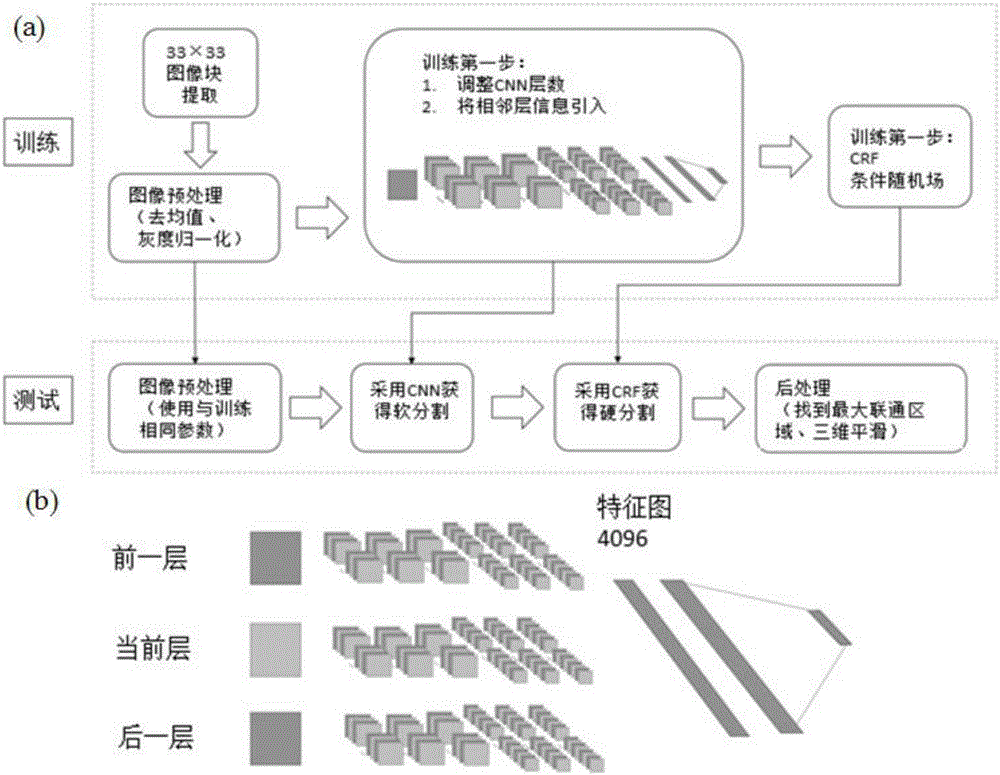
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
315 results about "Computer-aided diagnosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
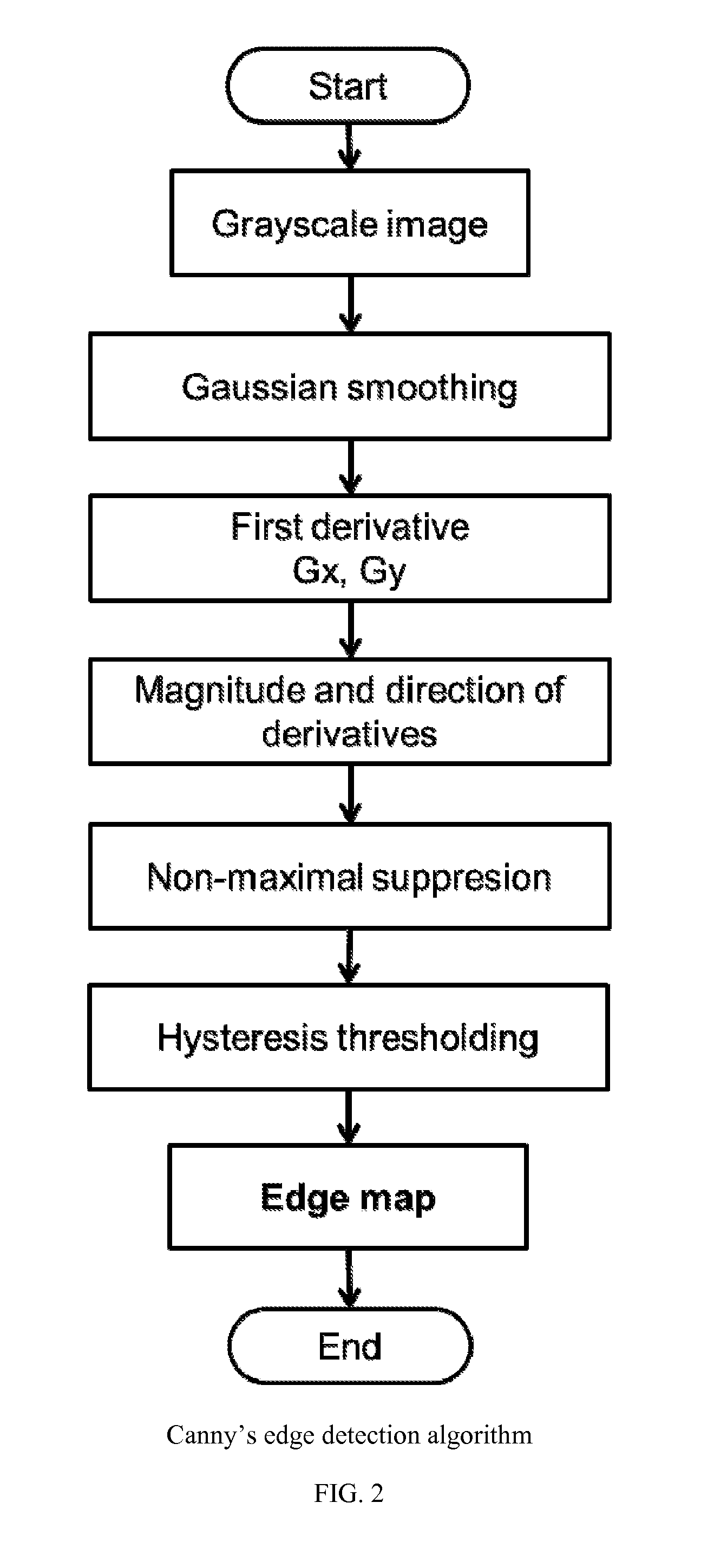
Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
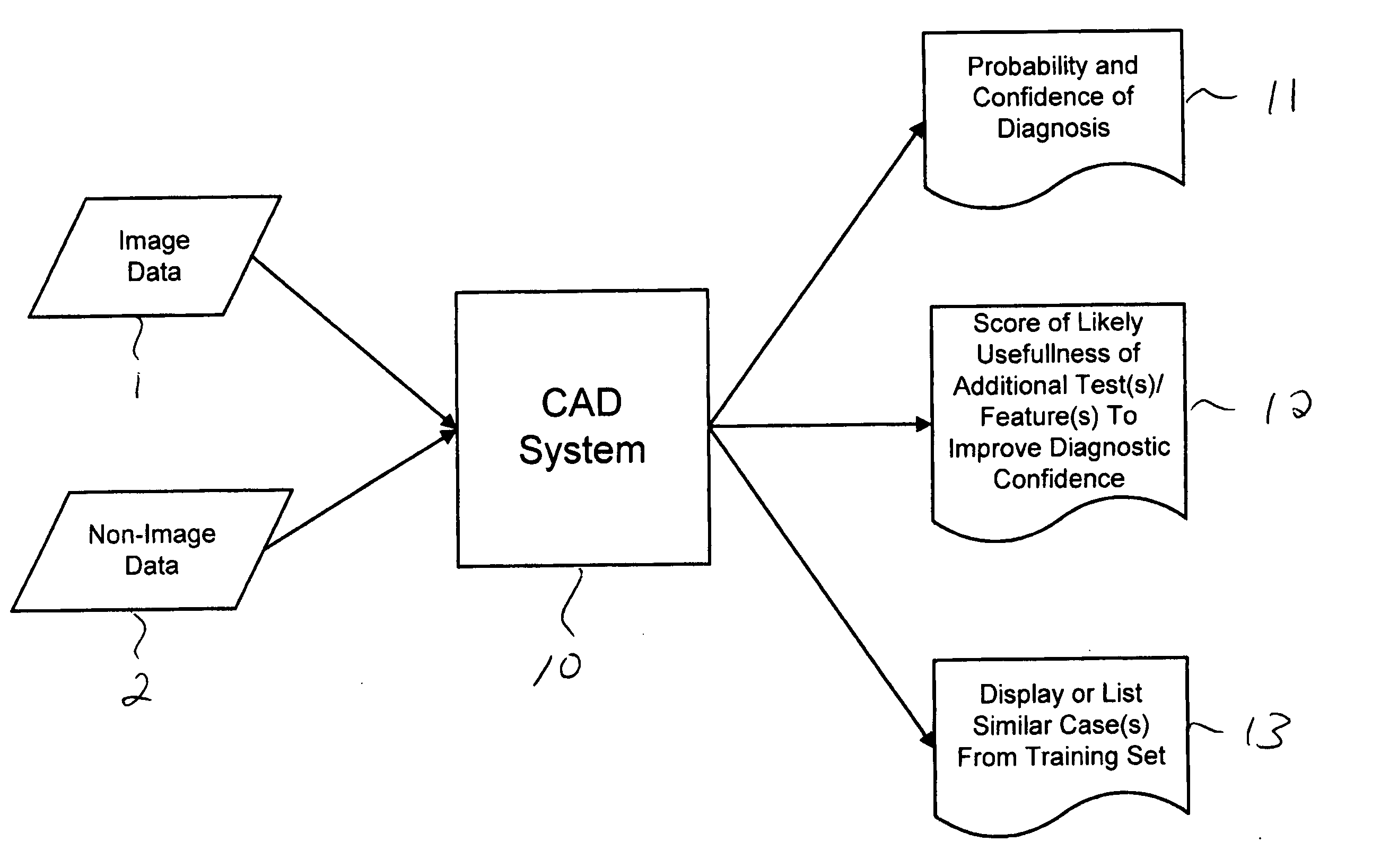
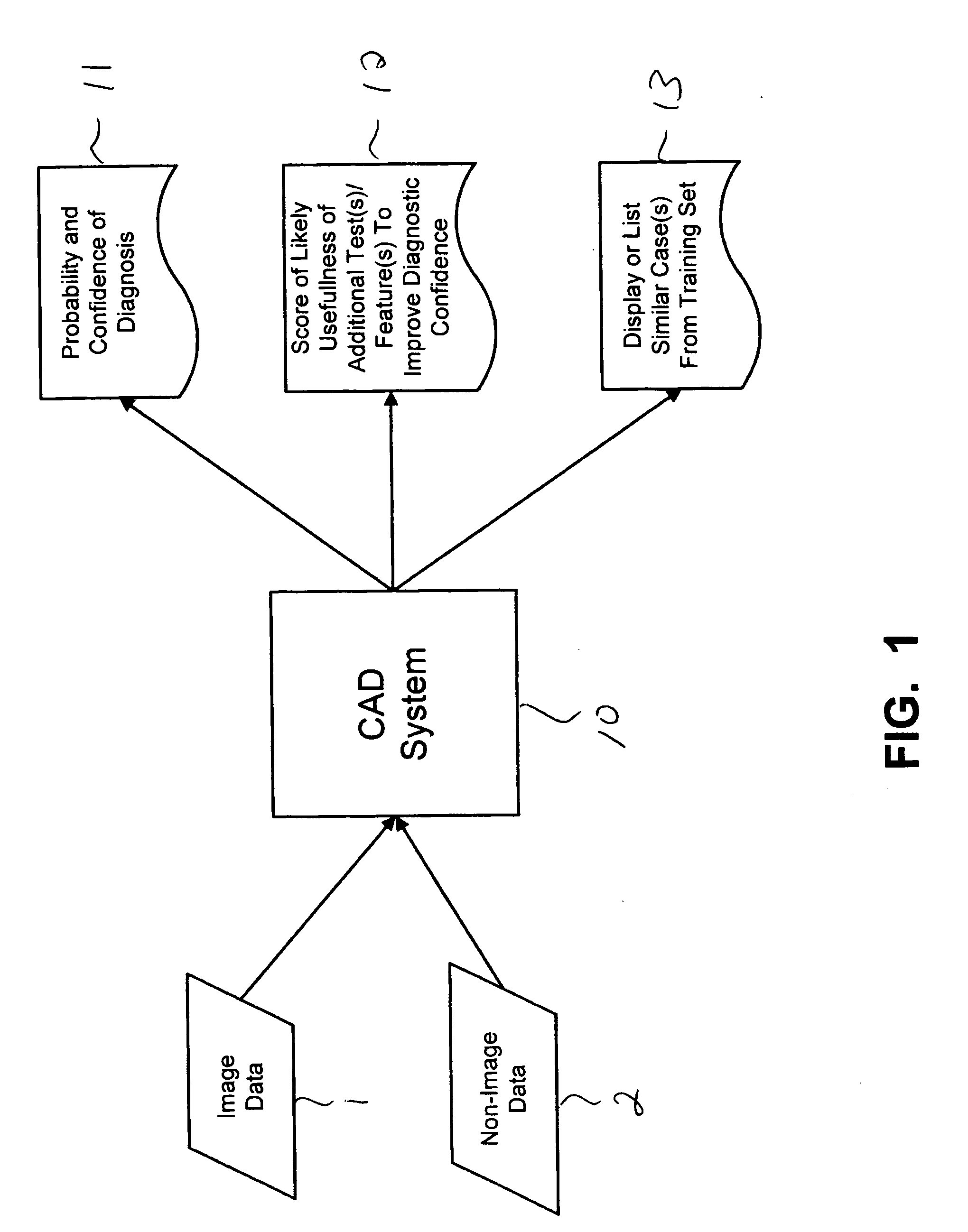
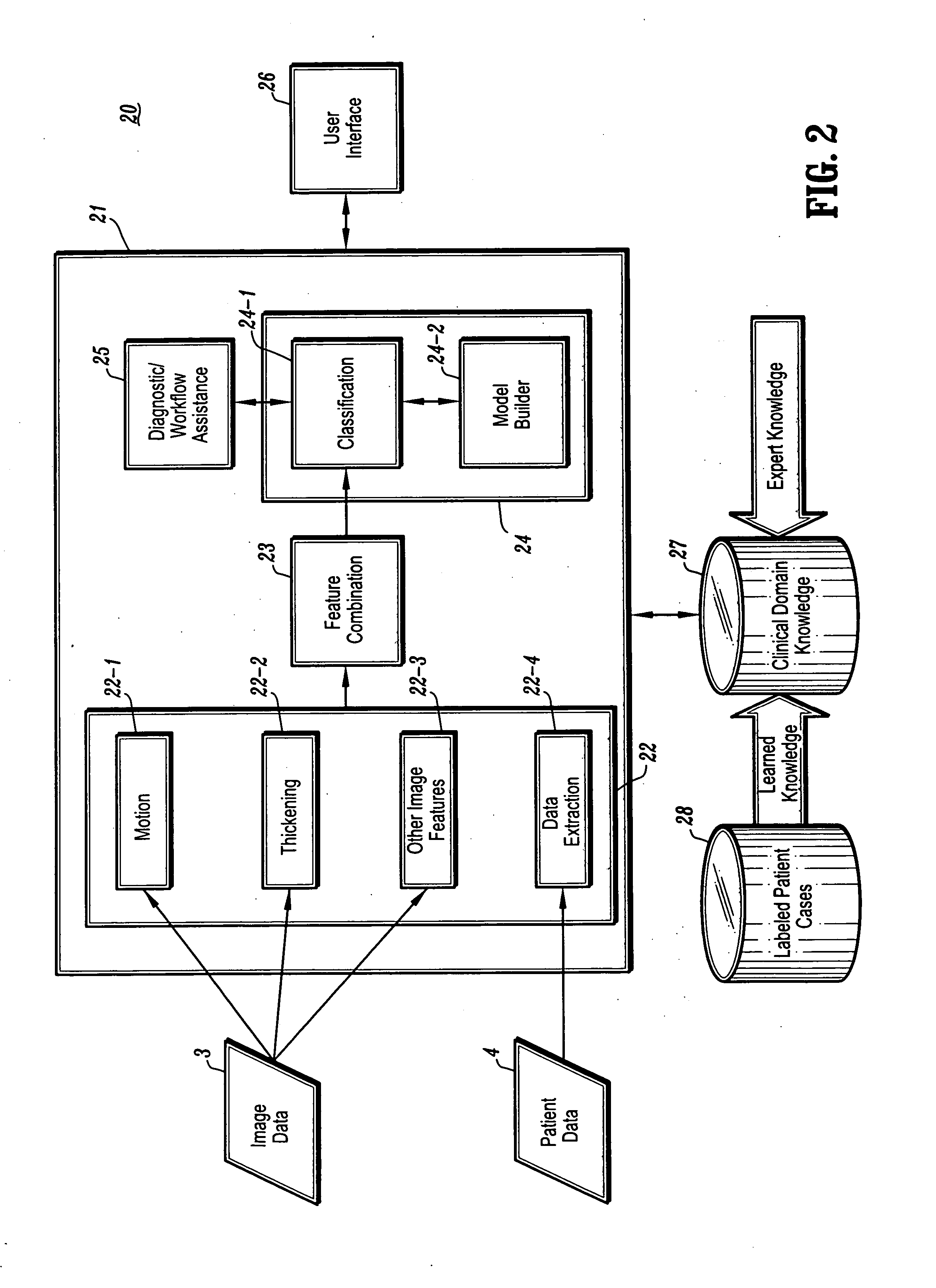
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for breast imaging
ActiveUS20050049497A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPatient dataDecision taking
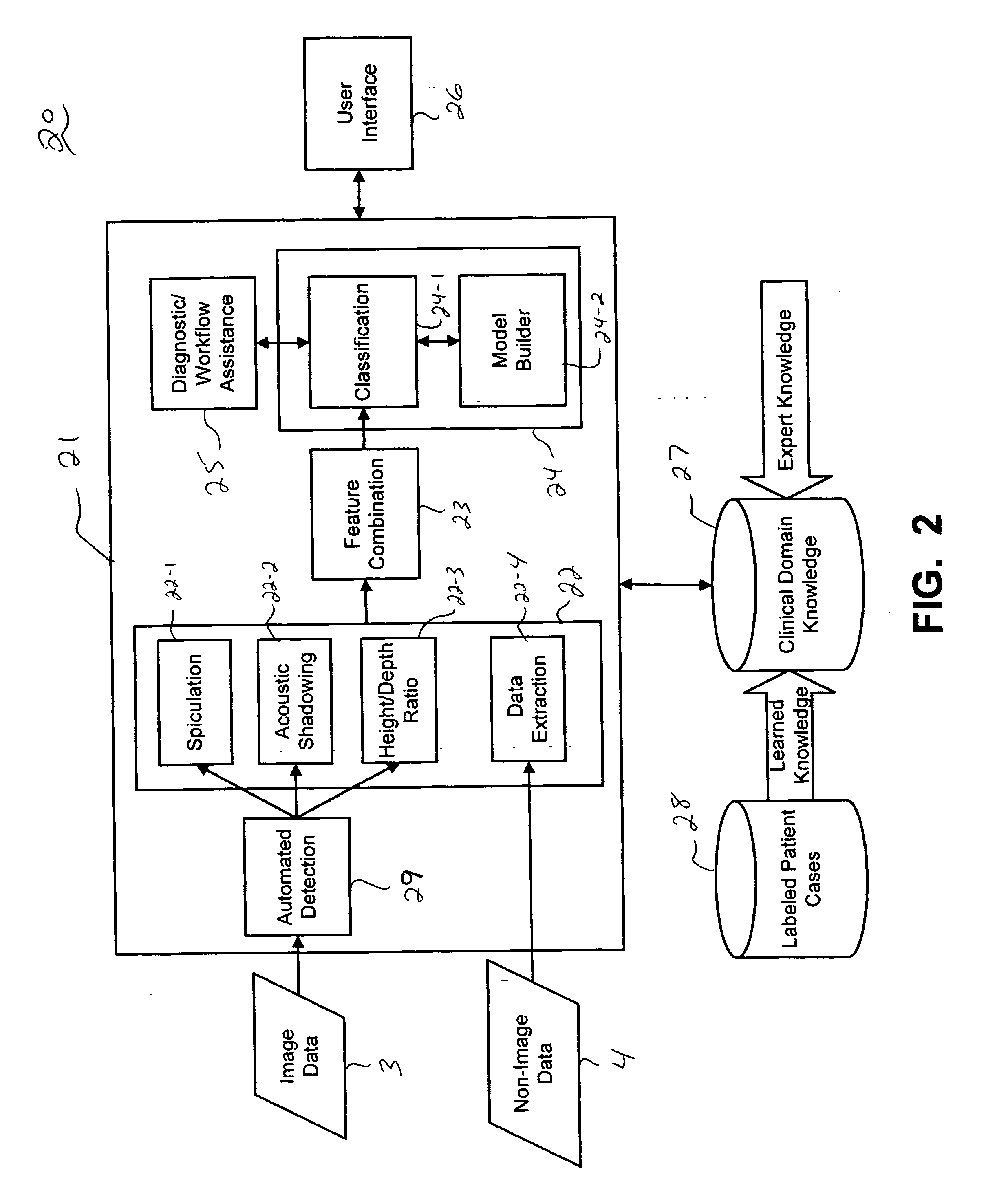
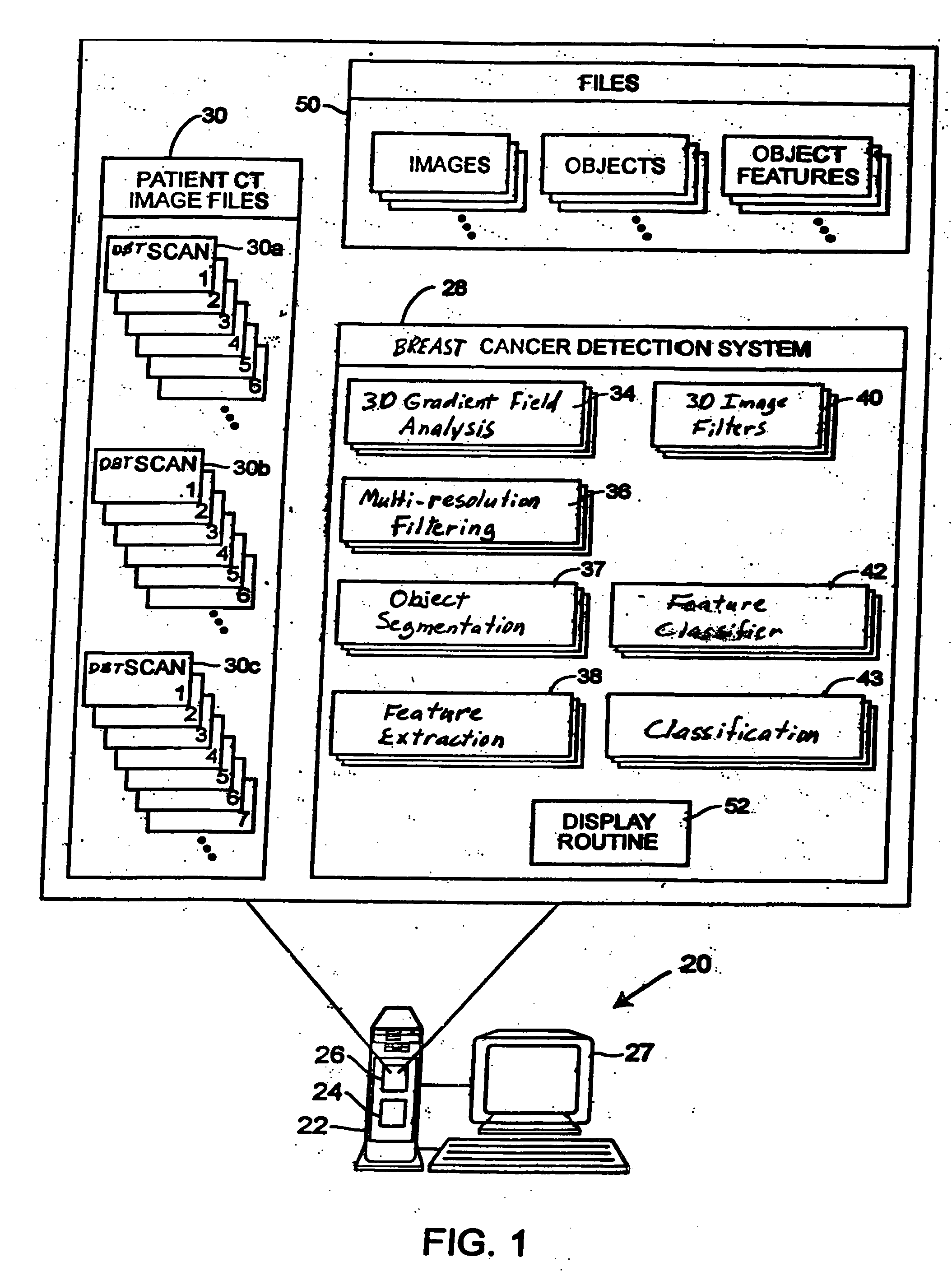
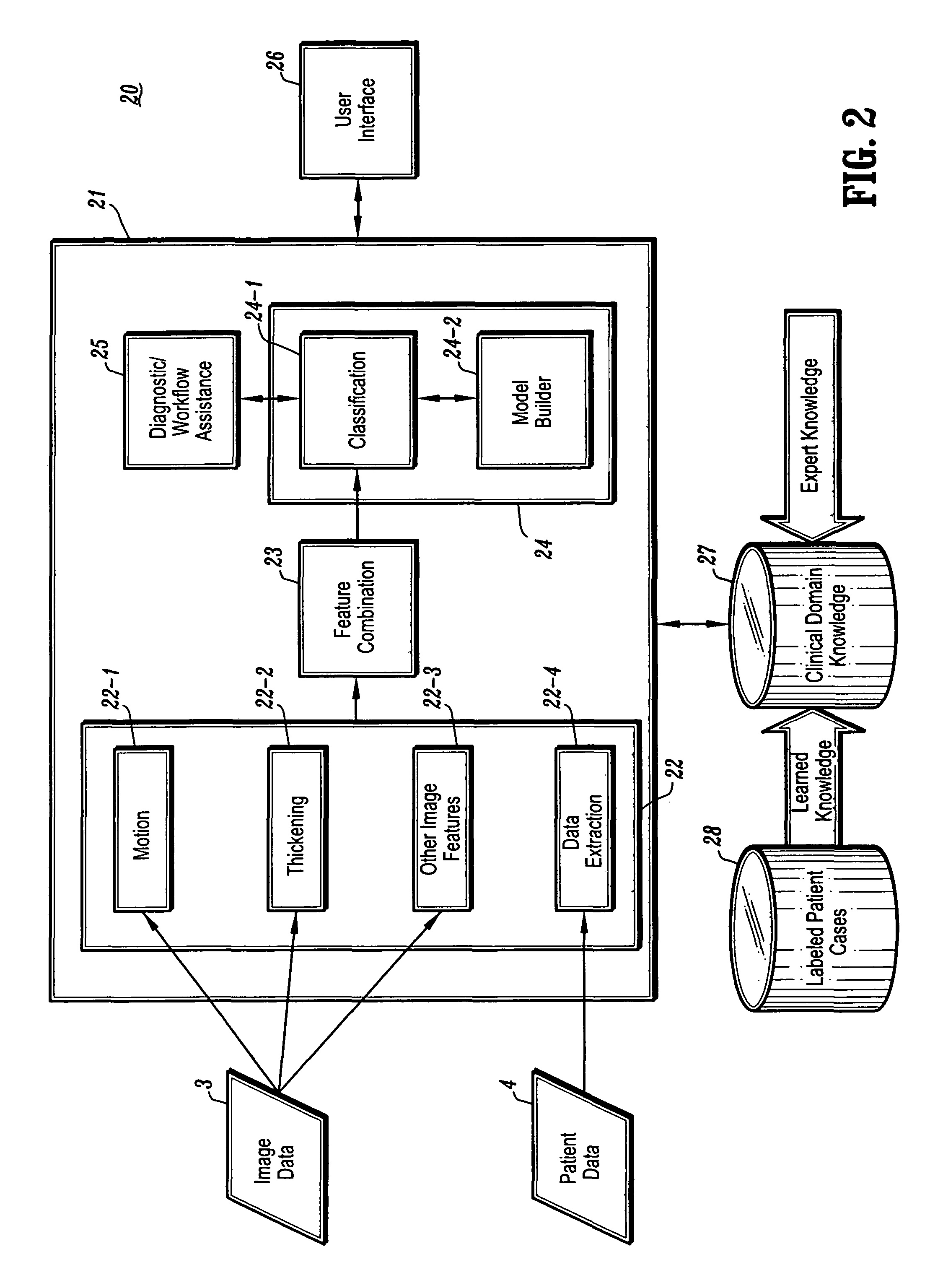
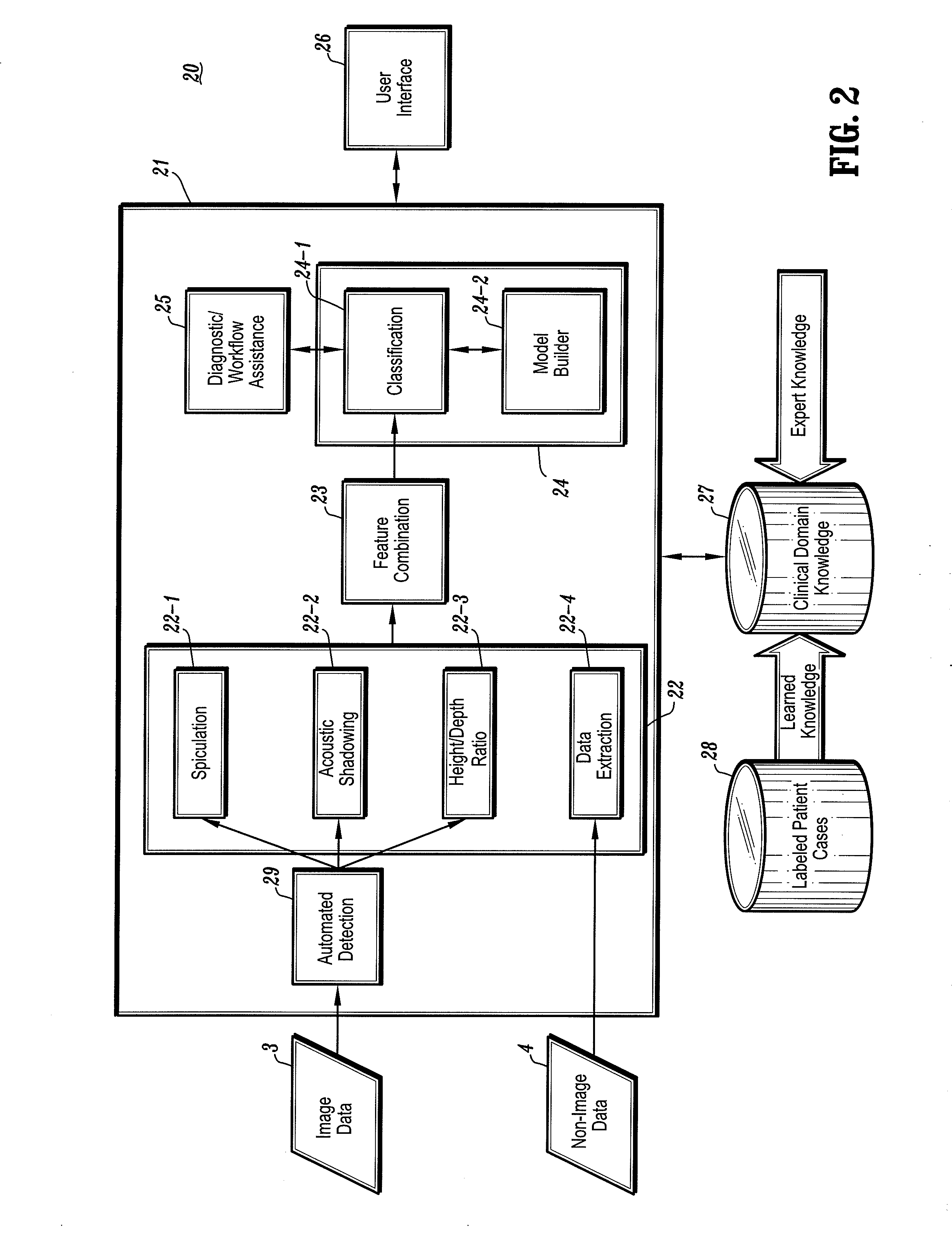
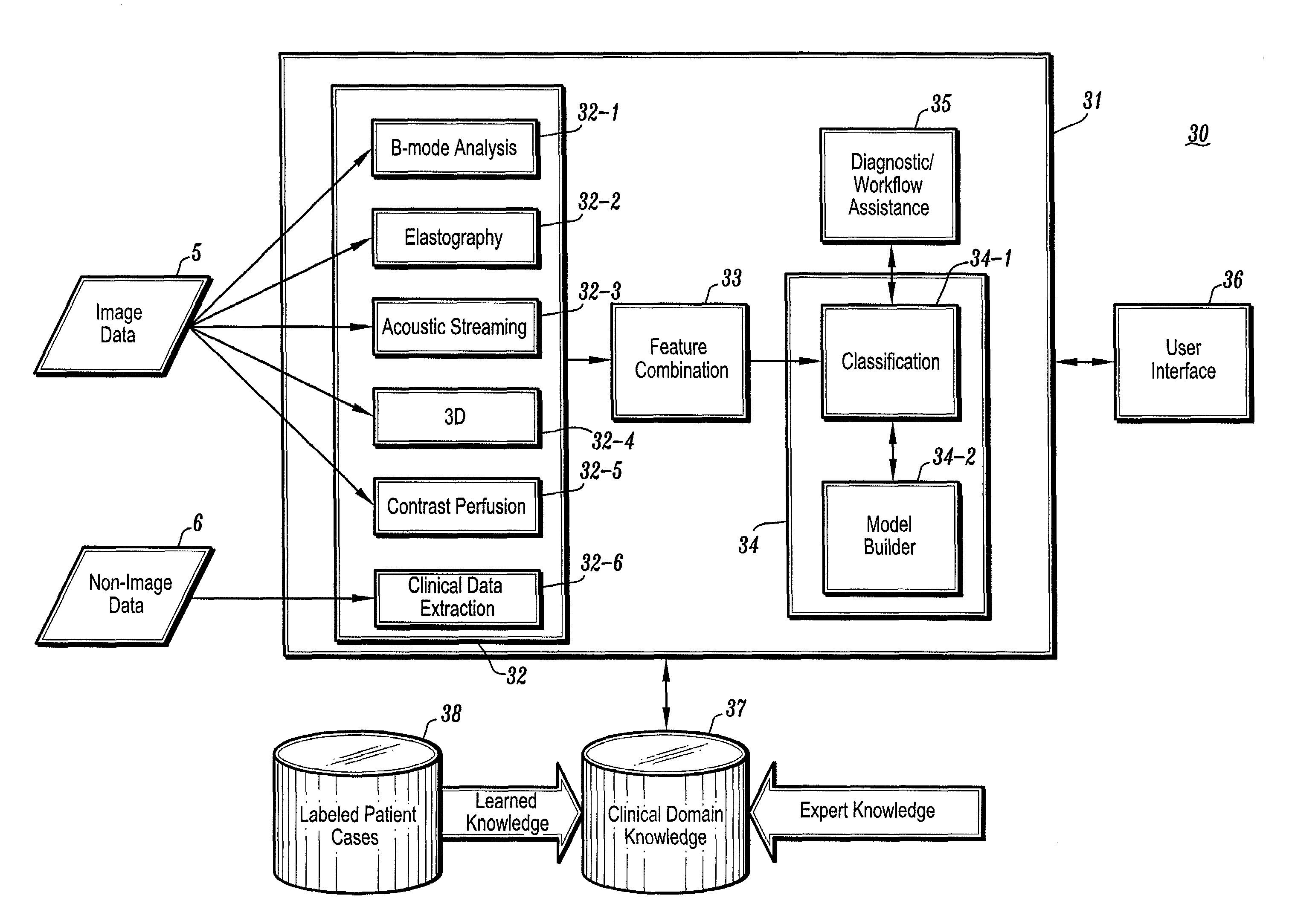
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for breast imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated diagnosis of breast cancer other automated decision support functions that enable decision support for, e.g., screening and staging for breast cancer. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
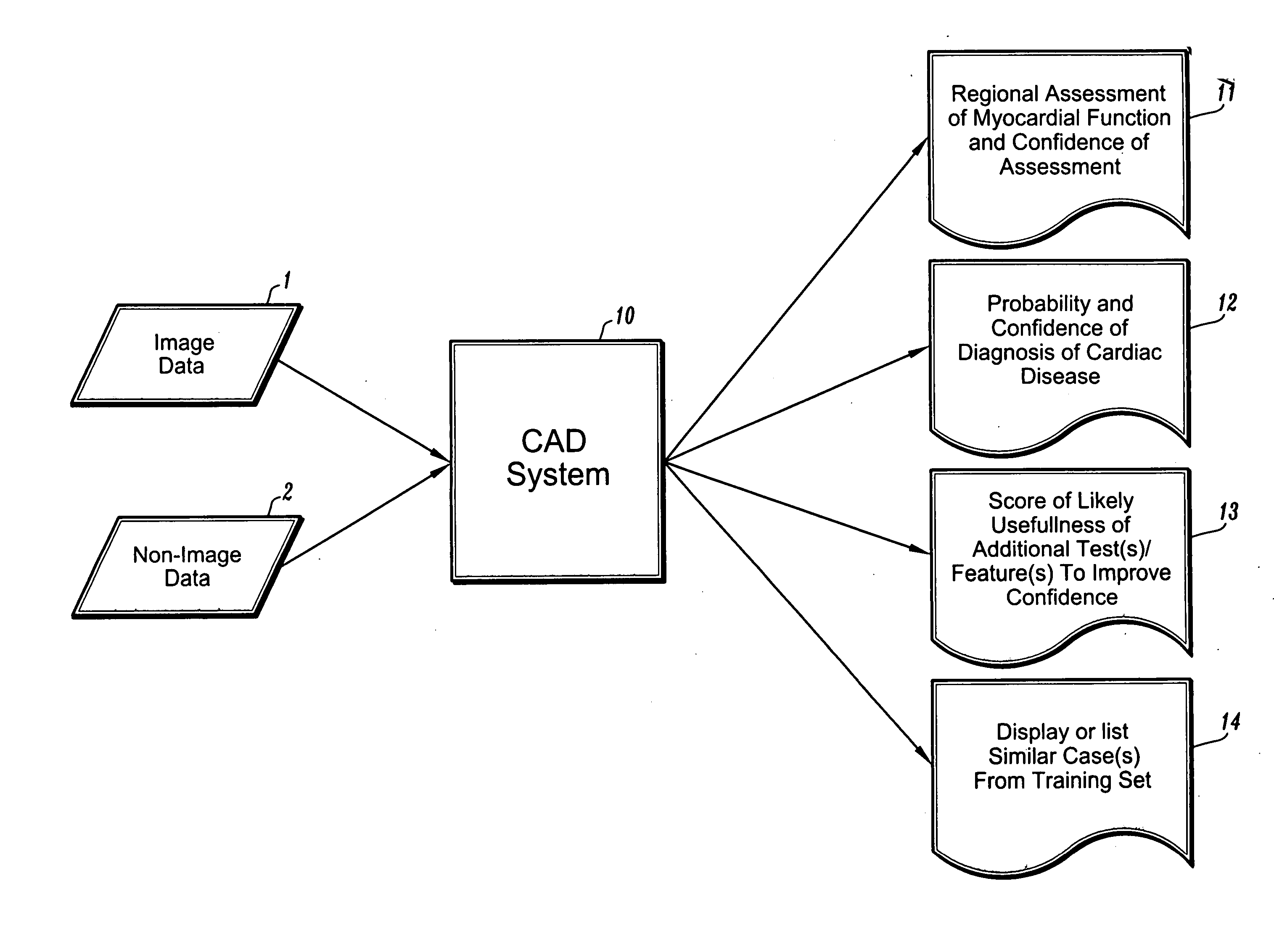
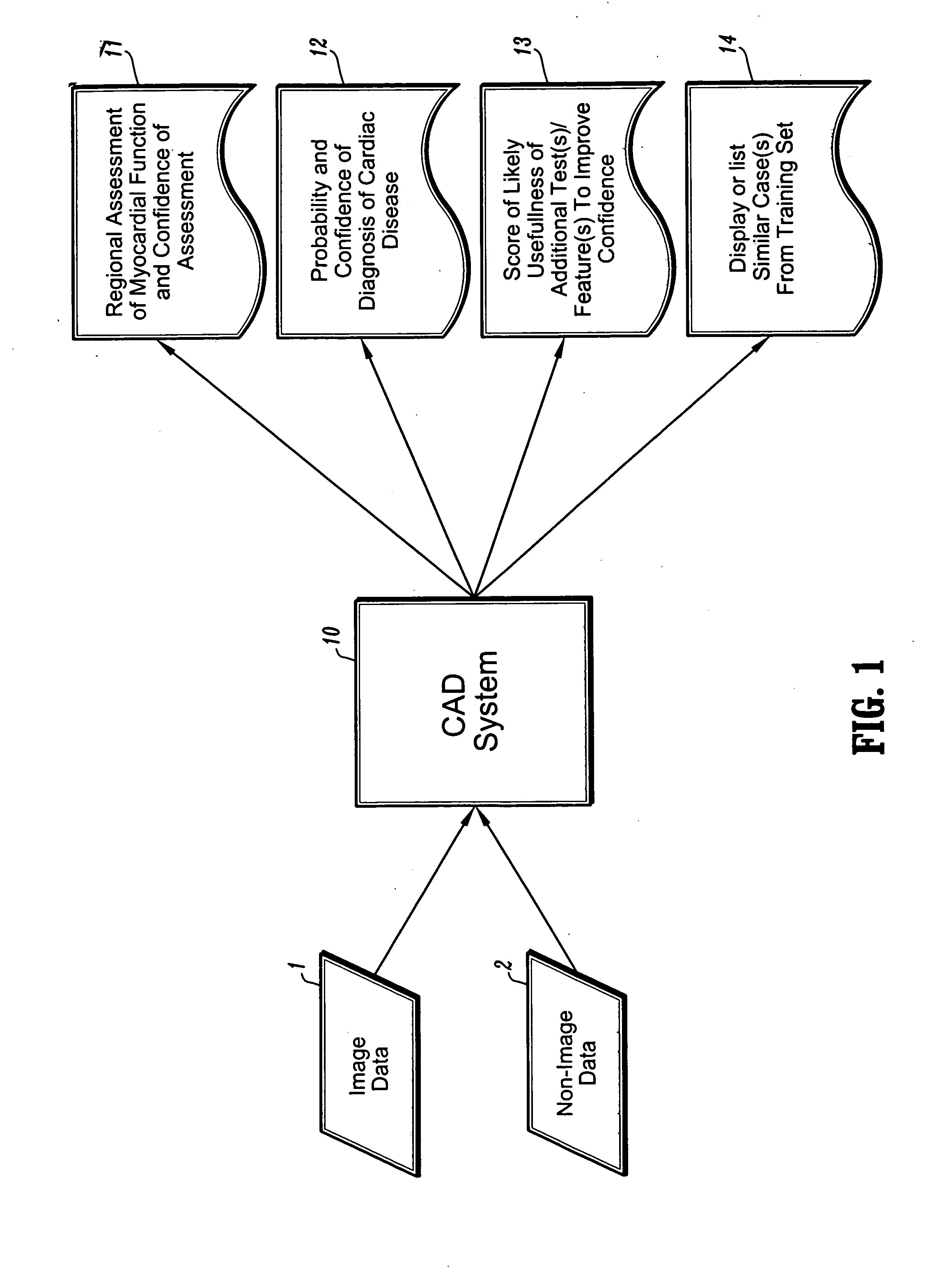
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for heart related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20050020903A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisCoronary artery diseasePatient data
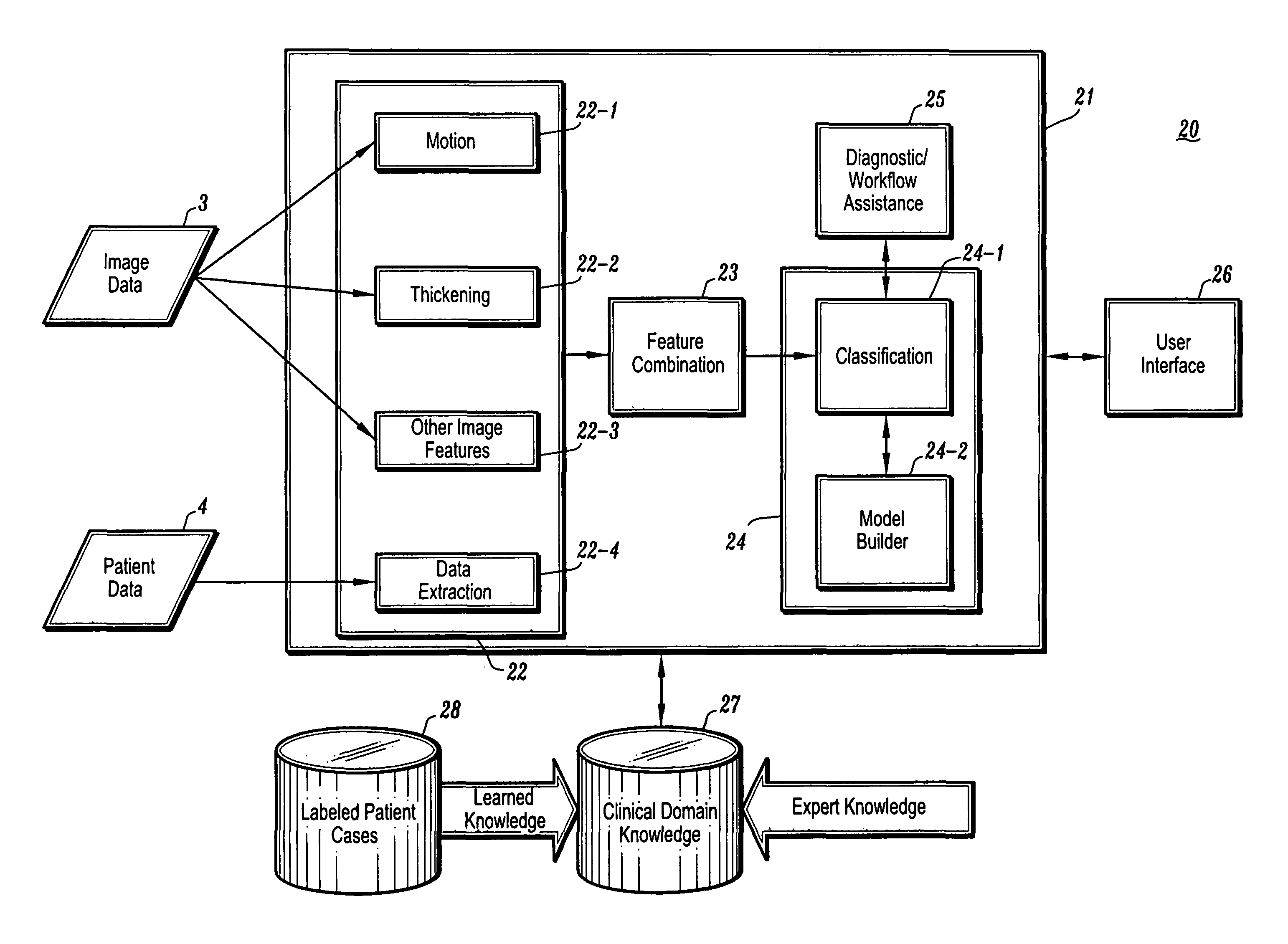
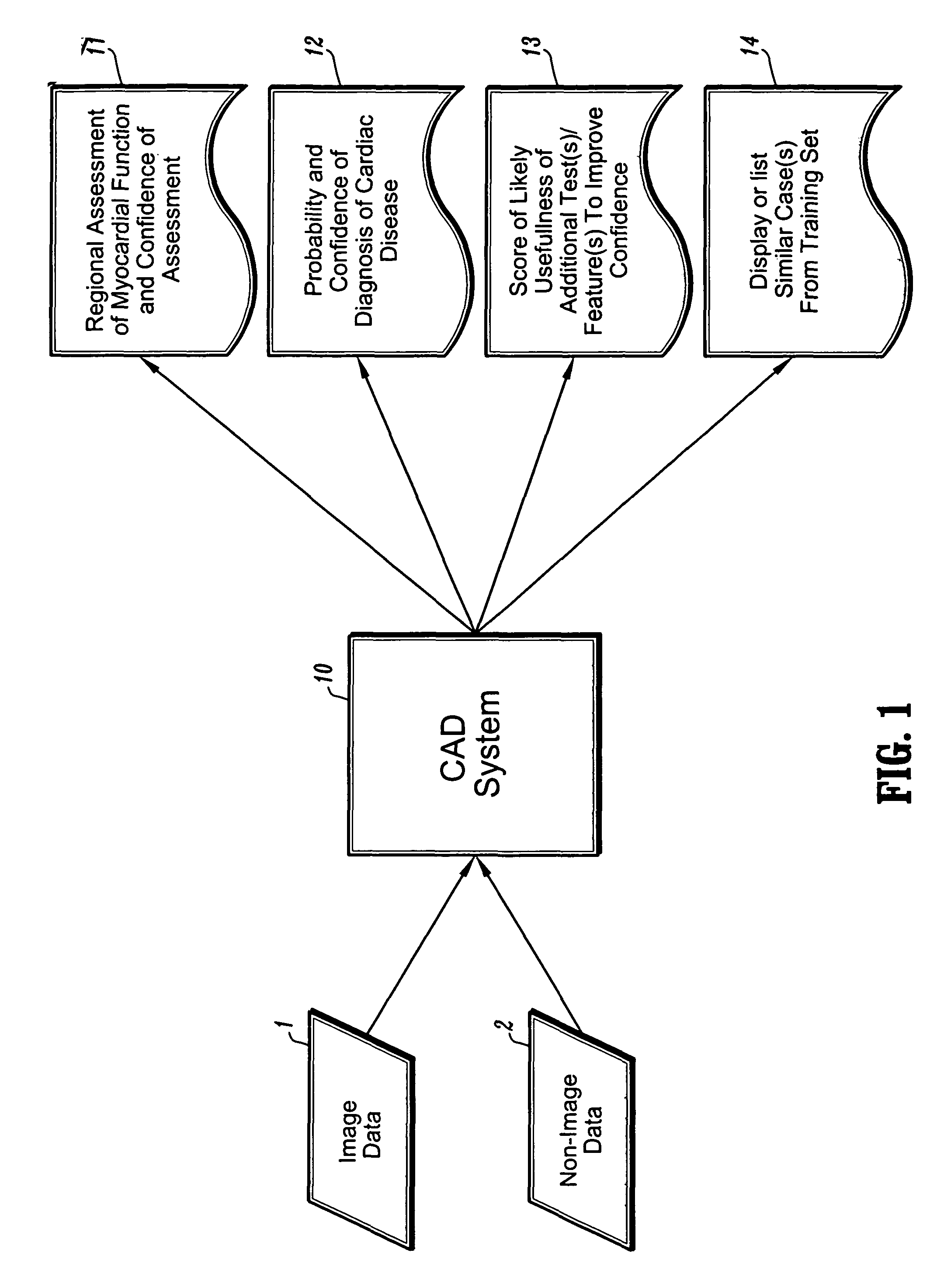
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for cardiac imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated assessment of regional myocardial function through wall motion analysis, automated diagnosis of heart diseases and conditions such as cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease and other heart-related medical conditions, and other automated decision support functions. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Method and apparatus for an improved computer aided diagnosis system
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
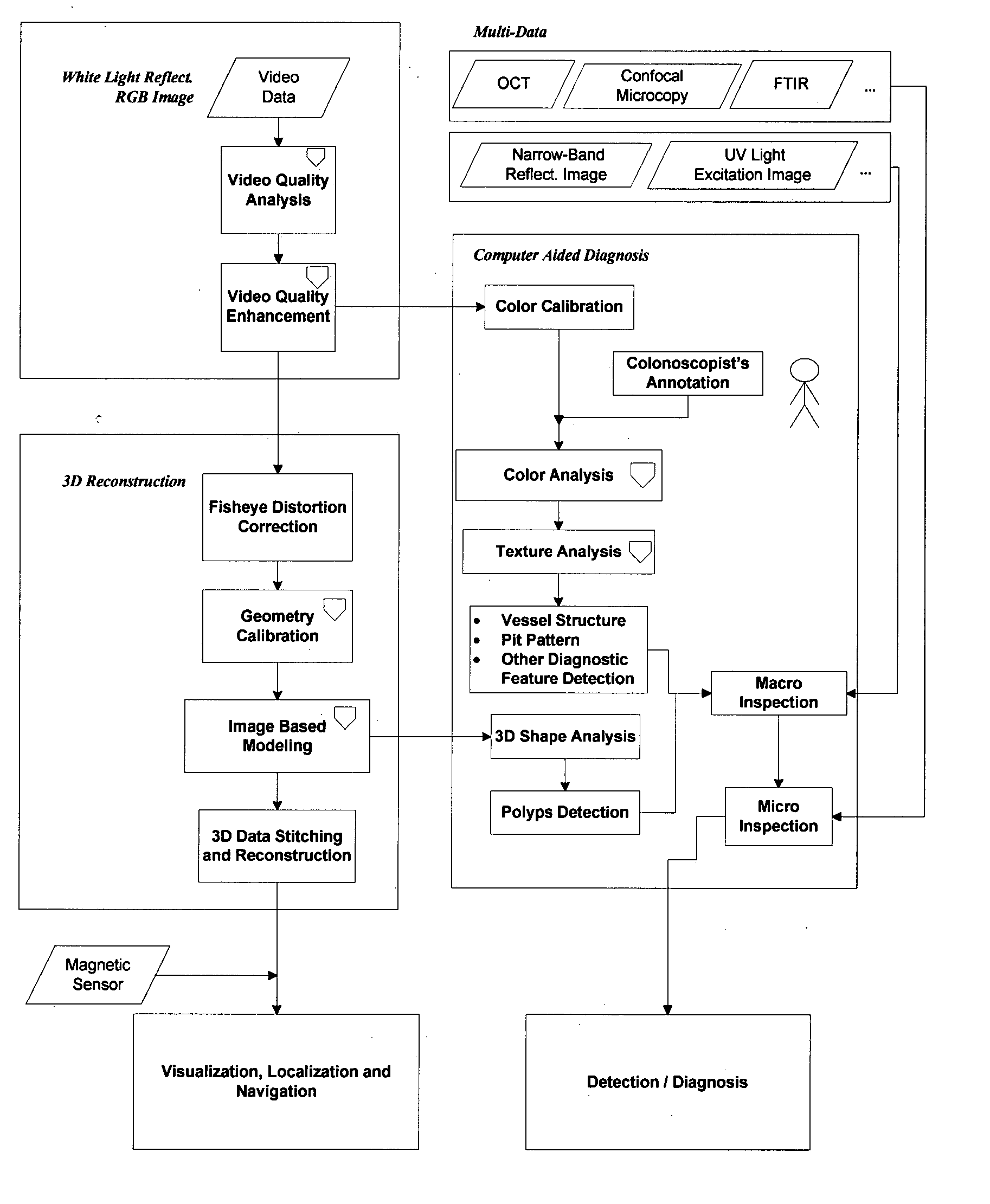
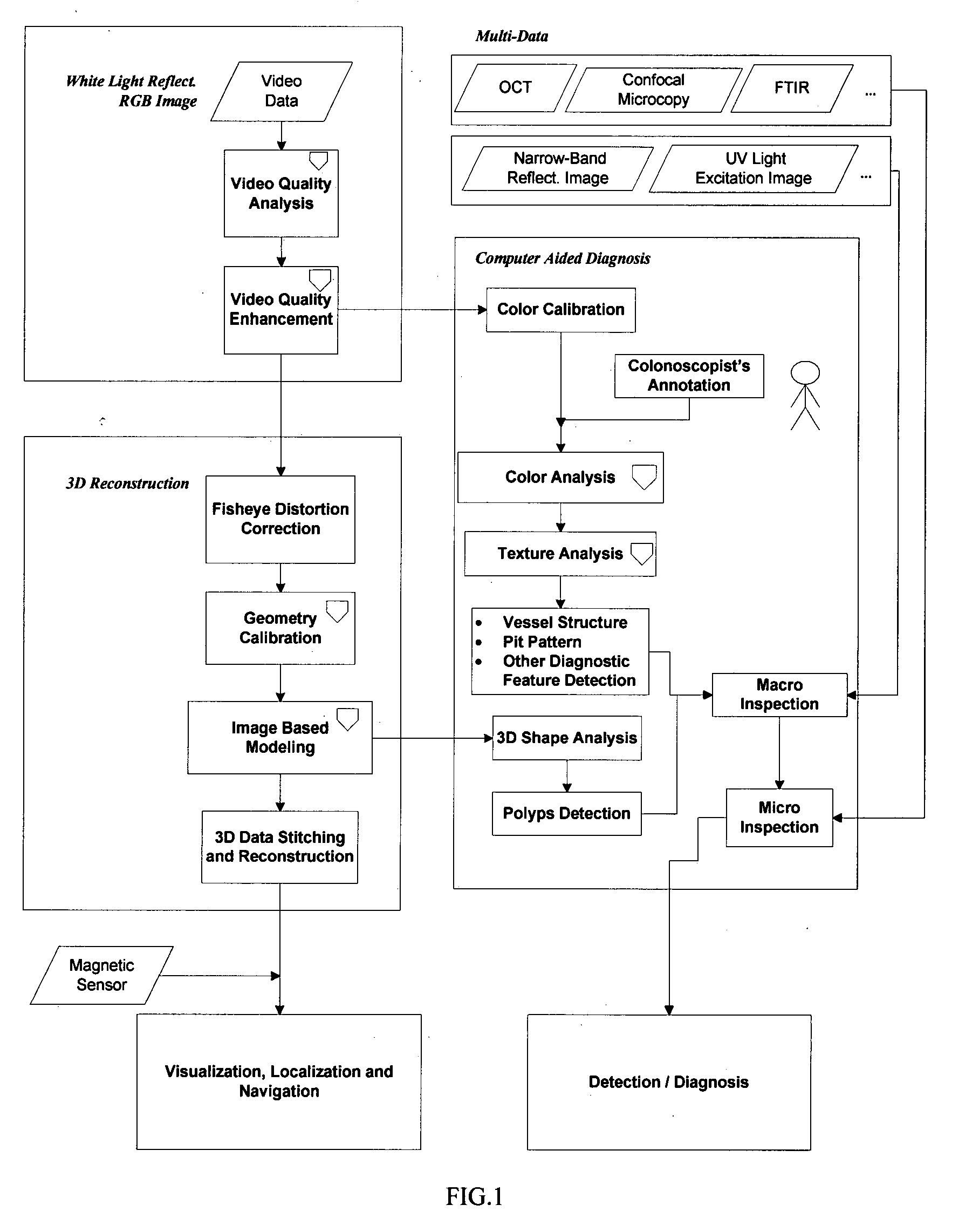
Computer aided diagnosis using video from endoscopes
