Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "More throughput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
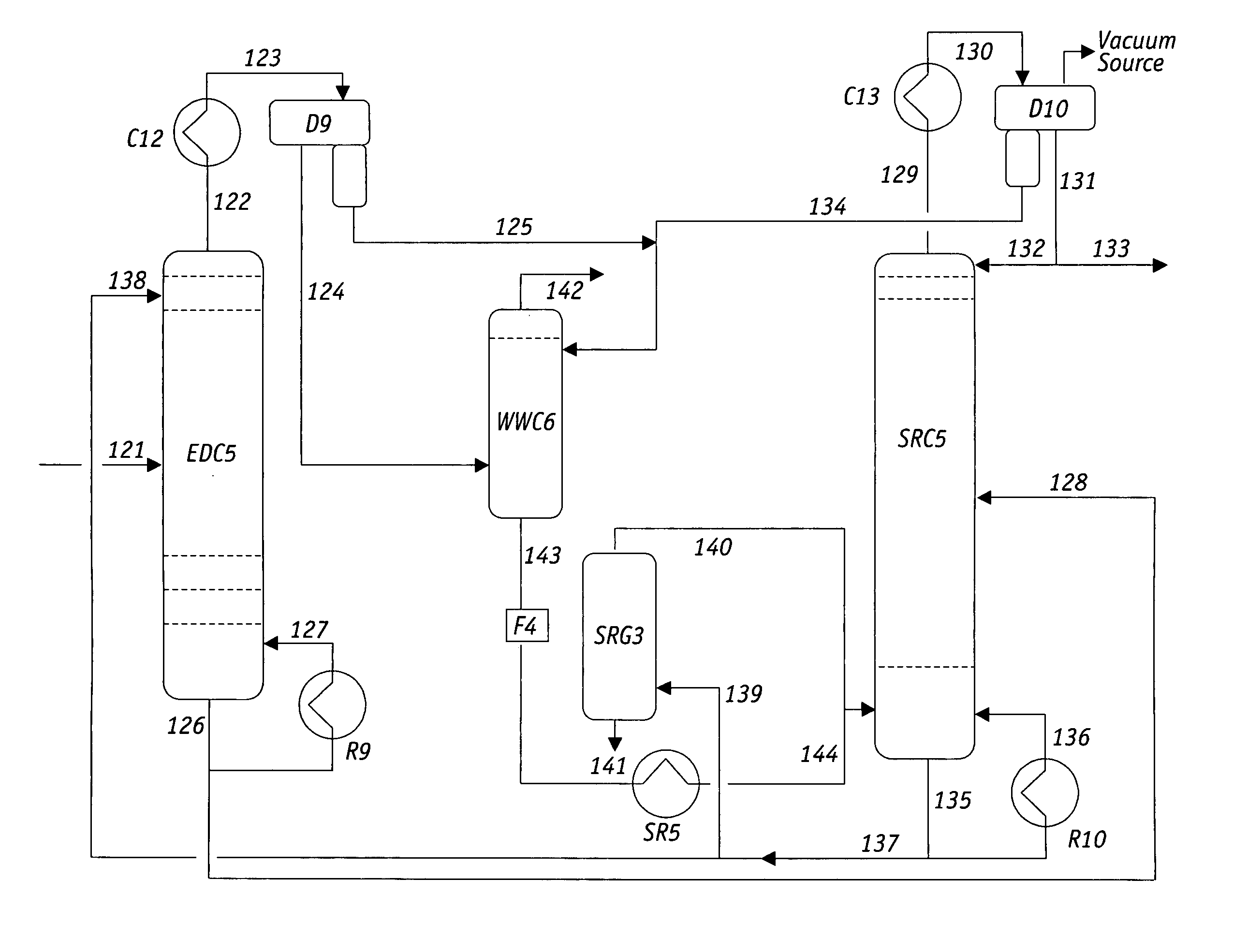
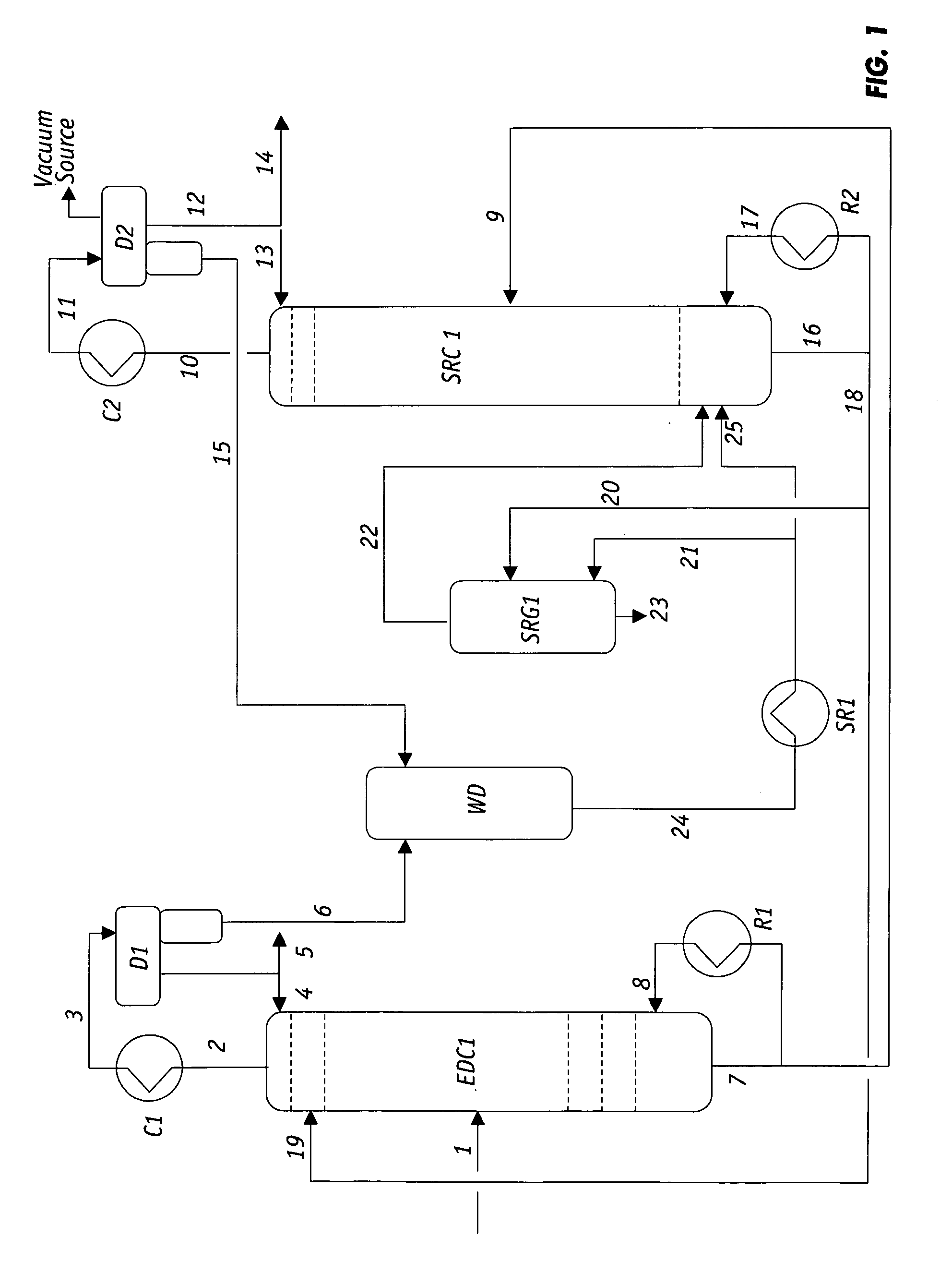
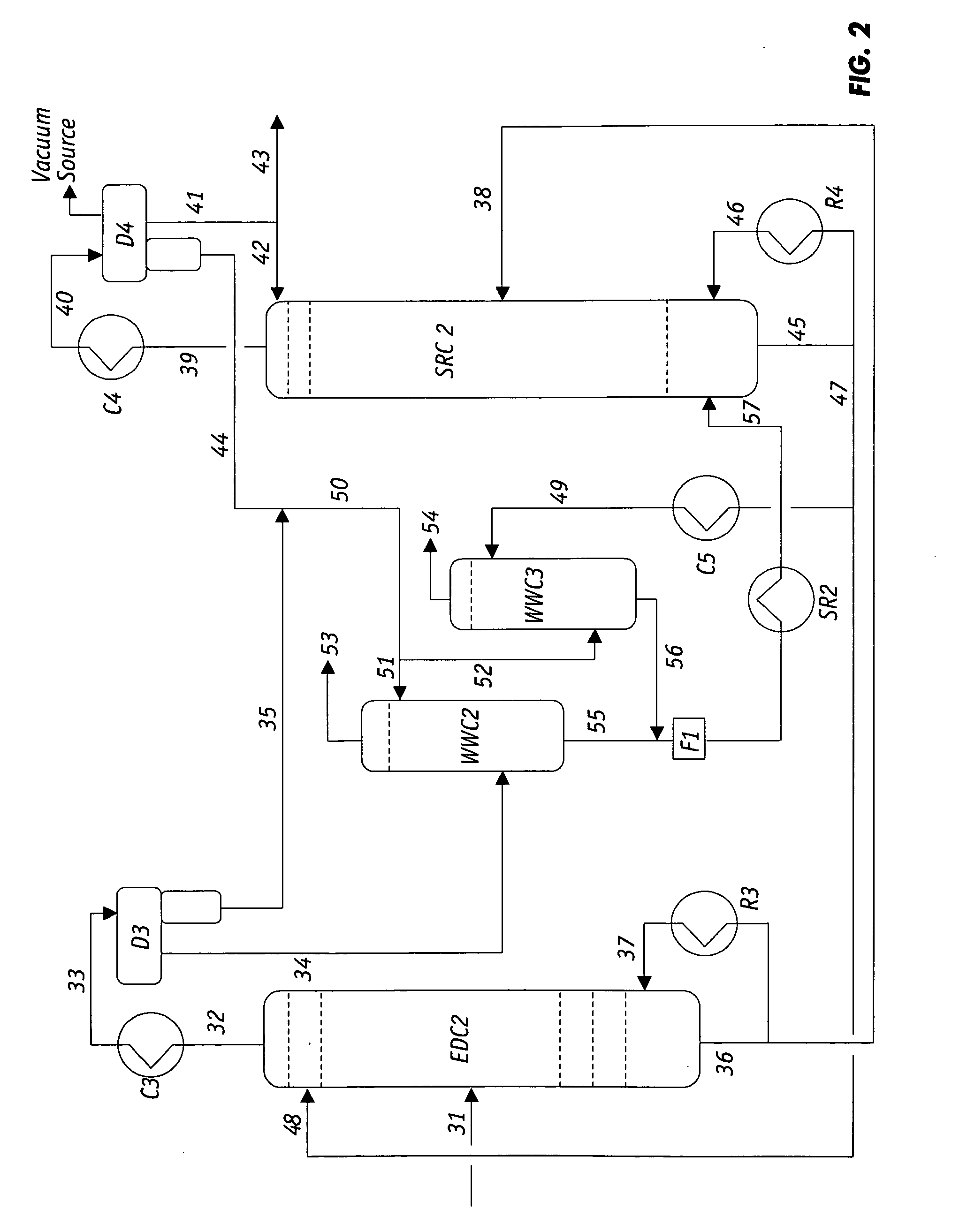
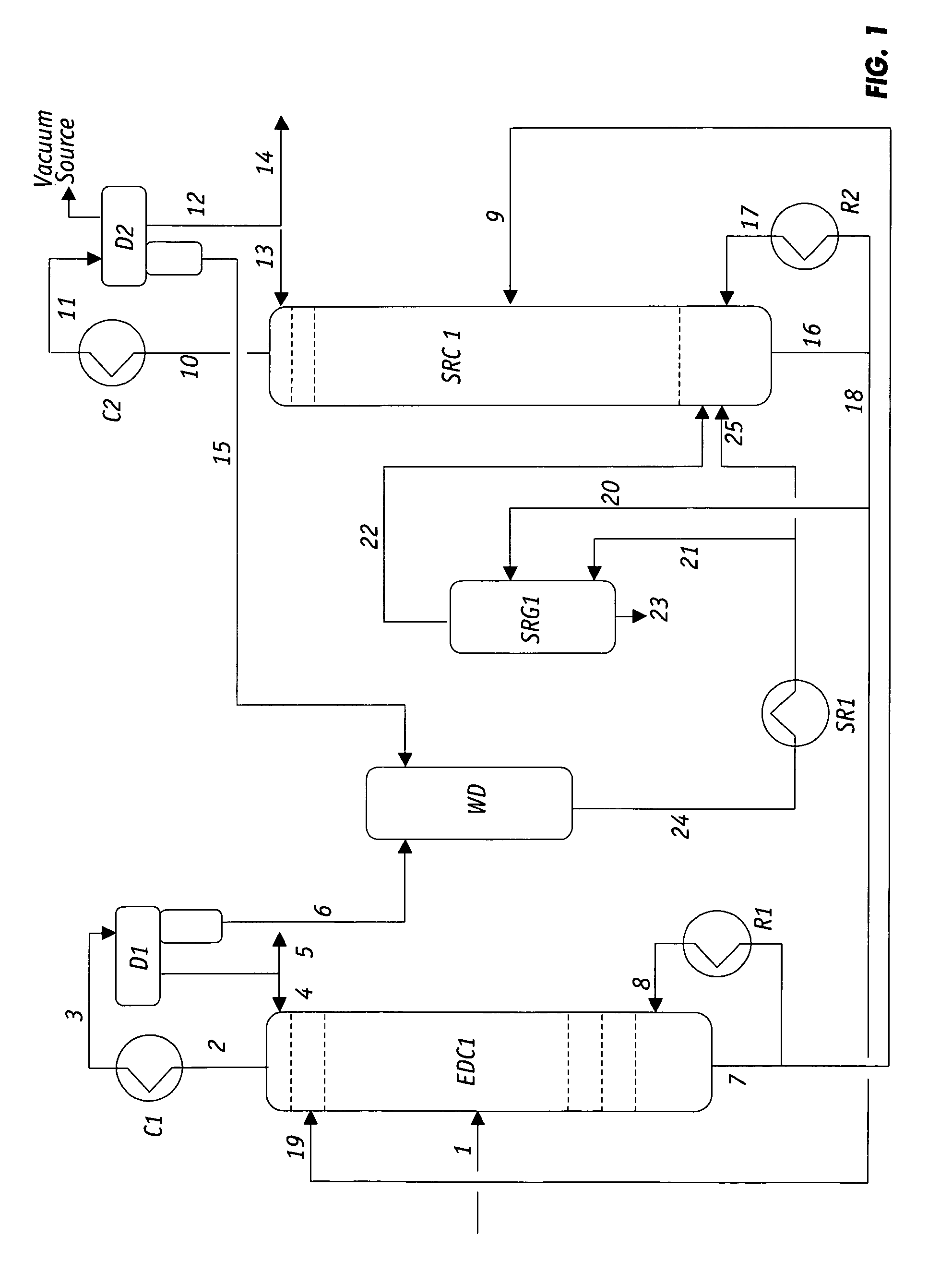
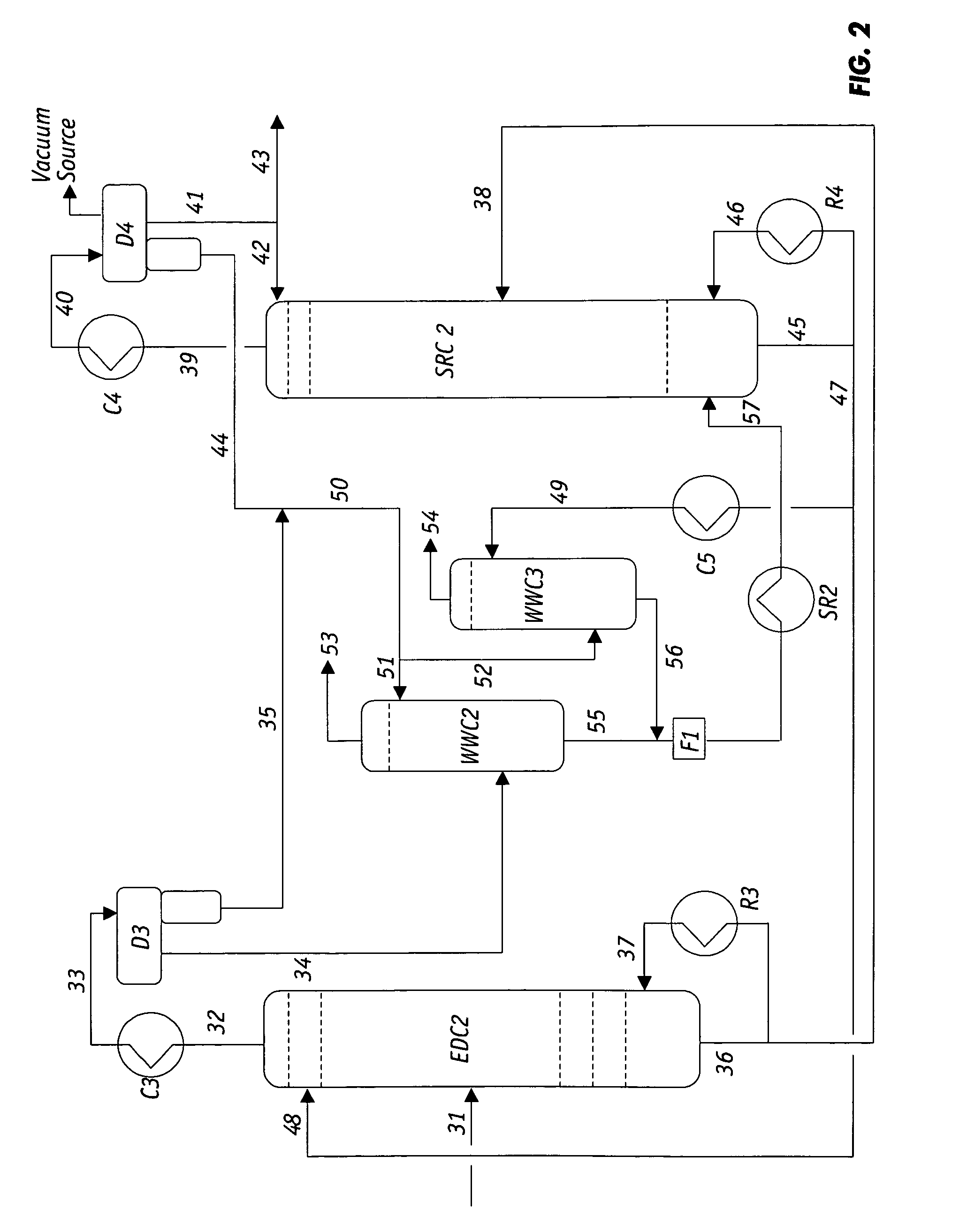
Extractive distillation processes using water-soluble extractive solvents
ActiveUS20090105514A1Reduce steam consumptionGood solvent resistanceHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsExtractive distillationWater soluble
Extractive distillation processes whereby water-soluble extractive distillation (ED) solvents are regenerated and recovered employ improved operations of the extractive distillation column (EDC) so that polar hydrocarbons are recovered and purified from mixtures containing polar and less polar hydrocarbons and measurable amounts of hydrocarbons that are heavier than intended feedstock and / or polymers that are generated in the ED process. The improved process can effectively remove and recover the heavy hydrocarbons and / or remove polymer contaminants from the solvent in a closed solvent circulating loop through mild operating conditions with no additional process energy being expended. With the improved process, the overhead reflux of the EDC may be eliminated to further reduce energy consumption and to enhance the loading and performance within the upper portion of the EDC, especially when two liquid phases exists therein.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
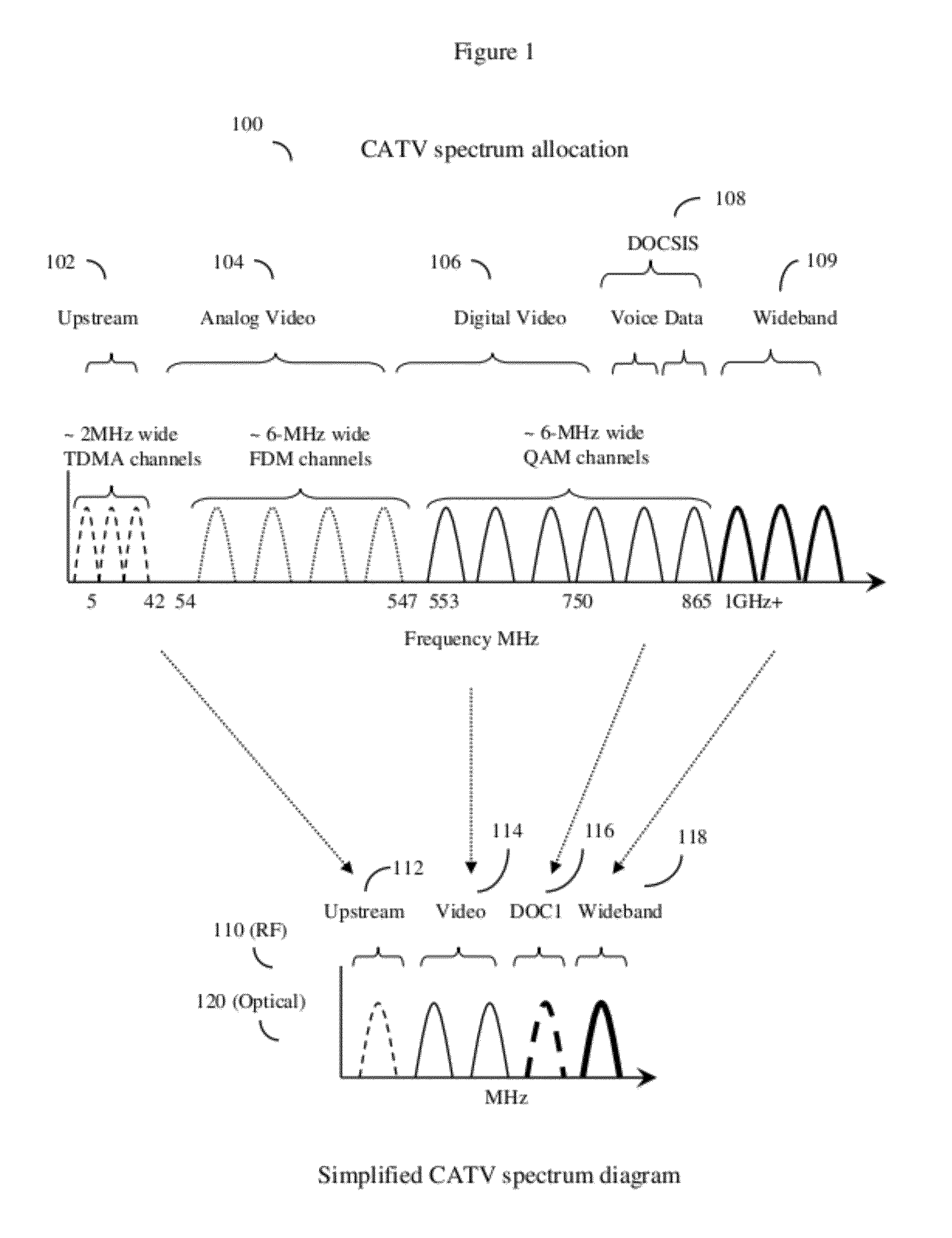
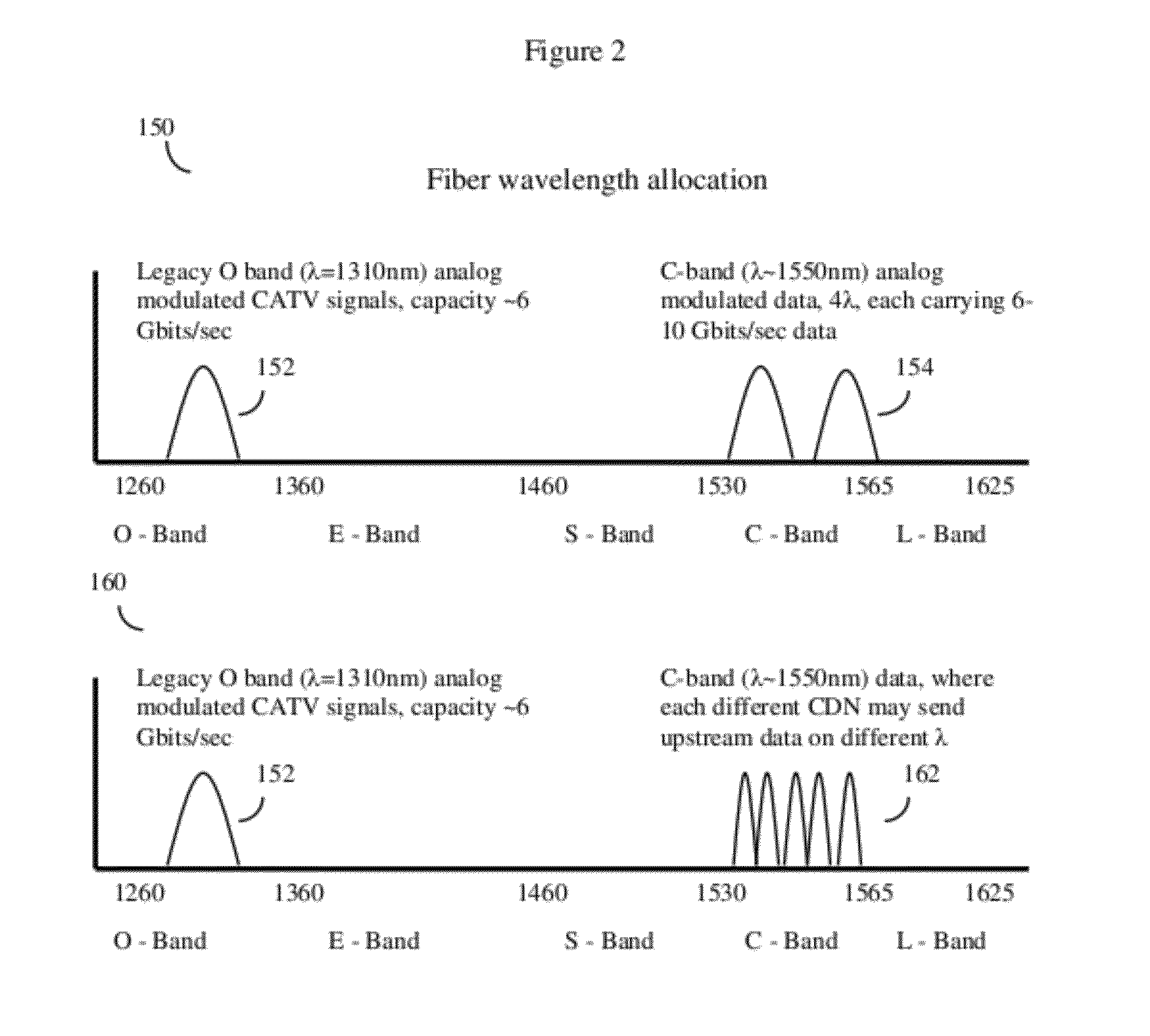
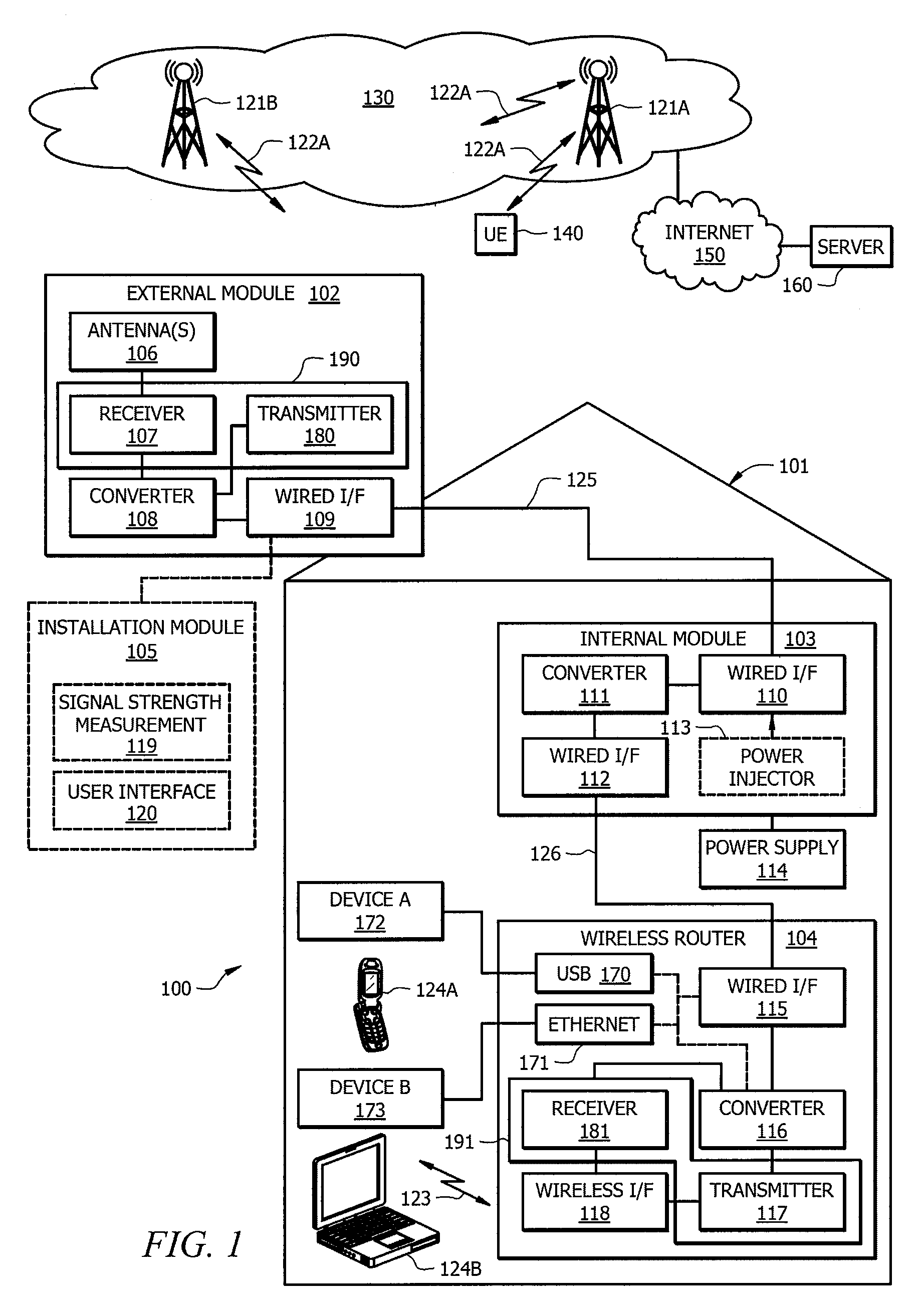
Hfc cable system with wideband communications pathway and coax domain nodes
ActiveUS20120110631A1Achieve backward compatibilityImprove data carrying capacityBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsDigital dataQam modulation
System and method to extend the data carrying capacity of a hybrid fiber cable (HFC) network by adding wideband RF signal capability above 1 GHz, and replacing at least some CATV active devices such as amplifiers with a new type of Coax Domain Node (CDN) device that acts to segment the CATV cable portion of the HFC network into a series of smaller domains. The CDN generally filter RF signals from 5-865 MHz, while amplifying and passing RF signals over 1 GHz. Upstream capability is enhanced because the CDN intercept 5-42 MHz upstream signals from each domain and convert to 1 GHz+ signals. Downstream capability is also enhanced because the CDN can take efficiently encoded 1 GHz+ digital data, QAM modulate it, and locally inject into each domain without crosstalk between domains. The system pushes data management and downstream from the head end to the CDN, creating more throughput.
