Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Traffic engineer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Traffic engineering is a branch of civil engineering that uses engineering techniques to achieve the safe and efficient movement of people and goods on roadways. It focuses mainly on research for safe and efficient traffic flow, such as road geometry, sidewalks and crosswalks, ...
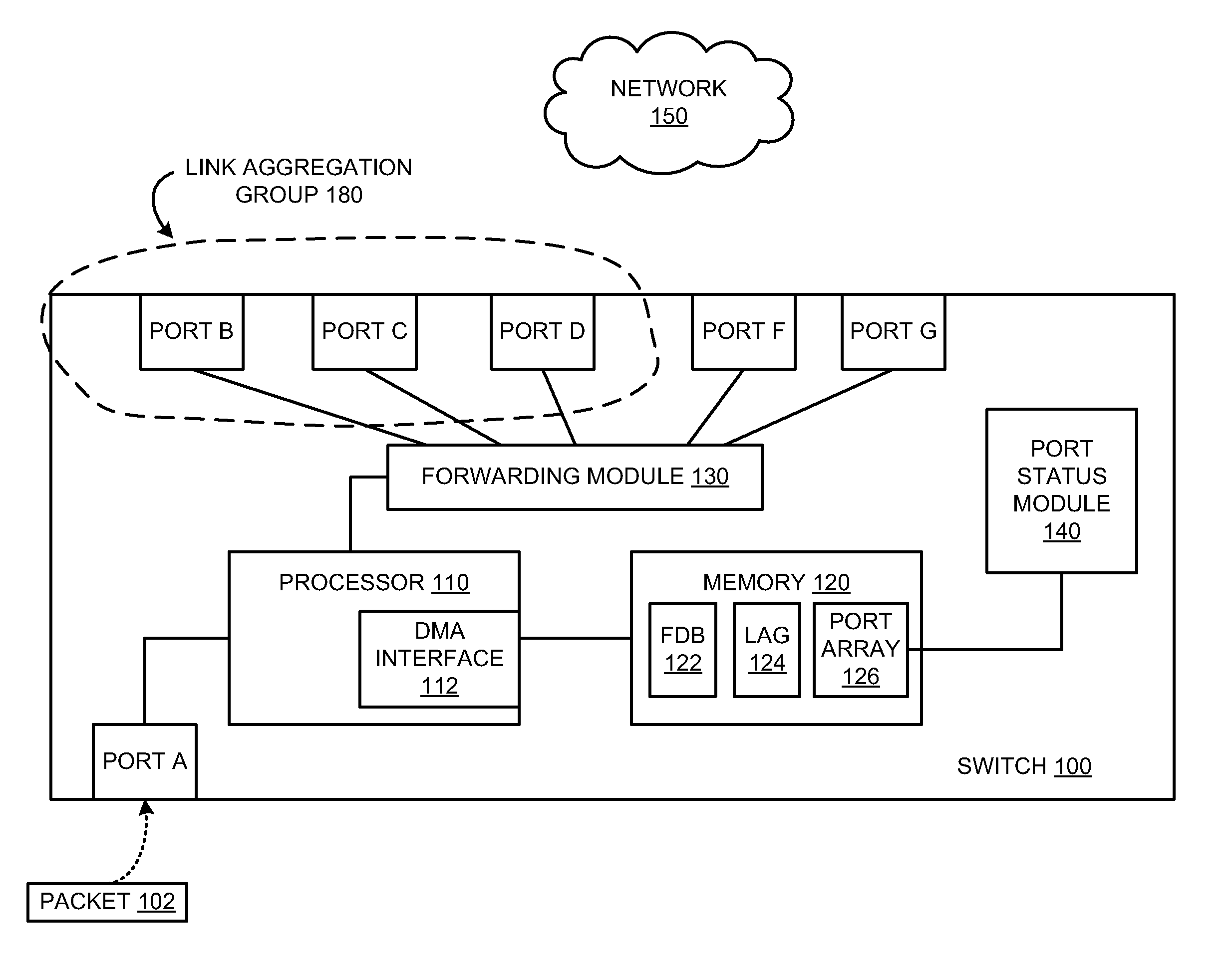
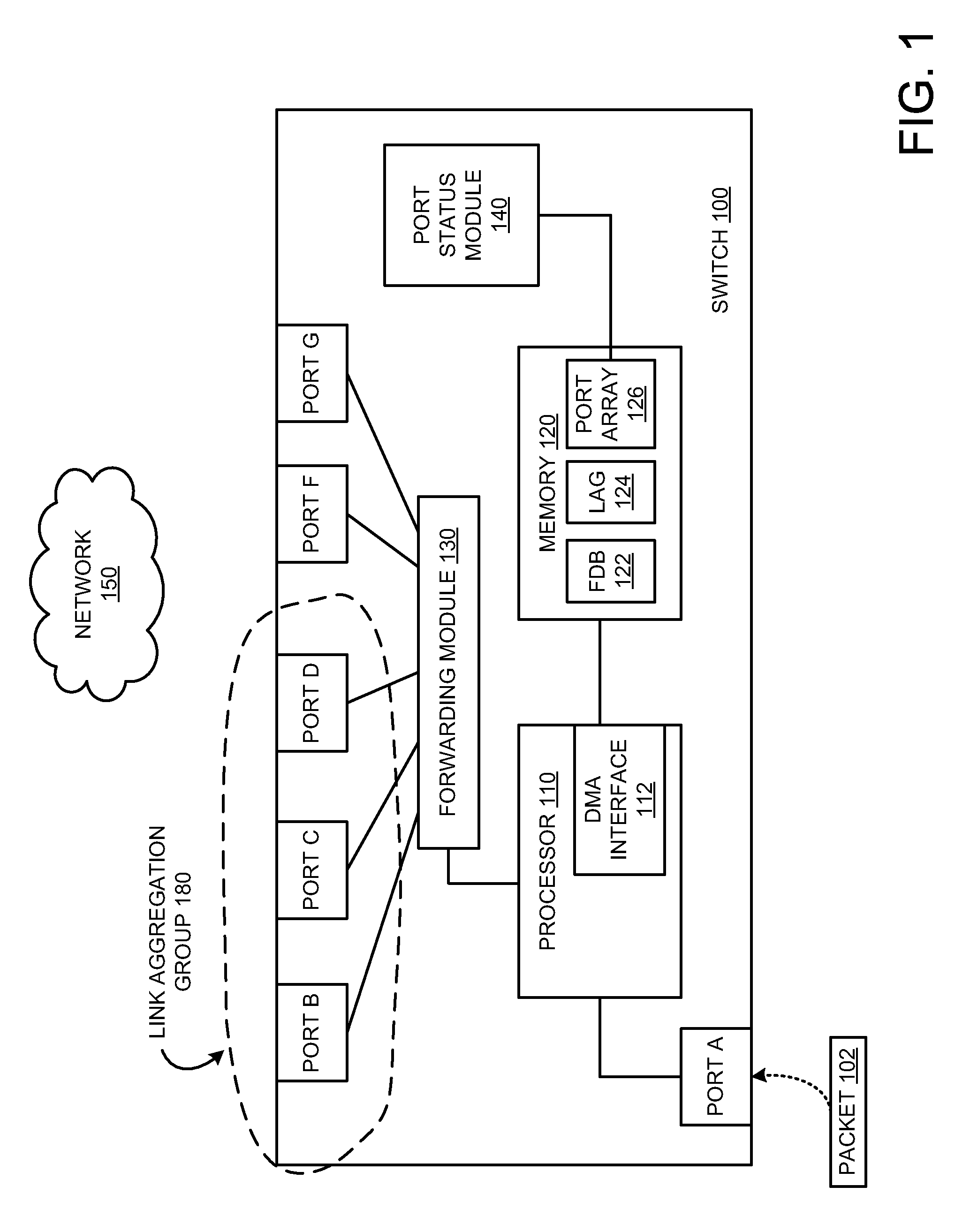
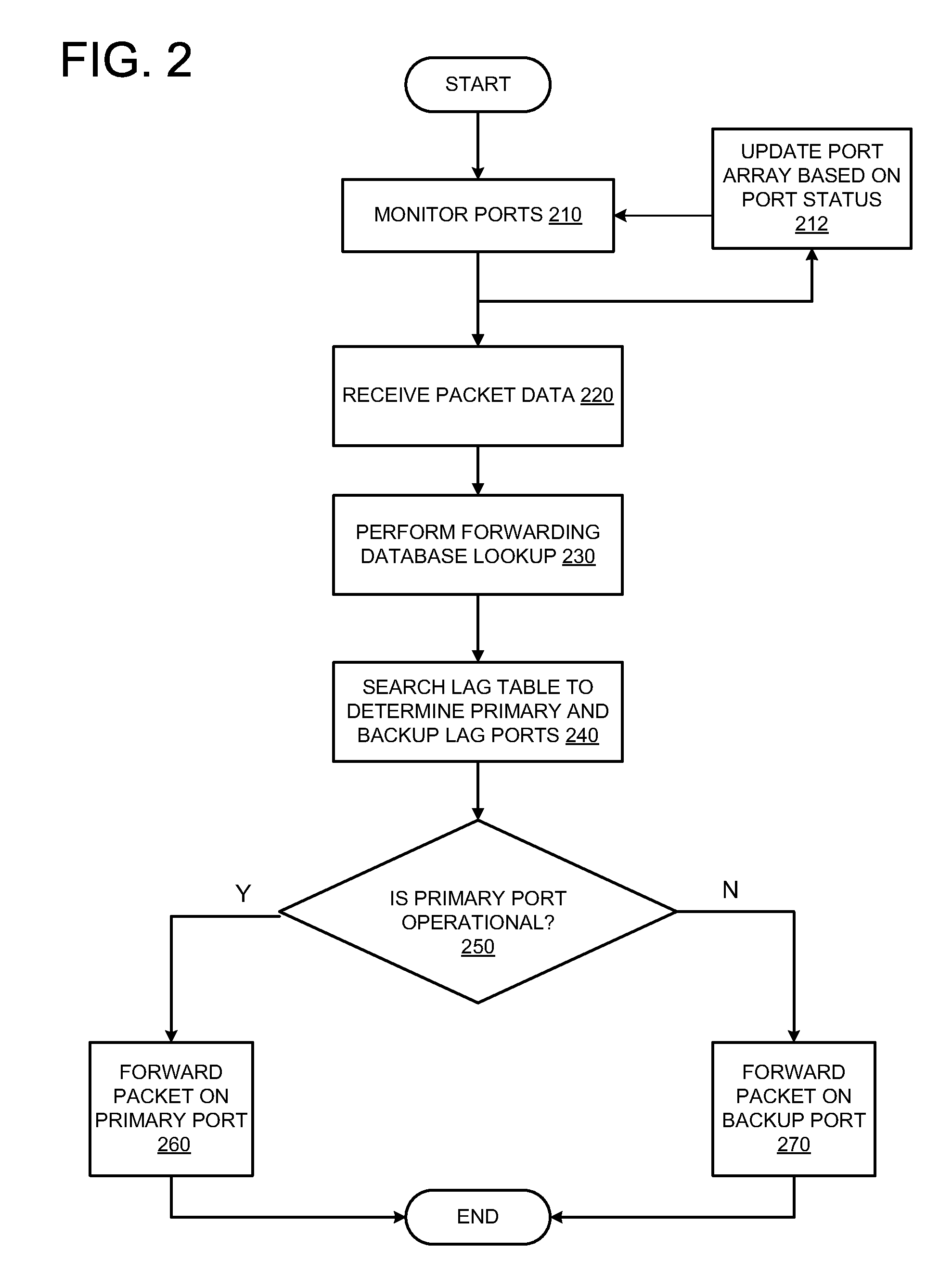
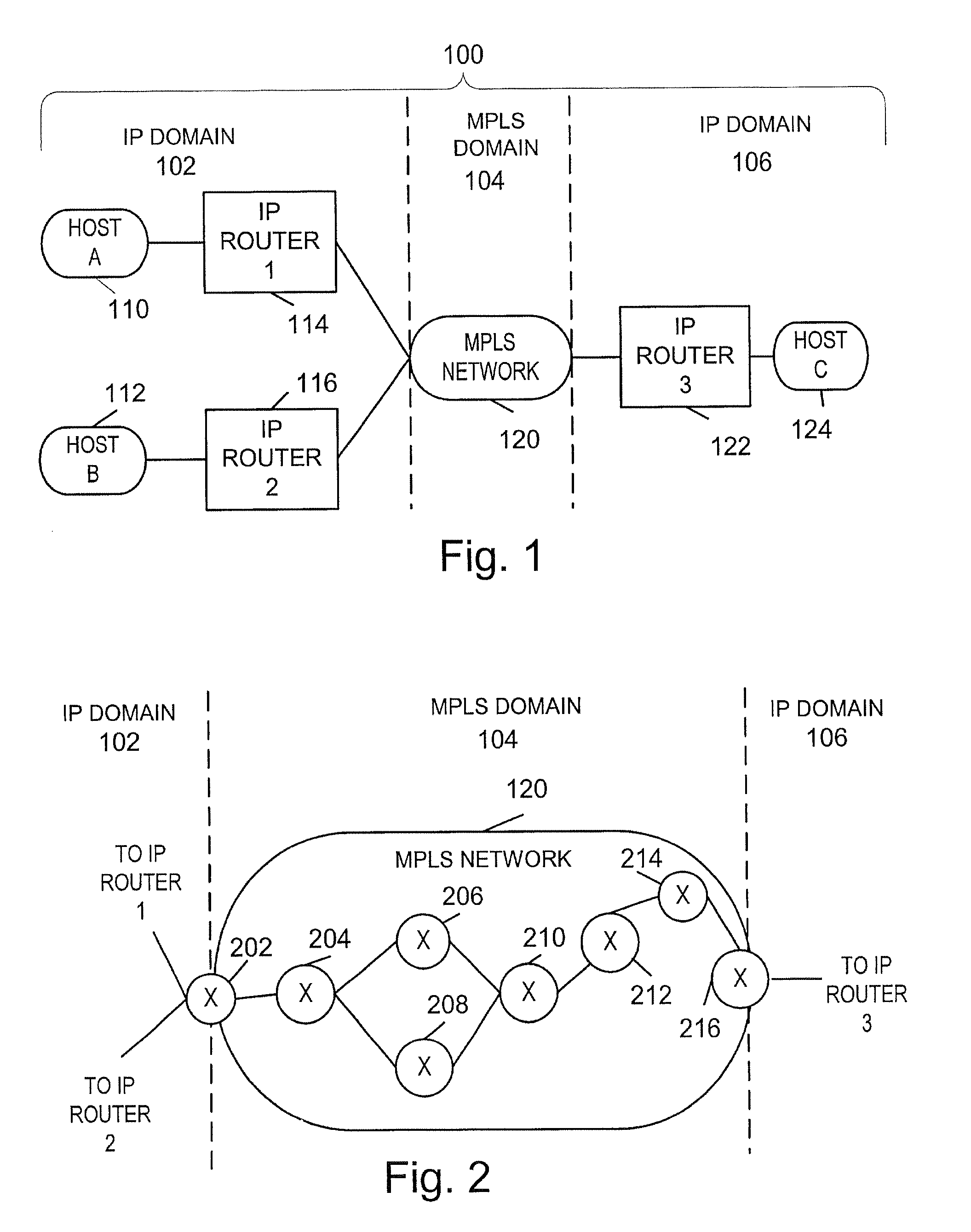
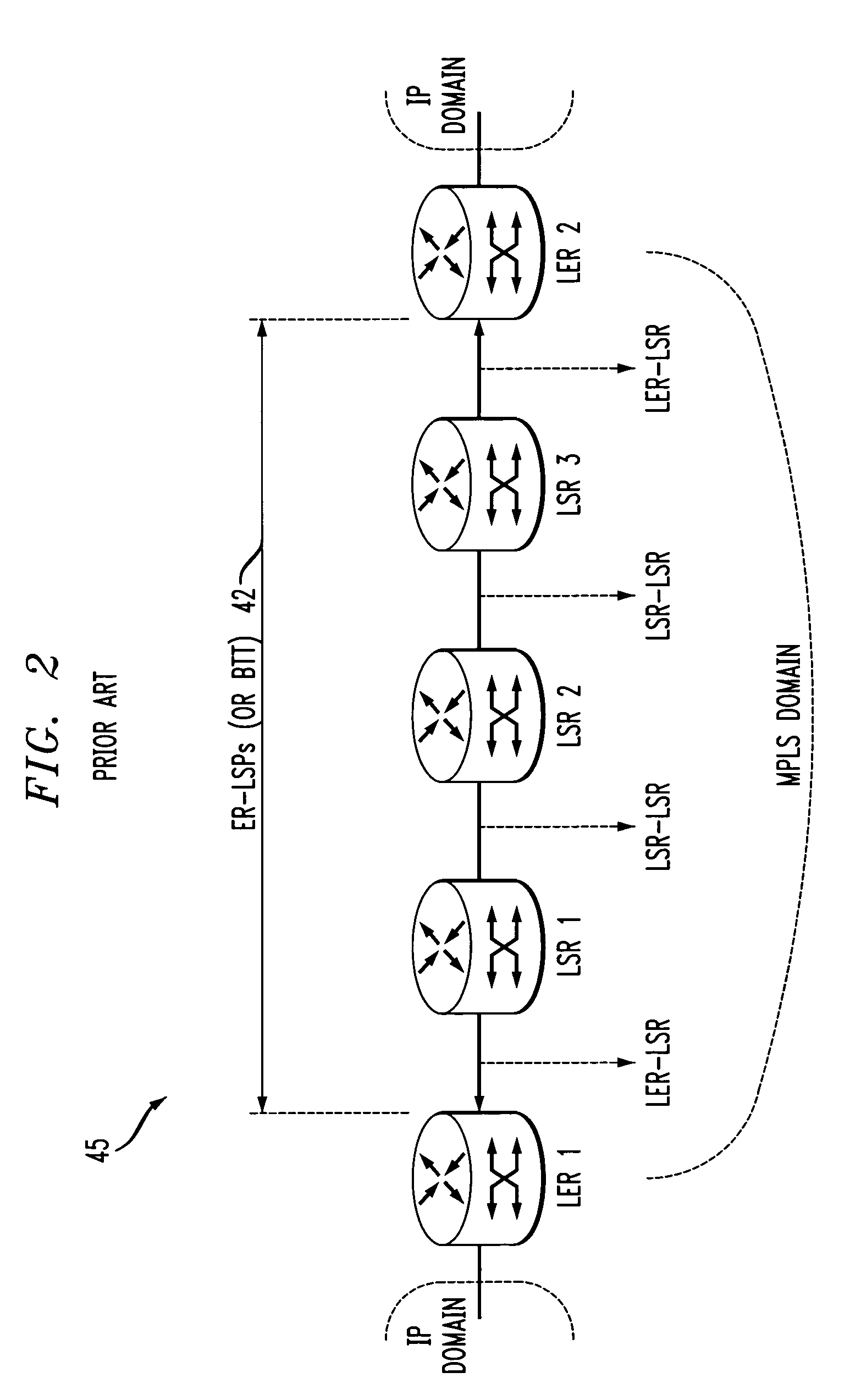
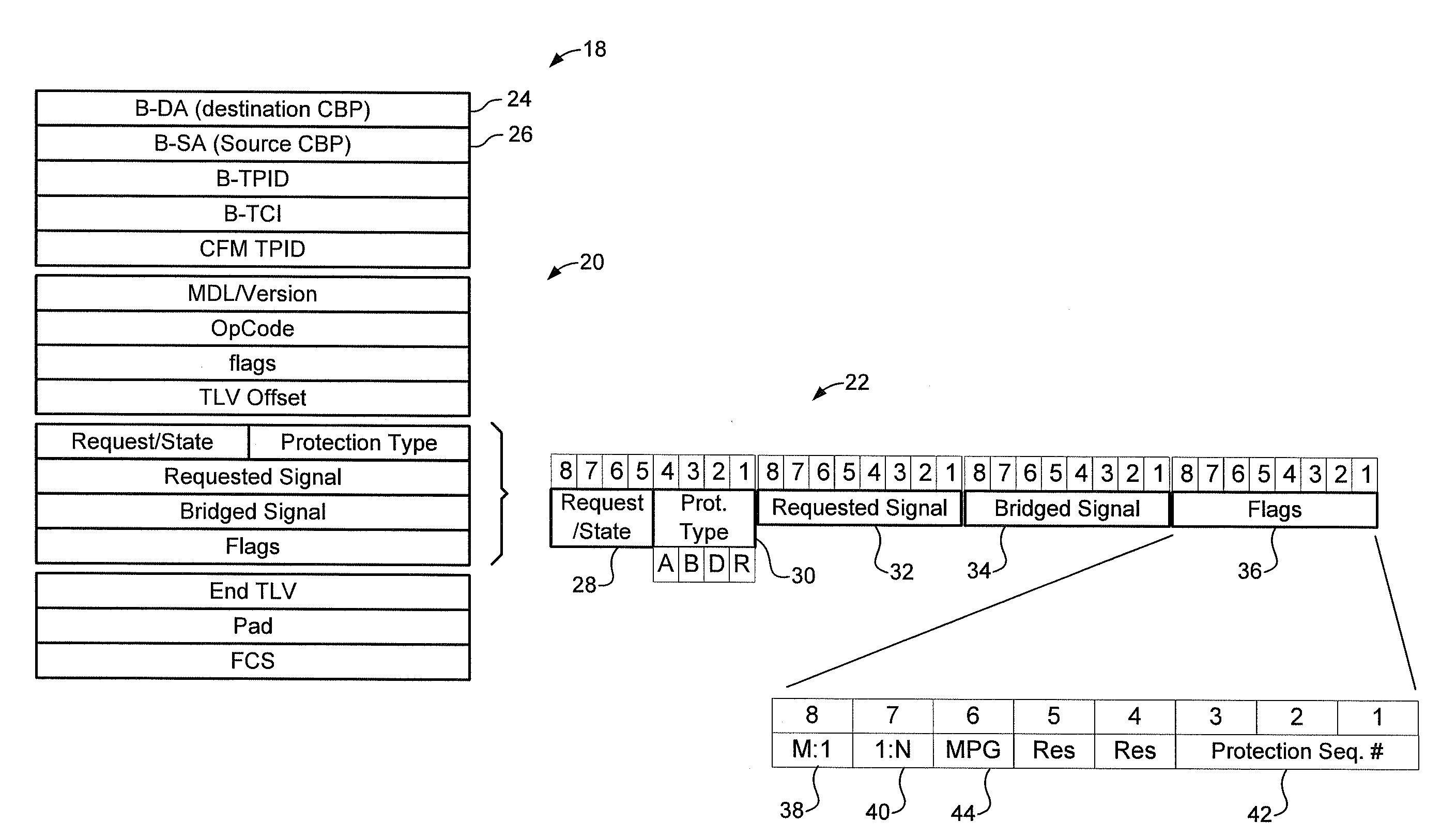
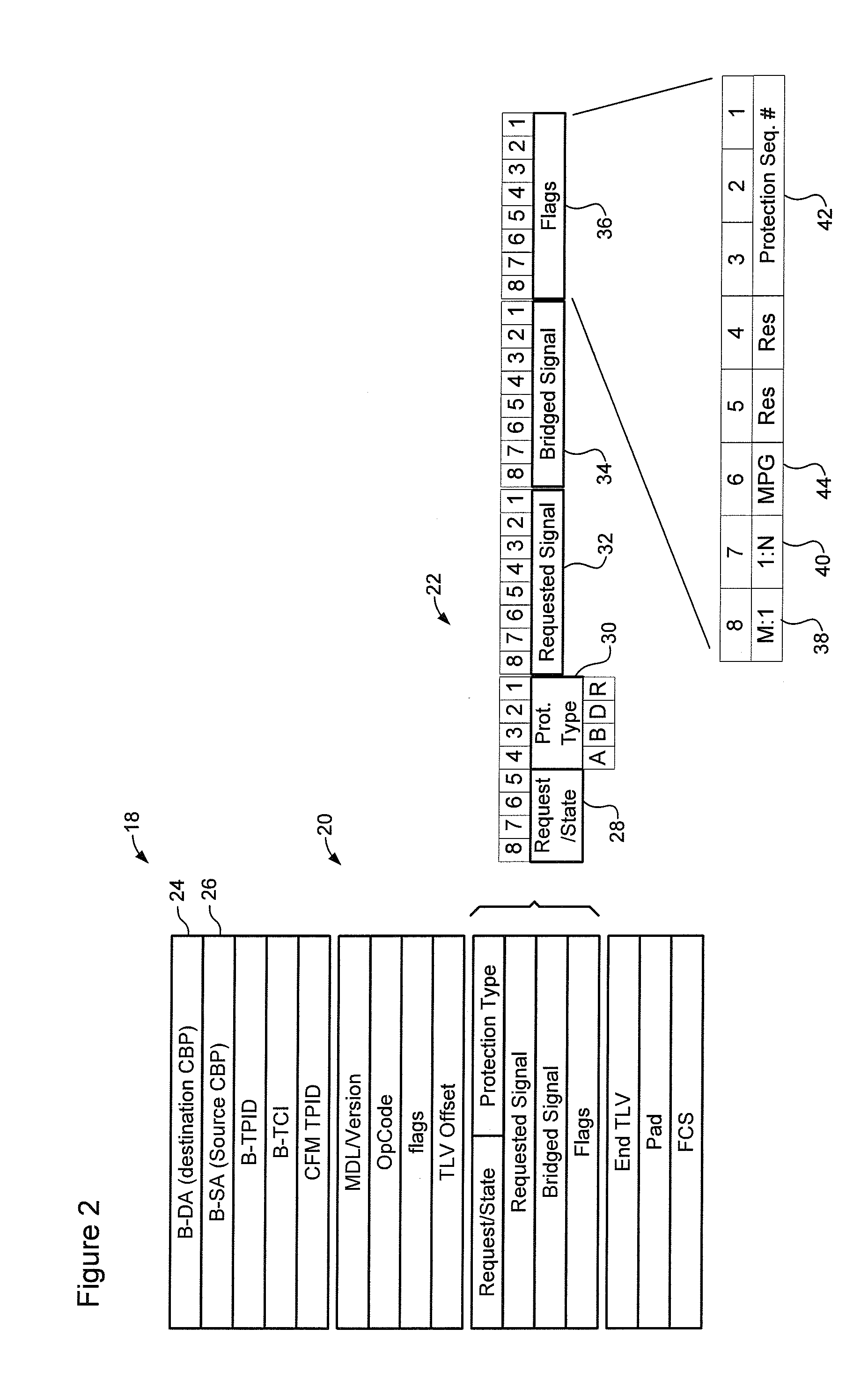
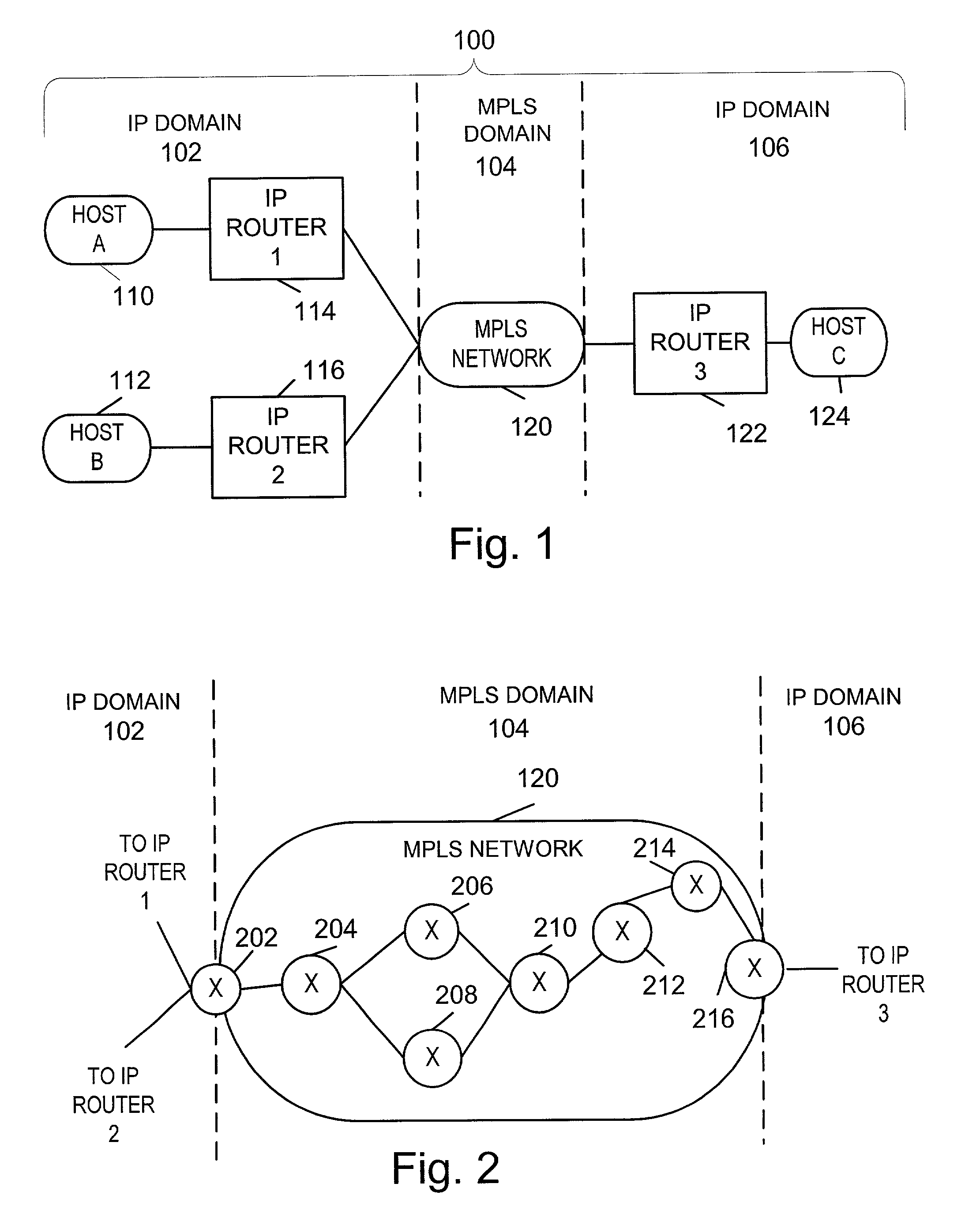
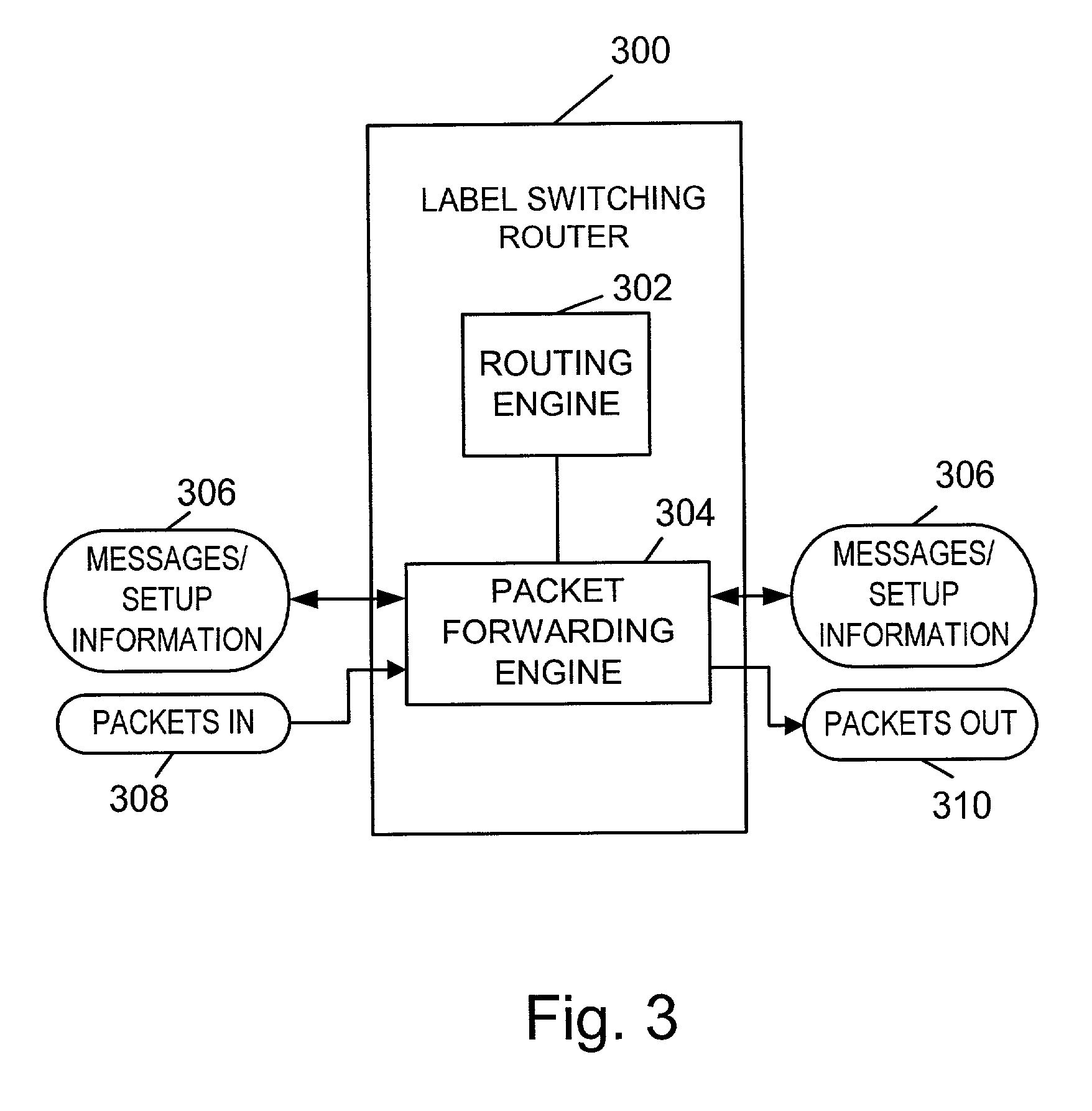
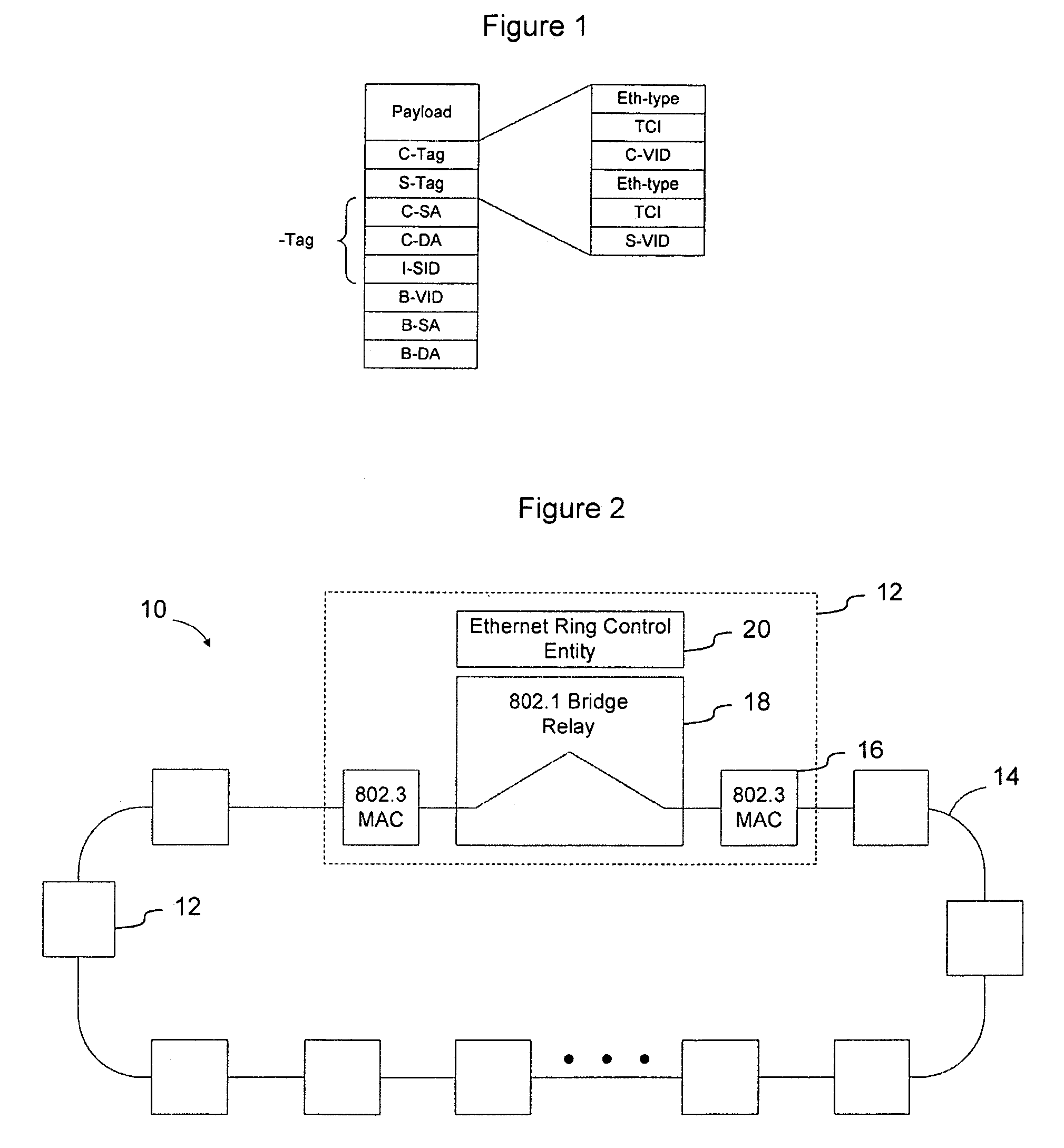
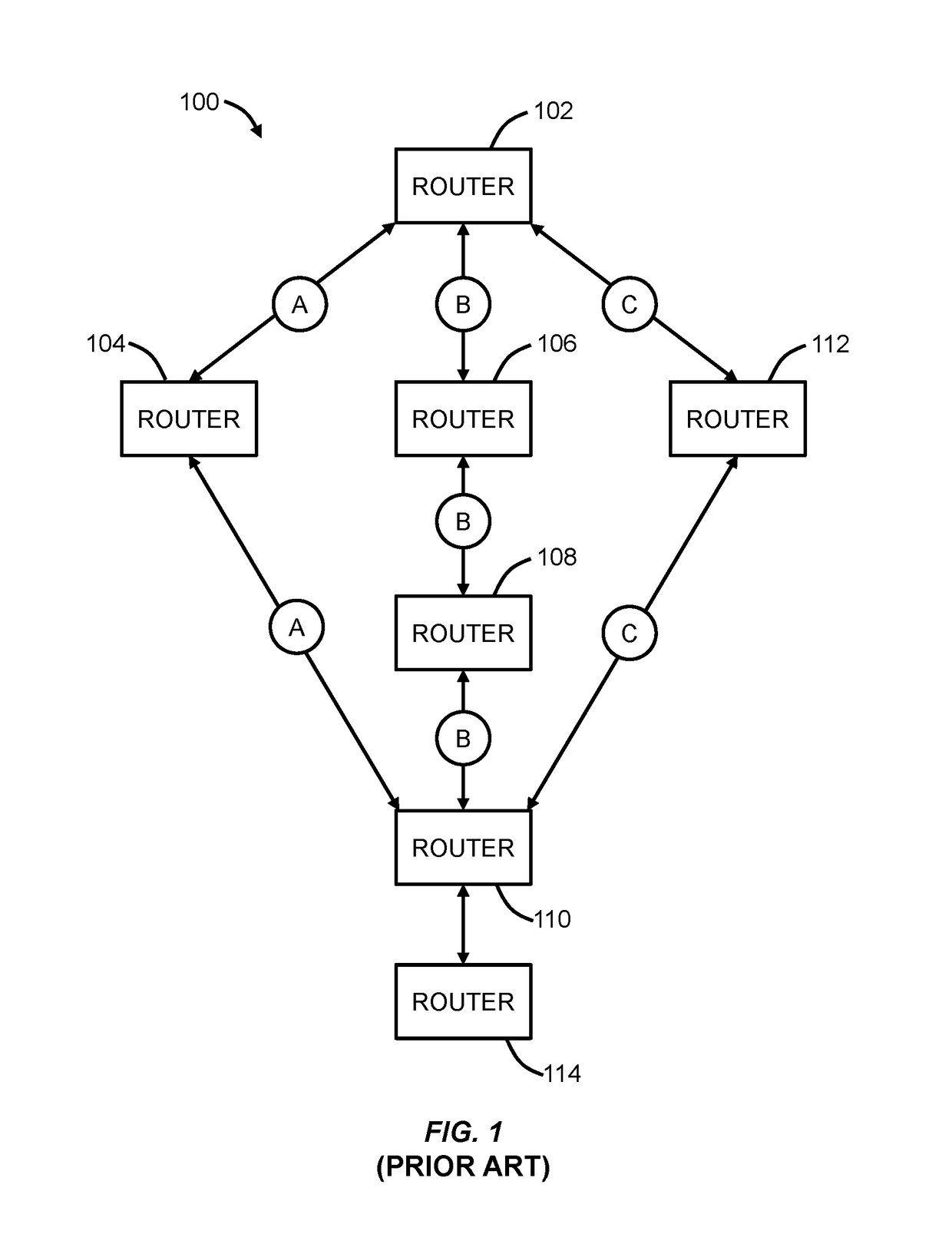
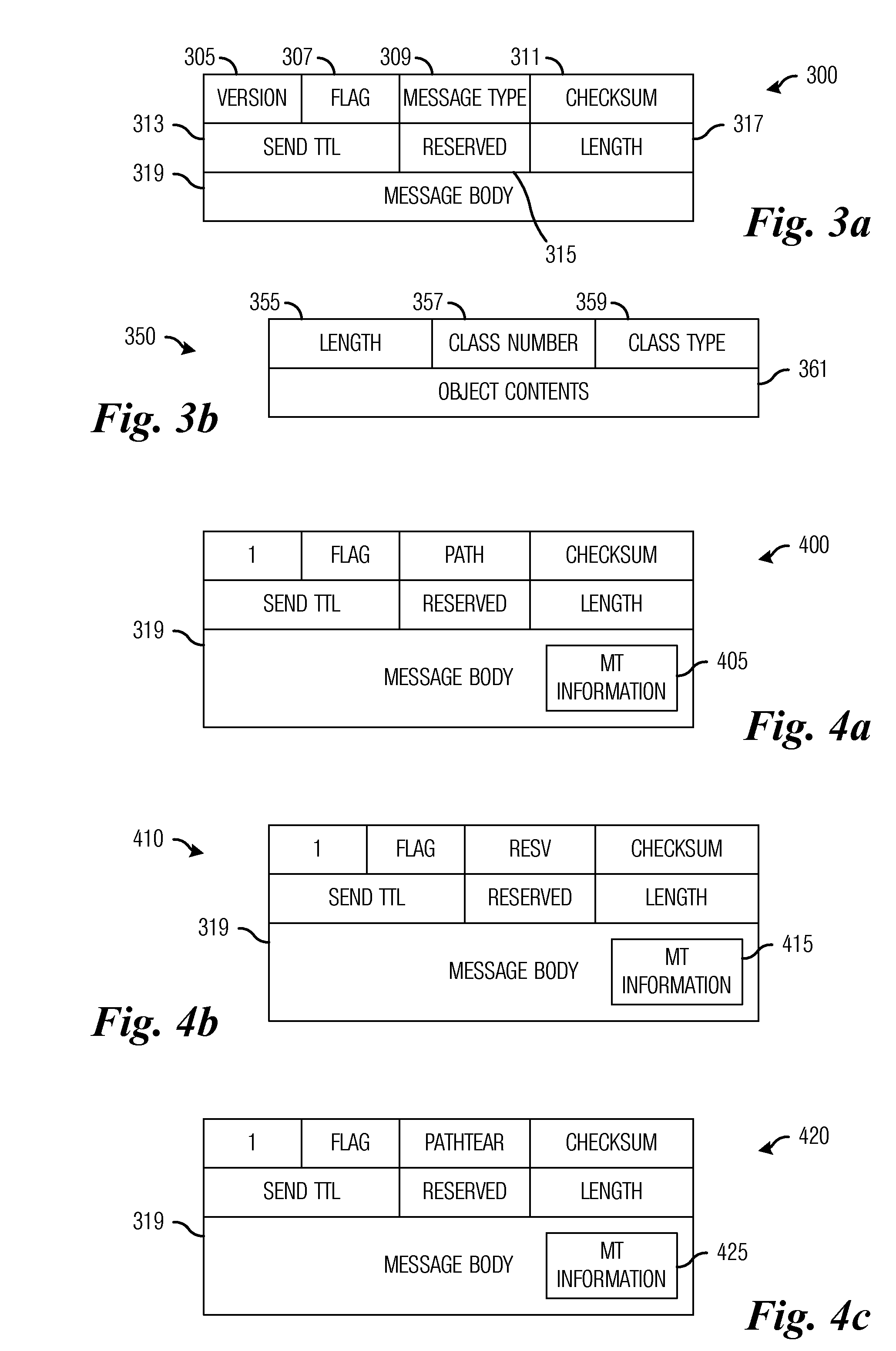
Traffic forwarding in a traffic-engineered link aggregation group
A data packet is received at a network switch. The packet has a destination address that is reached via a Link Aggregation group on a virtual local area network (VLAN). A forwarding database lookup is performed to determine a Link Aggregation port reference number for the data packet on the VLAN. A Link Aggregation port table is then searched to determine the primary Link Aggregation port and a backup Link Aggregation port for forwarding the packet. A port array for ports in the Link Aggregation group is searched to determine if the primary Link Aggregation port is valid. If the primary port is valid, then the packet is forwarded on the primary Link Aggregation port. If the primary port is not valid, then the packet is forwarded on the backup Link Aggregation port.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
