Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Load vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for coordination of motion determination over multiple frames
InactiveUS6157677AEasy to compressEasy to controlTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion fieldMultiple frame
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 01272 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 21, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 21, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 29679 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 26, 1996The present invention concerns improved motion estimation in signal records. A method for estimating motion between one reference image and each frame in a sequence of frames, each frame consisting of a plurality of samples of an input signal comprises the steps of: transforming the estimated motion fields into a motion matrix, wherein each row corresponds to one frame, and each row contains each component of motion vector for each element of the reference image; performing a Principal Component Analysis of the motion matrix, thereby obtaining a motion score matrix consisting of a plurality of column vectors called motion score vectors and a motion loading matrix consisting of a plurality of row vectors called motion loading vectors, such that each motion score vector corresponds to one element for each frame, such that each element of each motion loading vector corresponds to one element of the reference image, such that one column of said motion score matrix and one motion loading vector together constitute a factor, and such that the number of factors is lower than or equal to the number of said frames; wherein the results from the Principal Component Analysis on the motion matrix are used to influence further estimation of motion from the reference image to one or more of the frames.
Owner:IDT INT DIGITAL TECH DEUTLAND
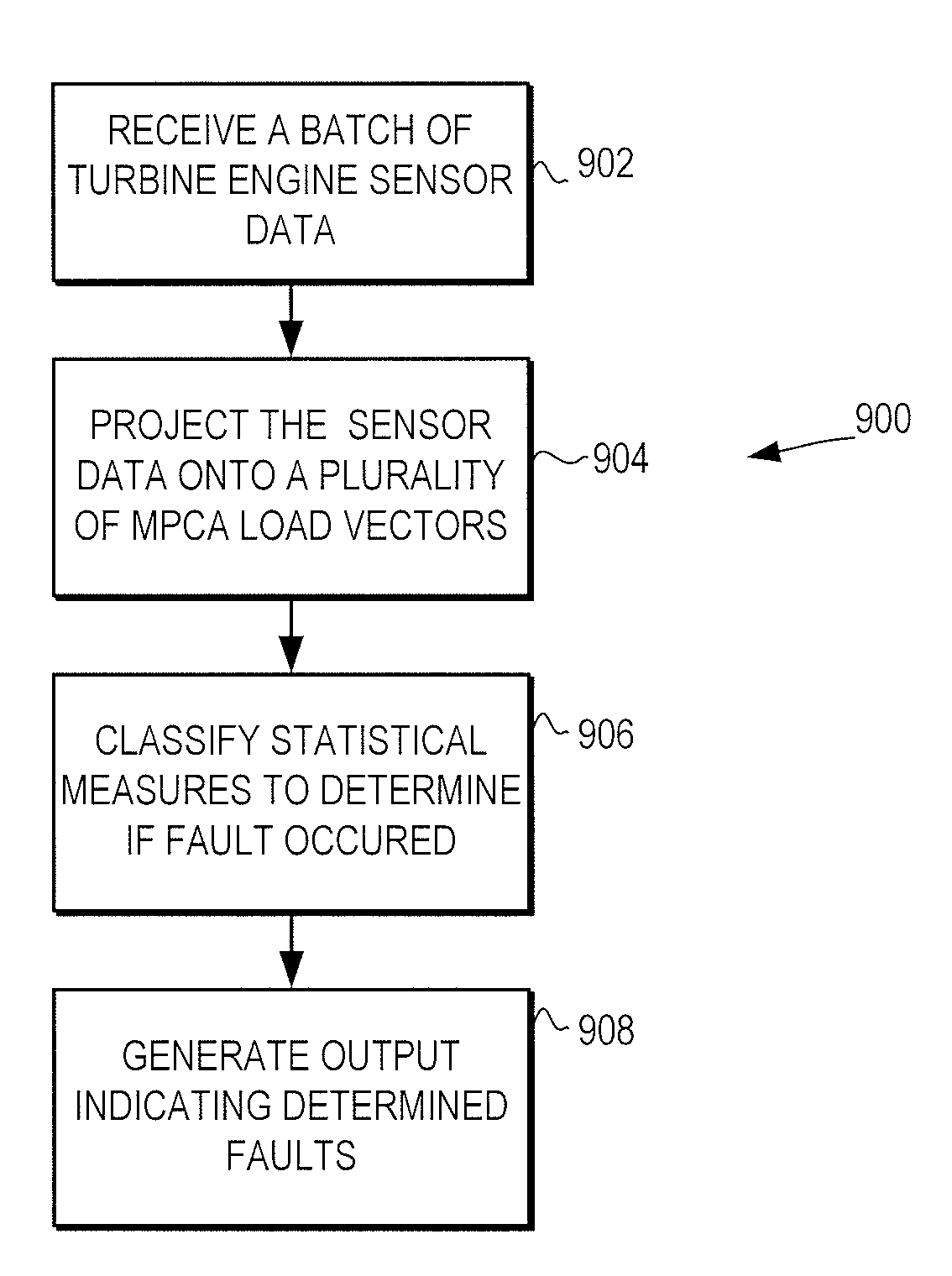
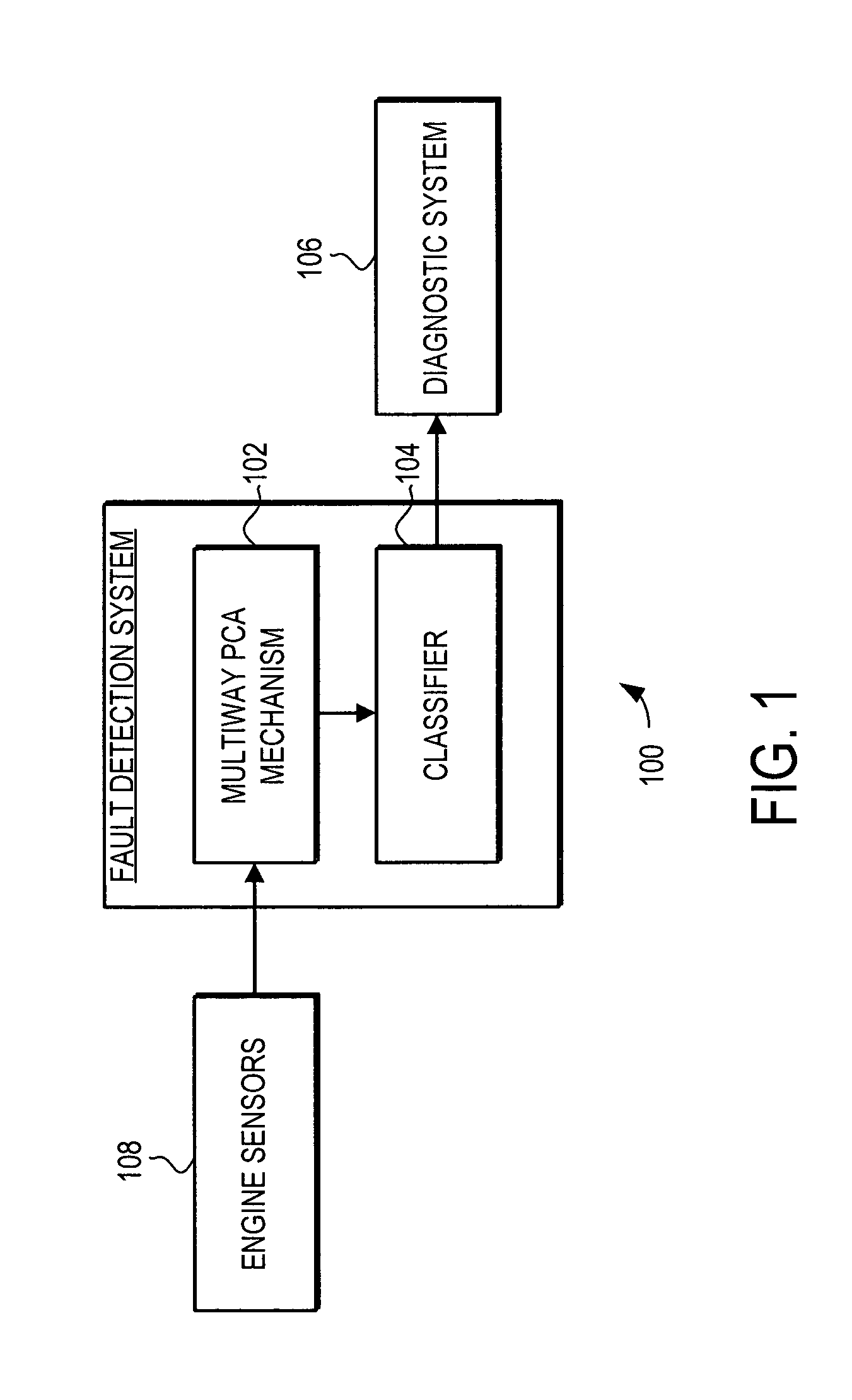
Fault detection system and method using multiway principal component analysis
InactiveUS20070124113A1Improve performanceVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesData setPrincipal component analysis
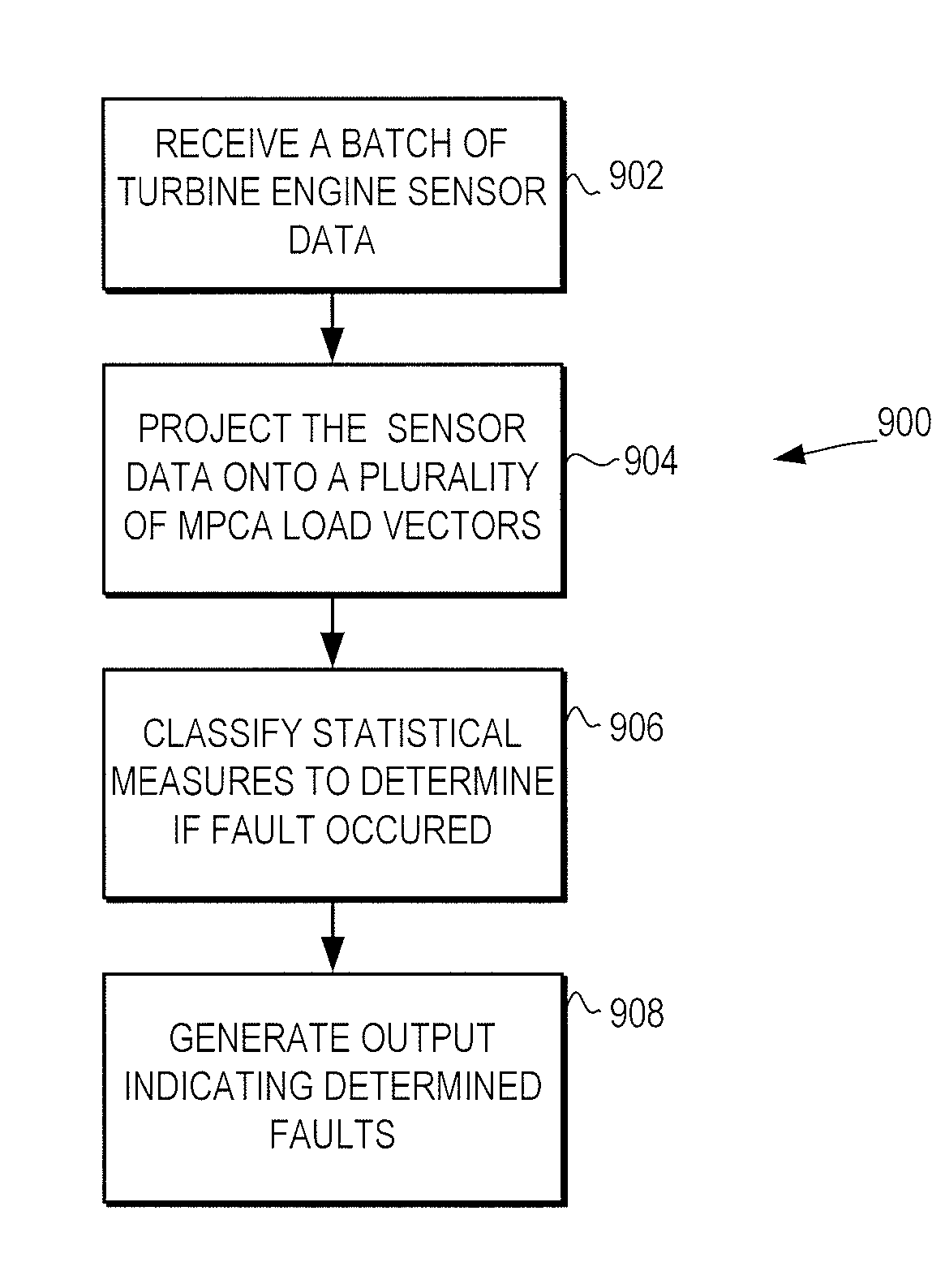
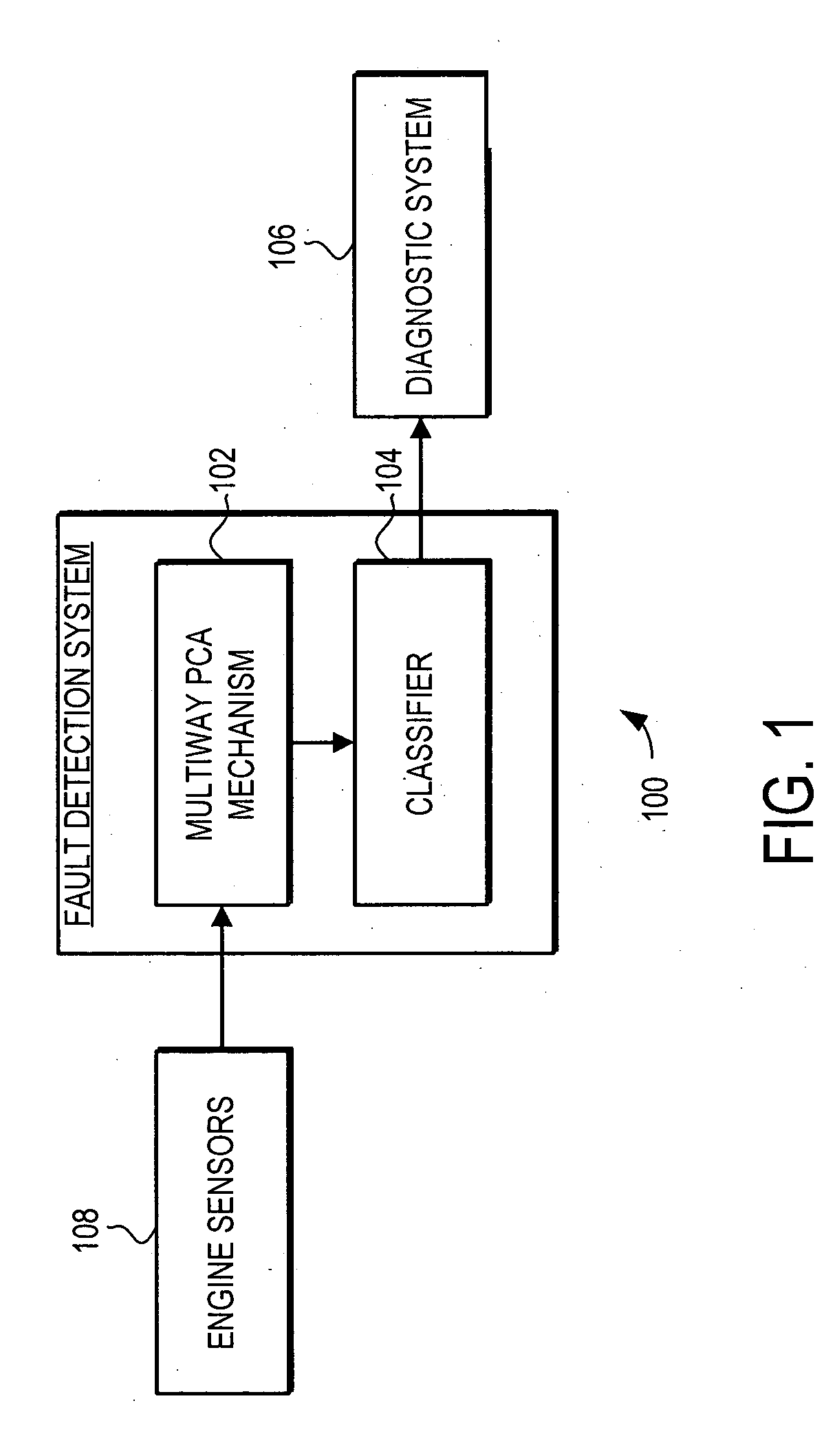
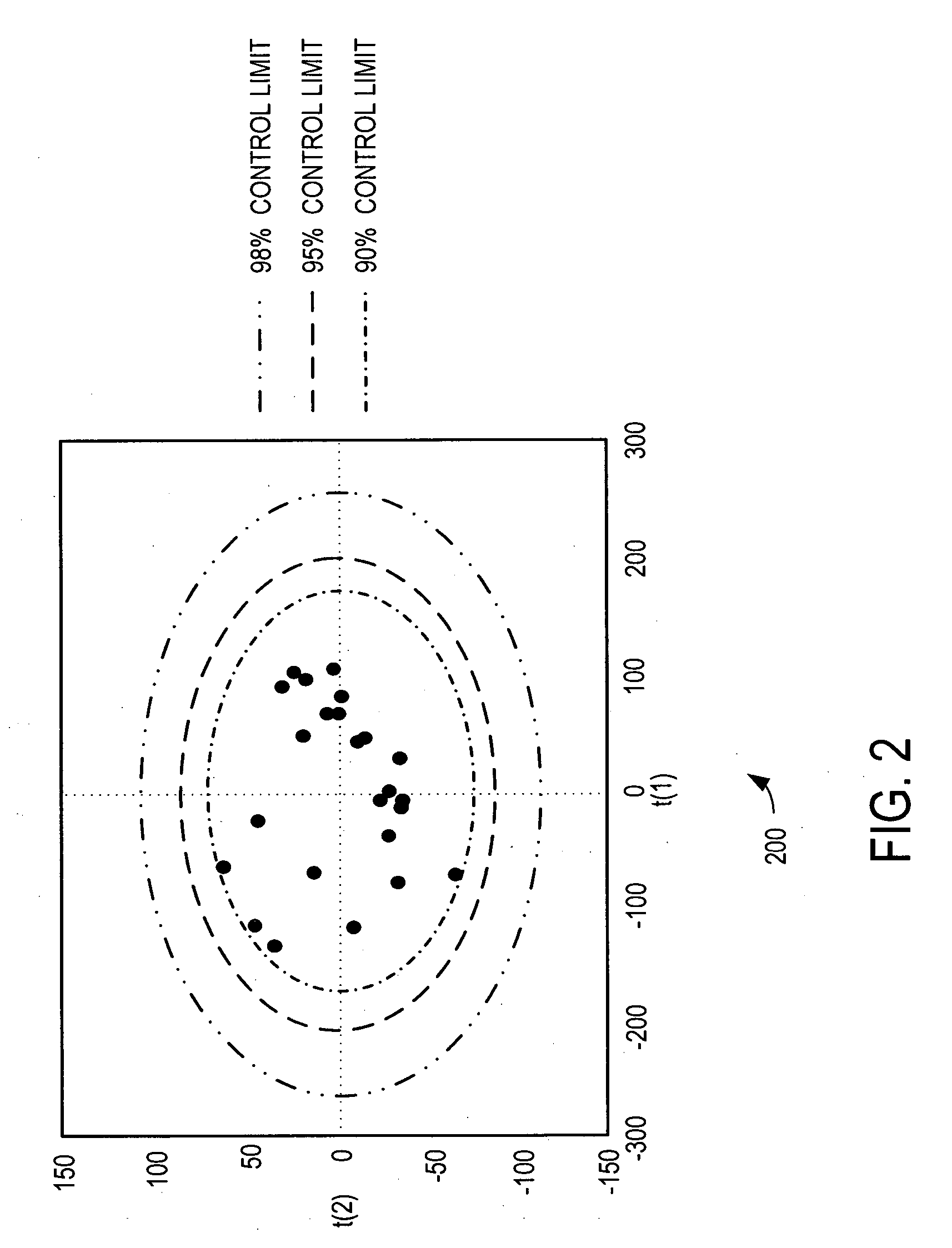
