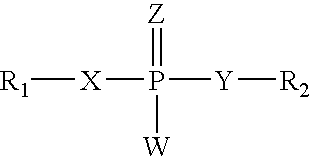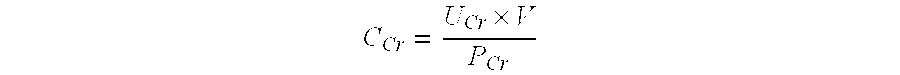Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Angiopoietin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
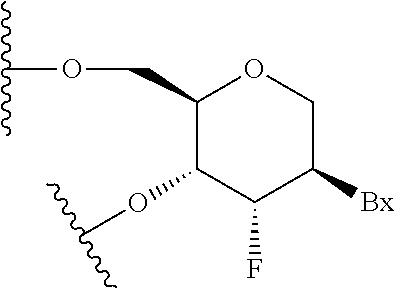
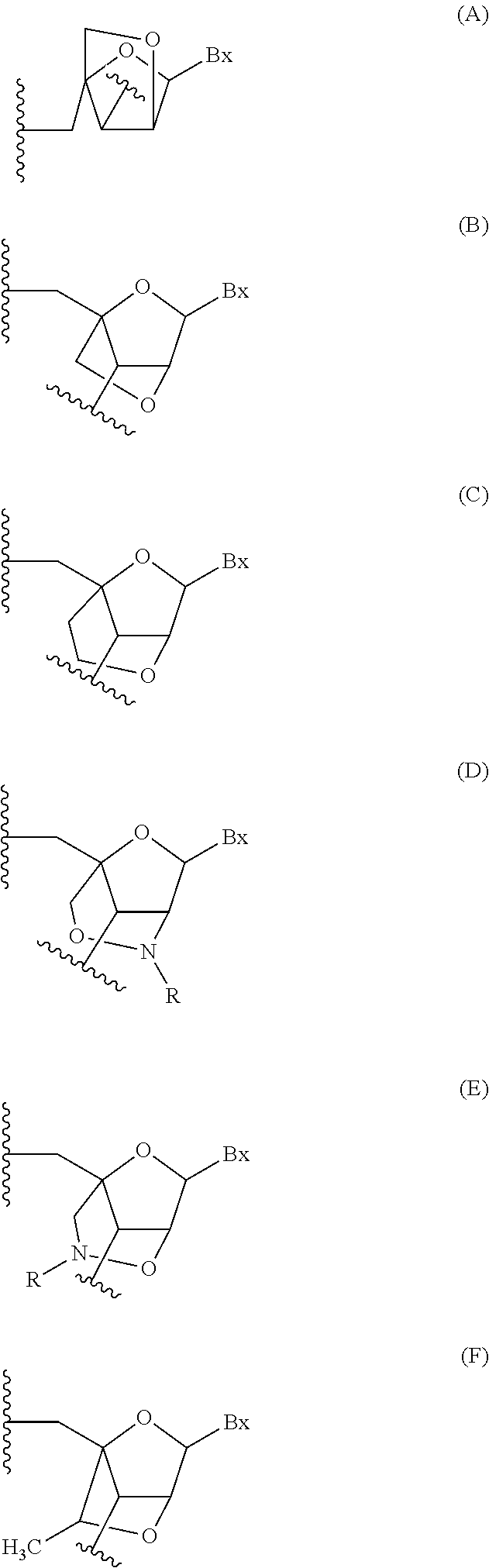
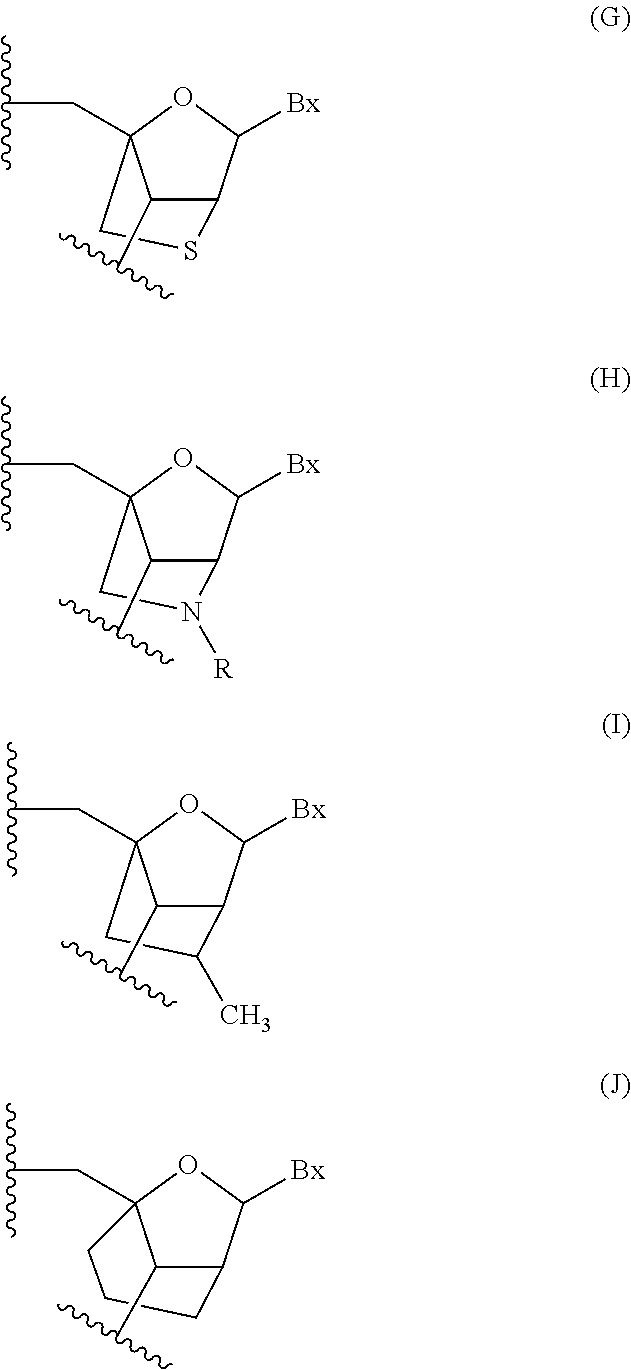
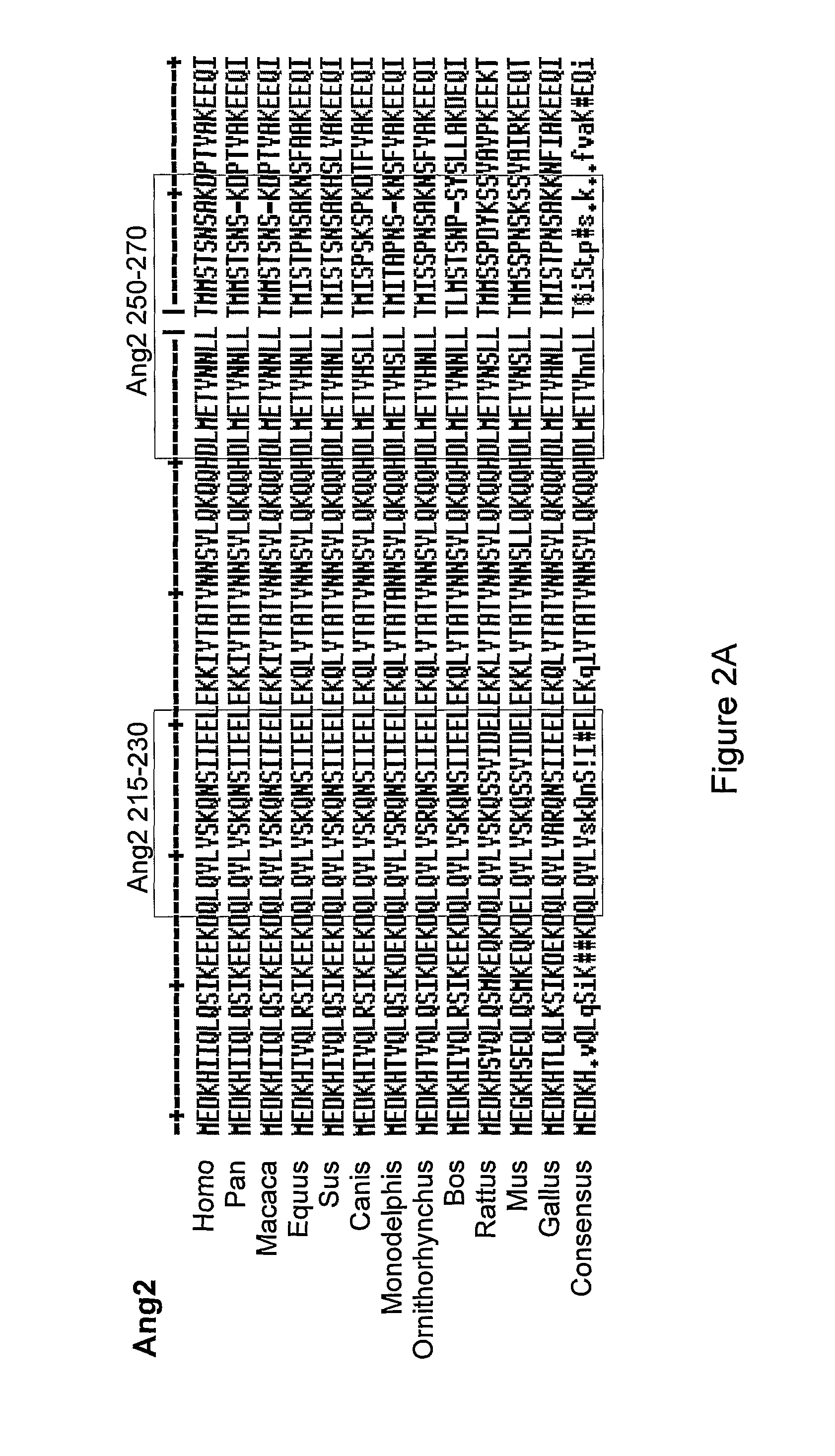
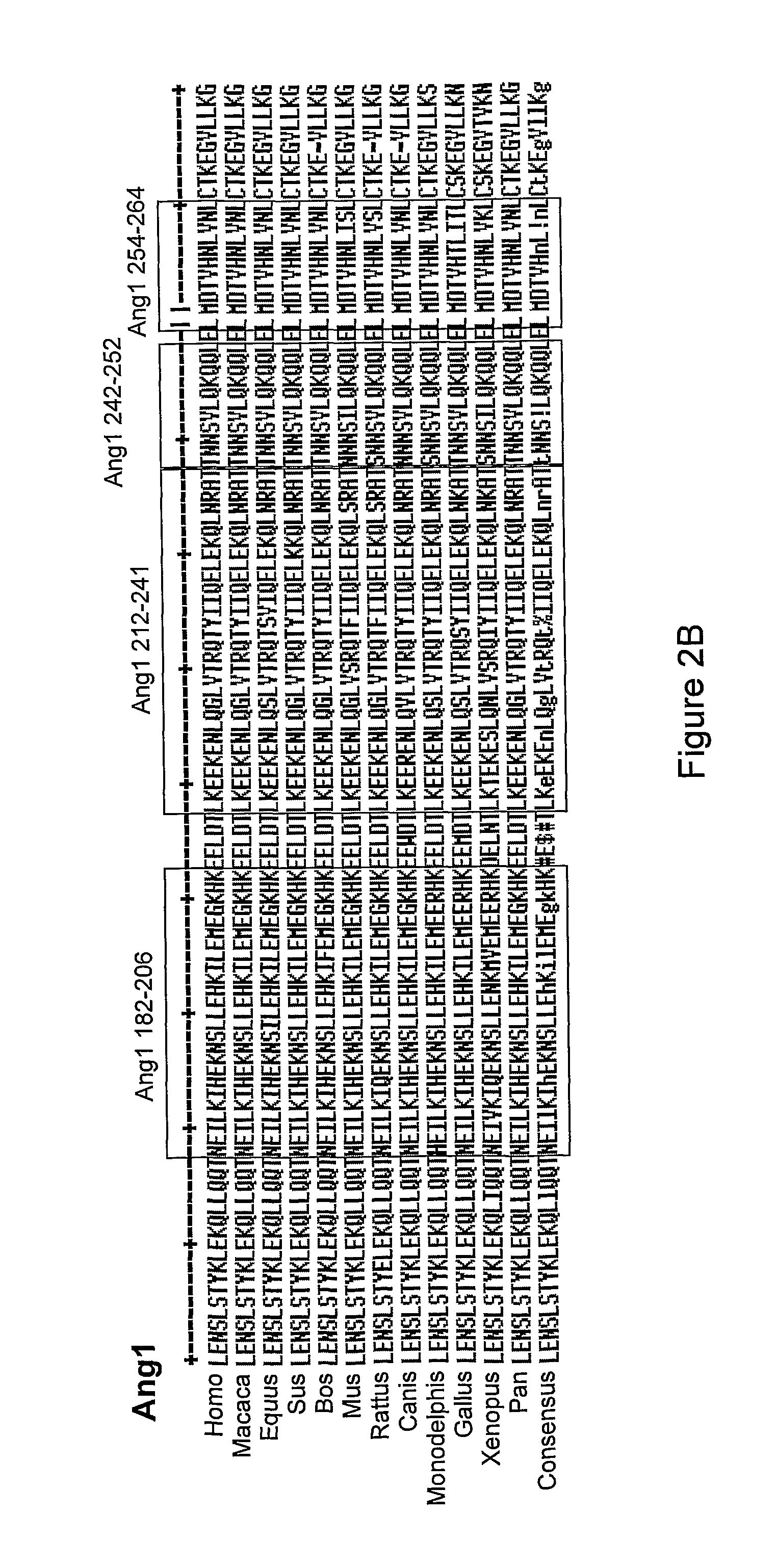
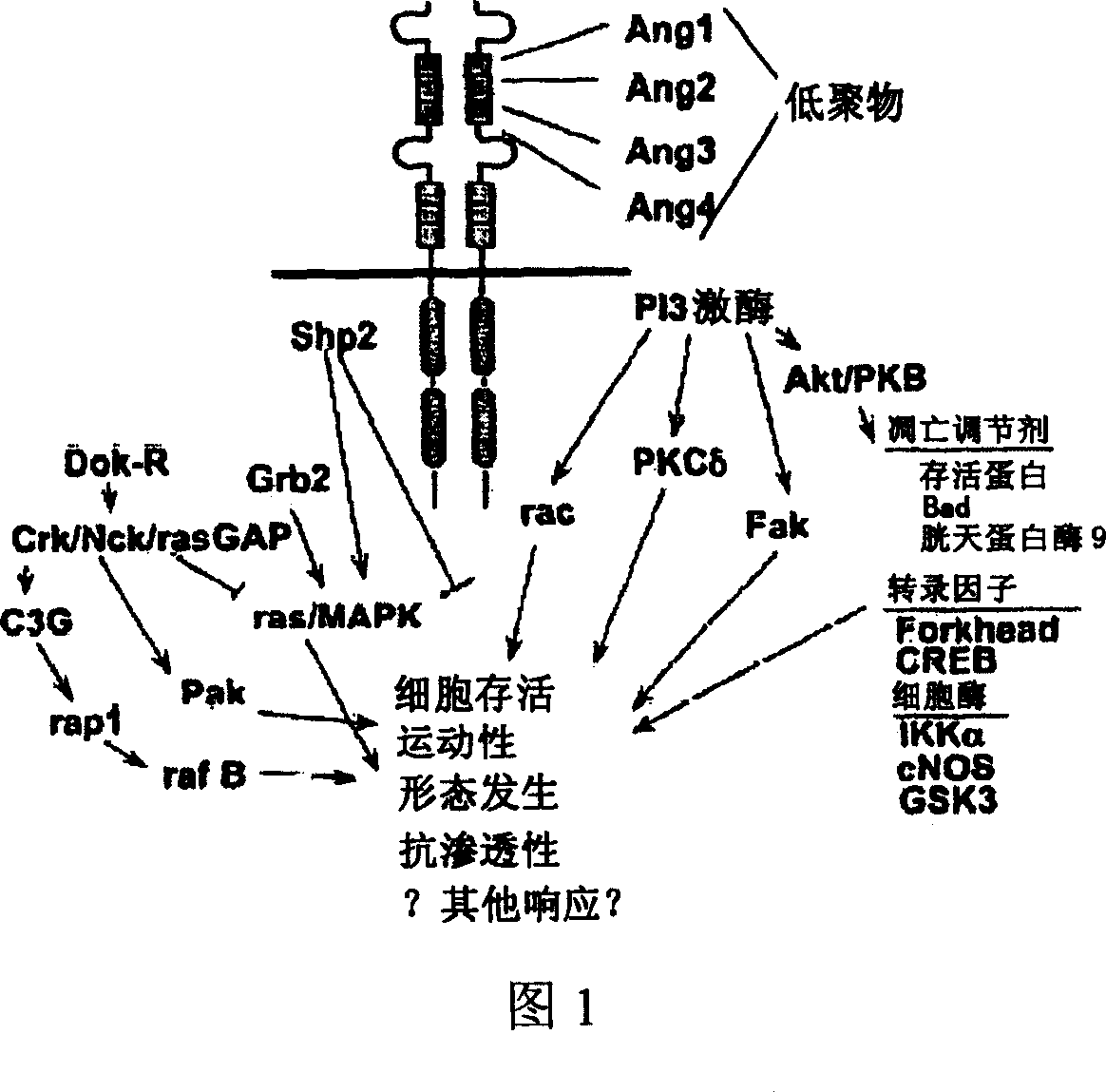
Angiopoietin is part of a family of vascular growth factors that play a role in embryonic and postnatal angiogenesis. Angiopoietin signaling most directly corresponds with angiogenesis, the process by which new arteries and veins form from preexisting blood vessels. Angiogenesis proceeds through sprouting, endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and vessel destabilization and stabilization. They are responsible for assembling and disassembling the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Angiopoietin cytokines are involved with controlling microvascular permeability, vasodilation, and vasoconstriction by signaling smooth muscle cells surrounding vessels. There are now four identified angiopoietins: ANGPT1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL3, ANGPT4.