Owner:VECIMA NETWORKS
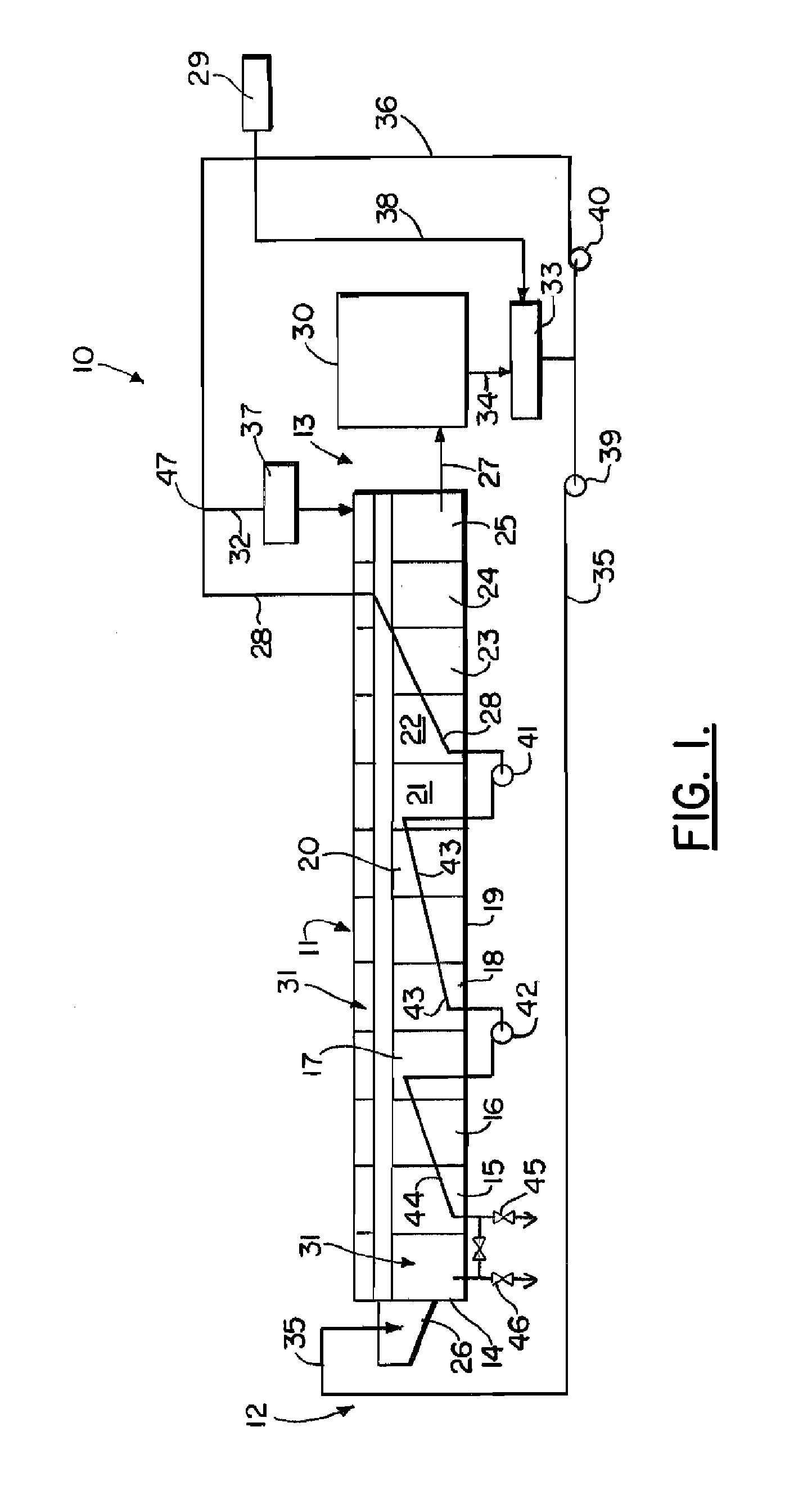
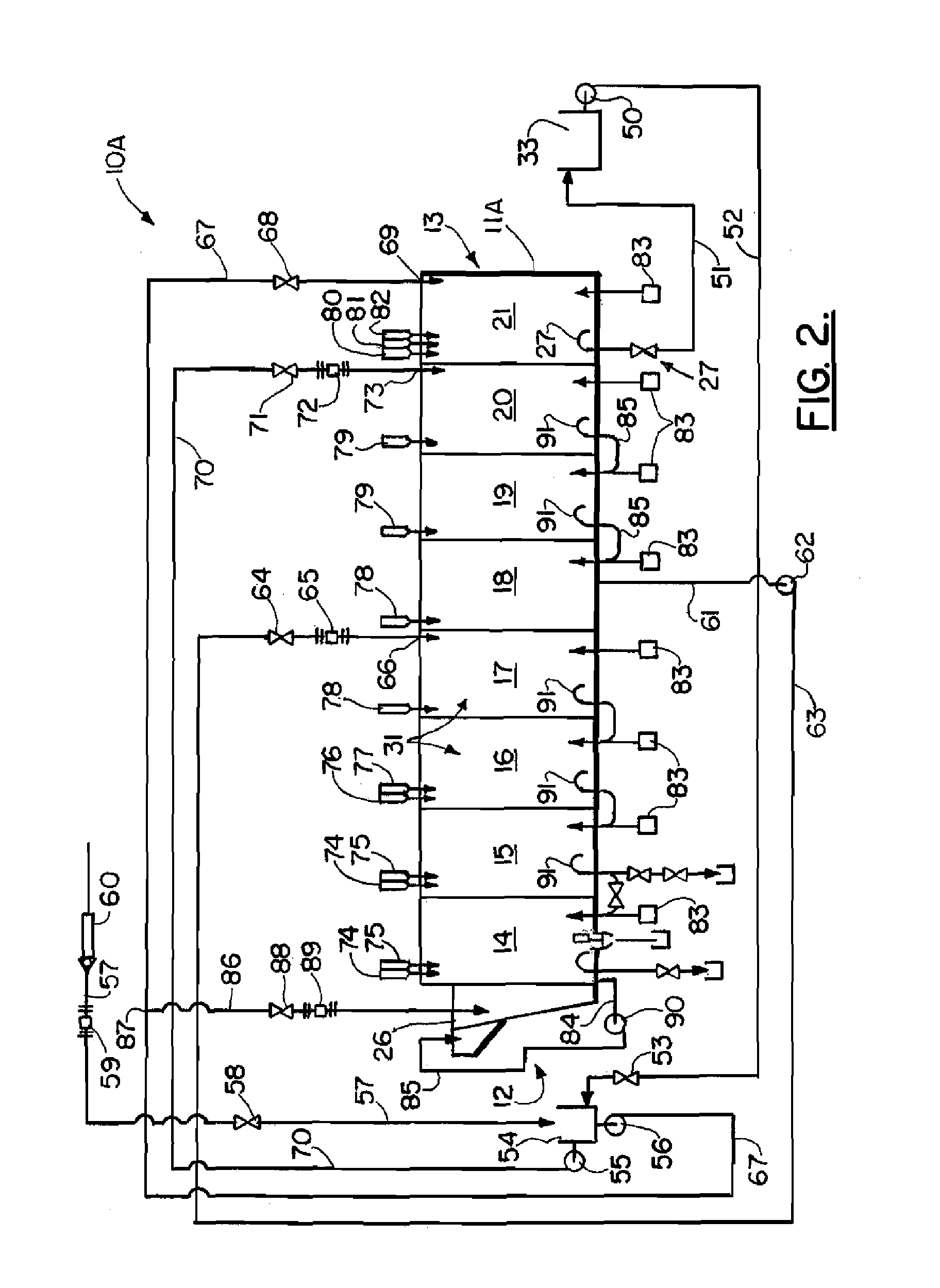
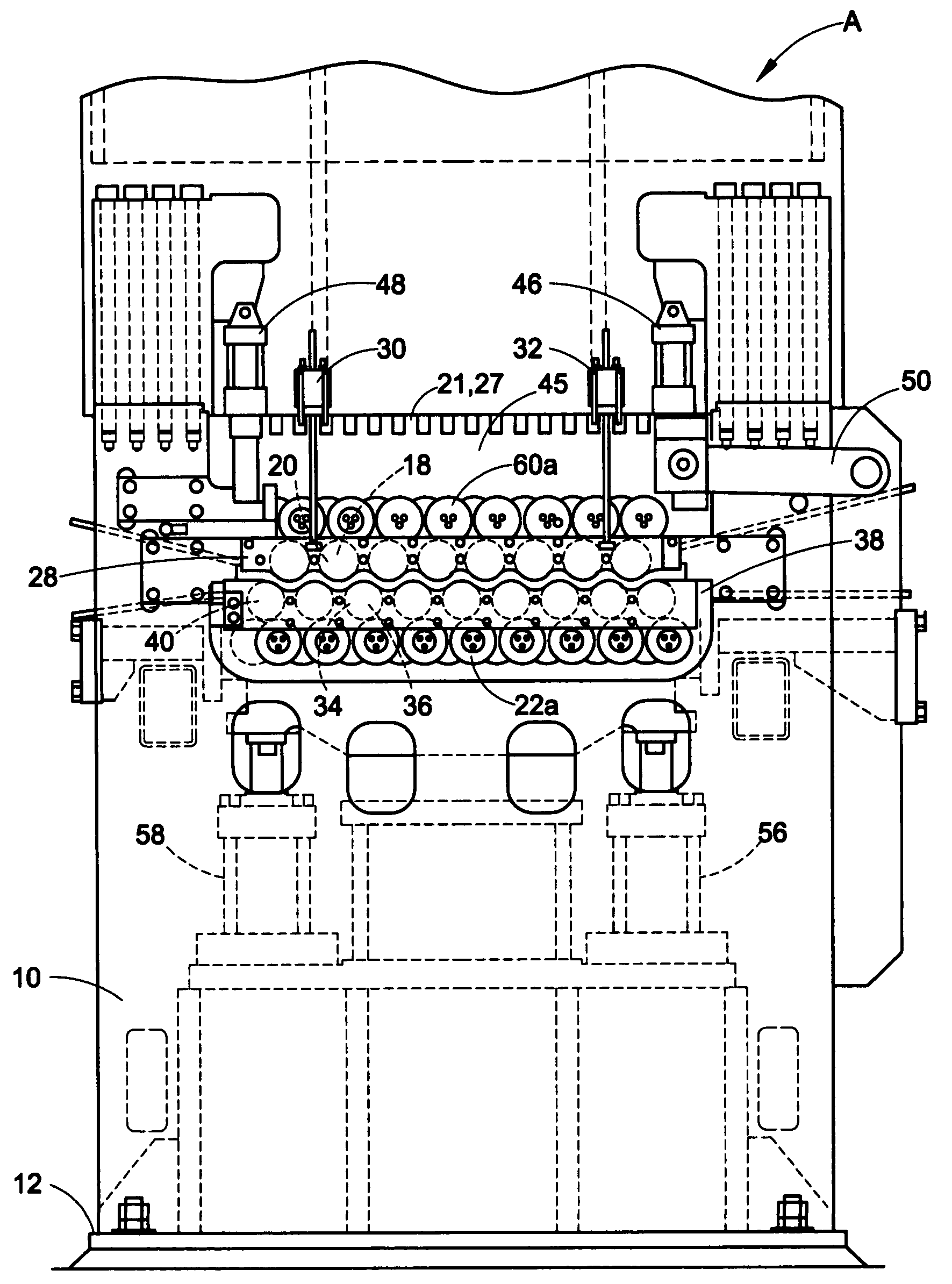
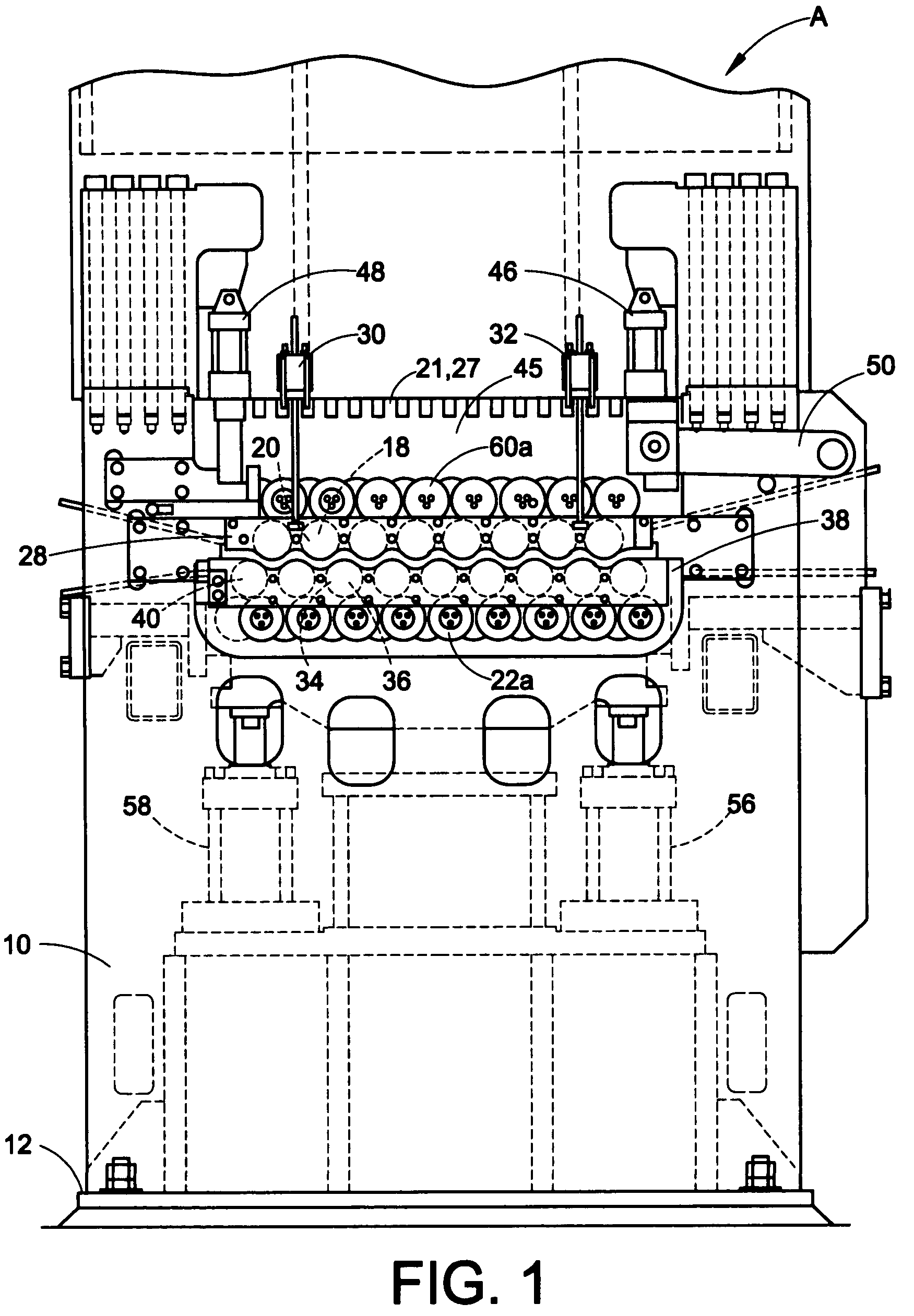
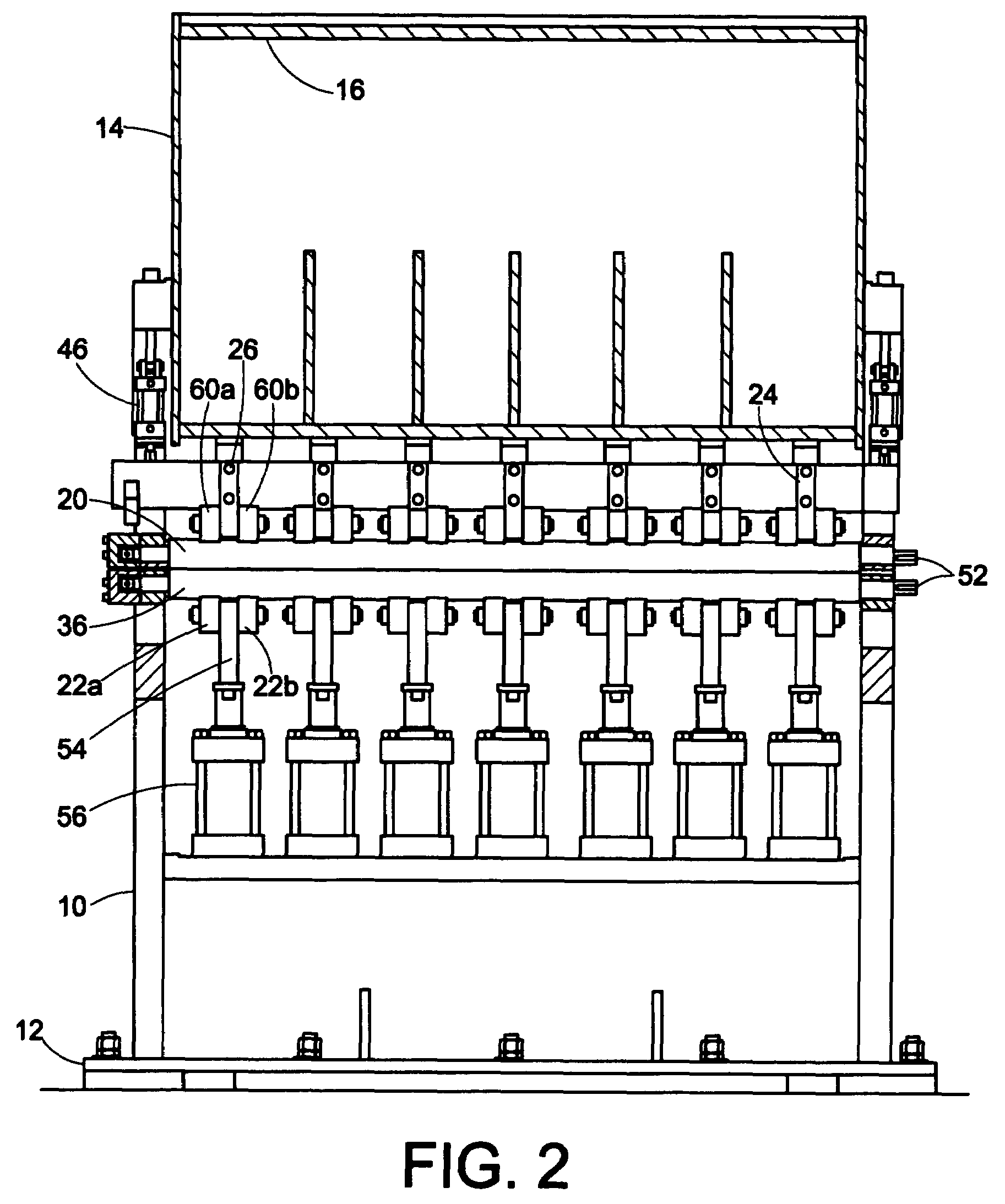
Continuous batch tunnel washer and method
ActiveUS20110296626A1Few modulesQuick rinseControl devices for washing apparatusDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesCounter flowEngineering
A method of washing fabric articles in a tunnel washer that includes moving the fabric articles from the intake of the washer to the discharge of the washer and through multiple modules or sectors. Liquid can be counter flowed in the washer interior along a flow path that is generally opposite the direction of travel of the fabric articles. A dual use zone includes multiple of the modules or sectors. In a dual use zone, a module or modules can be used to both wash and thereafter rinse the fabric articles. While counterflow rinsing, the flow rate can be maintained at a selected flow rate or flow pressure head. One or more booster pumps can optionally be employed to maintain constant counterflow rinsing flow rate or constant counterflow rinsing pressure head.
Owner:PELLERIN MILNOR
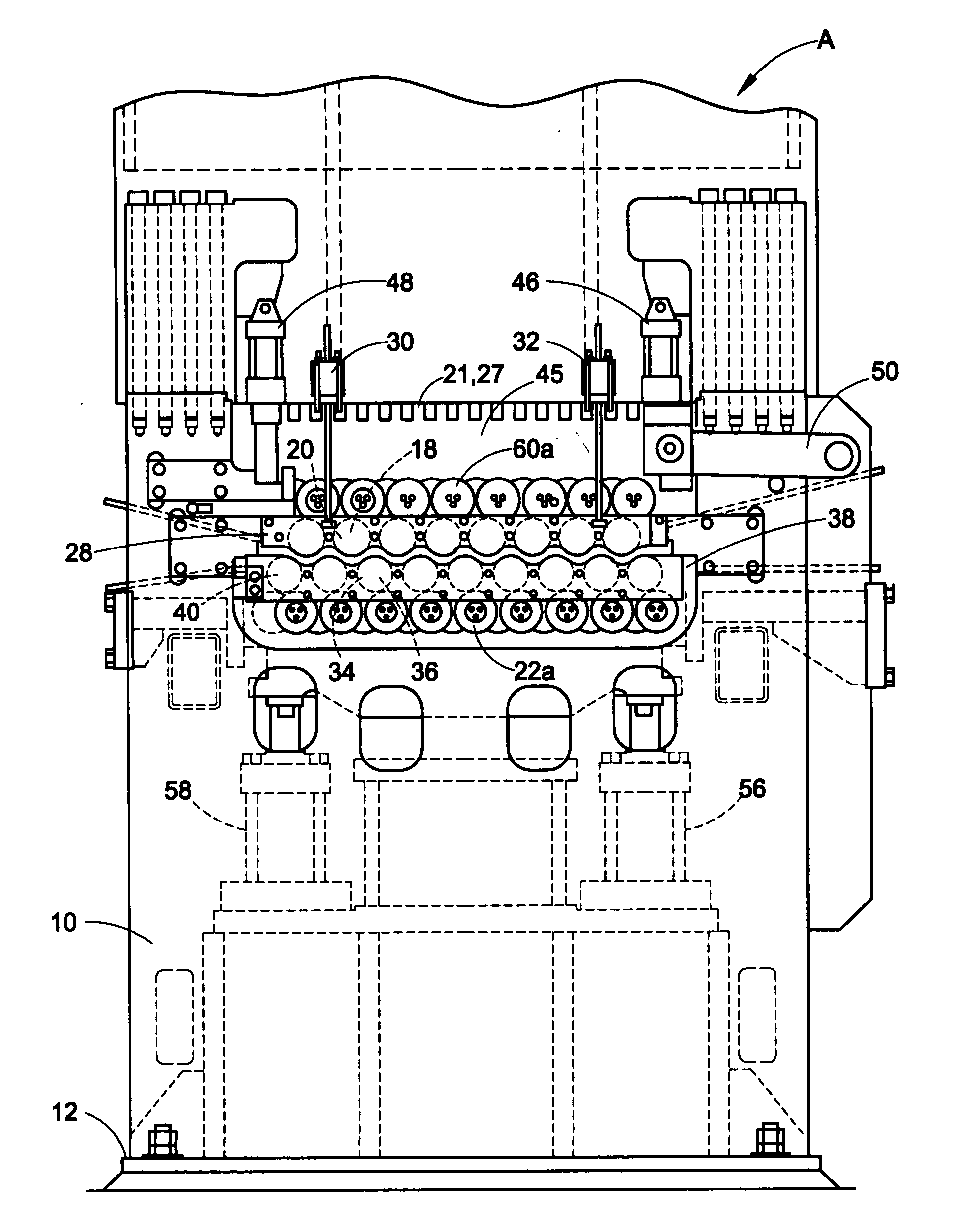
Cassette roller leveler with common back-up rolls
ActiveUS20080011036A1Shorten the timeLow costMetal rolling stand detailsMetal rolling arrangementsWork rollWork product
A roller leveler having a frame; a first bank of upper and lower work rolls journalled in the frame via a work roll journal housing; and a bank of back-up rolls in contact with the work rolls to support the work rolls. The work rolls perform leveling on a work product passing through a gap formed between upper and lower work rolls. The back-up rolls are mounted to the roller leveler frame via a back-up housing. The back-up rolls are movable to allow the first bank of work rolls to be removed and a second bank of work rolls to be installed wherein the second bank of work rolls includes work rolls of a different diameter than the first bank of work rolls.
Owner:BUTECH BLISS
Axial thrust bearing
InactiveUS7470064B2Reduce wearEasy to compressCrankshaftsGas turbine plantsTurbochargerThrust bearing
An axial thrust bearing for axially supporting a rotating shaft of an exhaust gas turbocharger connected to a lubricating oil circuit includes a profiled annular bearing surface which contacts an essentially flat sliding surface, the bearing surface having a plurality of radially extending grooves which are open on the outside circumference, a plurality of coplanar flat trap surfaces located between respective pairs of adjacent grooves, and a plurality of wedge surfaces located between adjacent pairs of respective grooves. Each wedge surface forms a lubricating oil gap which narrows circumferentially toward an adjacent flat trap surface and which narrows radially toward the outside circumference.
