Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101results about How to "Facilitate ablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
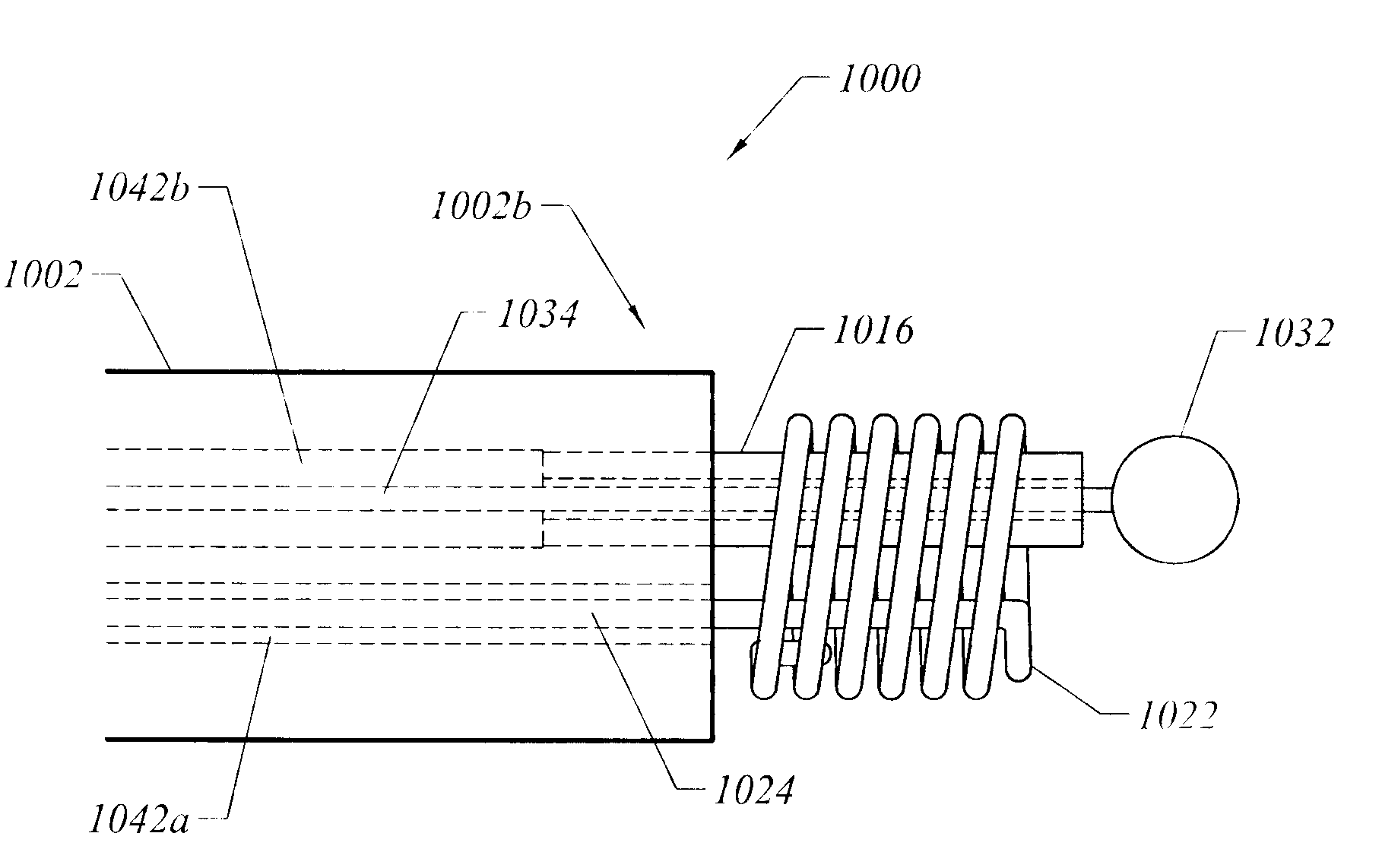
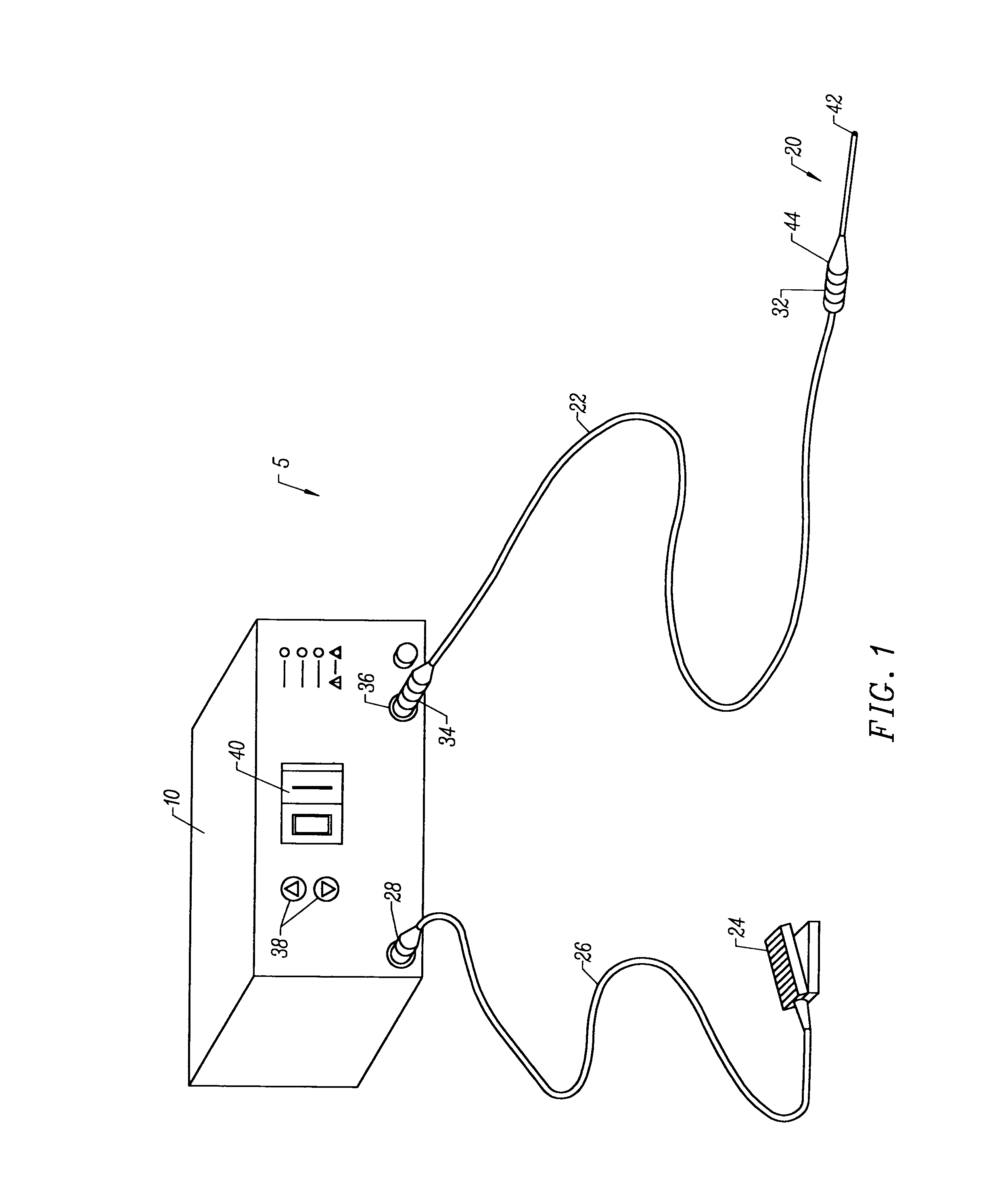
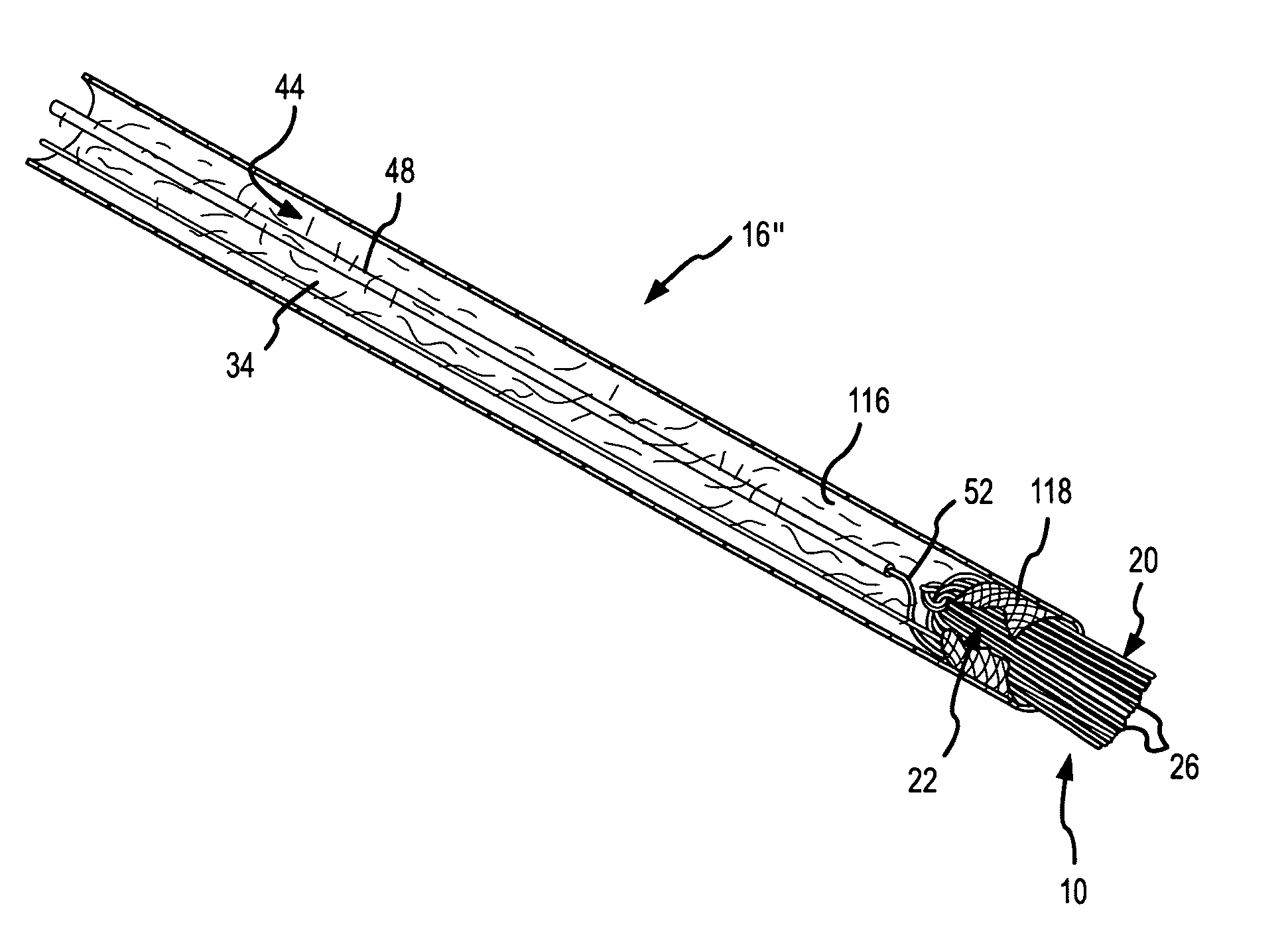
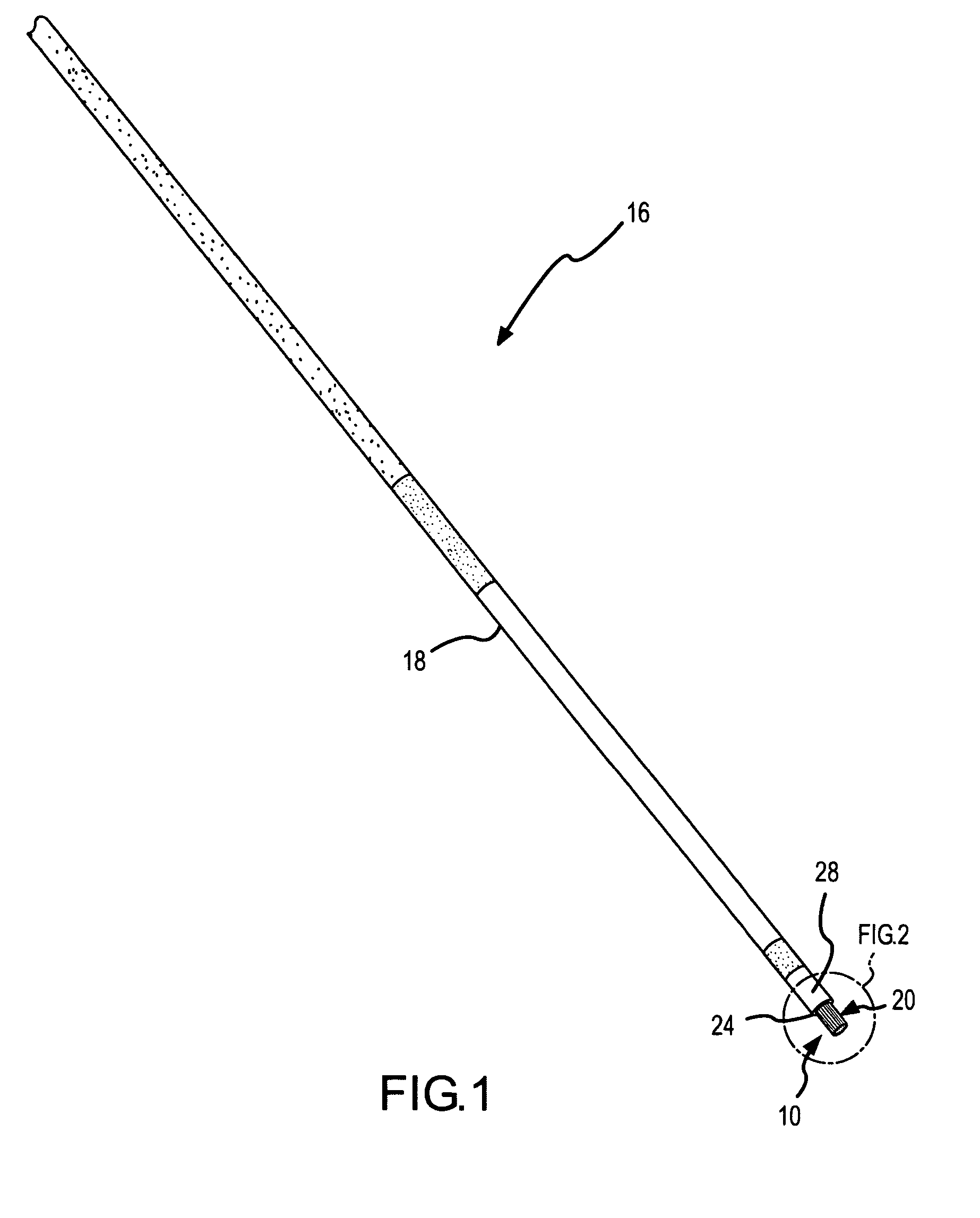
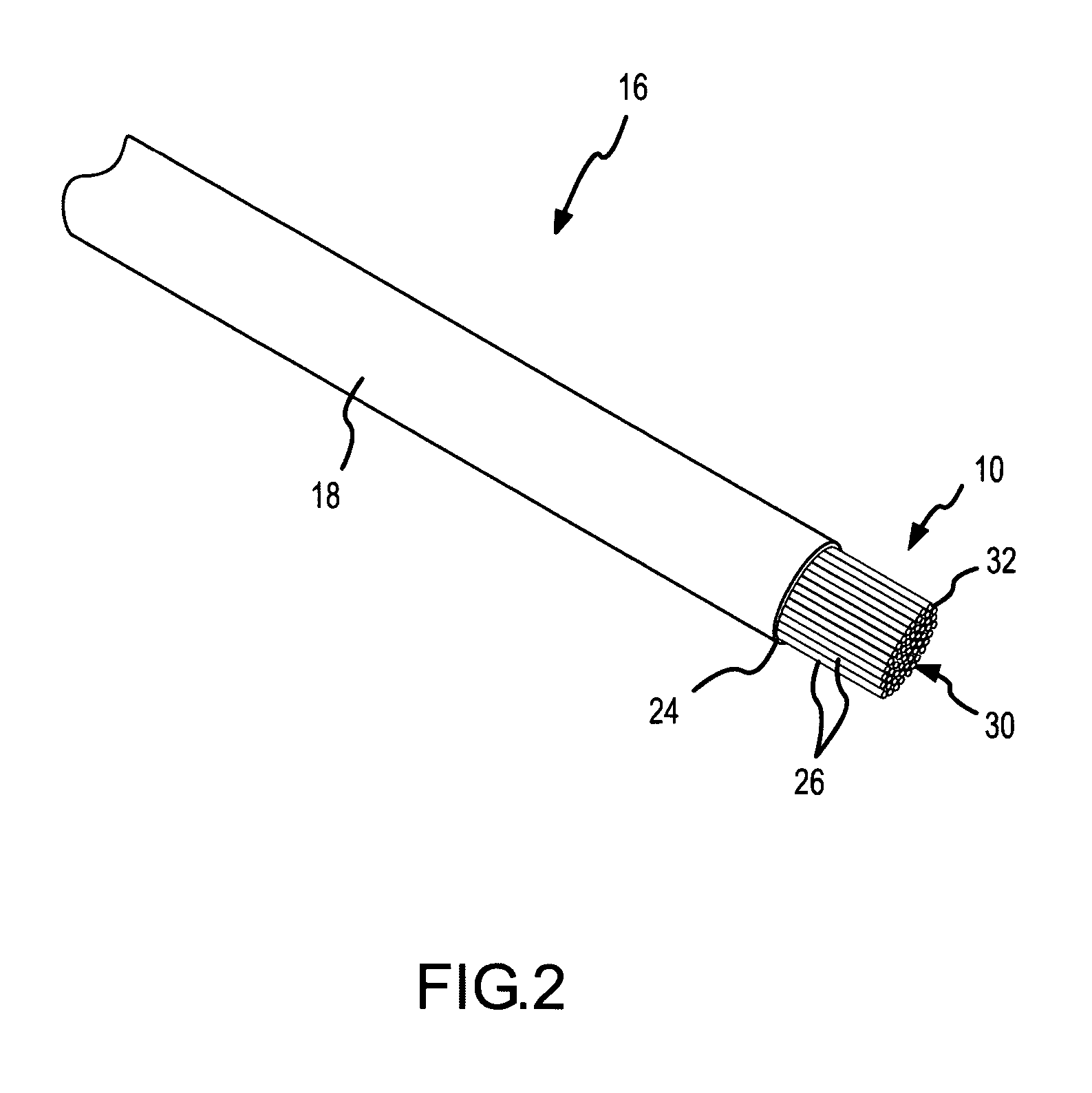
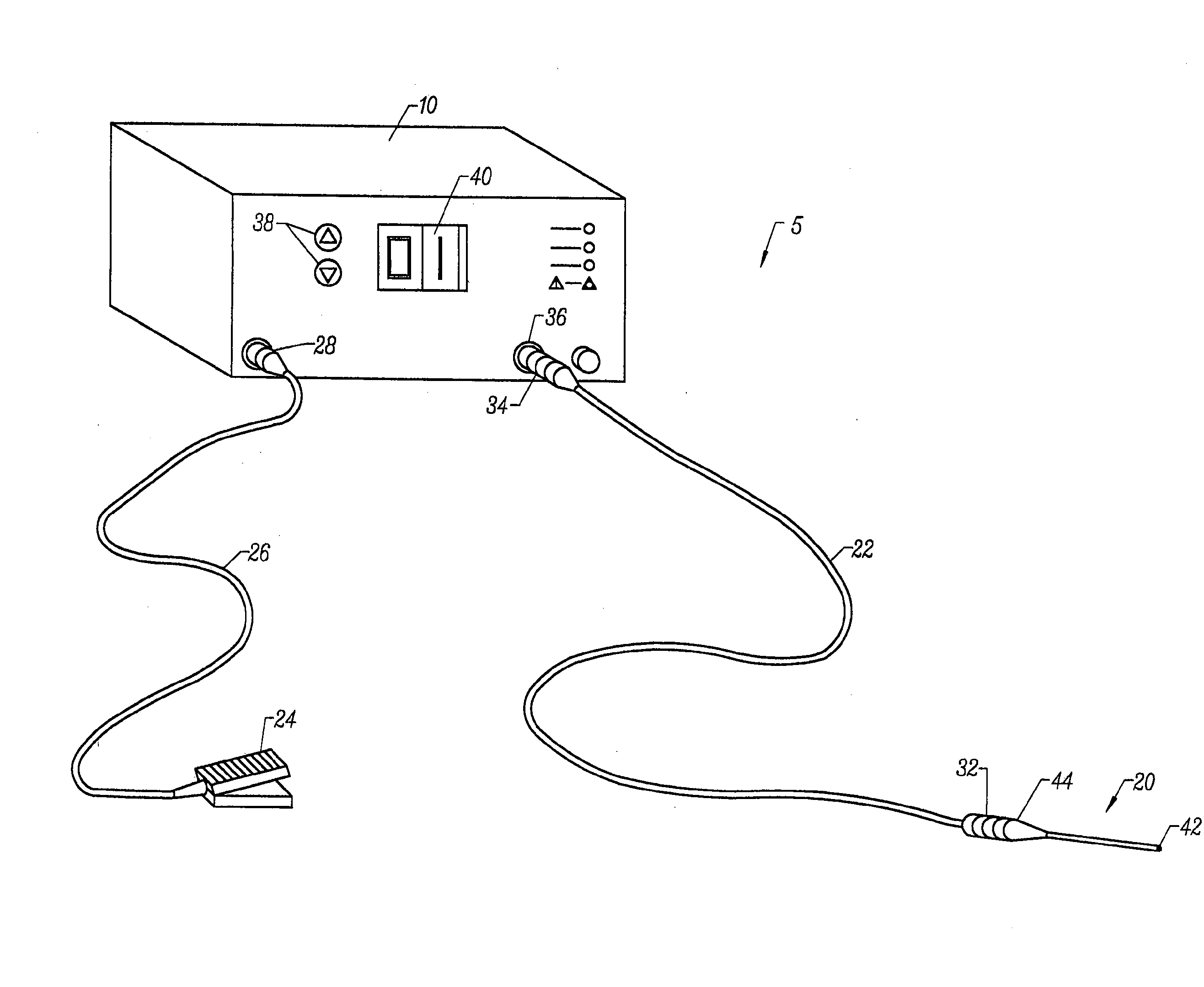
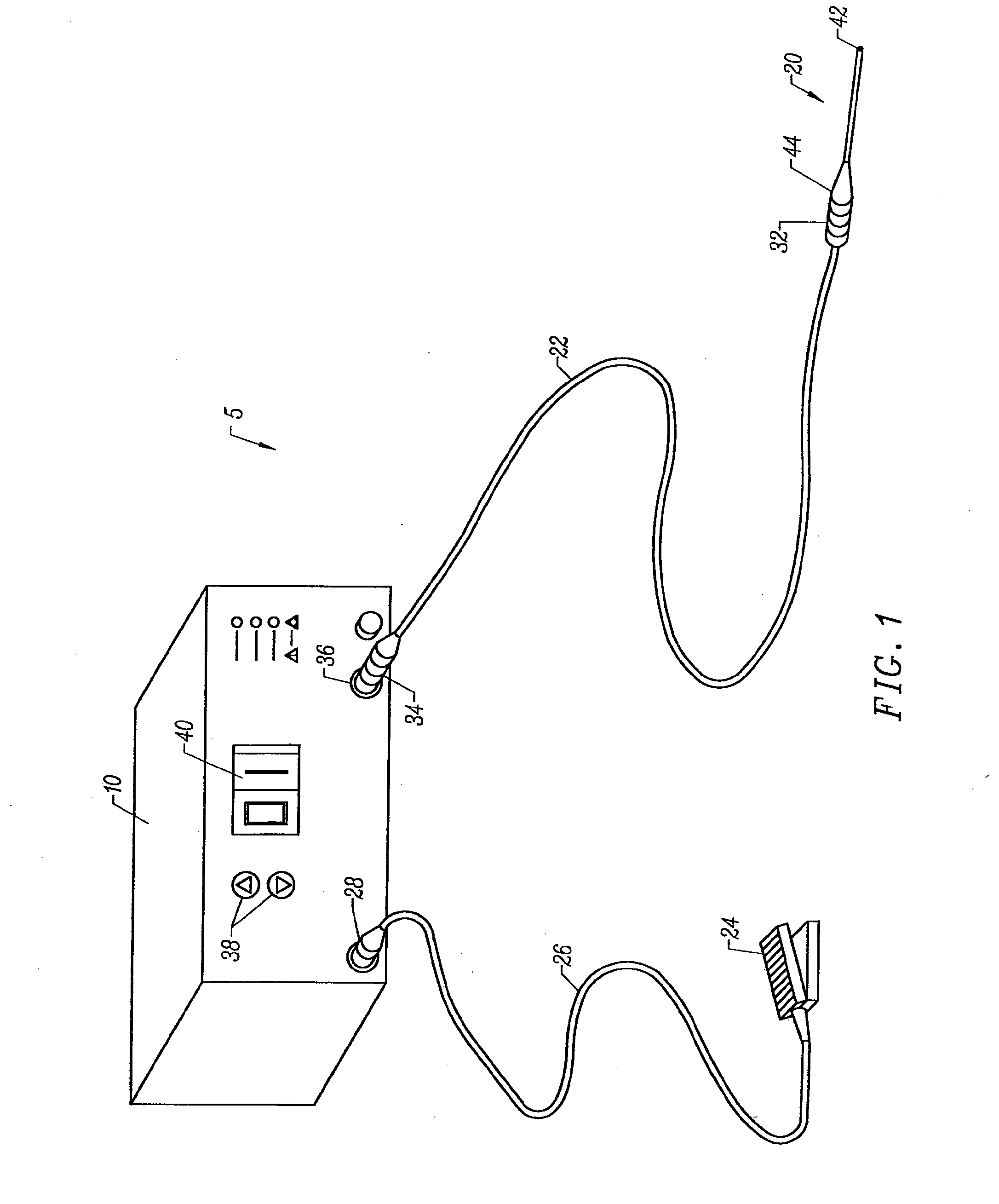
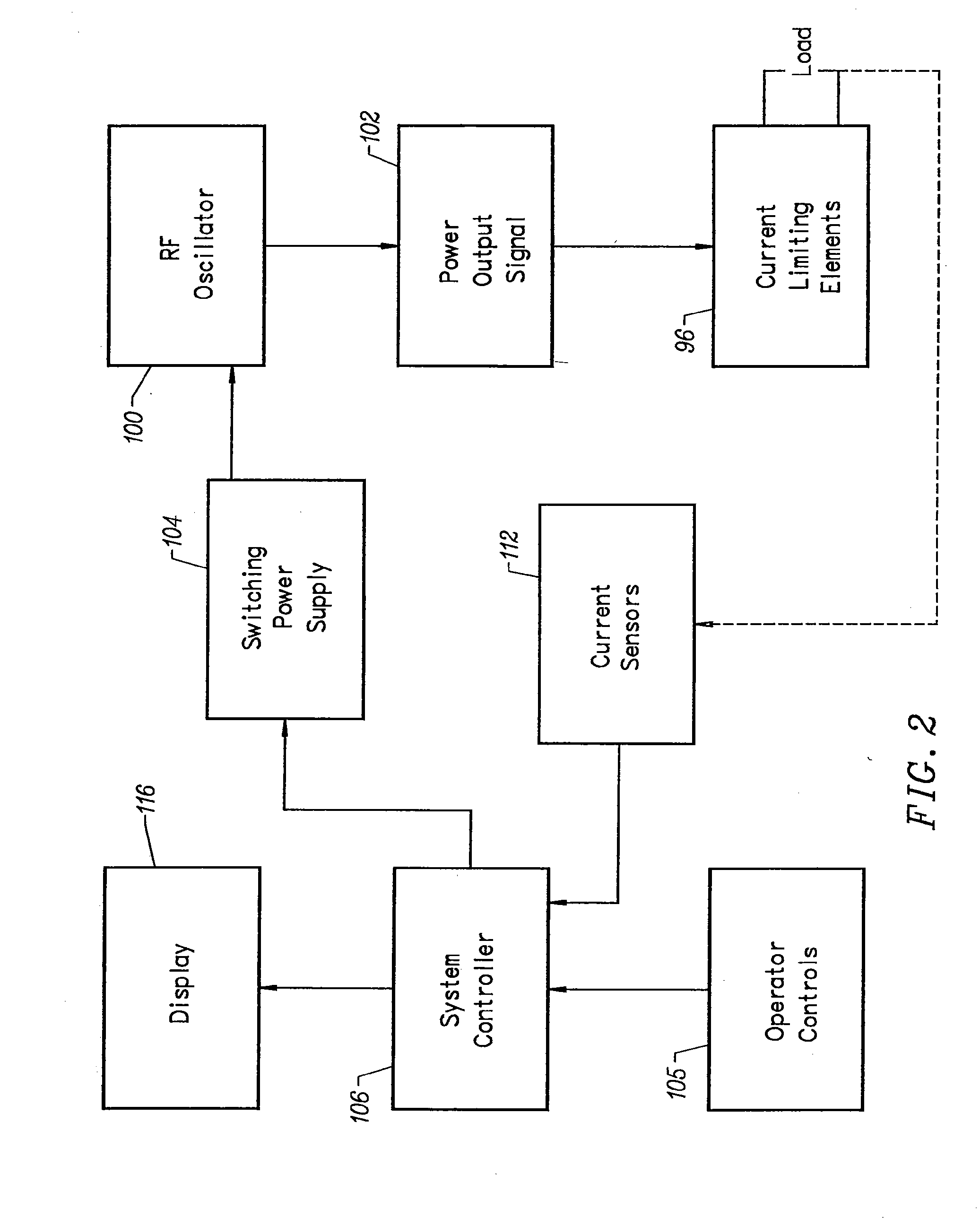
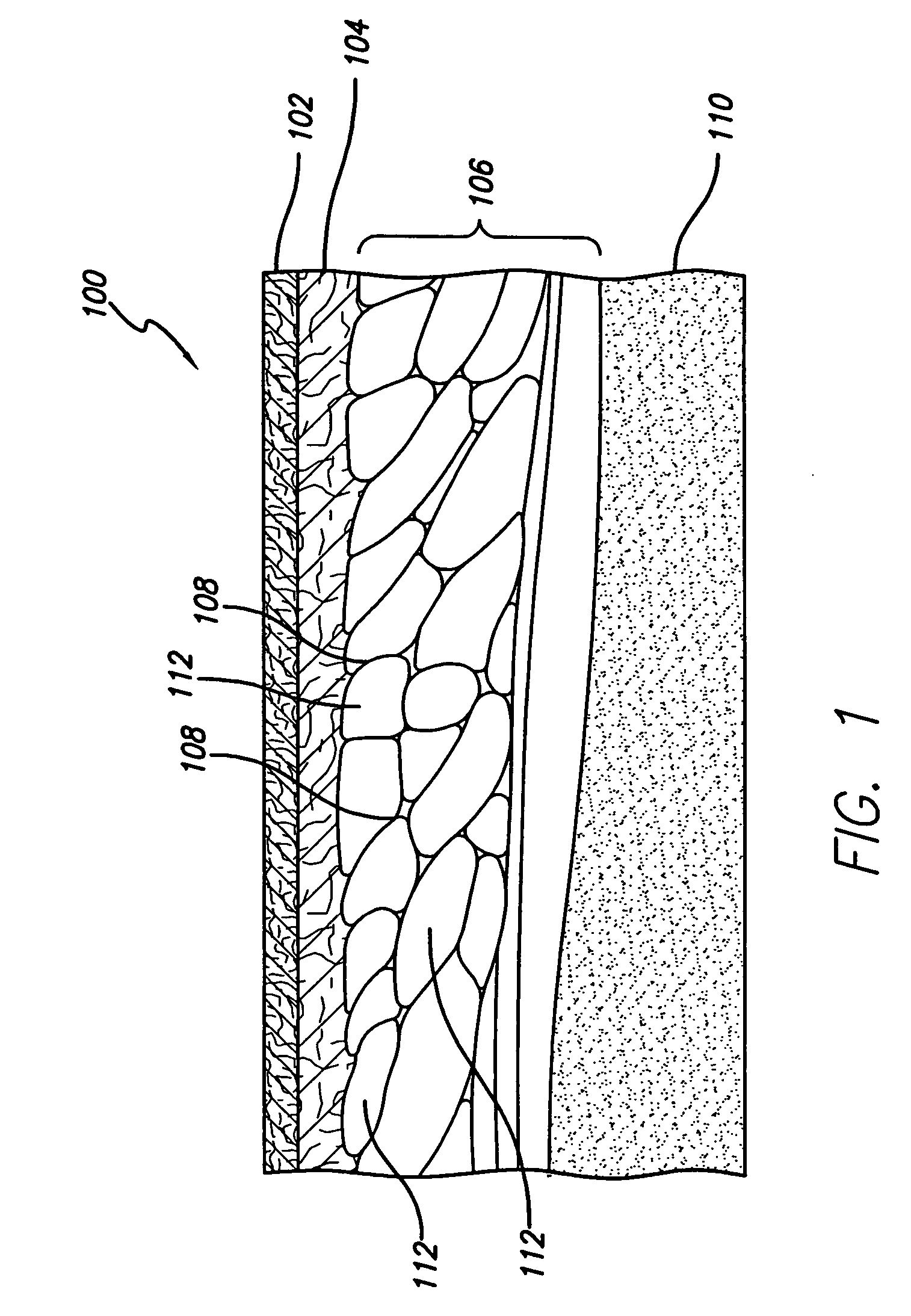
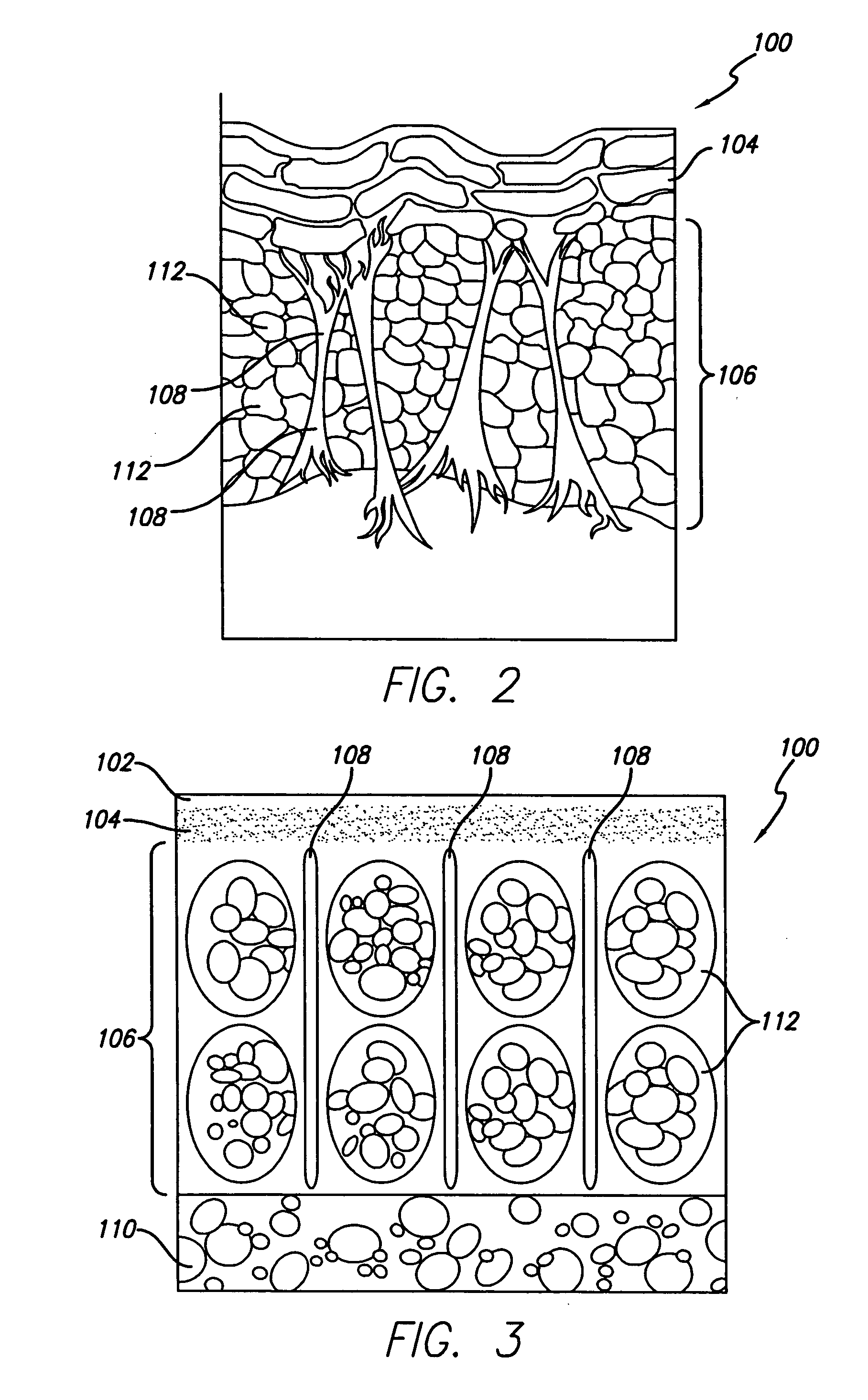
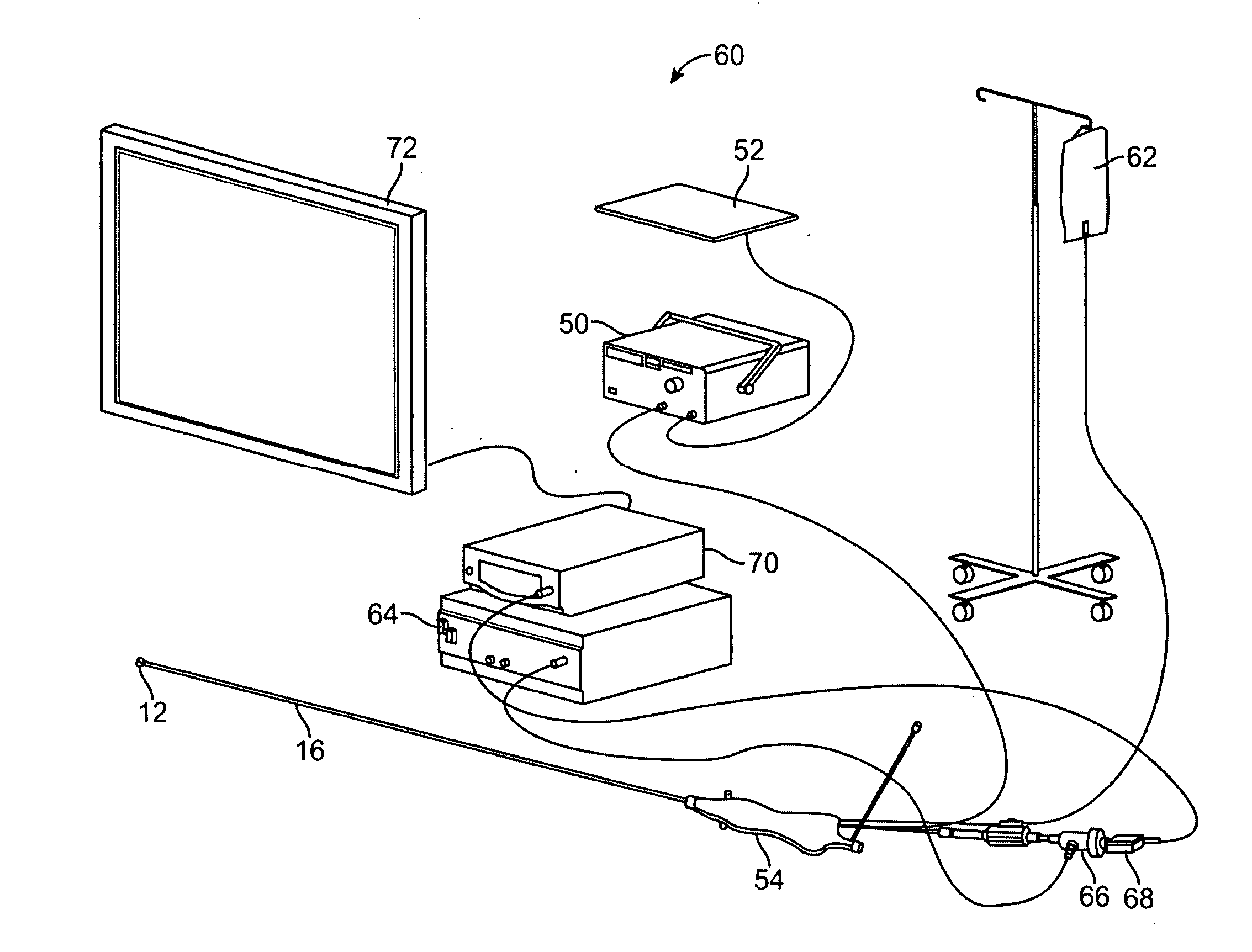
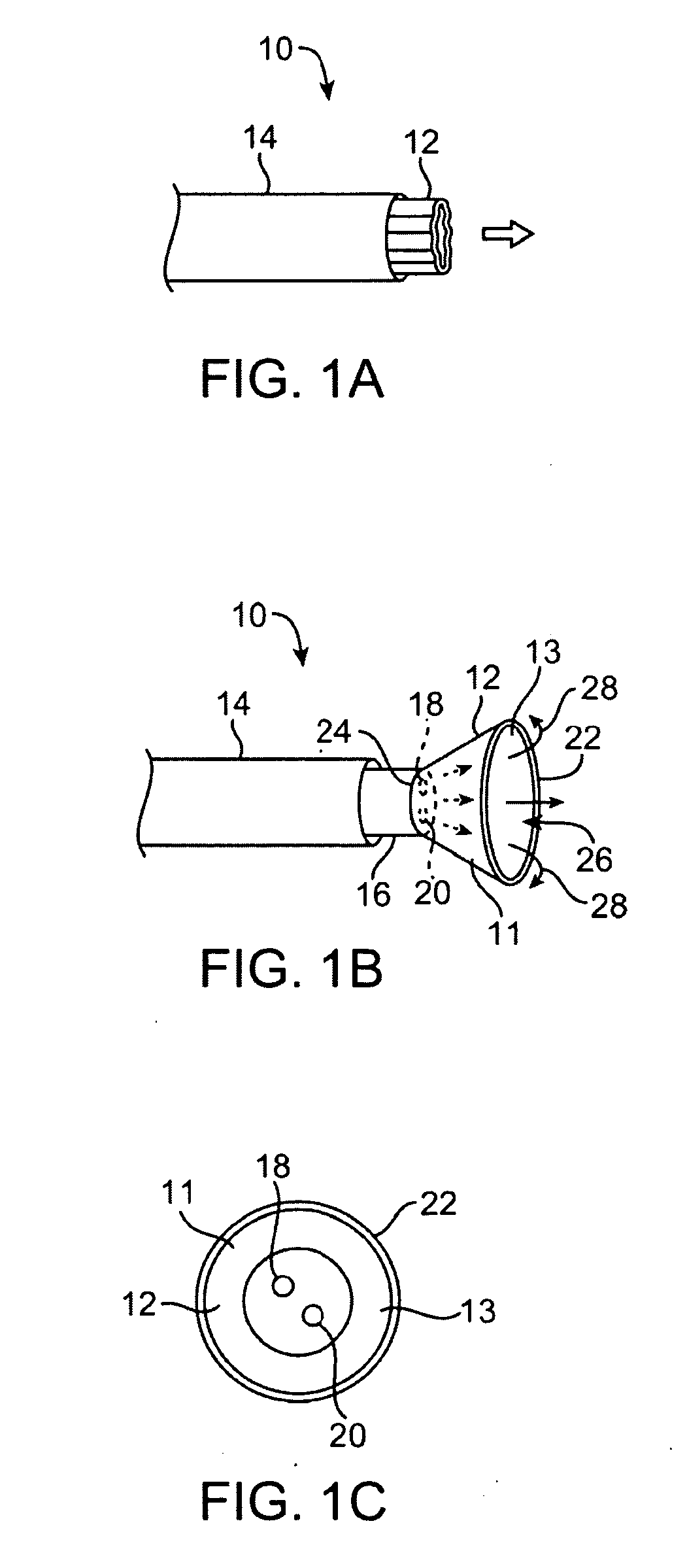
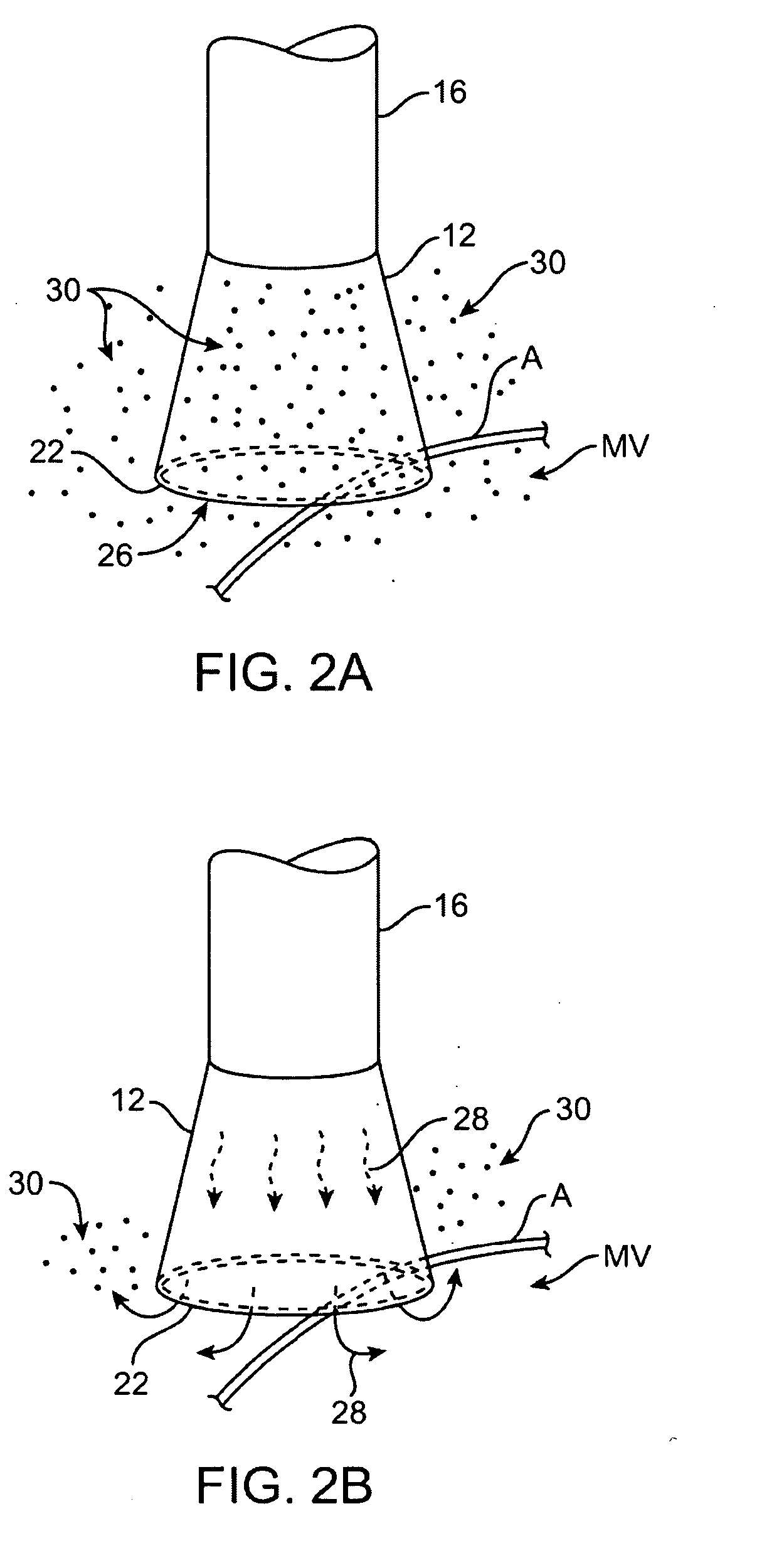
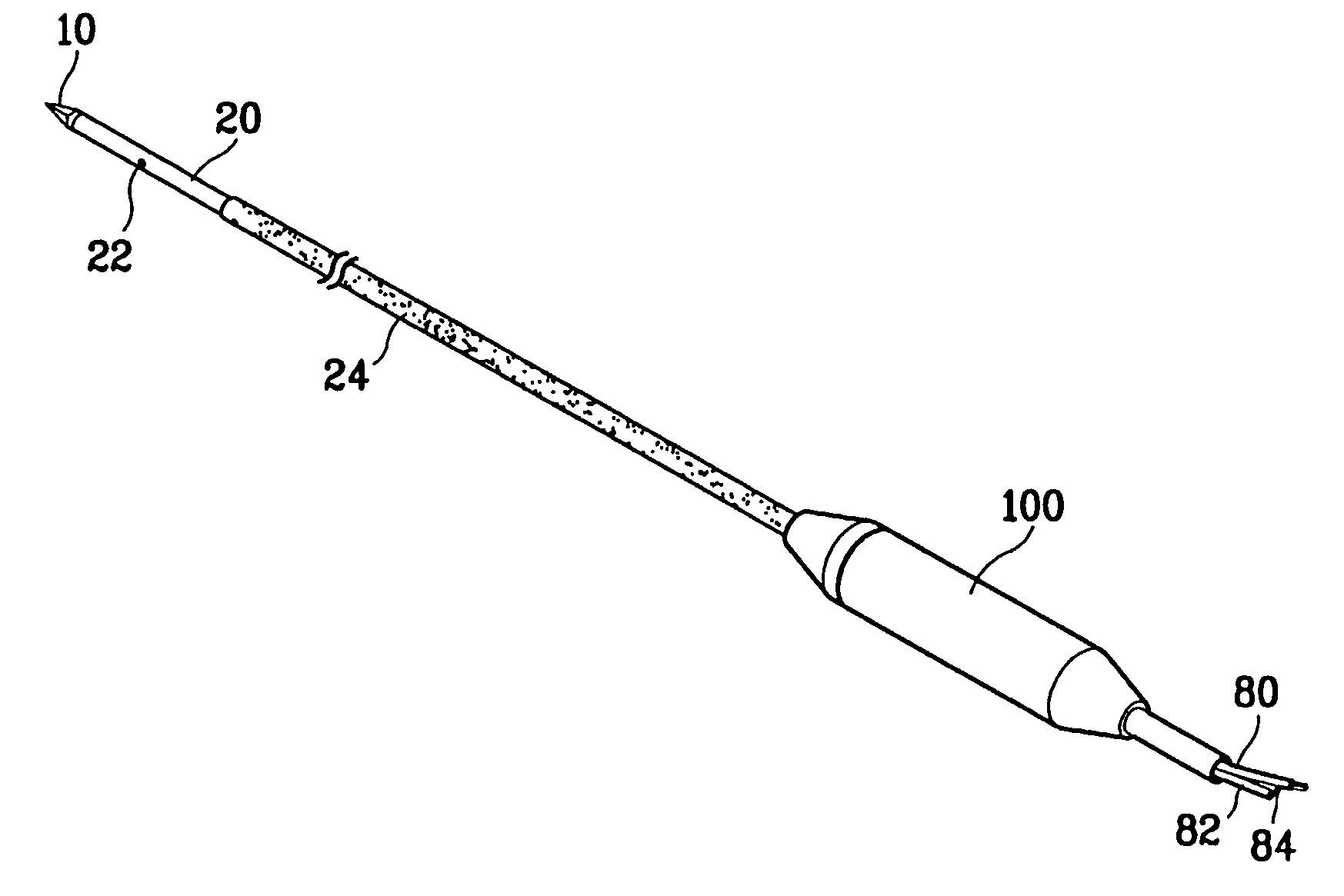
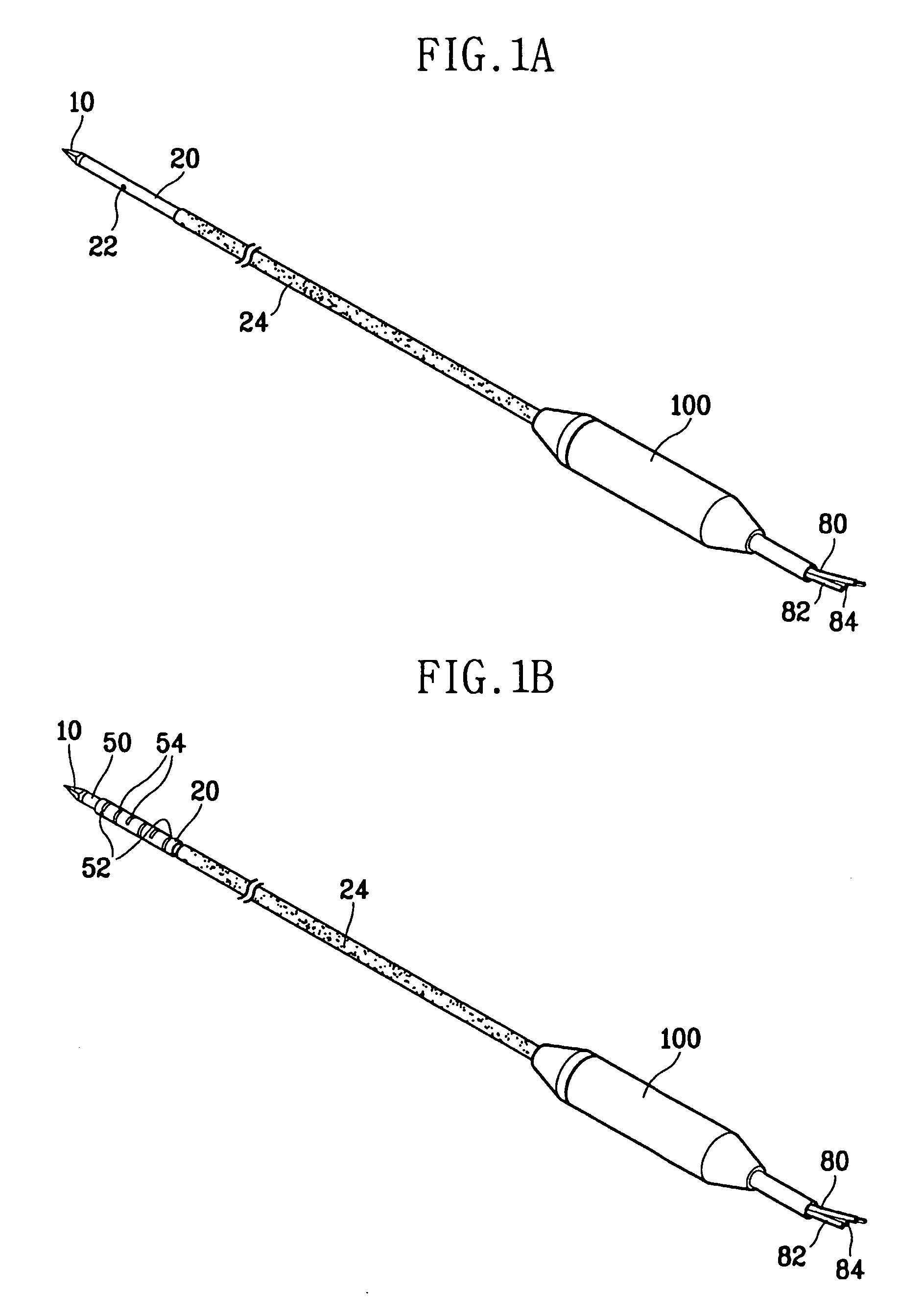
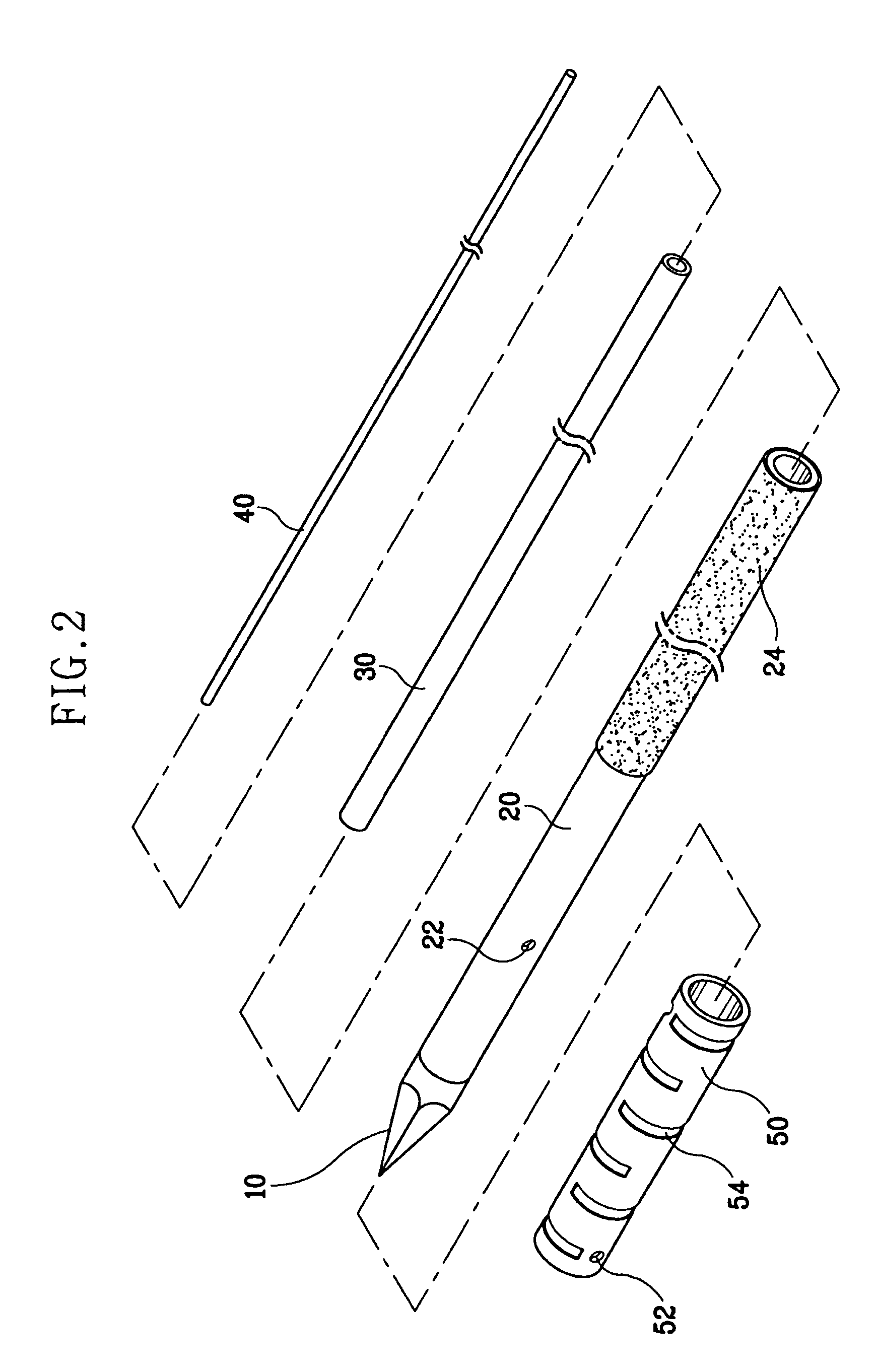
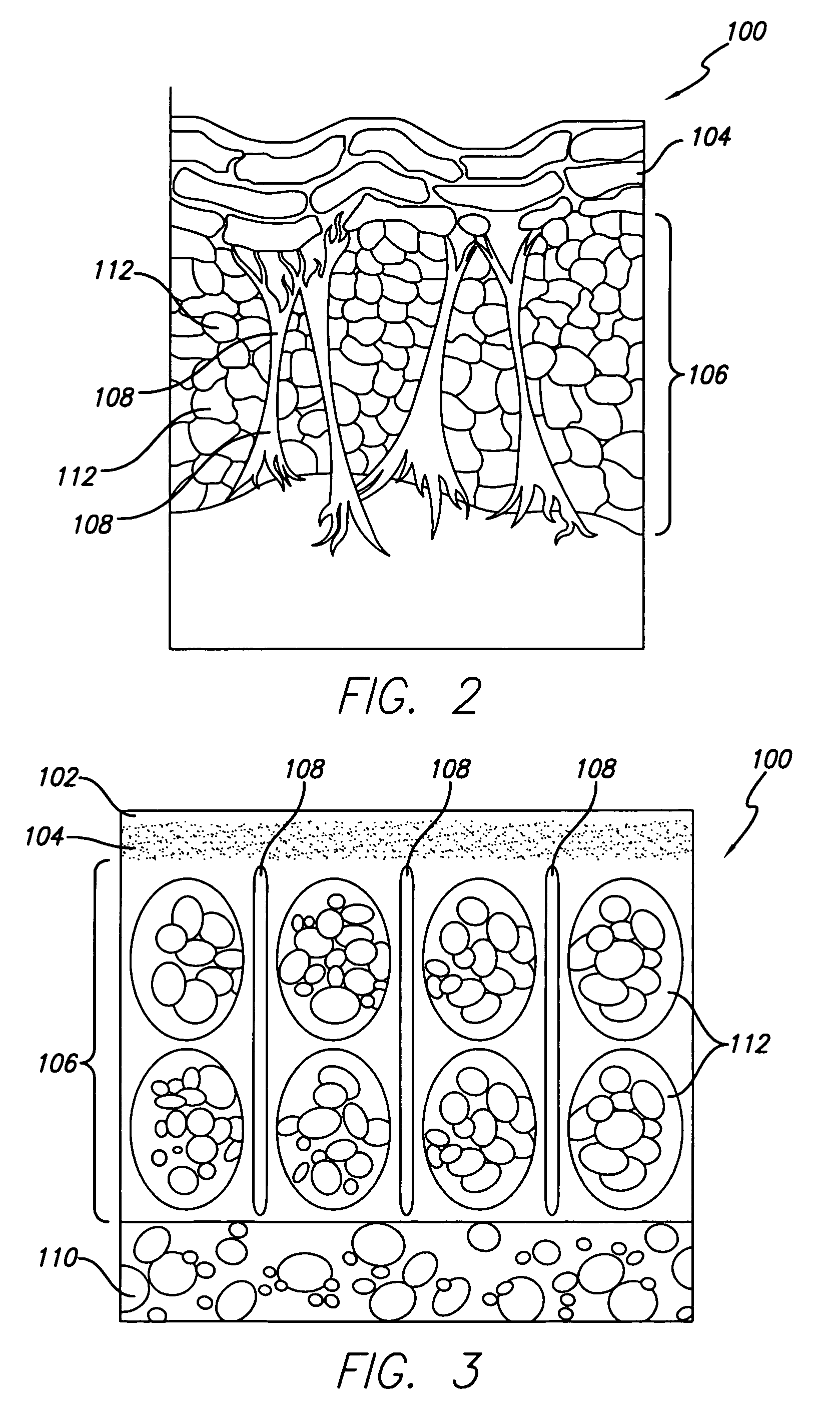
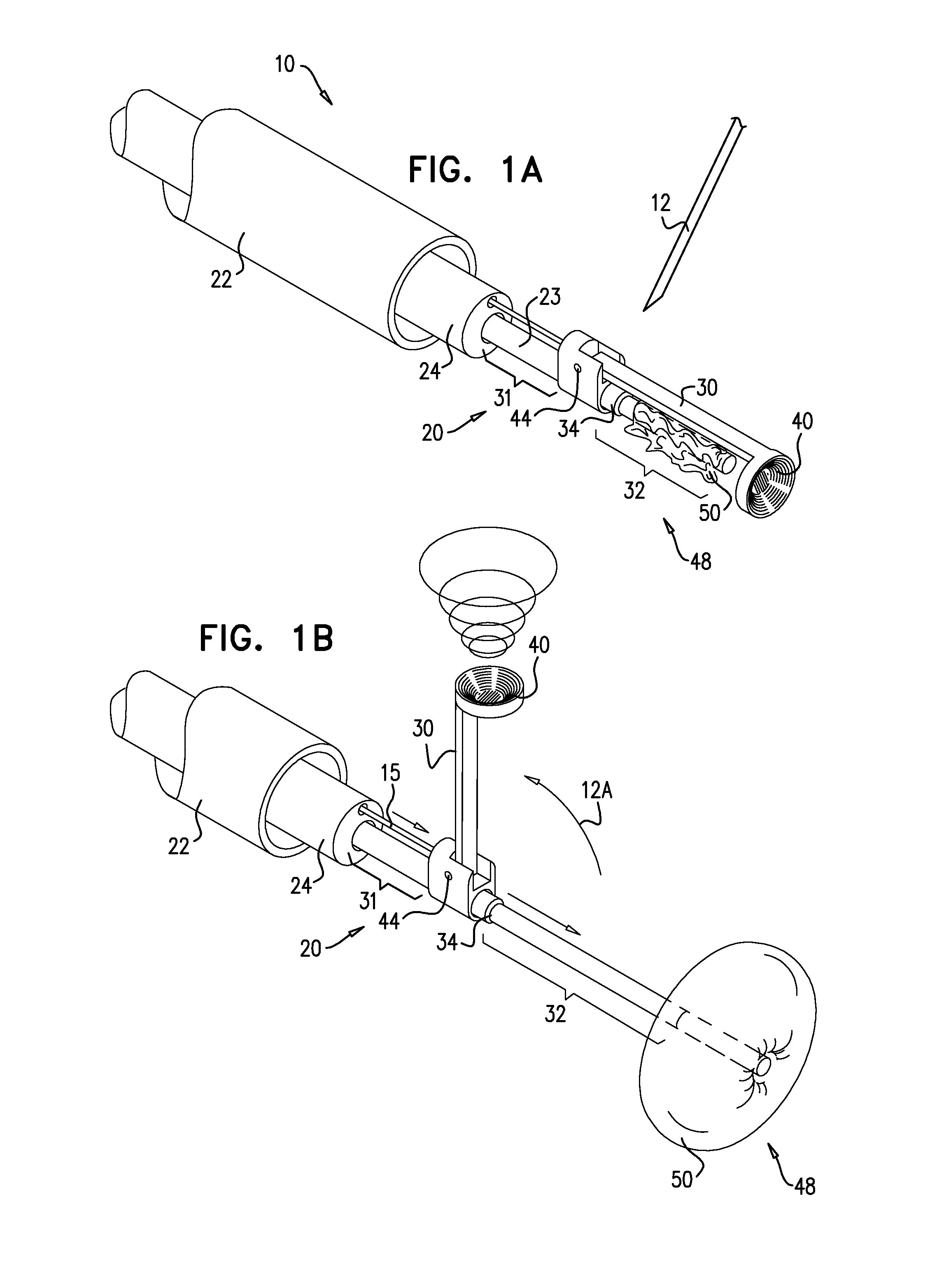
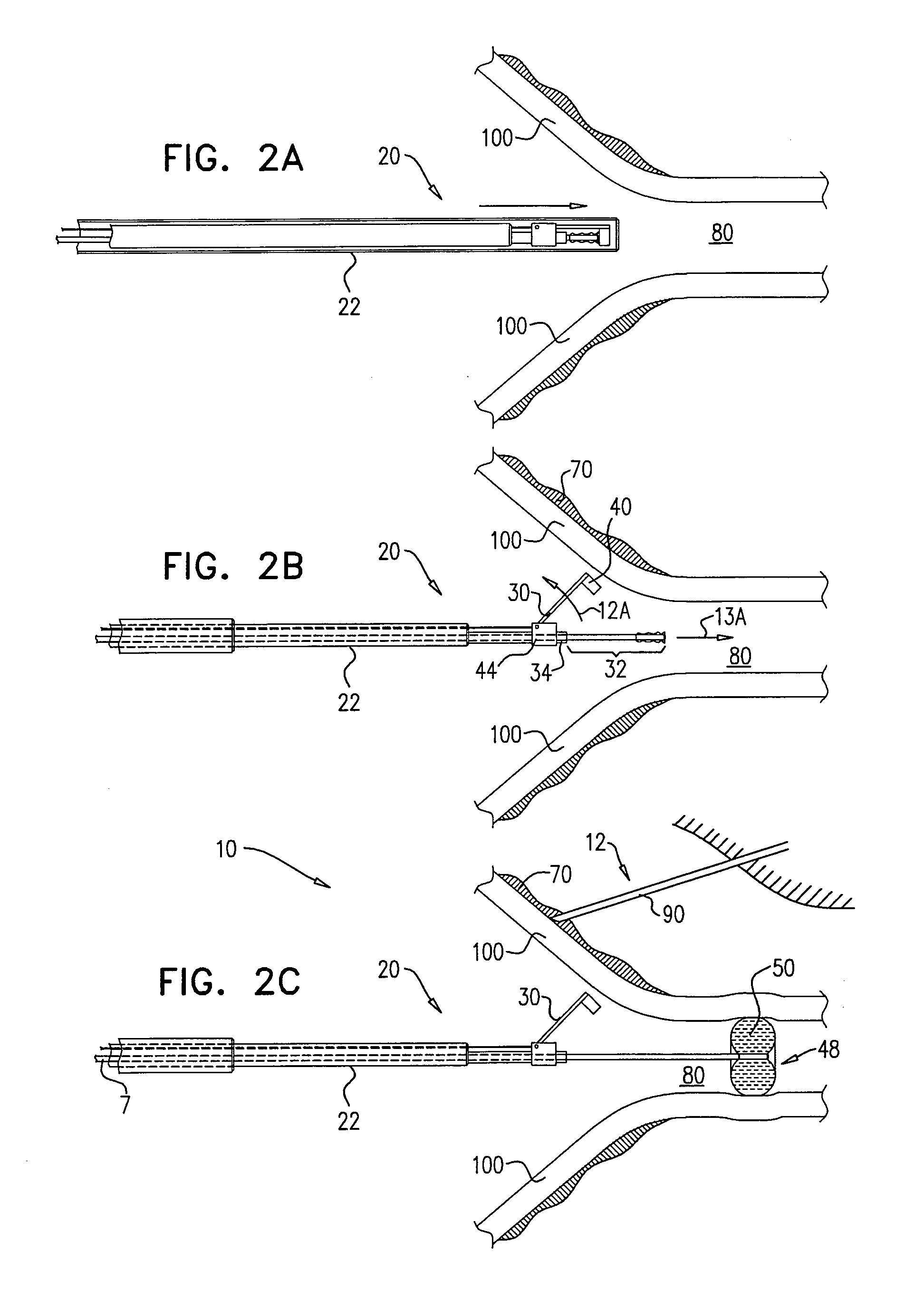
Electrosurgical apparatus and methods for treatment and removal of tissue
InactiveUS7186234B2Promote wettingReduce the possibilitySurgical instruments for heatingActive electrodeTarget tissue
Apparatus and methods for ablating, severing, cutting, shrinking, coagulating, or otherwise modifying a target tissue to be treated. In a method for treating a target tissue, an active electrode of an electrosurgical probe is positioned in at least close proximity to the target tissue in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid. A high frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein, the high frequency voltage is sufficient to volumetrically remove (ablate), sever, or modify at least a portion of the target tissue. The probe comprises a multi-lumen shaft having a plurality of internal lumens, and a return electrode coil oriented substantially parallel to the shaft distal end. The active electrode may be in the form of a metal disc, a hook, or an active electrode coil. In the latter embodiment, the active electrode coil is typically arranged substantially orthogonal to the return electrode coil. Methods of making an active electrode coil, a return electrode coil, and an electrosurgical probe are also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
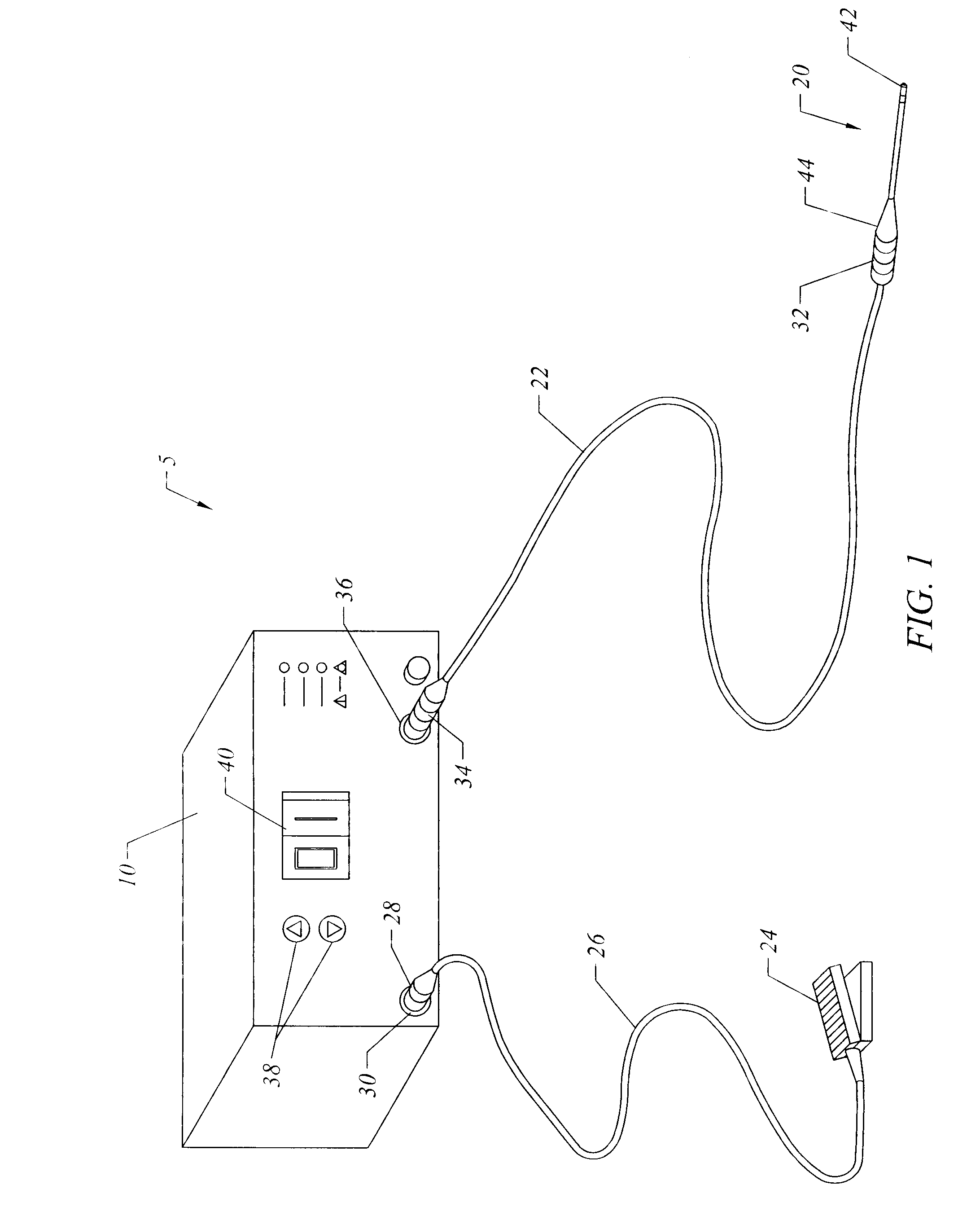
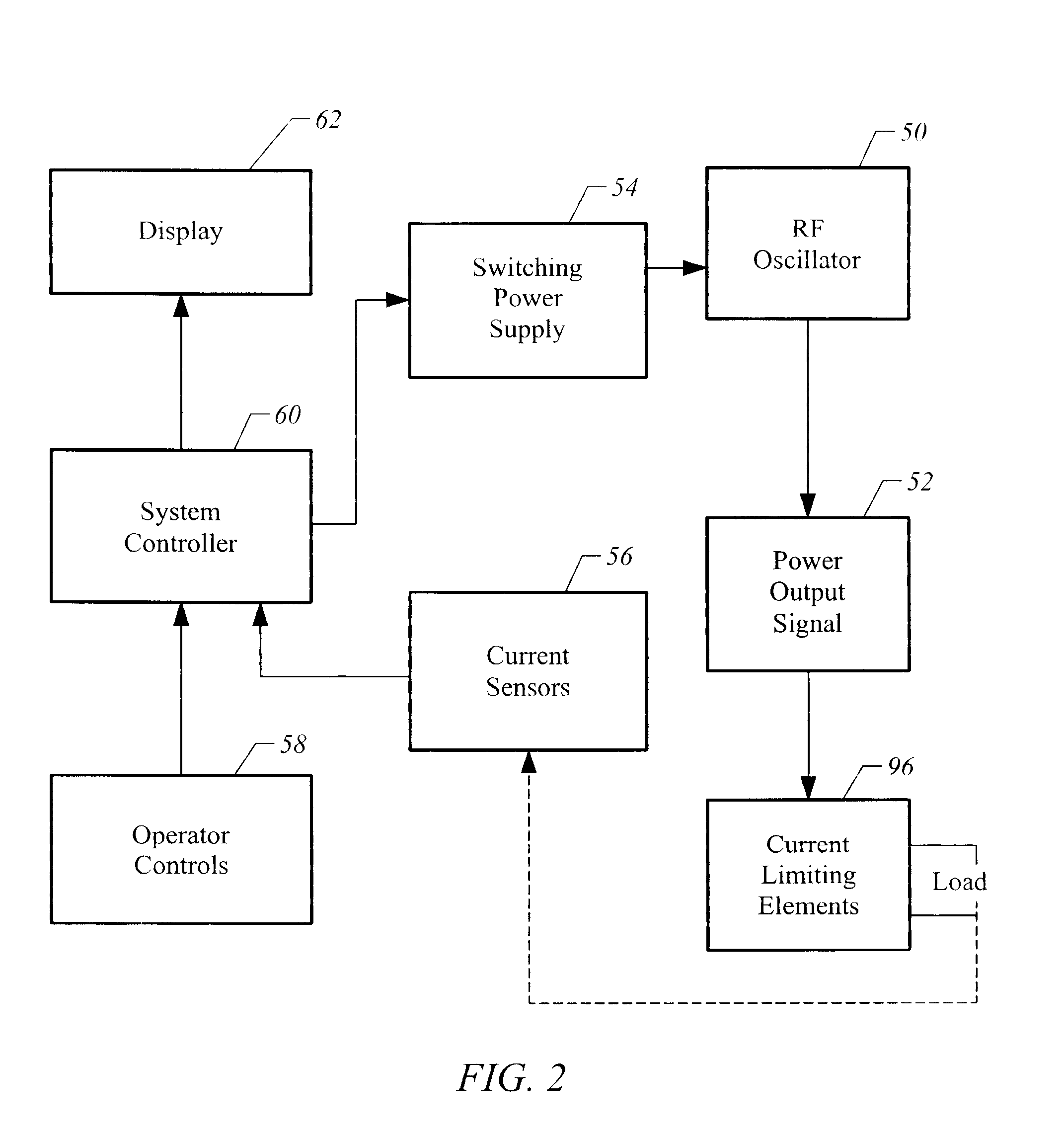
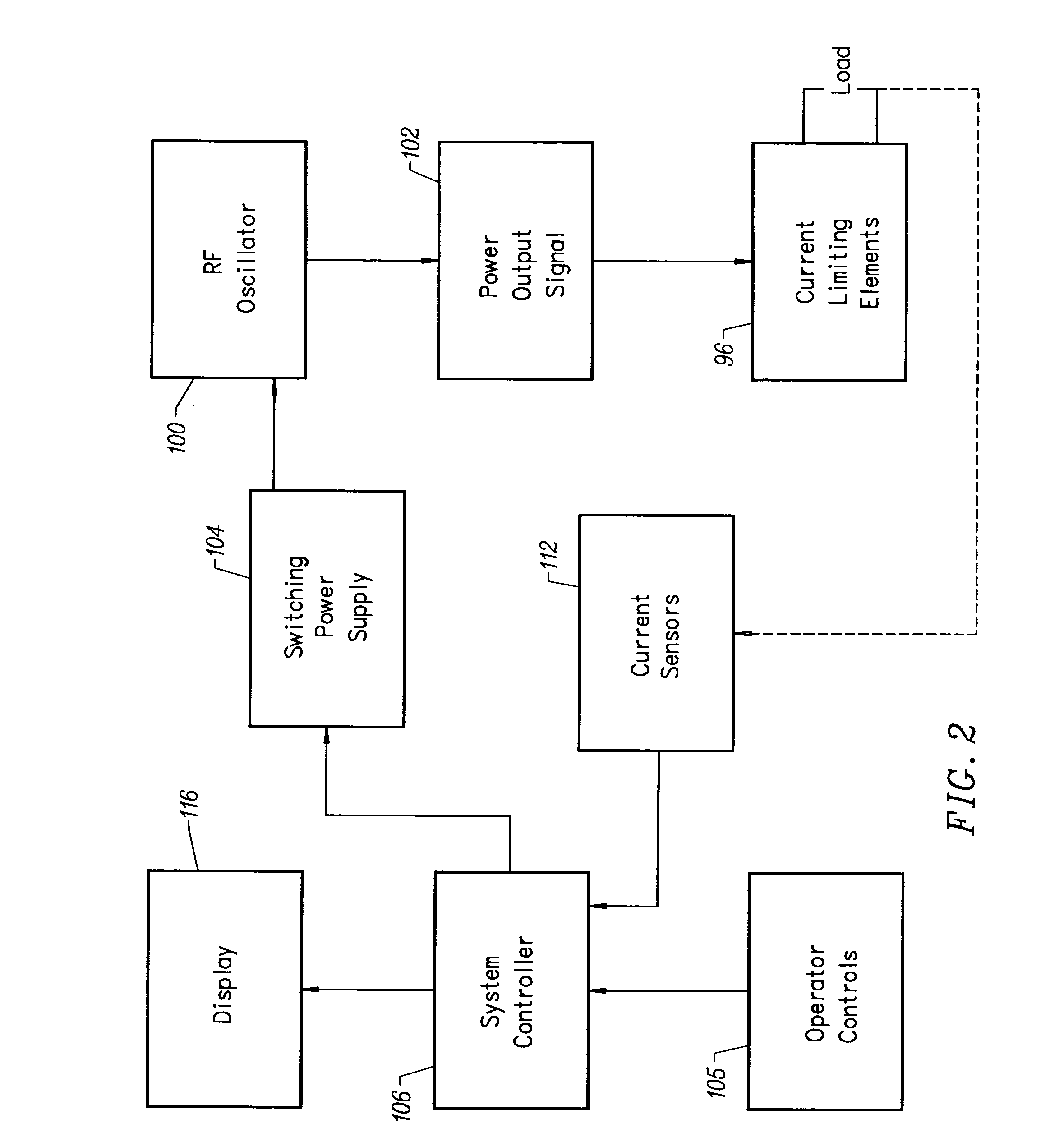
