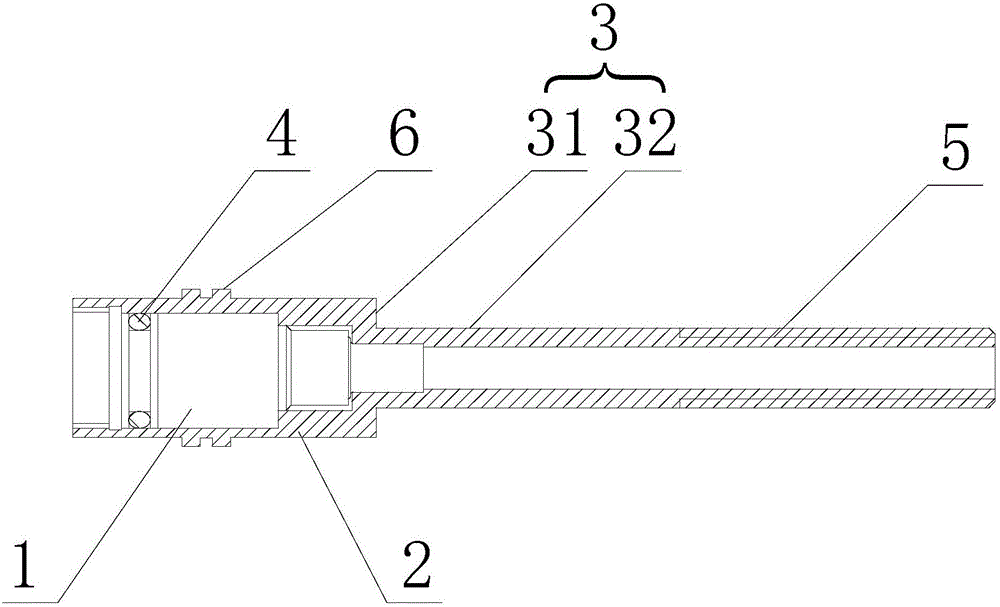
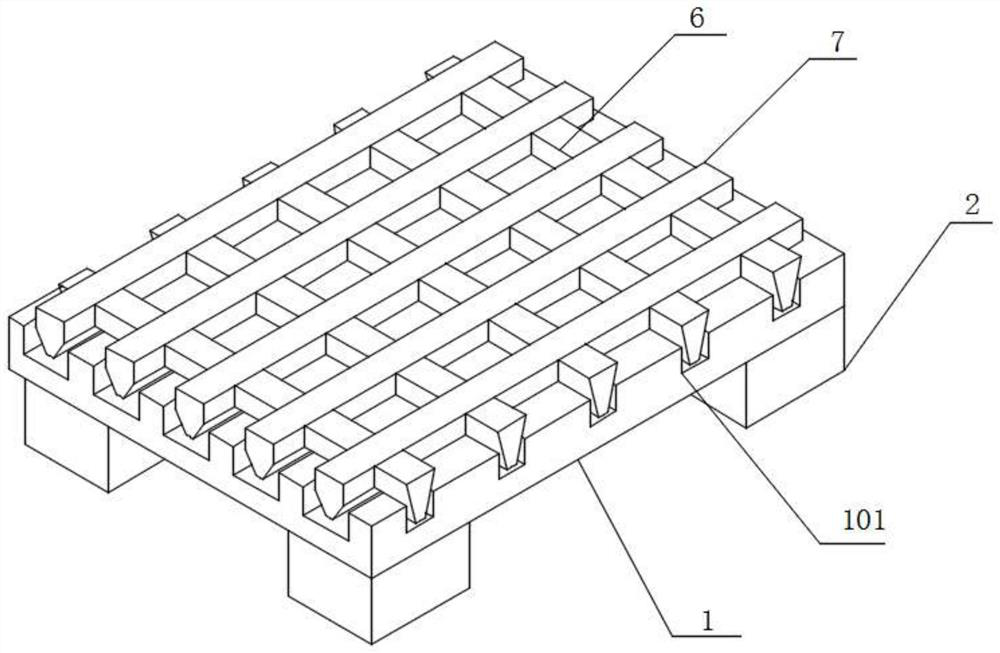
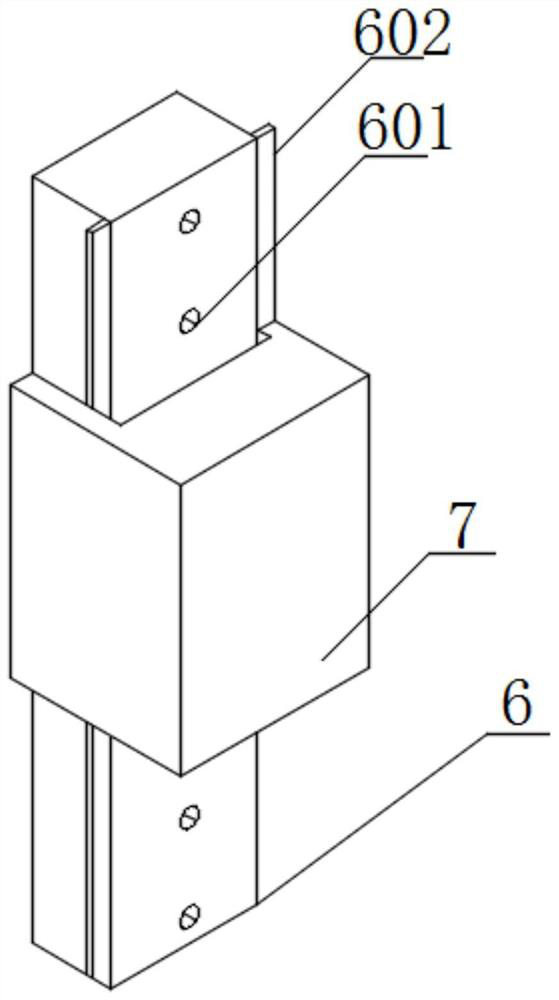
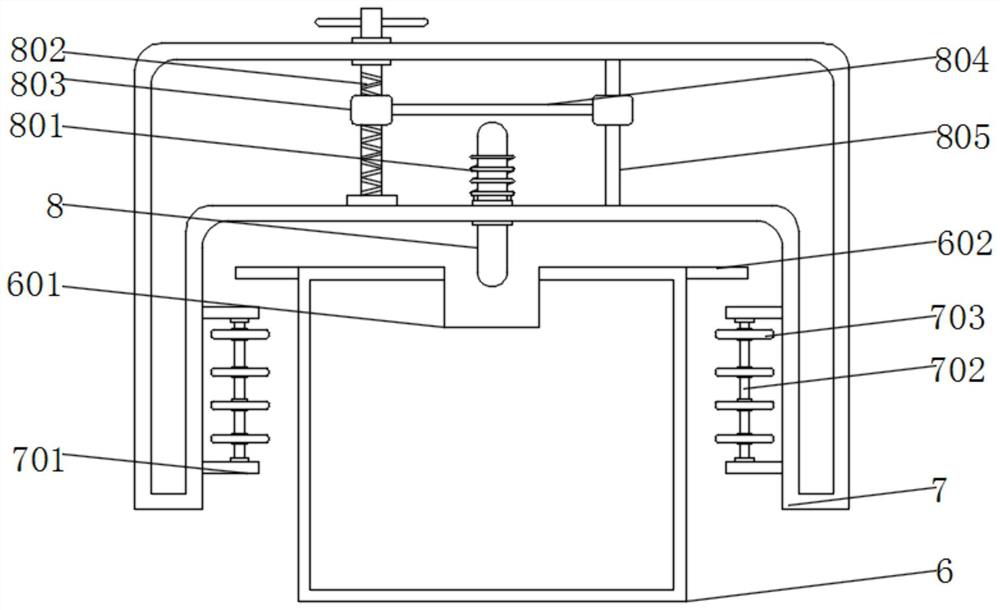
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66results about How to "Realize the connection function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
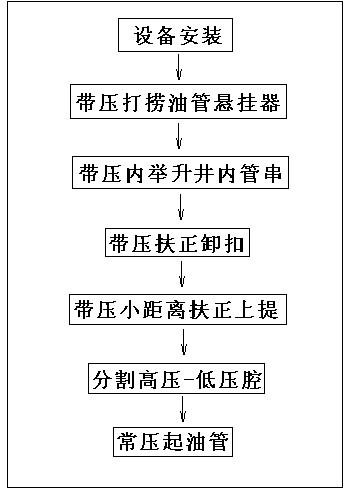
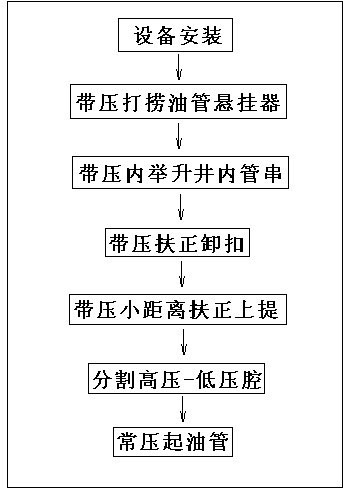
Lifting pressurized well-repairing technology in closed oil pipe
InactiveCN102561975AResolve rule movementSolve safe lifting and lowering operationsDrilling rodsSealing/packingMechanical engineeringPetroleum engineering
The invention relates to a lifting pressurized well-repairing technology in a closed oil pipe. The technology at least comprises the following steps: 1) mounting equipment, namely, mounting a lifting pressurized well-repairing device in the closed oil pipe; 2) fishing an oil pipe hanger under pressure; 3) lifting a pipe strand in the well under pressure; 4) holding a detaching buckle under pressure; 5) holding and lifting for a small distance under pressure; 6) dividing high-pressure and low-pressure chambers; and 7) lifting the oil pipe under normal pressure. According to the technology, a pressurized unplugged oil pipe in an oil-gas well is actively lifted up and pressed down in the high-pressure chamber of the device; the operations of holding the oil pipe in the high-pressure chamber and tools in the well and assembling and disassembling the buckle are performed according to an operation requirement; the separation of the high pressure and low pressure in the chamber is realized; the normal-pressure lifting / drilling operation can be completed by an operator at the well head; and the problem of safety lifting / drilling operation for the unplugged pipe strand in pressurized operation in the oil-gas well is efficiently solved.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD CHANGQING DOWNHOLE TECH CO
