Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about "ASR control systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
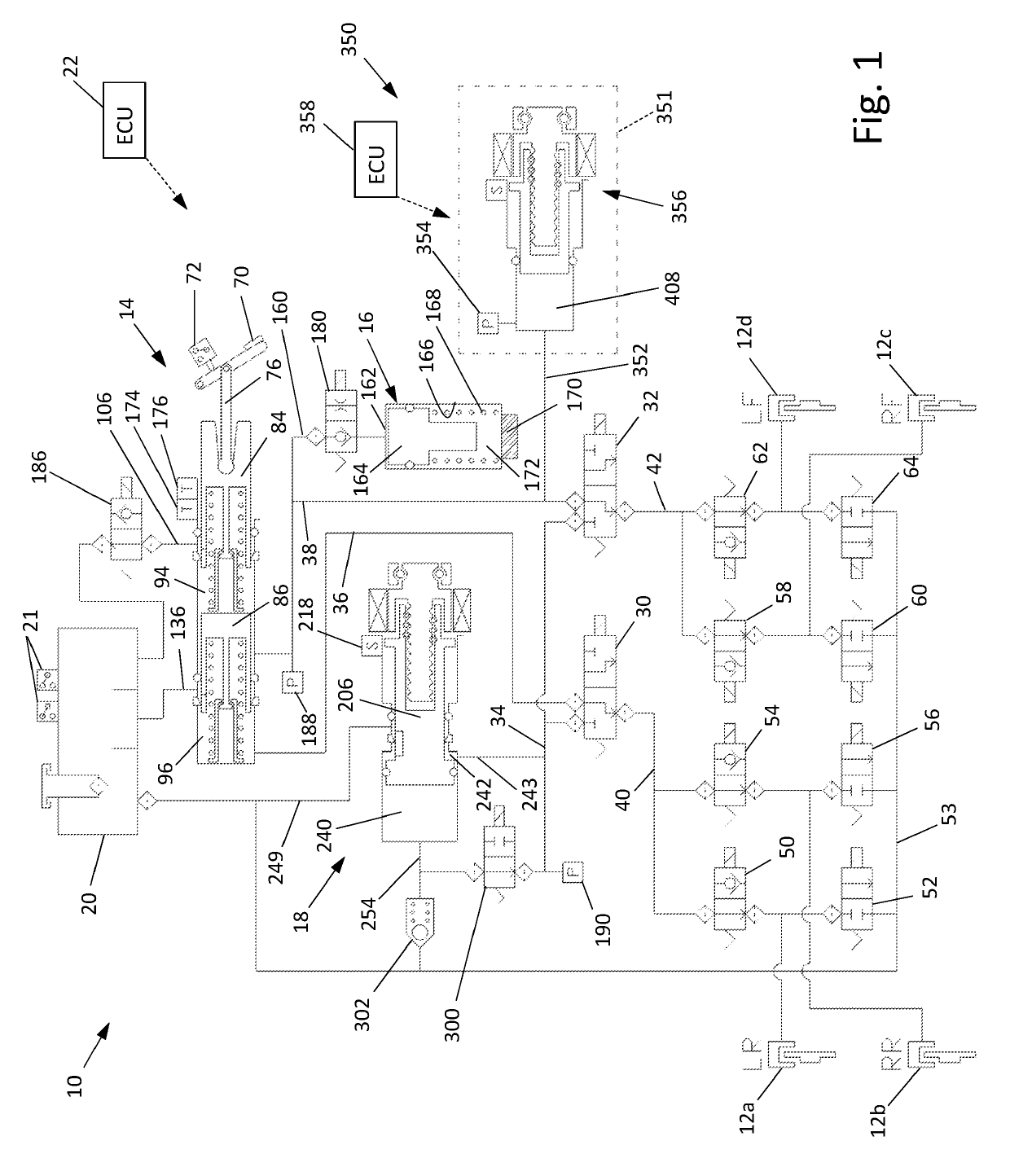
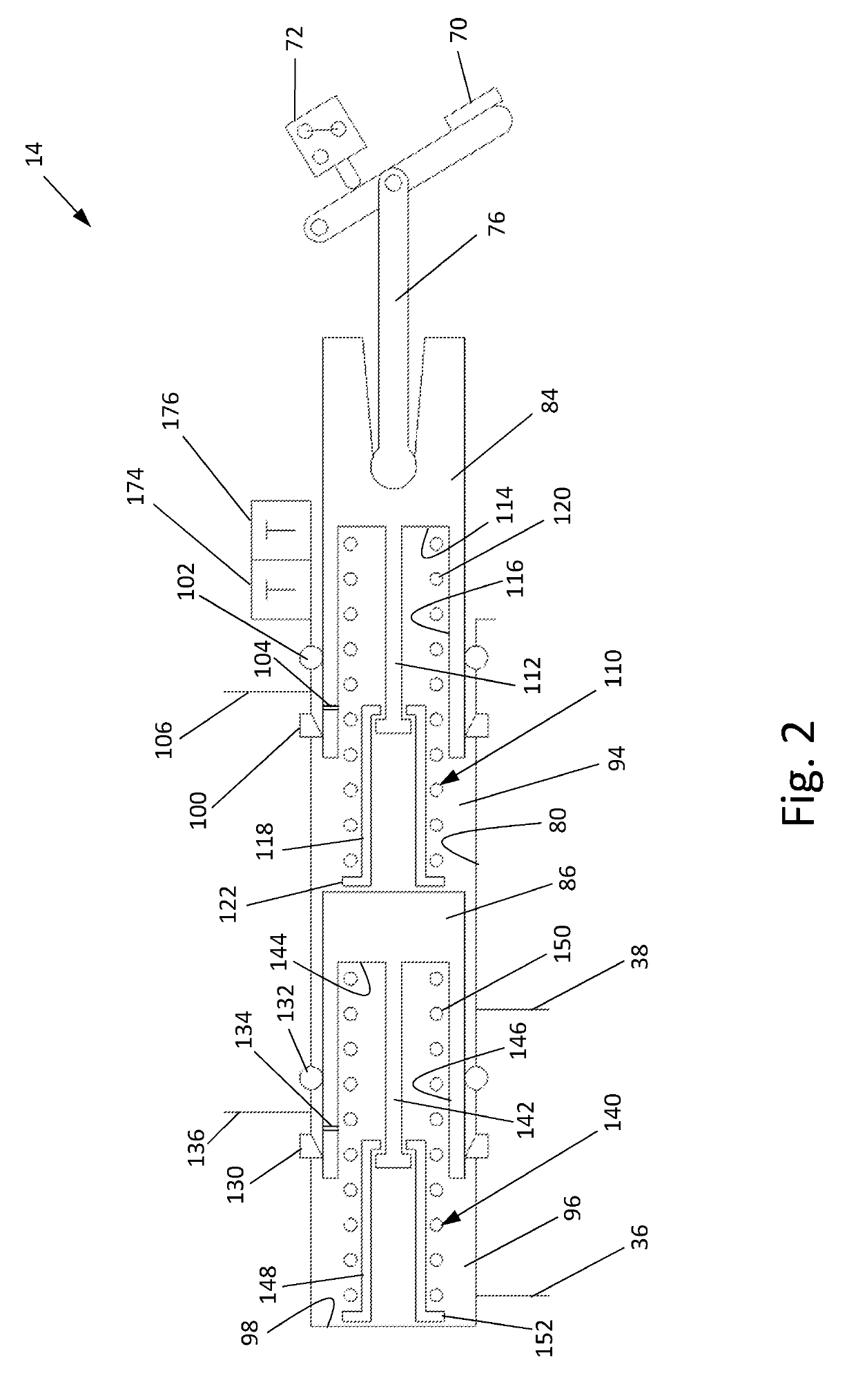
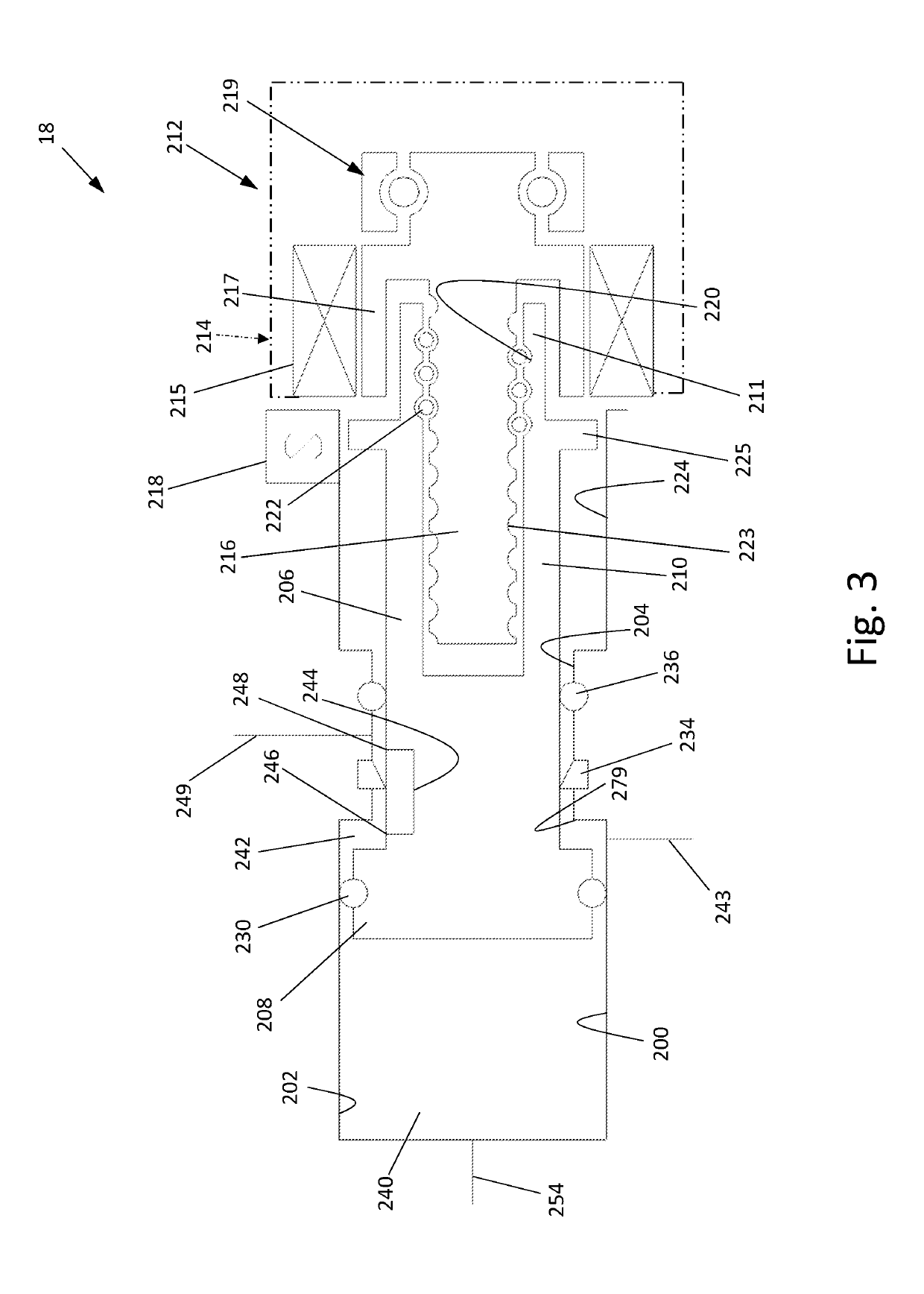
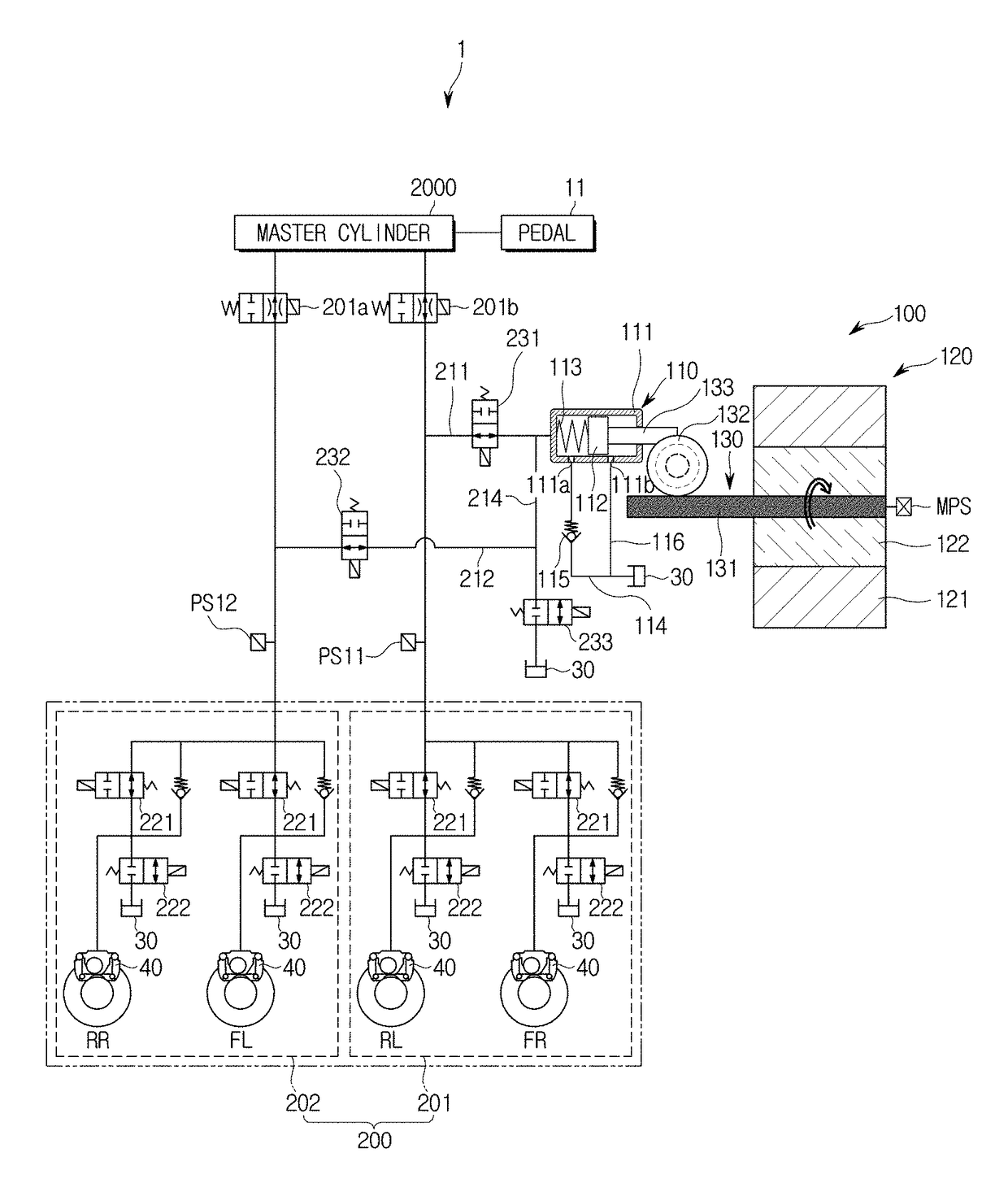
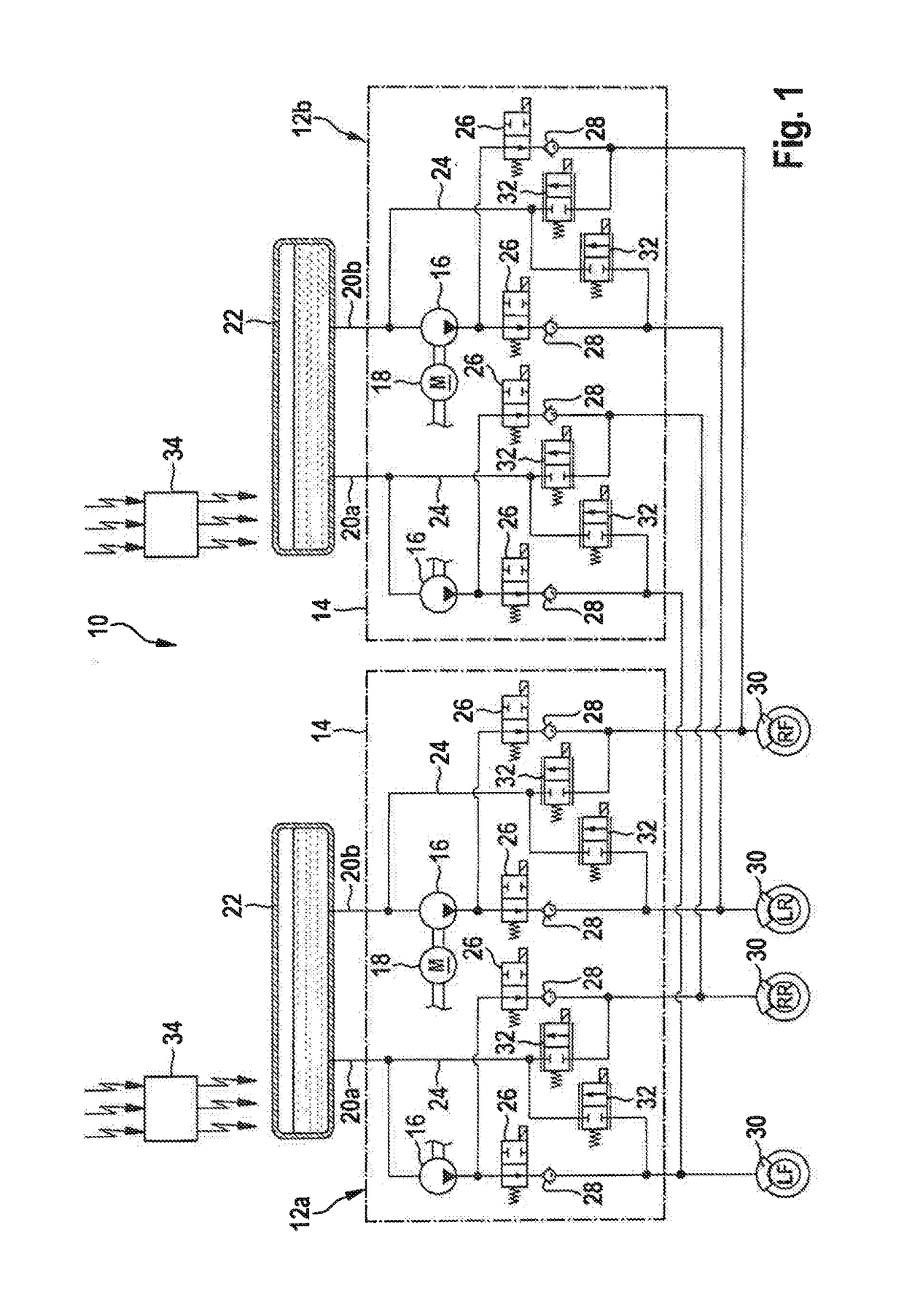
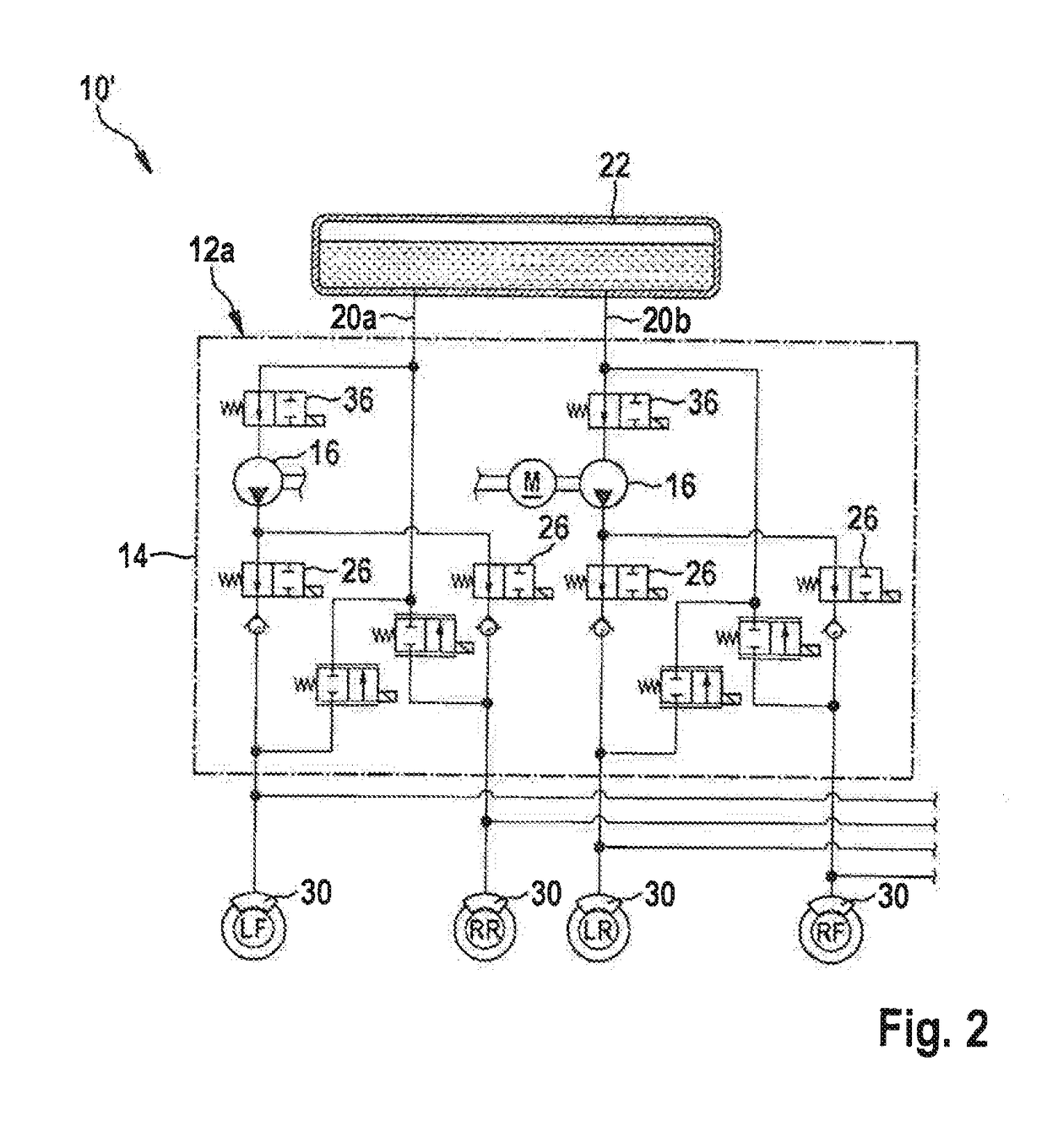
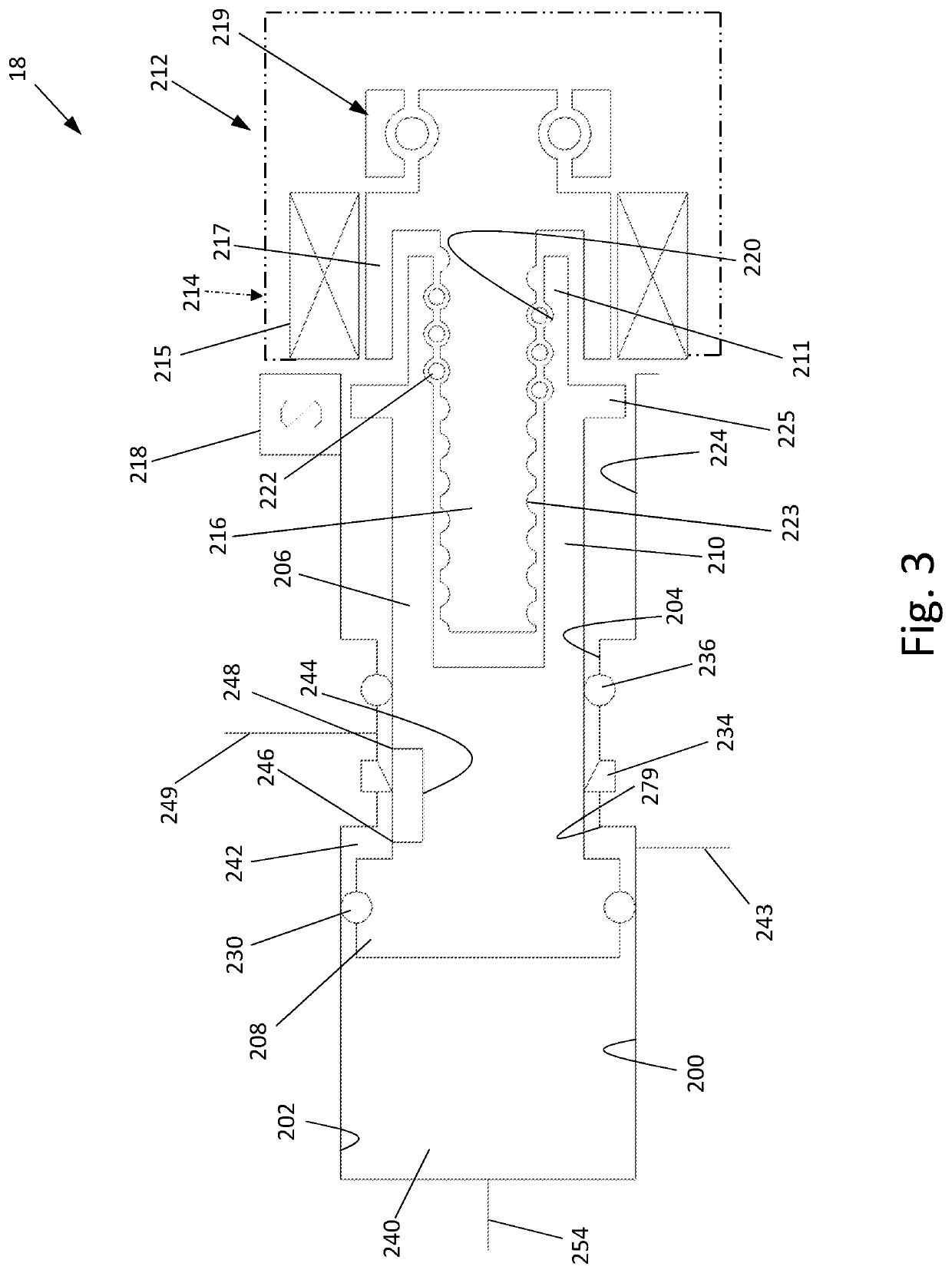
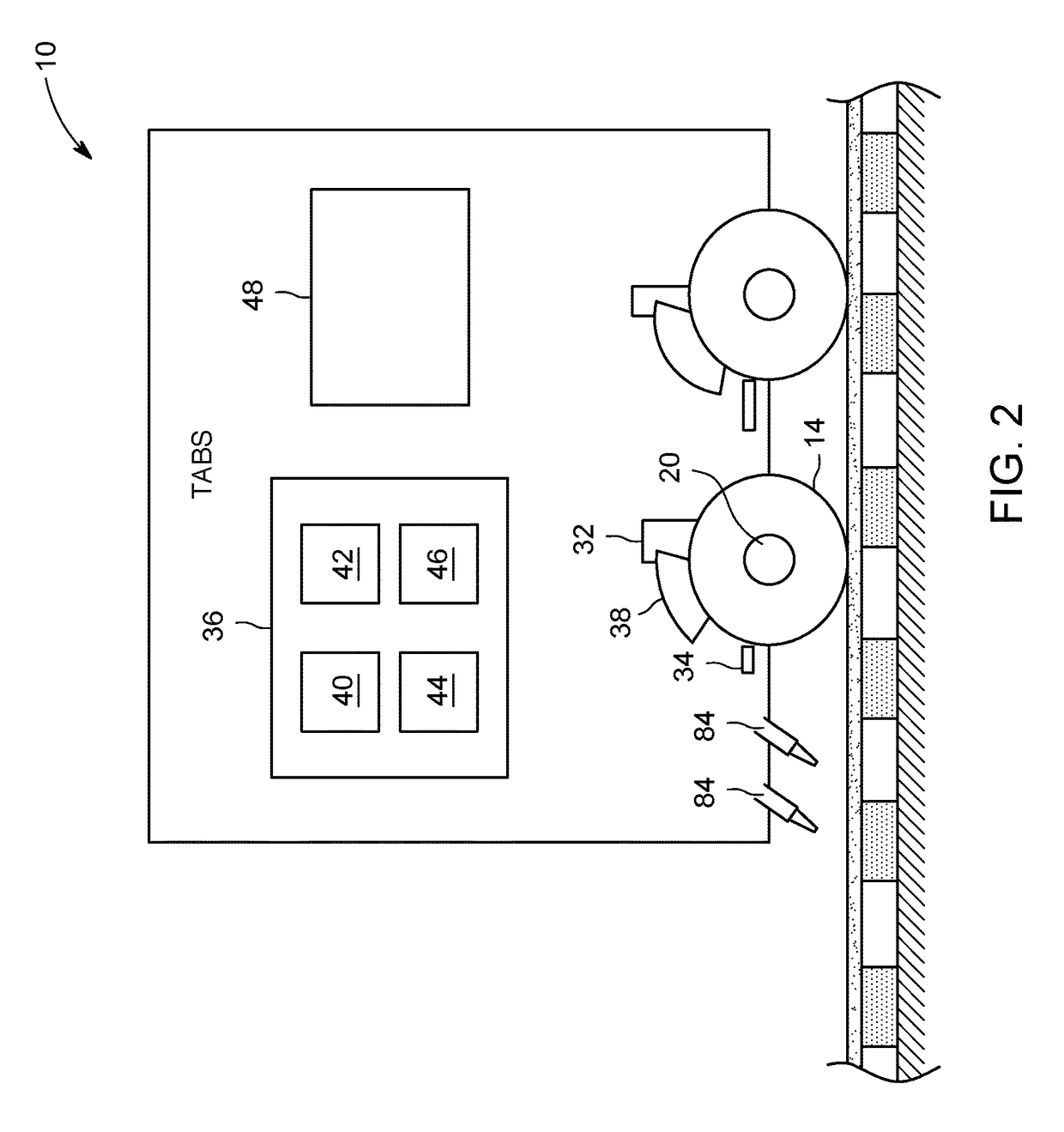
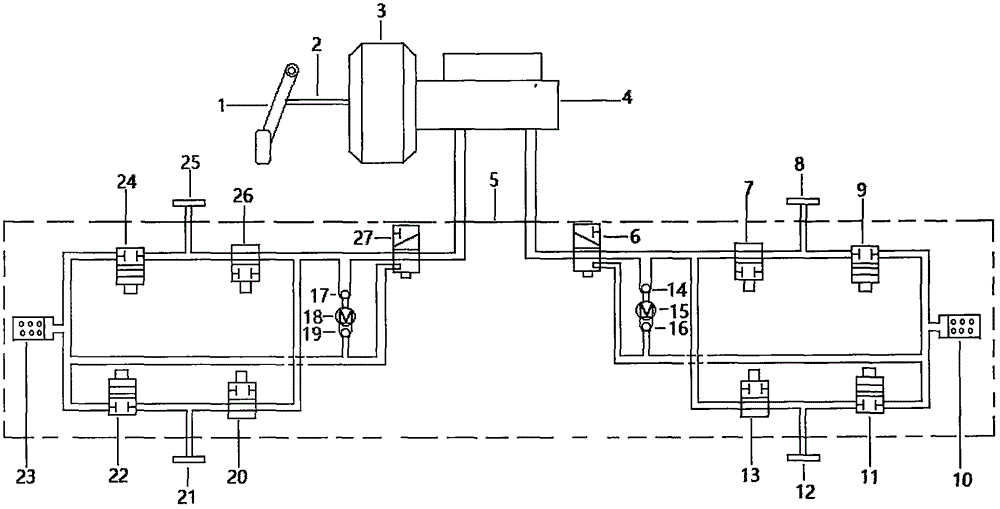
Vehicle Brake System With Secondary Brake Module
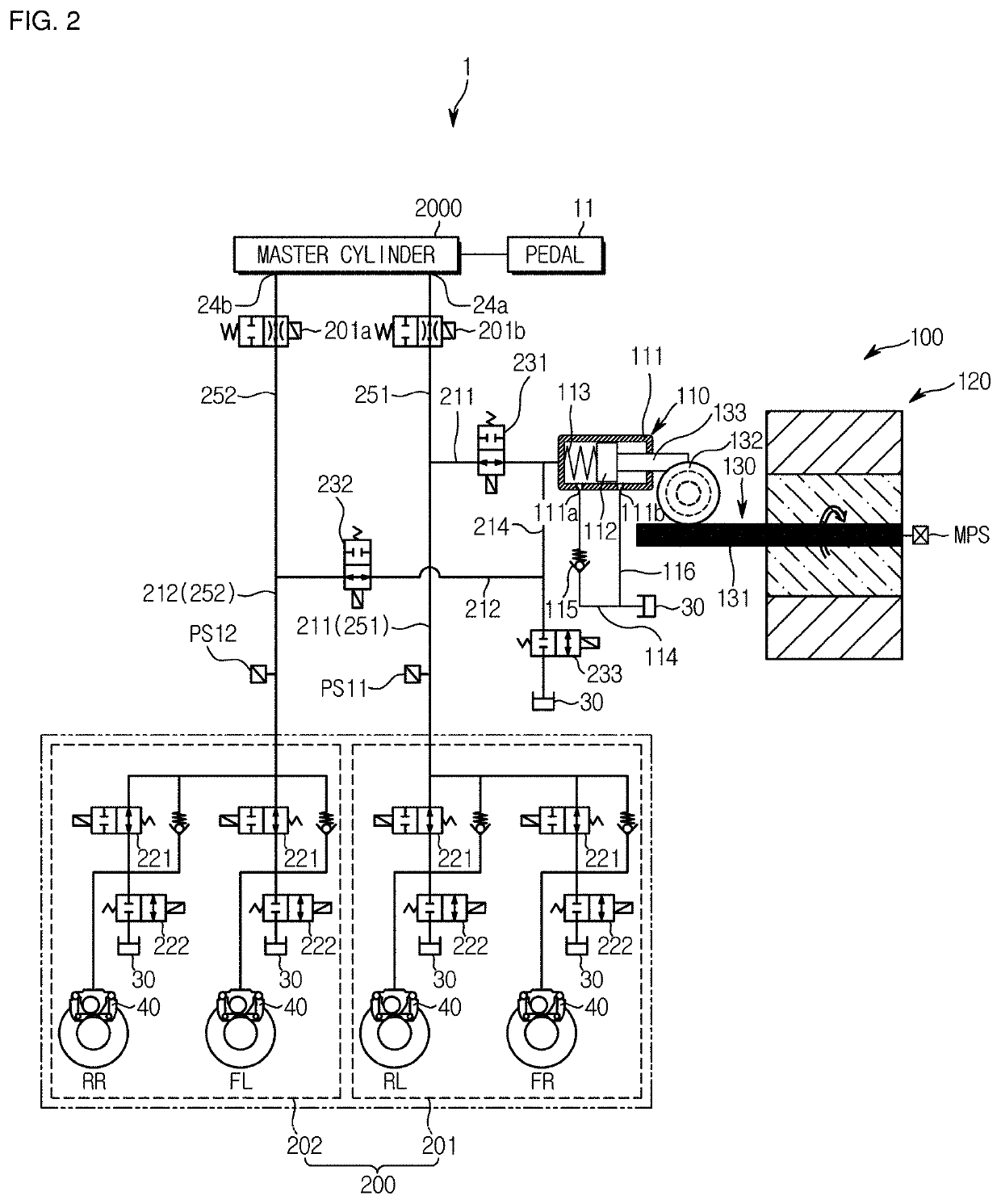
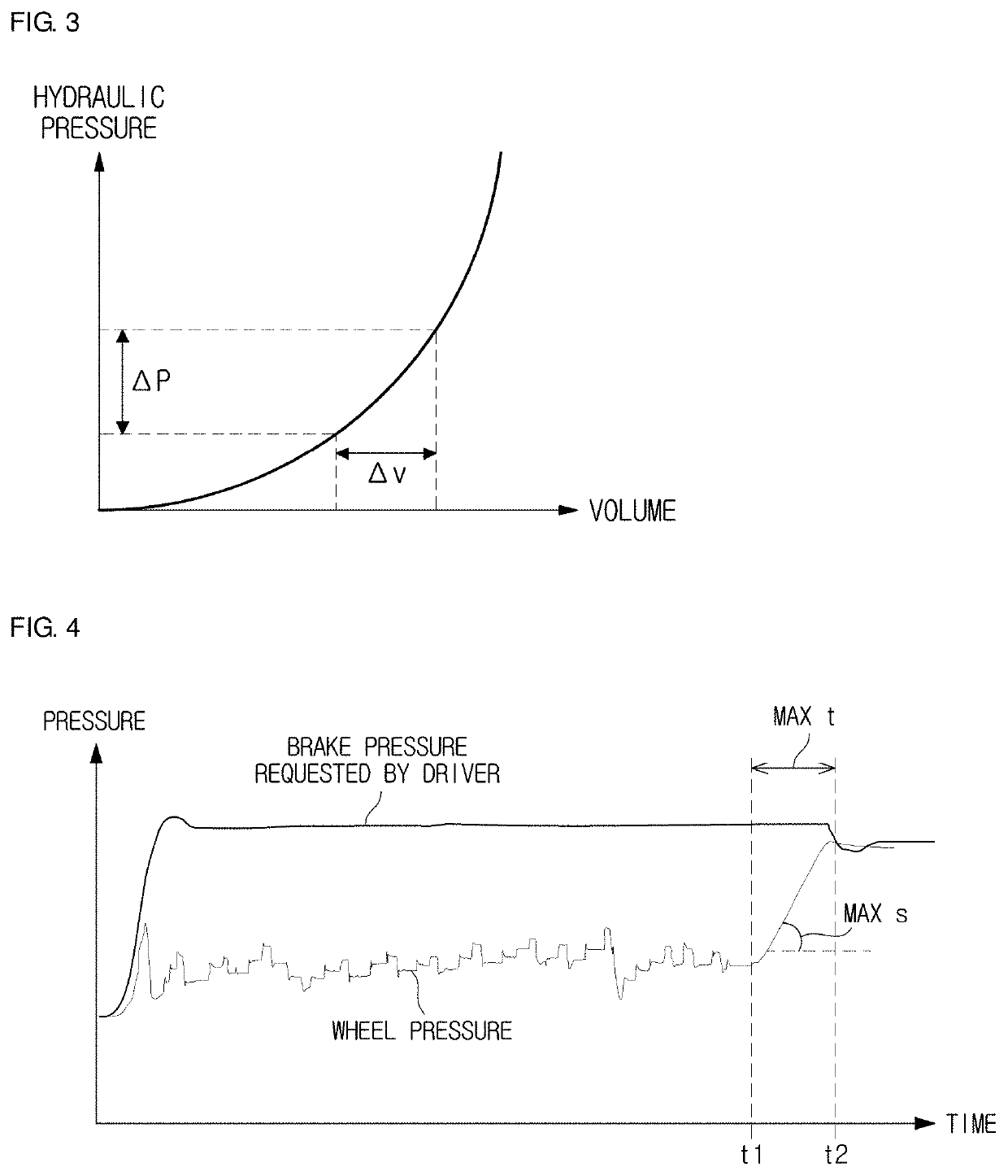
A brake system has a wheel brake and is operable under a non-failure normal braking mode and a manual push-through mode. The system includes a master cylinder operable by a brake pedal during a manual push-through mode to provide fluid flow at an output for actuating the wheel brake. A first source of pressurized fluid provides fluid pressure for actuating the wheel brake under a normal braking mode. A secondary brake module includes a plunger assembly for generating brake actuating pressure for actuating the wheel brake under the manual push-through mode.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Abs strategy for hybrid brake actuators
ActiveUS20180229705A1Efficient deliveryPotential failureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsActuatorBrake force
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
High-robustness wheel anti-skid control method, high-robustness wheel anti-skid control system and vehicle
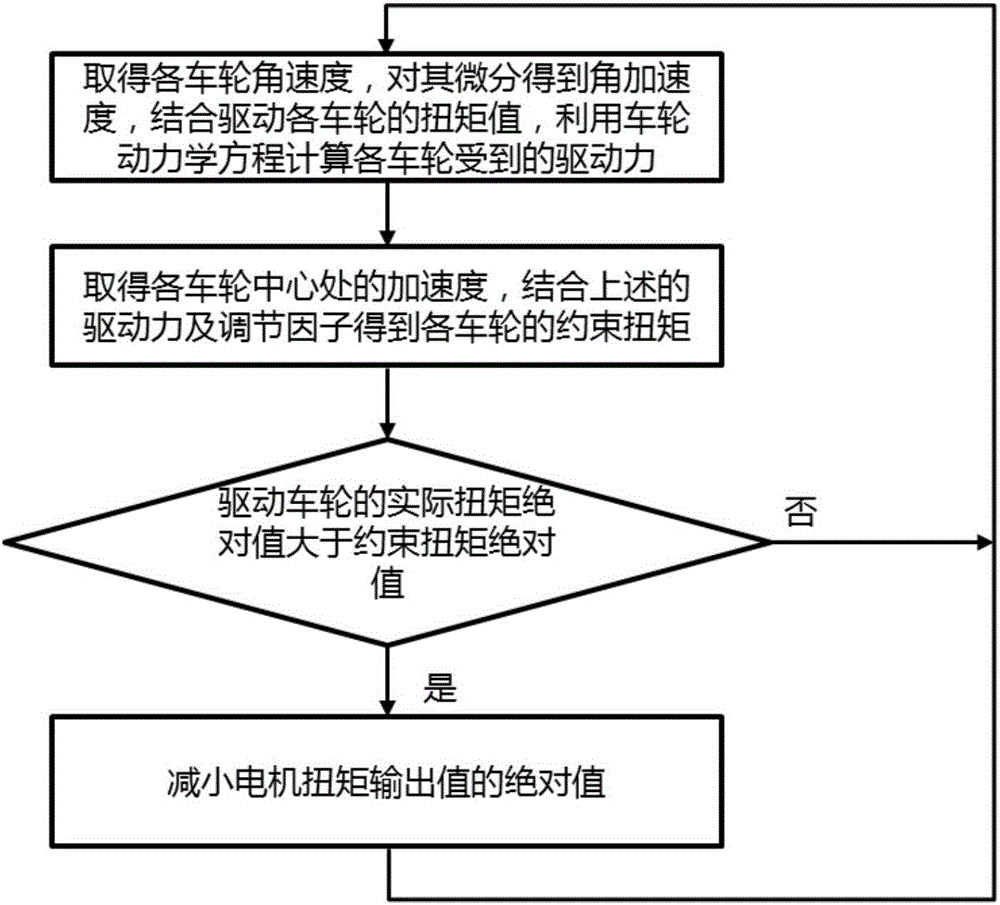
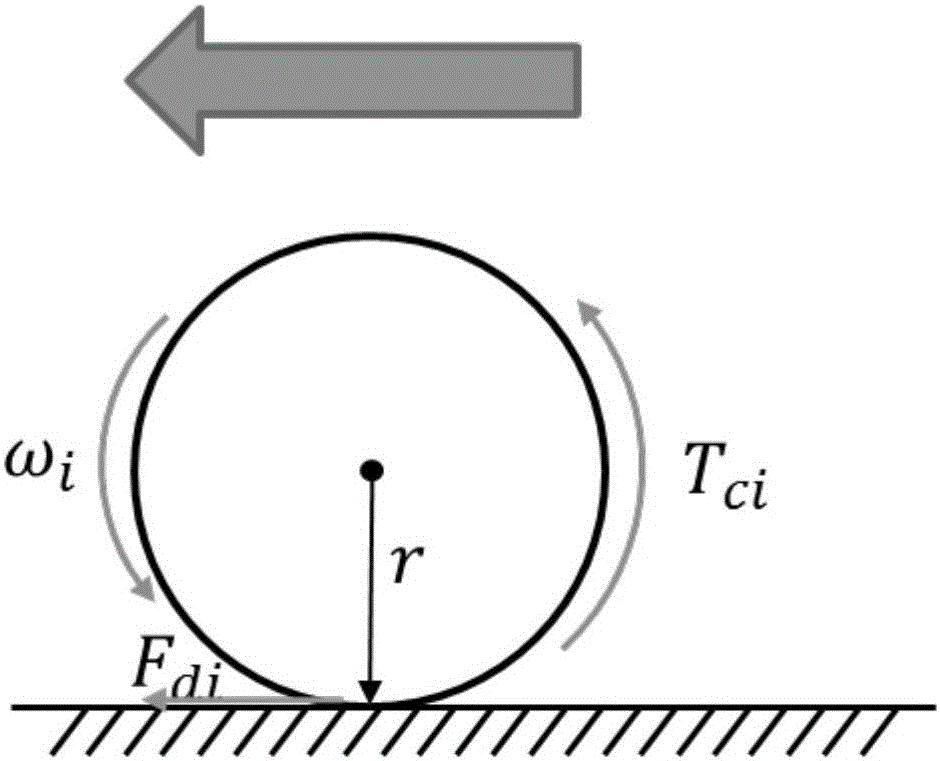
The invention provides a high-robustness wheel anti-skid control system. The control system is characterized in that an angular velocity of each wheel is subjected to differential calculation to obtain an angular acceleration; by means of combining the angular acceleration and a driving torque value of each wheel, a driving force applied to each wheel is calculated according to a wheel kinetic equation; by means of combining the driving force with a center acceleration of each wheel and regulatory factors, a constraint torque of each wheel can be obtained by calculation; by comparison of an upper torque output request value and a constraint torque numerical value, wheel driving torque output is controlled, and all wheels are enabled to have excellent anti-skid control effects under any conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solenoid valve and hydraulic braking system for vehicle
ActiveCN109863068AReduce complexityLow costOperating means/releasing devices for valvesABS control systemsMagnetic tension forceSolenoid valve
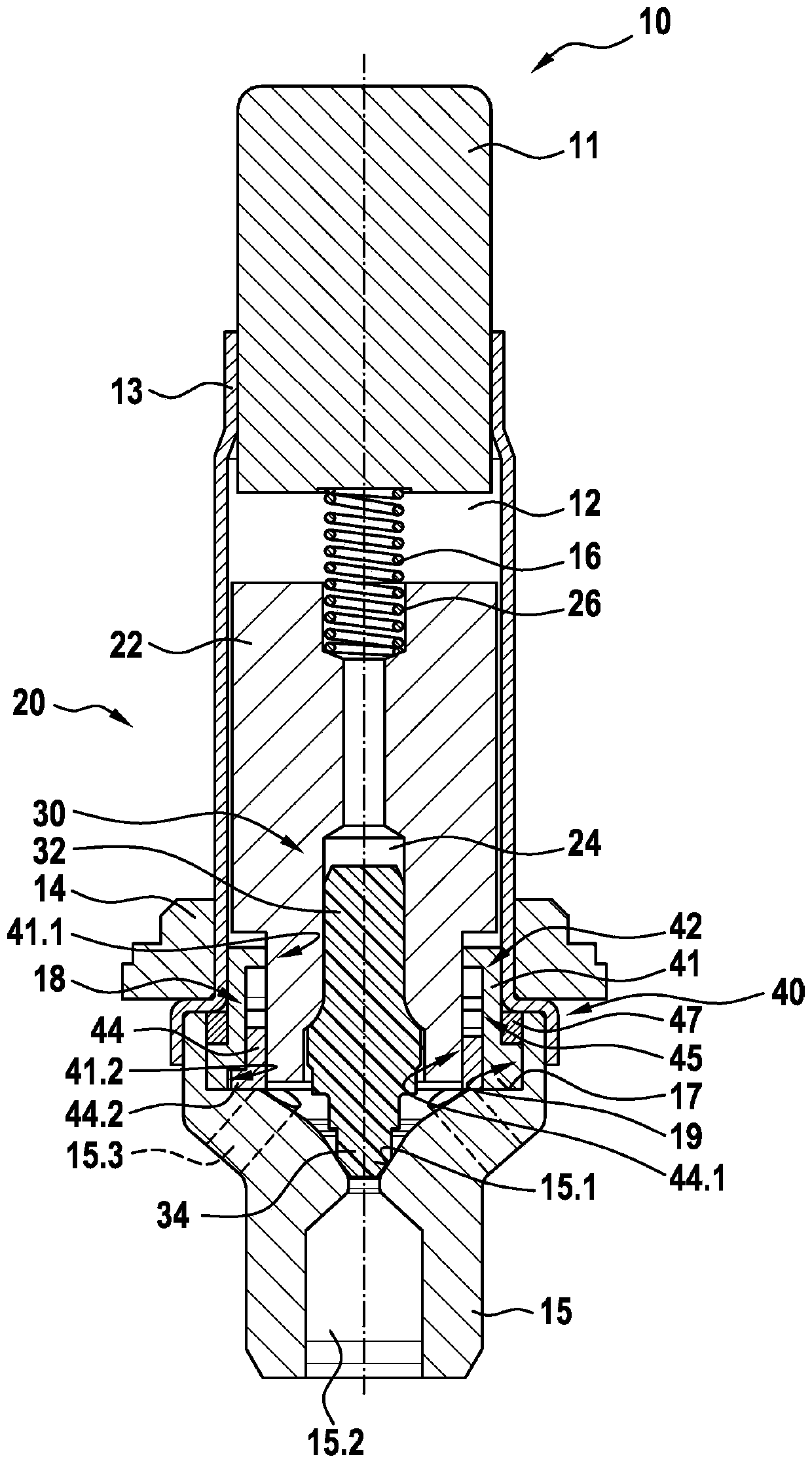
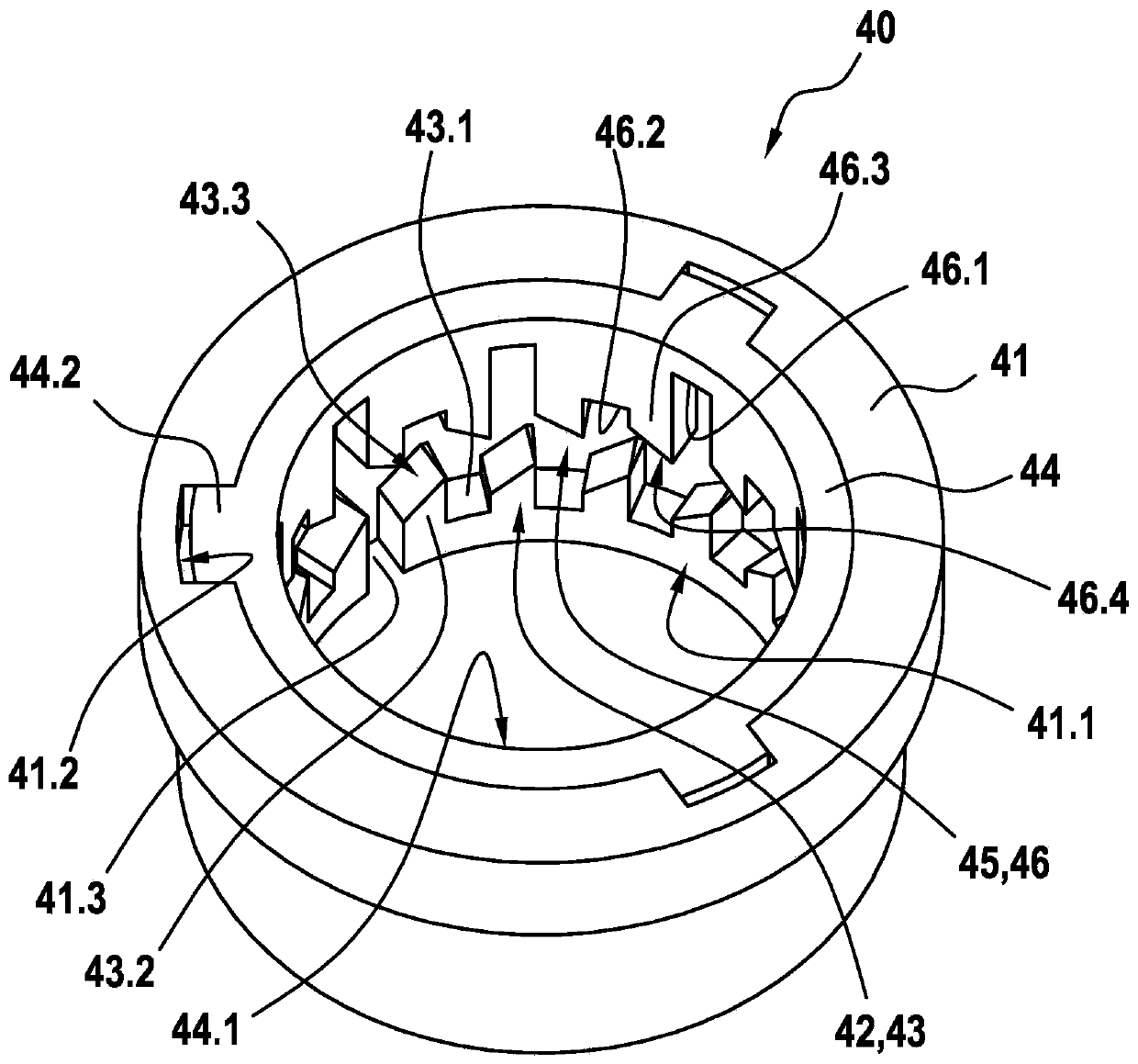
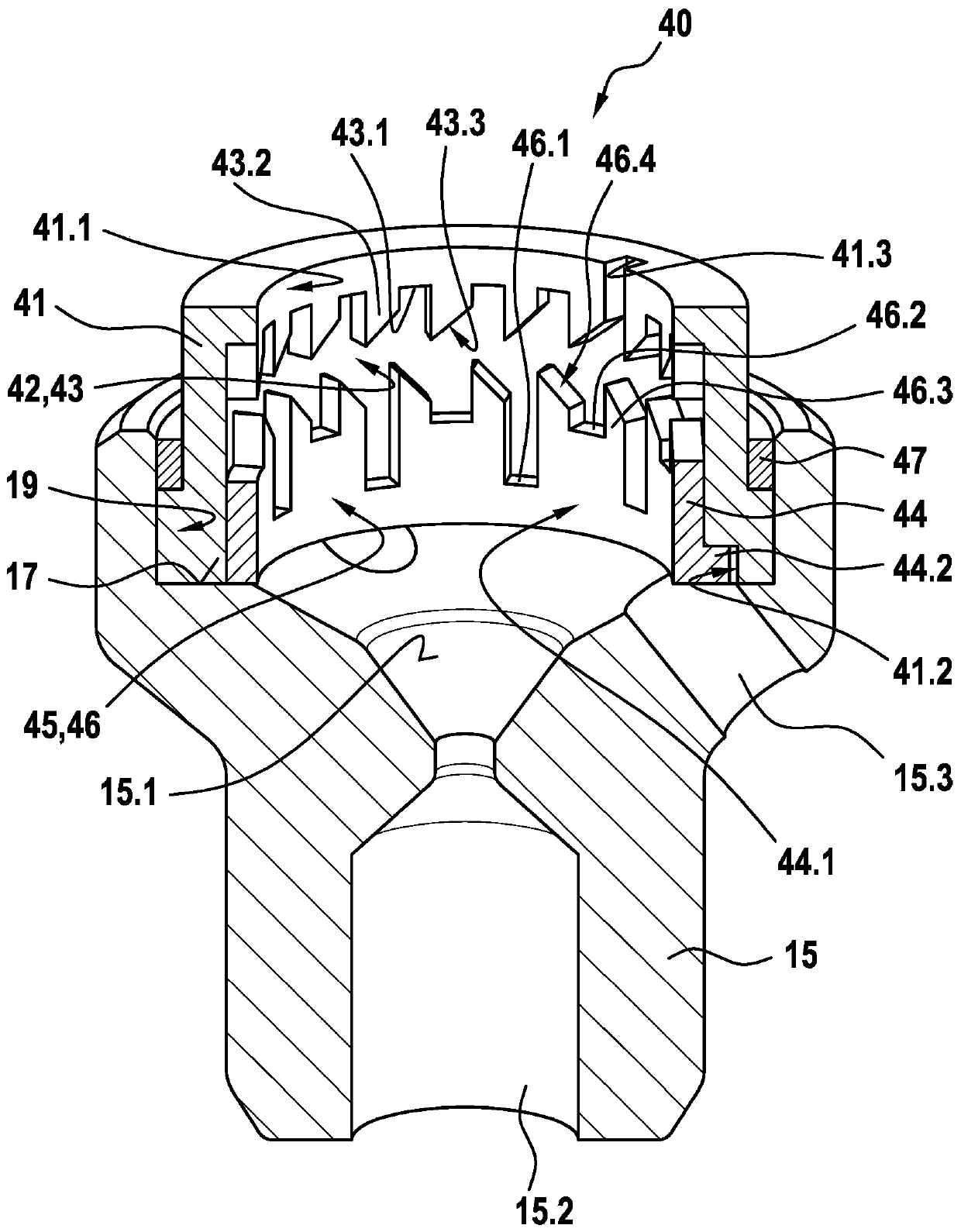
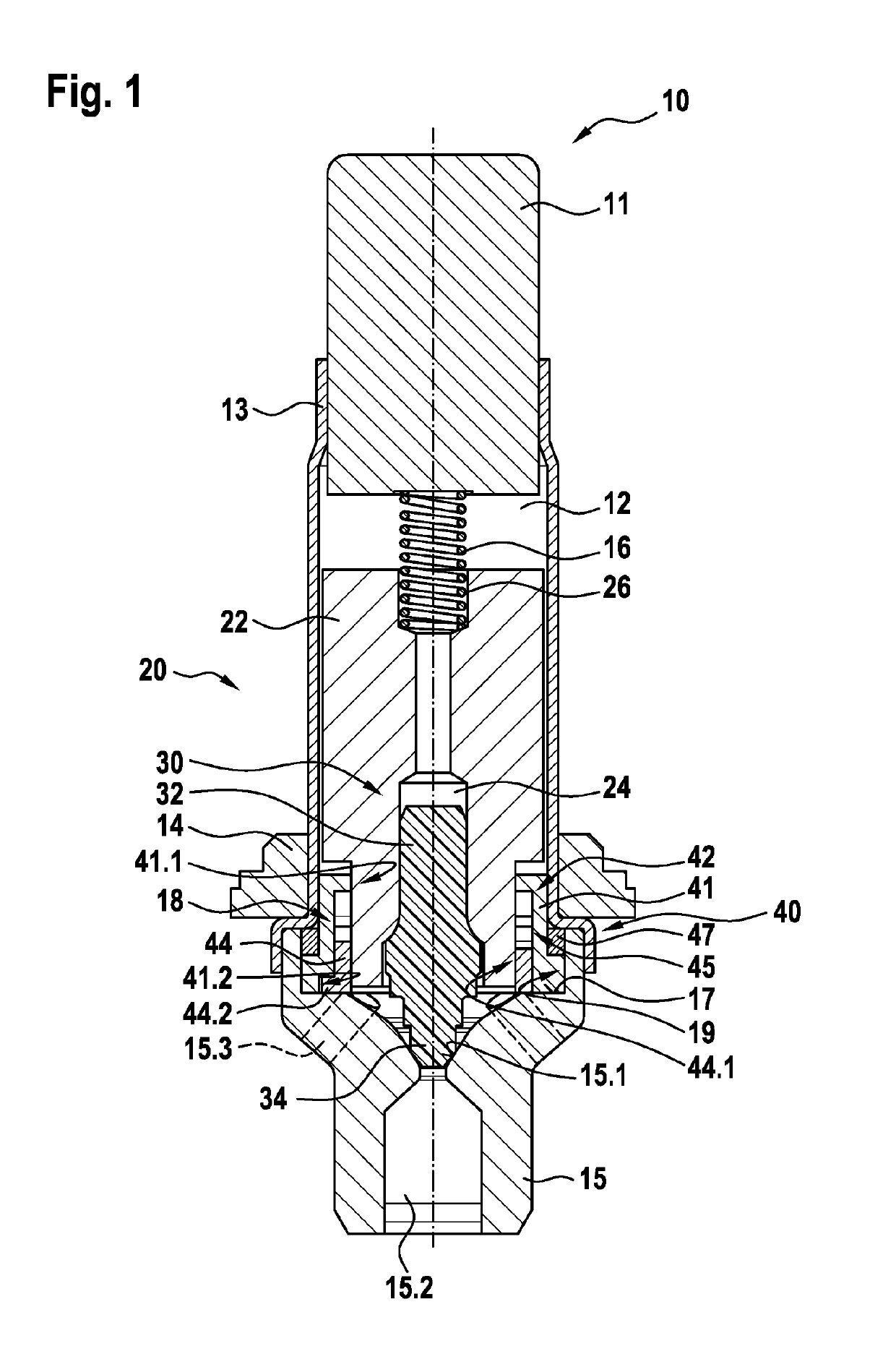
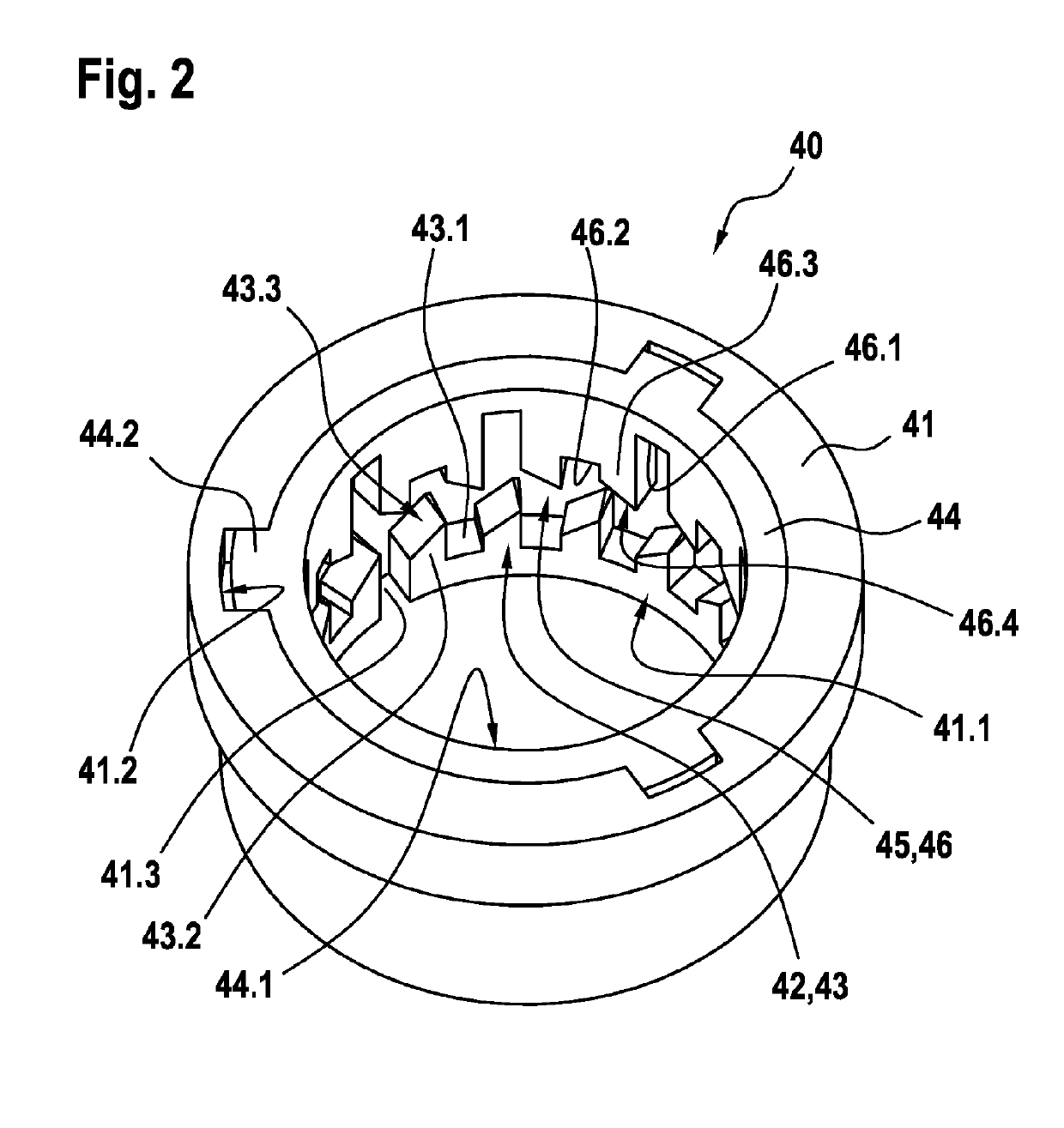
