Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89results about How to "Easily advanced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
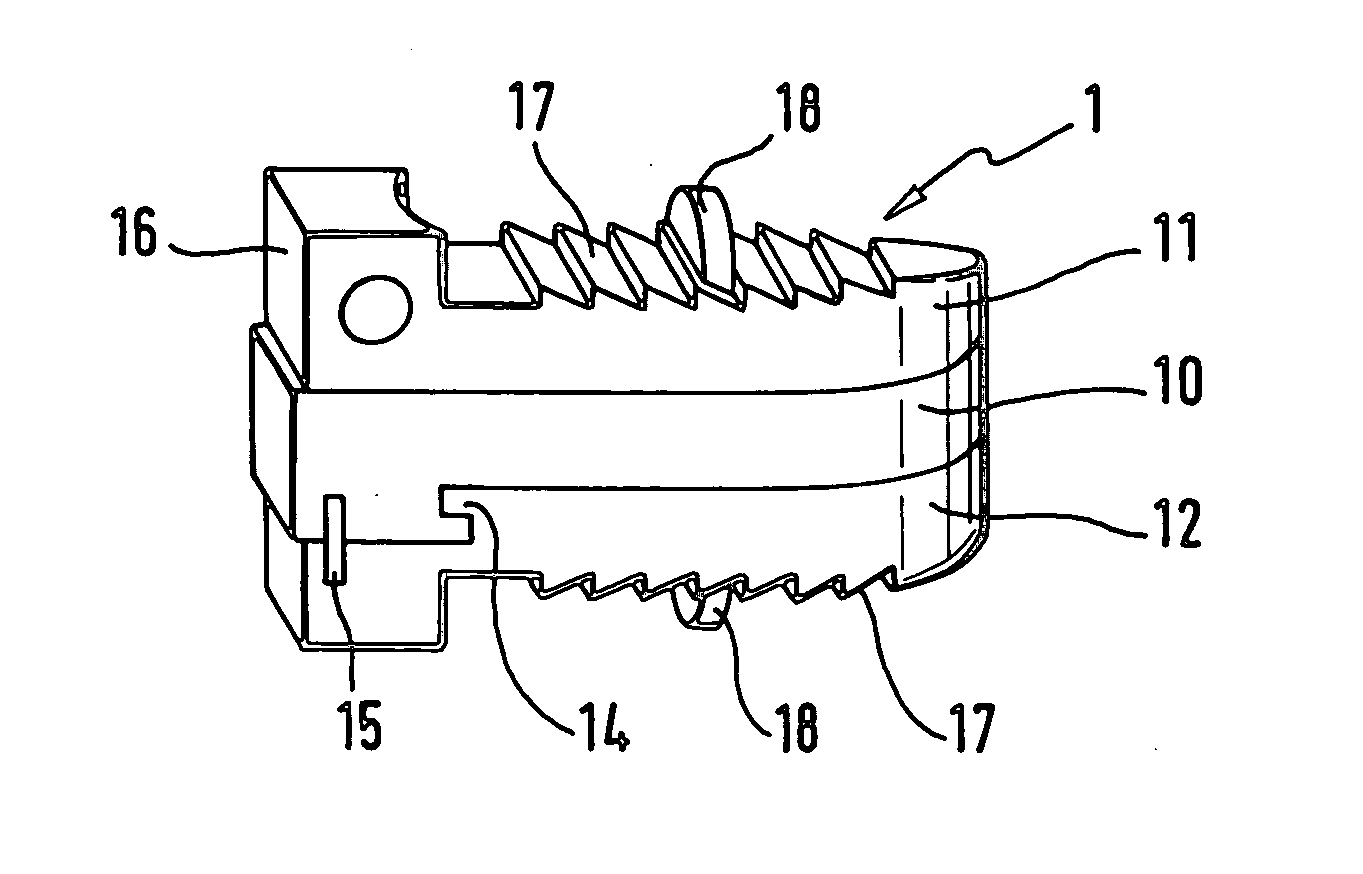
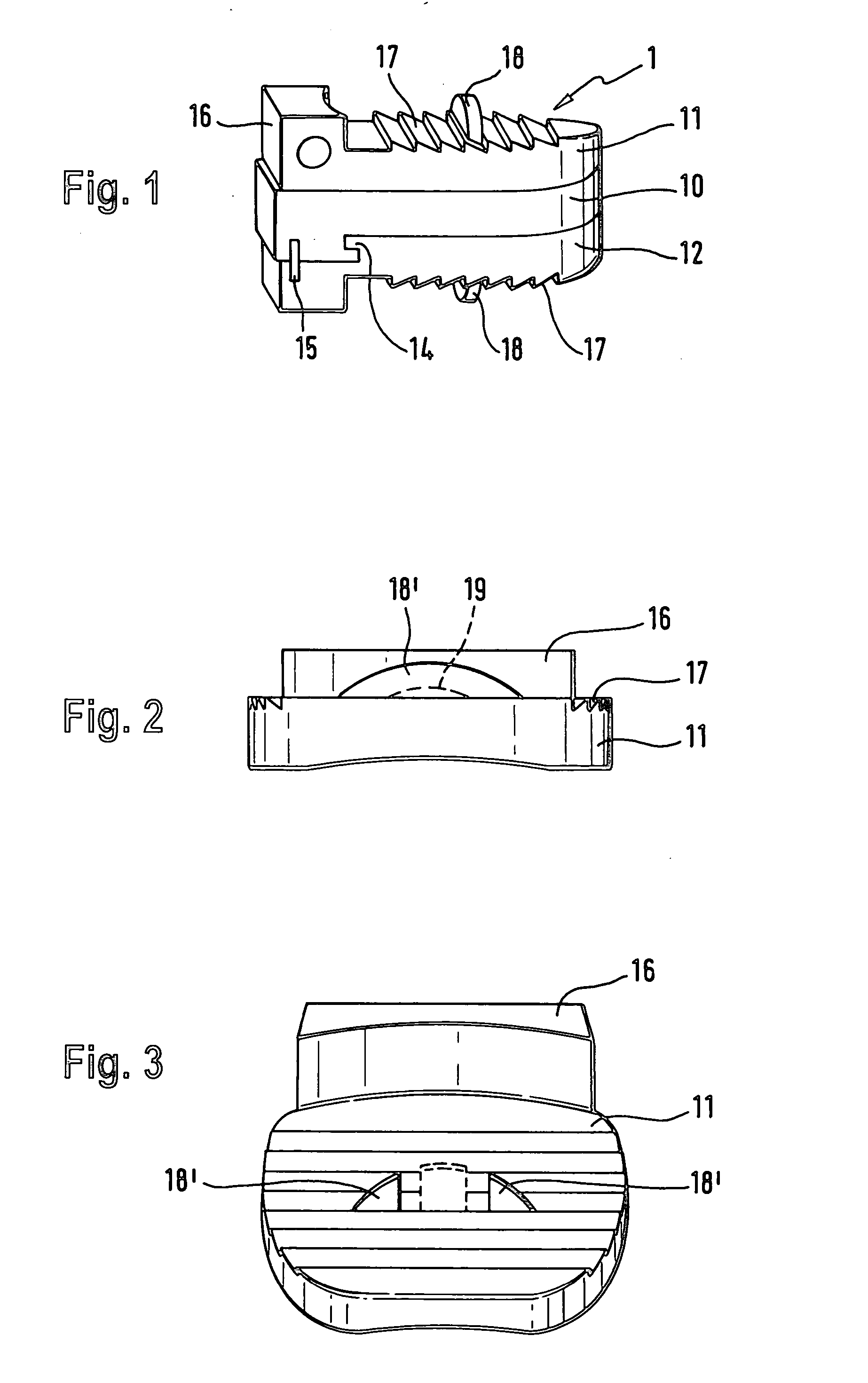
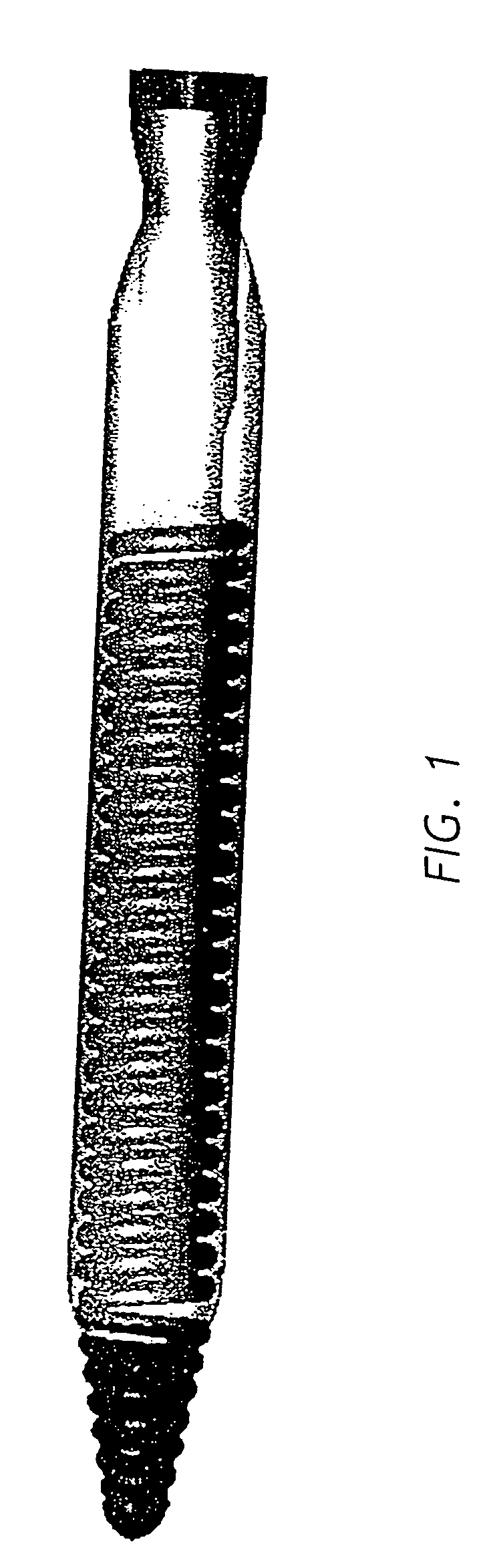
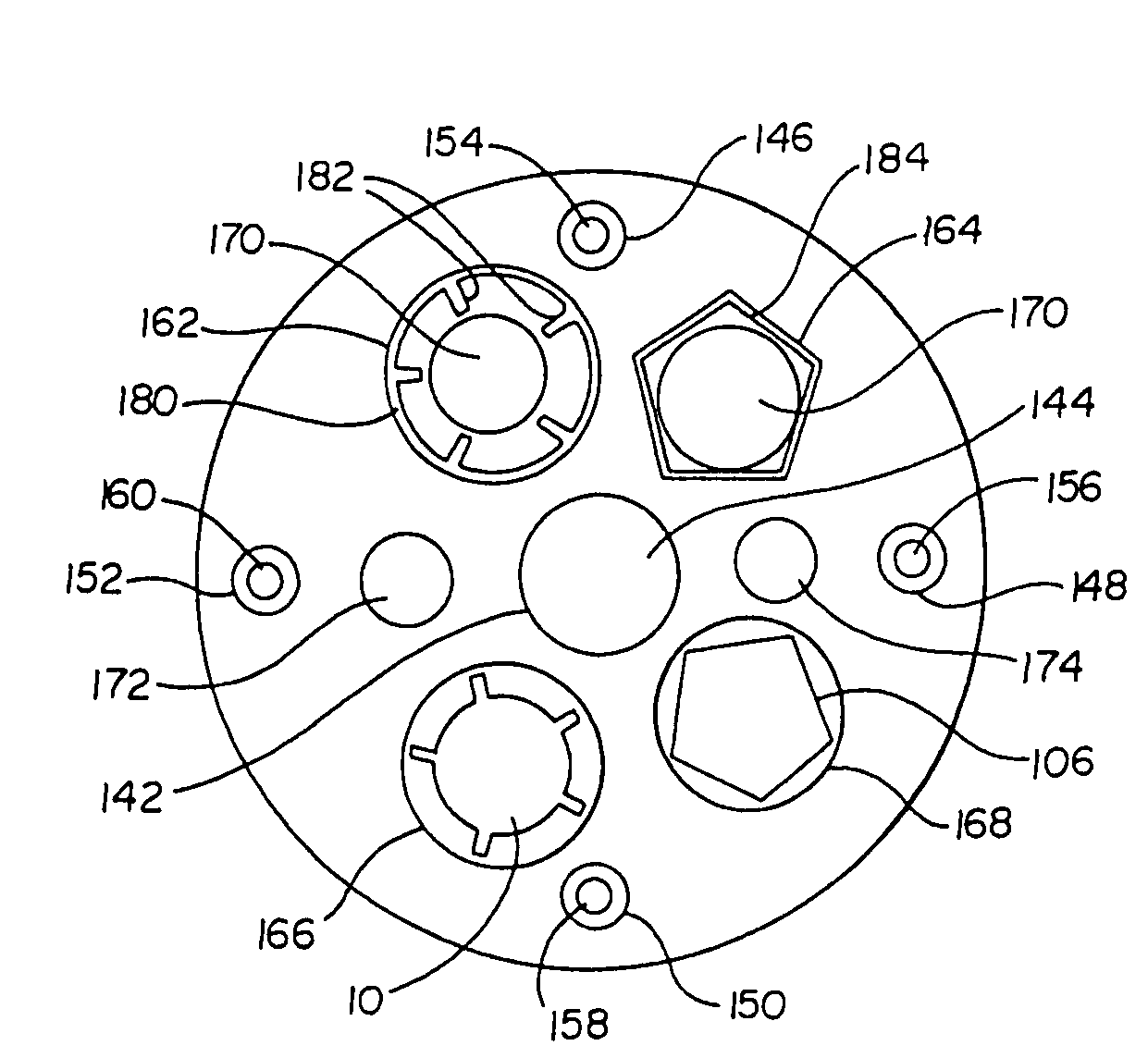
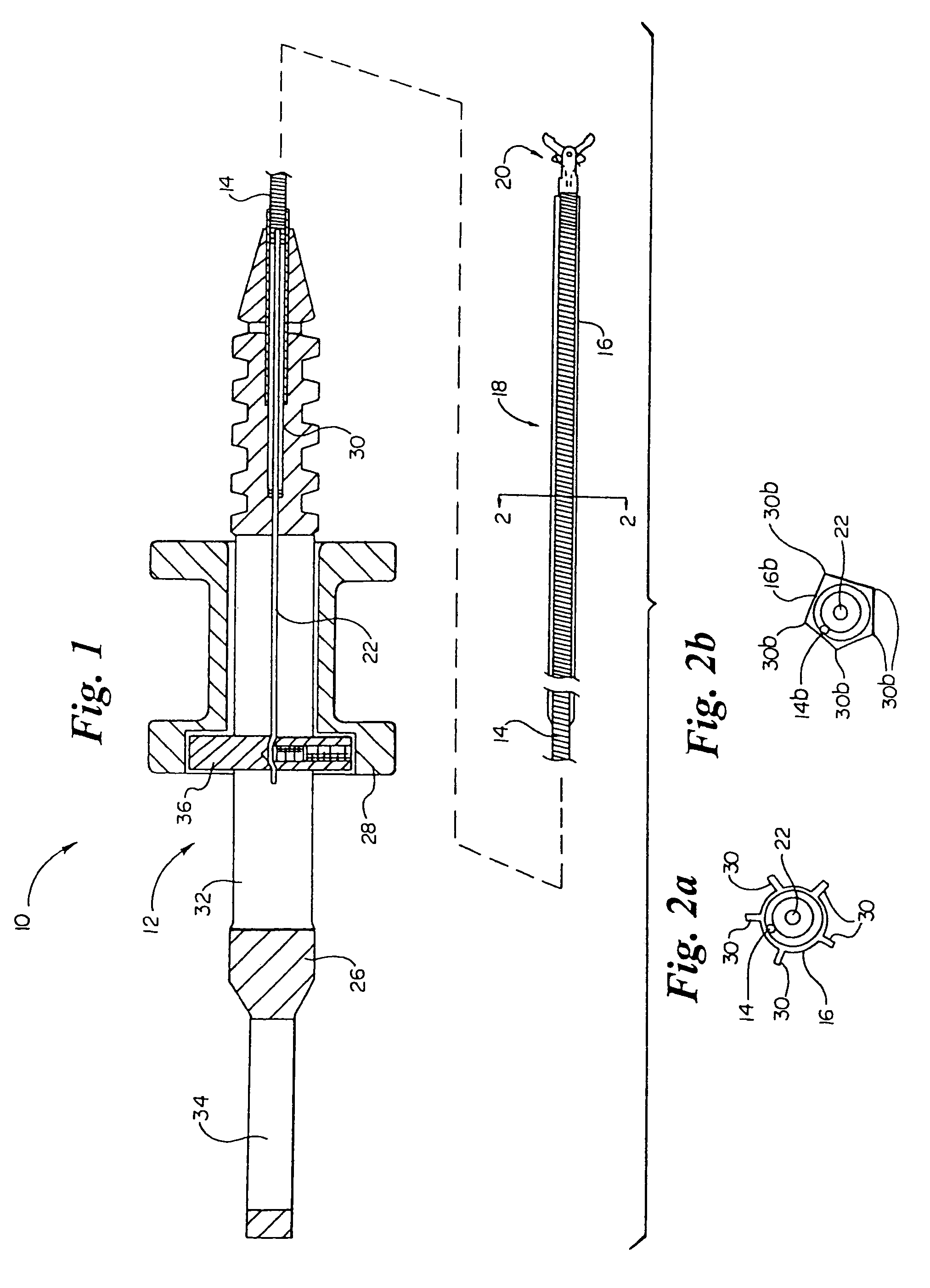
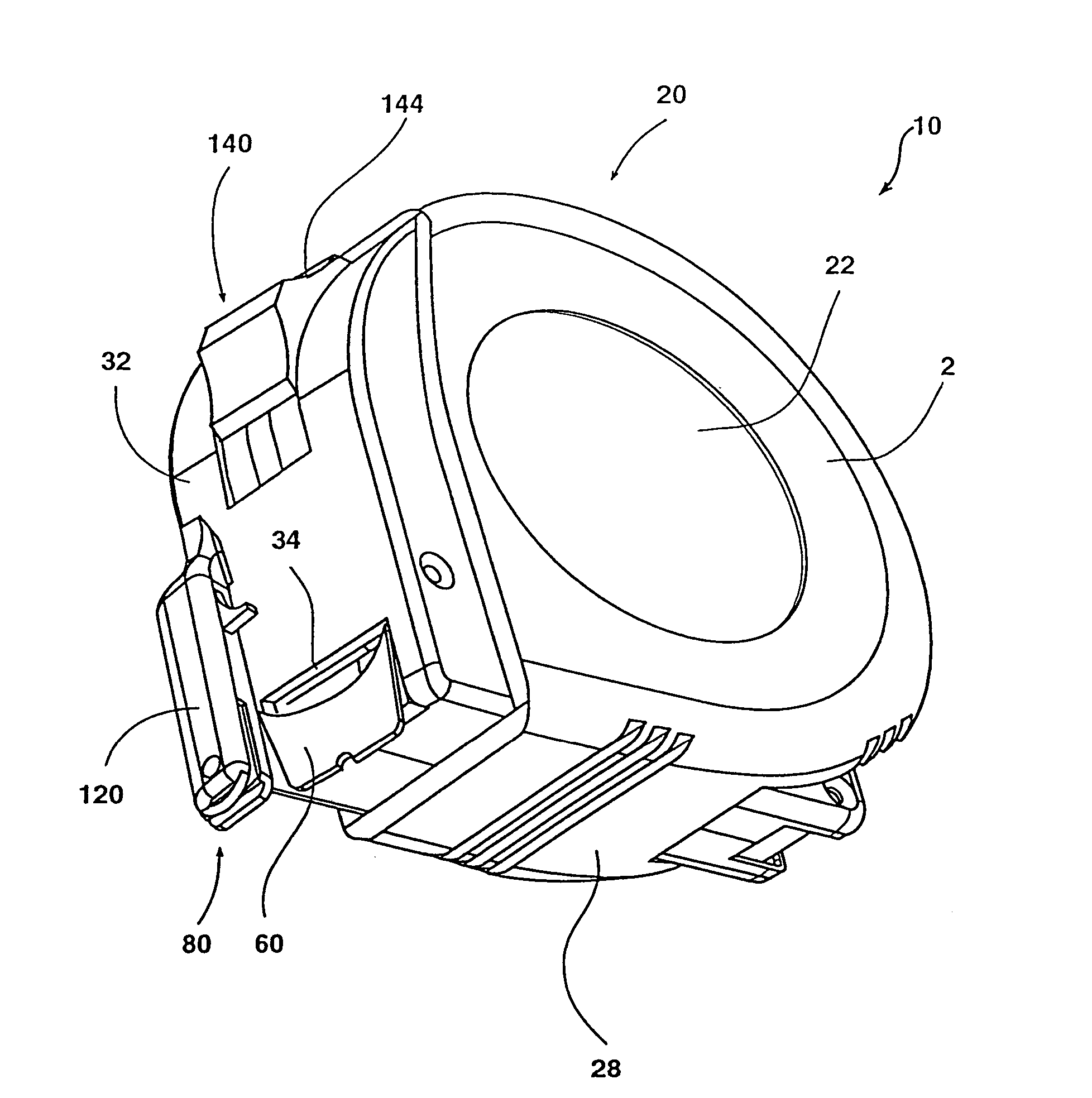
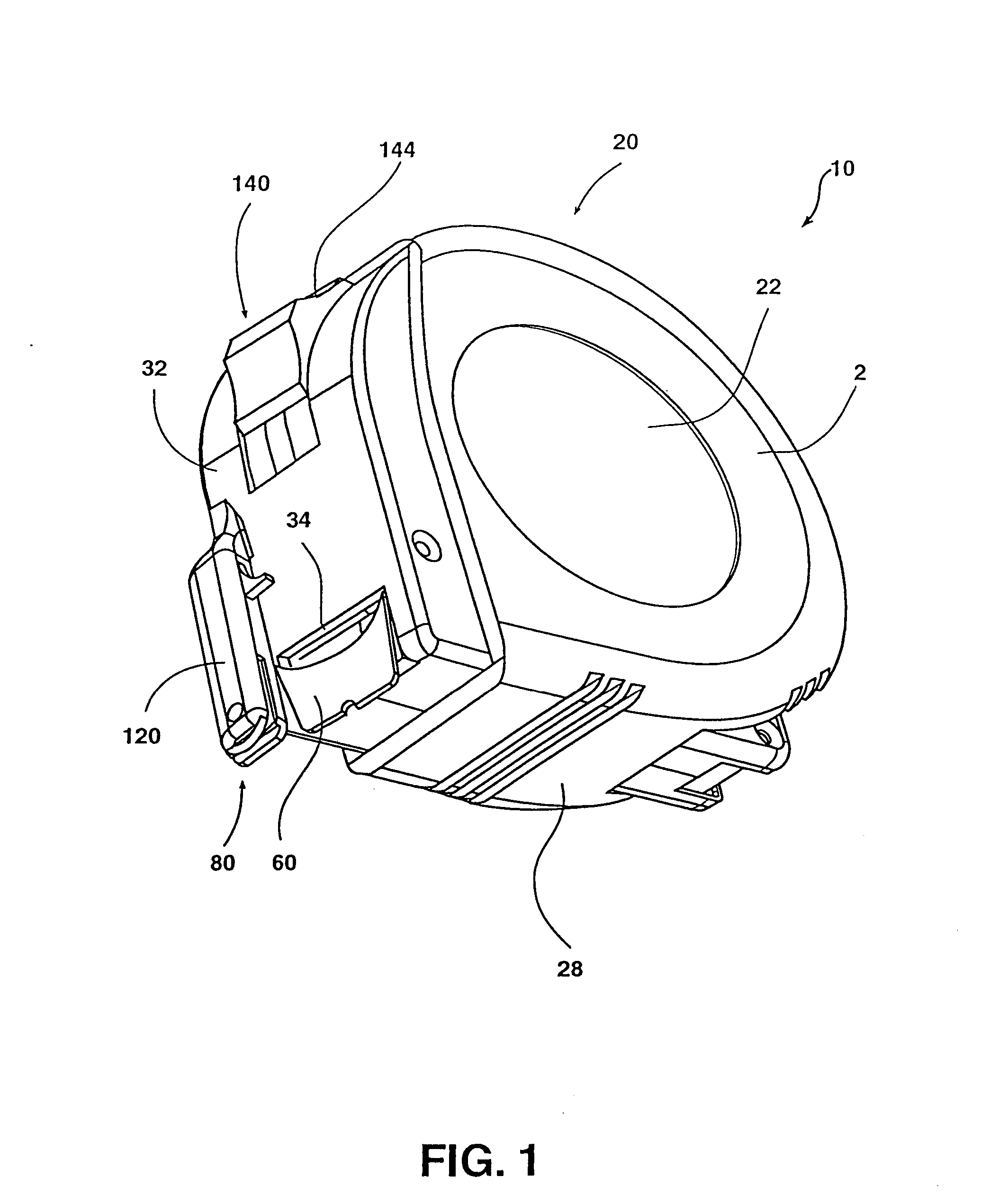
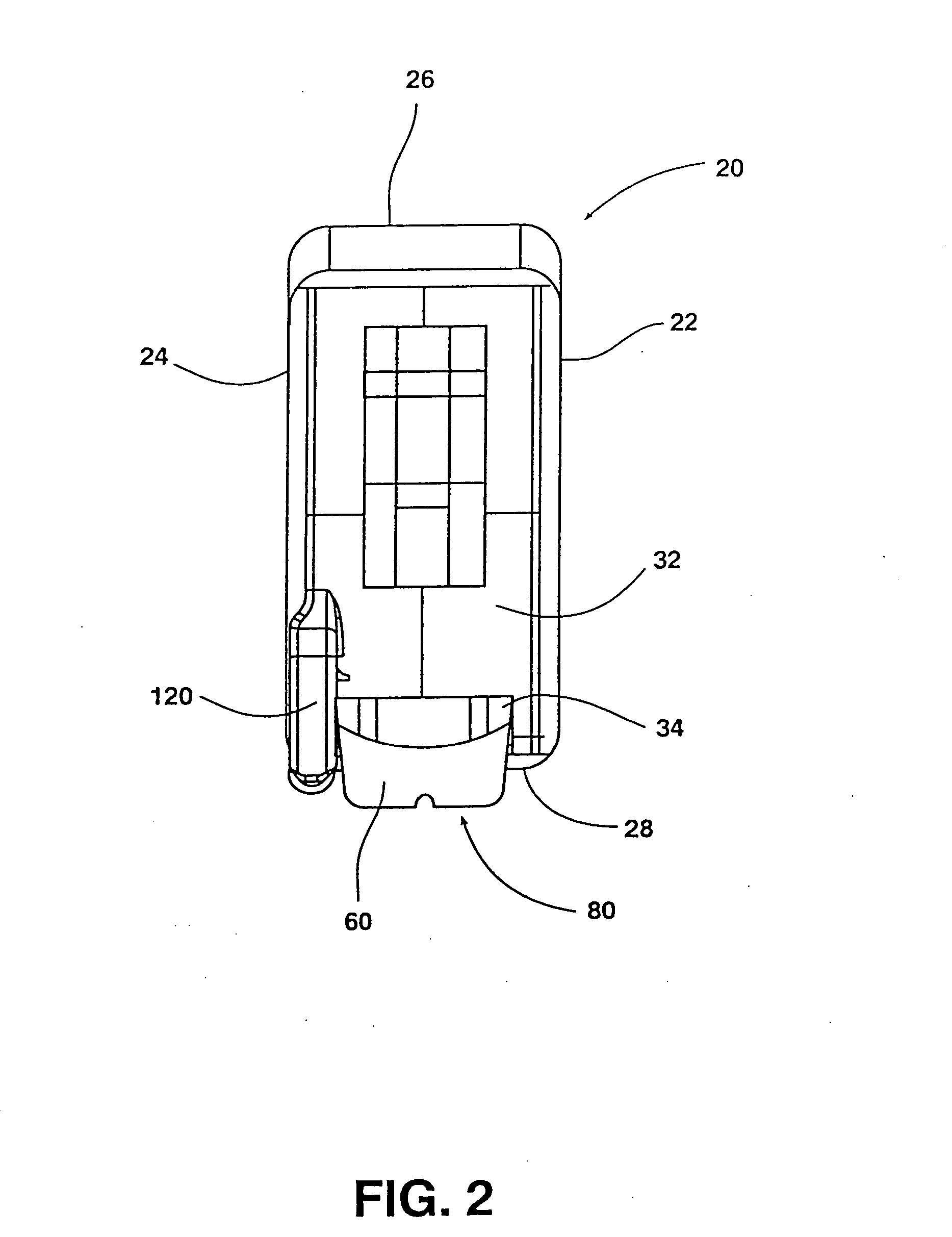
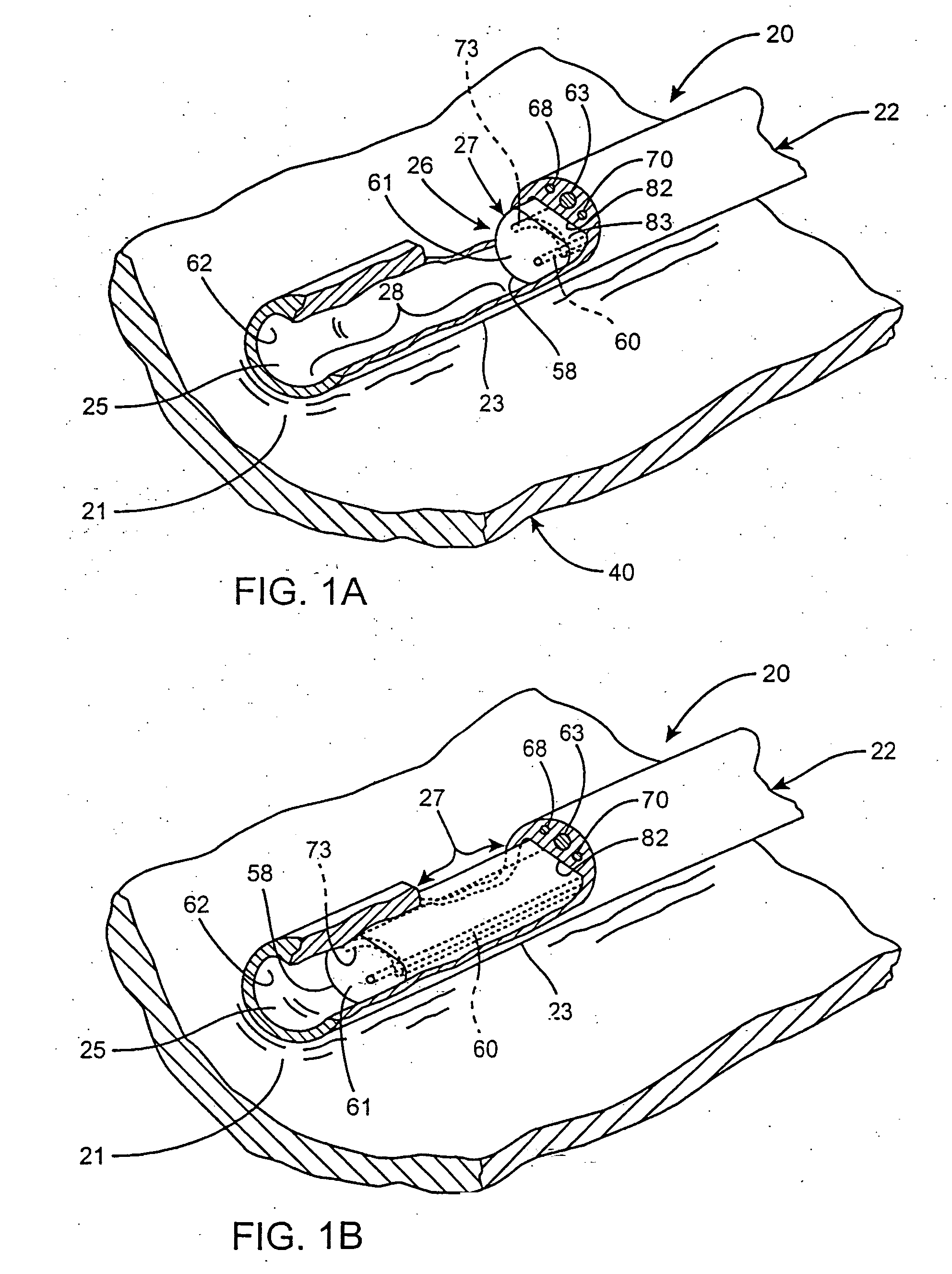
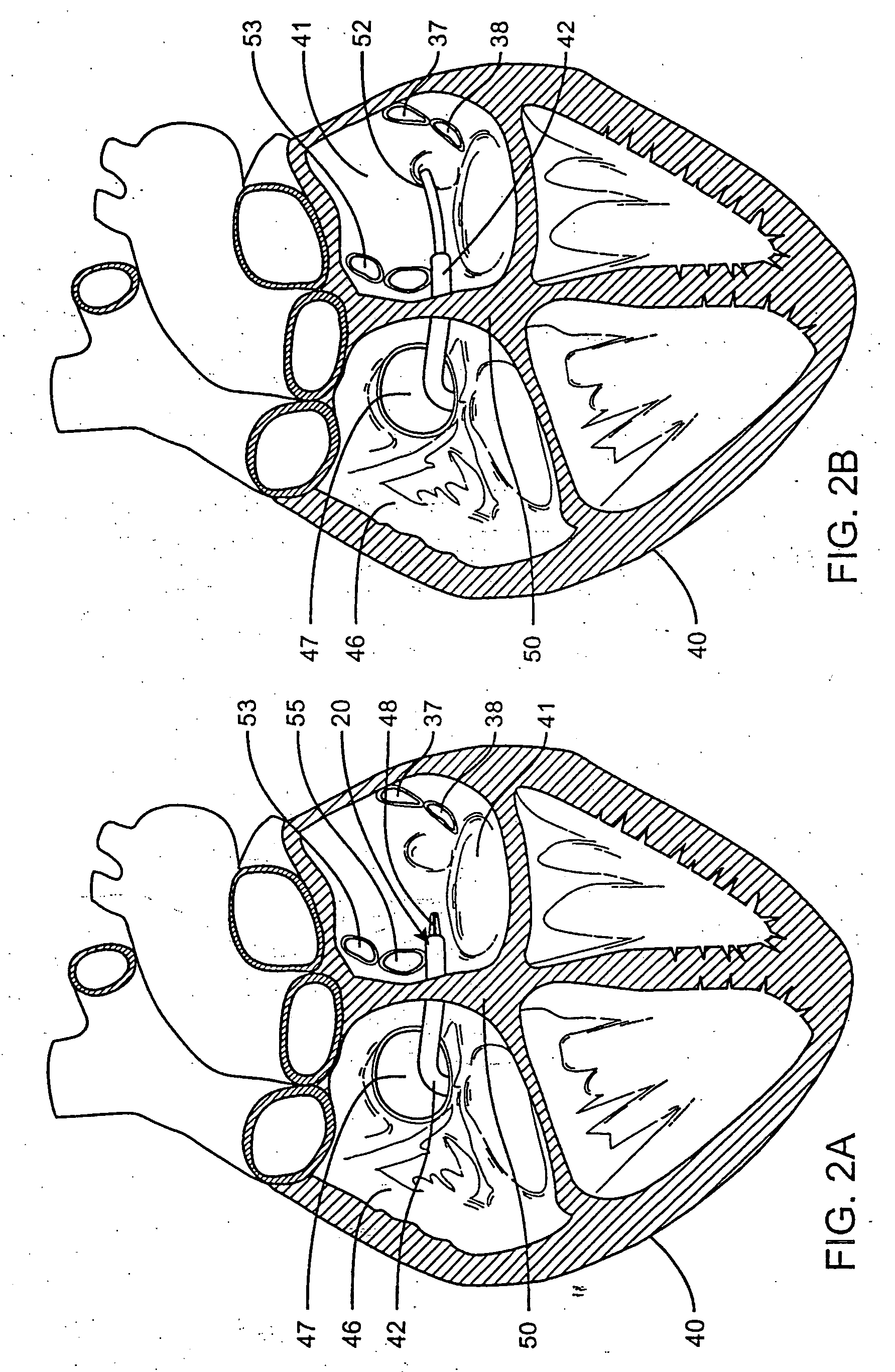
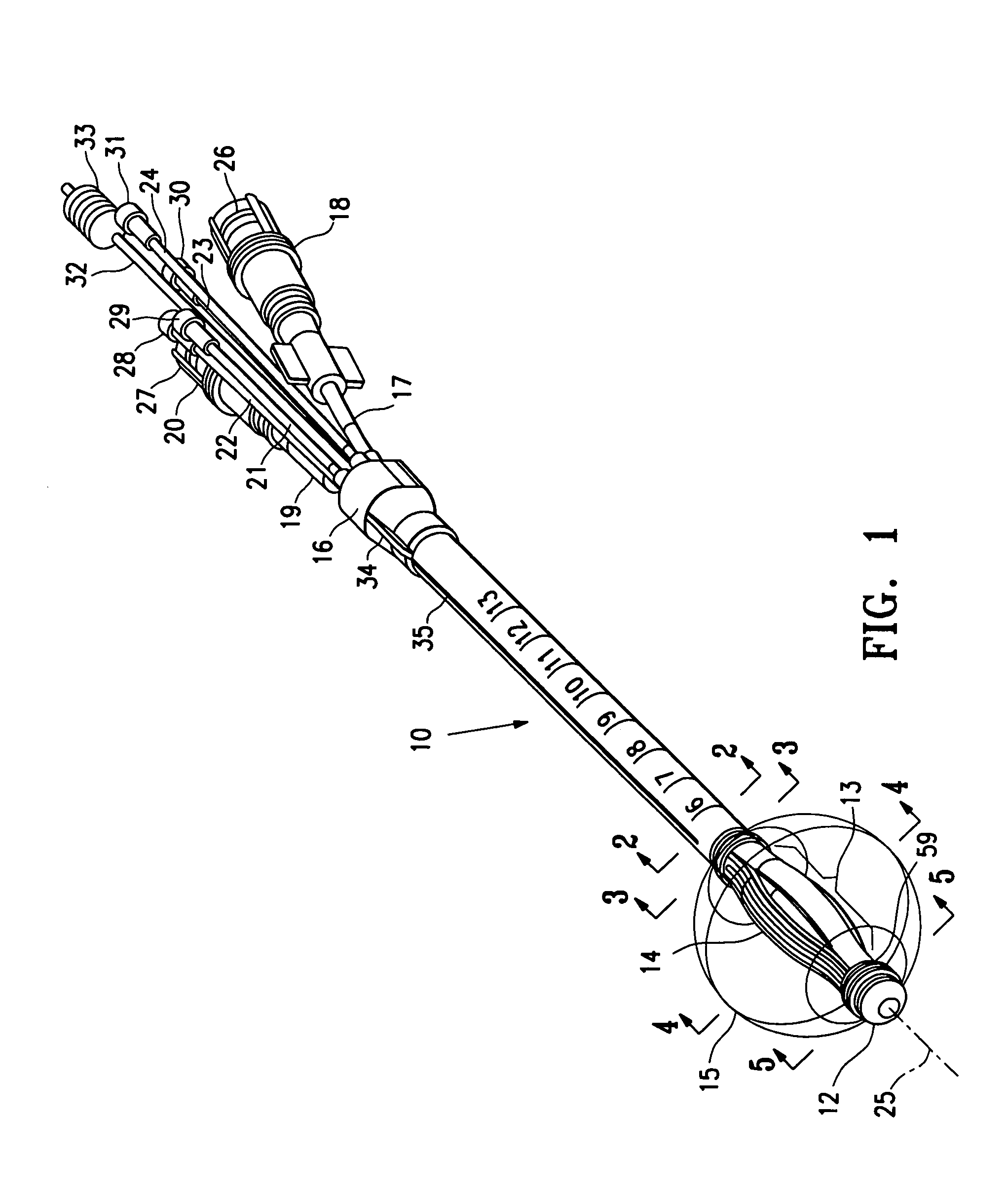
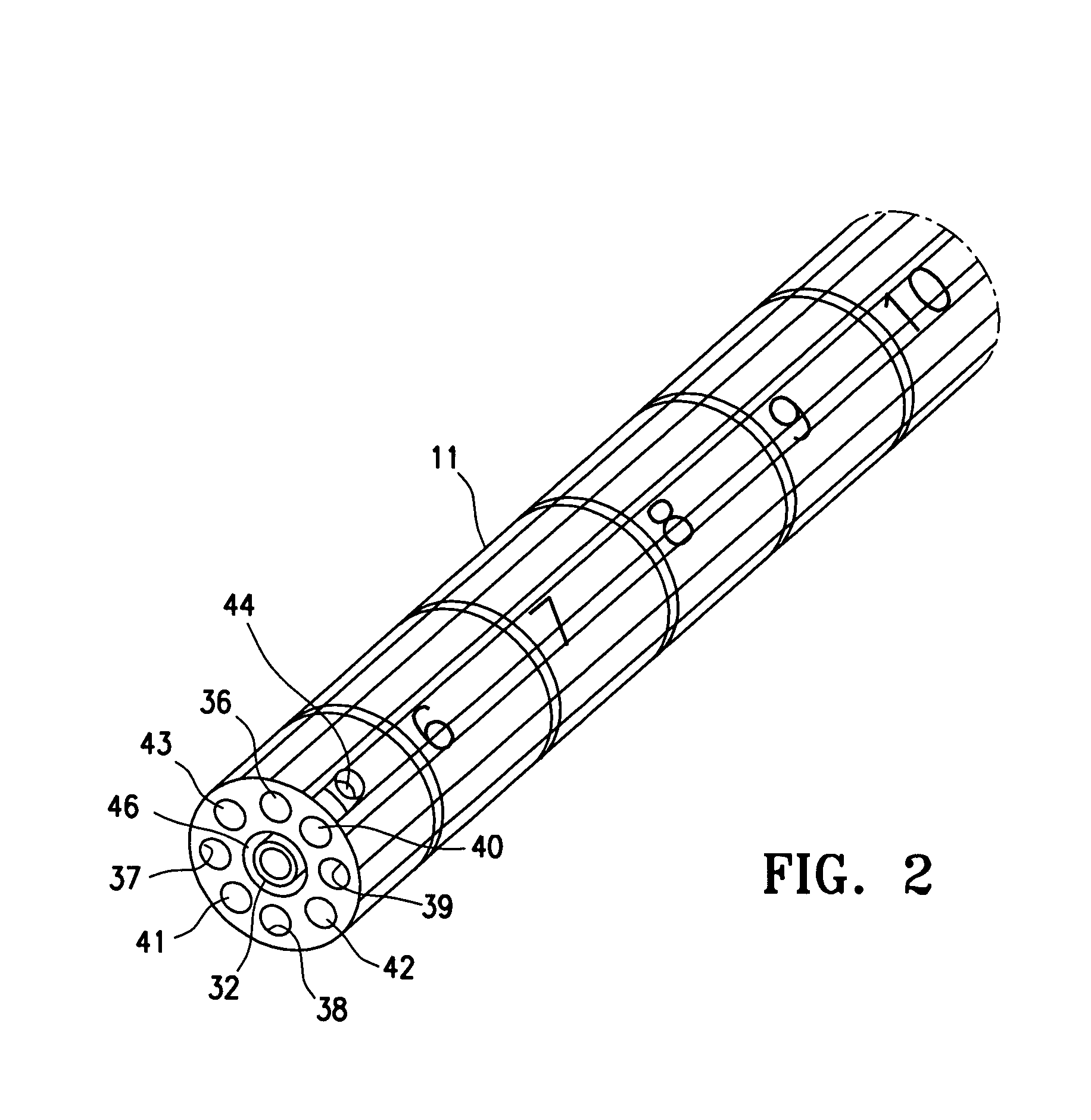
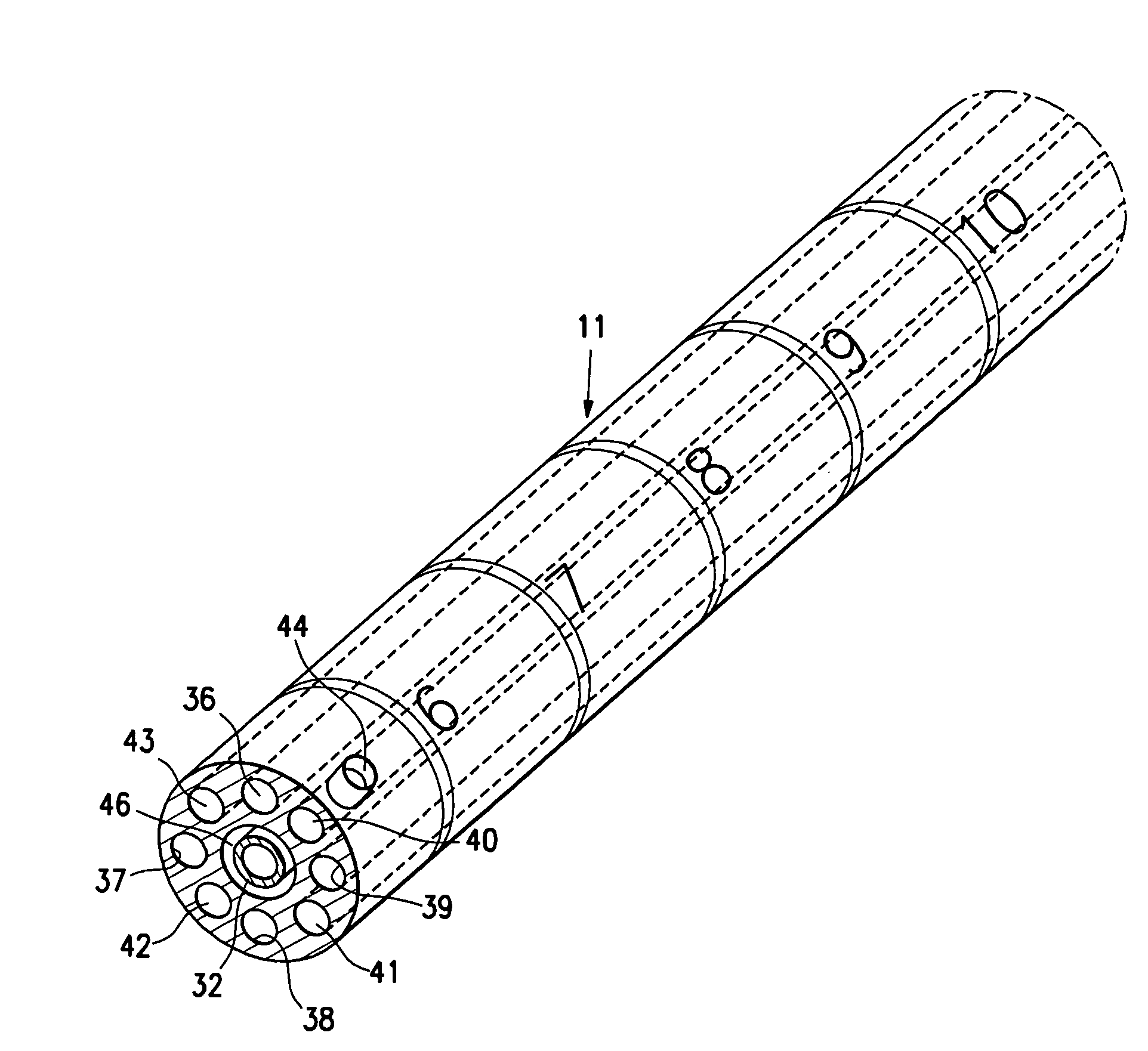
