Preparation method of aza-carbon-coated cobalt catalyst and unsaturated compound catalytic transfer hydrogenation method based on catalyst
A cobalt catalyst, transfer hydrogenation technology, applied in the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions, expensive precious metals, long reaction time, etc., and achieve fast reaction speed , raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the preparation method is simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
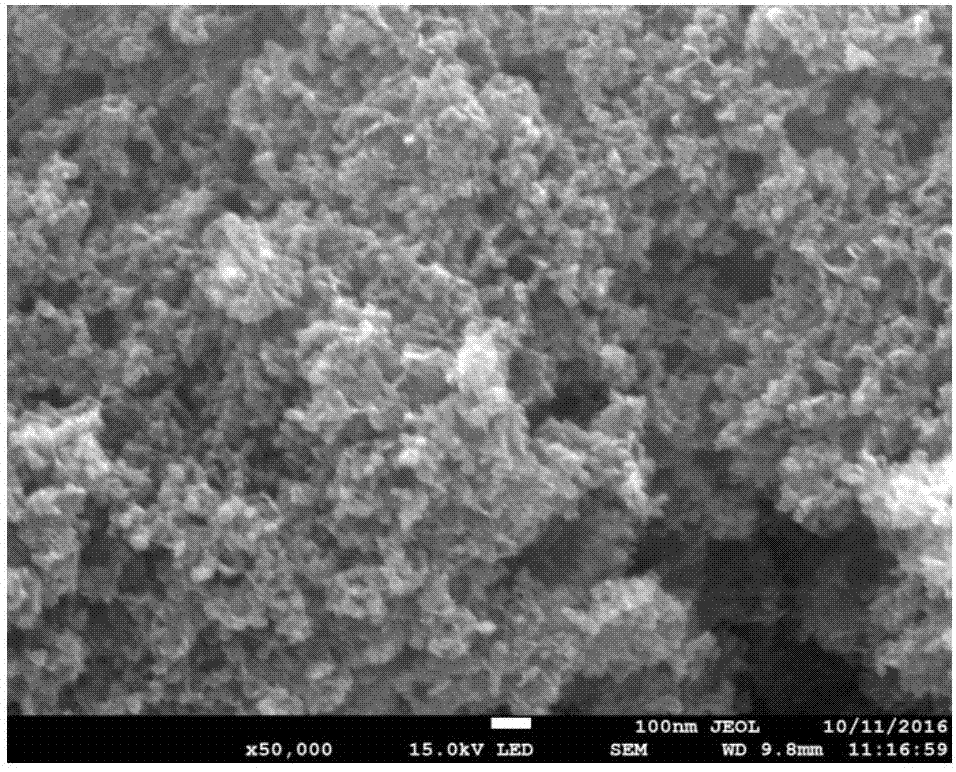
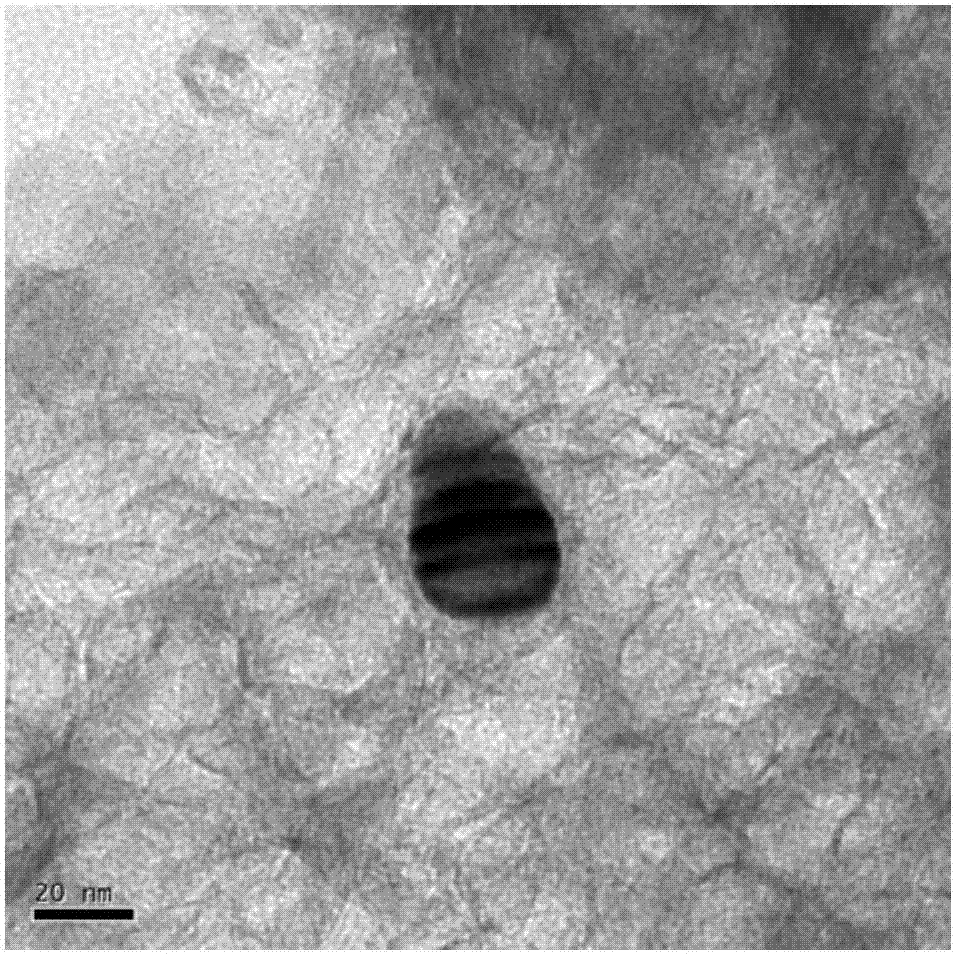
[0028] The preparation method of azacarbon-coated cobalt catalyst comprises the following steps:
[0029] 1) Mixing: Mix carbon source, nitrogen source, cobalt salt and solvent according to the mass ratio of x:(6-x):(1~6):(1~10) and stir evenly, x is 0~6, carbon The source is one or a combination of glucose, sucrose, and fructose, the nitrogen source is one of melamine, dicyandiamide or urea, and the cobalt salt is one of cobalt chloride, cobalt acetate, cobalt nitrate, and cobalt sulfate. Kind, the solvent is deionized water;
[0030] 2) Drying and roasting: After drying the mixed mixture, place it in a vacuum tube furnace and roast in nitrogen. The roasting temperature is 500-800°C, the heating rate is 1-10°C / min, and the roasting time is 1-5h. ;
[0031] 3) Post-treatment: acidify the calcined mixture in dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute nitric acid or dilute phosphoric acid, then separate the solid from the liquid through filtration, wash and dry the solid several times t...
Embodiment 1
