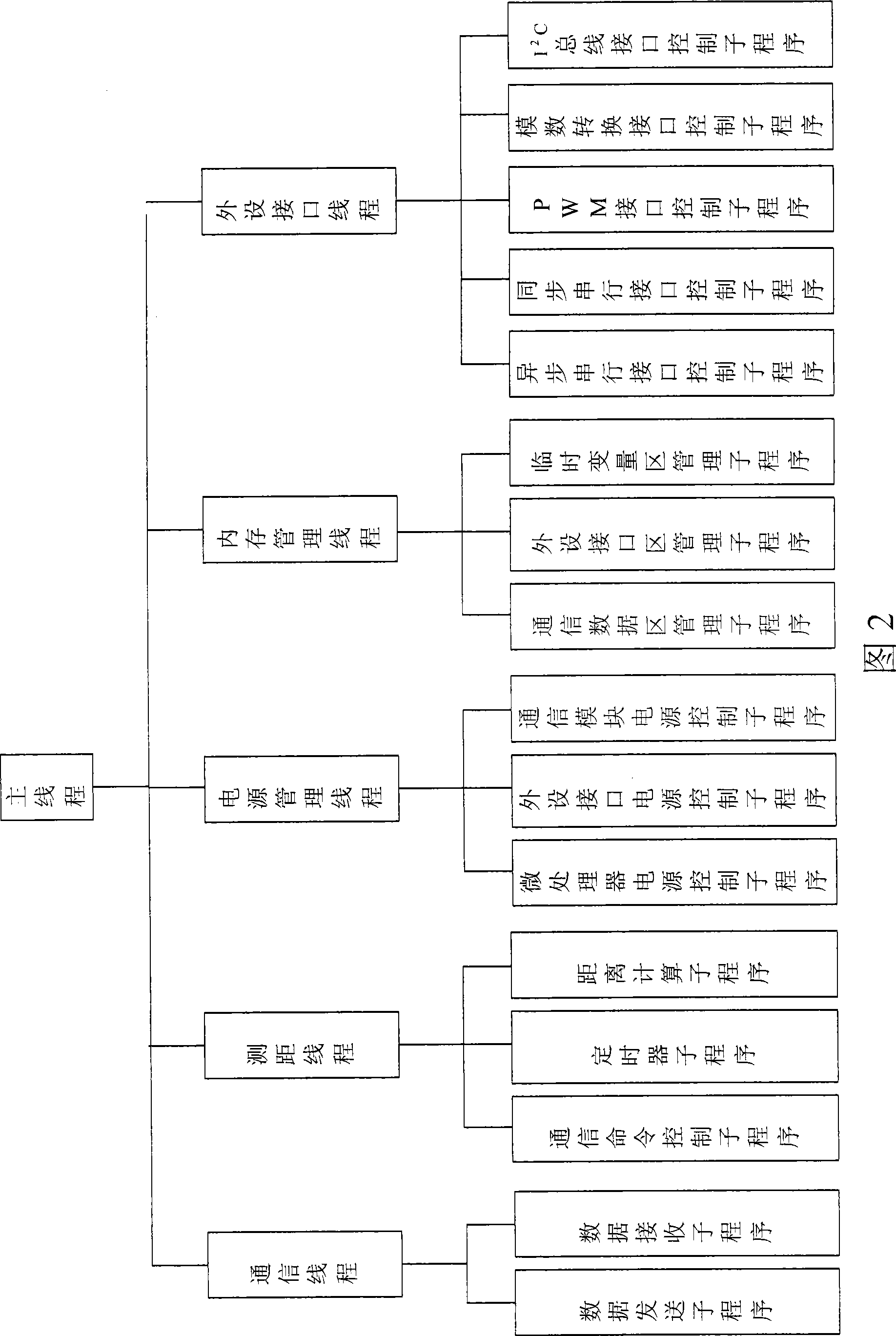
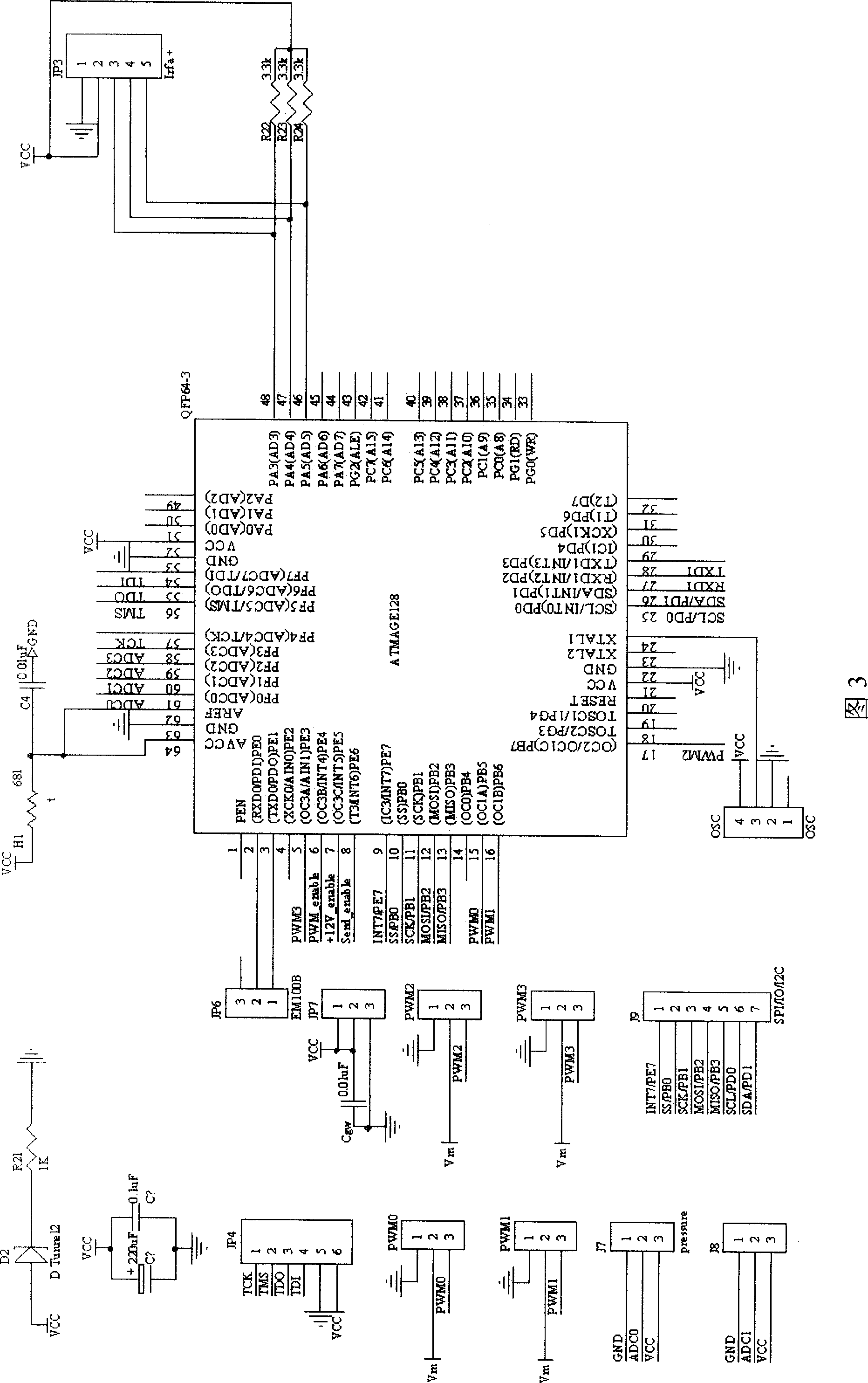
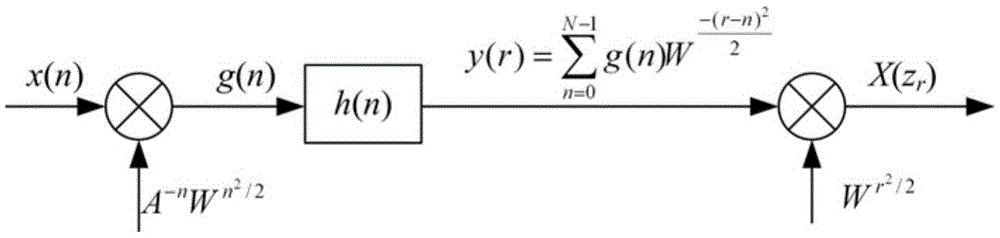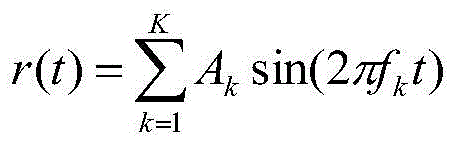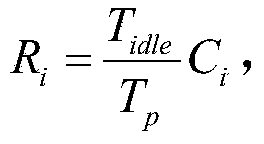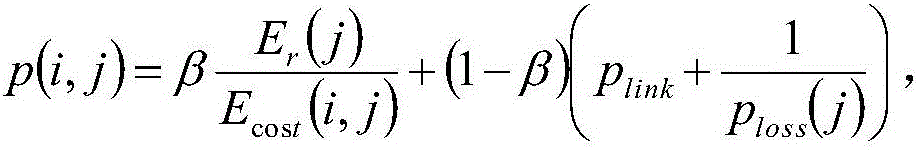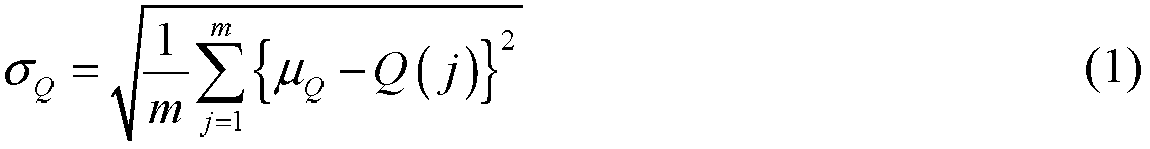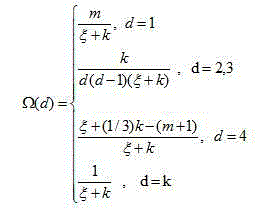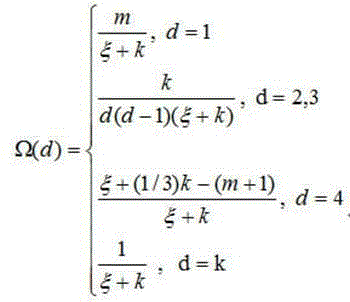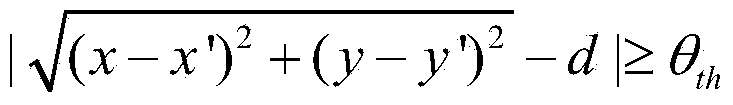Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
140 results about "Underwater wireless sensor networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
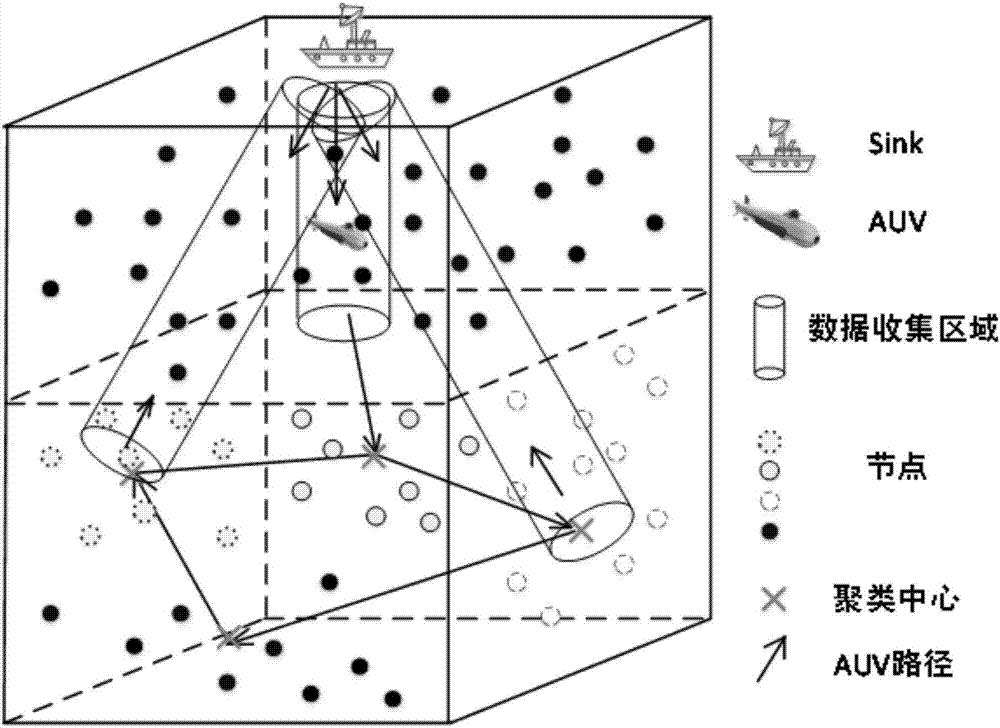
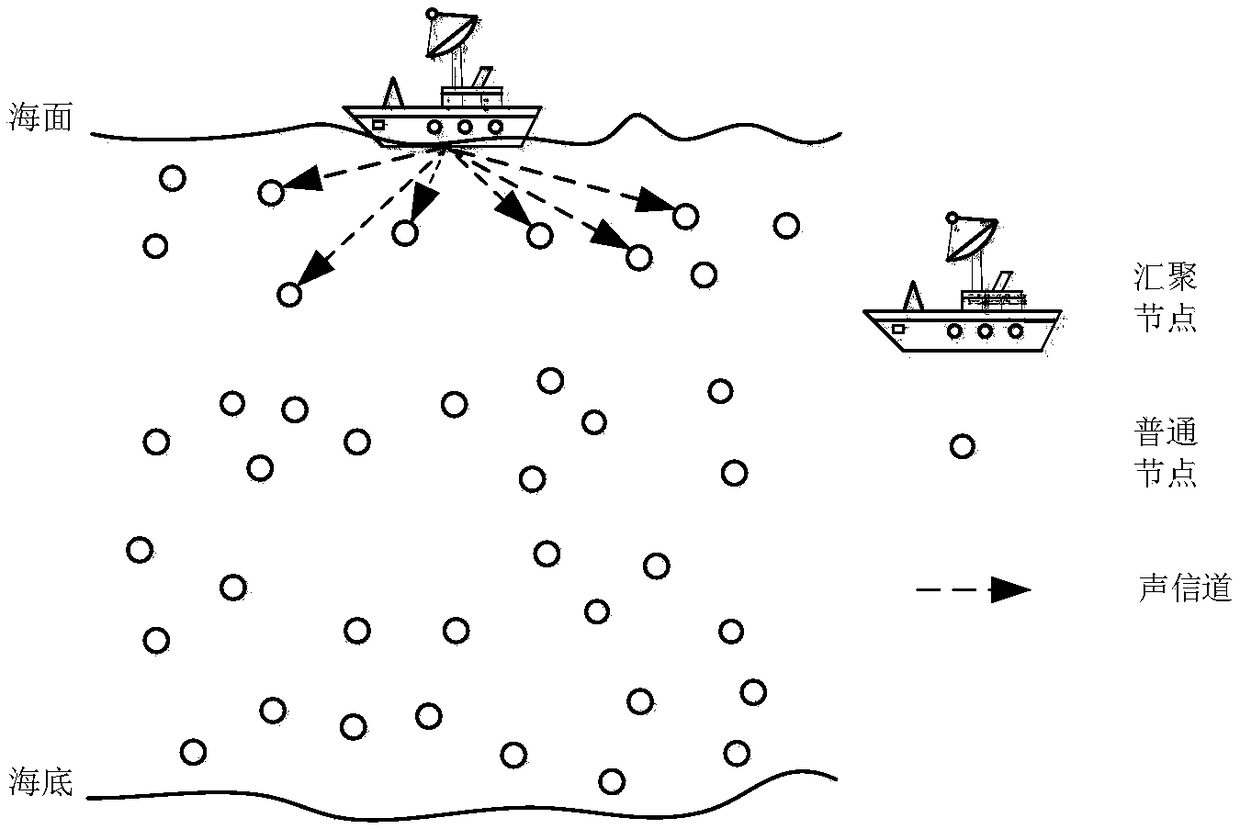
AUV data collection method in underwater wireless sensor network based on seawater layering
The invention discloses an AUV data collection method in an underwater wireless sensor network based on seawater layering. The AUV data collection method comprises: layering of the underwater wirelesssensor network is carried out through an oceanographic model; for different layering, different data collection strategies are adopted; an AUV cruises according to a predetermined path on a surface layer having relatively high mobility; a sensor node performs data forwarding by dynamically selecting a forwarding set at each hop through the factors, such as the forwarding probability and the residual energy, so that the data forwarding reliability of a mobile node is enhanced; simultaneously, in a lower-layer network, the node forms an AUV stop point through initialization operation includingaggregating, and then clustering; an AUV track is planned through a shortest path algorithm; data in the network is collected by utilization of the AUV used as an auxiliary tool; simultaneously, the energy consumption of the AUV is considered; therefore, the whole algorithm accords with a practical condition better; the cruising path of the AUV is reasonably planned; therefore, the data forwardinghop number is reduced; the energy consumption of the network is reduced; the problem that the energy consumption is non-uniform can be partly solved; and thus, the survival time of the network is prolonged.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
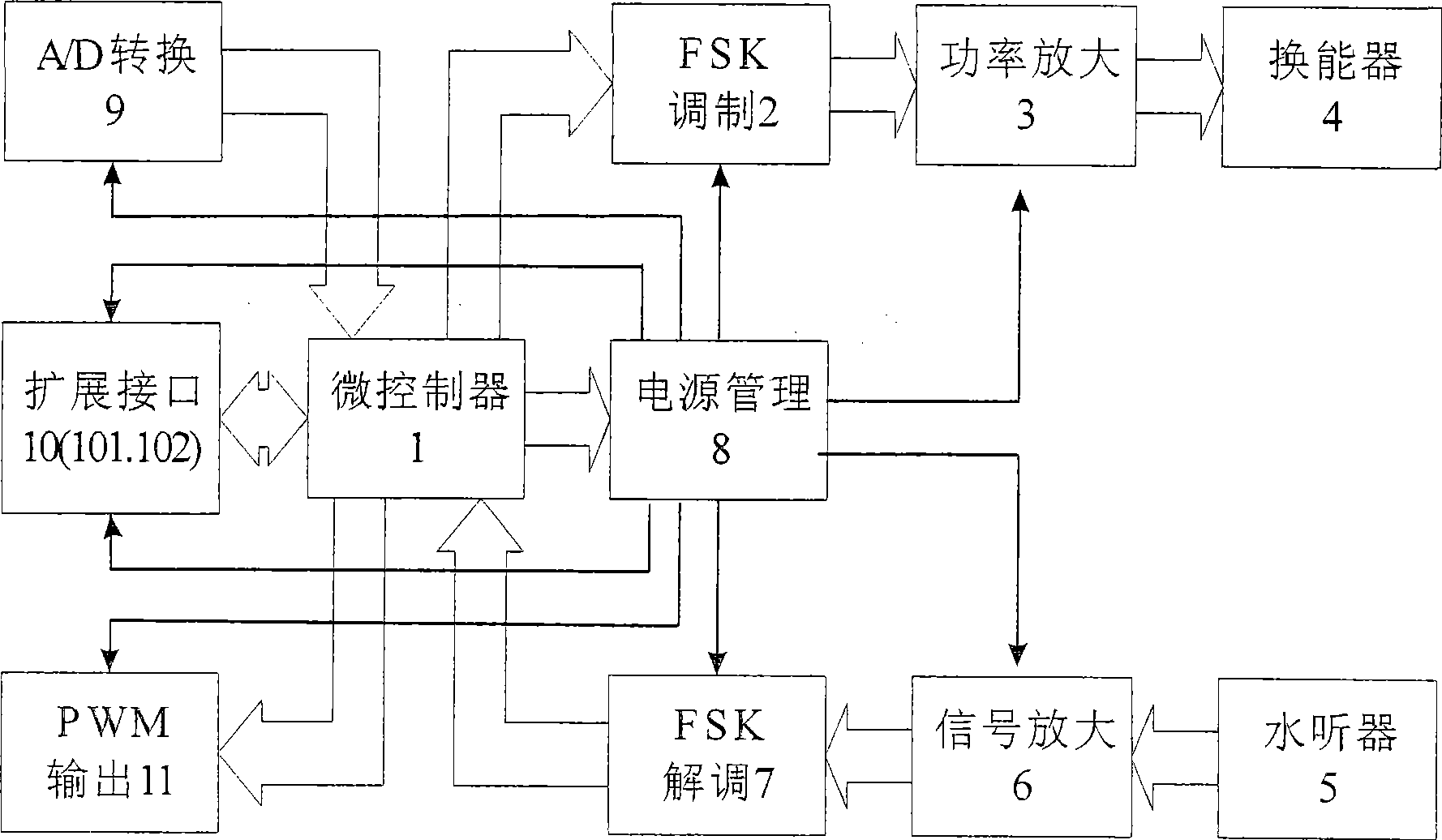
Method and apparatus for measuring network node of underwater sensor
InactiveCN101378293ALow costReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionMicrocontrollerSonification
The invention discloses a measuring method for network nodes of an underwater wireless sensor and a device. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out the interconversion of an electric signal and an ultrasonic signal by utilizing an ultrasonic transducer so as to complete underwater ultrasonic communication; calculating the relative distance between the nodes and the device by utilizing the transmission delay between node communication as well as the propagation velocity of ultrasound underwater; and collecting the underwater environmental data information from the position of the nodes by utilizing a sensor specially used in underwater detection. The device comprises a microcontroller, an FSK modulating and power amplifying module and a transducer which are connected in series; a hydrophone, a weak signal amplifier, an FSK demodulating chip and a microcontroller which are connected in series; a power management module is used for supplying power for a circuit and managing a power supply; and an external spreading interface module is used for connecting with a corresponding interface sensor and peripherals. The invention realizes the underwater sound communication function with low cost and low power consumption and the distance measuring function between the network nodes of the underwater wireless sensor.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for adaptively routing underwater sensor network on basis of difference
InactiveCN102868974ACutting costsLower latencyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPathPingEngineering
The invention generally relates to the technical field of network communication, and particularly relates to a method for routing an underwater sensor network. The method for routing comprises the following constituent parts: (1) node grade definition; (2) node grade information acquiring and updating processes; (3) neighbor node information recording; (4) directional flooding mechanism based on grade difference; (5) adaptive routing step based on the grade difference, node density and residual energy; and (6) differential geographical routing step based on the grade difference and distance. The method has the following advantages that the best next hop adaptive routing is determined on the basis of the neighbor table information to reduce redundant paths, so that the energy efficiency is improved to a great extent; and the adaptive routing adopts immediate routing, so that the inhibition time of the conventional underwater UWSN (underwater wireless sensor network) routing to a received package is avoided, and the time delay from terminal to terminal is reduced. A great deal of simulation experiments prove that through an underwater sensor network adaptive routing protocol based on the difference, the energy consumption can be reduced to a great extent, the time delay from terminal to terminal is reduced, the node utilization equity is improved, and the whole network life time is prolonged.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV +1
Tri-dimensional positioning method for underwater wireless sensor network node
InactiveCN101483818AImprove effectivenessSmall random noiseNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionControl communicationsComputer science
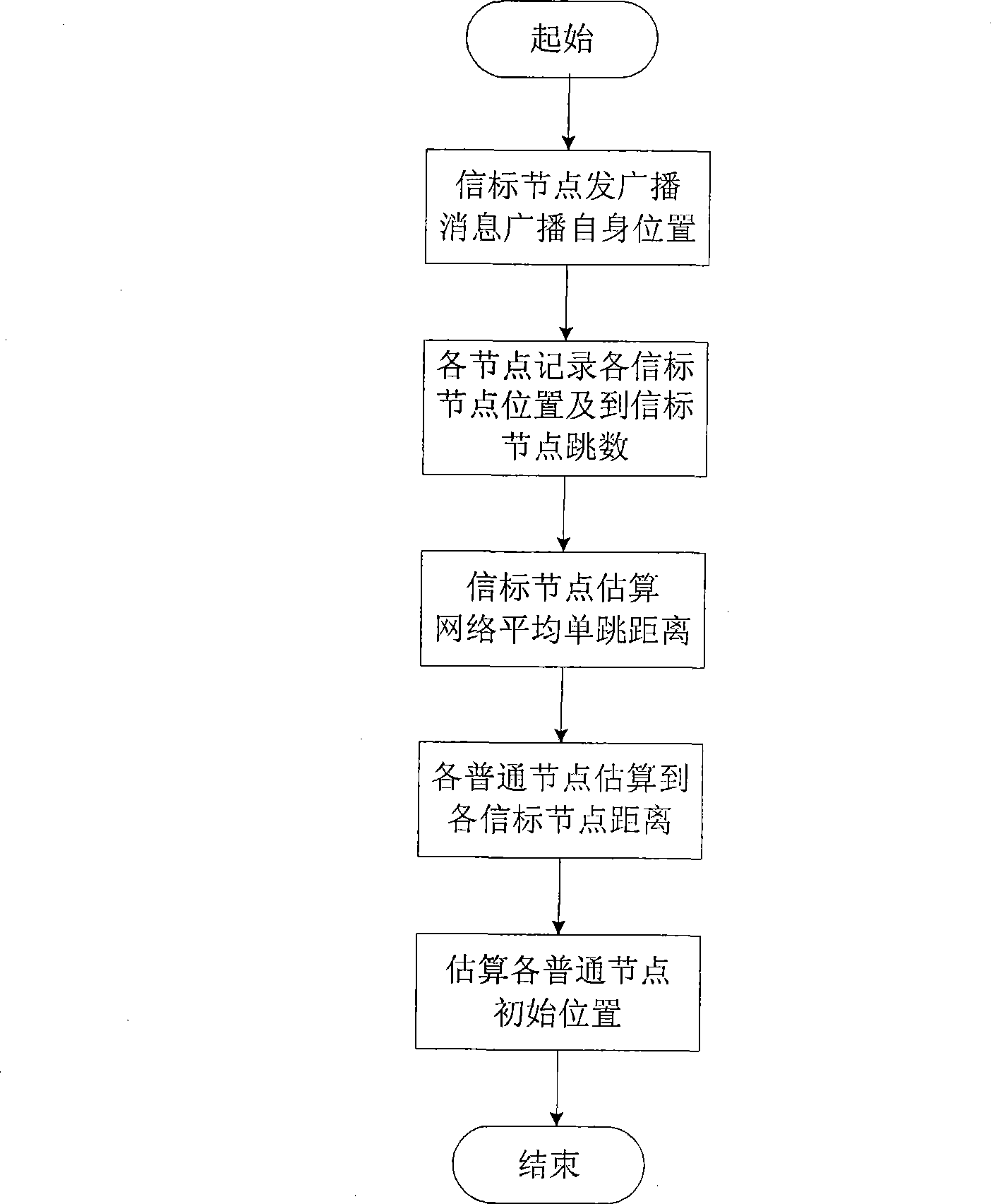
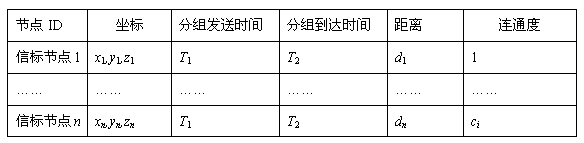
