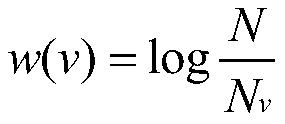Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Medical image computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
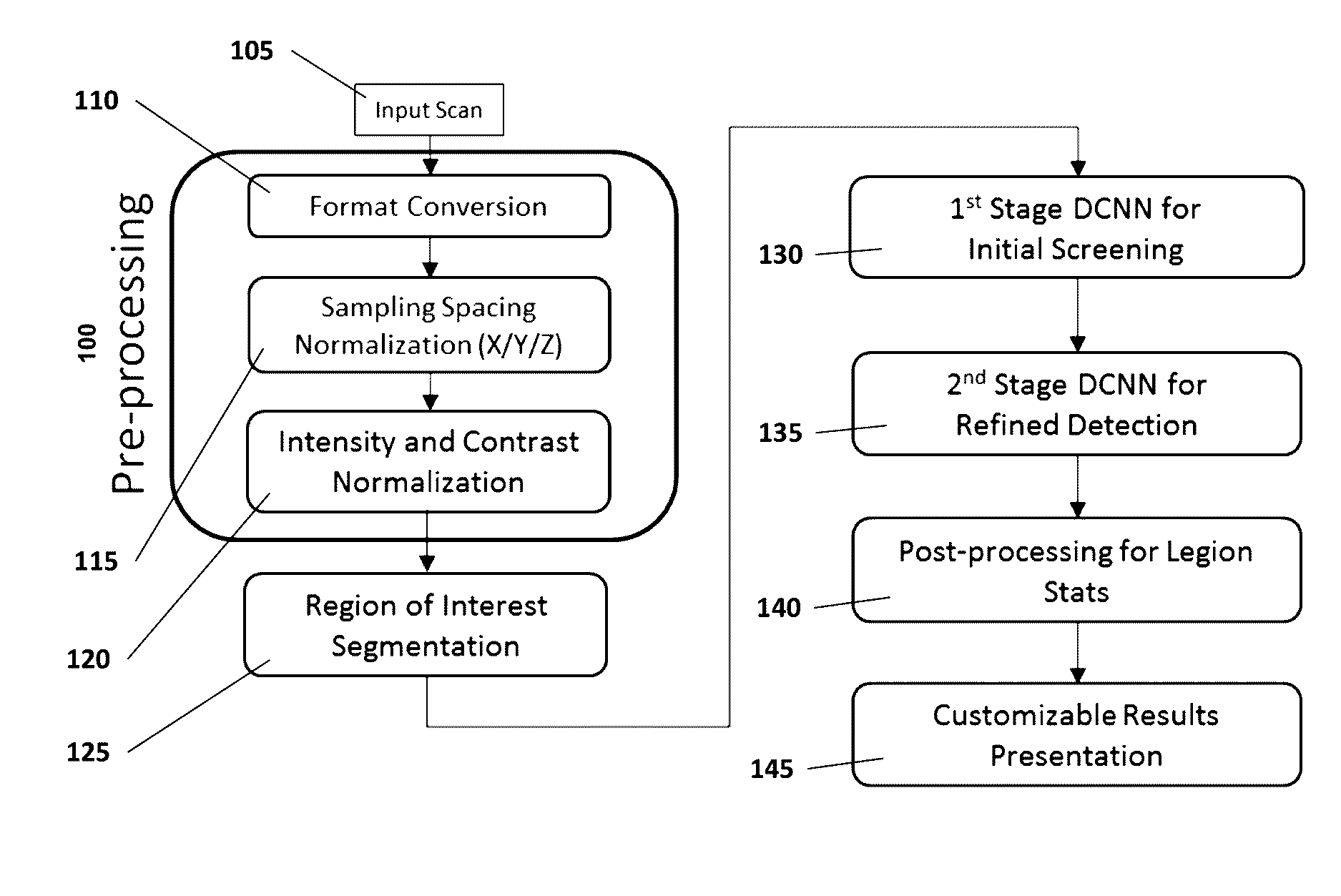
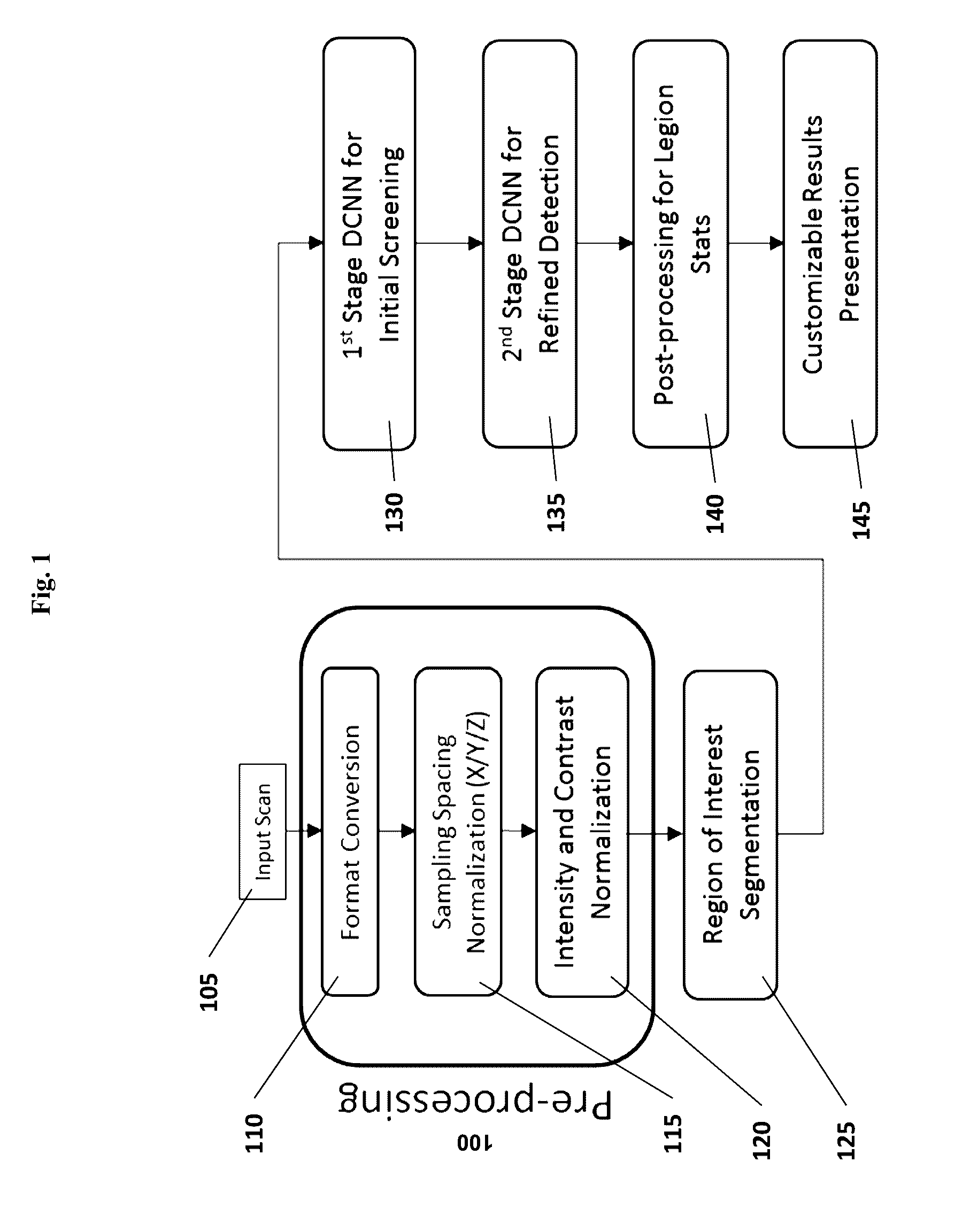
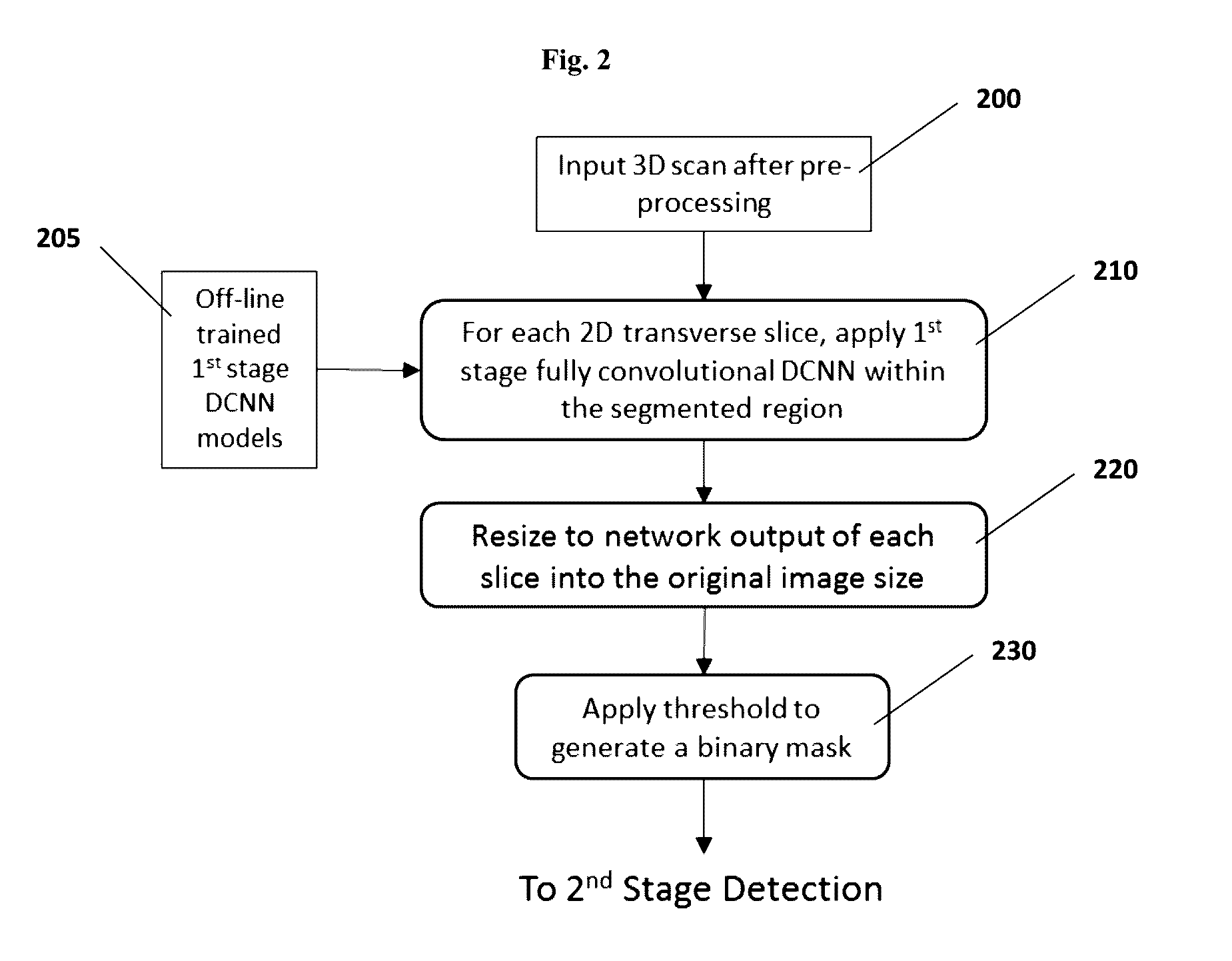
Medical image computing (MIC) is an interdisciplinary field at the intersection of computer science, information engineering, electrical engineering, physics, mathematics and medicine. This field develops computational and mathematical methods for solving problems pertaining to medical images and their use for biomedical research and clinical care.
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveUS9589374B1Examination time can be shortenedImprove diagnostic accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionAided diagnosis
Owner:12 SIGMA TECH
Method and system of computer-aided quantitative and qualitative analysis of medical images
ActiveUS20070133852A1Improve discriminationImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputer-aided
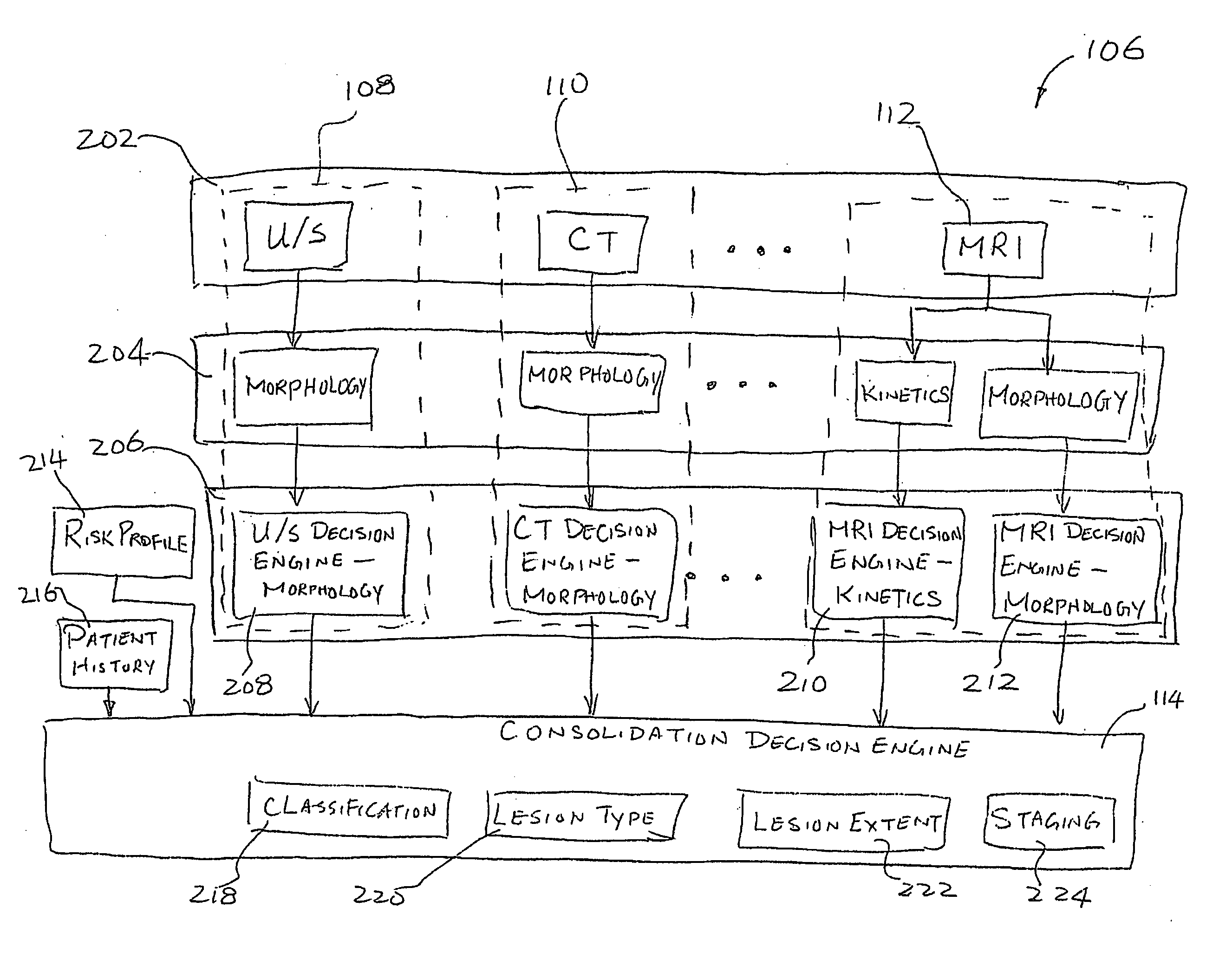
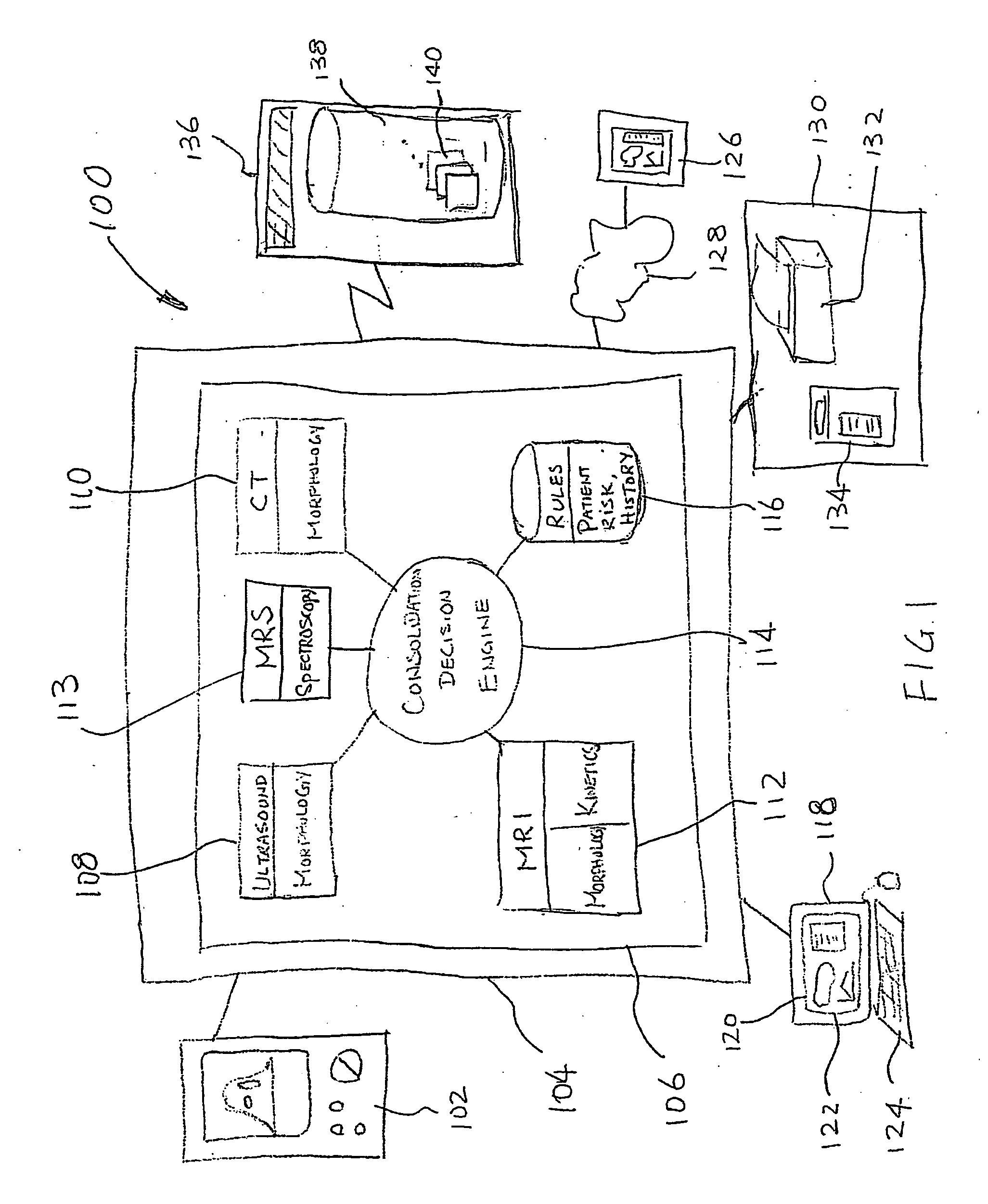
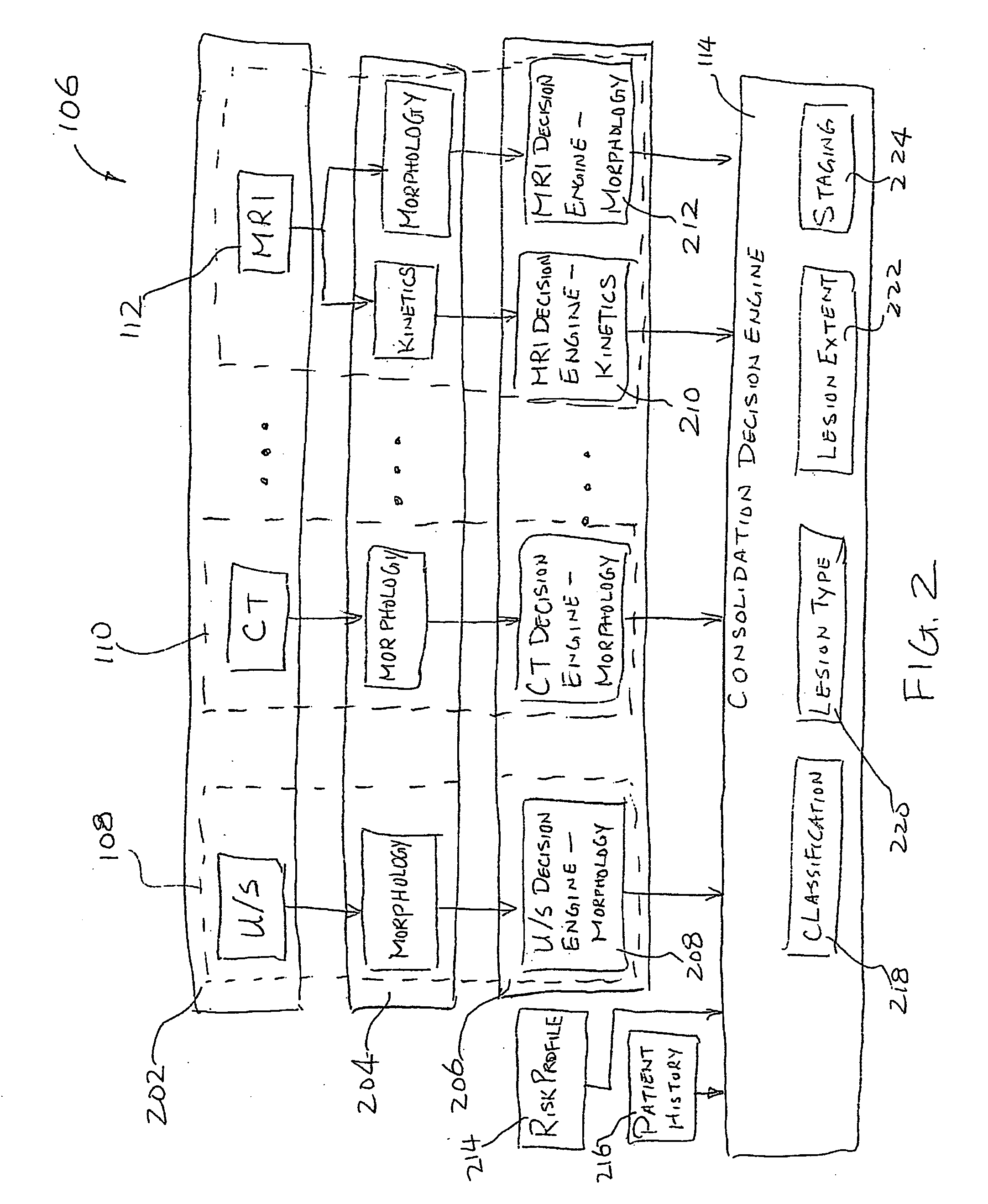
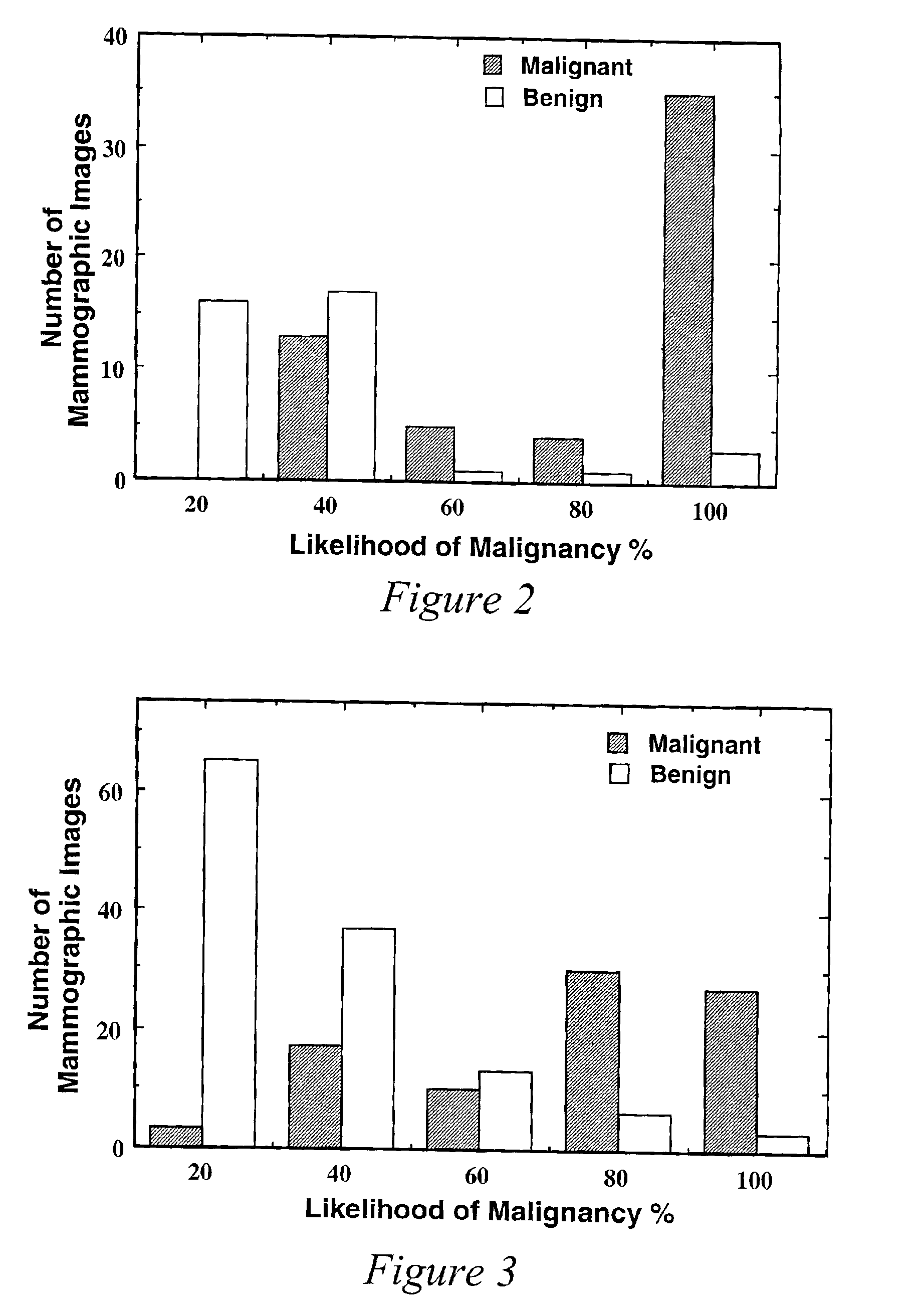
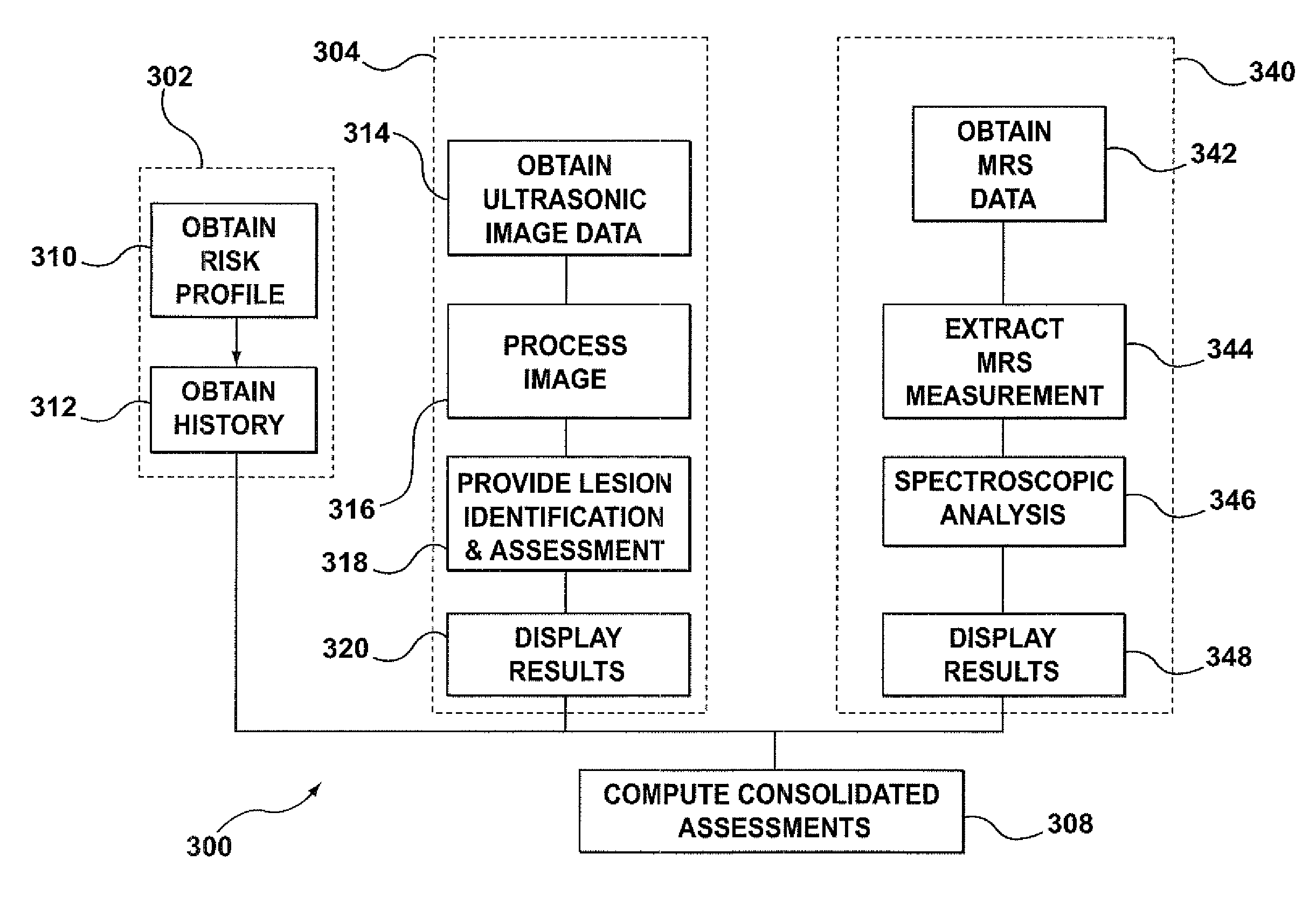
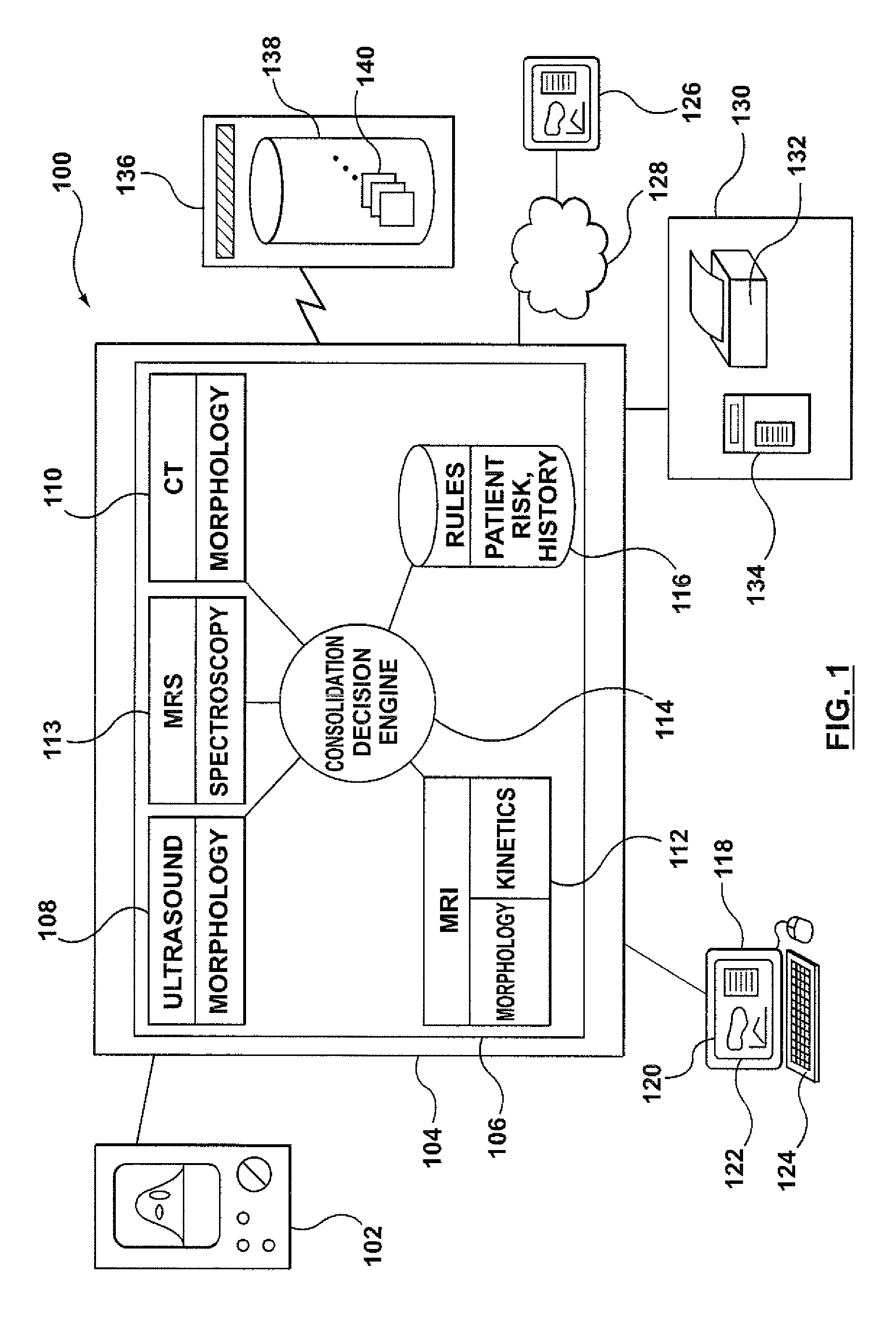
A system and method of computer aided analysis of medical images and detection of malignant lesions is described. Medical images obtained from multiple modalities are analyzed. Morphological features as well as temporal, i.e., kinetics features, are combined to compute a consolidated assessment of a possible lesion detected in the medical images. The system includes at least one kinetics module, which is capable of extracting kinetics features from a time sequence of MRI images or MRS data taken after administering a contrast enhancement agent to a patient. The consolidated assessment is presented to a user for confirmation or modification.
