Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Mycobacterium sp. e" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Target-dependent reactions using structure-bridging oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6709815B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to methods and compns. for treating nucleic acids, and in particular, methods and compns. for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and sequence changes. The invention provides methods for examg. the conformations assumed by single strands of nucleic acid, forming the basis of novel methods of detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. The present invention contemplates use of novel detection methods for, among other uses, clinical diagnostic purposes, including but not limited to the detection and identification of pathogenic organisms. Examples are presented for the analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and hepatitis C virus genes.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Methods of using a Mycobacterium tuberculosis coding sequence to facilitate stable and high yield expression of the heterologous proteins
InactiveUS7009042B1Stable and high yield expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousAmino acid
The present invention relates generally to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of a fusion polypeptide comprising a Mycobacterium tuberculosis polypeptide, and a heterologous polypeptide of interest, expression vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acids, and methods for producing such fusion polypeptides. In particular, the invention relates to materials and methods of using such M. tuberculosis sequence as a fusion partner to facilitate the stable and high yield expression of recombinant heterologous polypeptides of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic origin.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Quinoline derivatives and their use as mycobacterial inhibitors
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
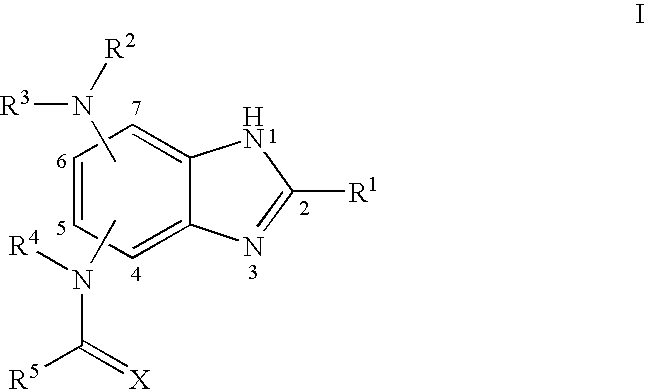
Benzimidazoles and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
The present invention relates to novel benzimidazole derivatives and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Another aspect of the invention relates to methods of treating a patient infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Francisella tulerensis by administering to the patient a benzimidazole derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Mycobacterial inhibitors
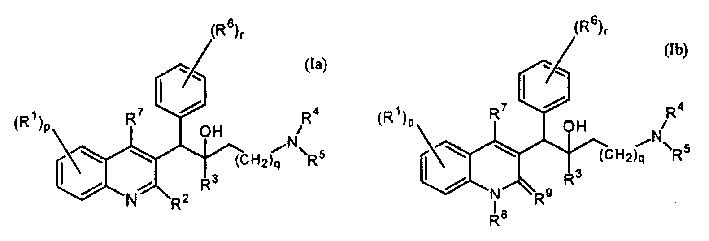
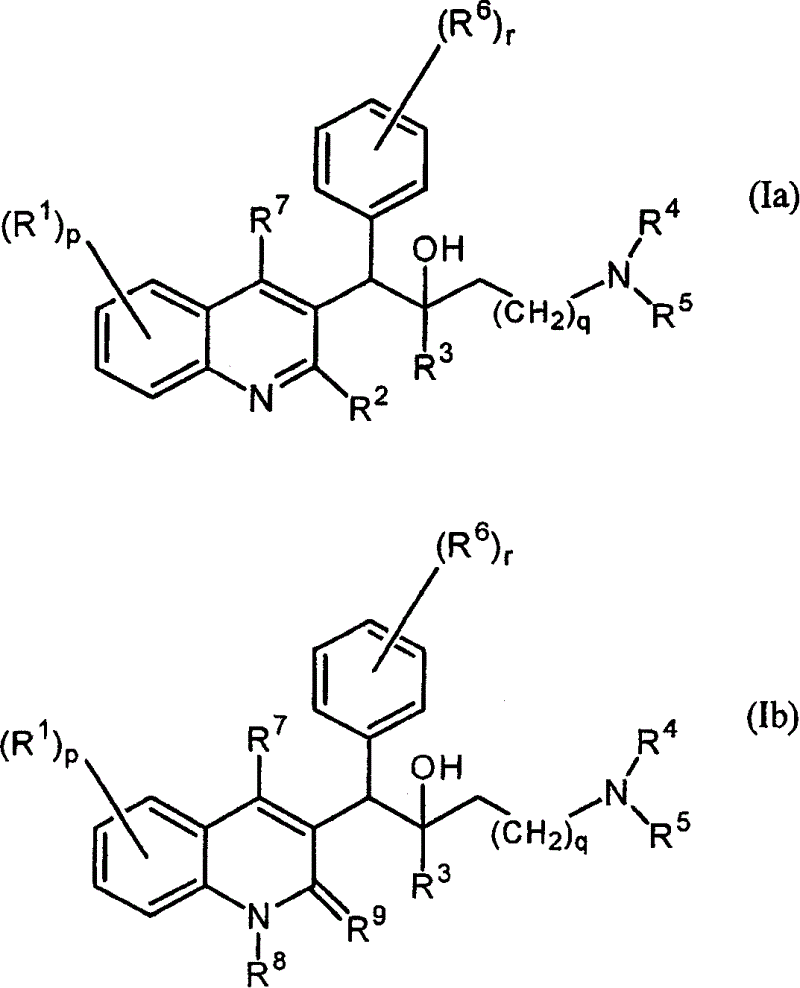
The present invention relates to novel substituted quinoline derivatives according to the general Formula (Ia) or the general Formula (Ib)the pharmaceutically acceptable acid or base addition salts thereof, the stereochemically isomeric forms thereof, the tautomeric forms thereof and the N-oxide forms thereof. The claimed compounds are useful for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases, particularly those diseases caused by pathogenic mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. avium and M. marinum. In particular, compounds are claimed in which, independently from each other, R1 is bromo, p=1, R2 is alkyloxy, R3 is optionally substituted naphthyl or phenyl, q=1, R4 and R5 each independently are hydrogen, methyl or ethyl, R6 is hydrogen, r is equal to 0 or 1 and R7 is hydrogen. Also claimed is a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and, as active ingredient, a therapeutically effective amount of the claimed compounds, the use of the claimed compounds or compositions for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases and a process for preparing the claimed compounds.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Kit for detecting nucleic acid of mycobacterium tuberculosis and method thereof
ActiveCN102373273AStrong specificityGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlContamination
The invention relates to a rapid detecting technology for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis through nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification and a kit for qualitative detection. The kit comprises an instrument-free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction kit, a mycobacterium tuberculosis nucleic acid constant-temperature amplification reaction liquid, a contamination-prevention nucleic acid amplification product detecting device, mycobacterium tuberculosis positive control, and mycobacterium tuberculosis negative control. The kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity and high reaction speed, wherein 1-1.5 hours are only needed from the step of processing a single sample to the step of completing the detection; and the kit can simultaneously meet requirements on sample detection of medium flux and low flux and is particularly suitable for being used in field detection and primary hospitals, and one constant-temperature instrument is only needed in the entire reaction process.