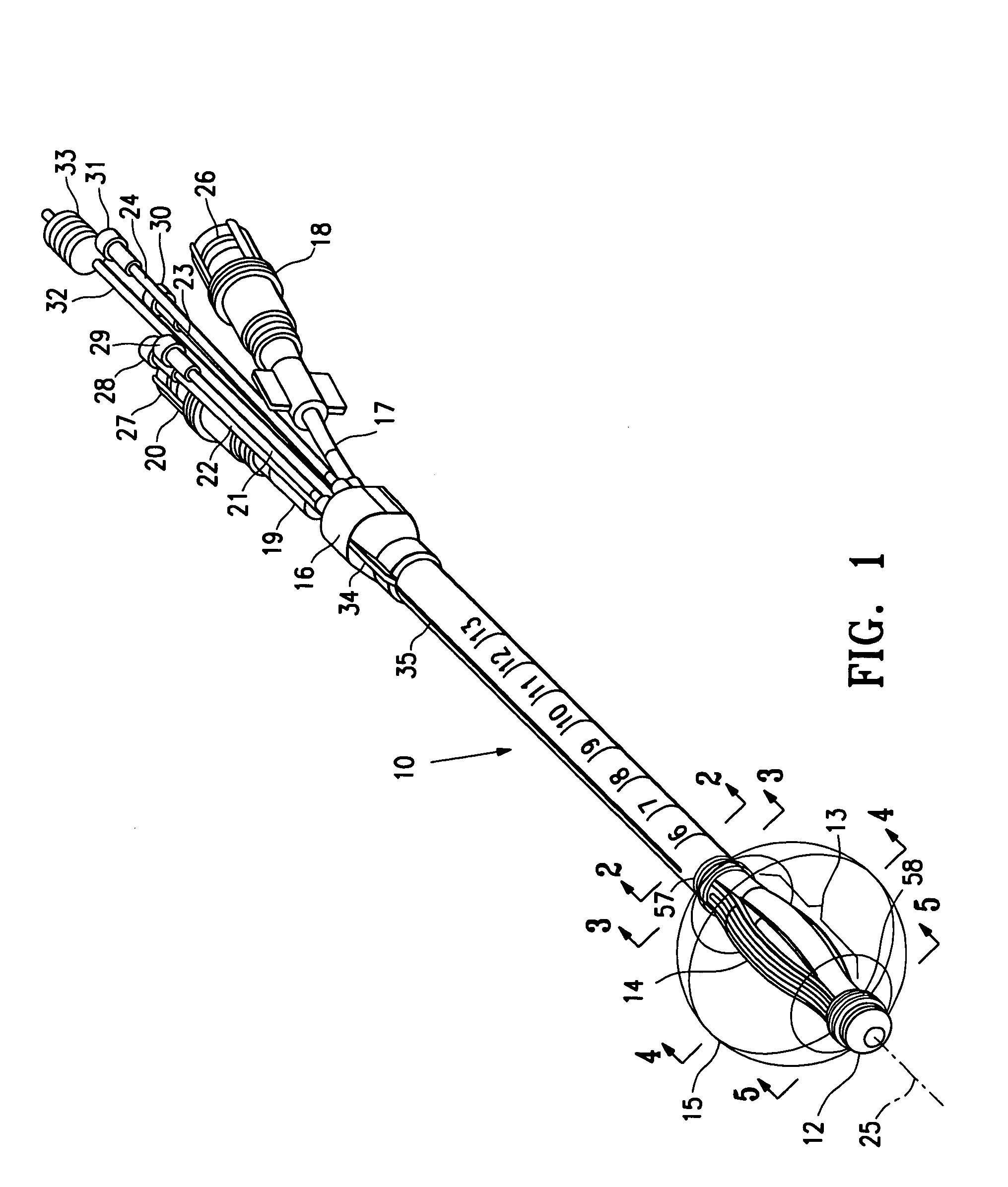
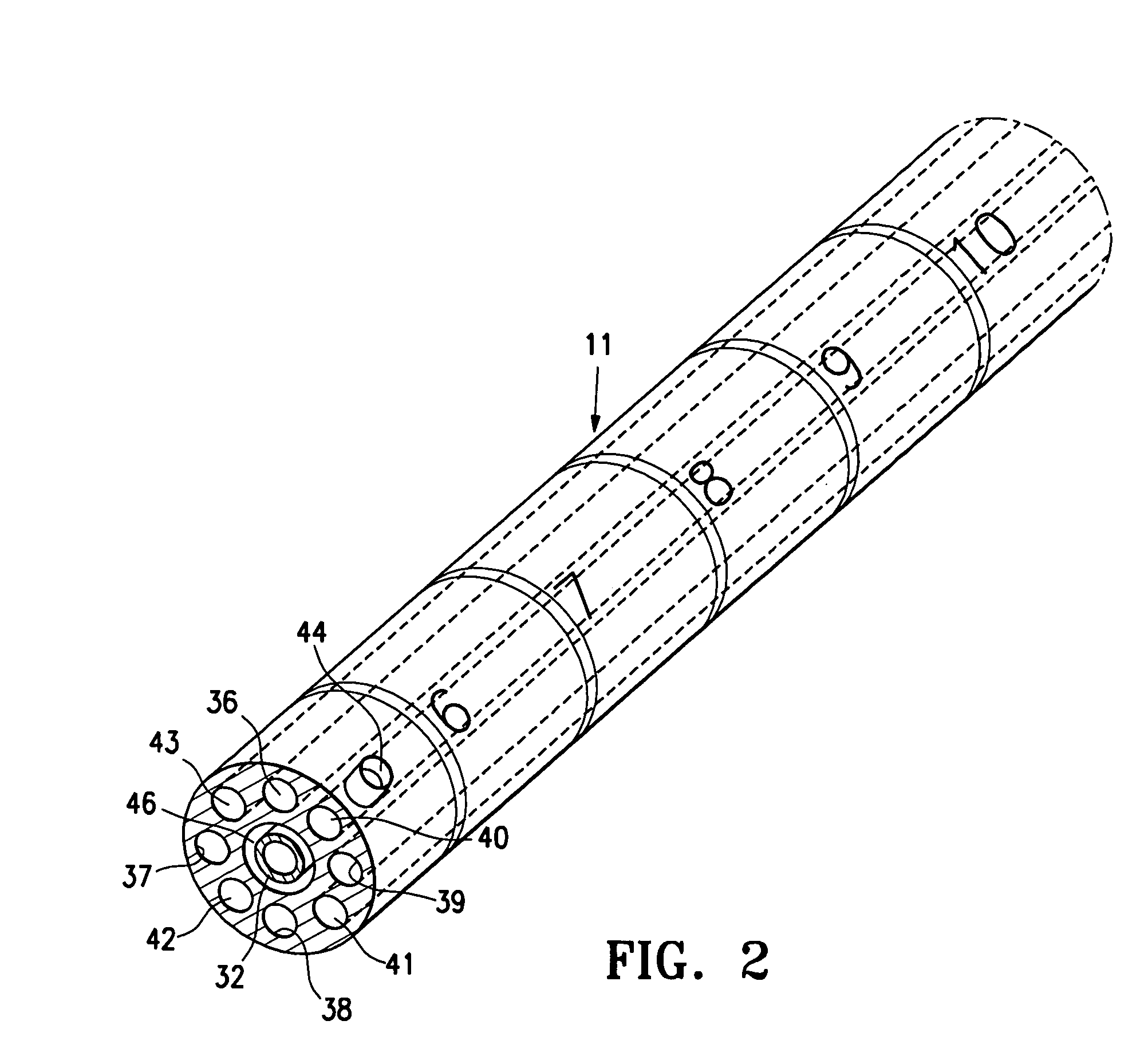
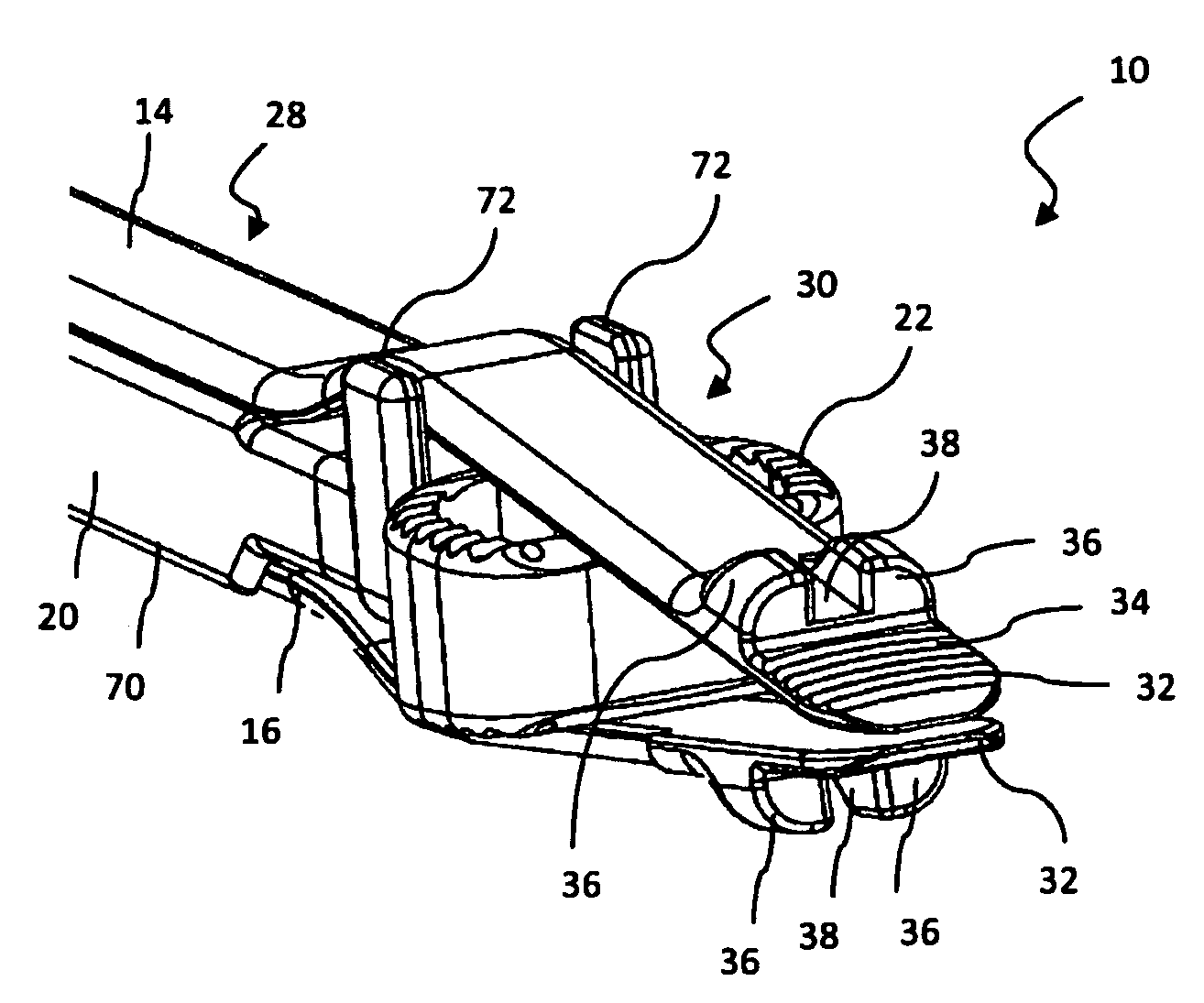
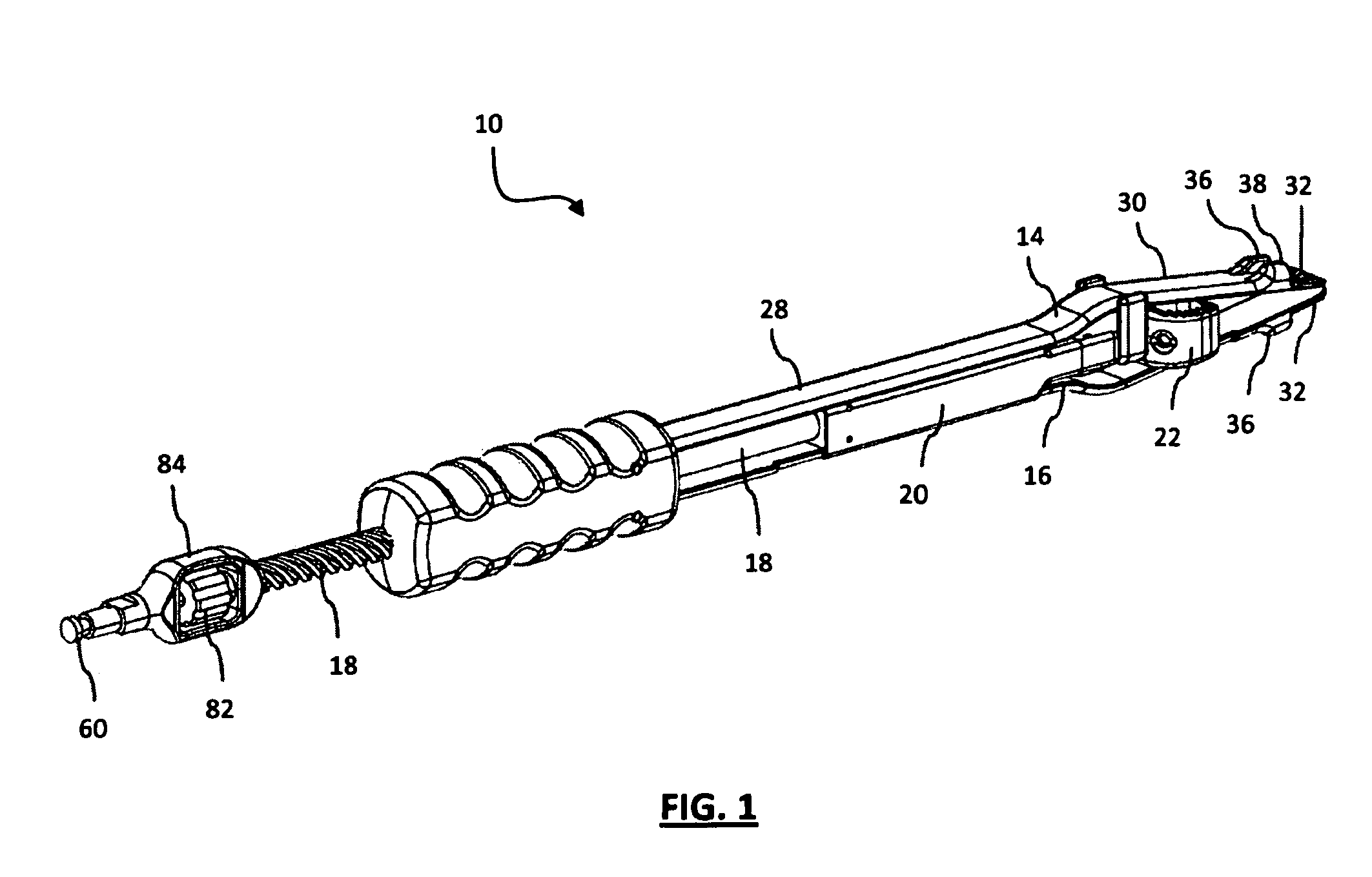
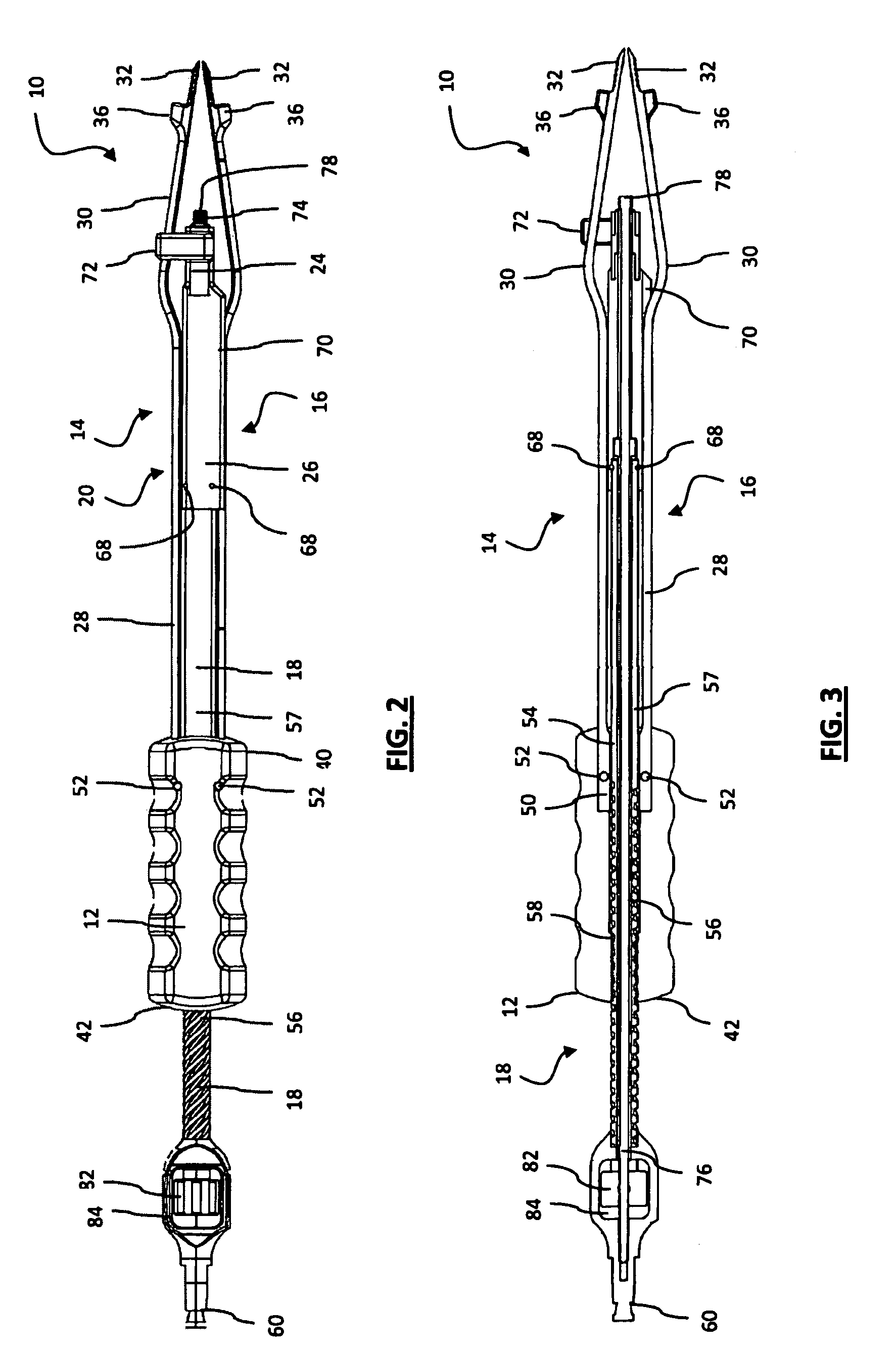
Cervical Intervertebral Disc Prosthesis Comprising An Anti-Dislocation Device And Instruments
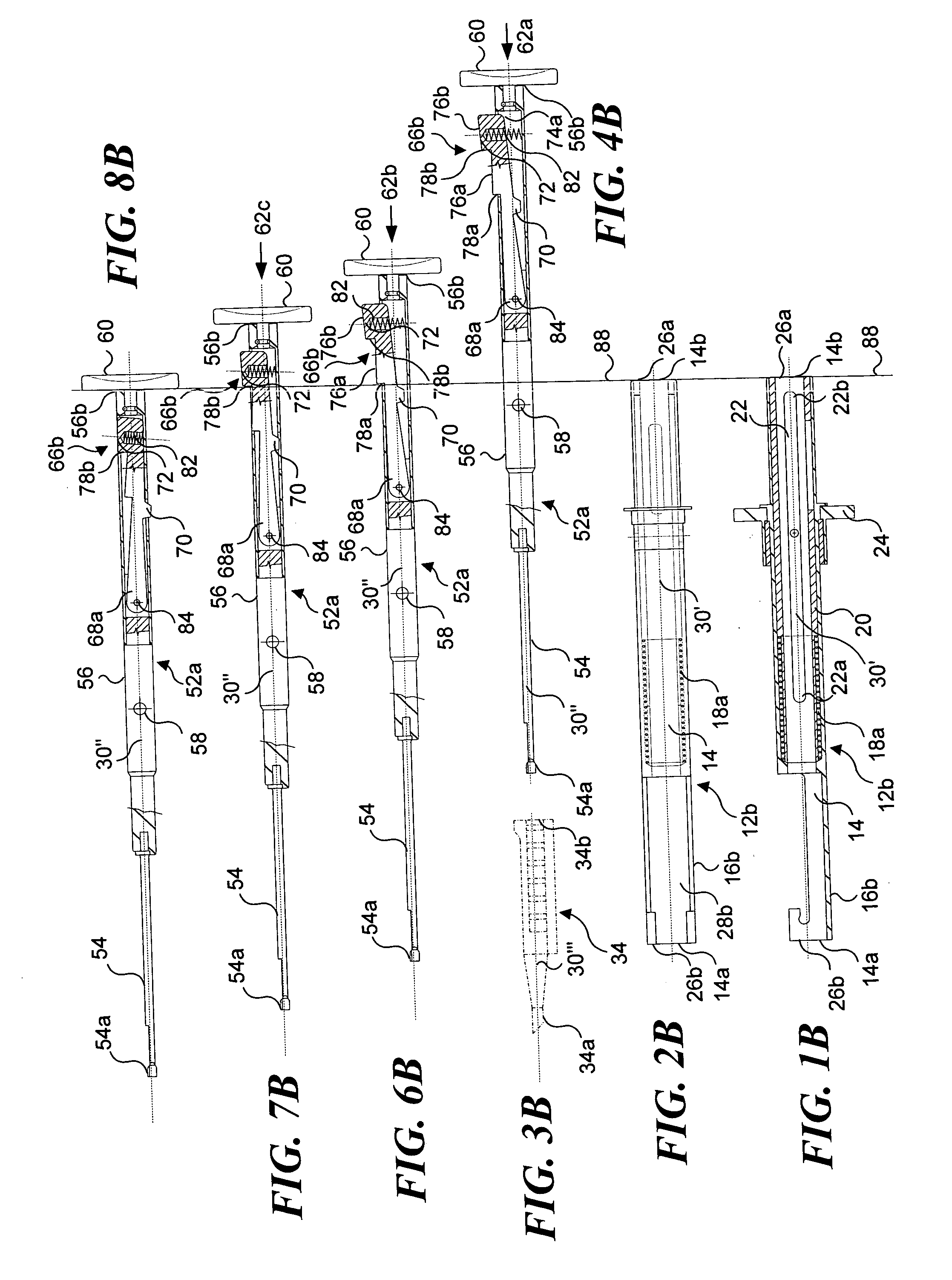
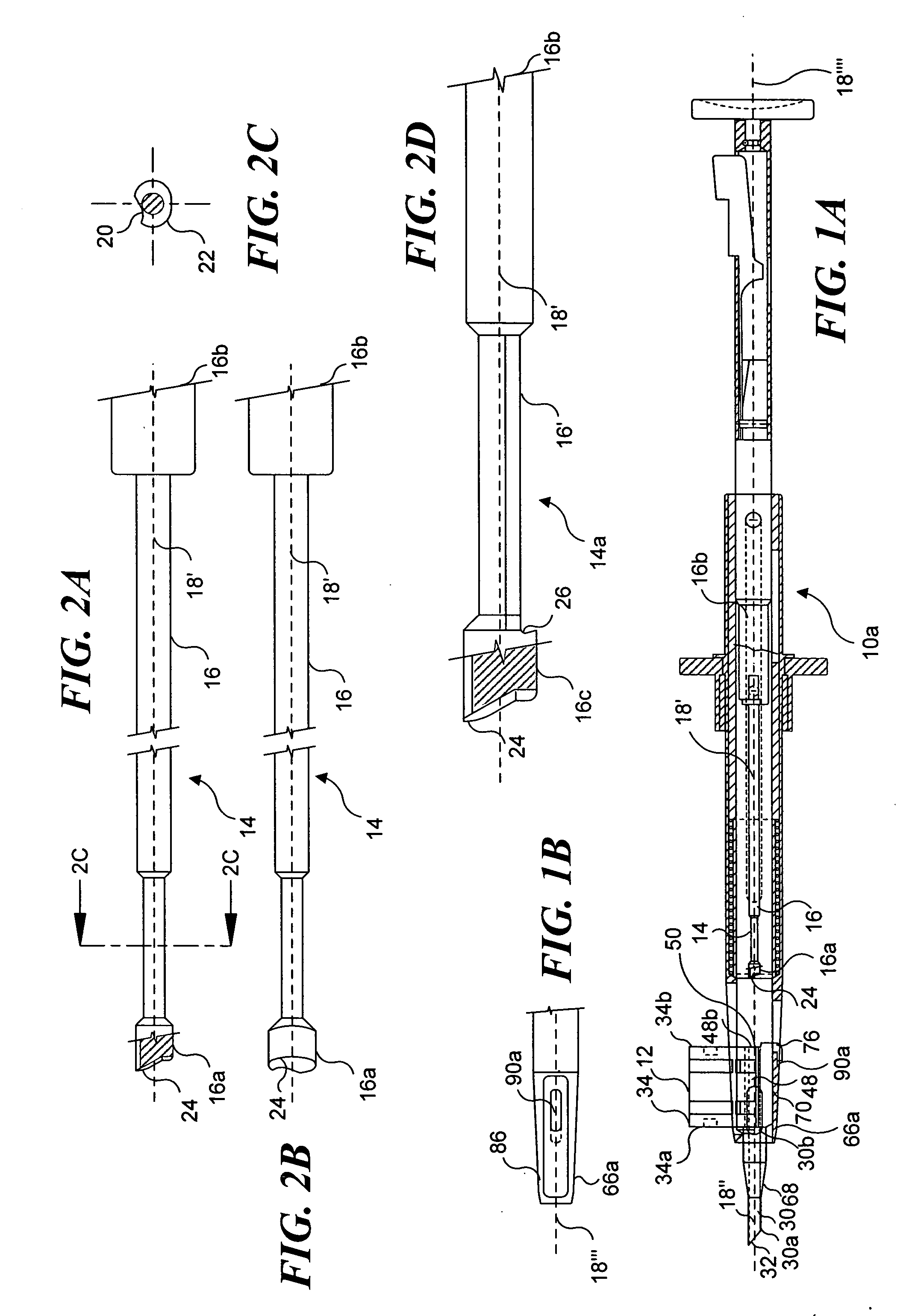
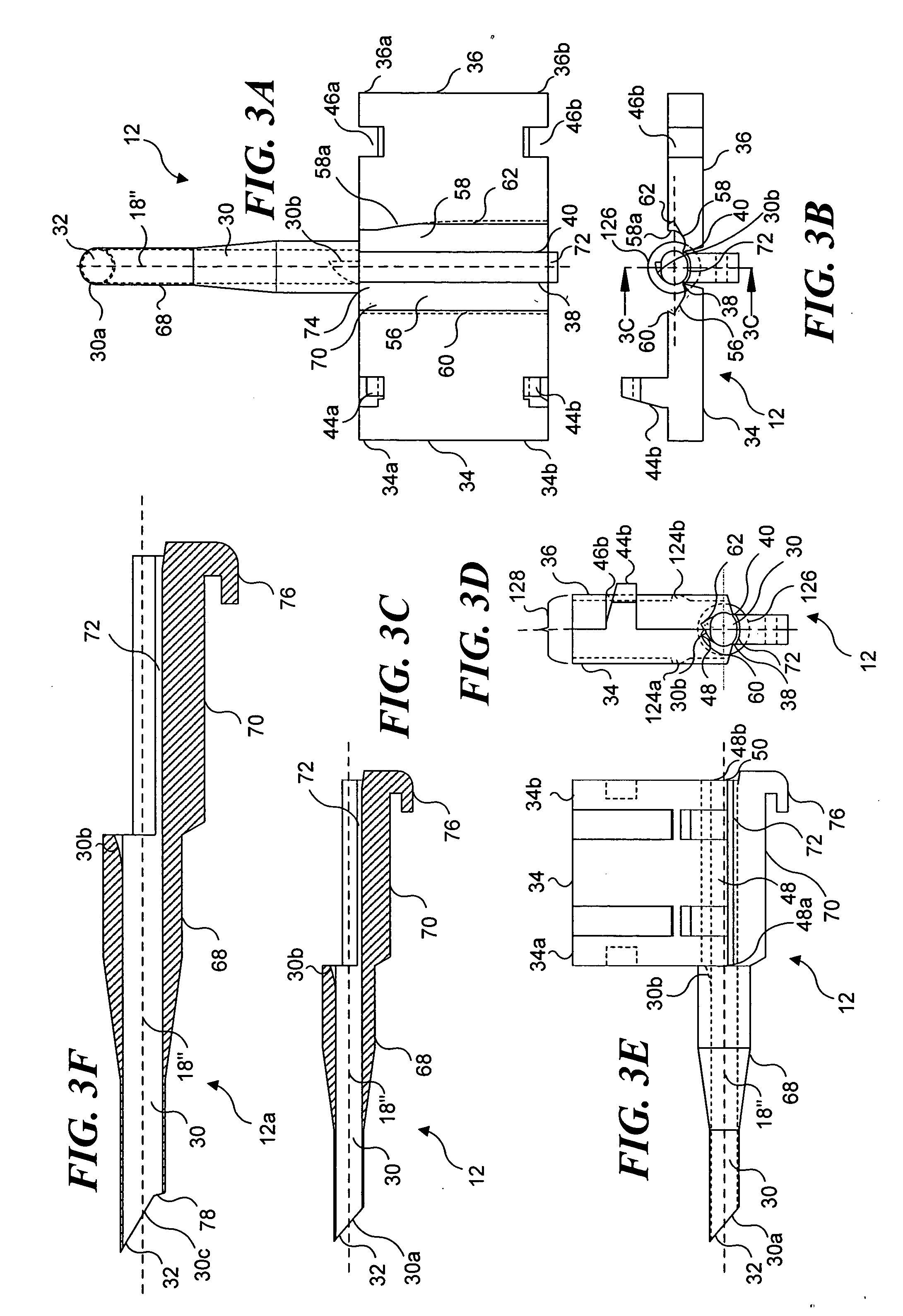
InactiveUS20080027550A1Easily advancedImprove connection reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsUnintended MovementSpinal column
A cervical intervertebral prosthesis includes lower and upper anchoring plates with a prosthesis core arranged between them to create an articulated connection. The anchoring plates are designed to bear with their anchoring plate surfaces on adjacent vertebral bodies. At least one anchoring plate surface has a rib-like projection thereon which can be used to engage in the vertebral body with a form fit. In order to produce a corresponding recess in the vertebral body, an instrument having a handle, a stem, a head part and an excavating element that can be retracted into the head part may be used. This permits considerably improved securing of the cervical intervertebral prosthesis against unintended movement. The medullary canal running along the posterior margin of the vertebral column is in this way protected from damage.