Owner:MAN ENERGY SOLUTIONS SA
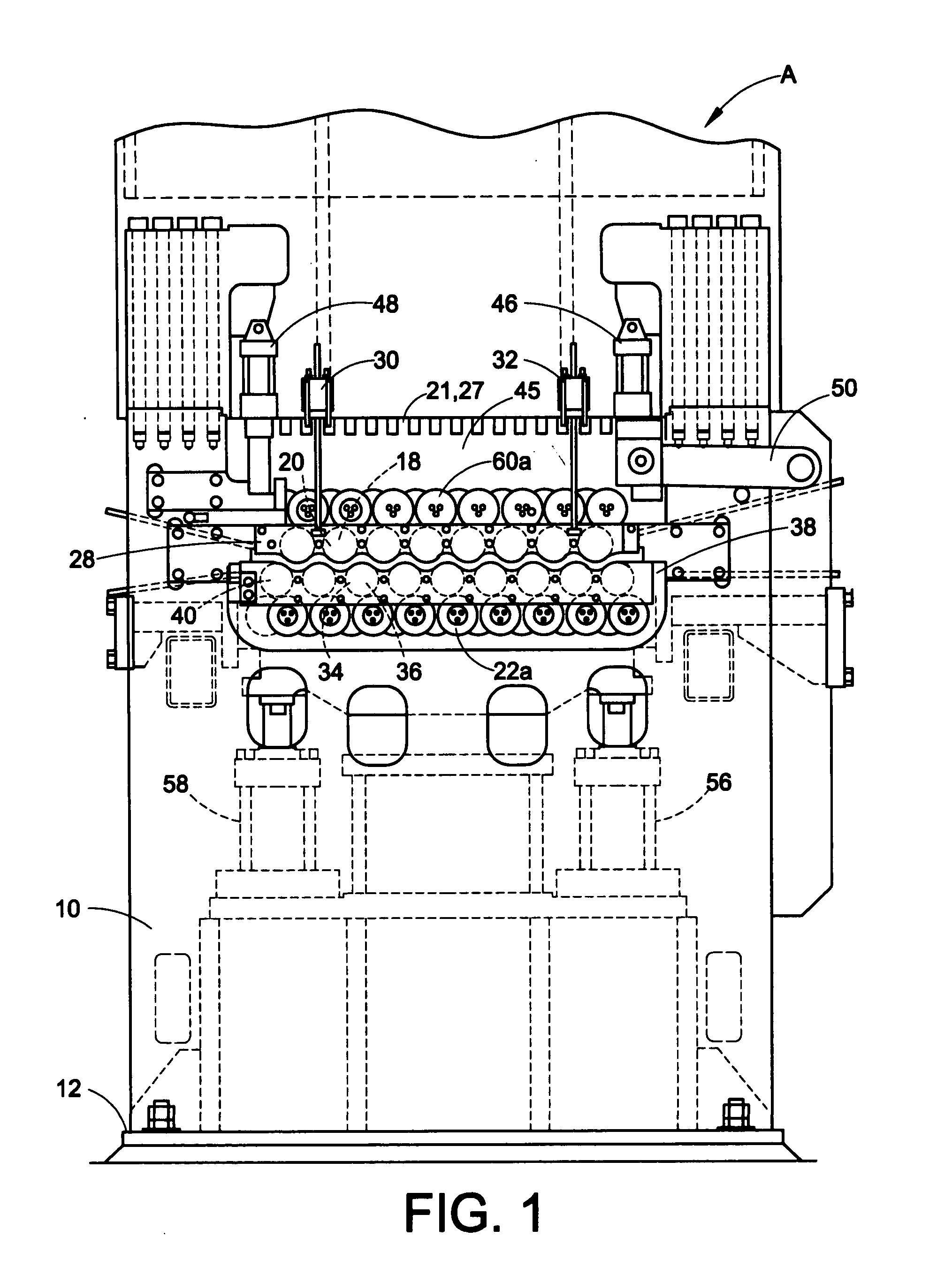
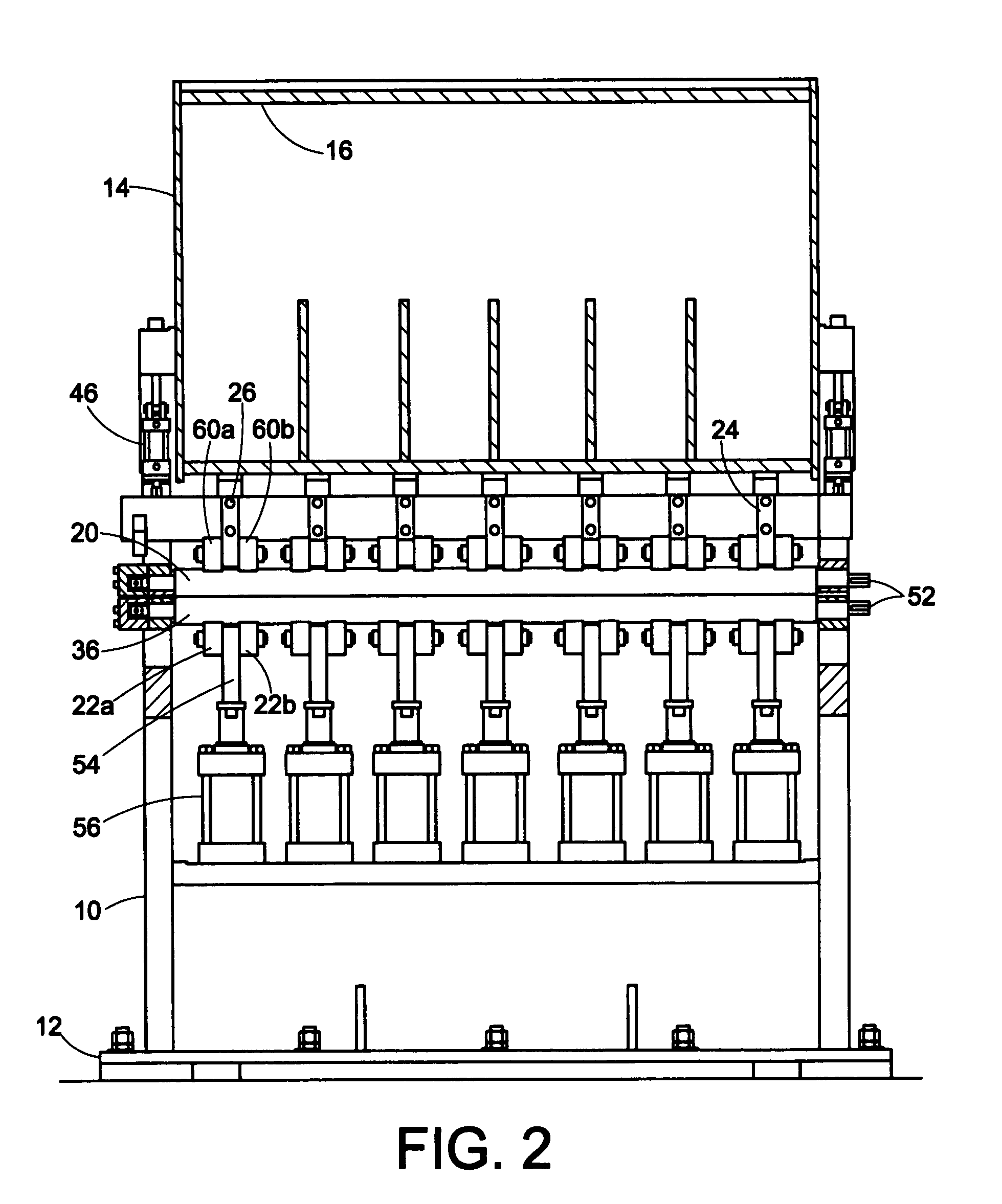
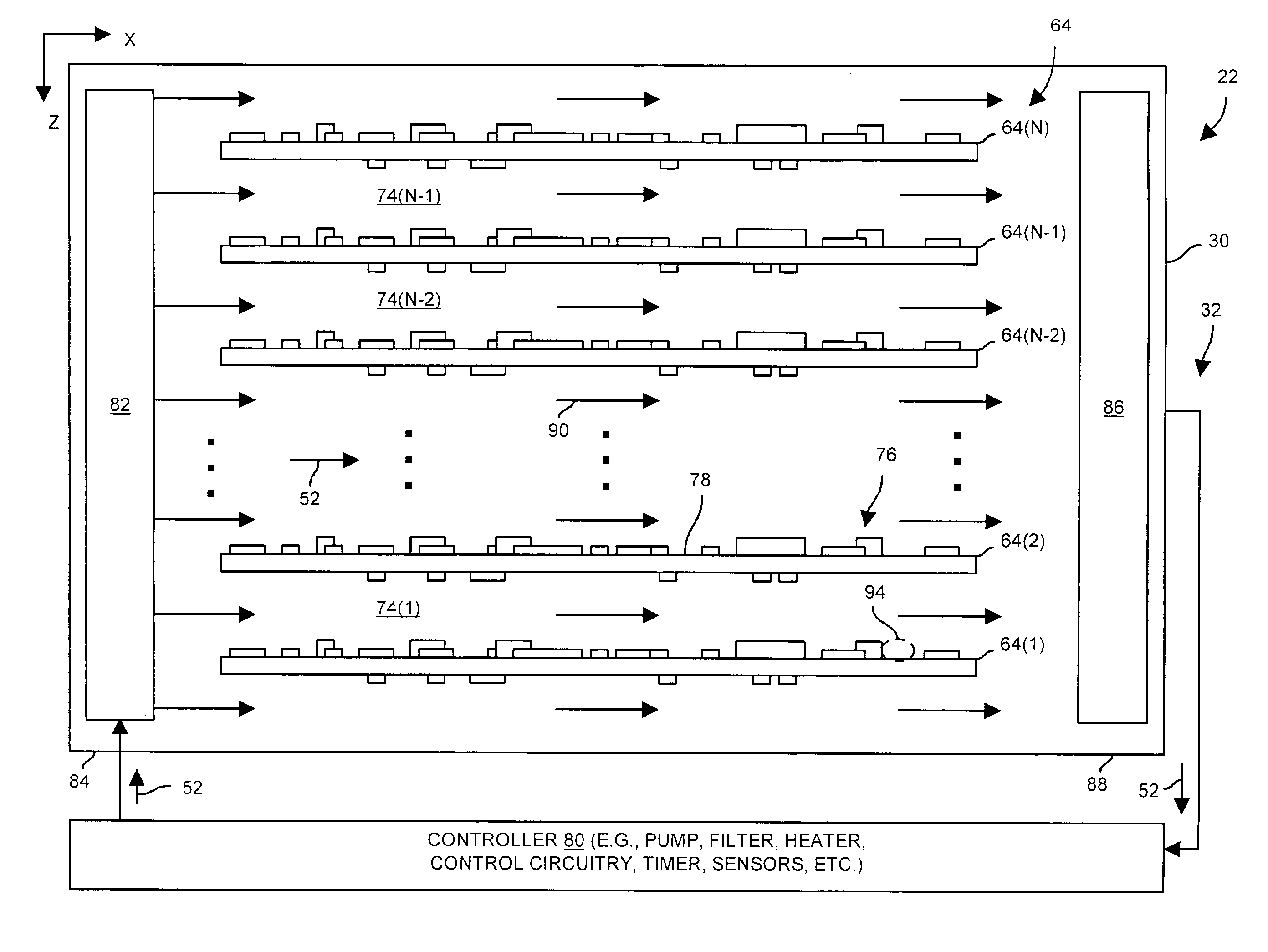
Systems and methods for processing a set of circuit boards
ActiveUS7252100B1Reduce the amount of energyReduce the amount of timeElectrostatic cleaningStacked spaced PCBsHandling systemElectrical and Electronics engineering
A circuit board processing system includes a wash tank configured to contain cleaning fluid, and a positioning subsystem configured to immerse a set of circuit boards into the wash tank. The system further includes a flow control subsystem having (i) a first set of nozzles disposed within the wash tank, (ii) a second set of nozzles disposed within the wash tank, and (iii) a controller. The controller is configured to direct the cleaning fluid through the first set of nozzles to provide a flow of the cleaning fluid in a first direction relative to the set of circuit boards. The controller is further configured to direct the cleaning fluid through a second set of nozzles to provide a flow of the cleaning fluid in a second direction relative to the set of circuit boards after providing the flow of the cleaning fluid in the first direction.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
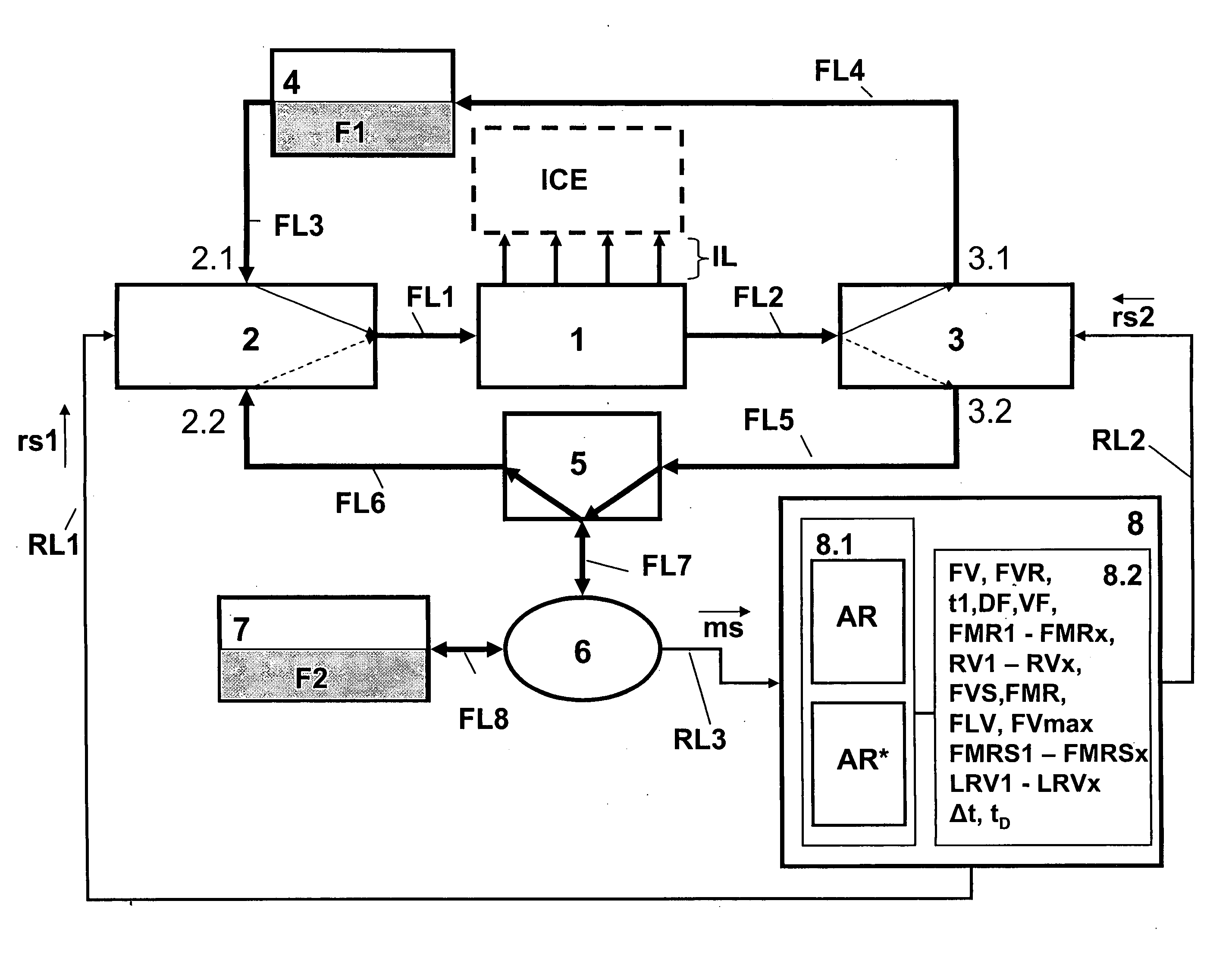
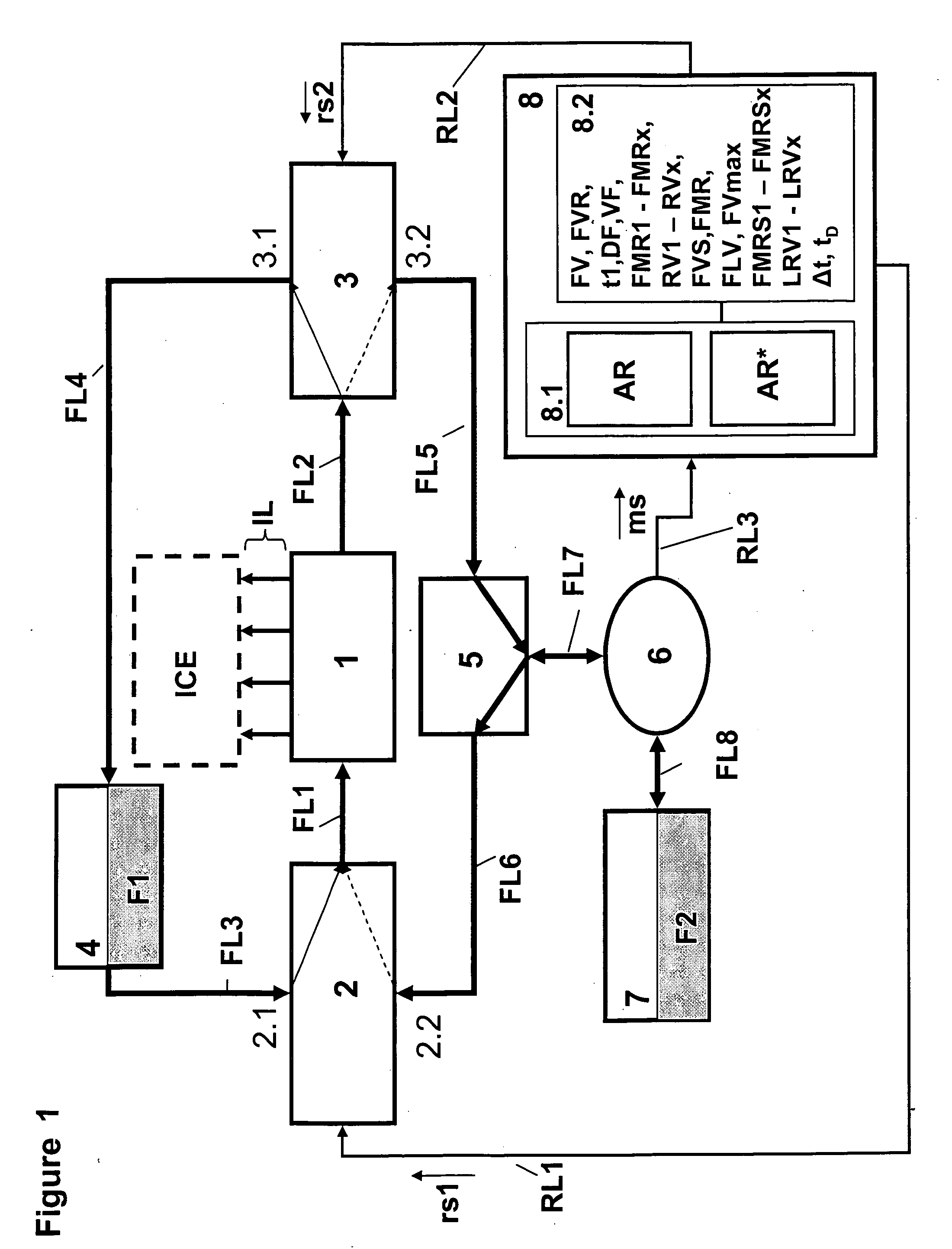
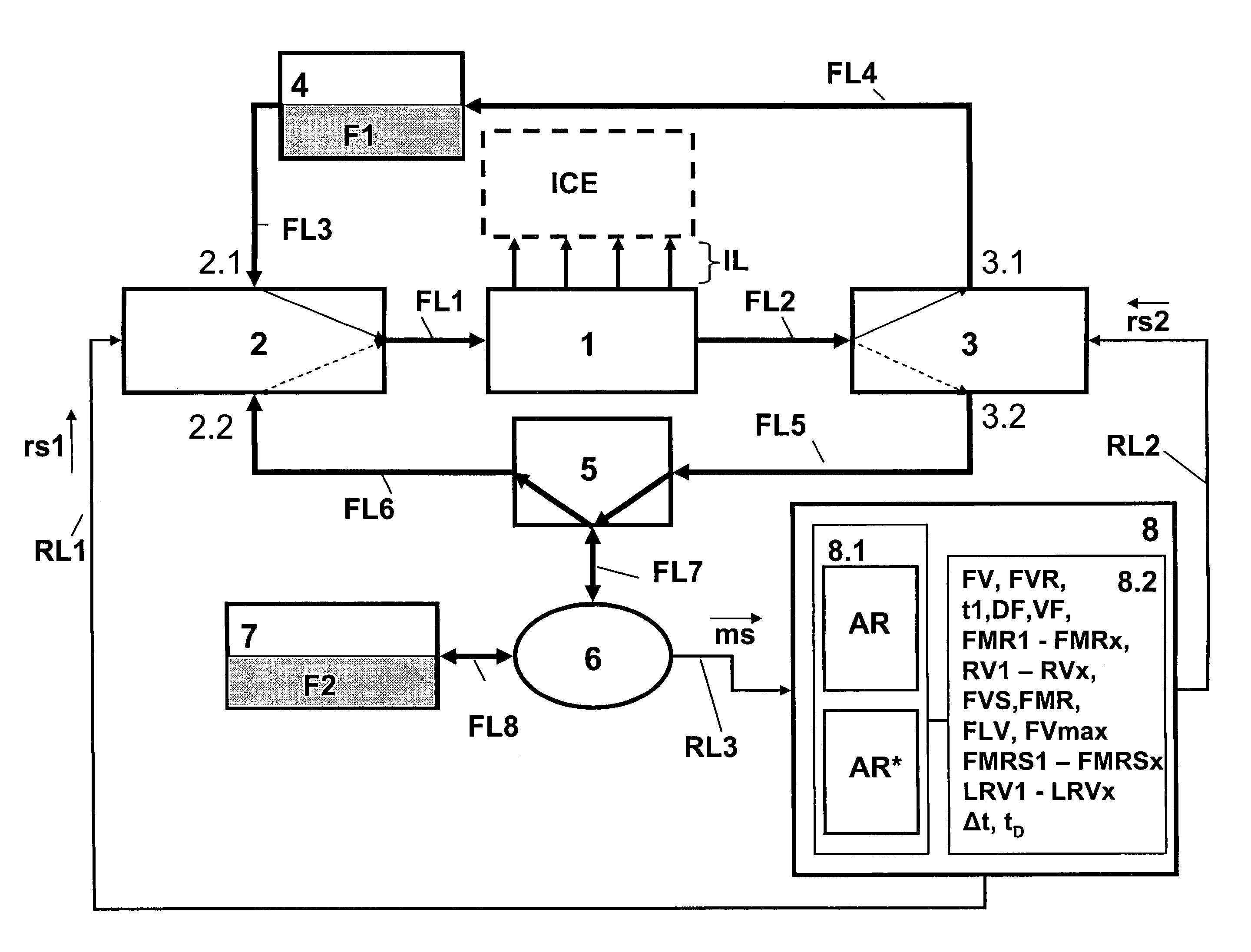
Method for verification of at least one given fuel mixture ratio
InactiveUS20060081230A1More throughputPrevents not only insufficient flushingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineFuel injection
A fuel injection system during operation of an internal combustion engine with at least two separately stored fuel types is supplied with at least one first fuel type. With the supply of a second fuel type or with the change from the supply of the first fuel type to the second fuel type, the fuel volume conveyed by the injection system is determined and dependent thereon the presence of a given fuel mixture ratio is verified.
Owner:KANGLER WOLFRAM
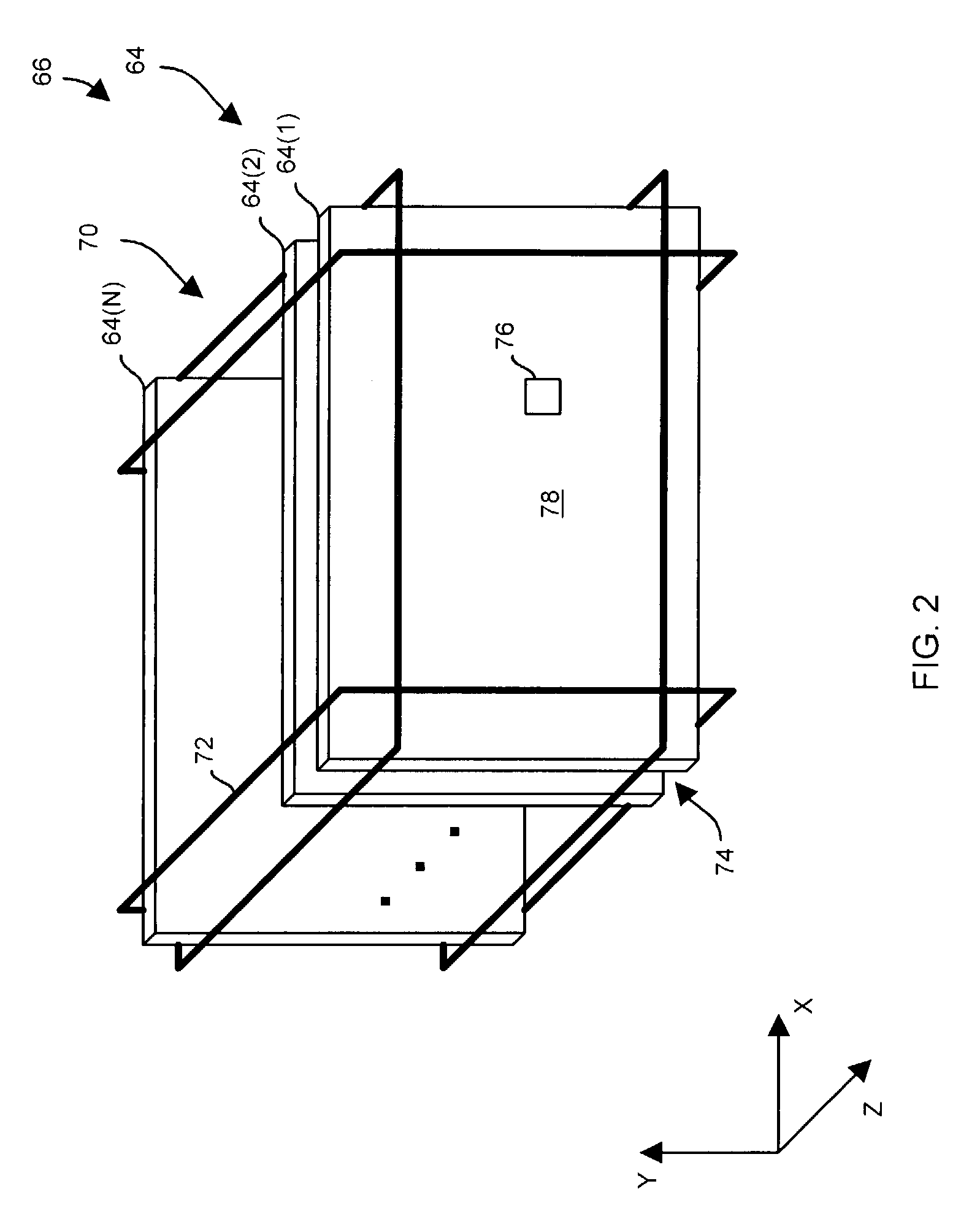
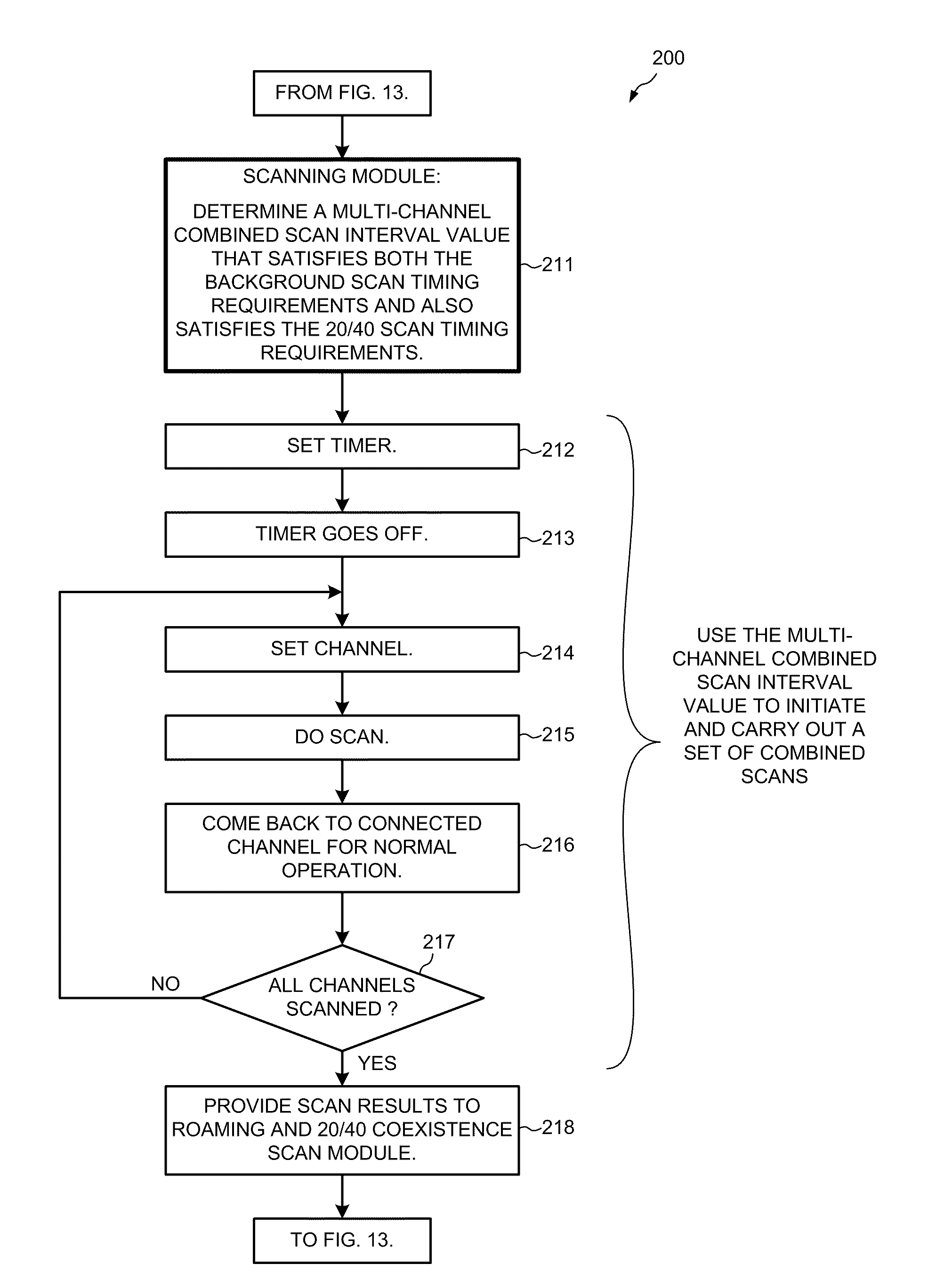
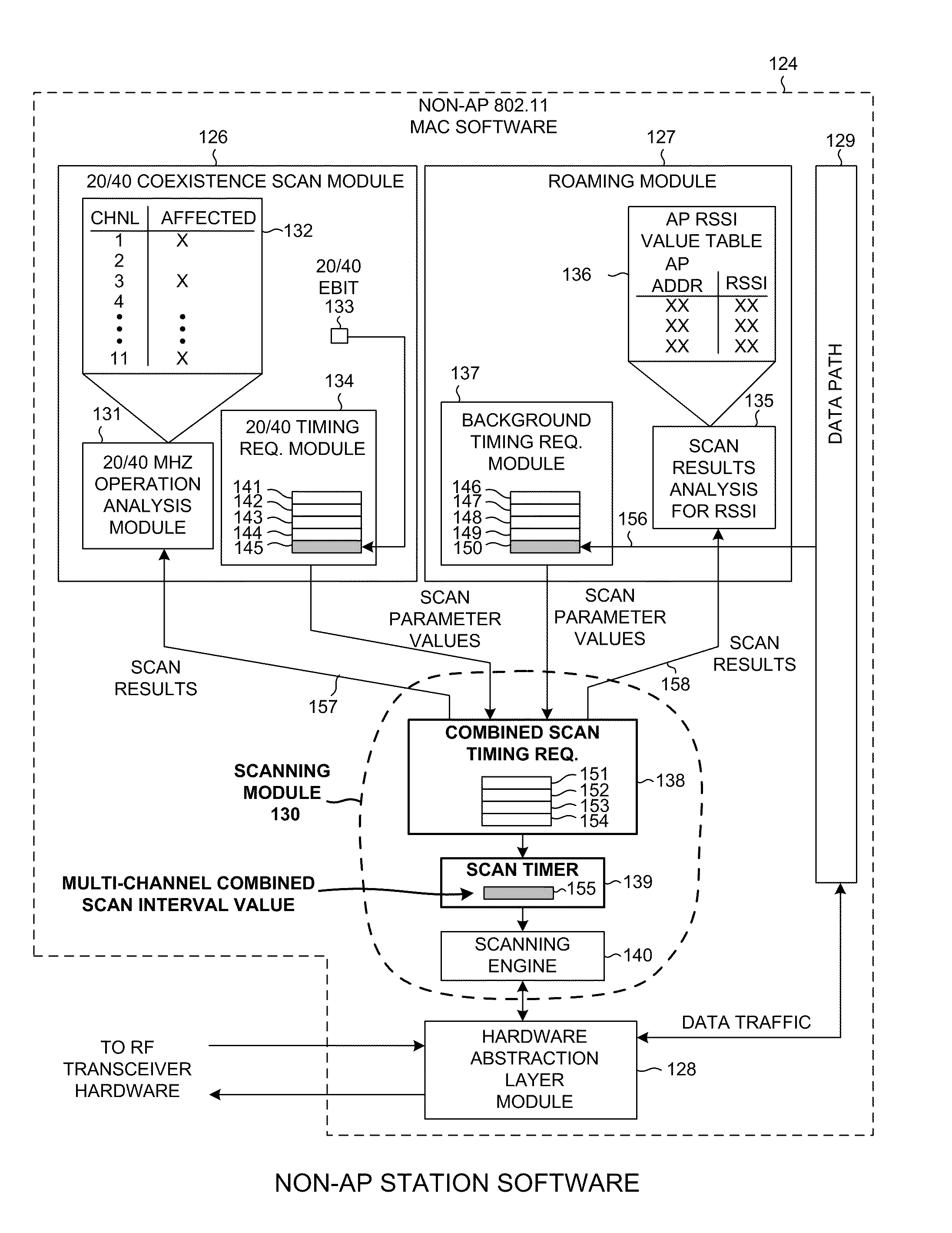
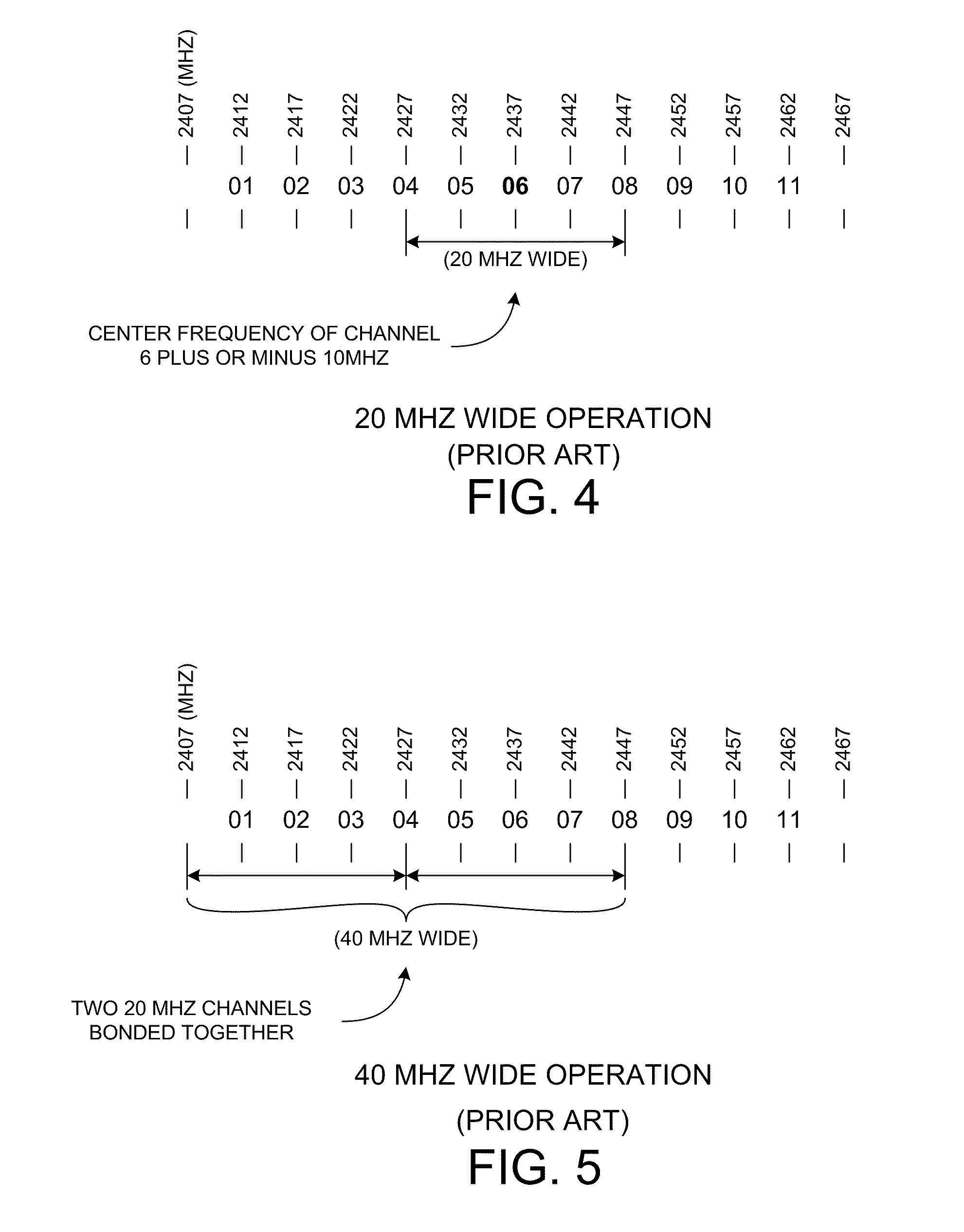
Combined background and 20/40 coexistence scan
InactiveUS20110165873A1Reduce in quantityIncreased data traffic throughputEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A scanning module within a non-AP station receives first scan parameter values for performing a first type of scan to obtain a first type of information, and receives second scan parameter values for performing a second type of scan to obtain a second type of information. From the first and second parameter values the scanning module determines combined scan parameter values that satisfy scan requirements for both types of scans. The combined scan parameter values are used to control a sequence of combined scans. A combined scan yields both the first and second type of information. In one example, an IEEE 802.11(n) non-AP station receives 20 / 40 coexistence scan parameters. The 20 / 40 parameters and locally-generated background scan parameters are used to determine parameters for performing combined background and 20 / 40 scans. Reducing the number of scans using combined scans has advantages including increasing data throughput, freeing processing resources, and reducing power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
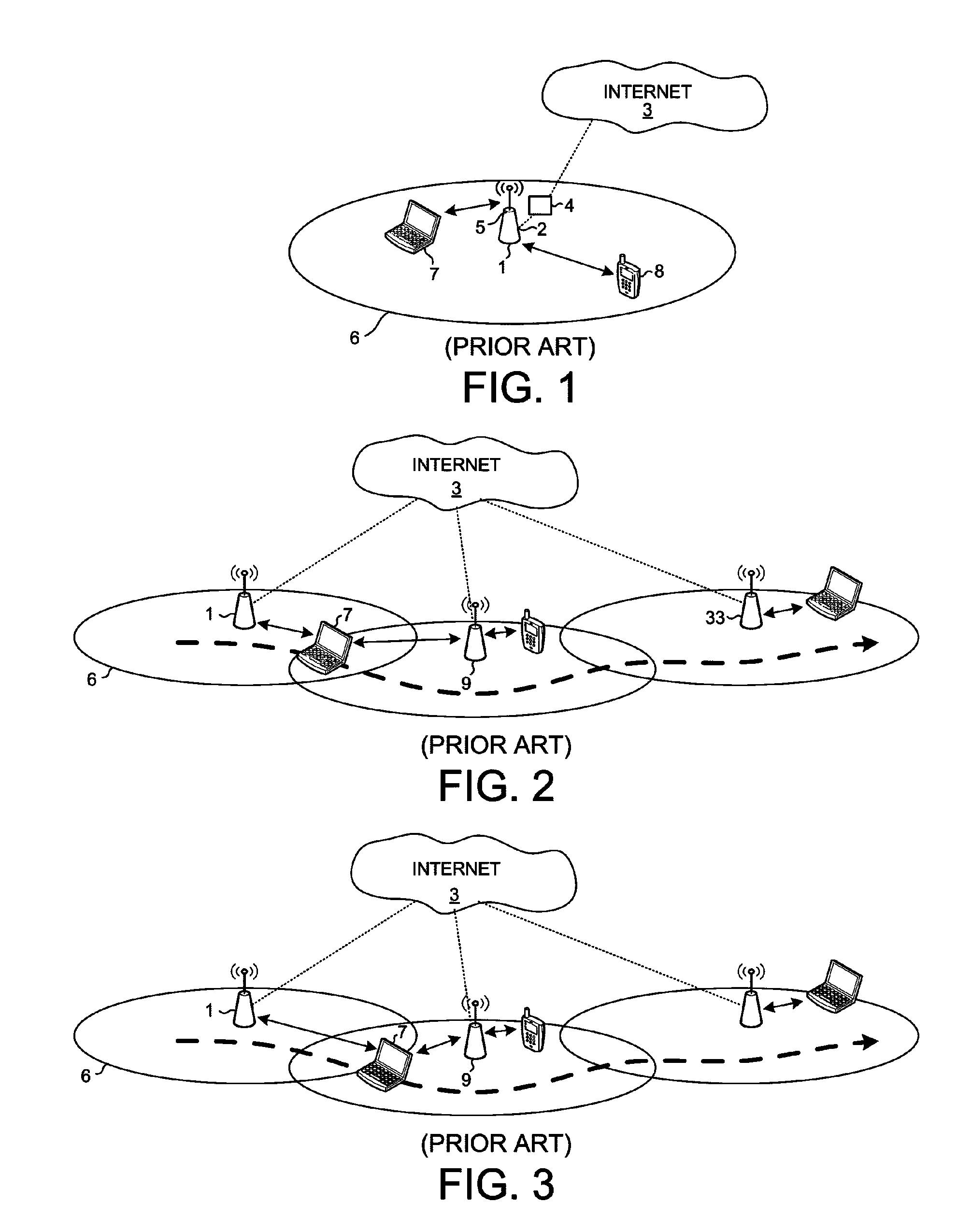
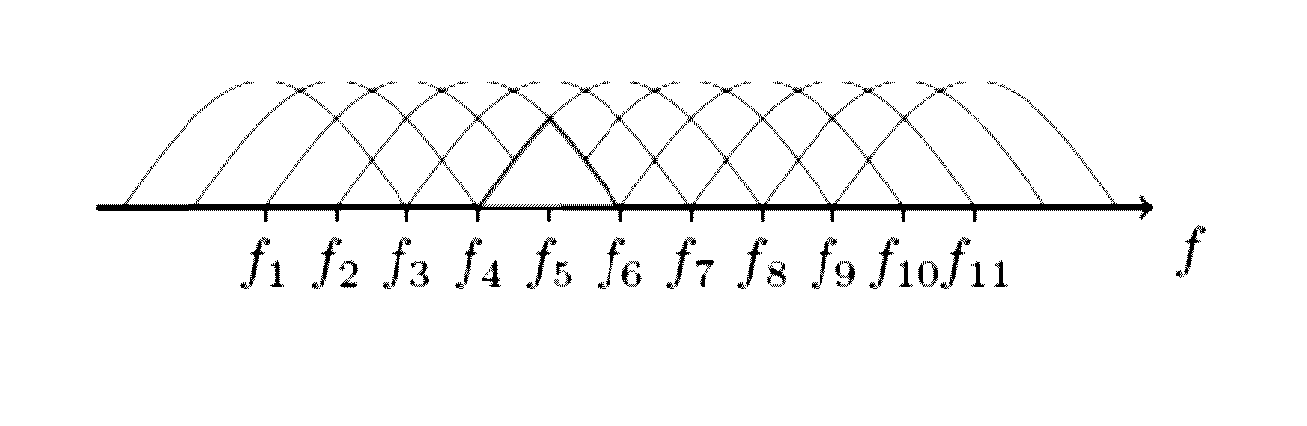
Method to optimize the communication parameters between an access point and at least one client device
ActiveUS20140307571A1Increase volumeWide bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsClient-side
A method to optimize the communication on a channel between an access point and at least one client device, said channel being characterized by a center frequency and a bandwidth, comprises: establishing a connection on a first channel according to a first center frequency and a first bandwidth; exchanging data through this first channel between the access point and the client device; monitoring a first interference level on the first channel; the access point, while the data are exchanged, executes: informing the client device to switch to a second channel having a different center frequency and / or a different bandwidth; determining a second interference level on the second channel; comparing the first interference level with the second interference level; deciding to switch back or keep the second channel based on the comparison.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method and apparatus for separating and dewatering slurries
