Method and system for improved measurement of t-wave alternans
An alternating measurement, odd number technique, used in the field of cardiology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
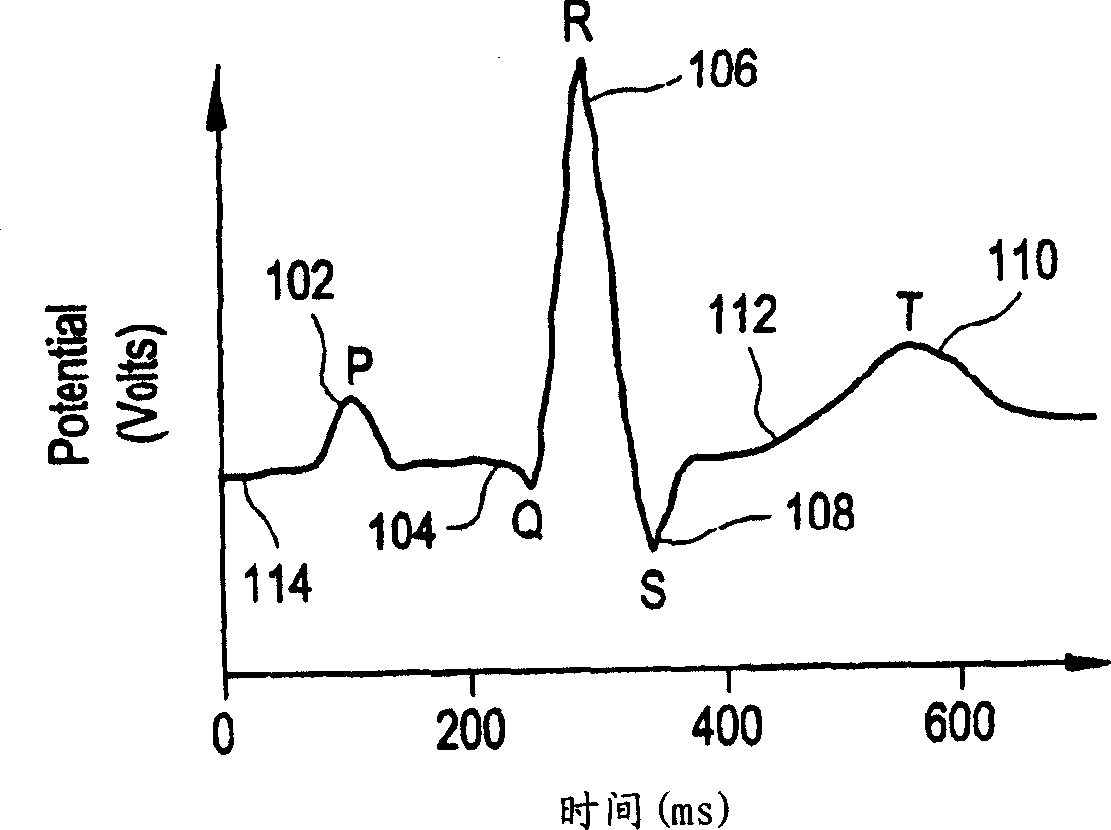
[0016] Figure 1A and 1B An example of a human surface ECG 100 is provided. The deflection 102 is called a "P wave" and is caused by atrial stimulation. Deflections 104, 106, and 108 are referred to as "Q waves," "R waves," and "S waves," respectively, and are caused by the contraction (depolarization) of the ventricles. The deflection 110 is called the "T wave" and results from the recovery (repolarization) of the ventricles.