Owner:SALIENT IMAGING +1
Method, system and computer readable medium for an intelligent search workstation for computer assisted interpretation of medical images
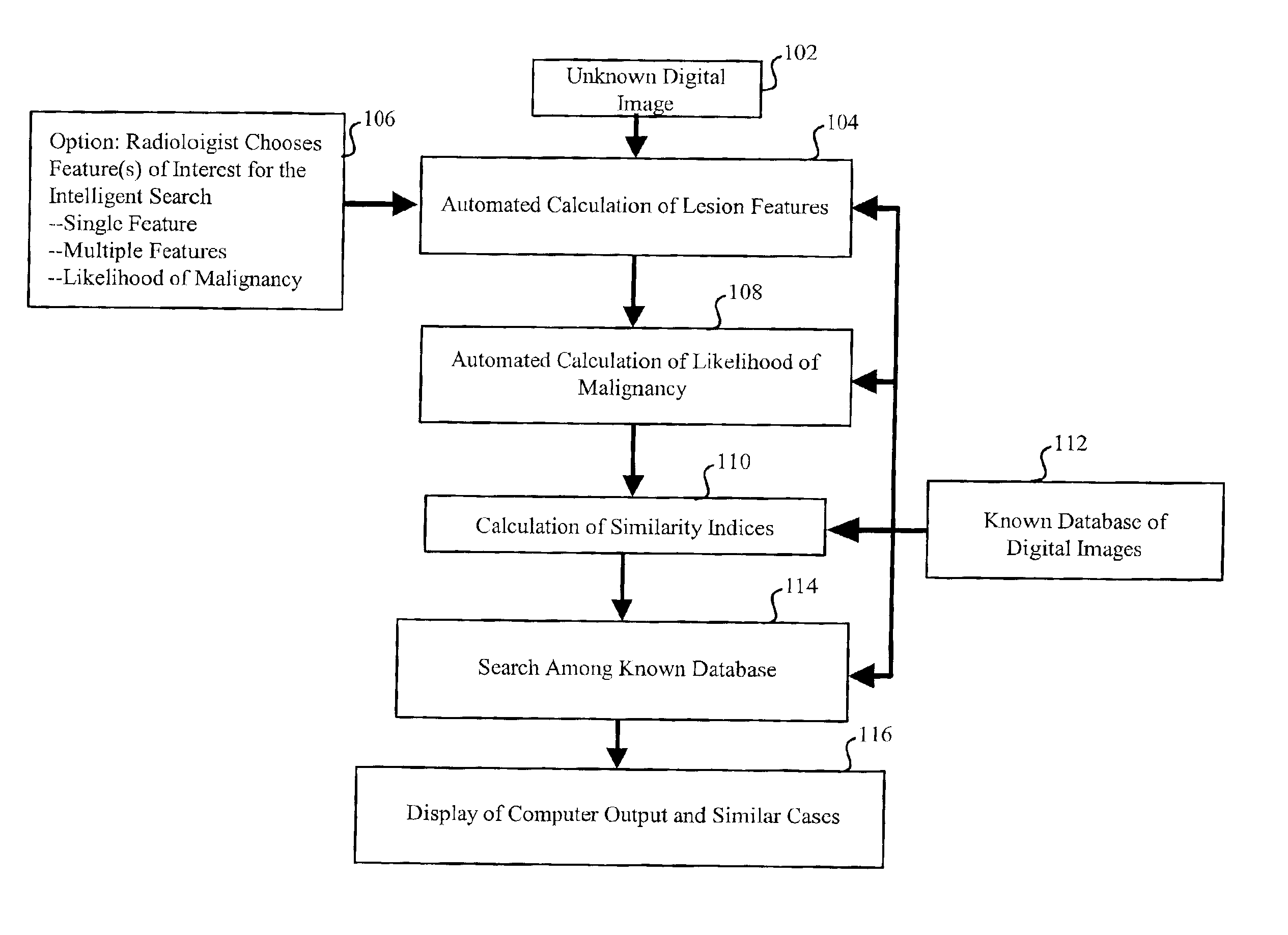
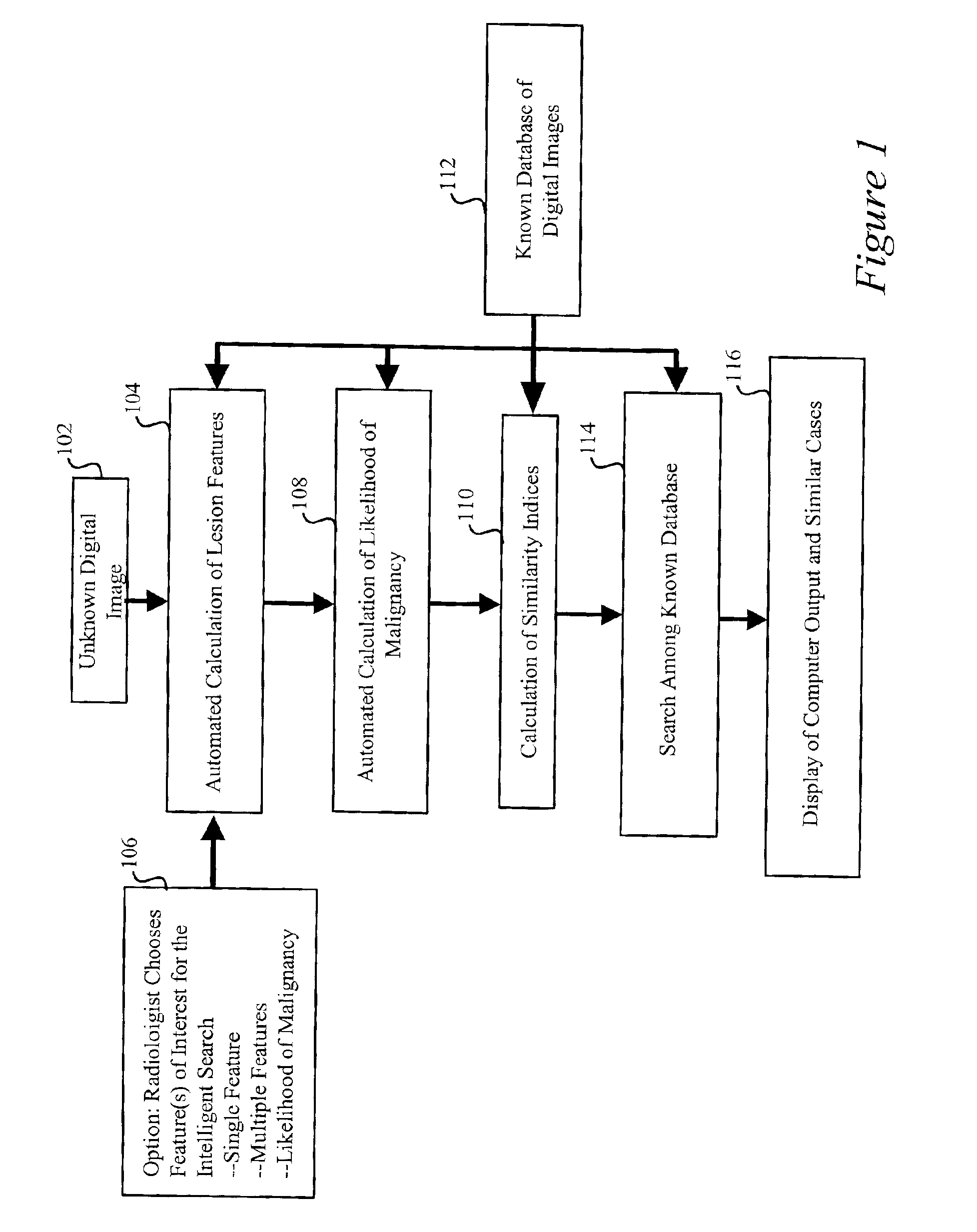
A method, system and computer readable medium for an intelligent search display into which an automated computerized image analysis has been incorporated. Upon viewing an unknown mammographic case, the display shows both the computer classification output as well as images of lesions with known diagnoses (e.g., malignant vs. benign) and similar computer-extracted features. The similarity index used in the search can be chosen by the radiologist to be based on a single feature, multiple features, or on the computer estimate of the likelihood of malignancy. Specifically the system includes the calculation of features of images in a known database, calculation of features of an unknown case, calculation of a similarity index, display of the known cases along the probability distribution curves at which the unknown case exists. Techniques include novel developments and implementations of computer-extracted features for similarity calculation and novel methods for the display of the unknown case amongst known cases with and without the computer-determined diagnoses.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Method and system of computer-aided quantitative and qualitative analysis of medical images
Owner:SALIENT IMAGING +1
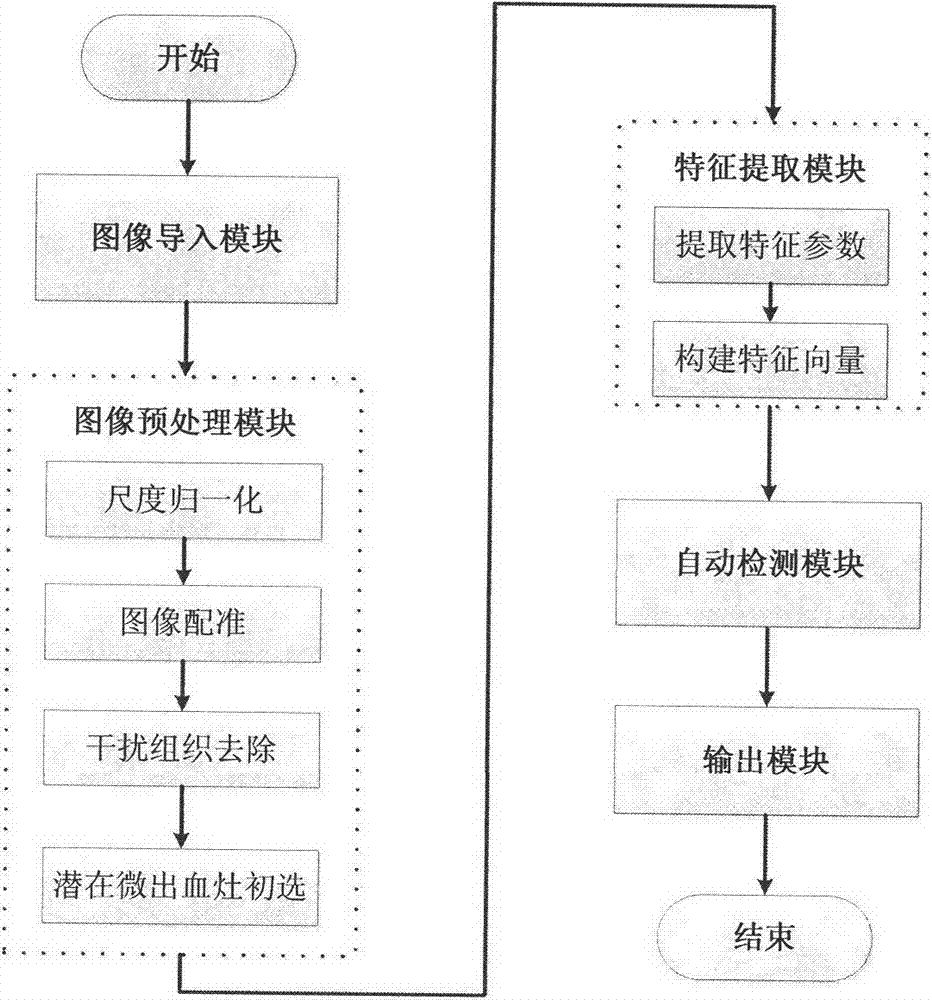
Magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system
InactiveCN104414636AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMR - Magnetic resonanceMedical image computing
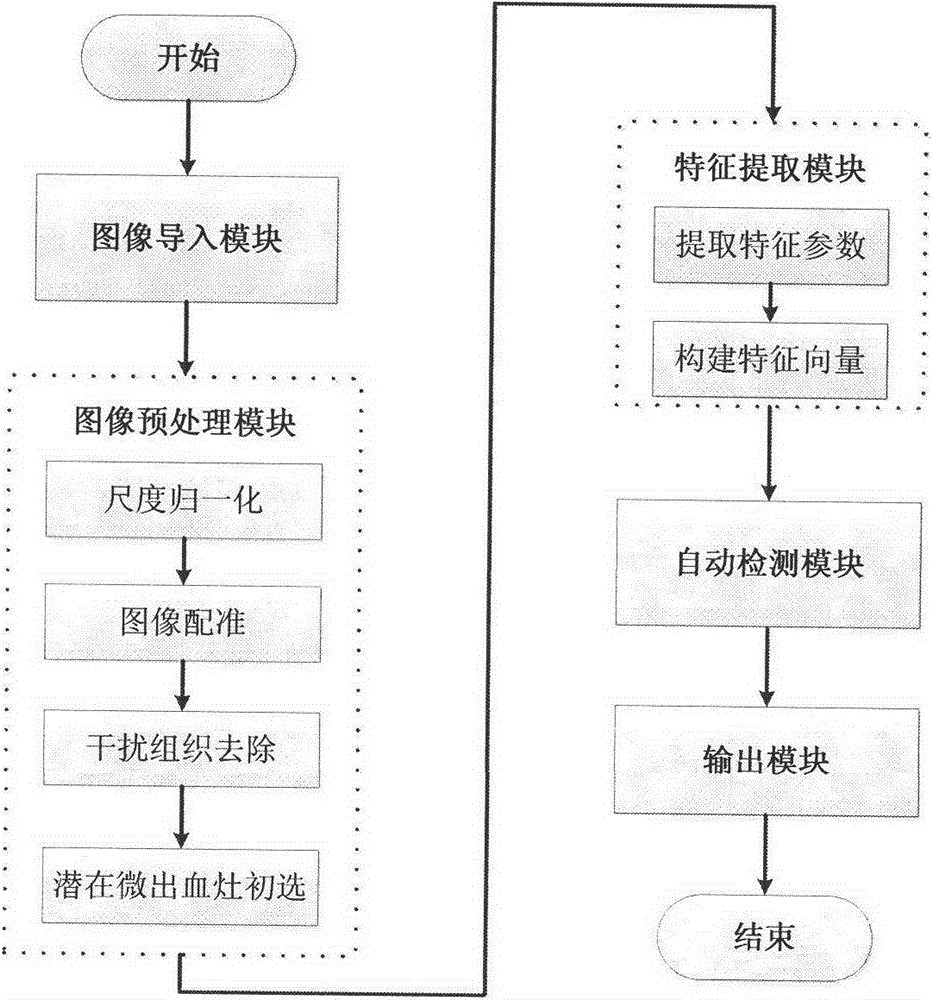
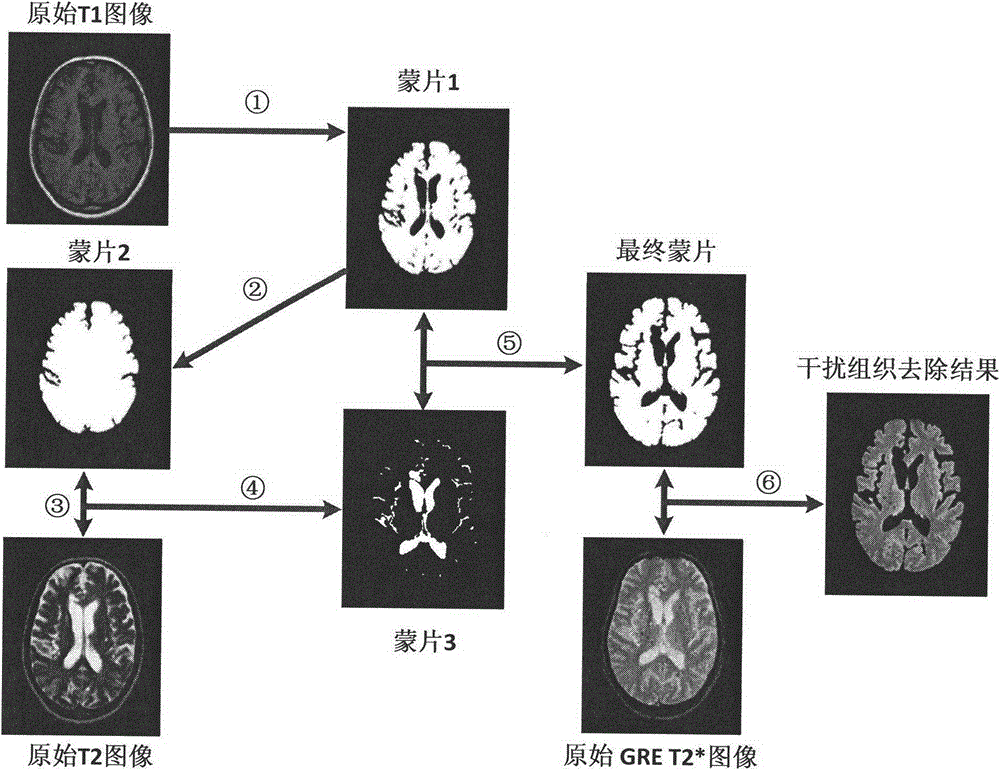
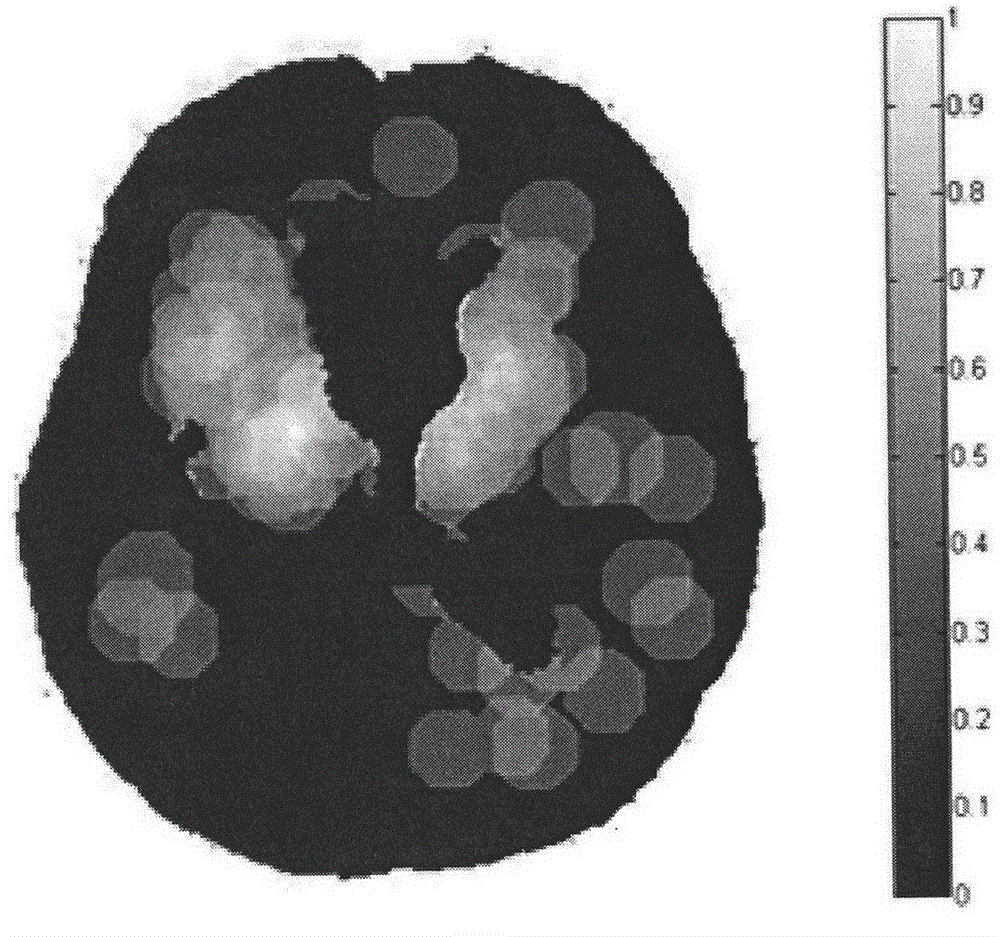
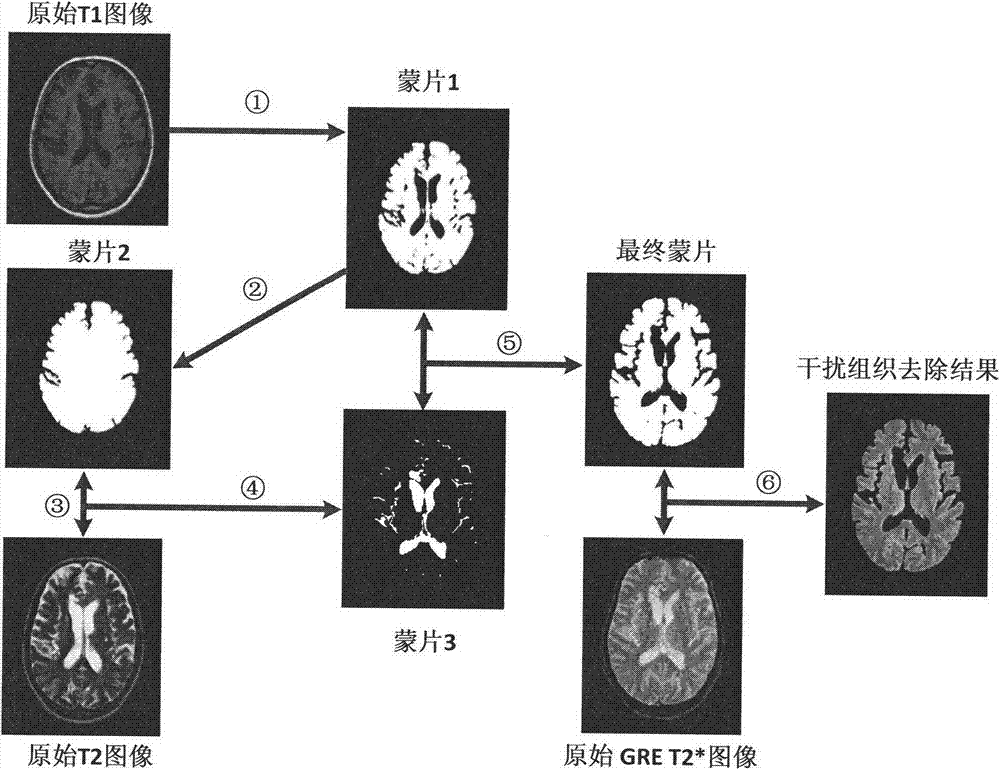
The invention provides a magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system and belongs to the medical image computer auxiliary detection field. The magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system comprises five portions of an image import module, an image preprocessing module, a characteristic extraction module, an automatic detection module and a cerebral micro-bleeding automatic detection report output module. According to the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system, the characteristics of T1, T2 and GRET2* images are comprehensively considered, the prior information of the cerebral micro-bleeding of different cerebral positions is obtained through a cerebral micro-bleeding focus prior distribution probability template, and a random forest classifier is combined to perform the automatic detection on the cerebral micro-bleeding focus; the system sensitivity is 0.890 and every case comprises 1.530 false positive focuses in average through a test; the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system is objective and high in repeatability in comparison with the traditional manual discriminant method and the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system is accurate and reliable in comparison with the existing computer auxiliary detection method; the operation is simple and convenient, the identification result of the cerebral micro-bleeding focus can be objectively provided, and meanwhile the abundant information is provided for the reference of doctors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
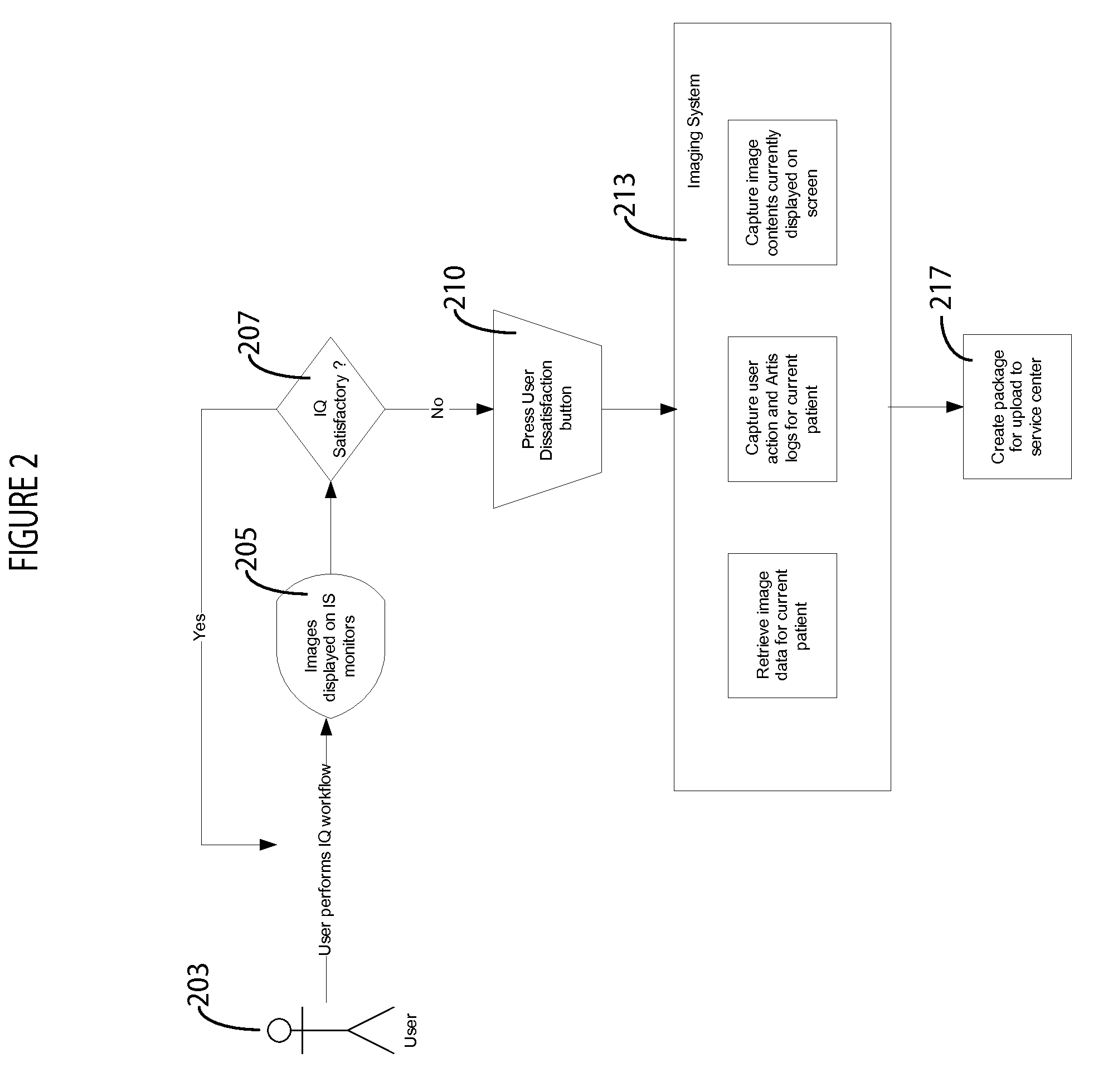
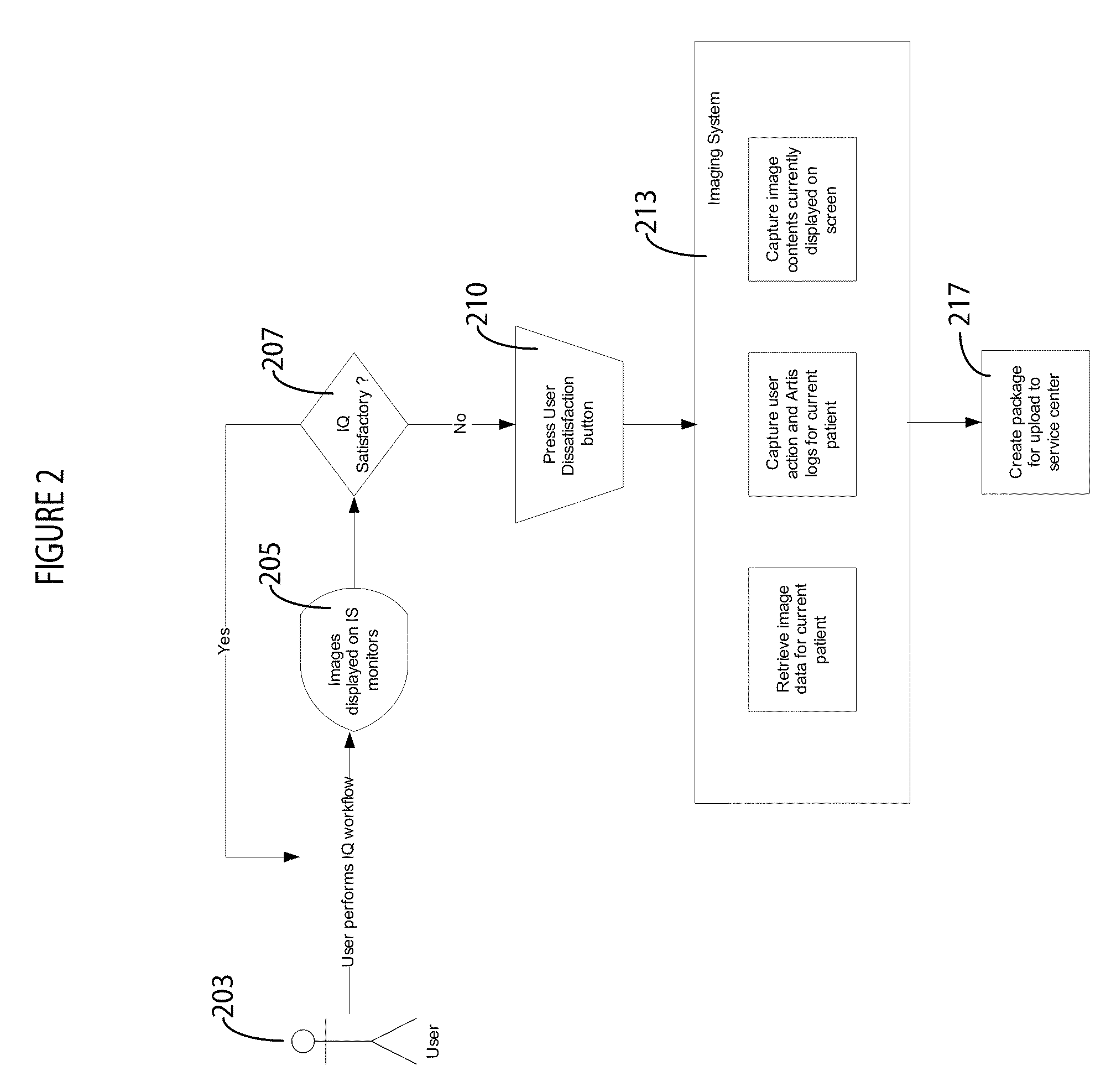
Medical Image Quality Monitoring and Improvement System