Owner:CERVITECH INC
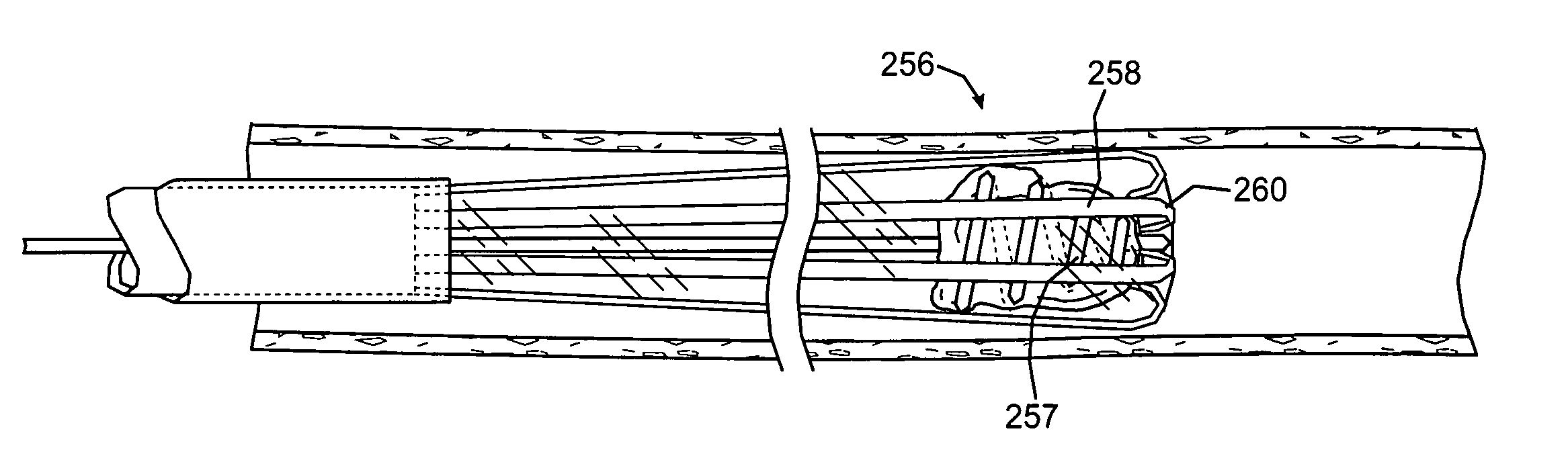
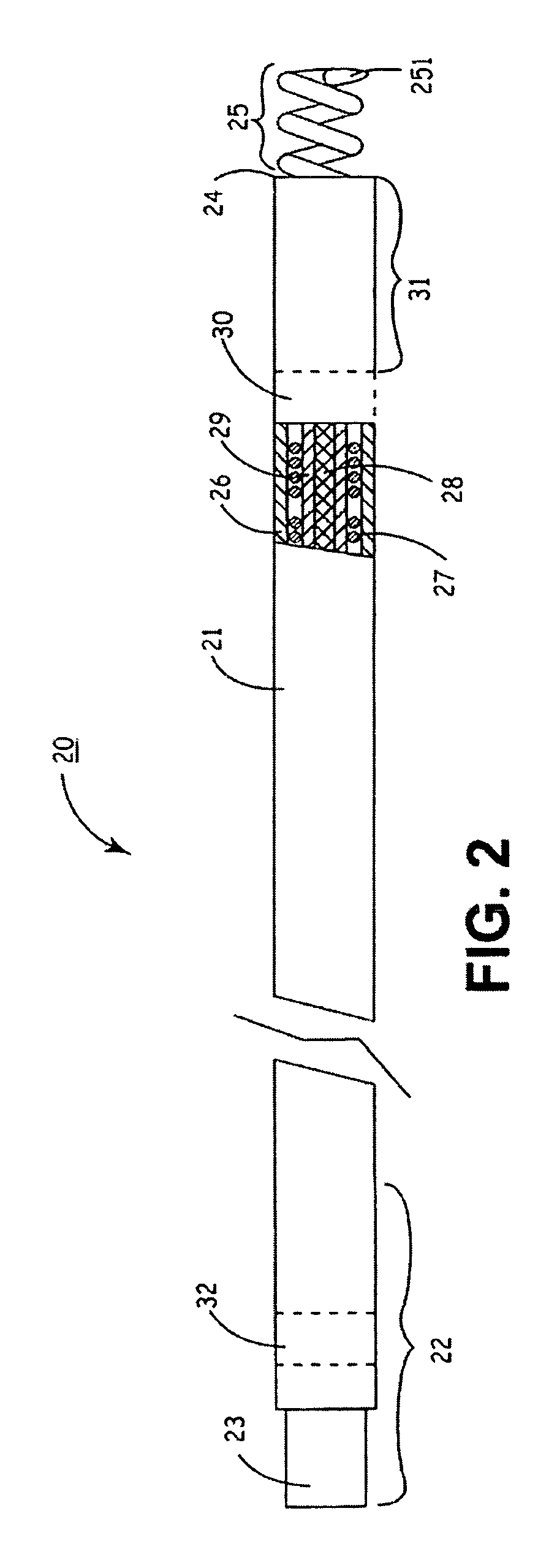
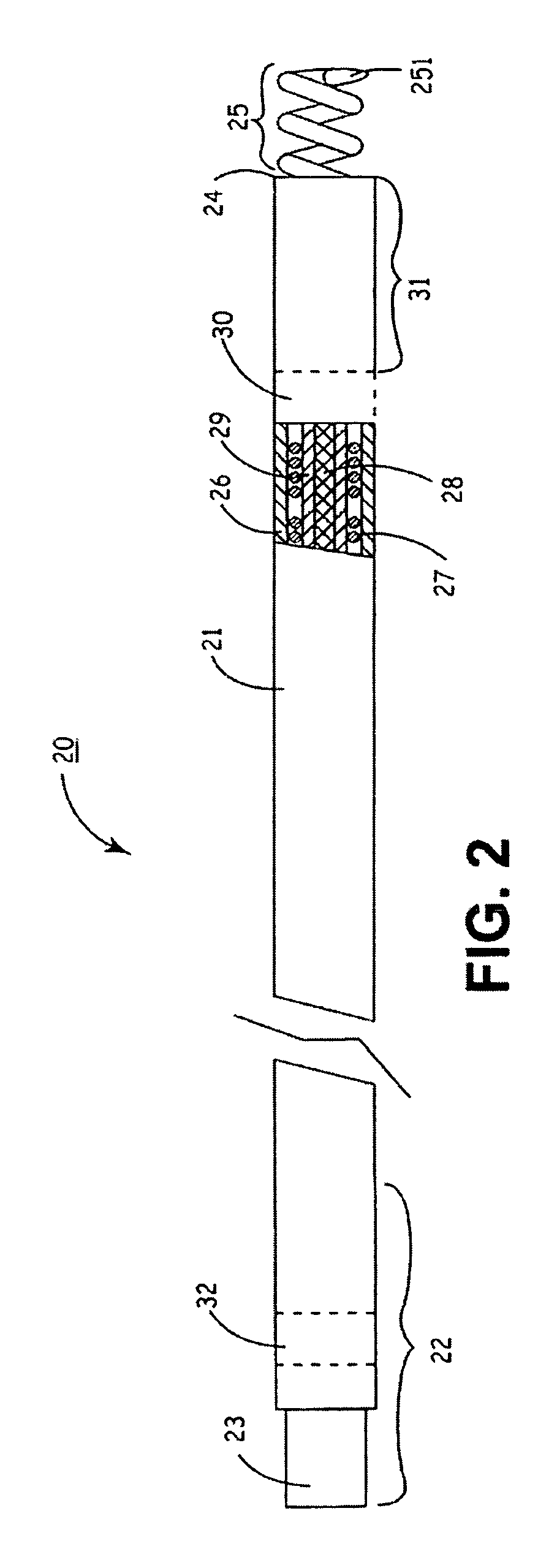
Systems, methods and devices for removing obstructions from a blood vessel
A system for removing an obstruction from a blood vessel includes an obstruction engaging element and an expandable capture element. The capture element preferably has a flexible cover and an expandable support structure. The engaging element engages the obstruction and moves the obstruction into the capture element. The capture element protects the obstruction when the obstruction is moved into the catheter.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Intraocular lens inserter
InactiveUS20060085013A1Easy to bendPrevent bucklingEye treatmentIntraocular lensDetentIntraocular lens insertion
An intraocular lens (IOL) inserter and method of use ensure that an artificial intraocular lens is controllably ejected from a cartridge and into a patient's eye by using successive, predefined detent positions. One embodiment has a distal pivotal portion that can be pivoted to a desired angle as a mover advances the IOL into the eye. A detent controls the motion of the mover. In one embodiment, the detent includes a longitudinally extending component with a plurality of stair steps, so that a face of each stair step engages the housing at each different predefined detent position. Other embodiments include at least one orifice in the housing, so that when the orifice is aligned with a pin or protrusion, it engages the orifice to define a detent step. Another embodiment includes a spring-loaded collar that biases a pin into a predefined detent step.
Owner:DUSEK VACLAV +1
Intraocular lens inserter system components
InactiveUS20060167466A1Avoid damageApply evenlyEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular lens insertionEngineering
Disclosed are an intraocular lens (IOL) push rod, an IOL cartridge, multiple embodiments of an IOL cartridge housing, and a method for folding an IOL for insertion into an eye during ocular surgery. The distal end of the push rod is contoured to apply force to a substantial portion of the perimeter of an IOL to advance the IOL through a bore of the cartridge. Two hinges couple flanges on the IOL cartridge to a central portion that supports an IOL when protected by a cover for an extended storage time. The IOL cartridge has a locking element that engages a cartridge housing or IOL inserter. Each cartridge housing accepts the IOL cartridge with the IOL in an unfolded state. The cartridge bore is unobstructed and is tapered to fold one side of the IOL over the other as the IOL is advanced through the bore and into an eye.
Owner:DUSEK VACLAV
Systems, methods and devices for removing obstructions from a blood vessel
InactiveUS20080109031A1Easily advancedInhibit bindingDilatorsSurgical instrument detailsEngineeringBlood vessel
A system for removing an obstruction from a blood vessel includes an obstruction engaging element and an expandable capture element. The capture element preferably has a flexible cover and an expandable support structure. The engaging element engages the obstruction and moves the obstruction into the capture element. The capture element protects the obstruction when the obstruction is moved into the catheter.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
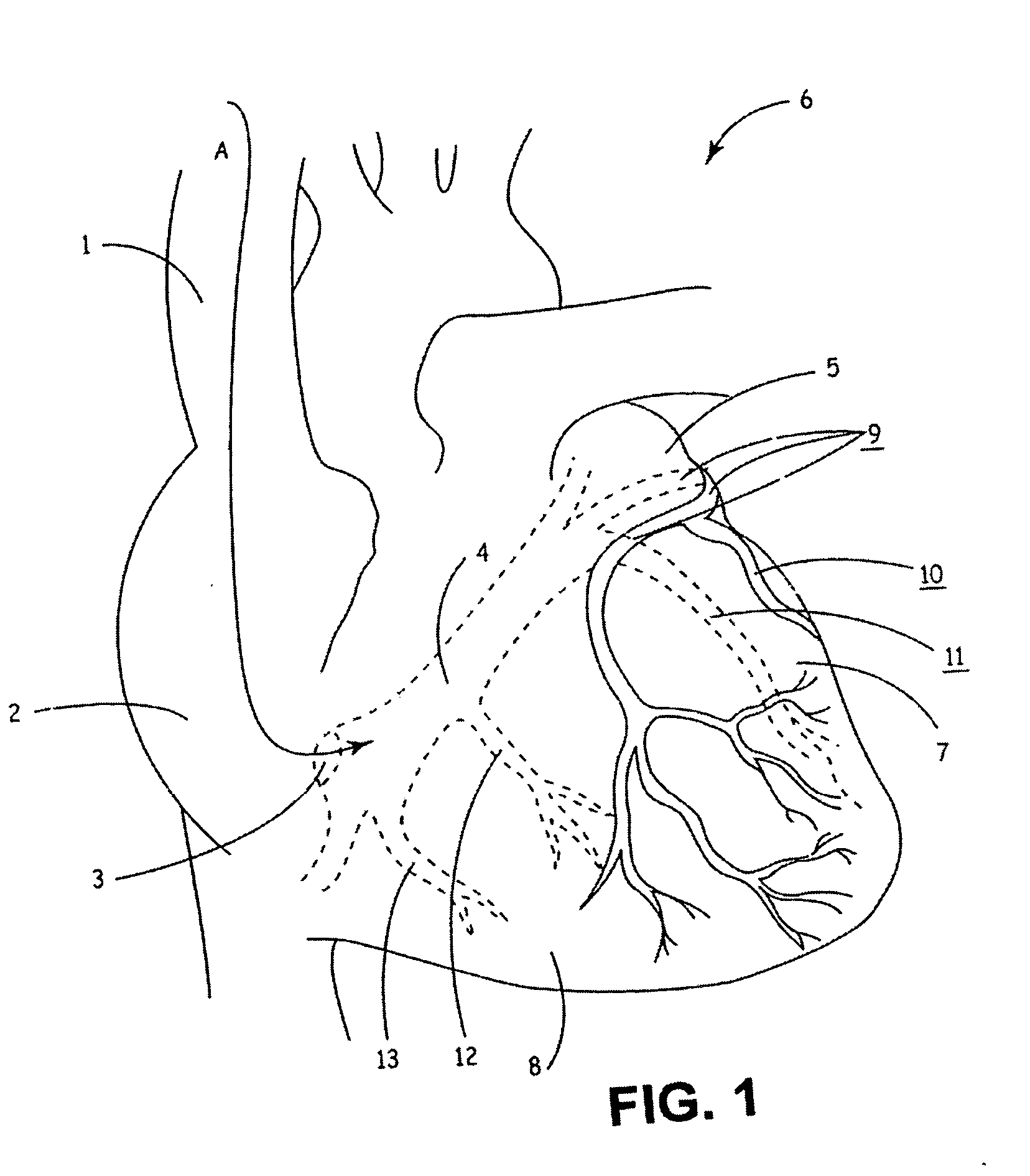
Bilumen guide catheters for accessing cardiac sites
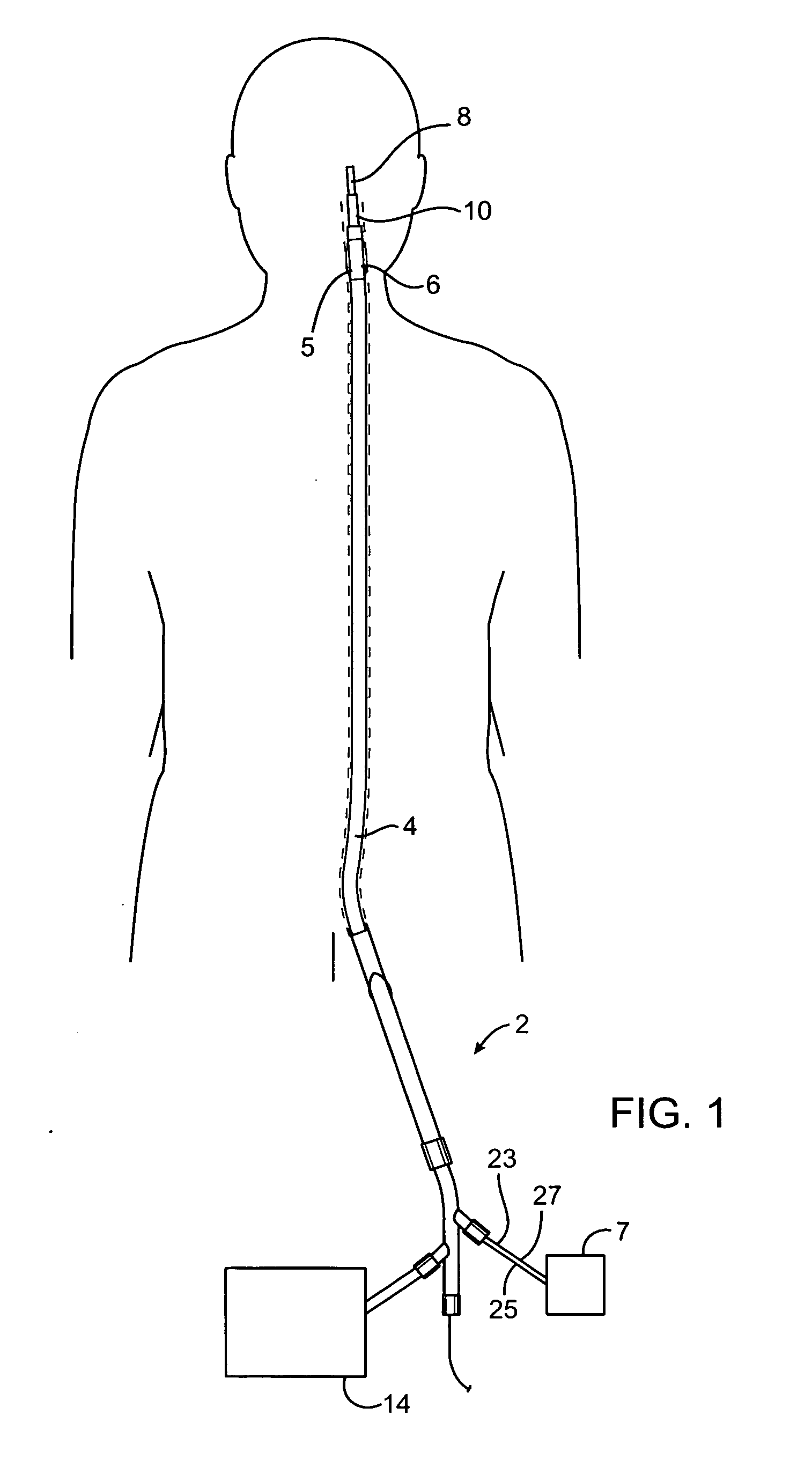
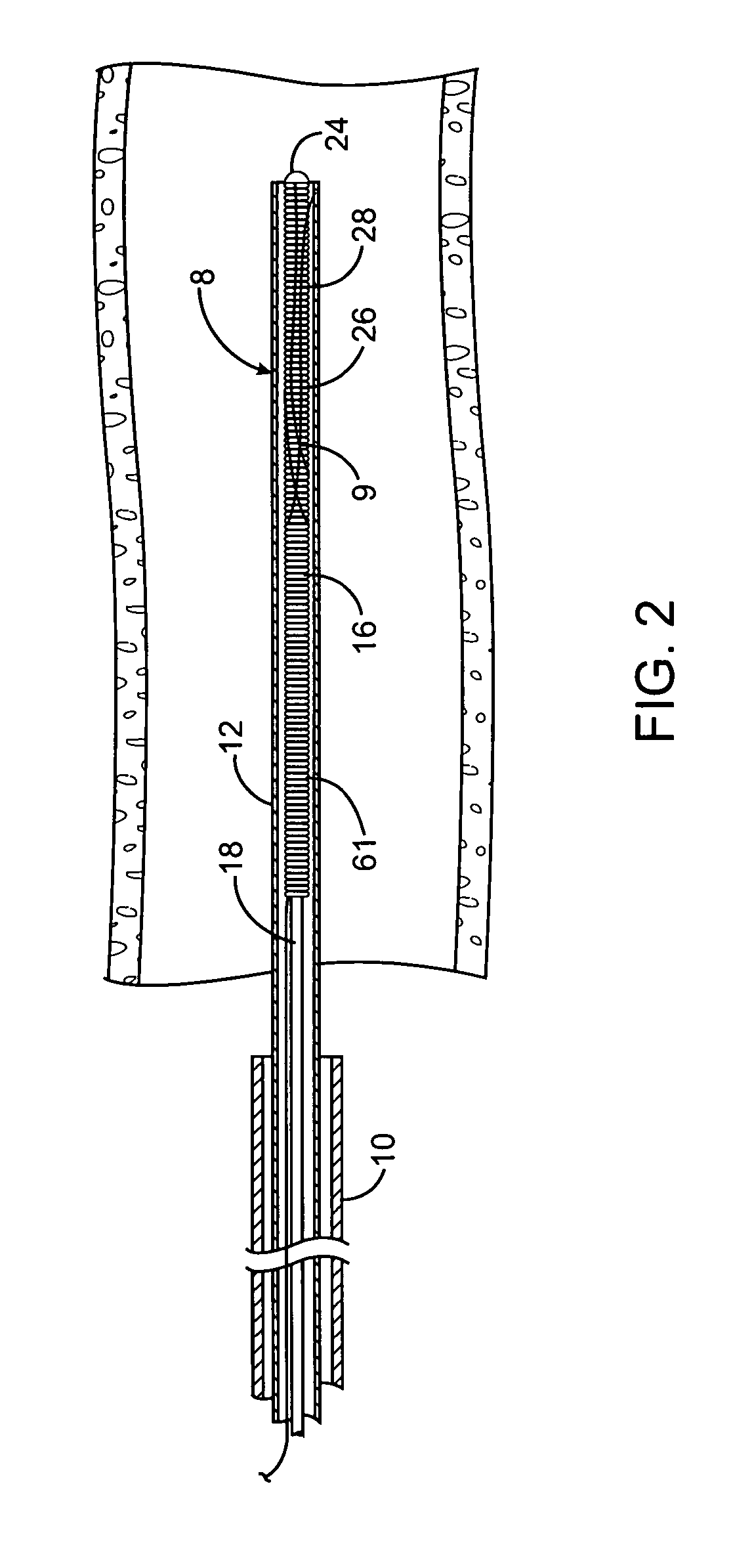
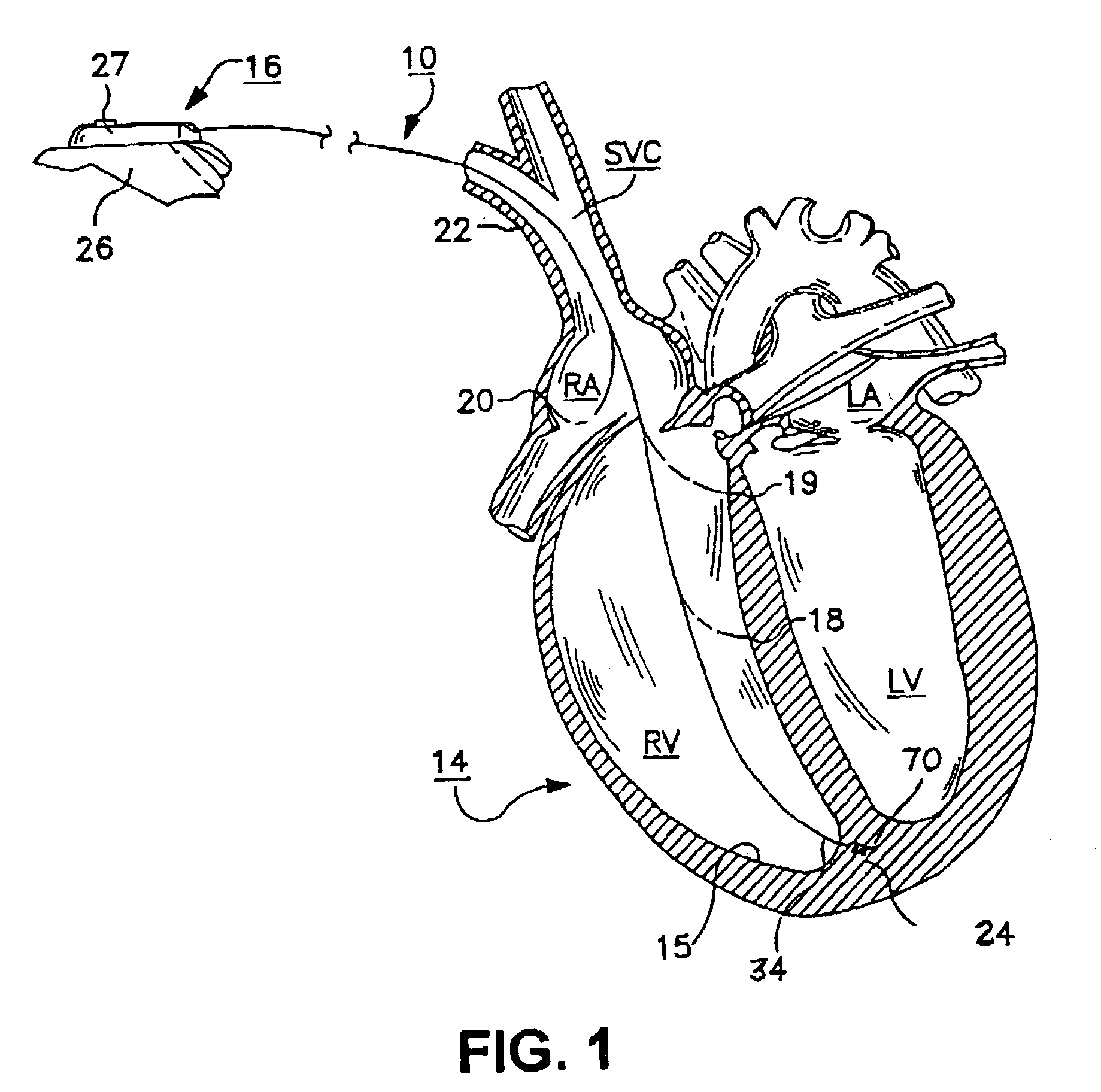
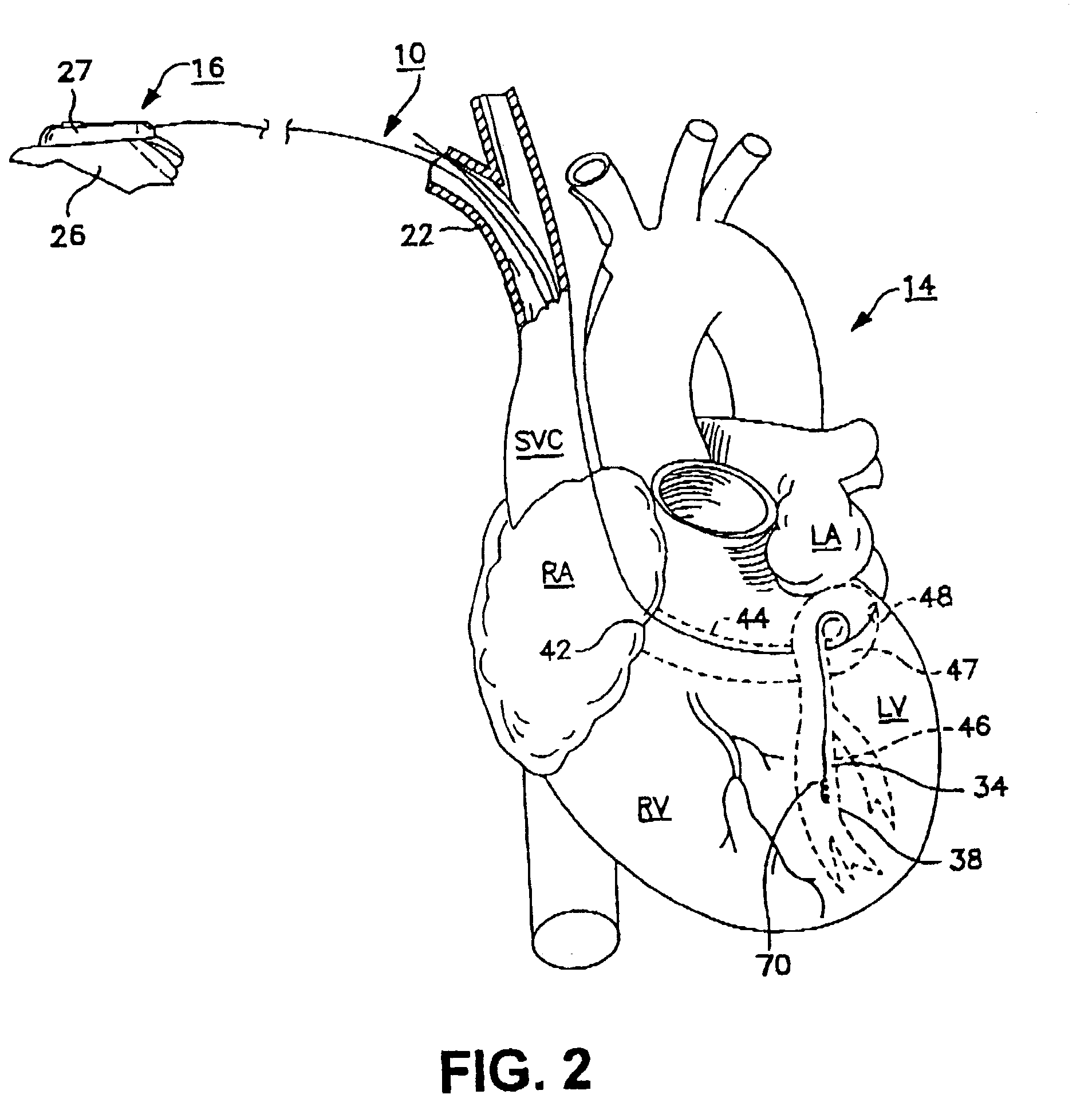
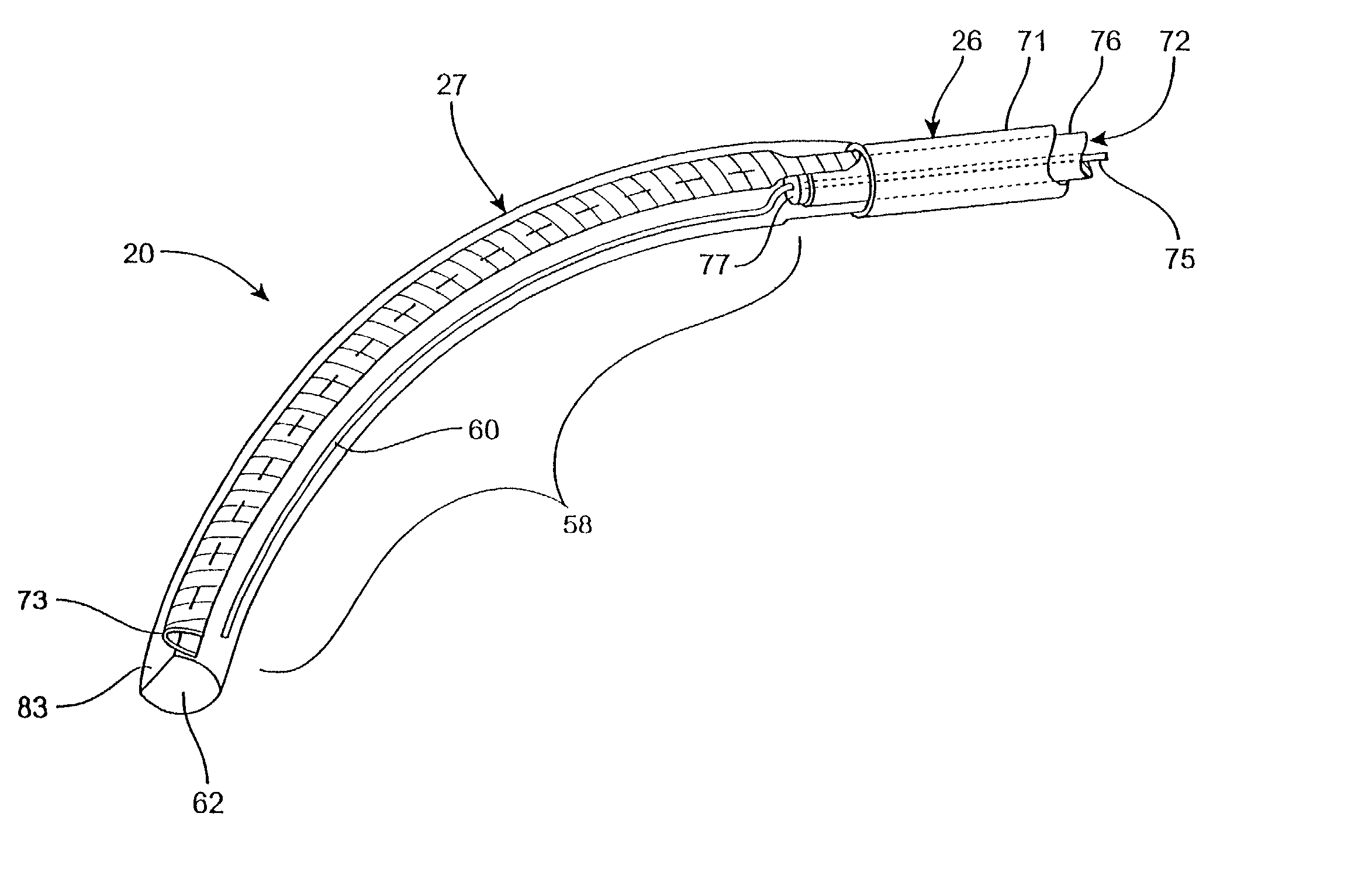
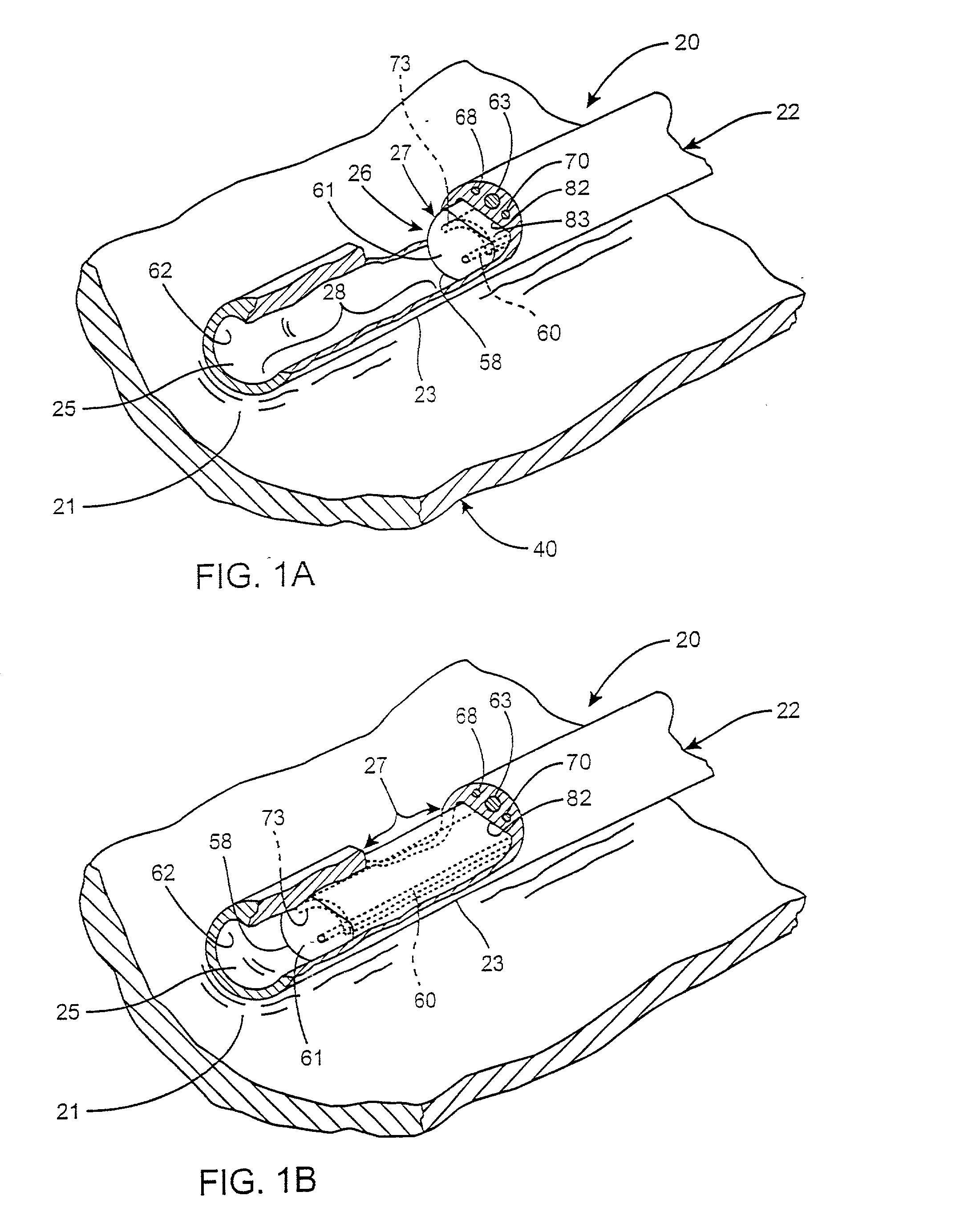
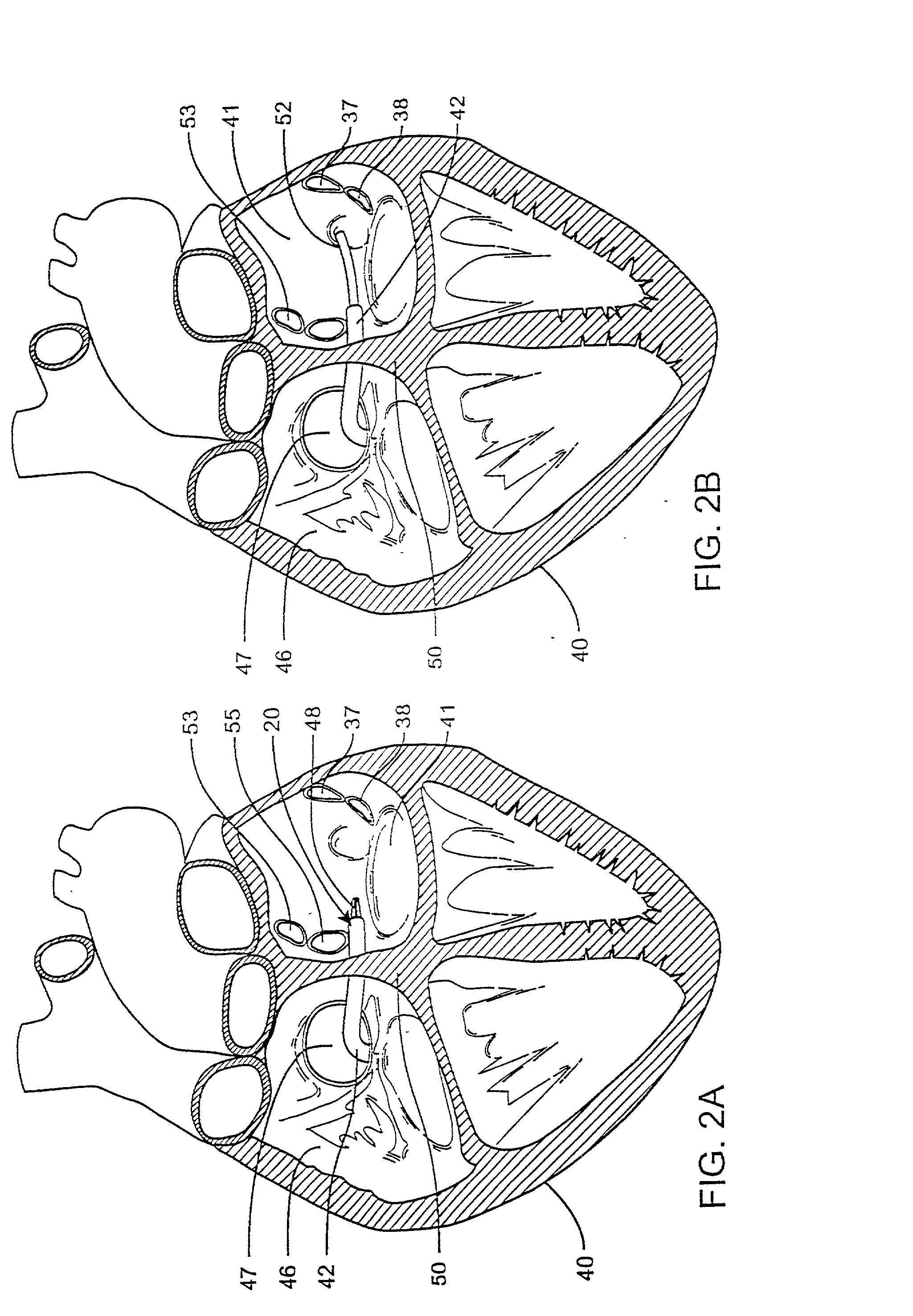
ActiveUS20040116878A1Meet actual needsAdvantageously employedTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterHeart chamberElectrical stimulations