Owner:USTAR BIOTECHNOLOGIES (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Novel bacteriological culture medium
The invention provides a novel bacteriological culture medium, which is used in a fermenting process for converting phytosterin into AD and ADD by adopting athrobacter nicotinovorans, mycobacteria ornocardia, contains corn steep liquor and inorganic salt, and contains 5 to 50ml of the corn steep liquor per liter preferably. The culture medium can improve the conversion ratio of biofermentation.
Owner:TIANJIN JINYAO GRP
Compounds for diagnosis of tuberculosis and methods of their use
InactiveUS20010012888A1Detect presenceBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenMycobacterium Infections
Compounds and methods for diagnosing tuberculosis are disclosed. The compounds provided include polypeptides that contain at least one antigenic portion of one or more M. tuberculosis proteins, and DNA sequences encoding such polypeptides. Diagnostic kits containing such polypeptides or DNA sequences and a suitable detection reagent may be used for the detection of M. tuberculosis infection in patients and biological samples. Antibodies directed against such polypeptides are also provided.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Composition And Method For Stabilizing And Maintaining The Viability Of Hardy Microorganisms
PendingUS20170226469A1Stabilizing and maintaining viabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBacteroides
The present application is to provide a composition and method for stabilizing and maintaining the viability of hardy microorganisms from sample collection to downstream analysis. In particular, there is a method for preserving viable hardy bacteria, such as Mycobacteria, Bacillus anthracis, or Clostridium difficile, in a biological sample, comprising contacting the biological sample with a stabilization composition, wherein the stabilization composition comprises a chelating agent, a denaturing, a salt and has a pH between about 6 and about 11.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN104232722AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation. Recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis is fermented to convert phytosterin to produce the 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant expression vector pMV261-ksh; constructing a recombinant strain; and carrying out culture propagation and fermentation conversion. Gene engineering means are utilized to obtain the gene engineering strain for overexpressing 3-sterone-9-alpha-hydroxylase gene (ksh); after the strain is fermented for 120 hours, the conversion rate of the phytosterin is up to 95% above; and the method has the characteristics of high yield, fewer byproducts, short fermentation time simple extraction, small pollution, low pressure for environmental protection and the like, and has huge advantages in industrial production.
Owner:宋浩雷
Biologically active substance on the basis of tetracyclic nitrogen heterocycles of pyrimidine row
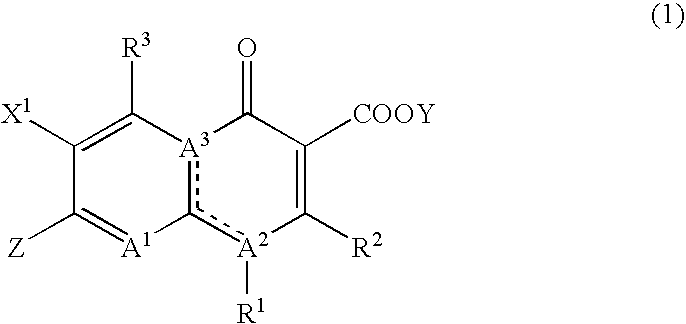
PCT No. PCT / RU97 / 00098 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 17, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 17, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 2, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 43982 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 10, 1998Biologically active substance on the basis of tetracyclicnitrogen heterocycles of pyrimidine row for treating tuberculosis, mycobacteriousis, viral diseases, infections caused by chlamydias, and also diseases which are accompanied by immunodeficiency, in particular malignant neoplasm, has high antimicrobial activity, in particular to strains of mycobacteria which are resistant to the prototype-isoniazid, and simultaneously possess antiviral activity (relative to herpes simplex viruses), antichylamidial activity and also stimulate production of endogenic interferons in organisms. It represents a derivative of 5-oxo-5H-[1]-benzopyrano-[5,6-b]-4-oxo-4H-[1,2]-pyrimido-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-1,3-thiazine (1) of general formula(1). (I-X) where: R1-H or halogen; R2-H, or halogen, or nitro-group, or hydroxy-group or methoxy-group.
