Method and system for secure transmission of biometric data
a biometric and data technology, applied in the field of biometrics, authentication/identification, secure communication, data management, etc., can solve the problems of increased input error rate, high vulnerability to fraudulent access, and difficulty in accessing data,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
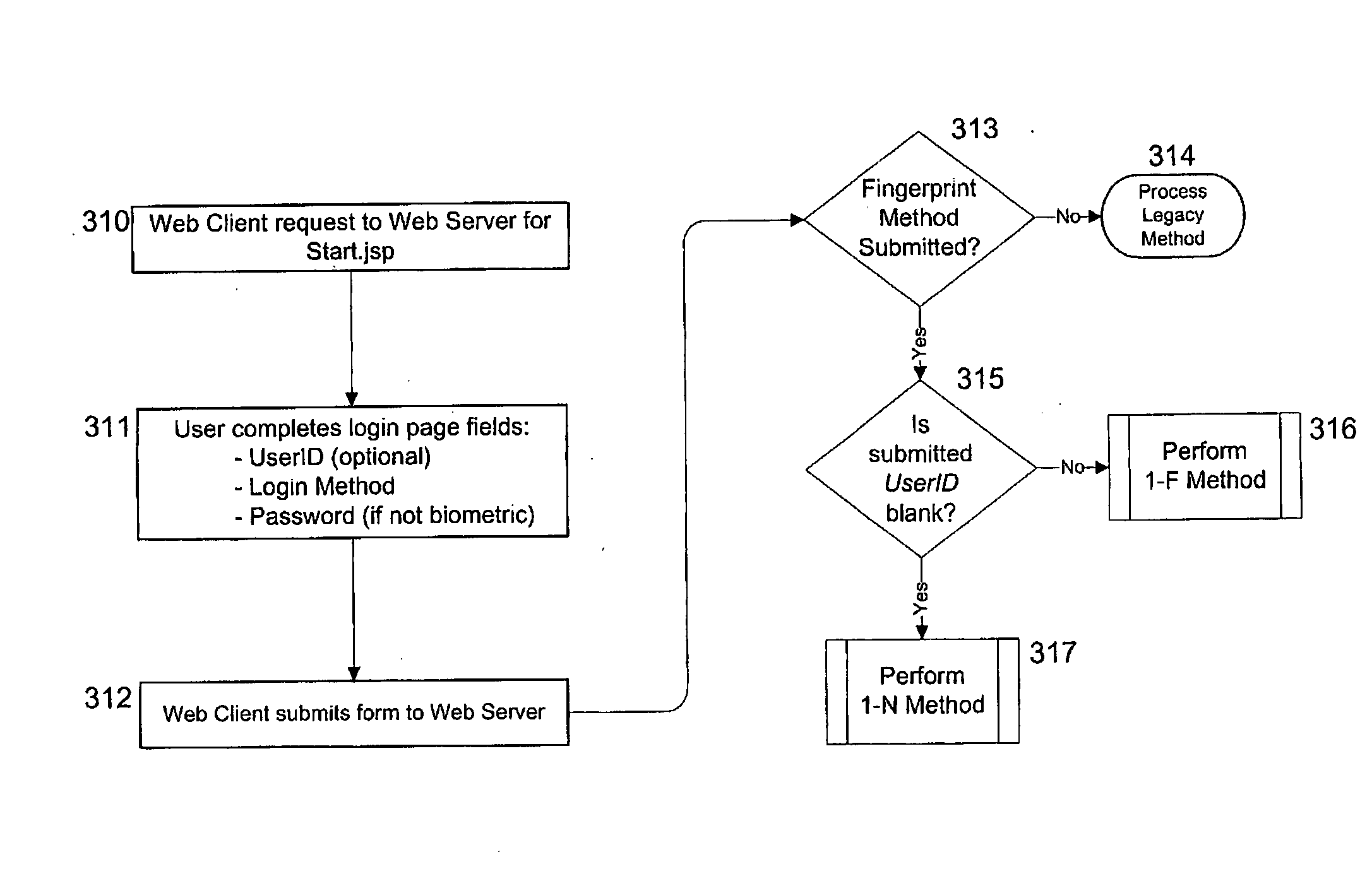
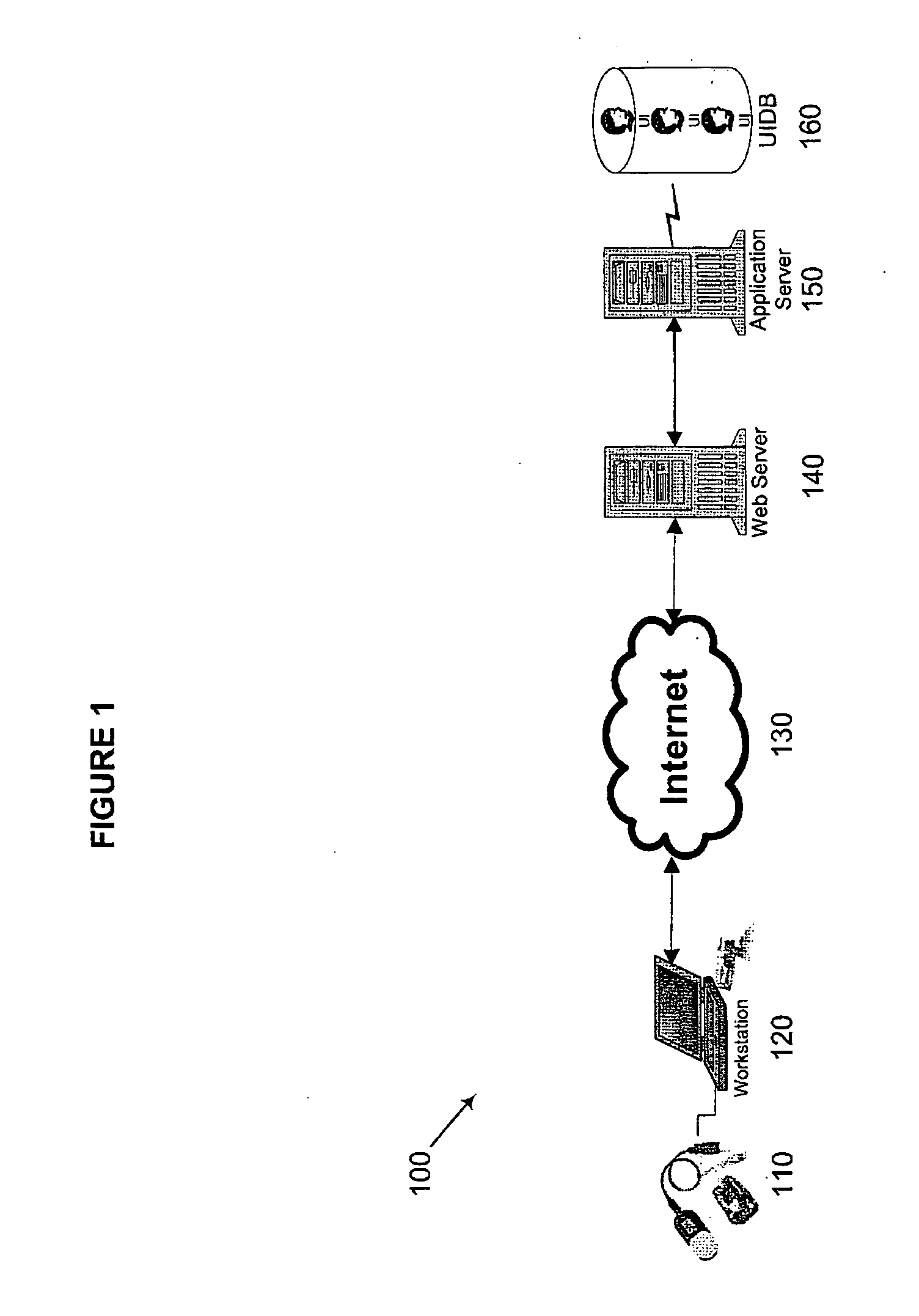
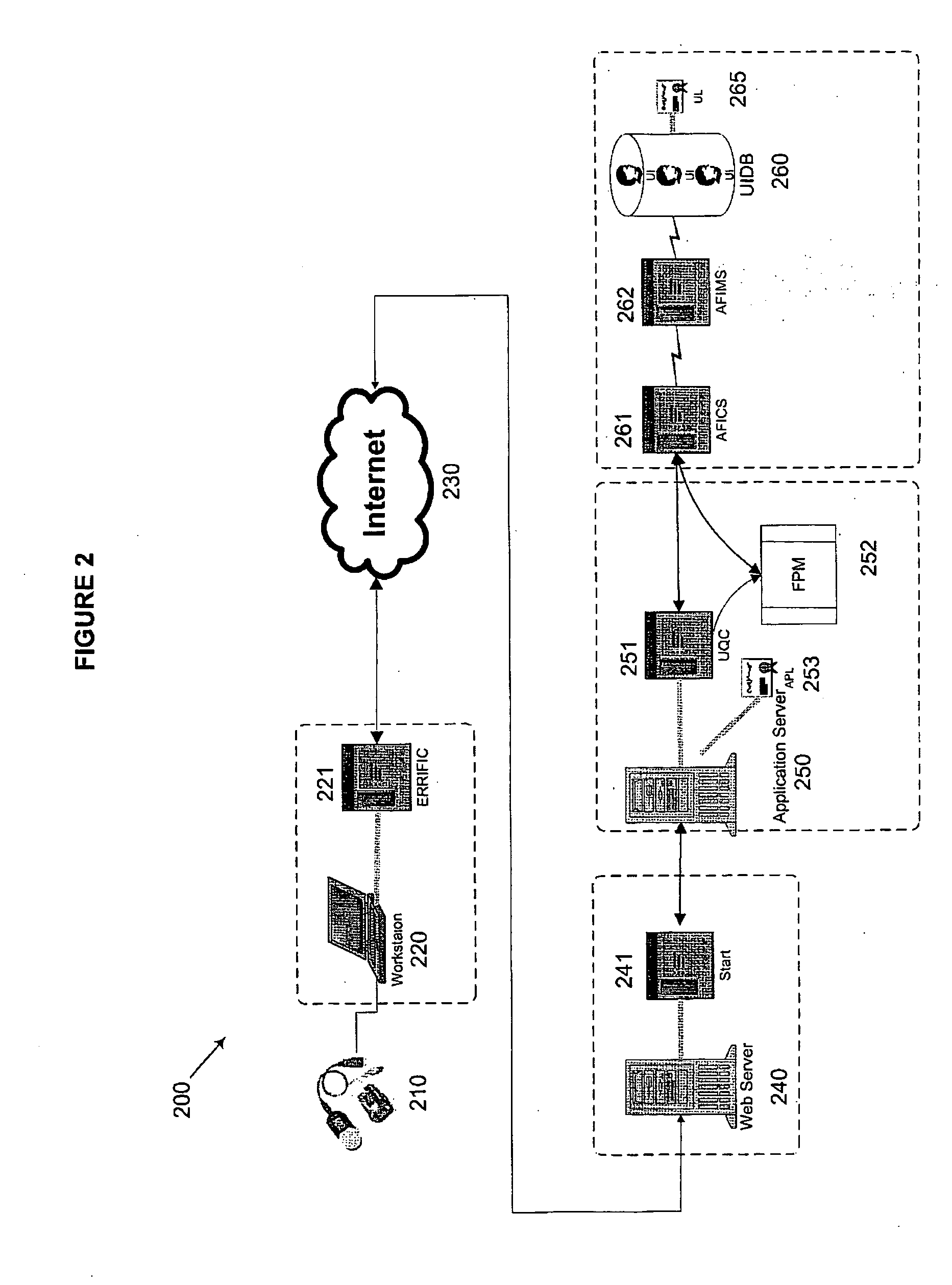
[0037] Methods and systems according to embodiments of the present invention relate to an integrated biometric authentication / identification and migration system with server side authentication and identification through the use of a four-tier architecture on a multi-platform, device-independent and device-interoperable structure. This architecture and novel aspects of the present invention provide an accurate, easy-to-use enrollment system and reduce the vulnerability of enterprise applications to access from unauthorized users without materially changing legacy hardware and software. Although a portion of the software for use with the present invention, as described herein, is written in the Java™ programming language, e.g., to enhance its portability and interoperability, other programming languages may be used without departing from the spirit of the present invention. Furthermore, it is to be understood that in the demonstrative embodiments described herein, the use of software...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com