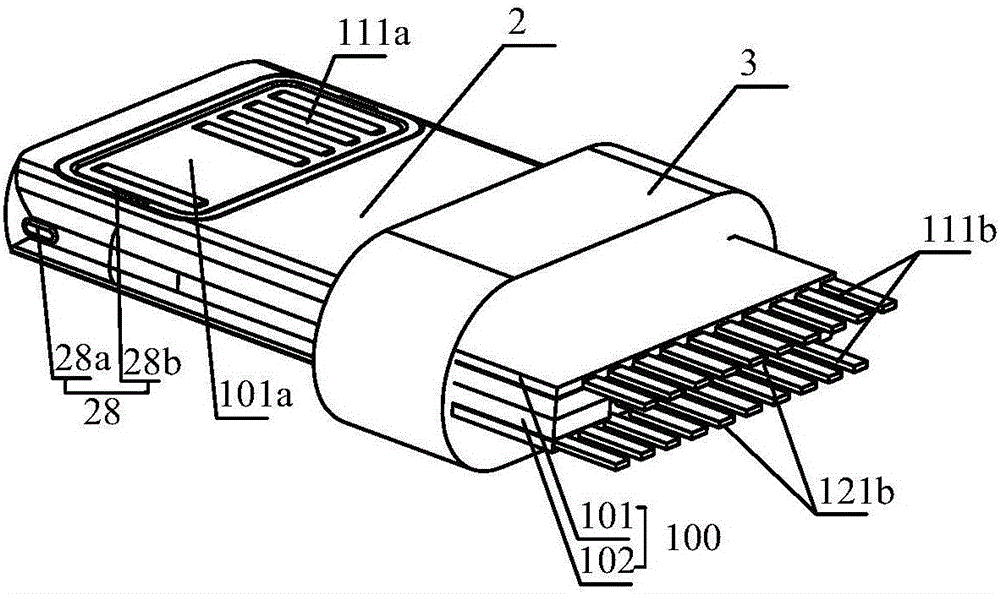
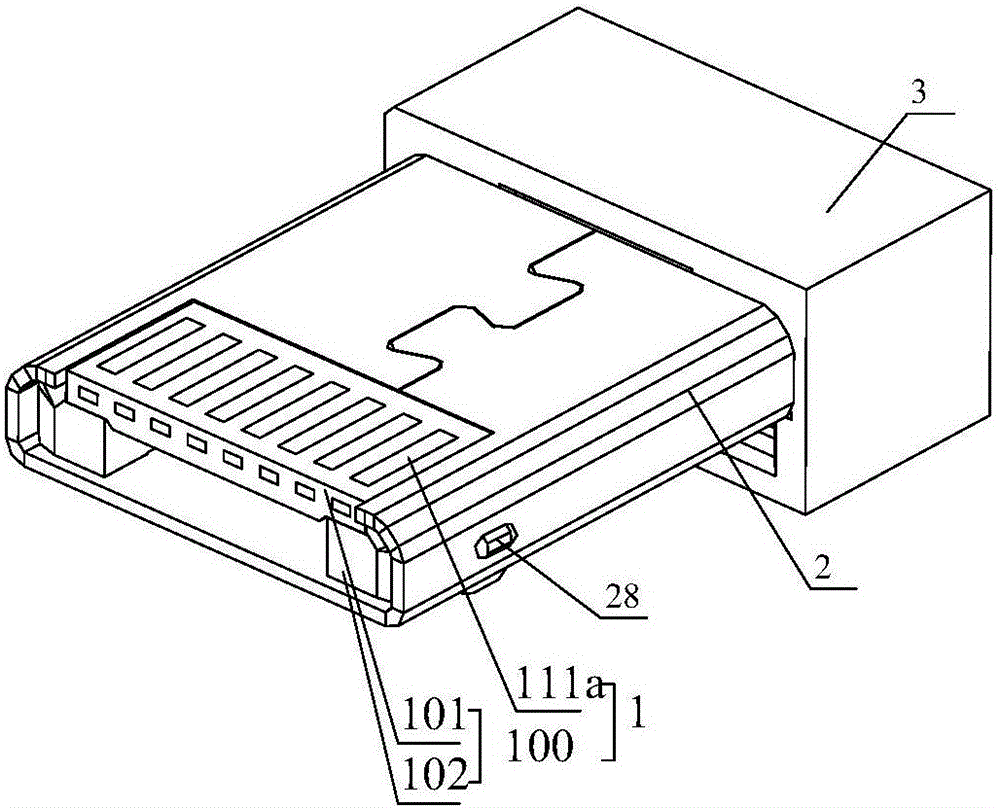
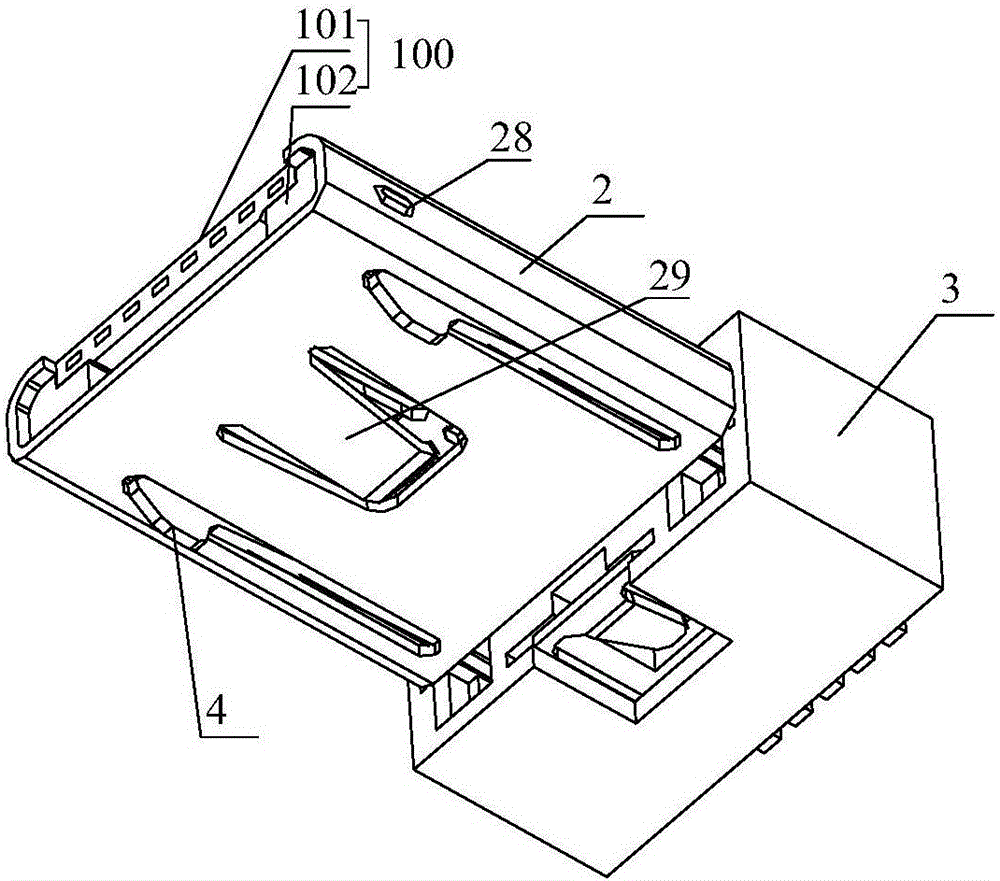
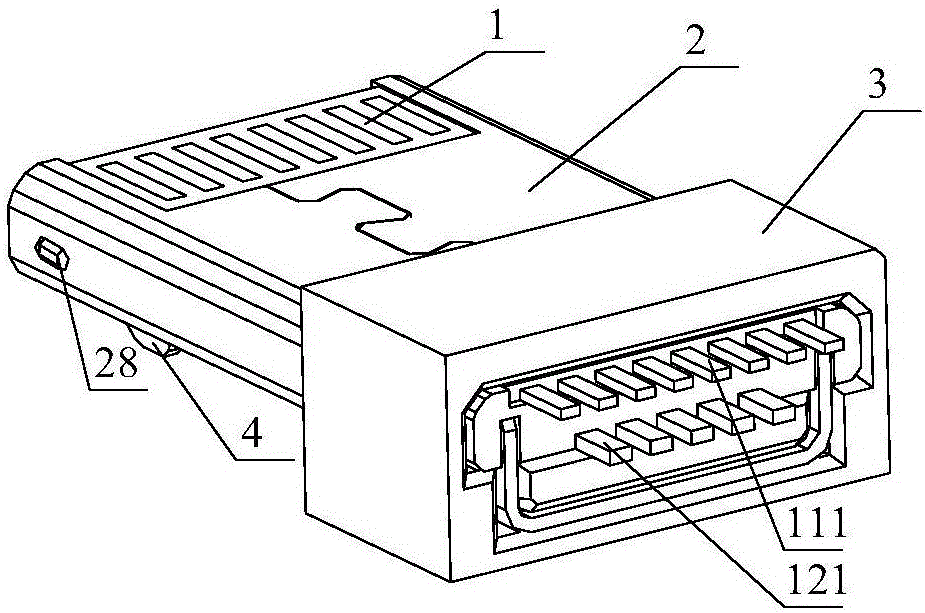
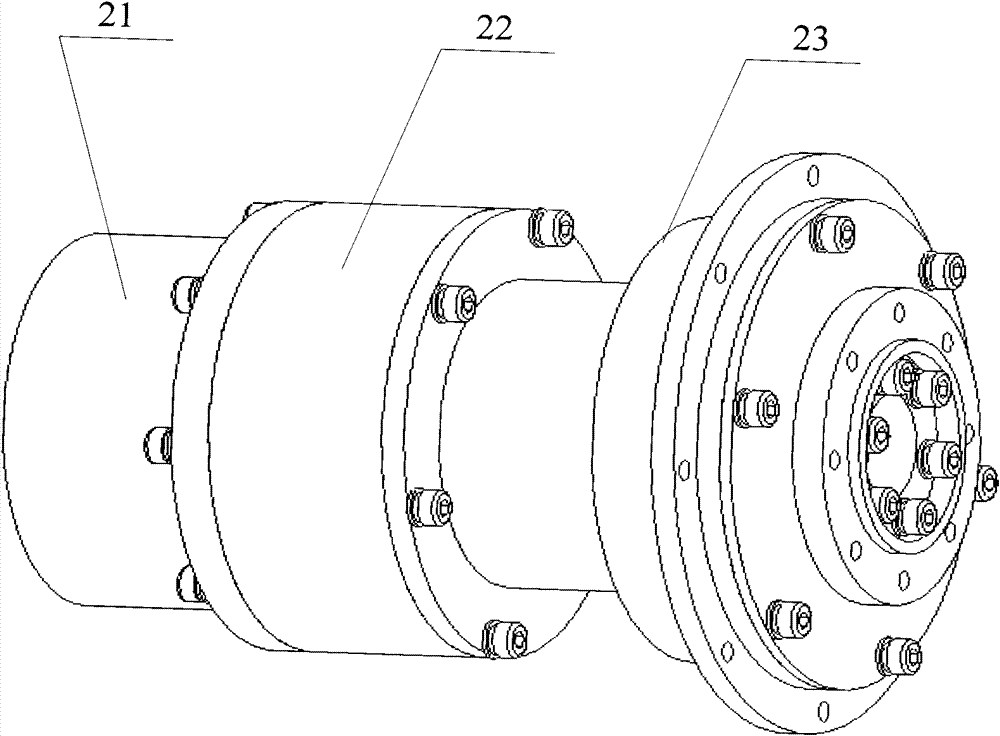
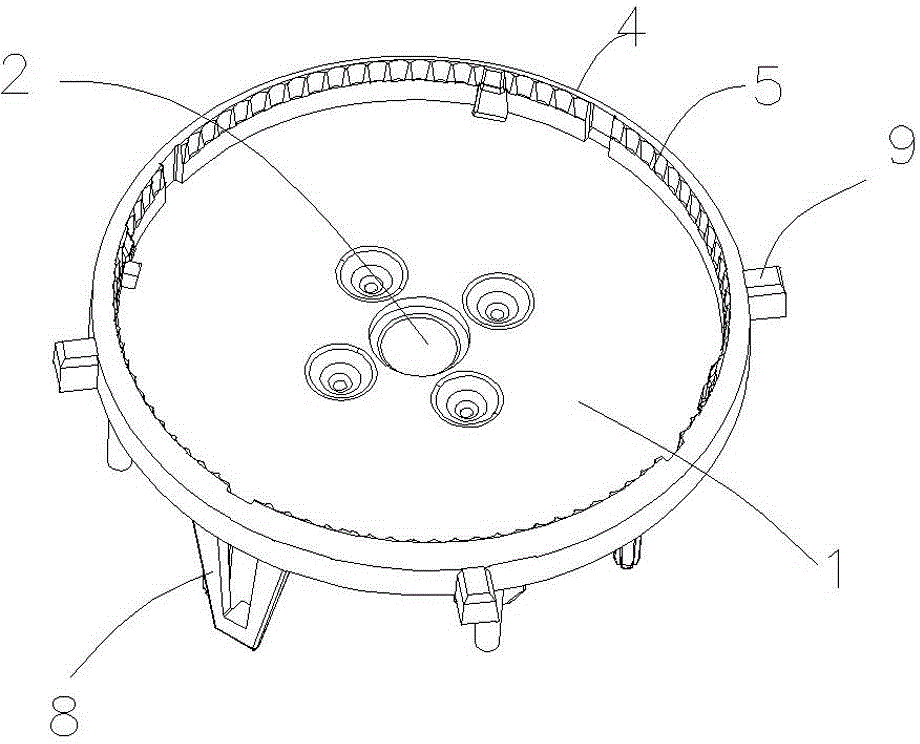
Double-sided dual-purpose forward and reverse plugging connector
ActiveCN105789957AEasy to assembleReduce production processCoupling contact membersEngineeringDual purpose
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPHASE ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Ejection and secondary extrusion device
The invention belongs to the technical field of extrusion forming machines and particularly relates to an ejection and secondary extrusion device for use in combination of a metal extrusion forming machine. The ejection and secondary extrusion device comprises an upper mounting plate and a lower driving plate, wherein the upper mounting plate is provided with an extrusion cylinder which passes through the center of the lower driving plate; the piston rod of the extrusion cylinder is a hollow piston; a secondary extrusion rod with a central through hole is inserted into the hollow piston rod; the hollow piston rod is fixedly connected with the secondary extrusion rod; the upper mounting plate is also provided with a stamping ejection device which comprises an ejection cylinder fixed on the upper mounting plate; the piston rod of the ejection cylinder is fixedly connected with the lower driving plate; and n ejection connecting rod is arranged at the bottom of the driving plate and is connected with an ejection connecting rod for demolding. The ejection and secondary extrusion device can realize secondary supplementation and provide an ejecting force in stamping and demolding effectively, can improve material performance effectively, and is convenient in stamping and demolding, compact in structure and convenient in installation and maintenance.