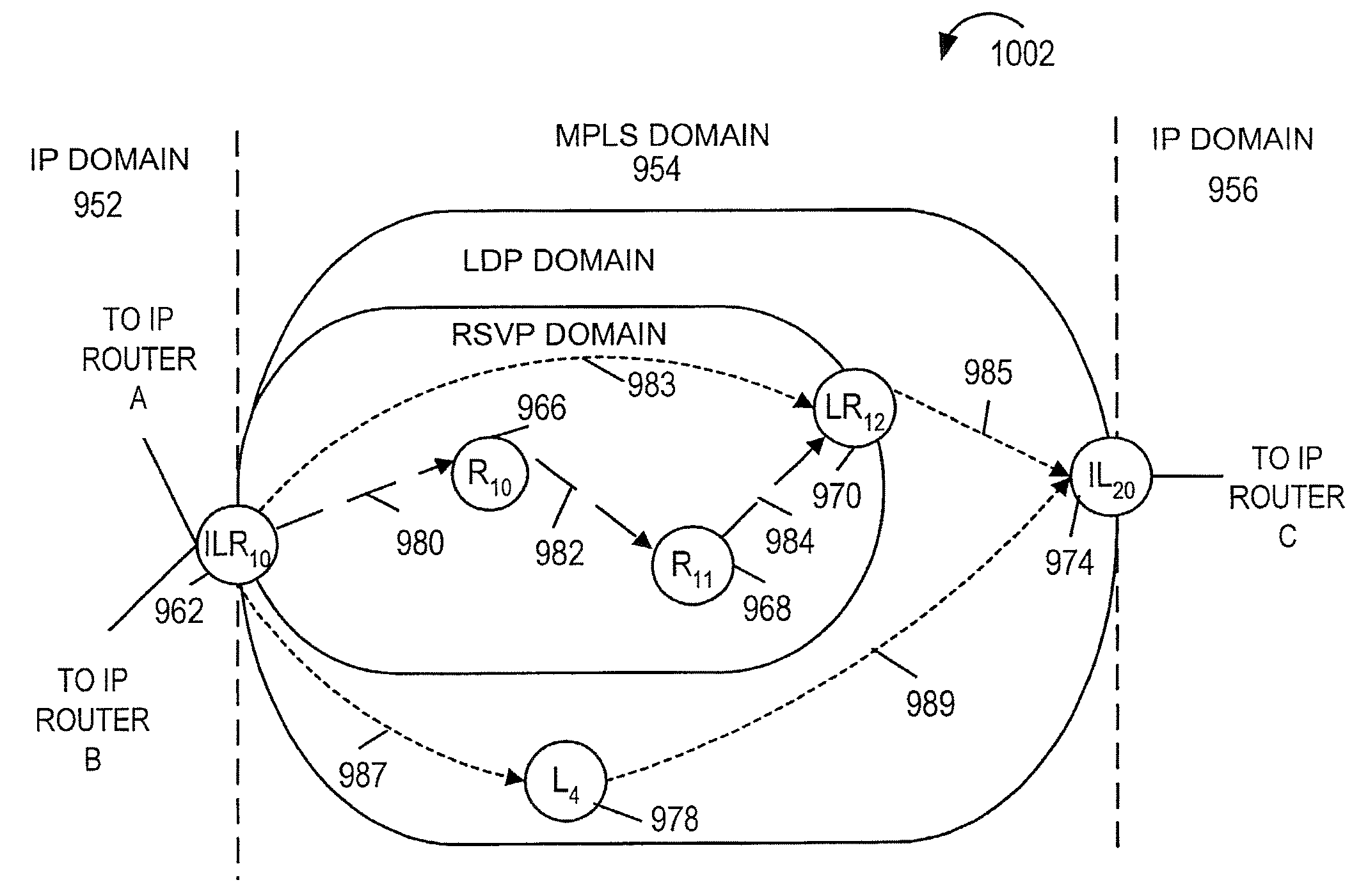
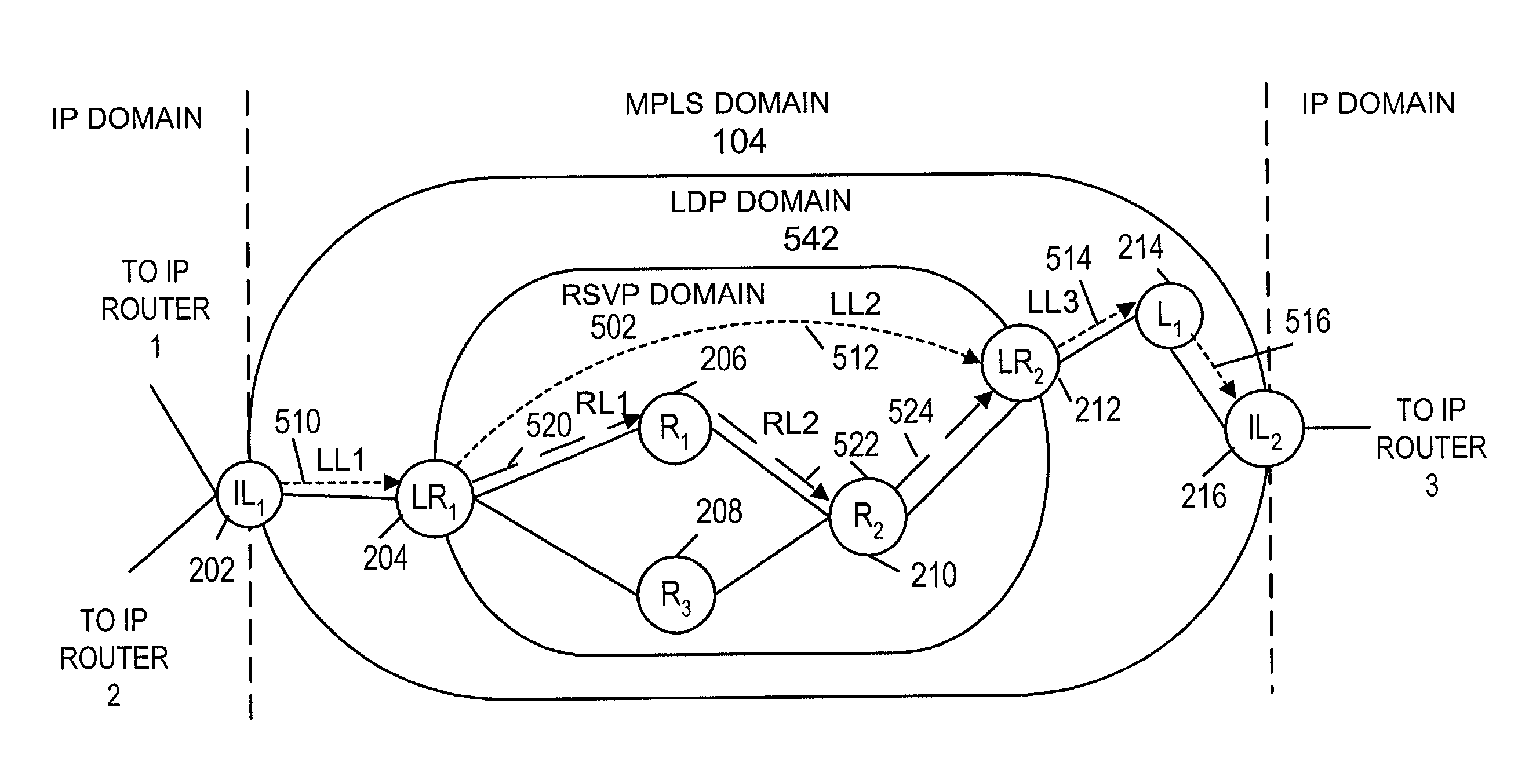
Methods and apparatus for using both ldp and rsvp in a communications system
InactiveUS20100142548A1Avoid the needDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationCommunications systemDistributed computing
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
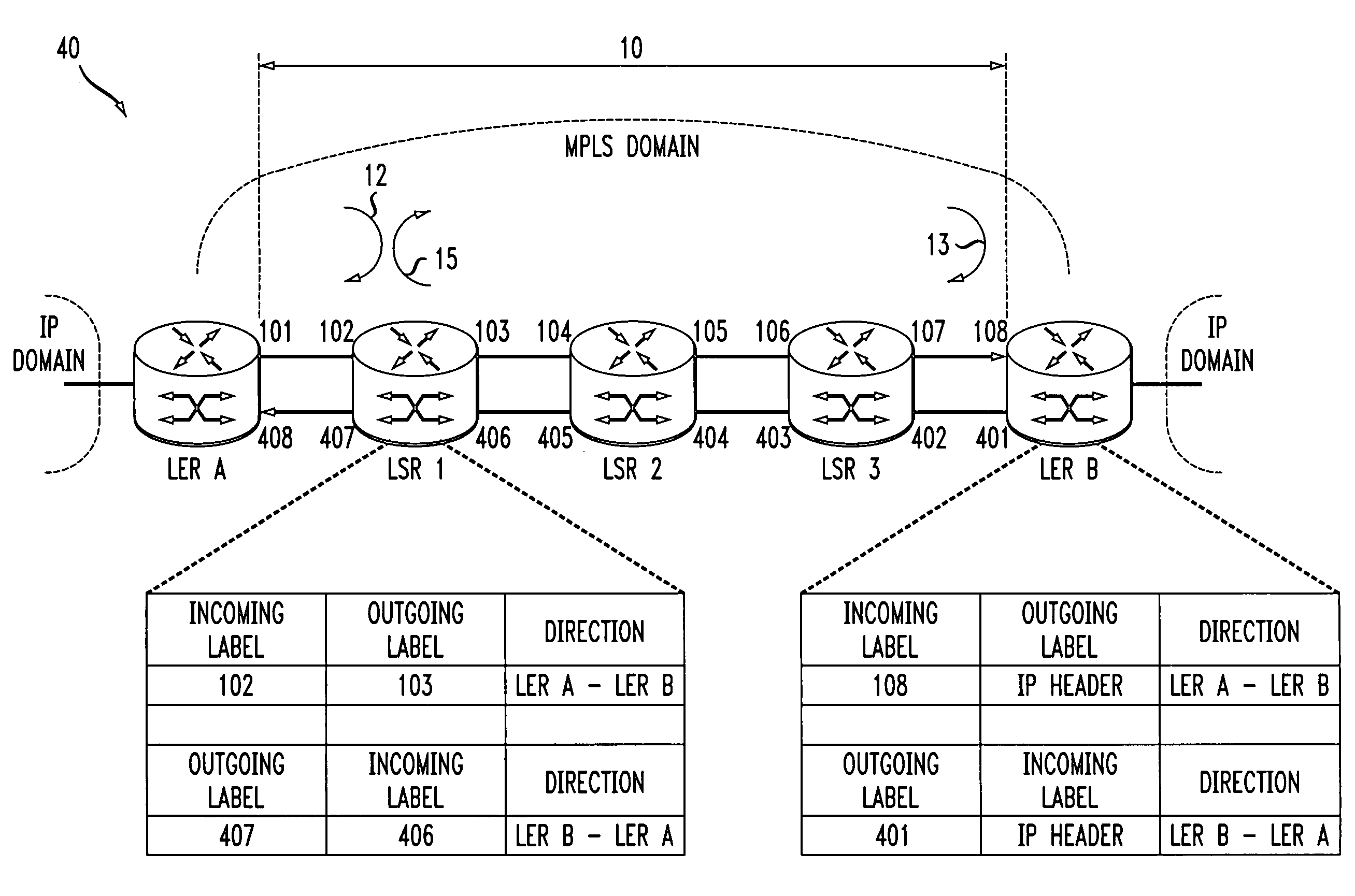
Loopback capability for bi-directional multi-protocol label switching traffic engineered trucks
InactiveUS6965572B1Simplify OA & MLower unit costError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceEngineering
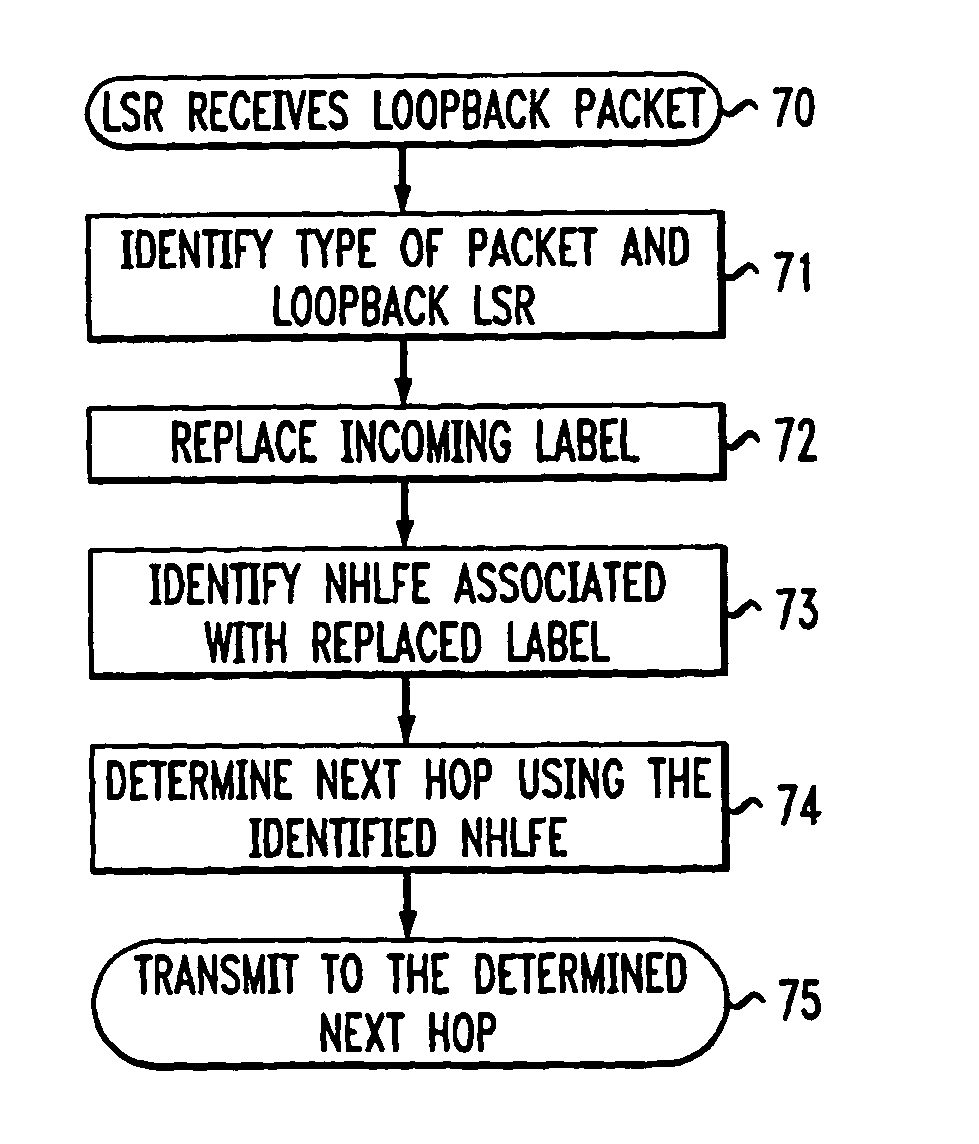
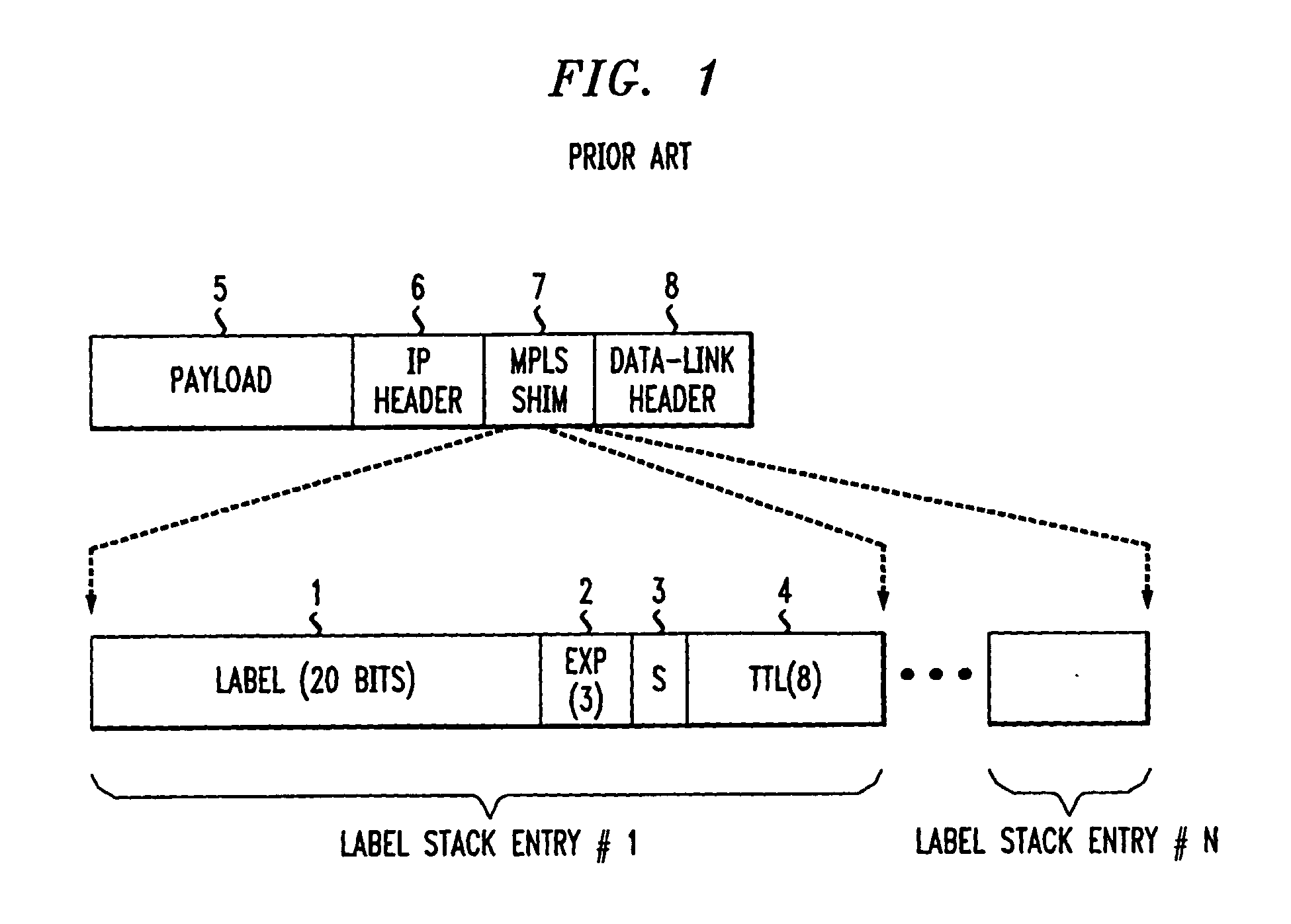
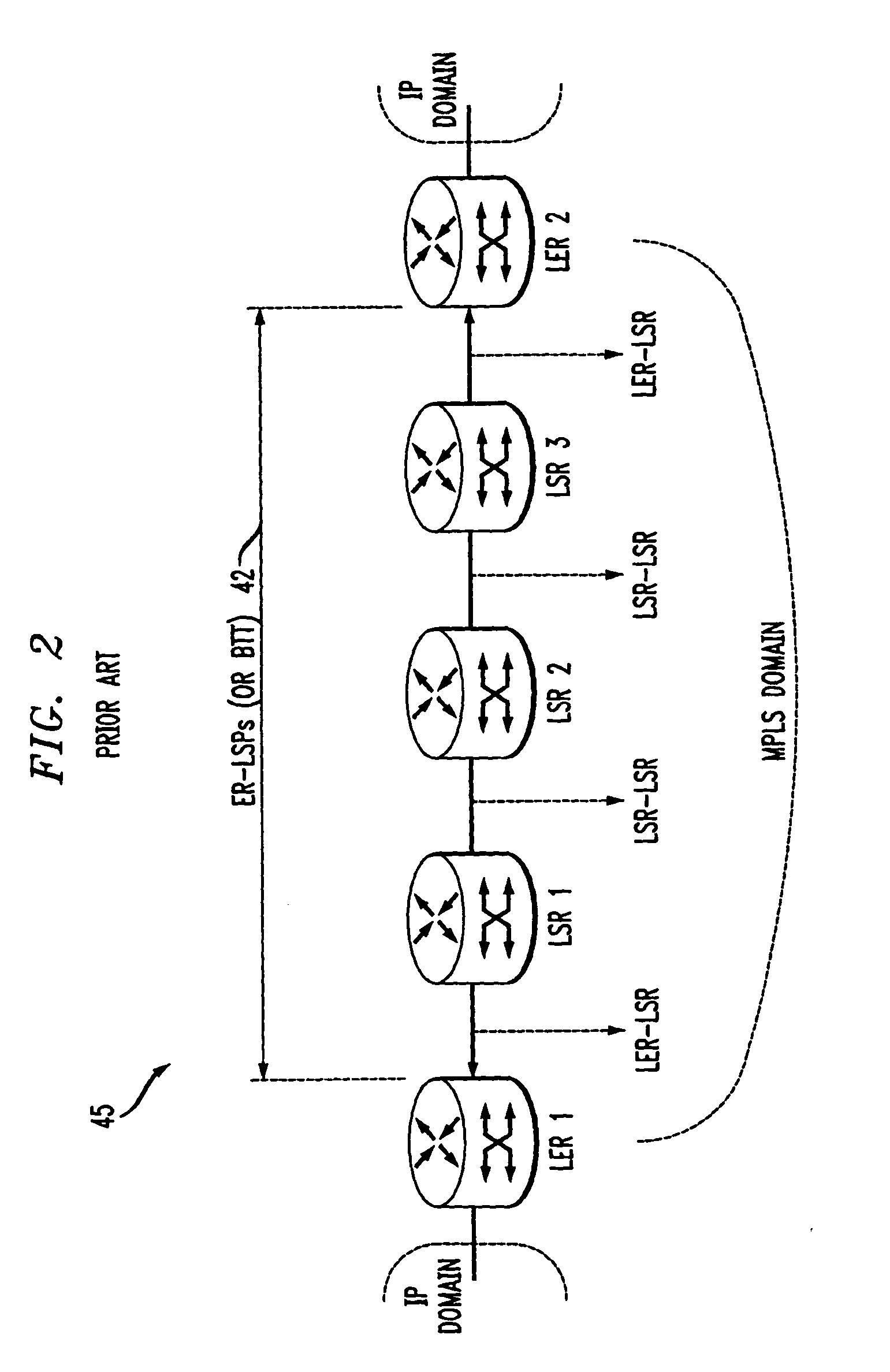
A system and method for introducing a loopback capability for Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) bi-directional traffic trunks are discussed. MPLS is an emerging technology, which integrates Internet Protocol (IP) routing with label switching techniques. MPLS intends to provide new capabilities in the area of traffic engineering for IP networks. These traffic engineering capabilities will have to be combined with a set of complementary operation, administration and maintenance (OA&M) functions for effectively managing and operating MPLS-based networks. One such function is loopback. A loopback function provides the capability to transmit a OA&M packet on one or more segments of a bi-directional traffic trunk (BTT) in a MPLS network. Using a loopback function, parameters of a BTT, such as connectivity, delay and other Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, can be tested. The system and method provide different techniques for implementing loopback in an MPLS network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