Bilumen catheters and methods of using same for facilitating implantation of cardiac leads for applying electrical stimulation to and / or sensing electrical activity of the heart through one or more electrode positioned at an implantation site within a heart chamber or cardiac vessel adjacent a heart chamber, and more particularly to a method and apparatus for introducing such a cardiac lead having low torqueability and pushability through a tortuous pathway to enable attachment of the cardiac lead at the implantation site employing a bilumen guide catheter are disclosed. The bilumen catheter body includes a relatively large diameter delivery lumen to introduce a small diameter cardiac lead and a small diameter guide lumen to receive a stylet or guidewire to locate the guide catheter body distal end at the implantation site. The small diameter lumen within a small diameter guide tube extends distally from the delivery exit port of the delivery lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical instrument positioning tool and method
InactiveUS20020128636A1Facilitate ablationEasily advancedElectrotherapyCatheterBiological targetSurgical department
A system and method for positioning a medical instrument at a desired biological target tissue site is provided. The system includes an elongated sheath having a deflectable distal end configured to deflect or otherwise position at least a portion of a medical instrument during a surgical procedure allowing for the placement of the deflected portion adjacent or proximate to a predetermined target tissue surface. The positioning system may be incorporated into the medical instrument. The medical instrument may be an ablation system.
Owner:AFX +1
System and method for positioning implantable medical devices within coronary veins
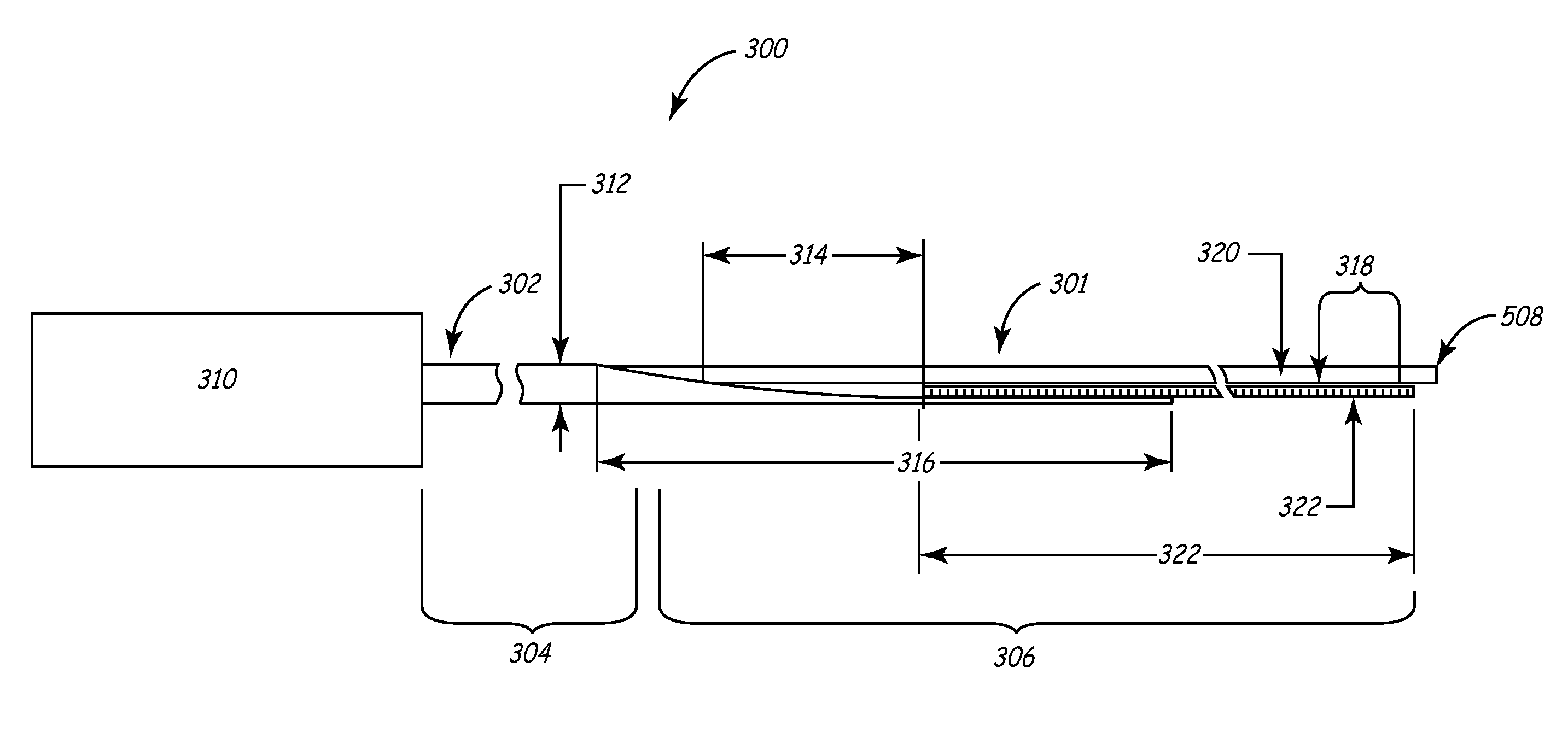
An improved system and method for placing implantable medical devices (IMDs) such as leads within the coronary sinus and branch veins is disclosed. In one embodiment, a slittable delivery sheath and a method of using the sheath are provided. The sheath includes a slittable hub, and a substantially straight body defining an inner lumen. The body comprises a shaft section and a distal section that is distal to, and softer than, the shaft section. A slittable braid extends adjacent to at least a portion of one of the shaft section and the distal section. In one embodiment of the invention, the sheath further includes a transition section that is distal to the shaft section, and proximal to the distal section. The transition section is softer than the shaft section, but stiffer than the distal section.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Low friction coated marked wire guide for over the wire insertion of a catheter
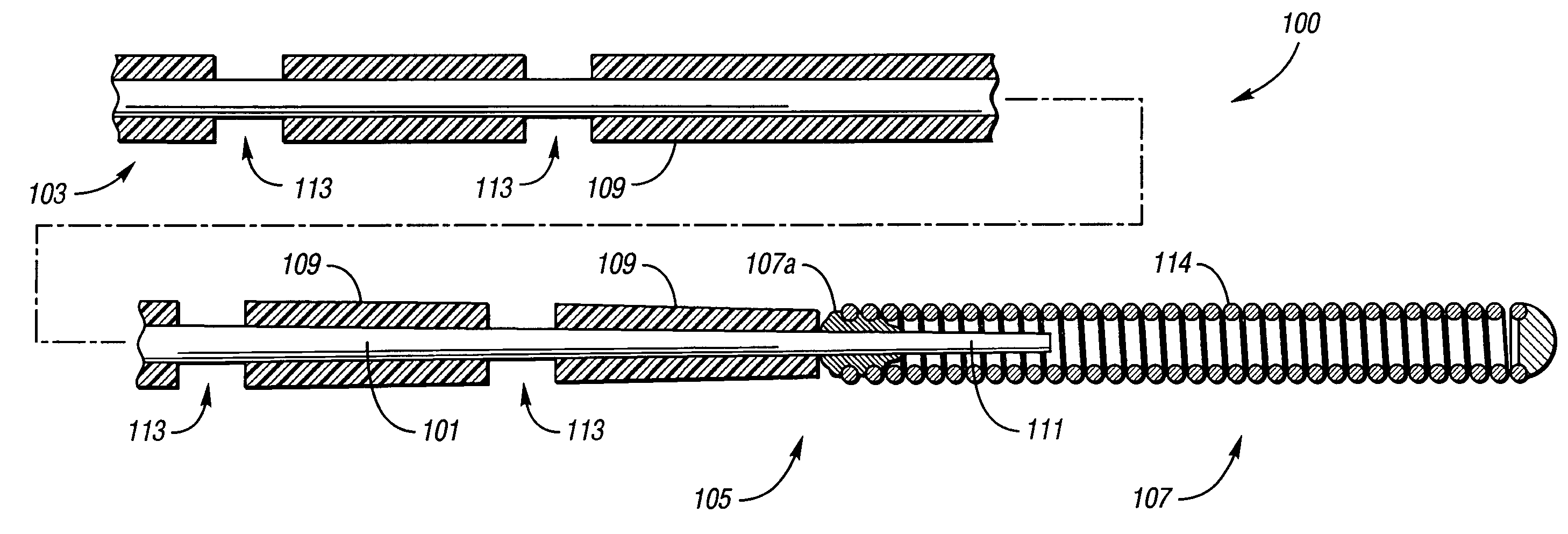
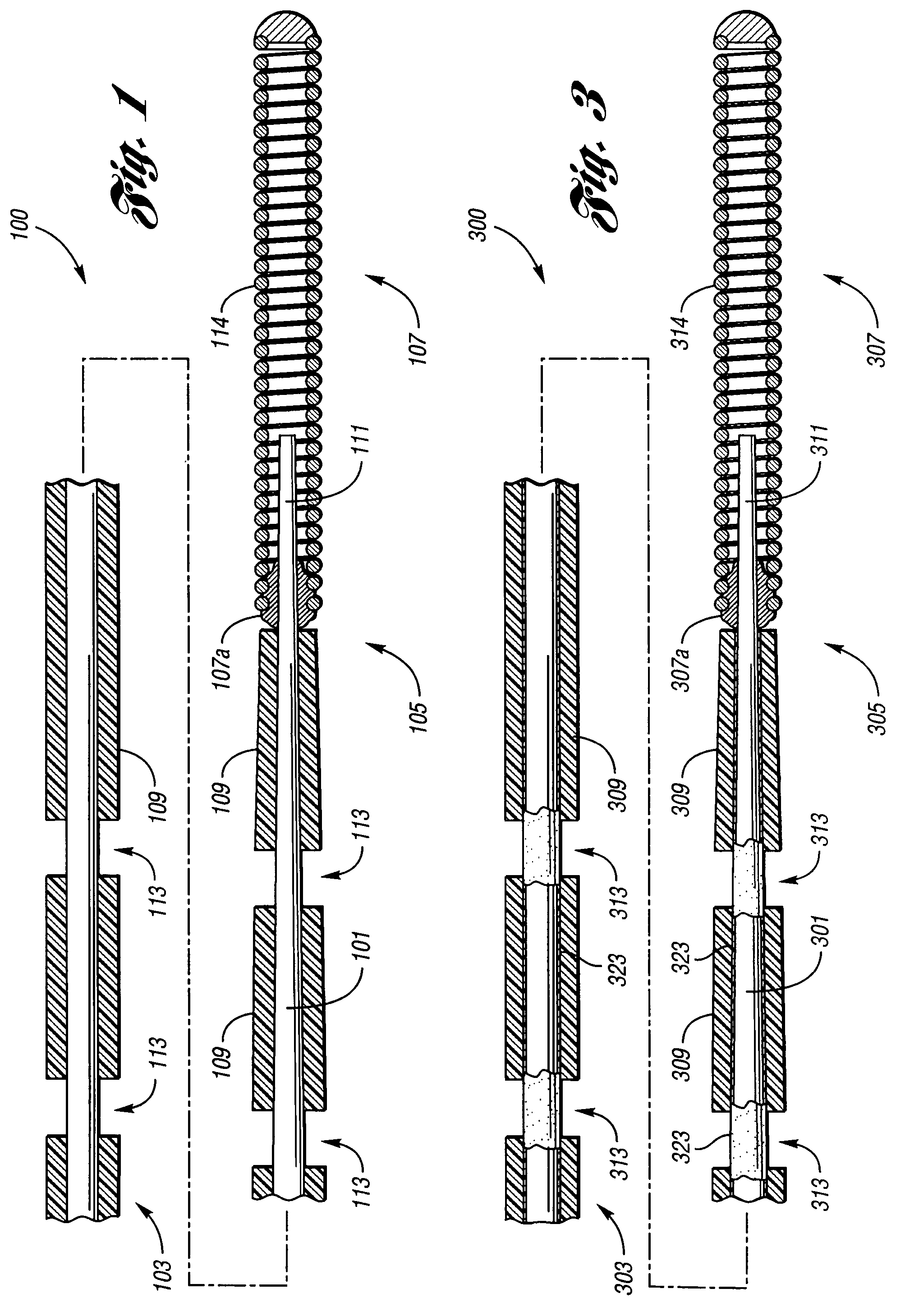
ActiveUS7651469B2Auxiliary judgmentEasily advancedInfusion syringesGuide wiresDistal portionGuide tube
A wire guide includes a mandrel that has a proximal portion and a distal portion. A coating having a low coefficient of friction is disposed on at least part of the proximal portion and the distal portion of the mandrel, where a part of the proximal portion and distal portion of the mandrel without the coating indicates a marking on the wire guide. This marking on the wire guide allows a user to determine a trimmable length of a catheter, and the low friction coating enables the user to easily advance the catheter over the wire guide.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
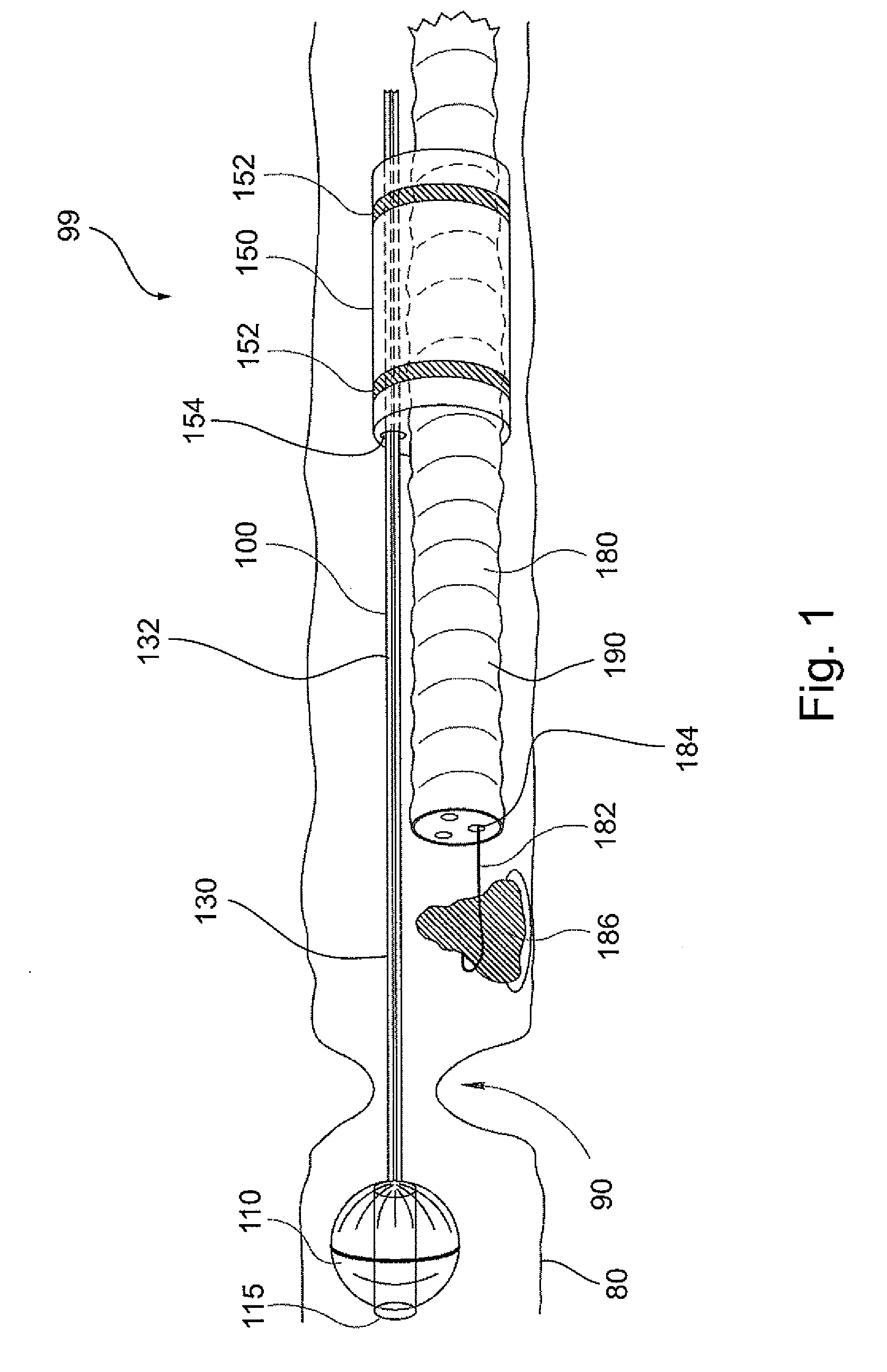
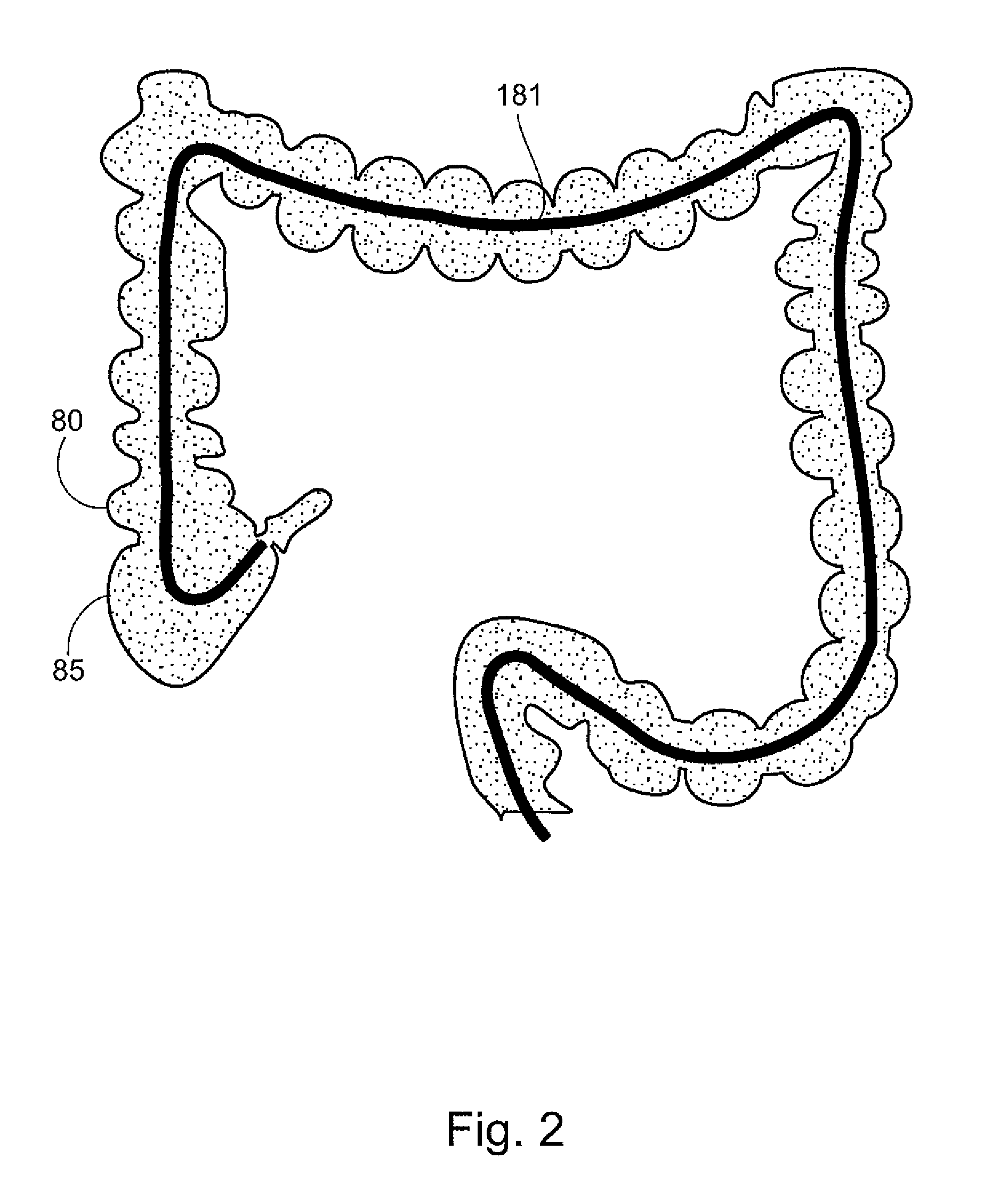
System and method for navigating a tool within a body conduit
InactiveUS20100105983A1Simple and rapid navigationFast displacementSurgeryEndoscopesBalloon catheterSurgical department
Apparatus and method for navigating surgical tools within a body cavity. Embodiments of the invention are particularly useful for displacing a surgical tool within a body conduit such as an intestine. Embodiments comprise a balloon catheter having a shaft, and a surgical tool operable to slide along that shaft. In some embodiments the surgical tool comprises a second balloon catheter.