A process for providing computer aided diagnosis from video data of an organ during an examination with an endoscope, comprising analyzing and enhancing image frames from the video and detecting and diagnosing any lesions in the image frames in real time during the examination. Optionally, the image data can be used to create a 3 dimensional reconstruction of the organ.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
Systems and methods for automated screening and prognosis of cancer from whole-slide biopsy images
InactiveUS20140233826A1Accurate and unambiguous measureReduce dependenceImage enhancementMedical data miningFeature setProstate cancer
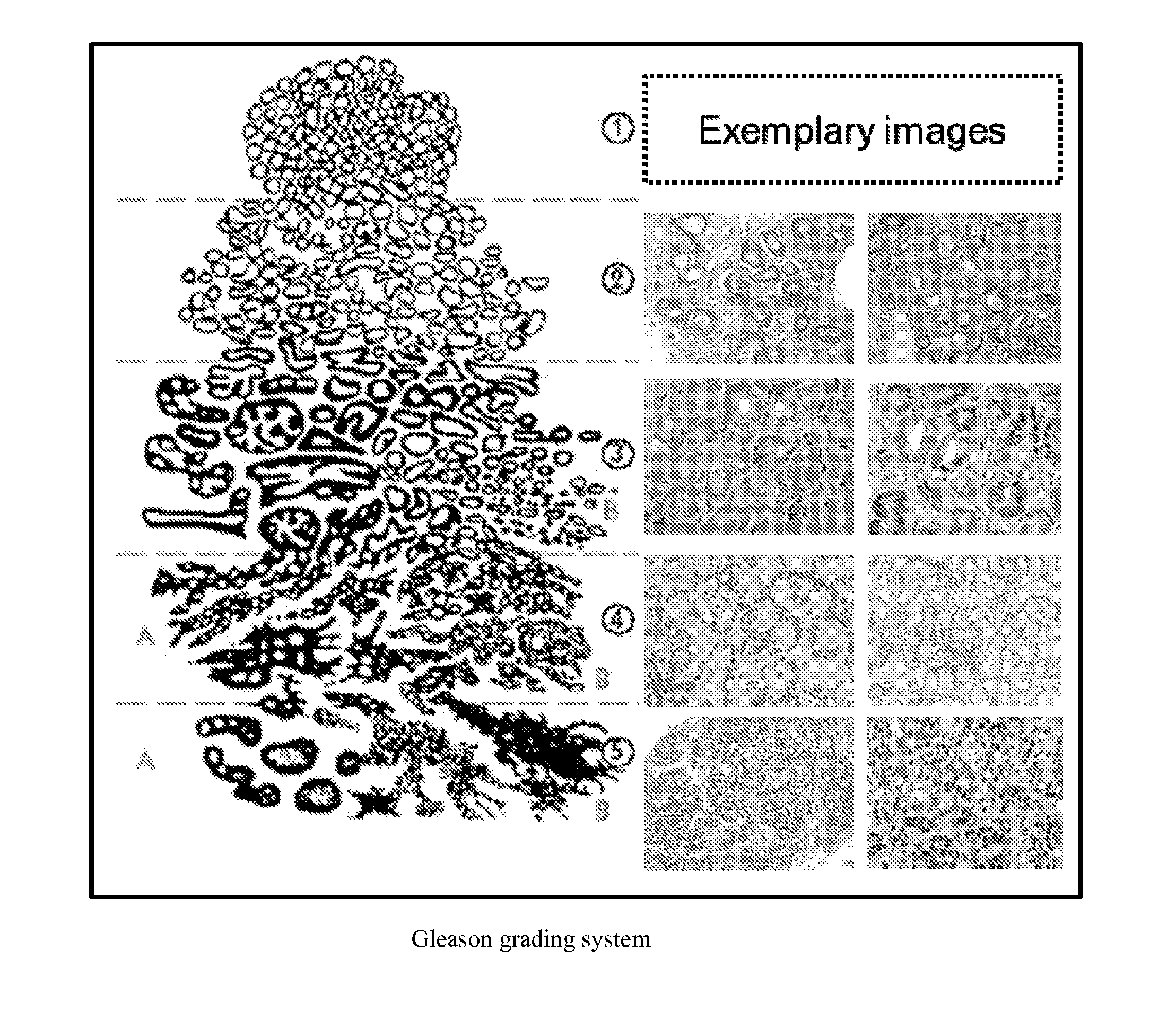
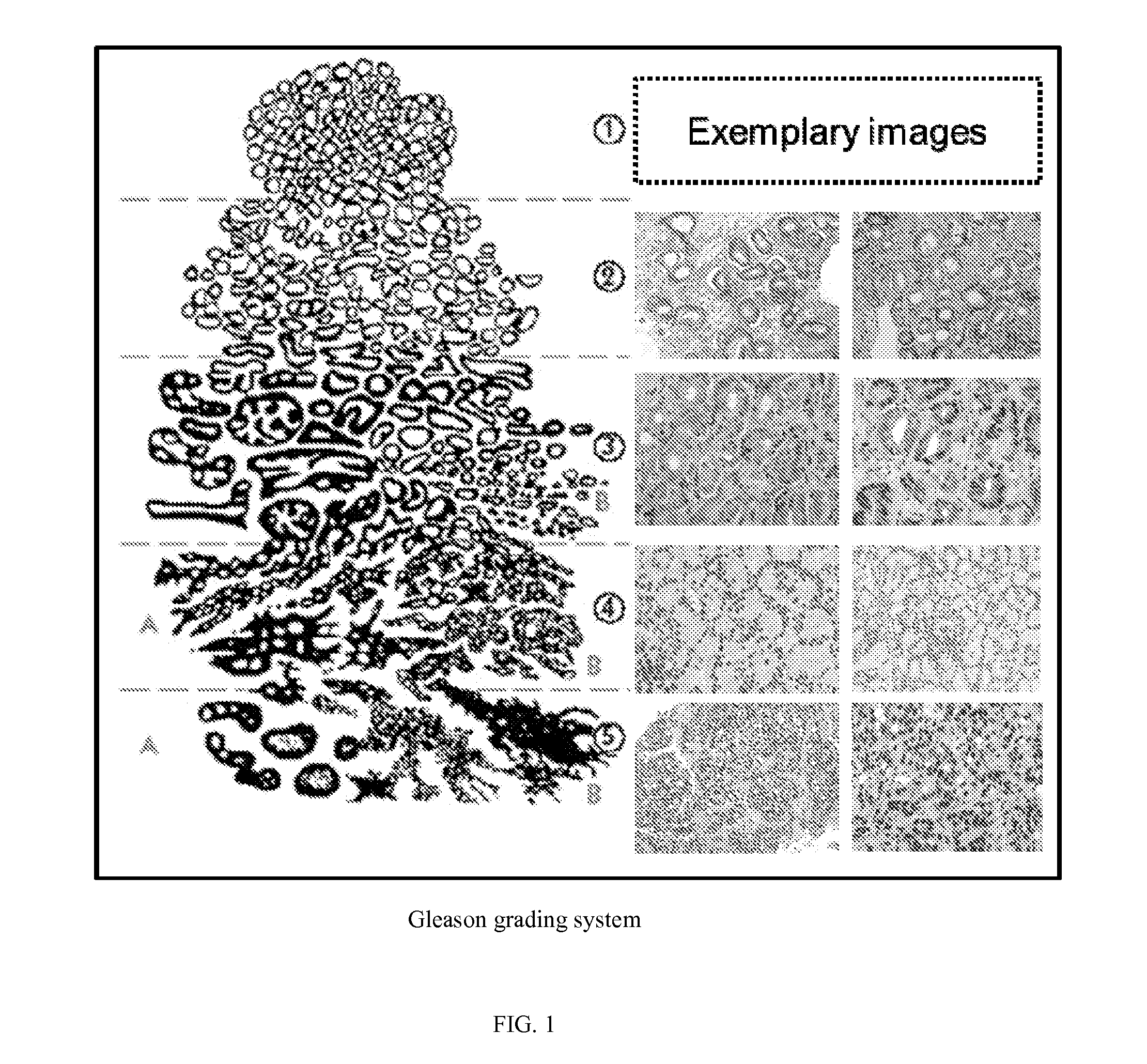
The invention provides systems and methods for detection, grading, scoring and tele-screening of cancerous lesions. A complete scheme for automated quantitative analysis and assessment of human and animal tissue images of several types of cancers is presented. Various aspects of the invention are directed to the detection, grading, prediction and staging of prostate cancer on serial sections / slides of prostate core images, or biopsy images. Accordingly, the invention includes a variety of sub-systems, which could be used separately or in conjunction to automatically grade cancerous regions. Each system utilizes a different approach with a different feature set. For instance, in the quantitative analysis, textural-based and morphology-based features may be extracted at image- and (or) object-levels from regions of interest. Additionally, the invention provides sub-systems and methods for accurate detection and mapping of disease in whole slide digitized images by extracting new features through integration of one or more of the above-mentioned classification systems. The invention also addresses the modeling, qualitative analysis and assessment of 3-D histopathology images which assist pathologists in visualization, evaluation and diagnosis of diseased tissue. Moreover, the invention includes systems and methods for the development of a tele-screening system in which the proposed computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems. In some embodiments, novel methods for image analysis (including edge detection, color mapping characterization and others) are provided for use prior to feature extraction in the proposed CAD systems.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