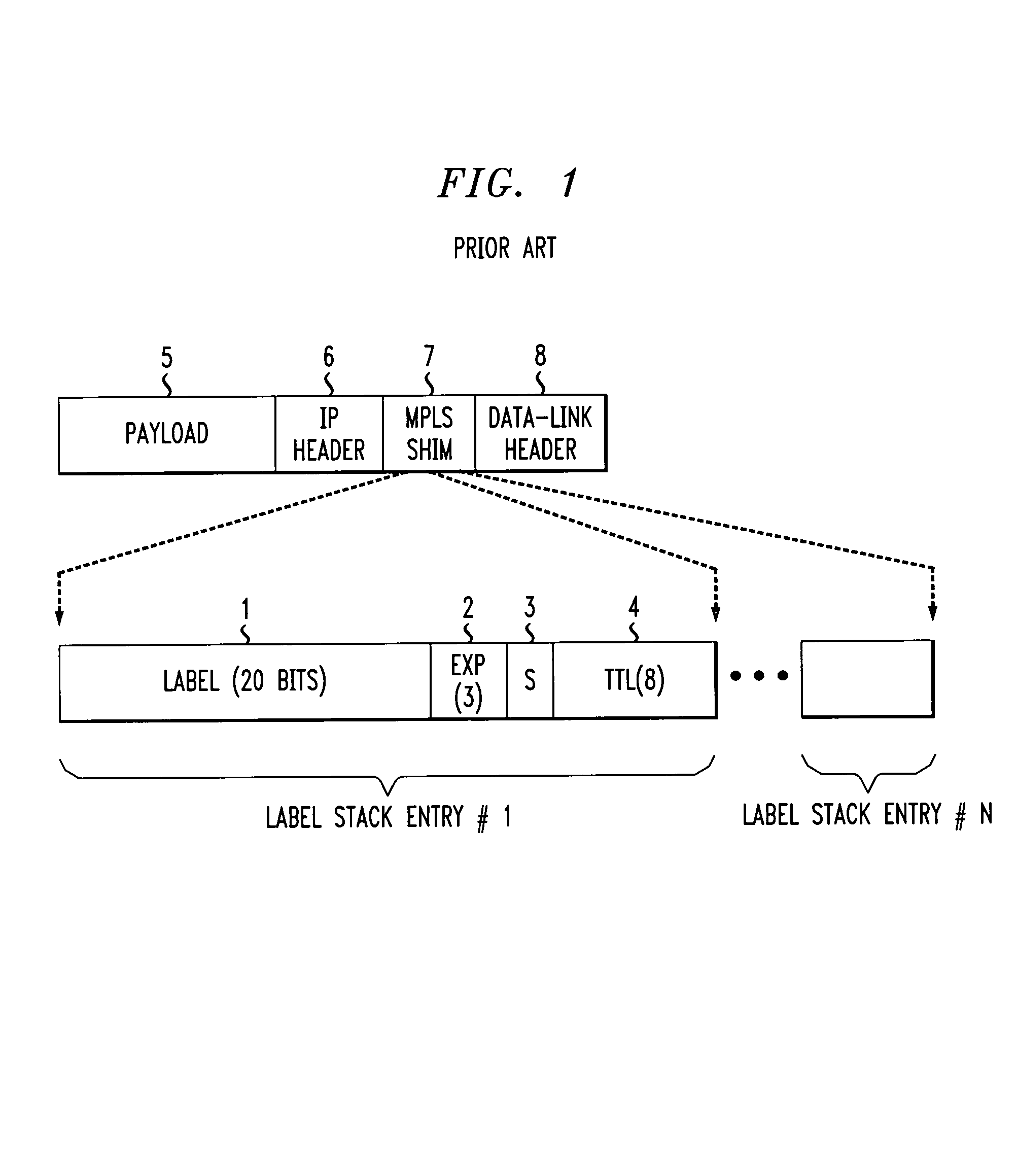
Mpls and gmpls tunnel flap dampening in traffic engineered networks
ActiveUS20150222557A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti protocolLabel switching
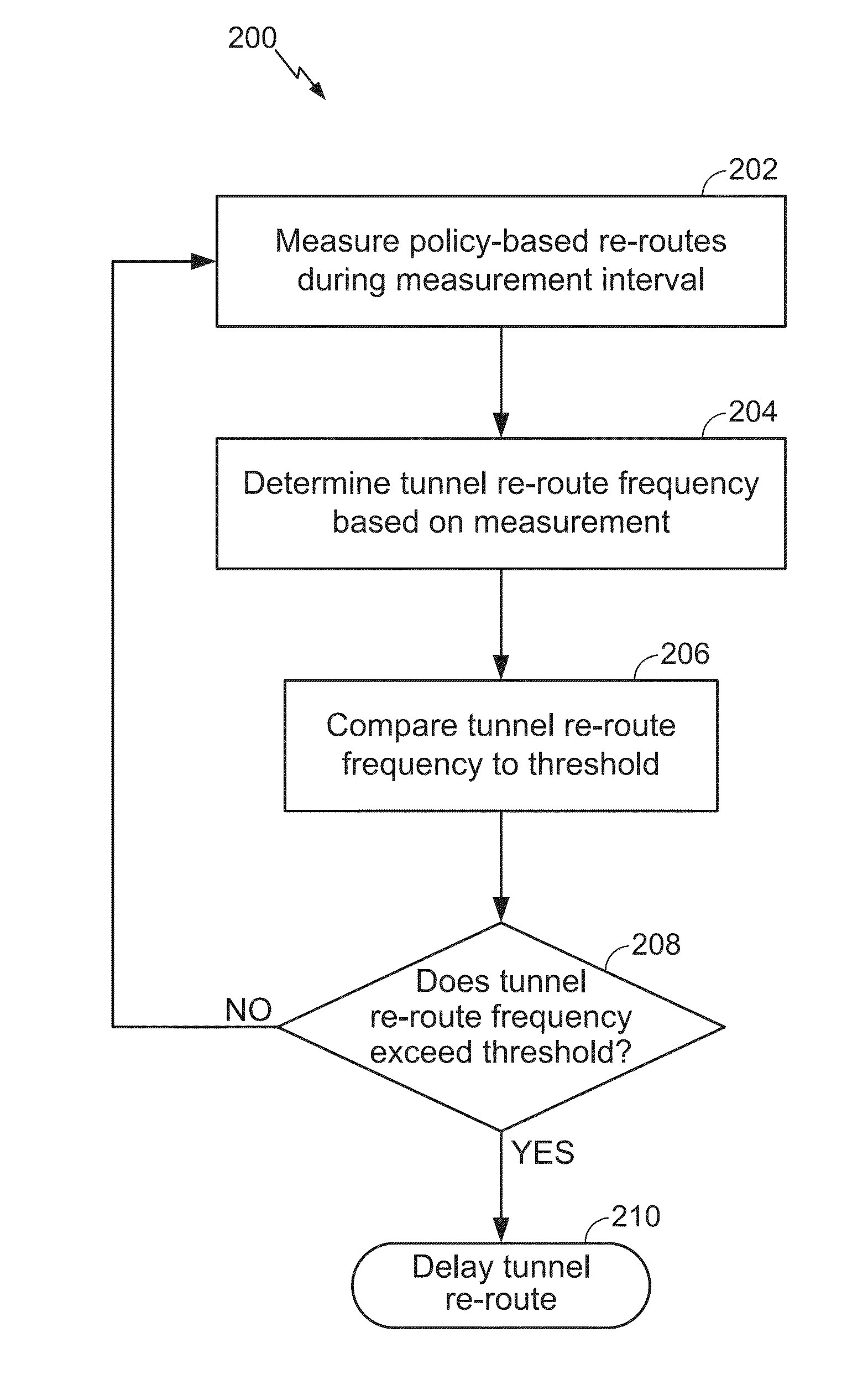
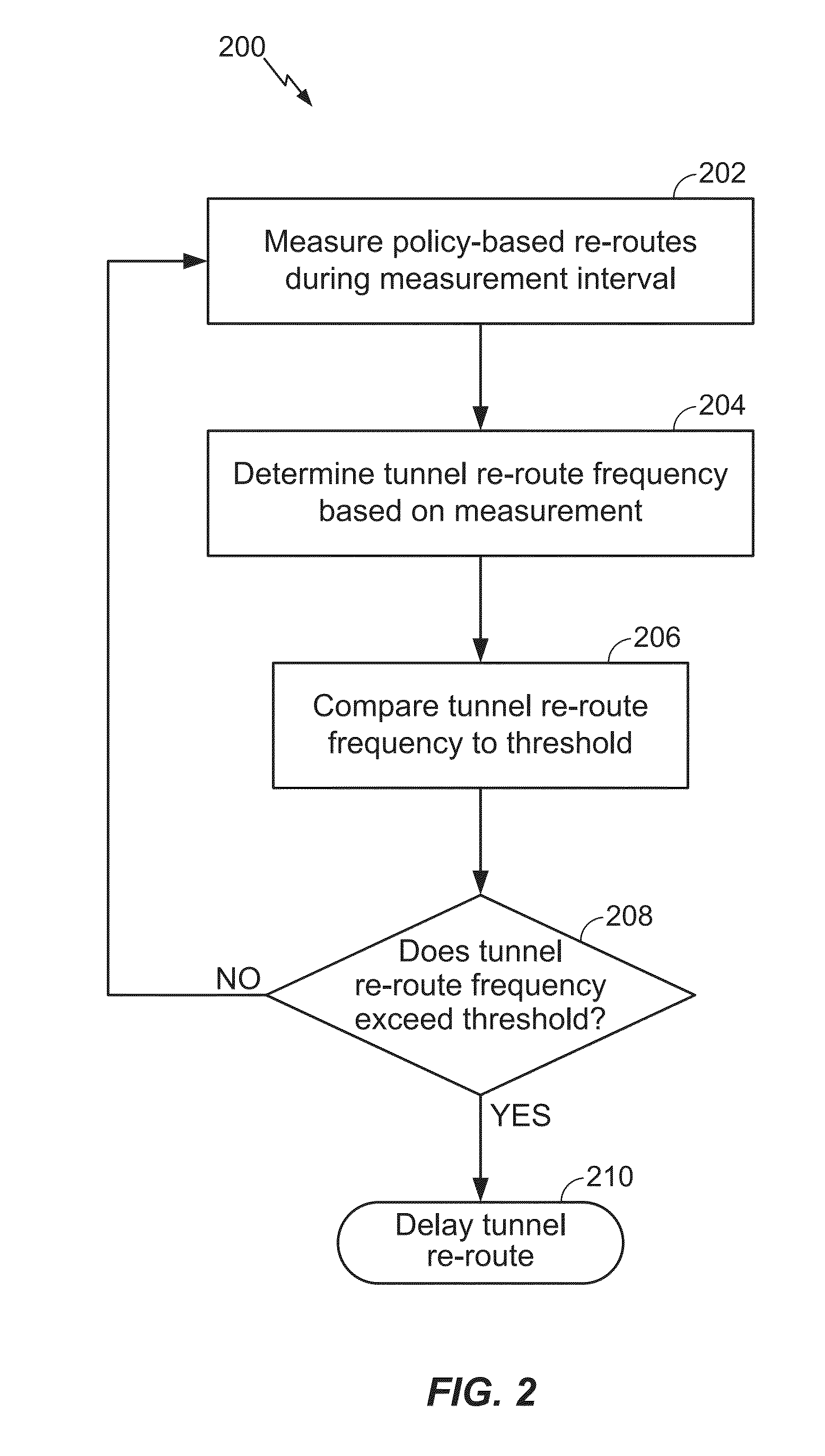
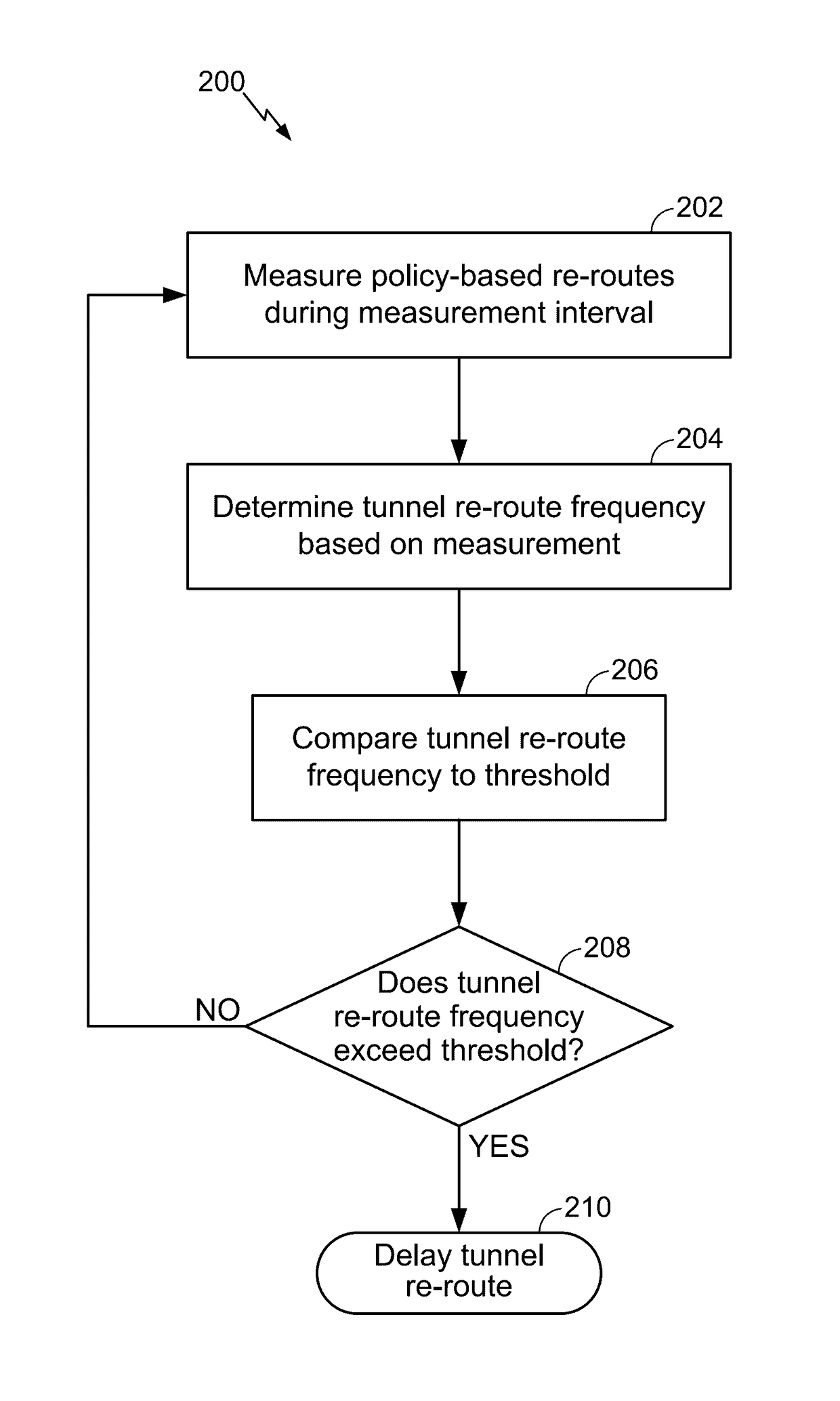
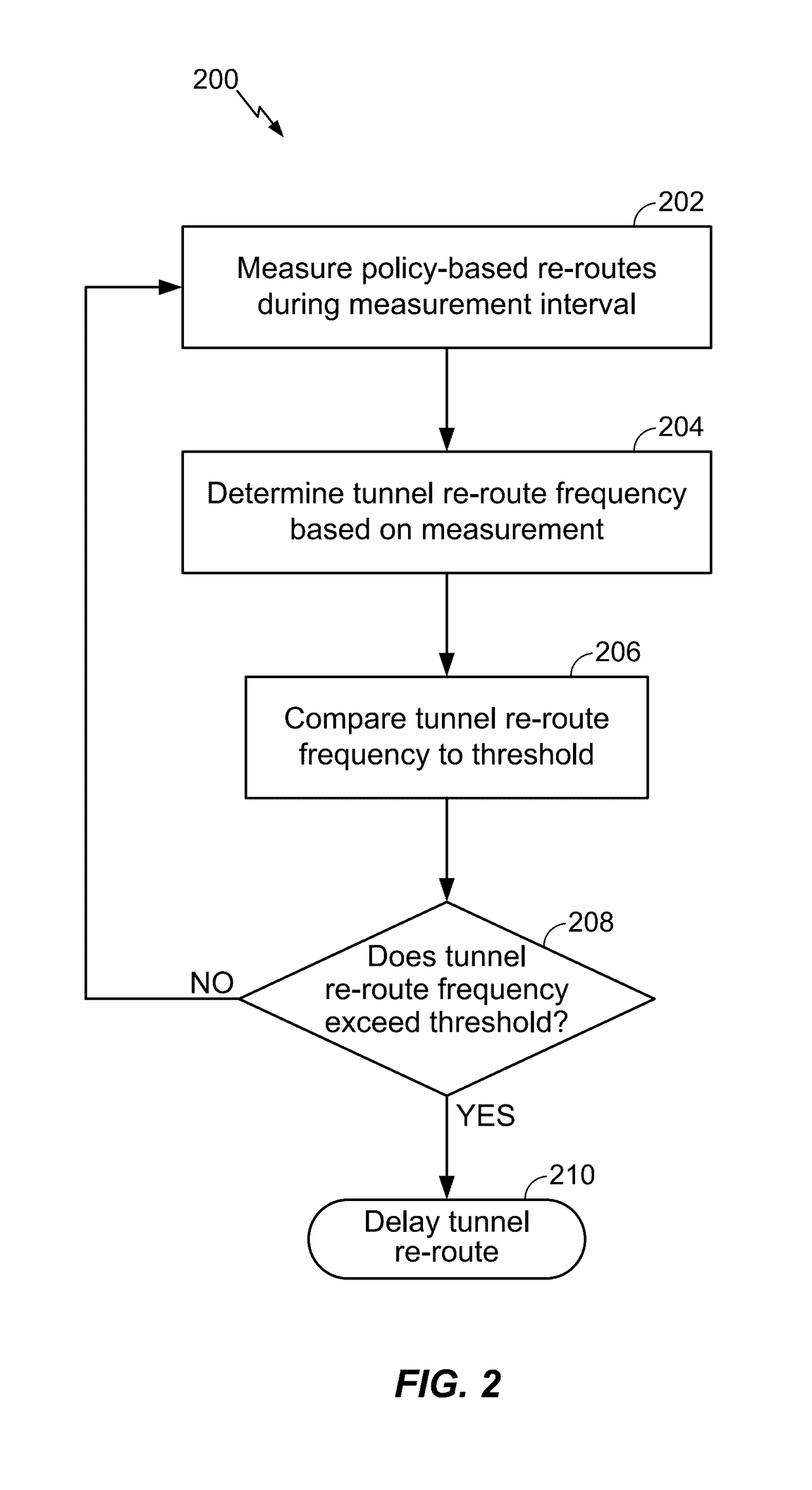
Embodiments of the disclosure are directed to tunnel flap damping in a traffic engineered network. One exemplary method for tracking a re-routing history of Multi-Protocol Label Switching (“MPLS”) / Generalized MPLS (“GMPLS”) tunnels over intervals includes measuring a number of policy-based re-routes during at least one measurement interval; determining a tunnel re-route frequency based on the measurement; comparing the tunnel re-route frequency to a frequency threshold; and determining if the tunnel re-route frequency exceeds the frequency threshold and, if the tunnel re-route frequency exceeds the frequency threshold, delaying at least one tunnel re-route.
Owner:CIENA
In-band signalling for point-point packet protection switching
InactiveUS20100135291A1Data switching by path configurationAutomatic protection switchingDistributed computing
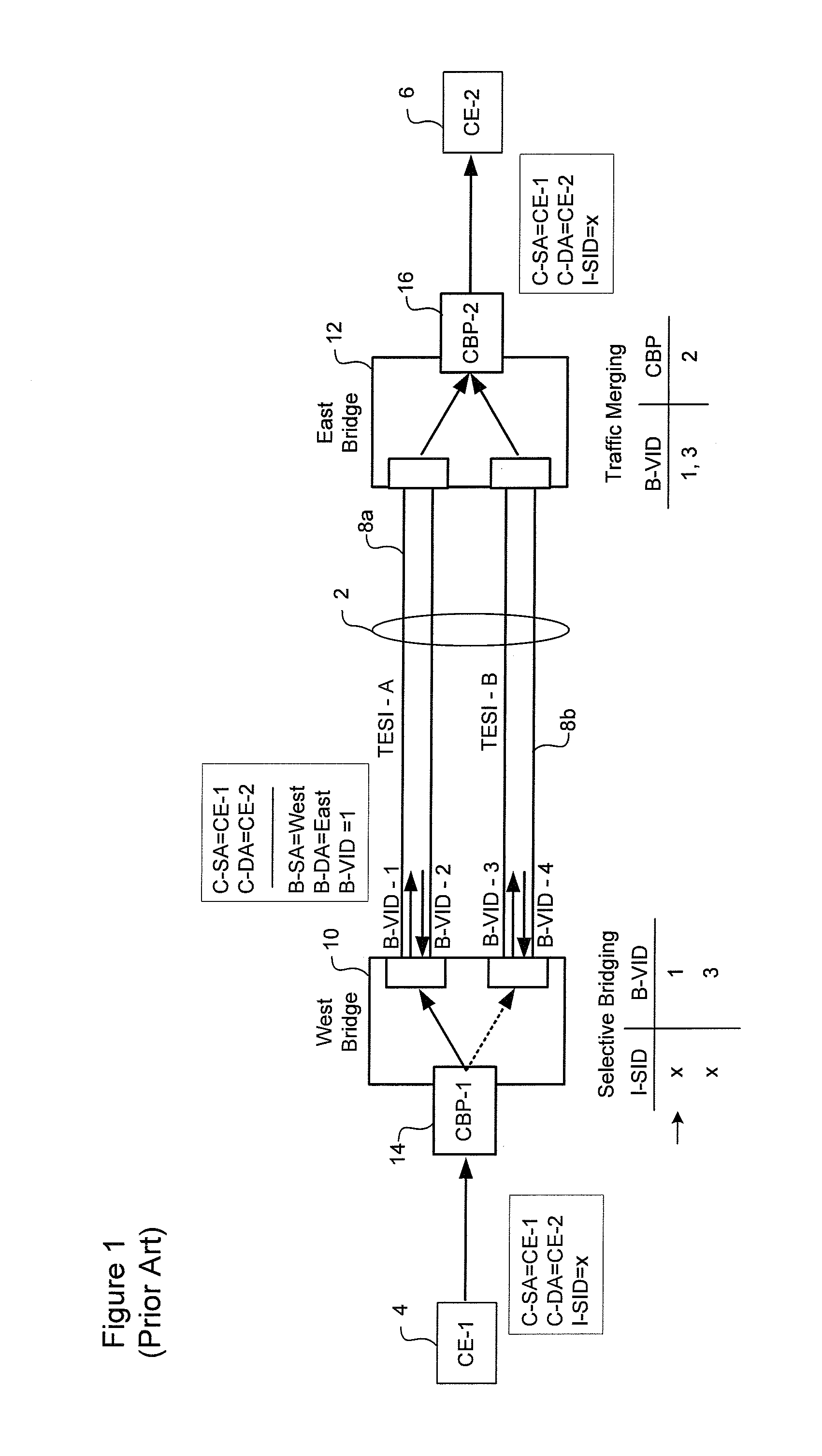
A method of controlling traffic forwarding in a Provider Backbone-Traffic Engineered (PBB-TE) network. A protection group (PG) is defined, and including N working Traffic Engineered Service Instances (TESIs) and M protection TESIs. An Automatic Protection Switching Protocol Data Unit (APS PDU) is defined, which includes information defining at least a state of the protection group. This APS PDU is forwarded only through the protection TESI(s).