Instrument for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7276063B2Low resistivityMinimizes production of heatSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
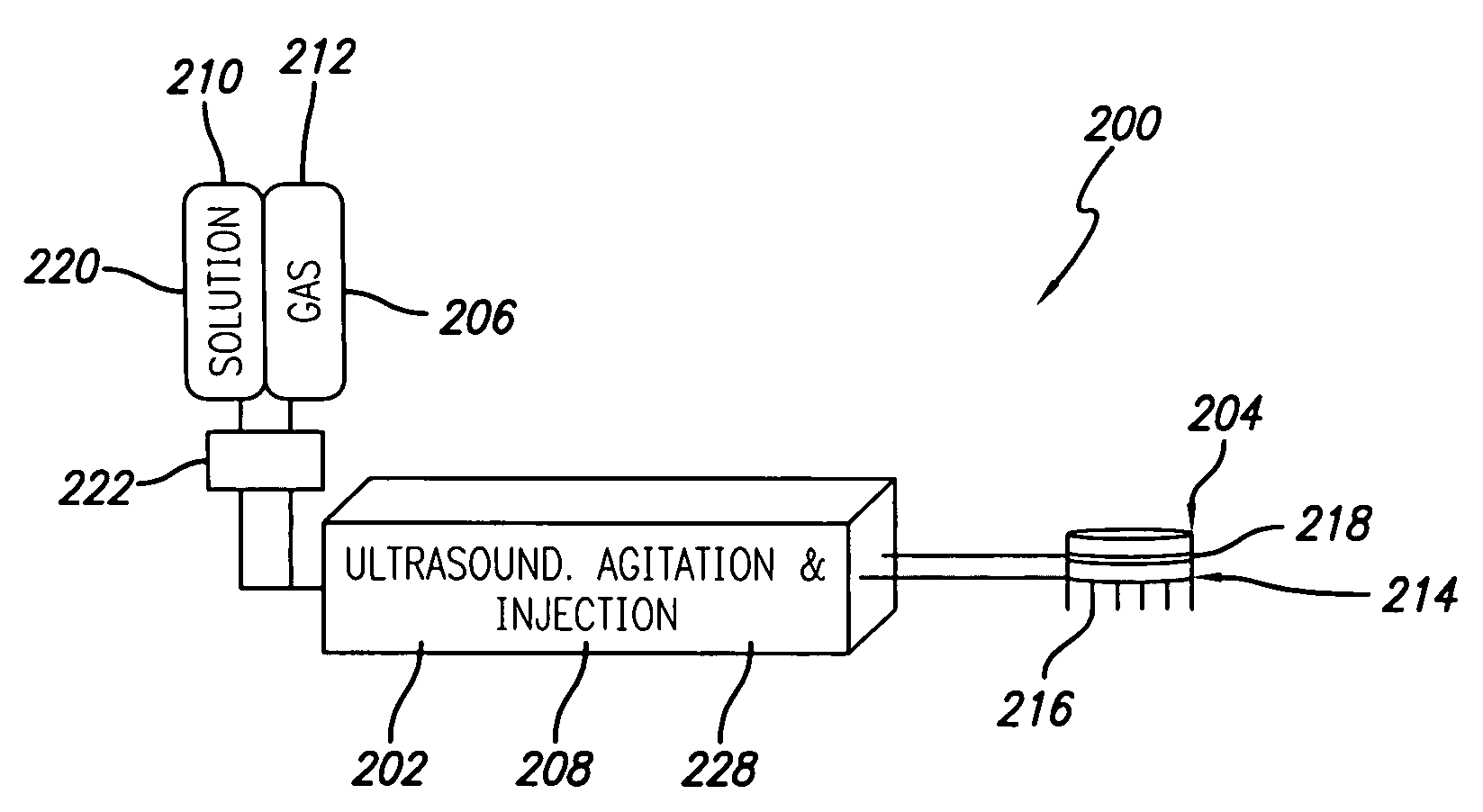
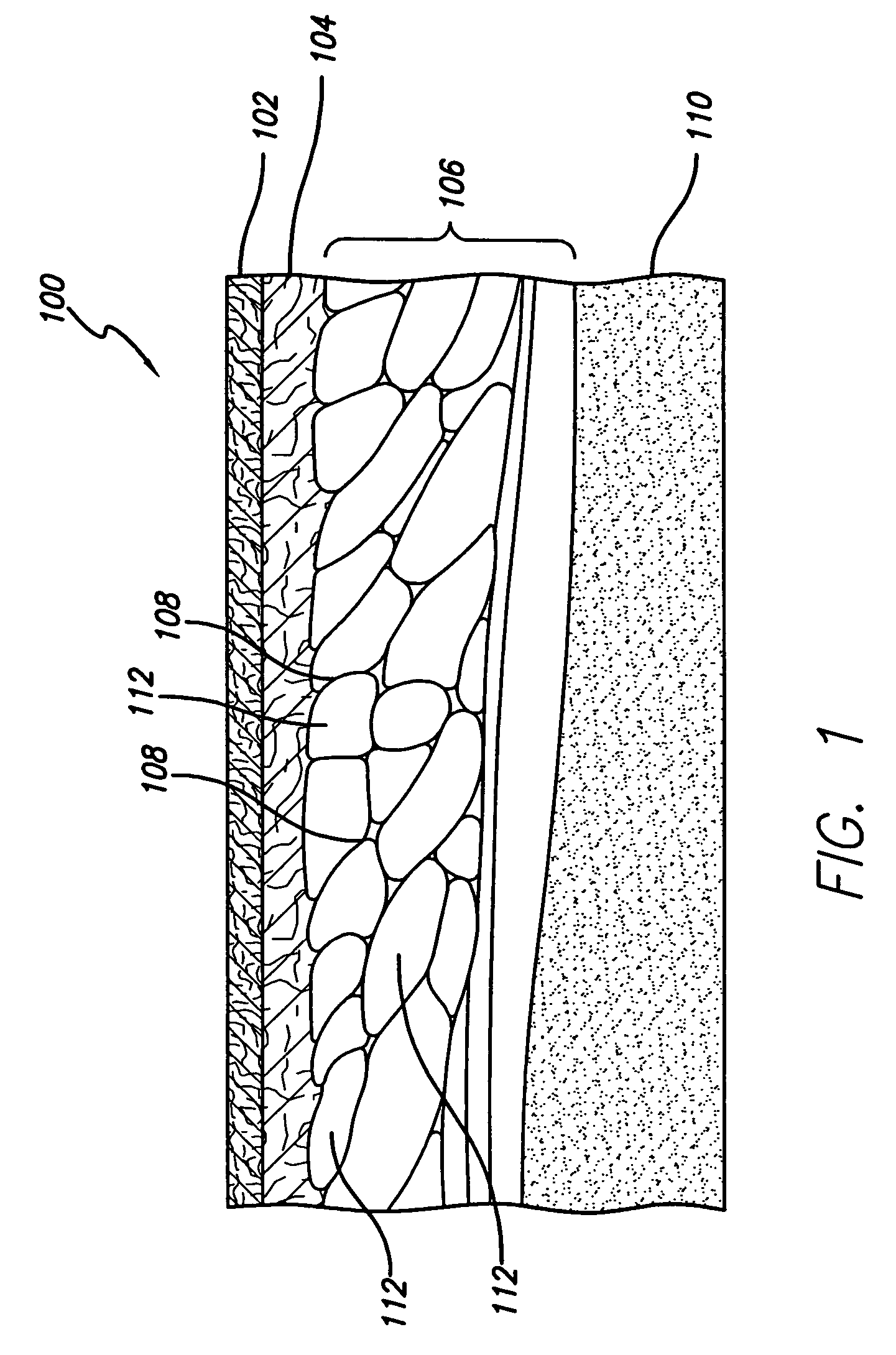
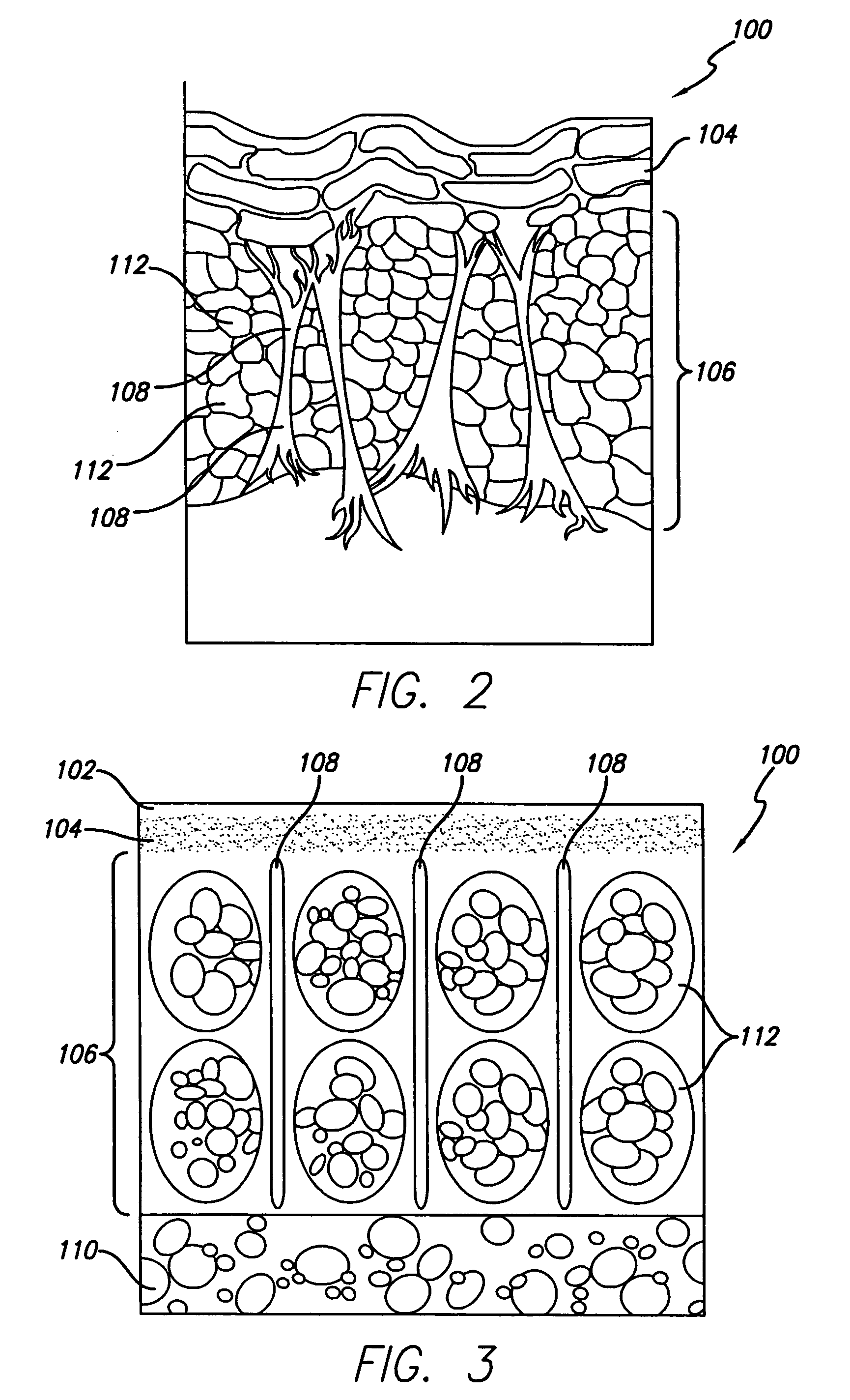
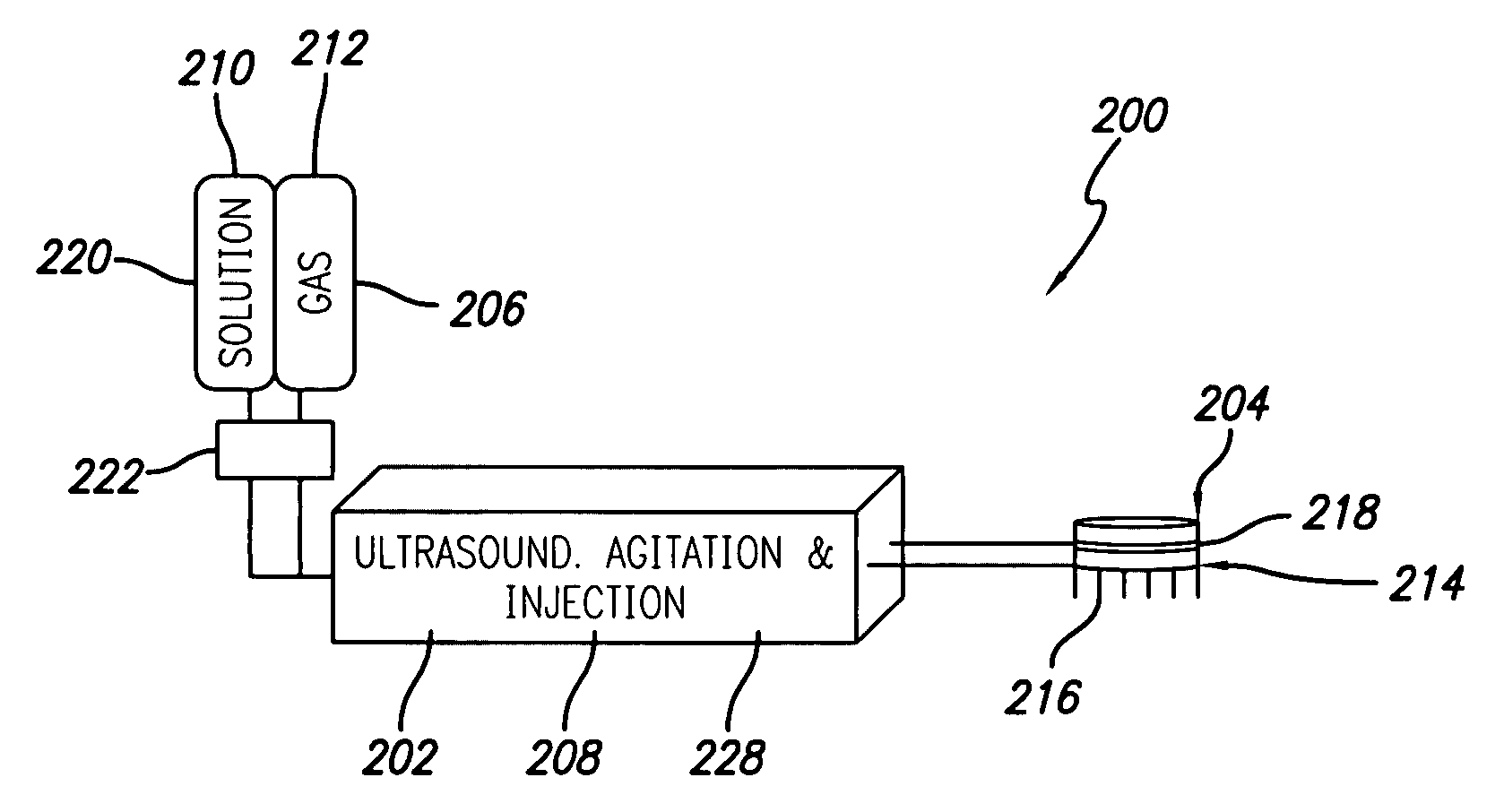
Method for treating subcutaneous tissues
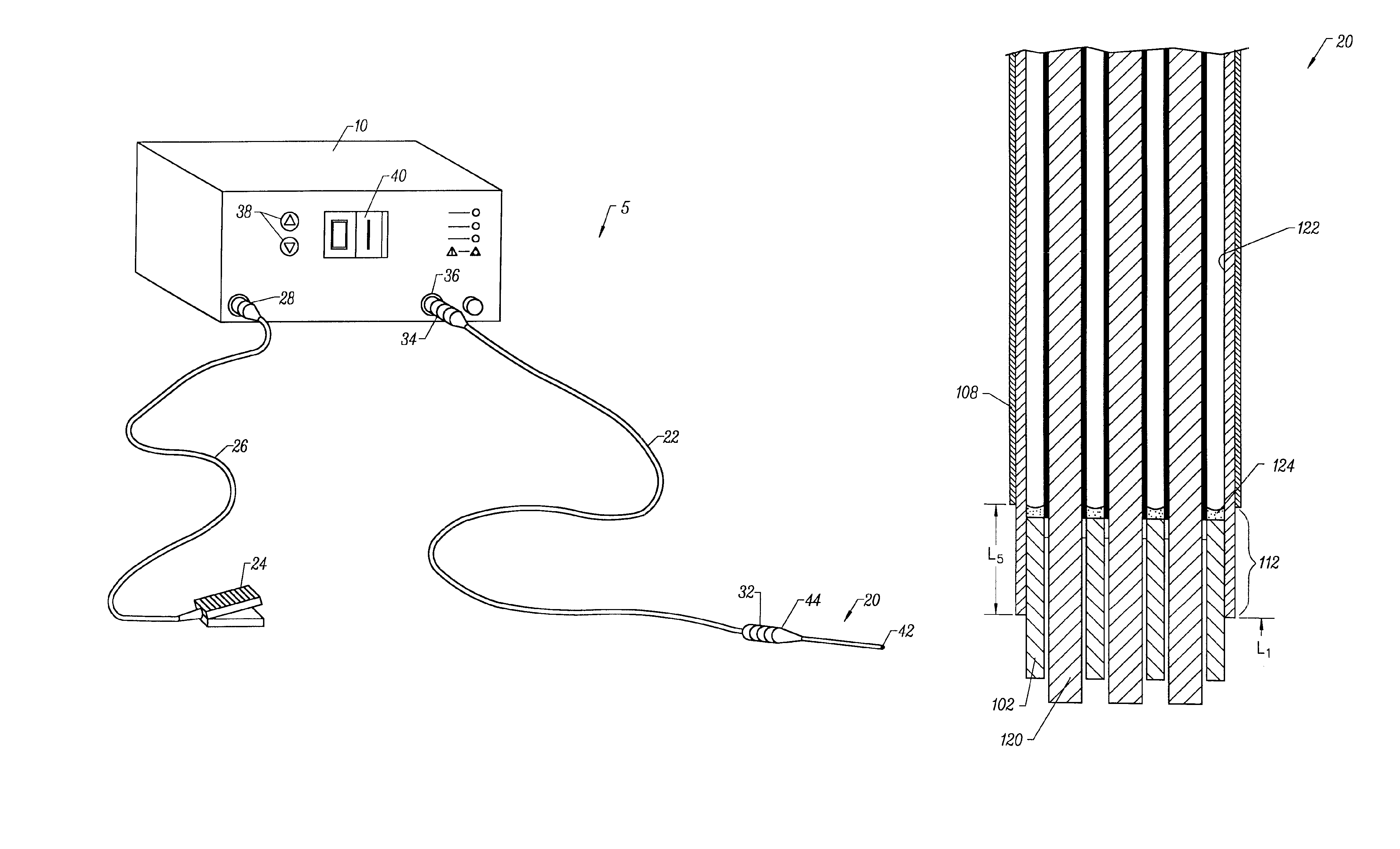
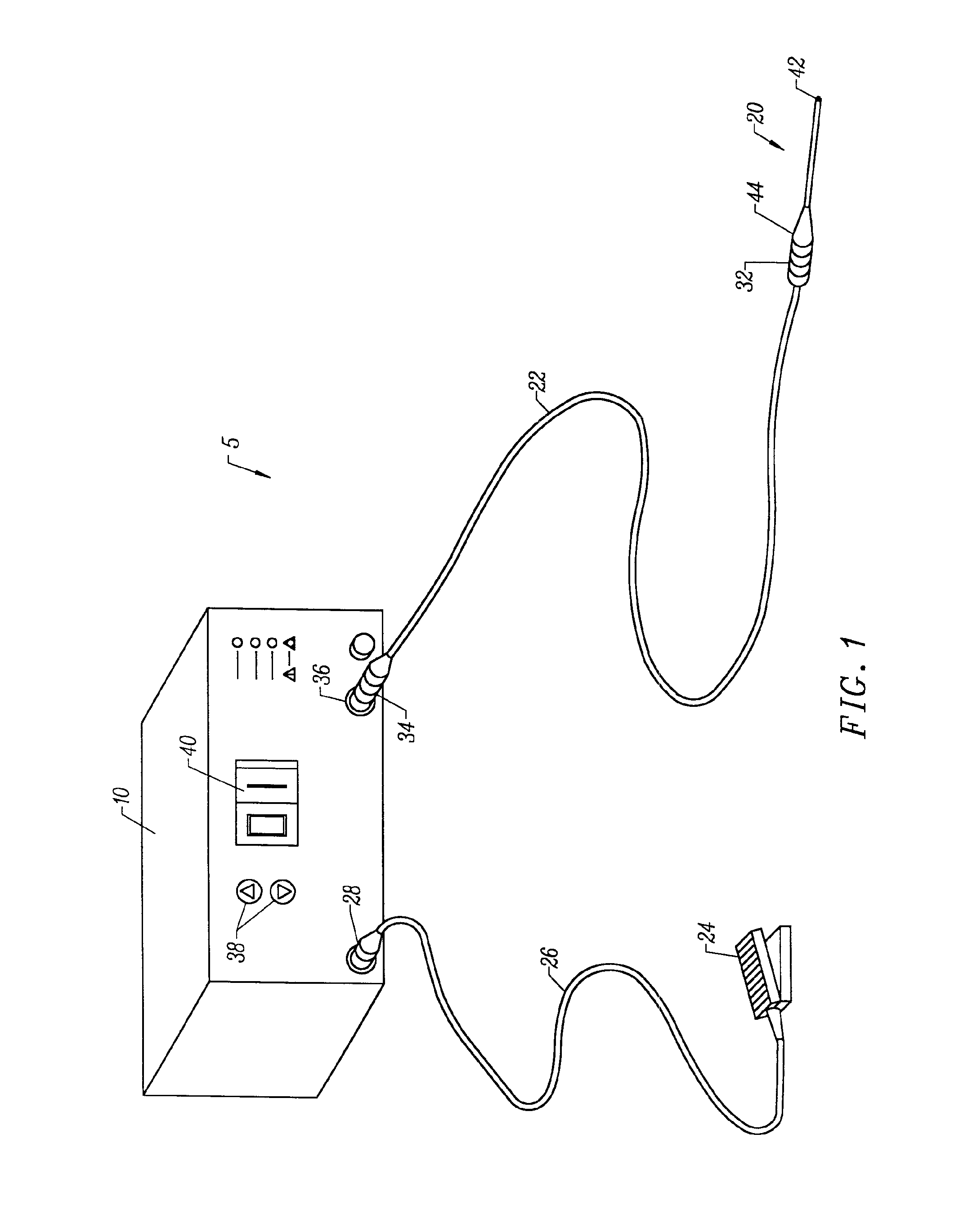
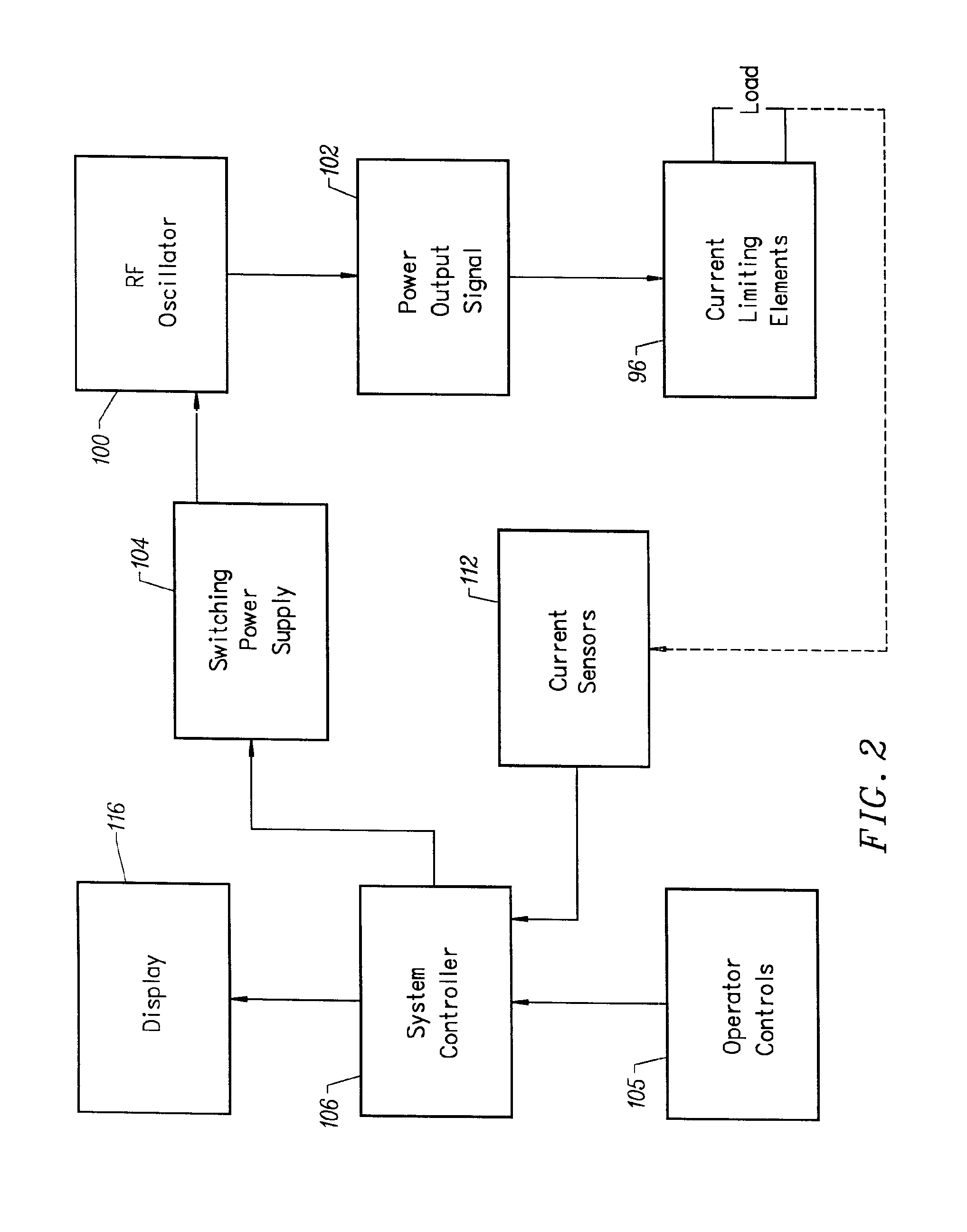
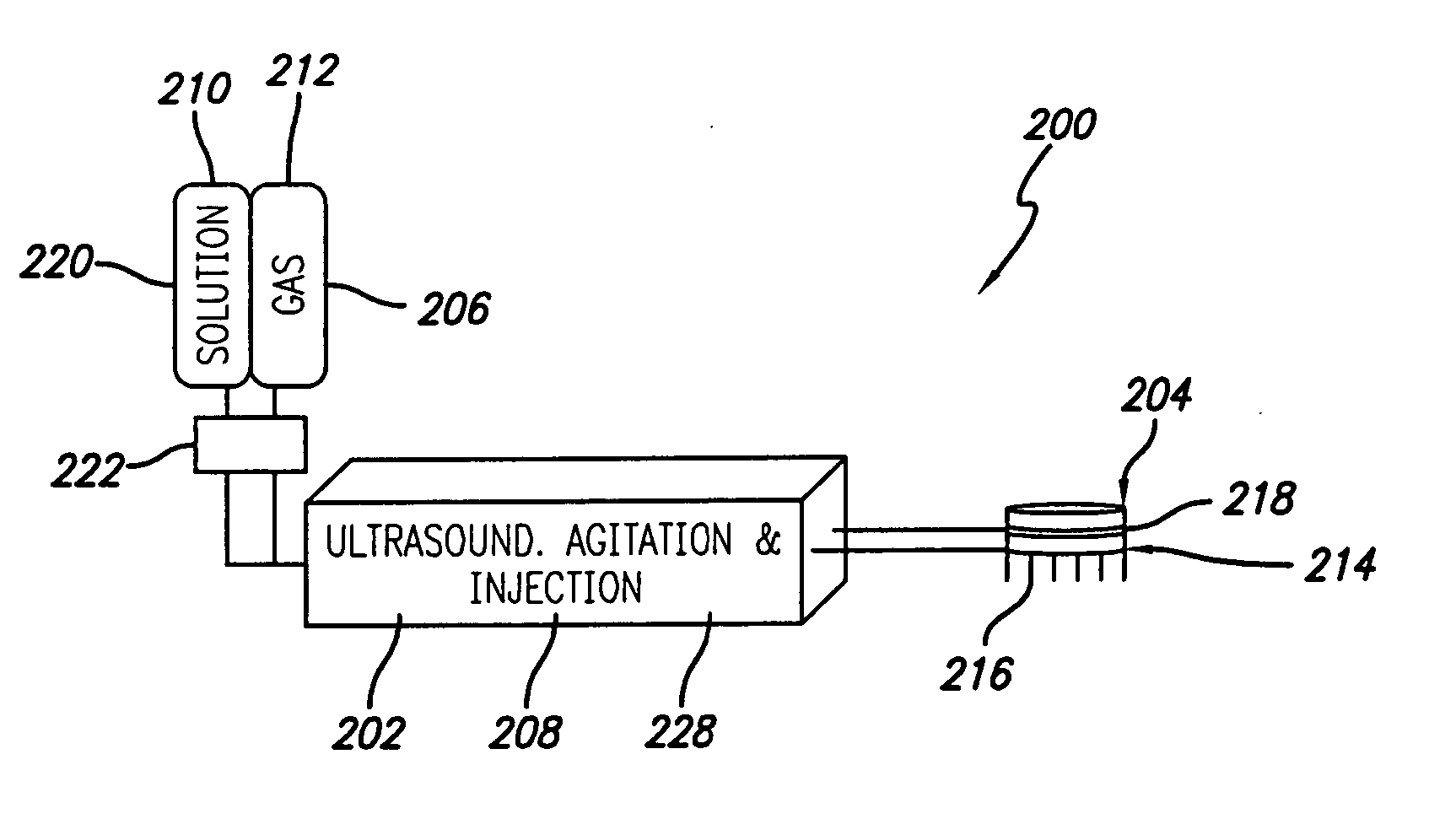
ActiveUS20070055179A1Sufficient powerEliminate riskUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyAbnormal tissue growthCavitation
An apparatus and method for treating subcutaneous tissues using acoustic waves in the range of low acoustic pressure ultrasound waves is disclosed. The method includes injections of enhancing agents, wherein disruption of subcutaneous tissues and subcutaneous cavitational bioeffects are produced by ultrasound waves having a power that will not produce tissue cavitation in the absence of the enhancing agents. The apparatus and method of use is useful for treatment of subcutaneous abnormalities including cellulite, lipomas, and tumors.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7435247B2Low resistivityMinimizes production of heatSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingActive electrodeTarget tissue
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. In one embodiment a tissue treatment surface includes spacers or a chamber for containing the electrodes.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
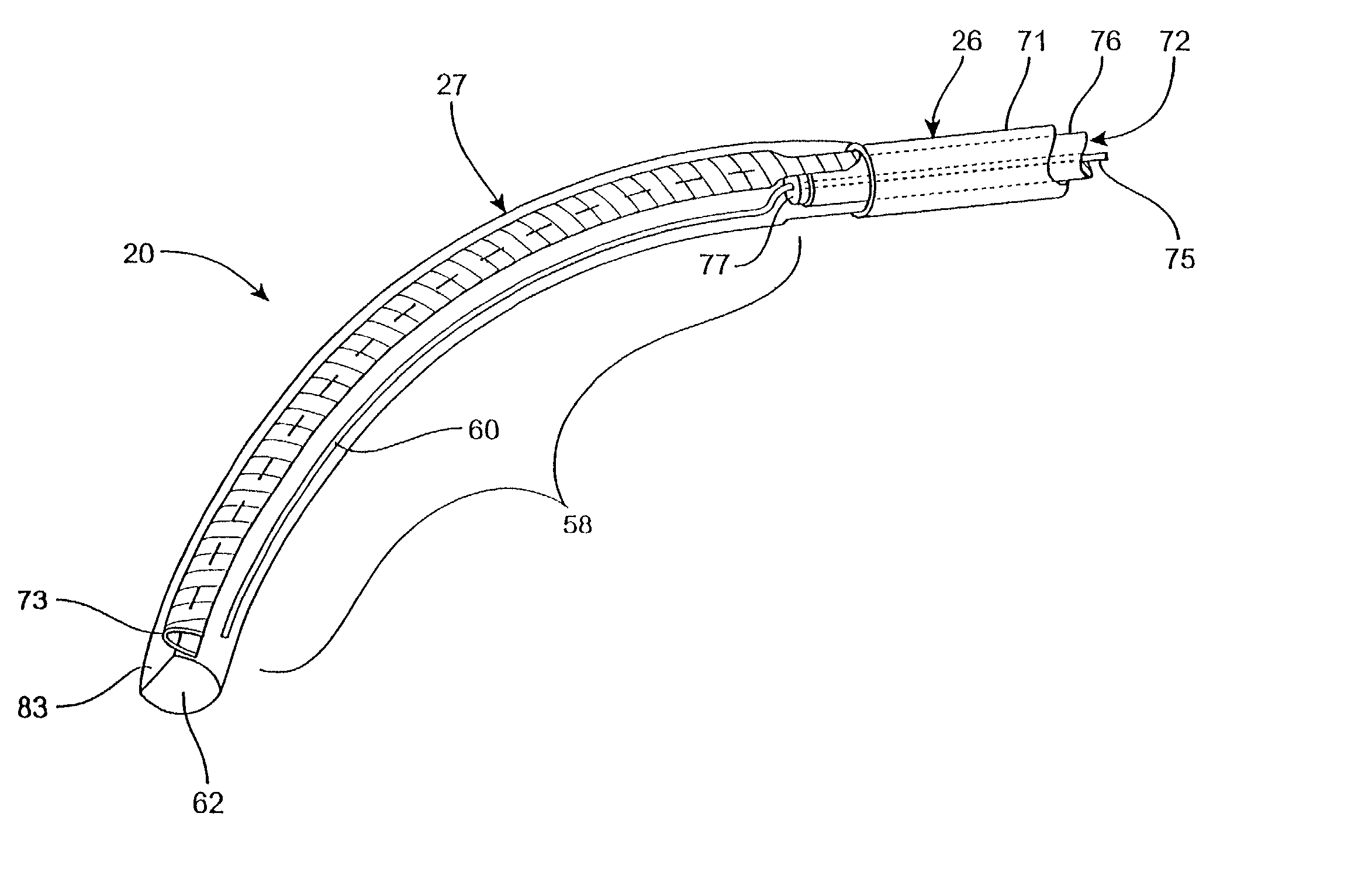
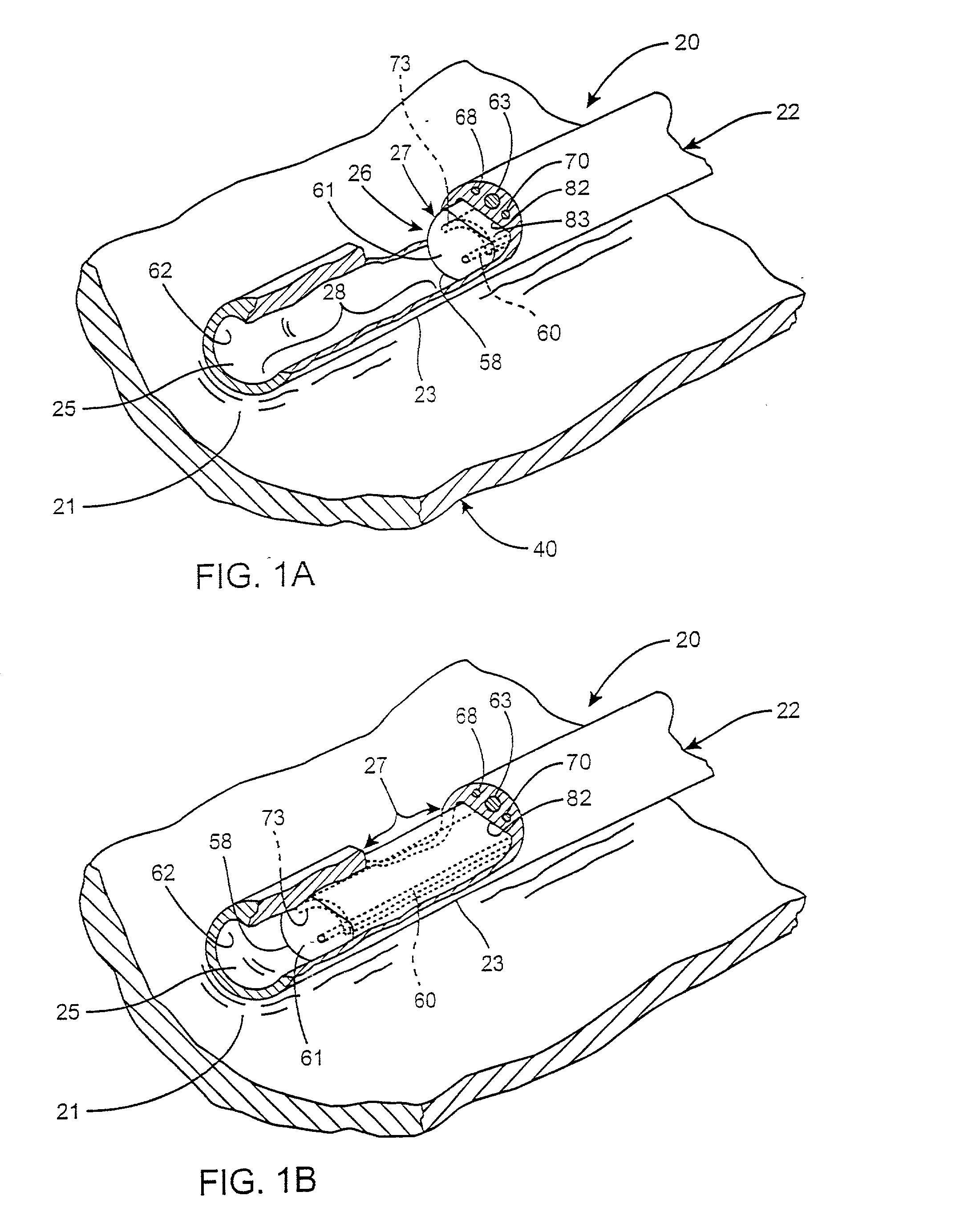
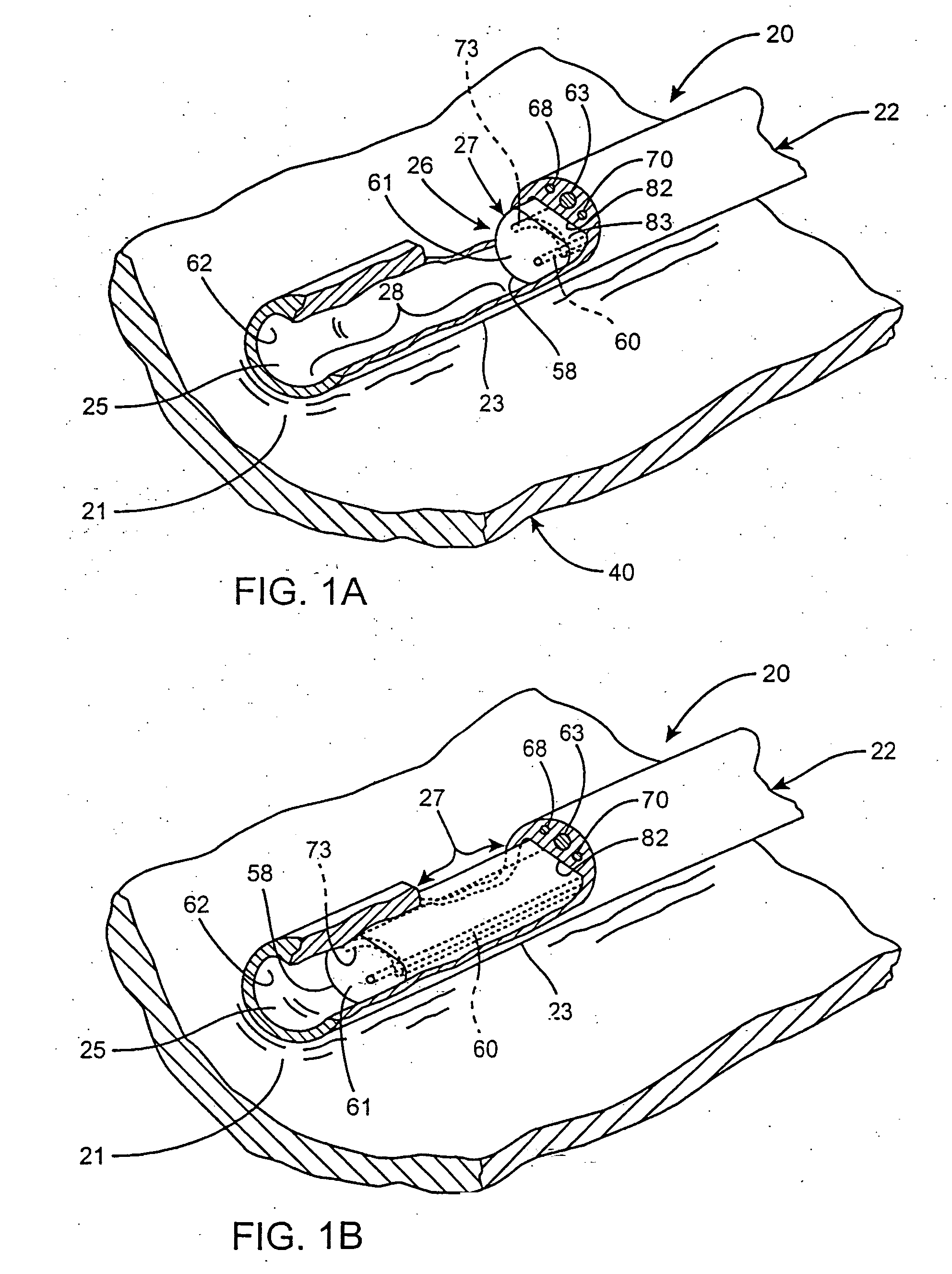
Conforming-electrode catheter and method for ablation
InactiveUS7326206B2Reduce formationReducing of of surfaceSurgical instruments for heatingBristleTissue ablation
A brush electrode catheter and a method for using the brush electrode catheter for tissue ablation are disclosed. The brush electrode catheter comprises a plurality of flexible filaments or bristles for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. Interstitial spaces are defined among the filaments of the brush electrode, and the interstitial spaces are adapted to direct conductive or nonconductive fluid, when present, toward the distal ends of the brush filaments. The brush electrode facilitates electrode-tissue contact in target tissue having flat or contoured surfaces. The flexible filaments may be selectively trimmed to give a desired tip configuration or a desired standoff distance between the tissue and the conductive filaments in the brush electrode. Also, the filaments may be grouped into clusters. A shielded-tip brush electrode, including a flexible boot, is also disclosed.