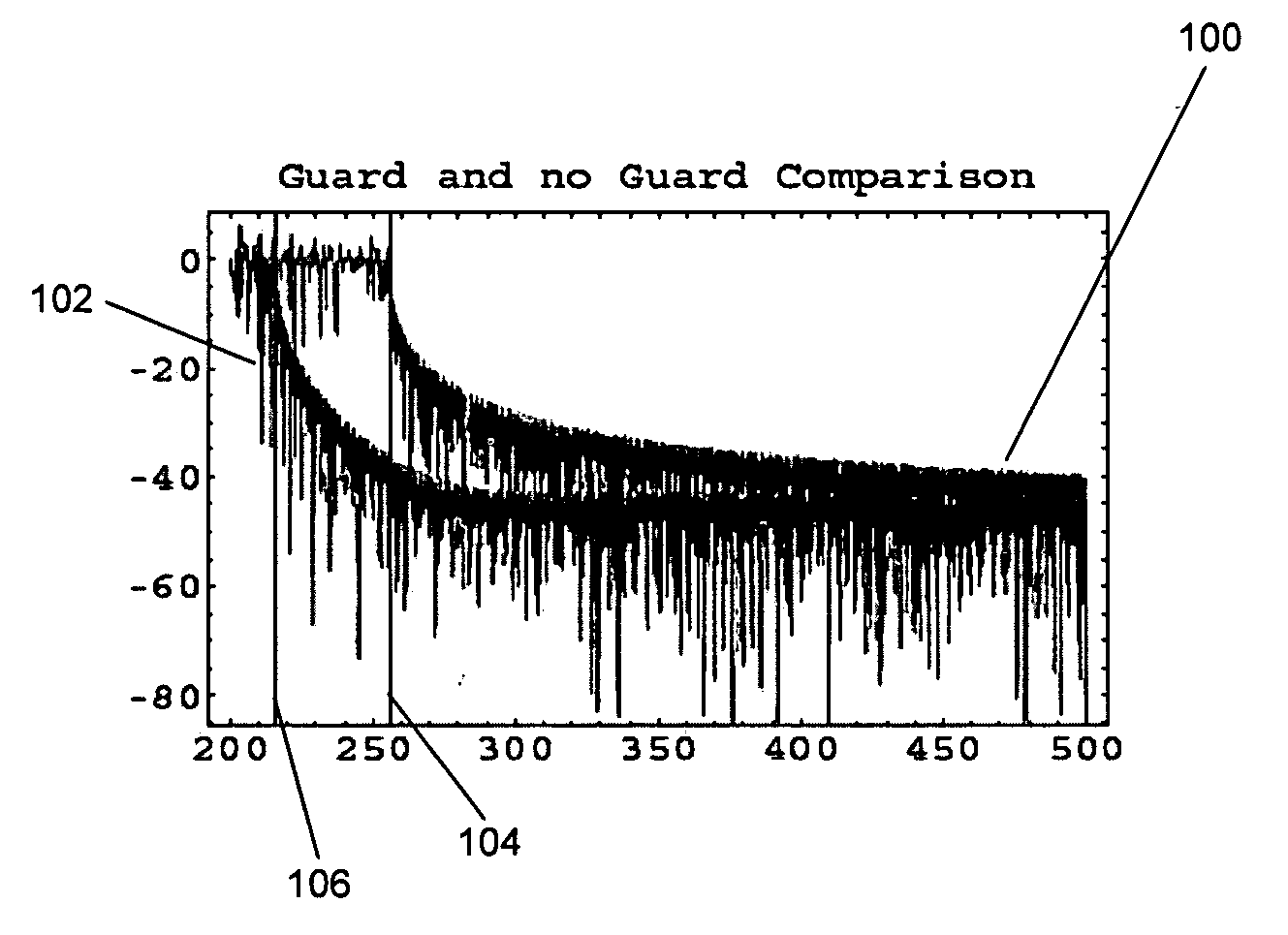
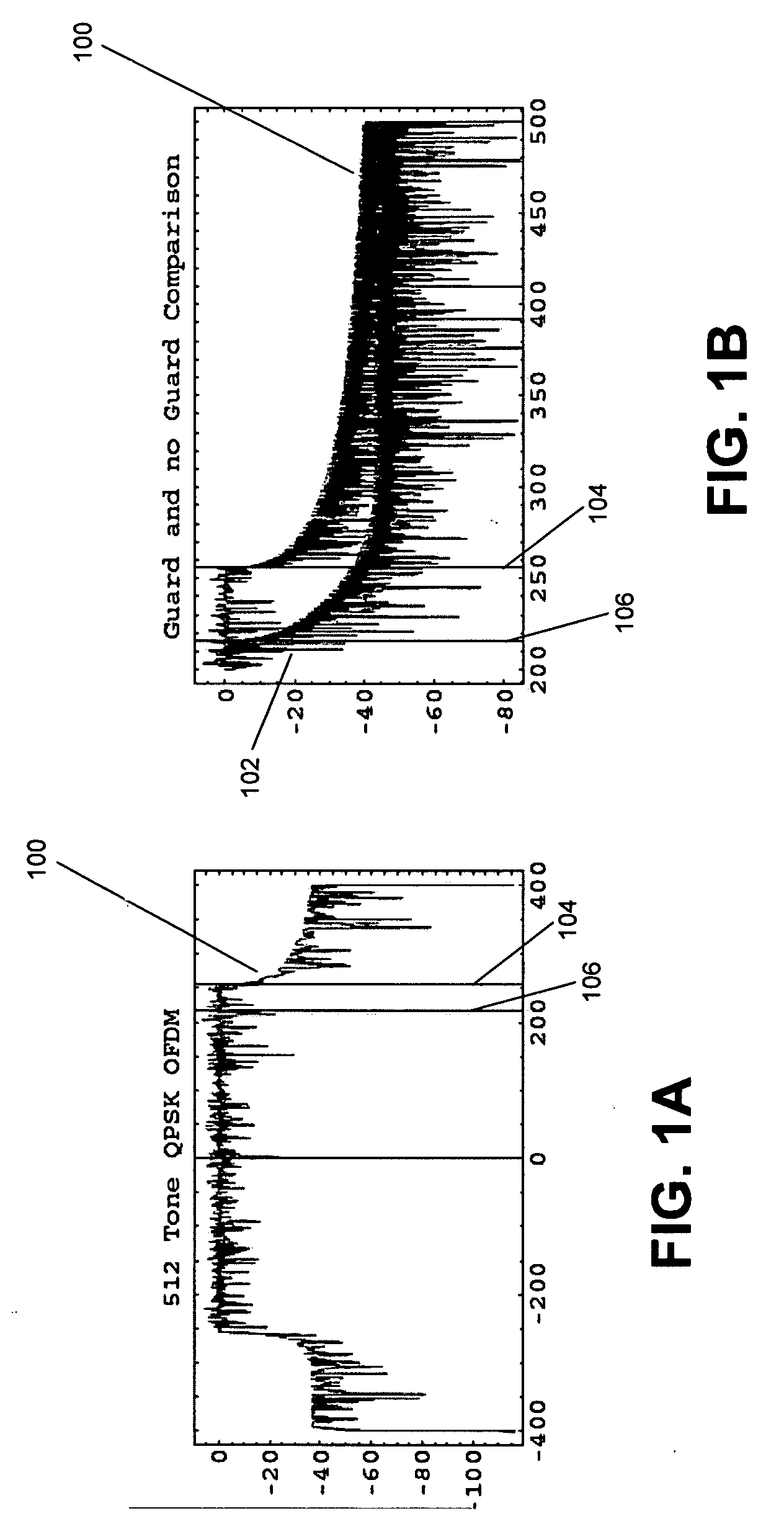
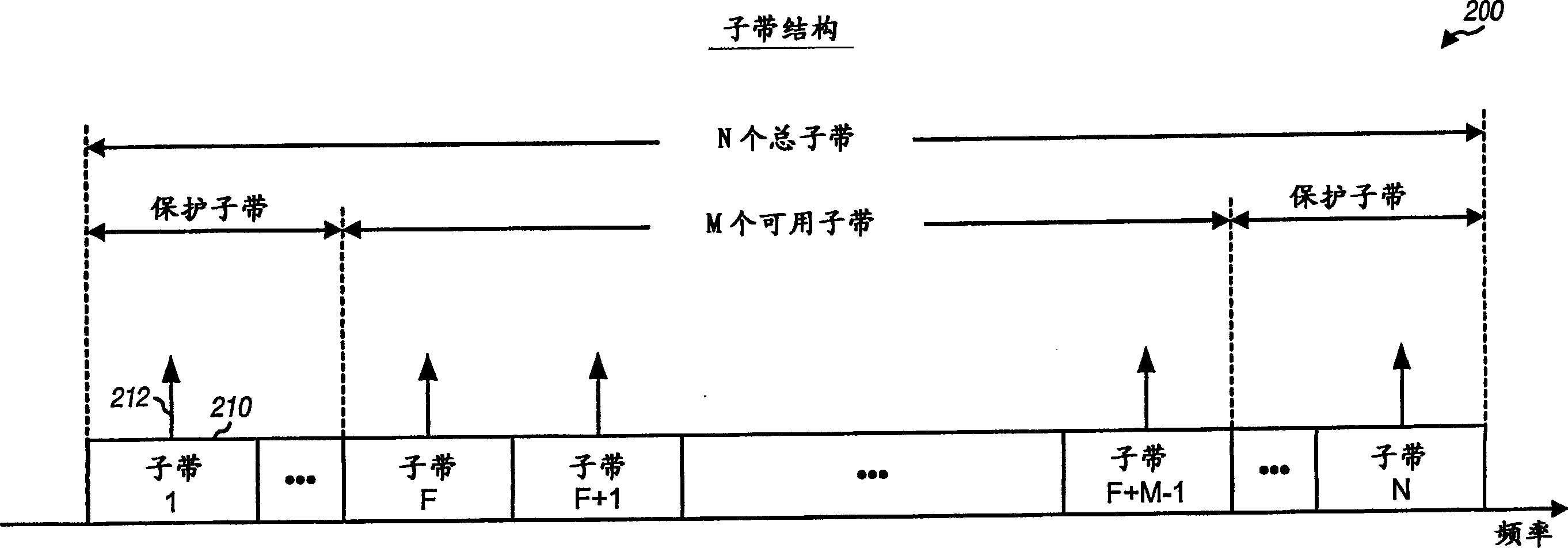
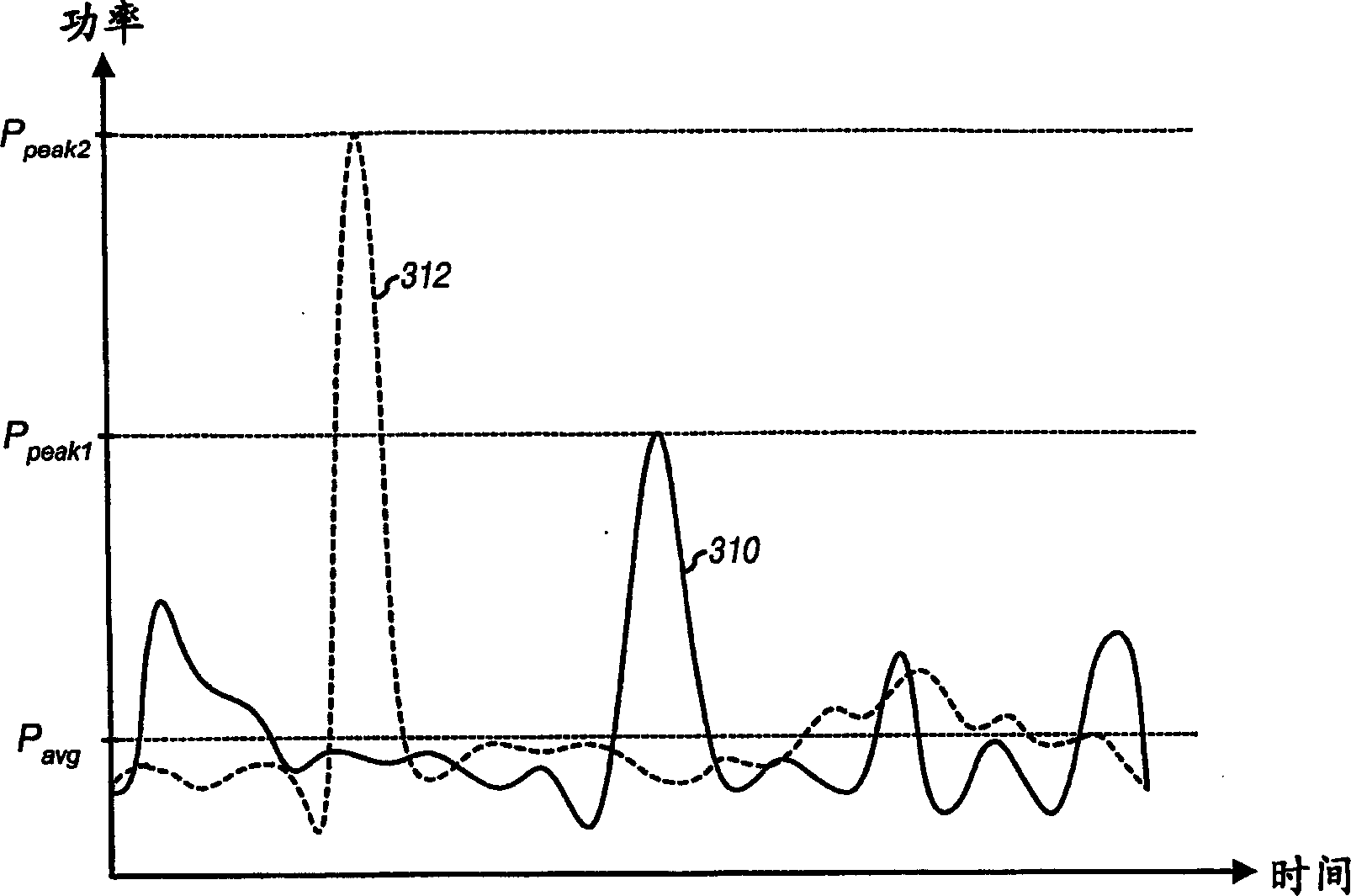
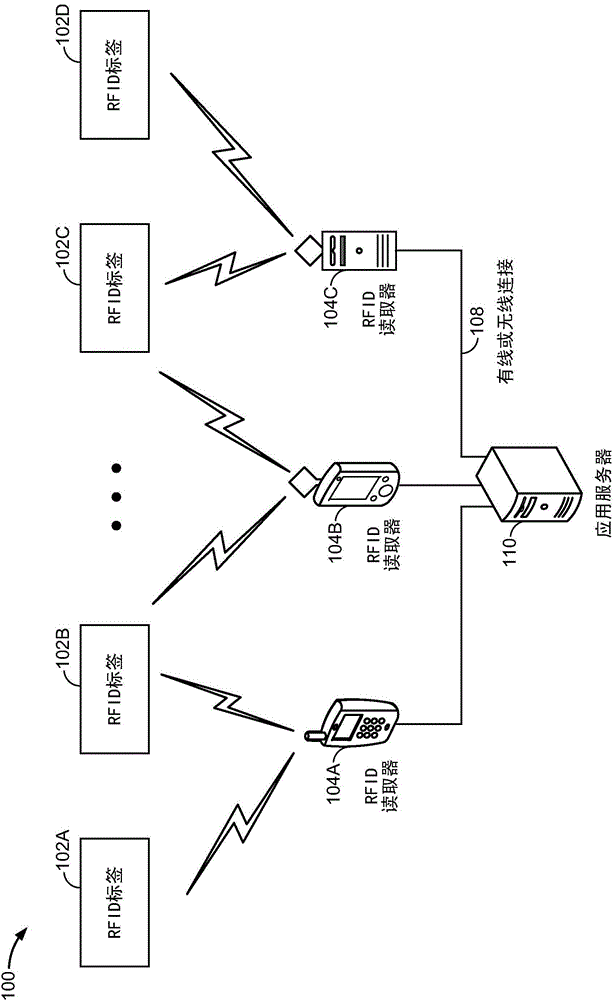
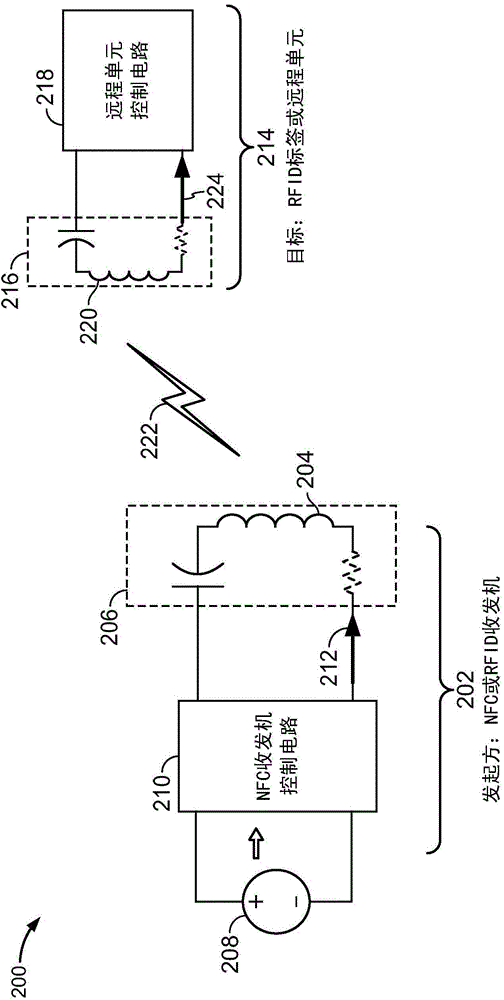
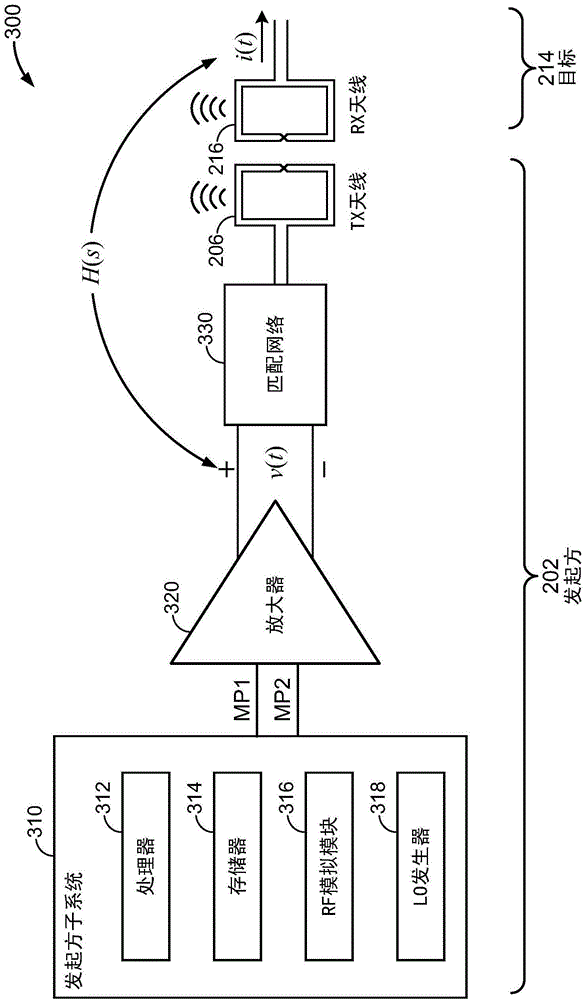
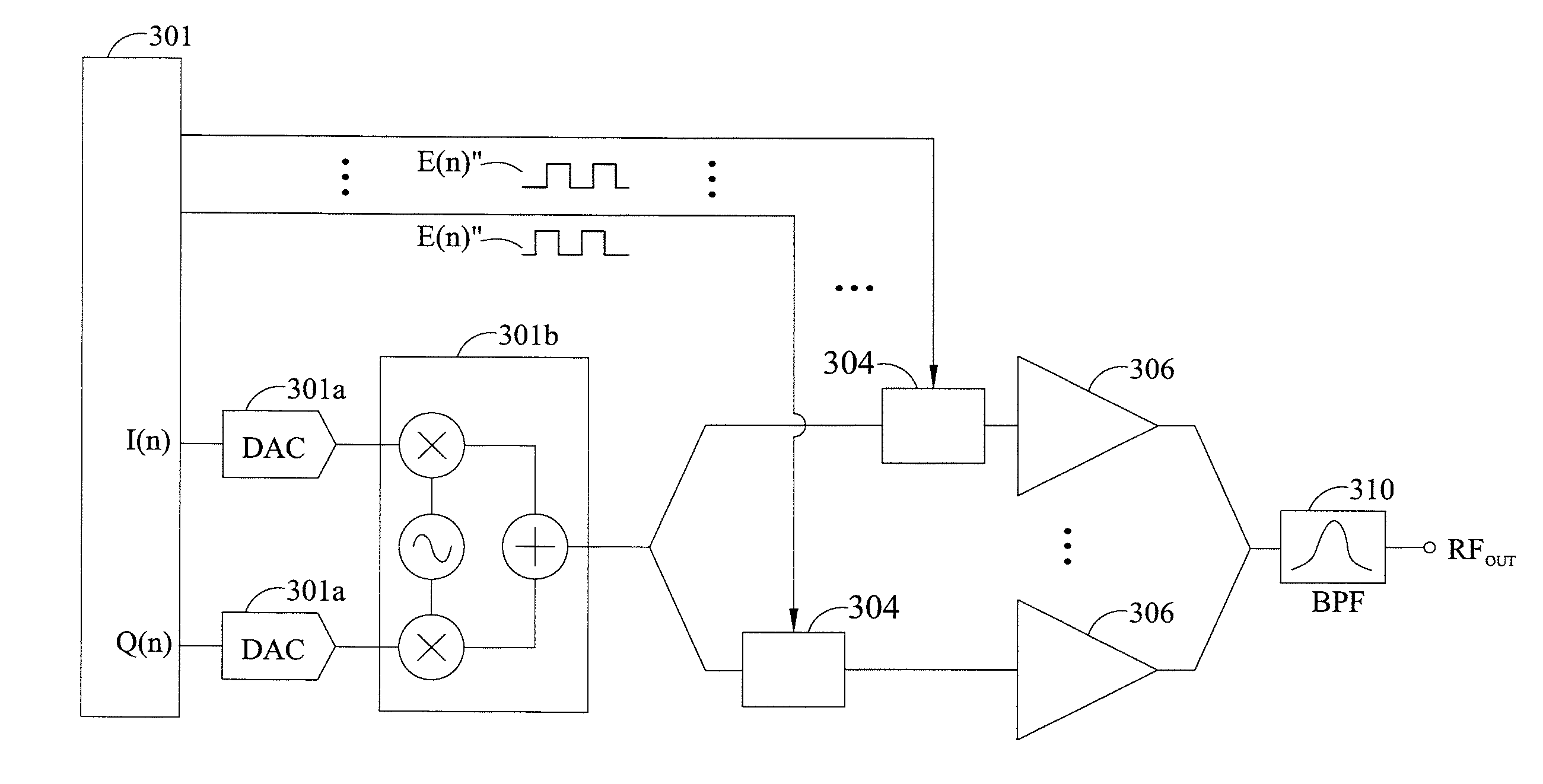
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Out of band emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Out-of-band emission. Out-of-band emission is emission on a frequency or frequencies immediately outside the necessary bandwidth which results from the modulation process. The level of out-of-band emission can not be reduced without affecting the corresponding transmission of information.