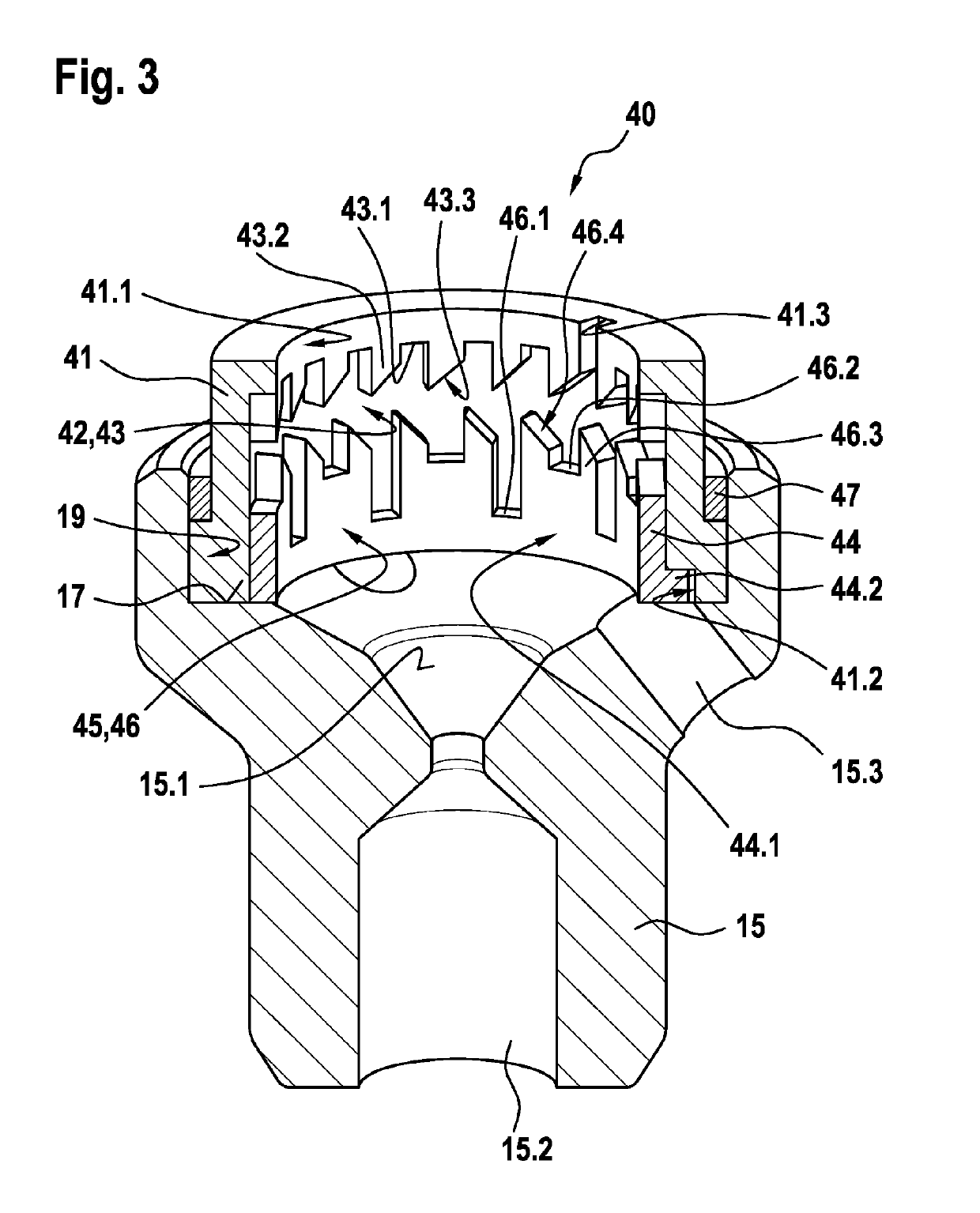
The invention relates to a solenoid valve (10) for a hydraulic braking system, comprising: a magnetic assembly; a pole core (11); a guide sleeve (13) joined to the pole core (11); a valve armature (20) running axially movably within the guide sleeve (13), the armature being drivable in opposition to a force of a restoring spring (16) by means of a magnetic force produced by the magnetic assembly,or being drivable by the force of the restoring spring (16), and said armature moving a plunger (30) comprising a closing element (34); and a valve body (15) connected to the guide sleeve (13) and comprising a valve seat (15.1) that is located between at least one first flow opening (15.2) and at least one second flow opening (15.3), the plunger (30) being fixedly connected to the valve armature (20). The invention also relates to a hydraulic braking system comprising a solenoid valve (10) of this type. The valve body (15) has a receiving region (19) which at least partially accommodates a guide assembly (40), the valve armature (20) running axially through at least one through-opening (41.1, 44.1) of the guide assembly (40), a mechanical detent device (18) being formed between the guide assembly (40) and the valve armature (20), the detent device releasing the valve armature (20) when the latter is in a de-energised closed position, such that the restoring spring (16) drives the valvearmature (20) and pushes the closing element (34) sealingly into the valve seat (15.1) to produce a sealing function, and said detent device fixes the valve armature (20) in a de-energised open position against the force of the restoring spring (16) in an axial detent position, such that the closing element (34) is raised from the valve seat (15.1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
System and method for traction control
ActiveUS20170334414A1Reduce speedReduce slidingASR control systemsPropulsion unit safety devicesTraction motorAutomotive engineering
A system includes a sensor and a controller. The sensor is configured to detect sliding of a wheel of a vehicle. The controller is configured to communicate with the sensor and a traction motor operatively connected to the wheel such that the traction motor selectively applies forces in at least one direction to the wheel during operation. The controller is further configured to direct the traction motor to apply a motoring slide reducing force to the wheel when the sensor detects sliding of the wheel resulting from a frictional braking force.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
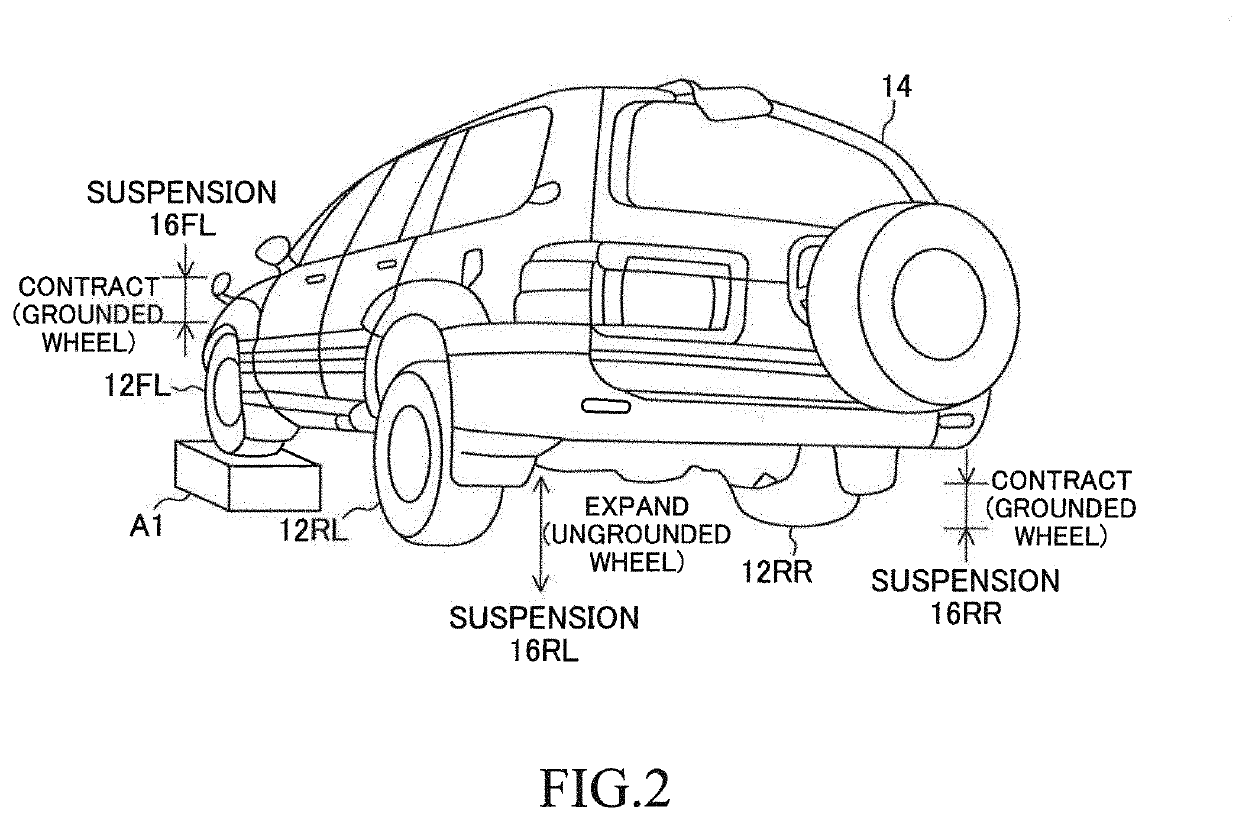
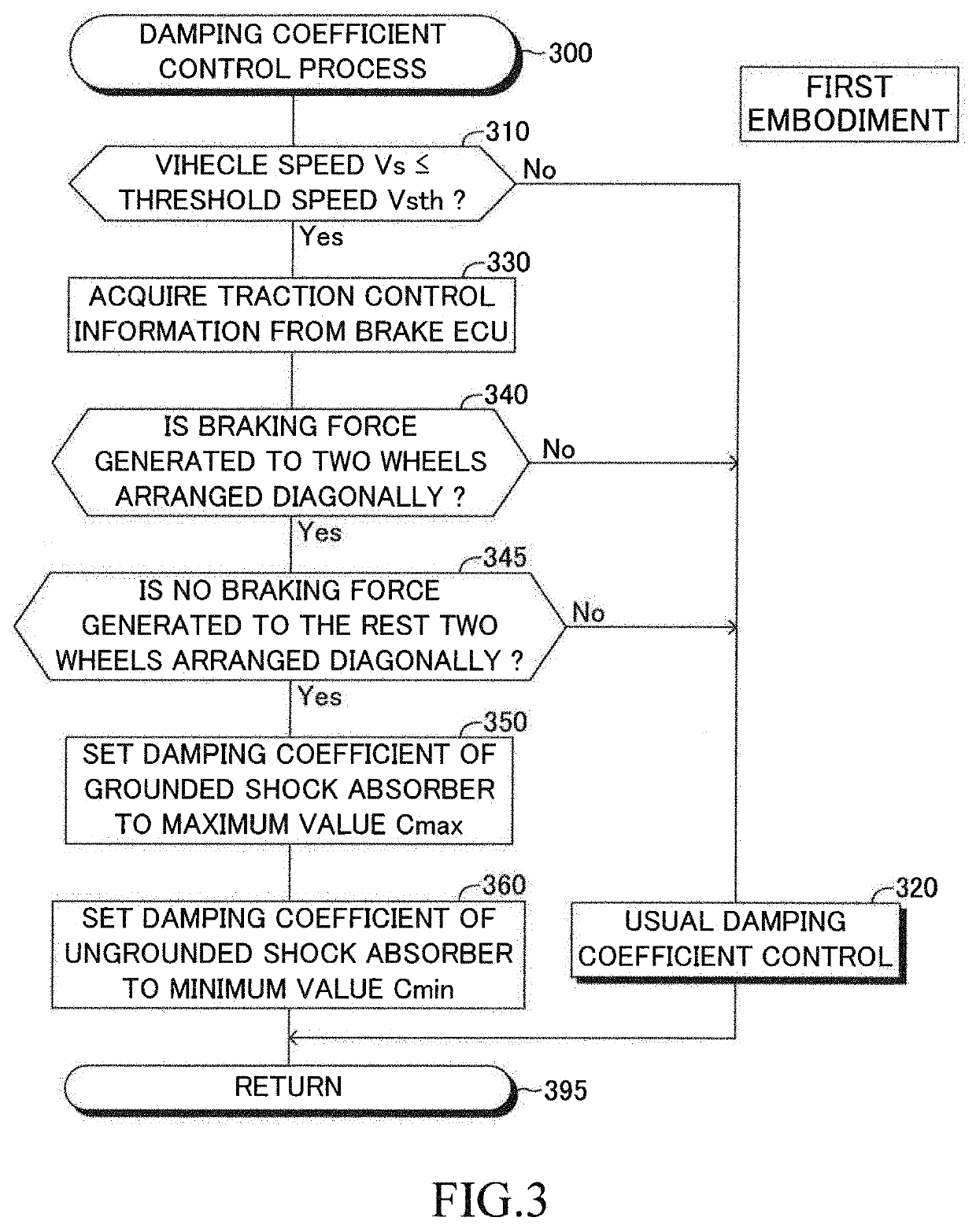
Damping force control device
ActiveUS20190351726A1Attenuate/reduce vibrationPrevent comfortabilityBrake system interactionsResilient suspensionsVertical vibrationSprung mass
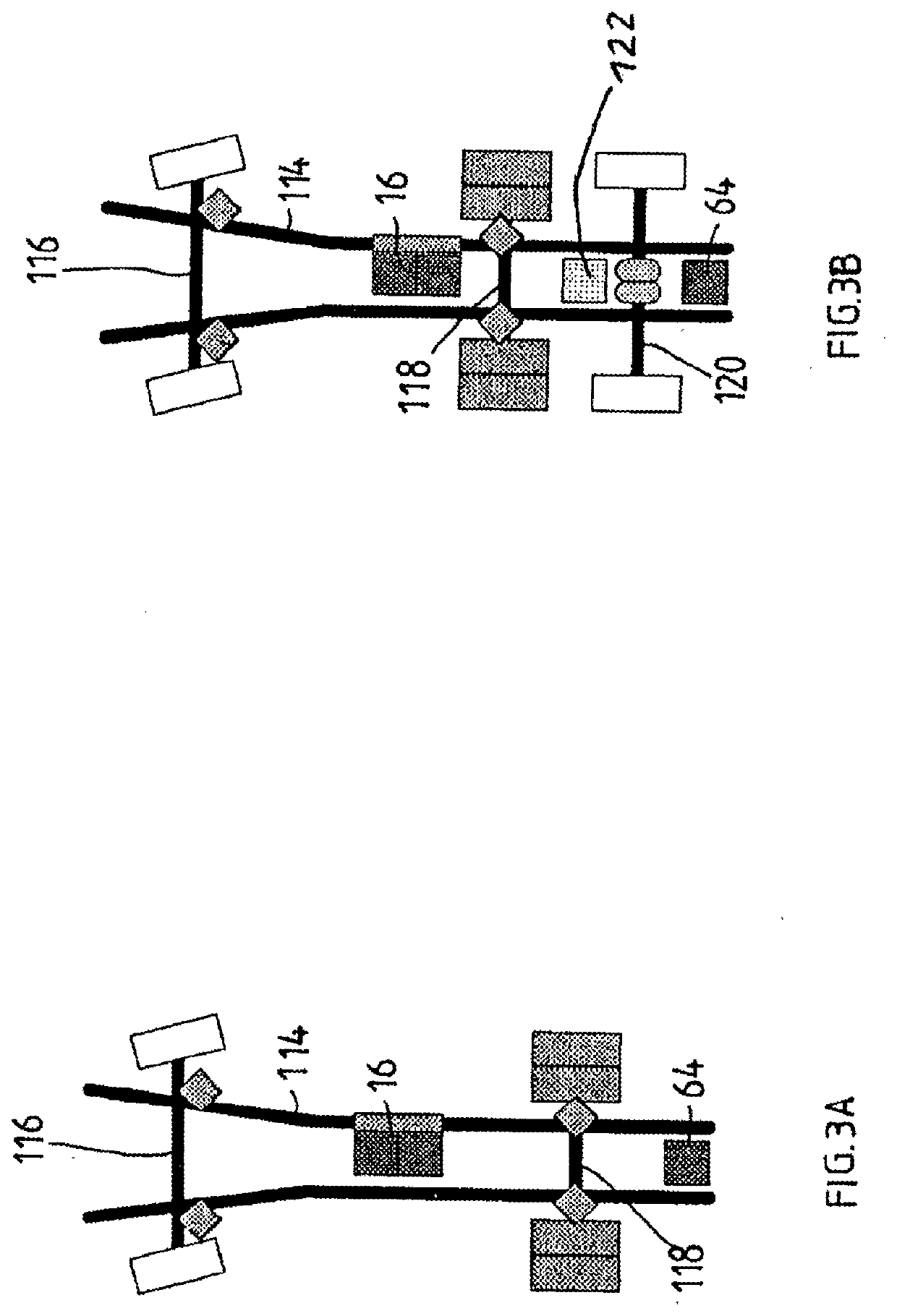
