Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Anatomical part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
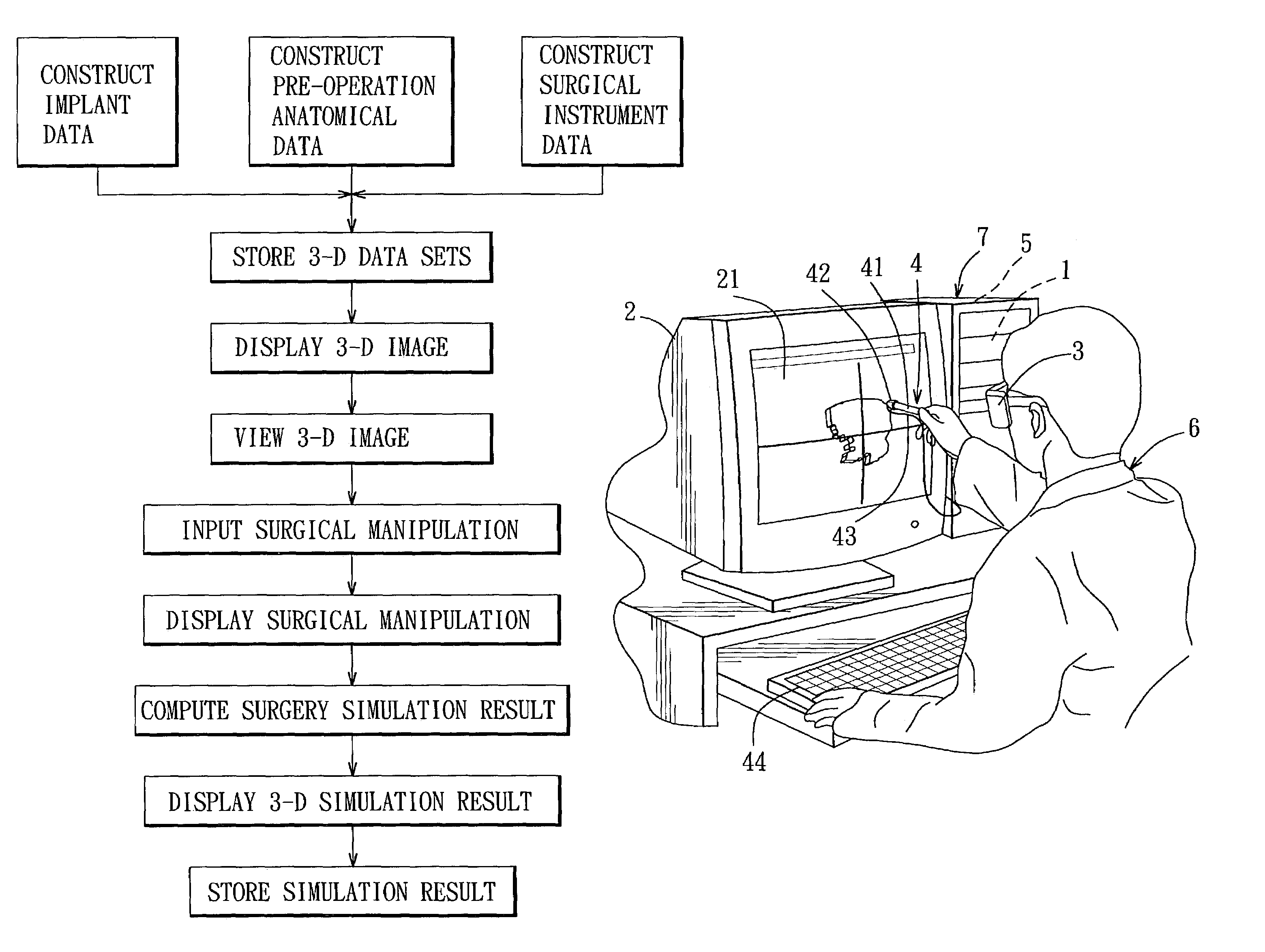
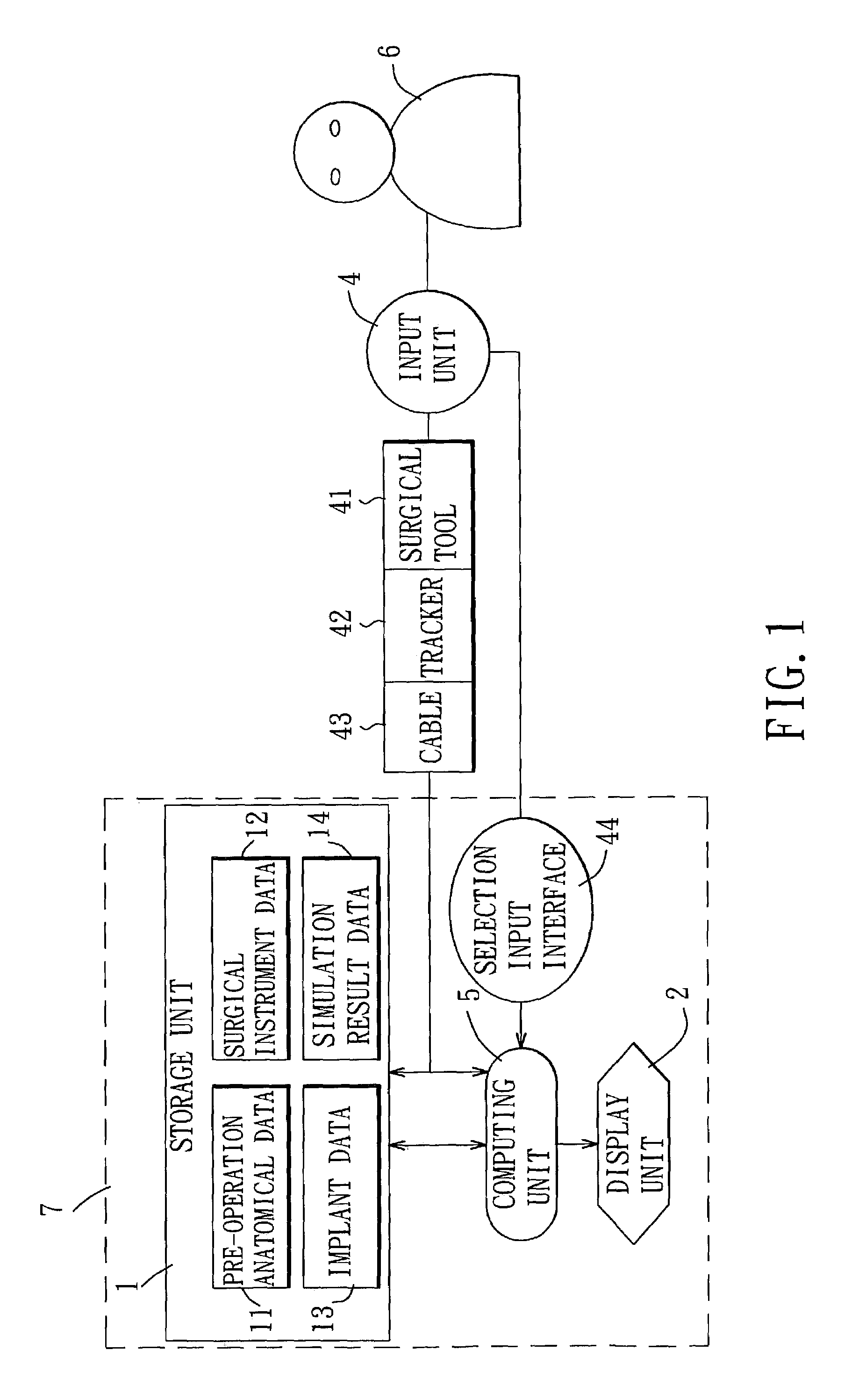
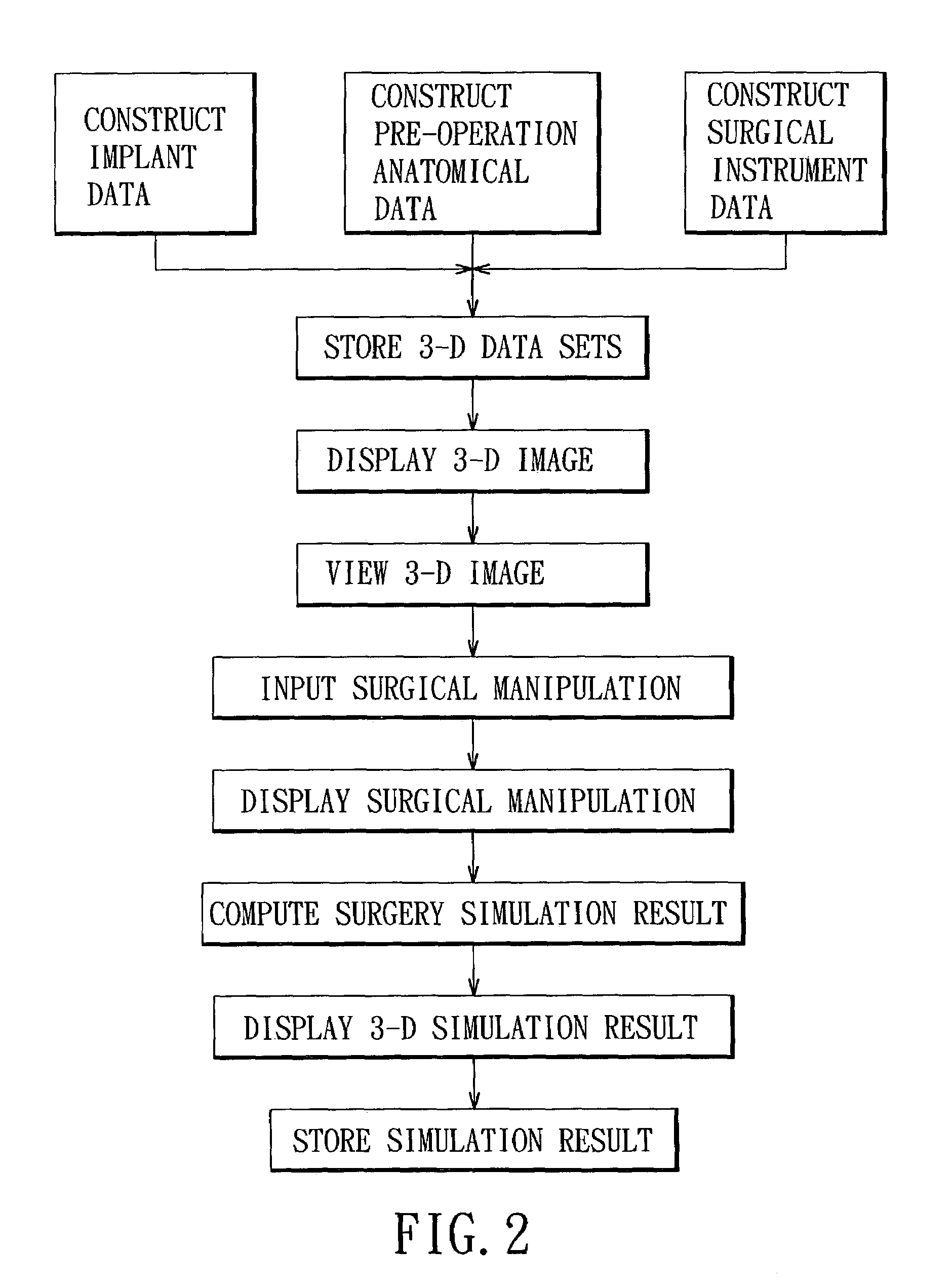
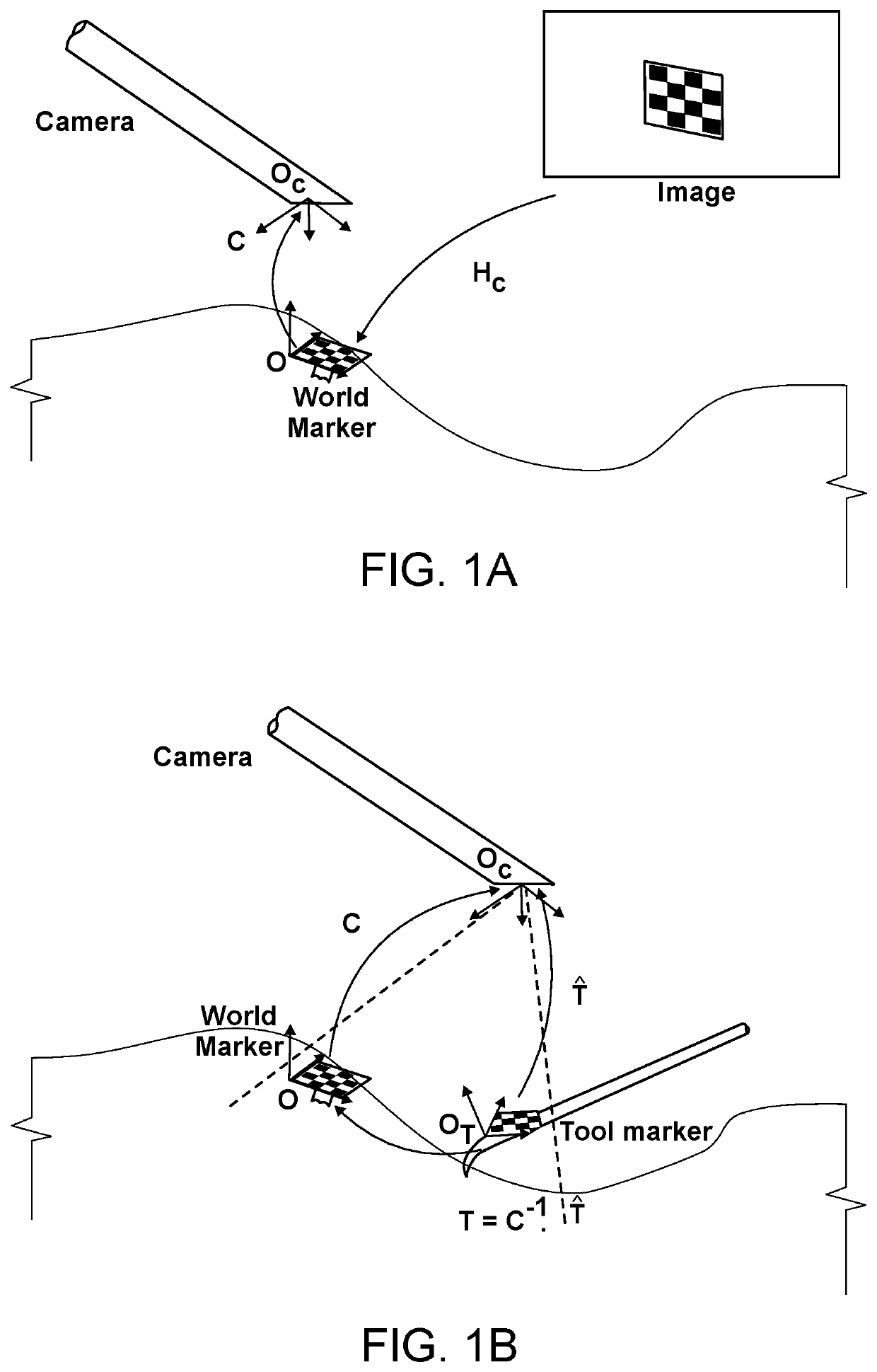
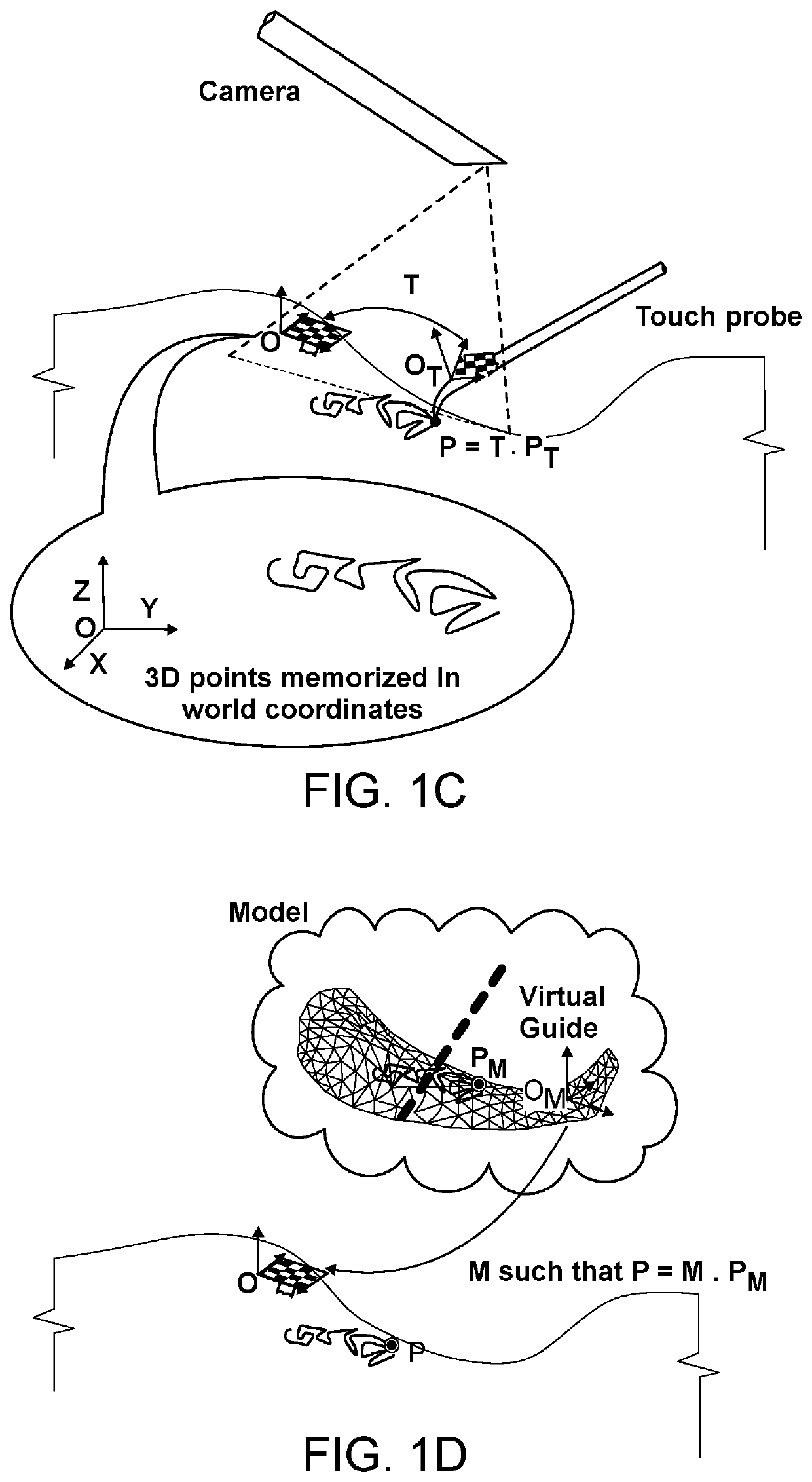
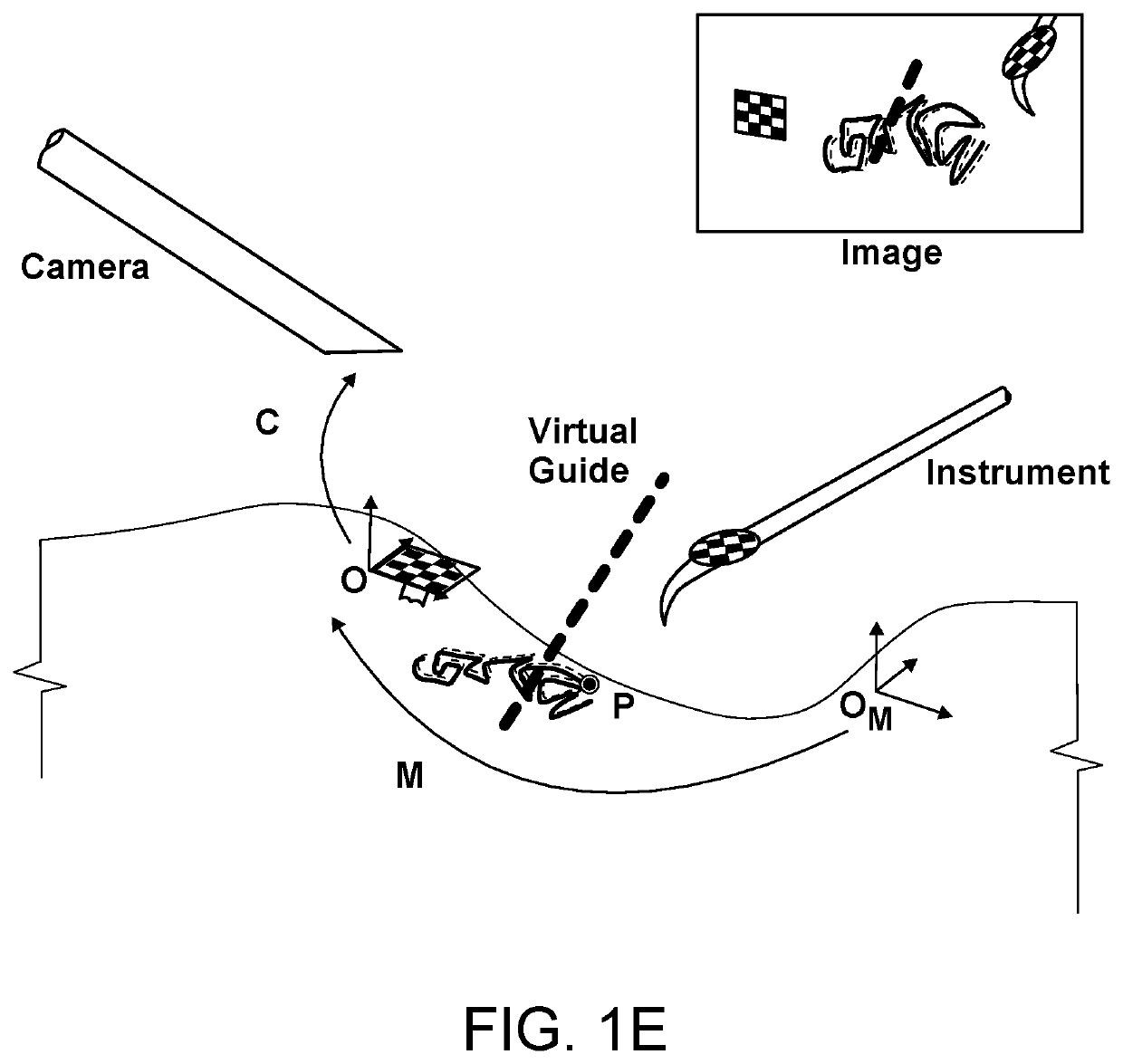
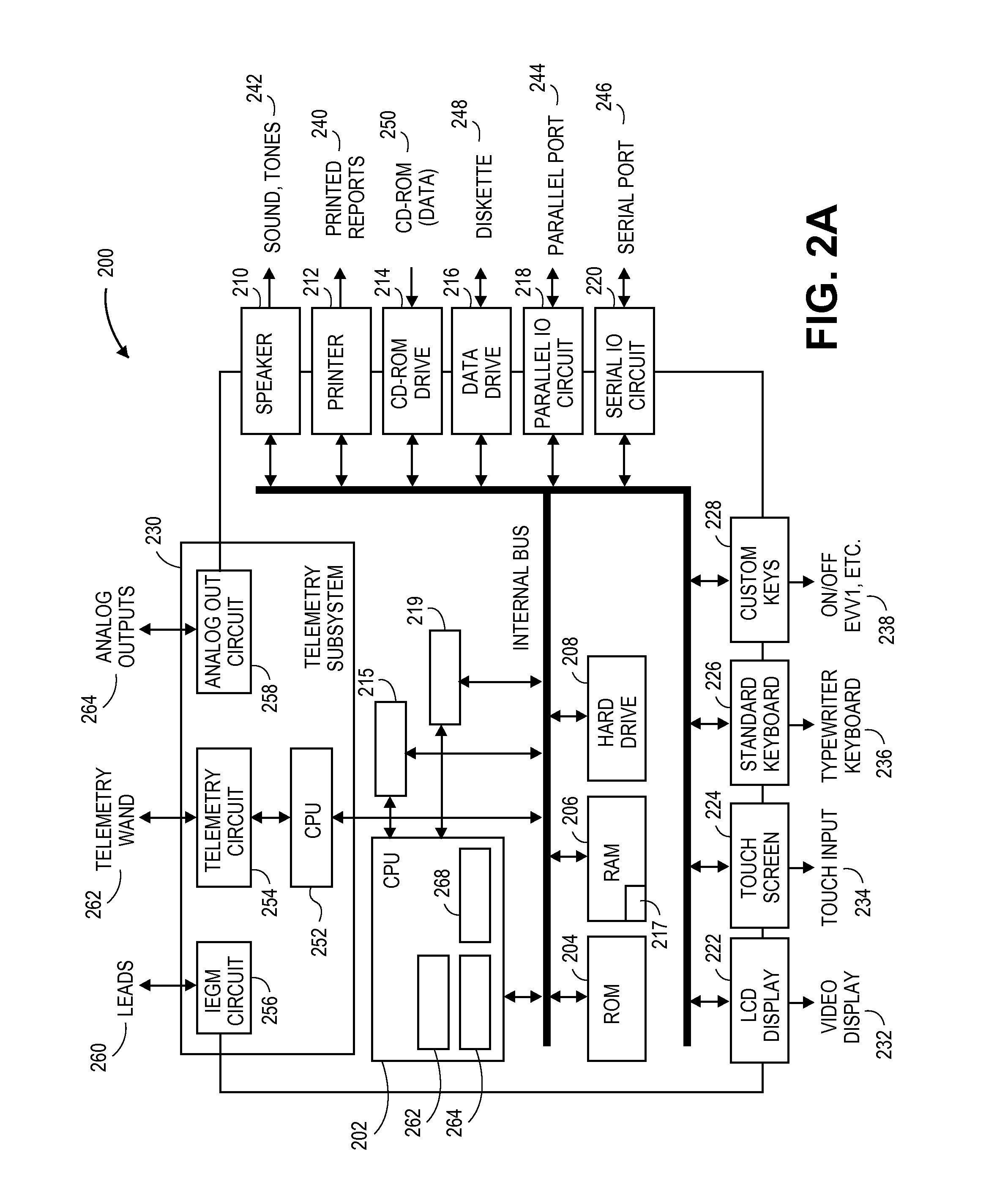
Three-dimensional surgery simulation system
ActiveUS7121832B2High simulationImprove accuracyCathode-ray tube indicatorsEducational modelsData setAnatomic Site
A three-dimensional surgery simulation system is provided for generating a three-dimensional surgery simulation result of an anatomical part undergoing a simulated surgical procedure. The system includes a display unit, a three-dimensional visual imaging unit, a storage unit for storing a plurality of voxelized three-dimensional model image data sets, an input unit for controlling progress of the simulated surgical procedure, and a computing unit for computing the simulation result data in accordance with the voxelized three-dimensional model image data sets and under the control of the input unit, and for controlling the display unit to permit viewing of the surgery simulation result in three-dimensional form thereon by an operator wearing the visual imaging unit.
Owner:OSSIM TECH INC
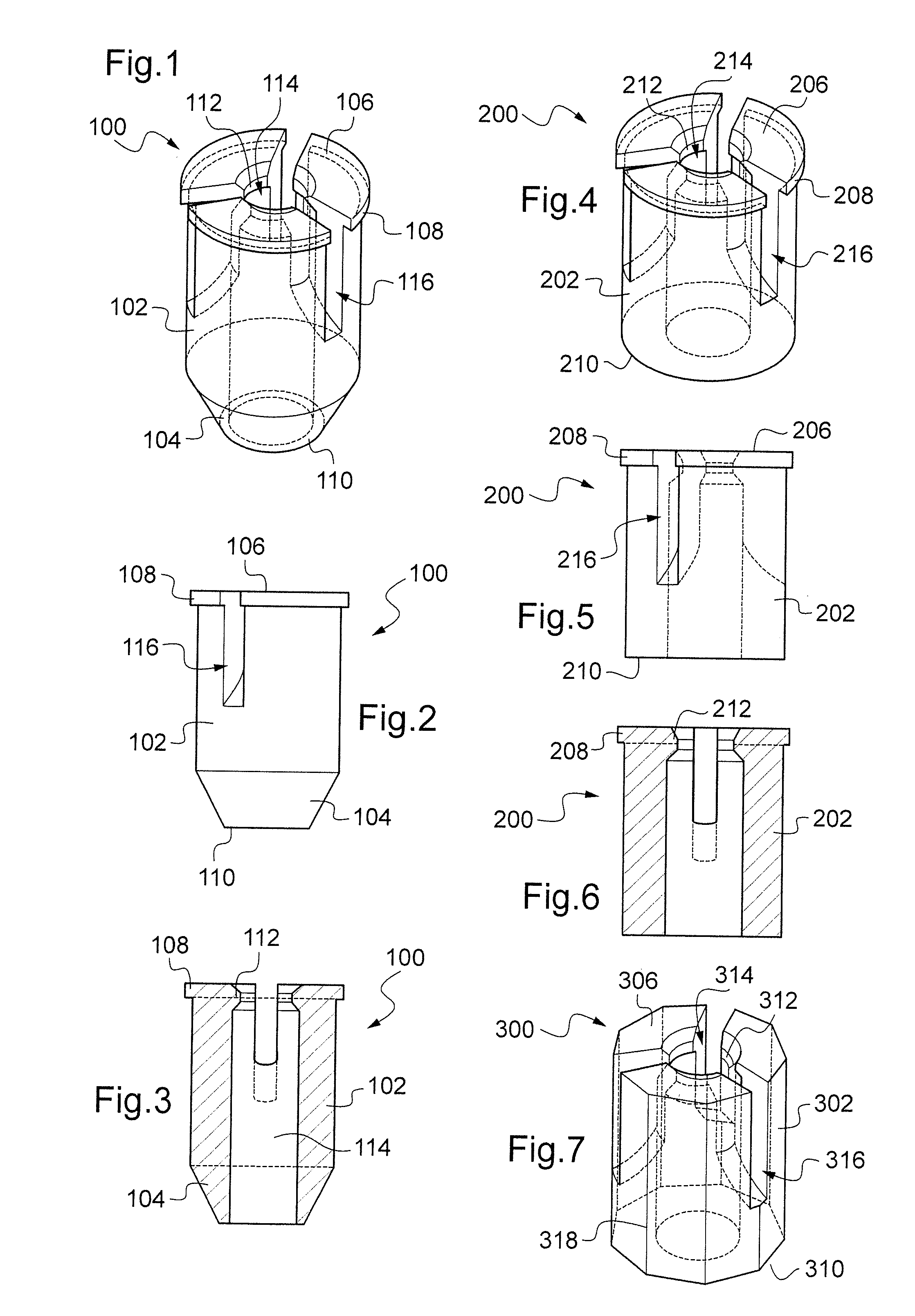
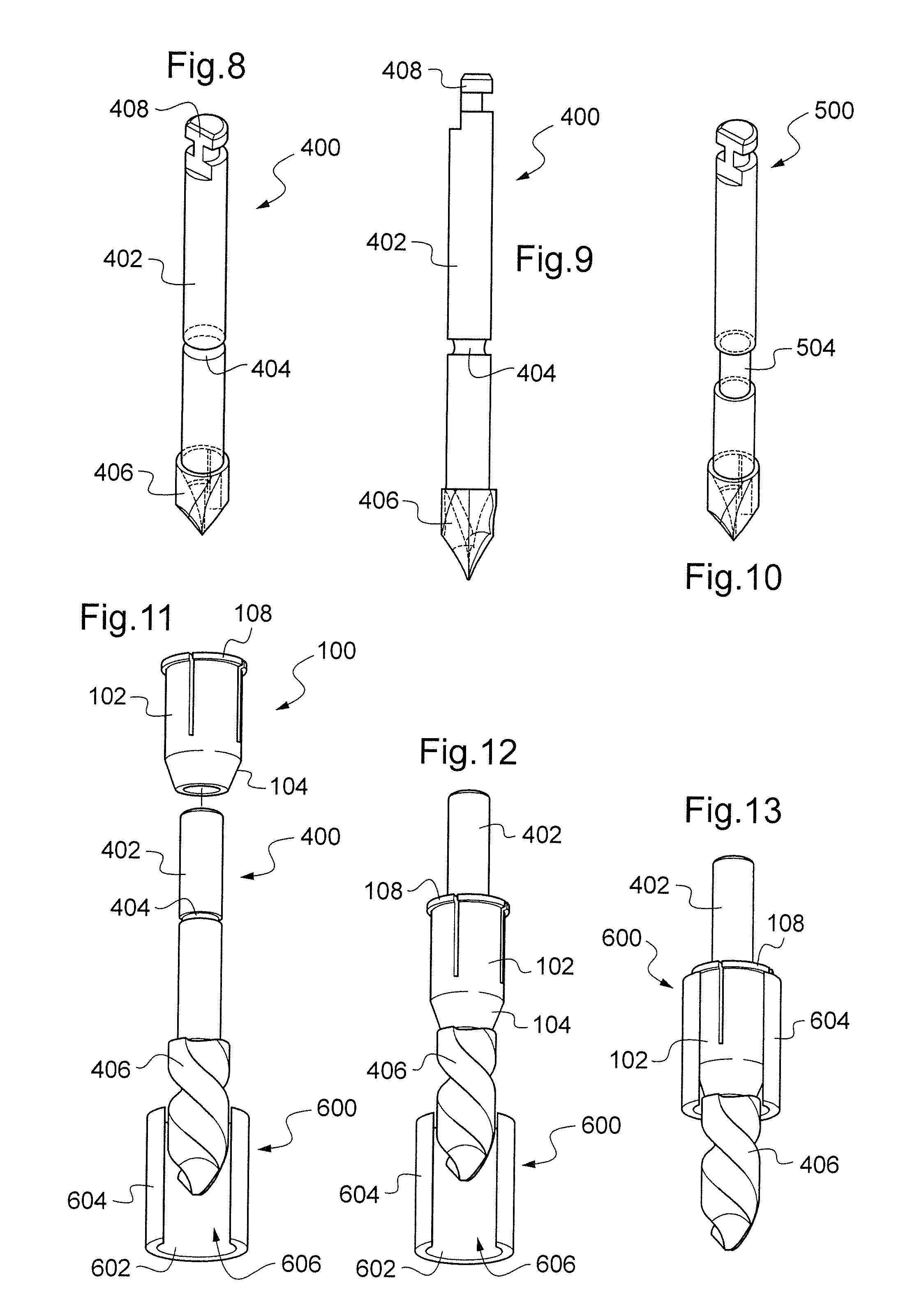
Drill assistance kit for implant hole in a bone structure
InactiveUS20110238071A1Improve general conditionOvercomes drawbackBoring toolsProsthesisBone structureAnatomic Site
The present invention provides a kit for bone surgery comprising a chirurgical drill and a base frame for positioning of said drill on an anatomical part of a patient. The base frame comprises at least one guiding tube with a cylindrical inner surface of predetermined diameter and also comprises a longitudinal cutout for direct view of the drilling site. The kit further comprises a burr-ring with a cylindrical outer surface of predetermined diameter arranged to be placed around the chirurgical drill. The diameter of the cylindrical outer surface of the burr-ring is slightly less than the diameter of the cylindrical inner surface of the guiding tube such that the burr-ring and the guiding tube are at most in a two-degree of freedom relationship along the longitudinal axis of the guiding tube when the burr-ring is engaged in the guiding tube. The invention also provides a bone surgery method using the kit.
