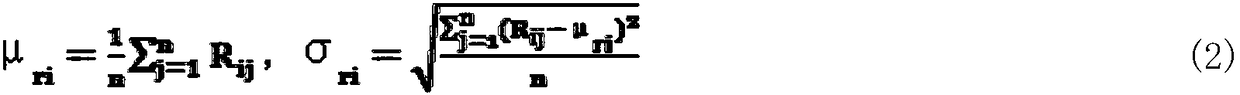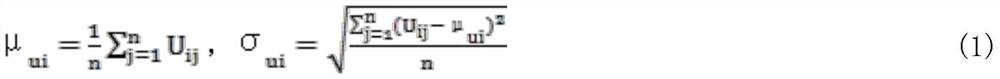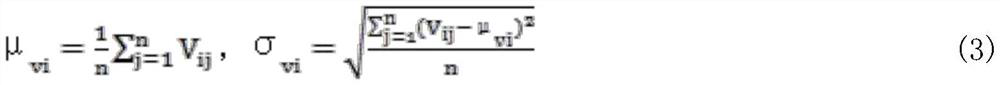Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Optimize calculation method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for autonomously localizing robots on basis of laser radar
ActiveCN107991683AAdd iterative optimizationEasy alignmentNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
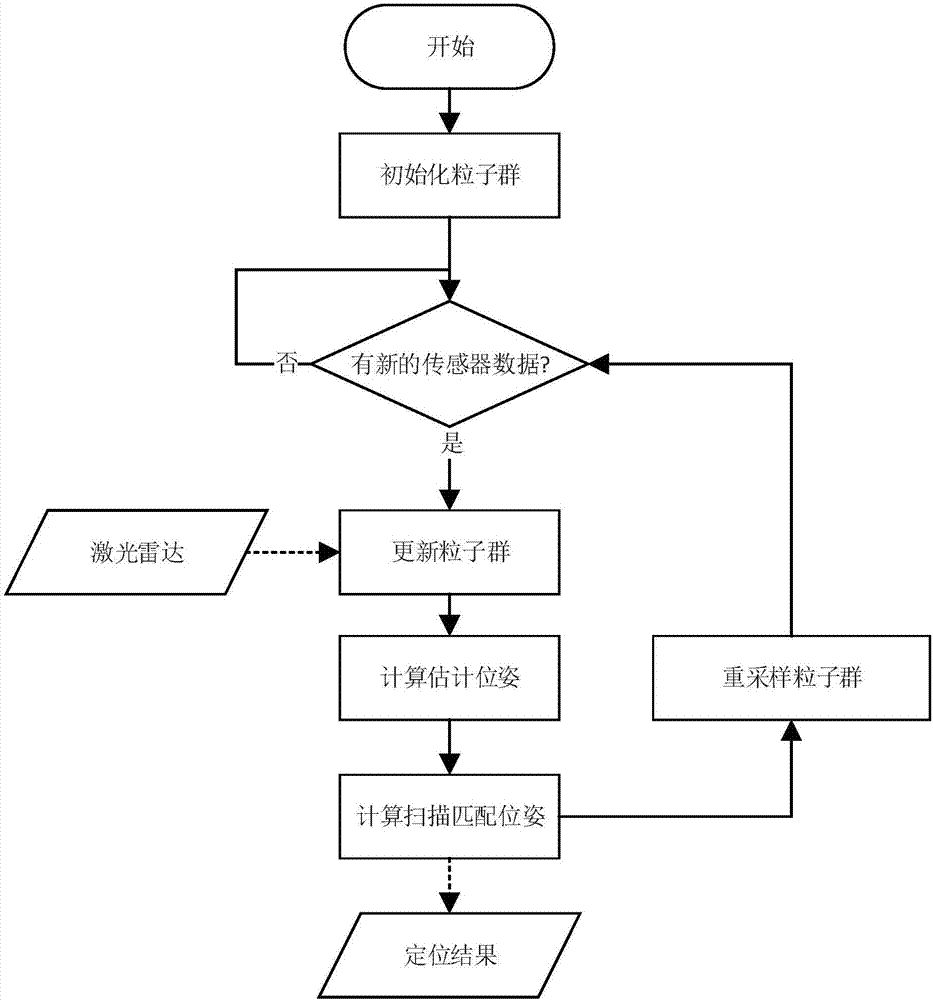
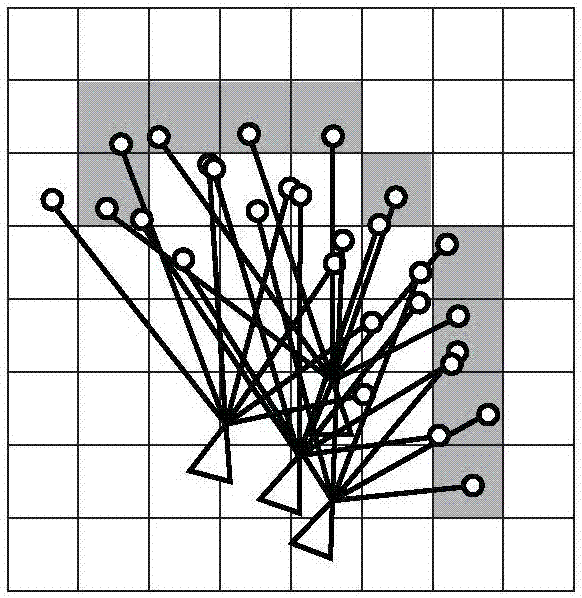
The invention discloses a method for autonomously localizing robots on the basis of laser radar. The method includes randomly generating N particles to form particle swarms around initial locations ofthe robots, and updating the particle swarms according to robot real-time movement distances and real-time rotation angles measured by sensors of the robots at current operation moments of the robots; computing the superposition quantity of point cloud of the laser radar and obstacles of maps for each particle to use the superposition quantity as a score of the particle, computing weighted position and posture average values of the particle swarms by the aid of the score, which is used as a weight, of each particle and utilizing the weighted position and posture average values as AMCL (adaptive Monte Carlo localization) estimation positions and posture; utilizing the AMCL estimation positions and posture as initial values, acquiring scanned and matched positions and posture by the aid ofscanning and matching algorithms on the basis of Gauss-Newton iterative processes and utilizing the scanned and matched positions and posture as the optimal positions and posture of the robots at thecurrent operation moments; re-sampling the particle swarms by the aid of AMCL algorithms to ultimately obtain the global optimal positions and posture of the robots during operation. The global optimal positions and posture of the robots are used as localization results. The method has the advantage that the localization convergence rate can be greatly increased, and the localization precision andthe localization stability can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
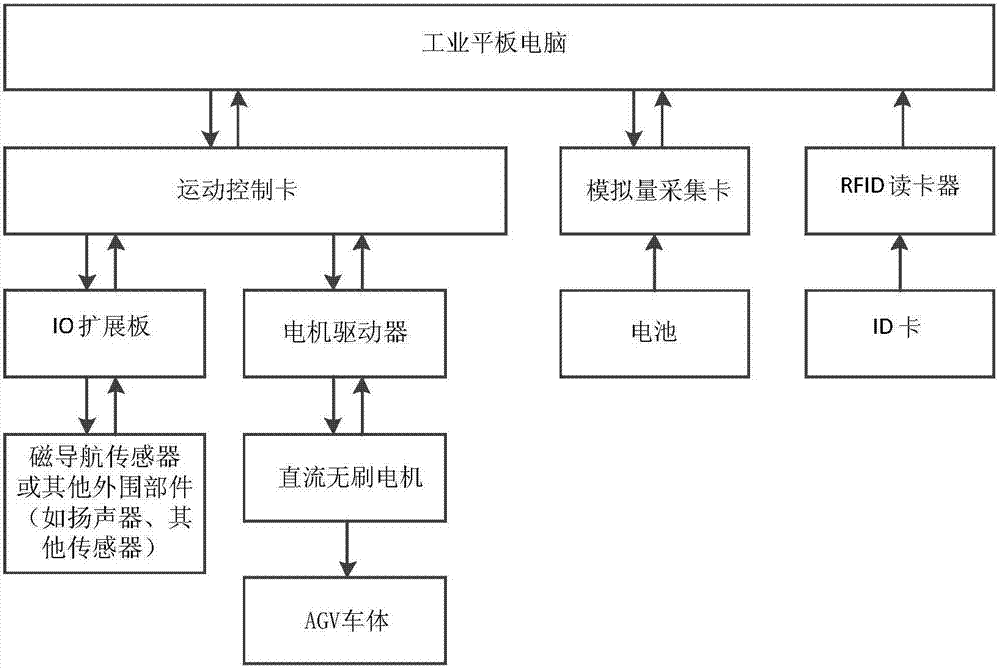
Single-drive one-direction AGV deviation rectification control system and method employing magnetic strip navigation
PendingCN107065864ATroubleshoot off-course issuesImprove work efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesTime deviationControl system
The invention discloses a single-drive one-direction AGV (Automatic Guided Vehicle) deviation rectification control system and method employing magnetic strip navigation. The system includes magnetic strips laid on ground and a single-drive one-direction AGV. The magnetic strips are laid on ground and the AGV can move along the ground with the magnetic strips. The vehicle body of the AGV is therein provided with a magnetic navigation sensor and a main controller. The main controller is in communicational connection with the magnetic navigation sensor. The main controller can perform real time deviation rectification control on the single-drive one-direction AGV according to position signals, collected by the magnetic navigation sensor, concerning to the vehicle body relative to the magnetic strips. According to the invention, through collecting signals of the magnetic navigation sensor in real time, an off-course problem of the AGV during operation is solved effectively and the working efficiency of the AGV is improved substantially.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
An image semantic segmentation method based on local region conditional random field model
InactiveCN109285162AReduce time complexityReduce calculationImage enhancementImage analysisRegion selectionConditional random field
The invention relates to an image semantic segmentation method based on a local area conditional random field model. A full convolution neural network structure of the invention extracts input picturefeatures and obtains a rough segmentation result. The region selection structure filters the edge of the segmentation result map, and selects the segmentation result as the largest circumscribed rectangle of the pedestrian, bicycle and motor vehicle parts. The local region conditional random field model establishes the conditional random field model in the rectangular region and refines the segmentation result of the rectangular region. The invention effectively combines the advantages of the precision of the conditional random field model with the advantages of the speed of the full convolution neural network. The computational method of the conditional random field model is optimized so that the time complexity of the model is greatly reduced. The segmentation accuracy of the traditional full convolution neural network is improved. The application of probability graph model and full convolution neural network is designed as an end-to-end system.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
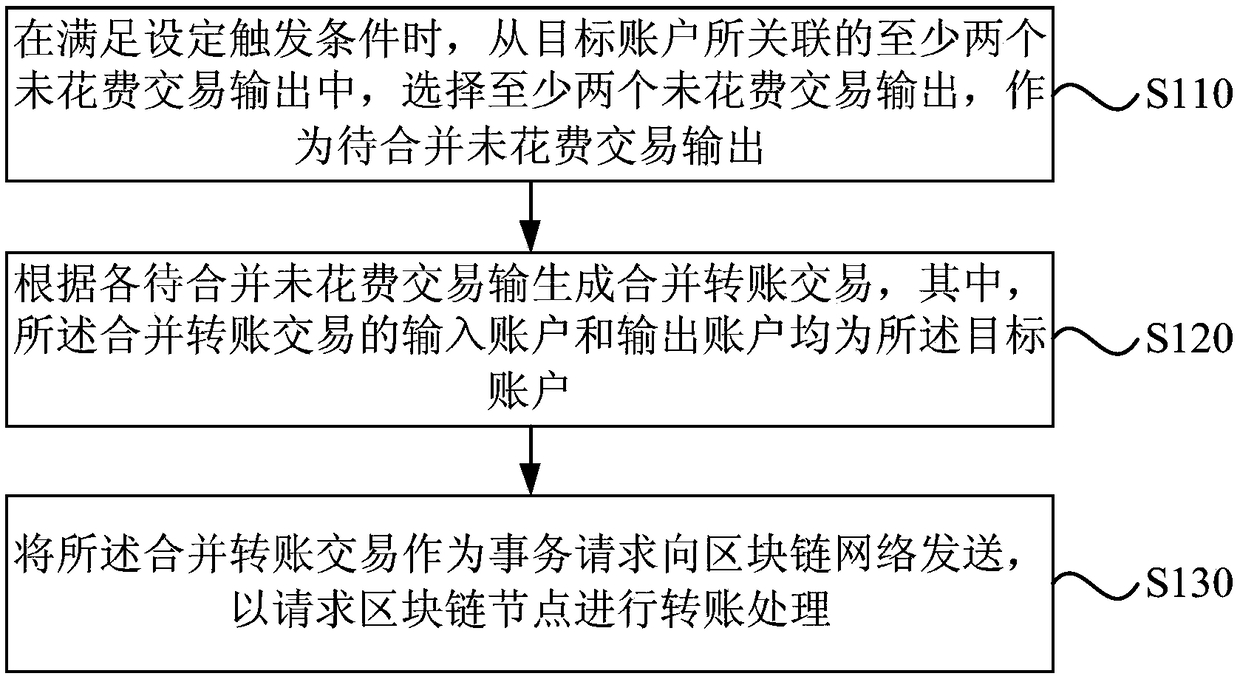
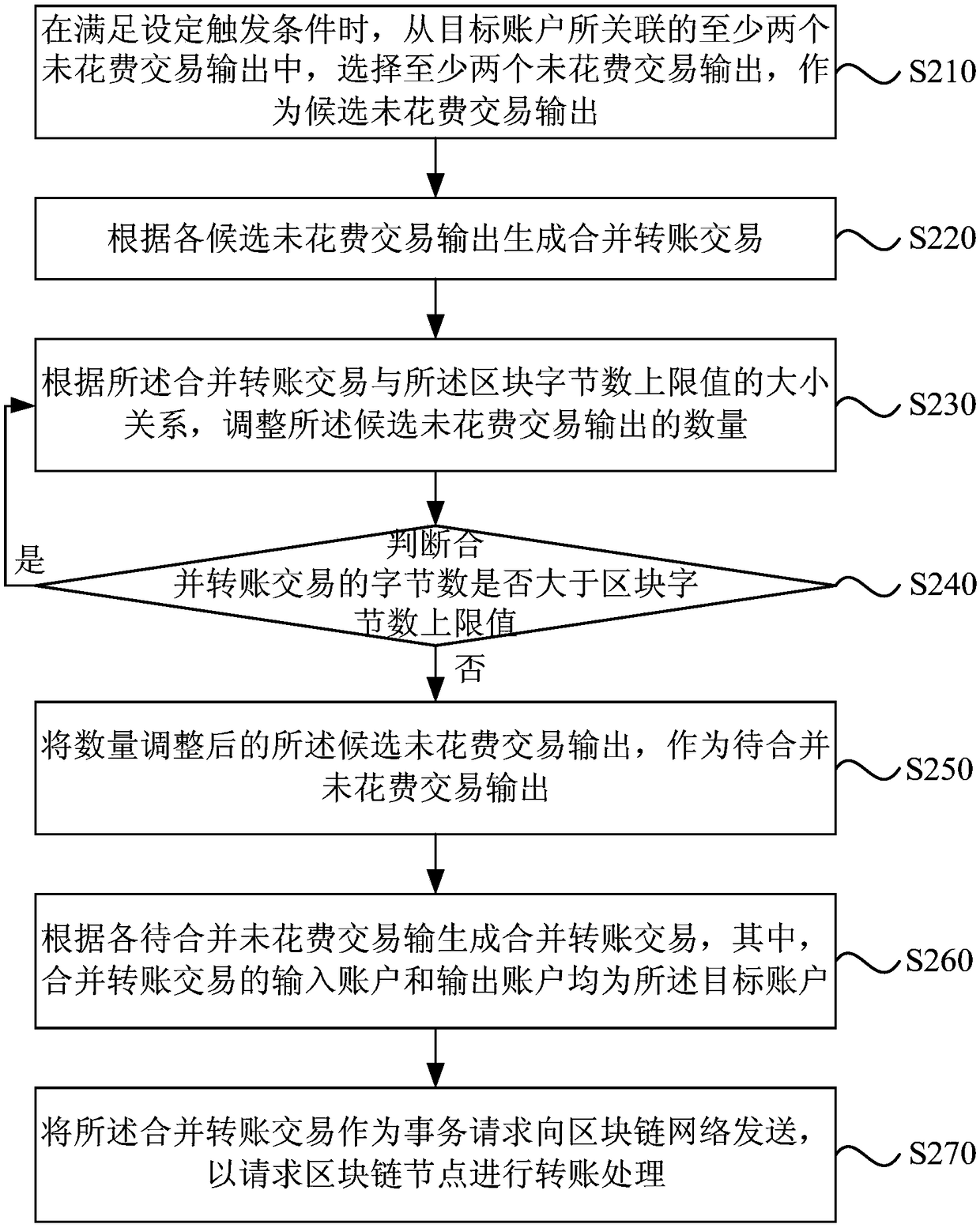
Block-chain transaction processing method, device and apparatus and medium
PendingCN109360101AOptimize calculation methodTroubleshoot time-consuming technical issuesFinanceFinancial transactionChain network
The embodiment of the invention discloses a block chain transaction processing method, device, and apparatus and a medium. The method includes that at least two unspent transaction output associated with the target account are selected as the unspent transaction outputs to be merged when the set trigger condition is met; A merge transfer transaction is generated according to that input of each unspent transaction to be merged, wherein the input account and the output account of the merged transfer transaction are both target accounts; A merge transfer transaction is sent to a block chain network as a transaction request to request a block chain node to carry out transfer process. As that technical scheme introduces the consolidated transfer transaction, A plurality of non-expended transaction outputs are transferred to own accounts to be combined into one non-expended transaction output, thereby solving the technical problem of calculating account balance based on the non-expended transaction output model in the prior art, optimizing the existing account balance calculation mode, saving processing time and system resources, and improving processing efficiency.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
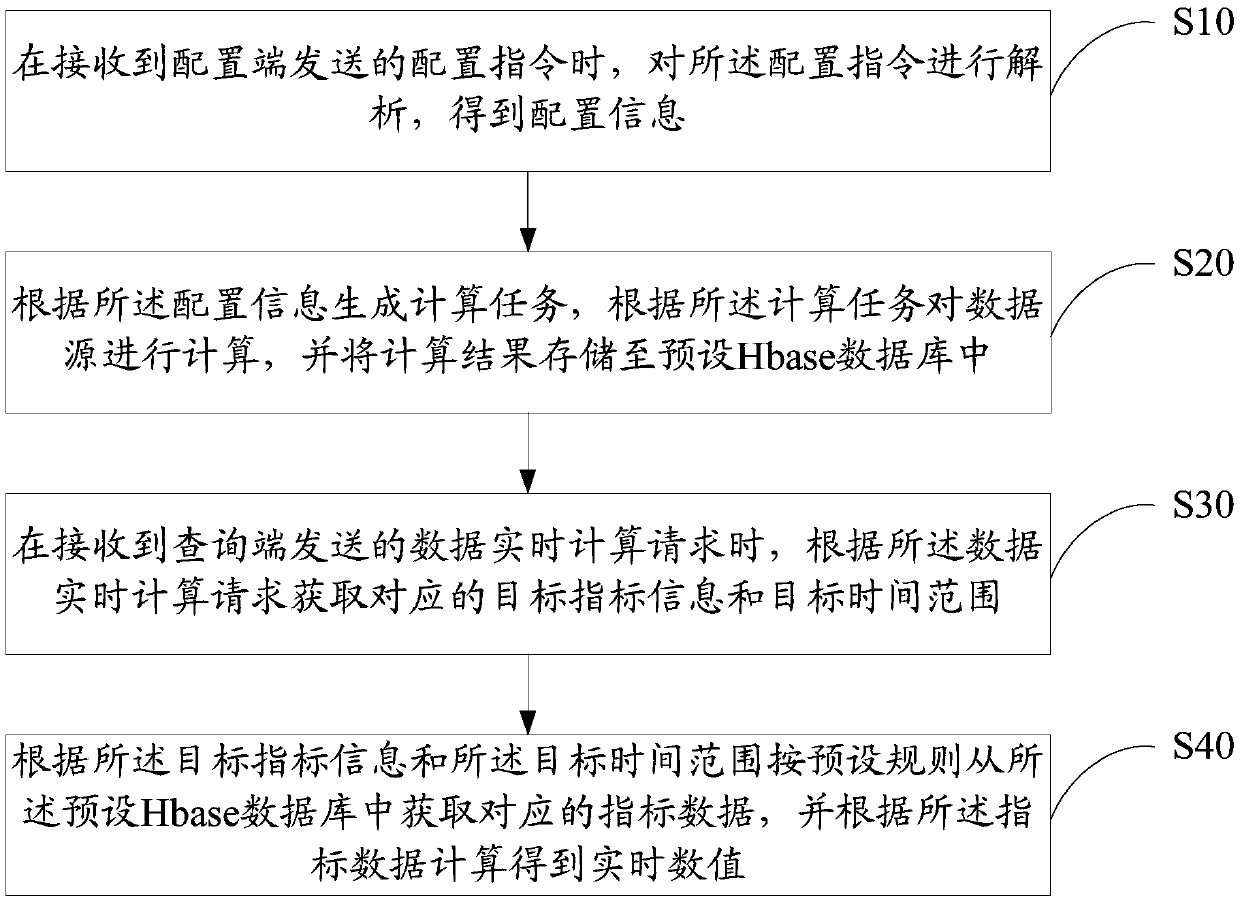
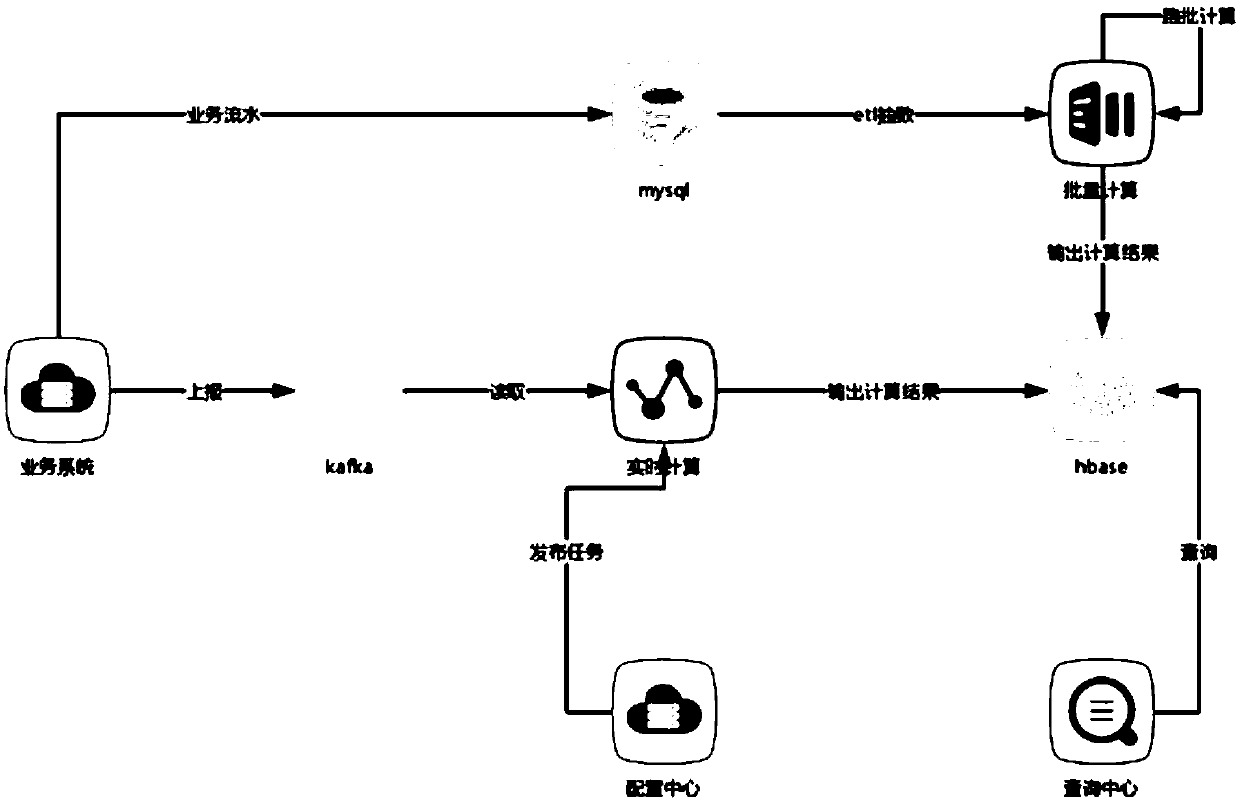
Real-time data calculation method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN109597842AImprove reuse rateReduced development effortDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsTime rangeReal-time data
The invention discloses a real-time data calculation method. The real-time data calculation method comprises the following steps: when a configuration instruction sent by a configuration end is received, analyzing the configuration instruction to obtain configuration information; generating calculation task is generated according to the configuration information, calculating a data source according to the calculation task, and storing a calculation result in a preset Hbase database; When a data real-time calculation request sent by a query end is received, obtaining corresponding target indexinformation and a target time range according to the data real-time calculation request; According to the target index information and the target time range, obtaining corresponding index data from the preset Hbase database according to a preset rule, and obtaining a real-time value through calculation according to the index data. The invention further discloses a data real-time calculation deviceand equipment and a computer readable storage medium. According to the invention, the development cost can be reduced, and the code reuse rate is improved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
Optical character recognition method based on LVQ neural network
InactiveCN103745213AReduce false recognition rateOptimize calculation methodBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage denoisingNerve cells
The invention relates to an optical character recognition method based on an LVQ (Learning Vector Quantization) neural network. The method includes the following steps: performing preprocessing including image denoising, character segmentation, binaryzation and characteristic extraction on a to-be-recognized character image; sending a single character characteristic into an input layer of the LVQ neural network and acquiring a winning competition-layer nerve cell according to a competition algorithm and performing a recognition rejection test; and inputting a character characteristic which complies with a recognition condition to the competition layer of the LVQ neural network for recognition and outputting the recognition result. The optical character recognition method based on the LVQ neural network is applicable to the field of automatic recognition of a small character set which has strict demands on false rate.