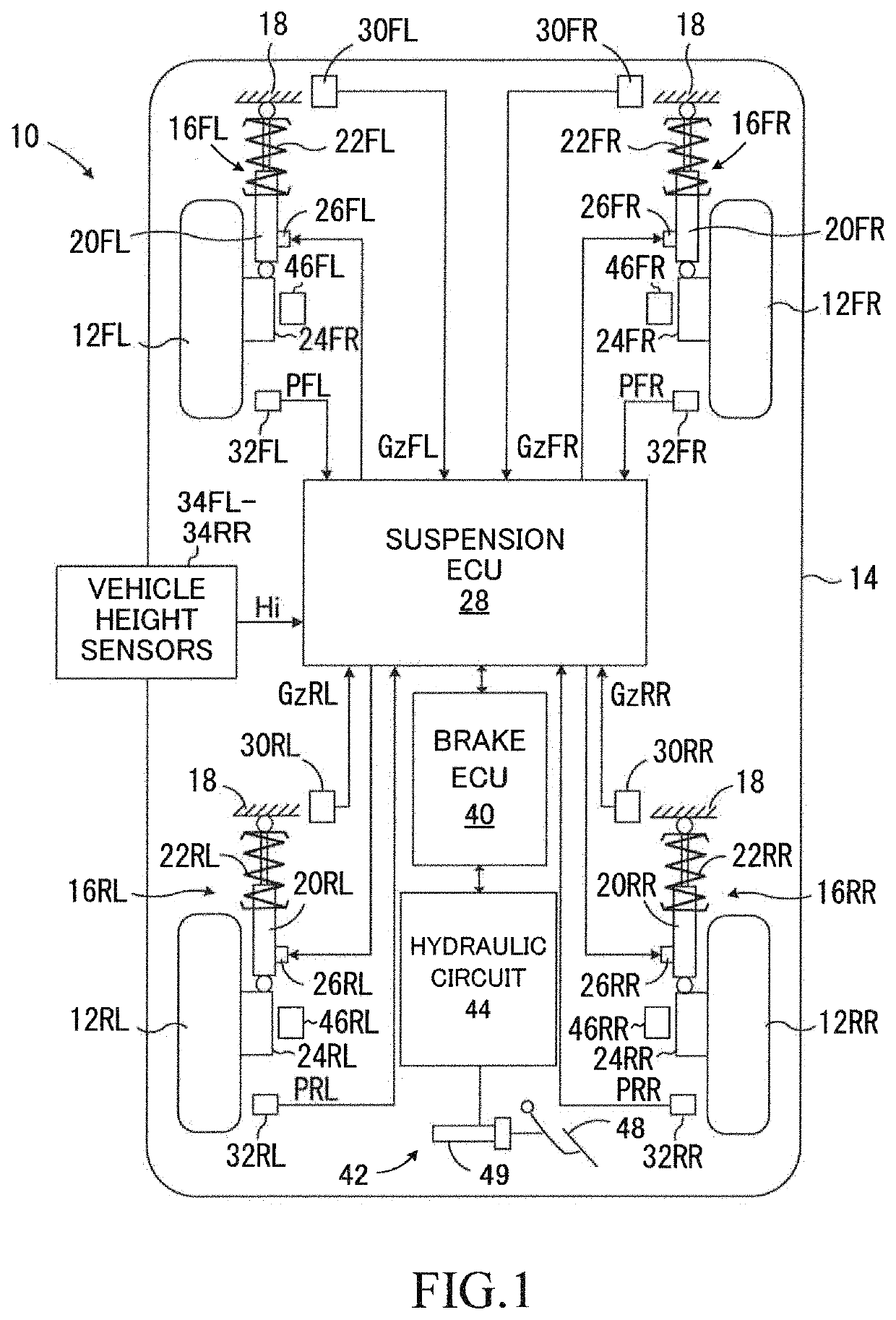
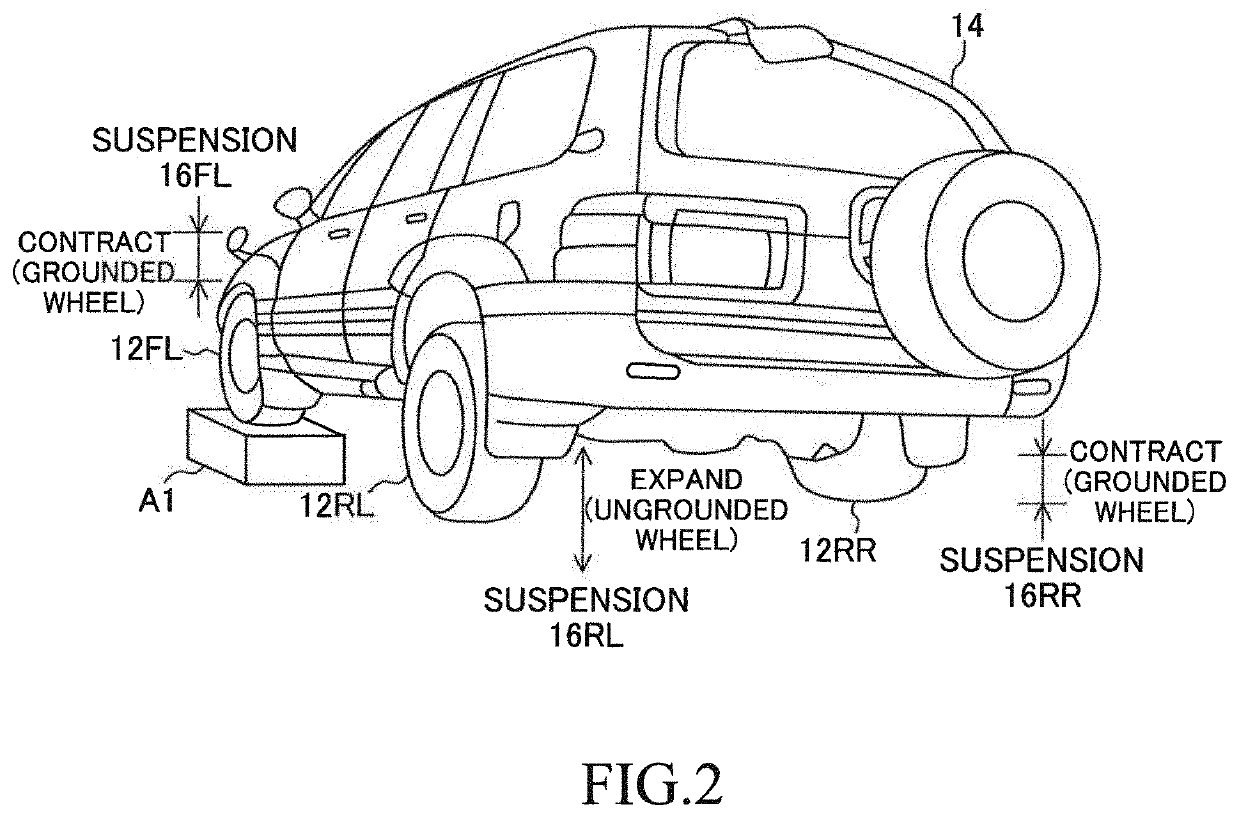
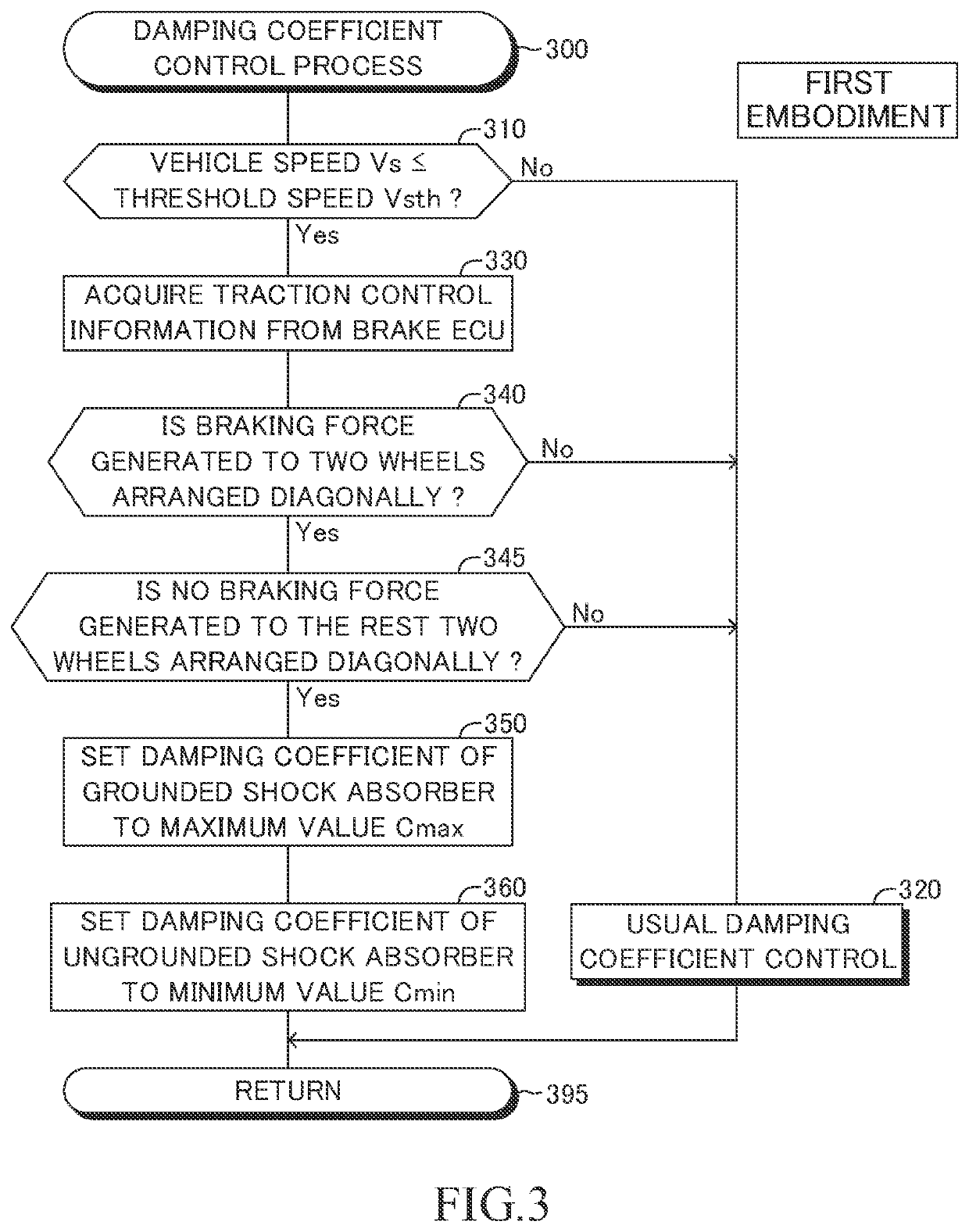
A damping force control device 10 comprises vary damping shock absorbers, a detector, and a controller. Each of the shock absorbers sets damping coefficient from a minimum value to a maximum value in order to adjust damping force. The detector detects vertical vibration state quantity relating to vibration of the sprung mass. The controller performs an ordinary control for setting the damping coefficient based on the vertical vibration state quantity and according to a predetermined control law suitable for an assumption that all of the wheels touch ground. The controller performs, when at least one of the wheels is an ungrounded wheel which does not touch the ground and each of the other wheels is a grounded wheel which touches the ground, a specific control for setting the damping coefficient of the shock absorber corresponding to the grounded wheel to a first specific value greater than the minimum value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle having controlled start
A vehicle and method are provided. The vehicle includes a system and method for limiting the slip of the wheels. In an embodiment, the system holds the brakes based on an acceleration characteristic measured by a sensor. In another embodiment, the system includes a transmission controller that applies an adjustment to limit an amount of clutch slip as the clutch temperature changes to change in clutch performance to reduce wheel slip. In another embodiment, the system monitors a wheel slip signal from a sensor and compares the wheel slip to a target slip value and controls clutch slip of the transmission clutch to maintain engine output torque during acceleration. In another embodiment, in response to an anticipated vehicle launch event, a drive motor applies a first torque to the input shaft to adjust a gear backlash of the differential unit.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for traction control
ActiveUS20170334415A1Prevent slidingIncreased riskASR control systemsPropulsion unit safety devicesBraking systemBrake force
A system includes a plurality of wheels, a braking system, and one or more sensors. The plurality of wheels includes a guardian wheel and at least one non-guardian wheel and is disposed on a wheeled vehicle. The braking system is operatively connected to the guardian and non-guardian wheels and applies a first braking force to the at least one non-guardian wheel and a second braking force to the guardian wheel. The second braking force increases a slide risk of the guardian wheel beyond a slide risk of the at least one non-guardian wheel. One or more sensors disposed within the wheeled vehicle detect sliding of the guardian wheel allowing a corrective action to be taken to prevent sliding of the at least one non-guardian wheel.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