Owner:山东八零特种电缆有限公司
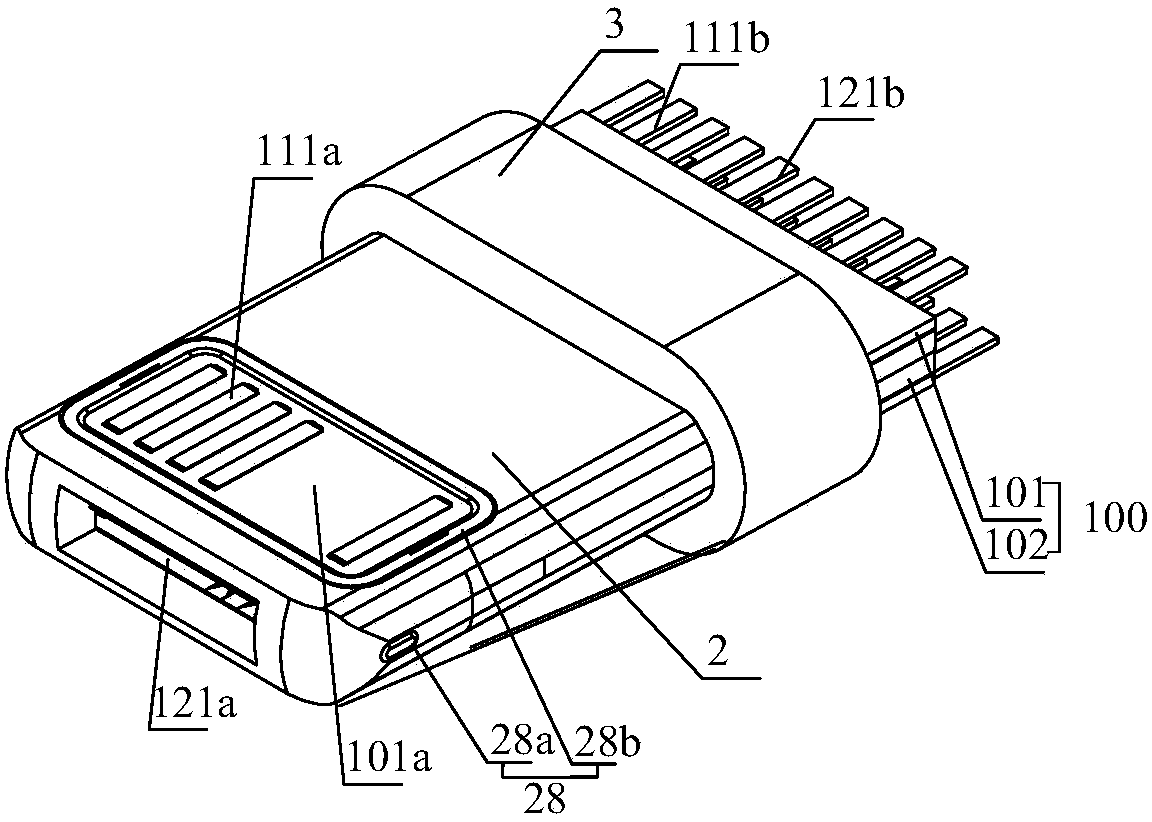
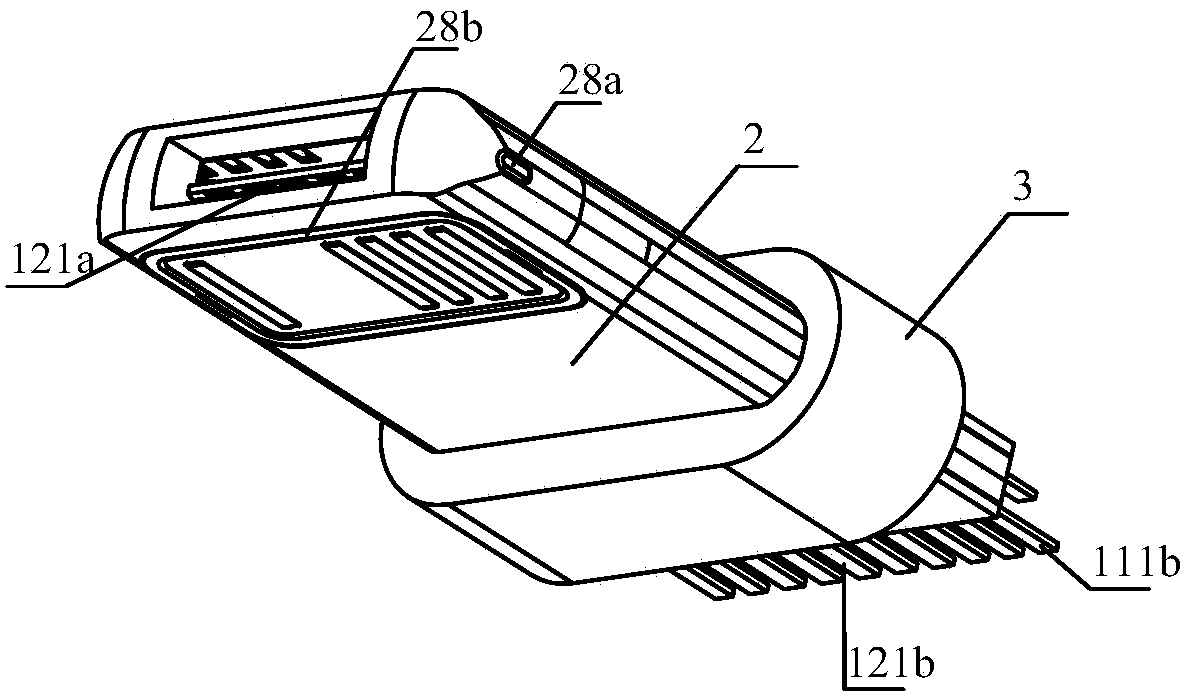
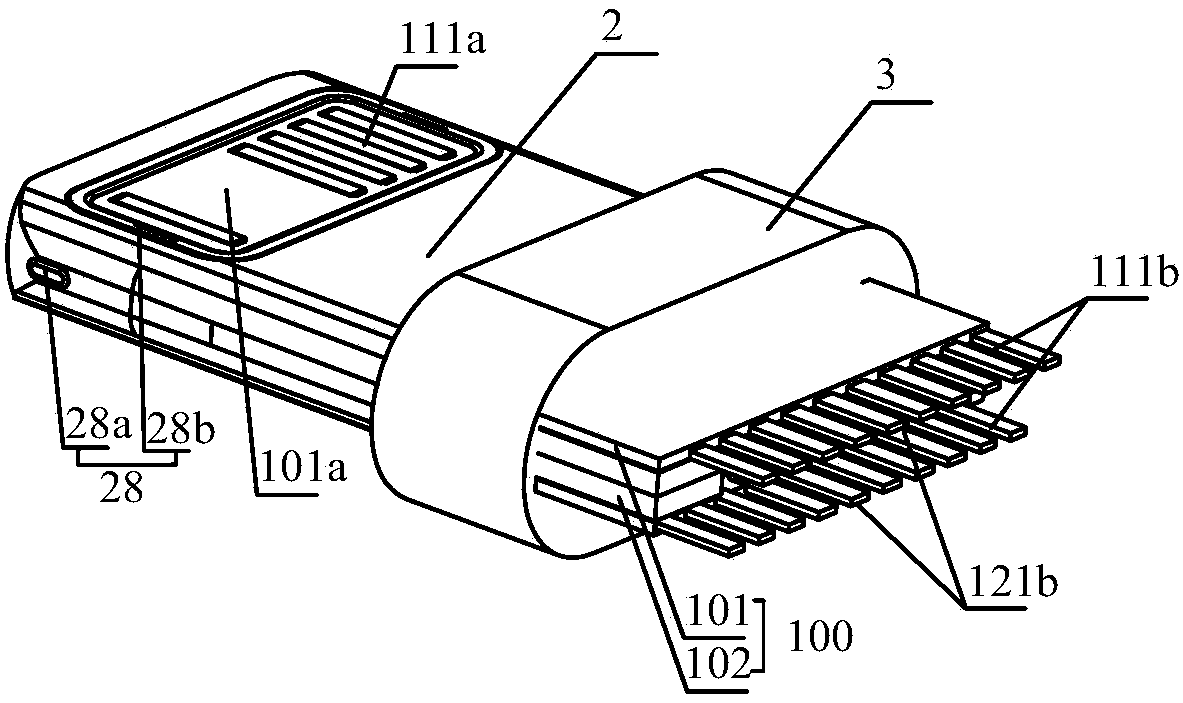
Two-sided connector
InactiveCN105680268AEasy to assembleReduce production processCoupling contact membersTelephony connectorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a two-sided connector, which comprises a terminal assembly, a shell, a rear seat and an elastic buckle, wherein the terminal assembly comprises a die body, and first terminals and second terminals for different data interfaces, and the first terminals and the second terminals are fixed via the die body and isolated; front-end connection parts of the first terminals and the second terminals are located at the front end of the die body; the rear seat is fixed at the rear part of the terminal assembly; rear ends of the first terminals and the second terminals extend outwardly from the rear part of the rear seat; the shell sleeves the terminal assembly for limiting and fixing the terminal assembly; the elastic buckle is inserted in the terminal assembly; the front part of the elastic buckle extends outwardly from the side surfaces of the terminal assembly and the shell; and the elastic buckle is limited and fixed with the rear seat via the terminal assembly. The connector is convenient to use, is compatible with interfaces with two different types of terminals and is directly matched with interfaces of existing various mobile phones.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPHASE ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
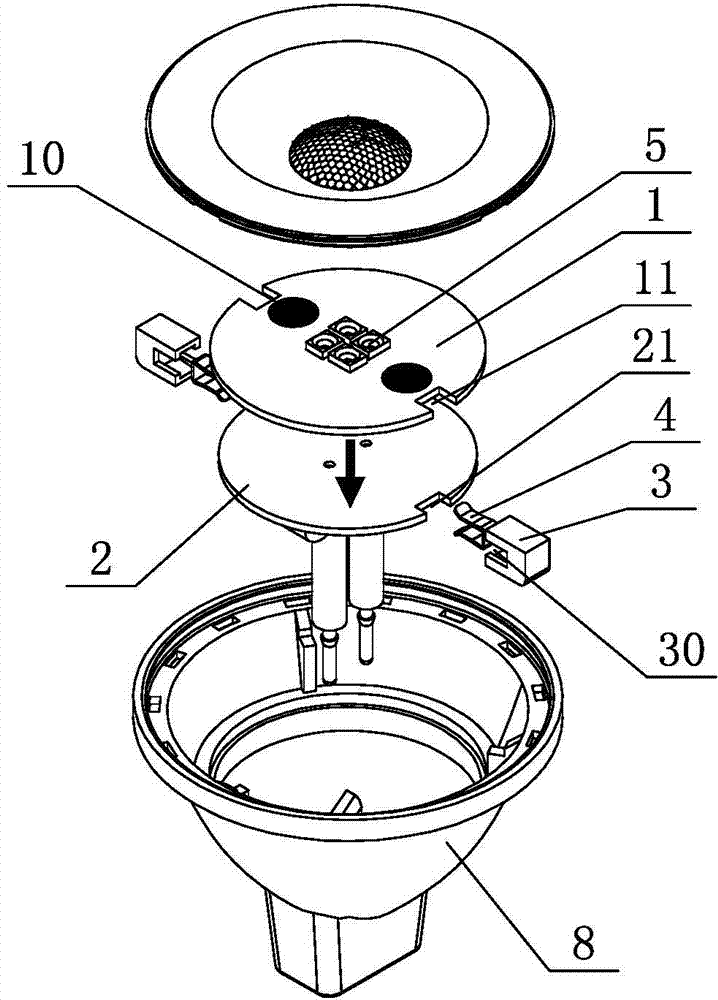
Double-sided substrate for LED (light-emitting diode) lighting and LED lighting device
InactiveCN104848069AEasy to processSimple structurePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsEffect lightEngineering
The invention discloses a double-sided substrate for LED (light-emitting diode) lighting and an LED lighting device which are simple in structure, low in processing cost and high in production efficiency. The lighting device comprises a lamp body (8) and the double-sided substrate. The double-sided substrate comprises a light source substrate (1) on which LEDs (5) are arranged, a power supply substrate (2) on which a driving circuit component is arranged, insulation clips (3) and elastic conductive clamping pieces (4), obverse side edges of the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2) are provided with two circuit junctions respectively which correspond to each other in position, each of the insulation clips (3) is provided with a clamping slot (30), the elastic conductive clamping piece (4) is embedded into the clamping slot (30), the reverse sides of the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2) are jointed together, the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2) are clamped by the insulation clips (3) through the clamping slots (30) at the circuit junctions, the elastic conductive clamping pieces (4) are electrically connected with the circuit junctions of the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2), circuits of the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2) are enabled to be connected, and the LEDs (5) carry out heat dissipation through the light source substrate (1) and the power supply substrate (2). The double-sided substrate for LED lighting and the LED lighting device can be widely applied to the field of LED lighting.