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
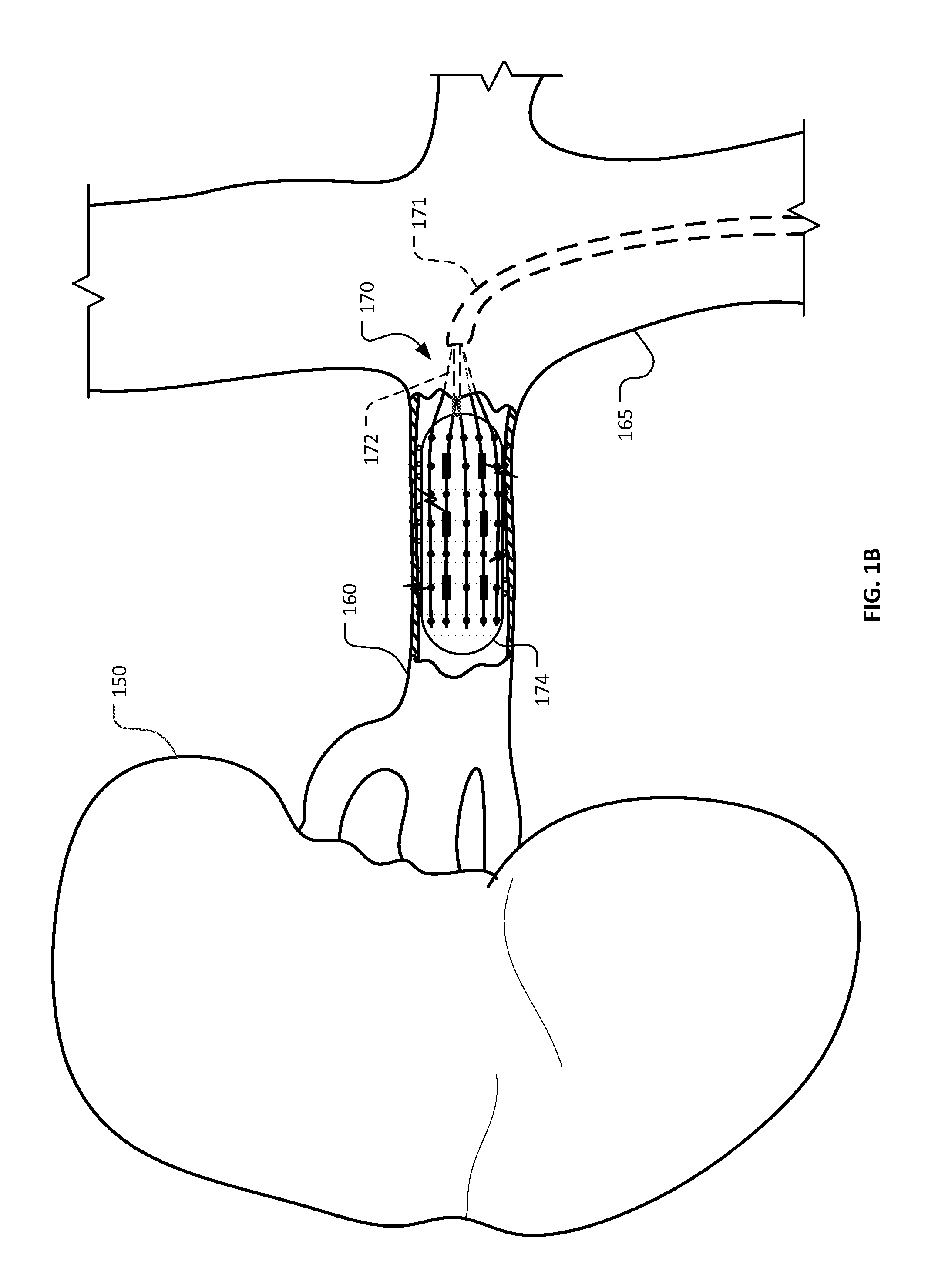
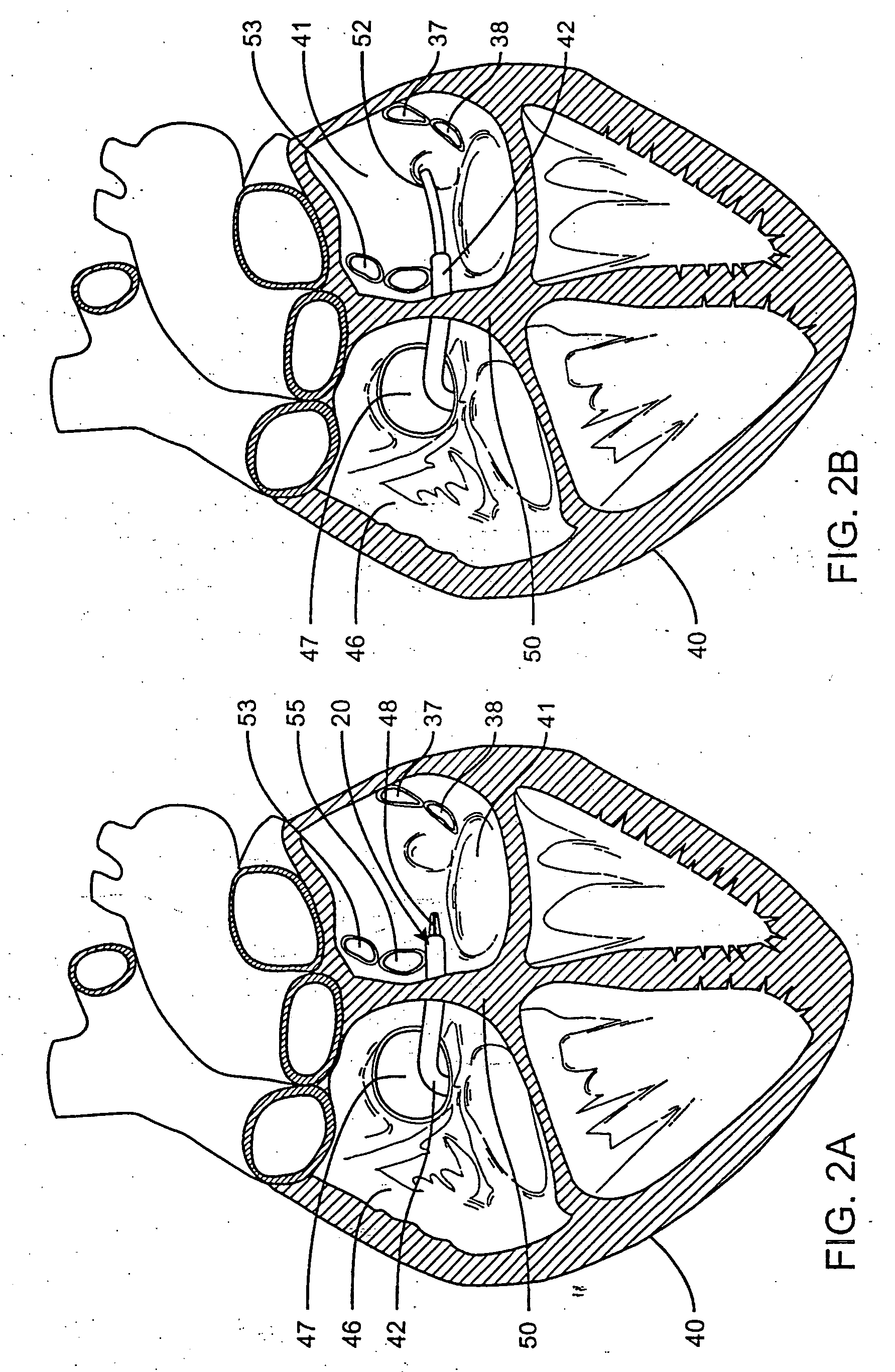
Deflectable catheter with a flexibly attached tip section
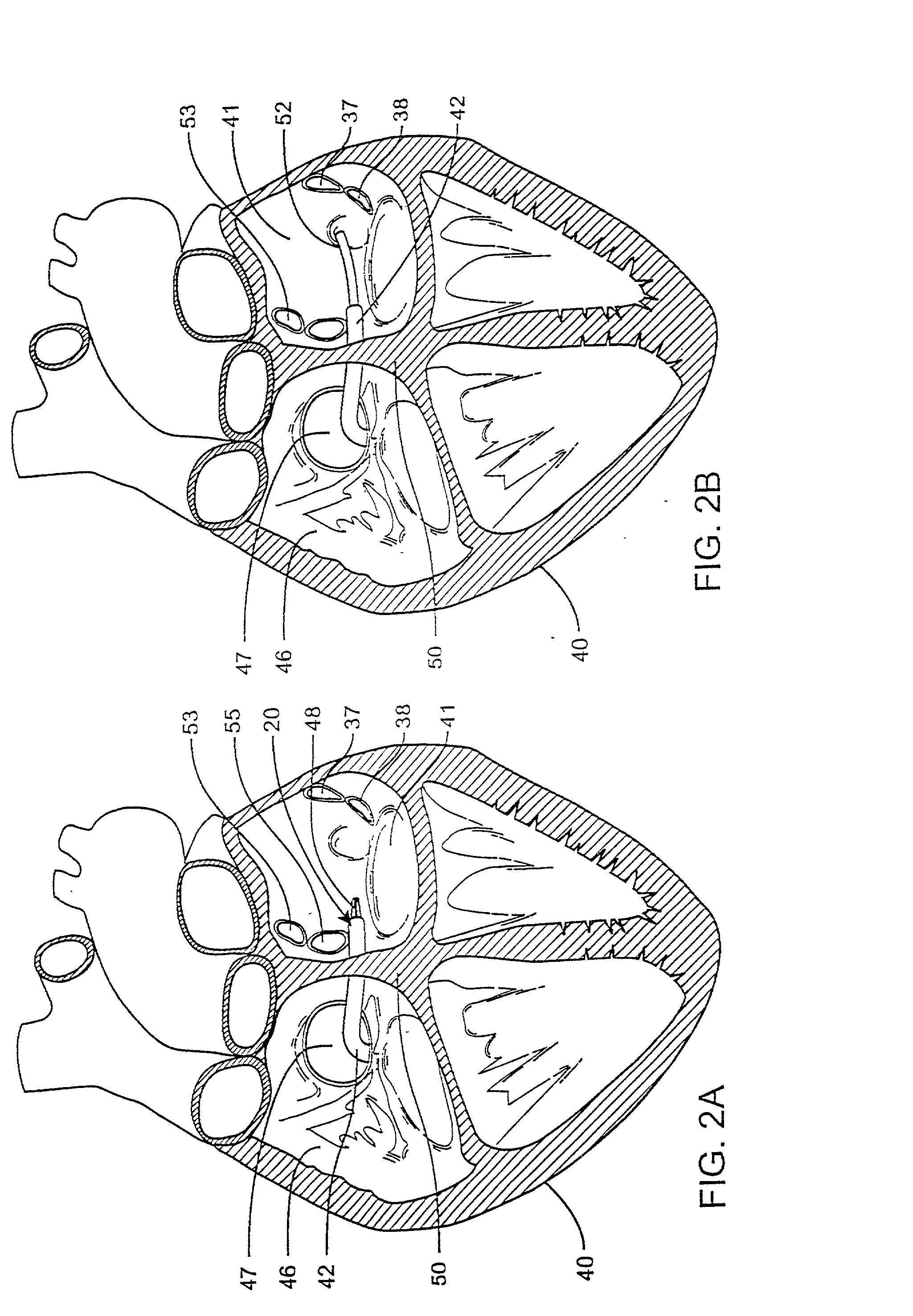
InactiveUS20070156114A1Improved and safe contactFacilitate ablationSurgical instrument detailsCatheterThrombusCatheter device
A catheter for mapping and / or ablating a region of the heart, comprises a catheter body with an intermediate section that is connected to a tip assembly by a highly flexible preshaped section. The highly flexible section presets the tip assembly at an off-axis and / or off-plane angles from the intermediate section, to provide the following: a) The intermediate section when deflected approximates the generally convex region of the cavo-tricuspid isthmus and the preset angle of the flexible section is off axis in the same plane and same direction as deflection of the intermediate section to enable the tip assembly to contact the cavo-tricuspid isthmus for ablation and / or mapping. b) The intermediate section when deflected approximates the generally concave region of the VA / RV / LA / LV and the preset angle in the same plane and opposite direction of deflection enables the tip assembly to contact the walls of the cavity for ablation and / or mapping. c) The intermediate section when deflected approximates the generally convex region of the His area and the preset off plane angle of the flexible section enable the tip assembly to contact the Bundle of His region. A high bending modulus of the flexible section enables the flexible section to absorb displacement force applied to the tip assembly, such as when the tip assembly encounters uneven tissue surface, without displacing the intermediate section. The flexible section prevents excessive force from being applied to the tip assembly, reducing the risk of any of the following: a) mechanical perforation, b) steam pop, c) burying the tip assembly in the myocardium resulting in high temperatures, low energy delivery, thrombus formation and char formation.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Methods and system for treating subcutaneous tissues