The invention provides a three dimensional locating method of underwater wireless sensor network nodes; first, the coordinates of each beaconing node is obtained and then the coordinates of each general node is assured. The coordinates of each general node is assured as followed, the three dimensional locating work of the coordinate of each general node is equivalently turned into two dimensional location; the general node makes use of distance vector arithmetic and the two dimensional coordinates of the beaconing node to the initial two dimensional coordinates; the two dimensional coordinates of adjacent node is used to iterate and update the two dimensional coordinate of the node till the coordinates is converged to actual two dimensional positions; at last the relation between the depth of water and the intensity of pressure are used to get the depth of water of general node. The method adopts certain message transmitting and iterating control mechanism to reduce the locating error to the lowest in the condition of effectively controlling communication overhead.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Two-stage isomerism clustering underwater wireless sensor network and routing method thereof
InactiveCN104010336AReduce energy consumptionProlong survival timeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementRemote controlIsomerisms
The invention discloses a two-stage isomerism clustering underwater wireless sensor network and a routing method of the underwater wireless sensor network. The two-stage isomerism clustering underwater wireless sensor network comprises upper-layer sensor nodes, lower-layer sensor nodes, an offshore sink node and a base station on land. All the sensor nodes in a monitoring region of the underwater wireless sensor network form a two-stage isomerism clustering structure. The lower-layer sensor nodes form first-stage clusters and first-stage cluster head nodes. The upper-layer sensor nodes form second-stage clusters and a dynamic cluster head chain. Second-stage cluster head nodes transmit data to the offshore sink node through the dynamic cluster head chain. The offshore sink node is in direct wireless communication with the base station on land, and then the base station transmits the data to a remote control center. Through the method, average energy consumption of the nodes can be effectively reduced, the survival time of the network can be prolonged, and the underwater wireless sensor network is suitable for monitoring an underwater application environment with numerous nodes, high in expandability, more balanced in node energy consumption and suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Underwater sensor network positioning method
InactiveCN102695126APositioning appliesNetwork topologiesLocation information based serviceUnderwater sensor networksEstimation methods
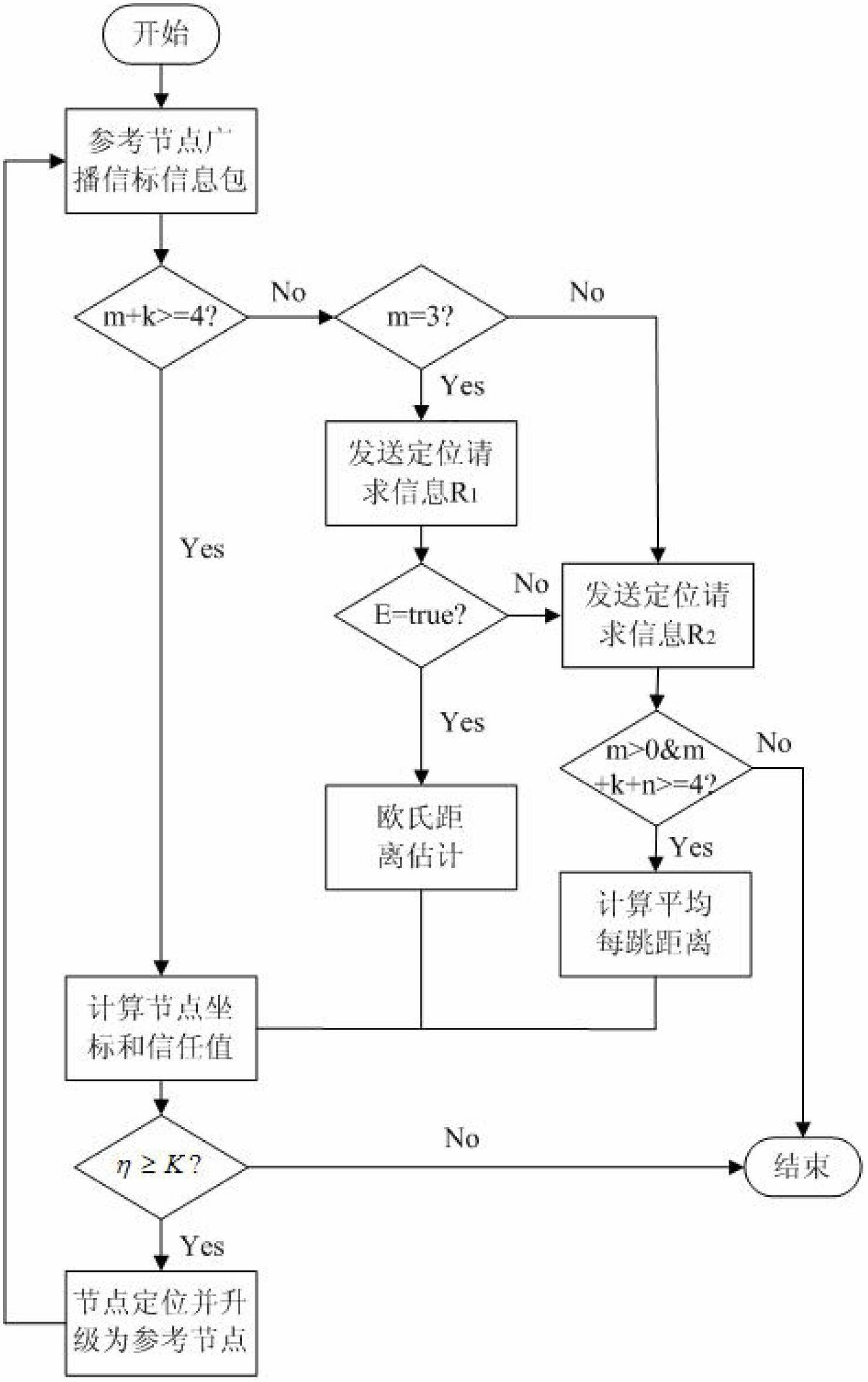
The invention discloses an underwater sensor network positioning method, which integrates a three-dimensional Euclidean distance estimation method, an iterative position estimation method and a DV-Hop algorithm, and for completing the positioning of common nodes, gives selection criteria of one-hop upgrade reference nodes, two-hop upgrade reference nodes and next-hop upgrade reference nodes for forwarding positioning request information packets. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the distance between a common node and a two-hop upgrade reference node by using the three-dimensional Euclidean distance estimation method and the DV-Hop algorithm, after the coordinates of the node are calculated by using a four-edge measurement method, calculating a positioning error and a trust value according to the coordinates and the distance between the node and a reference node, comparing the magnitude relation of the trust value and a threshold value, and determining whether the node is positioned successfully and becomes an upgraded reference node; and the iterative position estimation method is used for broadcasting a beacon information packet containing the position of a common node after the common node is positioned successfully, and assisting the positioning of other common nodes. The method disclosed by the invention is applicable to the static or dynamic positioning of nodes in large-scale underwater wireless sensor networks.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
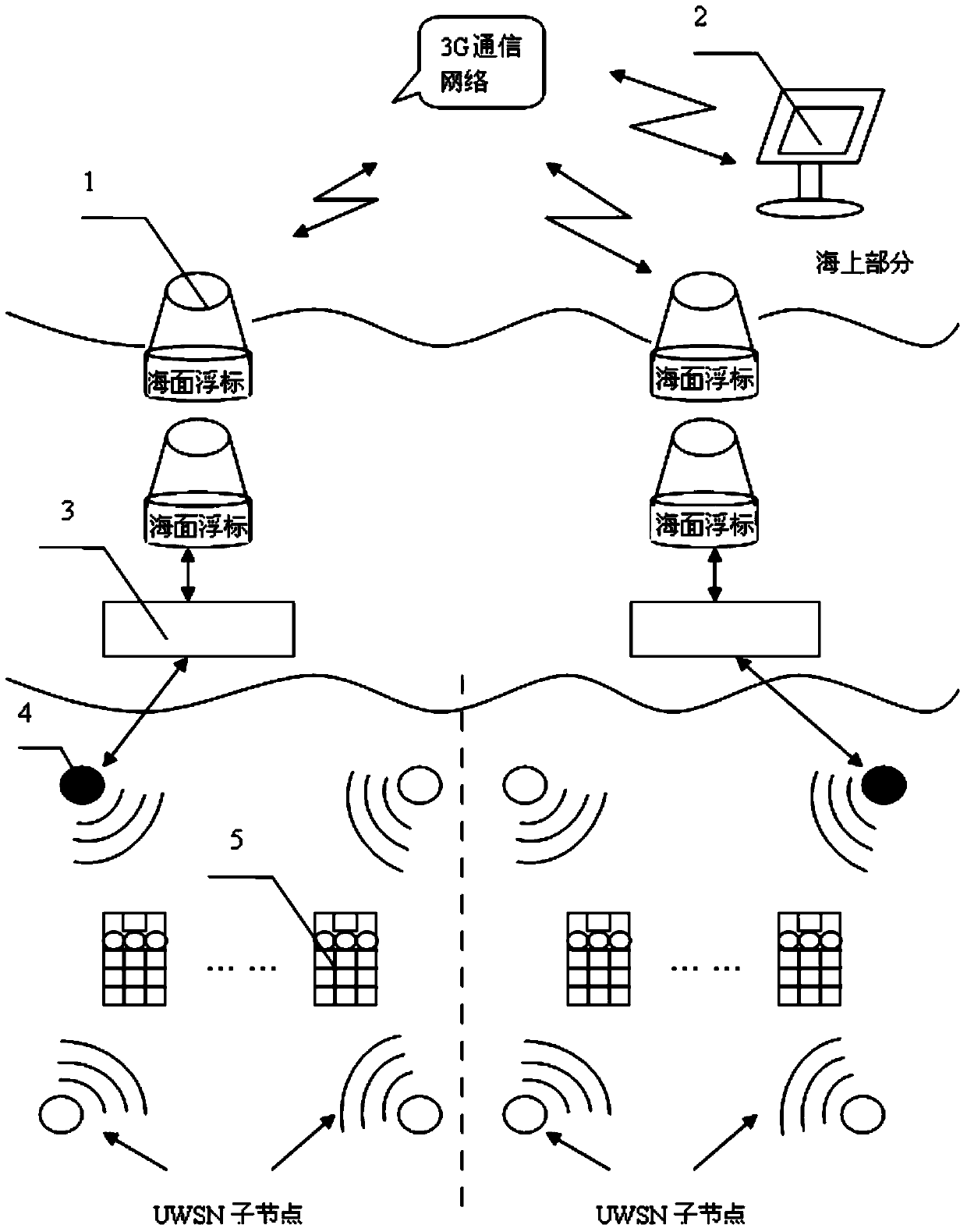
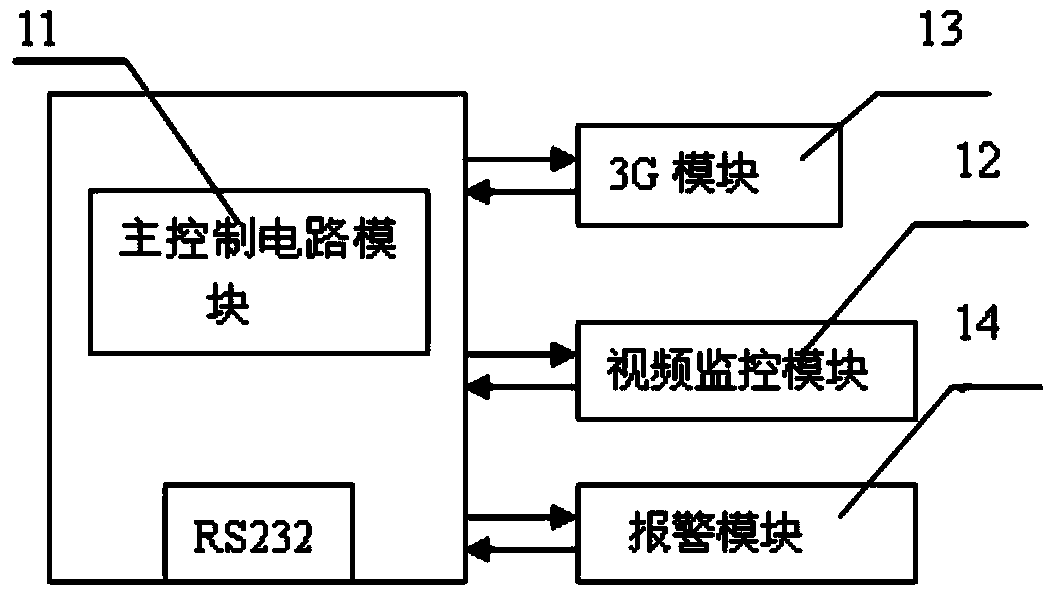
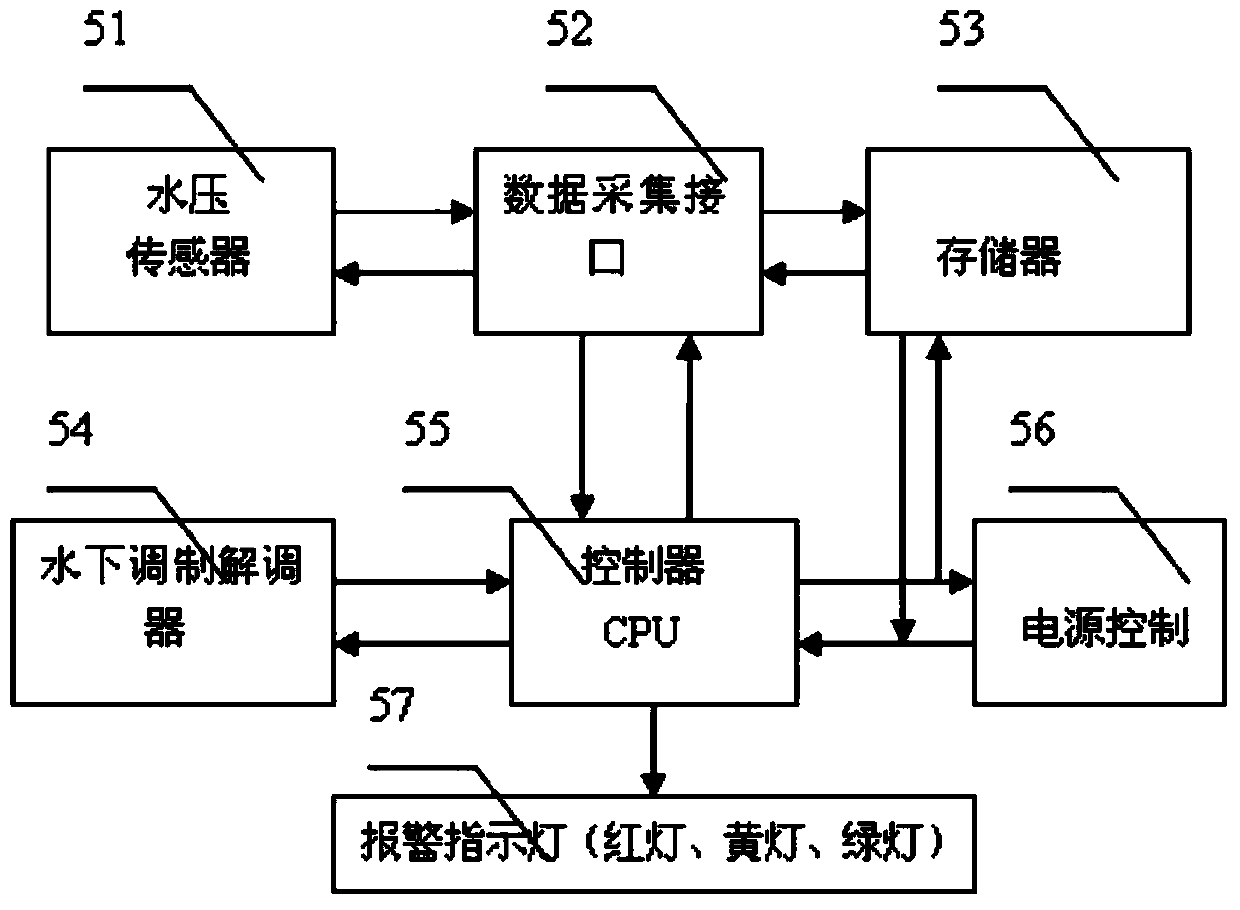
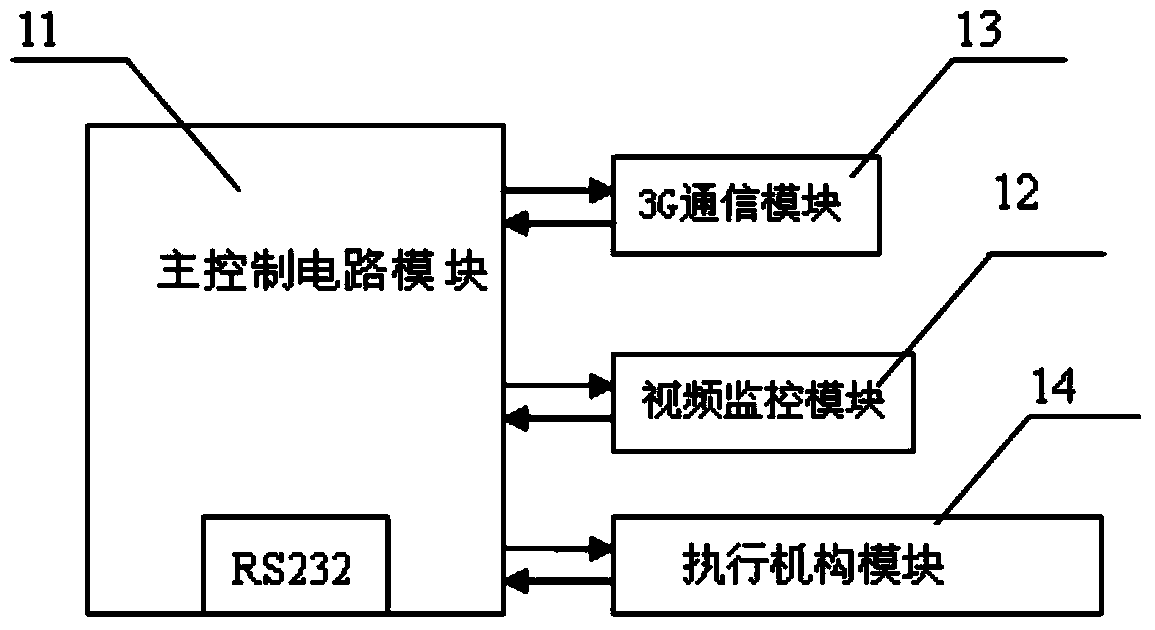
Positioning survival alarm system for bathing beach personnel
InactiveCN103634570ASolve precise positioningTimely rescueLife-buoysClosed circuit television systemsBathing BeachesWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a positioning survival alarm system for bathing beach personnel. The positioning survival alarm system comprises a water data transmission and alarm device, a remote monitor terminal device, an underwater sound communication device, an underwater wireless sensor network target positioning device and an underwater personnel survival device. By using the characteristics of the underwater wireless sensor network (UWSN), the positioning survival alarm system solves the problem of the precise positioning for the bathing beach personnel, a person not in the state of drowning can manually open the alarm device under special conditions, if the person is in the state of drowning, the alarm device can be automatically turned on according to the monitored water pressure parameter values through a water pressure sensor, so a signal is sent to seek help, and a monitoring center determines the position of the drowning person and rescues the person. An air sac device is arranged in the survival device and can be automatically opened during the dangerous condition, so the person can float on water.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mobile deep sea cultivation monitoring system
