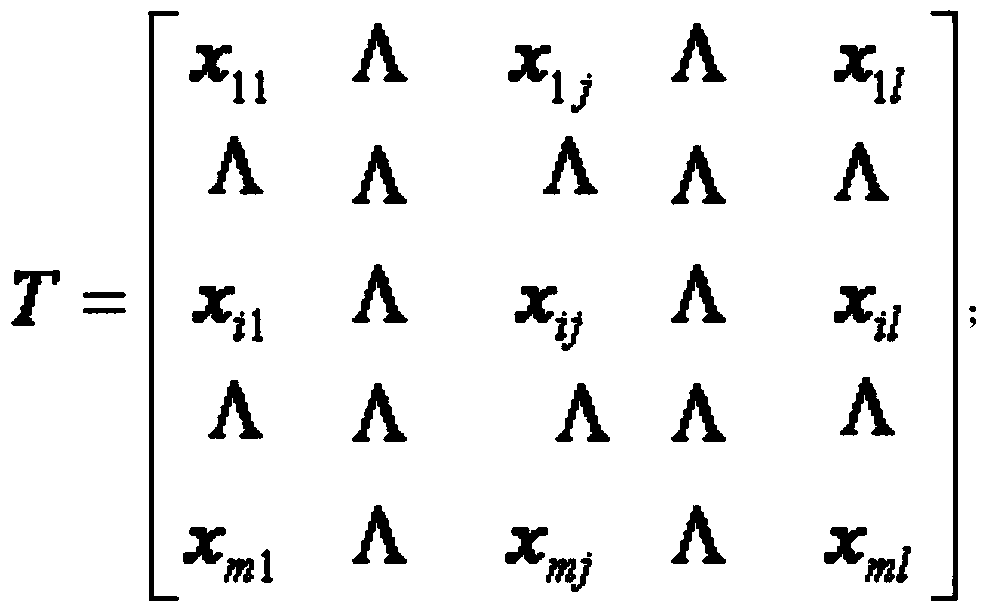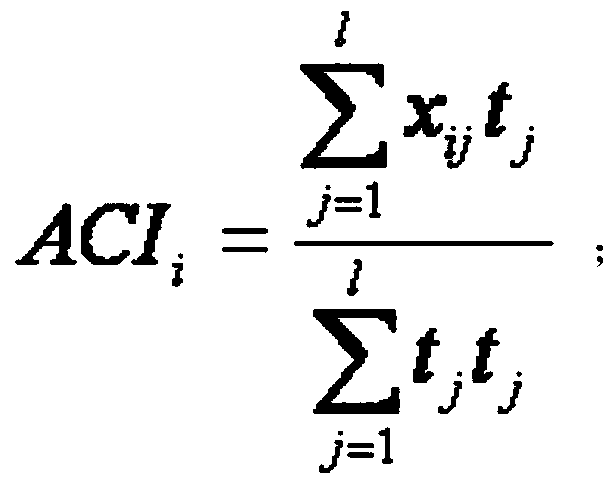Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "T wave alternans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
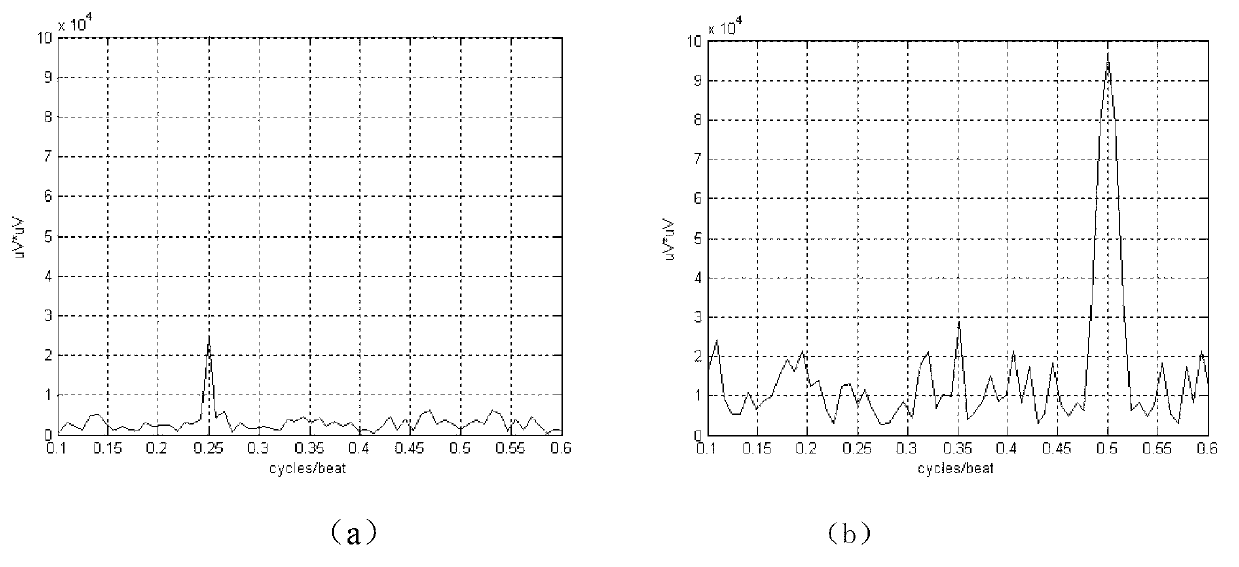
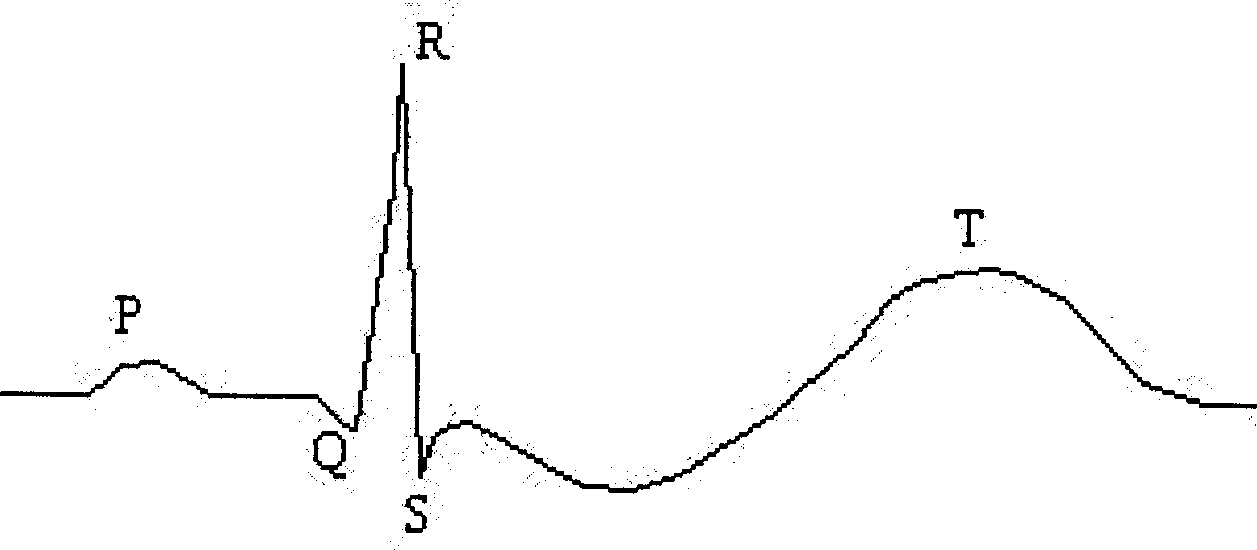
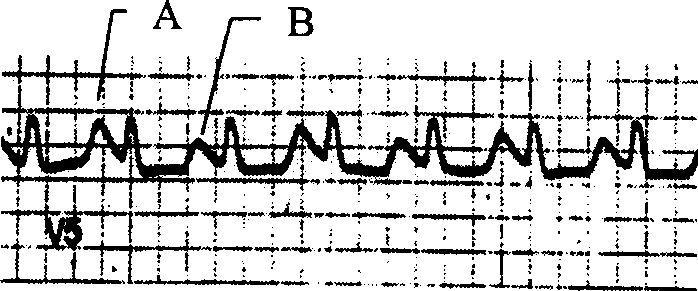
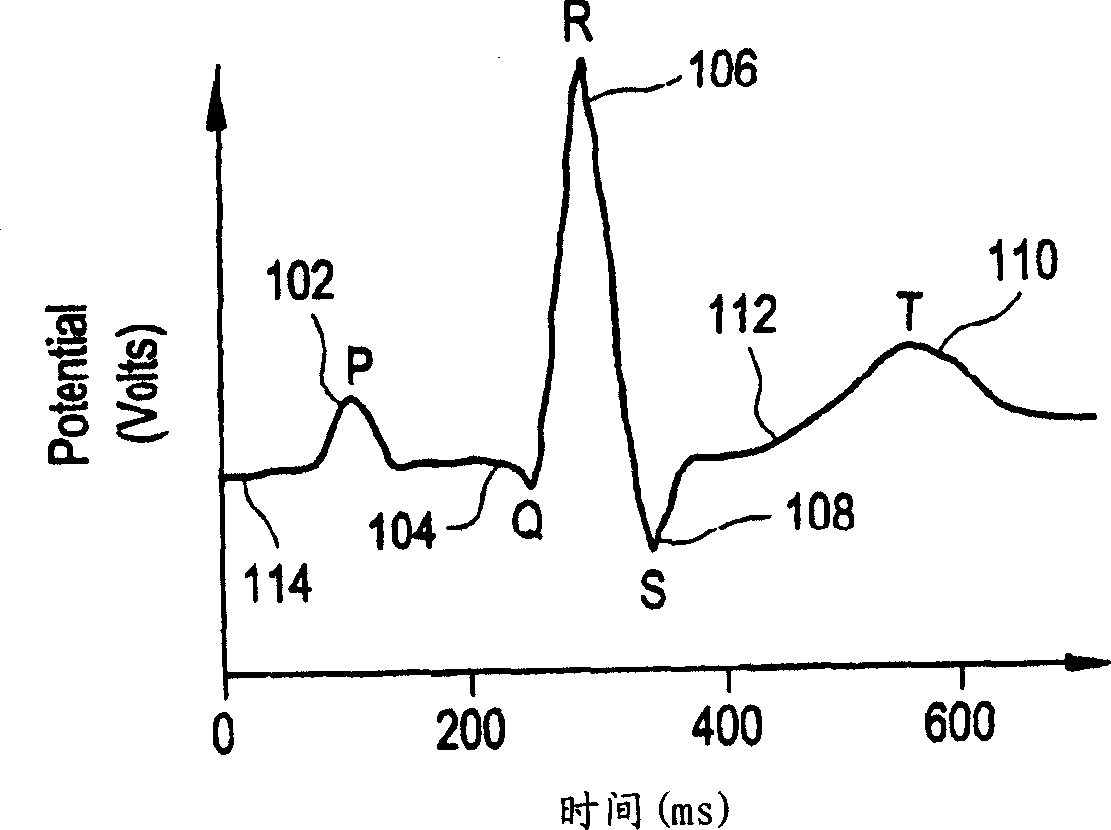
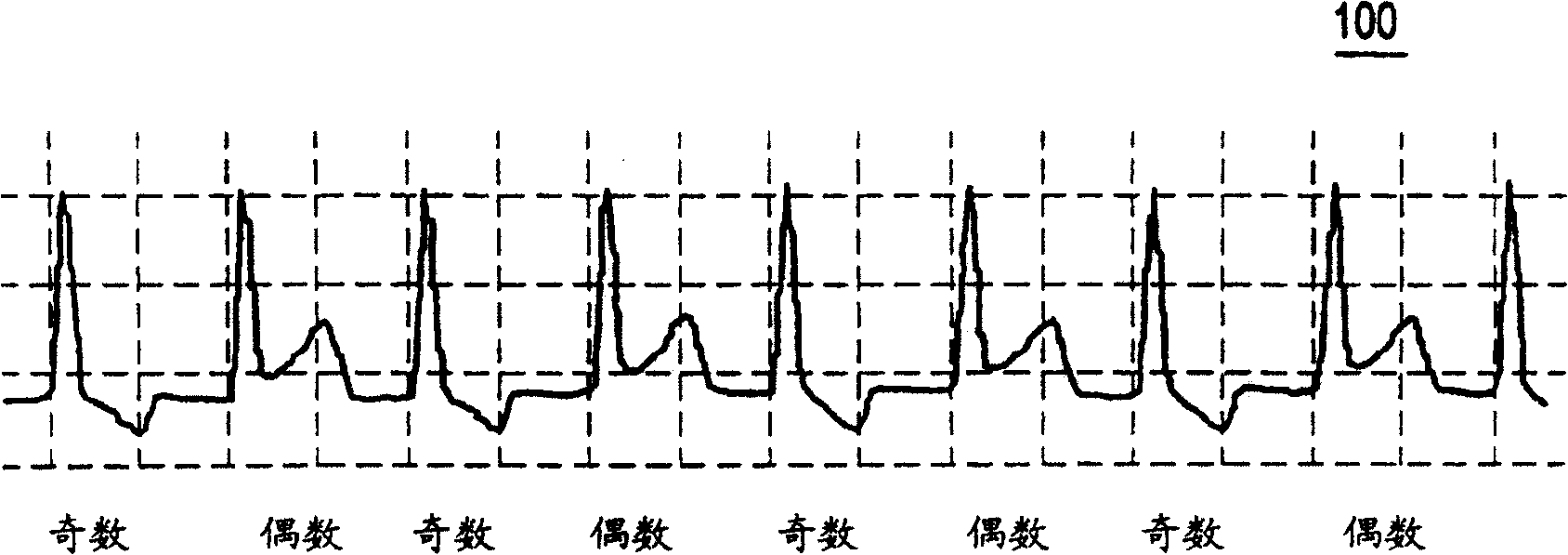
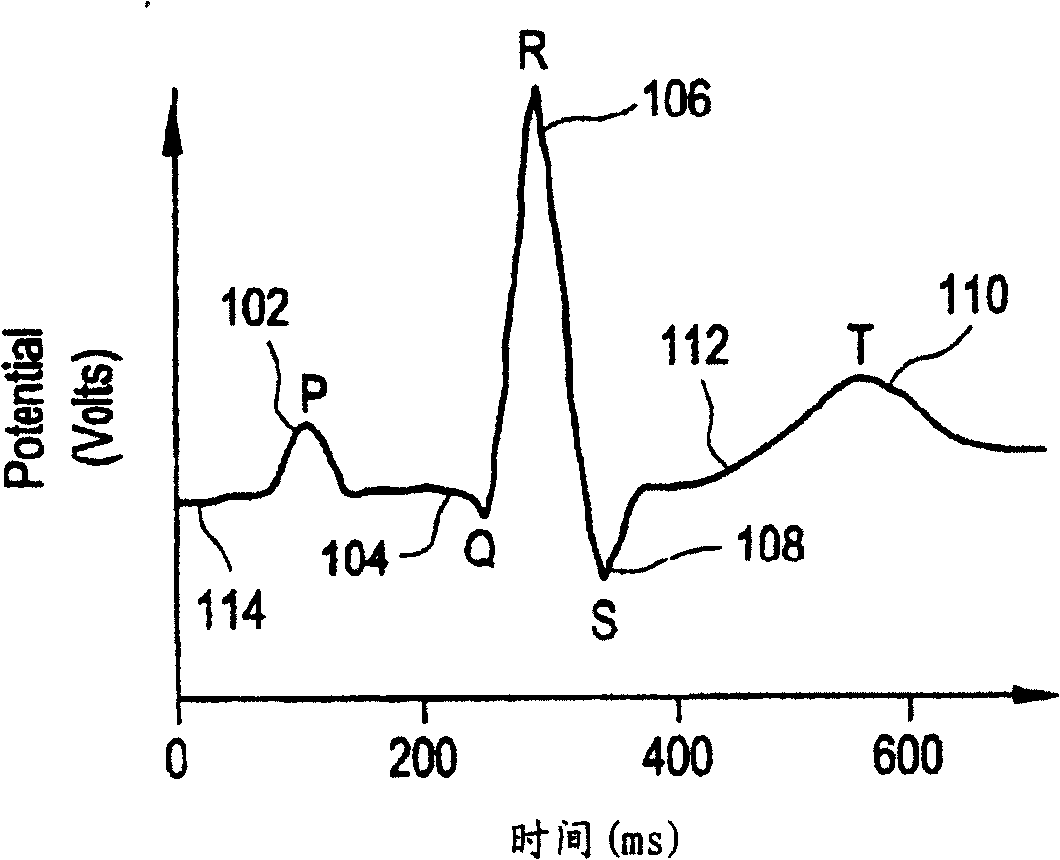
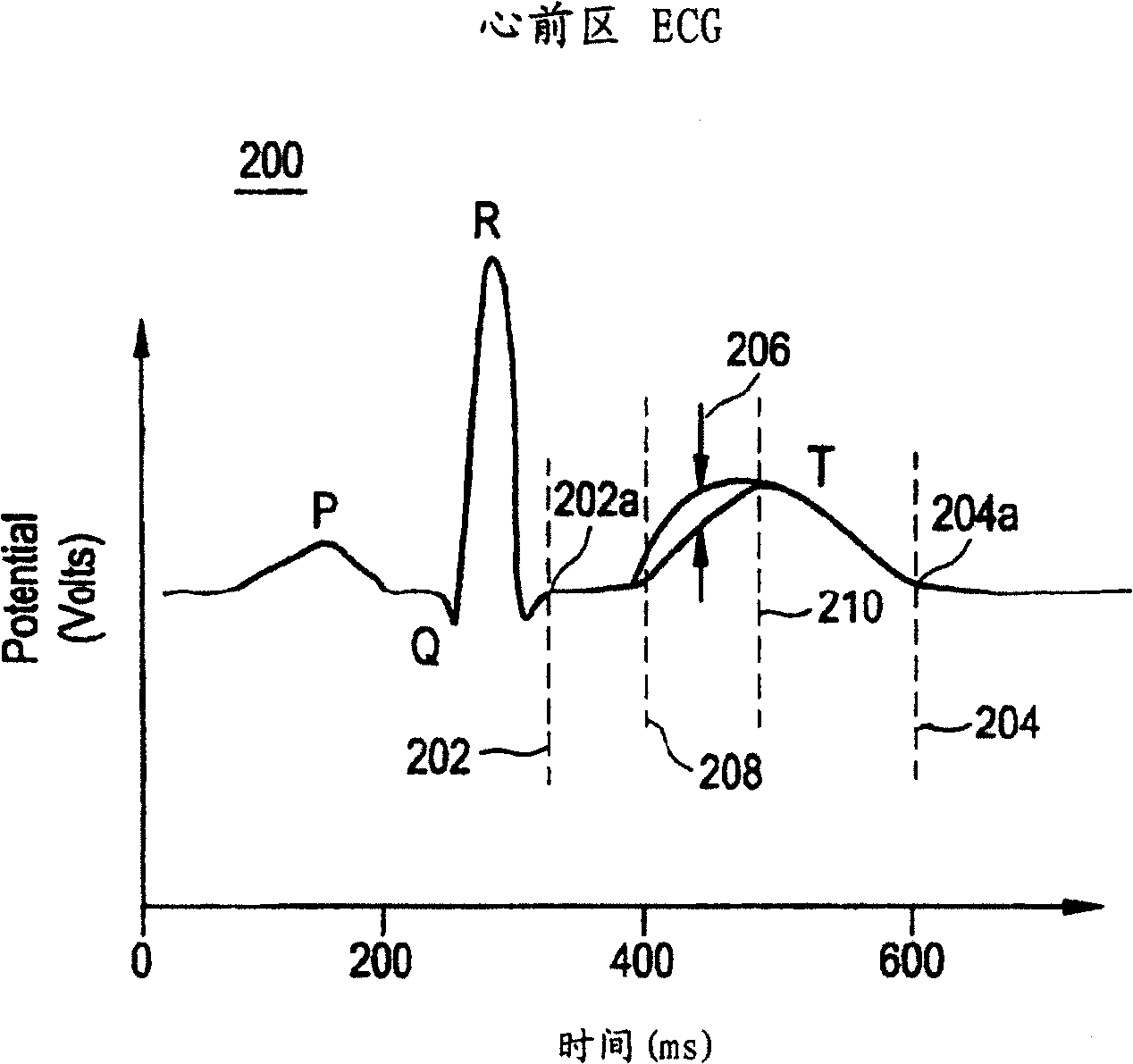
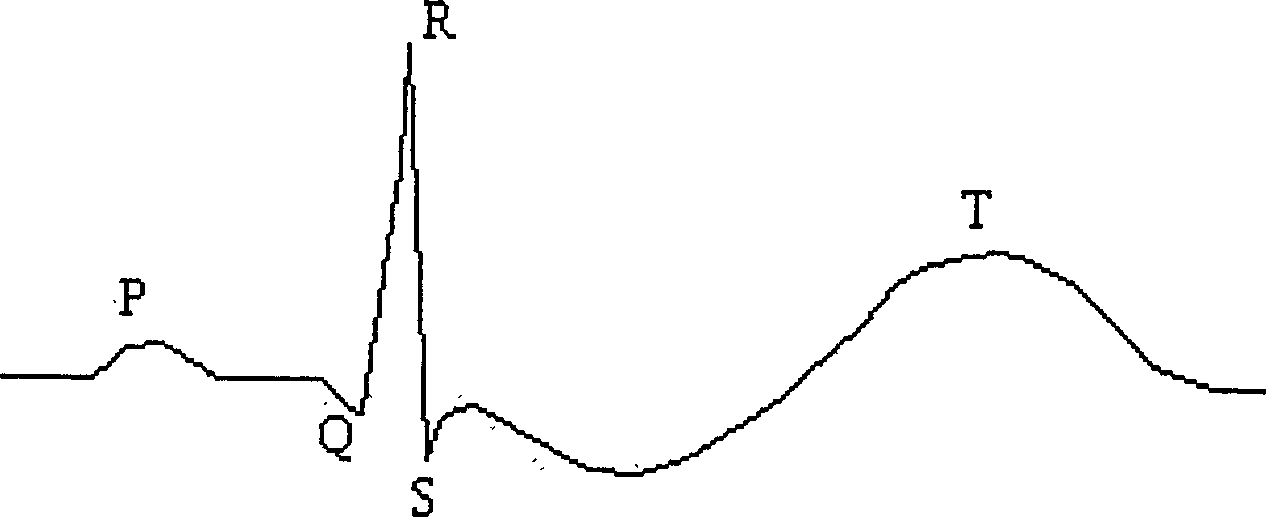
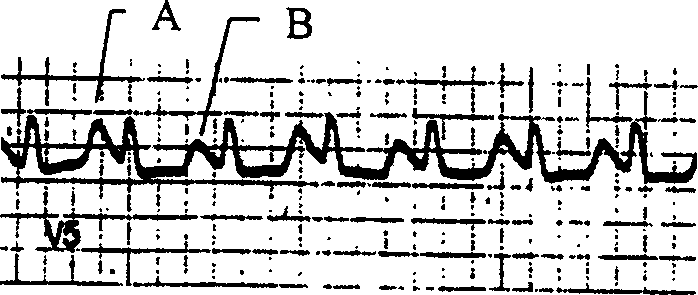
T wave alternans (TWA) is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations ("macroscopic" TWA) could be detected. Those large TWAs were associated with increased susceptibility to lethal ventricular tachycardias.
