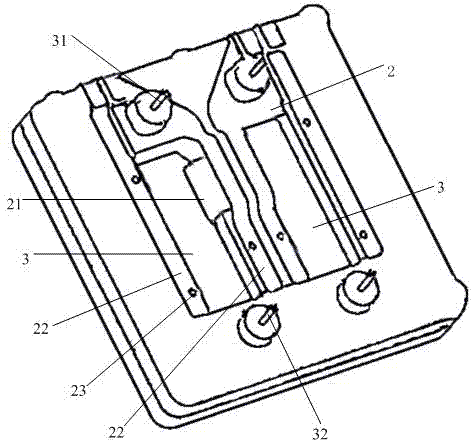
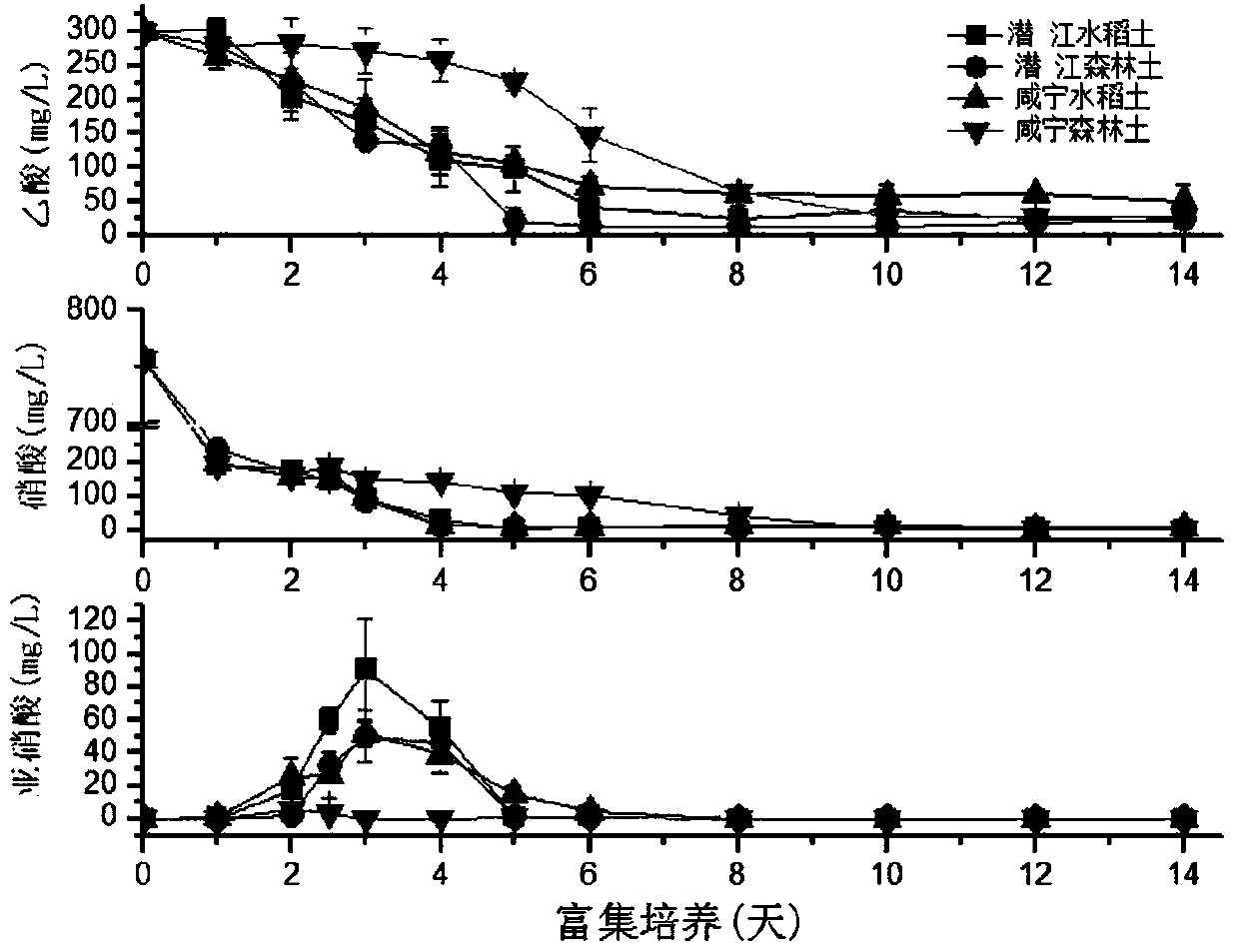
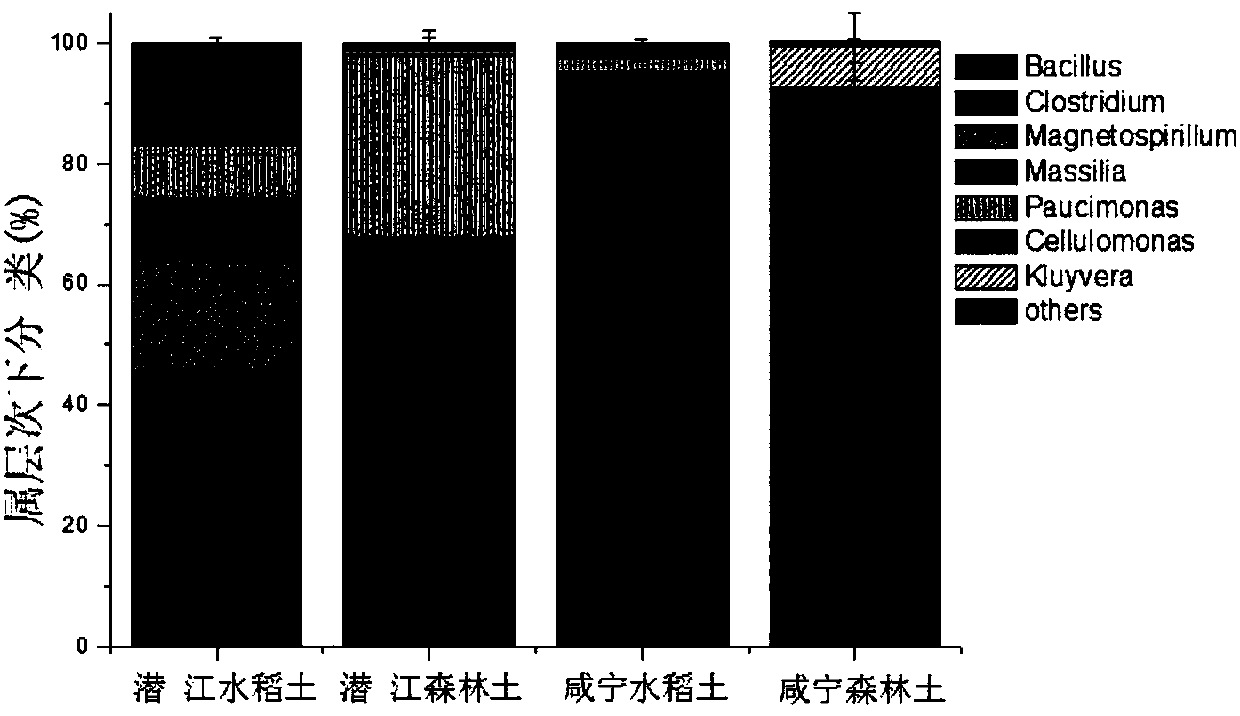
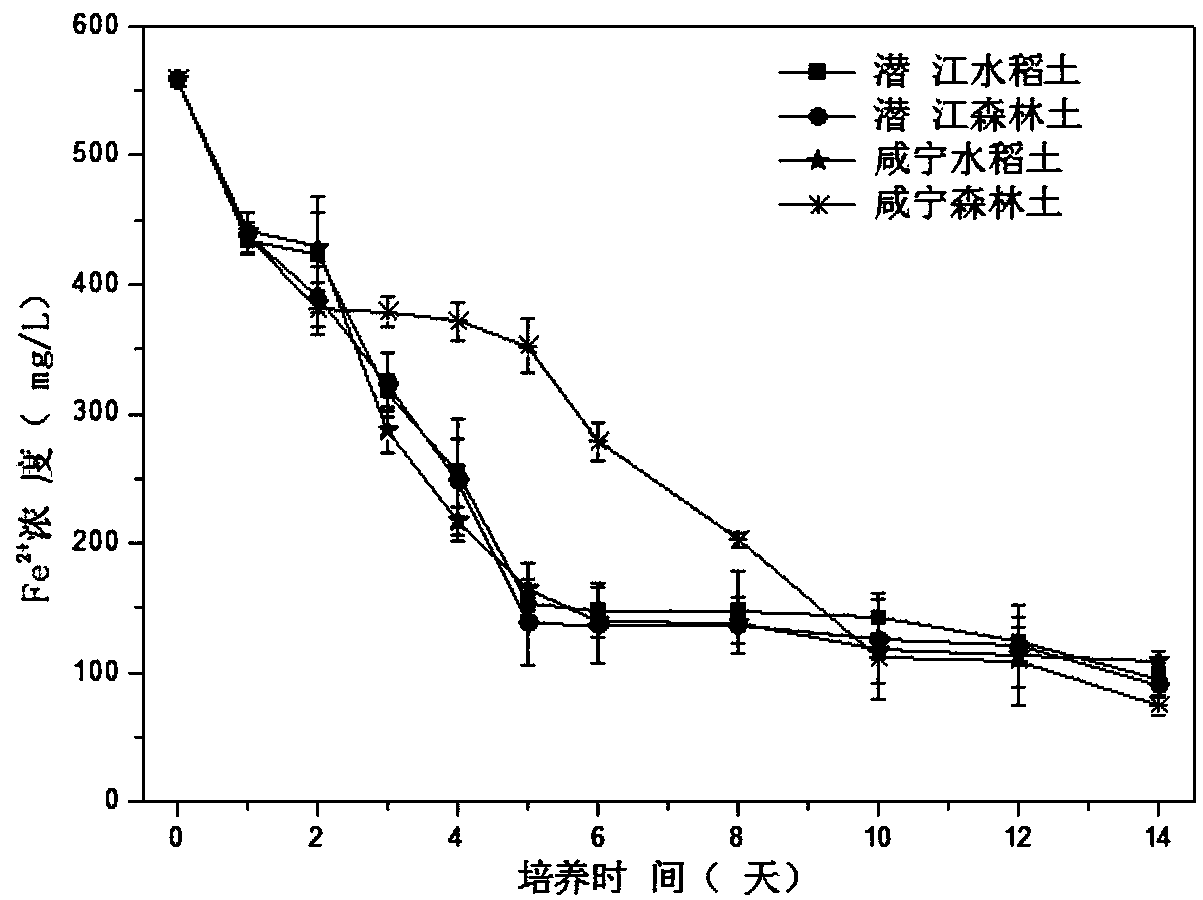
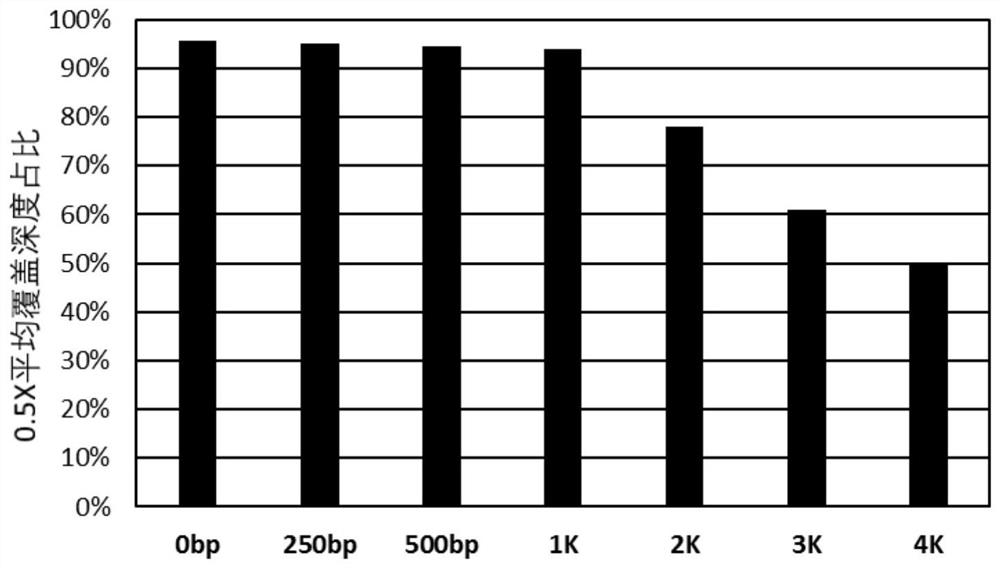
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "High sequencing throughput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
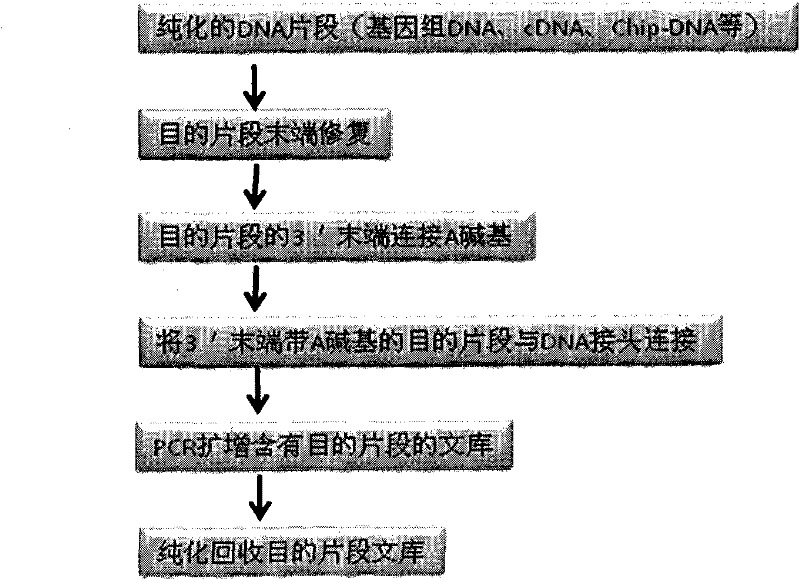
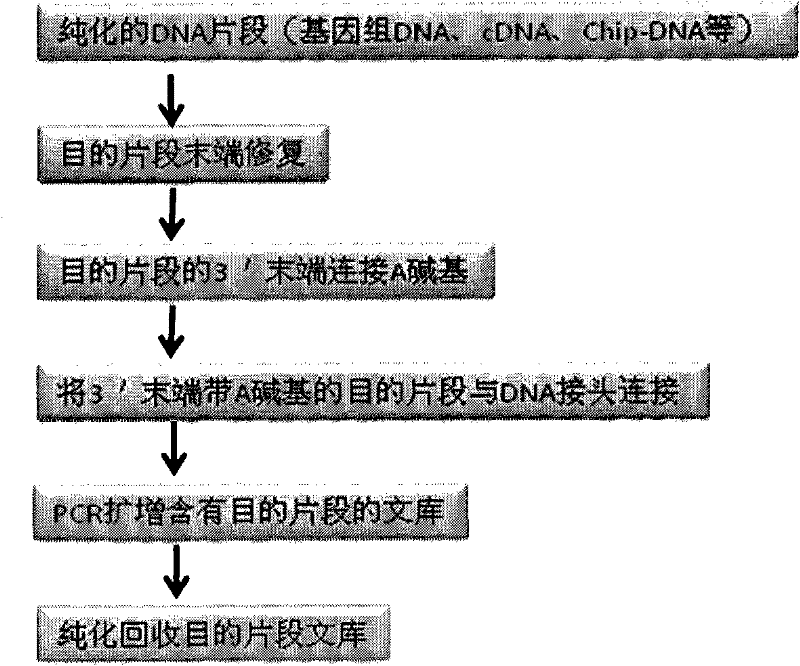
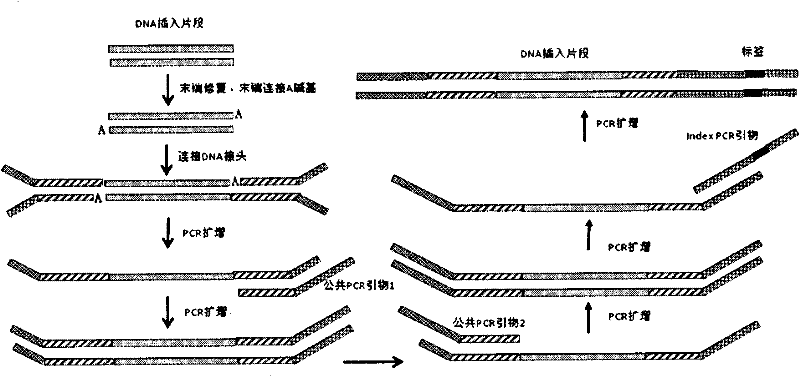
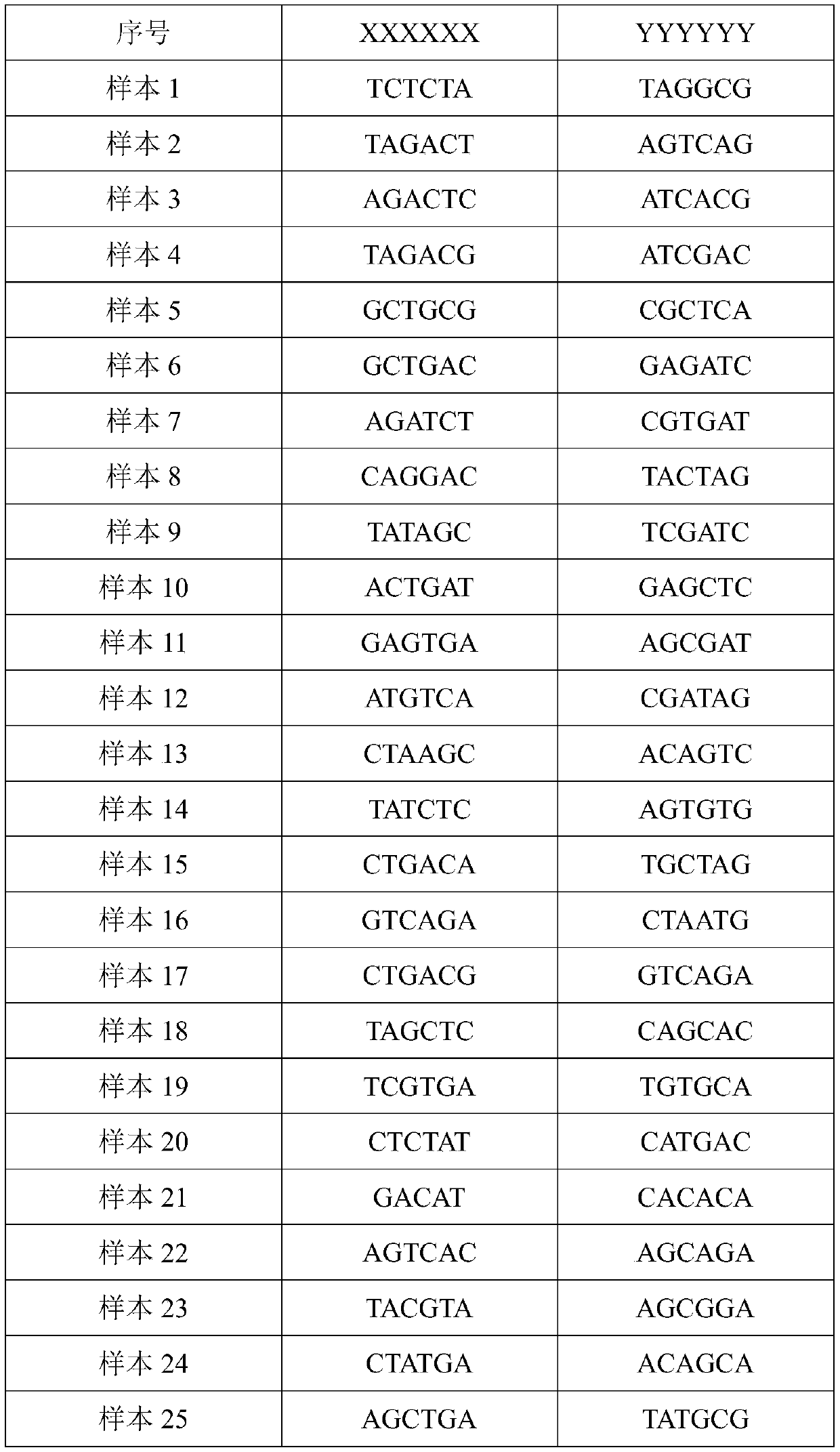
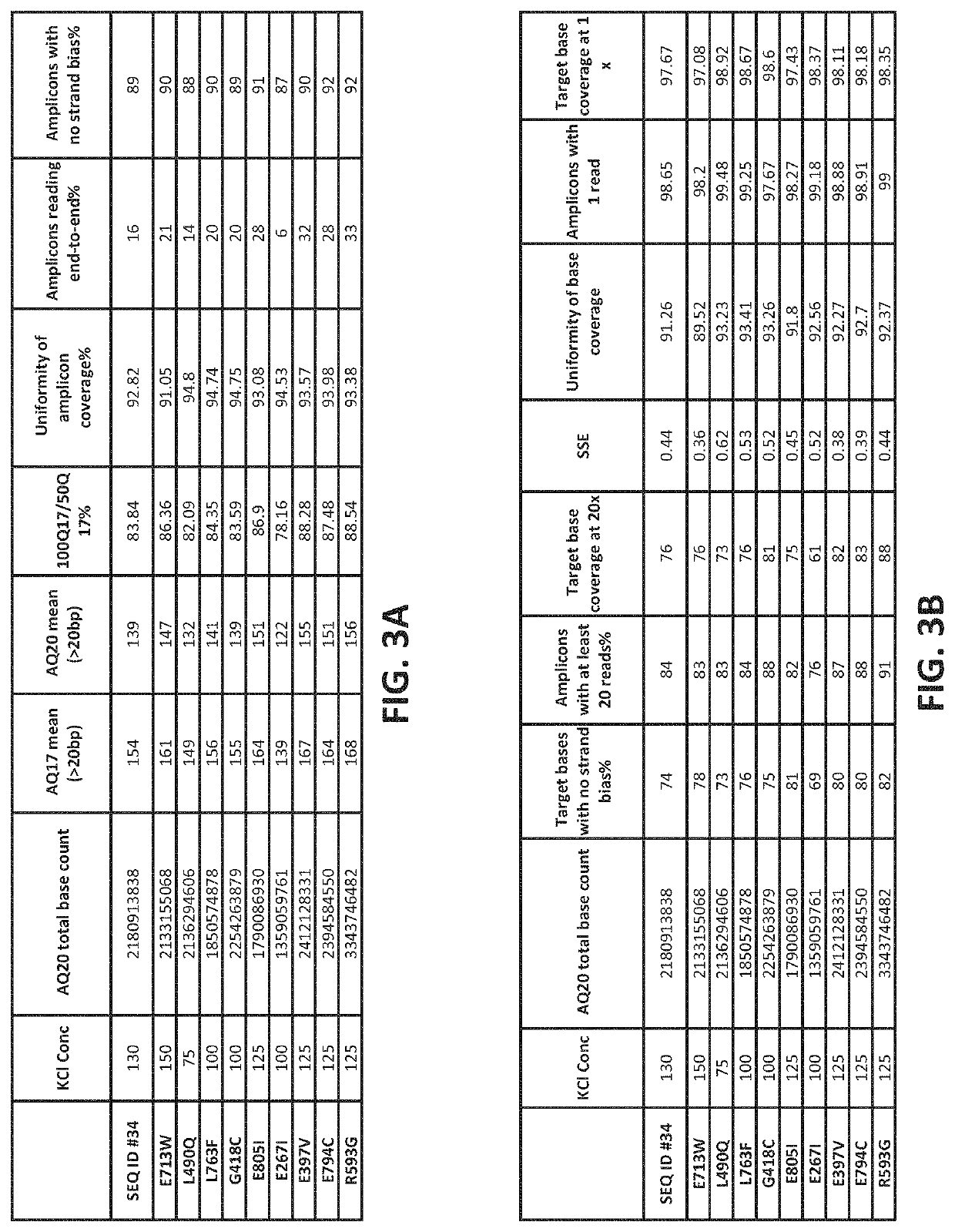
DNA index library building method based on high throughput sequencing
ActiveCN102409048AImprove production efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle sampleA-DNA
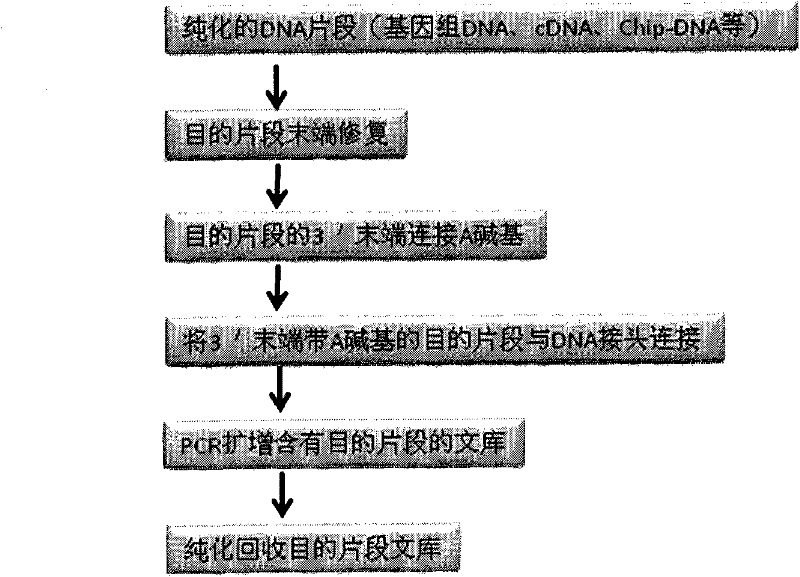
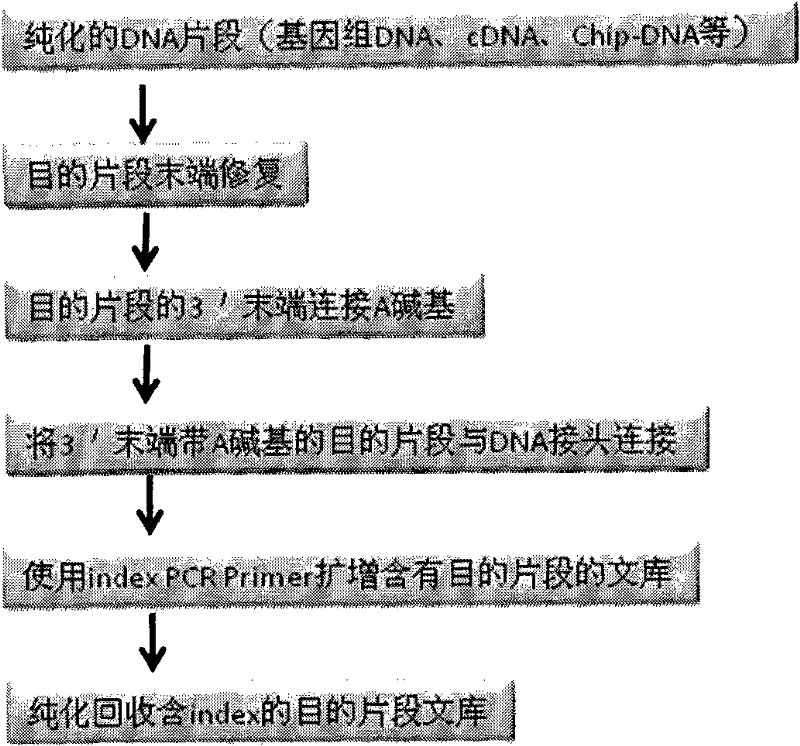
The invention provides unique index sequences with a length of 7bp. The index sequences can be respectively imported into a DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) index library through adapter link and PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The invention provides a method for building the DNA index library by using the index sequences based on a solexa sequencing platform of the current illumina company, and the method is applied to solexa DNA sequencing and has the effects on improving the preparation efficiency of the DNA index library, increasing the sequencing throughput of the DNA samples and lowering thesolexa sequencing cost of a single sample.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
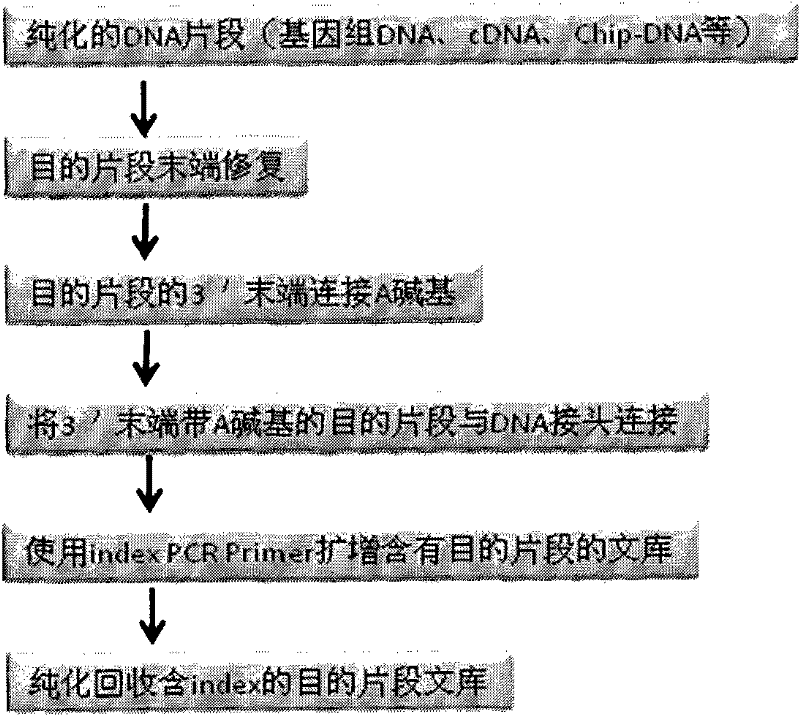
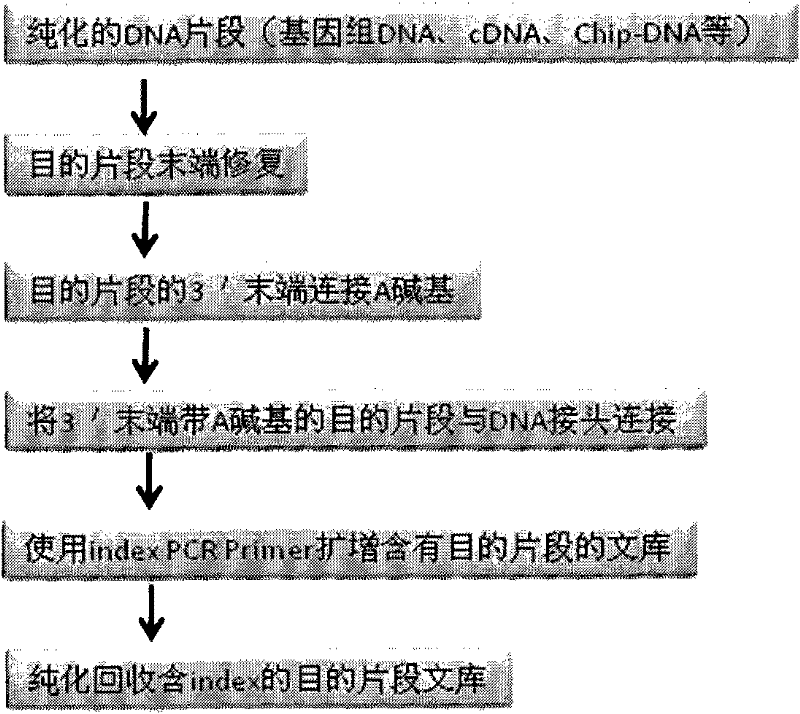
DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) index library building method based on PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
ActiveCN102409049AImprove production efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyInverse polymerase chain reaction