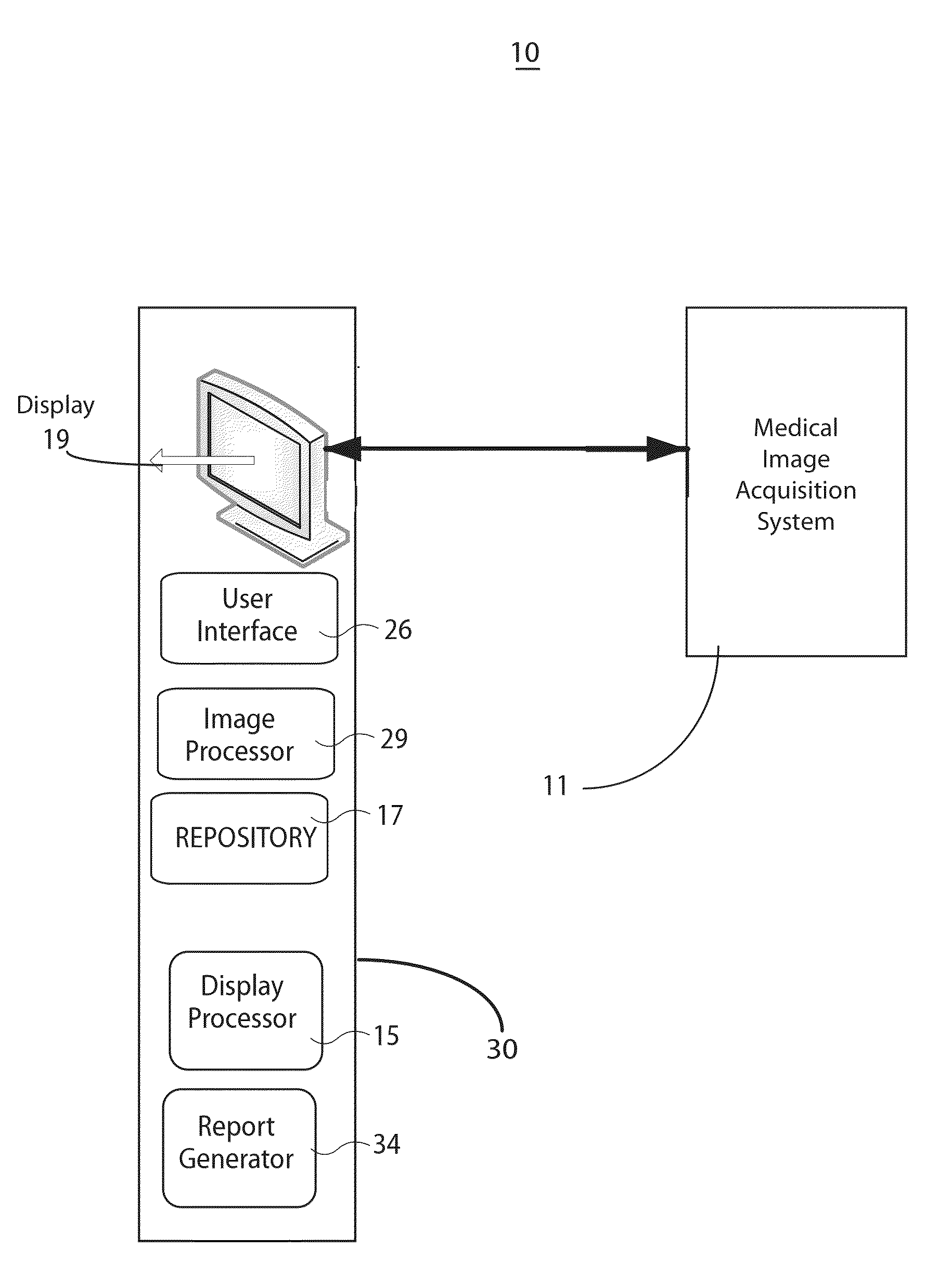
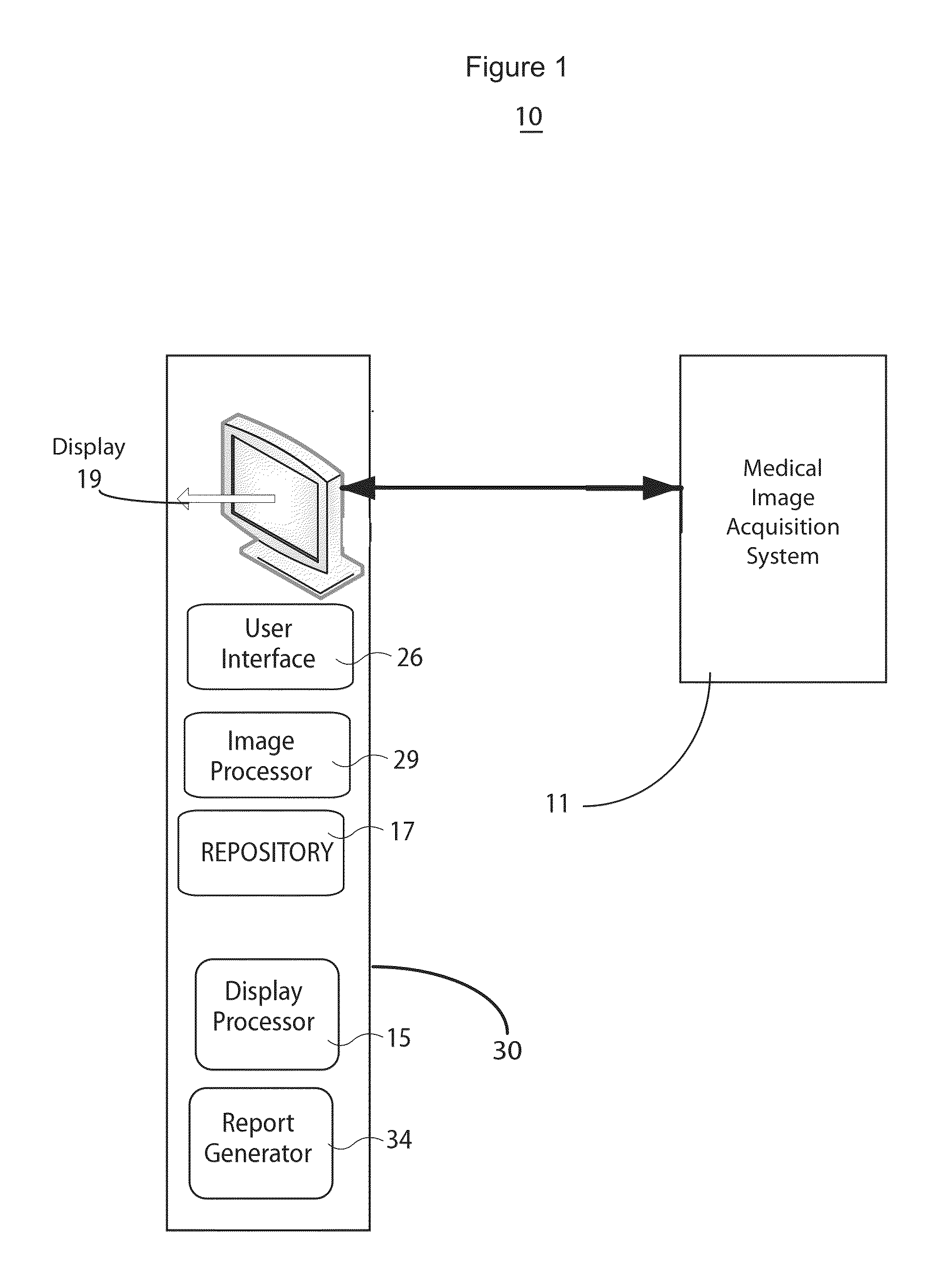
ActiveUS20130251219A1Express dissatisfactionQuality improvementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityMonitoring system
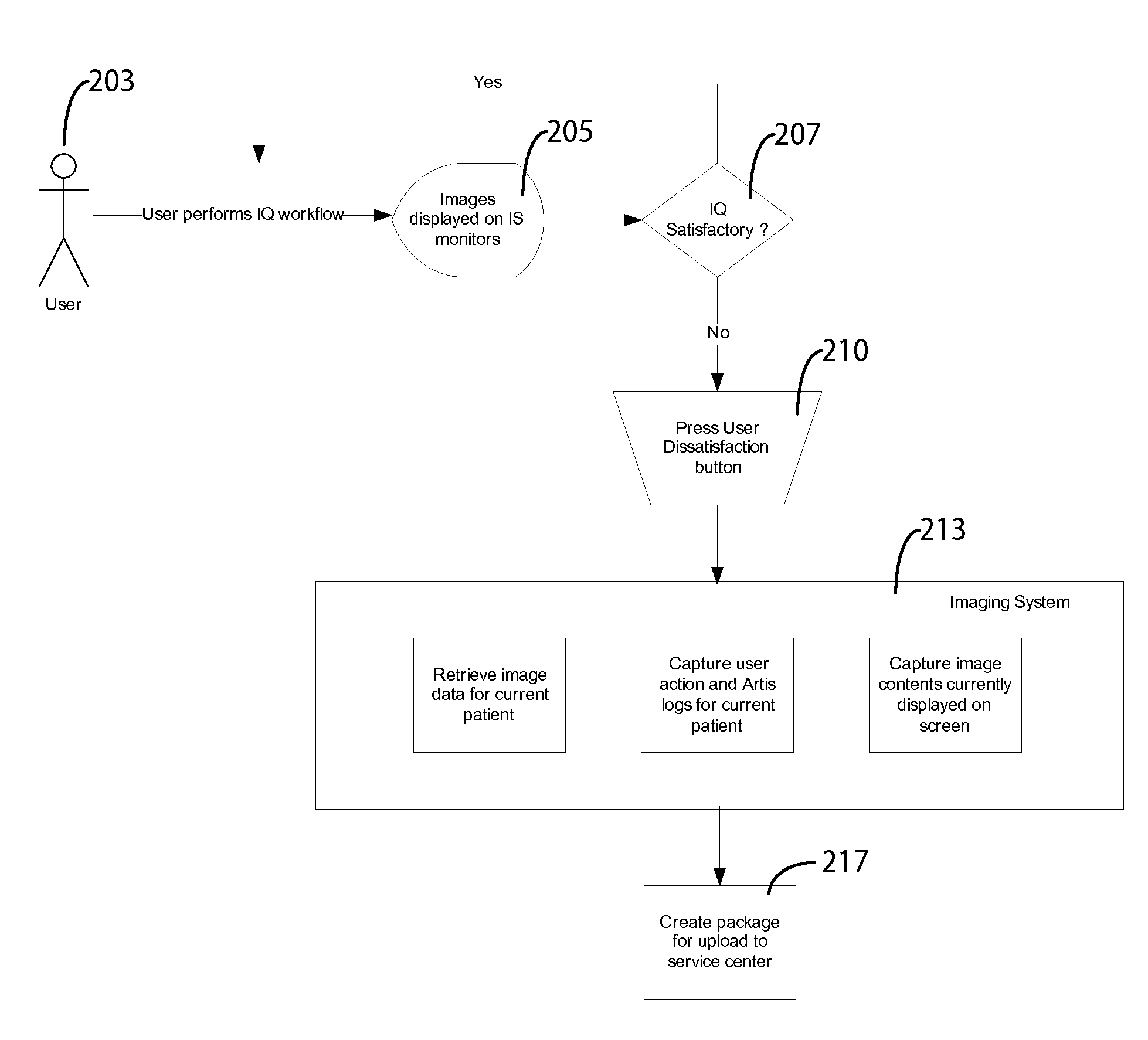
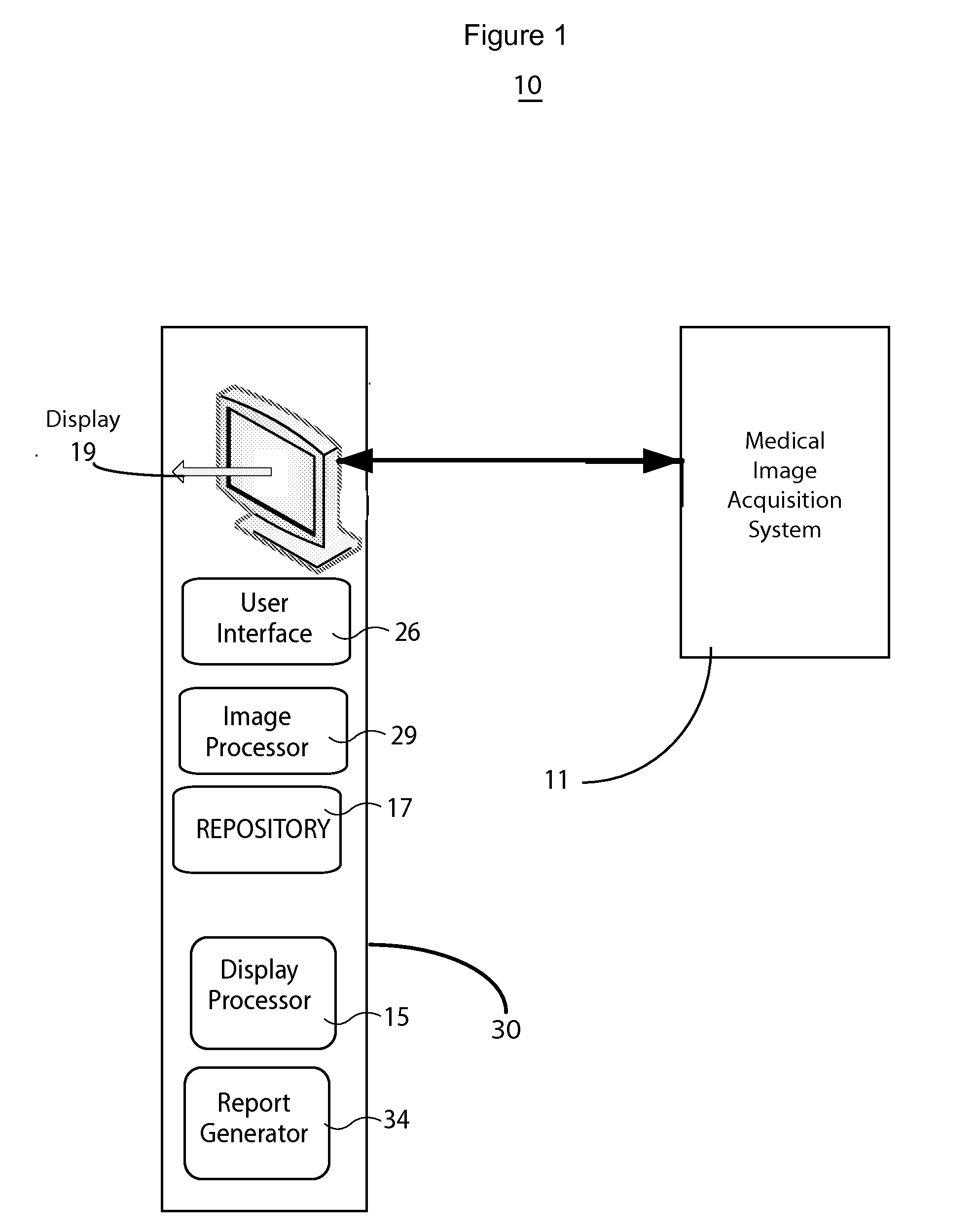
A medical image quality reporting and monitoring system for use in a medical imaging system comprises a medical image computer including, a display processor, a display and a report generator. The display processor generates data representing an image for display including a user selectable image element enabling a user to identify at least one medical image as having an image quality deficiency. The display presents the image. The report generator, in response to detection of selection of the image element, identifying at least one medical reduced quality image as having an image quality deficiency, automatically generates a report. The report comprises, data representing an anonymized reduced quality image having the image quality deficiency, a time of acquisition of the reduced quality image and imaging system acquisition settings used in acquiring the reduced quality image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
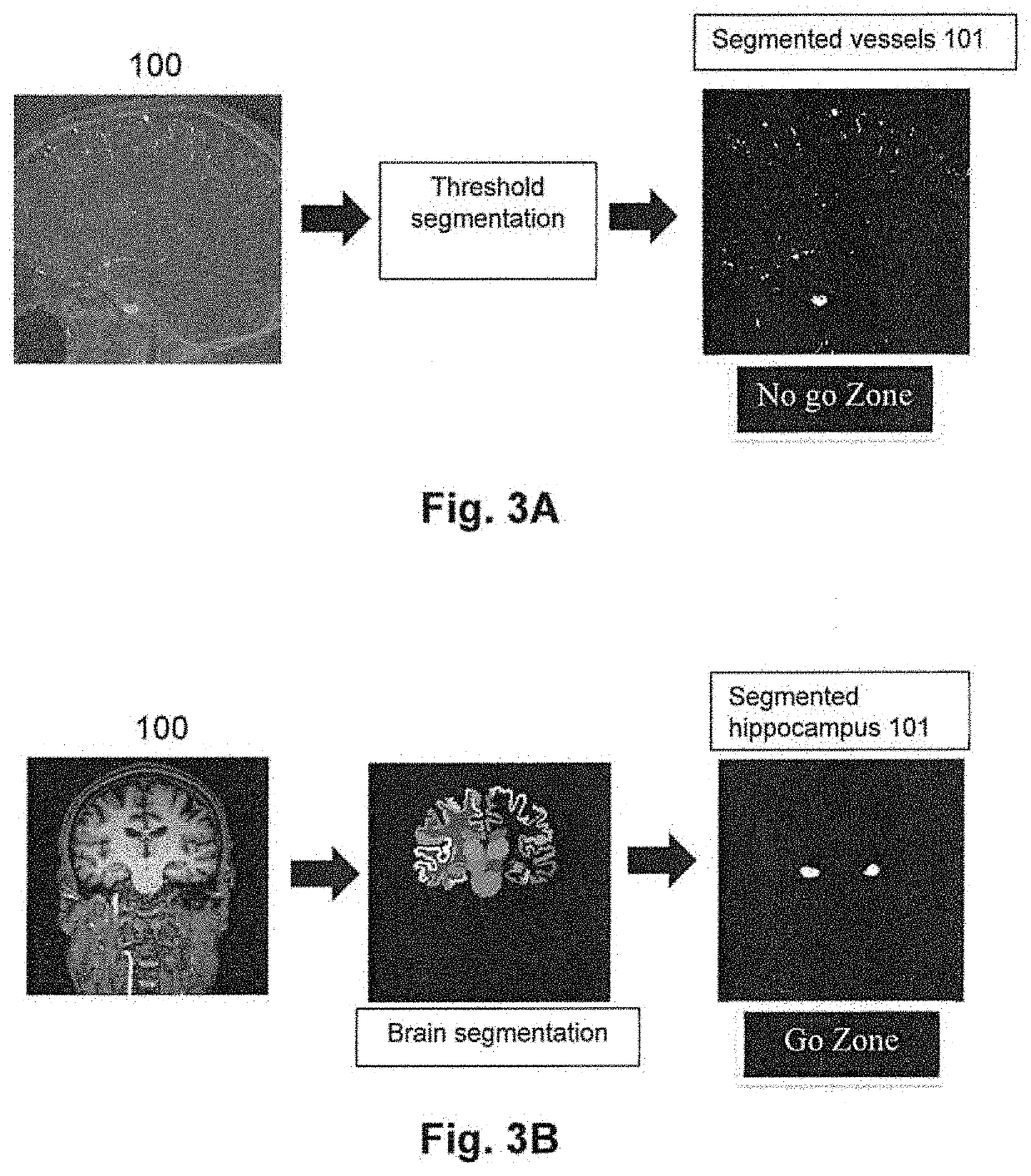
System and method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image
InactiveUS20050008205A1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnatomical partMedical image computing
A system and method for detecting a protrusion in a medical image are provided. The method comprises: acquiring a medical image, wherein the medical image is of an anatomical part; segmenting the medical image; calculating a distance map of the medical image; calculating a gradient of the distance mapped medical image; and processing the gradient to detect a protrusion in the medical image. The gradient is processed by: projecting a plurality of rays from a location in the distance mapped medical image; calculating a value for each of the plurality of rays based on features of each of the plurality of rays and the gradient of the distance mapped medical image; summing and scaling the value of each of the plurality of rays; and detecting one of a sphere-like and polyp-like shape using the summed and scaled values of the plurality of rays, wherein one of the sphere-like and polyp-like shapes is the protrusion.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
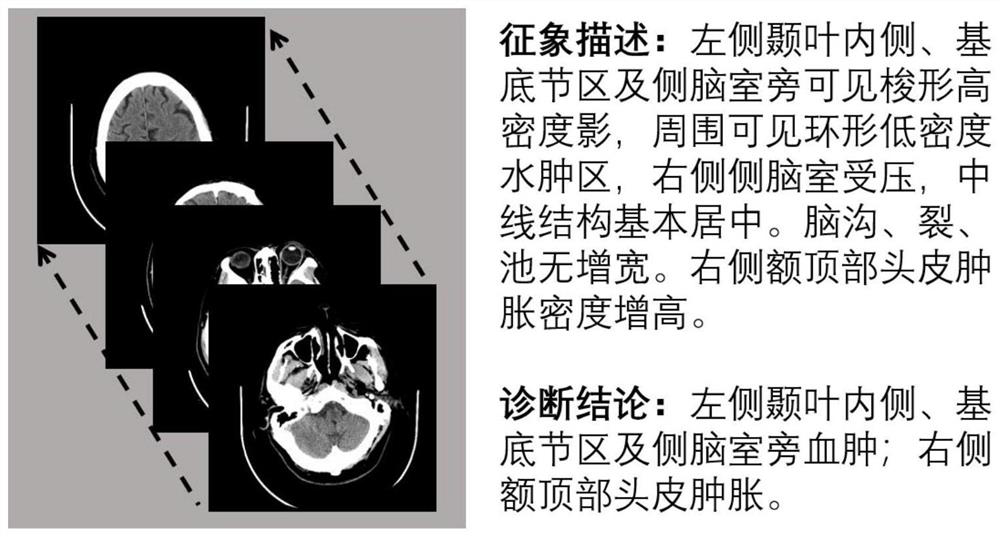
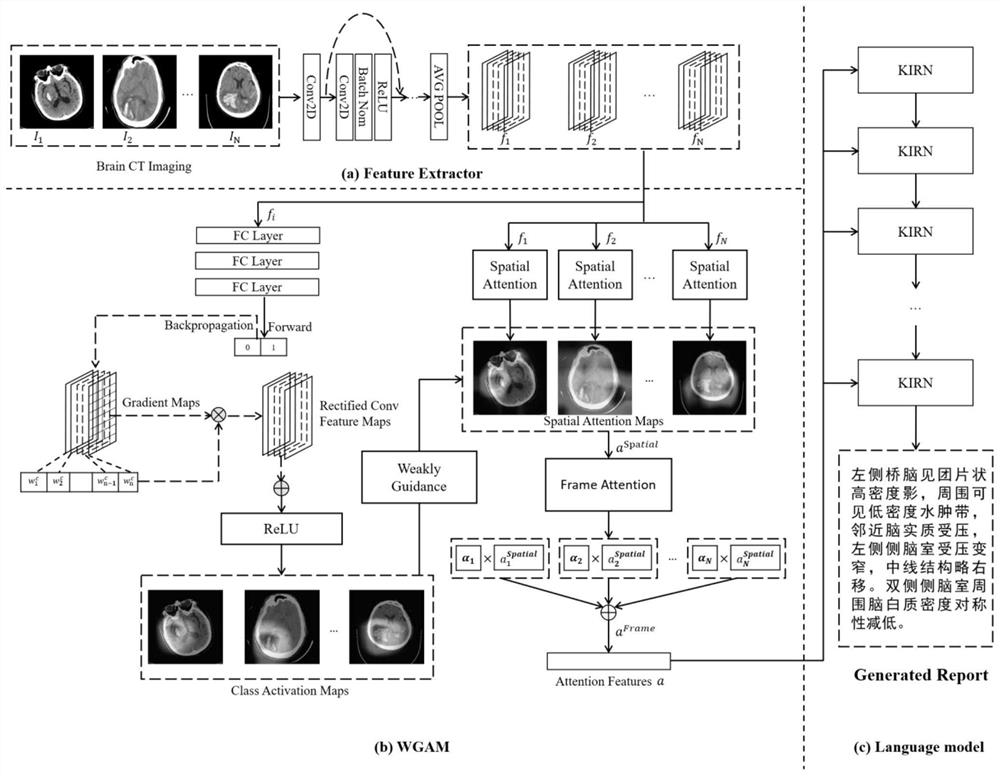
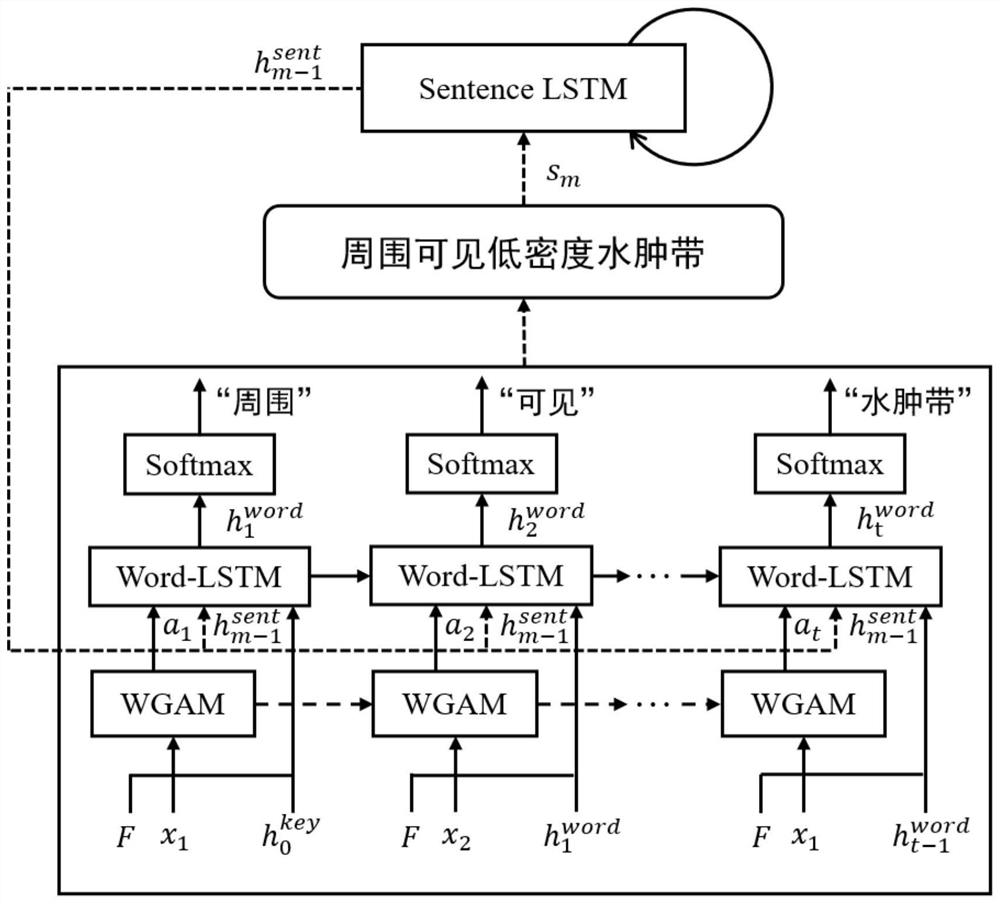
Brain CT medical report automatic generation method based on weak supervision attention
PendingCN113313199AImprove accuracyGood attentionCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical imagesBrain ctImaging report
The invention provides a method for automatically generating a brain CT medical report based on weak supervised attention, relates to the three fields of medical images, computer vision and natural language processing, and designs a weak supervised attention mechanism WGAM to clearly guide an attention model to focus on a focus region so as to improve the accuracy of medical report generation. WGAM is a hierarchical structure and comprises two attention mechanisms of space attention and sequence attention, and the space attention is weakly supervised by a gradient weighted class activation mapping algorithm to obtain a better attention effect. A keyword-driven interactive loop network KIRN is designed as a language generation module to generate a brain CT medical report, a hidden layer state of the language generation module is activated through keyword information containing focus position information, and the accuracy of generating a brain CT image report is improved through dynamic interaction of LSTMword and LSTMsen. According to the method, the work of automatically generating the brain CT medical report is explored for the first time, and effectiveness is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
