Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Macrodiversity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
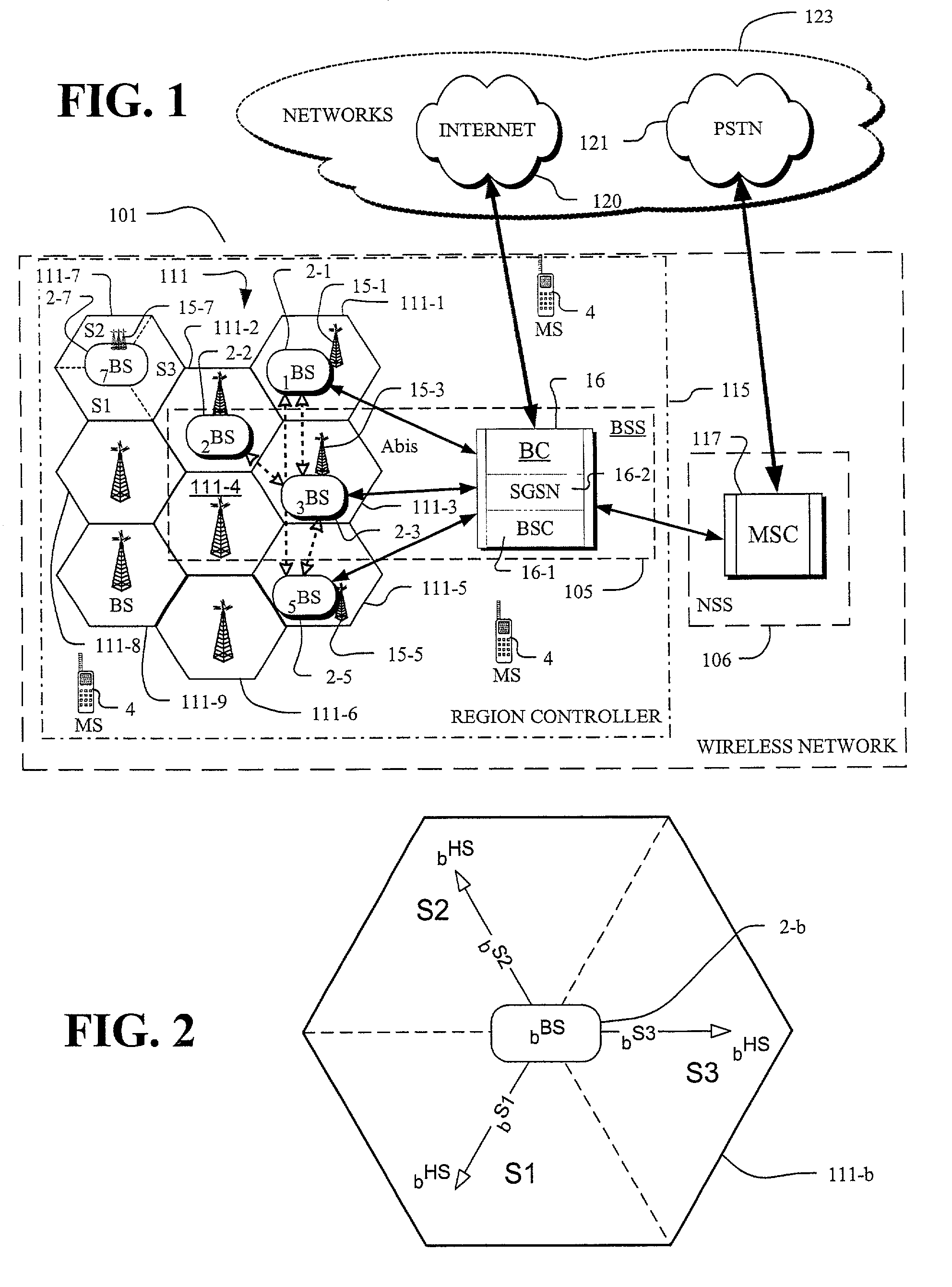
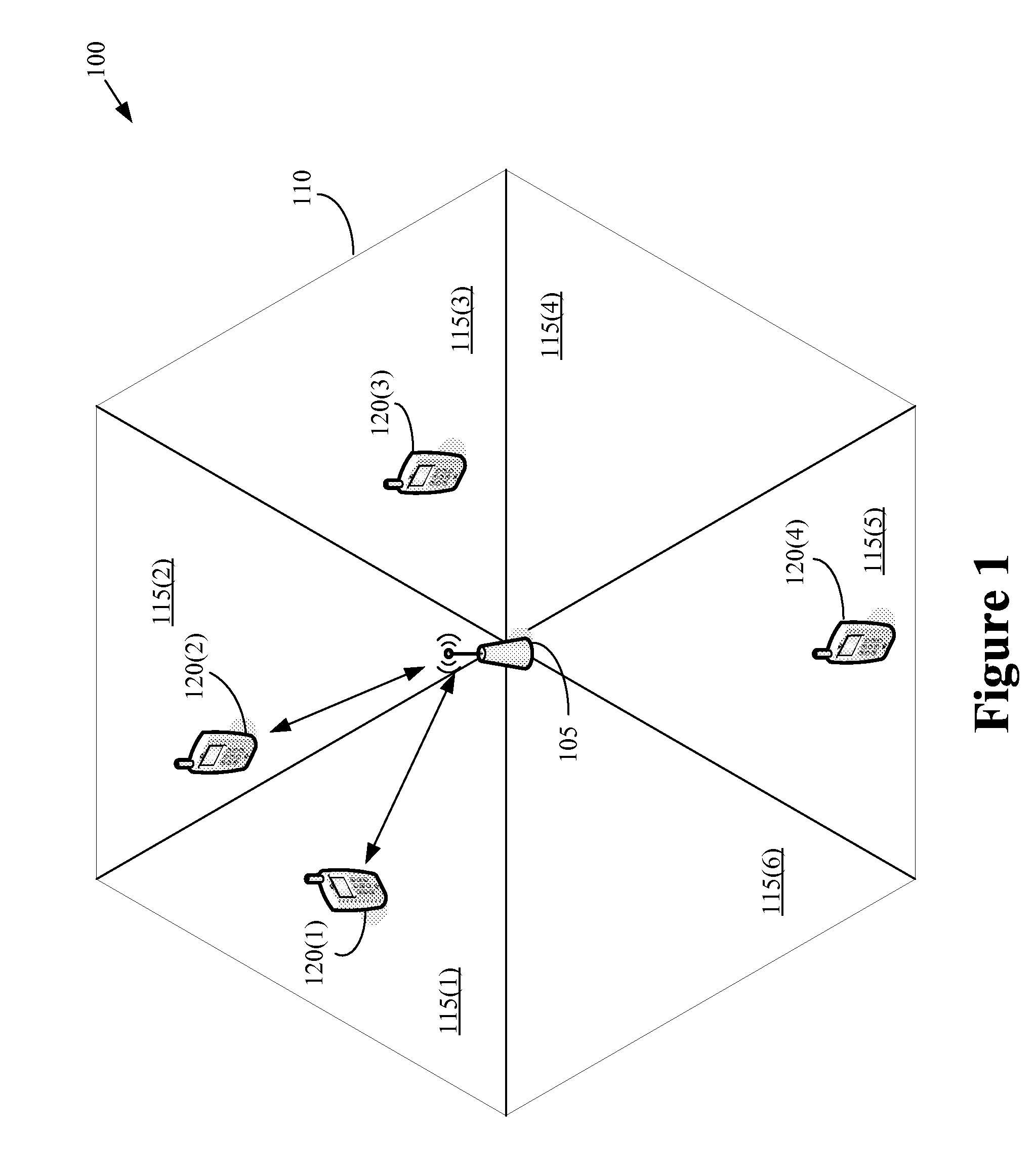
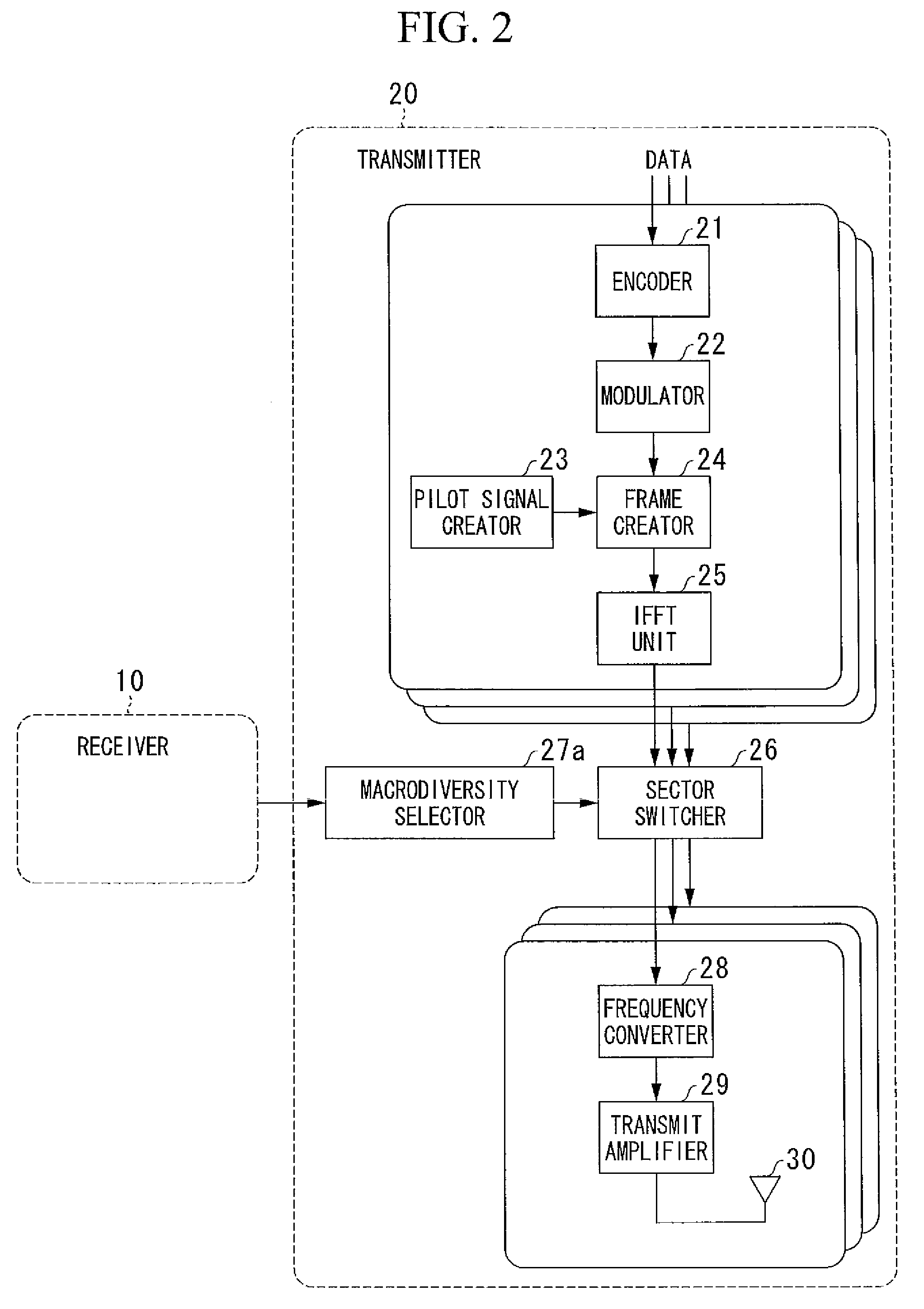
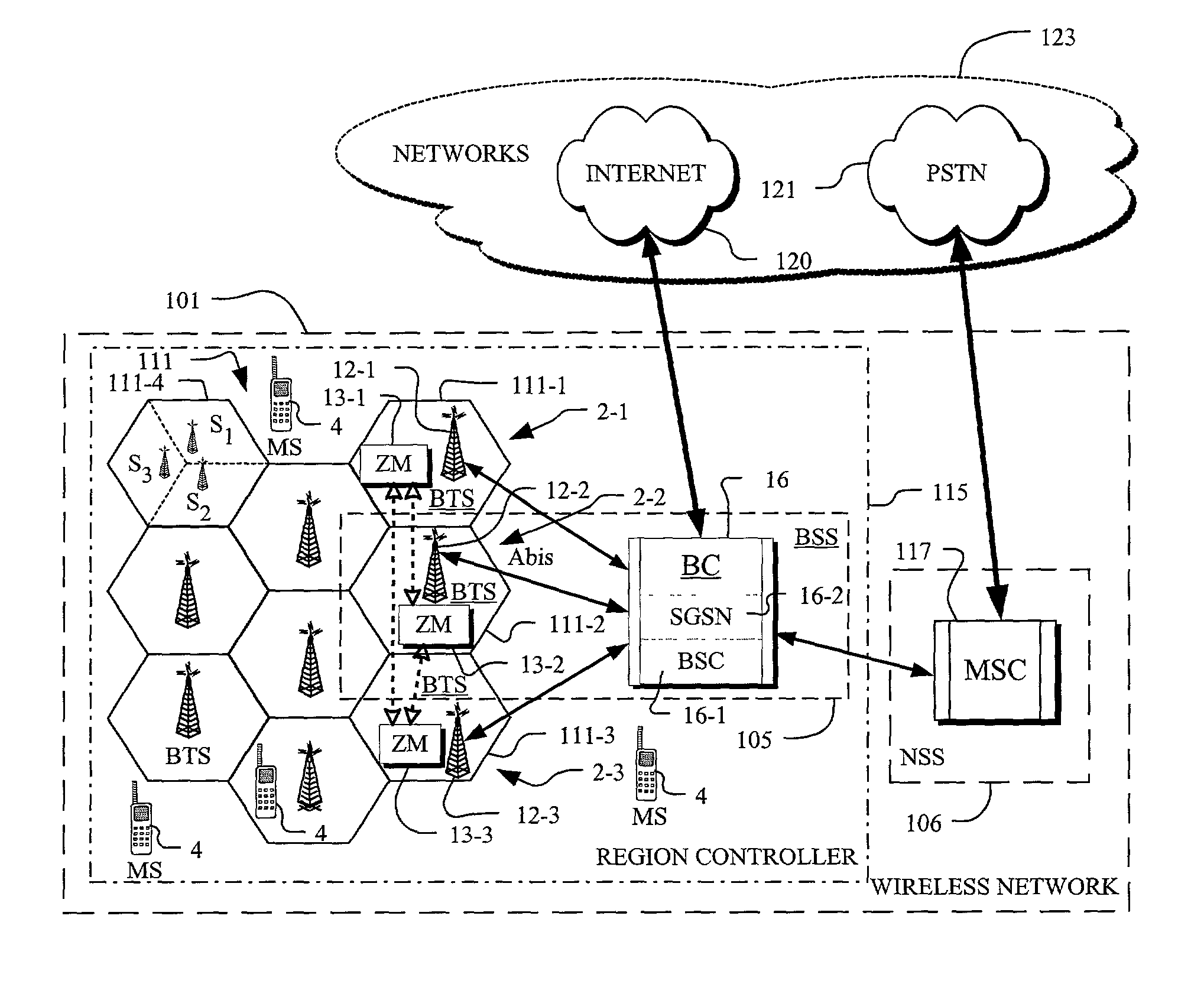
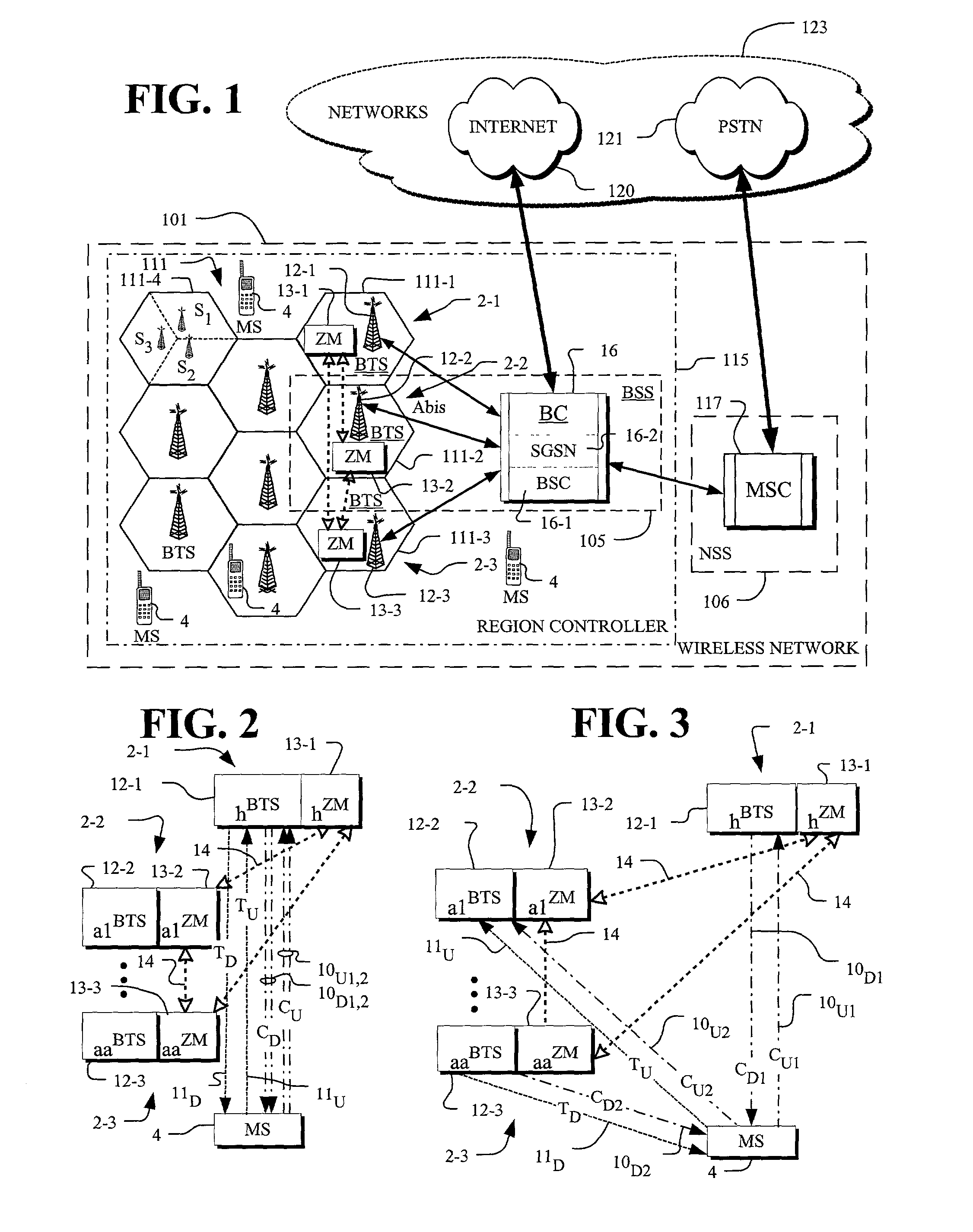
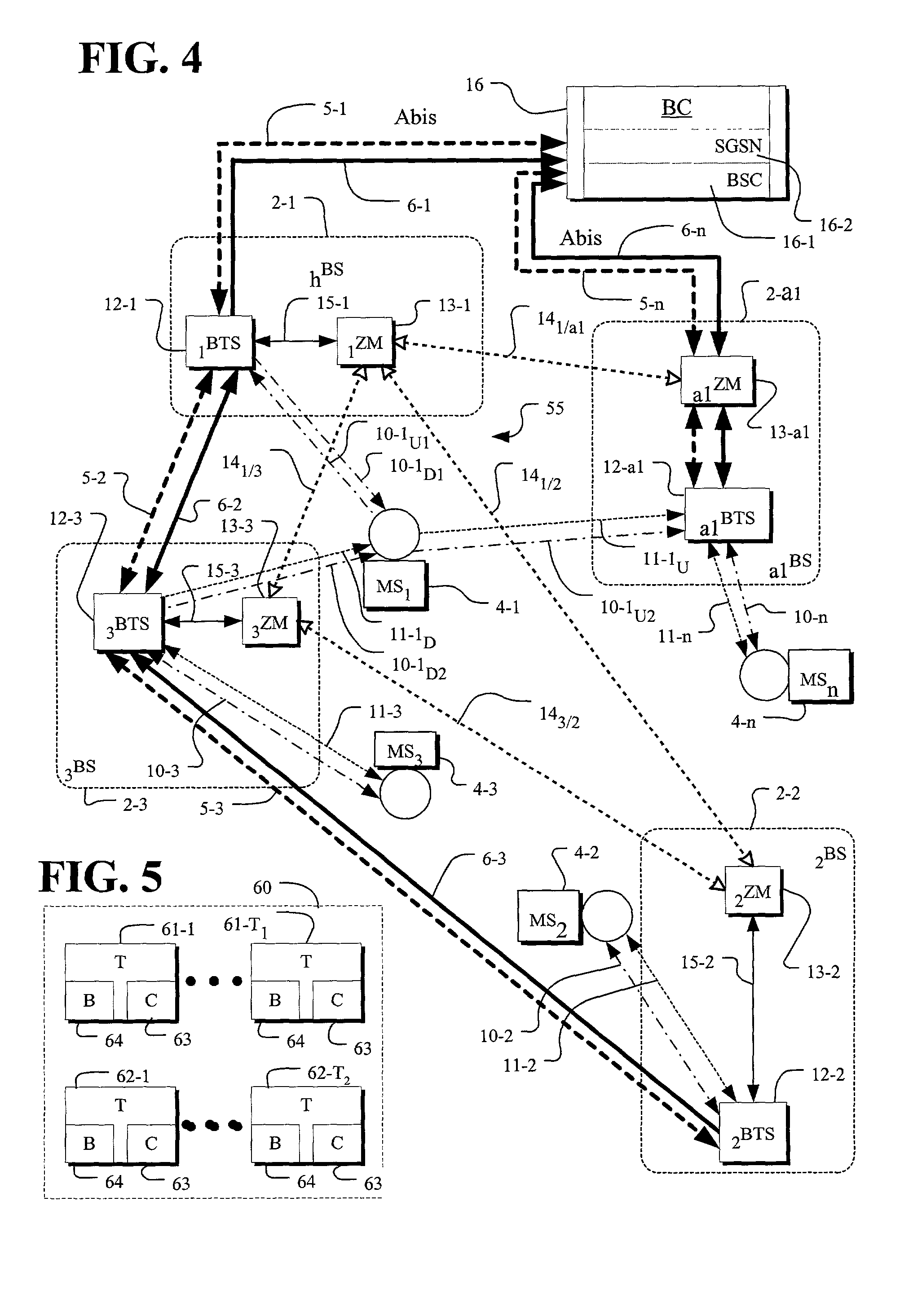
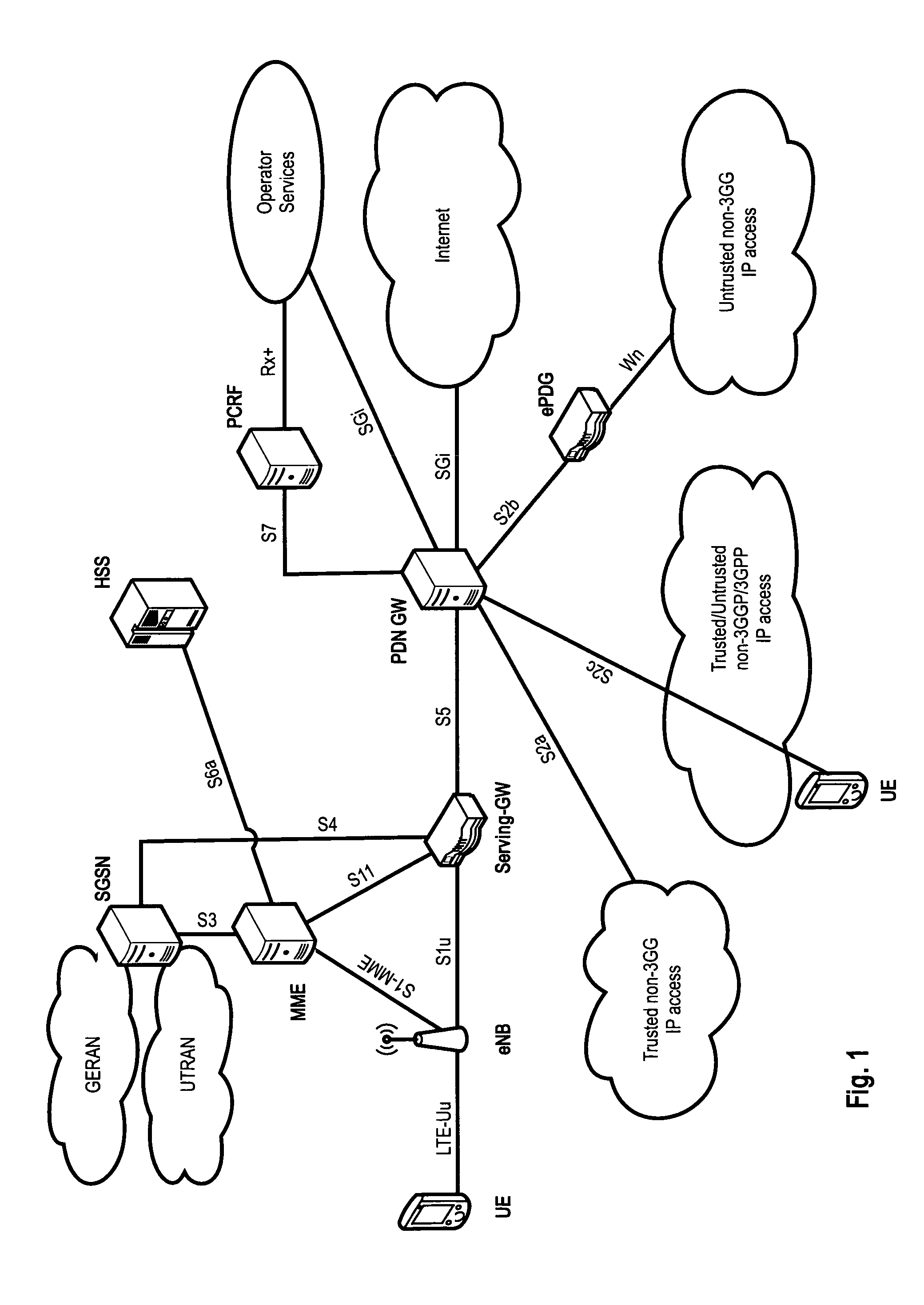
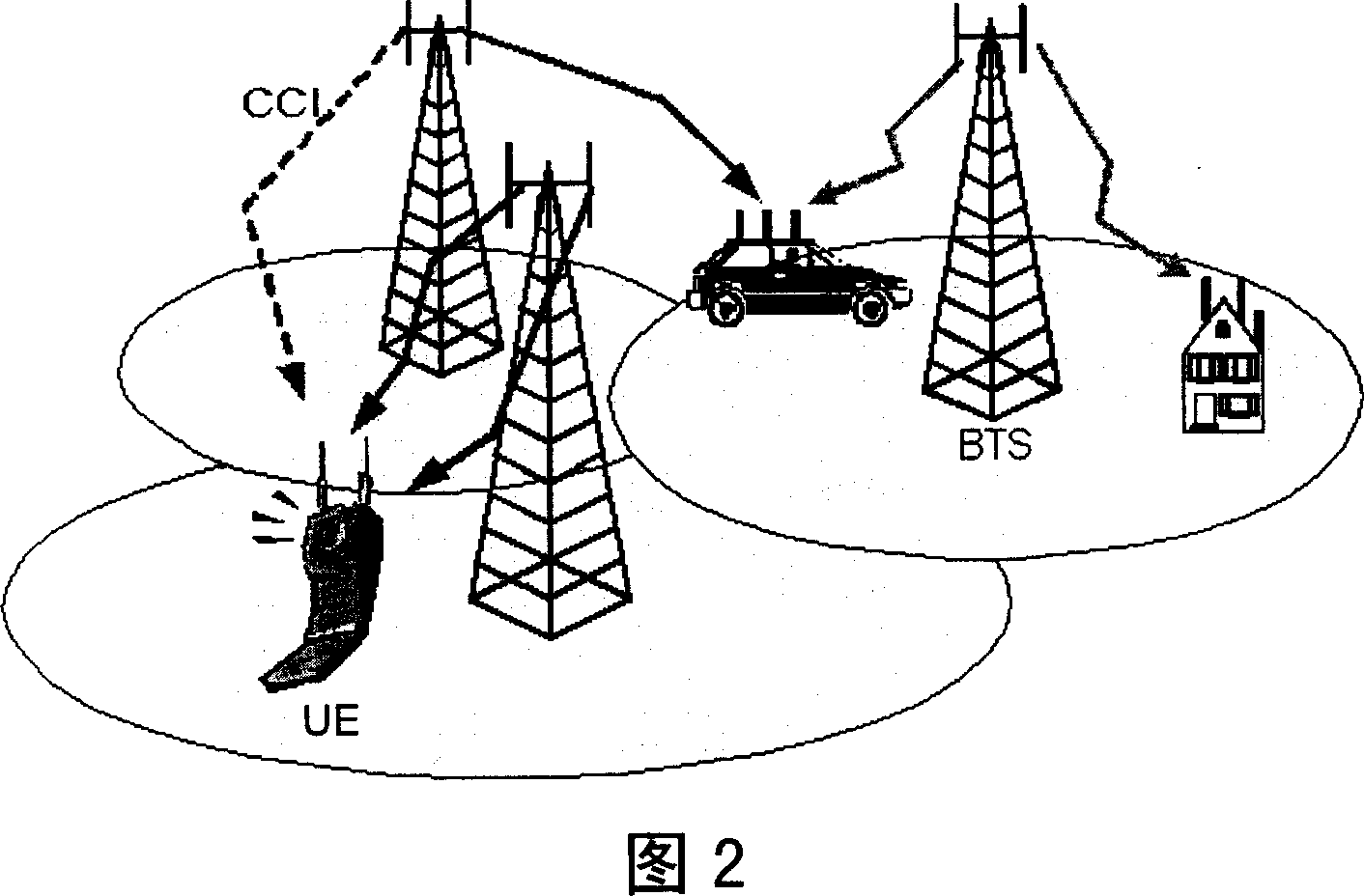
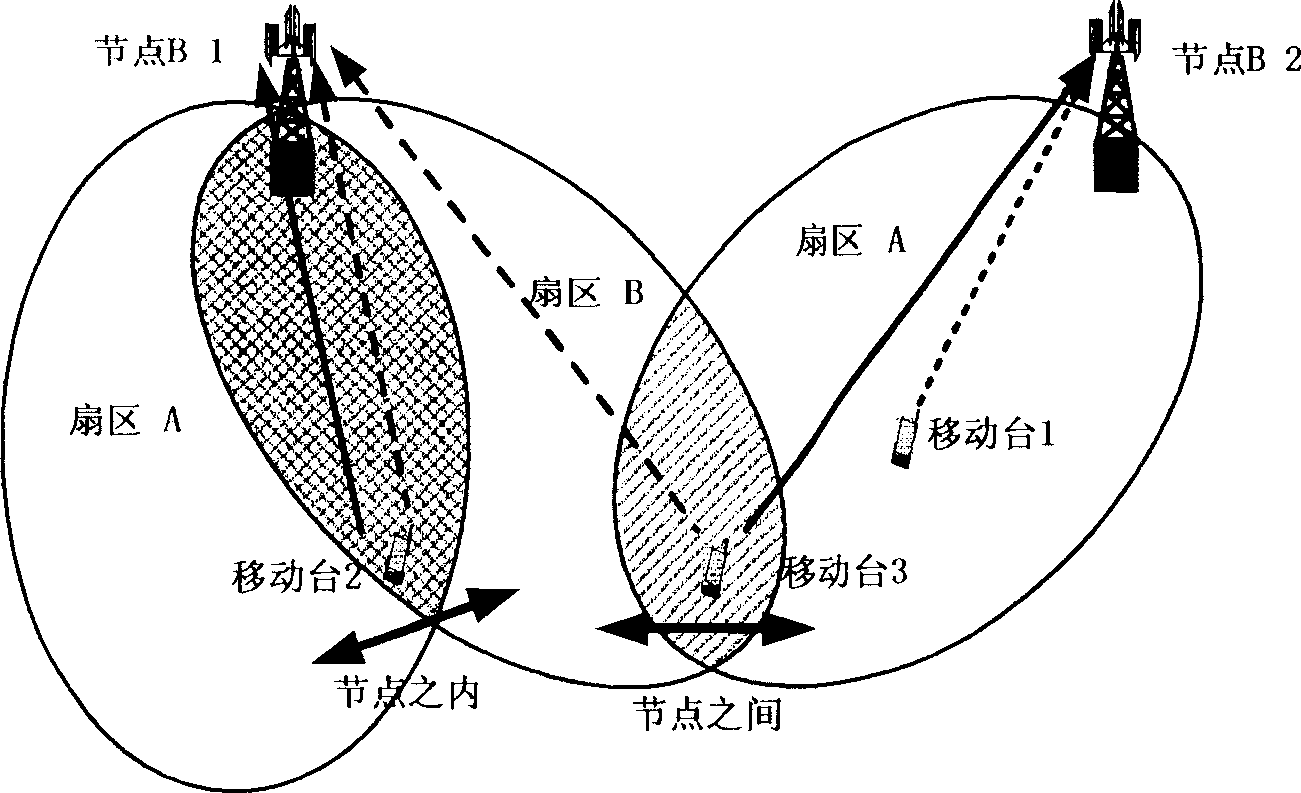
In the field of wireless communication, macrodiversity is a kind of space diversity scheme using several receiver antennas and/or transmitter antennas for transferring the same signal. The distance between the transmitters is much longer than the wavelength, as opposed to microdiversity where the distance is in the order of or shorter than the wavelength.