The invention designs 161 unique index sequences with a length of 8bp, and the indexes are embedded into DNA PCR (deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase chain reaction) primers to form DNA PCR index primers, thus being capable of importing the index sequences through PCR. The invention successfully establishes a method for building a DNA index library, and the method is applied to solexa DNA sequencing.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Method and equipment for neoantigen epitope prediction
ActiveCN105524984AImprove efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpitopeState dependent
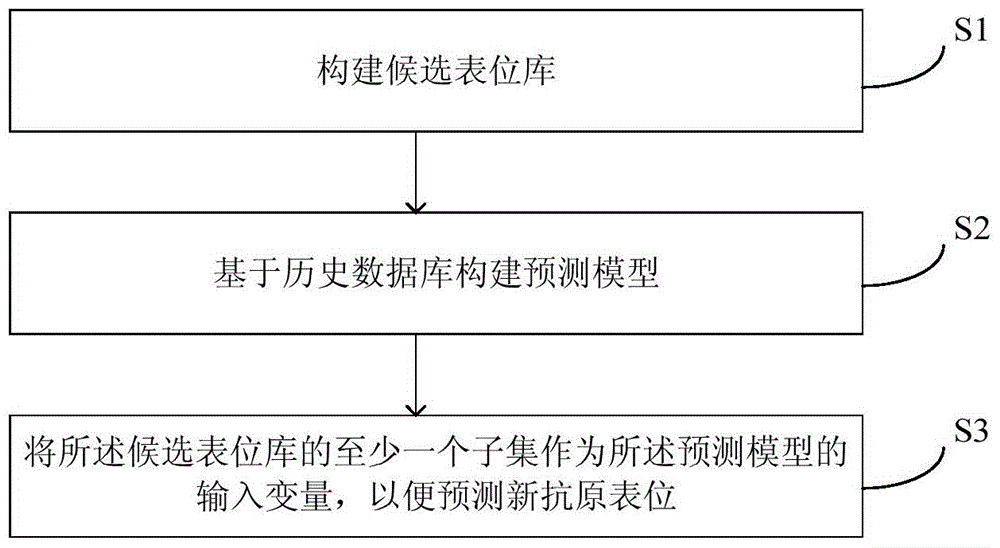
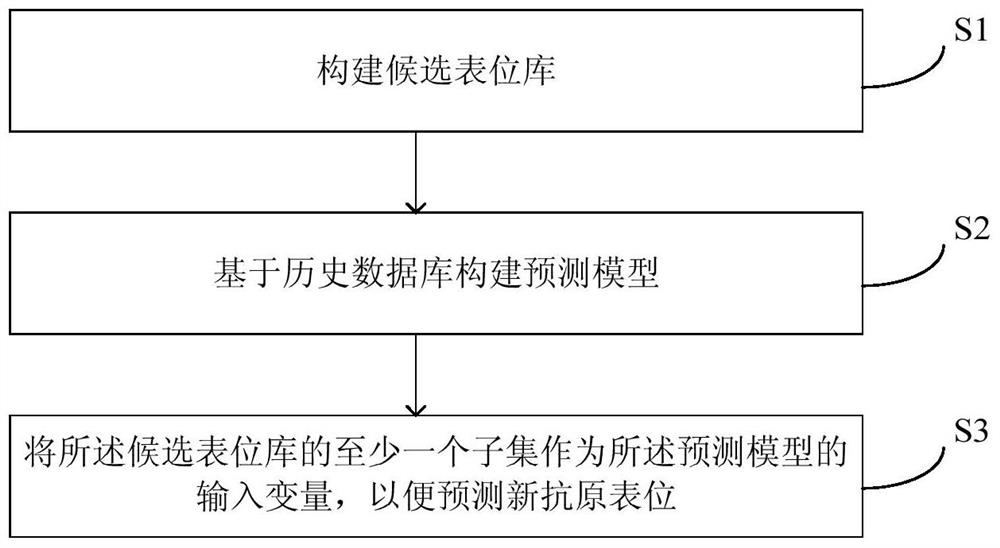
The invention provides a method and equipment for neoantigen epitope prediction. The method for neoantigen epitope prediction includes (1), building a candidate epitope library; (2), building a prediction model based on a historical database, and (3) taking at least one subset of the candidate epitope library as an input variable of the prediction model to predict neoantigen epitope. The candidate epitope library is composed of differential expression peptides which are peptides with difference between samples having predetermined state and samples having no predetermined state. The historical database is composed of known epitopes related with the predetermined state. By the method for neoantigen epitope prediction, antigen mutation information can be determined according to gene level and protein level really, neoantigen epitopes capable of being bound with MHC are acquired effectively rapidly, and binding capacity of neoantigen epitopes and NHC can be predicted precisely. Besides, the method is easy and convenient and capable of saving manpower and material resources greatly.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
Gene sequencing device and system
ActiveCN102517206AFully automatedImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlComputer module
