Apparatus and method for point-of-use treatment of effluent gas streams
a technology of effluent gas and apparatus, which is applied in the direction of perfluorocarbon/hydrofluorocarbon capture, crystal growth process, separation process, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, high temperature heated modules may accelerate corrosion downstream of thermal modules, and generation of nox resulting from ammonia oxidation, etc., to achieve high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
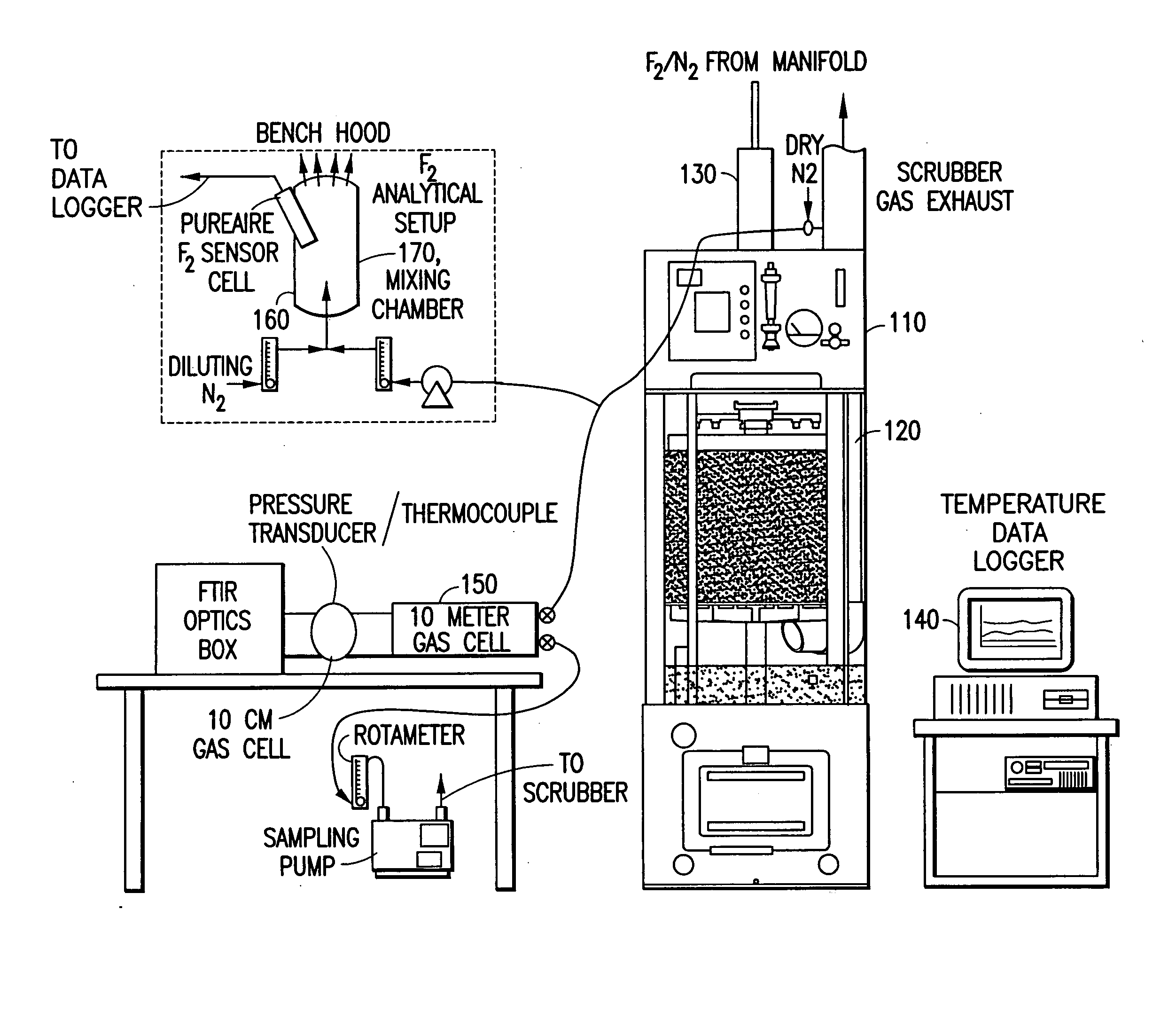
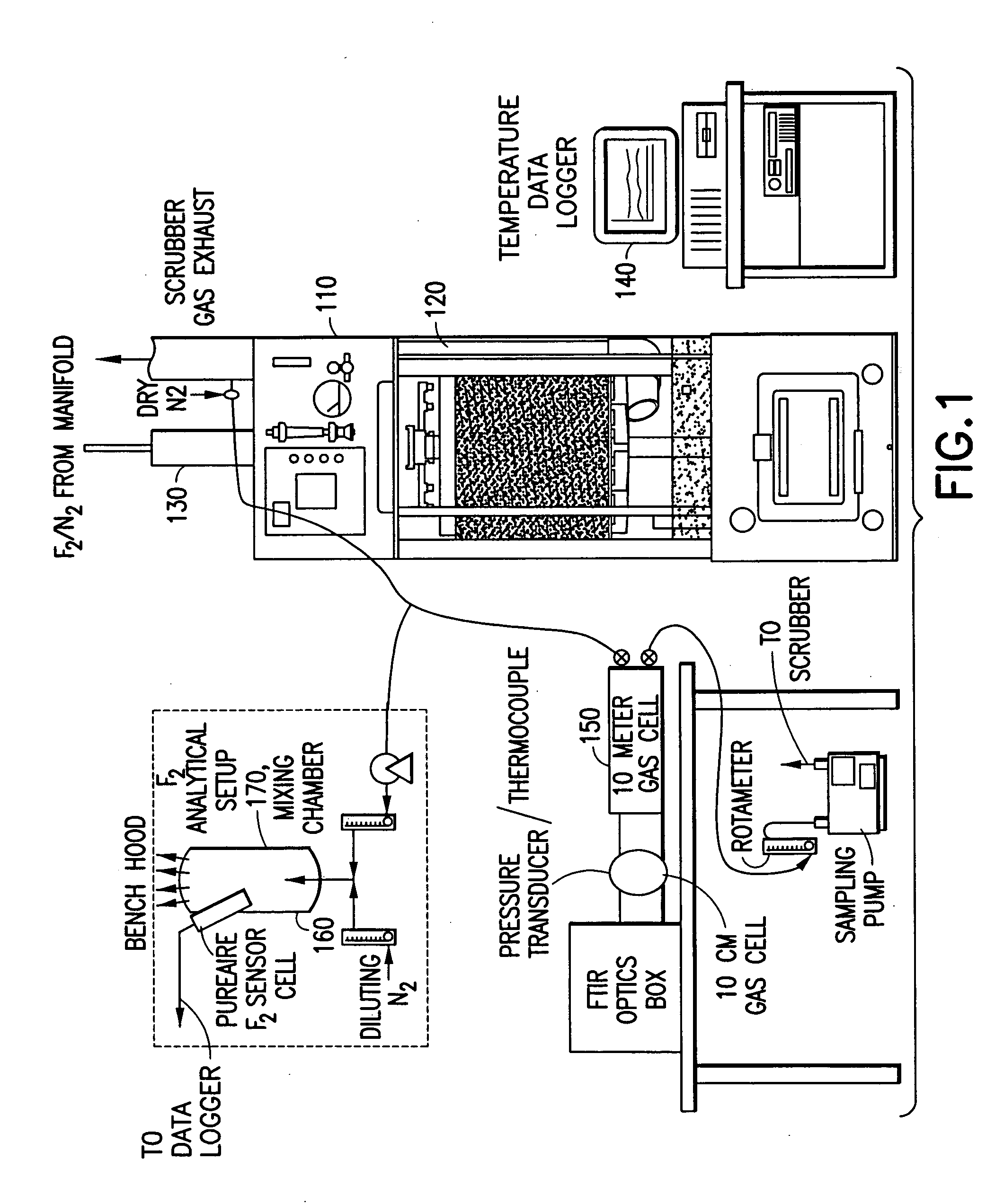
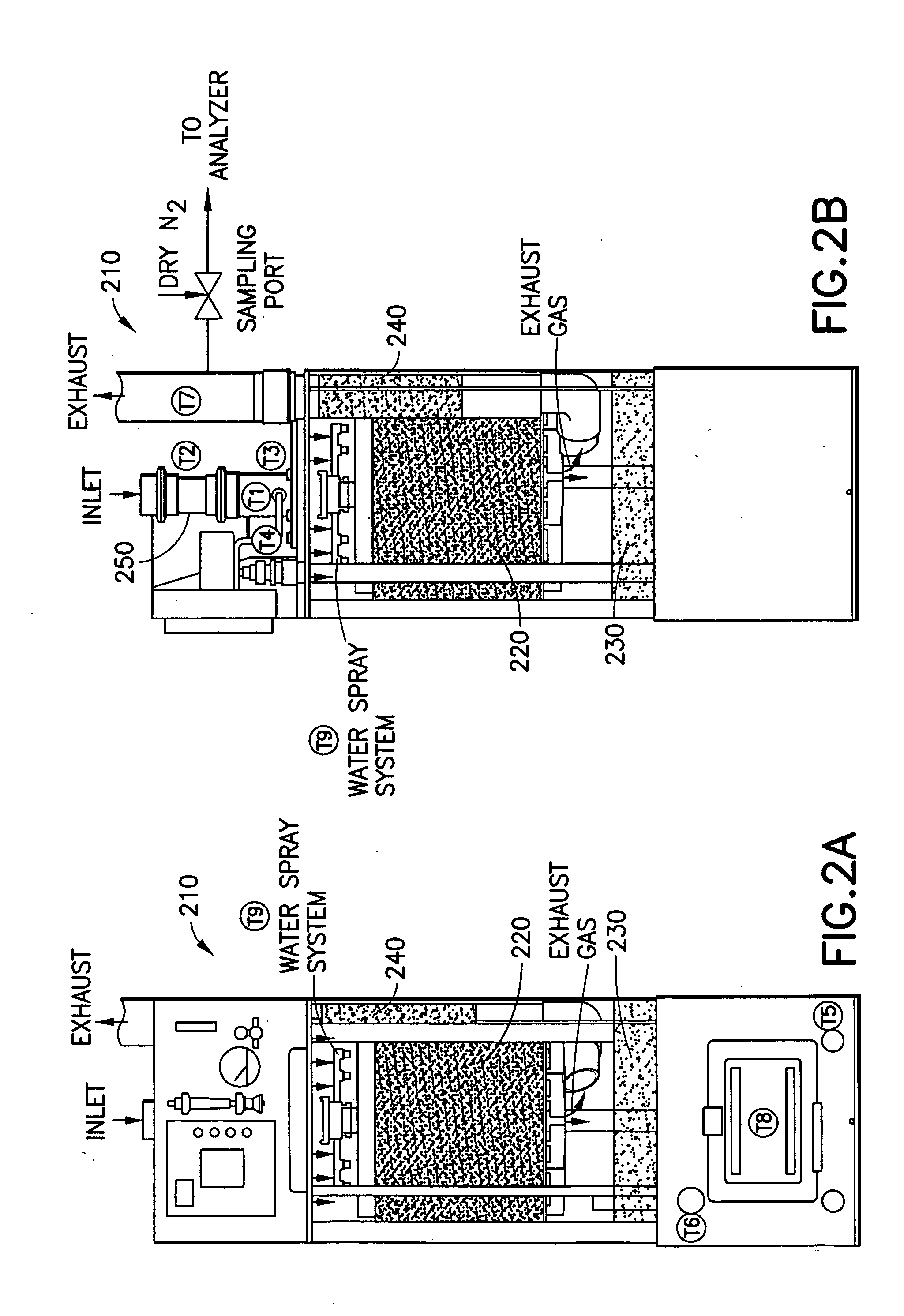
[0171] In a system of the general type shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, abatement of SiF.sub.4 was carried out using an effluent stream simulating effluent produced in a semiconductor manufacturing facility by cleaning of plasma reaction chambers.