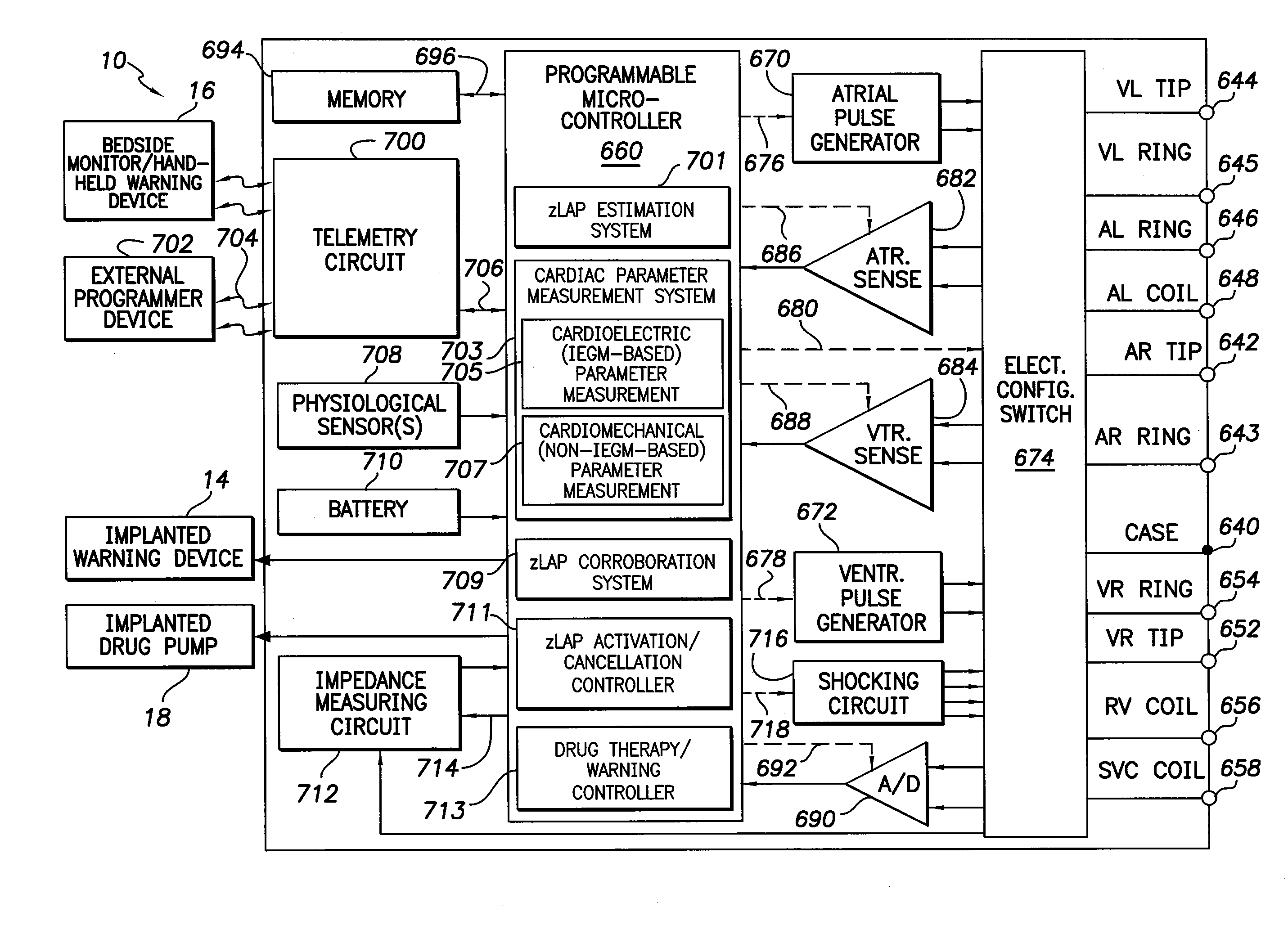
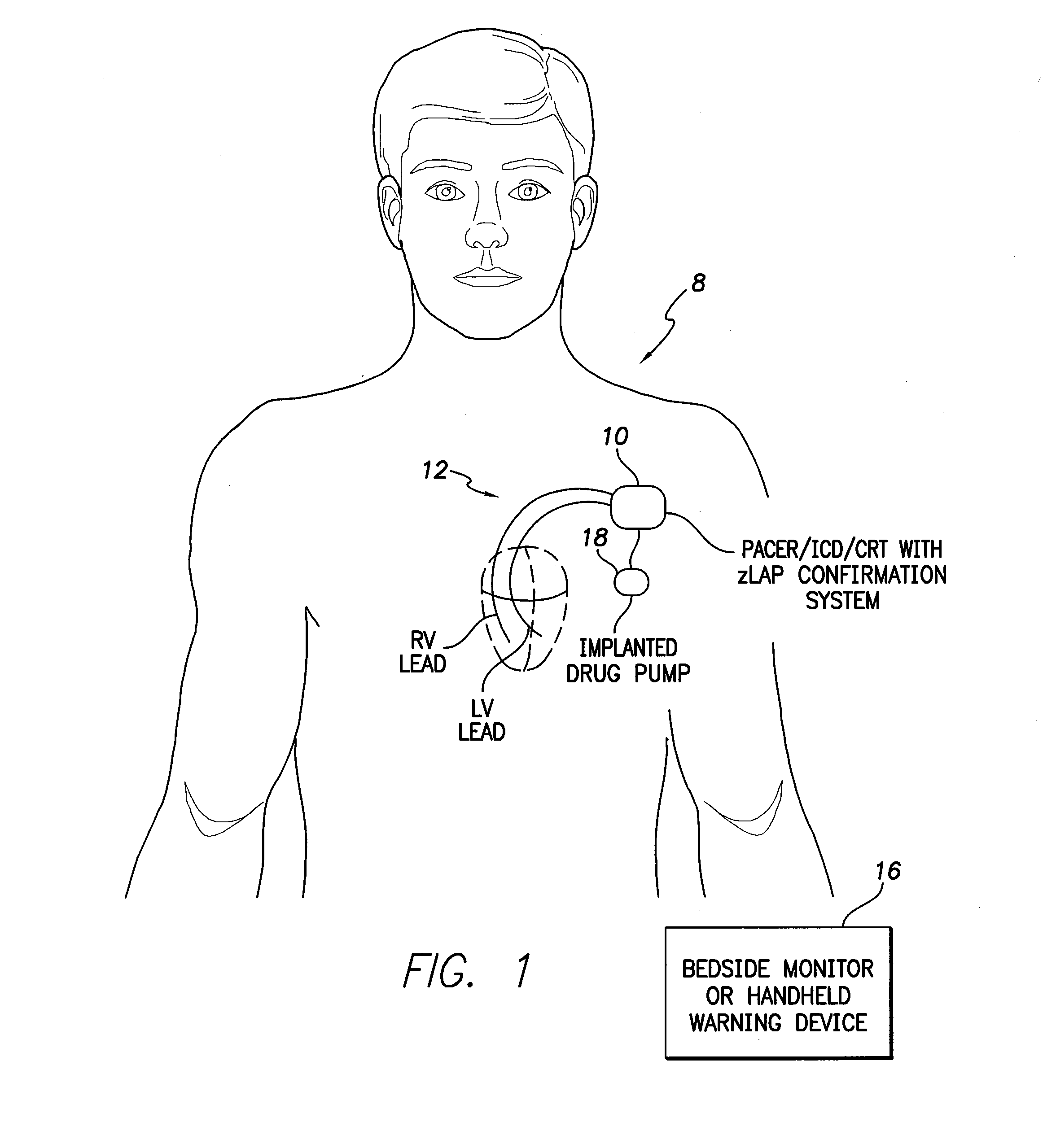
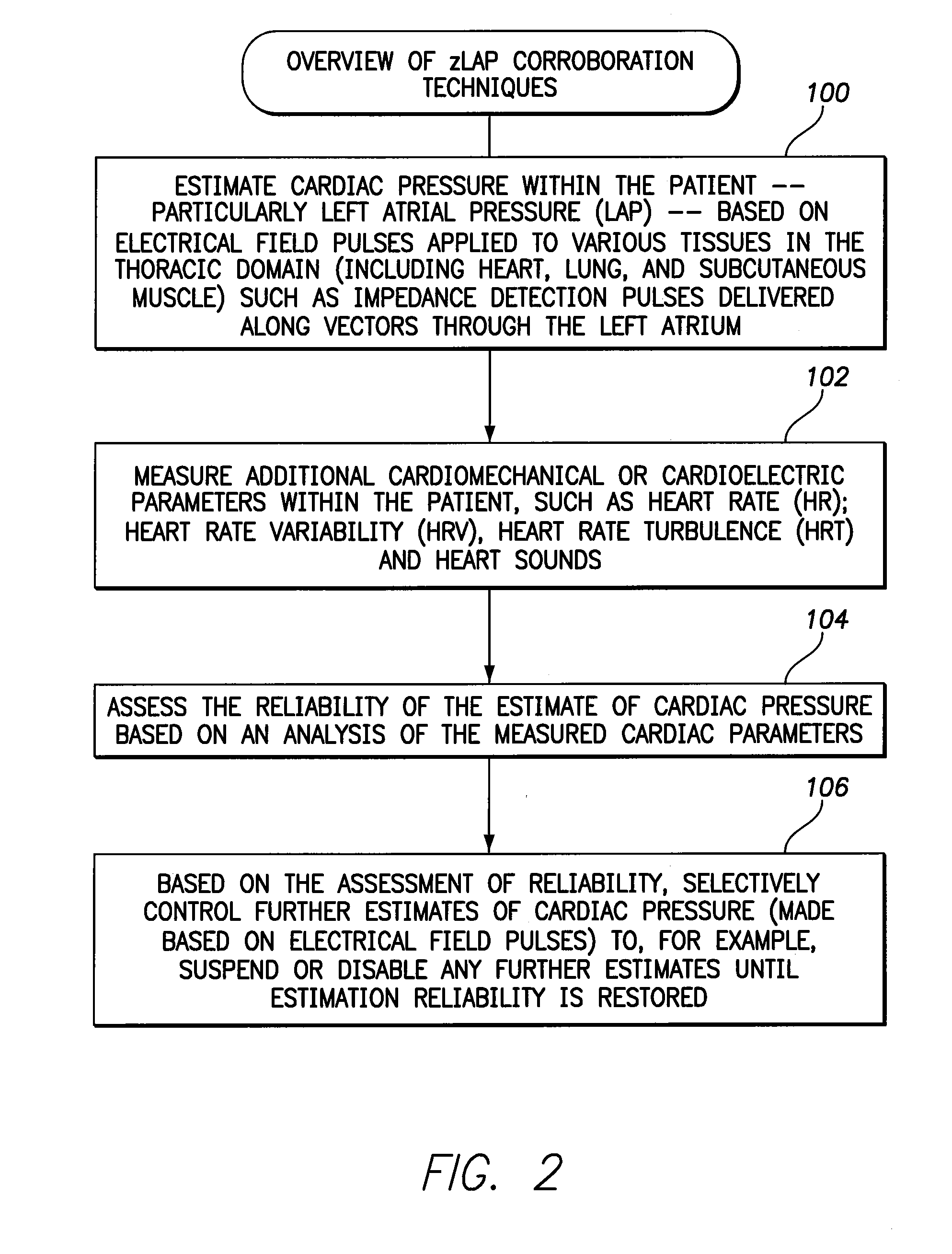
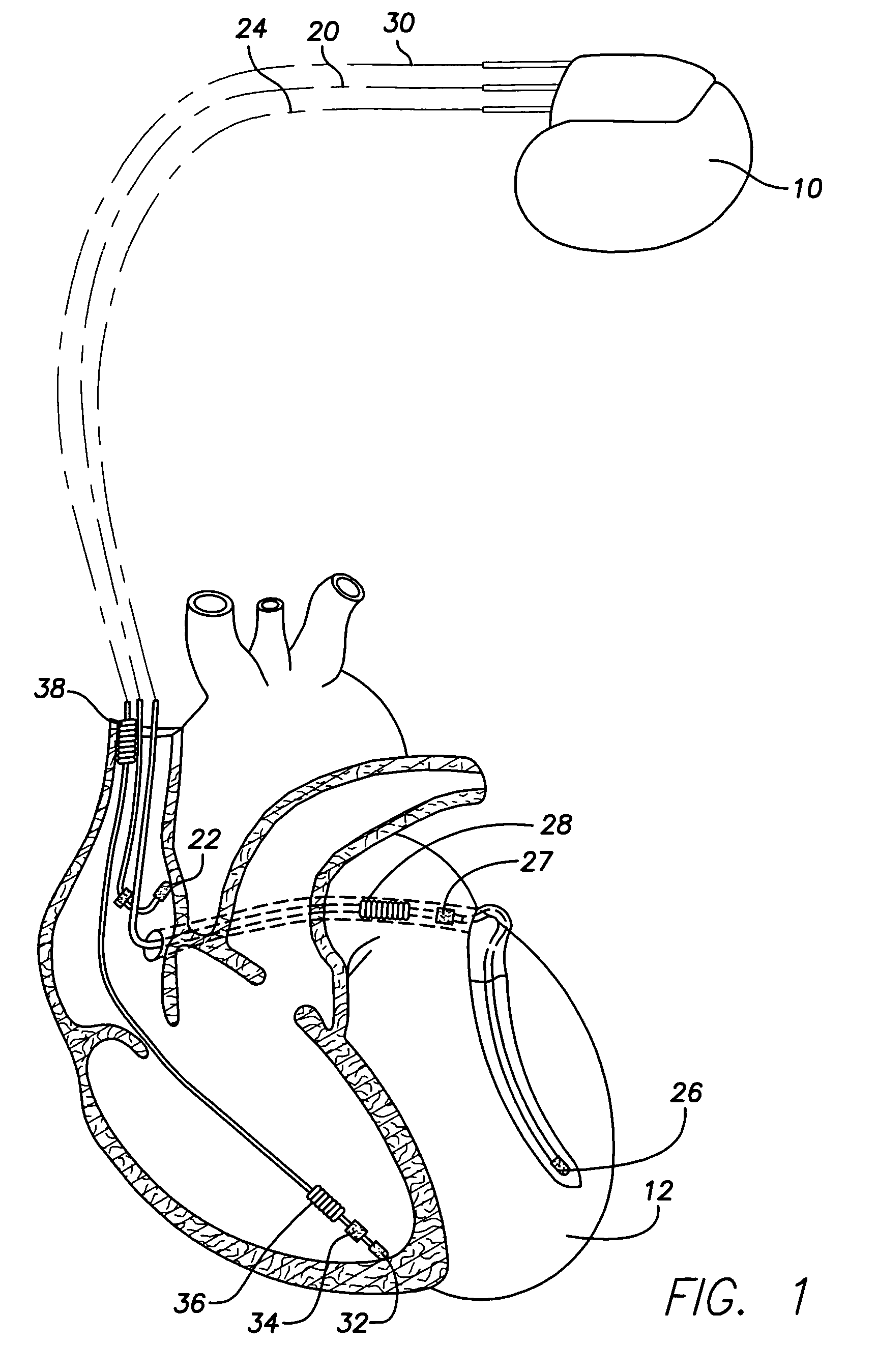
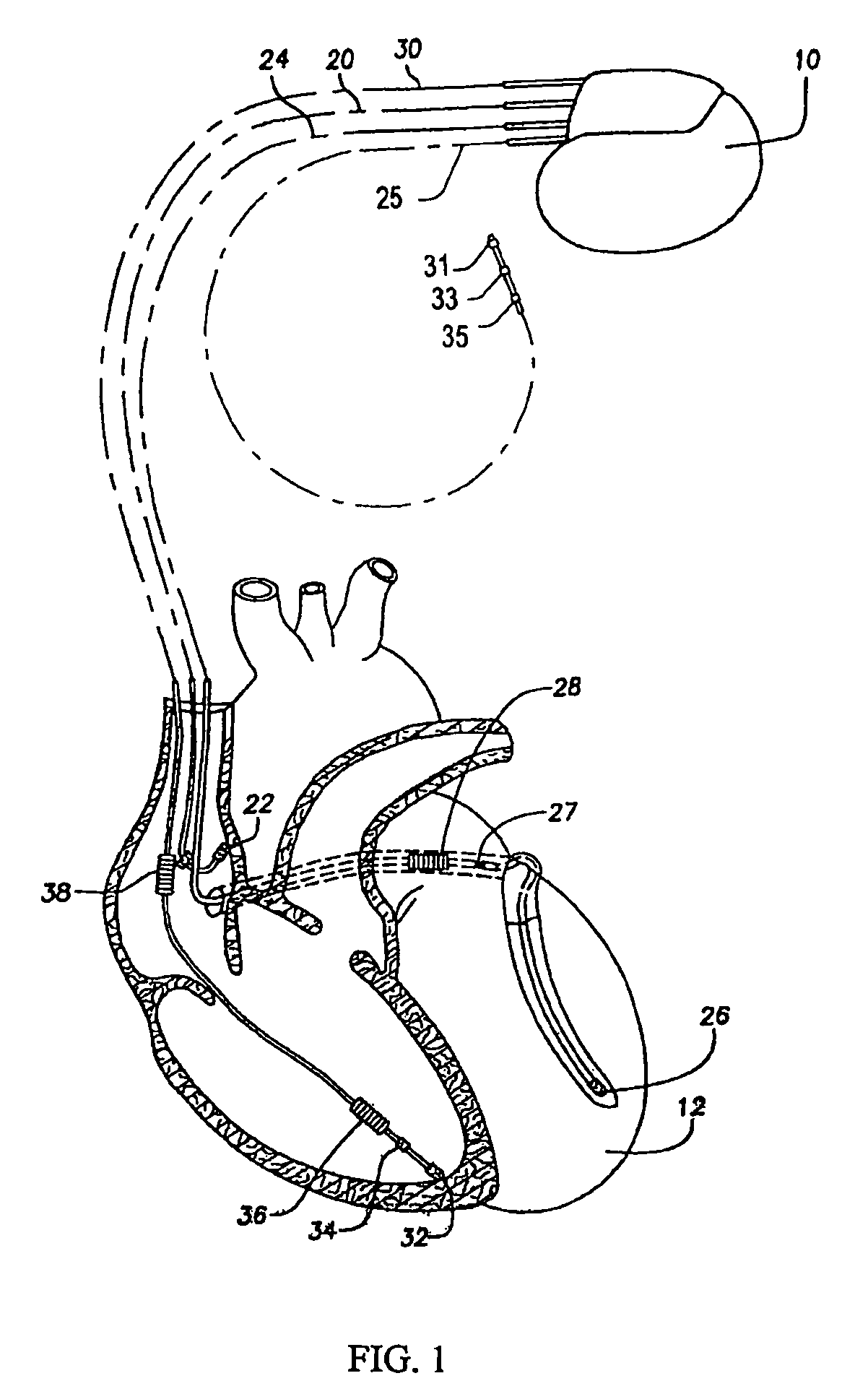
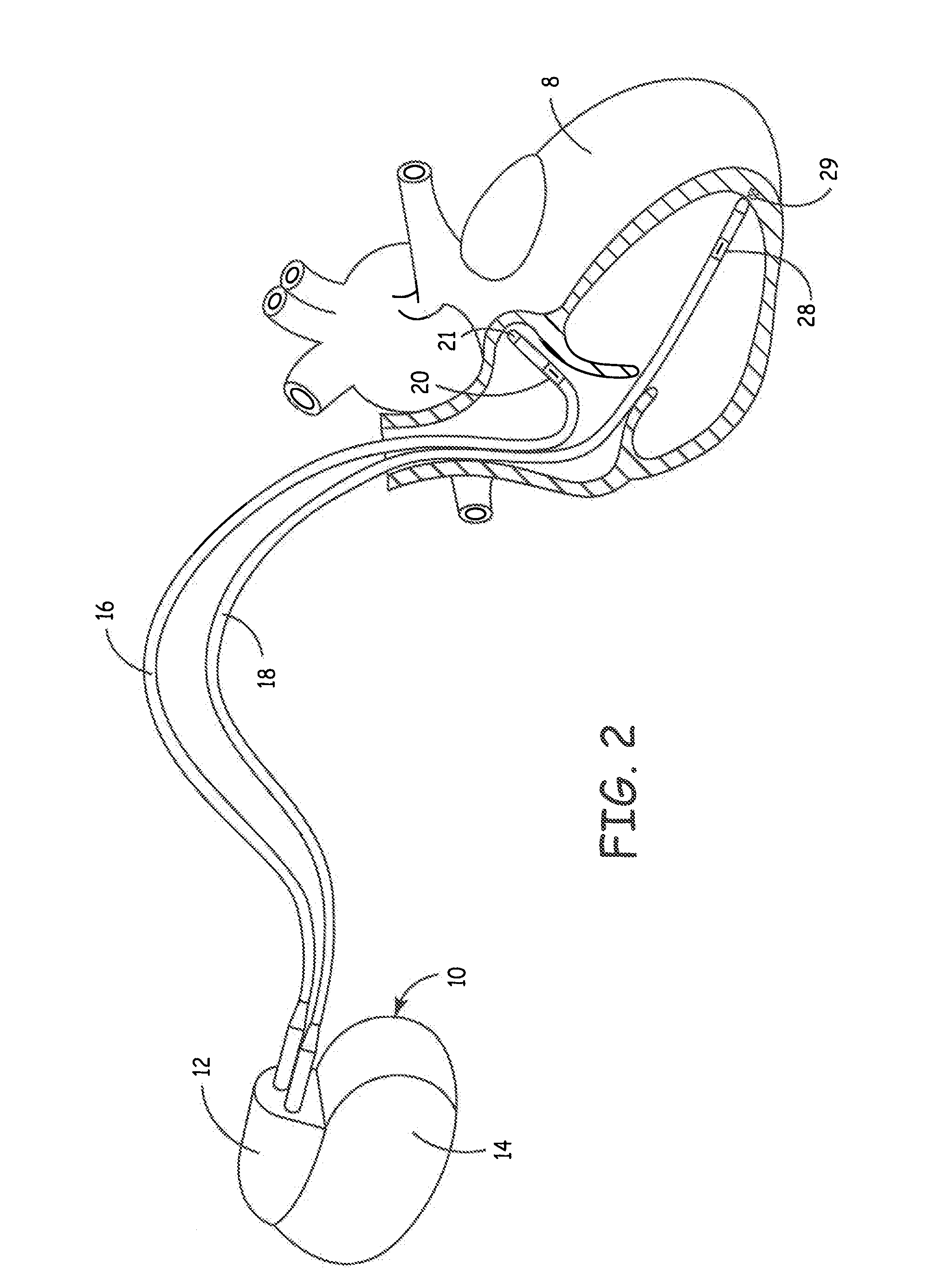
Systems and methods for corroborating impedance-based left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates for use by an implantable medical device
Various techniques are provided for assessing the reliability of left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates made by an implantable medical device based on impedance values or related electrical values. In one example, various cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters are used to corroborate LAP estimation in circumstances where the LAP estimates deviate from an acceptable, satisfactory or otherwise healthy range. The cardioelectric parameters include, e.g.: ST elevation; heart rate (HR); heart rate variability (HRV); T-wave alternans (TWA); QRS waveform parameters; P-wave duration; evoked response (ER) parameters; and intrinsic PV / AV / VV conduction delays. The cardiomechanical parameters include, e.g.: heart rate turbulence (HRT); cardiogenic impedance signals; heart sounds; and non-LAP blood pressure measurements, such as aortic pressure measurements. The device compares the cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters against corresponding baseline values to determine whether variations in the parameters corroborate the LAP estimates. If not, the LAP estimates are selectively cancelled or suspended, or the overall procedure is re-calibrated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
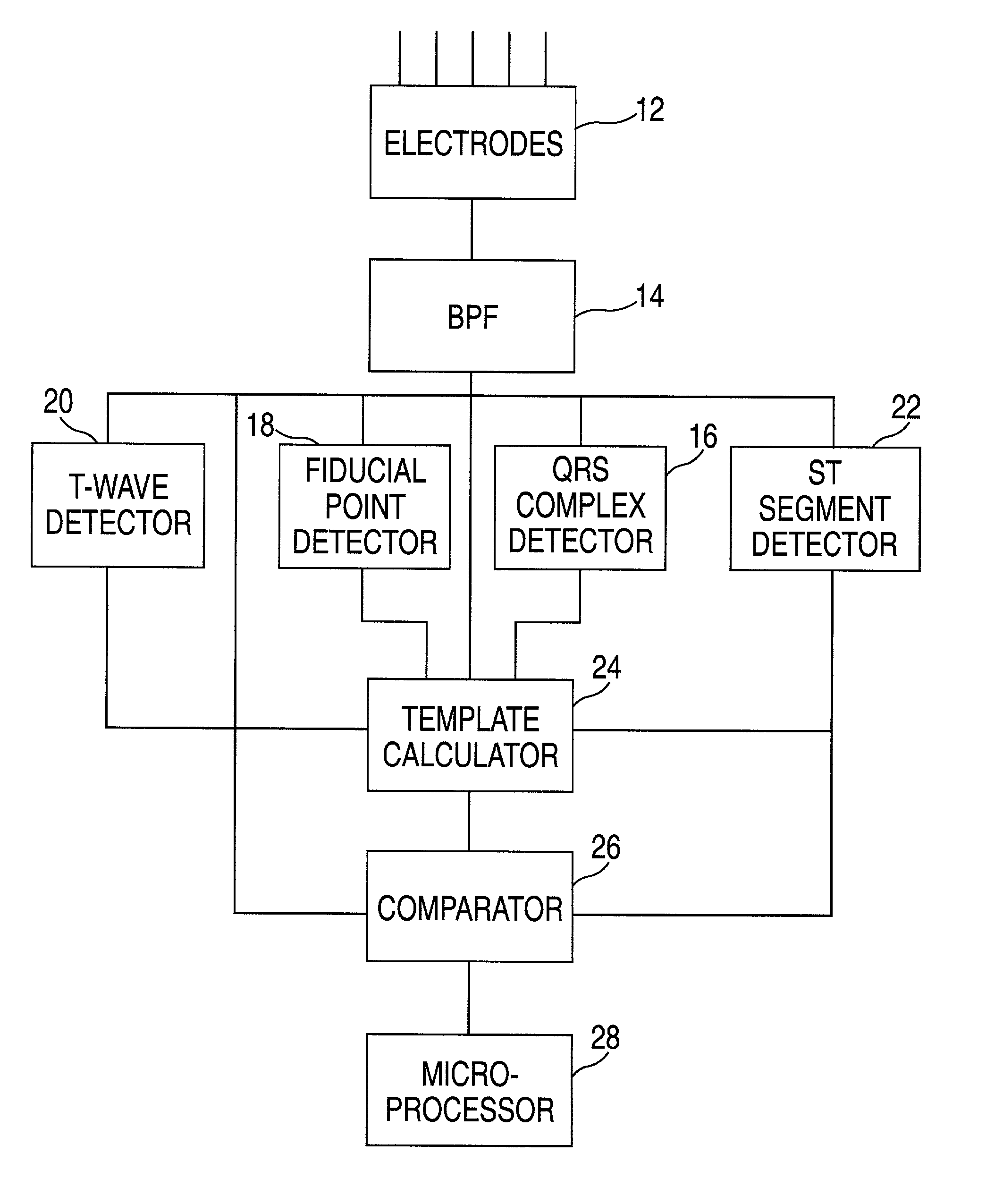
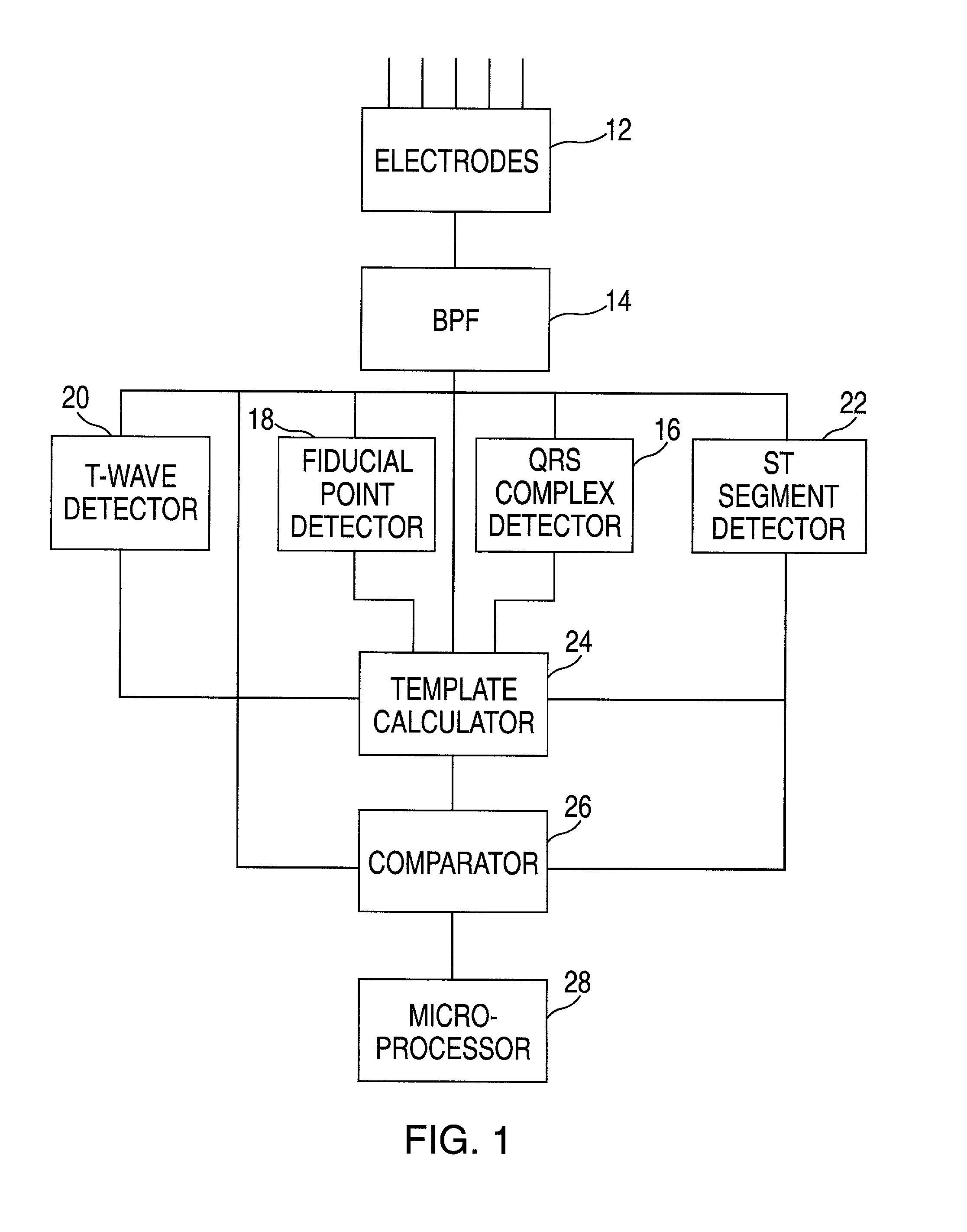
Method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac patients for T-wave alternans
InactiveUS6983183B2Eliminate the effects ofReliable measurementElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalArray data structure
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Dynamic electrocardiogram T wave alternate quantitative analysis method based on models
InactiveCN102512157ARealize dynamic estimationReal-time preventionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalSpatial model
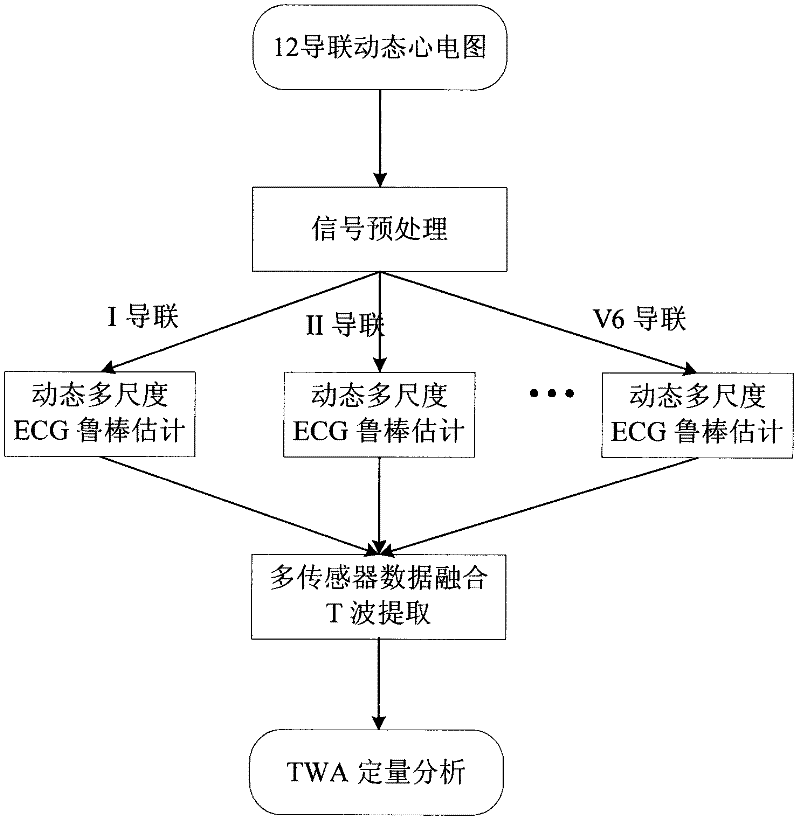
The invention discloses a dynamic electrocardiogram (ECG) T wave alternate quantitative analysis method based on models, which belongs to the technical field of biomedical signal processing. The dynamic electrocardiogram (ECG) T wave alternate quantitative analysis method includes steps of preprocessing 12 lead ambulatory electrocardiograms of a patient at first and removing random disturbance including baseline drift, power frequency disturbance, myoelectricity noise and the like; building various channel electrocardiosignal state space models and realizing robust estimation to electrocardiosignal waveforms by the aid of a dynamic multi-scale state estimation theory; applying a multi-sensor data fusion method to realize T wave fusion extraction and realizing T wave quantitative description; and finally realizing quantitative analysis for T wave alternate signals according to the analytic function of T waves. The dynamic electrocardiogram T wave alternate quantitative analysis method has the advantages that on the basis of the electrocardiosignal state spatial models, T wave quantitative analysis is realized at first, then dynamic electrocardiogram T wave alternate real-time detection and analysis are realized, and accordingly the dynamic electrocardiogram T wave alternate quantitative analysis method is convenient for catching T wave alternate electrocardio abnormal conditions suddenly caused in daily life and increases detecting level and diagnosis ability to patients in danger of sudden cardiac death.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
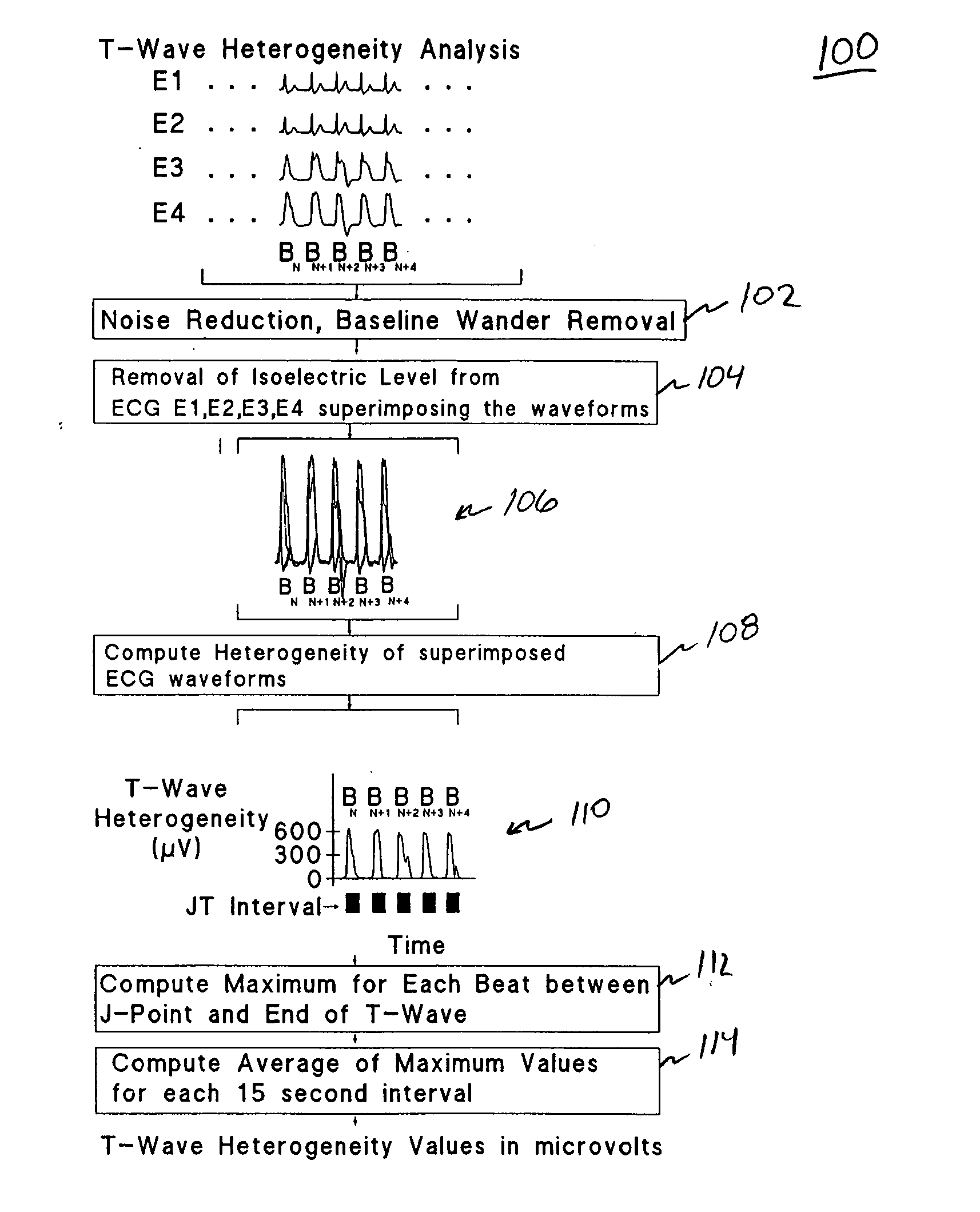
Spatial heterogeneity of repolarization waveform amplitude to assess risk of sudden cardiac death
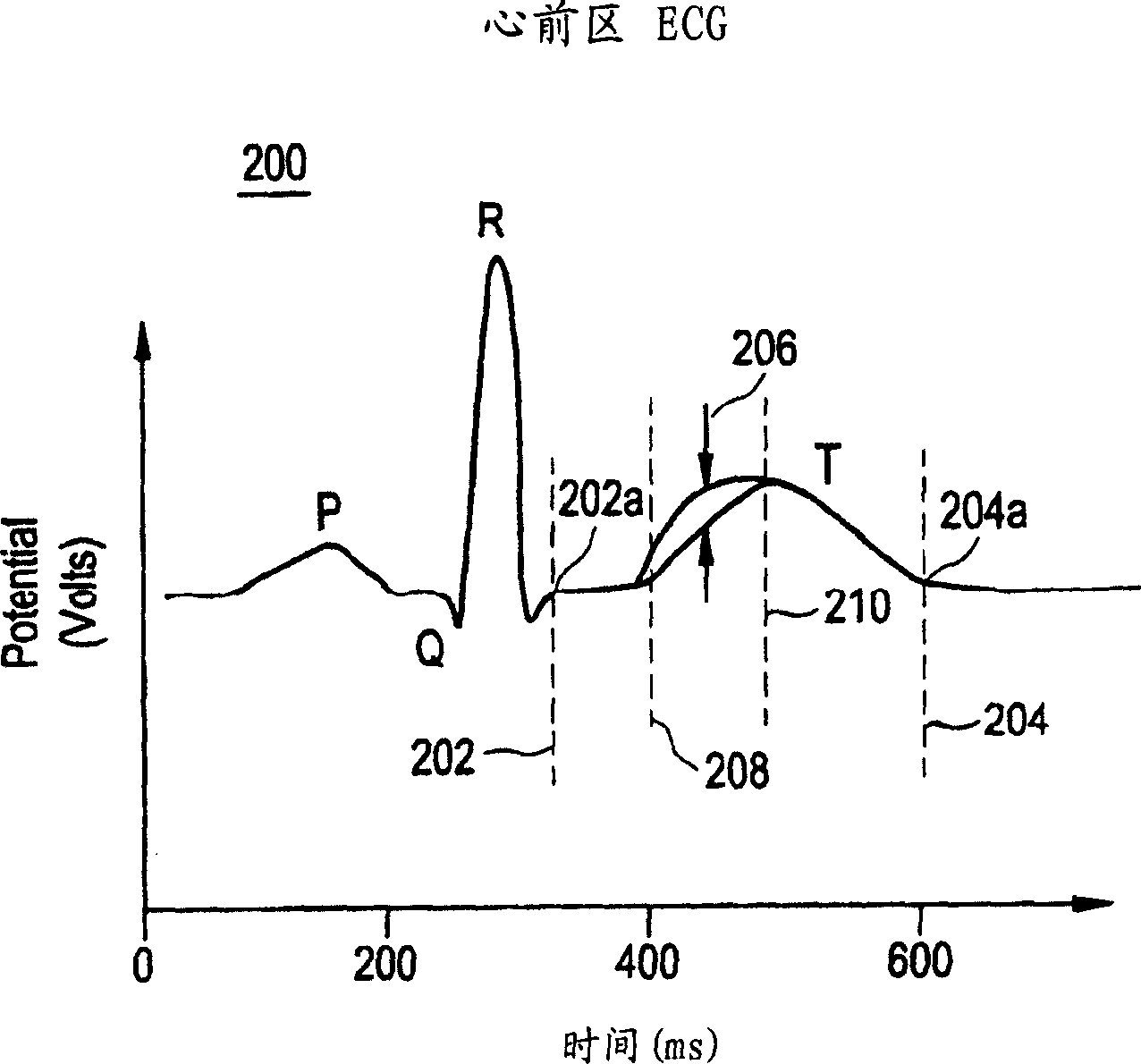
Exercise-induced T-wave alternans (TWA) in coronary artery disease patients reflects significant levels of spatial heterogeneity of repolarization, which may underlie the predictive utility of TWA in estimating risk of sudden cardiac death. A method for assessing spatial heterogeneity of repolarization of a heart of a patient includes the following steps: simultaneously sensing an ECG signal from each of a plurality of spatially separated leads attached to the patient; for a plurality of N beats in each of the ECG signals, identifying a JT interval of each beat; and for corresponding ones of the JT intervals of the ECG signals, calculating a second central moment indicative of spatial heterogeneity of repolarization.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
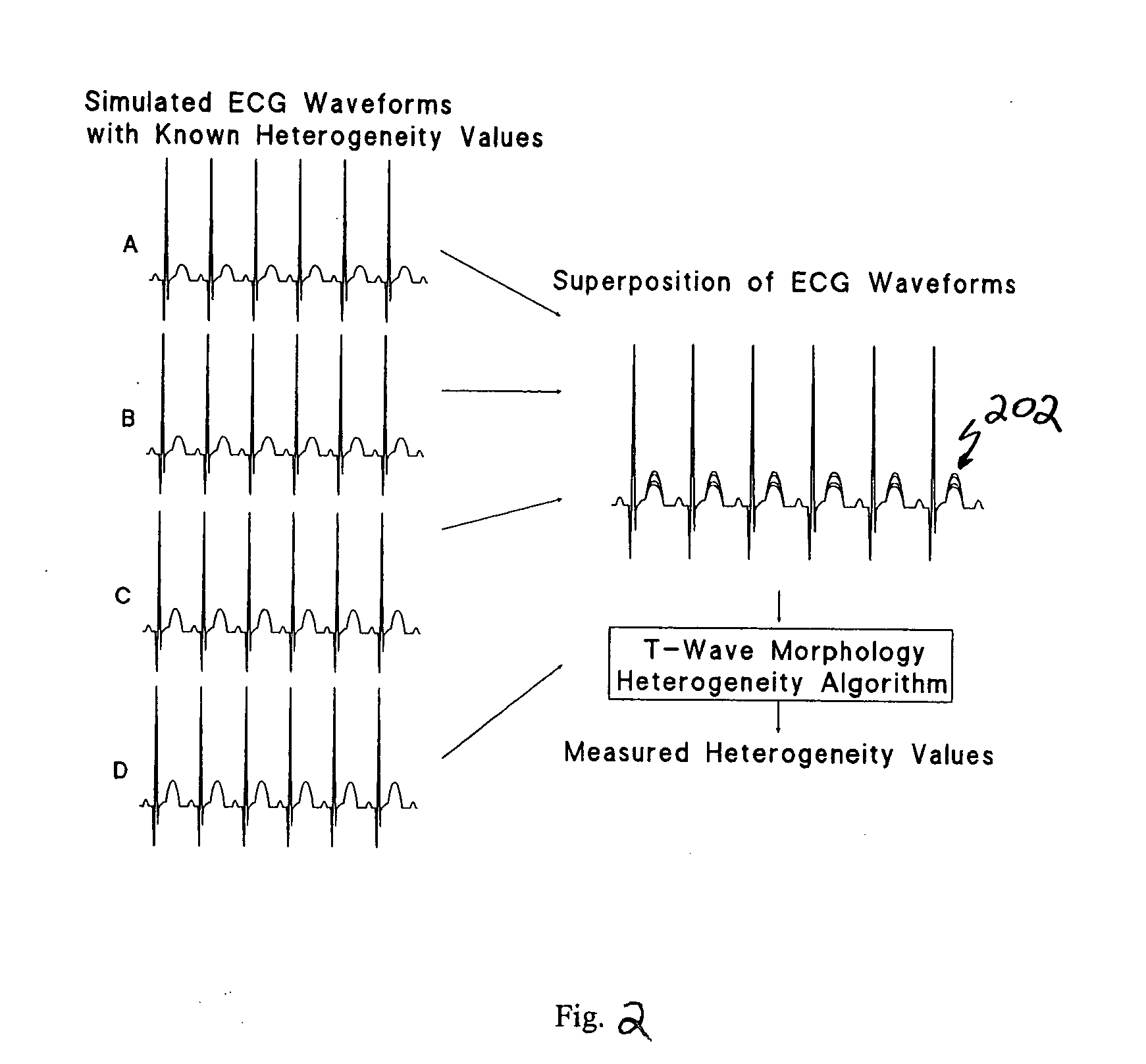
Electrocardiosignal analysis method of T wave alternans scatter diagram method based on morphology
InactiveCN103006207AReduce the drop in detection accuracyGood test resultDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalT wave