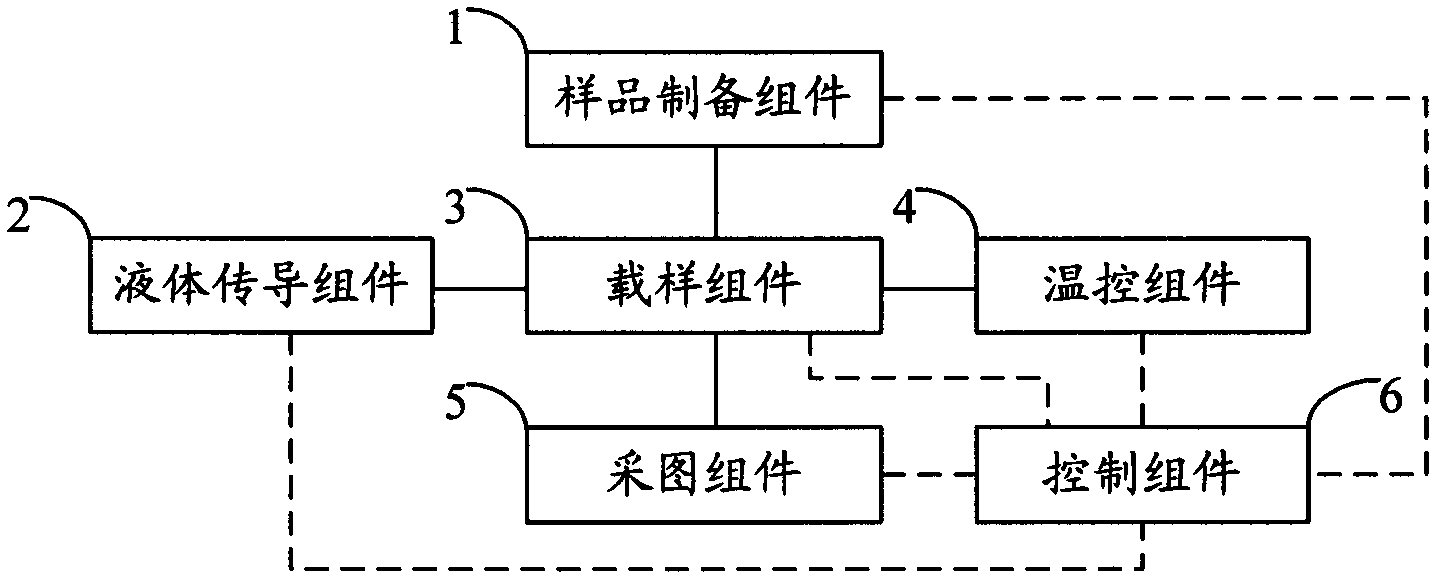
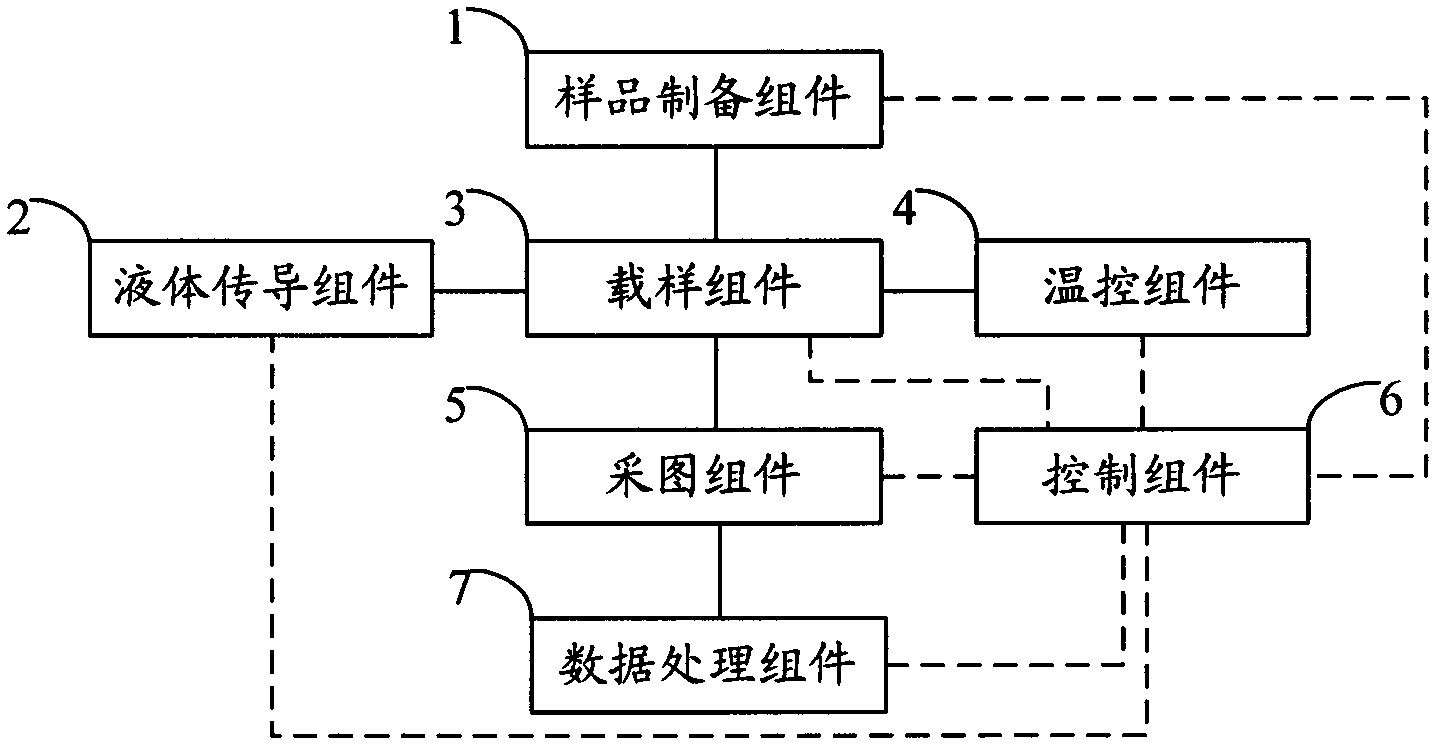
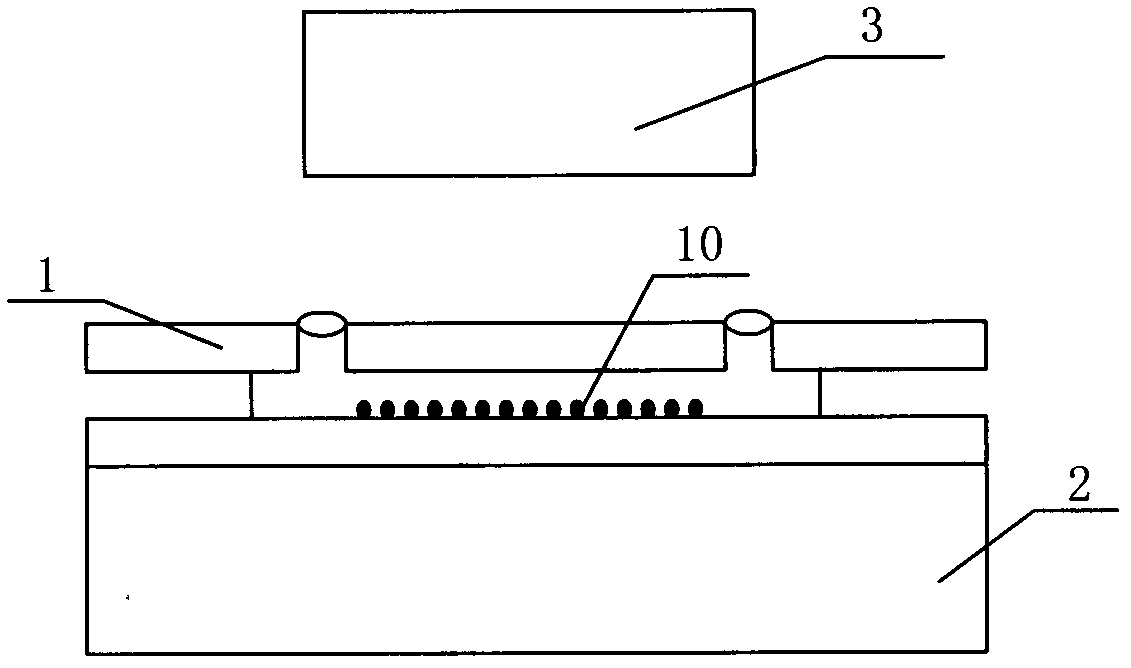
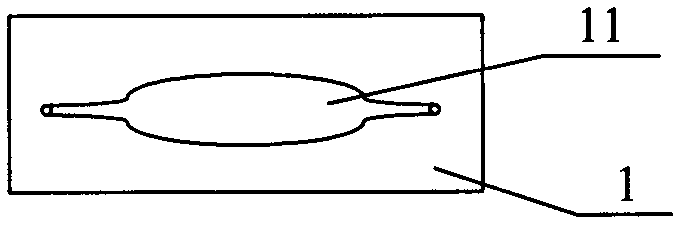
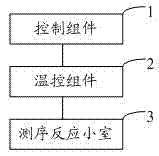
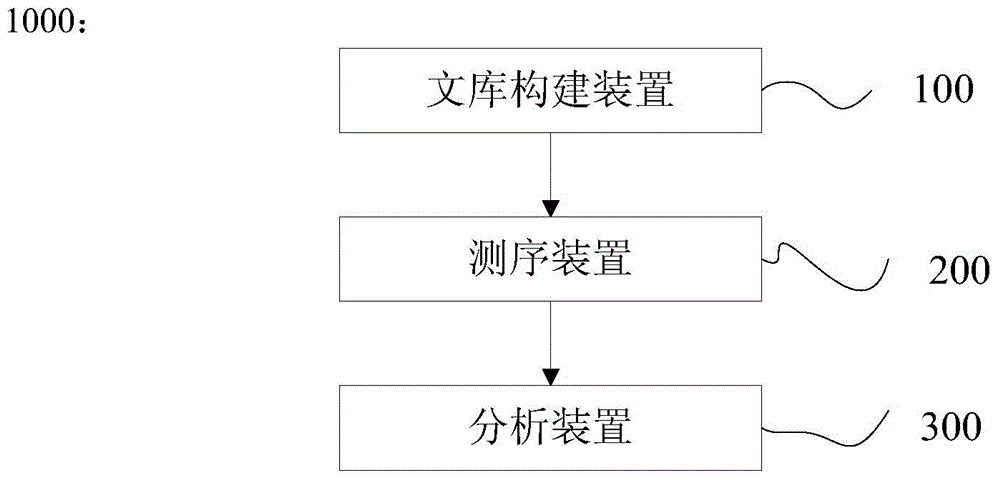
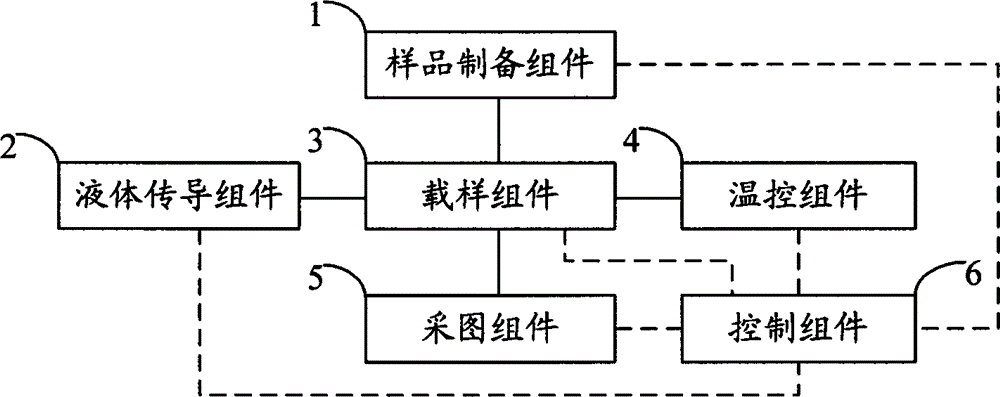
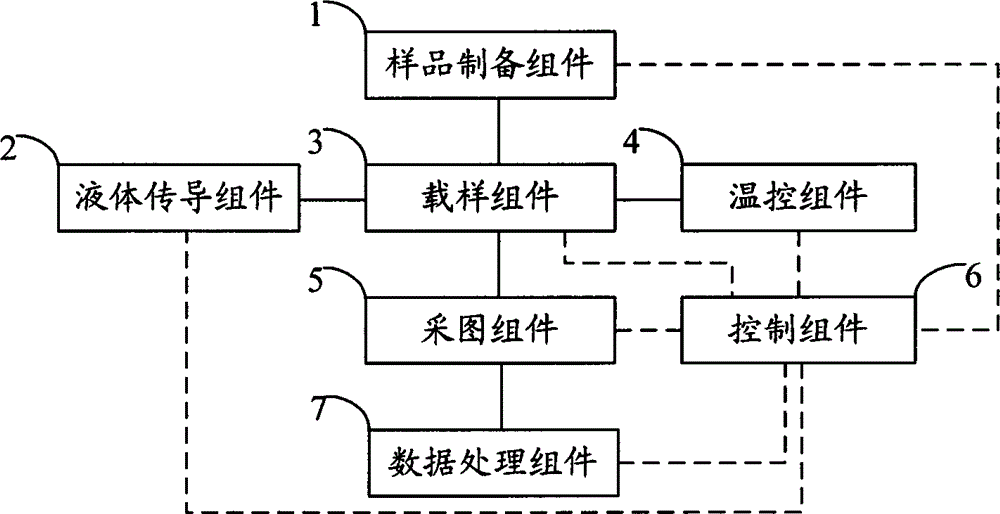
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a gene sequencing device and a gene sequencing system. The gene sequencing device comprises a sample preparation component, a liquid conduction component, a sample loading component, a temperature control component, an image acquisition component and a control component. The gene sequencing system comprises a sample preparation control module, a liquid conduction control module, a reaction control module, a temperature control module, an image acquisition control module and a control module. By adopting the gene sequencing device and the gene sequencing system, the integration from sample preparation to data processing can be realized, and full automation of gene sequencing can also be realized. Meanwhile, the high-pass and low-cost gene sequencing can be realized.
Owner:盛司潼
Tag library constructing method based on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) adapter connection as well as used tag and tag adapter
ActiveCN102409045AHigh sequencing throughputImprove efficiency and label recognition rateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyLibrary preparation
According to the invention, based on a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) tag library preparation method provided by a solexa sequencing platform of the illumine corporation, a special tag sequence with length of 6 bp is designed, the tags are embedded into DNA adapters, and the DNA adapters are connected to introduce the tag sequence, thus a library construction method of a DNA tag library is successfully constructed, and the constructed DNA tag library can be applied to solexa DNA sequencing.
