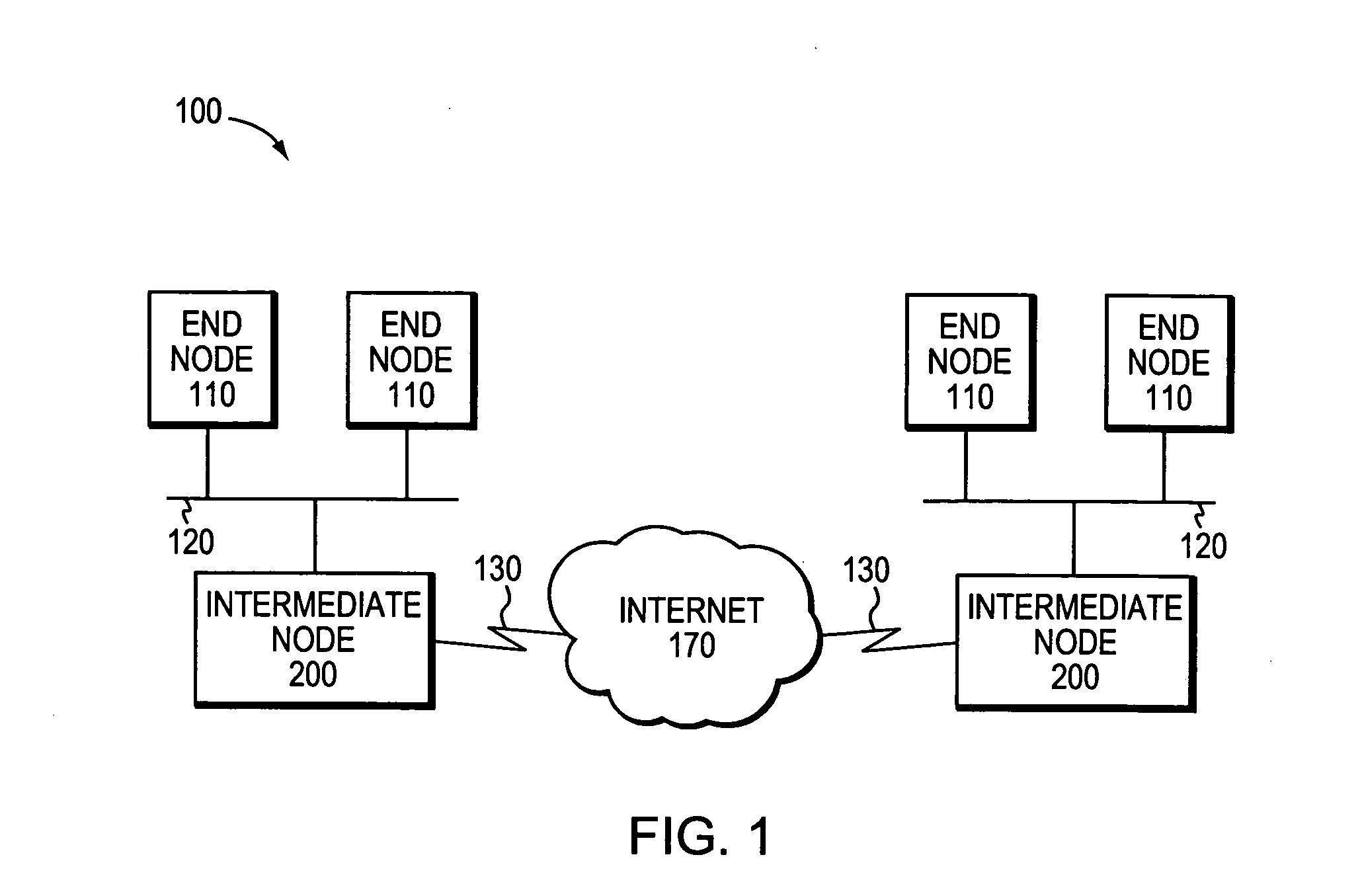
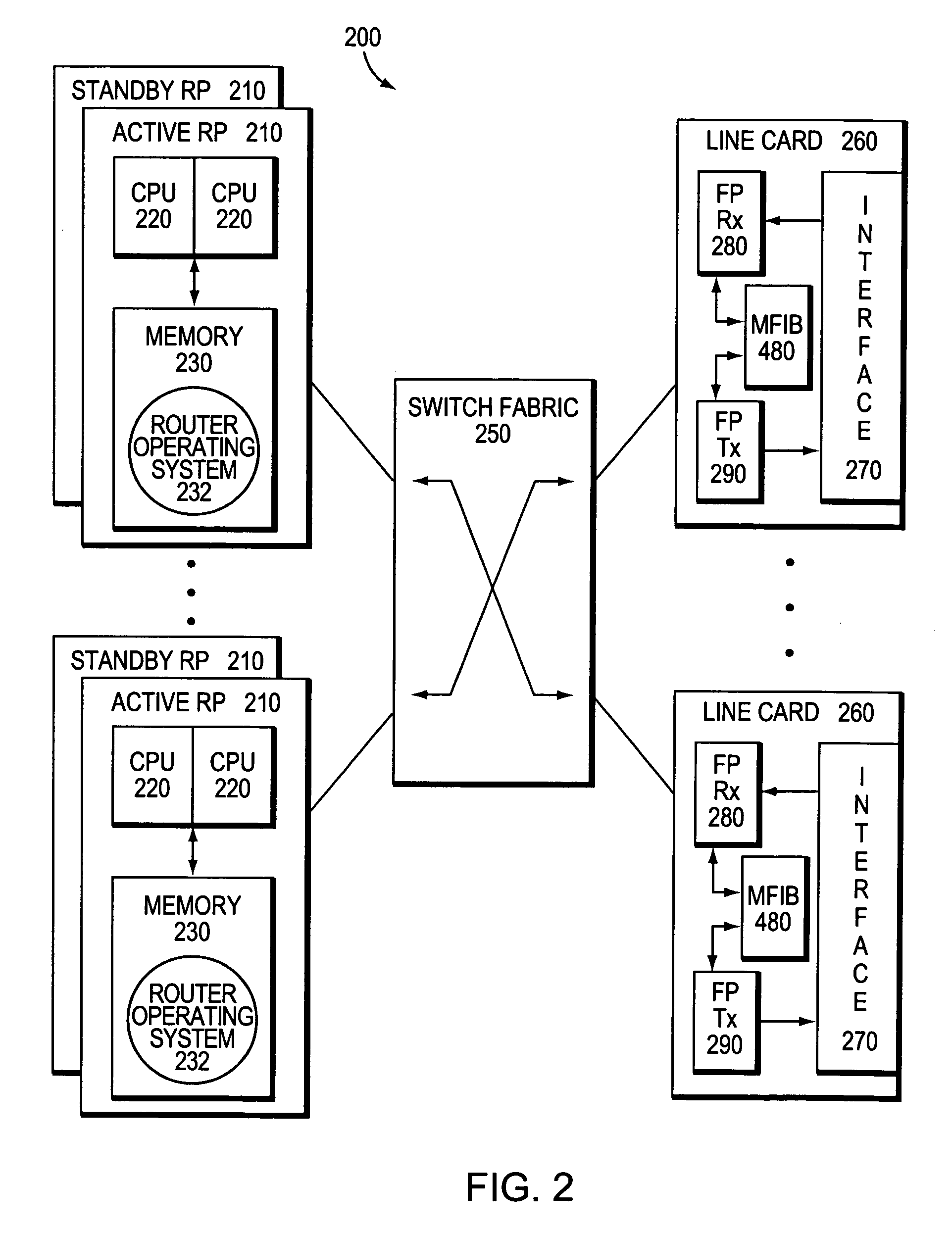
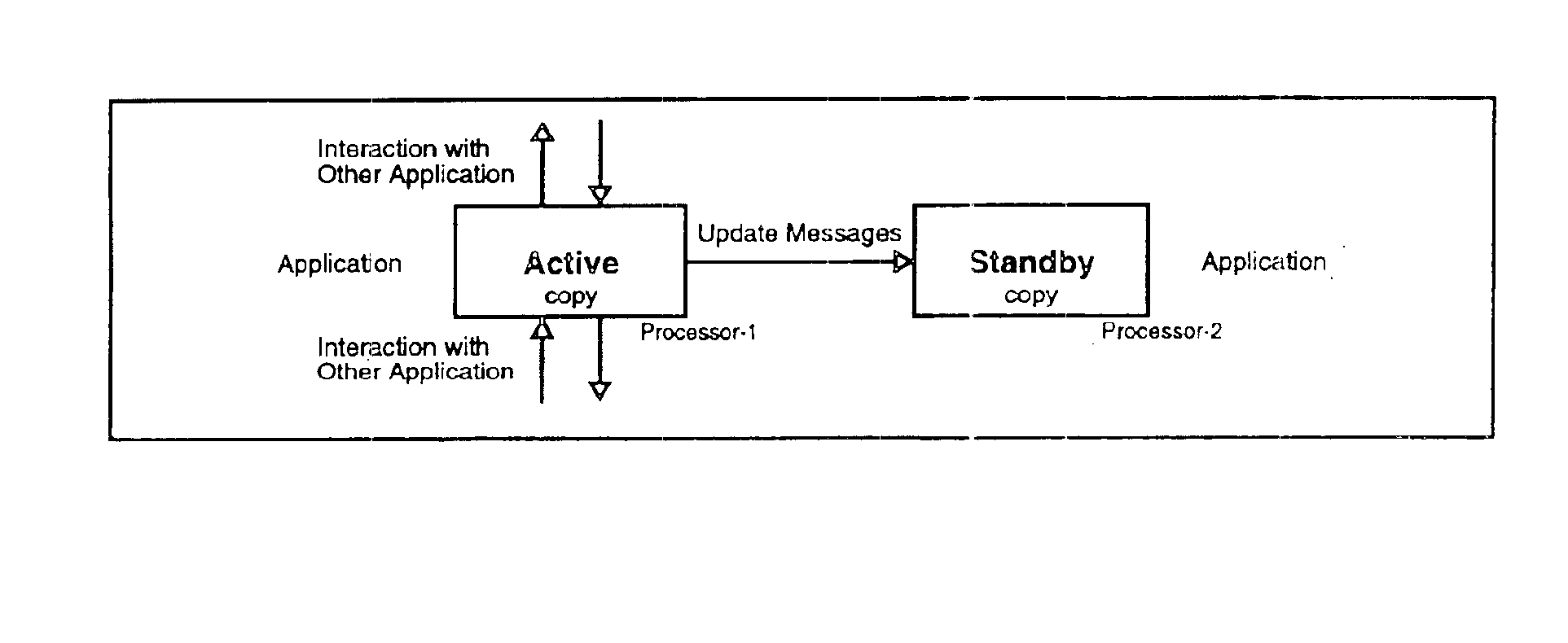
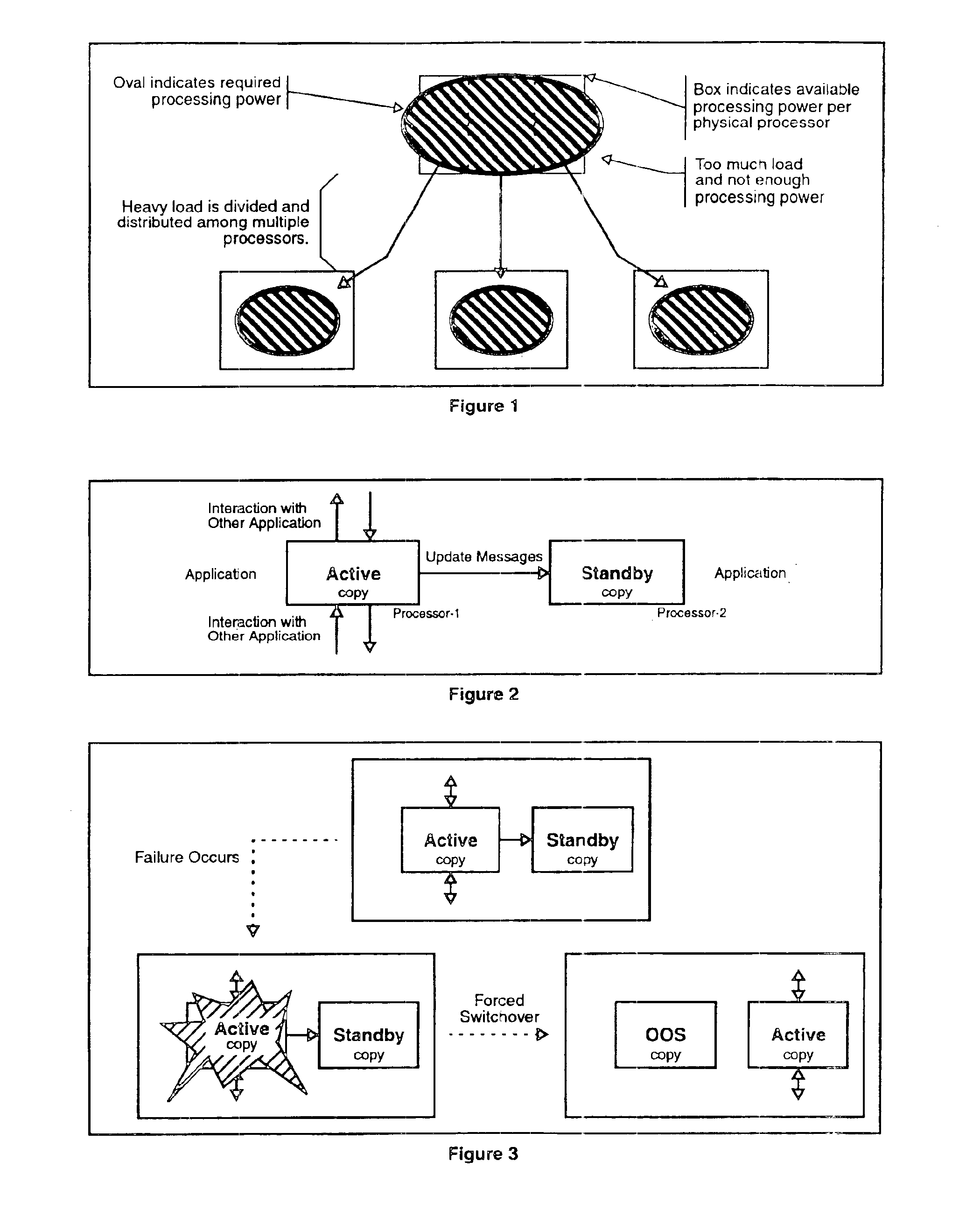
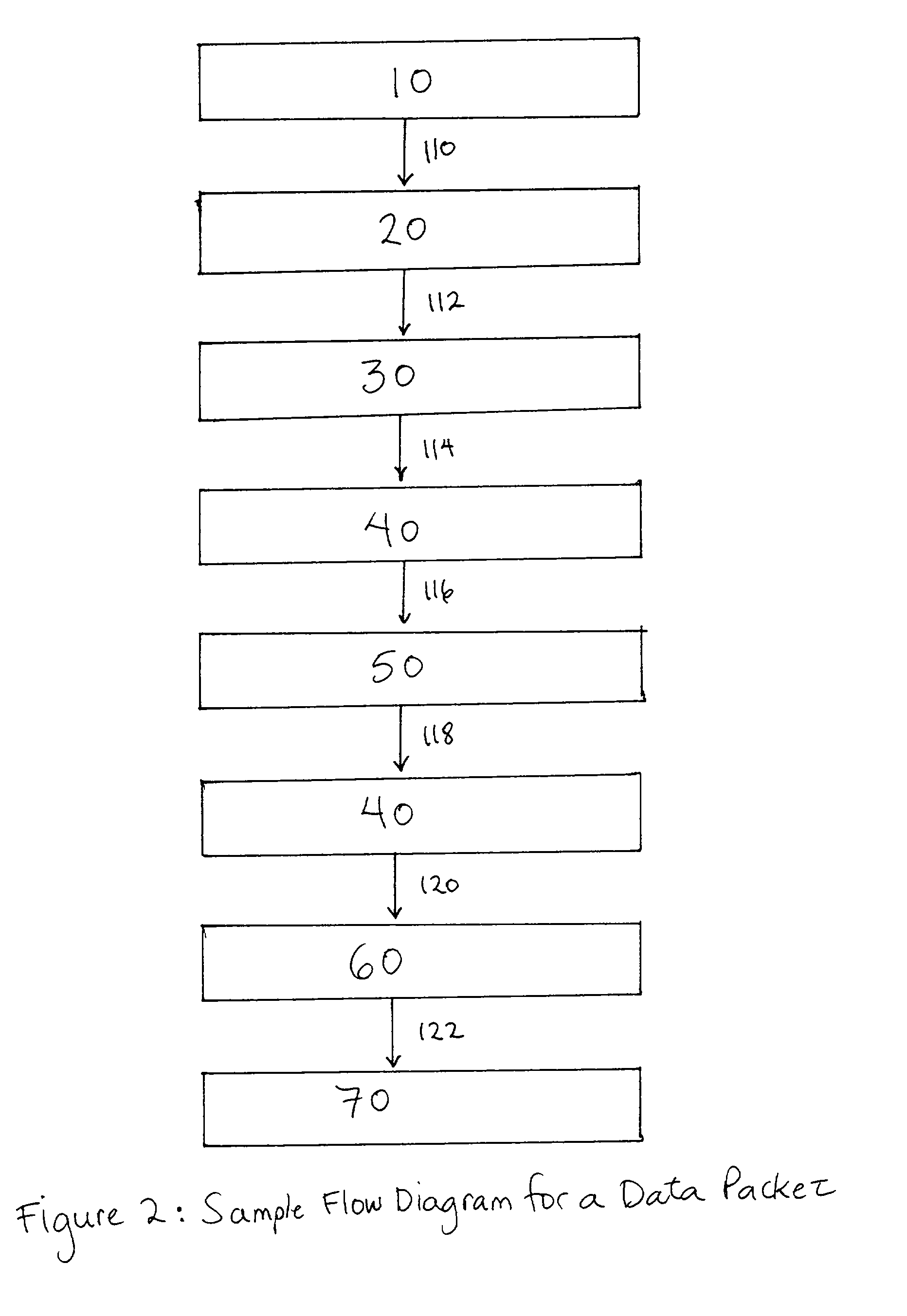
Patents
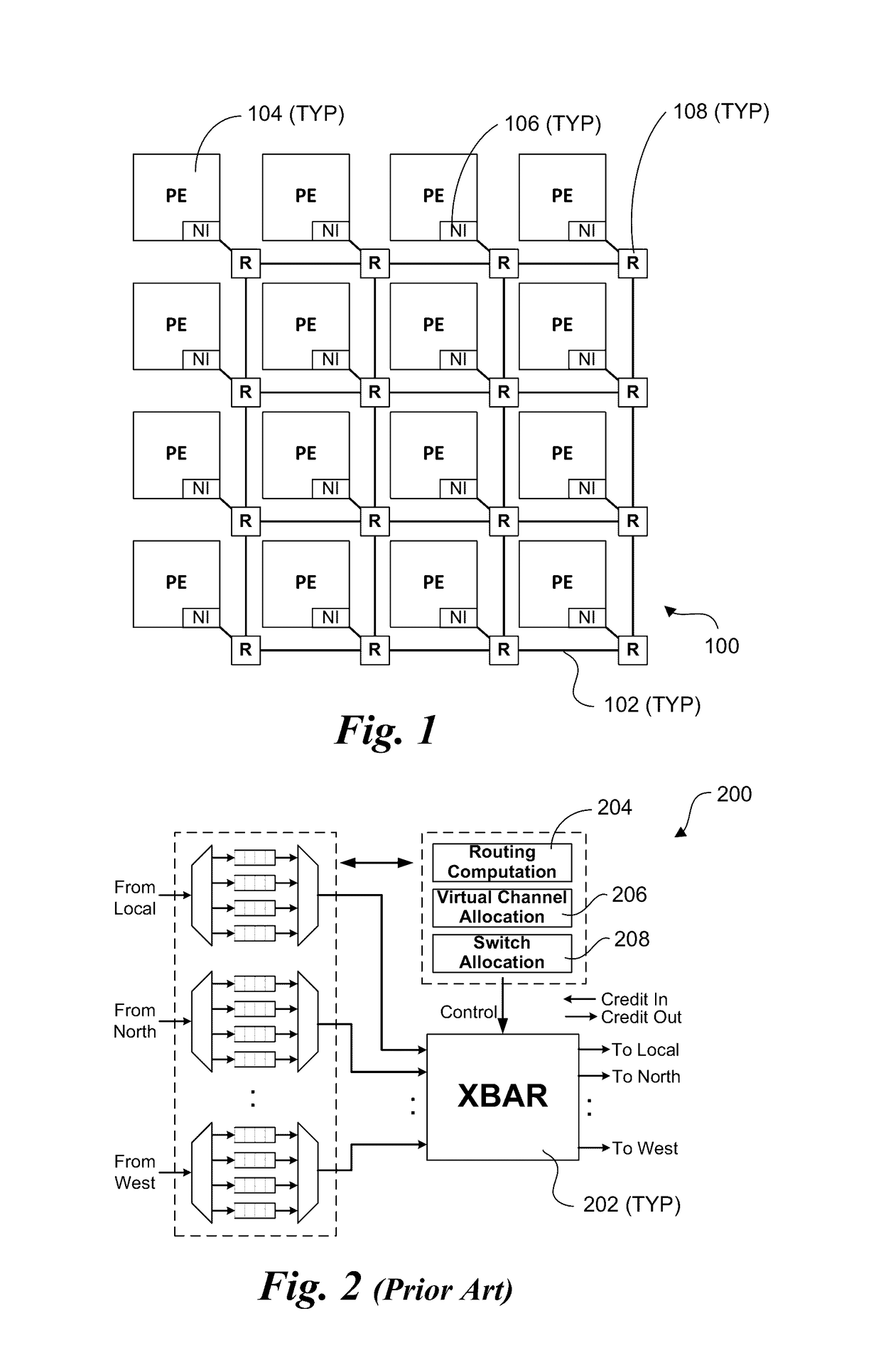
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Router architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
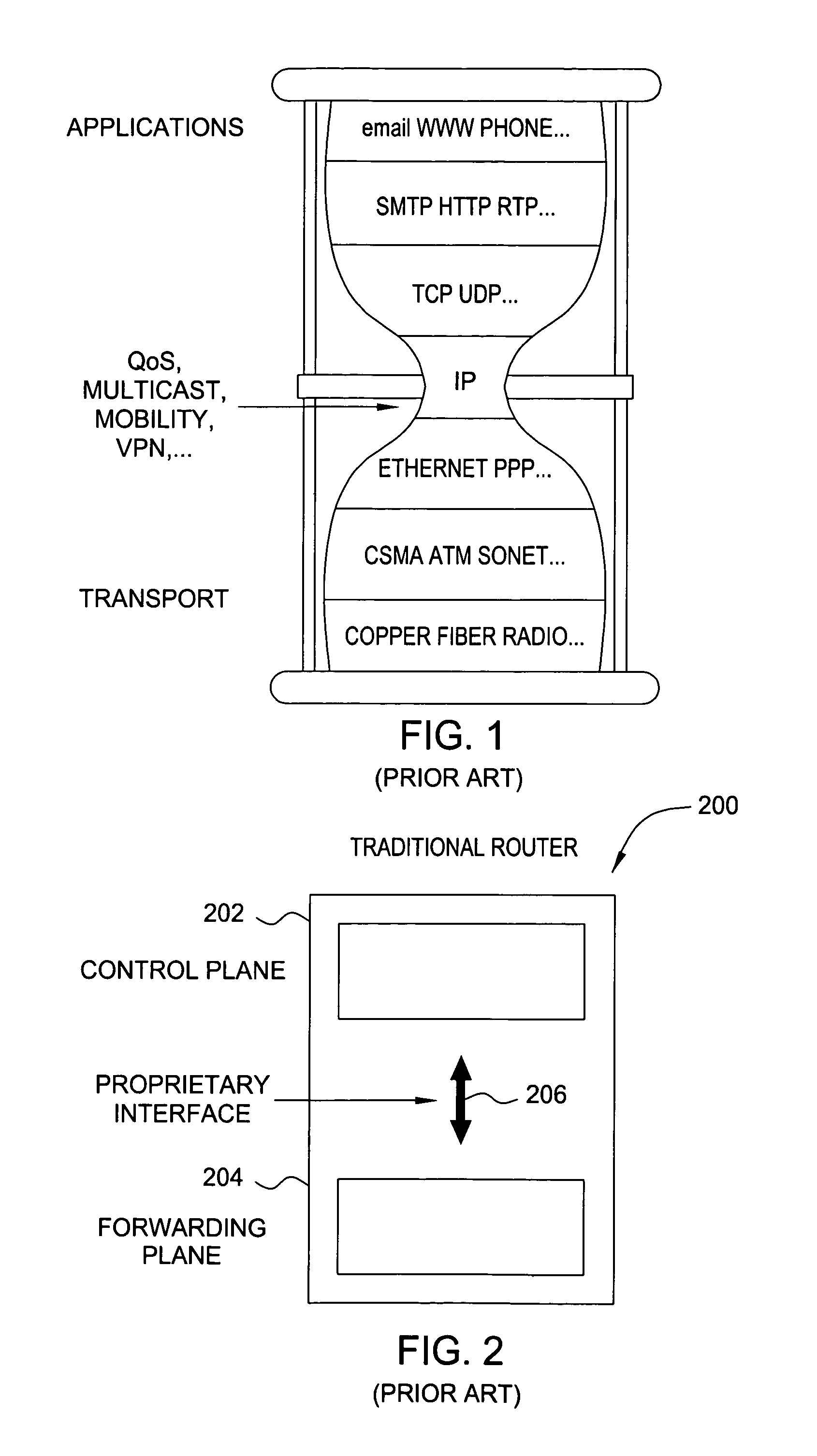
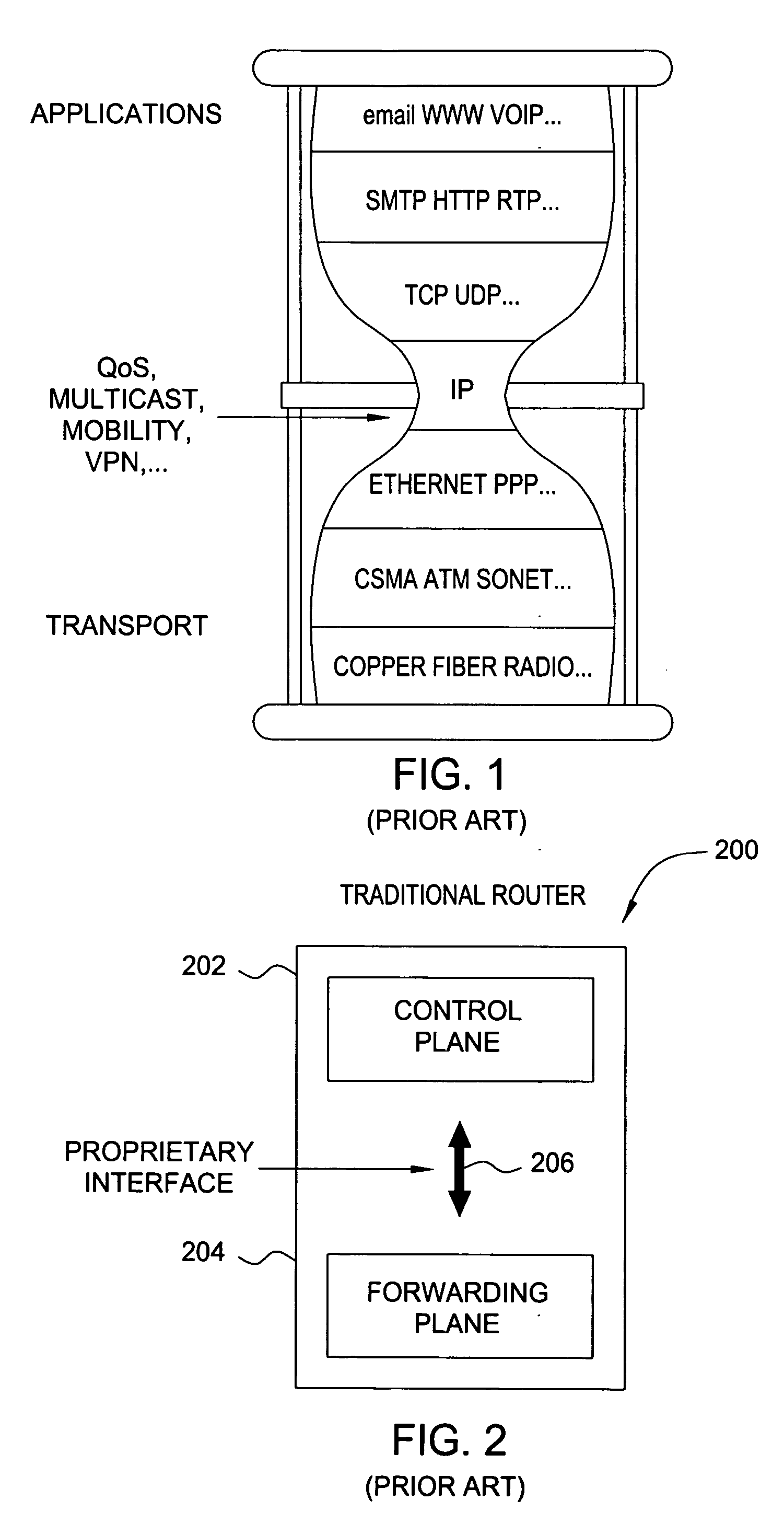