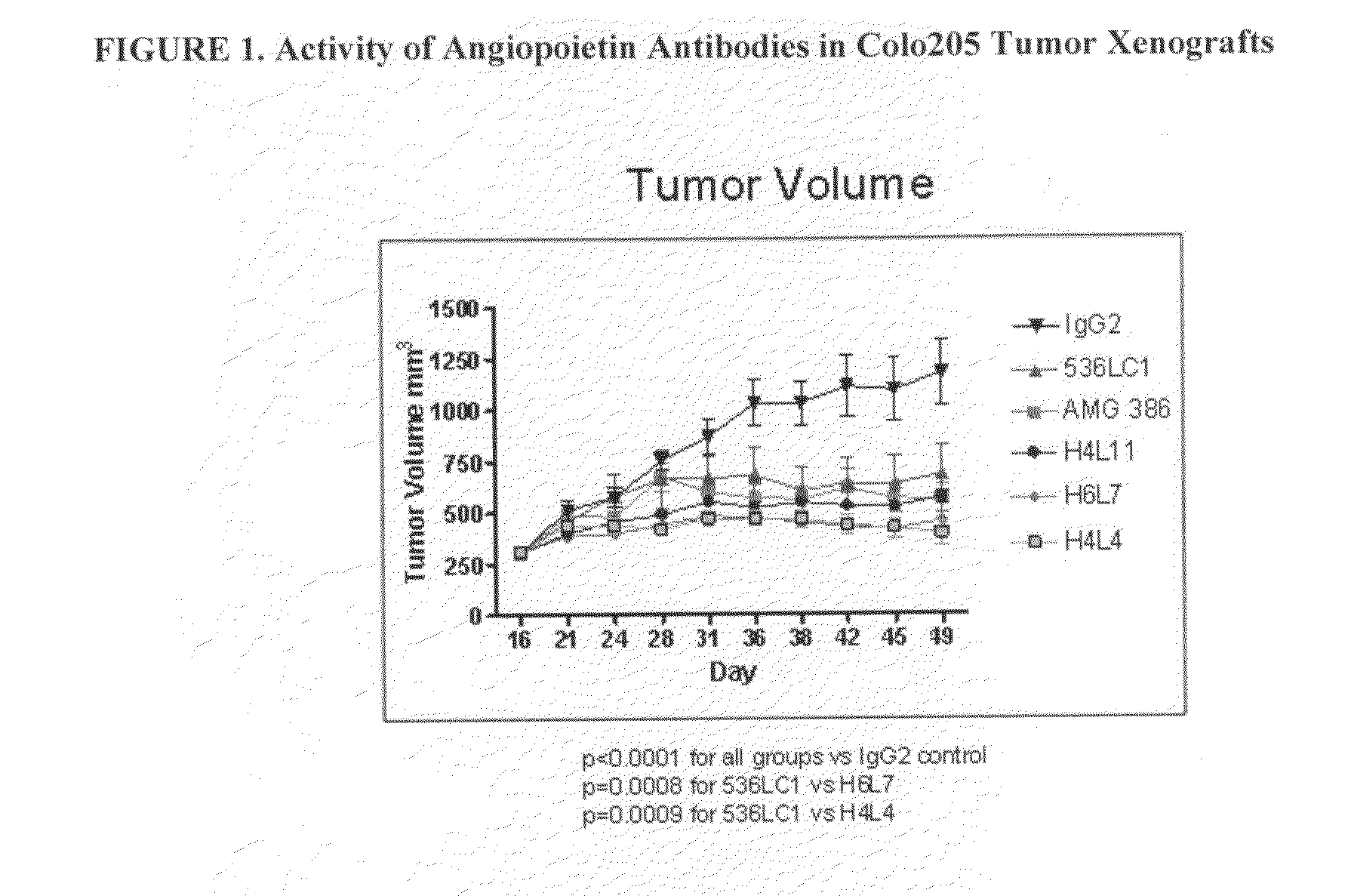
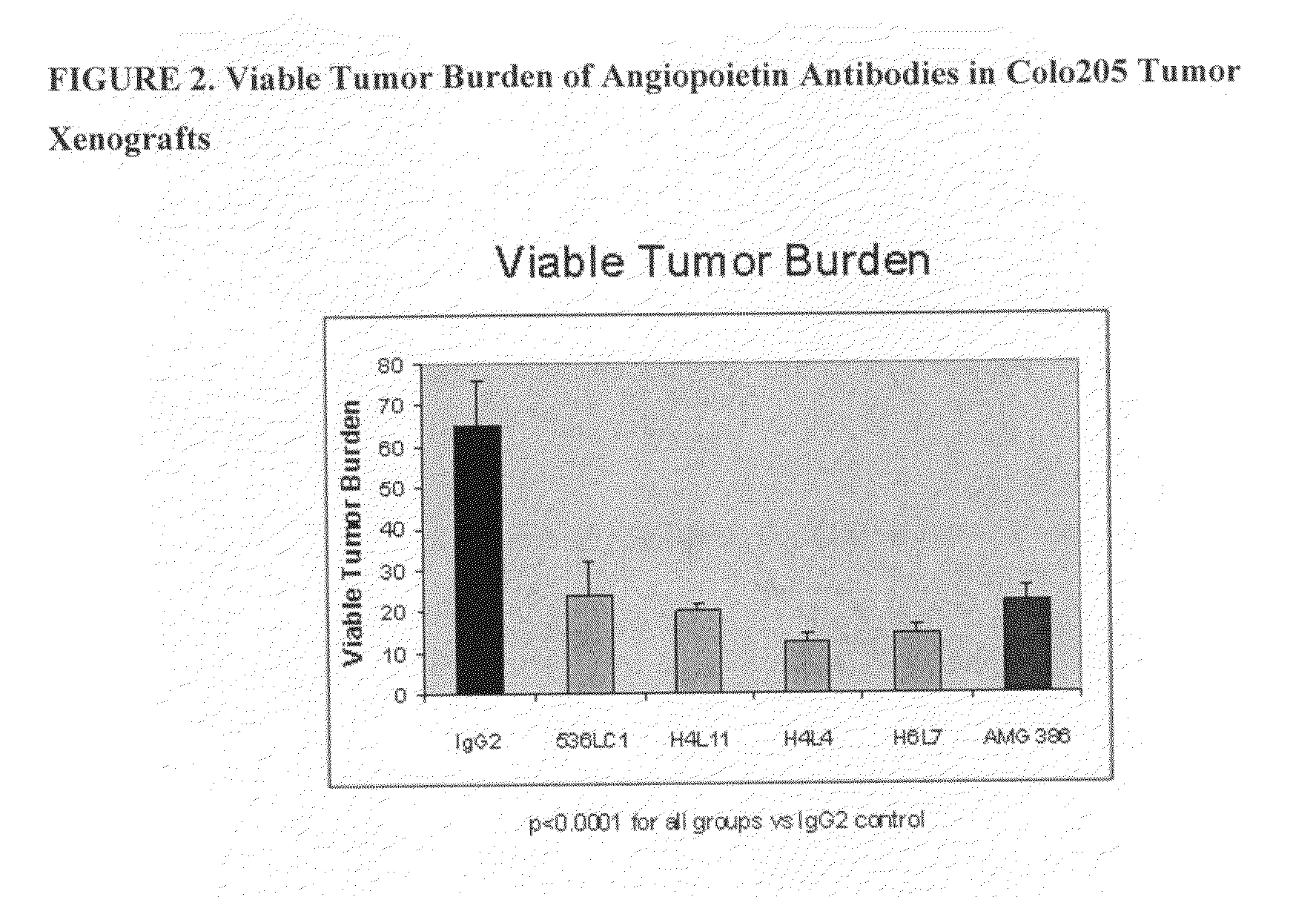
Specific binding agents of human angiopoietin-2
Owner:AMGEN INC
RNA interference mediated inhibition of angiopoietin gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050159380A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryFhit geneAngiopoietin-1
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating Angiopoietin gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of Angiopoietin gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (mRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of Angiopoietin genes, such as Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), Angiopoietin-3 (Ang-3), and Angiopoietin-4 (Ang-4).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Bispecific Anti-VEGF/Anti-ANG-2 Antibodies and their use in the Treatment of Ocular Vascular Diseases
ActiveUS20140017244A1Highly valuable propertyDiffusion slowAnimal cellsSenses disorderVascular diseaseBispecific antibody
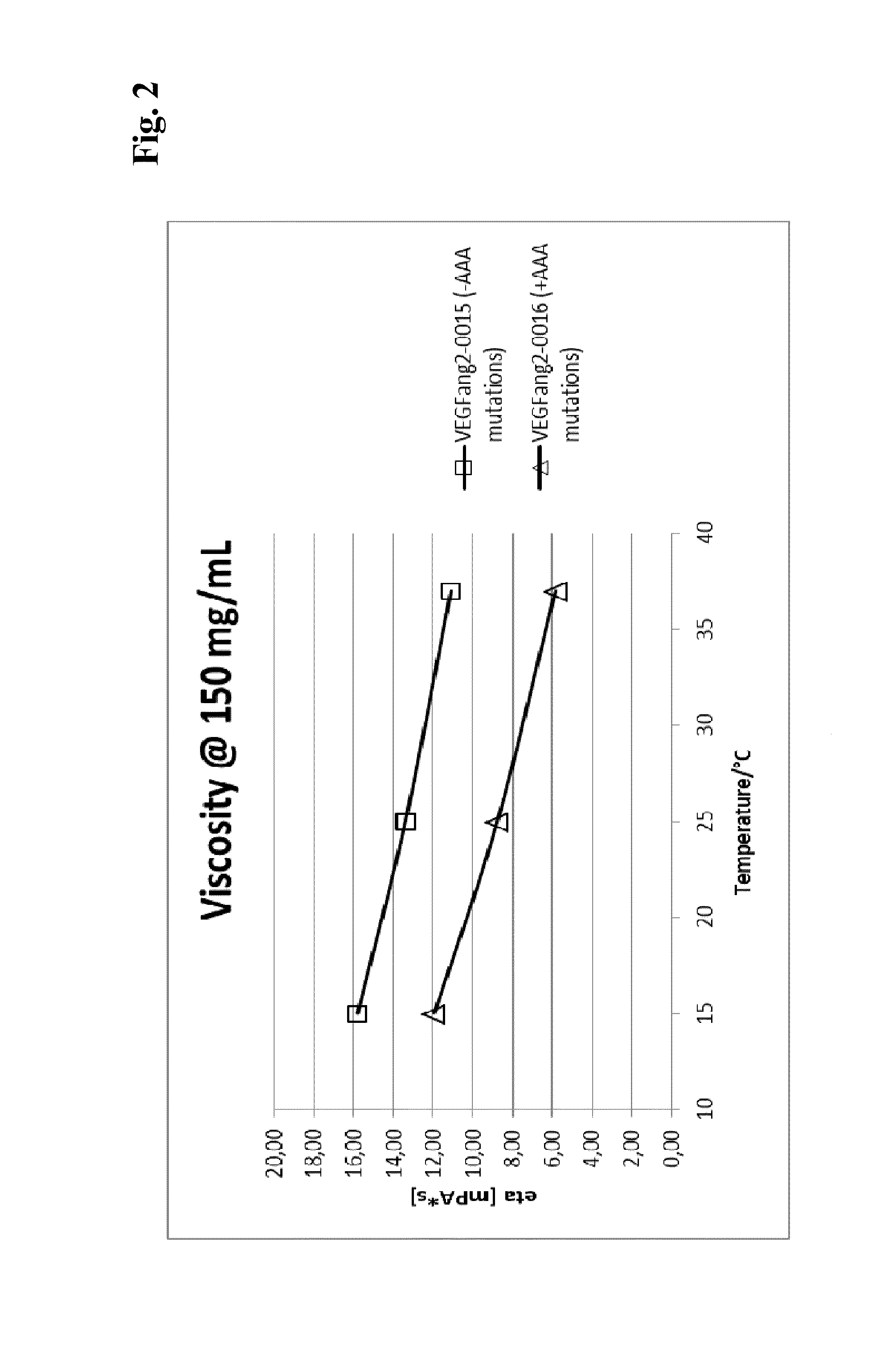
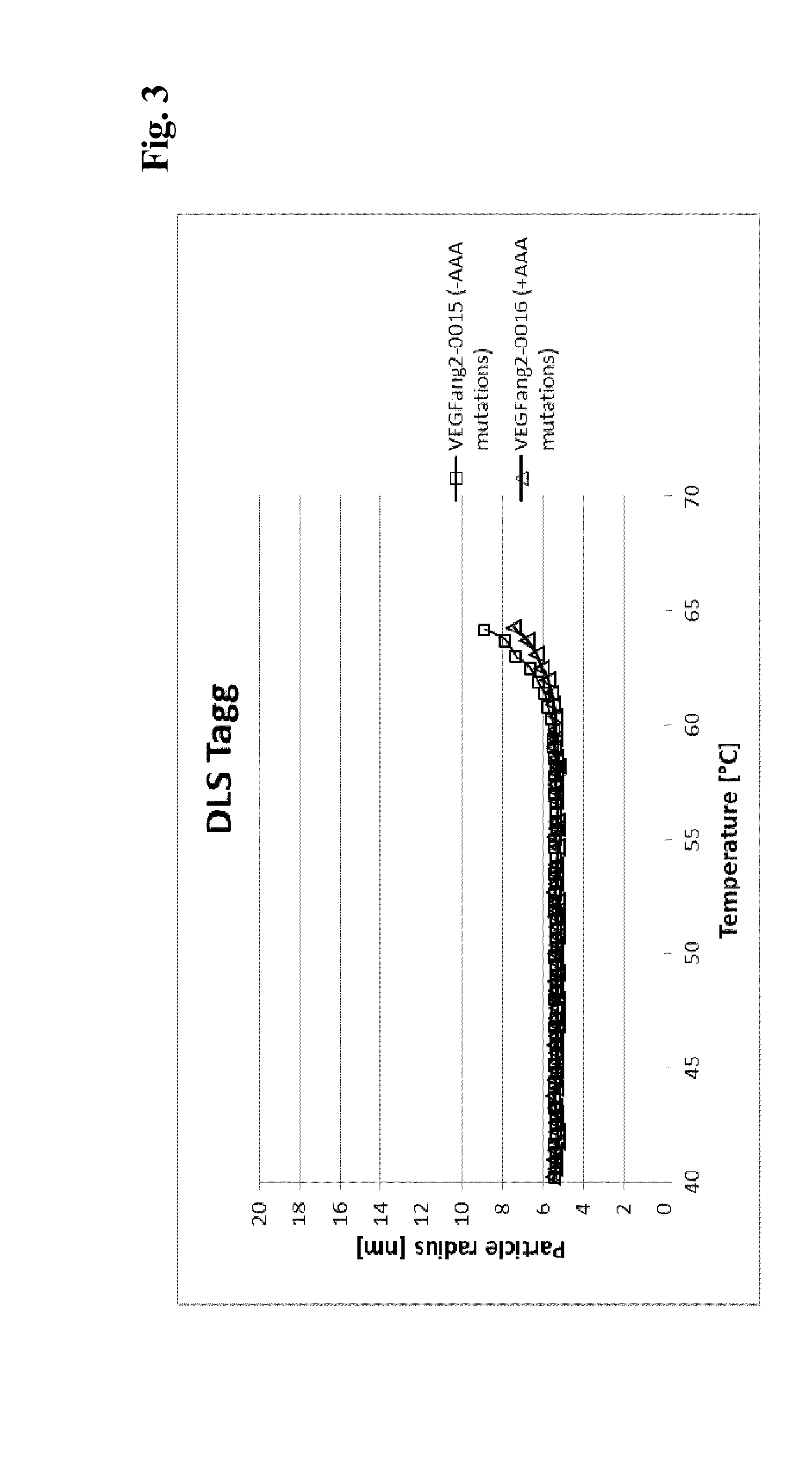
The present invention relates to bispecific antibody against human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF / VEGF-A) and against human angiopoietin-2 (ANG-2) of human IgG1 or IgG4 subclass with mutations I253A, H310A, and H435A, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing said antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Modulation of angiopoietin-like 3 expression
ActiveUS20130023579A1Reducing ANGPTL expressionReduces ANGPTL expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPlasma lipidsPlasma glucose
Provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing expression of an ANGPTL3 mRNA and protein in an animal. Also provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing plasma lipids, plasma glucose and atherosclerotic plaques in an animal. Such methods, compounds, and compositions are useful to treat, prevent, delay, or ameliorate any one or more of cardiovascular disease or metabolic disease, or a symptom thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
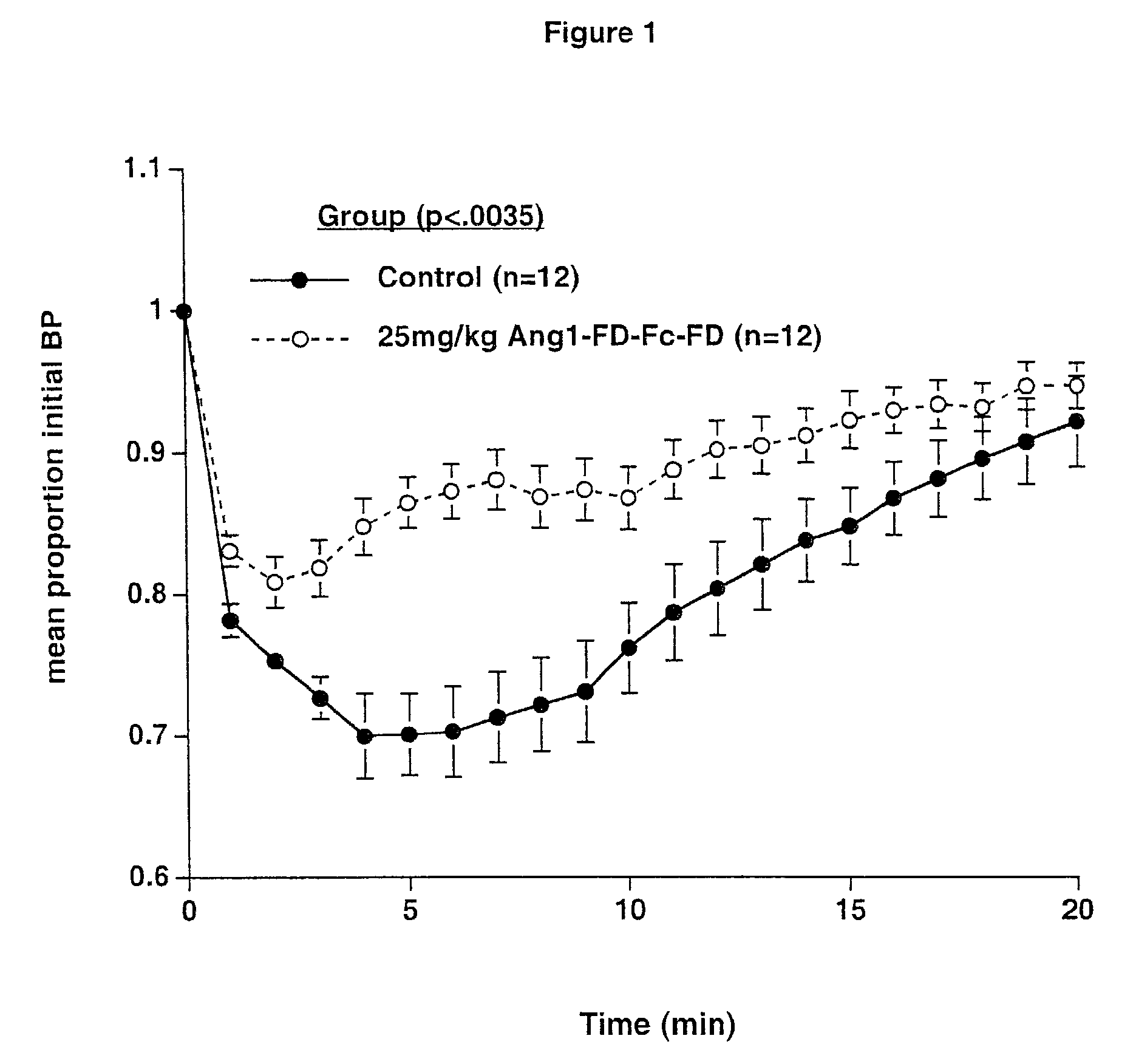
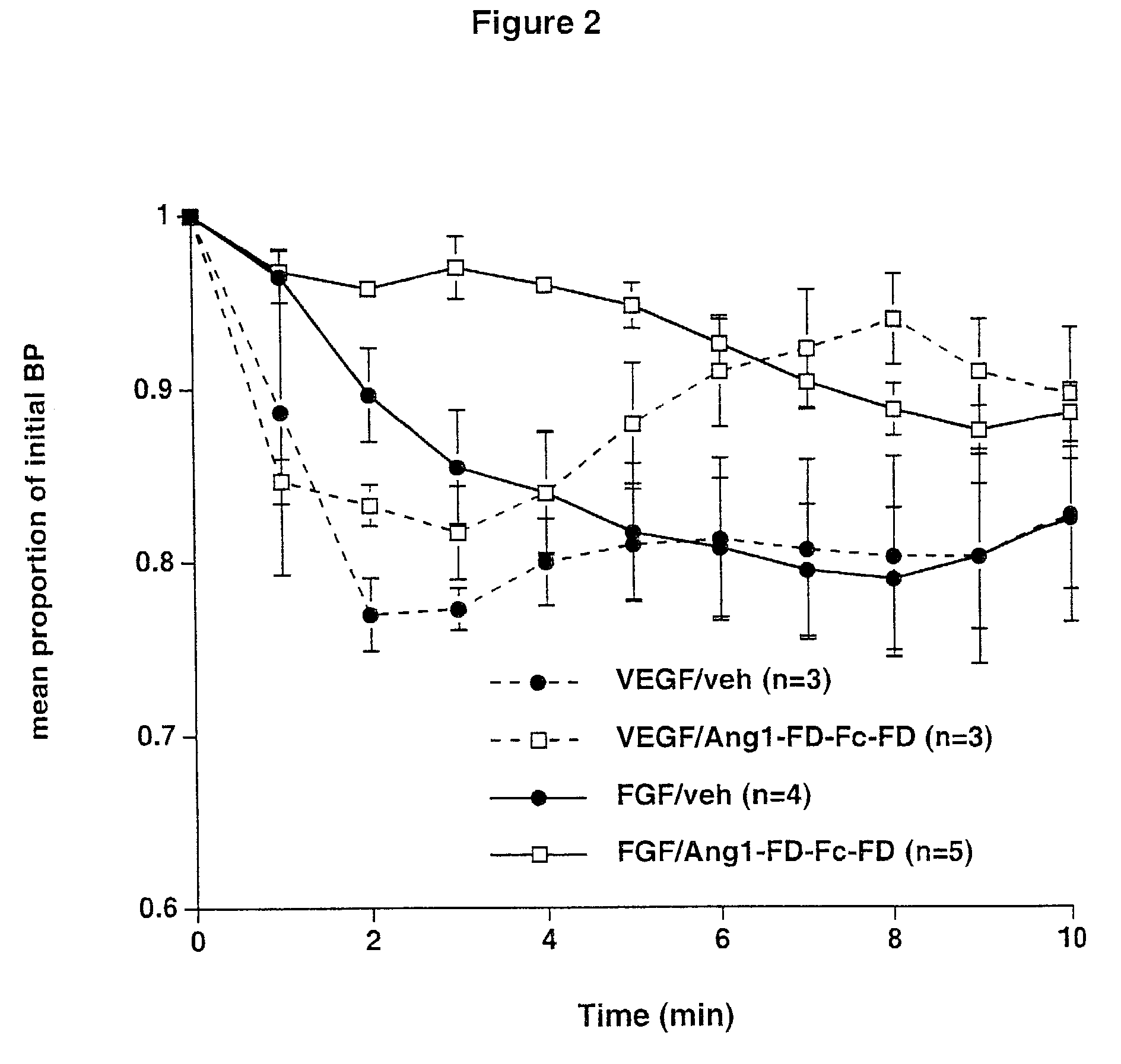
Angiopoietins and methods of treating hypertension
ActiveUS7052695B2Increase blood flowPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsArterial VasodilationHypotension shock
The invention generally relates to angiogenic factors and more particularly to the angiopoietin family of growth factors and to methods of using these growth factors to induce vasodilation and hypotension and reducing hypertension.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
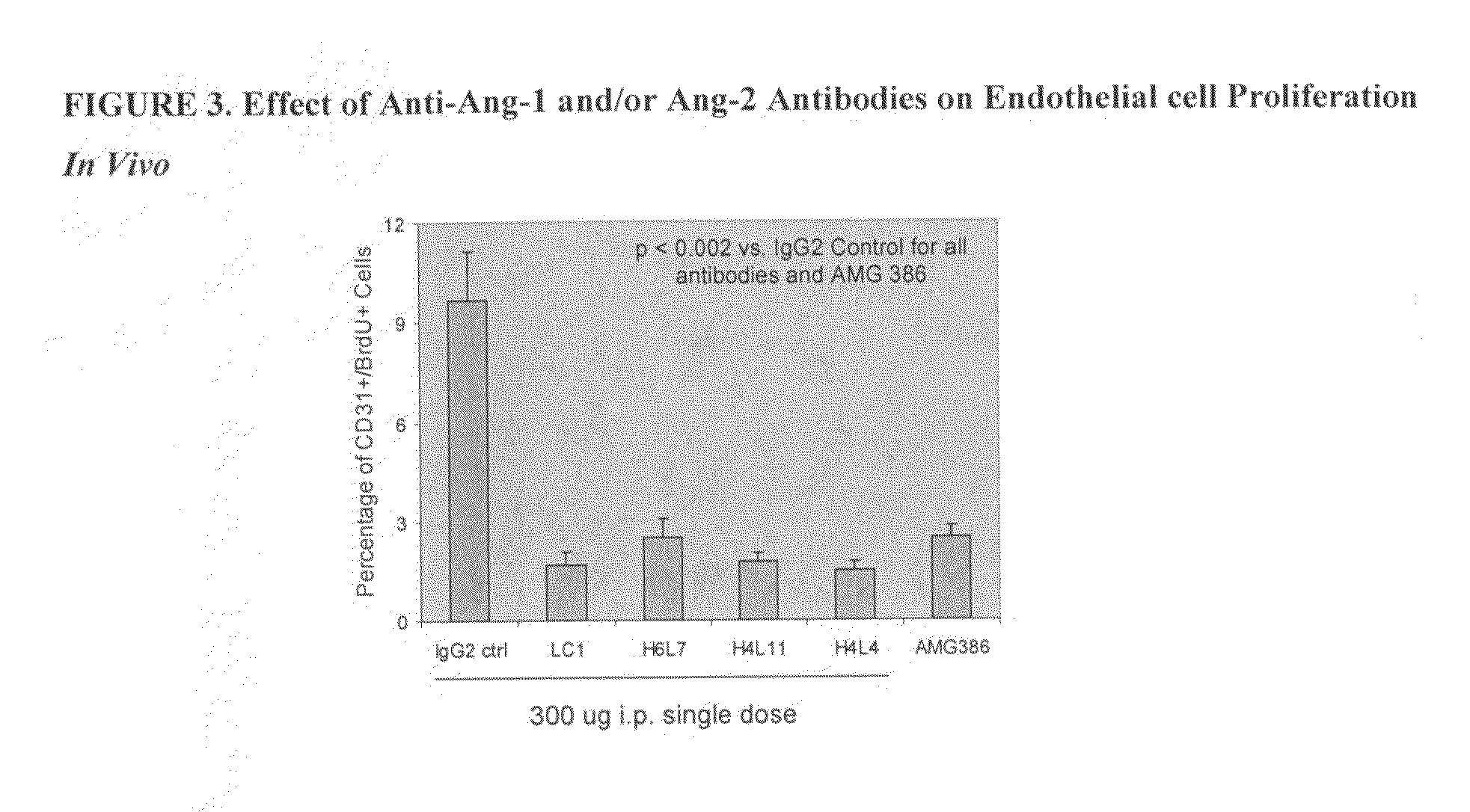
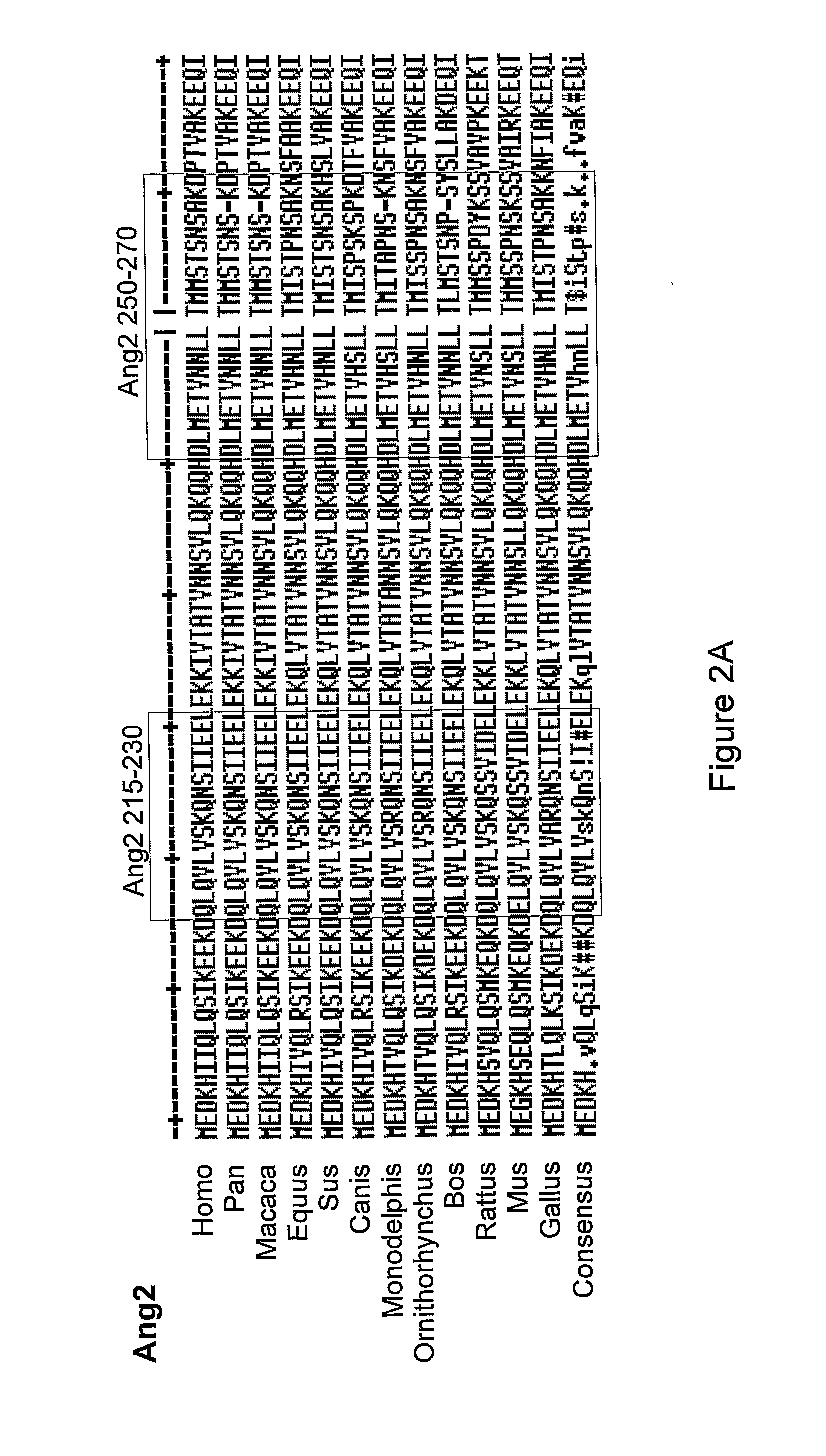
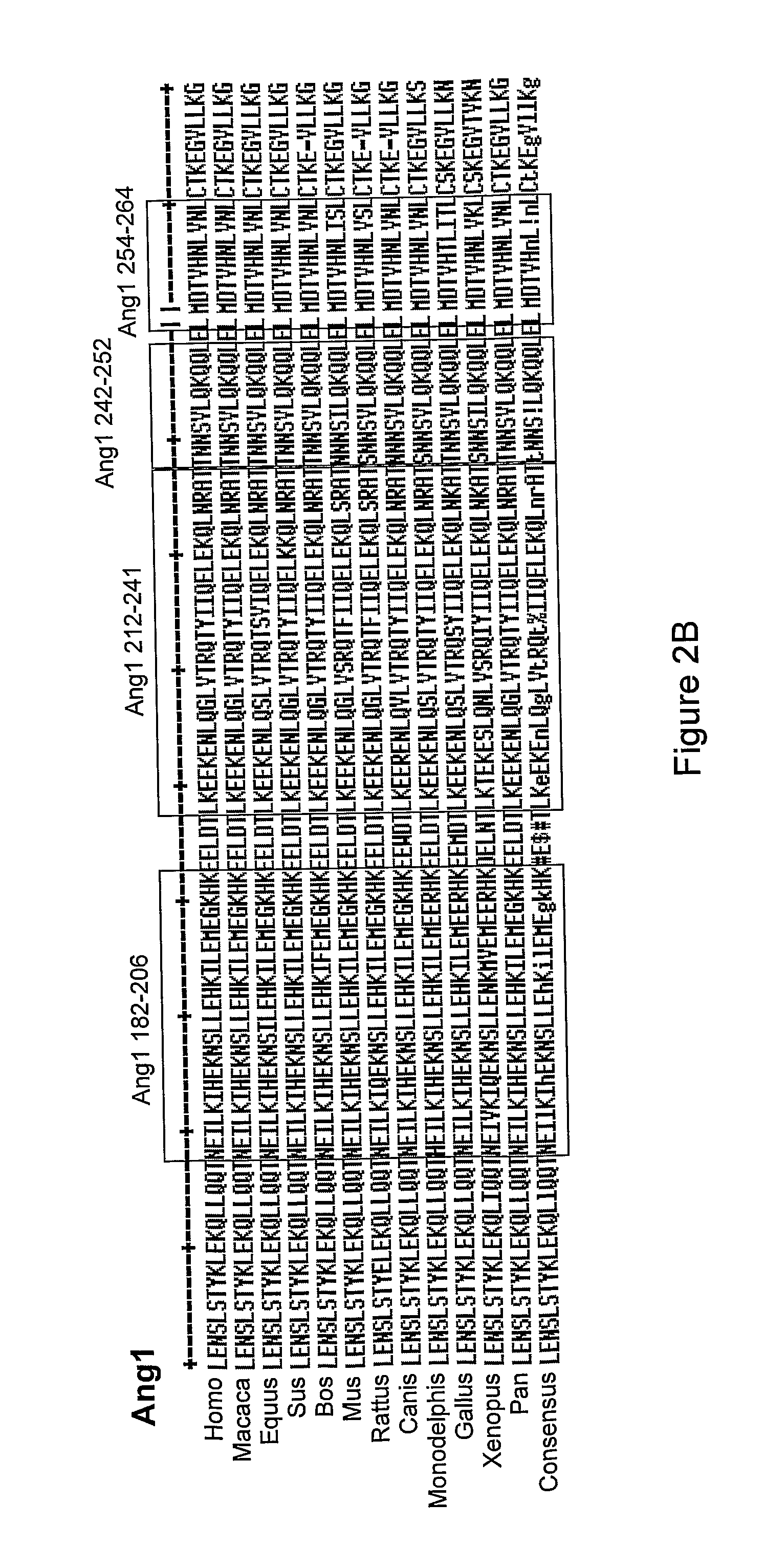
Antibodies directed to angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 and uses thereof
ActiveUS8030025B2Low effective concentrationInhibit physiological or pathological angiogenesisAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainCancer research
Owner:AMGEN INC
Angiopoietin derived peptides
Provided are angiopoietin-derived peptides or homologs or derivatives thereof, pharmaceutical composition including them, a use thereof for therapy and for the manufacture of a medicament, a method of treating a wide range of conditions, disorders and diseases therewith, nucleotide sequences encoding them, antibodies directed to epitopes thereof and fusion proteins including them.