InactiveUS20100314304A1Reduce Nutrient LoadMore throughputWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationLoose filtering material filtersFiberDrive motor
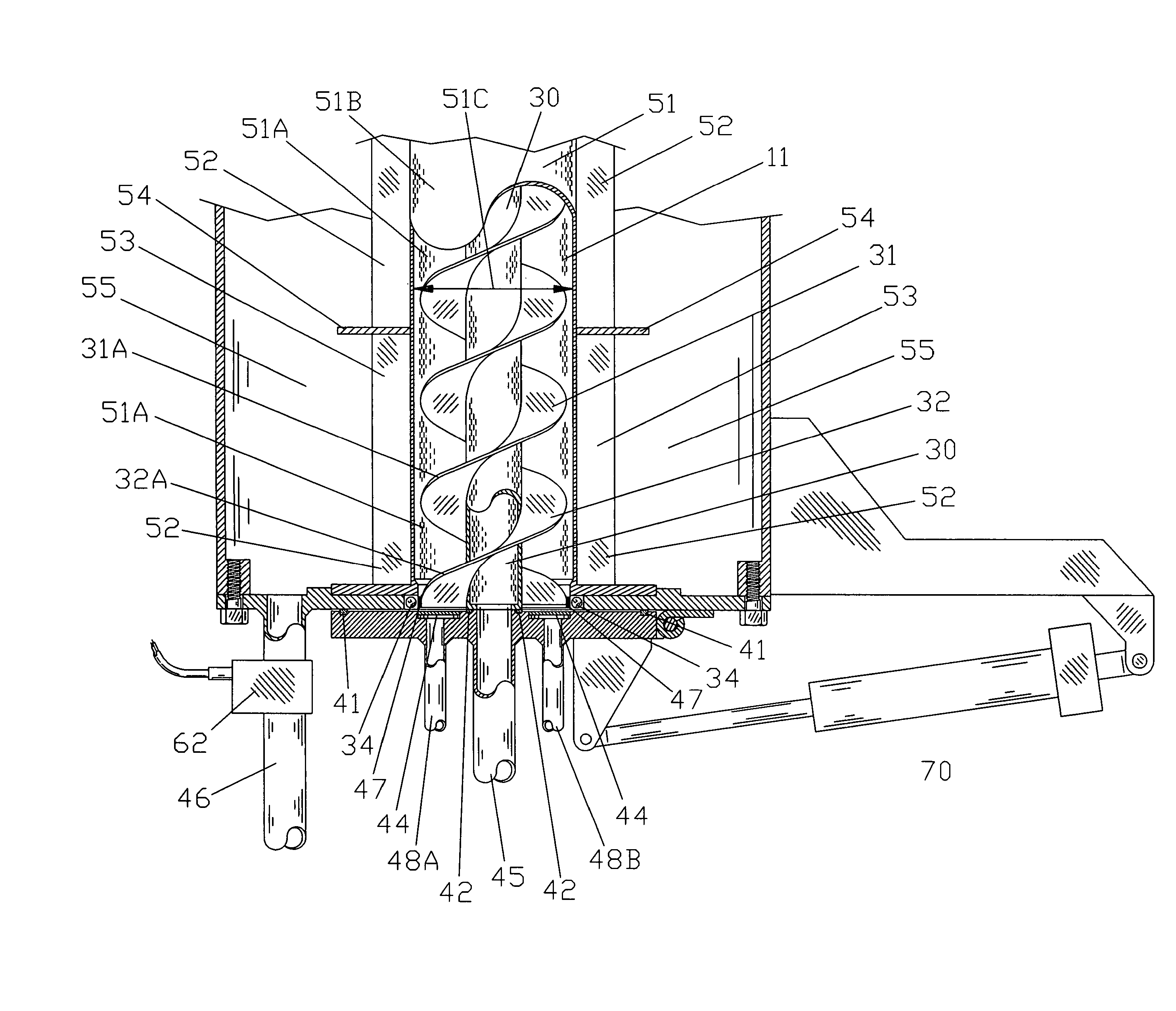
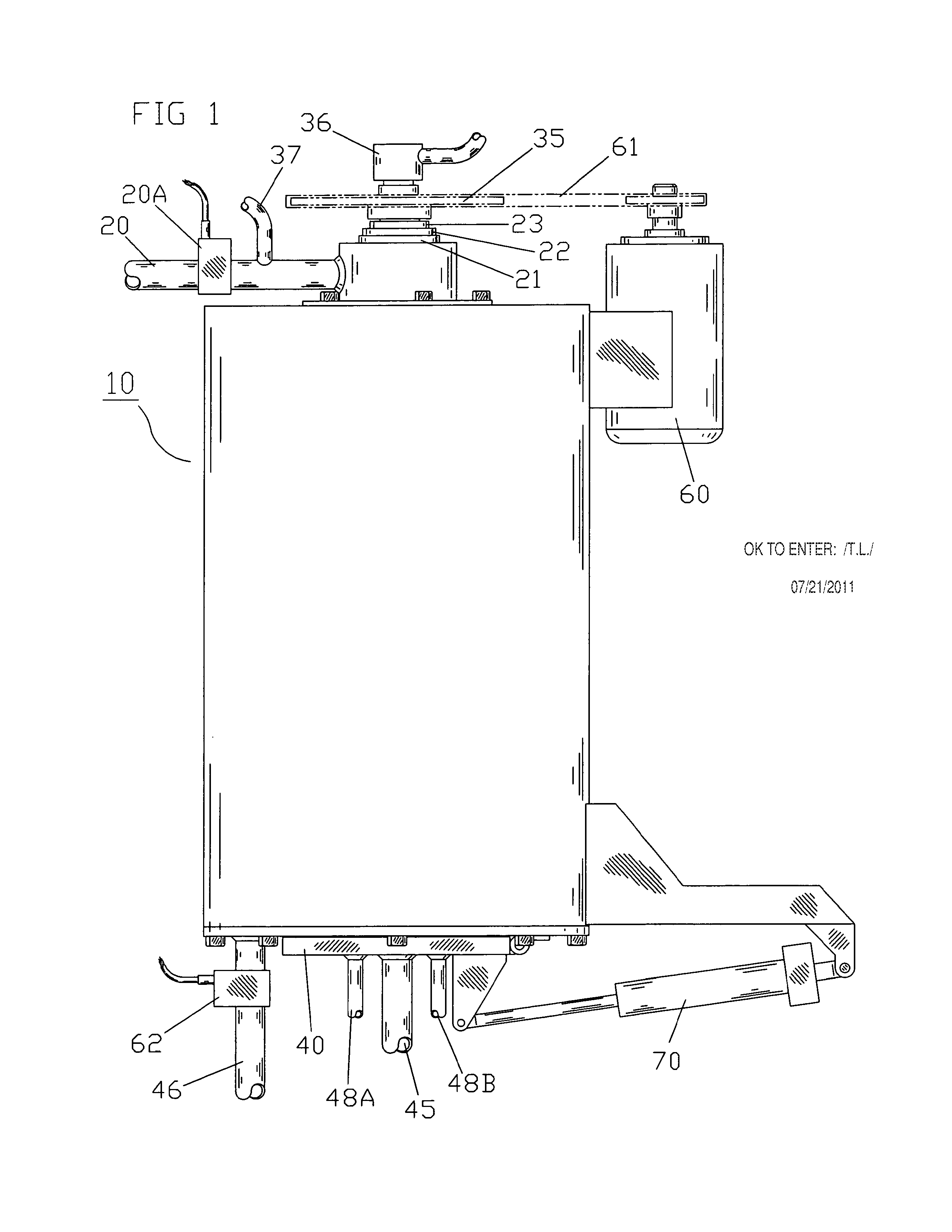
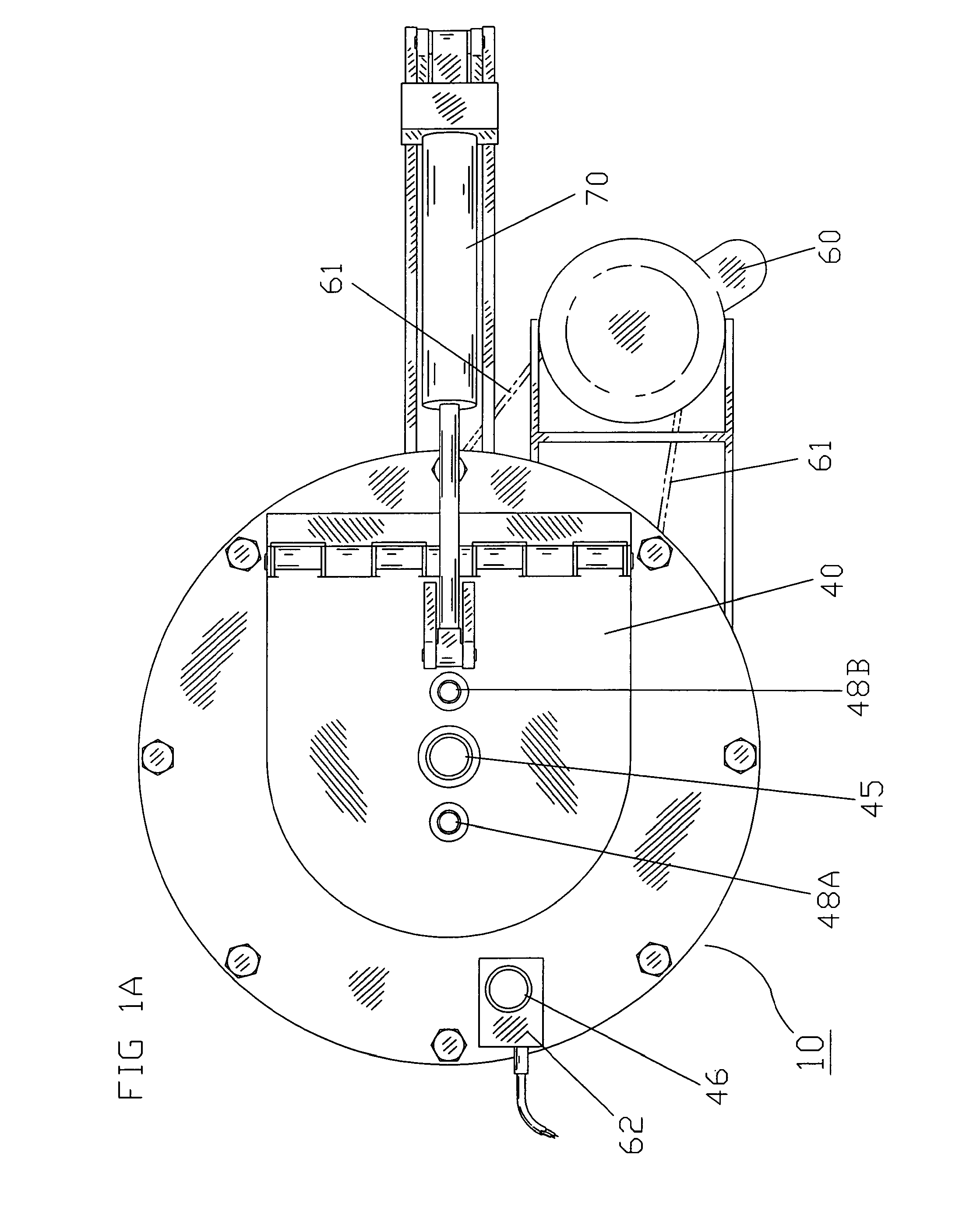
A vertical cylindrical dewatering apparatus for dewatering fibrous slurries, slurry of manure and water, or other similar slurries. The apparatus includes a housing that includes a defined chamber having an enclosed top end with a slurry injector into the chamber, a centrally disposed first filtering element that includes first and second flightings, and a second vertical cylindrical filtering element including a support grid. The first and second filtering elements define the chamber. The slurry in-flow port at the top of the apparatus directs the slurry spiraling down between the flightings. The particles start building up at the bottom of the chamber as the water is filtered out from the housing through filtrate drains. Compressed air supplied through a rotating seal down through the centrally disposed filtering element moves through the filter, and through the particles forcing the water from between the particles out through the outer filter element. After the moisture is removed from the particles, a hinge door is opened and a drive motor turns the first filter and flightings for particle removal. An alignment ring is attached to outer edges of the lower end of said flights in order to maintain a clearance of at least ¼ inch between the outer edges and the second filter element.
Owner:TAPP FLOYD G
Coordination of Wi-Fi P2P and LTE data traffic
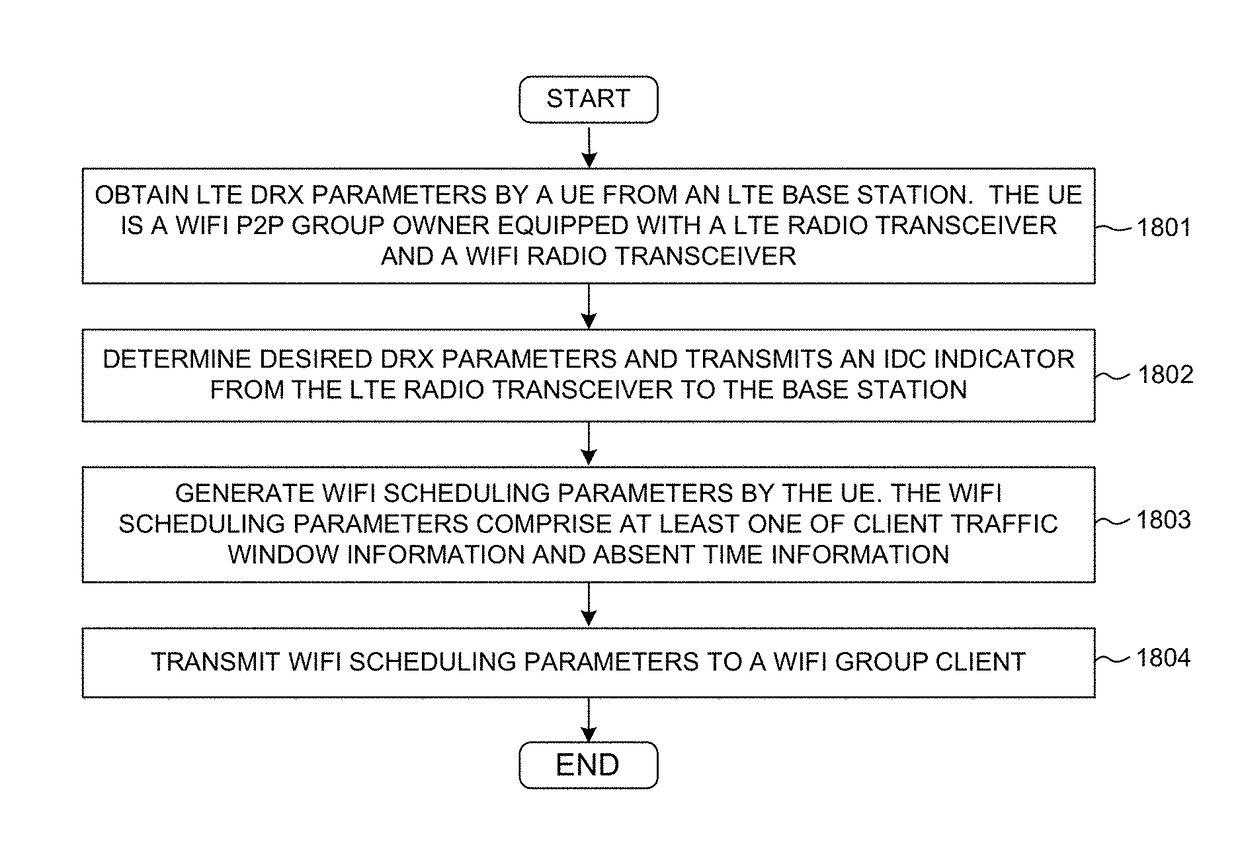
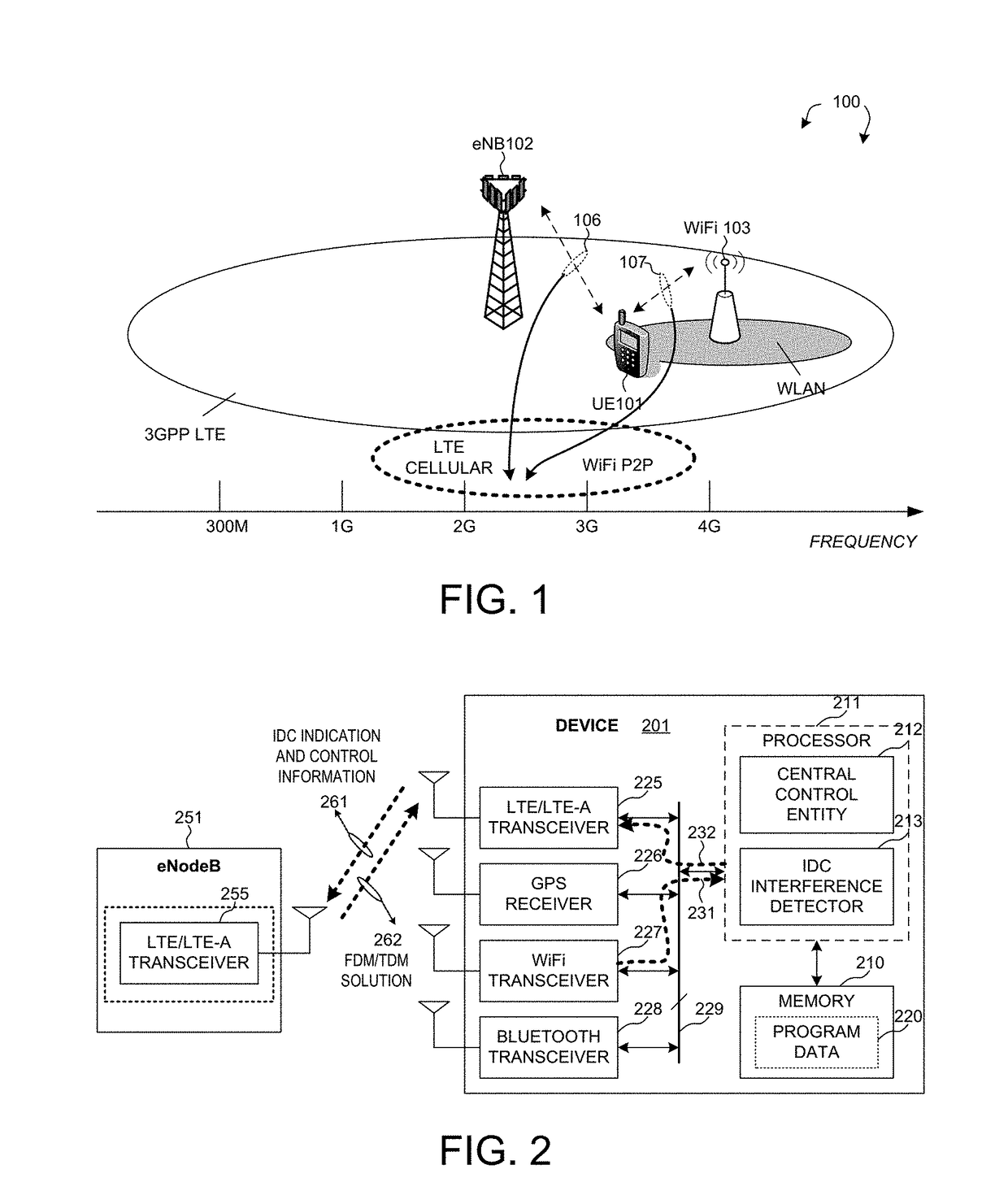
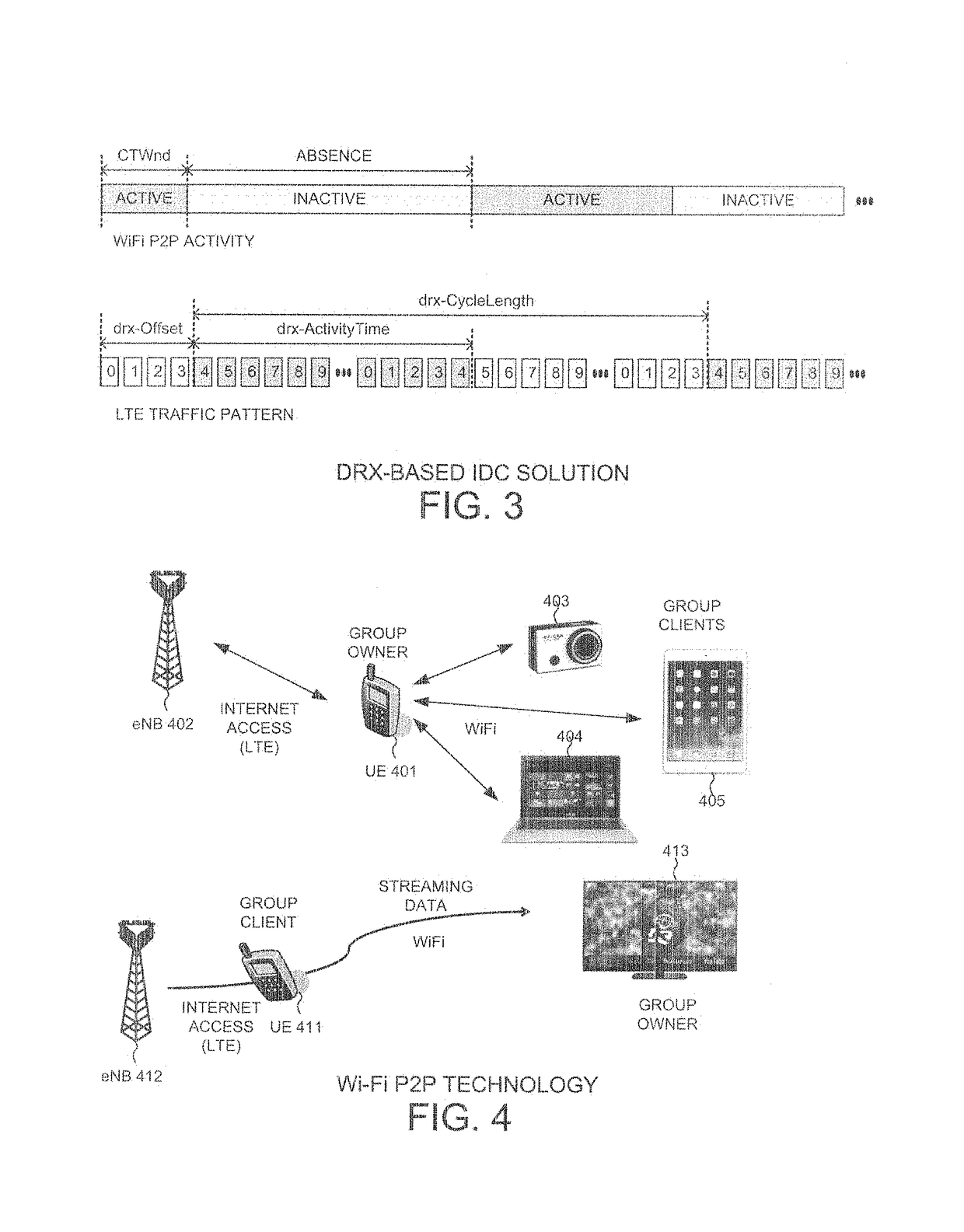
For LTE cellular data and Wi-Fi P2P technology coexistence scenario, a user equipment can generate in-device coexistence (IDC) indication message to the base station for DRX-based IDC solution. LTE data scheduling is described by a set of DRX parameters, while Wi-Fi P2P data scheduling is described by Opportunistic Power Saving (OppoPS) and Notification of Absence (NoA) parameters. When generating the IDC indication message for Wi-Fi P2P group client (GC), the DRX parameters must be selected carefully to maximize efficiency. Even though Wi-Fi shares less time, with proper time alignment, its coexistence performance could be better. For Wi-Fi P2P group owner (GO) with IDC TDM scheduling constraints, OppoPS and NoA should be aligned with DRX parameters to achieve best performance.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Extractive distillation processes using water-soluble extractive solvents
ActiveUS7871514B2Reduce amountGood solvent performanceHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsFluid phaseExtractive distillation
Extractive distillation processes whereby water-soluble extractive distillation (ED) solvents are regenerated and recovered employ improved operations of the extractive distillation column (EDC) so that polar hydrocarbons are recovered and purified from mixtures containing polar and less polar hydrocarbons and measurable amounts of hydrocarbons that are heavier than intended feedstock and / or polymers that are generated in the ED process. The improved process can effectively remove and recover the heavy hydrocarbons and / or remove polymer contaminants from the solvent in a closed solvent circulating loop through mild operating conditions with no additional process energy being expended. With the improved process, the overhead reflux of the EDC may be eliminated to further reduce energy consumption and to enhance the loading and performance within the upper portion of the EDC, especially when two liquid phases exists therein.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
Cassette roller leveler with common back-up rolls
ActiveUS7637133B2Shorten the timeMore productivityMetal rolling stand detailsMetal rolling arrangementsWork rollEngineering
A roller leveler having a frame; a first bank of upper and lower work rolls journalled in the frame via a work roll journal housing; and a bank of back-up rolls in contact with the work rolls to support the work rolls. The work rolls perform leveling on a work product passing through a gap formed between upper and lower work rolls. The back-up rolls are mounted to the roller leveler frame via a back-up housing. The back-up rolls are movable to allow the first bank of work rolls to be removed and a second bank of work rolls to be installed wherein the second bank of work rolls includes work rolls of a different diameter than the first bank of work rolls.