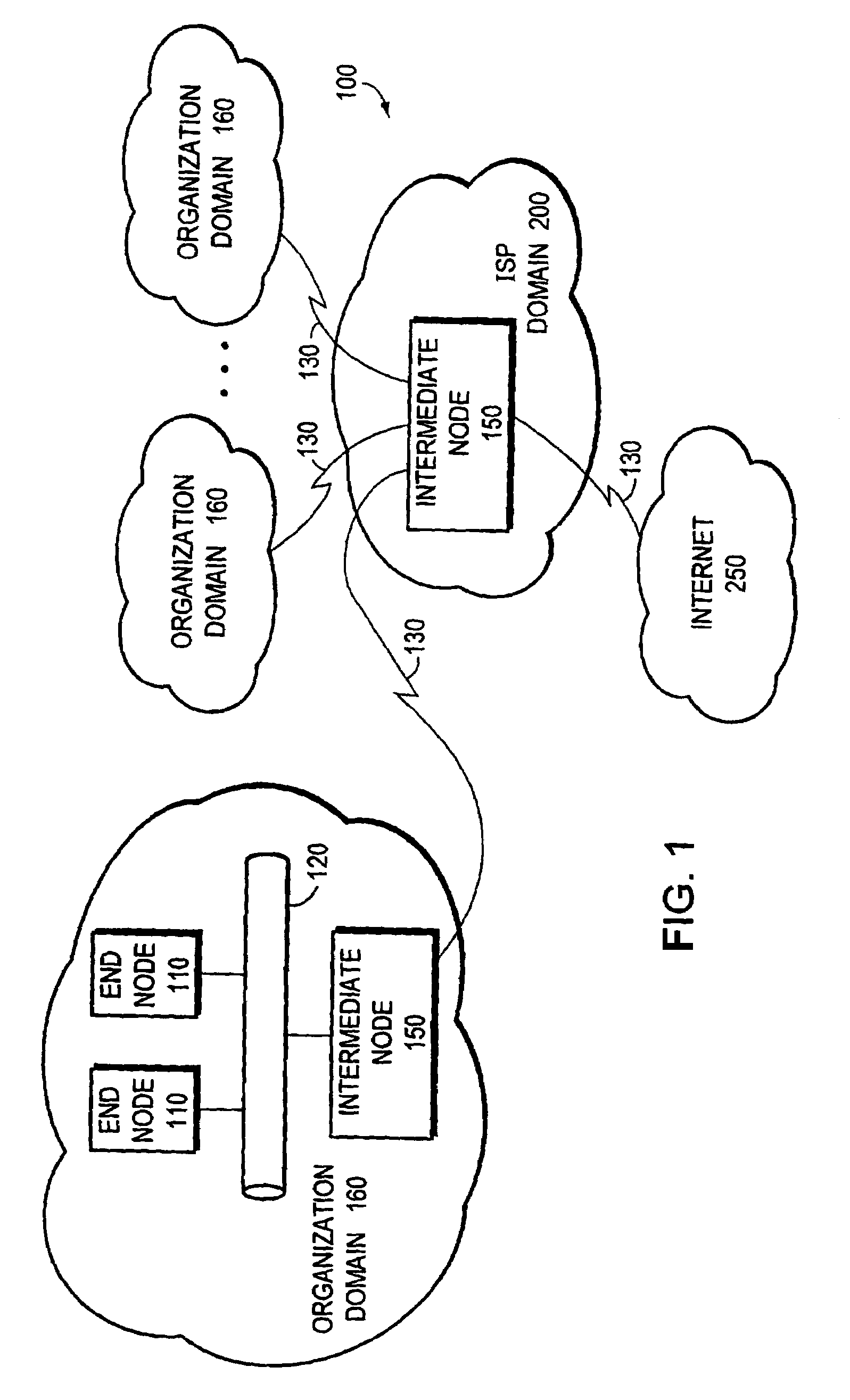
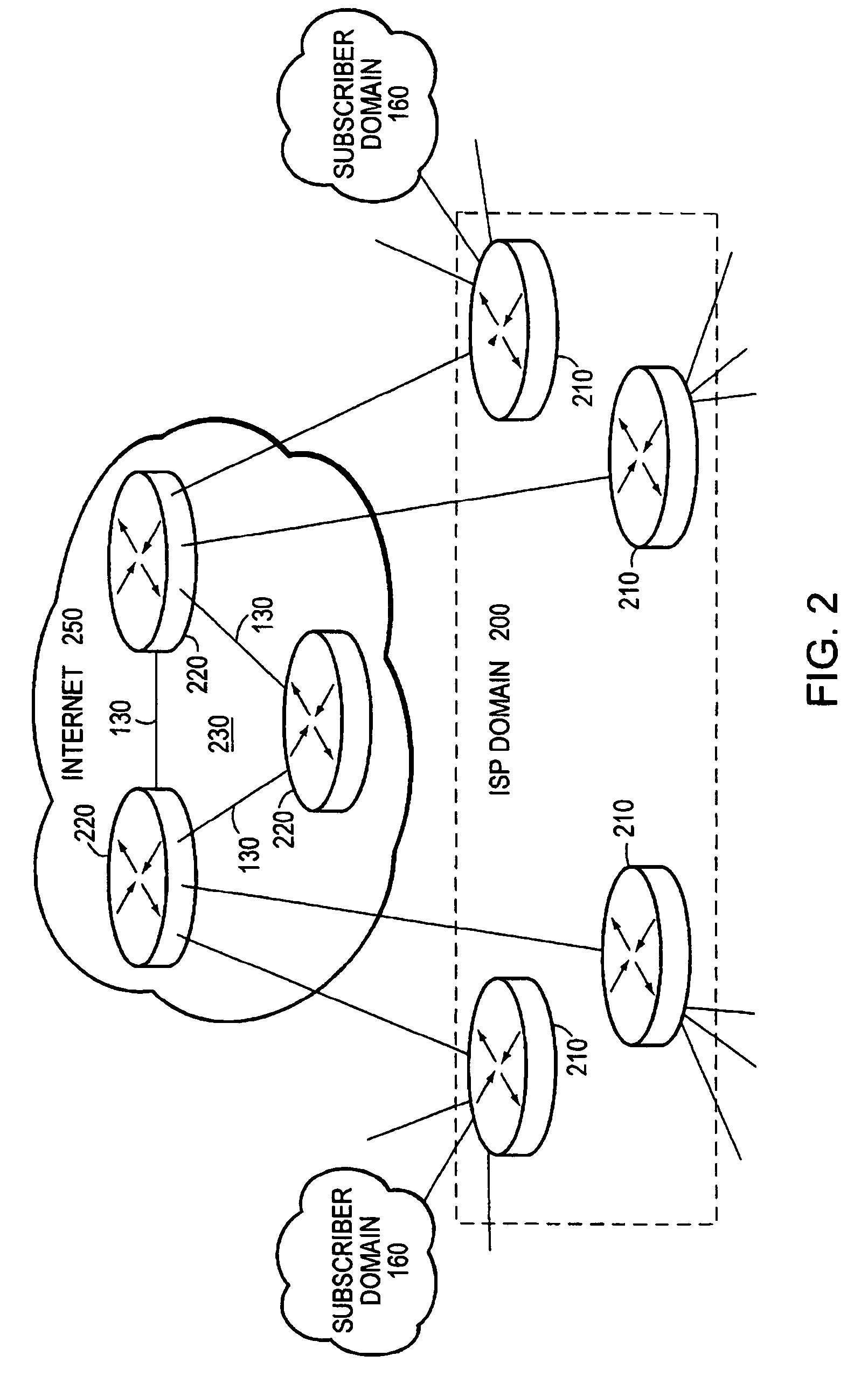
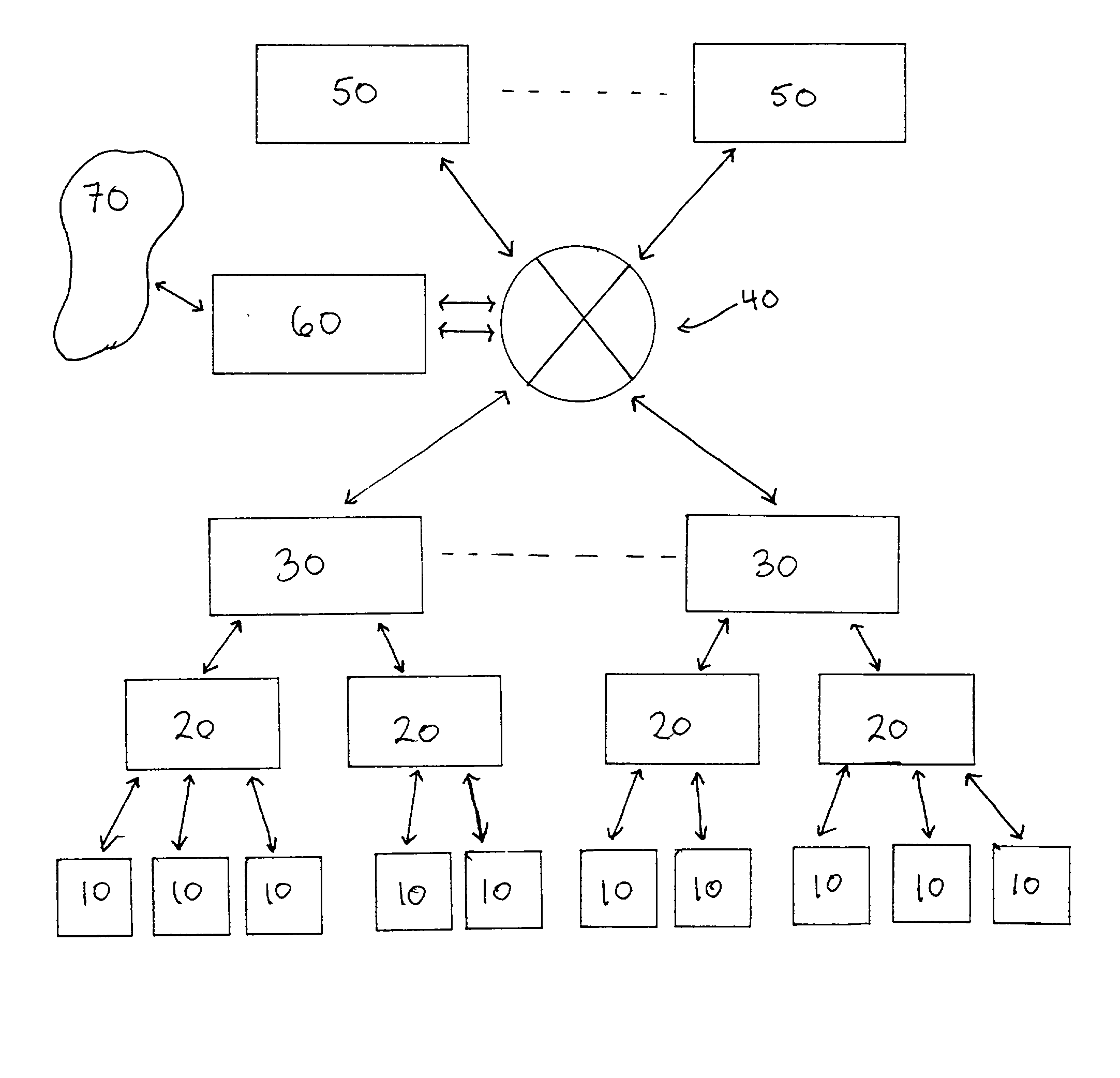
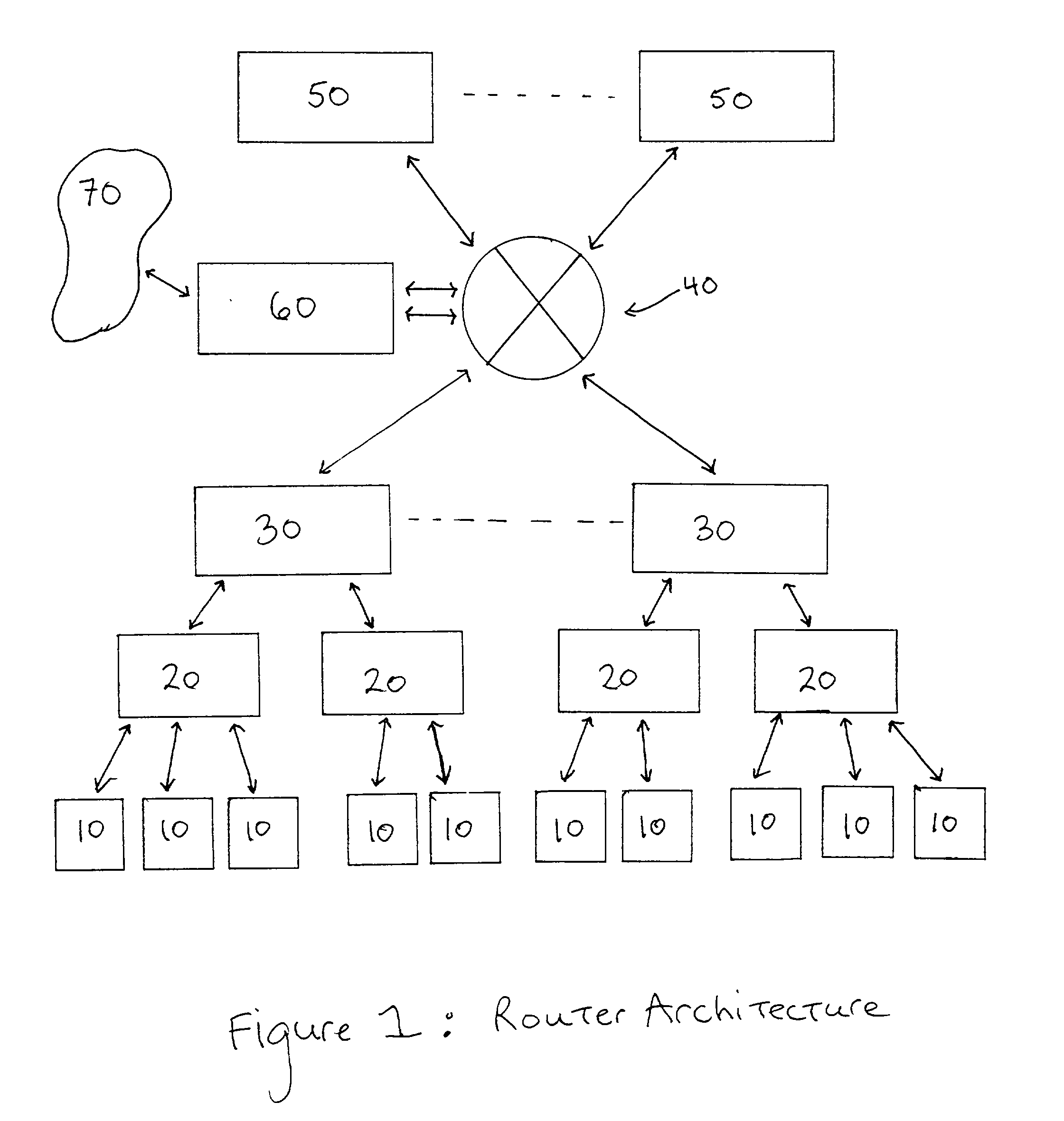
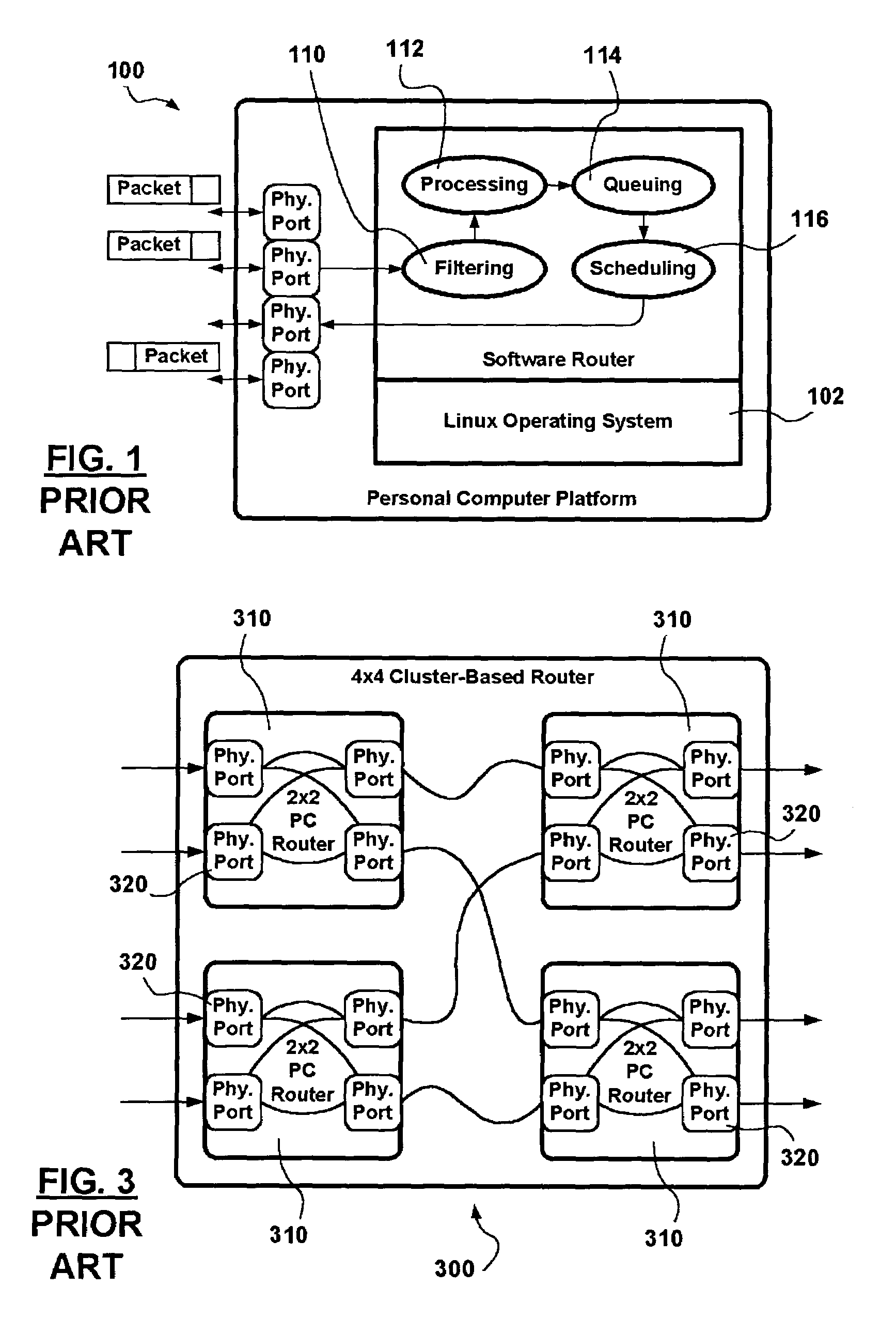
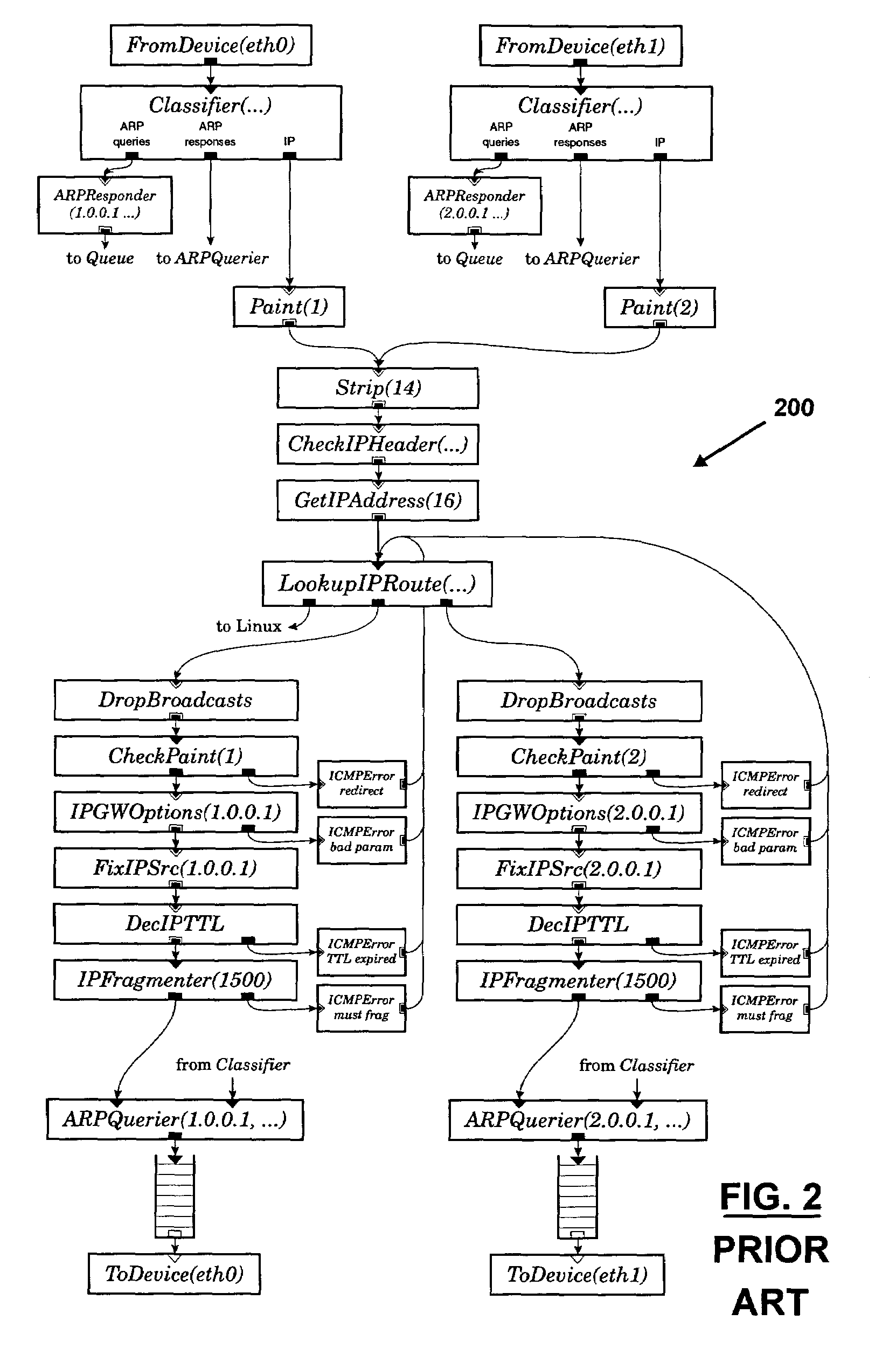
Router Architecture. Router architecture is designed so that routers are equipped to perform two main functions: process routable protocols and use routing protocols to determine best path.
