Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39results about How to "Improve anti-glue ability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Unsaturated C5 fraction and hydrogenation method
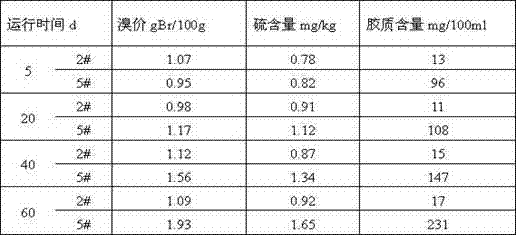
ActiveCN109439364AHigh hydrogenation selectivityReduce reactivityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsRefining by selective hydrogenationPotassiumFixed bed
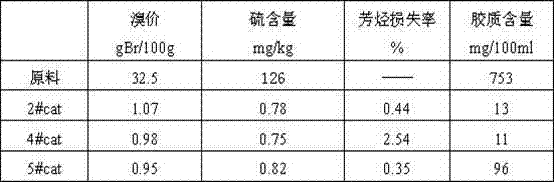
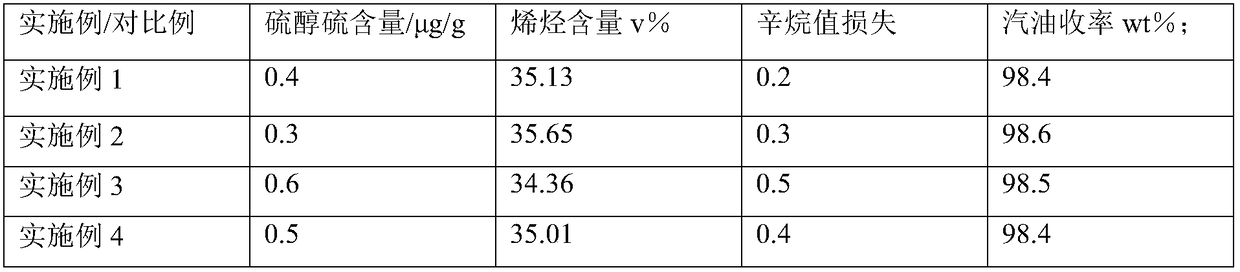
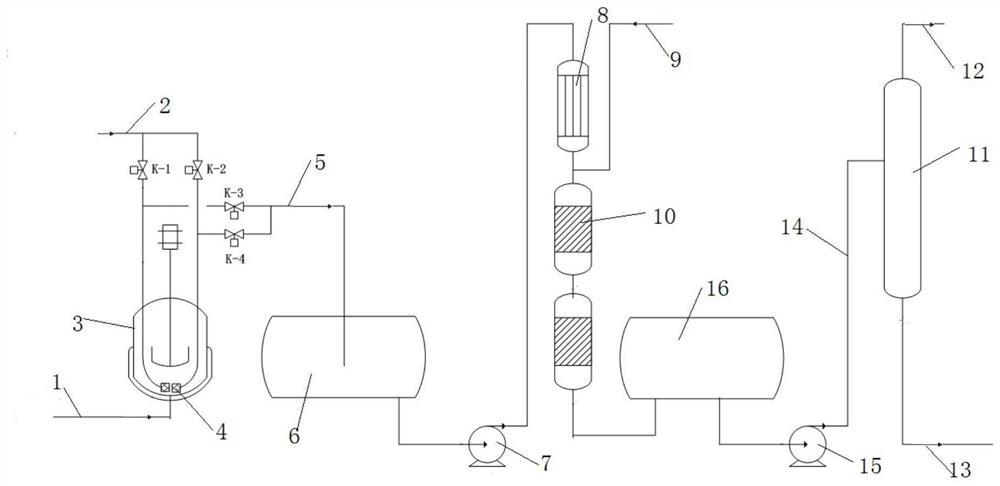
The invention relates to an unsaturated C5 fraction and hydrogenation method. According to the method, by the aid of a fixed bed reactor, a used catalyst is a nickel hydrogenation catalyst, and the catalyst is reduced by the aid of hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gas at the temperature of 350-500 DEG C. The catalyst comprises main active components and a silicon oxide-aluminum oxide composition, and the main active components include molybdenum, nickel, cobalt and potassium. Hydrogenation process conditions include that a reactor inlet temperature is 30-660 DEG C, reaction pressure is 1.5-6.0MPa, liquid volume per hour is 1.0-6.0h<-1>, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is 100:400. According to the unsaturated C5 fraction and hydrogenation method, the used nickel-based saturated hydrogenation catalyst has high hydrogenation activity and the advantages that the catalyst is resistant to sulfur, water and colloid, and hydrogenation reaction can be performed at low temperature.