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
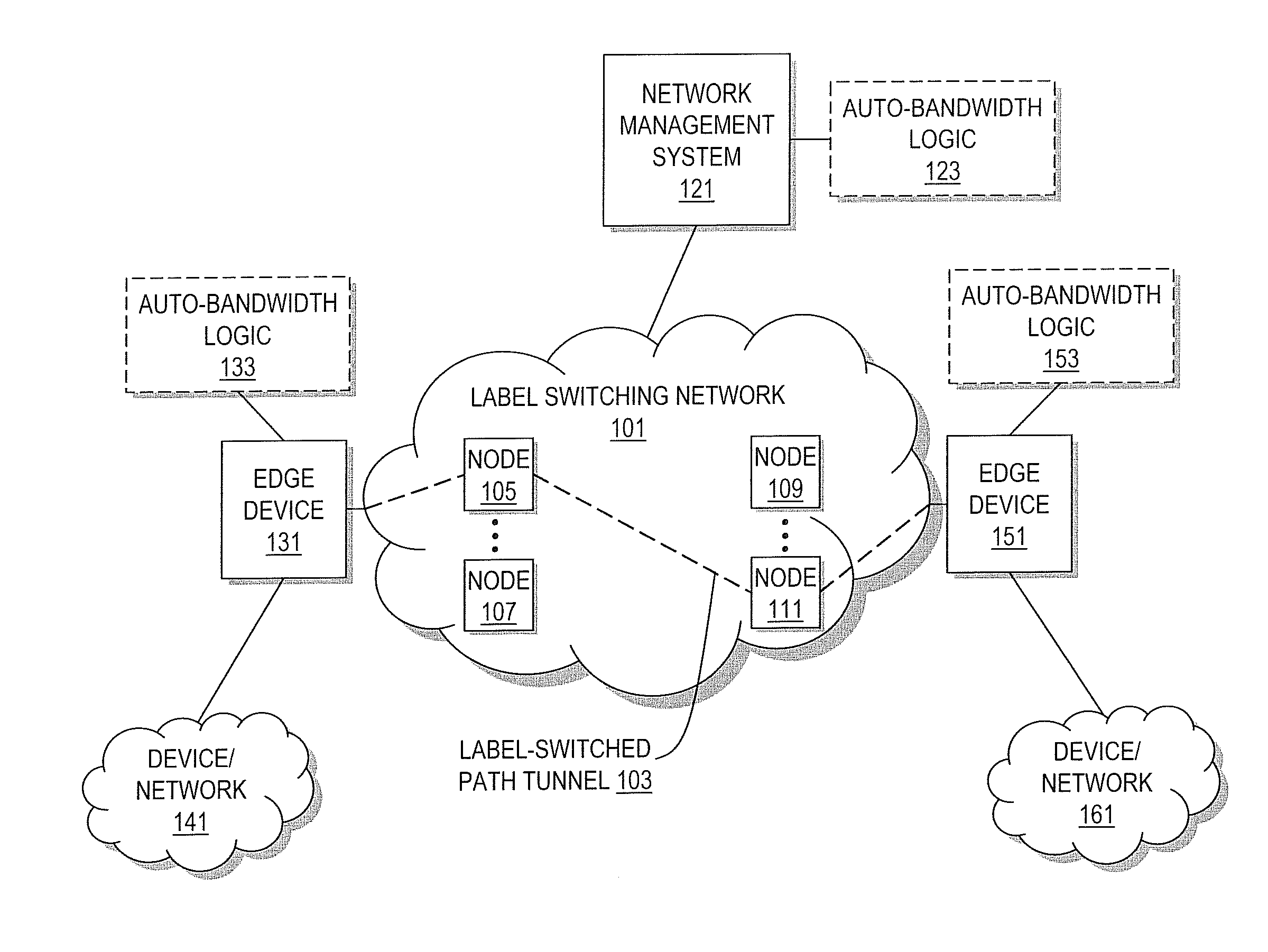
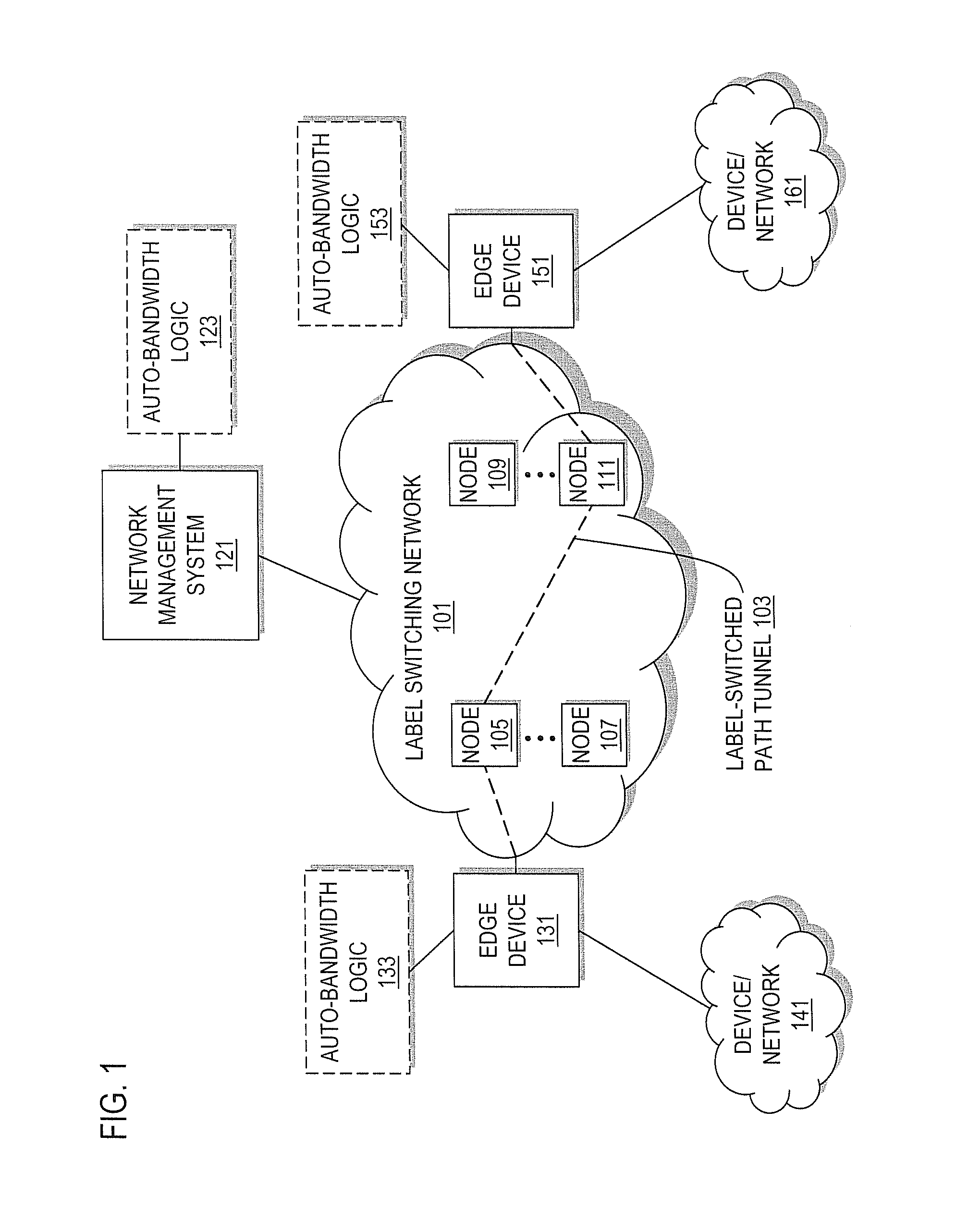
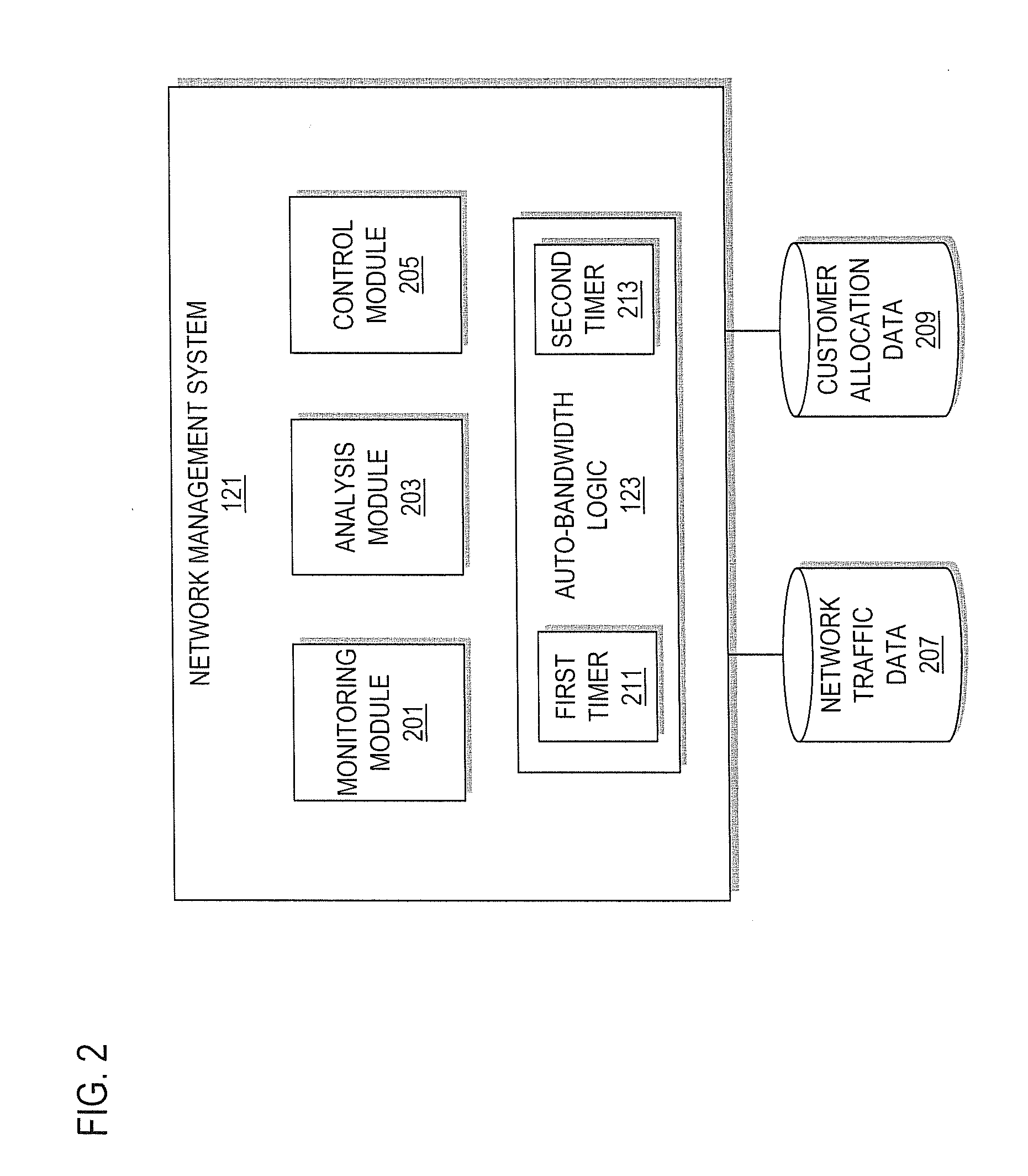
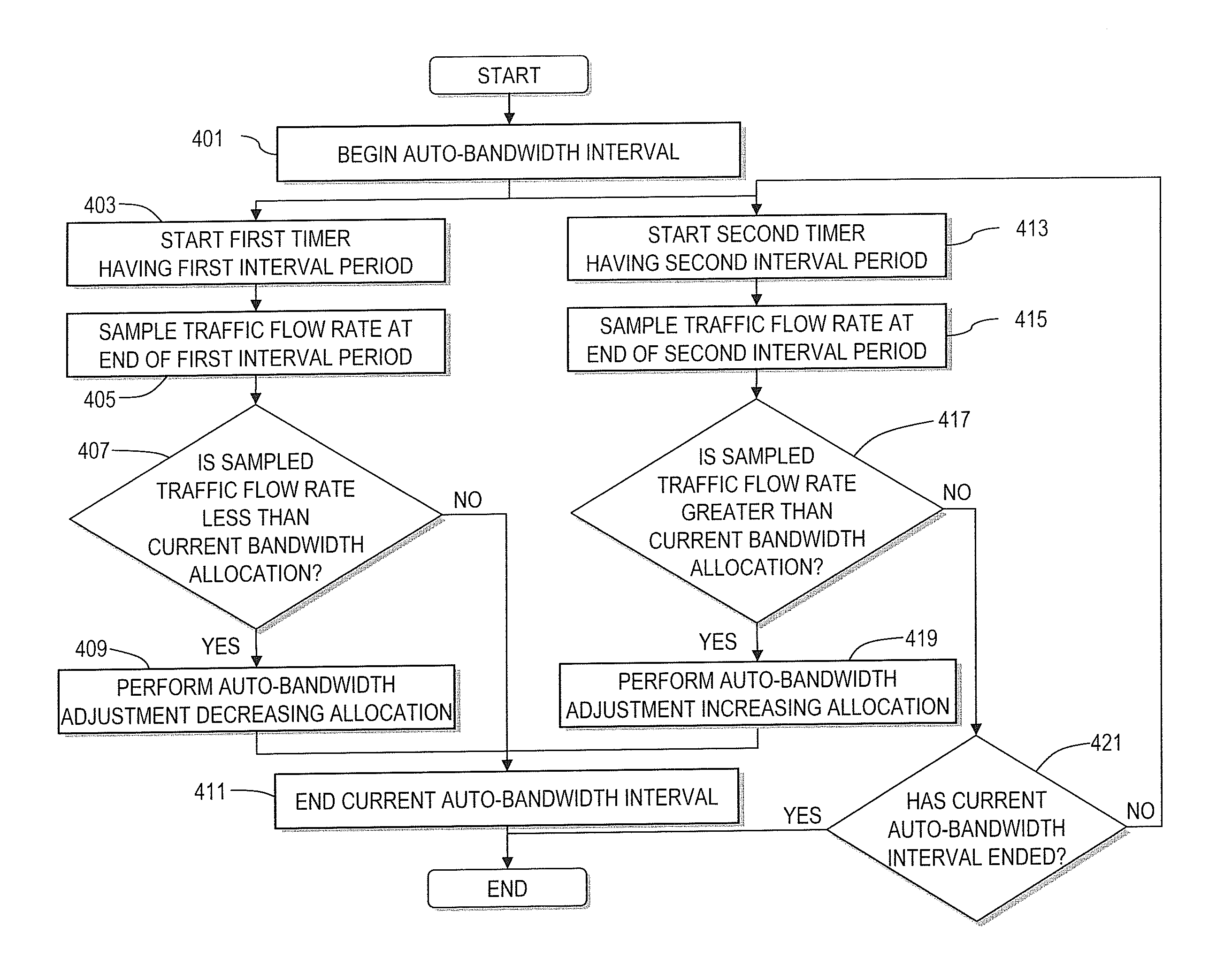
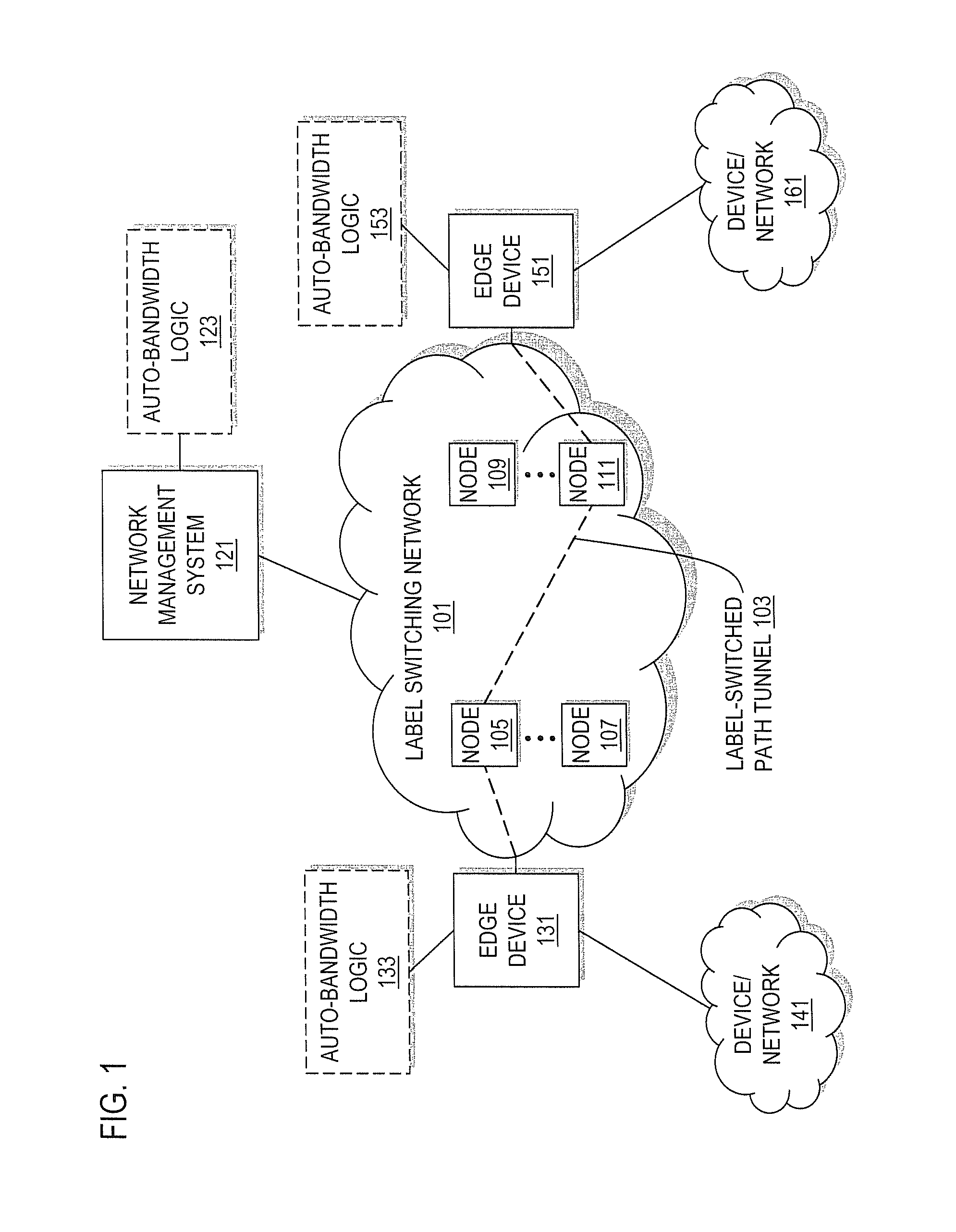
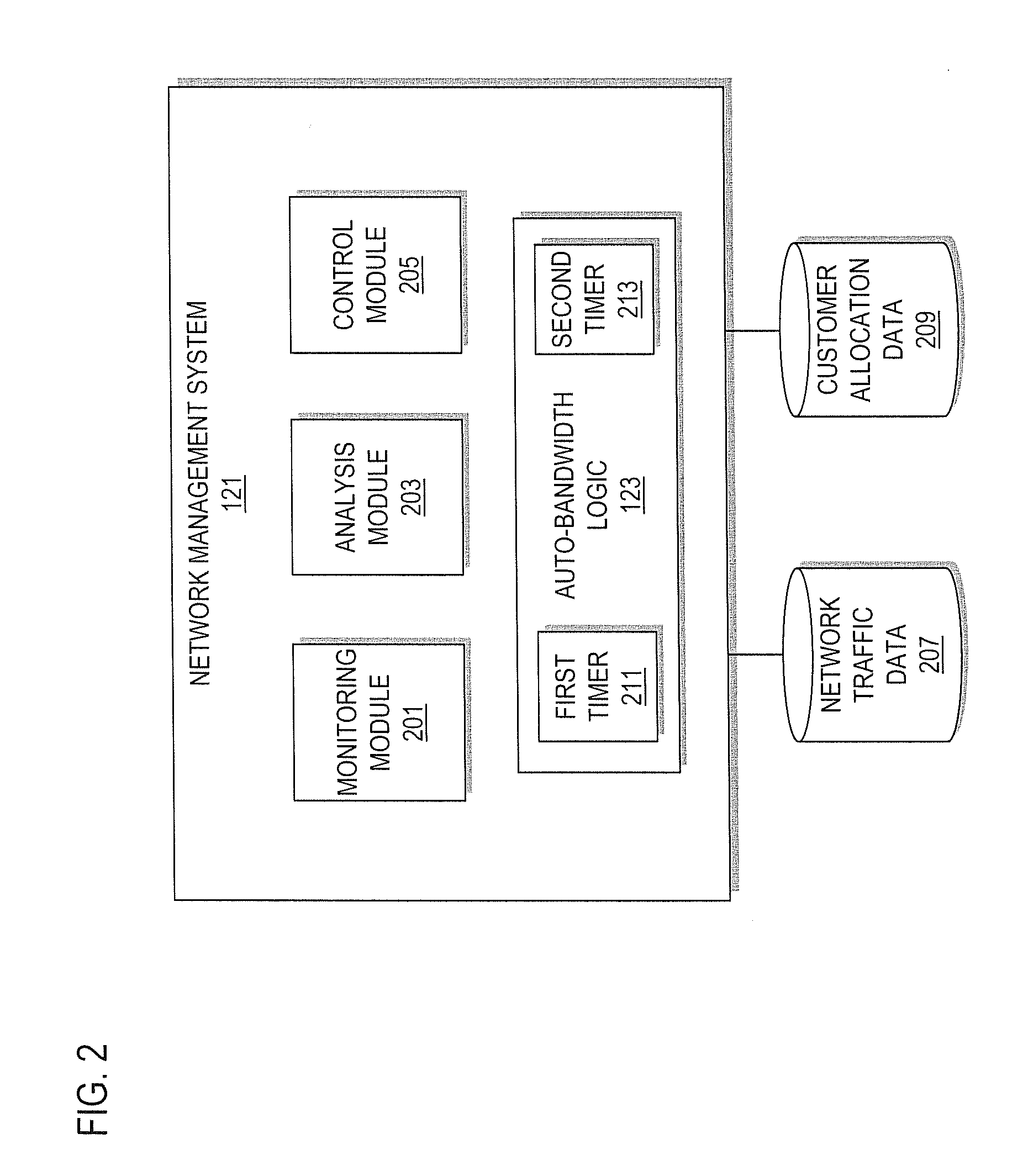
Method and system for adjusting bandwidth using multiple timers
An approach is provided for auto-bandwidth adjusting bandwidth allocations for traffic-engineered tunnels used to carry traffic along a network. Traffic over the tunnel is sampled at a first interval period and at a second interval period, where the second interval period is shorter than the first interval period. A determination is made as to whether the sampled traffic taken using the second interval period is greater than the bandwidth allocation, and the bandwidth allocation is adjusted upward based upon a determination that the sampled traffic taken using the second interval period is greater than the bandwidth allocation. Also, a determination can be made as to whether the sampled traffic taken using the first interval period is less than the bandwidth allocation, and the bandwidth allocation can be adjusted downward based upon a determination that the sampled traffic taken using the first interval period is less than the bandwidth allocation.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
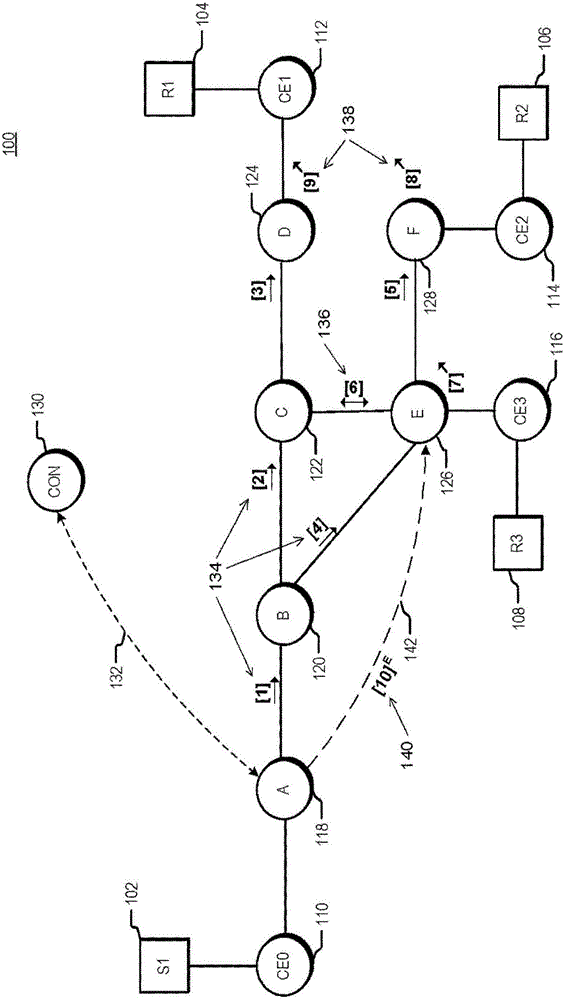
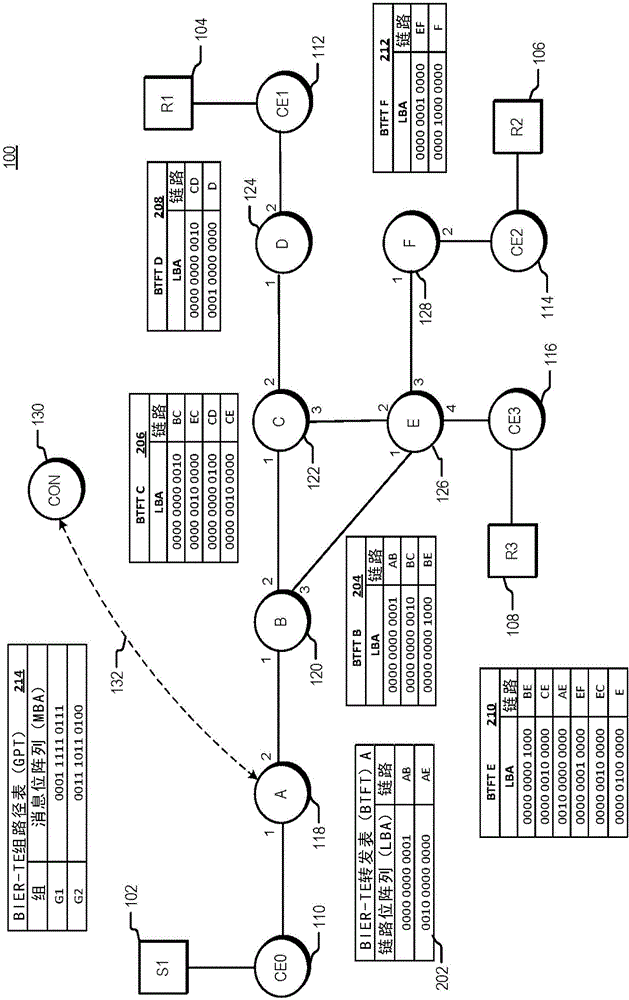
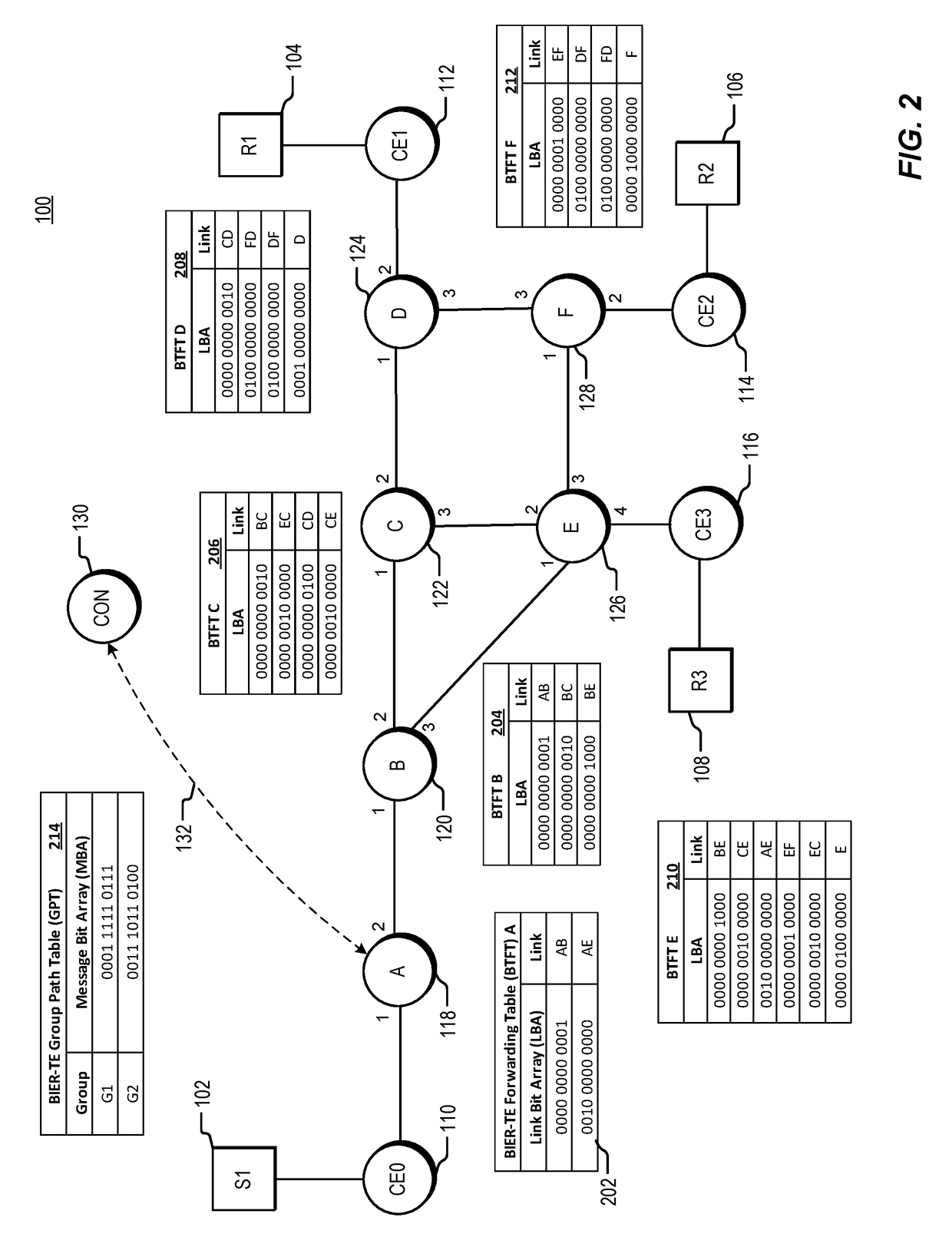
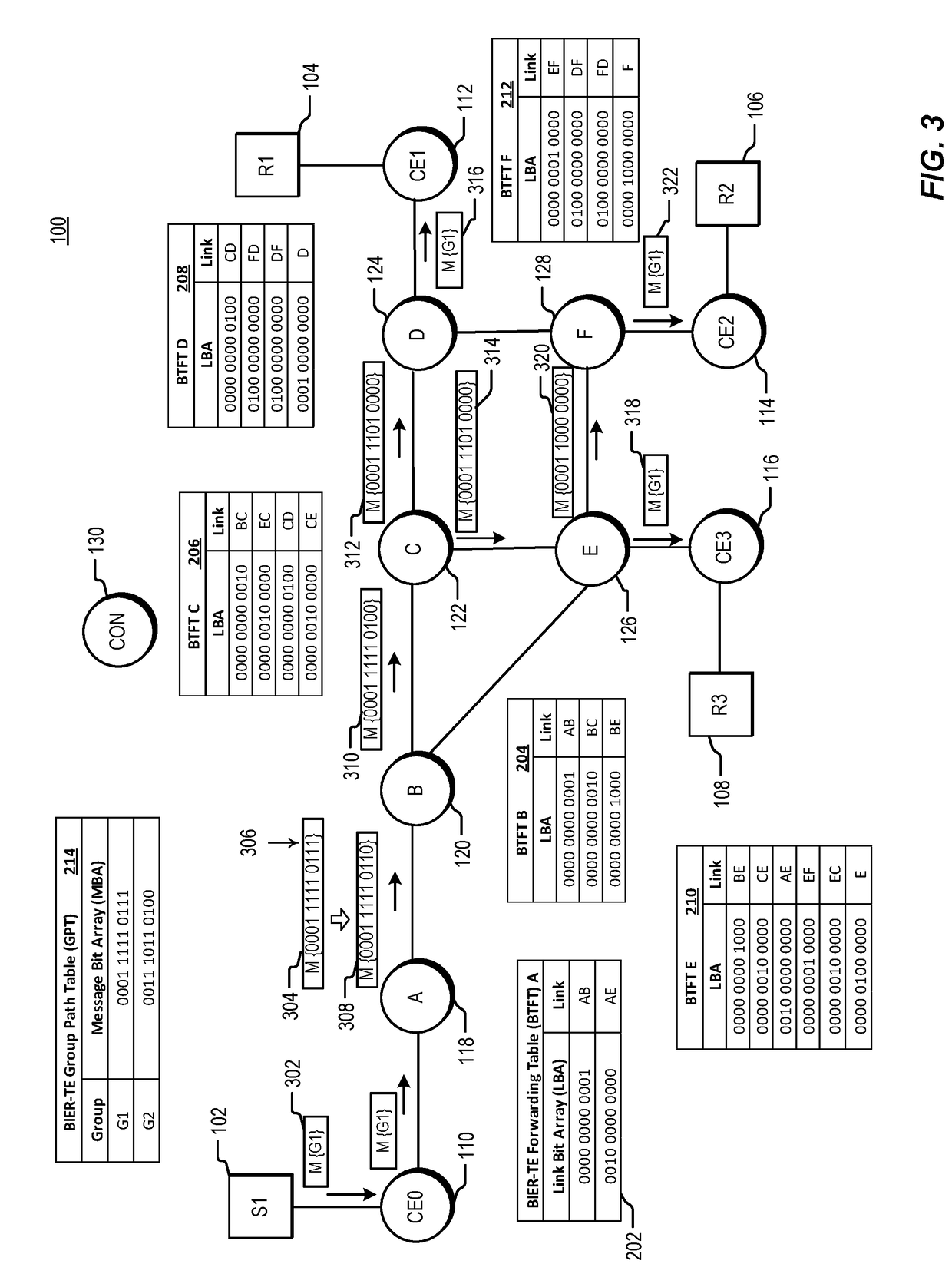
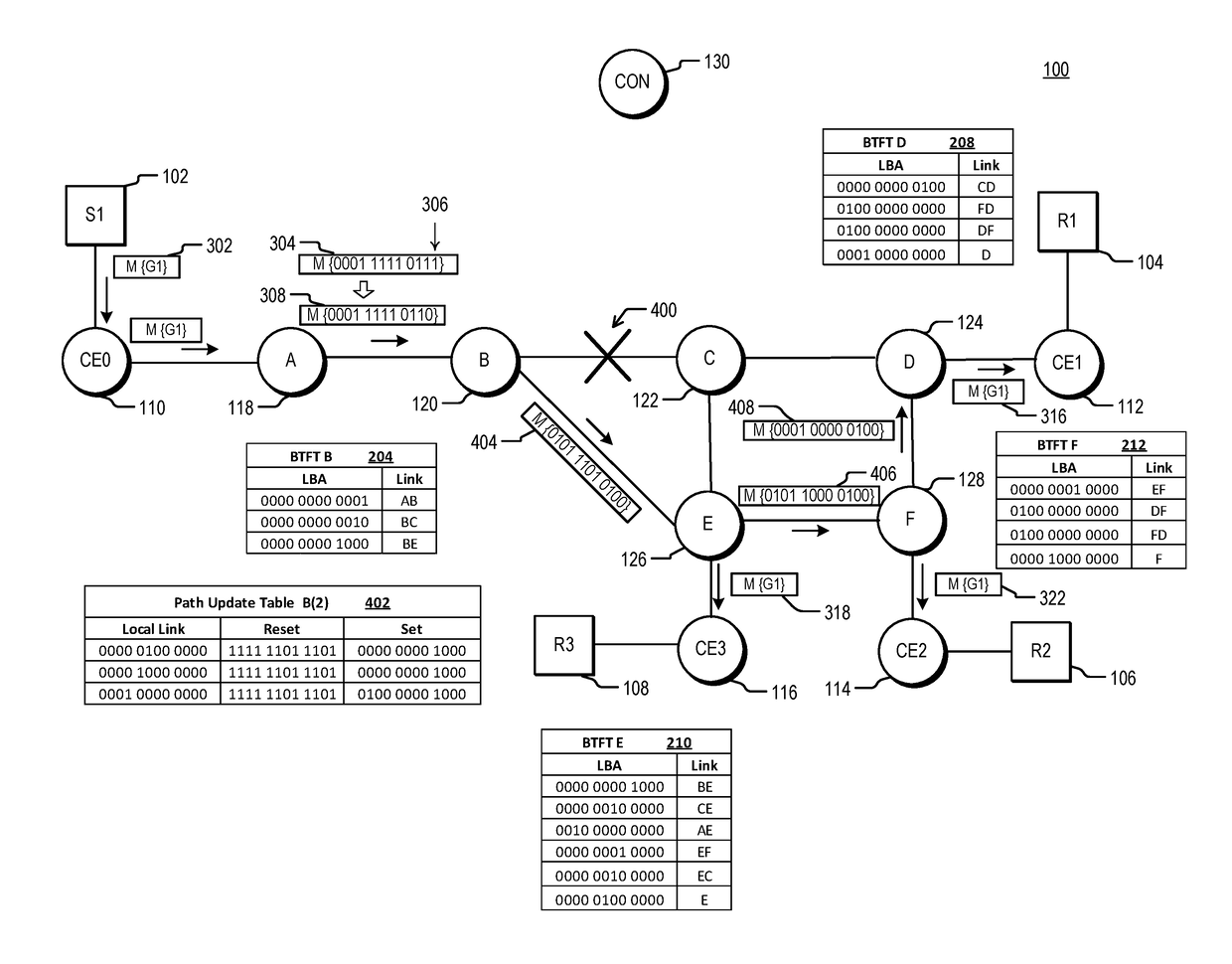
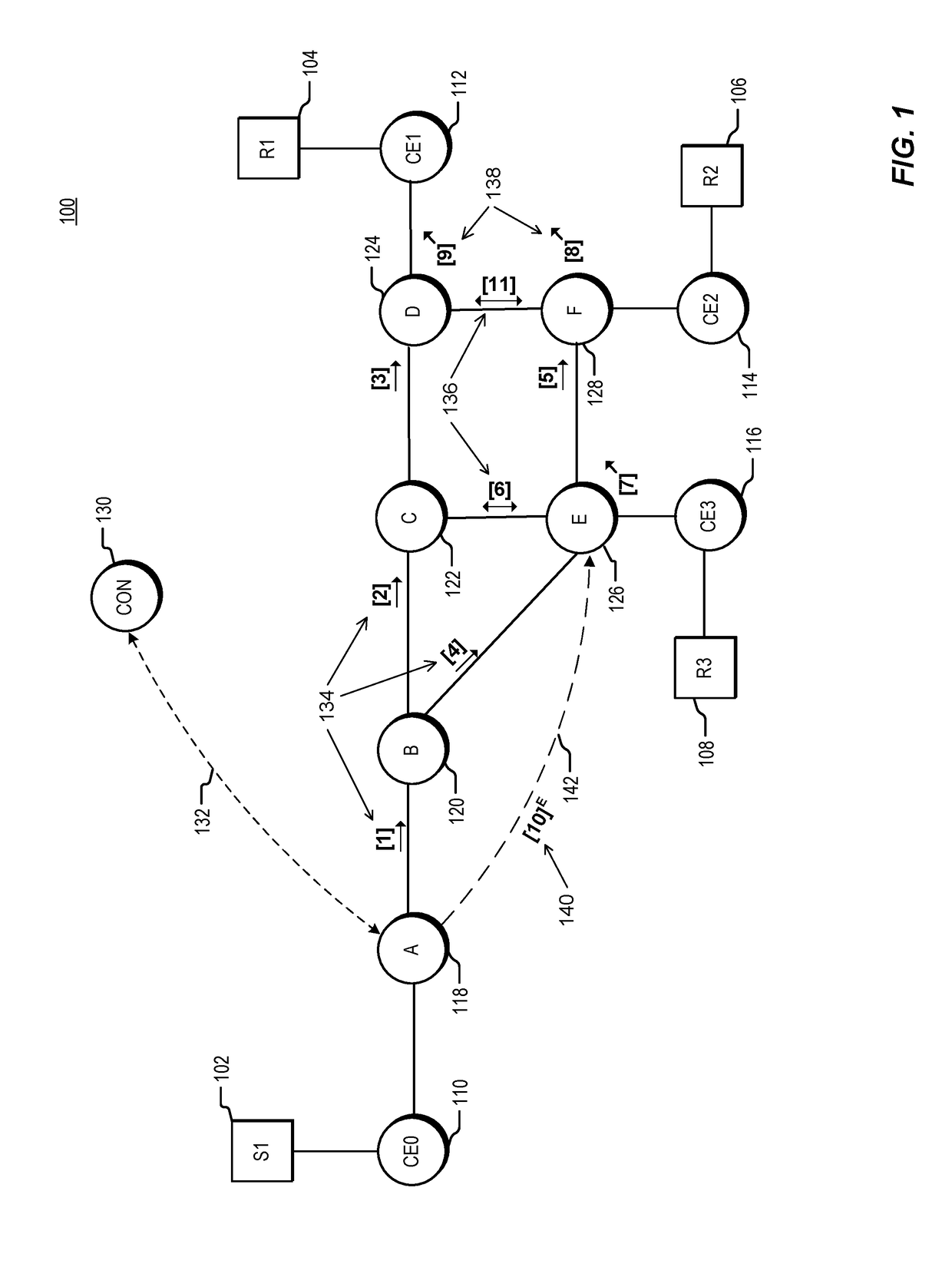
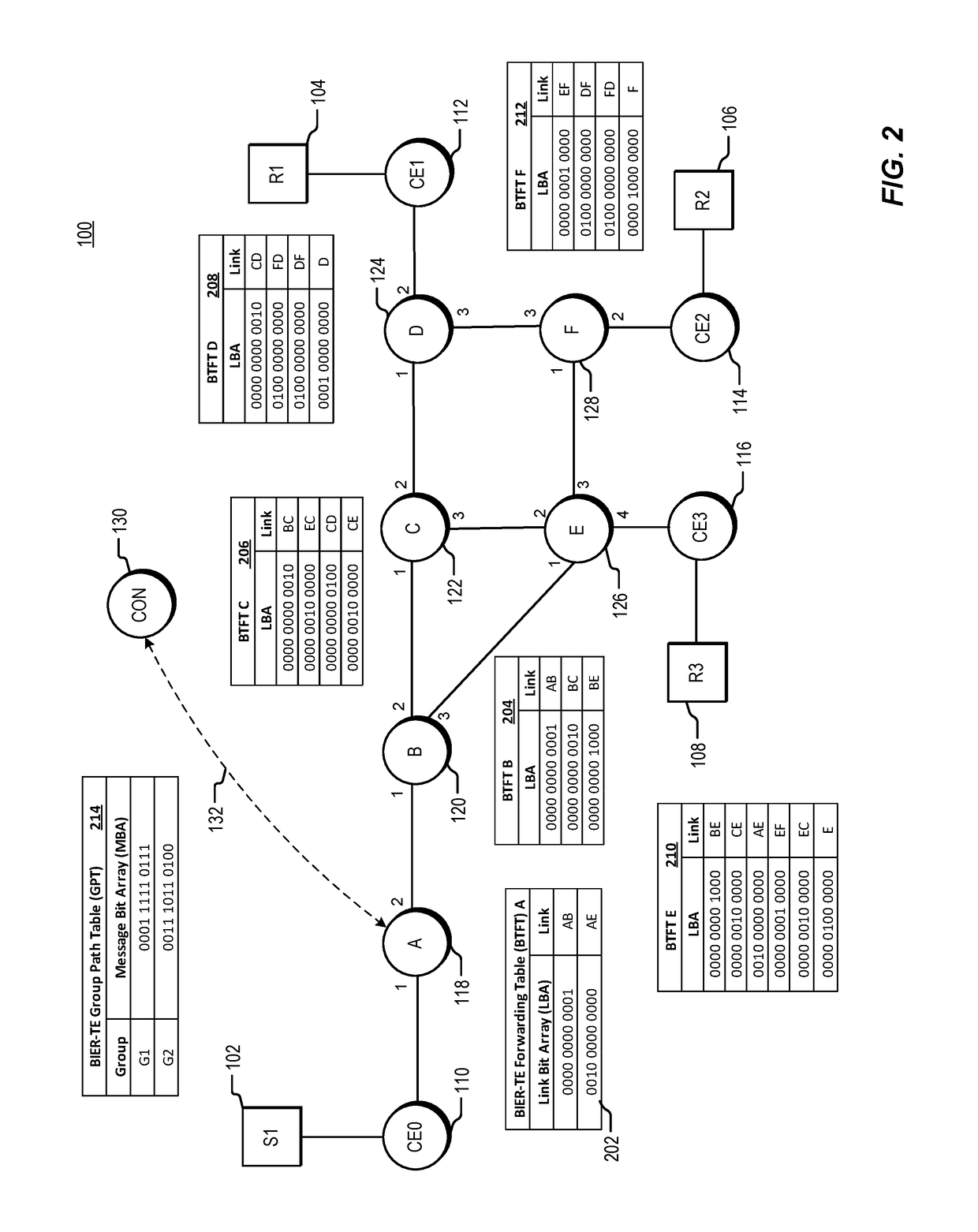
Traffic engineering for bit indexed explicit replication
The invention relates to a traffic engineering for bit indexed explicit replication. Methods and network devices are disclosed for traffic-engineered forwarding through a new form of bit indexed explicit replication. In one embodiment, a method includes receiving at a first node in a network a message comprising a message bit array, and comparing bit values at one or more bit positions in the message bit array to one or more entries in a forwarding table stored at the first node. The one or more bit positions correspond in this embodiment to links in the network. This embodiment of the method further includes forwarding the message over a link represented in the forwarding table if a result of the comparing indicates that the link is included in a path to be taken by the message. In a further embodiment of the method, the message is a multicast message and forwarding the message comprises forwarding a replica of the multicast message.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for using both LDP and RSVP in a communications systems
ActiveUS7664877B1Avoid the needDigital computer detailsTransmissionCommunications systemDistributed computing
Methods and apparatus for allowing routers in an autonomous system to implement LDP and RSVP at the same time. RSVP can be used in the network core with LDP being used in network regions surrounding the core. LDP LSPs are tunneled through the RSVP network core using RSVP LSPs and label stacking techniques. During route selection LDP LSPs which use an RSVP LSP tunnel are preferred over alternative LDP LSPs having an equal cost associated with them to create a preference for traffic engineered routes.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
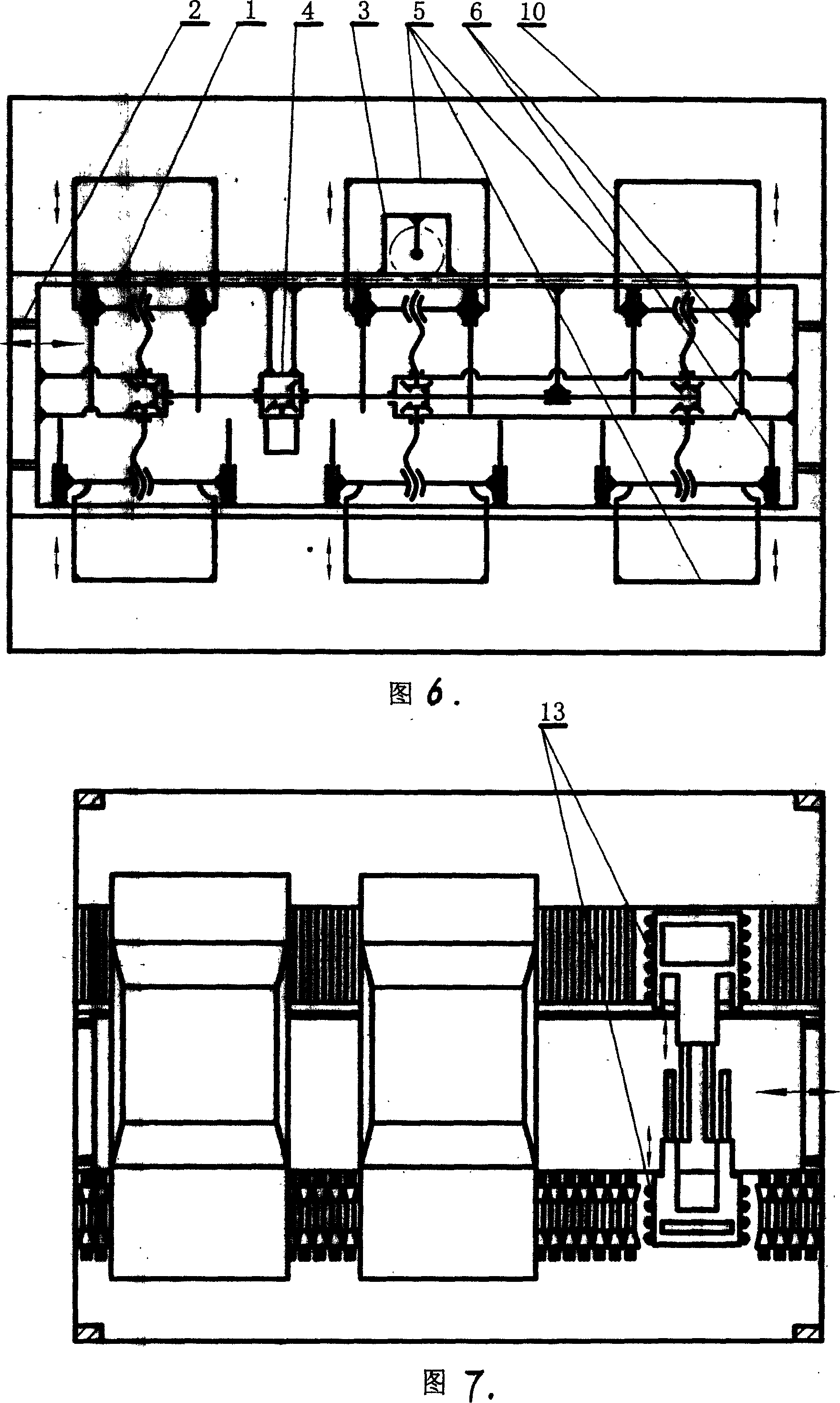
Joggle joint type bearing rail beam structure for middle and low-speed magnetic suspension traffic engineering low line
ActiveCN105714626AAchieving smoothness requirementsError will not occurRailway tracksLow speedReinforced concrete
The invention discloses a joggle joint type bearing rail beam structure for a middle and low-speed magnetic suspension traffic engineering low line. The joggle joint type bearing rail beam structure comprises reinforced concrete supporting structures; each reinforced concrete supporting structure comprises a reinforced concrete girder structure and a reinforced concrete bottom plate; each reinforced concrete bottom plate comprises a bottom plate main body structure, a tenon and a mortise; round corners are arranged on each tenon and each mortise, so that the tenon can rotate in the mortise, therefore, the adjacent two reinforced concrete bottom plates can rotate relative to each other, and further, the reinforced concrete girder structures borne by the two reinforced concrete bottom plates can also rotate relative to each other. According to the joggle joint type bearing rail beam structure disclosed by the invention, as the tenons and the mortises are arranged to form tenon connection, settlement and dislocation caused between the adjacent reinforced concrete girder structures due to different foundation treatment measures are avoided, so that the smoothness requirements for a magnetic suspension traffic engineering overhead structure and a low line transition section F rail are effectively satisfied.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