[0034] 3.0g glucose, 3.0g melamine, 3.0g cobalt chloride and 4.0g deionized water were mixed and stirred for 10min, transferred to a crucible, and placed in an oven at 80°C for 6h. Place the crucible in a vacuum tube furnace with N 2 As a protective gas, the temperature was raised to 500°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and roasted for 4h. After taking out the sample, soak it with 5% hydrochloric acid solution for 12h. Suction filtration, washing with deionized water, and drying to obtain Co@CN(1:1)-500 catalyst.
[0035] Take 50mg of the above-mentioned Co@CN(1:1)-500 catalyst, 76mg (0.5mmol) of vanillin, 10g of deionized water and 200mg of formic acid in the reactor, then tighten the reactor and fill it with N 2 Exhaust air, check airtightness, and fill with 0.5MPaN 2 For protective gas. Put the reaction kettle into a heater with a set temperature of 180°C, put the thermocouple in place, start stirring, and react for 4 hours. After the set reaction time, stop the reaction. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] 3.0g glucose, 3.0g melamine, 3.0g cobalt chloride and 4.0g deionized water were mixed and stirred for 10min, transferred to a crucible, and placed in an oven at 80°C for 6h. Place the crucible in a vacuum tube furnace with N 2 As a protective gas, the temperature was raised to 600°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and roasted for 4h. After taking out the sample, soak it with 10% hydrochloric acid solution for 12h. Suction filtration, washing with deionized water, and drying to obtain Co@CN(1:1)-600 catalyst.
[0038] According to the experimental procedure of Example 1, Co@CN(1:1)-600 was tested for activity. The experimental results show that the conversion rate of vanillin is 71.1%, and the selectivity of 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol is 100%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com