Owner:兰州金润宏成新材料科技有限公司
Hydrogenation method of C4 unsaturated hydrocarbon
ActiveCN109439365AHigh hydrogenation selectivityReduce reactivityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFixed bedSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a hydrogenation method of C4 unsaturated hydrocarbon. According to the method, by the aid of a fixed bed reactor, a nickel saturated hydrogenation catalyst is reduced outsidea hydrogenation reactor at the temperature of 350-500 DEG C, air is led in to passivate the catalyst, the passivated catalyst is reduced in the reactor by hydrogen at the temperature of 120-200 DEG C,the C4 unsaturated hydrocarbon is added, alkyne and diolefin in the C4 unsaturated hydrocarbon are hydrogenated into corresponding alkane, the nickel saturated hydrogenation catalyst comprises activecomponents and silicon oxide-aluminum oxide composition, and the active components include molybdenum, nickel , cobalt and magnesium. Reaction process conditions include that inlet temperature of thereactor is 30-55 DEG C, reaction pressure is 1.0-4.5MPa, liquid volume per hour is 1.5-4.5h<-1>, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is (120-450):1. According to the hydrogenation method of theC4 unsaturated hydrocarbon, the catalyst is good in hydrogenation activity, good in gelatine and water resistance and high in sulfur resistance.
Owner:兰州金润宏成新材料科技有限公司
Catalyst for pyrolysis C9 two-stage hydrogenation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103611562AAvoid large loss of aromaticsImprove anti-glue abilityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentMolecular sieveComposite oxide
The invention relates to a catalyst for pyrolysis C9 two-stage hydrogenation and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is prepared by taking a K and Ru modified composite oxide consisting of an HY molecular sieve, B2O3 and Al2O3 as a carrier and loading active components of Ni and Mo. The catalyst comprises the following active components in percentage by weight: 3.0-5.0% of NiO and 9.0-15.0% of MoO3. The catalyst provided by the invention is used for pyrolysis C9 two-stage hydrogenation, shows very high desulfurization activity and olefin saturation capacity, is strong in carbon deposition resistance and has a certain effect on macromolecular colloid pyrolysis, so that the colloid resistance of the catalyst is improved, and the service life of the catalyst is greatly prolonged.
Owner:WUHAN KELIN FINE CHEM
Total fraction cracking gasoline selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN109022025AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHydrocarbon oils refiningHydrocarbon oils treatment productsFixed bedReaction temperature
The invention relates to a total fraction cracking gasoline selective hydrogenation method. A fixed bed reactor is used; a catalyst is reduced in hydrogen gas atmosphere; after the reduction process is completed, the process condition is regulated to the reaction process conditions; gasoline raw material total fraction cracking is performed; selective hydrogenation reaction is performed; the catalyst is prepared from silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carriers and metal active ingredients of palladium loaded on the carriers; the content of the palladium is based on 0.15 to 0.45 weight percent of thetotal weight of the catalysts. The hydrogenation process conditions are shown as follows: the reaction inlet temperature is higher than or equal to 50 DEG C; the reaction temperature is 2.0 to 4.5MPa; the hydrogen oil volume ratio is (60 to 400):1; the liquid volume air speed is 2.5 to 5.0 h<-1>. The catalyst gum resistant capability is high; the arsenic resistant, sulfur resistant and water-resistant capability is high; the stability is high.
Owner:东营华浩化工有限公司
Method of removing mercaptan of catalytically cracked gasoline
ActiveCN109207191AHigh sweetening activityGood choicePhysical/chemical process catalystsRefining by selective hydrogenationReaction temperatureFixed bed
The invention relates to a method of removing mercaptan of catalytically cracked gasoline. According to the method, a fixed bed reactor is adopted; a catalyst comprises a silicon oxide-aluminum oxidecarrier, metal active components (nickel, molybdenum, and iron) loaded on the carrier, and an auxiliary agent (phosphorus); nickel oxide accounts for 2 to 15 wt% of the catalyst, molybdenum oxide accounts for 2 to 18 wt% of the catalyst, iron oxide accounts for 0.1 to 5.5 wt% of the catalyst, the auxiliary agent (phosphorus oxide) accounts for 0.01 to 2.2 wt% of the catalyst, the silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier accounts for 65 to 85 wt% of the catalyst, the micro pores, mesopores, macro pores are unevenly distributed in the carrier; the reaction temperature is 110 to 220 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 1.1 to 4.5 MPa, the volume air speed is 1.2 to 5.0 h<-1>, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is 7-25:1. The catalyst has the characteristics of high mercaptan removing activity, high selectivity of diolefin hydrogenation, few side reactions, and low octane value loss.