Owner:UNIT 63680 OF PLA
Object name editing distance calculating method and object name editing distance matching method based on information entropy
ActiveCN104572627AOptimize calculation methodGood effectNatural language data processingComplex mathematical operationsData matchingTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to an object name editing distance calculating method and an object name editing distance matching method based on information entropy. The object name editing distance calculating method comprises the following steps of (10) counting the using frequency of each character and the total number of object names and defining that the character which is frequently used in an object name only appears in the object name once; (20) calculating the information entropy of characters according to the ratio of the total number of the object names to the using frequency of the characters to obtain editing cost of the characters; and (30) enabling the editing cost of inserting or deleting of a character to be equal to the editing cost of the character when editing distances of the object names are calculated and performing substitution operation under the condition that the editing cost of substitution is zero if two characters are the same and the editing cost of the substitution is the sum of the two characters if the characters are different. The invention also provides the corresponding matching method. By the object name editing distance calculating method and the object name editing distance matching method based on the information entropy, the absolute difference between two object name character strings can be reflected accurately, the similarity between two object names can be recognized effectively, and an effect of handling the problem of matching of data such as names is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
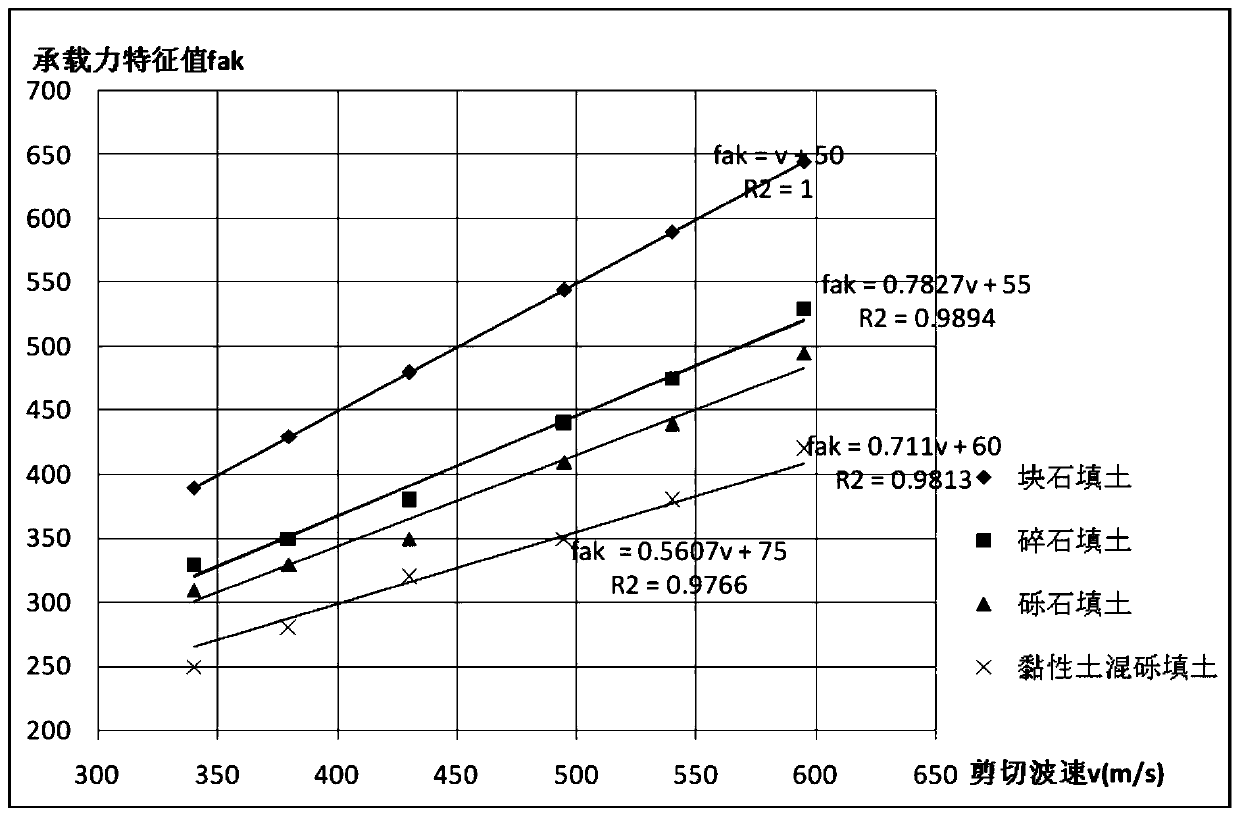
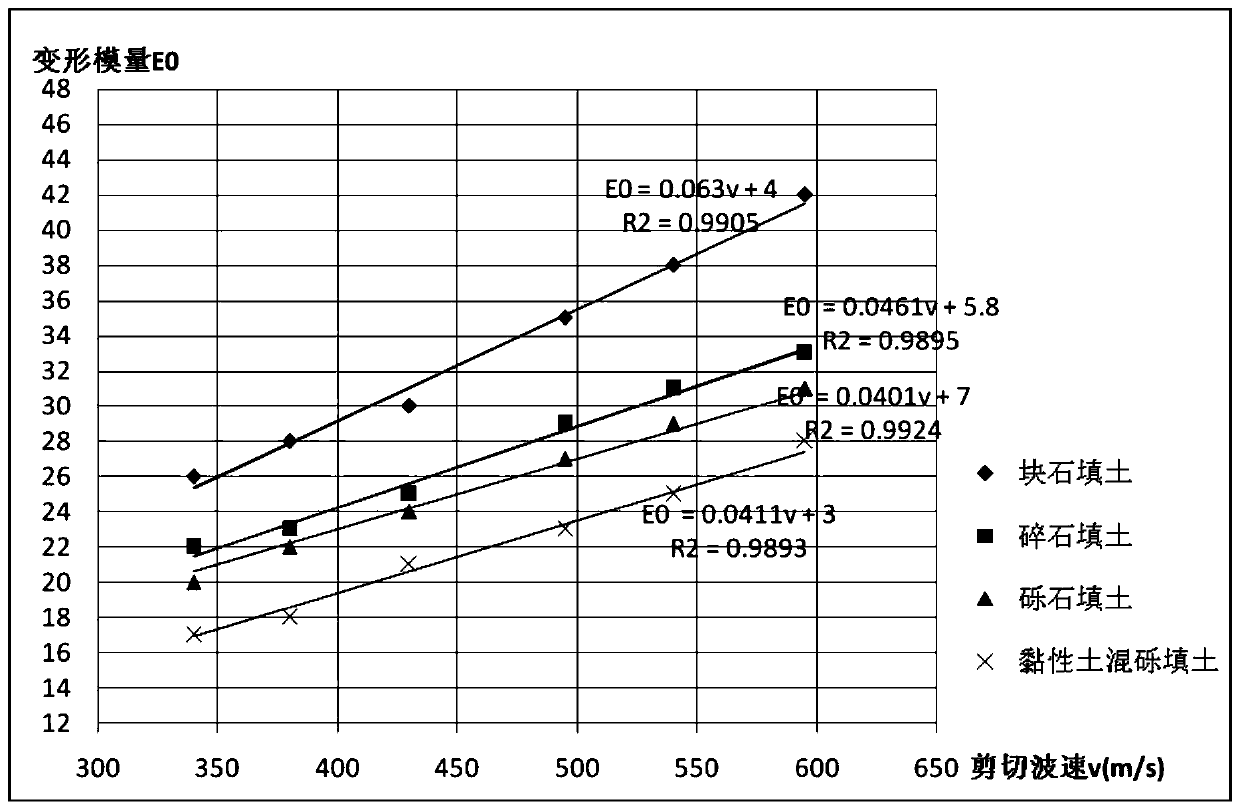
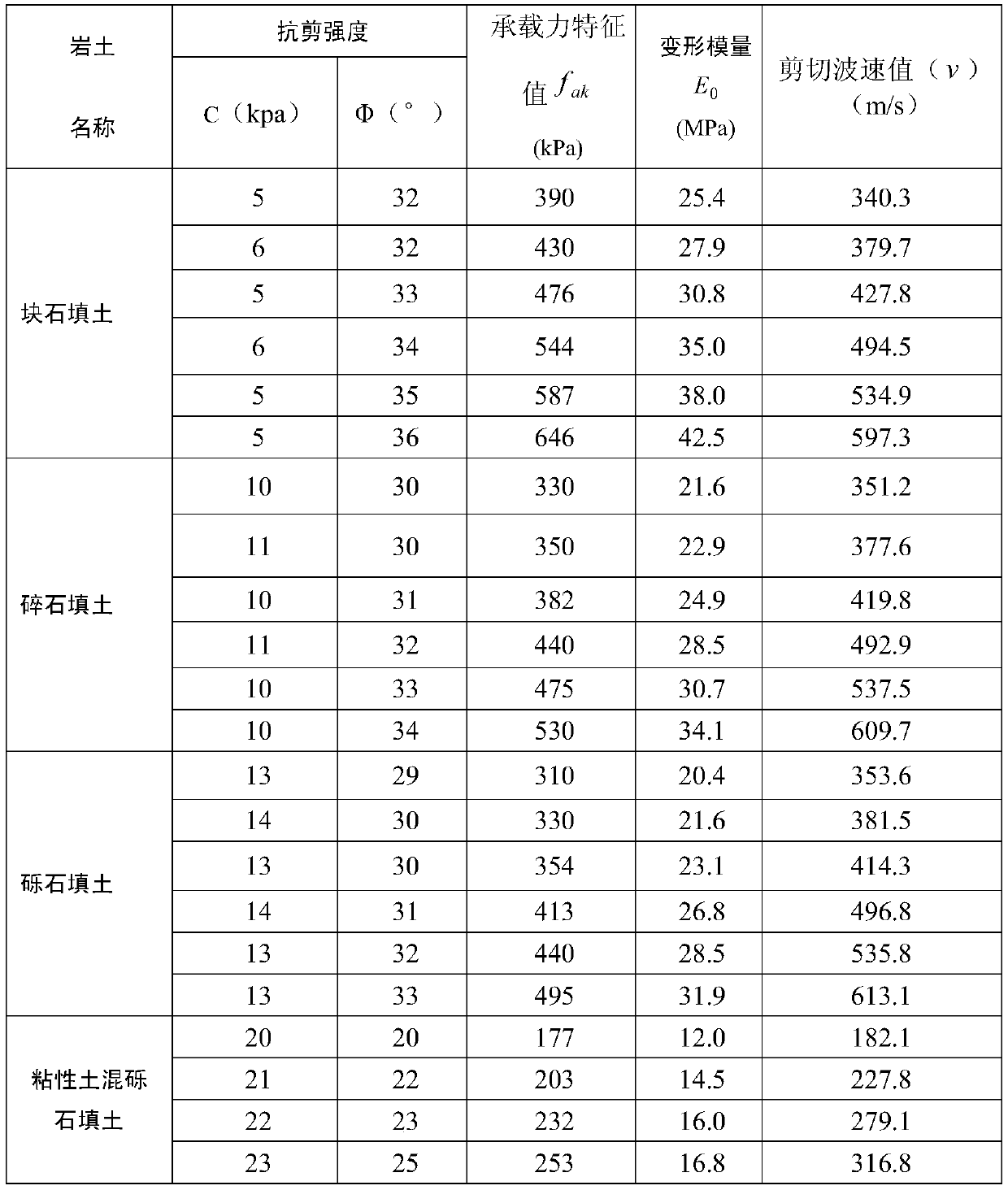
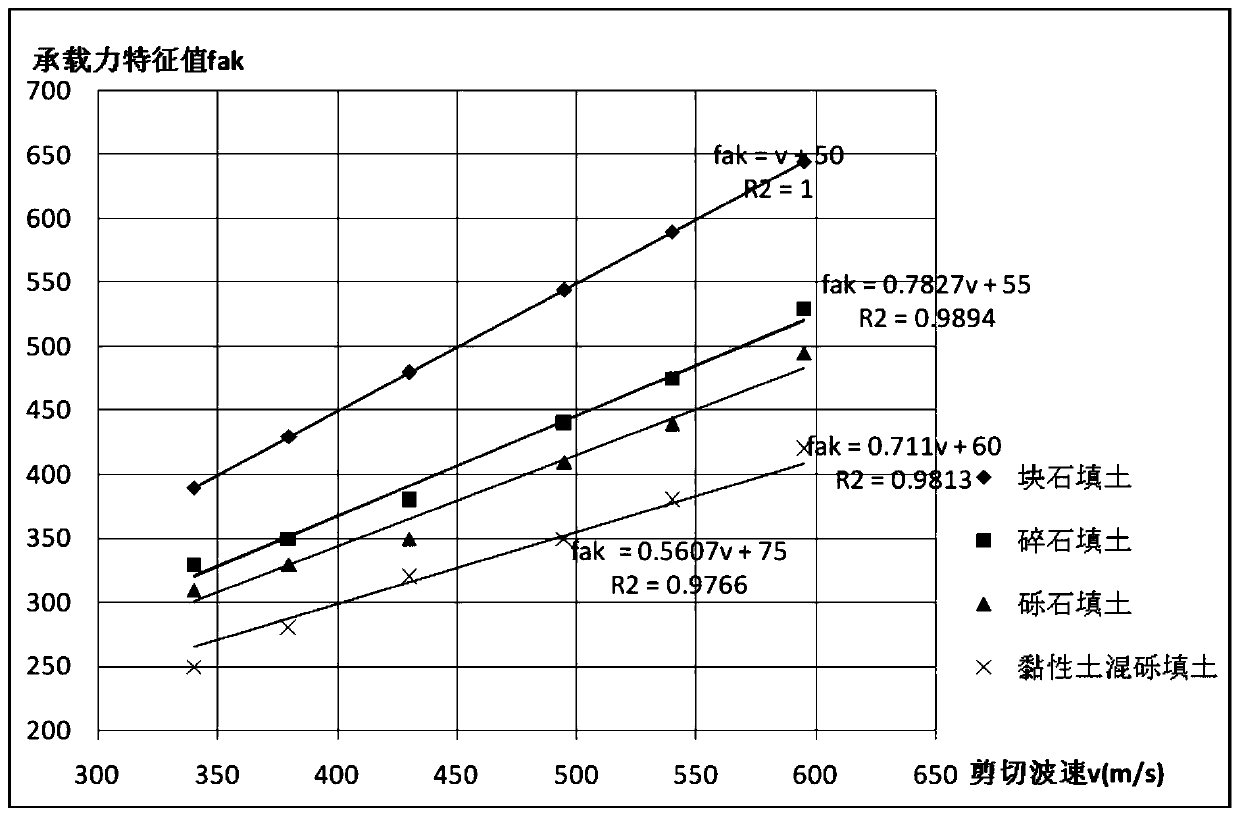
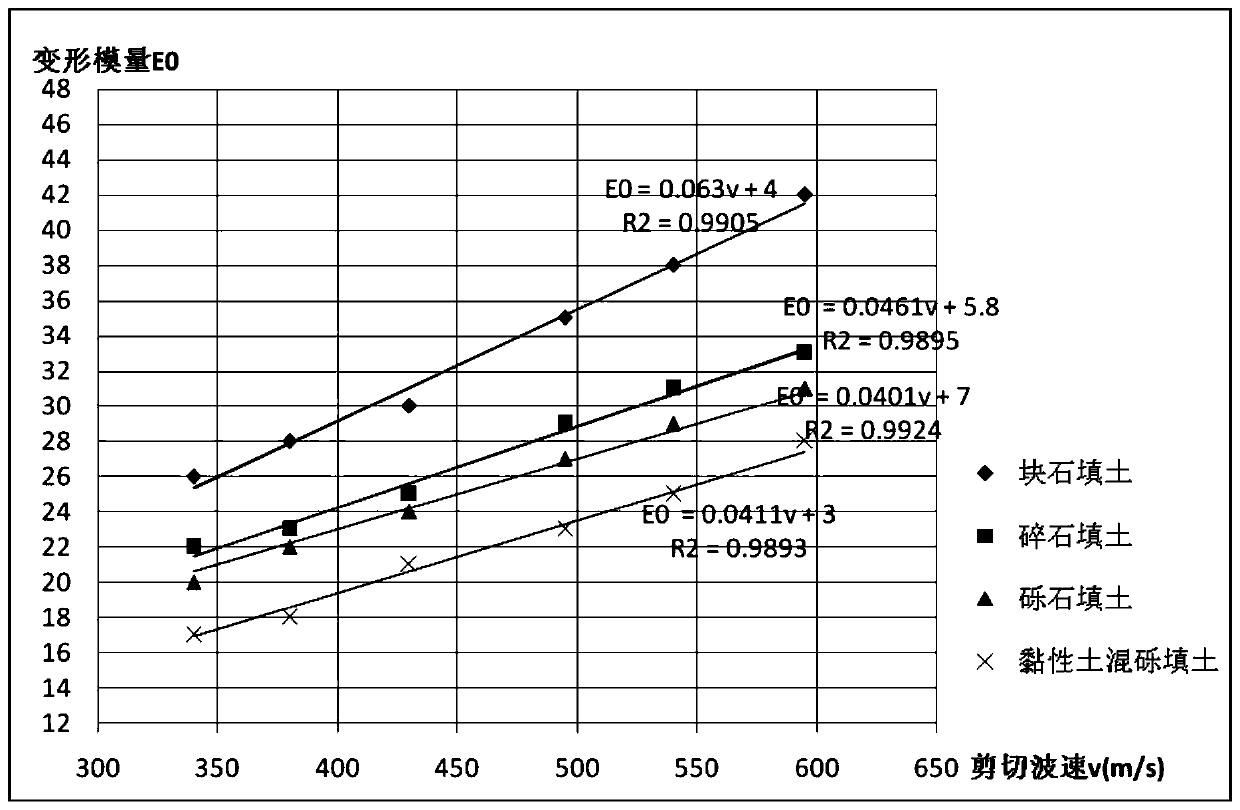
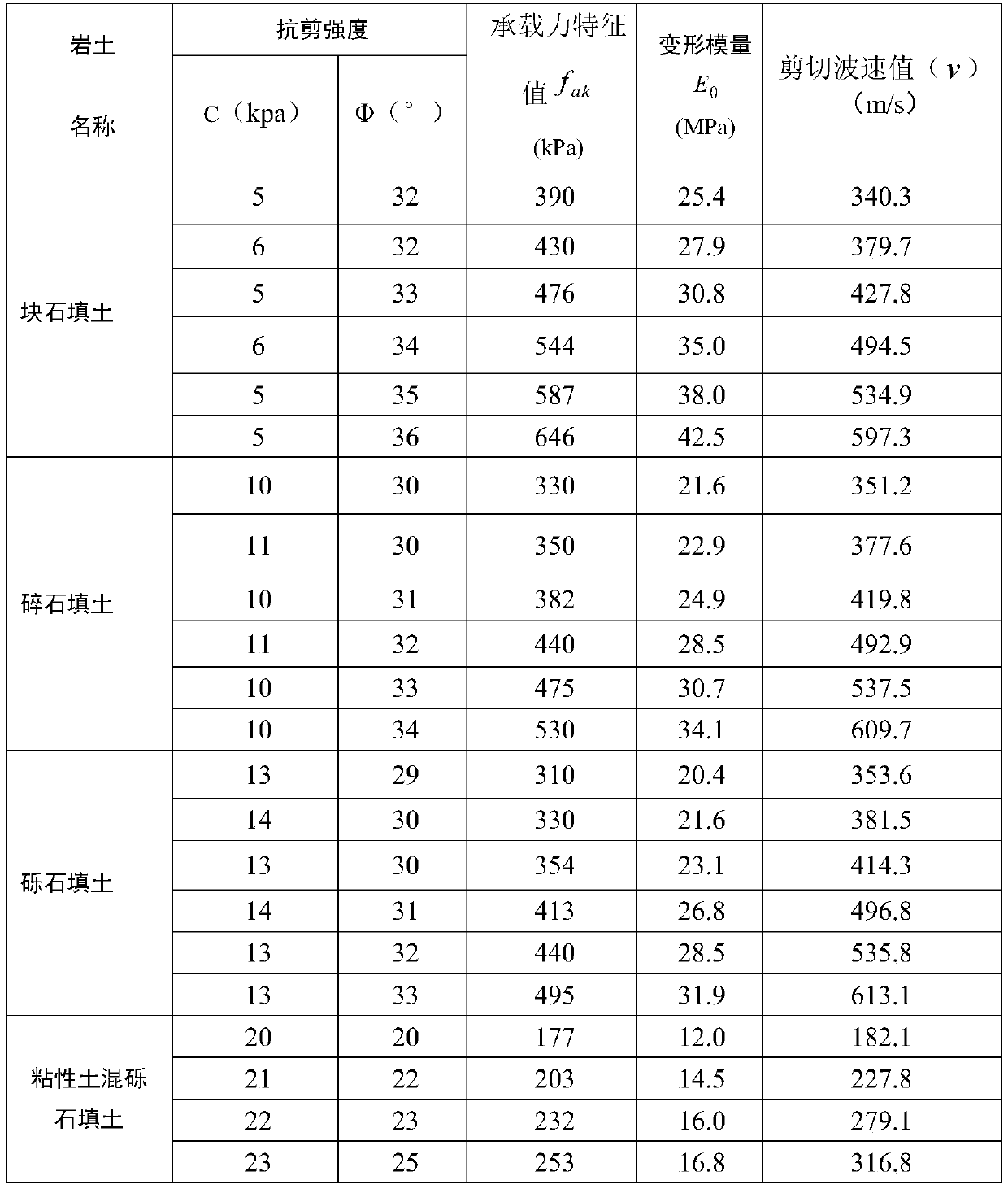
Method for determining bearing capacity characteristic values of tamped/compacted fill strata by using shear wave velocity
ActiveCN110130300AEasy to calculateOptimize calculation methodIn situ soil foundationDirect shear testSoil horizon
The invention provides a method for determining bearing capacity characteristic values of tamped / compacted fill strata by using the shear wave velocity. The method for determining the bearing capacitycharacteristic values of the tamped / compacted fill strata specifically includes the steps that the fill strata of a dynamic compaction (compacted) foundation are classified by using first stone backfill materials with different particle sizes, then the bearing capacity characteristic values of the fill strata calculated by adopting shear strength indexes (c and phi) of a direct shear test on sitecorrespondingly correspond to the shear wave velocity in a borehole to establish the relationship between the bearing capacity characteristic values and the shear wave velocity, and through the established correspondence, the accurate and fast method for determining the bearing capacity characteristic values of tamped / compacted foundation soil layers is provided in addition to a load test method.An accurate basis for valuing of the bearing capacity characteristic values is provided for valuing and evaluation of a tamped foundation and a compacted foundation in geotechnical engineering investigation.