Owner:SMALUX ELECTRICAL MFG
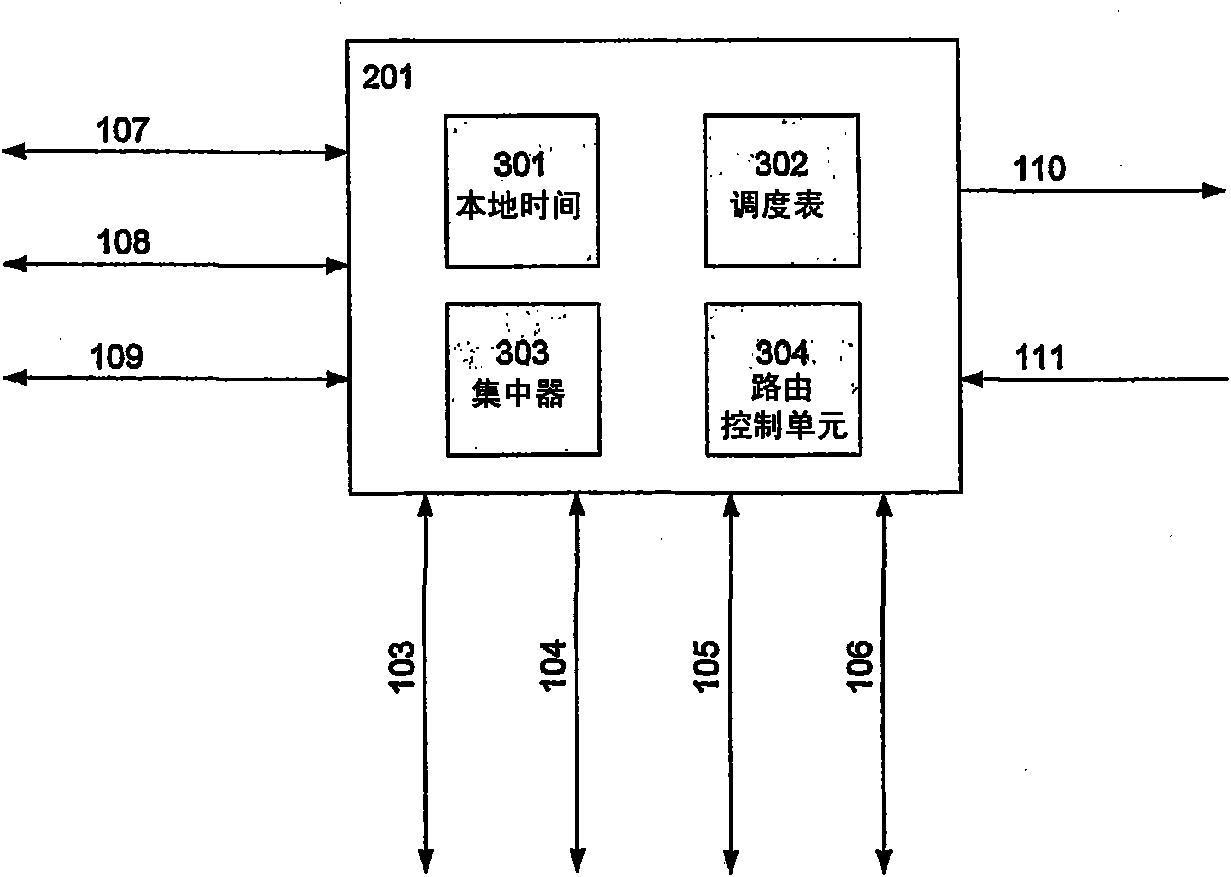
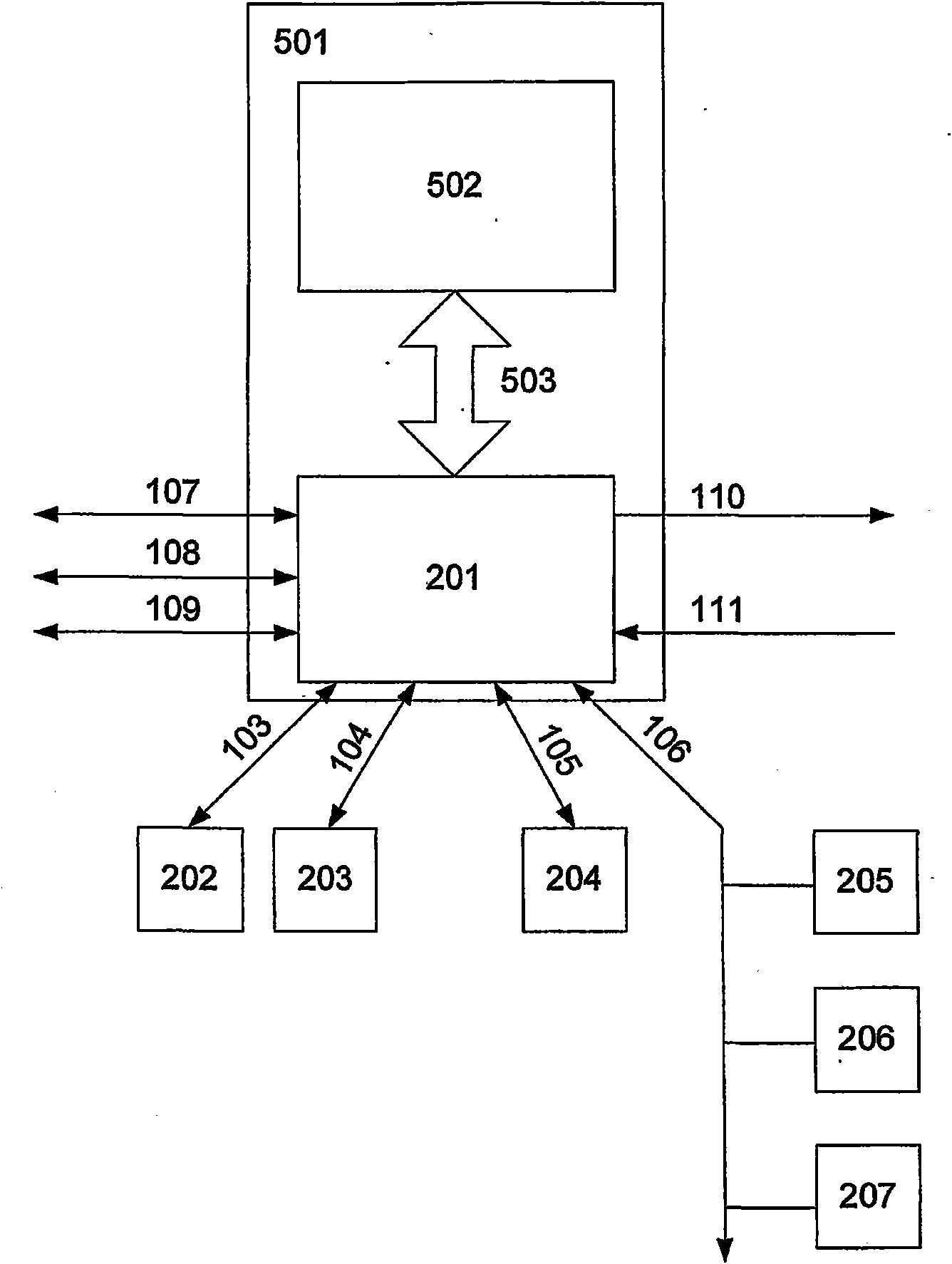
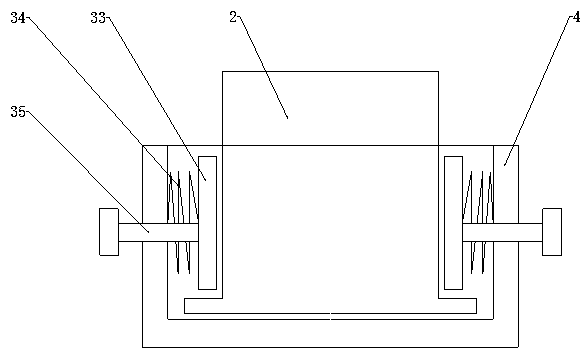
Method for switching from a distributed principle to a master-slave principle in a network
ActiveCN101843048AReduce complexityRealize the connection functionTime-division multiplexStar/tree networksEnd systemDistributed computing
A Method for switching from a distributed principle to a master-slave principle in a network, wherein the network is consisting of a number of end systems (202 - 207), and wherein the end systems (202 - 207) are capable of exchanging information in the form of messages, characterized in that at least one concentrator device (303) is provided in the network and wherein the at least one concentrator device (303) a) is capable of manipulating arbitrary messages of one or more protocol layers received of an end system (202 - 207) before relaying said message, with or without manipulation, to the end systems, and / or b) is capable of generating arbitrary messages of one or more protocol layers, which messages are relayed to the end systems (202 - 207), and wherein the messages relayed by the concentrator device (303) are used in the end systems (202 - 207) for realizing at least one system level function, for example for the synchronization of the local clocks. Furthermore, the invention relates to different devices such as the concentrator device and a network with such a concentrator device.
Owner:TTTECH COMPTECHN
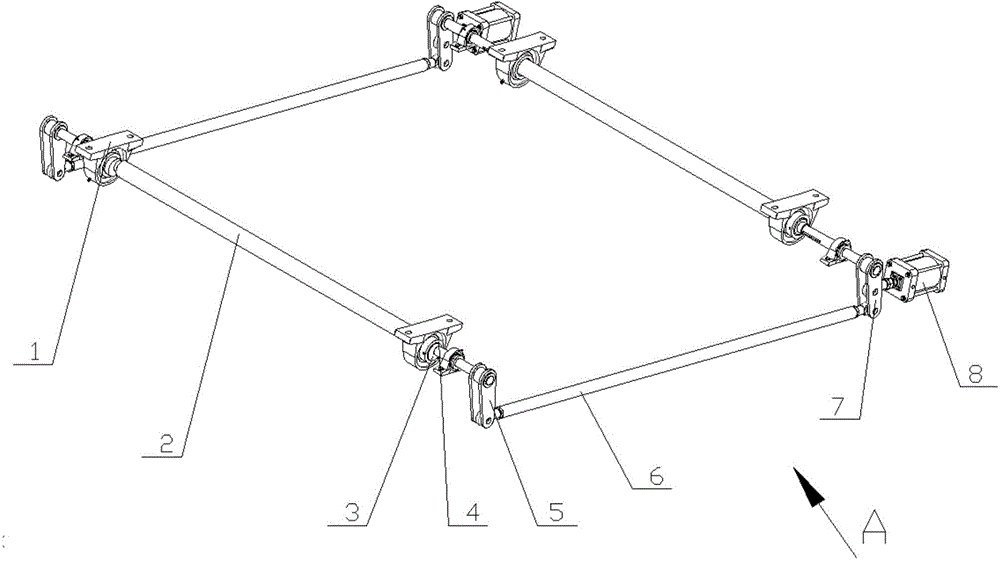
Interstitial cell for bidirectional connection of spatial cell robots
InactiveCN108890635ACompact structureCapable of bidirectional active connectionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSet screwCam
The invention relates to an interstitial cell for bidirectional connection of spatial cell robots. The interstitial cell for bidirectional connection of spatial cell robots consists of a servo motor,an L-shaped plate, a supporting plate, a transmission shaft, a cam, an incomplete bevel gear, a cross-shaped guide track, a sliding block, a guide track strut, a groove bevel gear, cover plates, a setscrew, connecting surfaces and bosses. The servo motor is a source power device of the interstitial cell, the electrifying phase sequence can be changed, and power for connection and disconnection ofcells is provided; the cam is in contact with the surface of the cross-shaped guide track, the sliding block is connected with the guide track strut to form a guide track assembly, the cam rotates, the cross-shaped guide track can be driven to move forwards, and meanwhile, the guide track assembly is driven to move linearly. The guide track strut is always tangential to a sinusoidal groove in thegroove bevel gear, and by rotation of the groove bevel gear, the guide track assembly can be driven to move in the radial direction. Two connecting mechanisms are fixedly connected through the set screw and the supporting plate to form a hexahedron structure of the interstitial cell. The connecting surfaces are connected with the cover plates through the bosses so as to jointly form a connectingsurface mechanism of the interstitial cell.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bracket for trailer based on industrial machinery
InactiveCN108819629ARealize the connection functionRealize the shock absorption functionTowing devicesEngineering
The invention provides a bracket for a trailer based on industrial machinery, which comprises a first fixing block, a first fixing frame, a clamping mechanism, a second fixing frame, a second fixing block, a groove, first springs, moving plates, clamping plates, second springs and a pull bolt, wherein the second fixing frame is welded at the left end of the second fixing block, the upper end faceof the second fixing frame is provided with a groove, the first fixing frame is arranged in the groove, the first fixing frame is welded on the right end of the first fixing block, the first springs are respectively arranged at the left end face and right end face of the groove, the moving plates are arranged on the inner side of the first springs, the second springs are respectively arranged on the front end face and rear end face of the groove, the clamping plates are all arranged in the second springs, the pull bolt penetrates through the front end face and rear end face of the fixing framerespectively, the design archives the connection of the trailer and a traction device and the function of damping, the device is convenient to use and convenient to operate, the clamping effect is perfect, the device has the damping function and high reliability.
Owner:王秀丽
Self-adaptive intelligent material moving device of laser cutting machine
InactiveCN114850696ADischarge in timeDoes not affect material transferLaser beam welding apparatusEngineeringLaser cutting
The invention relates to the technical field of laser cutting, in particular to a self-adaptive intelligent material moving device of a laser cutting machine, which comprises a base, a shell, a blanking device, a cutting device, a collecting mechanism and a sliding table, the placing assembly is arranged on the sliding table; the multiple bearing rods are sequentially arranged on the sliding table in the length direction of the sliding table in a sliding mode, and the through grooves are formed in the bearing rods in the length direction of the bearing rods in a penetrating mode. The multiple supporting pieces are evenly arranged on the upper portion of the bearing rod in the length direction of the bearing rod. The rotating shaft is rotatably arranged in the through groove along the axis of the through groove; the two rollers are respectively arranged at two ends of the rotating shaft along the axis of the rotating shaft; the connecting assembly is arranged on the roller; the driving assembly is arranged on one side of the rolling wheel and drives the rolling wheel to rotate through the connecting assembly. According to the laser cutting machine, by arranging the discharging device, it is guaranteed that cut finished products can be discharged in time, and therefore the influence on the laser cutting machine is reduced.
Owner:南通秋祥信息科技有限公司
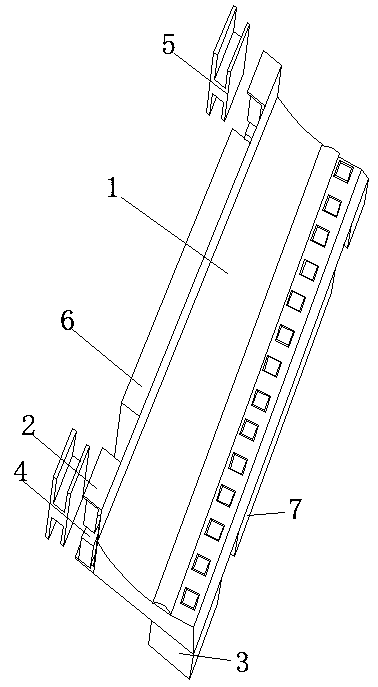
Novel corner fitting and connecting structure thereof
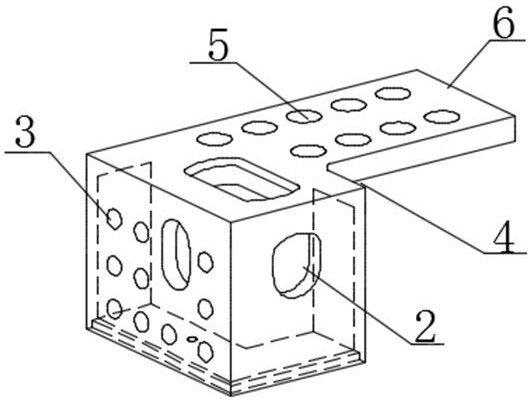
The invention discloses a novel corner fitting which comprises a corner fitting body. A flange plate extending outwards along the edge of the body is arranged on at least one side of the corner fitting body. The invention discloses a connecting structure of the novel corner fitting. The flange plate is arranged on one side of the corner fitting, the flange plate is used for enhancing the strengthof the corner fitting, and mounting holes can be formed in the flange plate, so that the corner fitting is conveniently connected with a connecting body; and the corner fitting is provided with secondmounting holes, and the corner fitting can realize a connecting function and can also realize a hoisting function.