Owner:宁夏瑞科新源环保科技研发有限公司
Selective hydrogenation method for full-range pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109364945AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLanthanumChemistry
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method for full-range pyrolysis gasoline, which adopts a reactor of an adiabat bed reactor. The catalyst comprises silica-alumina carrier and metal active component palladium loaded on the carrier, wherein the palladium is 0.15-0.45 percent of total weight of the catalyst; and the silica-alumina carrier is prepared from the following components inpercentage by weight: 0.1-12 percent of silica, 0.1-10 percent of nickel-doped lanthanum ferrite and 0.05-7.8 percent of magnesium. According to the hydrogenation process conditions, the reaction inlet temperature is more than or equal to 50 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 2.0-4.5MPa, the hydrogen-oil volume ratio is 60-450, and the liquid hourly space velocity is 3.0-5.0h<-1>. The catalyst has good gum resistance and strong performance of arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance.
Owner:毛琴飞
A kind of unsaturated hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN109433218BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsHydrocarbon oils refiningPtru catalystUnsaturated hydrocarbon
Owner:YANTAI BAICHUAN HUITONG TECH CO LTD
Selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109364929AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLanthanumMagnesium
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline. A catalyst comprises a silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier and a metal active component palladium loaded to the carrier. Palladium accounts for 0.15-0.45wt% of the total weight of the catalyst. The silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier comprises 0.1-12wt% of silicon oxide, 0.1-10wt% of nickel doped lanthanum ferriteand 0.05-7.8wt% of magnesium. The hydrogenation process conditions are as follows: the reaction inlet temperature is lower than or equal to 45 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 2.5-4.5 MPa, the hydrogenoil volume ratio is 60-450, and the liquid volume airspeed is 3.0-5.5h<-1>. The catalyst is good in colloid resistance and high in arsenic, sulfur and water resistance.
Owner:陈雅菁
Nickel selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109364934AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSulfurPotassium
The invention relates to a nickel selective hydrogenation catalyst. The catalyst is prepared from a silica-alumina carrier and metal active ingredients, including nickel, molybdenum and potassium, loaded on the carrier, and comprises the following components based on total weight of the catalyst: 9-25 weight percent of nickel oxide, 2.5-8 weight percent of molybdenum oxide, 0.02-2.5 weight percentof potassium oxide and 75-91 weight percent of silica-alumina carrier. The catalyst has strong colloid resistance, arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance.
Owner:江苏华海三联净化材料有限公司
Selective hydrogenation catalyst for pyrolysis gasoline and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109289868AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsHydrocarbon oils refiningPotassiumLanthanum
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation catalyst for pyrolysis gasoline. The catalyst includes a silica-alumina carrier and a metal active component palladium loaded on the carrier, the content of palladium is 0.15-0.45 wt% based on the total weight of the catalyst, and the silica-alumina carrier contains 0.1-12 wt% of silica, 0.1-10 wt% of nickel-doped lanthanum ferrite and 0.05-6.8 wt% of potassium; carrier mesopores account for 3-75% of total pores, and macropores account for 1.5-60% of the total pores. The catalyst has the advantages of good colloid resistant ability, and strongarsenic resistant, sulfur resistant and water resistant abilities, and is especially suitable for selective hydrogenation of first-section C6-C8 and C8 fractions of pyrolysis gasoline.