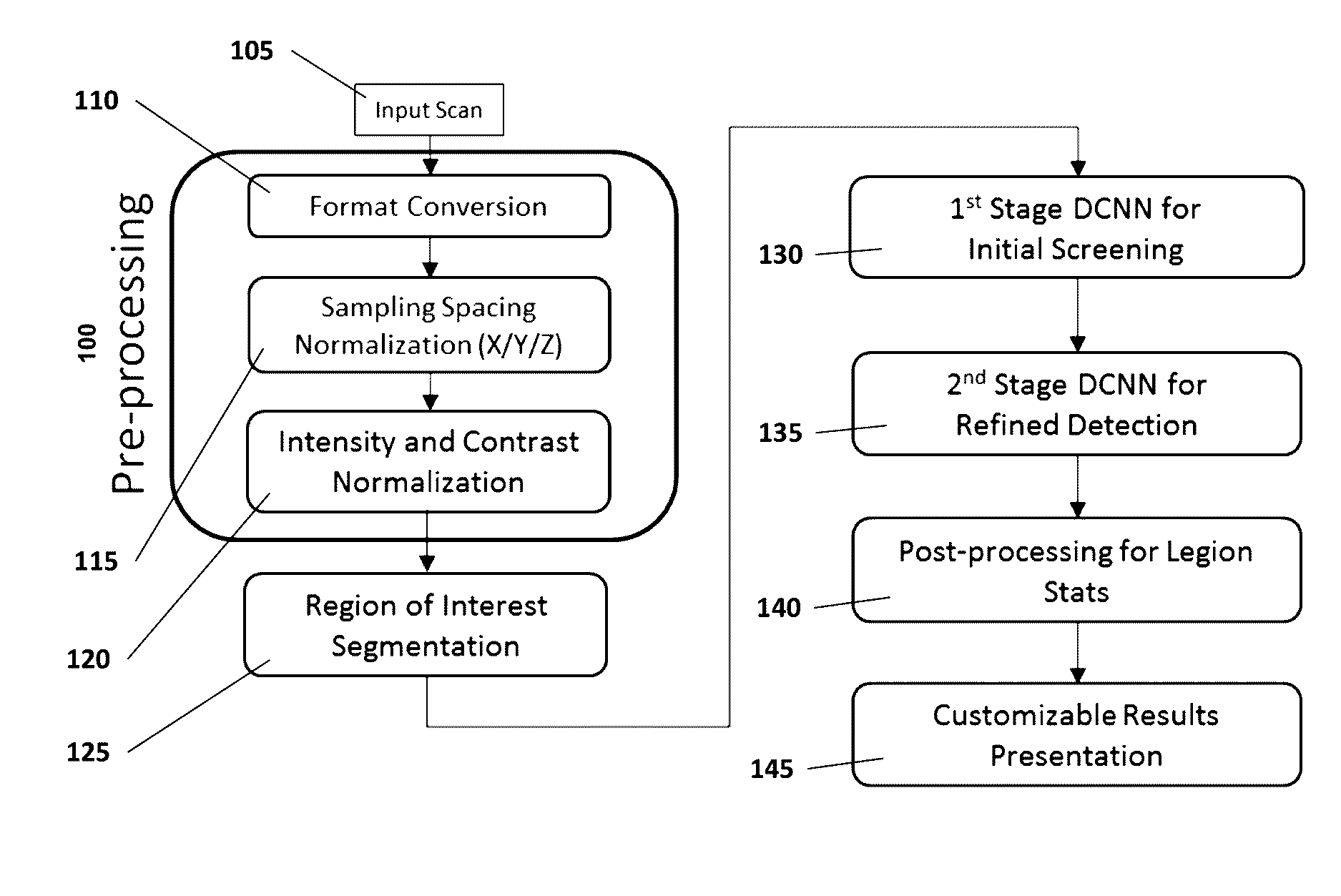
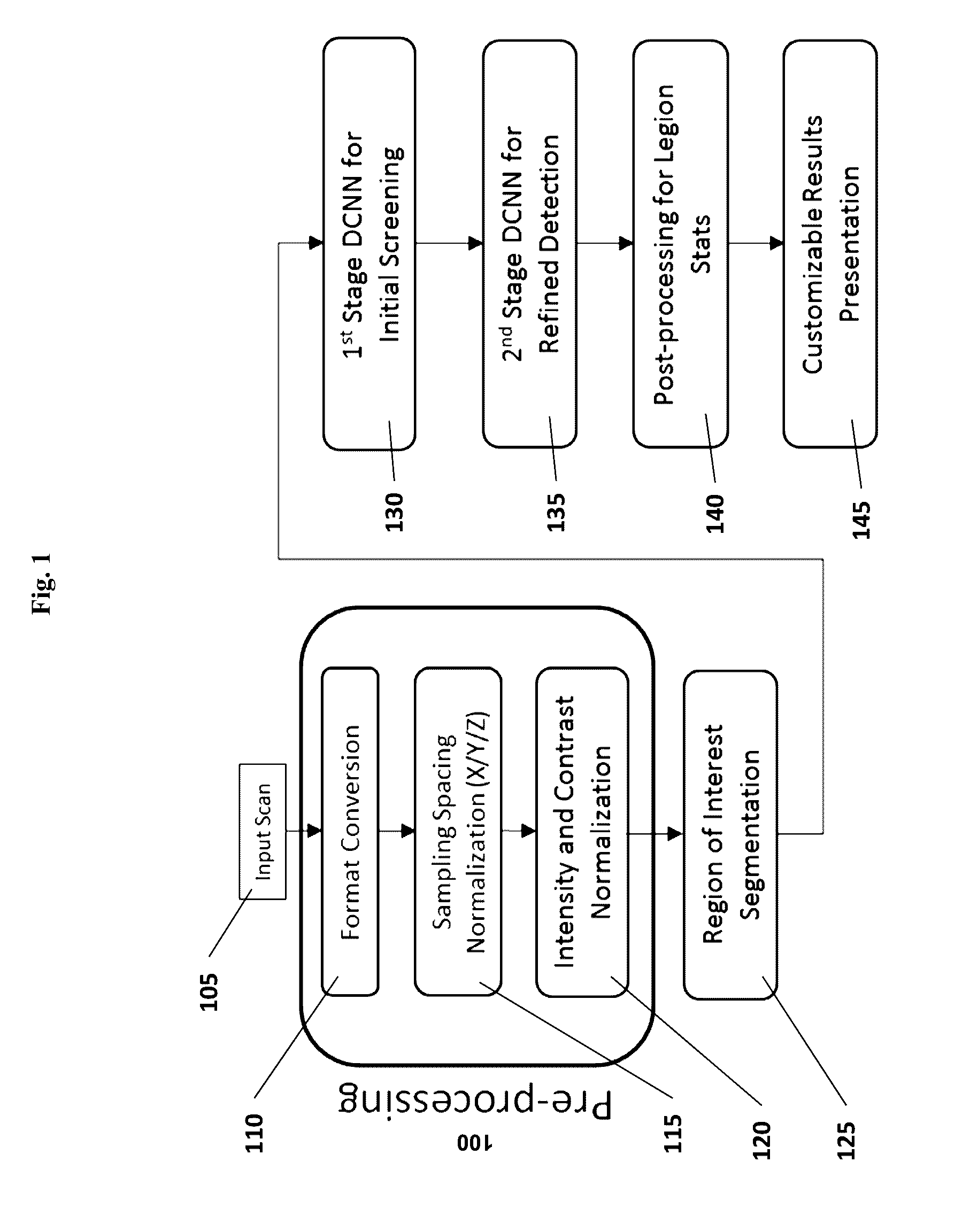
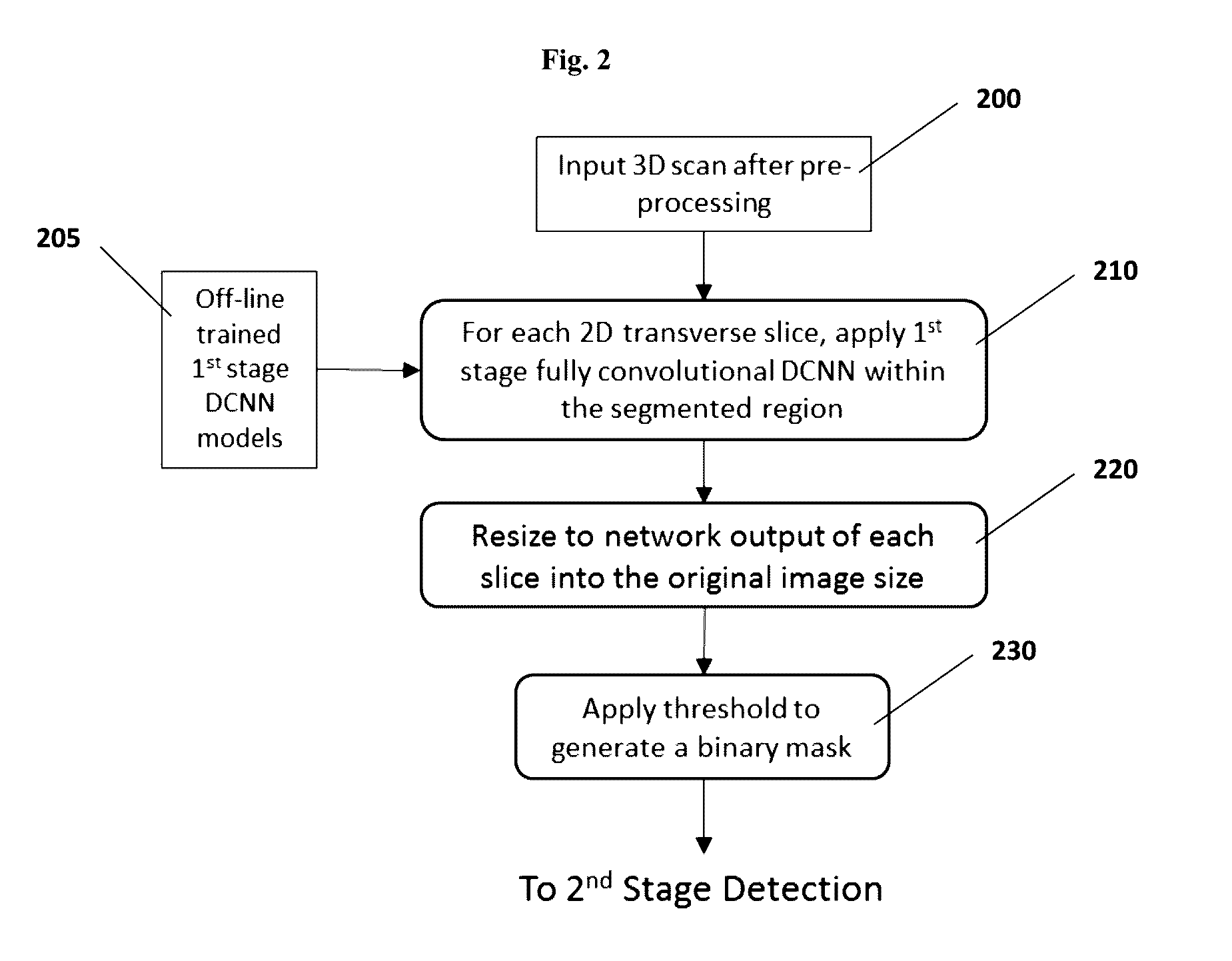
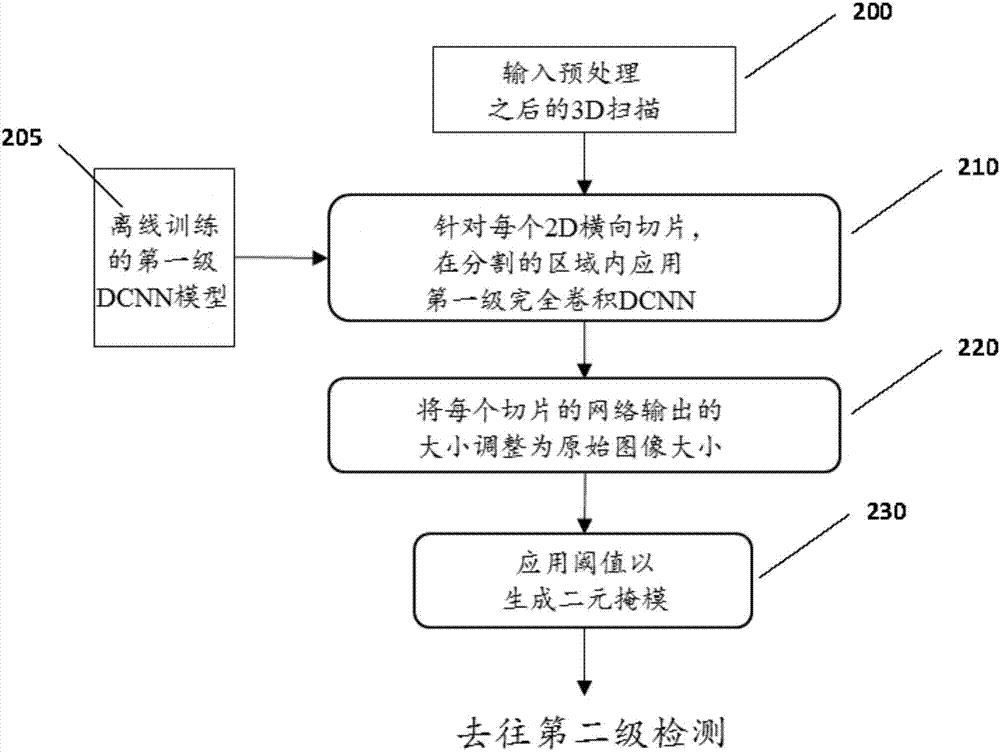
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveUS9589374B1Examination time can be shortenedImprove diagnostic accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionAided diagnosis
Owner:12 SIGMA TECH
Dynamic multi-spectral imaging with wideband seletable source
InactiveUS20040264628A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFiltrationX-ray
A multispectral X-ray imaging system uses a wideband source and filtration assembly to select for M sets of spectral data. Spectral characteristics may be dynamically adjusted in synchrony with scan excursions where an X-ray source, detector array, or body may be moved relative to one another in acquiring T sets of measurement data. The system may be used in projection imaging and / or CT imaging. Processed image data, such as a CT reconstructed image, may be decomposed onto basis functions for analytical processing of multispectral image data to facilitate computer assisted diagnostics. The system may perform this diagnostic function in medical applications and / or security applications.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
Graphical user interface for display of anatomical information
InactiveUS7072501B2Optimized for speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer aided diagnosticsGraphics
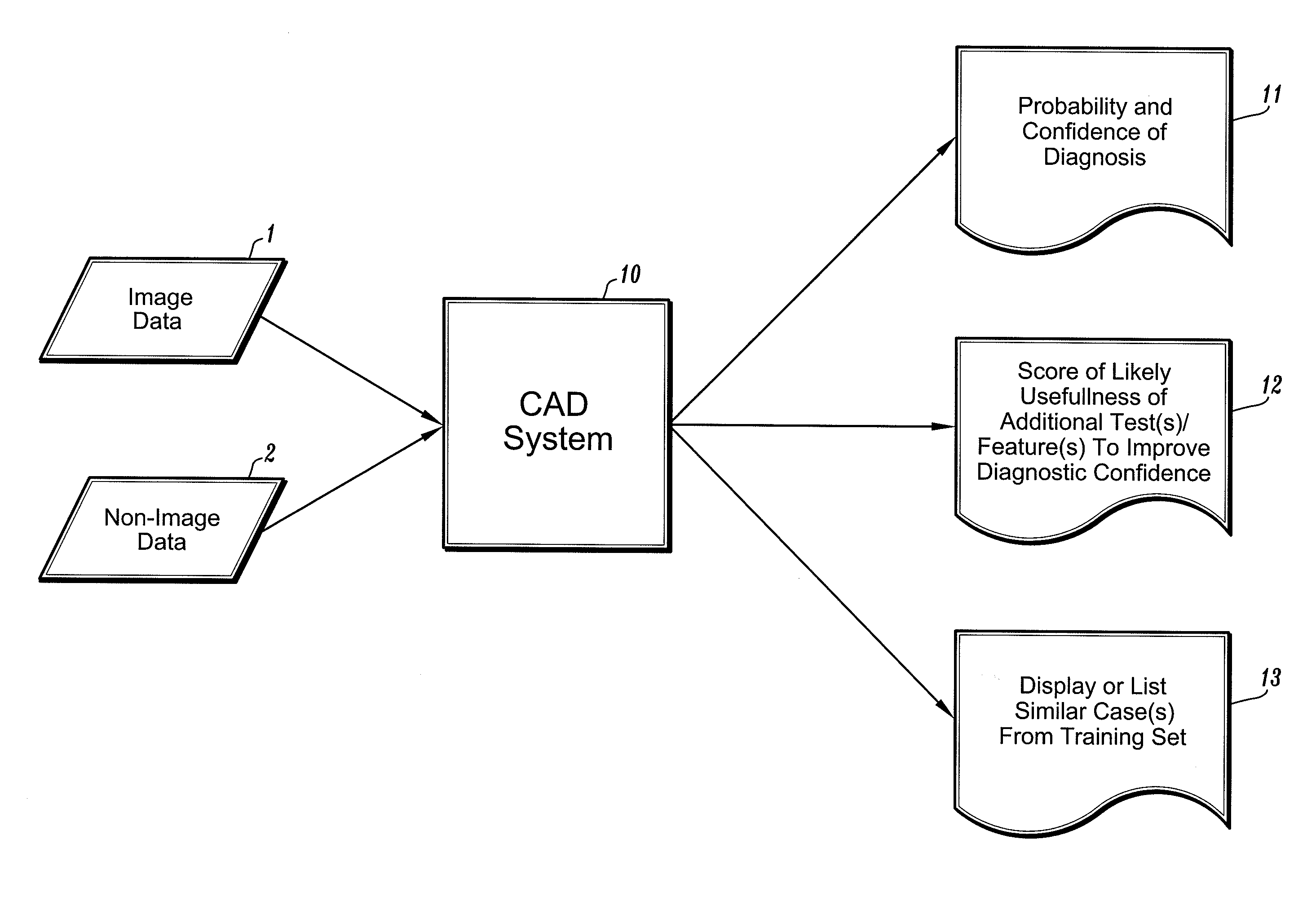
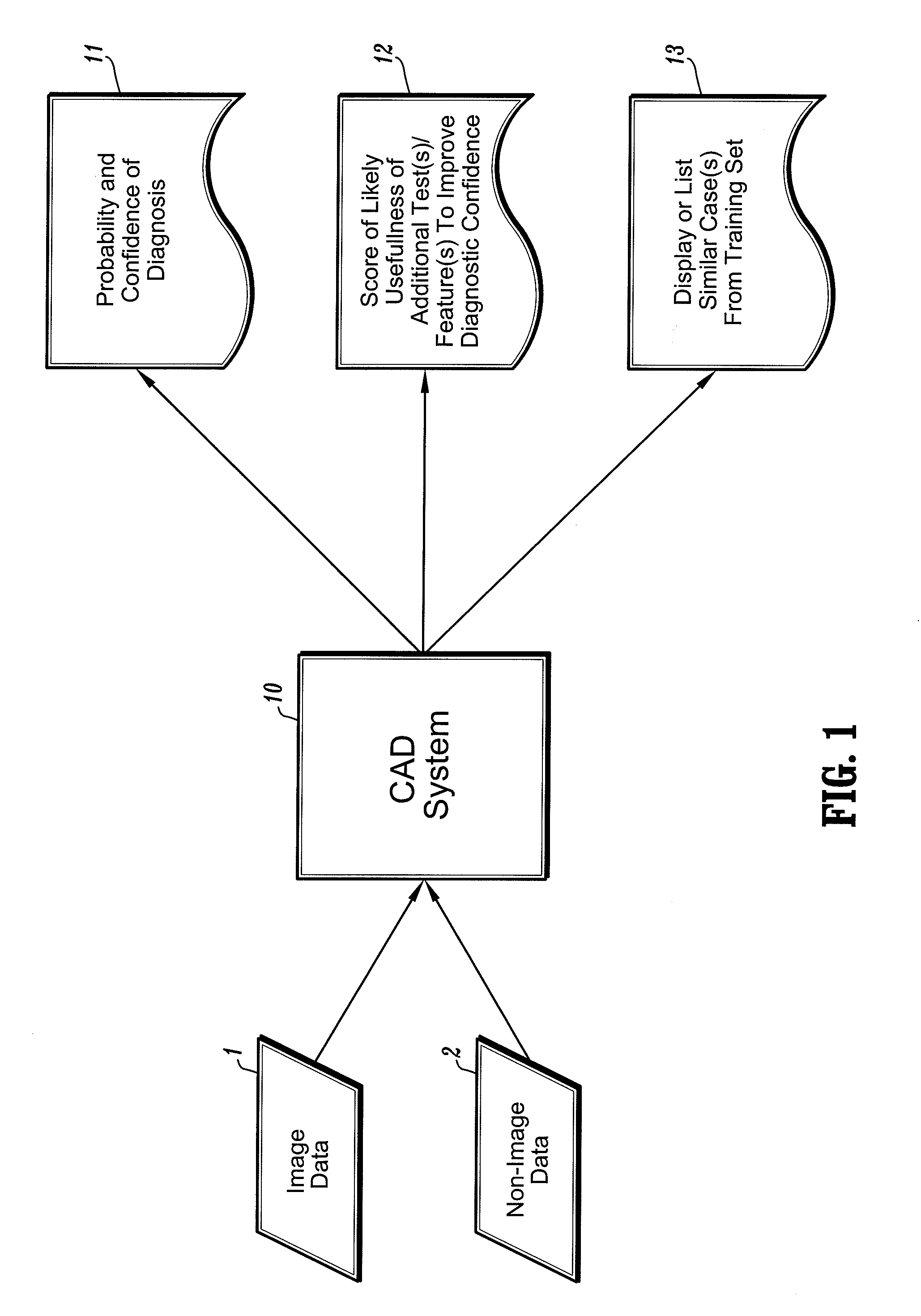
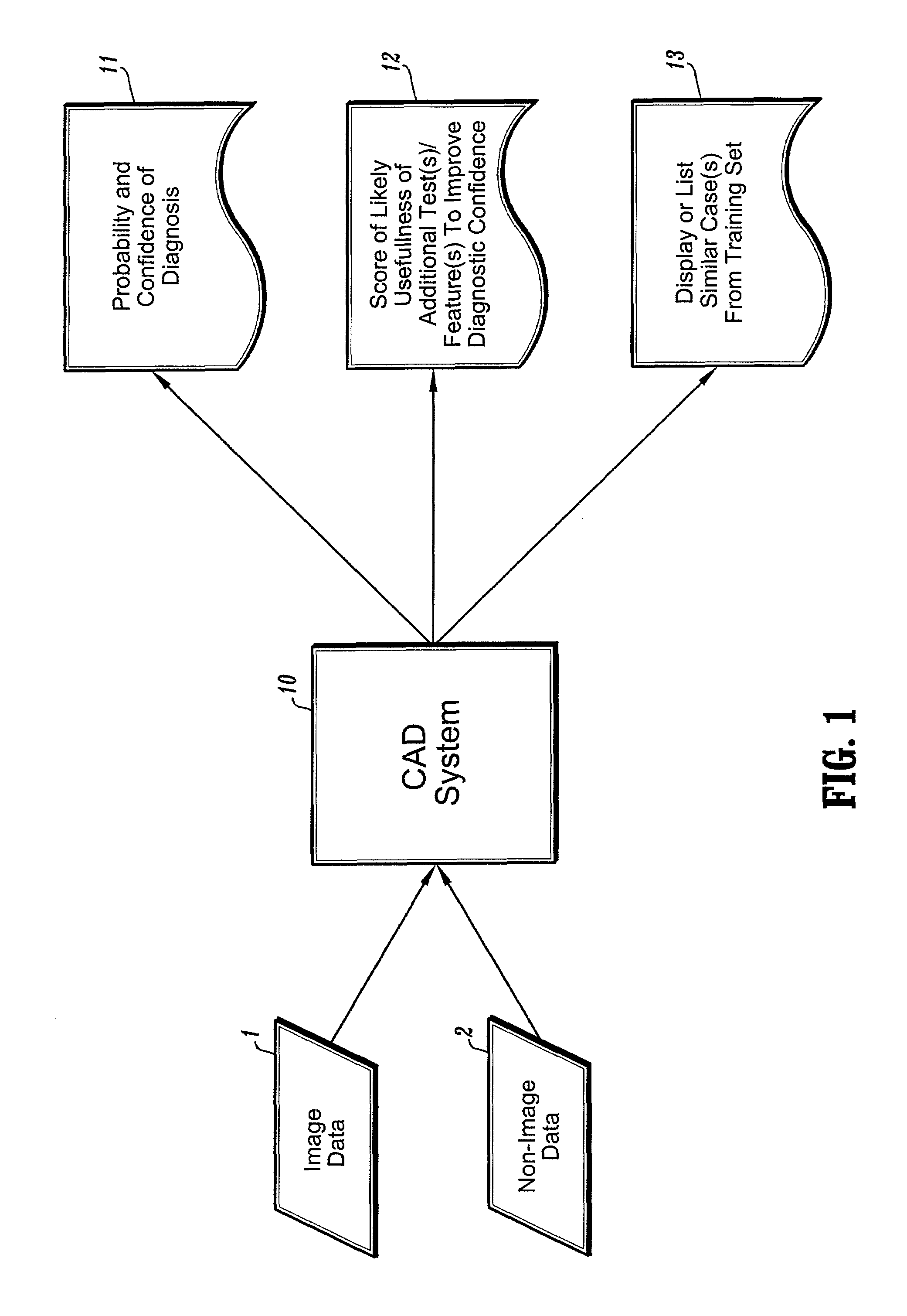
A computer-aided diagnostic method and system provide image annotation information that can include an assessment of the probability, likelihood or predictive value of detected or identified suspected abnormalities as an additional aid to the radiologist. More specifically, probability values, in numerical form and / or analog form, are added to the locational markers of the detected and suspected abnormalities. The task of a physician using such a system as disclosed is believed to be made easier by displaying markers representing different regions of interest.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