Owner:WUXI QINGLAN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
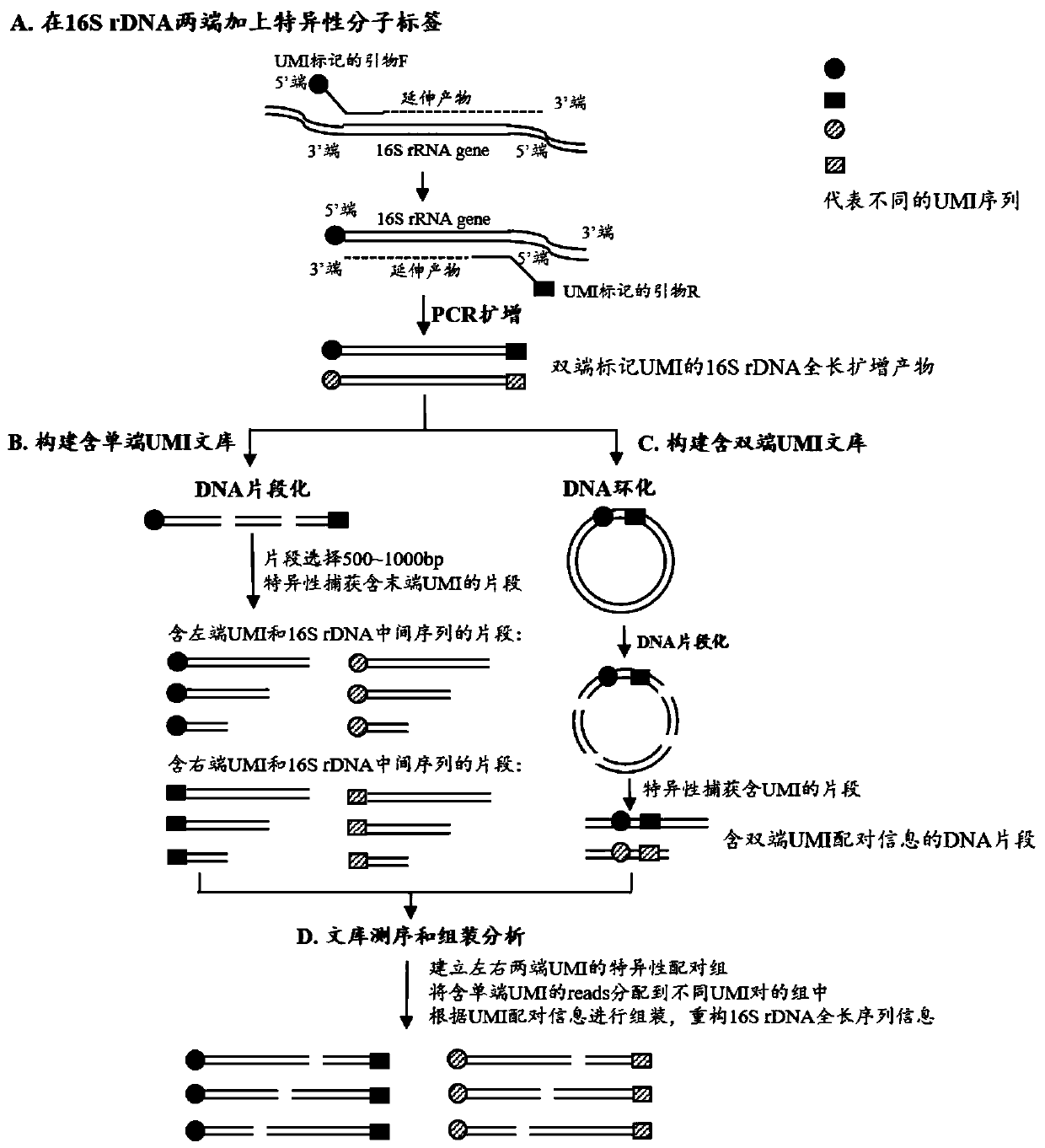
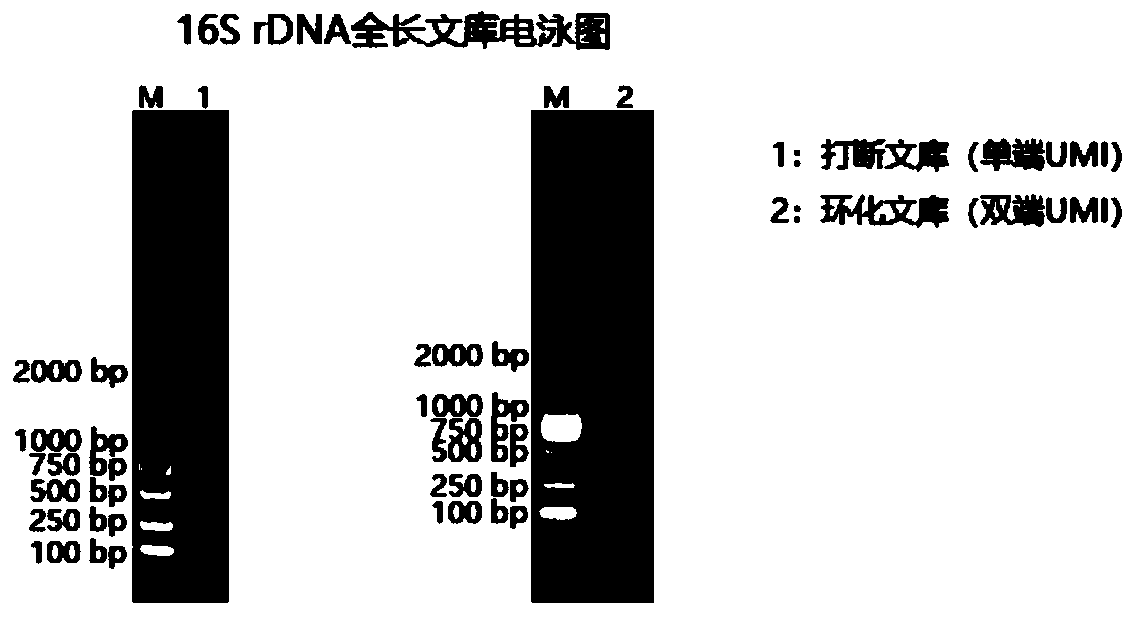
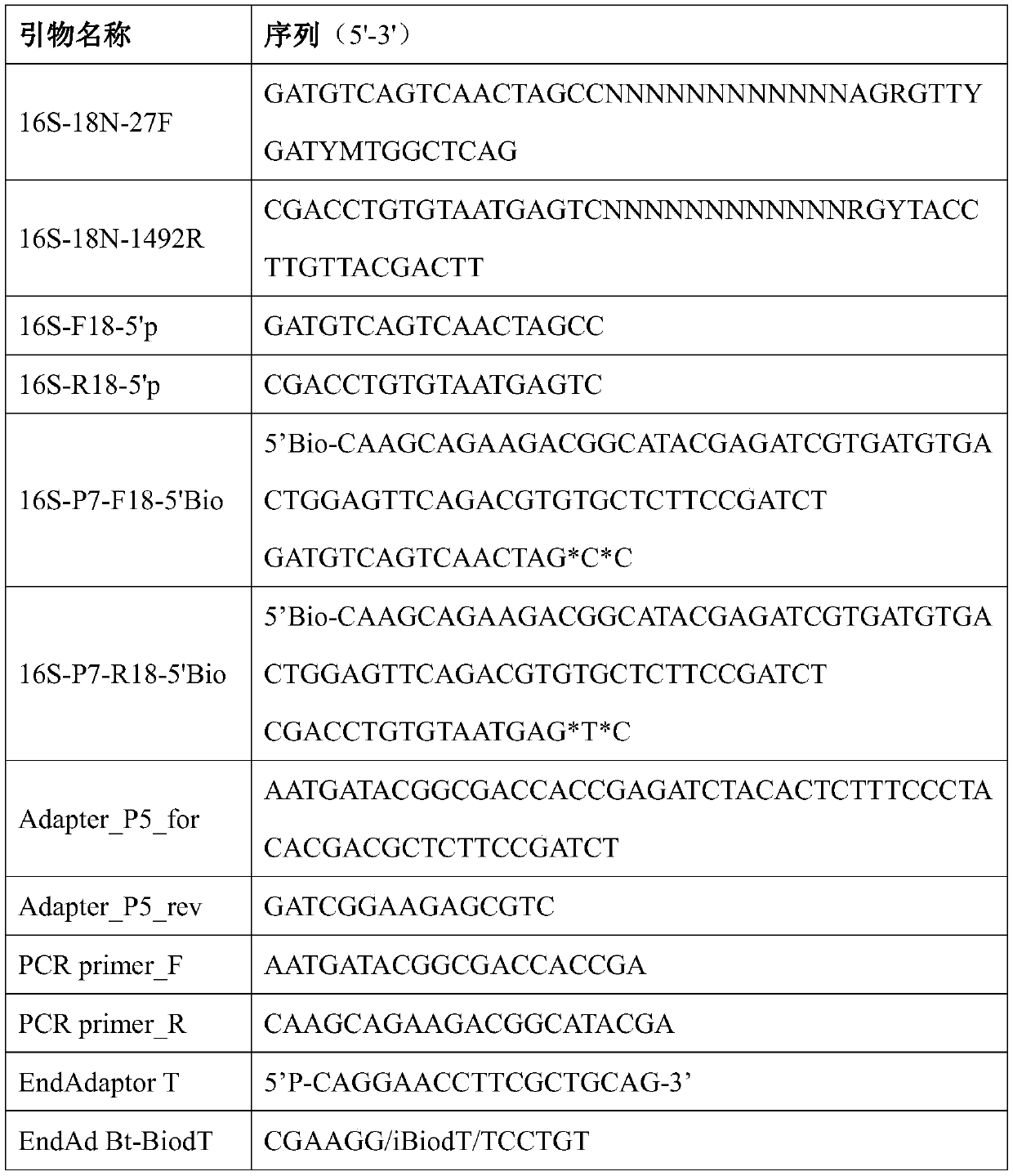
Method for constructing bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library
PendingCN110004210AHigh sequencing throughputLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMicroorganismBacterial 16S
The invention relates to a method for constructing a bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library, and relates to the field of microorganism high-throughput sequencing. The method comprises the steps of firstly, adding unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) which are composed of random base groups to the two ends of each 16S rDNA template molecule, conducting PCR amplificationto obtain multiple copied 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons with two ends containing specific UMIs, randomly breaking and connecting joints of the sequencing library, and conducting paired-end sequencing to obtain the UMI sequences and corresponding 16S rDNA fragment sequences; besides, through cyclizing of the 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons and sequencing, obtaining UMI pairing information oftwo ends of the same molecule; conducting reads assembly according to the same UMI and pairing UMI information to increase the splicing length accordingly, and finally conducting assembly to obtain 16S rDNA overall-length sequence information. The method is low in cost, high in accuracy and suitable for high-throughput sequencing platforms; meanwhile, the method can effectively eliminate the influence of PCR amplification preferences, amplification errors and sequencing errors through the UMIs, and thus the bacterium population abundance in a sample is more precisely quantified.