InactiveCN103491148ARealize mobile dynamic monitoringSolve data transmissionTransmissionTotal factory controlThird generationDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses a mobile deep sea cultivation monitoring system. The mobile deep sea cultivation monitoring system comprises a main control circuit terminal, an underwater acoustic communication module, a remote main monitoring center terminal, a remoter 3G mobile phone monitoring terminal, an underwater wireless sensor network positioning module and an underwater mobile monitoring terminal. According to the mobile deep sea cultivation monitoring system, the characteristics of an underwater vehicle are adopted, mobile dynamic monitoring of environmental parameters can be achieved, and the defect that fixed point monitoring in a fixed point area can only be achieved in a traditional mode is overcome. The mobile deep sea cultivation monitoring system not only can achieve environmental parameter monitoring in a seawater upper surface but also can achieve environmental parameter monitoring in a deep sea area of a cultivation area through an underwater mobile monitoring platform. The 3G communication technology and the UWSN technology are combined, and the data transmission problem between a seaborne remote monitoring terminal and the underwater mobile monitoring platform is solved. An automatic way-finding function of the underwater vehicle uses the positioning function of a UWSN, and the underwater mobile monitoring platform can be accurately positioned.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle)-assisted based underwater wireless sensor network positioning method
InactiveCN102869090AHigh positioning accuracyReduce consumptionNetwork topologiesEmbedded systemUnderwater wireless sensor networks
The invention discloses an AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle)-assisted based underwater wireless sensor network positioning method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out primary positioning on an unknown node by using a centroiding algorithm; estimating the positioning accuracy of the unknown node according to the number of beacon nodes around the unknown node, the distribution of the beacon nodes and the distance between each beacon node and the unknown node; screening out a plurality of nodes with a low positioning accuracy; and carrying out secondary positioning on the nodes by using an AUV. The method disclosed by the invention is less in calculation and communication consumption, and can fully use the AUV to improve the positioning accuracy of nodes and reduce the positioning errors, therefore, the method is applicable to the positioning of the unknown nodes of underwater wireless sensor networks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Distributed underwater network localization method based on mobile beacon
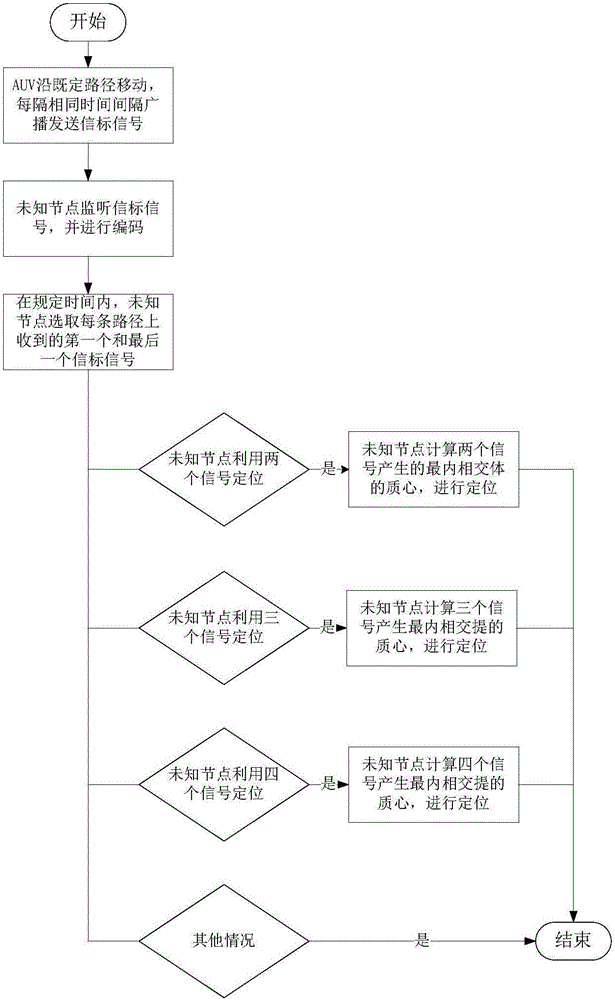
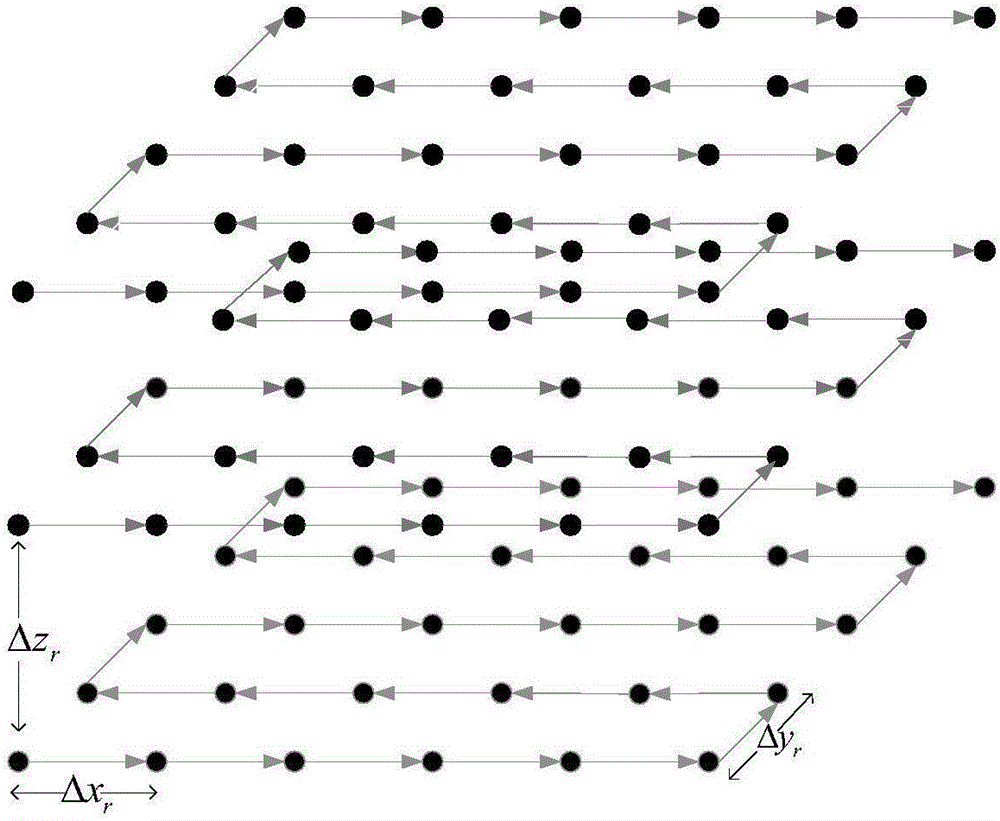
ActiveCN106028278AReduce consumptionImprove real-time performanceLocation information based serviceNetwork planningUnderwater networkUnderwater wireless sensor networks
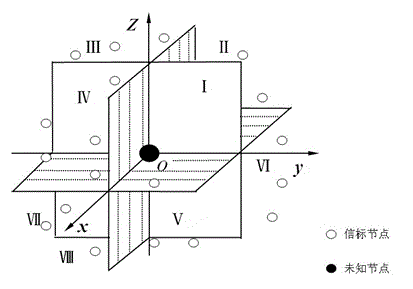
The invention discloses a distributed underwater network localization method based on a mobile beacon, and belongs to the technical field of an underwater wireless sensor network. The method comprises the steps that 1), an autonomous underwater vehicle AUV moves layer by layer and broadcasts and sends beacon signals at intervals of same time, and an unknown node encodes the signals according to the sequence of receiving the signals transmitted by the AUV; and 2), geometric models which are received by the unknown node in the signal coverage on adjacent paths are intersected to generate an innermost intersection body, and the mass center of the innermost intersection body is estimated as the location of the unknown node. The method is a three-dimensional distributed location method. The location of the unknown node is determined by calculating the mass center of the innermost intersection body. The experiment shows that the method has the advantages of relatively high node location accuracy and node location coverage.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Underwater multi-agent-oriented Q learning ant colony routing method
ActiveCN111065145AImprove convergence speedImprove robustnessNetwork topologiesEngineeringUnderwater wireless sensor networks
The invention provides an underwater multi-agent-oriented Q learning ant colony routing method, which is combined with reinforcement learning and ant colony algorithm to adapt to and learn characteristics of a dynamic underwater environment, and comprises the following steps of: a routing discovery stage, a routing maintenance stage and a routing hole processing mechanism. Pheromones in the ant colony algorithm are mapped into a Q value in Q learning. The delay and bandwidth of links and the residual energy and throughput of nodes are comprehensively considered as a Q value function to selecta next hop link. A routing protocol also realizes a hole sensing mechanism. ACK return time is recorded through node timing broadcast and a timer. Whether the nodes are in a routing holes are judged,and the network is prevented from using the nodes in the hole through a penalty function of Q learning. The energy and depth of the nodes and the link stability are considered, the end-to-end delay ofthe nodes is reduced through Q learning, the data delivery rate is increased, and the service life of the underwater wireless sensor network is prolonged.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Stable underwater communication node awakening signal detection method
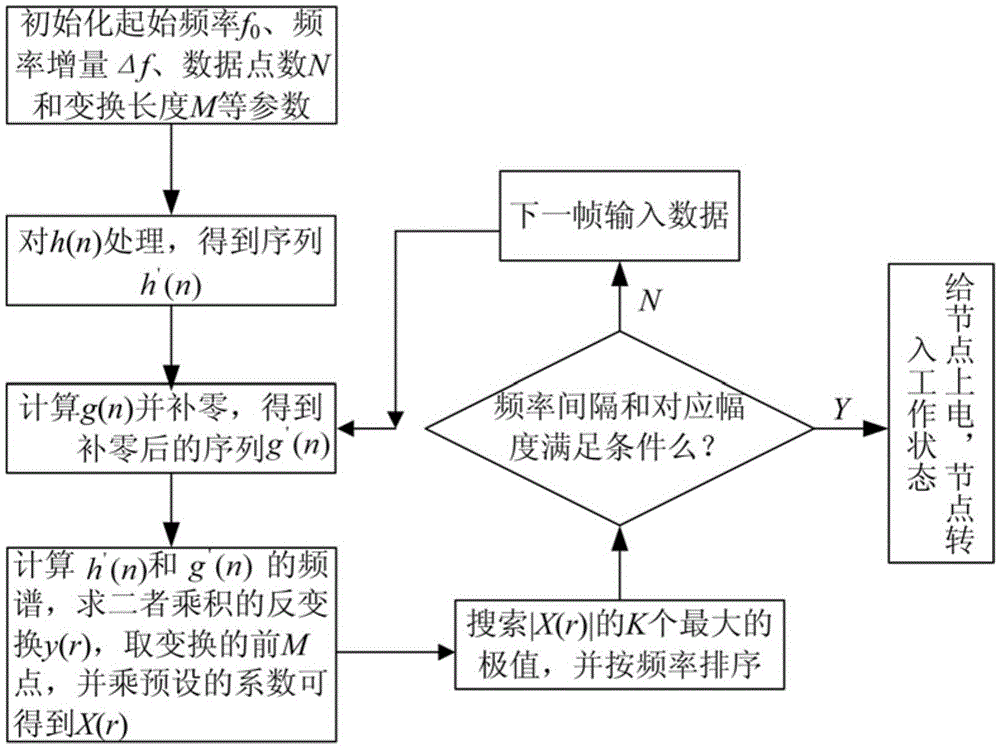
ActiveCN105472719AExtended service lifeHigh frequency resolutionPower managementTransmissionUnderwater wireless sensor networksFrequency interval