Medium and low speed maglev traffic engineering low line curve rail bearing beam structure
ActiveCN104452483AMeet stability requirementsMeet strength requirementsBallastwayReinforced concreteLow speed
The invention discloses a medium and low speed maglev traffic engineering low line curve rail bearing beam structure comprising a rail bearing beam, a sleeper pedestal fixed to the top of the rail bearing beam, a rail section fixed to the top of the sleeper pedestal, a reinforcement concrete base plate fixed to the interarea of the horizontal ground and guide rails arranged on two sides of the rail bearing beam; the top surface of the reinforcement concrete base plate is arranged obliquely corresponding to the level, the included angle between the top surface of the reinforcement concrete base plate and the level is alpha q, the bottom of the rail bearing beam is fixedly connected to the top of the reinforcement concrete base plate, the axle of the rail bearing beam, sleeper pedestal and rail section are perpendicular to the top surface of the reinforcement concrete base plate, the included angle between the central line of the rail section and the central line of the line is alpha, and alpha 1 = alpha. By the aid of the structure, the installation requirements for a maglev vehicle contacting with the rail can be met, the construction difficulty of soil engineering base below the rail bearing beam is not raised, and the long-term stability is not reduced.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
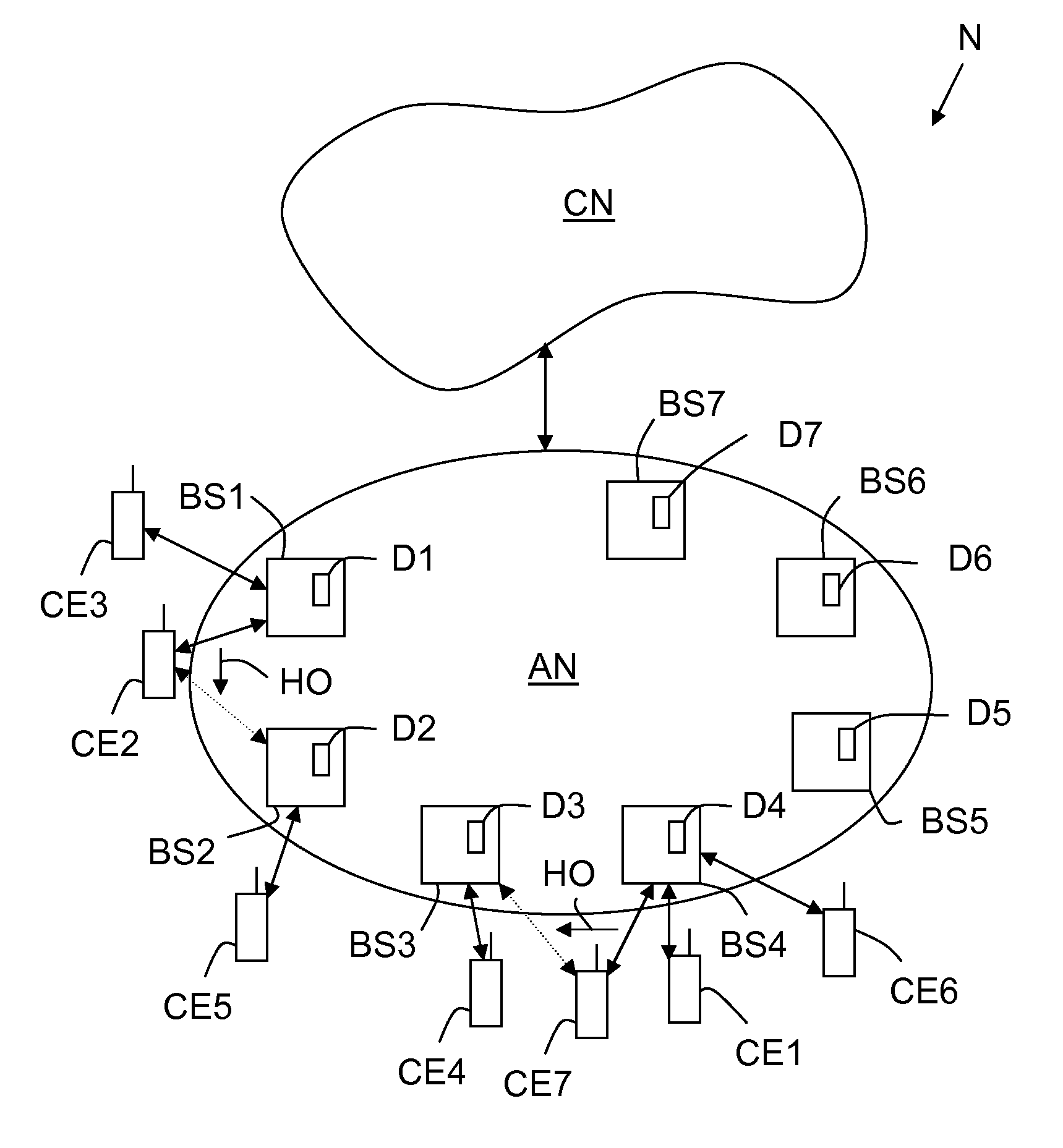
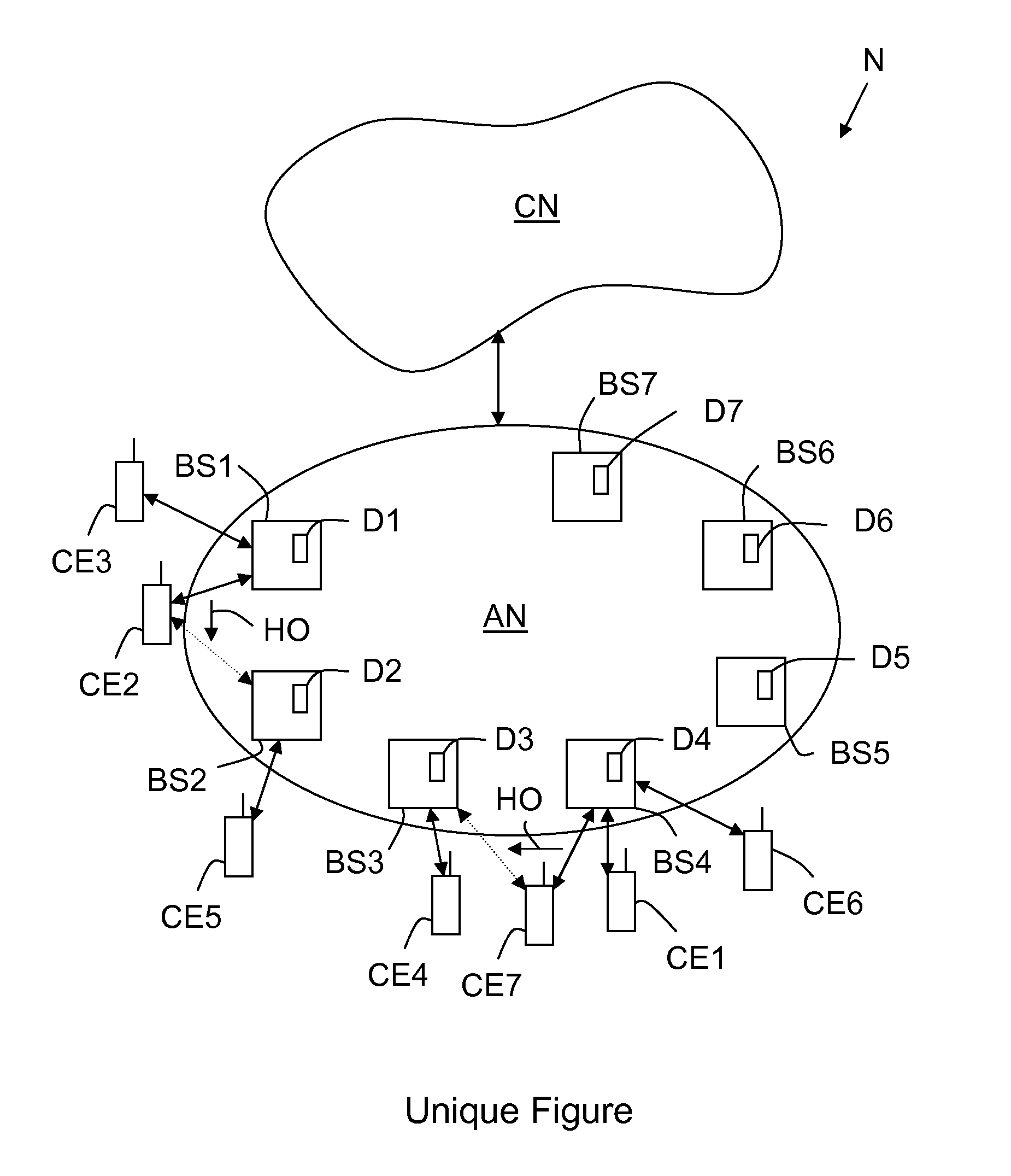
Multi-mode traffic engineered handover management device and method for a broadband wireless access network
InactiveUS20110170518A1Maximize successGood switching effectWireless commuication servicesAccess networkAlarm message
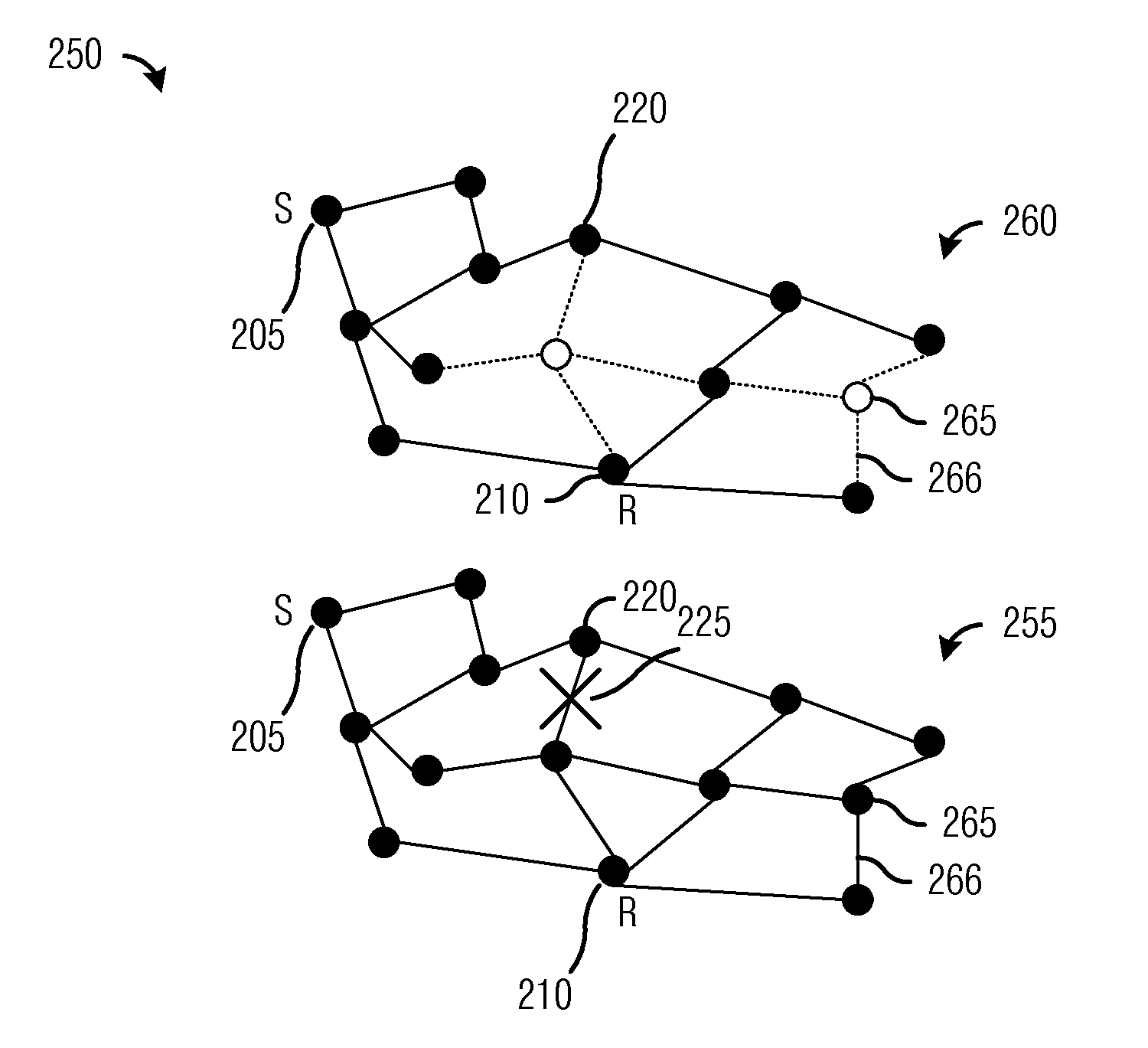
A handover management device (D1) is intended for a broadband wireless access network (AN) comprising a plurality of base stations (BS1-BS6) to which communication equipments (CE1-CE7) may be connected to. This device (D1) is arranged, when it receives, from either a base station (BS1) or a communication equipment (CE2) connected to this base station (BSi), an alarm message signalling either i) a degradation of at least one decision metric, representative either of the quality of a signal transmitted between this connected communication equipment (CE2) and this base station (BS1) or of a quality of service offered by this base station (BS1) to this connected communication equipment (CE2), or ii) an overload of this base station (BS1), for triggering a handover assisted either by this connected communication equipment (CE2) and possibly this base station (BS1) and involving a target base station (BS2) to be selected, or by a selected target communication equipment (CE5) and this base station (BS1) and involving a target base station (BS2) to be selected.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
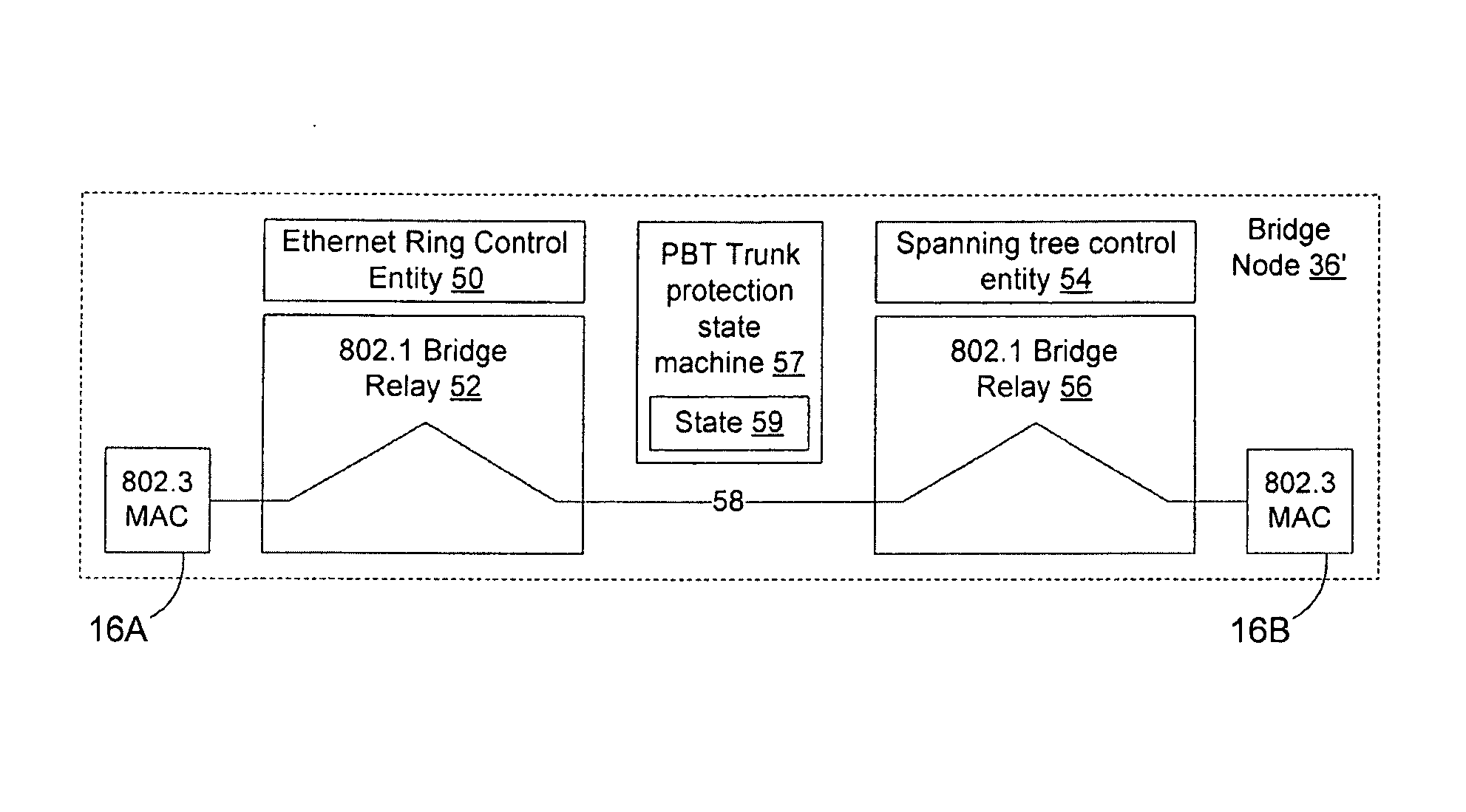
Interworking an ethernet ring network and an ethernet network with traffic engineered trunks
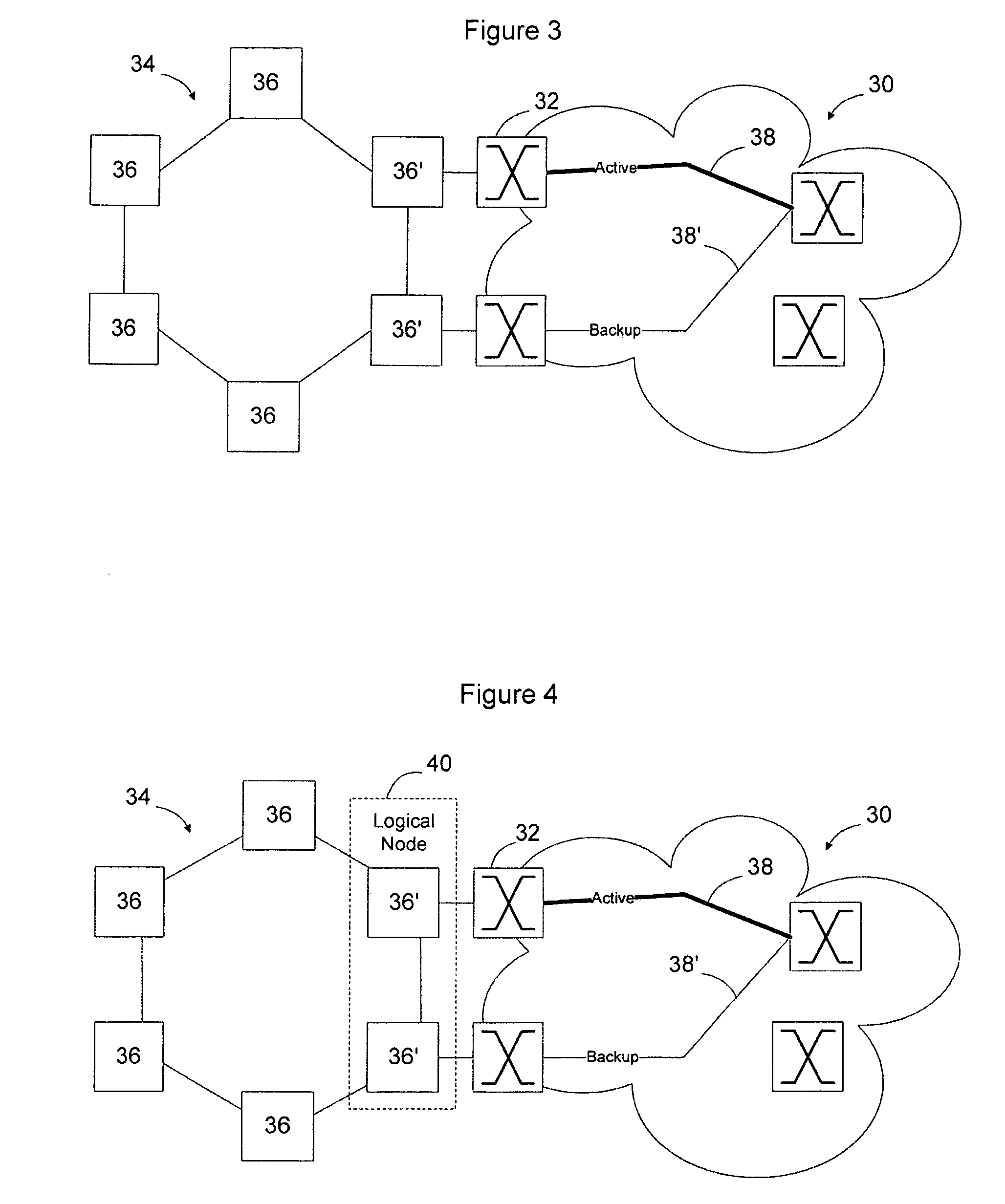
Interworking an Ethernet Ring network with an Ethernet network with traffic engineered trunks (PBT network) enables traffic engineered trunks to be dual homed to the Ethernet ring network to enable for protection switching between active and backup trunk paths in the PBT network. In one embodiment, the active path will terminate at a first bridge node on the Ethernet ring network and the backup path will terminate at a second bridge node on the Ethernet ring network. Trunk state information is exchanged between the bridge nodes to enable the bridge nodes to determine which of the active and backup paths should be used to forward data on the trunk. Upon a change in trunk state, a flush message is transmitted on the Ethernet ring network to enable the nodes on the Ethernet ring network to relearn the path to the new responsible bridge node.
Owner:CIENA
Loopback capability for Bi-directional multi-protocol label switching traffic engineered trunks