Owner:张跃
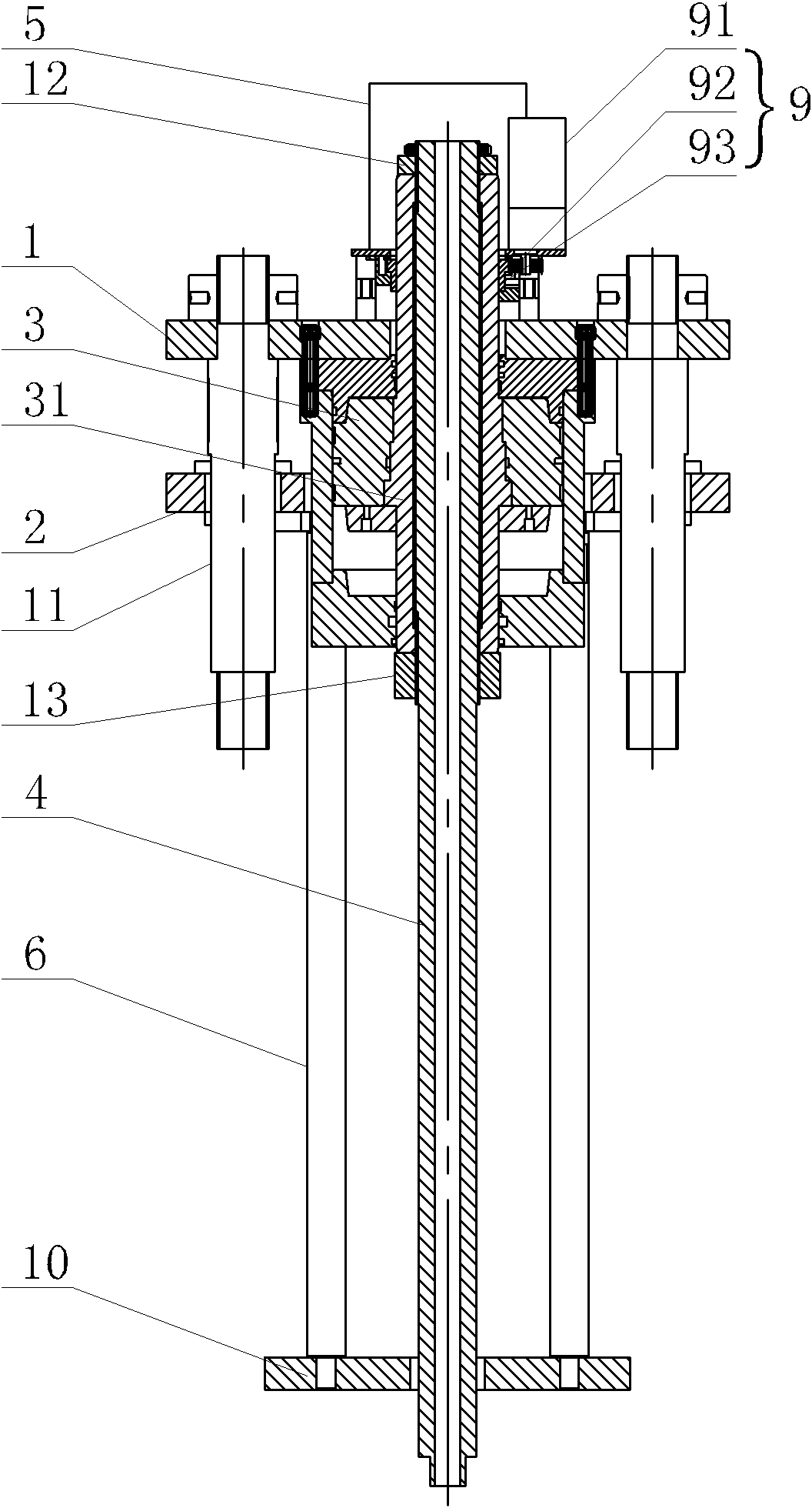
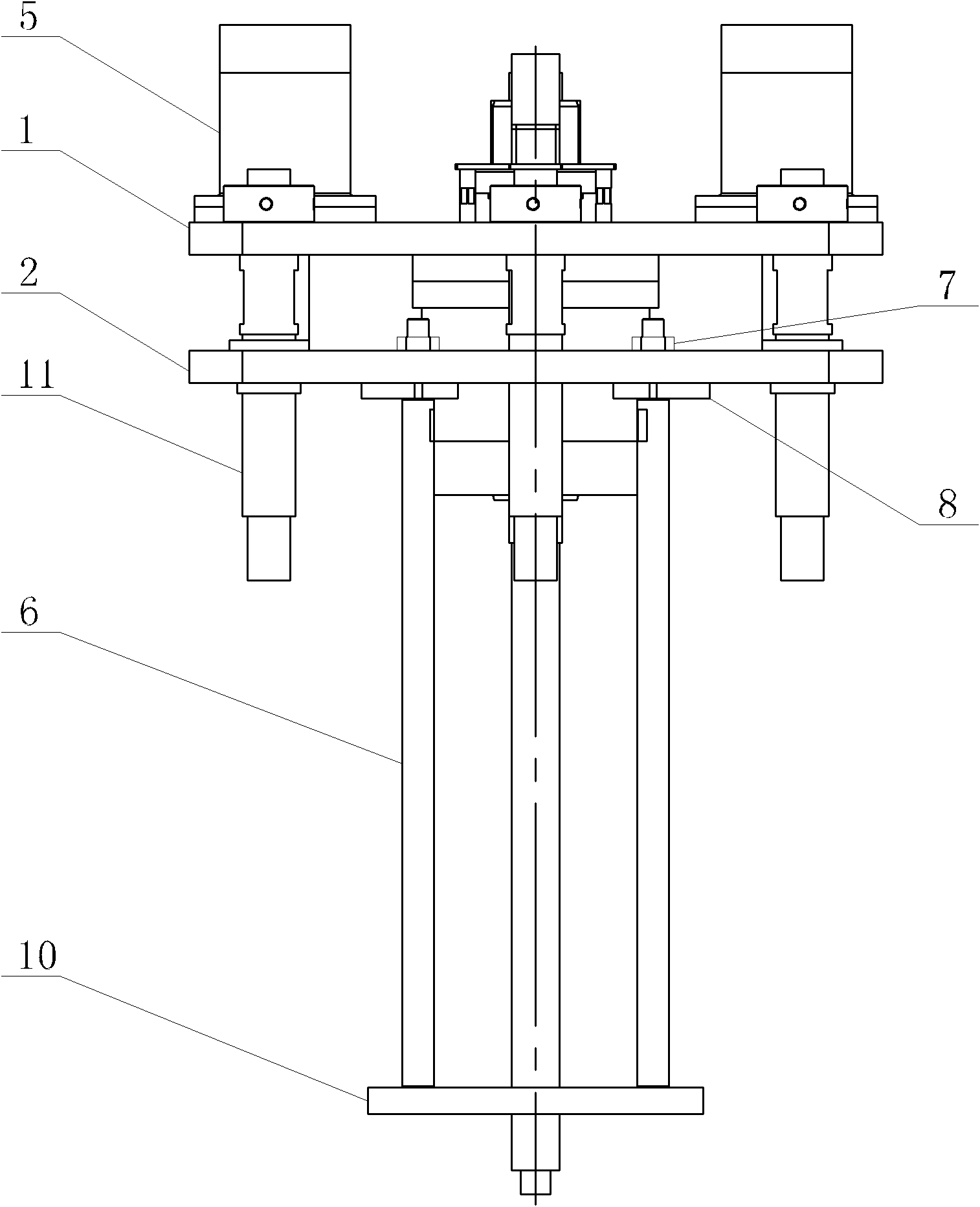
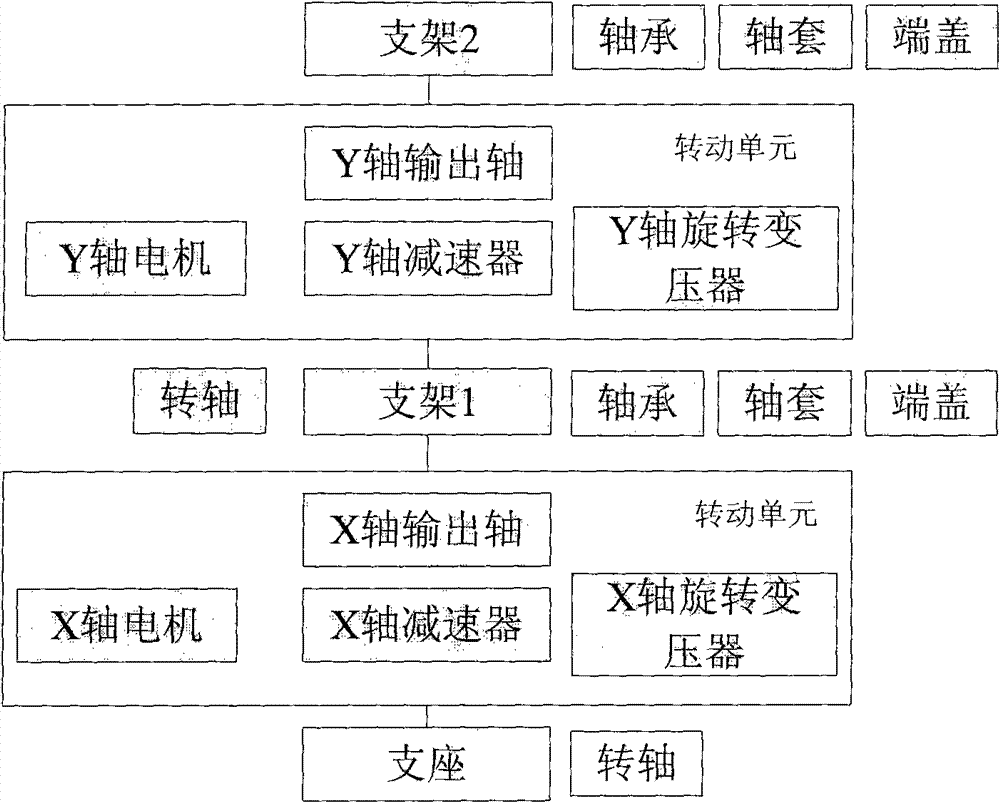
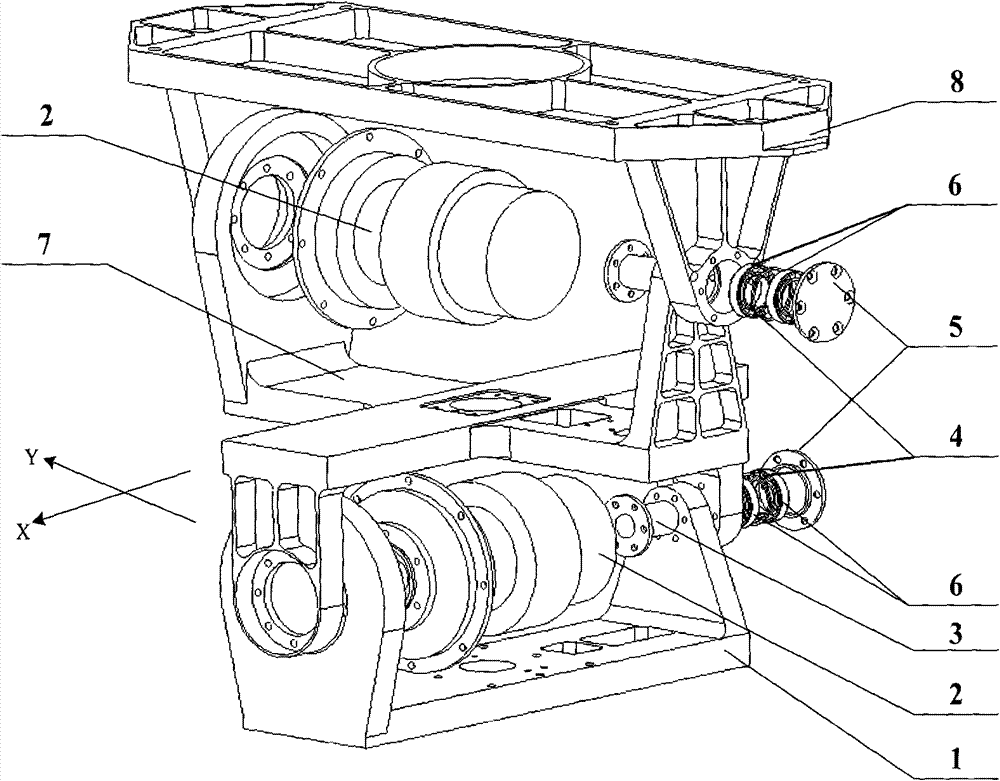
Rotating mechanism for spatial two-dimensional antenna
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
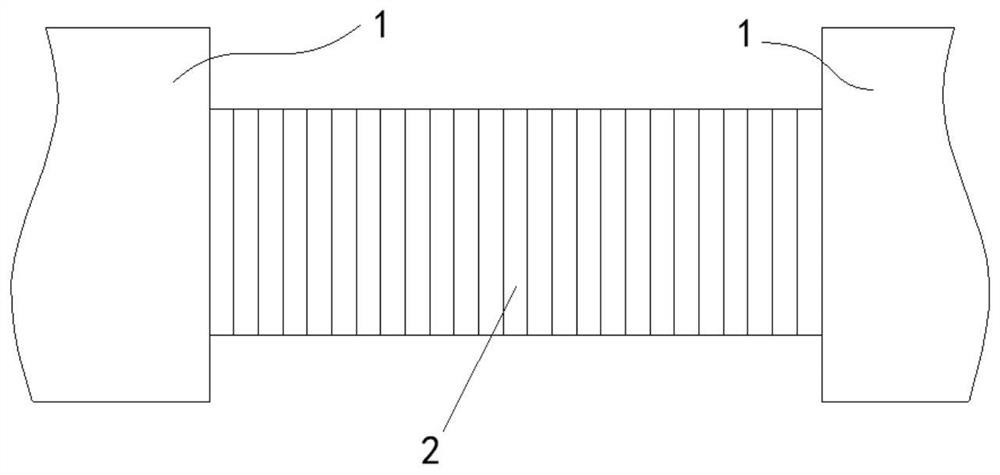
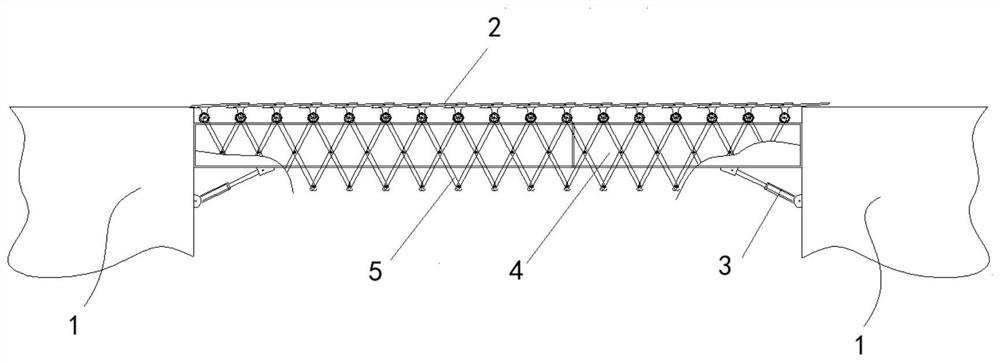
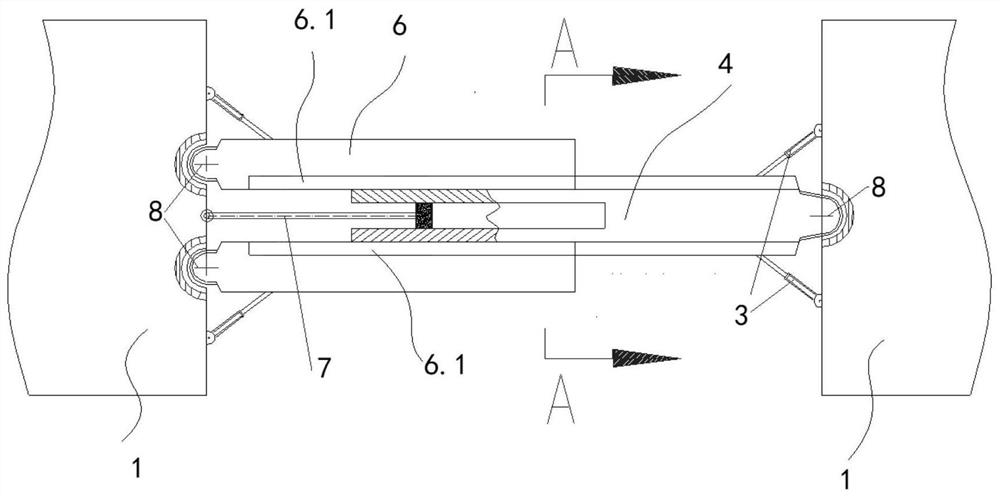
Flexible connecting bridge between large floating bodies capable of restraining motion
PendingCN113430911AInhibition of motor responseEasy to transportFloating bridgesOpen seaClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a flexible connecting bridge between large floating bodies capable of restraining motion. The flexible connecting bridge comprises a force bearing beam rotatably connected between floating bodies (1); a flexible folding blade (2) arranged above the force bearing beam; an equidistant displacement device (5) which is connected between the two floating bodies (1) and connected with rolling bodies (9) in an associated mode, wherein the blades are driven to move on a main beam (6) and a telescopic beam (4) at equal intervals to achieve bridge floor leveling; an axial motion damper (7) which is axially mounted between the main beam (6) and the telescopic beam (4); and rotary dampers (3) which are obliquely supported between the beams and the floating bodies (1) at the ends where the beams are located. The motion response between the floating bodies can be effectively improved, the working environment grade is improved, and compared with the current integral large floating body which is generally not higher than 5-grade sea conditions, the sea condition adaptation grade of open sea deployment can be improved to 6-grade or above after the floating bodies are adopted. And the flexible connecting bridge can also be used for flexible connection between medium-sized or conventional floating bodies.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