Owner:NATURAL DRUG SCI
Capture of micro-organisms
Micro-organisms, including fungi, viruses and bacteria such as Mycobacteria and / or fragments of micro-organisms such as cell wall components present in an aqueous liquid are captured to a solid surface by adding to the liquid a sufficient quantity of a water soluble polymer in the presence of the solid surface to displace the micro-organisms and / or fragments from the liquid to the solid surface. The surface may be provided by a bead. The water soluble polymer may be polyethyleneglycol or polyvinylpyrrolidone.
Owner:MICROSENS DIAGNOSTICS
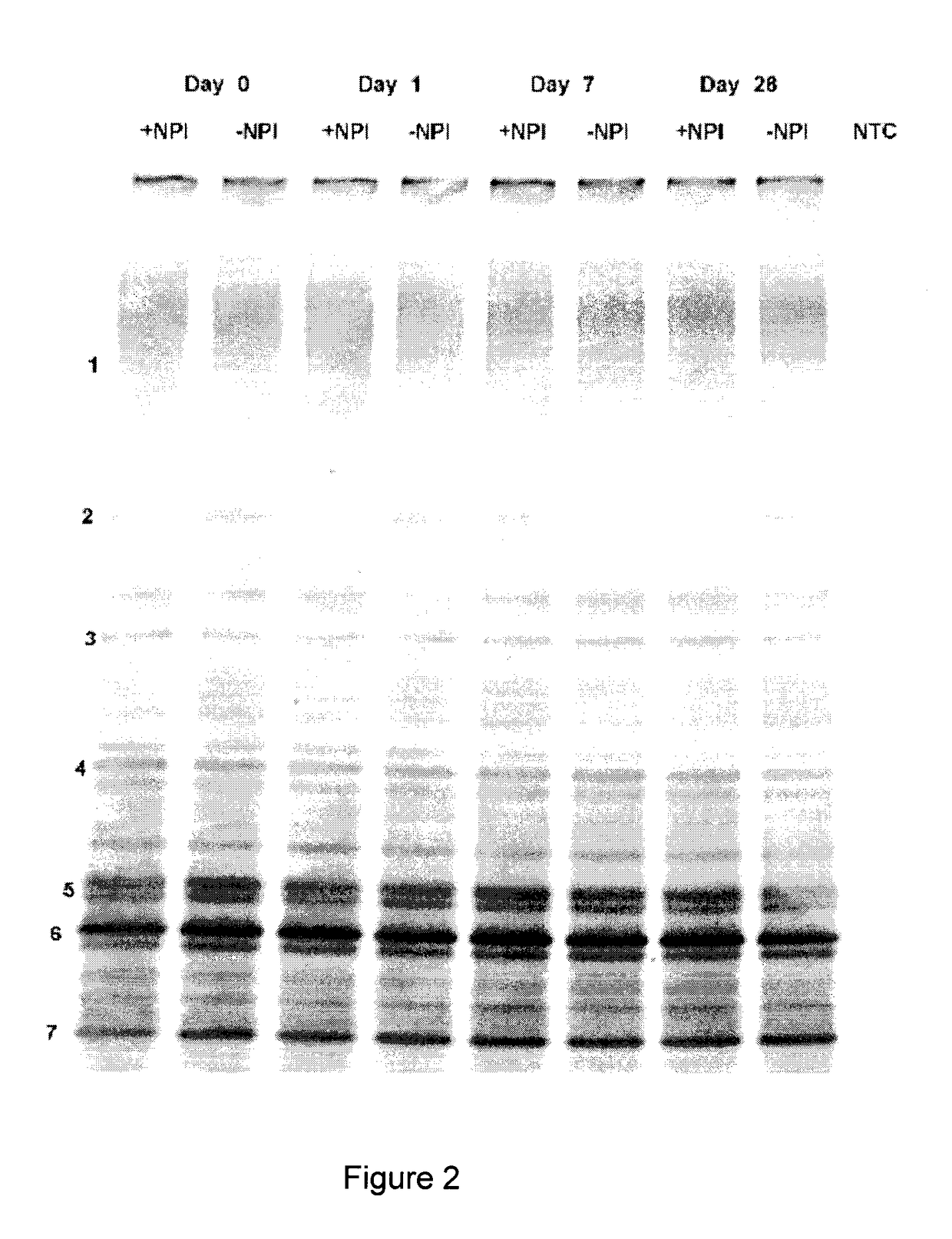
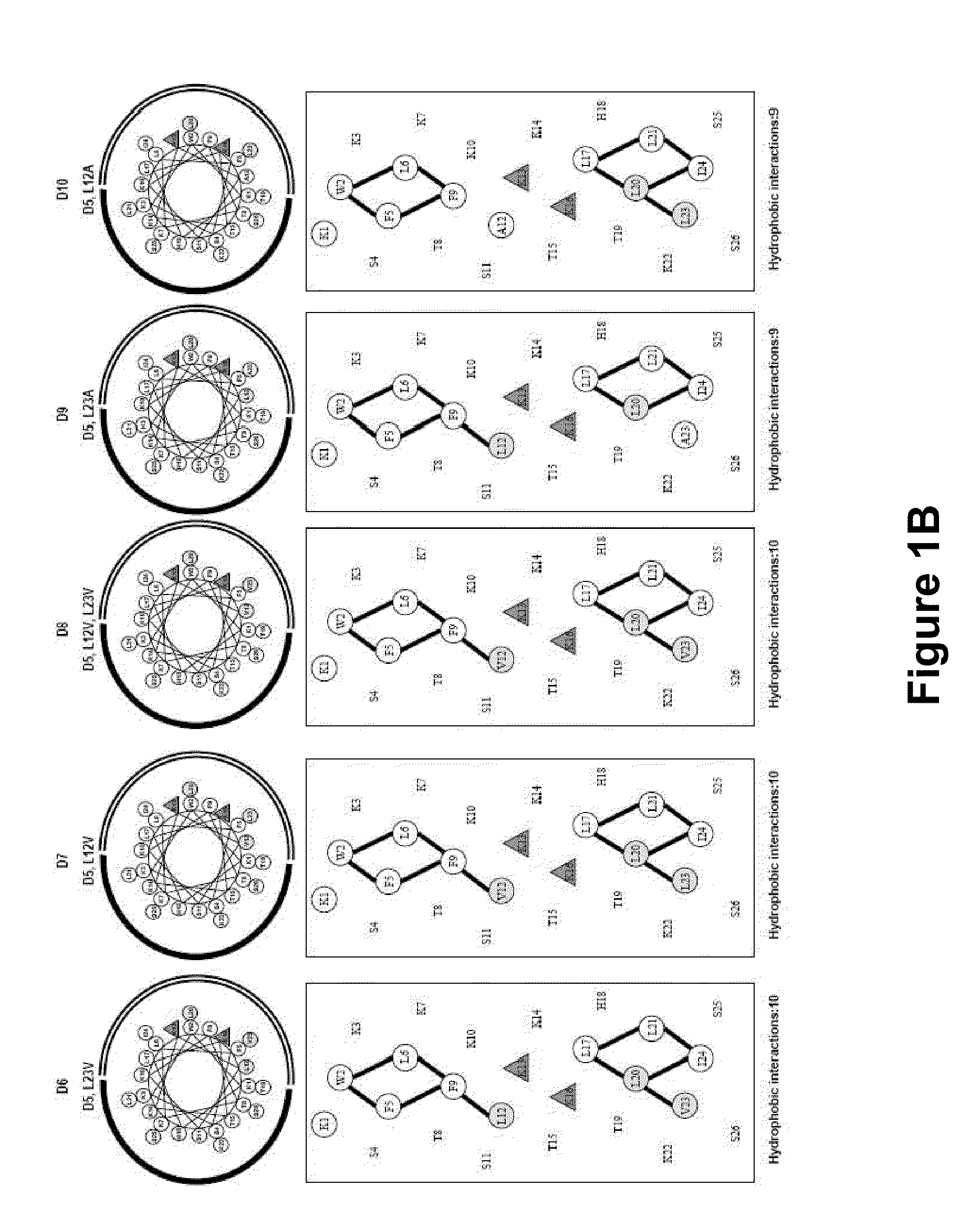
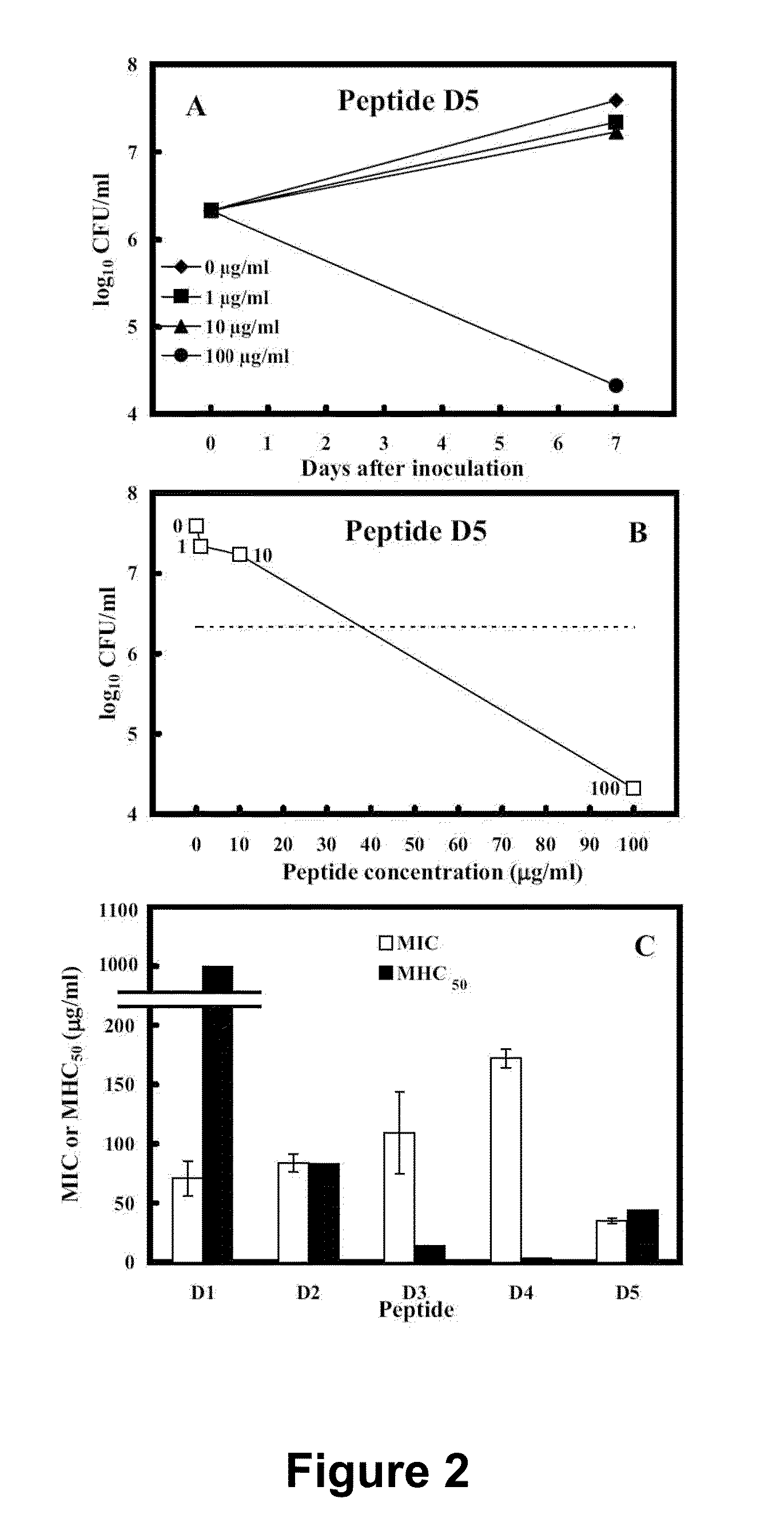
Antimicrobial Peptides and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20100099614A1Reduce morbidityReduce severityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesAcid-fast
Disclosed herein are antimicrobial peptides with useful and / or superior properties such as specificity, resistance to degradation, antimicrobial activity, desirably low levels of hemolytic activity, and a therapeutic index against a broad range of microorganisms including gram-negative, gram-positive and acid-fast bacteria, fungi and other organisms. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising these peptides and methods of using such peptides to control microbial growth or to treat or reduce incidence of infections caused by such microorganisms. Also disclosed are peptides at least one or all amino acids in the D configuration. Compositions disclosed herein are useful in the treatment of bacterial, mycobacterial and / or fungal infections or for reducing microbial cell numbers or growth on surfaces or in materials.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Lactic acid bacterial regulatable expression system
PCT No. PCT / DK97 / 00341 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1997 PCT Filed Aug. 22, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 10079 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 12, 1998Expression vectors capable of being replicated in lactic acid bacterial cells comprising a promoter region comprising (a) a promoter sequence element the function of which is regulatable by an environmental or growth condition factor and (b) at least one further nucleotide sequence element, the position, orientation, presence and / or sequence of which element has a regulatory effect on the expression of a gene operably linked to the promoter region in which vectors the position, orientation, presence and / or sequence of at least one of said elements (a) or (b) is modified relative to the position, orientation, presence and / or sequence