Owner:POSITDENTAL
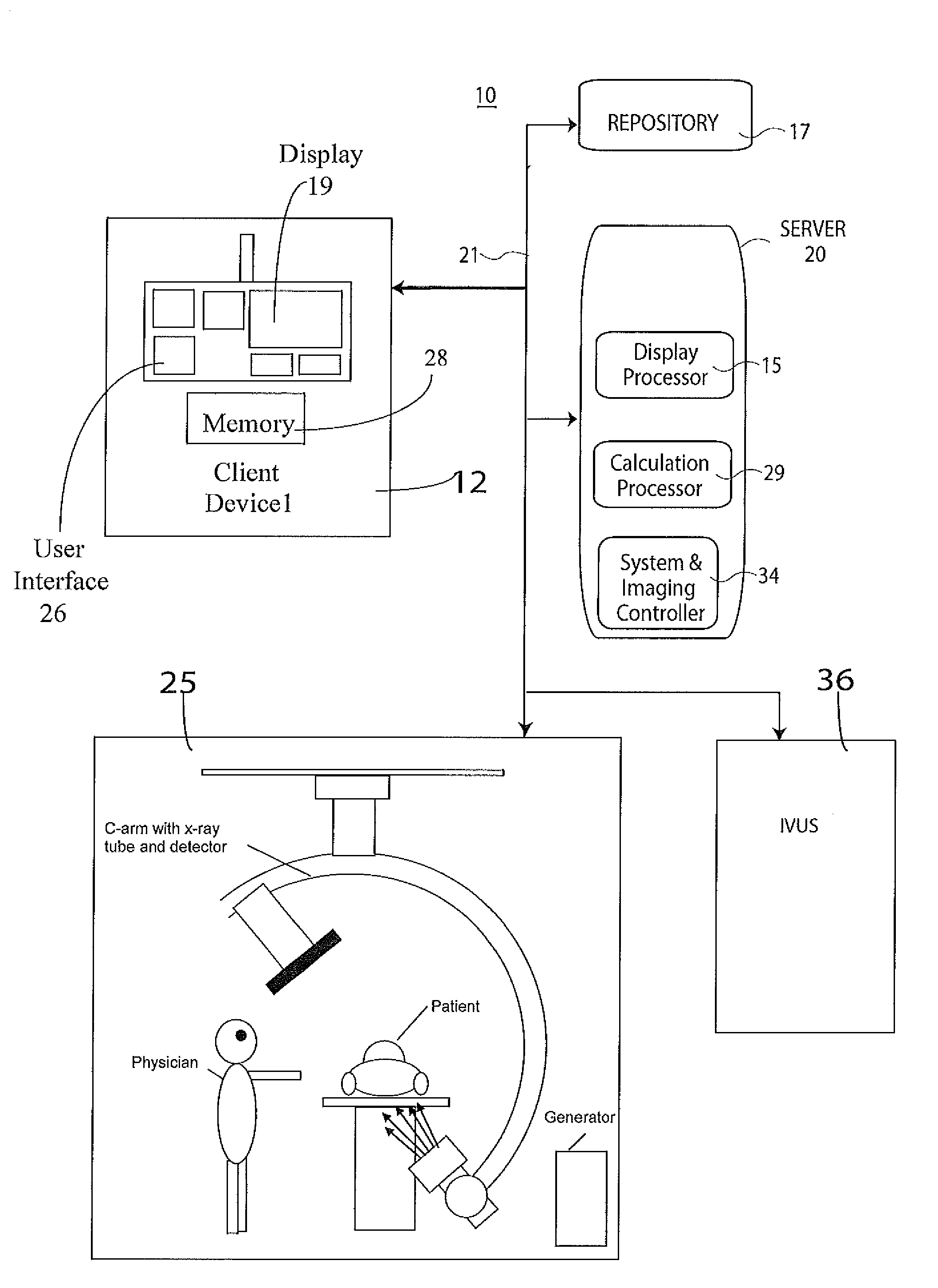
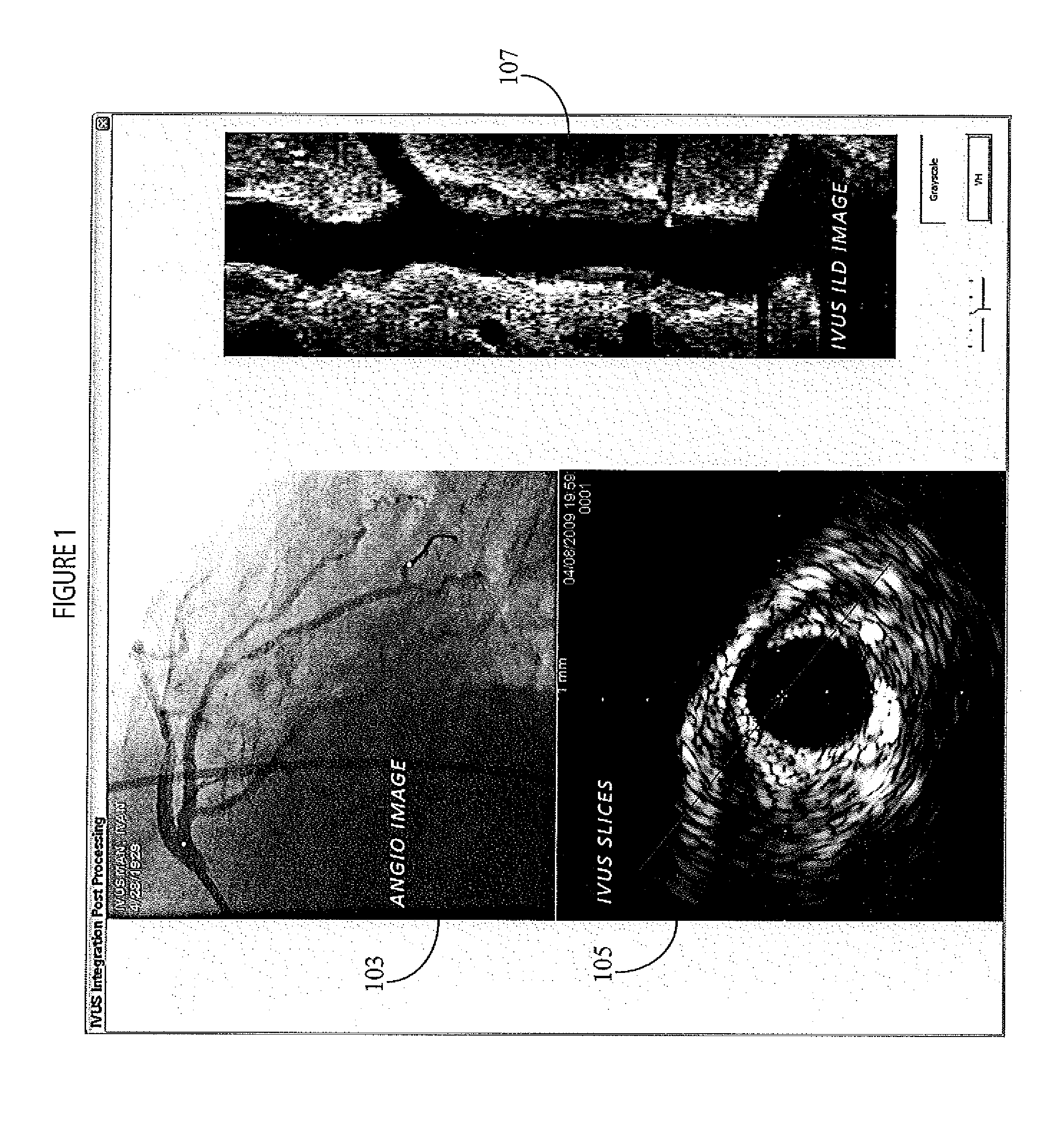
System for Processing Angiography and Ultrasound Image Data
ActiveUS20110034801A1Accurate locationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterSonificationAngio ct
A system provides a single composite image including multiple medical images of a portion of patient anatomy acquired using corresponding multiple different types of imaging device. A display processor generates data representing a single composite display image including, a first image area showing a first image of a portion of patient anatomy acquired using a first type of imaging device, a second image area showing a second image of the portion of patient anatomy acquired using a second type of imaging device different to the first type. The first and second image areas include first and second markers respectively. The first and second markers identify an estimated location of the same corresponding anatomical position in the portion of patient anatomy in the first and second images respectively. A user interface enables a user to move at least one of, (a) the first marker in the first image and (b) the second marker in the second image, to correct the estimated location so the first and second markers identify the same corresponding anatomical position in the portion of patient anatomy.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus, System and Method for Determining Cardio-Respiratory State
InactiveUS20090143655A1Early diagnosisEarly detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightAnatomic SiteMedicine
An apparatus, system and method provide data indicative of cardio-respiratory state of a patient. Two or more cardio-respiratory parameters of the patient are measured, and optionally monitored over time, the two or more cardio-respiratory parameters being different one from the other and being measured at a same anatomical part of said patient.