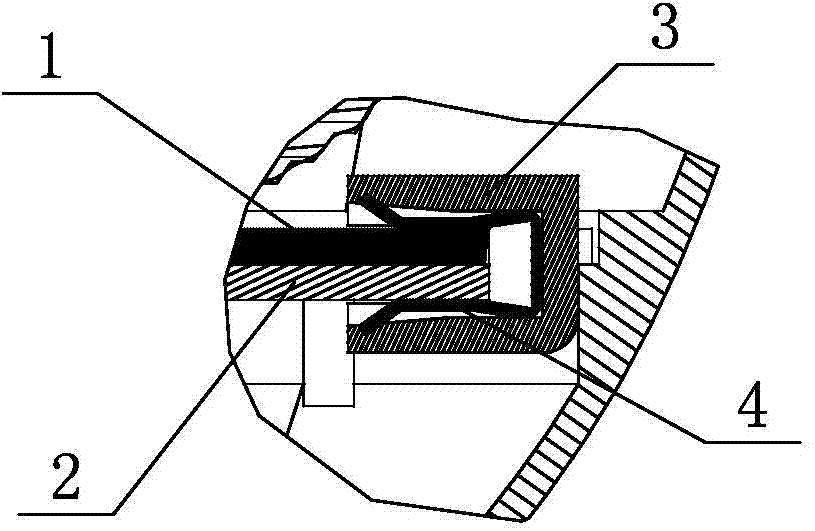
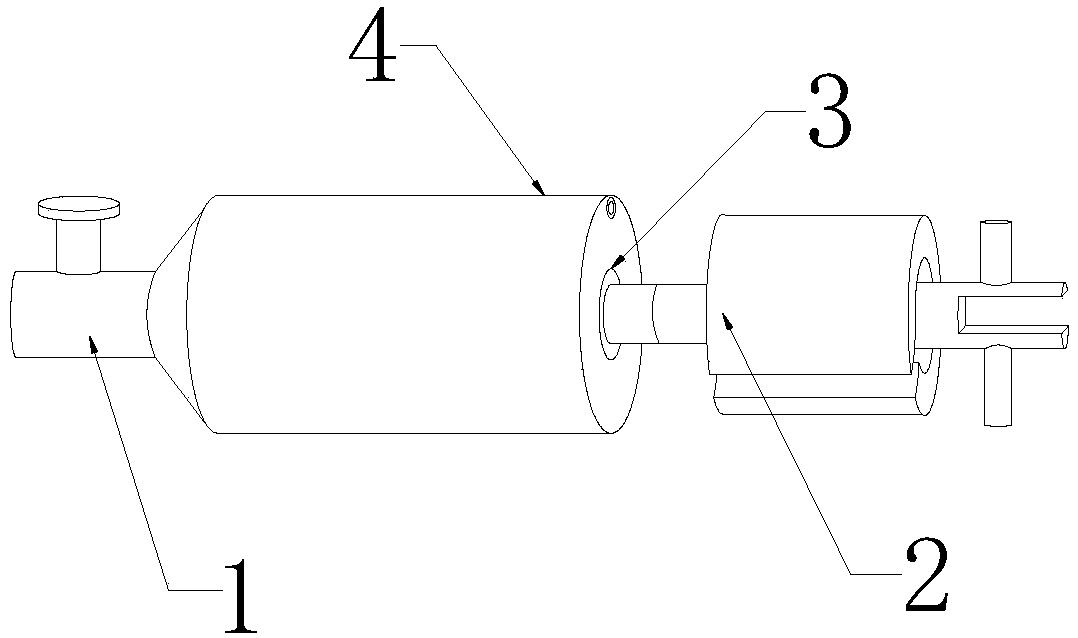
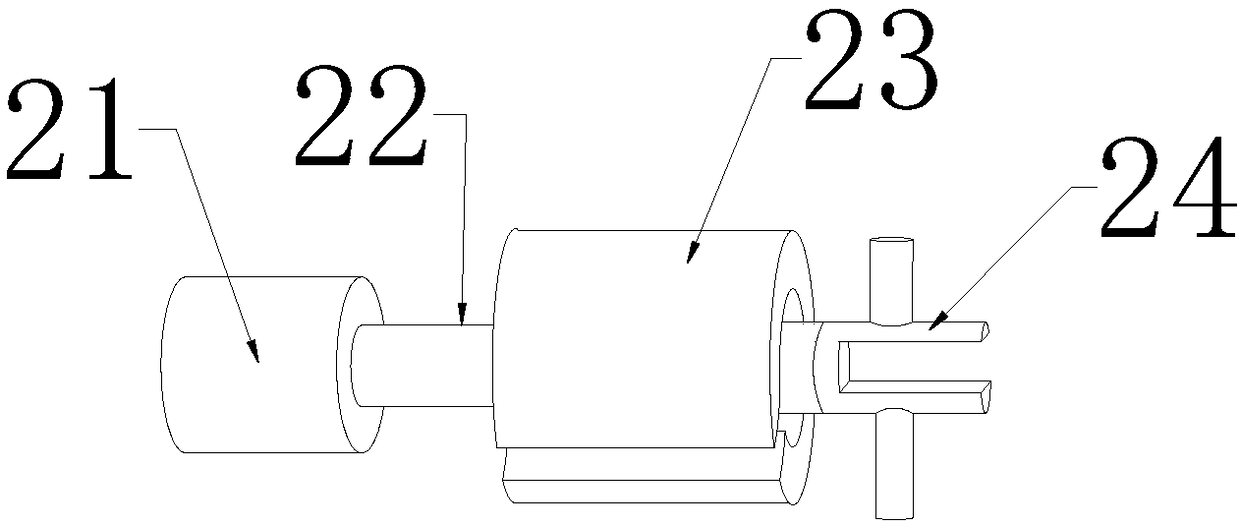
Sealed connecting rod for guiding
ActiveCN105870707ARealize the connection functionGuaranteed to workSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersCouplings bases/casesElectrical and Electronics engineeringContact element
The invention relates to a sealed connecting rod for guiding. The connecting rod comprises a high frequency contact element and a hollow rod body, a movable guiding structure is arranged on the outer side wall of the rod body, a sealing ring is connected to the high frequency contact element in the radial direction, a connecting segment is arranged at one end of the rod body, and a protruding edge is arranged at the other end of the rod body. The connecting rod has the advantages that the connecting segment and the protruding edge arranged on the rod body are connected with a sealing layer and a sealing layer of an electric coupler respectively, limited fixation of the sealing layer of the electric coupler is achieved through the movable guiding structure, the function of connecting the rod body with the electric coupler is achieved, a movable layer of the electric coupler can move leftward and rightward along the track of the movable guiding structure in the movement process through the movable guiding structure on the rod body, normal work of the movable layer is guaranteed, the guiding function of the rod body and the electric coupler is achieved, and the high frequency contact element with the sealing ring is mounted in the rod body, so that the sealing function of the rod body is achieved through sealing performance of the sealing ring.