of the corresponding non-modified element whereby the expression of the gene is altered, and a lactic acid bacterium which is transformed with such a vector as defined above are provided. The recombinant cells containing such a regulatable or inducible gene expression system are useful as food or feed starter cultures or as strains for the production of gene products such as pharmaceutically or immunologically active compounds including oligo- or polypeptides derived from a Mycobacterium species including M. tuberculosis.
Owner:BIONEER
Cofactor regeneration mycobacteria and its application in fermentation of oil-water two-liquid phase
PendingCN107779423ASolve the low conversion efficiencyIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPlant sterol
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological catalyst, and particularly relates to a mycobacteria genetically engineered bacterium with cofactor regeneration function and its applicationin fermentation of two liquid phases. Through a NADH oxidizing system in the cell, the genetically engineered bacterium for transforming plant sterol biology is structured and transformed for the NADH oxidizing system in the cell, thus the problem of low transforming efficiency of androstenedione in the oil water two-liquid-phase fermenting system is solved; the genetically engineered bacterium also provides possibility for the wide application of the oil water two-liquid-phase fermenting system in industrial production of the androstenedione. The genetically engineered bacterium MNR M3N2 structured by the invention can improve the AD (D) output by 1.4-2.9 times during the preparation process of androstenedione by degrading the phytosterol through the oil water two-liquid-phase fermentingsystem fermenting method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods for inactivation and extraction of acid-fast bacteria for characterization and/or identification using mass spectrometry
The present invention is directed to a method for inactivation and / or extraction of acid-fast bacteria (e.g., mycobacteria or nocardia), the method comprising the following sequential steps: (a) acquiring a test sample known to contain or that may contain acid-fast bacteria and suspending the test sample in a container containing ethanol and beads; (b) bead beating and / or vortexing the container to break up clumps and / or disrupt acid-fast bacteria cells in the container; and (c) subsequently incubating the suspension for at least about 3 minutes at room temperature to inactivate any acid-fast bacteria contained in the test sample. In accordance with the present invention, the test sample can subsequently be pelleted by centrifugation, resuspended with formic acid, acetonitrile added, and subjected to mass spectrometry for characterization and / or identification of the acid-fast bacteria.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