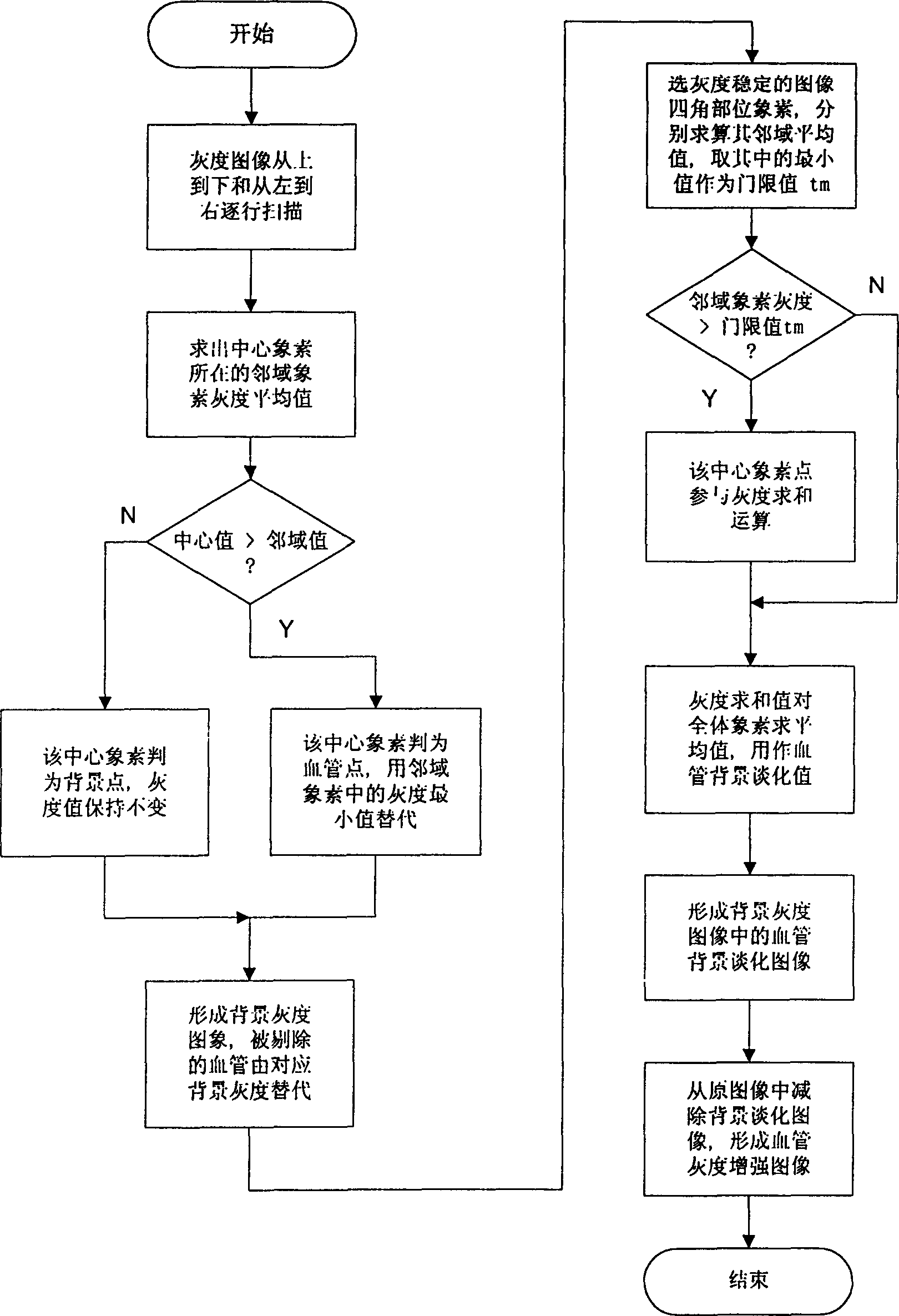
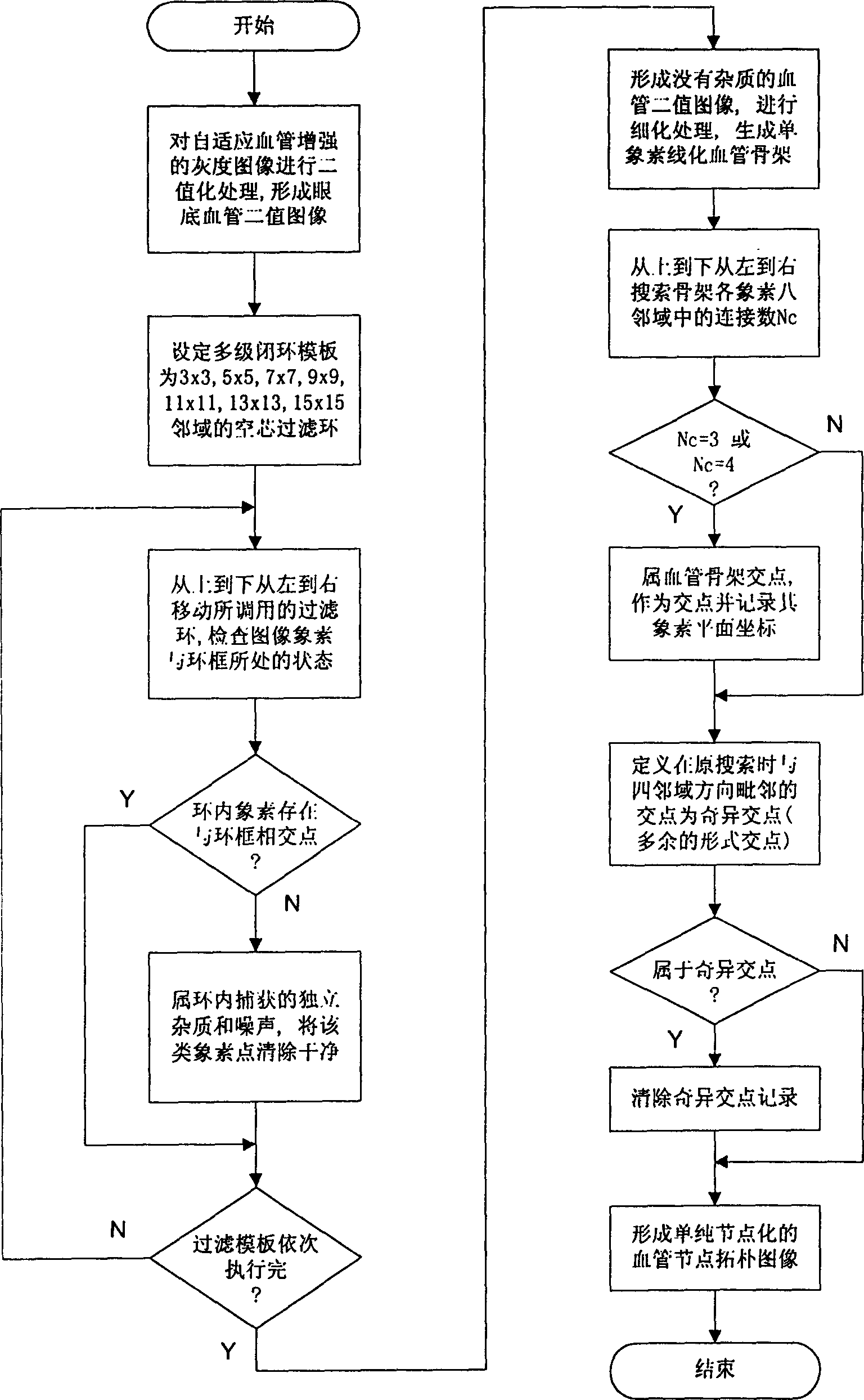
Computer aided characteristic registration identifying method for medical homolateral fundus image
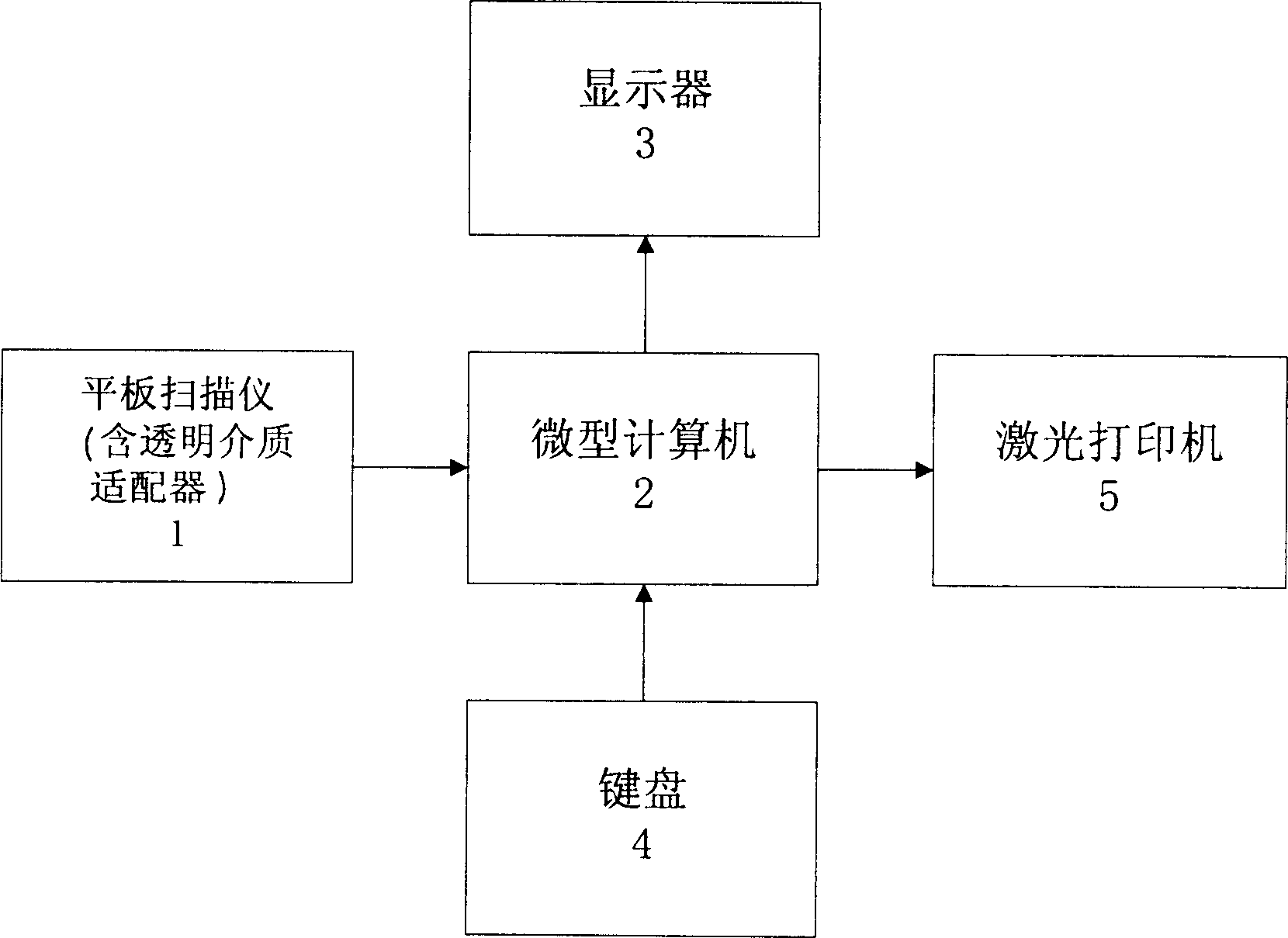
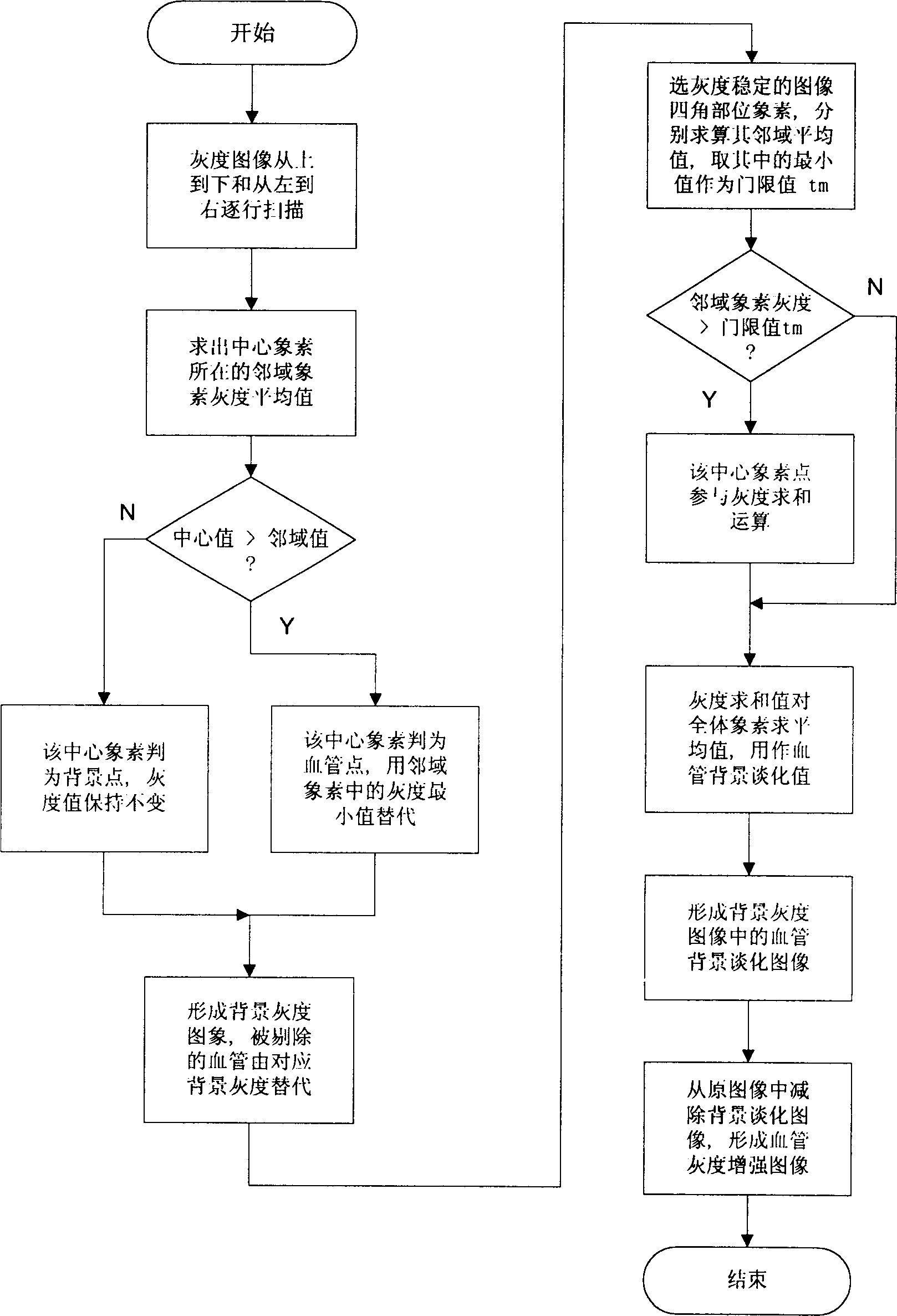
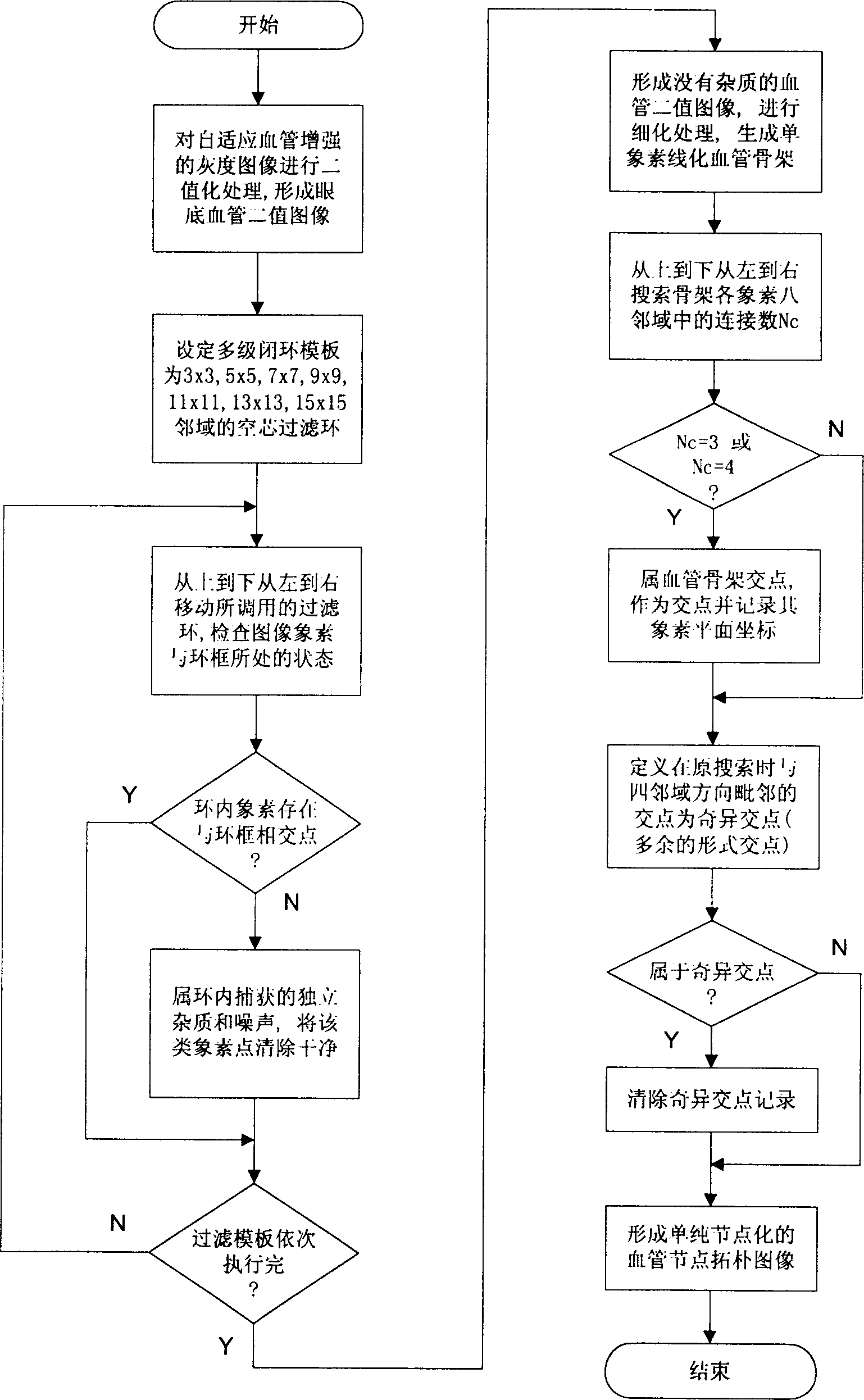
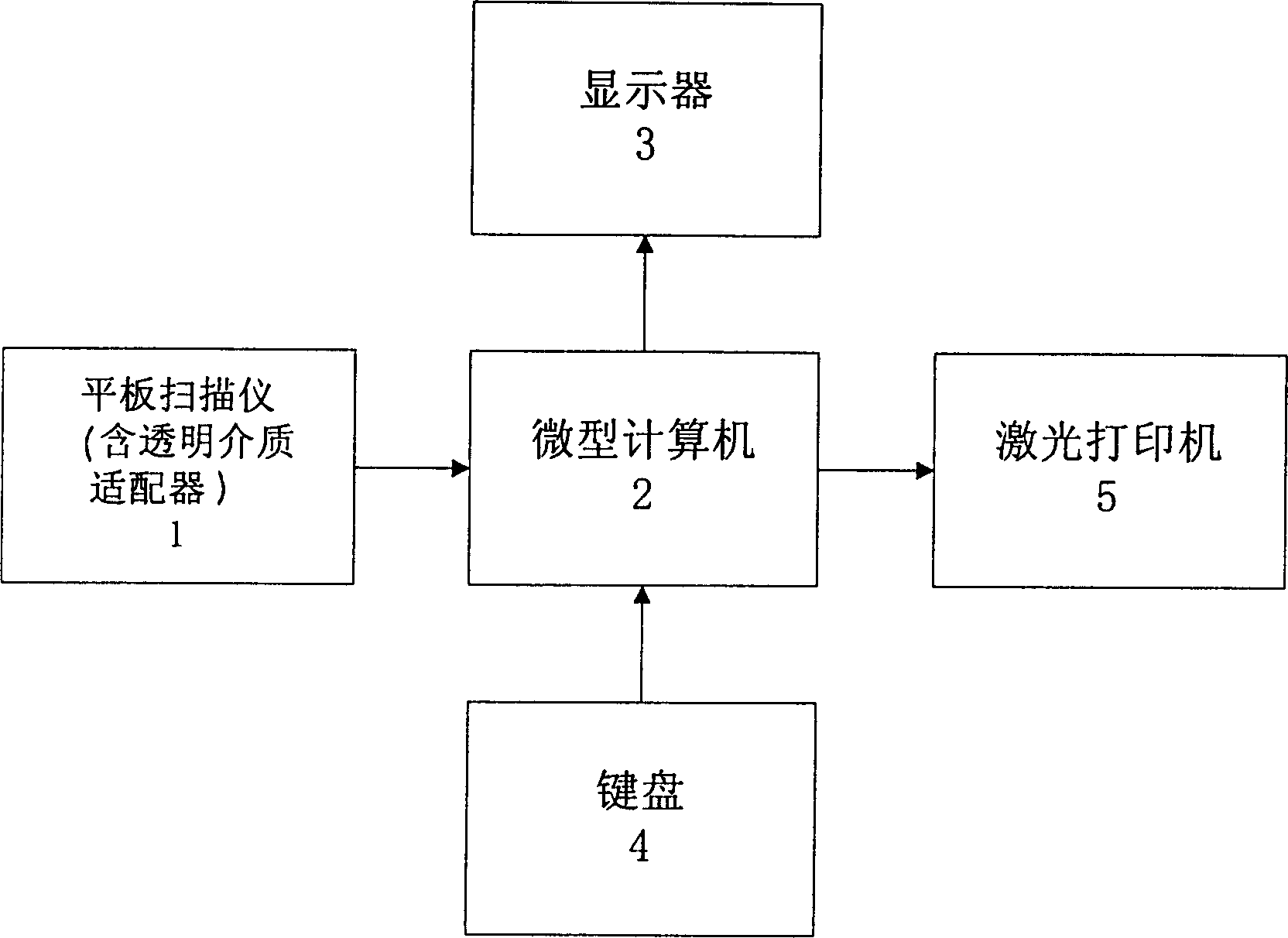
InactiveCN1378166AReduce distressReduce fatigueSpecial data processing applicationsComputer-aidedMedical image computing
The present invention relates to computer applying technology. The registration identifying system of the present invention consists of plate scanner with transparent medium adaptor, microcomputer with keyboard and display, laser printer electrically connected together via signal cables. The registration identifying process includes mainly adaptive enhancing of homolateral fundus vessel image; intersection point and pure node extraction of fundus vessel characteristic; normalization of fundus vessel characteristic nodes; and neighboring region registration and judgement of fundus vessel characteristic nodes. The computer-aided judgement means has light labor strength and other advantages.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
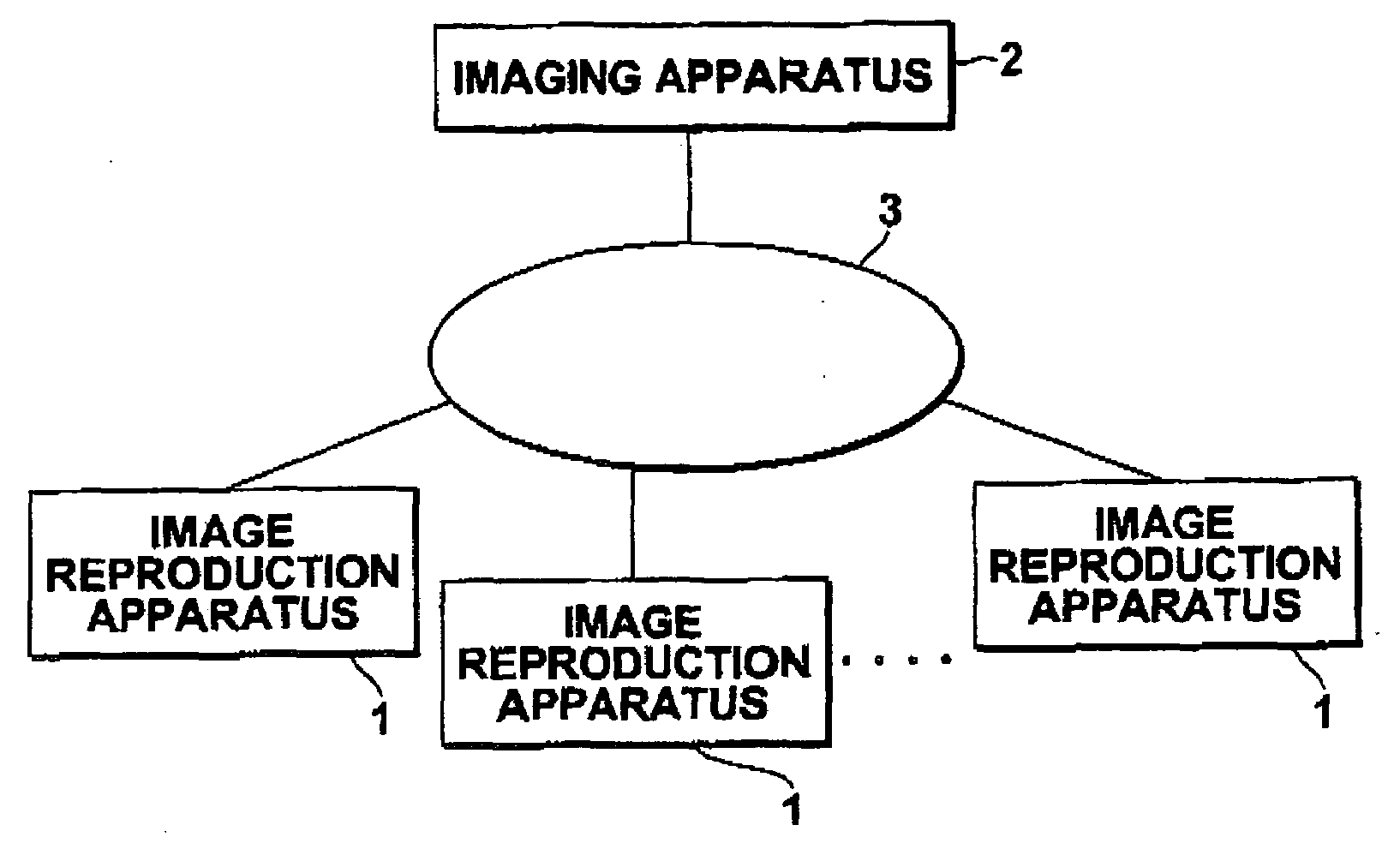
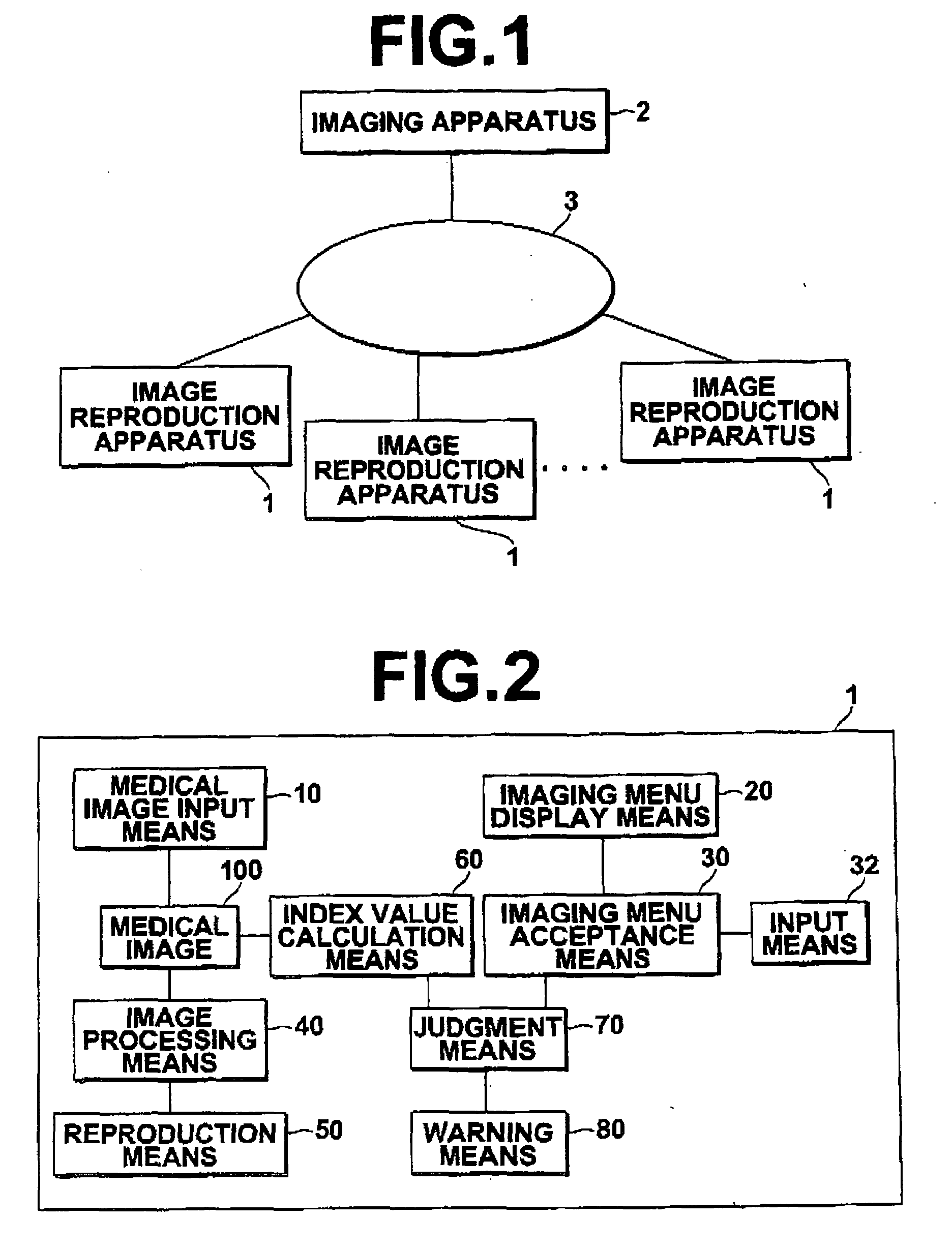
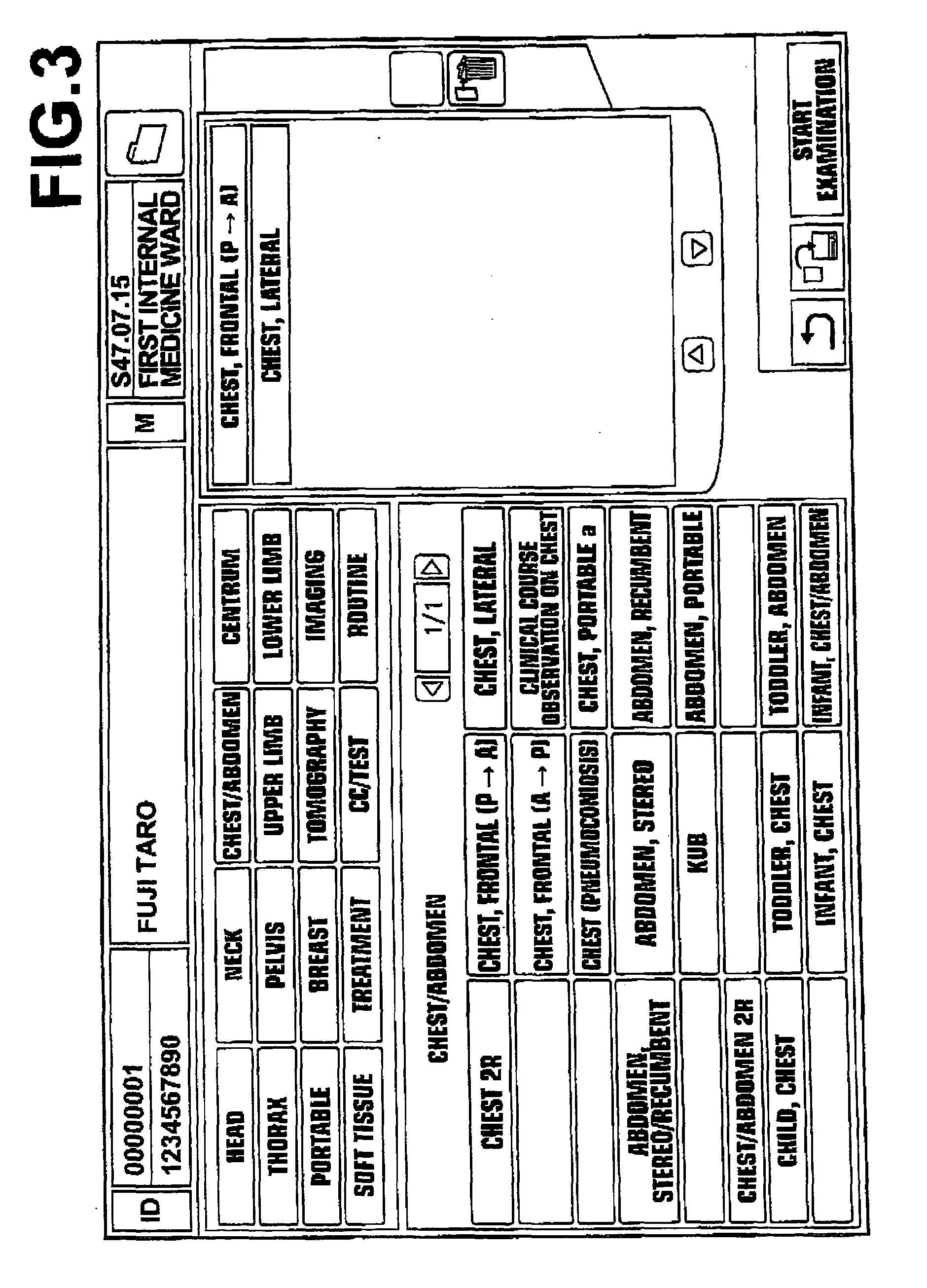
Image reproduction apparatus and program therefor
InactiveUS20070195061A1Easy to explainReduce generationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingImage conversion
A medical image is reproduced after being subjected to image processing appropriate for conversion into an image suitable for interpreting. Selection of a imaging menu item from a imaging menu being displayed is accepted, and the medical image is reproduced after being subjected to the image processing for converting the image into the image appropriate for the reproduction according to the selected imaging menu item. At this time, an index value representing an anatomical characteristic is calculated from the medical image, and the most appropriate imaging menu item to be selected from imaging menu items is judged based on the index value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Device for positioning surgical operation tools and positioning method thereof
InactiveCN108742877AReduced degrees of freedom requiredReduce complexityDiagnosticsSurgical needlesSurgical operationSupporting system
The invention relates to the field of medical equipment, in particular to a device for positing surgical operation tools and a positioning method thereof. The device for positing surgical operation tools comprises a medical imaging device which is used for shooting the medical image of the patient, a support system which is used for supporting the patient and translating the patient, a mechanicalarm for loading the surgical operation tools and driving the surgical tools to adjust the tool position, and a controller which is in communication connection with the medical imaging device, the support system and the mechanical arm and controls the support system and the mechanical arm; the controller calculates position data of the surgical operation tools relative to the patient according to the medical image and controls the movement of the supporting system and the mechanical arm according to the positioning data of the surgical operation tool relative to the patient. For the support system and the mechanical arm, one of them is able to move along a first direction and the other is able to translate along a second direction and a third direction. The first direction, the second direction, and the third direction are perpendicular to each other.