Owner:杭州进一生物科技有限公司
Gene sequencing equipment
ActiveCN102604826ASimple structurePrevent malfunctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlGene
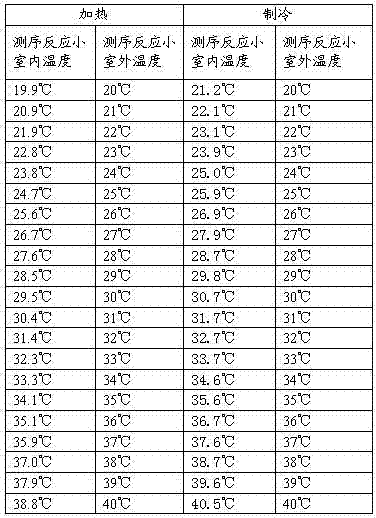
The invention relates to the field of biochemical equipment and provides gene sequencing equipment, which comprises a sequencing reaction chamber and a temperature control component. The sequencing reaction chamber is used for fixing samples and performing sequencing reaction; the temperature control component is fixed in an area of the sequencing reaction chamber when the samples are fixed and used for controlling temperature of the sequencing reaction chamber. The temperature of the sequencing reaction chamber rises and decreases quickly by the temperature control component, and sequencing reaction efficiency is improved.
Owner:盛司潼
Nucleic acid detection reaction platform and nucleic acid detection system
ActiveCN103087909AHigh-throughput sequencingHigh sequencing throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyReaction chamber
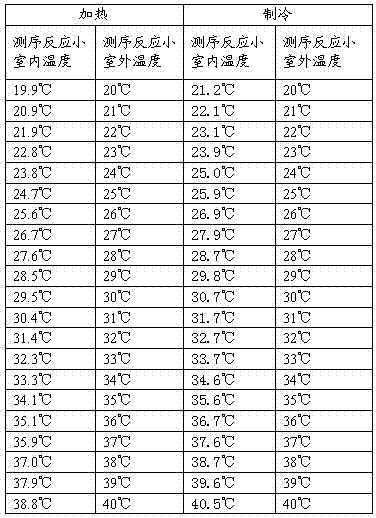
The invention relates to the field of biochemical equipment, and provides a nucleic acid detection reaction platform. The nucleic acid detection reaction platform comprises a temperature control component, a control component and at least two sequencing reaction chambers, wherein the control component is used for adjusting set temperature to target temperature and controlling a sequencing reaction to reach the target temperature from the current temperature and further used for sending a target temperature instruction to the temperature control component; the temperature control component is used for heating or cooling the sequencing reaction according to the target temperature instruction of the control component, and measuring and feeding back the current temperature of the sequencing reaction in real time; and the sequencing reaction chamber is used for parallel sequencing. The invention further provides a nucleic acid detection system containing the nucleic acid detection reaction platform. The nucleic acid detection reaction platform and the nucleic acid detection system related by the invention can improve the quality of the sequencing reaction and further can improve the sequencing throughput.
Owner:盛司潼
Magnetic bead enrichment technique based method for high-flux development of genome SSR markers
ActiveCN104212879AReduce the difficulty of buildingImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationHigh flux
The invention discloses a magnetic bead enrichment technique based method for high-flux development of genome SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers. The method comprises the steps of: (1) extracting target genome DNA; (2) subjecting the obtained genome DNA to random fragmentation; (3) constructing a genome random fragmented DNA library; (4) amplifying the DNA library; (5) utilizing a biotin labeled SSR probe to perform hybridization with a target fragment in the library; (6) carrying out streptavidin magnetic bead enrichment on the SSR sequence-containing DNA library fragments; (7) amplifying and purifying the enriched DNA library fragments; (8) subjecting the purified DNA fragments to emulsion PCR amplification and sequencing; and (9) searching sequences containing SSR loci in the obtained sequences. The method reduces the library construction difficulty, shortens the experimental period, improves the sequencing flux, lowers the sequencing cost, and can be widely used as an effective method for high-flux development of various species SSR markers.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
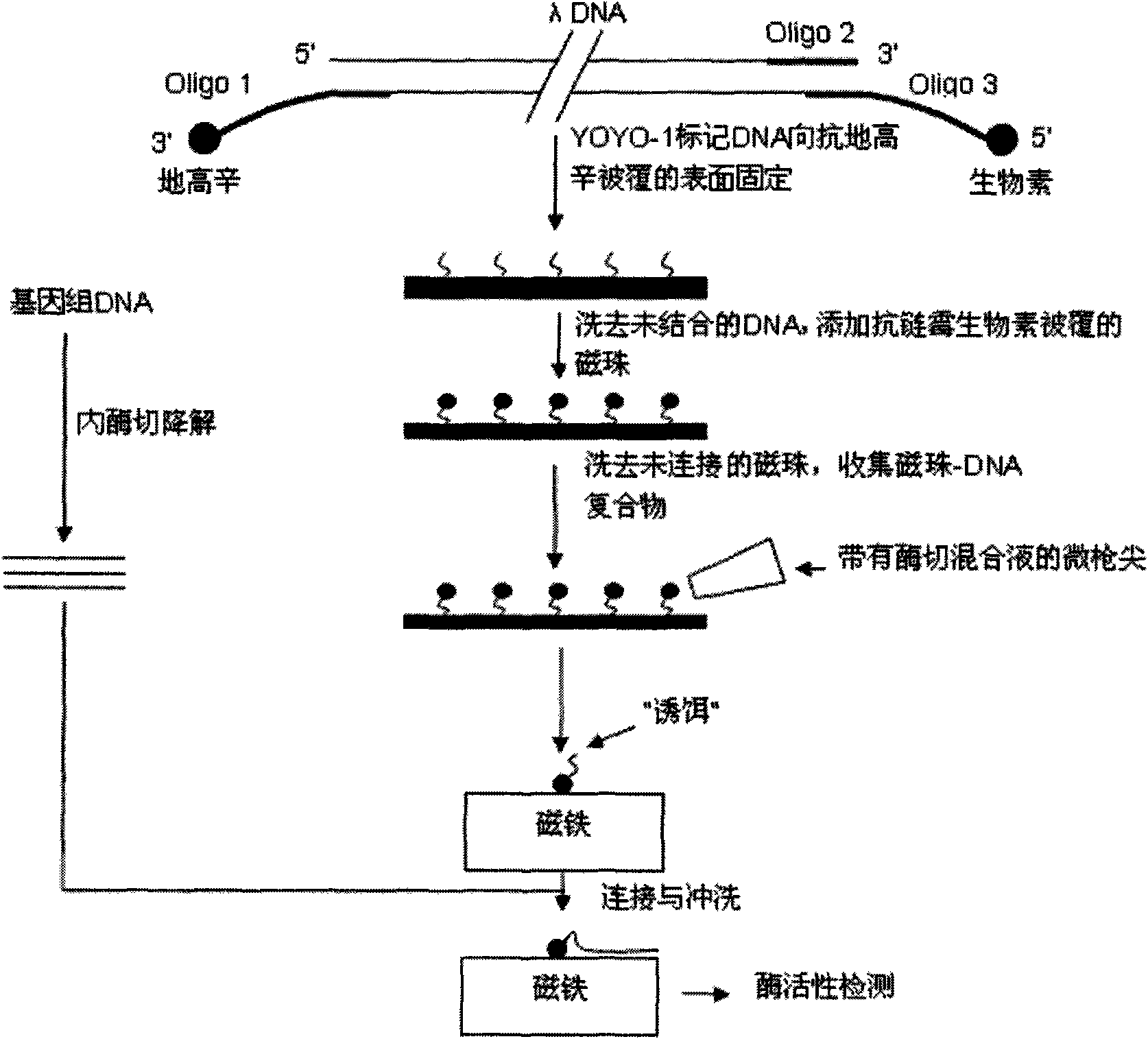
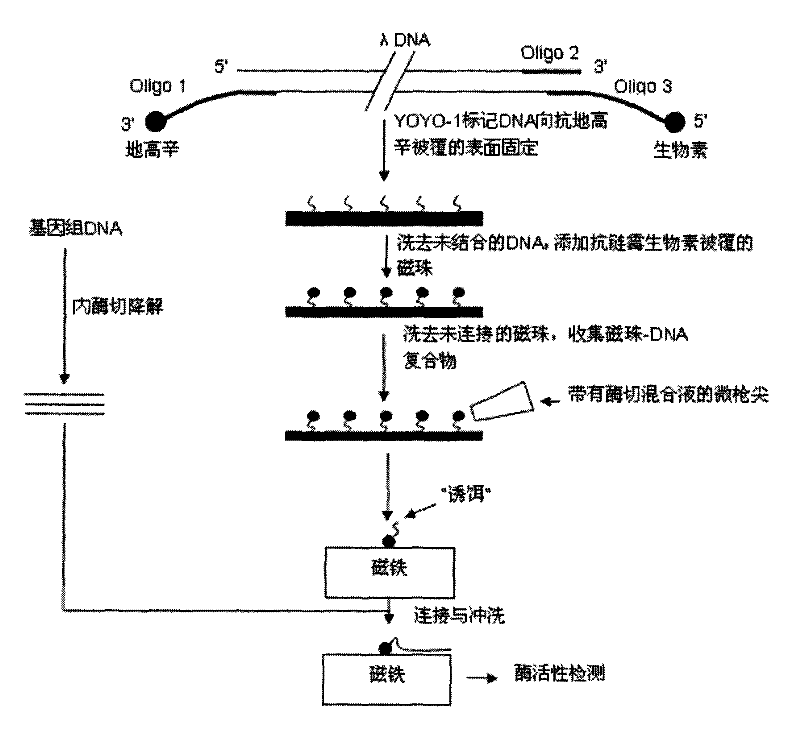
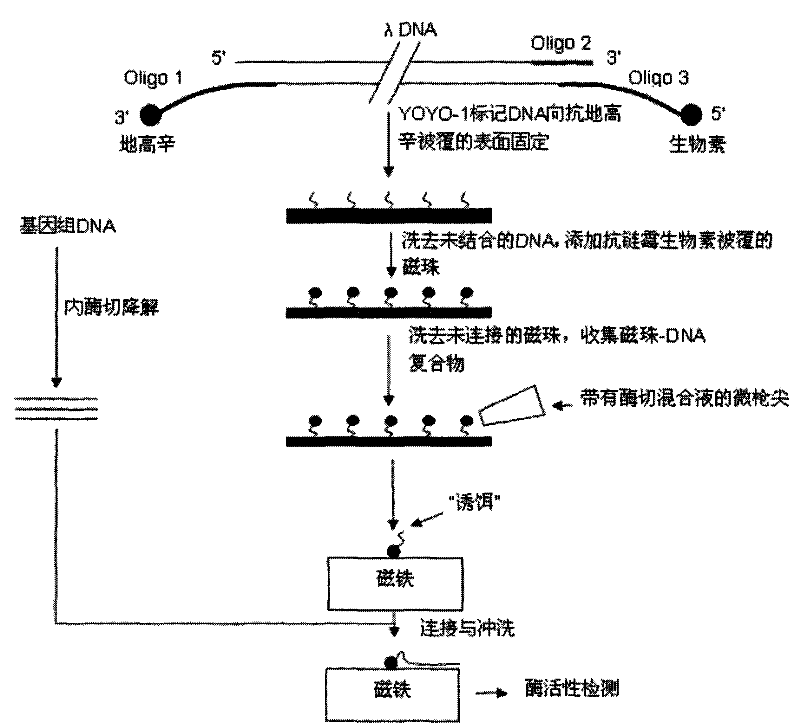
Method for linking monomolecular DNA to single magnetic bead
InactiveCN101619353AHigh sequencing throughputEnabling Single Molecule SequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBiotin
The invention relates to a method for linking monomolecular DNA to a single magnetic bead, belonging to the technical field of biology and comprising the following steps: performing fluorescence labeling to DNA, then labeling biotin at the end 3' of the DNA and labeling digoxin at the end 5' of the DNA; or labeling digoxin at the end 3' of the DNA and labeling biotin at the end 5' of the DNA; placing the DNA on glass to carry out an immunoreaction and washing the DNA by running water; carrying out the immunoreaction again; adding DNA endonuclease to the periphery of magnetic beads, after DNA molecules are degraded, collecting magnetic beads carrying DNA fragments one by one by a micro-gunpoint and placing the magnetic beads on a magnet; and cutting target DNA by the endonuclease and linking target DNA fragments with the DNA fragments on the magnetic beads under the action of ligase. The method for linking the monomolecular DNA to the single magnetic bead can acquire the sequence information of target fragments and realize the monomolecular sequencing of the DNA; and when nano-pores are produced into an array to be matched with a decoy array, sequencing throughput can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
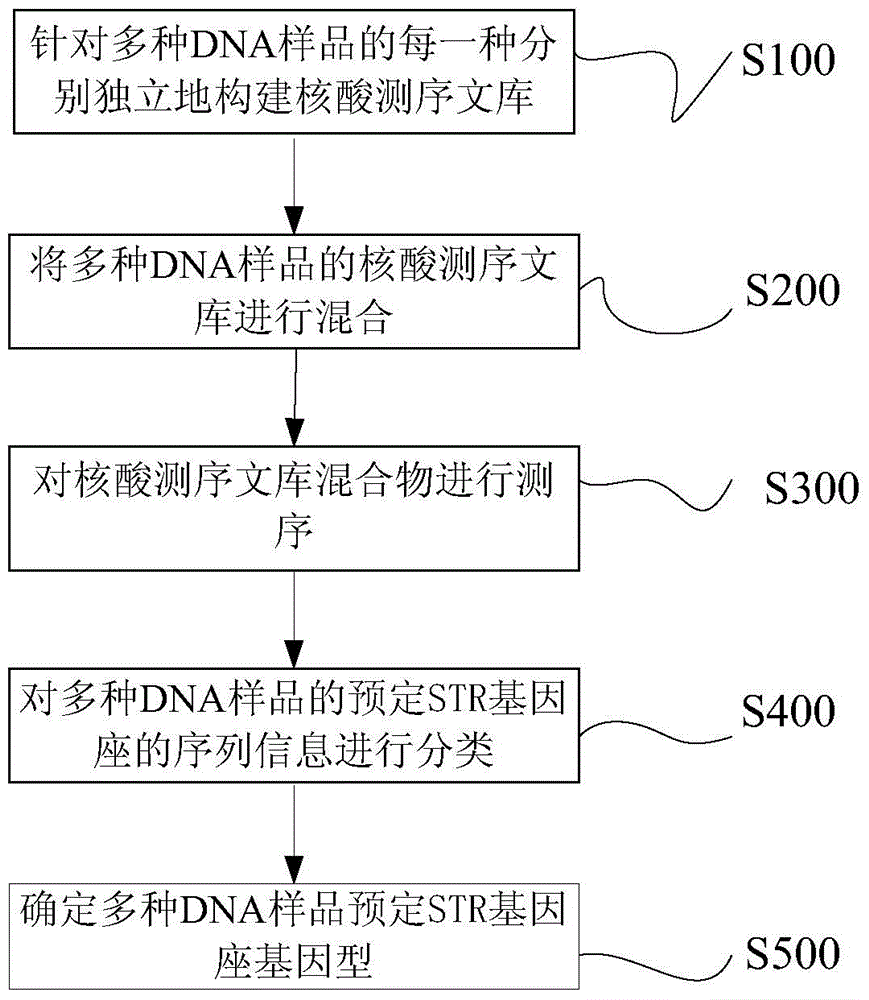
DNA tags, PCR primer and application thereof
ActiveCN105316320AHigh resolutionAvoid troubleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideGenotype
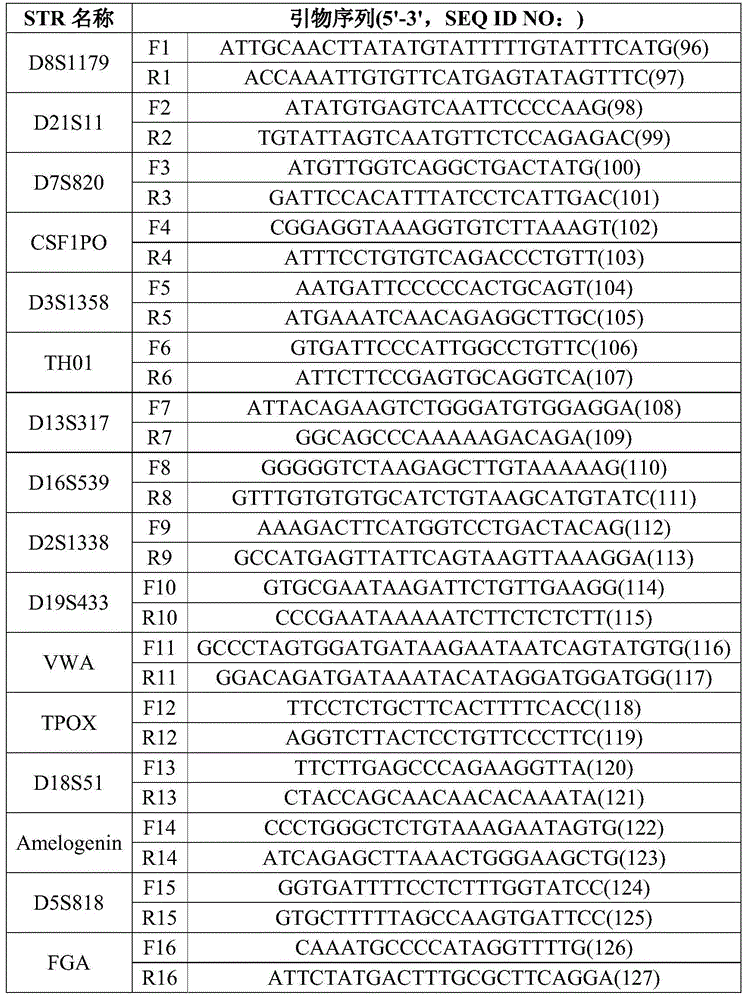
The invention discloses DNA tags, a PCR primer and application thereof. The DNA tags of one group are chosen from nucleotides shown as in SEQ ID NO:1-95 and can be used for building a nucleic acid sequencing library to accurately differentiate the nucleic acid sequencing library. The DNA tags and the PCR primer are utilized to build a tagged PCR primer, and by utilizing the tagged PCR primer, STR detection of at most 95 DNA samples can be realized at one step according to a method for determining preset STR gene locus genotype of various DNA samples.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +1
Larimichthys crocea genome breeding chip and application