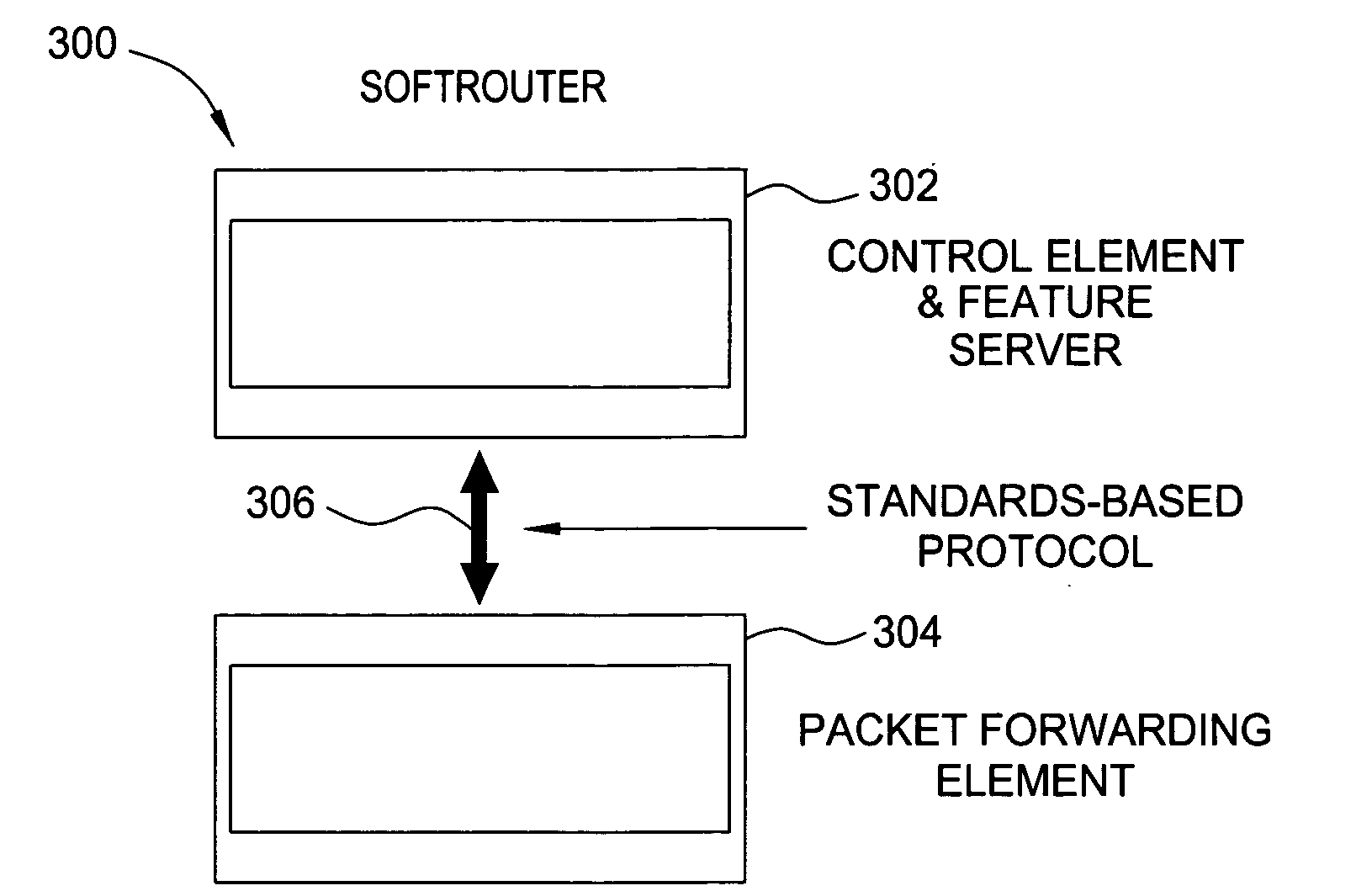
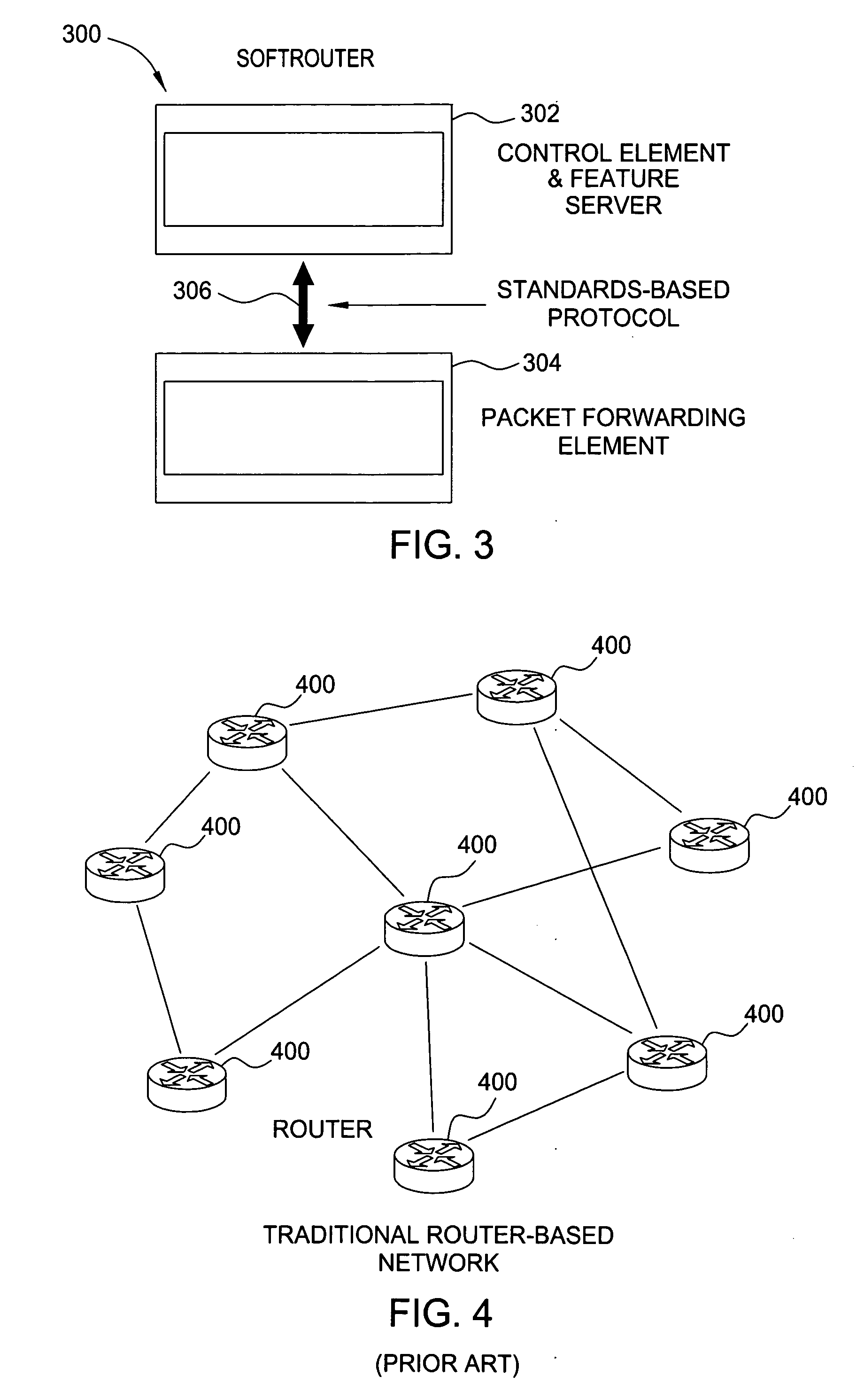
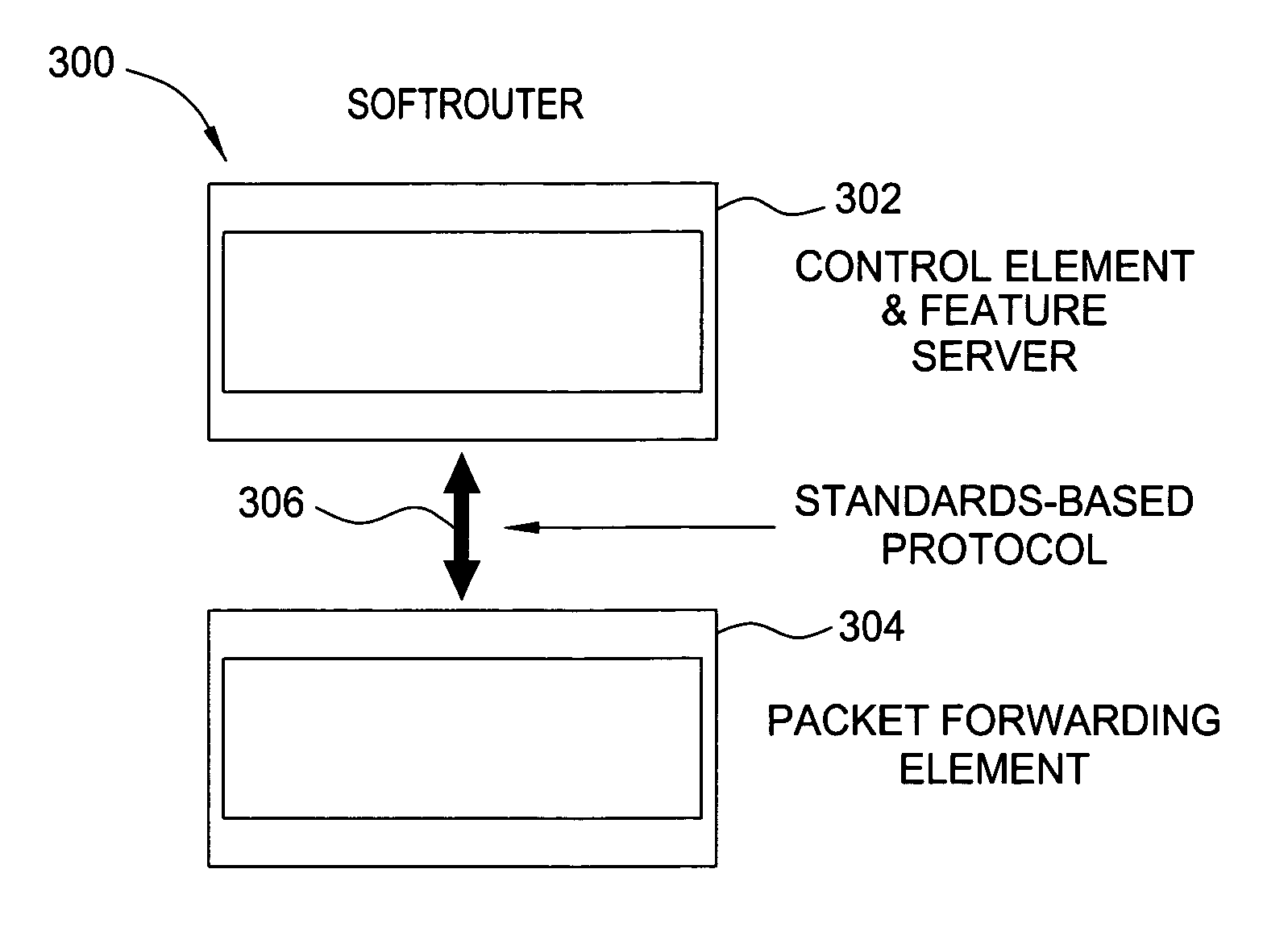
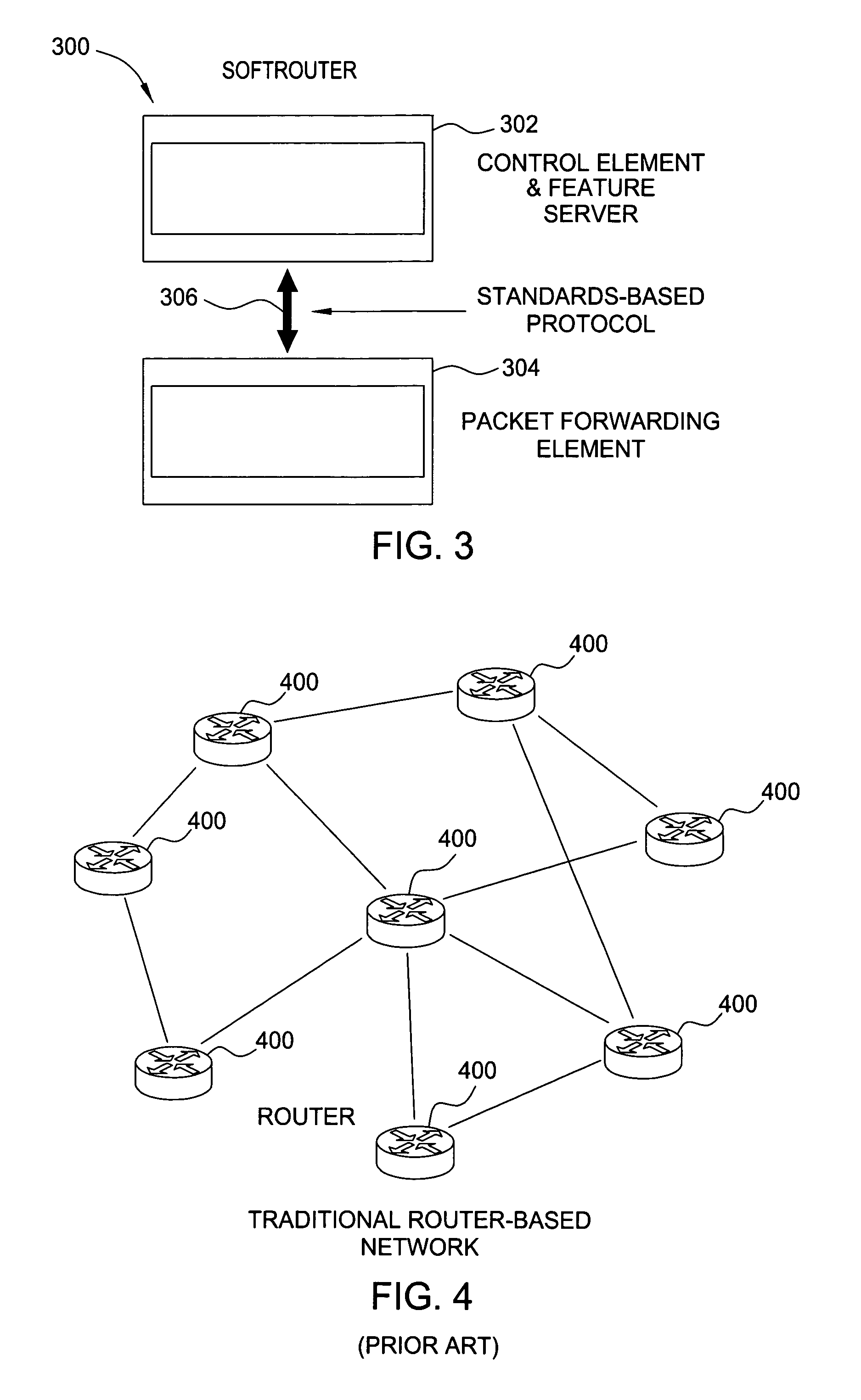
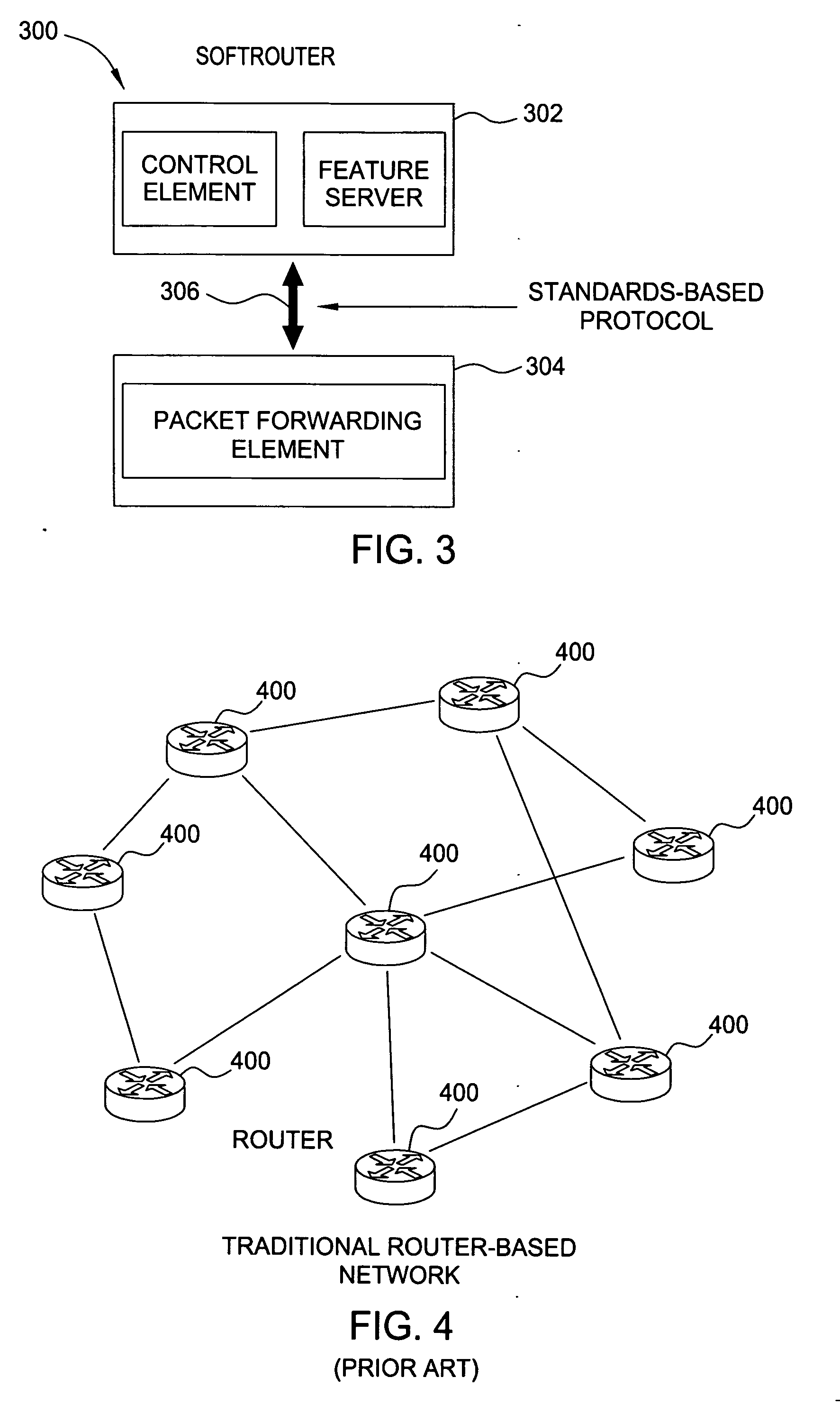
Softrouter separate control network
ActiveUS20060092976A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityExtensibility
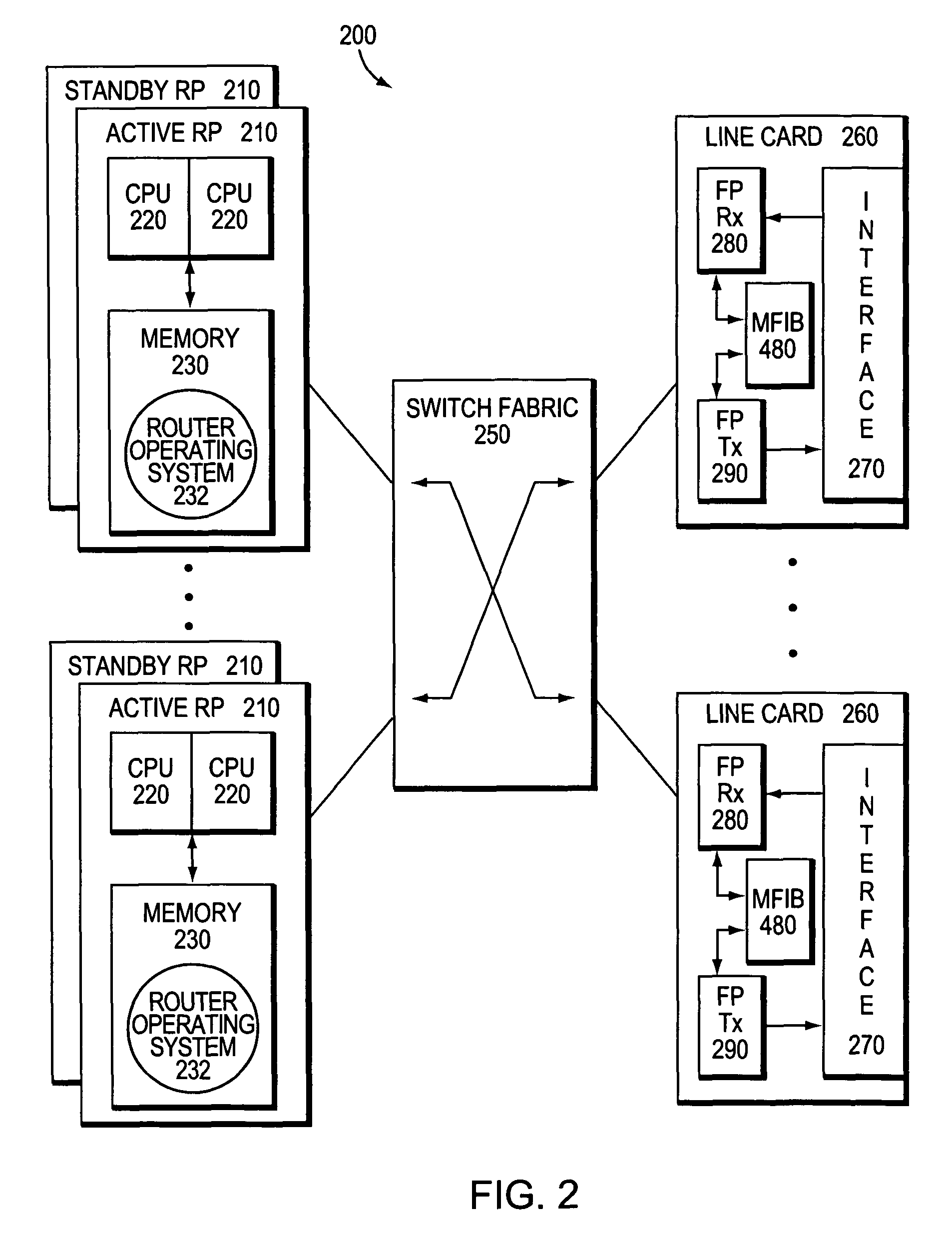
An embodiment of the exemplary SoftRouter architecture includes two physically separate networks, a control plane network and a data plane network. The data plane network is one physical network for the data traffic, while the control plane network is another physical network for the control traffic. The topology of the data plane network is made up of interconnected forwarding elements (FEs). The topology of the control plane network is made up interconnected control elements (CEs). This physical independence of the control plane network from the data plane network provides for a secure mechanism to communicate among the CEs in the control plane network. In addition, this physical independence provides improved reliability and improved scalability, when compared to the traditional router architecture, where control plane message are in-band with the data plane.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
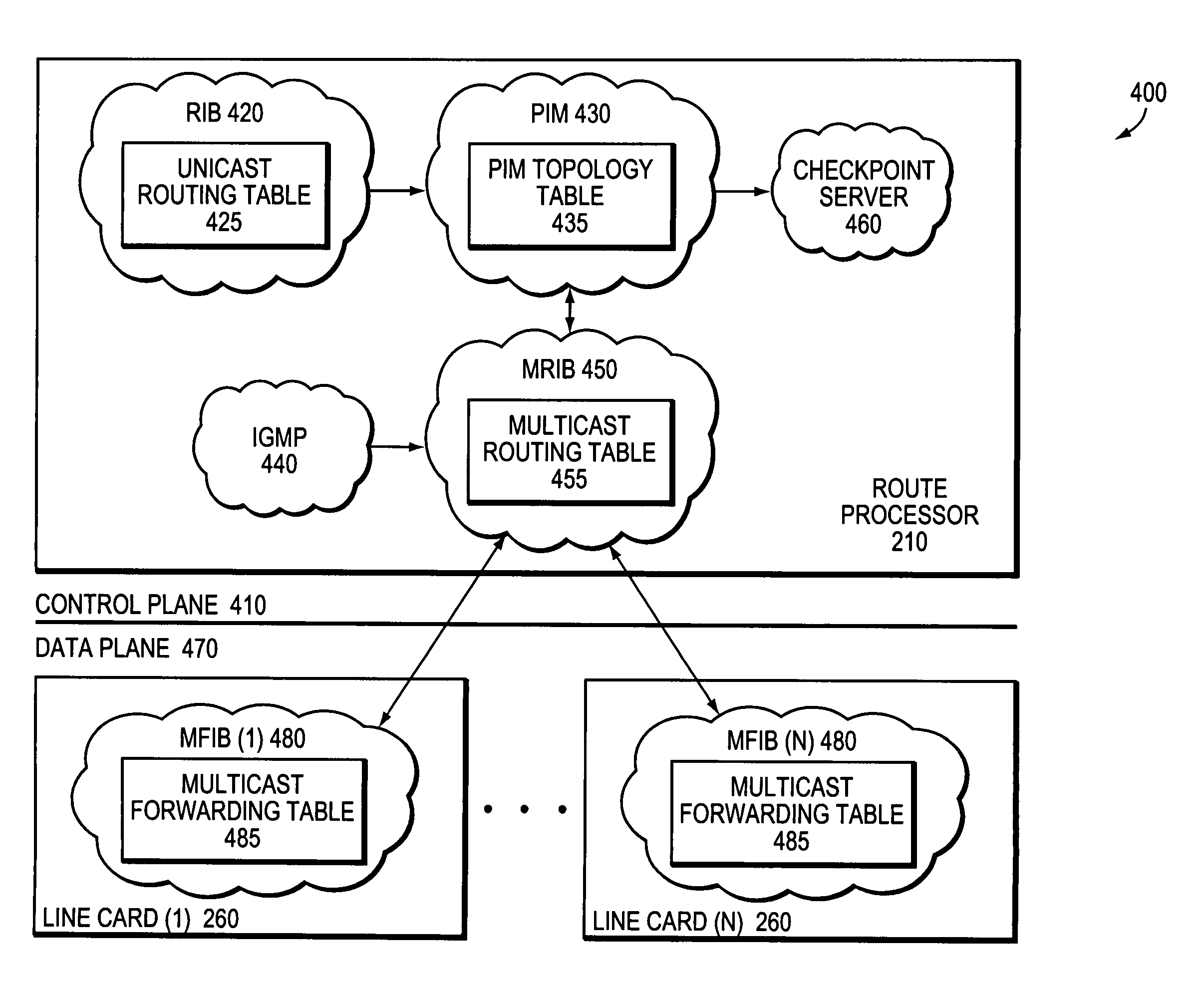
System and method for preserving multicast data forwarding during control failures in a router
ActiveUS20060018253A1Eliminate needImprove usabilityError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionHigh availability
A multicast non-stop forwarding (NSF) router architecture enhances high availability of a multicast router in a computer network. The router architecture further preserves multicast data forwarding through a data plane during NSF recovery of one or more failures in a control plane of the router. Various multicast components of the router cooperate to provide a checkpointing and recovery technique of the multicast NSF architecture that enables efficient restart and recovery of the control plane failures without loss of data connectivity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for building distributed fault-tolerant/high-availability computed applications
InactiveUS6865591B1Multiple failureOptimal hardware utilizationMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionOperational systemSystem maintenance
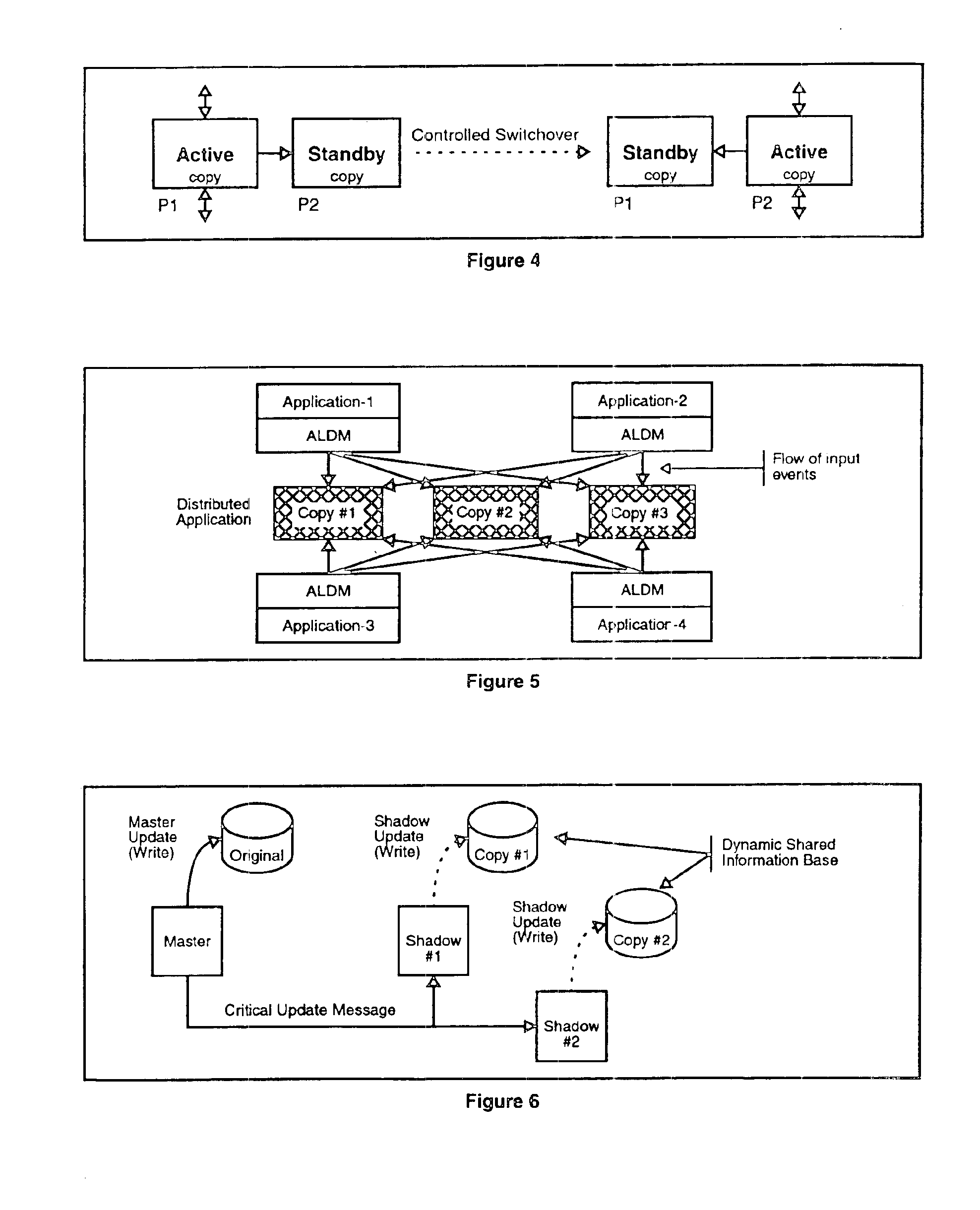
Software architecture for developing distributed fault-tolerant systems independent of the underlying hardware architecture and operating system. Systems built using architecture components are scalable and allow a set of computer applications to operate in fault-tolerant / high-availability mode, distributed processing mode, or many possible combinations of distributed and fault-tolerant modes in the same system without any modification to the architecture components. The software architecture defines system components that are modular and address problems in present systems. The architecture uses a System Controller, which controls system activation, initial load distribution, fault recovery, load redistribution, and system topology, and implements system maintenance procedures. An Application Distributed Fault-Tolerant / High-Availability Support Module (ADSM) enables an applications( ) to operate in various distributed fault-tolerant modes. The System Controller uses ADSM's well-defined API to control the state of the application in these modes. The Router architecture component provides transparent communication between applications during fault recovery and topology changes. An Application Load Distribution Module (ALDM) component distributes incoming external events towards the distributed application. The architecture allows for a Load Manager, which monitors load on various copies of the application and maximizes the hardware usage by providing dynamic load balancing. The architecture also allows for a Fault Manager, which performs fault detection, fault location, and fault isolation, and uses the System Controller's API to initiate fault recovery. These architecture components can be used to achieve a variety of distributed processing high-availability system configurations, which results in a reduction of cost and development time.