Owner:杭州航天电子技术有限公司
Pickling galvanized grid hanging tool with anti-falling protection function
InactiveCN114525515ARealize the connection functionEasy to moveElectrolysis componentsAdhesiveGear wheel
The pickling galvanized grid hanger comprises a bottom plate, a mounting block, a storage cavity, a vertical plate and a transverse plate, the mounting block is mounted at the bottom of the bottom plate, the storage cavity is mounted on the inner wall of the mounting block, a first gear is mounted on the inner wall of an open hole through a rotating shaft, and a second gear is mounted on the inner wall of the open hole through a rotating shaft. A detection rod is installed on the inner top wall of the bottom plate in a penetrating mode, and a limiting rod is installed on the inner wall of the transverse plate in a penetrating mode. An external connecting rod is firstly inserted into an open hole, then an inserting rod is inserted into an inserting groove under the driving of a first spring, the connecting rod is fixed, a second shaft rotates to enable a cable to contract, the cable contracts to drive a sealing plate to move upwards, the sealing plate extrudes an adhesive, then the adhesive enters a one-way valve of a liquid outlet pipe, and the liquid outlet pipe is connected with the liquid outlet pipe. And an adhesive impacts an extrusion plate, the extrusion plate moves to drive a second spring to contract, so that the adhesive flows out of a liquid outlet pipe, the connecting rod is bonded to the interior of an open hole, and the connecting function and automatic connection are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI YILANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Four-connecting-rod lifting system applied to roll gang
InactiveCN104787570ARealize the connection functionEasy to assembleConveyor partsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a four-connecting-rod lifting system applied to a roll gang. A four-connecting-rod system is formed by shafts and connecting rods. Eccentric wheels installed on the shafts play a role in enabling components needing to move to ascend and descend. According to the four-connecting-rod lifting system applied to the roll gang, the ascending and descending functions of the movable components are achieved through the eccentric wheels, the inner diameter parts and the outer diameter parts of the eccentric wheels are assembled with bearing blocks and the shafts, and meanwhile clamping points do not occur in the ascending and descending process. Assembling is easy, the connecting function of two components can be achieved, and meanwhile the movable components can ascend and descend in a flatness mode. Moving feasibility of the system can be guaranteed through the main shafts provided with the eccentric wheels, and meanwhile the load of the movable components can be borne.
Owner:CHINA TRIUMPH INT ENG
Wire pulling apparatus used for intelligent building installation engineering
InactiveCN108183429AImplement fixed functionPrevent loosening and fallingApparatus for laying cablesTransverse planeArchitectural engineering
The invention provides a wire pulling apparatus used for intelligent building installation engineering. The wire pulling apparatus comprises a lower half ring, an upper half ring, a bolt, a motor, a driving rod, a clamp ring and a turning rod. The lower half ring is arranged on the lower transverse plane in a hollow cylinder. The upper half ring is welded to the lower transverse plane of the bolt.The bolt is arranged above the hollow cylinder. Through the above design, the apparatus has a function of fixing a steel wire, is easy to operate, is high in fastening strength, and prevents the steel wire from loosening and falling. The motor is assembled in the hollow cylinder, the driving rod is arranged on the motor and passes through a circular hole, the clamp ring is assembled in the middleof the driving rod, and the turning rod is welded to the right transverse plane of the driving rod. The design enables the apparatus to have a wire joint function, the joint speed is fast, a way of twisting the steel wire and pulling a wire manually is changed, and the work efficiency is improved. The apparatus is reasonable in structure, wide in application range, high in practicability, good instability and high in reliability.
Owner:刘婷婷
Easily-installed ceiling line for decoration
InactiveCN109098398ARealize buffer adjustmentImprove tightnessBuilding constructionsVertical planeEngineering
The invention discloses an easily-installed ceiling line for decoration, and belongs to the technical field of sectional materials. The easily-installed ceiling line for the decoration comprises a plate body. The top plate face of the plate body is connected with two first installing plates distributed symmetrically, and one side, away from of the plate body, of the first installing plates is parallel to a horizontal plane. The back plate face of the plate body is connected with two second installing plates distributed symmetrically, and one side, away from the plate body, of the second installing plates is parallel to a vertical plane. The first installing plates and the second installing plates are provided with H-shaped limiting grooves, and H-shaped limiting blocks are locked and connected in the H-shaped limiting grooves. The easily-installed ceiling line for the decoration is capable of realizing convenient installing and detaching functions, and guaranteeing tightness and stability of connection.
Owner:湖州天辛环保科技有限公司
Power takeoff assembly and application
ActiveCN112178067AReduce loadAvoid starting difficultiesGearing controlInterengaging clutchesAutomotive engineeringHydraulic pump
The invention discloses a power takeoff assembly and application. The power takeoff assembly comprises a power takeoff shell, a power takeoff input shaft, a power takeoff output shaft, a sliding sleeve and a gear shifting shaft, wherein the power takeoff input shaft and the power takeoff output shaft are arranged in the power takeoff shell, one end of the power takeoff input shaft is rotationallyconnected with one end of the power takeoff output shaft, the other end of the power takeoff input shaft extends out of one end of the power takeoff shell and is used for being connected with a powertakeoff opening of a gearbox, and the other end of the power takeoff output shaft extends out of the other end of the power takeoff shell and is used for being connected with a hydraulic pump. Outer splines are arranged at the end, close to the power takeoff output shaft, of the power takeoff input shaft and the end, close to the power takeoff input shaft, of the power takeoff output shaft correspondingly, the sliding sleeve is provided with inner splines matched with the outer splines, and the rotating joint of the power takeoff input shaft and the power takeoff output shaft is sleeved with the sliding sleeve. One end of the gear shifting shaft extends into the power takeoff shell and is connected with the sliding sleeve. According to the power takeoff assembly, when an engine is startedat low temperature, the load can be reduced, and the problem that the engine is difficult to start is avoided.
Owner:SHAANXI FAST AUTO DRIVE GROUP CO LTD
Integrated sealing connector
PendingCN109149190AGood shielding effectGuaranteed reliabilityCoupling contact membersCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsRF connectorFirst glasses
The invention discloses an integrated sealing connector, comprising a connecting shell, wherein a radio frequency shell is arranged in the middle of the connecting shell, the radio frequency shell iscoaxial with the connecting shell, and a radio frequency pin is sintered in the radio frequency shell through a first glass insulator; A set of power supply pins is arranged between the RF housing andthe connecting housing, and the RF housing and the power supply pins are sintered and fixed with the connecting housing through a second glass insulator. The radio frequency connector and the commonpower connector are combined, and the connection function of the radio frequency power supply and the common power supply is realized at the same time. The radio frequency shell has good shielding function, so that the two power supplies do not interfere with each other when working, and the working reliability is guaranteed.
Owner:BENGBU FUYUAN ELECTRONICS TECH
Food processor and knife group mounting structure and stirring cup thereof
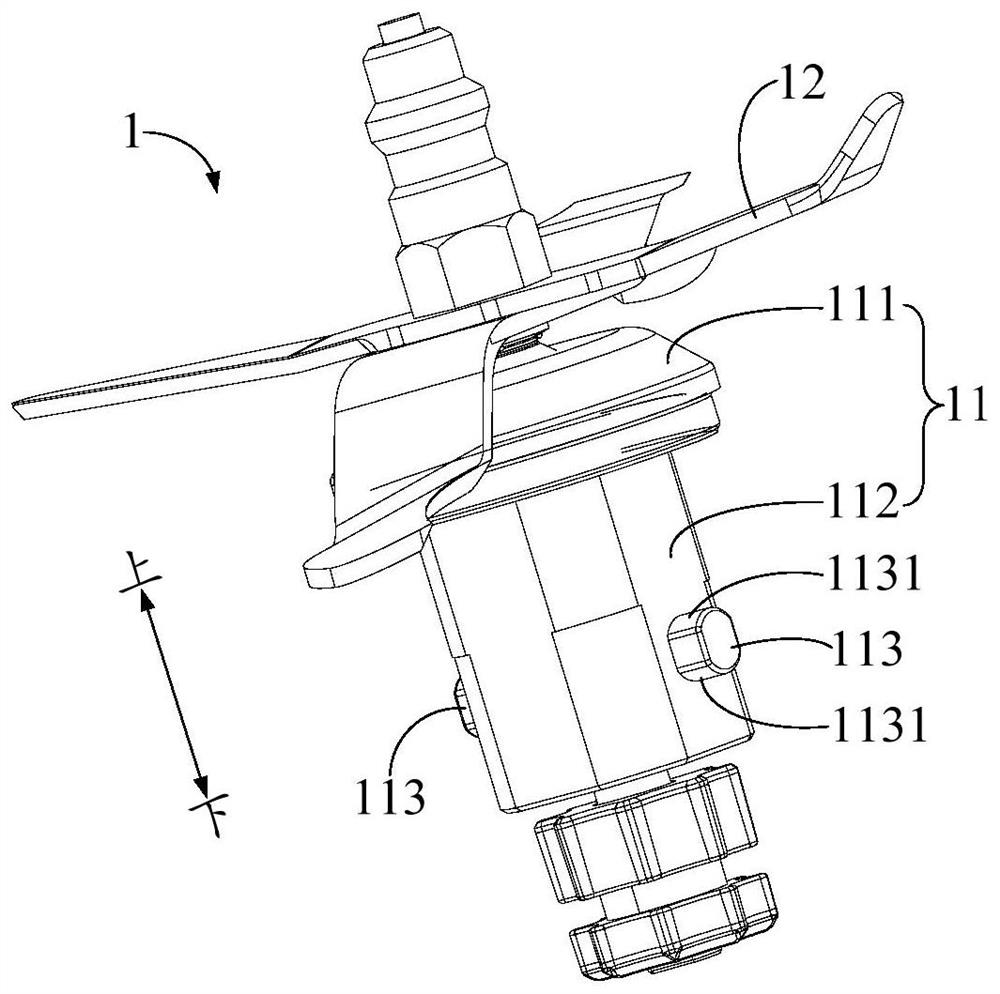
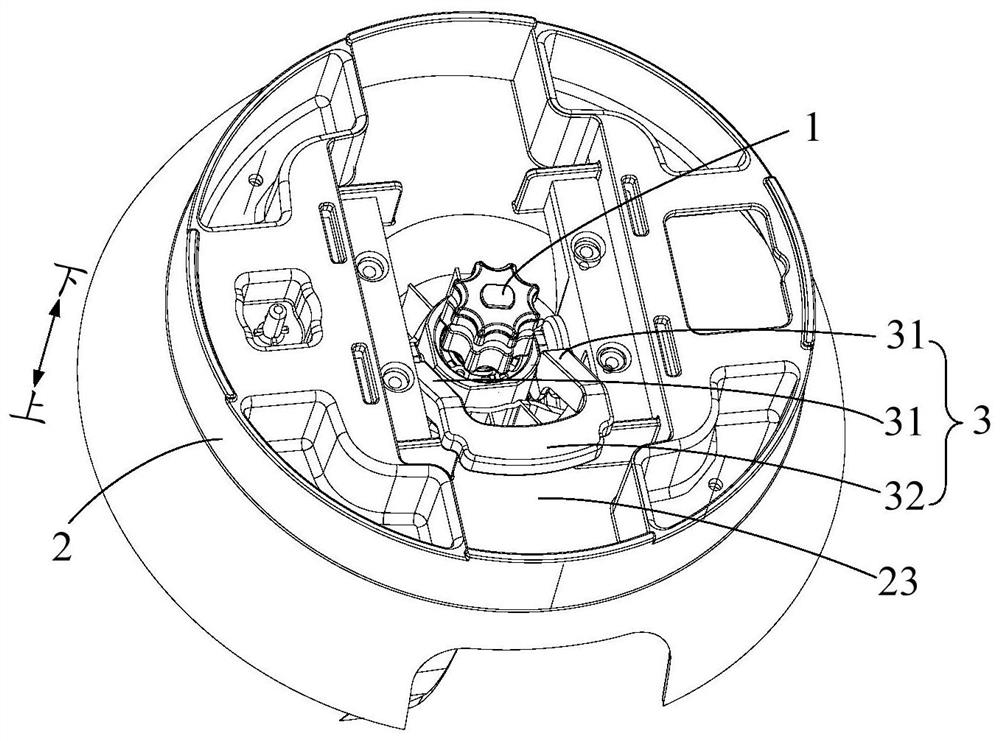
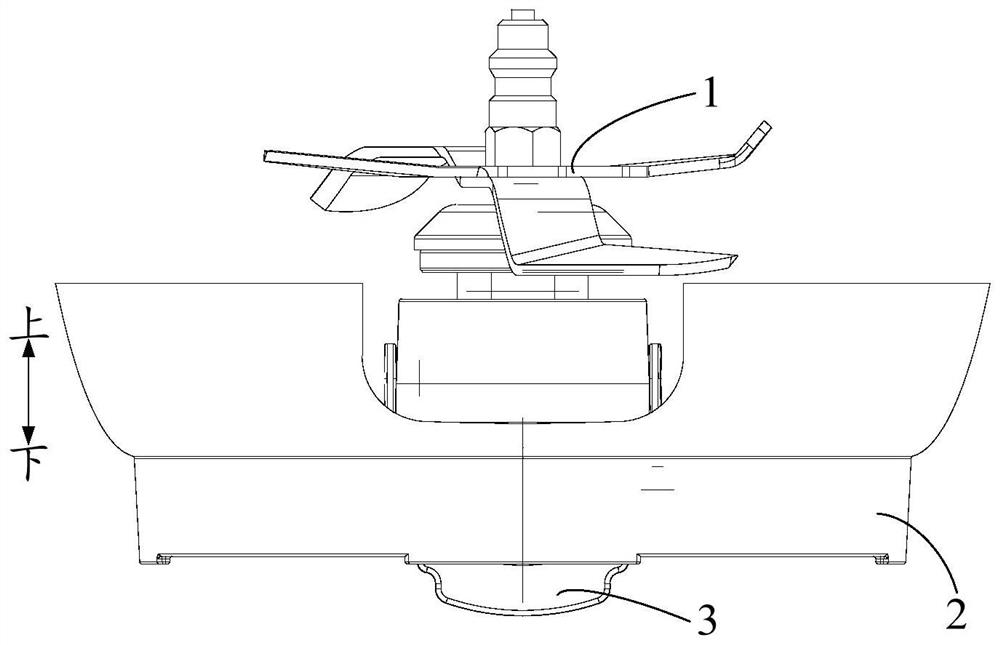
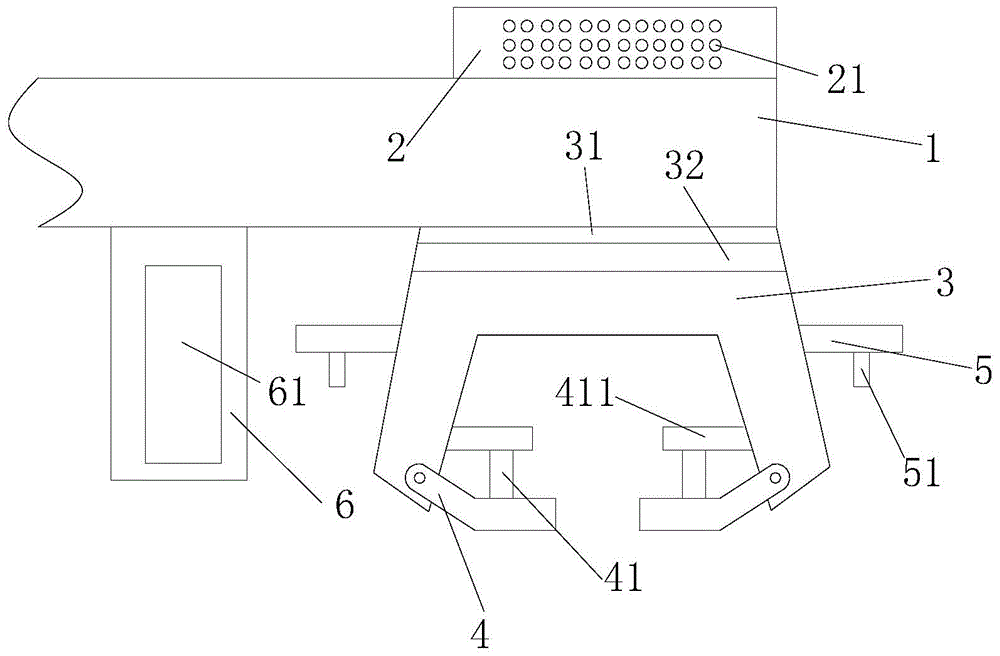
PendingCN112237388AHigh strengthImprove reliabilityStrainersReciprocating motionStructural engineering