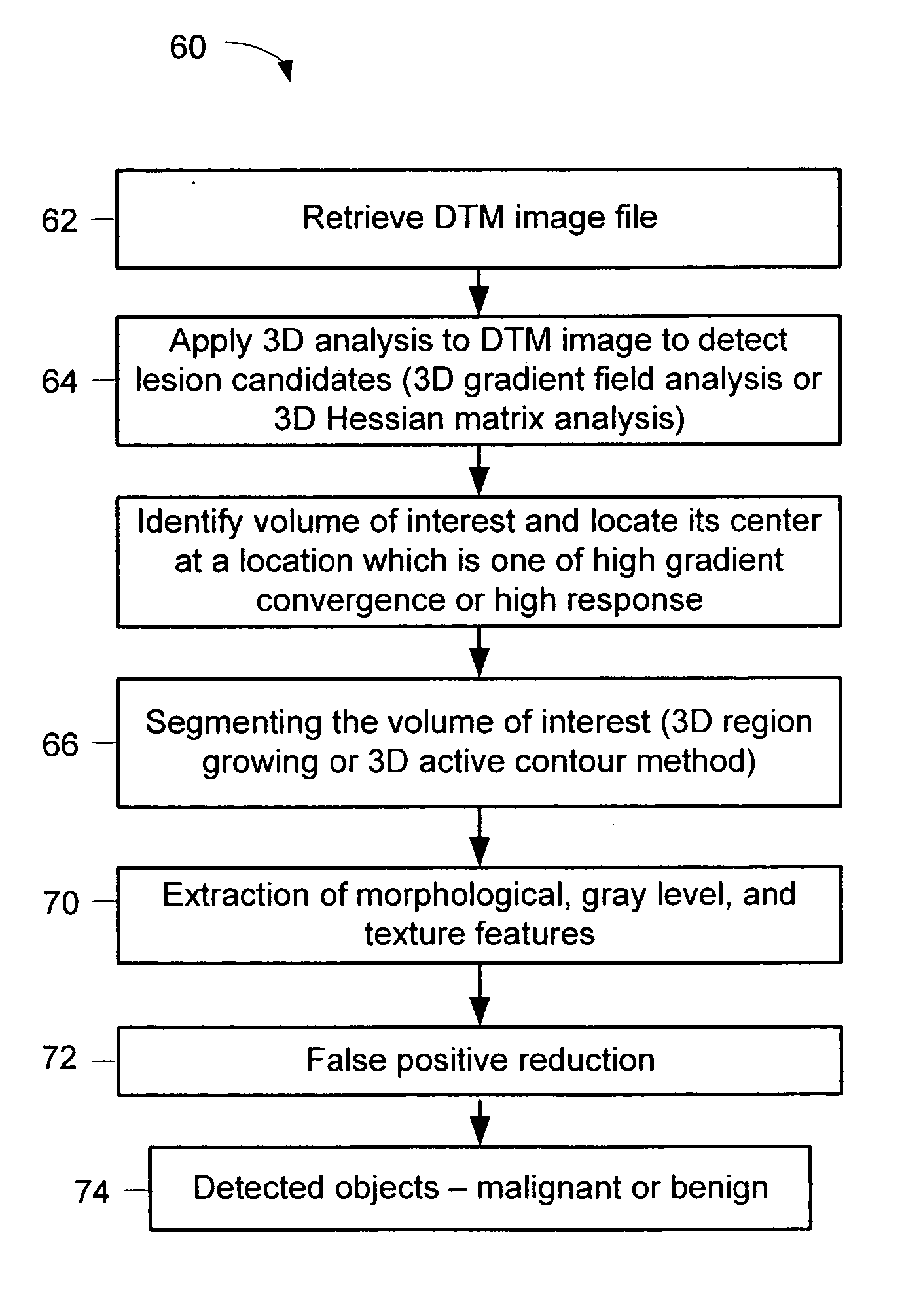
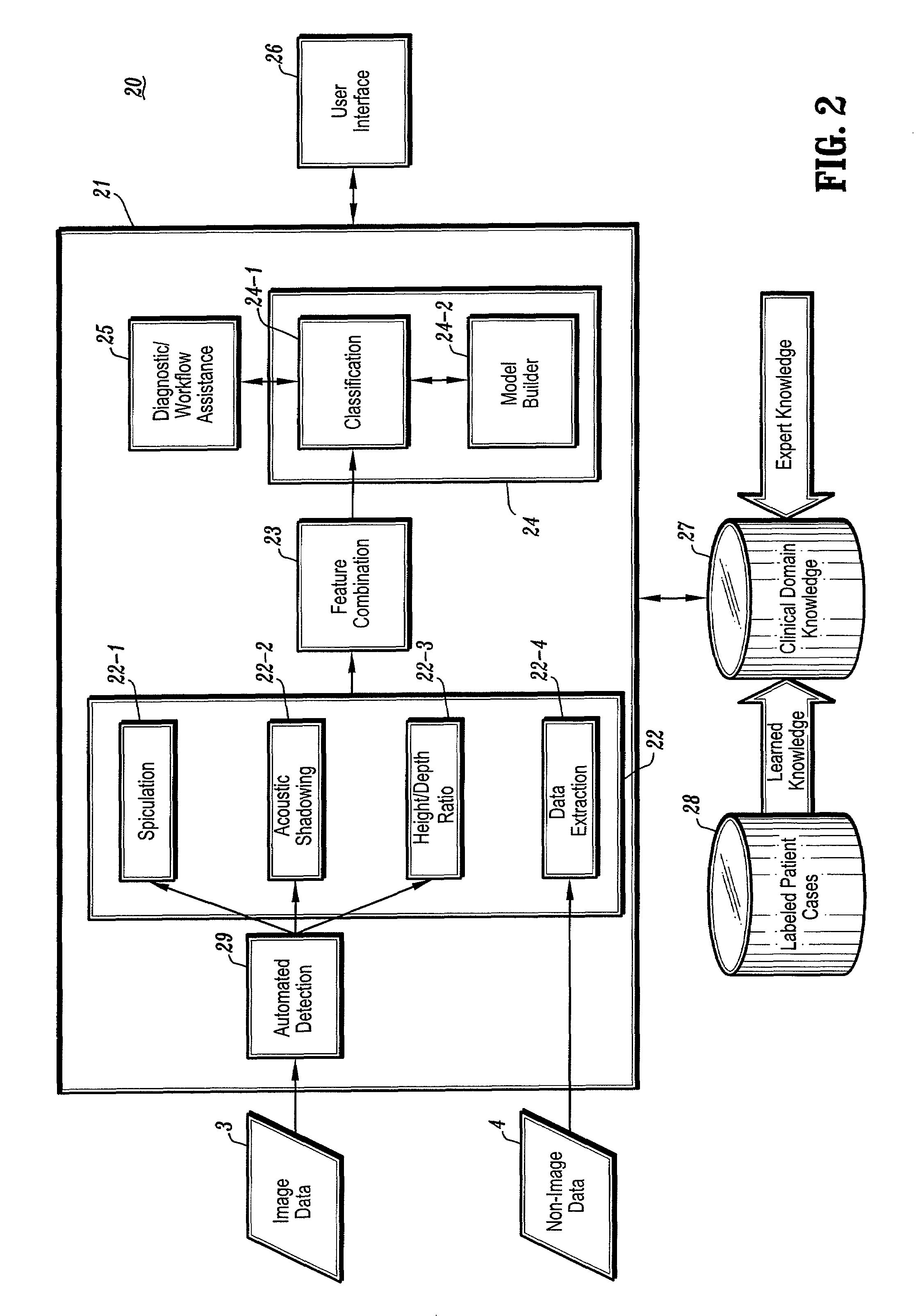
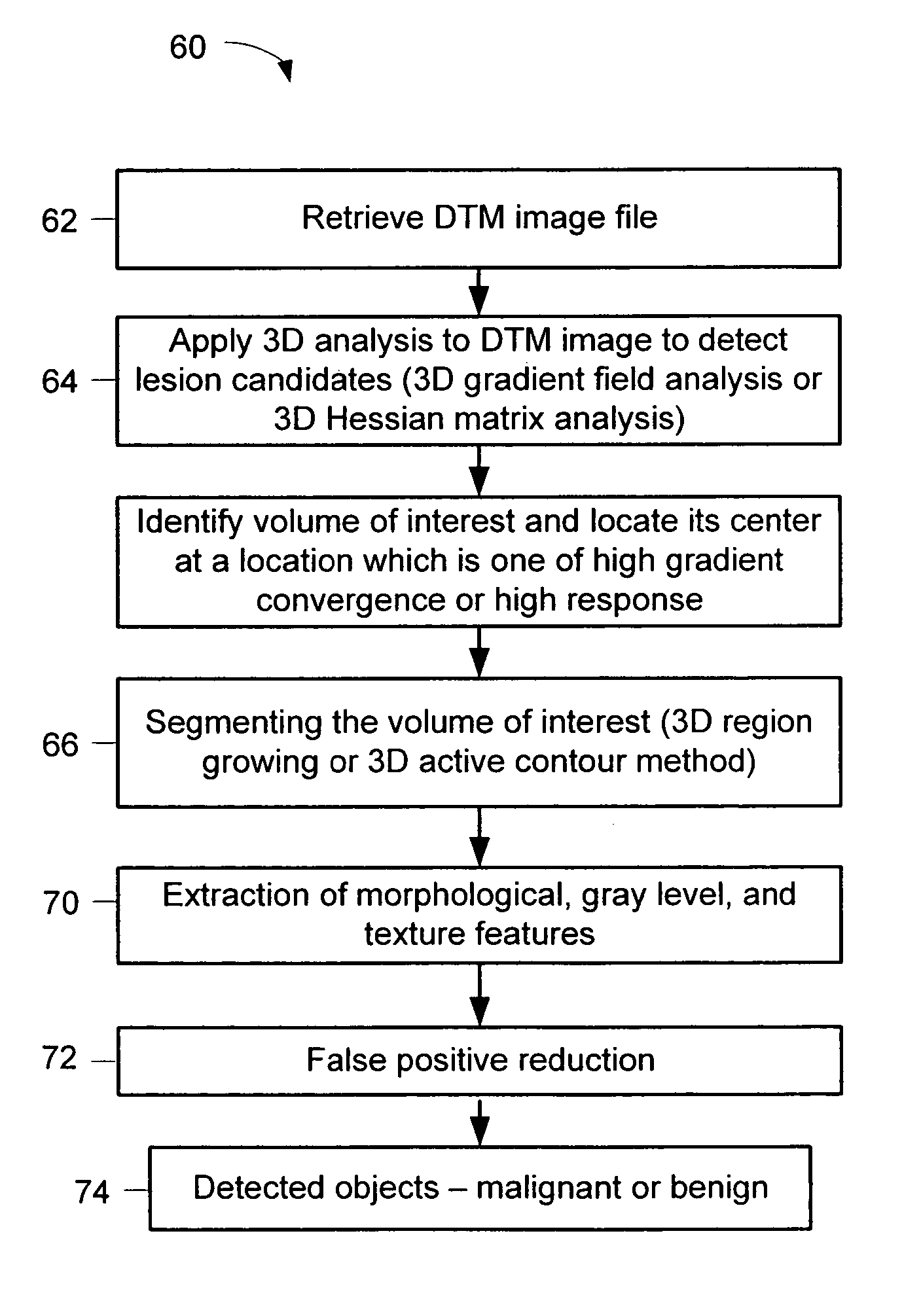
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for heart related diseases and conditions
InactiveUS7912528B2Medical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionCoronary artery diseasePatient data
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for cardiac imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated assessment of regional myocardial function through wall motion analysis, automated diagnosis of heart diseases and conditions such as cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease and other heart-related medical conditions, and other automated decision support functions. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Systems and Methods for Automated Diagnosis and Decision Support for Breast Imaging
InactiveUS20100121178A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMedicineDecision taking
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for breast imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated diagnosis of breast cancer other automated decision support functions that enable decision support for, e.g., screening and staging for breast cancer. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:KRISHNAN SRIRAM +3
Computer-aided diagnosis system and method
InactiveUS6434262B2Useful diagnostic informationGood presence and meaning and significanceImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayLow contrast
An x-ray system acquires an initial low-contrast, wide latitude (G=2.5, or G=2 or less) x-ray image of a breast. A processing system automatically finds suspected abnormalities in the breast by processing the low contrast initial image, and then automatically converts the initial x-ray image to a high-contrast, narrow latitude image at the locations of the found abnormalities to thereby facilitate diagnosis and patient care. The technology includes effective ways to produce, process and display the various images, and can be extended to other types of images.