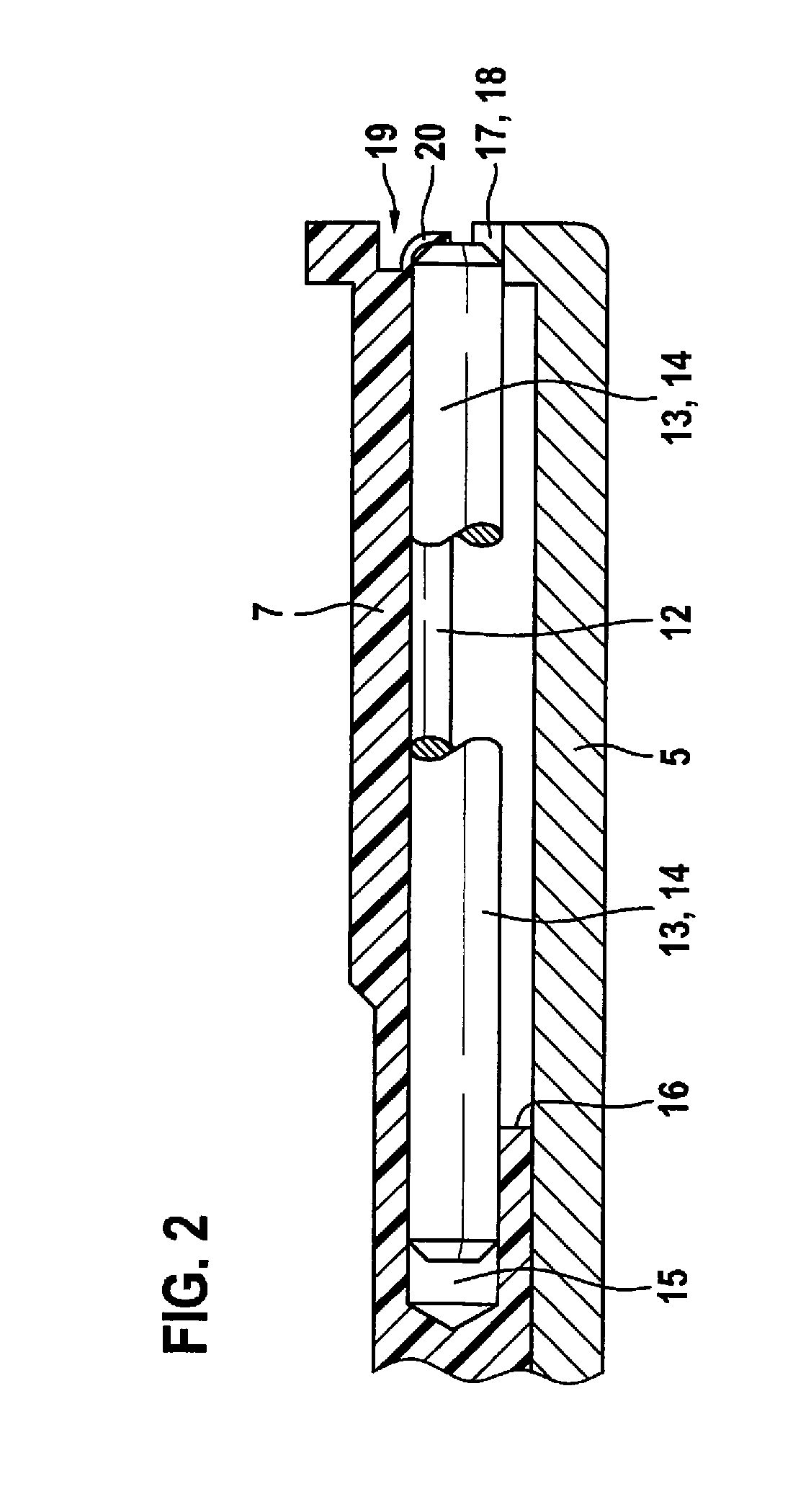
Piston pump assembly for a hydraulic power vehicle braking system
ActiveUS20190017502A1Simplifies and facilitates assemblyPositive displacement pump componentsBraking action transmissionGear wheelControl theory
A piston pump assembly for a hydraulic power vehicle braking system including an electric motor, a planetary gear set, a helical gear, and a piston which is displaceable in a cylinder. To prevent the piston from rotating in the cylinder, cylinder pins are situated in grooves at an inner side of the cylinder and engage with the recesses in a flange of the piston. Due to reshaping, the grooves are closed at one end, so that the cylinder pins are axially secured.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
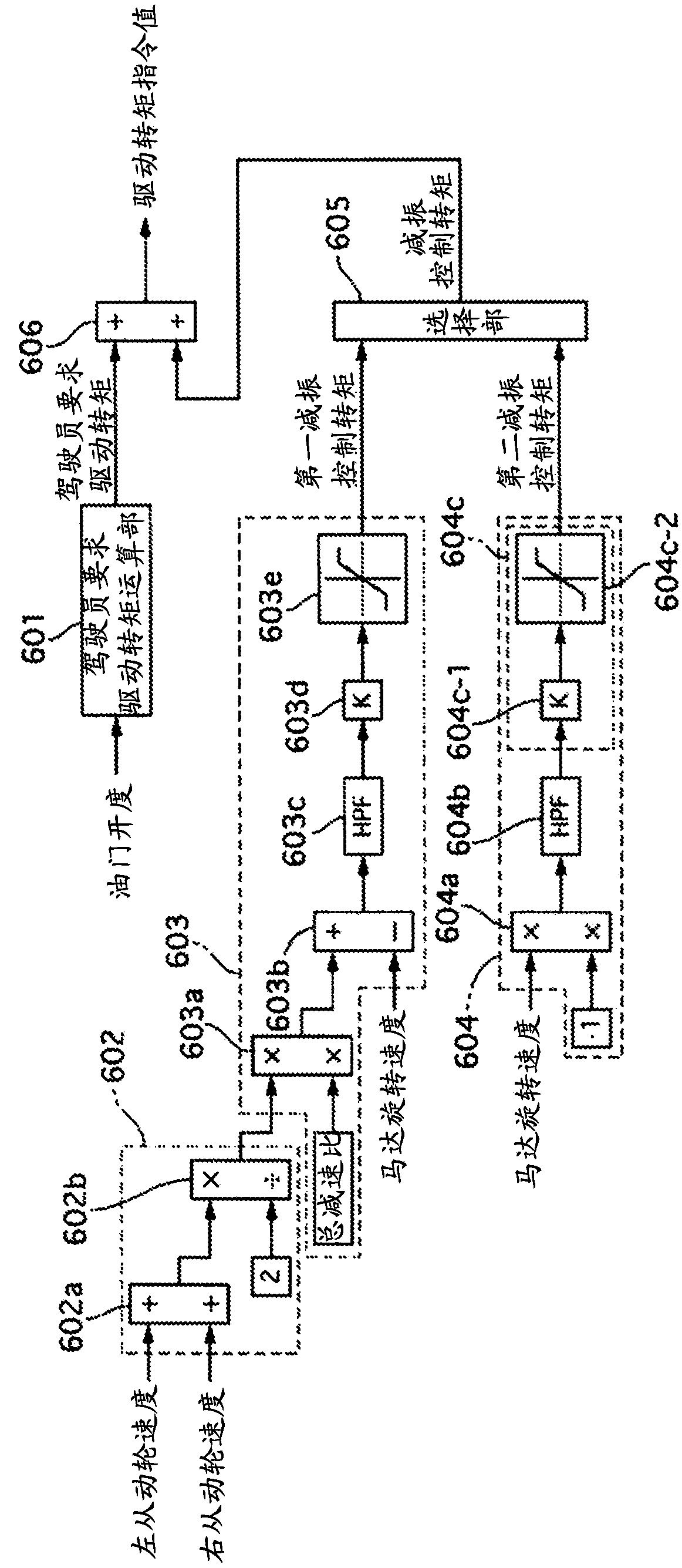
Electric vehicle control device, electric vehicle control system, and electric vehicle control method
InactiveCN108136932AVibration suppression effect obtainedSpeed controllerElectric devicesControl systemWheel speed sensor
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an electric vehicle control device capable of obtaining a vibration suppression effect regardless of the wheel rotation direction. A first vibration-dampening control torque and a second vibration-dampening control torque are selectively output in one embodiment of the present invention, said first vibration-dampening control torque being calculated by using a first calculation method on the basis of a wheel speed sensor signal during forward travel of the electric vehicle and said second vibration-dampening control torque being calculated byusing a second calculation method different from the first calculation method, during reverse travel of the electric vehicle.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Electric brake system and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20180304872A1Reduce noiseReduce vibrationBraking action transmissionVehicle sub-unit featuresRisk strokeElectric signal
An electric brake system and a method for controlling the same are disclosed. The electric brake system includes a hydraulic control device, a sensing unit, and a controller. The hydraulic control device generates hydraulic pressure using a piston operated by an electric signal generated in response to a displacement of a brake pedal. The sensing unit detects driver's braking intention. When an electronic stability control (ESC) of a vehicle operates, the controller calculates a change amount of stroke of the piston needed to output brake pressure corresponding to the driver's braking intention, and acquires the calculated stroke change amount so as to boost pressure of each wheel at a predetermined slope.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
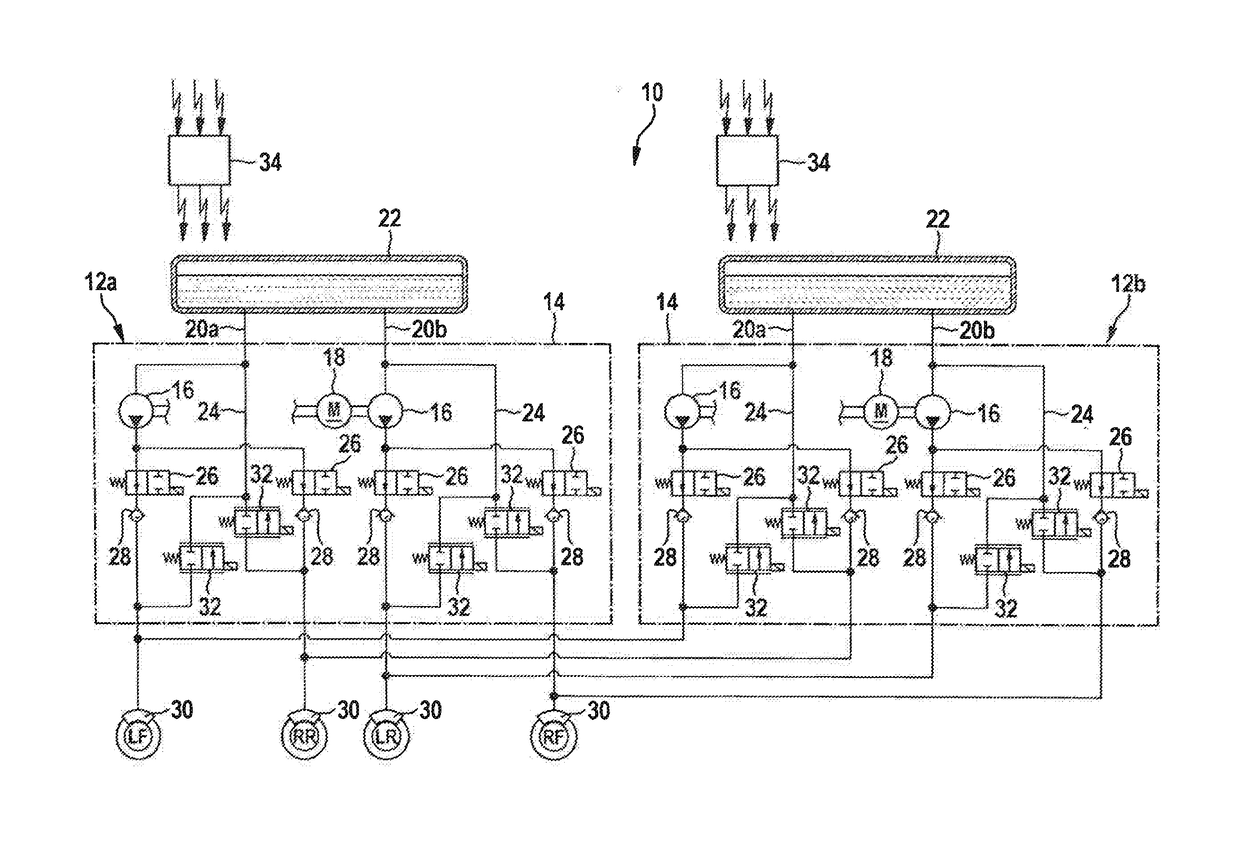