The invention discloses a stable underwater communication node awakening signal detection method. The stable underwater communication node awakening signal detection method comprises the following steps of: S1, emitting a dual-frequency or multi-frequency awakening signal; S2, according to a set initial frequency, transform point number and frequency resolution ratio, executing CZT (chirp z transform) on a unit circle on the awakening signal; S3, searching an extreme value of a zoom spectrum of CZT, judging a signal as the awakening signal if an estimated relative frequency interval and relative amplitude relationship between frequency components are kept unchanged, or judging the signal is not the awakening signal; and S4, after the signal is determined as the awakening signal, powering on an integral communication node to enable the node to be transferred into a working state, and when the node completes working, cutting off a power supply to enable the node to be transferred into a sleeping state. According to the stable underwater communication node awakening signal detection method disclosed by the invention, due to the high frequency resolution ratio, multiple groups of frequencies can be adopted for combination to awaken a plurality of nodes of an underwater sensor network without worrying about mutual interference, so that detection false-alarm is greatly reduced and a service life of the underwater wireless sensor network is prolonged.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Underwater wireless sensor network positioning method
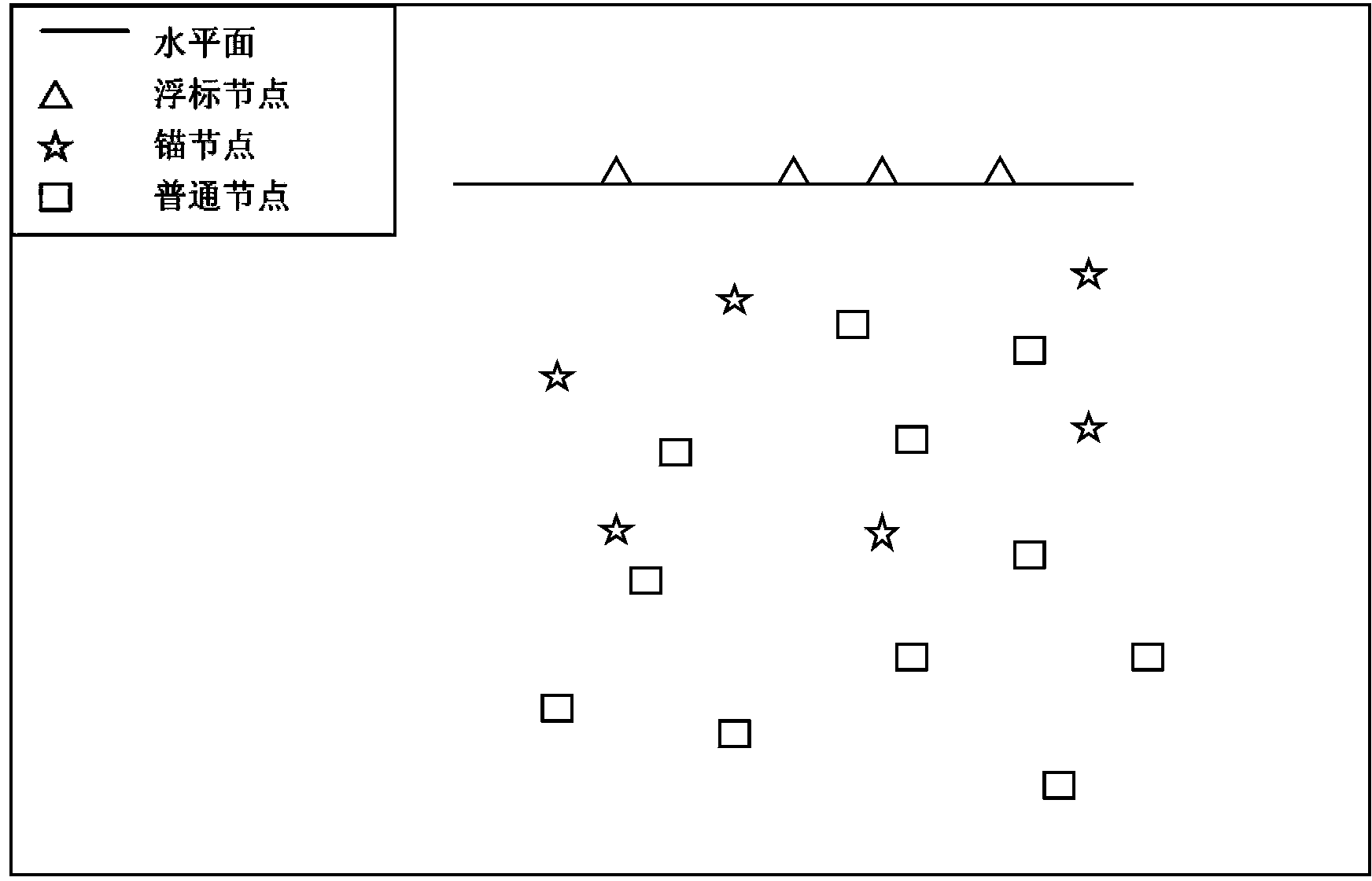
ActiveCN103415071AReduce the impact of failureIncrease coverageNetwork topologiesWireless sensor networkingBuoy
The invention provides an underwater wireless sensor network positioning method. A wireless sensor network comprises three types of nodes, namely buoy nodes, anchor nodes and ordinary nodes. The buoy nodes are satellite positioning nodes, the anchor nodes are in communication with the buoy nodes so that the anchor nodes can be positioned, and the anchor nodes and a part of positioned ordinary nodes constitute a reference node set. The ordinary nodes are in communication with the part of reference nodes in the reference node set so as to be positioned. When the anchor nodes are out of operation, the positioned ordinary nodes assist the ordinary nodes which can not be positioned to be positioned, positioning incapacity information does not need to be aggregated to a gateway, the ordinary node positioning problem is solved by itself in a region, thus, the positioning coverage rate is increased, and the node out-of-operation effect is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for positioning underwater wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102621522AAccurate measurementValid calibrationNetwork topologiesPosition fixationUnderwater wireless sensor networksReal-time computing
The invention relates to a method for positioning an underwater wireless sensor network, which belongs to the technical field of wireless sensor network positioning. The method includes: obtaining a primary estimation coordinate of an unknown node by means of primary weighted centroid algorithm according to a measured distance between a beacon node and the unknown node; and setting the weightiness according to the distance value to select a plurality of proper beacon nodes to obtain a secondary estimation coordinate of the unknown node by means of secondary weighted centroid algorithm, and finally determining the coordinate of the unknown node. The method is low in calculation complexity, positioning accuracy is improved, estimation errors are reduced, and the method is applicable to positioning of underwater wireless sensor networks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
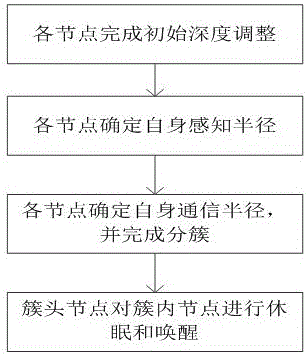
Novel underwater wireless sensor network point coverage control method
InactiveCN106028357ACheap methodSimple methodPower managementNetwork topologiesCoverage ratioCoverage control
The invention relates to a novel underwater wireless sensor network point coverage control method. In the method, node depth adjustment is taken as a feasible mobile mode. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, nodes determine depths of the nodes in reference to a distance between a Sink node and a water surface vertex and the depth of a monitoring water area; secondly, the nodes determine perception radiuses of the nodes according to a distance between the Sink node and a water bottom vertex in reference to a minimum perception radius and a maximum perception radius; thirdly, communication radiuses of the nodes are increased greatly till neighbor nodes with smaller depths are inquired, and a node with a smallest coverage target quantity is selected from a set of the nodes to take the selected node as a cluster head; and lastly, a cluster head node makes inner-cluster nodes hibernate and wake up. Compared with an existing relevant method, the method disclosed by the invention is more feasible. Moreover, indexes such as network coverage, a communication rate, energy consumption and balance, and a network life cycle can be optimized comprehensively.
Owner:柴俊沙
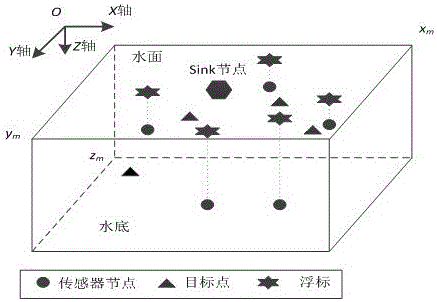
Underwater wireless sensor network cover control method based on surface even allocation
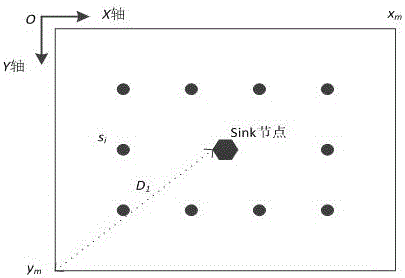
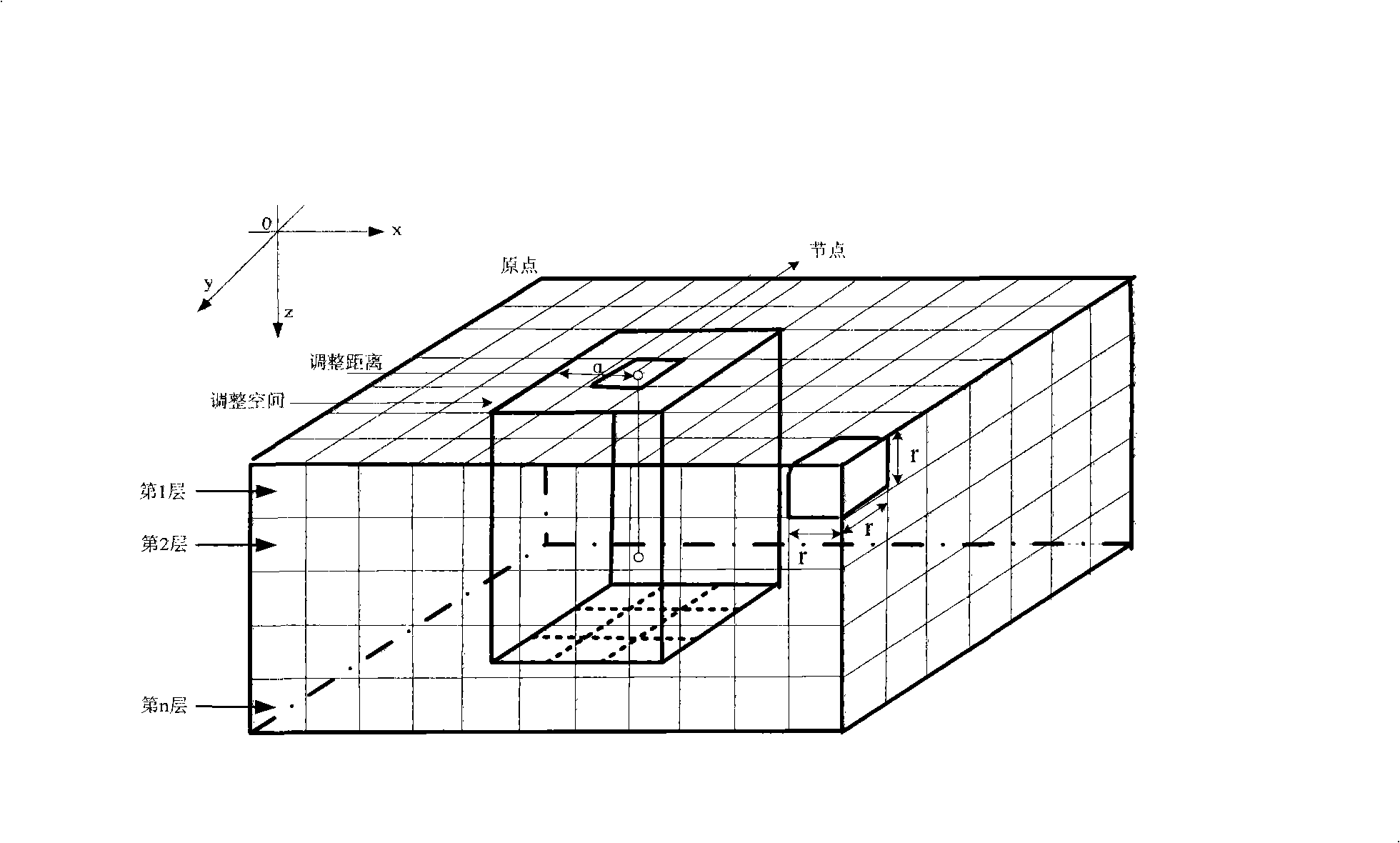
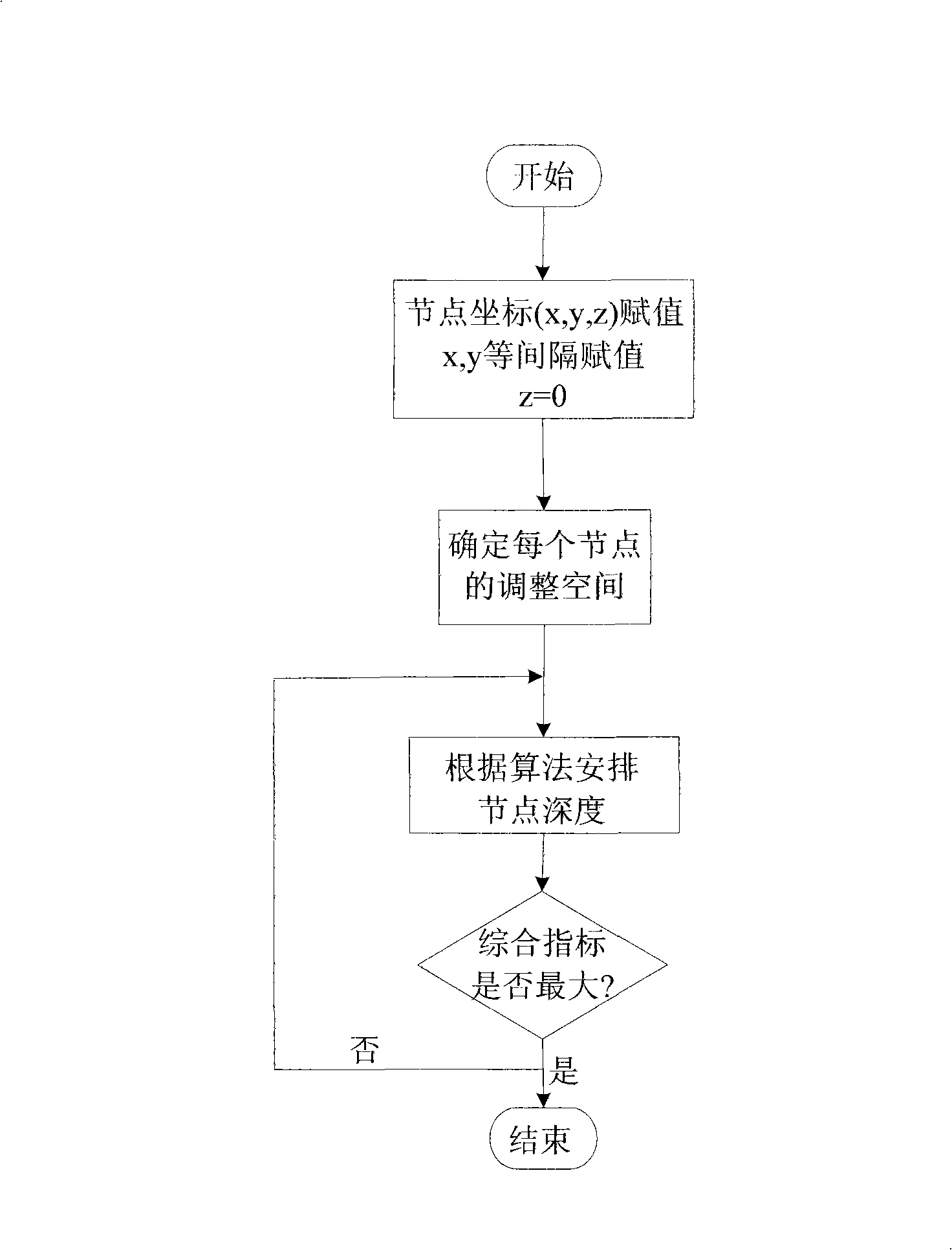
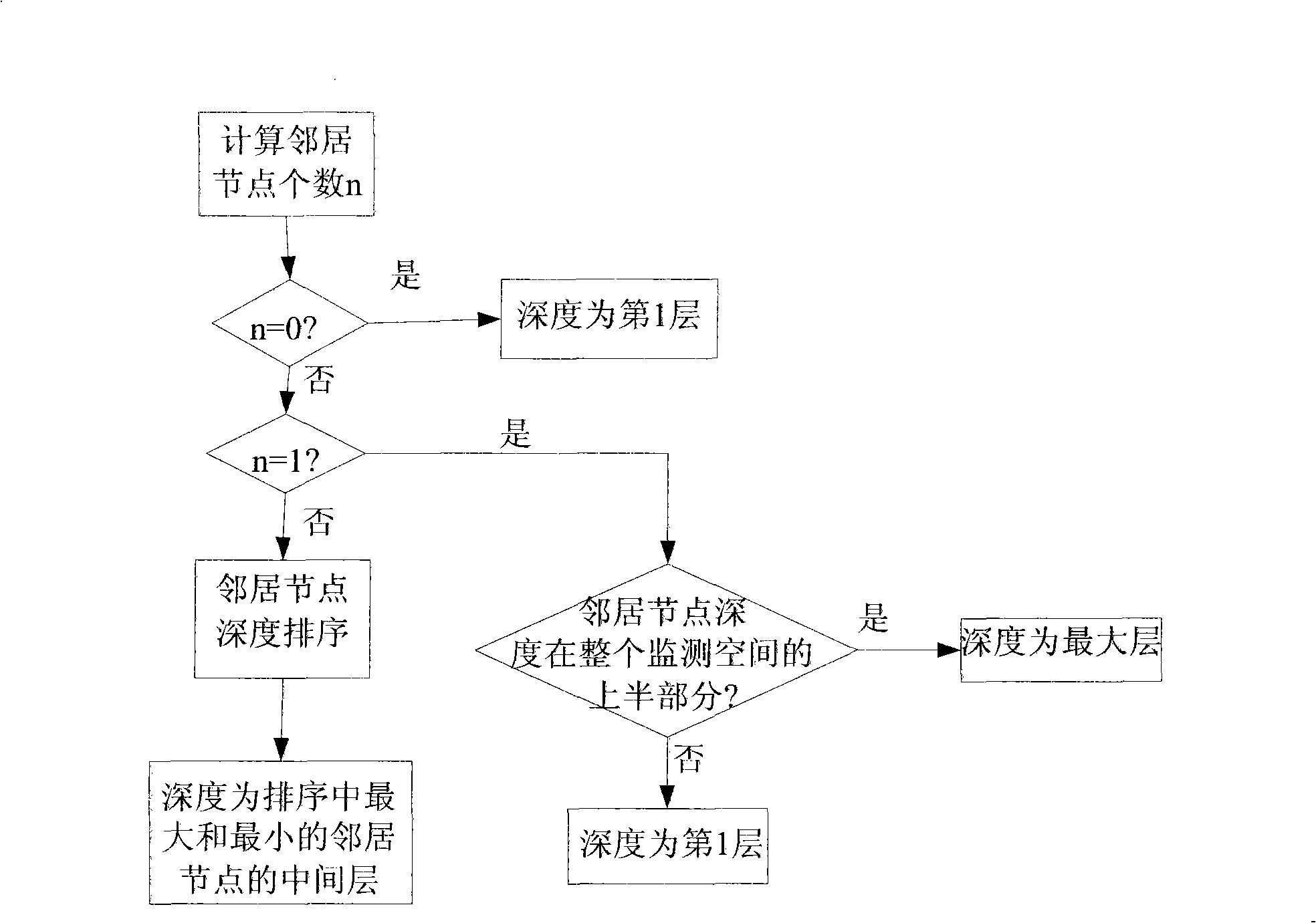