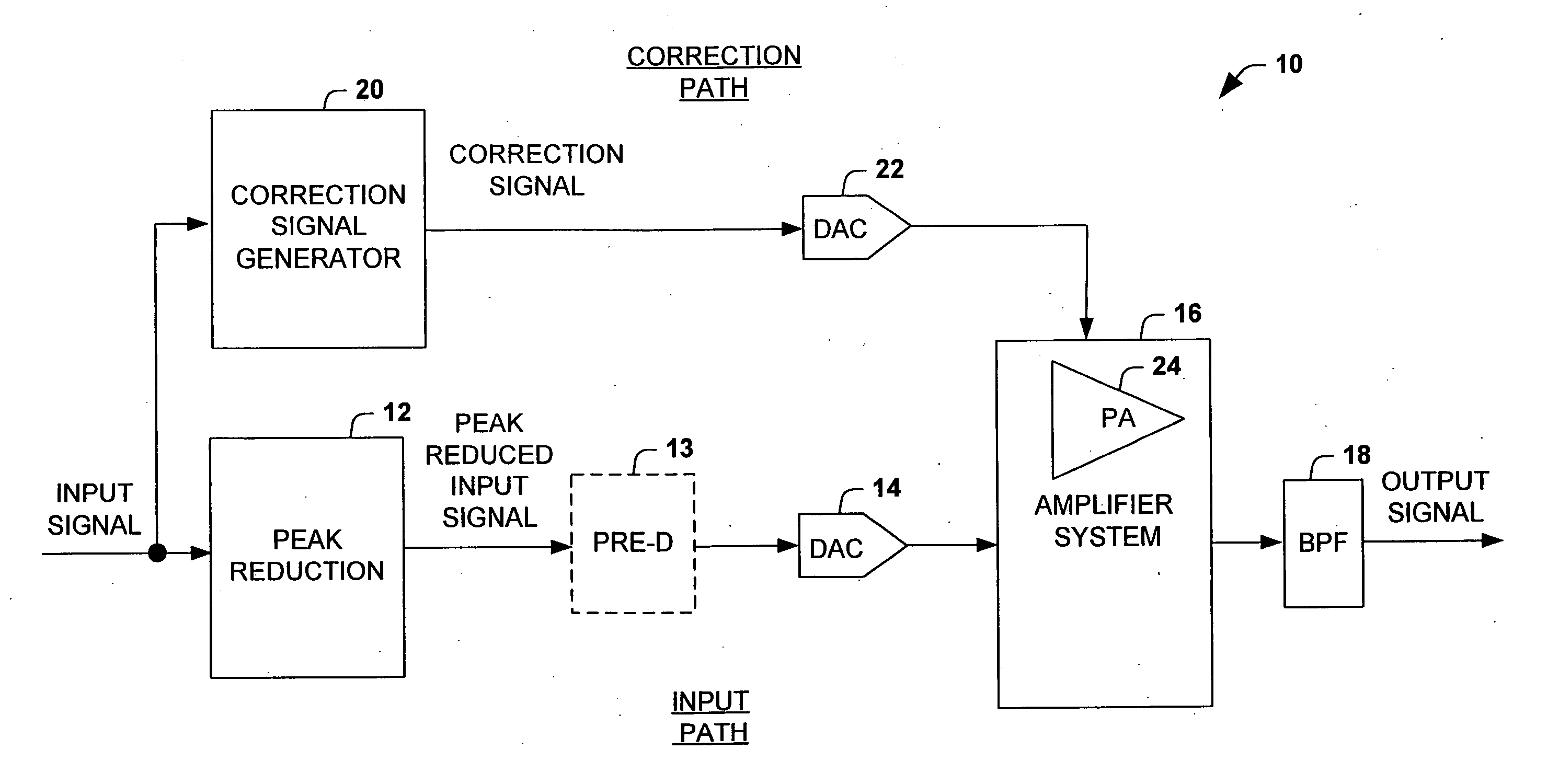
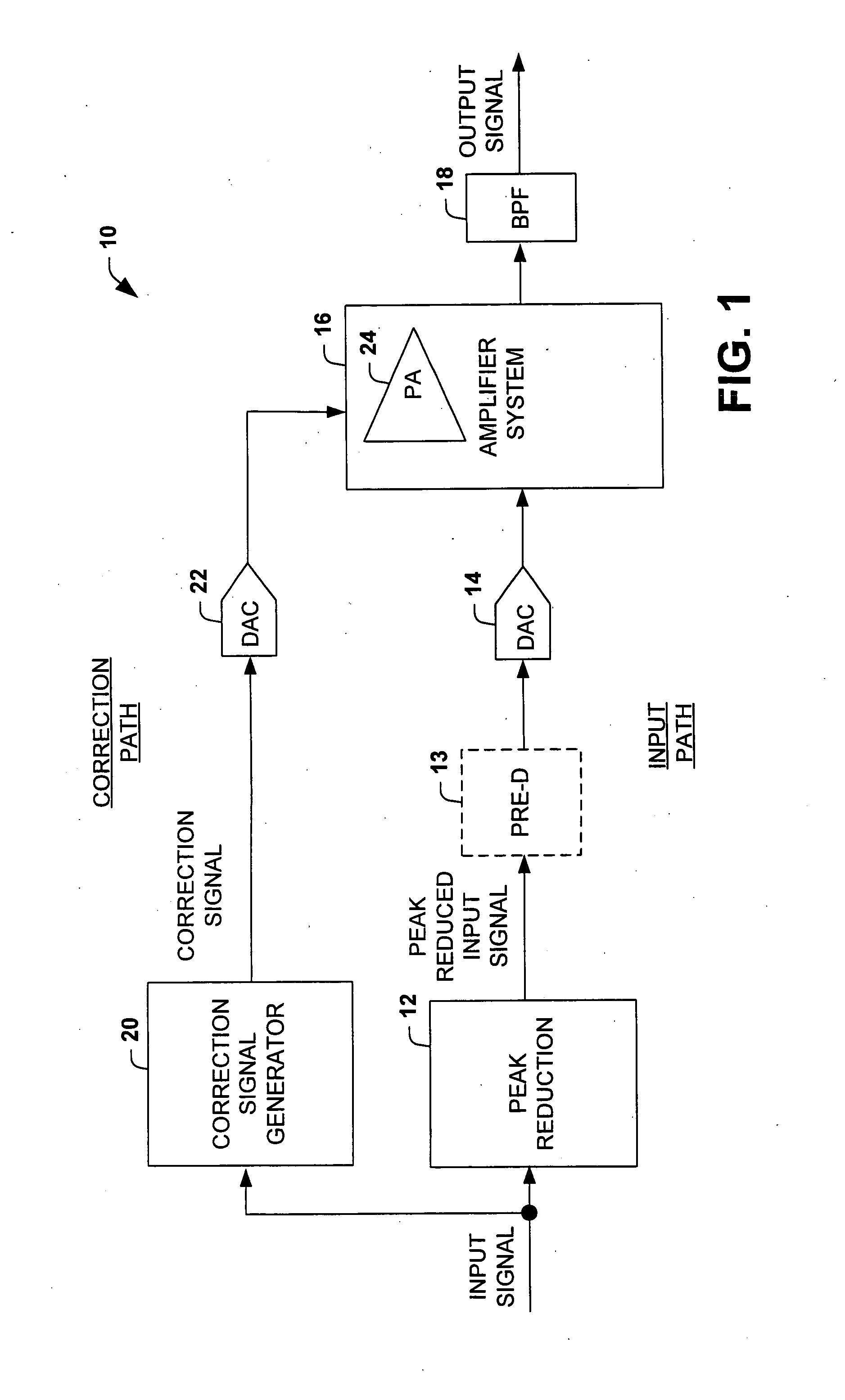
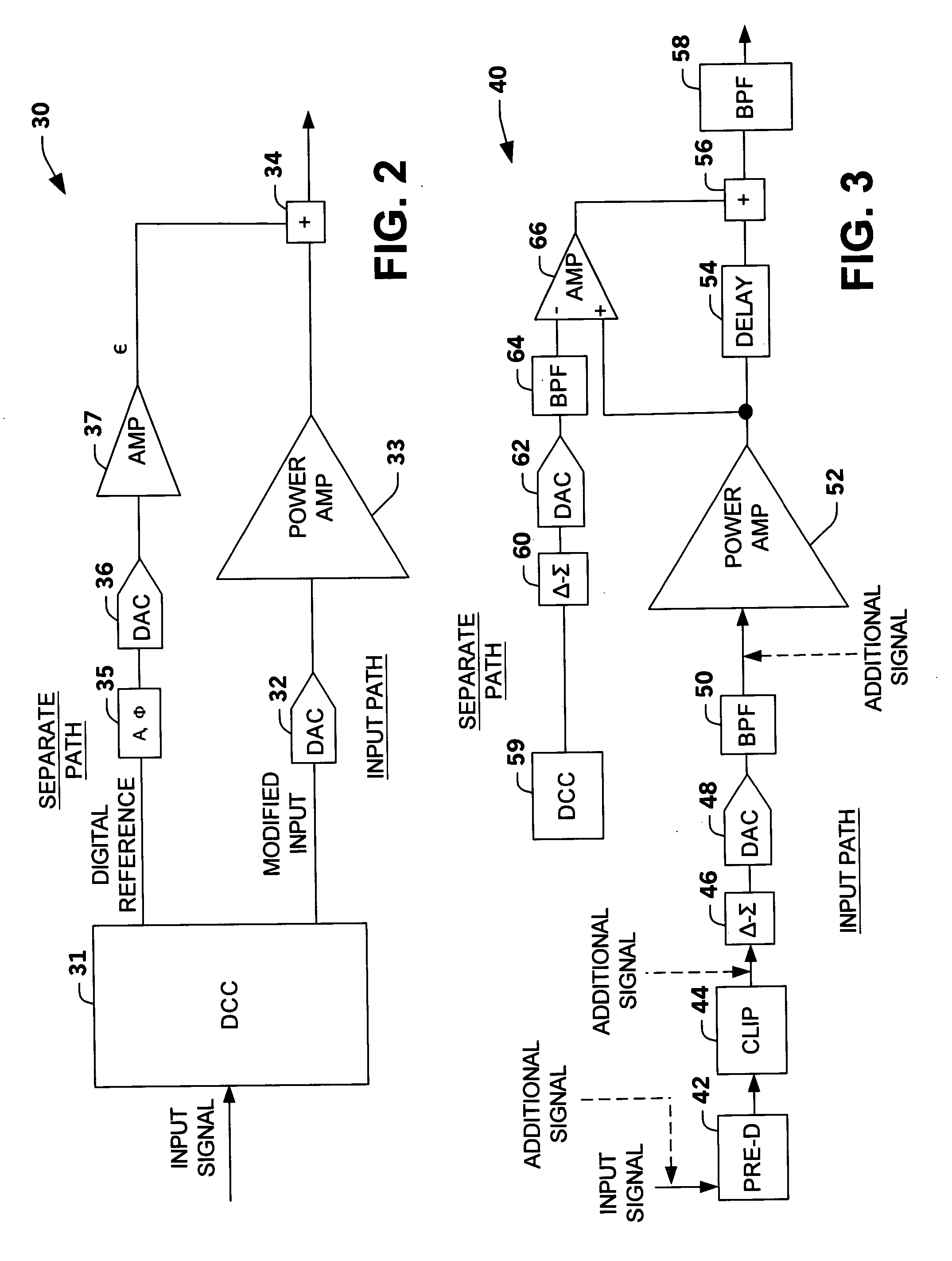
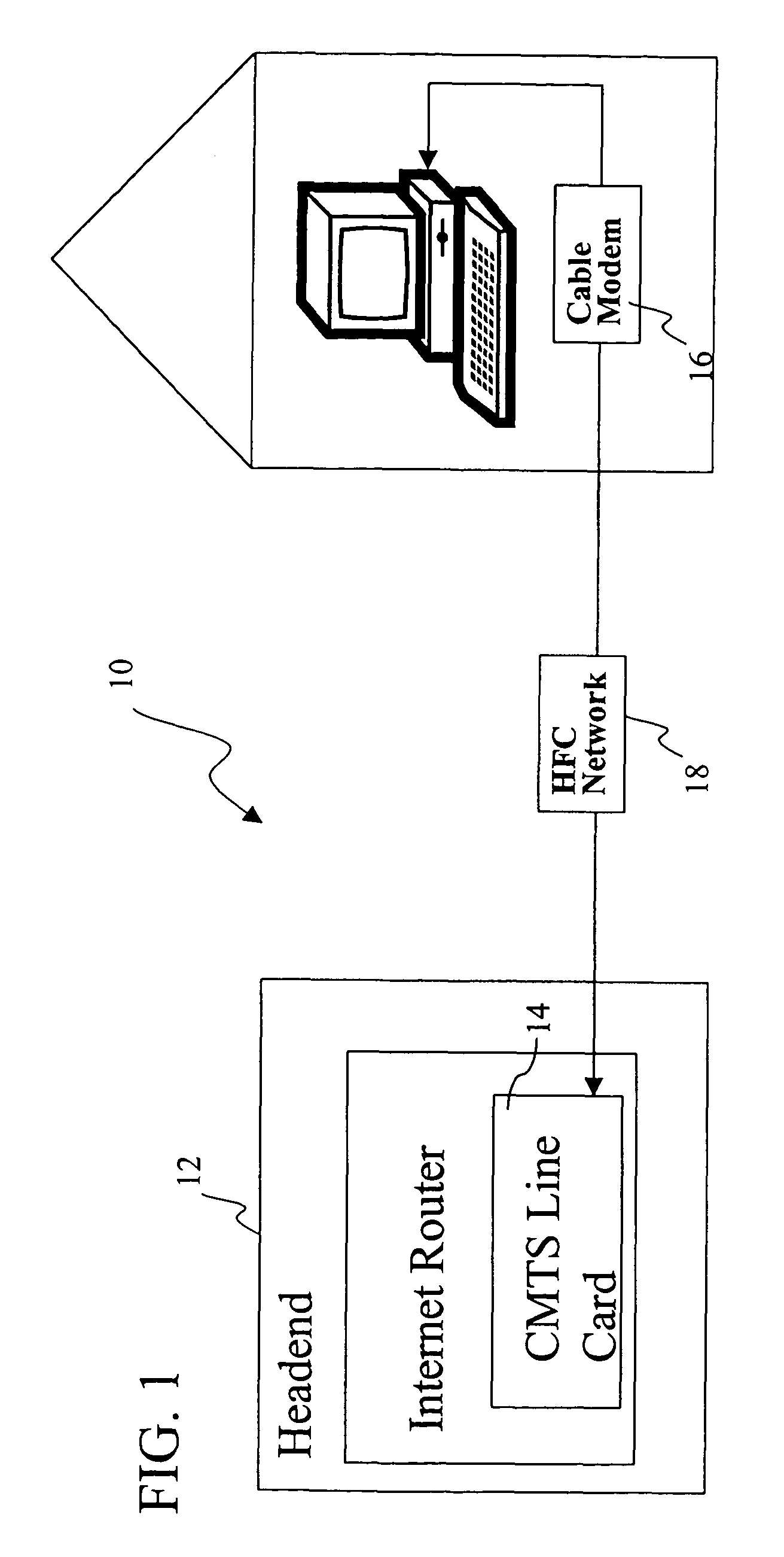
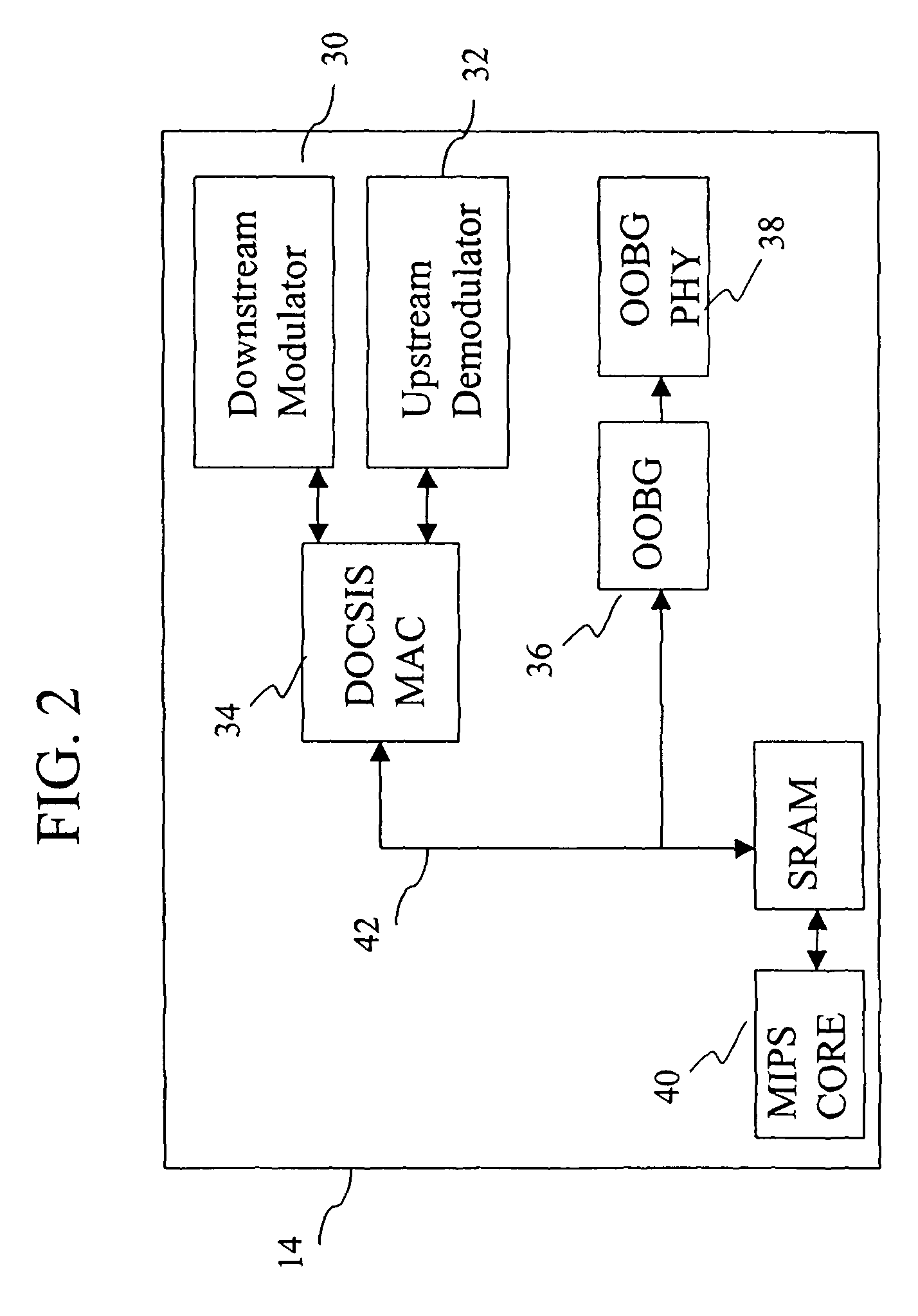
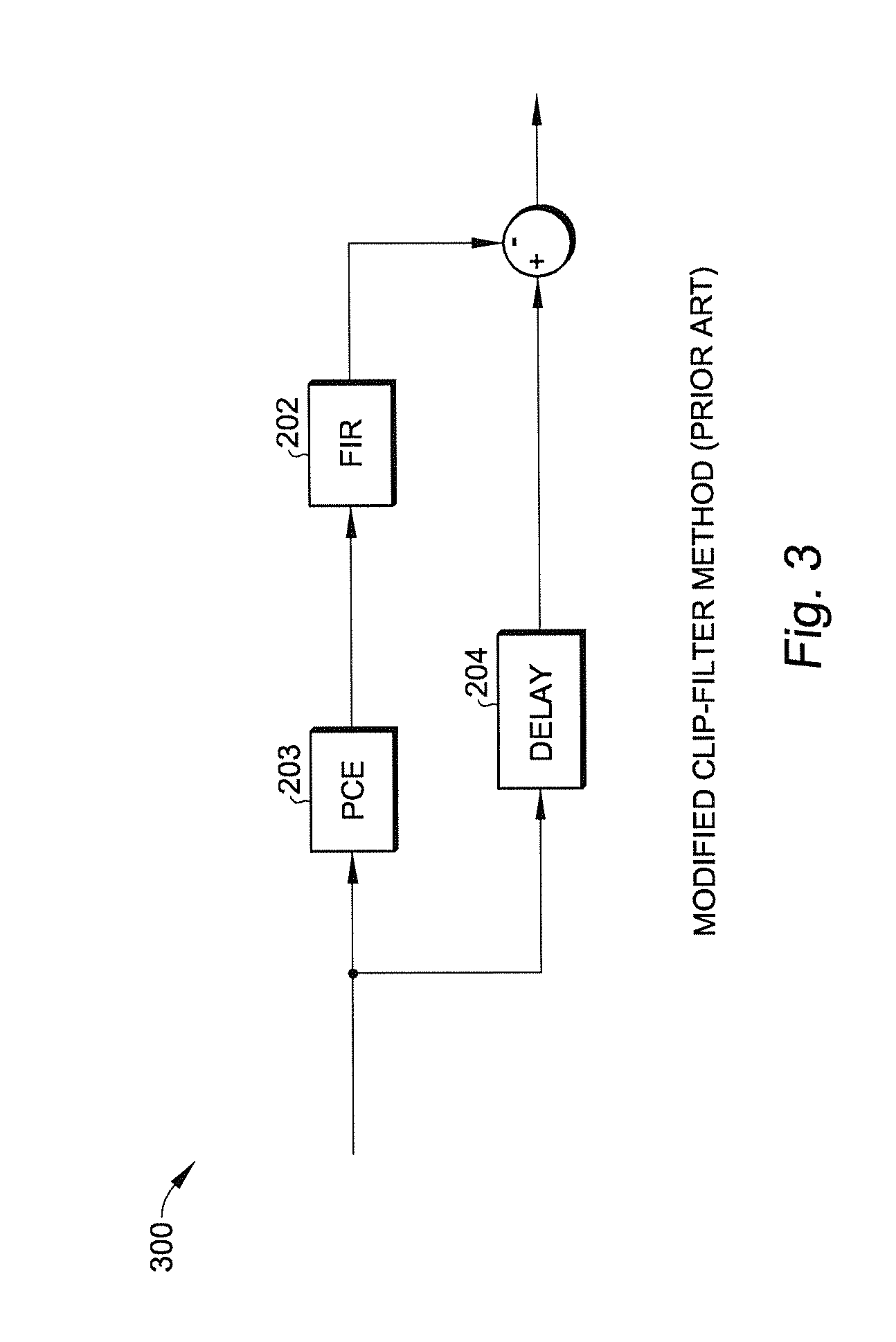
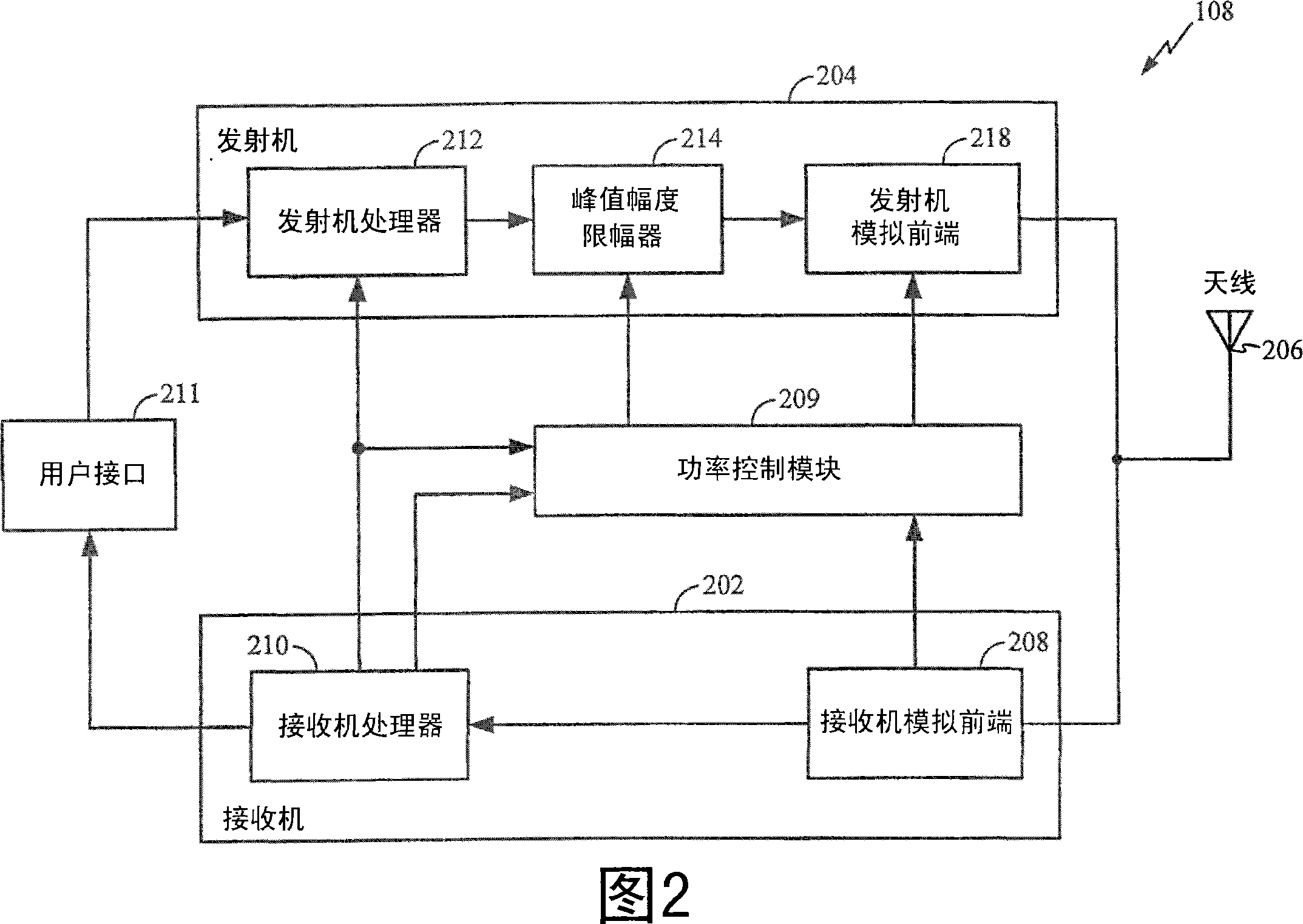
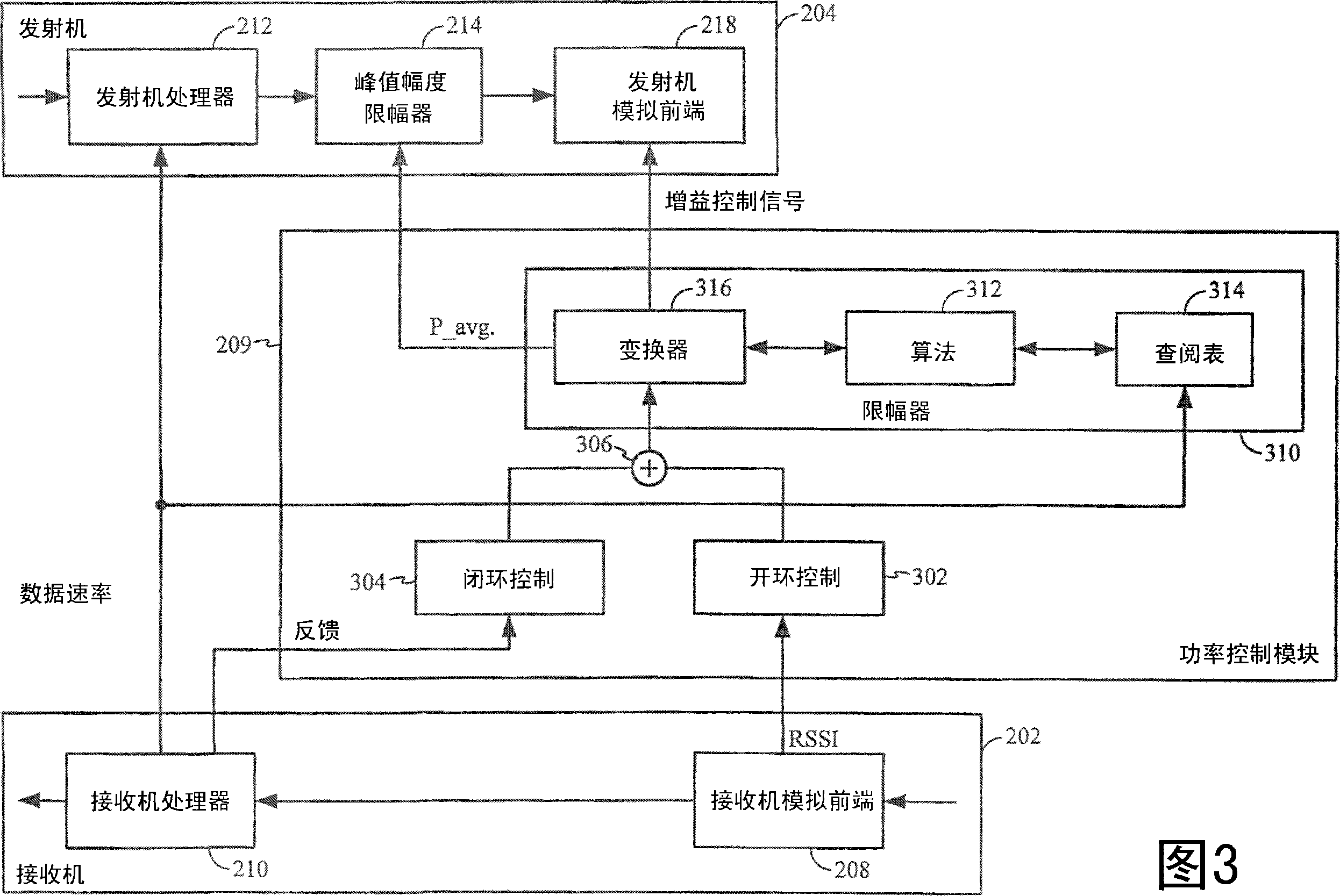
System and method for reducing dynamic range and improving linearity in an amplication system
InactiveUS20050129140A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpectral bandsEngineering
An amplification system and method is provided that reduces peaks associated with an input signal, and provides correction, in one or more spectral bands, to signal distortion and out-of-band emissions that result from the peak reduction. The correction signal that removes signal distortion and OOB emissions associated with the peak reduction can be calculated or electronically derived. The correction signal can be combined with the peak reduced signal prior to or after amplification of the peak reduced input signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
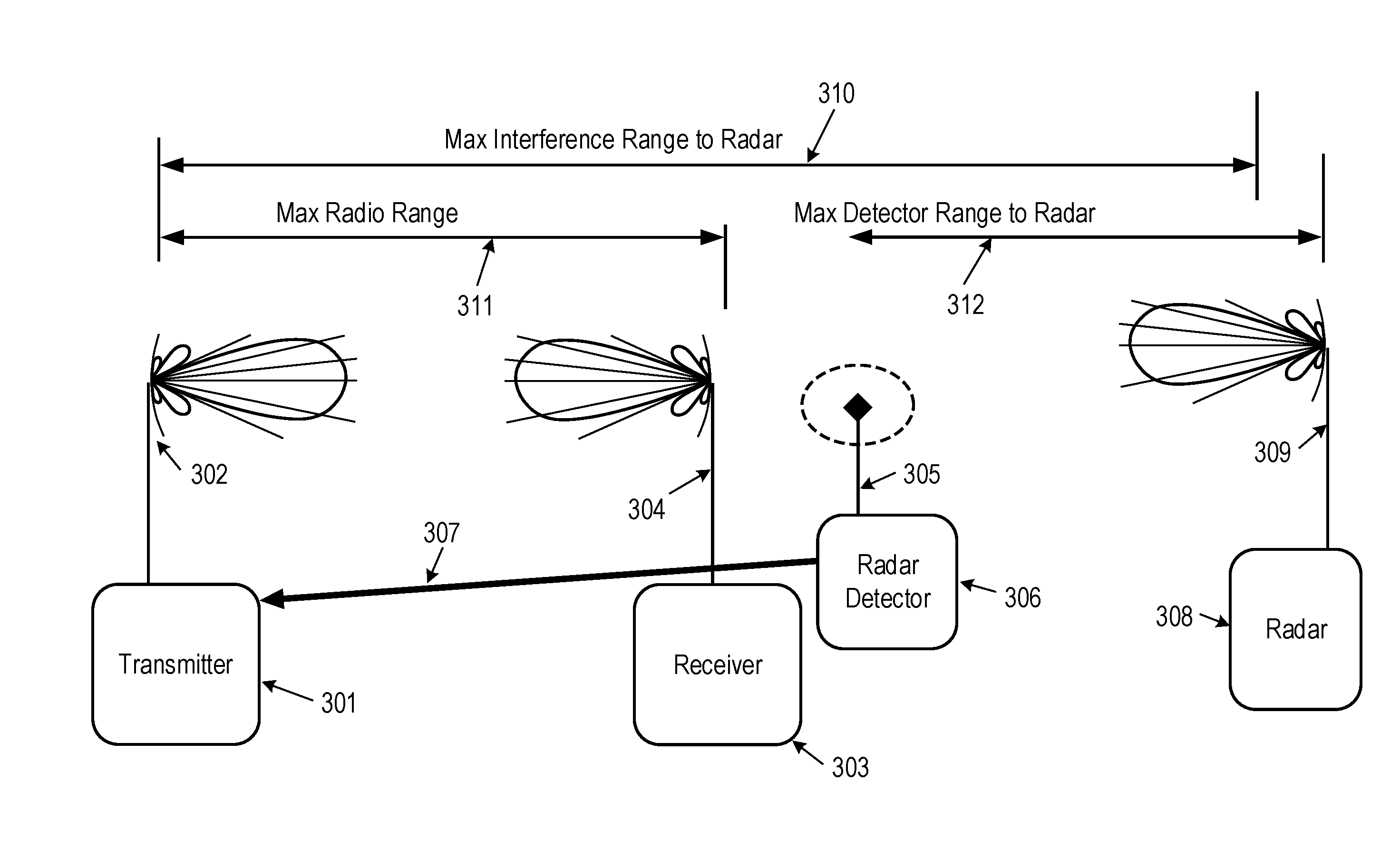
Radio with oobe victim detection
InactiveUS20160285611A1Improve performanceMitigating the losses from multipath fadingPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementWideband radarTransmitted power
A radar detector is used with a radio link, the radio link characterized by high duty factor operation of a radio transmitter. The radar detector is located a sufficient distance from the radio transmitter that the radar detector is not overwhelmed by the radio transmission signal in that channel and can detect sufficiently low level radar signals to ascertain potential radio interference at the radar from said radio transmitter. The results of the radar detection are communicated to the transmitter in a way that impacts the transmitter's use of the sensed channel. This communication can occur reactively when a radar detection is achieved (the absence of