Electronically pressure-controllable braking system and methods for controlling an electronically pressure-controllable braking system
ActiveUS20180334150A1Easy constructionReduce loadBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
An electronically pressure-controllable braking system and methods for controlling an electronically pressure-controllable braking system. Each wheel brake of the braking system is connected respectively to at least two brake circuits, pump units and valve devices of one brake circuit are operable respectively independently of the pump units and the valve devices of the respective other brake circuit. This provides a cost-effectively and compactly designed redundant braking system, which is suitable for use in autonomously, i.e., driverlessly drivable, motor vehicles.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
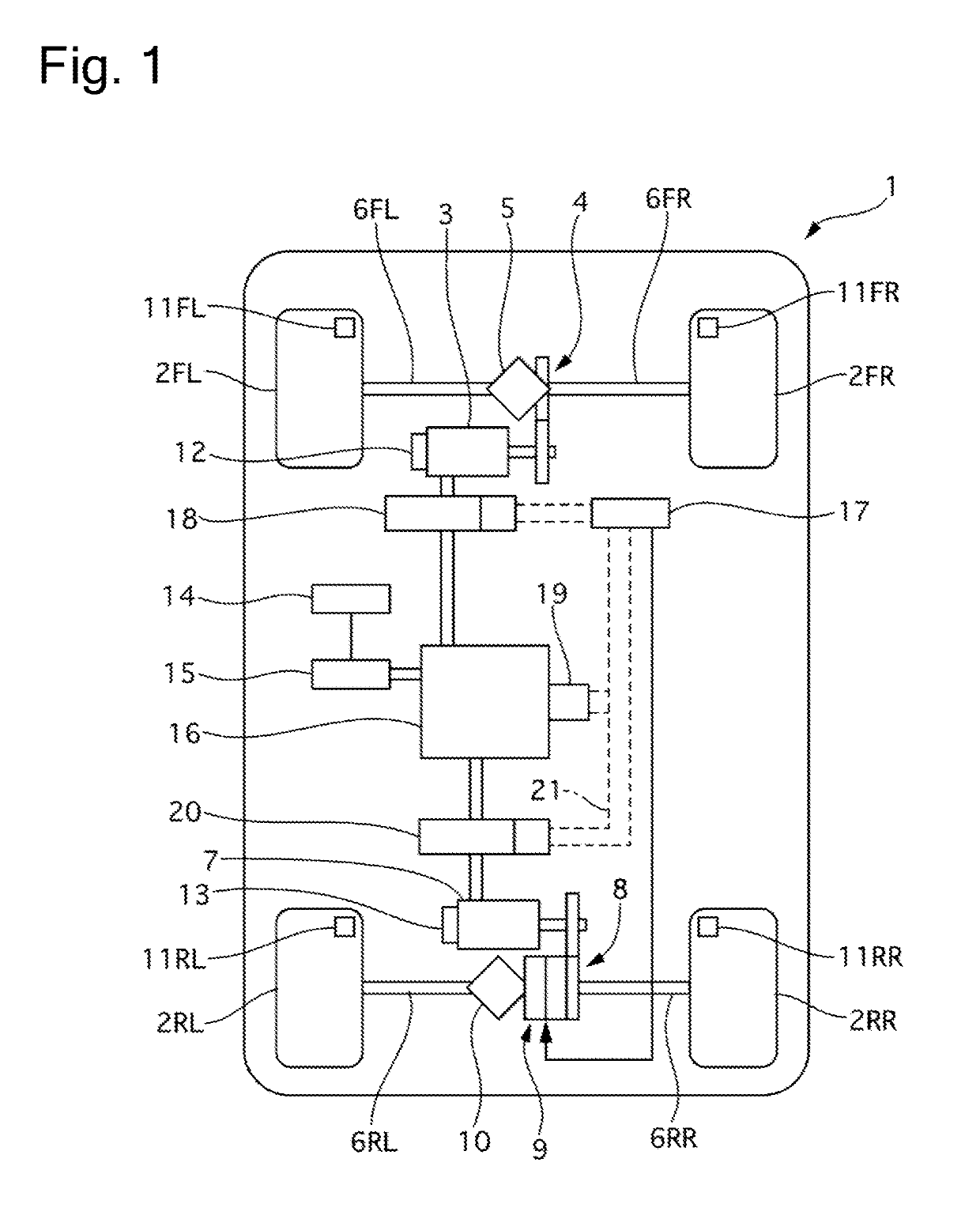
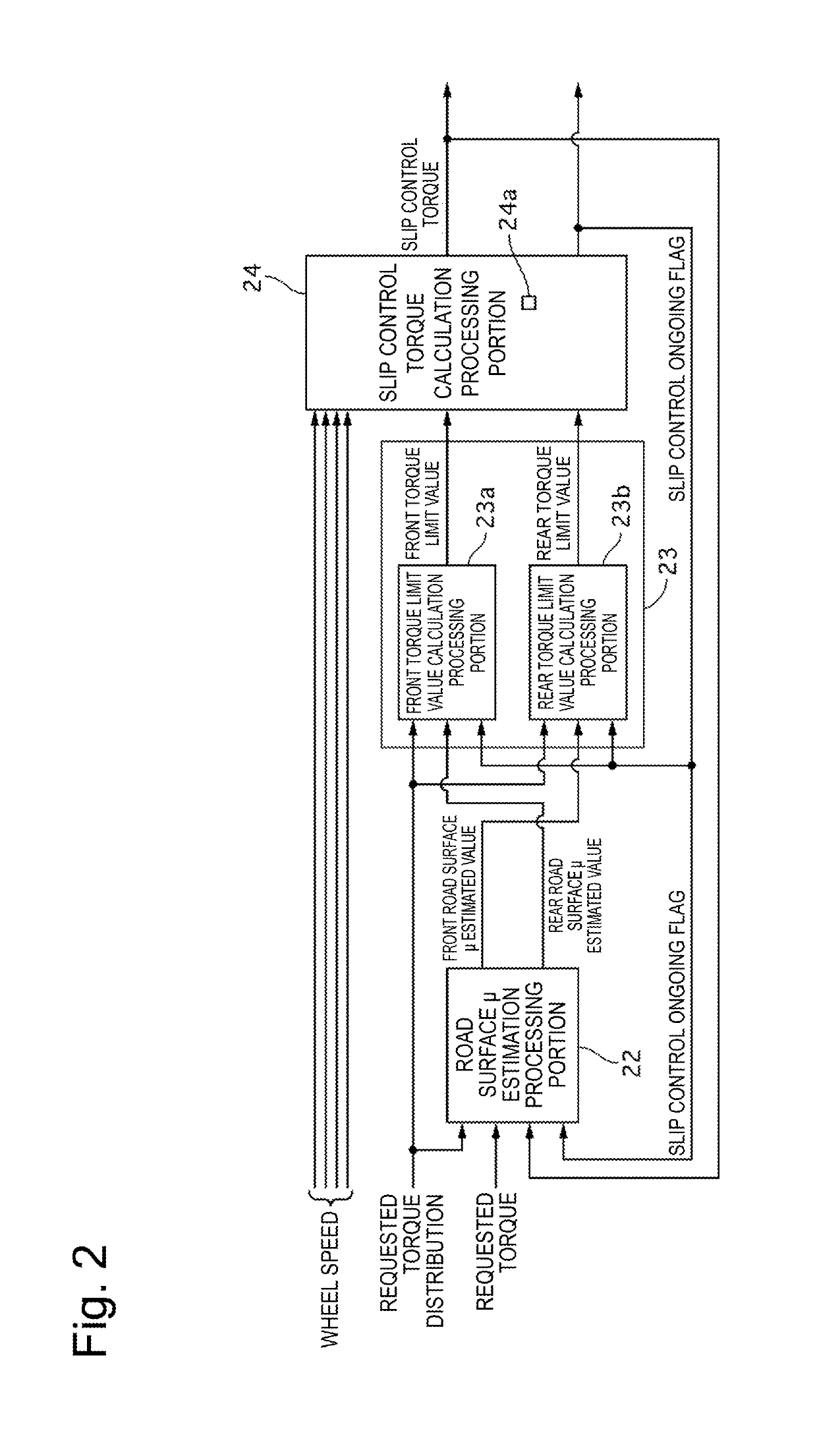
Control Apparatus, Control Method, and Control System for Electric Vehicle
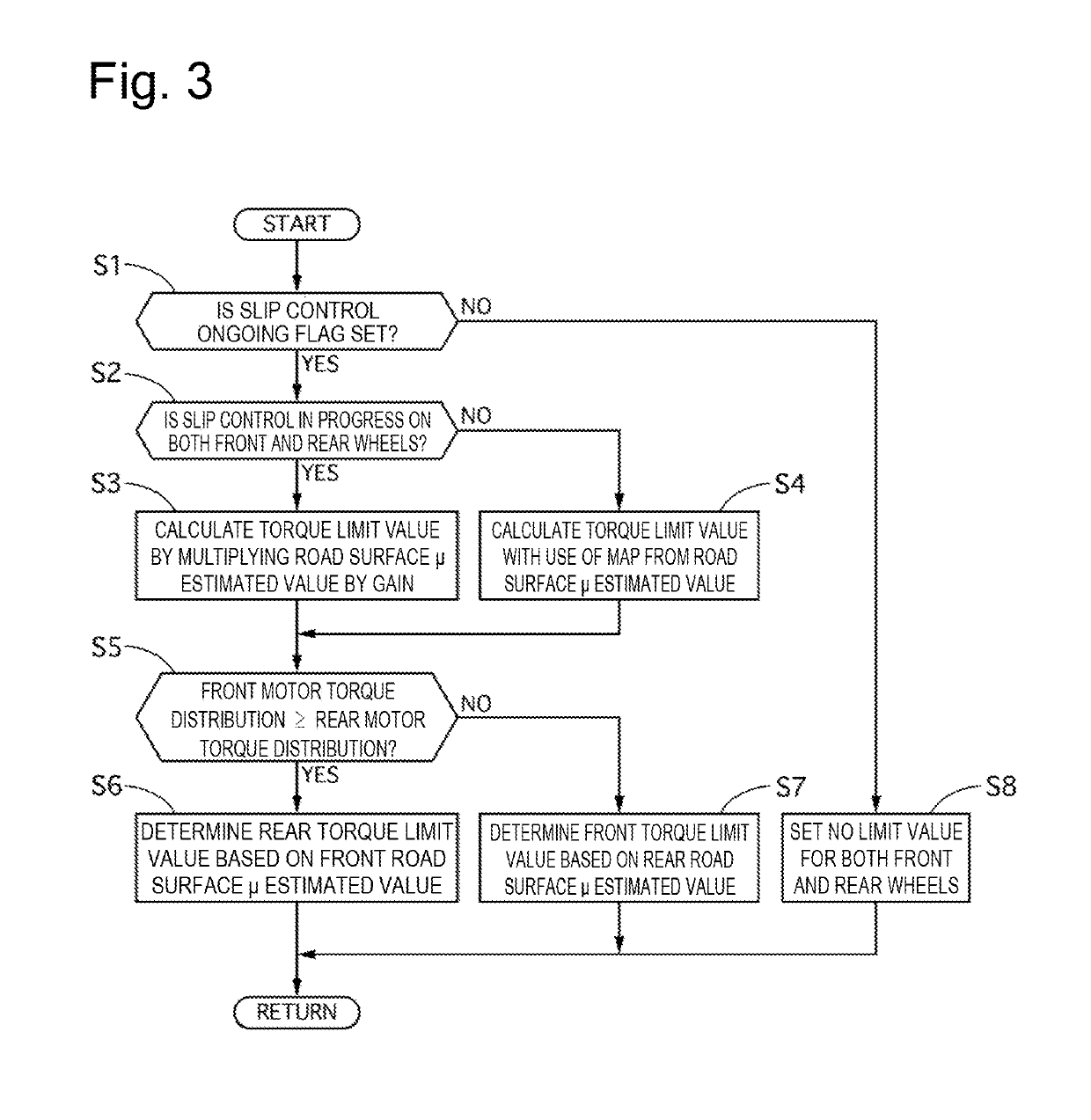
ActiveUS20190193577A1Unnecessary torque fluctuation on the wheel not targeted for the slip control can be prevented or reducedHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerControl systemElectric vehicle
Provided is a control apparatus, a control method, and a control system for an electric vehicle that can prevent or reduce an unnecessary torque fluctuation on a wheel not targeted for slip control. A control apparatus for an electric vehicle limits a torque to be output to a non-target wheel according to a torque output to a target wheel after target wheel slip control is started, and updates a limit value of the torque to be output to the non-target wheel when a fluctuation range of the torque output to the target wheel falls within a predetermined range during the limitation.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Solenoid Valve and Hydraulic Braking System for a Vehicle
ActiveUS20190210582A1Reduce energy consumptionReduce leakageOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBraking action transmissionSolenoid valveBraking system
In a solenoid valve for a hydraulic braking system, a valve body has a receiving region which at least partially accommodates a guide assembly, the valve armature running axially through at least one through-opening of the guide assembly. A mechanical detent device is formed between the guide assembly and the valve armature, the detent device releasing the valve armature when the latter is in a de-energised closed position, such that the restoring spring drives the valve armature and pushes the closing element sealingly into the valve seat to produce a sealing function, and said detent device fixes the valve armature in a de-energised open position against the force of the restoring spring in an axial detent position, such that the closing element is raised from the valve seat.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