Owner:YANTAI BAICHUAN HUITONG TECH CO LTD
First-stage selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109355094AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityRefining by selective hydrogenationHydrocarbon oils treatmentPotassiumReaction temperature
The invention relates to a first-stage selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline. The first-stage selective hydrogenation method is implemented by the aid of heat-insulation bed reactors.The first-stage selective hydrogenation method includes carrying out reduction on nickel catalysts in the presence of hydrogen under the condition of the temperature of 400-480 DEG C; carrying out cooling and passivation and then carrying out adjustment until reaction technological conditions are met. The reaction technological conditions include the reaction inlet temperatures of 45-120 DEG C, the reaction pressures of 2.5-5.5 MPa and the hydrogen-oil volume ratios of 60-220:1. The liquid volume space velocities are 2.0-6.5 h<-1>; the catalysts comprise silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carriers and metal active components including nickel, molybdenum and potassium, and the metal active components are loaded on the carriers. The first-stage selective hydrogenation method has the advantage thatthe catalysts are applicable to first-stage selective hydrogenation for the pyrolysis gasoline.
Owner:陈明海
Unsaturated hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109433218AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsHydrocarbon oils refiningSulfurUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a unsaturated hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation catalyst, which comprises a silicon-alumina carrier and metal active components such as nickel, molybdenum and magnesium loaded on the carrier. The catalyst comprises the following components based on the total weight of the catalyst: 7-18wt% of nickel oxide, 3.5-12wt% of molybdenum oxide, 0.05-2.0% of magnesium oxide, 75-91wt% of the silica-alumina carrier, 3-70% of mesopores of the carrier accounting for the total pores, and 1.5-55% of the macropores accounting for the total pores. The catalyst is prepared by an impregnation method. The catalyst has good colloid resistance, strong arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance.
Owner:YANTAI BAICHUAN HUITONG TECH CO LTD
All-fraction selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109355093AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityRefining by selective hydrogenationHydrocarbon oils treatmentSilicon oxideHydrogen
The invention relates to an all-fraction selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline. The all-fraction selective hydrogenation method includes procedures of carrying out reduction on nickelcatalysts in the presence of hydrogen under the condition of the temperature of 400-500 DEG C; carrying out cooling and passivation and then carrying out adjustment until reaction technological conditions are met. The reaction technological conditions include the reaction inlet temperatures of 45-110 DEG C, the reaction pressures of 2.0-4.5 MPa and the hydrogen-oil volume ratios of 60-200:1. The liquid volume space velocities are 2.0-5.5 h<-1>; the catalysts comprise silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carriers and metal active components including nickel, molybdenum and magnesium, and the metal active components are loaded on the carriers. The all-fraction selective hydrogenation method has the advantage that the catalysts are good in colloid resistance, high in arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance and applicable to long-period stable operation of devices.
Owner:陈明海
pyrolysis gasoline c 6 -c 8 Distillate oil selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN109355095BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityRefining by selective hydrogenationNickel catalystPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a cracked gasoline C6-C8 distillate selective hydrogenation method, comprising: performing reducing at 400-500 DEG C via a nickel catalyst in the presence of hydrogen, coolingfor passivation, and adjusting to reaction process conditions; subjecting raw oil, hydrogen and the catalyst to contact and selective hydrogenation under the reaction temperature of 40-160 DEG C, reaction pressure of 2.0-5.0 MPa, fresh oil space velocity of 1-10 h<-1> and hydrogen-oil volume ratio of (50-260):1, wherein the catalyst includes a silica-alumina carrier as well as metallic active components of nickel, molybdenum and potassium carried on the carrier; the catalyst has high resistance to gel, arsenic, sulfur and resistance. The method herein is highly adaptable to different materials.
Owner:陈明海
Catalyst for selective hydrogenation of pyrolysis gasoline and its preparation method
ActiveCN109289868BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsHydrocarbon oils refiningPtru catalystSilicon oxide
Owner:YANTAI BAICHUAN HUITONG TECH CO LTD
pyrolysis gasoline c 6 -c 8 Distillate hydrotreating catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN109317158BImprove anti-glue abilityImprove stabilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystSilicon oxide
The present invention relates to a kind of pyrolysis gasoline C 6 -C 8 Distillate hydrotreating catalyst, the catalyst uses molybdenum, cobalt, nickel, and potassium as active components, and uses silica-alumina as a carrier. Based on the total weight of the catalyst, the catalyst contains 6-22% of molybdenum oxide and 0.1-2.2% of cobalt oxide , nickel oxide 4.0-7.2%, potassium oxide content 0.1-3.0%, silica-alumina carrier content 75-88wt%, carrier mesopores account for 3-70% of total pores, macropores account for 1.5- 55%. The catalyst has good anti-colloid ability, strong anti-arsenic, anti-sulfur, and strong anti-water ability.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
One-stage selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109022026BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHydrocarbon oils refiningHydrocarbon oils treatment productsPtru catalystHydrogenation process
The invention relates to a pyrolysis gasoline one-section selective hydrogenation method. A catalyst is prepared from a silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier and a metal active ingredient palladium loaded on the carrier; the palladium content is 0.15 to 0.45 weight percent of the total weight of the catalyst; the pectin resistant capability of the catalyst is good; the anti-arsenic, anti-sulfur andwater-resistant capability is high. Under the hydrogenation process condition, the reaction inlet temperature is smaller than or equal to 45 DEG C; the reaction pressure is 2.5 to 4.5MPa; the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 60 to 450; the liquid volume space velocity is 3.0 to 5.5h<-1>. The catalyst has high adaptability on pyrolysis gasoline raw materials with different arsenic content, different sulphur content, water content and pectin content; the low-temperature activity of the catalyst is high.