InactiveCN112410435AQuality improvementImprove throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses a larimichthys crocea genome breeding chip and application, and relates to the technical field of genomics, bioinformatics, molecular biology and genome breeding. The larimichthys crocea whole-genome breeding chip is named as Ningxin No.1 and is manufactured on the basis of an Affymetrix gene chip technology of Thermofisher Company. Each chip can simultaneously detect 96 samples and contains 591,765 high-quality SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) sites, and the SNP sites have nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO.591765. The chip can be applied to detecting DNA samples of larimichthys crocea, genetic background analysis can be carried out on larimichthys crocea breeding materials, genotype identification can be carried out on closely-related species of larimichthys, and correlation analysis is carried out on economic traits of the larimichthys crocea. The method has the advantages of high throughput, good repeatability, simple data analysis,low cost of single labeled data and a wide application prospect.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Rice genome-wide breeding chip and its application
ActiveCN105008599BQuality improvementImprove throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeGenome
The present invention provides a rice genome-wide breeding chip and its application. The rice genome-wide breeding chip of the present invention is Rice60K, which is a SNP chip made based on Infinium chip manufacturing technology. Each chip can simultaneously detect 24 samples, including 58,290 SNPs These marker sites have the DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1-58290. The chip can perform molecular marker fingerprint analysis on rice variety resources, perform genotype identification on offspring of hybrid populations, and identify variety authenticity. The analysis and screening of the genetic background of breeding materials and the association analysis of agronomic traits have broad application prospects.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP +3
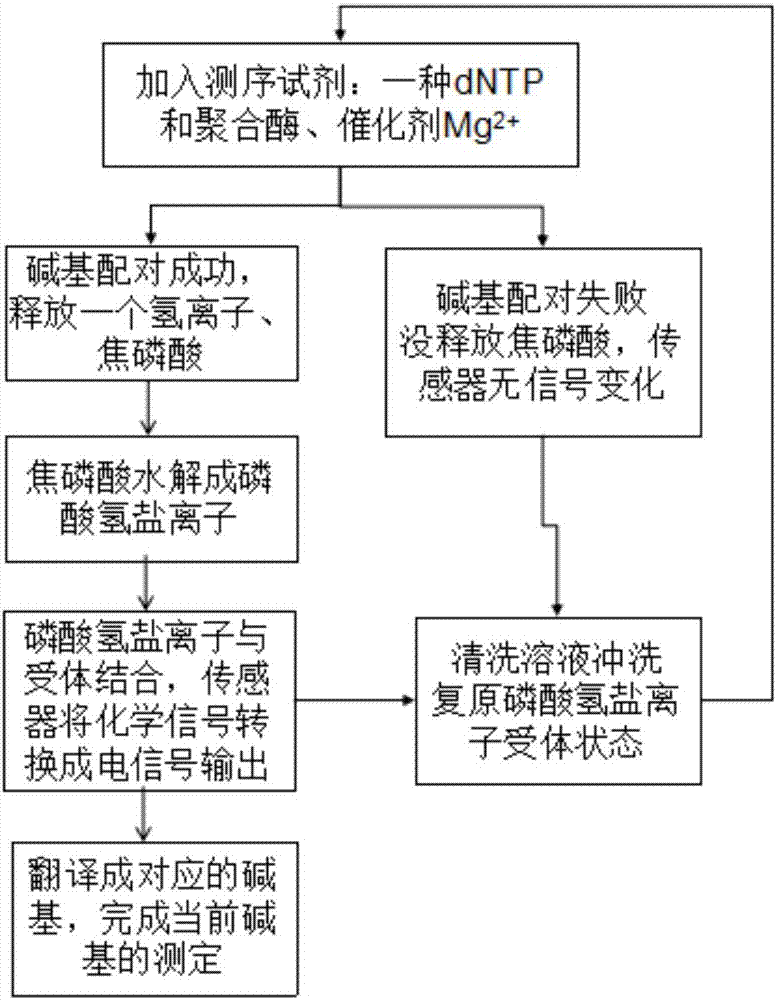
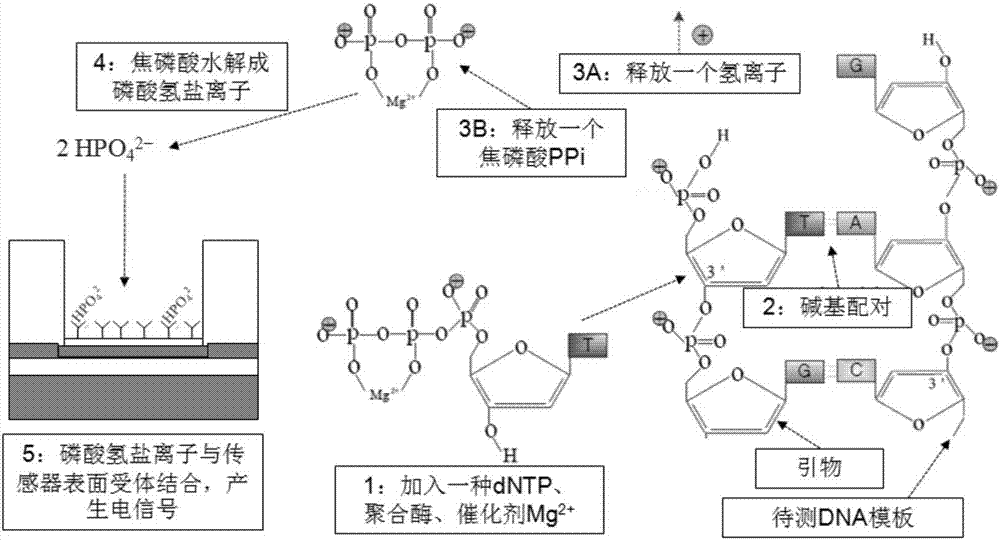
Gene sequencing method realized by detecting pyrophosphoric acid charges
InactiveCN107460233ALong electrical signalImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayEffective surface
The invention discloses a gene sequencing method capable of increasing the signal-to-noise ratio by detecting pyrophosphoric acid charges. According to the method, by adding dNTP, polymerases and catalysts to a reaction system, pyrophosphoric acid is released through base pairing, pyrophosphoric acid is hydrolyzed to generate hydrogen phosphate ions, and the hydrogen phosphate ions are combined with sensor surface receptors to generate electrical signals which are further translated into corresponding bases. Pyrophosphoric acid generated during amplification can be detected, the diffusion rate of pyrophosphoric acid is much slower than that of hydrogen ions because the relative molecular mass of pyrophosphoric acid is 174, electrical signals which can be detected last for a long time, and accuracy can be effectively improved. Besides, pyrophosphoric acid has four positive charges, diffusion is slowed down, effective surface concentration is high, the converted electric signals are strong, and the detected signal-to-noise ratio is high. The high signal-to-noise ratio allows the use of smaller sensors and a sensor array with higher density and larger scale, so that sequencing throughput can be further improved and sequencing cost can be reduced.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG ONECHIP BIO TECH CO LTD
Sebastiscus marmoratus gene screening and mining method based on simplified genome sequencing technology
ActiveCN110283892AQuality improvementIncreased enzyme cleavage rateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGenomic sequencingNucleotide
The invention provides a sebastiscus marmoratus gene screening and mining method based on a simplified genome sequencing technology, and belongs to the technical field of molecular marker development. The method comprises steps as follows: genome DNA extraction; genome DNA double digestion; linkage connection; PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification; sequence fragment recovery and high-throughput sequencing; data analysis and screening and gene locus mining. According to the method, extracted DNA has higher quality, enzyme cleavage rate is effectively increased, primer design difficulty is reduced, recovered fragments have more uniform size, the sequencing amount is larger, and a sequencing result is more accurate; areas such as a high-repetition area and the like with relatively higher methylation degree can be avoided, so that enzyme cleavage fragments with more specific sequences are collected, and marking effectiveness of SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) for following identification is higher; obtained nucleic acid molecules have quite low preference and high complexity, and therefore, the maximum gene coverage is obtained with the least sequencing data during sequencing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
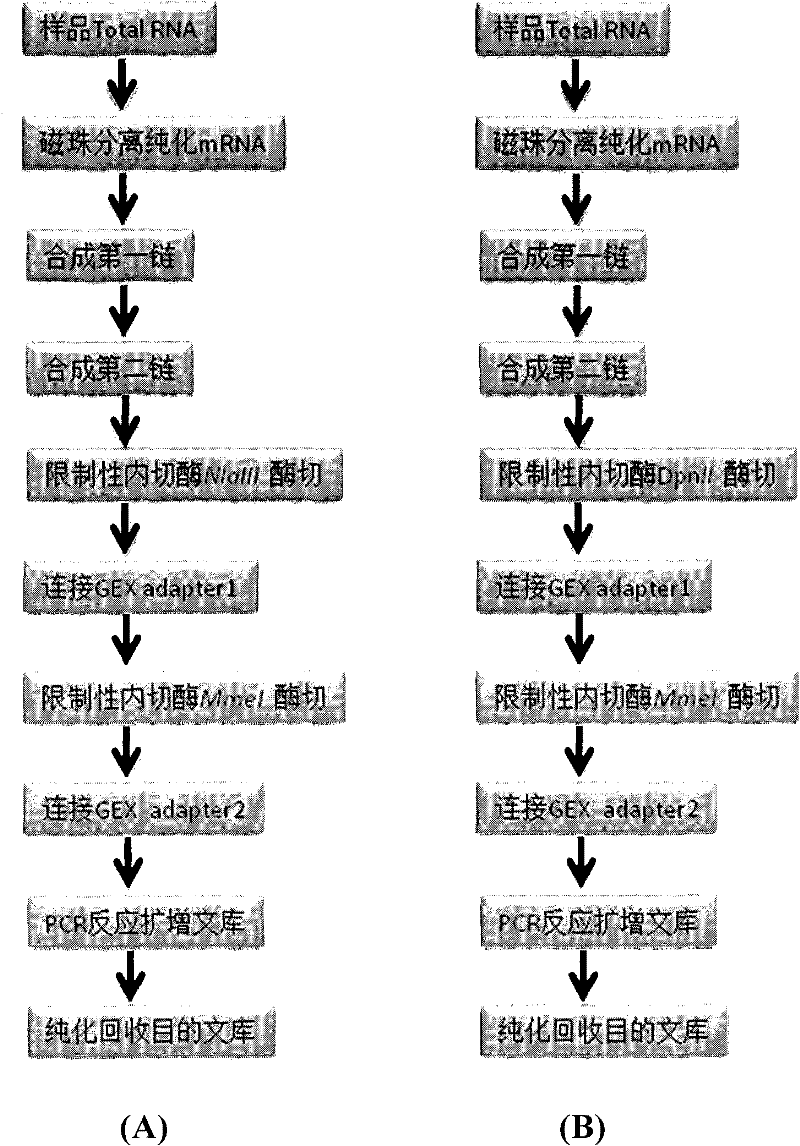
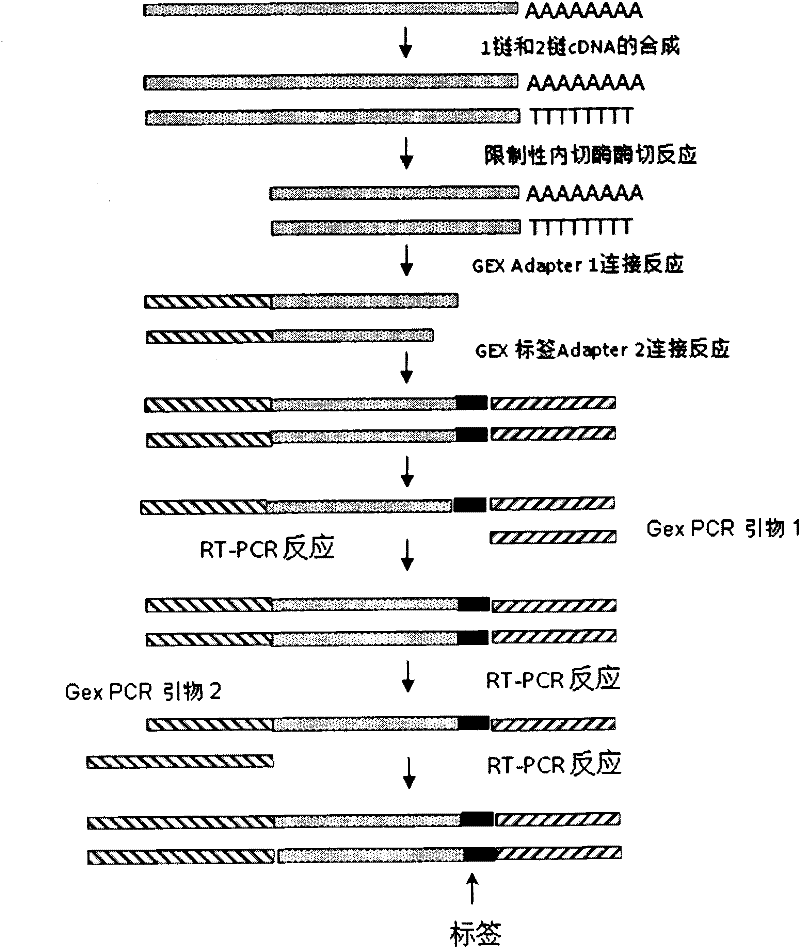
Indexes for digital gene expression profiling (DGE) and use method thereof
ActiveCN102409044AHigh sequencing throughputLow costNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyGene expression profiling
In the invention, a unique index sequence (index1-12) is designed aiming at a digital gene expression profiling (DGE) library sample building method based on a Solexa Single End sequencing platform provided by the current illumina company, and indexes are embedded in a 3' adapter in a DGE library by adapters, thus successfully establishing a DGE index library building method. The method is suitable for building the DGE index library of any eukaryote RNA sample and is successfully used for solexa sequencing, thus not only increasing the sequencing throughput of the DGE samples but also lowering the cost of solexa aiming at DGE sequencing.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Enrichment medium for nitrate dependent ferrous oxidizing flora, preparation method and application
InactiveCN107557312AAvoid changeGood varietyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetateMicrobial genetics