Owner:COMPUGEN
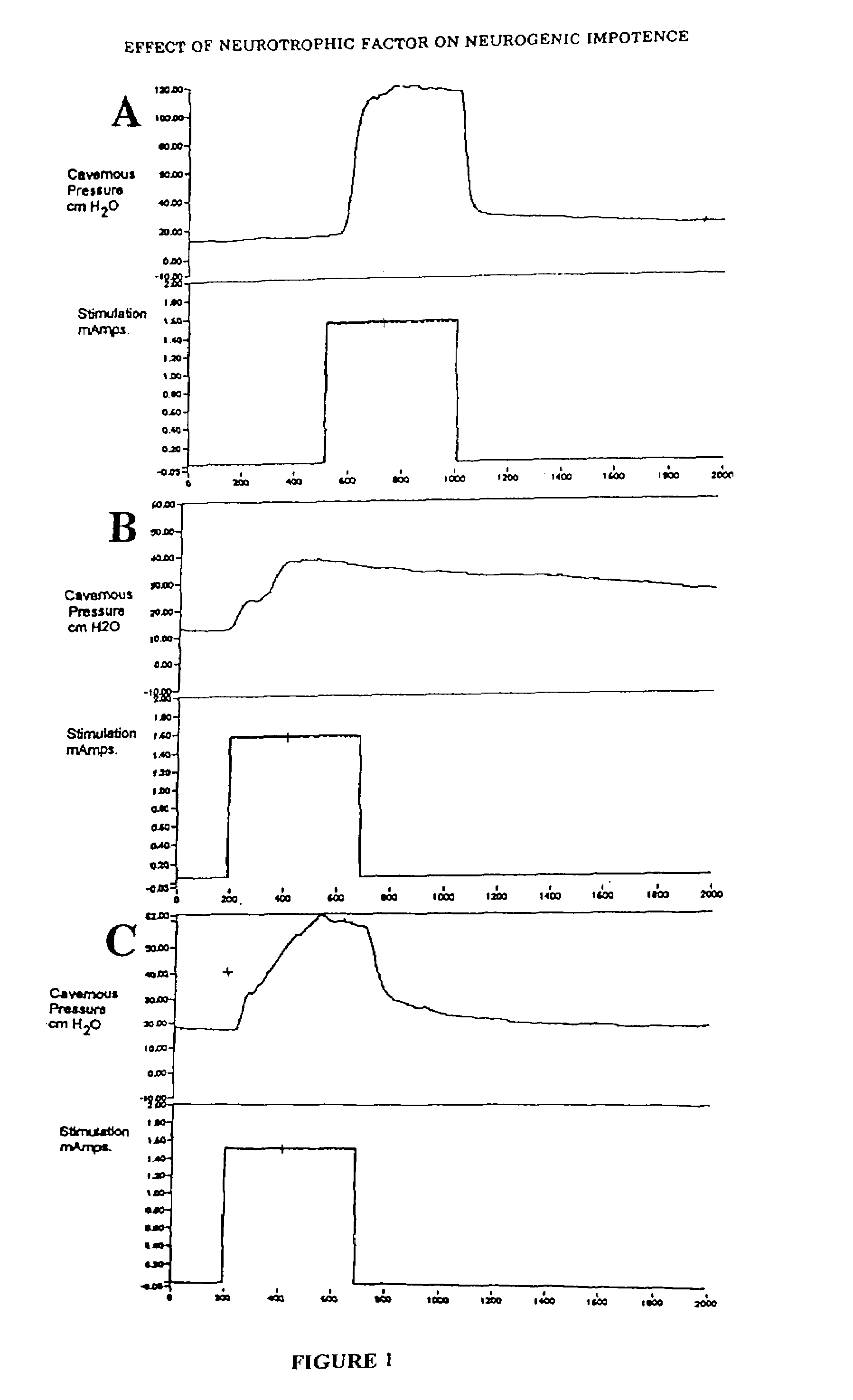
Methods and compositions for treating male erectile dysfunction
InactiveUS7265091B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderNeurotrophin-3
The invention provides a method for preventing or treating male erectile dysfunction or female sexual arousal disorder by administering an effective amount of one or more factors from a group of factors including vascular endothelial growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, neurotrophin-3, neurotrophin-4, or angiopoietin-1, wherein the factor is a full length protein or a nucleic acid encoding the factor, or a functional derivative or fragment thereof, or an agent that enhances production and / or male erection or female sexual arousal stimulating function of the factor(s). Combinations, kits, and combinatorial methods are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modulation of angiopoietin-like 3 expression
Provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing expression of an ANGPTL3 mRNA and protein in an animal. Also provided herein are methods, compounds, and compositions for reducing plasma lipids, plasma glucose and atherosclerotic plaques in an animal. Such methods, compounds, and compositions are useful to treat, prevent, delay, or ameliorate any one or more of cardiovascular disease or metabolic disease, or a symptom thereof.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
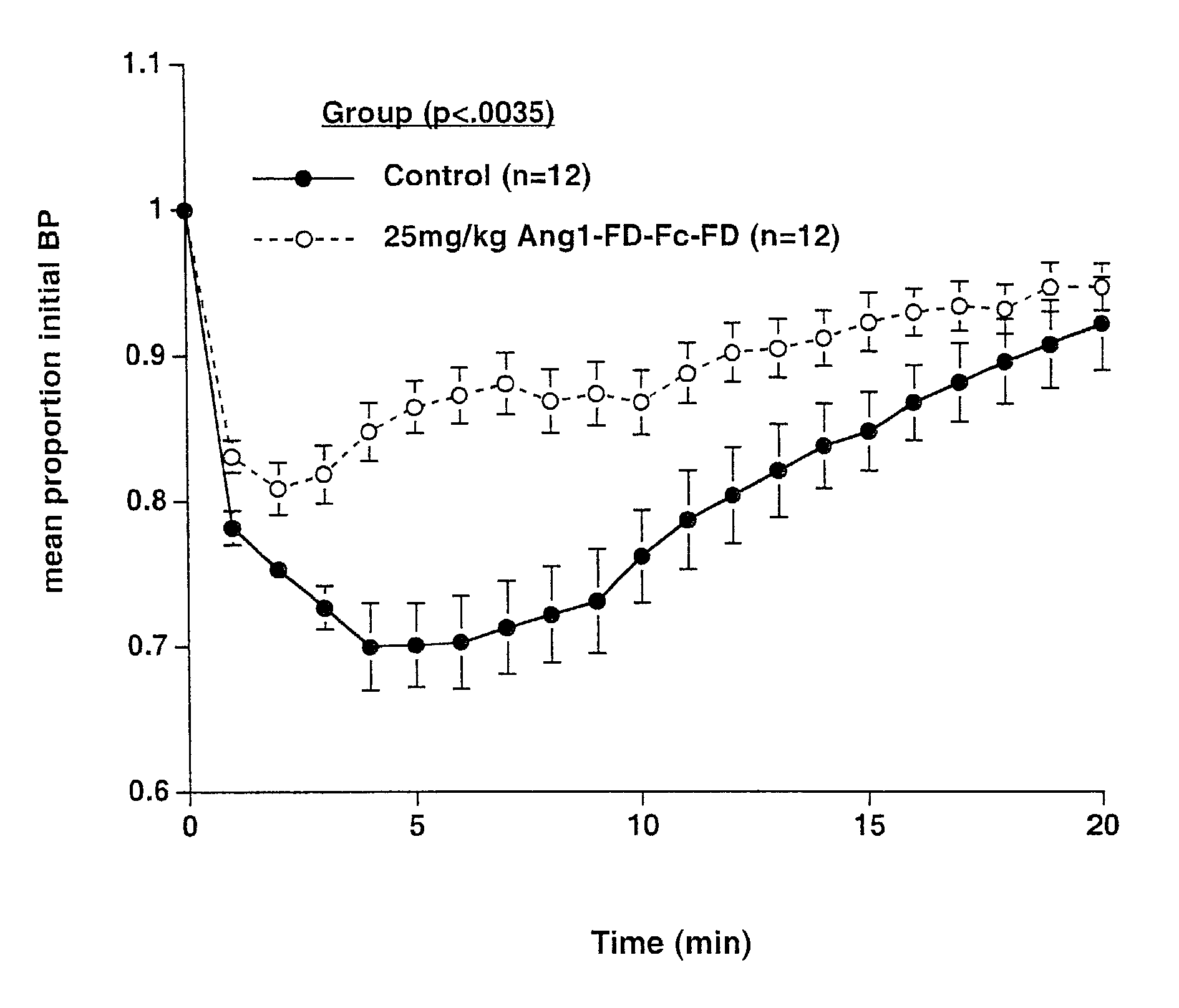
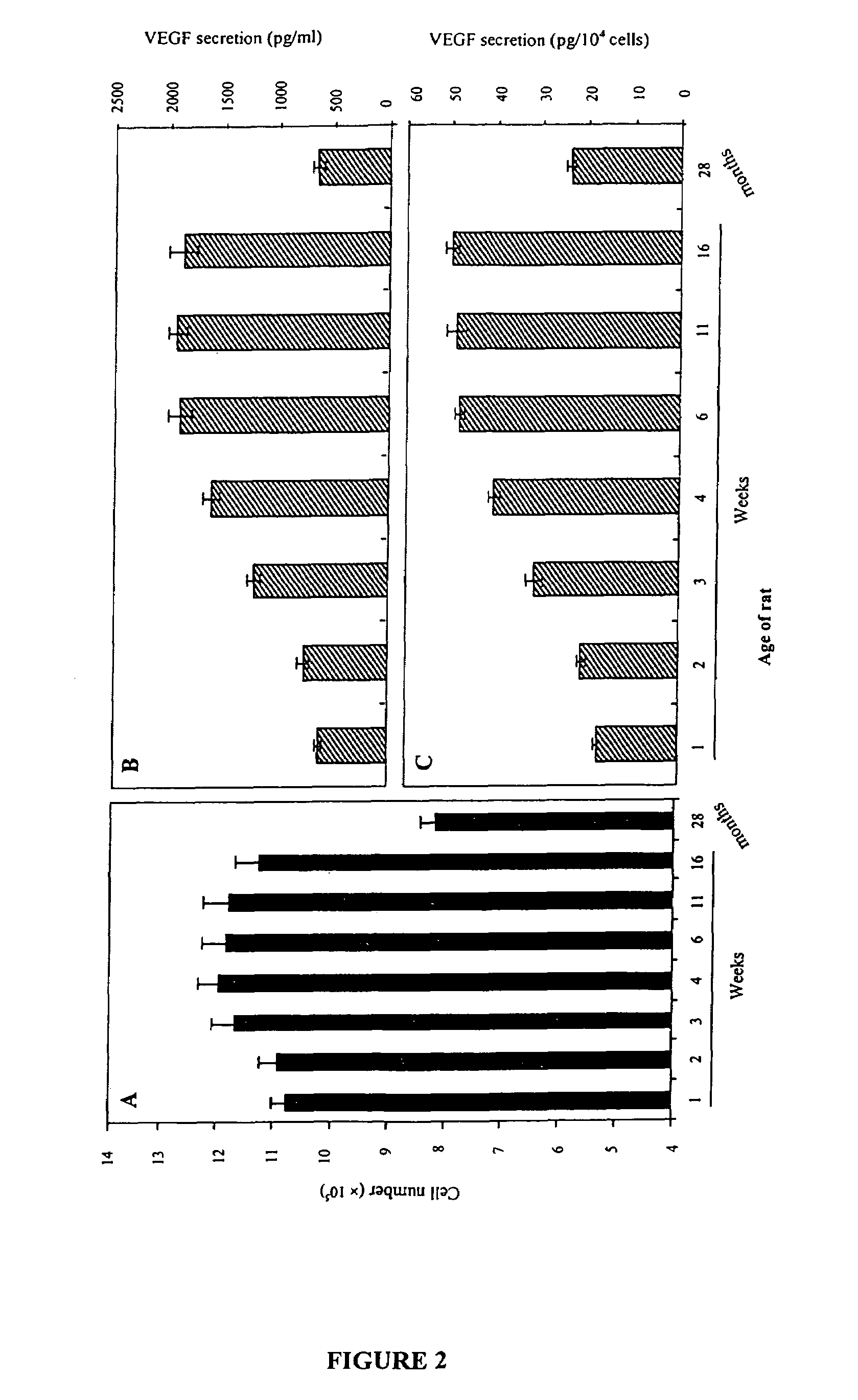
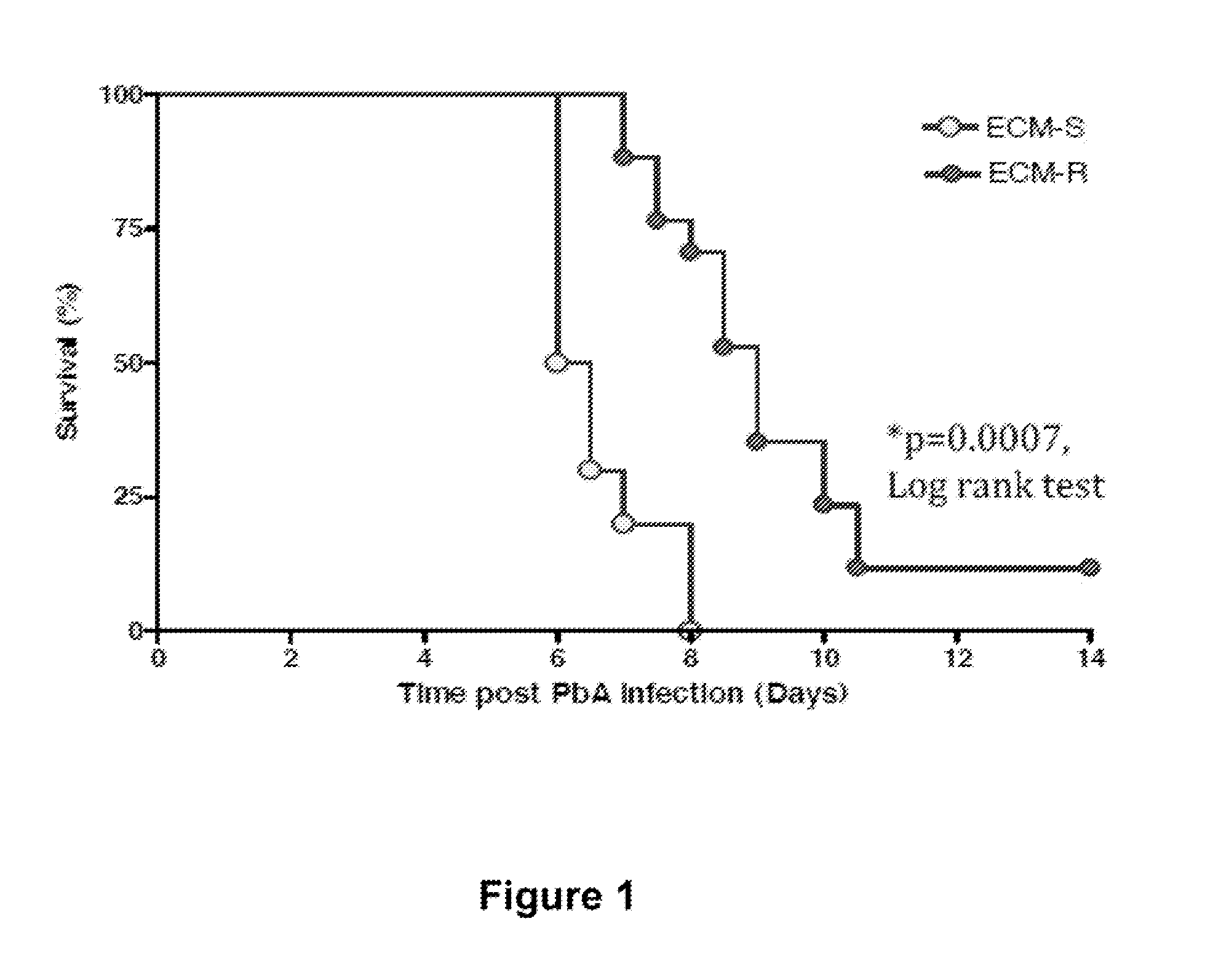
Angiopoietin-based interventions for treating cerebral malaria
ActiveUS20160045566A1Improving and increasing survivalPreventing vascular leakageAntibacterial agentsBiocideIntervention measuresMalaria
The present invention provides methods for treating, preventing or reducing the severity of cerebral malaria. The methods of the present invention comprise administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a modified angiopoietin molecule such as AngF1-Fc-F1.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +1
Fusion proteins binding to growth factors
The present application discloses an isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding a polypeptide capable of synchronously binding two different growth factors polypeptide components. Such a polypeptide is capable of synchronously binding VEGF polypeptide and Angiopoietin polypeptide.
Owner:APLOGEN CO LTD
Angiopoietin derived peptides
Provided are angiopoietin-derived peptides or homologs or derivatives thereof, pharmaceutical composition including them, a use thereof for therapy and for the manufacture of a medicament, a method of treating a wide range of conditions, disorders and diseases therewith, nucleotide sequences encoding them, antibodies directed to epitopes thereof and fusion proteins including them.