Owner:WANG SHIH PING
Systems and methods for automated diagnosis and decision support for breast imaging
ActiveUS7640051B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDecision takingPatient data
CAD (computer-aided diagnosis) systems and applications for breast imaging are provided, which implement methods to automatically extract and analyze features from a collection of patient information (including image data and / or non-image data) of a subject patient, to provide decision support for various aspects of physician workflow including, for example, automated diagnosis of breast cancer other automated decision support functions that enable decision support for, e.g., screening and staging for breast cancer. The CAD systems implement machine-learning techniques that use a set of training data obtained (learned) from a database of labeled patient cases in one or more relevant clinical domains and / or expert interpretations of such data to enable the CAD systems to “learn” to analyze patient data and make proper diagnostic assessments and decisions for assisting physician workflow.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
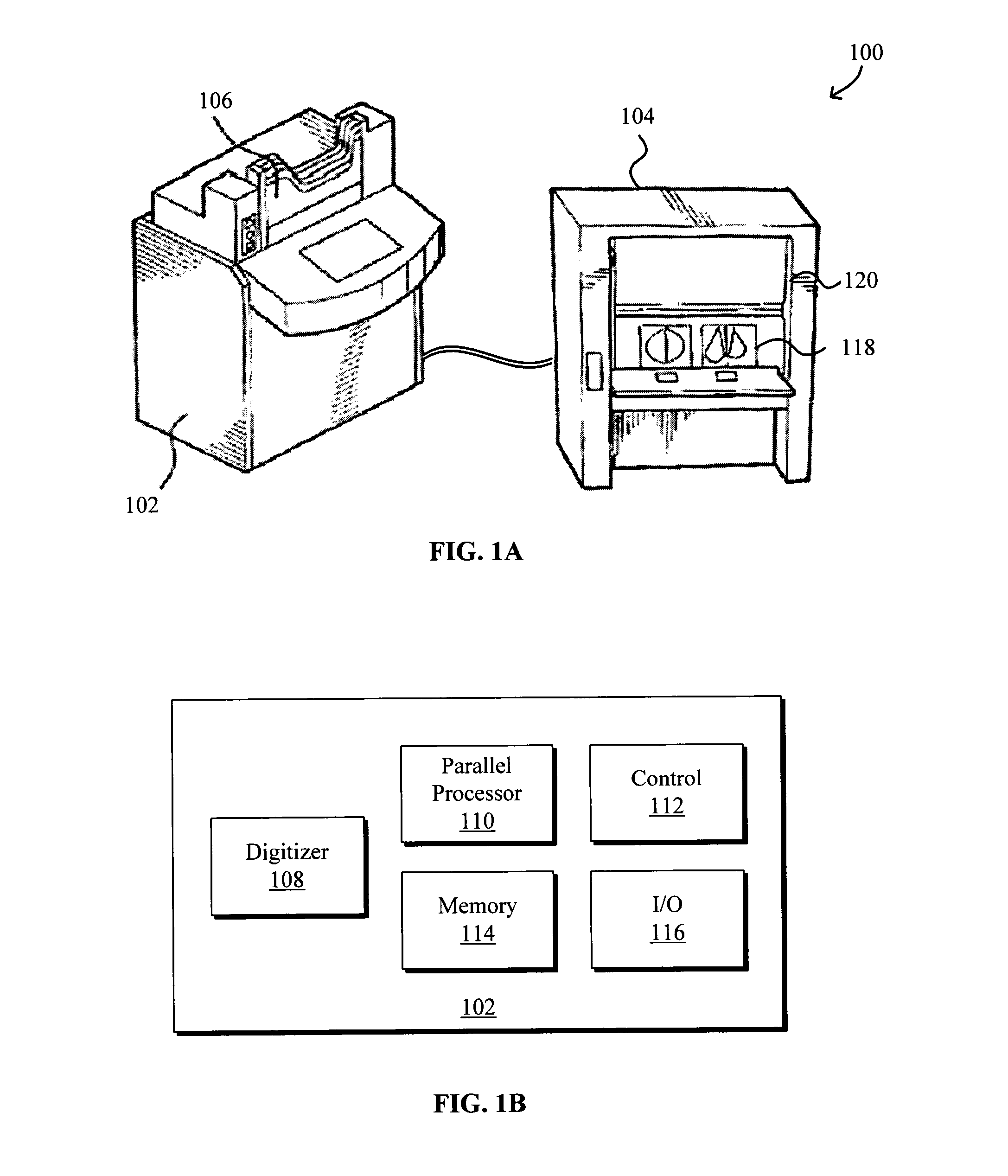
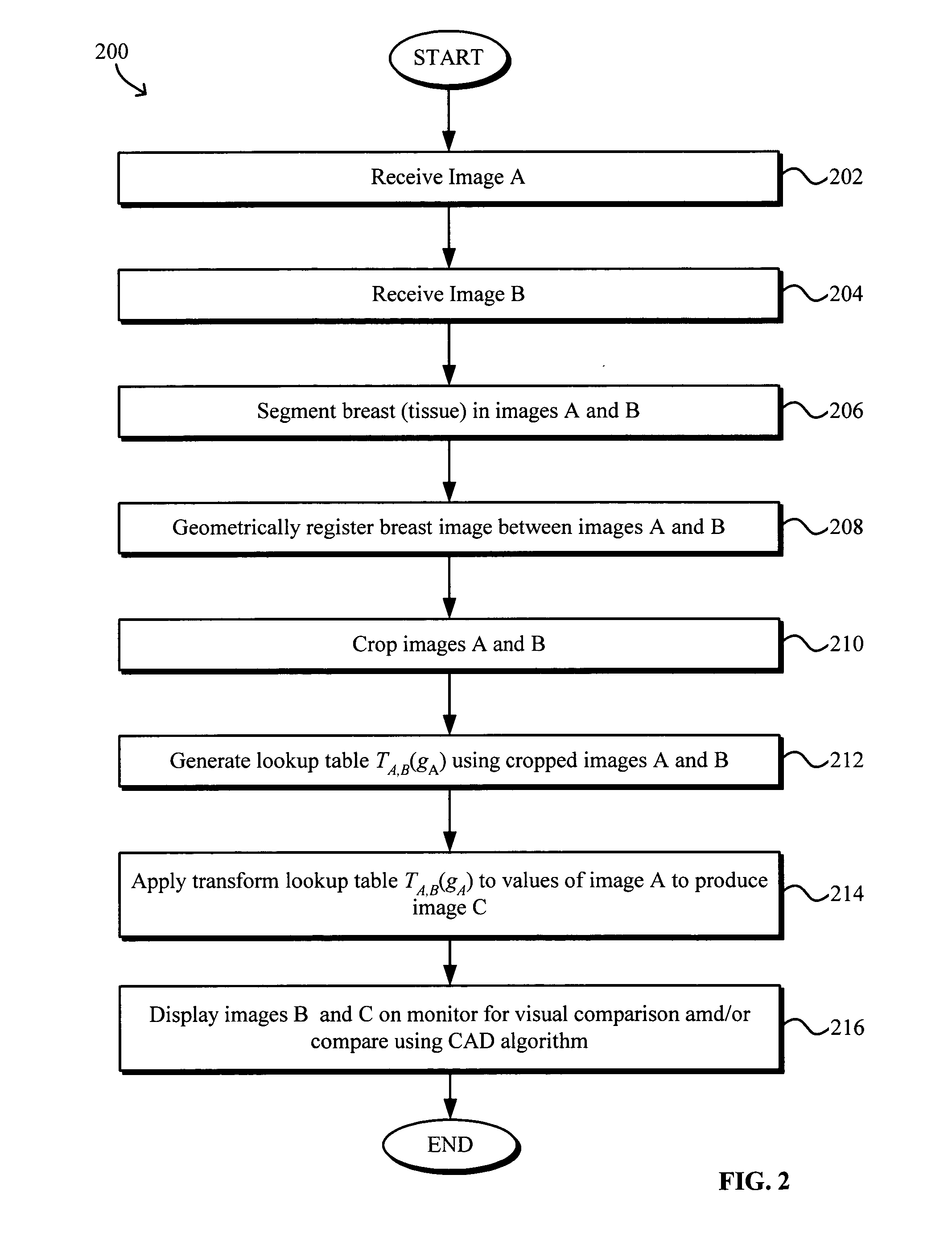
Model-based grayscale registration of medical images
ActiveUS20050013471A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPixel value differenceVisual perception
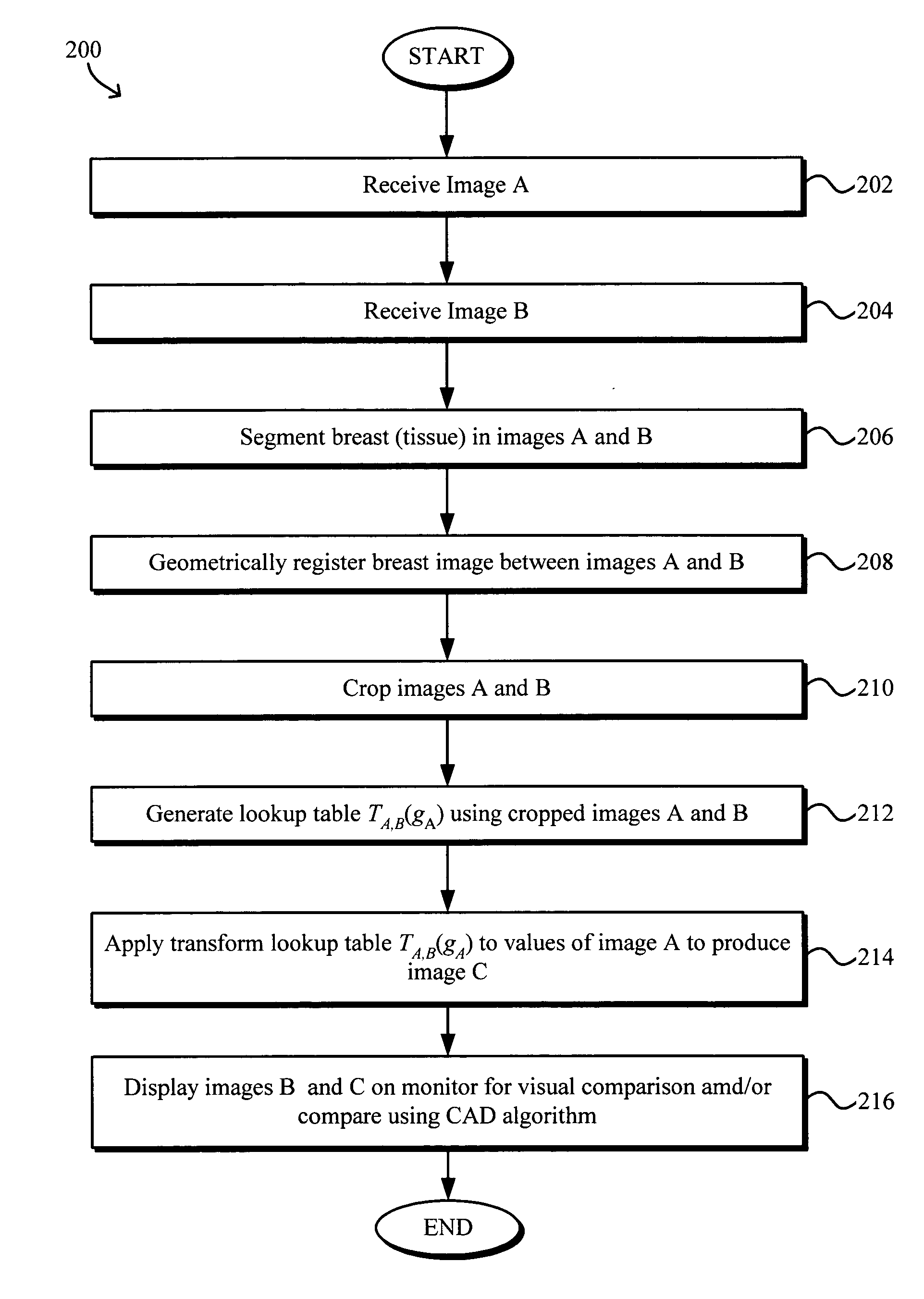
Numerical image processing of two or more medical images to provide grayscale registration thereof is described, the numerical image processing algorithms being based at least in part on a model of medical image acquisition. The grayscale registered temporal images may then be displayed for visual comparison by a clinician and / or further processed by a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system for detection of medical abnormalities therein. A parametric method includes spatially registering two images and performing gray scale registration of the images. A parametric transform model, e.g., analog to analog, digital to digital, analog to digital, or digital to analog model, is selected based on the image acquisition method(s) of the images, i.e., digital or analog / film. Gray scale registration involves generating a joint pixel value histogram from the two images, statistically fitting parameters of the transform model to the joint histogram, generating a lookup table, and using the lookup table to transform and register pixel values of one image to the pixel values of the other image. The models take into account the most relevant image acquisition parameters that influence pixel value differences between images, e.g., tissue compression, incident radiation intensity, exposure time, film and digitizer characteristic curves for analog image, and digital detector response for digital image. The method facilitates temporal comparisons of medical images such as mammograms and / or comparisons of analog with digital images.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Computer-aided diagnosis system for medical images using deep convolutional neural networks
InactiveCN106897573AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementNerve networkComputer vision
Owner:图兮深维医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
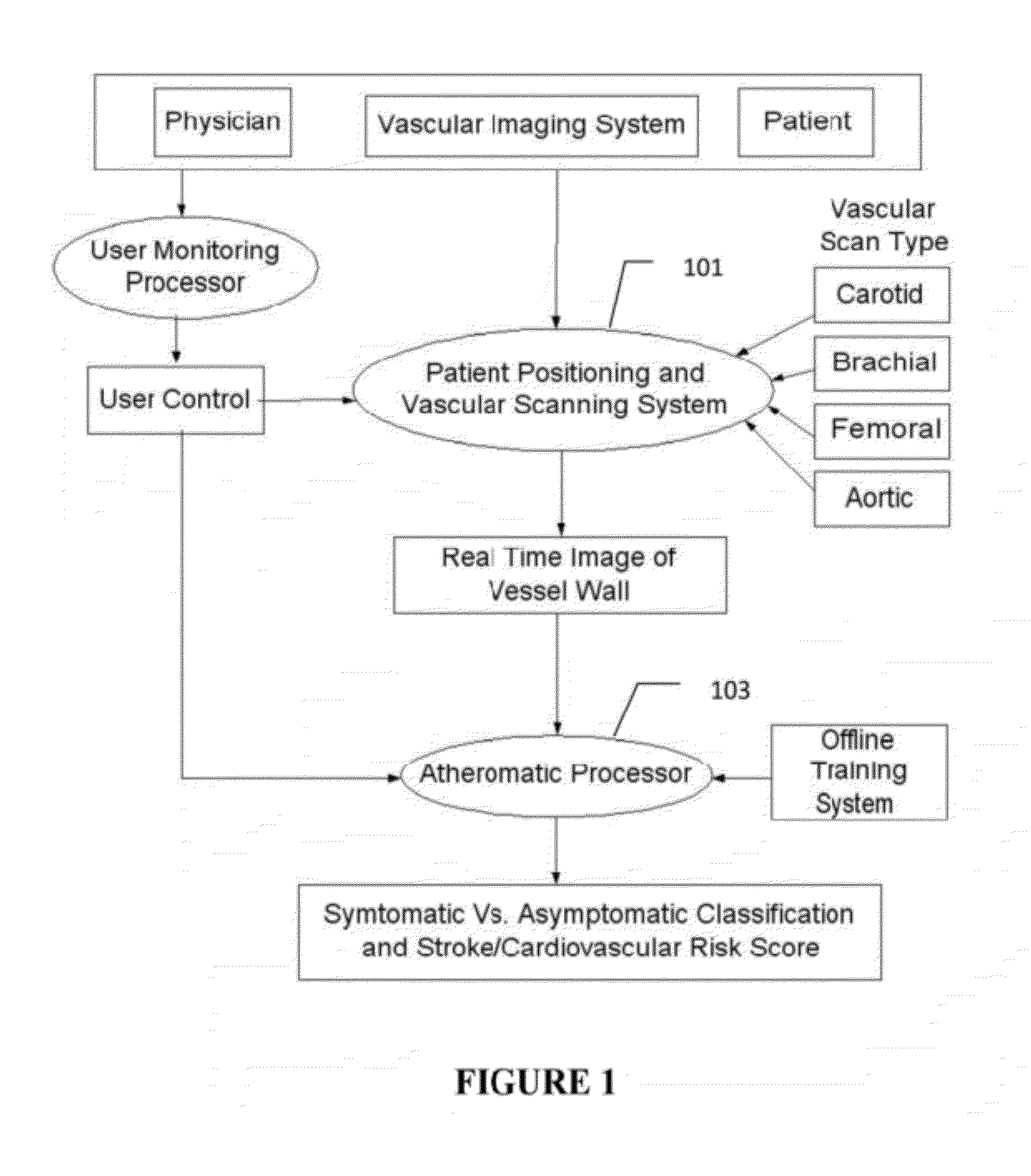
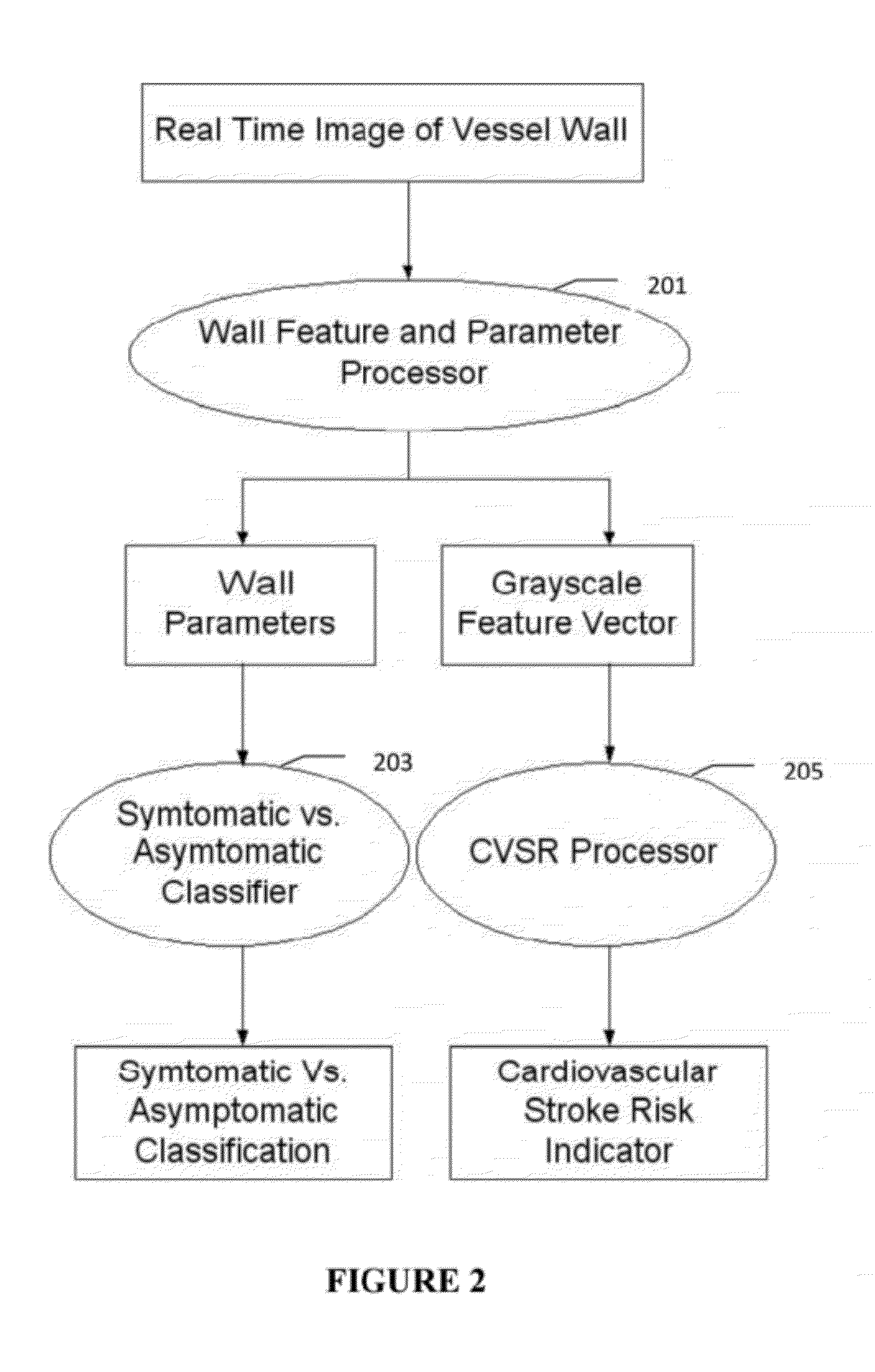
Imaging Based Symptomatic Classification Using a Combination of Trace Transform, Fuzzy Technique and Multitude of Features
InactiveUS20120078099A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsGray levelRadiology
A statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique is described for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which uses the combination: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Local Binary Pattern; (b) Law's Mask Energy and (c) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Trace Transform; (b) Fuzzy Grayscale Level Co-occurrence Matrix and (c) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line.