Owner:TRILLIUM DIGITAL SYST
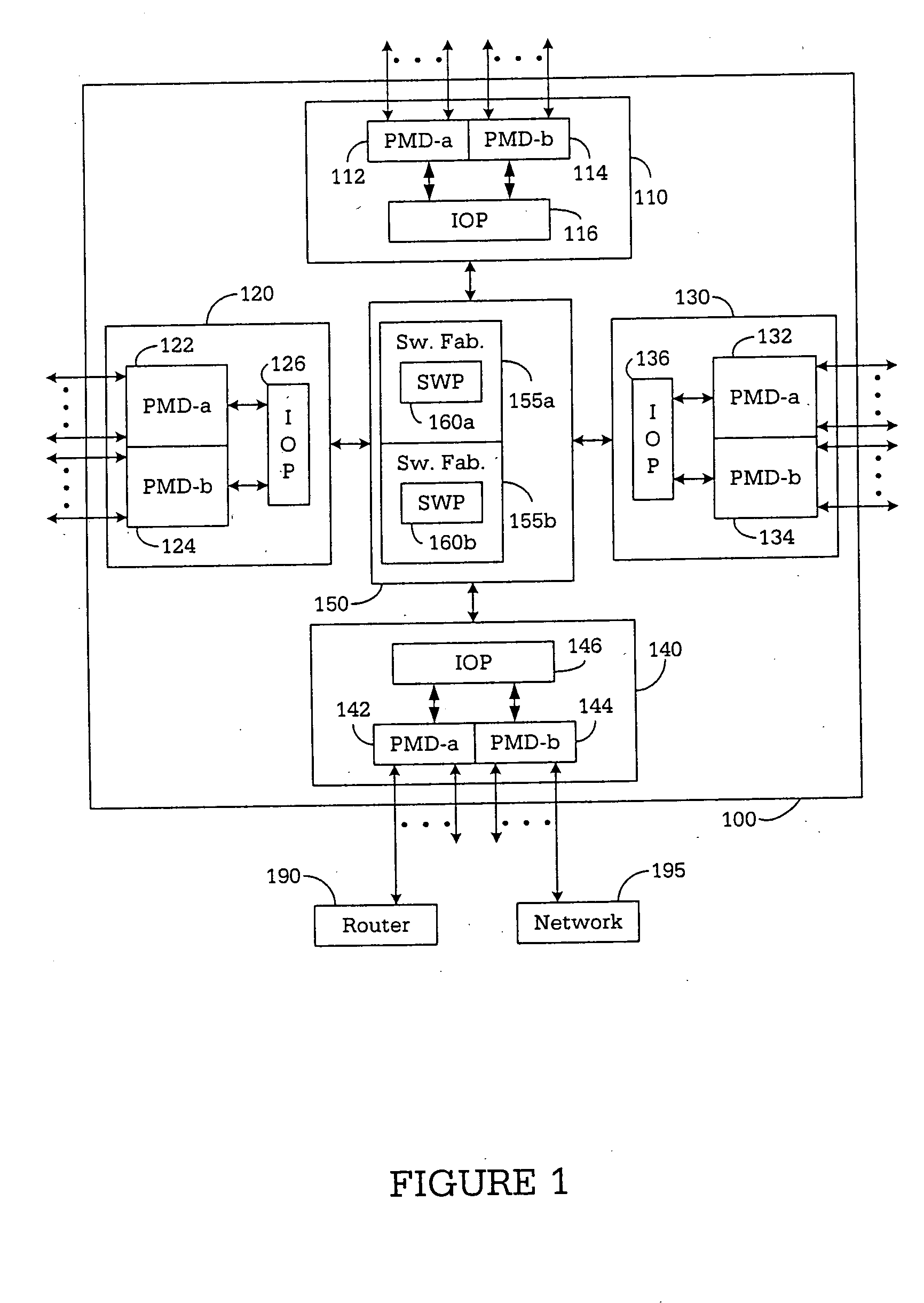
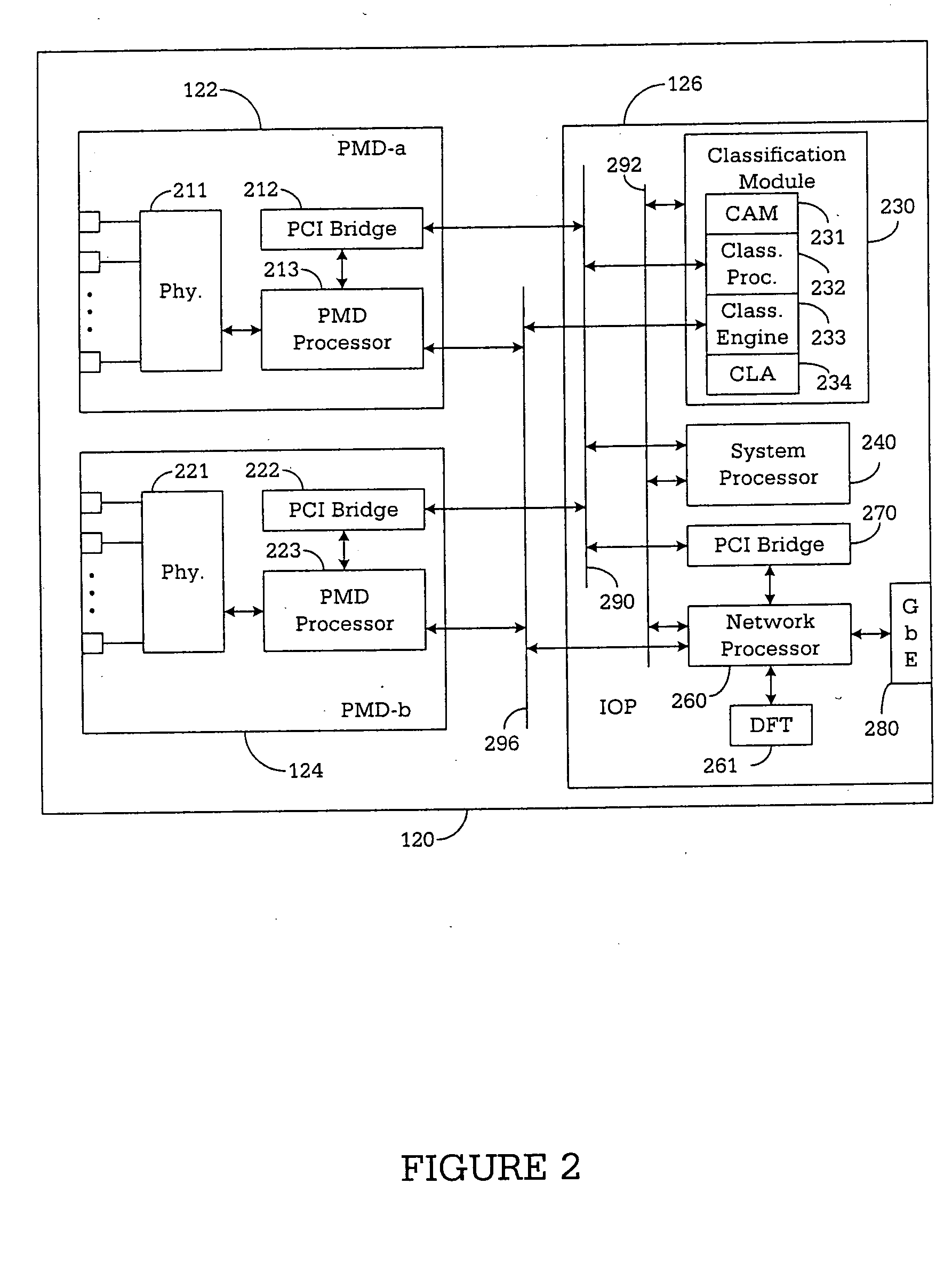
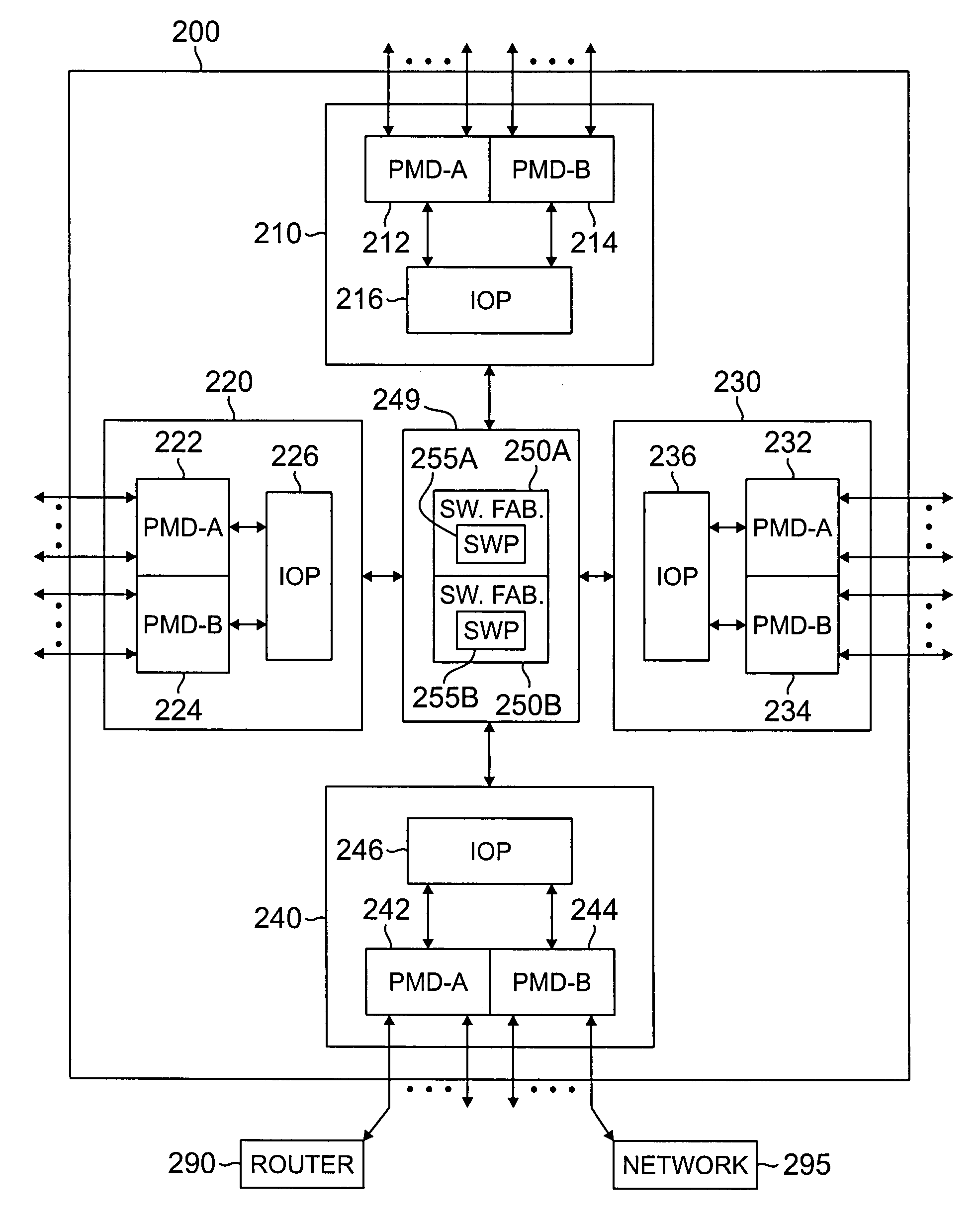
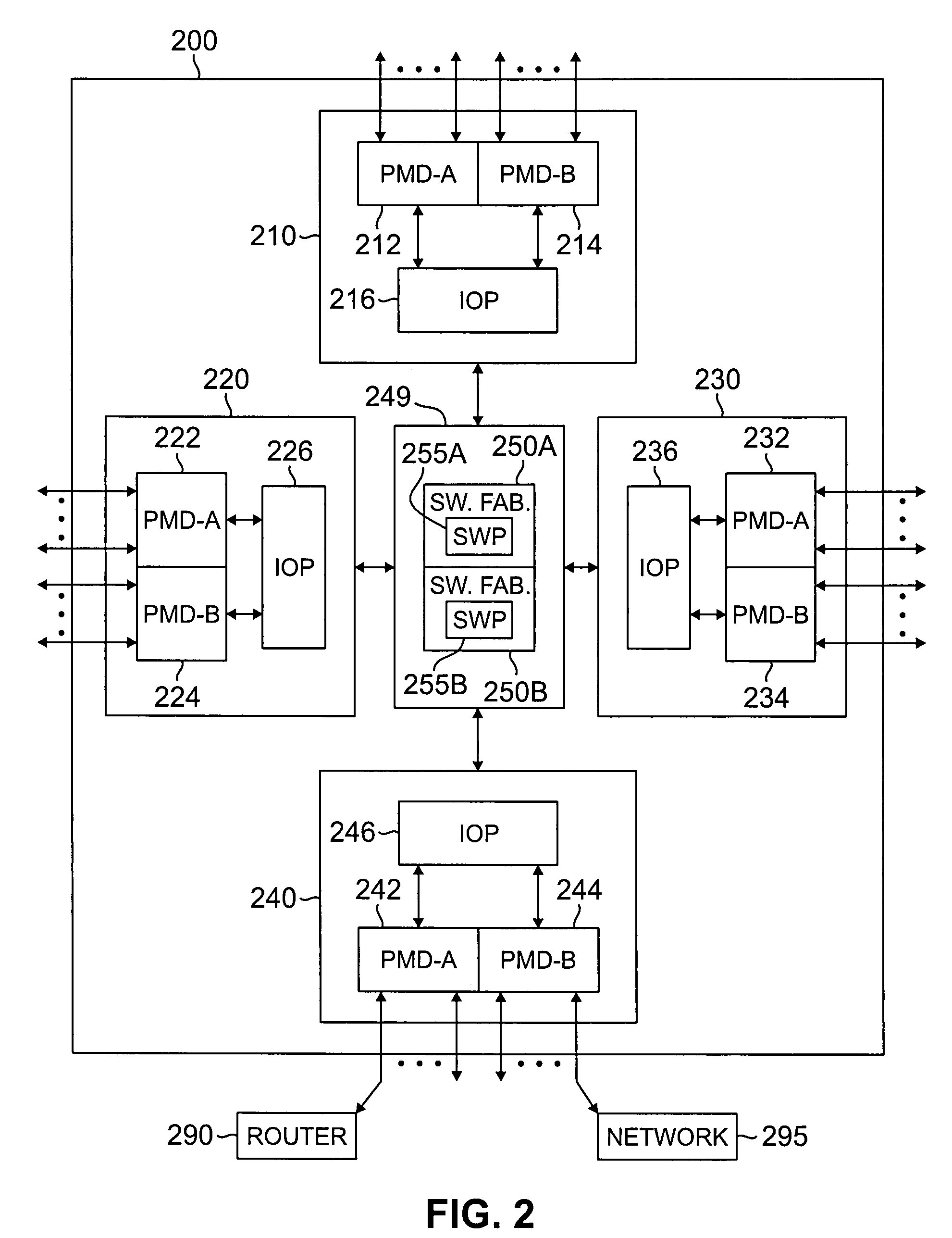
Apparatus and method for classifying traffic in a distributed architecture router
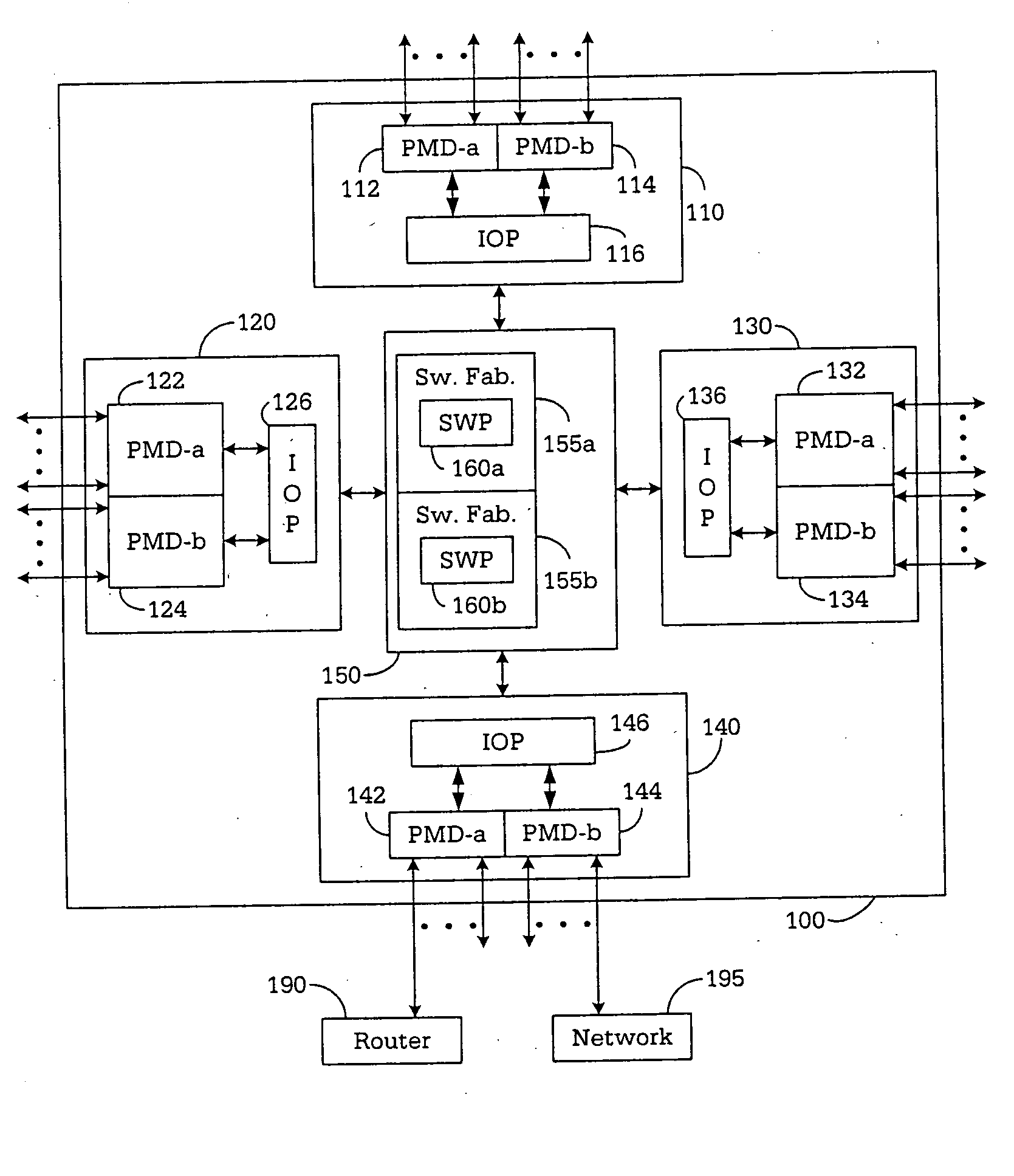
A router for interconnecting N interfacing peripheral devices. The router comprises a switch fabric and routing nodes coupled to the switch fabric. Each routing node comprises: i) a plurality of physical medium device (PMD) modules for transmitting data packets to and receiving data packets from selected ones of the N interfacing peripheral devices; ii) an input-output processing (IOP) module coupled to the PMD modules and the switch fabric for routing the data packets between the PMD modules and the switch fabric and between the PMD modules; and iii) a classification module associated with the IOP module for classifying a first data packet received from the IOP module. The classification module causes the IOP module to forward the first data packet based on the classification. The router architecture incorporates streams-based billing support, firewall capabilities, and data surveillance functionality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
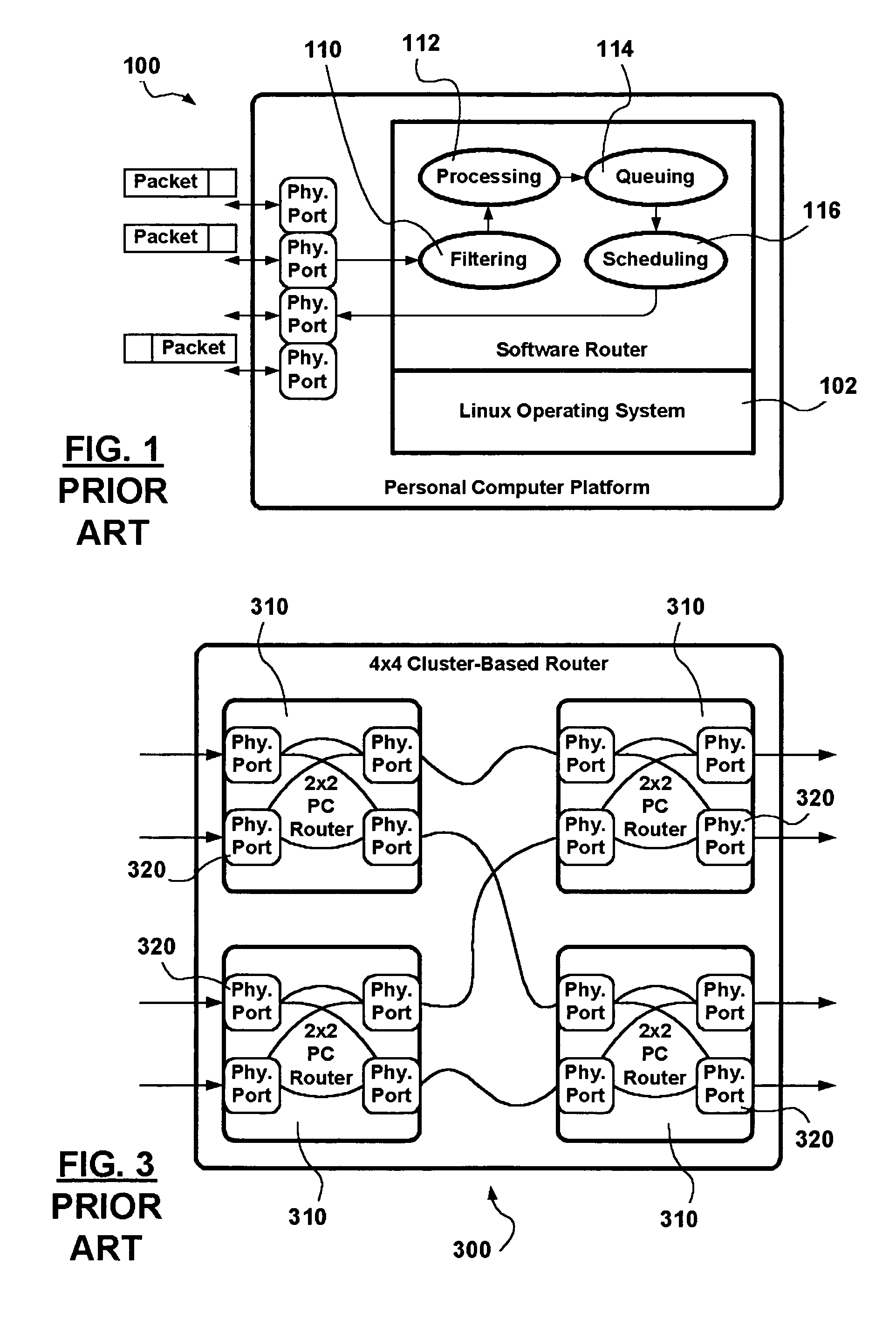
Software configurable cluster-based router using heterogeneous nodes as cluster nodes
ActiveUS20050108425A1Large capacityIncrease diversityError preventionTransmission systemsOff the shelfCluster based
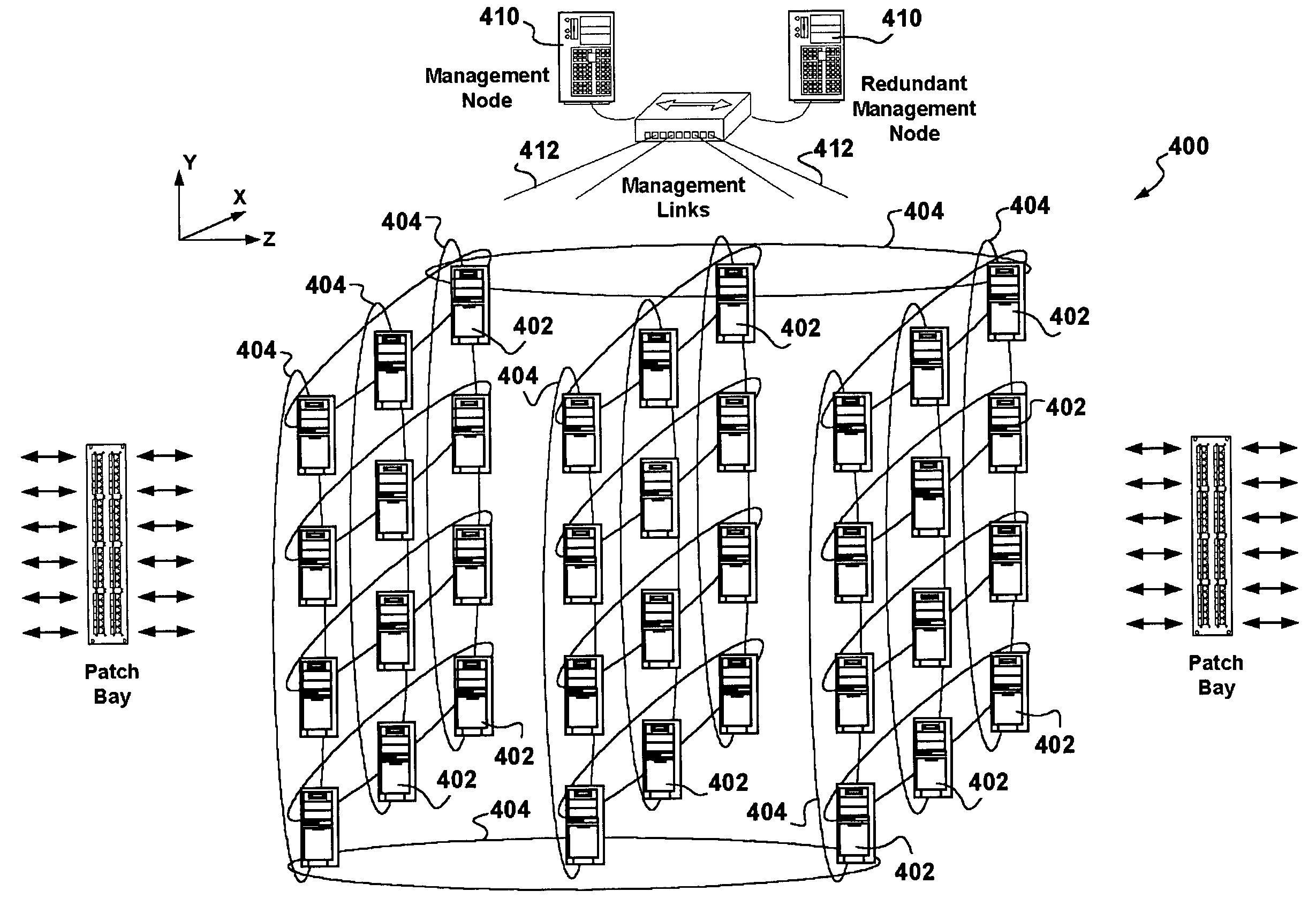
A cluster router architecture and methods for performing distributed routing are presented. The cluster router architecture includes off-the shelf Personal Computer (PC) hardware-based router cluster nodes interconnected in an intra-connection network in multiple dimensions. Each PC-based router cluster node is provided with the same routing functionality and a router-cluster-node-centric configuration enabling each router cluster node by itself or multiple router cluster nodes in the cluster router to provide routing responses for packets pending processing. Optimized packet processing in respect of specific functionality is provided via special purpose router cluster nodes not necessarily PC-based taking part as cluster nodes in the cluster router lattice. The method divides packet processing into entry packet processing and routing response processing; special processing; and exit processing. Entry packet processing and routing response processing is performed by router cluster nodes receiving packets from communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Exit packet processing is performed by router cluster nodes transmitting packets into communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Packet processing in accordance with the router-cluster-node-centric specification is interrupted on determining that special processing is required in respect of a packet, and the packet is handed over to a corresponding special purpose router cluster node. Advantages are derived from: a configurable, and scalable cluster router design providing a re-configurable high routing capacity using cost effective stock PC hardware; from the intra-connection network which provides a high degree of diversity ensuring resilience to equipment failure; from the use of a star topology with respect to management links which reduces management overheads in the intra-connection network; and from the ability to forward packets to designated special purpose router cluster nodes optimized to provide specific packet processing functionality.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
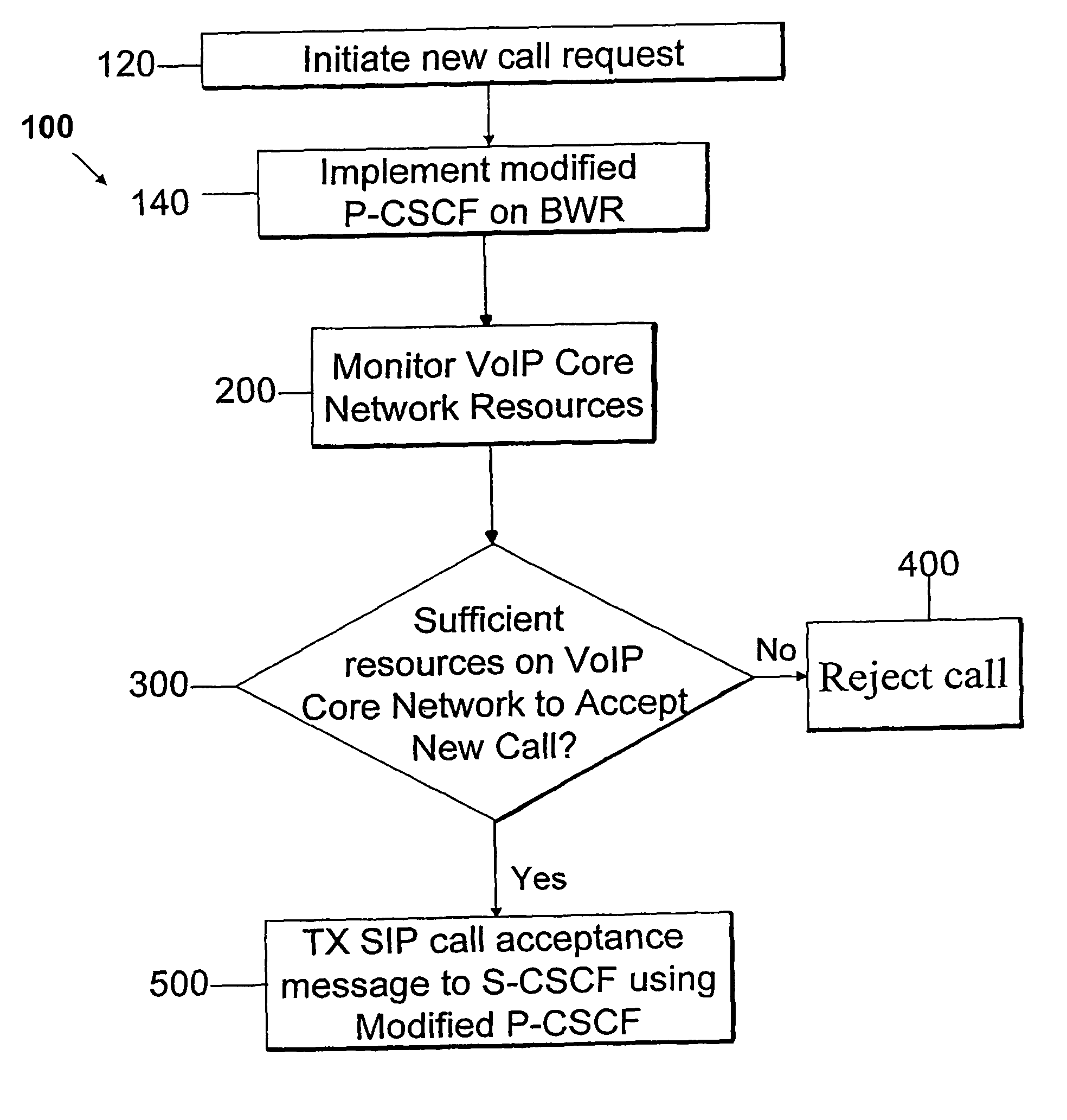
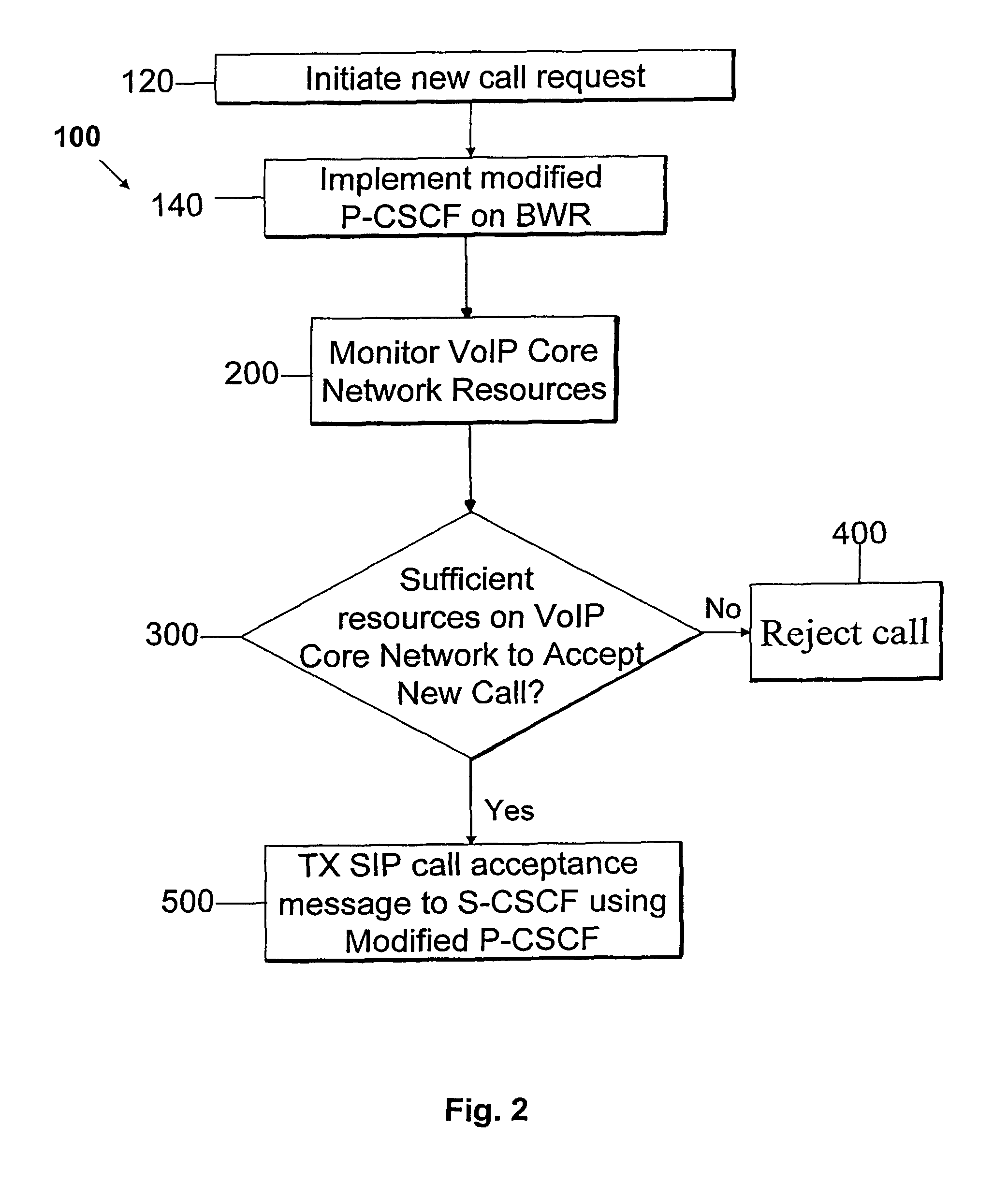
Broadband wireless router-architecture enhancements for VoIP
ActiveUS7853265B1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationWireless routerSession control
A method for providing enhanced service in an IP-based core network having a collapsed wireless system architecture comprises using a modified proxy-call session control function in a broadband wireless router to monitor the IP-based core network and, based on the amount of available resources, either accepting a call or rejecting the call into the network. Additionally, depending on an amount of available resources in the IP-based core network a quality of a call-in-progress or a user application may be adjusted.