Owner:CARDIOSENSE LTD
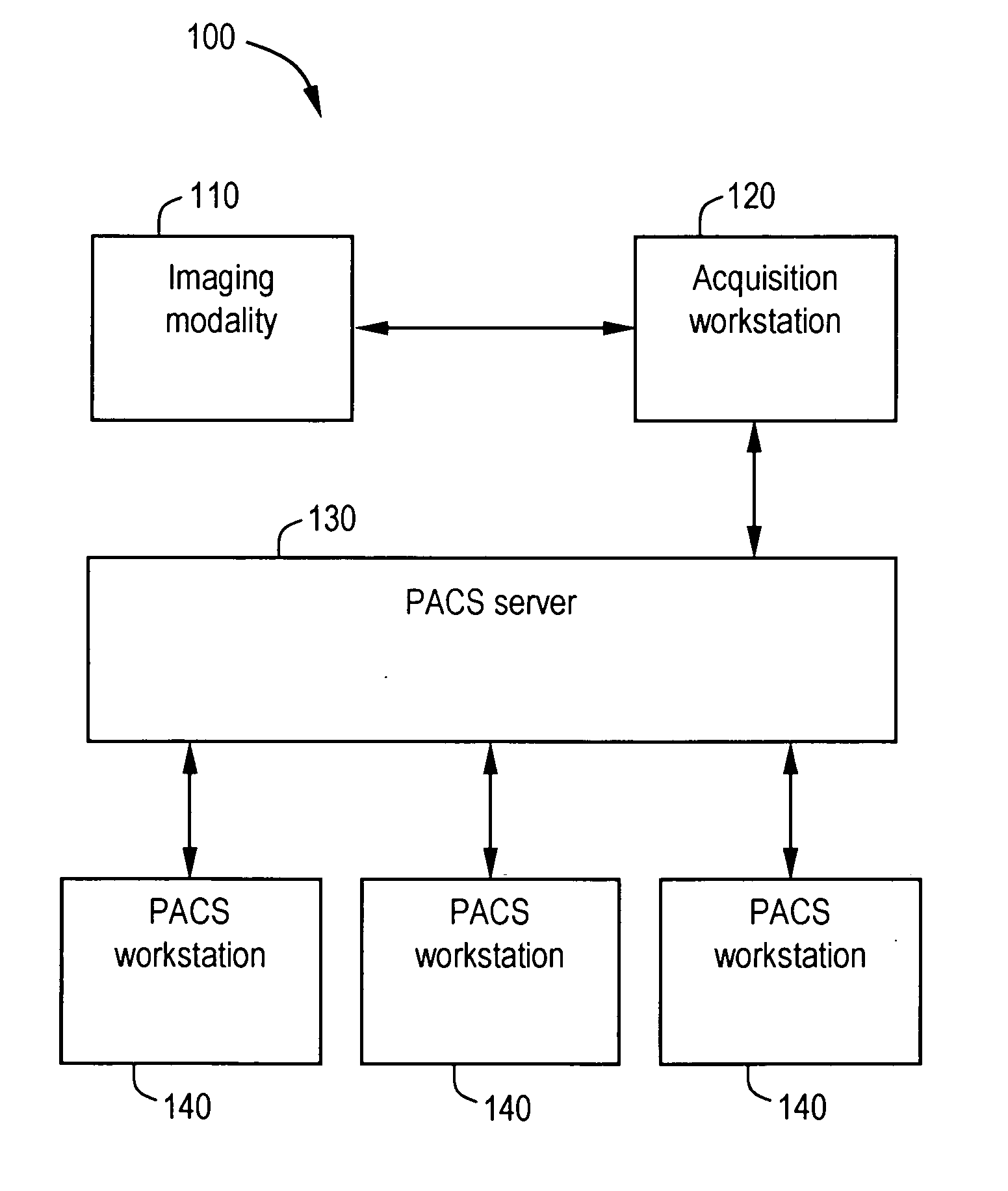
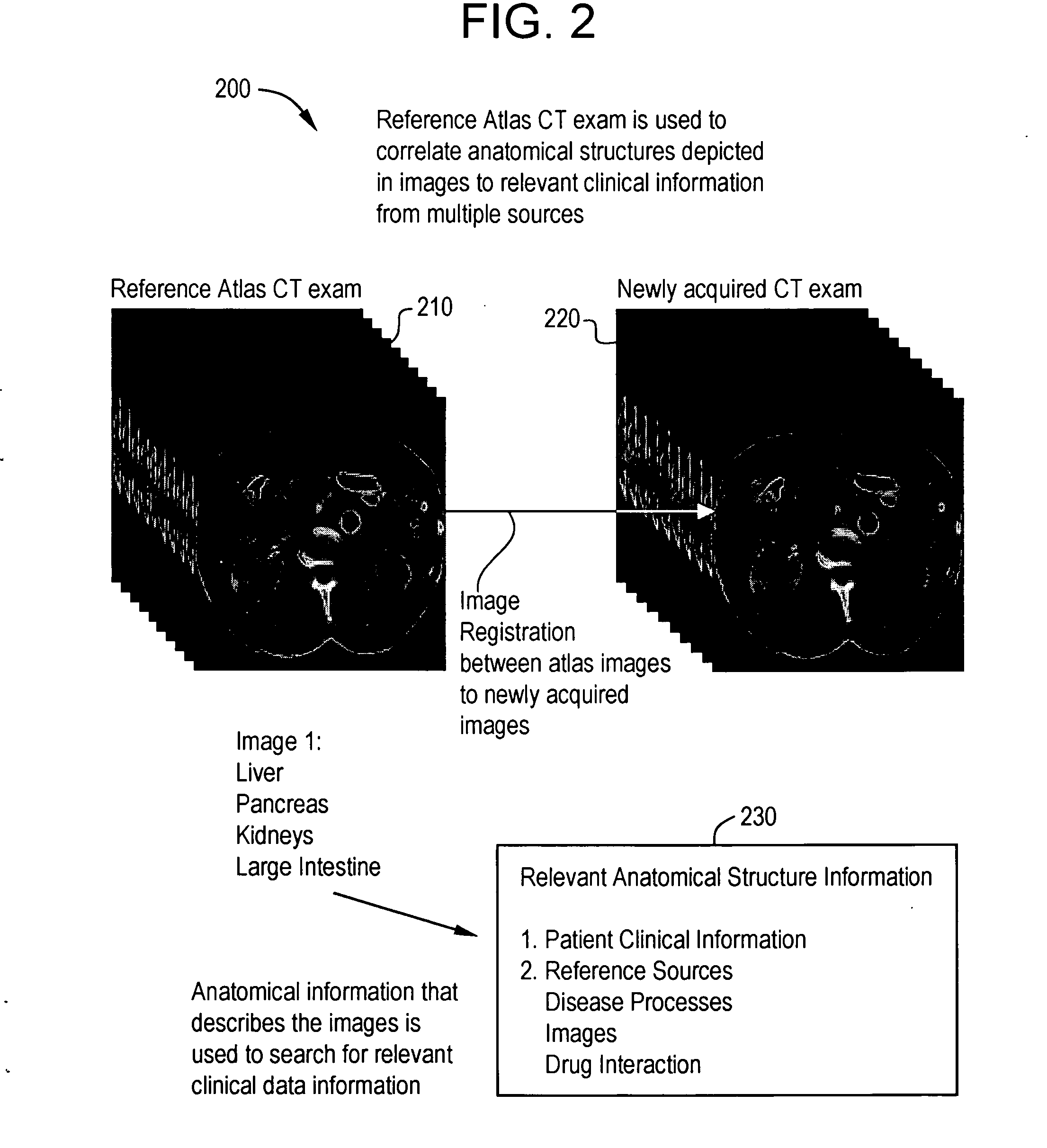
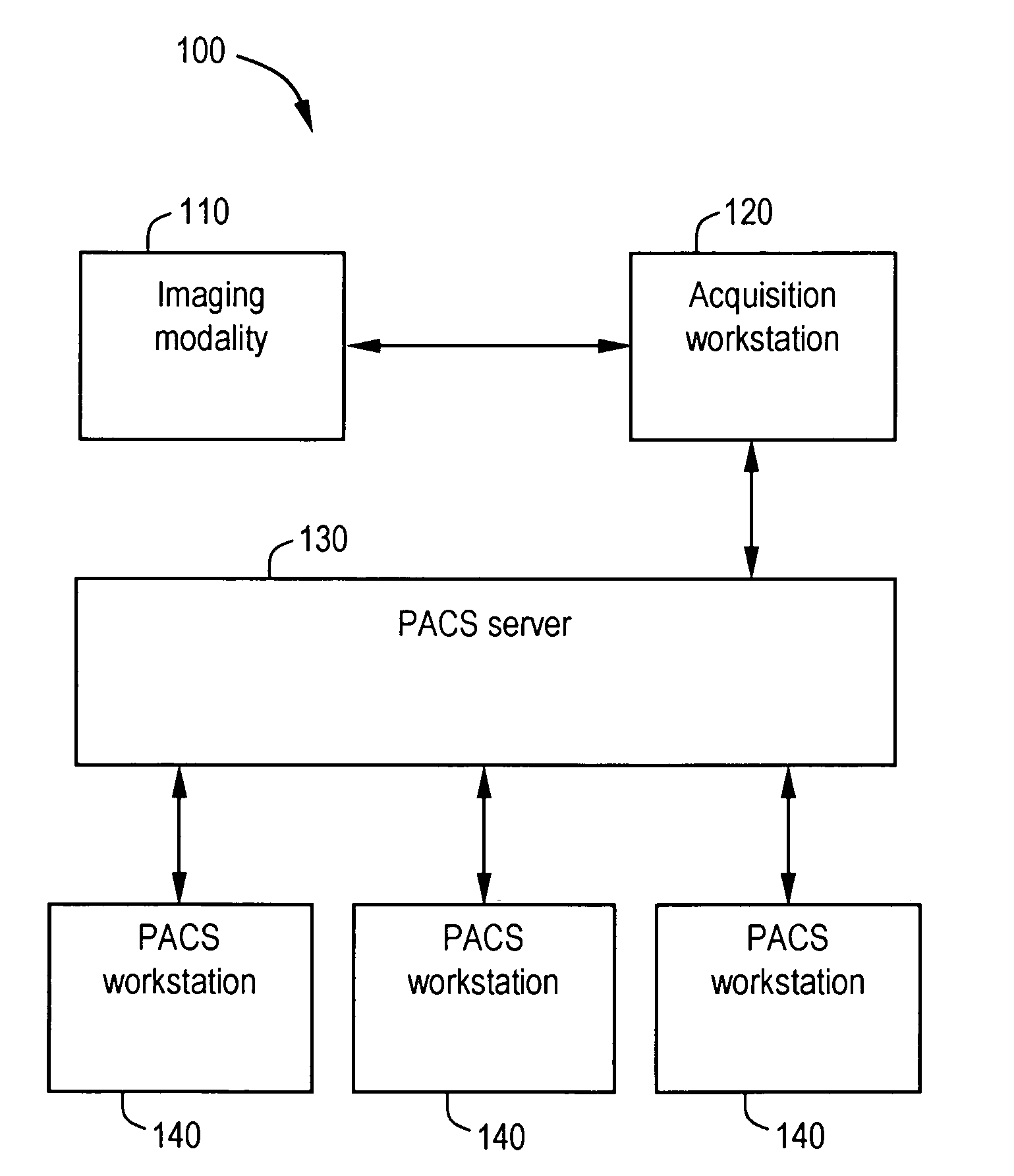
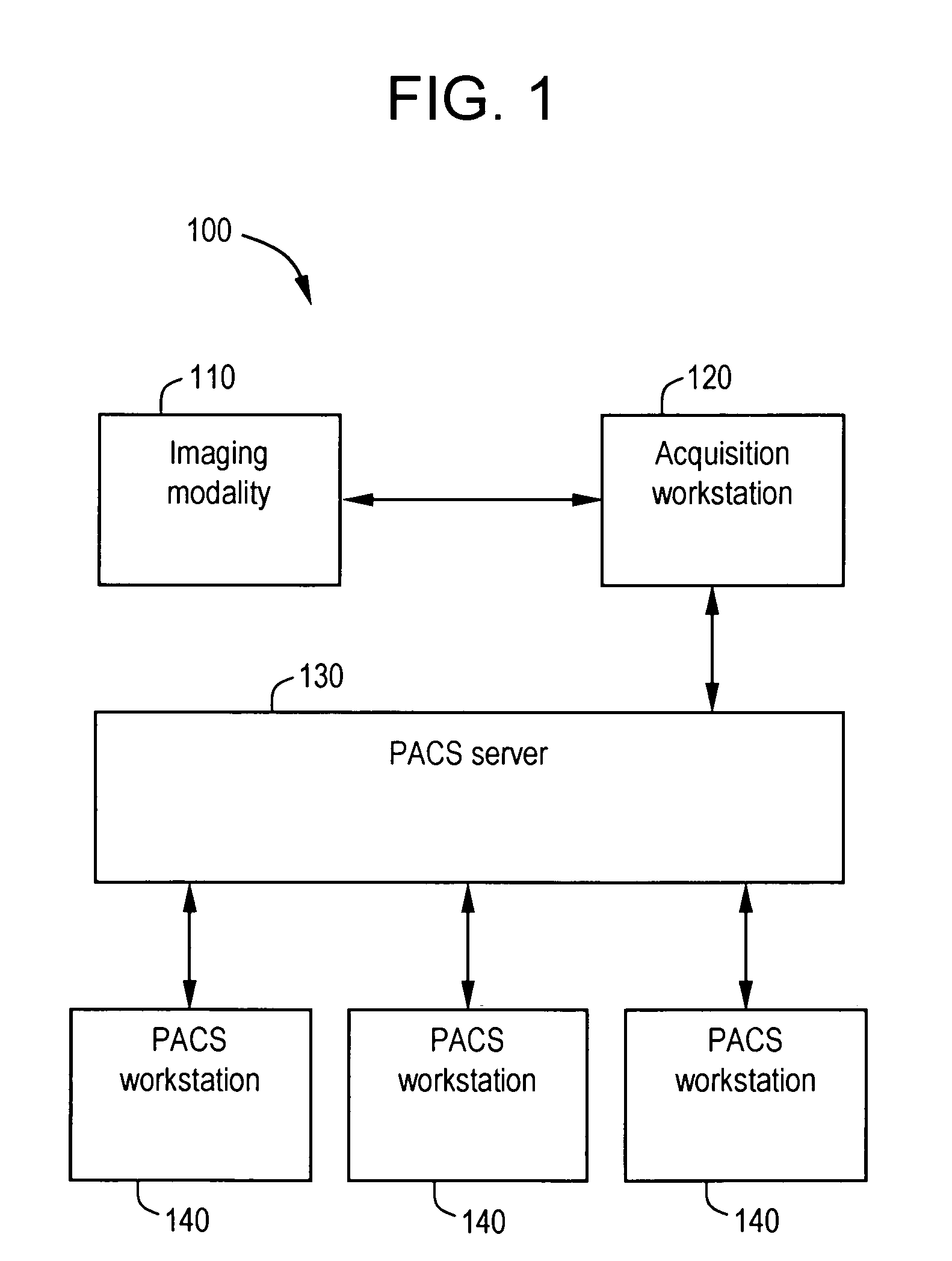
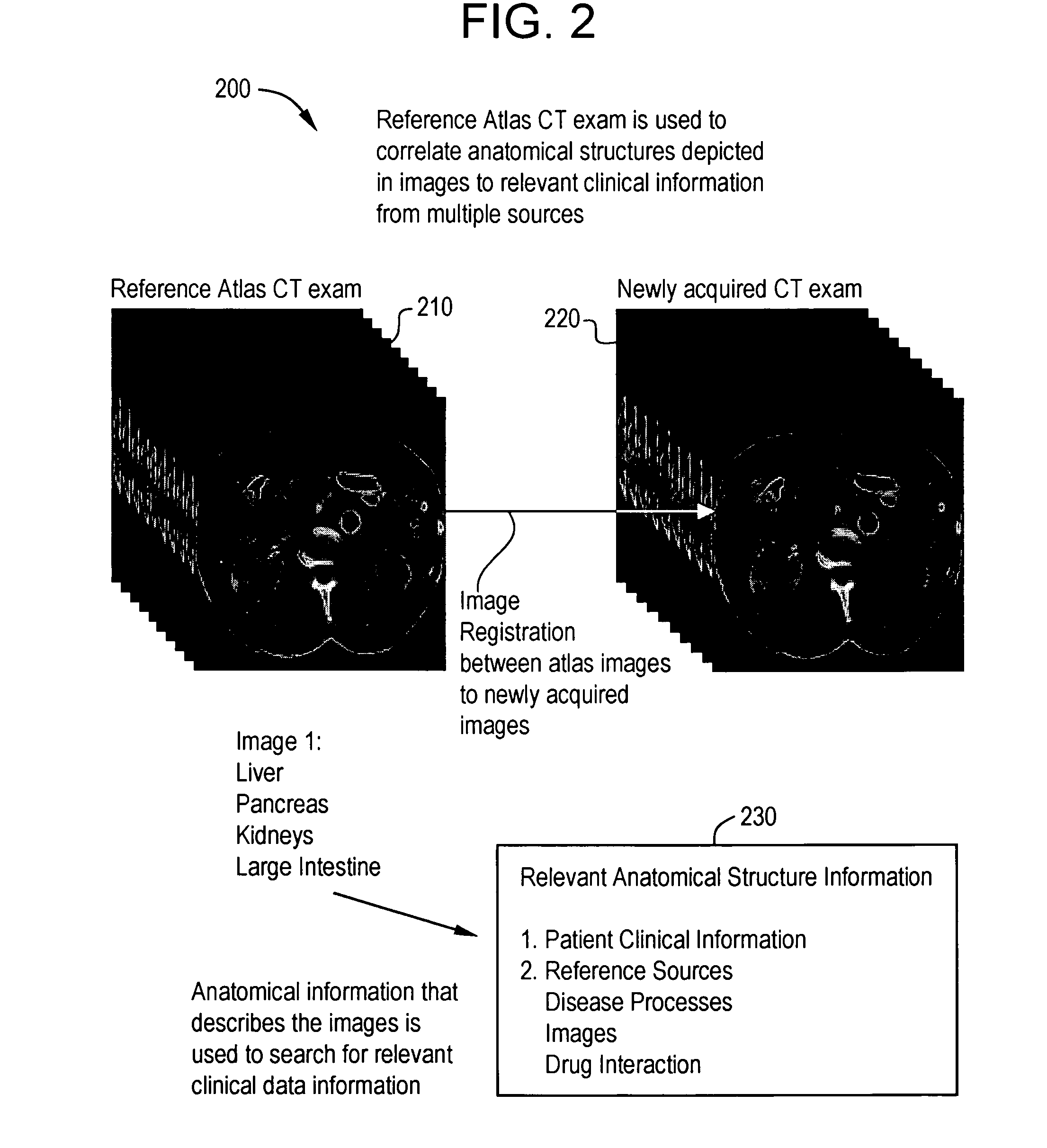
System and method for anatomy labeling on a PACS
ActiveUS20070127790A1Narrow selectionImage enhancementImage analysisClinical informationDrug interaction
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for image registration and display of relevant information. The method includes identifying one or more anatomical parts in an acquired image, mapping the acquired image to a reference image based on the one or more anatomical parts, storing anatomy information in relation to the acquired image, and displaying the acquired image based on the anatomy information. The method may also include controlling the displaying of the acquired image based on a voice command related to the anatomy information. Anatomy information may be displayed with the acquired image. Anatomy information may include clinical information, reference information, disease process information, a related image, and / or drug interaction information, for example. The acquired image may be displayed according to a display setting, such as a window level setting and / or other display setting, based on the anatomy information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for physical rehabilitation and motion training
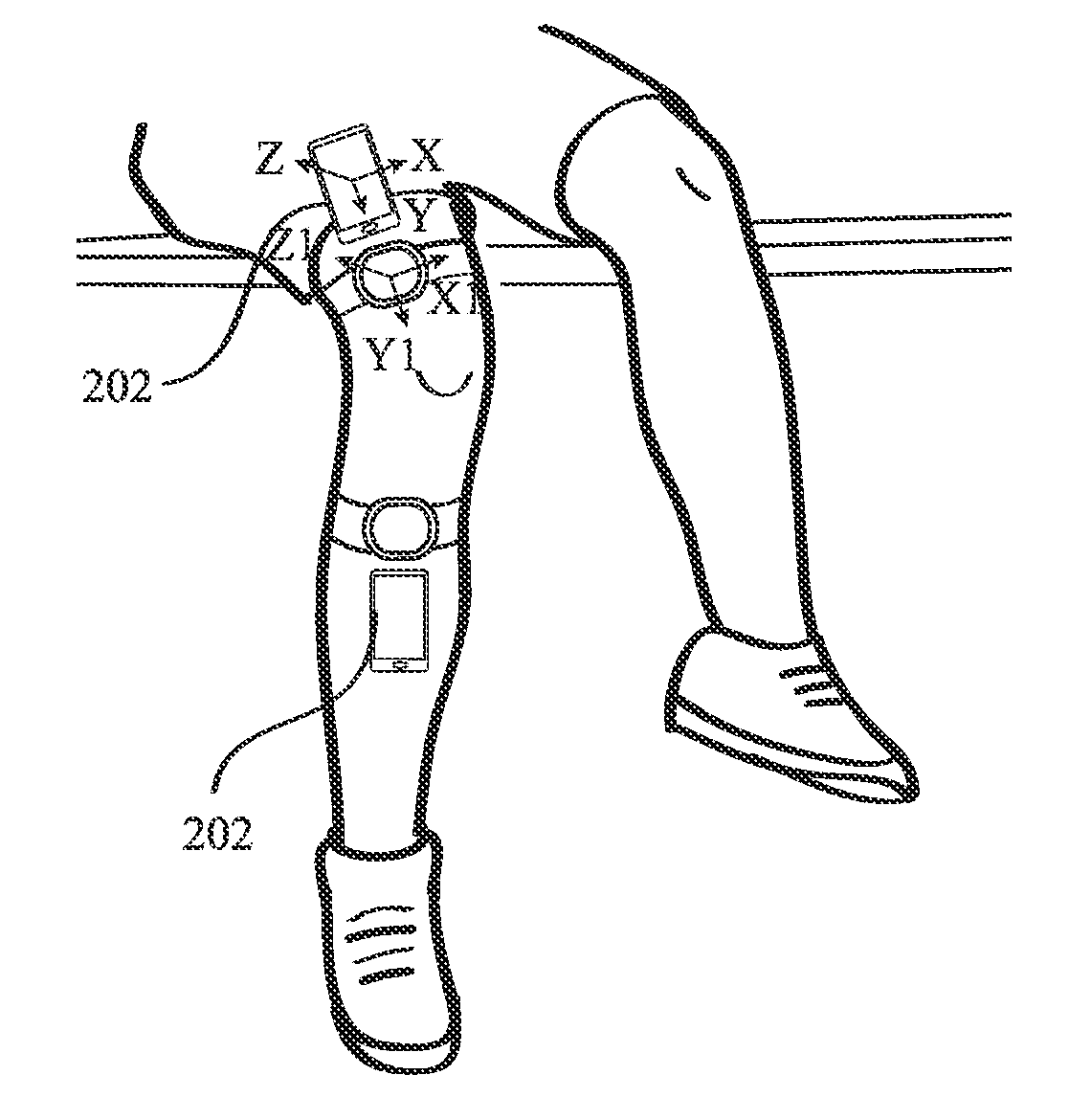
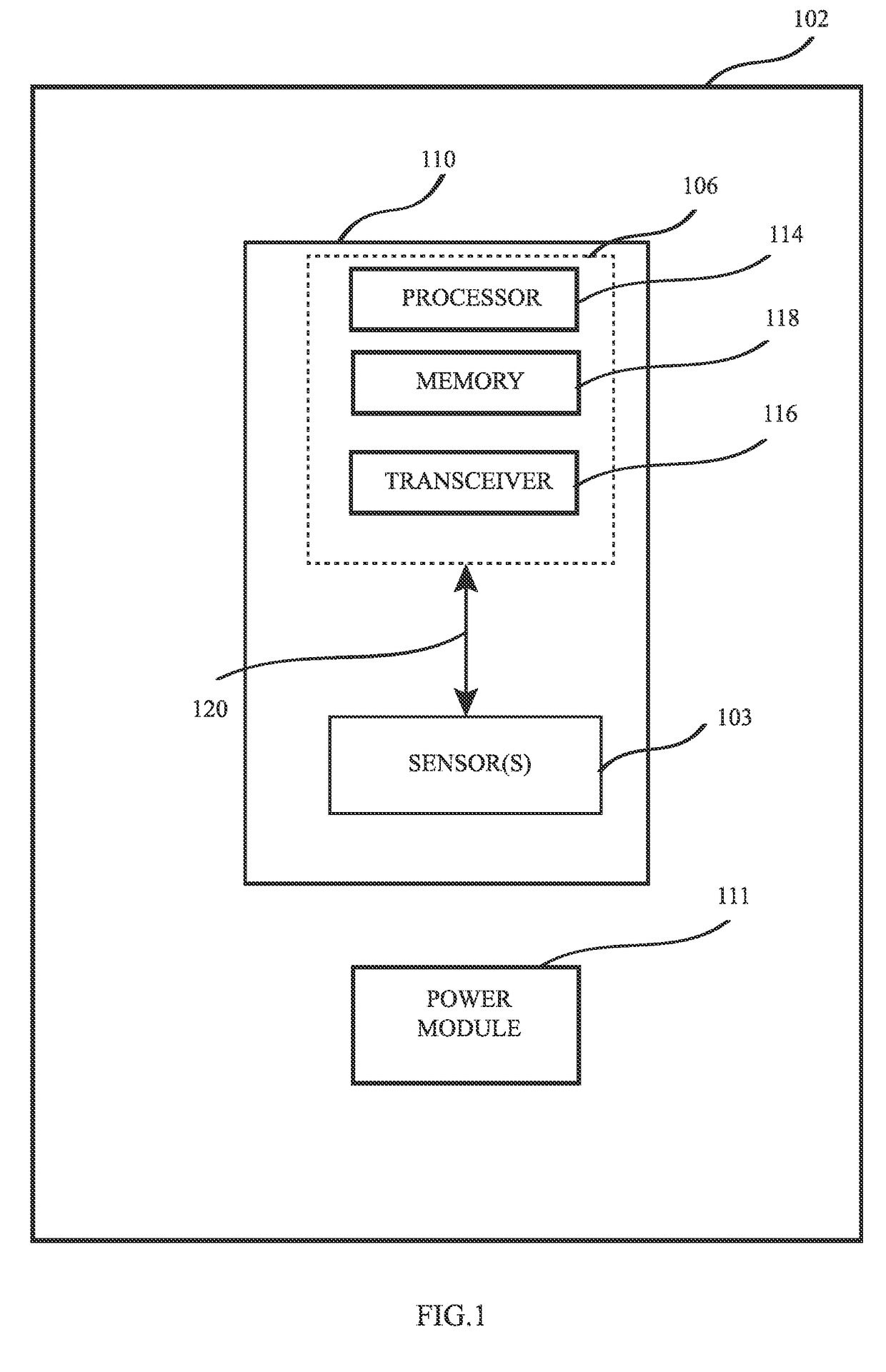
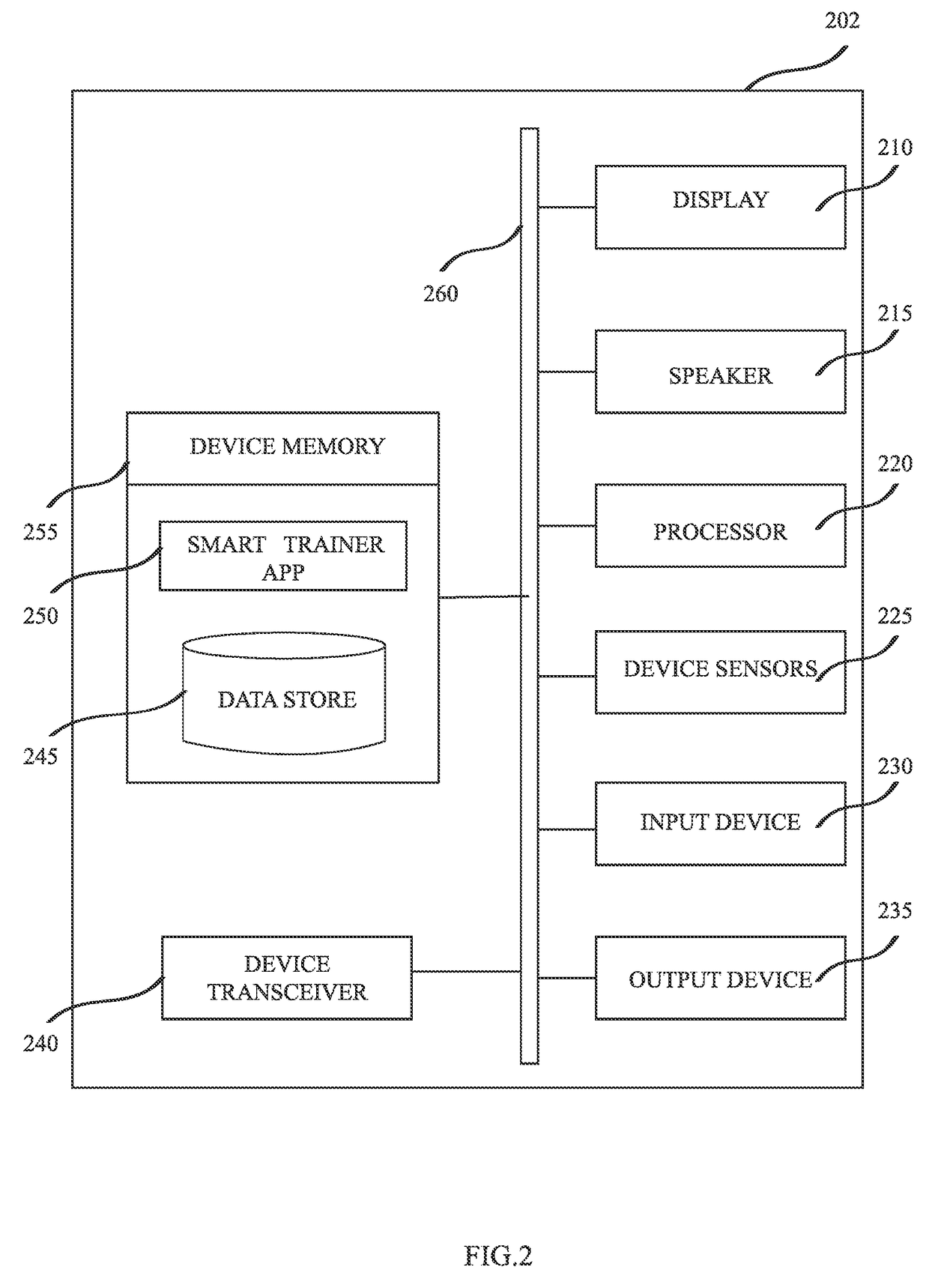
InactiveUS20170136296A1Reduce concentrationConvenient registrationPhysical therapies and activitiesTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsAnatomic SiteTransformation parameter
A system comprising wearable sensor modules and communicatively connected mobile computing devices for assisting a user in physical rehabilitation and exercising. The modules comprise sensors and the mobile computing device comprises device sensors. An application operably installed in memory of the mobile computing device provides a set of step-by-step instructions to a user for wearing the sensor modules in a particular way over an anatomical part depending on an exercise to be done by the user. The application further acquires a first set of data generated by the sensors and a second set of data generated by the device sensors. It then calculates a set transformation parameters based on the first set of data relative to the second set of data to do a sensor-anatomy registration of sensors to the anatomical part while the mobile computing device is placed substantially aligned with the wearable sensors over the anatomical part.