[0017] The portion 112 of ECG 100 between the end of S wave 108 and the beginning of T wave 110 is referred to as the "ST segment." As used throughout this application, the term "T-wave" refers to and includes the T-wave and ST segment portions of the ECG.
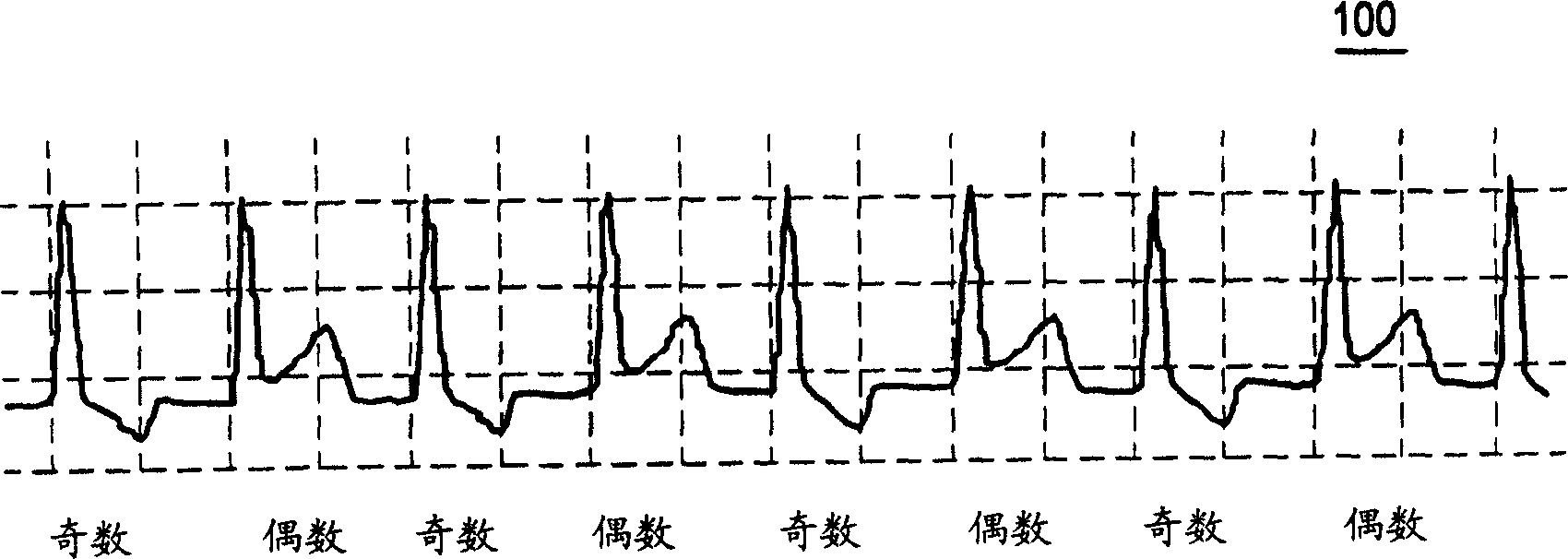
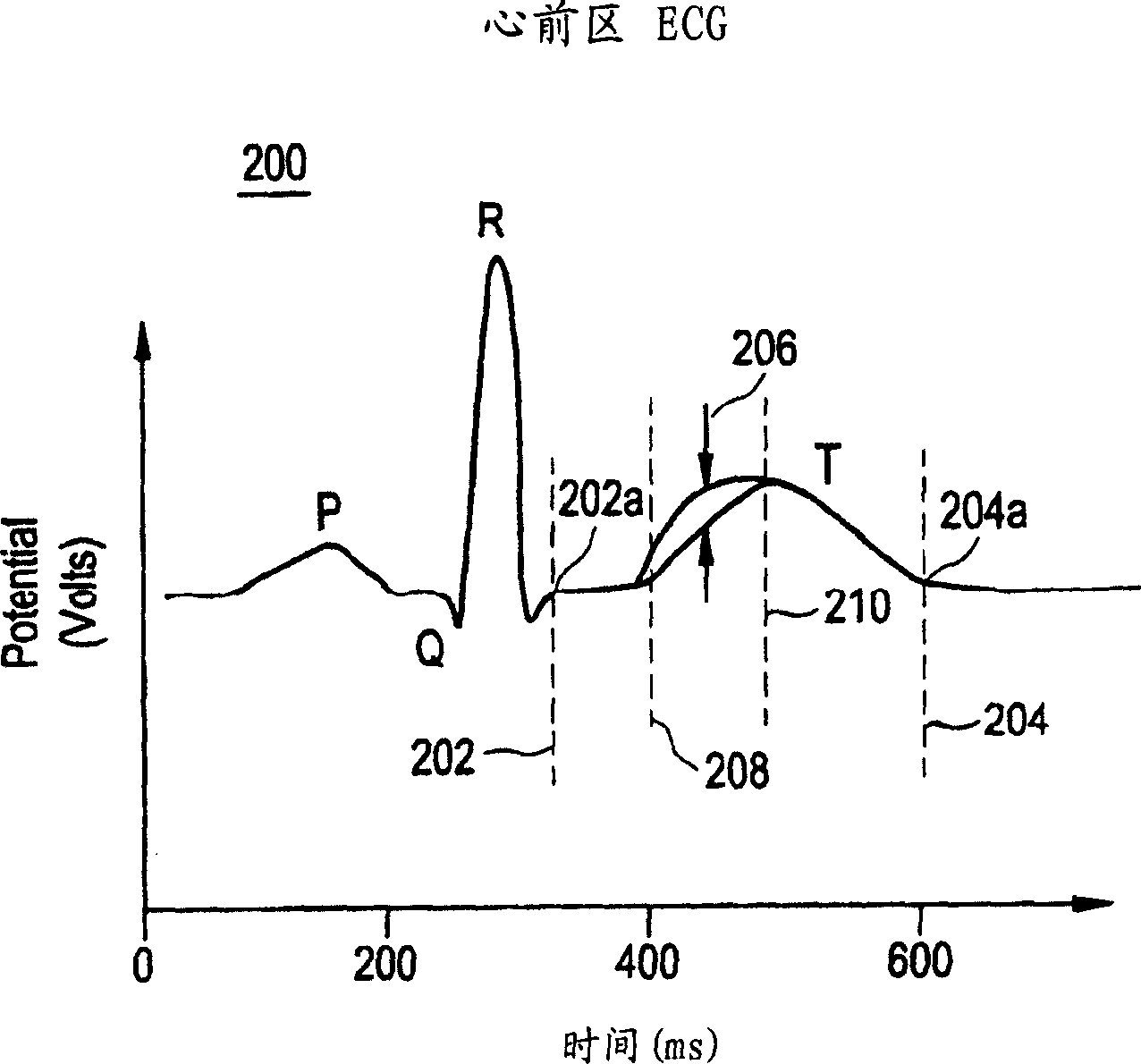
[0018] T-wave alternation is a regular or beat-to-beat variation of the T-wave of the ECG that repeats every two beats and connects to the underlying cardiac instability. figure 2 The principle of T wave alternation for the sampled precordial ECG signal 200 is shown. In ECG 200, several beats...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com