ActiveUS7588547B2Eliminate riskFacilitate ablationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationMedicine
An apparatus and method for treating subcutaneous tissues using acoustic waves in the range of low acoustic pressure ultrasound waves is disclosed. The method includes injections of enhancing agents, wherein disruption of subcutaneous tissues and subcutaneous cavitational bioeffects are produced by ultrasound waves having a power that will not produce tissue cavitation in the absence of the enhancing agents. The apparatus and method of use is useful for treatment of subcutaneous abnormalities including cellulite, lipomas, and tumors.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Medical instrument positioning tool and method
InactiveUS20020128636A1Facilitate ablationEasily advancedElectrotherapyCatheterBiological targetSurgical department
A system and method for positioning a medical instrument at a desired biological target tissue site is provided. The system includes an elongated sheath having a deflectable distal end configured to deflect or otherwise position at least a portion of a medical instrument during a surgical procedure allowing for the placement of the deflected portion adjacent or proximate to a predetermined target tissue surface. The positioning system may be incorporated into the medical instrument. The medical instrument may be an ablation system.
Owner:AFX +1
Instrument for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS20080021447A1Efficient ionizationLess heatSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Systems and methods for electrosurgical tissue treatment
InactiveUS7572251B1Reduce ionic strengthFacilitate initiationCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsEngineeringLow temperature plasma
Systems and methods are provided for applying a high frequency voltage in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to create a relatively low-temperature plasma for ablation of tissue adjacent to, or in contact with, the plasma. In one embodiment, an electrosurgical probe or catheter is positioned adjacent the target site so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into contact with, or close proximity to, a target tissue in the presence of electrically conductive fluid. High frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to non-thermally generate a plasma adjacent to the active electrode(s), and to volumetrically remove or ablate at least a portion of the target tissue. The high frequency voltage generates electric fields around the active electrode(s) with sufficient energy to ionize the conductive fluid adjacent to the active electrode(s). Within the ionized gas or plasma, free electrons are accelerated, and electron-atoms collisions liberate more electrons, and the process cascades until the plasma contains sufficient energy to break apart the tissue molecules, causing molecular dissociation and ablation of the target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
System for treating subcutaneous tissues
ActiveUS20070055180A1Eliminate riskFacilitate ablationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAbnormal tissue growthCavitation
An apparatus and method for treating subcutaneous tissues using acoustic waves in the range of low acoustic pressure ultrasound waves is disclosed. The method includes injections of enhancing agents, wherein disruption of subcutaneous tissues and subcutaneous cavitational bioeffects are produced by ultrasound waves having a power that will not produce tissue cavitation in the absence of the enhancing agents. The apparatus and method of use is useful for treatment of subcutaneous abnormalities including cellulite, lipomas, and tumors.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Conforming-electrode catheter and method for ablation
InactiveUS20050159741A1Easy to optimizeReduce decreaseSurgical instruments for heatingExternal electrodesBristleTarget tissue
A brush electrode catheter and a method for using the brush electrode catheter for tissue ablation are disclosed. The brush electrode catheter comprises a plurality of flexible filaments or bristles for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. Interstitial spaces are defined among the filaments of the brush electrode, and the interstitial spaces are adapted to direct conductive or nonconductive fluid, when present, toward the distal ends of the brush filaments. The brush electrode facilitates electrode-tissue contact in target tissue having flat or contoured surfaces. The flexible filaments may be selectively trimmed to give a desired tip configuration or a desired standoff distance between the tissue and the conductive filaments in the brush electrode. Also, the filaments may be grouped into clusters. A shielded-tip brush electrode, including a flexible boot, is also disclosed.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Tissue visualization and ablation systems