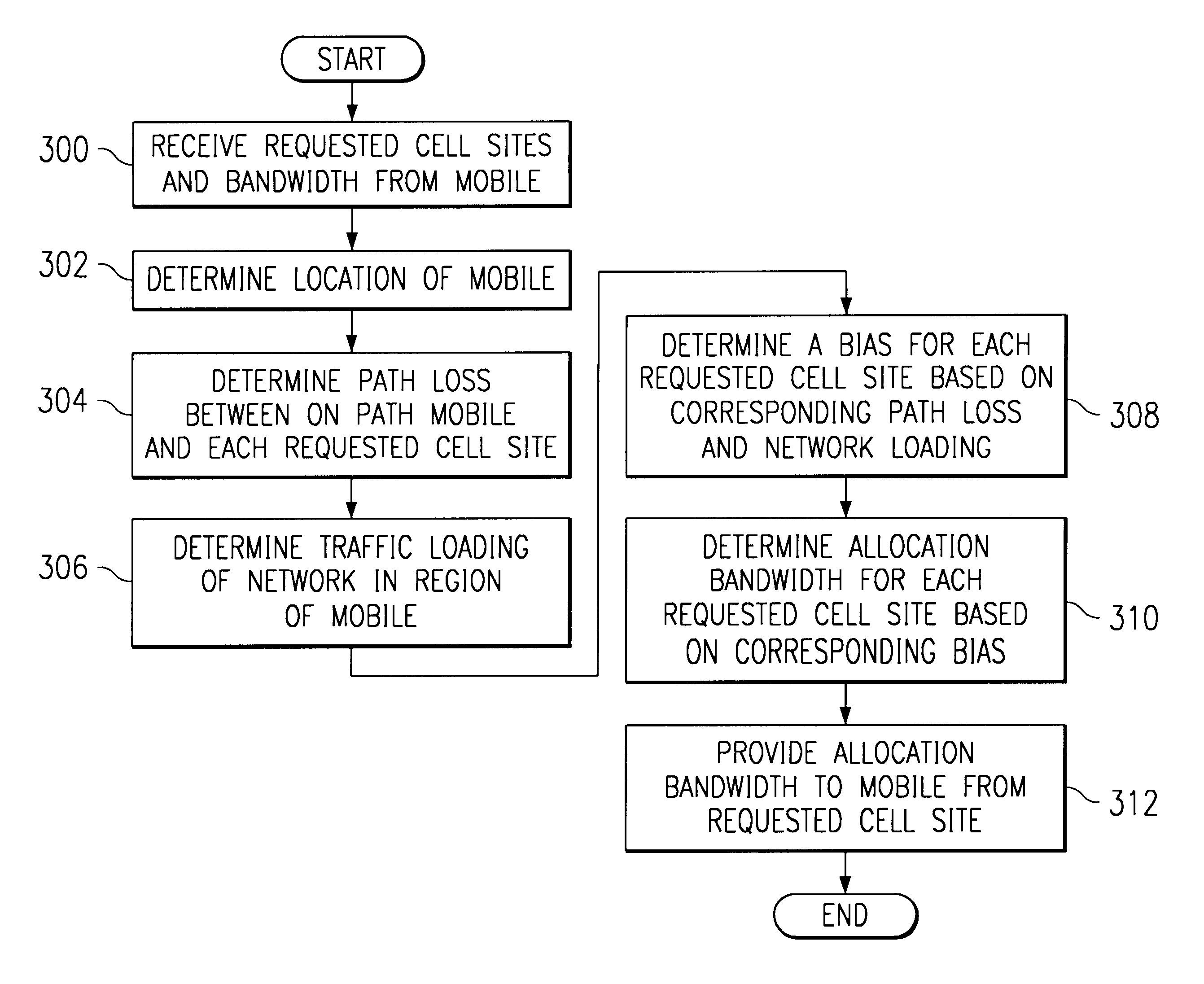
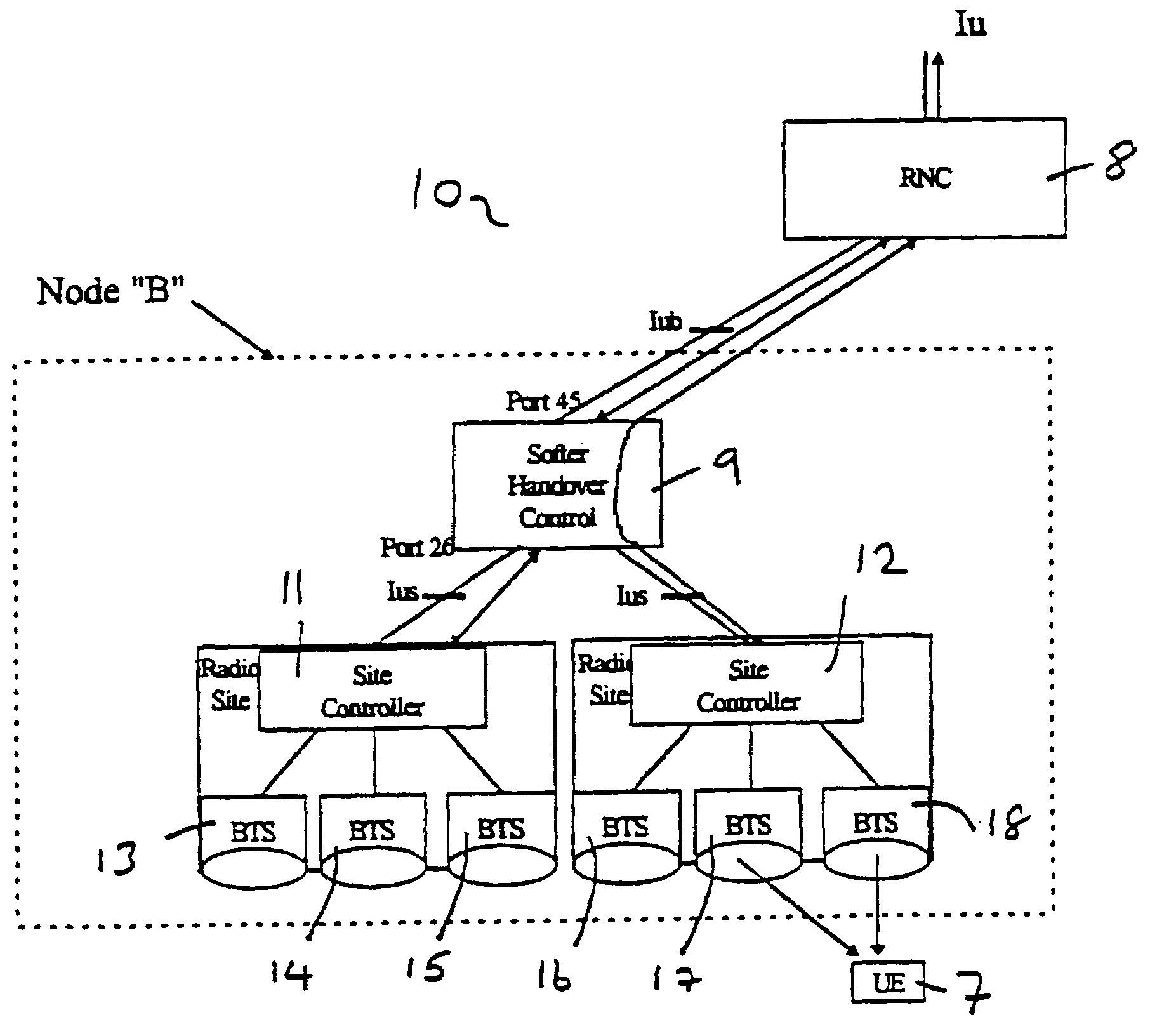
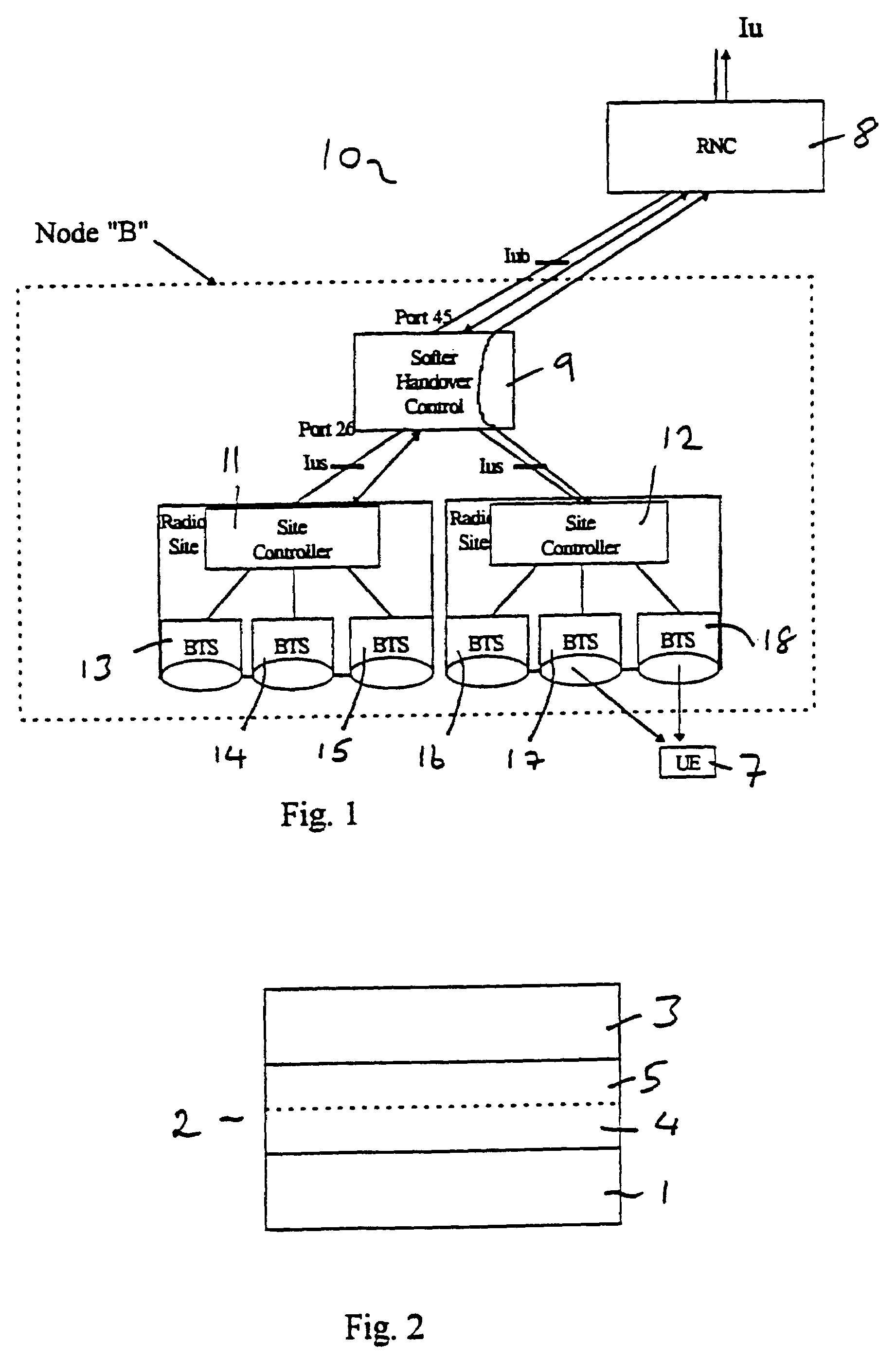
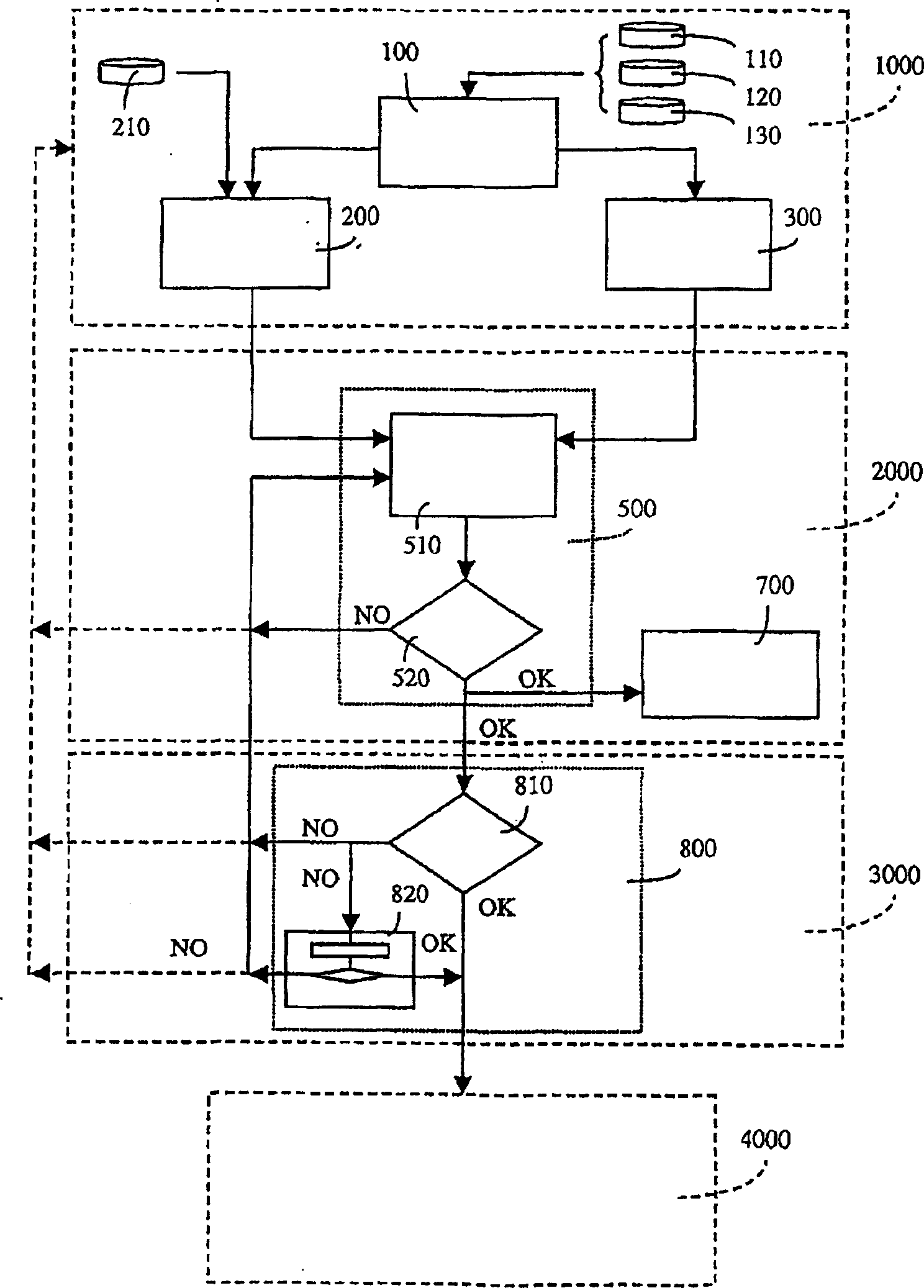
Method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless network
InactiveUS6907243B1Resource allocatedMinimize air-link congestionPower managementAccounting/billing servicesTelecommunicationsMobile device
A method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless communications network includes determining a wireless path characteristic individually for each path of a macro diversity connection between a mobile device and a plurality of wireless sites. Wireless resources are allocated for the macro diversity connection between the mobile device and the wireless sites based on the wireless path characteristic. The wireless path characteristic includes a location-based characteristic, a congestion-based characteristic, a subscriber-based characteristic and / or a performance-based characteristic.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
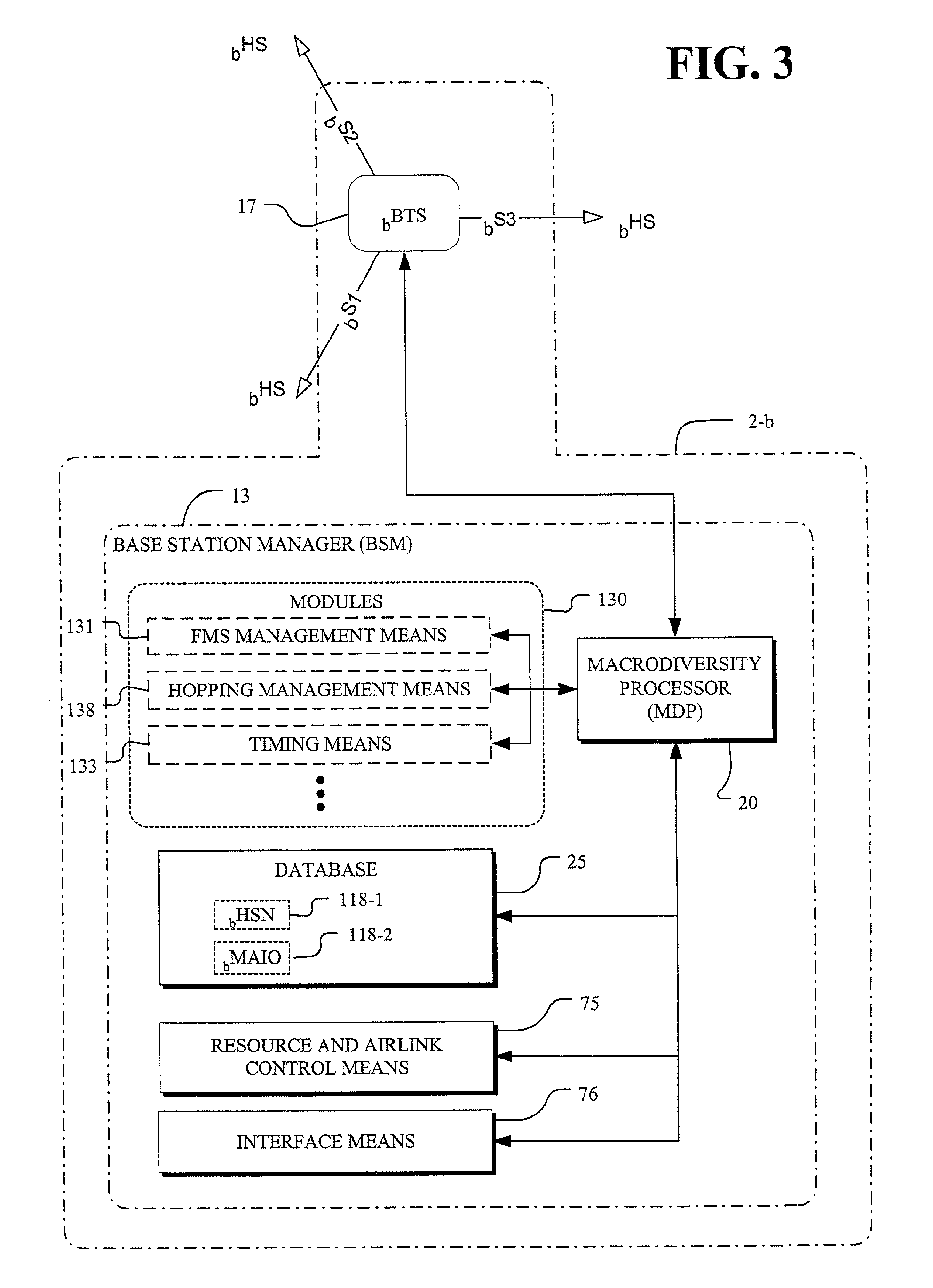
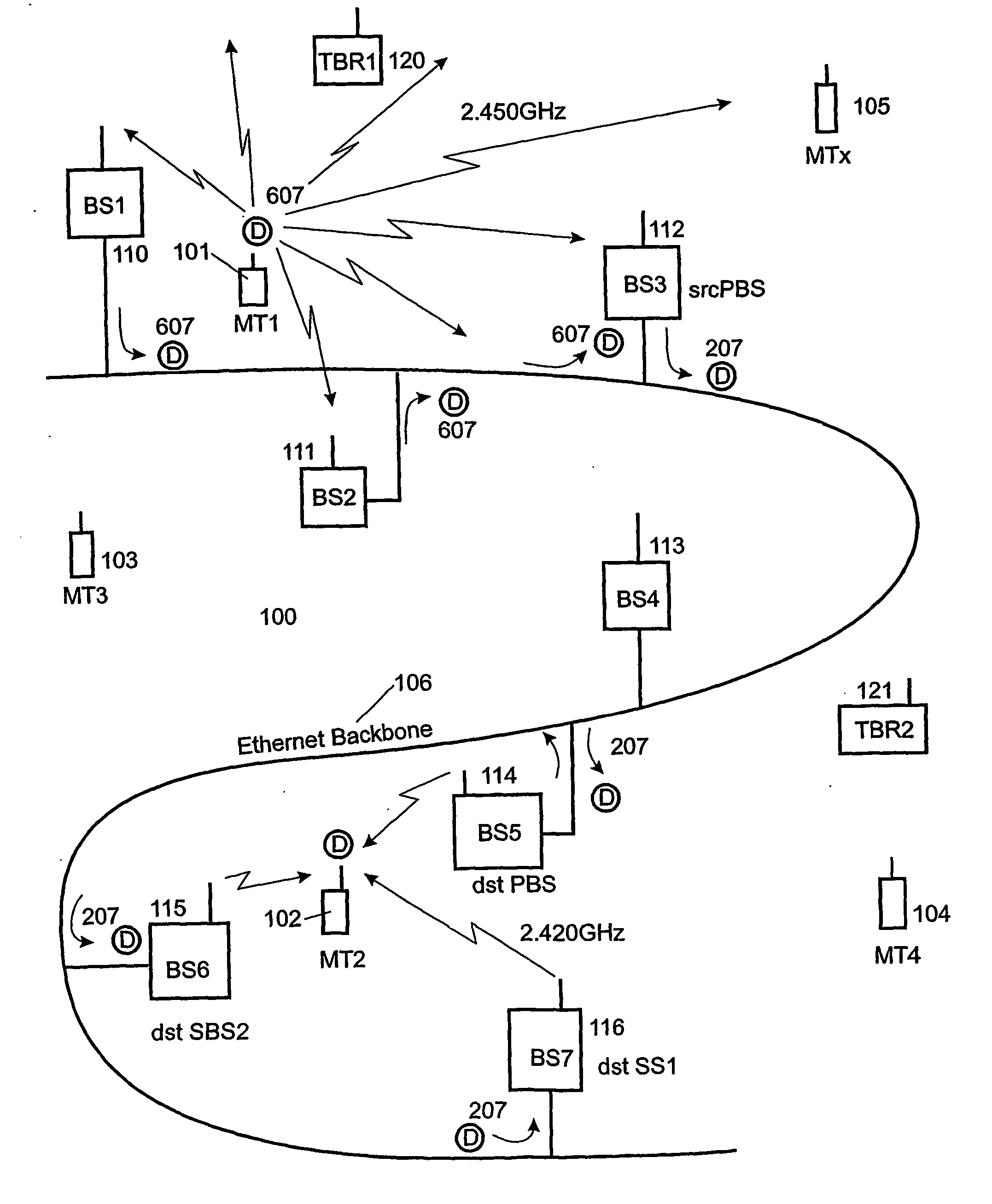
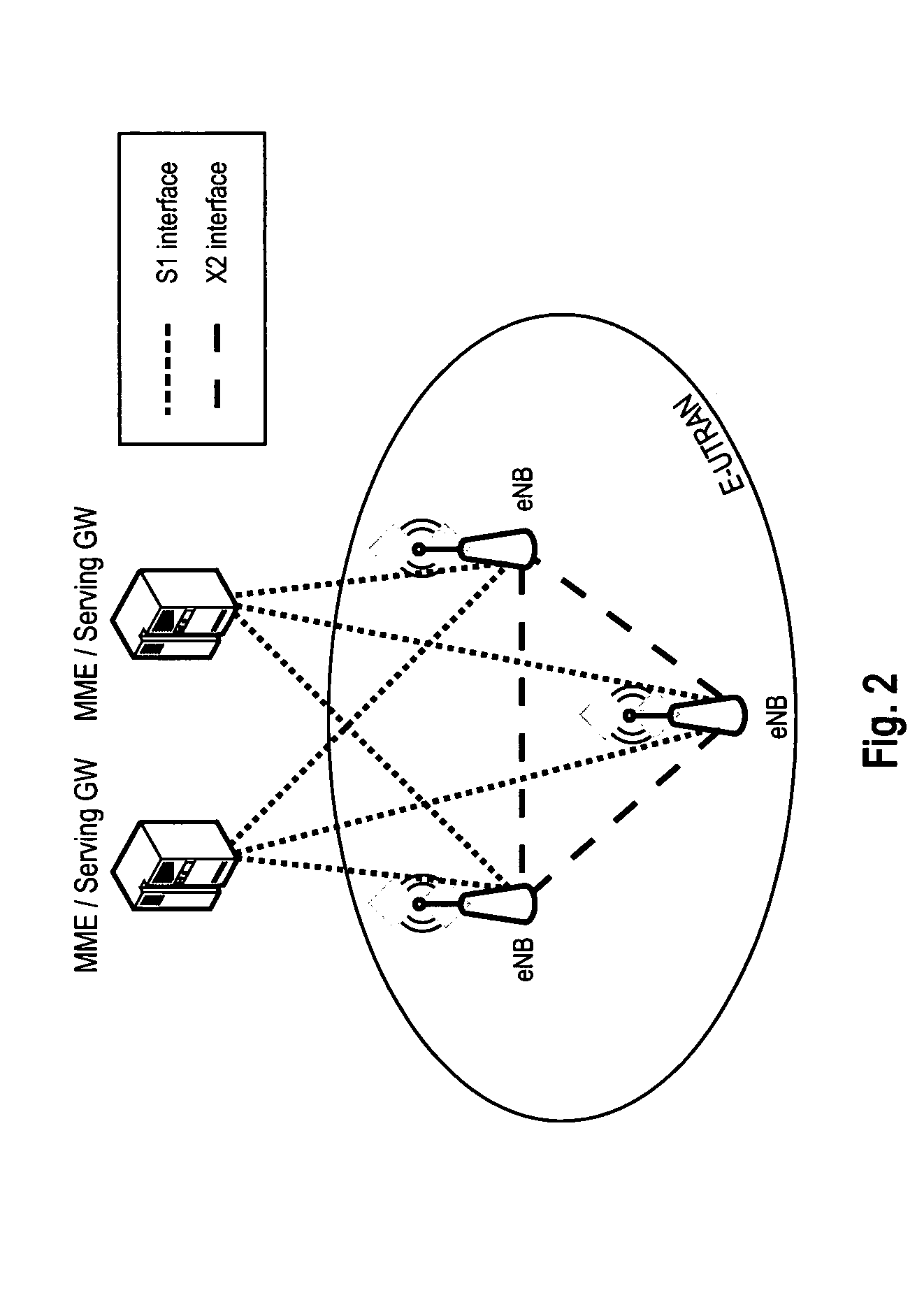
Virtual cell mapping in macrodiverse wireless networks with frequency hopping
InactiveUS7010015B2Interference minimizationSite diversitySecret communicationVirtual cellCommunications system
A communication system for communication with mobile stations through a plurality of base stations at macrodiverse locations and with frequency hopping (FH). Two or more adjacent base stations communicate with mobile stations in a region between the adjacent base stations using coordinated orthogonal frequency hopping sequences. The communication system operates with virtual cells formed of physical sectors from adjacent base stations. Where base stations each operate with three sectors, virtual cells use three adjacent sectors of three adjacent base stations, respectively, and the coordinated orthogonal frequency hopping sequences are used for the adjacent sectors of each of the virtual cells. For GSM, the coordinated orthogonal frequency hopping sequences in each virtual cell are defined by a single hopping sequence number (HSN) and a set of mobile allocation index offsets (MAIOs). Fast macrodiversity switching is employed in combination with FH.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
Radio communication systems
InactiveUS20070032241A1Easy to optimizeFacilitate communicationSite diversityNetwork topologiesCommunications systemTransceiver
A communications system including a plurality of base station transceivers linked by some means over which the base station transceivers communicate, a plurality of mobile transceivers adapted to communicate via the base station transceivers using macrodiversity, and wherein the mobile transceivers are further adapted to control allocation of system resorces to enable communication.