A fault detection system and method is provided that facilitates detection of faults that are manifest over a plurality of different operational phases. The fault detection system and method use multiway principal component analysis (MPCA) to detect fault from turbine engine sensor data. Specifically, the fault detection system uses a plurality of load vectors, each of the plurality of load vectors representing a principal component in the turbine engine sensor data from the multiple operational phases. The load vectors are preferably developed using sets of historical sensor data. When developed using historical data covering multiple operational phases, the load vectors can be used to detect likely faults in turbine engines. Specifically, new sensor data from the multiple operational phases is projected on to the load vectors, generating a plurality of statistical measures that can be classified to determine if a fault is manifest in the new sensor data.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
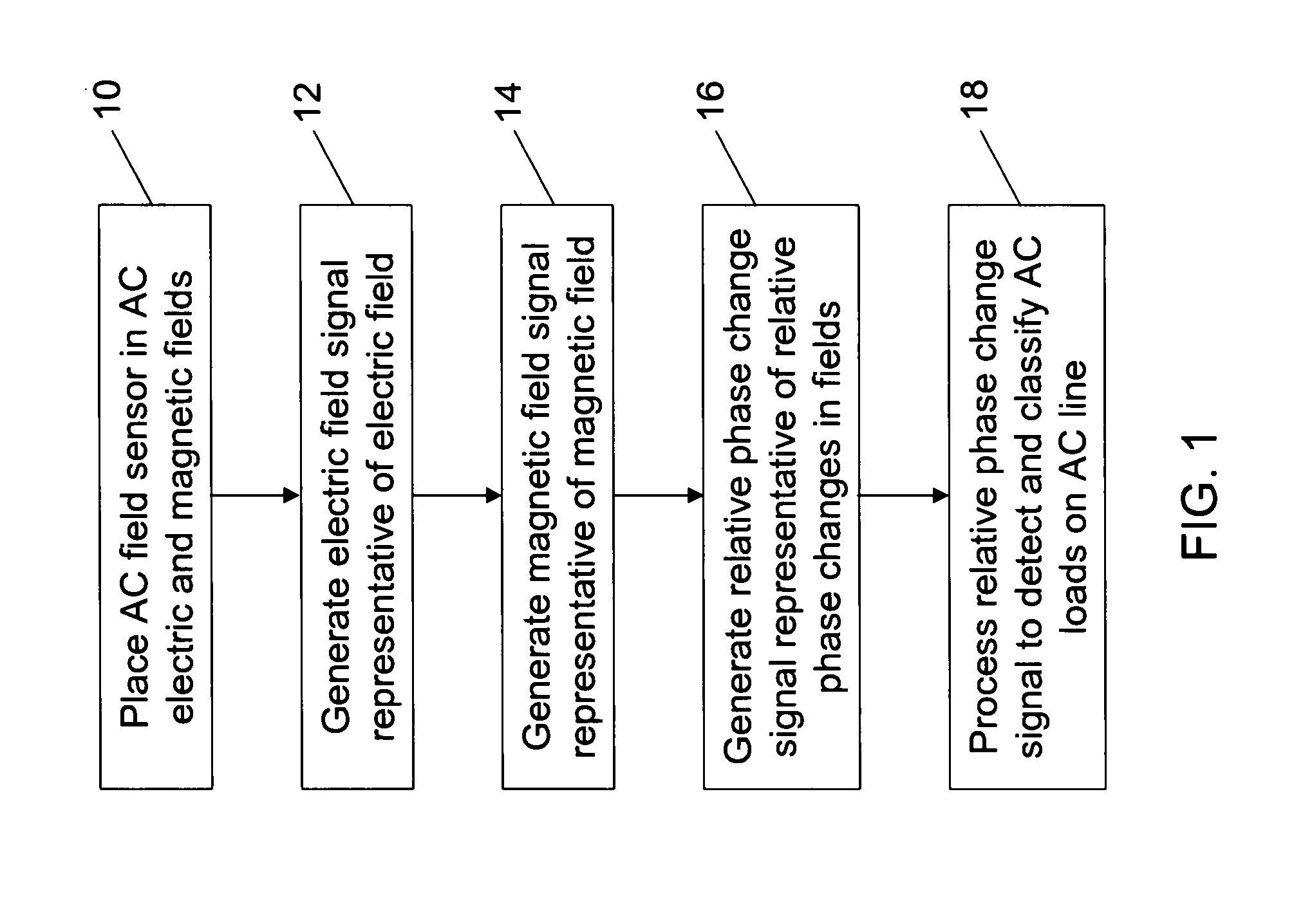
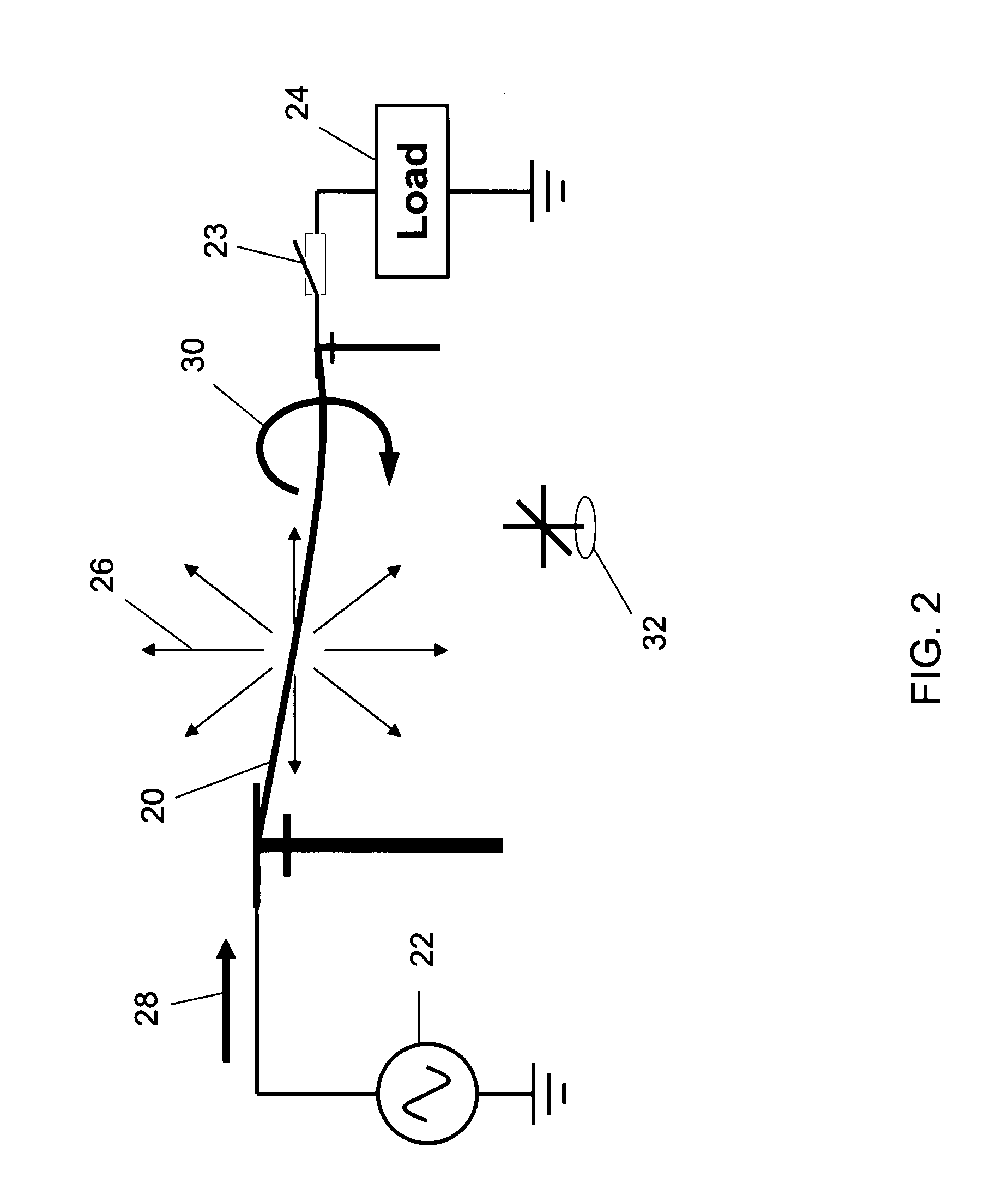
Methods for detecting and classifying loads on AC lines
InactiveUS20080048640A1Current/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase angleRelative magnitudeRelative phase
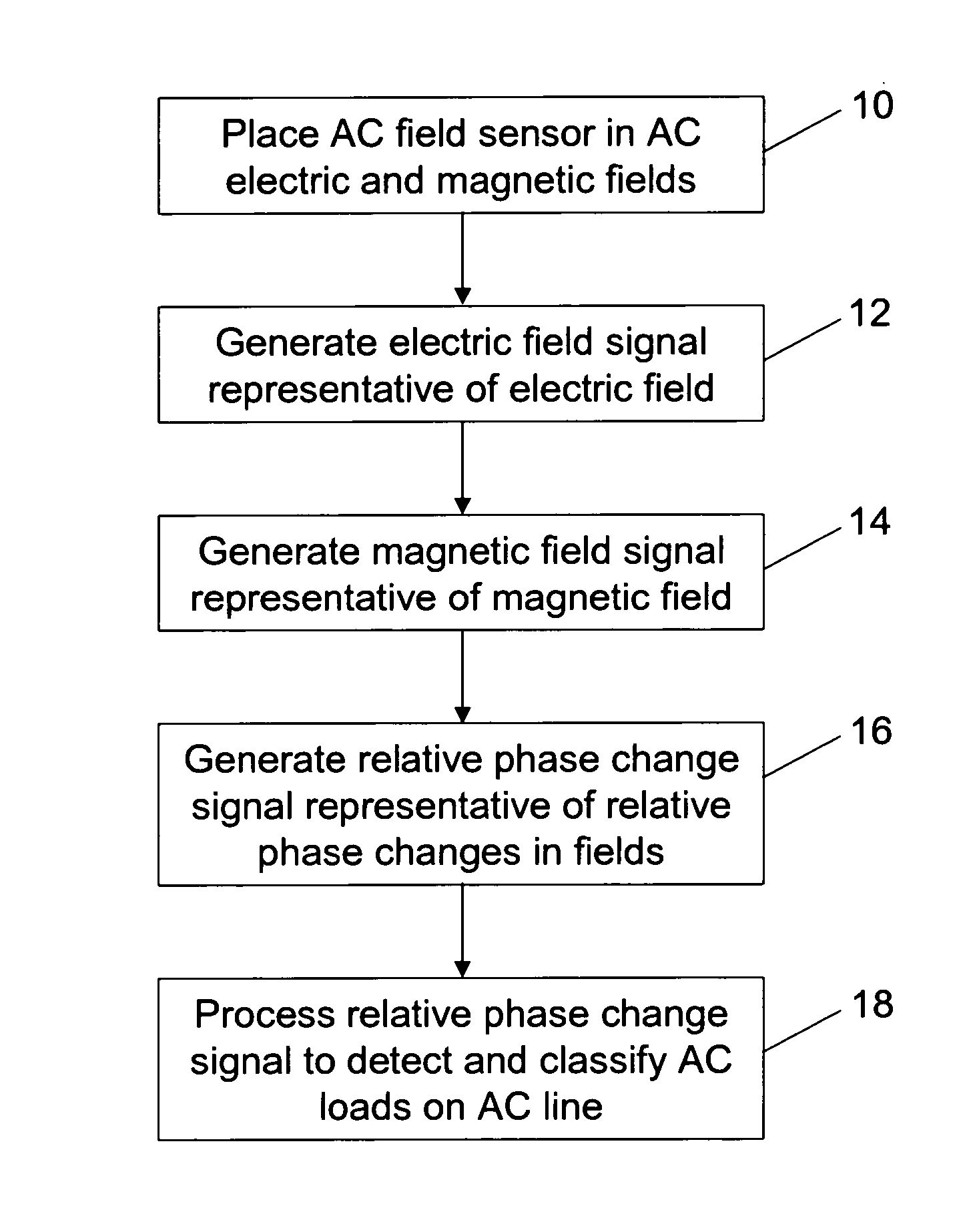
Methods for detecting and classifying loads on alternating current (AC) lines are provided. One such method includes the steps of placing an AC field sensor in AC electric and magnetic fields generated by an AC line, generating an electric field signal representative of the AC electric field received by the AC field sensor, generating a magnetic field signal representative of the AC magnetic field received by the AC field sensor, generating a relative phase signal representative of relative phase changes between the electric and magnetic fields, and processing the relative phase signal to detect and classify loads on the AC line. In another method, relative load vector signals representative of relative magnitude and phase changes in the magnetic field are generated and processed to detect and classify loads on the AC line.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Magneto-elastic sensor, load pin, ball-joint and tow coupling comprising this sensor, method of determining a direction of a load vector
ActiveUS9347845B2Reduce measurementGuaranteed uptimeForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsShear stressMagneto elastic