ActiveCN101257424AComprehensive index maximizationData switching by path configurationOpen water surveyMonitoring systemWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a method for controlling network coverage of a three-dimension underwater wireless sensor to solve the default of the prior control method. The method of the invention includes: evenly arranging sensor node array on a horizontal plane of the water area to be monitored and determining the three-dimension coordinate of each node in the array; determining the range of the adjusting space of each node based on the value of the adjusting distance; determining the adjusting depth of the node according to the number and depth of adjacent sensor nodes within the adjusting space of each sensor node; calculating the aggregative indicator value, which is weighting combined by a coverage degree and mean distance, based on the depth of each node so as to define the adjusting depth of each sensor node corresponding to the maximum aggregative indicator value as the final depth of the sensor node. The method of the invention is applicable for wetland aquatic environment real time monitoring system based on the wireless sensor network, and the maximum coverage of the three-dimension monitoring water area is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENXIANG ELECTROMECHANICAL
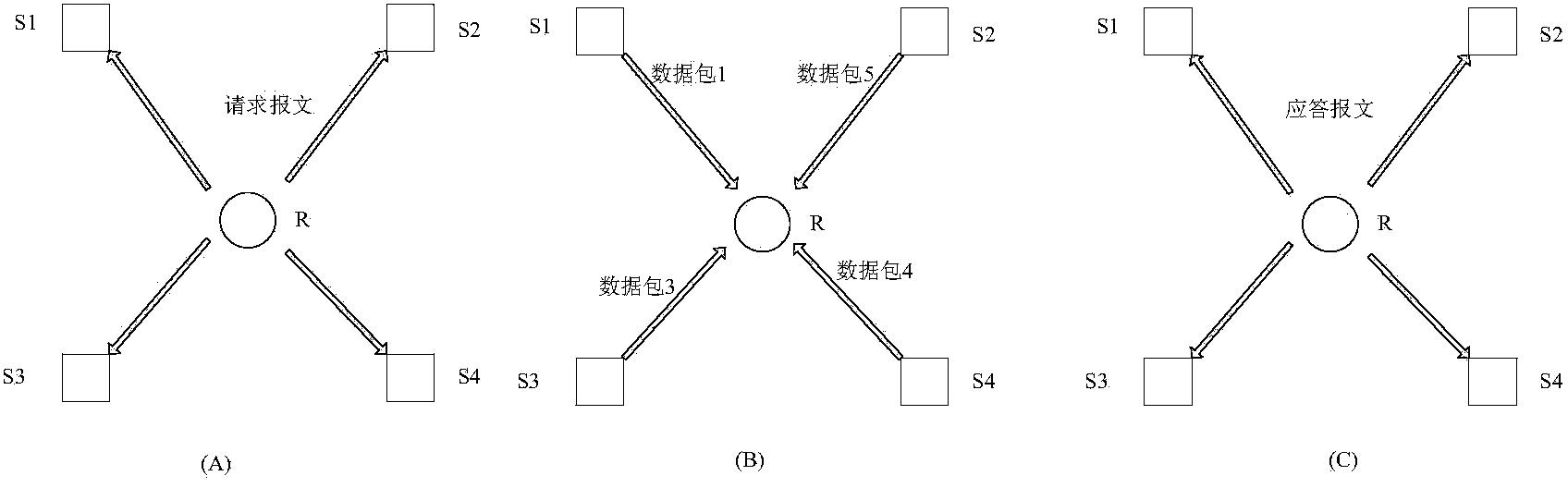
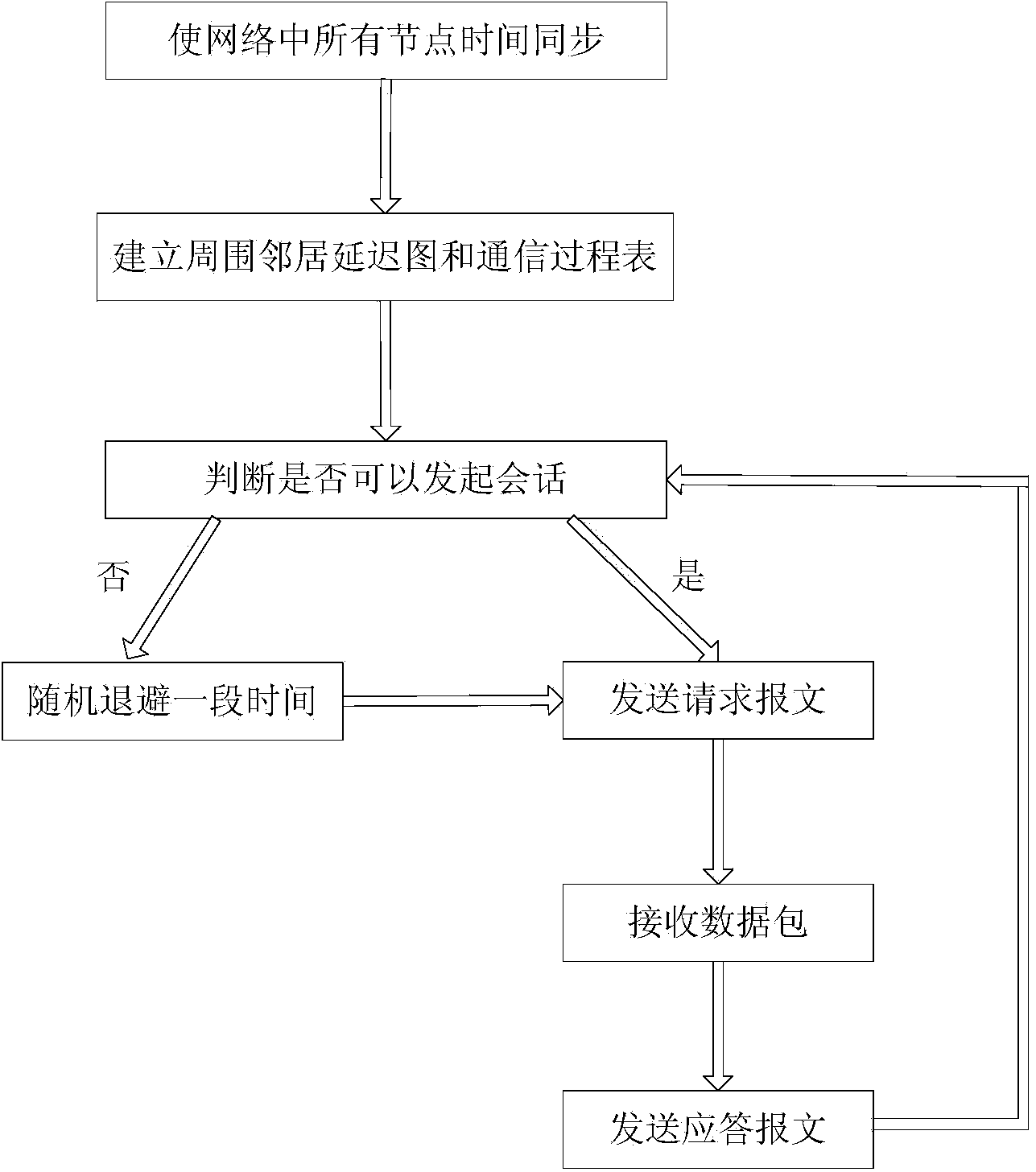
Media access control method and system suitable for underwater wireless sensor network
ActiveCN104080122AReduce the ratioCutting costsNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsNetwork packetMedia access control
The invention discloses a media access control method and system suitable for an underwater wireless sensor network. The method comprises the steps of enabling time of all nodes in the underwater wireless sensor network to be synchronized, enabling receiving nodes to establish delay diagrams and communication process tables of peripheral neighbor node by monitoring communication packets of the peripheral neighbor nodes, judging whether collision can be generated by launching dialogs according to the delay diagrams and the communication process tables, launching dialogs if no collision can be generated, calculating out residual bandwidth of the peripheral neighbor nodes and the time slot number distributed to the peripheral neighbor nodes, sending request message to the peripheral neighbor nodes through the receiving nodes according to the content requirements of control packets, sending data packets to the receiving nodes through the peripheral neighbor nodes according to the content of the request message, and broadcasting and sending response message to the peripheral neighbor nodes after the receiving nodes receive the data packets. According to the media access control method and system suitable for the underwater wireless sensor network, a protocol can reduce the cost for controlling data packets, the space-time multiplex ratio of channels is improved, the utilization rate of the channels is improved, and the communication efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
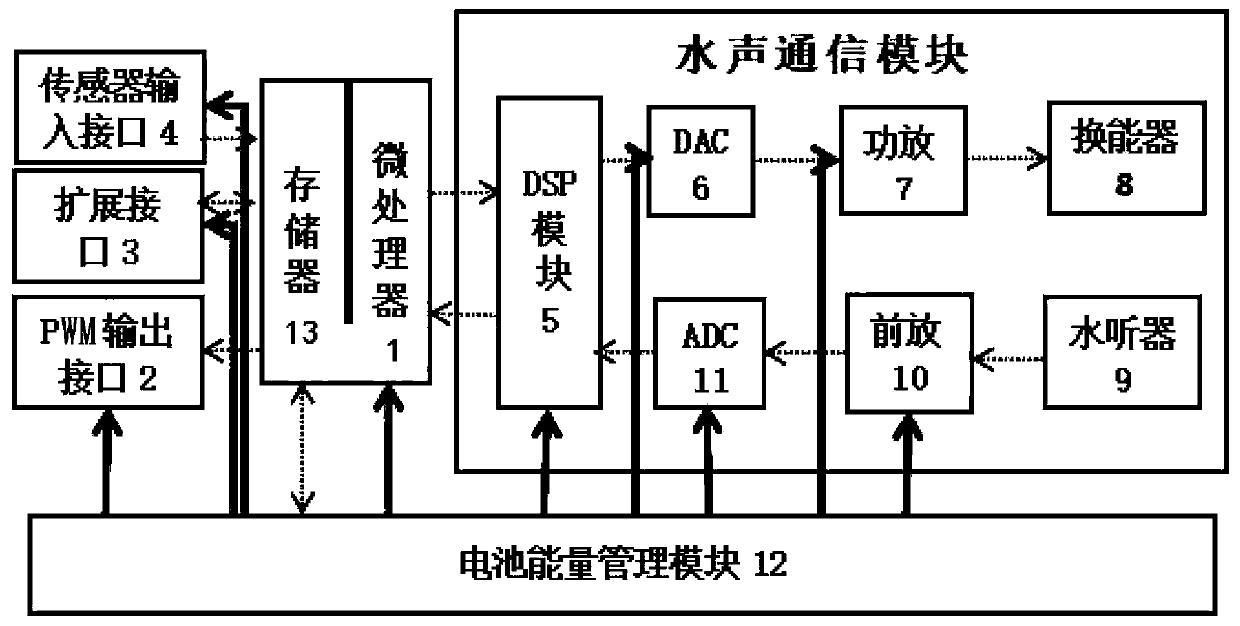
Underwater acoustic communication module and method and underwater wireless sensor network node device
InactiveCN109743117ARealize the function of cross-layer underwater acoustic communicationSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionNetwork topologiesSonificationUltrasonic sensor
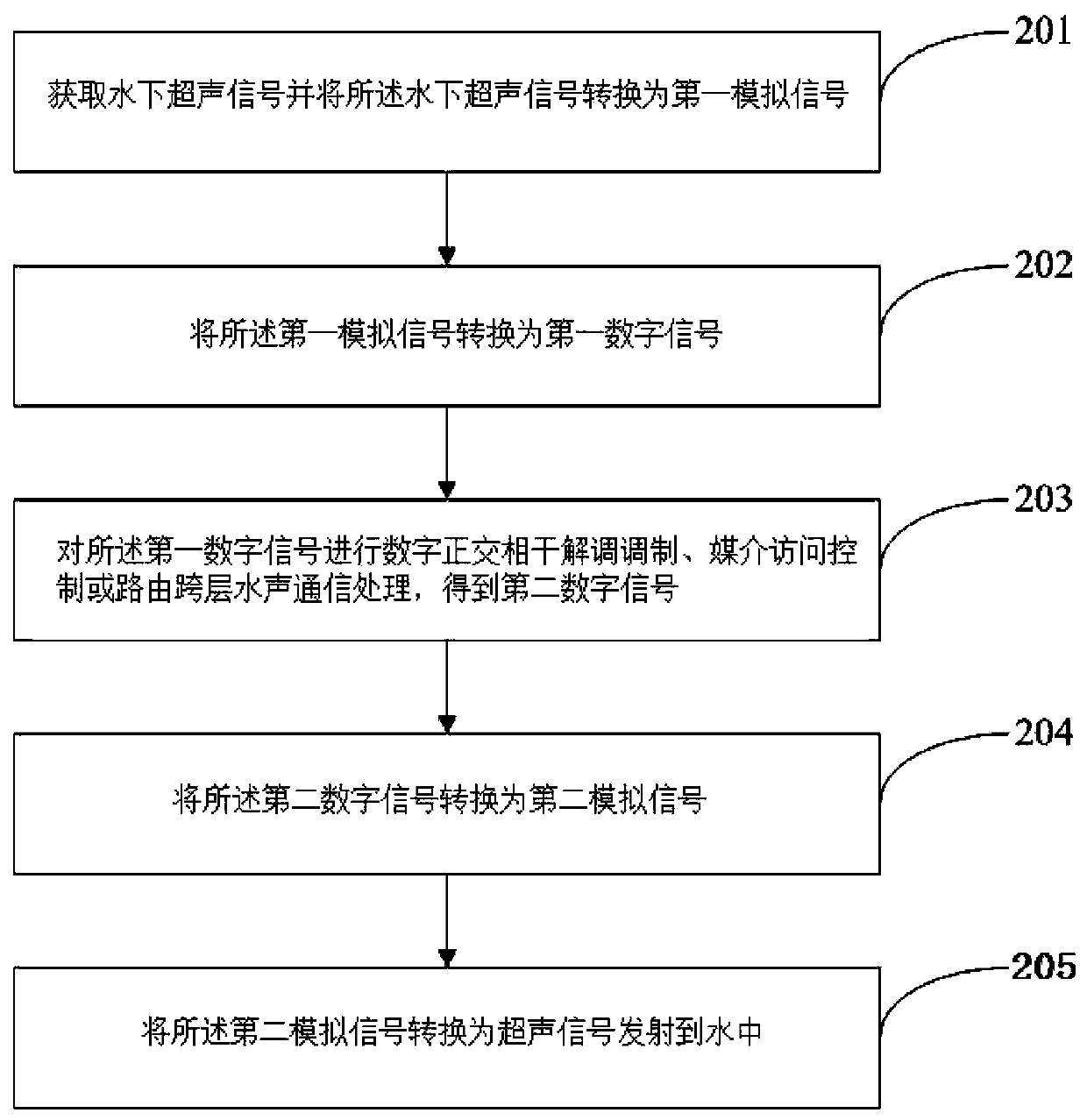
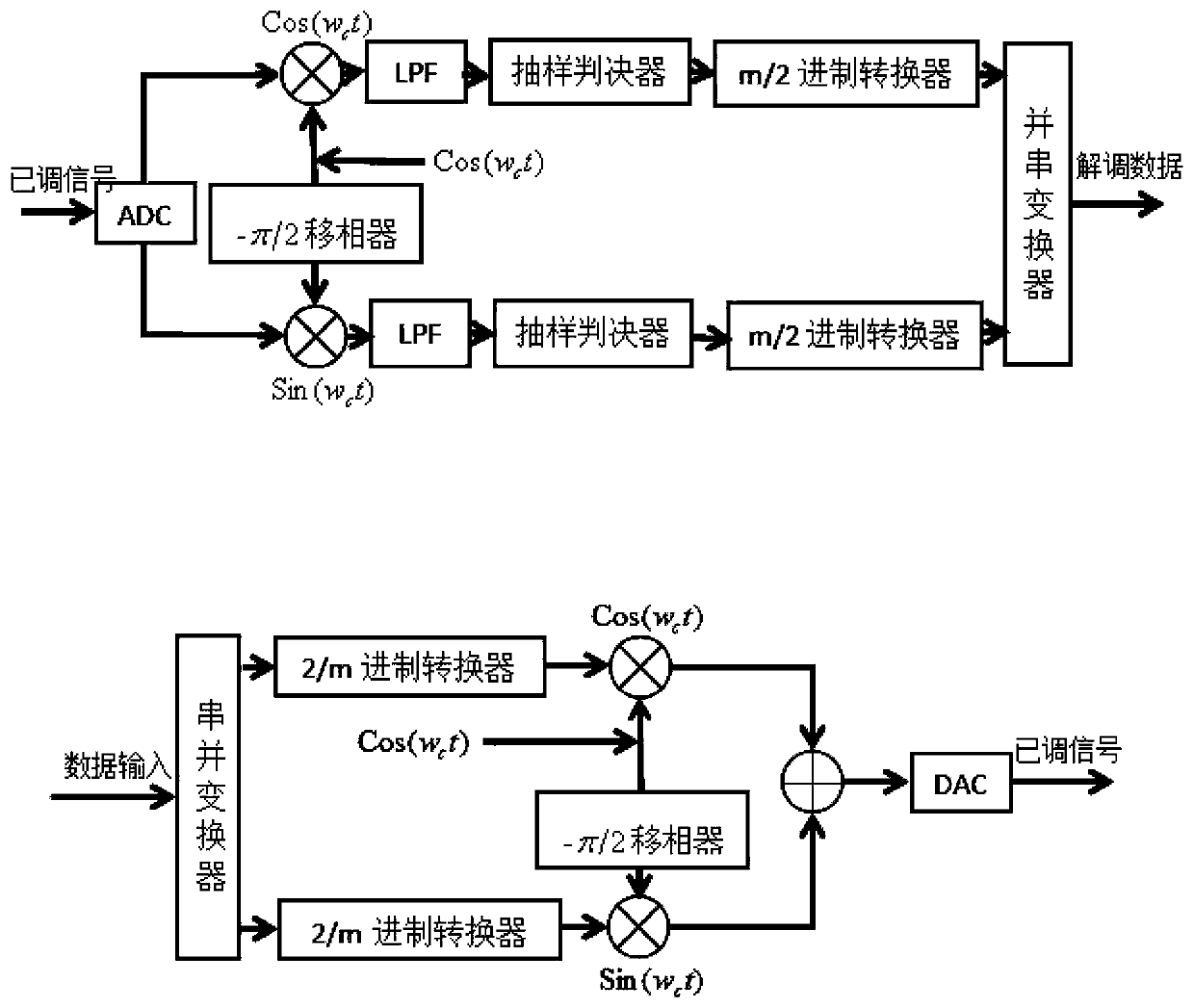
The invention discloses an underwater acoustic communication module and method and an underwater wireless sensor network node device. The underwater acoustic communication module comprises a digital signal processor, a digital-to-analog converter, an analog-to-digital converter, an ultrasonic transducer and a hydrophone. The hydrophone is used for acquiring an underwater ultrasonic signal and converting the underwater ultrasonic signal into a first analog signal; the analog-to-digital converter is used for converting a first analog signal into a first digital signal, and the digital signal processor is used for performing digital orthogonal coherent demodulation modulation, medium access control or routing cross-layer underwater acoustic communication processing on the first digital signalto obtain a second digital signal; The digital-to-analog converter is used for converting the second digital signal into a second analog signal; And the ultrasonic transducer is used for converting the second analog signal into an ultrasonic signal and transmitting the ultrasonic signal into water. According to the underwater acoustic communication module, the underwater acoustic communication method and the underwater wireless sensor network node device, a cross-layer underwater acoustic communication function can be realized without a complex hardware circuit.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF HUMANITIES SCI & TECH
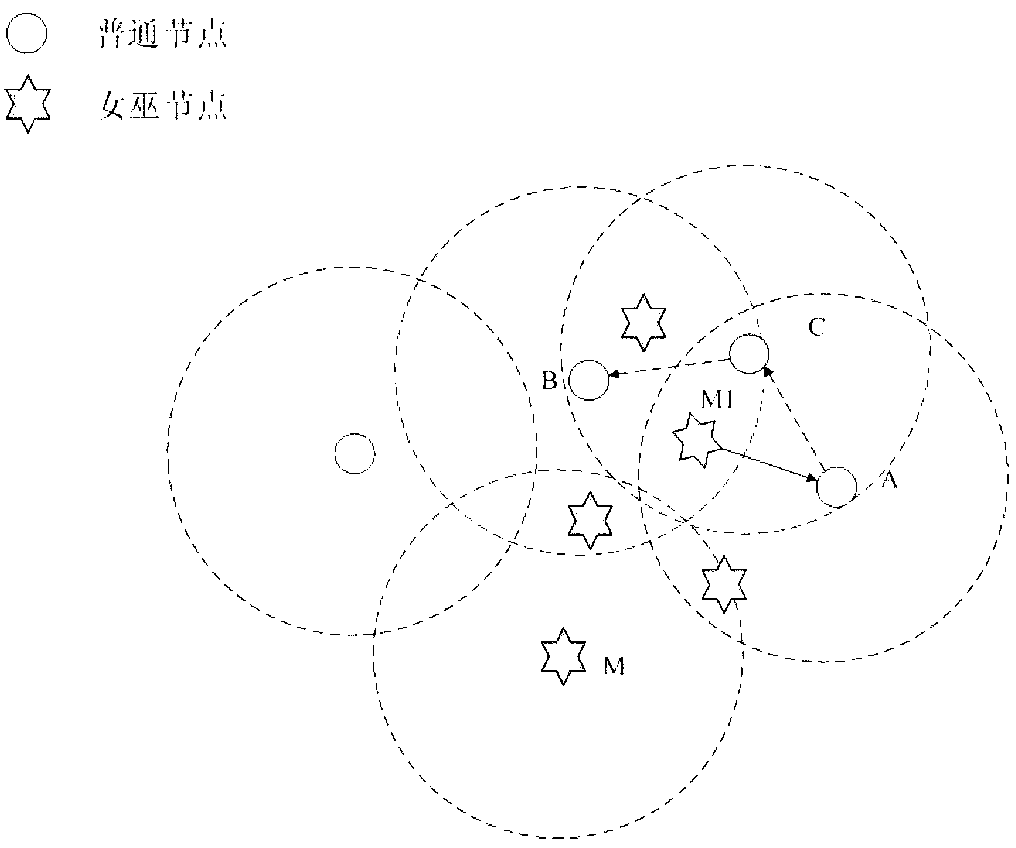
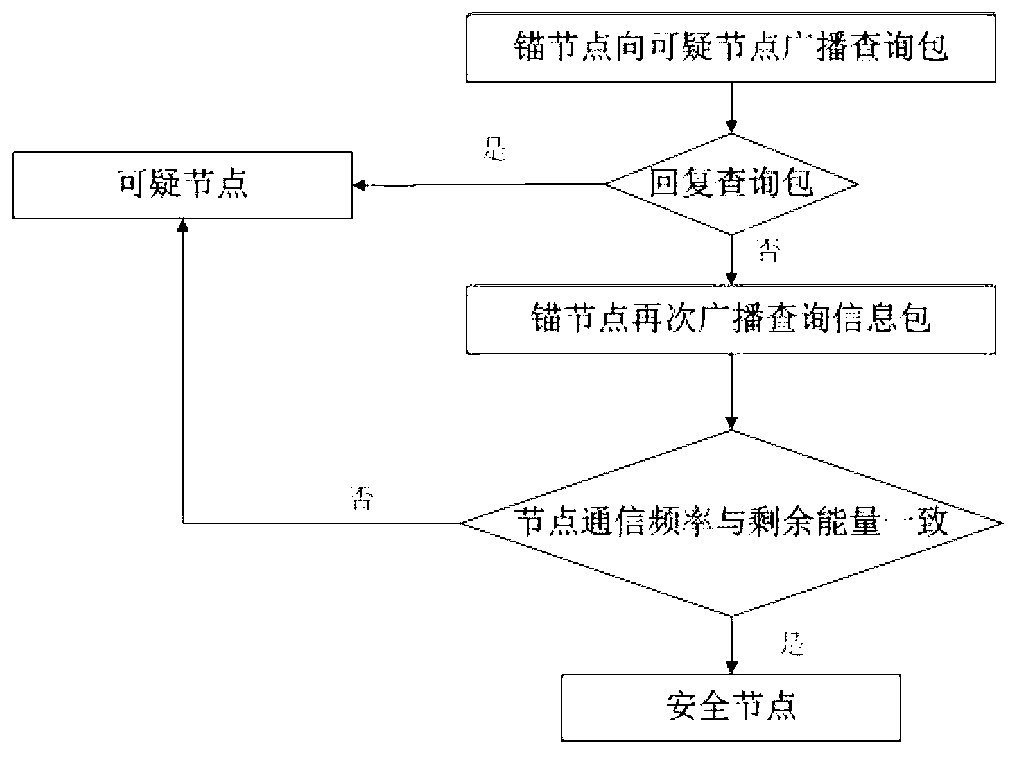
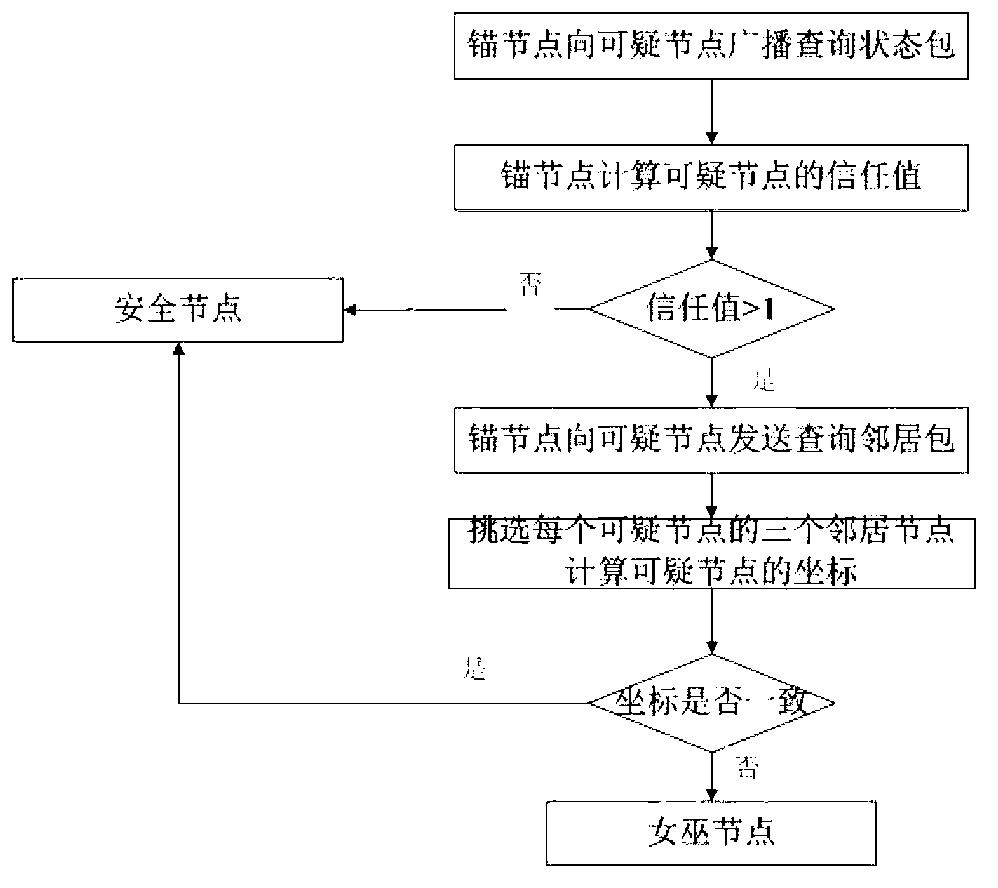
Method for detecting Sybil attack in underwater wireless sensor networks
ActiveCN103297973AEfficient detectionEnsure safetyNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementUnderwater sensor networksUnderwater wireless sensor networks
The invention relates to a method for detecting Sybil attack in underwater wireless sensor networks. The method includes three steps: by the aid of anchor nodes, (1) identifying suspicious nodes: identifying the suspicious nodes in the networks according to received information packets; (2) determining Sybil nodes: calculating state evaluation values of the suspicious nodes and determining the Sybil nodes by means of comparing with position information of the suspicious nodes; (3) separating the Sybil nodes: reporting the Sybil nodes to base stations which delete the Sybil nodes from the networks. The method has the advantages that hostile Sybil attack can be effectively detected, safety of the networks can be guaranteed, and hardware conditions for the nodes neither are limited strictly nor limited by specific information or specific nodes and have good expansibility.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
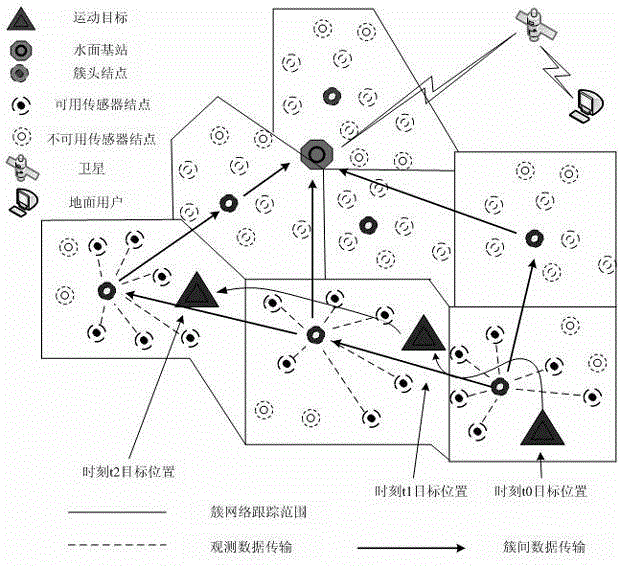
Target tracking method based on underwater wireless sensor network
InactiveCN103152791AImprove object tracking performanceWireless communicationPresent momentObservation data