Owner:BUTECH BLISS
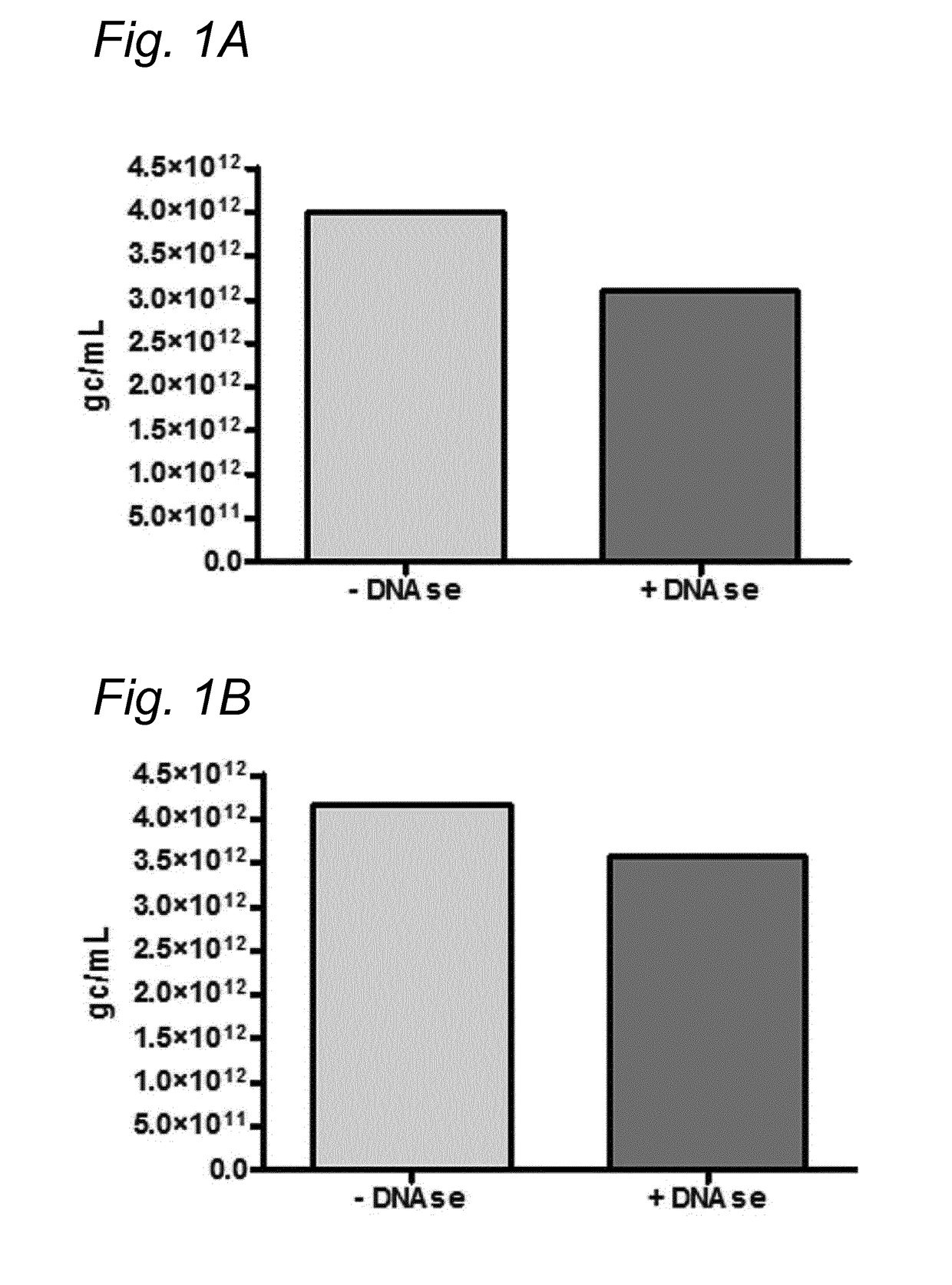
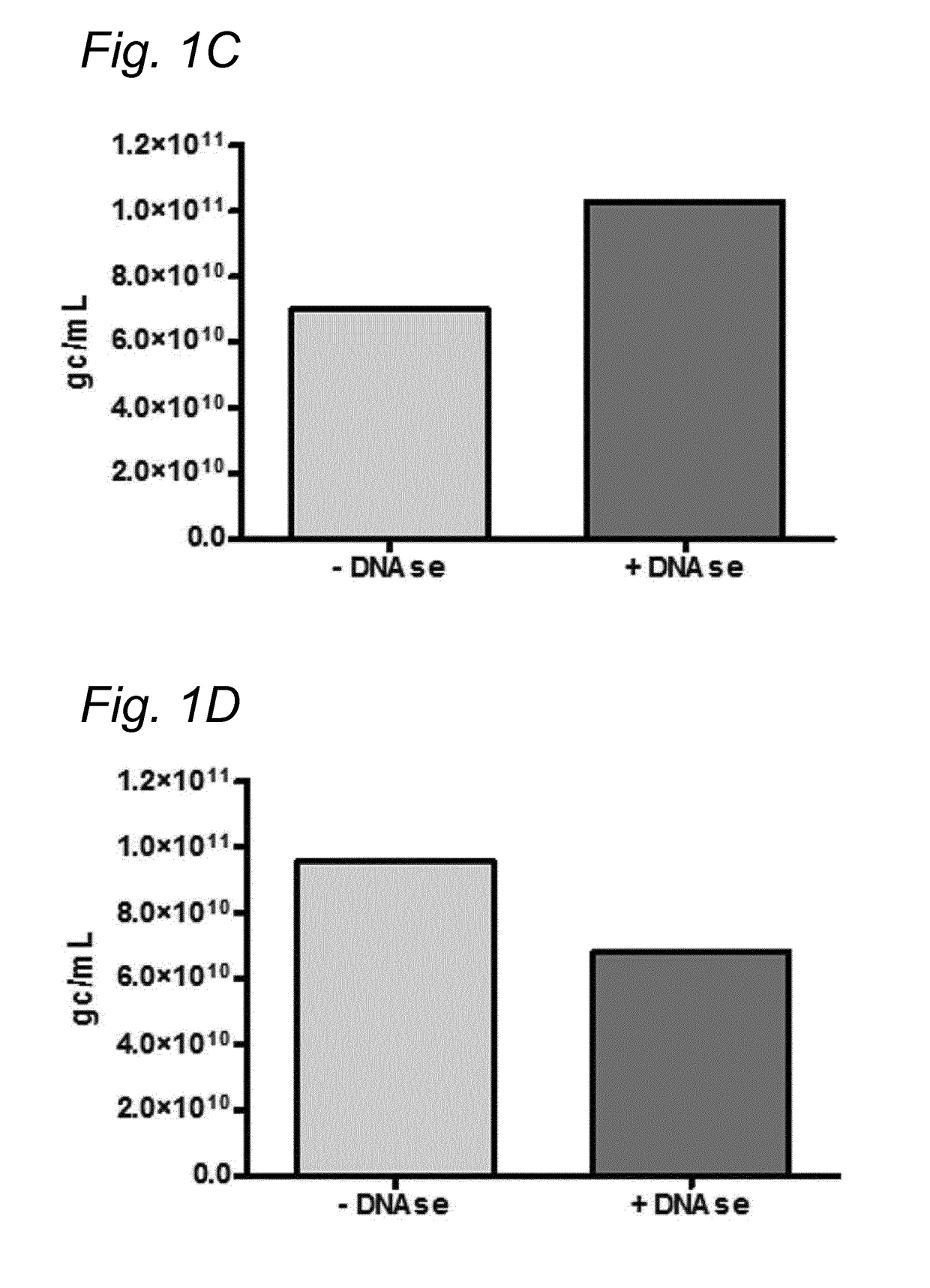
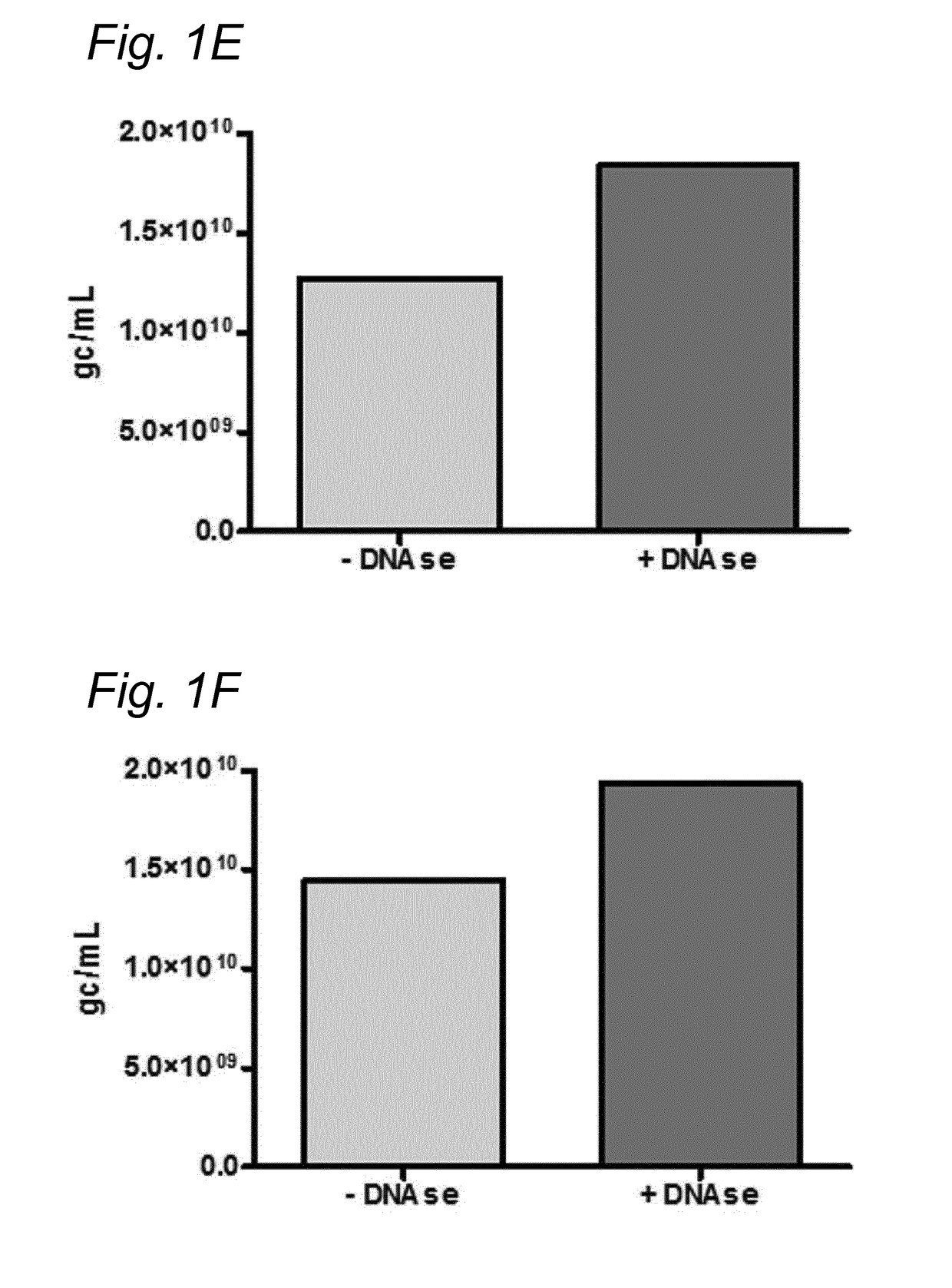
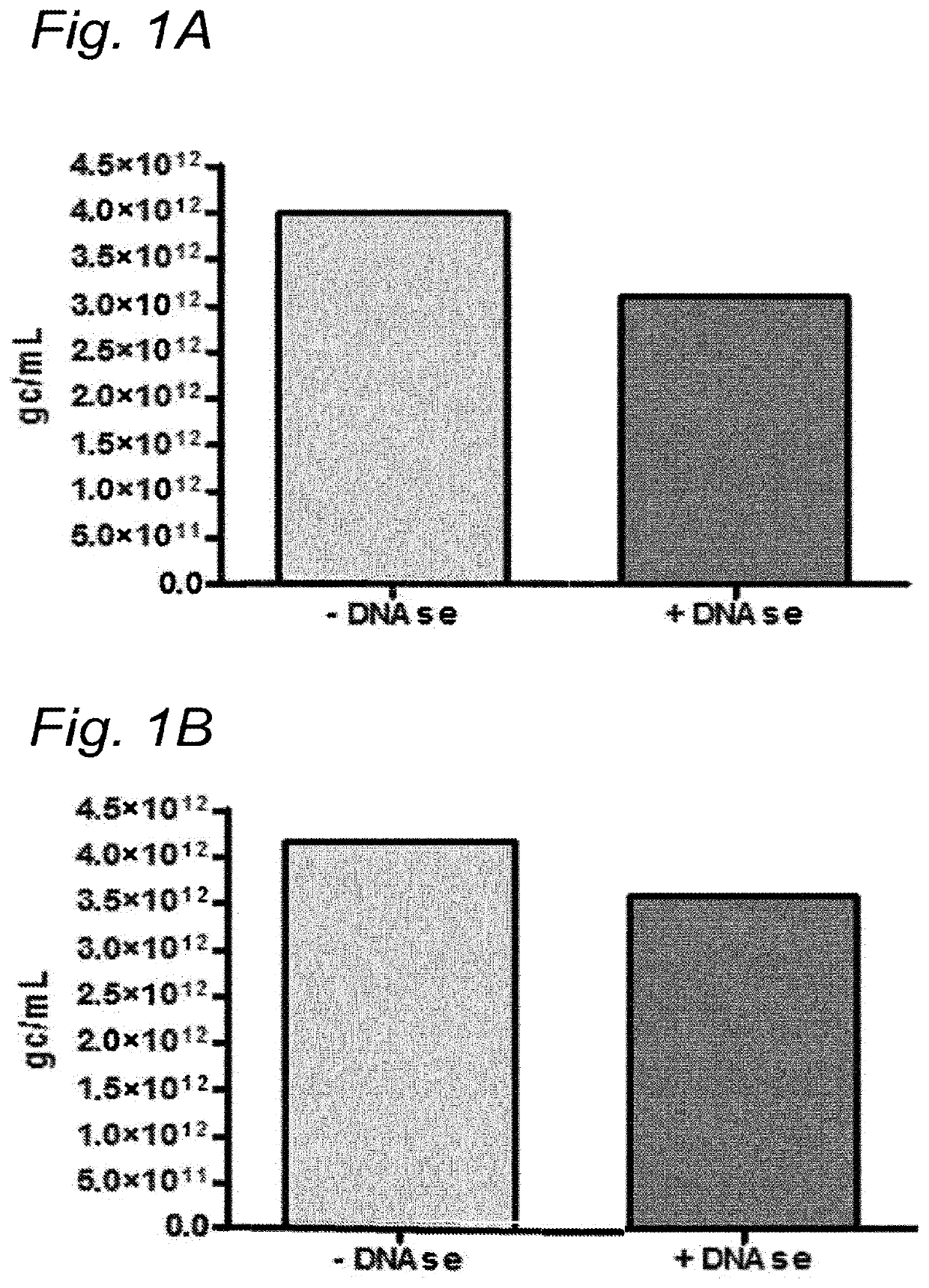
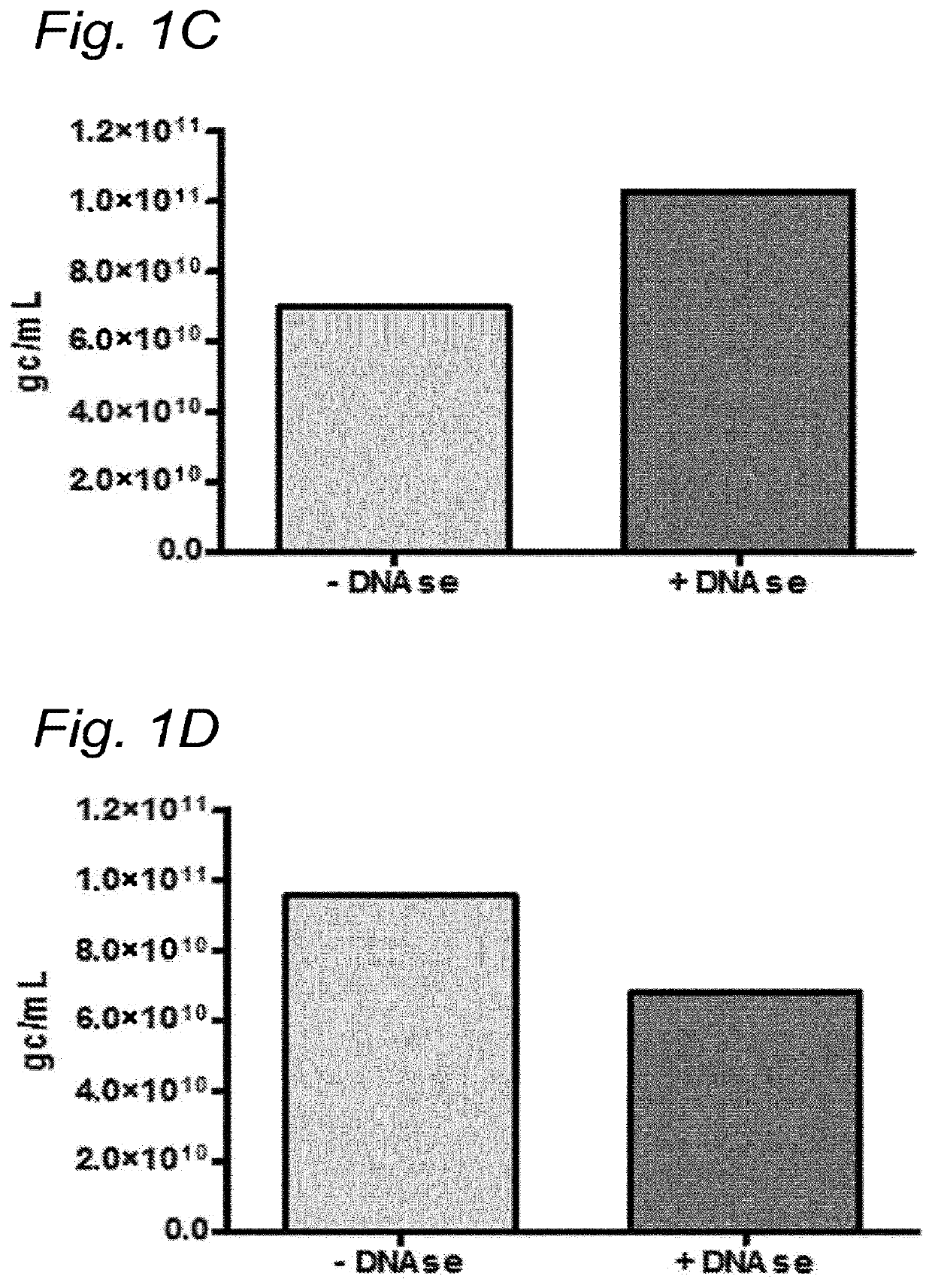
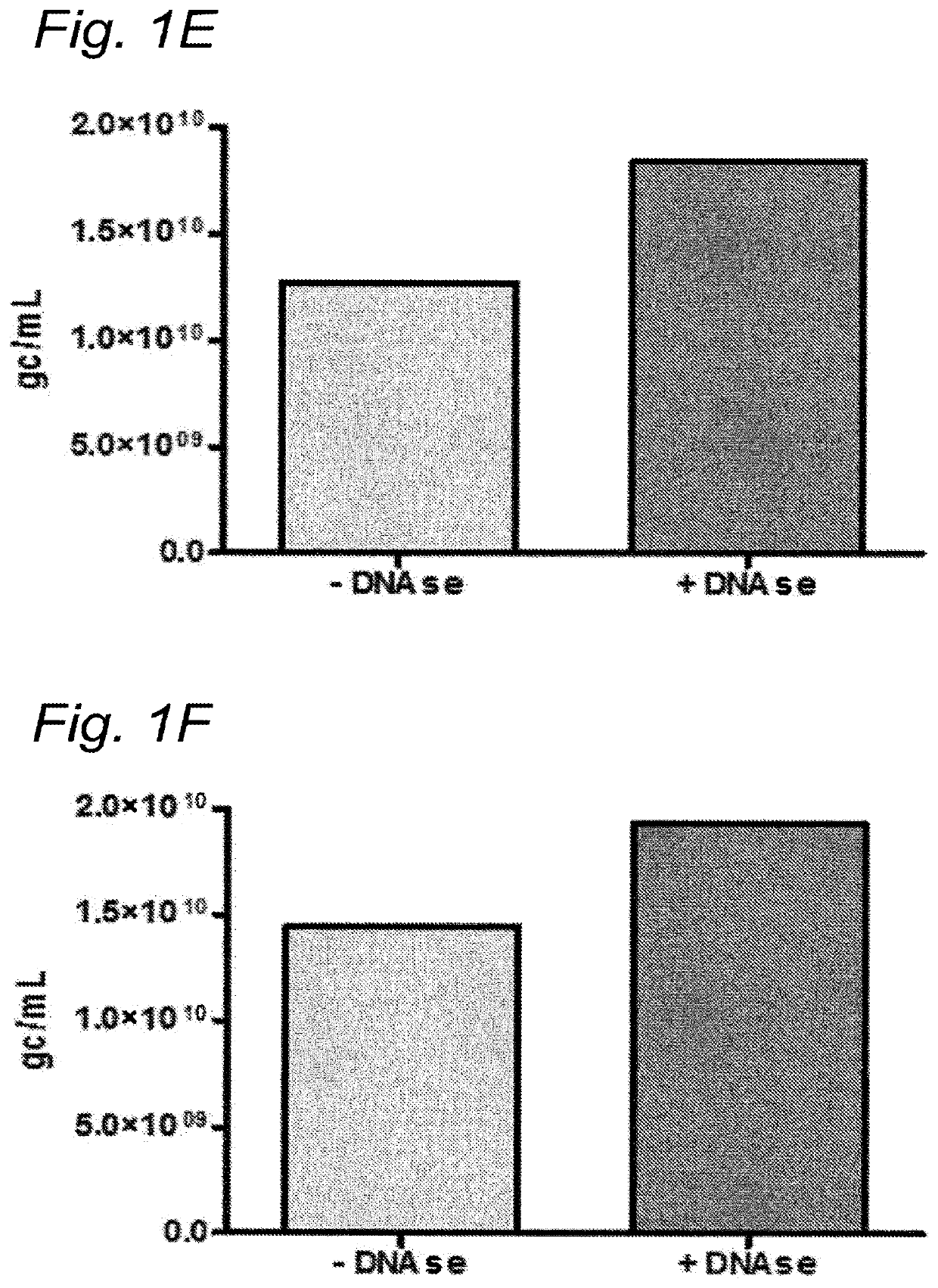
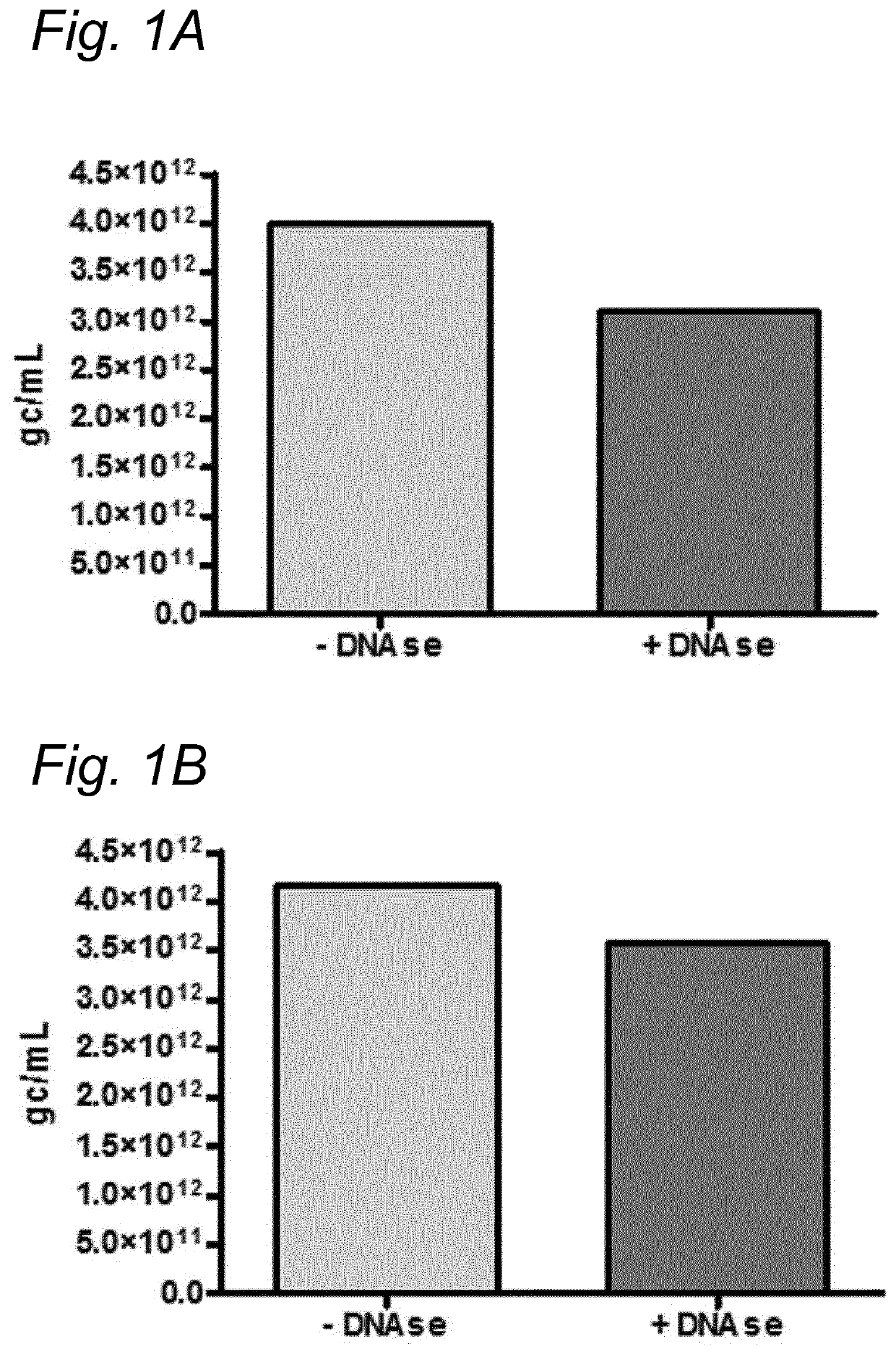
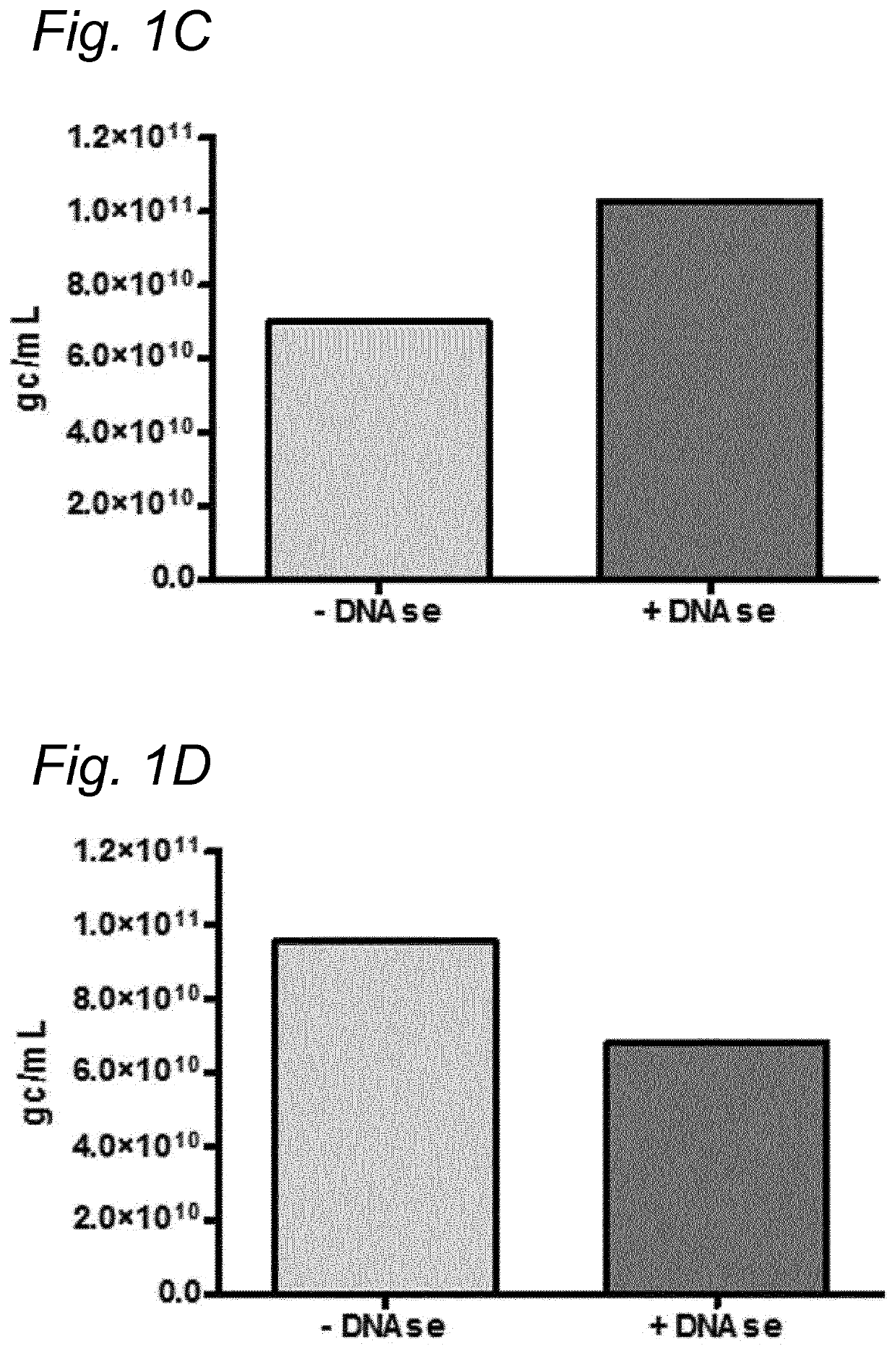
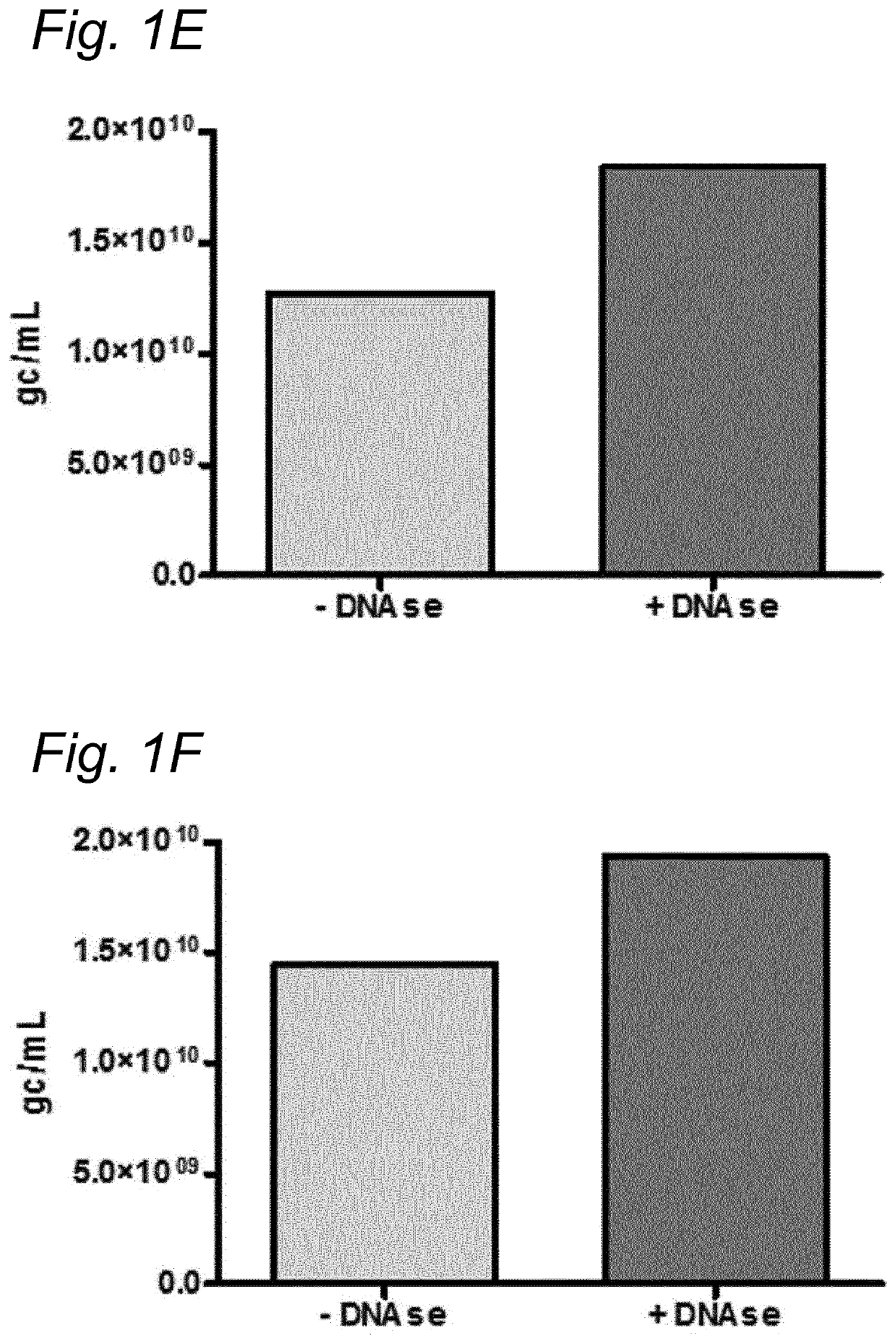
DNA impurities in a composition comprising a parvoviral virion
ActiveUS20170321290A1Efficiently cross-complementMore throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDsDNA virusesBiologyDNA
The current invention relates to nucleic acid impurities in a composition comprising a parvoviral vector. In particular, the current invention shows that DNA impurities are not randomly encapsulated within a parvoviral virion. The invention therefore relates to a method for identifying and quantifying a nucleic acid impurity in a composition comprising a parvoviral vector. Finally, the current invention relates to method of determining whether a composition comprising a parvoviral vector is regarded as clinically pure.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
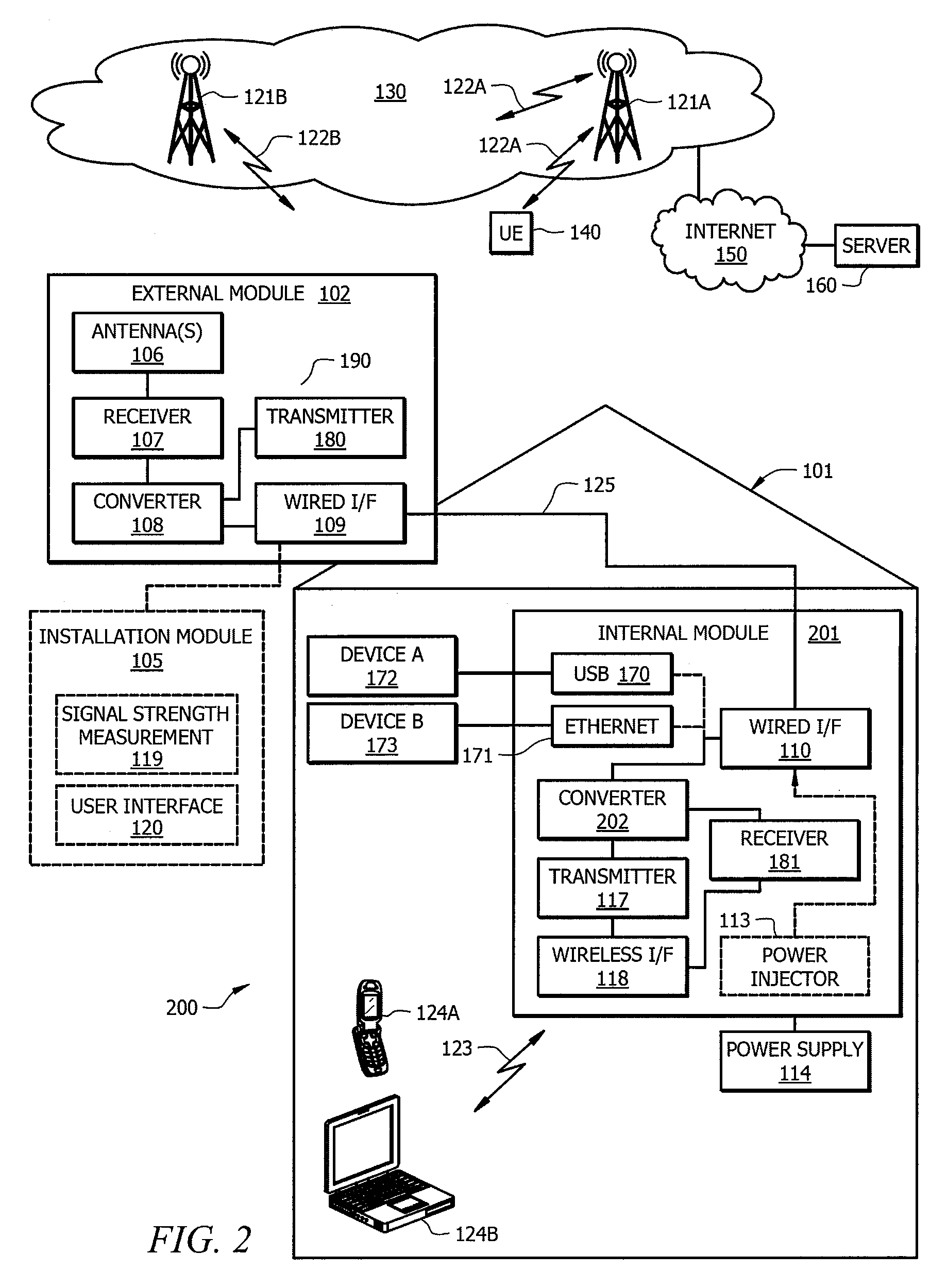
System and method for bridging to a LTE wireless communication network
ActiveUS9220128B2G-higher throughputLower latencyNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentCommunications systemNetwork Communication Protocols
A system and method for bridging user devices communicating according to a 3rd Generation (3G) communication protocol to a LTE wireless communication network, thereby enabling user devices that do not have sufficient signal strength for directly coupling to the LTE wireless communication network to nevertheless access such wireless communication systems and methods via a bridging system.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
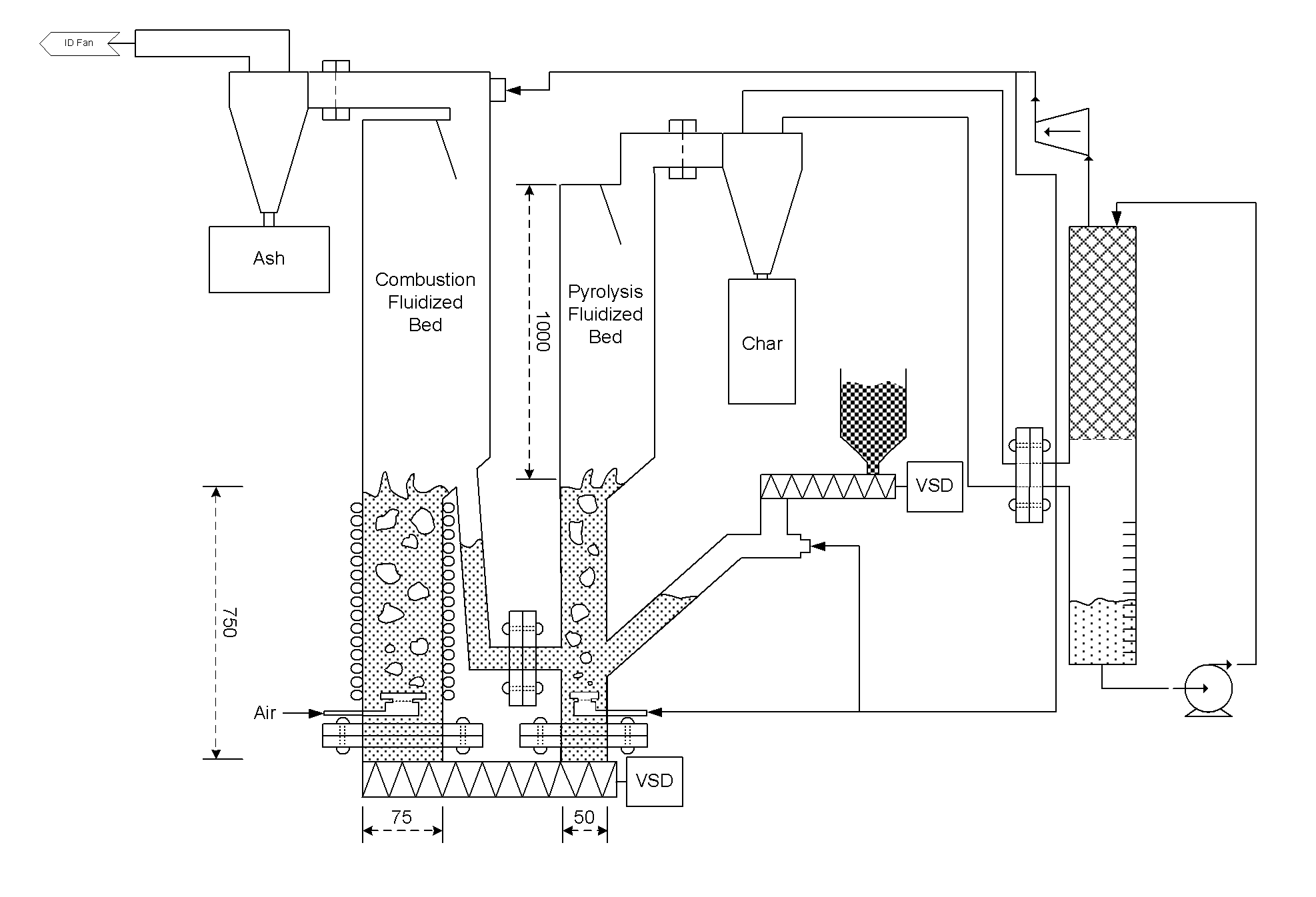
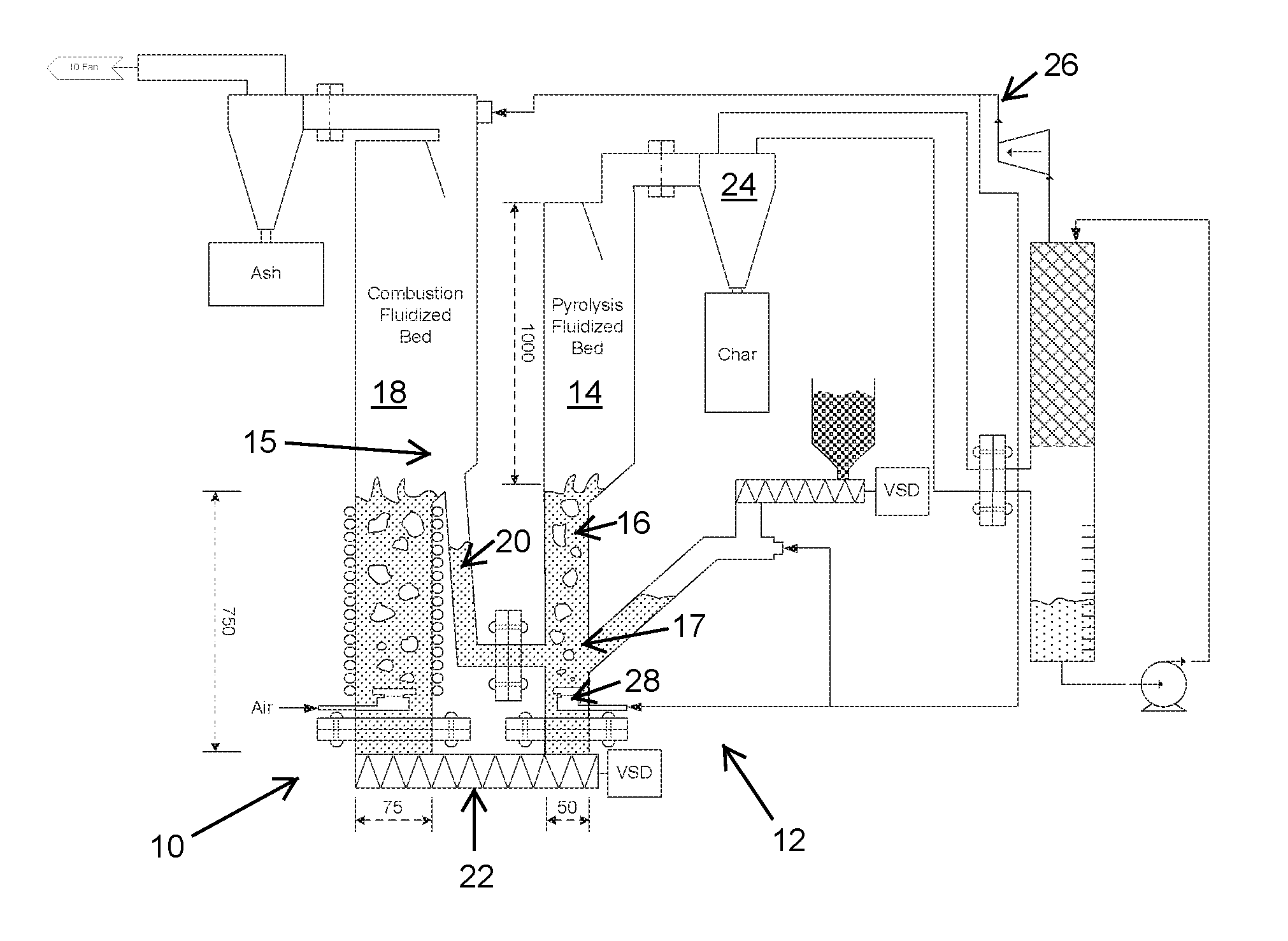
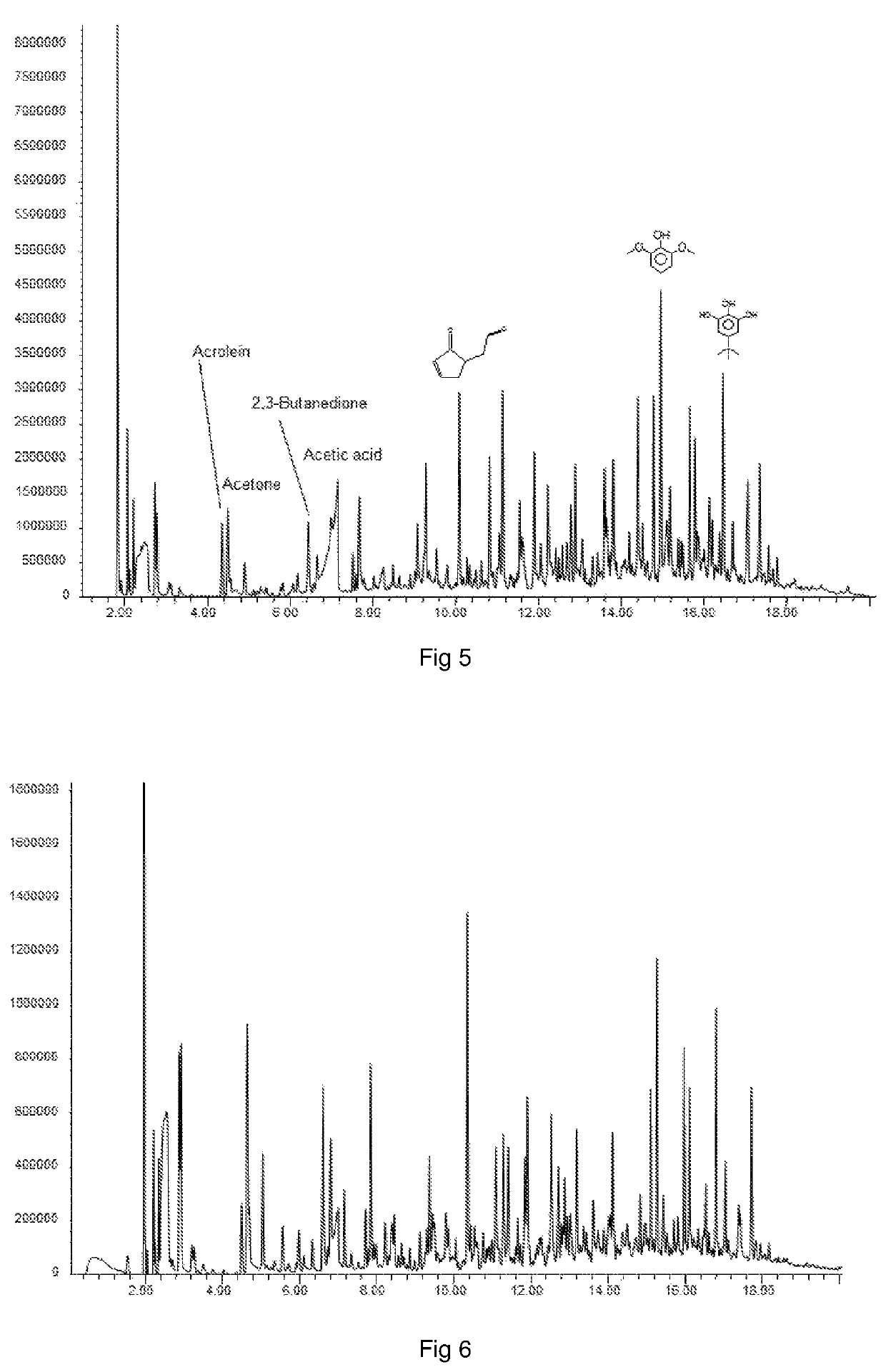
Fluidised bed pyrolysis apparatus and method
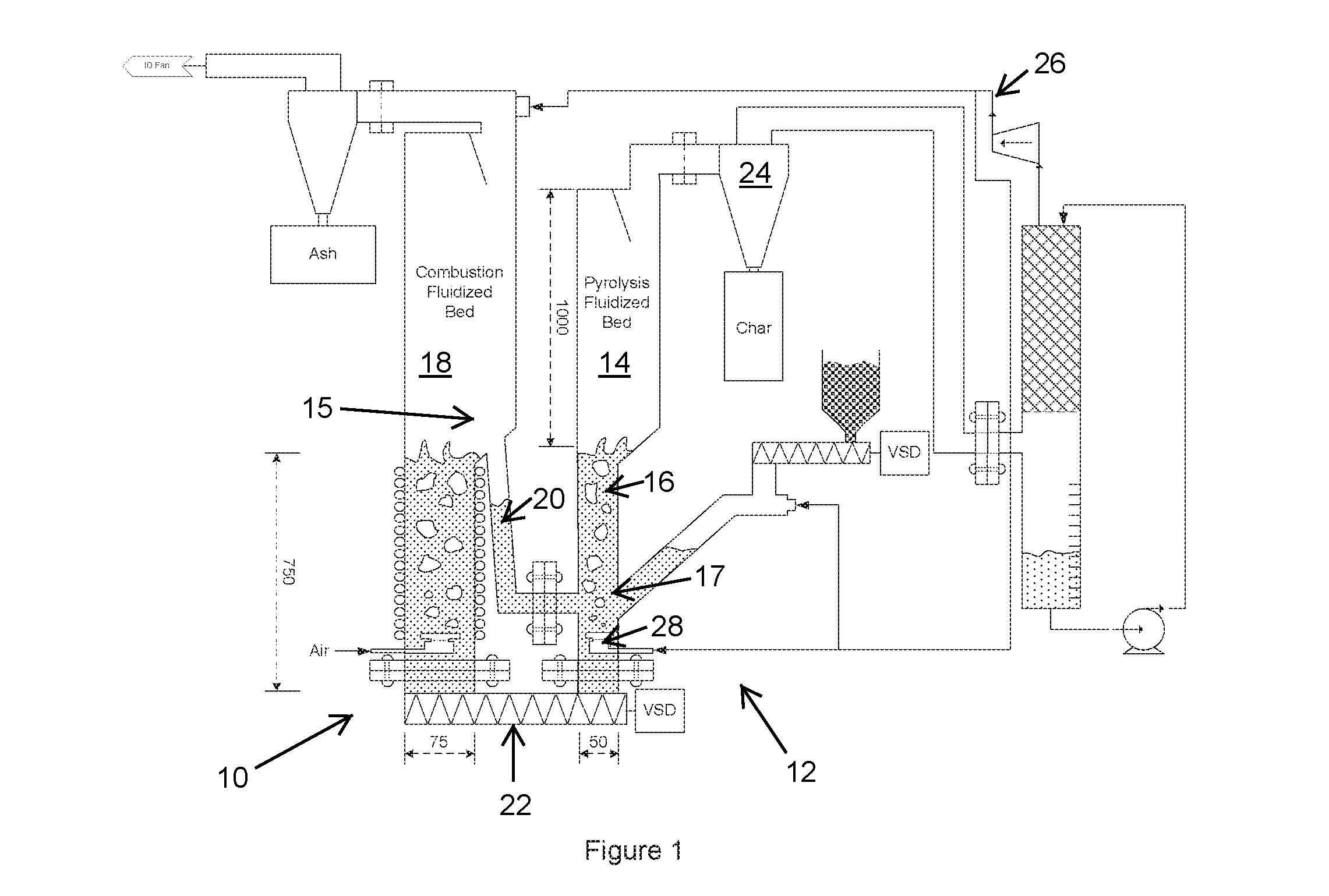
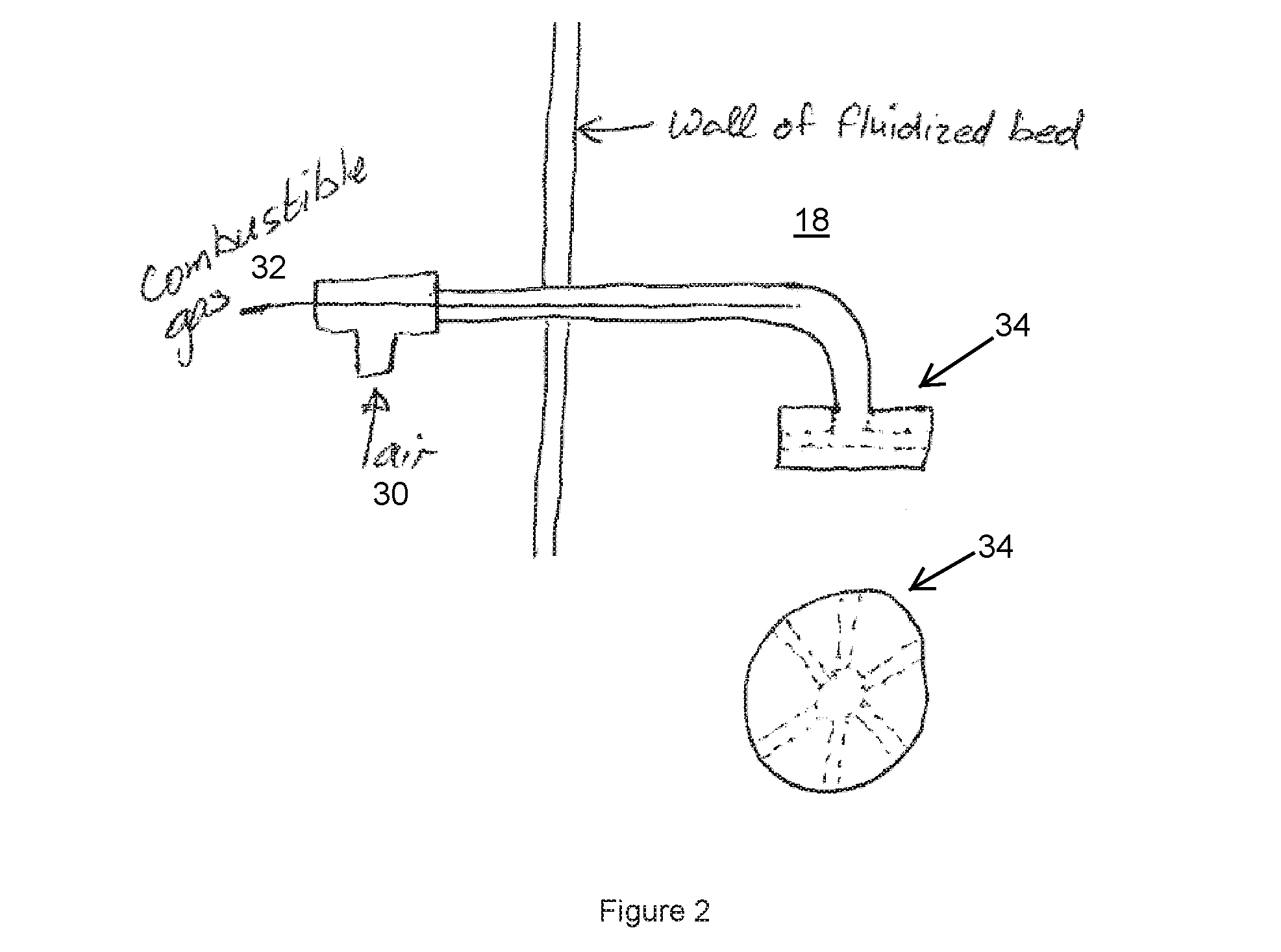
ActiveUS20140008205A1Less enthalpyIncreased superficial gas velocityFluidized bed combustionDirect heating destructive distillationCombustionFluidized bed
A carbonaceous feed pyrolysis apparatus is provided including two or more hot particle fluidised beds, and one or more positive displacement apparatus for the transfer of hot particles between two or more of the beds, wherein one or more of the fluidised beds contains a combustion zone. A bio-oil production process is also provided, including pyrolysis of a carbonaceous bio-mass using two or more fluidized beds, including a first combustion zone carried out in one or more combustion fluidized beds in which a particulate material is fluidized and heated, and a second pyrolysis zone carried out in one or more pyrolysis fluidized beds in which the hot particles heated in the combustion zone are used for pyrolysis of the bio-mass.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA +1
Method for verification of at least one given fuel mixture ratio
InactiveUS7258105B2Prevents not only insufficient flushingMore throughputElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineFuel injection