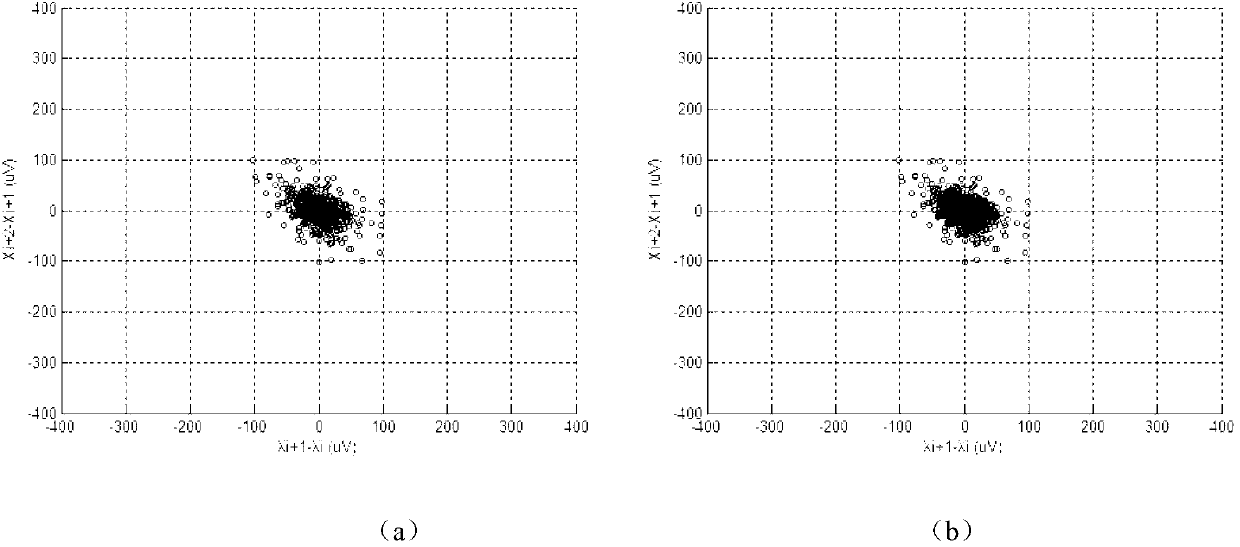
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal analysis method of a T wave alternans scatter diagram method based on morphology. Aiming at the defects of difficulty in detection of each heart beat T wave alternans amplitude value and complexity in calculation of T wave alternans detection by the spectrum analysis method, the T wave alternans scatter diagram method based on morphology is provided to provide a new effective quantitative index of T wave alternans detection for development of domestic related clinical researches. The method includes: using the T wave window analysis method for sampling T waves of 128 continuous heart beats selected from the American MIT-BIH standard heart beat irregularity database and the European ST-T electrocardio database, making a differential scatter diagram by the aid of the sample points, using vector angle index of the scatter diagram for quantitative analysis of T wave alternans to obtain a vector angle index range for judging whether T wave alternans exists or not, and comparing a T wave alternans detection result obtained by means of the vector angle index of the scatter diagram with the T wave alternans detection result obtained by means of the T wave alternans amplitude of the spectrum analysis method to judge reliability in detection of T wave alternans by the vector angle index.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Methods and systems for analyzing t-wave alternants
InactiveUS20090318822A1Optimizing antiarrhythmia therapyReduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyT waveInstability
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for detecting TWA (T wave alternans) in electrocardiogram
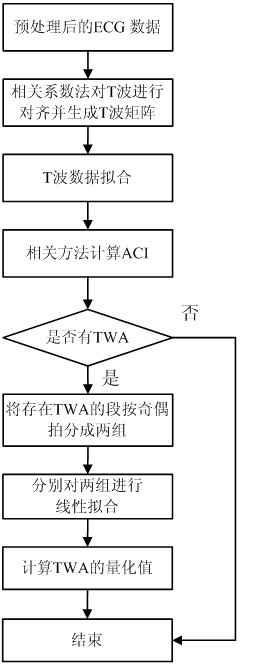
InactiveCN102579039AImprove time resolutionStrong anti-noise abilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalTime domain
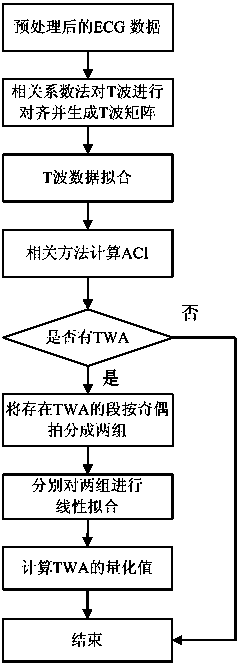
The invention discloses a method for detecting TWA (T wave alternans) in the electrocardiogram and belongs to the technical field of medical testing. The method comprises the following steps of: eliminating data sections with excessively high noise from selected electrocardiosignals by judging in the earlier stage so as to obtain relatively stable data suitable to analyze and carrying out analysis by taking M beats as an analysis window; firstly, extracting a T wave matrix for the M beats of electrocardiosignals and then carrying out data fitting on T waves in the T wave matrix to obtain a novel T wave matrix; respectively calculating alternans correlation indexes by a correlation analysis method to obtain an ACI (Allowable Concentration Index) of the integral analysis window); then judging whether the TWA exists in the integral analysis window by the correlation analysis method; if the TWA exists in the integral analysis window, respectively carrying out least square linear fitting on sectional odd and even beats of the existing TWA and calculating an actual TWA quantity; and if the TWA does not exist in the integral analysis window, intercepting a next analysis window to carry out analysis. According to the invention, the TWA signals can be effectively detected from the time domain angle and the TWA quantity is accurately quantized.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method and system having ultra-long record period and ultra-high storage capacity
InactiveCN102485171AAchieve playbackRealize monitoringDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMass storageConvalescence
The invention relates to a non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method having an ultra-long record period and an ultra-high storage capacity. By using the method, characteristic values of electrocardiographic waves can be safely, stably and clearly acquired under the natural physiological state of a human body within a long period (more than 15 days), microvolt-level measurements of T-wave alternans can be acquired, and the collection, processing and high-capacity storage of electrocardiographic waves can be completed; and multiple electrocardiographic recording pasters can be used to realize the simultaneous recording of multi-channel body surface electrocardiograms, and a computer data processing and analysis system can complete the data monitoring and analysis, image display, data storage and printing and output of the recorded signals and realize the networking transmission of the electrocardiosignals. The clinical indications of the device include: symptoms related to suspected arrhythmia; determination of arrhythmia property, and completion of reasonably evaluating anti-arrhythmia treatment and monitoring myocardial ischemia; evaluation of anemic heart disease treatment measures; instructions to acute myocardial infarction patients before leaving hospital and during convalescence; and installation, detection and function assessment of sudden cardiac death and heart pacemakers.