Owner:COGENTIX MEDICAL
Guide catheters for accessing cardiac sites
InactiveUS20060247751A1Reduce the overall diameterEasily advancedMulti-lumen catheterTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart chamberCardiac blood vessel
Guide catheters and methods of using same for facilitating implantation of cardiac leads for applying electrical stimulation to and / or sensing electrical activity of the heart through one or more electrode positioned at an implantation site within a heart chamber or cardiac vessel adjacent a heart chamber and more particularly to a method and apparatus for introducing such a cardiac lead having low torqueability and pushability through a pathway to enable attachment of the cardiac lead at the implantation site are disclosed. The catheter body comprises delivery lumen to introduce a small diameter cardiac lead and a guide lumen to receive a guide tool to locate the catheter body distal end at the implantation site. The small diameter lumen within a small diameter guide tube extends distally from the delivery exit port of the delivery lumen. The catheter body is shaped to bias the delivery lumen exit port toward the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Guide catheters for accessing cardiac sites
InactiveUS7974710B2Reduce the overall diameterEasily advancedMulti-lumen catheterTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart chamberElectrical stimulations
Guide catheters for facilitating implantation of cardiac leads for applying electrical stimulation to and / or sensing electrical activity of the heart through one or more electrodes positioned at an implantation site within a heart chamber or cardiac vessel adjacent a heart chamber. Such a cardiac lead has low torqueability and pushability through a pathway to enable attachment of the cardiac lead at the implantation site. The catheter body comprises a delivery lumen to introduce a small diameter cardiac lead and a guide lumen to receive a guide tool to locate the catheter body distal end at the implantation site. The small diameter lumen within a small diameter guide tube extends distally from the delivery exit port of the delivery lumen. The catheter body is shaped to bias the delivery lumen exit port toward the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
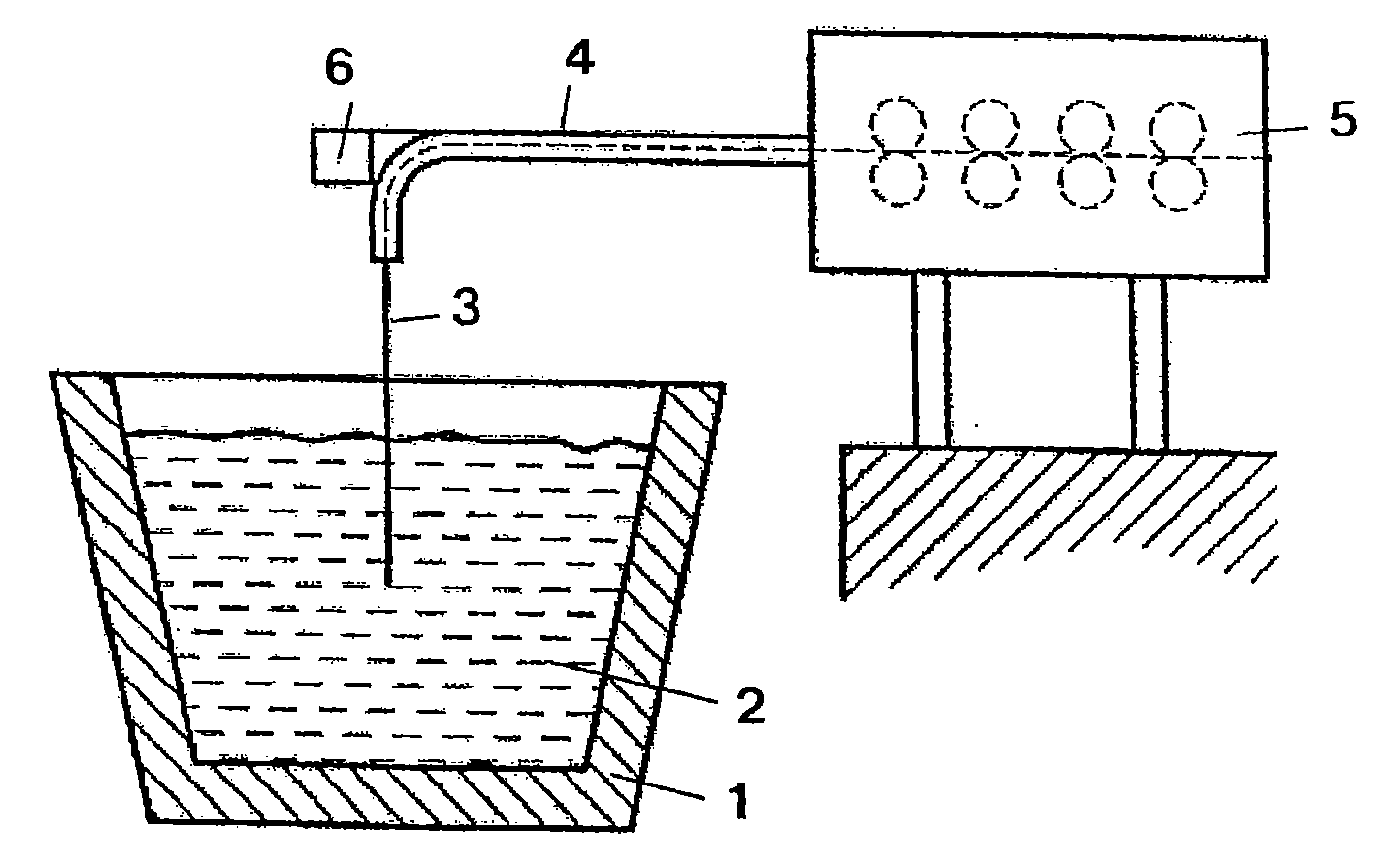
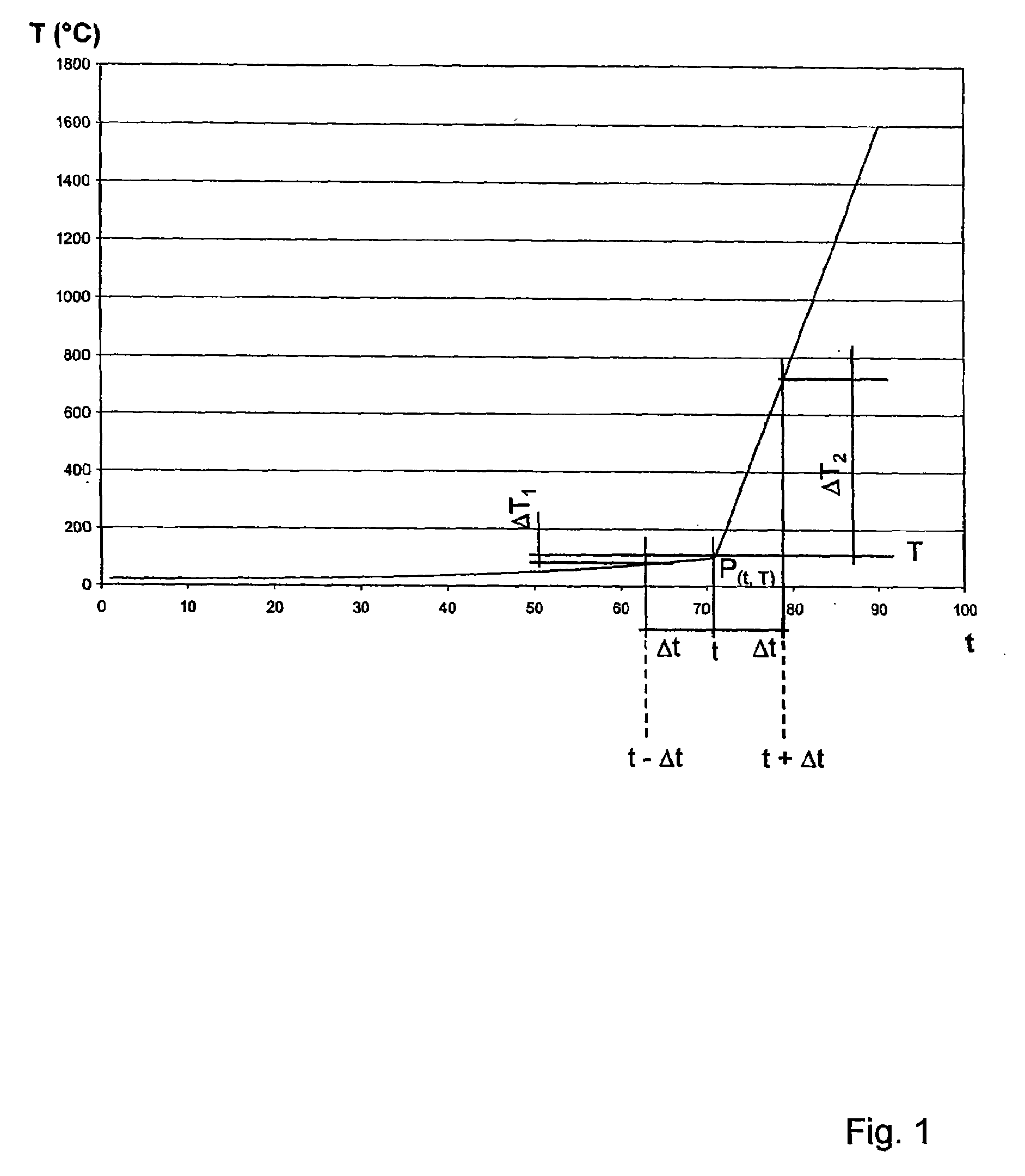
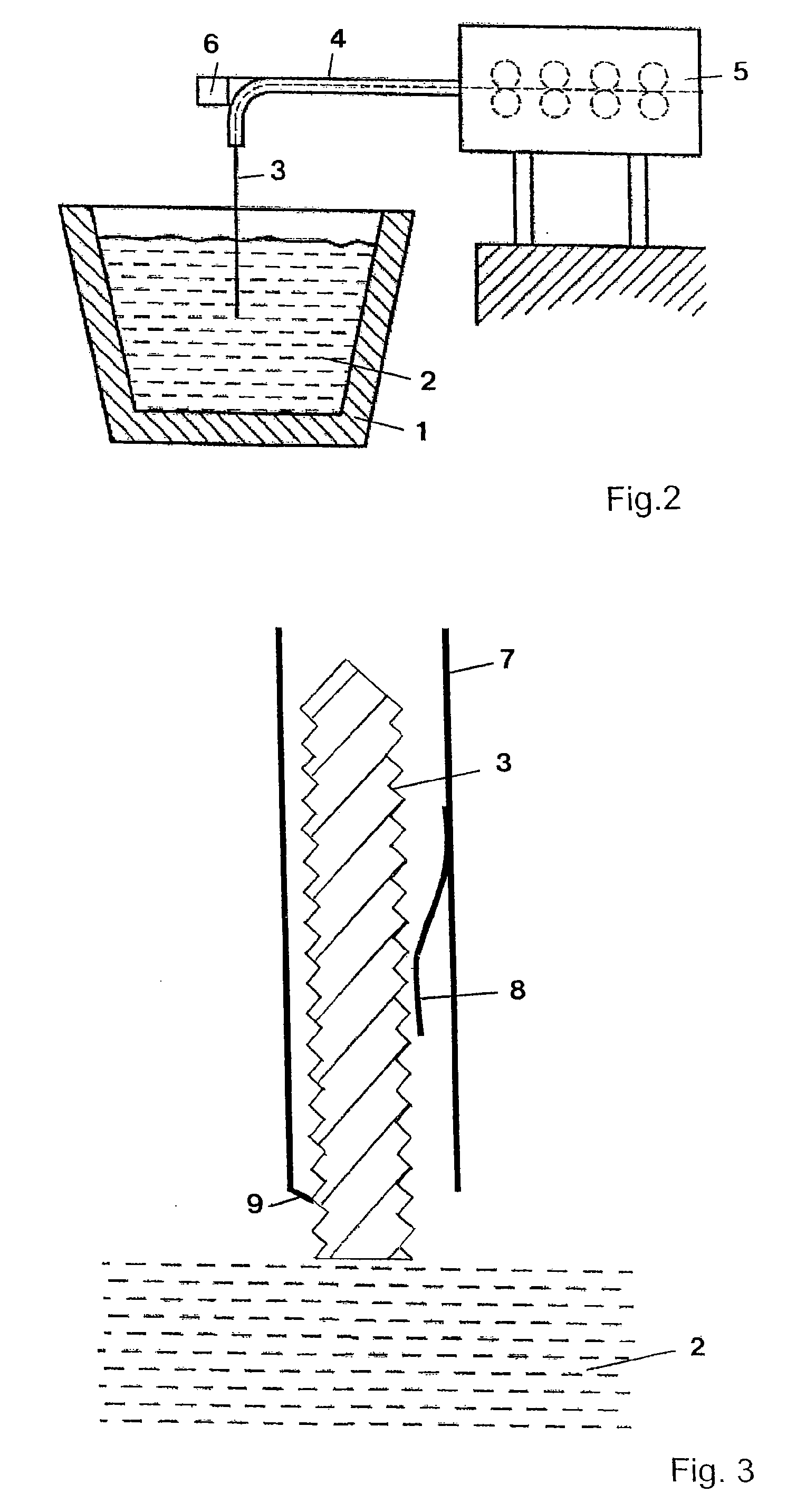
Method and device for measuring the temperature of a molten metal bath
ActiveUS20070268477A1Strong and effective changeIncrease heating speedThermometer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesMolten bathMolten metal
A method is provided for measuring a temperature of a molten metal bath by an optical fiber surrounded by a cover. The optical fiber is immersed in the molten bath, and the radiation absorbed by the optical fiber in the molten bath is fed to a detector, wherein the optical fiber is heated when immersed in the molten bath. The heating curve of the optical fiber has at least one point P(t0, T0), wherein the increase ΔT1 in the temperature T of the optical fiber over the time Δt in a first time interval t0−Δt up to the temperature T0 is smaller than the increase ΔT2 in the temperature of the optical fiber over the time Δt in an immediately following second time interval t0+Δt.
Owner:HERALUS ELECTRO NITE INT NV
Polymer coated guide wire
InactiveUS20060047224A1Easily advancedEnhanced Haptic FeedbackGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringGuide wiresPolymer coating
A guide wire having different polymers applied to different components thereof so as to differentially modify the performance characteristics of such components in order to achieve a desired performance behavior for such guide wire. A guide wire having a tapered distal coil coated with a highly conforming polymer while sections proximal thereto are coated with a substantially less conforming polymer will yield a guide wire that is more easily advanced through vasculature while nonetheless providing tactile feedback.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Medical instrument having a catheter and a medical guidewire
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
System and method for positioning implantable medical devices within coronary veins
InactiveUS20090131873A1Easily advancedMinimizing chanceGuide needlesBalloon catheterVeinDistal portion
An improved system and method for placing implantable medical devices (IMDs) such as leads within the coronary sinus and branch veins is disclosed. In one embodiment, a slittable delivery sheath and a method of using the sheath are provided. The sheath includes a slittable hub, and a substantially straight body defining an inner lumen. The body comprises a shaft section and a distal section that is distal to, and softer than, the shaft section. A slittable braid extends adjacent to at least a portion of one of the shaft section and the distal section. In one embodiment of the invention, the sheath further includes a transition section that is distal to the shaft section, and proximal to the distal section. The transition section is softer than the shaft section, but stiffer than the distal section.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Endoscope and endoscopic instrument system having reduced backlash when moving the endoscopic instrument within a working channel of the endoscope
An endoscopic instrument has a portion having an outer surface with a non-circular cross-sectional shape. The non-circular cross-sectional shape may be provided to the instrument by providing peripheral projections or fins along the length of the portion or by providing the periphery of the portion with a polygonal shape. Where fins are used, the fins are preferably quite small and only have a minimal effect on the fluid flow cross sectional area between the interior of the working channel and the endoscopic instrument. The resulting instrument has significantly reduced backlash while maintaining adequate fluid flow in the working channel. According to a second embodiment of the invention, a portion of the interior of the working channel of the endoscope has an interior surface having a non-circular cross sectional shape by the inclusion of a plurality of radially spaced and inwardly directed ribs or by being polygonally shaped. The resulting endoscope reduces the backlash of an endoscopic instrument inserted therein while maintaining adequate fluid flow in the working channel.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