Owner:宁夏宁鲁石化有限公司
Selective-hydrogenation catalyst for cracking gasoline and preparation method
ActiveCN109364930AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSilicon oxideLanthanum
The invention relates to a selective-hydrogenation catalyst for cracking gasoline and a preparation method. The selective-hydrogenation catalyst comprises a silicon oxide-aluminium oxide carrier and metal active-component palladium loaded on the carrier, wherein the content of the palladium is 0.15-0.45wt% of the total weight of the catalyst; the silicon oxide-aluminium oxide carrier contains silicon oxide, nickel-doped lanthanum ferrite and magnesium oxide; mesopores of the carrier account for 3-75% of total pores, and macropores account for 1.5-60% of the total pores. The selective-hydrogenation catalyst is prepared by adopting an impregnation method and is good in colloid resistance, arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance.
Owner:东营天喜化工有限公司
Pyrolysis gasoline C6-C8 fraction hydrofinishing catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN109317158AImprove anti-glue abilityImprove stabilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPotassiumSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a pyrolysis gasoline C6-C8 fraction hydrofinishing catalyst. The catalyst takes molybdenum, cobalt, nickel and potassium as active components, and silicon oxide-aluminum oxideas a carrier. Measured by the total weight of the catalyst, the catalyst comprises 6-22% of molybdenum oxide, 0.1-2.2% of cobalt oxide, 4.0-7.2% of nickel oxide, 0.1-3.0% of potassium oxide, and 75-88w% of the silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier. In the carrier, mesopores account for 3-70% of total pores, and macropores account for 1.5-55% of the total pores. The catalyst has good colloid resistance and high arsenic resistant, sulphur resistant and water resistant abilities.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
Non-noble metal Ni-based catalyst, preparation method thereof and method for preparing cyclopentane through cyclopentadiene hydrogenation
PendingCN113492012AReduce self-focusingImprove anti-glue abilityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationPentaneNon noble metal
The present invention relates to the field of cyclopentane preparation, and discloses a non-noble metal Ni-based catalyst, a preparation method thereof, and a method for preparing cyclopentane through cyclopentadiene hydrogenation, the non-noble metal Ni-based catalyst contains a carrier, and a Ni active metal component and a metal auxiliary agent component loaded on the carrier, at least part of the nickel element exists in the form of nickel elementary substance and / or nickel carbide. The catalyst can reduce the self-coalescence coking phenomenon of cyclopentadiene in preparation of cyclopentane through hydrogenation of cyclopentadiene, so that the colloid resistance of the catalyst is improved, and the catalyst has the advantages of high activity, good selectivity, high reuse rate, difficulty in inactivation and the like, and further has the advantages of simple preparation process, low cost and the like. In the process of preparing cyclopentane through cyclopentadiene hydrogenation, no extra solvent or diluent needs to be added, and inactivation is not prone to occurring. In addition, according to the method for preparing cyclopentane through cyclopentadiene hydrogenation, due to the fact that the catalyst is used and matched with a two-stage hydrogenation process, high selectivity and yield are achieved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Ethylene cracking C6-C8 distillate oil hydrorefining method
PendingCN109266383AImprove anti-glue abilityImprove stabilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentCobalt oxideChemistry
The invention relates to an ethylene cracking C6-C8 distillate oil hydrorefining method, which is characterized in that a heat insulation bed reactor is used; a nickel and molybdenum series catalyst is vulcanized by vulcanizing oil and then put into raw material oil; the catalyst uses molybdenum, cobalt, nickel and potassium as active ingredients; silicon oxide-aluminum oxide is used as a carrier;through being metered by the total weight of the catalyst, the catalyst contains 6 to 22 percent of molybdenum oxide, 0.1 to 2.2 percent of cobalt oxide, 4.0 to 8.2 percent of nickel oxide, and 0.1 to 3.0 percent of potassium oxide, and 75 to 88 percent by weight of the silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier. The reaction process conditions are as follows: the reaction pressure is 2.8MPa or higher;the inlet temperature is 220 to 380 DEG C; the volume space velocity of fresh raw material oil is 1.5 to 3.5h<-1>; through being metered by the fresh oil, the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is from(180:1) to (350:1). The catalyst is good in anti-colloid capability; the arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance capabilities are strong; the stability is good.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