The invention provides a food processor and a knife group mounting structure and a stirring cup thereof, the knife group mounting structure comprises: a container bottom, wherein the bottom wall of the container bottom is provided with a mounting hole; a tool apron which is mounted at the mounting hole and is used for mounting a tool of the food processor; and a locking part which is arranged at the bottom of the container, is matched with the tool apron, is suitable for doing reciprocating motion between a tool dismounting position and a tool locking position relative to the bottom of the container, locks the tool apron to fix the tool apron when moving to the tool locking position, and unlocks the tool apron to loosen the tool apron when moving to the tool dismounting position. Accordingto the invention, the knife group can be disassembled and assembled by operating the locking part, and rapid disassembly and assembly of the knife group are facilitated. Meanwhile, the locking part is directly mounted at the bottom of the container and cannot be separated from the bottom of the container in the using process, so that the locking part can be prevented from being lost or confused with other tools; and loosening of the tool apron due to loosening of the nut when the tool rotates in one direction can be prevented, so that the use reliability of the product is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA CONSUMER ELECTRICS MFG CO LTD
A vibration damping device for men's casual running shoes
InactiveCN105124856BAchieve ventilation and vibration reductionRealize the connection functionSolesInsolesDamping functionEngineering
Owner:杨静 +2
Flash memory storage device based on cold and hot data analysis technology
ActiveCN114596885APrevent slippingRealize the connection functionReducing temperature influence on carrierCarrier indicating/warning arrangementsGear wheelEngineering
The invention discloses a flash memory storage device based on cold and hot data analysis technology, the flash memory storage device comprises a main body, a heat dissipation frame, a circulator, a mounting hole and a warning indicator, the top of the main body is provided with a connecting hole, the inner wall of the main body is provided with a rotating shaft, the front side of the main body is provided with the heat dissipation frame, the top of the heat dissipation frame is provided with a temperature detector, and the temperature detector is provided with a temperature sensor. And a warning indicator is mounted on the front surface of the main body. Rapid connection and disassembly can be achieved by installing a connecting hole, when connection is conducted firstly, a connecting block is inserted into the connecting hole, an inclined plate collides with a movable rod, the movable rod returns to the original position under the action of a first spring, the inclined plate is limited, the inclined plate and the connecting block are prevented from sliding off, and the connecting function is achieved; a pressing rod moves to drive a second spring to extend, the pressing rod drives a gear groove to move, a driving gear and a rotating shaft are made to rotate, a cable is tightened to drive a movable rod to contract, and therefore an inclined plate is not limited any more, and the dismounting function is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUACUN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Double-sided substrate for led lighting and led lighting device
InactiveCN104848069BEasy to processSimple structureElectric circuit arrangementsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectricityEngineering
Owner:SMALUX ELECTRICAL MFG
Condenser connection block and air conditioner
ActiveCN111473508BRealize the connection functionGuaranteed connection reliabilityEvaporators/condensersSpace heating and ventilation detailsControl theoryMechanical engineering
Owner:NINGBO AUX ELECTRIC +1
Spacecraft unlocking and separating device
The invention relates to a spacecraft unlocking and separating device which is used in mechanical devices in the field of the aerospace industry. A device combination mainly comprises two structural parts namely separating hexagon bolts, wherein the two structural parts can move oppositely. The two structural parts which can move oppositely are solidified through a hot melt adhesive, and when the hot melt adhesive is melted by changing temperature, the two structural parts are separated. When the device serves as a connecting piece, the two structural parts are solidified through the hot melt adhesive, the connecting function is achieved in the mode similar to the connecting mode of a common bolt or a common stud, and two objects can be connected into a whole through screwing up a nut or a bolt body. When the two connected bodies are to be separated, the set temperature reaches the melting temperature of the hot melt adhesive, so that the two structural parts of the device break away, and then the two objects are separated rapidly under the action of a spring. According to the spacecraft unlocking and separating device, an electrical heating mode is adopted for melting the hot melt adhesive to unlock the two connected parts, and negative influence on a spacecraft caused by dynamic impact generated in the unlocking process is effectively avoided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Coupling of refrigerating machine
The invention provides a coupling of a refrigerating machine. The coupling comprises a connecting base plate, a connecting shaft, a clamping roller and an abutting piece, wherein the connecting shaftis arranged in the middle of the connecting base plate, a plurality of arc-shaped clamping grooves are uniformly formed in the side wall of the connecting shaft, and skid resistance rubber pads are attached to the groove walls of the clamping grooves; a sliding groove is further formed in the connecting base plate, and a clamping roller is connected to one end of the sliding groove in a sliding mode; the clamping roller is correspondingly arranged at the front end of each clamping groove; the diameter of the connecting base plate is 20-50mm larger than the diameter of the connecting shaft; andthe connecting shaft is in threaded connection with the connecting base plate, and the middle of the connecting base plate is provided with a threaded hole as a blind hole. According to the coupling,the rotating shaft with the shaft wall bulge is connected with the coupling, the coupling is specially designed to effectively clamp the rotating shaft, and meanwhile, the clamping roller is used forfurther adjusting, so that the connecting function of the coupling is finally realized.
Owner:XINCHANG XIANGYUN MACHINERY
Automobile clock backlight plate
InactiveCN105782907AUniform light brightnessAchieve high brightnessMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceCircular discLight guide
An automobile clock backlight plate comprises a disk; a pointer hole is formed in the middle of the disk; a plurality of light guiding protrusions are arranged on the lower side of the disk and surround the pointer hole; a circle of edges are upwards arranged on the edge of the disk; light refraction scales are arranged on the inner sides of the edges; a plurality of positioning columns are arranged on at the position, backing to the edges, of the back side of the disk; a plurality of inserting columns are arranged on the back side of the disk; a plurality of positioning buckles are arranged on the back side of the disk; and three light guiding columns are arranged around the disk. The automobile clock backlight plate has the beneficial effects that high-brightness automobile clock backlight illumination can be achieved through a small number of lamps, illumination brightness is uniform, and light guiding uniformity is 70% or above.
Owner:慈溪市锦辉导光板厂
Double-sided dual-use positive and negative plug connector
InactiveCN105789957BRealize the connection functionEasy to assembleCoupling contact membersDual purposeMobile phone
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPHASE ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
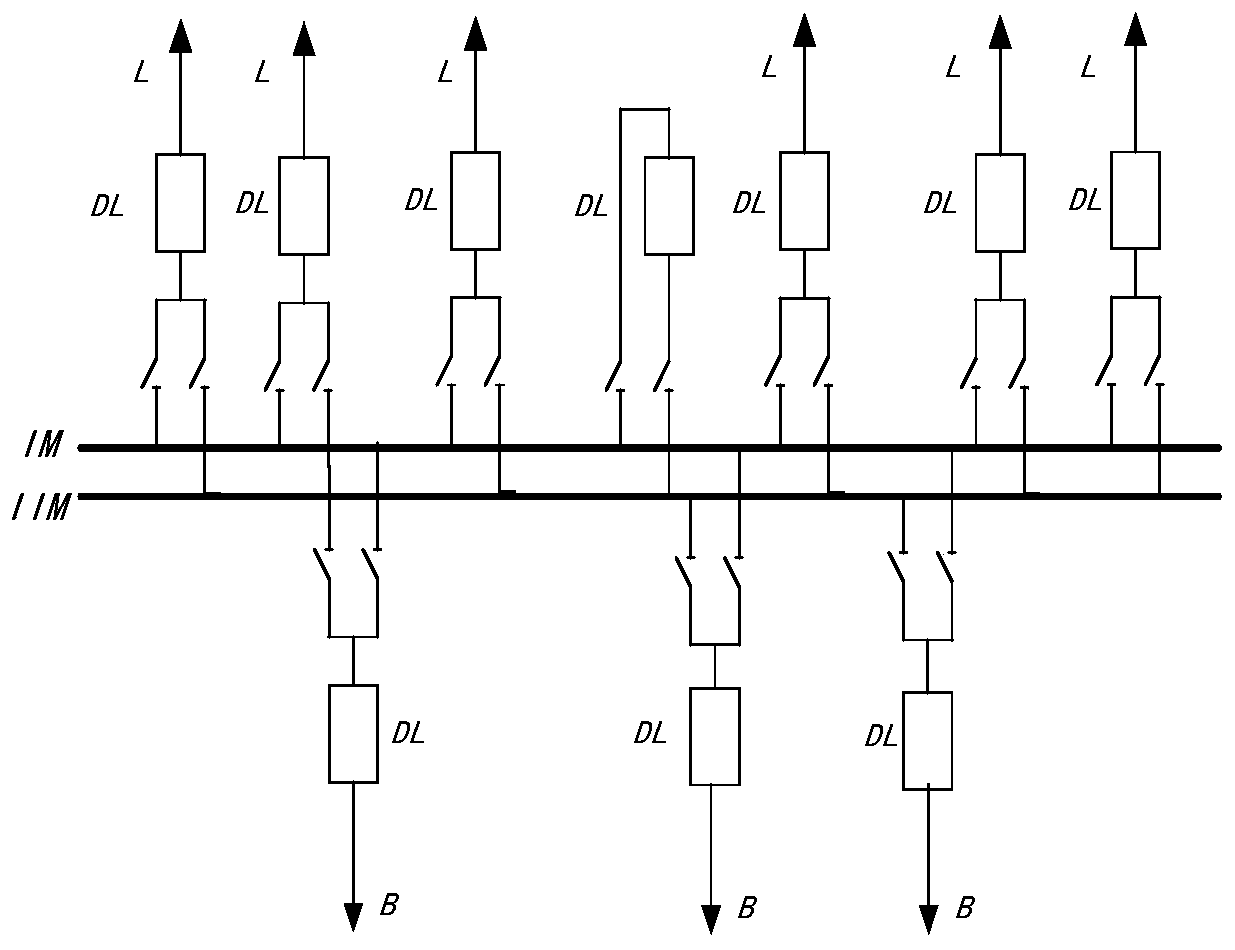
Polygonal wiring 220kV GIS power distribution device and arrangement method
InactiveCN110571692ARealize the connection functionReduce vertical sizeNon-enclosed substationsBus-bar/wiring layoutsTransformerEngineering
The invention provides a polygonal wiring 220kV GIS power distribution device and an arrangement method. In the invention, a circuit breaker main ring and incoming and outgoing line loops are arranged, the circuit breaker main ring is arranged in an end-to-end connection mode, the incoming and outgoing line loops are arranged at connection points between circuit breakers in a staggered mode so asto achieve a connection function of electric appliances between different loops and a power supply function of the loops, arrangement of 220kV GIS is realized, an application range of a GIS power distribution device is expanded, and flexibility of main wiring selection in a scheme design of a transformer substation is improved. After the polygonal wiring 220kV GIS power distribution device of theinvention is adopted, a longitudinal width of a 220kV transformer substation power distribution device chamber with a same scale can be reduced from 12m to 8m, a size of a building is reduced by 1 / 3,and the size of the building and an occupied area of a transformer substation are greatly decreased. A polygonal wiring main ring selects a horizontal circuit breaker structure and overall arrangementis vertical to an incoming and outgoing line direction so that a longitudinal size of the power distribution device is greatly reduced, and a building area of the power distribution device chamber isgreatly decreased.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
A filling-type self-service flexible point-contact guiding cable dragging device for mines
ActiveCN114268069BOvercoming difficult problemsImplement self-regulating behaviorArrangements using take-up reel/drumElectric cablesTowing
Owner:徐州新路智能科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com