Owner:NEXTEL COMMUNICATIONS
Softrouter separate control network
ActiveUS9014181B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsTraffic capacityStructure of Management Information
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
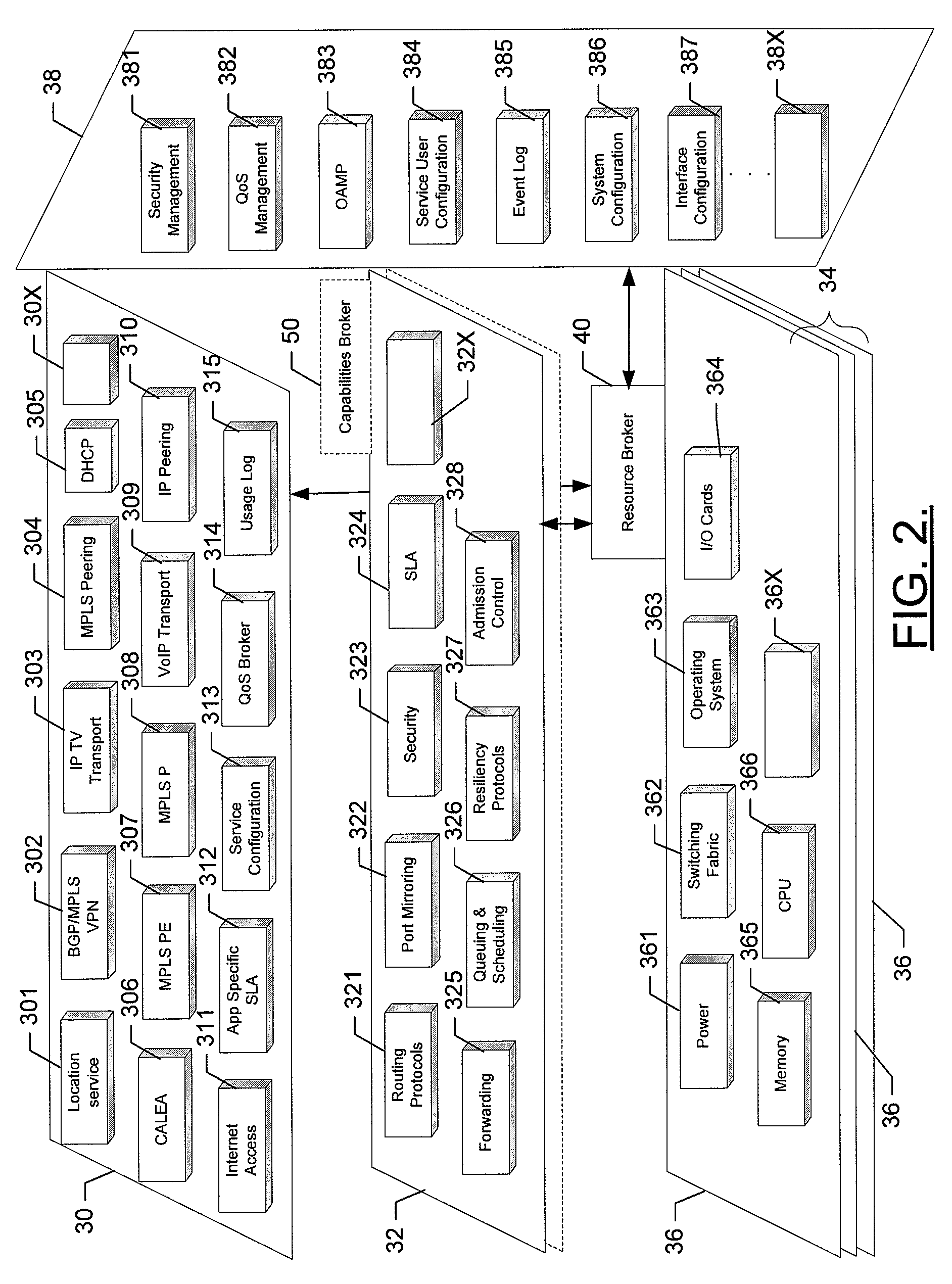
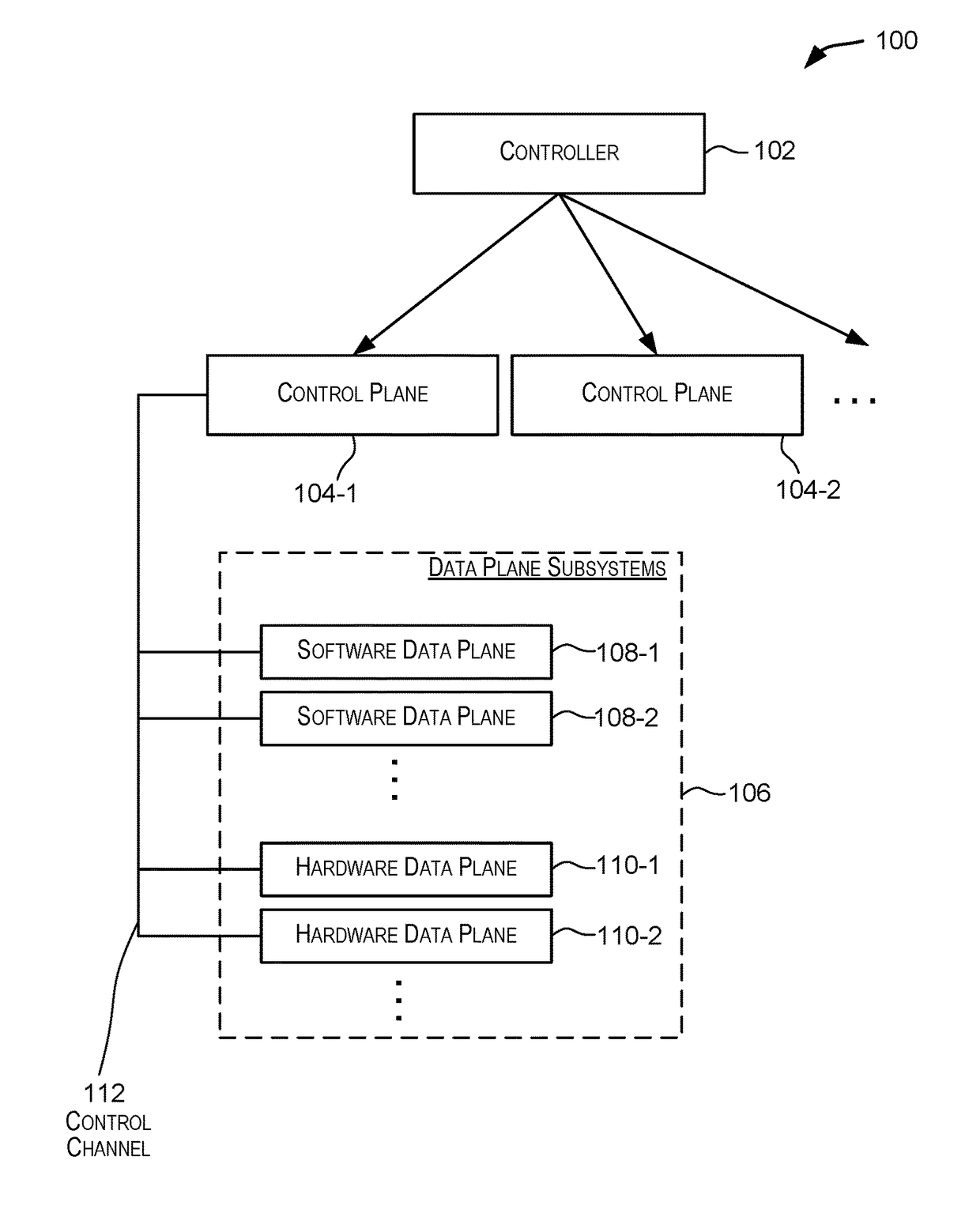
Multilayered distributed router architecture
A distributed multilayered network routing architecture comprises multiple layers including a controller layer comprising a controller, a control plane layer comprising one or more control plane subsystems, and a data plane layer comprising one or more data plane subsystems. A controller may be coupled to one or more control plane subsystems. A control plane subsystem may in turn be coupled to one or more data plane subsystems, which may include one or more software data plane subsystems and / or hardware data plane subsystems. In certain embodiments, the locations of the various subsystems of a distributed router can be distributed among various devices in the network.
Owner:CIENA
Software configurable cluster-based router using stock personal computers as cluster nodes
InactiveUS20050018665A1Increase capacityIncrease diversityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsData packCost effectiveness
A cluster router architecture and methods for performing distributed routing is presented. Implementations include off-the shelf Personal Computer (PC) hardware. The cluster router architecture includes PC-based router cluster nodes toroidally interconnected in an intra-connection network in multiple dimensions. The cluster router may further make use of a management node. Each router cluster node is provided with the same routing functionality and a node centric configuration enabling each router cluster node by itself or multiple router cluster nodes in the cluster router to provide routing responses for packets pending processing. The method divides packet processing into entry packet processing and routing response processing; and exit processing. Entry packet processing and routing response processing is performed by router cluster nodes receiving packets from communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Exit packet processing is performed by router cluster nodes transmitting packets into communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Advantages are derived from: a configurable, and scalable cluster router design providing a high routing capacity using cost effective stock PC hardware; from the toroidal topology of the intra-connection network which provides a high degree of diversity ensuring resilience to equipment failure, and from the use of the star topology of the management links which reduces management overheads in the intra-connection network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
System and method for preserving multicast data forwarding during control failures in a router
ActiveUS7787360B2Improve usabilityEliminate needError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionHigh availability
A multicast non-stop forwarding (NSF) router architecture enhances high availability of a multicast router in a computer network. The router architecture further preserves multicast data forwarding through a data plane during NSF recovery of one or more failures in a control plane of the router. Various multicast components of the router cooperate to provide a checkpointing and recovery technique of the multicast NSF architecture that enables efficient restart and recovery of the control plane failures without loss of data connectivity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Software configurable cluster-based router using heterogeneous nodes as cluster nodes
ActiveUS7483998B2Increase capacityIncrease diversityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOff the shelfHeterogeneous network
A cluster router architecture and methods for performing distributed routing are presented. The cluster router architecture includes off-the shelf Personal Computer (PC) hardware-based router cluster nodes interconnected in an intra-connection network in multiple dimensions. Each PC-based router cluster node is provided with the same routing functionality and a router-cluster-node-centric configuration enabling each router cluster node to provide routing responses for packets pending processing. Packet processing is divided into entry packet processing and routing response processing; special processing; and exit processing. Exit packet processing is performed by router cluster nodes transmitting packets into communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Packet processing is interrupted on determining that special processing is required in respect of a packet, and the packet is handed over to a corresponding special purpose router cluster node.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Softrouter feature server
ActiveUS20060092935A1Remove complexityEasy to introduceData switching by path configurationExtensibilityOff the shelf
A network architecture includes one or more feature servers and control servers in a control plane that is logically separate from a data plane that includes forwarding elements. Feature servers facilitate adding network-based functionality in a centralized way that is has better scalability than the traditional router architecture. Some examples of network-based functionality are voice over IP, enhancing QoS support, scaling BGP route reflectors, network-based VPN support, scaling mobile IP support, introducing IPv6 into existing and future networks, and enhancing end-to-end network security. Feature servers remove complexity from routers, allow functions to be implemented on a standard-off-the-shelf server platform, facilitate easy introduction of value-added functions, and scale well.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