which indicates no radar has been detected) and / or can be a periodic or event-driven indication that the channel is available for operation (the information expiring if the result is not refreshed). A highly sensitive radar detector apparatus that can detect wideband radar signals at very low levels and overcome the disparity of detection range versus interference range is described. A signal detector is also described that detects energy from other users that is not in the operating channel or operating band of the transmitter to determine if the out of band emissions or out of channel emissions of the operating transmitter's signal need to be adjusted through such settings as transmit power, operating channel, filtering, or a combination.
Owner:SKYLINE PARTNERS TECH LLC
Transmit Power Dependent Reduced Emissions From a Wireless Transceiver
InactiveUS20080176575A1Reducing transmit emissionEmission reductionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementWireless transceiverTransceiver
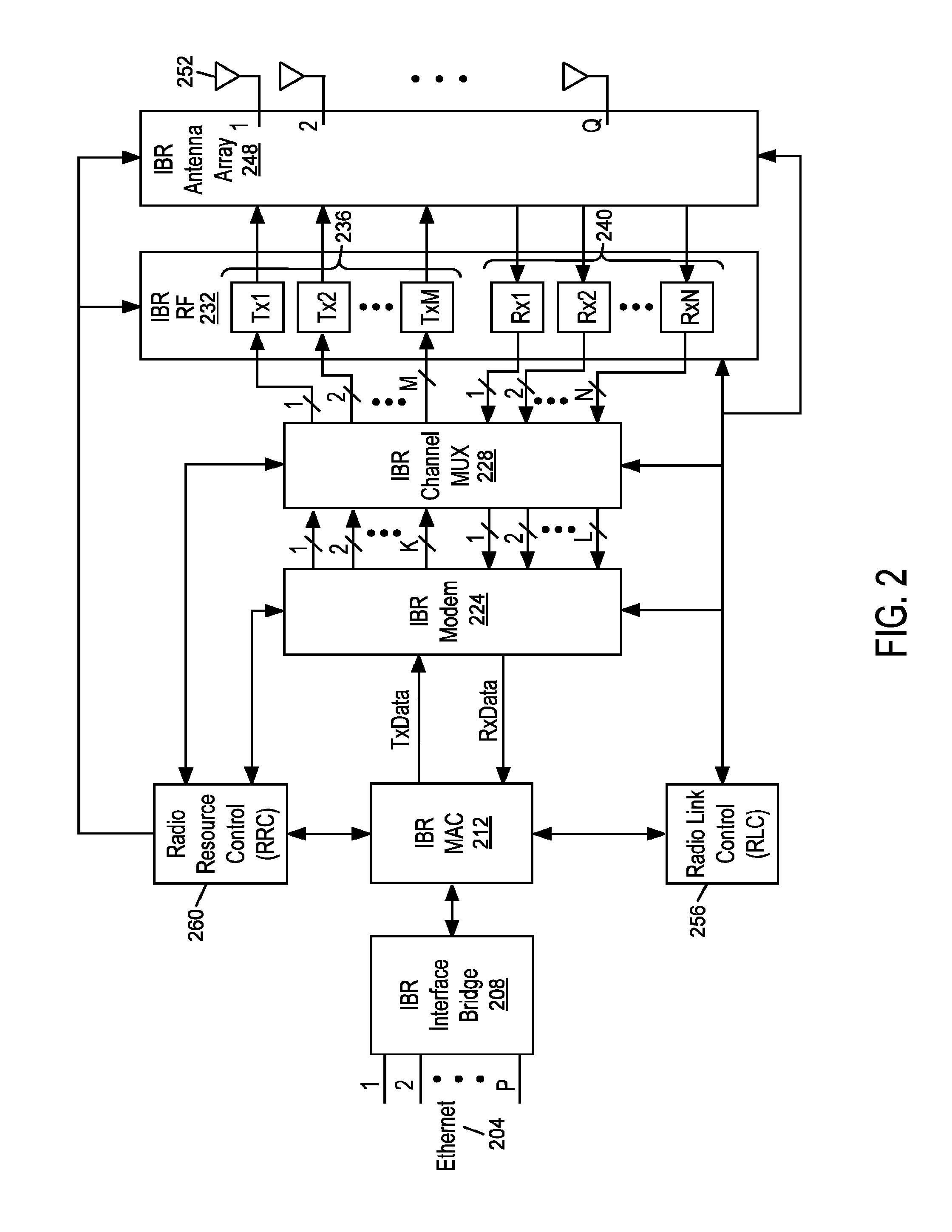
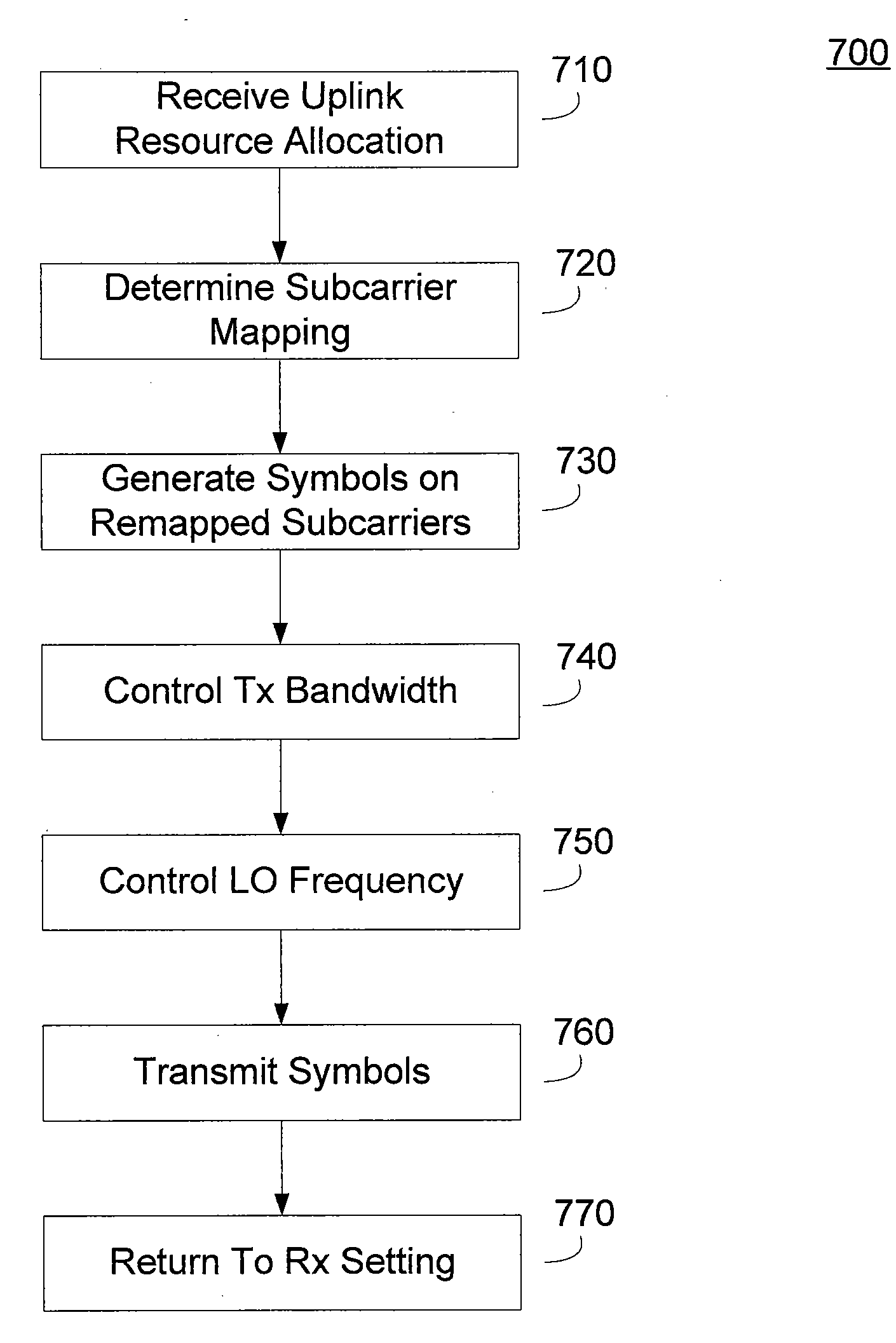
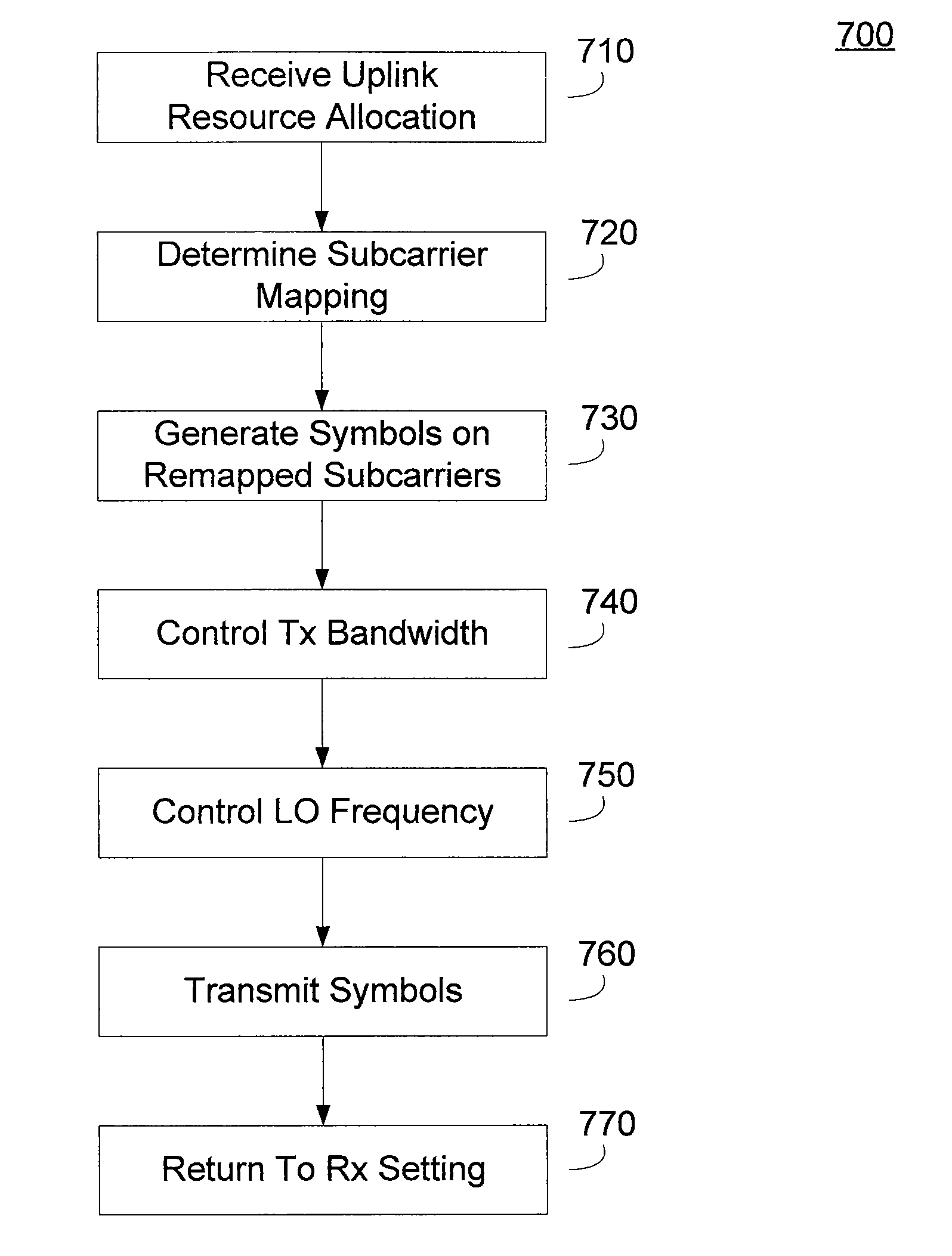
Methods and apparatus for reducing out of band emissions through selective resource allocation, transmit power control, or a combination thereof. A resource controller, such as a base station, can allocate uplink resources to a requesting subscriber station based in part on an expected transmit power. The base station can allocate uplink bandwidth to the subscriber station based on an expected subscriber station uplink transmit power and a frequency of a restricted emissions band. Those subscriber stations having higher expected transmit powers are allocated bandwidth further from the restricted emissions band. The subscriber station can perform complementary transmit power control based on allocated uplink resources. The subscriber station can limit a transmit power based in part on a bandwidth allocation, modulation type allocation, or some combination thereof.