A system and method for introducing a loopback capability for Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) bi-directional traffic trunks are discussed. MPLS is an emerging technology, which integrates Internet Protocol (IP) routing with label switching techniques. MPLS intends to provide new capabilities in the area of traffic engineering for IP networks. These traffic engineering capabilities will have to be combined with a set of complementary operation, administration and maintenance (OA&M) functions for effectively managing and operating MPLS-based networks. One such function is loopback. A loopback function provides the capability to transmit a OA&M packet on one or more segments of a bi-directional traffic trunk (BTT) in a MPLS network. Using a loopback function, parameters of a BTT, such as connectivity, delay and other Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, can be tested. The system and method provide different techniques for implementing loopback in an MPLS network.
Owner:BOODAGHIANS SAMSON
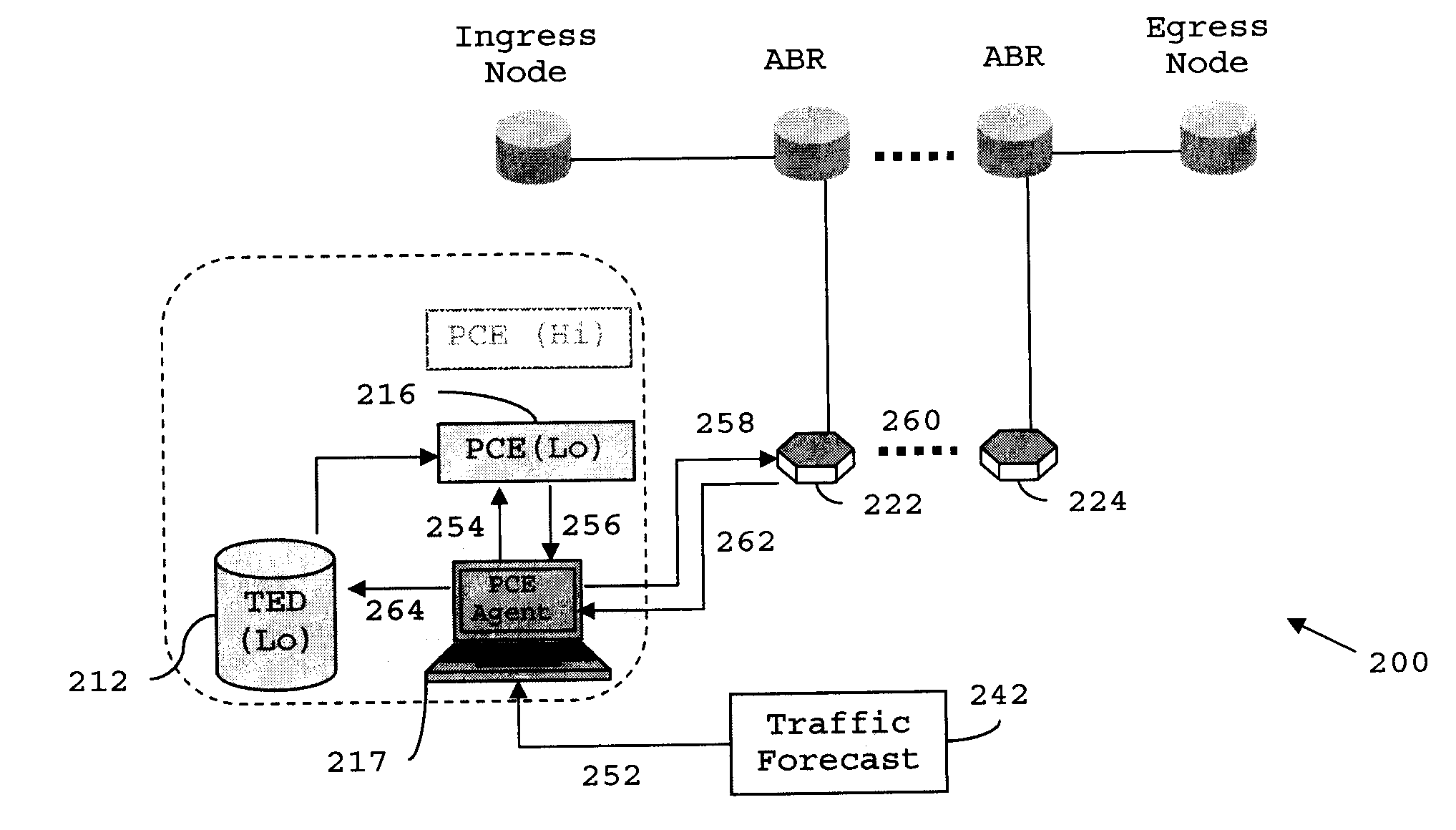
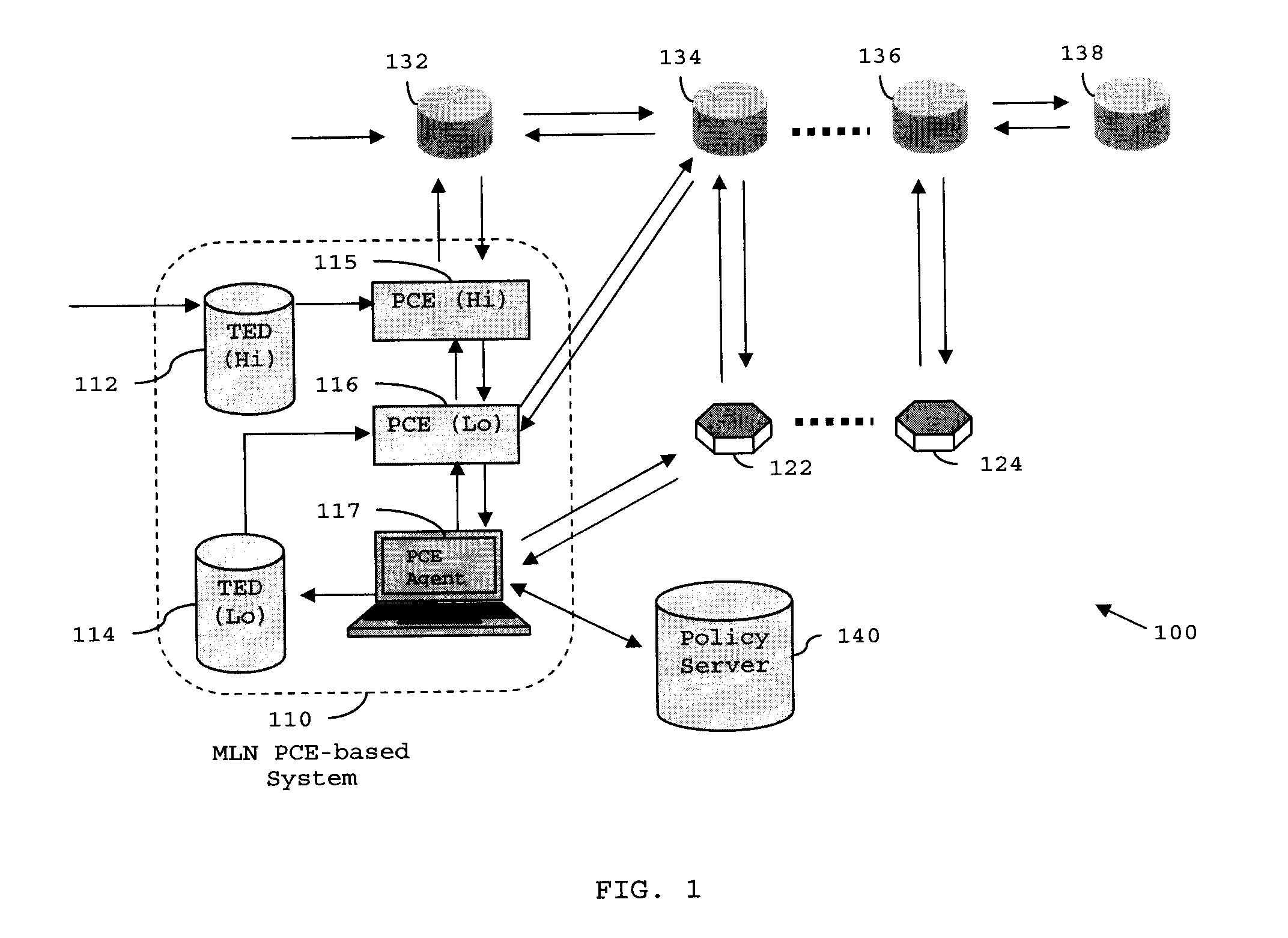
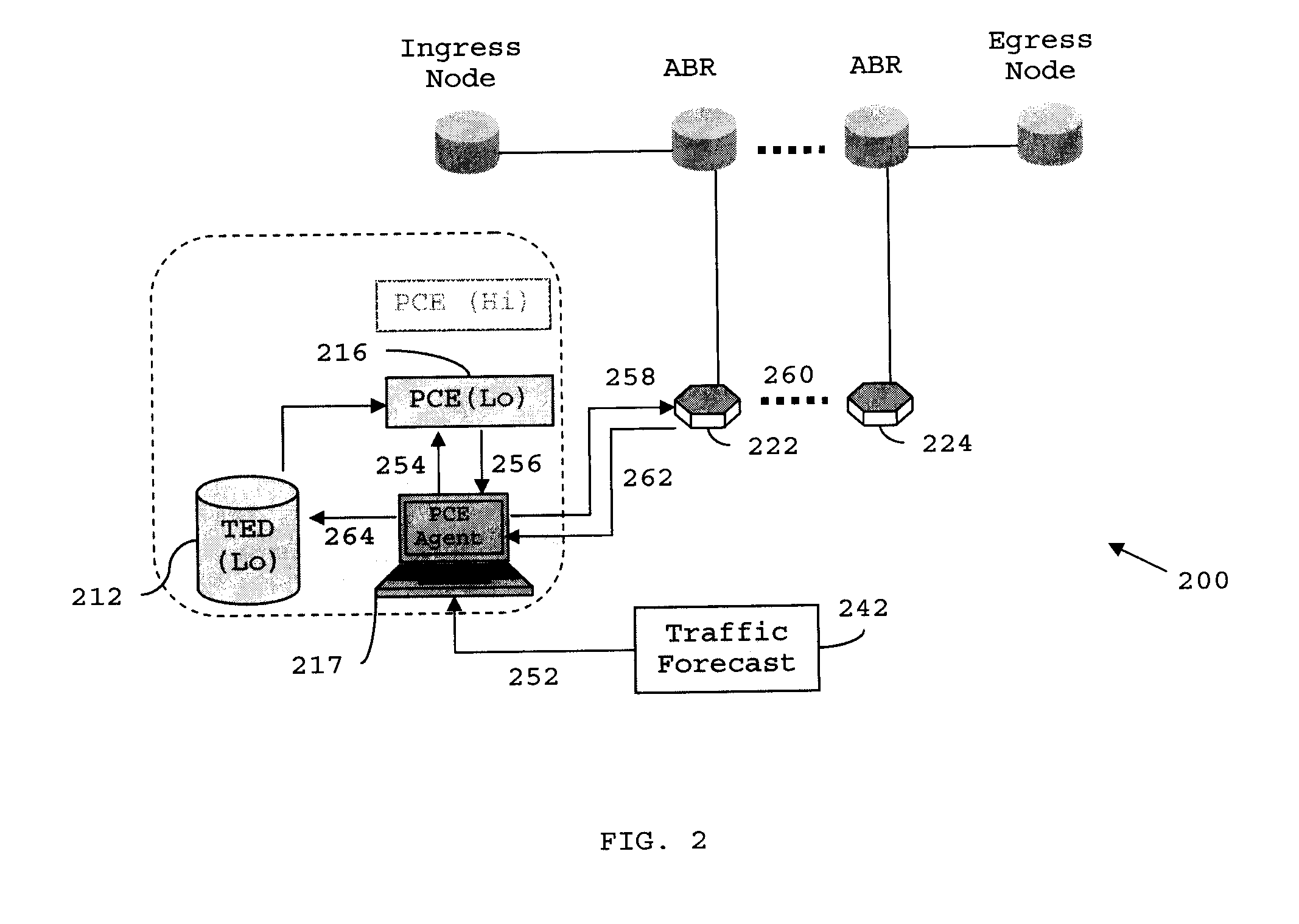
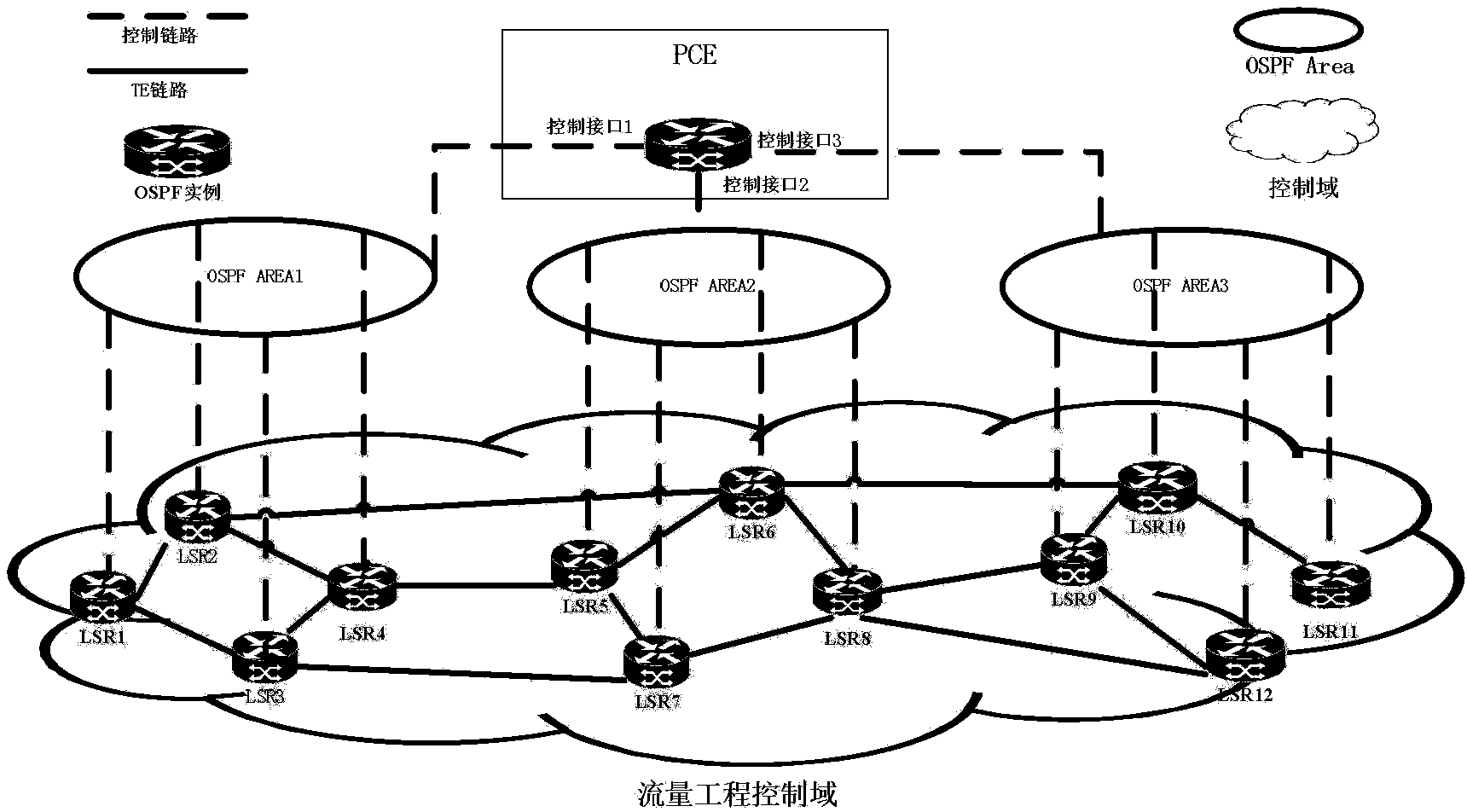
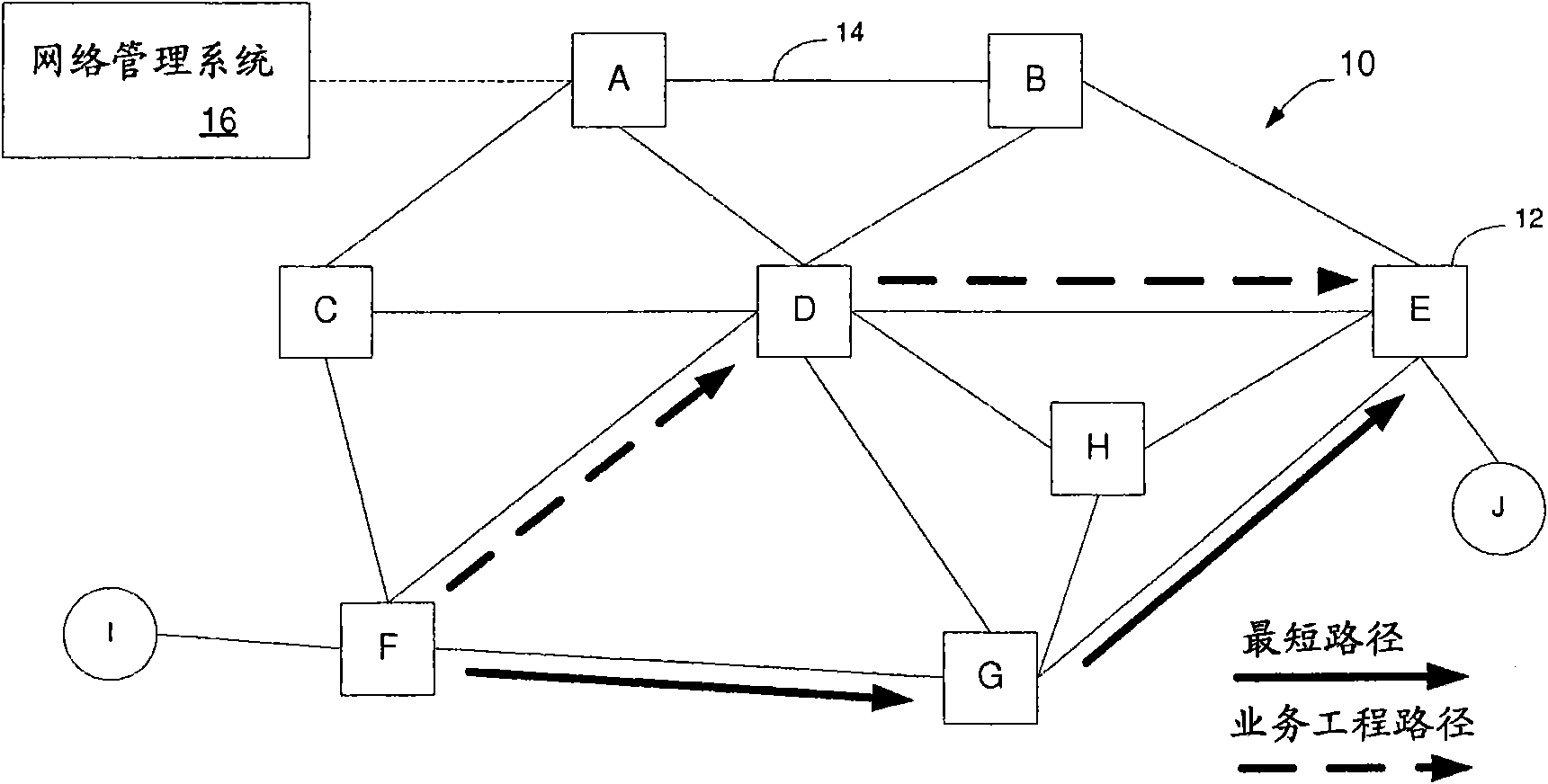
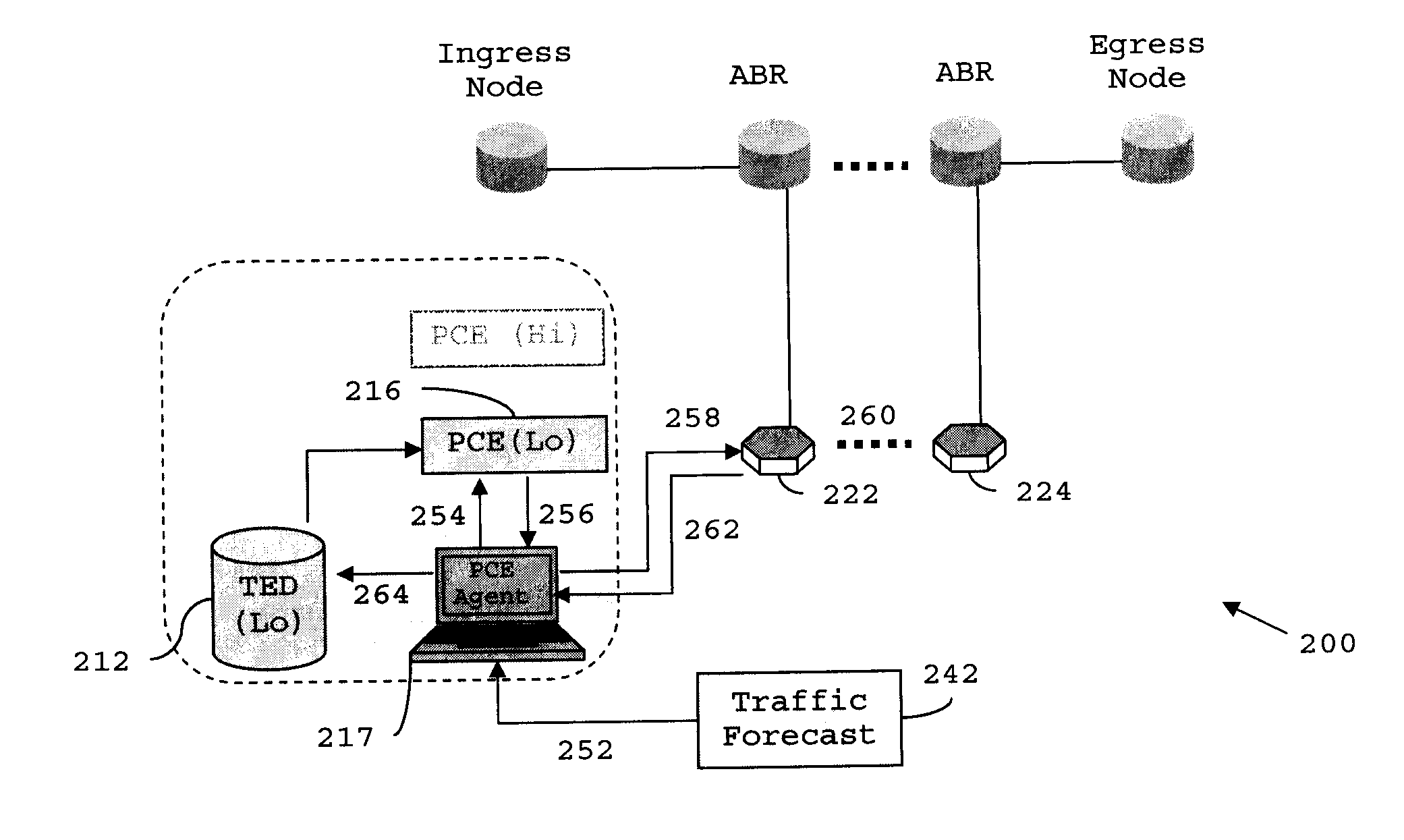
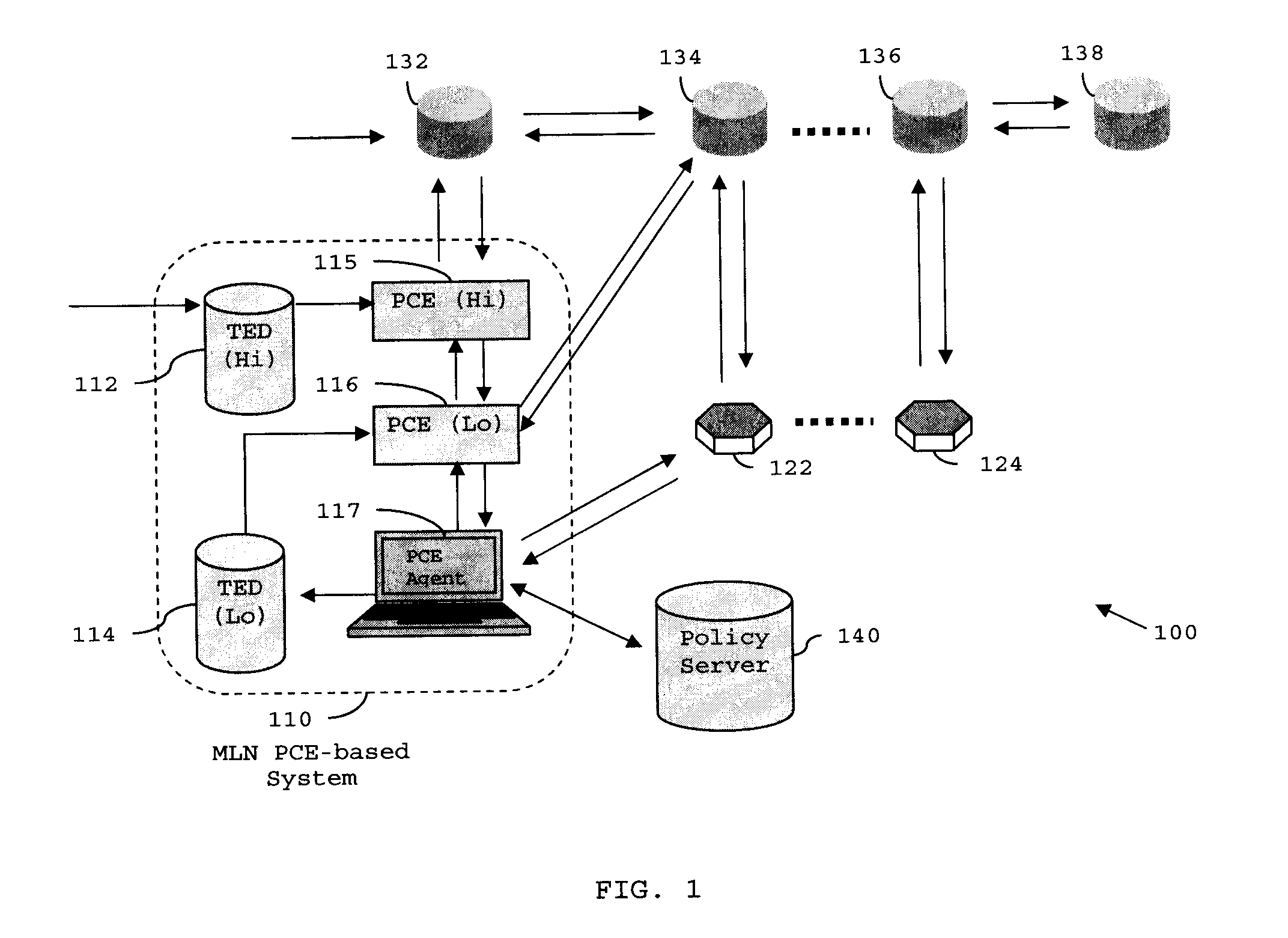
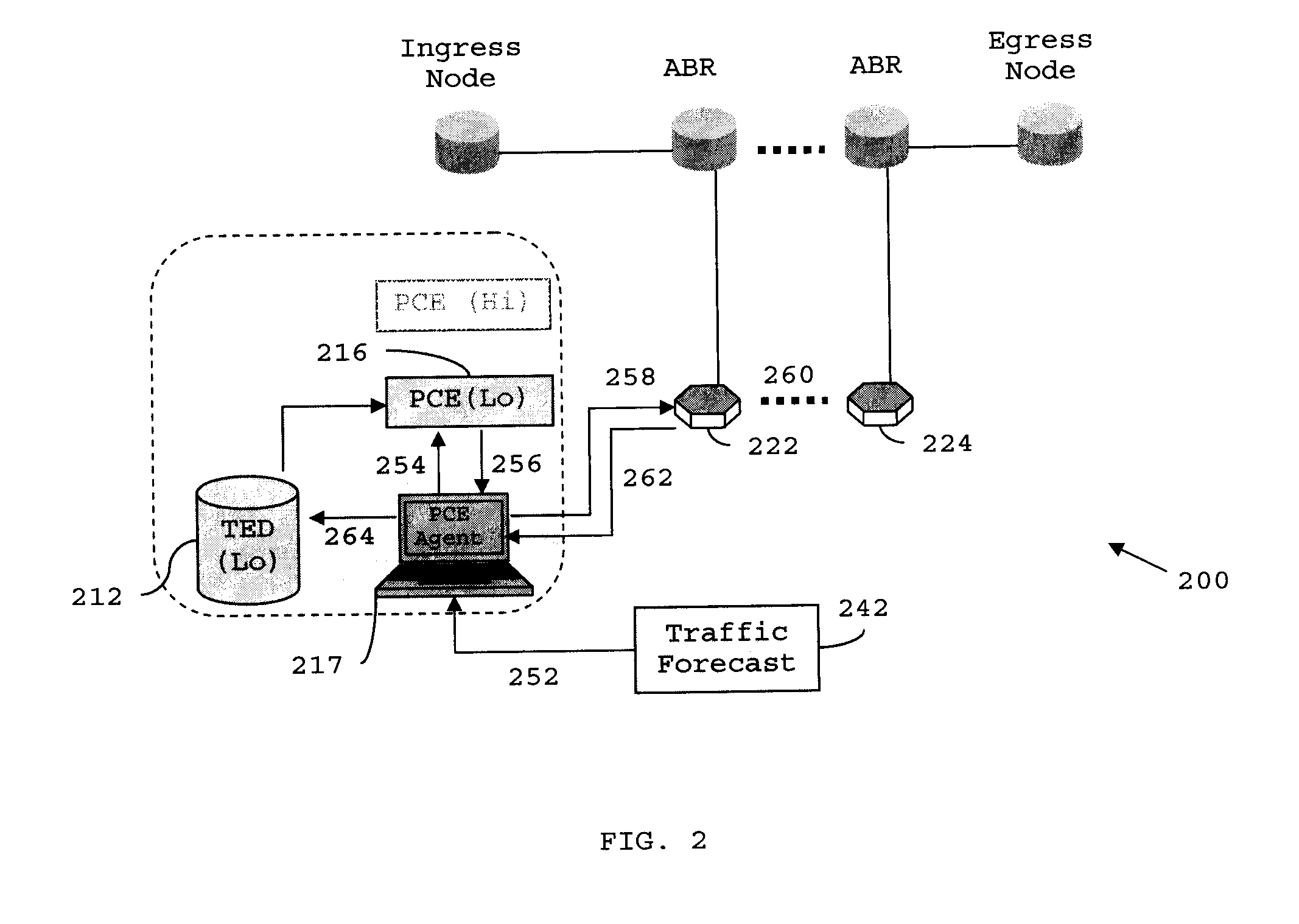
Distributed pce-based system and architecture in multi-layer network
A distributed path computation element based system in a multi-layer network. The system comprises at least one higher-layer path computation element, and at least one lower-layer path computation element, adapted to provide dynamic multi-layer path computations; at least one higher-layer traffic engineering database, and at least one lower-layer traffic engineering database, adapted to provide multi-layer traffic engineering label switched paths, while maintaining layer-specific traffic engineered database in a distributed fashion; and at least one path computation element agent, adapted to provide static optical layer path provisioning, and reconfiguration of optical layer label switched paths in cooperation with the at least one lower-layer path computation element.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Failure protection for traffic-engineered bit indexed explicit replication
Methods and network devices are disclosed for failure protection in traffic-engineered bit indexed explicit replication networks. In one embodiment, a method includes receiving at a node in a network a message comprising a message bit array, where bit positions in the message bit array correspond to respective links in the network. The method further includes evaluating a bit value at a bit position in the message bit array, where the bit position corresponds to a network link represented in a forwarding table for the node, checking for a failure state of the link represented in the forwarding table, and, responsive to a determination of a failure state of the link, modifying one or more bit values in the message bit array. In one embodiment a network device includes a network interface, a memory configured to store a forwarding table, and a processor configured to carry out the methods.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Urban rail traffic engineering civil air defense system
ActiveCN103276749AEnsure safe trafficEffective fortificationArtificial islandsLighting and heating apparatusElectronic systemsRail traffic
The invention discloses an urban rail traffic engineering civil air defense system which comprises a building subsystem, a structure subsystem, an air subsystem, a water subsystem and an electronic subsystem, wherein a civil air defense ventilation subsystem is composed of an air shaft, a ventilation channel communicating an underground station main body structure and the air shaft, and a station environmental controlling device arranged in the underground station main body structure; the ventilation channel is composed of a clean type air inlet duct, a clean type air exhaust duct, an isolated type air inlet duct and an isolated type air exhaust duct, part of a clean type air duct protecting section is arranged in the clean type air inlet duct and the clean type air exhaust duct, part of an isolated air duct protecting section is arranged inside the isolated type air inlet duct and the isolated type air exhaust duct, the clean type air inlet duct, the clean air exhaust duct, the isolated type air inlet duct and the isolated type air exhaust duct are communicated with the station environmental controlling device, and the station environmental controlling device is composed of a clean type air inlet device, an isolated type air inlet device, a clean type air outlet device and an isolated type air outlet device. The urban rail traffic engineering civil air defense system has the functions of ensuring staff safe traffic, transferring and cargo transportation, and is good in ventilation performance.
Owner:4TH DESIGN & RES INST OF ENGINEER CENT STAFF PLA
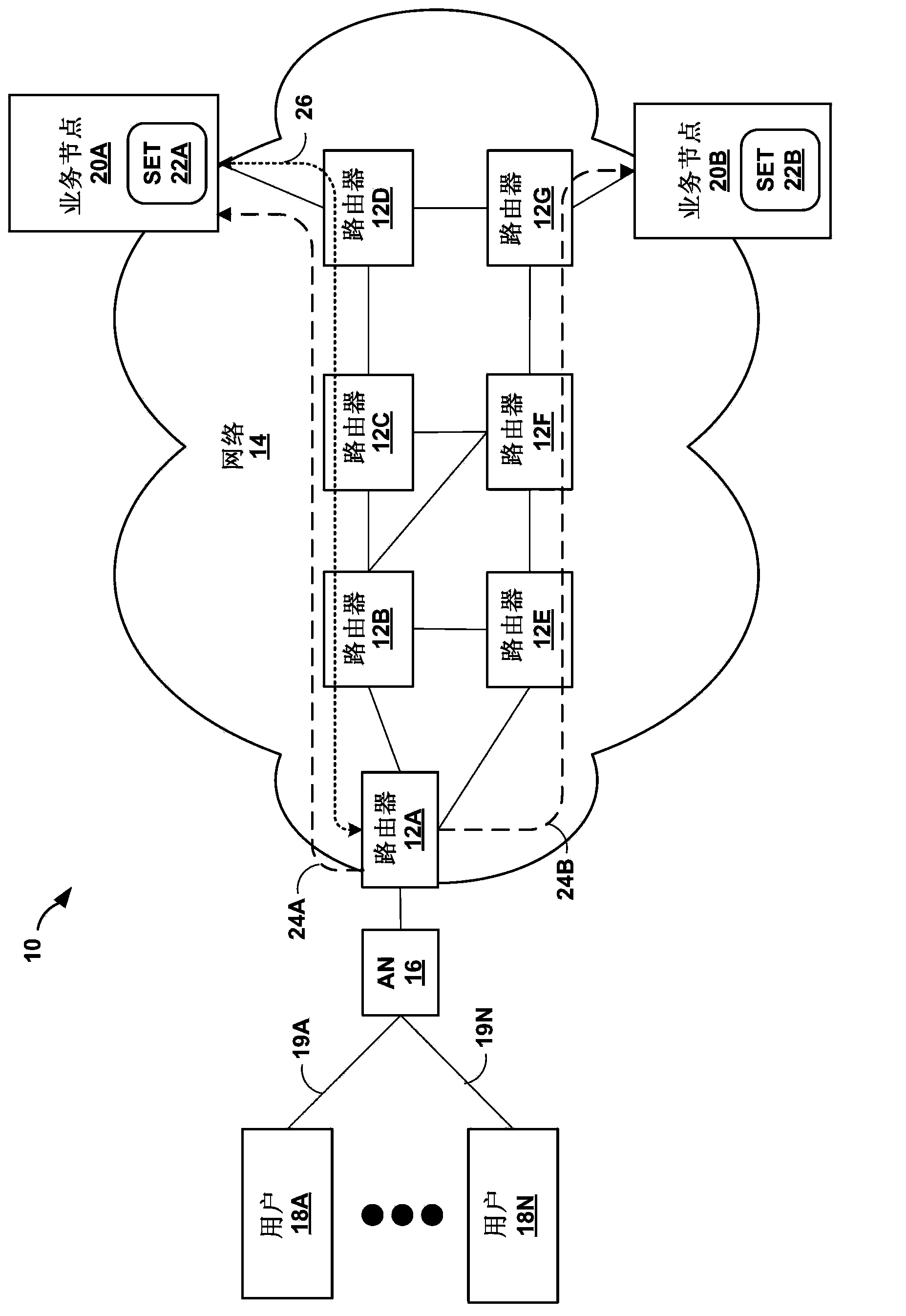
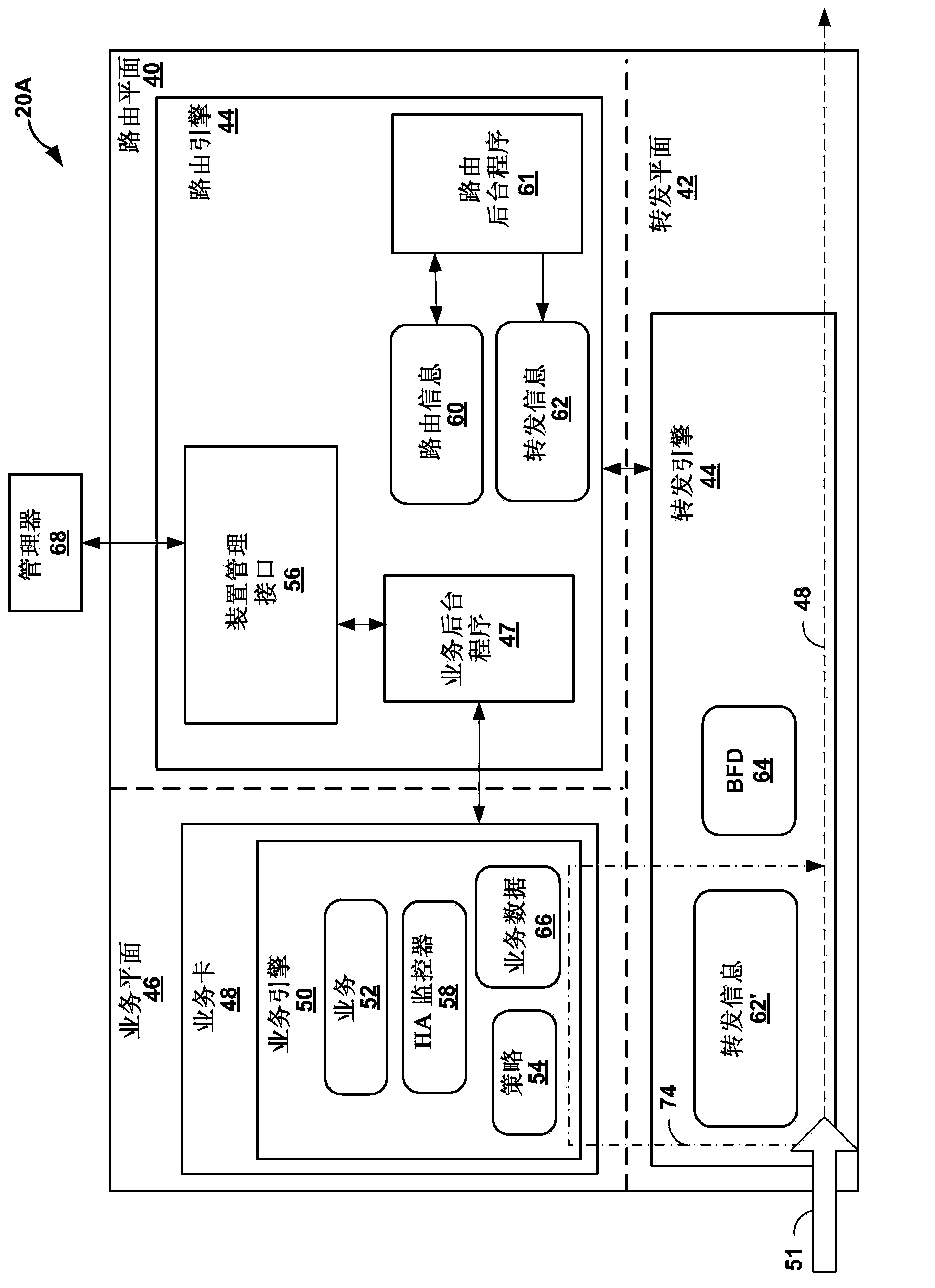