InactiveUS20090125022A1Facilitate conductionSlow flowBioelectric signal measurementEndoscopesRf ablationControl manner
Visualization and ablation system variations are described which utilize various tissue ablation arrangements. Such assemblies are configured to facilitate the application of energy delivery, such as RF ablation, to an underlying target tissue for treatment in a controlled manner while directly visualizing the tissue during the bipolar ablation process.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
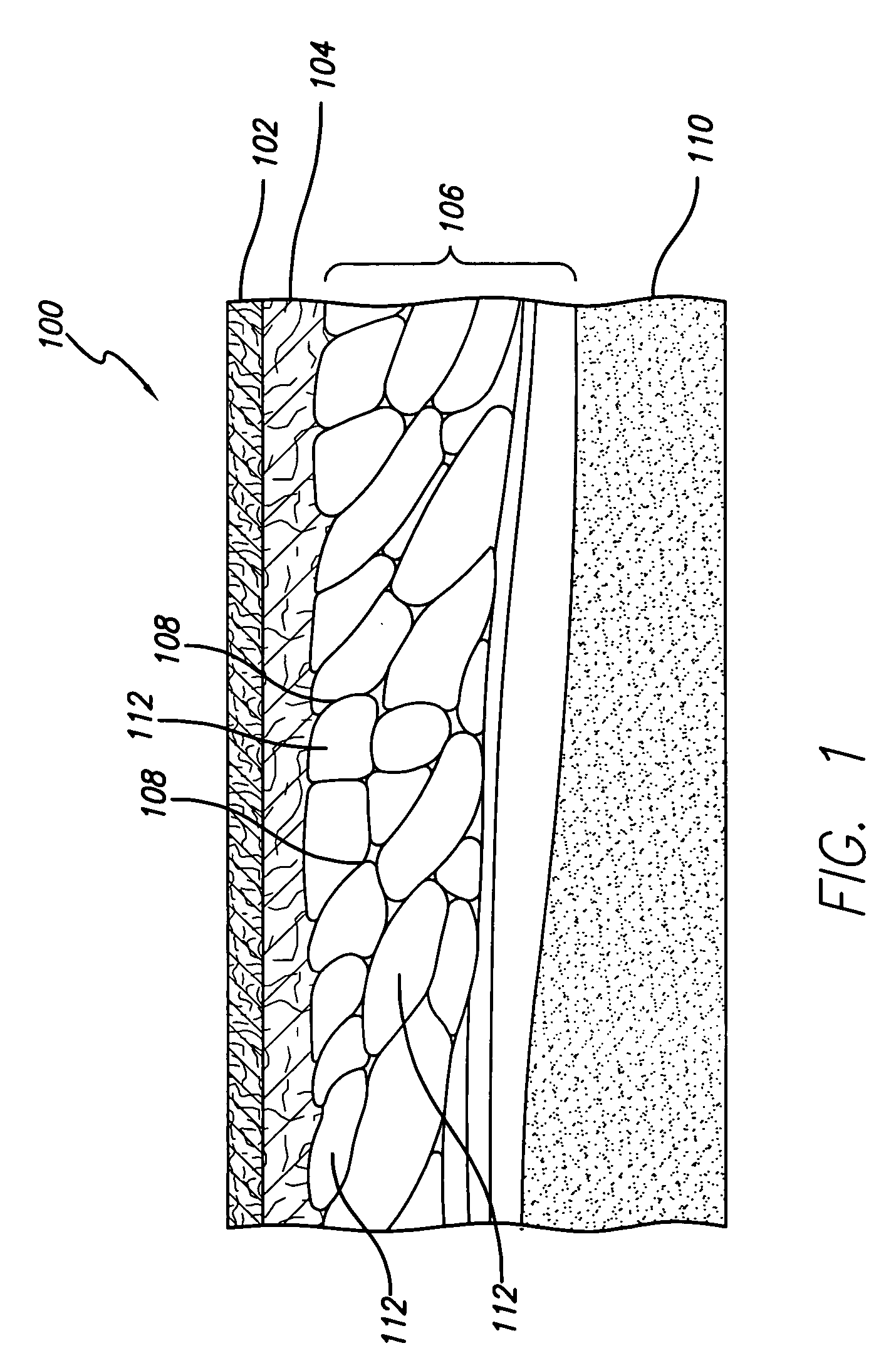
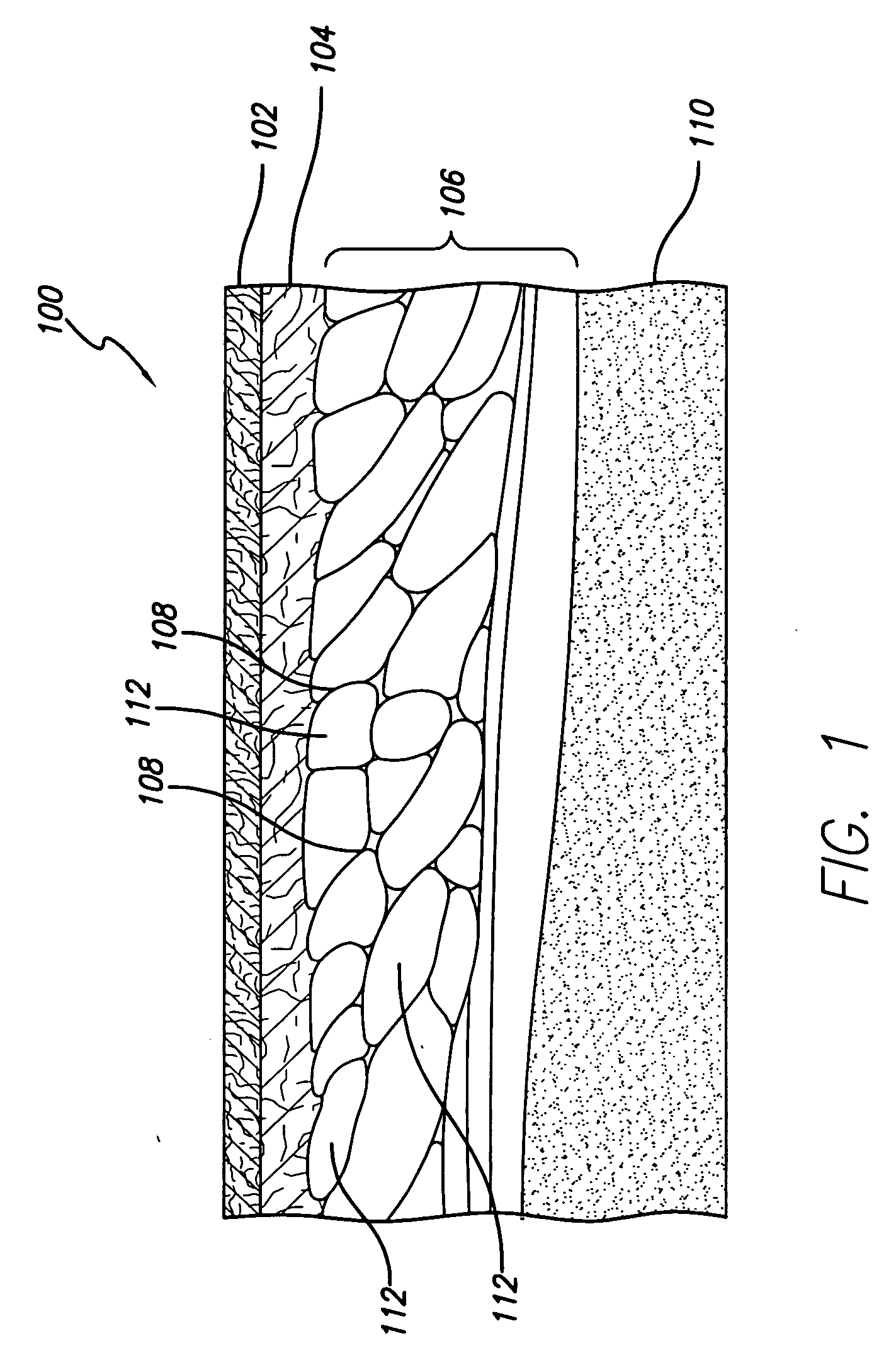
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
InactiveUS20060122593A1Facilitate ablationReduce ablationSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingSaline solutionsRefrigerant
The present invention discloses an electrode for an electric operation device including a hollow electrode being formed in a hollow tube shape extended long from a closed tip, and having an insulation-coating on the outside surface except a predetermined length of the closed tip side, a refrigerant tube having a smaller diameter than a diameter of the hollow electrode, and being inserted into the hollow electrode, the refrigerant tube supplying refrigerants for cooling a living tissue contacting the closed tip and the hollow electrode into the hollow electrode, and externally discharging the heat-exchanged refrigerants from the living tissue through the gap between the refrigerant tube and the hollow electrode, at least one first hole formed on the outside surface of the hollow electrode where the insulation coating has not been formed, for externally discharging some of the refrigerants supplied through the refrigerant tube from the hollow electrode, and a flow control means formed on the outside surface of the hollow electrode where the insulation coating has not been formed, and operated as a discharge resistance to the refrigerants discharged from the first hole, for controlling a flow of the refrigerants, whereby supplying an electrode structure using both a method for water-cooling the inside of the electrode and a method for discharging the saline solution.