Rapid detection of volatile organic compounds for identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a sample
In various embodiments, the invention relates to a method for identifying the presence of particular bacteria in a sample. The method includes collecting a sample that includes or has been exposed to the particular bacteria and detecting, in the sample, at least one volatile organic compound indicative of the presence of the bacteria.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Mycobacterium cosmeticum with capacity of degrading benzene compound and application thereof
ActiveCN101624576AEfficient degradationPromote degradationBacteriaDispersed particle separationMycobacterium cosmeticumChemistry
The invention provides a mycobacterium cosmeticum byf-4 with the capacity of degrading a benzene compound and an application thereof. The mycobacterium cosmeticum byf-4 is stored in Chinese typical culture storage center which has an address: Wuhan University Wuhan China, 430074, a storage date: Oct. 29, 2008 and a storage number: CCTCC No. M 208180. The invention has the advantages that the strain can rapidly degrade various benzene compounds with high efficiency and has an important meaning to the engineering practice of biologically purifying contaminants caused by the benzene compounds and the derivatives thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Two phase Roe's culture medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1699592APromote rapid growthImprove culture positive rateMicrobiological testing/measurementPurplish redMicrobiology
The present invention discloses a preparation method of a new type incubation medium, belonging to the medical inspection field. The method can promote growth of mycobacteria. The incubation medium comprises a solid part and a liquid part: the solid part is the modified Roche's incubation medium that is generally used at home and abroad and the liquid part consists of basic incubation medium, growth promoter and bacteria inhibitor. The incubation medium can not only promote growth of mycobacteria, but also inhibit other bacteria. The growing mycobacteria can form violet red bacteria colony on the solid inclined plane of incubation medium, which is beneficial to elementary appraisal. The incubation medium can shorten incubation time obviously, increase incubation positive rate considerably, very suitable for fast inspection of mycobacteria for the hospitals and the sanitation and anti-epidemic institutions.