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
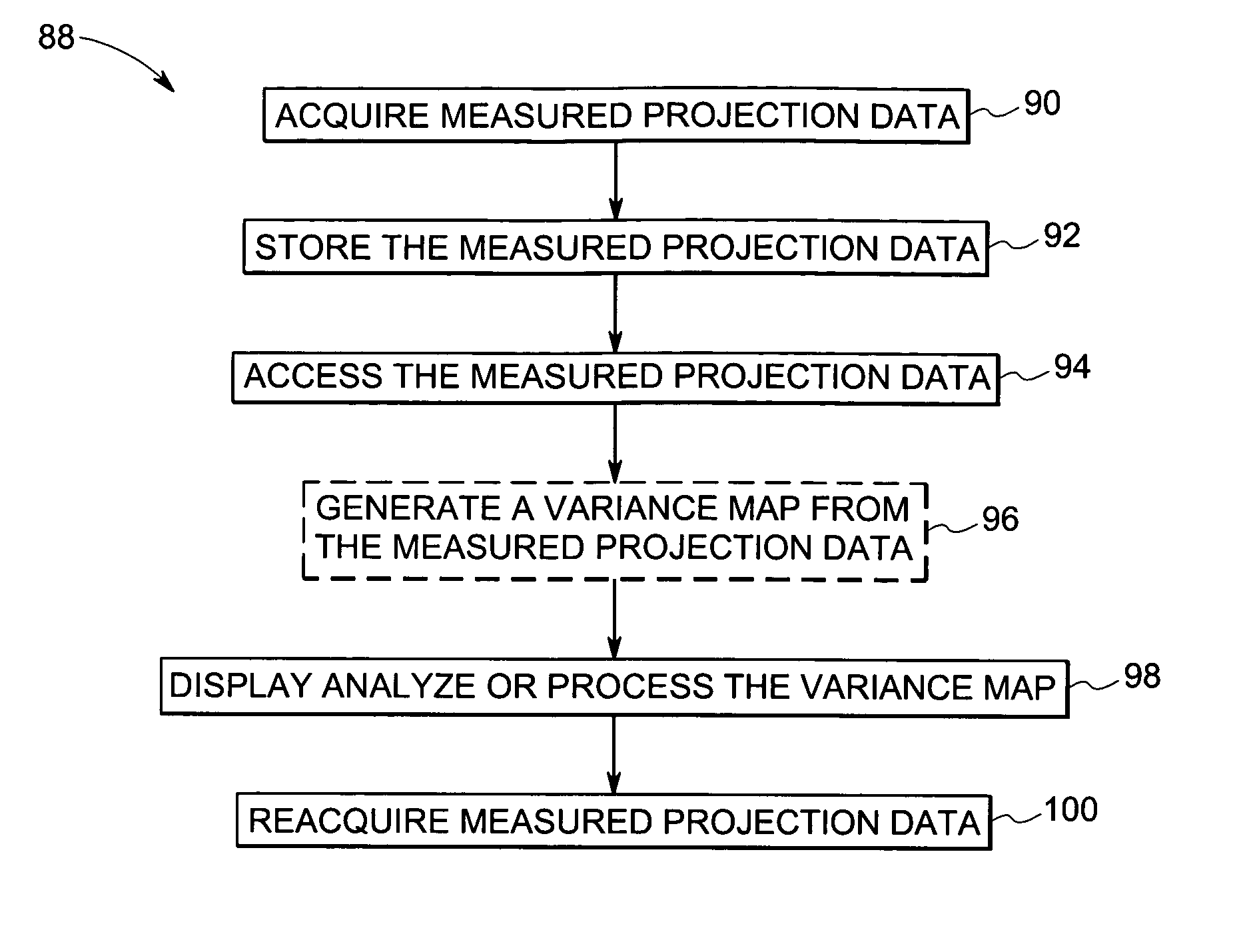
Method and apparatus for efficient calculation and use of reconstructed pixel variance in tomography images
ActiveUS20050226484A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging analysisData acquisition
A technique is disclosed for generating variance data and a variance map from measured projection data acquired from a tomography system. The method comprises accessing the measured projection data from the tomography system. The method further comprises generating the variance map from the measured projection data and displaying, analyzing or processing the variance map. The variance data is determined based upon a statistical model from measured image data, and may be used for image analysis, data acquisition, in computer aided diagnosis routines, and so forth.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
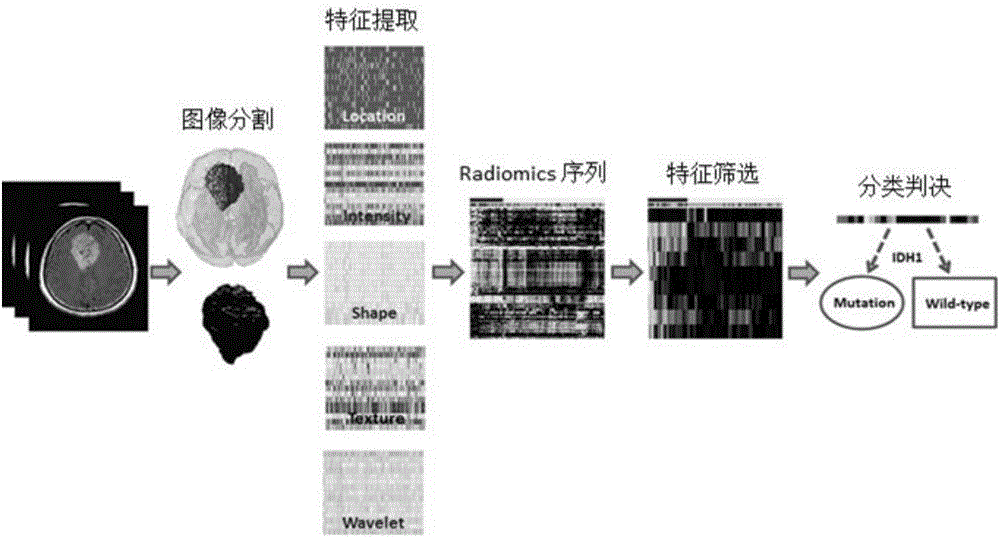
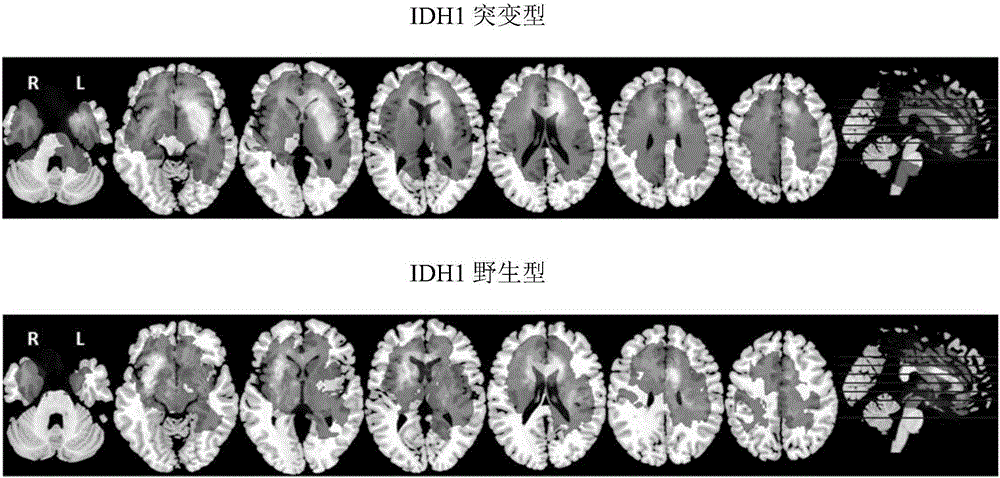
Brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and prediction system based on radiomics
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis, and specifically relates to a brain glioma molecular marker nondestructive prediction method and a prediction system based on radiomics. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image automatic segmentation method based on a convolution neural network; registering a tumor obtained from segmentation to a standard brain atlas, and acquiring 116 position features of tumor distribution; getting 21 gray features, 15 shape features and 39 texture features through calculation; carrying out three-dimensional wavelet decomposition on the gray features and the texture features to get 480 wavelet features of eight sub-bands; acquiring 671 high-throughput features from the three-dimensional T2-Flair magnetic resonance image of each case; using a feature screening strategy combining p-value screening and a genetic algorithm to get 110 features highly associated with IDH1; and using a support vector machine and an AdaBoost classifier to get a classification of which the IDH1 prediction accuracy is 80%. As a novel method of radiomics, the method provides a nondestructive prediction scheme of important molecular markers for clinical diagnosis of gliomas.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
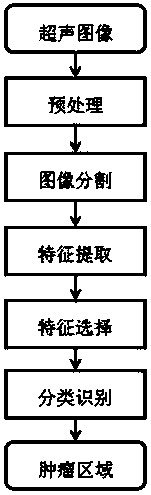
Method for automatically identifying breast tumor area based on ultrasound image
InactiveCN104143101AImprove automation performanceReduce manual operationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSonificationImage segmentation algorithm
The invention discloses a method for automatically identifying a breast tumor area based on an ultrasound image. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring the ultrasound image of the breast, and preprocessing the ultrasound image; segmenting the ultrasound image subjected to preprocessing through an image segmentation method to obtain a plurality of segmented subareas; extracting a grey level histogram, texture features, gradient features and morphological features of the ultrasound image, and combining the grey level histogram, the texture features, the gradient features and the morphological features of the ultrasound image with two-dimensional position information to obtain high-dimensionality feature vectors; selecting the most effective feature subset of the high-dimensionality feature vectors through feature ordering based on biclustering and a selection method; performing learning classification on the selected most effective feature subset through a classifier, and then automatically identifying the breast tumor area. By means of the method, the breast tumor area can be identified automatically from segment results of the breast tumor ultrasound image, therefore, automation performance of computer-aided diagnosis is improved, manual operation of clinical doctors is reduced, and subjective influence of clinical doctors is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
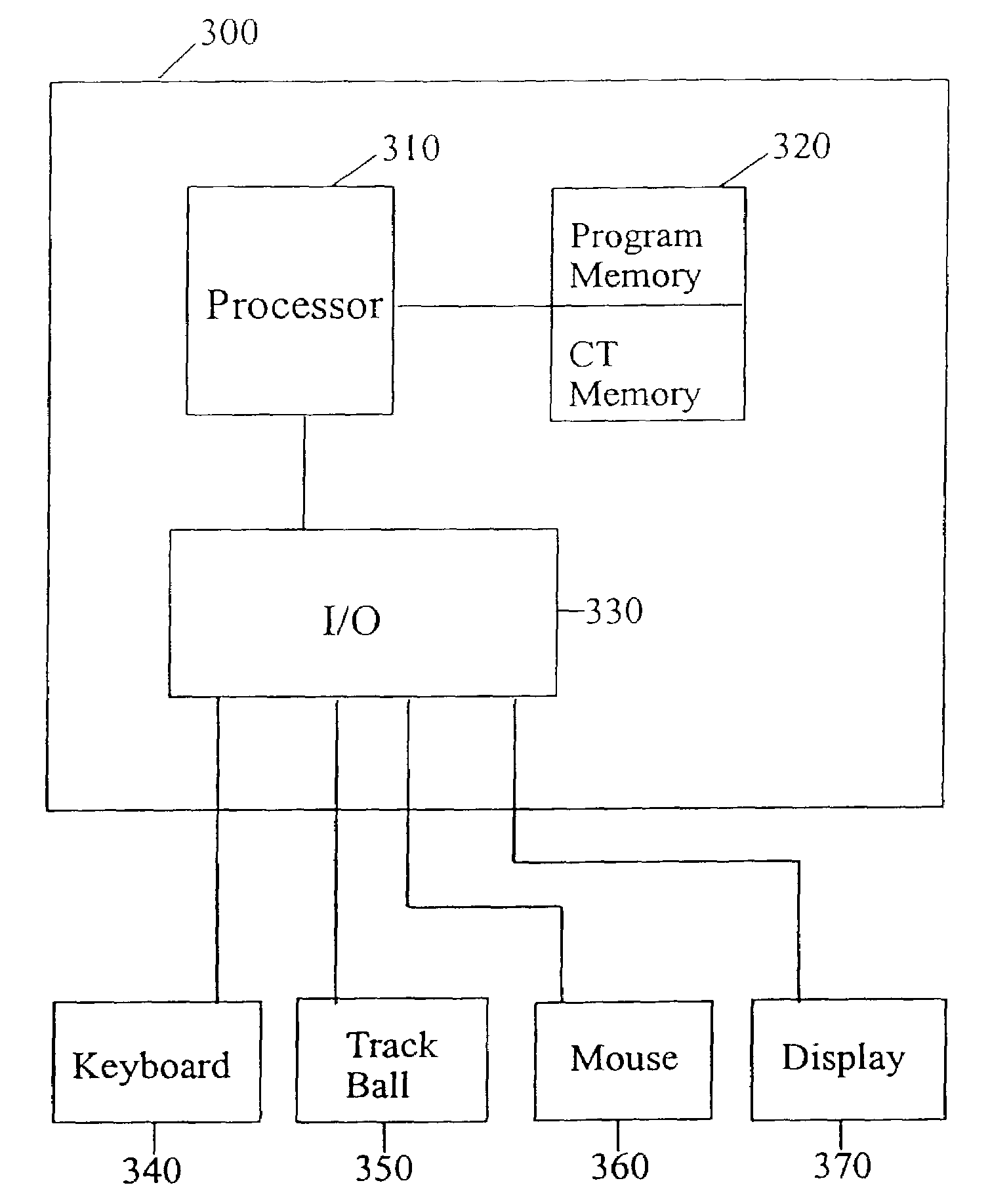
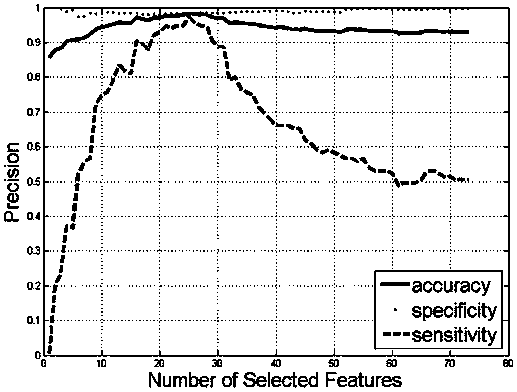
Computer-aided diagnosis apparatus and method
A computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) apparatus and method. The CAD apparatus includes an area divider configured to divide a current image frame into a first area and a second area based on location of a region of interest (ROI) detected in a previous image frame. The CAD apparatus further includes a functional processor configured to perform different functions of the CAD apparatus for the first area and the second area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
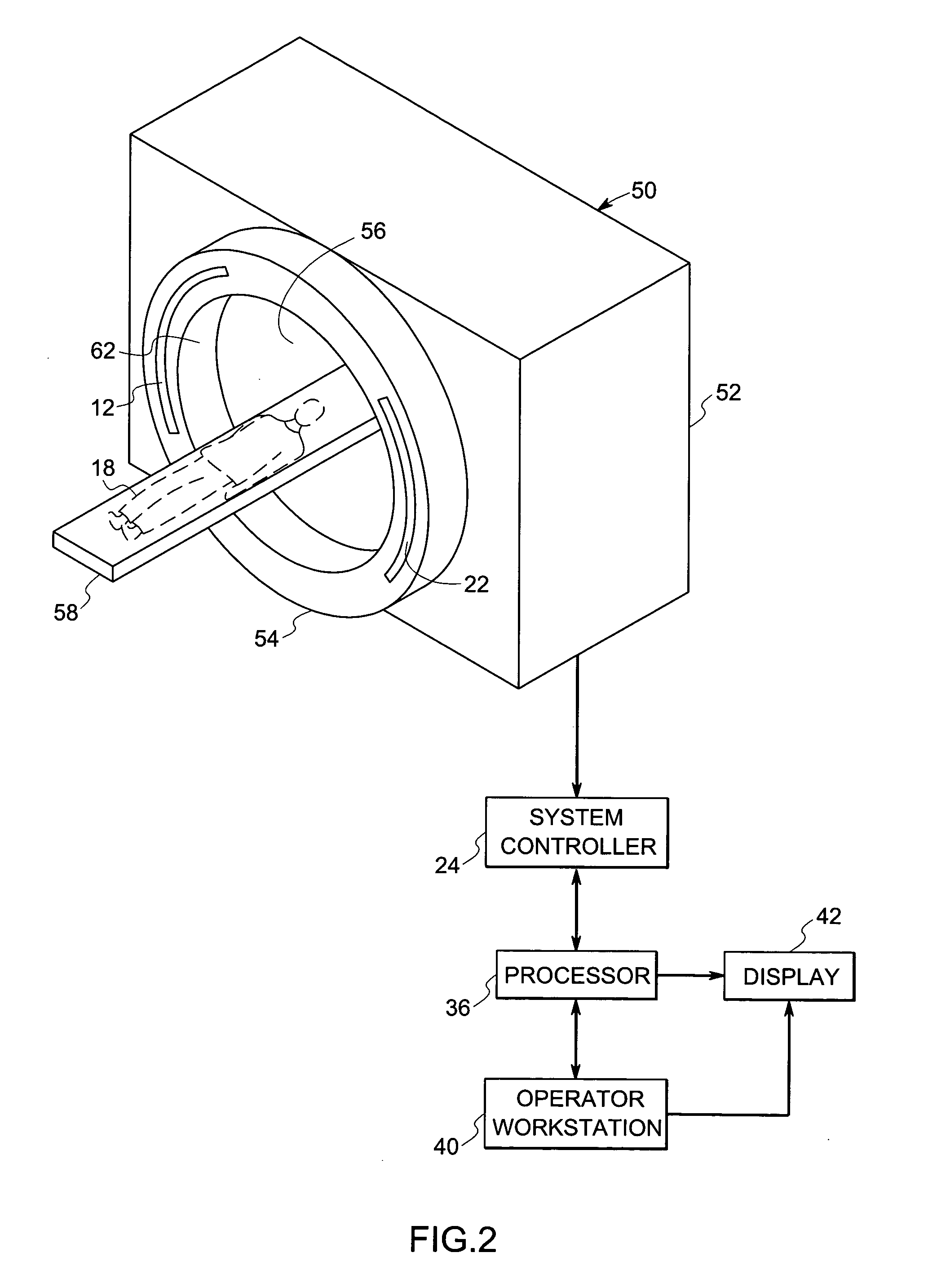
3D display system and method
InactiveUS20050285853A1Program controlSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
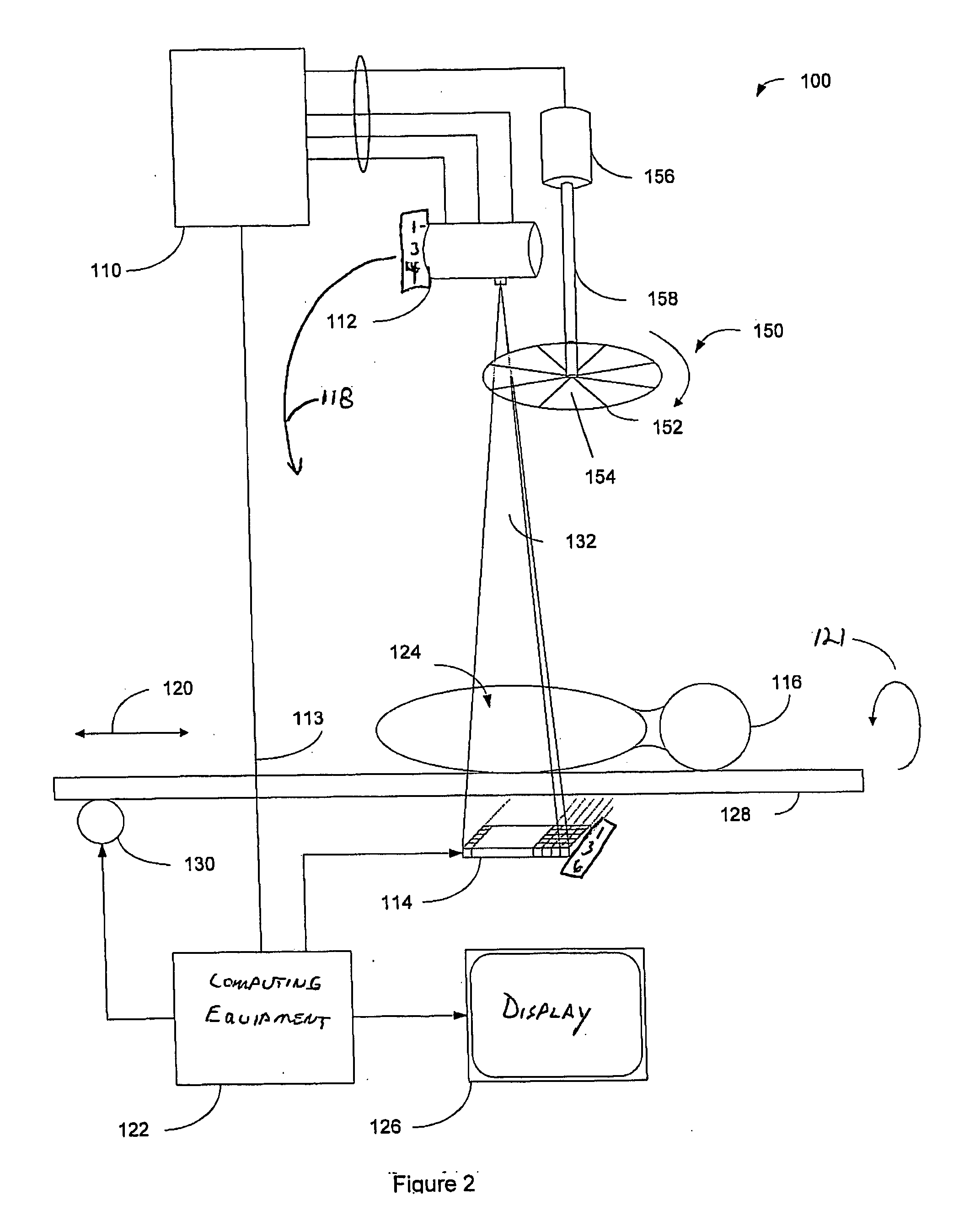
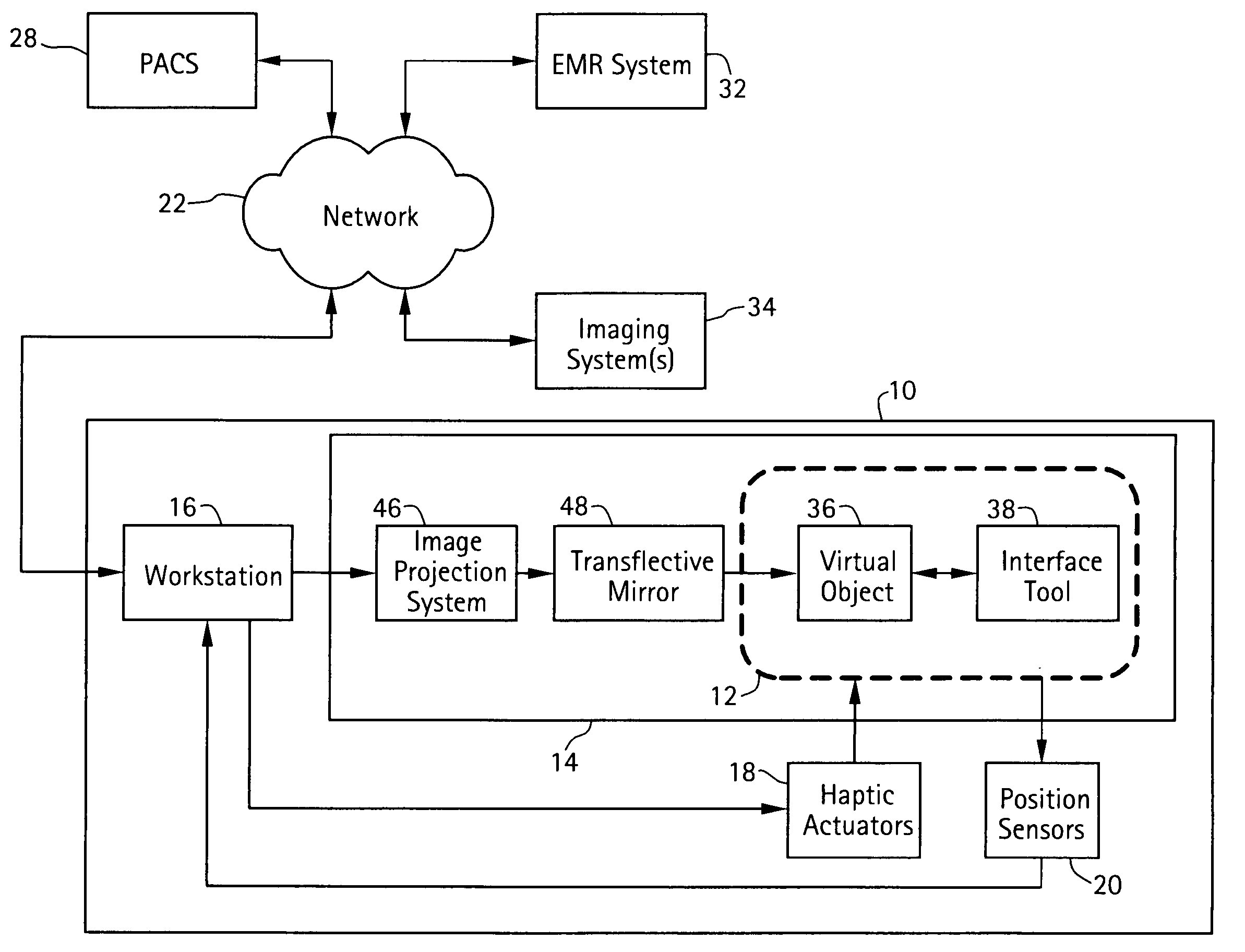
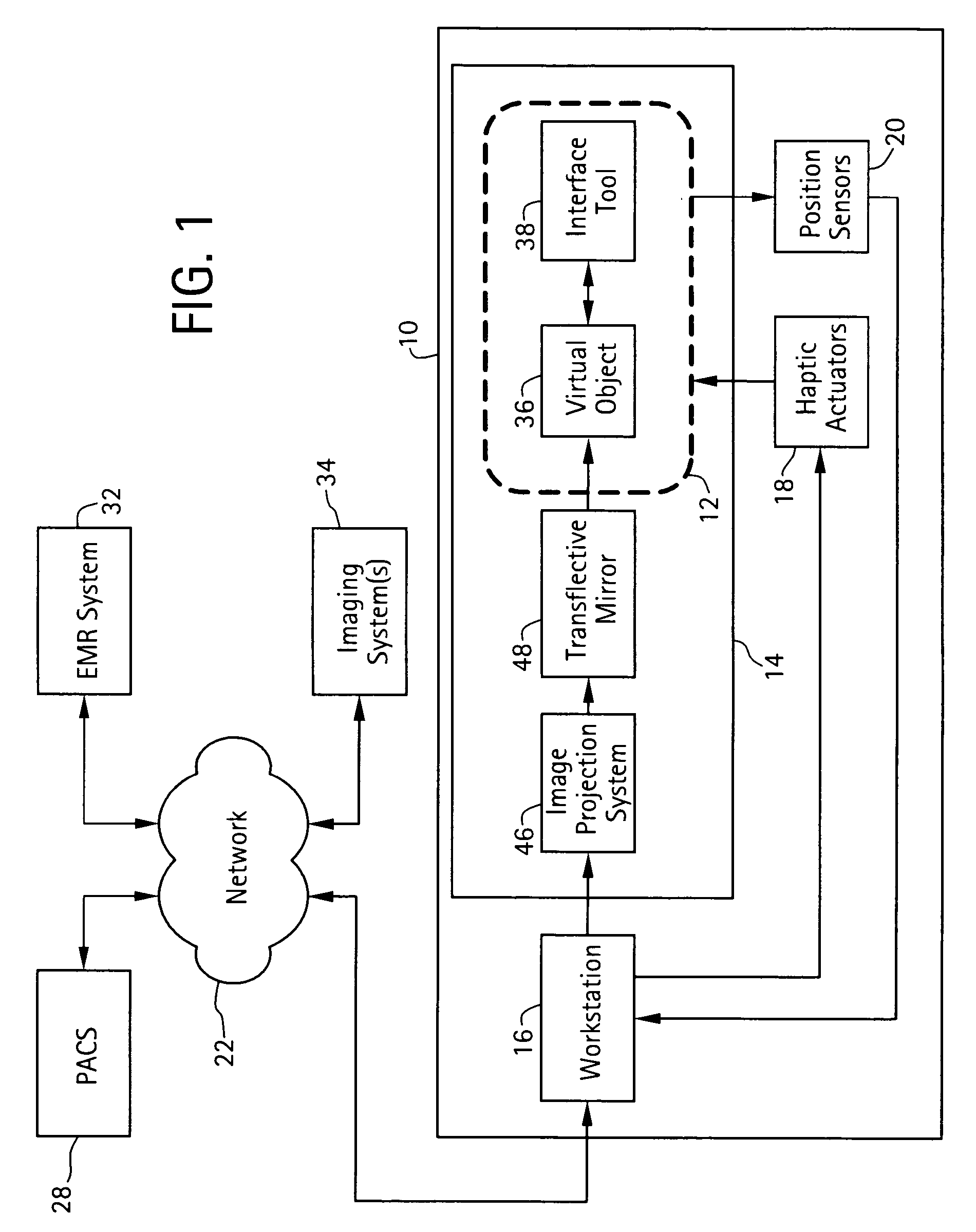
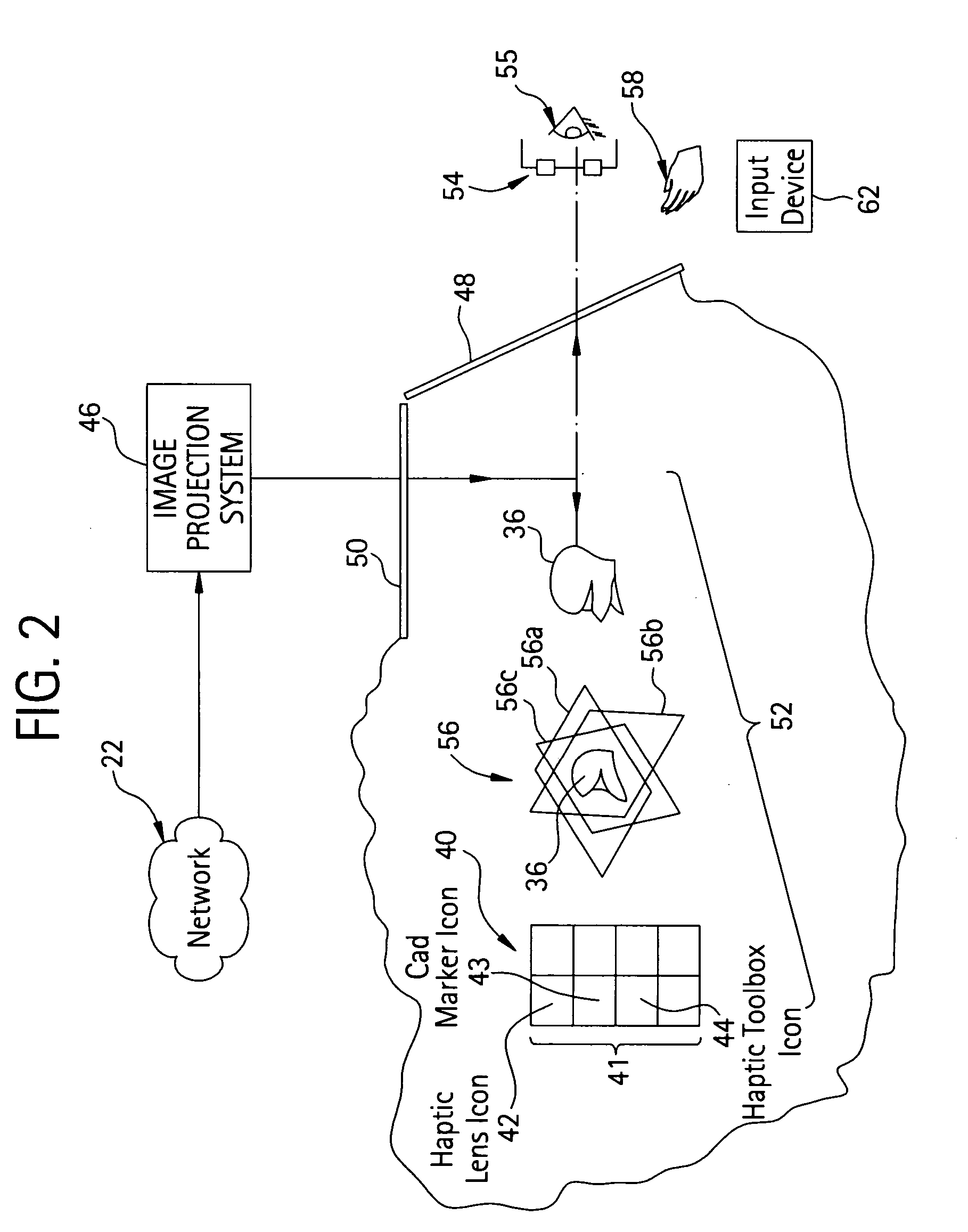