Owner:TAIT
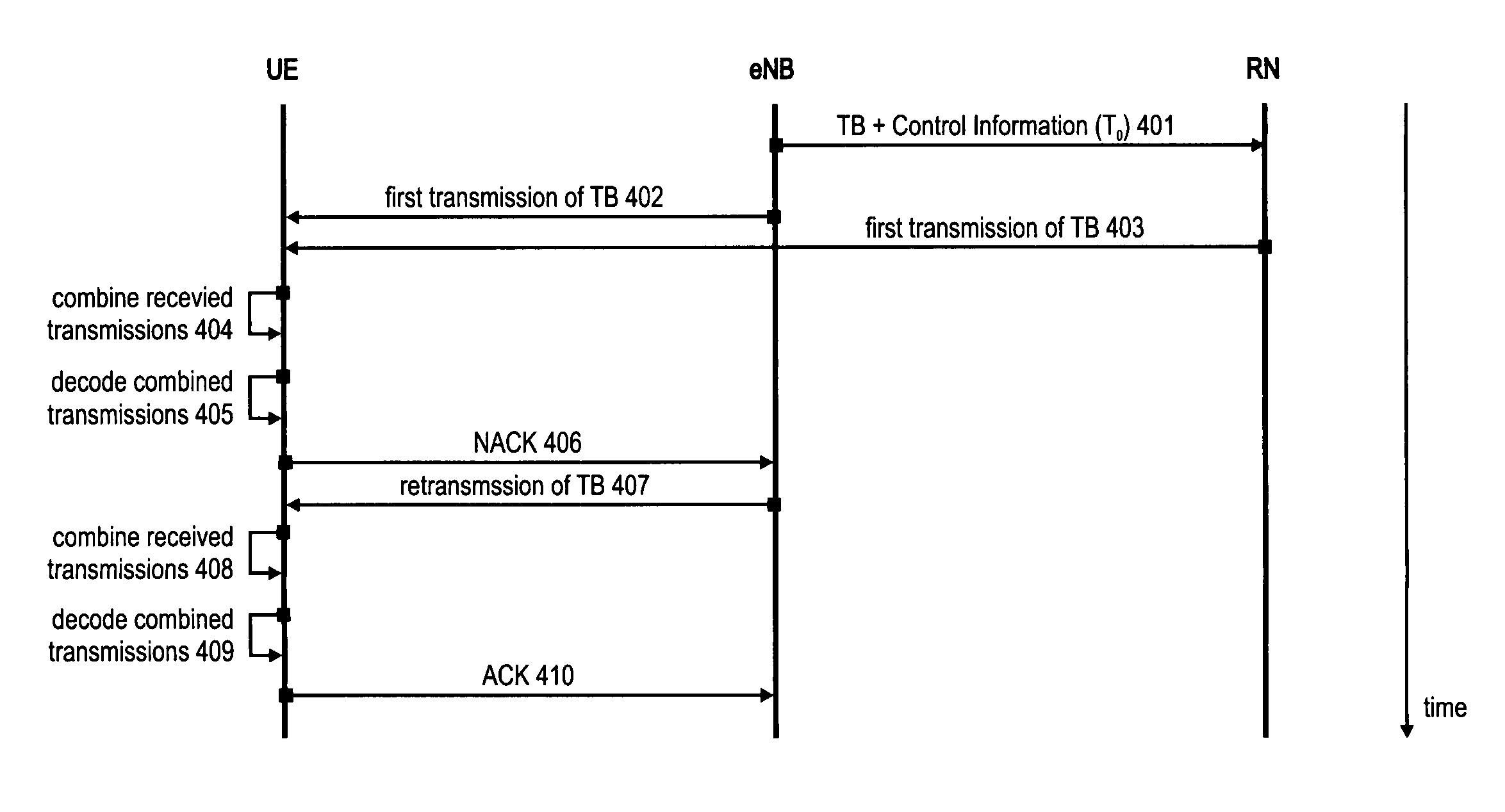
HARQ operation for macro-diversity transmissions in the downlink
ActiveUS20110305213A1Reduce delaysWireless commuication servicesTransmission link error control systemData transmissionComputer science
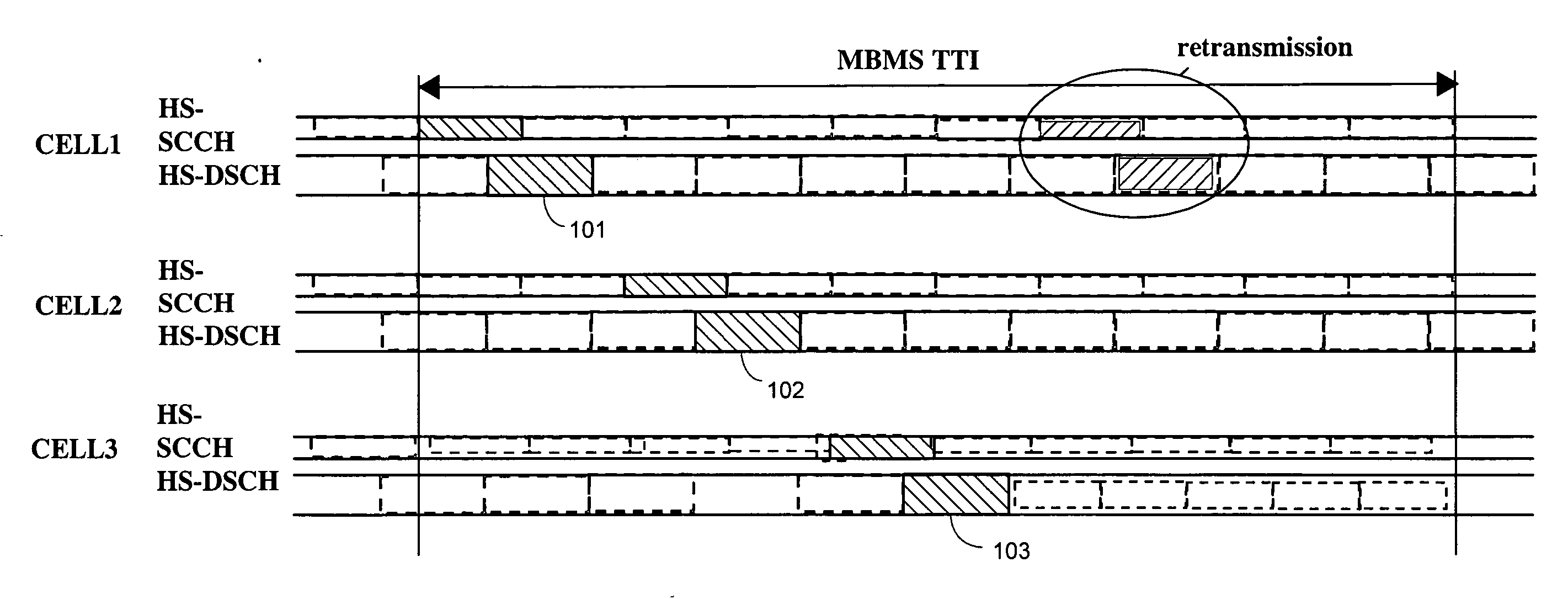
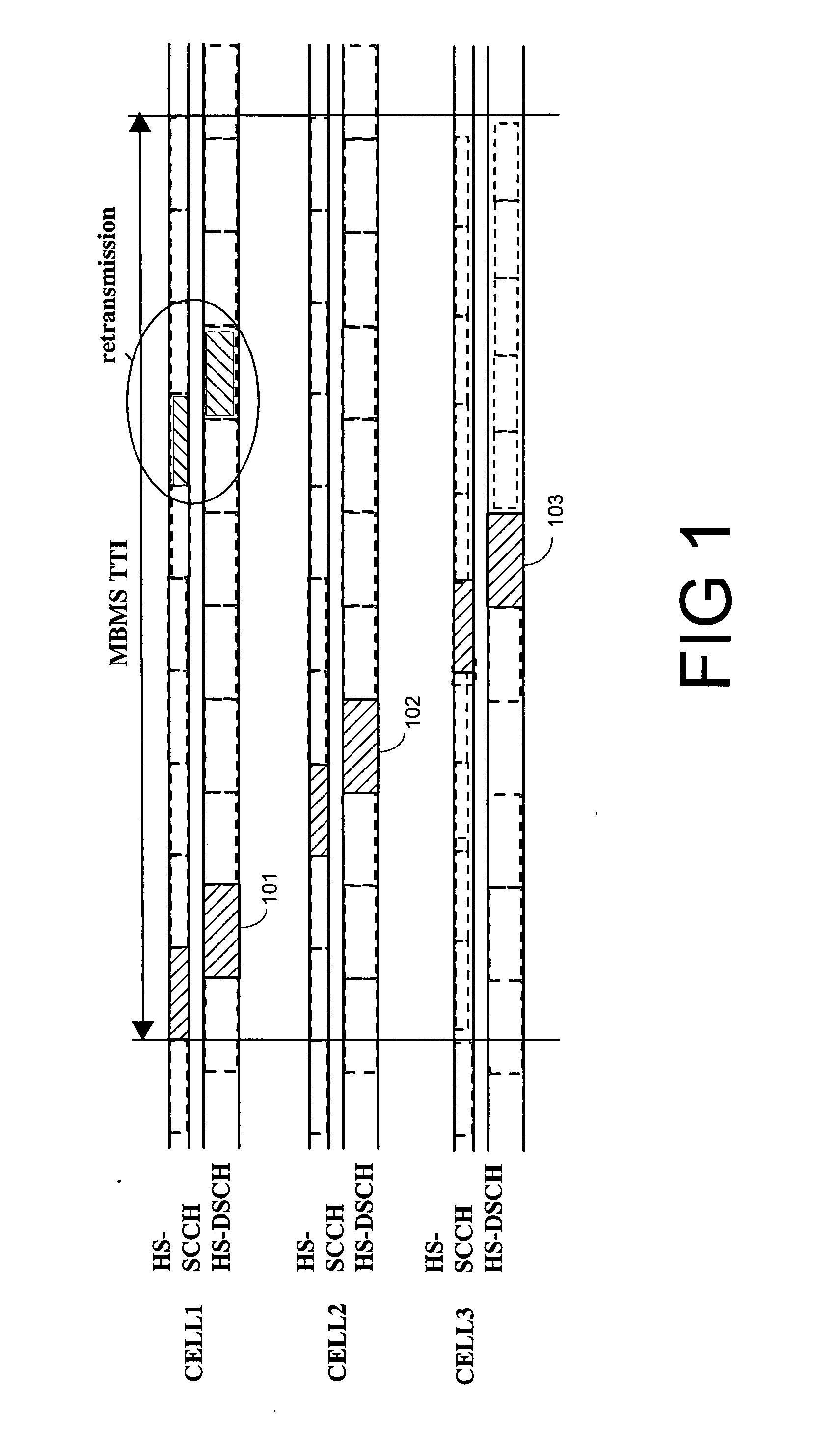
The invention relates to a downlink transmission scheme that supports downlink HARQ operation and macro-diversity that is capable of overcoming the problem of HARQ protocol de-synchronization when using HARQ in the downlink with multiple data transmitting network nodes. In this scheme, a distributed HARQ protocol operation for downlink data transmissions involving multiple network nodes is provided, where only one network node is terminating downlink HARQ protocol operation towards to mobile terminal, i.e. retransmissions of a data packet are sent from a single network node, a single HARQ transmitter, to the mobile terminal. The multiple network nodes send a first transmission of the data packet to the mobile terminal in a single transmission time interval using HARQ. One of the multiple network nodes is designated as the HARQ terminating node that controls / handles all retransmissions of the data packet.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Communication system employing transmit macro-diversity
InactiveUS6996380B2Reduce and eliminate transmit powerExcessive transmission powerSpatial transmit diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTransmitter
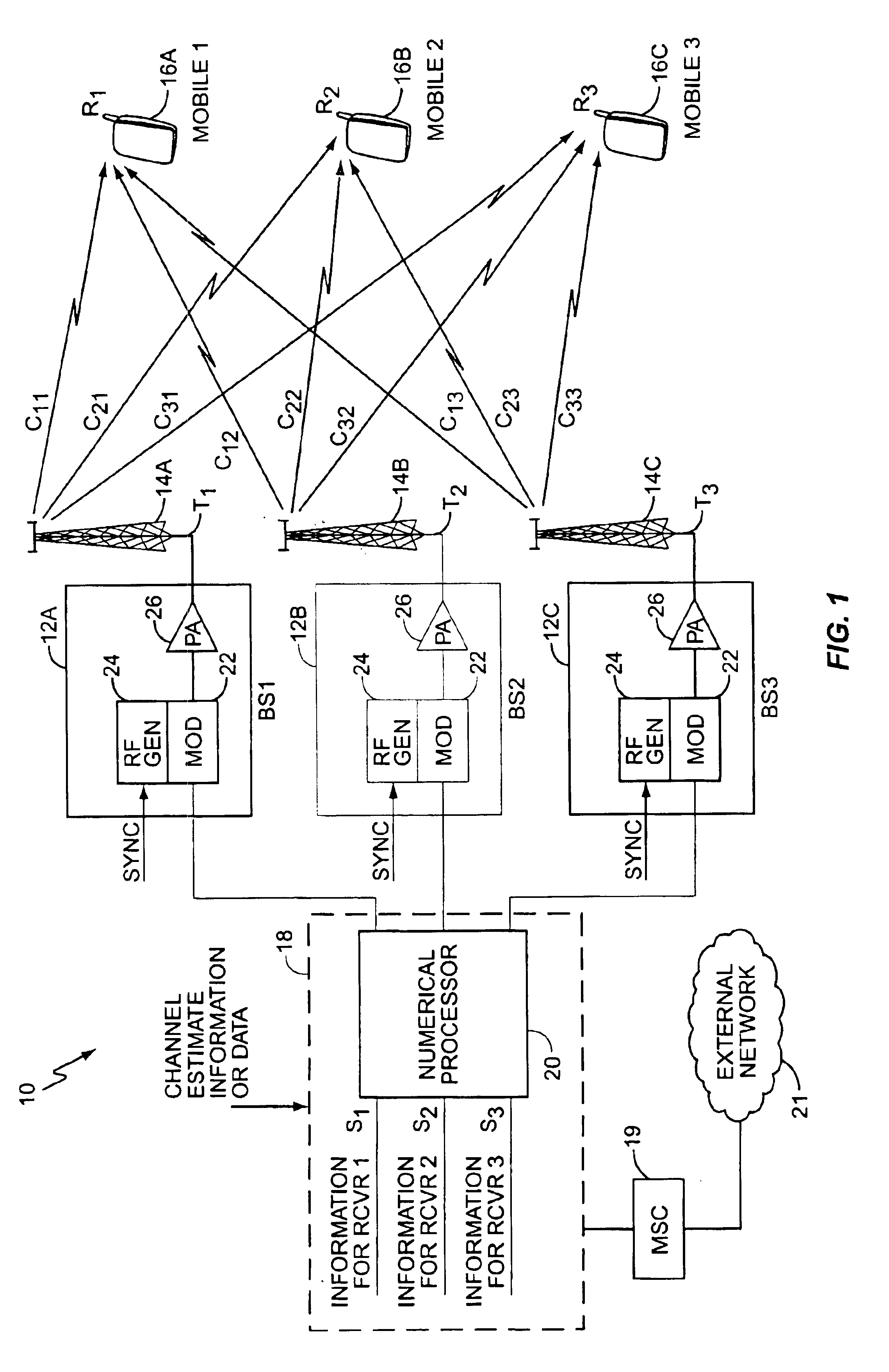
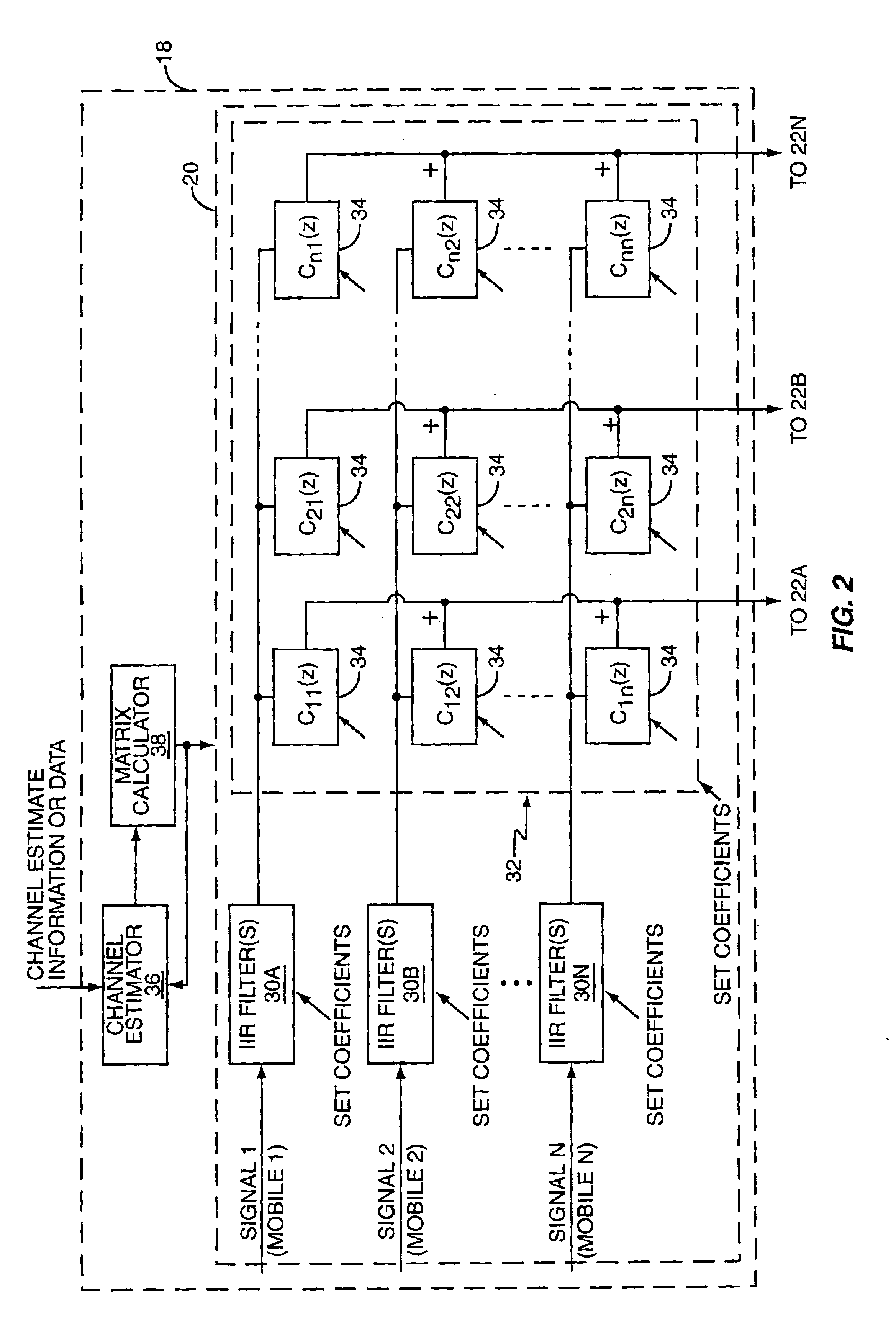
Coherent transmit macro-diversity involves transmitting simultaneous signals from one or more transmitters to one or more wireless receivers. Transmit signals are formed as weighted combinations of the individual information signals for each of the wireless receivers. By properly weighting these receiver-specific signals, the combined signals combine at each receiver to cancel all but the desired information signal for that receiver. This improves reception performance and allows multiple receivers to operate on the same communication channel in the same area if desired. The weighting factors used to form the combined signals are based on propagation path characteristics between each of the transmit antennas and each of the receivers. This information is generally referred organized as a channel estimate matrix and is used to filter the information signals such that they may be combined in the required weighted combinations.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Method and apparatus for changing radio link configurations in a mobile telecommunications system with soft handover
InactiveUS7043244B1Minimum qualityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionTransceiverAir interface
A telecommunications system and a method of operating the same are described in which mobile terminals may communicate with base station transceivers over an air interface, a communication to another user terminal being supported in macrodiversity by radio links between a plurality of base station transceivers and a mobile terminal. The radio links in macrodiversity have a set of common radio link configuration parameters. When a change in the common configuration is necessary, the system transmits a radio link configuration change message to each of the base station transceivers and the mobile terminal and waits before implementation of the radio link configuration change until an acknowledgement has been received from at least one base station transceiver in transmitting communication with the mobile terminal, at least one base station transceiver in receiving communication with the mobile terminal and the mobile terminal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
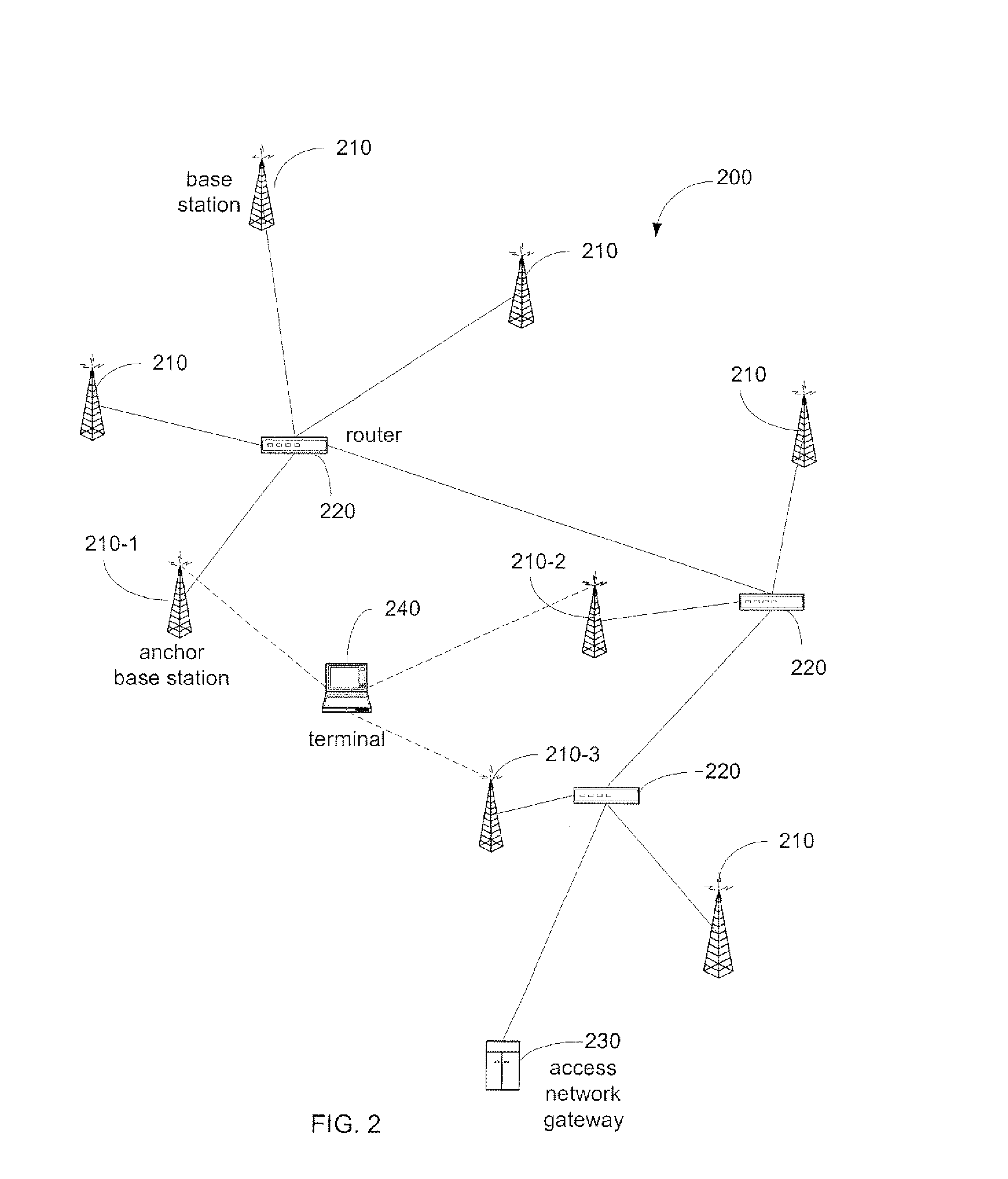
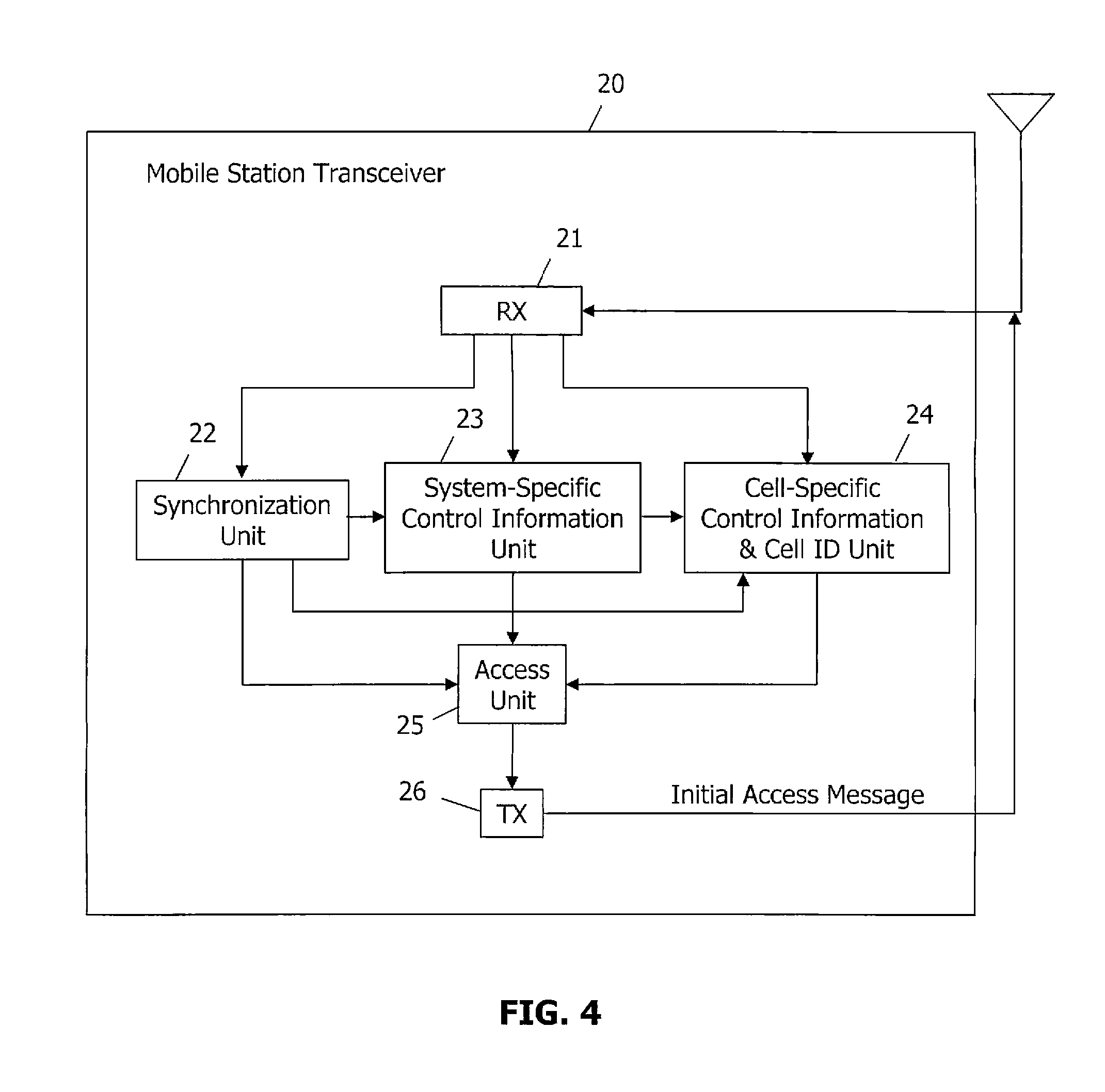
Broadcast-centric cellular communication system
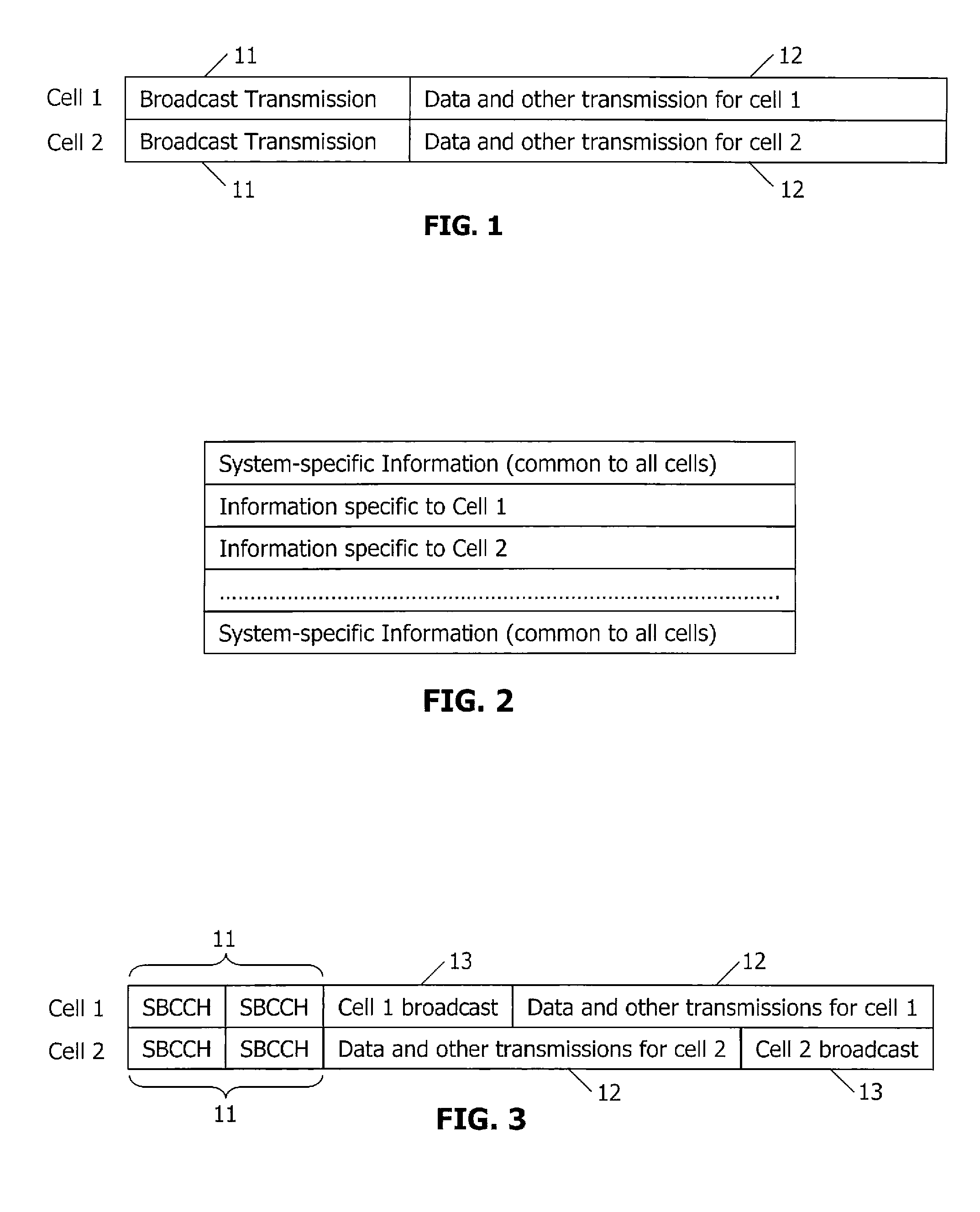
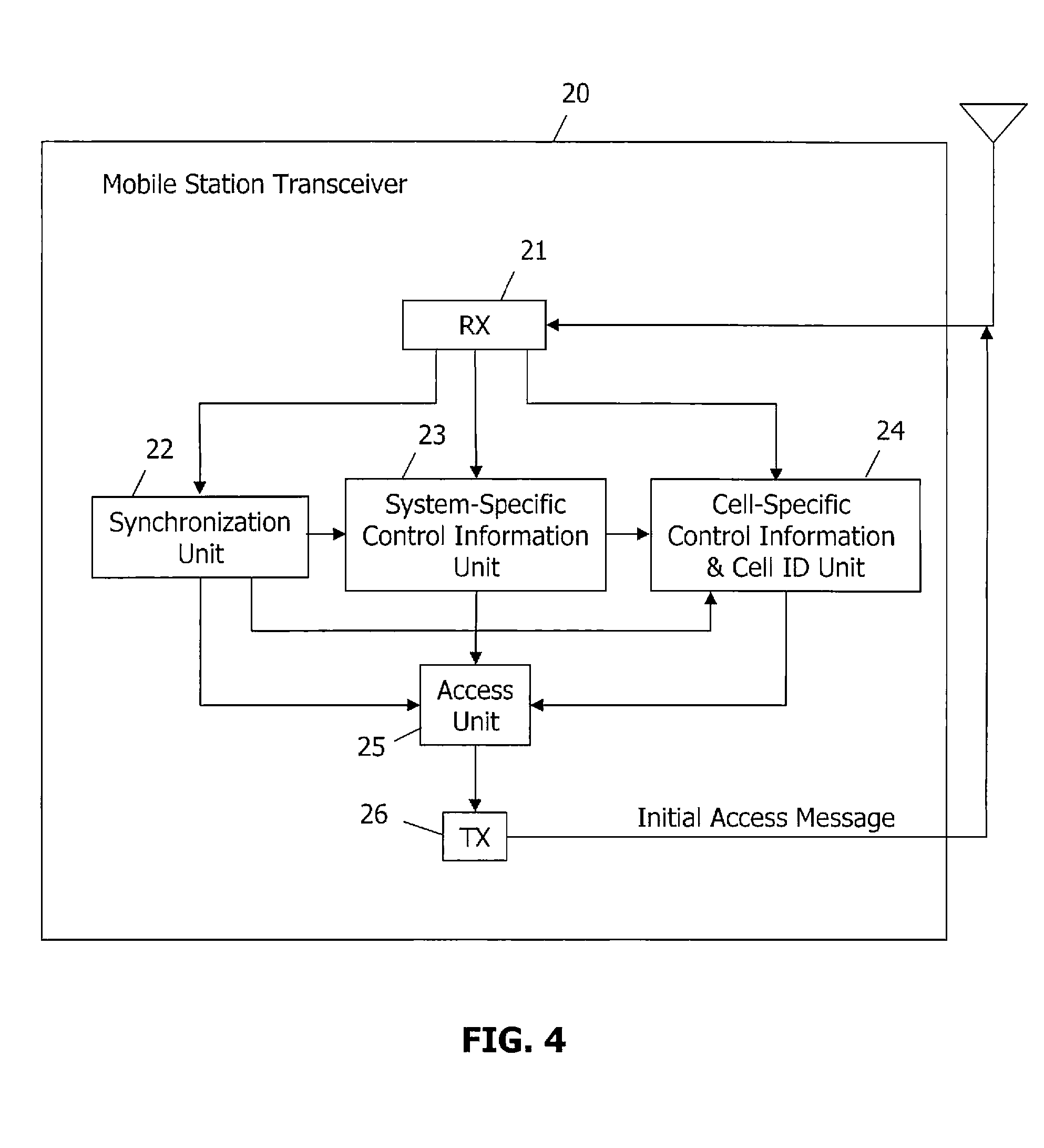
ActiveUS20070167180A1Improve performanceImprove channel performanceSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionCell specificBroadcast channels