Owner:JUN MYONG KI
Apparatus for treating subcutaneous tissues
ActiveUS20070055181A1Sufficient powerEliminate riskUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyAbnormal tissue growthCavitation
An apparatus and method for treating subcutaneous tissues using acoustic waves in the range of low acoustic pressure ultrasound waves is disclosed. The method includes injections of enhancing agents, wherein disruption of subcutaneous tissues and subcutaneous cavitational bioeffects are produced by ultrasound waves having a power that will not produce tissue cavitation in the absence of the enhancing agents. The apparatus and method of use is useful for treatment of subcutaneous abnormalities including cellulite, lipomas, and tumors.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
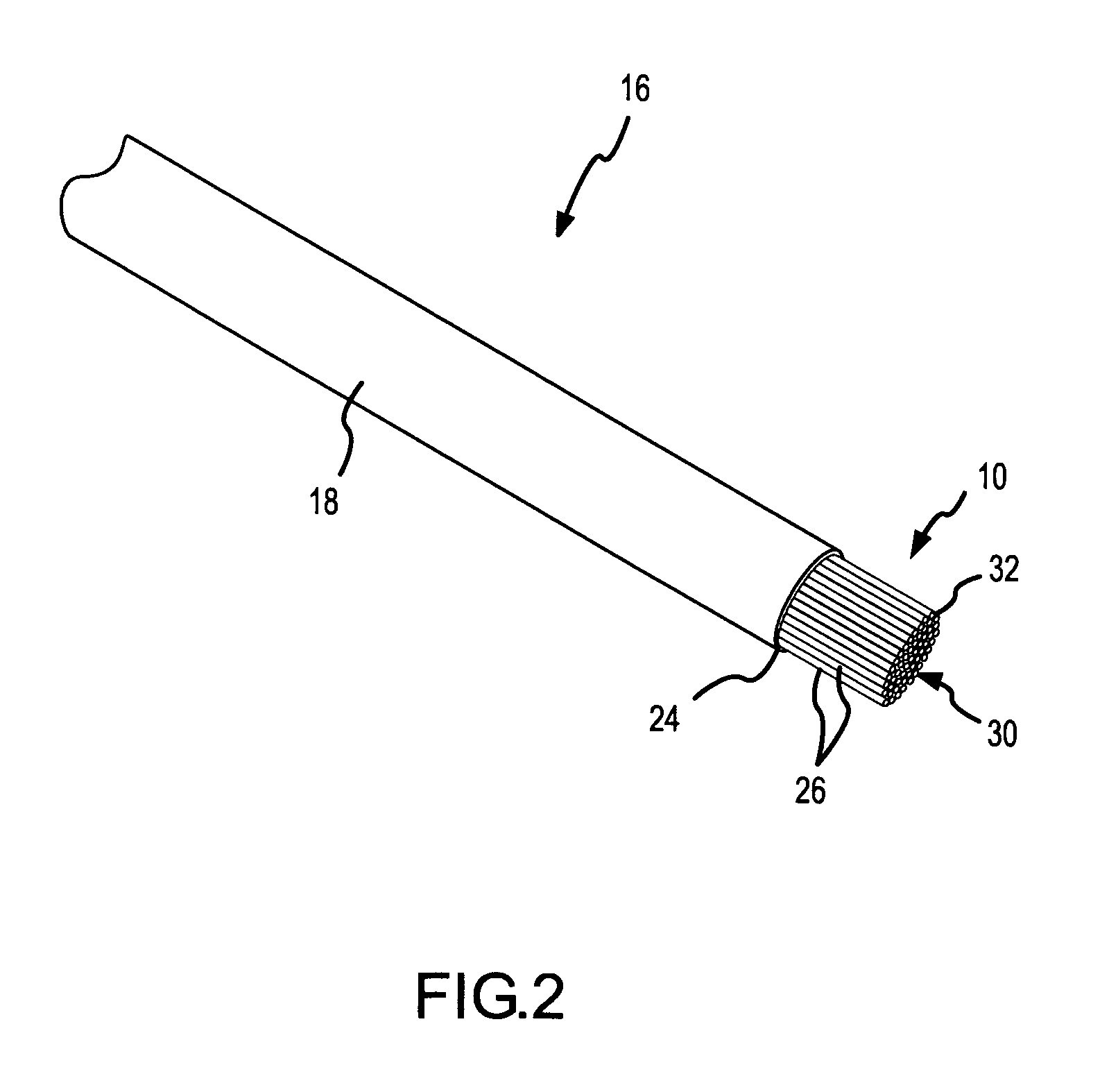
Brush electrode and method for ablation
InactiveUS7326204B2Reduce formationReducing of of surfaceSurgical instruments for heatingBristleTissue ablation
A brush electrode and a method for using the brush electrode for tissue ablation are disclosed. The brush electrode comprises a plurality of flexible filaments or bristles for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. Interstitial spaces are defined among the filaments of the brush electrode, and the interstitial spaces are adapted to direct conductive or nonconductive fluid, when present, toward the distal ends of the brush filaments. The brush electrode facilitates electrode-tissue contact in target tissue having flat or contoured surfaces. The flexible filaments may be selectively trimmed to give a desired tip configuration or a desired standoff distance between the tissue and the conductive filaments in the brush electrode. Also, the filaments may be grouped into clusters. A shielded-tip brush electrode, including a flexible boot, is also disclosed.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
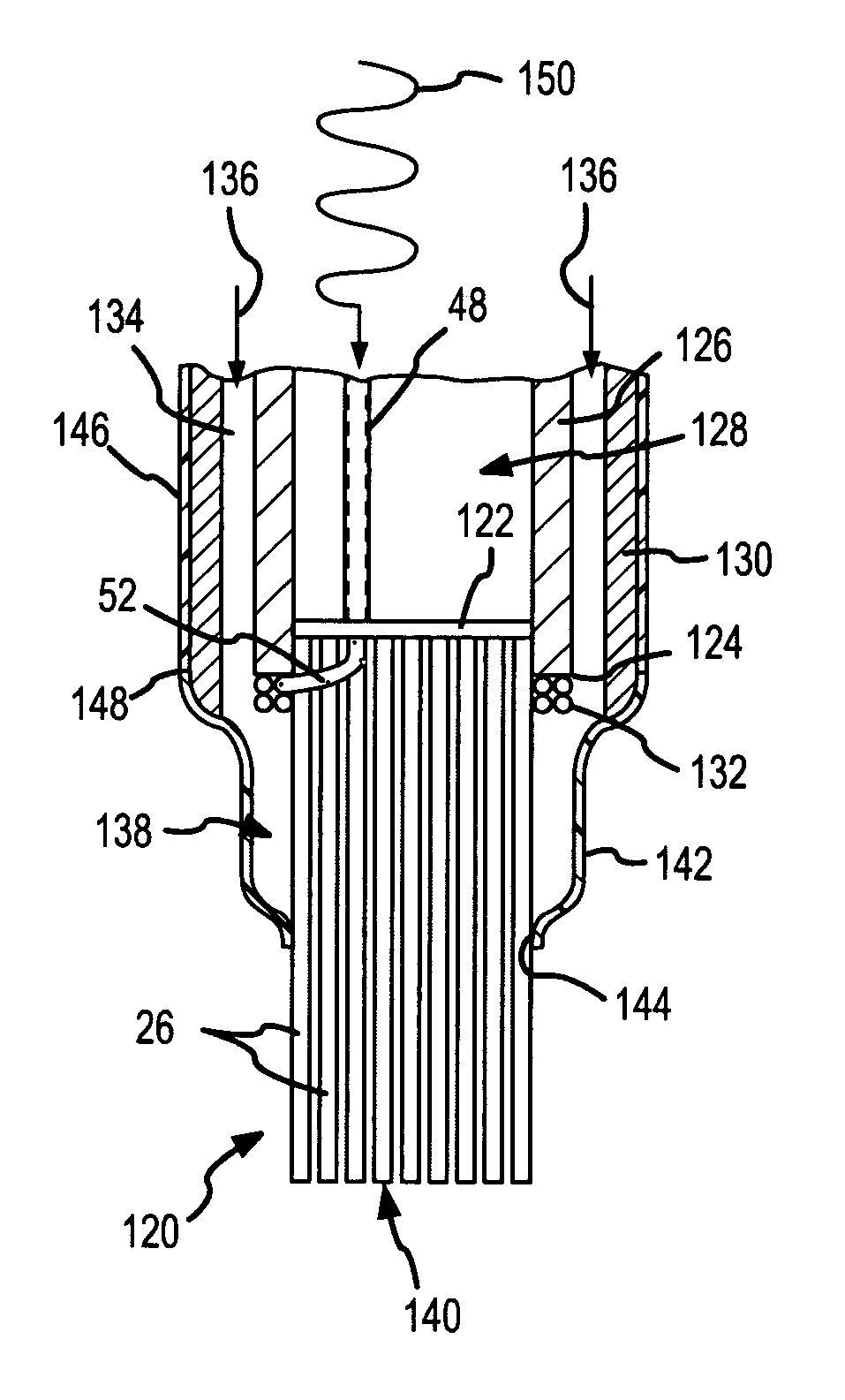
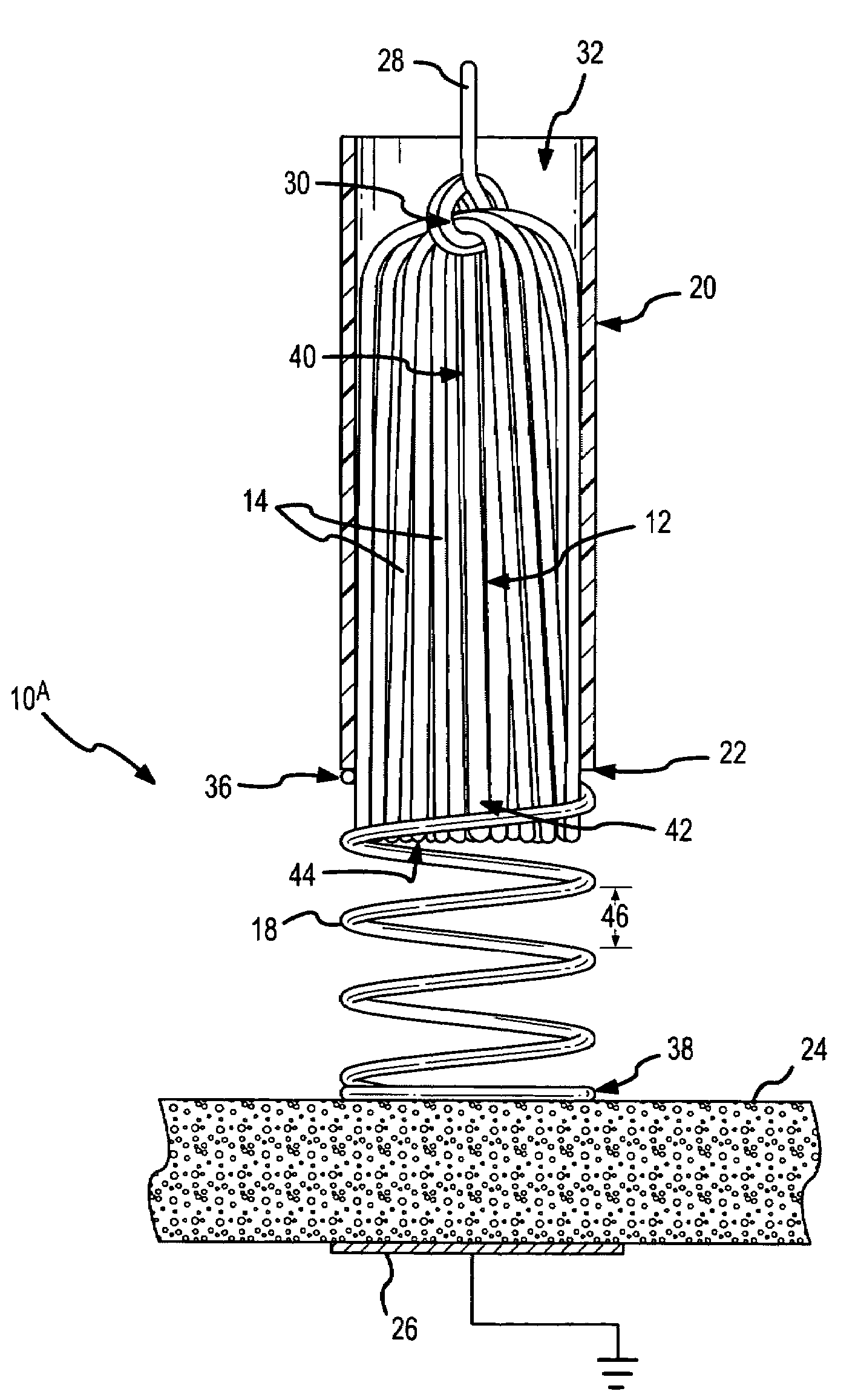
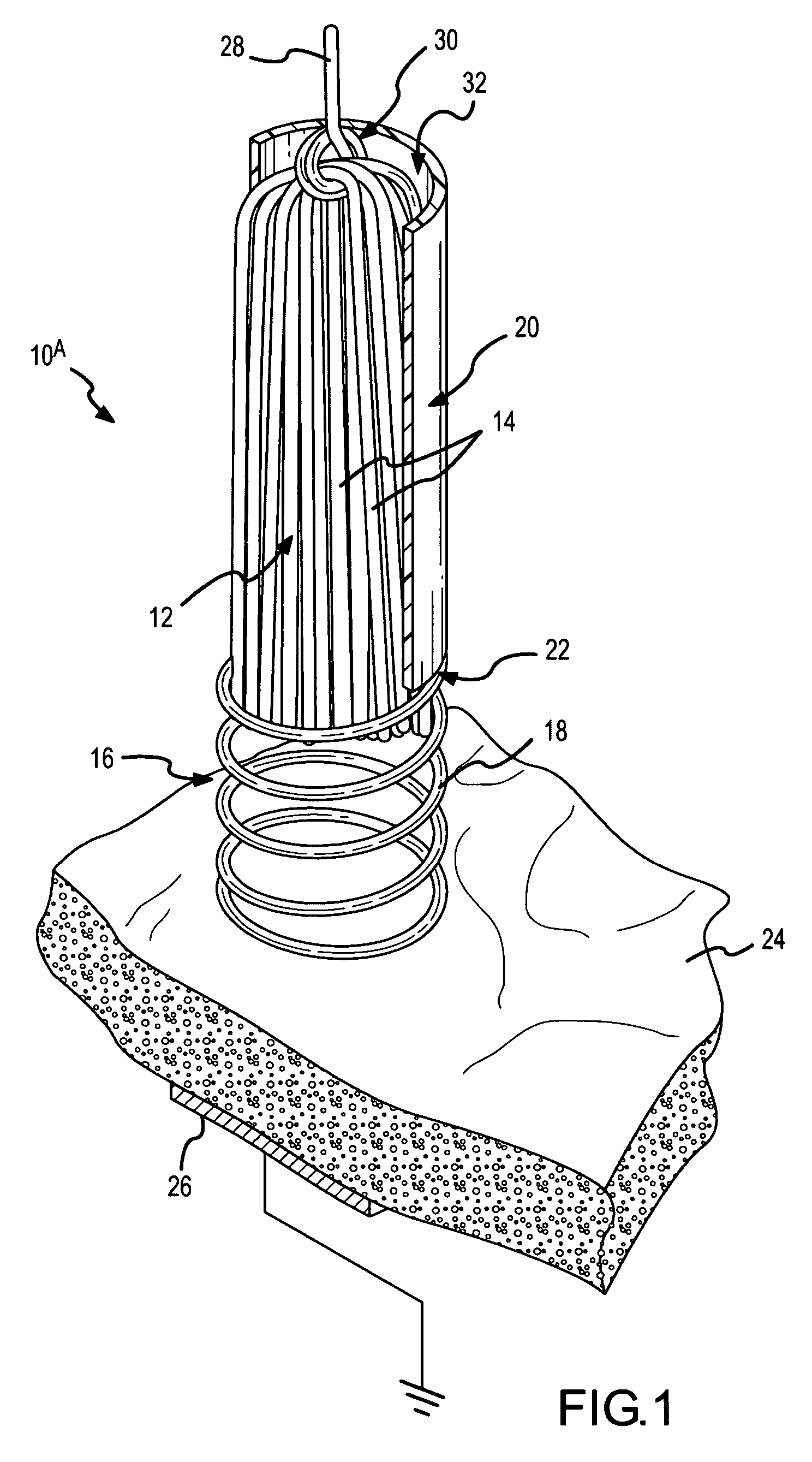
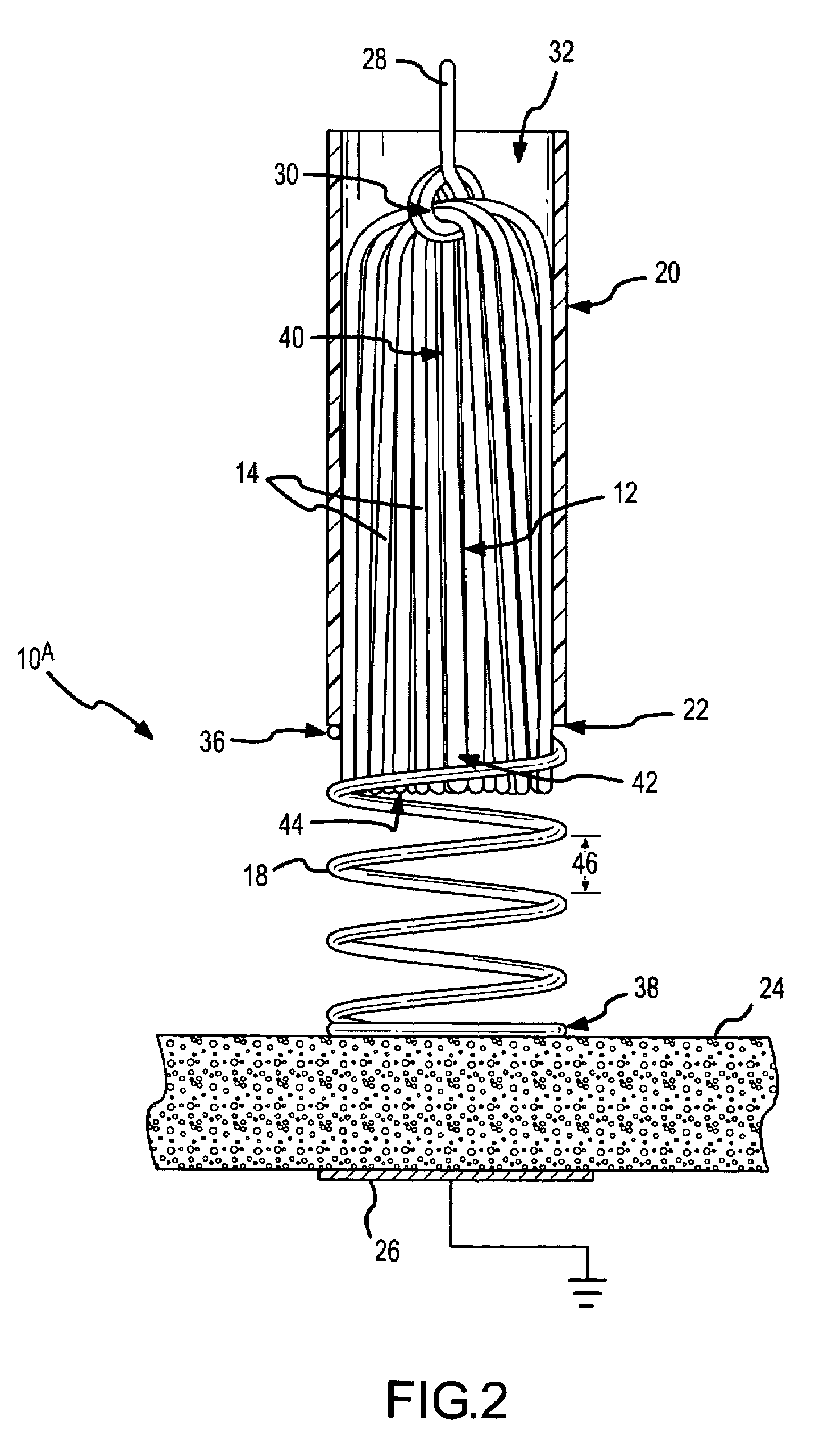
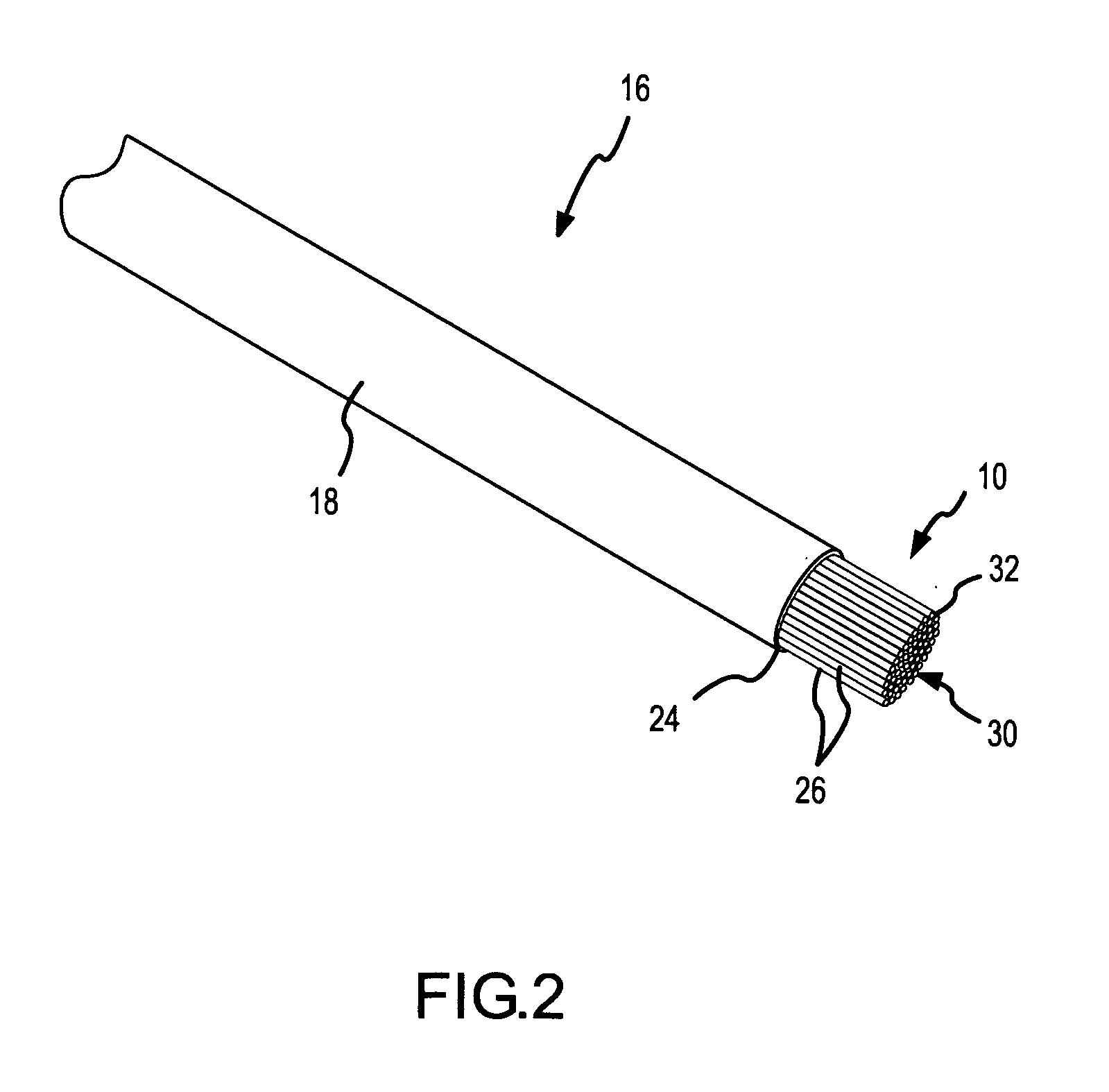
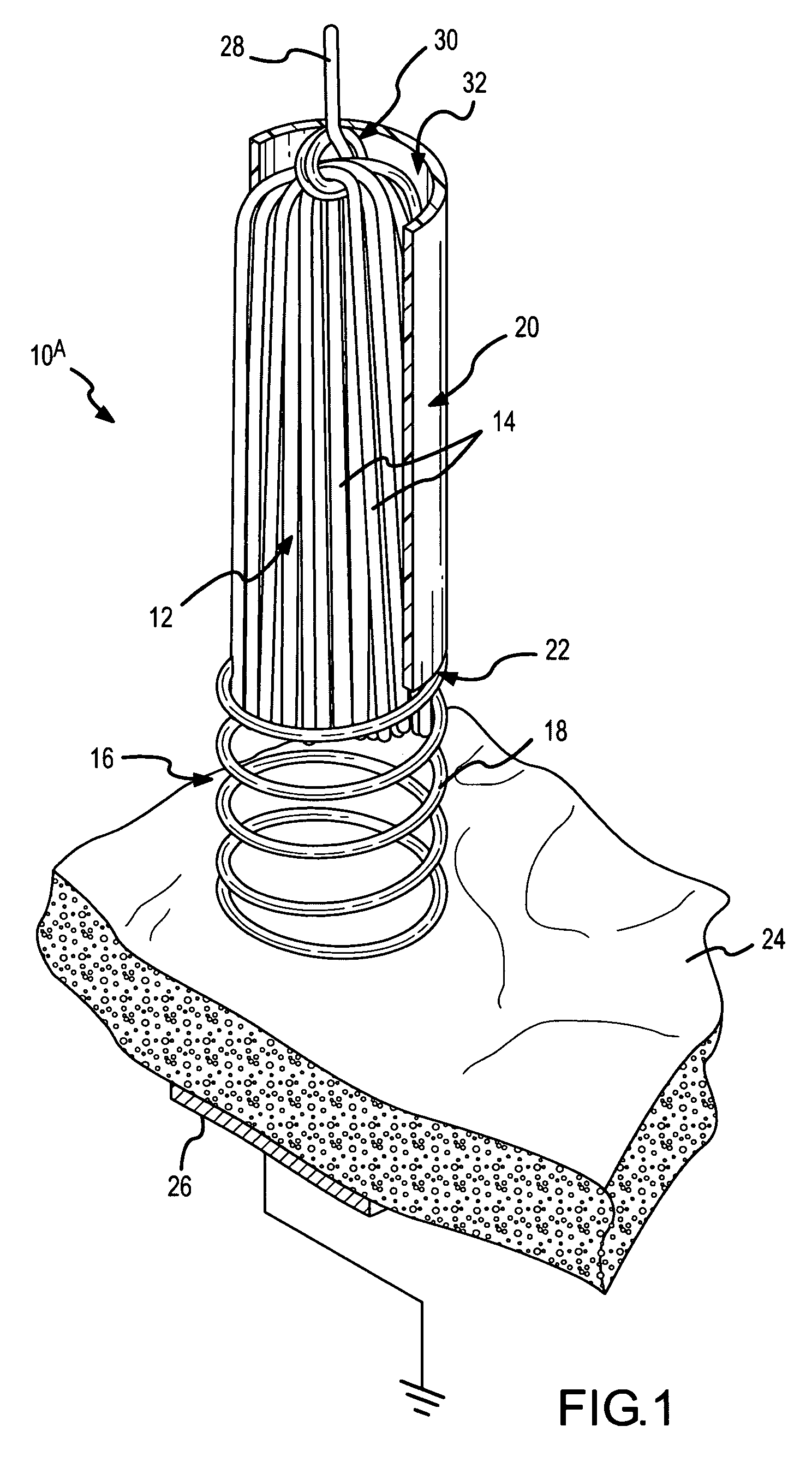
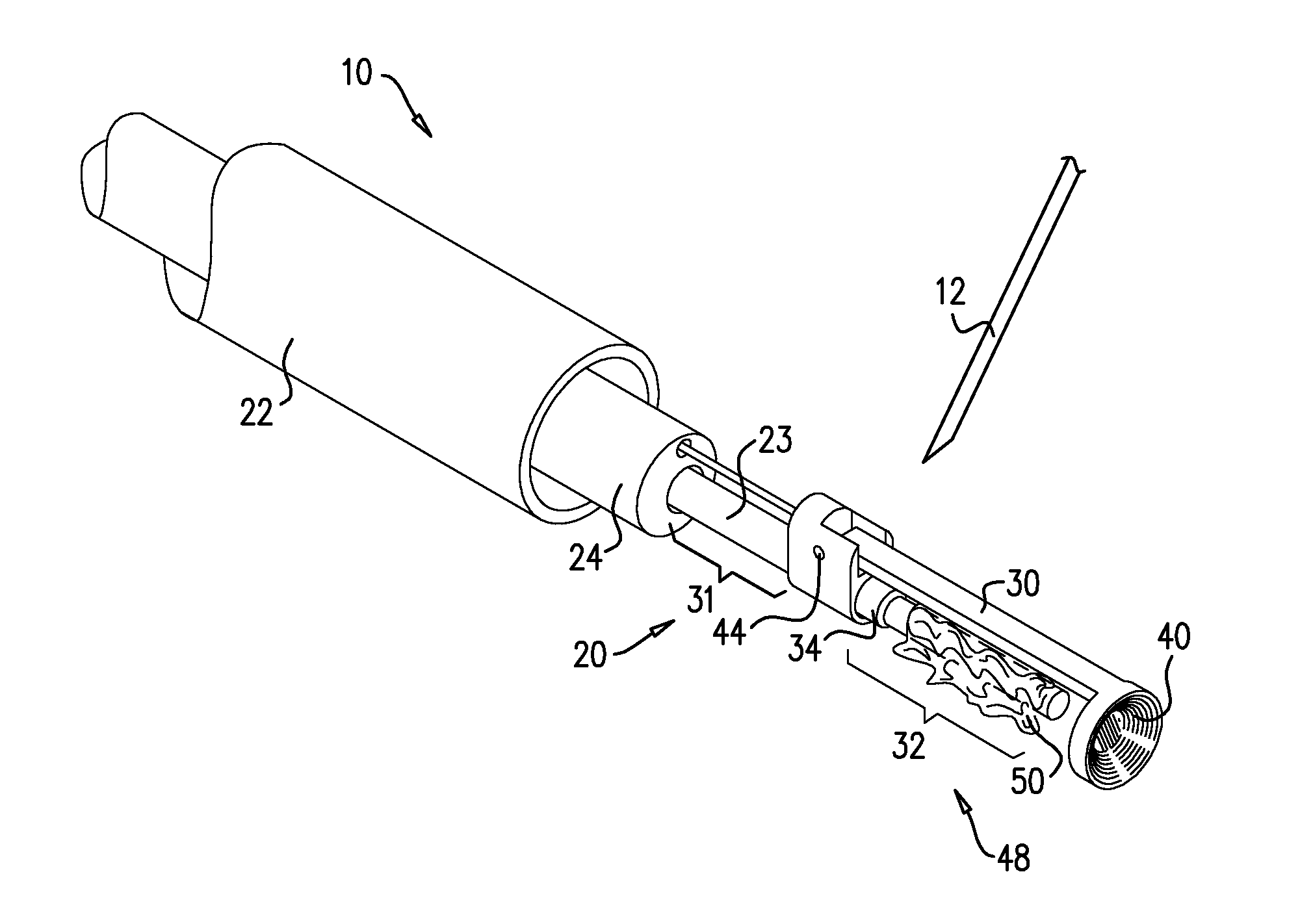
Spring-tip, flexible electrode catheter for tissue ablation
InactiveUS7311704B2Reduce formationReducing of of surfaceInternal electrodesEndoscopesBristleAxial compression
A spring-tip, flexible electrode, and a method for using that electrode for tissue ablation, are disclosed. The spring-tip, flexible electrode comprises an enshrouded flexible electrode (e.g., an enshrouded plurality of flexible brush filaments or bristles) for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. The spring of the spring tip may comprise compressible coils, compressible mesh, or compressible bellows, among other things. The spring provides axial suspension and is capable of axial compression and extension, and is flexible enough for deflection and bending. The axial suspension of the spring tip facilitates the desired contact between the electrode and the tissue surface. A shielded, spring-tip, flexible electrode is also disclosed, and includes a flexible nipple or shield. The spring-tip, flexible electrode facilitates enhanced tissue contact in difficult environments (e.g., during ablation of a contoured or trabeculated surface inside a beating heart) since the flexible electrode readily conforms to surface contours while the bending stress of the spring enhances the contract pressure on the tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Brush electrode and method for ablation
InactiveUS20050159739A1Easy to optimizeReduce decreaseSurgical instruments for heatingBristleEngineering
A brush electrode and a method for using the brush electrode for tissue ablation are disclosed. The brush electrode comprises a plurality of flexible filaments or bristles for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. Interstitial spaces are defined among the filaments of the brush electrode, and the interstitial spaces are adapted to direct conductive or nonconductive fluid, when present, toward the distal ends of the brush filaments. The brush electrode facilitates electrode-tissue contact in target tissue having flat or contoured surfaces. The flexible filaments may be selectively trimmed to give a desired tip configuration or a desired standoff distance between the tissue and the conductive filaments in the brush electrode. Also, the filaments may be grouped into clusters. A shielded-tip brush electrode, including a flexible boot, is also disclosed.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Energy delivery systems and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130165915A1Reduced flexibilityFacilitate ablationDiagnosticsSurgical needlesVascular thrombosisThrombus
The present invention relates to comprehensive systems, devices and methods for delivering energy to tissue for a wide variety of applications, including medical procedures (e.g., tissue ablation, resection, cautery, vascular thrombosis, treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and dysrhythmias, electrosurgery, tissue harvest, etc.). In certain embodiments, systems, devices, and methods are provided for treating a tissue region (e.g., a tumor) through application of energy.