Owner:BARRERA OSVALDO ANDRES +1
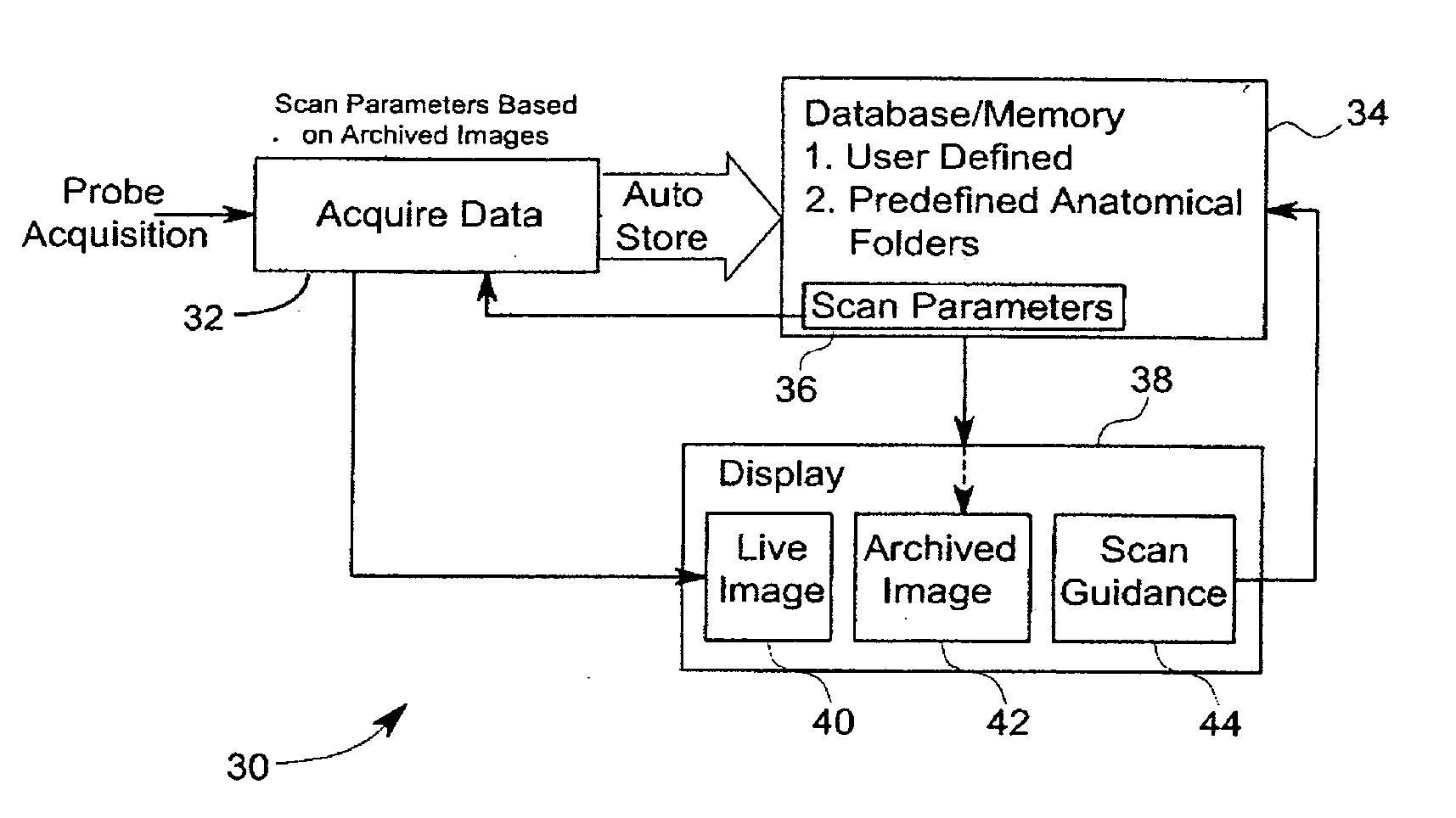
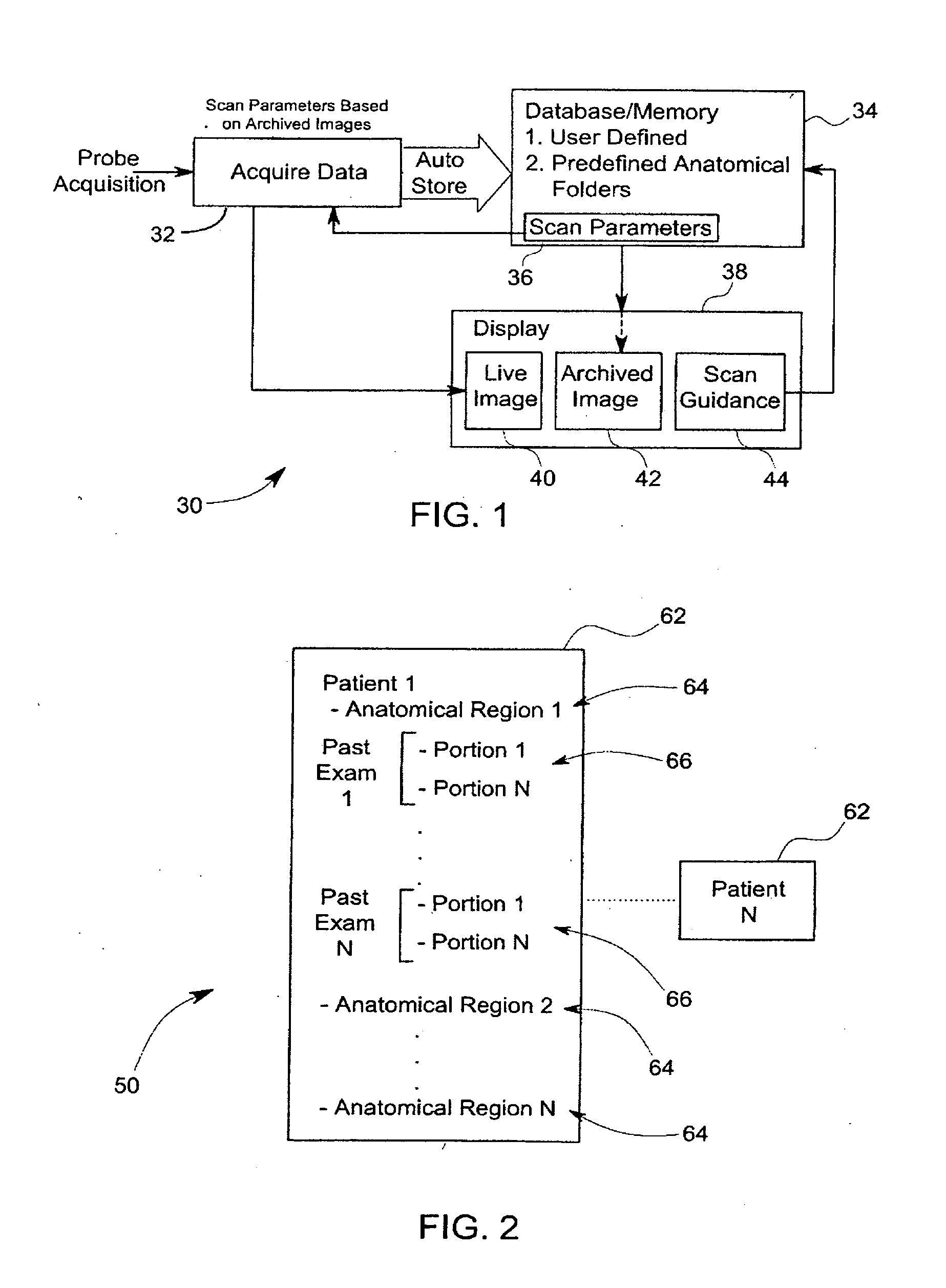
Method and system for organizing stored ultrasound data
InactiveUS20120108960A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUser input
Methods and systems for organizing stored ultrasound data are provided. One method includes displaying selectable anatomical identification guidance information having a plurality of identifiers corresponding to a plurality of anatomical portions of an anatomical region and receiving a user input selecting one of the plurality of identifiers. The method further includes storing a subsequently acquired image and associating the stored image with the anatomical potion of the anatomical region corresponding to the selected identifier.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and systems for computer-aided surgery using intra-operative video acquired by a free moving camera
ActiveUS10499996B2Avoids significant investmentImprove accuracyPhysical therapies and activitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionAnatomical structuresVisual marking
Owner:UNIVE DE COIMBRA
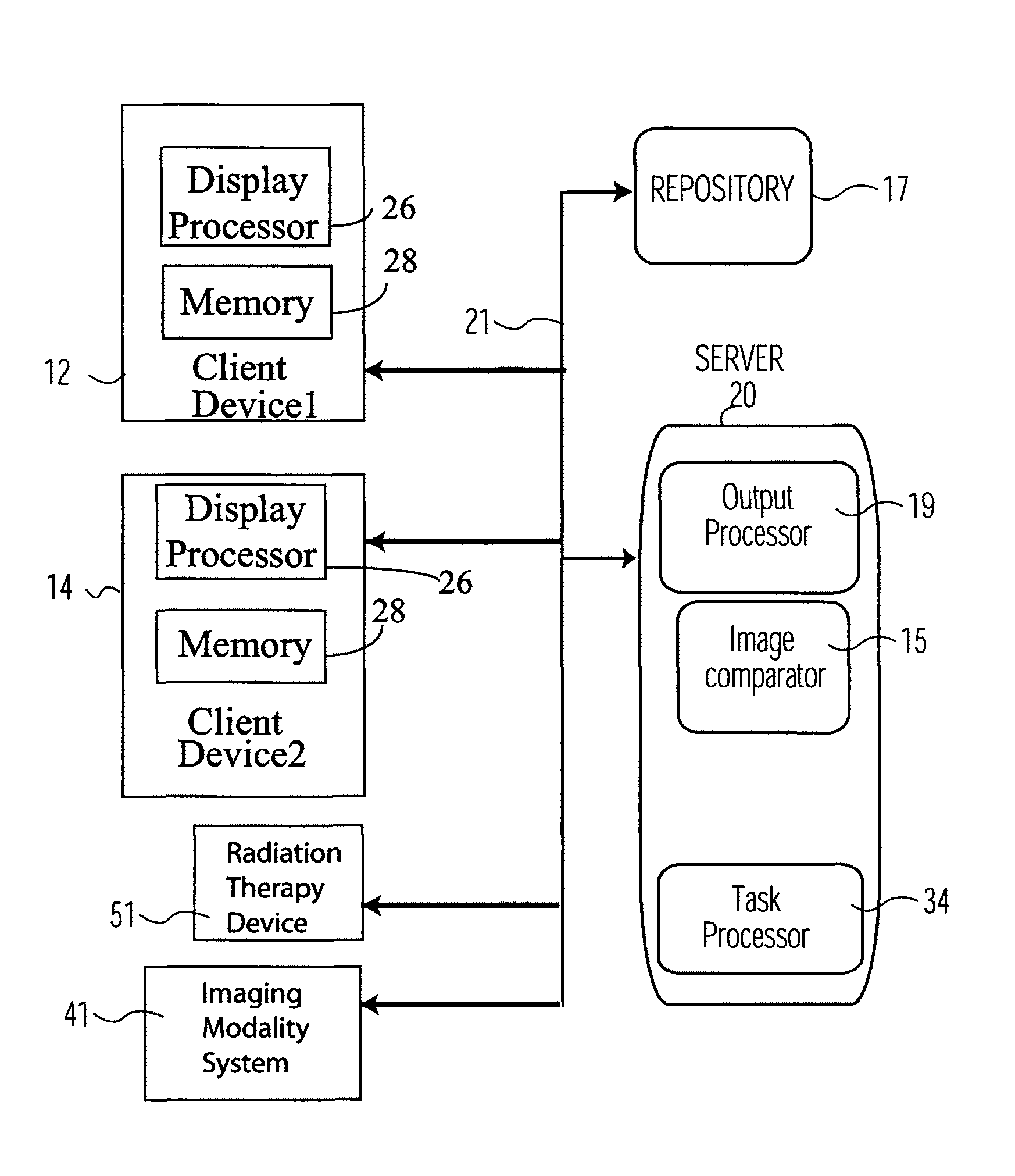
Medical imaging processing and care planning system
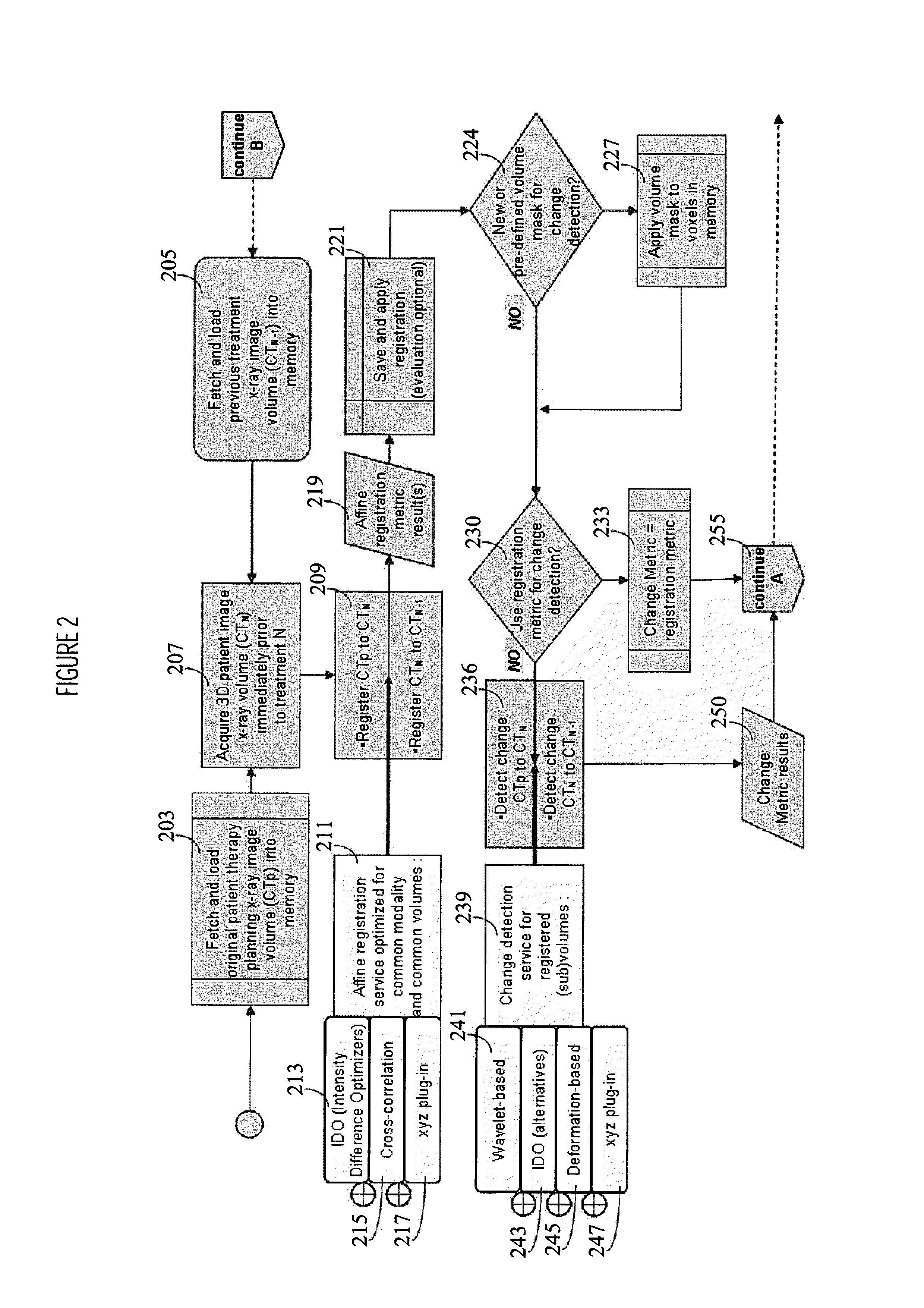
A system automatically compares radiotherapy 3D X-Ray images and subsequent images for update and re-planning of treatment and for verification of correct patient and image association. A medical radiation therapy system and workflow includes a task processor for providing task management data for initiating image comparison tasks prior to performing a session of radiotherapy. An image comparator, coupled to the task processor, in response to the task management data, compares a first image of an anatomical portion of a particular patient used for planning radiotherapy for the particular patient, with a second image of the anatomical portion of the particular patient obtained on a subsequent date, by image alignment and comparison of image element representative