Owner:WUHAN SURVEYING GEOTECHN RES INST OF MCC
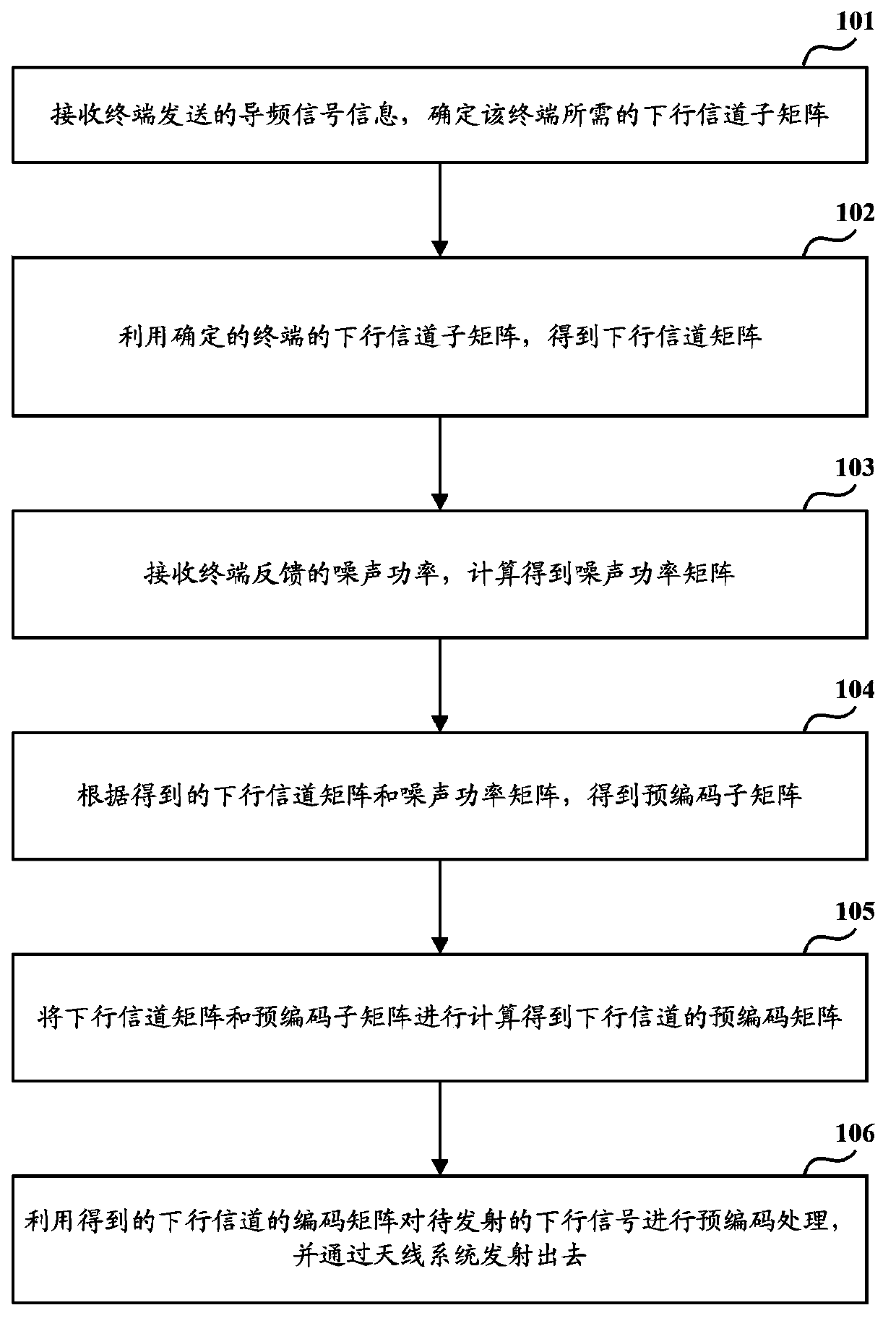
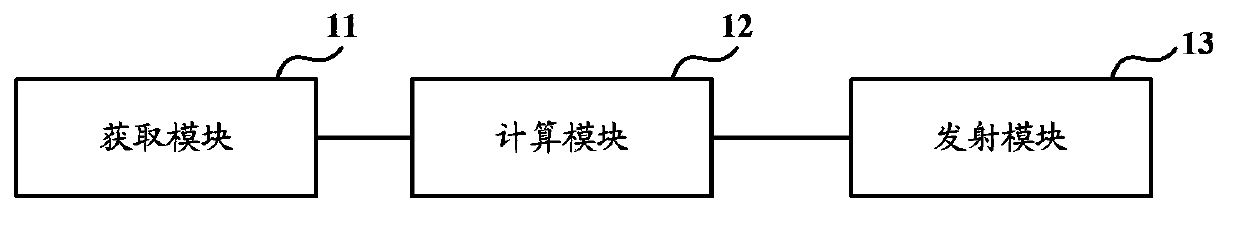
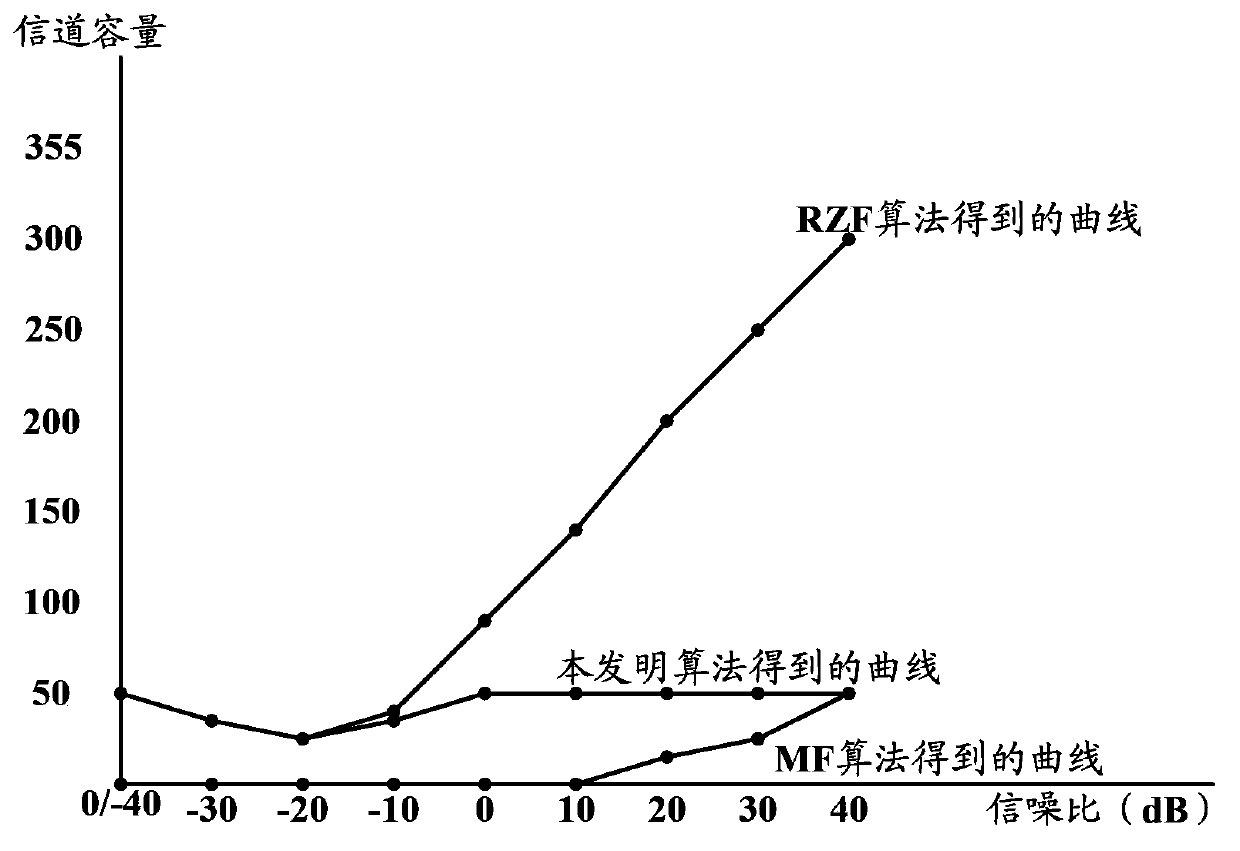
Downlink signal sending method and downlink signal sending equipment in multiaerial system
ActiveCN103873125AOptimize calculation methodSimplify complexitySpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesComputation complexityPrecoding matrix
The invention discloses a downlink signal sending method and downlink signal sending equipment in a multiaerial system. The downlink signal sending method mainly comprises the following contents: obtaining a downlink channel submatrix required by a terminal by virtue of receiving pilot signal information sent by the terminal; determining a downlink channel matrix of an aerial system and obtaining a noise power matrix according to noise power fed back by each terminal; obtaining a precoding submatrix by use of the downlink channel matrix and the noise power matrix, and determining the precoding matrix of the downlink channel, so that the influence of interference and noises among the terminals on the system performance is taken into consideration in a precoding matrix acquisition process; obtaining a precoding submatrix C according to the obtained downlink channel matrix H and noise power matrix X. According to the method and the equipment, the computation complexity is simplified, the precoding matrix computing mode in the prior art is improved, meanwhile, the precoding matrix of antennae is determined by virtue of considering the factor that different terminals are influenced by noises, and the downlink signal power of the antennae is optimized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
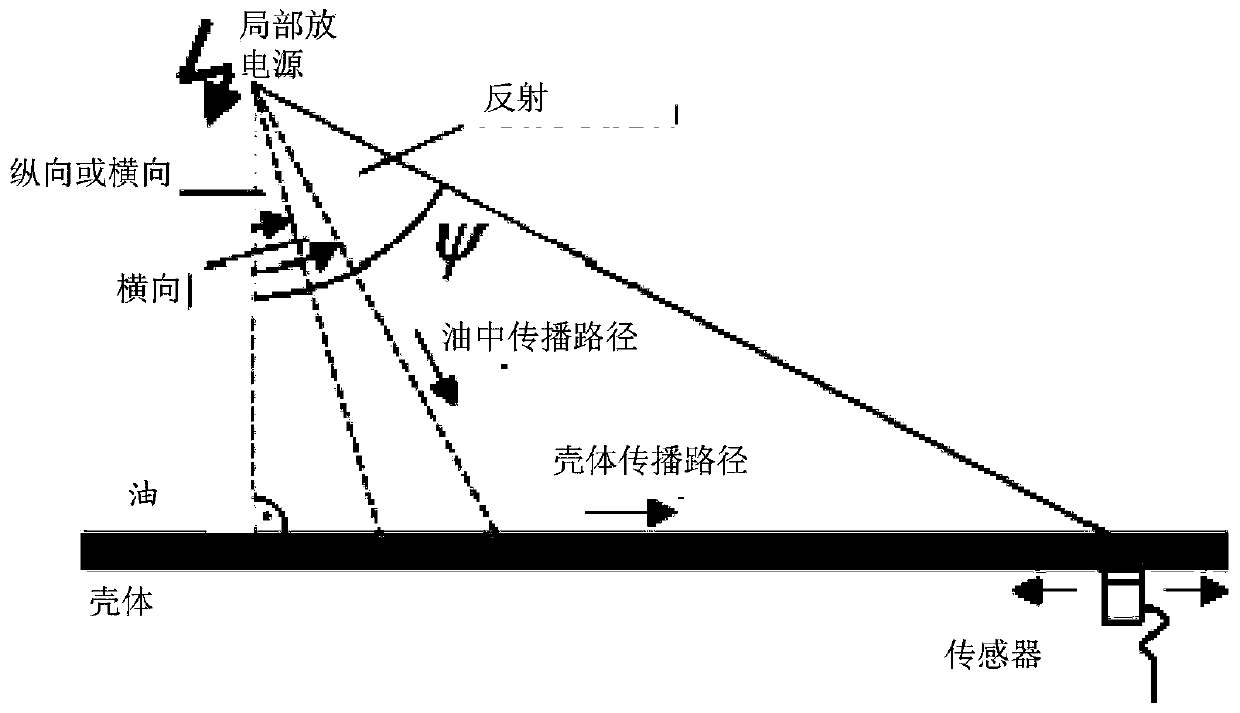
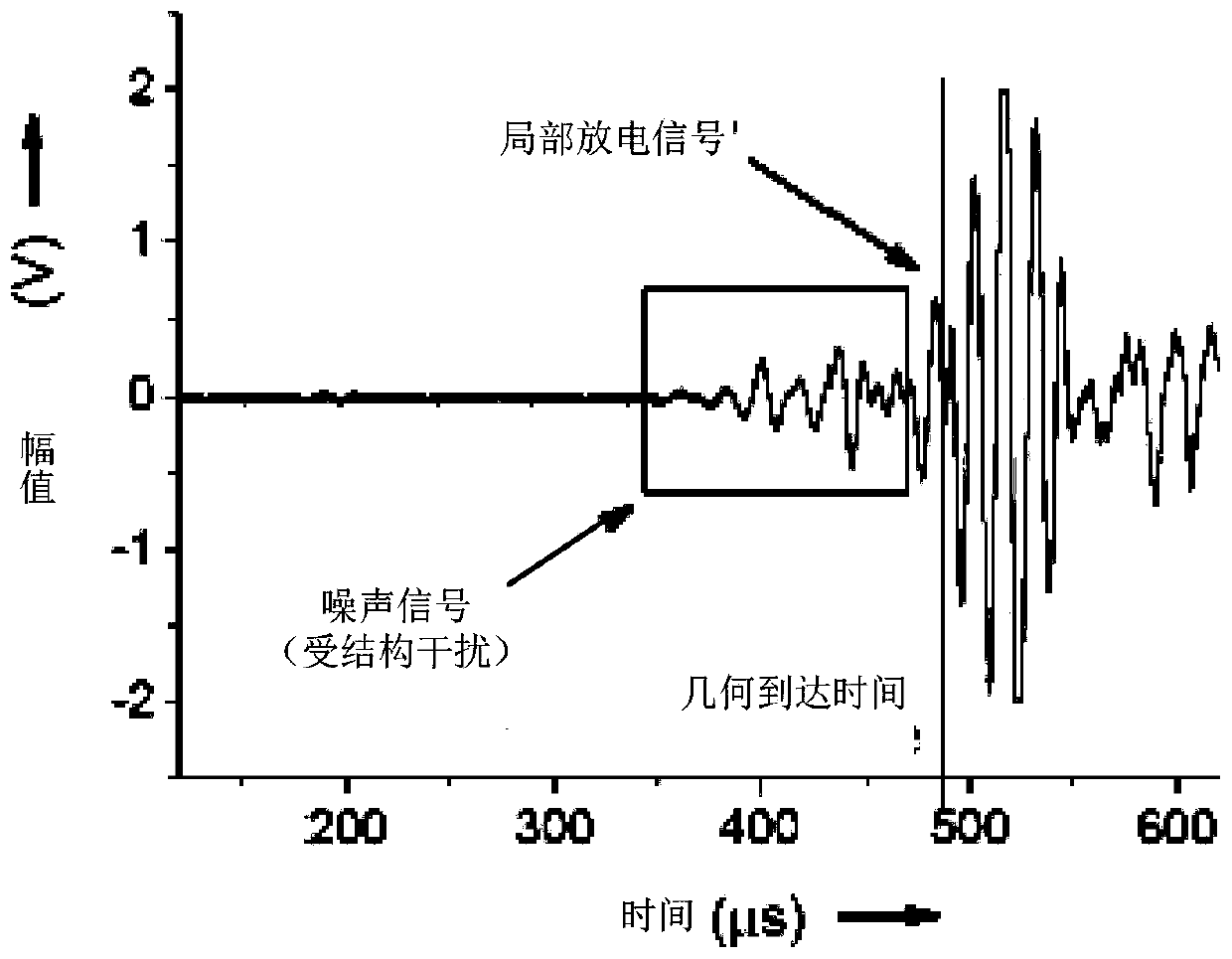
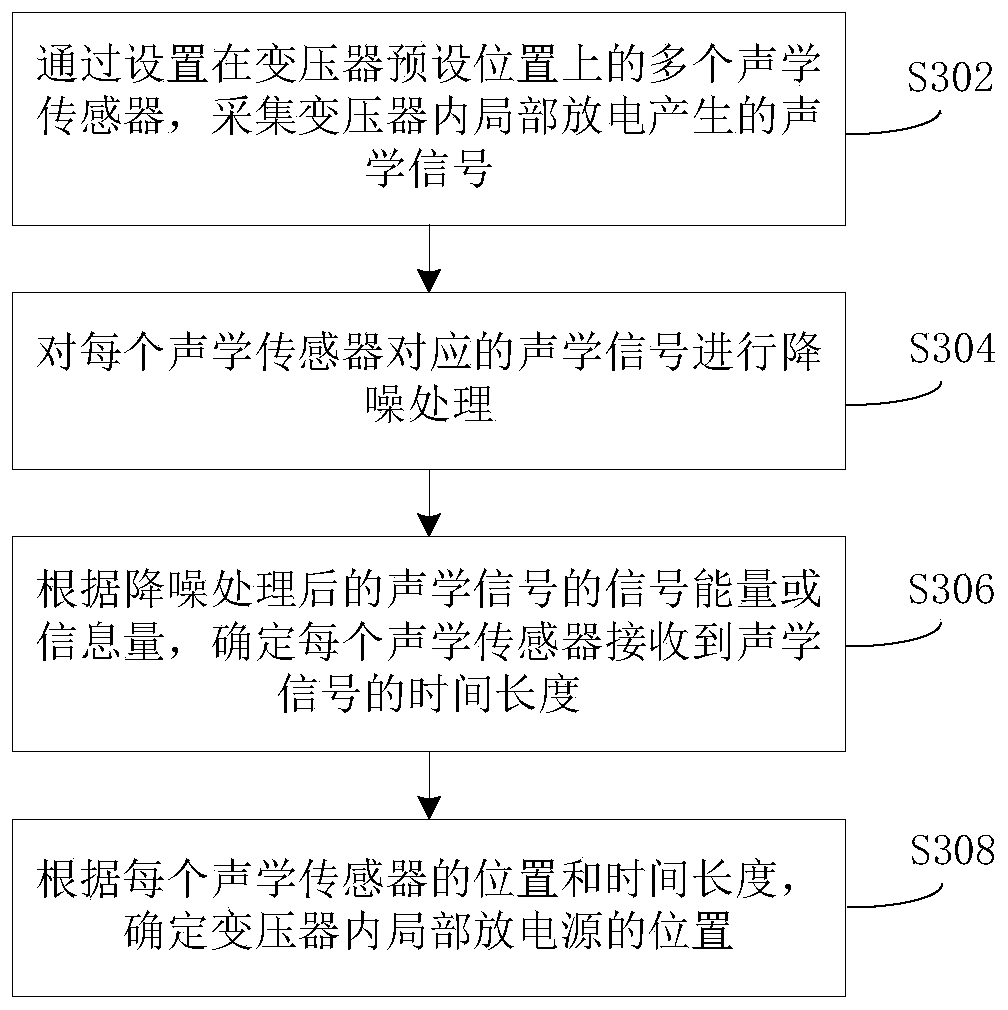
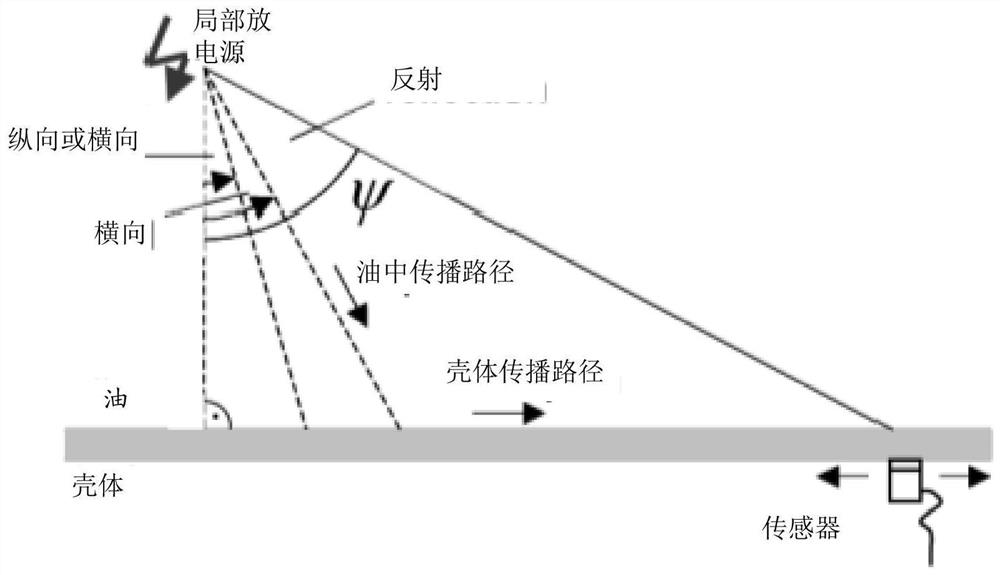
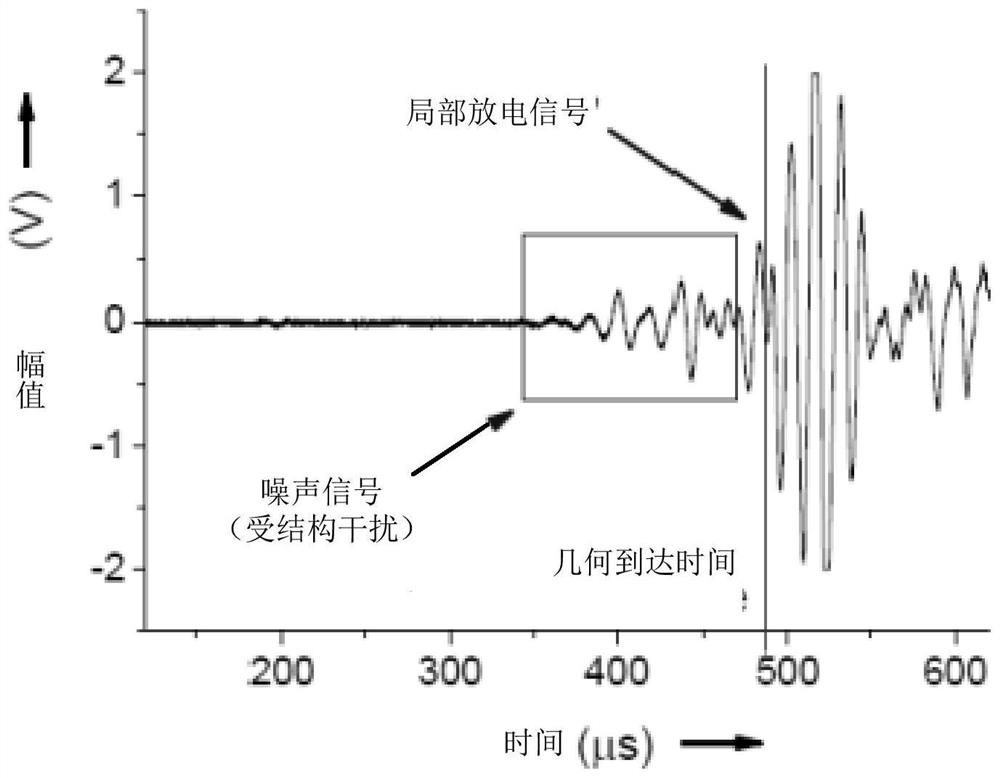
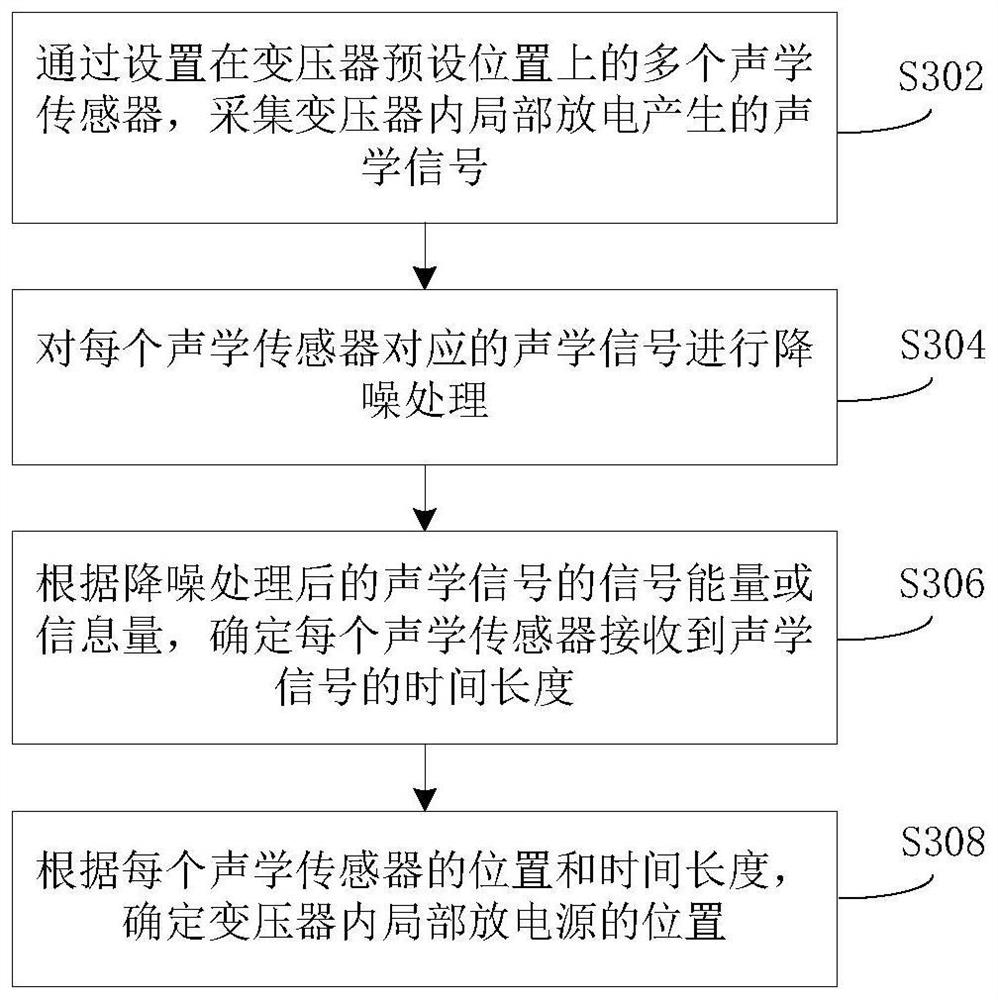
Partial discharge source location method and device in transformer, and server
ActiveCN109917252AHigh precisionOptimize calculation methodTesting dielectric strengthTransformerEngineering
The present invention provides a partial discharge source location method and device in a transformer, and a server. The method comprises the steps of: collecting acoustic signals generated by partialdischarge in a transformer by employing a plurality of acoustic sensors arranged at preset positions of the transformer; performing noise reduction processing of the acoustic signals corresponding tothe each acoustic sensor; according to the signal energy or the information amount of the acoustic signals after noise reduction processing, determining the time length of each acoustic sensor receiving the acoustic signals; and according to the position and the time length of each acoustic sensor, determining the position of the partial discharge source in the transformer. In the invention, thereference time point when each acoustic sensor starts to collect signals at the same time as reference to determine the time length of each acoustic sensor receiving the acoustic signals, and therefore, the relative time mode facilitates optimization of the late computing mode of partial discharge source location in the transformer so as to improve the accuracy of partial discharge source locationin the transformer.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
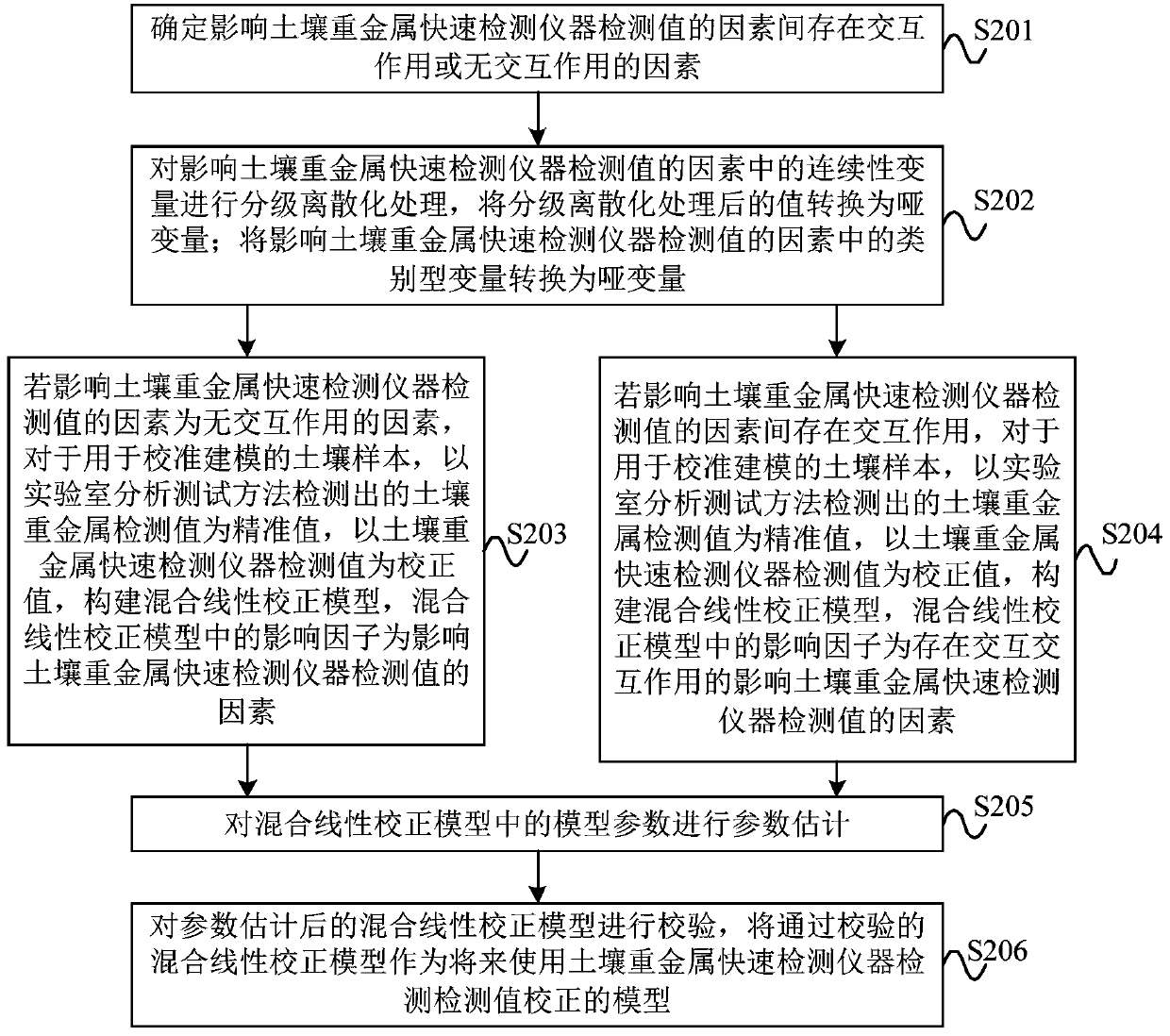