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
Method and apparatus of peak-to-average power ratio reduction
InactiveUS7409009B2Reducing peak-to-average power ratioReduce total powerSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDigital videoFrequency spectrum
A technique of reducing the Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) of Multi-Carrier (MC) modulated signals in which peaks in the baseband signal that lie above a threshold amplitude are detected and used to generate a pulse sequence signal which, after shaping, is subtracted from the baseband signal to reduce its PAPR. The method is spectrally efficient, has a low degree of implementation complexity and hence it is also suitable for low-power, portable implementation. Moreover, it is compatible with existing standard-based Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) systems. As an example of the performance of the proposed scheme, the amplifier back-off requirement in a Terrestrial Digital Video Broadcast (DVB-T) system can be reduced from 12 to 6 dB, while satisfying the of out-of-band emission specifications imposed by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) spectral mask.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Predistortion with integral crest-factor reduction and reduced observation bandwidth
ActiveUS8446979B1Reduced observation bandwidthReduce processing requirementsResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsAudio power amplifierError vector magnitude
Apparatus and methods configure digital predistortion linearizers for power amplification of bandlimited signals using non-linear amplifiers. The predistorter is configured to achieve both crest factor reduction (CFR) and predistortion for linearization. One embodiment advantageously reduces processing requirements conventionally associated with CFR by considering only the in-band component, that is, the information bearing component, of the desired signal to be reproduced for those cases in which the mitigation of in-band error vector magnitude (EVM) is preferred over the reduction of spurious out-of-band emissions.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Wireless Transceiver with Reduced Transmit Emissions
InactiveUS20080176523A1Reducing transmit emissionEmission reductionTransmission path divisionTransmission path sub-channels allocationTransceiverWireless transceiver
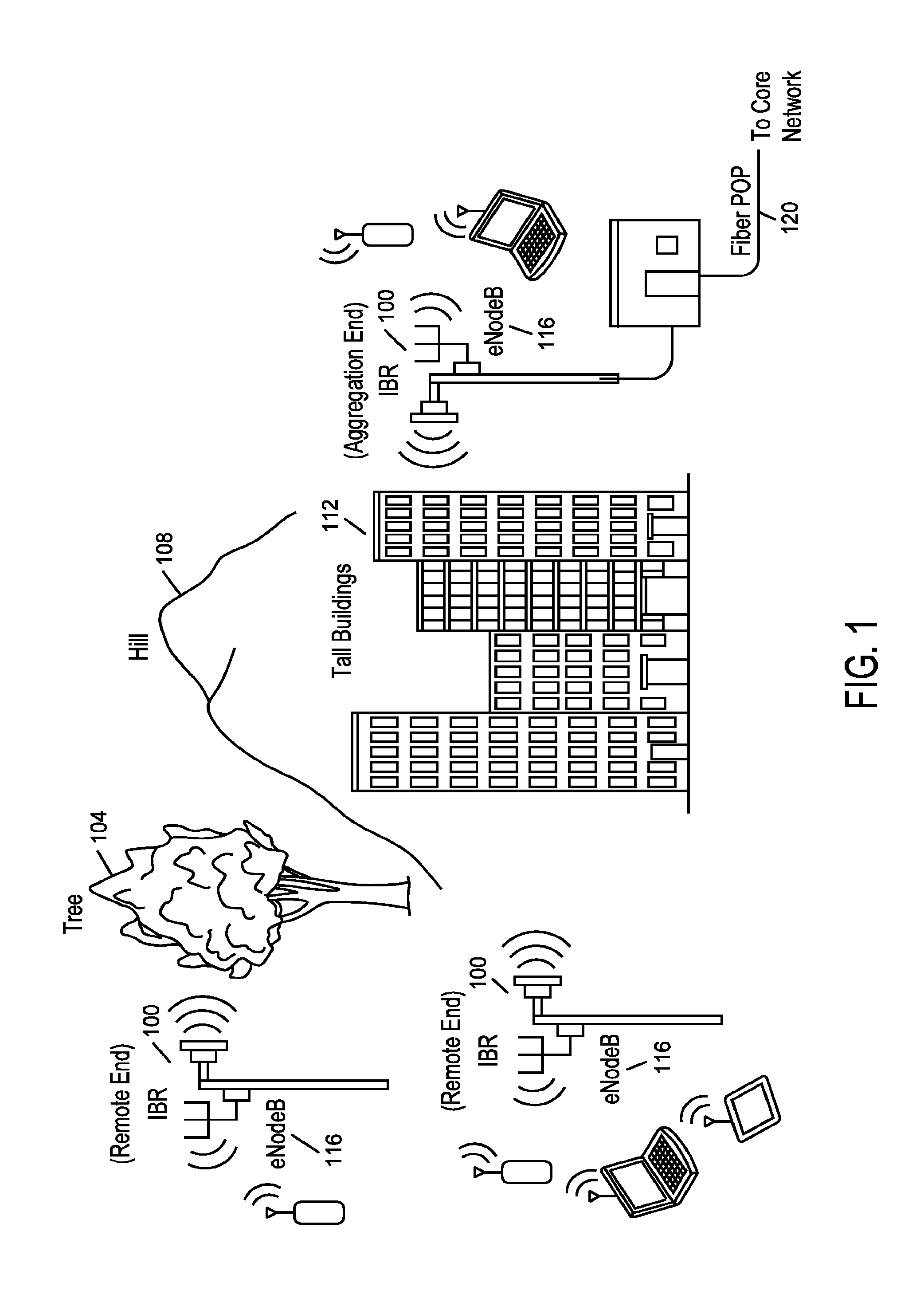
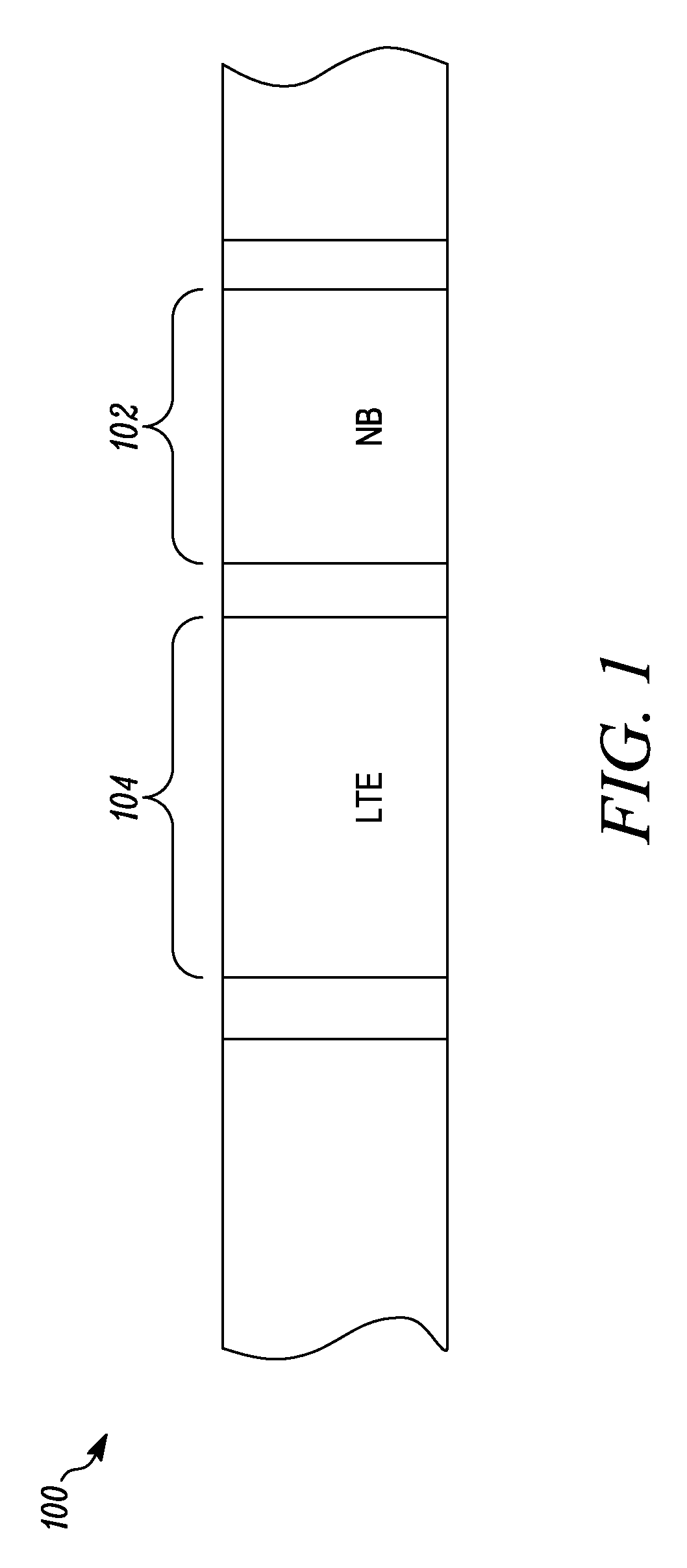
Methods and apparatus for reducing transmit emissions are described herein. The transmit out of band emissions in an adjacent band can be reduced while complying with existing wireless communication standards through utilization of one or more of reduced transmit bandwidth, transmit operating band offset, and channel index remapping. The transceiver can support a receive operating band that is substantially adjacent to a band edge. The transmit operating band can be offset from an adjacent frequency band, and can use a narrower operating band than is supported by the receiver. The transmit baseband signal can have a reduced bandwidth to reduce the amount of noise. The frequency offset can introduce a larger transition band between the transmit operating band edges and the adjacent frequency band of interest. The transceiver can remap channel assignments to compensate for the frequency offset such that the frequency offset introduced in the transmitter is transparent to channel allocation.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Duplexer and method for separating a transmit signal and a receive signal
ActiveUS20110080856A1Improve performanceReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equalisingUltrasound attenuationOut of band emission
The present disclosure provides a duplexer for separating a transmit signal and a receive signal. The duplexer comprises a transmit filter, a receive filter and an analogue quadrature splitter, a first filtering element and a second filtering element. By choosing the first filtering element and the second filtering element substantially identical, it is possible to transform filtering characteristics of the first and second filtering element such that stop bands are substantially transformed into an effective pass band, and vice versa. The analogue quadrature splitter is adapted to increase an attenuation of the transmit signals outside the transmit band, such as in the receive band. Therefore out-of-band emissions by the transmitter will be substantially reduced. The present disclosure further provides a method for separating a transmit signal and a receive signal, and computer program products for the manufacture for carrying out the method of separating transmit signals and receive signals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
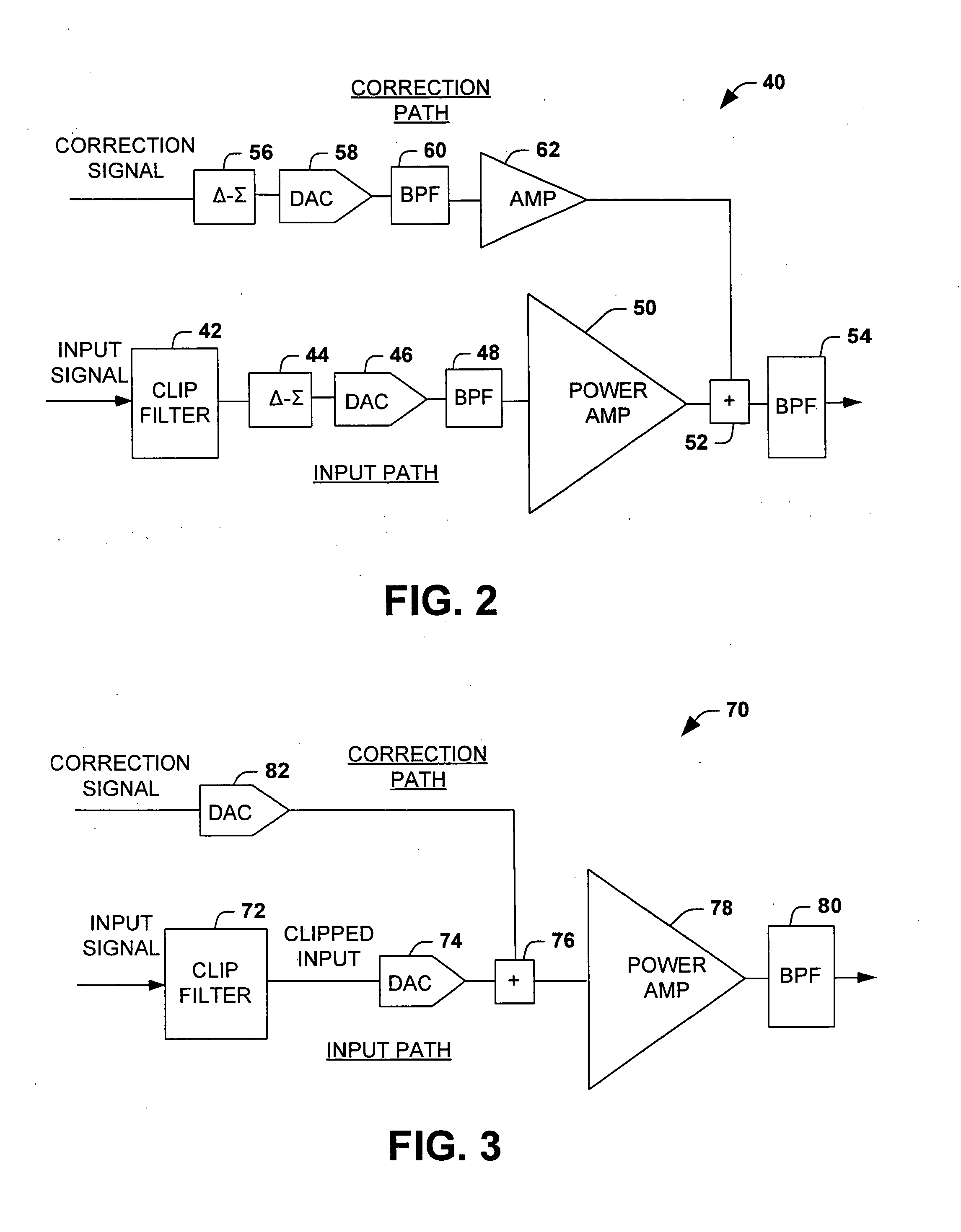
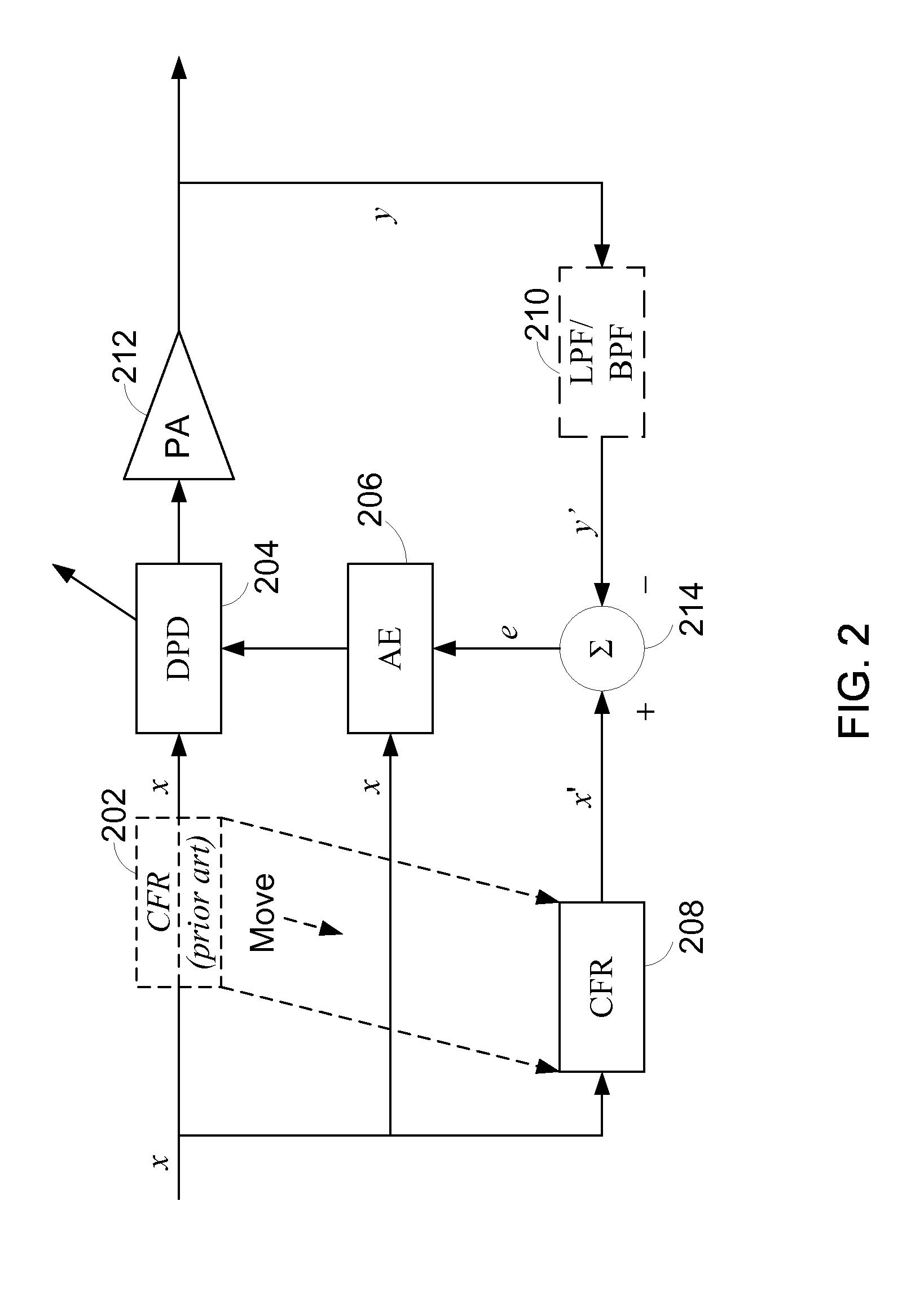
Digital cross cancellation system
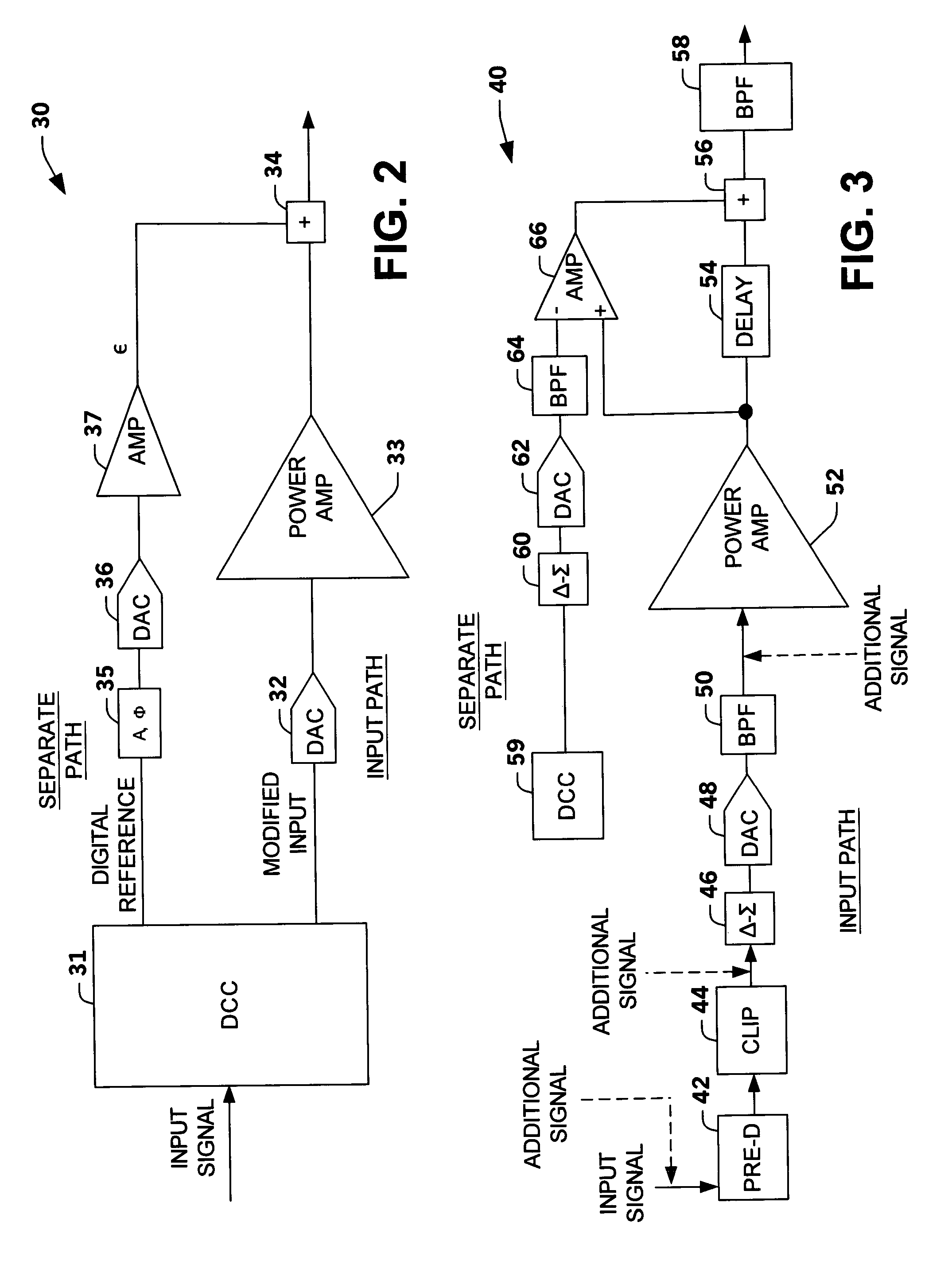
ActiveUS20050017802A1Attenuation of signal levelEmission reductionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierDistortion
An amplification system and method is provided that employs a digital cross-cancellation technique which provides a separate digital signal to be input to a separate DAC to generate a cancellation signal. The cancellation signal is added to the output of the amplifier to produce a final signal with substantially reduced distortion and / or out-of-band emissions. The cancellation signal can be pre-computed or derived by generating an inverted version of the wanted signal, and combining it with a portion of the output signal to determine the error or unwanted portion of the output signal. This error signal is then combined with a delayed version of the output signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