Owner:杰升生物科技(上海)有限公司 +2
Method for quantitatively detecting microvolt T-wave alternans
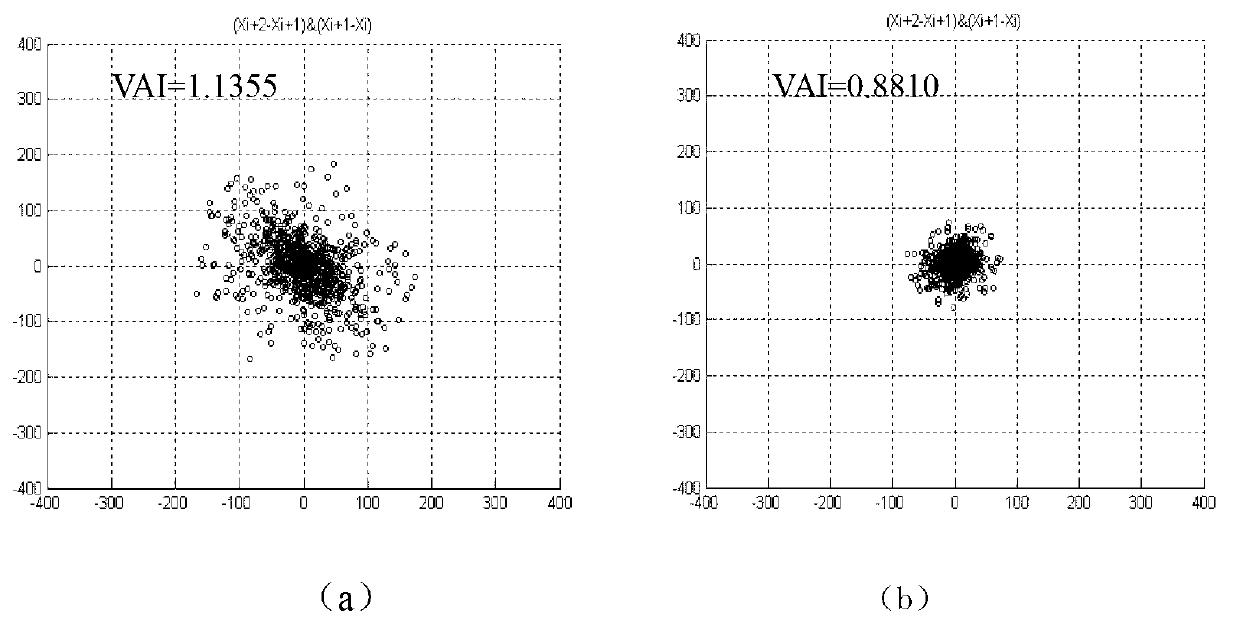
InactiveCN103006206ANo high quality requirementsSimple calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPoint sequenceT wave
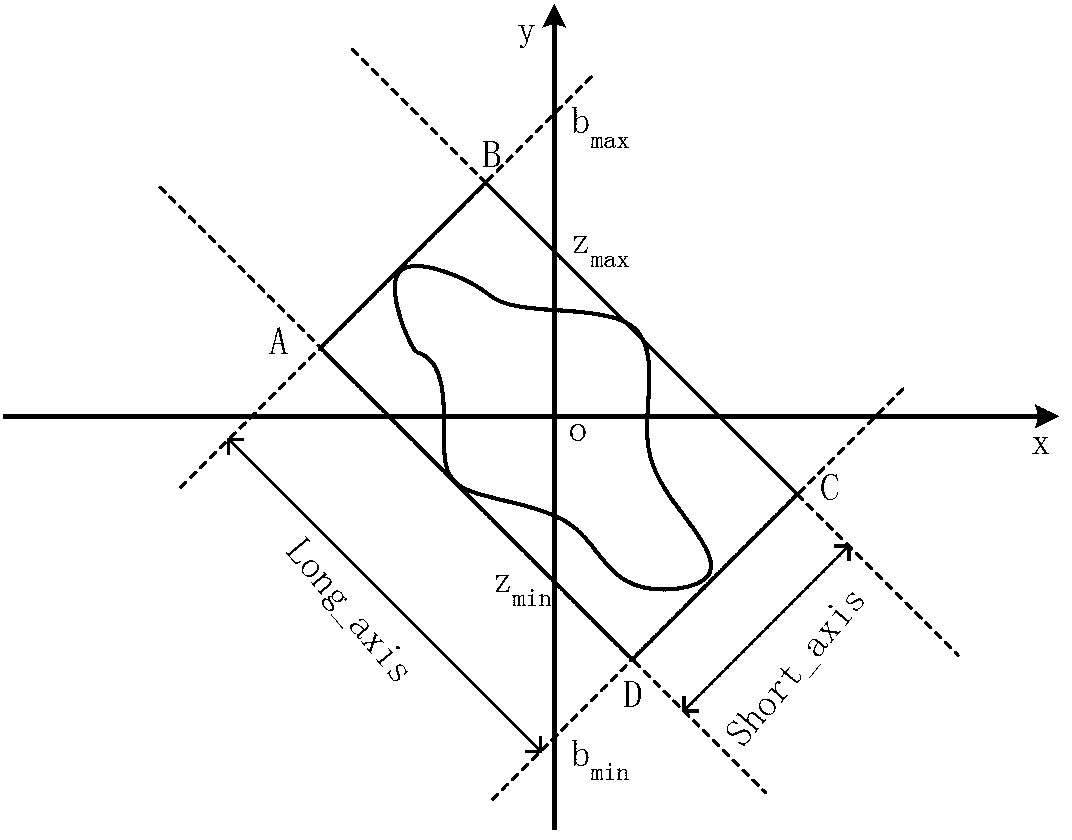
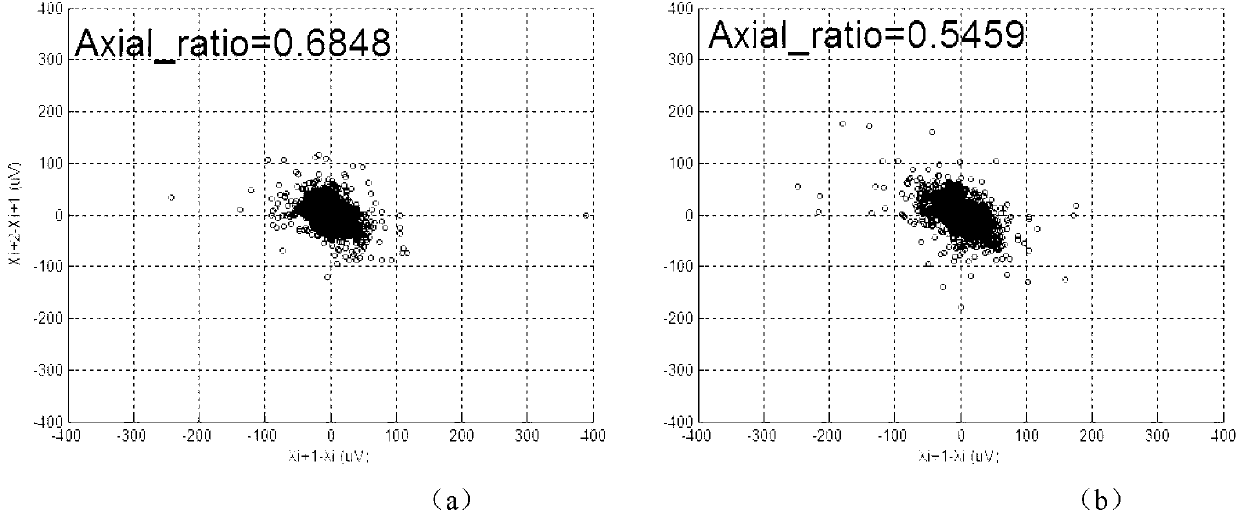
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting microvolt T-wave alternans. A new effective quantitative TWA (T-wave alternans) detection index is provided by analyzing external shape of a T-wave alternans scatter diagram according to the relation of the external shape and the T-wave alternans. By means of improved T-wave window analysis method, the method includes: subjecting 128 continuous heartbeat T-wave sampling point sequences to first difference and drawing a scatter diagram, analyzing the relation of the external shape of the scatter diagram and the T-wave alternans, researching an effective 'cross searching method' to subject the scatter diagram to edge extraction, then defining three quantitative parameters of short axis, long axis and the ratio of the short axis to the long axis at the 'edge' of the scatter diagram, utilizing the ratio of the short axis to the long axis as quantitative detection index Axial_ratio, and finding a proper threshold to judge whether the T-wave alternans exist or not.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Alternating T-wave measuring method for sports electrocardiogram
The present invention belongs to the field of medical test technology, and the T-wave alternation measuring method for sports electrocardiogram beings from the No.113 beat of electrocardiogram signaland analyzes in 16 beats as one analysis window unit. Maximum heart rate is first judged to estimate the noise level. The power spectrum is then analyzed and judged based on noise, whether to exist obvious RR interphase alternation is judged, and if no, the ratio of component at 0.25 and the alternative component before deducing noise level is calculated. When the ratio is smaller than some value, obvious T-wave alternation is considered found out. The method of the present invention solves the problem of detecting weak T-wave alternation signal for predicting malignant arrhythmia.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
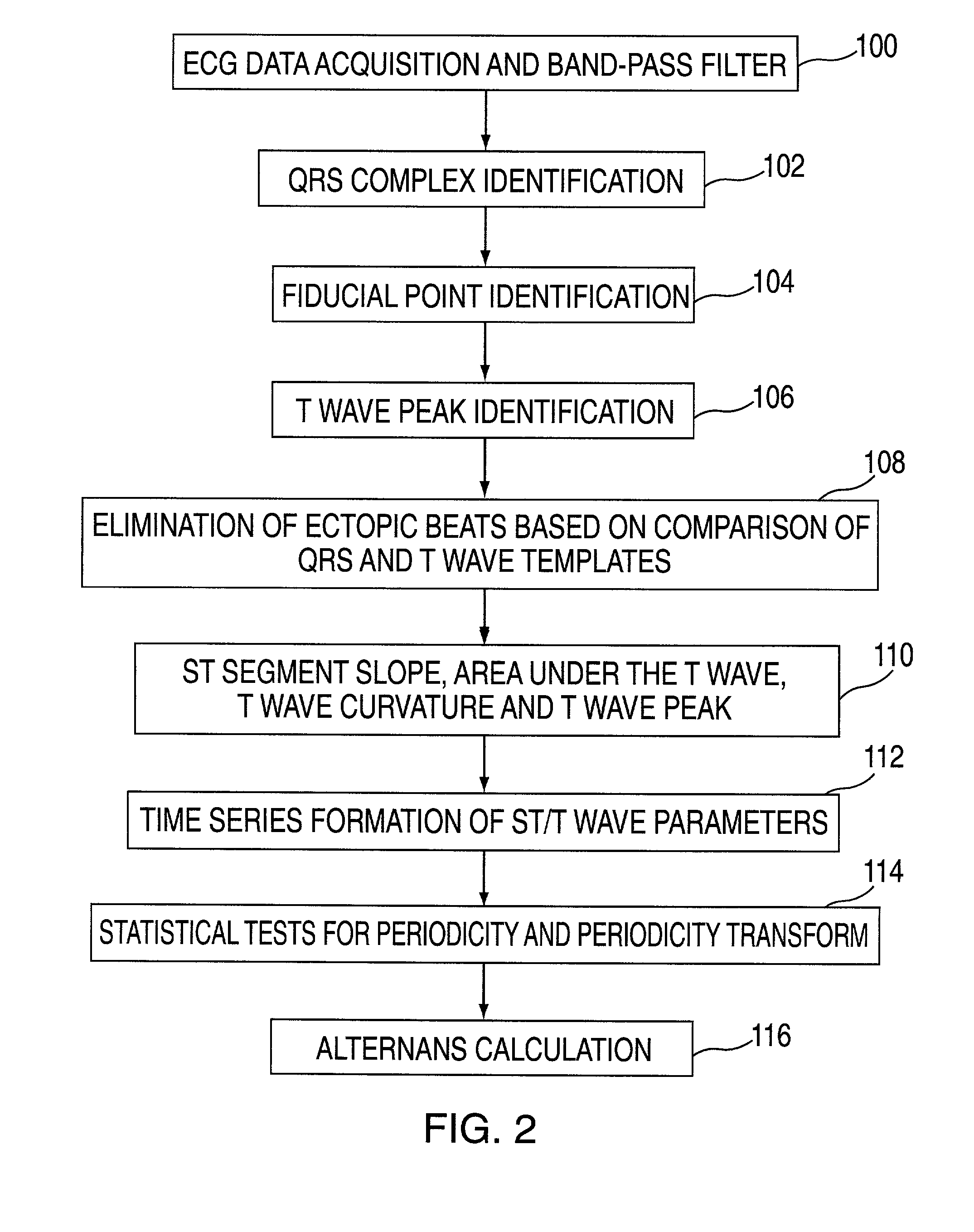
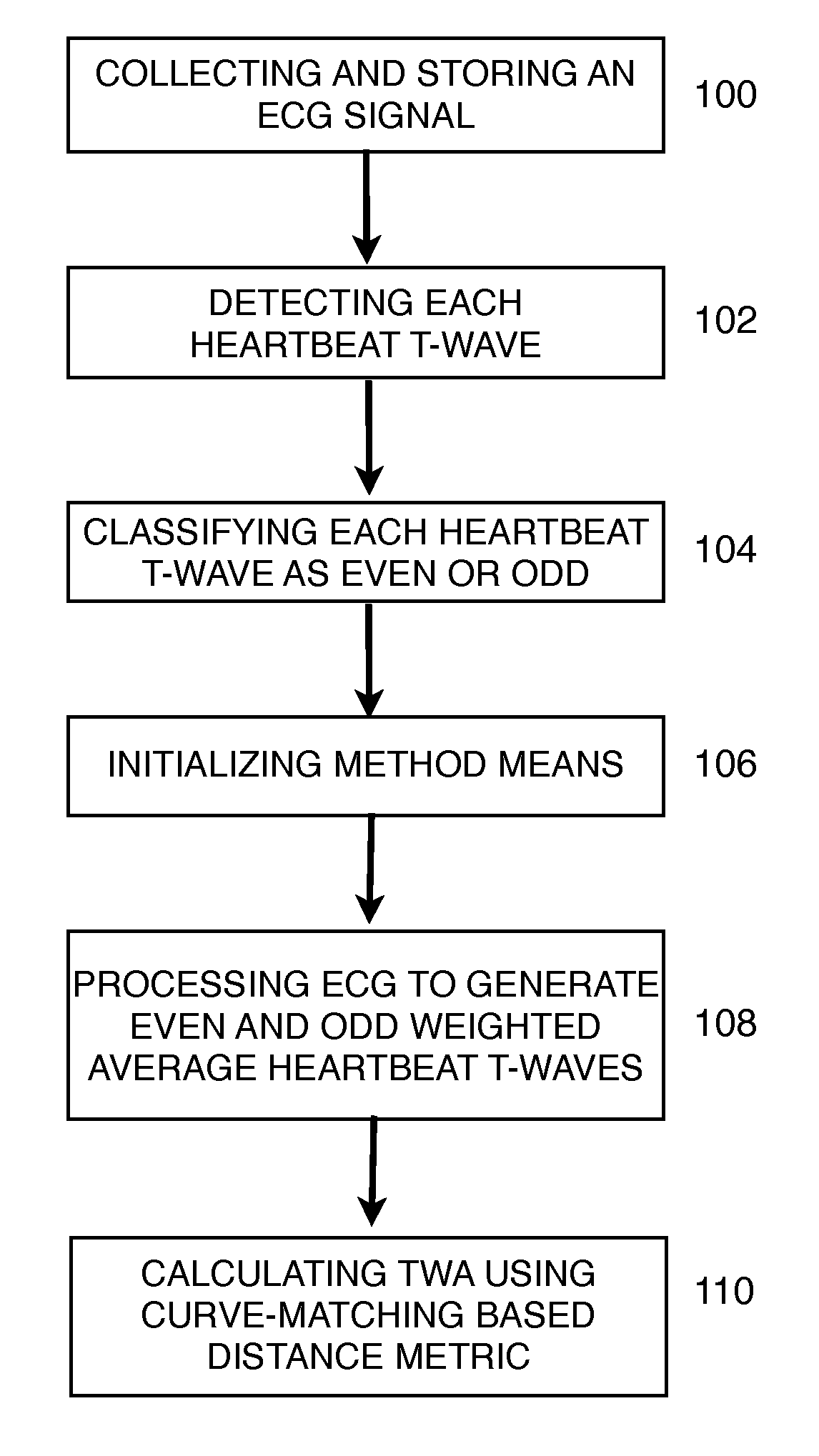
Method and apparatus for automatic analysis of t-wave alternans
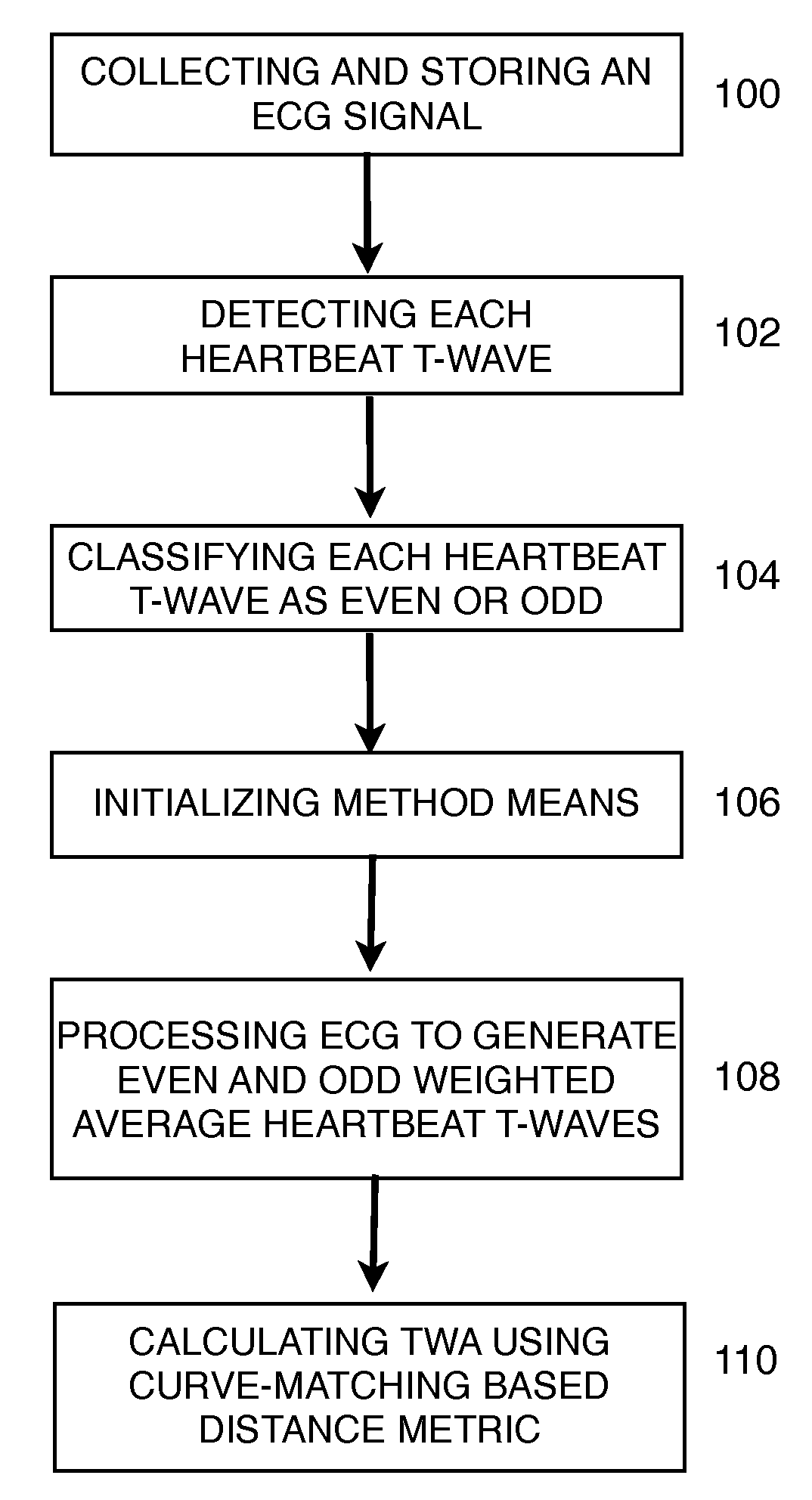
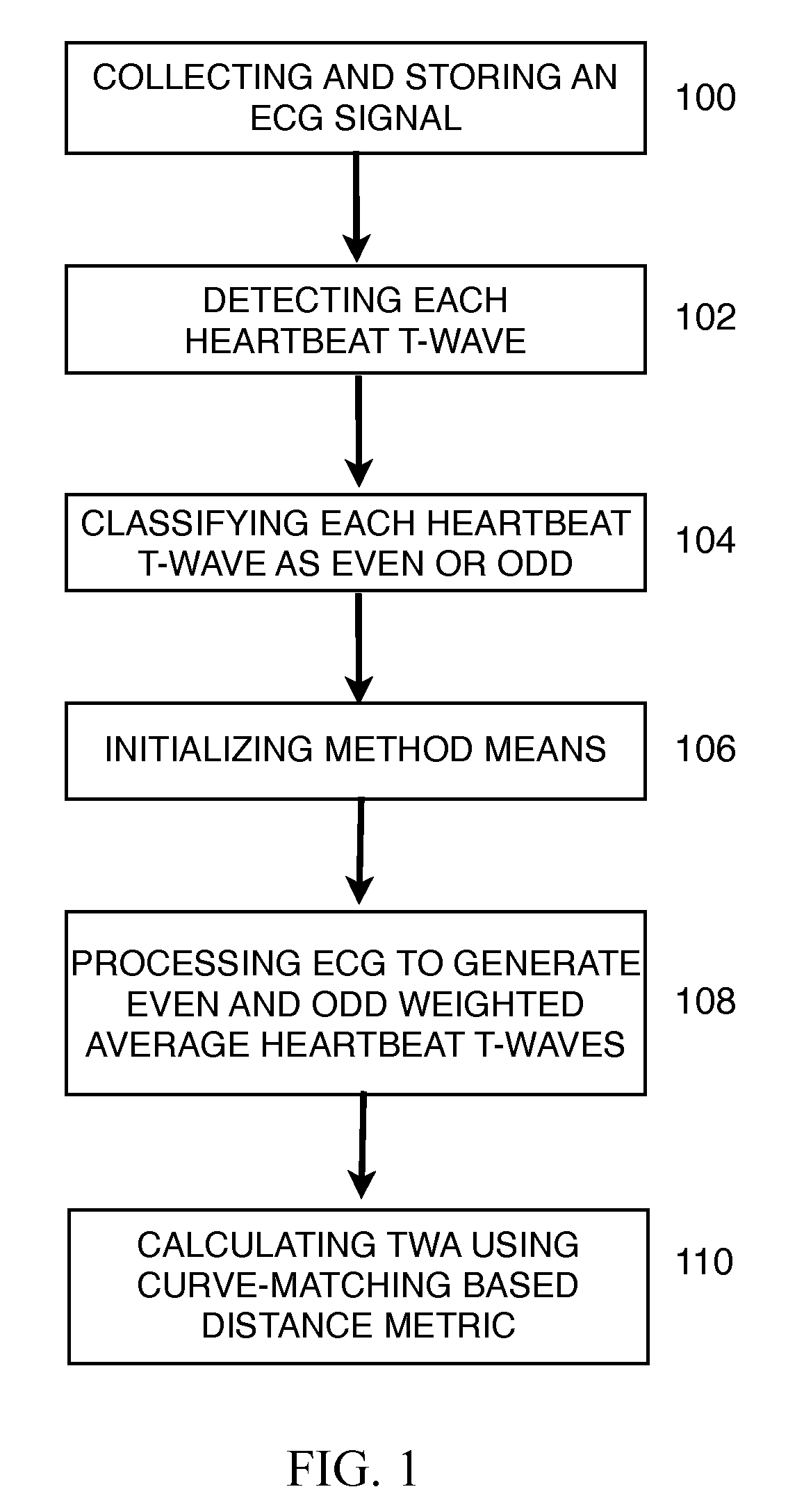
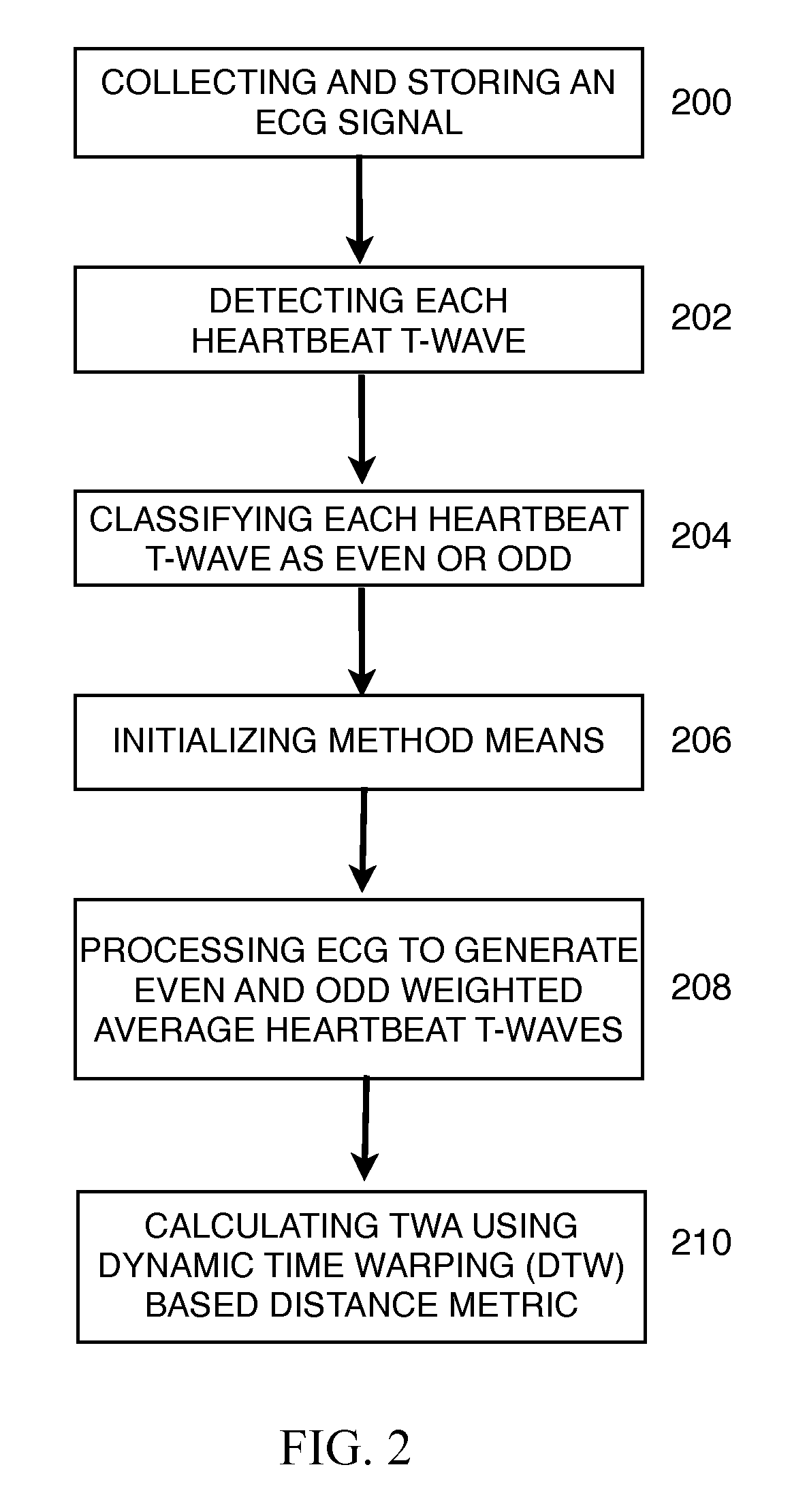
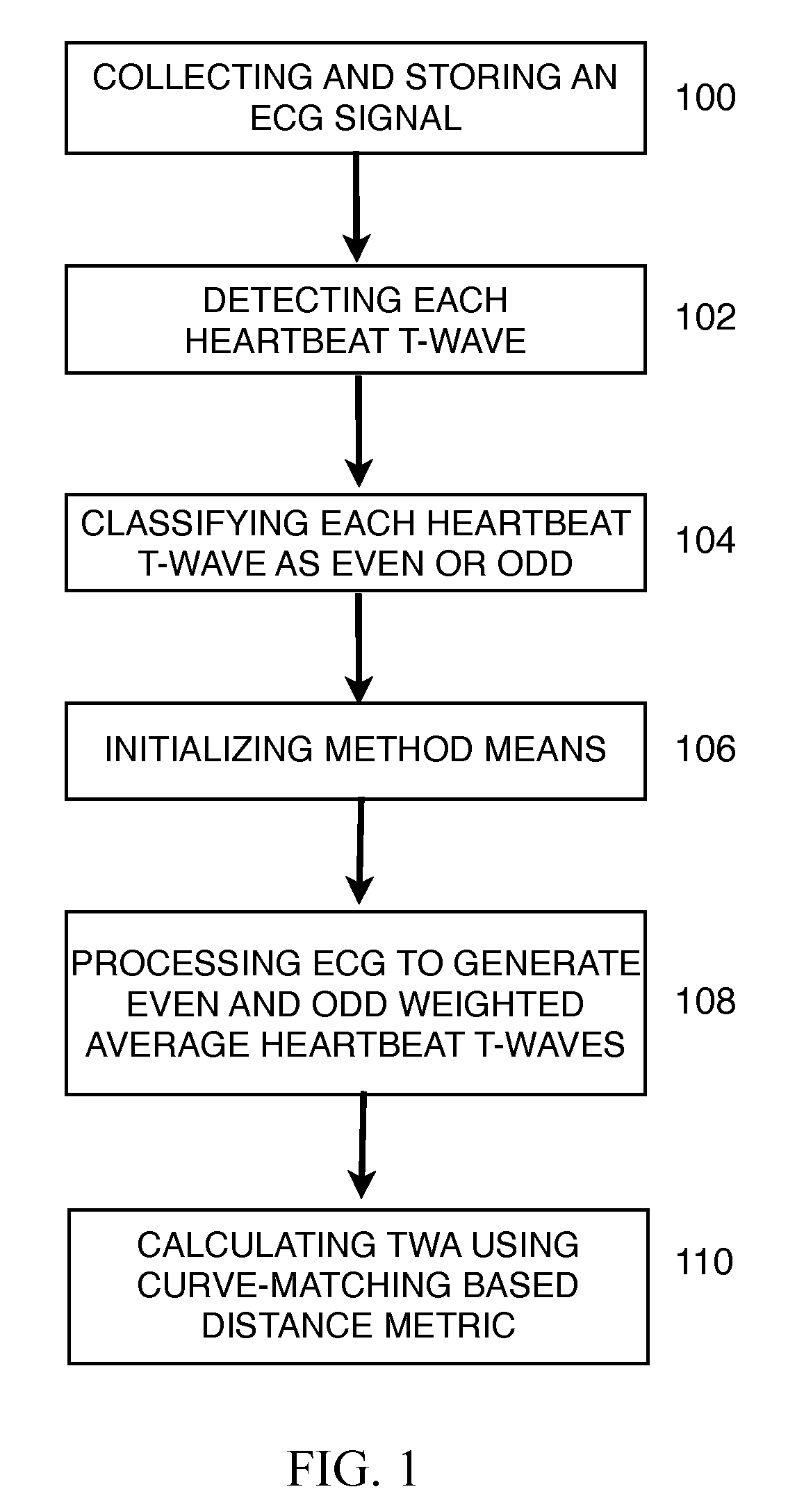
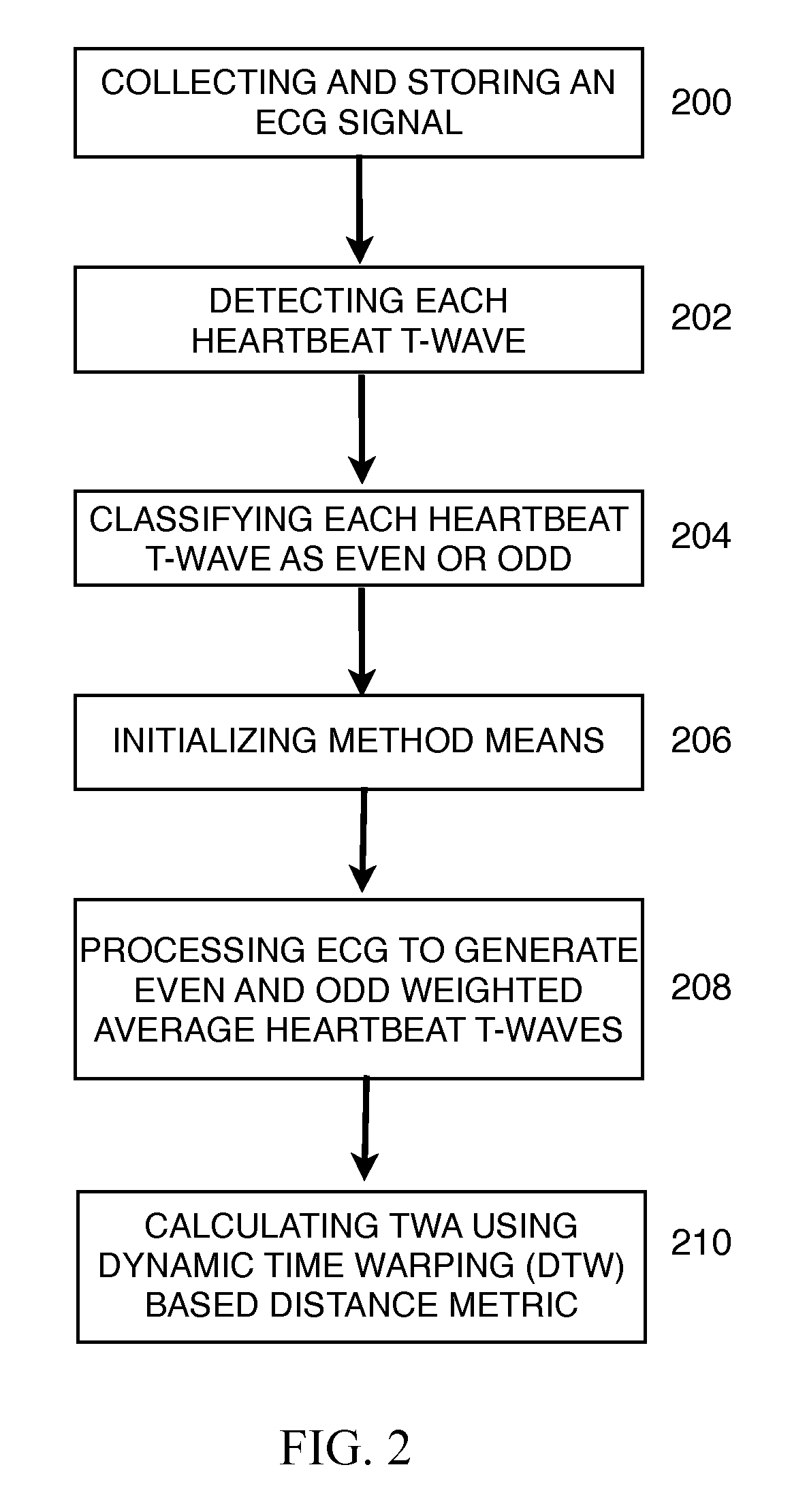
The invention disclosed includes a method and apparatus for calculation of T-wave alternas in electrocardiographic (ECG) signals; said method comprises the following method steps: (a) collecting and storing an ECG signal; (b) detecting each heartbeat T-wave in the ECG signal using an automatic detection and segmentation algorithm; (c) classifying said heartbeat T-wave as an even or odd heartbeat T-wave; (d) initializing said method by taking the first even and the first odd heartbeat T-wave as their respective initial average; (e) processing all the heartbeat T-waves in the ECG signal to generate an even heartbeat T-wave weighted average and odd heartbeat T-wave weighted average; and (f) calculating TWA using a distance metric between the even heartbeat weighted average and the odd heartbeat weighted average, said distance metric including curve matching Continuous Dynamic Time Warping (CDTW).