data of aligned first and second images to determine an image difference representative remainder value and determines whether the image difference representative remainder value exceeds a first predetermined threshold. An output processor, coupled to the image comparator, initiates generation of an alert message indicating a need to review planned radiotherapy treatment for communication to a user in response to a determination the image difference representative remainder value exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for anatomy labeling on a PACS
ActiveUS7590440B2Narrow selectionImage enhancementImage analysisDrug interactionRelevant information
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Surgically implantable perineal urinary incontinence device
InactiveUS20060004246A1Efficient user controlOvercome deficienciesAnti-incontinence devicesUrethraAnatomical part
An incontinence device for attachment to the inferior ischio-pubic rami in the anterior perineal triangle of a user. The device may include a generally semi-flexible bi-parabolic membrane configured to deflect from an engaged position in which the device exerts pressure upon the user's urethra, or a similar anatomical part. The membrane may deflect to a disengaged position with a first force applied by the user, and be configured to deflect back to the engaged position from the disengaged position upon a further second force applied by the user. Additionally, the device may include bolster connected to the membrane. The bolster may exert pressure upon the user's urethra, or similar anatomical part, when the membrane is in the engaged position and relieve pressure when the membrane is in the disengaged position.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
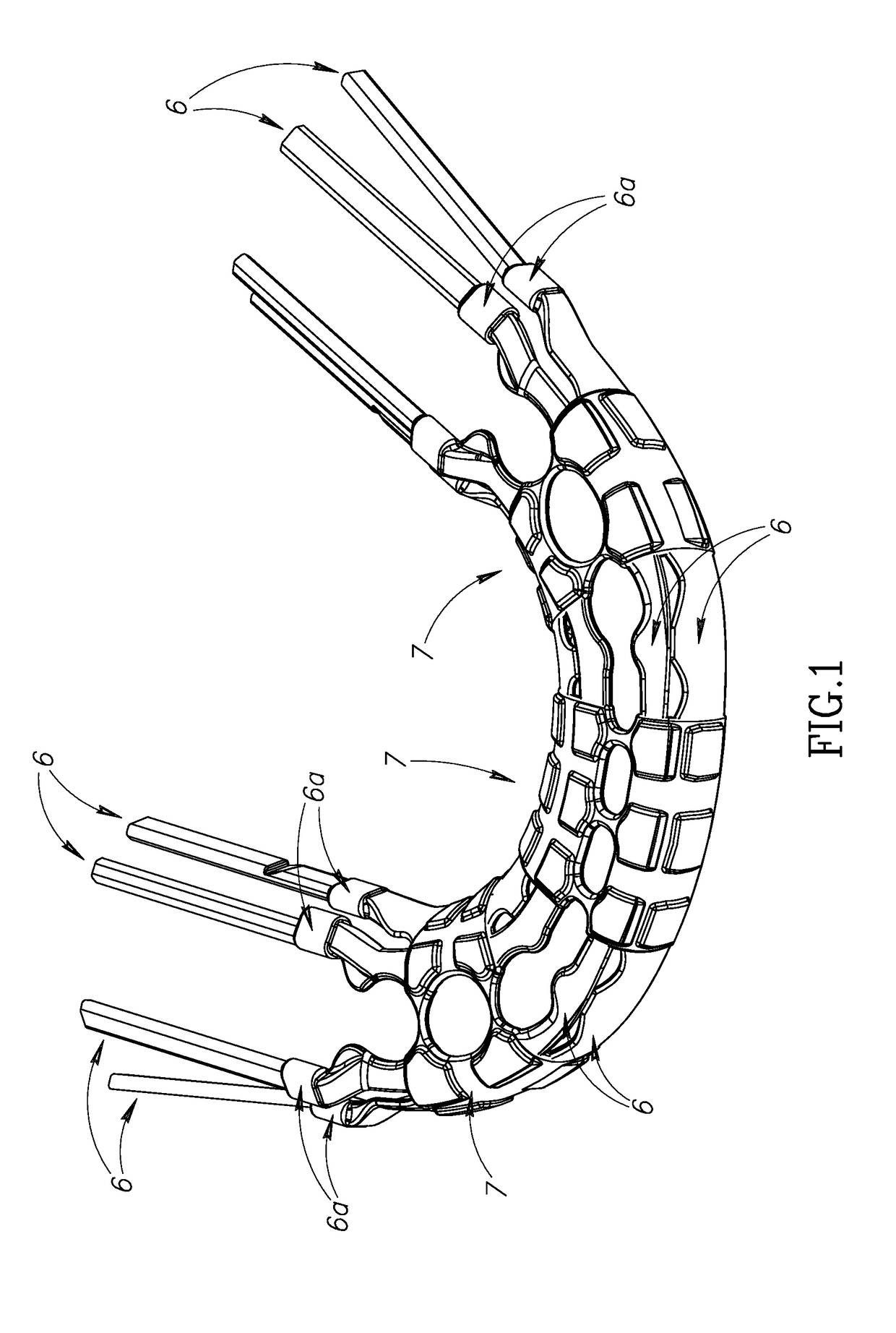
Guides with pressure points
ActiveUS8984731B2Precise positioningMaximize useAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisAnatomic SiteAnatomical part
The application provides methods for providing a surgical guide for placement on an anatomical part wherein the guide is provided with one or more dedicated push features that can be used as pressure points for applying force onto the surgical guide. The application further provides guides comprising one or more push features which can be used as a pressure point for applying force onto said guide.