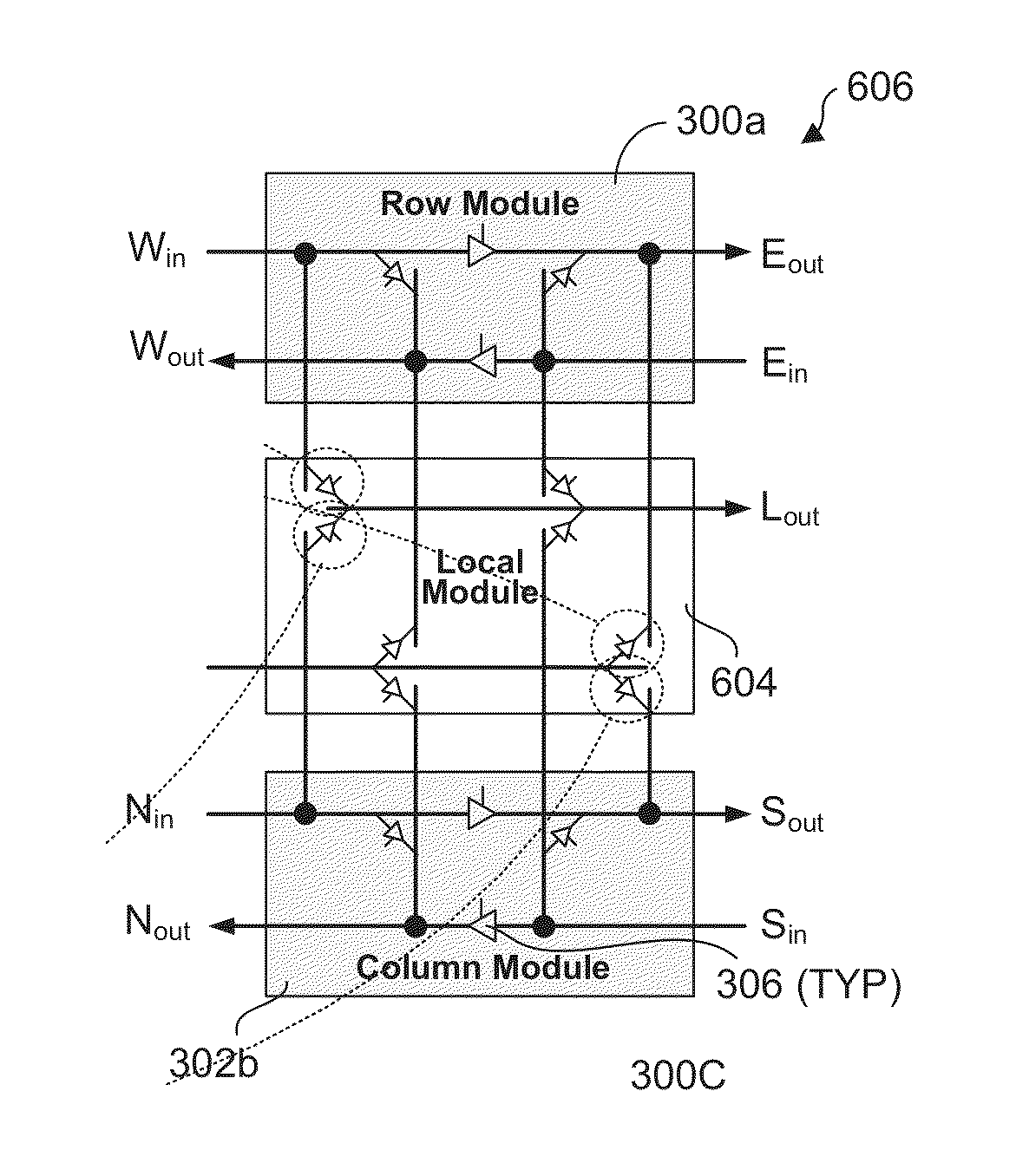
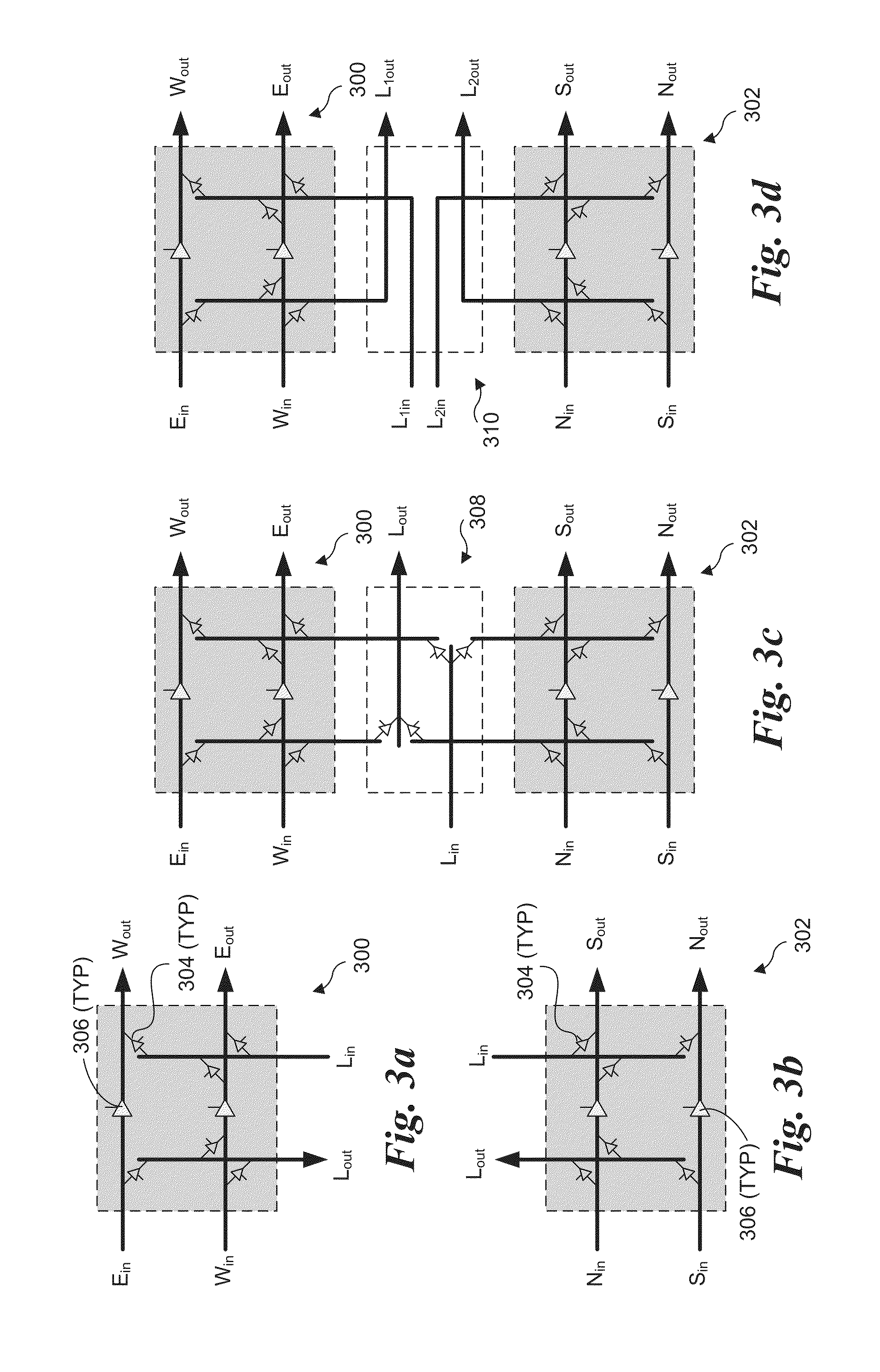
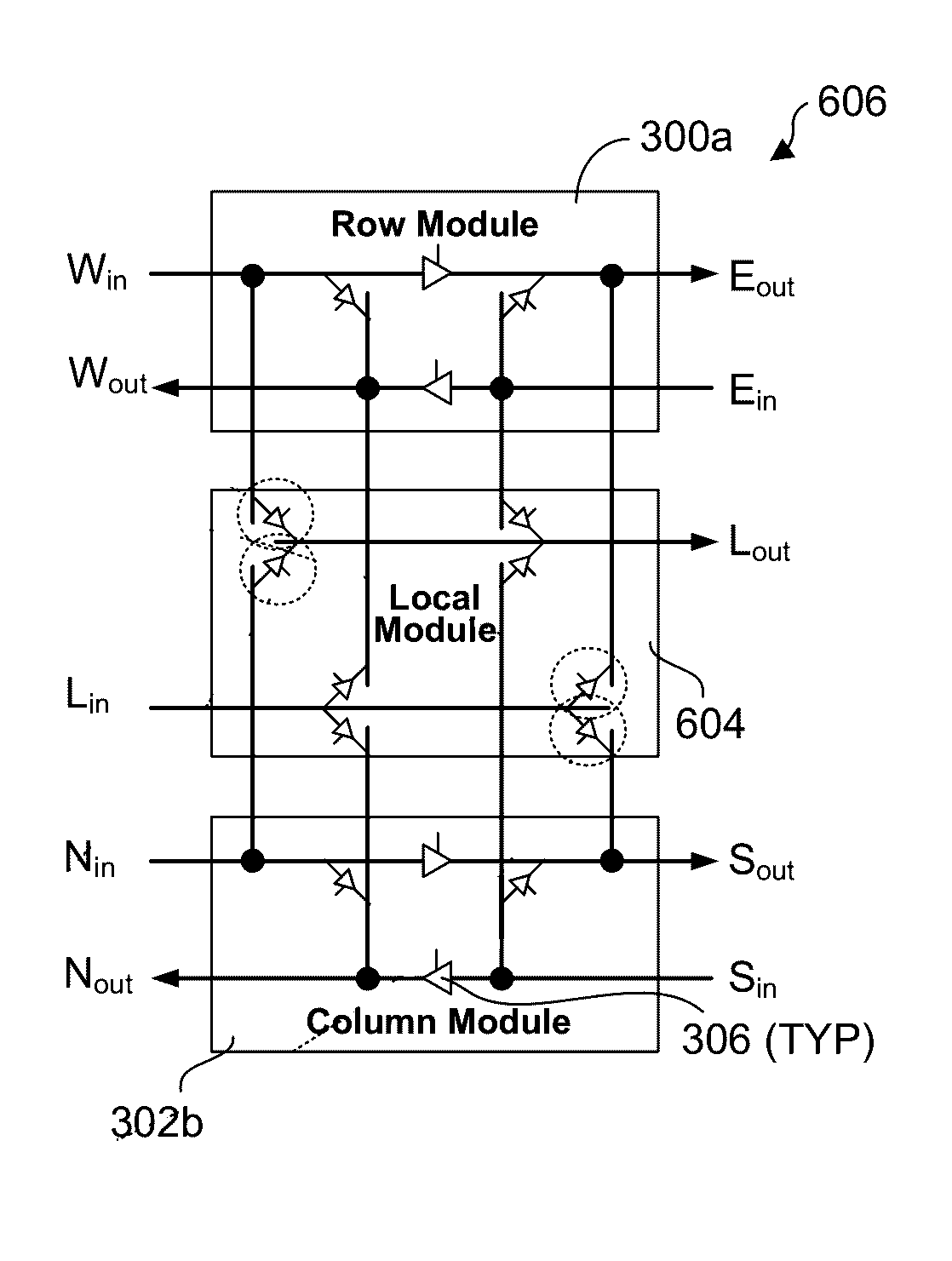
Modular decoupled crossbar for on-chip router
InactiveUS20140376557A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchComputer network
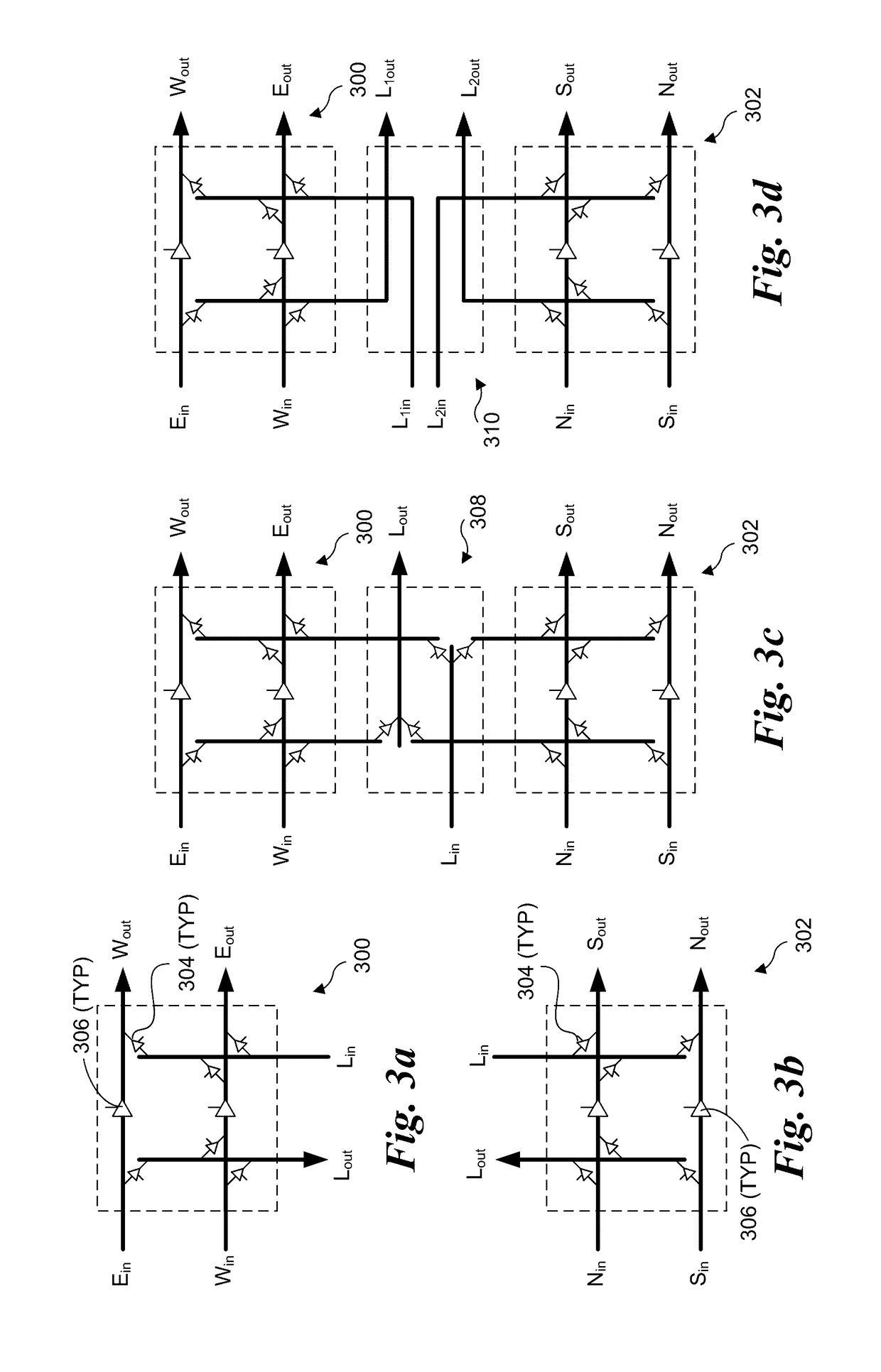
Layout-aware modular decoupled crossbar and router for on-chip interconnects and associated micro-architectures and methods of operation. A crossbar and router architecture called MoDe-X (Modular Decoupled Crossbar) is disclosed that supports 5-port routing for use in 2D mesh interconnects and is implemented through use of decoupled row and column sub-crossbar modules in combination with feeder wiring and control logic that enables routing between ports on the row and column sub-crossbar modules. The corresponding MoDe-X router supports 5-port routing between various router input and output port combinations while reducing both router area and power consumption when compared with a conventional 5×5 crossbar design and implementation. The MoDe-X micro-architecture can be configured to support both single and dual local port injection configurations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Route/service processor scalability via flow-based distribution of traffic
InactiveUS6853638B2Increase volumeHigh interface rateError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityExtensibility
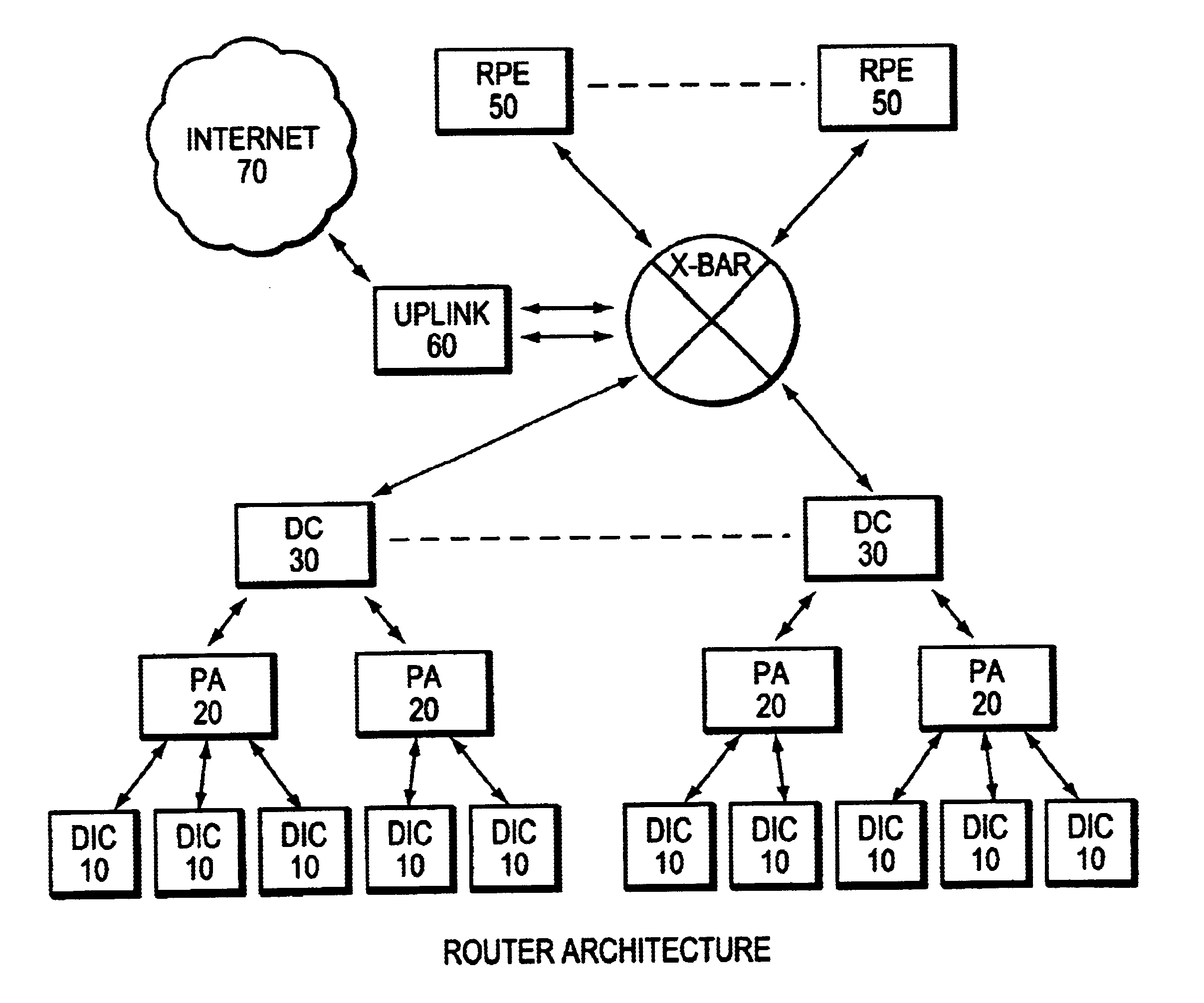
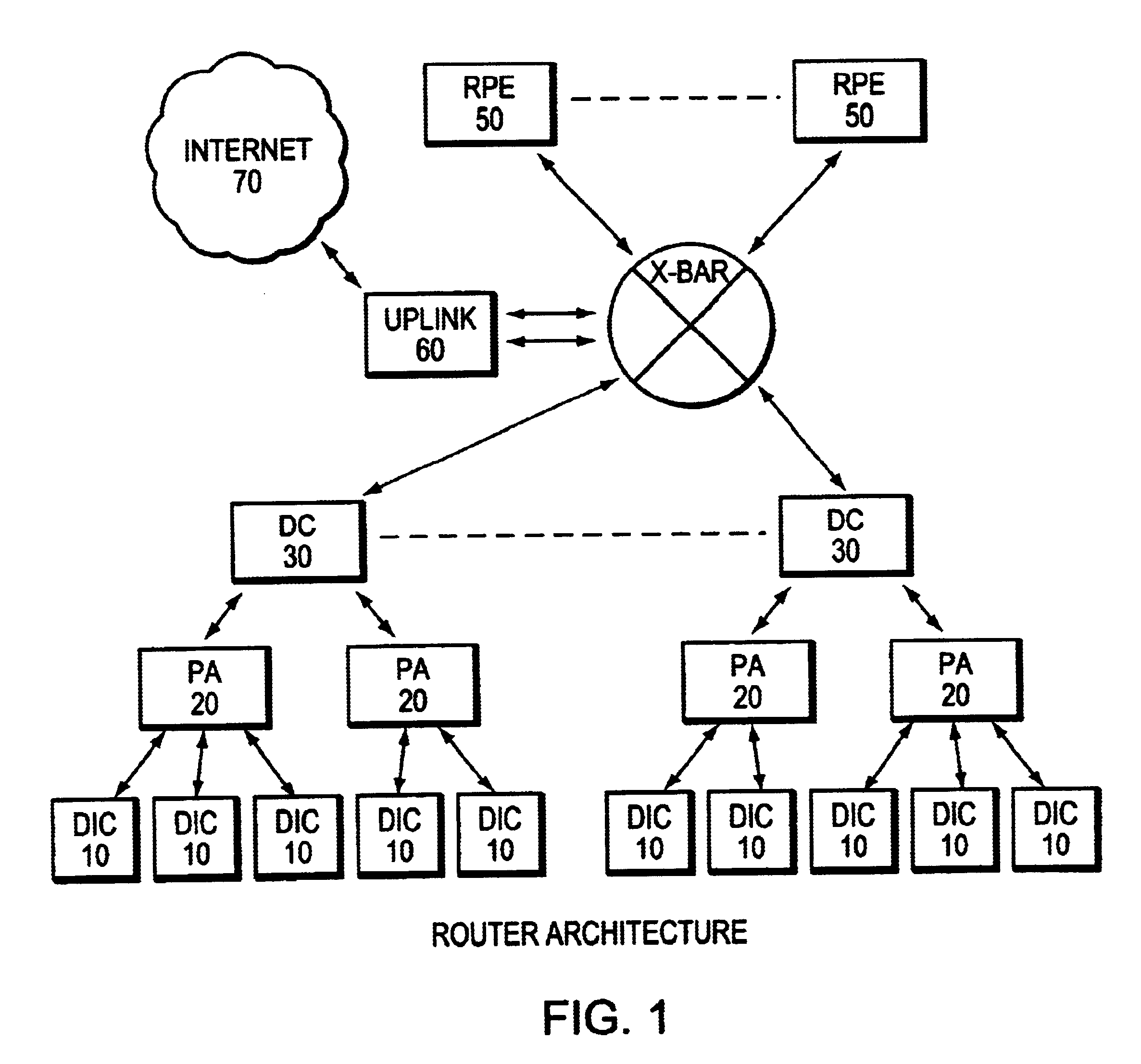
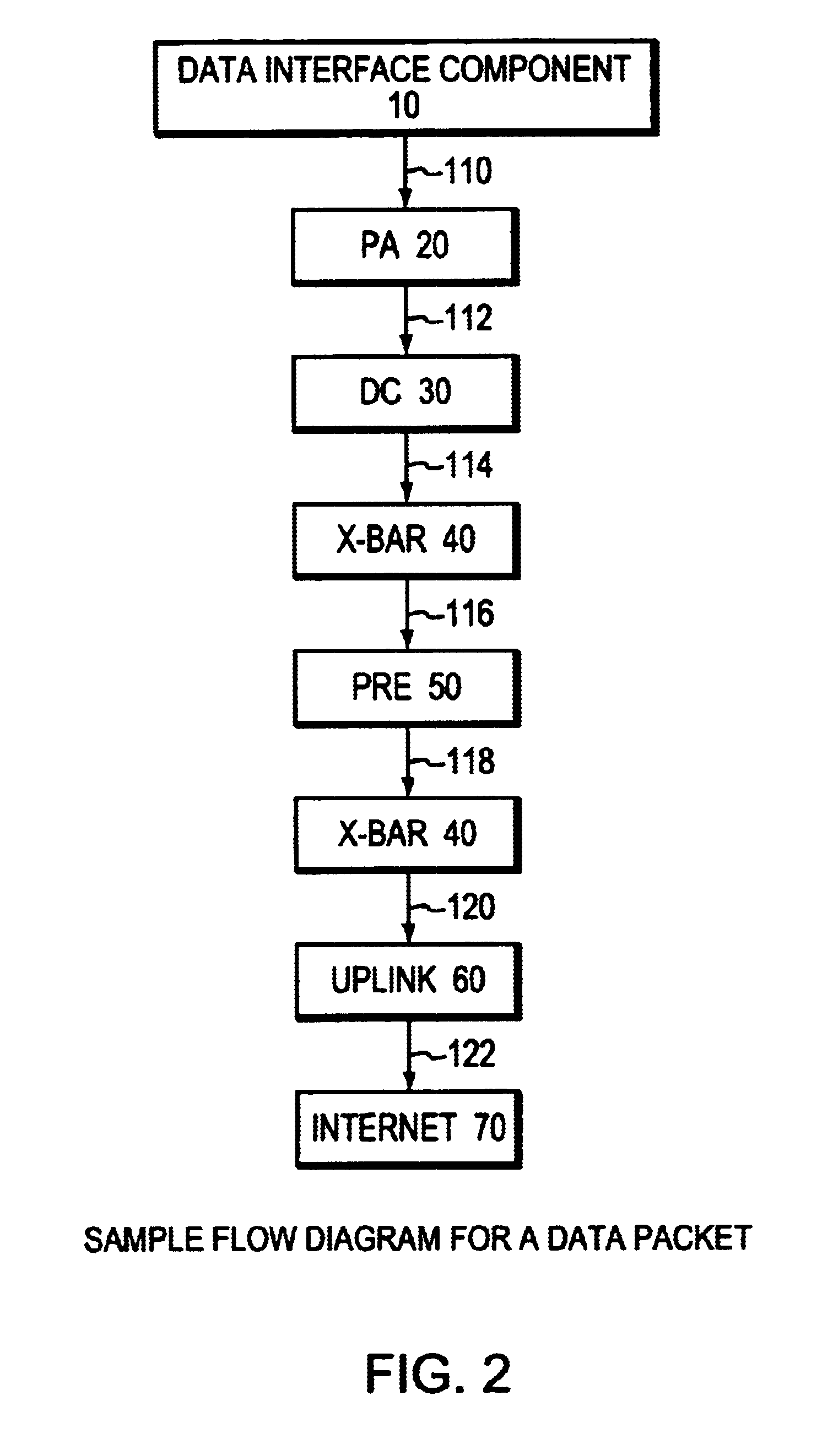
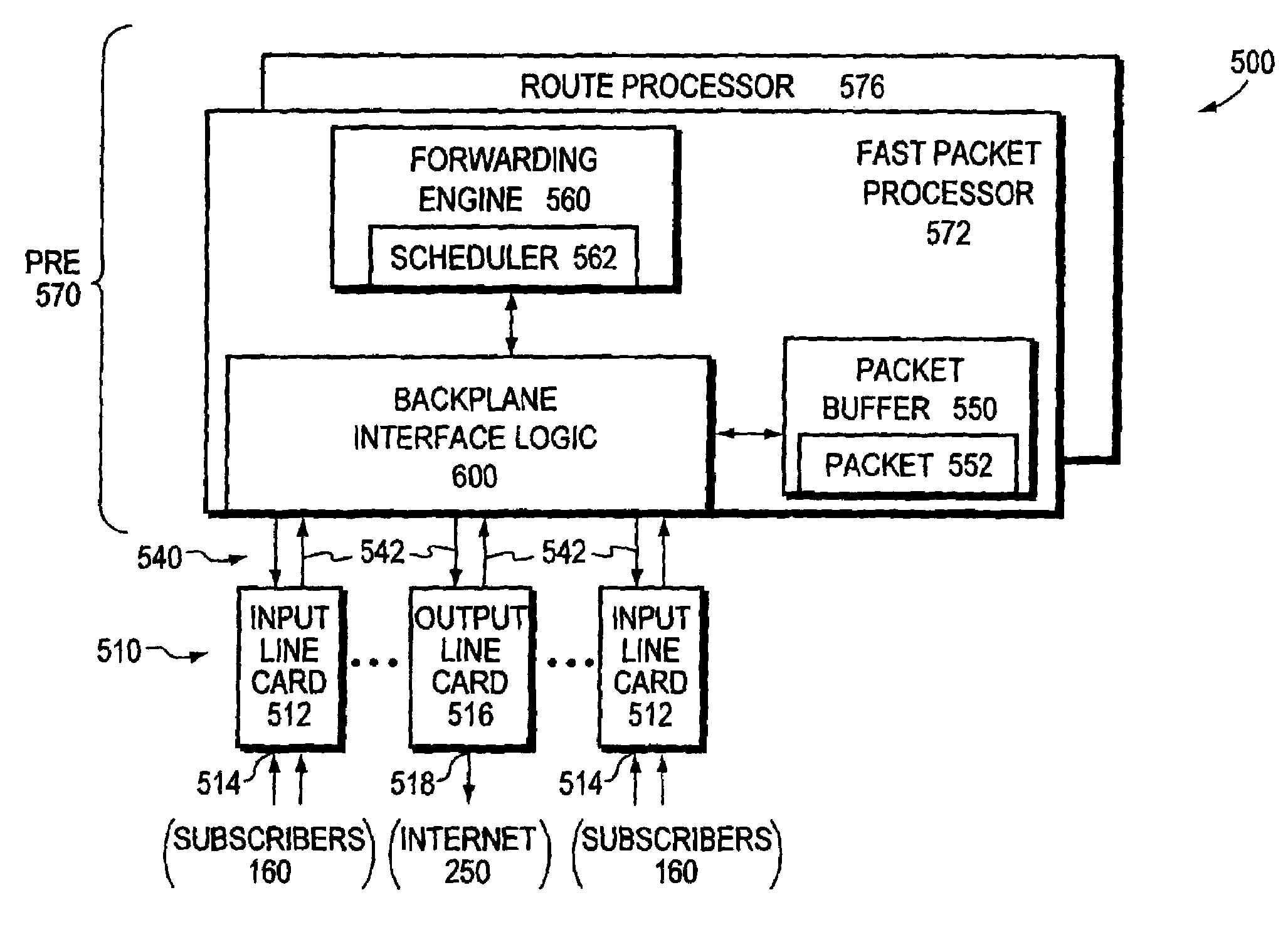
The invention provides a router architecture that is scalable, that is, as more processing power is desired, more individual processors can be added. The data flow from each line can be distributed among all of the processors in the system. As desired services are added, increasing the amount of “touch” or processing performed on the packets in the system, more processors can be added to carry the increased load. The router architecture is also able to distribute the high interface rate of an uplink connection in the same manner. Packets are allocated to processors in a manner that allows the original order of data packets within the same flow to be maintained. The system uses a hash function to distribute the flows, making sure that packets within the same flow are sent to the same processor so that the original packet order in each flow is maintained. Different flows may be sent to different processors.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
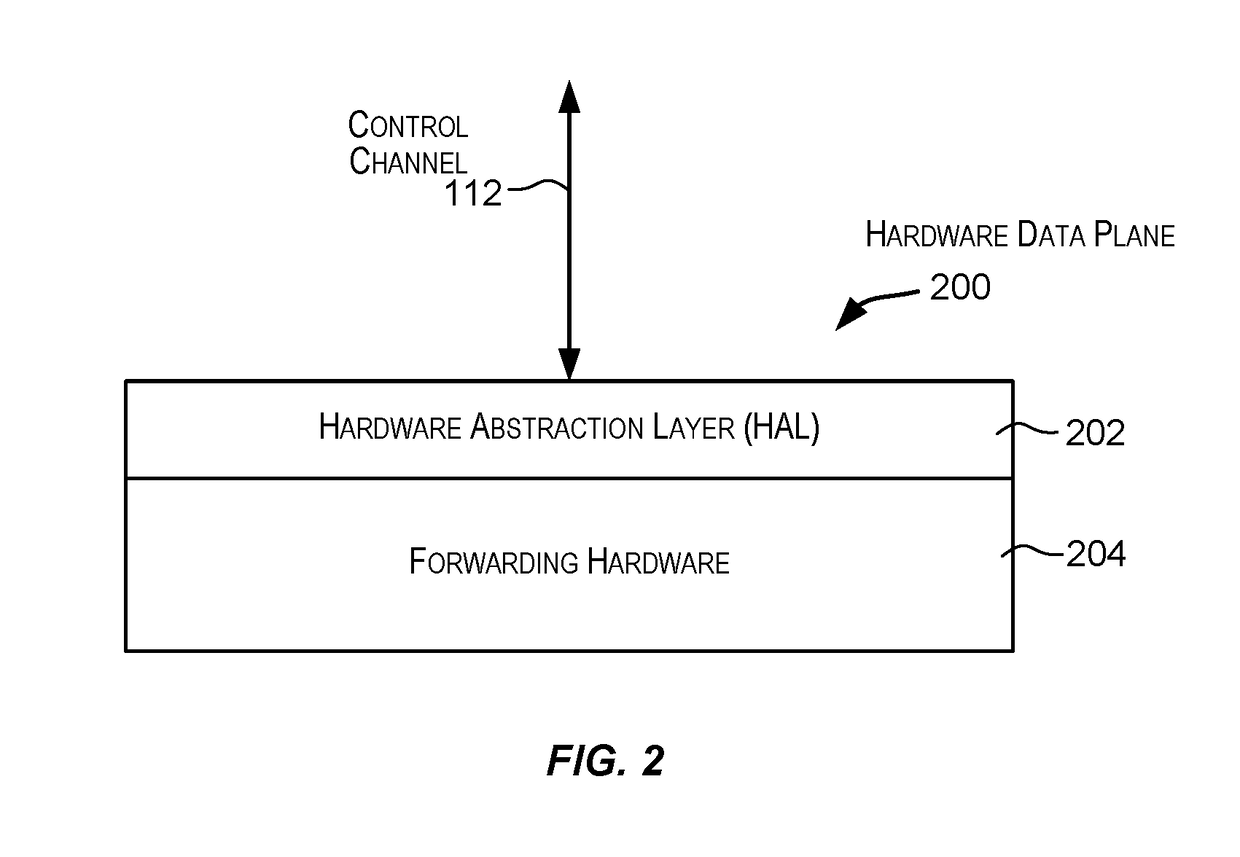
High performance interface logic architecture of an intermediate network node
ActiveUS7286532B1Improve congestionImprove latencyData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceUser input
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Route/service processor scalability via flow-based distribution of traffic
InactiveUS20020097736A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityHash function
The invention provides a router architecture that is scalable, that is, as more processing power is desired, more individual processors can be added. The data flow from each line can be distributed among all of the processors in the system. As desired services are added, increasing the amount of "touch" or processing performed on the packets in the system, more processors can be added to carry the increased load. The router architecture is also able to distribute the high interface rate of an uplink connection in the same manner. Packets are allocated to processors in a manner that allows the original order of data packets within the same flow to be maintained. The system uses a hash function to distribute the flows, making sure that packets within the same flow are sent to the same processor so that the original packet order in each flow is maintained. Different flows may be sent to different processors.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
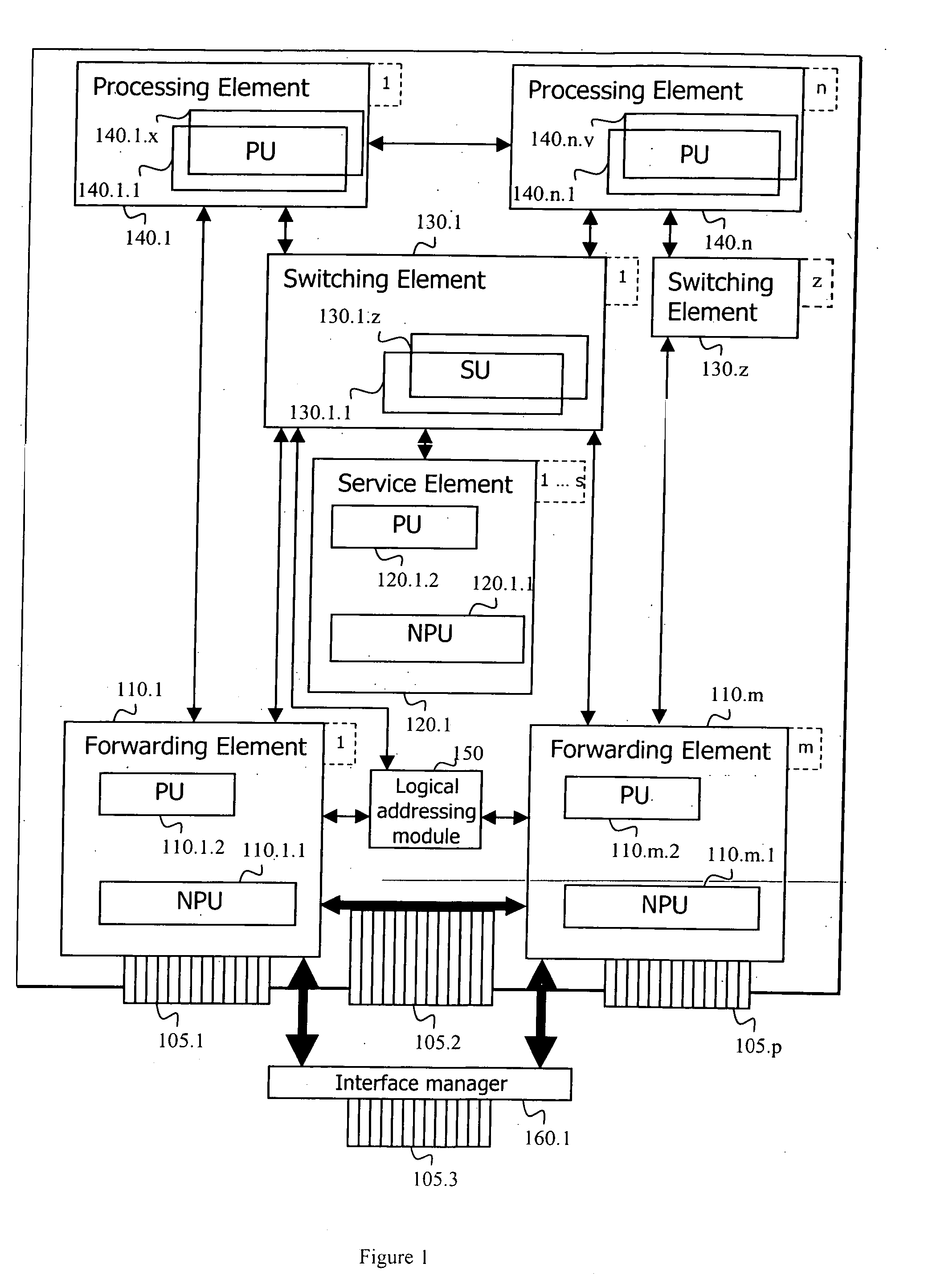
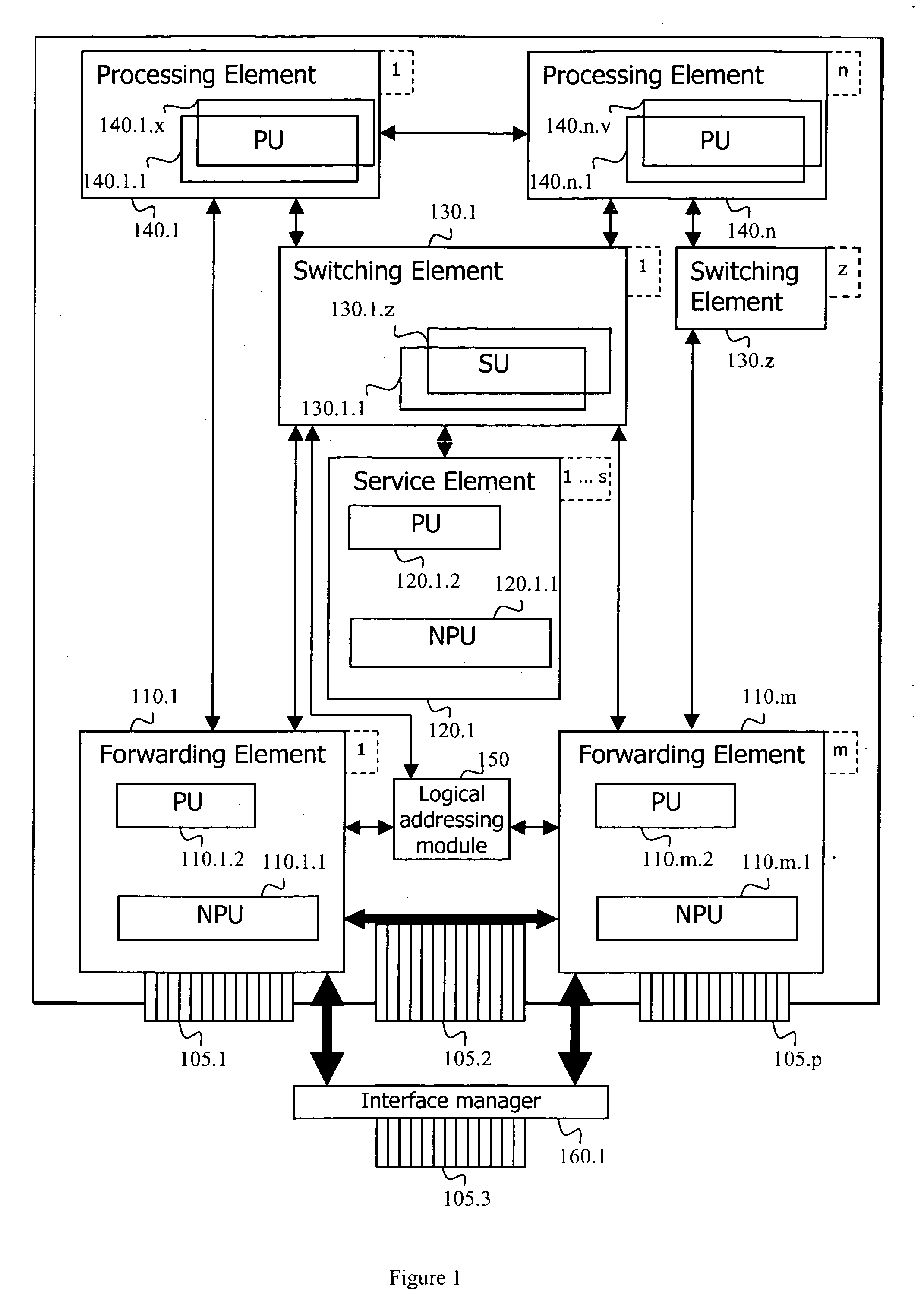
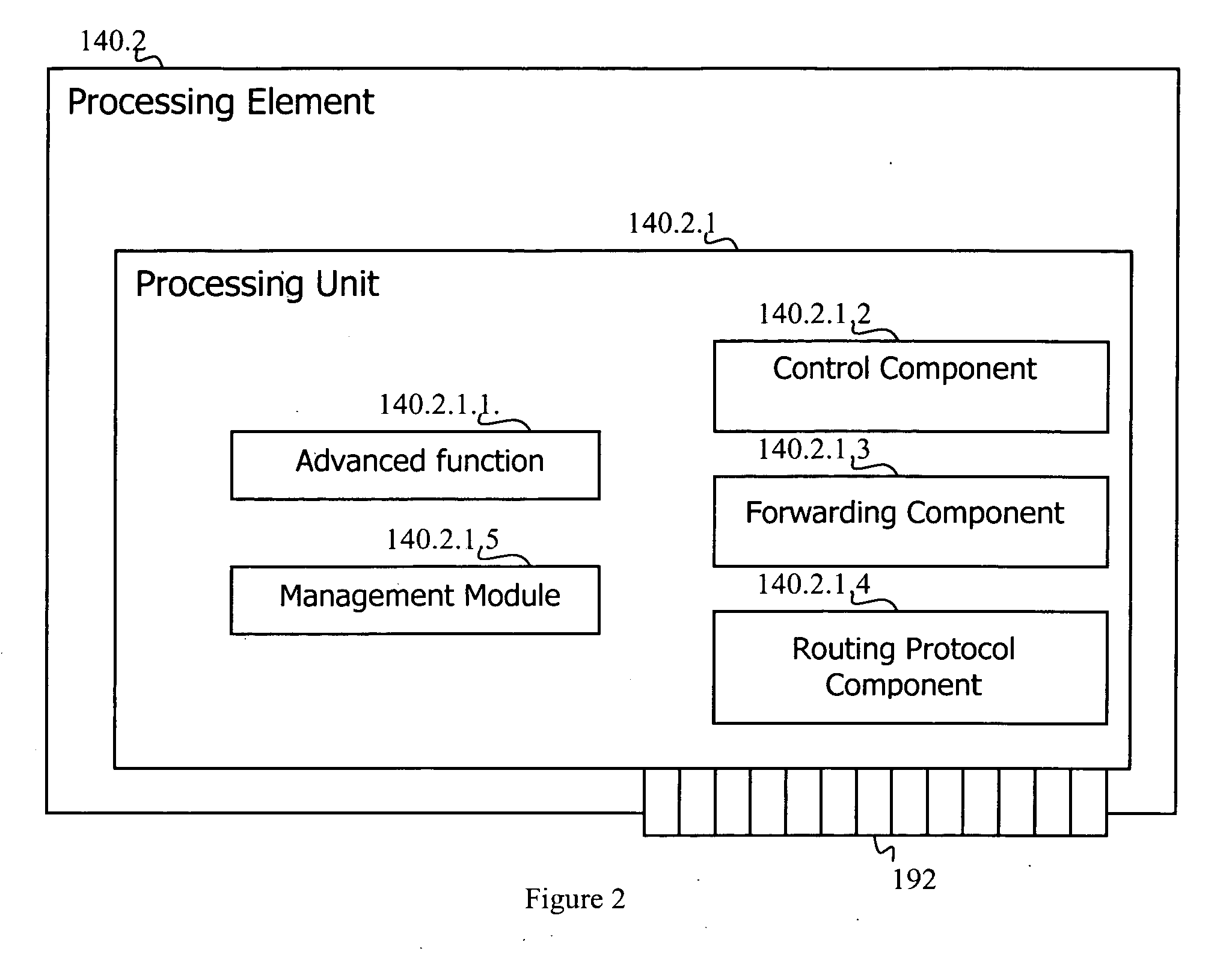
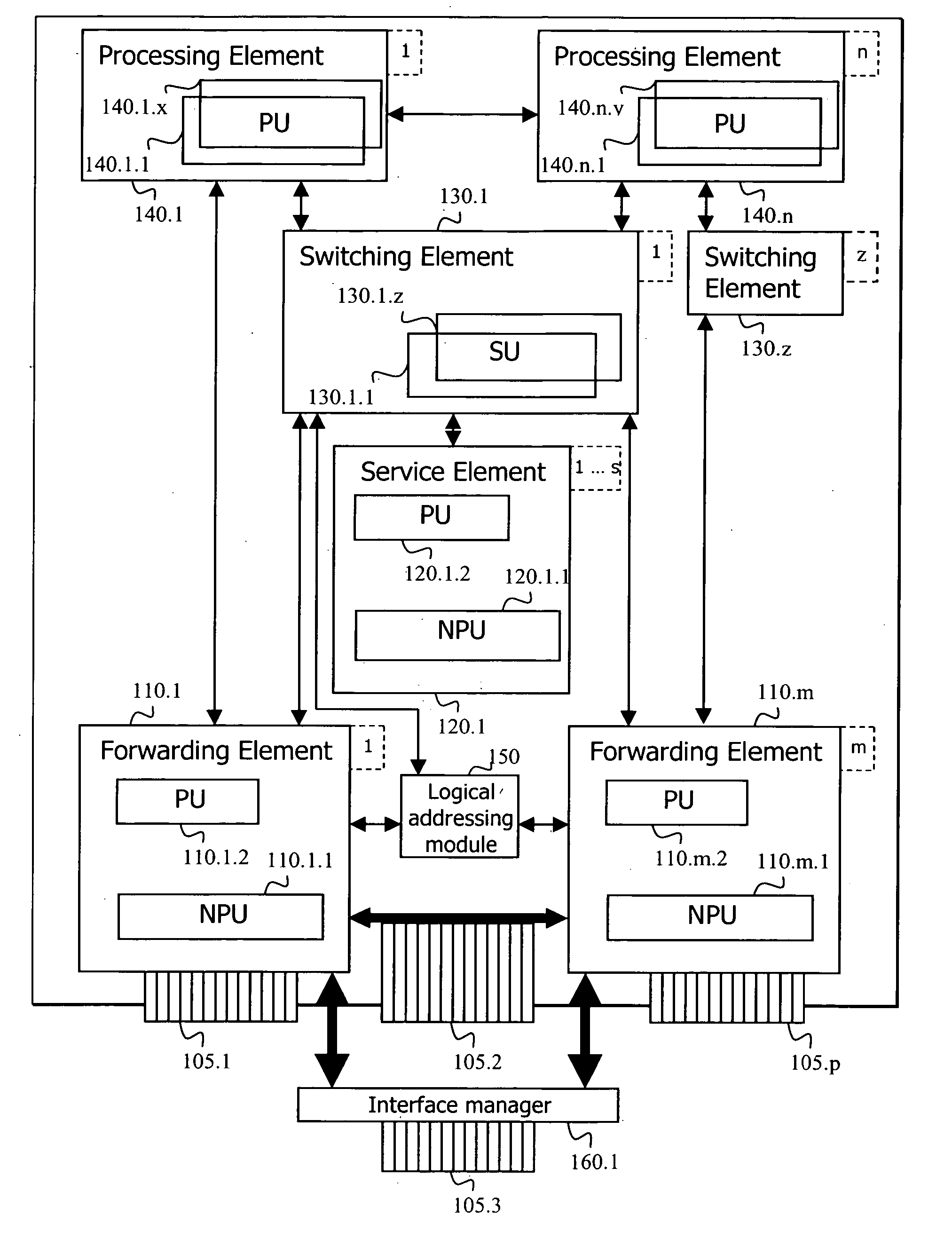
Adaptive router architecture enabling efficient internal communication
A router comprising a plurality of elements, each having an element identifier, subdivided into a plurality of groups of at least one element. Each group has a common identifier and each member within each group shares redundant capabilities. Each element is capable of communicating with another element by addressing information to the common identifier instead of the element identifier. Optionally, one element can be a member of more than one group. Another option suggests that all elements within a group share essential information associated with a service provided by the group. Another option is implemented through one element of the router identifying a primary element for a group, wherein the primary element serves requests addressed the corresponding common identifier. Yet another option suggests that one element is identified through configuration of the router as a primary element in its group to serve requests addressed to the common identifier.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus and method for classifying traffic in a distributed architecture router