A fuel injection system during operation of an internal combustion engine with at least two separately stored fuel types is supplied with at least one first fuel type. With the supply of a second fuel type or with the change from the supply of the first fuel type to the second fuel type, the fuel volume conveyed by the injection system is determined and dependent thereon the presence of a given fuel mixture ratio is verified.
Owner:KANGLER WOLFRAM
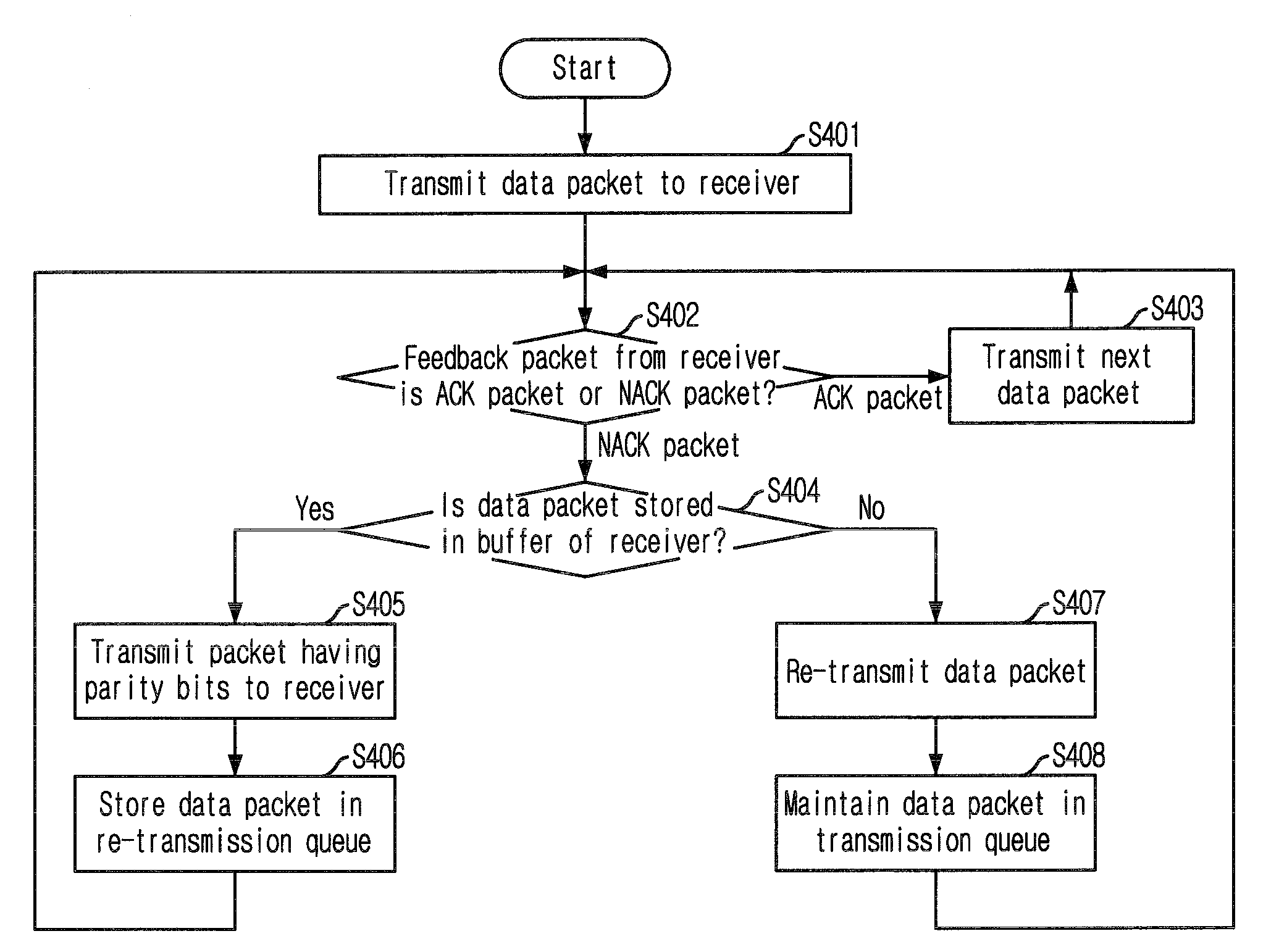
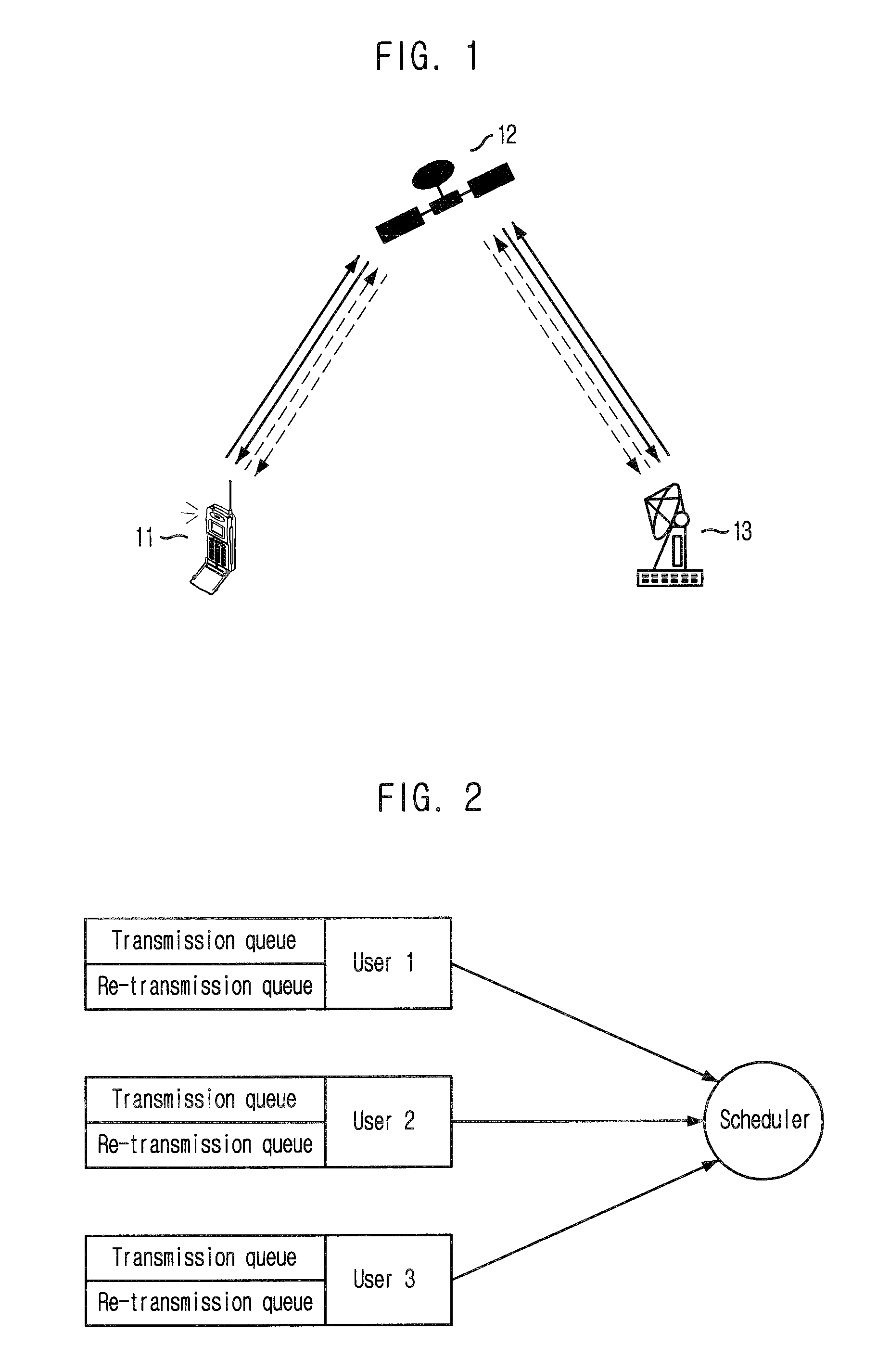
Method for preventing consecutive packet errors in selective hybrid ARQ system
InactiveUS20100050035A1Wasteful of errorsWasteful useError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsAutomatic repeat requestNetwork packet
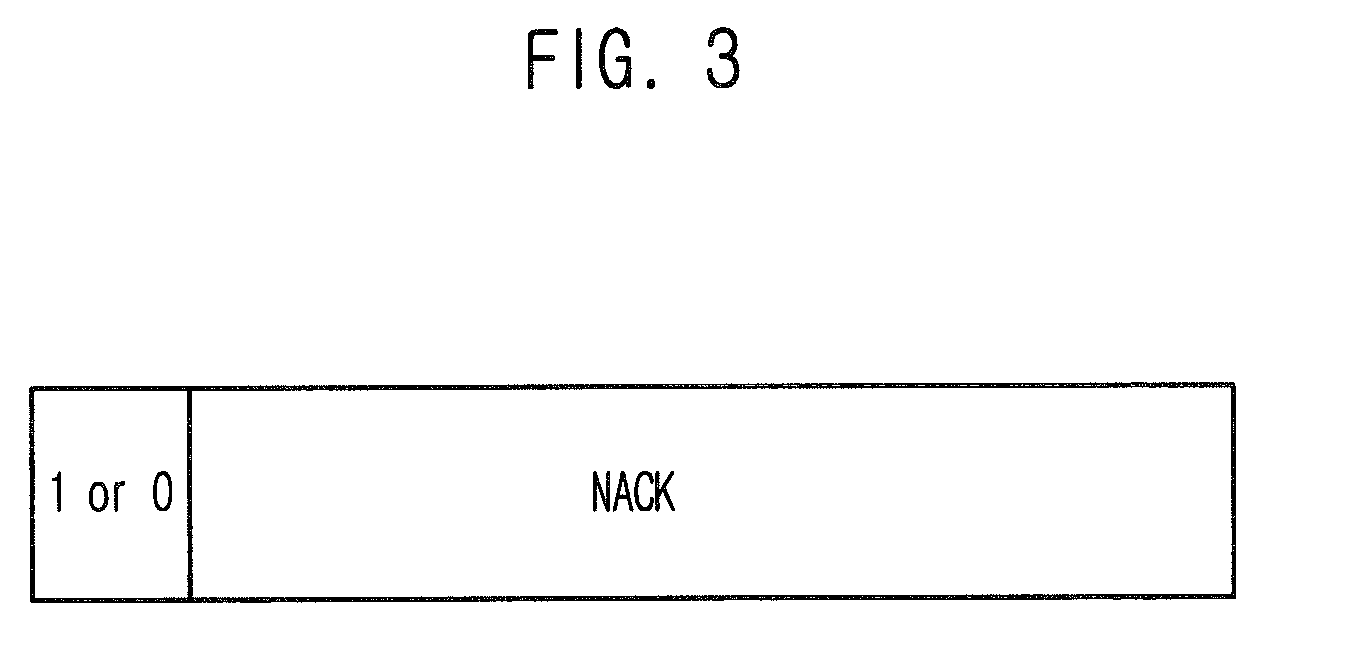
Provided is a method for preventing consecutive packet errors in a transmitter by combining a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) type II with a selective automatic repeat request (ARQ), including: transmitting a data packet from the transmitter to a receiver; when a negative acknowledgement (NACK) packet corresponding to the data packet is received from the receiver, checking stored information in the NACK packet wherein the stored information represent whether or not the data packet is stored in a buffer; when the data packet is stored in the buffer, transmitting a packet having parity bits to the receiver and storing the data packet in a retransmission queue; and when the data packet is not stored in the buffer, re-transmitting the data packet and maintaining the data packet stored in a transmission queue.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for separating and dewatering slurries
InactiveUS8025156B2Reduce Nutrient LoadMore throughputWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationLoose filtering material filtersFiberDrive motor
A vertical cylindrical dewatering apparatus for dewatering fibrous slurries, slurry of manure and water, or other similar slurries. The apparatus includes a housing that includes a defined chamber having an enclosed top end with a slurry injector into the chamber, a centrally disposed first filtering element that includes first and second flightings, and a second vertical cylindrical filtering element including a support grid. The first and second filtering elements define the chamber. The slurry in-flow port at the top of the apparatus directs the slurry spiraling down between the flightings. The particles start building up at the bottom of the chamber as the water is filtered out from the housing through filtrate drains. Compressed air supplied through a rotating seal down through the centrally disposed filtering element moves through the filter, and through the particles forcing the water from between the particles out through the outer filter element. After the moisture is removed from the particles, a hinge door is opened and a drive motor turns the first filter and flightings for particle removal. An alignment ring is attached to outer edges of the lower end of said flights in order to maintain a clearance of at least ¼ inch between the outer edges and the second filter element.