Owner:胡忠义
Mycobacterium sp. strain for biosynthesis of 20-hydroxy-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one and synthetic method thereof
ActiveCN106854630AHigh yieldReduce pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a mycobacterium sp. strain FJH0105-16 and a method for producing 20-hydroxy-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one through fermentation of phytosterol with the strain. The stain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 3, 2016, with an accession number of CGMCC No. 13234. The production method comprises the following steps: with the mycobacterium sp. strain FJH0105-16 as a bacterial strain, carrying out slant seed culture, primary seed culture and fermentation and transformation in a fermentation tank; then adding ethyl acetate for extraction; carrying out drying with anhydrous sodium sulfate; then removing a solvent under reduced pressure so as to obtain a crude 20-hydroxy-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one product, wherein the mol yield of the crude product is no less than 71%; and subjecting the crude product to recrystallization so as to obtain a finished 20-hydroxy-23,24-bisnorchol-4-ene-3-one product, wherein the finished product has a purity of greater than 95%.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Probe And Primer For Tubercle Bacillus Detection, And Method Of Detecting Human Tubercle Bacillus Therewith
ActiveUS20080241826A1False positive reactionAccurate detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyHuman tubercle bacillus
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel primer and prove for detecting tubercle bacillus capable of avoiding false positive, and an easy-to-use, rapid and high-sensitivity method for detecting human tubercle bacillus (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) using the same. The present invention relates to an oligonucleotide comprising a part of or an entire sequence of the nucleic acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7 or SEQ ID NO:8, or a part of or an entire sequence of the complementary sequence thereof, wherein the oligonucleotide has a property of hybridizing with the nucleic acid sequence of IS6110 gene in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a primer and a probe containing the oligonucleotide for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and a method for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis using the primer and the probe.
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP
An electrochemical biochip sensor array for rapidly detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis and a preparing method
InactiveCN104878075AVisualization of test resultsAvoid slow detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSensor arrayMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the technical fields of bioelectrochemistry and biochip sensors and relates to an electrochemical biochip sensor array for mycobacterium tuberculosis 16SrDNA and for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis and a preparing method thereof. Starting with molecular level detection of the mycobacterium tuberculosis 16SrDNA, Fe3O4@SiO2 composite nanometer particles and a nanometer Au structure material are adopted as mediators, a novel and functionalized nanometer electrochemical biochip superparamagnetism nano-detection microsphere sensor interface is designed, the mycobacterium tuberculosis is subjected to double enrichment extraction and purification detection, and the electrochemical biochip sensor array for rapidly detecting the mycobacterium