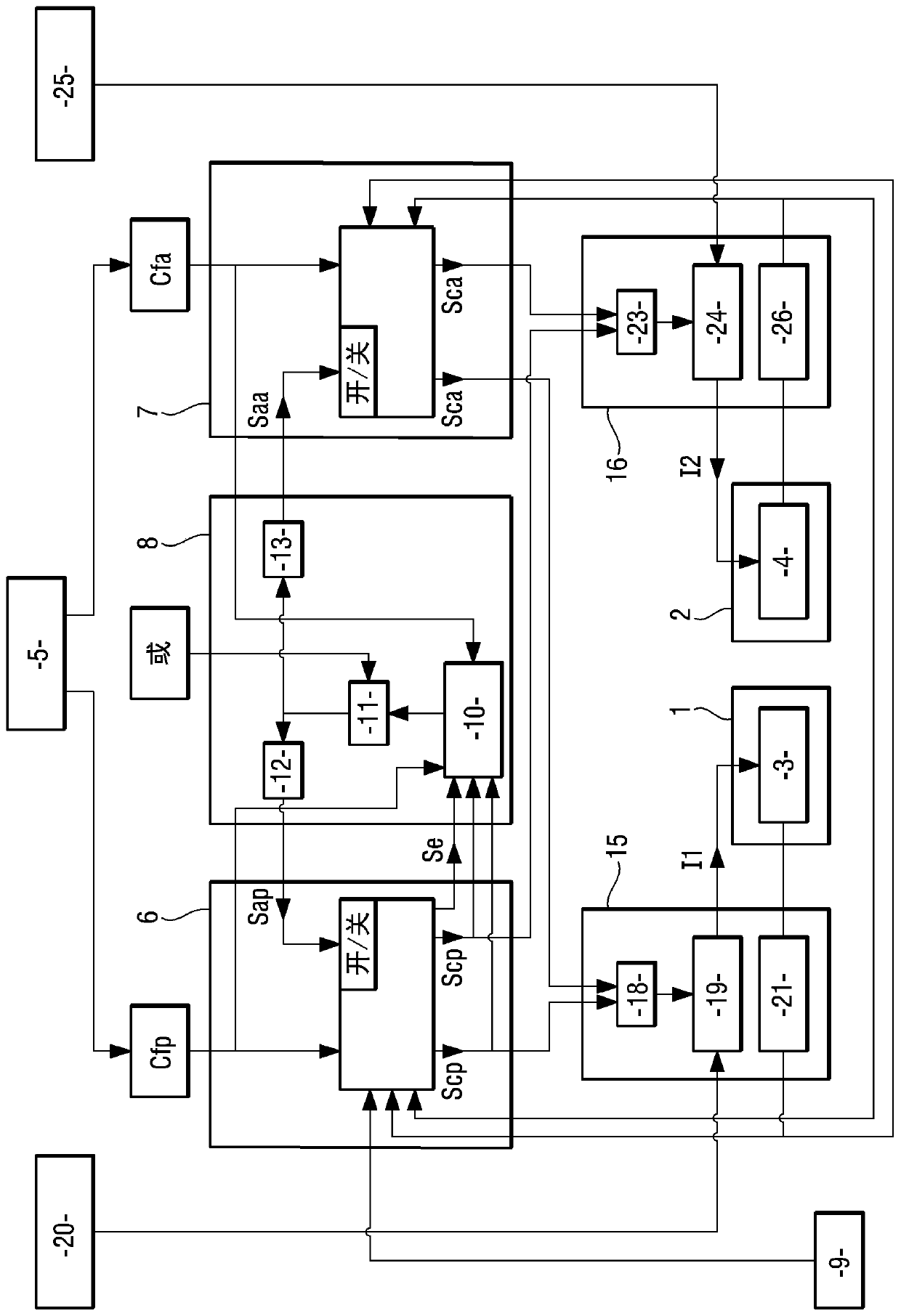
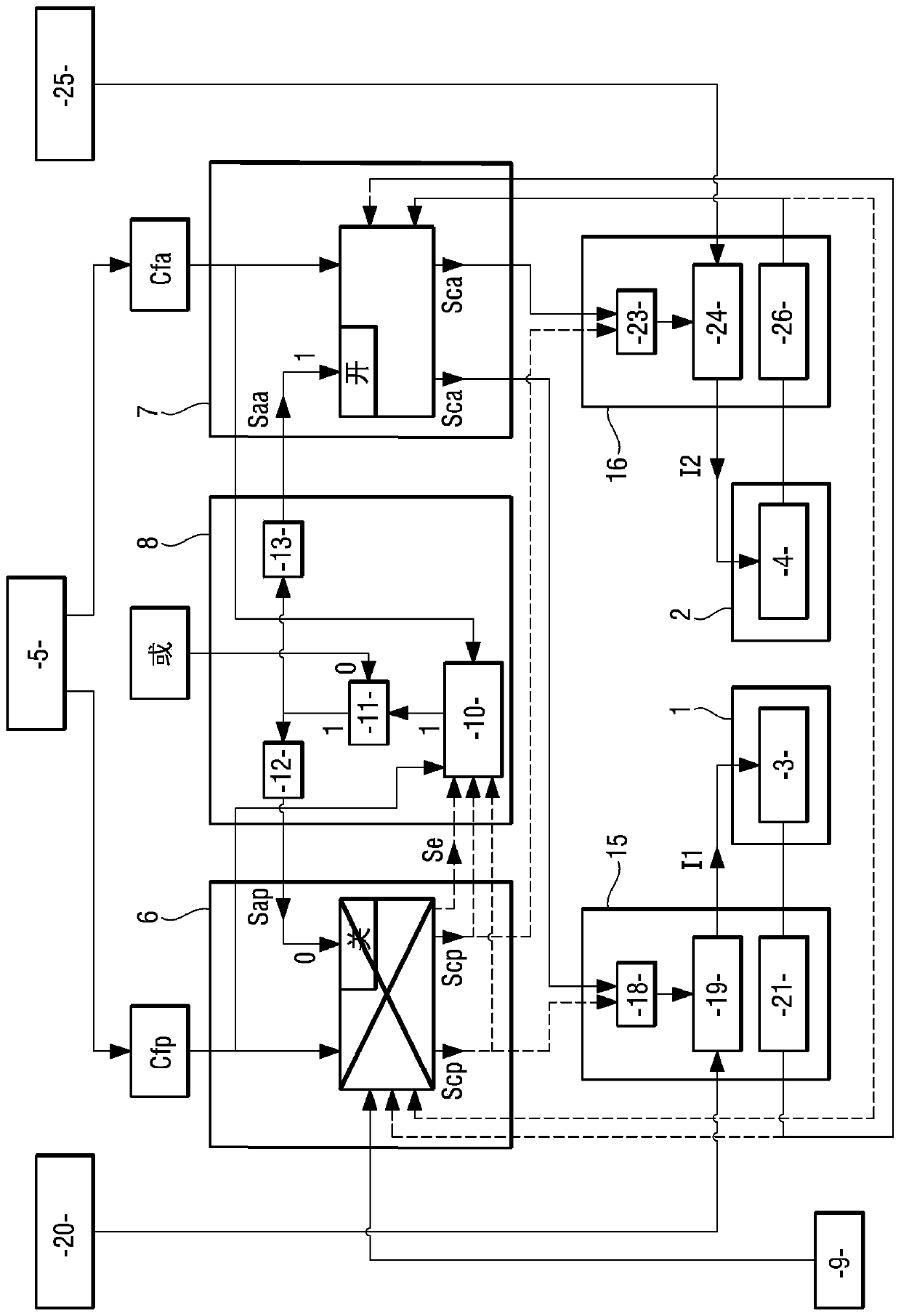
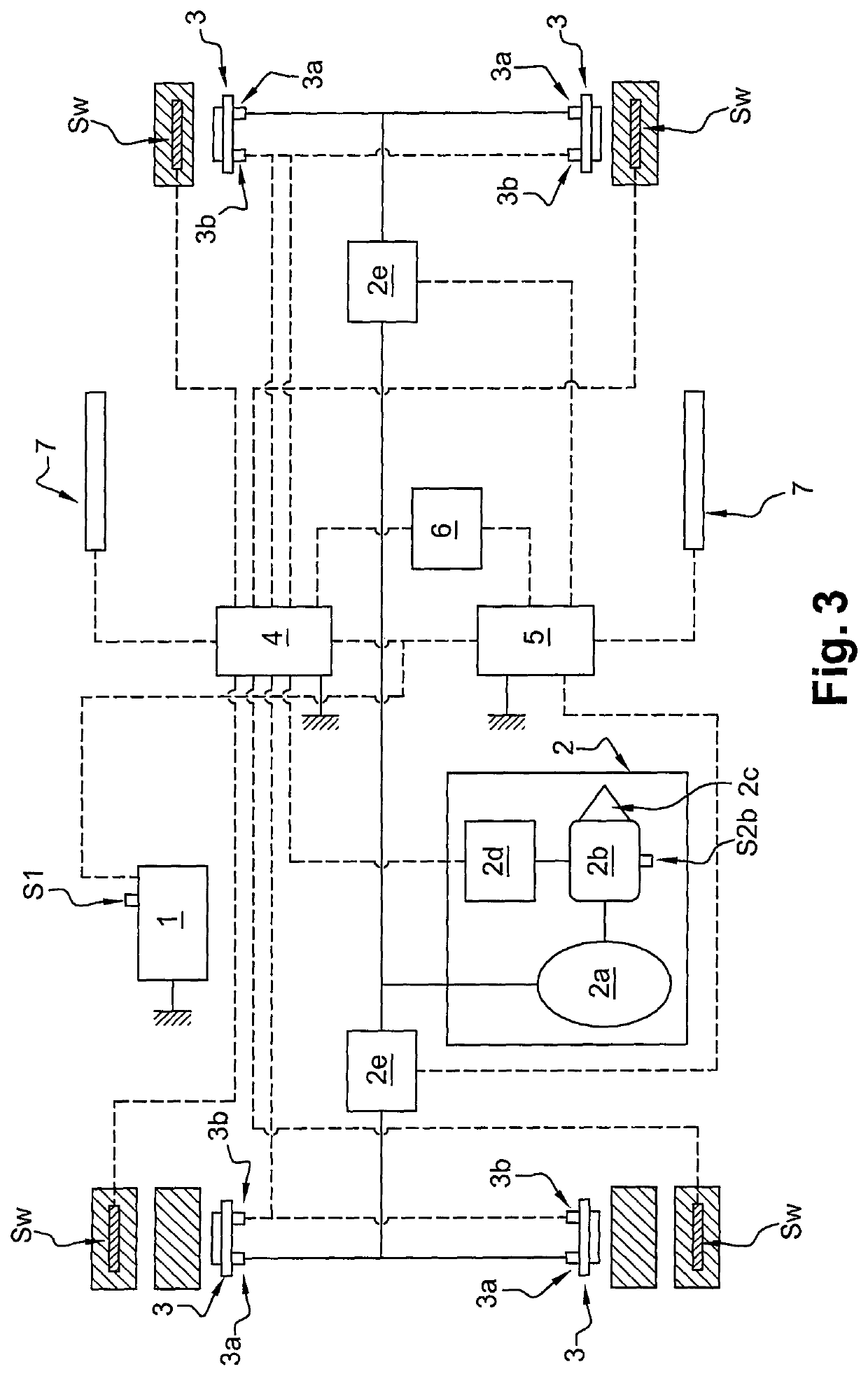
Architecture of an aircraft braking system
ActiveCN110963025ABraking action transmissionAircraft brake actuating mechanismsControl signalFlight vehicle
Disclosed is an architecture of an aircraft braking system, including: brakes including electromechanical actuators (1,2); a main control channel (6) and an alternative control channel (7), wherein the main control channel (6) and the alternative control channel (7) comprise electrical components at least partly different and adapted to provide at least partly different main brake control functions and alternative brake control functions, power modules (15, 16), wherein the power modules (15, 16) comprise electrical components at least partly different and adapted to generate supply current (I1, I2) based on the main control signal or an alternative control signal, a supervision unit (8). The supervision unit (8) is adapted to ensure that the main control signal is used in normal operationand that the replacement control signal is used to generate the supply current in the event of a fault.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS
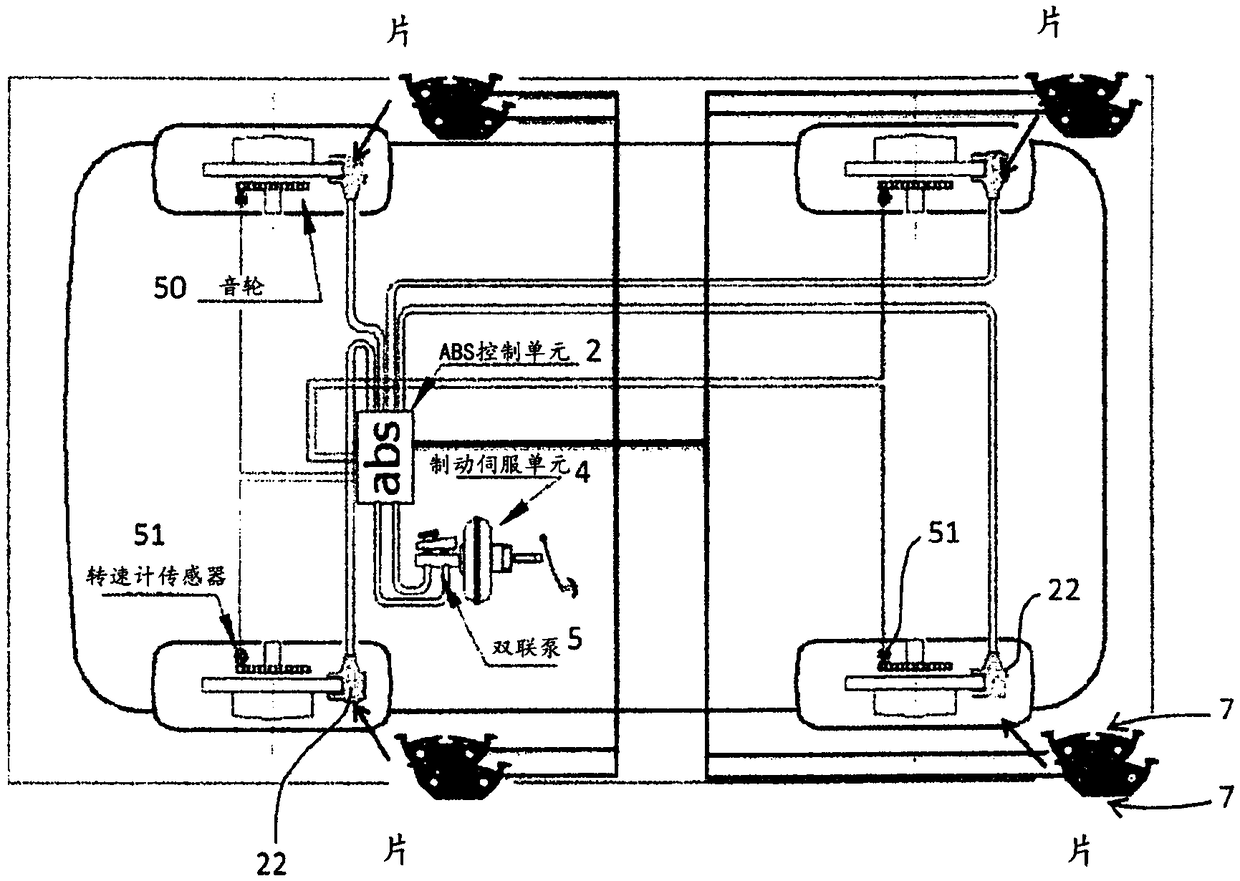
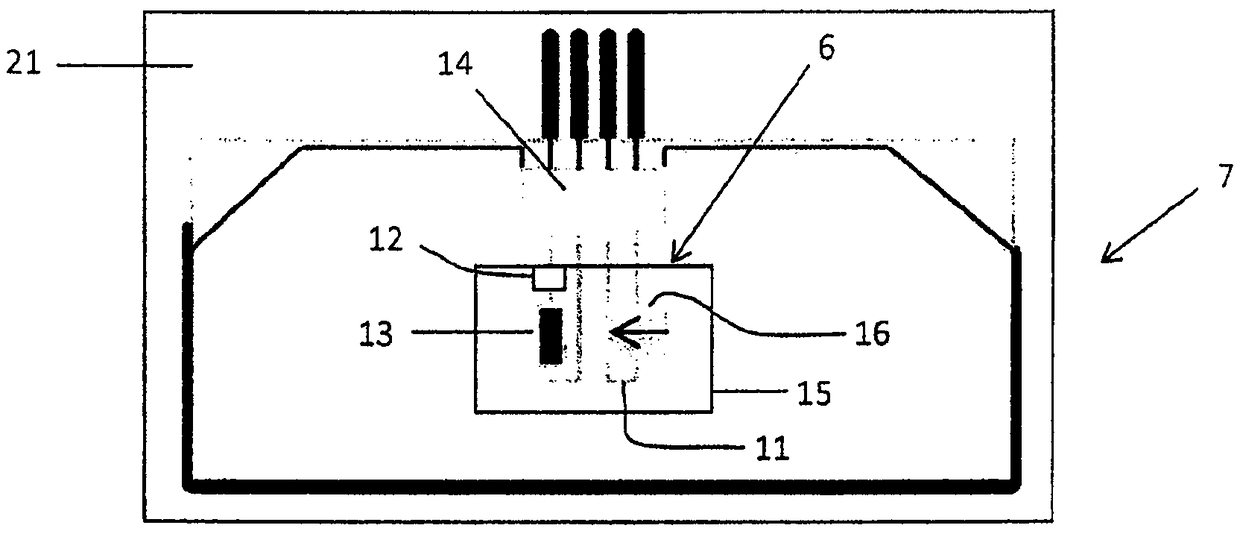
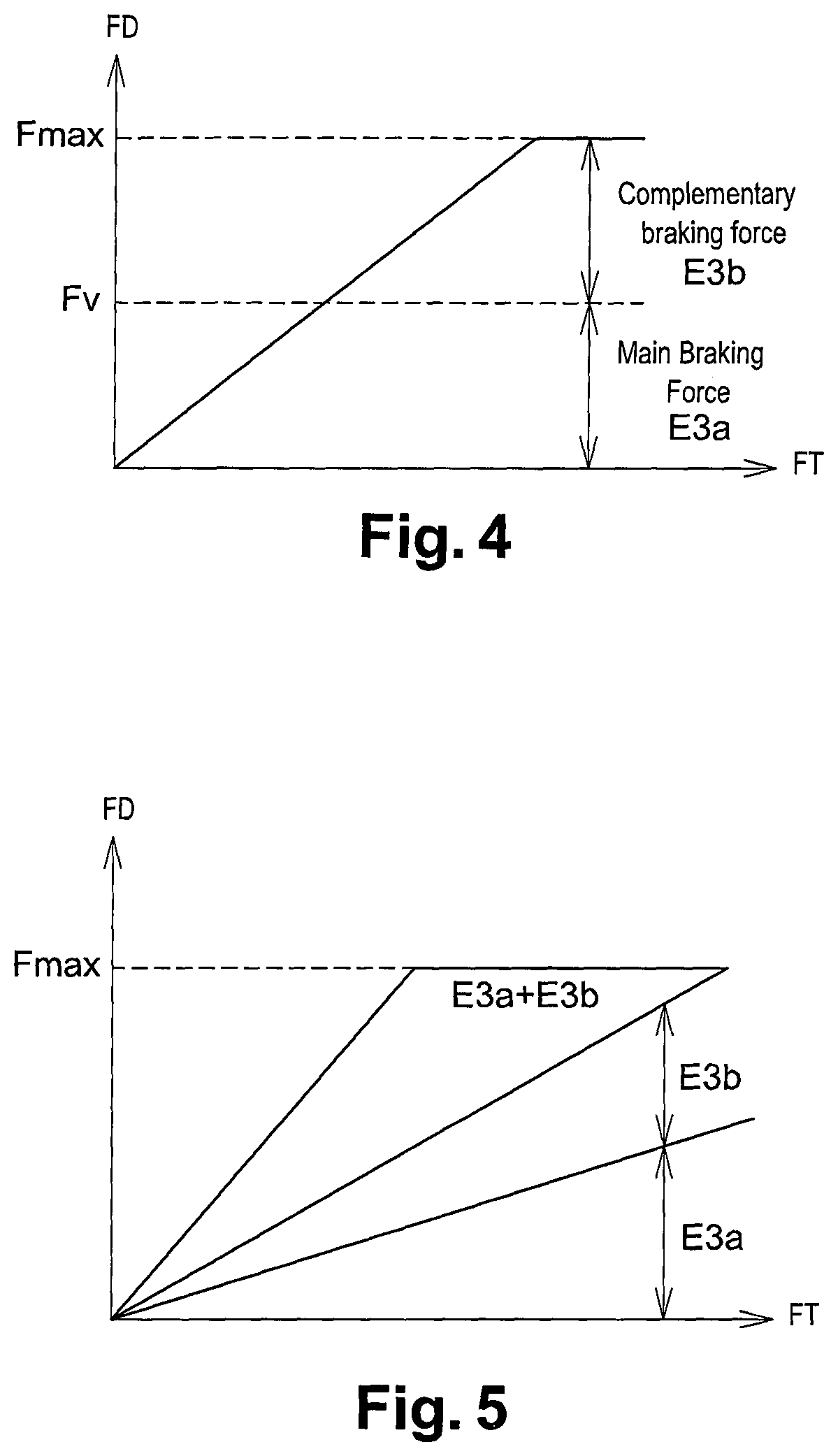
Device and method for improving the performance of an antilock braking and Anti-slip regulation of a vehicle
ActiveCN108698575AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityABS control systemsBraking elementsBrake torqueSolenoid valve
Device for improving the performance of an antilock braking (ABS) and / or anti-slip regulation (ASR) and / or electronic stability control (ESC) system of a vehicle comprising at least a fluid-dynamic system for controlling the braking pressure composed of at least one standard ABS management control unit and a brake-servo unit and a fluid pressure pump, solenoid valves connected to pipes for oil orair and at least phonic wheels and tachometer sensors respectively present one for each wheel of the vehicle, the device comprises additional intelligent sensors associated with at least one of the braking pads acting upon the braking disk of each wheel in order to collect additional data and at least one dedicated ECU control unit for managing said additional data and interacting with at least said ABS control unit. The method consists in detecting, by means of the pad and the dedicated control unit, the actual value of the tire-ground coefficient of friction that is constantly updated duringbraking using the braking torque data derived from the braking pad in order to adjust the braking pressure profile to the value of the actual coefficient of friction present between the tire and theground during the braking of the vehicle.