An apparatus configured to display 3D volumetric data acquired from a patient by an imaging system comprises a 3D volumetric display system configured to generate a real-time 3D diagnostic display of the 3D volumetric data. The 3D volumetric display system includes a graphical user interface configured to permit a user to access, view, and manipulate the 3D volumetric data. The graphical user interface also includes a plurality of 3D computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) markers, each plurality of 3D CAD markers having a delineator configured to navigate through the 3D volumetric data to locate pathology and to permit a user to compile and to prepare a report containing diagnosis information in a virtual-reality environment.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Image segmentation method based on annotated image learning
InactiveCN102436583AImprove cognitive abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionModel parametersImage segmentation
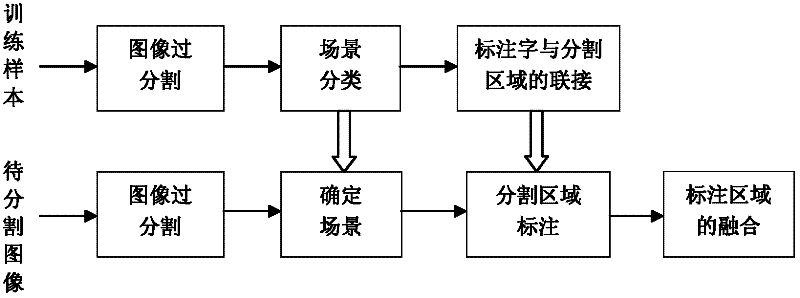
The invention provides an image segmentation method based on an annotated image learn. The method comprises two processes of: 1, learning an annotated training sample, namely segmenting the training image, performing scene classification on the training image, and establishing connection between the annotated words and the segmentation region on a special scene; and 2, determining the annotated words of the region to be segmented according to a model parameter acquired by learning in the process 1, performing information fusion according to the annotated information of the region and finishing segmentation. According to the method, the image segmentation and the identification process are fused by learning the annotated image; the annotated words serve as connecting link of the image segmentation and object identification; connection is established between low-grade visual stimulation and the annotated words representing high-grade semantic information to guide the image segmentation process, so that the cognitive ability of the image segmentation result is improved. The method can be directly applied to the actual application fields such as automatic image annotation, computer-aided diagnosis of a medical image, segmentation and classification of remote sensing images, multimedia information retrieval and the like.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS7646902B2Breast enlargementExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
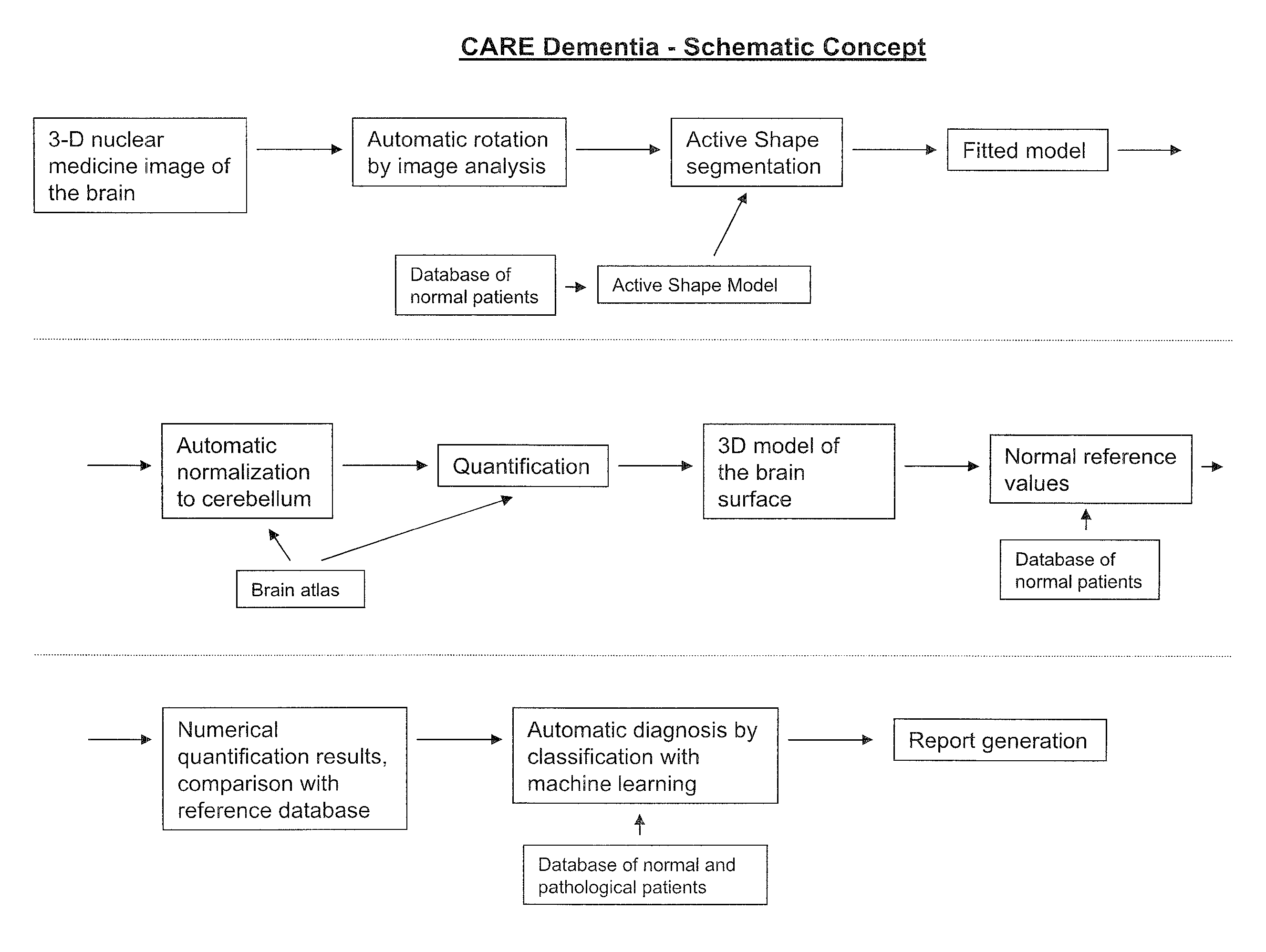
Automatic interpretation of 3-D medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS8199985B2Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
Texture analysis for mammography computer aided diagnosis
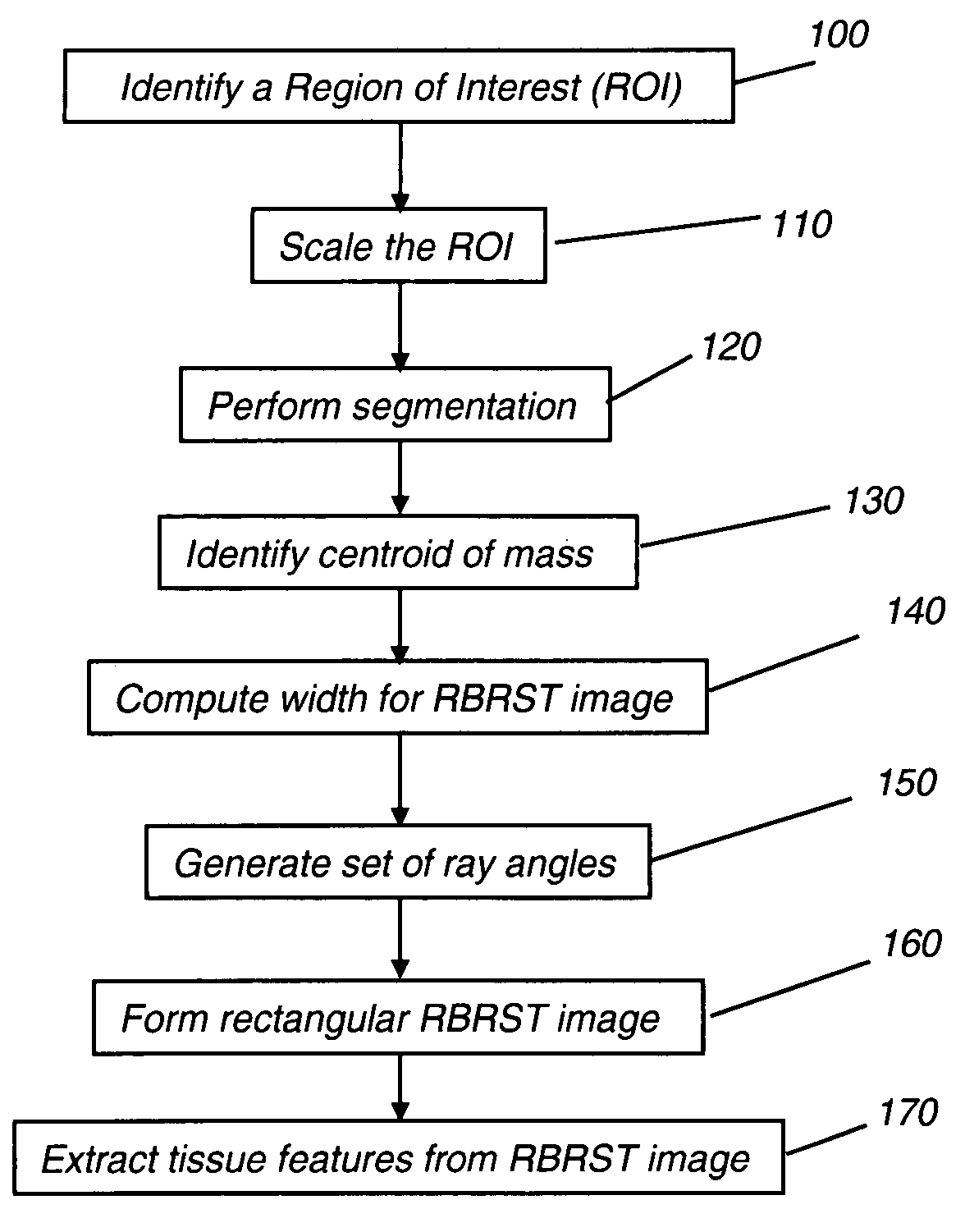
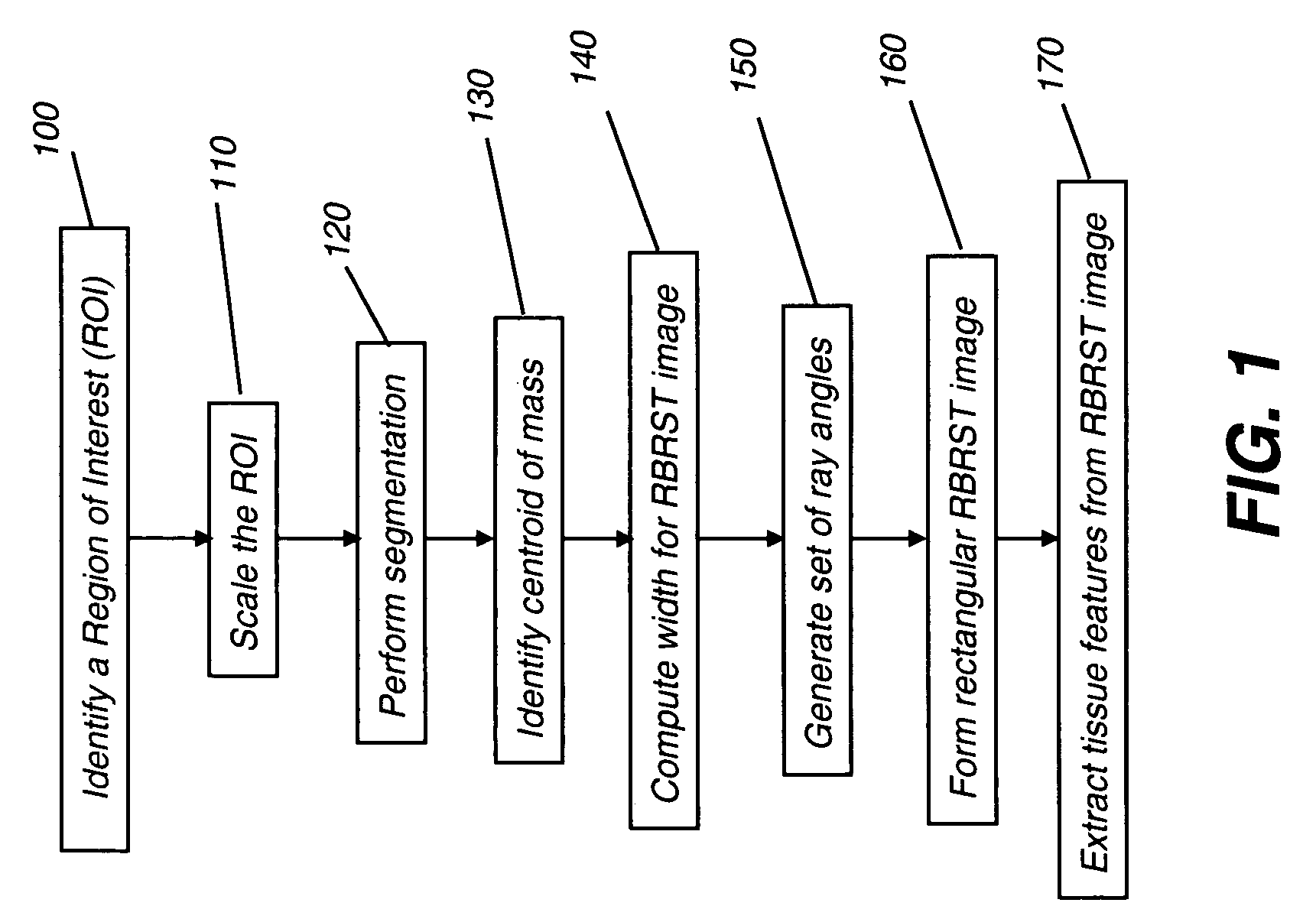
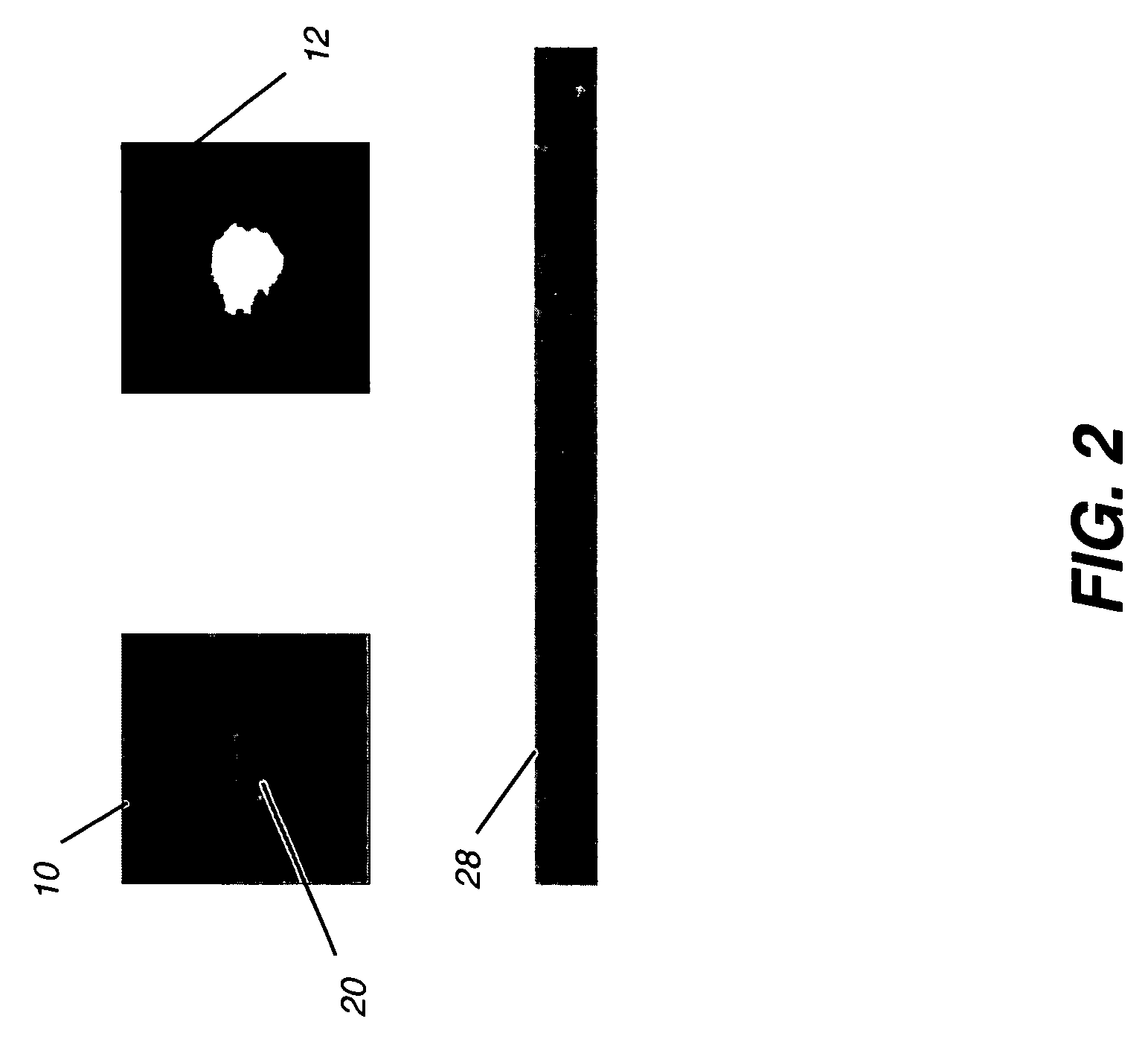
InactiveUS20080031506A1MinimizesMinimizes under-samplingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramAided diagnosis
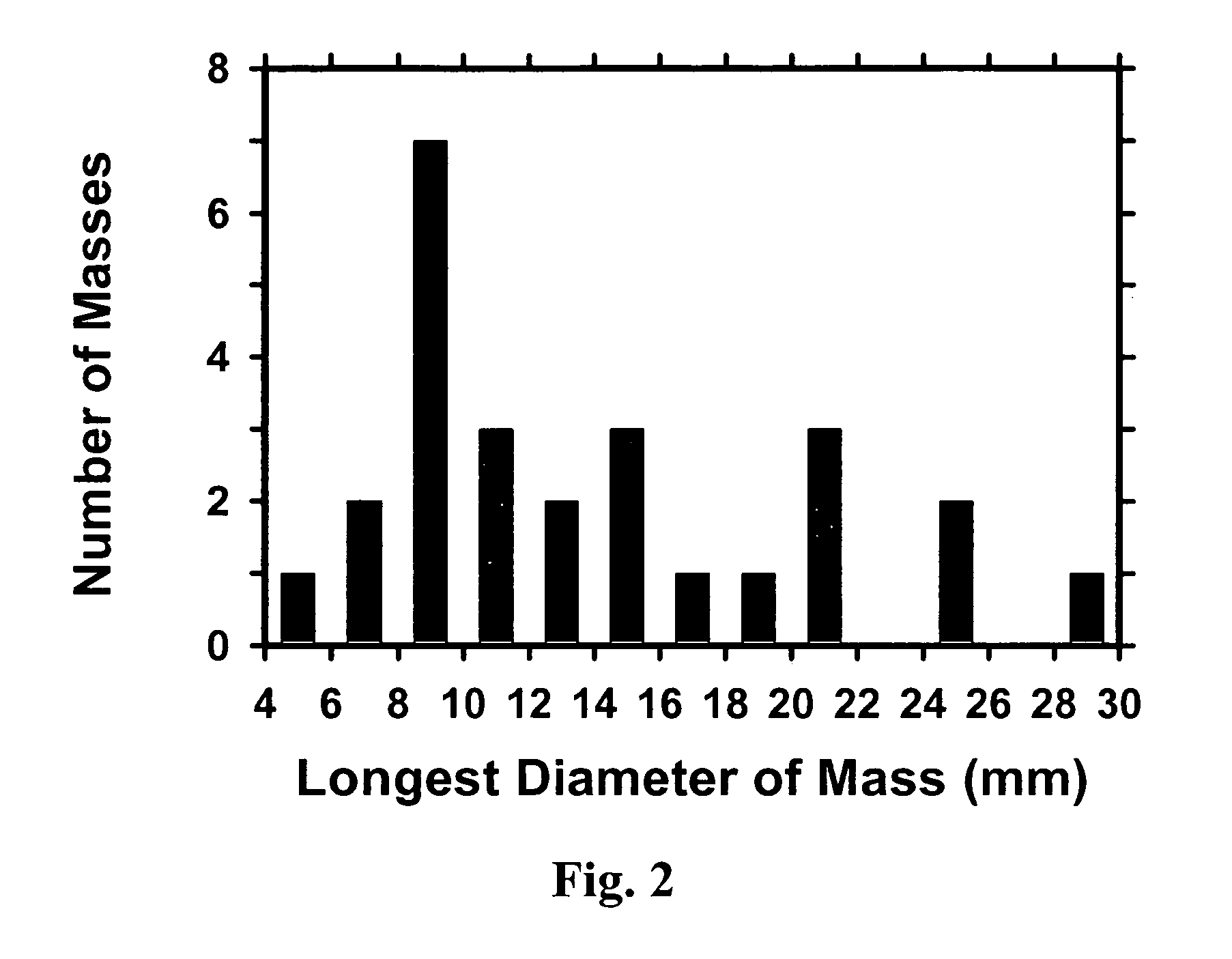
A method of characterizing a mass within a digital mammogram. A region of interest is identified that includes the mass and surrounding tissue. A border outline of the mass is identified. A rectangular image is formed wherein each column of the image is formed by repetition of steps. A vector is employed for each of a set of ray angles, wherein the vector extends from a central point of the mass and intersects the border outline at an intersection point. A starting pixel along the vector is identified, between the intersection point and the central point, at a first distance before the intersection point. An ending pixel along the vector is identified at a second distance beyond the intersection point. Pixels along the vector, from the starting pixel to the ending pixel, are remapped as the respective column in the rectangular image. Texture features are extracted from the formed rectangular image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
System and Method for Lesion Detection Using Locally Adjustable Priors
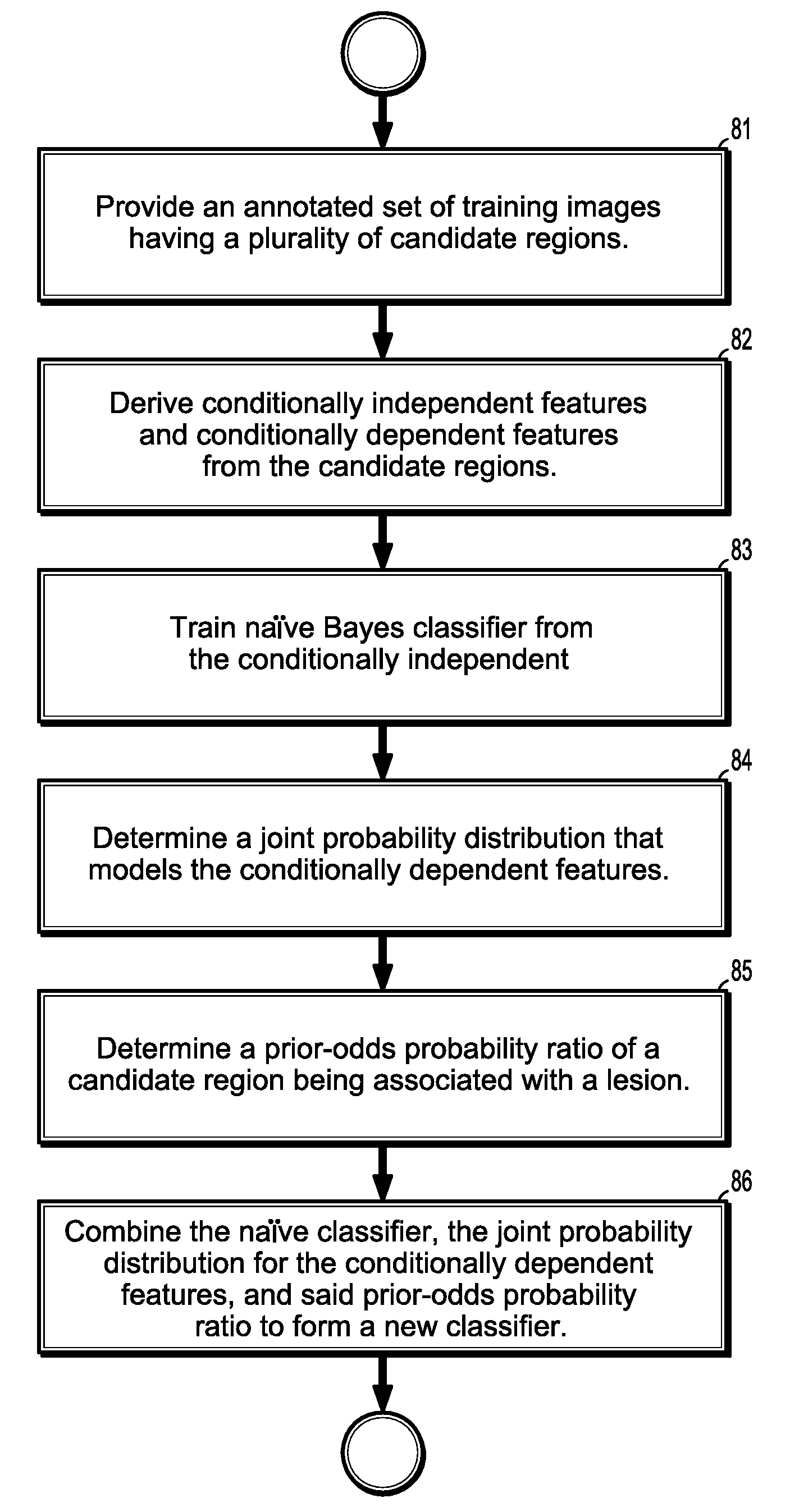
According to an aspect of the invention, a method for training a classifier for classifying candidate regions in computer aided diagnosis of digital medical images includes providing a training set of annotated images, each image including one or more candidate regions that have been identified as suspicious, deriving a set of descriptive feature vectors, where each candidate region is associated with a feature vector. A subset of the features are conditionally dependent, and the remaining features are conditionally independent. The conditionally independent features are used to train a naïve Bayes classifier that classifies the candidate regions as lesion or non-lesion. A joint probability distribution that models the conditionally dependent features, and a prior-odds probability ratio of a candidate region being associated with a lesion are determined from the training images. A new classifier is formed from the naïve Bayes classifier, the joint probability distribution, and the prior-odds probability ratio.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
System and Method for Multiple-Instance Learning for Computer Aided Diagnosis
InactiveUS20090080731A1Increase probabilityDiagonal elementCharacter and pattern recognitionMalignancyTraining set