The invention discloses a target tracking method based on an underwater wireless sensor network. The method selects cluster head nodes according to a strongest signal principle at first. Then, a cluster network is formed according to single hop distance principle to observe a target. If observation signal strength exceeds a threshold value, observation data are sent to cluster head nodes. The cluster head nodes receive the data which are transmitted by thick internal nodes. A resampling particle filtering algorithm is utilized to estimate a target position and variance at present moment. The cluster head nodes are constantly updated according to target movements. A node state estimating value and a variance value of a previous cluster head node are transmitted to a present cluster head node. The present cluster head node estimates moving target positions through a modified resampling particle filtering algorithm until the moving target exceeds a tracking range of the underwater wireless sensor network. The target tracking method based on the underwater wireless sensor network can estimate the position and the variance of the underwater target by utilizing the filtering tracking method of the modified resampling particle algorithm. Target tracking property of the underwater wireless sensor network is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Underwater wireless sensor network topology control method based on balanced energy consumption
ActiveCN105764114ALoad balancingExtend the life cycleNetwork topologiesData switching networksBalancing networkWireless mesh network
The invention relates to an underwater wireless sensor network topology control method based on balanced energy consumption, belonging to the technical field of wireless sensor network. The underwater wireless sensor network topology control method includes the steps: utilizing a non-cooperative game theory to select nodes with higher residual energy from all the nodes as cluster heads to enable the energy consumption level of the whole network to achieve balance; adding the nodes which can receive a cluster head message into the cluster through a neighbor principle; for the nodes which cannot receive a cluster head signal, selecting reliable relay nodes and adding the reliable relay nodes into the cluster according to the principle of minimizing the energy consumption in the cluster; and preparing through a route of adjacent clusters, so that the whole network forms a tree-shaped structure to guarantee starting of a standby route when a link fails, wherein if some nodes fail, the network starts the maintenance process to perform networking again to guarantee normal operation of the network. The underwater wireless sensor network topology control method based on balanced energy consumption reduces communication and energy consumption in an underwater topology network structure, balances network energy consumption, and prolongs the network life cycle.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Energy consumption balancing and coverage keeping method for underwater wireless sensor network
InactiveCN108055683AGuaranteed coverageReduce energy consumptionPower managementNetwork topologiesCoverage ratioDecomposition
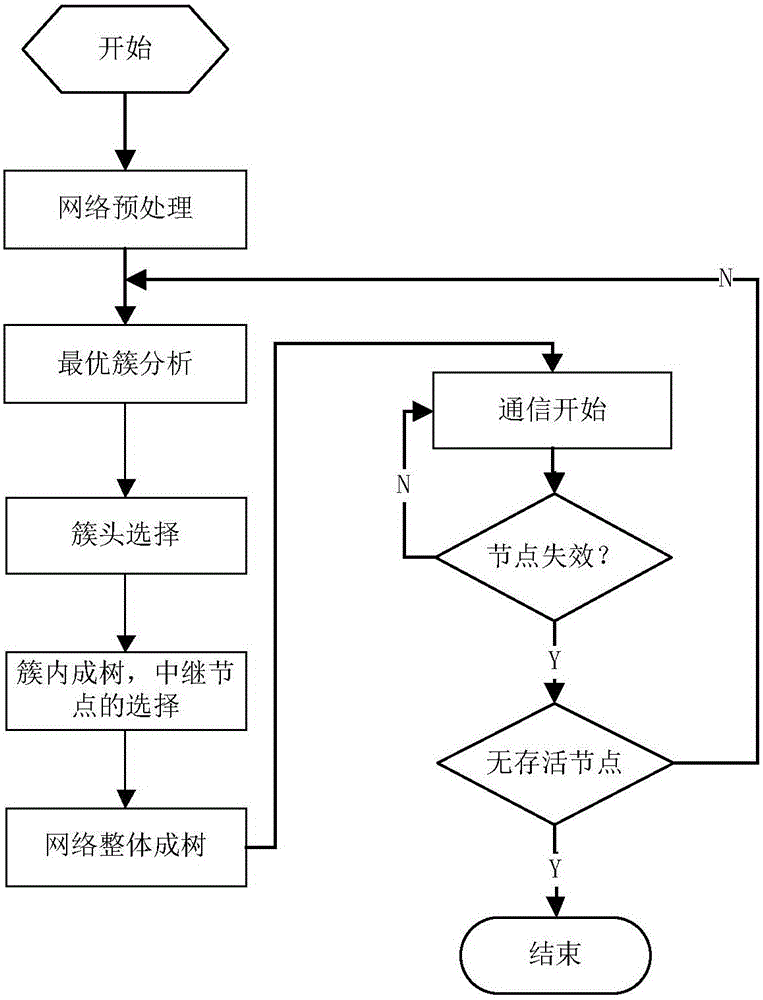
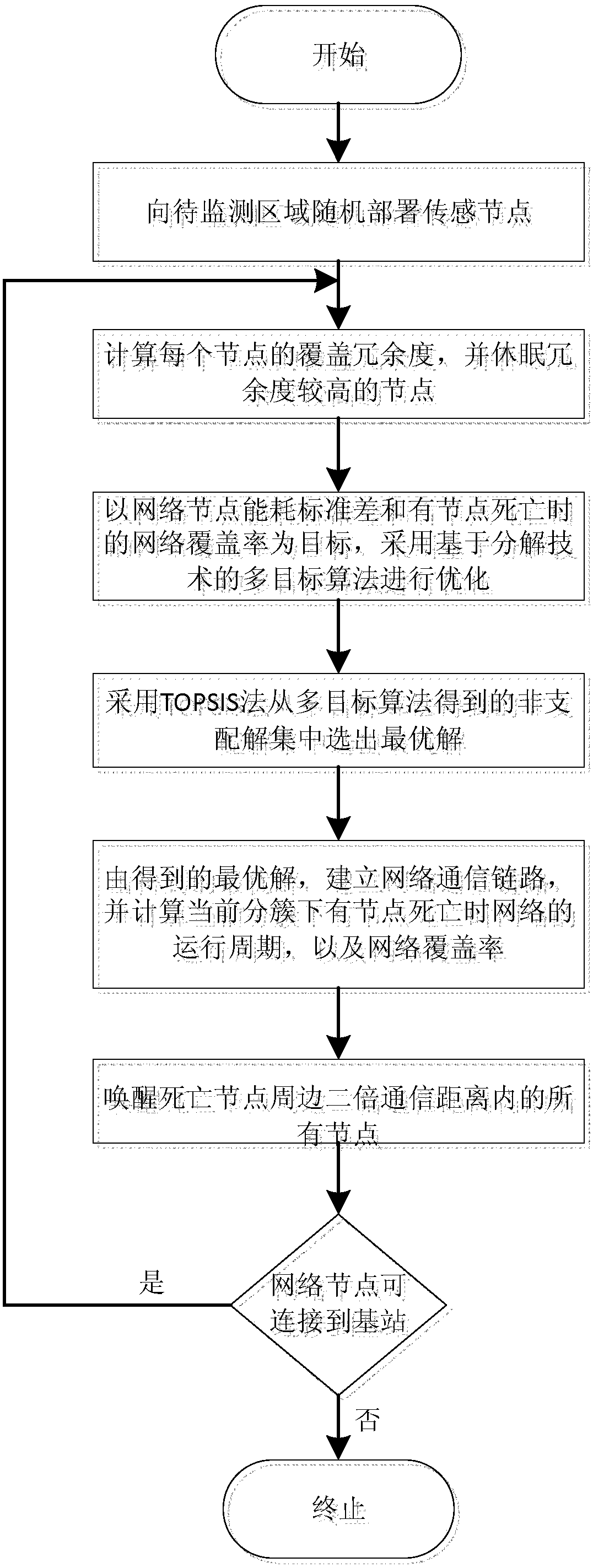
The invention discloses an energy consumption balancing and coverage keeping method for an underwater wireless sensor network, belongs to the field of underwater wireless sensor networks, and aims toovercome the defects in an existing underwater wireless sensor network link technology. The method comprises the following steps: randomly distributing nodes in a region to be monitored; hibernating the nodes with relatively high redundancy; clustering a network in which redundant nodes are hibernated: optimizing and acquiring a group of non-dominant solutions through a multi-target algorithm based on a decomposition technology by taking network coverage and a standard difference of energy consumption as target functions, and selecting a better solution from the group of non-dominant solutionsto serve as a clustering way by a TOPSIS method; if a certain node is monitored to die, awakening dormant nodes around the dead node, and then hibernating the redundant nodes in the awakened nodes according to a hibernation principle; and repeating the steps above until the nodes cannot be connected to a base station.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Hop-by-hop reliable transmission control method for underwater wireless sensor network
InactiveCN104539387AReliable transmissionReduce codec complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelSimplex communicationReliable transmission
The invention discloses a hop-by-hop reliable transmission control method for an underwater wireless sensor network. Based on a digital fountain code technology irrelevant to a code rate, optimized degree distribution and recursive coding ideas are adopted, and an RLT (recursive LT) coding scheme is designed, so that rapid and efficient coding and decoding are realized; packet collision and end-to-end delay are reduced; and the network throughput is increased. Through collection of feedback information of a receiving node, the packet corruption probability of an underwater acoustic channel is accurately estimated, and the coding packet quantity of next transmission is further computed, so that the transmission overhead of extra packets is reduced. The fourth-layer reliable transmission mechanism and the second-layer medium access control mechanism of a conventional TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) protocol stack are organically fused, so that block-by-block and hop-by-hop reliable transmission of the underwater wireless sensor network is realized on the basis of RLT coding, and transmission-reception conflicts, multi-transmission-single-reception conflicts and data-ACK conflicts caused by simplex communication of an underwater Modem are reduced. As an effective and practicable technical scheme, the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:杜秀娟