Owner:COMPUGEN
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
InactiveUS20140147864A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisFactor iiRenal Failures
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using a one or more assays configured to detect a kidney injury marker selected from the group consisting of Proheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor, Tenascin C, Angiopoietin-related protein 4, Fibroblast growth factor 19, Fibroblast growth factor 21, Heparin-binding growth factor 1, Angiopoietin-related protein 6, Proepiregulin, Probetacellulin, Amphiregulin, Angiogenin, Thrombospondin-2, and Collagen alpha-1 (XVIII) chain as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
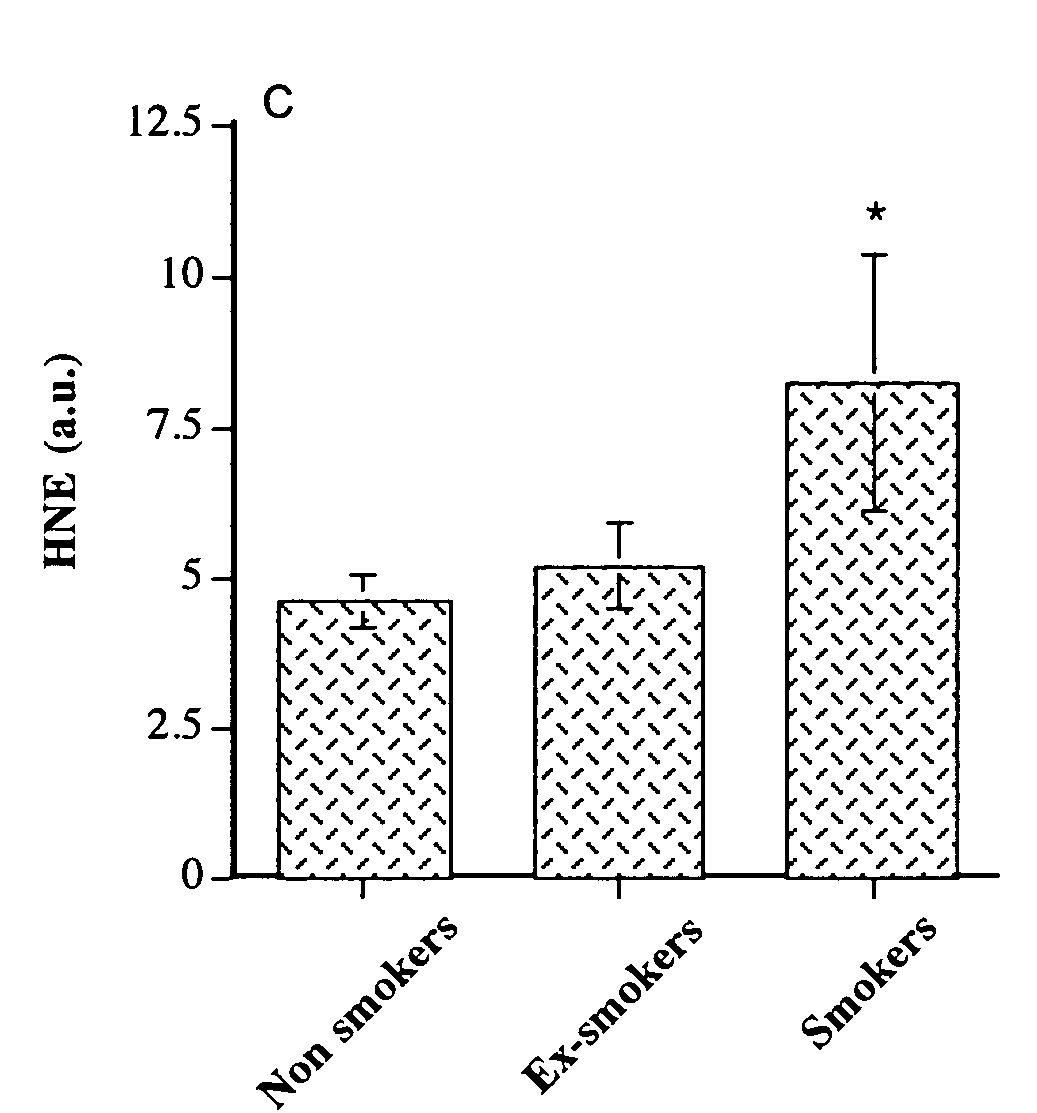
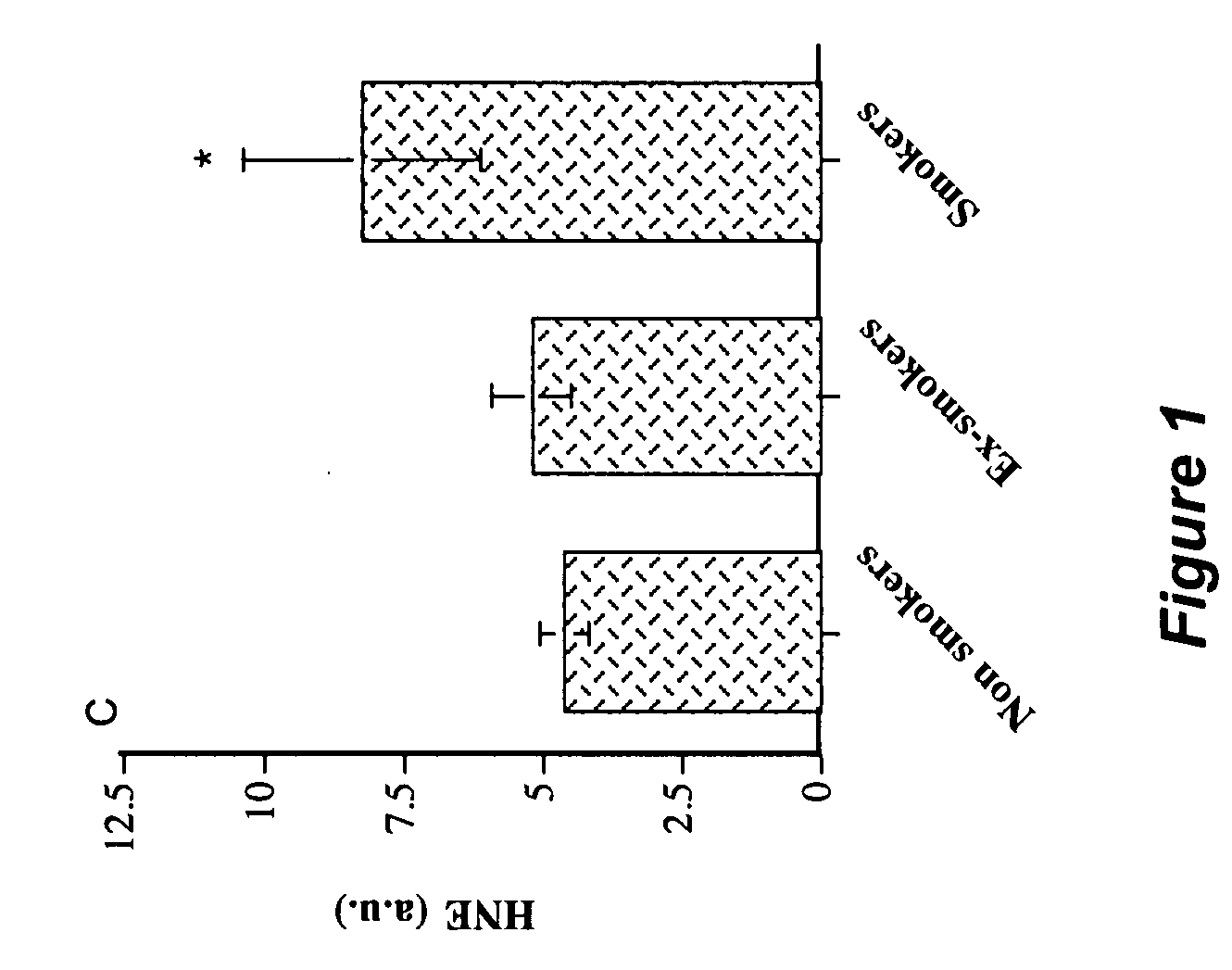
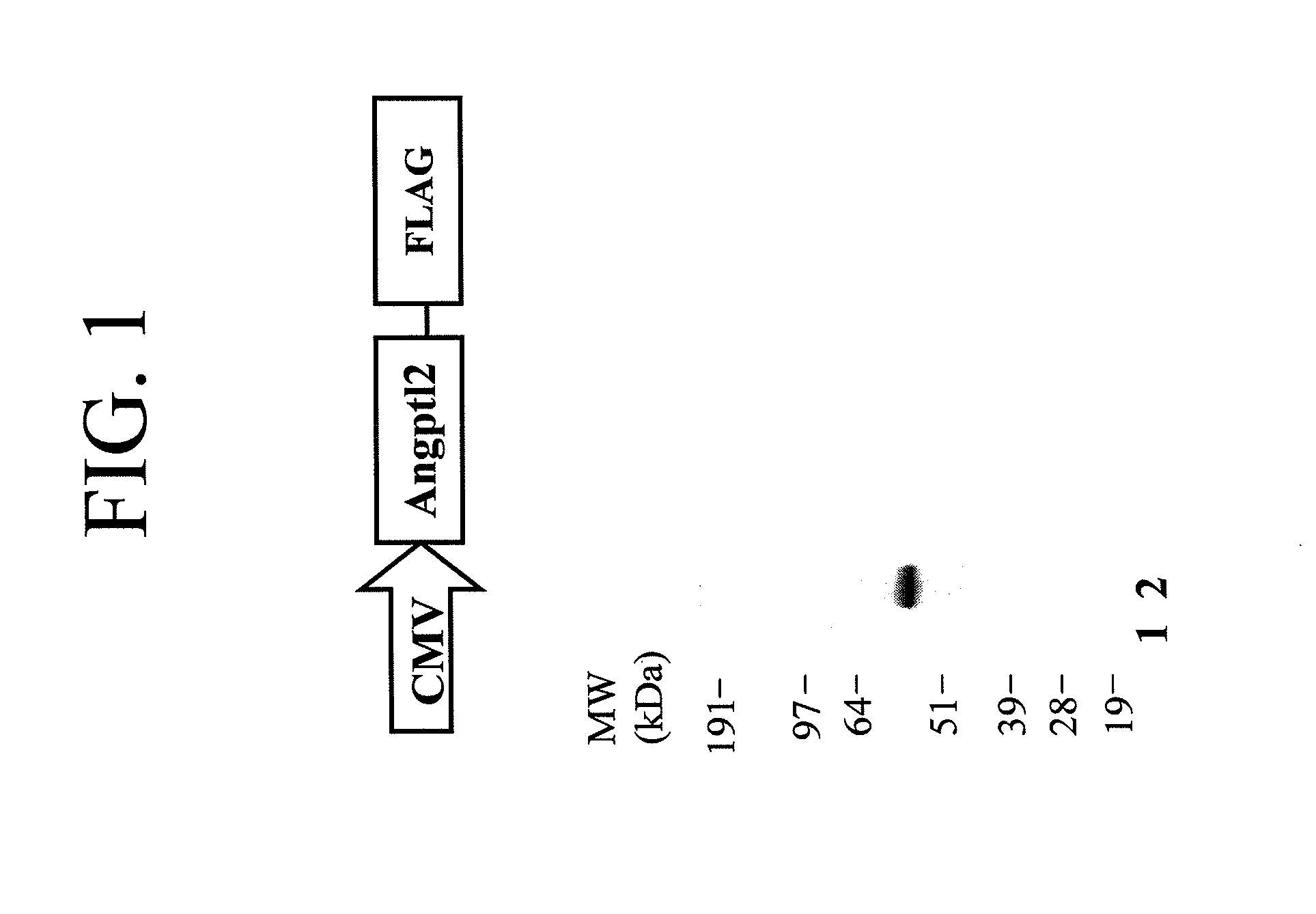
Angiopoietin-like 2 as a biomarker of vascular endothelial cell abnormal function and senescence
InactiveUS20080166717A1Great oxidative stressImproves oxidative stressMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisVascular endotheliumMammal
A method for assessing a physiological state of a mammal. The method includes: obtaining from the mammal a biological sample; measuring the expression of angiopoietin-like 2 in the biological sample; and assessing the physiological state of the mammal by comparing the measured expression of the angiopoietin-like 2 to a predetermined normal expression level in normal subjects, wherein an increase in angiopoietin-like 2 level over the predetermined normal expression level indicates an abnormal physiological state.
Owner:INST DE CARDIOLOGIE DE MONTREAL
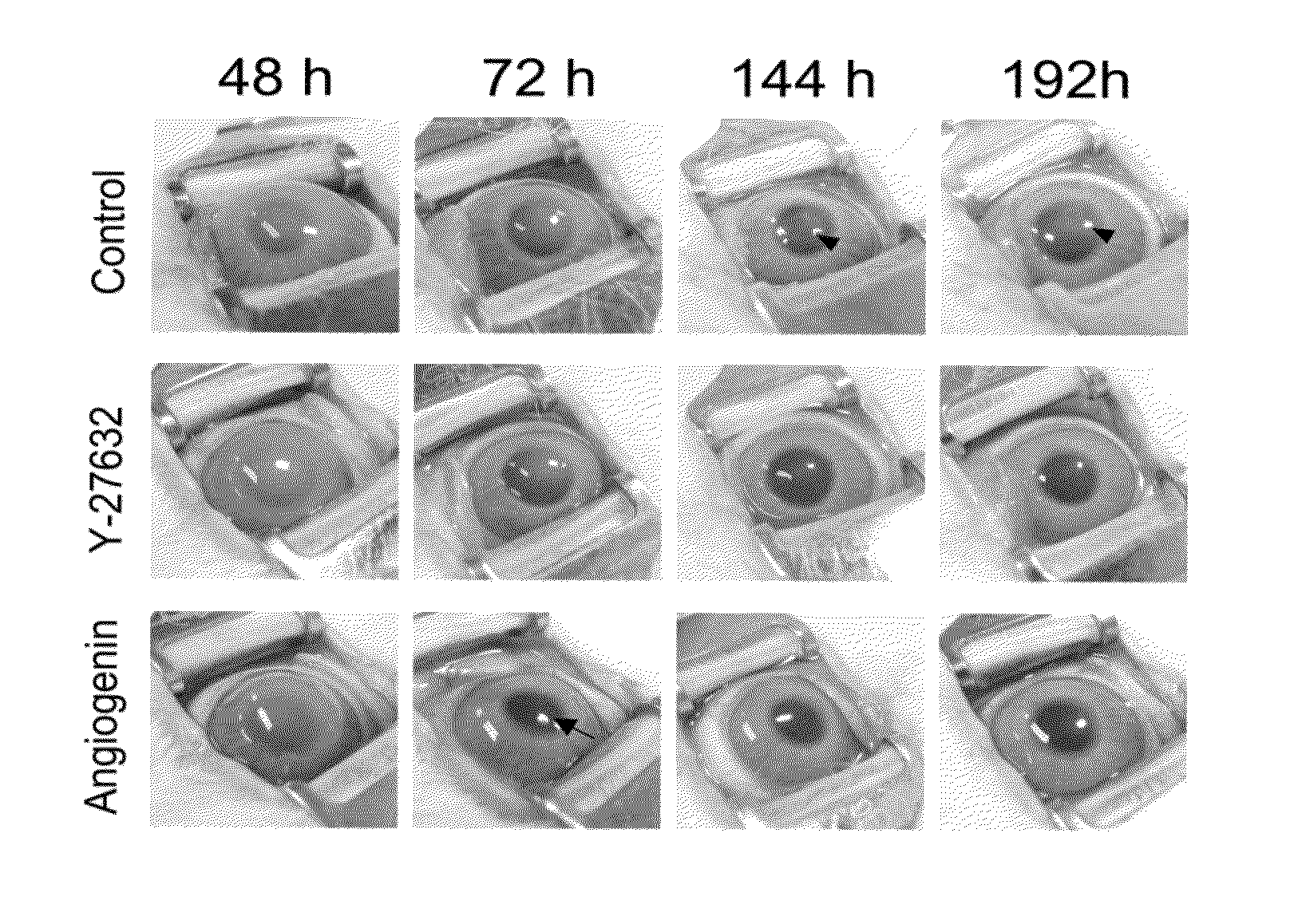
ANGIOGENIN COMPLEXES (ANGex) WITH ANABOLIC HORMONES FOR IMPROVING BONE HEALTH
InactiveUS20150174218A1Efficient assimilationReduce frequencyBiocideDispersion deliveryHormoneLactoferrin
Compositions are described which contain lactoferrin, angiogenin and an anabolic hormone. The described compositions are useful in treatment of a variety of conditions, particularly in promoting bone health.