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
Conduit harvesting instrument and method
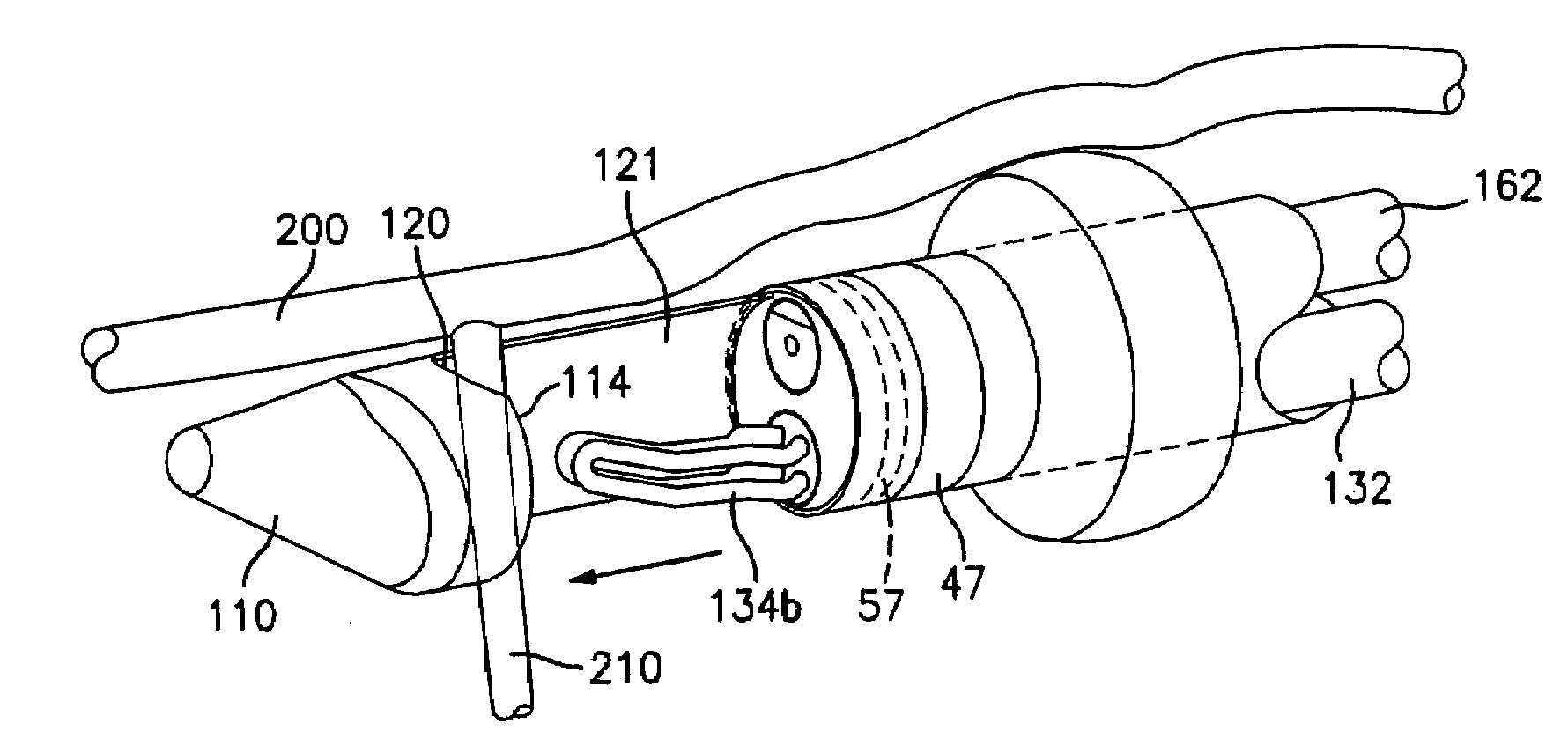
InactiveUS7699861B2Facilitate blunt dissectionEasy to operateCannulasEndoscopesProximateAnatomical part
A surgical instrument for harvesting vessels from the body includes an elongated shaft having distal and proximal ends and a plurality of lumens disposed therethrough. The shaft also includes a tip having a dissecting portion disposed at a distal end thereof and a cradle section. The tip is movable from a first position proximate the distal end of the shaft to at least one additional position distally further from the distal end of the shaft to expose the cradle section. The instrument also includes an endoscope disposed in one of the plurality of lumens and at least one additional surgical instrument disposed in one of the remaining lumens. Methods are disclosed for utilizing the surgical instrument.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Individually-contoured seat cushion and shape capturing and fabricating method for seat cushion
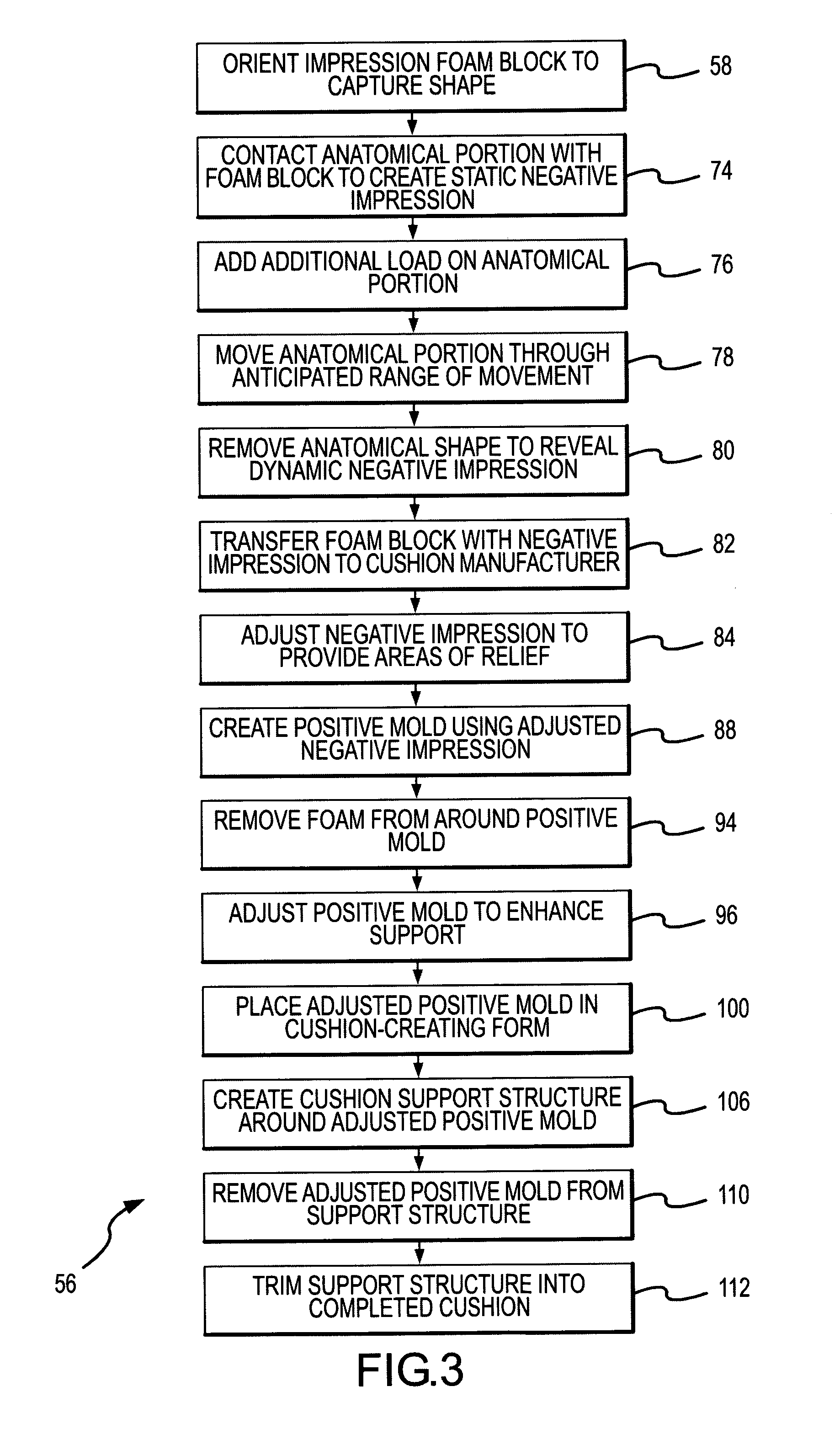
ActiveUS20050025953A1Easy to transportConvenient to accommodateLayered productsWheelchairs/patient conveyanceWheelchairConstant force
A negative impression of an anatomical portion of a person is captured by forcing the anatomical portion into impression foam to collapse the impression foam into the negative impression. The impression foam has a crush characteristic of approximately constant resistance force over a relatively wide predetermined range of collapse distances. The negative impression is obtained by collapsing the impression foam within the range of constant-force collapse distances, thereby creating the negative impression under conditions which reflect an equally-loaded anatomical portion. A cushion support contour created from the equally-loaded negative impression is beneficial in more appropriately supporting the anatomical portion. The present invention is particularly useful in fabricating wheelchair seat cushions.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
Individually-contoured seat cushion and shape capturing and fabricating method for seat cushion
InactiveUS7220376B2Shape-capturing equipment of the invention is relatively inexpensiveEasy to transportWheelchairs/patient conveyanceNursing bedsWheelchairConstant force
A negative impression of an anatomical portion of a person is captured by forcing the anatomical portion into impression foam to collapse the impression foam into the negative impression. The impression foam has a crush characteristic of approximately constant resistance force over a relatively wide predetermined range of collapse distances. The negative impression is obtained by collapsing the impression foam within the range of constant-force collapse distances, thereby creating the negative impression under conditions which reflect an equally-loaded anatomical portion. A cushion support contour created from the equally-loaded negative impression is beneficial in more appropriately supporting the anatomical portion. The present invention is particularly useful in fabricating wheelchair seat cushions.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
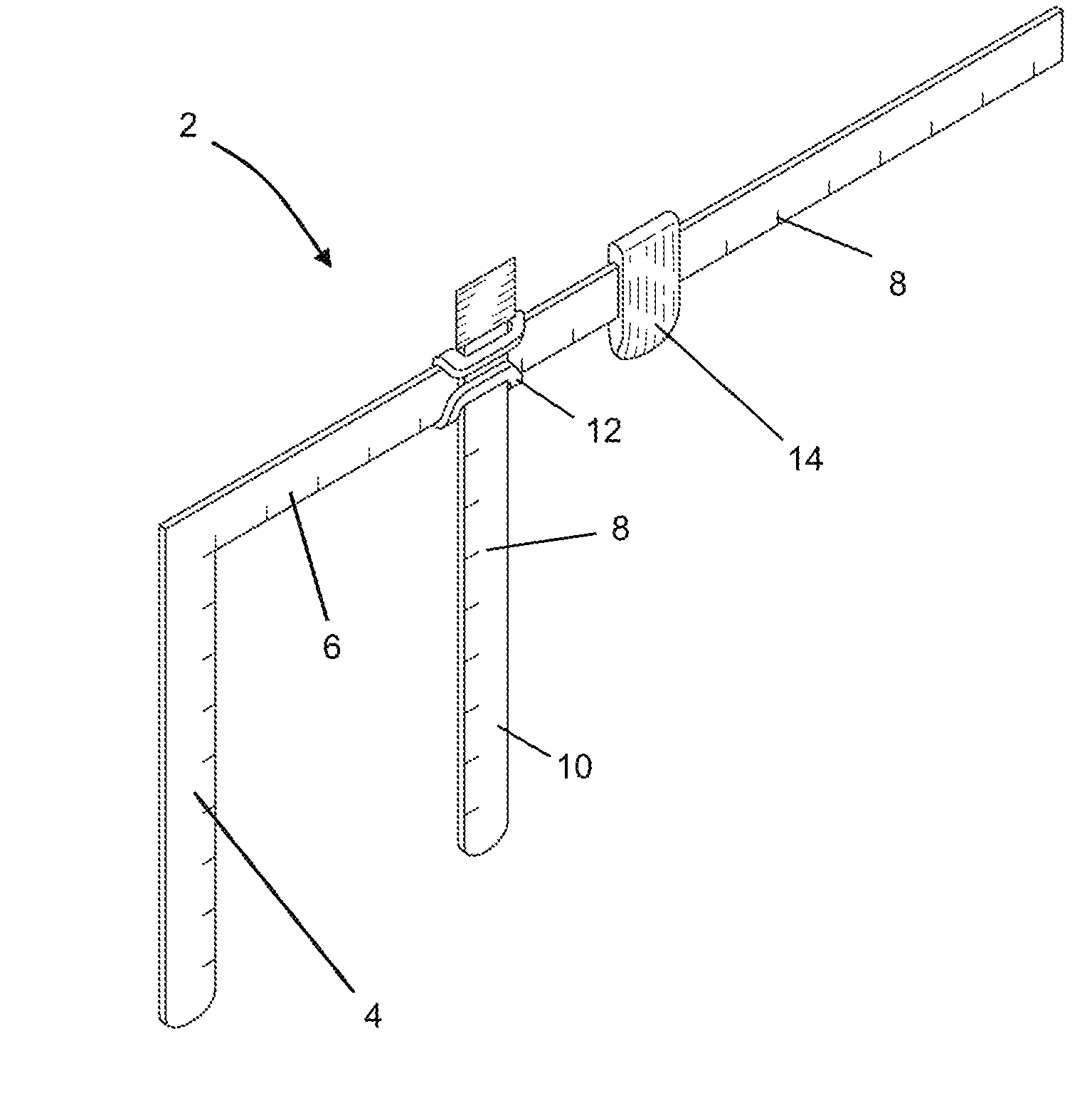
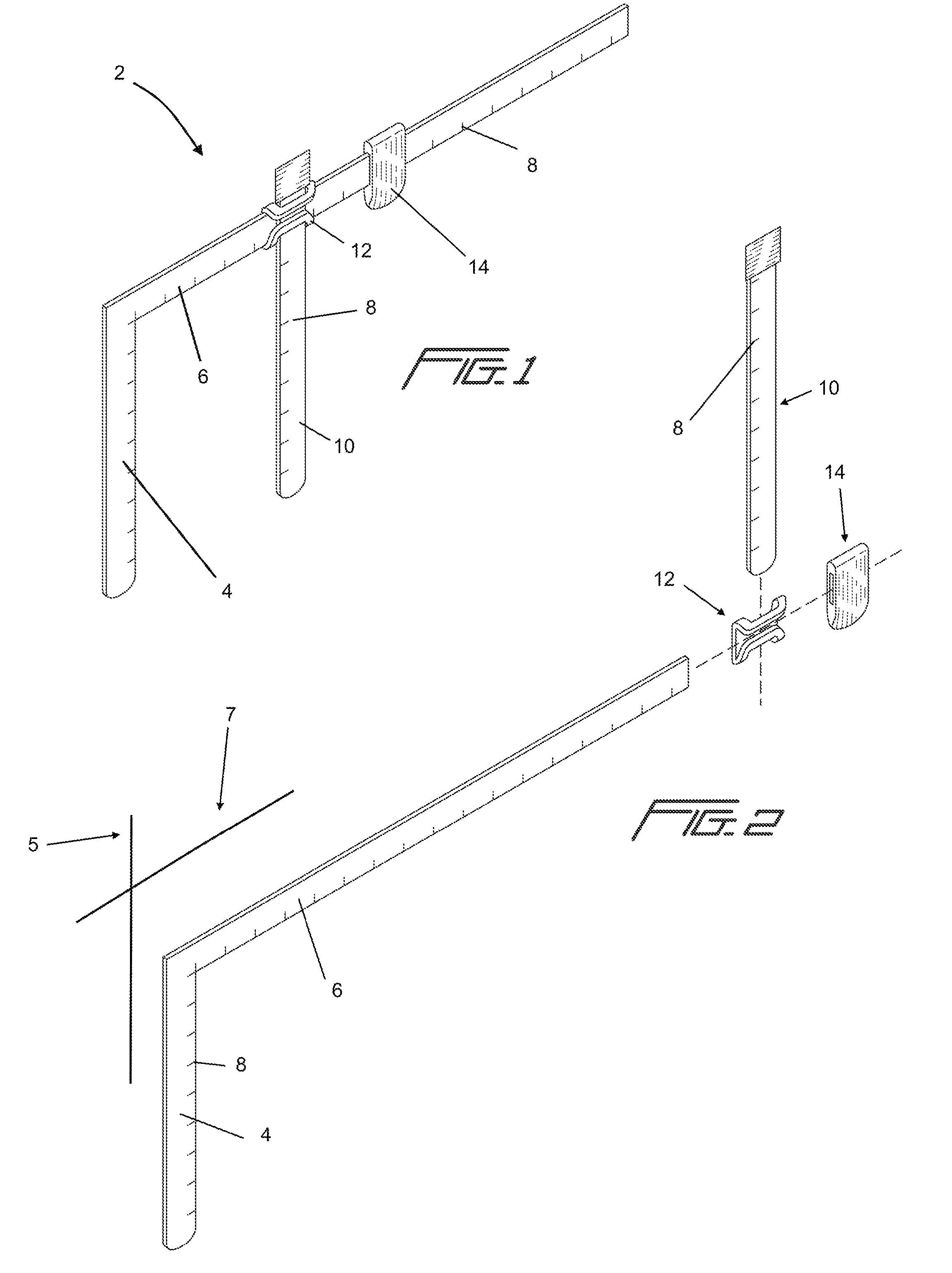
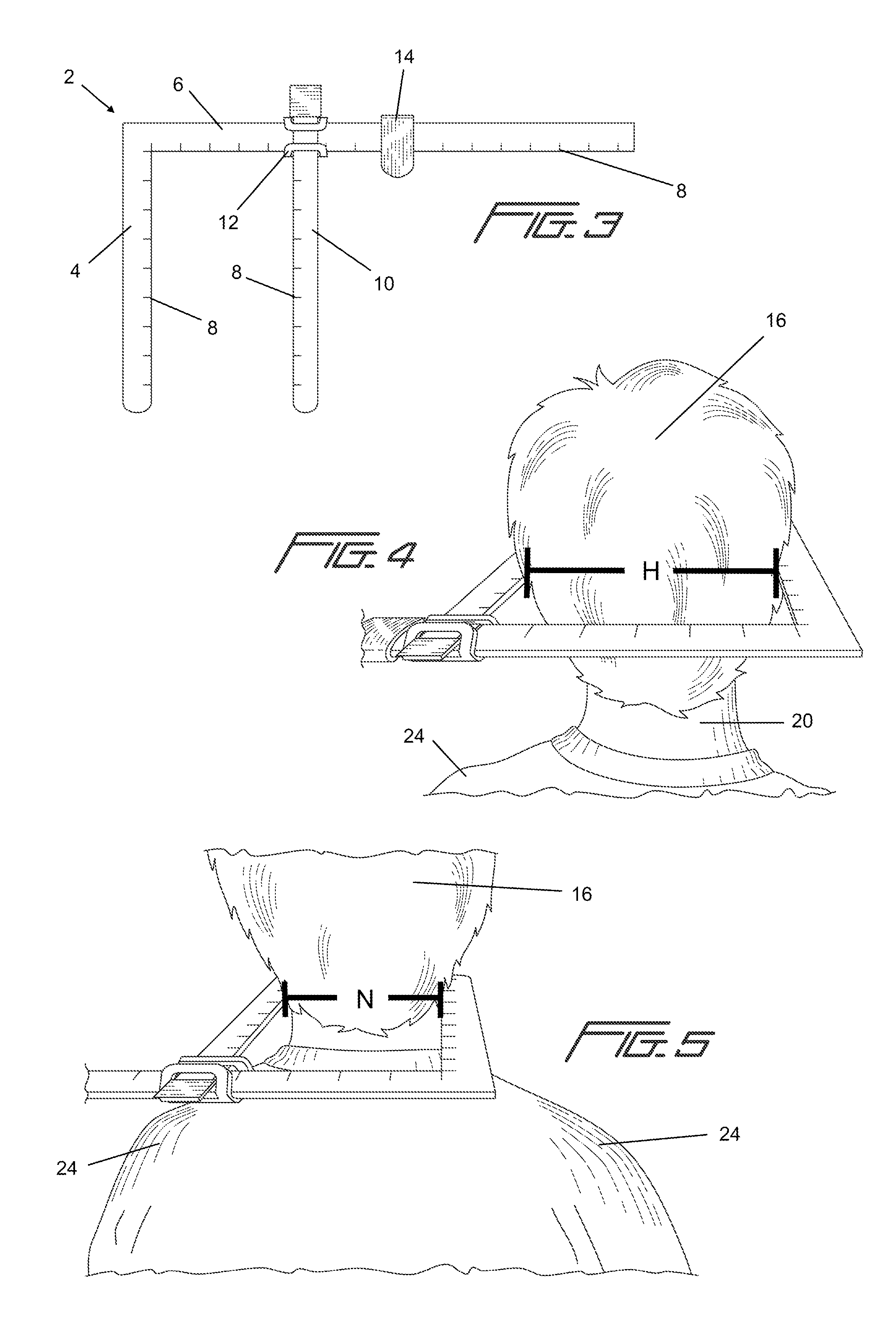
Pillow measurement device
A pillow measurement device and a method of using it are provided. Certain embodiments of the device include a first leg, a second leg, a first movable portion slidably affixed to the second leg, a means for affixing the first movable portion to the second leg, and a second movable portion. One or more of these components may have measurement indicia imprinted on them. The device can be used to measure various anatomical parts of a person, such as head width, neck width, shoulder width, cervical length and cervical depth. Measurements taken using the device may be used to custom build a pillow for a person.