The invention discloses an enrichment medium for nitrate dependent ferrous oxidizing flora, a preparation method and an application. The enrichment medium is prepared from calcium chloride, potassiumchloride, magnesium chloride, ammonium chloride, monopotassium phosphate, sodium acetate, SL-10, piperazine-1,4-bisethanesulfonic acid, ferrous sulfate, sodium nitrate and vitamin B1 in certain ratio.The preparation method comprises steps as follows: (1), preparation of the medium: a solution A, a solution B and a solution C are prepared; (2), sterilization of the medium: a sterilization method for the solution A and the solution C comprises the step that suction-filtration sterilization is performed by a polyether sulfone membrane under the aseptic condition, and a product is standby; (3), sterilization of the solution B: the sterilized solution A, solution B and solution C are sequentially poured into a culture flask for subpackaging, and a sterile culture solution is obtained. Microbial genetic information obtained after three generations or more of enrichment subculture and high-throughput sequencing is high in flux and specificity, defects of a traditional screening culture method are overcome, and information of nitrate dependent ferrous oxidizing flora in the environments such as soil, sediment, underground water and the like is disclosed comprehensively and accurately.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Detection probe, kit and method for Dystrophin gene
PendingCN111607642AEasy to detectImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBioinformaticsBiological organism
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a Dystrophin gene detection probe, a kit and a method. The invention also relates to a design method of the probe. The primerand the kit provided by the invention can be combined with a three-generation sequencing method to effectively sequence the human Dystrophin gene and analyze mutation in the human Dystrophin gene.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH
a gene sequencing device
ActiveCN102604826BSimple structurePrevent malfunctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlGene
The invention relates to the field of biochemical equipment and provides gene sequencing equipment, which comprises a sequencing reaction chamber and a temperature control component. The sequencing reaction chamber is used for fixing samples and performing sequencing reaction; the temperature control component is fixed in an area of the sequencing reaction chamber when the samples are fixed and used for controlling temperature of the sequencing reaction chamber. The temperature of the sequencing reaction chamber rises and decreases quickly by the temperature control component, and sequencing reaction efficiency is improved.
Owner:盛司潼
Construction method and application of sequencing library of circular small non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
PendingCN113684247AImprove accuracyIncrease credibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCulture cellTotal rna
The invention relates to a construction method and application of a sequencing library of circular small non-coding RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing cells; (2) extracting total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from the cells; (3) extracting RNA by using a small RNA extraction kit, and removing 28S and 18S rRNA; (4) further removing 5S and 5.8 S rRNA by an RAP method; (5) removing linear RNA; and (6) constructing the sequencing library of the circular small non-coding RNA. The constructed sequencing library of the circular small non-coding RNA has the advantages of few rRNA residues, high detection efficiency of the circular RNA, high sequencing flux, better data repeatability and high success rate of verification of a sequencing result. The whole method is simple and convenient to operate, low in cost and time consumption, high in stability and very good in repeatability and reliability.
Owner:深圳市龙华区中心医院
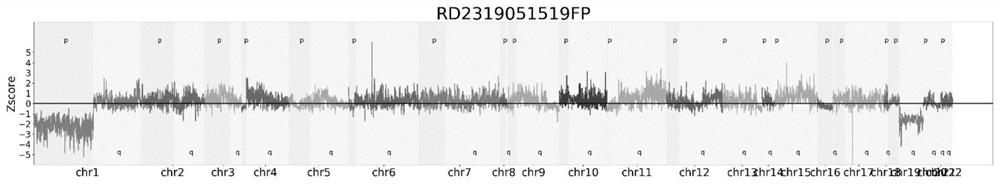
A method and system for analyzing chromosomal aneuploidy
ActiveCN111091868BImprove detection accuracyReduce the impact of the result judgmentBiostatisticsProteomicsStatistical analysisAllele frequency
The invention provides a chromosome aneuploidy analysis method and a chromosome aneuploidy analysis system. According to the method, sample sequencing depth is subjected to statistical analysis basedon a Zscore algorithm, and the condition of chromosome aneuploidy is comprehensively judged in combination with statistical analysis of SNP allele frequency of samples. The method provided by the invention is high in accuracy, is not influenced by the SNP locus number of a sample to be detected, has high specificity and sensitivity (up to 100%), and can also be used for judging whether abnormal chromosomes are deleted or amplified.
Owner:SIMCERE DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +2
Gene sequencing device and system
ActiveCN102517206BFully automatedImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenetic engineeringComputer science
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a gene sequencing device and a gene sequencing system. The gene sequencing device comprises a sample preparation component, a liquid conduction component, a sample loading component, a temperature control component, an image acquisition component and a control component. The gene sequencing system comprises a sample preparation control module, a liquid conduction control module, a reaction control module, a temperature control module, an image acquisition control module and a control module. By adopting the gene sequencing device and the gene sequencing system, the integration from sample preparation to data processing can be realized, and full automation of gene sequencing can also be realized. Meanwhile, the high-pass and low-cost gene sequencing can be realized.
Owner:盛司潼
Nucleic acid detection reaction platform and nucleic acid detection system
ActiveCN103087909BAccurate temperature controlHigh-throughput sequencingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlNucleic acid detection
The invention relates to the field of biochemical equipment, and provides a nucleic acid detection reaction platform. The nucleic acid detection reaction platform comprises a temperature control component, a control component and at least two sequencing reaction chambers, wherein the control component is used for adjusting set temperature to target temperature and controlling a sequencing reaction to reach the target temperature from the current temperature and further used for sending a target temperature instruction to the temperature control component; the temperature control component is used for heating or cooling the sequencing reaction according to the target temperature instruction of the control component, and measuring and feeding back the current temperature of the sequencing reaction in real time; and the sequencing reaction chamber is used for parallel sequencing. The invention further provides a nucleic acid detection system containing the nucleic acid detection reaction platform. The nucleic acid detection reaction platform and the nucleic acid detection system related by the invention can improve the quality of the sequencing reaction and further can improve the sequencing throughput.