Owner:赛诺联合医疗科技(北京)有限公司
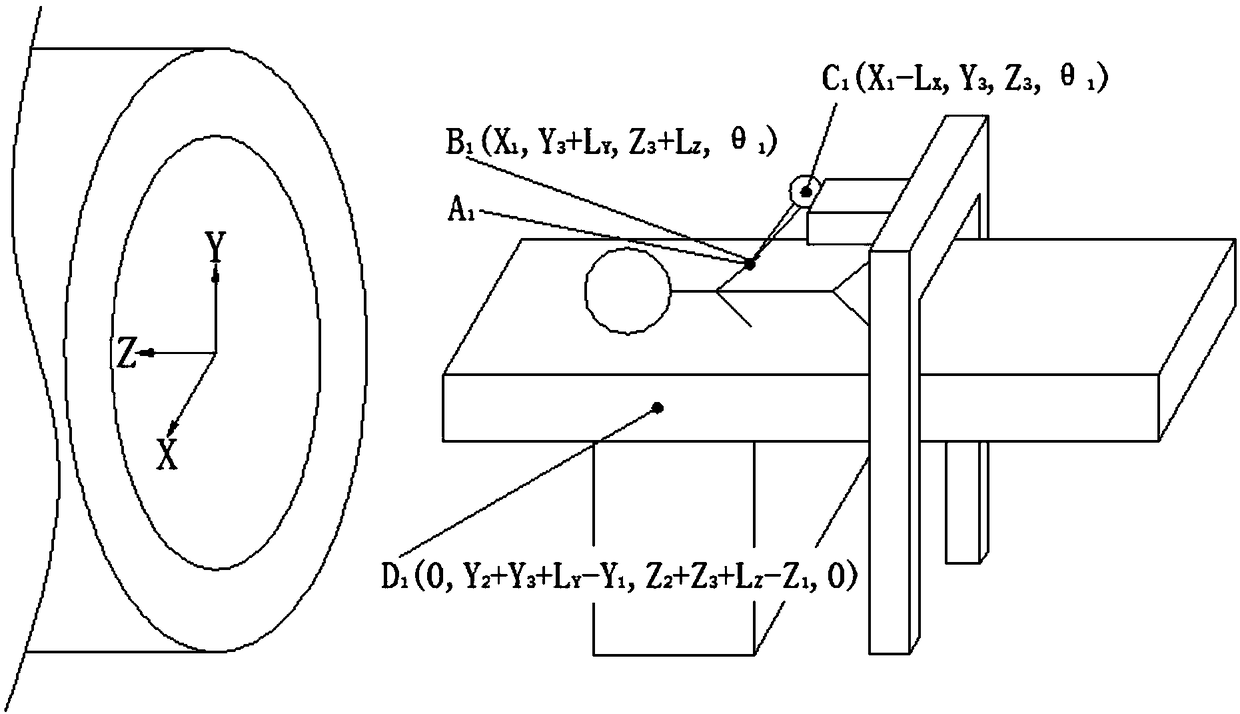
Method for determining position of orthodontics mini-screw and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20130196280A1Accurately determineShorten the overall cycleDental implantsOthrodonticsBone densityOrthodontic wire
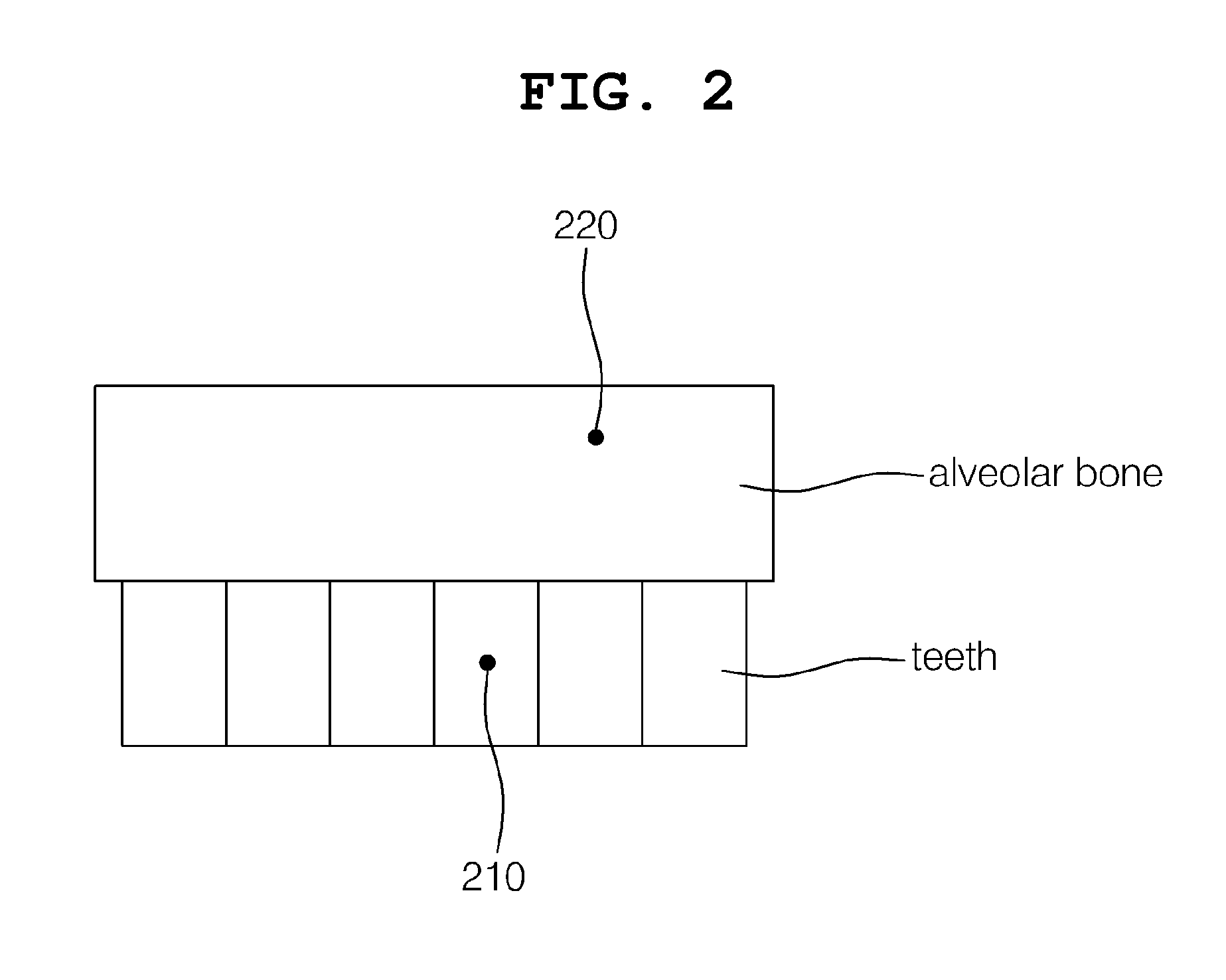
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for determining the location of an orthodontic fastener. In the method, a first location on a tooth and a second location on alveolar bone are set on a patient's medical image. Thereafter, a first rectilinear line including two points, that is, the set first and second locations, is generated. Thereafter, bone density values at the locations of the alveolar bone on the generated first rectilinear line are computed using the medical image. Finally, the location of the alveolar bone at which a first fastener is inserted is determined based on the computed bone density values.
Owner:INFINITT HEALTHCARE CO LTD
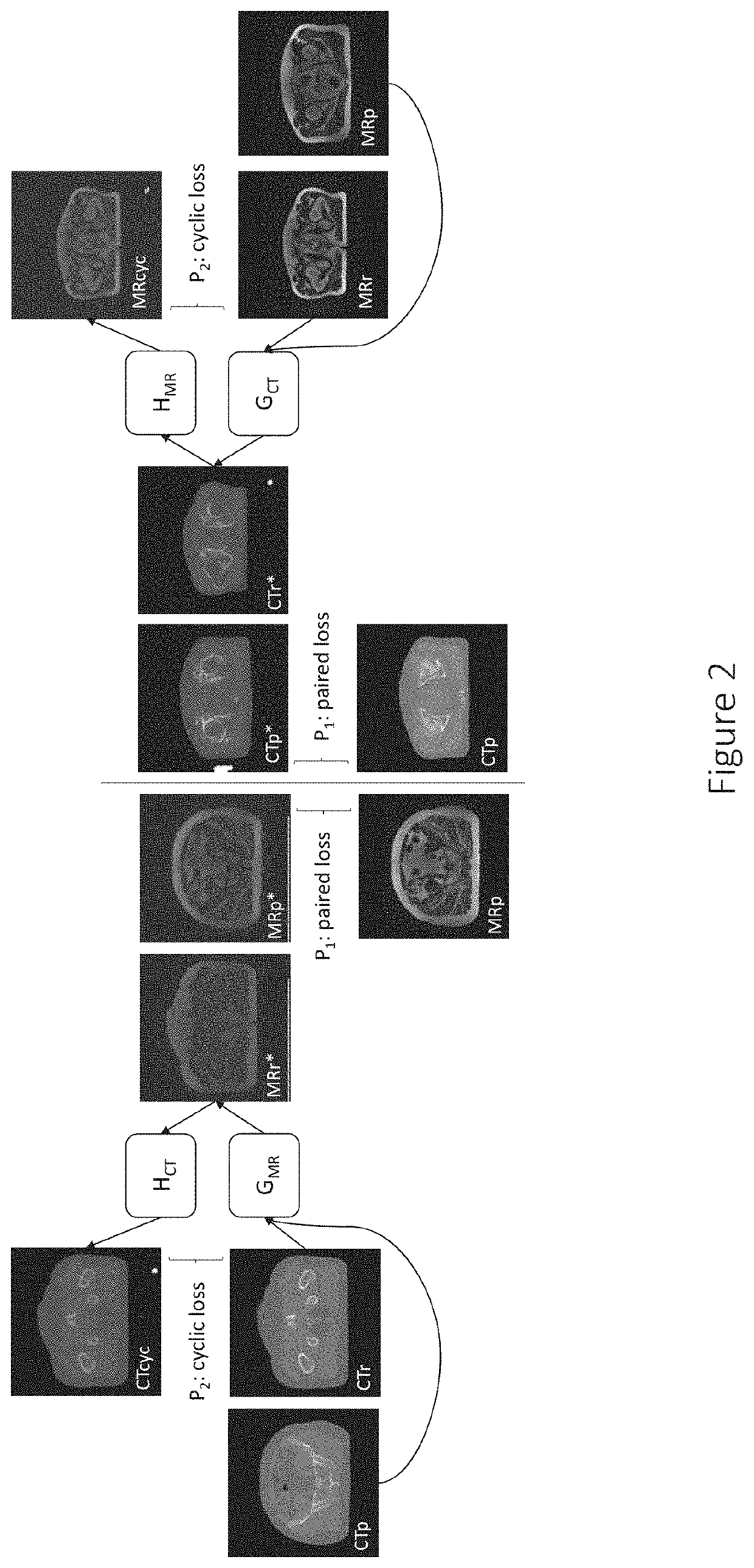
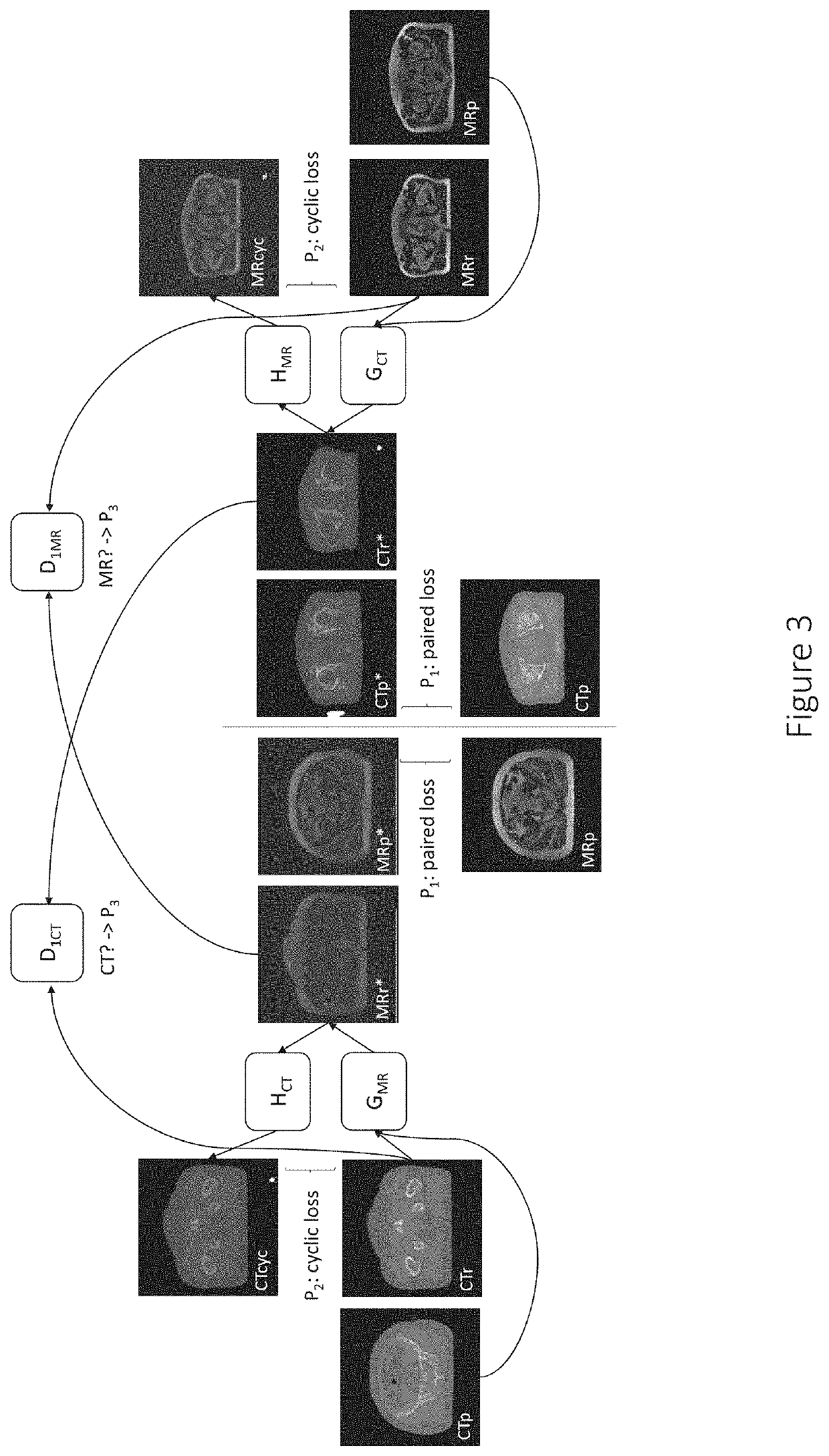
Medical image conversion
InactiveUS20210201546A1Accurate optimized parametrizedMinimize said first and second penaltiesImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage conversionImage pair
In accordance with one or more embodiments herein, a system for generating an optimized parametrized conversion function T for converting an original medical image of a first image type into a converted medical image of a second image type is provided. The system comprises at least one processing unit configured to: obtain original medical images of the first and second image types; obtain an initial parametrized conversion function G to convert original medical images of the first image type into converted medical images of the second image type; calculate a first penalty P1 based on at least one comparison of a first original medical image of the second image type with a first converted medical image of the second image type, that has been generated by applying a first parametrized conversion function G1, which is based on the initial parametrized conversion function G, to a first original medical image of the first image type that forms an image pair with the first original medical image of the second image type and has thereby been determined to show the same part of the same patient; calculate a second penalty P2 based on at least one comparison of an original medical image of the first image type and a converted medical image of the second image type that has been generated by applying a second parametrized conversion function G2, which is based on the initial parametrized conversion function G, to the original medical image of the first image type, after converting the original medical image of the first image type and / or the converted medical image of the second image type into images of the same image type; and generate the optimized parametrized conversion function T based on the parameters of the initial parametrized conversion function G and at least said first and second penalties P1 and P2.