Owner:NAIDU LP
Methods for Expansion and Analysis of Cultured Hematopoietic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20110196343A1Improve scalabilityIncrease the number ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideCulture cellGlycoprotein
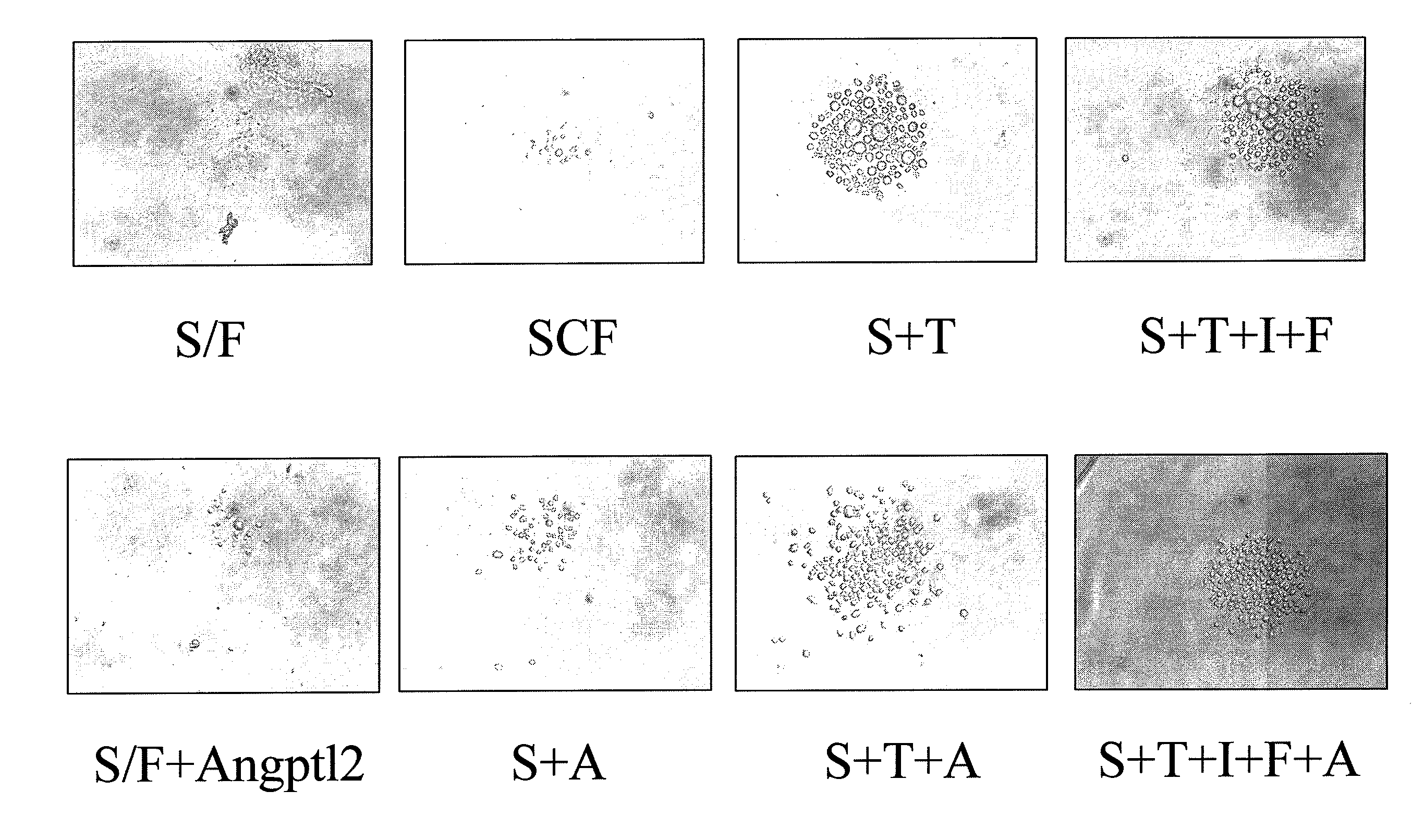
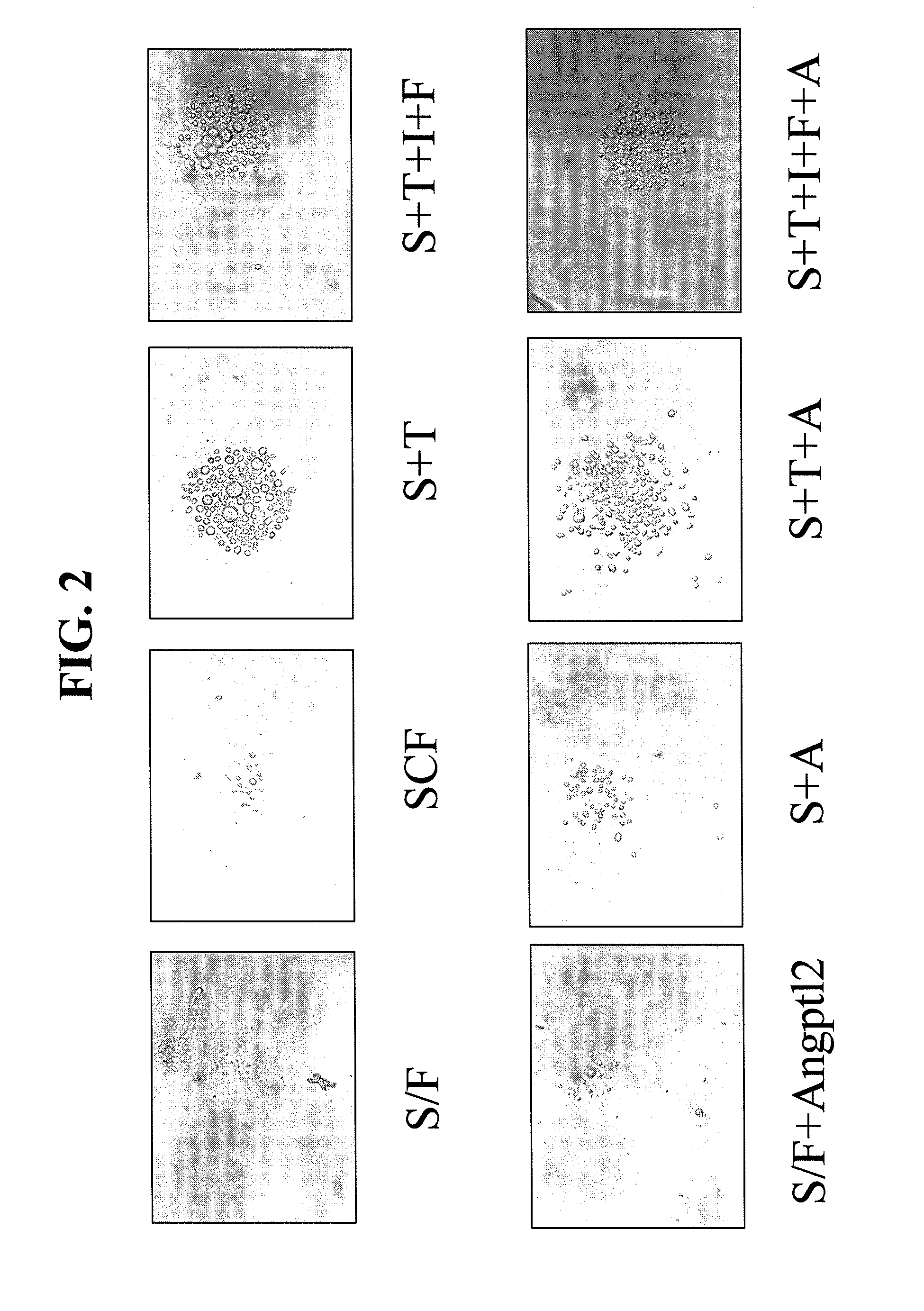
Methods and kits for propagating hematopoietic stem cells are provided. The methods comprise culturing cells in medium comprising one or more angiopoietin-like proteins, under conditions sufficient for expansion of HSCs. Angiopoietin-like proteins include angiopoietin-like protein 2, angiopoietin-like protein 3, angiopoietin-like protein 4, angiopoietin-like protein 5, angiopoietin-like protein 7, and microfibrillar-associated glycoprotein (Mfap4). Methods for identifying hematopoietic stem cells are provided and isolated hematopoietic stem cells are also provided.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method of blocking vascular leakage using an anti-ANG2 antibody
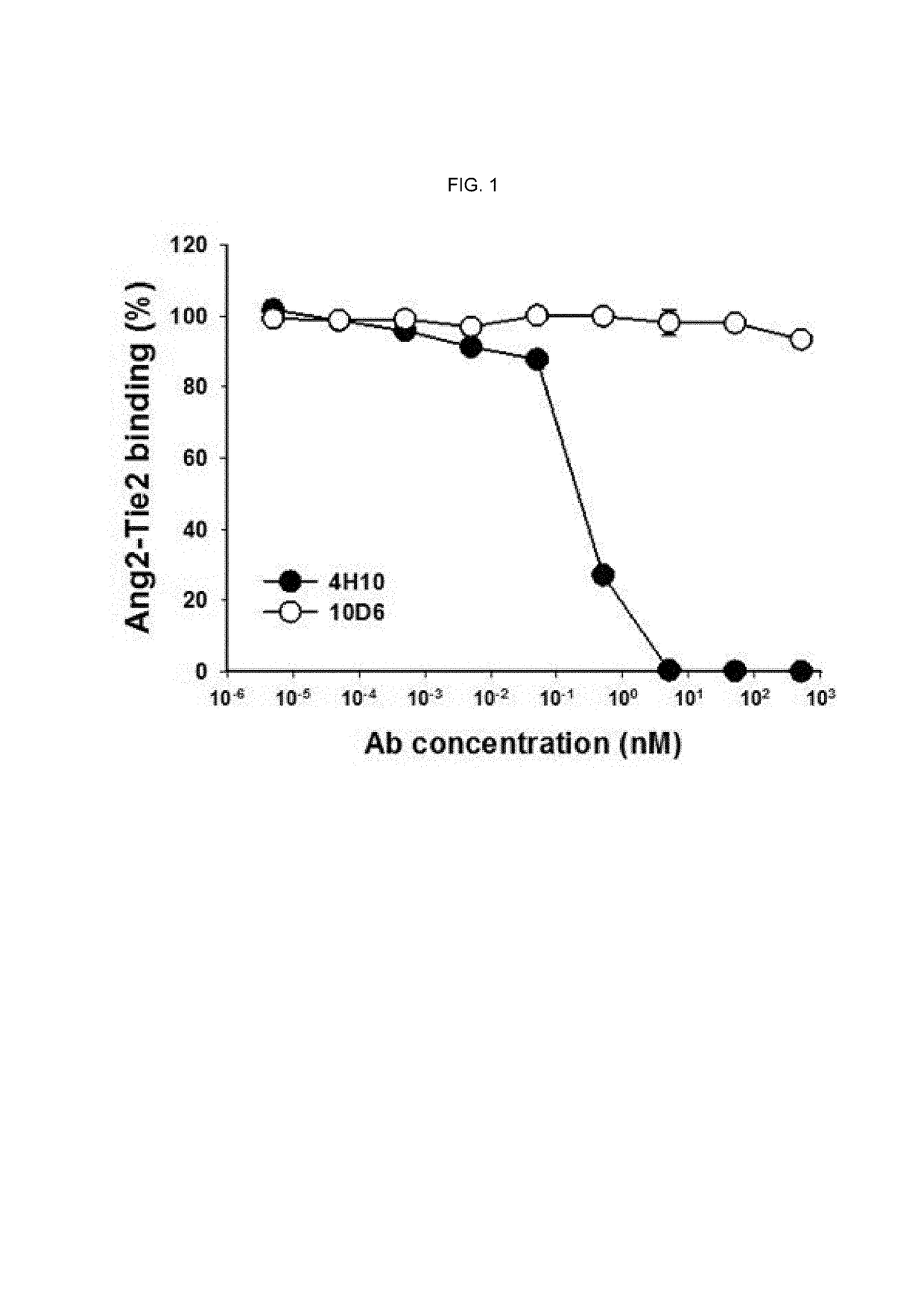
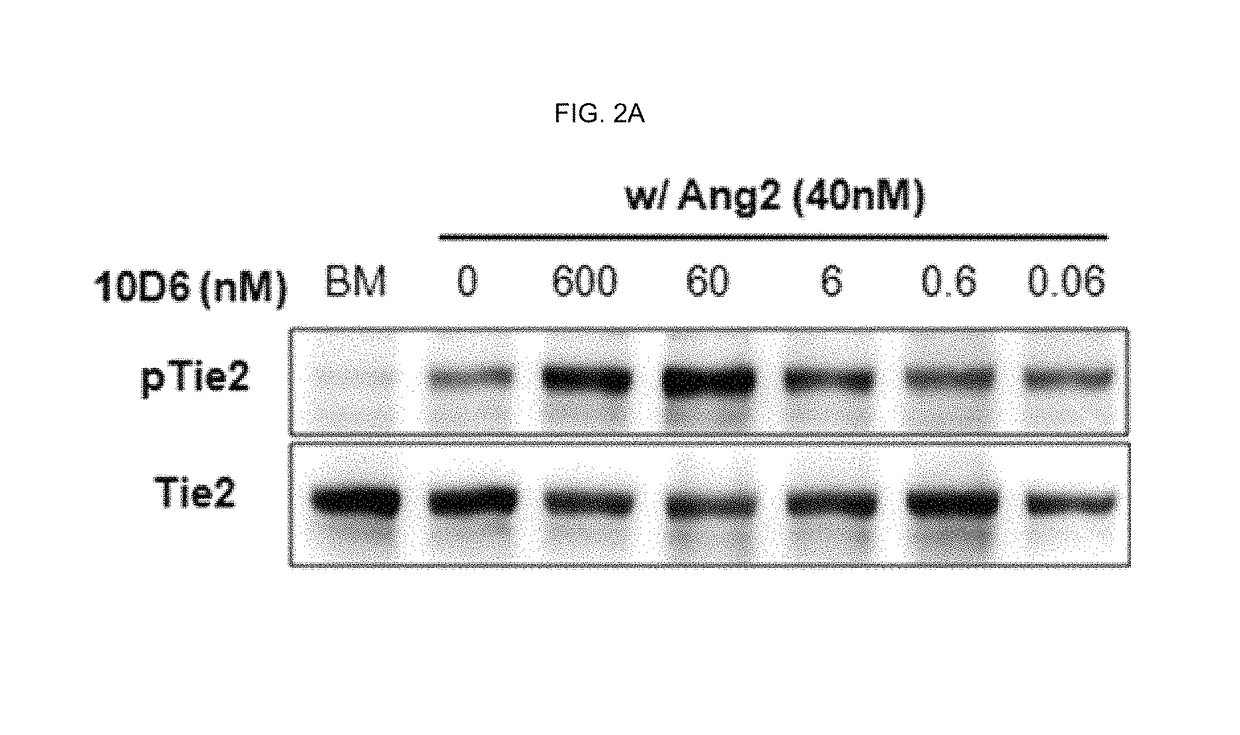
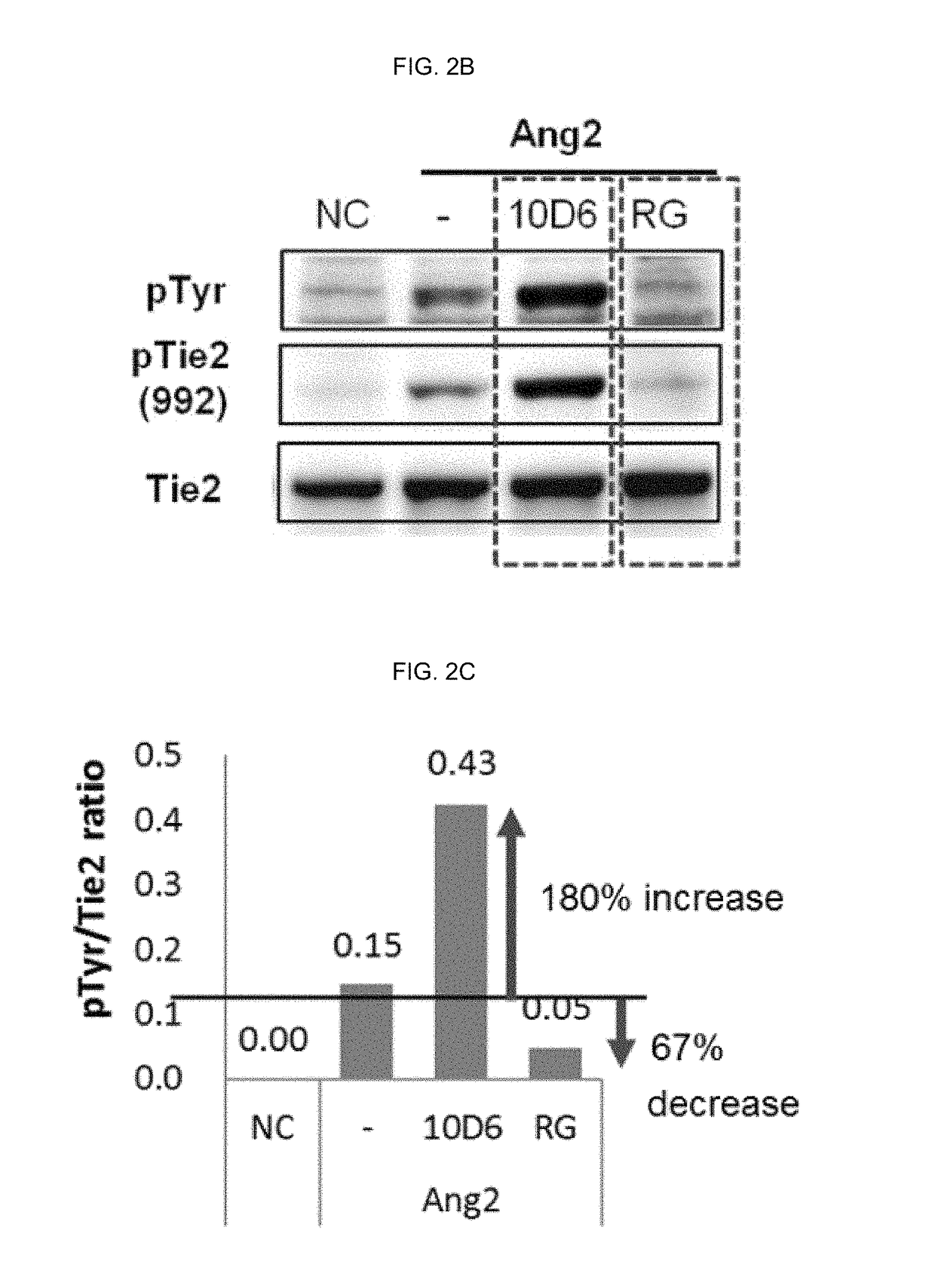
A method for the prevention and / or treatment of a disease accompanied by vascular leakage and / or vascular inflammation comprising administering an anti-Ang2 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof that specifically binds to an angiogenesis-inducing factor Angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) and forms a complex with a Tie2 receptor and Ang2.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
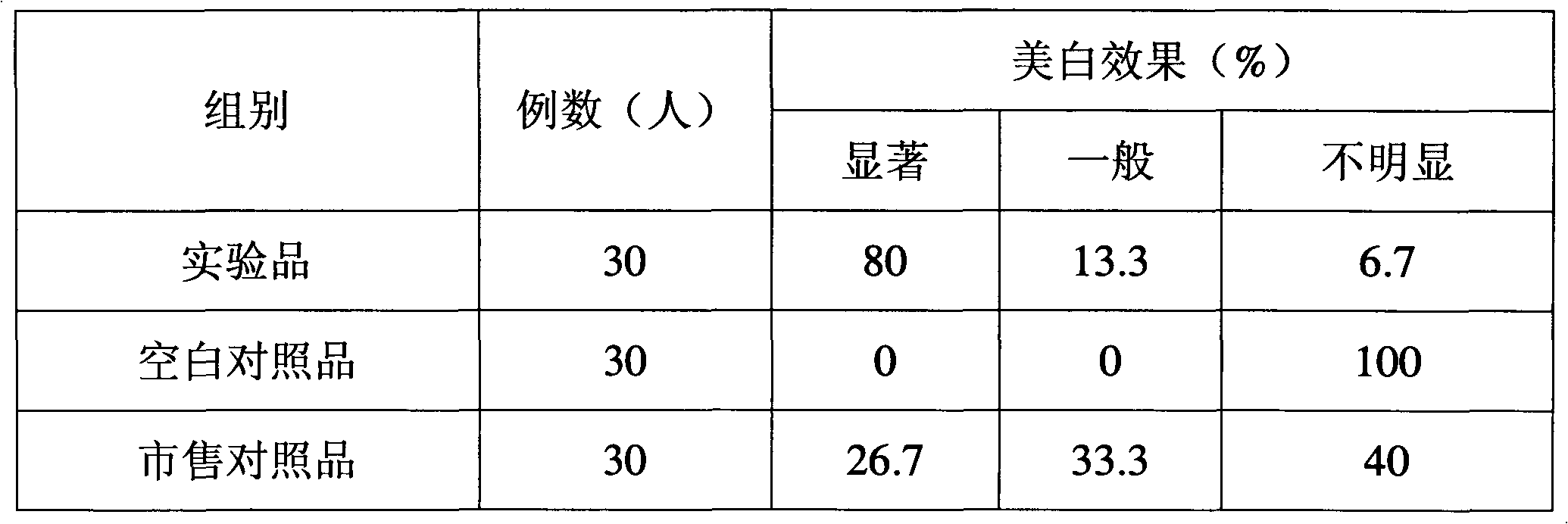
Freeze-dried gel cosmetic and preparation method and application thereof
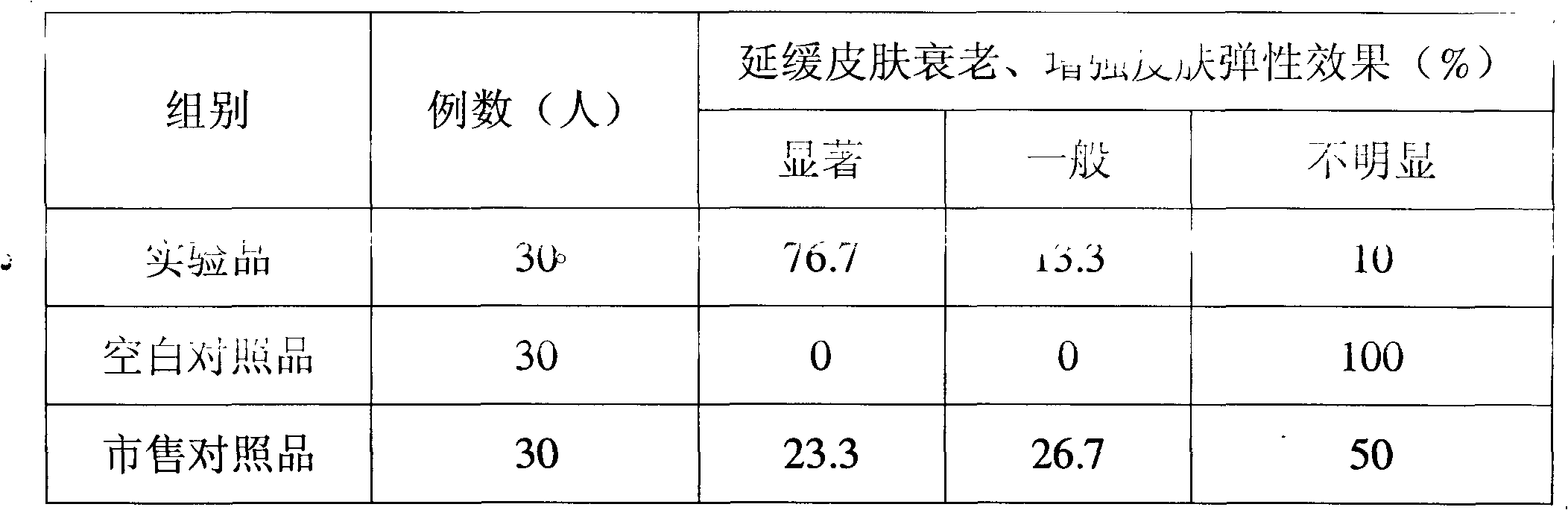
ActiveCN101953757AExtended shelf lifeIncrease elasticityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin elasticityHeparin sodium
The invention discloses a freeze-dried gel cosmetic and preparation method and application thereof. The freeze-dried gel cosmetic of the invention comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.5-3% of chitosan, 1-10% of stabilizing agent, 0.0001-0.001% of coenzyme Q10, 0.00001-0.001% of metallothionein, 0.00001-0.001% of recombinant human angiopoietin-1 and 0.01-0.2% of low molecular weight heparin sodium, the balance of water. The freeze-dried gel cosmetic of the invention can be used for daily skin care and has the beauty effects of whitening, postponing senility and enhancing skin elasticity.