Owner:盛司潼
Novel tetracycline resistance gene tetX and application thereof
PendingCN113481215AHigh sequencing throughputRead longMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesNucleotide sequencMolecular biology
The invention discloses a novel tetracycline resistance gene tetX and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the novel tetracycline resistance gene tetX is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the potential tetracycline resistance gene tetX found in the invention, a database of the tetracycline resistance gene is supplemented, help is provided for understanding the resistance mechanism of tetracycline, and theoretical support is also provided for subsequent tetracycline action target research.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Novel tet34 resistance gene of tetracycline and application of novel tet34 resistance gene
PendingCN113502340AImprove accuracyHigh sequencing throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisResistant genesNucleotide
The invention discloses a novel tet34 resistance gene of tetracycline and application of the novel tet34 resistance gene. The nucleotide sequence of the tetracycline novel tet34 resistance gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the potential tetracycline resistance gene tet34 found in the application, a database of the tetracycline resistance gene is supplemented, help is provided for understanding the resistance mechanism of tetracycline, and a theoretical support is also provided for subsequent tetracycline action target research.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and equipment for predicting neoantigen epitopes
ActiveCN105524984BHigh sequencing throughputEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigen epitopeProtein level
The present invention provides a method and equipment for predicting neoantigen epitopes. The method for predicting neoantigen epitopes includes: (1) constructing a candidate epitope library, wherein the candidate epitope library is composed of differentially expressed peptides, and the expression differentially Peptides are peptides that differ between samples with the predetermined state and samples without the predetermined state; (2) building a predictive model based on a historical database composed of known antigenic epitope composition; and (3) using at least a subset of the candidate epitope library as an input variable of the prediction model, so as to predict new antigenic epitopes. Using this method of predicting neoantigen epitopes, it is possible to truly determine the mutation information of antigens from the gene level and protein level, and then quickly and effectively obtain neoantigen epitopes that can bind to MHC, and can accurately predict the relationship between antigen epitopes and NHC At the same time, the method is simple and convenient, and can greatly save manpower and material resources.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
Polymerase compositions and methods of making and using same
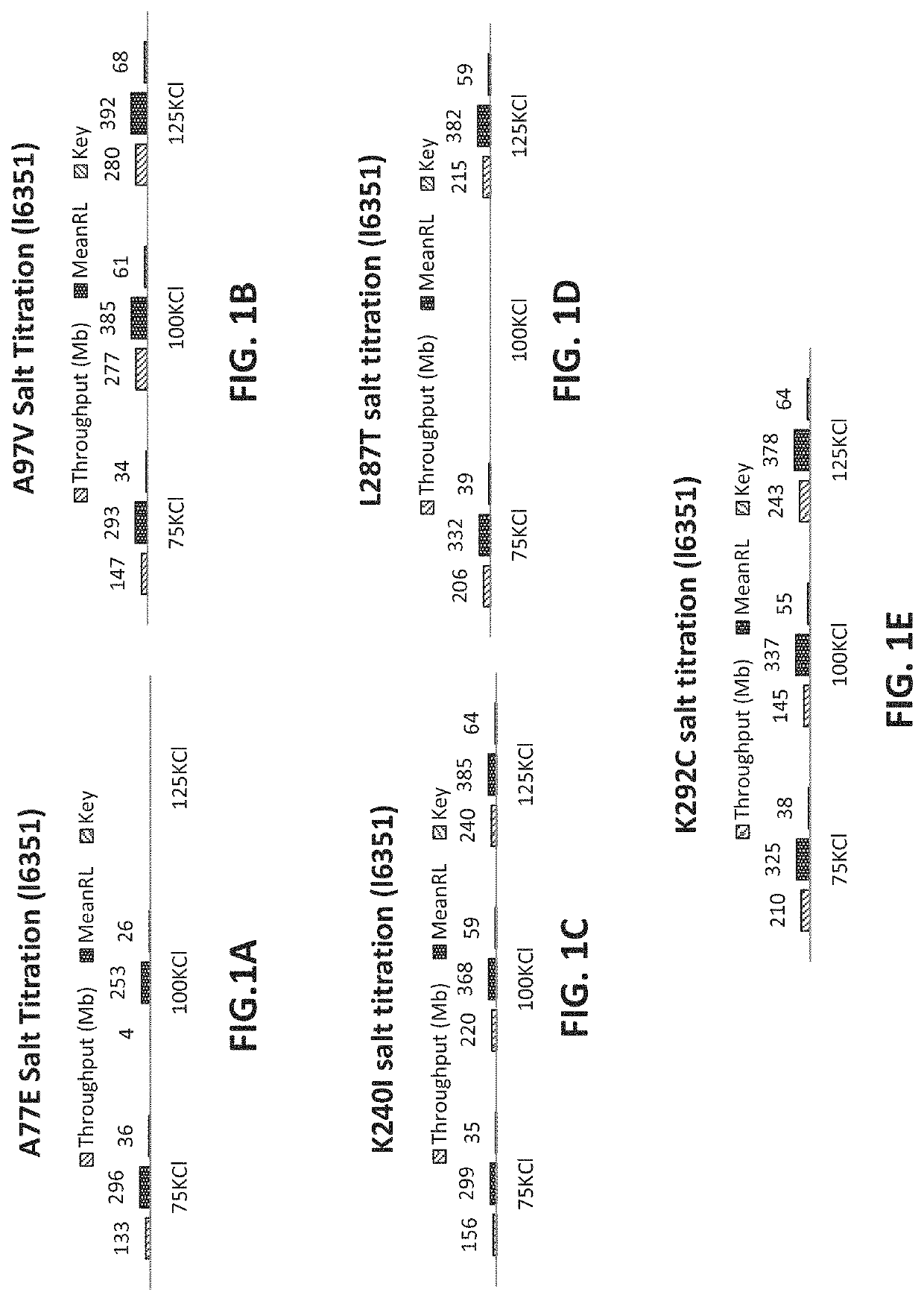
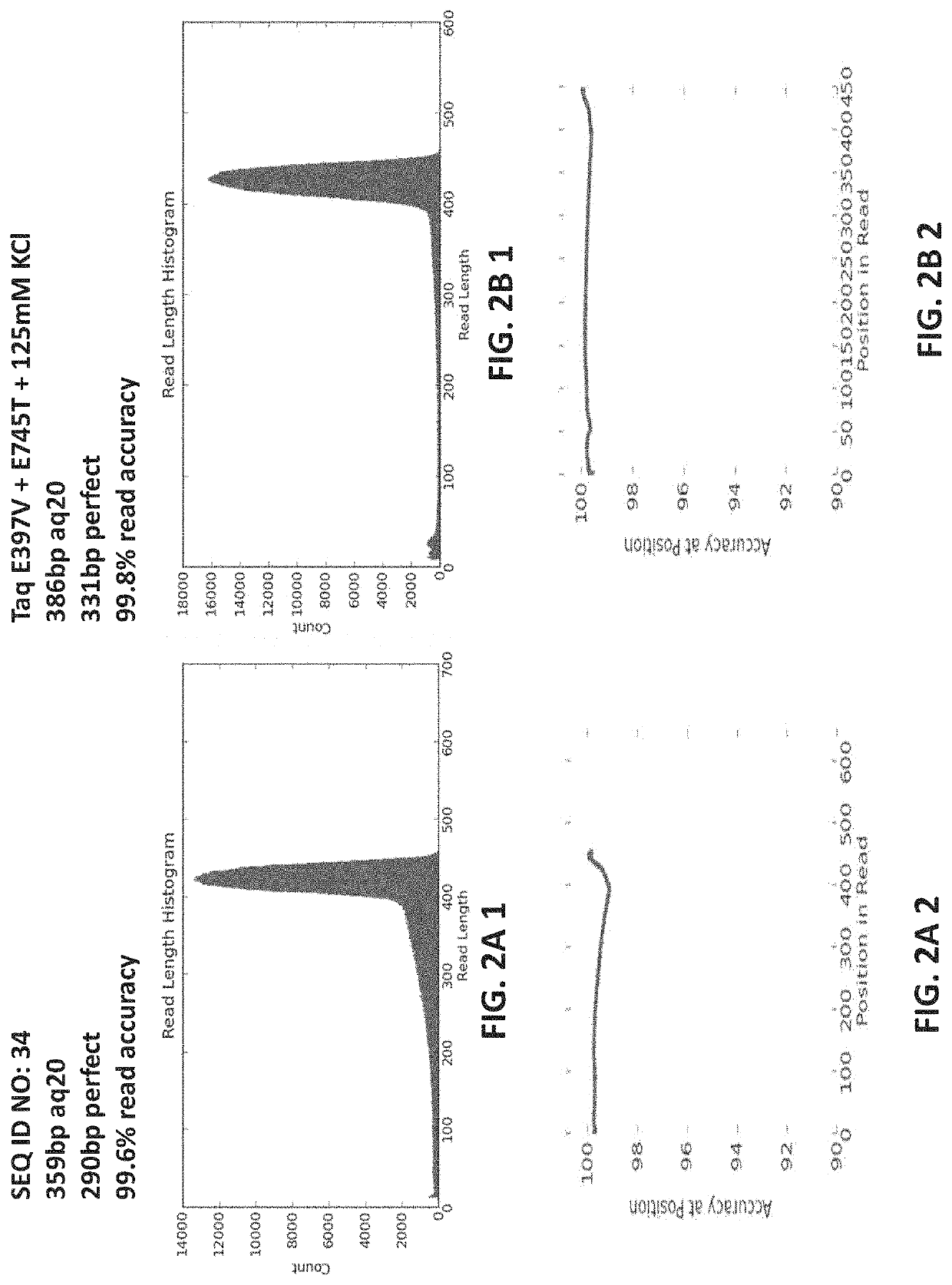
PendingUS20220307071A1Reduced strand biasExpand coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPHA polymeraseTaq polymerase
The present disclosure provides compositions, methods, kits, systems and apparatus that are useful for nucleic acid polymerization. In particular, modified polymerases and biologically active fragments thereof, such as modified Taq polymerases, are provided that allow for improved nucleic acid amplification. In some aspects, the disclosure provides modified polymerases having improved thermostability, accuracy, processivity and / or read length as compared to a referenceTaq polymerase. In some aspects, the disclosure relates to modified polymerases or biologically active fragments thereof, useful for amplification methods, and in practically illustrative embodiments, emulsion PCR.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
A method for high-throughput development of genomic SSR markers based on magnetic bead enrichment
ActiveCN104212879BReduce the difficulty of buildingImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a magnetic bead enrichment technique based method for high-flux development of genome SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers. The method comprises the steps of: (1) extracting target genome DNA; (2) subjecting the obtained genome DNA to random fragmentation; (3) constructing a genome random fragmented DNA library; (4) amplifying the DNA library; (5) utilizing a biotin labeled SSR probe to perform hybridization with a target fragment in the library; (6) carrying out streptavidin magnetic bead enrichment on the SSR sequence-containing DNA library fragments; (7) amplifying and purifying the enriched DNA library fragments; (8) subjecting the purified DNA fragments to emulsion PCR amplification and sequencing; and (9) searching sequences containing SSR loci in the obtained sequences. The method reduces the library construction difficulty, shortens the experimental period, improves the sequencing flux, lowers the sequencing cost, and can be widely used as an effective method for high-flux development of various species SSR markers.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for linking monomolecular DNA to single magnetic bead
InactiveCN101619353BEnabling Single Molecule SequencingHigh sequencing throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for linking monomolecular DNA to a single magnetic bead, belonging to the technical field of biology and comprising the following steps: performing fluorescence labeling to DNA, then labeling biotin at the end 3' of the DNA and labeling digoxin at the end 5' of the DNA; or labeling digoxin at the end 3' of the DNA and labeling biotin at the end 5' of the DNA; placing the DNA on glass to carry out an immunoreaction and washing the DNA by running water; carrying out the immunoreaction again; adding DNA endonuclease to the periphery of magnetic beads, after DNA molecules are degraded, collecting magnetic beads carrying DNA fragments one by one by a micro-gunpoint and placing the magnetic beads on a magnet; and cutting target DNA by the endonuclease and linking target DNA fragments with the DNA fragments on the magnetic beads under the action of ligase. The method for linking the monomolecular DNA to the single magnetic bead can acquire the sequence information of target fragments and realize the monomolecular sequencing of the DNA; and when nano-pores are produced into an array to be matched with a decoy array, sequencing throughput can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Three-color high-throughput sequencing reagent and sequencing method
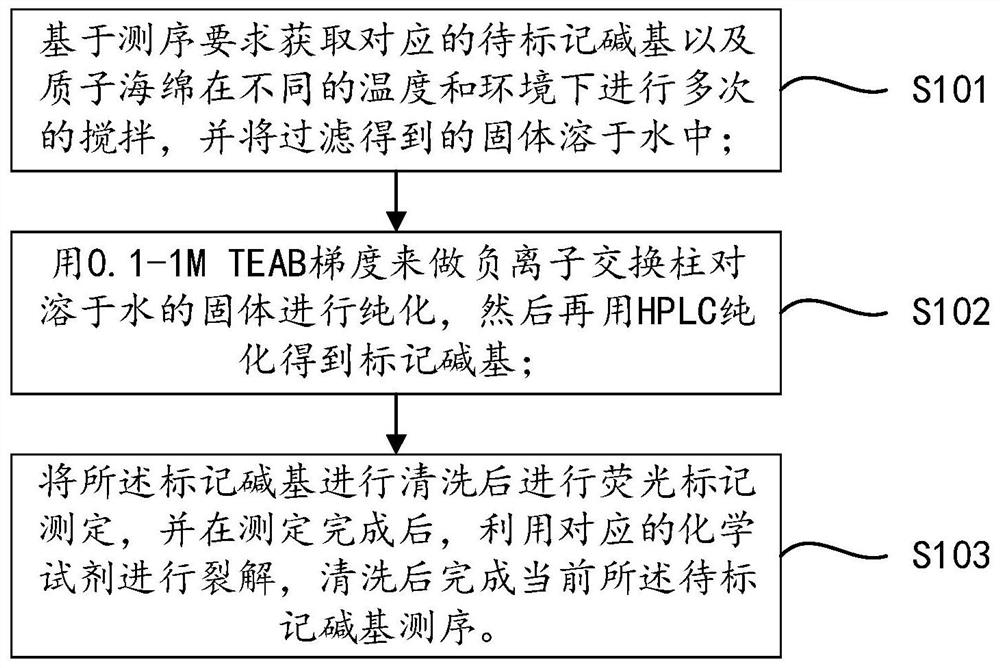
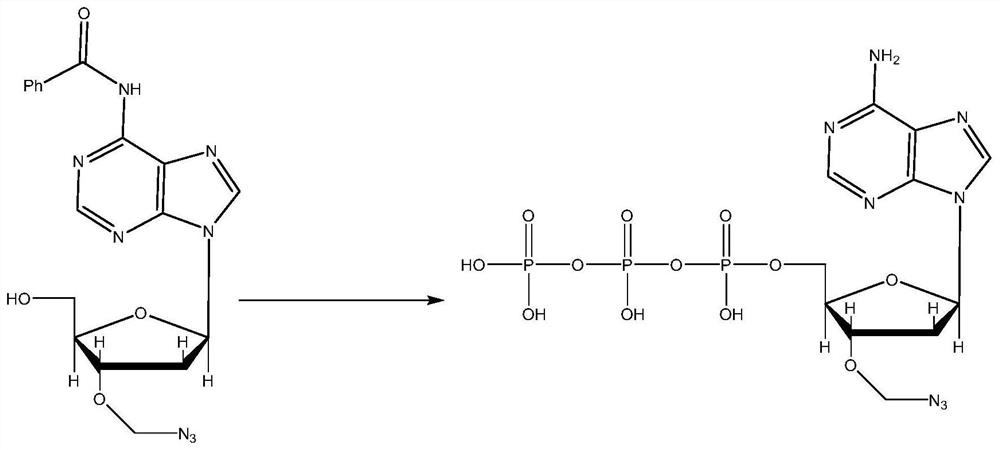
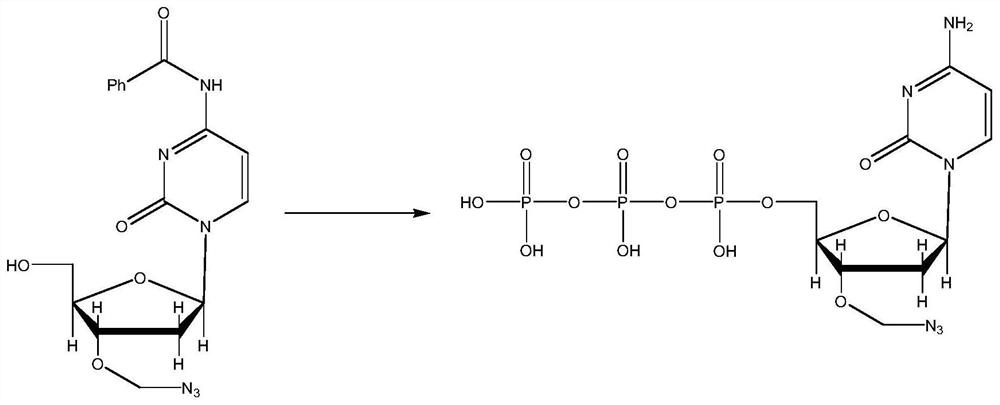
PendingCN113341058AFast sequencingSequencing length is not affectedComponent separationHigh fluxIon exchange
The invention belongs to the field of high-throughput sequencing, and discloses a three-color high-throughput sequencing reagent and a sequencing method. The method comprises the steps that corresponding to-be-labeled basic groups and proton sponge are obtained on the basis of sequencing requirements and stirred for multiple times under different temperatures and environments, and solids obtained through filtering are dissolved in water; a TEAB gradient is used as a negative ion exchange column to purify a solid dissolved in water, and then HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) is used for purifying to obtain a labeled basic group; the labeled basic group is cleaned and then subjected to fluorescence labeling determination, after determination is completed, a corresponding chemical reagent is used for splitting, sequencing of the current to-be-labeled basic group is completed after cleaning, the processes of reaction, cleaning, basic group reading, splitting and cleaning are circularly conducted on each sequencing process, the used three-color sequencing technology accelerates the sequencing speed like a two-color sequencing technology, base signals are not separately detected, and the sequencing length is not influenced and is increased, so that the sequencing efficiency and the sequencing flux are improved.
Owner:NANJING SUPERYEARS GENE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com