A broadcast-centric cellular communication system improves broadcast channel performance by exploiting the benefits of macro-diversity in a cellular communication system having a plurality of base stations that transmit signals within a plurality of associated cells. System-specific control information common to all cells is synchronously and simultaneously broadcast from multiple base stations using a broadcast channel that is identical across the entire system. Cell-specific control information is transmitted individually from each base station. Mobile stations use the broadcast information for initial synchronization to the system, and to obtain most relevant system information. After system synchronization, the mobile stations identify the connected cell through a physical layer characteristic, and perform initial access to the system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
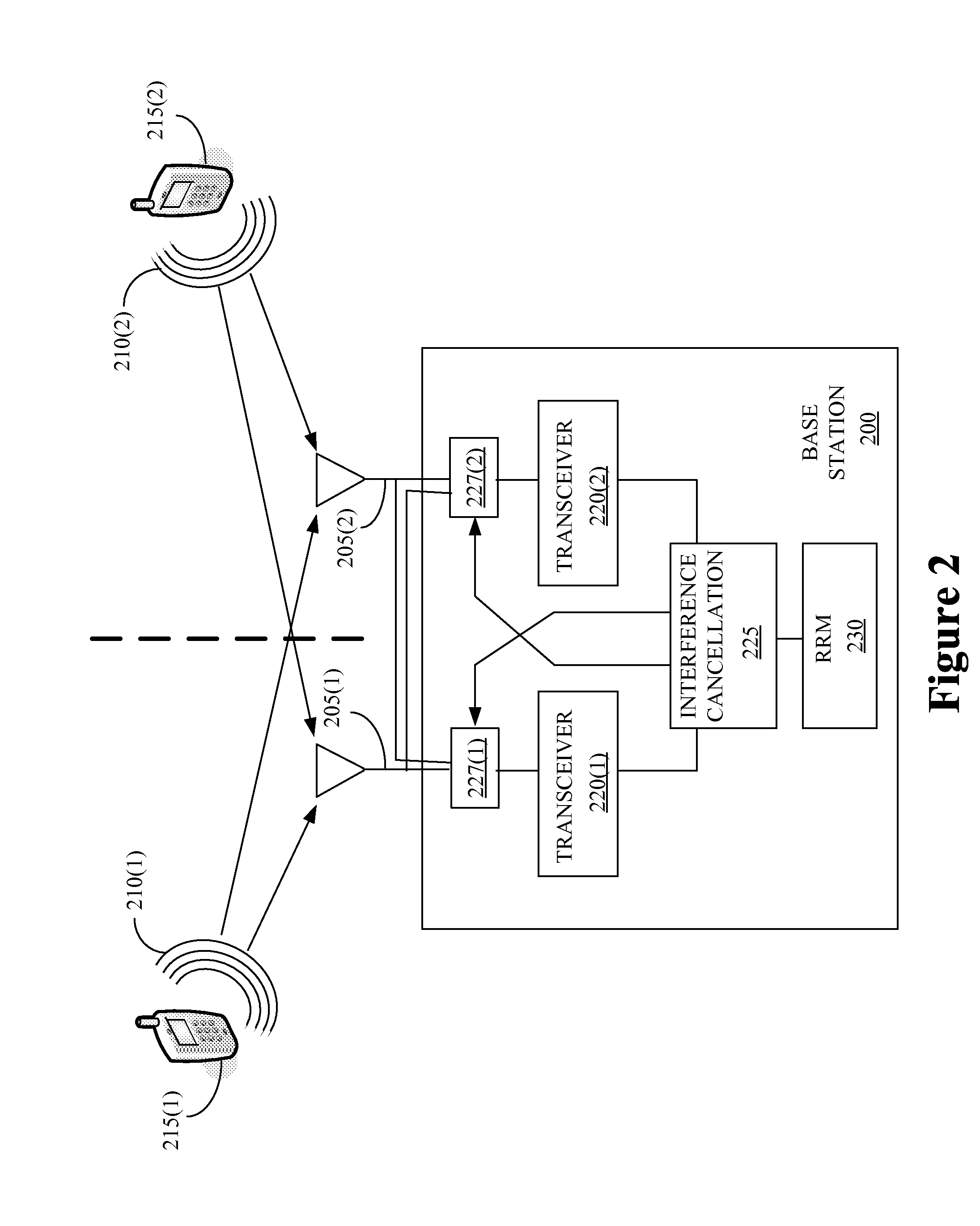
System and apparatus for interference suppression using macrodiversity in mobile wireless networks
InactiveUS20080318613A1Reduce amountMaximize data transfer rateSite diversityModulated-carrier systemsMobile wirelessWireless network
In a wireless network, plural downlink signals from plural base stations are transmitted to a terminal. The plural downlink signals all carry the same information to the terminal. The terminal provides feedback on the downlink channels. The feedback provides information on the taps of the channels. The amount of information fed back is constrained. Based on the feedback, transmission parameters of the downlink signals are adjusted. The process of transmitting, providing feedback, and adjusting the parameters continue so that the energy of the downlink signal is enhanced at the terminal location and suppressed elsewhere. Beam forming can be used to further suppress the energy signature at locations other than the terminal location.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
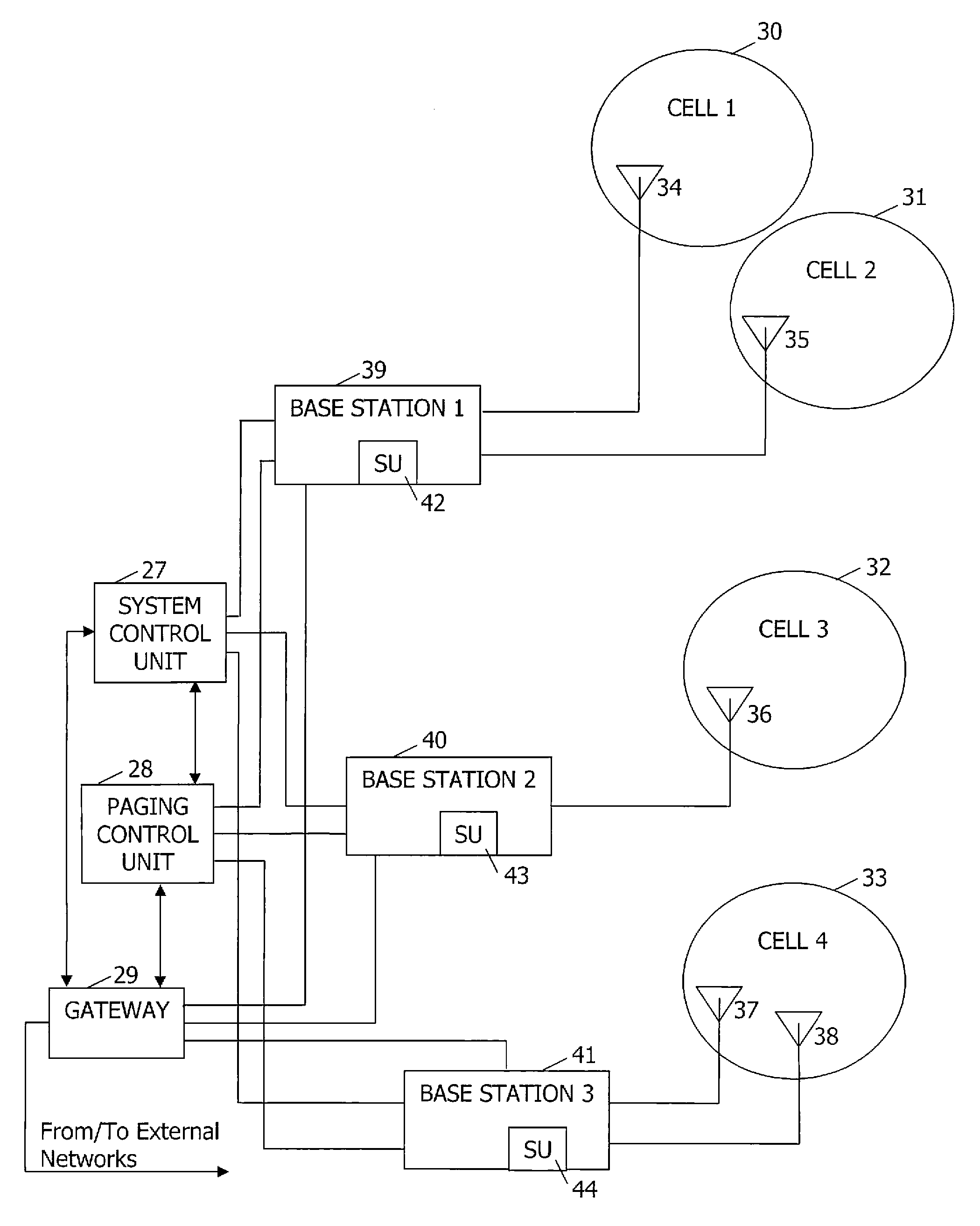
Broadcast-centric cellular communication system, method, and mobile station
InactiveUS20070167159A1Improve performanceSite diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBroadcast channelsSignal quality
A broadcast-centric cellular communication system improves broadcast channel performance by exploiting the benefits of macro-diversity in a cellular communication system having a plurality of base stations that transmit signals within a plurality of associated cells. The system constructs an identical paging signal at the plurality of base stations, and controls the base stations to simultaneously transmit the identical paging signal. A mobile station camps on a paging channel that is common to the plurality of base stations, and listens to paging messages being simultaneously broadcast by the plurality of base stations. The mobile station selects a base station having a suitable signal quality, and transmits to the selected base station, a response to a paging message addressed to the mobile station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
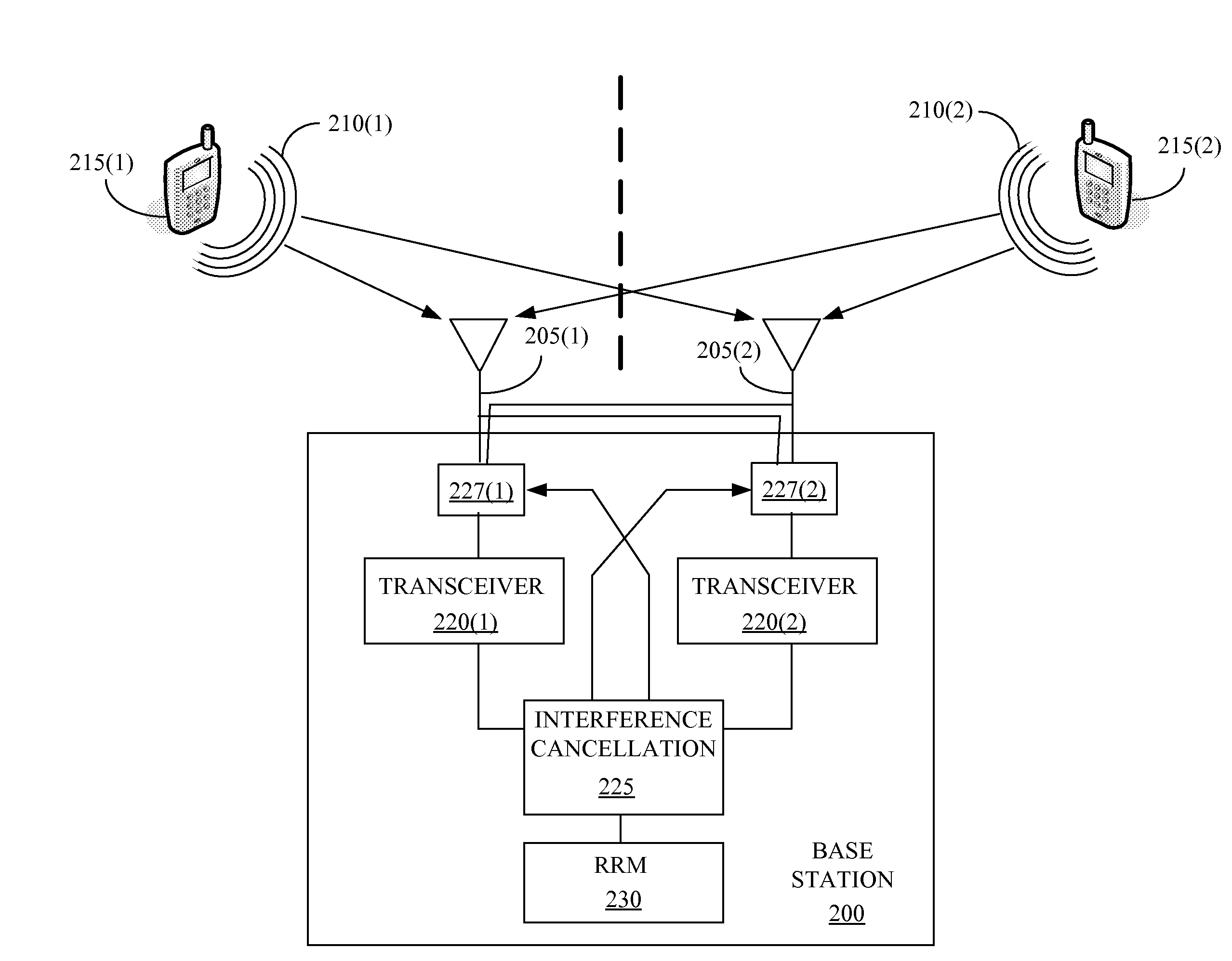
Inter-sector macrodiversity interference cancellation and scheduling
InactiveUS20090312042A1Well formedCancel any interferenceSite diversityCriteria allocationCommunications systemInterference cancelation
The present invention provides a method for interference cancellation in a wireless communication system. One embodiment of a method includes accessing information indicative of one or more first signals transmitted by one or more first mobile units from one or more first sectors. The method also includes accessing information indicative of one or more second signals transmitted by one or more second mobile units from one or more second sectors different than the first sectors. The method further includes canceling interference caused in the second signal(s) by the first signal(s) using the accessed information indicative of the first signal(s) and the second signal(s). The method also includes jointly scheduling and allocating resources to one or more mobile stations in one or more sectors of one or more base stations.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
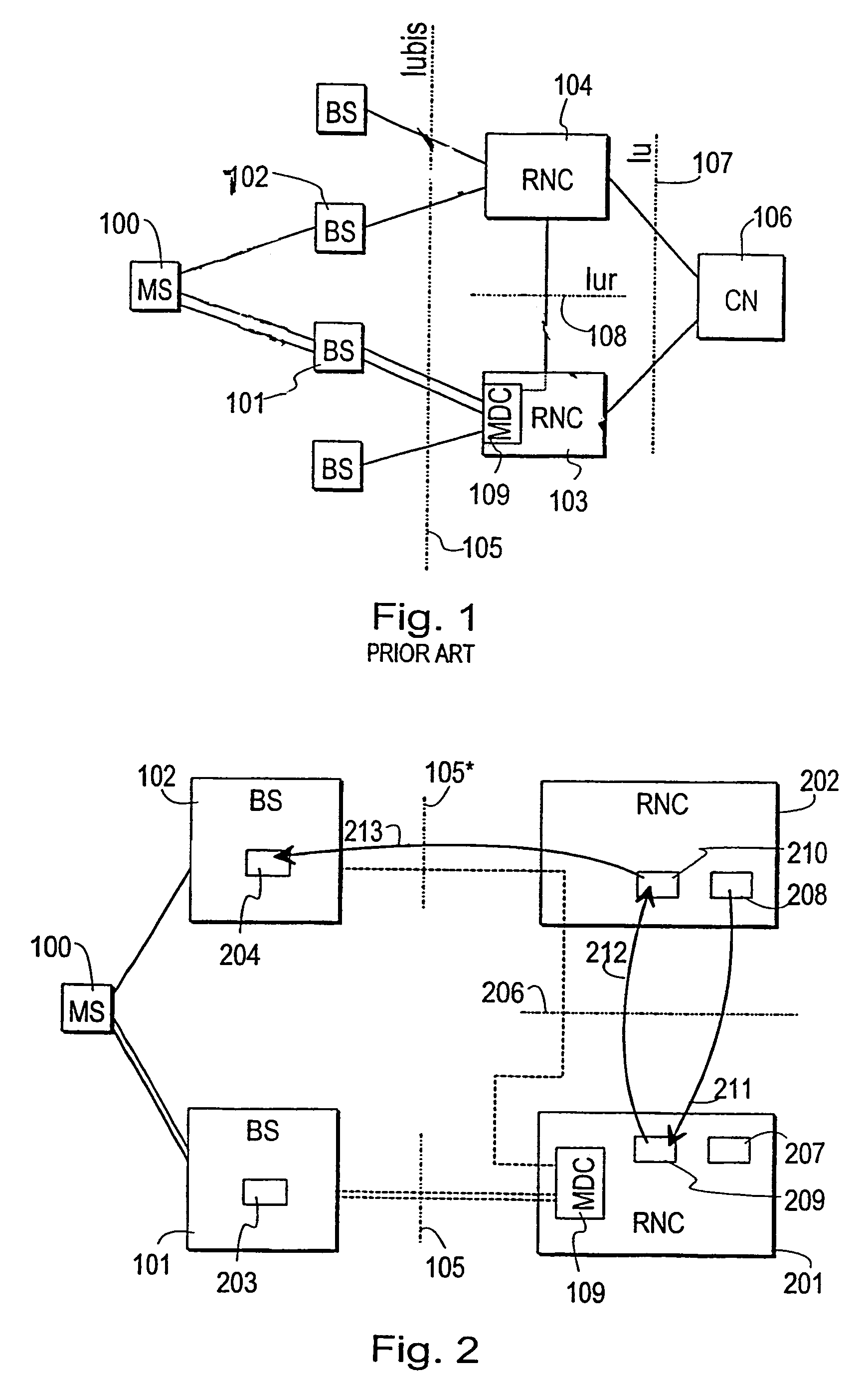
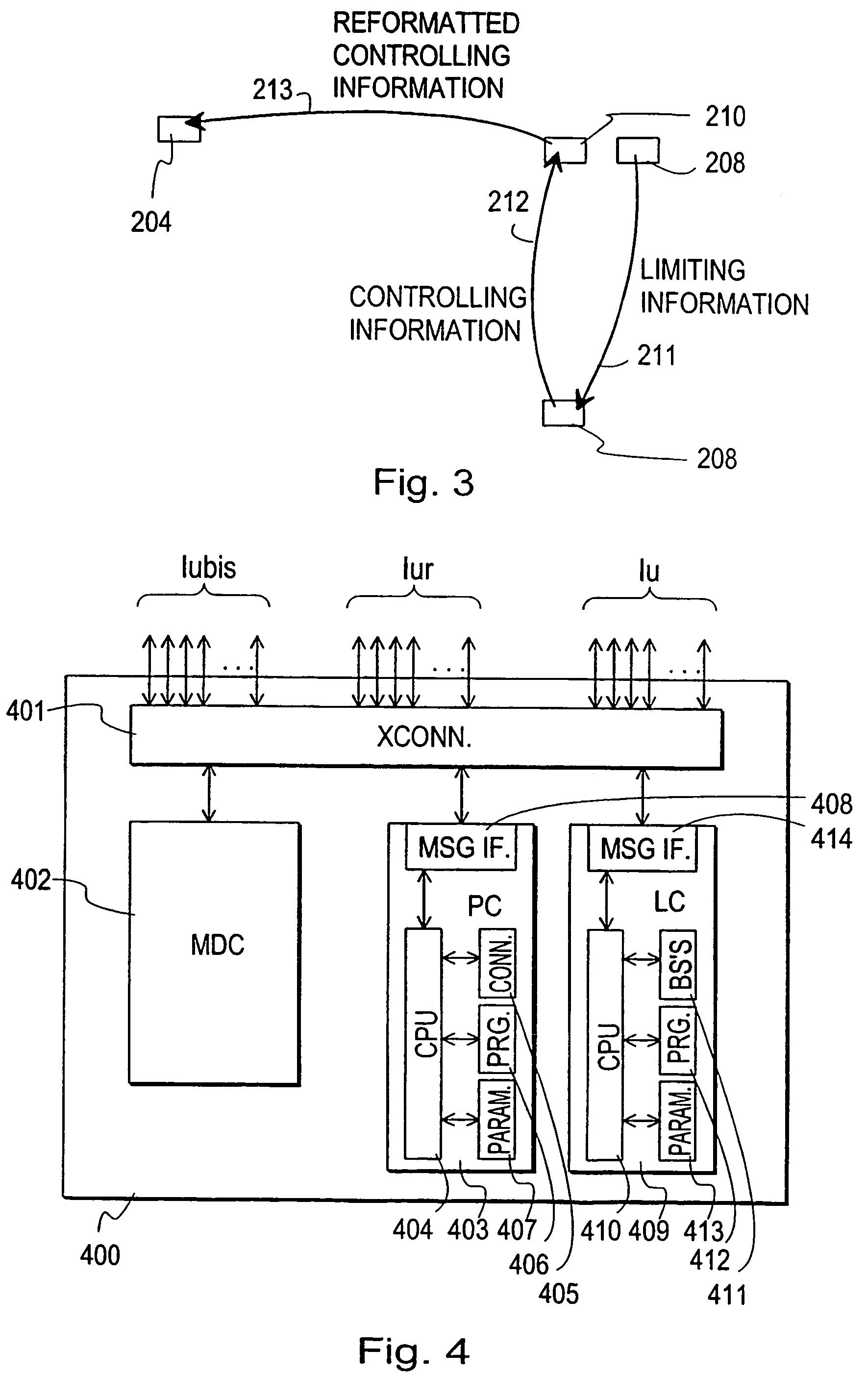
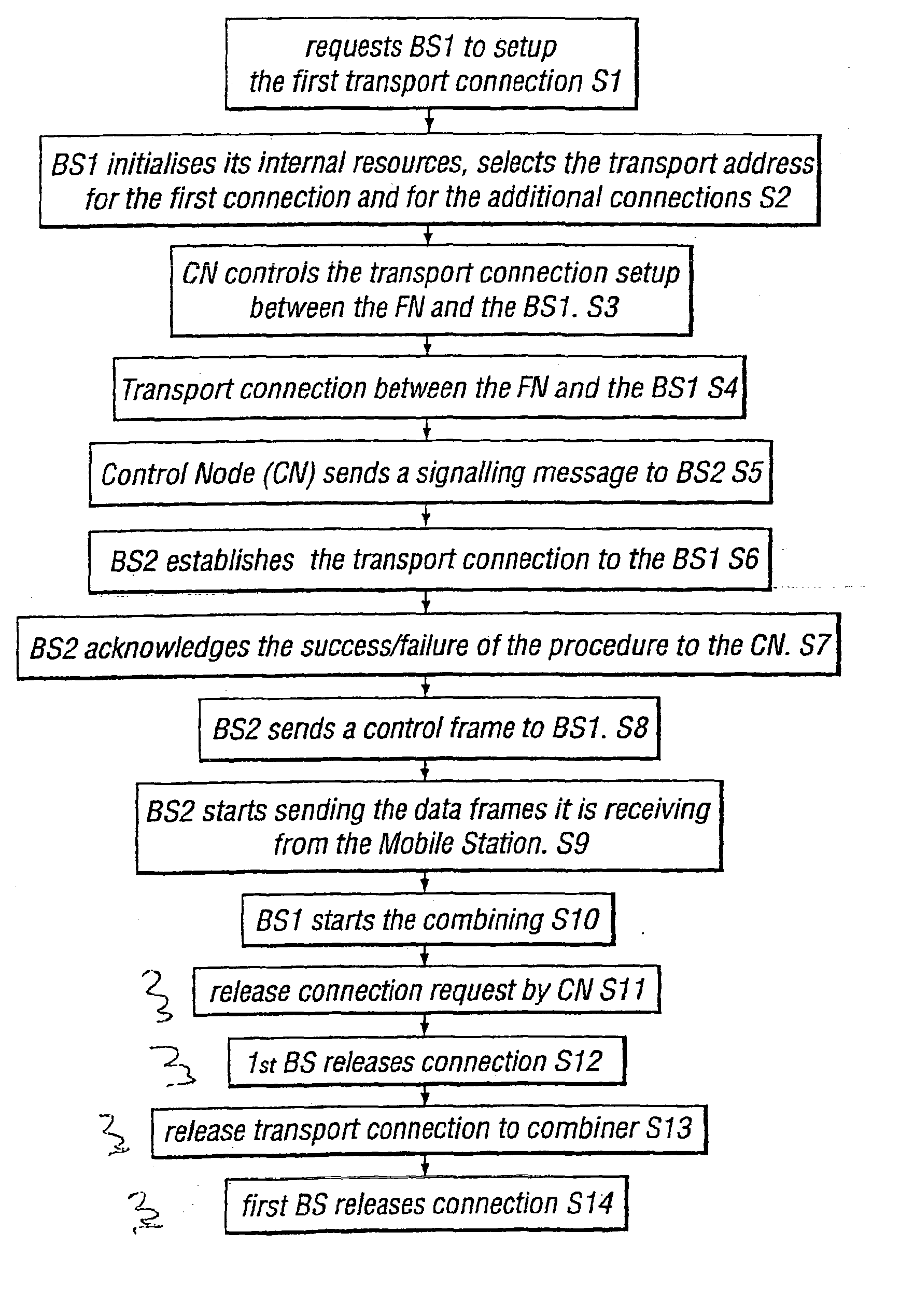
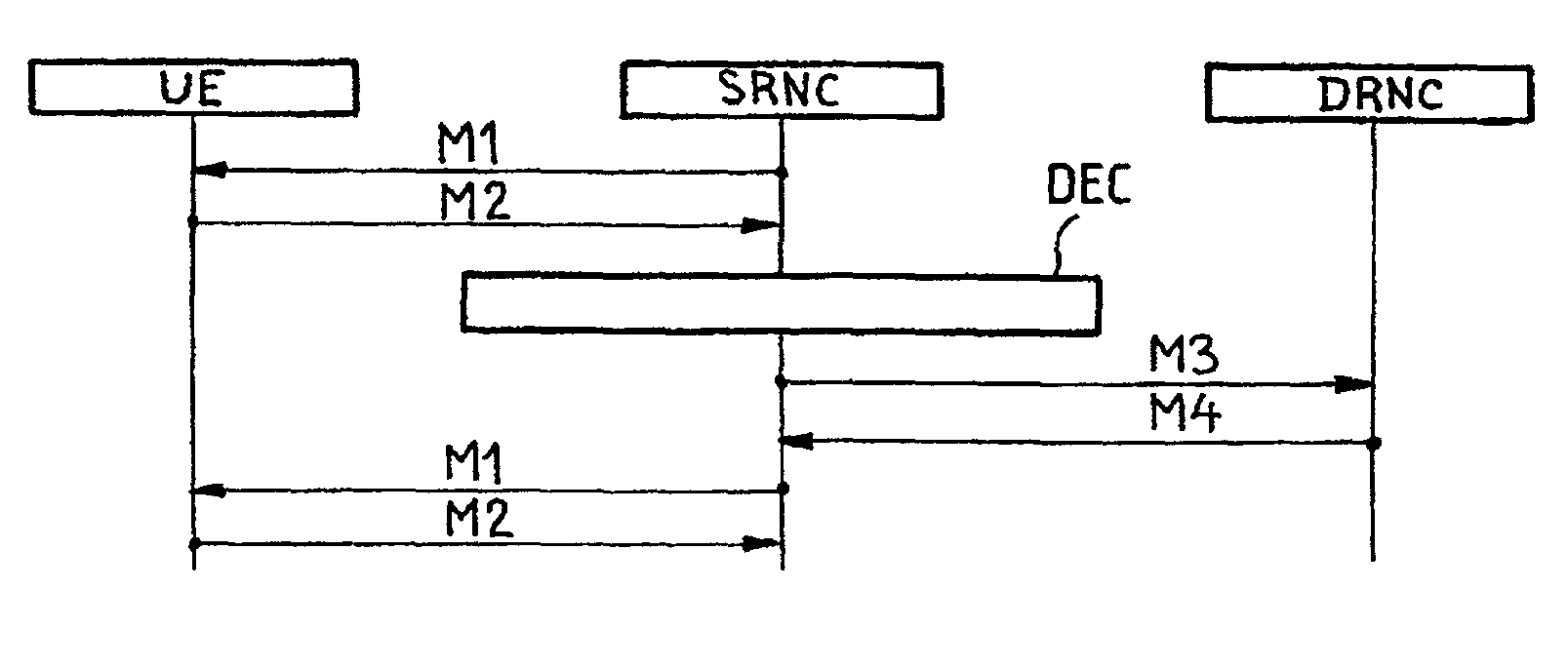
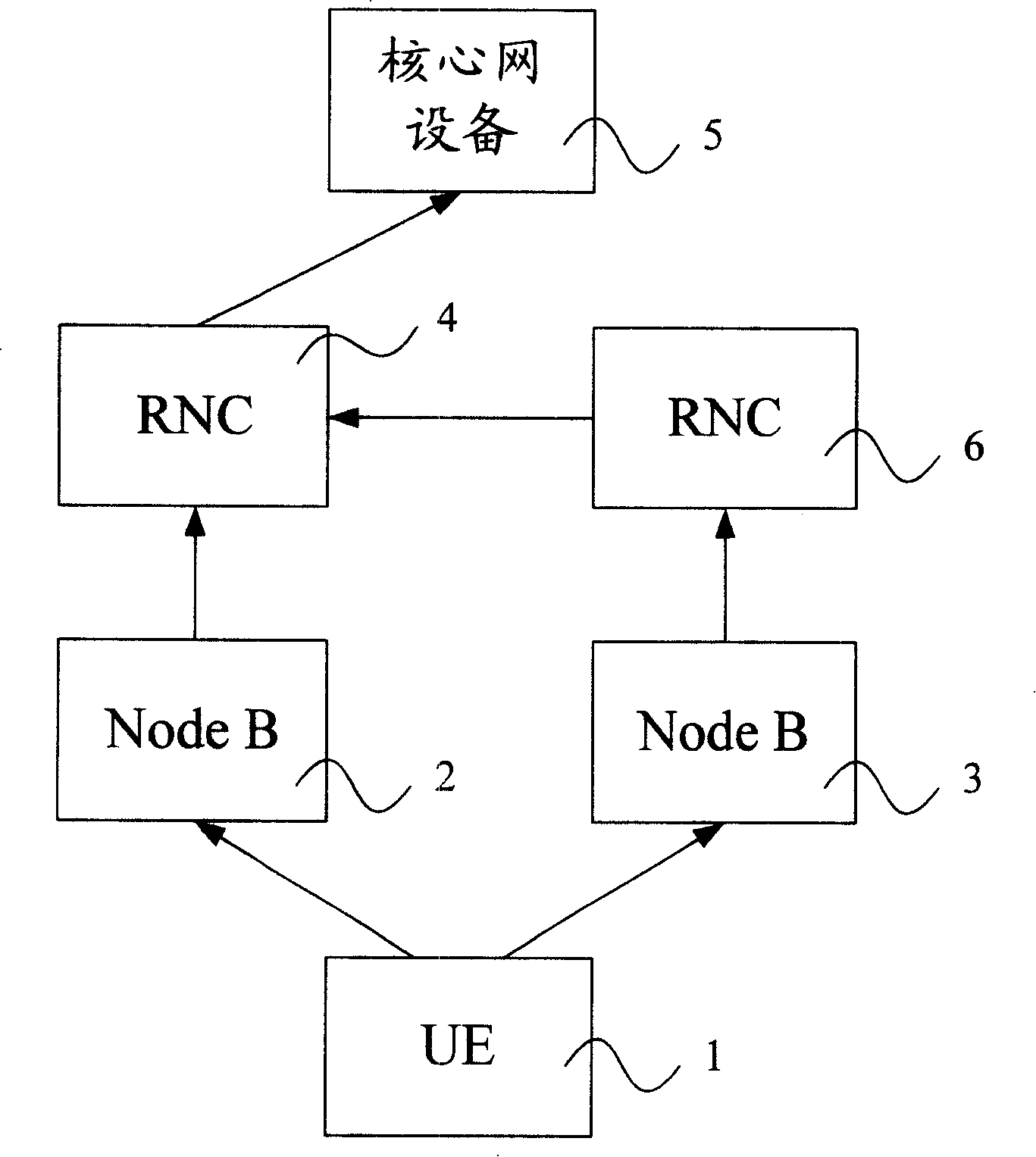
Method and a system for controlling a macrodiversity connection through at least two radio network controllers