Owner:YU CHANG JUN
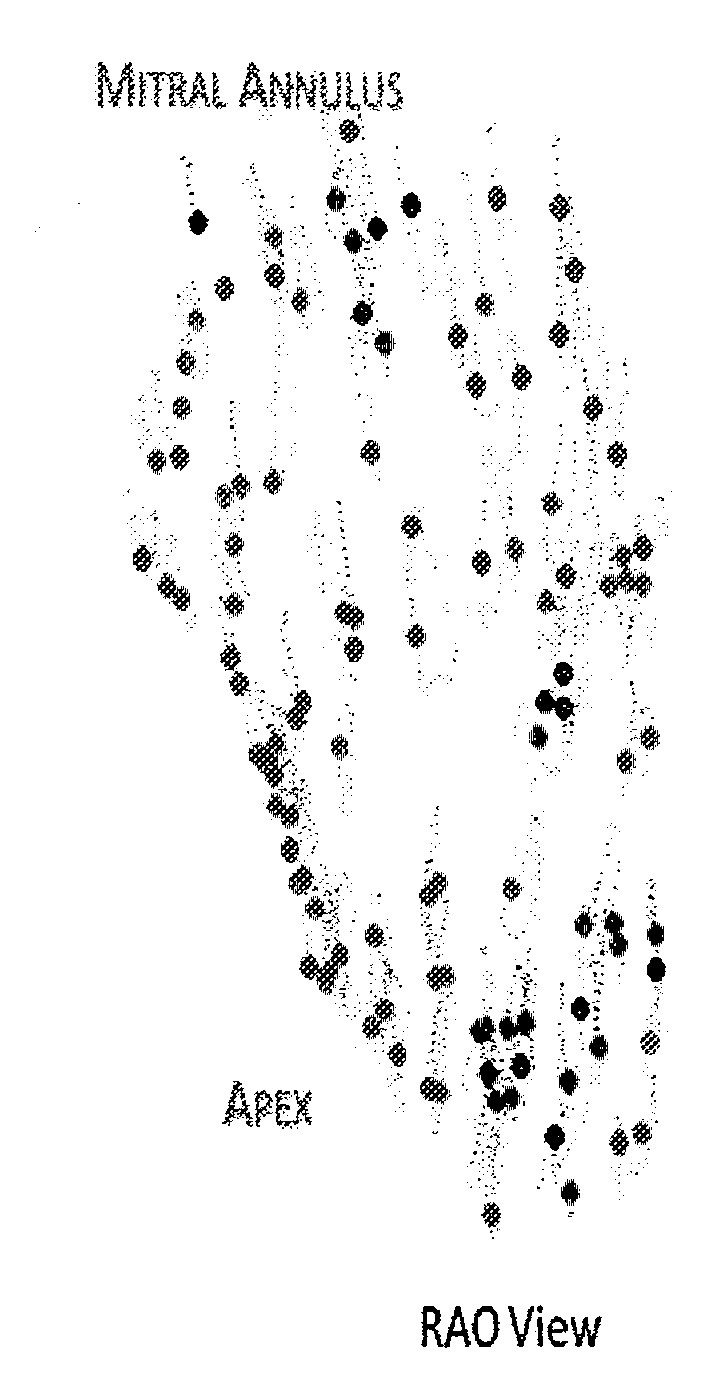
Method and system to automatically assign map points to anatomical segments and determine mechanical activation time
A method and system are provided for assigning map points to anatomical segments of a heart. The method and system utilize an intravascular mapping tool configured to be inserted into at least one of the endocardial or epicardial space. The mapping tool is maneuvered to select locations proximate to surfaces of the heart, while collecting map points at the select locations to form a ROI data set. The method and system store the ROI data set in a data storage and defines apical, basal and circumferential landmarks within the ROI data set. The method and system automatically calculate circumferential and longitudinal segment boundaries, associated with wall segments of the heart, based on the apical, basal and circumferential landmarks. The method and system automatically assign segment identifiers (IDs) to the map points based on locations of the map points relative to the circumferential and longitudinal boundaries, the segment IDs associated with wall segments of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
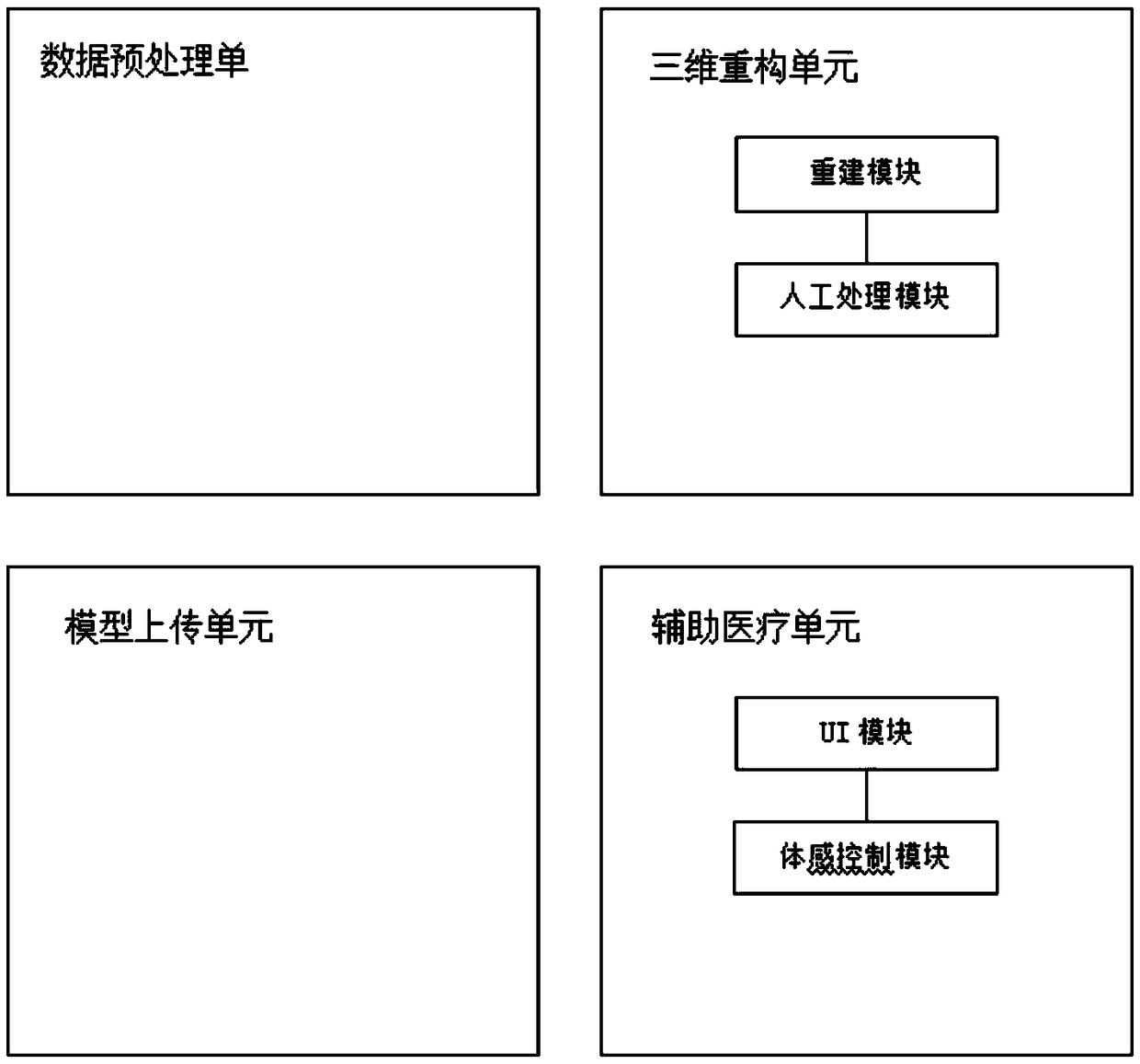
MR-based 3D visualized auxiliary diagnosis and treatment system
InactiveCN109036548AImplementation processLow costMedical communicationMedical automated diagnosisHuman bodyMixed reality
The invention relates to an MR(mixed reality)-based 3D visualized auxiliary diagnosis and treatment system that comprises a data preprocessing unit for receiving a medical image provided by a hospitalon a cloud platform, and converting the medical image into a commonly used Dicom format for subsequent digitization processing; a 3D reconstruction unit for volume rendering the medical image by using a reconstruction technology in a vtk environment, generating an available STL format, then manually processing a 3D model to improve the model; a model uploading unit for converting the format of the model to generate a file format available for a MR system and uploading a file; and an auxiliary medical treatment unit for covering the human body with the 3D model by a MR device through a visualoverlay technology during an operation to help a doctor perform the operation. The application of the auxiliary diagnosis and treatment system in the medical field solves the problem that the doctor cannot perform the accurate operation by enabling the 3D displayed human body structure to correspond to the actual anatomical parts of a patient during the operation.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG TUOMENG TECH CO LTD
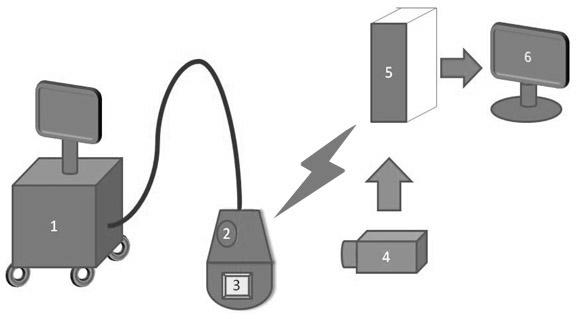
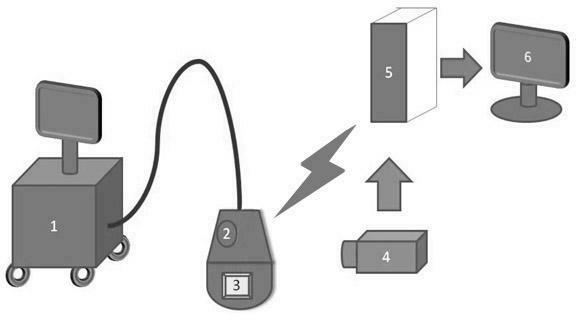
Three-dimensional spatial positioning system for medical ultrasonic probe relative to part to be checked and method
InactiveCN102499762AAccurate analysisAccurate diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographySpatial positioning
The invention discloses a three-dimensional spatial positioning system for a medical ultrasonic probe relative to a part to be checked, which comprises an image acquisition module, an ultrasonic probe, a communication module and a computer module. The inside or surface of the ultrasonic probe is provided with a three-axis gyroscope. In a specific positioning method, video signals of the probe on a specific anatomical part of a human body are obtained through the image acquisition module, the three-axis gyroscope is used for determining the state of the three-dimensional space with the ultrasonic probe, and the communication module is used for respectively transmitting data obtained by the three-axis gyroscope and the image acquisition module to the computer module; and the computer module is used for processing the video signals of the probe on the specific anatomical part obtained through the image acquisition module and information on the state of the space with the probe sensed by the three-axis gyroscope, and promptly and synchronously displaying the information on a screen. The defect of no probe information in the current ultrasonic diagnosis can be overcome, and necessary diagnostic information can be provided for ultrasonic diagnosis.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
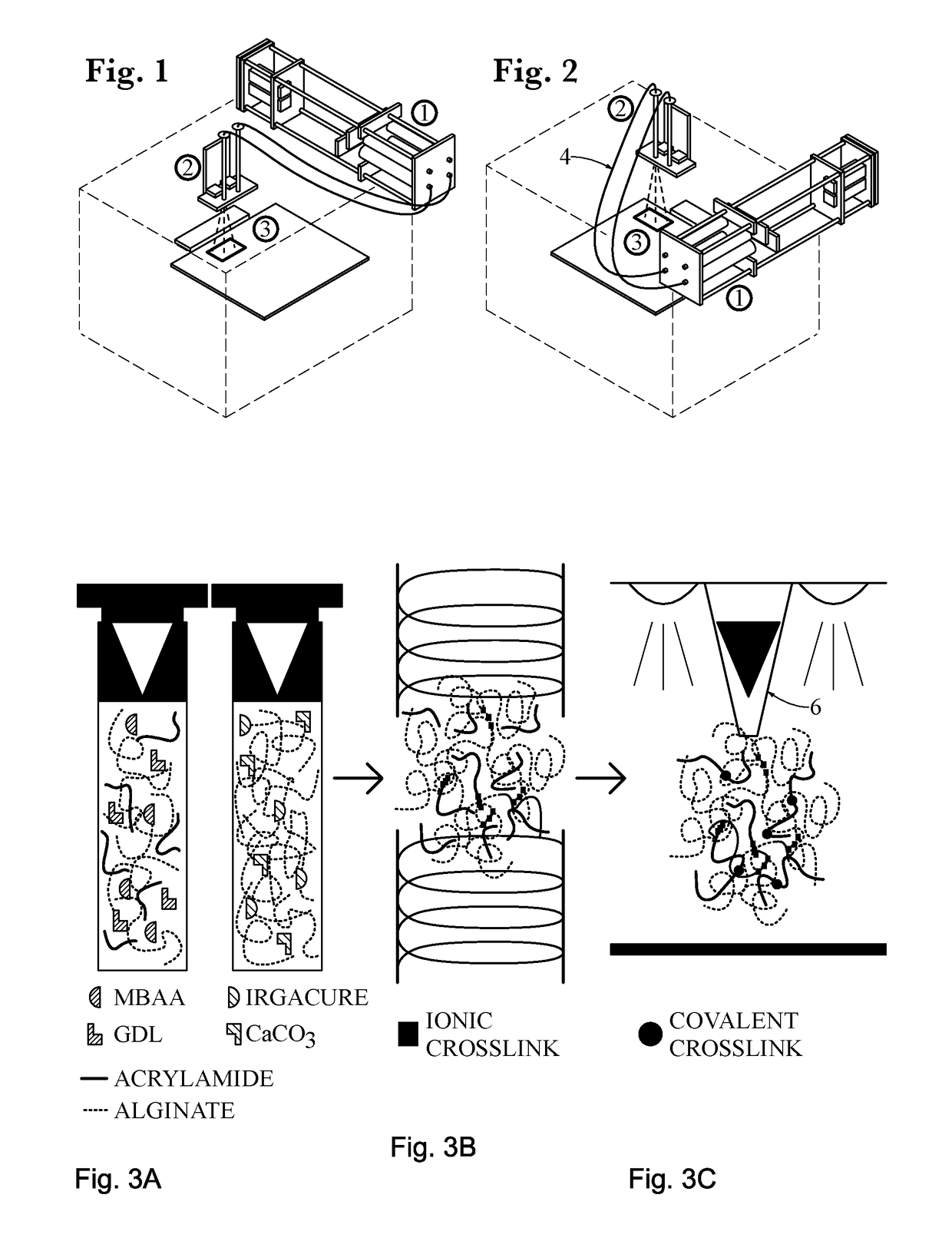
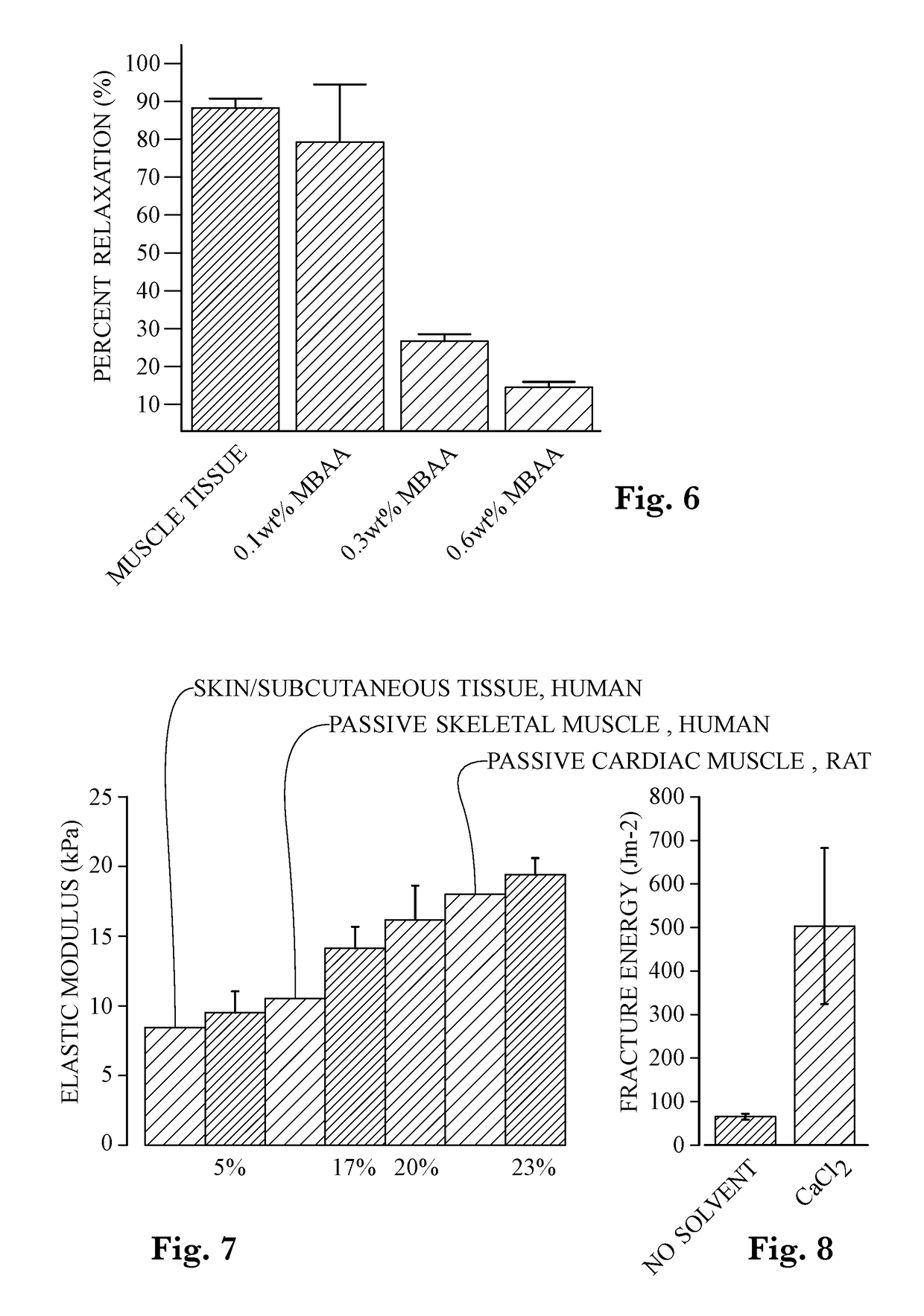
Method, apparatus and formulation for an interpenetrating network polymer
InactiveUS20170145202A1Impart propertyEasy to controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsVolumetric Mass DensityStress relaxation
An alginate-polyacrylamide IPN hydrogel formulation for 3D printing using a dual syringe system where the components that initiate polymerization of each network remain separated until printing. The dual syringe system may use a single motor and mixing head to combine both parts of the hydrogel formulation for controlled polymerization of the material. The elastic and time-dependent viscoelastic properties (stress relaxation) are tuned to match mammalian tissues by changing the crosslink density and monomer concentration. The fracture energy of the material may be increased by soaking in a calcium chloride solution. The resulting IPN polymer material may find application in soft tissue medical simulation devices, particularly because the mechanical properties may be tuned to mimic the elastic and viscoelastic properties of muscle tissue and may be 3D printed in the shape of anatomical parts.
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERSITY
System and method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image
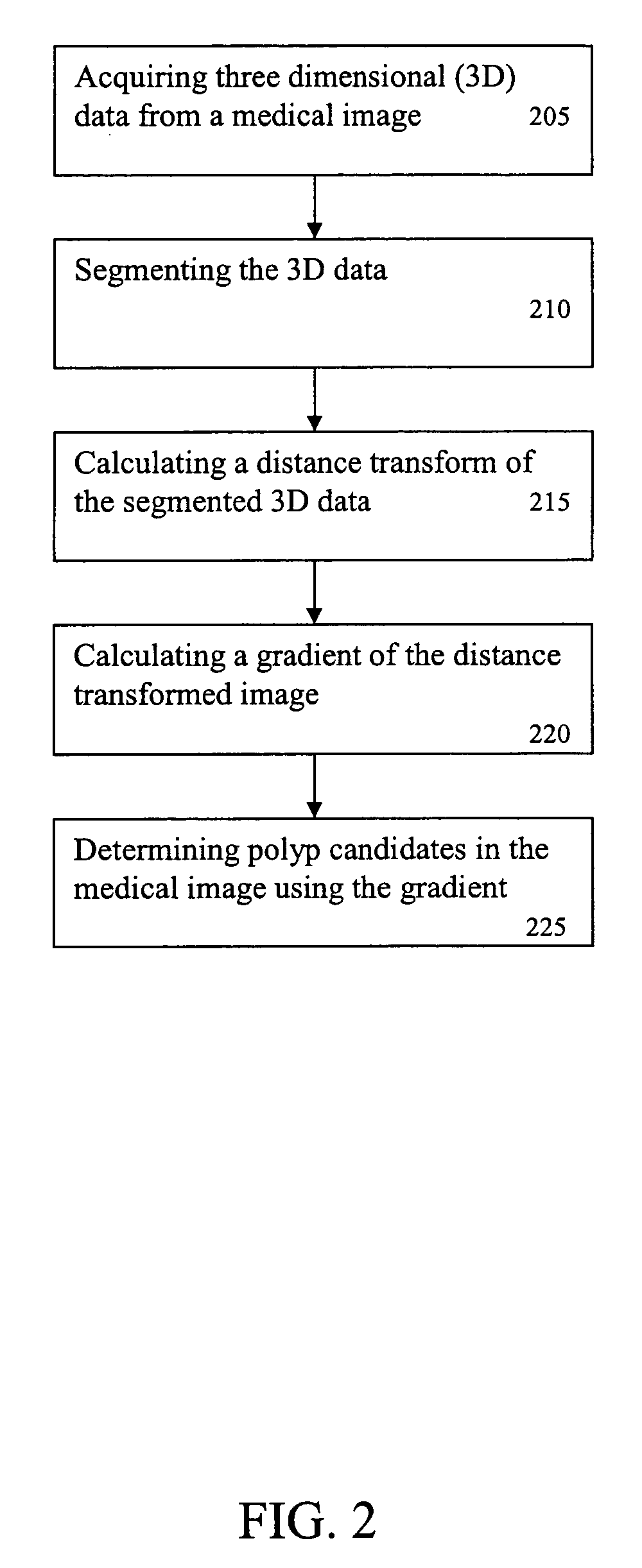
InactiveUS20050008205A1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnatomical partMedical image computing
A system and method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image are provided. The method comprises: acquiring a medical image, wherein the medical image is of an anatomical part; segmenting the medical image; calculating a distance map of the medical image; calculating a gradient of the distance mapped medical image; and processing the gradient to detect a protrusion in the medical image. The gradient is processed by: projecting a plurality of rays from a location in the distance mapped medical image; calculating a value for each of the plurality of rays based on features of each of the plurality of rays and the gradient of the distance mapped medical image; summing and scaling the value of each of the plurality of rays; and detecting one of a sphere-like and polyp-like shape using the summed and scaled values of the plurality of rays, wherein one of the sphere-like and polyp-like shapes is the protrusion.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
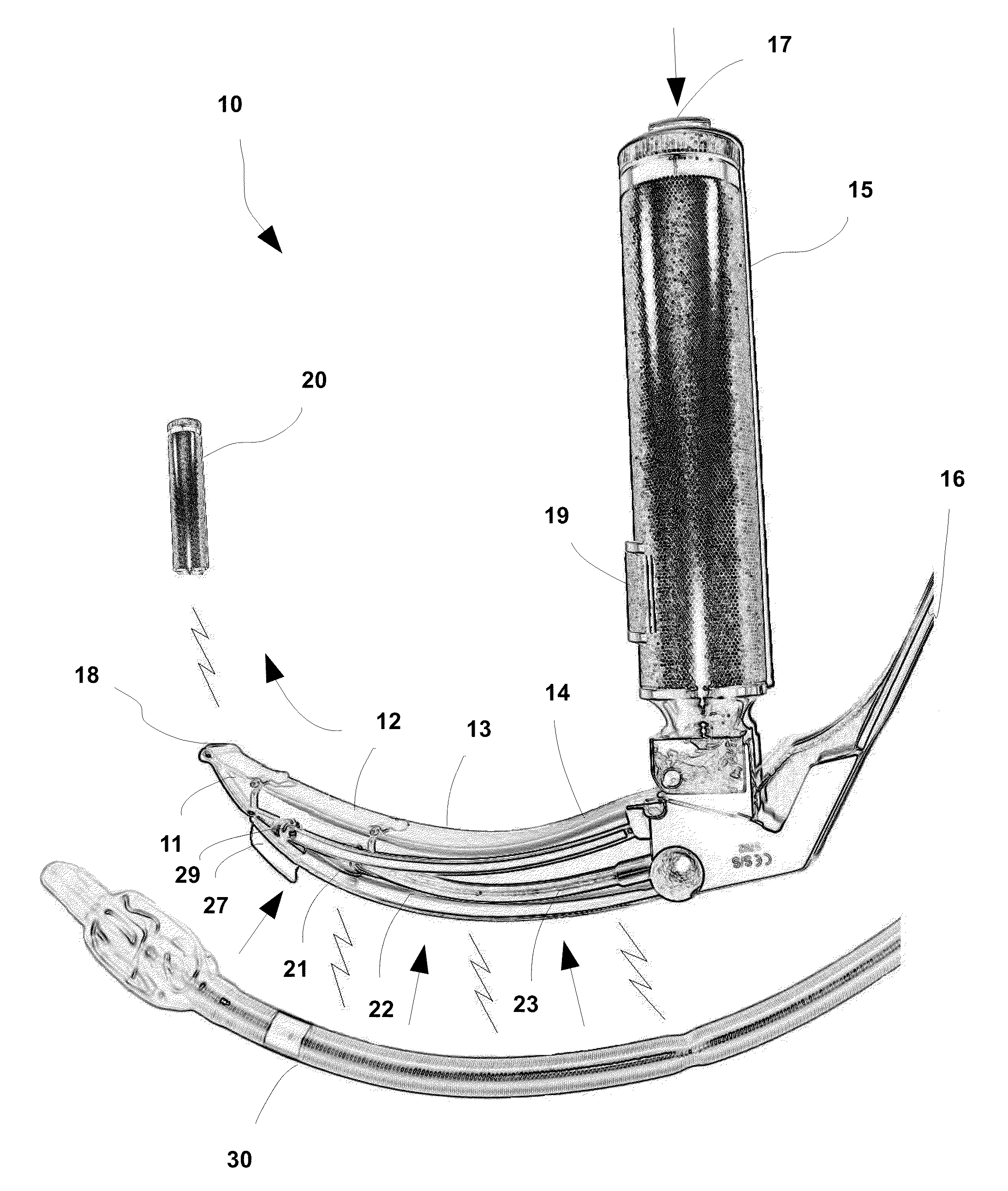
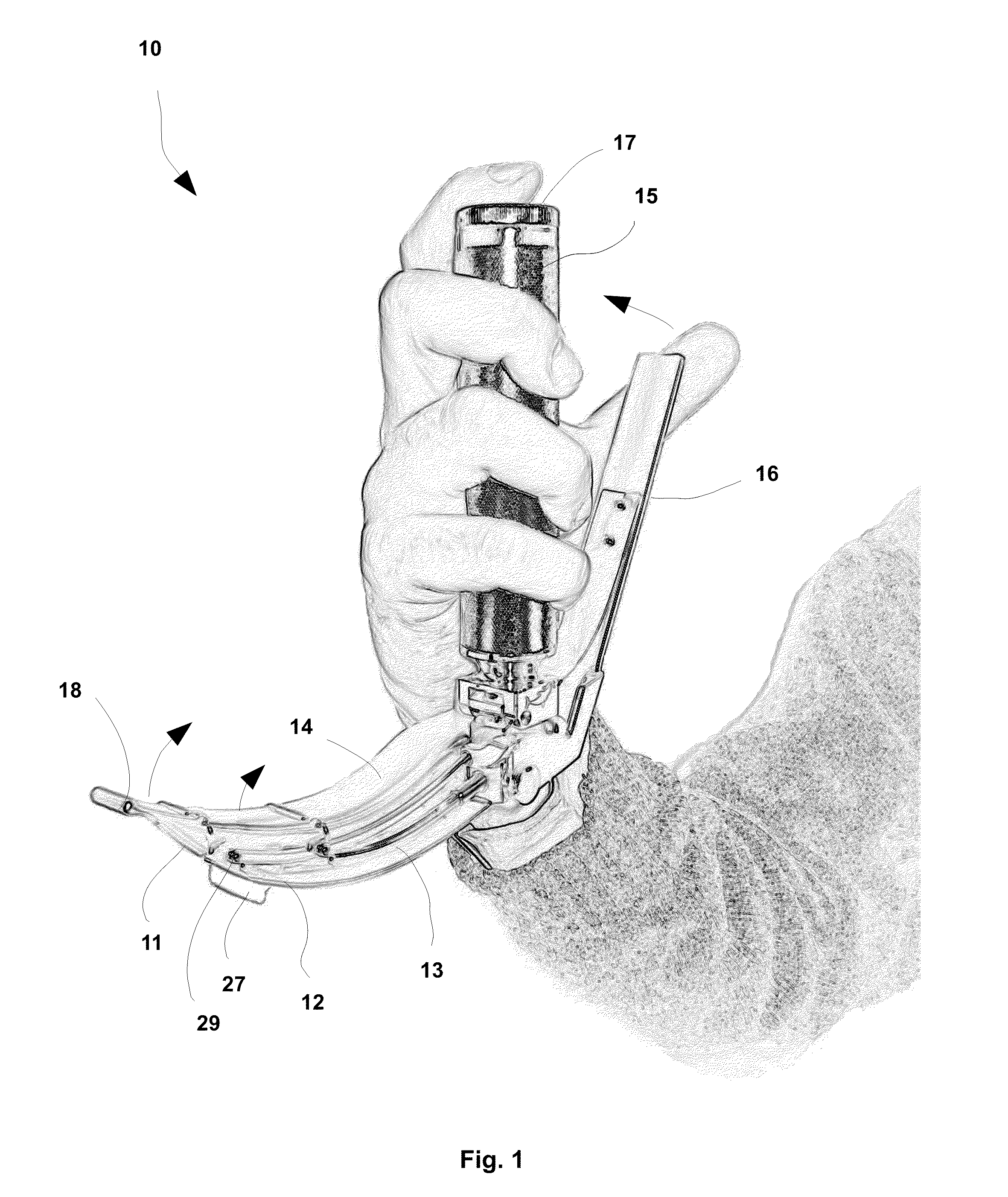
Laryngoscope, comprising a set of magnetic elements
InactiveUS20120022332A1Easy to viewFast and precise and comfortableRespiratorsBronchoscopesAnatomic SiteEndotracheal intubation
Owner:DE DOMENICO ANDREA
System and method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image
A method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image includes: acquiring a medical image, wherein the medical image is of an anatomical part; segmenting the medical image; calculating a distance map of the medical image; calculating a gradient of the distance mapped medical image; and processing the gradient to detect a protrusion in the medical image. The gradient is processed by: projecting a plurality of rays from a location in the distance mapped medical image; calculating a value for each of the plurality of rays based on features of each of the plurality of rays and the gradient of the distance mapped medical image; summing and scaling the value of each of the plurality of rays; and detecting one of a sphere-like and polyp-like shape using the summed and scaled values of the plurality of rays, wherein one of the sphere-like and polyp-like shapes is the protrusion.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Neural network for generating synthetic medical images