Soil heavy metal detection value correction method, device and computer storage medium
ActiveCN110018294AAchieve correctionDrawbacks of Improving ConnectivityEarth material testingSoil heavy metalsModel parameters
The invention discloses a soil heavy metal detection value correction method, device and a computer storage medium. The soil heavy metal detection value correction method includes the steps that factors affecting the detection value of a soil heavy metal rapid detection instrument are determined; for soil samples used for calibration modeling, by taking the soil heavy metal detection value detected by a laboratory analysis test method as an accurate value and taking the soil heavy metal rapid detection instrument detection value as a correction value, a mixed linear correction model is built;and model parameters of the mixed linear calibration model are estimated and verified, and the verified mixed linear calibration model is used as a soil heavy metal detection value correction model detected by the soil heavy metal rapid detection instrument in the future. The soil heavy metal detection value correction method, device and the computer storage medium are used for improving the detection accuracy of the soil heavy metal content of the soil heavy metal rapid detection instrument.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
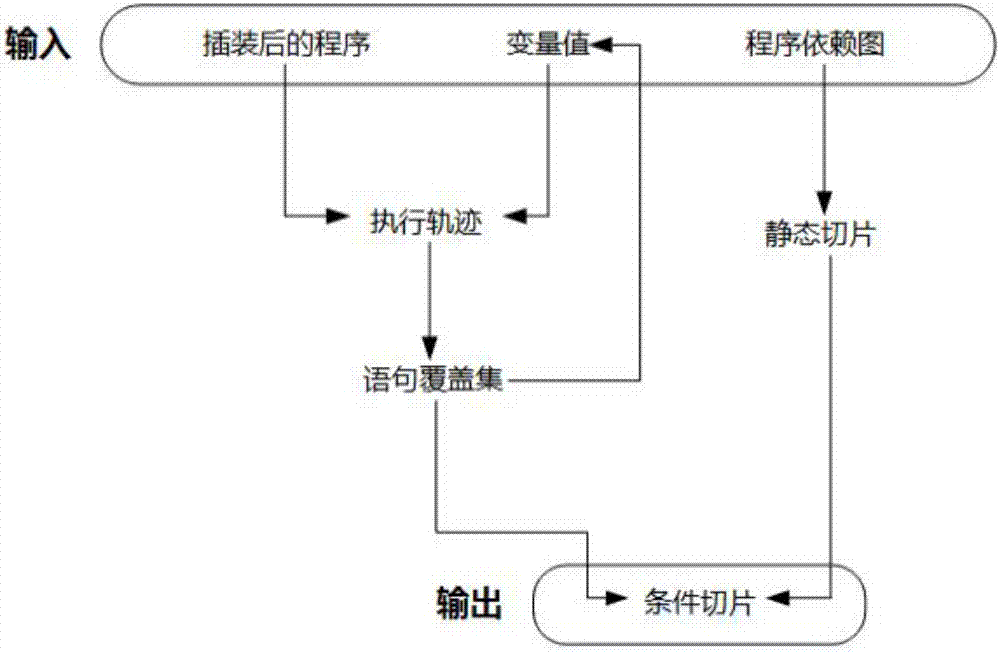
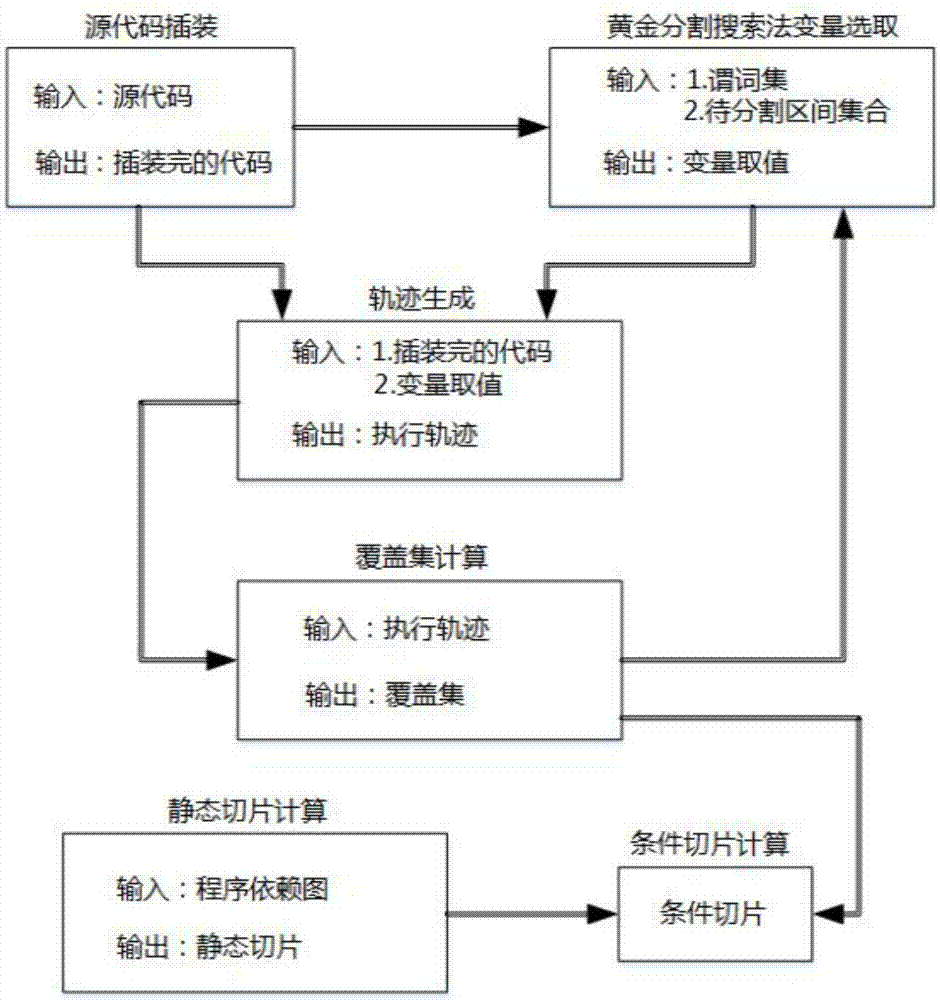
Condition slicing method based on golden section search and software execution trace
ActiveCN107391124ALow space complexityEasy access to trajectory informationReverse engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsGolden section searchSoftware execution
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
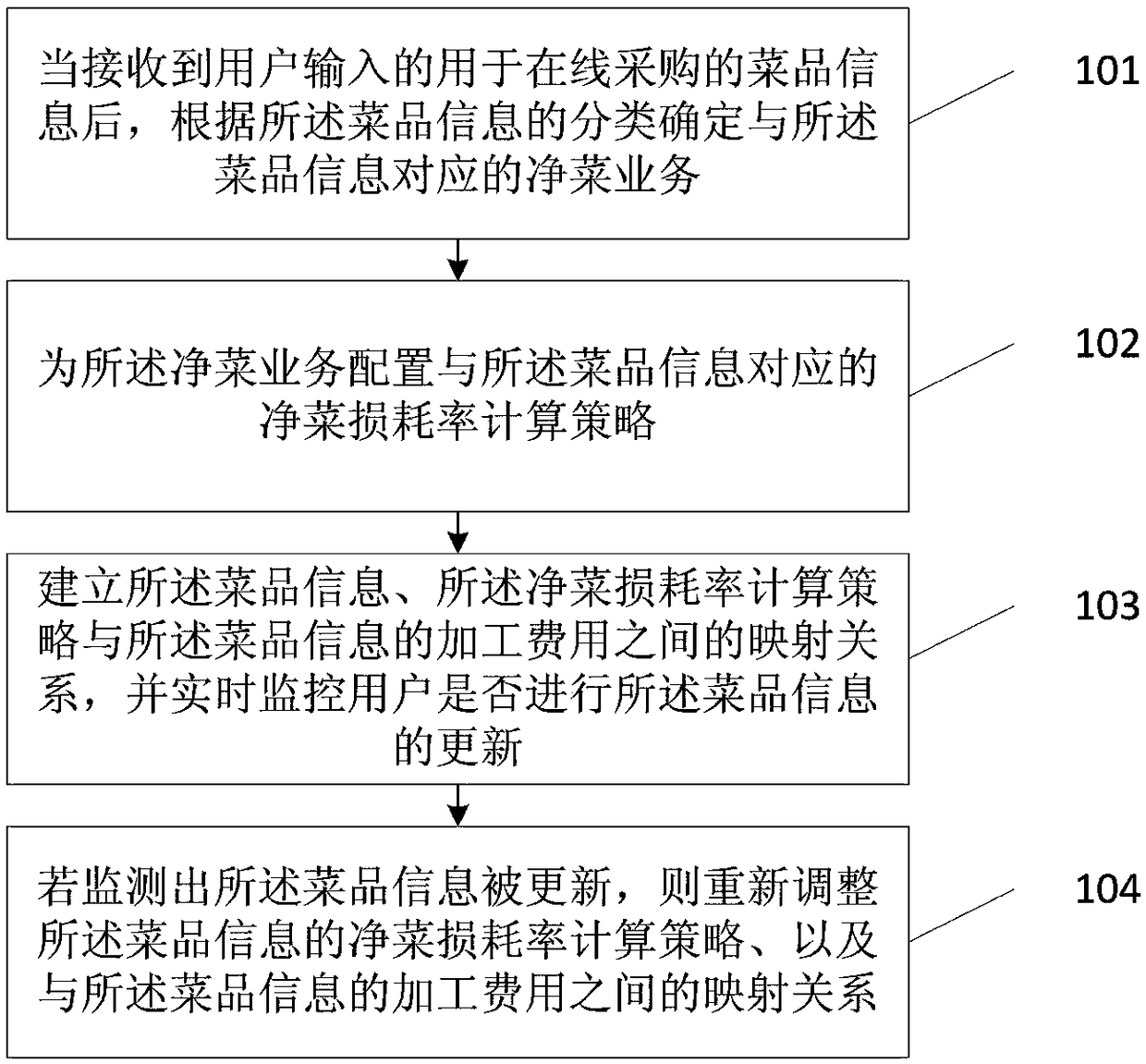
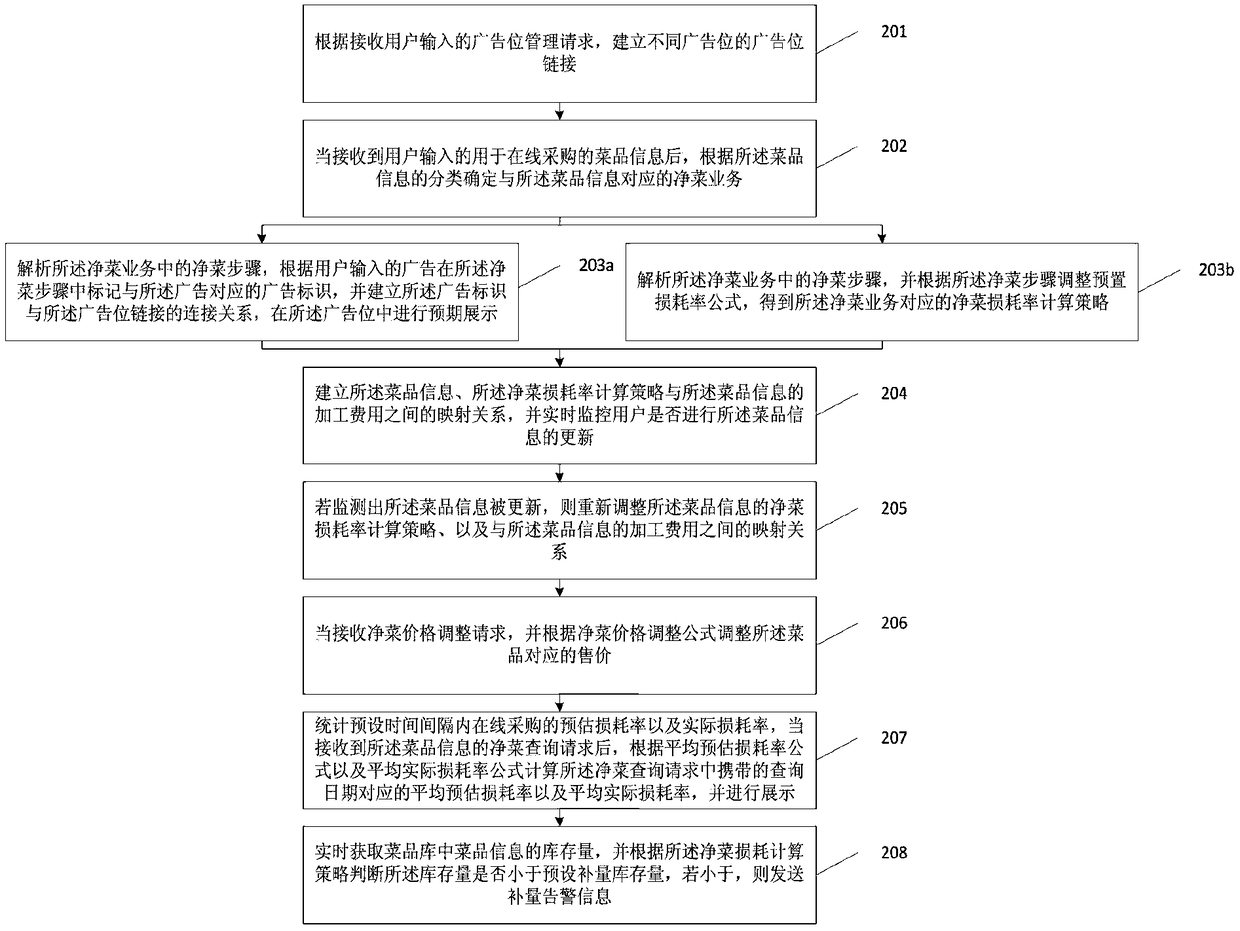
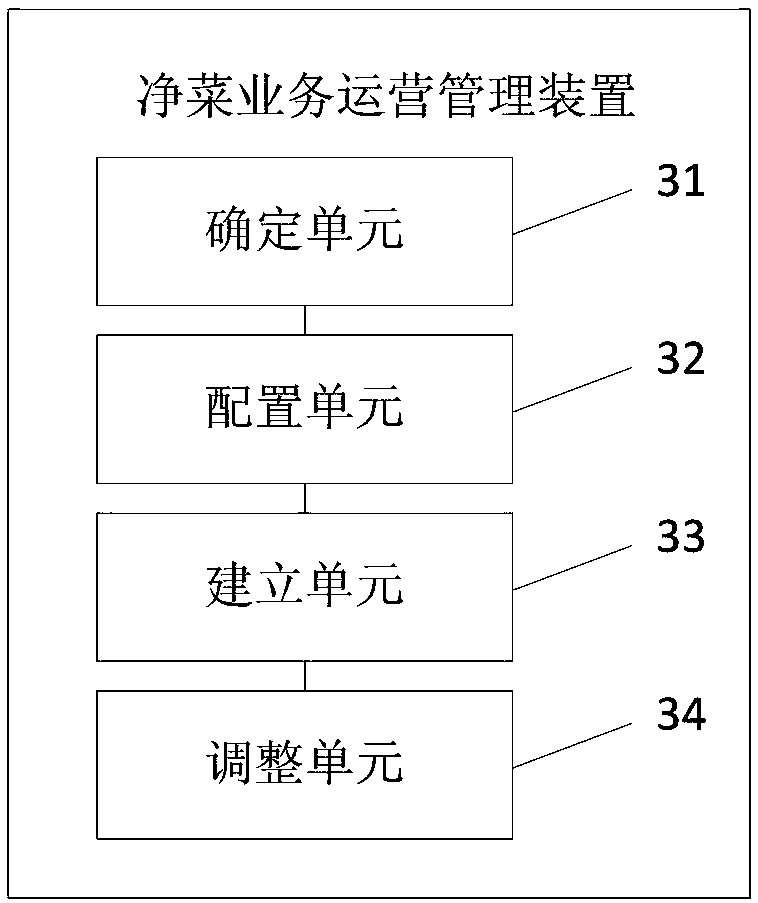
Minimally processed vegetable service operation management method and device
ActiveCN108960589AOptimize calculation methodImprove efficiencyAdvertisementsResourcesUser inputProcessing cost
The invention discloses a minimally processed vegetable service operation management method and device, and relates to the technical field of on-line purchase. The minimally processed vegetable service operation management method and device mainly aim to solve the problem that at present, there is still no specific method for operation management of minimally processed vegetable service to meet the demand for different merchants or suppliers. The minimally processed vegetable service operation management method includes the steps: after receiving dish information for on-line purchase, input bya user, determining the minimally processed vegetable service corresponding to the dish information according to classification of the dish information; configuring a minimally processed vegetable waste rate calculation strategy corresponding to the dish information for the minimally processed vegetable service; establishing a mapping relationship between the dish information, the minimally processed vegetable waste rate calculation strategy, and the processing cost of the dish information Mapping the relationship, and monitoring whether the user updates the dish information in real time; andif monitoring that the dish information is updated, iteratively adjusting the minimally processed vegetable waste rate calculation strategy of the dish information, and the mapping relationship withthe processing cost of the dish information.