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA
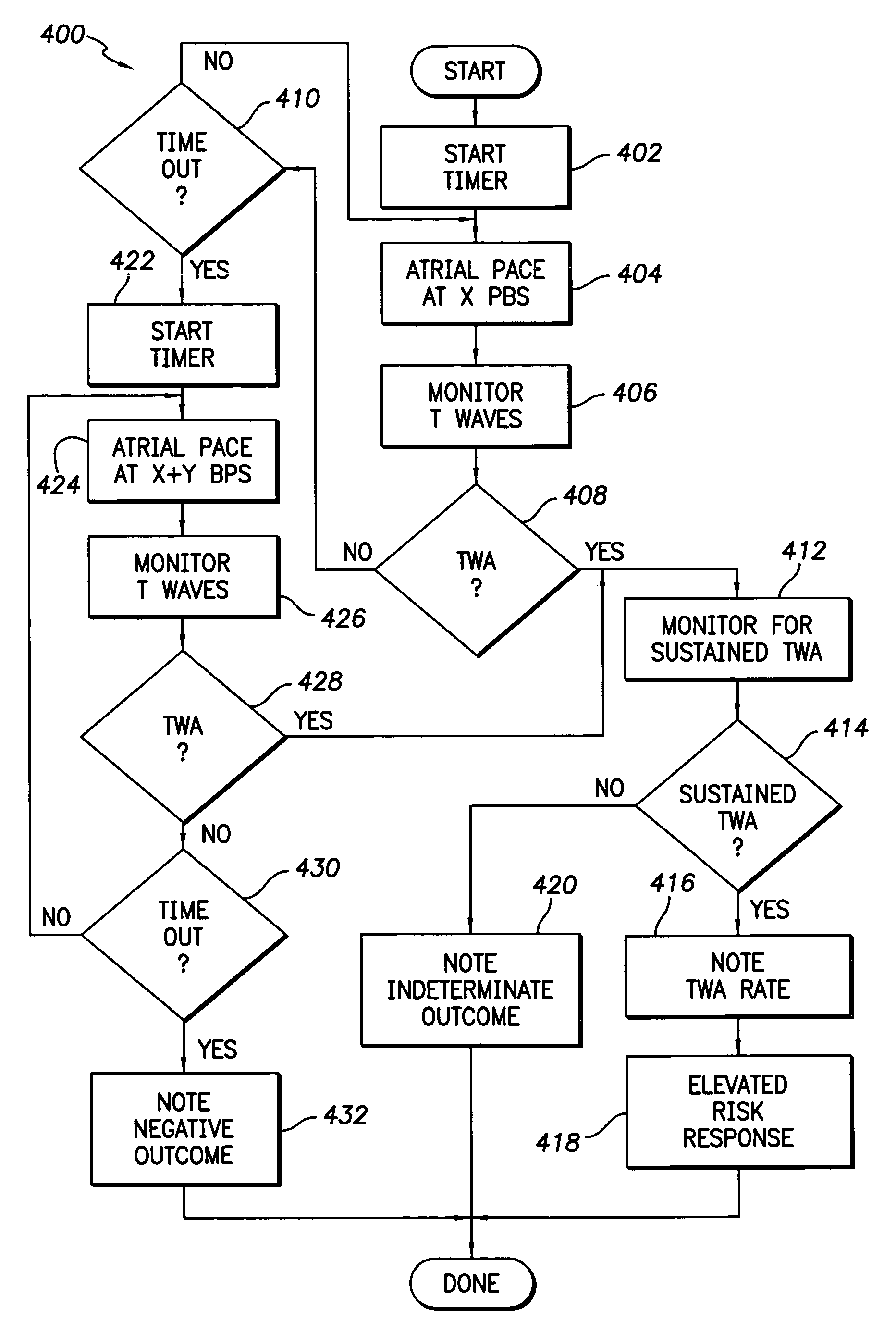
Pacing schemes for revealing T-wave alternans (TWA) at low to moderate heart rates
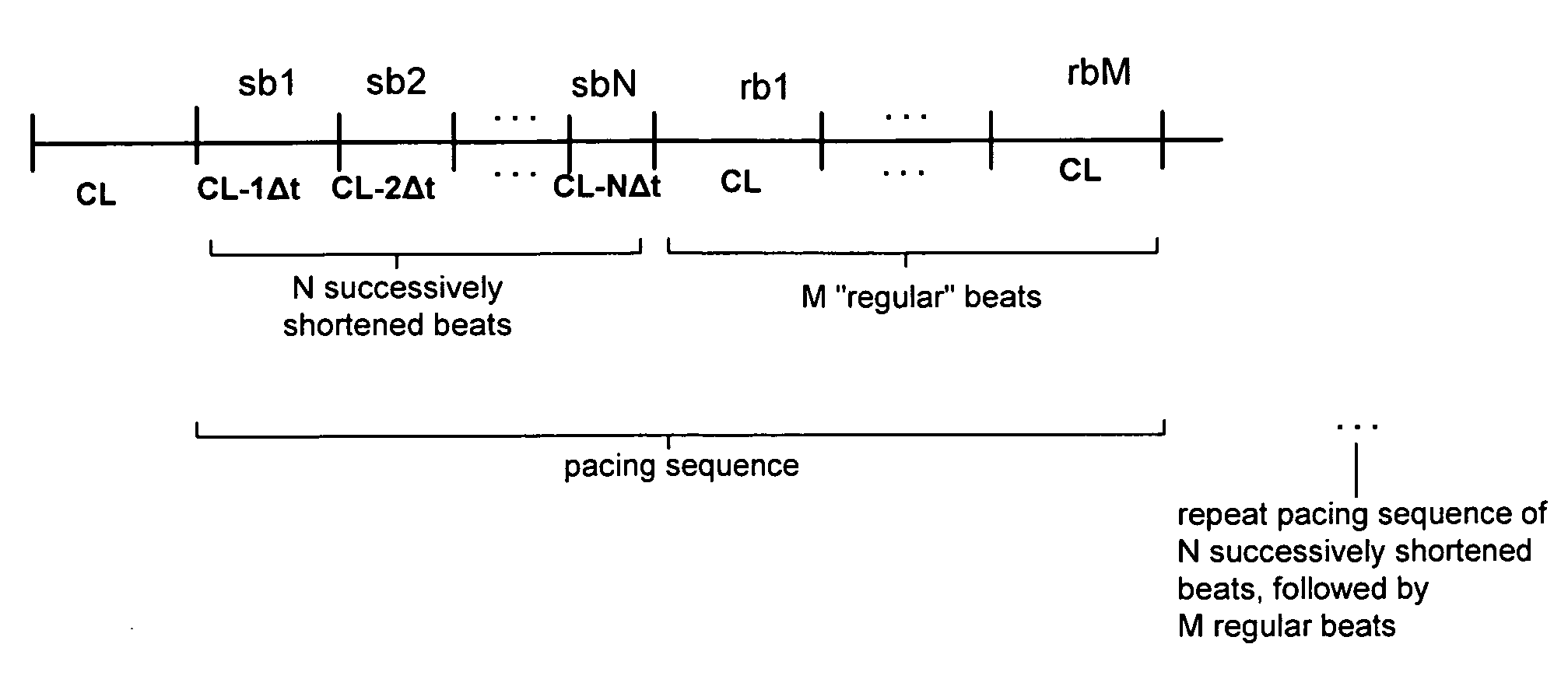
Implantable systems that can monitor myocardial electrical stability, and methods for use therewith, are provided. Also provided are novel pacing sequences that are used in such monitoring. Such pacing sequences are designed to reveal alternans at low to moderate heart rates.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
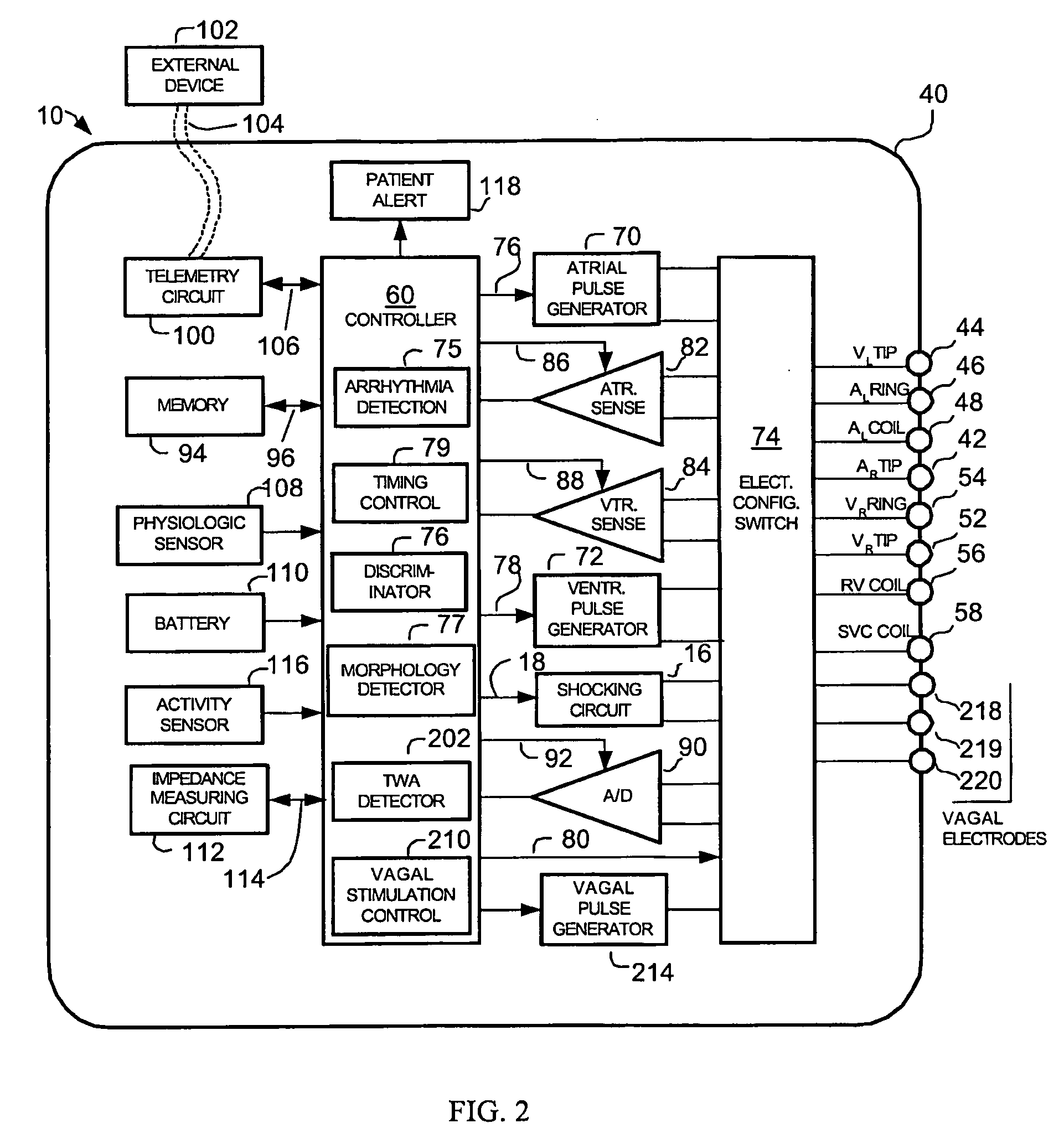
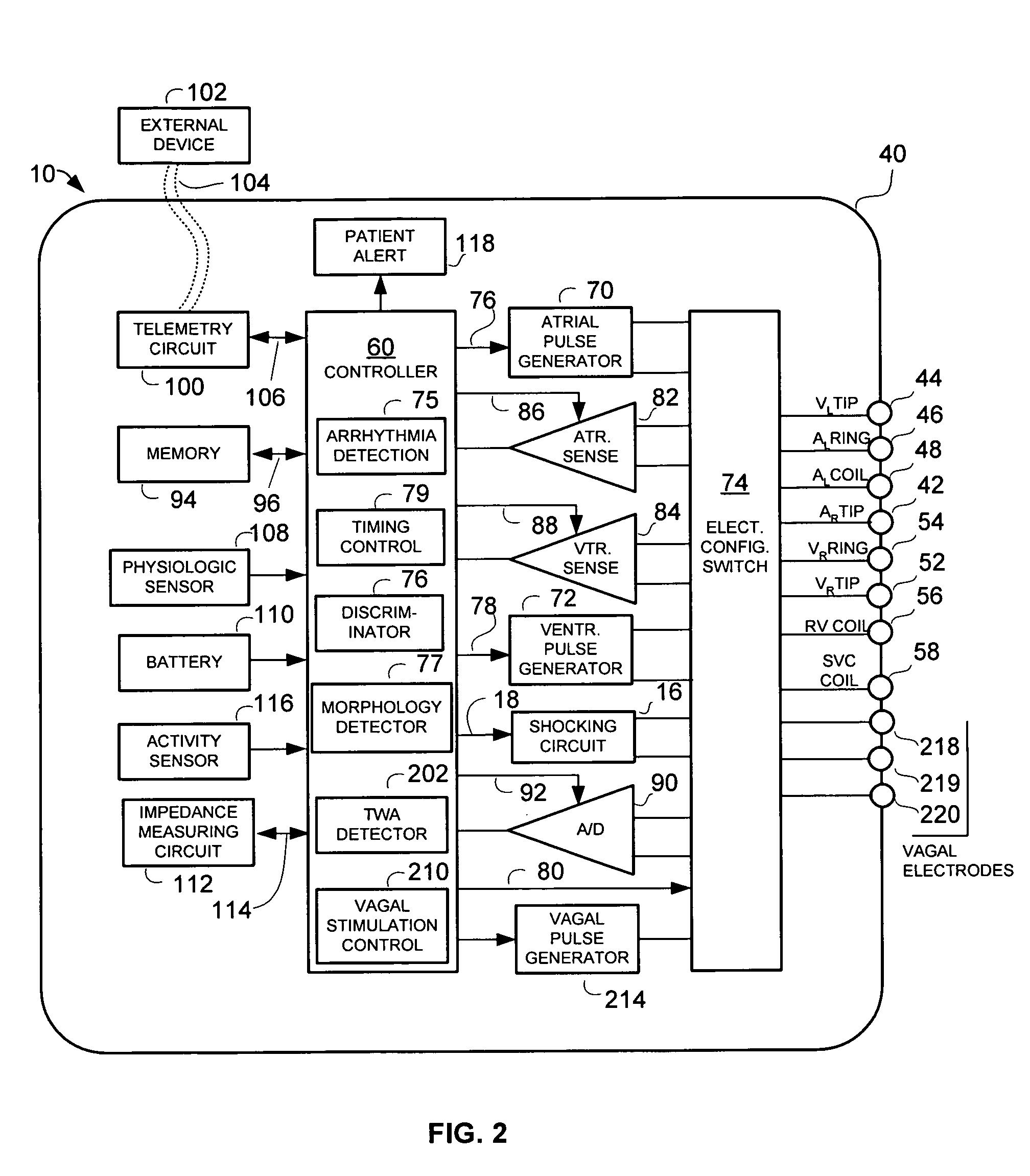
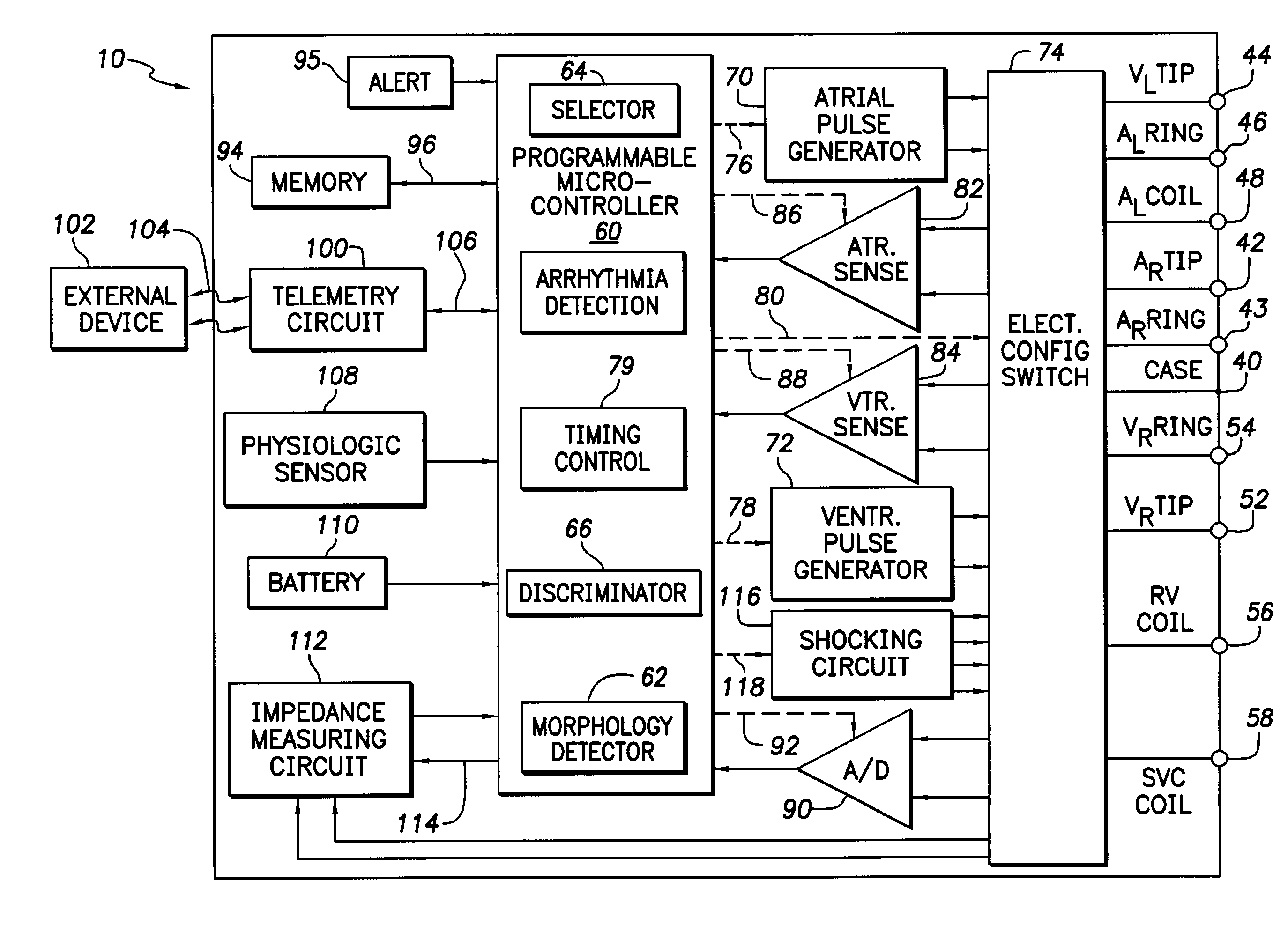
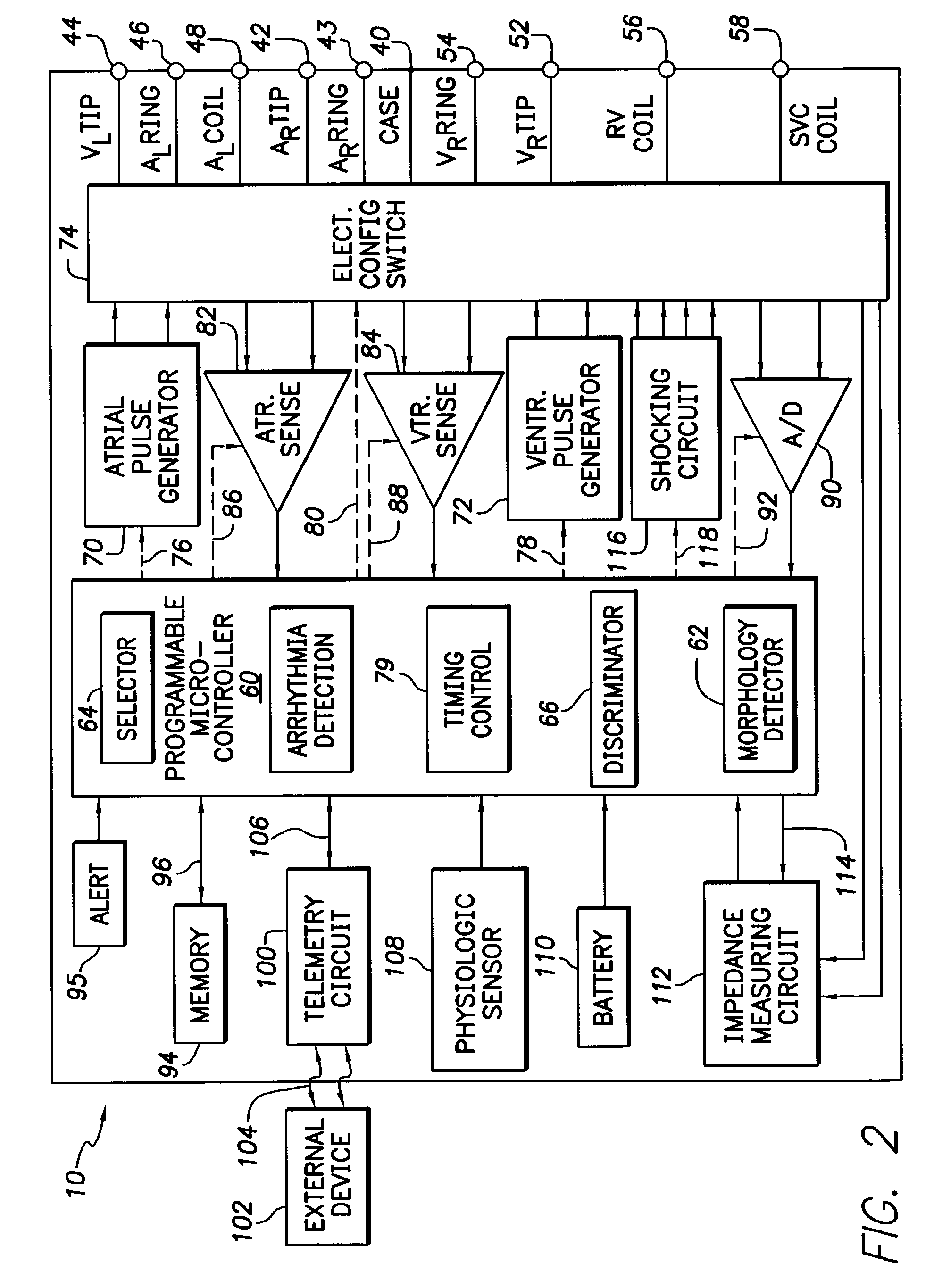
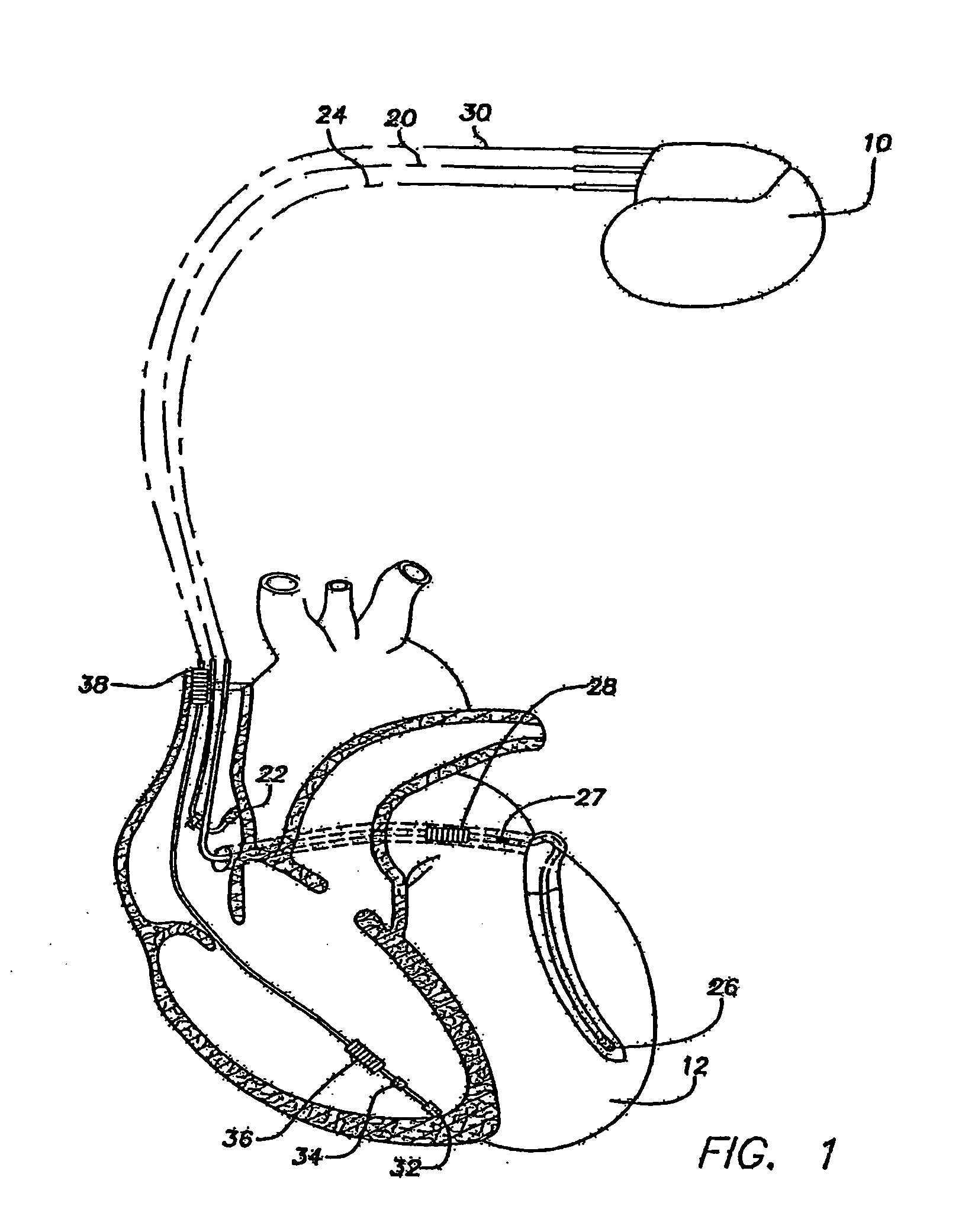
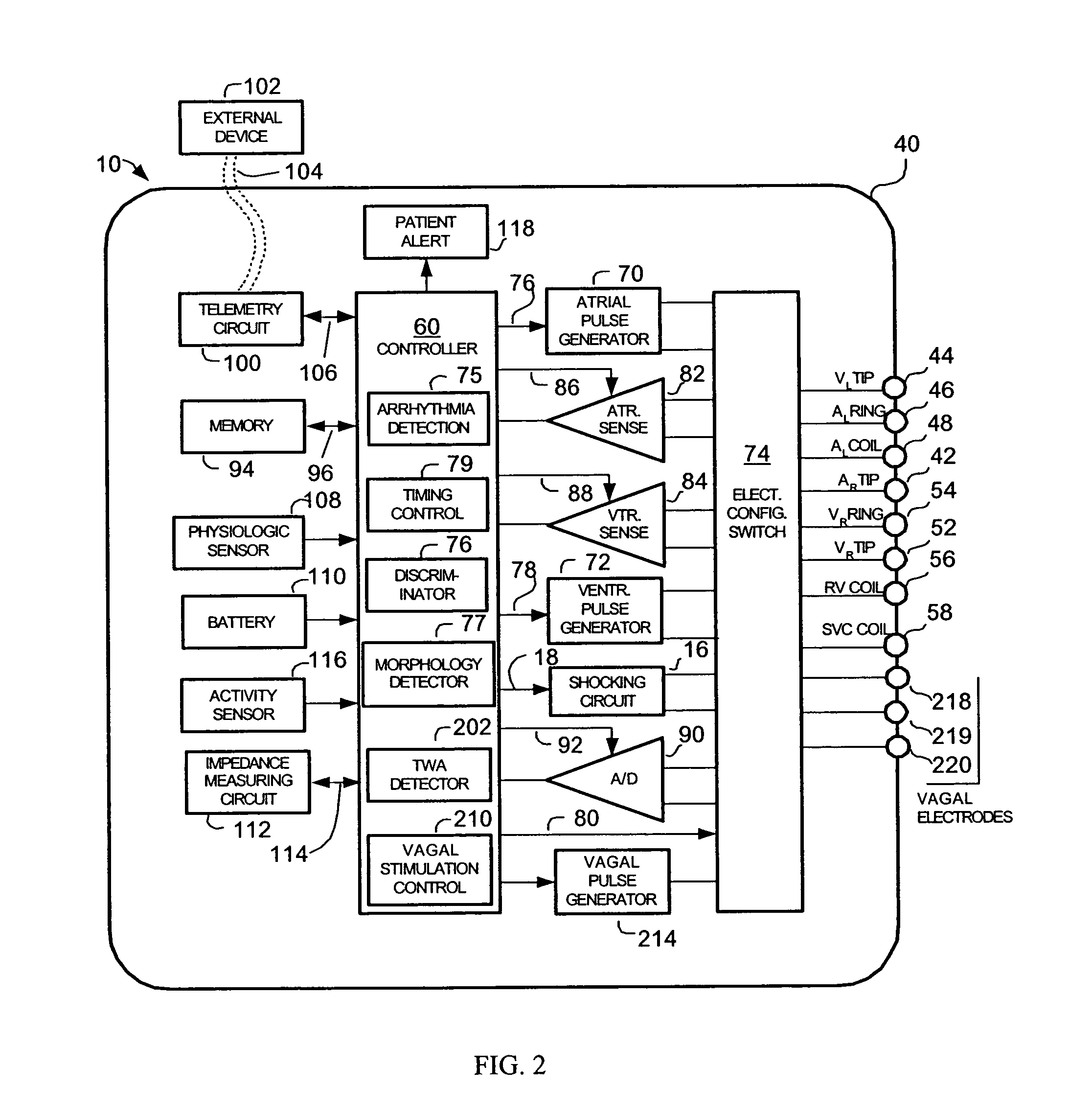
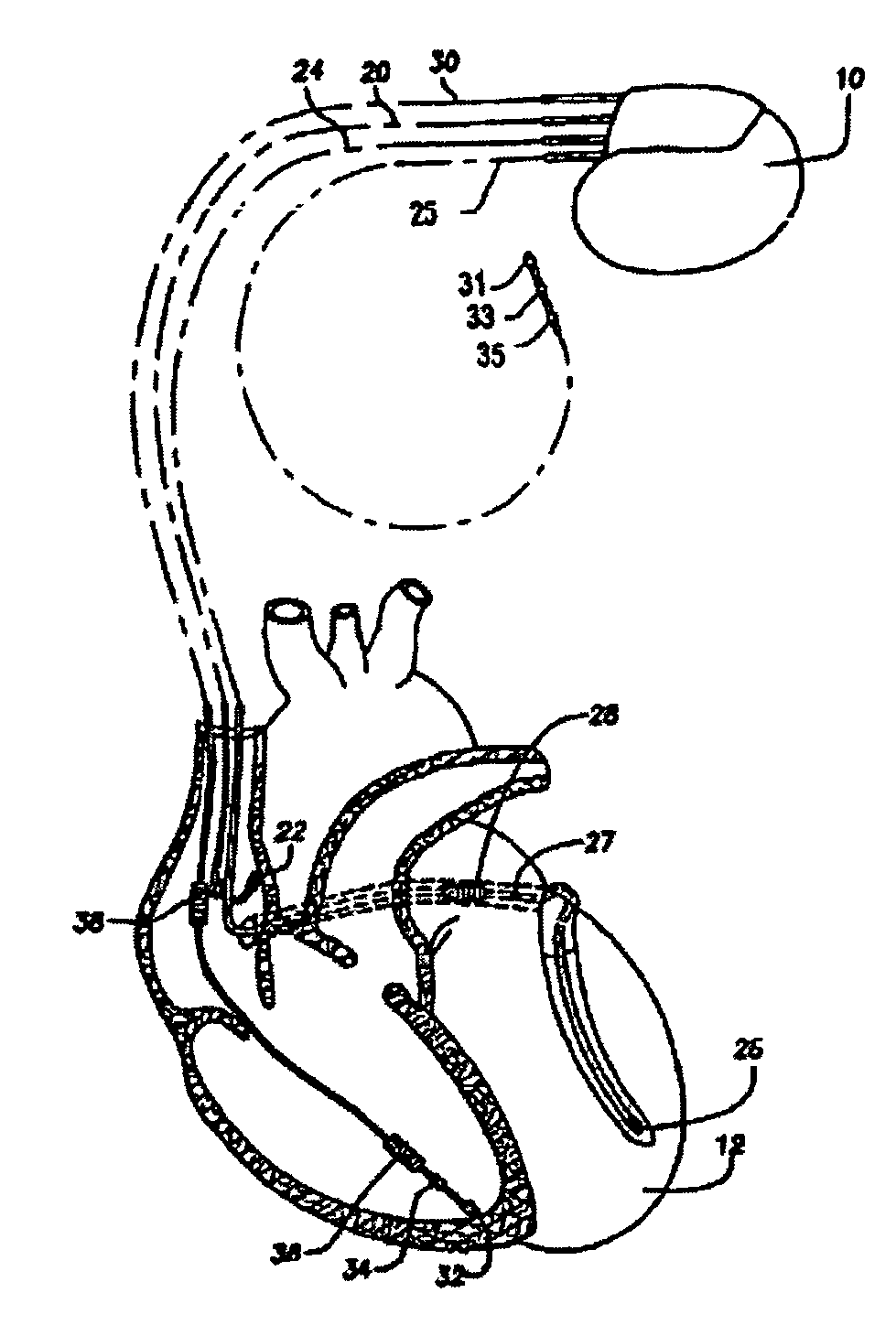
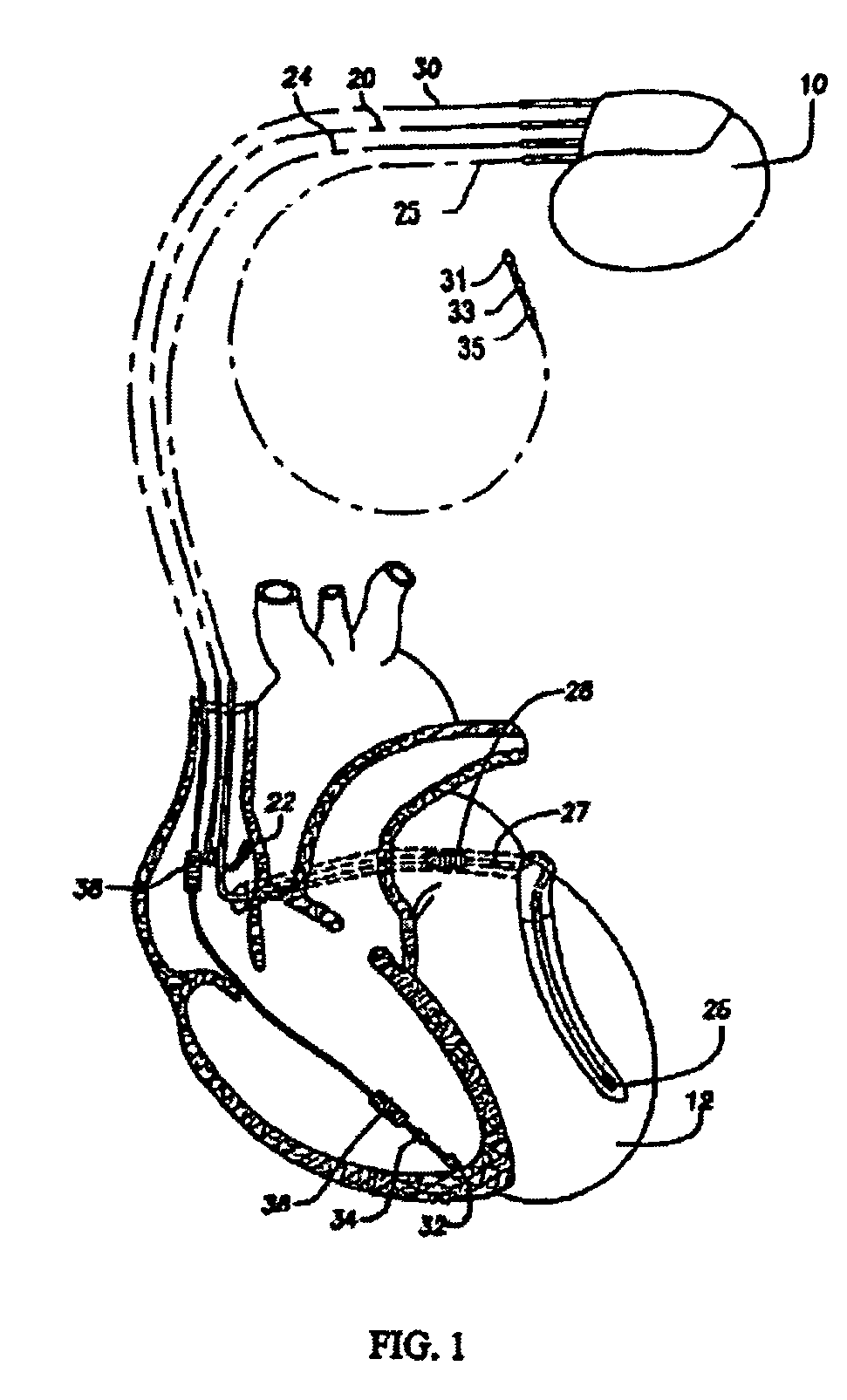
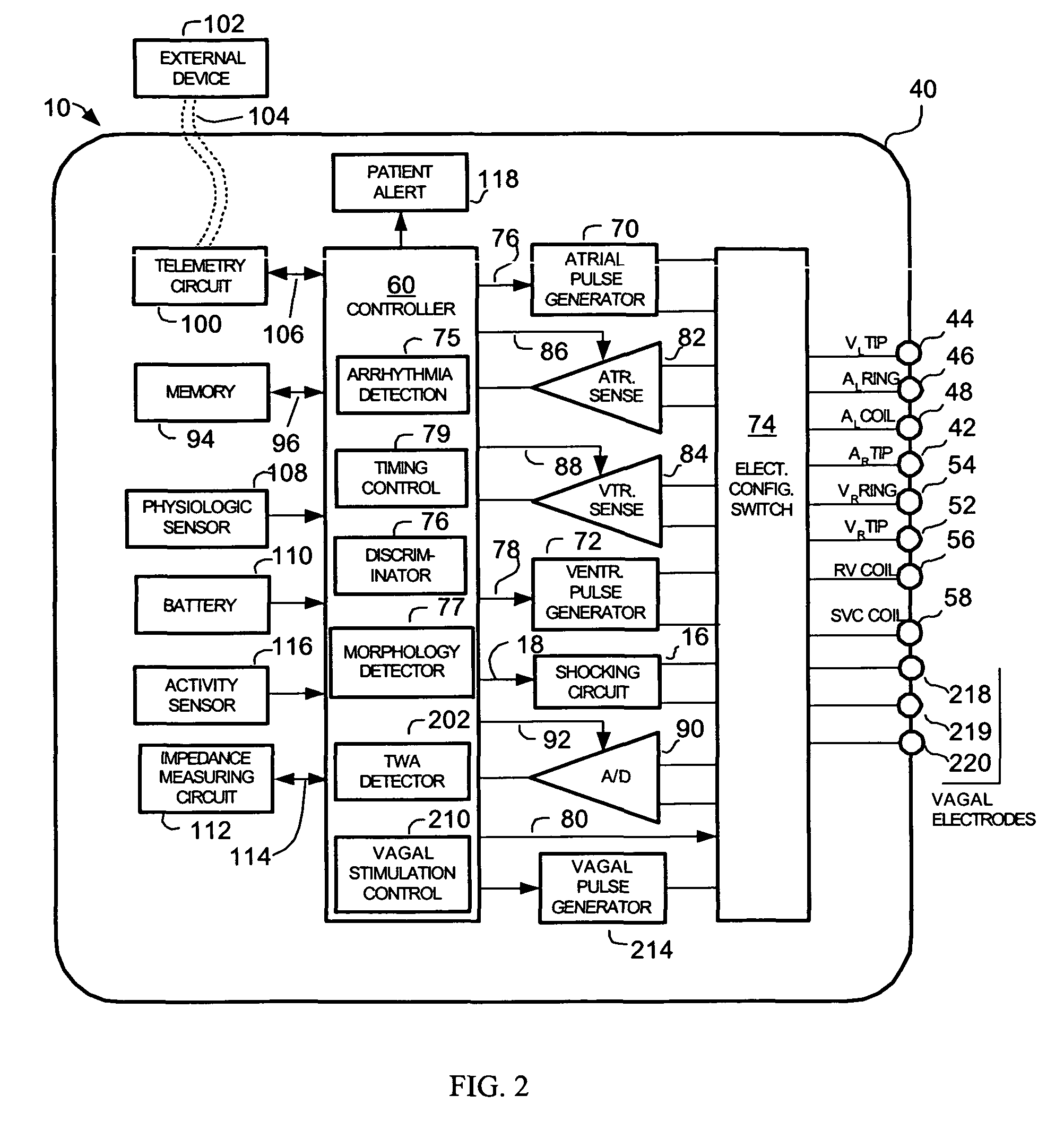
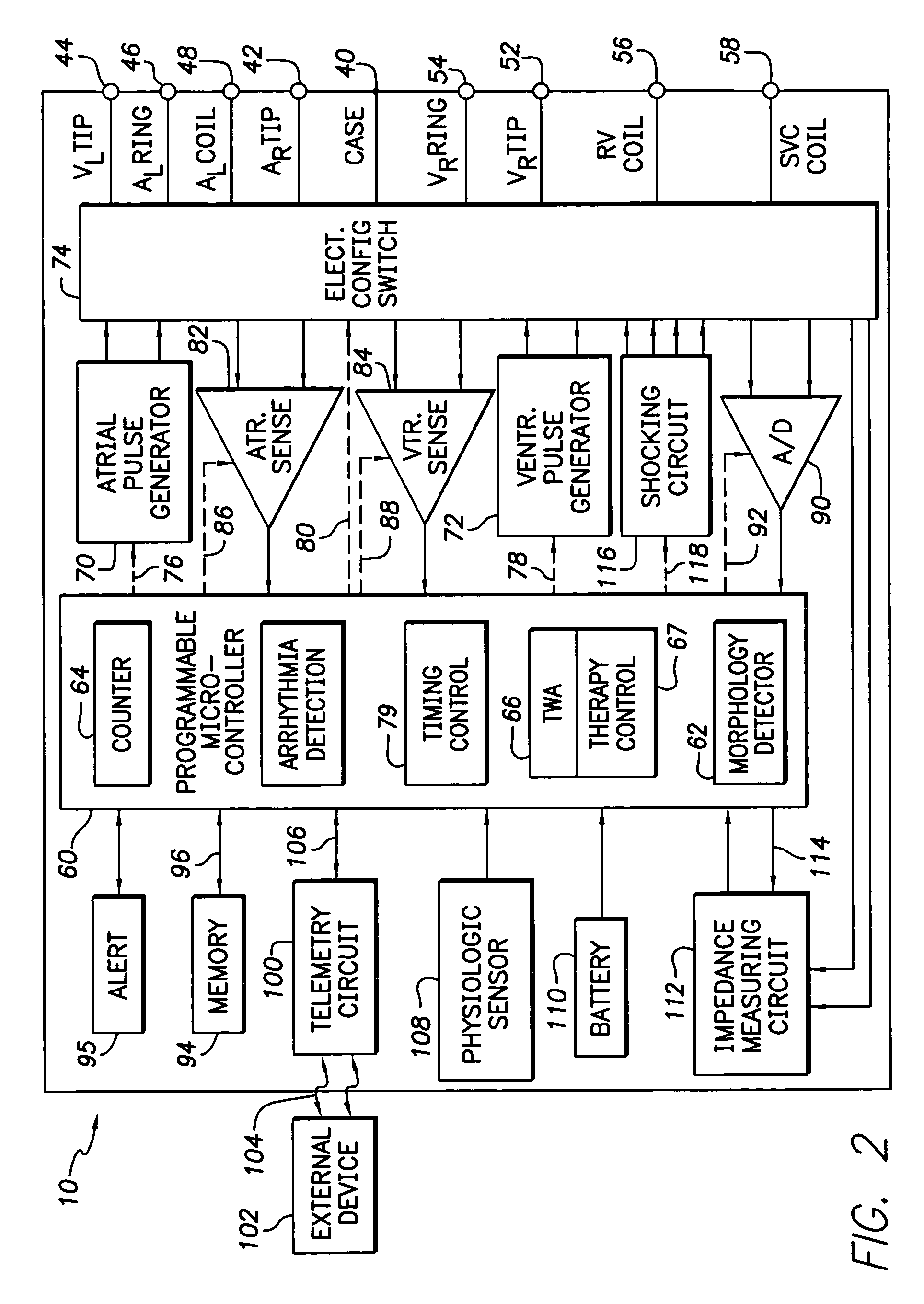
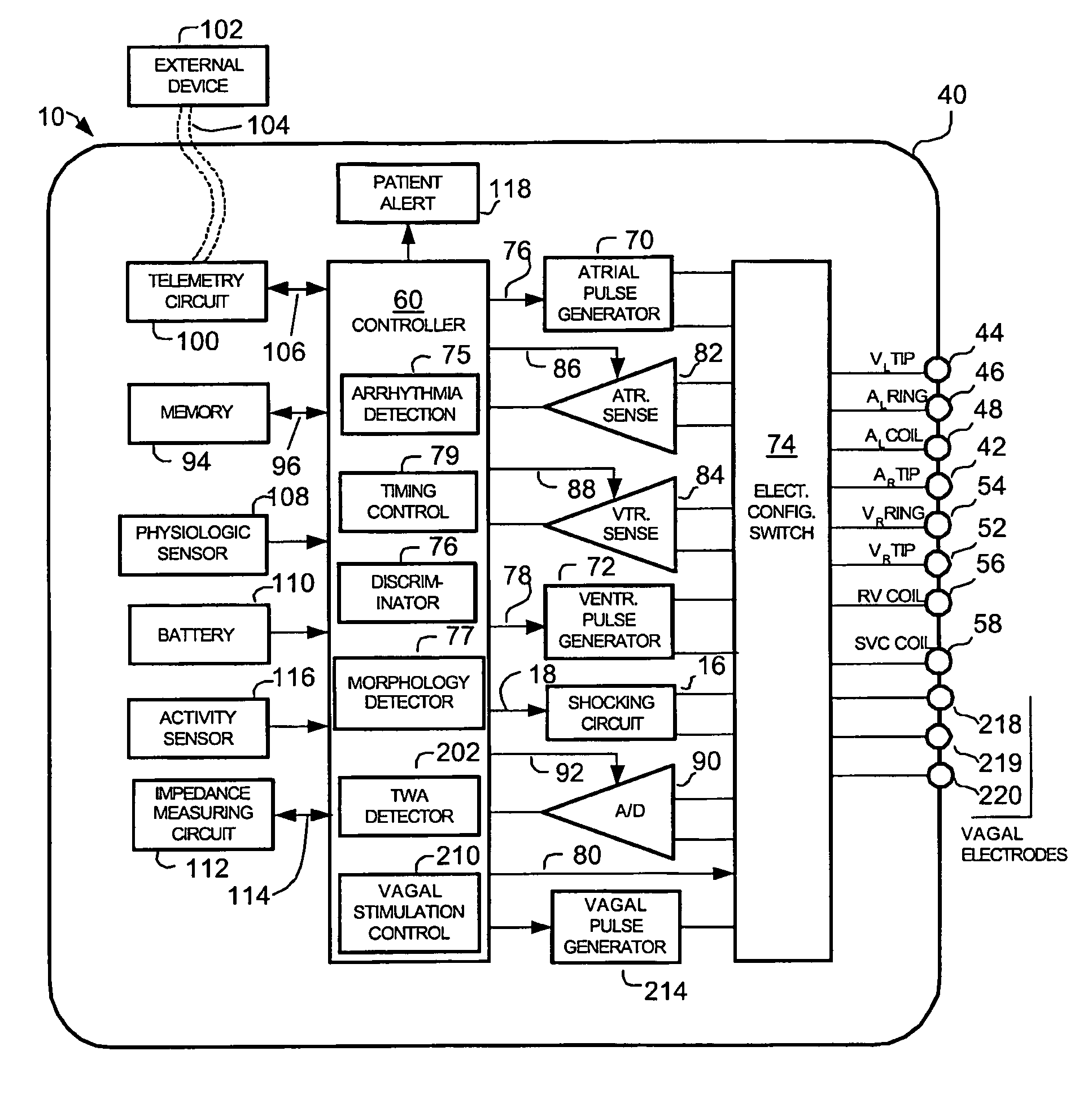
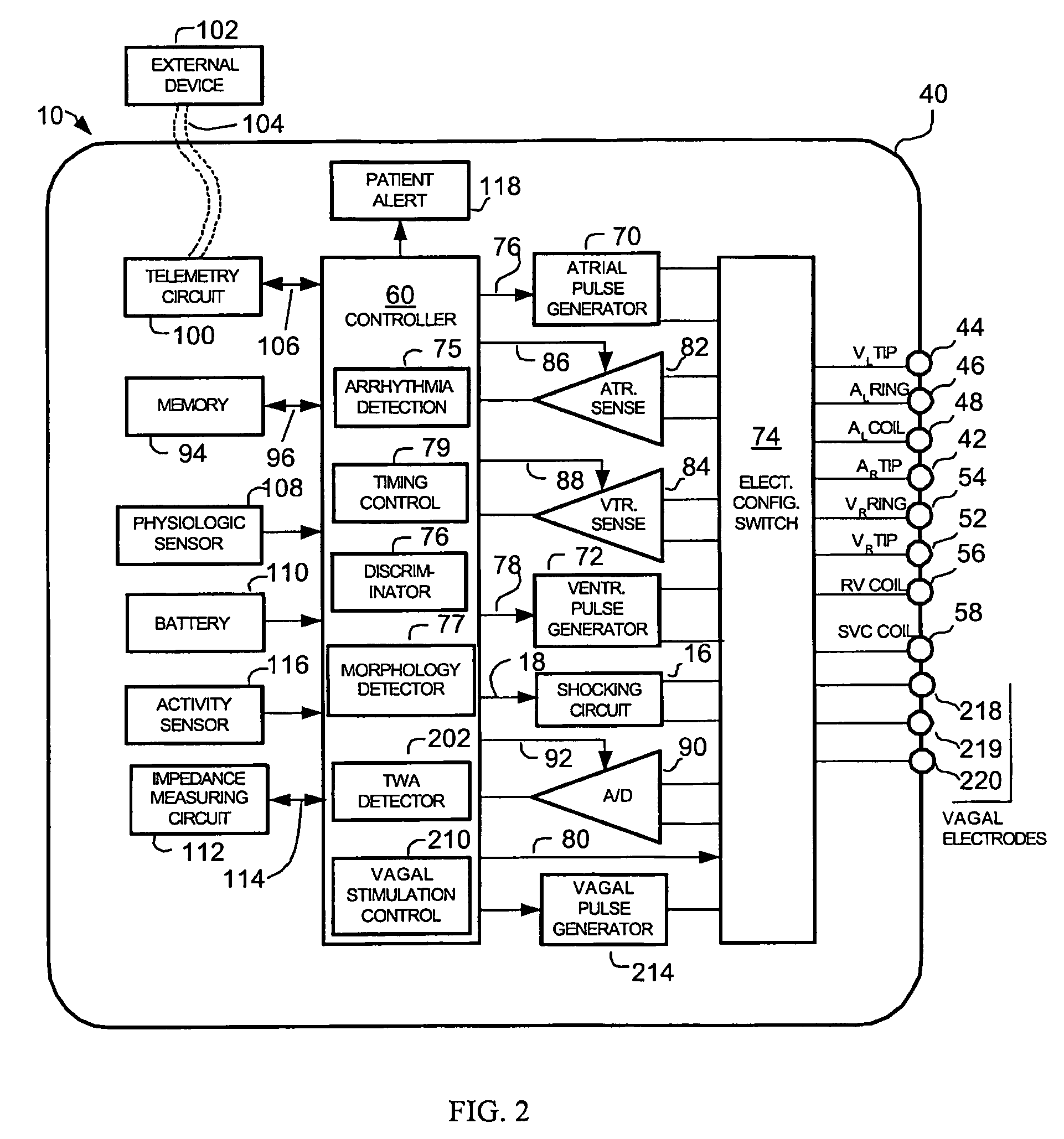
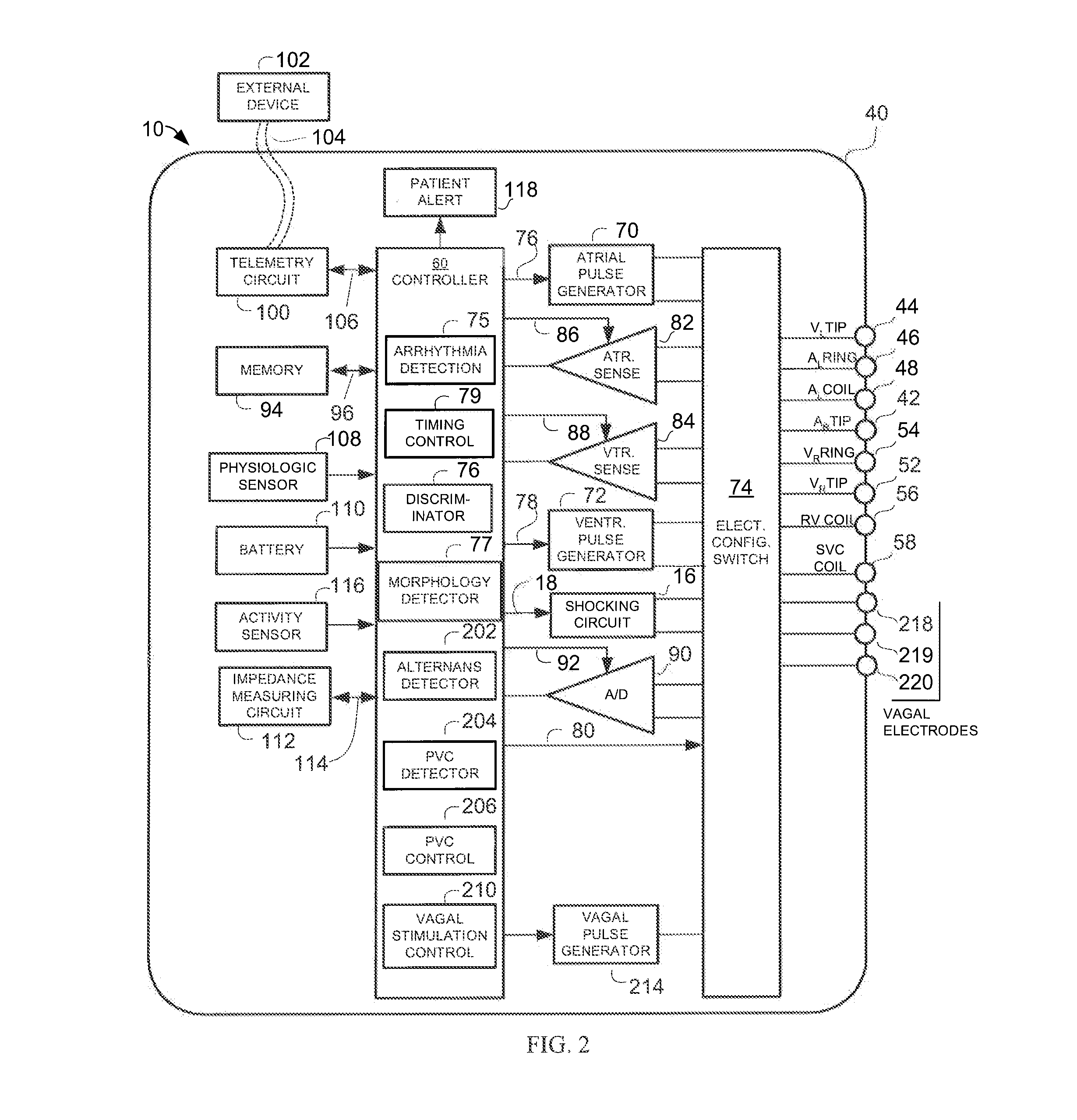
Implantable cardiac device having a system for detecting T wave alternan patterns and method
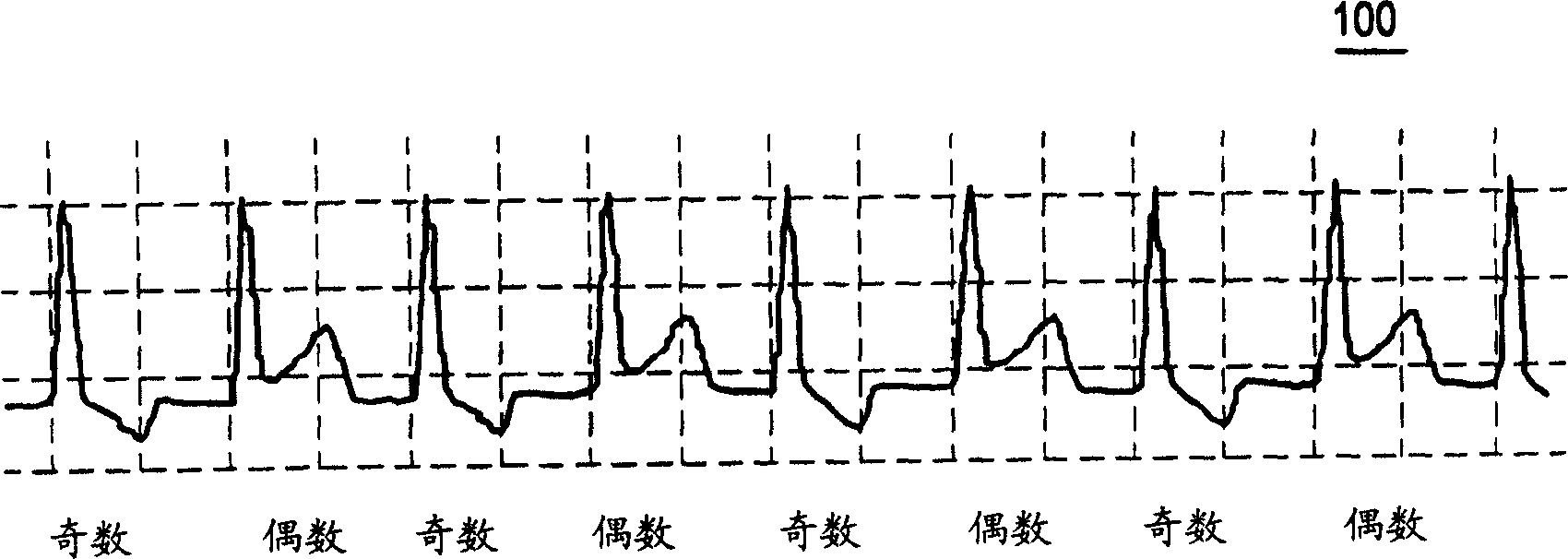
A system and method for use in an implantable cardiac device that delivers electrical therapy to a patient's heart determines if a T wave alternan pattern of the patient's heart exists. The system includes a sensing circuit that generates an electrical signal representing electrical activity of the patient's heart. A morphology detector measures a magnitude of a T wave characteristic of each T wave in the electrical signal of a predetermined number of cardiac cycles of the heart. A discriminator then determines, responsive to the measured T wave characteristic magnitudes, if a T wave alternan pattern exists. A T wave alternan pattern may be determined to exist if the number of measured T wave characteristic magnitudes greater than and less than a T wave characteristic magnitude baseline are substantially equal and each greater than a given number.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and systems for detecting the presence of T-wave alternans
Embodiments of the present invention relate to implantable systems, and method for use therein, that can detect T-wave alternans. In accordance with specific embodiments of the present invention, intrinsic premature contractions of the ventricles are detected, and at least one metric of T-waves is measured in a specified number of beats that follow each detected intrinsic premature contraction of the ventricles. A determination of whether T-wave alternans are present is made based on the measured T-wave metrics. In alternative embodiments, rather than waiting for intrinsic premature contractions of the ventricles, premature contractions of the ventricles are caused on demand by inducing premature atrial contractions. In still other embodiments, a patient's vagus nerve is stimulated to simulate premature contractions of the ventricles. This abstract is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and systems for detecting the presence of T-wave alternans