A method for training a classifier for classifying candidate regions in computer aided diagnosis of digital medical images includes providing a training set of images, each image including one or more candidate regions that have been identified as suspicious by a computer aided diagnosis system. Each image has been manually annotated to identify malignant regions. Multiple instance learning is applied to train a classifier to classify suspicious regions in a new image as malignant or benign by identifying those candidate regions that overlap a same identified malignant region, grouping each candidate region that overlaps the same identified malignant region into a same bag, and maximizing a probabilityP=∏i=1Npiyi(1-pi)1-yi,wherein N is a number of bags, pi is a probability of bag i containing a candidate region that overlaps with an identified malignant region, and yi is a label where a value of 1 indicates malignancy and 0 otherwise.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
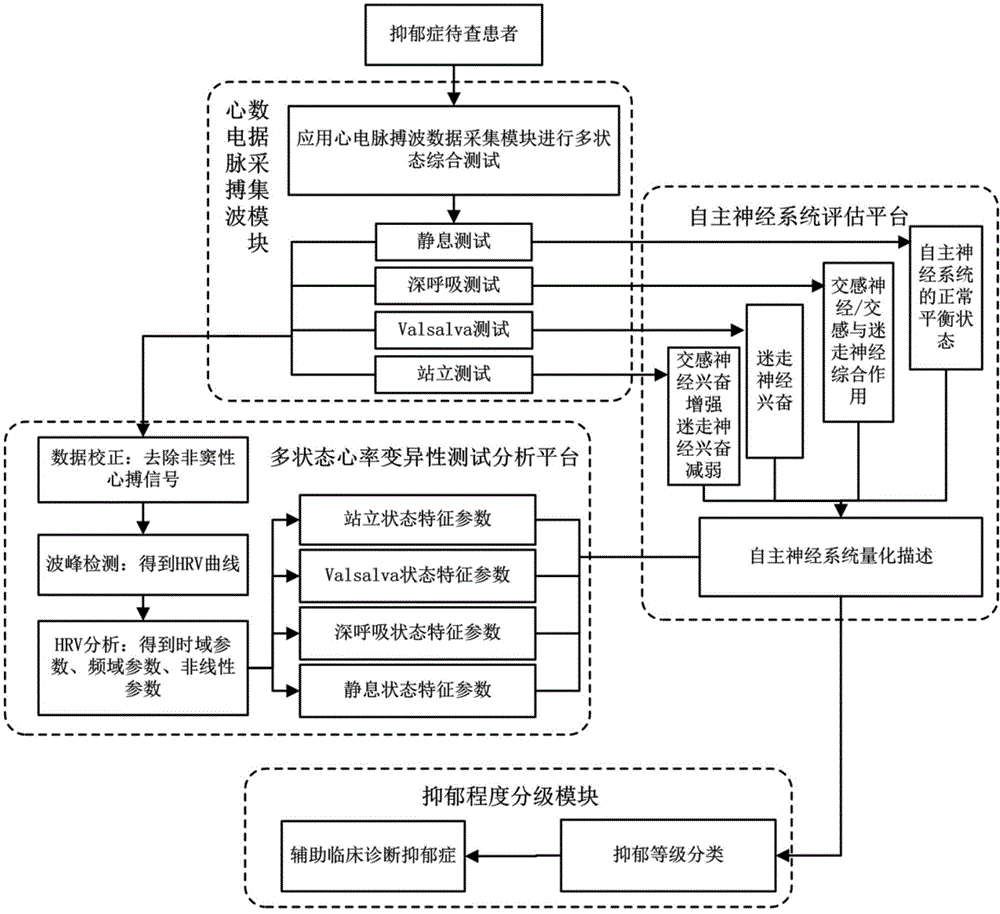
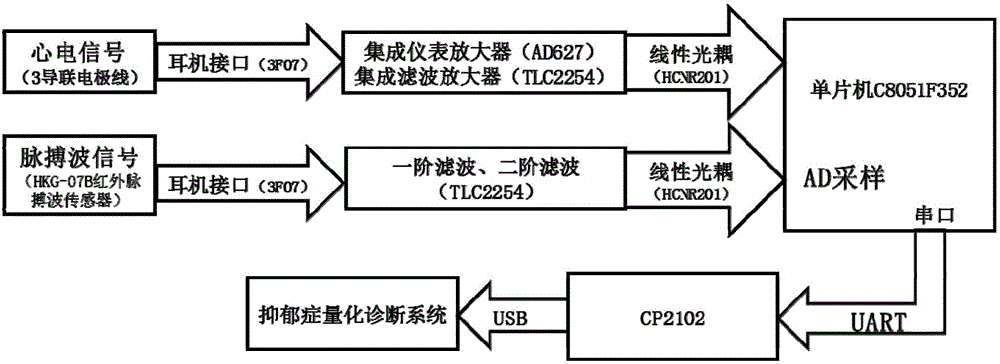
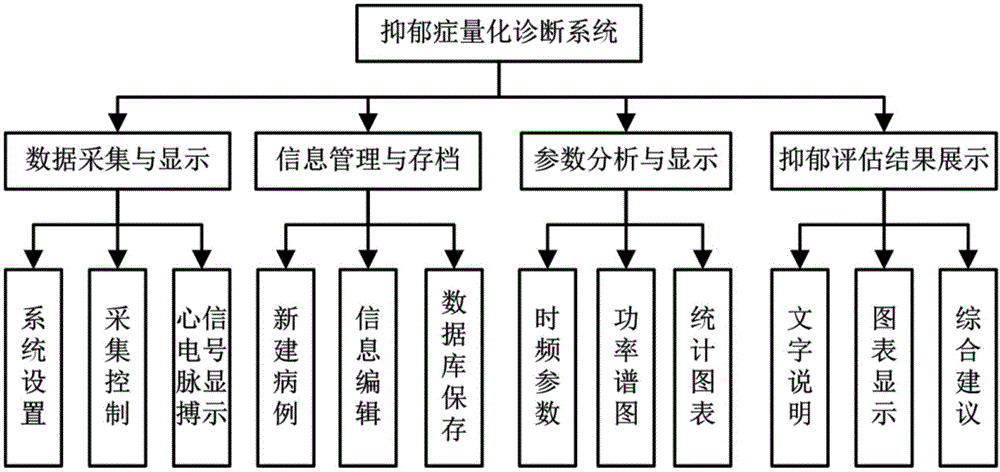
Evaluating system and evaluating method of depressive disorder degree quantization
ActiveCN104127193AAvoid subjectivityAvoid variabilitySensorsPsychotechnic devicesNervous systemData treatment
The invention discloses an evaluating system of depressive disorder degree quantization. The system comprises an electrocardio and pulse wave integral detection device, a data transmission device and a data processing platform. The invention further discloses an evaluating method of depressive disorder degree quantization. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, human physiological information under different states is acquired through a multi-state comprehensive test platform; secondly; HRV characteristic parameters under the different states are obtained on the basis of the heart rate variability analysis principle; thirdly, the function balance states of sympathetic nerves and pneumogastric nerves in the automatic nervous system are evaluated; fourthly, a depressive disorder degree quantization evaluation model is built, and the depressive disorder degree level of a tested person is evaluated fast and objectively. The system and method belong to the technical field of computer-aided diagnosis, depressive disorder degree quantization evaluation is achieved, the blank of the technical field of depressive disorder inspection is filled up, and the system and method are easy and convenient to implement, save medical resources and have the good clinic practicality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
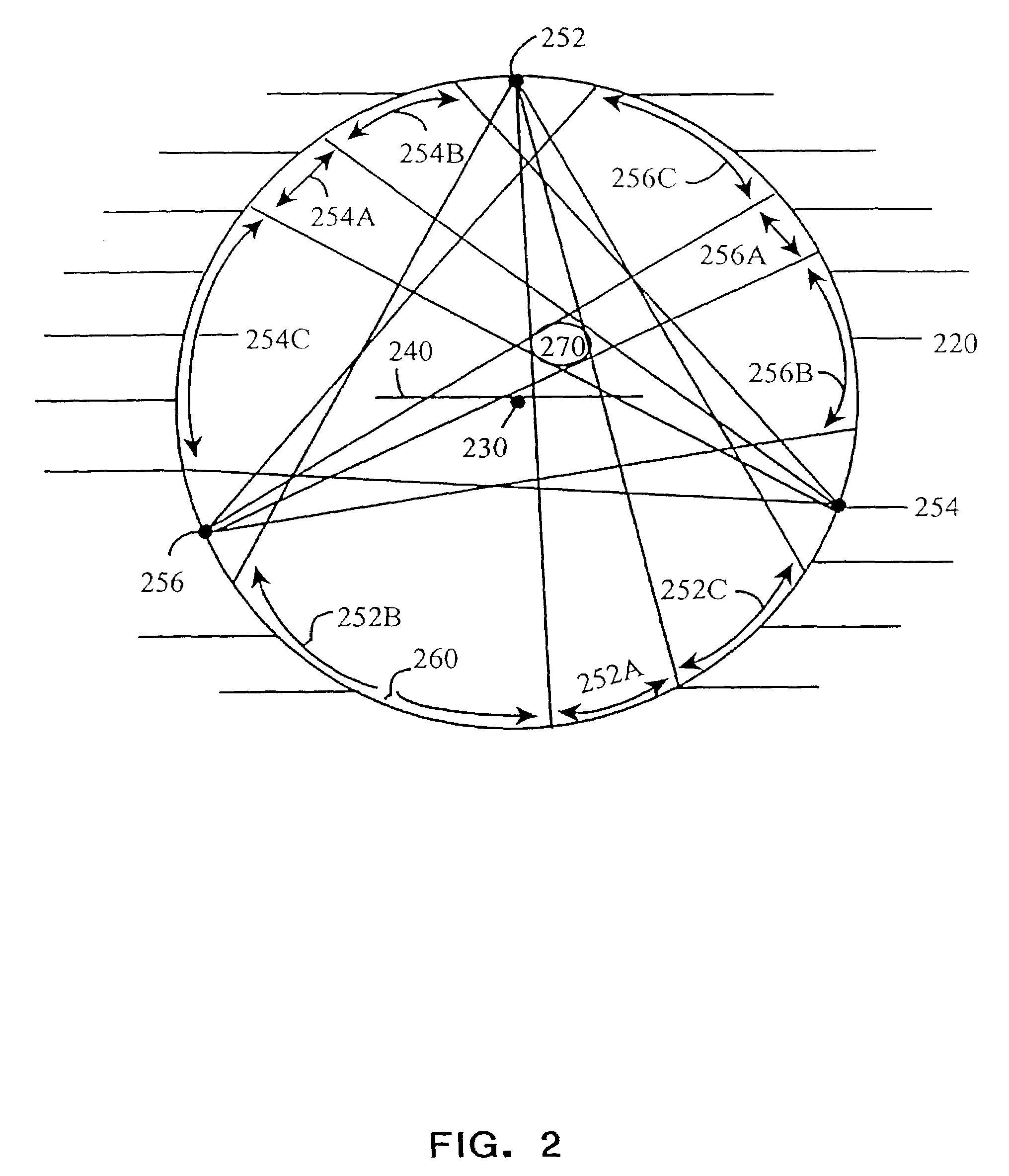
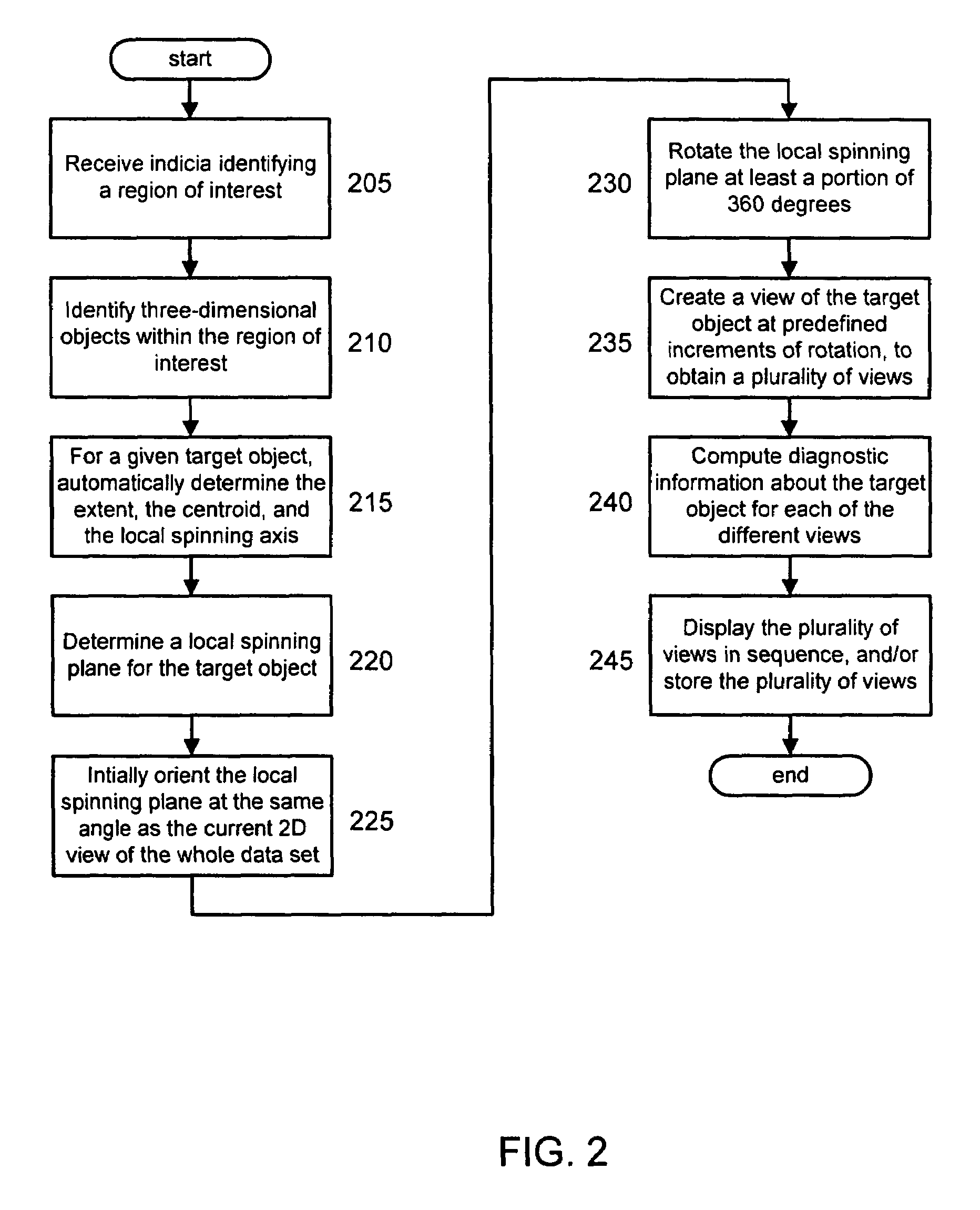
Computer-aided diagnosis method for aiding diagnosis of three dimensional digital image data
There is provided a computer-assisted diagnosis method for assisting diagnosis of three-dimensional digital image data. The method includes the step of receiving indicia identifying at least one region of interest in a digital medical image. Three-dimensional objects within the at least one region of interest are identified. For a given three-dimensional (3D) object within the at least one region (ROI), an extent, a centroid, and a local spinning axis of the given object are determined. Moreover, a local spinning plane is determined for the given object, the local spinning plane being centered at the centroid and the local spinning axis. The local spinning plane is rotated at least a portion of 360 degrees. The rotating step includes the step of creating a view of the given object at predefined increments of rotation, so as to result in a plurality of views of the given object.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +1
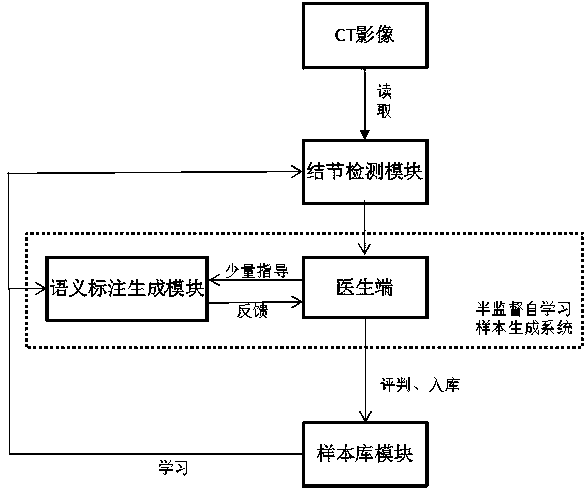
Medical image aided diagnosis and semi-supervised sample generation system
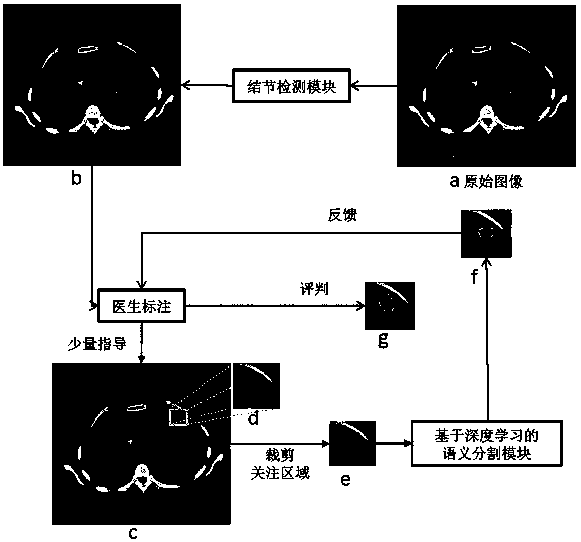
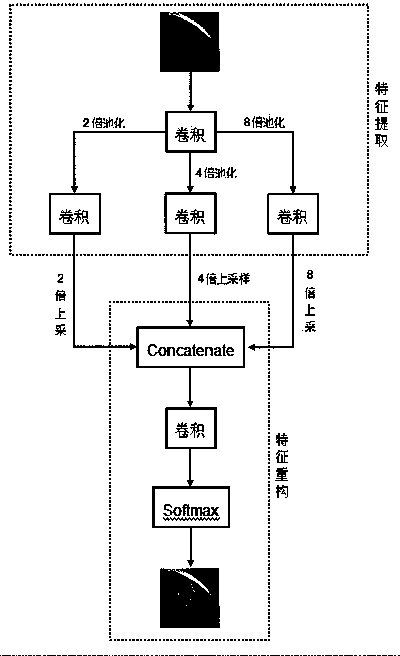
InactiveCN107563383AImprove labeling efficiencyImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsClosed loopComputer-aided
The invention relates to the technical field of medical image computer aided diagnosis, and discloses a medical image auxiliary diagnosis and semi-supervised sample generation system. The medical image aided diagnosis and semi-supervised sample generation system comprises a hospital image filing and communication module (a), a pulmonary nodule-based automatic detection module (b), a deep learning-based semantic annotation generation module (c) and a sample library module (d), wherein the hospital image filing and communication module is used for filing image data; the pulmonary nodule-based automatic detection module is used for automatically detecting pulmonary nodules to generate suspected pulmonary nodule positions; the deep learning-based semantic annotation generation module is used for receiving a small quantity of instructions of doctors and generating samples with accurate pulmonary nodule profiles and pulmonary nodule ingredient properties; and the sample library module is used for storing qualified samples so that online learning can be carried out by other self-learning systems. According to the system, the problem that computer aided software cannot feed closed loops back, cannot generate high-quality samples and cannot carry out self-learning is solved, and a feasible method is provided for a self-learning computer aided diagnosis system of CT images.
Owner:杭州健培科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com