Owner:METHODE ELECTRONICS MALTA LTD
Online updating method of principal component analysis monitoring model
ActiveCN102662321AEnsure consistencyReduce false alarm rateAdaptive controlKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
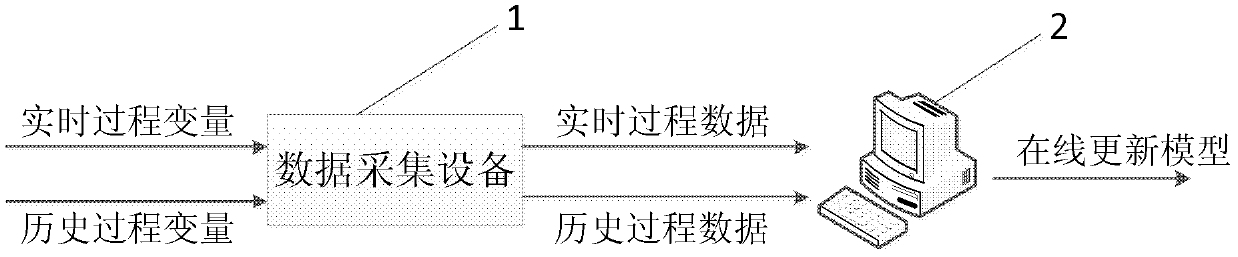
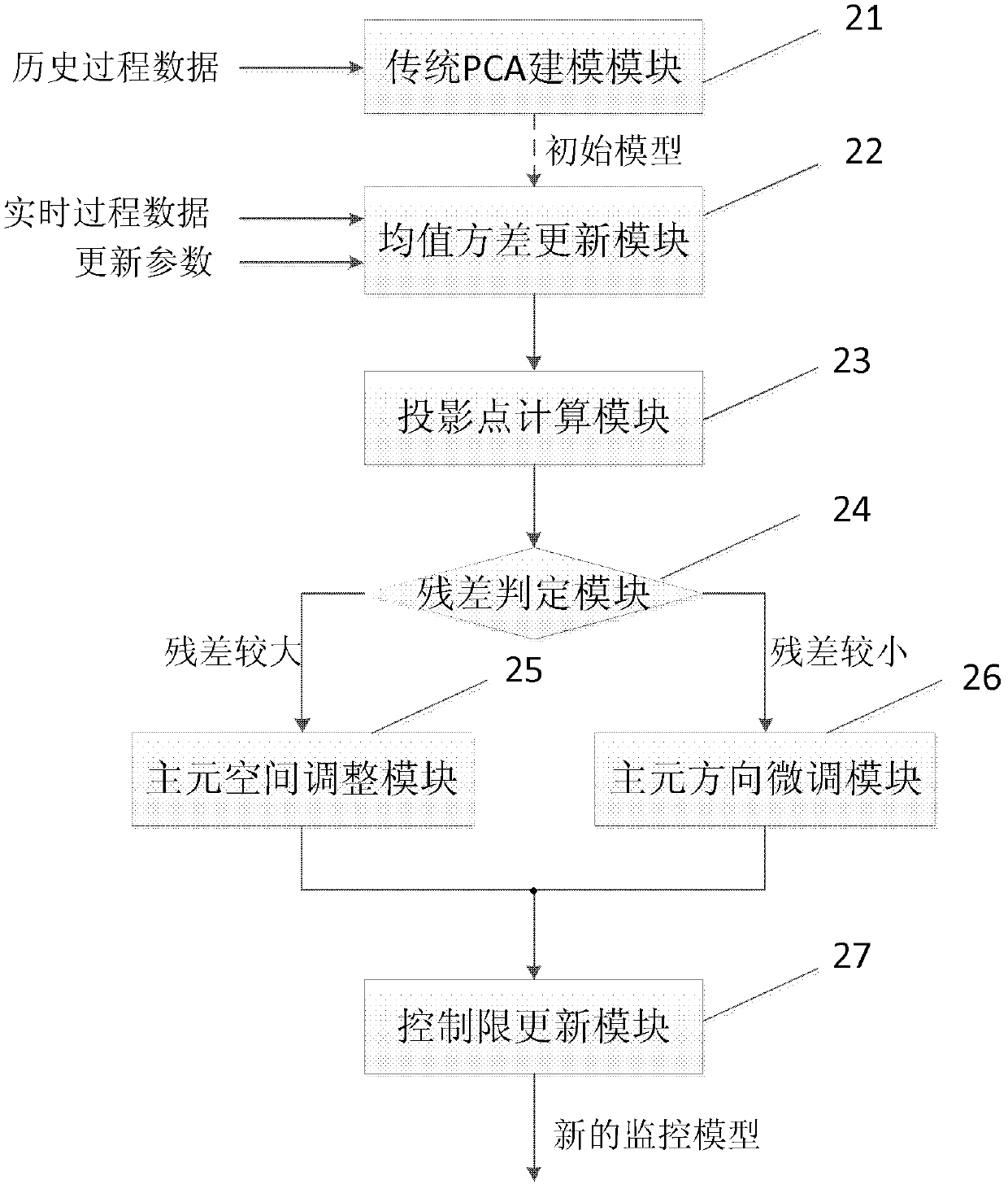
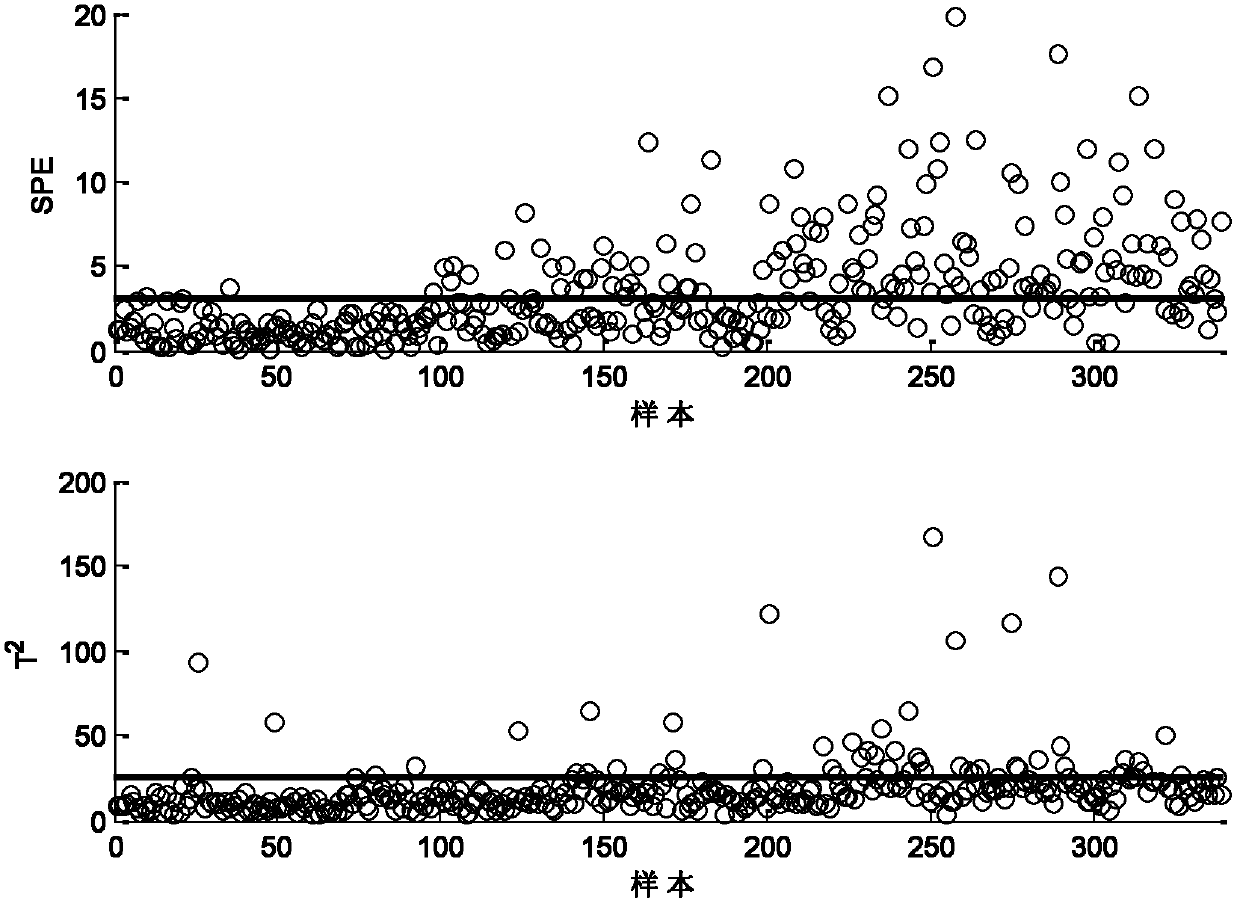
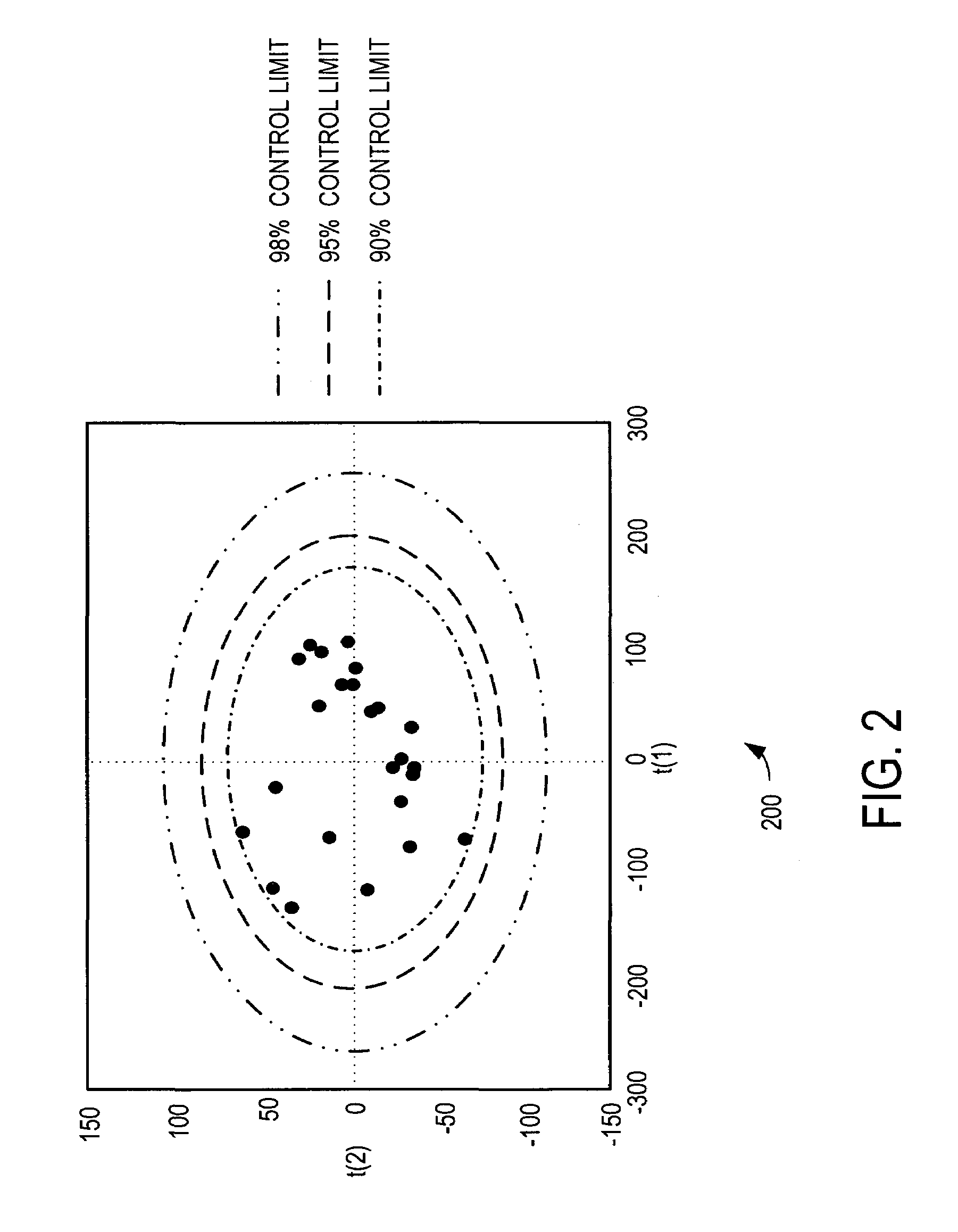
The invention relates to an online updating method of a principal component analysis monitoring model. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) A model online updating system comprising data acquisition equipment and a monitoring computer is arranged in industry field; 2) A traditional principal component analysis (PCA) modeling module uses historical data to establish a PCA initial monitoring model; 3) After the monitoring begins, a mean value variance updating module calculates a mean value and a standard deviation sigma' of a new model according to real-time process data and the current PCA model; 4) A projection point calculation module calculates a residual vector of a new sample and transmits to a residual determination module; 5) The residual determination module determines an updating method of a projection direction according to a size of a residual vector die; if the residual is large, a principal component space adjusting module is called; if the residual value is small, a principal component direction fine adjusting module is called; finally a load vector P' nk and a characteristic value matrix lambda' kk of the new model is obtained; 6) A control limit updating module carries out control limit and updating on statistical magnitude of the model; the system finally outputs the new model omega' which is used for online monitoring and fault diagnosis during an industrial process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
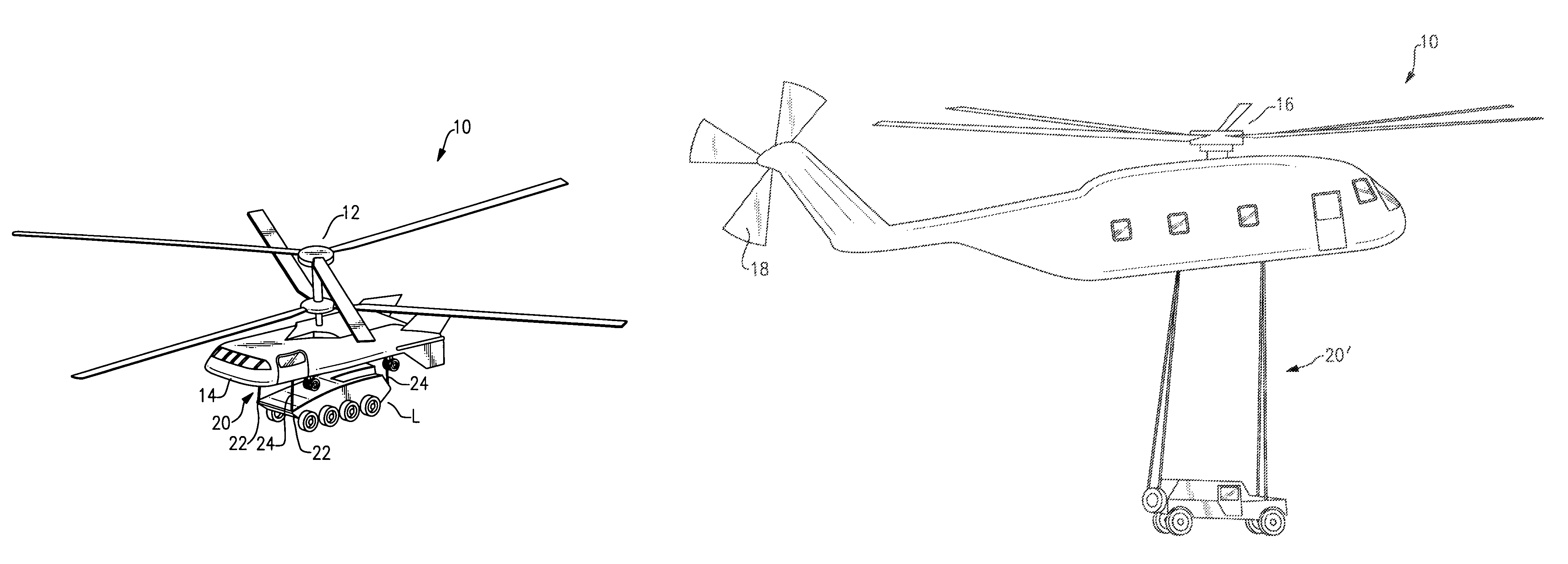
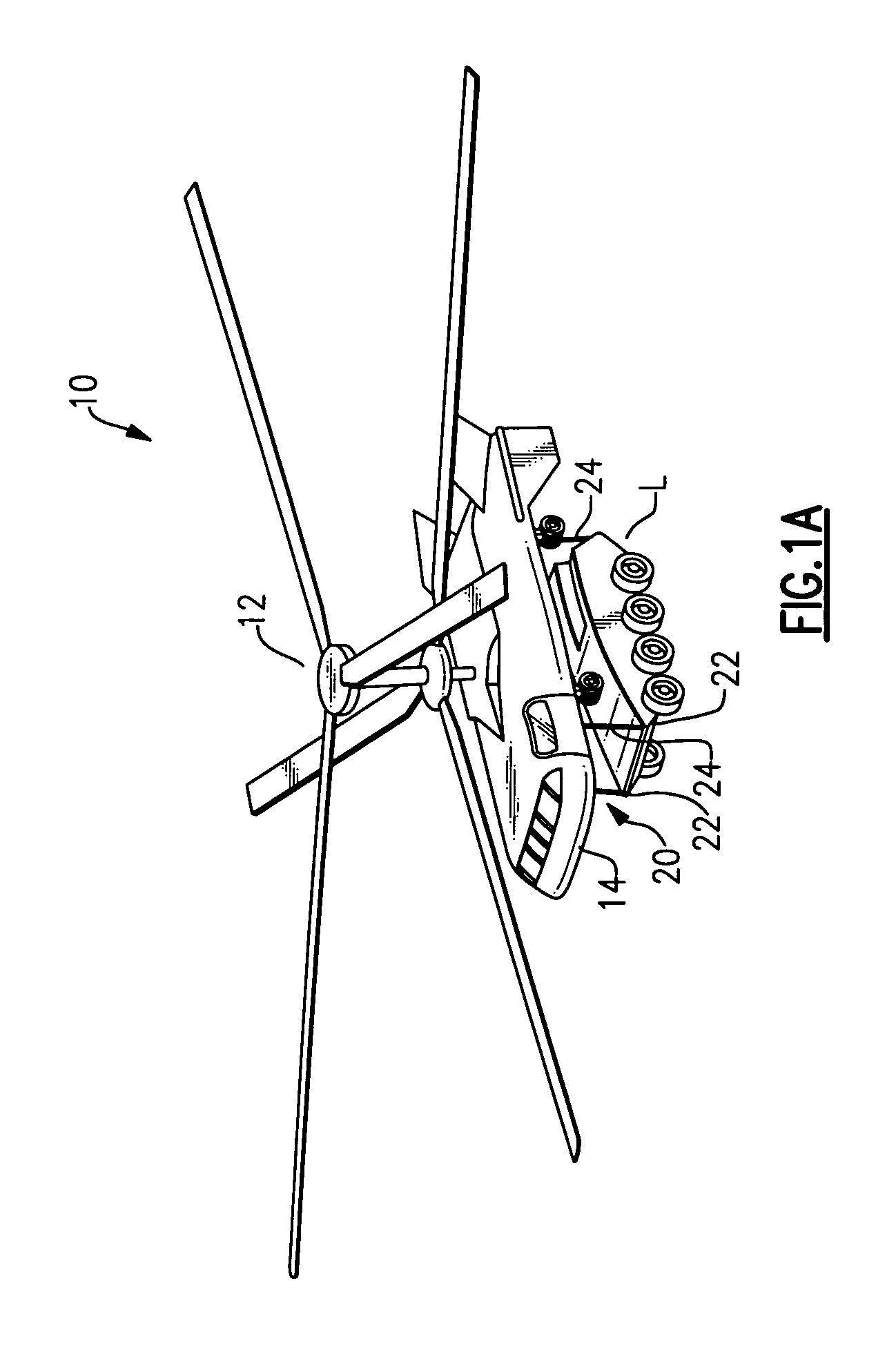
System and method for improved rotary-wing aircraft performance with interior/external loads
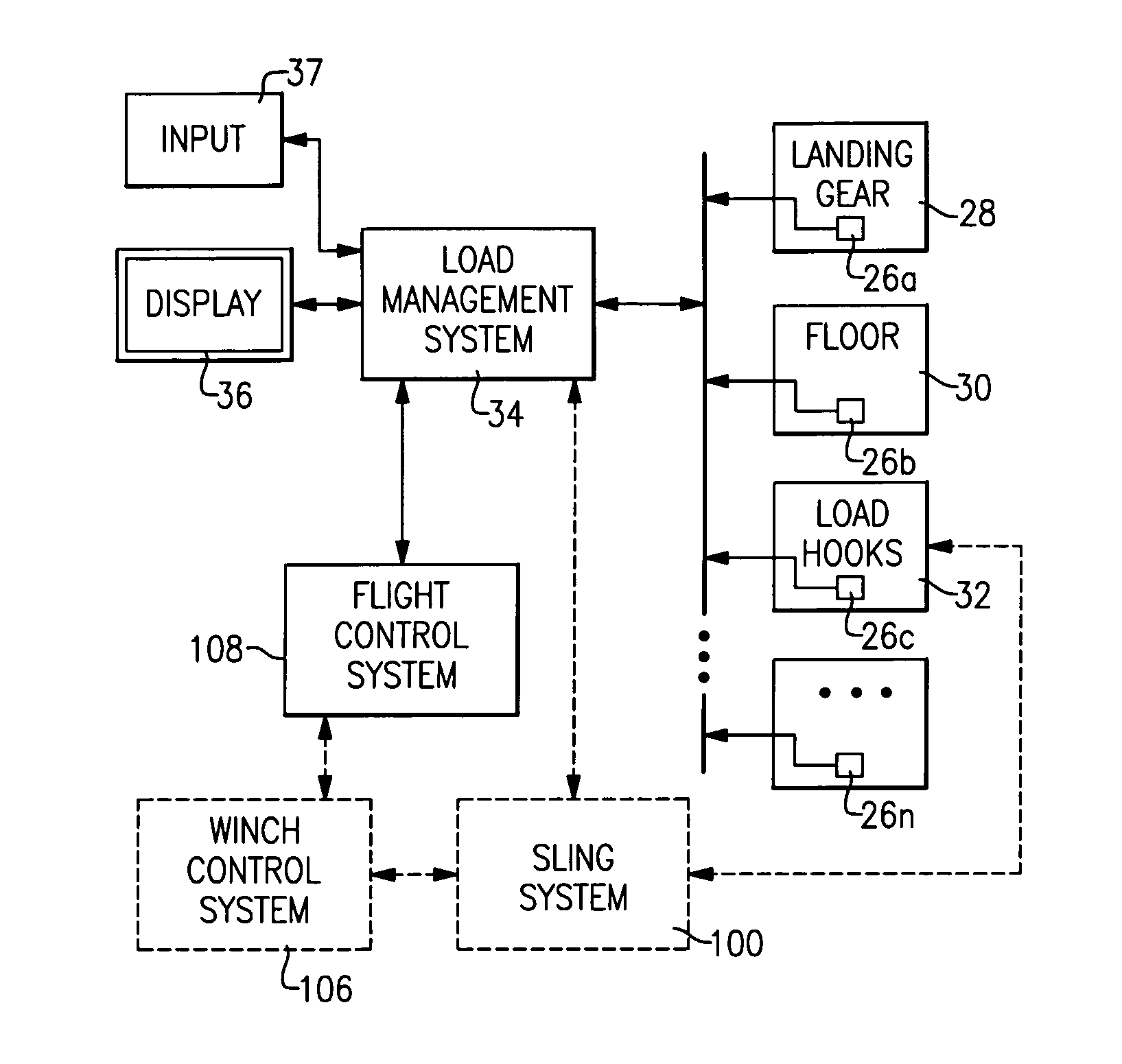
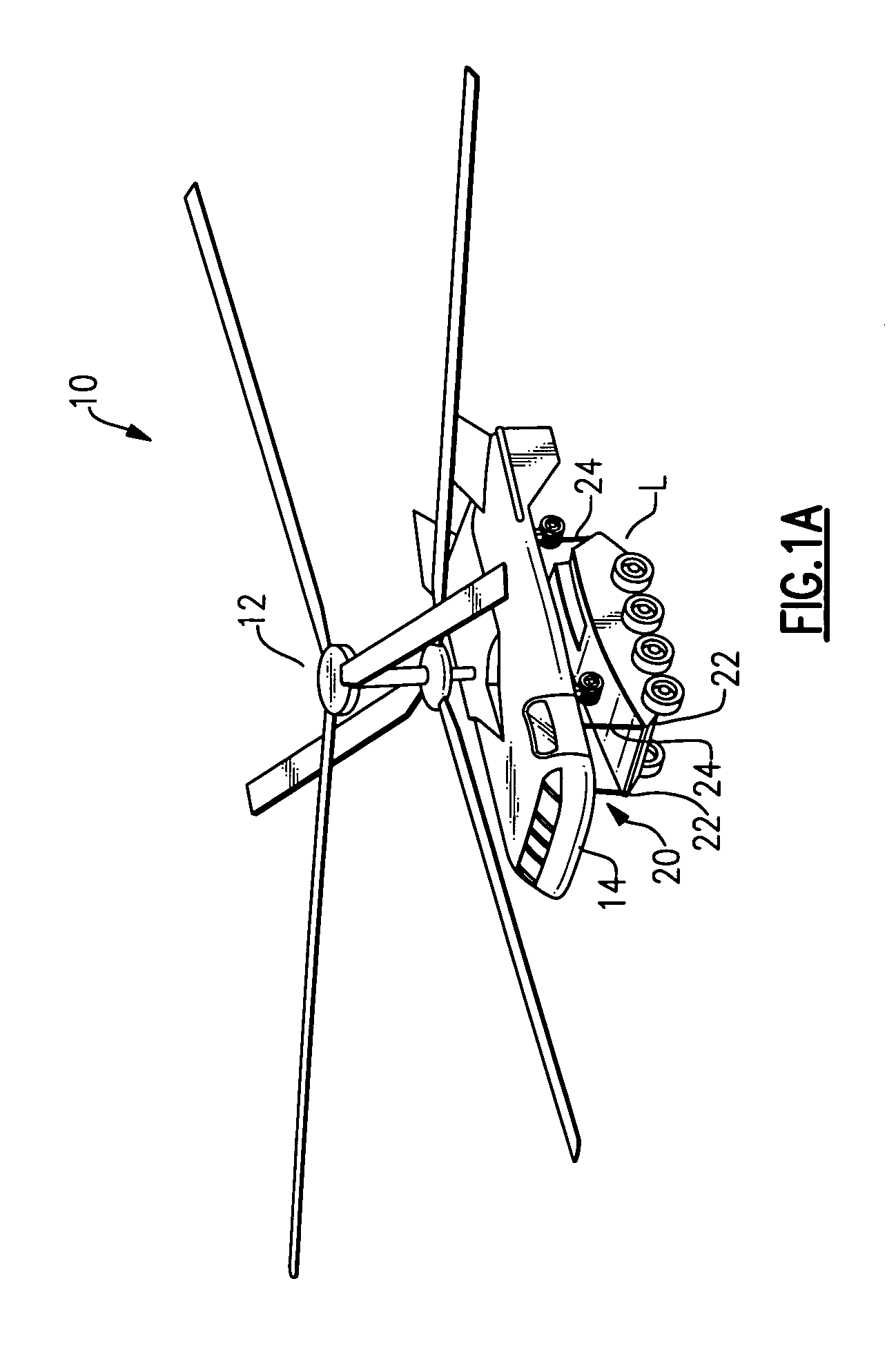
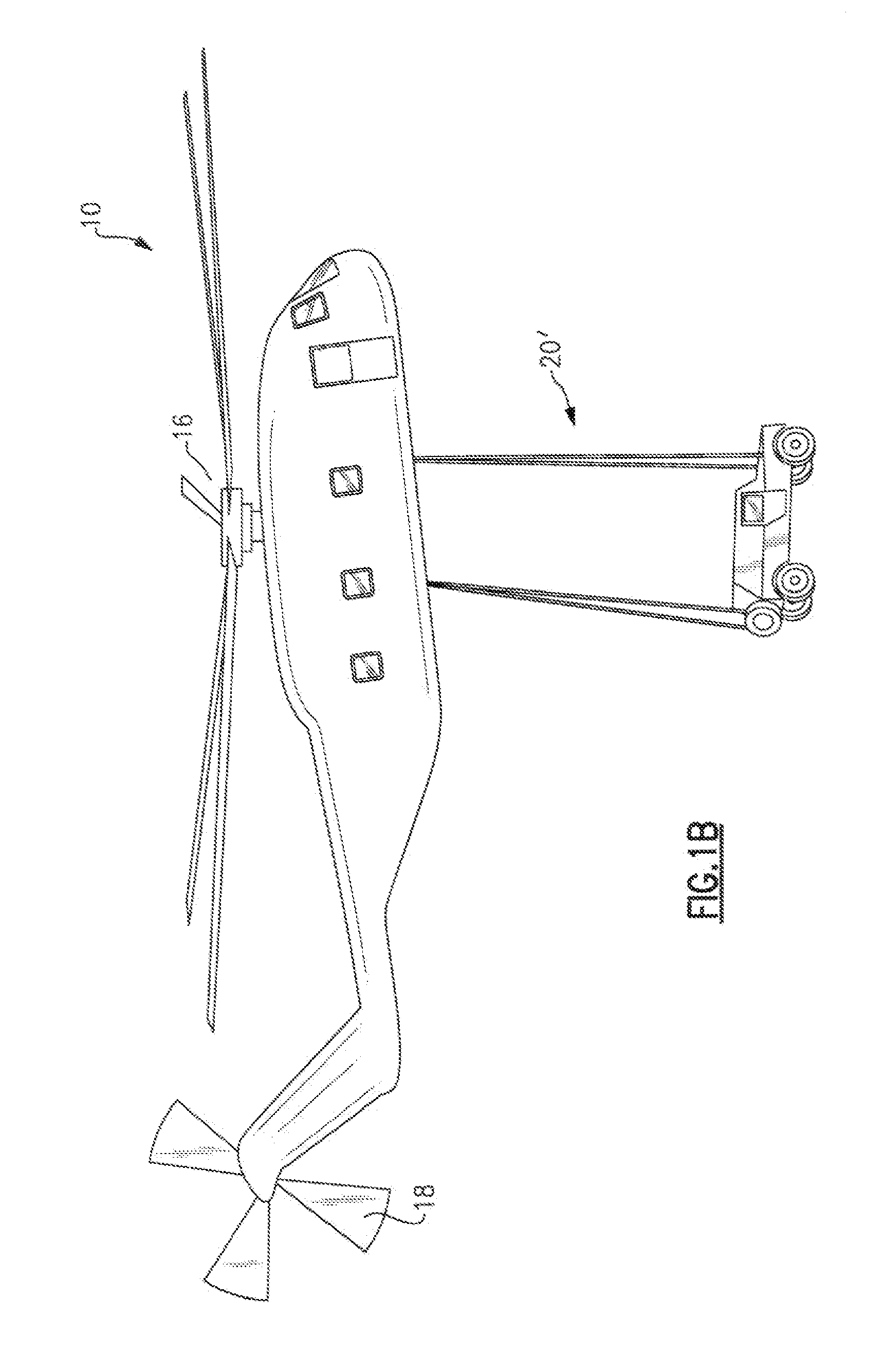