Owner:阳光易购(北京)科技有限公司
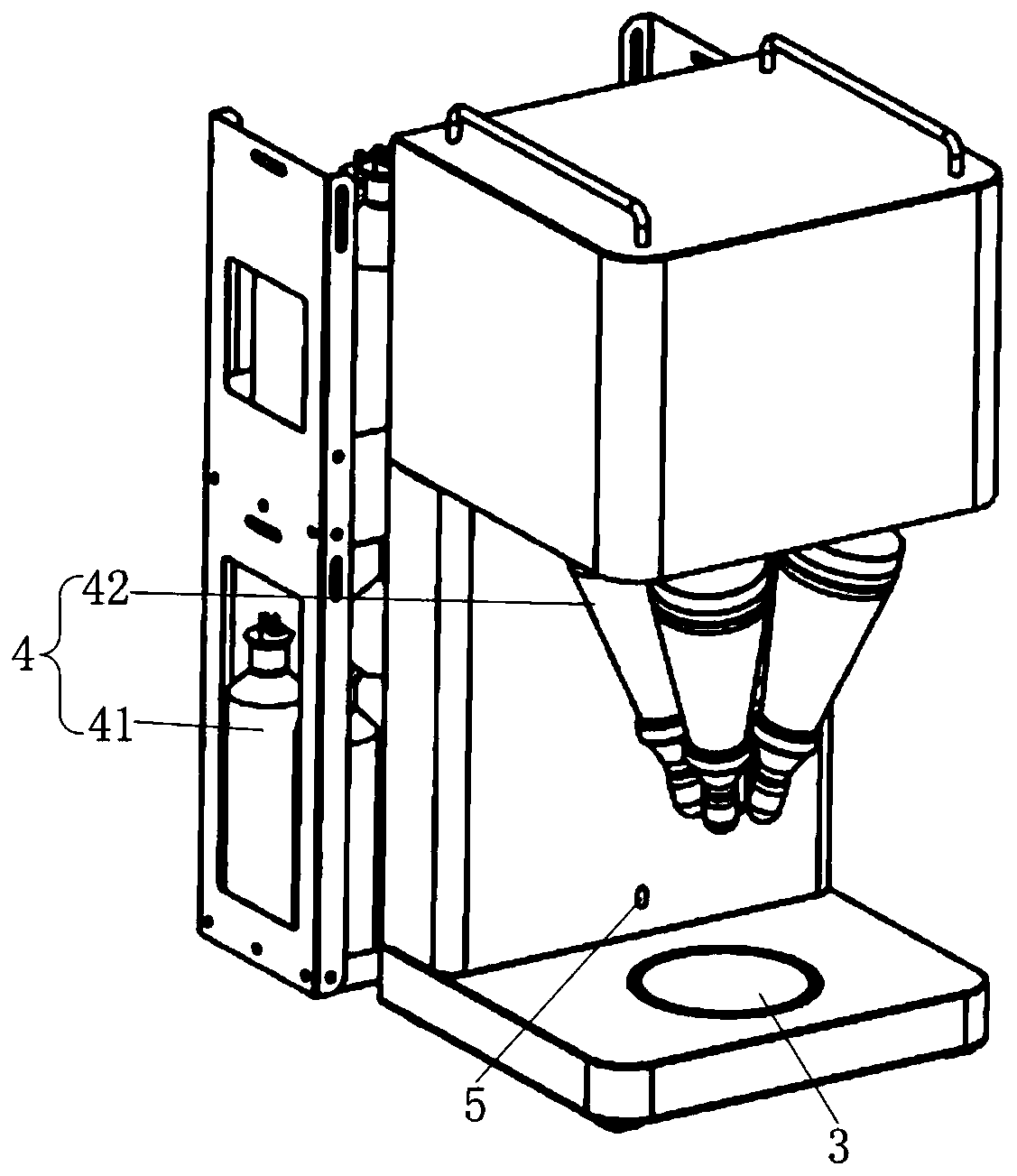
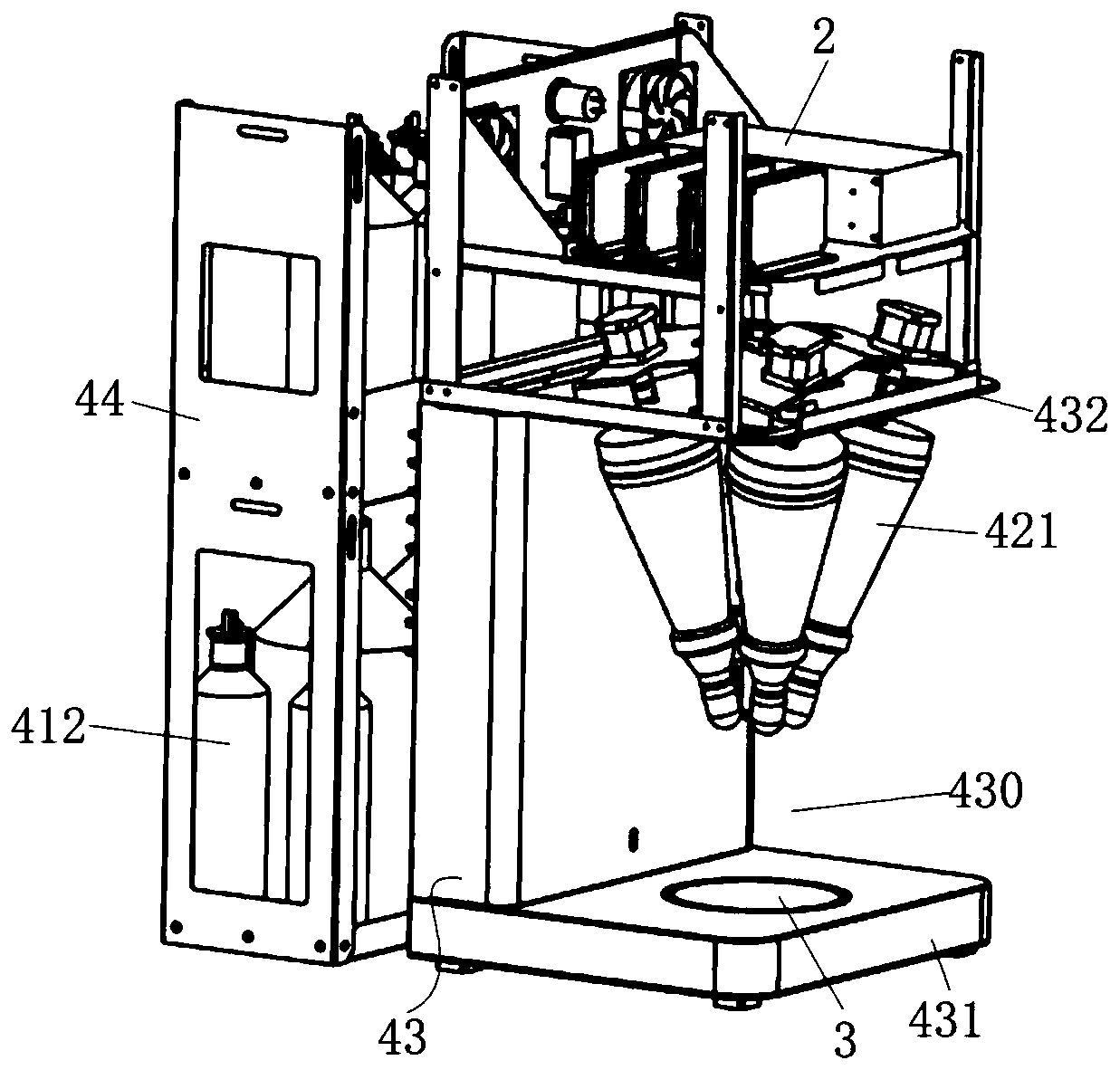
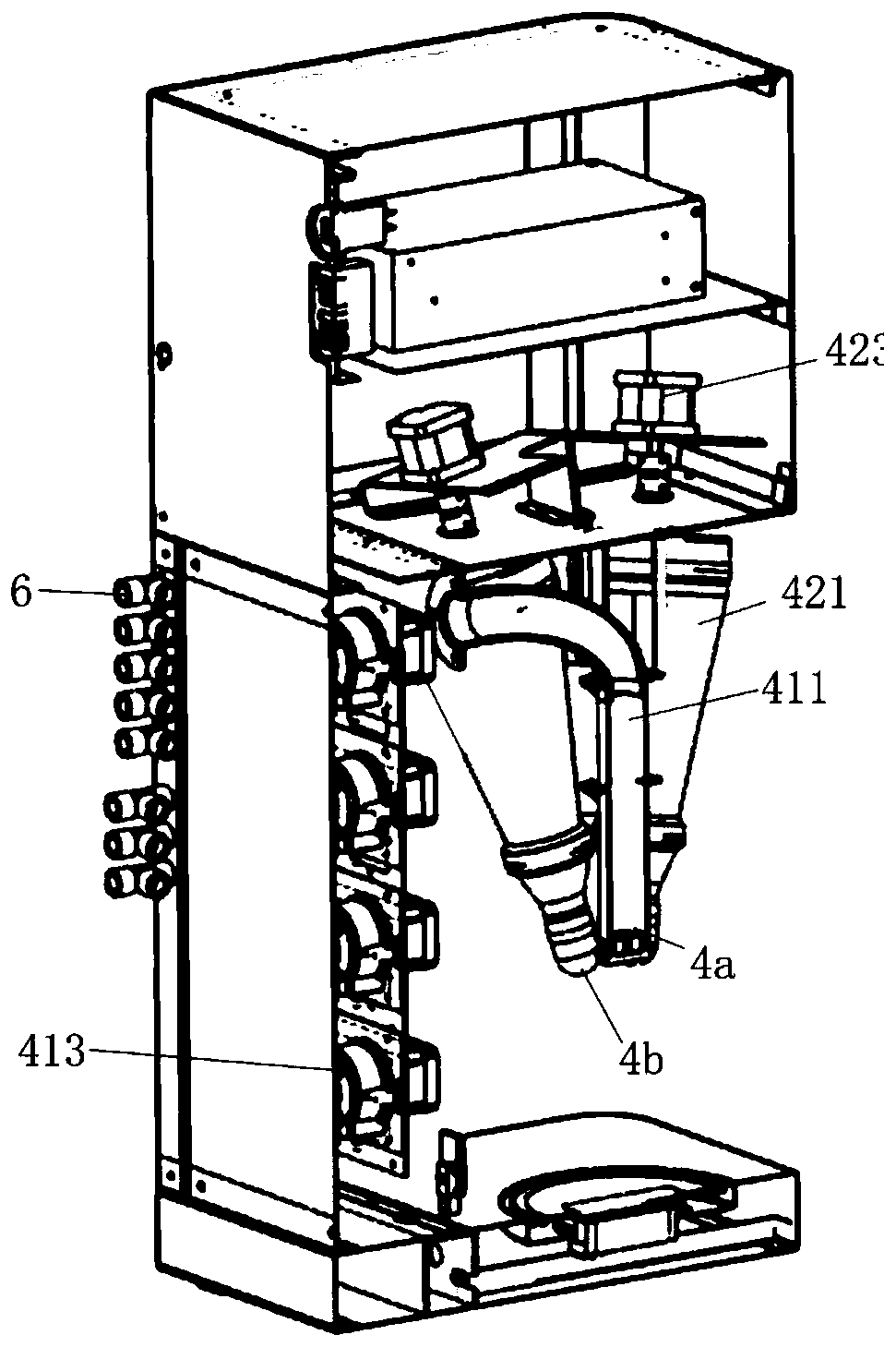
Automatic proportioning flavoring machine
The invention discloses an automatic proportioning flavoring machine which comprises a setting device for presetting seasoning proportion, a control device for communicative connection with the setting device, a weighing device connected with the control device and for weighing a utensil below a discharging port and sending weight data to the control device, and a discharging device provided witha plurality of driving parts for driving discharging. The control device sends the obtained weight data to the setting device, the setting device obtains the weight data and then calculates driving parameters of the driving parts according to preset seasoning proportion, and the control device obtains the driving parameters and controls the driving parts to work. The automatic proportioning flavoring machine can dynamically adjust seasonings according to the weights of food materials, thereby improving the accuracy of seasoning proportioning.