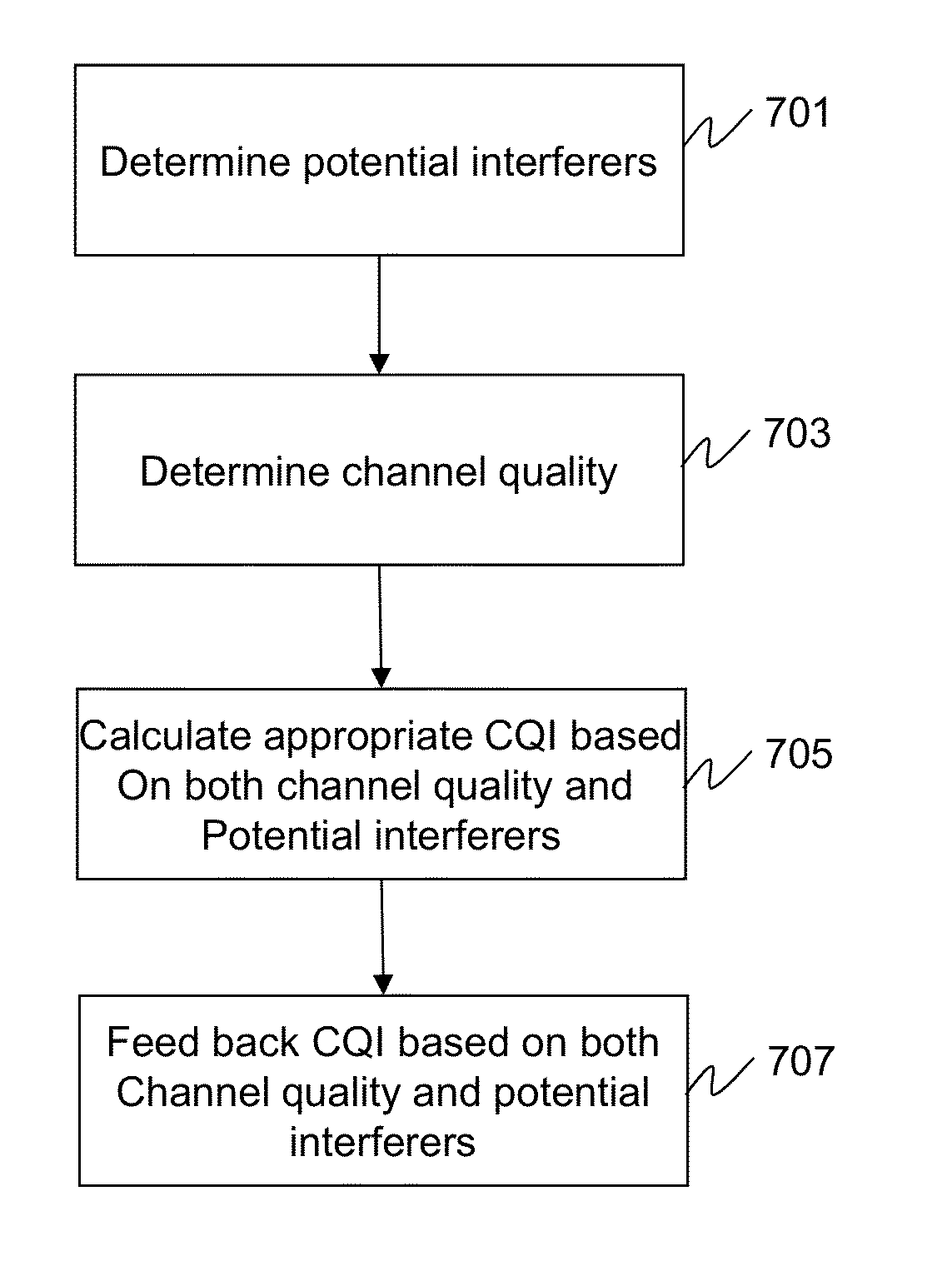
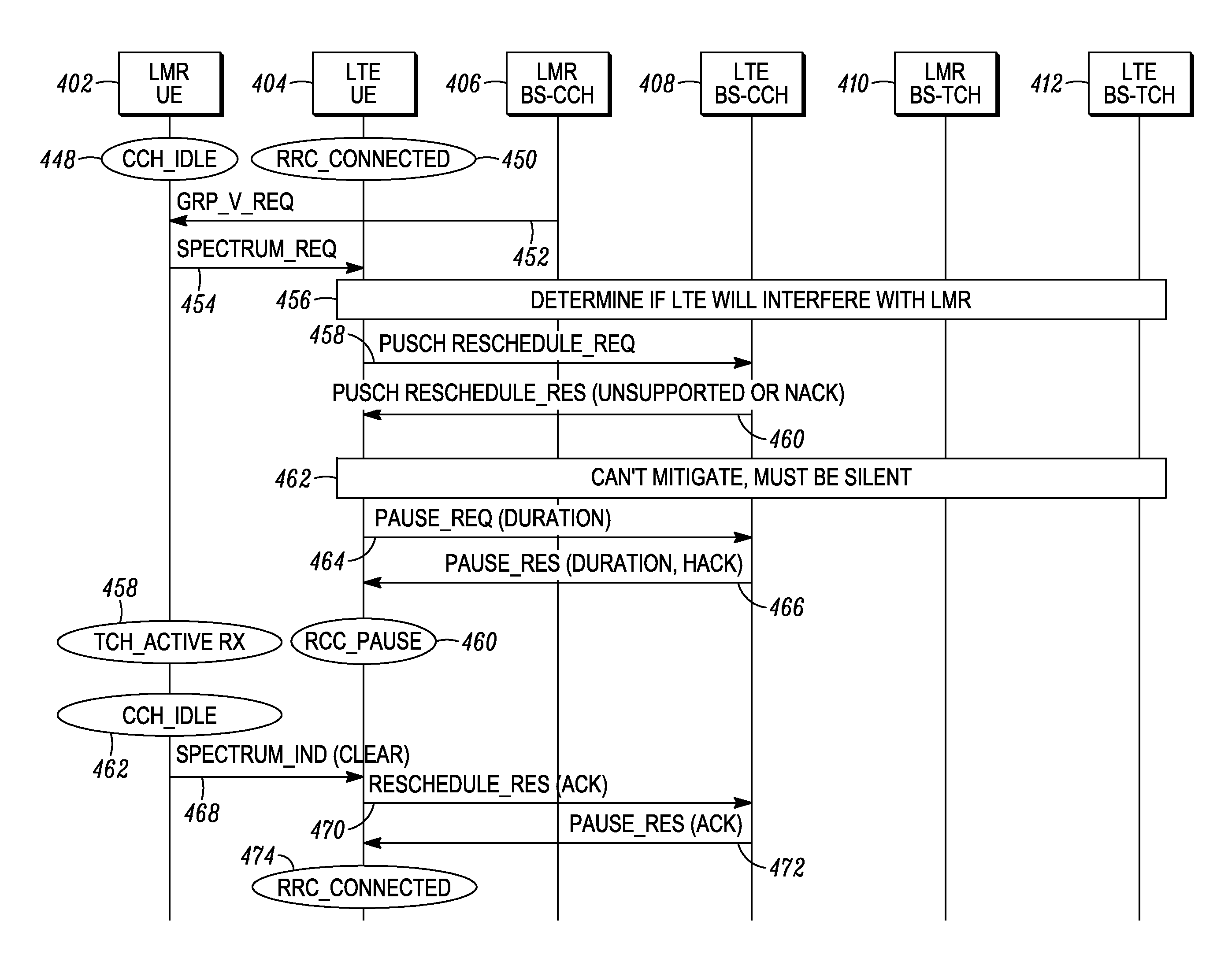
Methods and apparatus for mitigating interference between co-located collaborating radios
ActiveUS20130272436A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method and apparatus for mitigating out of band emissions among user equipment and base stations operating at geographically co-located and spectrally distinct wireless communication systems are provided herein. During operation, a wireless radio will determine potential interferers. Preferably, these interferers comprise user equipment and base stations operating at geographically co-located and spectrally distinct wireless communication systems. Once determined, a channel quality indicator (CQI) will be adjusted accordingly to accommodate for any potential interferer. Because the CQI will take into effect any potential interferer, transmissions to / from the wireless radio will be made more robust, decreasing channel interference.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Peak-to-average power ratio management for multi-carrier modulation in wireless communication systems
InactiveUS20100067474A1Power managementEnergy efficient ICTAudio power amplifierCommunications system
Techniques for managing peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) for multi-carrier modulation in wireless communication systems. Different terminals in a multiple-access system may have different required transmit powers. The number of carriers to allocate to each terminal is made dependent on its required transmit power. Terminals with higher required transmit powers may be allocated fewer carriers (associated with smaller PAPR) to allow the power amplifier to operate at higher power levels. Terminals with lower required transmit powers may be allocated more carriers (associated with higher PAPR) since the power amplifier is operated at lower power levels. The specific carriers to assign to the terminals may also be determined by their transmit power levels to reduce out-of-band emissions. Terminals with higher required transmit powers may be assigned with carriers near the middle of the operating band, and terminals with lower required transmit powers may be assigned with carriers near the band edges.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive digital predistortion method and apparatus for wireless transmitter
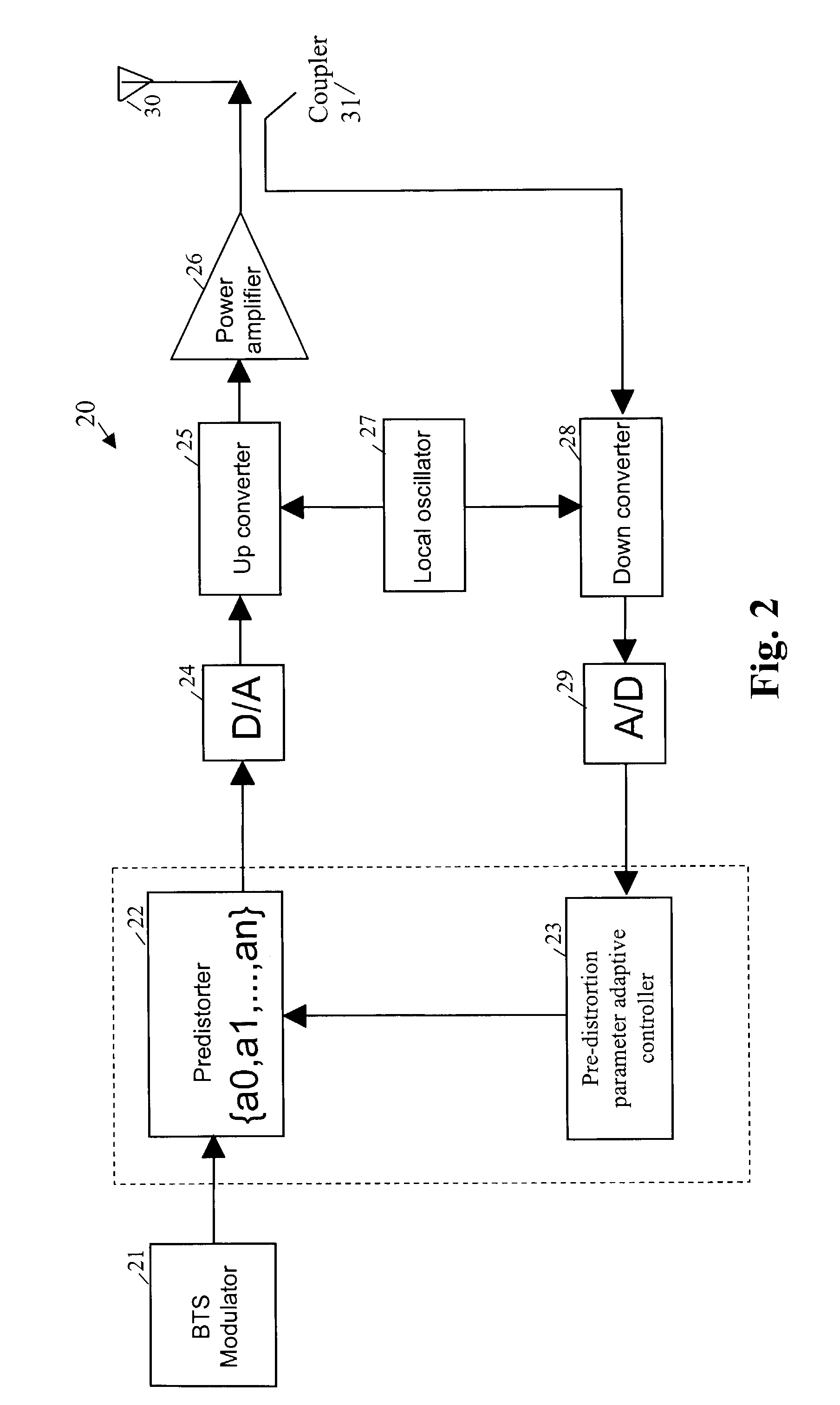
InactiveUS7136628B2Overcome disadvantagesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasUp conversionWireless transmitter
An adaptive digital predistortion apparatus and method for transmitting broadband digital signals from a wireless transmitter to a transmitting channel are provided. In the adaptive digital predistortion process, a non-linearity conversion opposite to the transmitting channel characteristic is performed by a digital predistorter for input baseband signals. The predistorted signals are amplified by a power amplifier via an up conversion channel. A part of the signals outputted from the power amplifier are fed back to an adaptive controller via a coupler. The feedback signals are processed by the adaptive controller to obtain out-of-band emission energy of the feedback signals. Using the out-of-band emission energy as a target function, the predistortion parameters are updated by employing a multi-parameter optimum seeking module. Accordingly, broadband signals to be transmitted are predistorted by the digital predistortion system to cancel out the non-linear characteristic of the transmitting channels, and to suppress the out-of-band emission energy of the outputting signals. Meanwhile, by using a multi-parameter optimization seeking module, the predistortion parameters are adjusted adaptively by the digital predistortion system based on the slow variation of non-linearity of the transmitting channels.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Digital cross cancellation system
InactiveUS7129778B2Emission reductionLower Level RequirementsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierOut of band emission
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Electromagnetic compatibility optimizing method for receiver in targeted frequency ranges
ActiveCN101873144AKnow the interference environmentGet informed about the disturbanceTransmissionBroadbandWide band
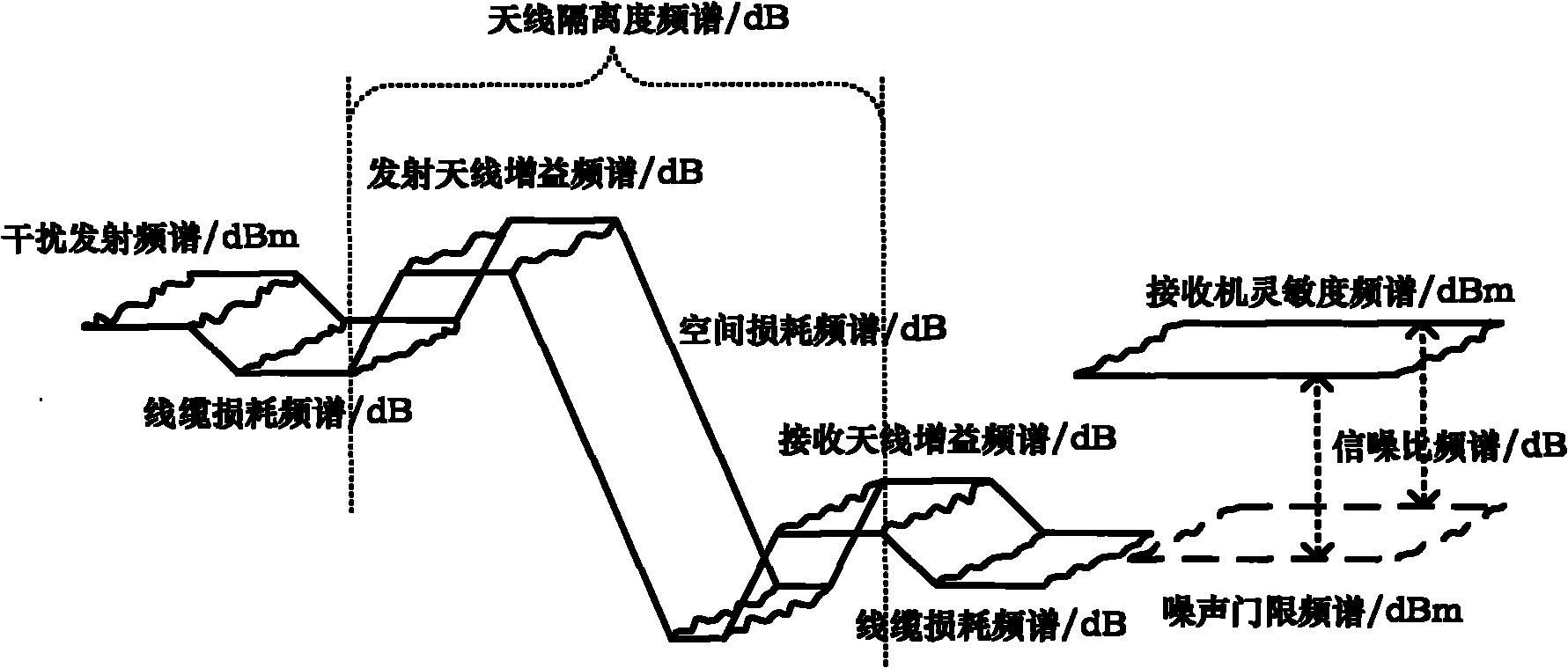
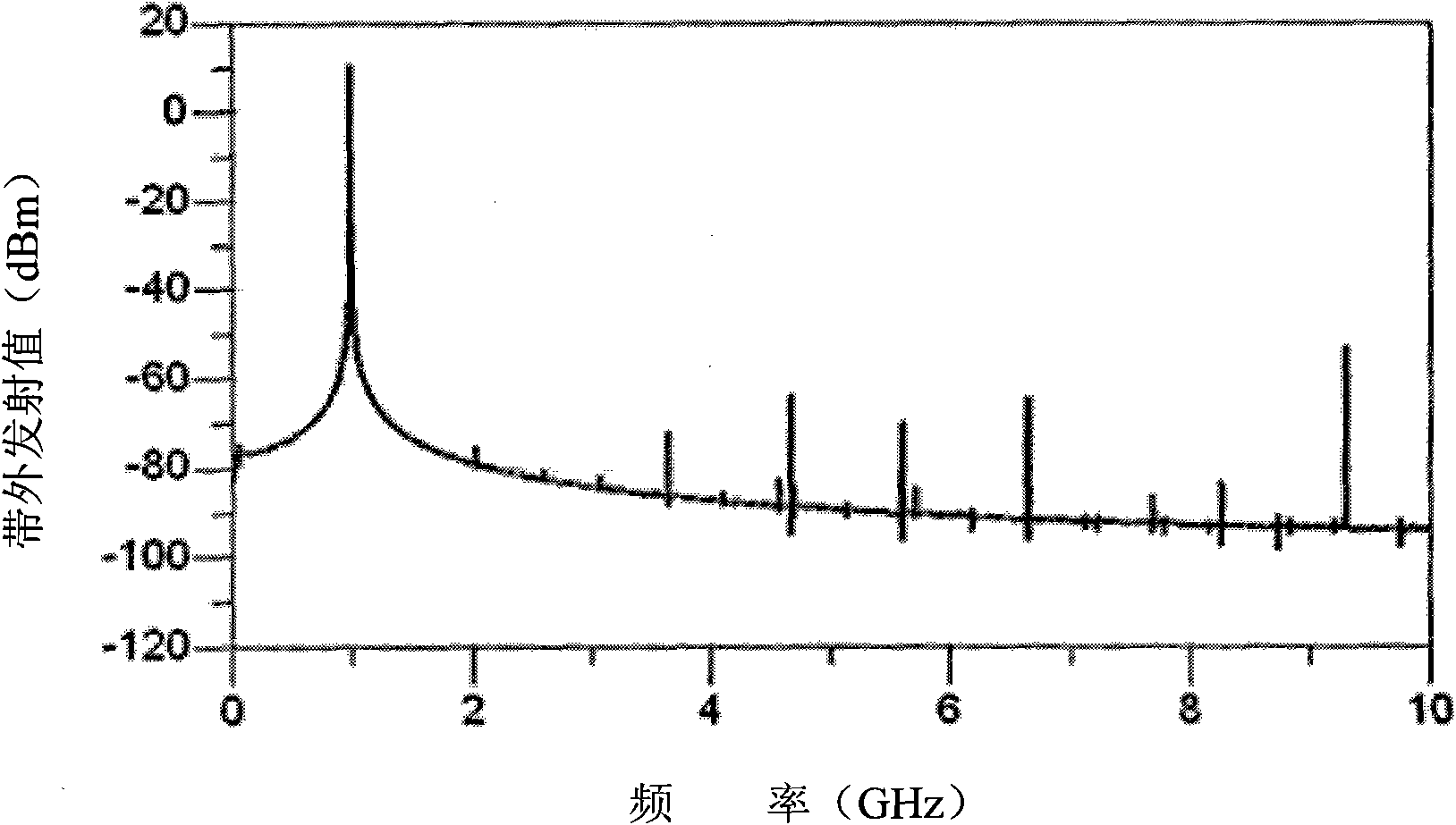
The invention discloses an electromagnetic compatibility optimizing method for a receiver in targeted frequency ranges. A plurality of interference devices and a width-band receiver are associated by using simulation software and the simulation computing power of a computer, and comprehensive consideration is given to the interference characteristic of each interference device, the interfered characteristic of the receiver and the spatial isolation degree so as to extract an interference leading source; and the interference leading source is used to systematically perform targeted electromagnetic compatibility optimization on the out-of-band emission of the interference devices, the spatial isolation degree of antennae and the interfered threshold of the wide-band receiver according to the priority. The method defines the optimization target and improves the optimization speed on the premise of ensuring the optimization effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Latency reduction in a communications system