Systems, computer-implemented methods, and computer readable media for generating a synthetic image of an anatomical portion based on an origin image of the anatomical portion acquired by an imaging device using a first imaging modality are disclosed. These systems may be configured to receive the origin image of the anatomical portion acquired by the imaging device using the first imaging modality, receive a convolutional neural network model trained for predicting the synthetic image based on the origin image, and convert the origin image to the synthetic image through the convolutional neural network model. The synthetic image may resemble an imaging of the anatomical portion using a second imaging modality differing from the first imaging modality.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Express-registering regions of the body
ActiveUS20100307516A1Improve accuracySurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomic SiteAnatomical part
The present invention relates to a method for determining the region of the body in which an anatomical part of the body is situated, said method including the following steps:anatomical point data is provided which includes information concerning a spatial pattern of positions of patient landmarks of a part of a patient's body which corresponds to the anatomical part of the body;landmark data is provided which includes information concerning a spatial pattern of positions of model landmarks of a model of the anatomical part of a patient's body;wherein, assuming thatthe patient landmarks represent the same landmarks as the model landmarks,the region of the body in which the part of the patient's body is situated is determined on the basis of the landmark data and the anatomical point data.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Surgical navigation registration system
ActiveCN110547872AReduce distractionsImprove navigation accuracySurgical navigation systemsAnatomic SiteAnatomical part
The invention discloses a surgical navigation registration system. The surgical navigation registration system is provided with a registration probe, an image acquisition device and a navigation terminal, wherein the registration probe is used for detecting an electromagnetic intensity signal of a marking point through an electromagnetic sensor and calibrating the position of the marking point through an optical mark; the image acquisition device acquires optical image information of the optical mark; and the navigation terminal acquires scanning image information including the marking point and an anatomical part, and carries out marking point positioning by adopting an electromagnetic positioning mode and an optical positioning mode, so that the conversion relation between the surgical space required by the electromagnetic surgical navigation and the computer space, and the conversion relation between the surgical space required by the optical surgical navigation and the computer aredetermined.
Owner:CHONGQING BOSSCAN TECH CO LTD
Anatomical adaptable drape device
An anatomical drape (1a or 1b), such as a dental drape, for covering a treatment area of an anatomical part, the drape comprising an elastomeric material capable of conforming to the contours of the anatomical part and including a curing agent (9) contained within internal channels distributed in the drape; and wherein activation of the curing agent, for example by a light source, causes hardening of the material to at least partially set the drape in a configuration conforming to the anatomical part. The semi-rigid set drape is liquid impermeable but gas permeable. A method of manufacturing the drape is also disclosed.
Owner:MAVRIK DENTAL SYST
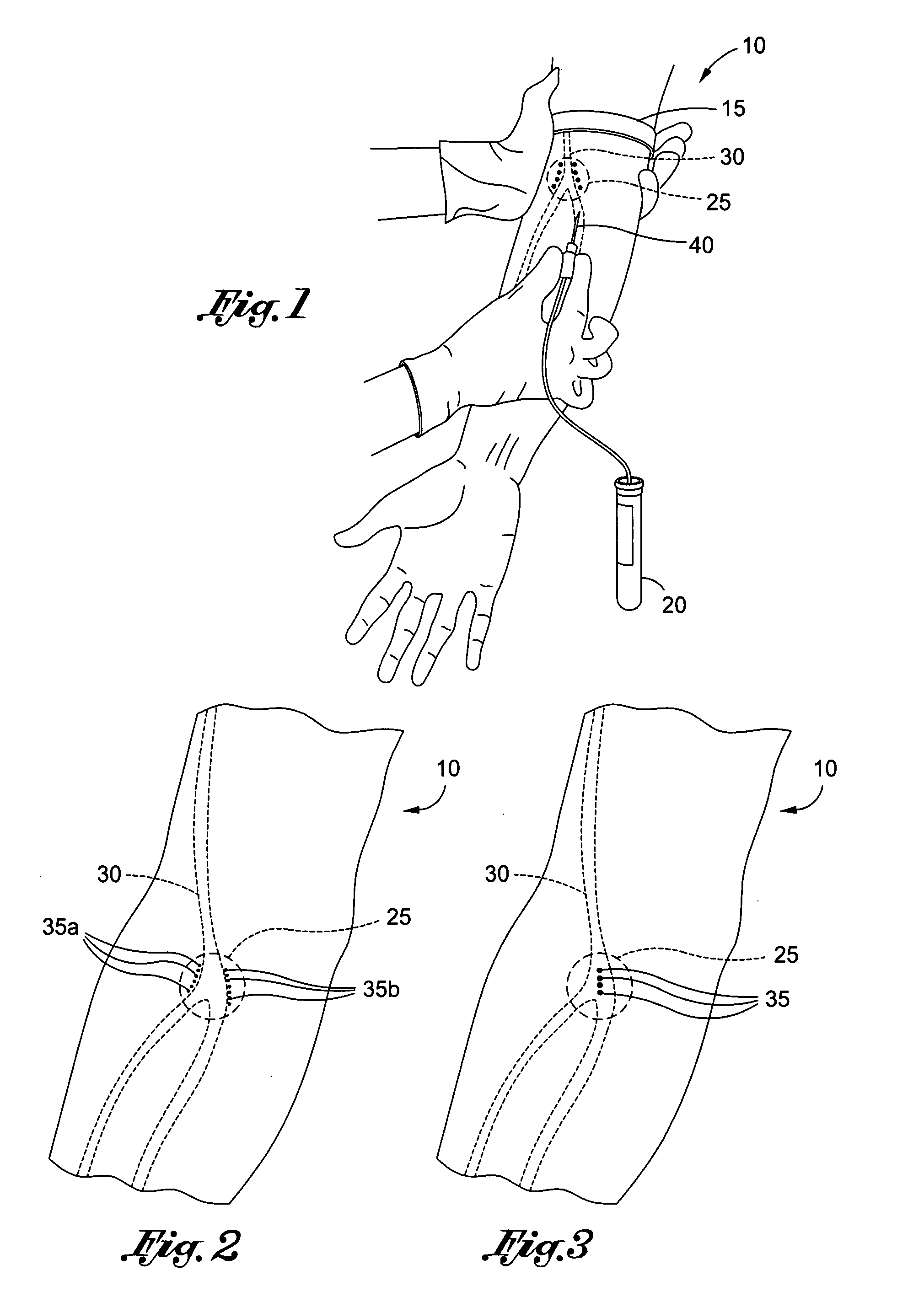
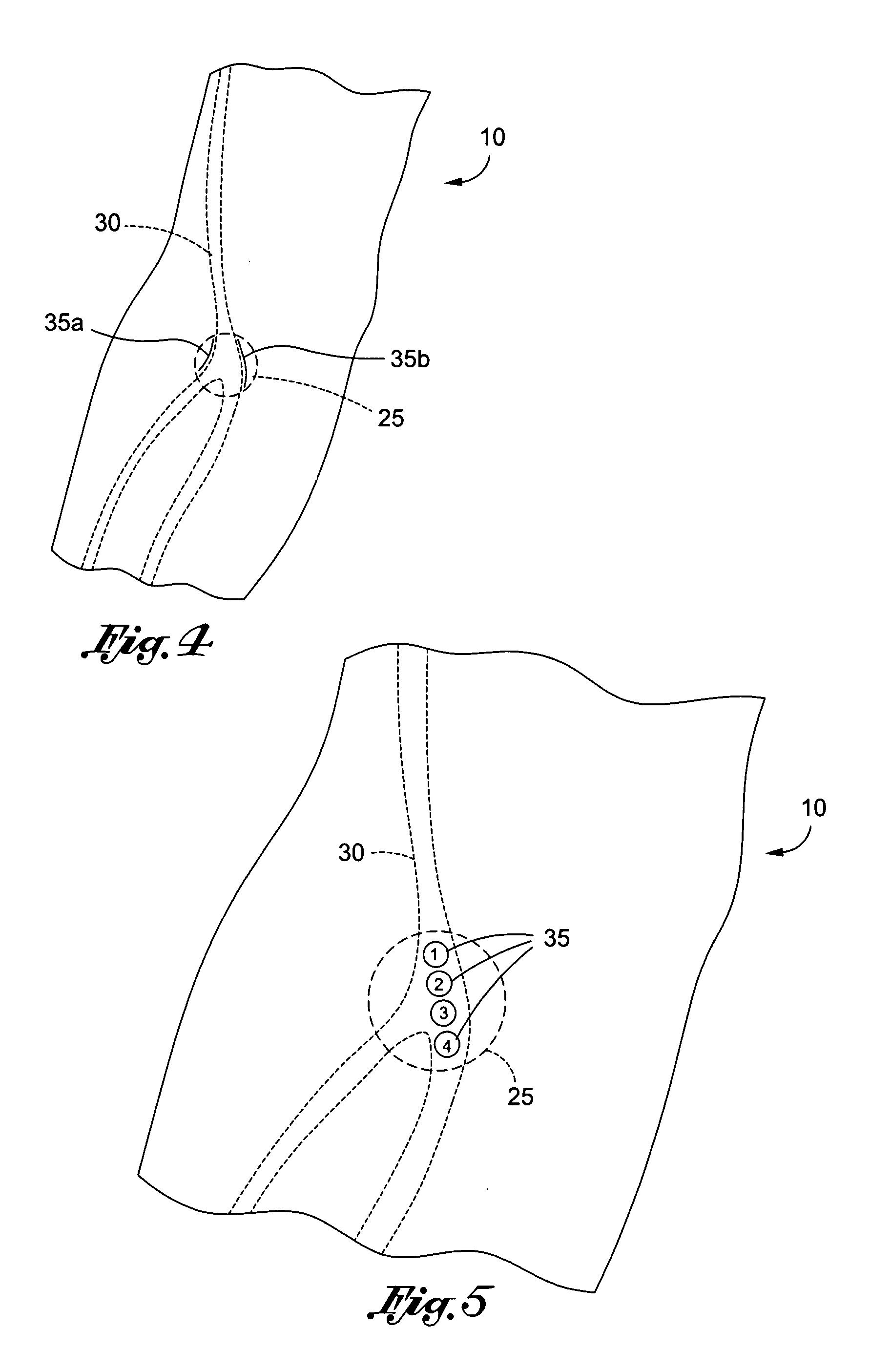
Method of locating vessel puncture access sites via tattoo or permanent marking
A method of marking the boundaries of at least one vessel with a vessel access marking for locating a vessel puncture access site to facilitate the introduction or withdrawal of fluid from the vein in connection with a medical procedure, the method comprising the steps of: designating an anatomical portion of an individual on which the medical procedure is performed; locating a vessel along the anatomical portion of the individual; applying a marking material to designate the boundaries of the vein, the marking material defining a region for vessel puncture access; cleansing an area proximate the vessel access marking and accessing the region of vessel puncture access using the vessel access marking as a visual reference.
Owner:COOK HAROLD D
Anatomical data processing method, device and system
ActiveCN107248353AReduce usageAlleviate the current situation of resource shortageImage enhancementImage analysisData processing systemHuman body
The invention provides an anatomical data processing method, device and system. The anatomical data processing method is applied to a server in the anatomical data processing system, and comprises the steps of receiving a first anatomical data processing request which is sent by a terminal and caries a target anatomical part identifier; determining a target anatomical part three-dimensional model corresponding to the target anatomical part identifier according to a pre-generated mapping relation between anatomical part identifiers and anatomical part three-dimensional models, and sending the target anatomical part three-dimensional model to the terminal, wherein the target anatomical part three-dimensional model is a foundation or basis for the terminal to perform display. According to the method disclosed by the invention, display of the terminal for the target anatomical part three-dimensional model is realized through data interaction between a server and the terminal, and a user can watch the anatomical part effectively in real time by using the terminal, so that utilization of a human body anatomical specimen is reduced, thus the current situation that the human body anatomical specimen source is shortage is effective relieved, and further a problem that students sitting far away cannot watch when the number of learning people is great is also avoided.
Owner:山东数字人科技股份有限公司
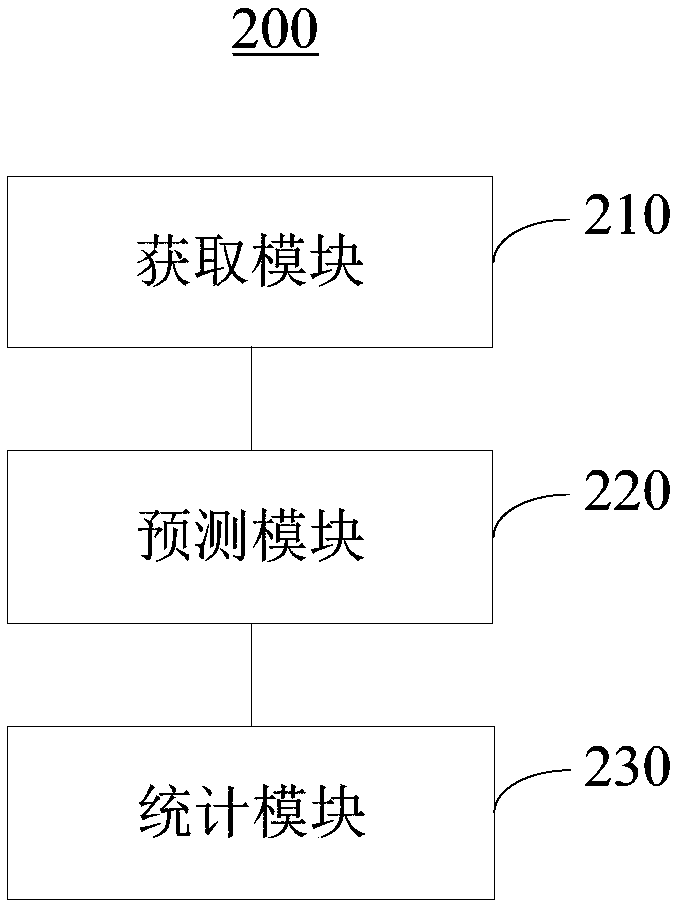
Endoscopic image recognition method and device
InactiveCN109446627AReduce workloadRelieve painAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsDesign optimisation/simulationEndoscopic operationsCLARITY
The embodiments of that present application provide the endoscopic image recognition method and device. By acquiring a first number of frame key frames from a unit time video stream in an endoscopically acquired medical image, then, based on the pre-trained anatomical part prediction model, and predicting the anatomical part in each key frame of the first number of frames, a the prediction resultof each key frame is obtained, wherein the prediction result includes the confidence level of each anatomical part in the key frame of the frame. Finally, the prediction result of each key frame is counted, and if the same prediction result exceeds the second number, the corresponding endoscopic image recognition result is output. Thus, the anatomical part in each key frame can be automatically collected and recognized, and the doctor does not need to care about the quantity, quality, and clarity of the collected images, so that the doctor has more energy to focus on the endoscopic operation and observation, thereby lightening the workload of the doctor, improving the examination quality, and reducing the pain of the patient in the examination process.
Owner:青岛美迪康数字工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com