Owner:广东顺德新厨网络科技有限公司 +1
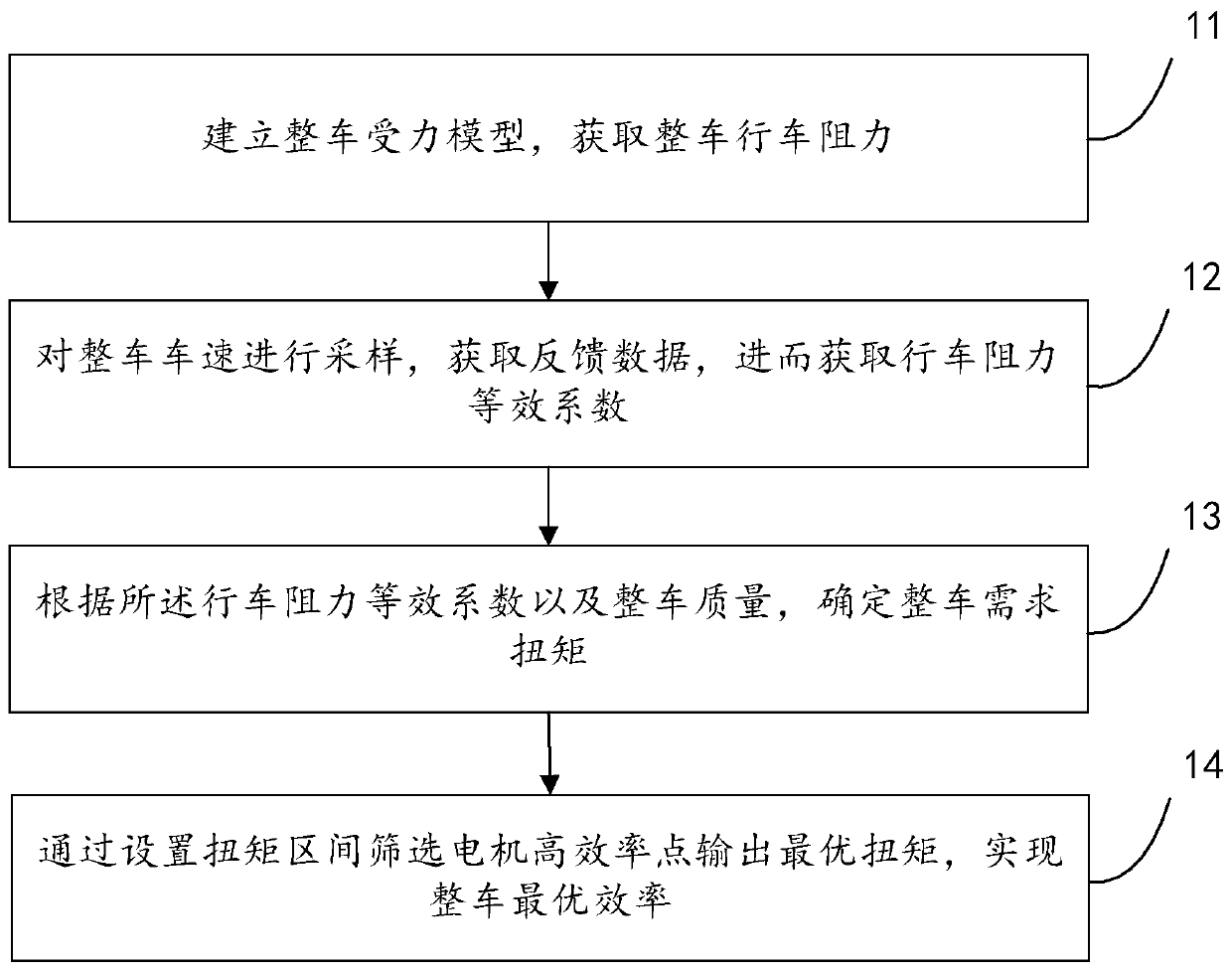
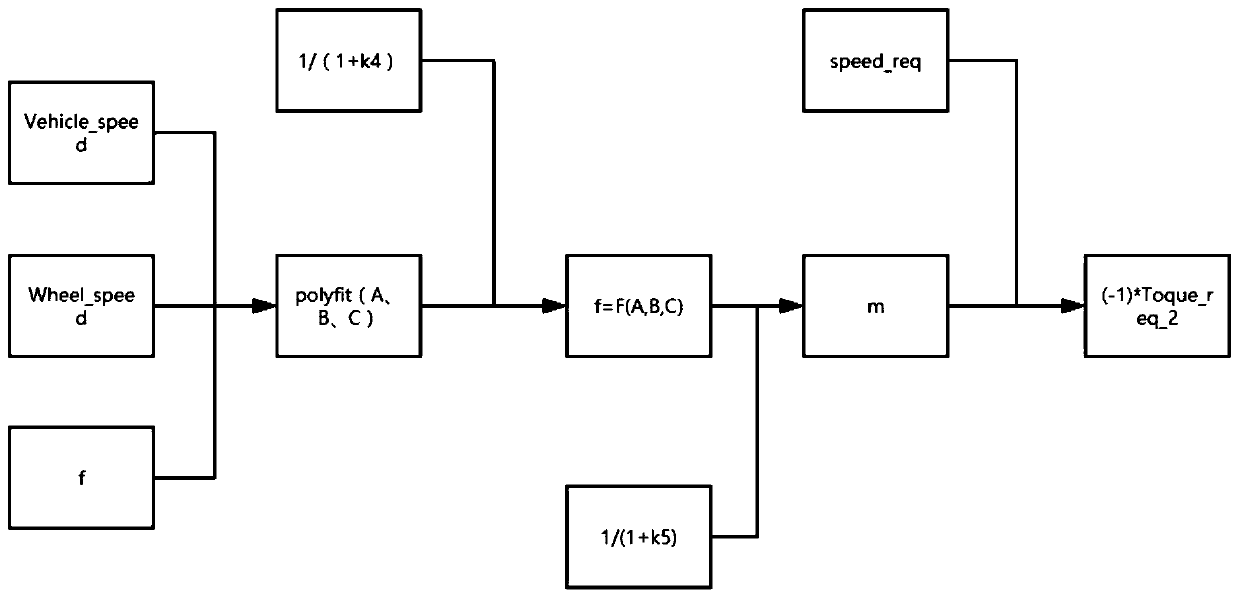
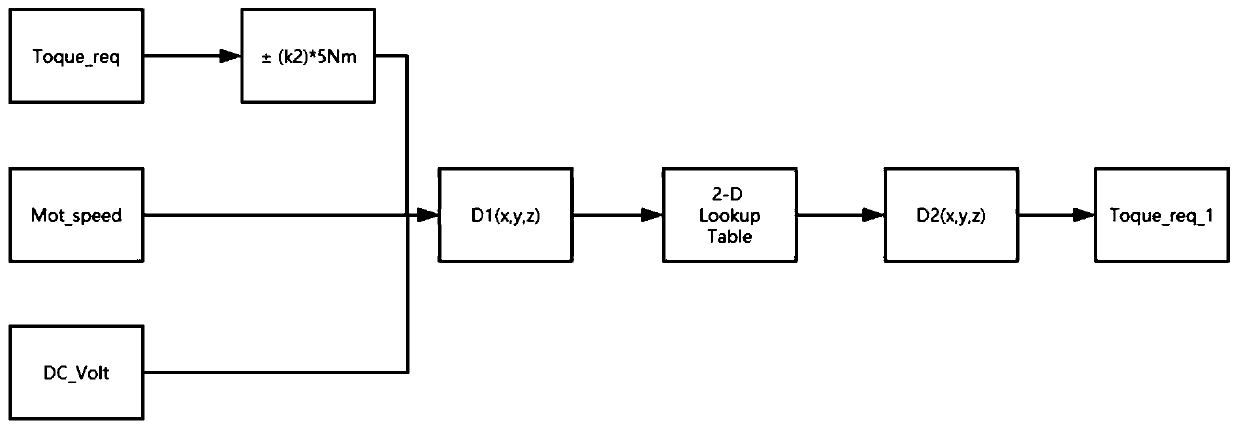
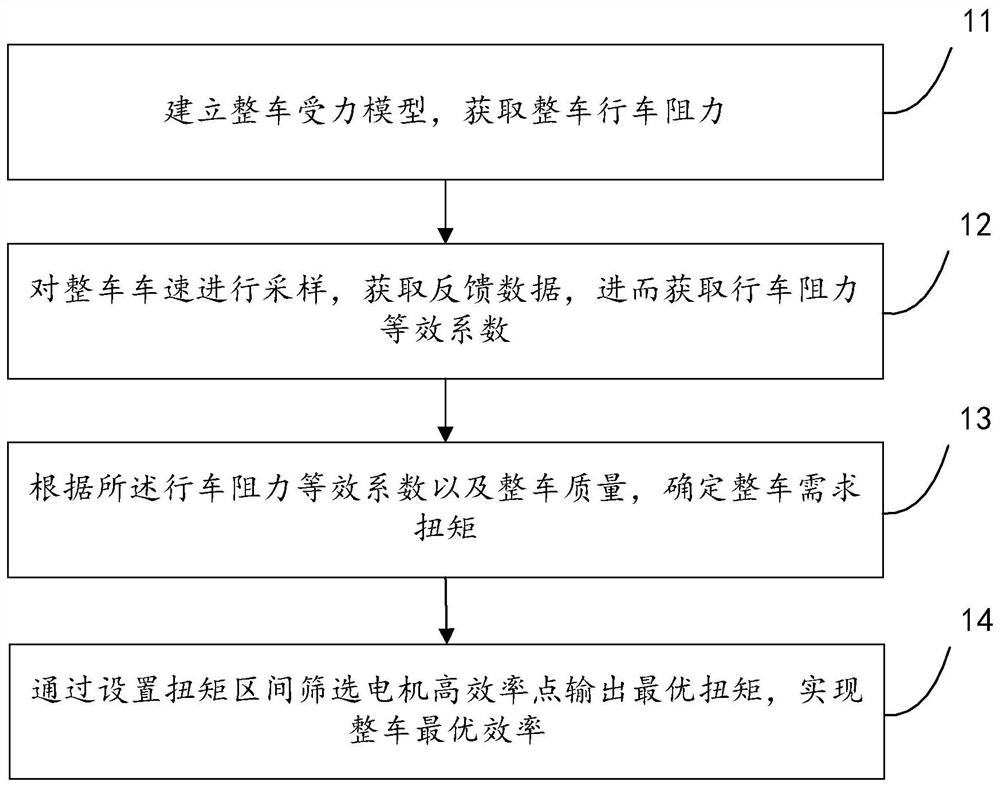
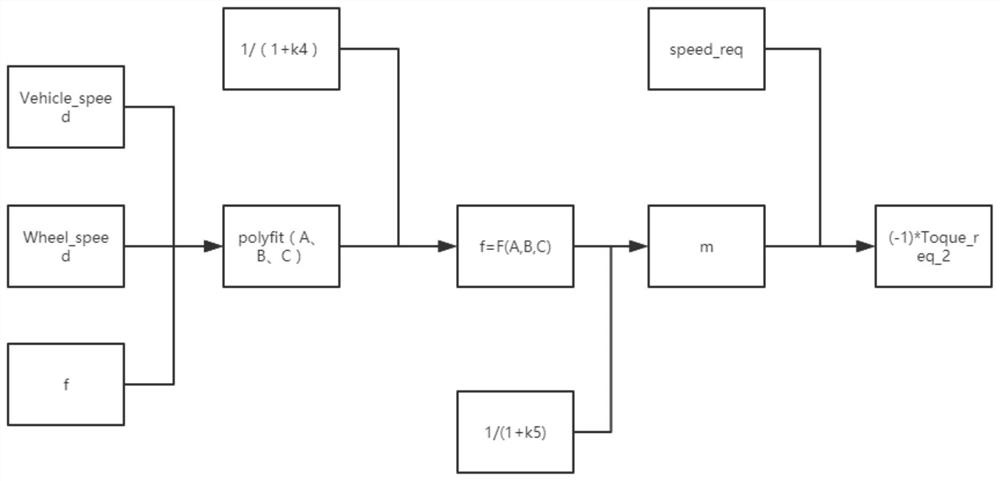
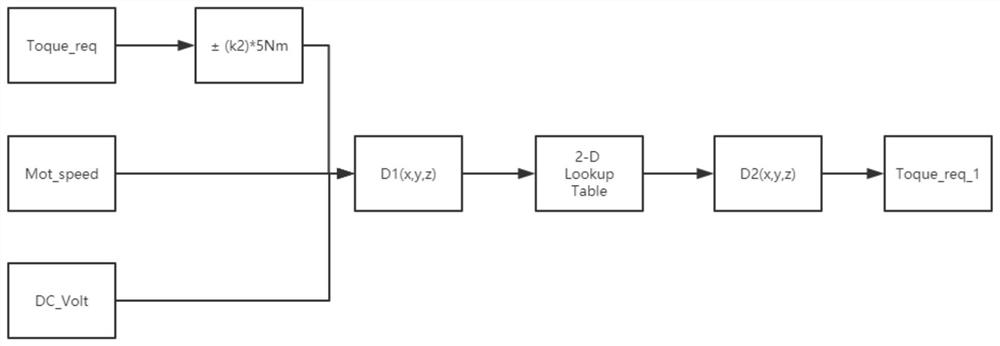
Vehicle optimal efficiency obtaining method and system
ActiveCN111497857AImprove computing efficiencyOptimal efficiency achievedVehicle condition input parametersElectric machineryAutomotive engineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a vehicle optimal efficiency obtaining method and system, and the method comprises the steps: building a whole vehicle stress model; sampling the vehicle speed of the whole vehicle to obtain feedback data, and obtaining driving resistance equivalent coefficients A, B and C according to the stress model of the whole vehicle; determining the required torqueof the whole vehicle according to the driving resistance equivalent coefficients A, B and C and the mass of the whole vehicle; screening the optimal torque output by the motor high-efficiency point bysetting a torque interval, and achieving the optimal efficiency of the whole vehicle. According to the scheme, the whole vehicle mathematical model is established, the whole vehicle stress equivalentcoefficient is used for closed-loop adjustment, and various working conditions in whole vehicle operation are met. And the calculation efficiency is improved by optimizing a calculation mode, lookingup a table, obtaining a difference value and a weight, calibrating in advance and the like.
Owner:智车优行科技(上海)有限公司
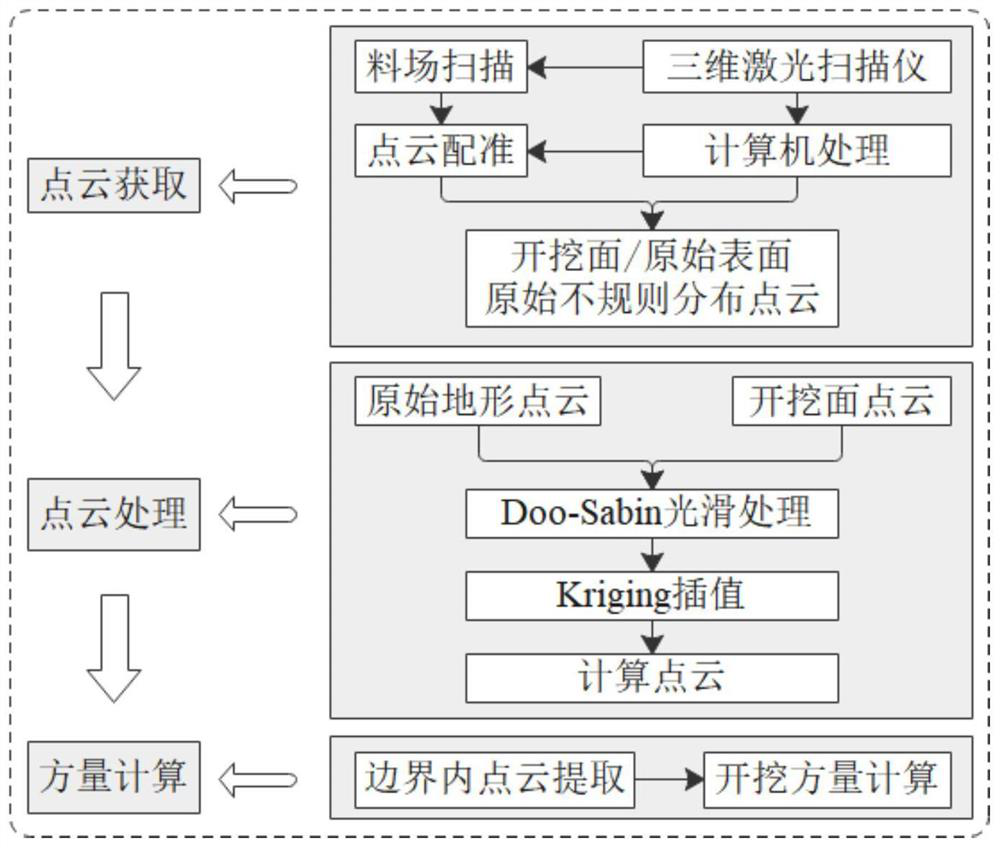
Earth and rockfill dam complex borrow pit excavation volume calculation method based on grid subdivision algorithm
ActiveCN112734929ARetain regularityReserve completenessImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudGrid based
An earth and rockfill dam complex borrow pit excavation volume calculation method based on a grid subdivision algorithm comprises the following steps that three-dimensional point cloud data of a borrow pit excavation face are scanned, registration of point clouds of different scanning batches is achieved through a point cloud registration algorithm, so that point clouds which are originally and irregularly distributed on the excavation face are obtained; the obtained original irregularly distributed point cloud is processed through a Doo-Sabin subdivision algorithm, and the point cloud forms a relatively regular excavation surface; then, Kriging interpolation calculation is performed to obtain a spatial point cloud participating in excavation volume calculation; a grid subdivision algorithm is compiled through MATLAB, and calculation of the excavation volume is achieved. According to the earth and rockfill dam complex borrow pit excavation volume calculation method based on the grid subdivision algorithm, the borrow pit excavation volume can be rapidly estimated, and the method has the advantages of being small in workload, relatively safe in measurement and high in efficiency.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
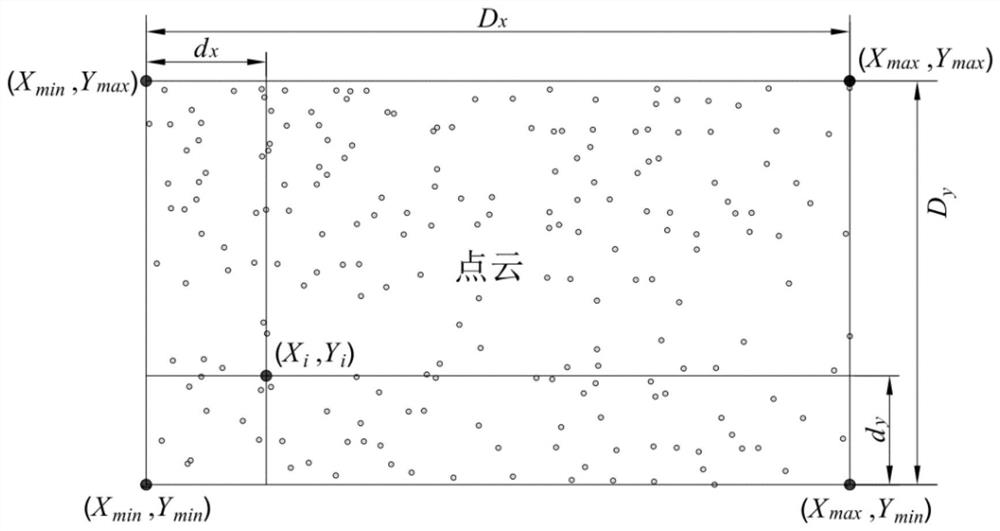
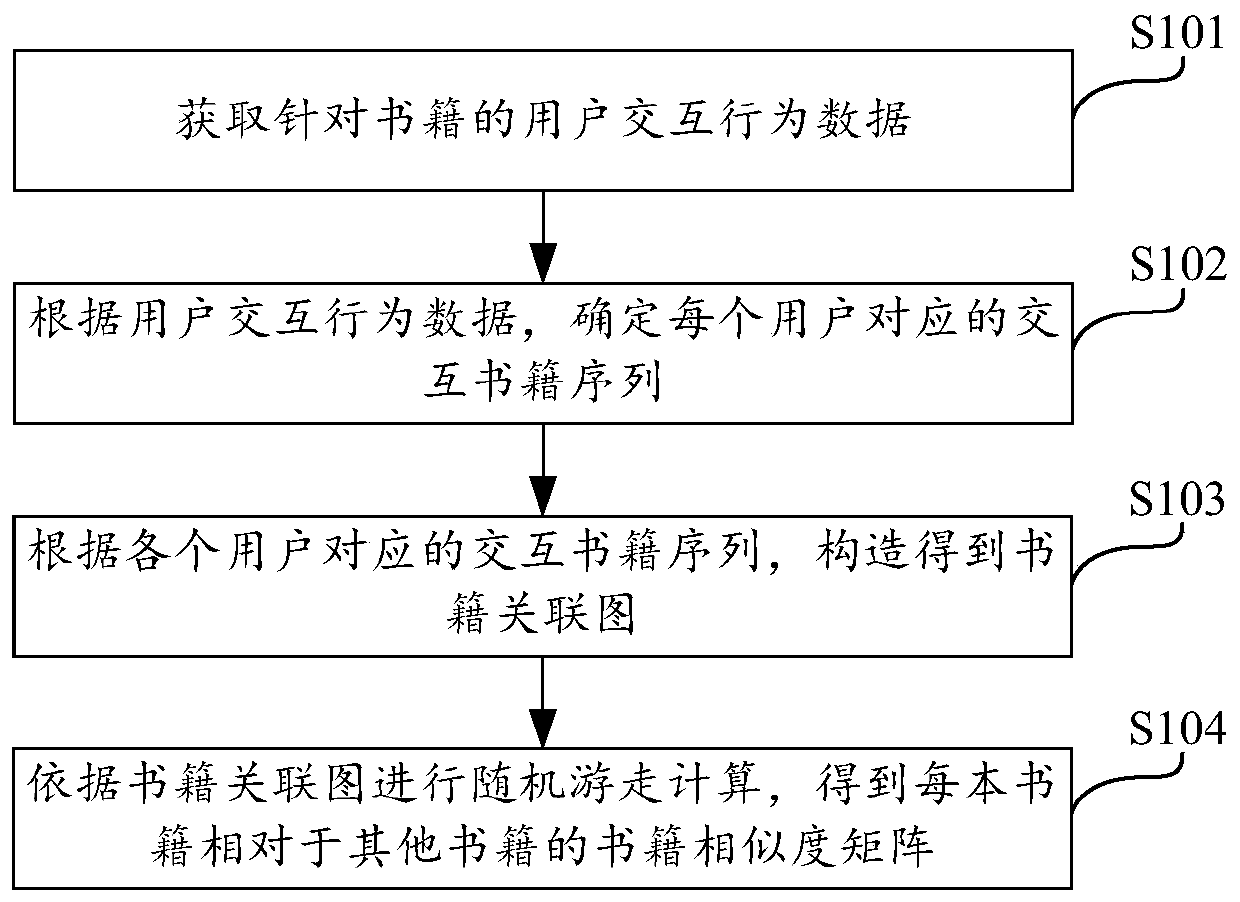
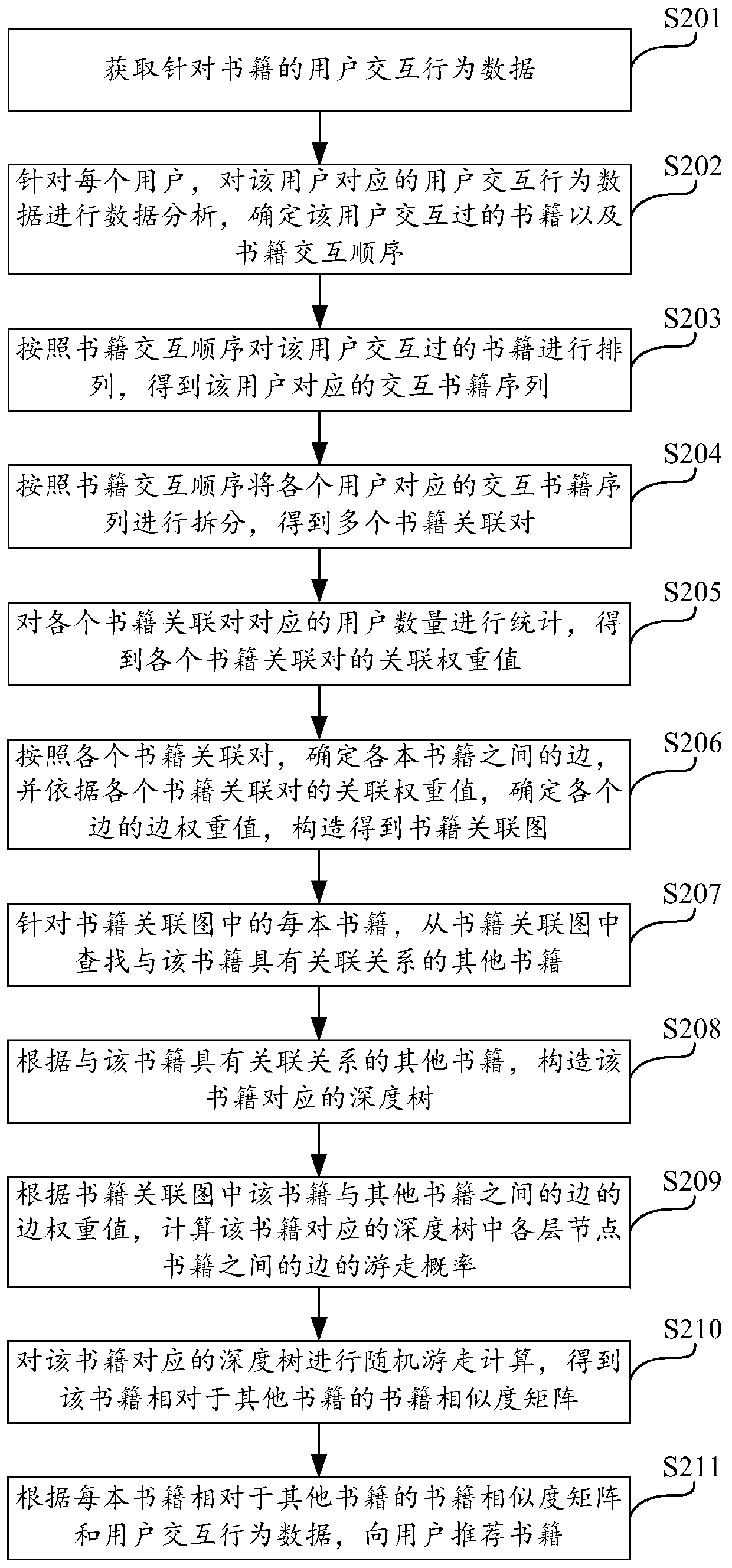
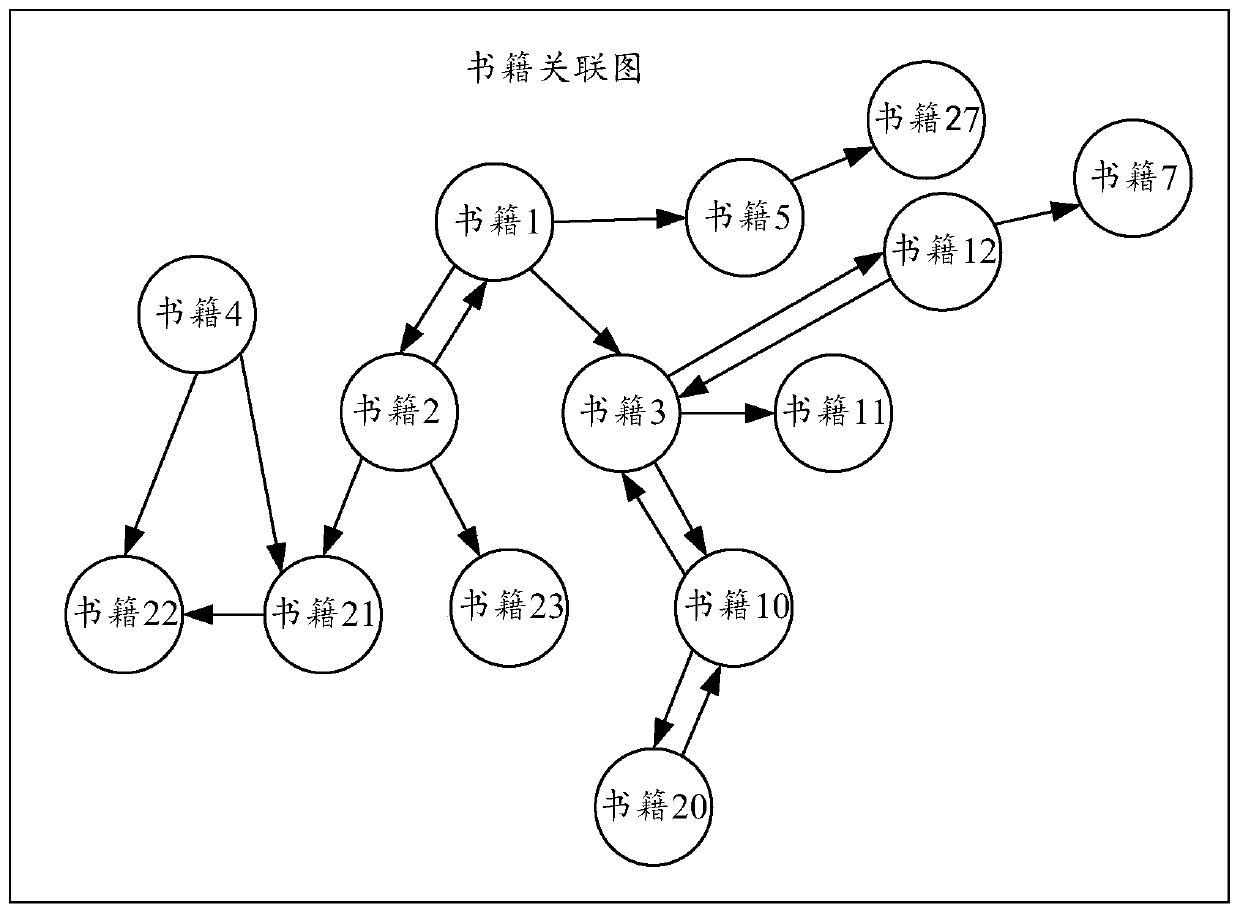
Book similarity calculation method based on random walk and electronic equipment
PendingCN110532528AImprove calculation accuracyOptimize calculation methodSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionElectronic equipment
The invention discloses a book similarity calculation method based on random walk, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining user interaction behavior data for a book; determining an interactive book sequence corresponding to each user according to the user interaction behavior data; constructing a book association graph according to the interactive book sequence corresponding to each user; performing random walk calculation according to the book association graph to obtain a book similarity matrix of each book relative to other books. According to user interaction behavior data for books, the book association graph can be conveniently and rapidly constructed. Random walk calculation is made according to the book association graph, the book similarity matrix of each book relative to other books is rapidly obtained, the similarity between the books is accurately and effectively reflected from the perspective of a user, the calculation accuracy of the book similarity is effectively improved, and the calculation mode of the book similarity is optimized.