Embodiments of the present invention relate to implantable systems, and method for use therein, that can detect T-wave alternans. In accordance with specific embodiments of the present invention, intrinsic premature contractions of the ventricles are detected, and at least one metric of T-waves is measured in a specified number of beats that follow each detected intrinsic premature contraction of the ventricles. A determination of whether T-wave alternans are present is made based on the measured T-wave metrics. In alternative embodiments, rather than waiting for intrinsic premature contractions of the ventricles, premature contractions of the ventricles are caused on demand by inducing premature atrial contractions. In still other embodiments, a patient's vagus nerve is stimulated to simulate premature contractions of the ventricles. This abstract is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and system for improved measurement of t-wave alternans
The method and system comprise receiving digitized ECG data including a plurality of alternating consecutive odd and even beats (302), calculating a variability for at least one odd or even beat (304), and excluding certain beats from T-wave alternant measurements according to an exclusion procedure (310).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
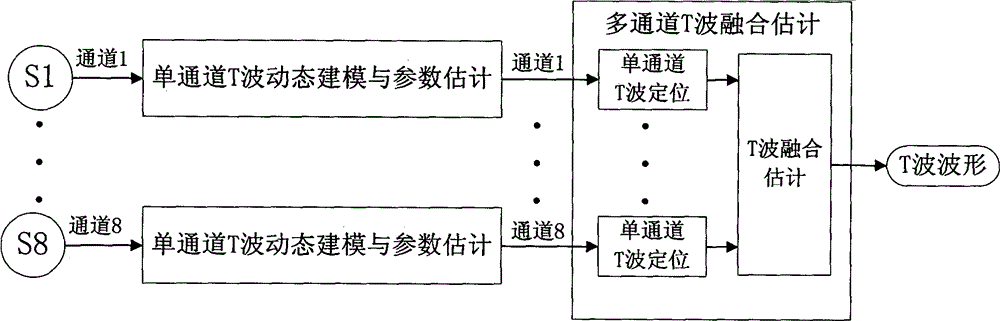
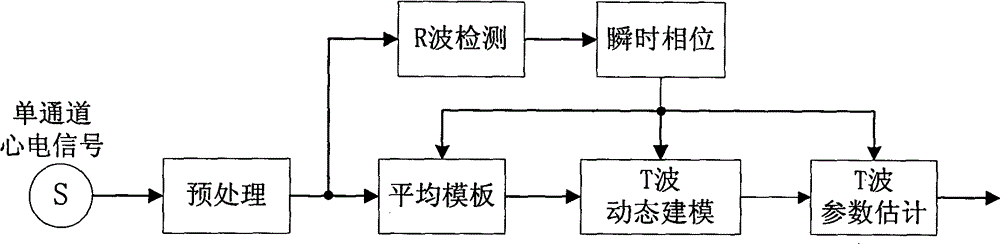
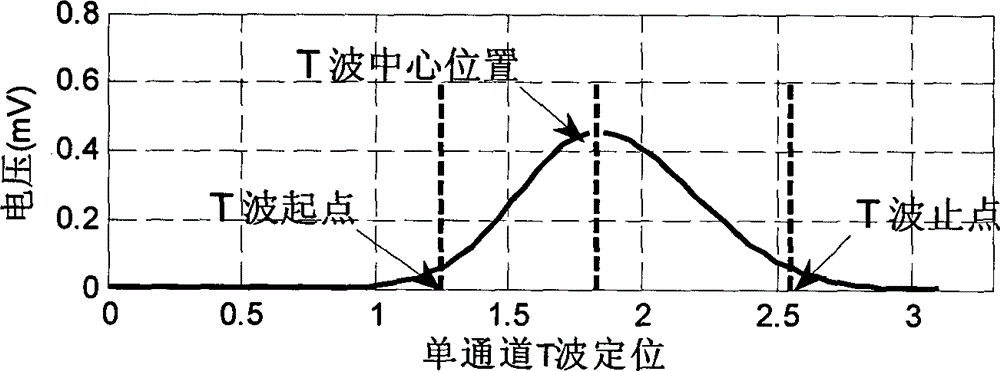
T wave dynamic modeling and multi channel estimation fusion method
InactiveCN104462867AAutomate analysisImplement extractionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses a T wave dynamic modeling and multi channel estimation fusion method. Aiming to solve the problems of T wave asymmetry, beat-to-beat dynamic change, myoelectricity pulses in highly dynamic monitoring environment and electrode pulse noise interference, a T wave state space model adaptive to the beat-to-beat dynamic estimation is provided, on the basis of extended Kalman filter, a multi-channel T wave estimation fusion frame is established, T wave parameters with eight independent channels are combined, and T wave robustness estimation in strong noise background can be implemented. The method has the advantages that the sectional characteristics of electrocardiosignals are utilized completely, an analysis module adaptive to asymmetrical T wave estimation is established, the T wave analysis presentation is utilized, the T wave data with eight independent channels are fused completely, the robustness of the T wave beat-to-beat dynamic estimation is improved, and necessary theoretical and technical basis is provided for beat-to-beat detection and estimation of T wave alternating signals in the highly dynamic monitoring environment.
Owner:CHONGQING TELECOMMUNICATION INSTITUTE
Method and apparatus for automatic analysis of T-wave alternans