Owner:RAYSEARCH LAB
Computer aided characterstic registration identifying method for medical homolateral fundus image
InactiveCN1147815CReduce distressReduce fatigueSpecial data processing applicationsMicrocomputerDisplay device
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
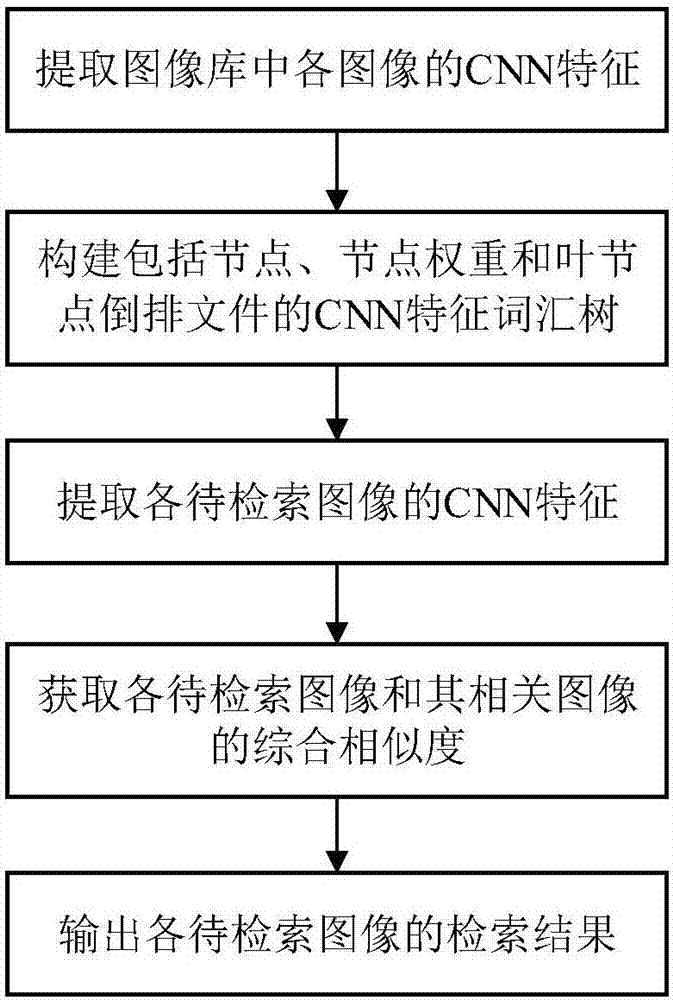
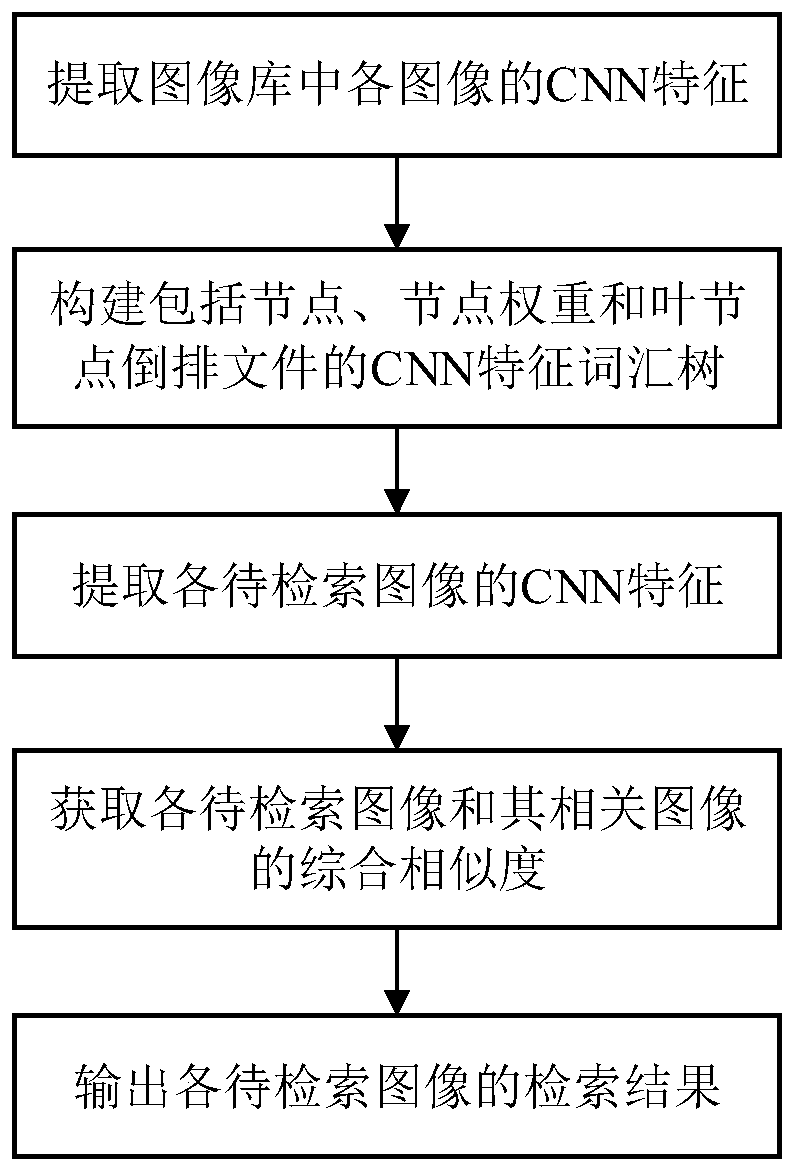
Image retrieval method based on CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) feature vocabulary tree
ActiveCN107423379AImprove accuracyEasy to learnCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalDiagnostic system
The invention discloses an image retrieval method based on a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) feature vocabulary tree, and aims to solve the technical problem of low accuracy in an existing vocabulary tree method. The method comprises the following implementation steps that: firstly, generating the derivative image of each image in an image library, and extracting the CNN feature of each image in the image library; according to the extracted CNN feature, constructing the CNN feature vocabulary tree; then, generating the derivative image of each image to be retrieved, and extracting the CNN feature of each image to be retrieved; comparing the path of the CNN feature of each image to be retrieved with the path of the CNN feature of the relevant image of the image to be retrieved in the CNN feature vocabulary tree; calculating a distance between the image to be retrieved and the relevant image, and combining the distance between the image to be retrieved and the relevant image with initial similarity; and finally, according to the comprehensive similarity of each image to be retrieved and the relevant image, outputting the retrieval result of each image to be retrieved. The method is high in image retrieval accuracy and can be used for a medical image computer-assisted diagnostic system and a search-by-image system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Using Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy Slopes to Define Glial Cells that Diagnose Brain Disorder
InactiveUS20190125272A1Minimal energyAttracting forceImage enhancementMedical imagingMinimum free energySchizophrenia
A method of diagnosing a disorder includes obtaining a medical image of a subject. A Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy is computed from the medical image. A negative slope of the Helmholtz Minimum Free Energy is determined, from which a glial force is computed. The existence of a disorder in the subject is diagnosed if a value of the glial force is within a predetermined range. The disorder can be, for example, a brain disorder, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and / or schizophrenia. Other examples of disorders are epilepsy and rheumatoid arthritis. The subject can be, for example, a human subject.
Owner:SZU HAROLD
Computer-aided detection system for cerebral microbleeds based on magnetic resonance images
InactiveCN104414636BIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMri brainMR - Magnetic resonance
The invention provides a magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system and belongs to the medical image computer auxiliary detection field. The magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system comprises five portions of an image import module, an image preprocessing module, a characteristic extraction module, an automatic detection module and a cerebral micro-bleeding automatic detection report output module. According to the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system, the characteristics of T1, T2 and GRET2* images are comprehensively considered, the prior information of the cerebral micro-bleeding of different cerebral positions is obtained through a cerebral micro-bleeding focus prior distribution probability template, and a random forest classifier is combined to perform the automatic detection on the cerebral micro-bleeding focus; the system sensitivity is 0.890 and every case comprises 1.530 false positive focuses in average through a test; the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system is objective and high in repeatability in comparison with the traditional manual discriminant method and the magnetic resonance image based cerebral micro-bleeding computer auxiliary detection system is accurate and reliable in comparison with the existing computer auxiliary detection method; the operation is simple and convenient, the identification result of the cerebral micro-bleeding focus can be objectively provided, and meanwhile the abundant information is provided for the reference of doctors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
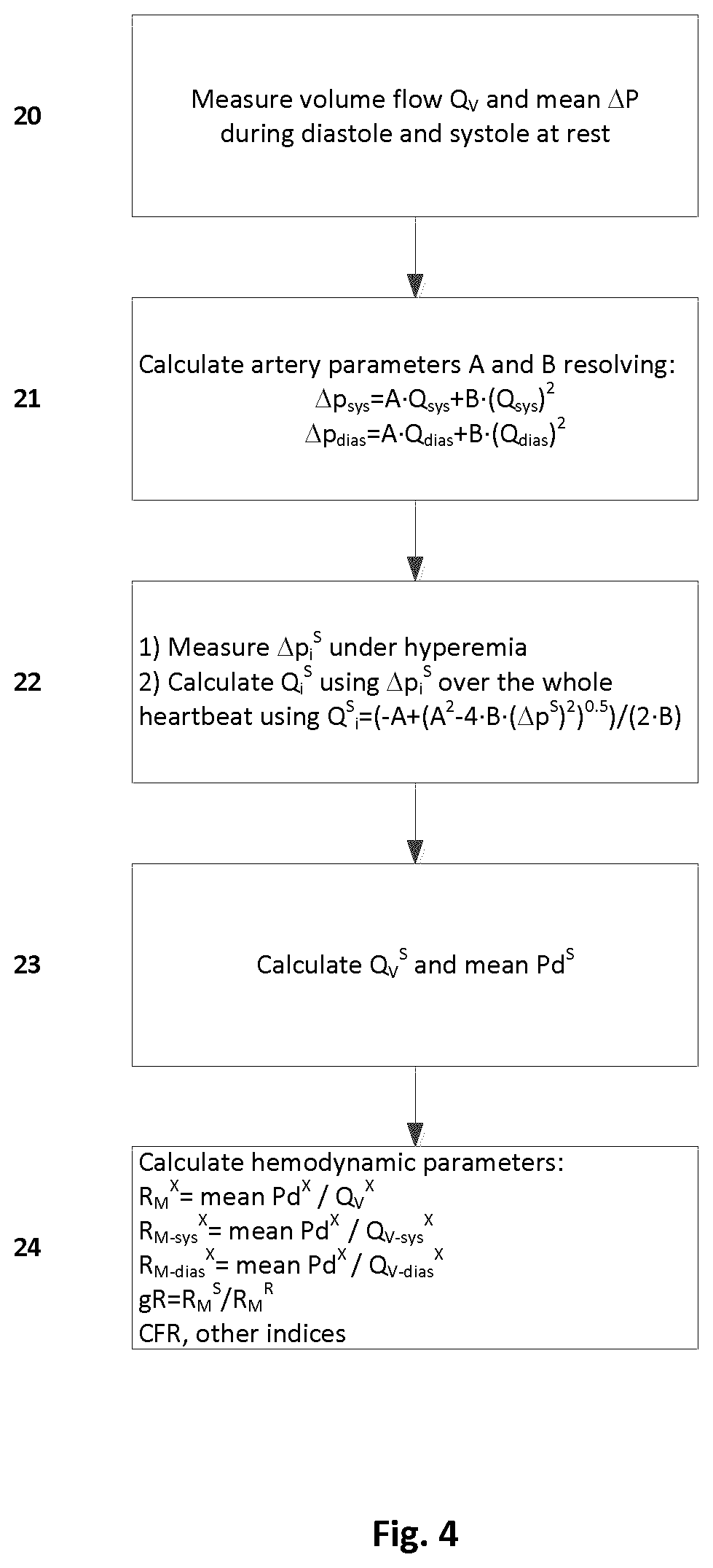
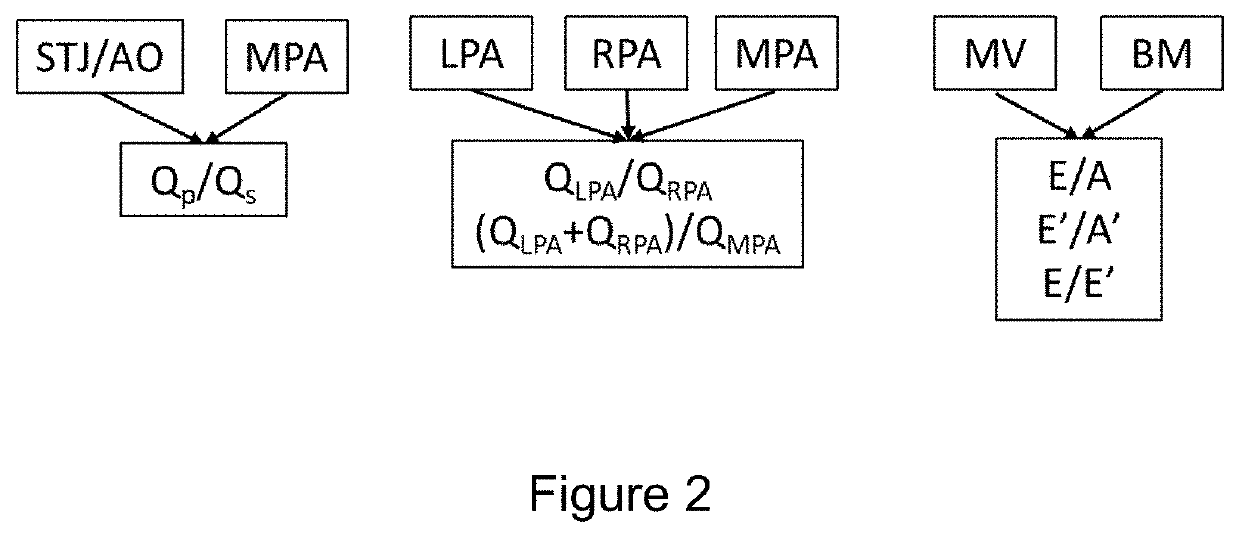
Hybrid image-invasive-pressure hemodynamic function assessment
ActiveUS11369277B2Diagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationMedical imagingNuclear medicine
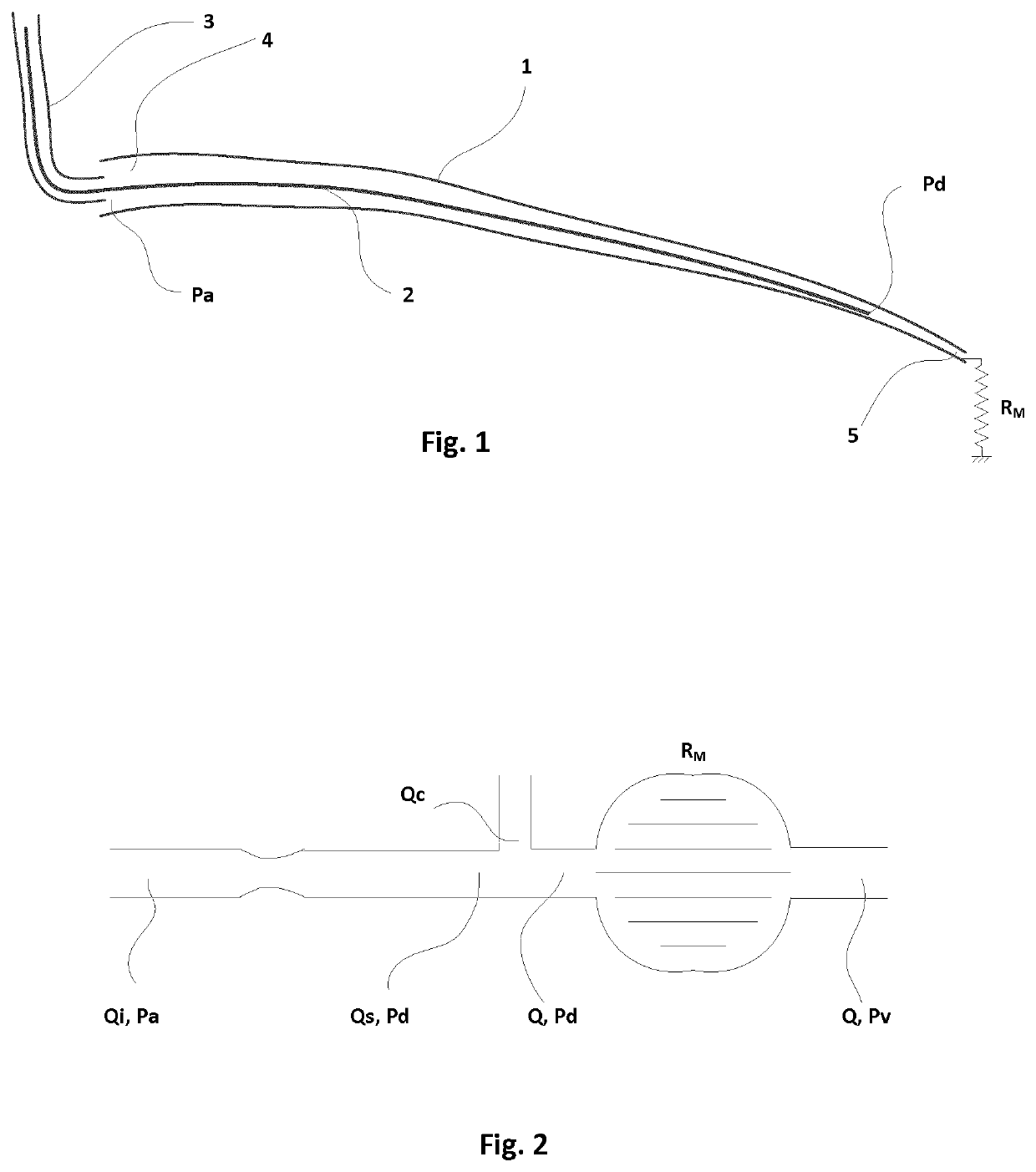
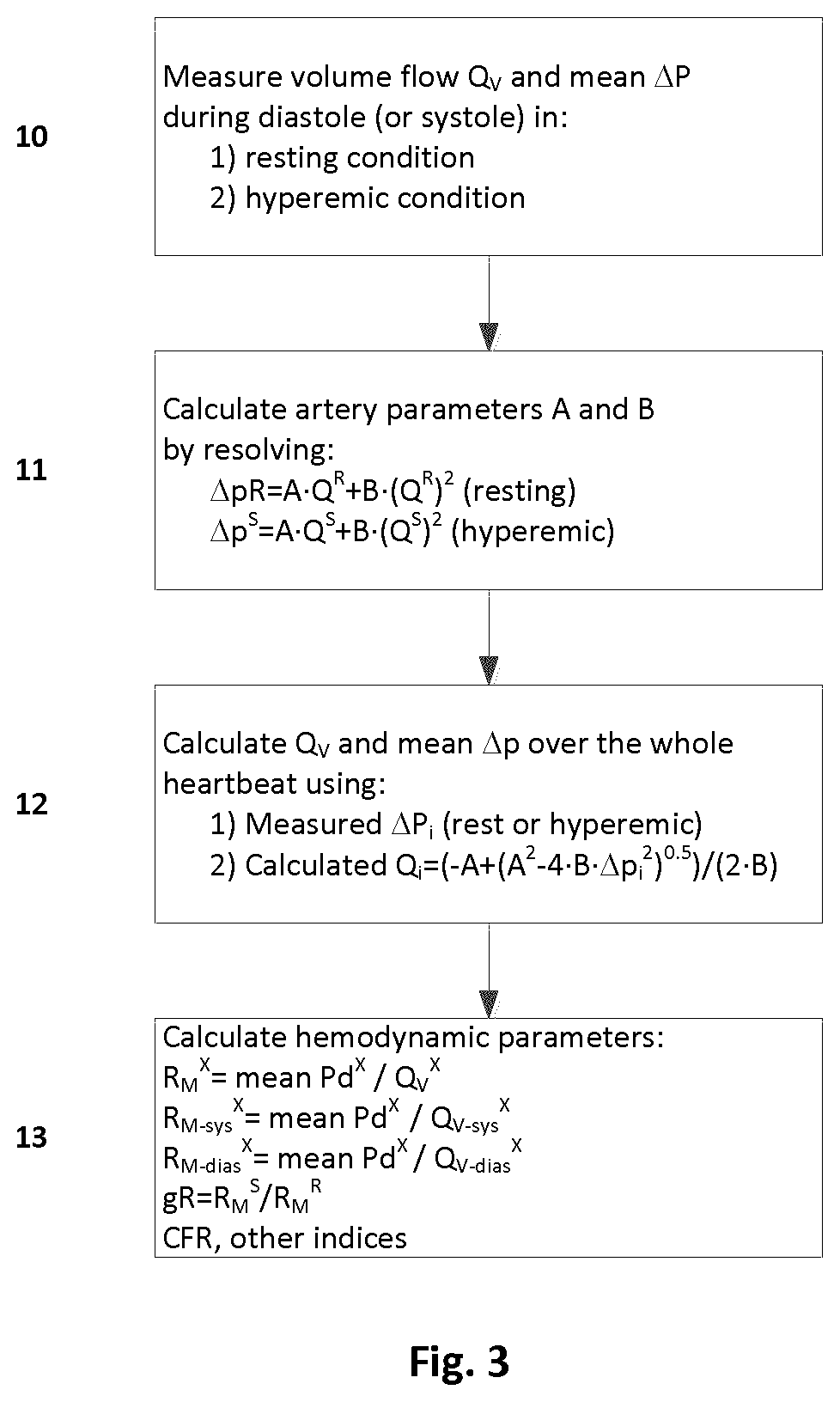
There is described a method for calculating a patient-specific hemodynamic parameter. The method comprises measuring at least one pressure measurement in an artery using an intravascular pressure measurement device, and taking at least one medical image of the artery from a medical imaging instrument, the at least one medical image of the artery being synchronous with the at least one pressure measurement. Both the pressure measurement and the medical image are fed to a computing system to calculate a flow from the at least one medical image, to calculate parameters of the artery from at least two artery pressure drops and corresponding flow components, and based on the flow and the parameters of the artery, to calculate a patient-specific hemodynamic parameter or a plurality thereof.
