Complex microbial agent capable of efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and application of complex microbial agent
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and compound bacterial agent technology, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, can solve the problems of slow growth, low growth and slow degradation rate of mycobacteria, achieve strong application prospects and promotion value, improve degradation effect, and fermentation time. short effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Using PCR-DGGE method to screen degrading strains and synergistic strains
[0032] 1.1 Isolation and cultivation of strains: including separation, identification and cultivation of strains
[0033] Two culture media are used for the culture of bacteria, namely bacterial culture medium I and II:
[0034] Bacterial culture medium I: 2.5 g ammonium sulfate, 0.28 mg ferrous sulfate, 1.5 g disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.36 g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.25 g magnesium sulfate, 10.7 mg calcium chloride, 0.5 g sodium chloride, ferric chloride 0.004 g, 1 mL trace metal solution, 1 mL vitamin complex solution, add water to 1000 mL and control pH at 7.2-7.4, shake well and use as liquid medium for later use, if it is solid medium, add 1.5% agar powder. The composition of the trace metal liquid is: CoCl 2 ·6H 2 0 35 mg, CuCl 2 0. 20mg, H 3 BO 3 6.0 mg, MnCl 2 4H 2 O 25 mg, Na 2 MoO 4 2H 2 O 3.0 mg, NiCl 2 2H 2 O 2.0 mg, ZnCl 2 2.5 mg, add water to 1...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 The degradation effects of three kinds of single bacteria on pyrene respectively
[0062] Pyrene to be degraded (final concentration 200ppm) was used as the only carbon source. In the liquid containing bacterial culture medium I, three kinds of single bacteria cultured in equal amounts were respectively added. , 10d to extract and detect by GC-MS; by figure 2 It can be seen that mycobacteria have a strong ability to decompose pyrene, and the degradation rate of the pyrene solution with a final concentration of 200ppm is 77.1% on the 10th day, while the decomposition ability of single microbacteria and Acinetobacter is very weak to pyrene. The 10-day degradation rates were 18.1% and 13.2%, respectively.
Embodiment 3
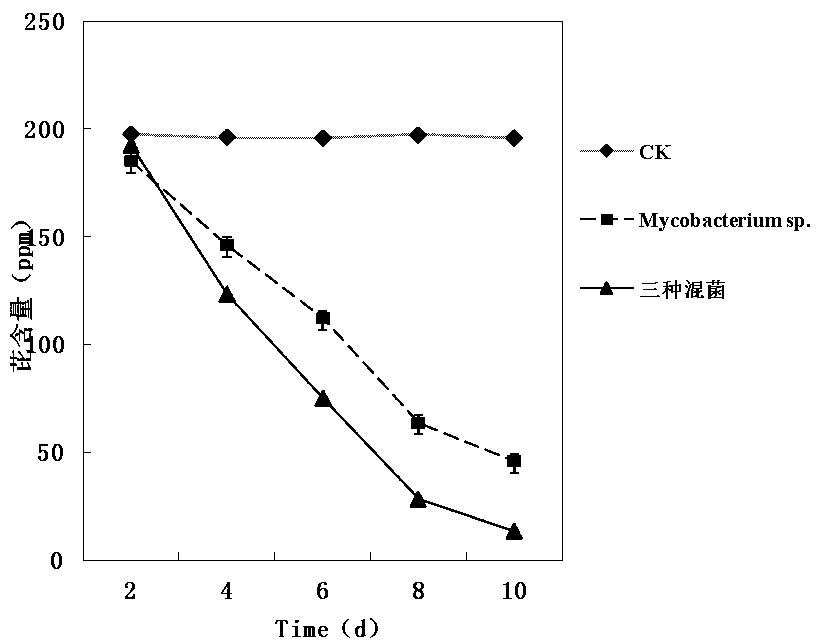
[0063] Example 3 Degradation effect of single mycobacterium and three kinds of mixed bacteria on pyrene
[0064]Pyrene to be degraded (final concentration 200ppm) was used as the only carbon source, and cultured single mycobacterium and three kinds of mixed bacteria were respectively added to the liquid containing bacterial culture medium I. 6, 8, and 10d were extracted and detected by GC-MS; by image 3 It can be seen that mycobacteria have a strong ability to decompose pyrene, and the degradation rate of the pyrene solution with a final concentration of 200ppm is 77.1% on the 10th day. Three kinds of mixed bacteria (mycobacteria: microbacteria: Acinetobacter=2; 1; 1) The degradation ability was further enhanced, and the degradation rate of pyrene by the mixed bacteria was detected to be 93.2% on the 10th day. Therefore, it can be concluded that Microbacteria and Acinetobacter have a synergistic strengthening effect, and the application effect of the mixed bacteria is better....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com