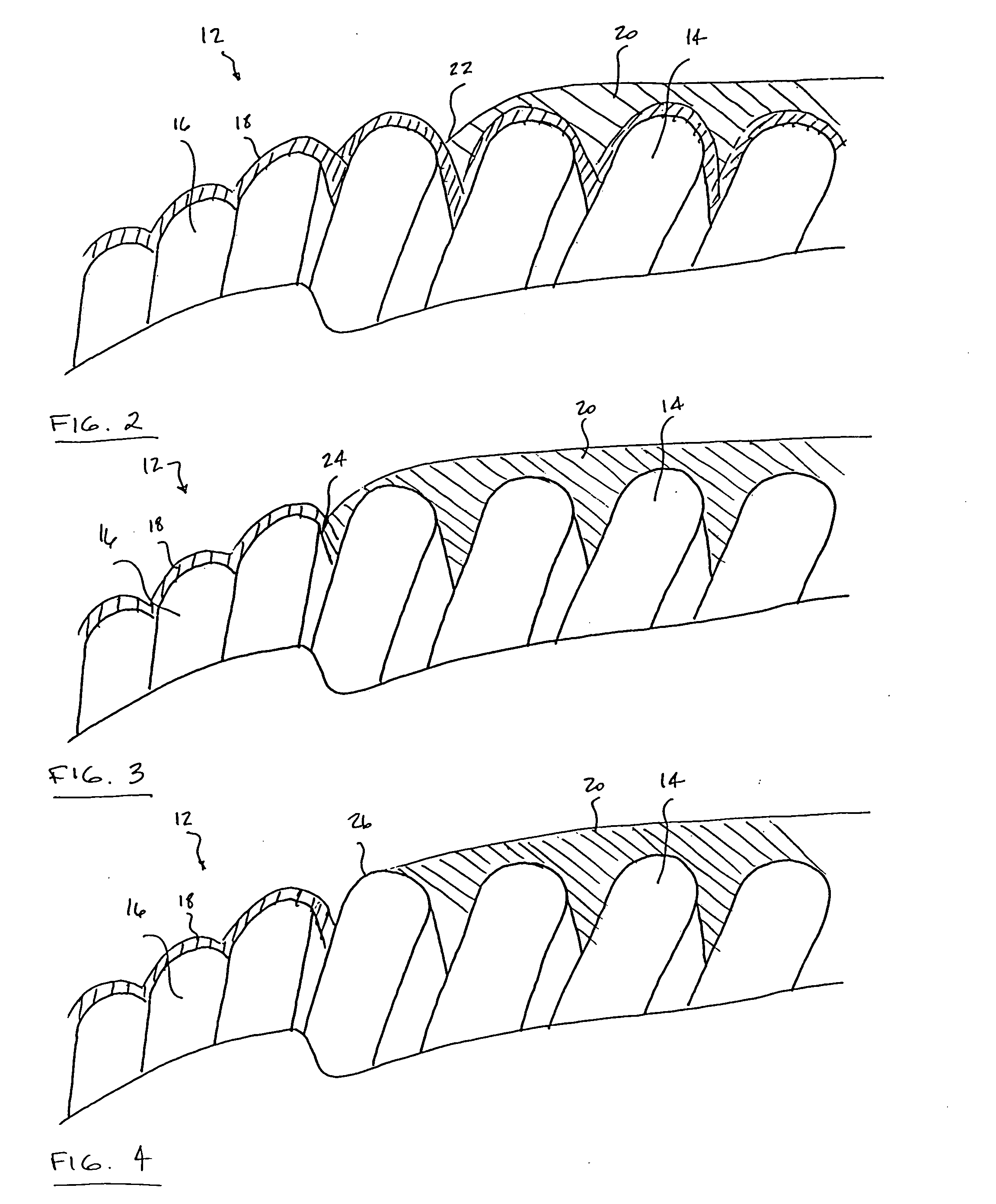
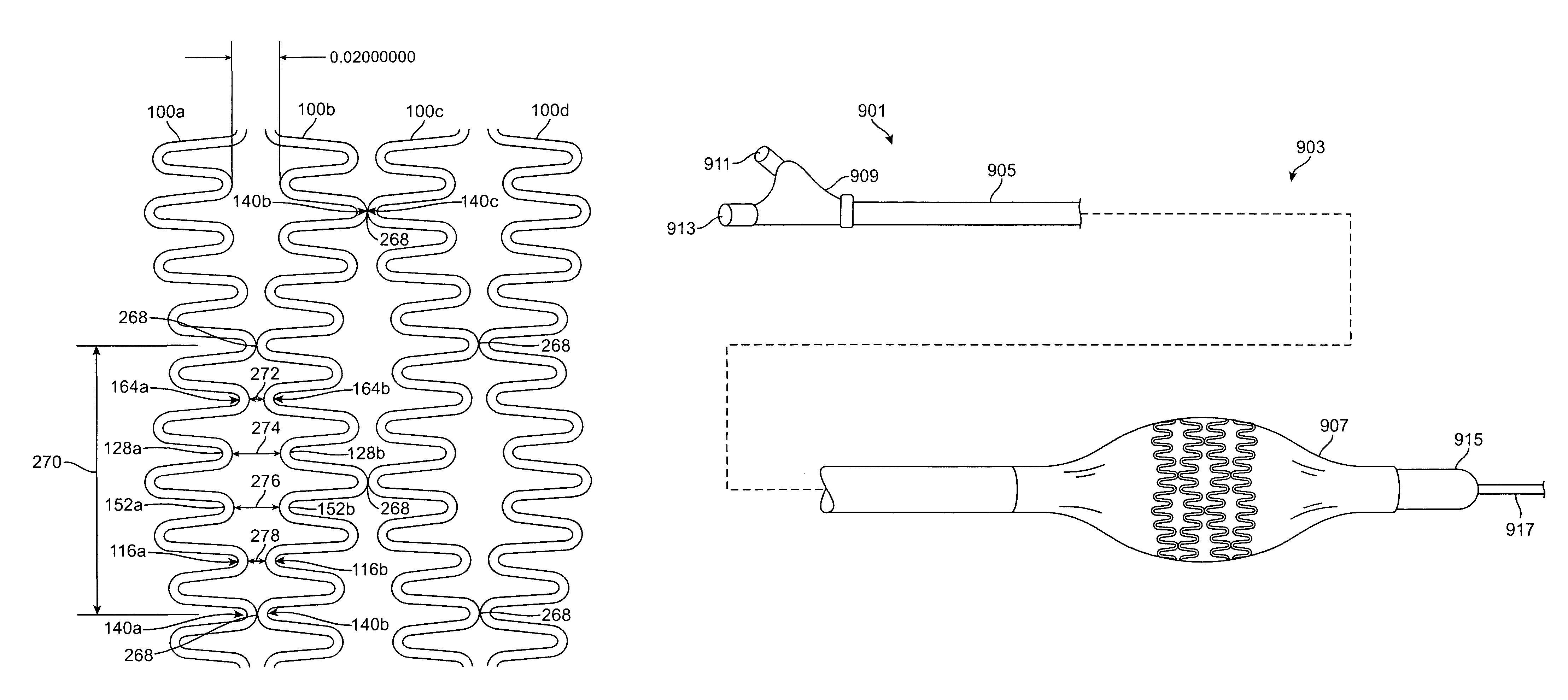
Intraluminal flexible stent device
InactiveUS8052738B2Good flexibilitySolve the real problemStentsBlood vesselsLong segmentBiomedical engineering
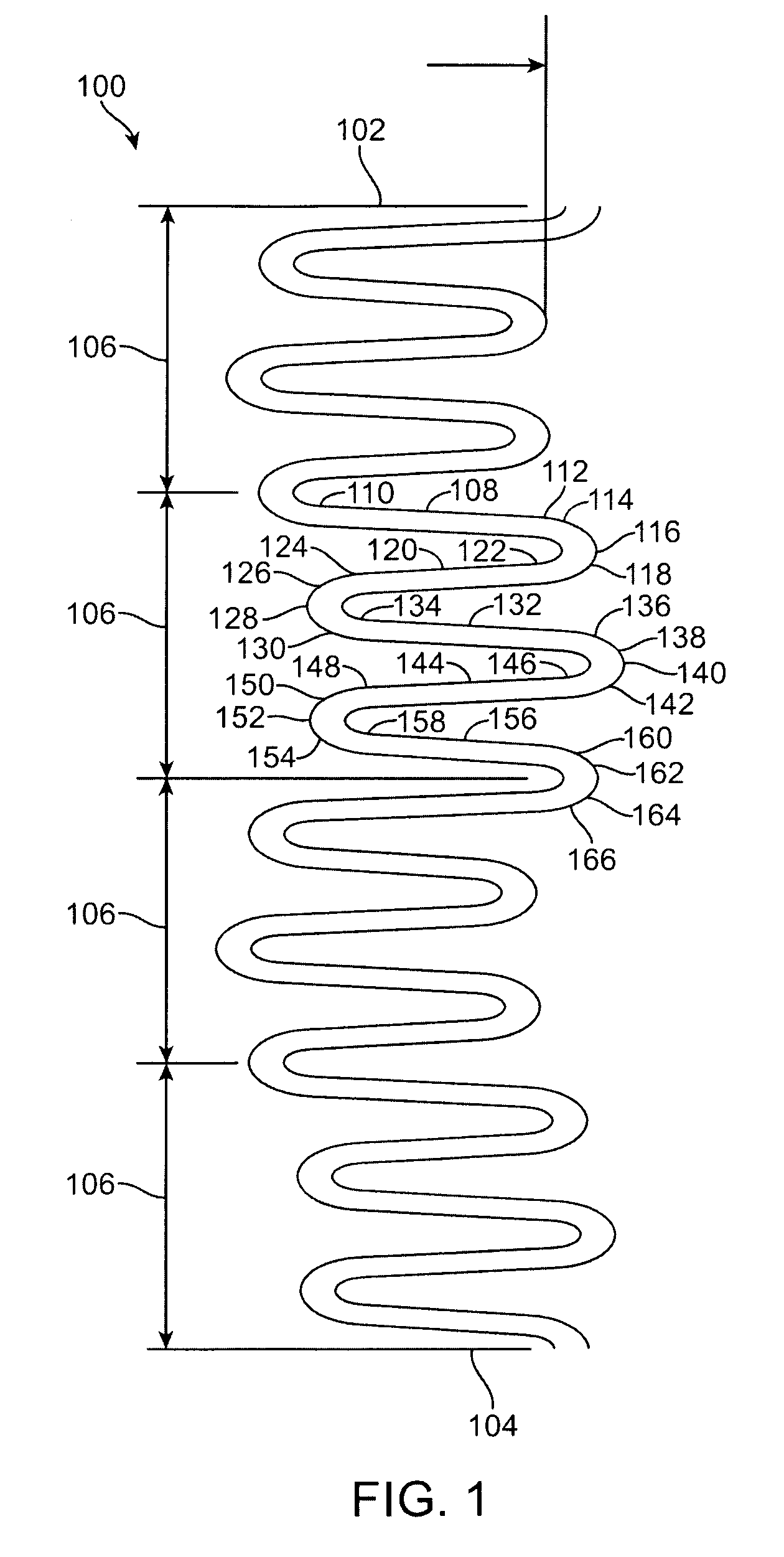
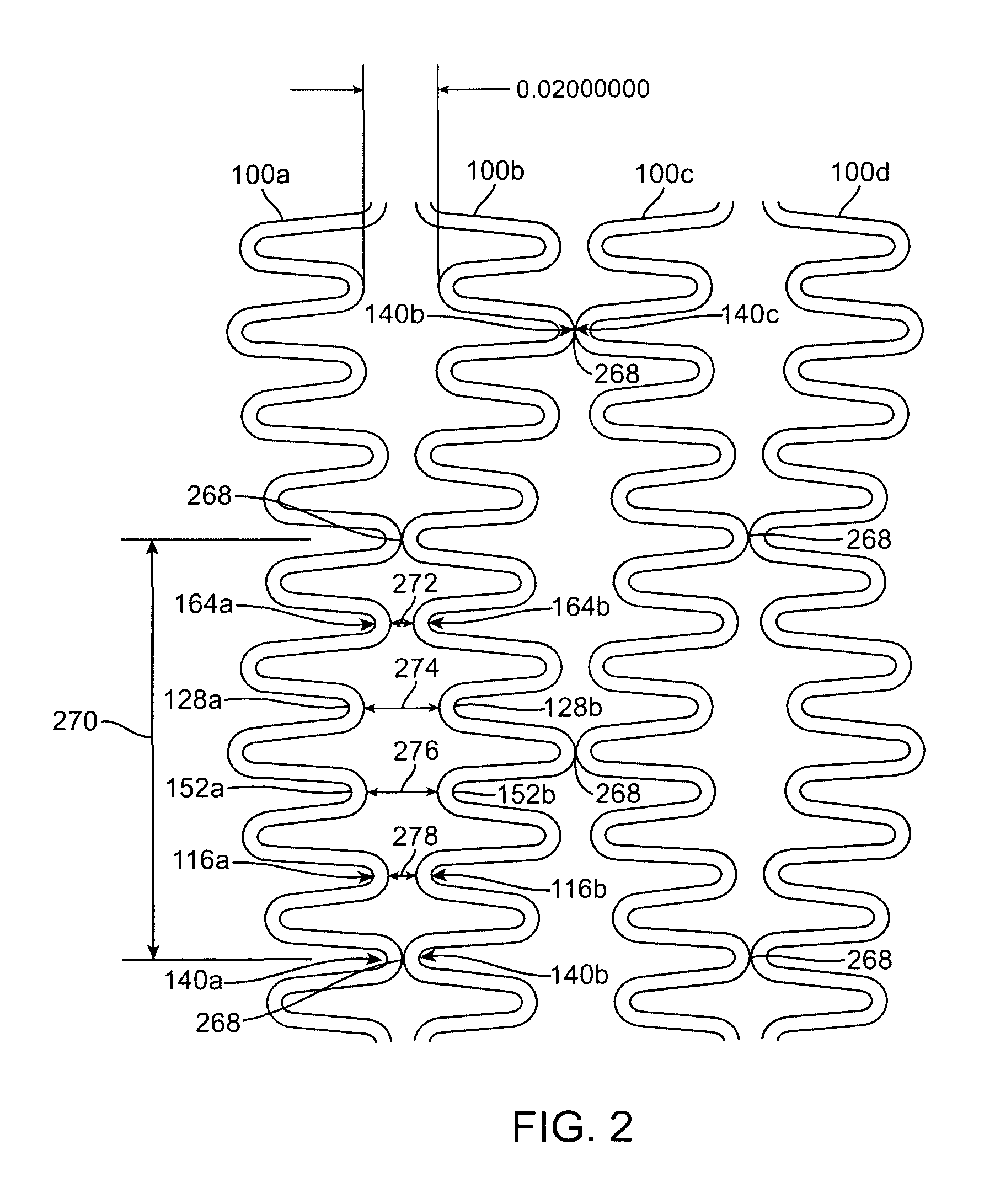
A stent made up of at least two connected bands, each band having a pattern of undulations formed from long, short and mid-sized segments connected together by turns. In particular, the pattern includes a repeating series having five segments: a long segment, a short segment, a mid-sized segment, a mid-sized segment, a short segment (LSMMS). When adjacent bands are connected together to form the stent body, the LSMMS segment configuration forms a series of consecutive tapered gaps between the consecutive unconnected close ended turns of adjacent bands which provide greater flexibility for the stent. The series of consecutive tapered gaps allow the stent to flex with little or no interference with adjacent bands when the stent is tracked around a small radius bend in a vessel. In addition, the length of the longest rigid element of the stent is decreased to further improve flexibility. A rigid element is formed by the lengths of the segments on both sides of a connection between adjacent bands. By decreasing the length of this rigid element, the length which must be tracked around the bends of a vessel is shortened and thus the stent is easier to advance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Flexible system for delivering an anchor
ActiveUS20140005690A1Minimize patient discomfortImpart tensionSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesDiseaseBiomedical engineering
A system and associated method for manipulating tissues and anatomical or other structures in medical applications for the purpose of treating diseases or disorders or other purposes. In one aspect, the system includes a delivery device including a flexible portion that is suited to access target anatomy. The flexibility of an elongate portion of the delivery device can be varied. Additionally, the delivery device can include structure that maintains the positioning of the delivery device in patient anatomy.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
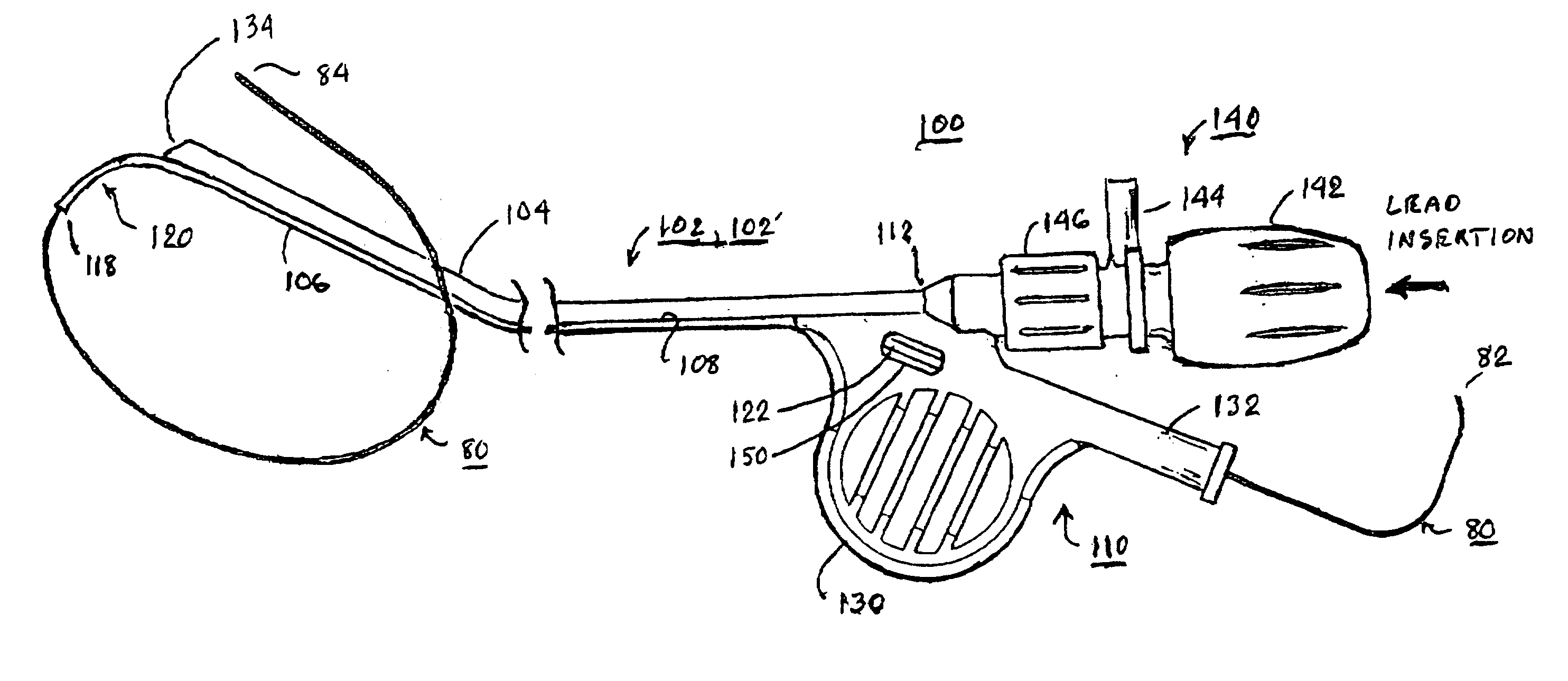
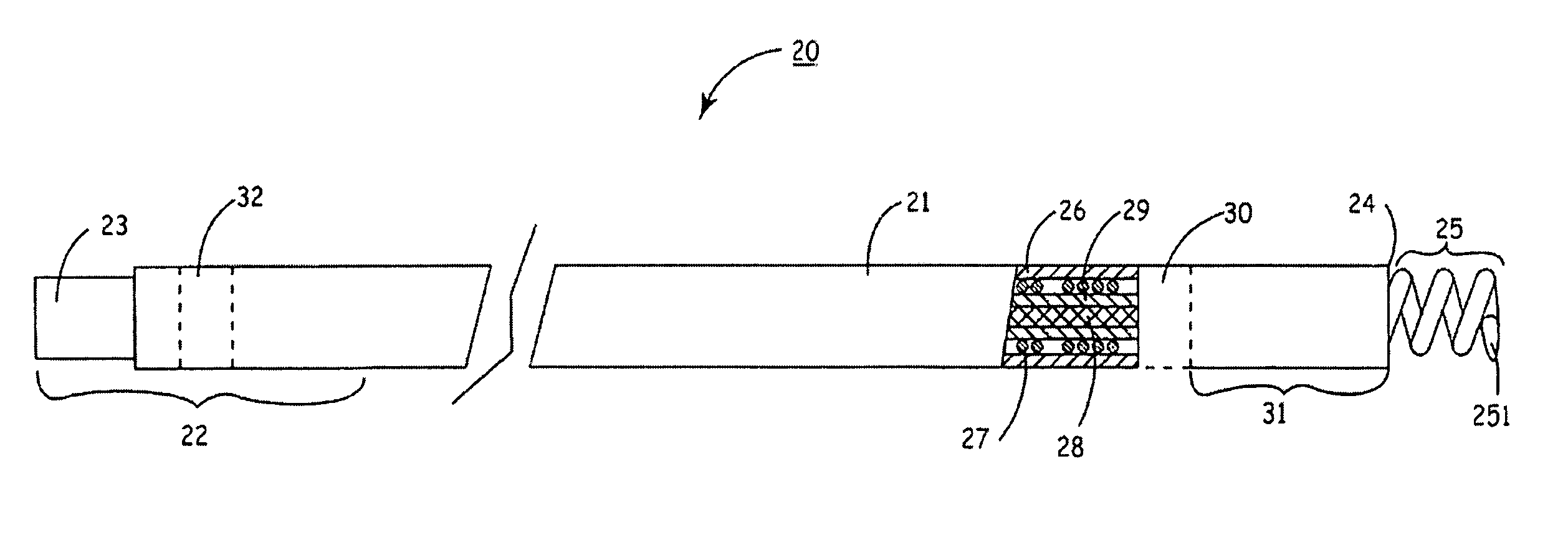
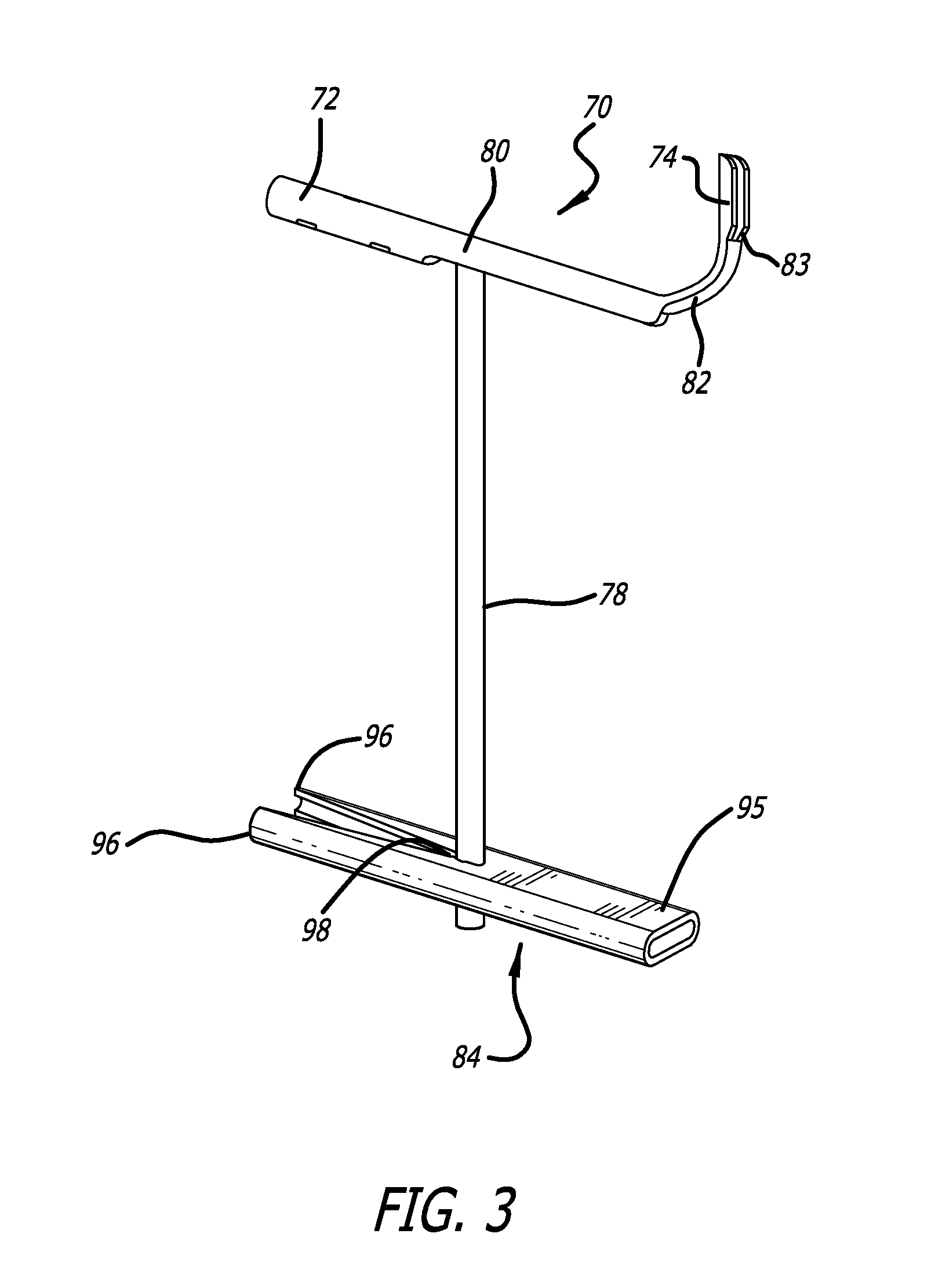
Double sleeve endoscope
Endoscopic apparatus, including a probe (9) having an anterior component (12) and a posterior component (14), and a flexible dual-sleeved tube (31). The flexible dual-sleeved tube consists of a flexible external sleeve (26) and a flexible internal sleeve (36) within the external sleeve. The sleeves are coupled between the anterior component and the posterior component so as to define an enclosure (37) between the sleeves, which enclosure is inflated in order to propel the anterior component within a lumen (49).
Owner:STRYKER GI
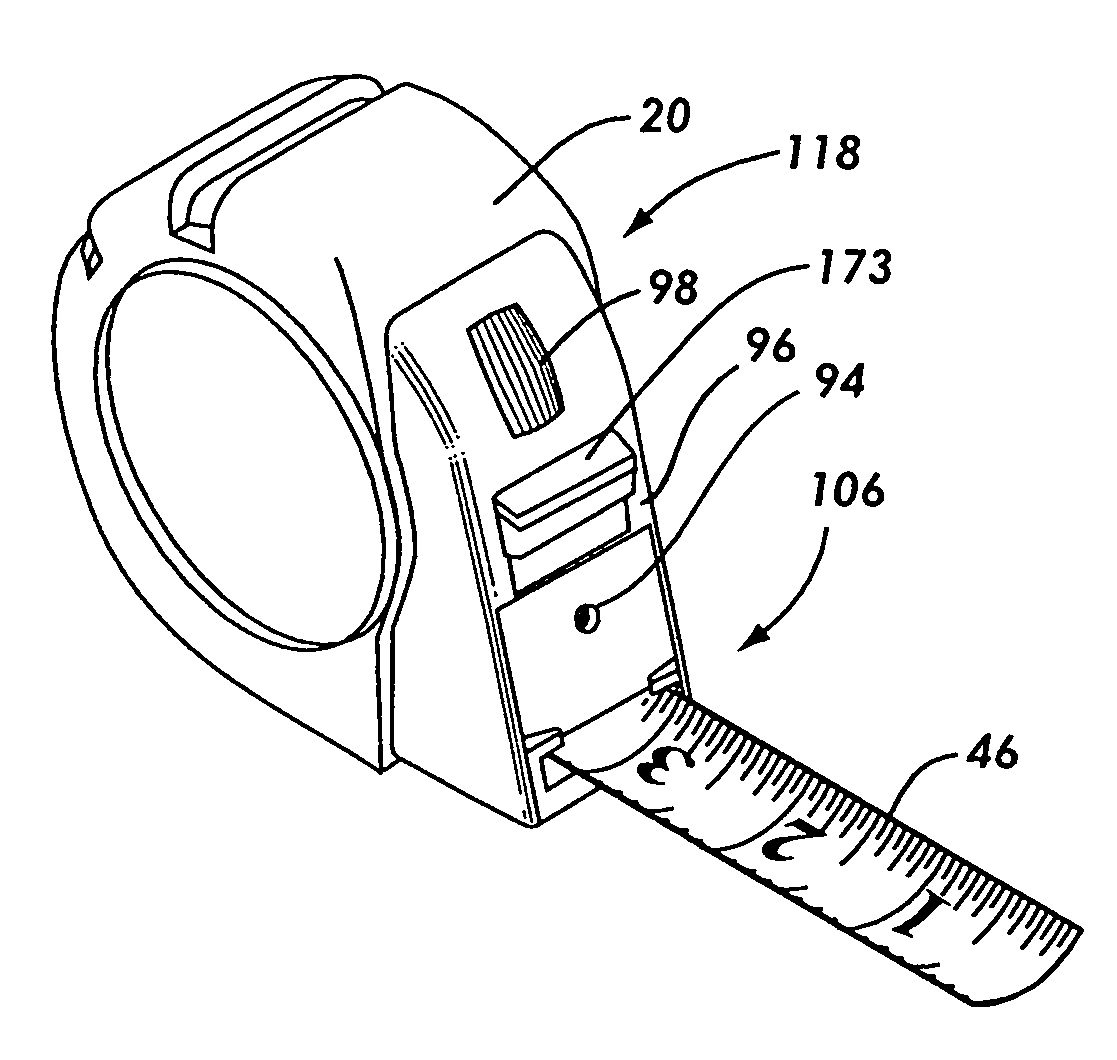
Tape measure that incorporates a chalk line style marking device
InactiveUS20060185185A1Efficient and economicalEasily advancedMeasuring tapesTape measureElectrical and Electronics engineering
A tape measure that incorporates a marking device for allowing an individual to measure and mark a wide variety of materials in a more efficient and economical manner, and for measuring and marking the beginning point of reference and the measured position point simultaneously. The tape measure has a housing, a coiled measuring tape, a tape tip, a chalk line, a chalk receptacle, a chalk line recharger, an activator, and an advancer. The chalk line is easily advanced and retracted for making marks at varying distances. The chalk is stored in a chalk storage receptacle that allows the chalk line to be re-chalked and is refillable for multiple uses. The activator allows the retractable chalk line to transfer a chalk substance from the chalk line to the surface to be measured and marked.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Method of positioning a medical instrument
InactiveUS20060217694A1Facilitate ablationEasily advancedElectrotherapyCatheterProximateBiological target
A system and method for positioning a medical instrument at a desired biological target tissue site is provided. The system includes an elongated sheath having a deflectable distal end configured to deflect or otherwise position at least a portion of a medical instrument during a surgical procedure allowing for the placement of the deflected portion adjacent or proximate to a predetermined target tissue surface. The positioning system may be incorporated into the medical instrument. The medical instrument may be an ablation system.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
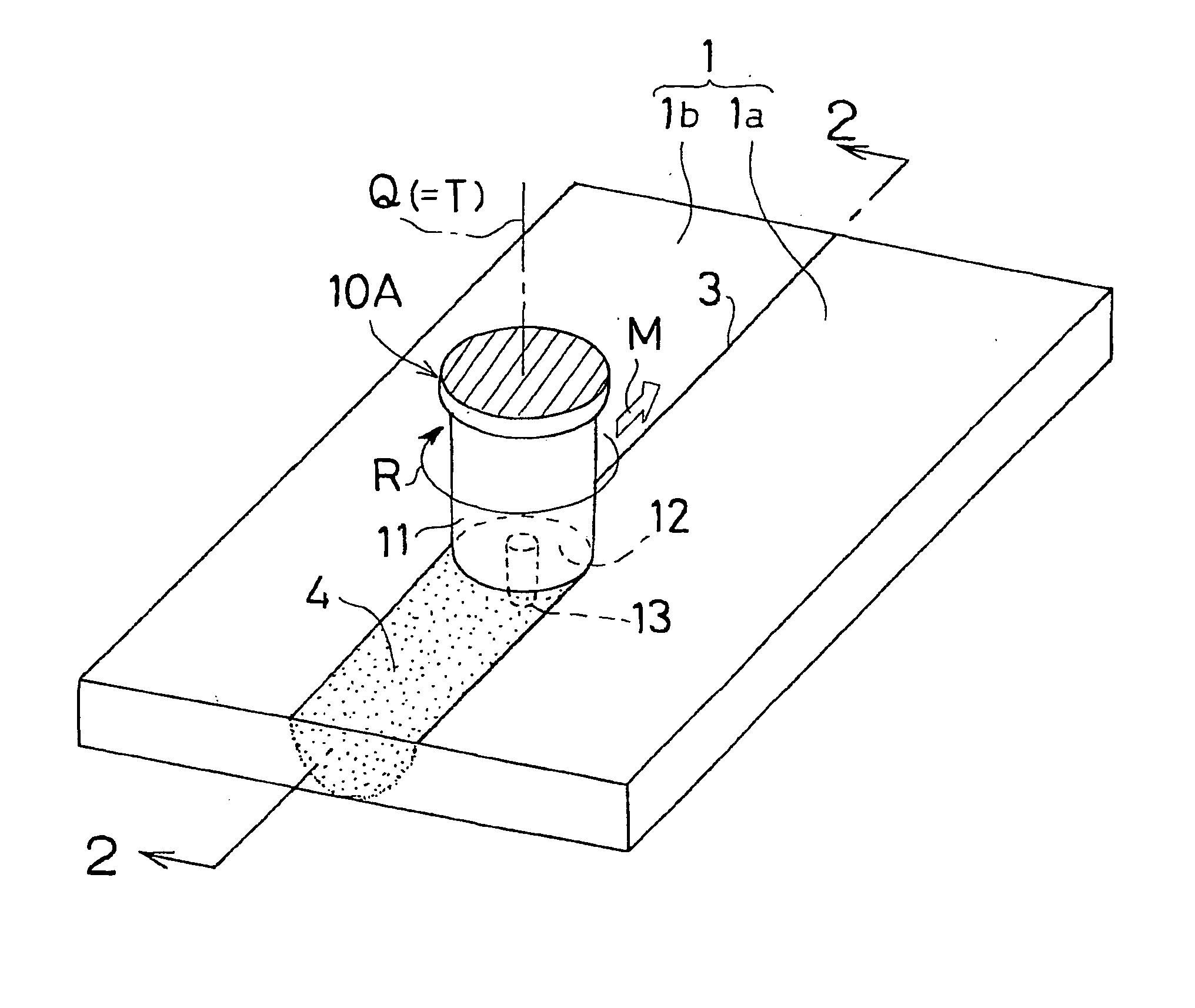
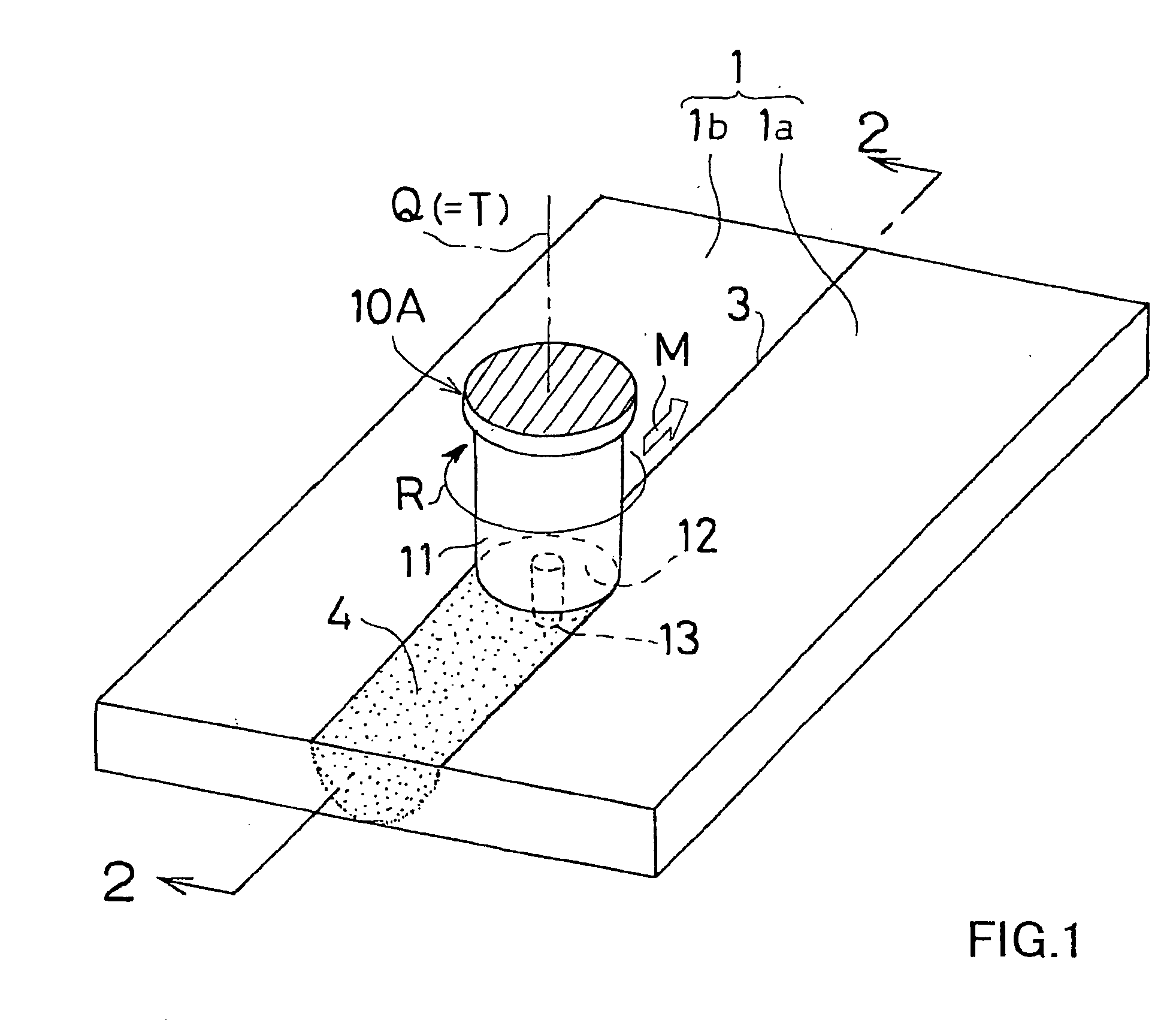
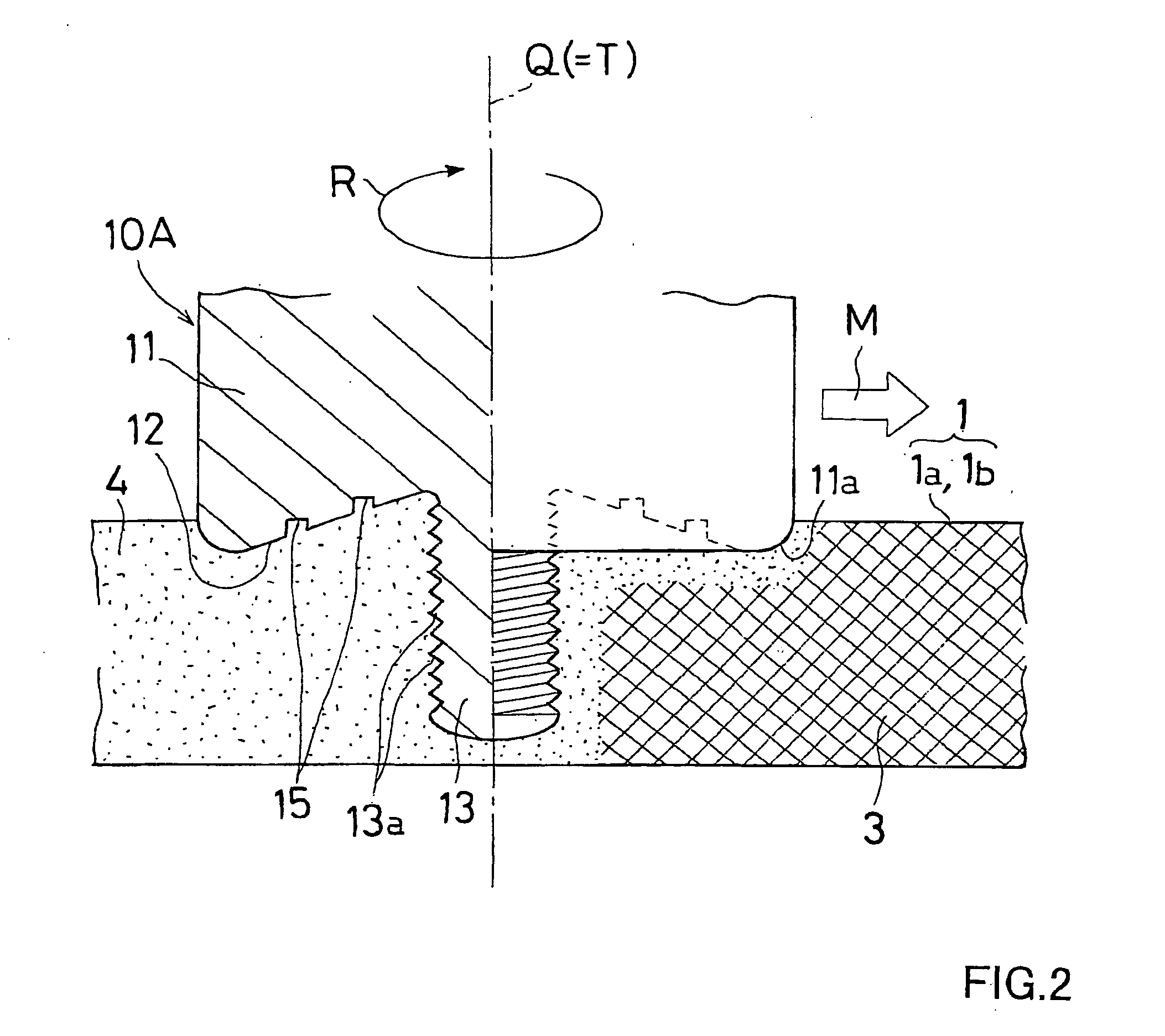
Friction agitation joining tool, friction agitation joining method and joined member manufacturing method
InactiveUS20040108359A1Prevent escapeHold steadyWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
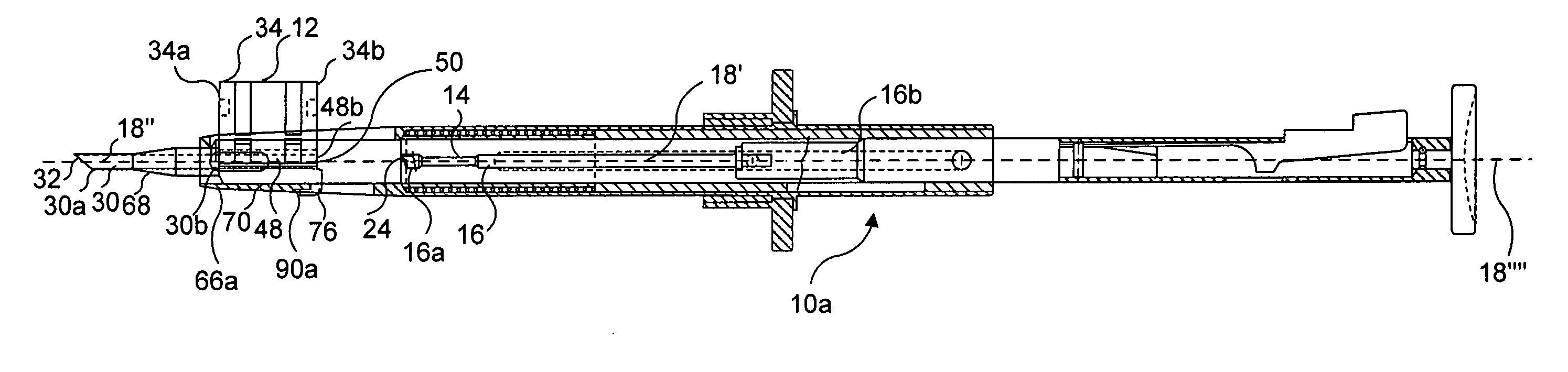