A method of changing connection parameters in a cellular radio system comprising terminals, base stations, and radio network controllers, and where at least one terminal is in a macrodiversity connection wherein at least one diversity branch goes between the serving radio network controller and the terminal through the drift radio network controller and the drift base station, and which further comprises a load control wherein the radio network controller monitors and balances the use of radio resources in the base stations that operate under it, and a call control wherein the serving radio network controller sets and changes the connection parameters of its connections, and being characterized in that it comprises observing that the load control of the drift radio network controller demands a change in the connection parameters of the terminal communicating through the base station that operates under it, and controlling the serving radio network controller to change the connection parameters of said terminal.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
High speed downlink packet access communication in a cellular communication system
InactiveCN101433124AConnection managementStore-and-forward switching systemsTransceiverCellular communication systems
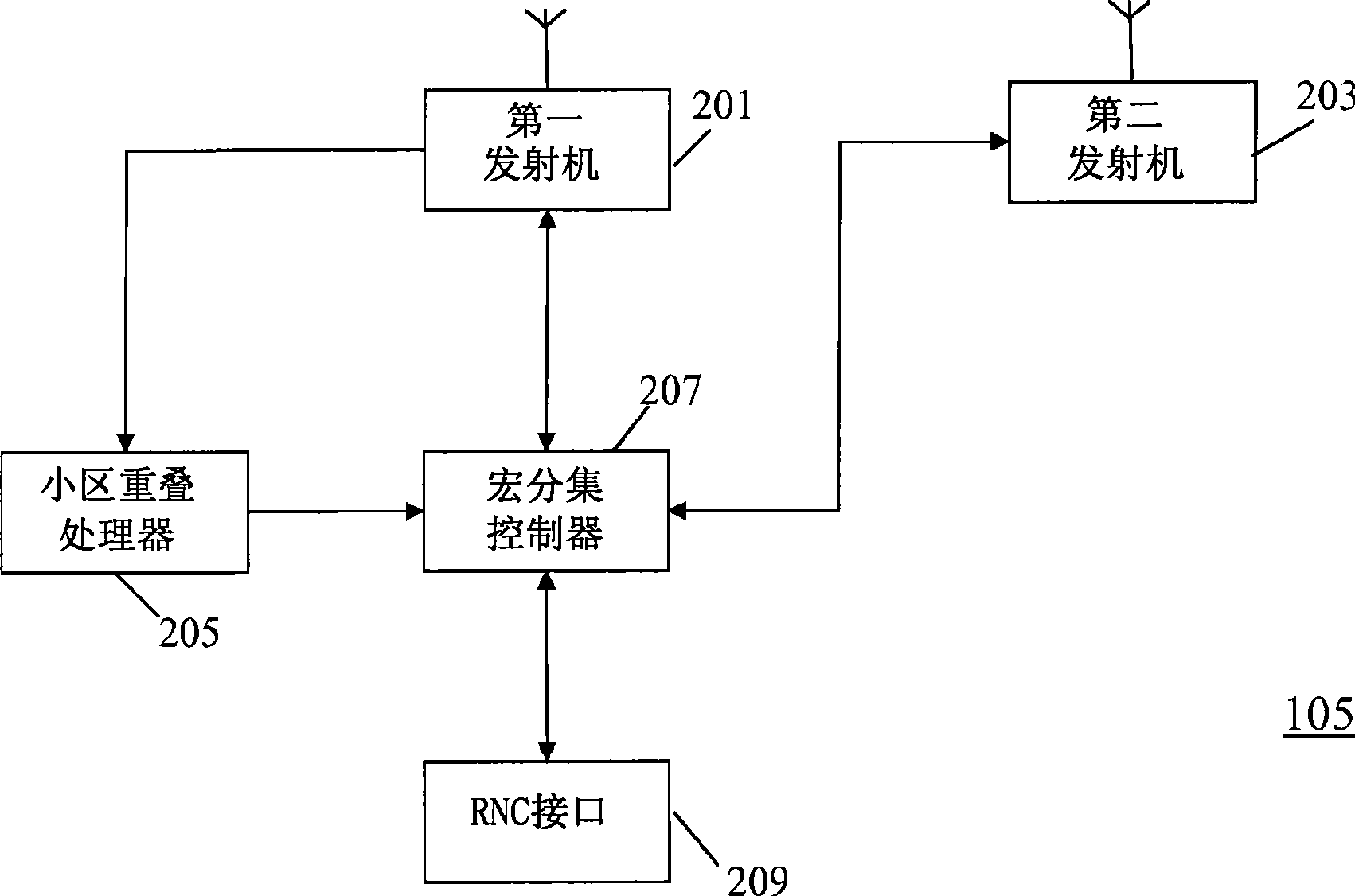
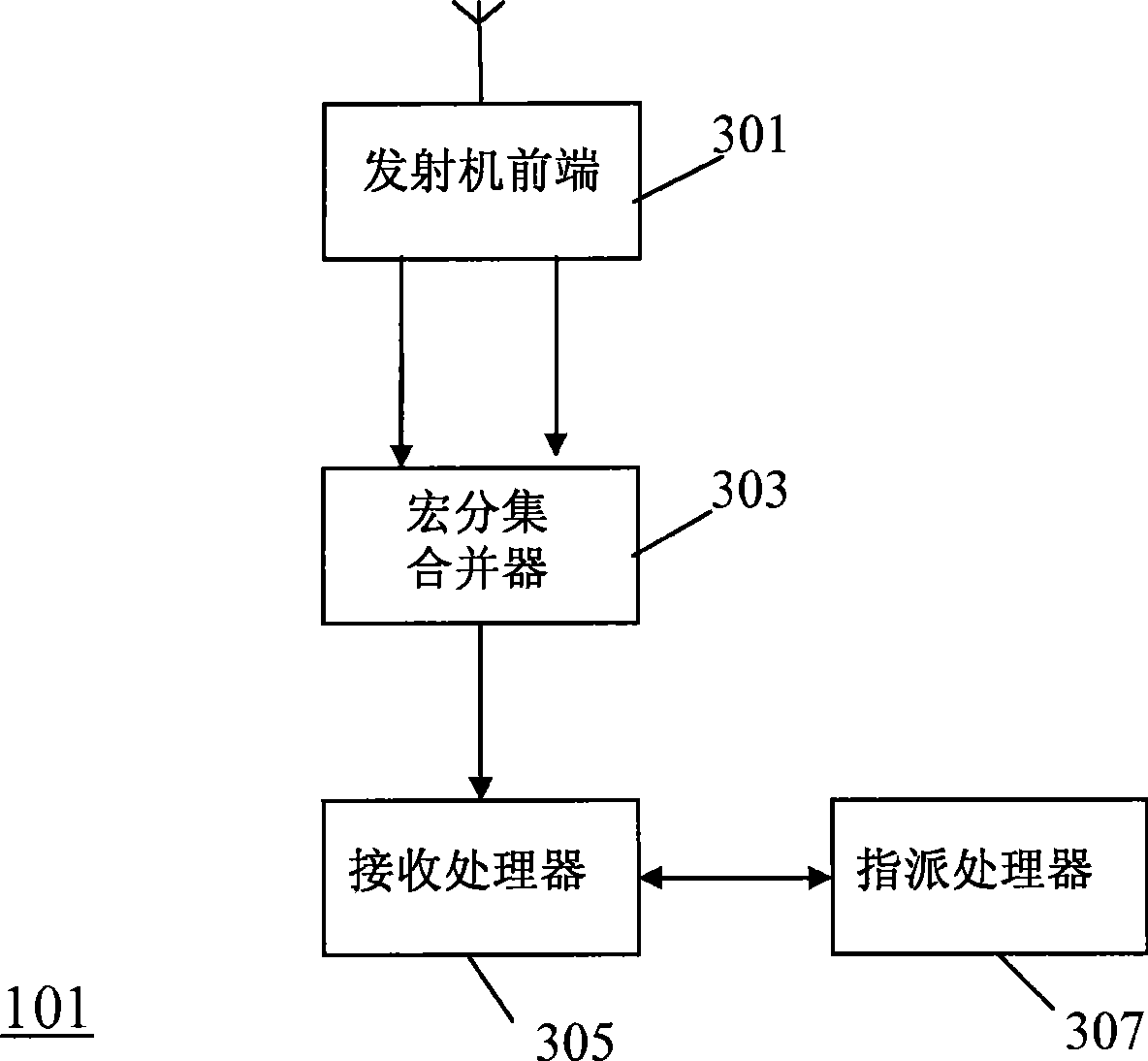
A cellular communication system supports High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) services. A first transceiver (201) transmits HSDPA downlink packet data in a first cell and a second transceiver (203) transmits HSDPA downlink packet data in a second cell. A cell overlap processor (205) can determine that a remote station (101) is in a cell overlap region between the first cell and the second cell. A macro-diversity controller (207) causes the first transceiver (201) to transmit first HSDPA data to the remote station (101) as a first signal in the first cell and the second transceiver (203) to transmit the first HSDPA data to the remote station (101) as a second signal in the second cell. The first and second signals are macro-diversity signals. The remote station (101) comprises a macro-diversity combiner (303) which receives the first downlink HSDPA packet data by combining the first signal and the second signal. The invention may allow improved support of HSDPA services in cell overlap areas.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
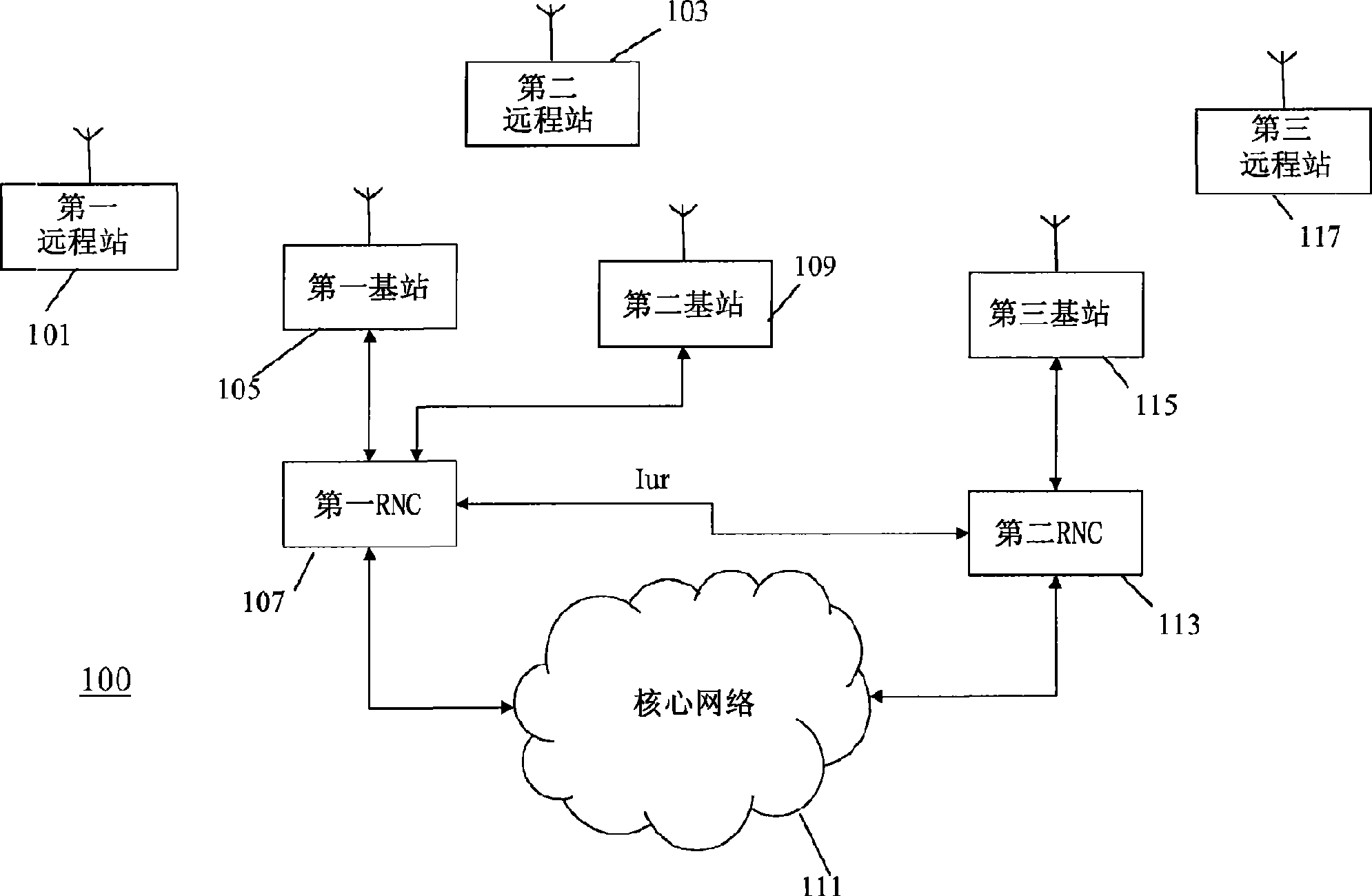
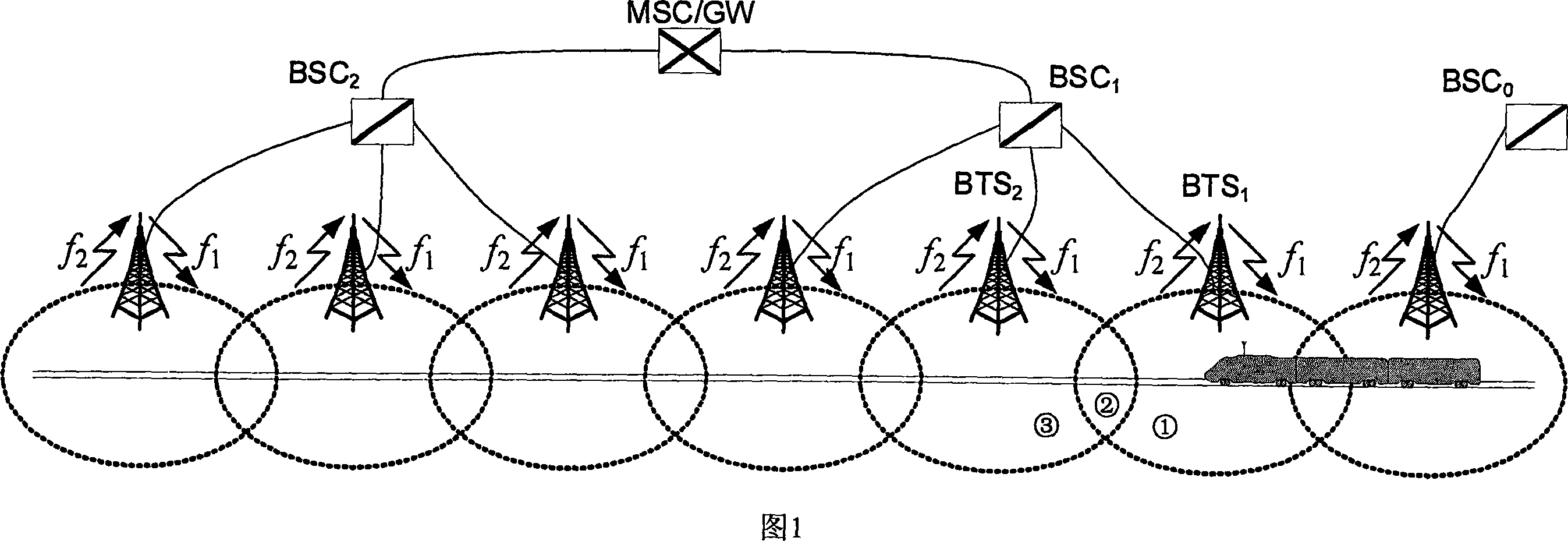
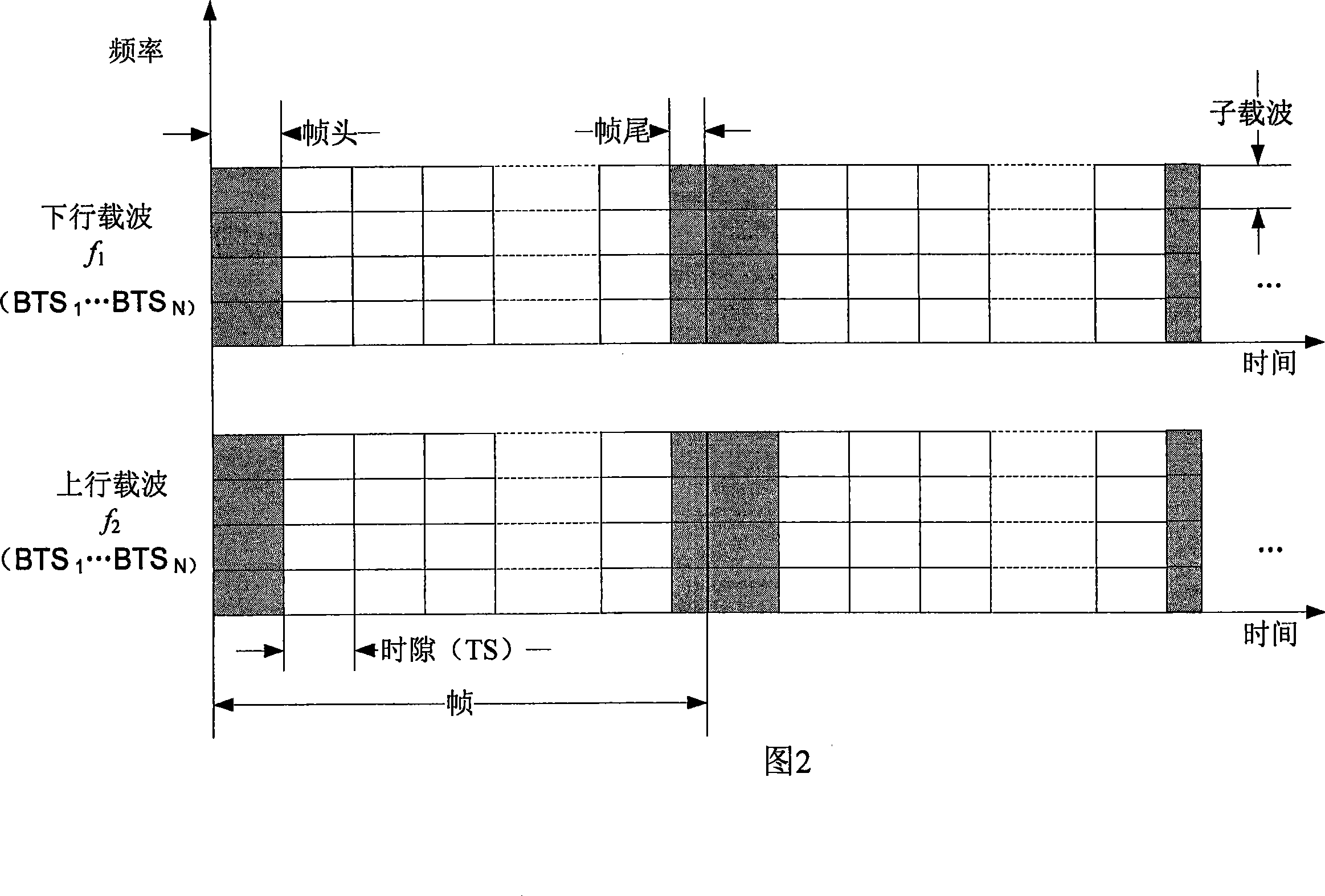
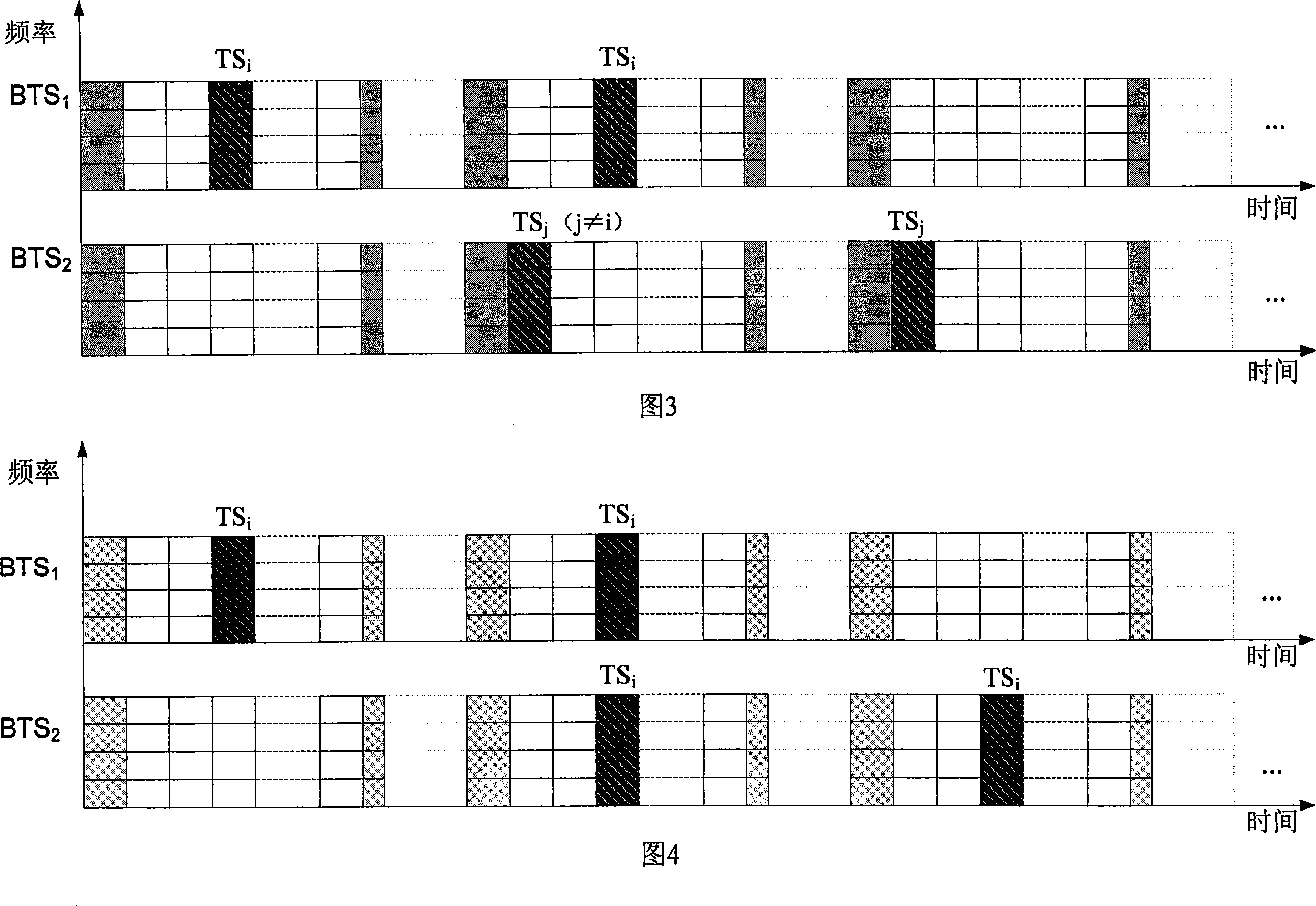
Mobile communication system based on OFDM and channel switching distribution method
InactiveCN101022643AImprove transmission performanceImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesCommunications systemDistribution method
A mobile communication system based on OFDM is prepared as forming service region by multiple sub-network and forming each sub-network by a numbers of cells, switching-in mobile table with fixed network through radio link with BTS and BSC as well as MSC / GW, using the same downlink carrier frequency and the same uplink carrier frequency synchronous operation by all BTS in sub-network. The method for switching over channel distribution is also disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Macrodiversity system with signal combining in the base station
A method for processing signals in a communications system comprising a first station and a plurality of second stations, said method comprising the steps of receiving at said plurality of second stations signals from said first station; sending said received signals to a designated one of said plurality of second stations; and processing in said designated second station the signals received by plurality of second stations to provide a single signal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Wireless communication system, base station device, mobile station device, and macrodiversity selection method
InactiveUS20090137237A1Blocking signal transmissionIncrease reception strengthSite diversitySubstation equipmentCommunications systemMobile station
A wireless communication system, a base station device, a mobile station device, and a macrodiversity selection method of the invention, in a base station device including a macrodiversity function among a plurality of sectors, select a macrodiversity method for the mobile station device from a plurality of macrodiversity methods, in accordance with a predetermined determination reference based on reception conditions of the mobile station device.