Owner:广州泰润合投资有限公司
Antiobesity drug
An antiobesity drug, a remedy for diabetes and / or a remedy for hyperlipemia containing angiopoietin-related growth factor (AGF) or a polynucleotide encoding the same as the active ingredient; a functional food or a health food containing AGF as the active ingredient and having a function of ameliorating obesity, diabetes and / or hyperlipemia imparted thereto; a method of preventing or treating obesity, diabetes and / or hyperlipemia which comprises administering AGF or a polynucleotide encoding the same; and utilization of AGF or a polynucleotide encoding the same for producing an antiobesity drug, a remedy for diabetes and / or a remedy for hyperlipemia.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
Angiopoietin-based interventions for treating cerebral malaria
ActiveUS9592271B2Improving and increasing survivalPrevent leakageAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMalariaCerebral Malaria
The present invention provides methods for treating, preventing or reducing the severity of cerebral malaria. The methods of the present invention comprise administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a modified angiopoietin molecule such as AngF1-Fc-F1.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +1
Preparation method and kit of human stem cell with prolonged service life and enhanced angiogenesis
ActiveCN105018524AExtend your lifeEnhanced angiogenesisMammal material medical ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseVirus type
The invention provides a preparation method of a human stem cell with prolonged service life and enhanced angiogenesis. The preparation method comprises the following steps of establishing gene segments of a RNA (ribonucleic acid) testis signal transduction and activating body and angiogenin-1; and recombining the gene segments to a virus expression vector. The service life of the cell can be prolonged by transfection of the human stem cell, the angiogenesis of the human stem cell is improved, and tumorigenesis is avoided. The invention also provides a kit of the human stem cell with the prolonged service life and the enhanced angiogenesis, and the human stem cell is expected to treat ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases well.
Owner:广州赛琅生物技术有限公司
Protection of cardiac myocardium
InactiveUS20060019891A1Improve survivalPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesVascular tissuePlatelet
The invention provides compositions and methods for protecting vascular tissues from injury that occurs, for example, during occlusion of one or more arteries. In some embodiments, the injury is myocardial infarction. The compositions of the invention include combinations of platelet derived growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and angiopoietin-2.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Sustained release preparation for therapy of coronary stenosis or obstruction
InactiveUS20060148691A1Prominent effectIncrease blood flowPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCoronary arteriesAngiogenesis Factor
A pharmaceutical composition for therapy of coronary artery narrowing or blockage, which comprises a sustained release preparation containing an angiogenesis factor or a gene encoding the same and a gelatin hydrogel is disclosed. Examples of the angiogenesis factor which may be used include e.g., bFGF and other FGFs, VEGF, HGF, PDGF, TGF, angiopoietin, HIF, cytokine, chemokine, adrenomeduline and the like.
Owner:MEDGEL CORP
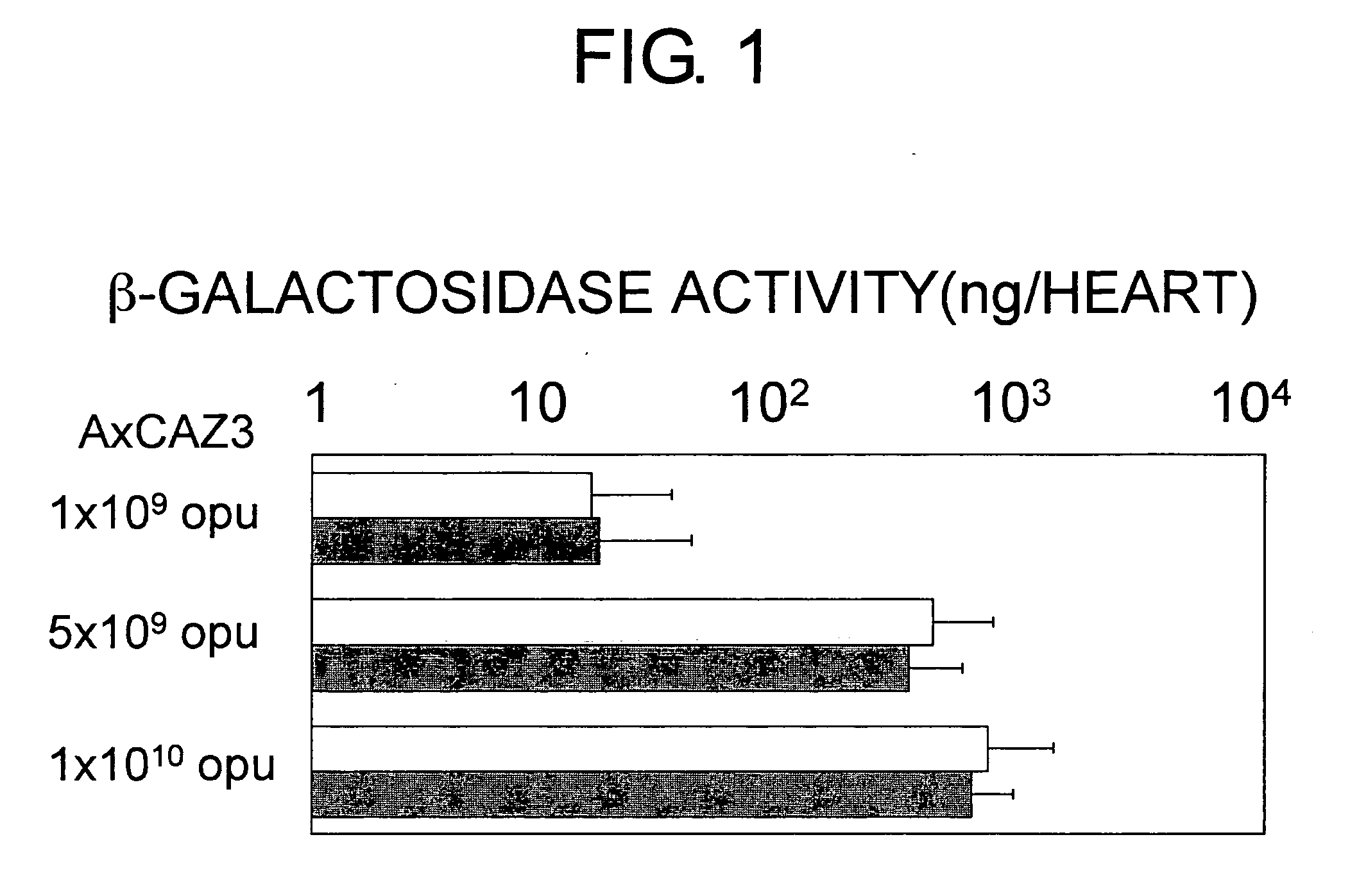
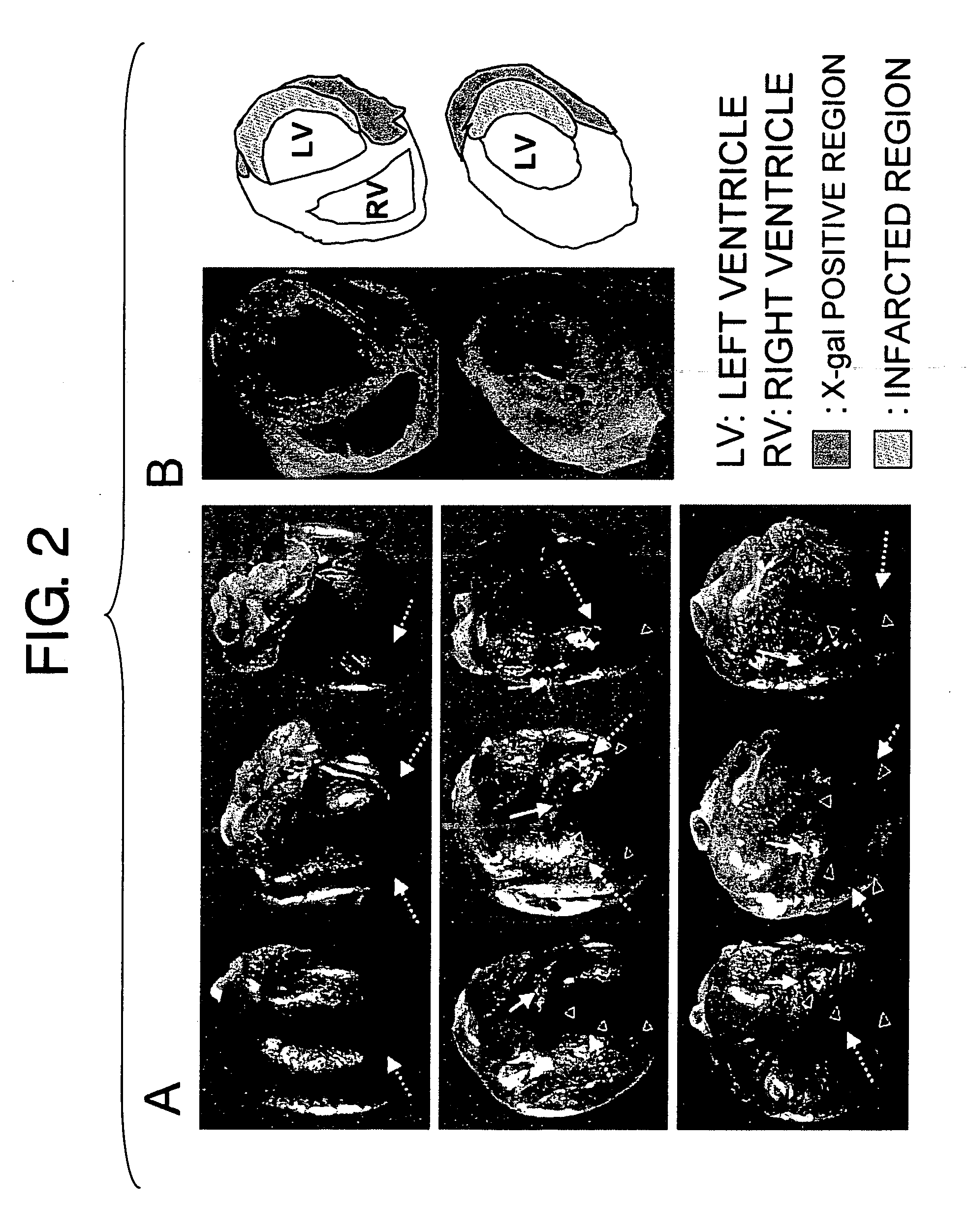
Method for treating ischemic diseases
InactiveUS20070036756A1Suppresses necrosisFunction increaseBiocideVirusesLimb ischemiaMortality rate
The present invention provides methods for treating ischemic diseases, which comprise the step of administering angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) or an Ang1-encoding vector. The present invention also provides ischemic disease treatment kits which comprise Ang1. Ang1-expressing vectors were prepared, and each was administered alone intramyocardially to rats in the acute phase of myocardial infarction to express Ang1 in the local cardiac muscle. The results indicate that marked effects have been obtained, such as decrease in post-infarction mortality rate, increase in blood vessel number in myocardium, reduction of myocardial infarct size, and improvement of cardiac function. Administration of the required VEGF was not necessary for the angiogenic activity of Ang1. Furthermore, when an Ang1viral expression vector was administered alone to an animal model of severe limb ischemia, in which ischemia had been induced by arterial ligation, a remarkable limb salvage effect was obtained. The Ang1 gene therapy is excellent as a safe and effective therapeutic method for ischemic diseases such as ischemic heart diseases and limb ischemia.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
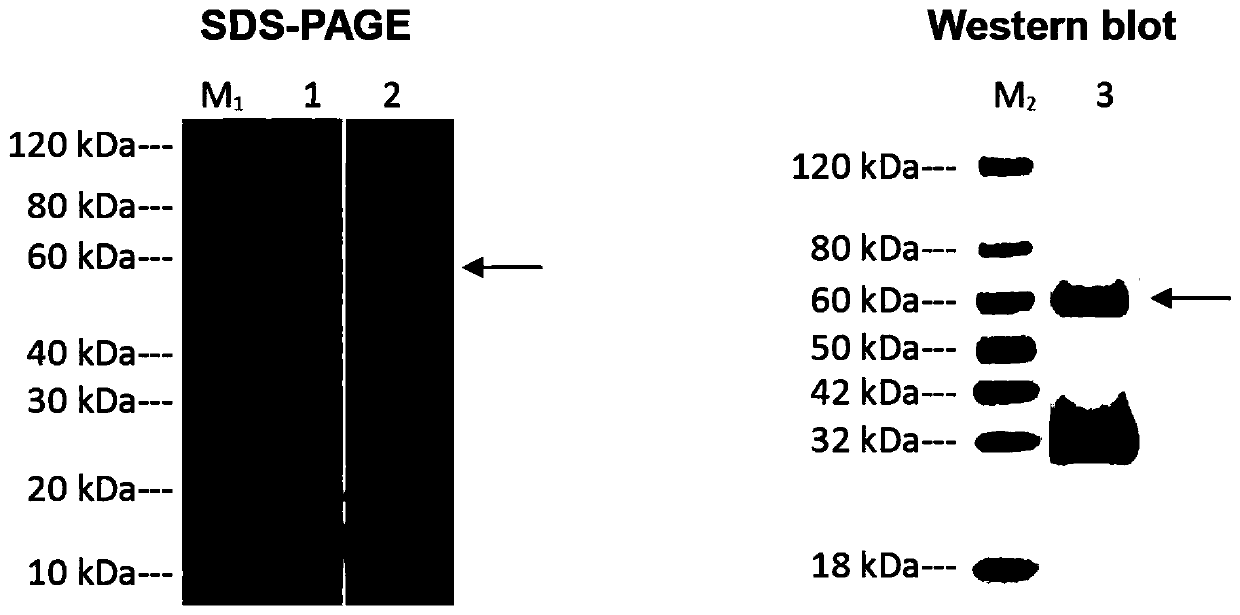
Anti-ANGPTL3 (angiopoietin-like protein) monoclonal antibody and purpose thereof in preparing medicine capable of treating nephrotic syndrome
ActiveCN110938144AAntagonistic injuryAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibodies monoclonal
The invention discloses an anti-ANGPTL3 (angiopoietin-like protein) monoclonal antibody. The heavy chain amino acid sequence of the monoclonal antibody is SEQ ID: No 1, the light chain amino acid sequence of the monoclonal antibody is SEQ ID: No 2, the heavy chain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the monoclonal antibody is SEQ ID: No 3, and the light chain DNA sequence of the monoclonal antibody is SEQ ID: No 4. The invention also discloses application of the anti-ANGPTL3 monoclonal antibody in preparing a medicine capable of treating a nephrotic syndrome. The anti-ANGPTL3 monoclonal antibody specifically identifies an ANGPTL3, blocks a fibrinogen-like structural domain of the ANGPTL3, and antagonizes the injury of the ANGPTL3 to sertoli cells. The invention can be used for detecting the ANGPTL3 and is hopefully used for treating nephrotic syndrome proteinuria.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Novel cheese and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20150343029A1Prevention and treatmentReduce usagePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesAngiogeninHydrolysate
The invention relates to a cheese includes angiogenin and / or angiogenin hydrolysate in an amount of 6.5 mg / 100 g to 160 mg / 100 g, and lactoperoxidase and / or lactoperoxidase hydrolysate in the mass ratio to the angiogenin and / or angiogenin hydrolysate of 0.3 to 33.