An interactive aircraft load management system automates calculation and provides simulation capability to changes in an aircraft C.G. limit for display on a three-dimensional aircraft symbology. The aircraft load management system also communicates with a fly by wire (FBW) flight control system wherein the aircraft's control system is programmed to automatically compensate for C.G. excursions and to alter control laws. The aircraft load management system also selectively reels-in and reels out sling lines as the aircraft pitches and rolls to maintain a load vector from a slung load along the aircraft centerline. Load vector travel is accomplished by coupling a winch control system into the flight control system.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Fault detection system and method using multiway principal component analysis
InactiveUS7243048B2Improve performanceVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for analyzing static strength characteristics of turbomachinery blade based on CPU+GPU heterogeneous parallel computing
ActiveCN106570204AShorten the design cycleAccurate static strength characteristic analysis resultsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelParallel algorithm
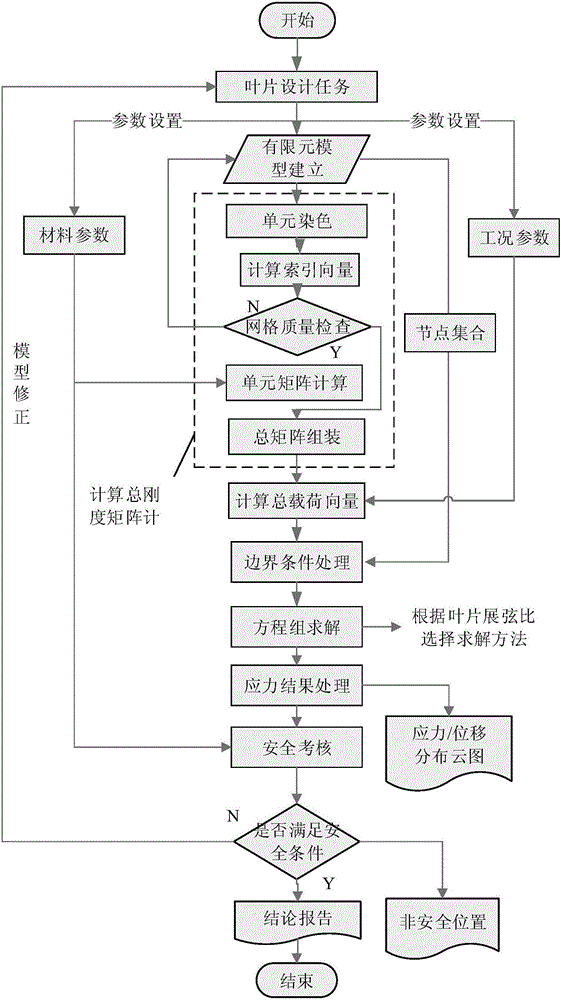
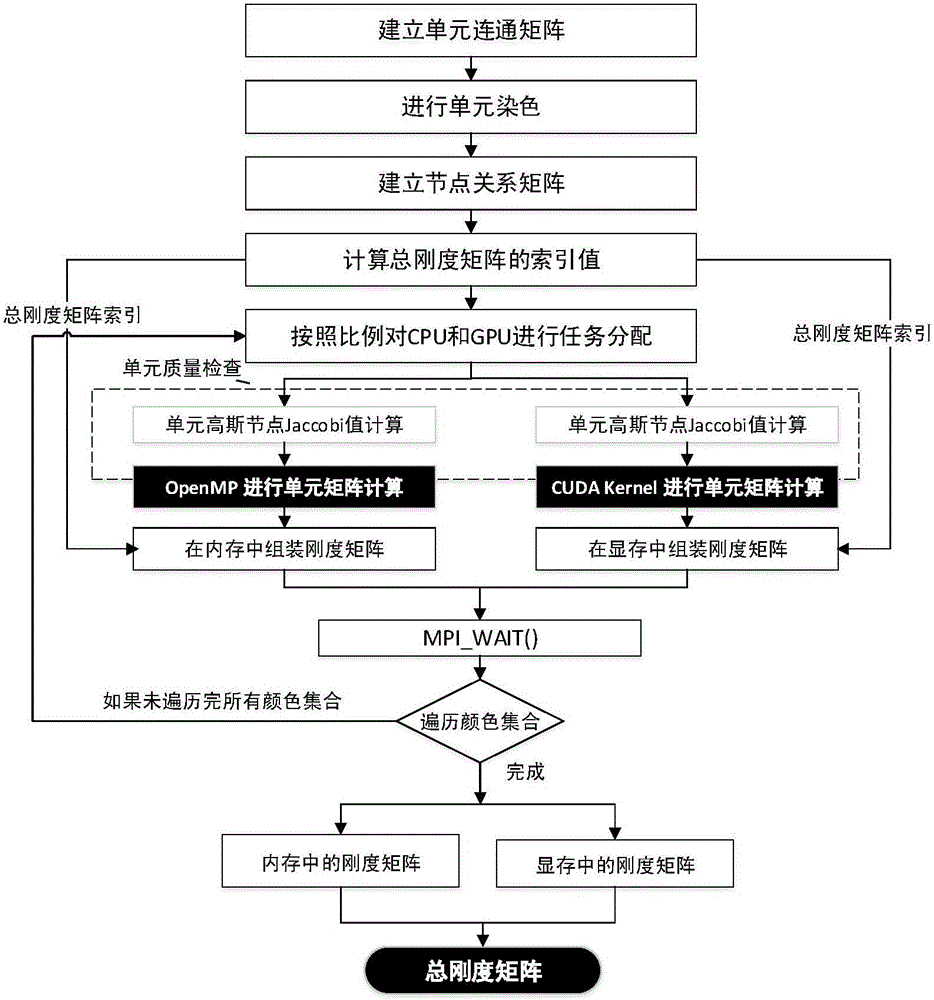
The invention discloses a method for analyzing static strength characteristics of a turbomachinery blade based on CPU+GPU heterogeneous parallel computing. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, establishing a finite element model, computing the total stiffness matrix of the model, then, computing the centrifugal load vector and the pneumatic load vector of the turbomachinery blade, performing displacement constraint and coupling of a node, and correcting the total stiffness matrix; and then, solving an equation set formed by the total stiffness matrix and the load vector in parallel by using CPU+GPU, obtaining a node displacement vector, then, computing the principal strain and the VonMises equivalent stress, drawing a distribution cloud picture, and finally, performing safety check. By means of the method disclosed by the invention, for static strength analysis and design of the turbomachinery blade, project planners can perform operation conveniently; simultaneously, due to an adopted CPU+GPU parallel algorithm, the computing speed of a finite element method can be effectively increased; an accurate and rapid blade static strength characteristic analysis result is provided for design of the turbomachinery blade; and the design period of the turbomachinery blade is greatly shortened.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for improved rotary-wing aircraft performance with interior/external loads