Owner:SHARP KK
Predictive collision avoidance in macrodiverse wireless networks with frequency hopping using switching
A communication system using fast macrodiversity switching (FMS) and frequency hopping (FH) for wireless signals including downlink signals to and uplink signals from mobile stations. Frequency hopping sequences are determined for the uplink and downlink signals for the mobile stations. A plurality of transceiver stations employ broadcast channels and dedicated channels for communications with the mobile stations. A zone manager controls fast macrodiversity switching of dedicated channels among the mobile stations while broadcast channels remain unswitched. The zone manager extracts frequency hopping information to form predictions of dedicated channel collisions, and based upon the predictions, controls the dynamic switching of dedicated channels to avoid collisions.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC
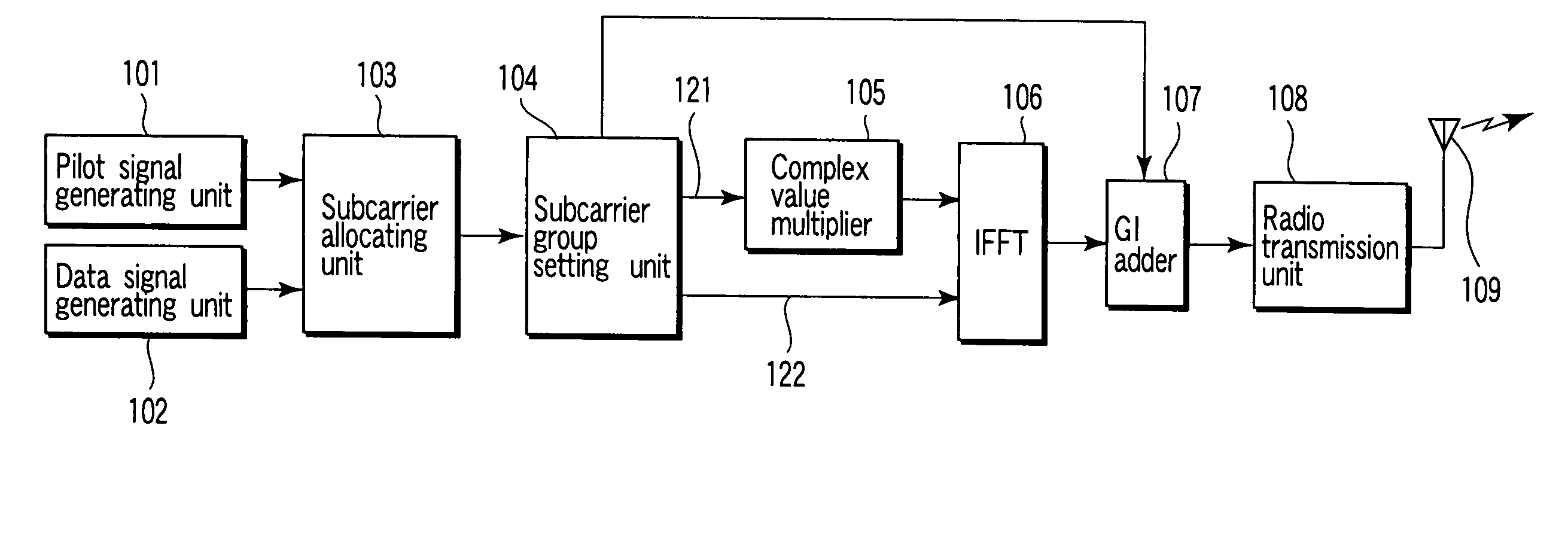
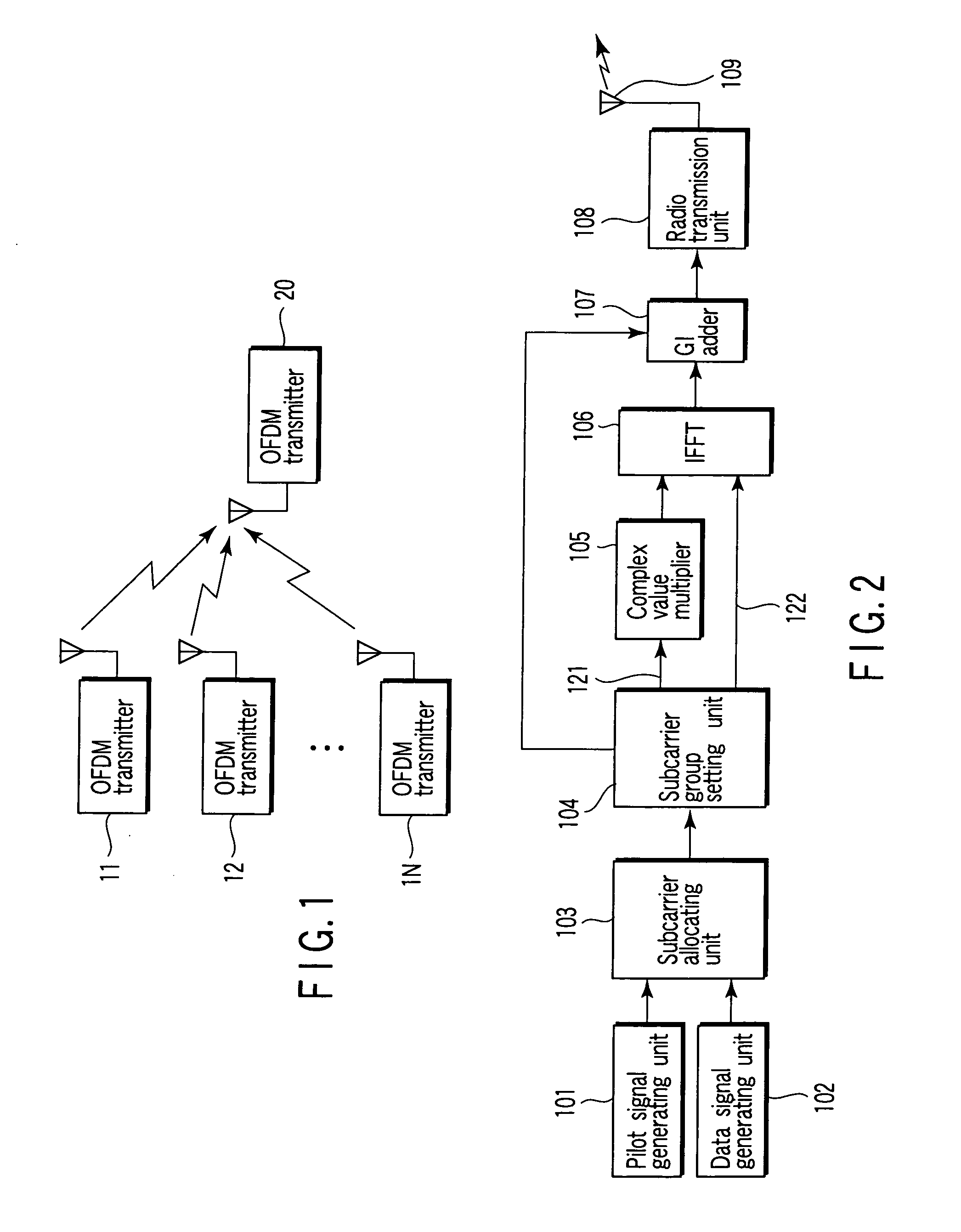
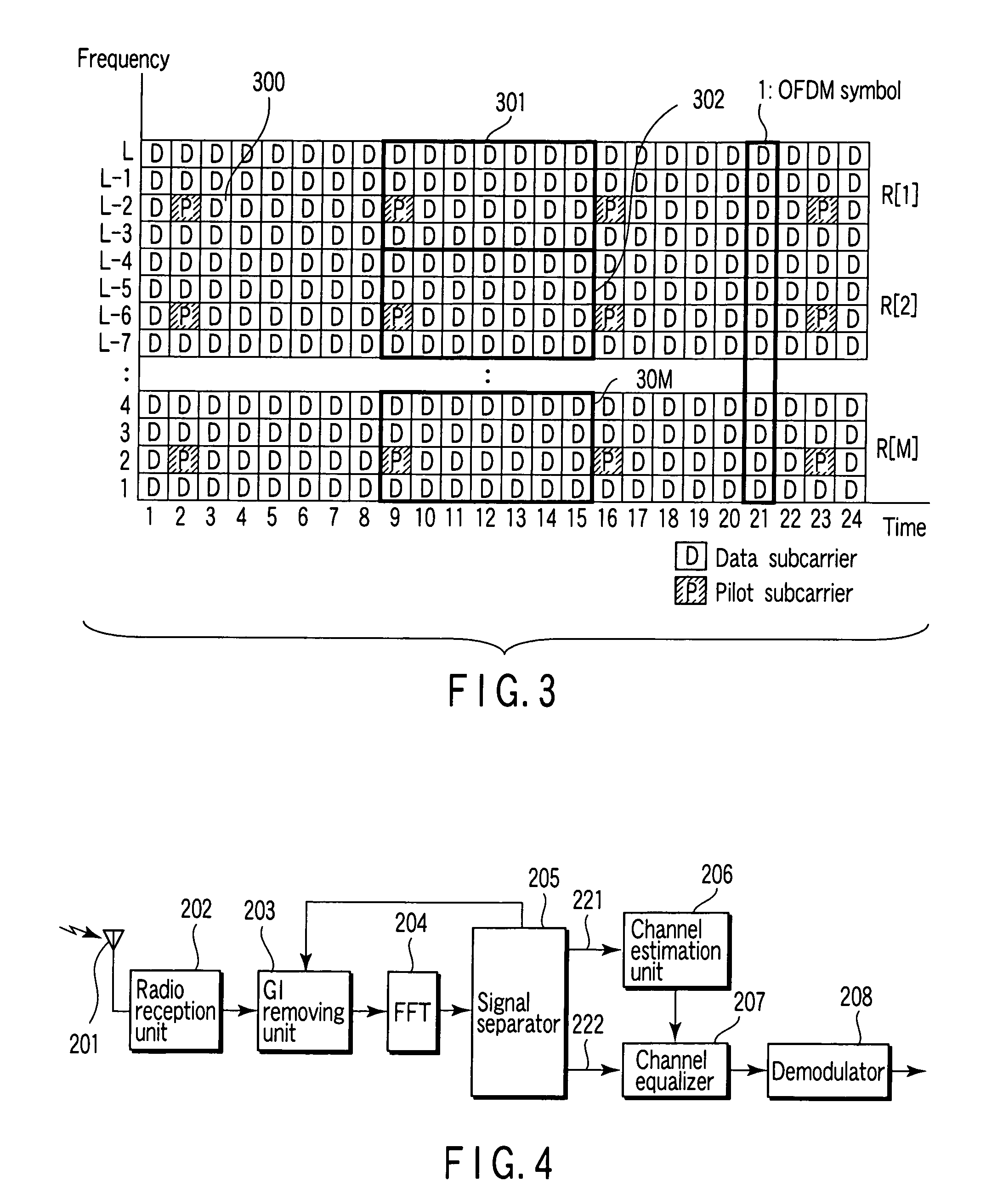
OFDM radio communications system
InactiveUS20070189149A1Small amount of calculationEasy to controlTransmission control/equlisationSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringRadio communications
A transmitter forms each subcarrier group of only frequency locations of subcarriers to which at least one pilot signal is allocated, and conducts transmission by allocating a macro-diversity signal into the subcarrier group and allocating a non-macro-diversity signal to other frequencies (outside the subcarrier group). As for the macro-diversity signal, a receiver conducts channel estimation on the basis of the pilot signal in the same subcarrier group as the macro-diversity signal. As for the non-macro-diversity signal outside the subcarrier group, the receiver conducts channel estimation on the basis of the pilot signal, and results of channel estimations of the macro-diversity signal and other non-macro-diversity signals.
Owner:FUJITSU TOSHIBA MOBILE COMM LTD
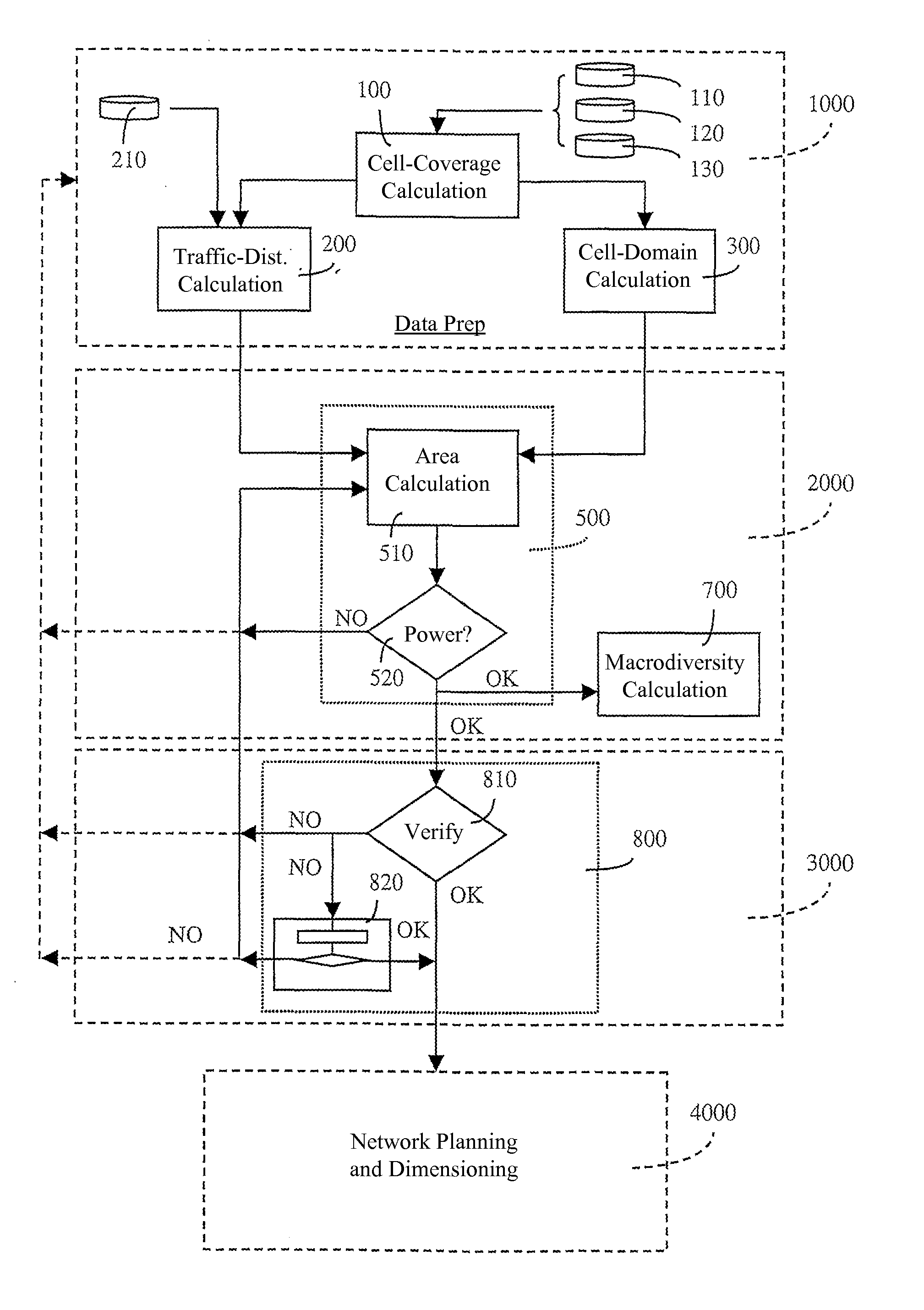
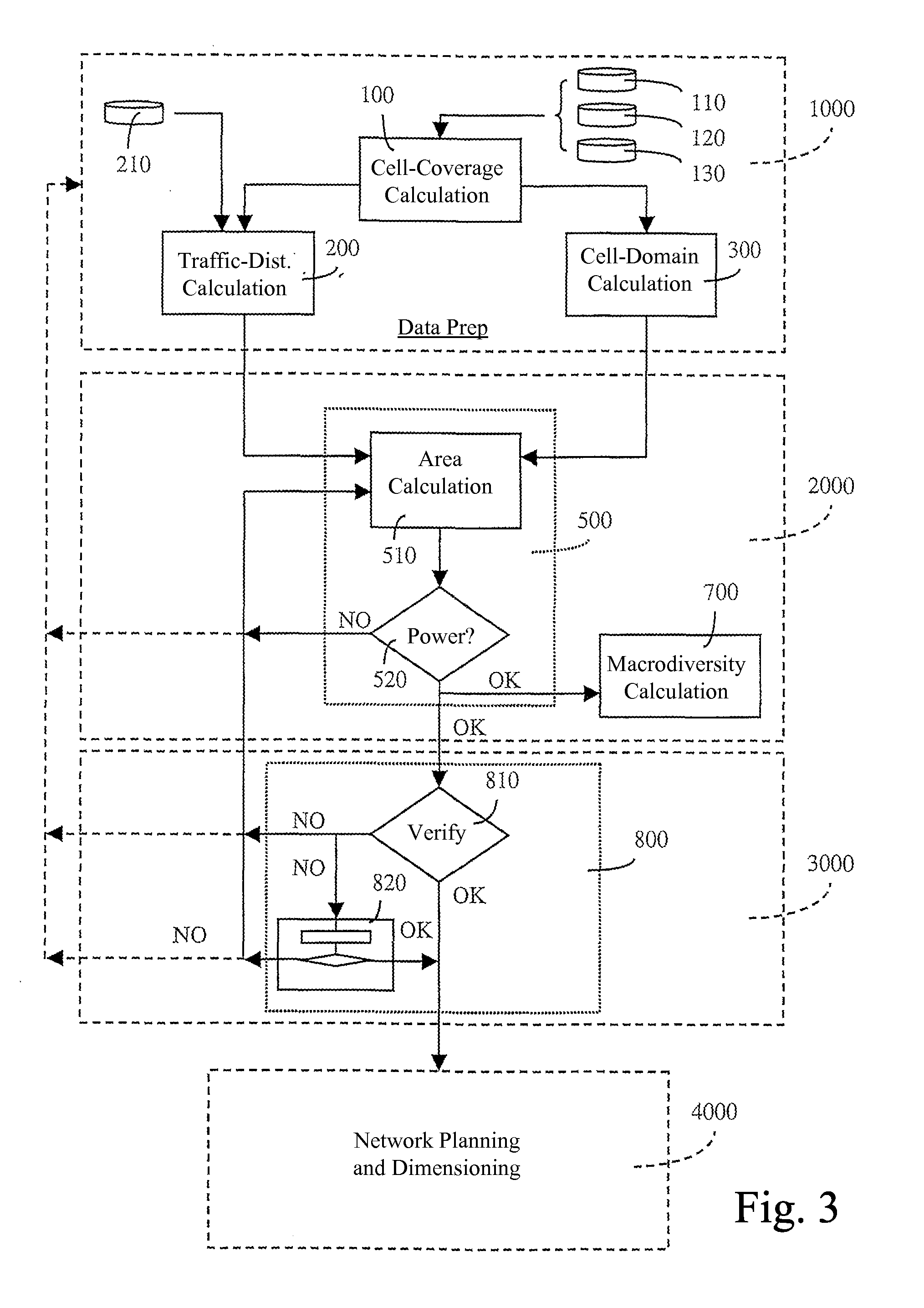
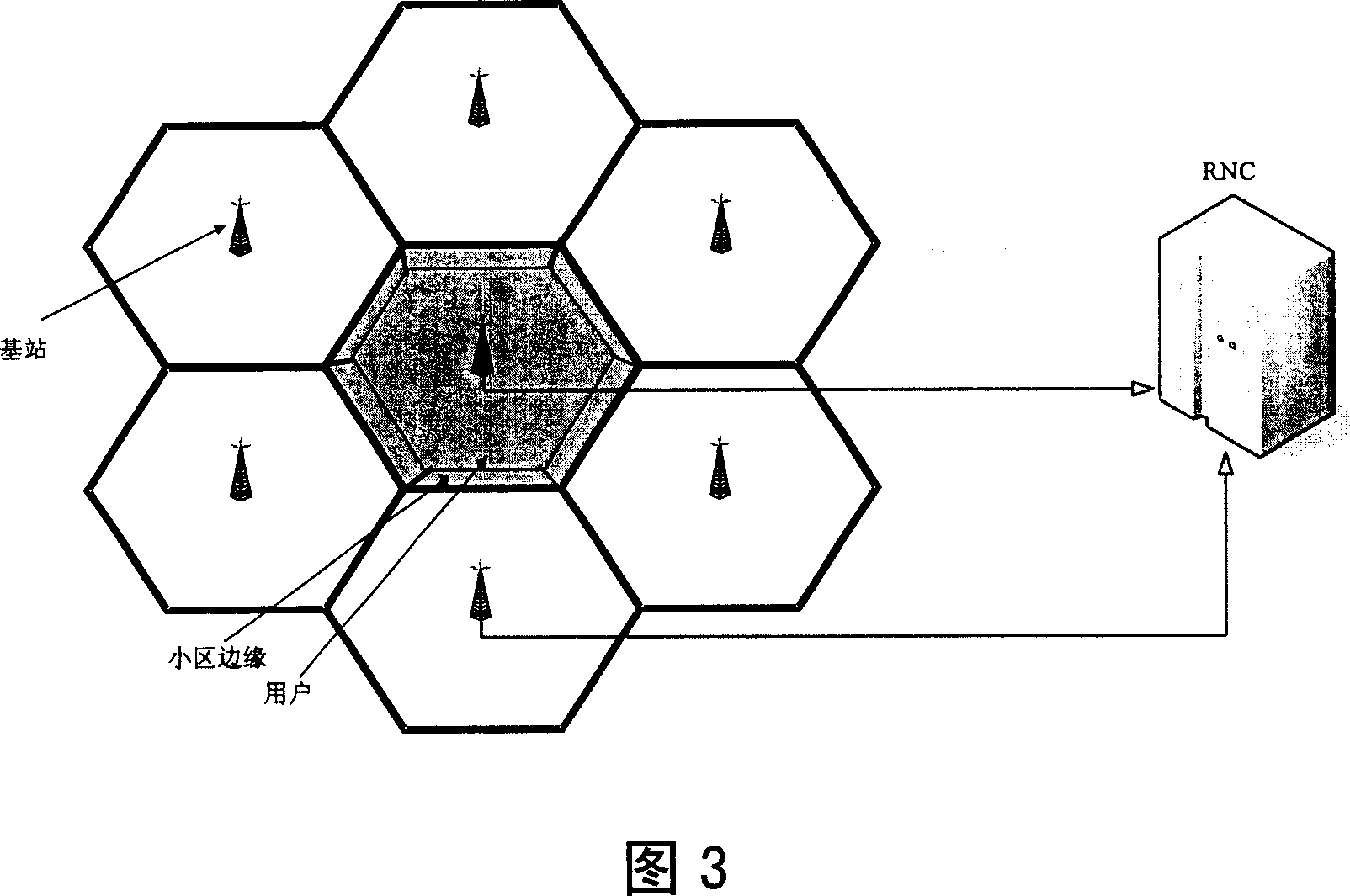
System and method for planning a telecommunications network for mobile terminals
InactiveUS7596377B2Telephonic communicationRadio transmissionTraffic capacityTelecommunications network
The present invention relates to a system and method for planning networks for mobile terminals that use a radio interface based on the Code Division Multiple Access or CDMA technique. More particularly, the system and method provide a step 500 whereby the Service Areas in these networks can be calculated using, as a reference, Domains calculated by means of a step 300 on the basis of real propagation models and taking a predetermined or estimated traffic into account on a pixel by pixel basis. In addition, the system and method make it possible to calculate the Macrodiversity Areas by means of a step 700, and thus to take the areas in which mobile terminals are capable of exchanging information with more than one radio base station into account at the planning step.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
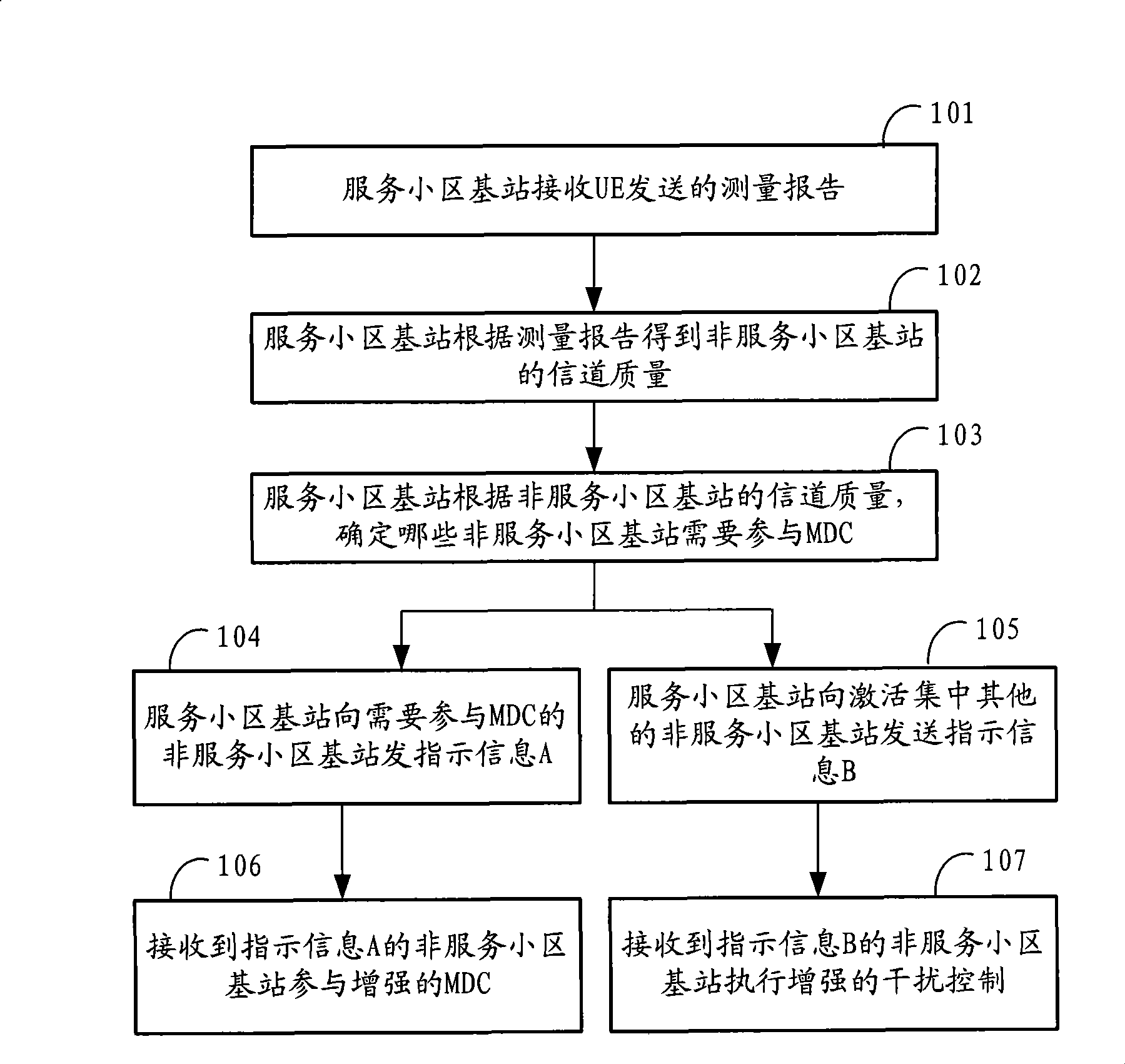
Integrated realizing method, system and base station for macrodiversity incorporating and interference control
ActiveCN101364826AImprove performanceImprove system performanceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingCell basedDiversity combining
The inventive embodiment provides a comprehensive implementation method of macro-diversity combining and interference control, a system and a base station. The method comprises the following steps: determining a non-serving cell base station needing to participate in macro-diversity combining MDC in a UE active set by a serving cell base station; transmitting an indication information to the non-serving cell base station needing to participate in MDC by the serving cell base station to indicate the non-serving cell base station to participate in MDC; and transmitting an indication information to other non-serving cell base stations in the active set by the serving cell base station to indicate the other non-serving cell base stations to carry out interference control operation. The system comprises the serving cell base station, the non-serving cell base stations, and a user terminal. The technical scheme can achieve macro-diversity combining and interference control in a more flexible manner, thereby optimizing the system performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