Owner:OPSENS
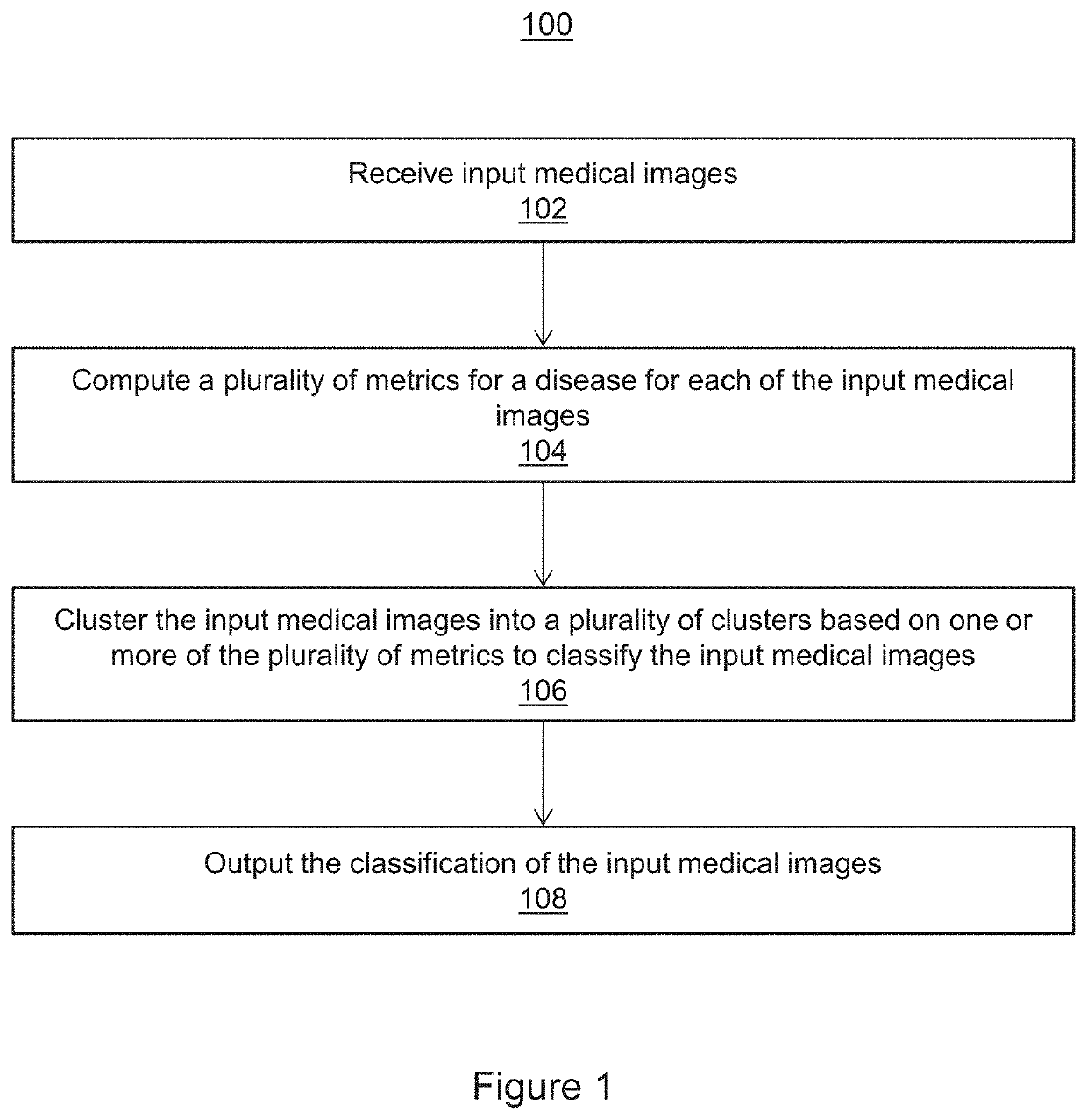
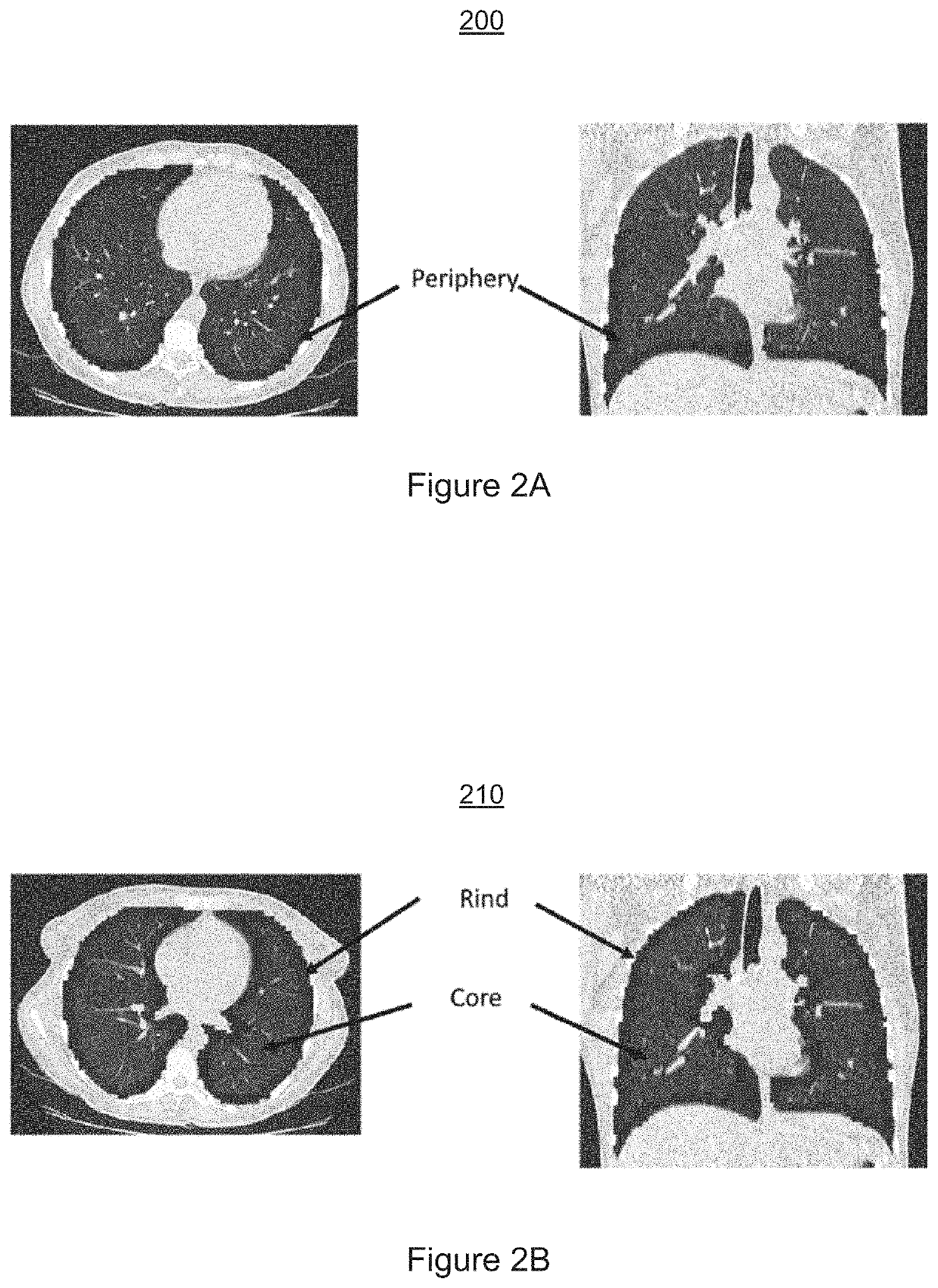
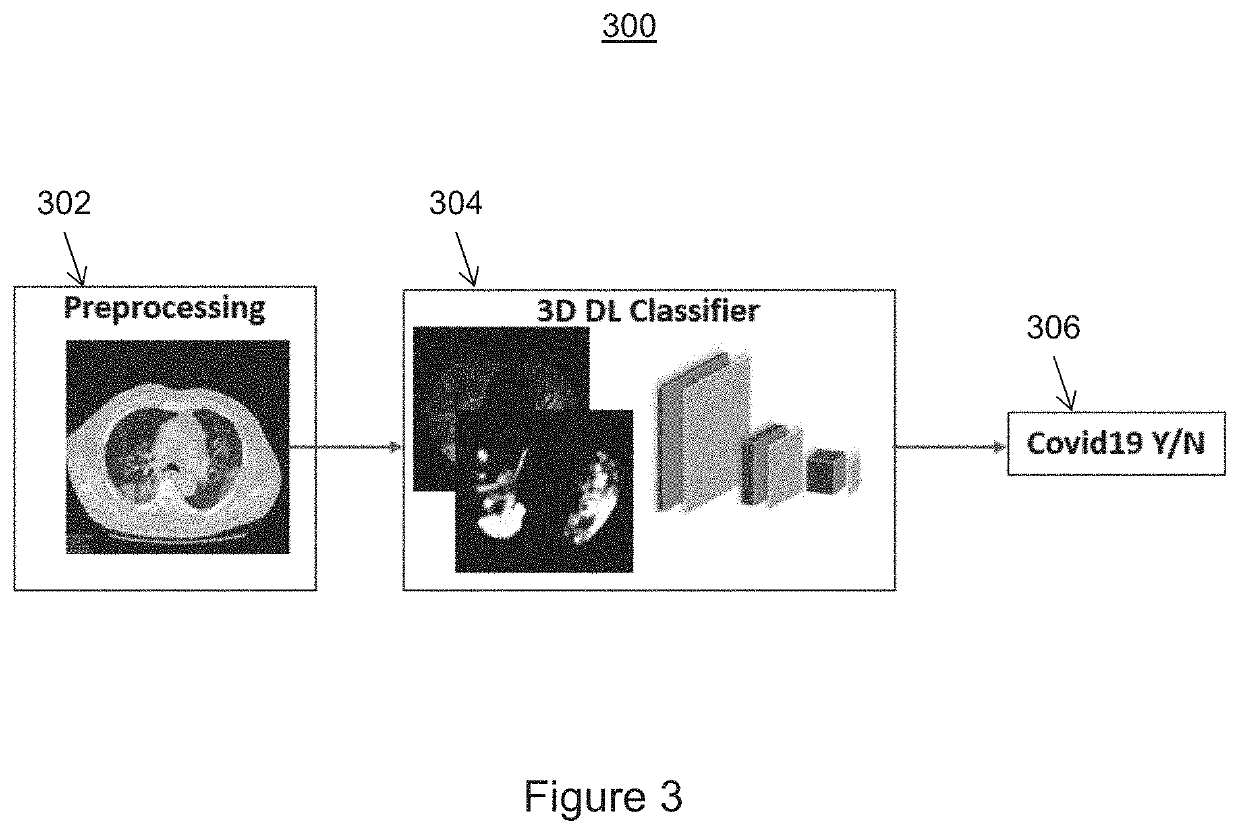
Automatic detection of covid-19 in chest ct images
Systems and methods for automatically detecting a disease in medical images are provided. Input medical images are received. A plurality of metrics for a disease is computed for each of the input medical images. The input medical images are clustered into a plurality of clusters based on one or more of the plurality of metrics to classify the input medical images. The plurality of clusters comprise a cluster of one or more of the input medical images associated with the disease and one or more clusters of one or more of the input medical images not associated with the disease. In one embodiment, the disease is COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
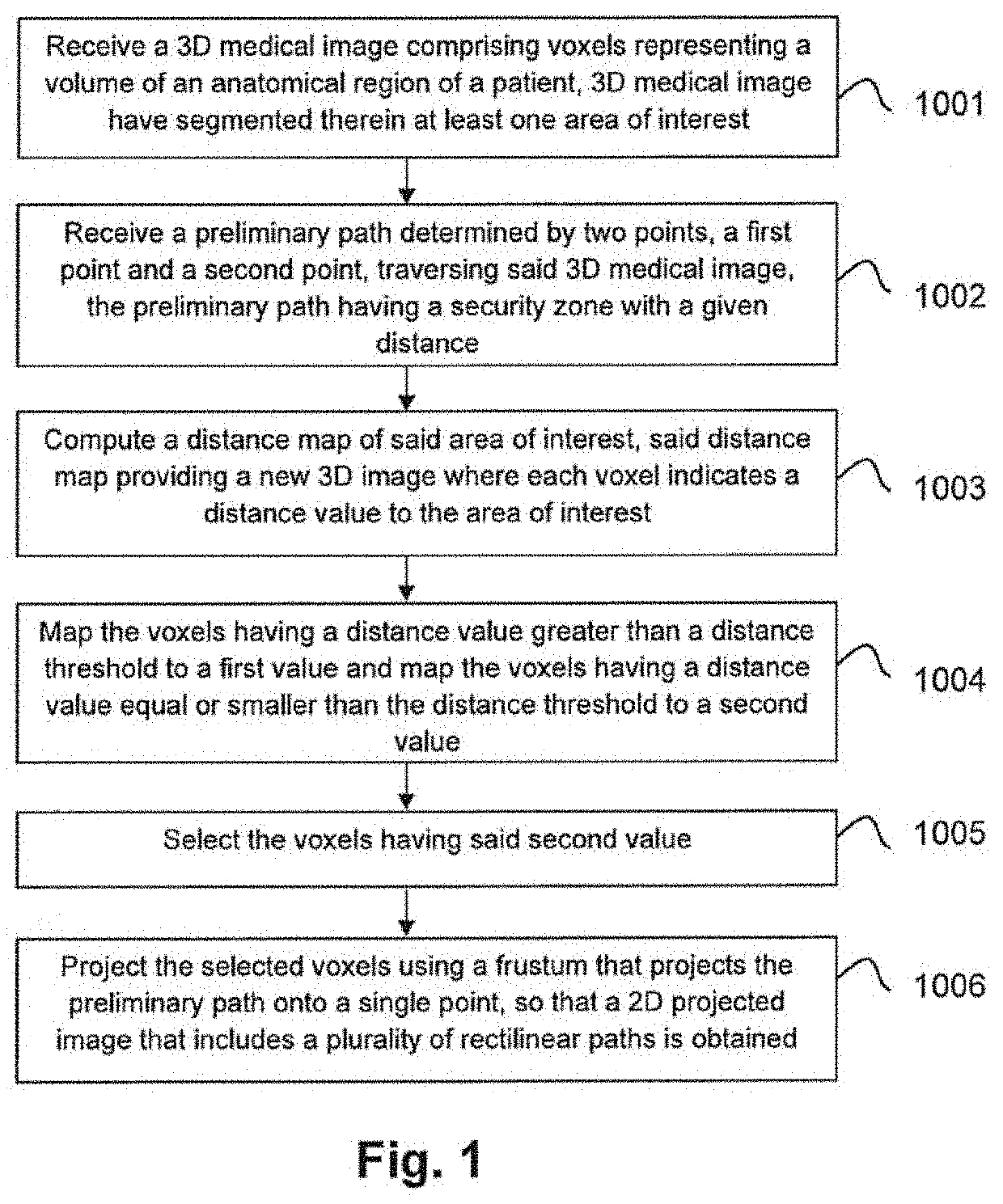
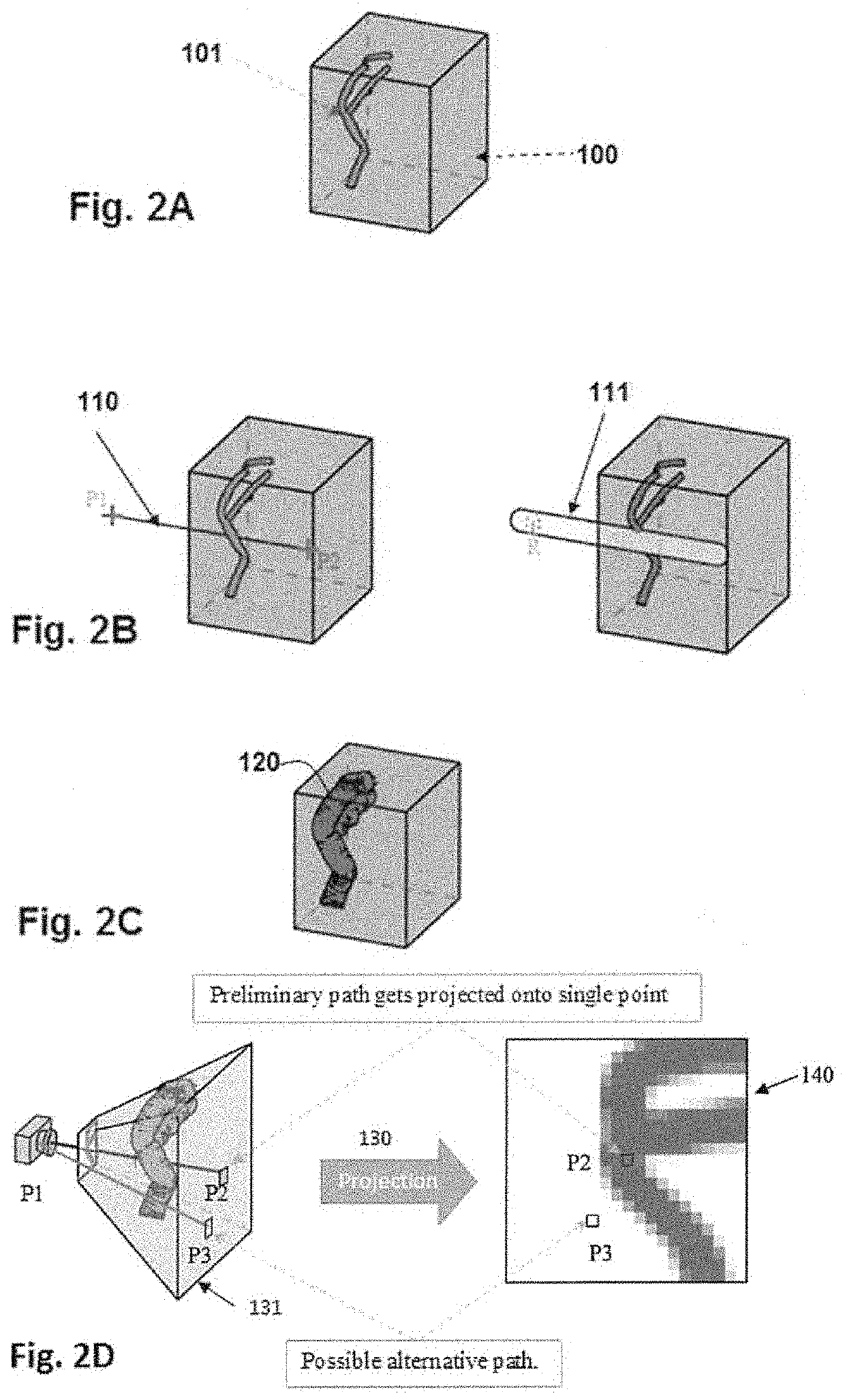
Computer implemented method, a system and computer programs for computing simultaneous rectilinear paths using medical images
ActiveUS20200394833A1Less powerValid checkImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsVoxelProjection image
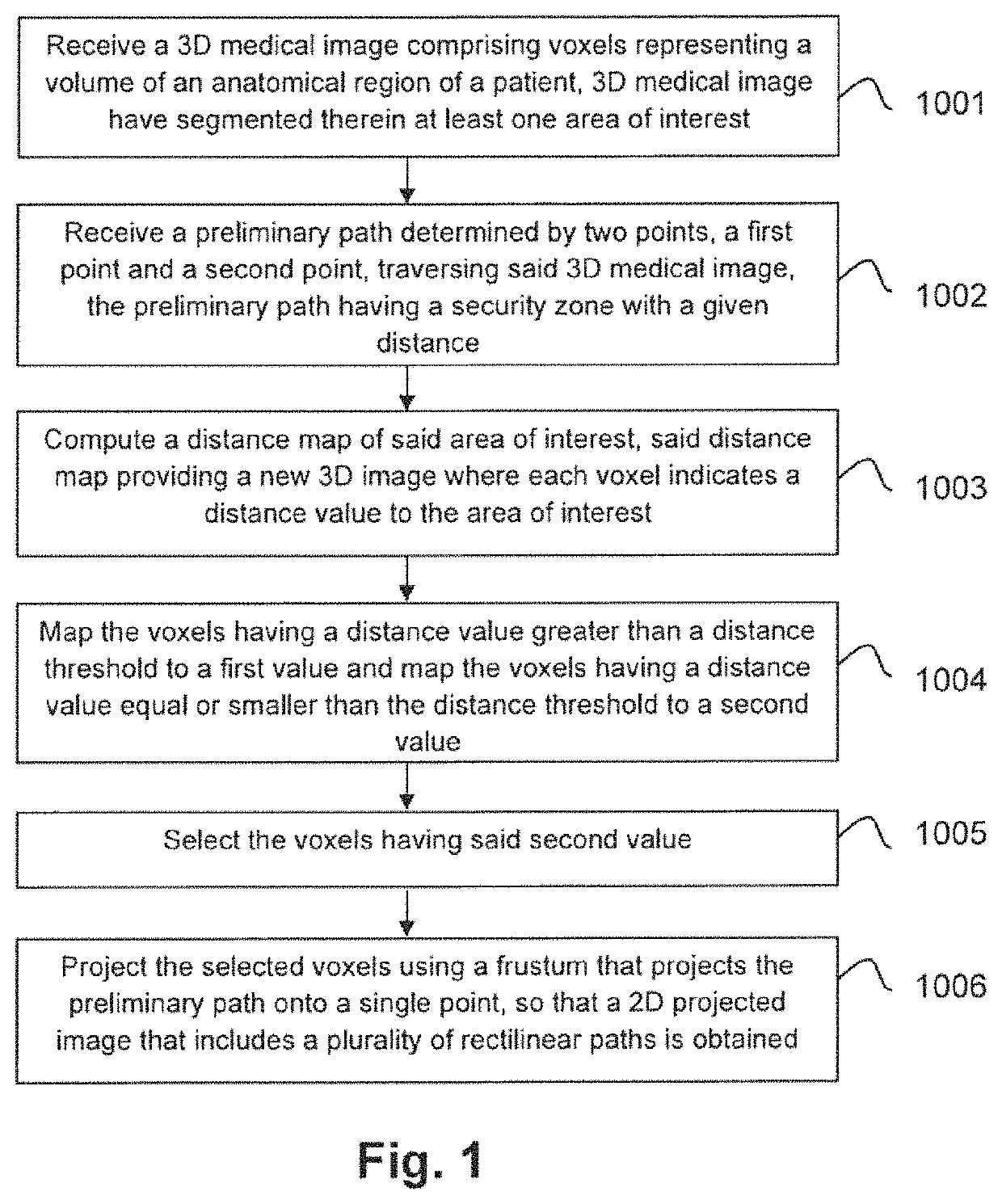
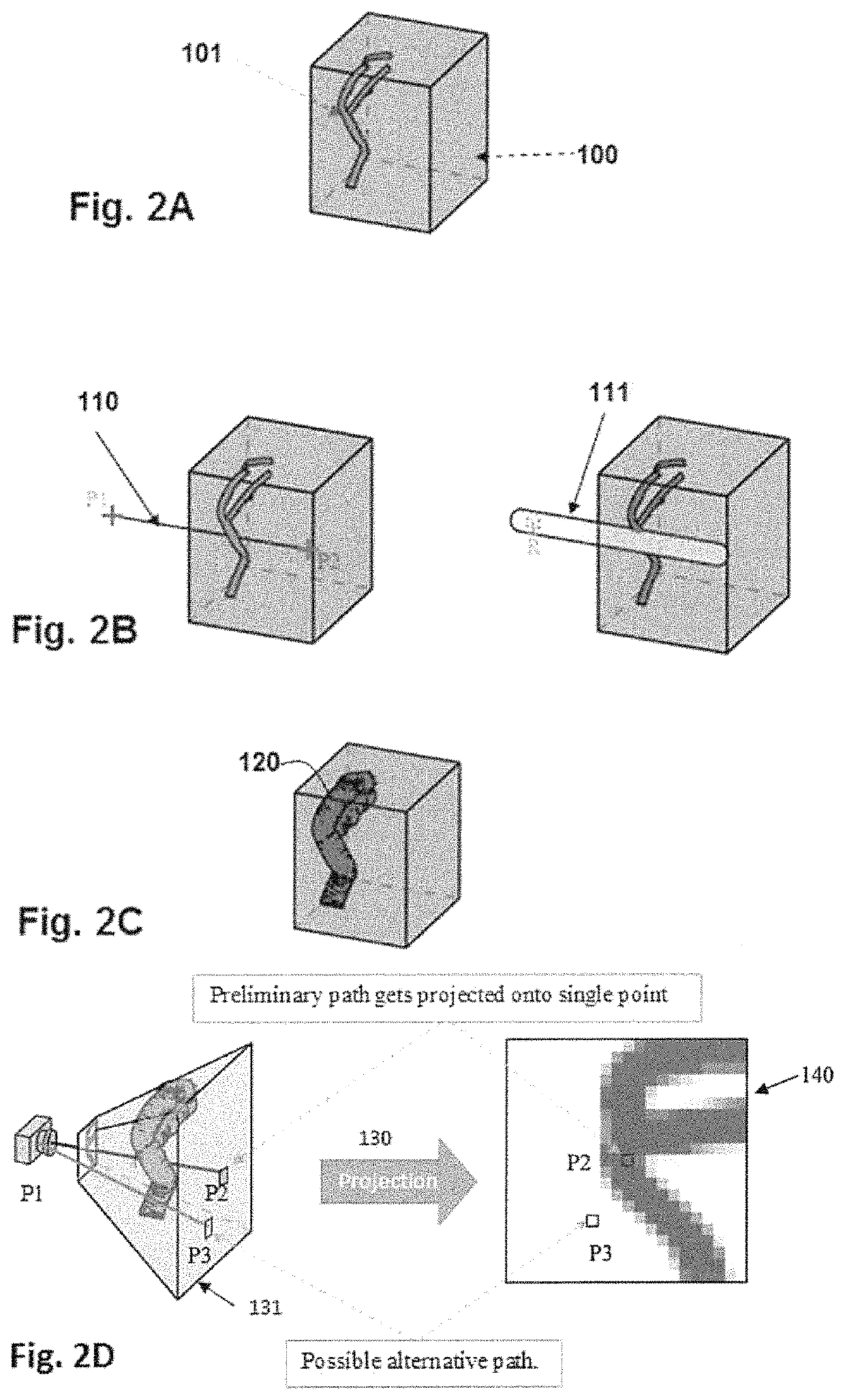
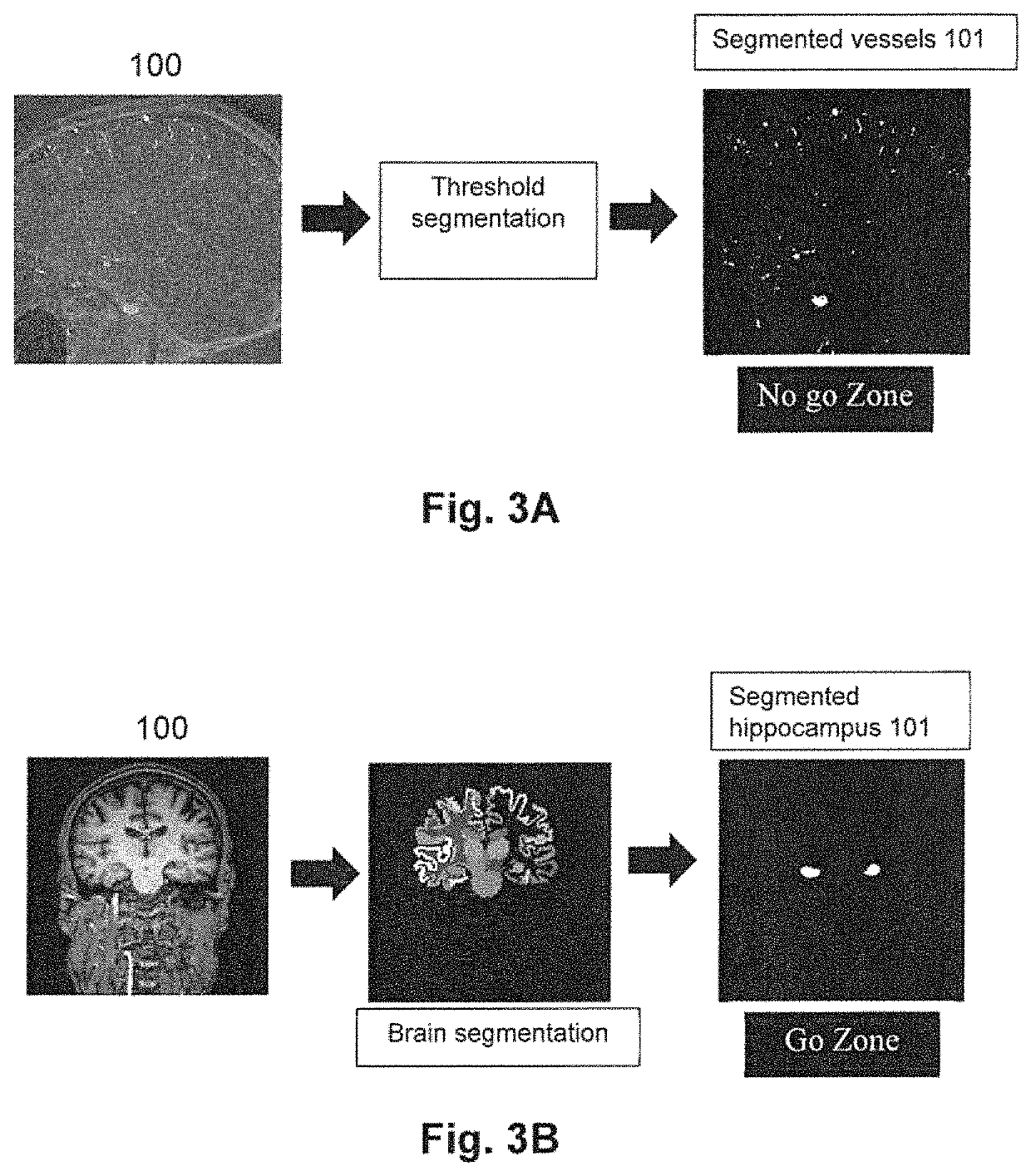
A method, system and computer programs for computing simultaneous rectilinear paths using medical images are disclosed. The method comprises receiving a 3D medical image comprising voxels representing a volume of an anatomical region of a patient and a preliminary path determined by two points traversing said 3D medical image, wherein said 3D medical image has segmented therein at least one area of interest, the preliminary path comprising a security zone with a given distance; computing a distance map of said area of interest and mapping its voxels to a first value or to a second value depending on a distance threshold, the latter being equal to said given distance of the security zone; selecting the voxels having said second value and projecting them using a frustum that projects the preliminary path onto a single point, to obtain a 2D projected image that includes a plurality of rectilinear paths.
Owner:GALGO MEDICAL +3
Bone Repositioning Based on an Automated Assignment
ActiveUS20160321807A1Precise positioningEasy to adaptImage enhancementImage analysisComputer moduleComputer vision
A method and a control module for calculating and displaying result data based on at least one medical image, which has been captured by an imaging device, are provided. At least one image is captured by the imaging device in a digital format with a plurality of bone fragments. Subsequently, a segmentation method is applied to the captured image for identification of the bone fragments contained in the image. Thereafter, a fragment-matching algorithm is executed on the segmented bone fragments for calculation of result data. The result data includes instruction data for assembling at least a part of the bone fragments, which is output on the monitor in a configurable format.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Medical image preprocessing method and system
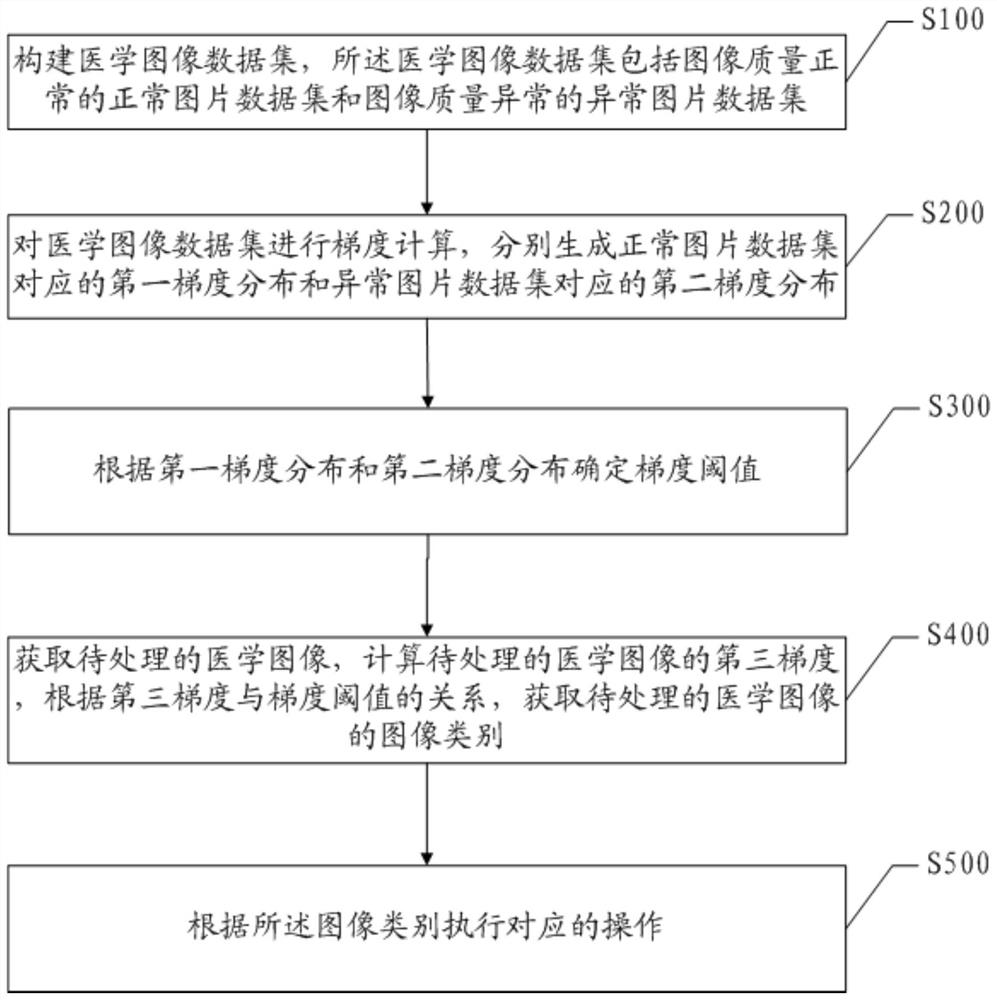
The embodiment of the invention discloses a medical image preprocessing method and system, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a medical image data set which comprises a normal image data set with normal image quality and an abnormal image data set with abnormal image quality; performing gradient calculation on the medical image data set, and respectively generating first gradient distribution corresponding to the normal image data set and second gradient distribution corresponding to the abnormal image data set; determining a gradient threshold according to the first gradient distribution and the second gradient distribution; acquiring a to-be-processed medical image, calculating a third gradient of the to-be-processed medical image, and acquiring an image category of the to-be-processed medical image according to a relationship between the third gradient and a gradient threshold; and executing corresponding operation according to the image category. According to the embodiment of the invention, before the medical picture data is input into the deep learning model for learning, the pictures with whitening or blackening quality are screened out, the noise of the pictures with poor quality is filtered out, and the training accuracy of the subsequent deep learning model is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SMART IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Computer implemented method, a system and computer programs for computing simultaneous rectilinear paths using medical images
ActiveUS11282263B2Less powerValid checkDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementVoxelProjection image
A method, system and computer programs for computing simultaneous rectilinear paths using medical images are disclosed. The method comprises receiving a 3D medical image comprising voxels representing a volume of an anatomical region of a patient and a preliminary path determined by two points traversing said 3D medical image, wherein said 3D medical image has segmented therein at least one area of interest, the preliminary path comprising a security zone with a given distance; computing a distance map of said area of interest and mapping its voxels to a first value or to a second value depending on a distance threshold, the latter being equal to said given distance of the security zone; selecting the voxels having said second value and projecting them using a frustum that projects the preliminary path onto a single point, to obtain a 2D projected image that includes a plurality of rectilinear paths.