Owner:ZHANGYUE TECH CO LTD
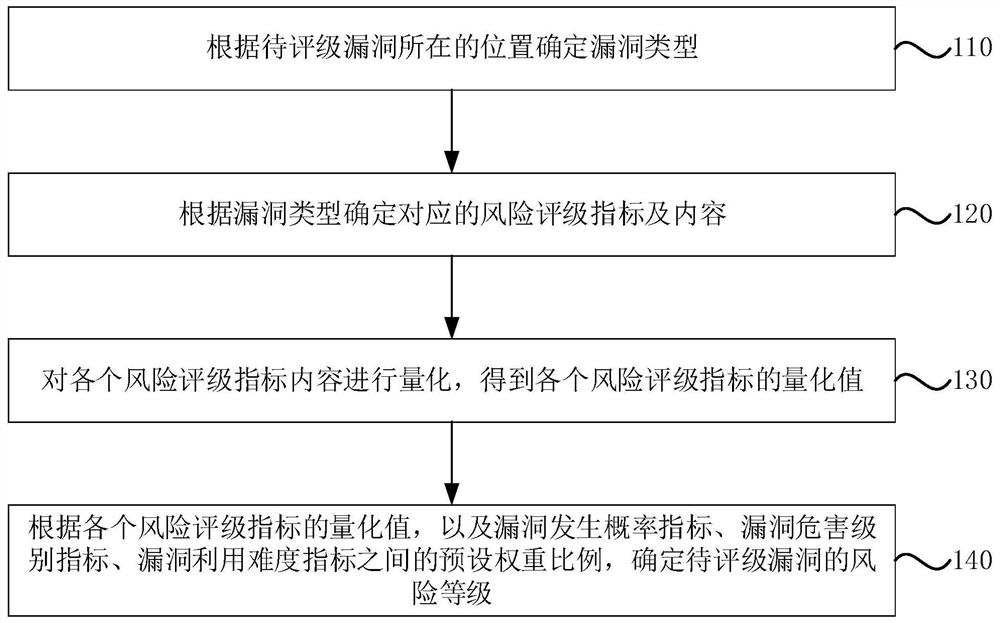
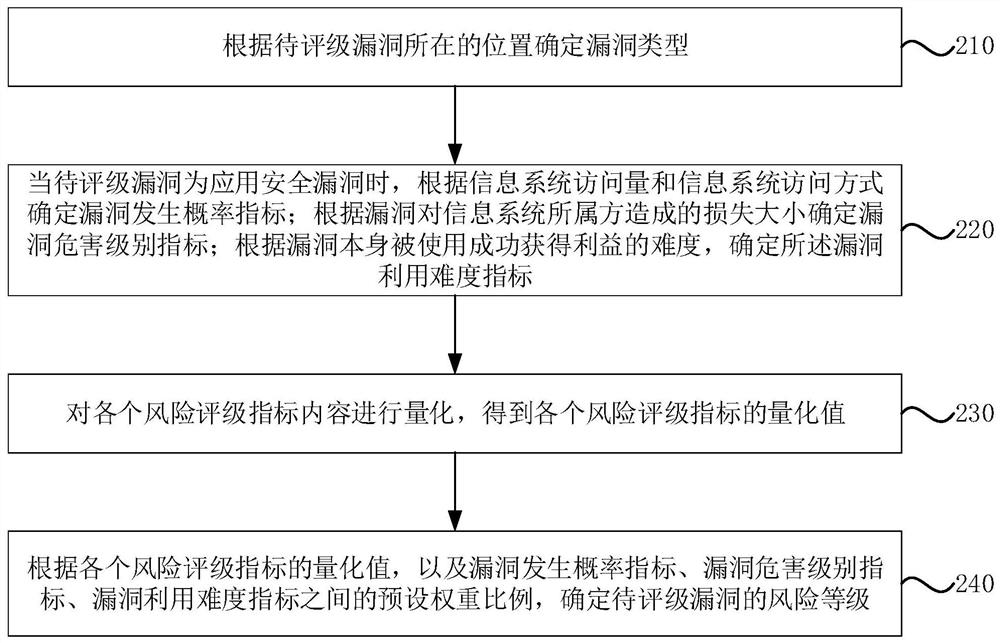
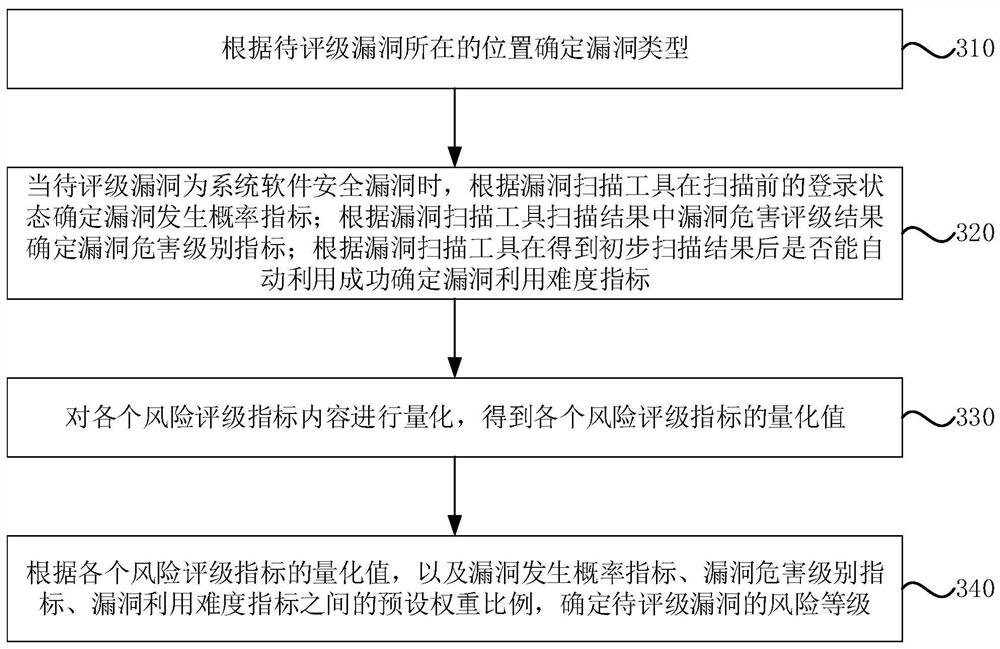
Risk rating method and device for security vulnerabilities of information system, equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113987509AImprove applicabilityOptimize calculation methodPlatform integrity maintainanceResourcesSystem safetySecurity bug
The embodiment of the invention discloses a risk rating method and device for security vulnerabilities of an information system, equipment and a storage medium. The risk rating method for the security vulnerabilities of the information system comprises the following steps: determining vulnerability types according to positions of to-be-rated vulnerabilities; determining a corresponding risk rating index and content according to the vulnerability type, wherein the risk rating indexes comprise a vulnerability occurrence probability index, a vulnerability hazard level index and a vulnerability utilization difficulty index; quantifying the content of each risk rating index to obtain a quantized value of each risk rating index; and according to the quantized value of each risk rating index and a preset weight ratio among the vulnerability occurrence probability index, the vulnerability hazard level index and the vulnerability utilization difficulty index, determining the risk level of the to-be-rated vulnerability. Through the method, the security vulnerabilities of the information system can be graded quickly.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUDONG DEVELOPMENT BANK
Method for determining battery performance by multi-parameter weighting
The invention relates to the technical field of operation and maintenance and monitoring on a substation DC system, specifically, relates to a method for determining battery performance by multi-parameter weighting, comprising the following steps of : 1 collecting the cell voltage of each cell in real time and recording it once every hour; 2 automatically performing an internal resistance test every month, and recording the internal resistance and discharge voltage of each battery in the internal resistance test. The method for determining battery performance by multi-parameter weighting assigns weights according to categories, and then calculates the integrated value of each battery. The battery with the highest combined value is the worst performing battery. The calculation method is simple and accurate.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY
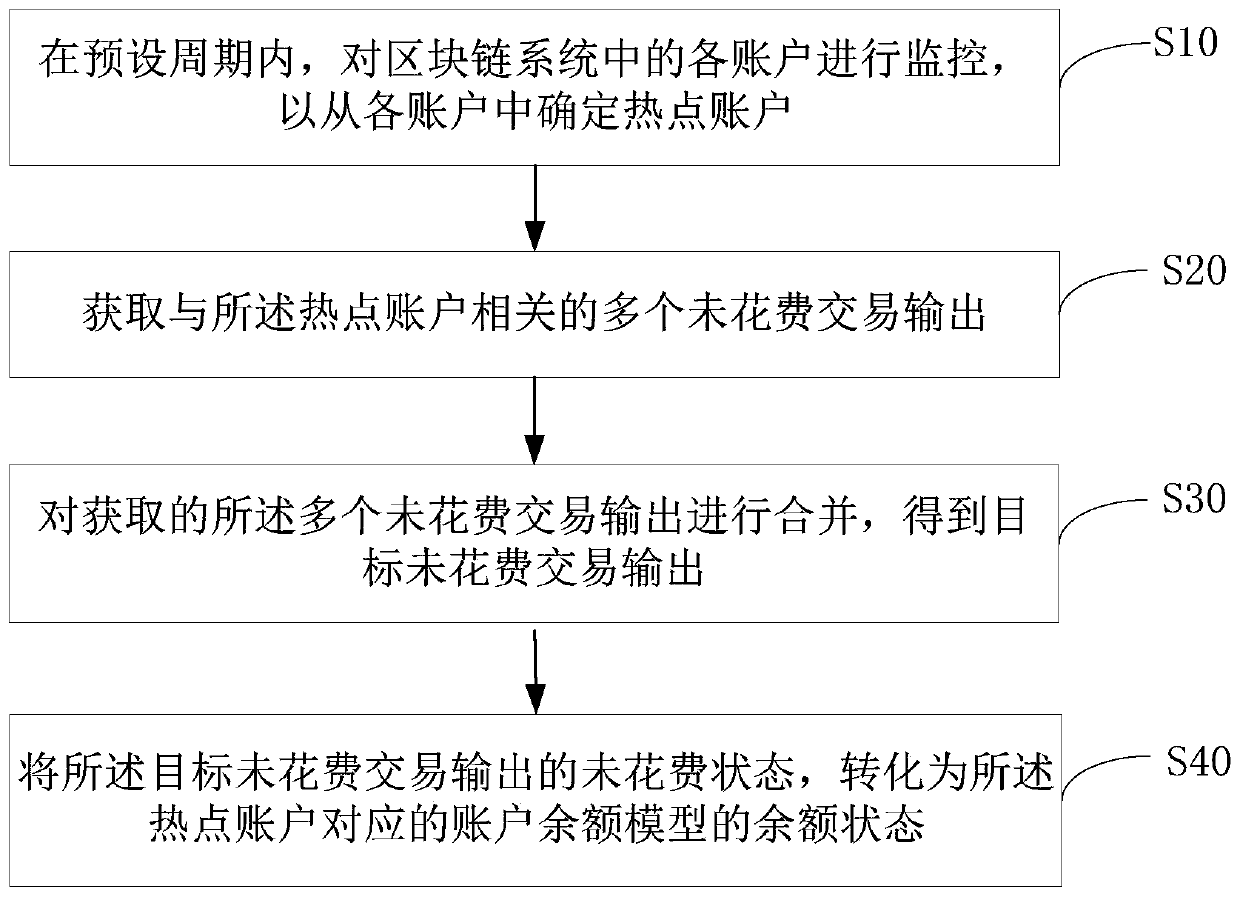
Block chain data processing method, apparatus and device and readable storage medium
InactiveCN110728504AOptimize calculation methodImprove operational efficiencyPayment protocolsPayment circuitsEngineeringFinancial transaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of data processing, and provides a block chain data processing method, which comprises the steps of monitoring each account in a block chain system in a preset period so as to determine a hotspot account from each account; acquiring a plurality of unspent transaction outputs related to the hotspot account; combining the plurality of obtained unspent transaction outputs to obtain a target unspent transaction output; and converting the unspent state output by the target unspent transaction into a balance state of an account balance model correspondingto the hotspot account. The invention further provides a block chain data processing apparatus and device and a readable storage medium. According to the block chain data processing method, the account balance calculation mode can be optimized, and the operation efficiency of the block chain system is improved, and the query experience of the account balance is improved.
Owner:PINGAN YIQIANBAO E COMMERCE CO LTD
Multi-parameter weighted method for judging battery performance
ActiveCN109212429BHigh precisionOptimize calculation methodElectrical testingElectrical batteryInternal resistance
The invention relates to the technical field of operation and maintenance and monitoring on a substation DC system, specifically, relates to a method for determining battery performance by multi-parameter weighting, comprising the following steps of : 1 collecting the cell voltage of each cell in real time and recording it once every hour; 2 automatically performing an internal resistance test every month, and recording the internal resistance and discharge voltage of each battery in the internal resistance test. The method for determining battery performance by multi-parameter weighting assigns weights according to categories, and then calculates the integrated value of each battery. The battery with the highest combined value is the worst performing battery. The calculation method is simple and accurate.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY
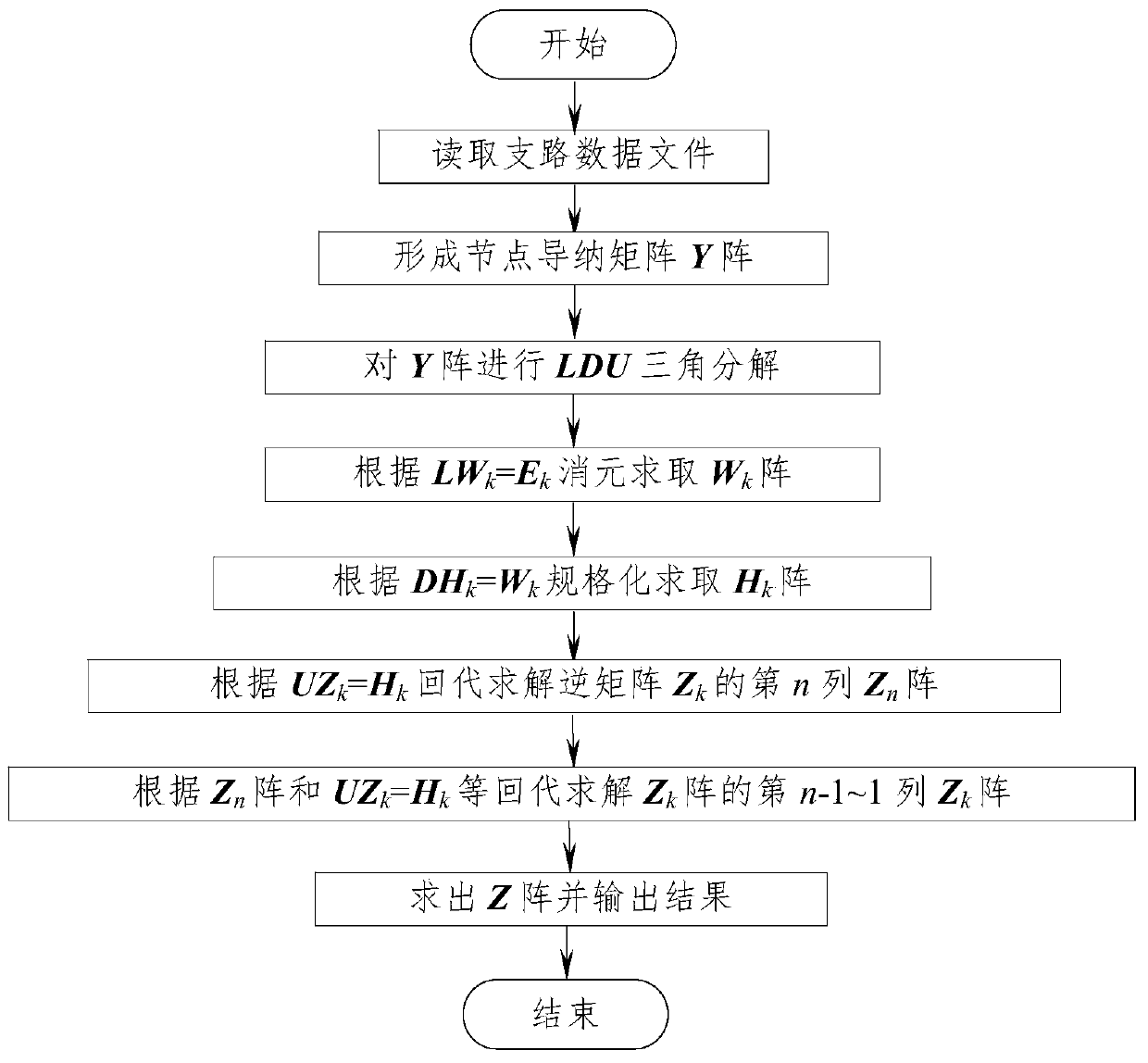
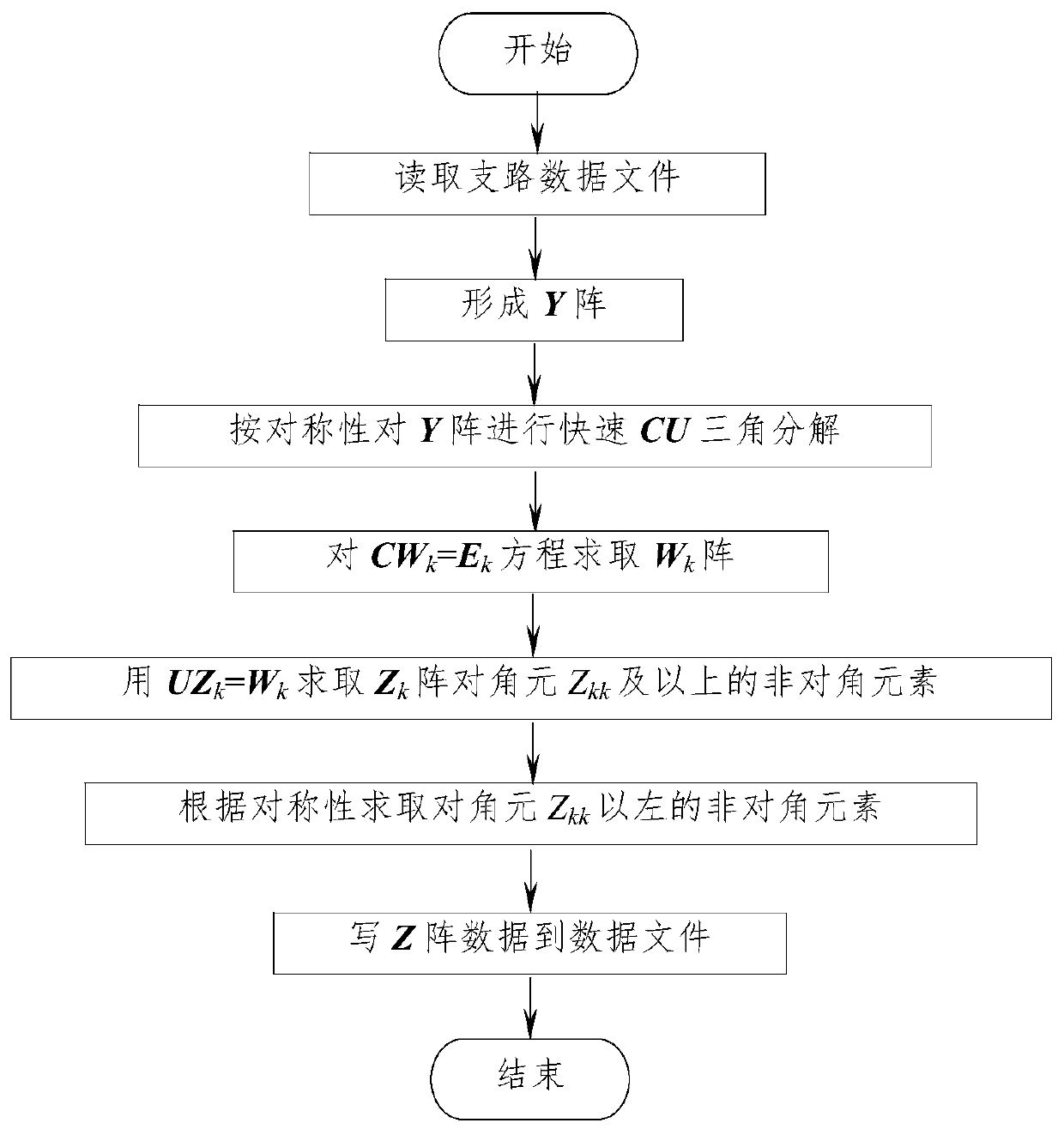
A Method of Obtaining Power System Node Impedance Matrix Based on cu Triangular Decomposition
ActiveCN104657337BImprove computing efficiencySave storage unitComplex mathematical operationsElectric power systemData file
The invention relates to an electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition and belongs to the field of electric power system analysis and computing. The method mainly includes the steps of forming a node admittance matrix Y; performing quick CU triangular decomposition on the matrix Y; solving a matrix Wk through CWk=Ek; solving non-diagonal elements of a diagonal element Zkk and the diagonal element above the diagonal element Zkk of a matrix Zk through UZk=Wk; solving non-diagonal elements on the left of the diagonal element Zkk in accordance with the symmetry; writing data of a matrix Z to a data file. According to the electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition, a CU triangular decomposition method higher in calculation efficiency than a LDU triangular decomposition method is used for solving elements of the matrix Z, the symmetrical relationship between elements of a matrix Y and elements of a matrix C and a matrix U is used for quickly forming a composite matrix of a factor matrix C and a factor matrix U, and the symmetry of the matrix Z and the calculation order of elements of the matrix Zk is used for omitting back substitution solving of lower triangular elements of the matrix Z for achieving direct solving, so that the speed of formation of the matrix Z is greatly improved. Compared with the traditional LDU triangular decomposition method, the electric power system node impedance matrix Z solving method based on CU triangular decomposition has the calculation speed increased by about 33% when the method is used for IEEE-30, IEEE-57 and IEEE-118 node system checking calculation.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Method for Determining Characteristic Values of Bearing Capacity of Rammed/Compacted Fill Layer Using Shear Wave Velocity
ActiveCN110130300BEasy to calculateOptimize calculation methodIn situ soil foundationDynamic compactionSoil science
The invention provides a method for determining bearing capacity characteristic values of tamped / compacted fill strata by using the shear wave velocity. The method for determining the bearing capacitycharacteristic values of the tamped / compacted fill strata specifically includes the steps that the fill strata of a dynamic compaction (compacted) foundation are classified by using first stone backfill materials with different particle sizes, then the bearing capacity characteristic values of the fill strata calculated by adopting shear strength indexes (c and phi) of a direct shear test on sitecorrespondingly correspond to the shear wave velocity in a borehole to establish the relationship between the bearing capacity characteristic values and the shear wave velocity, and through the established correspondence, the accurate and fast method for determining the bearing capacity characteristic values of tamped / compacted foundation soil layers is provided in addition to a load test method.An accurate basis for valuing of the bearing capacity characteristic values is provided for valuing and evaluation of a tamped foundation and a compacted foundation in geotechnical engineering investigation.