Owner:SNOW BRAND MILK PROD CO LTD
Pharmaceutical composition for treatment of corneal endothelial wounds containing angiogenin
InactiveUS9050301B2Improve proliferation and migrationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCorneal endothelial woundCorneal endothelial cell
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition for treating corneal endothelium wounds, the composition including angiogenin as an effective ingredient. The present invention relates to a new topical therapeutic use of angiogenin for treatment of corneal endothelium wounds, wherein the angiogenin that is generally known to be involved in angiogenesis activates a PI3K / Akt / eNOS pathway thereof in ocular corneal endothelium to increase migration and proliferation of corneal endothelial cells that are not capable of self-proliferation and to promote prevention and treatment of corneal endothelial cell wounds.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +2
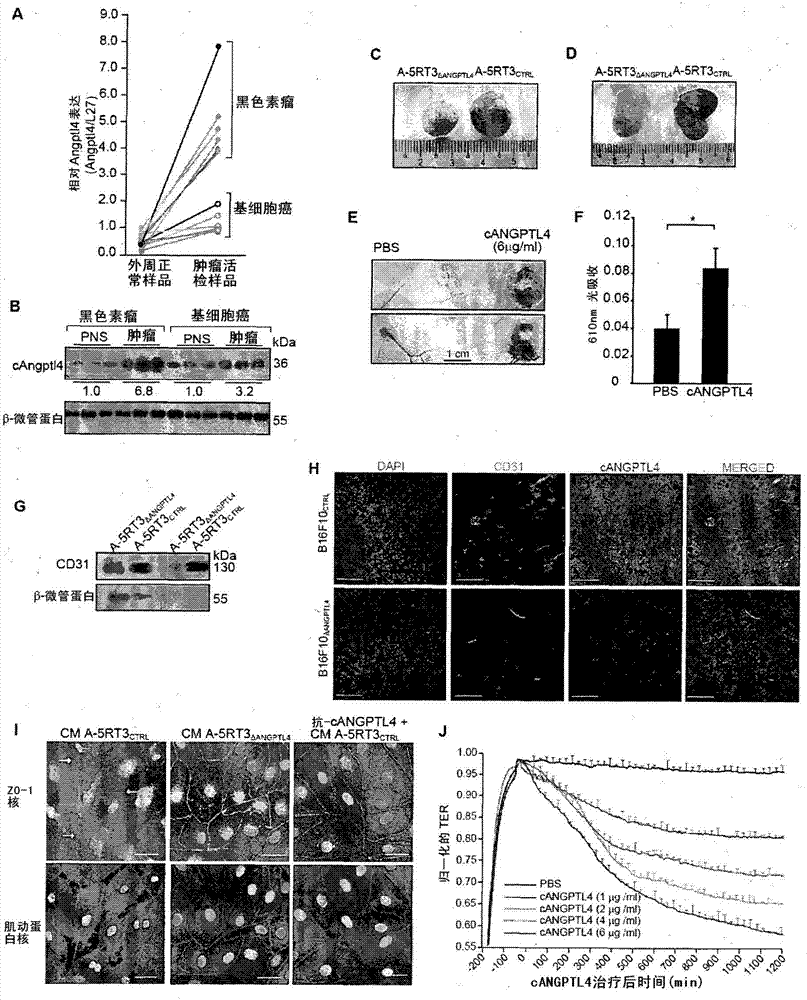
Angiopoietin-like 4 and its use in modulating cell leakiness
Vascular disruption induced by interactions between tumor-secreted permeability factors and adhesive proteins on endothelial cells facilitates metastasis. The role of tumor secreted angiopoietin-like 4 (cANGPTL4) in vascular leakiness and metastasis is controversial due to the lack of understanding of how cANGPTL4 modulates vascular integrity. Here, we show that cANGPTL4 instigated the disruption of endothelial continuity by directly interacting with three novel binding partners, integrin [alpha]5[beta]1, VEcadherin and claudin-5, in a temporally sequential manner, thus facilitating metastasis. We showed that cANGPTL4 binds and activates integrin [alpha]5[beta]1-mediated Rac1 / PAK signaling to weaken cell-cell contacts. Subsequently, cANGPTL4 is associated with and declusters VE-cadherin and claudin-5, leading to endothelial disruption. Interfering with the formation of these cANGPTL4 complexes delayed vascular disruption. In vivo vascular permeability and metastatic assays performed using ANGPTL4-knockout and wild-type mice injected with either control or ANGPTL4-knockdown tumors confirmed that cANGPTL4 induced vascular leakiness and facilitated lung metastasis in mice. Therefore, our findings elucidate how cANGPTL4 induces endothelial disruption. Our findings have direct implications for targeting cANGPTL4 to treat cancer and other vascular pathologies.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
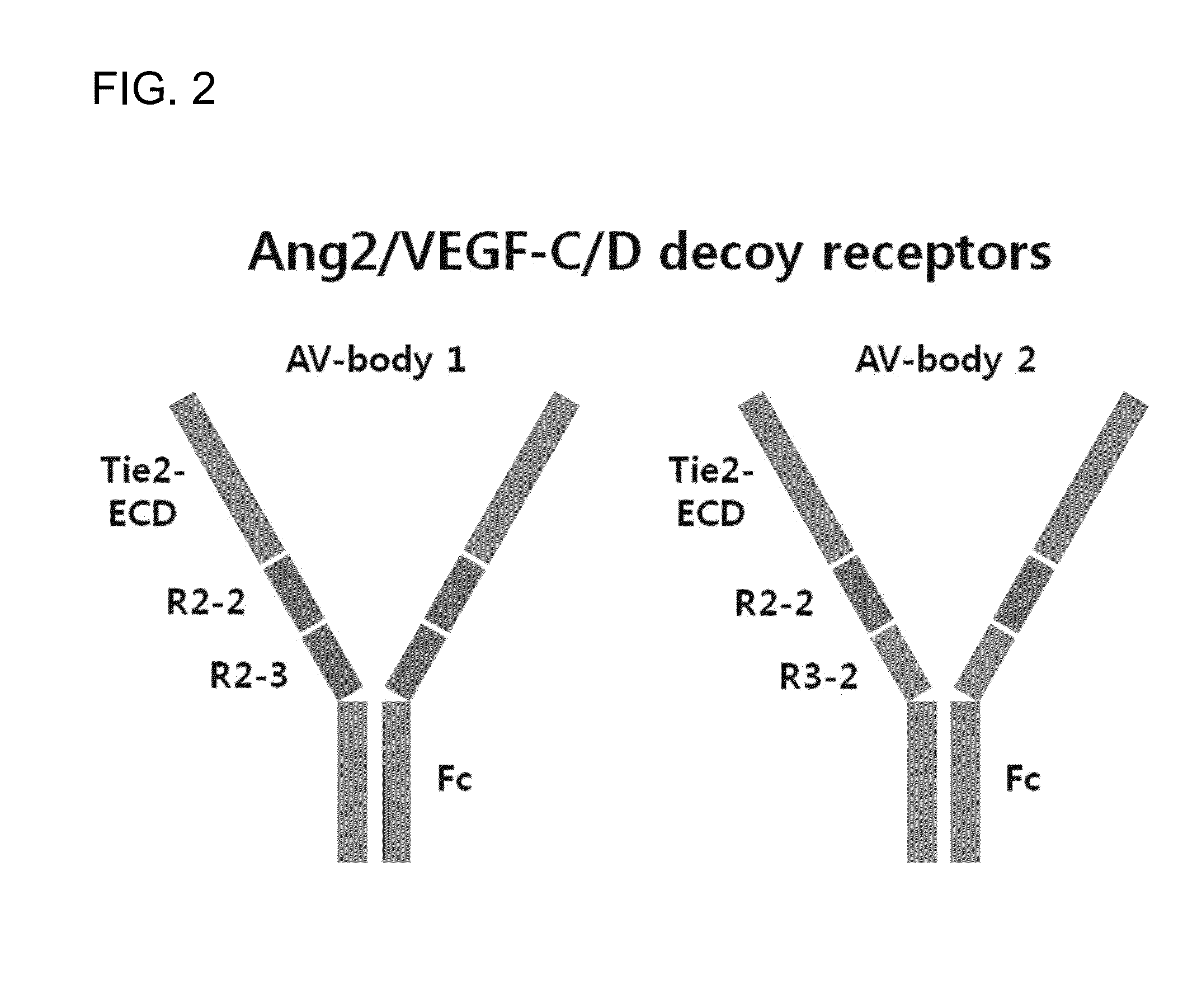
Fusion polypeptide inhibiting vegf-c, vegf-d and/or angiopoietin-2, and use thereof
ActiveUS20150023958A1Prevent proliferationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAngiopoietin 2
A fusion polypeptide capable of binding simultaneously to angiopoietin 2, VEGF-C and VEGF-D; or capable of binding simultaneously to VEGF-C and VEGF-D, and methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
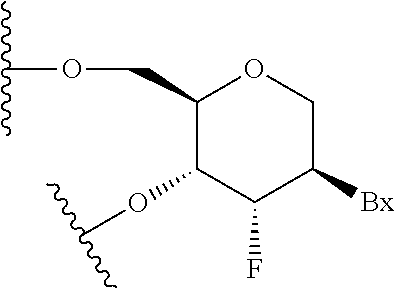
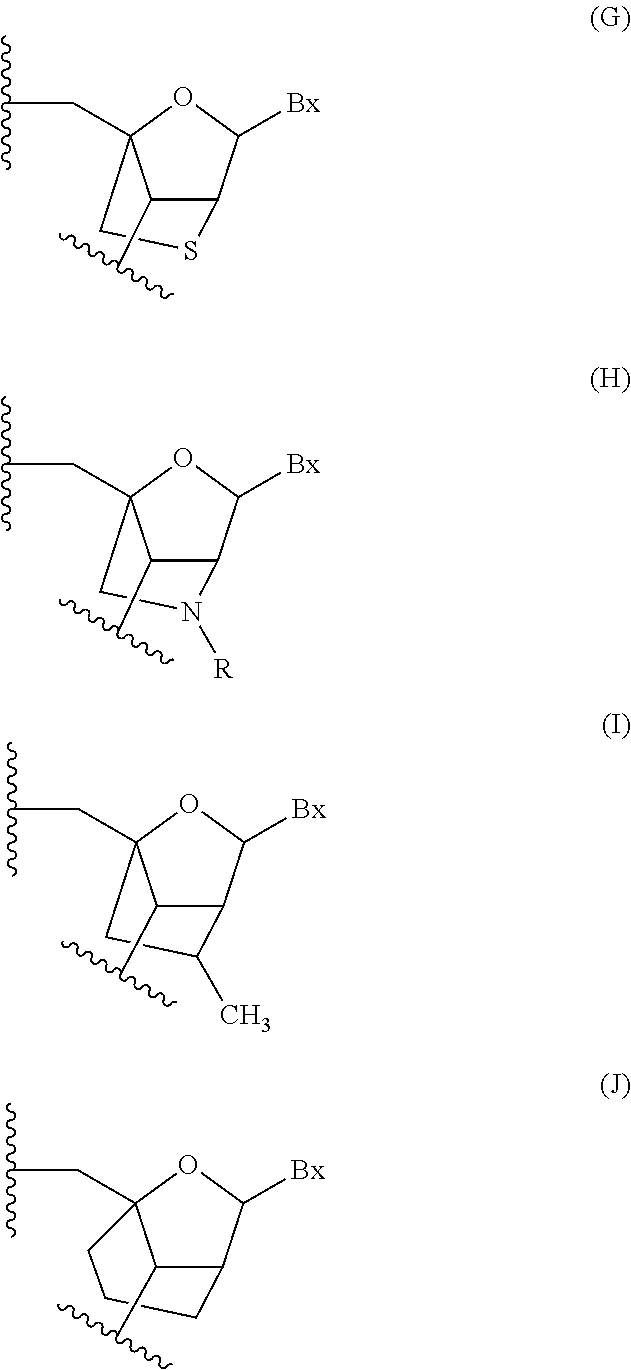
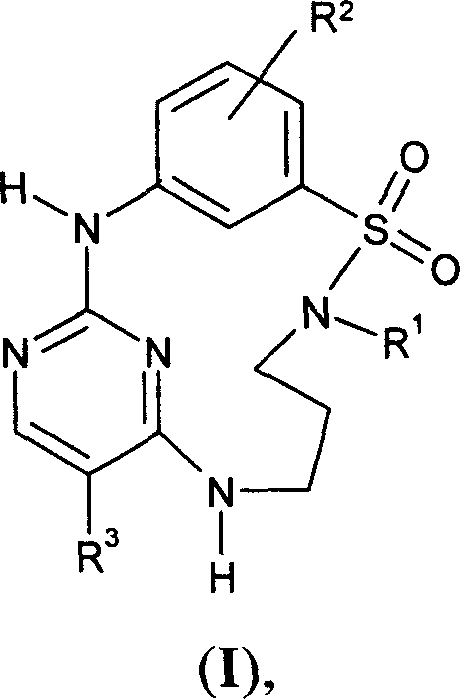
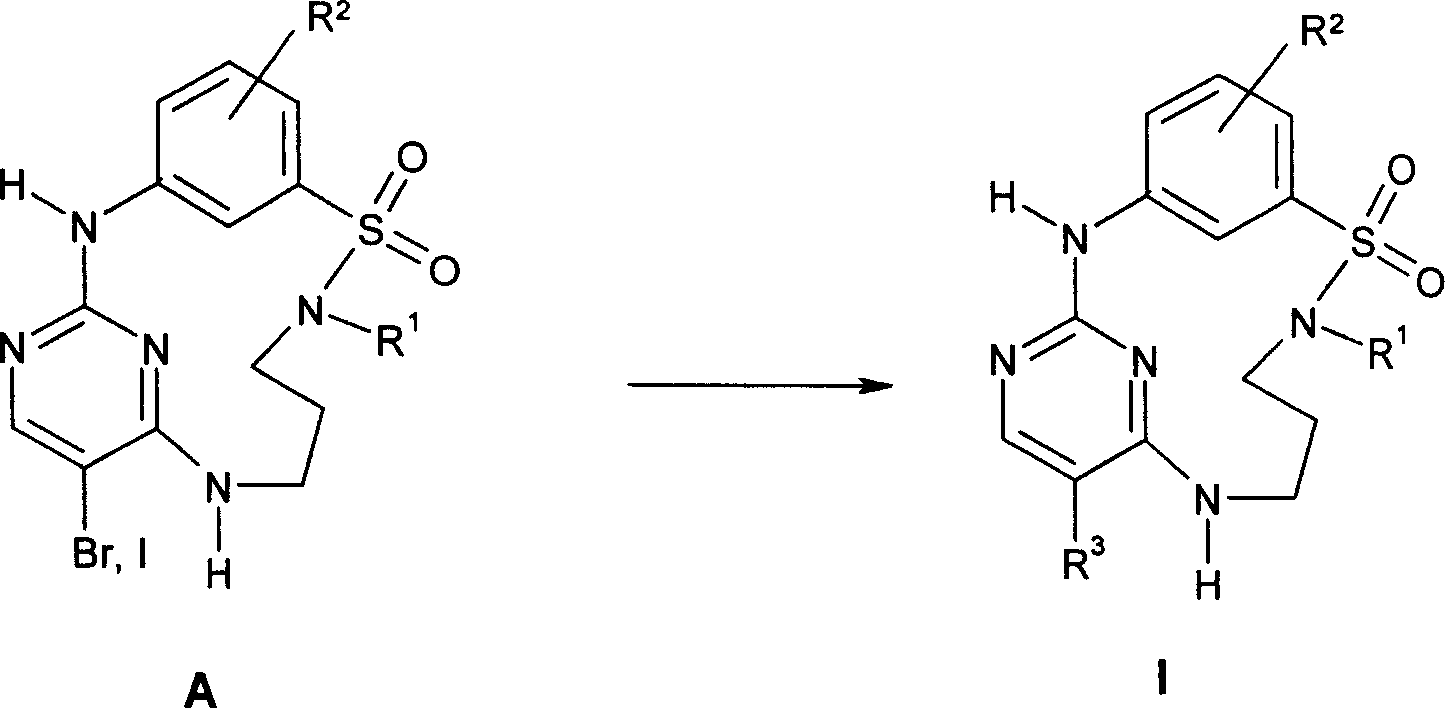
Sulfonamido-macrocycles as tie2 inhibitors
The invention relates to sulfonamido-macrocycles according to the general Formula I and the salts thereof, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the sulfonamido-macrocycles and to a method of preparing the sulfonamido-macrocycles as well as the use thereof for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of diseases of dysregulated vascular growth or of diseases which are accompanied with dysregulated vascular growth, wherein the compounds effectively interfere with angiopoietin and therefore influence Tie2 signalling, wherein R<1>, R<2> and R<3> have the meaning as given in the specification and the claims.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com