Owner:NEUWAVE MEDICAL
Devices and methods for ablation of tissue
ActiveUS20160374754A1Avoid flowFacilitate ablationElectrotherapyBalloon catheterDiseaseMedical disorder
This document provides devices and methods for the treatment of heart conditions, hypertension, and other medical disorders. For example, this document provides devices and methods for treating atrial fibrillation by performing thoracic vein ablation procedures, including pulmonary vein myocardium ablation. In some embodiments, the ablation is performed in coordination with the delivery a pharmacological agent that can abate the formation of tissue stenosis or neointimal hyperplasia caused by the ablation.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Spring-tip, flexible electrode catheter for tissue ablation
InactiveUS20050267332A1Easy to optimizeImproves catheter-tissue contactInternal electrodesEndoscopesBristleAxial compression
A spring-tip, flexible electrode, and a method for using that electrode for tissue ablation, are disclosed. The spring-tip, flexible electrode comprises an enshrouded flexible electrode (e.g., an enshrouded plurality of flexible brush filaments or bristles) for applying ablative energy (e.g., RF energy) to target tissue during the formation of spot or continuous linear lesions. The spring of the spring tip may comprise compressible coils, compressible mesh, or compressible bellows, among other things. The spring provides axial suspension and is capable of axial compression and extension, and is flexible enough for deflection and bending. The axial suspension of the spring tip facilitates the desired contact between the electrode and the tissue surface. A shielded, spring-tip, flexible electrode is also disclosed, and includes a flexible nipple or shield. The spring-tip, flexible electrode facilitates enhanced tissue contact in difficult environments (e.g., during ablation of a contoured or trabeculated surface inside a beating heart) since the flexible electrode readily conforms to surface contours while the bending stress of the spring enhances the contract pressure on the tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment
ActiveUS20110282249A1Facilitate ablationPromote rapid formationUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesSonificationHeart chamber
Apparatus is provided that includes an ultrasound ablation system, which includes a reflection-facilitation element, configured to be placed at an extramyocardial site of a subject, and to provide an extramyocardial reflective region. The system further includes an ultrasound tool, which comprises at least one ultrasound transducer configured to be positioned within a heart chamber of the subject, and to ablate myocardial tissue by applying ultrasound energy to the myocardial tissue such that at least a portion of the transmitted energy is reflected by the reflective region onto the myocardial tissue. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
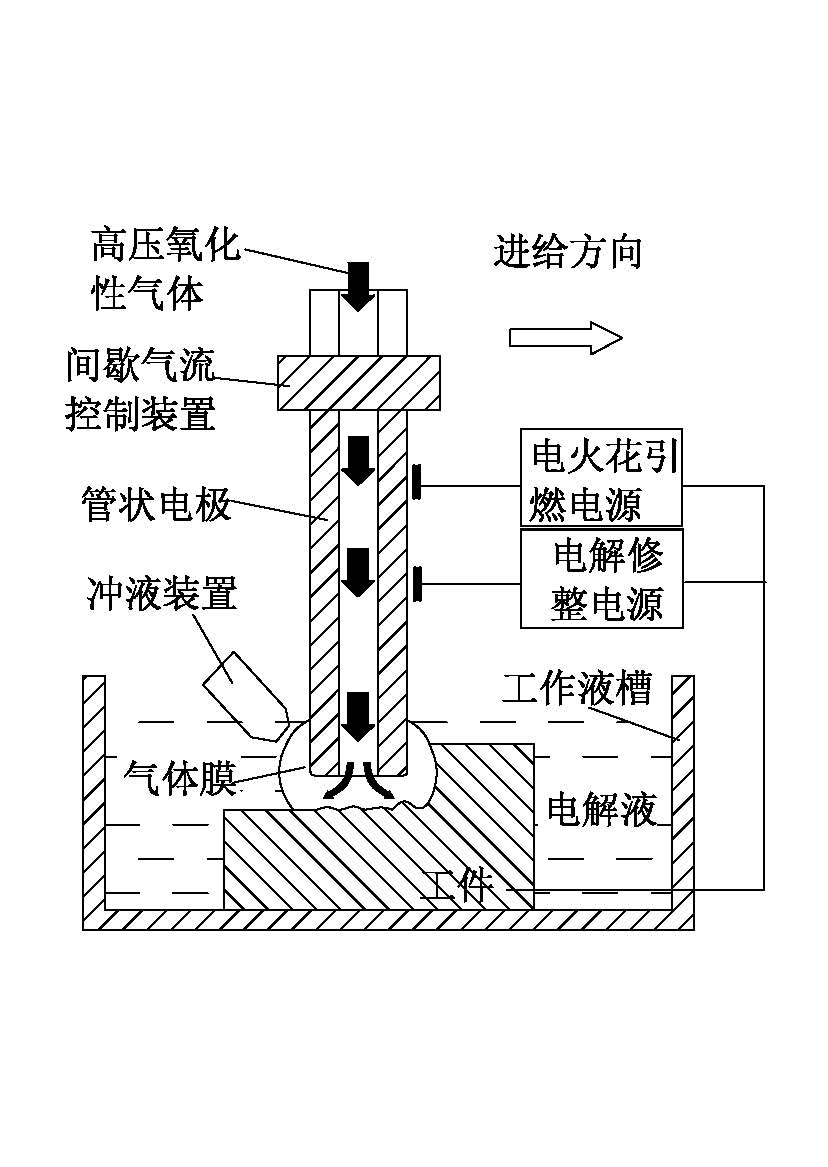
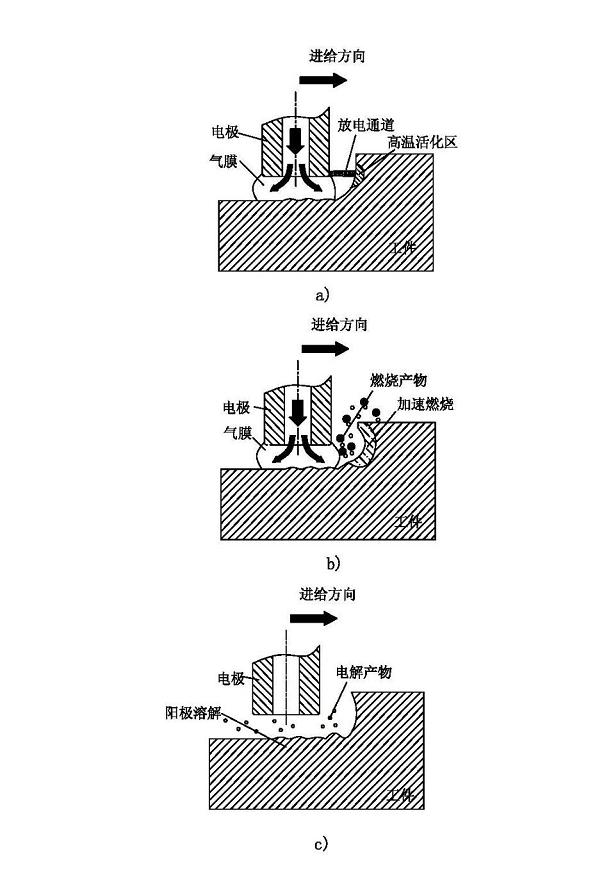
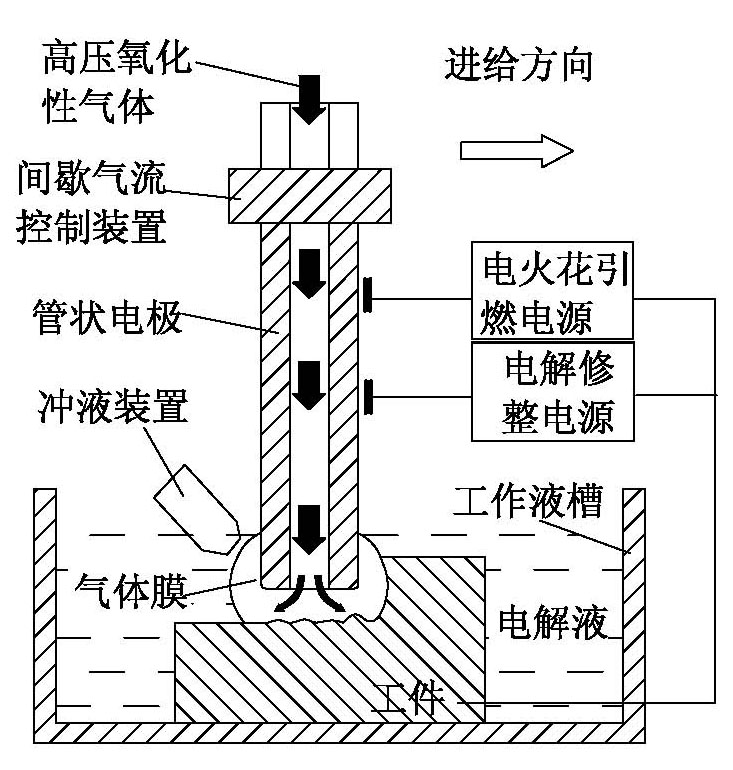
Electric spark induction controllable erosion and electrolysis compound efficient machining method
The invention discloses an electric spark induction controllable erosion and electrolysis compound efficient machining method which is characterized by comprising the steps of: with electrolyte as a working medium, immersing one end of a to-be-machined workpiece electrode and a tool electrode in the working medium, intermittently introducing air to a machining area and forming an air film between the to-be-machined workpiece electrode and the tool electrode; generating electric spark discharge between the to-be-machined workpiece electrode and the tool electrode under the action of an electric spark power supply to ensure that the to-be-machined workpiece generates an oxidation exothermic reaction with the introduced air under the action of electric spark discharge ignition and forms a burning effect so that efficient ablation is realized; in an air closed stage, carrying out electrochemical machining and surface dressing on the ablation surface under the action of an electrolysis power supply; and alternating to start an electric spark ignition pulse power supply and an electrolysis eroding power supply and moving the tool electrode until machining is finished. The invention has the advantages of high material eroding efficiency up to be several times, even tens of times of that of the conventional electric spark machining and also be higher than that of the conventional electrolysis machining under the same electrical parameters on the premise of ensuring machining quality and precision, good surface quality, precision and controllability and capability of eliminating surface residual stress.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment and monitoring
InactiveUS20110282203A1Preventing cardiac arrhythmiaFacilitate ablationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMedicineTransducer
A method comprising providing a reflective region at a far side of tissue of a subject is provided. The method includes assessing whether the reflective region is in a desired location, by means of acoustic sensing; and in response to assessing that the reflective region is in the desired location, activating an ultrasound transducer to ablate the tissue by applying ultrasound energy to a near side of the tissue, such that at least a portion of the transmitted energy is reflected by the reflective region onto the tissue of the subject. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
Method of positioning a medical instrument
InactiveUS20060217694A1Facilitate ablationEasily advancedElectrotherapyCatheterProximateBiological target
A system and method for positioning a medical instrument at a desired biological target tissue site is provided. The system includes an elongated sheath having a deflectable distal end configured to deflect or otherwise position at least a portion of a medical instrument during a surgical procedure allowing for the placement of the deflected portion adjacent or proximate to a predetermined target tissue surface. The positioning system may be incorporated into the medical instrument. The medical instrument may be an ablation system.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Laser pulse synthesis system
ActiveUS8675699B2Reduce processing stepsFacilitate ablationLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionOptoelectronicsUltrashort laser
A laser pulse synthesis system is provided. A further aspect of the present system uses a phase-only modulator to measure ultrashort laser pulses. An additional aspect achieves interferences between split subpulses even though the subpulses have different frequencies. Yet another aspect of a laser system employs multi-comb phase shaping of a laser pulse. In another aspect, a laser system includes pulse characterization and arbitrary or variable waveform generation through spectral phase comb shaping.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment
ActiveUS8617150B2Facilitate ablationPromote rapid formationUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingSonificationHeart chamber
Apparatus is provided that includes an ultrasound ablation system, which includes a reflection-facilitation element, configured to be placed at an extramyocardial site of a subject, and to provide an extramyocardial reflective region. The system further includes an ultrasound tool, which comprises at least one ultrasound transducer configured to be positioned within a heart chamber of the subject, and to ablate myocardial tissue by applying ultrasound energy to the myocardial tissue such that at least a portion of the transmitted energy is reflected by the reflective region onto the myocardial tissue. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment and monitoring
ActiveUS20130103028A1Preventing cardiac arrhythmiaFacilitate ablationUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsHeart chamberTransducer
Apparatus comprising an ultrasound ablation system (10), which comprises a reflection-facilitation element (12), configured to be placed at an extramyocardial site of a subject, and to provide an extramyocardial reflective region; and an ultra-sound tool (20), which comprises at least one ultrasound transducer (40) configured to be positioned within a heart chamber of the subject. The ultrasound transducer (40) is configured to ablate myocardial tissue by applying ultrasound energy to the myocardial tissue such that at least a portion of the transmitted energy is reflected by the reflective region onto the myocardial tissue. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
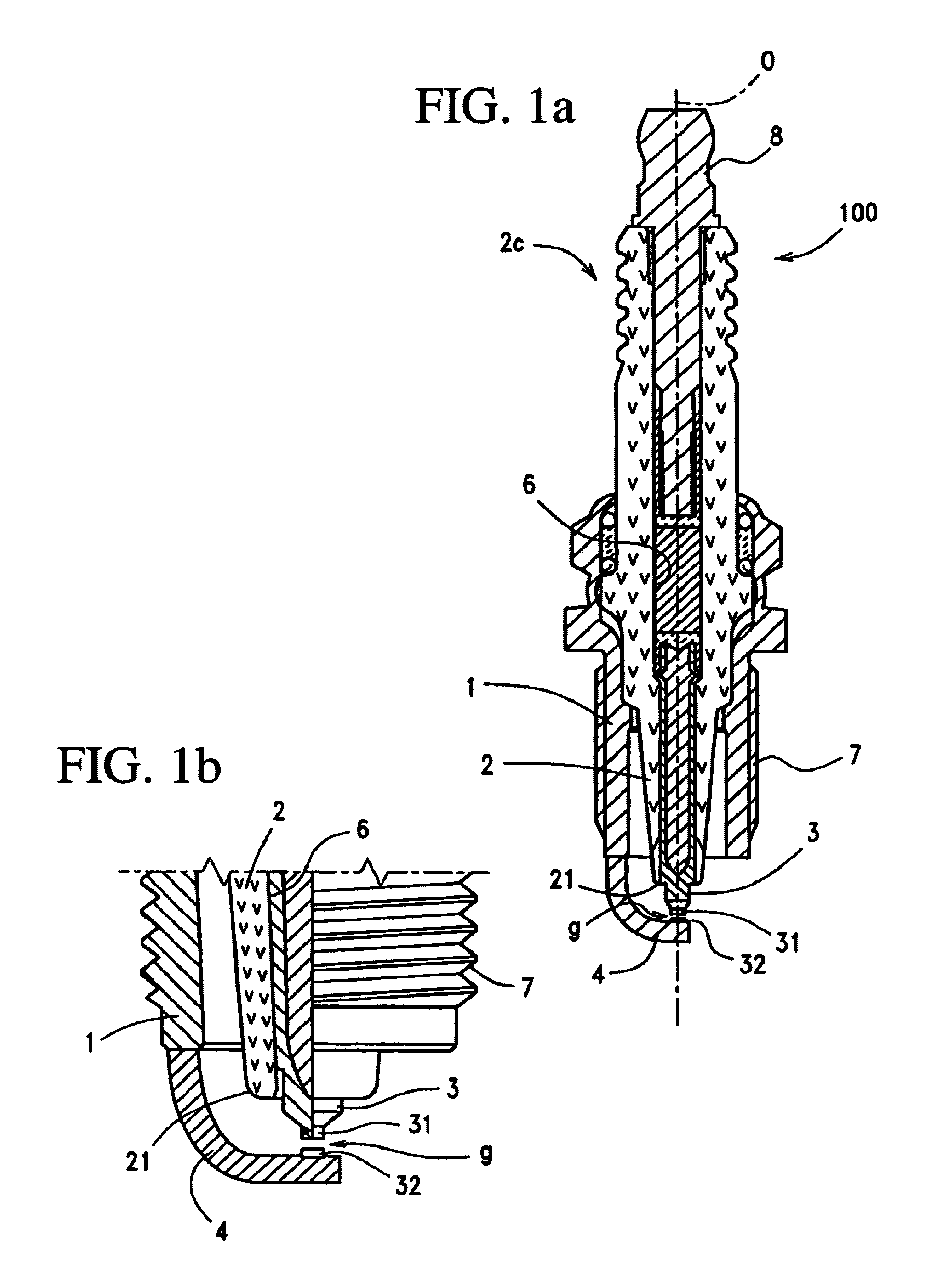
Method for manufacturing a spark plug, and spark plug
InactiveUS6997767B2Increase energy densityIncreased durabilitySpark gapsFuel injection apparatusFiberRefractive index
A method for manufacturing a spark plug which reduces the generation of spatters and the possibility of insufficient weld strength resulting from penetration depth insufficiency of a weld metal portion is disclosed. In accordance with the method, a chip joint face formation portion of a center electrode is formed from a heat-resistant alloy predominantly containing Fe or Ni. A noble metal chip is attached to a chip joint face of the chip joint face formation portion to thereby form a chip-attached assembly. A full-circled laser-beam weld metal portion is formed on the chip-attached assembly in such a manner as to intrude into the noble metal chip and into the chip joint face formation portion. A graded-index-type fiber optic cable is used as an optical transmission path extending between a laser beam generator and an optical emission section. A laser beam which is transmitted from the laser beam generator through the cable irradiates the chip-attached assembly while being condensed.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
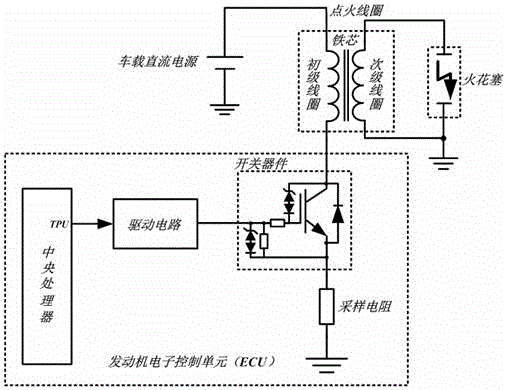
Spark duration time monitoring circuit for engine ignition system
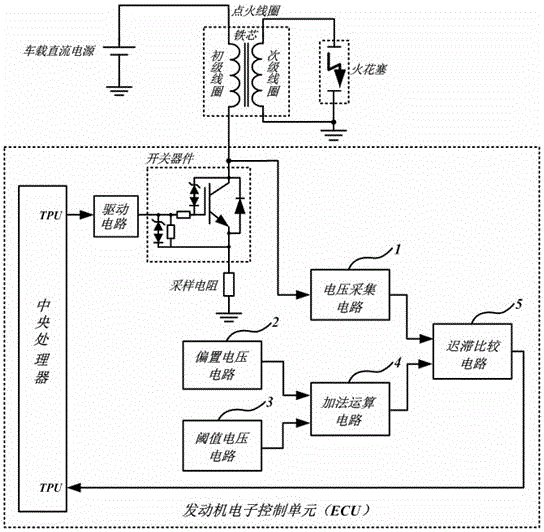
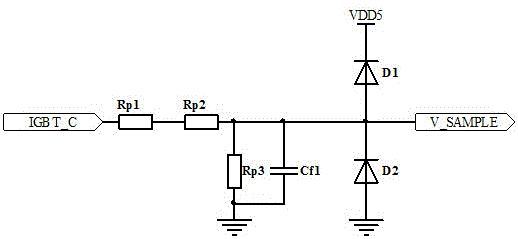
ActiveCN106286072AReduced service lifeGuaranteed to burnOther installationsMachines/enginesIgnition coilEngineering
The invention relates to a spark duration time monitoring circuit for an engine electronic control ignition system. The spark duration time monitoring circuit is characterized in that a time processing unit channel of a central processing unit is connected with the grid electrode of a switching element IGBT through a drive circuit of the switching element IGBT; the collector electrode of the switching element IGBT is connected with the first end of an ignition primary coil; the second end of the ignition primary coil is connected with a vehicle-mounted direct-current power source; the collector electrode voltage of the switching element IGBT is connected to a time processing unit input port of the central processing unit after passing the spark duration time monitoring circuit, the central processing unit regulates the charging time, namely ignition energy of the primary coil in real time according to the monitored spark duration time, and the spark duration time is controlled within a certain range (please see the range in the specification). By means of feedback signals of the spark duration time monitoring circuit of the ignition system, the charging time, namely the ignition energy of the primary coil is regulated in real time, the spark duration time is controlled within a certain range, and the purposes that it is guaranteed that mixed gas in an air cylinder is completely burned every time when ignition of an engine is carried out, and the situation that erosion of electrodes of a sparking plug is accelerated due to tool much ignition energy is provided and the service life of the sparking plug is shortened is avoided are achieved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com