A kind of pyrolysis gasoline hydrotreating catalyst and its preparation method
ActiveCN109317159BImprove anti-glue abilityImprove stabilityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystStrontium
The invention relates to a pyrolysis gasoline hydrogenation catalyst. The catalyst uses molybdenum, cobalt, nickel, and strontium as active components, and uses silicon oxide-alumina as a carrier. Based on the total weight of the catalyst, the catalyst includes 9-19 wt% of molybdenum oxide , 3.0-8.5wt% cobalt oxide, 0.2-3.5wt% nickel oxide, 0.1-2.0wt% strontium oxide, silica-alumina carrier content of 75-85wt%, micropores, mesopores and macropores in the carrier Uneven distribution. The catalyst has good anti-colloid ability, strong anti-arsenic, anti-sulfur, and strong anti-water ability.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
FCC gasoline mercaptan etherification method
ActiveCN109207189AHigh activityReduce lossesCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsReaction temperatureFixed bed
The invention relates to a FCC gasoline mercaptan etherification method. A fixed bed reactor is adopted, gasoline is introduced into the reactor, under the action of a catalyst, mercaptan in the gasoline and dialkene carry out etherification reactions, and the catalyst comprises a composite carrier and metal active components: nickel, molybdenum and magnesium. The reaction conditions are: reactionpressure 0.1-5 MPa, volume ratio of hydrogen to oil 2:1-30:1, reaction temperature 60-200 DEG C, and air speed 0.5-8 h<-1>. The catalyst has the characteristics that the mercaptan etherification activity is high and the loss of octane value is low and can adapt to various raw materials.
Owner:博兴兴业精细化工产业发展有限公司
Pyrolysis gasoline one-section selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN109022026AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityHydrocarbon oils refiningHydrocarbon oils treatment productsSilicon oxideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a pyrolysis gasoline one-section selective hydrogenation method. A catalyst is prepared from a silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier and a metal active ingredient palladium loaded on the carrier; the palladium content is 0.15 to 0.45 weight percent of the total weight of the catalyst; the pectin resistant capability of the catalyst is good; the anti-arsenic, anti-sulfur andwater-resistant capability is high. Under the hydrogenation process condition, the reaction inlet temperature is smaller than or equal to 45 DEG C; the reaction pressure is 2.5 to 4.5MPa; the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 60 to 450; the liquid volume space velocity is 3.0 to 5.5h<-1>. The catalyst has high adaptability on pyrolysis gasoline raw materials with different arsenic content, different sulphur content, water content and pectin content; the low-temperature activity of the catalyst is high.
Owner:宁夏宁鲁石化有限公司
A kind of fcc gasoline mercaptan etherification method
ActiveCN109207189BImprove anti-glue abilityImprove stabilityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsPtru catalystFixed bed
The invention relates to a FCC gasoline mercaptan etherification method. A fixed bed reactor is adopted, gasoline is introduced into the reactor, under the action of a catalyst, mercaptan in the gasoline and dialkene carry out etherification reactions, and the catalyst comprises a composite carrier and metal active components: nickel, molybdenum and magnesium. The reaction conditions are: reactionpressure 0.1-5 MPa, volume ratio of hydrogen to oil 2:1-30:1, reaction temperature 60-200 DEG C, and air speed 0.5-8 h<-1>. The catalyst has the characteristics that the mercaptan etherification activity is high and the loss of octane value is low and can adapt to various raw materials.