InactiveUS7930000B2Lower latencyFacilitate controlled communicationEnergy efficient ICTBroadband local area networksPower modeCommunications system
A two way communication system is adapted to reduce latency while the communications system is operating in a low power mode. The two way communication system includes a local host having a first primary communication channel and a secondary out of band transmitter; and customer premise equipment having a primary communication channel for communicating with the first primary communication channel of the local host and a secondary low power out of band receiver that receives out of band control signals from the out of band transmitter during low power operation of the customer premise equipment.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
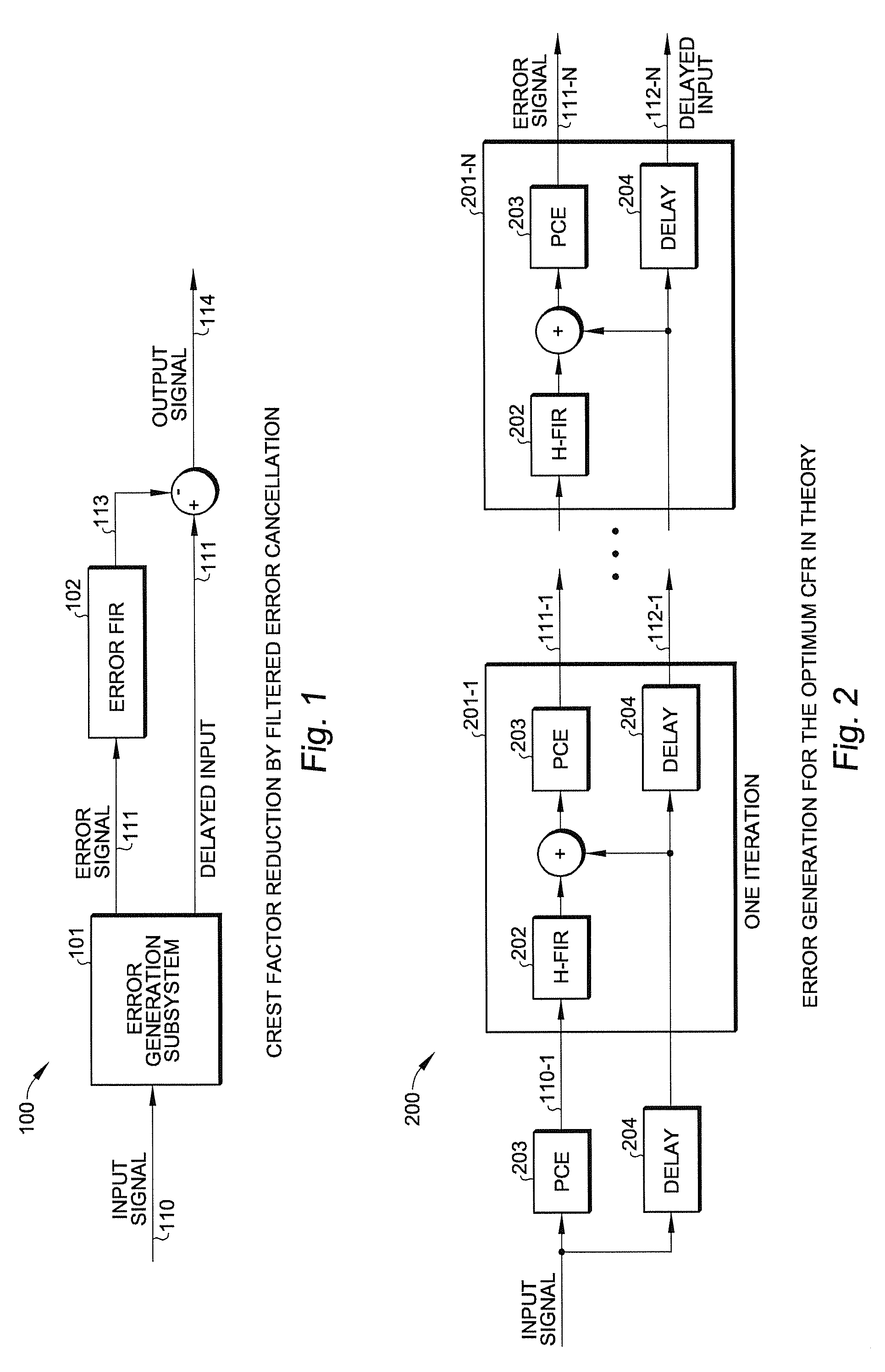
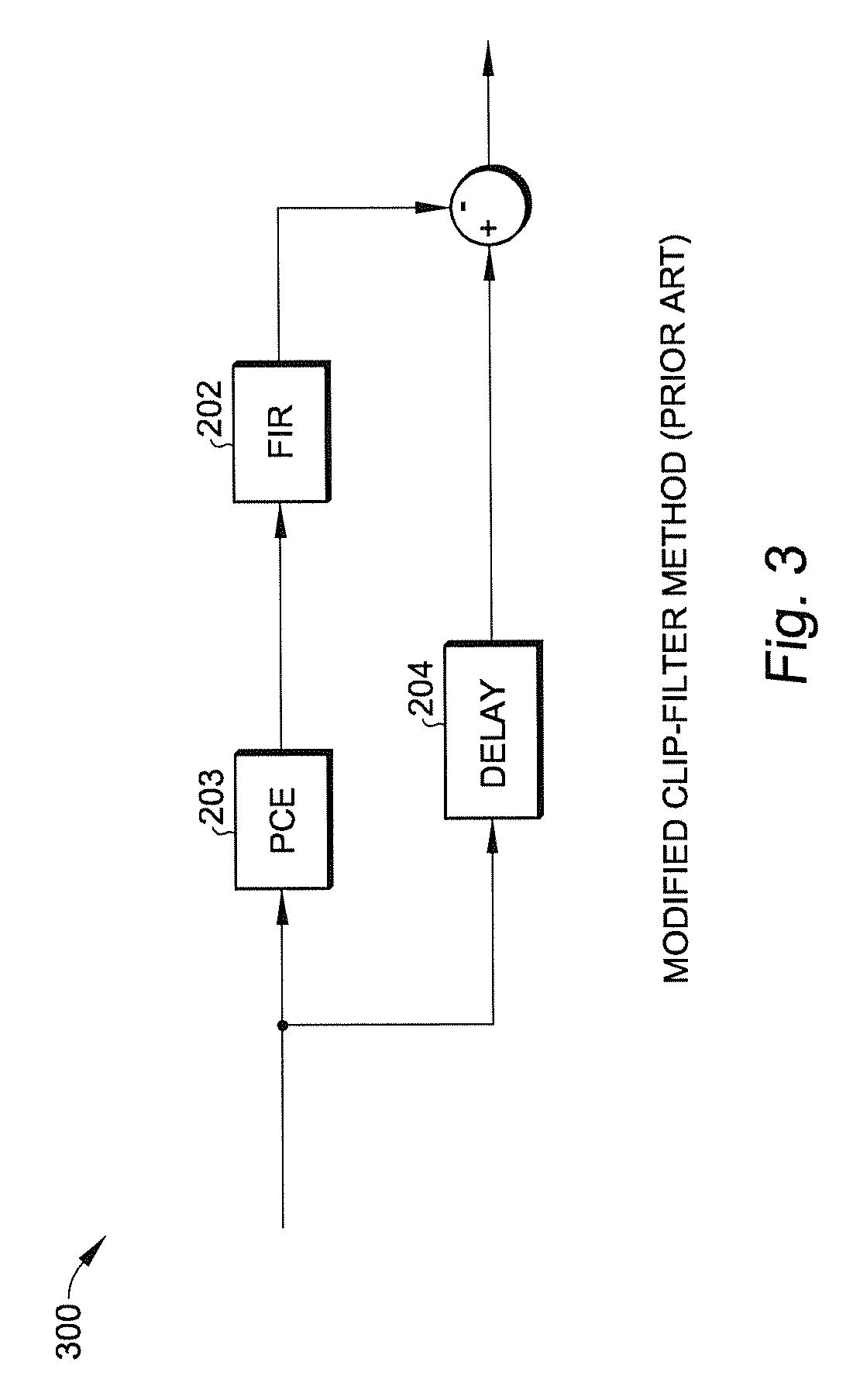
Crest factor reduction for band-limited multi-carrier signals
ActiveUS20140341316A1Reduce rateIncrease in out-of-band emissionModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationComputation complexityCarrier signal
A crest factor reduction (CFR) circuit reduces the peak-to-average (PAR) power of a digitally modulated signal in a complex baseband is achieved by post-processing the input signal, with negligible increase in out-of-band emissions. The CFR circuit takes advantage of a procedure that solves for an optimum CFR using a constraint-optimization approach. In one embodiment, the CFR circuit, which receives an input signal and provides an output signal, includes: (a) an error generation circuit that receives the input signal and provides an error signal representative of a measure of circuit-induced distortion and a delayed input signal, the delayed input signal being the input signal delayed by a predetermined value; (b) a linear-phase filter receiving the error signal to provide a correction signal; and (c) a summer that subtracts the correction from the delayed input signal to provide the output signal. This circuit can achieve near optimal CFR for arbitrary multi-carrier signals without incurring high computational complexity.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS +1
Power transfer measurement circuit for wireless systems
ActiveUS20050020218A1Resonant long antennasResistance/reactance/impedenceAudio power amplifierWireless lan
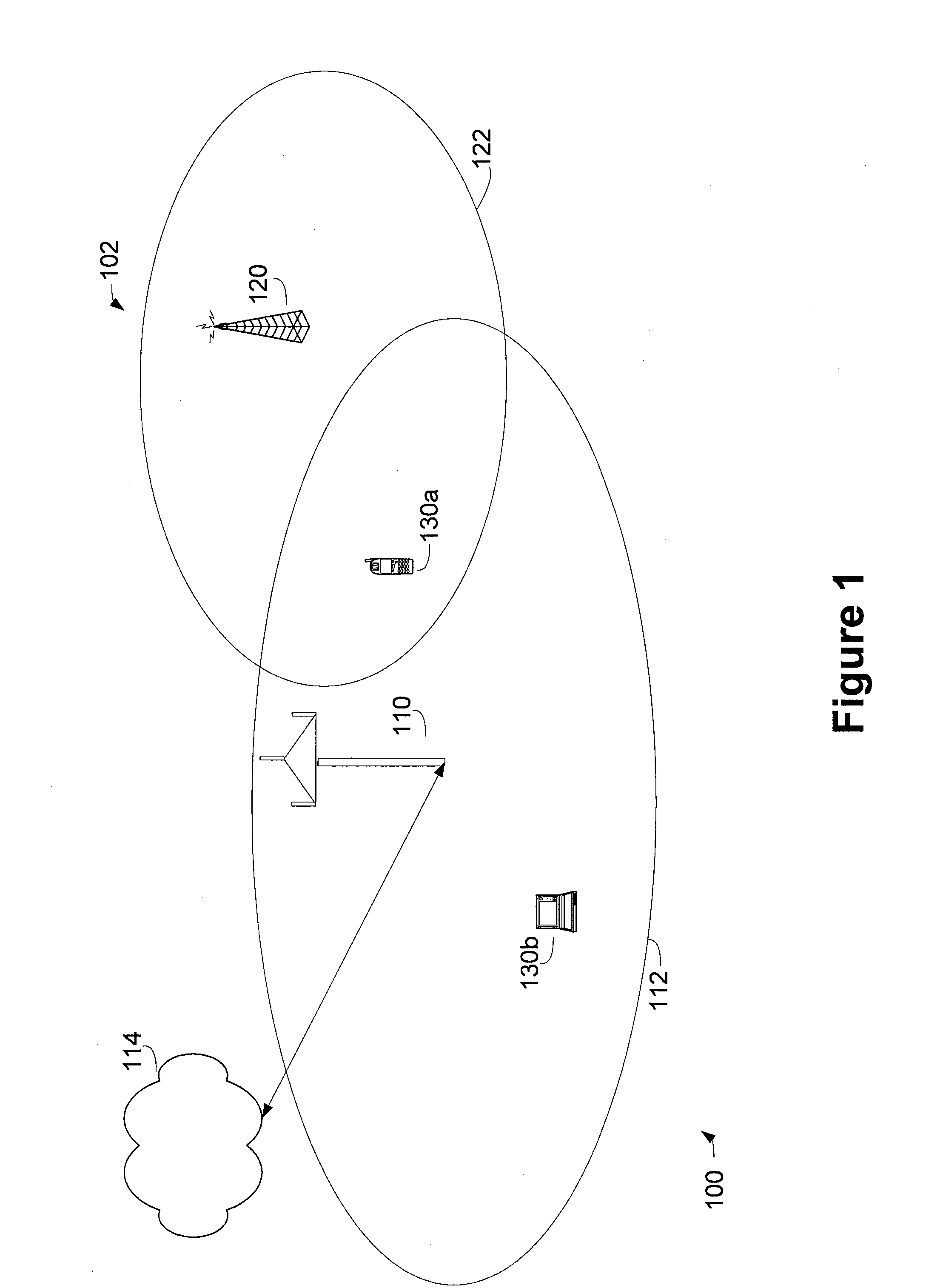
The purpose of the invention is to provide an accurate measurement of RF signal power transfer between a power amplifier circuit and an antenna in the presence of supply voltage variations, temperature variations and VSWR mismatch. Knowing the VSWR mismatch enables modification of a control loop for the PA and thus allows for output power adjustment in order to make the PA more efficient and robust against VSWR changes. Having an indication of power delivered to the load and the VSWR is desirable for many wireless applications especially in those applications where the PA can generate emissions that are out of band and all emissions subject to industry standards. In particular, the embodiments of the invention are applicable to wireless LANs (WLANs).
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
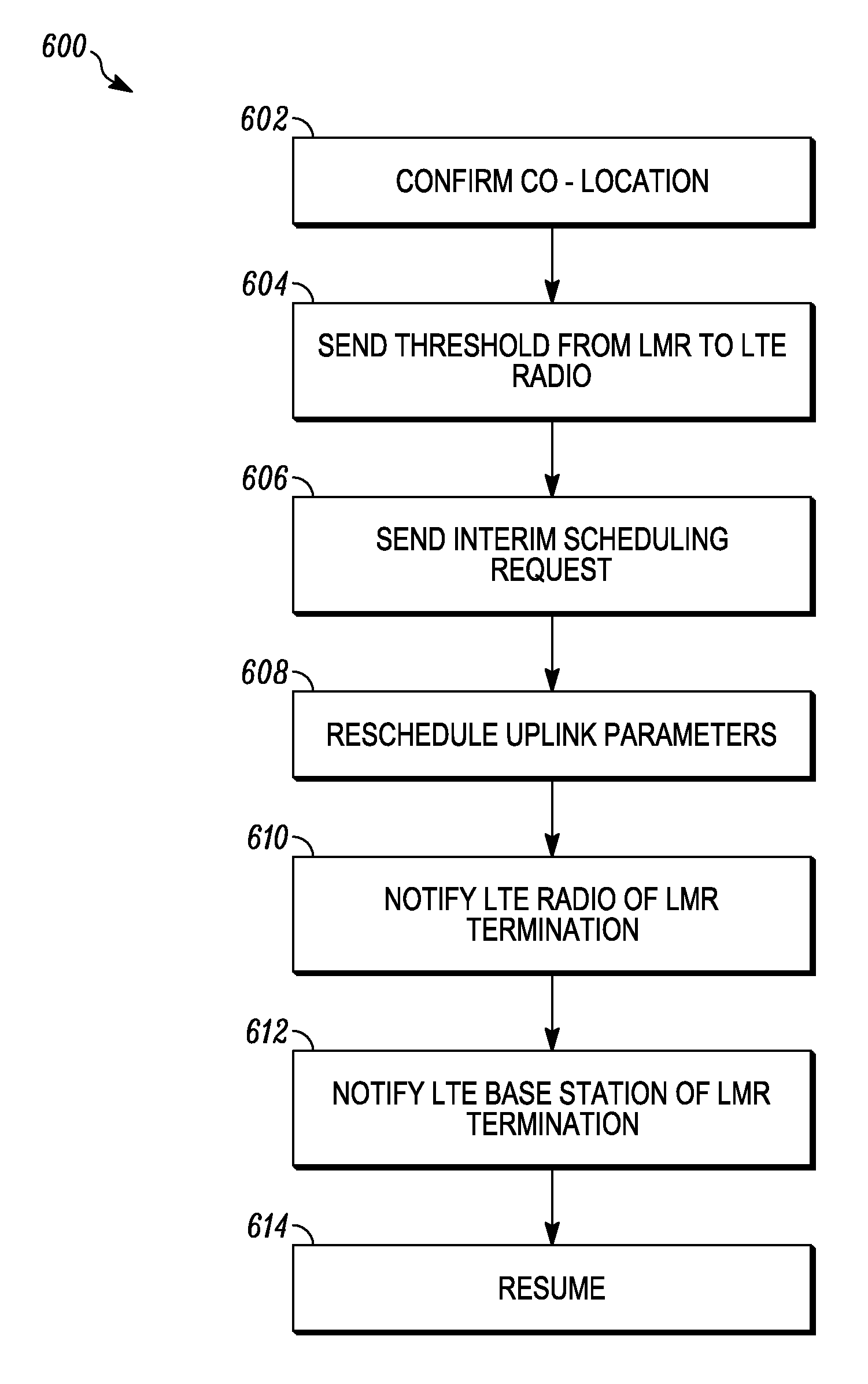
Methods and apparatus for mitigating interference between co-located collaborating radios
Methods and apparatus are provided for mitigating interference between spectrally distinct wireless communication networks employing co-located, collaborating radios. A first base station is in a first network and communicates with a first radio within a first frequency range, and a second base station is in a second network and communicates with a second radio in a second frequency range. The first and second radios are geographically co-located, for example, within a public safety vehicle. The first radio determines a maximum level of interference it will accept based on current operational parameters, and communicates a corresponding threshold value to the second radio through a data link. The second radio sends a request to its base station to employ interim scheduling constraints governing uplink transmissions from the second radio, to thereby limit out of band emissions received by the first radio to a range that is less than the threshold interference level.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
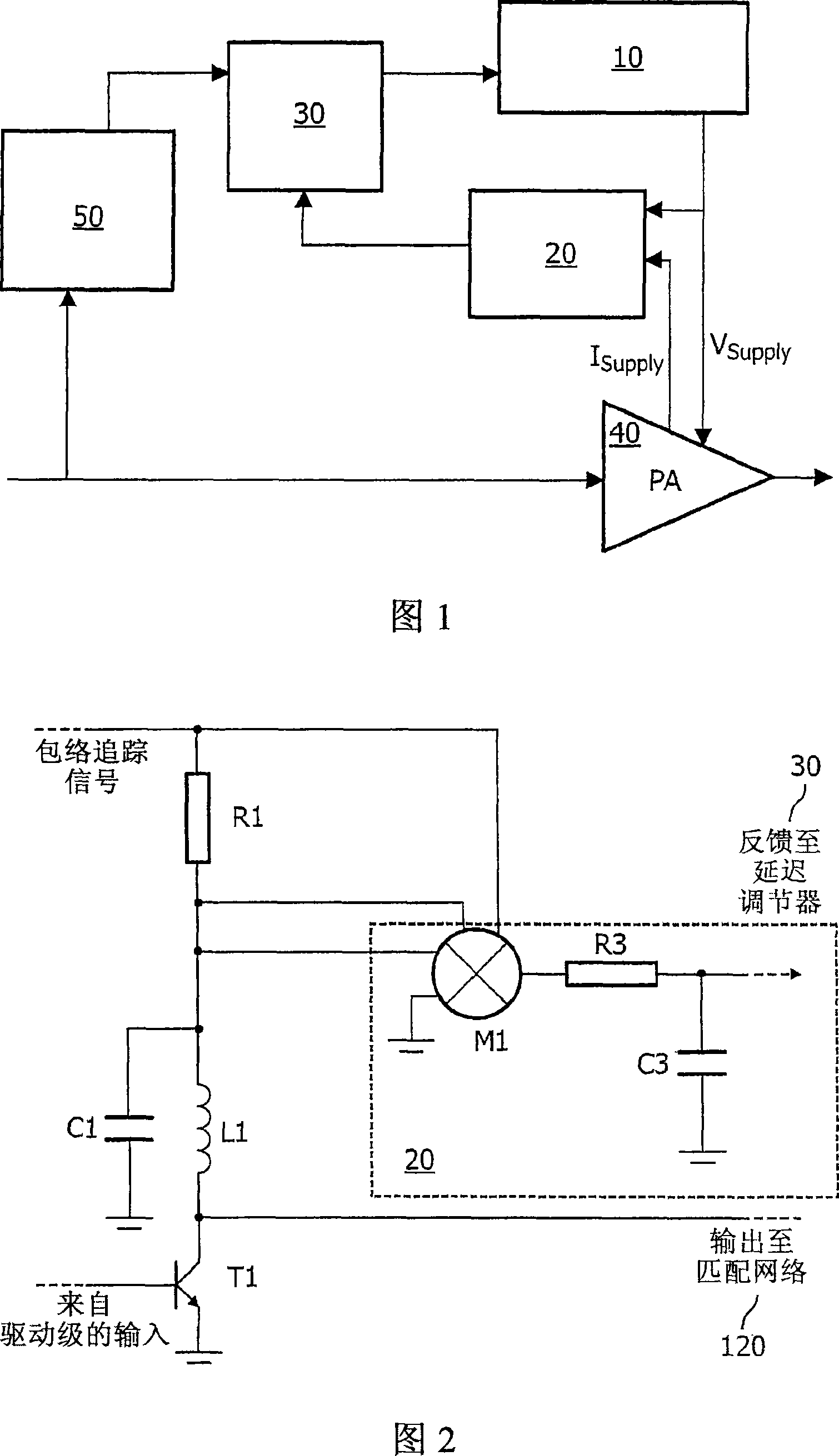
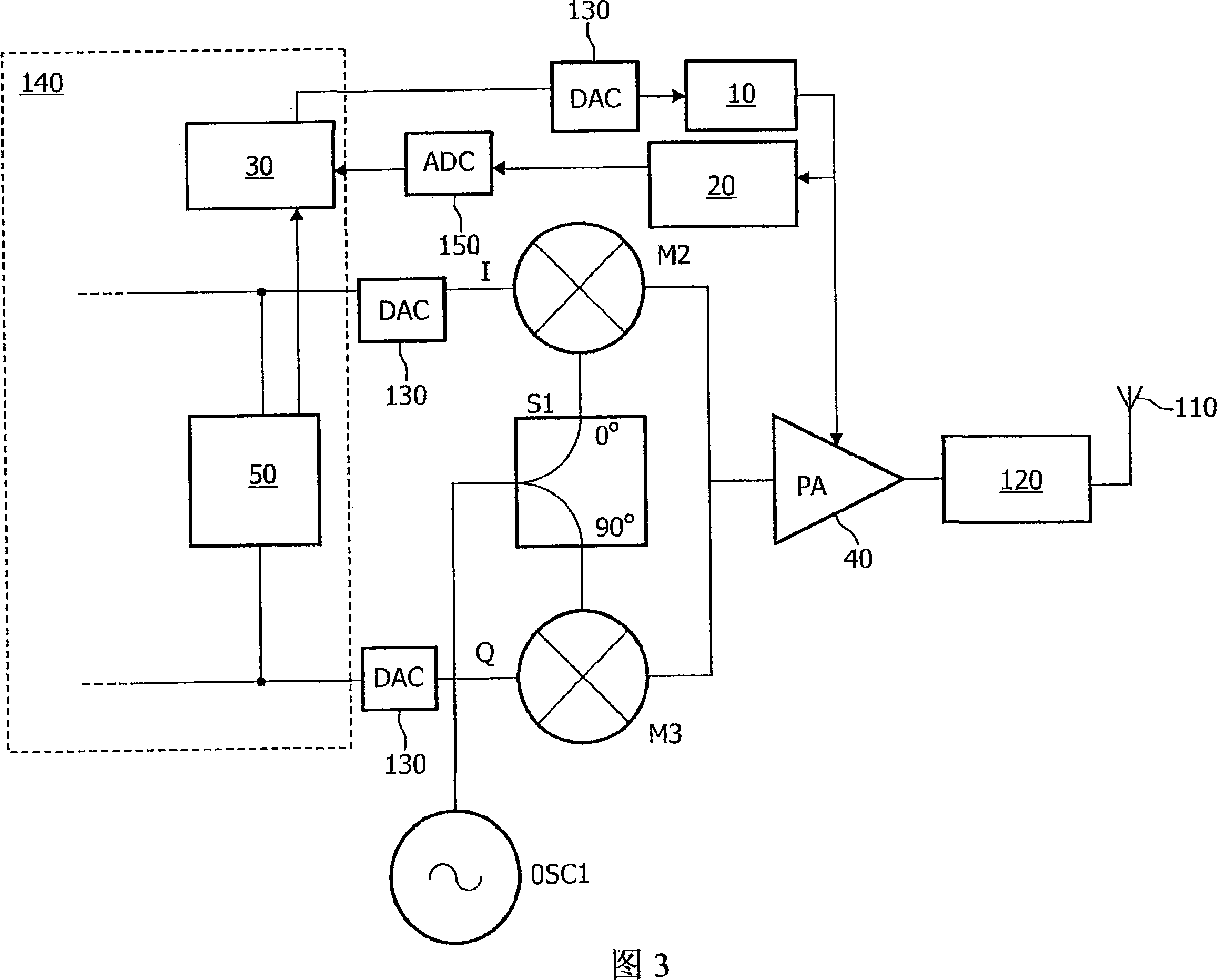
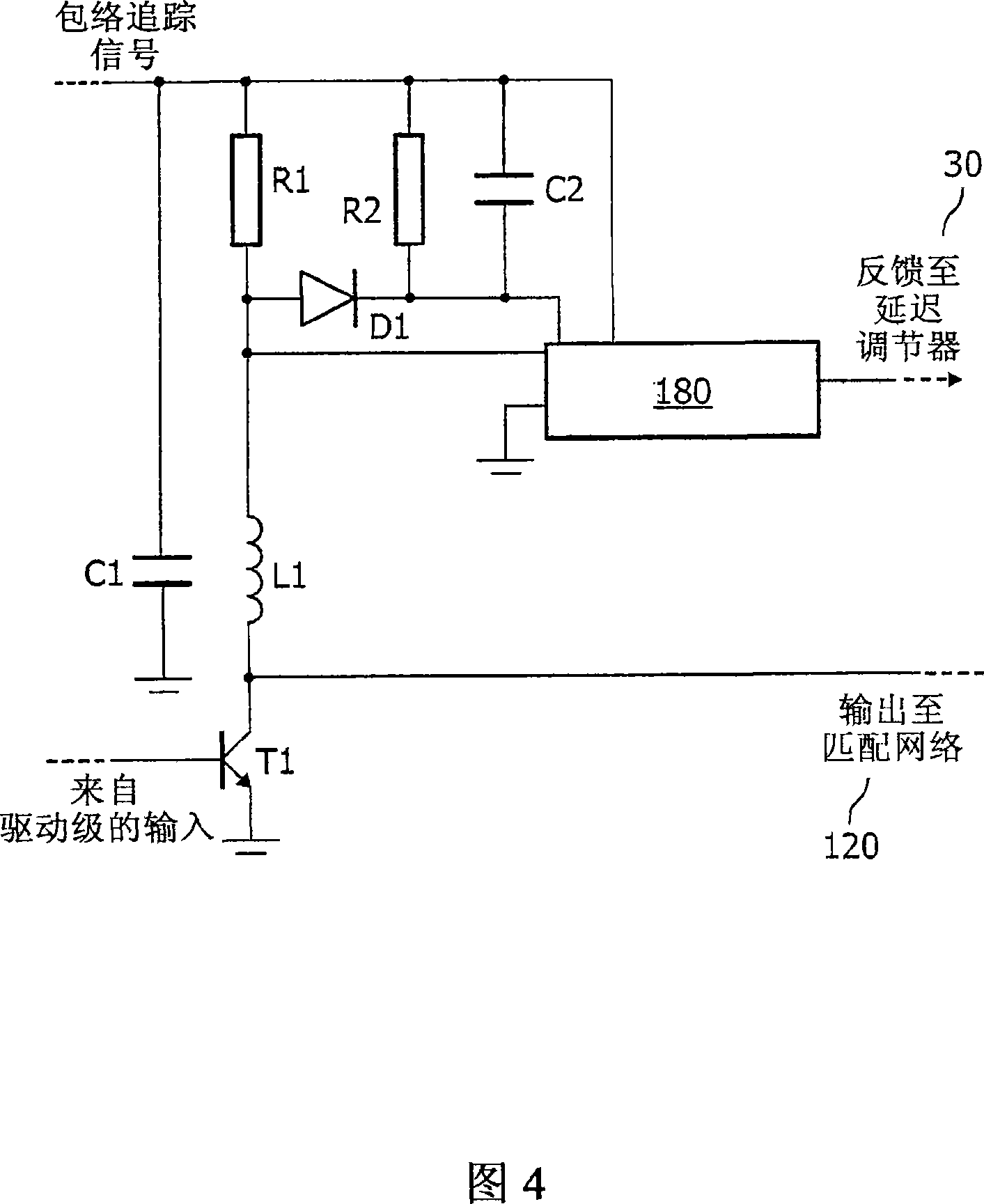
RF transmitter with compensation of differential path delay
InactiveCN101233681AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl delay
A transmitter has a power amplifier (40) to amplify an input signal having amplitude modulation, a supply voltage controller (10) to control a supply voltage of the power amplifier (40) according to the envelope, a sensor (R1) for sensing a modulation of a current drawn by the power amplifier (40), a delay detector (20) for detecting a delay of the controlled supply voltage relative to the sensed current, and a delay adjuster (30) for compensating the relative delay according to the detected delay. By sensing a current drawn, the delay detected can include any delay contributed by the power amplifier (40) up to that point, and yet avoid the more complex circuitry needed to derive the delay from an output of the power amplifier. Thus the distortion and out of band emissions caused by differential delays can be reduced more effectively.