HARQ operation for macro-diversity transmissions in the downlink
ActiveUS8855069B2Reduce delaysError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless commuication servicesData transmissionTransmitter
The invention relates to a downlink transmission scheme that supports downlink HARQ operation and macro-diversity that is capable of overcoming the problem of HARQ protocol de-synchronization when using HARQ in the downlink with multiple data transmitting network nodes. In this scheme, a distributed HARQ protocol operation for downlink data transmissions involving multiple network nodes is provided, where only one network node is terminating downlink HARQ protocol operation towards to mobile terminal, i.e. retransmissions of a data packet are sent from a single network node, a single HARQ transmitter, to the mobile terminal. The multiple network nodes send a first transmission of the data packet to the mobile terminal in a single transmission time interval using HARQ. One of the multiple network nodes is designated as the HARQ terminating node that controls / handles all retransmissions of the data packet.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
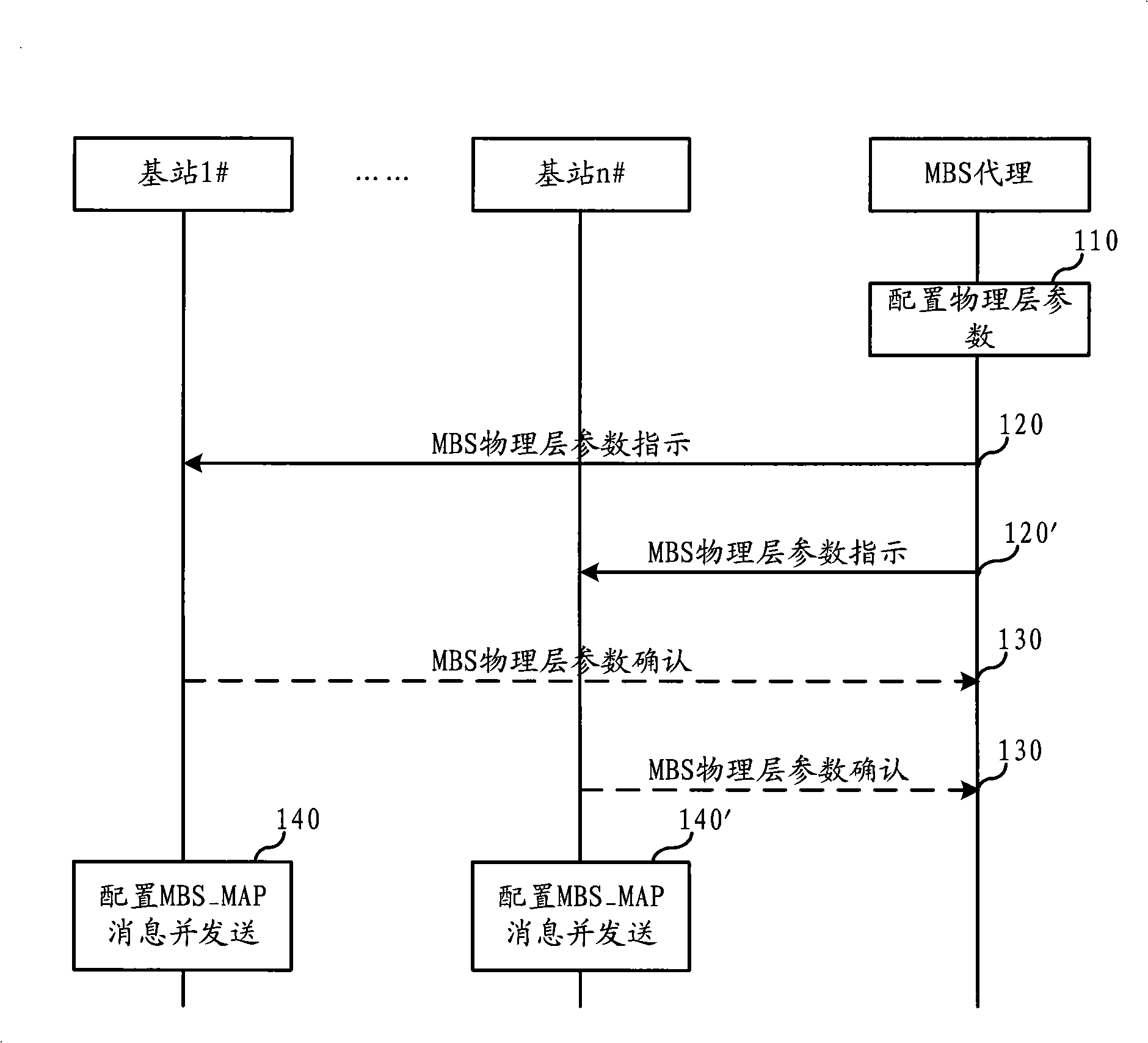
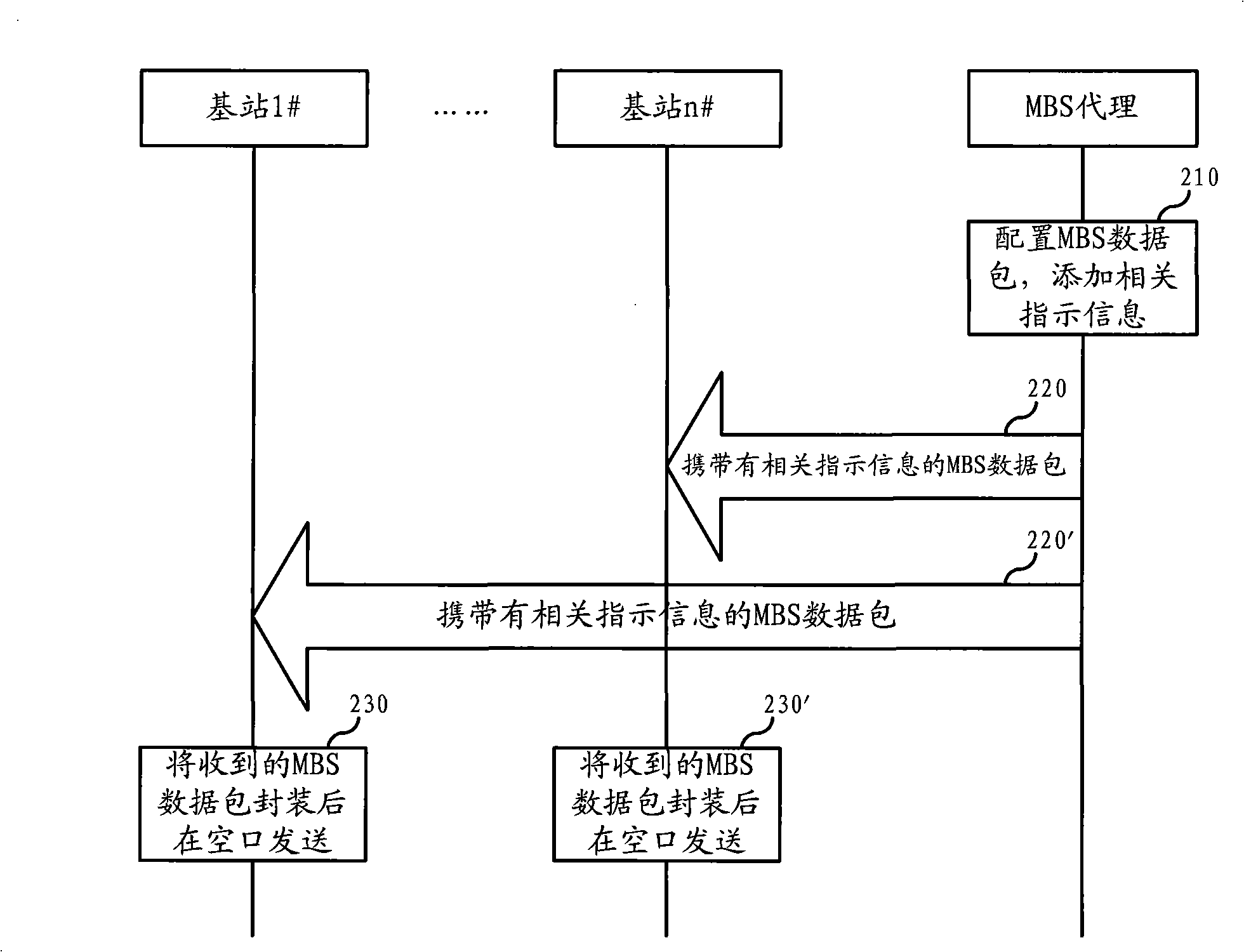
Method for collocating and receiving multi-broadcast service mapping message and its unit
InactiveCN101257398ASpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationRadio networksManagement unit
The invention relates to communication field and discloses a configuring method, a receiving method and a unit of multicast broadcast service mapping message, which realizes the macro diversity of MBS, enhances the receiving performance of MBS in the communication system. In the invention, the message unit of MBS transmits the physical layer parameter necessary for configuration of MBS mapping message MBS_MAP to all of the MBS operating units in one MBS field; the operating unit of MBS transmits the configured MBS_MAP to the receiving unit of MBS after configuring MBS_MAP based on the received physical layer parameter; the receiving unit of MBS receives MBS service based on MBS_MAP. The invention realizes the macro diversity of MBS in the radio network and enhances the receiving performance of MBS. When applied in WiMAX network, the management unit of MBS is a MBS agent, the operating unit of MBS is a base station, the receiving unit of MBS is a terminal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Intersystem call transfer method for use in cellular mobile radio systems
InactiveUS7162245B2Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentRadio networksCall forwarding
A method for intersystem transfer of calls from a first cellular mobile radio system using the macrodiversity transmission technique to a second cellular mobile radio system, the macrodiversity transmission using a radio network controller of the first system, referred to as the serving controller, and at least one other radio network controller of the first system, referred to as the drift controller, wherein adjoining cell information relating to the second system is signaled to the serving controller by at least one drift controller controlling at least one serving cell belonging to the first system and having at least one adjoining cell belonging to the second system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
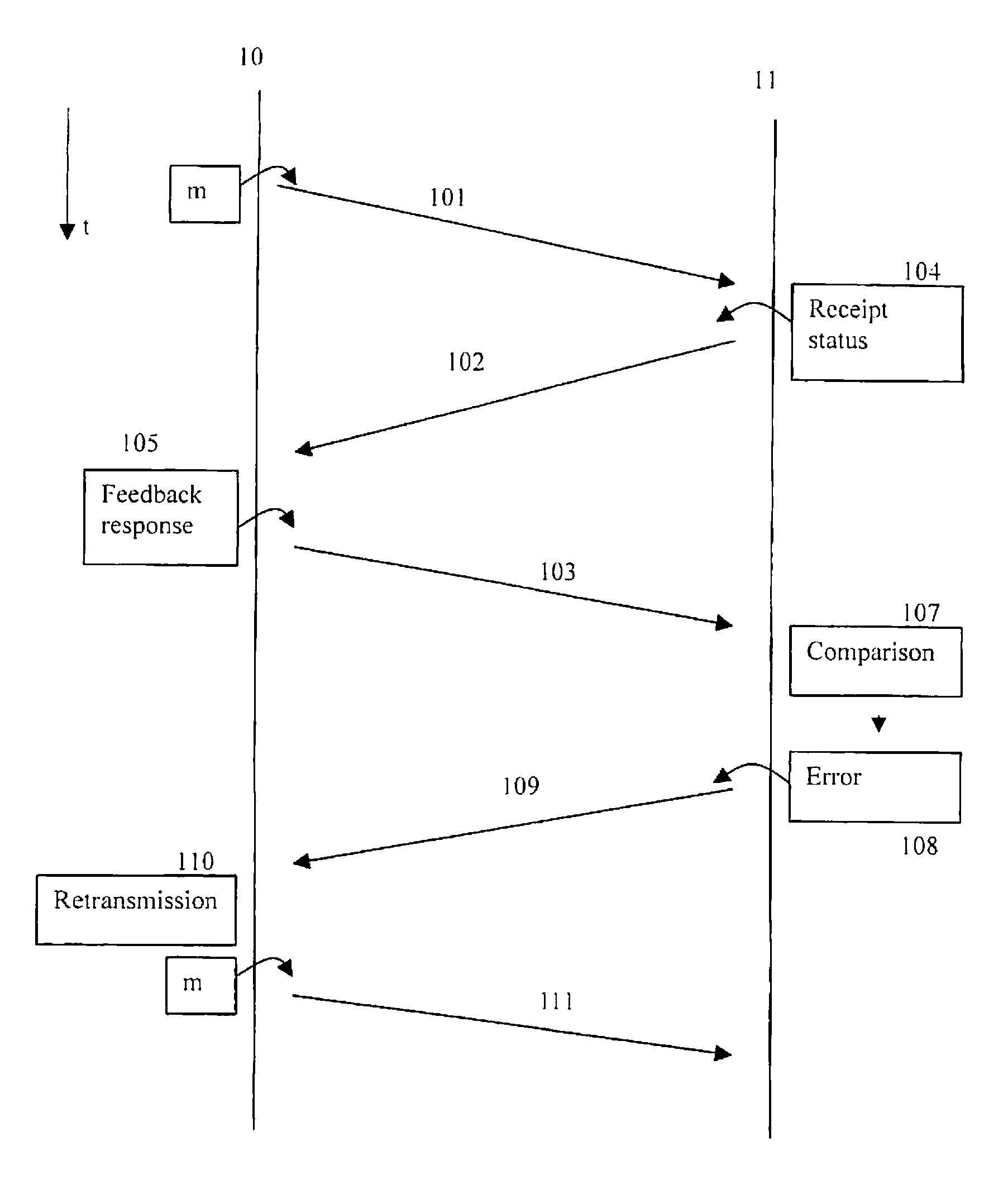
Forward feedback for ul macrodiversity
InactiveUS20090222704A1Optimal control methodImproved receiverError prevention/detection by using return channelSite diversityTransmitterReal-time computing
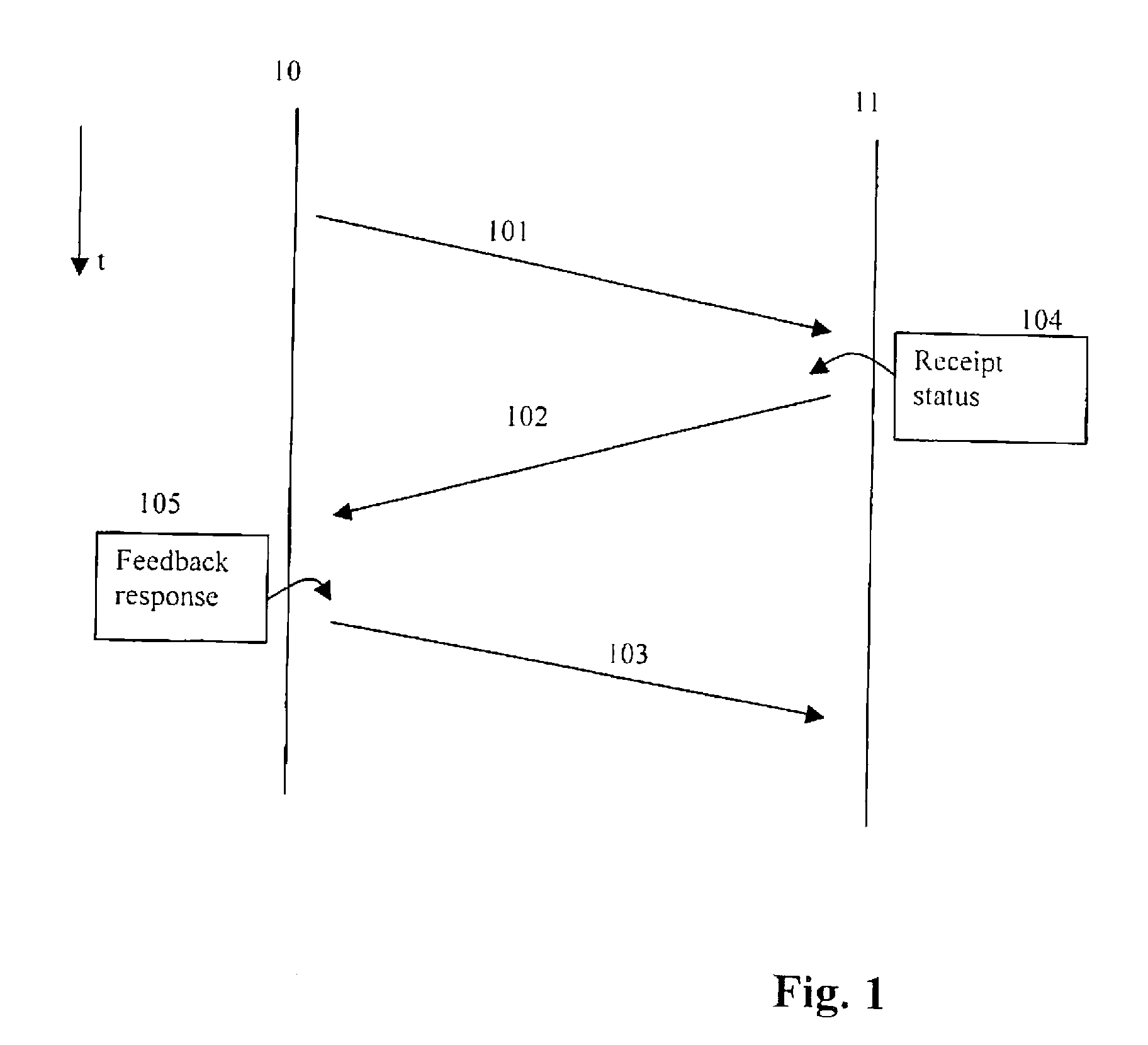
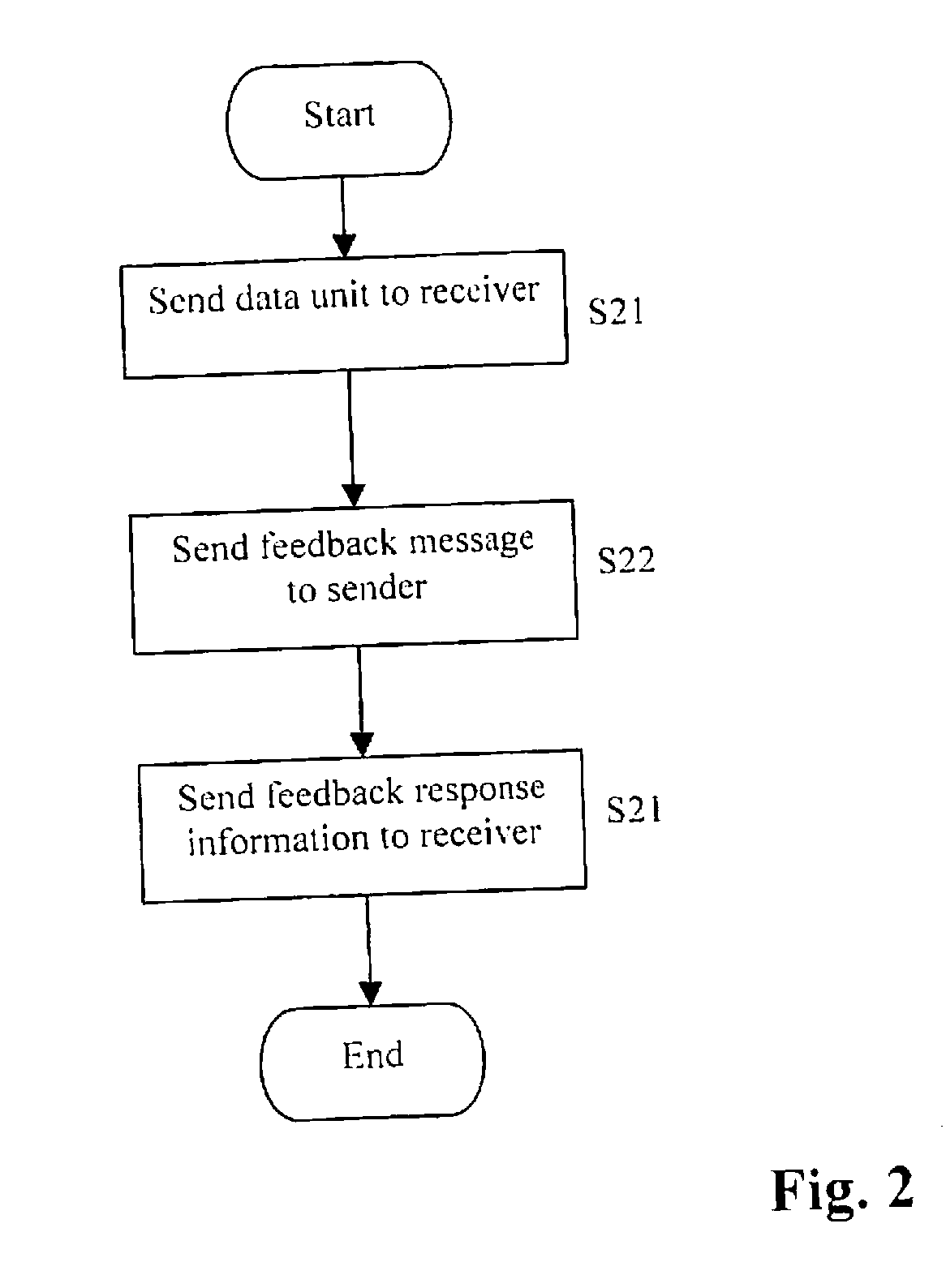
A method of controlling a data unit transmission from a sender (10) to a receiver (11) is described, comprising the steps: the sender (10) sending a data unit (101) to the receiver (11), the receiver (11) sending to the sender (10) a feedback message (102) comprising receipt status information (104) for the data unit (101) indicating one of at least correct receipt and incorrect receipt, and the sender (10), subsequent to receiving the feedback message (102), sending to the receiver (11) feedback response information (105) indicating a receipt status indicated in the received feedback message (102).