An interactive aircraft load management system automates calculation and provides simulation capability to changes in an aircraft C.G. limit for display on a three-dimensional aircraft symbology. The aircraft load management system also communicates with a fly by wire (FBW) flight control system wherein the aircraft's control system is programmed to automatically compensate for C.G. excursions and to alter control laws. The aircraft load management system also selectively reels-in and reels out sling lines as the aircraft pitches and rolls to maintain a load vector from a slung load along the aircraft centerline. Load vector travel is accomplished by coupling a winch control system into the flight control system.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
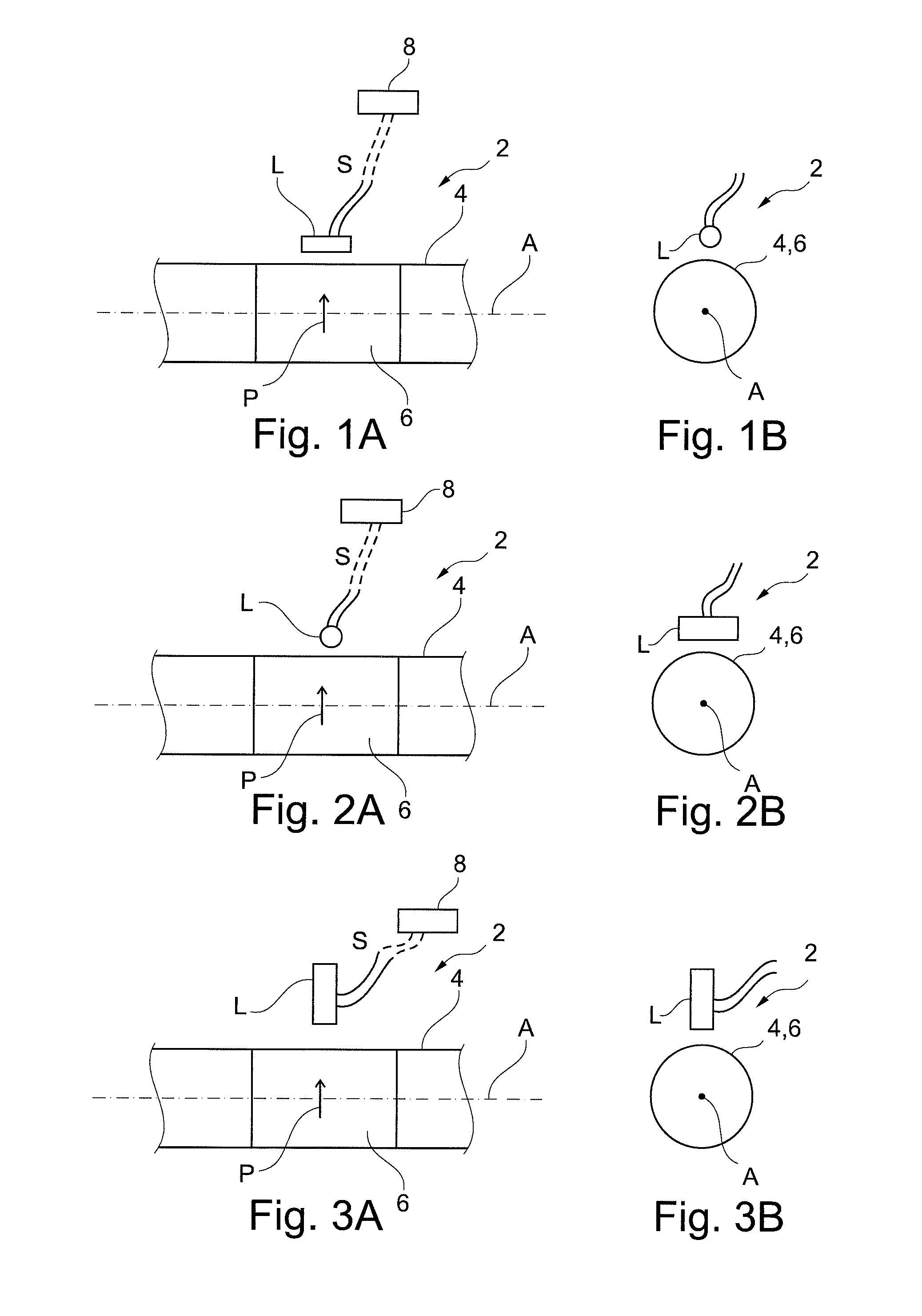
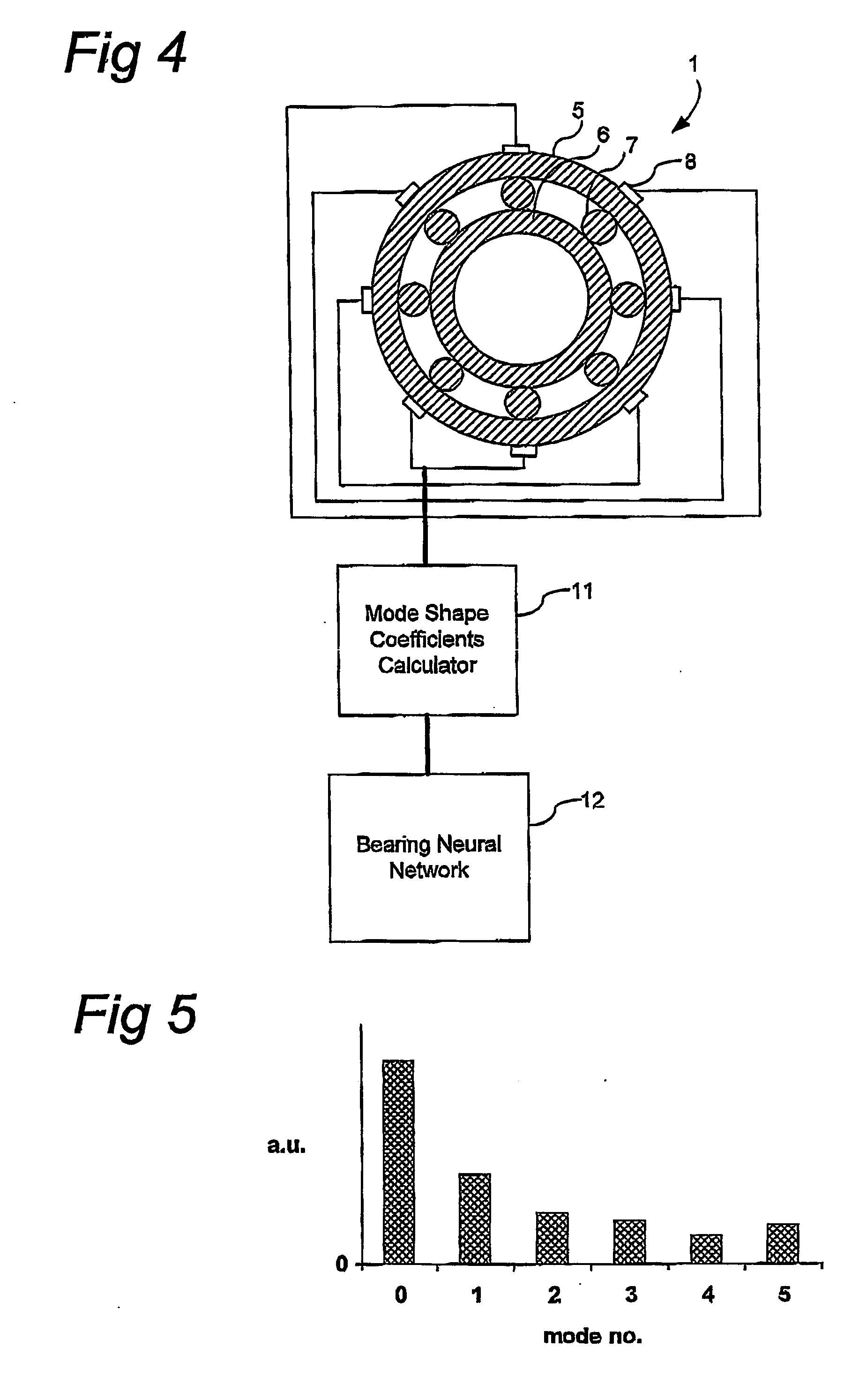
Method and sensor arrangement for load measurement on rolling element bearing based on model deformation
ActiveUS7389701B2Measurement qualityMachine part testingRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingEngineering
Owner:AB SKF
KPCA-based fused magnesium furnace fault diagnosis method for fault separation and reconstruction
InactiveCN104898646AEliminate the alarm phenomenon of detection statistics exceeding the limitTo achieve the purpose of fault separationElectric testing/monitoringElectricityDecomposition
The invention provides a KPCA-based fused magnesium furnace fault diagnosis method for fault separation and reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring historical normal data of a fused magnesium furnace, historical fault data when the fused magnesium furnace generates a fault, and test data when a fault occurs in online monitoring; performing preprocessing on the historical normal data of the fused magnesium furnace and the historical fault data; performing high-dimension mapping and then PCA decomposition on the historical normal data of the fused magnesium furnace by use of a nucleus principal component analytical method; and performing diagnosing and fault reconstruction on the test fault data when the fault occurs in the online monitoring by use of a fault load vector set, determining a fault type, and recovering the fault data to corresponding normal data so that the fault is eliminated. According to the method provided by the invention, the fault