InactiveUS20050053074A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationData packEngineering
A router for interconnecting N interfacing peripheral devices. The router comprises a switch fabric and routing nodes coupled to the switch fabric. Each routing node comprises: i) a plurality of physical medium device (PMD) modules for transmitting data packets to and receiving data packets from selected ones of the N interfacing peripheral devices; ii) an input-output processing (IOP) module coupled to the PMD modules and the switch fabric for routing the data packets between the PMD modules and the switch fabric and between the PMD modules; and iii) a classification module associated with the IOP module for classifying a first data packet received from the IOP module. The classification module causes the IOP module to forward the first data packet based on the classification. The router architecture incorporates streams-based billing support, firewall capabilities, and data surveillance functionality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
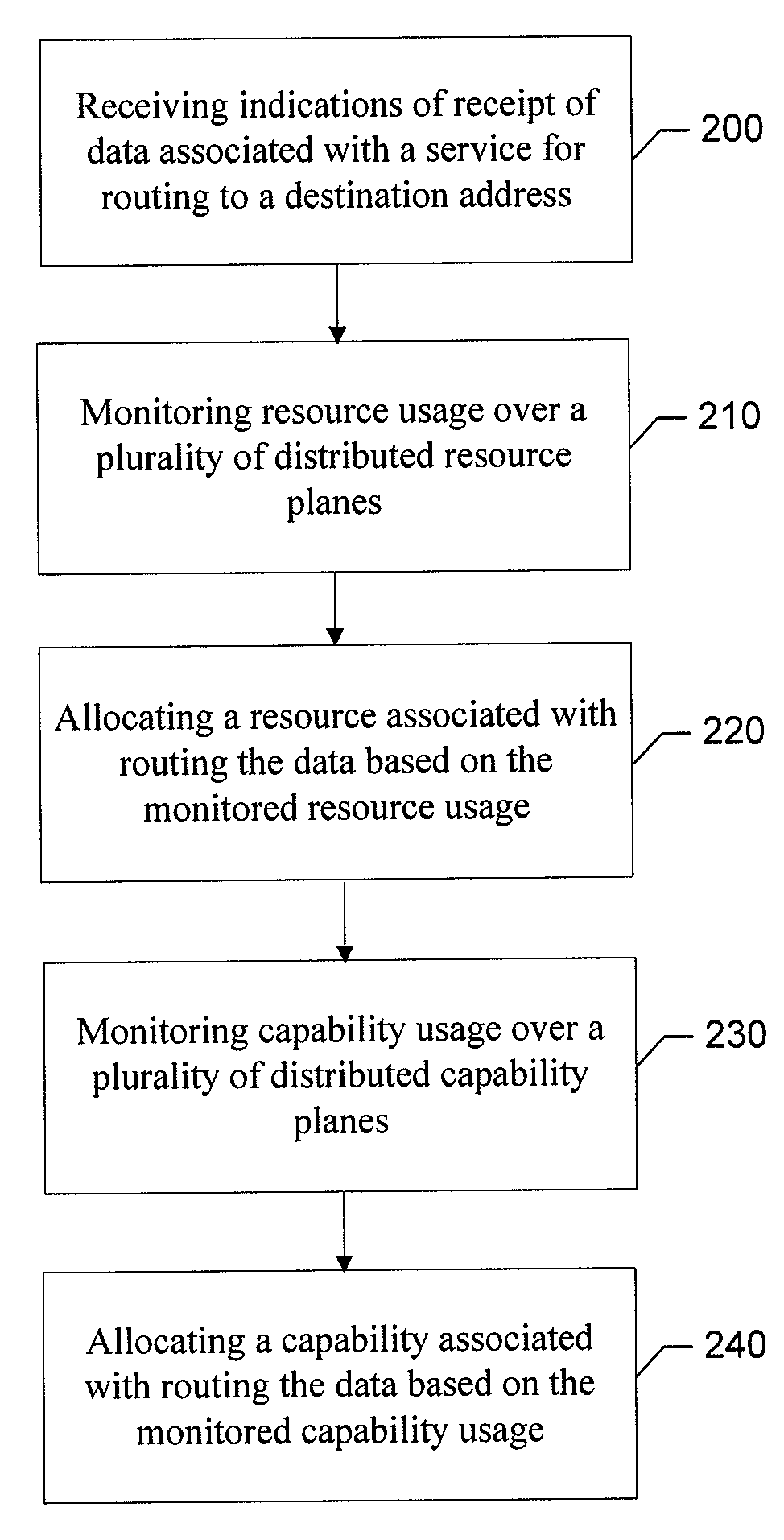
Method, computer program product, and apparatus for providing a distributed router architecture
An apparatus for providing a distributed router architecture includes a processing element and a resource availability element. The processing element may be configured to receive indications of receipt of data associated with a service for routing to a destination address. The resource availability element may be in communication with the processing element and may be configured to monitor resource usage over a plurality of distributed resource planes. The processing element may be further configured to allocate a resource associated with routing the data based on the monitored resource usage.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
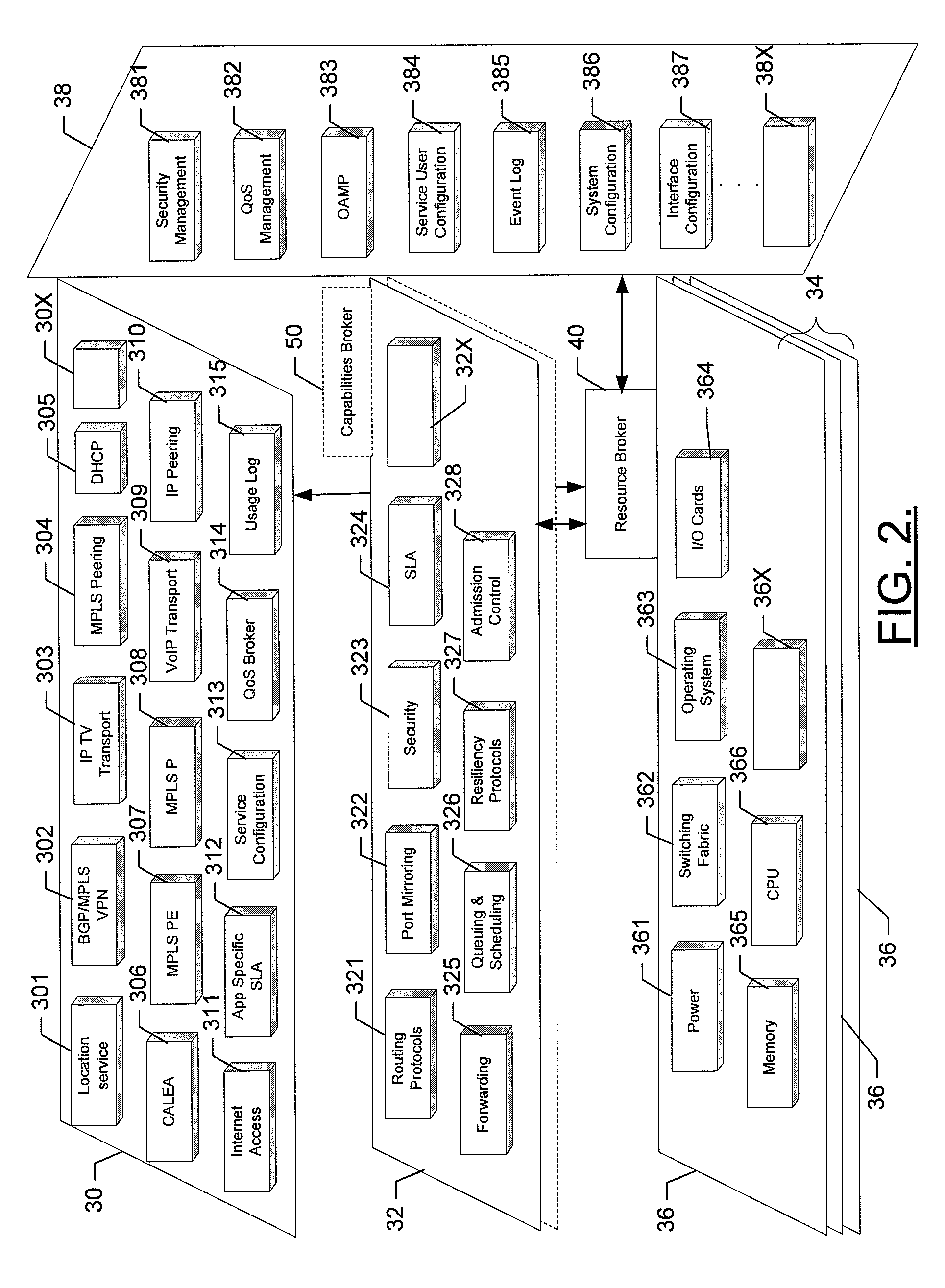
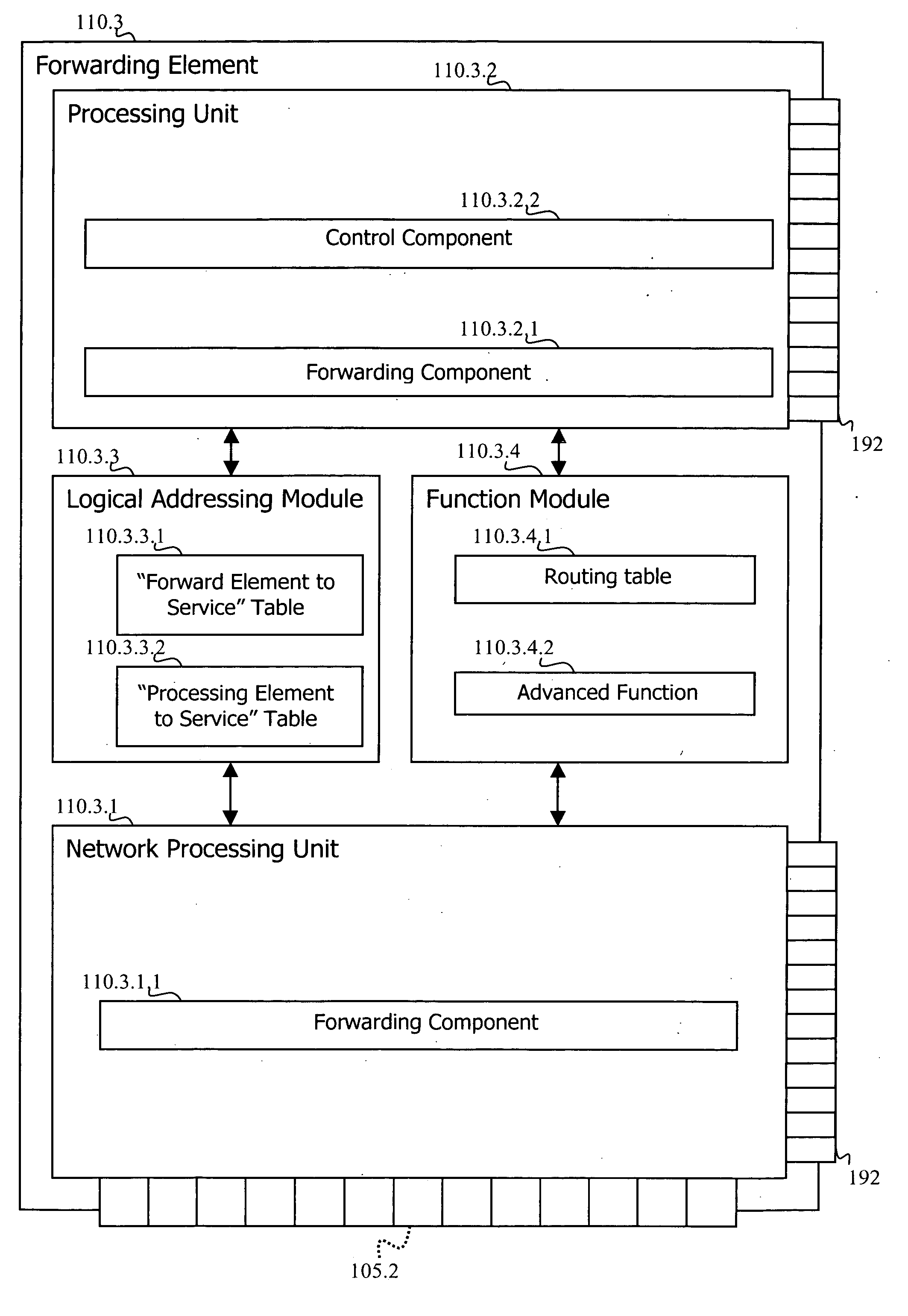
Adaptive router architecture using logical internal addressing
ActiveUS20060140194A1Hybrid switching fabricsData switching by path configurationAdaptive routingSelf adaptive
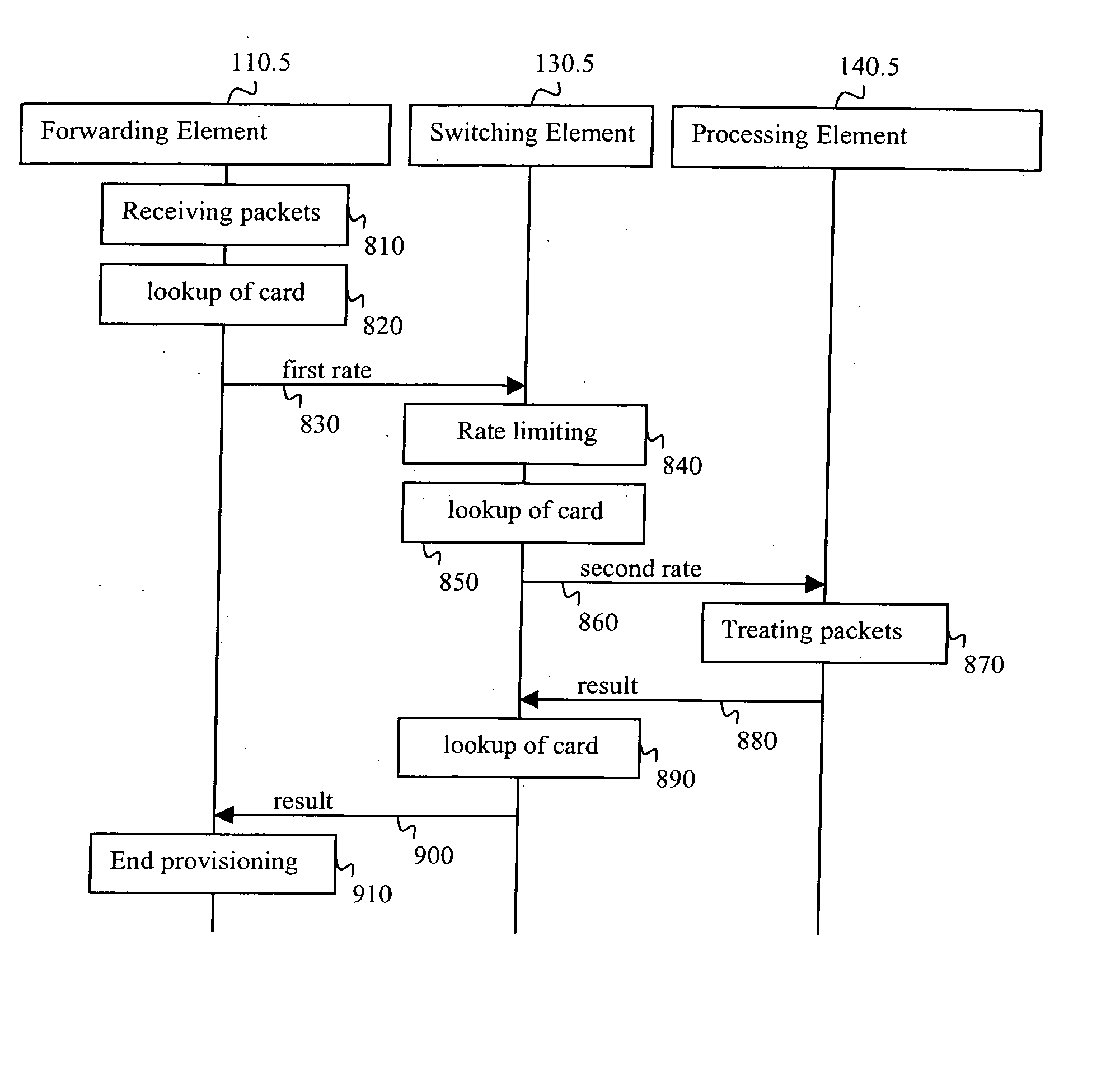
A method and a related router comprising a network interface, a logical addressing module and a forwarding element card. The logical addressing module is capable of maintaining at least one local table associating at least one card of the router with at least a portion of at least one service provided by the router. The forwarding element card is capable of receiving a packet stream on the network interface, detecting that the packet stream requires further treatment from a further card of the router and, upon detection, consulting the local table to find an identifier, to which the further card is linked, based on information found in the packet stream before forwarding the packet stream toward the further card.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
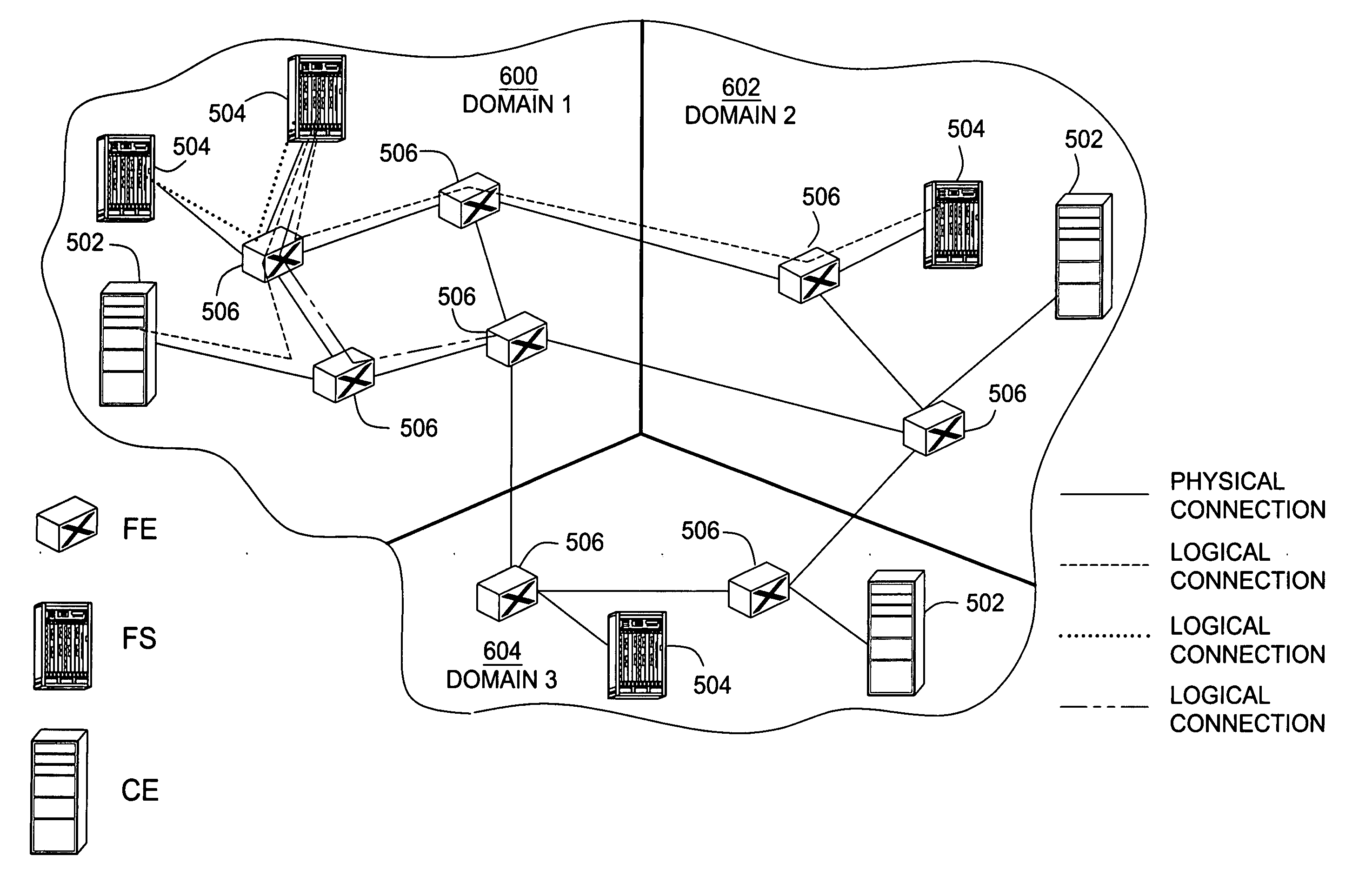
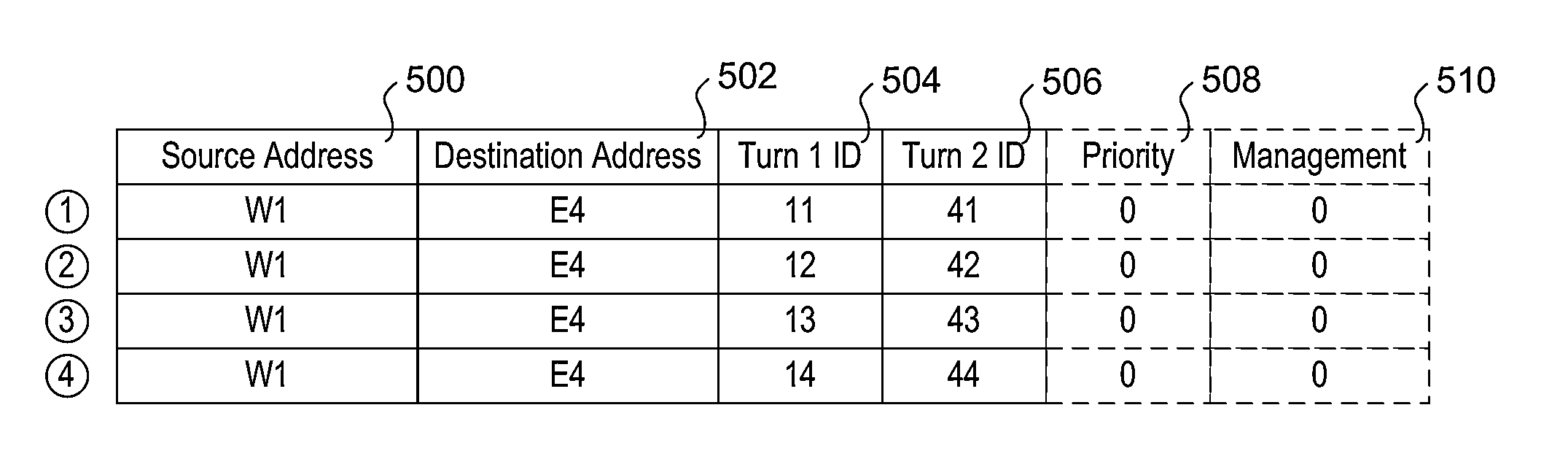
Routing coordination protocol for a massively parallel router architecture
InactiveUS7254111B2Reduce traffic problemsReduce decreaseError preventionTransmission systemsMassively parallelComputer network
A parallel router comprising: 1) a plurality of routing nodes, each of the plurality of routing nodes capable of receiving message packets from and transmitting message packets to external devices, wherein each of the routing nodes maintains a routing table suitable for routing message packets from transmitting ones of the plurality of routing nodes to receiving ones of the plurality of routing nodes; and 2) a switch fabric capable of transmitting the messages packets between the transmitting nodes and the receiving nodes, wherein a designated one of the plurality of routing nodes is operable to receive from non-designated ones of the plurality of routing nodes link state advertisement (LSA) message packets containing link state information, wherein the designated routing node aggregates the LSA message packets to thereby form a link-state database.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
IPSecVPN (Internet Protocol Security Virtual Private Network) realizing system and method based on NetFPGA (Net Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN102065021AImprove processing speedRealize forwarding functionNetworks interconnectionData streamControl layer
The invention relates an IPSec VPN (Internet Protocol Security Virtual Private Network) realizing system and method based on a NetFPGA (Net Field Programmable Gate Array), wherein a control layer of a router is additively provided with an IKE (Internet Key Exchange) module, a security relation database mapping module and a security policy database, and a key management module is used for dynamically managing the key, the security relation and the security policy; and a forward layer is additionally provided with two independently designed IPSec input and output process modules in the originalNetFPGA standard router architecture by sufficiently utilizing the modularization reusable idea of a NetPGA development board. The scheme of the invention can realize the route forward function of the data flow in a hardware manner, and can also realize the great mass of calculation functions required by the IPSecVPN in a hardware manner, such as safe detaching / packing load and completeness authentication; in addition, the invention can effectively make a compromise on the data flow forward performance and the IPSec protocol processing performance.