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
Method and device for adjusting distribution positions of frequency-domain resources
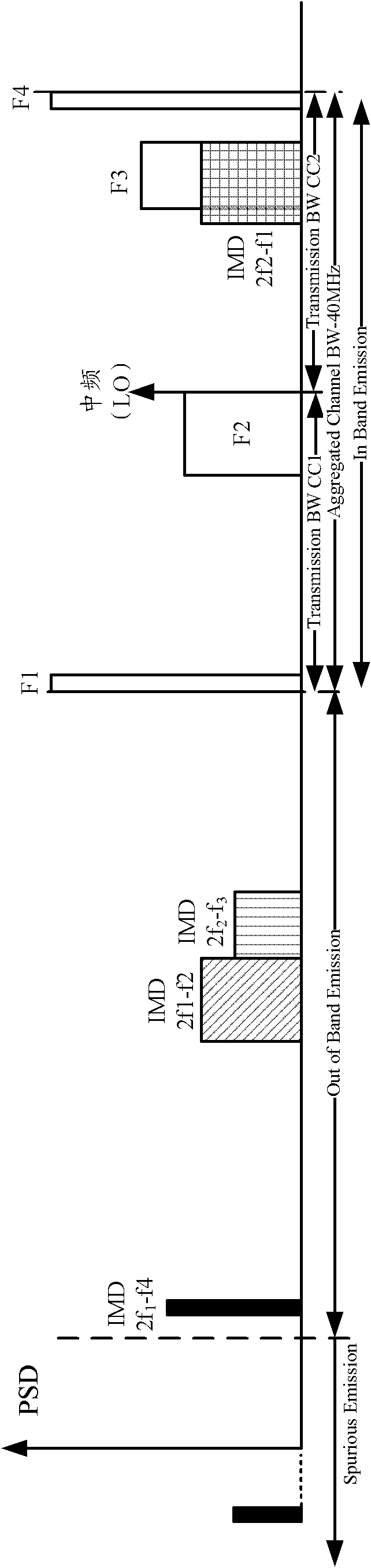
ActiveCN102075951AReduce out-of-band leakageGuaranteed transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementInter user/terminal allocationSignal qualityUplink transmission
The invention relates to the communication field, and discloses a method and device for adjusting distribution positions of frequency-domain resources, so as to ensure signal quality of a terminal when an uplink transmission is performed based on discontinuous frequency-domain resources. The method comprises the following steps: in a case that the uplink transmission is performed by using discontinuous frequency-domain resources in an LTE-A (long term evolution-advanced) system, a terminal can obtain a corresponding largest frequency-domain interval according to a network-environment-based MPR (multiple protocol router) threshold value; and then based on the largest frequency-domain interval, the distribution positions of discontinuous frequency-domain resources used by the terminal are adjusted, so as to ensure the interval between each frequency-domain resource not to exceed the determined largest frequency-domain interval. Therefore, when signals are transmitted on the adjusted discontinuous frequency-domain resources, out-of-band emission due to inter-modulation (IMD) generated between each frequency-domain resource is effectively reduced, and thus the transmission quality of uplink signals are ensured, so that adverse effects to system coexistence and system performance are avoided while gain for user performance brought by the discontinuous frequency-domain transmission is fully used.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for mitigating interference between co-located collaborating radios
Methods and apparatus are provided for mitigating interference between spectrally distinct wireless communication networks employing co-located, collaborating radios. A first base station is in a first network and communicates with a first radio within a first frequency range, and a second base station is in a second network and communicates with a second radio in a second frequency range. The first and second radios are geographically co-located, for example, within a public safety vehicle. The first radio determines a maximum level of interference it will accept based on current operational parameters, and communicates a corresponding threshold value to the second radio through a data link. The second radio sends a request to its base station to employ interim scheduling constraints governing uplink transmissions from the second radio, to thereby limit out of band emissions received by the first radio to a range that is less than the threshold interference level.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Wireless transceiver with reduced transmit emissions
InactiveUS8290447B2Attenuation bandwidthEmission reductionTransmission path divisionTransmission path sub-channels allocationTransceiverWireless transceiver
Methods and apparatus for reducing transmit emissions are described herein. The transmit out of band emissions in an adjacent band can be reduced while complying with existing wireless communication standards through utilization of one or more of reduced transmit bandwidth, transmit operating band offset, and channel index remapping. The transceiver can support a receive operating band that is substantially adjacent to a band edge. The transmit operating band can be offset from an adjacent frequency band, and can use a narrower operating band than is supported by the receiver. The transmit baseband signal can have a reduced bandwidth to reduce the amount of noise. The frequency offset can introduce a larger transition band between the transmit operating band edges and the adjacent frequency band of interest. The transceiver can remap channel assignments to compensate for the frequency offset such that the frequency offset introduced in the transmitter is transparent to channel allocation.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Fft spreading among selected OFDM sub-carriers
InactiveCN101675637ATransmission path divisionMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalDiversity scheme
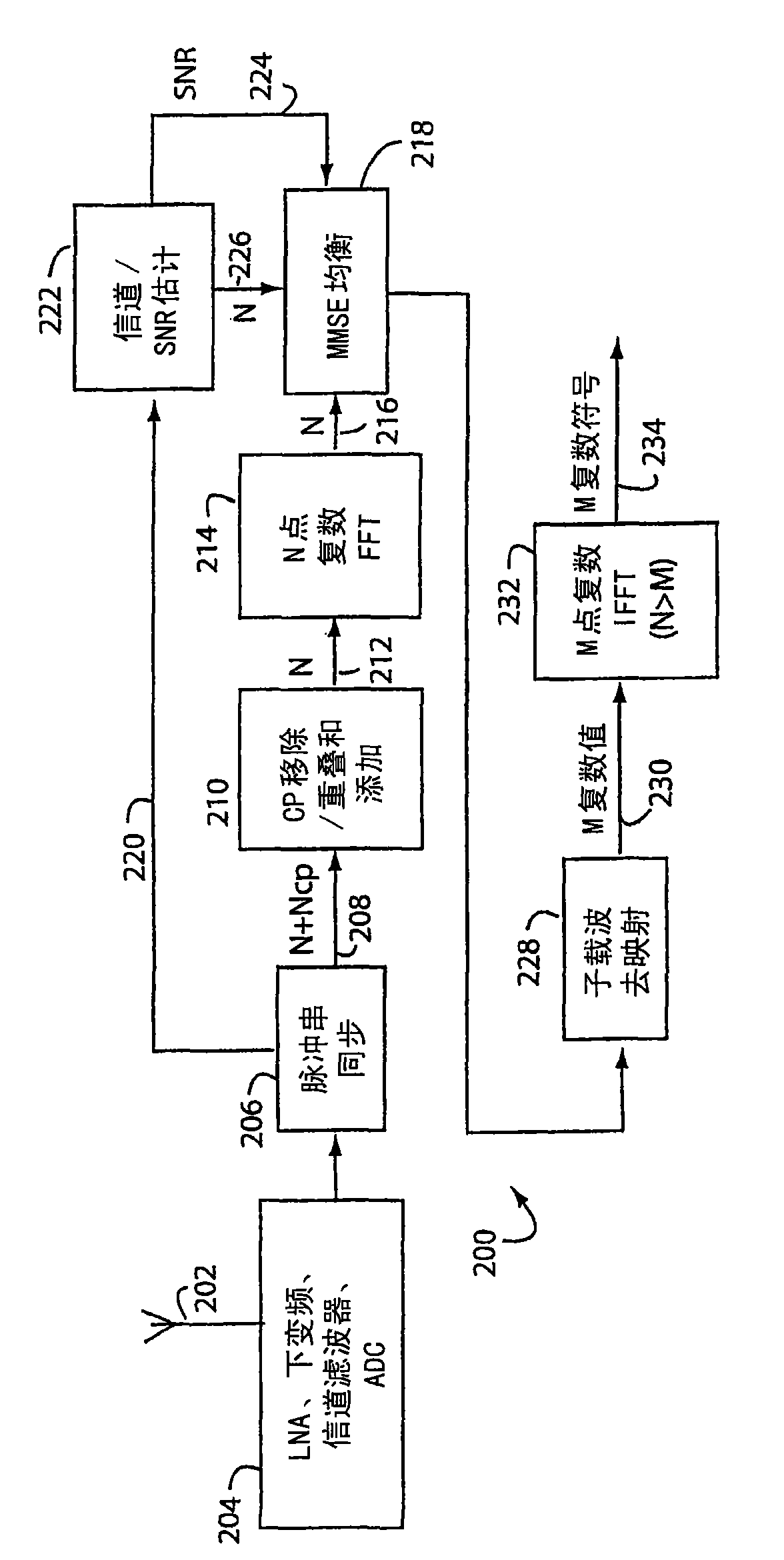
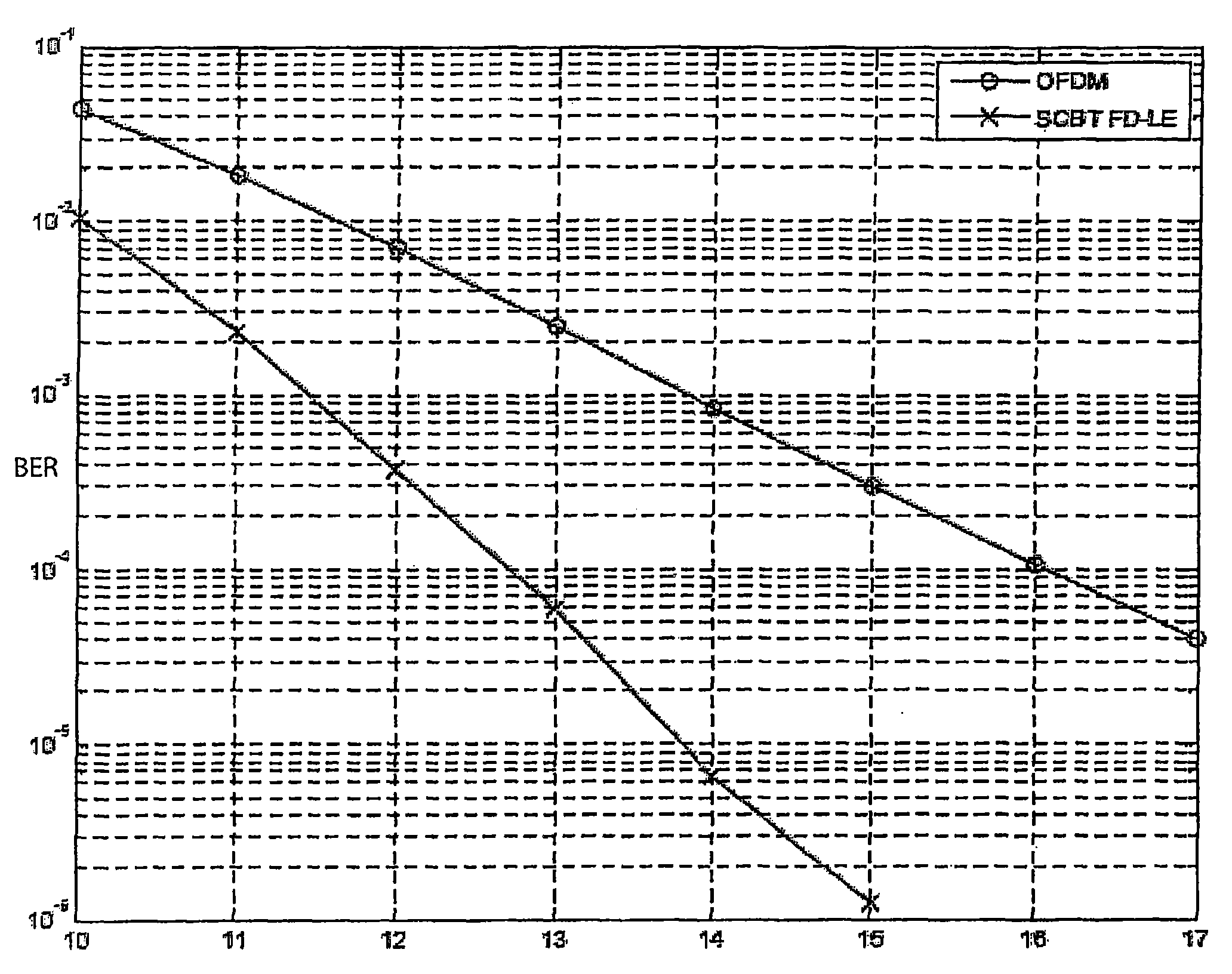
An improved communications system for frequency-selective fading channels spreads the data-bearing modulation symbols across many OFDM sub-carriers using a discrete Fourier transform (FFT) at the transmitter, and despreads them using an inverse discrete Fourier transform (IFFT) at the receiver. An IFFT is included at the transmitter to form the OFDM symbols in the usual way, and a corresponding FFT is used at the receiver for the frequency-domain processing of the received signal. The difference is, the size of the FFT used for spreading at the transmitter is smaller than that of an IFFT usedjust after the FFT to create the OFDM symbols for transmission. This results in improved bit-error-rate, similar to single carrier block transmission (SCBT), while retaining the frequency domain benefits of conventional OFDM, e.g., low out of band emissions and the ability to control the power spectral density using active interference cancellation and other frequency-domain techniques. The improved frequency diversity is especially useful in the higher data rate modes of WLAN or WiMedia Physical Layer Standards, and in other cases where low redundancy forward error correction is employed.