The invention disclosed includes a method and apparatus for calculation of T-wave alternas in electrocardiographic (ECG) signals; said method comprises the following method steps: (a) collecting and storing an ECG signal; (b) detecting each heartbeat T-wave in the ECG signal using an automatic detection and segmentation algorithm; (c) classifying said heartbeat T-wave as an even or odd heartbeat T-wave; (d) initializing said method by taking the first even and the first odd heartbeat T-wave as their respective initial average; (e) processing all the heartbeat T-waves in the ECG signal to generate an even heartbeat T-wave weighted average and odd heartbeat T-wave weighted average; and (f) calculating TWA using a distance metric between the even heartbeat weighted average and the odd heartbeat weighted average, said distance metric including curve matching Continuous Dynamic Time Warping (CDTW).
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA
Implantable cardiac device providing rapid pacing T wave alternan pattern detection and method
An implantable cardiac device that delivers electrical therapy to a patient's heart determines if a T wave alternan pattern of the patient's heart exists. The device includes a sensing circuit that generates an electrical signal including T waves representing paced electrical activity of the heart and a morphology detector that measures a metric of each T wave in the electrical signal. A T wave alternan pattern detector determines, responsive to the measured T wave metrics, if a paced activity T wave alternan pattern is present. The T wave alternan pattern detector may also detect for intrinsic T wave alternan patterns. A therapy control initiates suitable different responses for a paced T wave alternan pattern detection and an intrinsic T wave alternan pattern detection.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
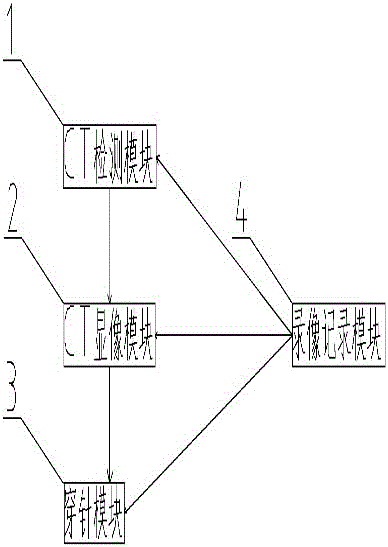
Multifunctional puncture system for department of pediatrics
InactiveCN106175891ADone successfullySimple structureSurgical needlesSensorsEcg signalImaging processing
The invention discloses a multifunctional puncture system for the department of pediatrics. The multifunctional puncture system is characterized in that an image processing module is built in a CT imaging module and comprises an image capture unit, a data acquisition unit, a data conversion unit, an identification pattern generation unit, an image processing unit and a detection optimization module; a puncture module is provided with an intelligent electrocardiogram analysis module and an emotion sensing module; the intelligent electrocardiogram analysis module comprises an intelligent analysis unit as well as an electrocardiogram signal noise analysis unit and a T-wave alternans scatter diagram electrocardiogram signal analysis unit which are connected with the intelligent analysis unit. CT detection is performed on a puncture part, internal images are displayed on the CT imaging module during detection, a puncture operation can be performed on a patient visually with a puncture needle, physical signs are monitored in the whole operation process by means of the CT imaging module, the intelligent electrocardiogram analysis module and the emotion sensing module, and smooth finishing of the puncture operation is facilitated.