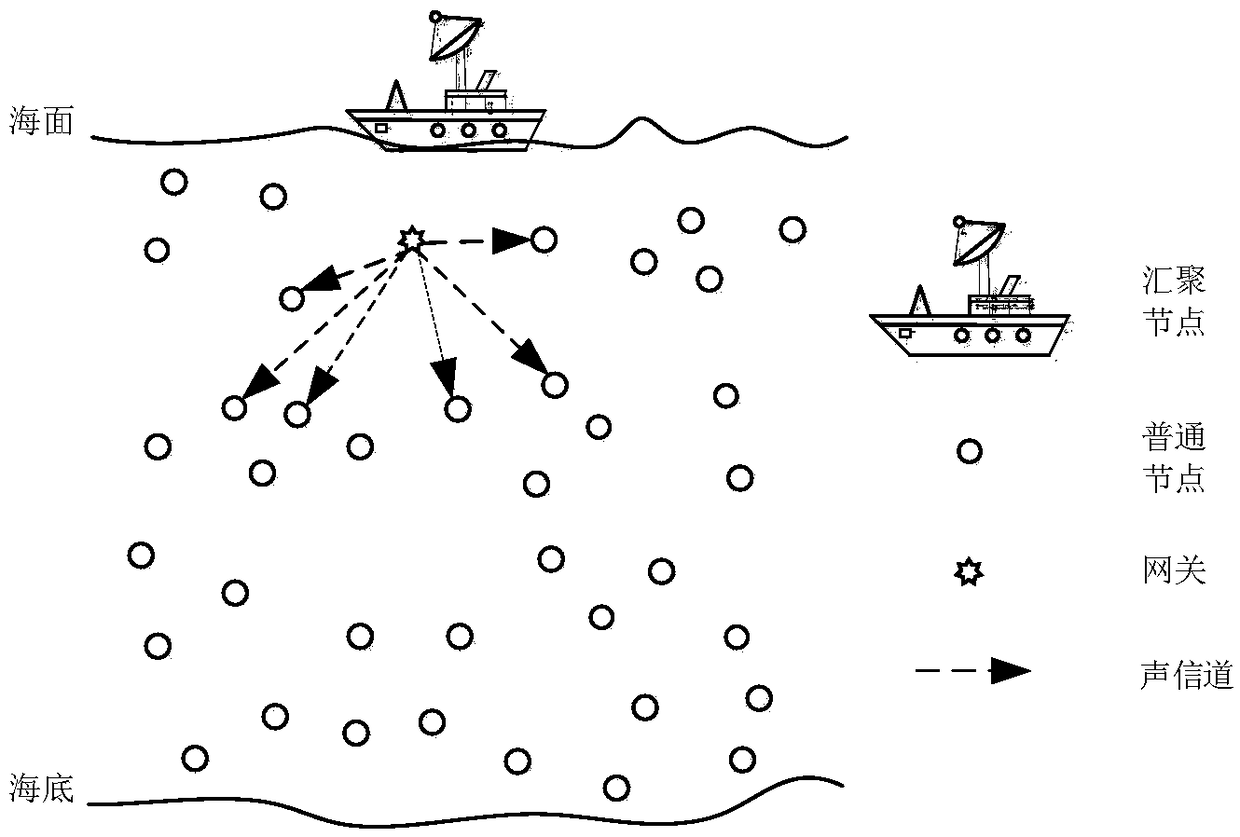
Reliable data transmission method for network cross layer of underwater wireless sensor
ActiveCN108696926ASave energyAvoid communication interferencePower managementNetwork topologiesCross layer designSensor node
The invention discloses a reliable data transmission method for a network cross layer of an underwater wireless sensor. In the method, underwater sensor nodes are arranged in a three-dimensional underwater space, and an aggregation node is arranged on the water surface; the nodes are classified into different clusters according to depths; the nodes close to the perpendicular line of the aggregation node are selected as gateway nodes, and common nodes acquire data packets and transmit the data packets to the gateway nodes in the clusters of the common nodes within an appointed time slot; the gateway nodes fuse the data packets in the clusters and then perform inter-cluster data transmission along a perpendicular direction; the aggregation node schedules node communication time slots in a unified manner; adjacent inter-cluster nodes perform dislocated communication within the same time slot so as to avoid mutual interference of signals; and the nodes in the clusters communicate with oneanother by using a network encoding-based CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) improved mechanism to reduce transmission collision and reduce the number of times of retransmission. Through the designof transmission between adjacent clusters at different time slots, the method disclosed by the invention realizes a network cross layer design and avoids the data transmission collision to an extremely large extent, so that the data transmission reliability is improved, and the communication time delay is shortened.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
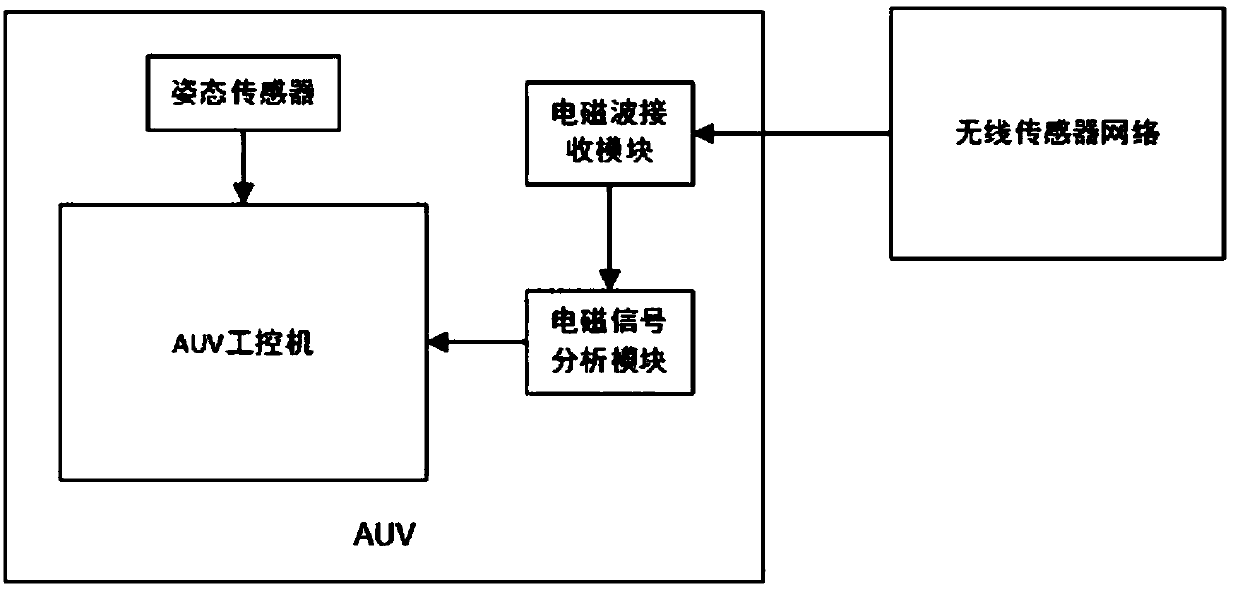
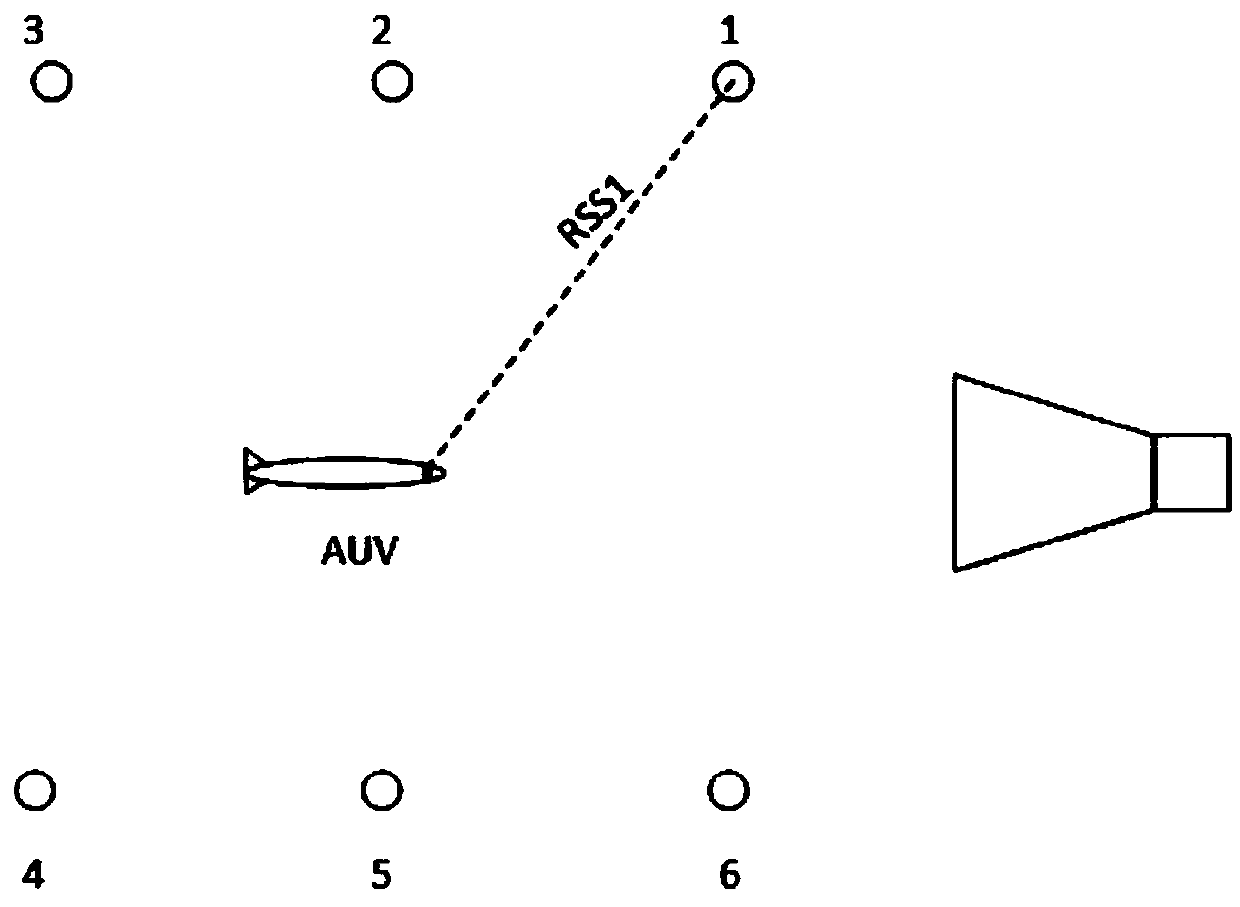
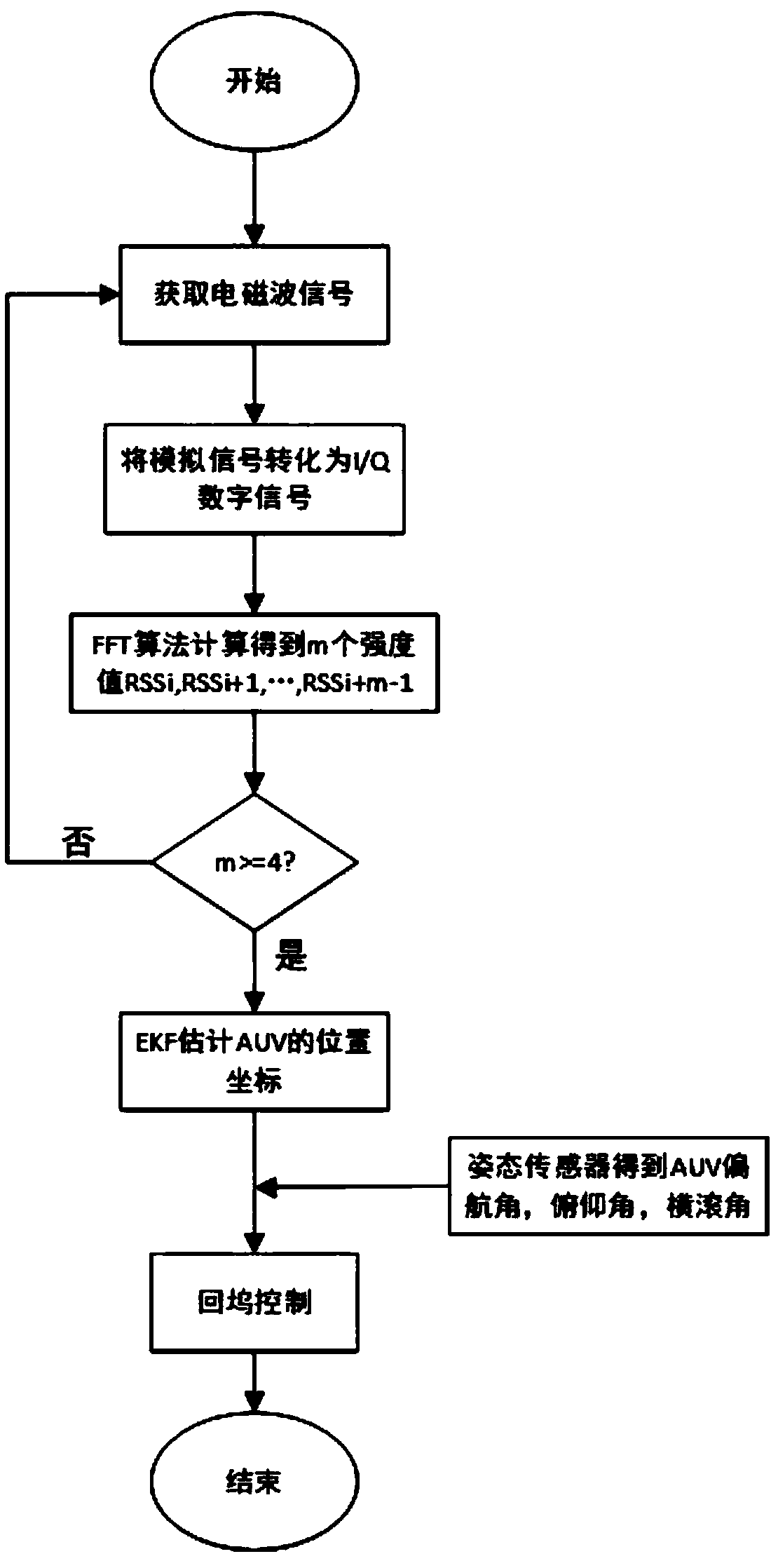
AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) return-dock navigation system and method based on electromagnetic wave attenuation principle
InactiveCN108680170ANot easily affected by the surrounding environmentAvoid disadvantagesNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationEnvironmental noiseWater quality
The invention discloses an AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) return-dock navigation system based on an electromagnetic wave attenuation principle. The AUB return-dock navigation system comprises anelectromagnetic wave receiving module, an electromagnetic signal analysis module, an industrial personal computer and an underwater wireless sensor network, wherein the electromagnetic wave receivingmodule is carried on AUV and is used for receiving an electromagnetic wave signal emitted by a wireless radio frequency sensor and transmitting the electromagnetic wave signal to the electromagnetic signal analysis module; the electromagnetic signal analysis module is carried on the AUV and is used for enabling the electromagnetic wave signal to be converted from an analog signal into a digital signal and transmitting the digital signal to the industrial personal computer; the industrial personal computer is used for calculating intensity of the electromagnetic wave signal according to an electromagnetic wave digital signal and carrying out return-dock navigation on the AUV according to a preset navigation method; the underwater wireless sensor network is arranged in an AUV return-dock water domain and comprises a plurality of wireless radio frequency sensors with different emission frequencies. The invention also discloses a method for carrying out return-dock navigation based on theAUV return-dock navigation system. According to the AUV return-dock navigation system disclosed by the invention, high-precision navigation in a small range can be realized, and meanwhile, the systemcannot be affected by water quality, environmental noise and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A multi-AUV efficient data collection method based on VOI in an underwater wireless sensor network
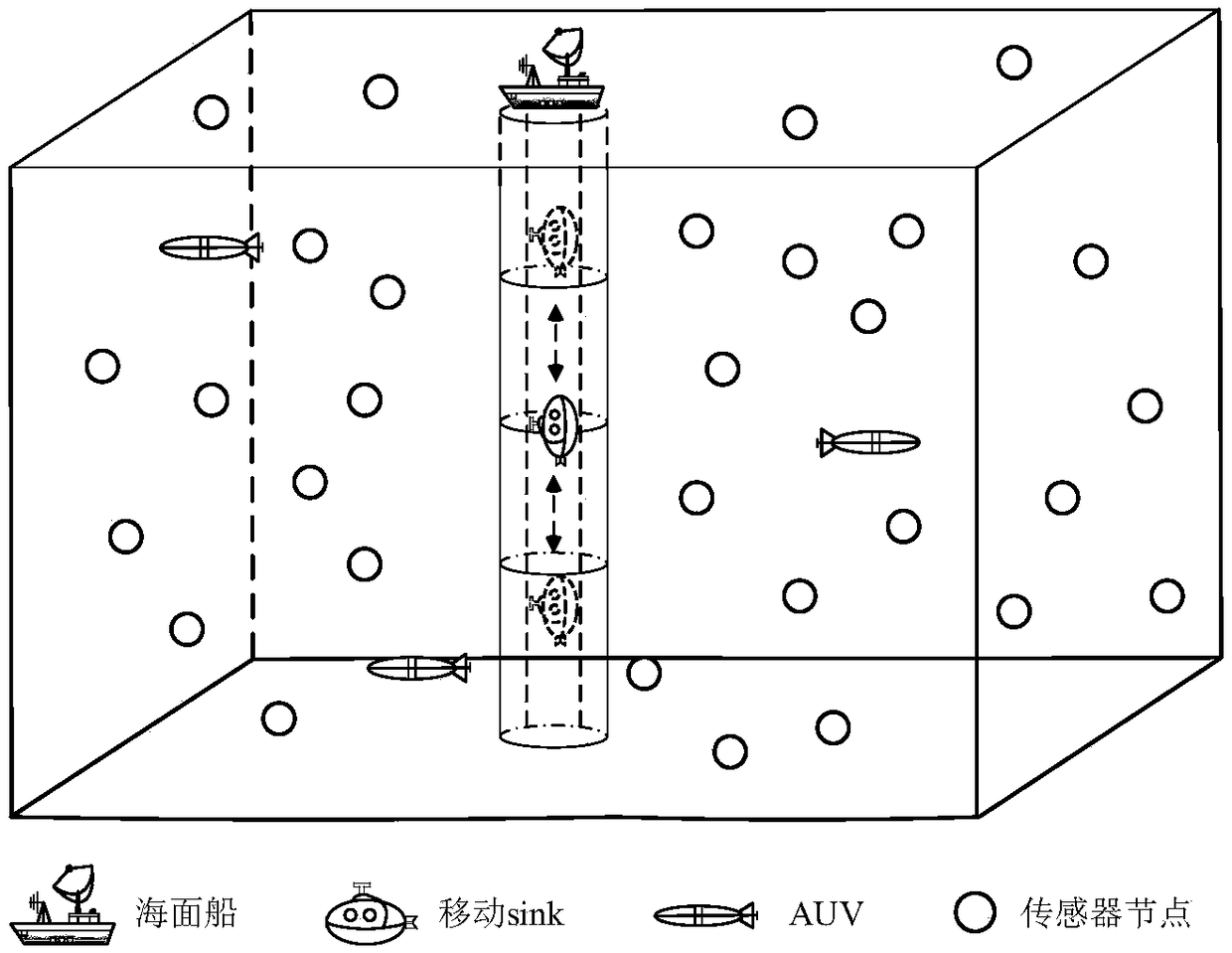
ActiveCN109275099ASolve complex data collection tasksExtend your lifeNetwork topologiesTransmissionFault toleranceResource distribution
The invention discloses a multi-AUV efficient data collection method based on VOI in an underwater wireless sensor network, which comprises the following steps: (1) a high VOI data packet is transmitted to a cluster head firstly; (2) The determination of moving Sink position and the division of space region in 3D underwater environment; (3) Path planning of AUV in sub-region; (4) Multiple AUVs compete dynamically to handle emergent tasks. By utilizing the spatial distribution characteristics of multiple AUVs and the characteristics of resource distribution, It can effectively solve the complexdata collection task in underwater wireless sensor networks. The multi-AUV data collection method has good fault tolerance and improve the system robustness. Its advantages of high reliability and low latency are not possessed by a single AUV system. Combined with AUV path planning, the three-dimensional underwater area division adopts multi-AUV dynamic competition mechanism to deal with emergencies and collect network data dynamically, which balances the network energy consumption and prolongs the network lifetime.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Underwater wireless sensor network target tracking method based on sensor node strategy selection
InactiveCN103096444AReduce energy consumptionReduce communication loadPower managementNetwork topologiesUnderwater sensor networksSensor node