Owner:TAPP FLOYD G
DNA impurities in a composition comprising a parvoviral virion
PendingUS20210332447A1More throughputMinimization requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDsDNA virusesVirosomeDNA
The current invention relates to nucleic acid impurities in a composition comprising a parvoviral vector. In particular, the current invention shows that DNA impurities are not randomly encapsulated within a parvoviral virion. The invention therefore relates to a method for identifying and quantifying a nucleic acid impurity in a composition comprising a parvoviral vector. Finally, the current invention relates to method of determining whether a composition comprising a parvoviral vector is regarded as clinically pure.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Combined background and 20/40 coexistence scan
InactiveUS8620312B2Reduce in quantityImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceThroughput
A scanning module within a non-AP station receives first scan parameter values for performing a first type of scan to obtain a first type of information, and receives second scan parameter values for performing a second type of scan to obtain a second type of information. From the first and second parameter values the scanning module determines combined scan parameter values that satisfy scan requirements for both types of scans. The combined scan parameter values are used to control a sequence of combined scans. A combined scan yields both the first and second type of information. In one example, an IEEE 802.11(n) non-AP station receives 20 / 40 coexistence scan parameters. The 20 / 40 parameters and locally-generated background scan parameters are used to determine parameters for performing combined background and 20 / 40 scans. Reducing the number of scans using combined scans has advantages including increasing data throughput, freeing processing resources, and reducing power consumption.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
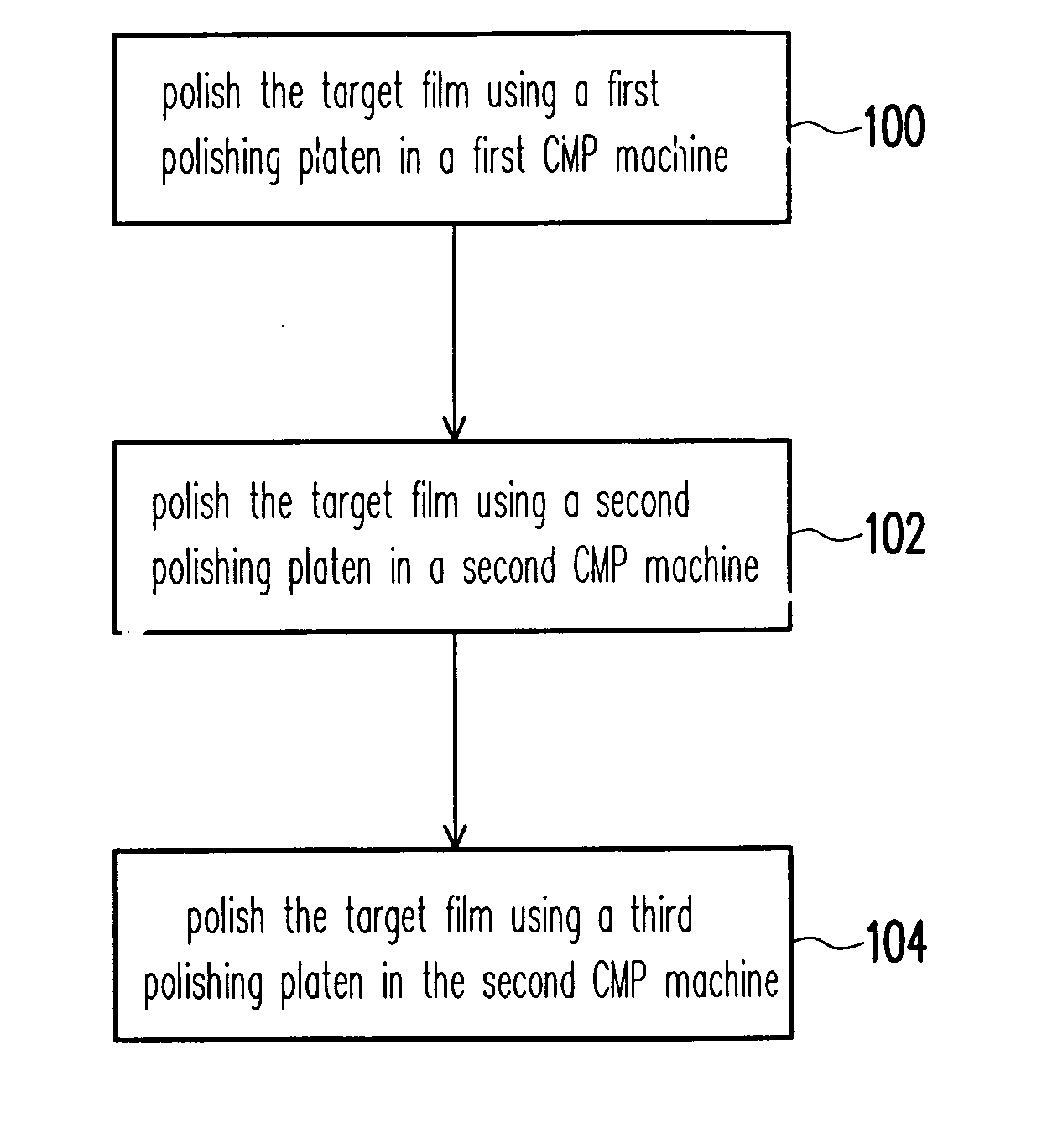
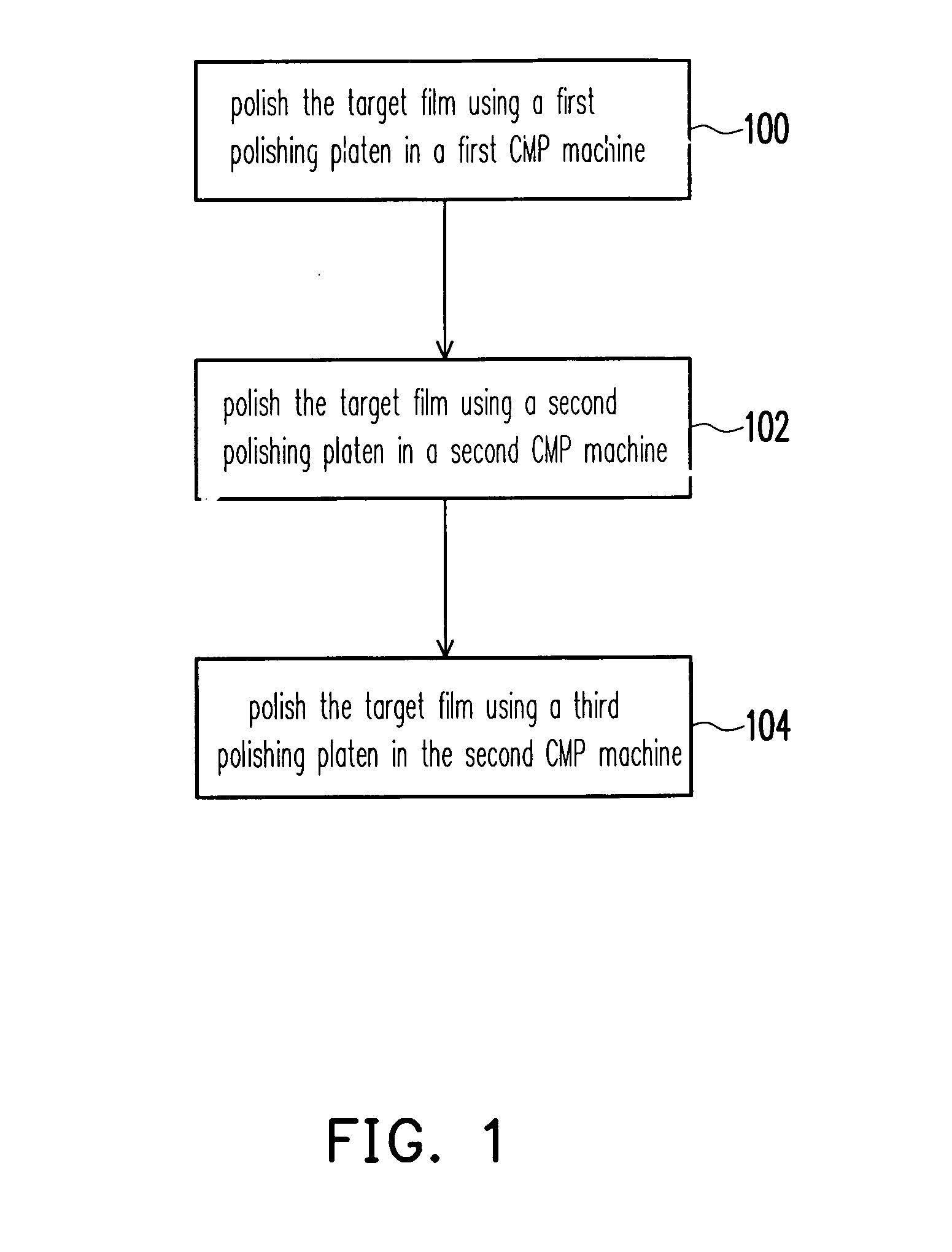
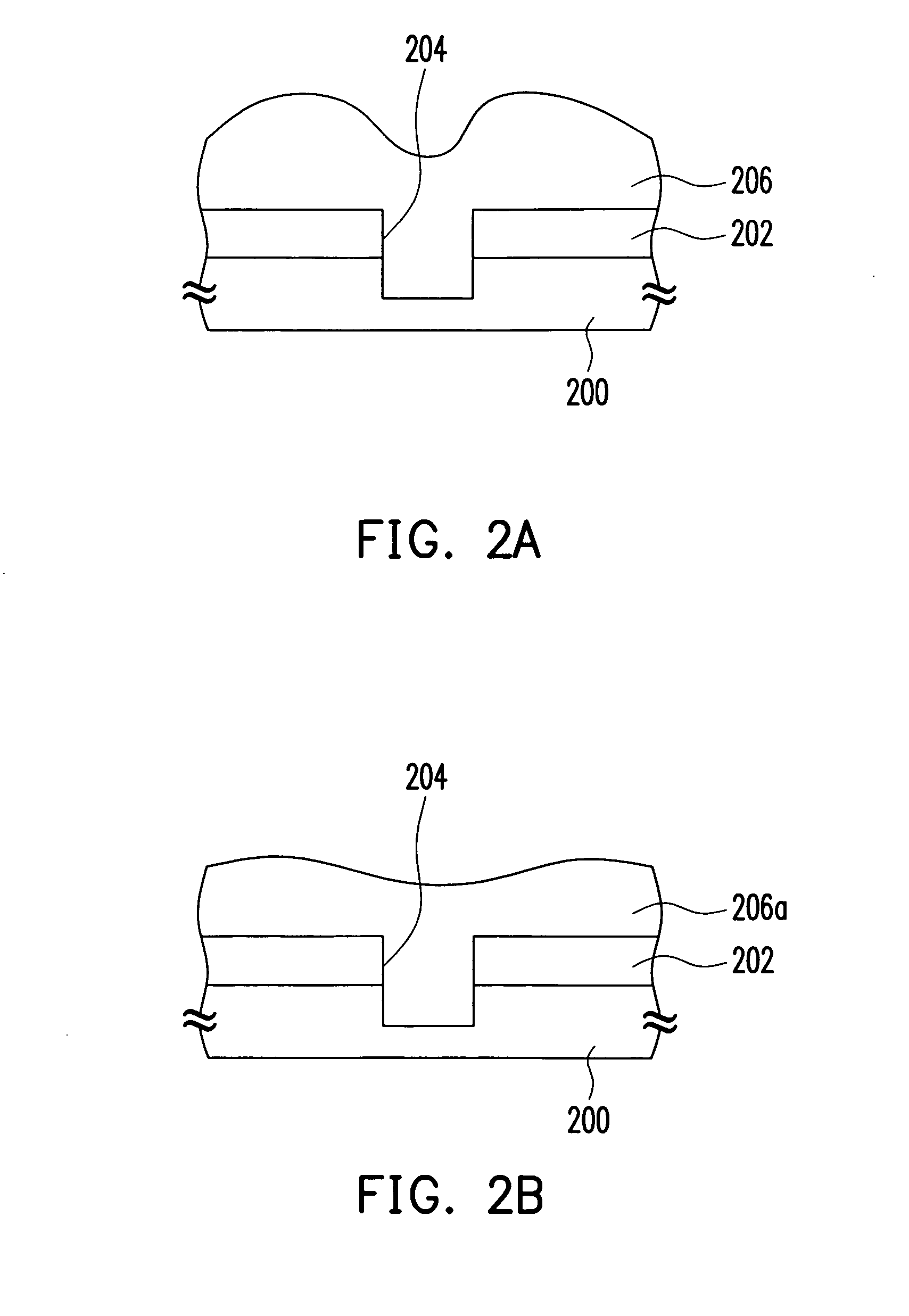
Complex CMP process and fabricating methods of STI structure and interconnect structure
InactiveUS20070062910A1Improve polishing efficiencyImprove throughputDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineering
A complex CMP process is described. A target film is coarsely polished using a first polishing platen in a first CMP machine. The remaining target film is then fine polished using successively a second polishing platen and a third polishing platen in a second CMP machine that is different from the first CMP machine.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
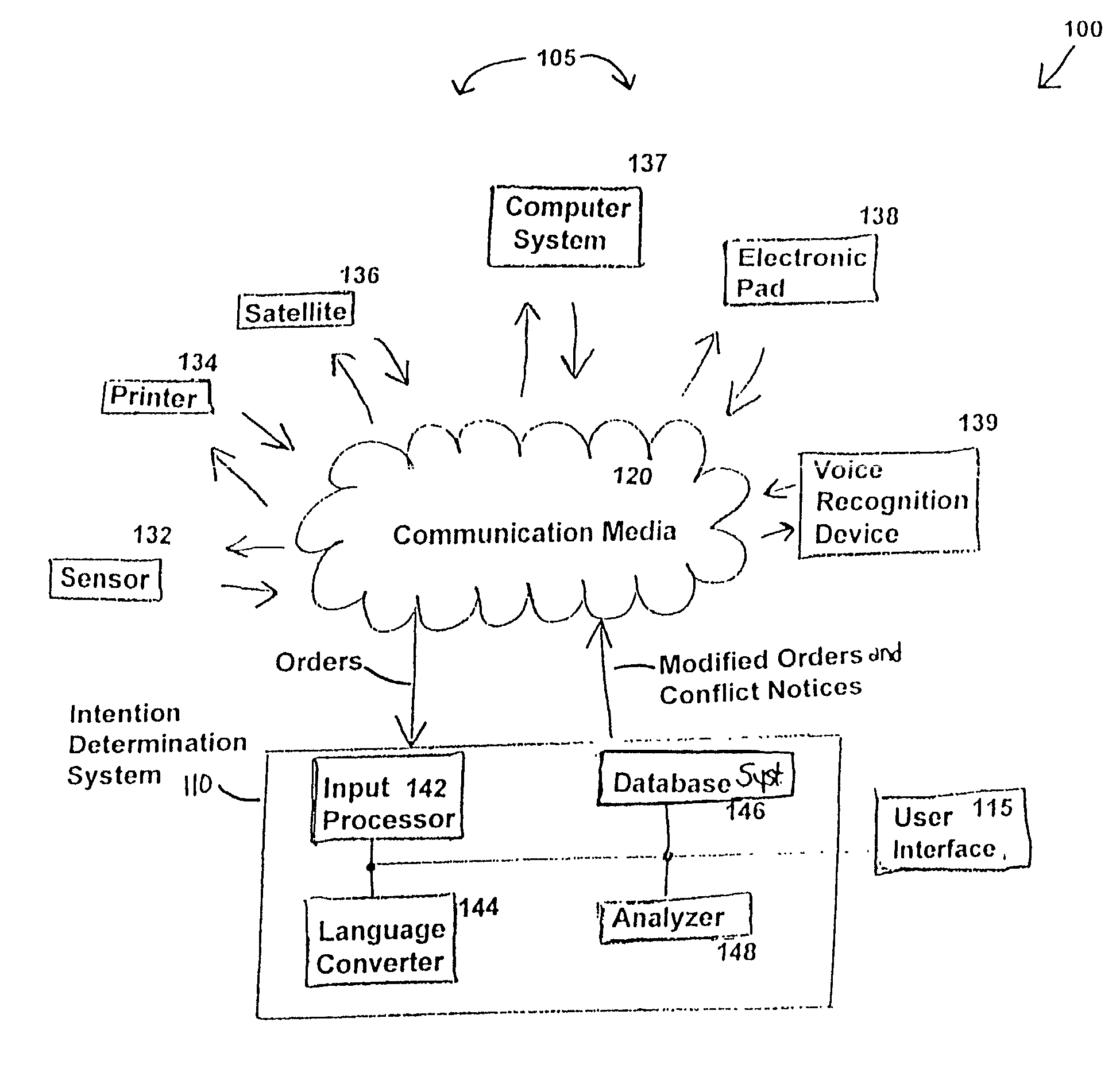
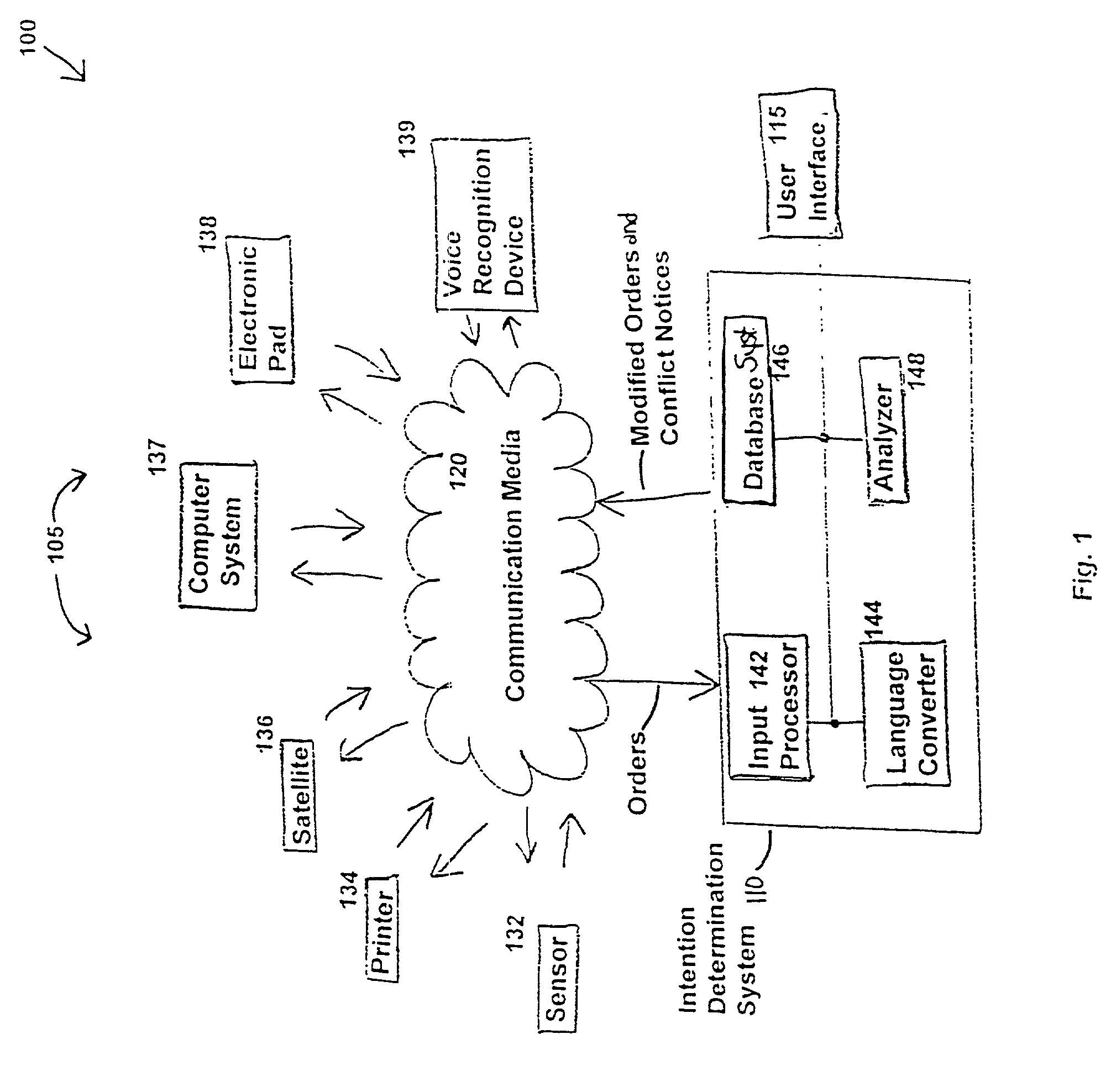
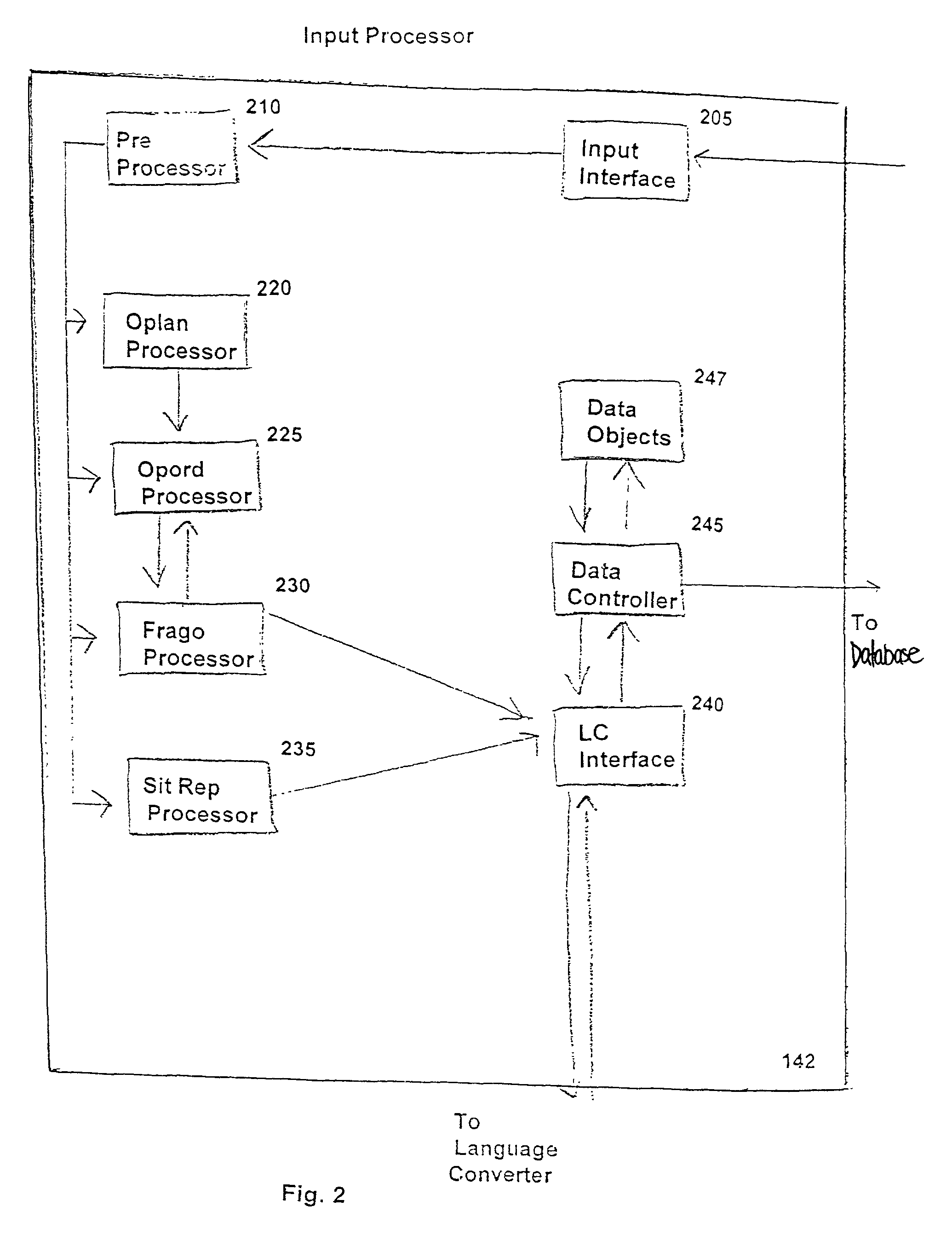
Intention-based automated conflict prediction and notification system
ActiveUS8407281B2Increased Intention AwarenessFacilitate communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsResourcesDisplay deviceNavigation system
Input devices such as satellites, field sensors, electronic pads, cellular phones, and / or radio transmitters communicate information representing queries, reports, and / or instructions to an intention determination system that is accessible by a user interface with a display. The intention determination system includes an input module for processing the information received from the input devices; a language converter for converting the information from a natural language format to a restructured form in a position-based format; a database system for storing the received information, the restructured information, and reference information; and a rule-based analyzer for periodically retrieving and processing the stored information. The analyzer sends an alert to the user interface to notify the user if execution of one the instructions creates a potential conflict with the other stored information. The user interface can include a node-based navigation system that allows user customization of how the alert is displayed.
Owner:GARDNER GROFF MEHRMAN & JOSEPHIC P C
Method to optimize the communication parameters between an access point and at least one client device
ActiveUS9549328B2Increase volumeWide bandwidthData switching networksWireless communicationTelecommunicationsData exchange
A method to optimize the communication on a channel between an access point and at least one client device, said channel being characterized by a center frequency and a bandwidth, comprises: establishing a connection on a first channel according to a first center frequency and a first bandwidth; exchanging data through this first channel between the access point and the client device; monitoring a first interference level on the first channel; the access point, while the data are exchanged, executes: informing the client device to switch to a second channel having a different center frequency and / or a different bandwidth; determining a second interference level on the second channel; comparing the first interference level with the second interference level; deciding to switch back or keep the second channel based on the comparison.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
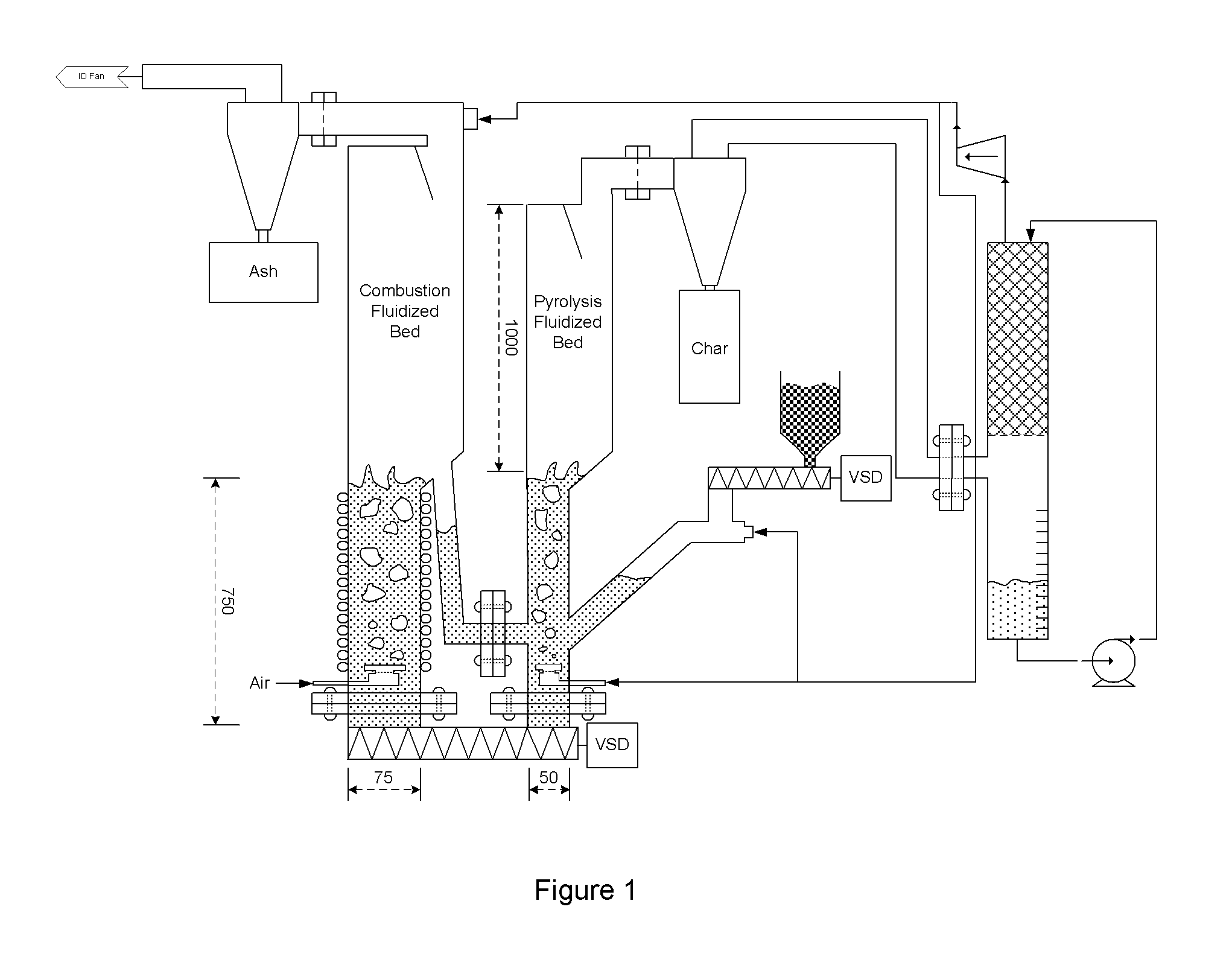
Fluidised bed pyrolysis apparatus and method
ActiveUS9580657B2More throughputLess endothermicProductsFluidized bed combustionCombustionFluidized bed
A carbonaceous feed pyrolysis apparatus is provided including two or more hot particle fluidized beds, and one or more positive displacement apparatus for the transfer of hot particles between two or more of the beds, wherein one or more of the fluidized beds contains a combustion zone. A bio-oil production process is also provided, including pyrolysis of a carbonaceous bio-mass using two or more fluidized beds, including a first combustion zone carried out in one or more combustion fluidized beds in which a particulate material is fluidized and heated, and a second pyrolysis zone carried out in one or more pyrolysis fluidized beds in which the hot particles heated in the combustion zone are used for pyrolysis of the bio-mass.