Owner:ITT ITAL SRL
Brake system and brake control method
ActiveUS20170144639A1Suppressing wasteful consumptionLimit wasteFluid braking transmissionABS control systemsParking brakeBraking system
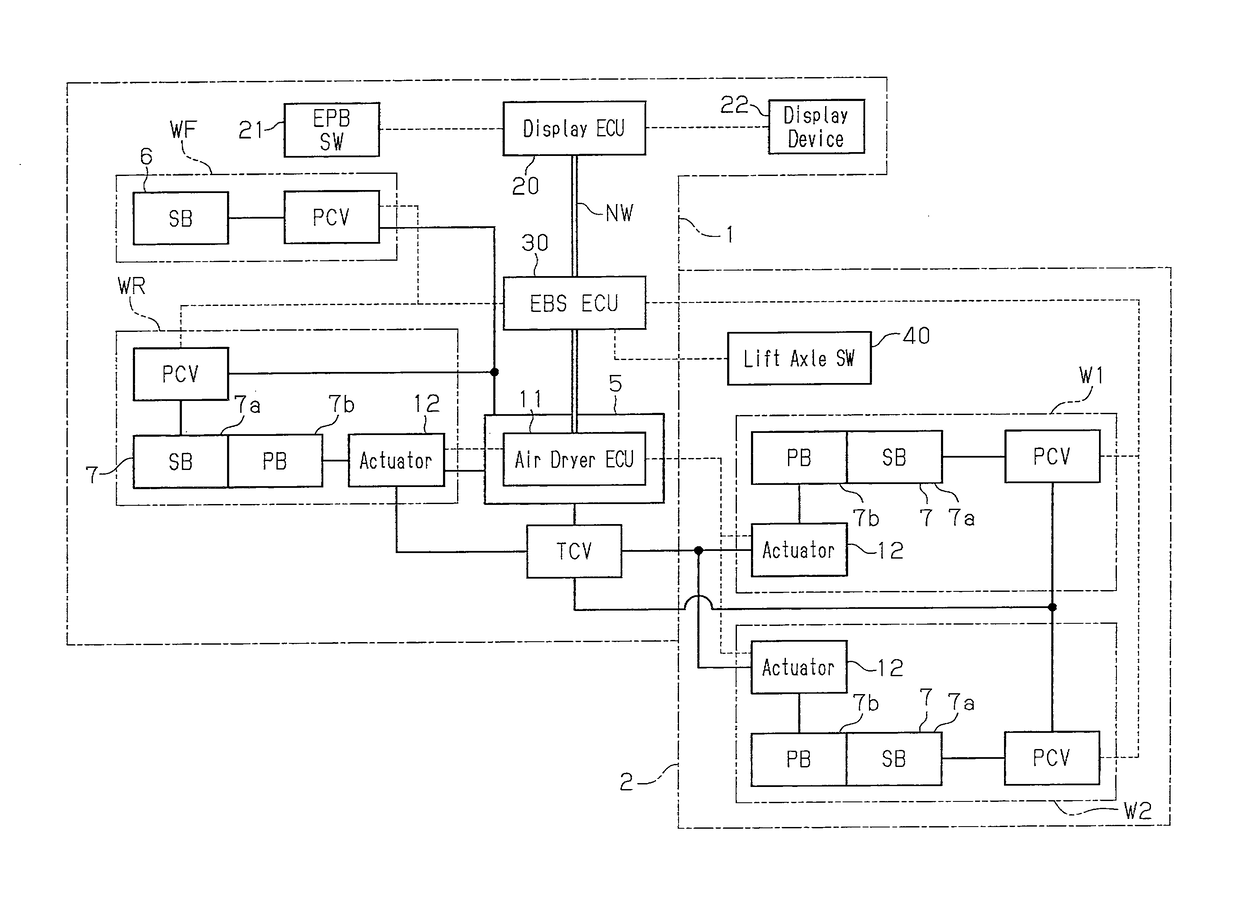
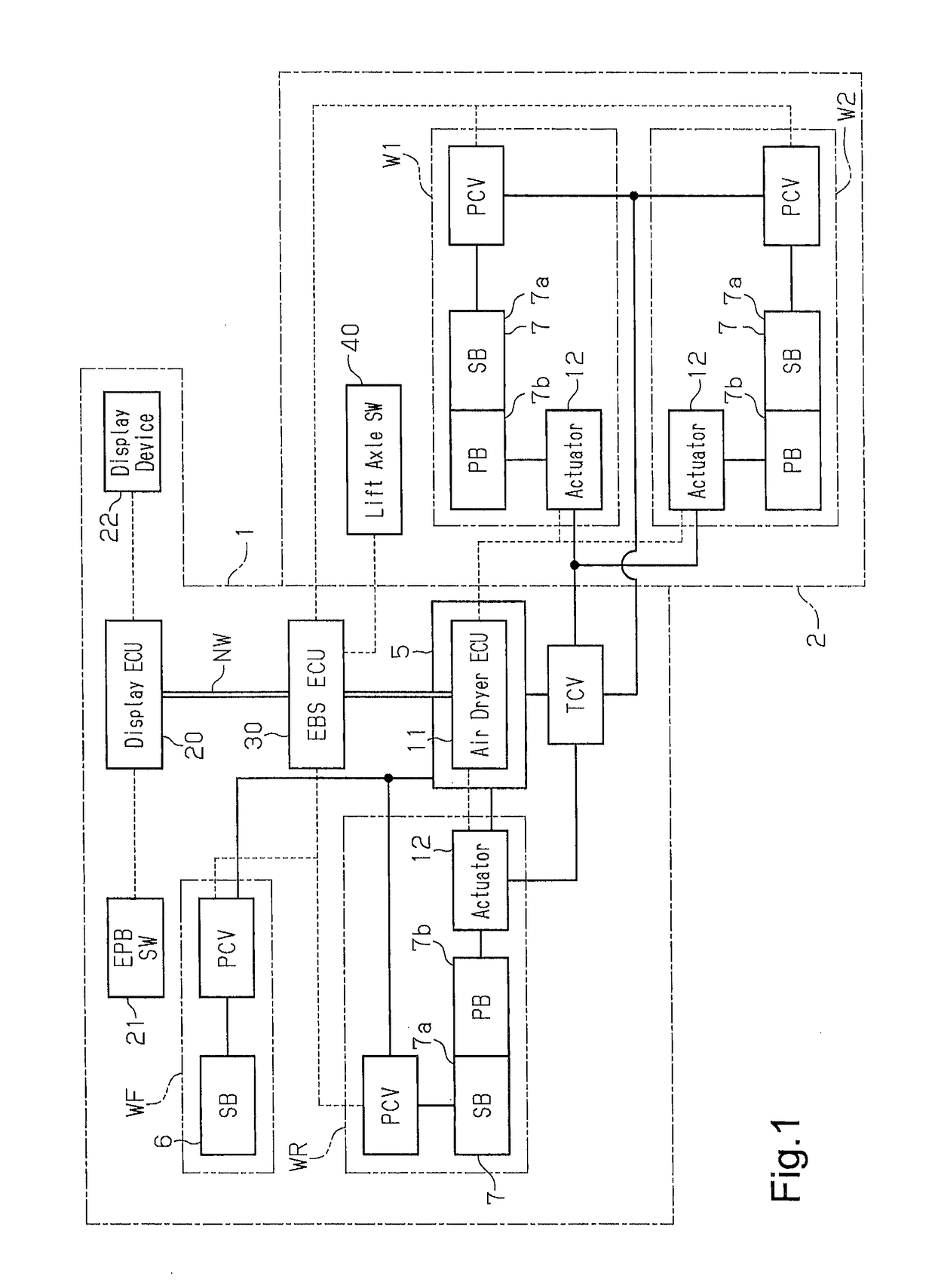
A brake system includes a service brake and a parking brake that brake a vehicle including a lift axle capable of ascending and descending. The brake system further includes a brake blocker device and a controller that controls the brake blocker device. The brake blocker device blocks at least one of supply of compressed air to the service brake and supply of compressed air to the parking brake. The service brake and the parking brake act on the lift axle. The controller actuates the brake blocker device when the lift axle is at a lifted position.
Owner:NABTESCO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
Vehicle brake system with secondary brake module
A brake system has a wheel brake and is operable under a non-failure normal braking mode and a manual push-through mode. The system includes a master cylinder operable by a brake pedal during a manual push-through mode to provide fluid flow at an output for actuating the wheel brake. A first source of pressurized fluid provides fluid pressure for actuating the wheel brake under a normal braking mode. A secondary brake module includes a plunger assembly for generating brake actuating pressure for actuating the wheel brake under the manual push-through mode.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Automatic parking method based on ASR system
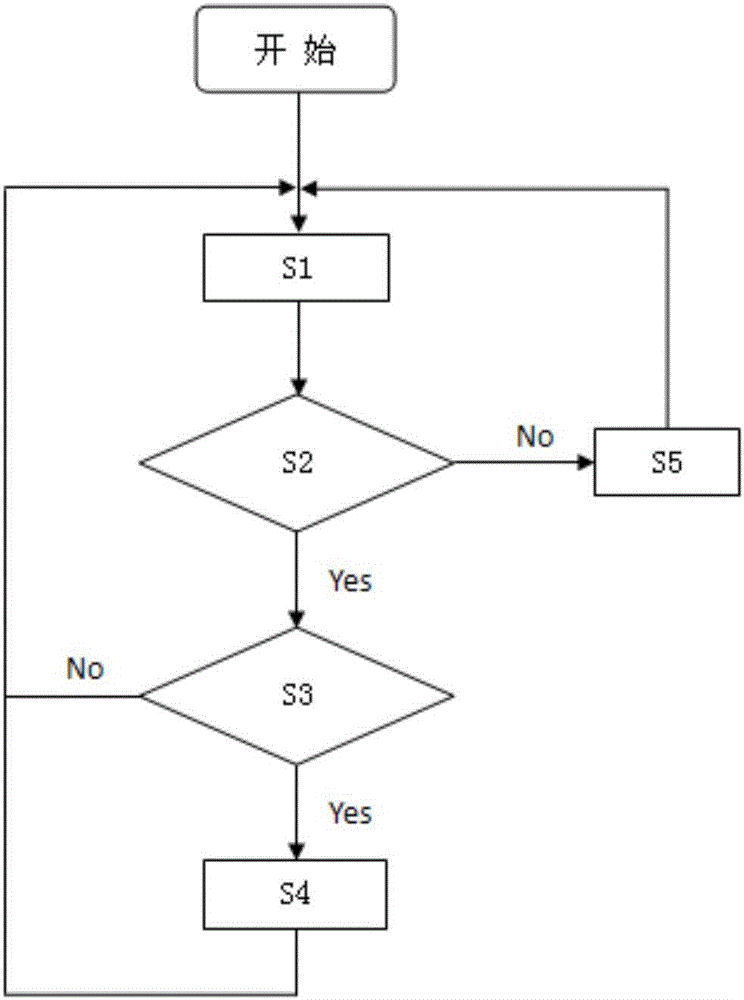
InactiveCN106364468AImprove reliabilityWill not change the layout structureBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsElectronic controllerThrottle position sensor
The invention relates to the field of automobile control devices, and provides an automatic parking method based on an ASR system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, monitoring the revolving speed of wheels and the position of a throttle valve through a wheel revolving speed sensor and a throttle valve position sensor of the ASR system, and then executing a step S2; S2, judging whether the conditions that the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in an idling state are simultaneously met, executing a step S3 if the conditions that the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in the idling state are simultaneously met, and executing a step S5 if the conditions that the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in the idling state are not simultaneously met; S3, judging whether the lasted duration at which the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in the idling state reaches the preset duration through timing by an ECU interior timer, executing a step S4 if the lasted duration at which the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in the idling state reaches the preset duration, and executing the step S1 if the lasted duration at which the wheel revolving speed is zero and the throttle valve position is in the idling state does not reach the preset duration; S4, starting brake control, and then executing the step S1; and S5, removing the brake control, and then executing the step S1. No additional components are needed to be installed, the original automobile layout structure is not changed, facilities adopted in the method can be shared with the corresponding function components of the ASR antiskid system, and the method can be implemented just through the program updating in an electronic controller ECU, thereby being low in implementation cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
ABS strategy for hybrid brake actuators
ActiveUS10766472B2Reduce weightReduce energy consumptionBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsEngineeringControl theory
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
System and method for traction control
ActiveUS9845084B2Shorten speedSlow vehicleASR control systemsPropulsion unit safety devicesTraction motorAutomotive engineering
A system includes a sensor and a controller. The sensor is configured to detect sliding of a wheel of a vehicle. The controller is configured to communicate with the sensor and a traction motor operatively connected to the wheel such that the traction motor selectively applies forces in at least one direction to the wheel during operation. The controller is further configured to direct the traction motor to apply a motoring slide reducing force to the wheel when the sensor detects sliding of the wheel resulting from a frictional braking force.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
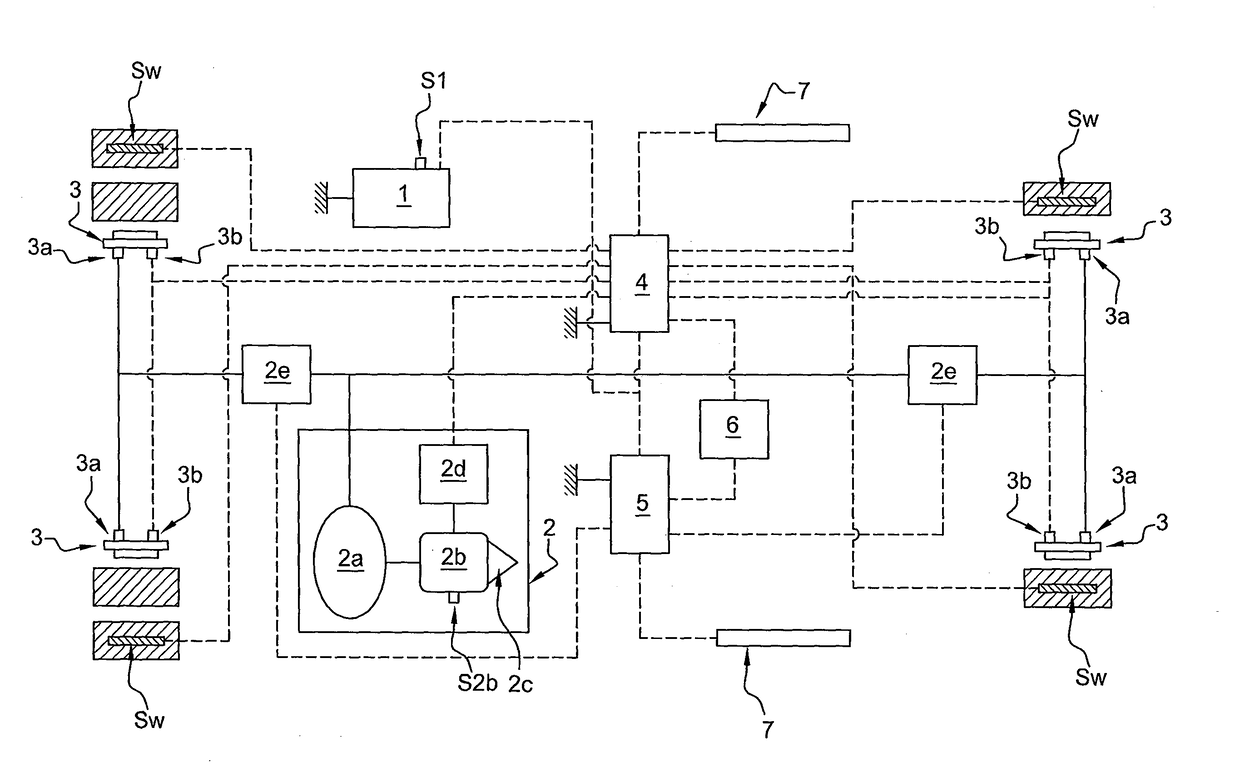
Method for operating a driver assistance system of a motor vehicle and corresponding driver assistance system
ActiveCN106255629BGreat driving potentialSmall drive potentialVehicle sub-unit featuresASR control systemsDriver/operator
The invention relates to a method for operating a driver assistance system of a motor vehicle (1). The method is characterized by the steps of: respectively acquiring the drive potentials of all drive wheels (3, 4) of at least one axle (3) of the motor vehicle (1); comparing these drive potentials; The power is used to actuate the braking device, so that the wheels (3) with a lower driving potential are braked.