separation and reconstruction problems of non-linear data of the fused magnesium furnace are solved, the test data when the fault occurs in the online monitoring can be monitored, only a fault model corresponding to a current fault can correctly remove fault information in the data, based on this, the fault type can be determined, and the purpose of fault separation is realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades
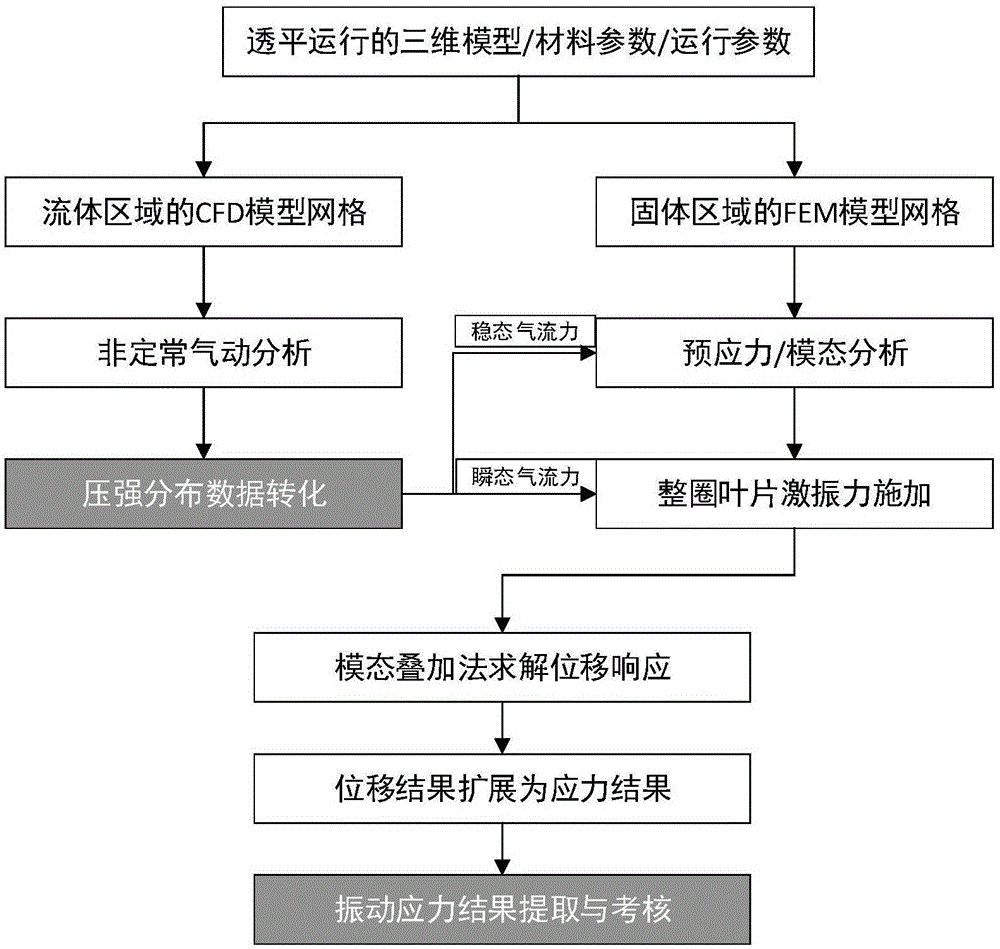
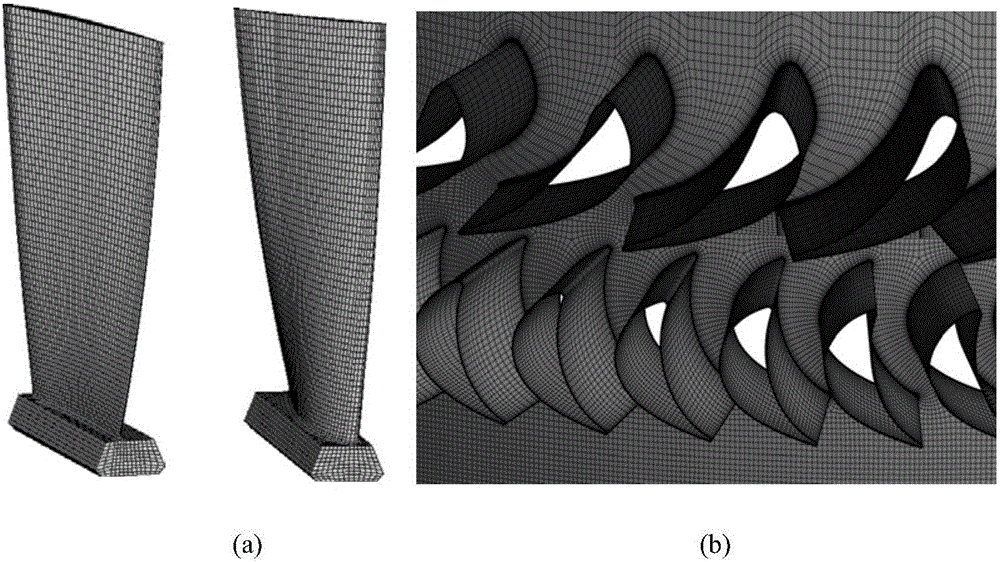
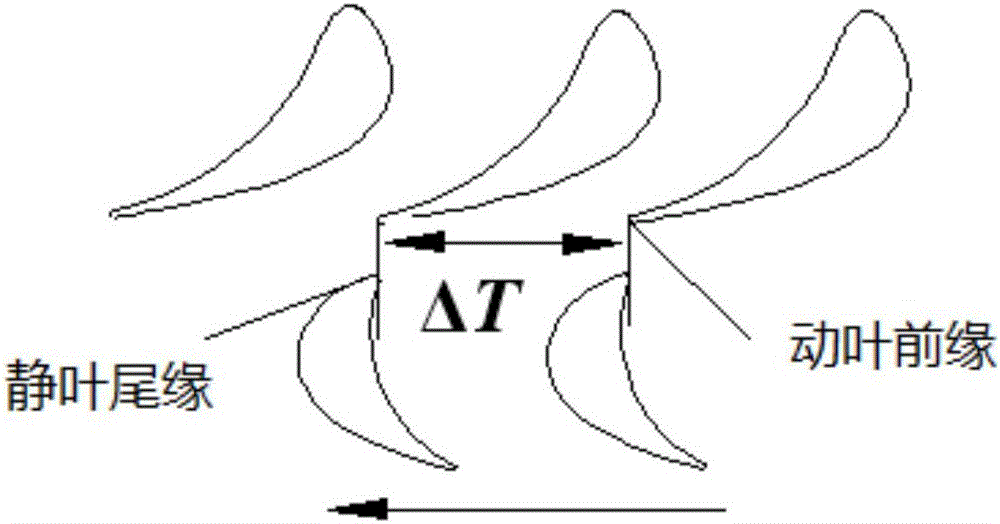
ActiveCN106528932AImprove calculation accuracyCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionEngineering
The invention discloses a vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades. The method comprises the steps of 1, building an FEM model of a solid region of an entire circle of the blades and CFD models of periodically symmetric fluid regions; 2, obtaining steady-state pressure intensity field distribution of meshes of the fluid regions of the blades and instant pressure intensity field distribution of each time step in a pneumatic period; 3, converting pressure intensity field distribution data; 4, performing finite element mode analysis of the entire circle of the blades; 5, obtaining node force load vectors of blade surfaces of all time steps; 6, solving a vibration displacement response by a mode superposition method; 7, expanding a displacement response result into a stress result; and 8, performing vibration stress result extraction and check. According to the method, the pressure intensity distribution of the blade surfaces is obtained by adopting a non-steady computing method, and an accurate air exciting-vibration force load is obtained by interpolation from the meshes of the fluid regions of the blades to the pressure intensity of the meshes of the solid region, so that the computing precision is improved; and each sector adopts a CPU+GPU heterogeneous parallel computing mode, so that the computing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
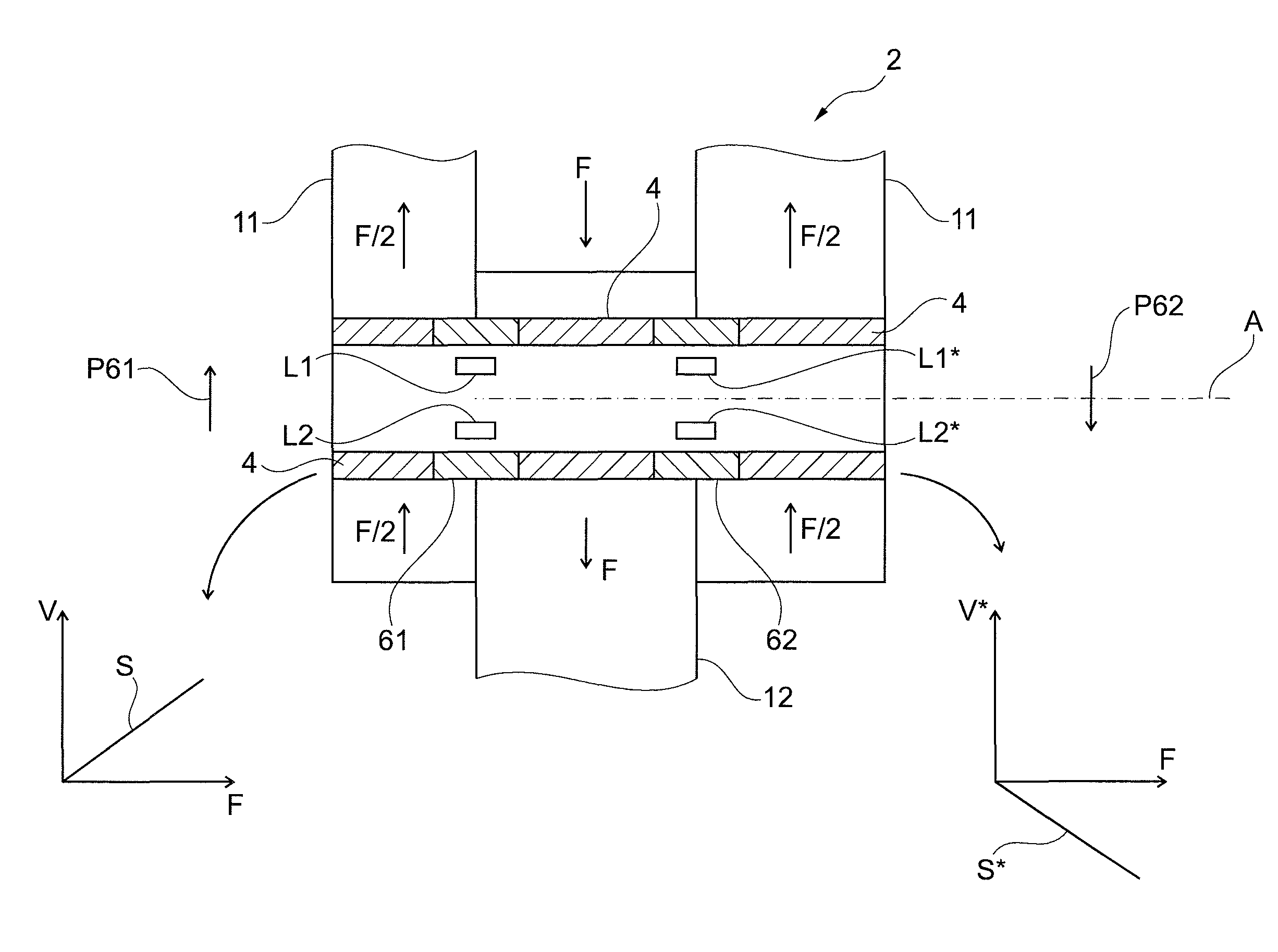
Simple shear connection structure pin load vector measuring method and measuring instrument thereof
InactiveCN102519648AEnables direct measurementLow costApparatus for force/torque/work measurementMeasuring instrumentEngineering