Owner:王磊
Methods and systems for analyzing T-wave alternans
InactiveUS8255043B2Convenient treatmentReduce in quantityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyT waveInstability
Owner:PACESETTER INC
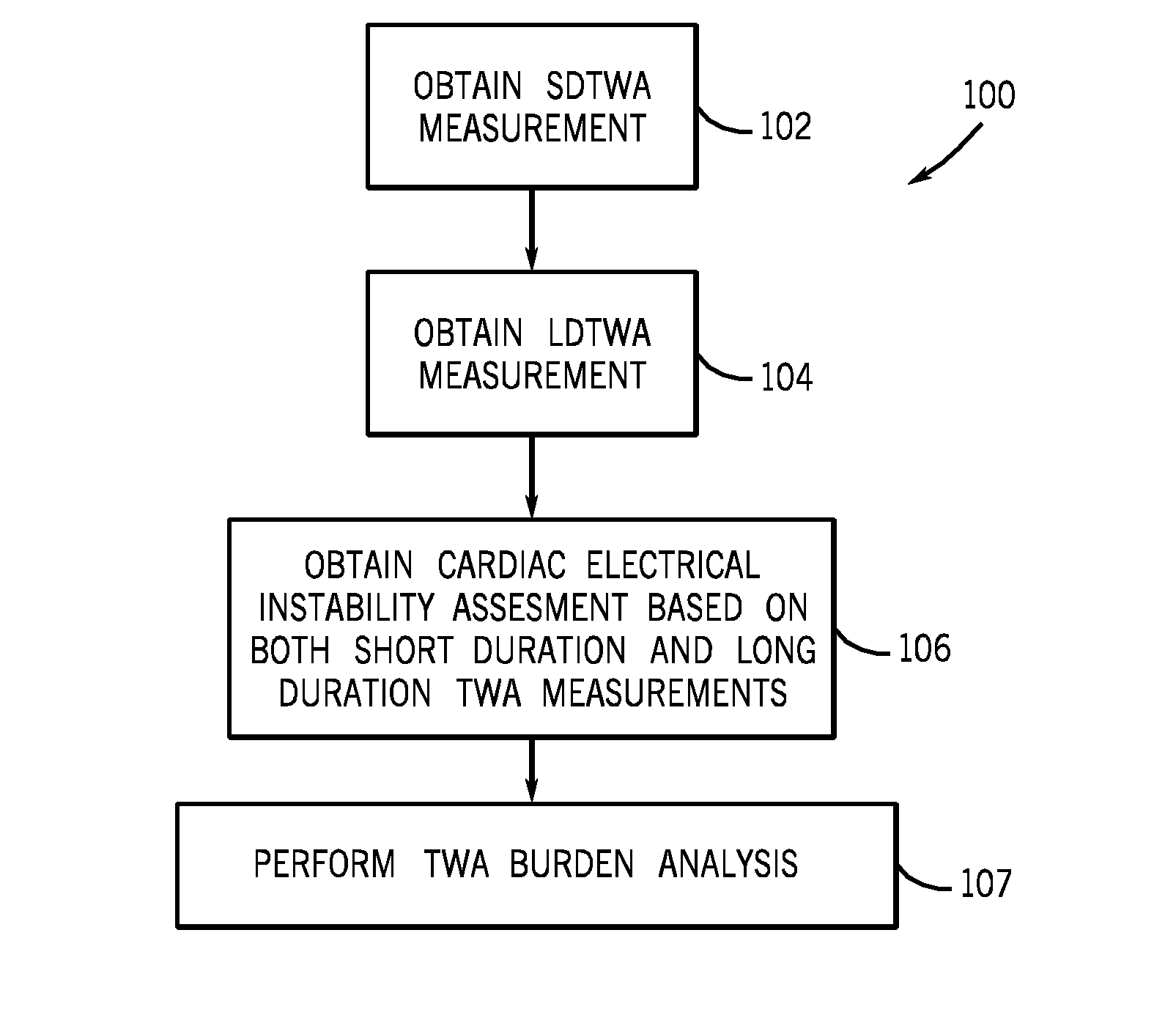
Method and system for detecting T-wave alternans
A method for generating a cardiac electrical instability assessment is disclosed herein. The method includes obtaining a short duration T-wave alternans (SDTWA) measurement, obtaining a long duration T-wave alternans (LDTWA) measurement, and obtaining a cardiac electrical instability assessment based on both the SDTWA measurement and the LDTWA measurement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
T-wave alternans train spotter
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
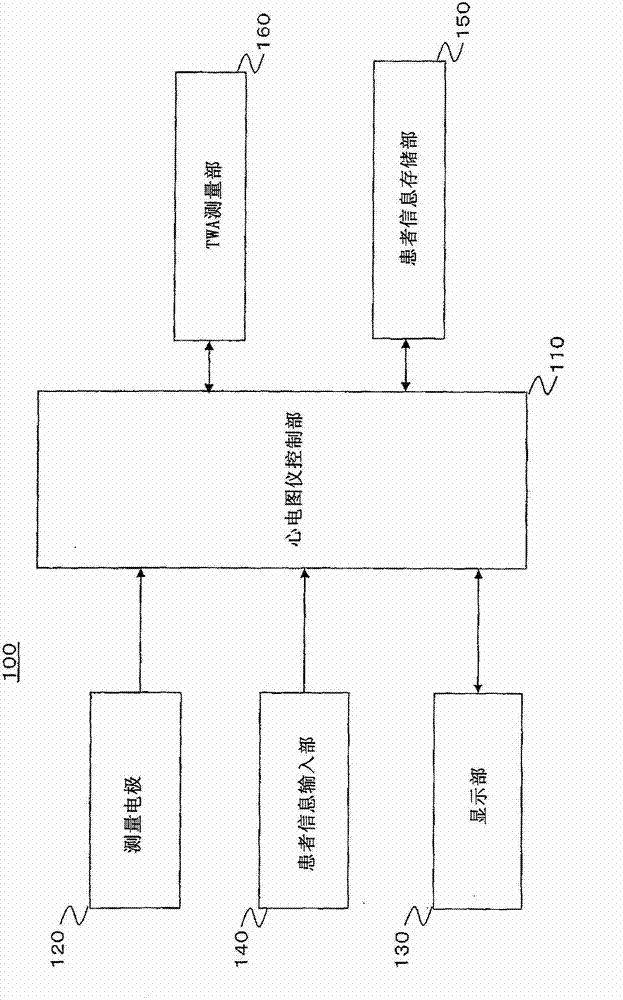
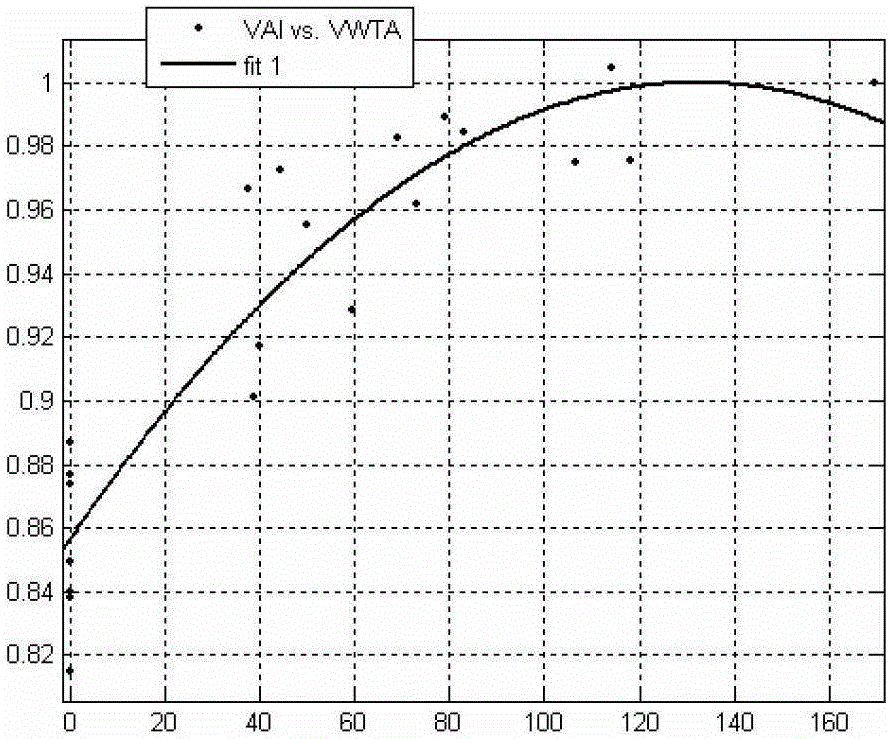
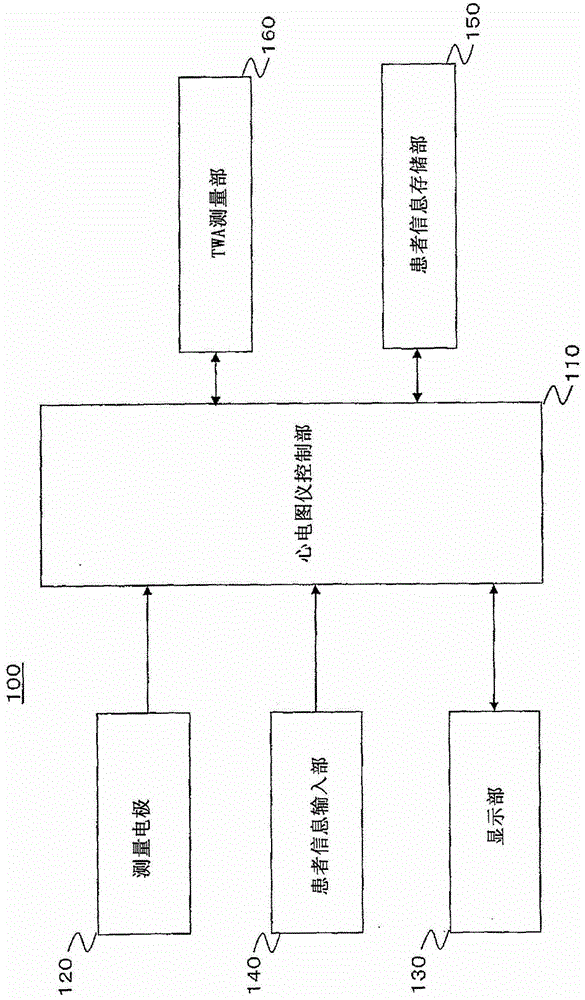
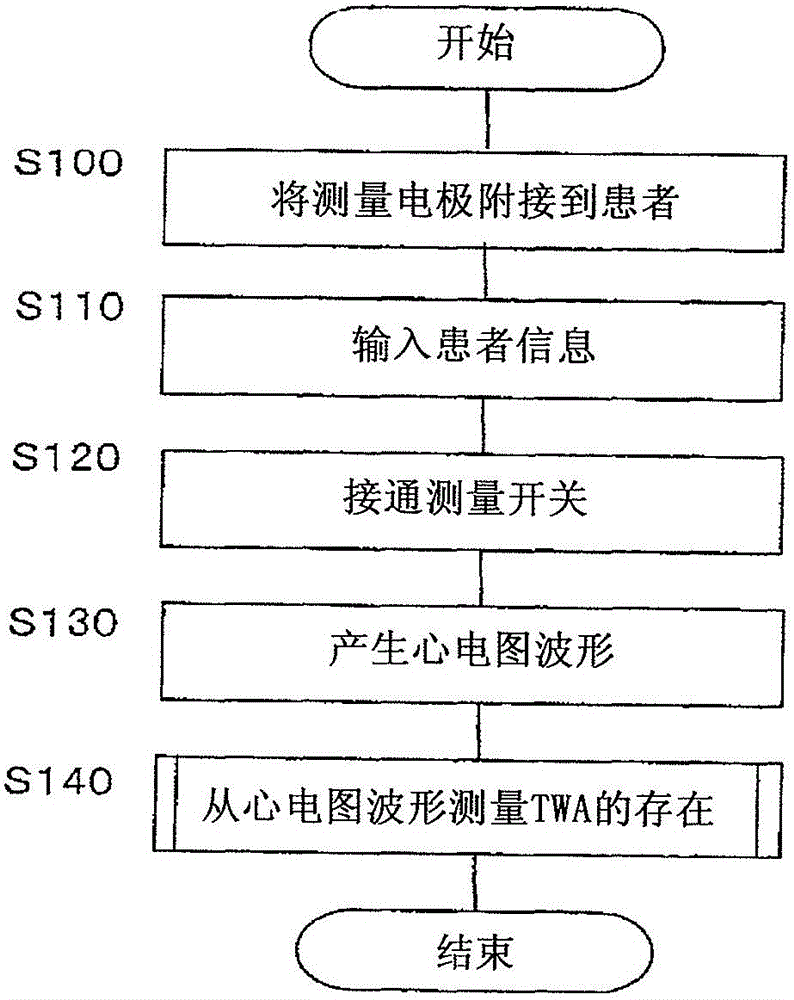
TWA measuring apparatus and TWA measuring method
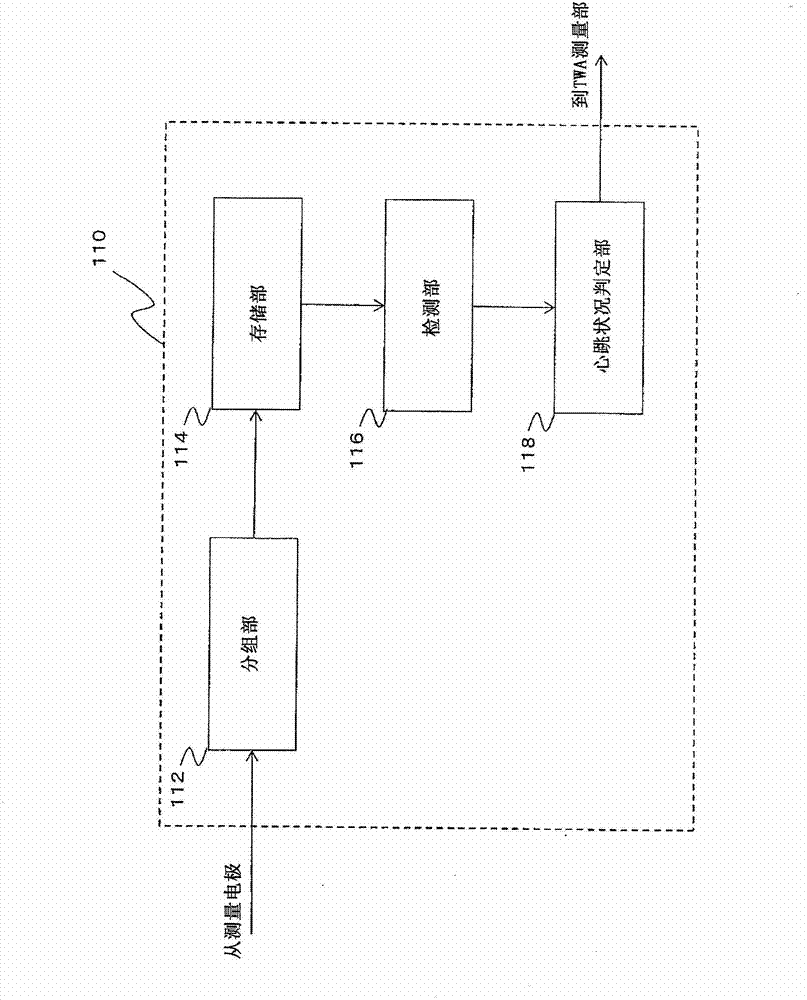
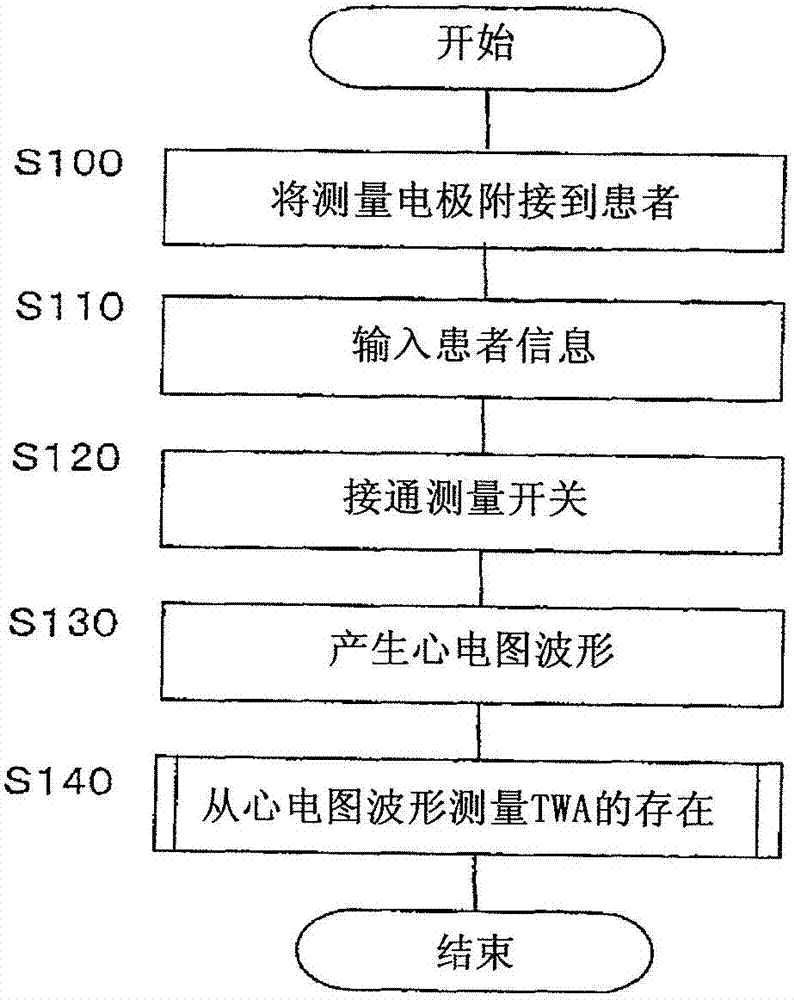
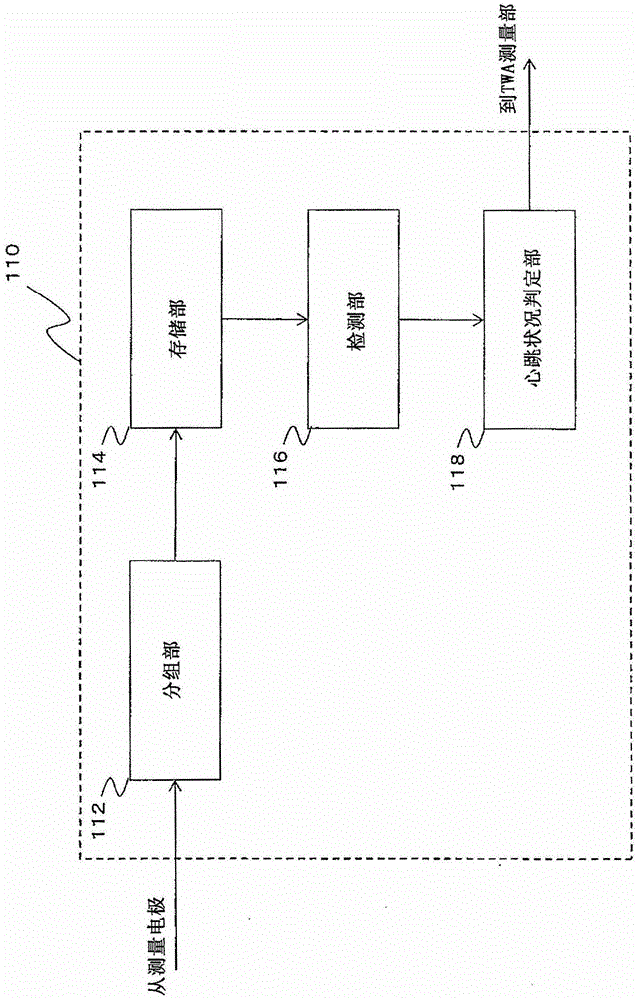
A T-wave alternans (TWA) measuring apparatus is configured to group electrocardiogram (ECG) waveforms in increments of a first beat, to test a statistical intergroup difference for the correponding first groups, and to determine that a heartbeat condition is unstable, when a significant statistical difference exists between the first groups. The apparatus is further configured to determine the magnitude of TWA when it is determined that the heartbeat condition is unstable. The ECG waveforms may further be grouped in increments of a second beat number to generate second groups, and to determine that the heartbeat condition is unstable when a significant statistical difference exists between the first groups but not between the second groups.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Method and system for improved measurement of t-wave alternative
Methods and systems for improved measurement of T-wave alternation in ECG signals are disclosed. The method and system includes receiving digitized ECG data (302) comprising a plurality of alternating consecutive odd and even beats, calculating (304) a variability for at least one of the odd or even beats and, according to a process of exclusion, dividing certain beats from T Wave alternation measurements are excluded (310).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Alternating T-wave measuring method for sports electrocardiogram
The present invention belongs to the field of medical test technology, and the T-wave alternation measuring method for sports electrocardiogram beings from the No.113 beat of electrocardiogram signal and analyzes in 16 beats as one analysis window unit. Maximum heart rate is first judged to estimate the noise level. The power spectrum is then analyzed and judged based on noise, whether to exist obvious RR interphase alternation is judged, and if no, the ratio of component at 0.25 and the alternative component before deducing noise level is calculated. When the ratio is smaller than some value, obvious T-wave alternation is considered found out. The method of the present invention solves the problem of detecting weak T-wave alternation signal for predicting malignant arrhythmia.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
ECG signal analysis method based on t-wave alternating scattergram method based on morphology
InactiveCN103006207BReduce the drop in detection accuracyGood test resultDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalMedicine
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal analysis method of a T wave alternans scatter diagram method based on morphology. Aiming at the defects of difficulty in detection of each heart beat T wave alternans amplitude value and complexity in calculation of T wave alternans detection by the spectrum analysis method, the T wave alternans scatter diagram method based on morphology is provided to provide a new effective quantitative index of T wave alternans detection for development of domestic related clinical researches. The method includes: using the T wave window analysis method for sampling T waves of 128 continuous heart beats selected from the American MIT-BIH standard heart beat irregularity database and the European ST-T electrocardio database, making a differential scatter diagram by the aid of the sample points, using vector angle index of the scatter diagram for quantitative analysis of T wave alternans to obtain a vector angle index range for judging whether T wave alternans exists or not, and comparing a T wave alternans detection result obtained by means of the vector angle index of the scatter diagram with the T wave alternans detection result obtained by means of the T wave alternans amplitude of the spectrum analysis method to judge reliability in detection of T wave alternans by the vector angle index.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
twa measuring device and twa measuring method
A TWA measuring device, comprising: a grouping section configured to: group electrocardiogram waveforms of a subject under inspection in increments of a first beat number to generate a plurality of first groups; a storage section, the storage section configured to store electrocardiogram waveforms; a detection section configured to: detect a statistical difference between groups of measured values of electrocardiogram waveforms of the first group; a heartbeat condition determination section configured to: determining that the heartbeat condition is unstable when there is a significant statistical difference between one group; and a TWA measurement section configured to measure the heartbeat using the stored electrocardiogram waveform when it is determined that the heartbeat condition is unstable changes on.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
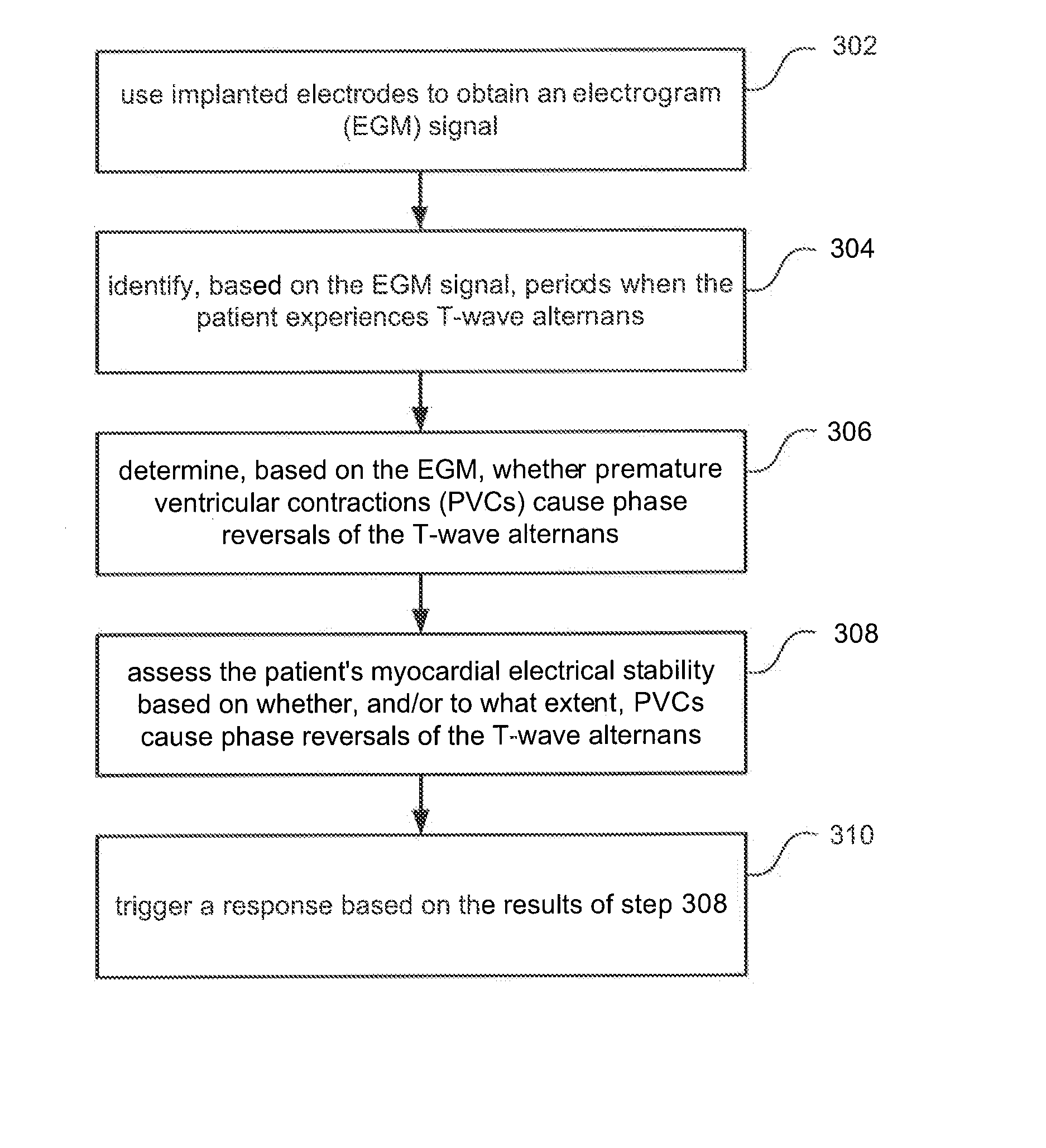
Implantable systems and methods for monitoring myocardial electrical stability by detecting PVC induced t-wave alternans reversals
Embodiments of the present invention relate to implantable systems, and methods for use therewith, for assessing a patients' myocardial electrical stability. Implanted electrodes are used to obtain an electrogram (EGM) signal, which is used to identify periods when the patient experiences T-wave alternans. Additionally, the EGM signal is used to determine whether premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) cause phase reversals of the T-wave alternans. The patient's myocardial electrical stability is assessed based on whether, and in a specific embodiment the extent to which, PVCs cause phase reversals of the T-wave alternans. This abstract is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for detecting TWA (T wave alternans) in electrocardiogram
InactiveCN102579039BImprove time resolutionStrong anti-noise abilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalTime domain
The invention discloses a method for detecting TWA (T wave alternans) in the electrocardiogram and belongs to the technical field of medical testing. The method comprises the following steps of: eliminating data sections with excessively high noise from selected electrocardiosignals by judging in the earlier stage so as to obtain relatively stable data suitable to analyze and carrying out analysis by taking M beats as an analysis window; firstly, extracting a T wave matrix for the M beats of electrocardiosignals and then carrying out data fitting on T waves in the T wave matrix to obtain a novel T wave matrix; respectively calculating alternans correlation indexes by a correlation analysis method to obtain an ACI (Allowable Concentration Index) of the integral analysis window); then judging whether the TWA exists in the integral analysis window by the correlation analysis method; if the TWA exists in the integral analysis window, respectively carrying out least square linear fitting on sectional odd and even beats of the existing TWA and calculating an actual TWA quantity; and if the TWA does not exist in the integral analysis window, intercepting a next analysis window to carry out analysis. According to the invention, the TWA signals can be effectively detected from the time domain angle and the TWA quantity is accurately quantized.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com