Owner:AUDI AG
Method for braking a vehicle, and drive train of a vehicle
PendingCN110650879AFast transferCommunicate with each other quicklyBrake system interactionsAutomatic initiationsTransmission brakeControl theory
The invention relates to a method for braking a vehicle, the vehicle having a transmission (2) controlled by a transmission control unit (3). In a method in which a transmission brake is not required,the transmission control unit (3) electronically requests a braking intervention.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Electro-pneumatic pressure control module implemented as a component and having an integrated inertial sensor
PendingUS20210354675A1Simpler and robust constructionHigh level of functional reliabilityBrake system interactionsBraking action transmissionElectronic componentControl theory
An electro-pneumatic central pressure control module having at least a single channel, and which is implemented as a component for an electro-pneumatic service brake of a vehicle, having at least one pressure control channel which is electrically controllable with regard to a brake pressure. Also described is an electronic control device of the pressure control module having a board carrying electrical and electronic components, at least one inertial sensor being arranged on or at the at least one board and being electrically conductively connected to at least several of the electrical and electronic components on the board, in which an arrangement / apparatus ensures a lower vibration load of the inertial sensor on the board.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Damping force control device
ActiveUS11279196B2Attenuate/reduce vibrationPrevent comfortabilityBrake system interactionsResilient suspensionsVertical vibrationSprung mass
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Multifunctional automobile control system
InactiveCN106004845AImprove braking effectImprove driving stabilityBraking action transmissionABS control systemsWheel speed sensorAutomotive control systems
The invention discloses a multifunctional automobile control system which comprises a control unit. The signal input end of the control unit is connected with a wheel speed sensor, a steering wheel rotating angle sensor, a transverse deflection rate sensor, an ignition switch, a brake switch and an ASR / ESP switch. The first control output end of the control unit is connected with an engine control unit through a CAN bus and used for controlling an electronic throttle through the engine control unit. The second control output end of the control unit is connected with a hydraulic control unit and controls all electromagnetic valves and an oil return pump in the hydraulic control unit. The multifunctional automobile control system integrates the functions of systems such as the ABS, the ASR and the ESP, the braking performance and running stability and safety of an automobile can be greatly improved, the structure and the control principle are simple, the integration of execution elements is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:WUXI INST OF COMMERCE
System and method for traction control
ActiveUS10053070B2Prevent slidingIncreased riskASR control systemsPropulsion unit safety devicesBraking systemBrake force
A system includes a plurality of wheels, a braking system, and one or more sensors. The plurality of wheels includes a guardian wheel and at least one non-guardian wheel and is disposed on a wheeled vehicle. The braking system is operatively connected to the guardian and non-guardian wheels and applies a first braking force to the at least one non-guardian wheel and a second braking force to the guardian wheel. The second braking force increases a slide risk of the guardian wheel beyond a slide risk of the at least one non-guardian wheel. One or more sensors disposed within the wheeled vehicle detect sliding of the guardian wheel allowing a corrective action to be taken to prevent sliding of the at least one non-guardian wheel.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Power hop anticipation and mitigation
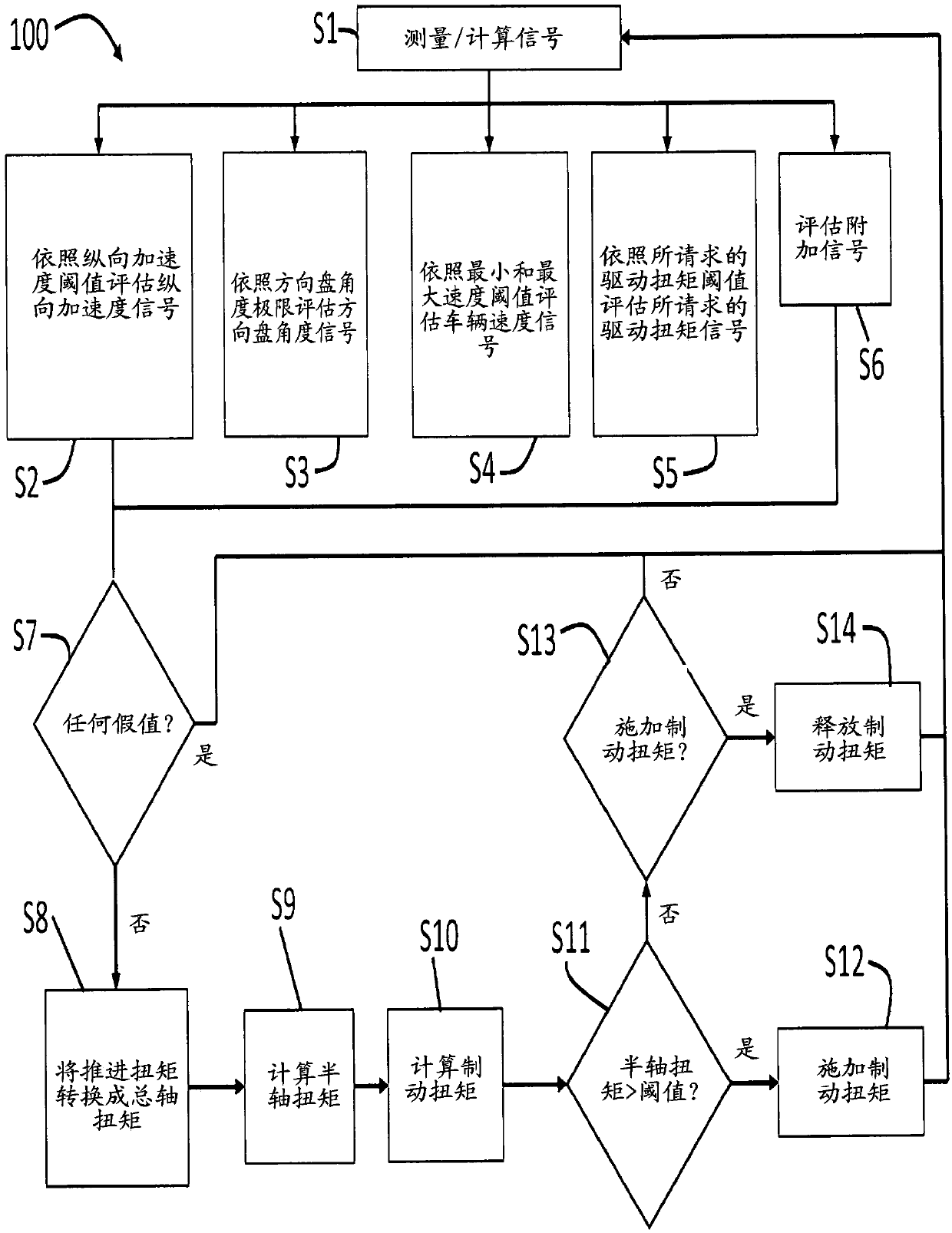
ActiveCN109641592AExternal condition input parametersVehicle condition input parametersBrake torqueControl theory
Longitudinal acceleration, intended travel angle, wheel speed, and requested drive torque signals are measured for a vehicle. The longitudinal acceleration, intended travel angle, wheel speed, and requested drive torque signals are then evaluated. A brake torque is calculated as a function of a propulsive torque, wherein the propulsive torque is produced by a power source for the vehicle. The brake torque is applied when the longitudinal acceleration signal exceeds a longitudinal acceleration threshold, the intended travel angle signal is between intended travel angle limits, the wheel speed signal is less than a minimum speed threshold, the requested drive torque signal exceeds a requested drive torque threshold, and a torque threshold is exceeded.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Electric brake system and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS10654457B2Reduce noiseReduce vibrationBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsDriver/operatorControl system
An electric brake system and a method for controlling the same are disclosed. The electric brake system includes a hydraulic control device, a sensing unit, and a controller. The hydraulic control device generates hydraulic pressure using a piston operated by an electric signal generated in response to a displacement of a brake pedal. The sensing unit detects driver's braking intention. When an electronic stability control (ESC) of a vehicle operates, the controller calculates a change amount of stroke of the piston needed to output brake pressure corresponding to the driver's braking intention, and acquires the calculated stroke change amount so as to boost pressure of each wheel at a predetermined slope.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
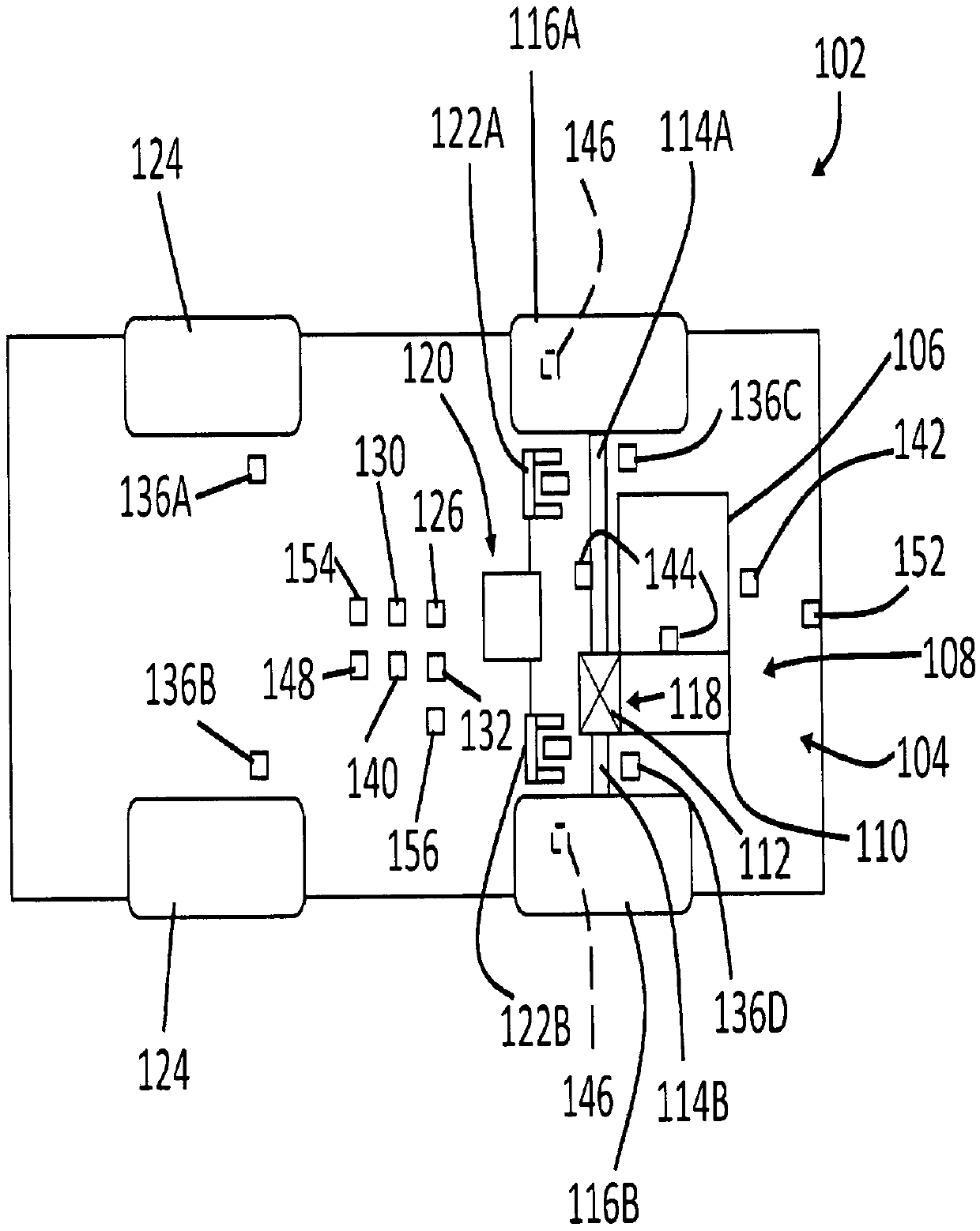
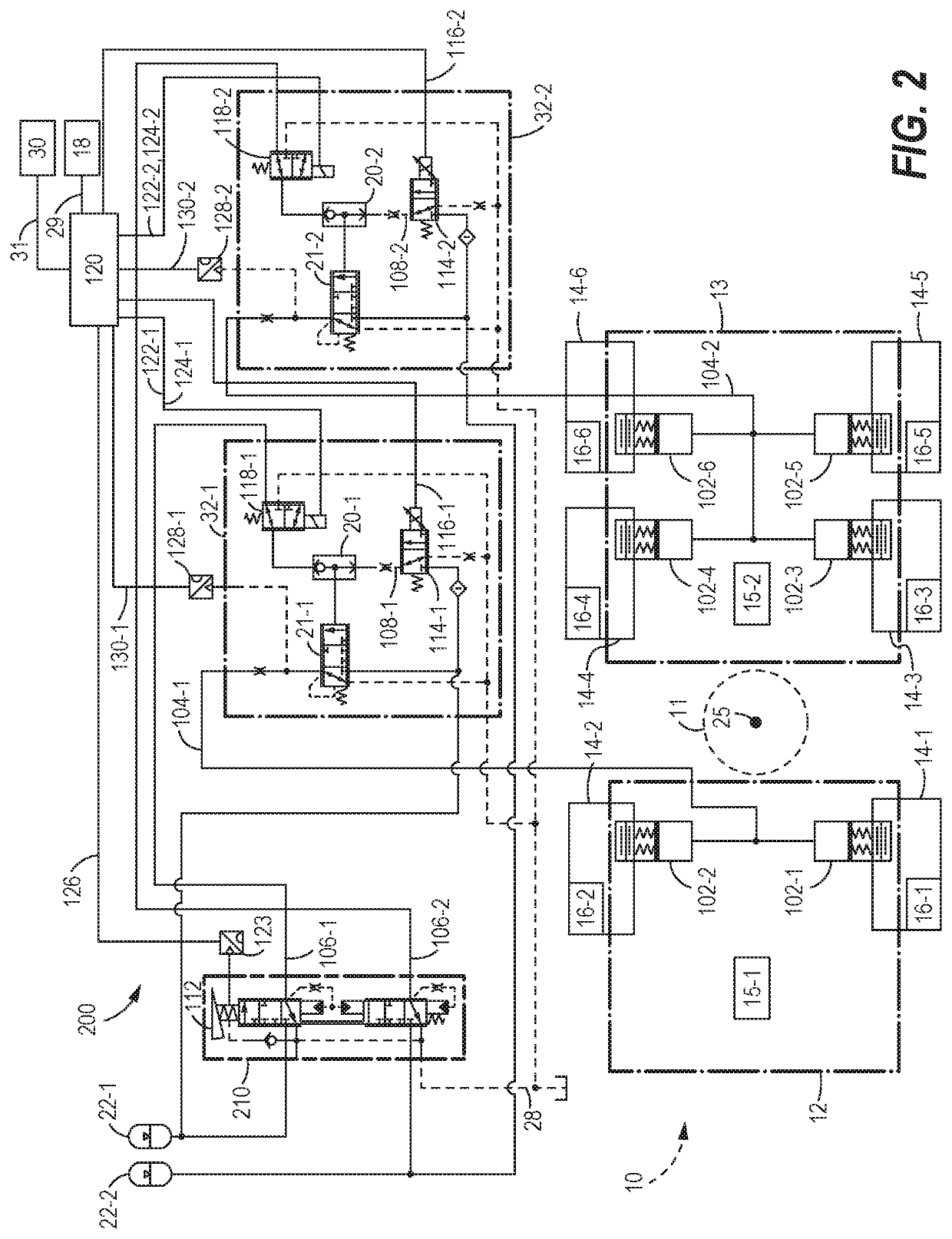
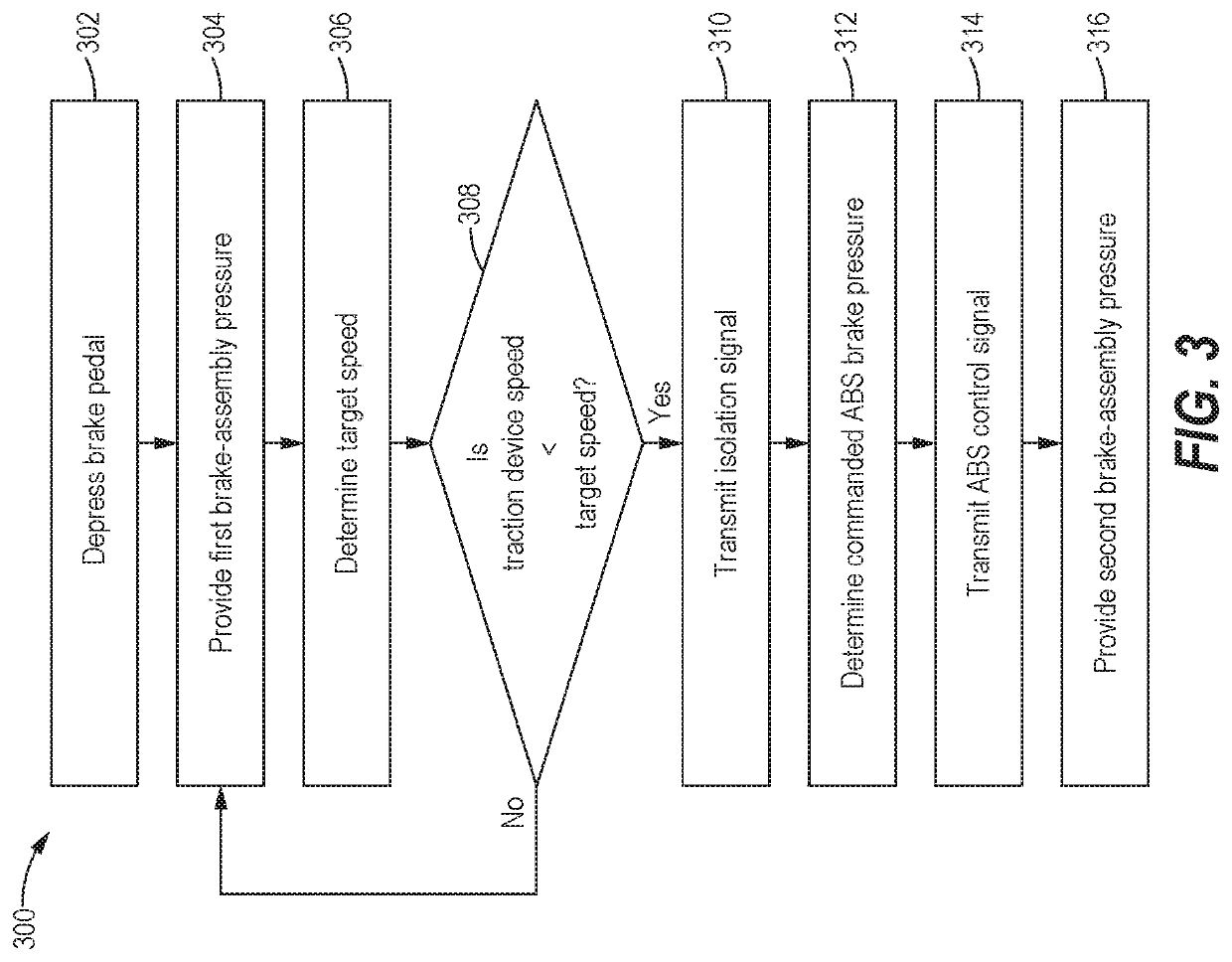
Brake system for an articulated vehicle
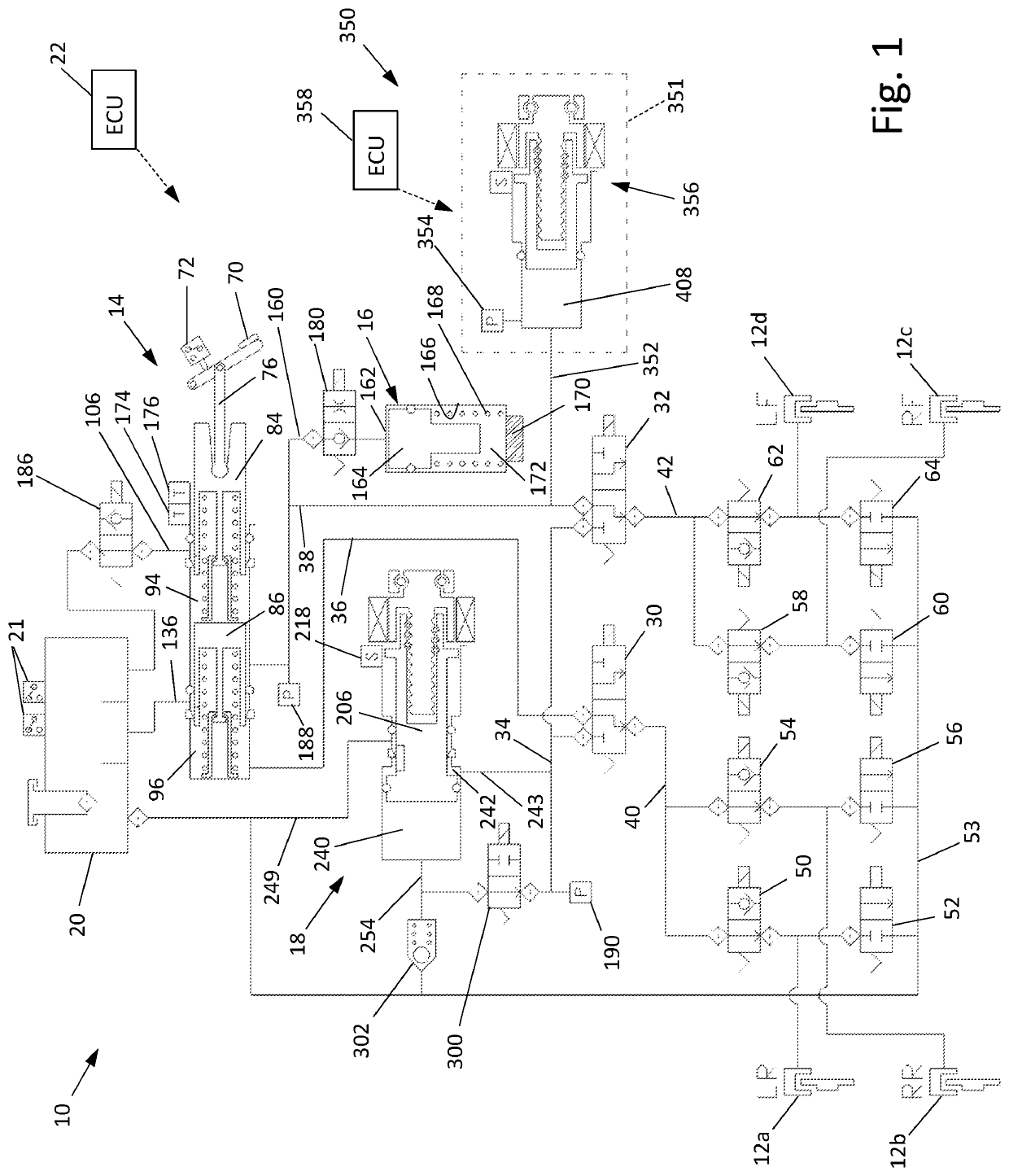
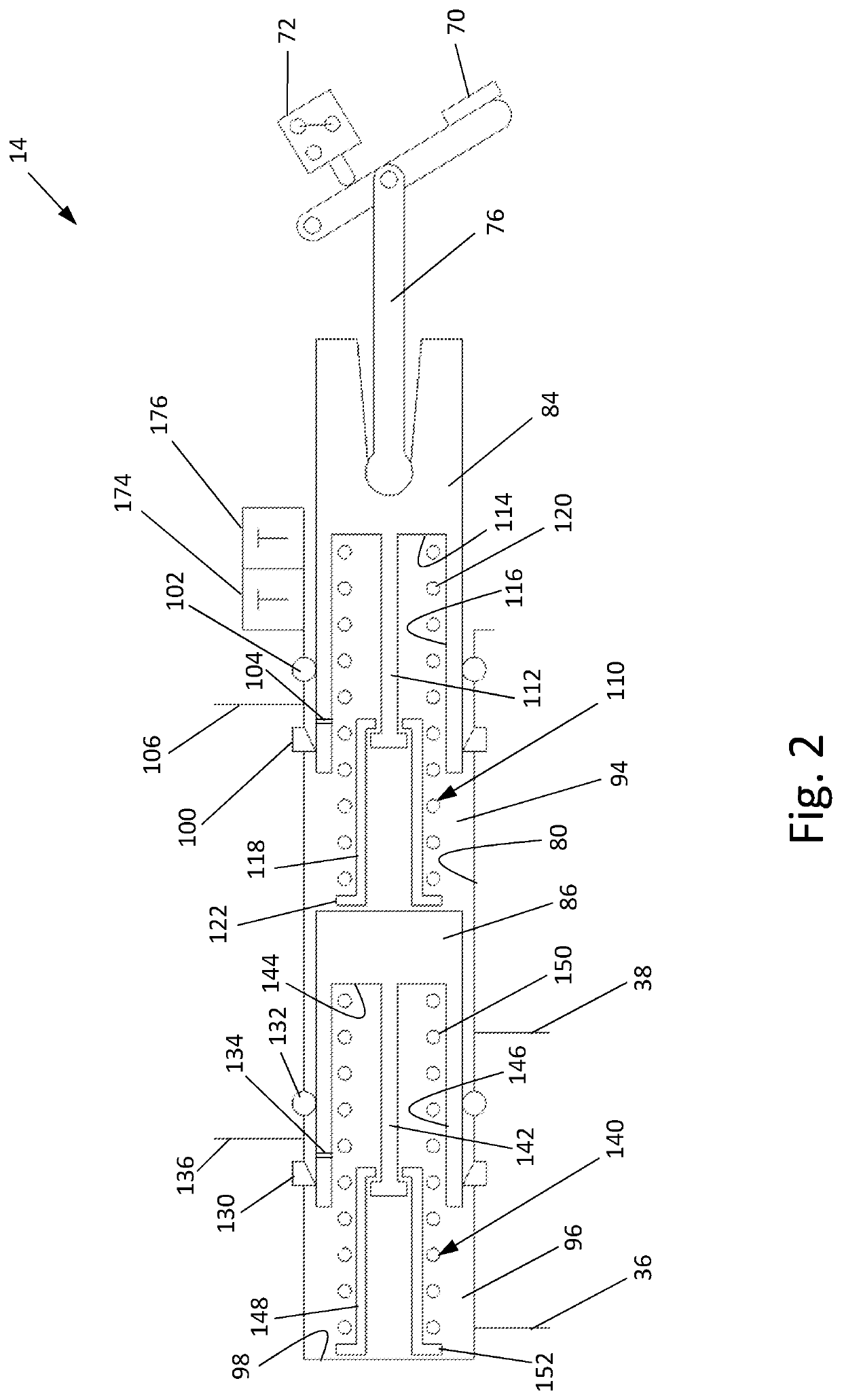
A brake system for an articulated vehicle is disclosed. The brake system includes a brake assembly coupled to a traction device, the brake assembly being configured to apply a brake-assembly pressure based on one of a hydro-mechanical pressure signal and an electro-mechanical pressure signal. A blocking valve is configured to block the hydro-mechanical pressure signal when closed. A brake controller, is configured to transmit an isolation signal configured to close the blocking valve and transmit an ABS control signal that is based on a commanded ABS brake pressure.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com