The invention discloses an underwater wireless sensor network target tracking method based on sensor node strategy selection. According to the method, firstly, a node which is closest to an initial position in estimated distance is used as a processing node, wherein the node is selected according to initial position estimation and variance estimation of a moving target, then the node is used as a circle center, estimated triple distance of standard deviation is used as a radius to select an observing node, and when the distance between the position of the observing node and the position of a target is smaller than observing range of a sensor, observing data is sent to the processing node which is used for estimating a target position estimation value and a variance estimation value using kalman filtering according to the observing value. A sensor node closest to the target position is selected according to the target position estimation value and used as a processing node of the next time, and the position estimation value and the variance estimation value of the processing node of the previous time are sent to the current processing node until the moving target exceeds the tracking range of an underwater sensor network. By means of the underwater wireless sensor network target tracking method based on sensor node strategy selection, energy consumption and communication load of underwater wireless sensor network target tracking are effectively lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dynamic self-adaptation positioning method of underwater wireless sensor network
ActiveCN104080169AImprove effectivenessReduce adverse effectsNetwork topologiesPosition errorSelf adaptive
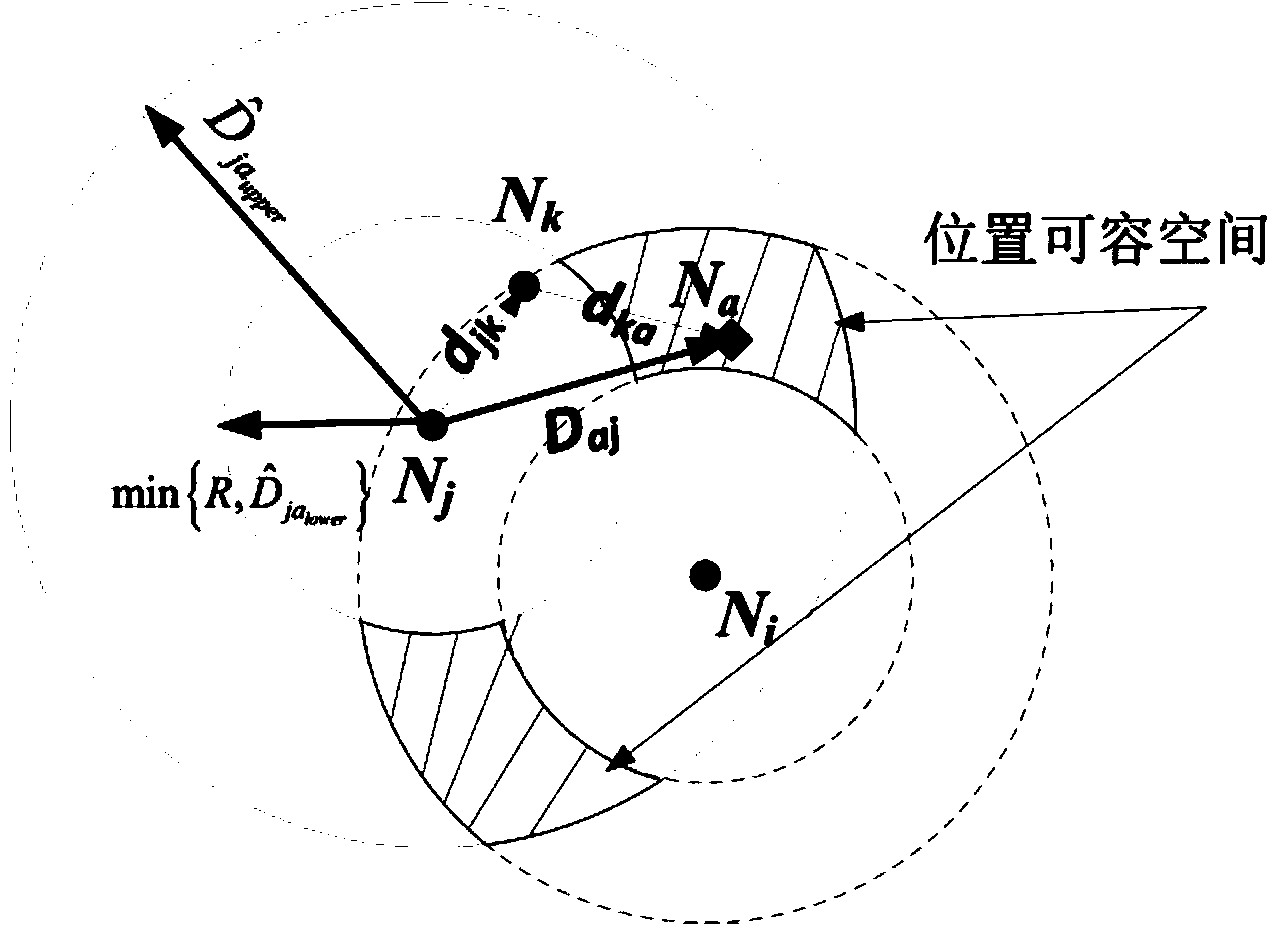
The invention discloses a dynamic self-adaptation positioning method of an underwater wireless sensor network, and belongs to the technical field of positioning of the underwater wireless sensor network. The dynamic self-adaptation positioning method of the underwater wireless sensor network comprises the following steps that firstly, an anchor node evaluates the accuracy of the coordinates of the self-statement position; secondly, a node to be positioned builds a dynamic updatable positioning set; thirdly, the positioning set carries out multi-hop distance estimation with the deviation corrected in a self-adaptation mode; fourthly, the position accommodation space of the node to be positioned is solved; fifthly, coordinate estimation and accuracy evaluation of the node to be positioned are carried out. The accuracy of the coordinates of the statement position of the anchor node is evaluated and calibrated on line, the adverse influence on positioning performance from the position error of the anchor node is reduced, the accuracy of multi-hop distance estimation is improved through multi-hop distance estimation with the deviation corrected in the self-adaptation mode, the on-line cognition and dynamic self-adaptation capacity of a complex positioning environment of a sensor network node are improved, ad the positioning performance of the underwater wireless sensor network is improved.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Safe locating method for underwater sensor network
InactiveCN103763704AEnsure safetyGuaranteed reliabilityPosition fixationSecurity arrangementUnderwater sensor networksDependability
The invention provides a safe locating method based on malicious anchor node detection in an underwater wireless sensor network. A trust management module and a locating module are related in the safe locating method, wherein in the trust management module, the direct trust values of nodes are described by adopting Beta distribution and observing interbehaviors among the nodes, and the direct trust values of the nodes are updated timely by updating interaction records. Contradictory factors are obtained by carrying out variance calculation on the direct trust values among the nodes and the global trust values, the contradictory factors are compared with a contradictory threshold value, and malicious slander nodes with the contradictory factors larger than the contradictory threshold value are removed. A cluster head collects the trust value information of all the nodes in a cluster, the nodes with the global trust values higher than a trust threshold value are judged as trusted nodes, and the trusted nodes are stored in a trusted node list. According to the safe locating method, the defamation aggressive behaviors of malicious nodes are detected based on a trust mechanism, the safety and reliability of the network are guaranteed thereof, and the safe locating method is especially suitable for the underwater wireless sensor network.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Three-dimensional underwater network topology control method based on potential game and rigid subgraph
ActiveCN111132200ACompatible with underwater environmentImprove robustnessNetwork topologiesTransmissionSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional underwater network topology control method based on a potential game and a rigid subgraph. The method comprises the steps of 1, constructing an underwater wireless sensor network topology; 2, executing a network topology game; 3, removing redundant links; and 4, carrying out self-adaption and maintenance of the network topology. According to the method,underwater factors are fully considered, a UWSNs topology control method comprising a plurality of optimization targets such as connectivity, coverage, energy consumption, transmission delay, a data transmission success rate and a signal to interference plus noise ratio of a network is designed, the redundant links in network topology are eliminated by utilizing an optimal rigid subgraph principle, and the load of nodes is reduced; and meanwhile, the network can resist different underwater environments by adjusting a weight factor in the network, so that the method has relatively strong adaptability.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com