A friction agitation joining tool (10A, 10B) includes a rotor (11) having an end portion to be pressed onto at least one of surfaces of joining members (11a, 1b) and a probe (13) to be inserted into a joining portion (3) of the joining-members (1a, 1b), wherein the probe (13) has a diameter smaller than a diameter of the rotor (11). An end face (12) of the end portion of the rotor (11) is formed into a concave surface dented from a periphery of the end face (12) toward a rotational center of the end face (12). The probe (13) is protruded from the rotational center of the end face (12). The end face (12) is provided with a spiral groove (15) or an annular groove (16) surrounding the probe (13). By performing the joining operation with the joining tool (10A, 10B), a joined member with a good joint can be obtained.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Tape measure that incorporates a chalk line style marking device
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Multilumen brachytherapy balloon catheter
ActiveUS20090198095A1Easily advancedAvoid excessive radiationElectrotherapyBalloon catheterDistal portionBrachytherapy
The disclosure describes a device for asymmetrical irradiation of a body cavity or site, such as after removal of tissue, e.g. biopsy or lumpectomy. The device includes an elongated tubular shaft having an inner lumen and a tubular wall with a plurality of lumens extending within the wall which are configured for receiving a radiation source. The distal portion of the tubular shaft is cut into a plurality of longitudinally separated wall segments with a lumen extending within at least one of the wall segments. A support member is positioned within the separated wall segments to support and position the wall segments in a desired configuration for brachytherapy. An expandable member such as an inflatable balloon is mounted on the distal shaft portion about the separated wall segments wall which when inflated secures the distal shaft portion within a desired intracorporeal site for brachytherapy treatment.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Multimen brachytherapy balloon catheter
InactiveUS20090188098A1Minimizing damaging irradiationThin and stretchElectrotherapyBalloon catheterDistal portionBrachytherapy
The disclosure describes a device for asymmetrical irradiation of a body cavity or site, such as after removal of tissue, e.g. biopsy or lumpectomy. The device includes an elongated tubular shaft having an inner lumen and a tubular wall with a plurality of lumens extending within the wall which are configured for receiving a radiation source. The distal portion of the tubular shaft is cut into a plurality of longitudinally separated wall segments with a lumen extending within at least one of the wall segments. A support member is positioned within the separated wall segments to support and position the wall segments in a desired configuration for brachytherapy. An expandable member such as an inflatable balloon is mounted on the distal shaft portion about the separated wall segments wall which when inflated secures the distal shaft portion within a desired intracorporeal site for brachytherapy treatment.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
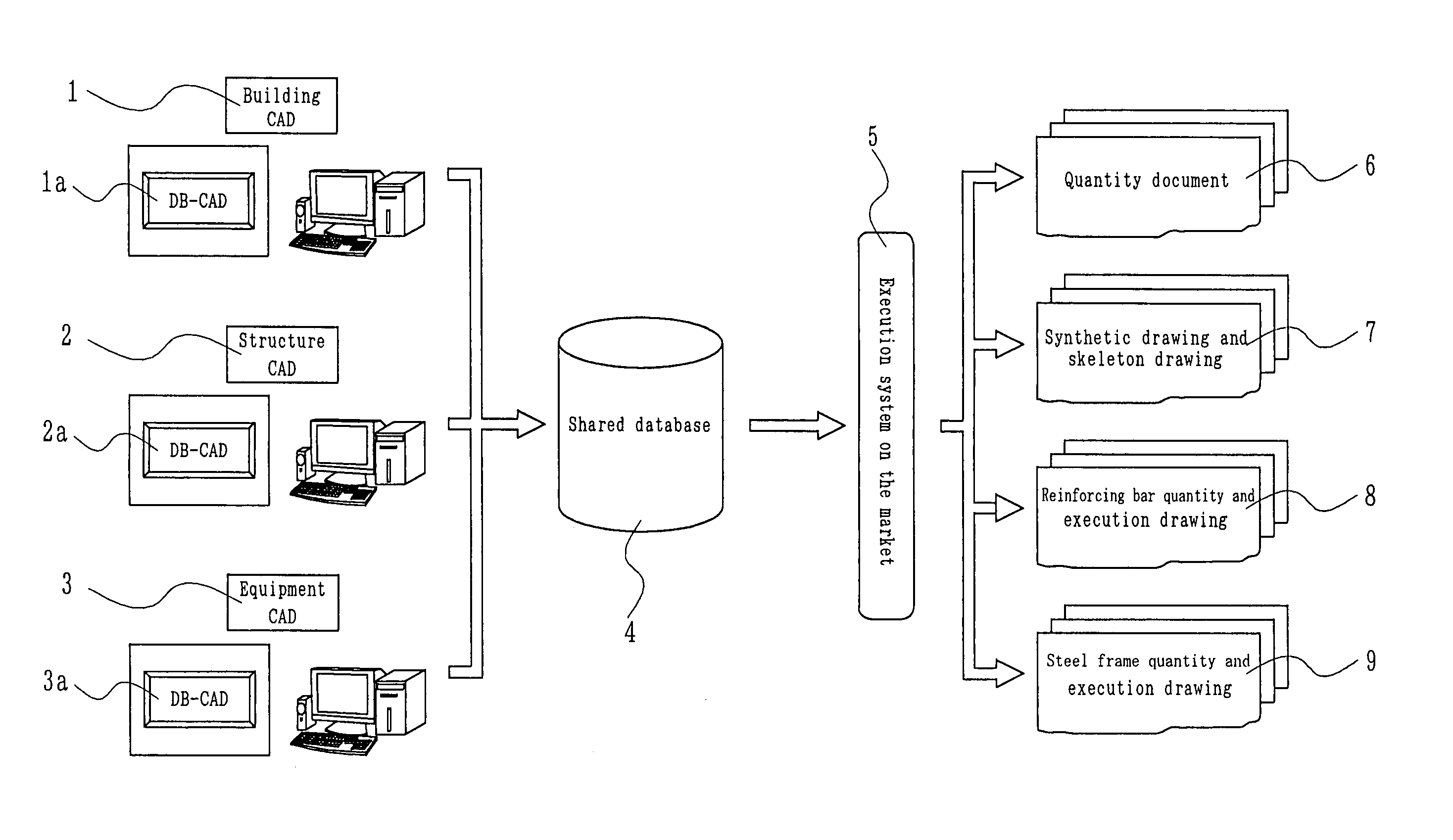
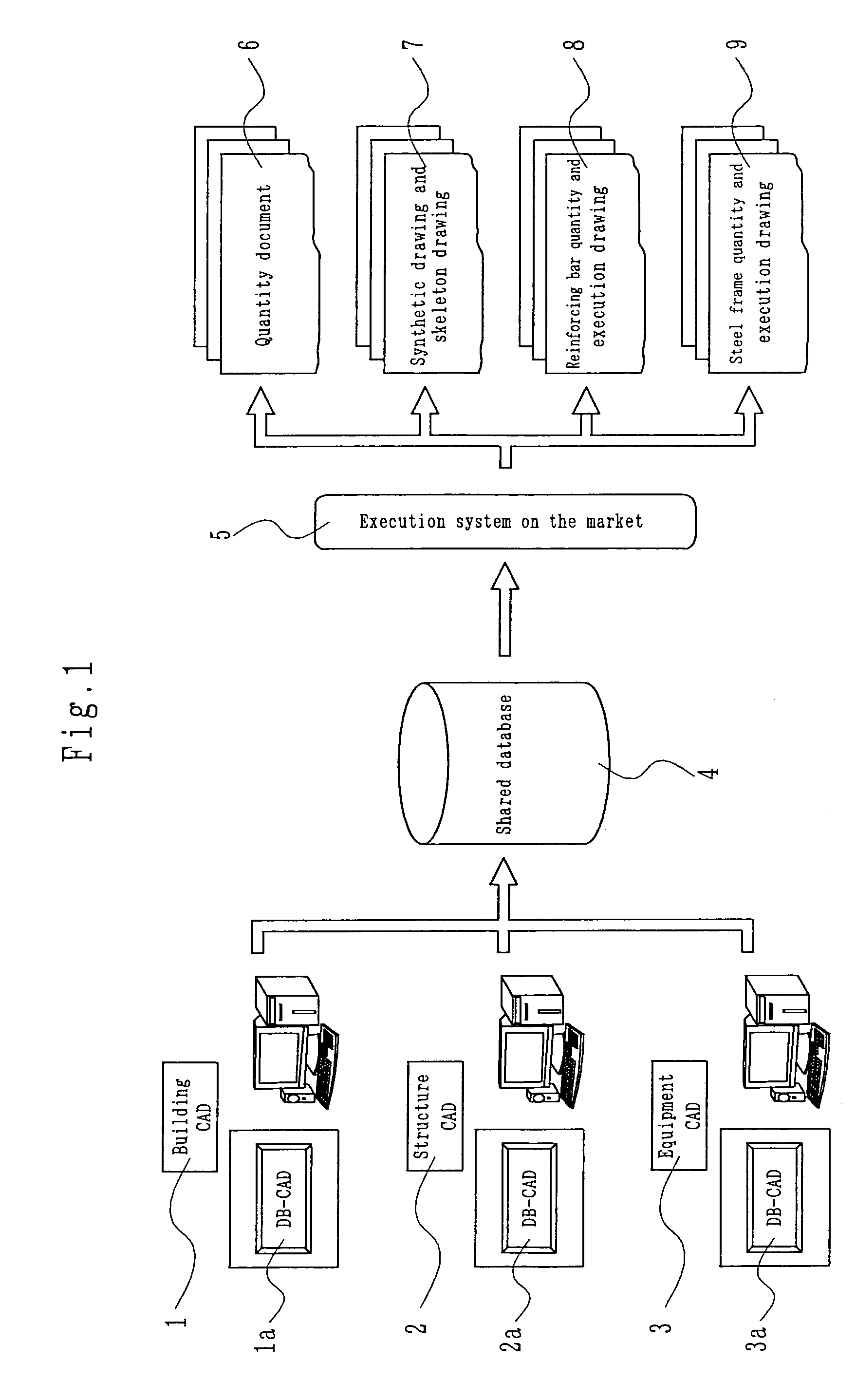
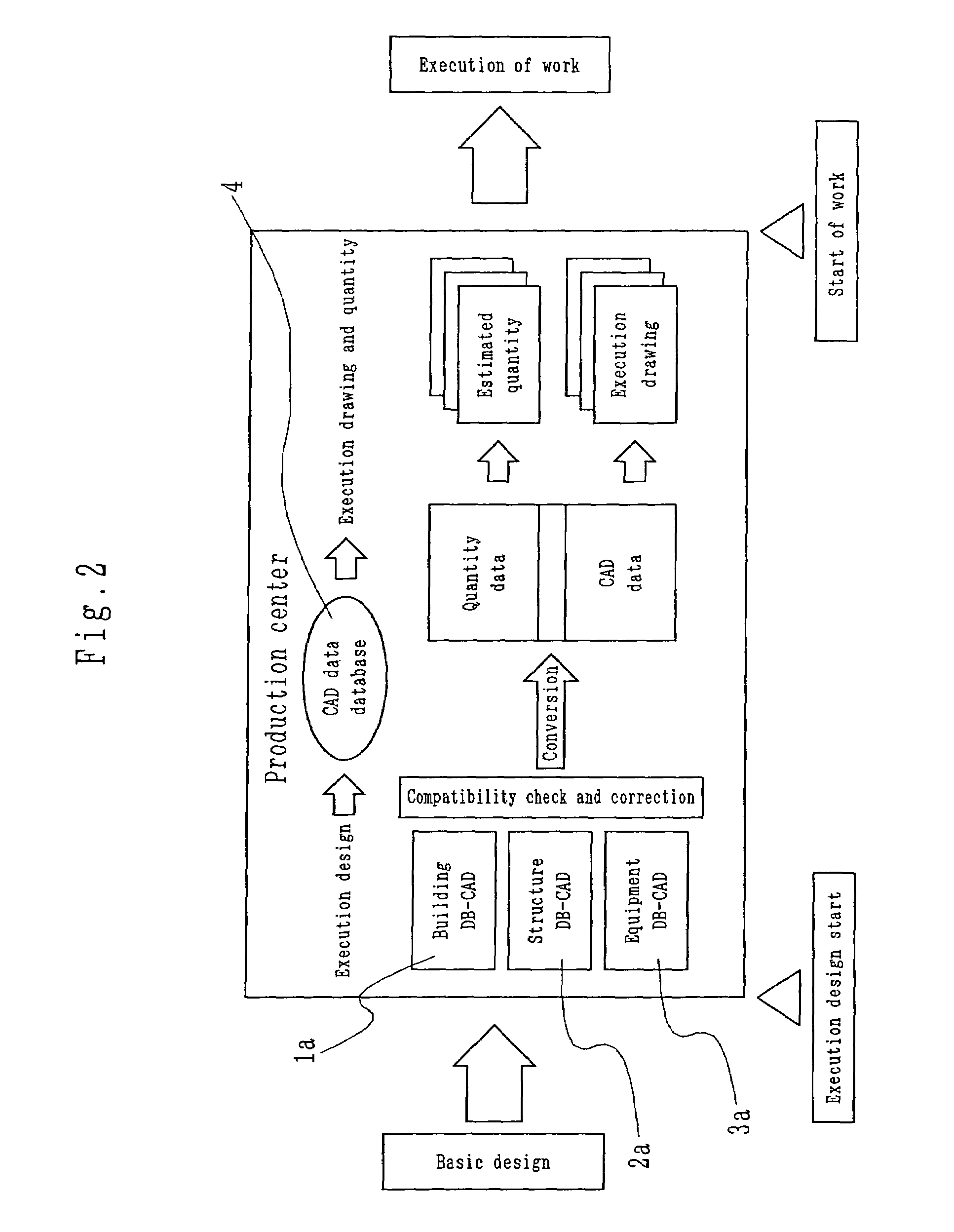
Integrated building production information system
InactiveUS7130775B2Improve design qualityImprove compatibilityGeometric CADData processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignSteel frame
An integrated building production information system including design CAD (computer-aided-design) based on software of building, structure, and equipment, and databases built in the outside separately from the design CAD, the databases making an integrated DB (shared database)-CAD system of building, structure and equipment as an execution-linked system in DB-CAD's sharing of a standard database, wherein the integrated building production information system stores the information made compatible by three-dimensional superposition at the time of design into a shared database (DB) of the integrated DB-CAD system, and further receives and links information of this shared database to extemal systems such as a skeleton drawing CAD, a reinforcing bar and steel frame system and the like and produces execution information.
Owner:KAJIMA CORP
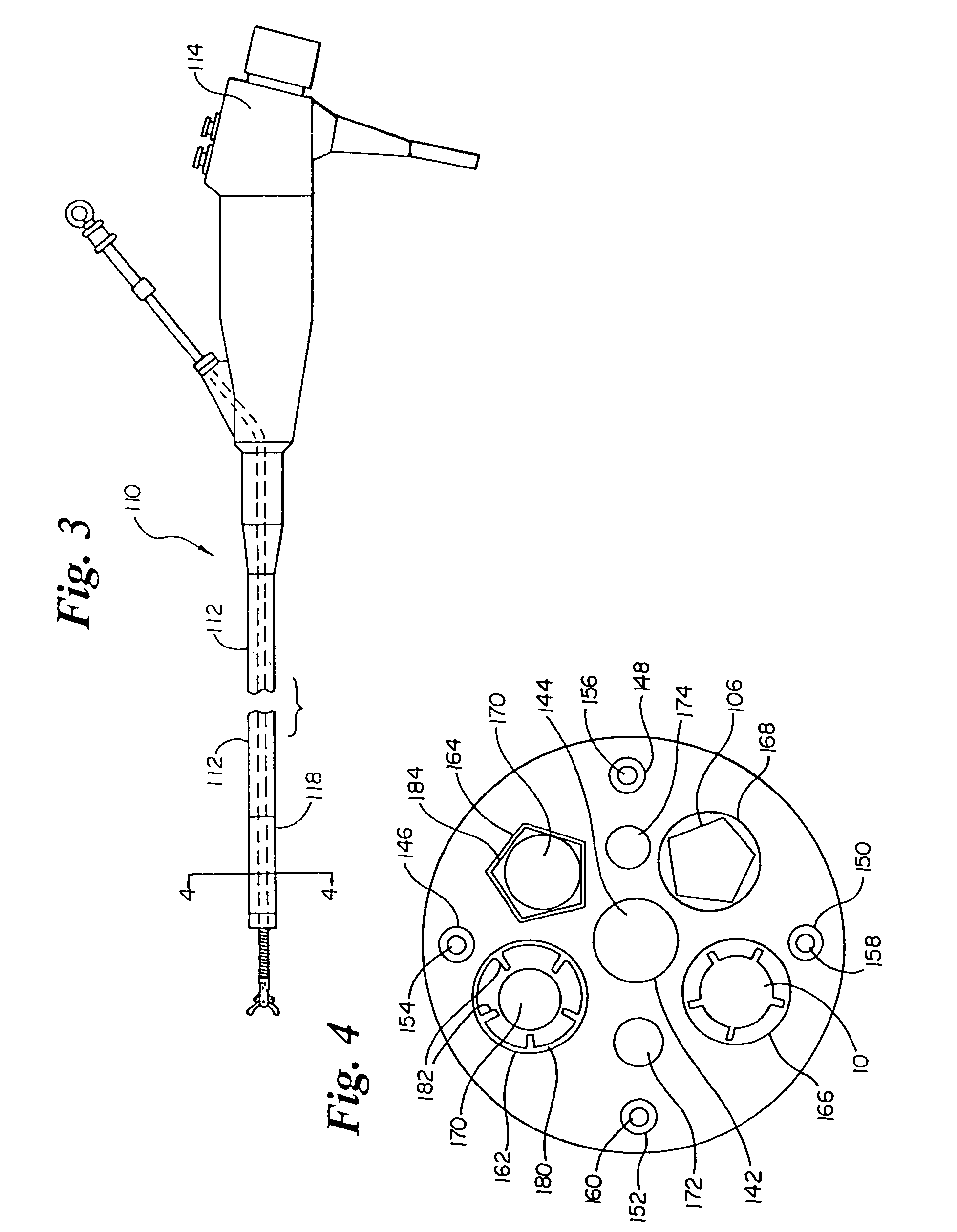
Spinal implant installation device
ActiveUS8343163B1Convenient to accommodateIncrease engagementSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesSpinal columnDistal portion
An implant installation device is provided for delivering an implant to a target implantation site including a handle with a first and second arms extending distally therefrom. A translation member extends through the handle such that a distal portion lies between the first arm and second arm while a proximal portion extends beyond the proximal end of the handle. An inserter is coupled at the distal end of the translation member and also lies between the first arm and second arm. With an implant positioned proximate the distal end of the inserter, the distal ends of the arms may be inserted between the pair of vertebrae. The translation member may be operated to drive the inserter distally, which in turn pushes the implant toward the implantation site.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Screwstrip advance mechanism and feeder for a power screwdriver
ActiveUS20110232430A1Easily advanceEasily repositionSpannersWrenchesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SIMPSON STRONG TIE
Guide for a cutting tool
InactiveUS7127976B1Cutting and similar operationEasy to cutDovetailed workMulti-purpose machinesEngineeringKnife blades
A guide comprises one or more brackets for securing the guide to a cutting tool, a horizontal support member secured to and moveable with respect to the brackets, and one or more arm assemblies secured to the horizontal support member and adapted to secure a working piece relative to the horizontal support member. With the working piece secured to the guide in this manner, the working piece may be readily advanced over a blade of the cutting tool by grasping and moving the horizontal support member relative to the brackets, thus ensuring a precise cutting of the working piece while also allowing a user to keep their hands away from the blade.
Owner:FITZSIMMONS GEORGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com