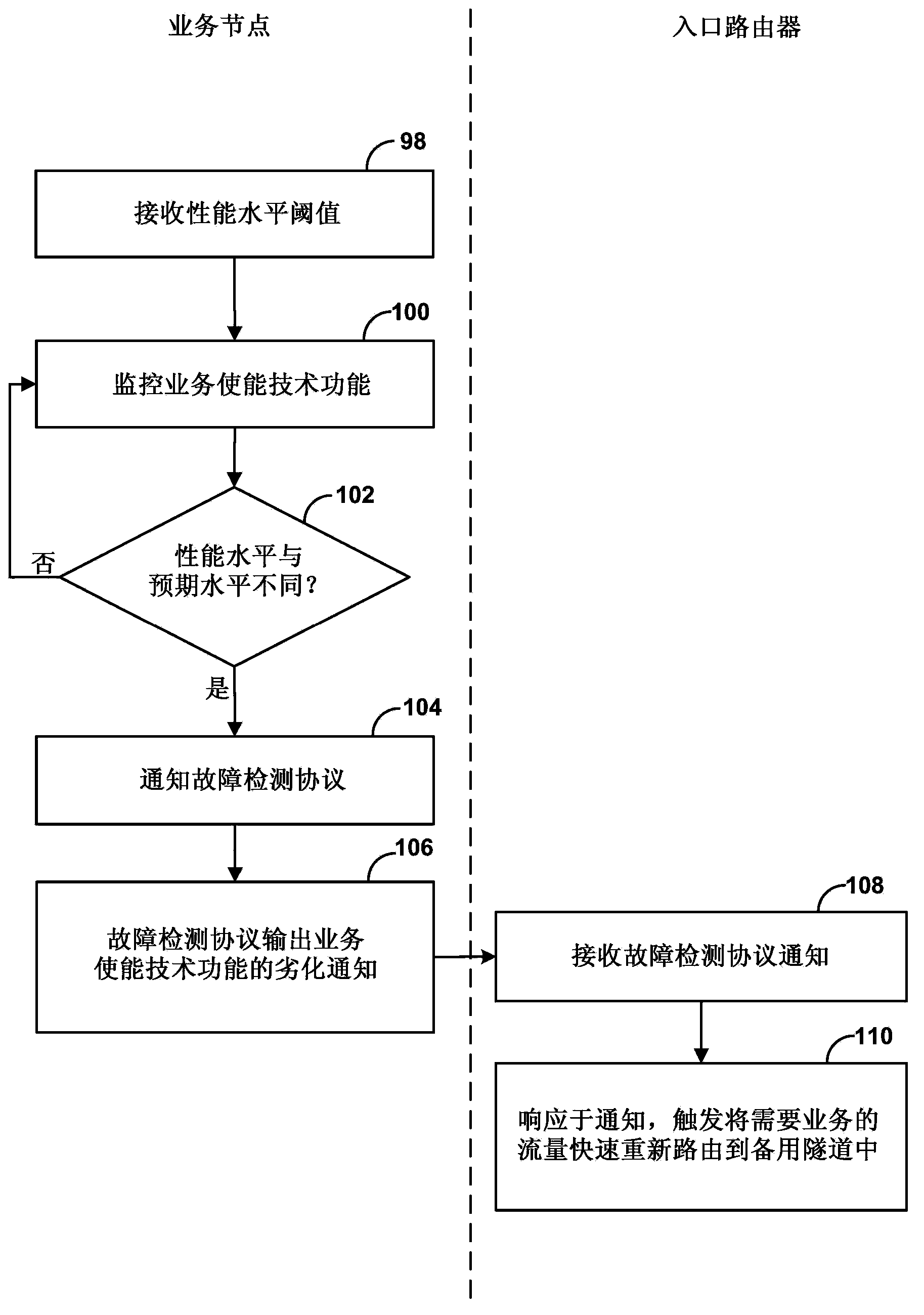
Service plane triggered fast reroute protection
Techniques are described for detecting failure or degradation of a service enabling technology function independent from an operational state of a service node hosting the service enabling technology function. For example, a service node may provide one or more service enabling technology functions, and service engineered paths may be traffic-engineered through a network to service node network devices that host a service enabling technology function. A monitor component at the service layer of the service node can detect failure or degradation of one or more service enabling technology functions provided by the service node. The monitor component reports detection of failure or degradation to a fault detection network protocol in a forwarding plane of the service node. The fault detection network protocol communicates with an ingress router of a service engineered path to trigger fast reroute by the ingress of traffic flows to bypass the affected service enabling technology function.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
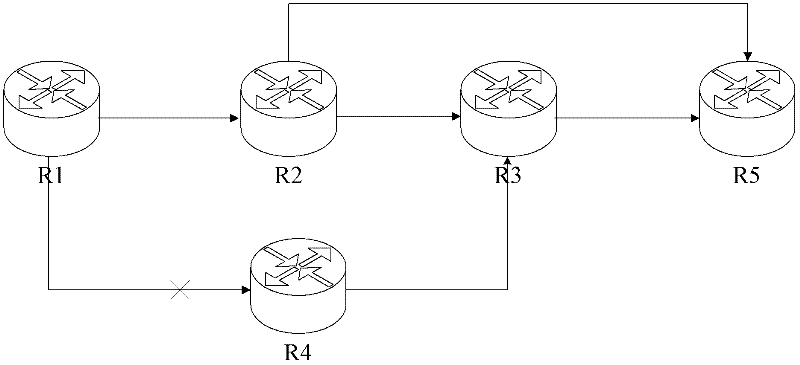
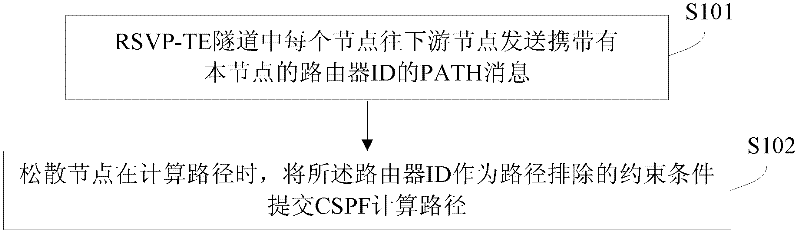
Loose node in RSVP-TE (Resource Reservation Protocol-Traffic Engineer) tunnel and path calculation method of loose node
InactiveCN102647340AReduce generationReduce the possibility of loopsData switching networksConstrained Shortest Path FirstCalculation methods
The invention discloses a path calculation method of a loose node in an RSVP-TE (Resource Reservation Protocol-Traffic Engineer) tunnel, the loose node, a non-loose node and the RSVP-TE network. The method comprises the following steps that: each node in the RSVP-TE network sends a PATH message carrying the router ID (Identifier) of the node to a downstream node; when the path of the loose node is calculated, the router ID is used as a constraint condition of path exclude to submit to CSPF (Constrained Shortest Path First) to calculate the path. The loose node comprises a receiving module, a path calculation module and a message generating module; the non-loose node comprises a message generating module and a sending module; and the RSVP-TE network comprises the loose node and the non-loose node. The local router ID of an upstream node is used as a constraint condition of the path exclude, so that the possibility of a loop generated when the path of the loose node is calculated is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Vehicle partition-positioned transverse shifting accessing device adopting mobile positioning type activator
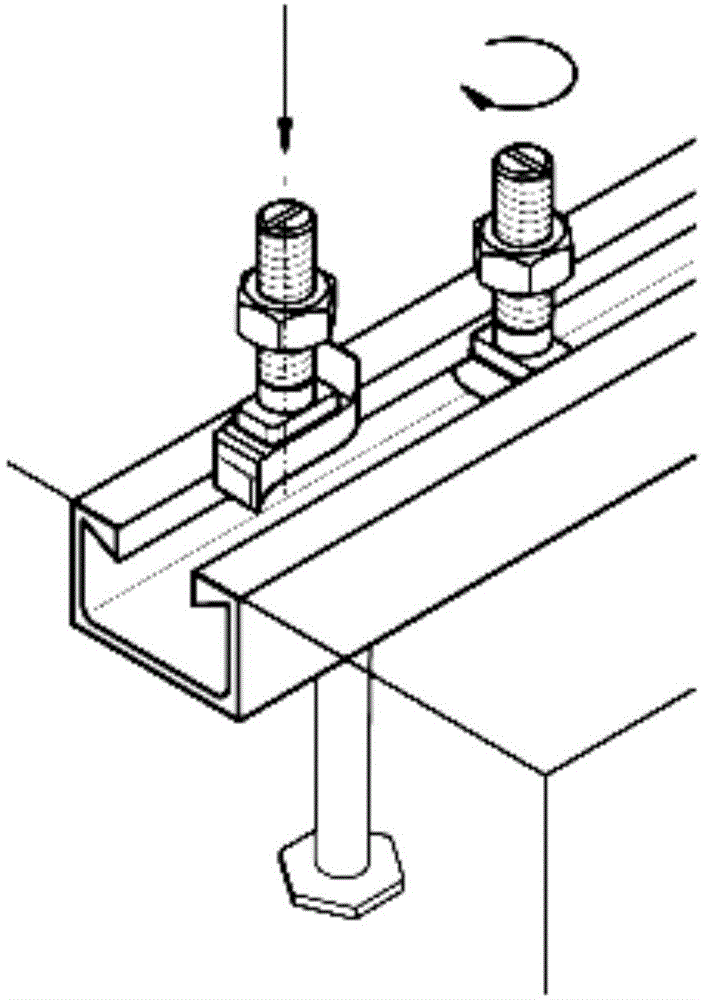
The invention is a vehicle separating, locating, lateral shifting accessing device adopting mobile locating actuators, belonging to the field of traffic engineer mechanical parking equipment, comprising: lateral shifting underframe, lateral shifting guide mechanism, lateral shifting drive mechanism, locating drive mechanism, mobile locating actuators, and mobile locating guide mechanism, where the lateral shifting underframe is arranged between front and rear wheel trays of parking equipment and stretches across several parking spaces in the park and can be driven by the lateral shifting drive mechanism to shift right and left along the guide rails of the lateral shifting guide mechanism by a parking space, respectively, the lateral shifting underframe is equipped with a mobile locating actuator corresponding to each parking space, where the mobile locating actuator is driven by the locating drive mechanism and restricts reverse shifting by the mobile locating guide mechanism to be spread for locating or be drawn in, and after spread, blocks inside wheel rings of all wheels of a vehicle, and moves with the lateral shifting underframe to push and pull the vehicle. And it has simple structure, working reliability and acts a vehicle accessing device in parallel multi-parking space tray parking equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
MPLS and GMPLS tunnel flap dampening in traffic engineered networks
Embodiments of the disclosure are directed to tunnel flap damping in a traffic engineered network. One exemplary method for tracking a re-routing history of Multi-Protocol Label Switching (“MPLS”) / Generalized MPLS (“GMPLS”) tunnels over intervals includes measuring a number of policy-based re-routes during at least one measurement interval; determining a tunnel re-route frequency based on the measurement; comparing the tunnel re-route frequency to a frequency threshold; and determining if the tunnel re-route frequency exceeds the frequency threshold and, if the tunnel re-route frequency exceeds the frequency threshold, delaying at least one tunnel re-route.