Owner:UNIV OF PRETORIA +1
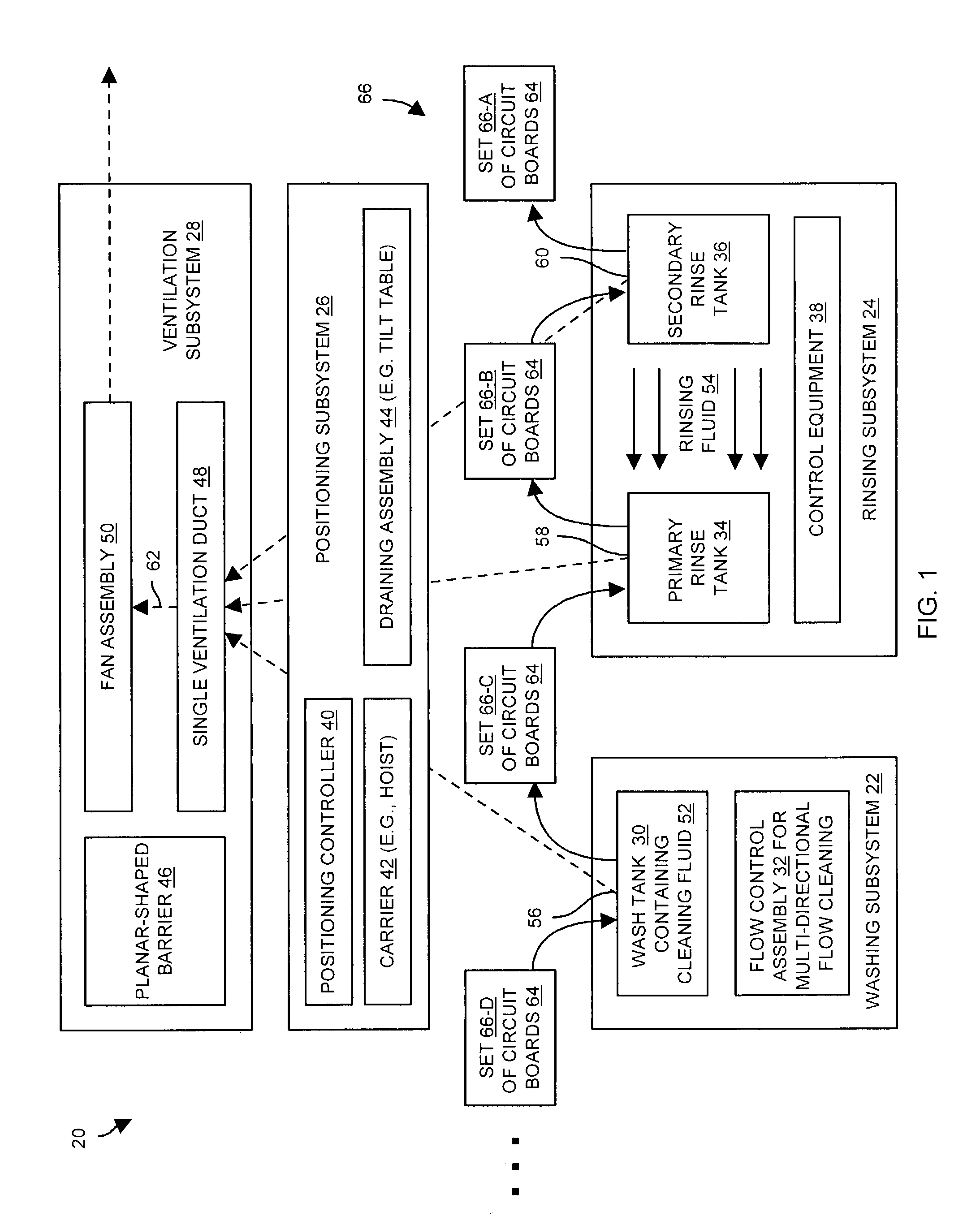
Continuous batch tunnel washer and method
ActiveUS10161079B2Few modulesQuick rinseOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusCounter flowComputer module
Owner:PELLERIN MILNOR
Top feed droplet generator
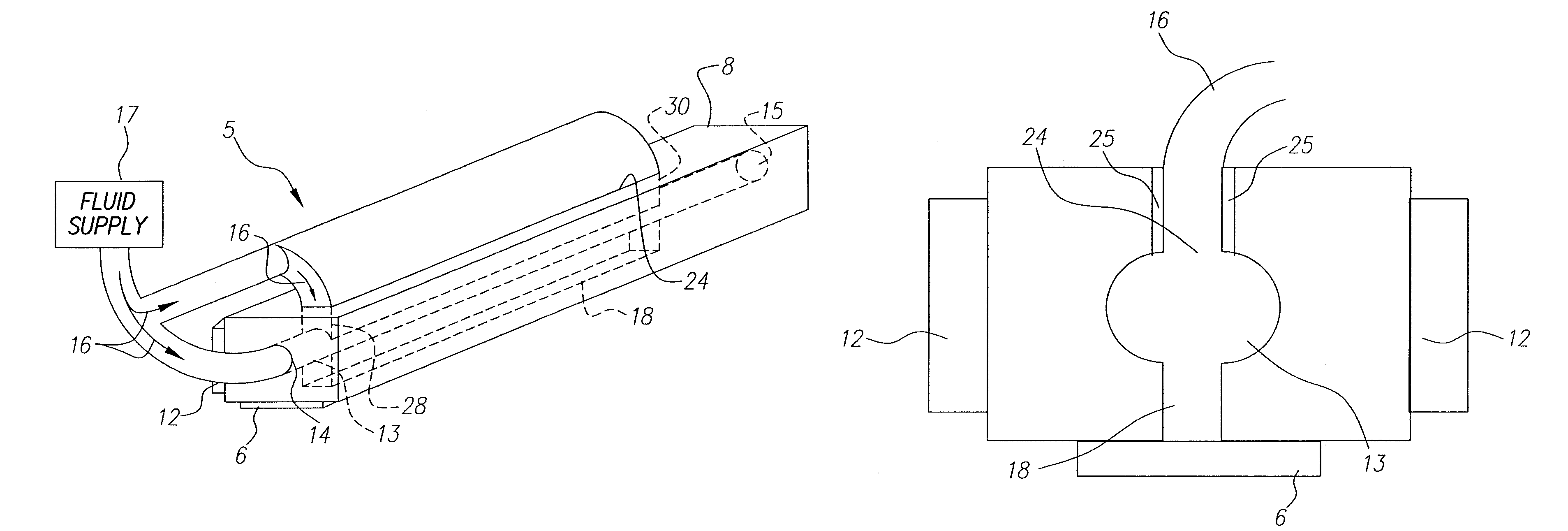
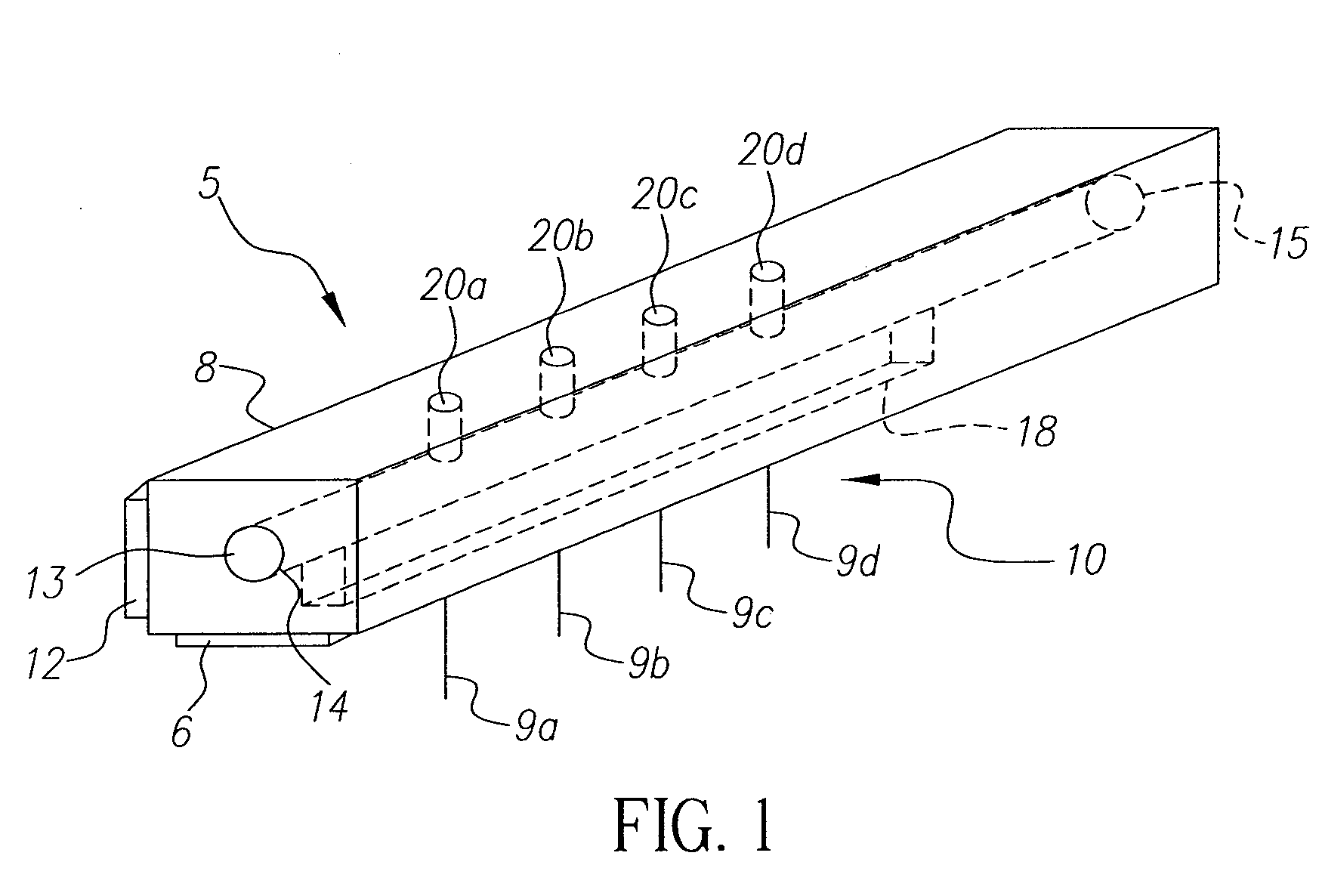
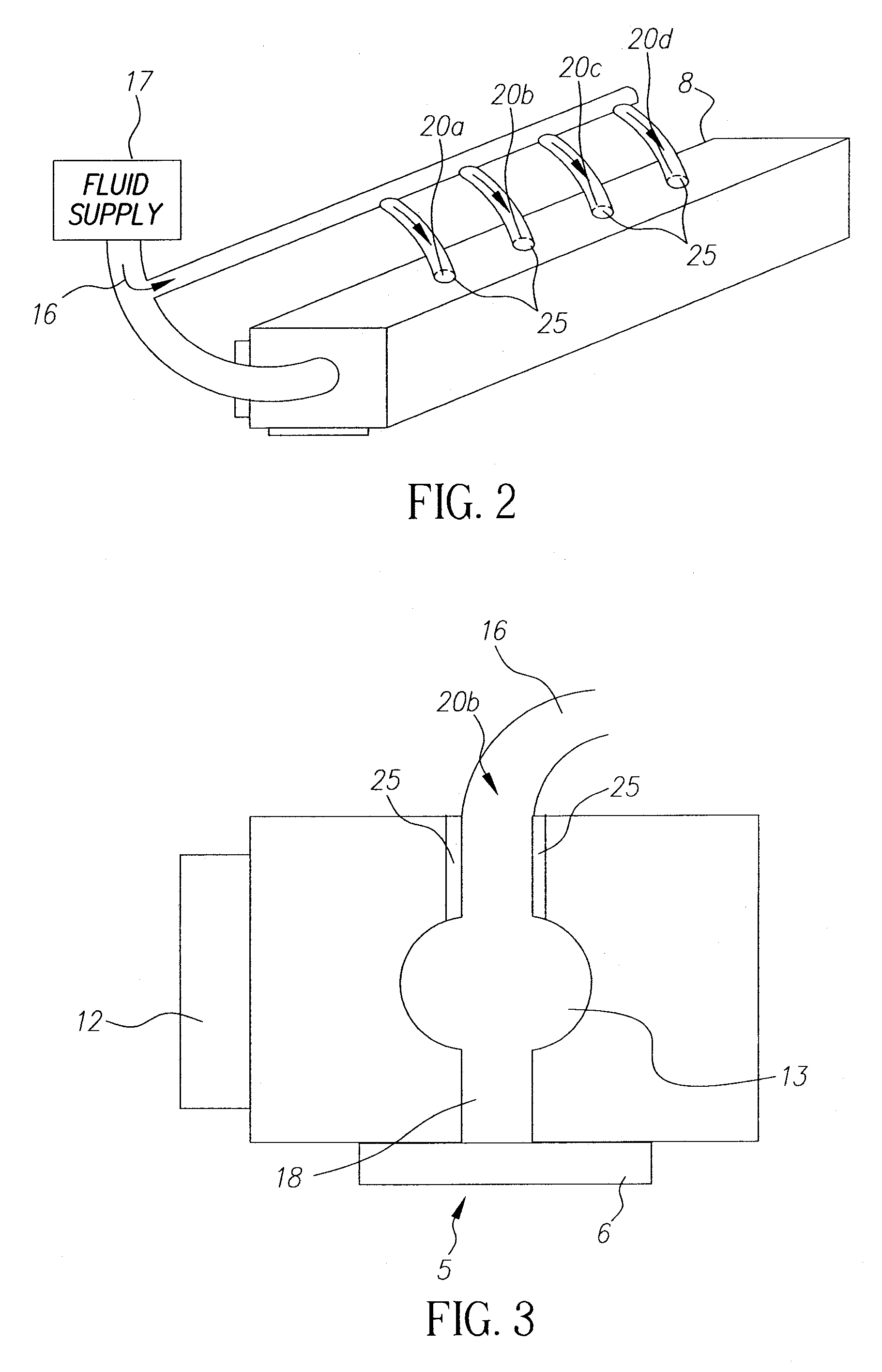
An ink jet droplet generator body for an ink jet droplet generator comprising an orifice plate with a plurality of nozzles forming a jet array entails a throughbore with an entrance and exit port, the throughbore provides a path through that flows fluid from a fluid supply to the first slot. The first slot connects the throughbore to the orifice plate. One or more holes or a slot are located in the top of the generator body to direct fluid or a secondary source of fluid to the first slot and then the orifice plate.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
DNA impurities in a composition comprising a parvoviral virion
ActiveUS11021762B2More throughputMinimization requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDsDNA virusesVirosomeDNA
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
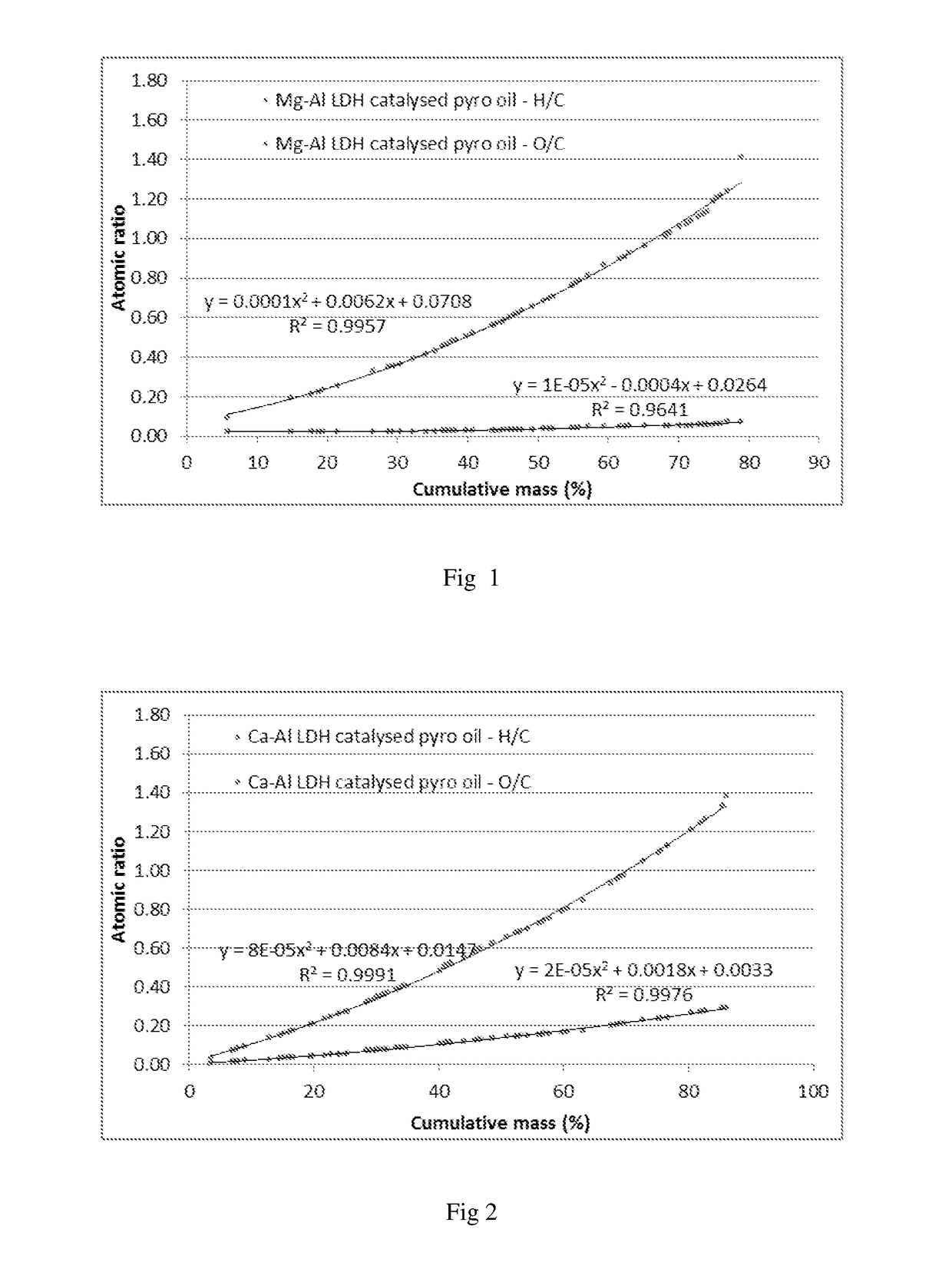
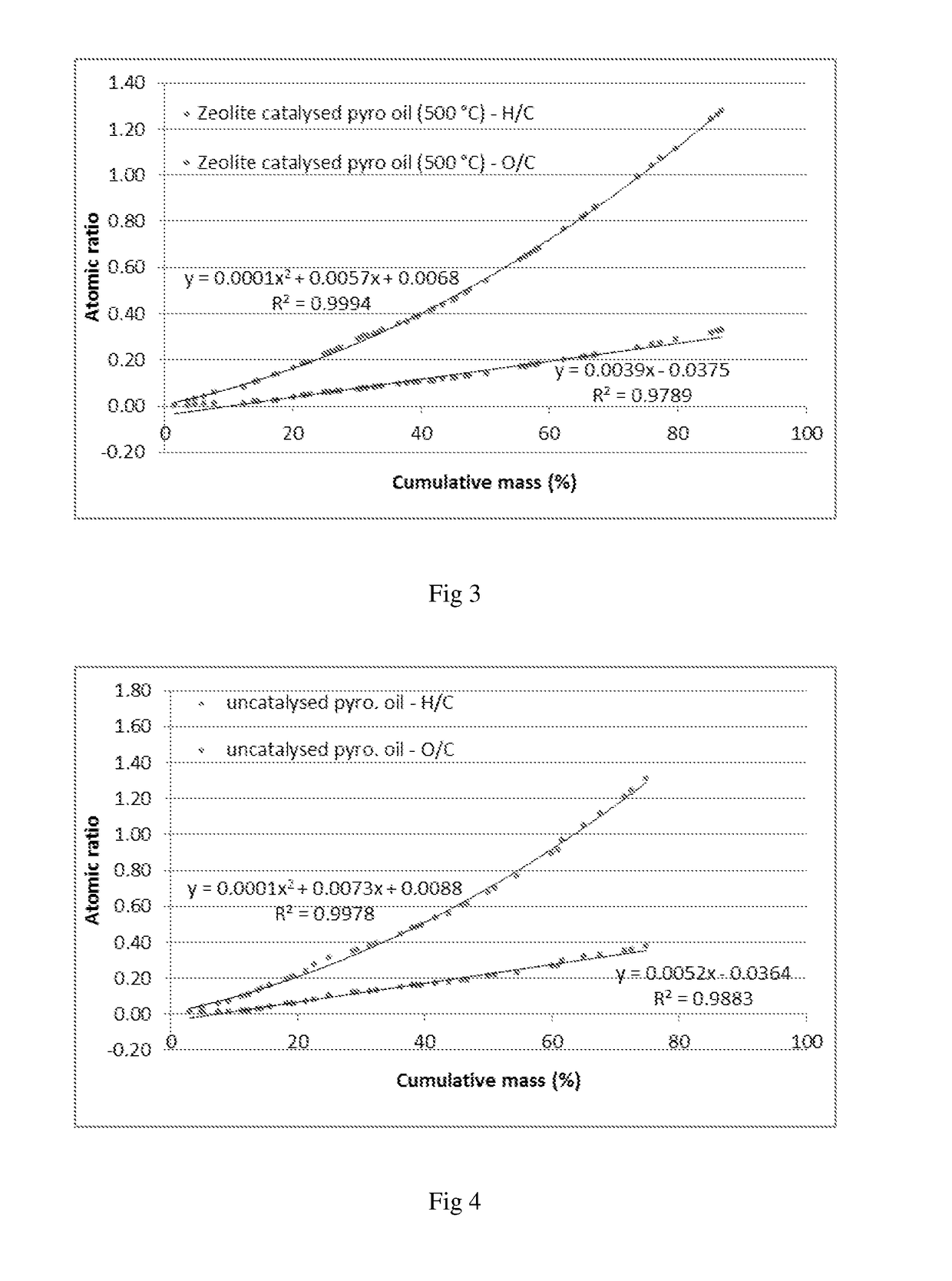
Oxygenate reduction catalyst and process
ActiveUS20190070593A1More throughputLess endothermicBiofuelsCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCombustionSulfate
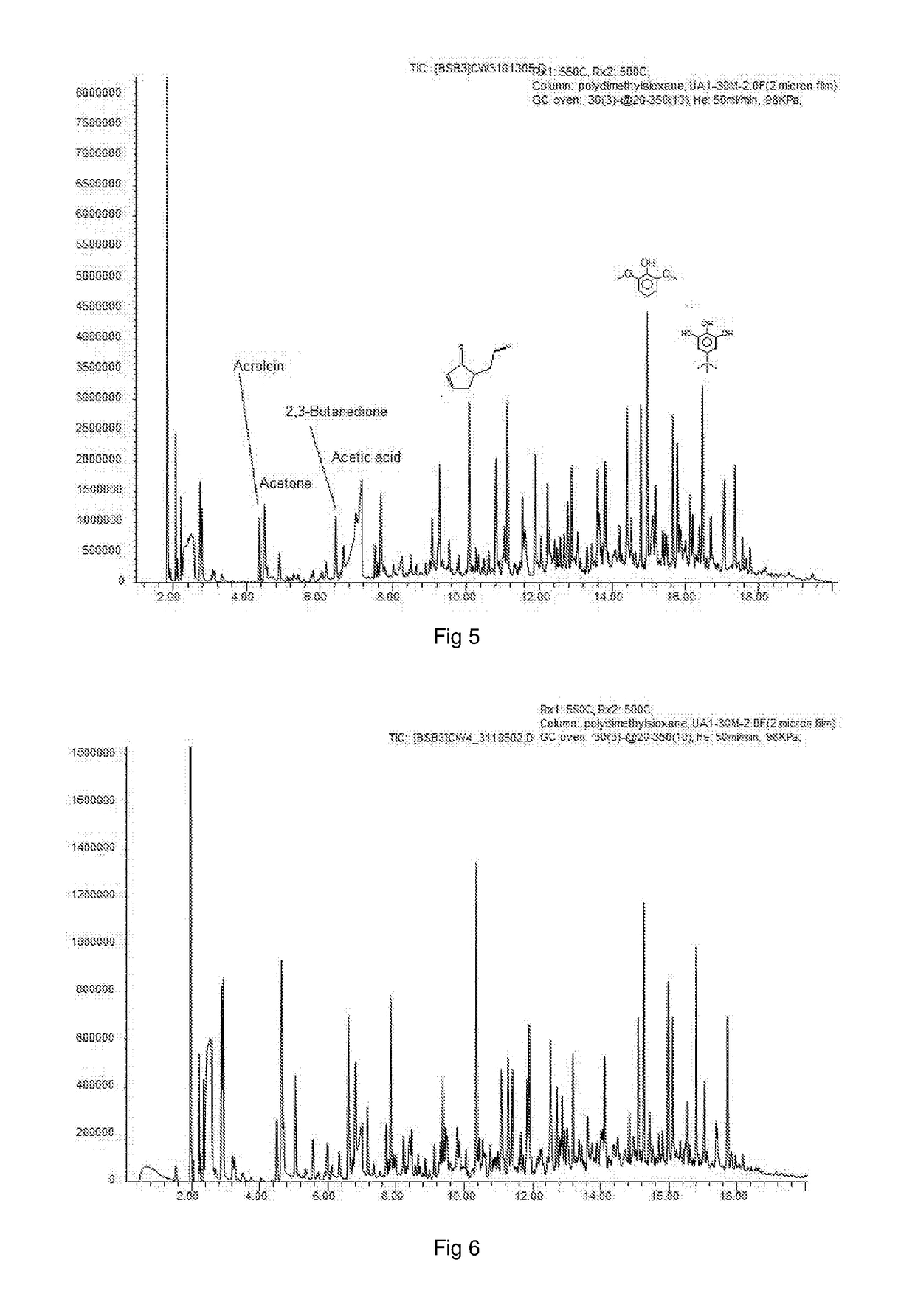
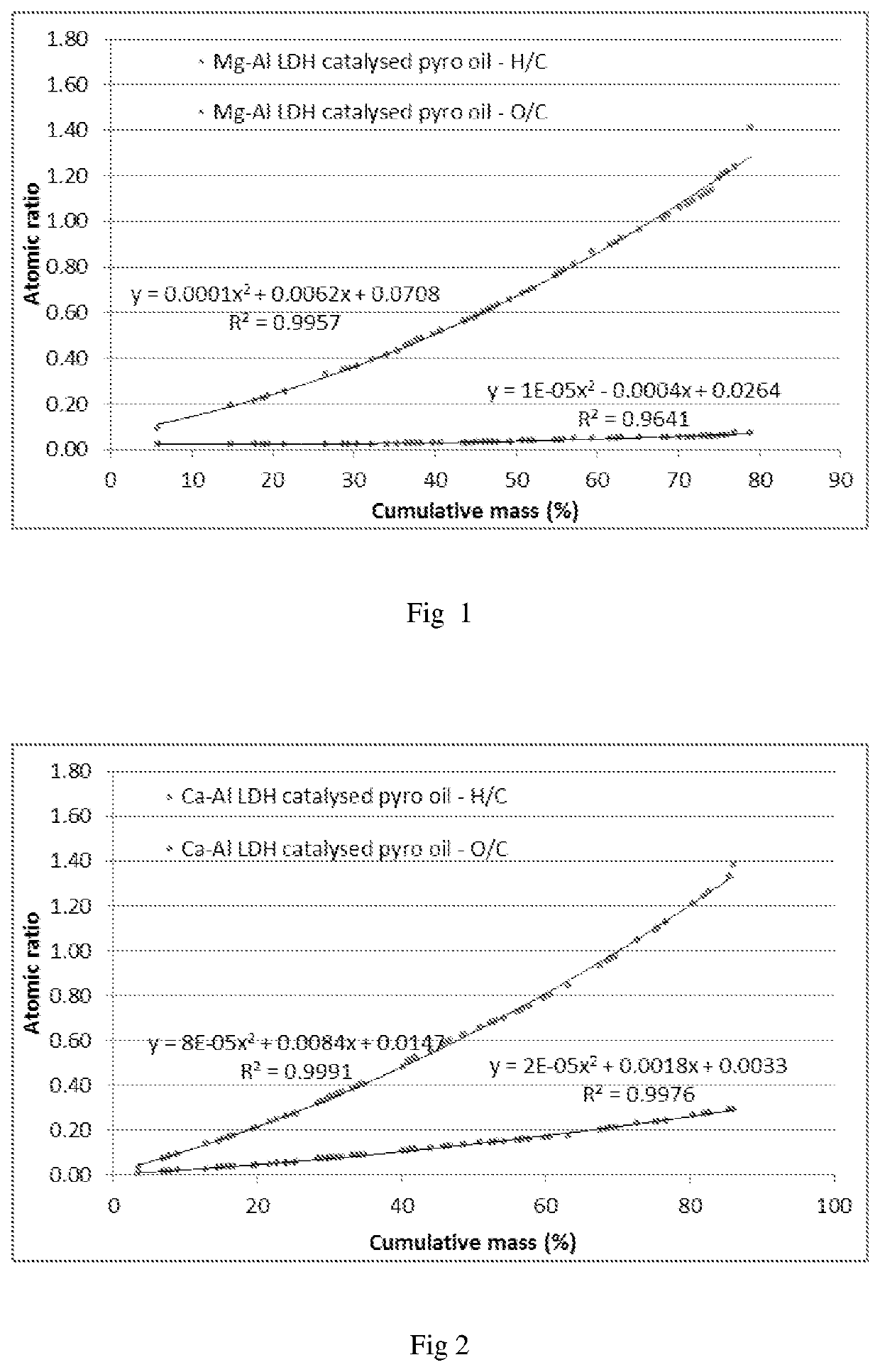
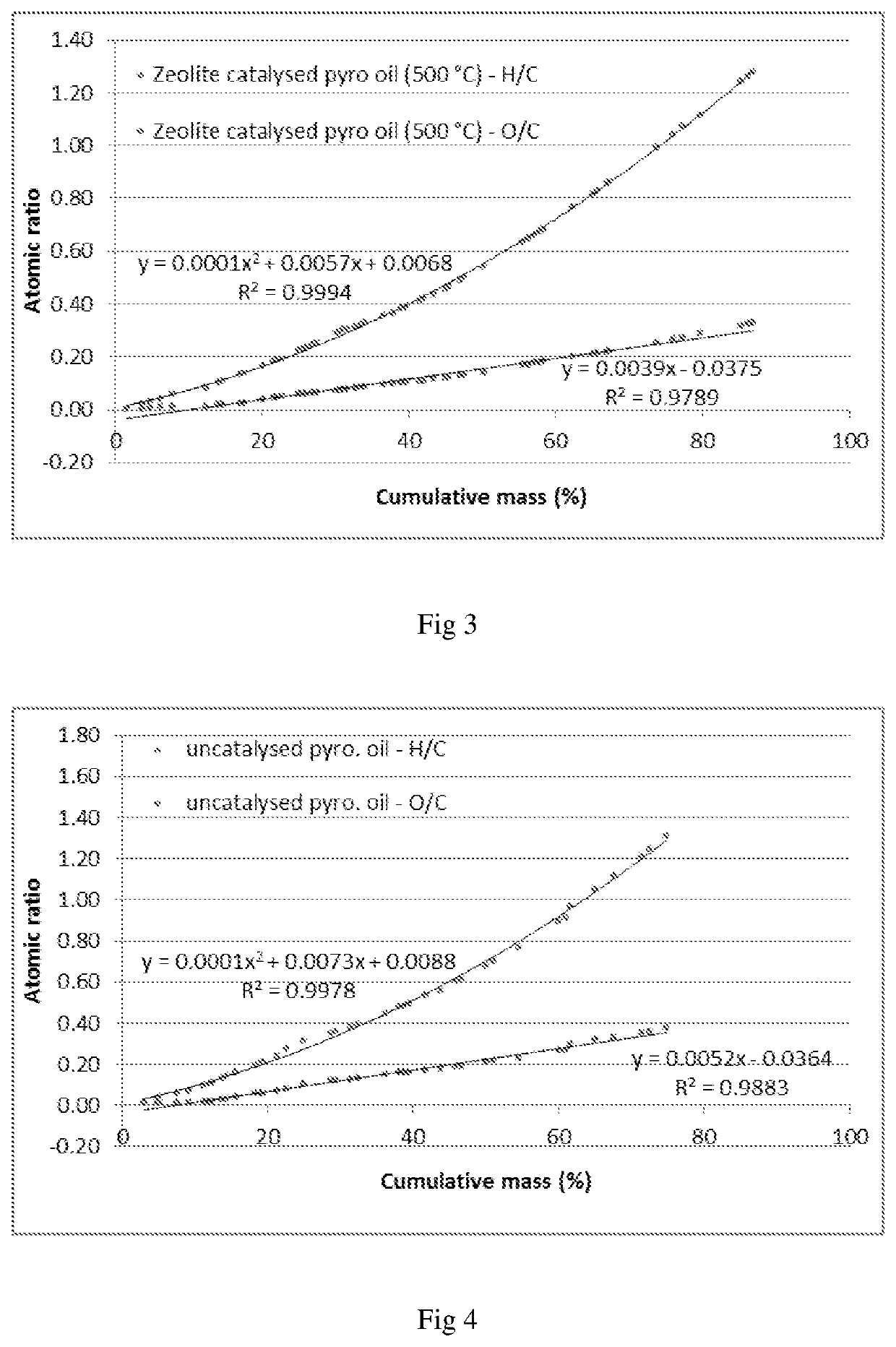
The invention provides a catalyst system and method for the deoxygenation of hydrocarbons, such as bio-oil, using a sulphide-sulfate or an oxide-carbonate (LDH) system. The invention extends to a pyrolysis process of a carbonaceous bio-mass wherein a first combustion zone is carried out in one or more combustion fluidised beds in which a particulate material including chemically looping deoxygenation catalyst particles is fluidised and heated, and a second pyrolysis zone carried out in one or more pyrolysis fluidised beds in which the hot particles, including the catalyst particles, heated in the combustion zone are used for pyrolysis of the bio-mass, said combustion zone being operated at a temperature of from 250° C. to 1100° C., typically around 900° C., and the pyrolysis zone being operated at a temperature of from 250° C. to 900° C., typically 450° C. to 600° C., said catalyst particles being oxygenated in the pyrolysis zone in the presence of oxygenates in the pyrolysis oil and regenerated in the combustion zone either by calcining to drive off the carbon oxides, such as CO2, or by reduction to its form which is active for deoxygenation of the pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA
Oxygenate reduction catalyst and process
ActiveUS10786806B2Low oxygenQuality improvementBiofuelsCatalyst regeneration/reactivationPtru catalystOxygen compound
The invention provides a catalyst system and method for the deoxygenation of hydrocarbons, such as bio-oil, using a sulphide-sulfate or an oxide-carbonate (LDH) system. The invention extends to a pyrolysis process of a carbonaceous bio-mass wherein a first combustion zone is carried out in one or more combustion fluidised beds in which a particulate material including chemically looping deoxygenation catalyst particles is fluidised and heated, and a second pyrolysis zone carried out in one or more pyrolysis fluidised beds in which the hot particles, including the catalyst particles, heated in the combustion zone are used for pyrolysis of the bio-mass, said combustion zone being operated at a temperature of from 250° C. to 1100° C., typically around 900° C., and the pyrolysis zone being operated at a temperature of from 250° C. to 900° C., typically 450° C. to 600° C., said catalyst particles being oxygenated in the pyrolysis zone in the presence of oxygenates in the pyrolysis oil and regenerated in the combustion zone either by calcining to drive off the carbon oxides, such as CO2, or by reduction to its form which is active for deoxygenation of the pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com