The invention relates to a simple shear connection structure pin load vector measuring method and a measuring instrument thereof. The measuring instrument is formed by processing an ordinary bolt. Four strain gauge pasting grooves are processed on the contact surface of the bolt and a bolt hole, positions of the strain gauge pasting grooves are evenly distributed on the contact surface and respectively located at both ends of two perpendicular diameters. A strain gauge group is pasted axially along the bolt in each strain gauge pasting groove, each strain gauge group is formed by two strain gauges, and the two strain gauges and the bolt axially form an angle of +45 degrees and an angle of -45 degrees. The upper end of each strain gauge pasting groove is provided with a wire leading hole used for leading a wire out of each strain gauge. Due to the fact that the two strain gauges of +45 degrees and -45 degrees in each strain gauge group have a common wire, each wire leading hole needs to lead three wires out, and the total number is 12. The led wires of the strain gauges which are led out are connected on a strain measuring instrument. The measuring instrument achieves direct measurement of simple shear connection structure pin load size and orientation and pin axial force, and is directly formed by processing a standard bolt, low in cost and wide in application scope.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
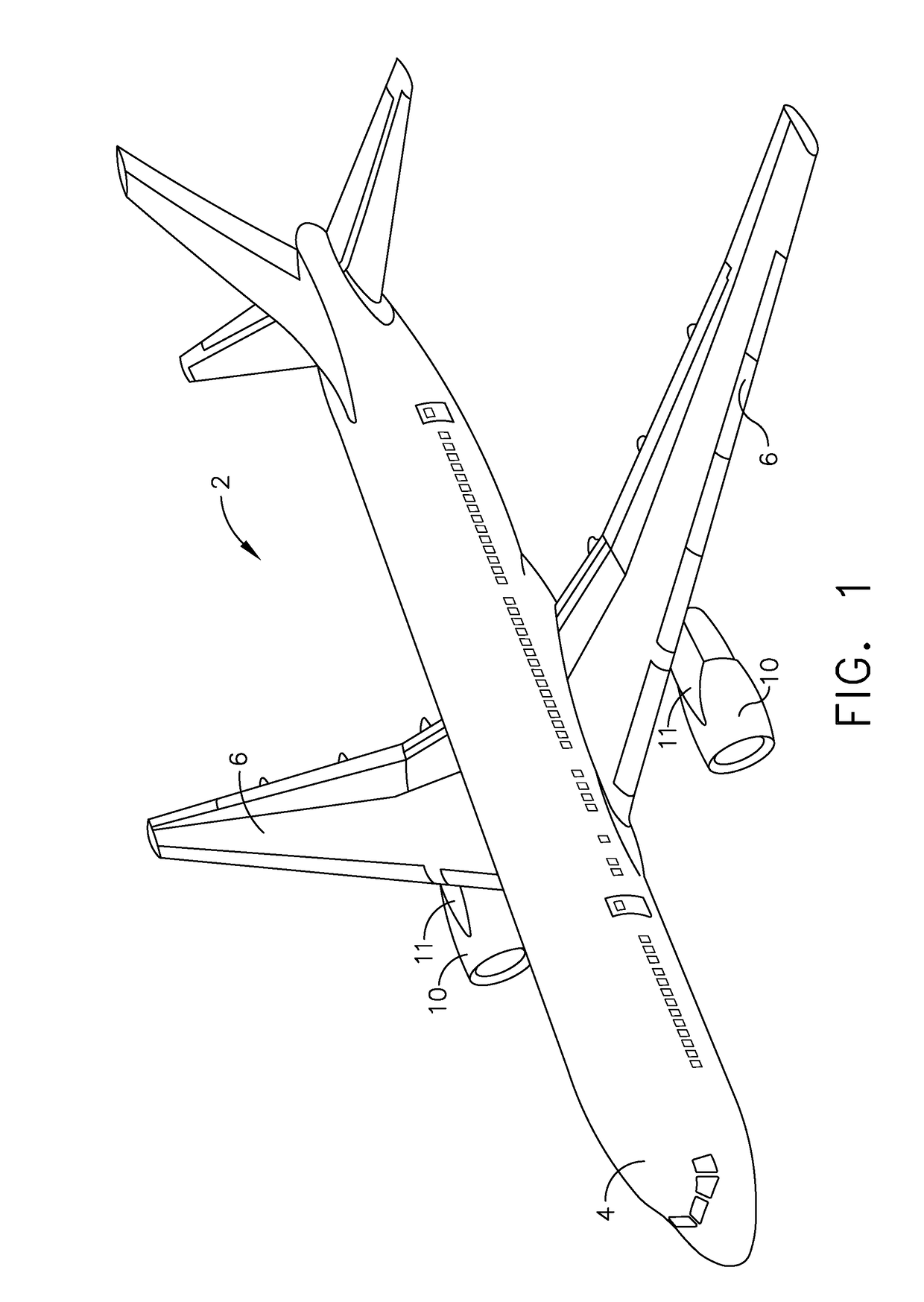
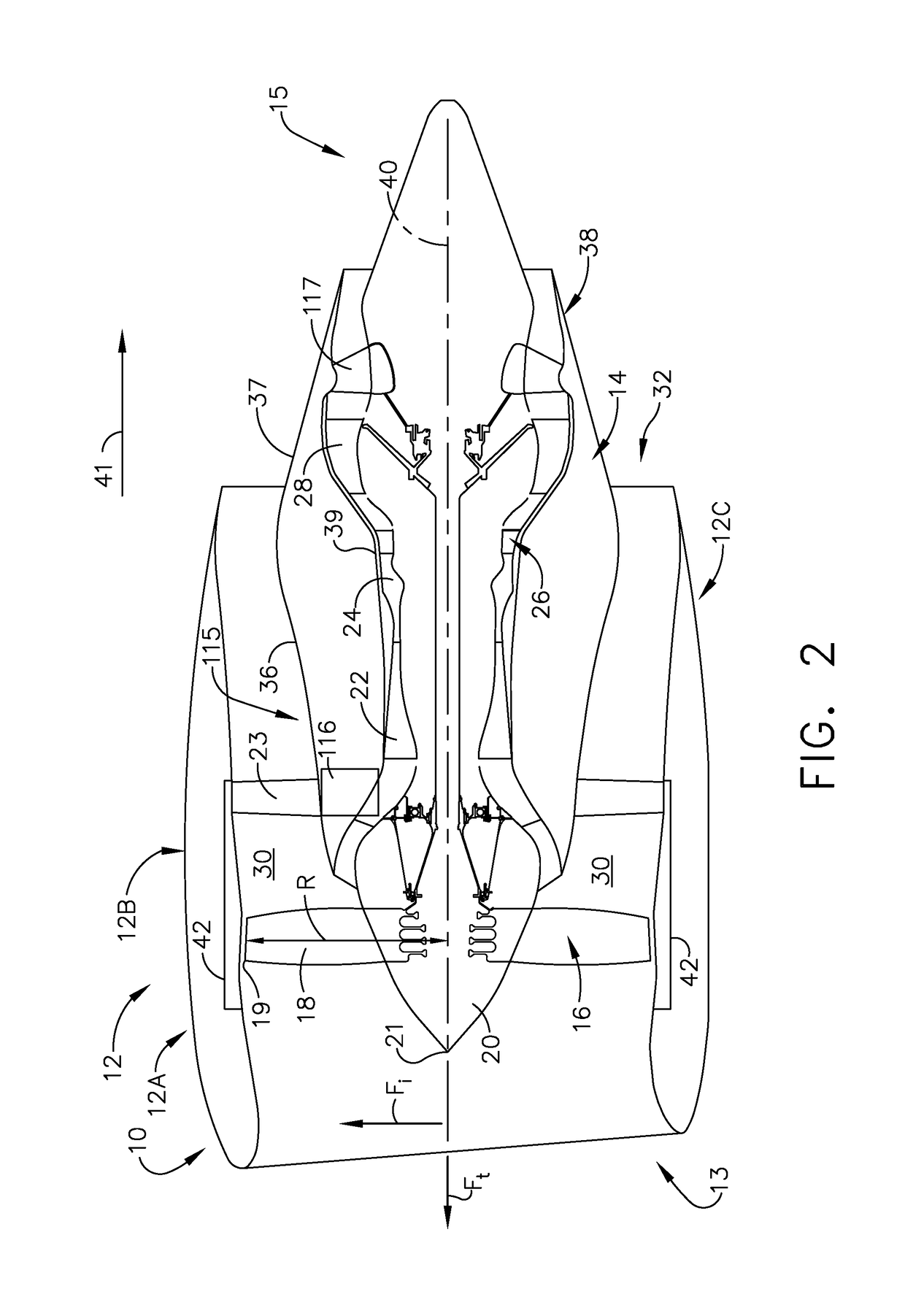
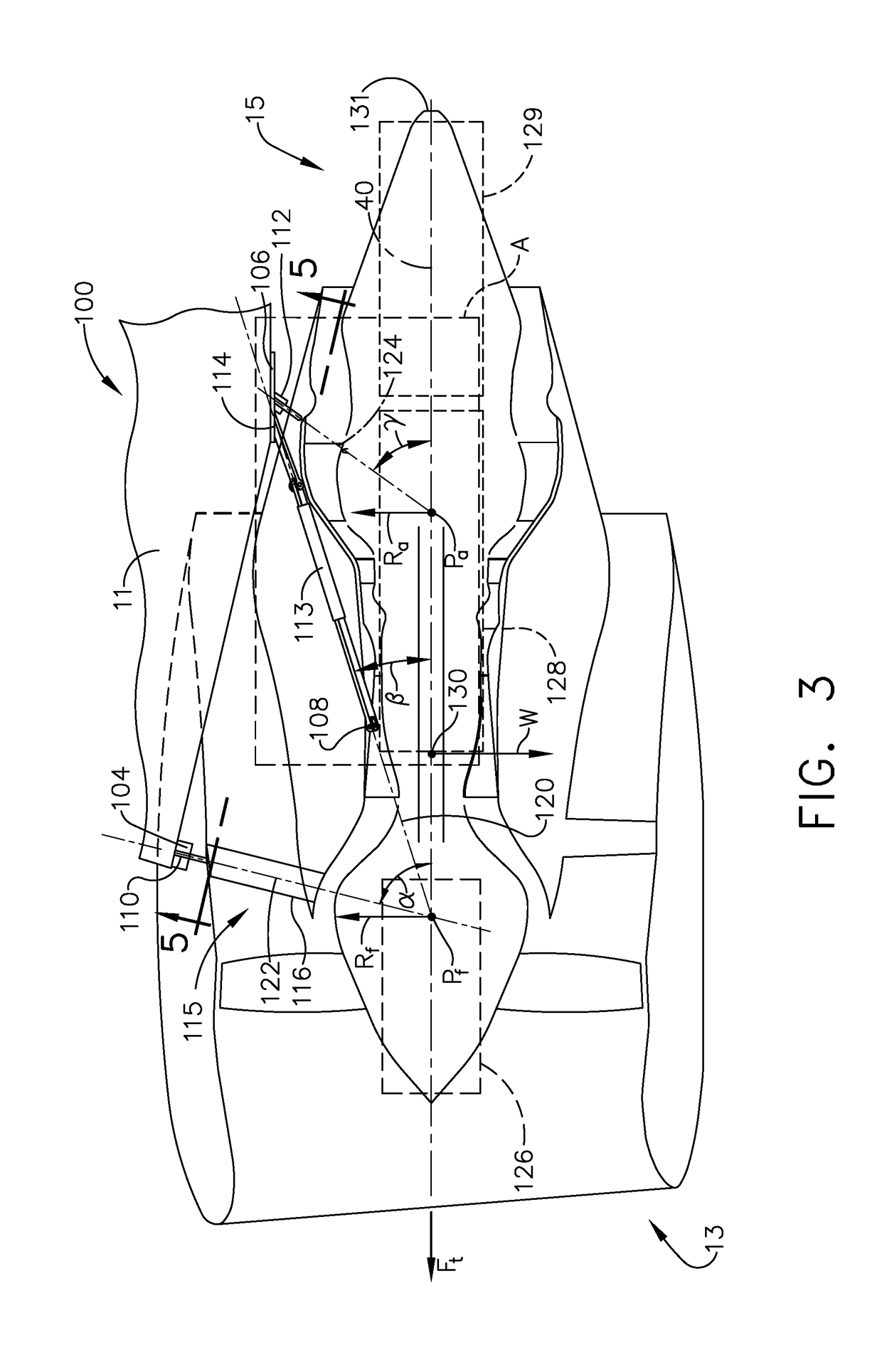
Method and system for mounting an aircraft engine
ActiveUS20180362170A1Gas turbine type power plantsPower plant constructionVertical planeFlight vehicle
A system for mounting an engine to an aircraft includes an engine forward mount angled toward the forward end of the engine at a first angle. At least two thrust links extend between an engine aft mount to a link support connection at a second angle. The engine aft mount is angled toward the forward end of the engine at a third angle. A projection of a load vector of the engine forward mount onto a vertical plane extending through the axis of rotation of the engine and a projection of a load vector of each of the at least two thrust links onto the vertical plane intersect the axis of rotation of the engine within a first vertical plane segment extending between a forward end of a nose of a fan assembly and forward of a forward mount interface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