tuberculosis is constructed. A clinical sample containing the mycobacterium tuberculosis is directly added into a magnetic reaction micropore. A mycobacterium tuberculosis 16SrDNA specific sequence can be subjected to double enrichment and biological stabilization through utilizing a capture probe labeled by the Fe3O4@SiO2 composite nanometer particles and a nanometer Au labeled detecting probe respectively. A high mycobacterium tuberculosis target molecule separating efficiency and high detection sensitivity are expected to be achieved by utilization of nano-detection microsphere superparamagnetism. In addition, target molecule "on-chip" separation is expected to be achieved through characteristics of the electrochemical biochip sensor array without the need of extra separating steps, thus largely simplifying operation procedures and shortening the detection time.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF YIBIN
Anti acid-fast bacterial agent containing pyridonecarboxylic acids as active ingredient
InactiveUS7176313B2High antibacterial activityImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAcid-fastCarboxylic acid
An anti acid-fast bacterial agent containing, as an active ingredient, a pyridonecarboxylic acid derivative represented by the following general formula (1), a salt thereof, or a hydrate thereof, which shows excellent antibacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and atypical acid-fast bacteria and exhibits good pharmacokinetics and safety
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Therapeutic agents
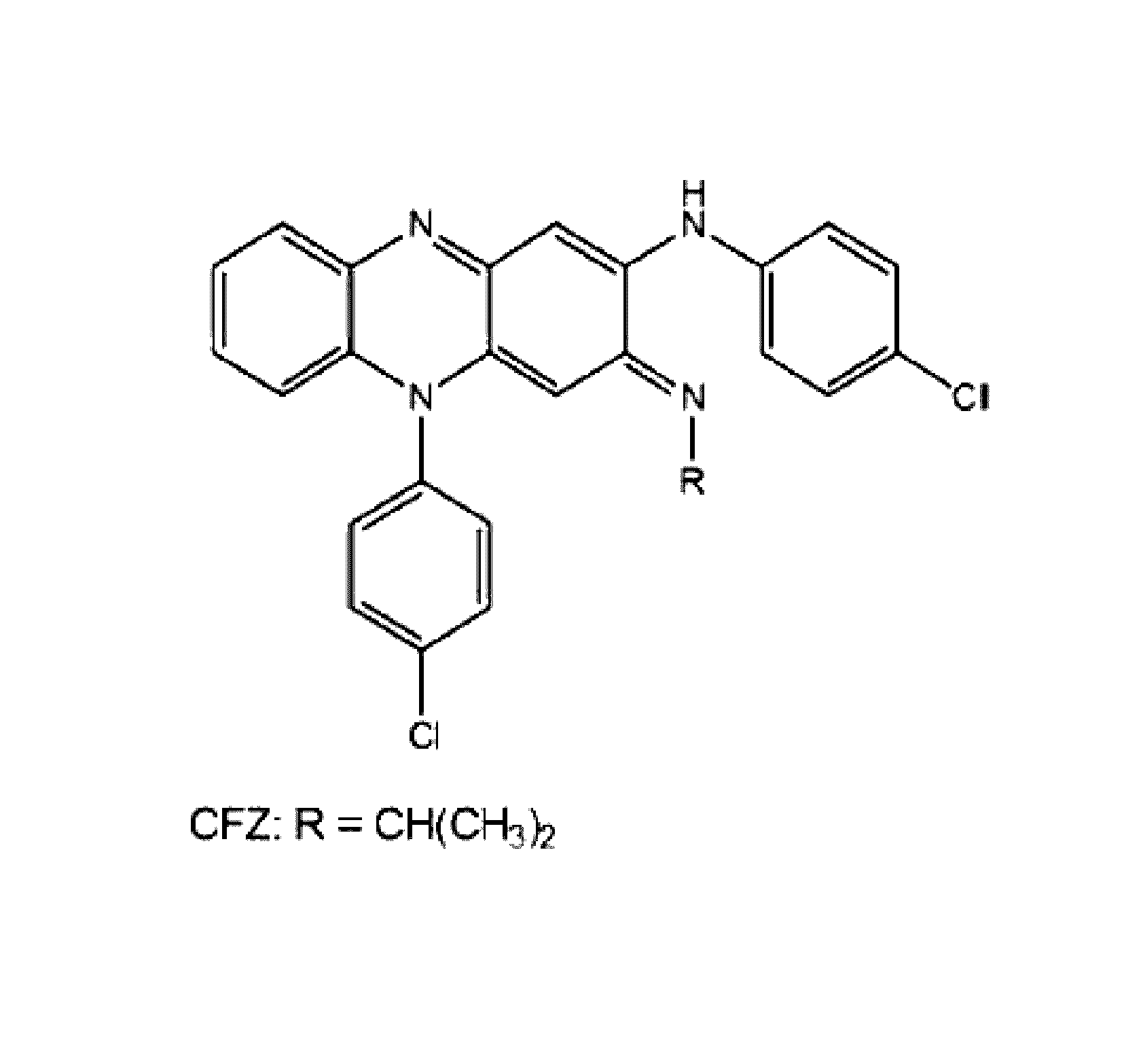
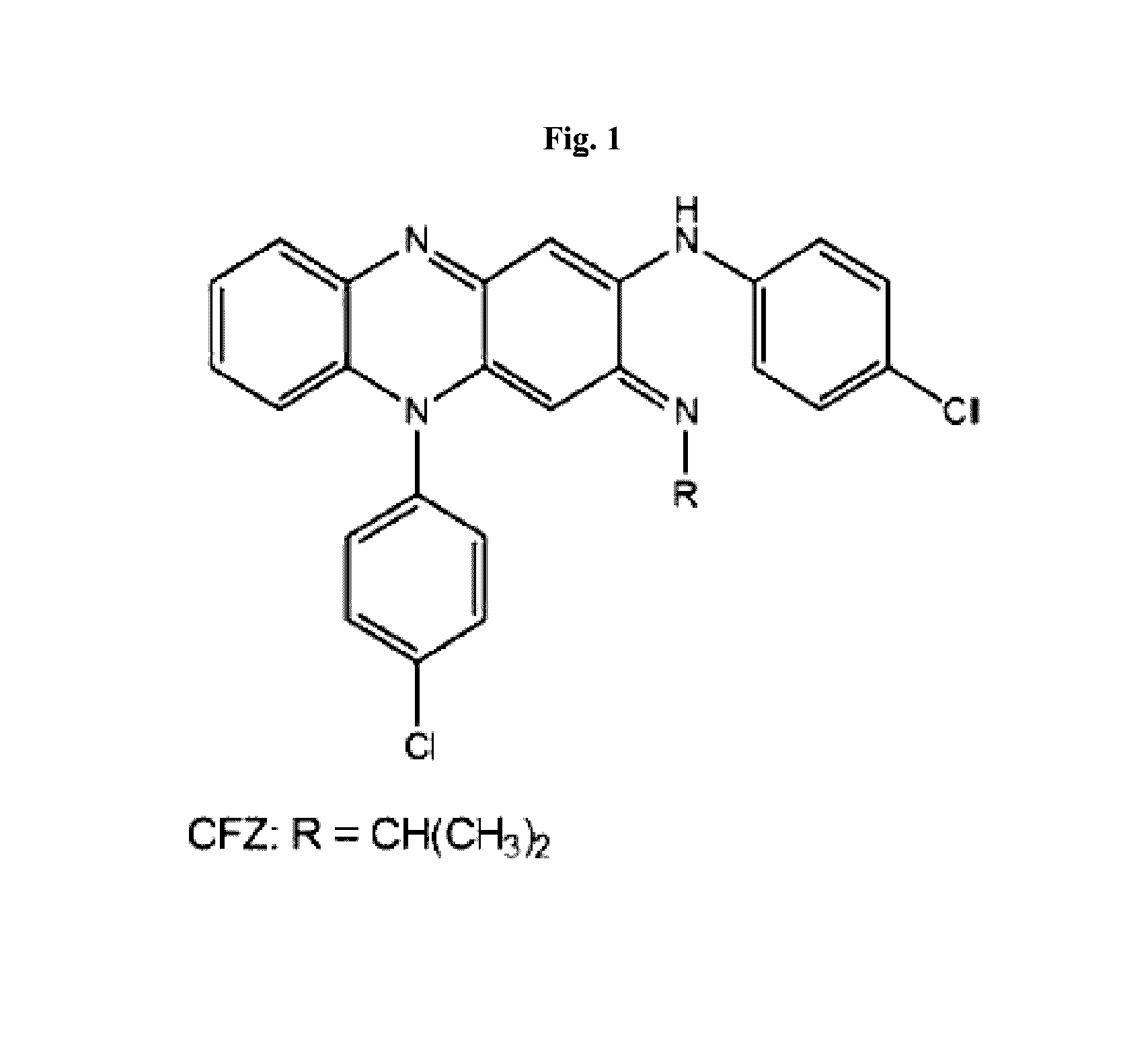
The present invention includes a method of treating or preventing a disease or disorder such as a mycobacterial infection, a Gram-positive bacterium infection, a yeast infection, an inflammatory condition, an auto-immune disorder and / or a proliferative disorder in a subject in need thereof. The method comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of at least one compound of the invention, which includes clofazimine derivatives.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for producing A ring degradation products through plant sterol fermentation
InactiveCN104404099AAvoid degradationHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlant sterolFermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing A ring degradation products through plant sterol fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: (A) preparing a liquid inoculant containing mycobacterium fortuitum; (B) carrying out fermentation culture; (C) extracting and separating so as to obtain the A ring degradation products. The provided fermentation method for preparing A ring degradation products is carried out in an oil-free condition, thus the ring opening of A ring and B ring is effectively inhibited, thus the degradation is inhibited, the yield is increased, and the weight yield can reach 35 to 40%.
Owner:江西赣亮医药原料有限公司
Antituberculous drug drug-resistance gene and screening method thereof
InactiveCN106048019AEasy to operateEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAntituberculous drugScreening method
The invention discloses an antituberculous drug drug-resistance gene and a screening method thereof. The antituberculous drug drug-resistance gene is pks12, pks5, PPE34, Rv1978, Rv1847, hemK, PPE3, glyA1, PE_PGRS27, PE_PGRS19, Rv1520, Rv1505c, Rv2407, mmuM, vapB17, Rv3727 and Rv3737. The novel candidate drug target gene is provided for a further understanding of drug resistance mechanism of MDR / XDR mycobacterium tuberculosis and the therapy of MDR / XDR-TB.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