Owner:NXP BV
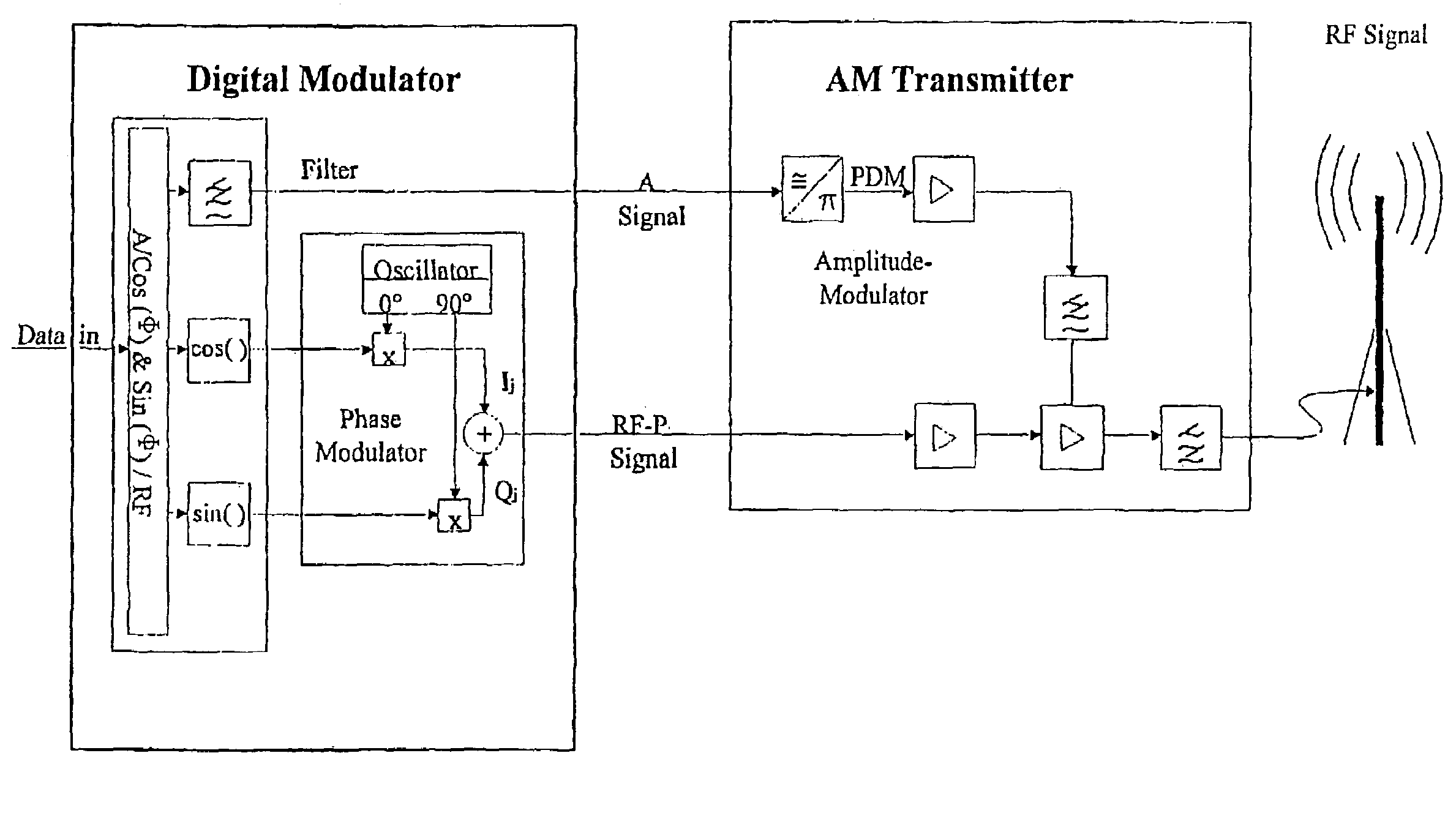
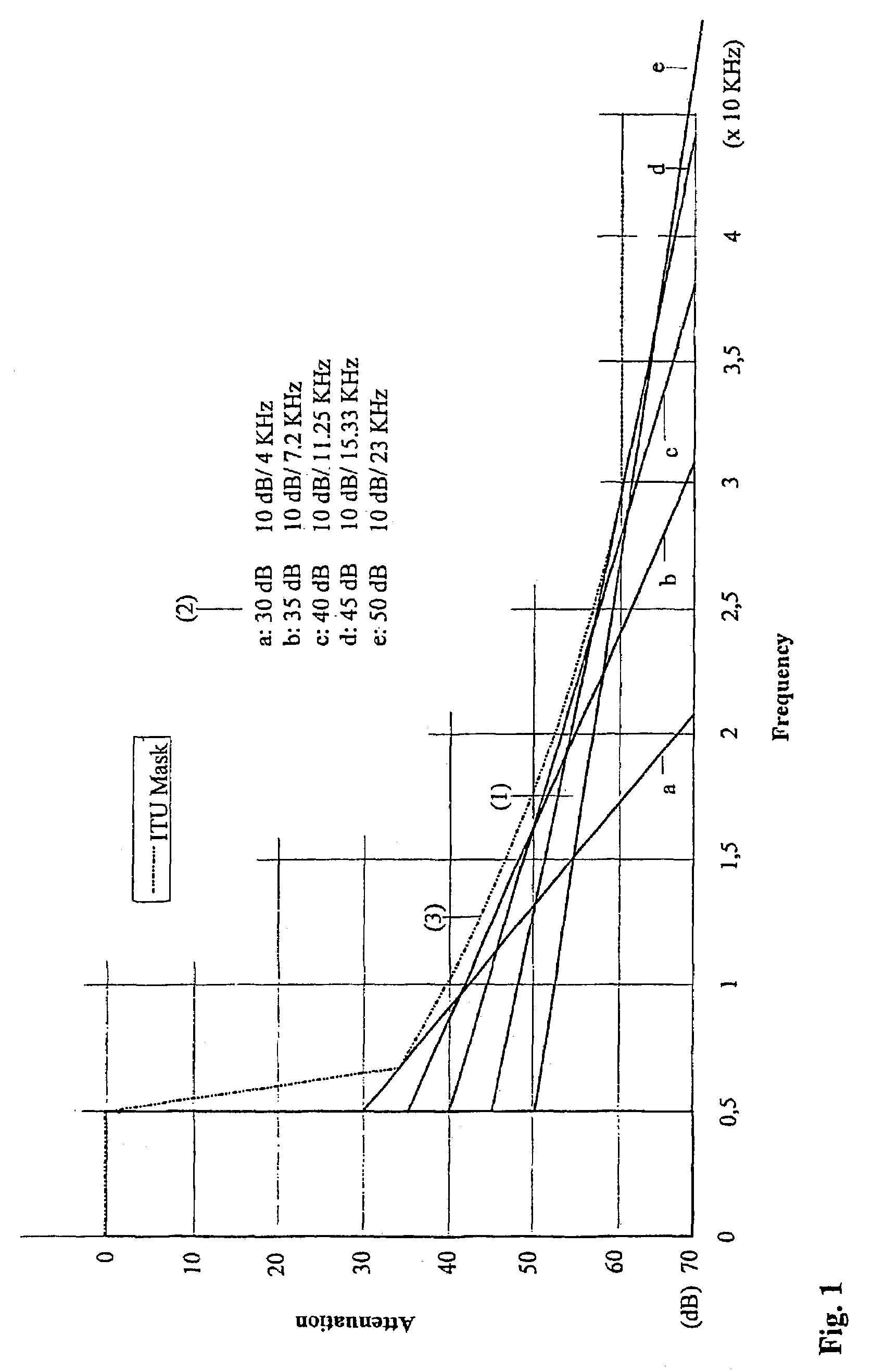
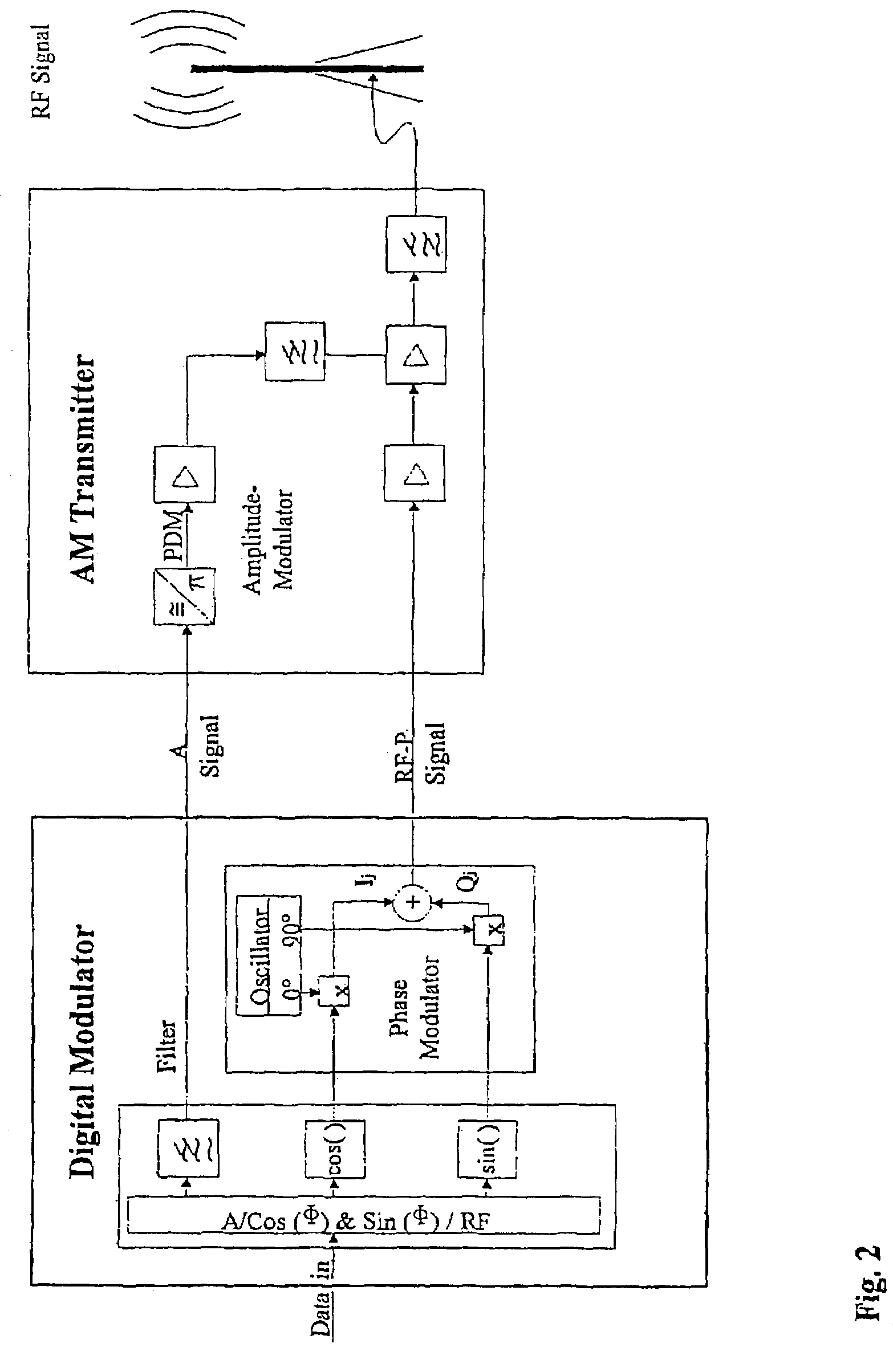
Method for reducing the out-of-band emission in AM transmitters for digital transmission
ActiveUS7248639B2Reducing unwanted emissionReducing out-of-band emissionSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierFrequency spectrumRadio frequency signal
A method for reducing out-of-band emission in an AM transmitter for digital transmission includes generating, from a digital modulation signal, an amplitude signal and a phase-modulated radio frequency signal configured to control the AM transmitter. A digital modulation process is used in which a hole is formed around a 0 / 0 point so that a zero crossing is avoided by a substantial margin in a vector diagram representation. Thereby a respective bandwidth of the amplitude signal and the phase-modulated radio frequency signal is limited so that the out-of-band emission decreases as a function of a shoulder distance achievable by the AM transmitter at a rate where a spectrum mask is not exceeded.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power in a wireless communications device
Systems and techniques for wireless communications are disclosed. The systems and techniques include the generation of a signal, the setting of an average transmit power of the signal transmission as a function of a first threshold relating to out-of-band emissions, the clipping of the signal as a function of a second threshold relating to peak transmit power, and the transmission of the signal over a wireless medium.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Crest factor reduction for brand-limited multi-carrier signals
ActiveUS8937993B2Reduce rateIncrease in out-of-band emissionMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkComputation complexityPhase filter
A crest factor reduction (CFR) circuit reduces the peak-to-average (PAR) power of a digitally modulated signal in a complex baseband is achieved by post-processing the input signal, with negligible increase in out-of-band emissions. The CFR circuit takes advantage of a procedure that solves for an optimum CFR using a constraint-optimization approach. In one embodiment, the CFR circuit, which receives an input signal and provides an output signal, includes: (a) an error generation circuit that receives the input signal and provides an error signal representative of a measure of circuit-induced distortion and a delayed input signal, the delayed input signal being the input signal delayed by a predetermined value; (b) a linear-phase filter receiving the error signal to provide a correction signal; and (c) a summer that subtracts the correction from the delayed input signal to provide the output signal. This circuit can achieve near optimal CFR for arbitrary multi-carrier signals without incurring high computational complexity.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS +1
Method for suppression of OFDM energy spectral density for minimization of out of band emission or utilization of fractured spectrum
ActiveUS20080037668A1Suppressing Orthogonal Frequency Division MultiplexingRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsTransmission systemsFrequency spectrumEngineering
The Energy spectral density of OFDM signals inherently rolls off slowly. Slow OFDM spectral rolloff has system level implications traditionally mitigated by some combination of the following: addition of bandlimiting filtering; use of significant guard bands of zeroed tones; and, guard time shaping. Each of these techniques negatively impact system performance and / or flexibility. This application presents a methodology for active cancellation of out of band spectral energy. The technique can be used by itself or in conjunction with above traditional methods to help control out of band emission. Examples of the use of the new technique are provided. Computational cost of the new technique is also discussed.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
Peak-to-average power ratio management for multi-carrier modulation in wireless communication systems
Techniques for managing peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) for multi-carrier modulation in wireless communication systems. Different terminals in a multiple-access system may have different required transmit powers. The number of carriers to allocate to each terminal is made dependent on its required transmit power. Terminals with higher required transmit powers may be allocated fewer carriers (associated with smaller PAPR) to allow the power amplifier to operate at higher power levels. Terminals with lower required transmit powers may be allocated more carriers (associated with higher PAPR) since the power amplifier is operated at lower power levels. The specific carriers to assign to the terminals may also be determined by their transmit power levels to reduce out-of-band emissions. Terminals with higher required transmit powers may be assigned with carriers near the middle of the operating band, and terminals with lower required transmit powers may be assigned with carriers near the band edges.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Pulse shaping for generating nfc initiator transmit waveform
InactiveCN104662808ANear-field transmissionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesPower flowAudio power amplifier
The present systems and methods may shape signals to meet emission mask requirements, current consumption requirements, and overshoot / undershoot requirements relating to the interaction that, for example, occurs when a near field communications (NFC) target comes within range of an NFC initiator, and the initiator generates and transmits an NFC waveform. In some implementations, a pair of bit patterns are defined whose differential output from an amplifier is a shaped pulse width modulated waveform. Varying individual bits of the bit patterns can vary the shaped pulse waveform with predictability. The pulse width modulated waveform may be filtered using a matching network that reduces higher order harmonics, thereby reducing out-of-band emissions.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
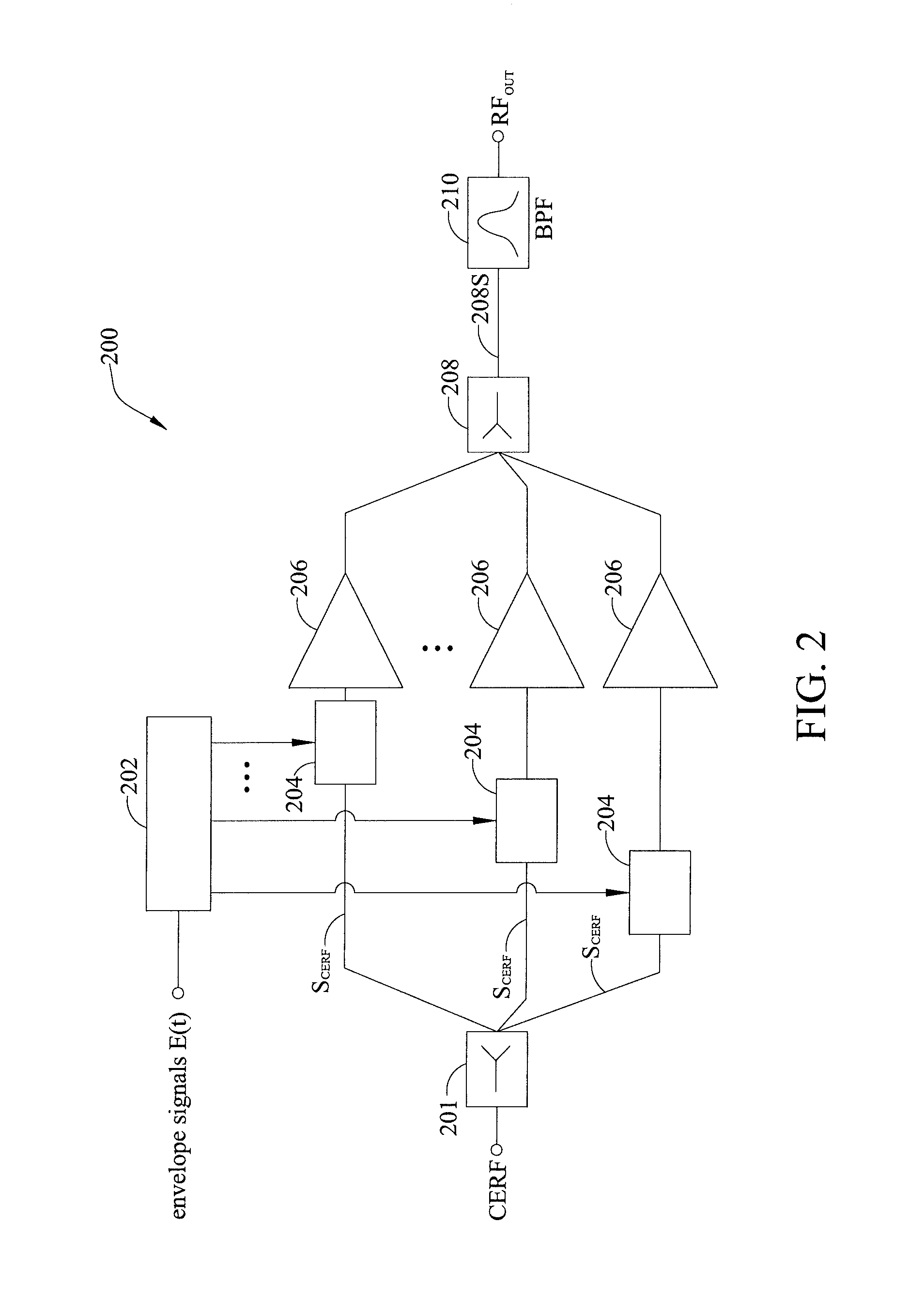
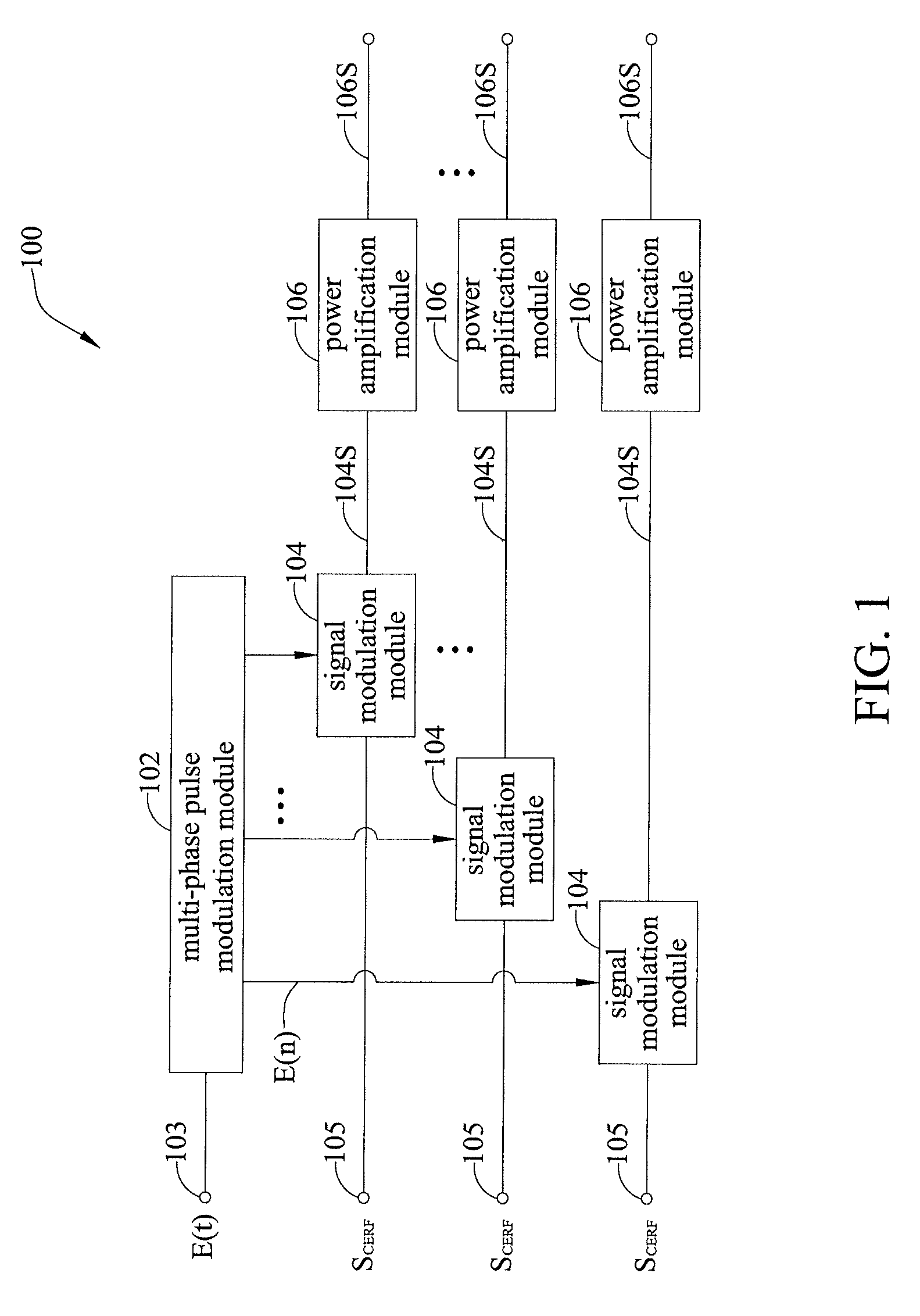
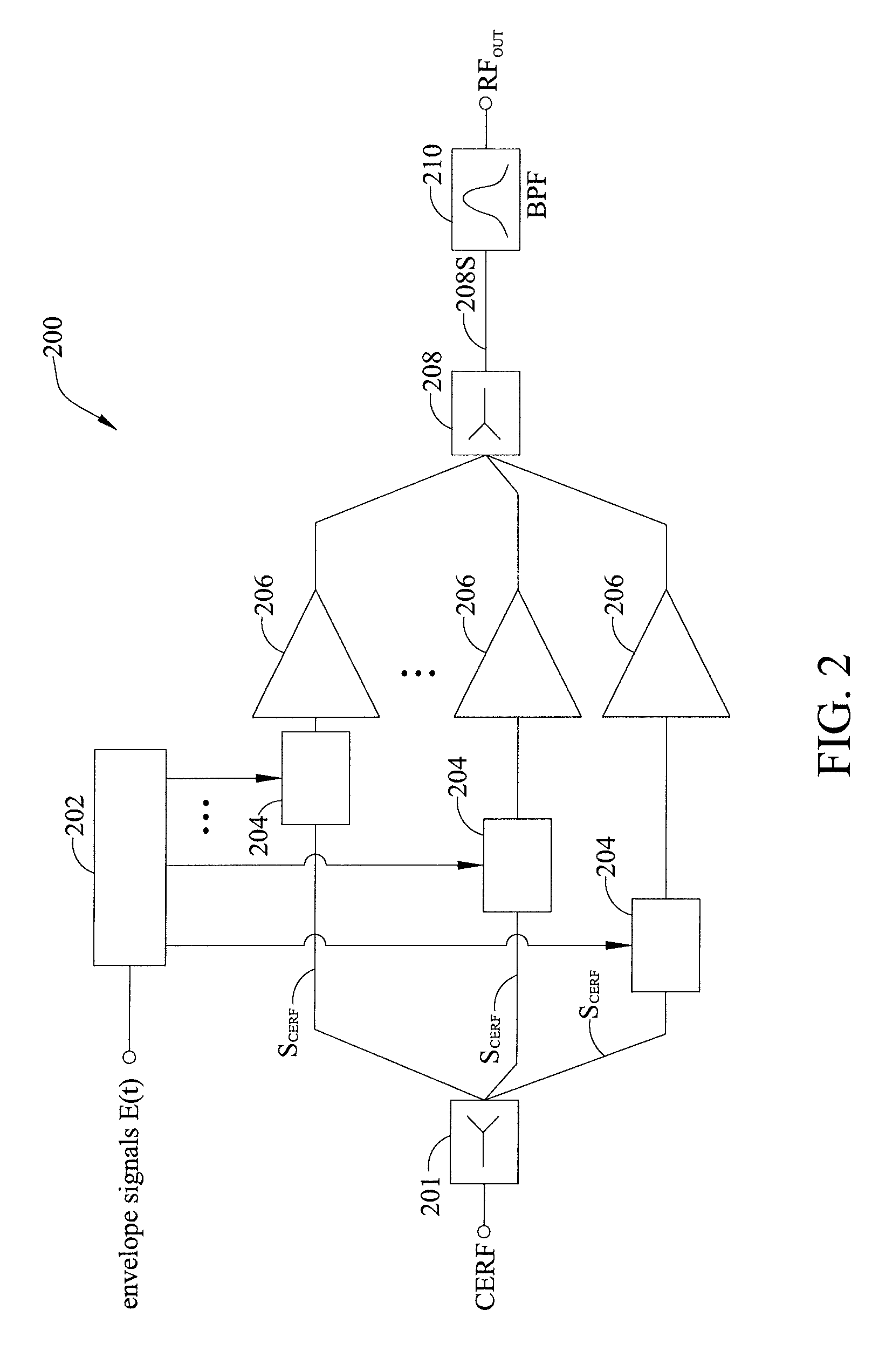
Multi-phase pulse modulation polar transmitter and method of generating a pulse modulated envelope signal carrying modulated RF signal
ActiveUS20110254636A1Synchronization is simpleHigh bandwidthPhase-modulated carrier systemsPulse duration/width modulationAudio power amplifierCombined use
A multi-phase pulse-modulated polar transmitter and a method of generating a pulse-modulated envelope signal carrying modulated RF signal. Multi-phase pulse modulation technique or similar multi-phase pulse modulation techniques are employed in conjunction with a plurality of power amplifiers to enhance the bandwidth of the transmitter and to reduce out-of-band emissions and noises while easily synchronizing the phase and envelope of the input signal.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Multi-phase pulse modulation polar transmitter and method of generating a pulse modulated envelope signal carrying modulated RF signal
ActiveUS8169272B2Synchronization is simpleHigh bandwidthPhase-modulated carrier systemsPulse duration/width modulationAudio power amplifierPolar transmitter
A multi-phase pulse-modulated polar transmitter and a method of generating a pulse-modulated envelope signal carrying modulated RF signal. Multi-phase pulse modulation technique or similar multi-phase pulse modulation techniques are employed in conjunction with a plurality of power amplifiers to enhance the bandwidth of the transmitter and to reduce out-of-band emissions and noises while easily synchronizing the phase and envelope of the input signal.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com