[0172] Table 1 below summarizes results for the abatement (destruction and removal efficiency, % DRE) of SiF.sub.4, with and without the injection of caustic. The abatement in this instance did not include the introduction of a reducing agent.
[0173] Fixed concentrations (300 ppm) of silicon tetrafluoride balanced with 120 slpm of nitrogen were introduced into the water scrubber. The experimental conditions were chosen to represent or exceed effluent gas concentrations released during typical plasma chamber cleans. Abatement efficiencies were measured as a function of water flow rates (0.5 and 1 gpm), and scrubber pH (with and without caustic injection). In all cases investigated, measured scrubber outlet concentrations of HF and SiF.sub.4 were sligh...
example 2
[0174] Fluorine gas flow rates ranging between 0.5 to 5 slpm were delivered into a Vector.RTM.-100 water scrubber (ATMI Ecosys Corporation, San Jose, Calif.) that was equipped with a passivated manifold. These streams were diluted with 50 slpm of balanced nitrogen resulting in challenges between 1 and 6% F.sub.2. In addition, the effects of residence time within the scrubber were studied by increasing the nitrogen flow rate to 200 slpm. The performance of the scrubber unit was tested using standard (1.2 gpm) and low (0.75 gpm) water flow rates. Sodium thiosulfate was used during high fluorine gas challenges to improve fluorine gas removal and to eliminate the formation of OF.sub.2 as a by-product.
[0175] Table 2 summarizes the experimental data, and illustrates the enhancement achieved by injection of sodium thiosulfate as a reducing agent.
2TABLE 2 Summary of Fluorine Abatement Results OF2 Water N2 F2 Flow HF Out. F2 Out. Out. Outlet F2 Flow Balance Rate F2 inlet Chem. Conc. Conc. Co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com