Bacterial Ribonucleic Acid Cell Wall Compositions and Methods of Making and Using Them
ActiveUS20140170189A1Anti-cancer activity of the present compositions is maximizedImmune stimulatory activity is maximizedOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsCell wallRNA
Owner:TELESTA THERAPEUTICS IP
Complex microbial agent capable of efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and application of complex microbial agent
ActiveCN109370931APromote degradationShort fermentation timeBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAcenaphthyleneMicrobial agent
The invention provides a complex microbial agent capable of efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The active ingredients include Mycobacterium sp. having a collection number of CGMCCNo. 6531, Acinetobacter sp. having a collection number of CGMCC No. 6532, and Microbacterium sp. having a collection number of CGMCC No. 6530. The complex microbial agent can take the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, such as fluorine, naphthalene, anthracene, acenaphthene, acenaphthylene, dibenzothiophen, carbazole, chrysene, phenanthrene, pyrene, fluoranthene, benzofluoranthrene, benzanthraceneor benzopyrene as the unique carbon source. The complex microbial agent disclosed by the invention is capable of obviously improving the degradation effect of single colony on organic contaminated soil, the fermentation time of three strains is short, the effect is obvious, and the cost is low. Therefore, the complex microbial agent has strong application prospects and popularization value on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon heavy contaminated soil and water.
Owner:北京市科学技术研究院资源环境研究所
Biosensor materials and methods
InactiveUS6849442B1Improve efficiencyMinimises host restriction difficultySugar derivativesBacteriaShuttle vectorMycolic acid
Disclosed are methods for generating mycolic acid bacterial biosensors for particular analytes (especially industrial pollutants) by the use of innovative methods for isolating DNA encoding an inducible promoter which is induced in response to the specific analyte (and / or associated operon proteins), the methods generally comprising the steps of: (a) culturing a source of mycolic acid bacteria in a selective medium containing said specific analyte and being selective for oligotriphic bacteria; (b) identifying mycolic acid bacteria capable of subsisting on said medium, especially those which do not display catabolic repression; (c) extracting DNA from said mycolic acid bacteria; (d) incorporating said DNA into vectors, such as various shuttle vectors; (e) cloning said vector into a suitable host cell (which may be E. coli strain carrying one or more of the mcrABC mrr hsdSRM recA and recO mutations); (f) screening that host cell (or a second host cell which is preferably a corynebacterium) for said inducible promoter. The methods are exemplified by the isolation of the R. corallina ohp operon.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD
Compositions and methods for the detection and analysis of mycobacterium tuberculosis
ActiveUS20160024561A1Accurate identificationAccurate isolationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyReagent
Provided herein are compositions and methods useful for the detection of MTB. In particular, provided herein are kits, reagents, reaction mixtures, and methods involving such for nucleic acid amplification and detection procedures, which specifically and sensitively detect MTB in samples.
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com