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Apparatus, method, system and software product involving a macrodiversity arrangement for a multicast service on a high speed transport channel
InactiveUS20080070606A1Easy to receiveSite diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData transportUser equipment
An apparatus, method, system and software product are for receiving a broadcast service or a multicast service. User equipment receives information about transmissions of data for a broadcast or multicast. The data is transmitted in non-overlapping signals from a plurality of cells. The user equipment then uses this information to attempt to decode at least one of the signals, if decoding another of the signals failed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Uplink macrodiversity incorporating method
ActiveCN1842050AQuality improvementImprove delivery efficiencyData switching networksNetwork packetQuality data
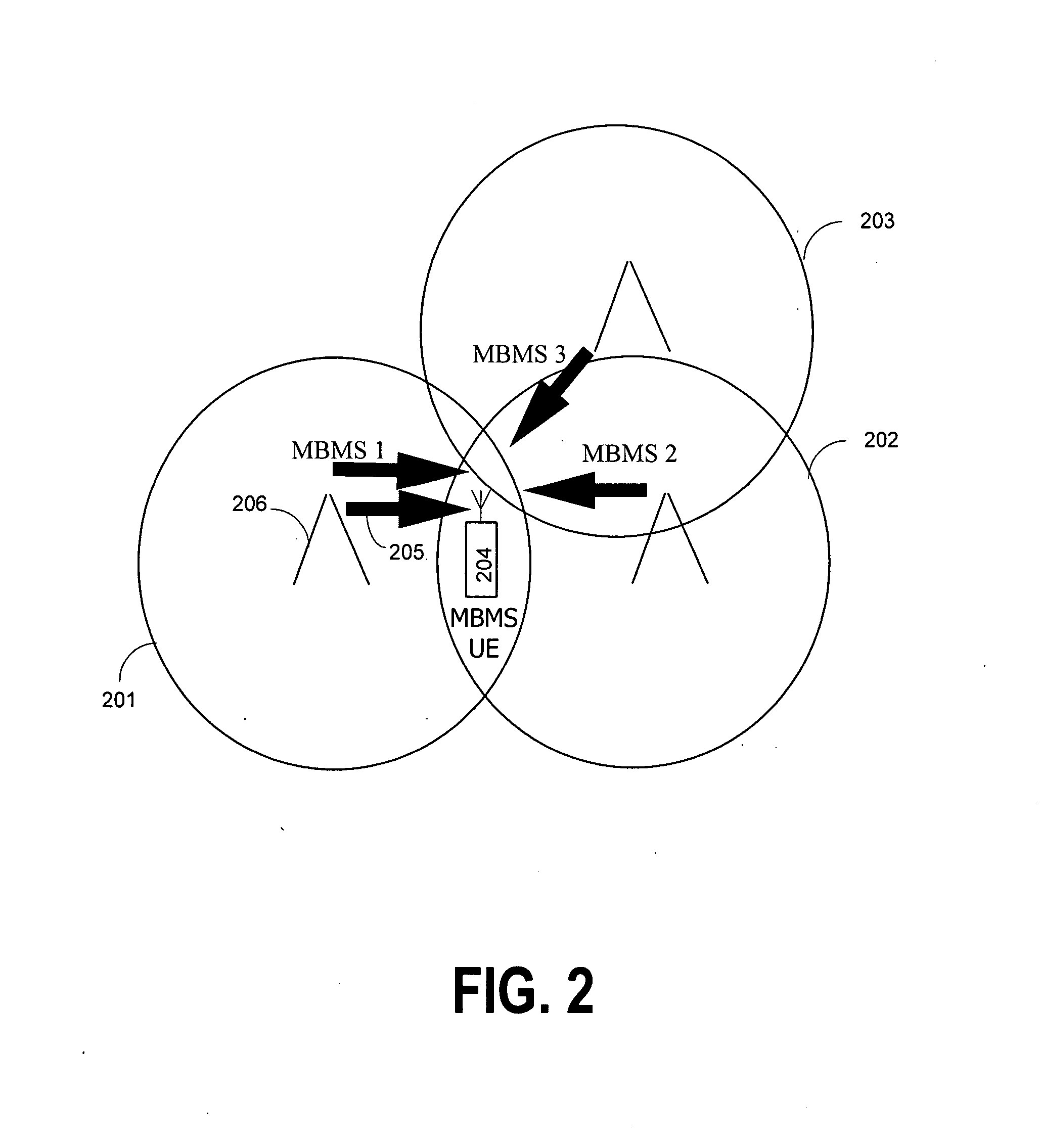
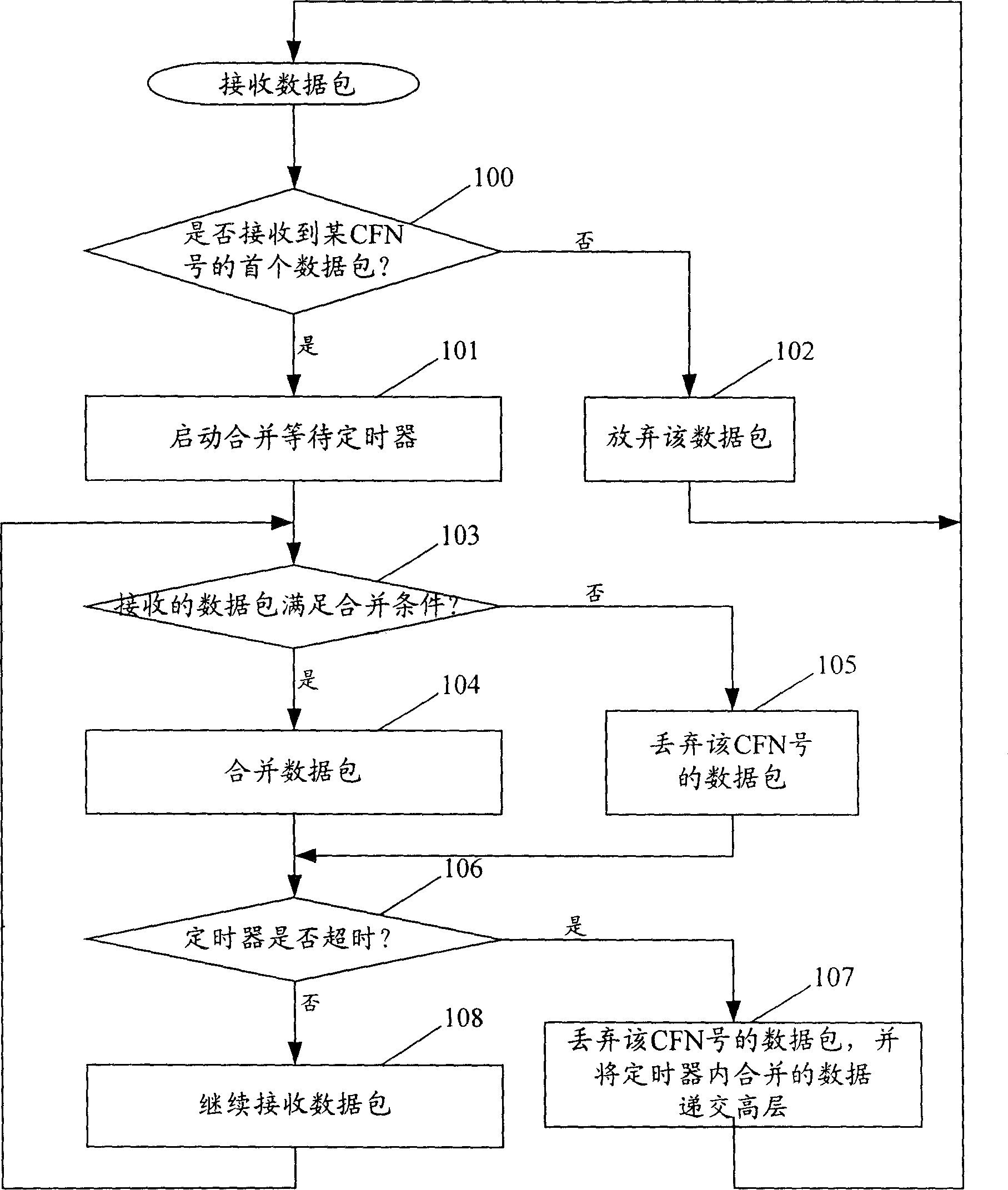
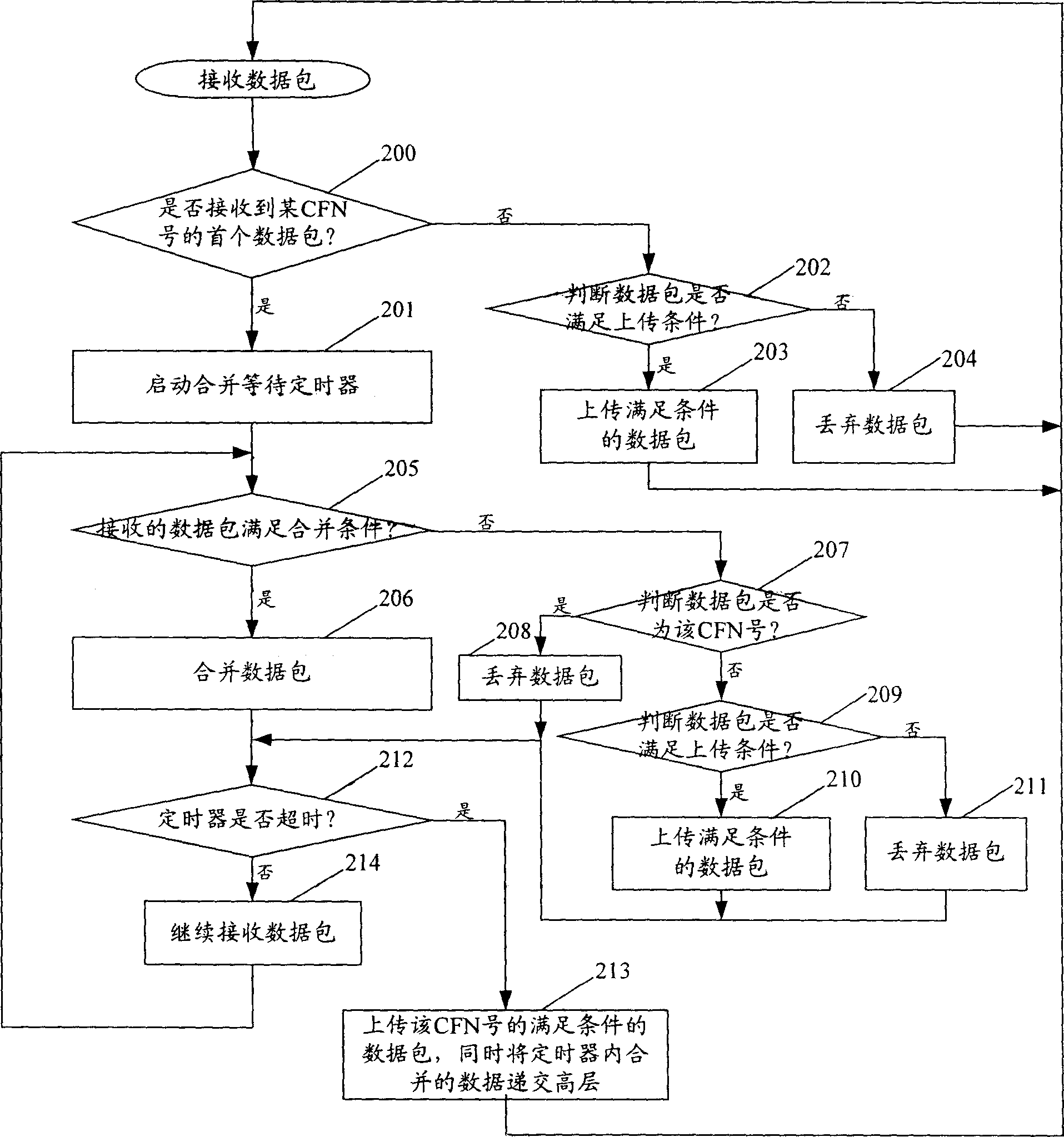
The invention discloses a method of ascending macro diversity combination, which mainly considers the data package quality of the CFN number when it receives the different branch data package; if the quality is good and meets the combining condition in the combining timer, it can do the combination and the bed quality data package is abandoned.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
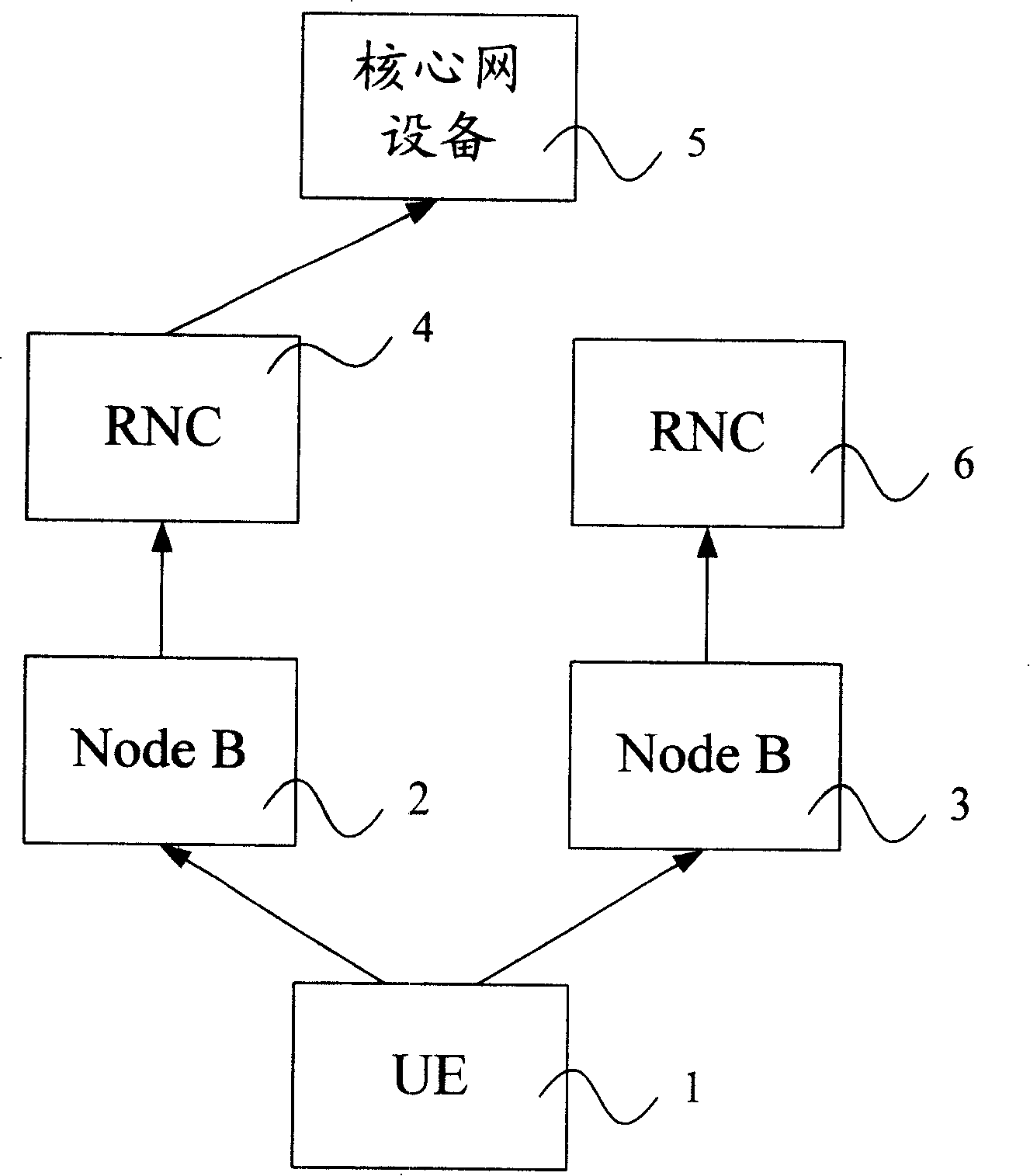
Uplink macro diversity method in mobile communication system
ActiveCN101242565AReduce loadReduce network trafficRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationNetwork communicationRadio Network Controller
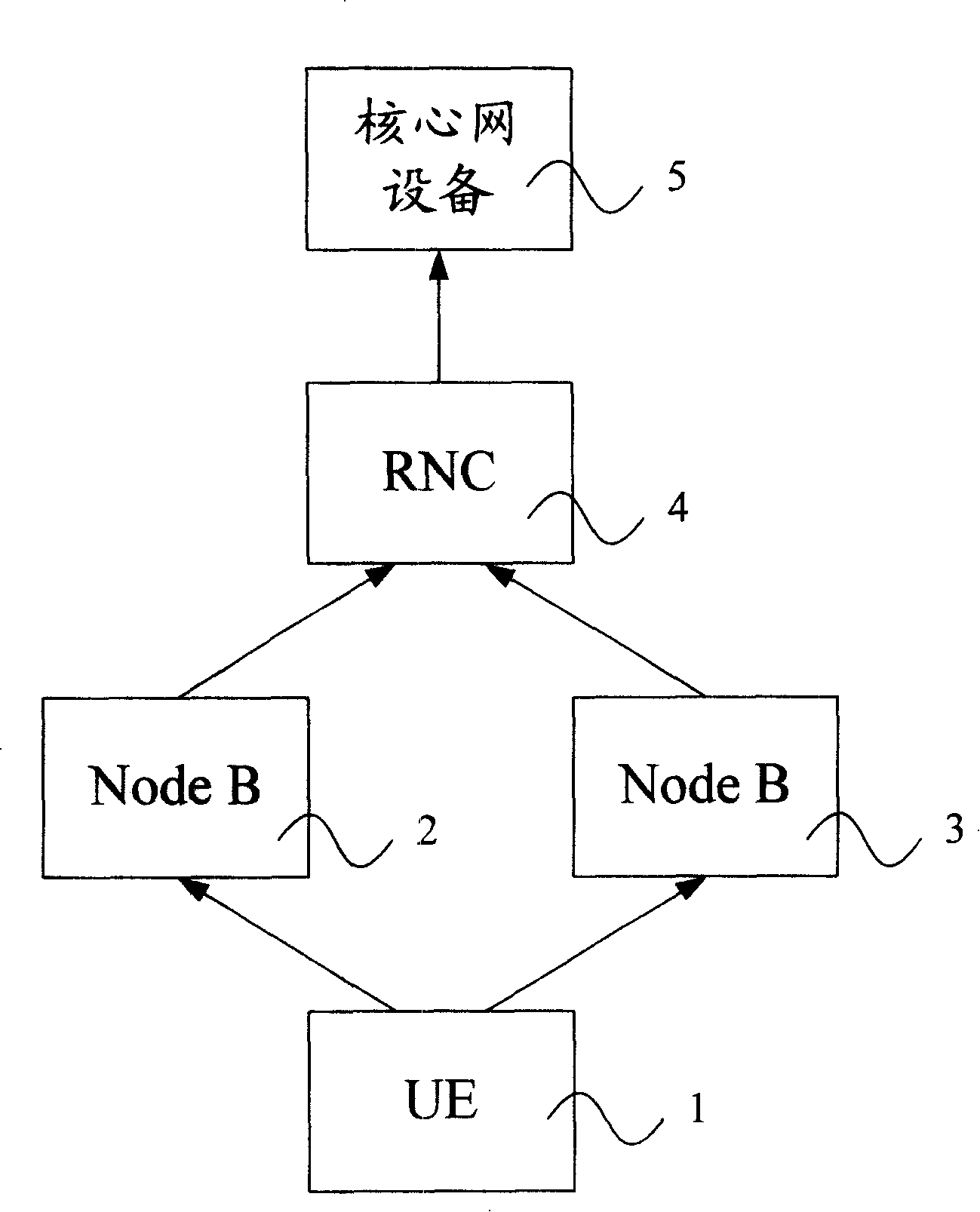
The present invention provides an upper macro diversity method of mobile communication system, under the soft switching course, including: unpacking measurement report when the radio network controller or base station receiving the measurement report aquiring link quality of each data link; analyzing the unpacked measurement report, if the quality for executing the first radio network controller of the upper macro diversity or the link being highest, then direct uploading the data received from the data link to the core network equipment. The invetion processes unpacking to the measurement report to judge which data lind has the best quality, direct uploading the best data lind to the core network equipment by the radio network controller or base station for the upper macro diversity, data or signaling not the best data does not transmitted between the radio network controller or base station under the course, reducing network communications volume of the upper macro diversity when processing the soft switching, and reducing the network load.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
System and method for planning telecommunications network for mobile terminals
InactiveCN1478361ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningTelecommunications networkRadio Base Station
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Uplink sub-macro method used for multiantenna, orthogonal frequency division multiple access cellular system
InactiveCN1968042AAvoid Signal HandlingReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Carrier signal
The invention relates to an ascending macro grouping method used in multi-antenna orthogonal frequency-division multiple cellular systems, wherein said network comprises user terminal, base station and wireless network controller; the method comprises that: each one of base stations via channel evaluation, obtains the channel gain matrix factor between user terminal and base station; via channel gain, calculating out the signal / noise ratio of each antenna branch of each base station; sequencing the signal / noise ratios, form all antennas of all base stations, selecting the multi-amplitude antenna relative to the user antennas with high signal / noise ratio; based on selected antenna branch, the base station of said antenna branch uses relative carrier wave to process fast Fourier transform demodulation; and the wireless network controller processes multi-antenna check or decode on demodulated signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method, device and system for deleting links
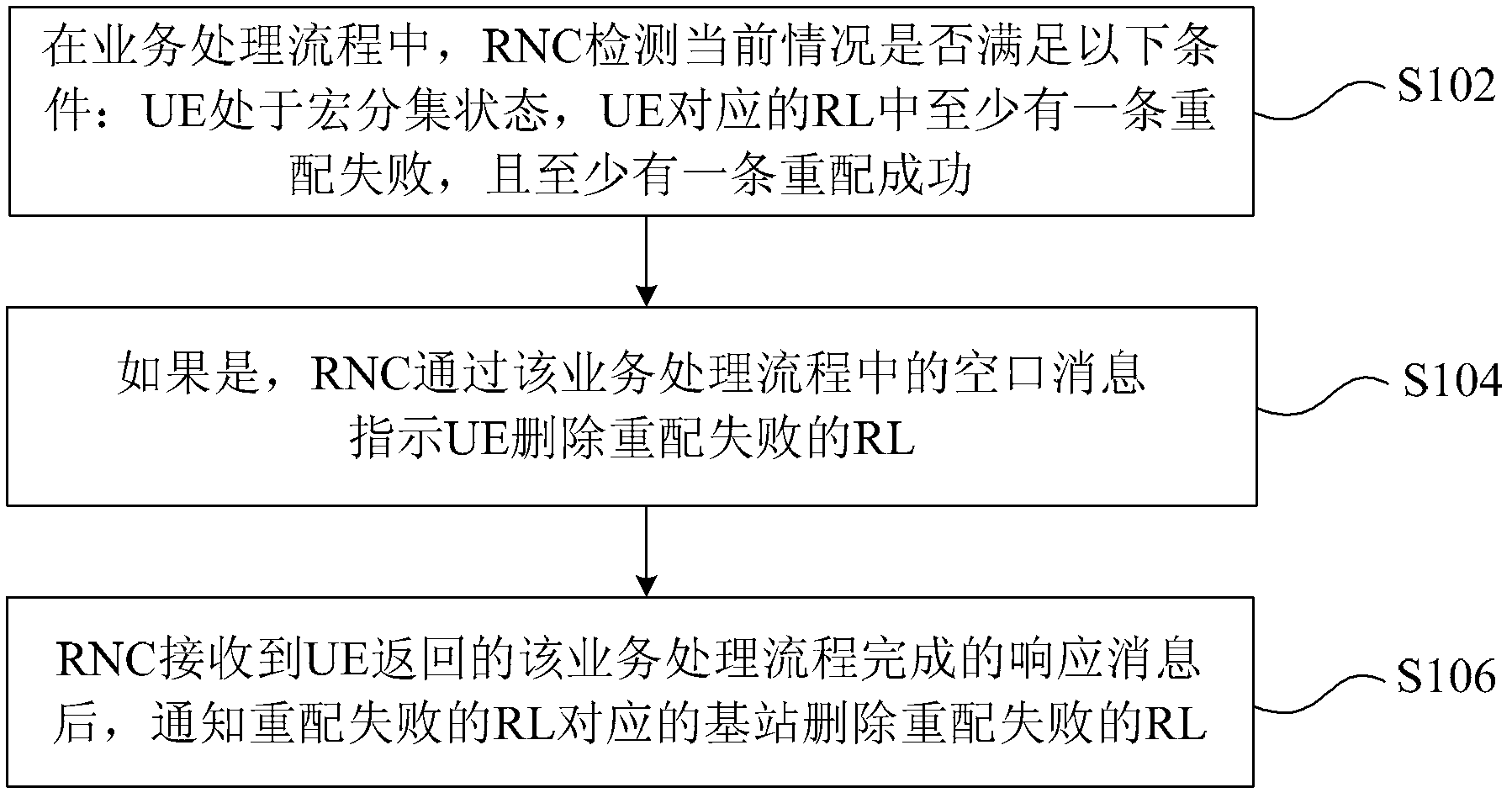
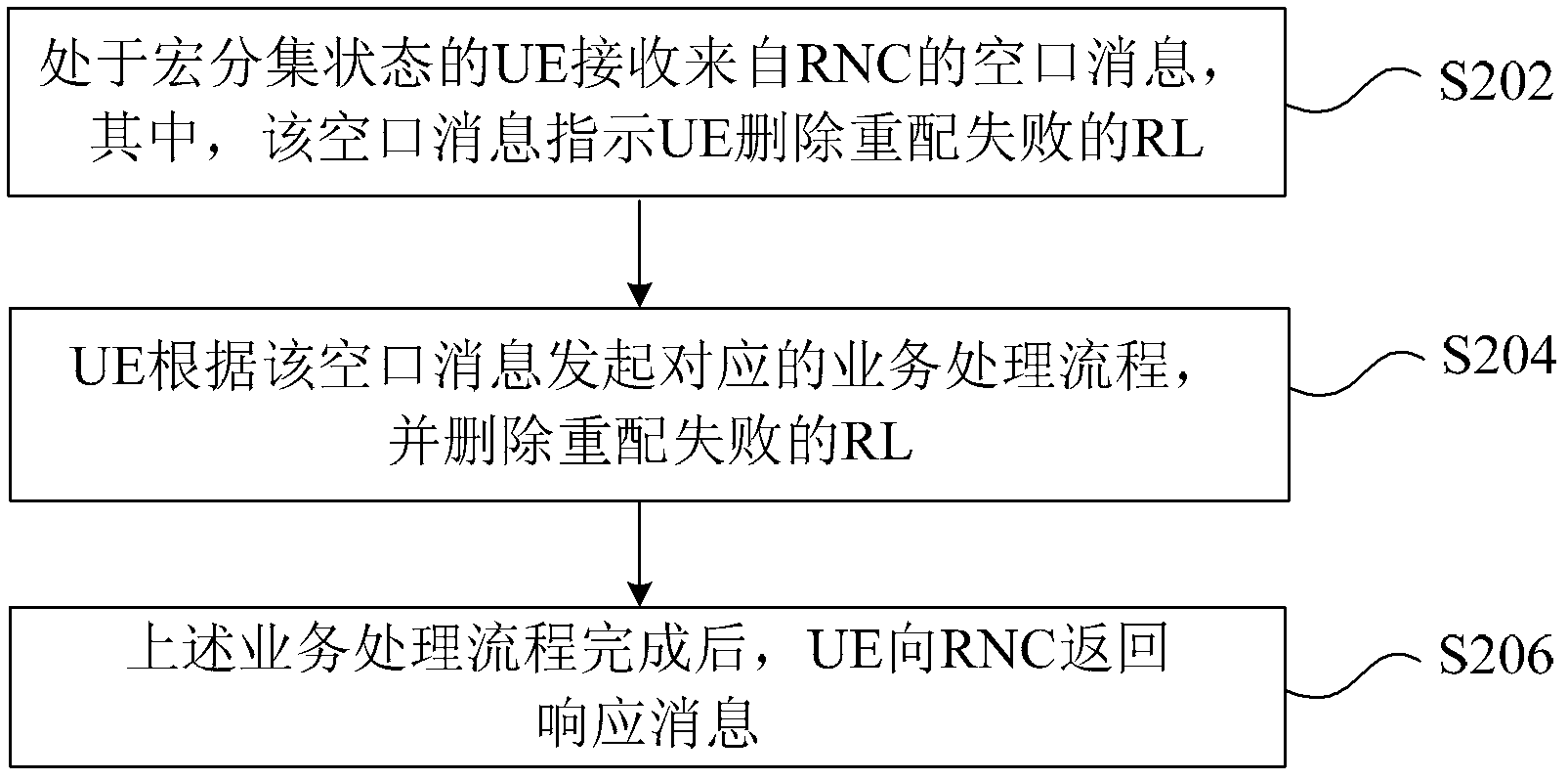
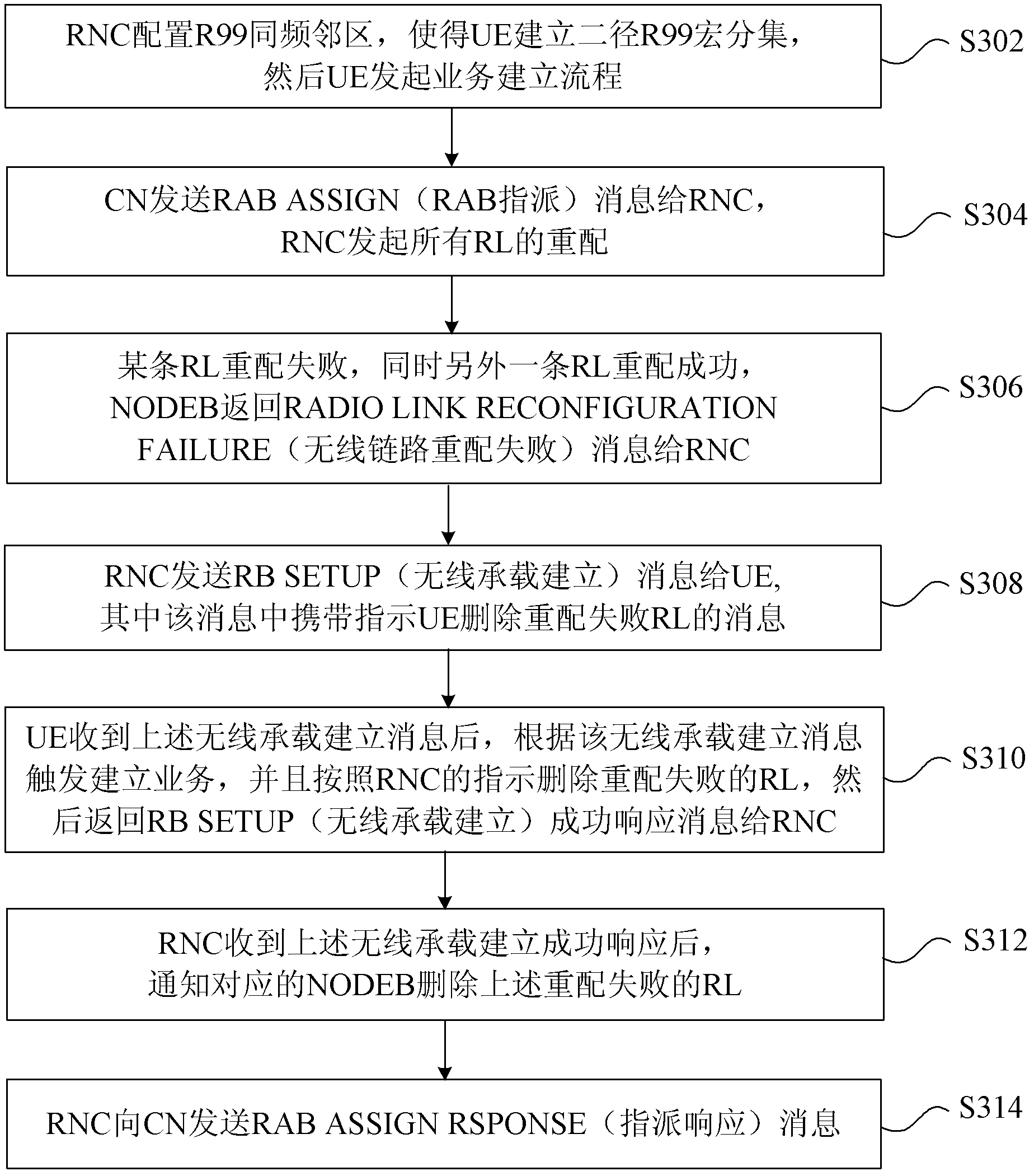
ActiveCN103179687AEasy to handleReduce the number of air interface interactionsNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementTime delaysAir interface
The invention discloses a method, a device and a system for deleting links. The method comprises that a radio network controller (RNC) detects whether a current situation meets following conditions: user equipment (UE) is in a macrodiversity state, at least one radio link (RL) corresponding to the UE fails in reconfiguration, and at least one RL succeeds in reconfiguration; if the conditions are met, the RNC indicates that the UE delete the RL failing in reconfiguration; and the RNC informs a base station corresponding to the RL failing in reconfiguration to delete the failed RL after receiving response information completed by a business processing flow which is returned by the UE. By means of the method, the device and the system for deleting links, the business processing flow is optimized, the processing time delay is shortened, the air interface interaction is reduced, and air interface resources are saved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Uplink macro-diversity reception method of orthogonal frequency division multiplex cellular communication system
ActiveCN1913391AReduce capacityDoes not increase transmission burdenSpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
This invention discloses a receiving method for up-stream macro-diversities of OFDM cellular communication including: 1, the system selects multiple base station antennas with the optimum chain performance to receive the up-line signals of users of the edges of non-sector local areas in the cellular communication system, 2, said system selects multiple fan area antennas with the best chain performance to receive the up-line signals of the users at the edges of sector areas, 3, these antennas demodulate the received signals by quick Fourier transform and make the maximum S / N ratio combination to the information on the sub-carriers used by the users so as to increase the up-line rate of the users.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com