Owner:CIENA
Urban rail traffic engineering electromechanical equipment embedded part installation method
InactiveCN104452977AImprove carrying capacityExtend the service life of the projectBuilding insulationsConcrete beamsFilling materials
The invention discloses an urban rail traffic engineering electromechanical equipment embedded part installation method. The method comprises the steps that a steel sliding groove is embedded in concrete, the large heads of T-shaped bolts are buckled into a C-shaped groove of the steel sliding groove, a component to be installed is then fixed through the T-shaped bolts, and channel steel is filled with foam stuffing or bar-shaped stuffing materials; insulation nylon sleeve pipes are embedded in concrete beams and concrete walls which need to be provided with pipelines and equipment supporting and hoisting frames in a dot type, and the insulation nylon sleeve pipes are used in cooperation with steel sliding groove embedded parts. According to the urban rail traffic engineering electromechanical equipment embedded part installation method, the insulation nylon sleeve pipes and the steel sliding groove are used in cooperation, are high in bearing capability which can reach 32 kN / m or 128 kN / m and can be used for static and dynamic bearing; no damage to a tunnel structure is caused, and the engineering service life is prolonged; installation is convenient, adjustment is easy, the operation maintenance cost is lowered, and equipment is convenient to replace; the cost for drilling and detecting is saved; the construction period is shortened, and the efficiency is increased by 3 times compared with that of a traditional installation technology; noise and dust are avoided in the installing process, and the construction environment is good; after surface anti-corrosion processing is conducted, the anti-corrosion performance is good.
Owner:刘卡丁 +3
Plane intersection left turn waiting area setting evaluation method
InactiveCN110111569AJudging scientificallyJudging rationalityDetection of traffic movementControl setSimulation
The preset invention discloses a plane intersection left turn waiting area setting evaluation method, and relates to the field of traffic organization design of urban road intersections. The method comprising following steps: Step 1, through investigating a left-turn traffic flow, evaluating whether setting a left-turn waiting area is required; Step 2: through calculating length of the left-turn waiting area, deterining whether the left-turn waiting area can be set; Step 3: through drawing a left-turning vehicle driving track, determining whether the left turn waiting area can be set; step 4,through a signal control setting mode, determining whether the left turn waiting area can be set. Compared with past where senior transportation engineers are required to determine through experience,the method confirms implementation effect through a large number of data surveys, the evaluation method is more scientific and reasonable, reduces manpower and material resources.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHENYE UCTRL TECH CORP LTD
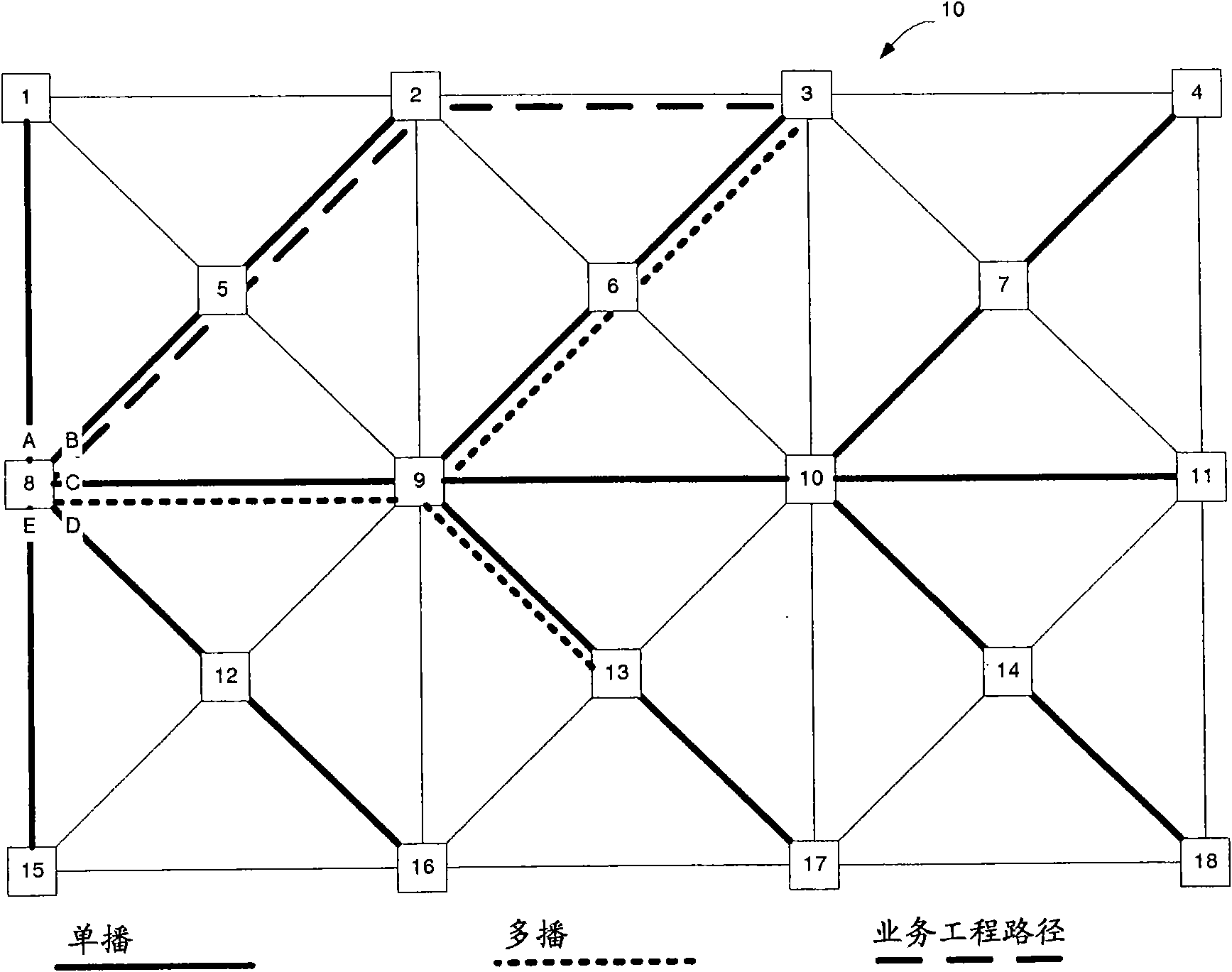
System and Method for Multi-Topology Support
ActiveUS20090303904A1Improve performanceData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTopology information
A system and method for providing multi-topology support in RSVP-TE in a multi-protocol label switching network is provided. A method includes reserving path states for a traffic engineered label switched path (TE LSP), and releasing the reserved path states. The TE LSP is established within a single network topology in an environment of multiple network topologies, and the reserving path states includes sending a first resource reservation protocol with traffic engineering (RSVP-TE) message containing multi-topology information.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Failure protection for traffic-engineered bit indexed explicit replication
Methods and network devices are disclosed for failure protection in traffic-engineered bit indexed explicit replication networks. In one embodiment, a method includes receiving at a node in a network a message comprising a message bit array, where bit positions in the message bit array correspond to respective links in the network. The method further includes evaluating a bit value at a bit position in the message bit array, where the bit position corresponds to a network link represented in a forwarding table for the node, checking for a failure state of the link represented in the forwarding table, and, responsive to a determination of a failure state of the link, modifying one or more bit values in the message bit array. In one embodiment a network device includes a network interface, a memory configured to store a forwarding table, and a processor configured to carry out the methods.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
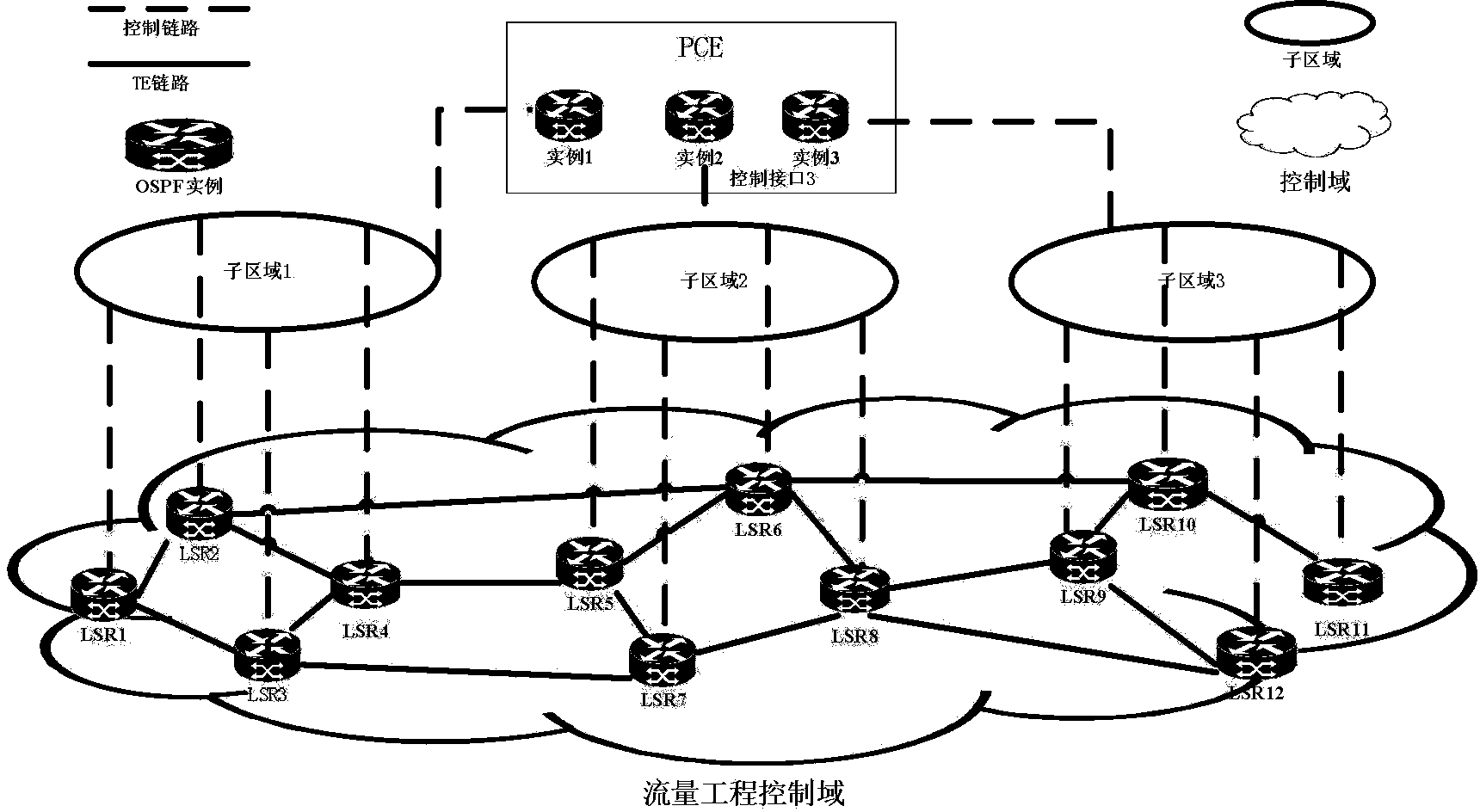
Method and system for network topology
ActiveCN104301219ASpeed up flooding convergenceGuaranteed rich featuresHybrid transportNetwork sizeTopological graph
A method and system for network topology. The method includes: dividing Label Switching Routers in a single control area into multiple sub-areas, wherein the Label Switching Routers in each sub-area constitute Open Shortest Path First neighbors; obtaining Traffic Engineer resource information on each said sub-area, collecting the Traffic?Engineer resource information on all the sub-areas, and generating a network topology diagram in the single control area.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING SOFTWARE
Method and system for adjusting bandwidth using multiple timers
An approach is provided for auto-bandwidth adjusting bandwidth allocations for traffic-engineered tunnels used to carry traffic along a network. Traffic over the tunnel is sampled at a first interval period and at a second interval period, where the second interval period is shorter than the first interval period. A determination is made as to whether the sampled traffic taken using the second interval period is greater than the bandwidth allocation, and the bandwidth allocation is adjusted upward based upon a determination that the sampled traffic taken using the second interval period is greater than the bandwidth allocation. Also, a determination can be made as to whether the sampled traffic taken using the first interval period is less than the bandwidth allocation, and the bandwidth allocation can be adjusted downward based upon a determination that the sampled traffic taken using the first interval period is less than the bandwidth allocation.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Medium and low speed maglev traffic engineering low line solid bearing-trail beam structure and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106049201AImprove structural rigidityStrong resistance to deformationRailway track constructionLow speedReinforced concrete
The invention belongs to the field of bearing-trail beams and discloses a medium and low speed maglev traffic engineering low line solid bearing-trail beam structure; the bearing-trail beam structure comprises a reinforced concrete base plate, reinforced concrete solid beams, multiple rows of rail bearing pedestals, a track panel, and guide rail supports; the reinforced concrete solid beam is integrated on the reinforced concrete base plate; the reinforced concrete solid beams are arranged in the line direction in sections and an expansion joint is arranged between adjacent reinforced concrete solid beams; tops of the reinforced concrete solid beams are provided with the multiple rail bearing pedestals; beam grooves are uniformly installed at a left side and a right side of each reinforced concrete solid beam; multiple guide rail supports are installed at the left side and the right side of each reinforced concrete solid beam. The medium and low speed maglev traffic engineering low line solid bearing-trail beam structure has large rigidity and strong anti-deformation ability which can be prepared by cast-in-situ or prefabrication and lifting; the structure and construction process are simple; the construction precision is easy to control.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
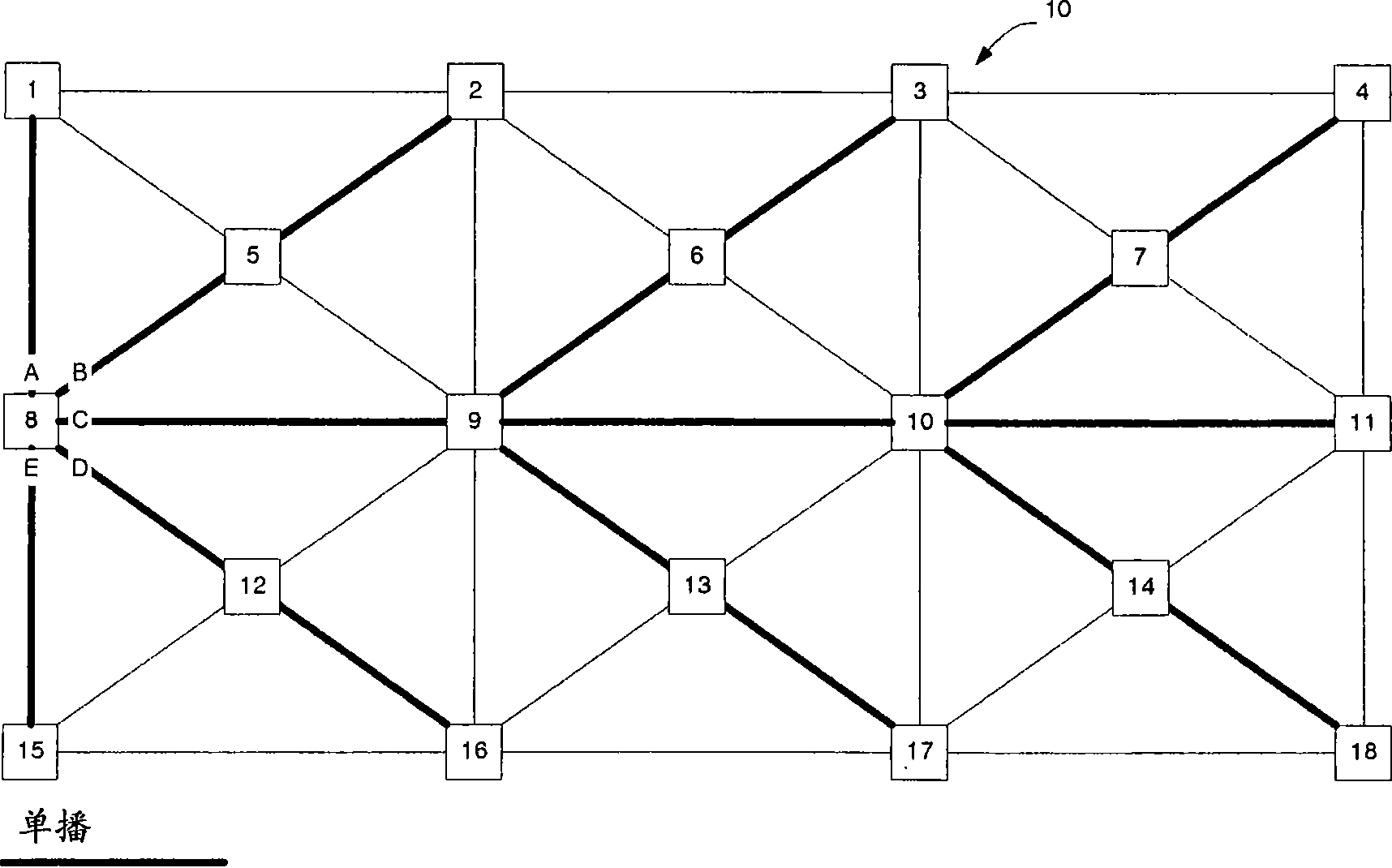
Traffic engineered paths in a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network
InactiveCN101529829ADistribution modificationData switching networksLink-state advertisementEthernet
Traffic Engineered (TE) paths may be created over a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network by causing explicit paths to be installed by network elements on the link state protocol controlled Ethernet network and used to forward traffic on the network. The network elements exchange routing information using link state advertisements to enable each node on the network to build a link state database that may be used to determine shortest paths through the network. The shortest paths are used as a default forwarding state for traffic that is not associated with one of the traffic engineered paths. The link state advertisements 'may also be used to carry the TE path definitions. Where the TE paths are to be used exclusive of other routes, forwarding state for particular service instances may be removed to prevent traffic from traversing the network other than over the TE path.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Distributed PCE-based system and architecture in multi-layer network
A distributed path computation element based system in a multi-layer network. The system comprises at least one higher-layer path computation element, and at least one lower-layer path computation element, adapted to provide dynamic multi-layer path computations; at least one higher-layer traffic engineering database, and at least one lower-layer traffic engineering database, adapted to provide multi-layer traffic engineering label switched paths, while maintaining layer-specific traffic engineered database in a distributed fashion; and at least one path computation element agent, adapted to provide static optical layer path provisioning, and reconfiguration of optical layer label switched paths in cooperation with the at least one lower-layer path computation element.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
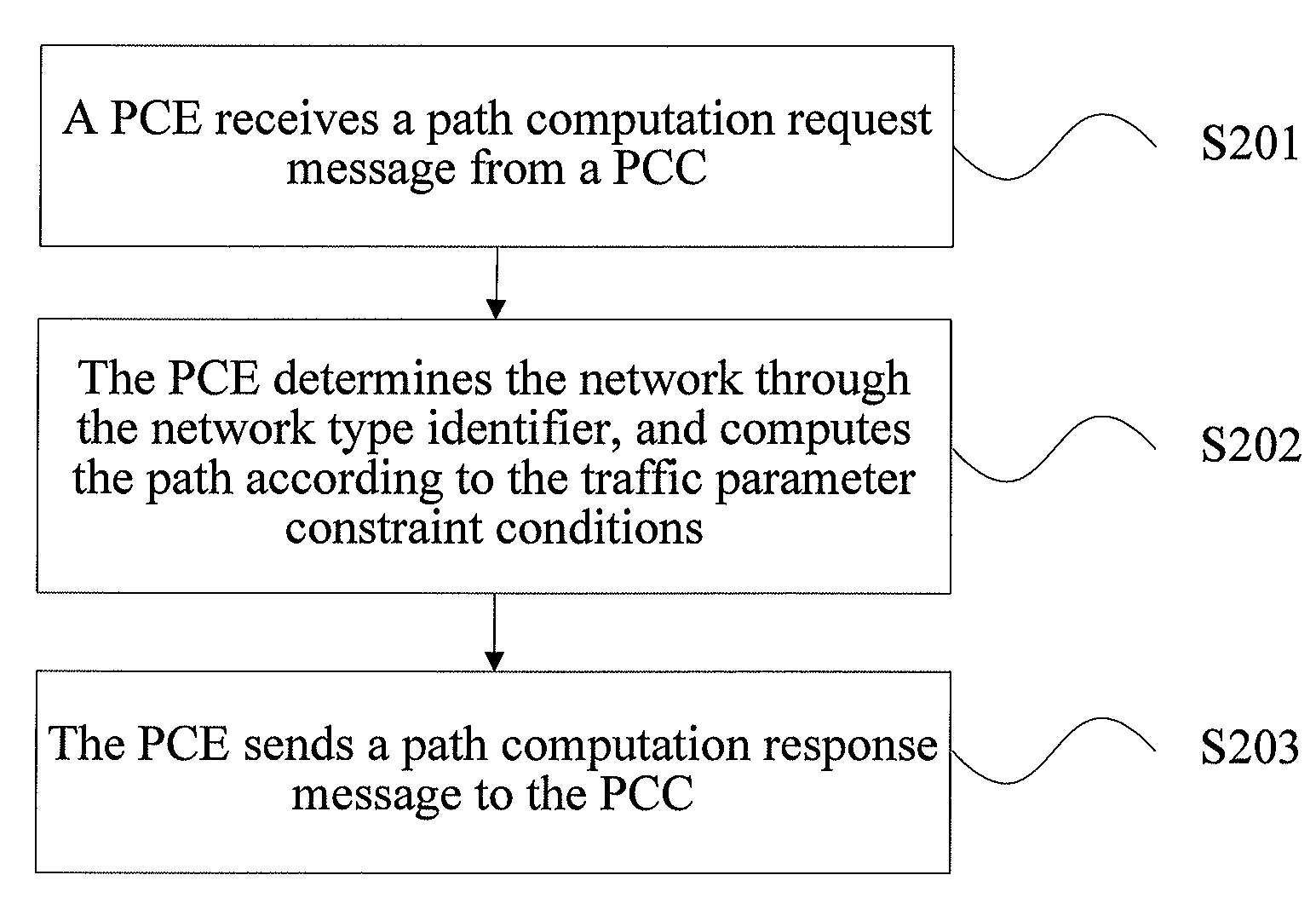
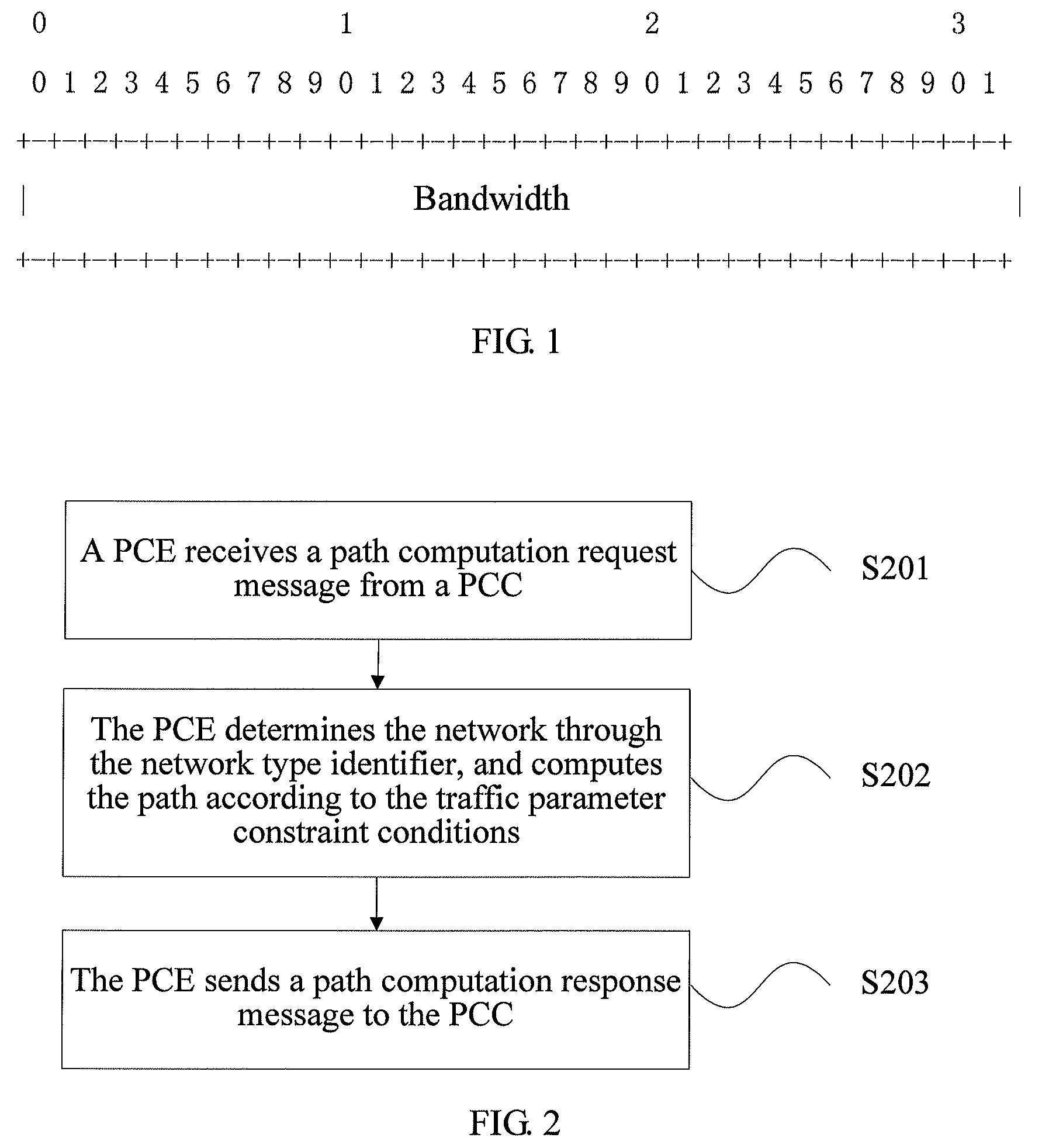
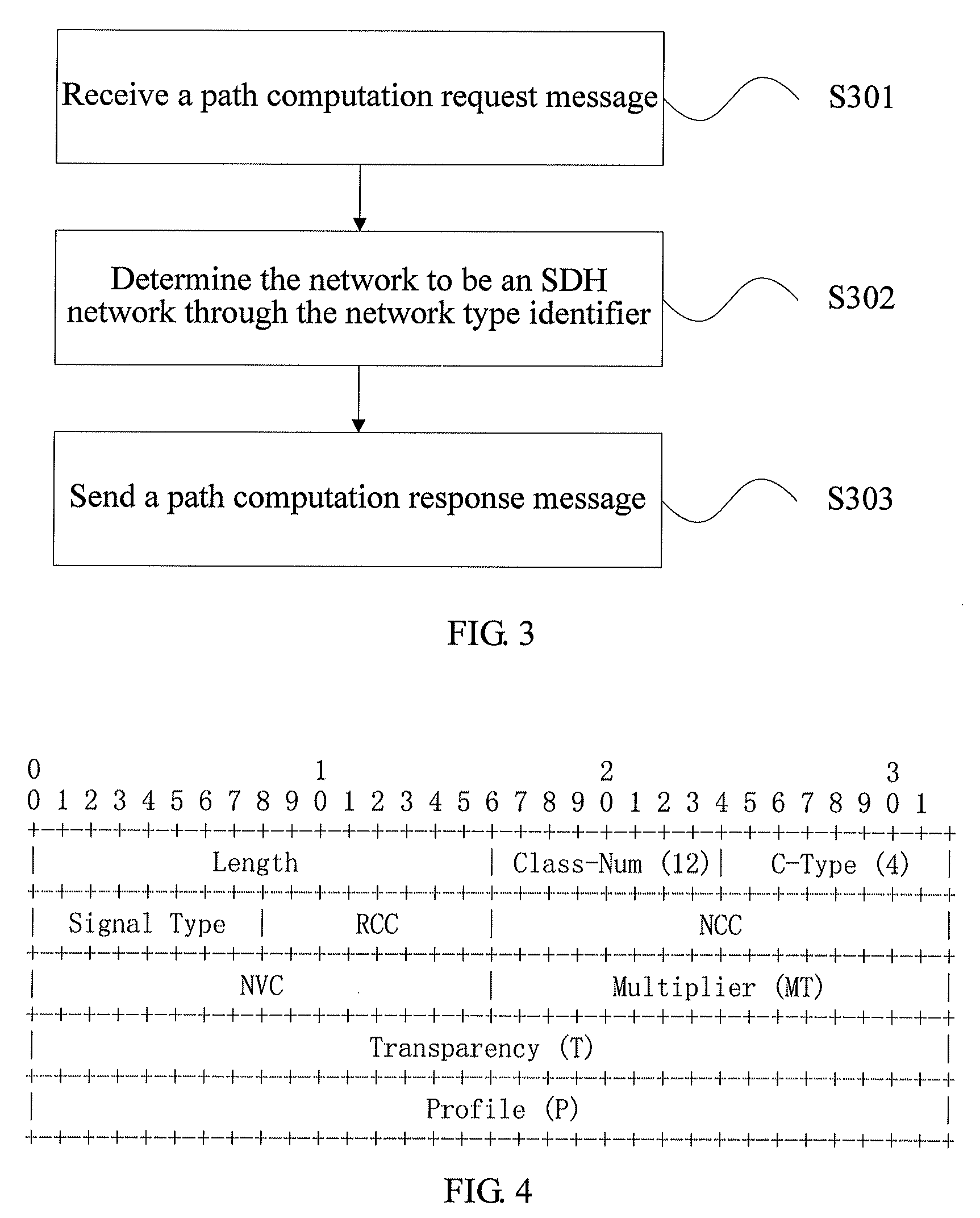
Path computation method, path computation element, node device, and network system
ActiveUS9054944B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPath computation elementNetworked system
The present invention provides a path computation method, a Path Computation Element (PCE), a node device, and a network system. The method includes: receiving a path computation request message (S201), where the path computation request message carries a network type identifier and traffic parameter constraint conditions of a path required to be computed, and the network type identifier indicates a type of a network where the path required to be computed locates; determining the network through the network type identifier, and computing the path in the network according to the traffic parameter constraint conditions (S202); and sending a path computation response message (S203), where the path computation response message carries the computed path. The problem of distinguishing and computing Traffic Engineer (TE) paths for various types of services in a multi-region convergence network is solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com