RF transmitter with compensation of differential path delay
A transmitter and relative delay technology, applied in the parts, electrical components, amplifiers and other directions of the amplifying device, which can solve the problems of chip area and extravagant power consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
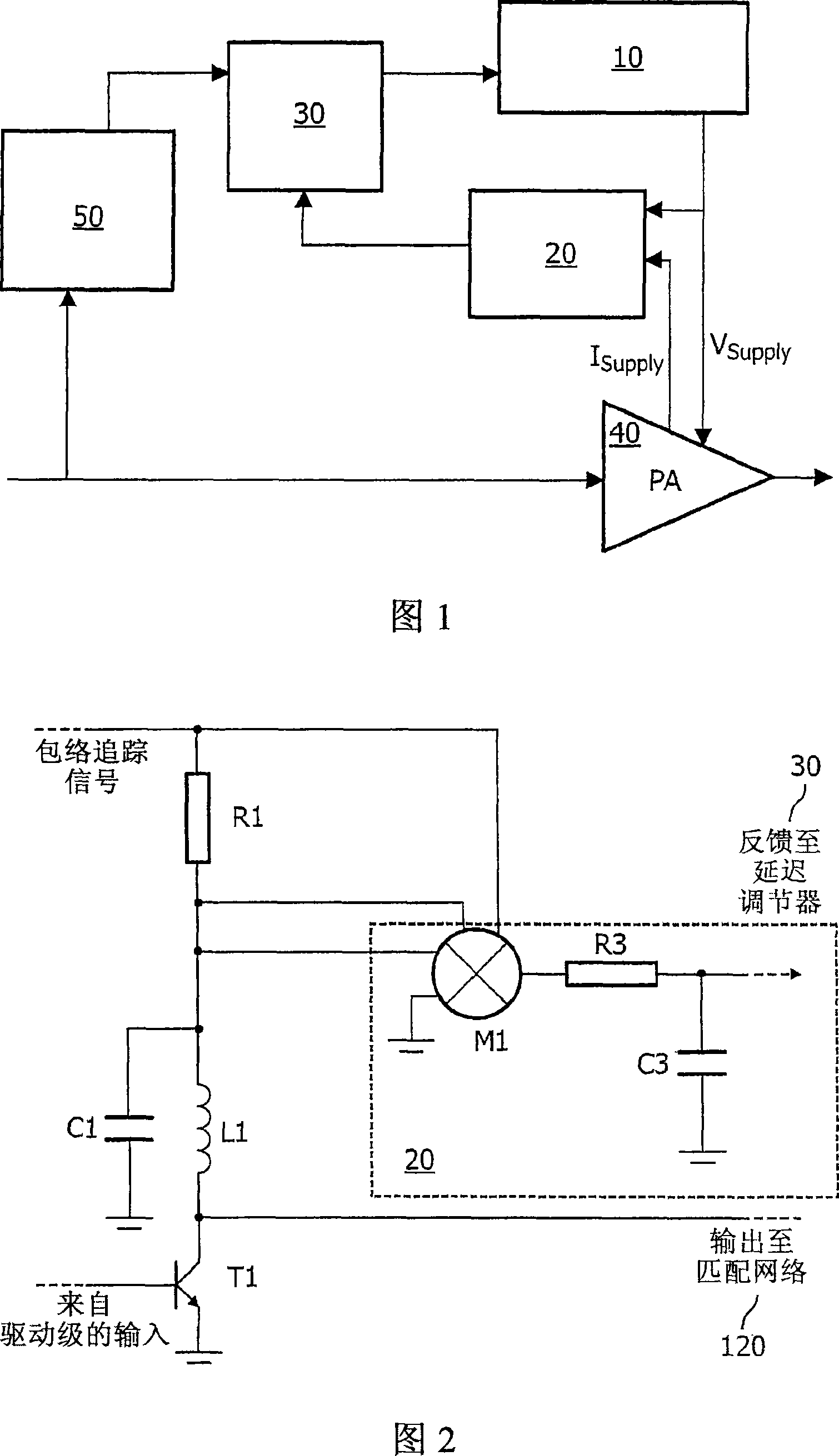
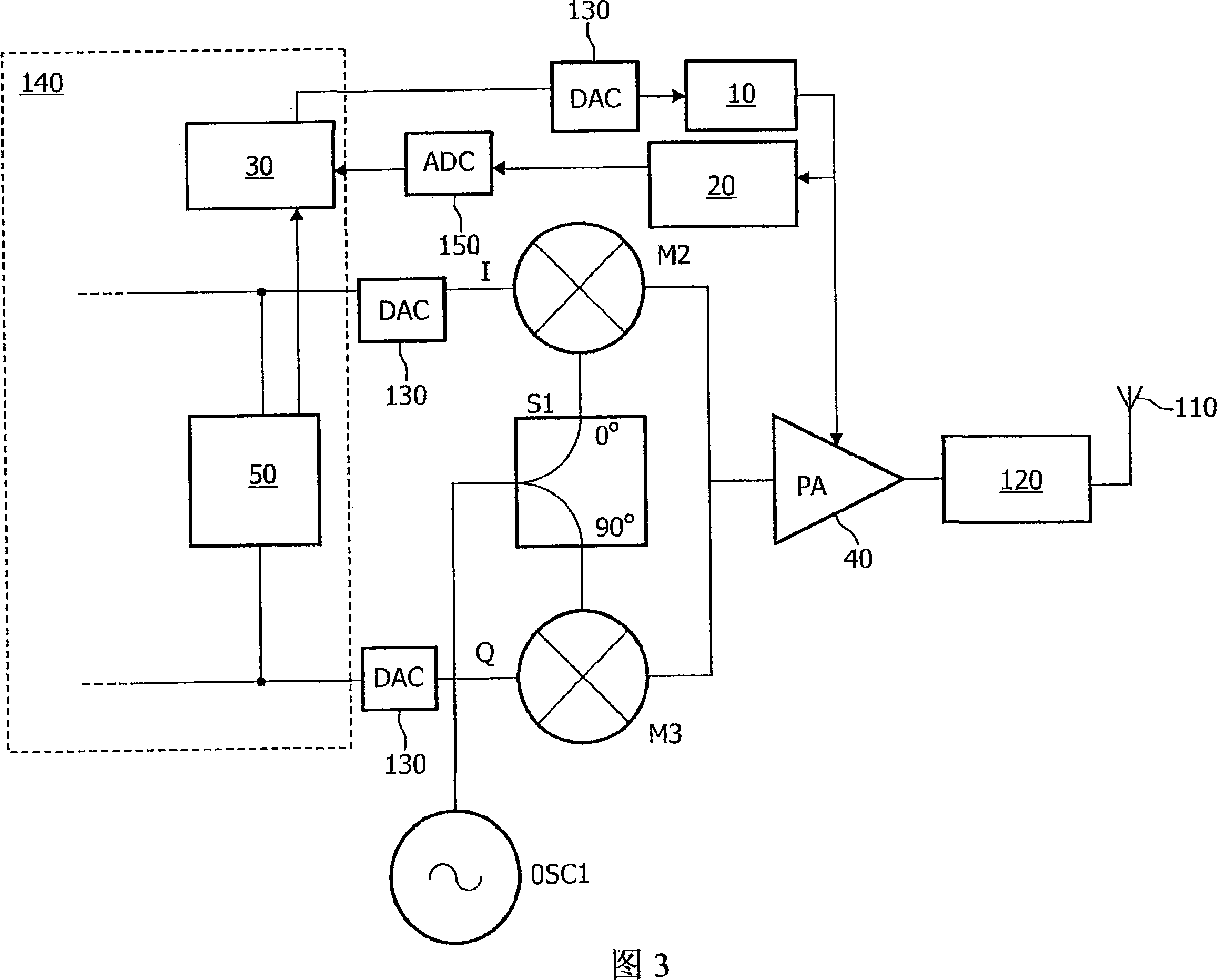
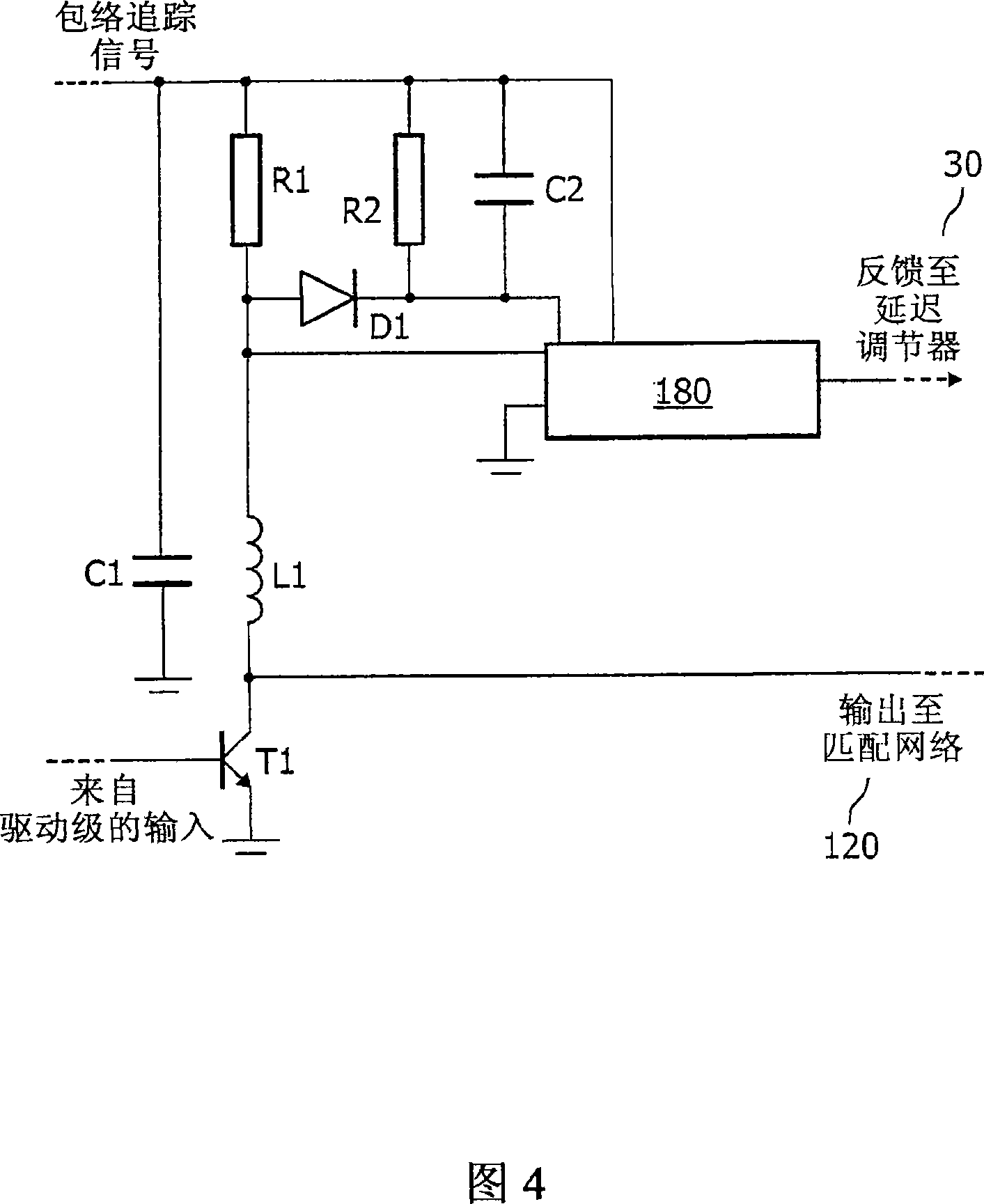
[0020] The described embodiment provides means for detecting the existence of any delay between the main signal channel and the channel carrying the envelope of the fully modulated signal without down-converting the output signal. For envelope tracking, this is possible because the power amplifier is driven by a fully modulated signal, rather than a constant envelope signal that contains only the phase component of the fully modulated signal. Similarly, this embodiment can be extended to polarization modulation, as long as some modulation is performed in the amplified signal (such as a small part of the envelope of the driving signal). In principle, it is possible to specifically generate voltage modulation and current modulation to detect the delay, instead of using the amplitude modulation obtained from the information content of the transmitted signal to detect the delay. As long as the relative delay can be measured, and the desired output spectrum is not excessively polluted,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com