Owner:北京地平线轨道技术有限公司
Software configurable cluster-based router using stock personal computers as cluster nodes
InactiveUS7436775B2Increase capacityIncrease diversityError preventionTransmission systemsTorus interconnectPersonal computer
A cluster router architecture and methods for performing distributed routing is presented. Implementations include off-the shelf Personal Computer (PC) hardware. The cluster router architecture includes PC-based router cluster nodes toroidally interconnected in an intra-connection network in multiple dimensions. The cluster router may further make use of a management node. Each router cluster node is provided with the same routing functionality and a node centric configuration enabling each router cluster node by itself or multiple router cluster nodes in the cluster router to provide routing responses for packets pending processing. The method divides packet processing into entry packet processing and routing response processing; and exit processing. Entry packet processing and routing response processing is performed by router cluster nodes receiving packets from communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Exit packet processing is performed by router cluster nodes transmitting packets into communication networks in which the cluster router participates. Advantages are derived from: a configurable, and scalable cluster router design providing a high routing capacity using cost effective stock PC hardware; from the toroidal topology of the intra-connection network which provides a high degree of diversity ensuring resilience to equipment failure, and from the use of the star topology of the management links which reduces management overheads in the intra-connection network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method, computer program product, and apparatus for providing a distributed router architecture
ActiveUS7656797B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProcessing elementDistributed computing
An apparatus for providing a distributed router architecture includes a processing element and a resource availability element. The processing element may be configured to receive indications of receipt of data associated with a service for routing to a destination address. The resource availability element may be in communication with the processing element and may be configured to monitor resource usage over a plurality of distributed resource planes. The processing element may be further configured to allocate a resource associated with routing the data based on the monitored resource usage.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
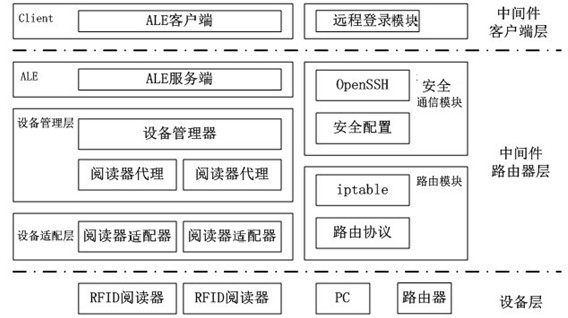
An RFID router architecture system
InactiveCN102281197AEasy to call remotelySolve the current situation of insufficient network integrationData switching networksClient-sideMiddleware
The invention belongs to the technical field of RFID, and in particular relates to an RFID router architecture system. It includes the middleware client layer that provides the RFID intermediate call interface and the remote login function of the RFID router; the middleware router layer responsible for providing the core middleware function, routing function and security configuration function of the RFID router; including the RFID middleware control The device layer of the reader, the computer participating in the networking and the router; the middleware client layer, the middleware router layer and the device layer are connected in sequence. The invention effectively solves the problem of insufficient combination of the RFID middleware and the RFID network, and provides technical support for introducing the RFID reader into the internal network of the enterprise and self-organizing and constructing the RFID network meeting the requirements of the enterprise.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
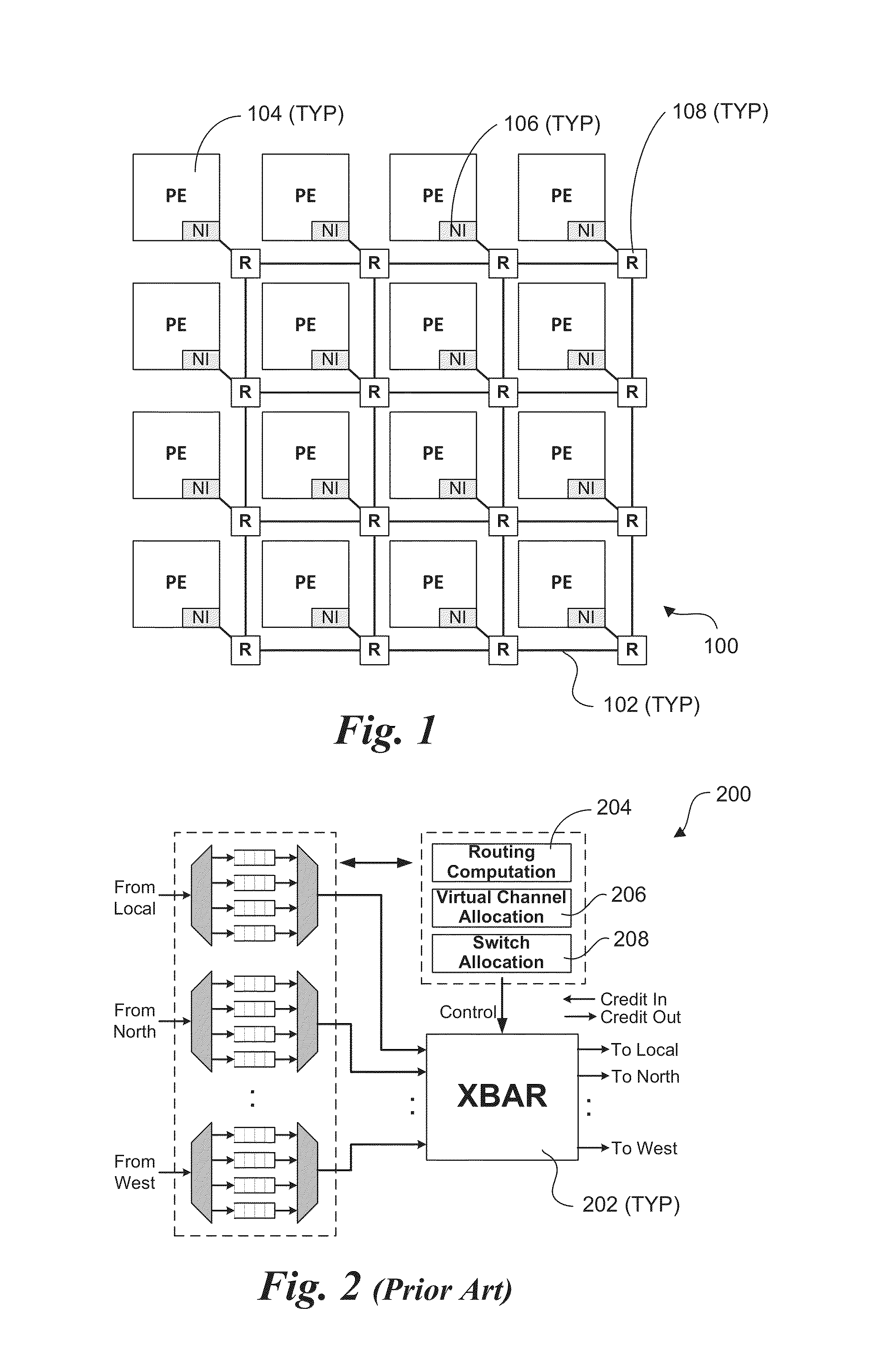
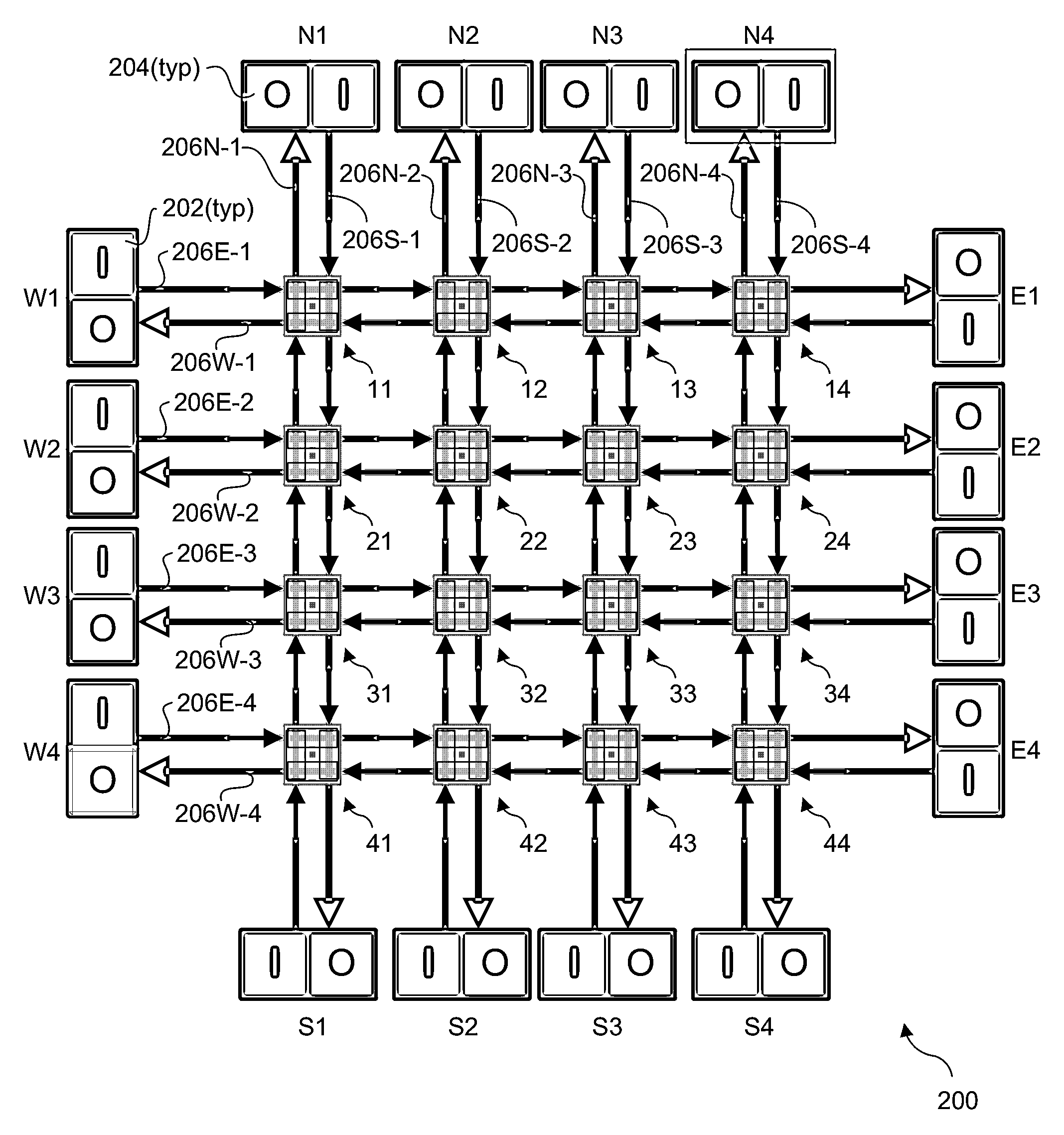
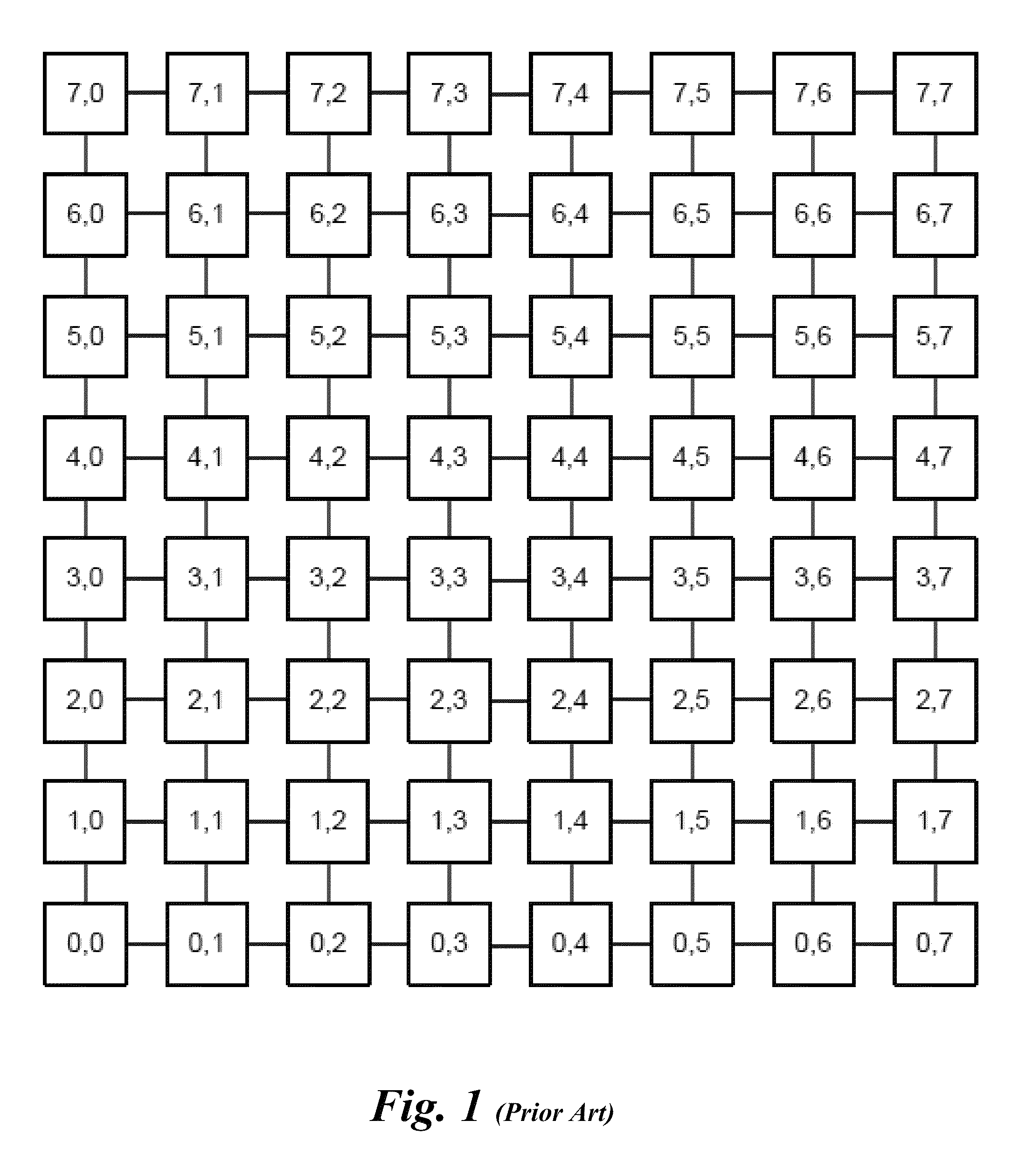
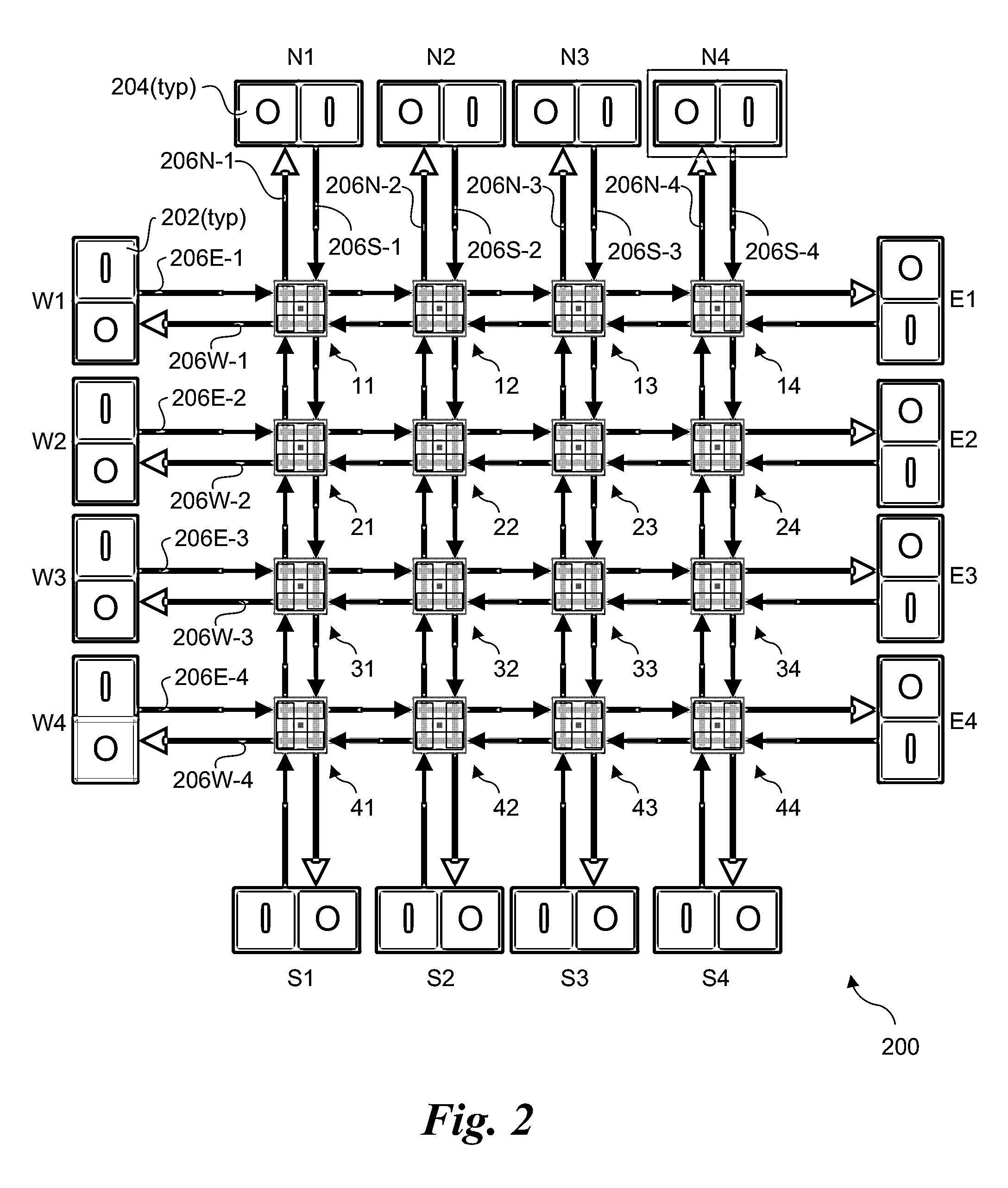
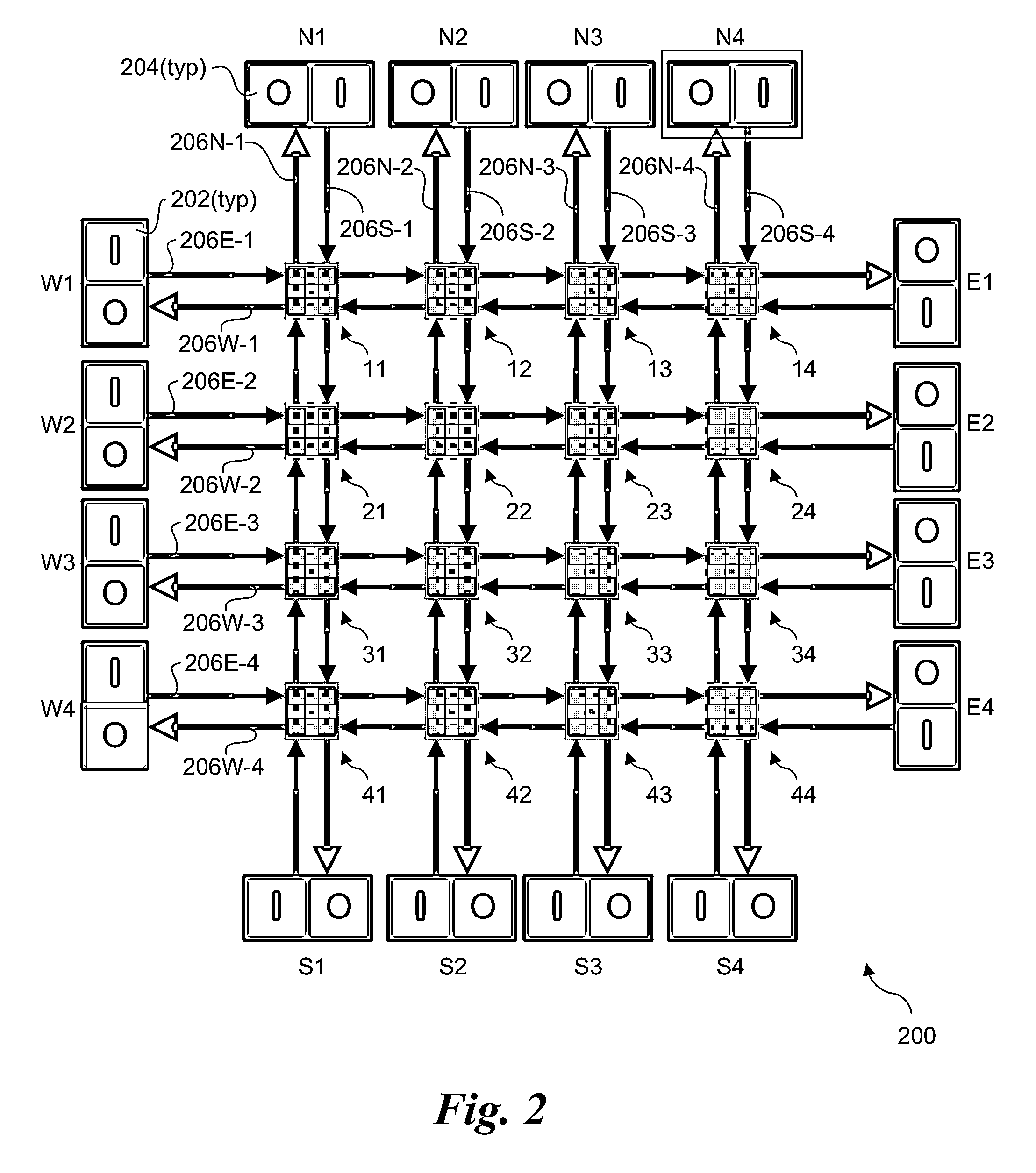
Scalable multi-layer 2D-mesh routers
Architectures, apparatus and systems employing scalable multi-layer 2D-mesh routers. A 2D router mesh comprises bi-direction pairs of linked paths coupled between pairs of IO interfaces and configured in a plurality of rows and columns forming a 2D mesh. Router nodes are located at the intersections of the rows and columns, and are configured to forward data units between IO inputs and outputs coupled to the mesh at its edges through use of shortest path routes defined by agents at the IO interfaces. Multiple instances of the 2D meshes may be employed to support bandwidth scaling of the router architecture. One implementation of a multi-layer 2D mesh is built using a standard tile that is tessellated to form a 2D array of standard tiles, with each 2D mesh layer offset and overlaid relative to the other 2D mesh layers. IO interfaces are then coupled to the multi-layer 2D mesh via muxes / demuxes and / or crossbar interconnects.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Modular decoupled crossbar for on-chip router
InactiveUS9674114B2Energy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationComputer networkModularity
Owner:INTEL CORP
Scalable multi-layer 2d-mesh routers
InactiveUS20150003281A1Data switching by path configurationComputer graphics (images)Crossover switch
Architectures, apparatus and systems employing scalable multi-layer 2D-mesh routers. A 2D router mesh comprises bi-direction pairs of linked paths coupled between pairs of IO interfaces and configured in a plurality of rows and columns forming a 2D mesh. Router nodes are located at the intersections of the rows and columns, and are configured to forward data units between IO inputs and outputs coupled to the mesh at its edges through use of shortest path routes defined by agents at the IO interfaces. Multiple instances of the 2D meshes may be employed to support bandwidth scaling of the router architecture. One implementation of a multi-layer 2D mesh is built using a standard tile that is tessellated to form a 2D array of standard tiles, with each 2D mesh layer offset and overlaid relative to the other 2D mesh layers. IO interfaces are then coupled to the multi-layer 2D mesh via muxes / demuxes and / or crossbar interconnects.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multilayered distributed router architecture
Owner:CIENA
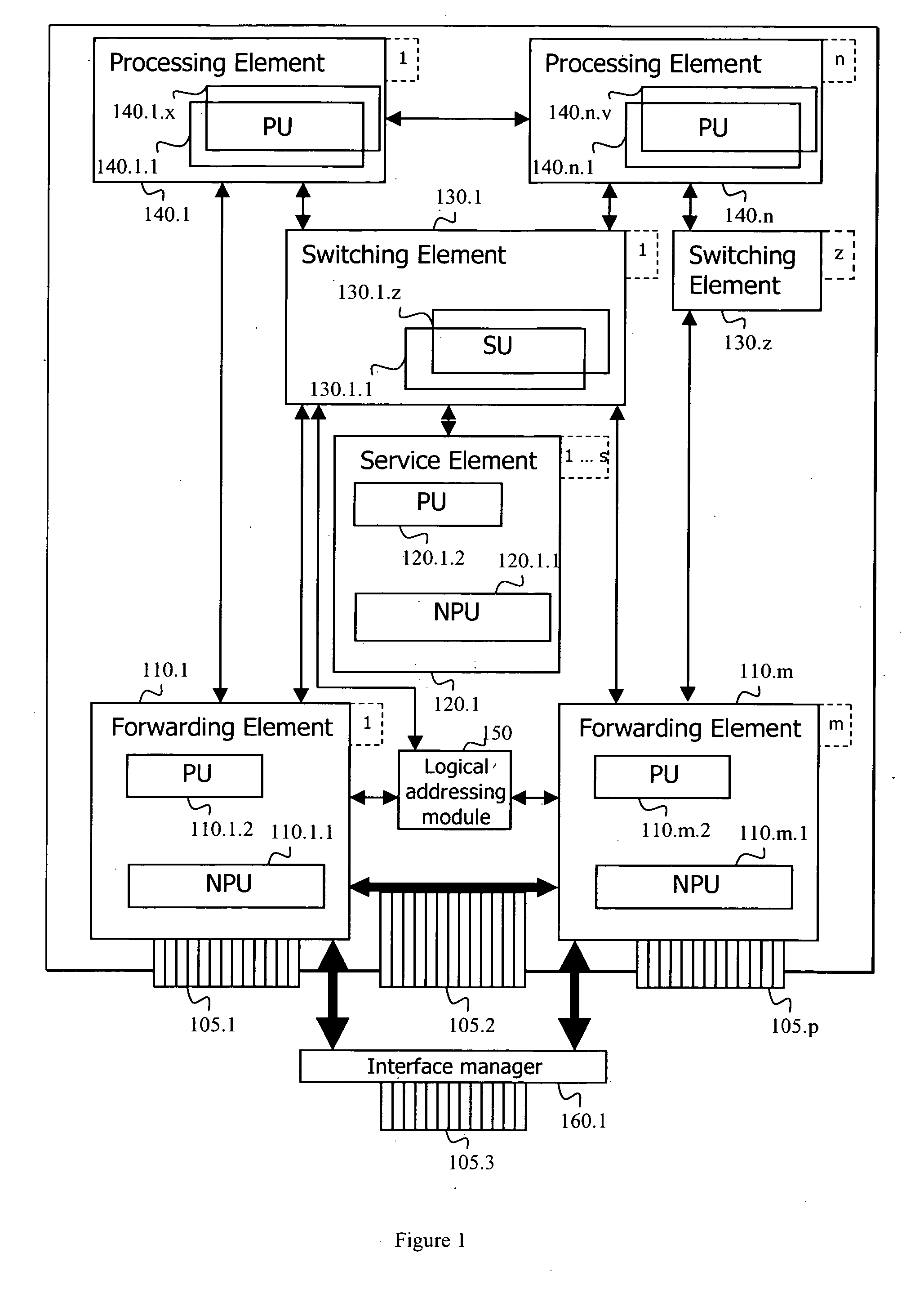
Adaptive router architecture
A router and a router architecture comprising at least one network interface, a plurality of processing elements, at least one switching element and a plurality of forwarding elements. Each of the plurality of processing elements comprises at least one processing unit, wherein each processing unit is capable of processing network traffic to provide at least a portion of a network service. The switching element is capable of acting as a proxy of the plurality of processing elements while each of the plurality of forwarding elements is capable of receiving network traffic on the at least one network interface of the router and delegating processing of network traffic toward at least one of the plurality of processing elements through the at least one switching element.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com