Owner:GALGO MEDICAL +3
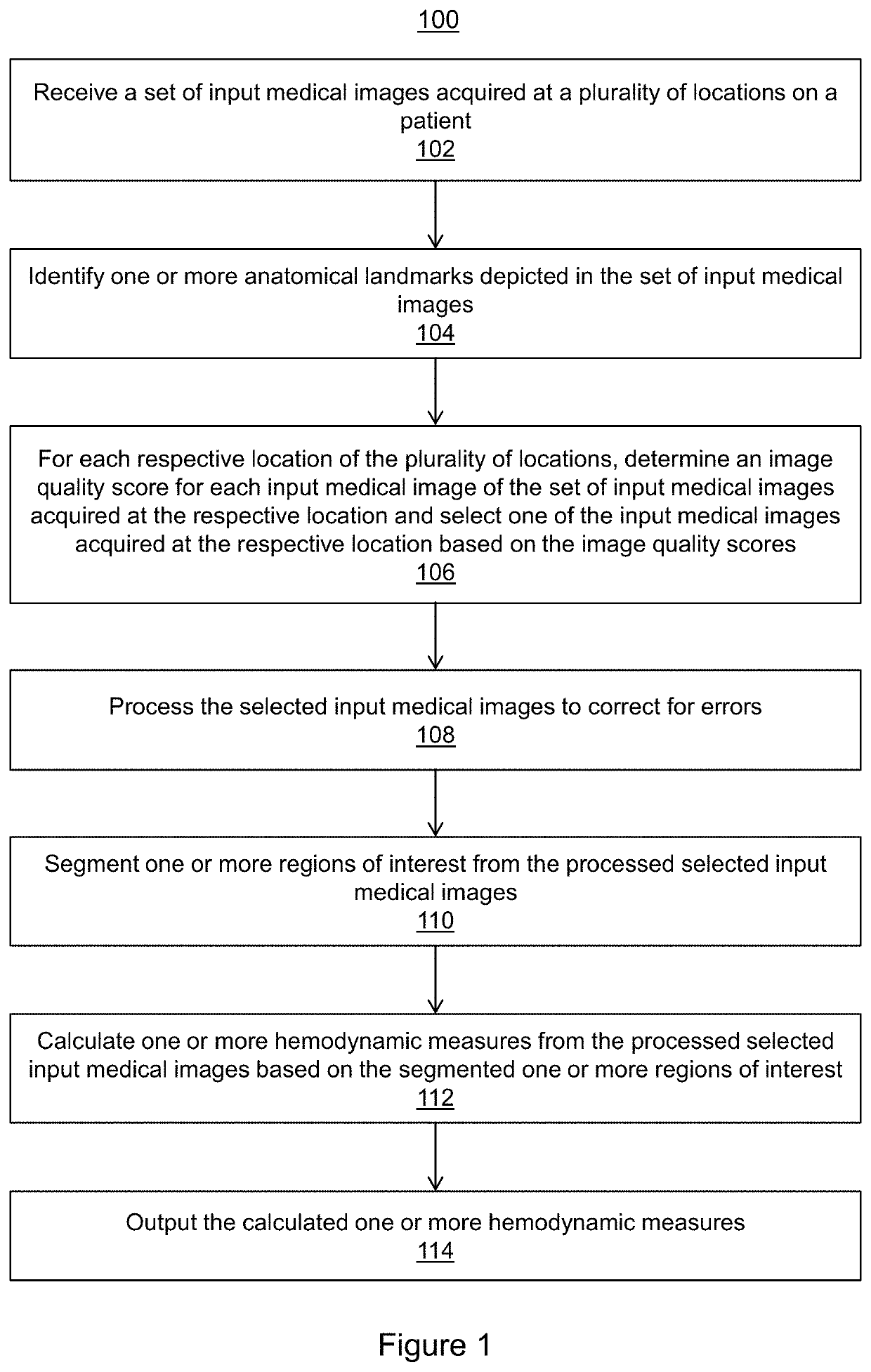
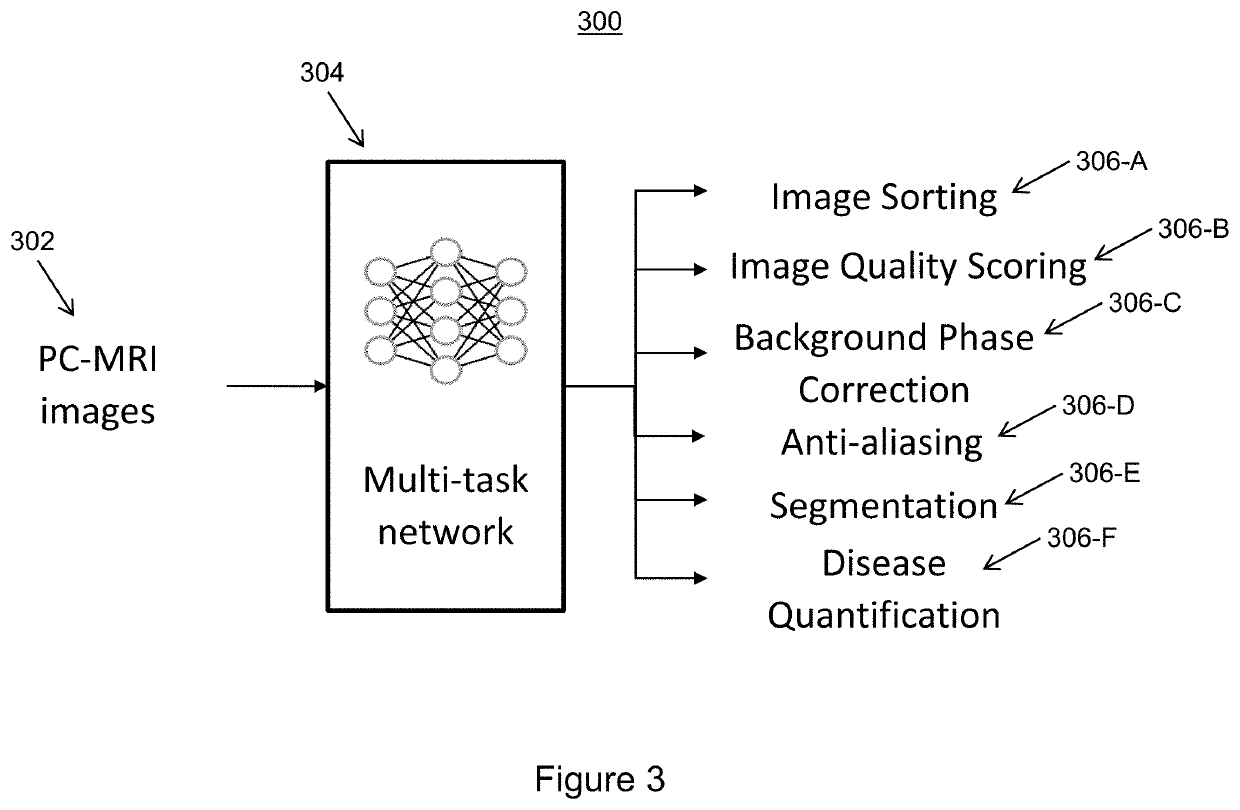
Fully automatic inline processing for pc-mri imagesfully automatic inline processing for pc-mri images using machine learning
PendingUS20220270240A1Correction errorImage enhancementMedical data miningImaging qualityHemodynamics
Systems and methods for automatic processing of input medical images are provided. A set of input medical images acquired at a plurality of locations on a patient is received. For each respective location of the plurality of locations, an image quality score is determined for each input medical image of the set of input medical images acquired at the respective location and one of the input medical images acquired at the respective location is selected based on the image quality scores. The selected input medical images are processed to correct for errors. One or more regions of interest are segmented from the processed selected input medical images. One or more hemodynamic measures are calculated from the processed selected input medical images based on the segmented one or more regions of interest. The calculated one or more hemodynamic measures are output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for automatic determination of the change of a hollow organ
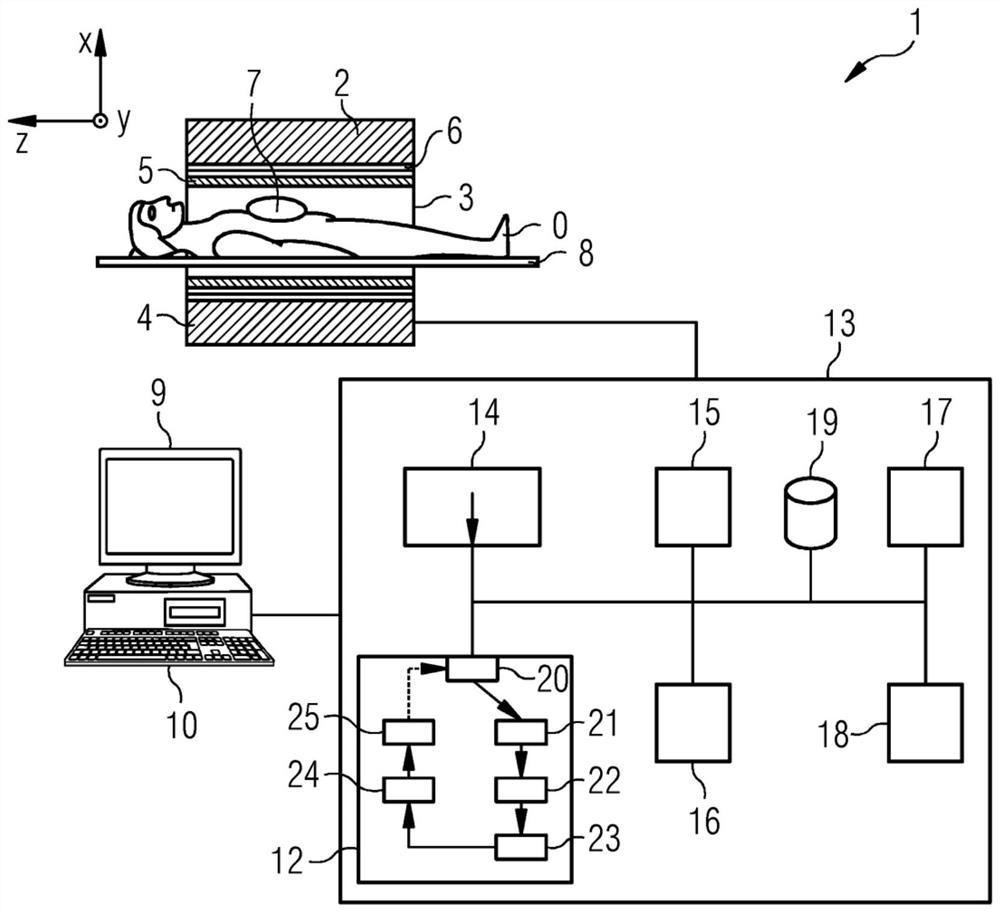
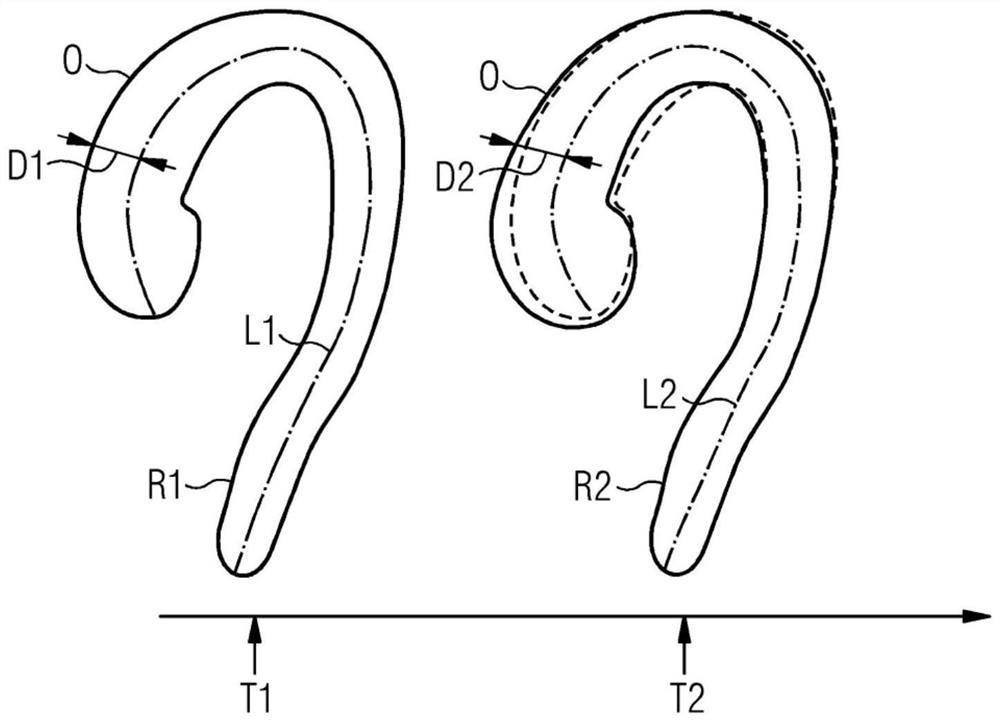
PendingCN112488988AIntuitive and quick instructionsImage enhancementImage analysisMedical imagingSurgery
The invention describes a method and a device for automatic determination of the change of a hollow organ. The method comprises the steps: providing a first medical image of the organ recorded at a first point of time, computing a first representation of the organ in the first image, computing a first reference-line of the organ based on the first representation of the organ, providing a second medical image of the organ recorded at a second point of time, computing a second representation of the organ in the second image, computing a second reference-line of the organ based on the second representation of the organ, registering of the first reference-line and the second reference-line to obtain a matching of the two representations of the organ and / or features derived from the representations, comparing the matched representations of the organ and / or the features derived from these representations. The invention further describes a related device, a related control device and a related medical imaging system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Medical image quality monitoring and improvement system
ActiveUS9449380B2Express dissatisfactionQuality improvementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityMonitoring system
A medical image quality reporting and monitoring system for use in a medical imaging system comprises a medical image computer including, a display processor, a display and a report generator. The display processor generates data representing an image for display including a user selectable image element enabling a user to identify at least one medical image as having an image quality deficiency. The display presents the image. The report generator, in response to detection of selection of the image element, identifying at least one medical reduced quality image as having an image quality deficiency, automatically generates a report. The report comprises, data representing an anonymized reduced quality image having the image quality deficiency, a time of acquisition of the reduced quality image and imaging system acquisition settings used in acquiring the reduced quality image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image retrieval method based on CNN feature vocabulary tree
ActiveCN107423379BImprove accuracyEasy to learnDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage retrievalDiagnostic system
The invention discloses an image retrieval method based on a CNN feature vocabulary tree, and aims to solve the technical problem of low accuracy existing in the existing vocabulary tree method. The implementation steps are as follows: first generate the derivative images of each image in the image library, and extract the CNN features of each image in the image library, then construct a CNN feature vocabulary tree according to the extracted CNN features, then generate derivative images of each image to be retrieved, and extract The CNN feature of each image to be retrieved, by comparing the path of the CNN feature of each image to be retrieved and its related image in the CNN feature vocabulary tree, calculate the distance between the image to be retrieved and its related image, and compare the image to be retrieved and its related image The distance is combined with the initial similarity, and finally the retrieval results of each image to be retrieved are output according to the comprehensive similarity of each image to be retrieved and its related images. The image retrieval accuracy rate of the invention is high, and can be used in medical image computer aided diagnosis systems and image search systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
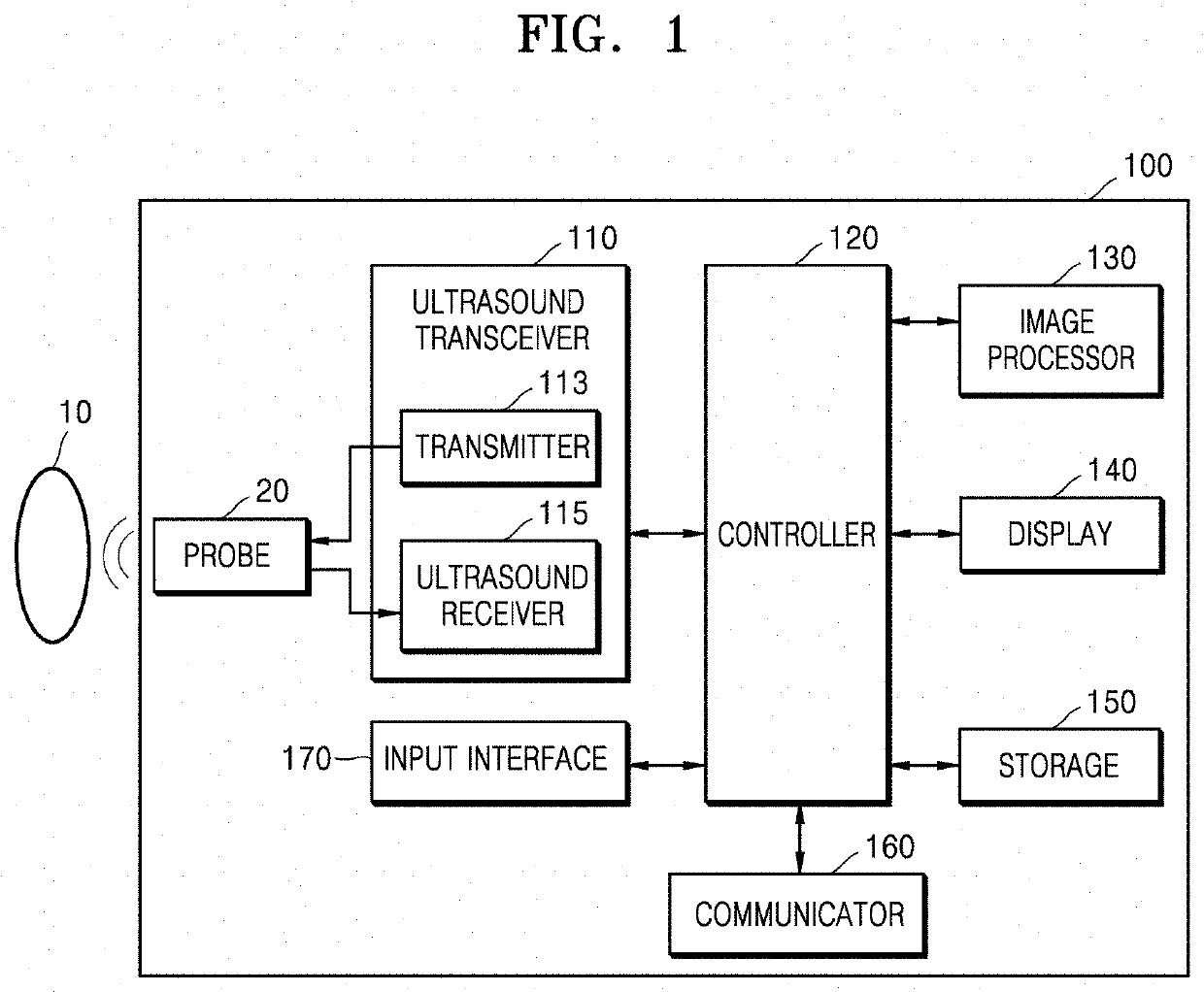
Ultrasound imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and computer program
PendingUS20210282750A1Easy to viewWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasonic imagingRadiology
Provided are an ultrasound imaging apparatus and a control method thereof, the ultrasound imaging apparatus including: an input / output interface; a storage; and at least one processor configured to: display, via the input / output interface, at least one resulting value calculated based on a plurality of medical images; when one of the at least one resulting value is selected by an input via the input / output interface, retrieve, from the storage, a plurality of measurement values and a plurality of medical images used to calculate the selected resulting value; and output, via the input / output interface, the retrieved plurality of measurement values and the retrieved plurality of medical images on a single display.
Owner:SAMSUNG MEDISON
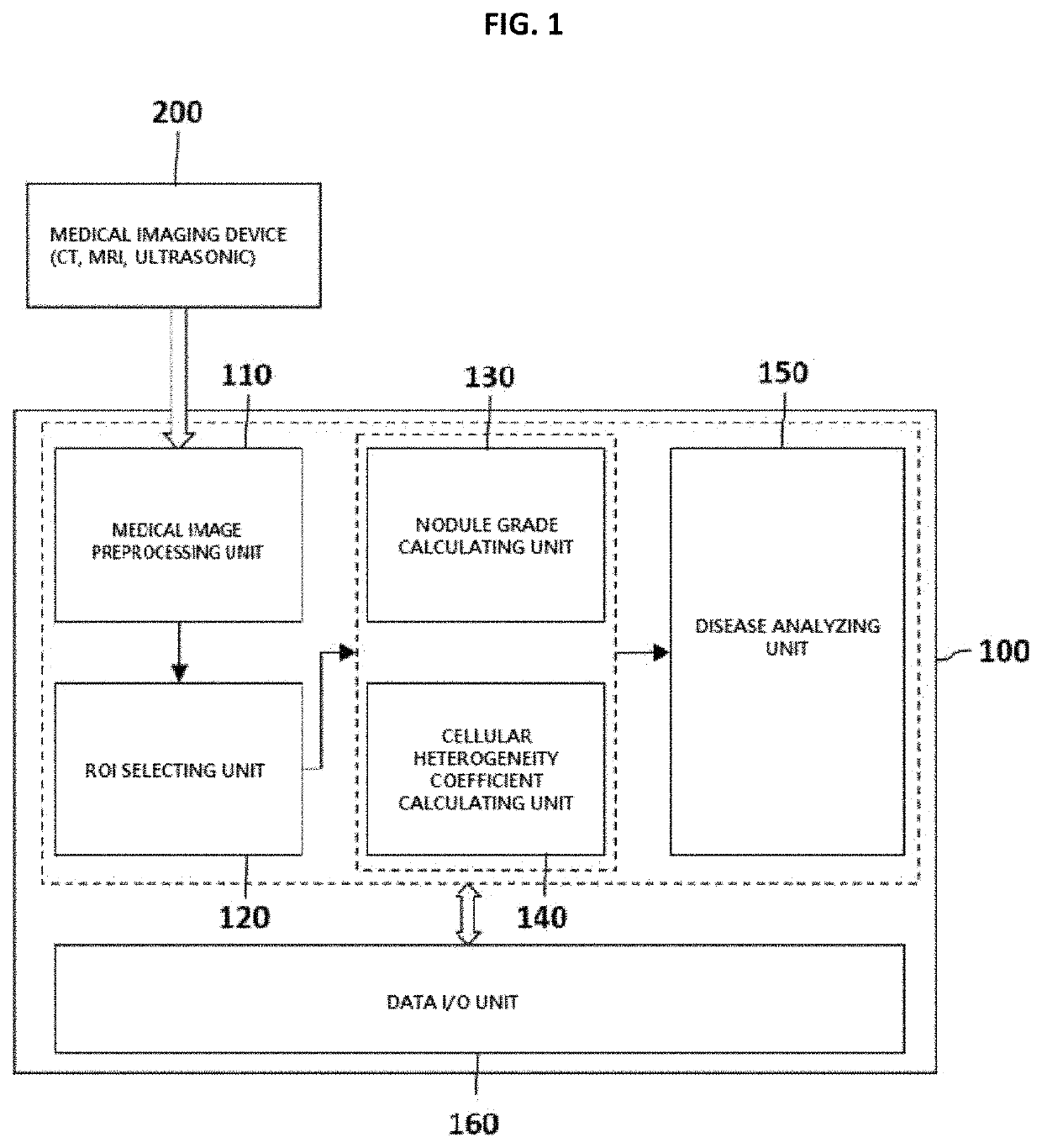
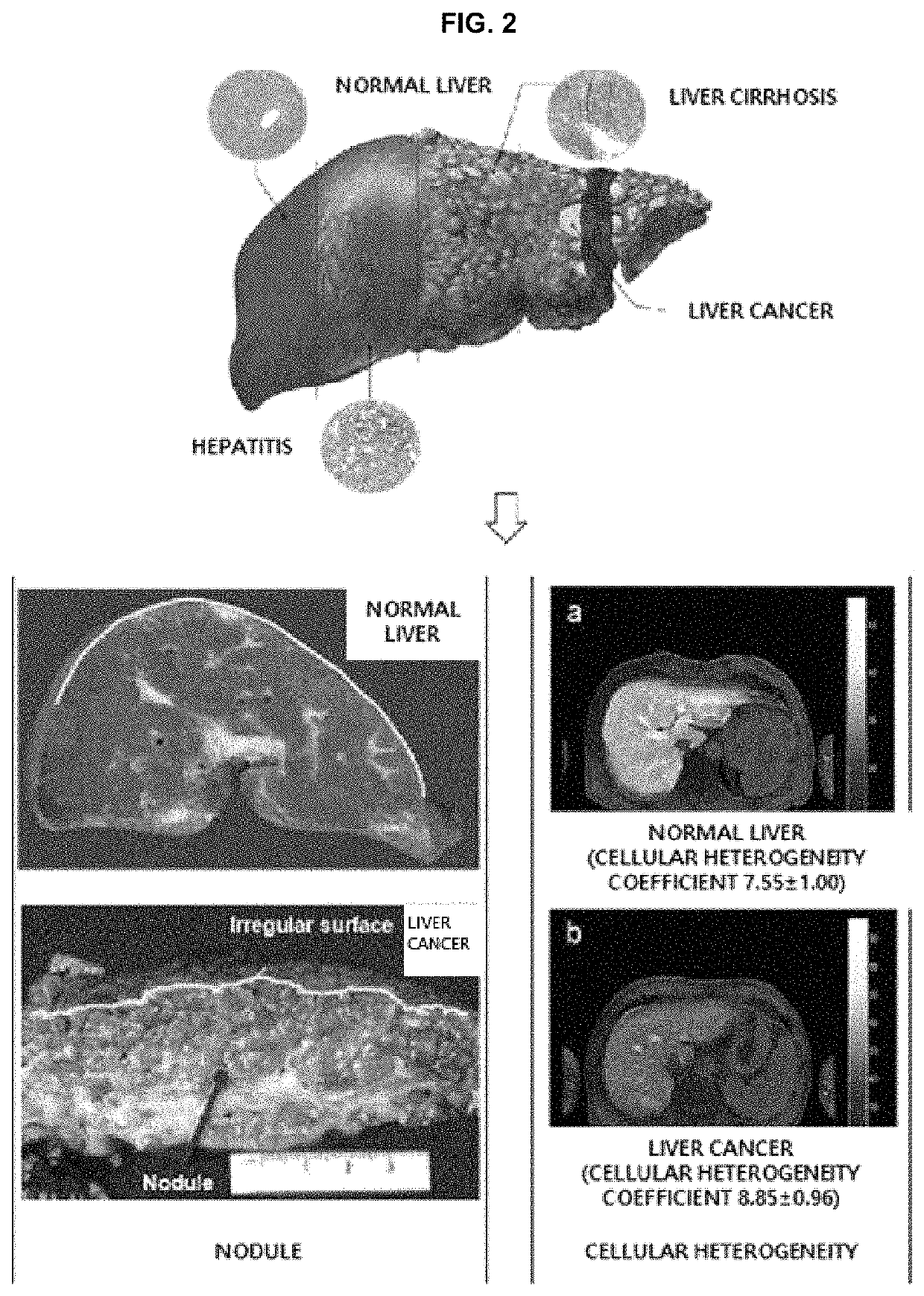
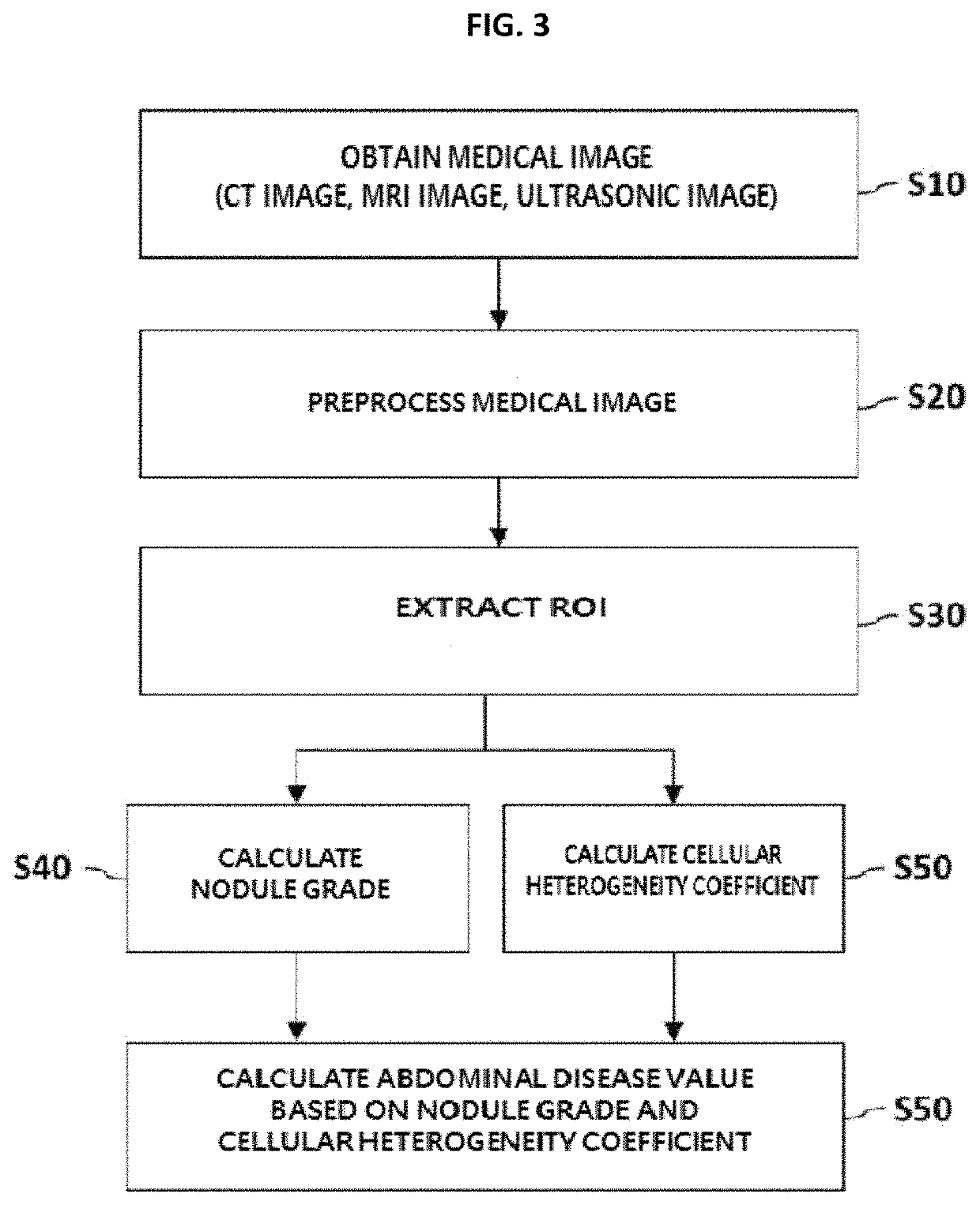
Method and apparatus for calculating abdominal disease diagnosis information based on medical image
ActiveUS11069061B2Low costShorten the timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDiseaseRadiology
A method for analyzing an abdominal disease based on a medical image, includes receiving and preprocessing a medical image obtained by photographing an abdominal region of a patient to detect a plurality of analysis candidate regions and setting one of the plurality of analysis candidate regions as a ROI, calculating a nodule grade based on surface unevenness of the ROI, calculating a cellular heterogeneity coefficient based on pixel homogeneity of the ROI, and predicting and outputting an abdominal disease value based on the nodule grade and the cellular heterogeneity coefficient.
Owner:WONKWANG UNIV CENT FOR IND ACAD COOPERATION
Digital grid method and terminal
PendingCN114240909AScatter effects effectively and thoroughlyEffective and thorough suppression of scattering effectsImage enhancementImage analysisImage correctionComputational physics
The invention discloses a digital grid method and a terminal, and the method comprises the steps: determining a simulated boundary spread function curve based on a preset scattering simulation model, and carrying out the fitting of the simulated boundary spread function curve, and obtaining a scattering model; receiving a scattering correction request of a to-be-corrected medical image; according to the scattering correction request, a scattering boundary spread function curve corresponding to the to-be-corrected medical image is obtained through calculation based on the scattering model and the to-be-corrected medical image, and a scattering kernel is determined according to the scattering boundary spread function curve; scattering correction is carried out on the to-be-corrected medical image based on the scattering core, a corrected medical image is obtained, a digital grid is achieved, a physical simulation model of scattered rays is analyzed, a simulated ESF curve is determined, the scattering model can better reflect the physical effect of scattering and better fit the actual scattering condition, and the medical image correction accuracy is improved. And the scattering influence in the medical image is suppressed more effectively and thoroughly, so that the scattering influence in the medical image is effectively eliminated.
Owner:安健科技(重庆)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com