Owner:WUHAN SURVEYING GEOTECHN RES INST OF MCC
A method and system for obtaining optimal efficiency of a vehicle
ActiveCN111497857BOptimal efficiency achievedMeet working conditionsVehicle condition input parametersMathematical modelControl engineering
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a method and system for obtaining optimal vehicle efficiency, wherein the method includes: establishing a force model of the vehicle; sampling the speed of the vehicle to obtain feedback data, and obtaining driving resistance according to the force model of the vehicle Equivalent coefficients A, B, C; according to the equivalent coefficients A, B, C of driving resistance and the mass of the vehicle, determine the required torque of the vehicle; set the torque interval to filter the motor high-efficiency point to output the optimal torque to realize the vehicle optimal efficiency. This scheme establishes the mathematical model of the whole vehicle, and uses the equivalent force coefficient of the whole vehicle in the closed-loop adjustment to meet various working conditions in the operation of the whole vehicle. Optimize the calculation method, look up the table, difference, weight, advance calibration and other methods to improve the calculation efficiency.
Owner:智车优行科技(上海)有限公司
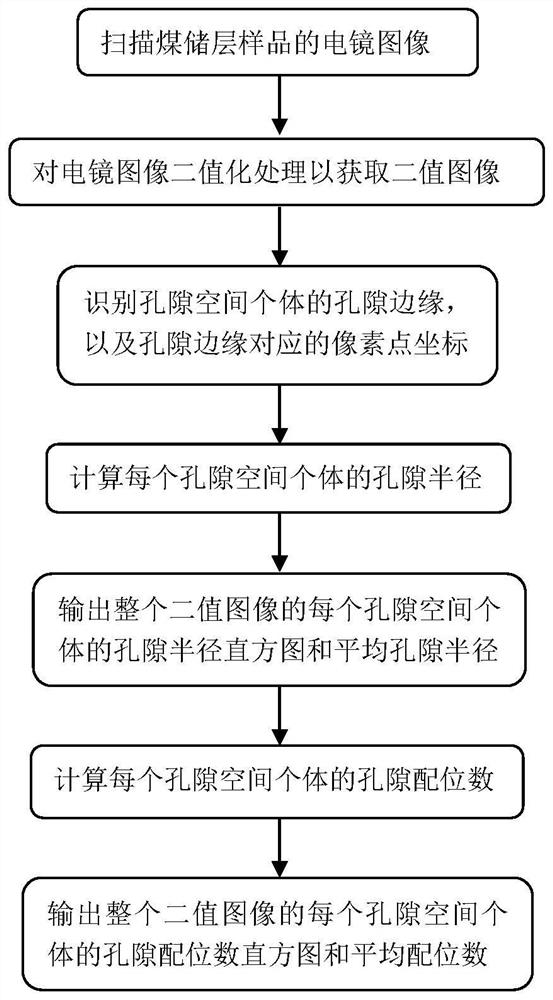
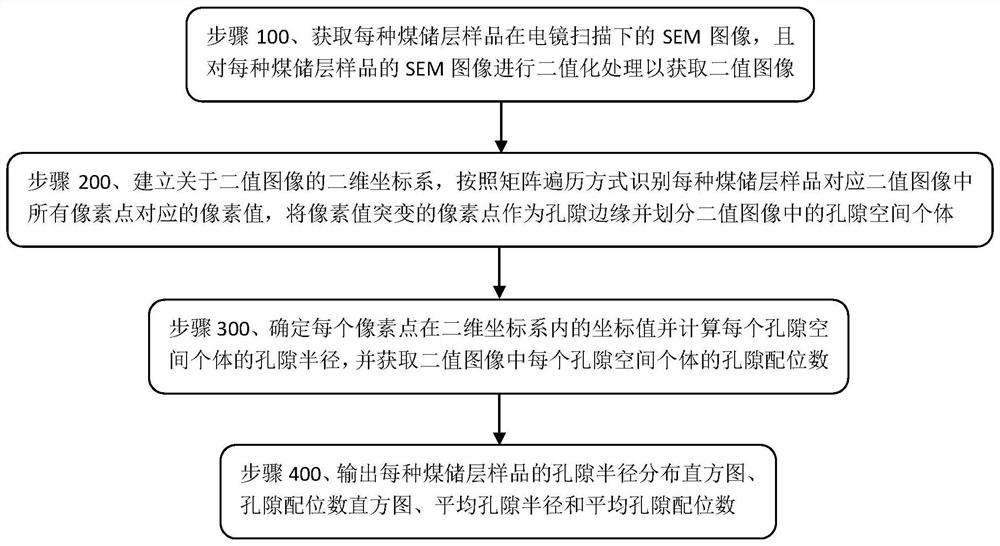
A Quantitative Analysis Method of Coal Reservoir Pore Structure Parameters Based on SEM Image
ActiveCN113533158BImprove calculation accuracyAdding Computational ImpactImage analysisPermeability/surface area analysisComputational scienceStatistical physics
The invention discloses a method for quantitative analysis of pore structure parameters of coal reservoirs based on SEM images. Perform binarization processing to obtain a binary image; establish a two-dimensional coordinate system about the binary image, identify the pixel values corresponding to all pixel points in the binary image corresponding to each coal reservoir sample according to the matrix traversal method, and mutate the pixel values The pixel points are used as the pore edge and divide the pore space individuals in the binary image; determine the coordinate value of each pixel point in the two-dimensional coordinate system and calculate the pore radius of each pore space individual, and obtain each pore space in the binary image. Pore coordination number of individual pore space; output histogram of pore radius distribution, pore coordination number histogram, average pore radius and average pore coordination number of each coal reservoir sample; The calculation accuracy is high and the implementation cost is low.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Calculation method and device for platform-based log analysis
ActiveCN105404579BOptimize calculation methodAvoid redundant calculationsHardware monitoringAlgorithmDegree of association
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
A Novel Text Recognition Method Based on Counting Focusing Model
ActiveCN108009539BOptimize calculation methodLow implementation requirementsCharacter and pattern recognitionText recognitionAlgorithm
The present invention relates to a novel text recognition method based on a counting focus model, the counting focus model includes an encoder and a decoder, and the recognition method includes the following steps: S1. Using an encoder based on a convolutional neural network to process an input image The high-level features are extracted to obtain the high-level feature map; S2. The decoder based on the long-term short-term memory network and the focusing mechanism decodes the characters from left to right in sequence from the high-level feature map.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
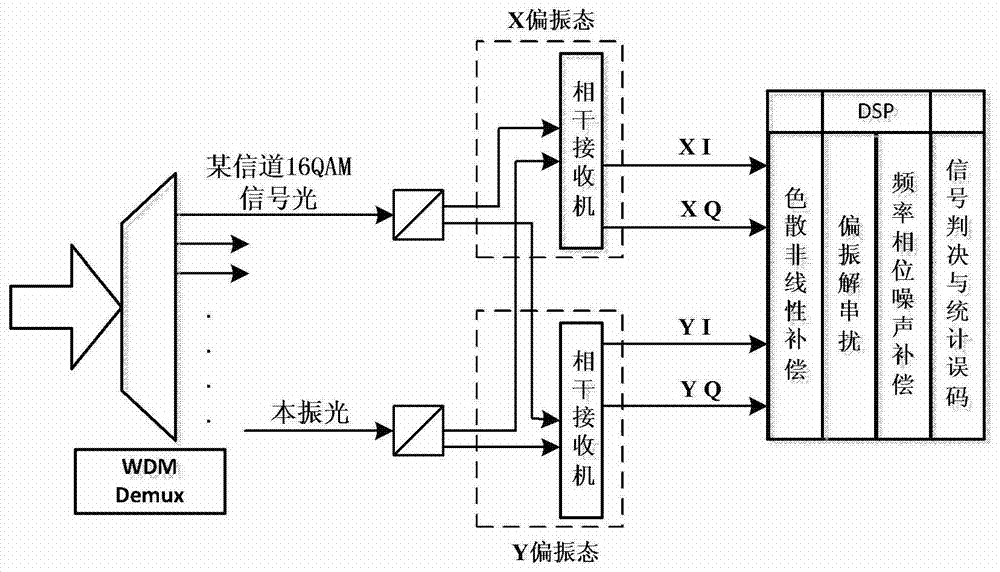
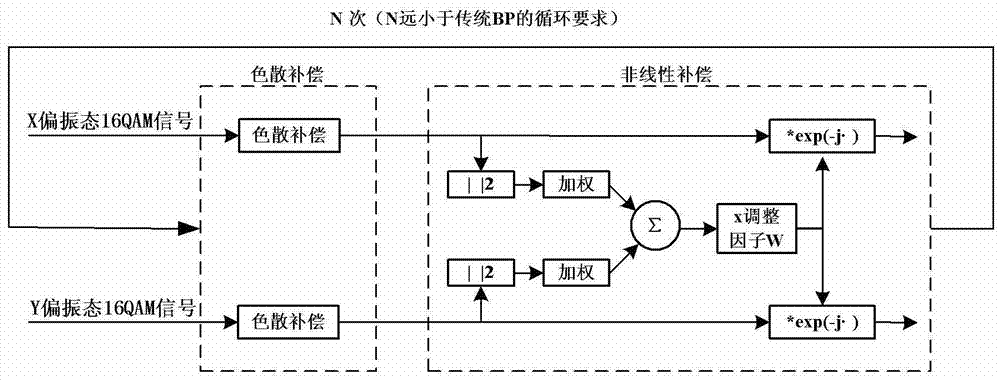
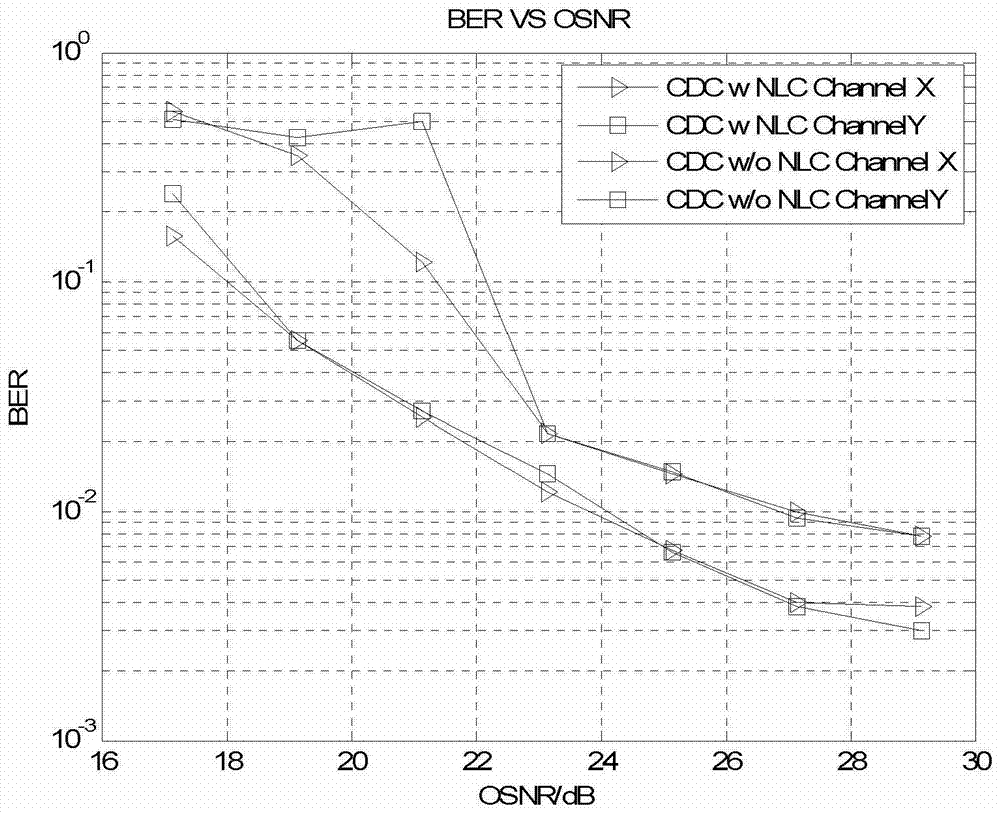
Dispersion and nonlinear compensation method and system in coherent optical communication system
ActiveCN102983910BOptimize calculation methodIncrease step sizeDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical transmissionComputation complexityCommunications system
The invention discloses a dispersion and nonlinear compensation method and system in a coherent optical communication system, and relates to the communication field. The method disclosed in the present invention includes: dividing the total length of the optical fiber into N steps of equal length, first performing dispersion compensation in each step, and then performing nonlinear compensation; wherein, when performing nonlinear compensation in each step, the The current sampling point is the center, and the X and Y value polarization states of the current sampling point are sampled at 2k+1 sampling points, and the power of 2 (2k+1) sampling points is calculated, and the samples with the same position on the X and Y polarization states are Add the power of the points to get 2k+1 power values, weight and sum the 2k+1 power values, and then multiply the weighted sum value by the set coefficient W to get the nonlinear phase angle of the current sampling point, according to Non-linear phase angle compensation. The invention also discloses a dispersion and nonlinear compensation system in the coherent optical communication system. The technical solution of the present application improves the calculation method of the nonlinear phase angle and reduces the calculation complexity.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method, device and server for locating partial discharge source in transformer
ActiveCN109917252BHigh precisionOptimize calculation methodTesting dielectric strengthTransformerEngineering
The present invention provides a method, device and server for locating partial discharge sources in transformers, wherein the method includes: collecting acoustic signals generated by partial discharges in transformers through a plurality of acoustic sensors arranged at preset positions of transformers; The acoustic signal corresponding to each acoustic sensor is subjected to noise reduction processing; according to the signal energy or information amount of the acoustic signal after the noise reduction processing, determine the time length for each acoustic sensor to receive the acoustic signal; according to the position and time length of each acoustic sensor , to determine the location of the partial discharge source within the transformer. In the present invention, the time length for each acoustic sensor to receive the acoustic signal is determined based on the reference time point at which each acoustic sensor starts to collect signals at the same time. This relative time method is conducive to optimizing the calculation of the location of the partial discharge source in the subsequent transformer. way, thereby improving the accuracy of the location of the partial discharge source in the transformer.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
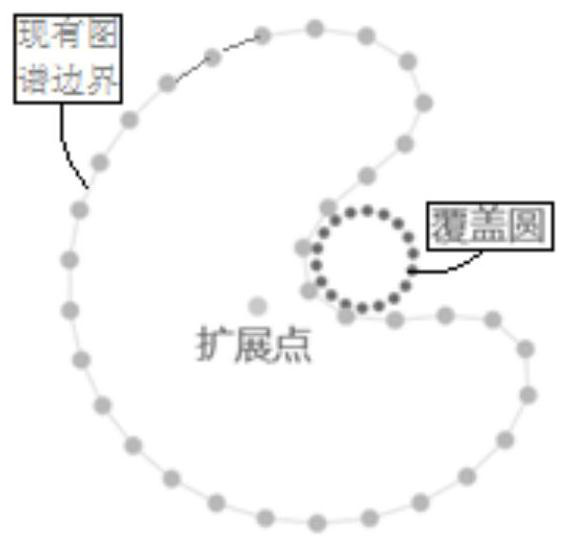
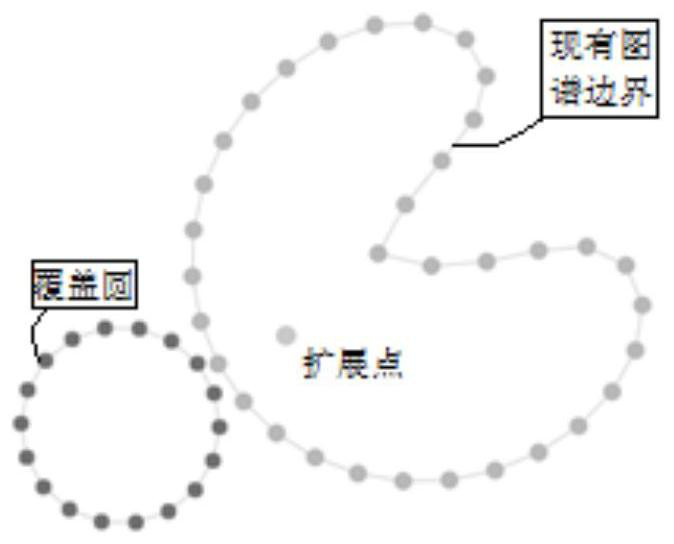
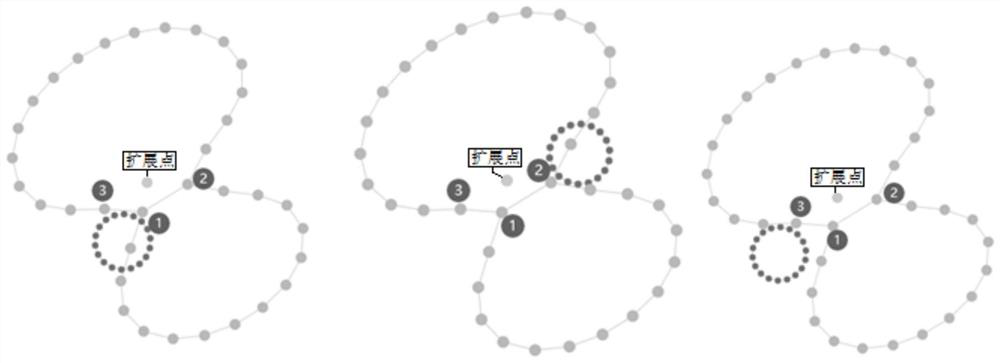
Map extension layout method
PendingCN113886597AEnsure layout stabilityOptimize calculation methodKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer visionEngineering
The invention discloses a map extension layout method, and relates to the field of data visualization analysis. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an existing map boundary, forming an ordered coordinate set of the boundary, performing node positive sequence arrangement according to the distance between an extension node and a node coordinate in the ordered coordinate set to obtain an ordering result, calculating a coverage circle and an original position of the coverage circle for a newly-added node which is not in an existing map and is associated with the extension node, obtaining a moving route of the coverage circle in the existing map according to the sorting result, determining a layout positioning circle by moving the coverage circle according to the moving route, and adjusting the layout positioning circle to complete layout extension of the map.
Owner:INSPUR SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com