Owner:博兴兴业精细化工产业发展有限公司
Catalyst for removing diolefins from distillate oil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109468142BImprove anti-glue abilityReduce surface coking processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsAlkadienePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a catalyst for removing alkadiene in distillated oil. The catalyst comprises a silica-alumina carrier and active metal components loaded on the silica-alumina carrier such asNi, Mo and Sr. The catalyst comprises the following components in mass percent: 2-18 wt% of nickel oxide, 2-12 wt% of molybdenum oxide, 0.05-4.5 wt% of strontium oxide and 67-85 wt% of the silica-alumina carrier. The catalyst is high in hydrogenation activity, good in selectivity, resistant in gelatination and strong in water resistance.
Owner:山东省安正安全咨询服务有限公司
A kind of cracking carbon nine second-stage hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103611562BImprove performanceModerate performanceMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentMolecular sieveActive component
The invention relates to a catalyst for pyrolysis C9 two-stage hydrogenation and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is prepared by taking a K and Ru modified composite oxide consisting of an HY molecular sieve, B2O3 and Al2O3 as a carrier and loading active components of Ni and Mo. The catalyst comprises the following active components in percentage by weight: 3.0-5.0% of NiO and 9.0-15.0% of MoO3. The catalyst provided by the invention is used for pyrolysis C9 two-stage hydrogenation, shows very high desulfurization activity and olefin saturation capacity, is strong in carbon deposition resistance and has a certain effect on macromolecular colloid pyrolysis, so that the colloid resistance of the catalyst is improved, and the service life of the catalyst is greatly prolonged.
Owner:WUHAN KELIN FINE CHEM
A kind of pyrolysis gasoline middle distillate unsaturated hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN109321270BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentPtru catalystUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a method for selective hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons in the middle distillate of pyrolysis gasoline, which includes the following process: nickel catalyst is reduced at 400-500°C in the presence of hydrogen, and adjusted to the reaction process conditions after cooling and passivation: reaction Inlet temperature 45-110°C, reaction pressure 2.0-4.5MPa, hydrogen-oil volume ratio 60-200:1; liquid volume space velocity 2.0-5.5h ‑1 ; The catalyst includes a silica-alumina carrier and metal active components nickel, molybdenum and magnesium loaded on the carrier. The catalyst has good colloidal resistance, strong resistance to arsenic, sulfur and water, and is suitable for long-term stable operation of the device.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
Selective hydrogenation method of middle distillate unsaturated hydrocarbon of pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109321270AHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrocarbon oils treatmentSilicon oxideMetallic Nickel
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method of middle distillate unsaturated hydrocarbon of pyrolysis gasoline. The selective hydrogenation method comprises the following process: in thepresence of hydrogen and under the condition of 400 to 500 DEG C, reducing a nickel catalyst; adjusting to reaction process conditions after cooling passivation: the temperature of a reaction inlet is 45 to 110 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 2.0 to 4.5 MPa, the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is (60 to 200) to 1 and the liquid volume airspeed is 2.0 to 5.5 h<-1> ; the catalyst comprises a silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carrier and metal active components such as nickel, molybdenum and magnesium loaded on the carrier. The catalyst has good colloid resistance, as well as high arsenic resistance,sulfur resistance and water resistance, and is suitable for long-cycle stable operation of a device.
Owner:泉州市利泰石化科技有限公司
A method for selective hydrogenation of whole distillates of pyrolysis gasoline
ActiveCN109355093BHigh hydrogenation selectivityImprove anti-glue abilityRefining by selective hydrogenationHydrocarbon oils treatmentPtru catalystSilicon oxide
The invention relates to an all-fraction selective hydrogenation method for pyrolysis gasoline. The all-fraction selective hydrogenation method includes procedures of carrying out reduction on nickelcatalysts in the presence of hydrogen under the condition of the temperature of 400-500 DEG C; carrying out cooling and passivation and then carrying out adjustment until reaction technological conditions are met. The reaction technological conditions include the reaction inlet temperatures of 45-110 DEG C, the reaction pressures of 2.0-4.5 MPa and the hydrogen-oil volume ratios of 60-200:1. The liquid volume space velocities are 2.0-5.5 h<-1>; the catalysts comprise silicon oxide-aluminum oxide carriers and metal active components including nickel, molybdenum and magnesium, and the metal active components are loaded on the carriers. The all-fraction selective hydrogenation method has the advantage that the catalysts are good in colloid resistance, high in arsenic resistance, sulfur resistance and water resistance and applicable to long-period stable operation of devices.
Owner:陈明海
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com