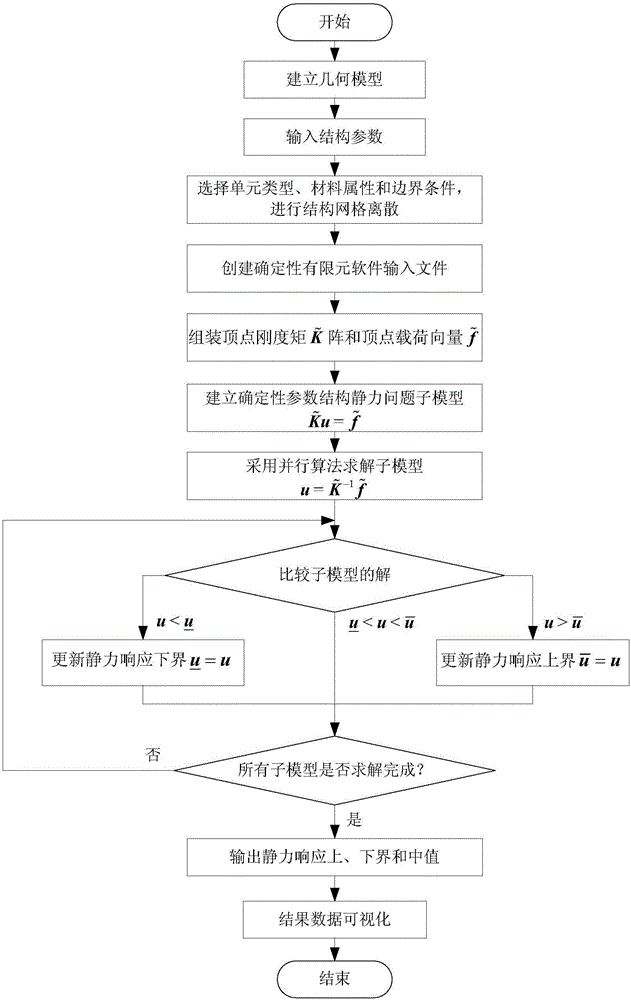
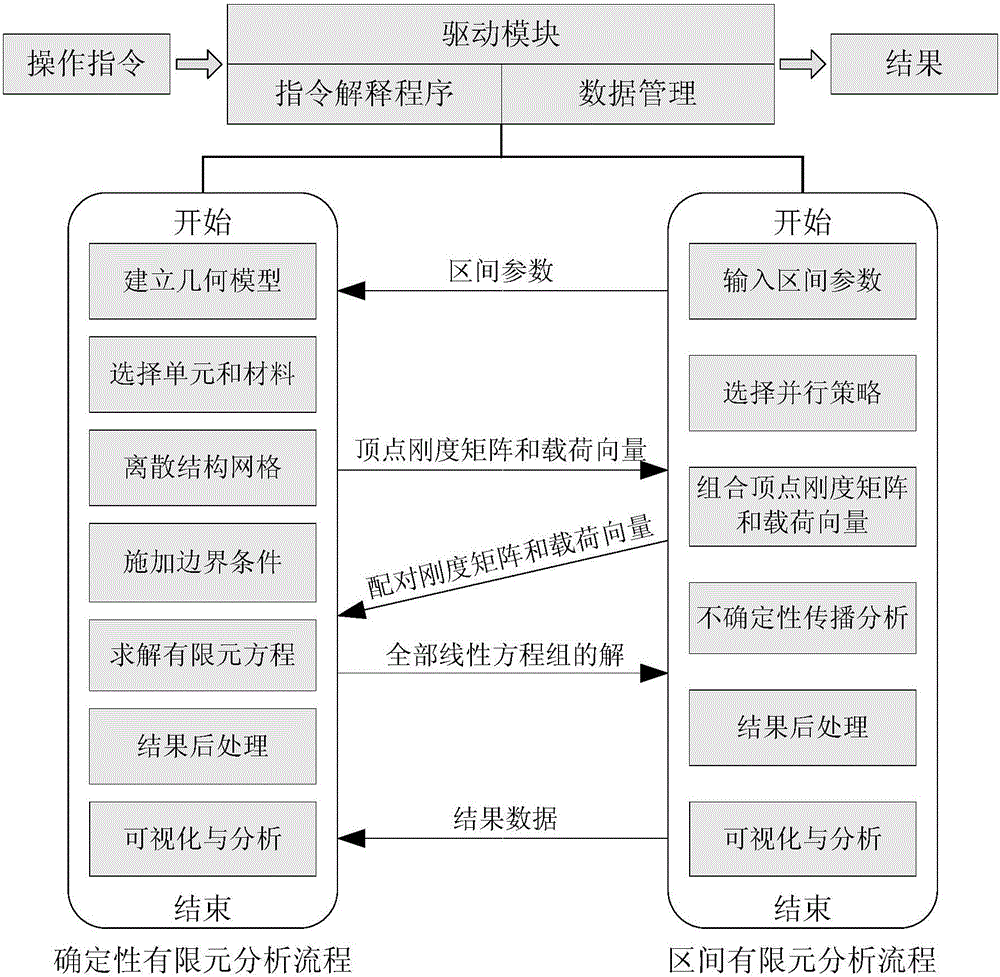
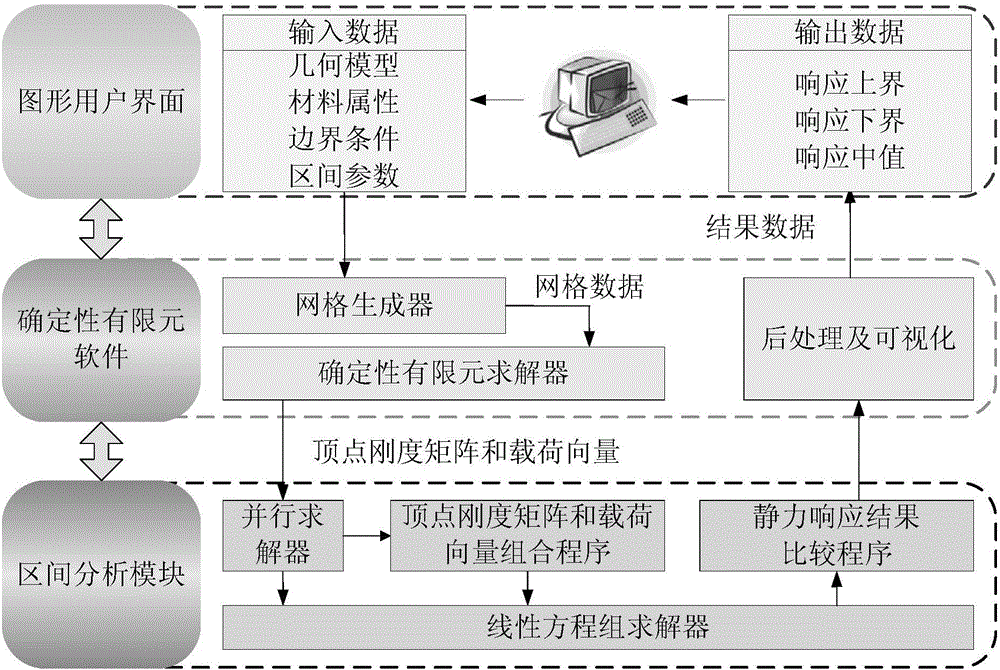
Method for applying deterministic finite element software to analysis of simple or large-size complicated structure containing interval parameters
ActiveCN106021824ASolve problemsMeet the practical needs of uncertainty analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStructure analysisStructural geometry
The invention discloses a method for applying deterministic finite element software to the analysis of a simple or large-size complicated structure containing interval parameters. The method for applying the deterministic finite element software to the analysis of the simple or large-size complicated structure containing the interval parameters comprises the following steps of (1), establishing the geometric model of the structure; (2), inputting the interval parameters of the structure; (3), selecting a unit type, a material attribute and a boundary condition, and carrying out grid discretization on the structure; (4), getting back data in steps (2) and (3) to construct an input file of the deterministic finite element software; (5), running the deterministic finite element software to generate a vertex stiffness matrix and a vertex load vector; (6), converting the static problem of the structure containing the interval parameters into a series of sub-models of the static problem of a structure containing deterministic parameters according to a vertex solution theorem; (7), solving the sub-models by adopting a parallel algorithm, so as to obtain structural static responses of all the sub-models; (8), carrying out post processing on a result to obtain the upper bounds, the lower bounds and the mid-values of the structural static responses, and carrying out result visualization as required. By using the method for applying the deterministic finite element software to the analysis of the simple or large-size complicated structure containing the interval parameters, a succinct and effective method is provided for solving the interval analysis of the complicated structure.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and sensor arrangement for load measurement on rolling element bearing based on model deformation
ActiveUS20070143039A1Improve measurement result qualityMeasurement qualityMachine part testingRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingEngineering
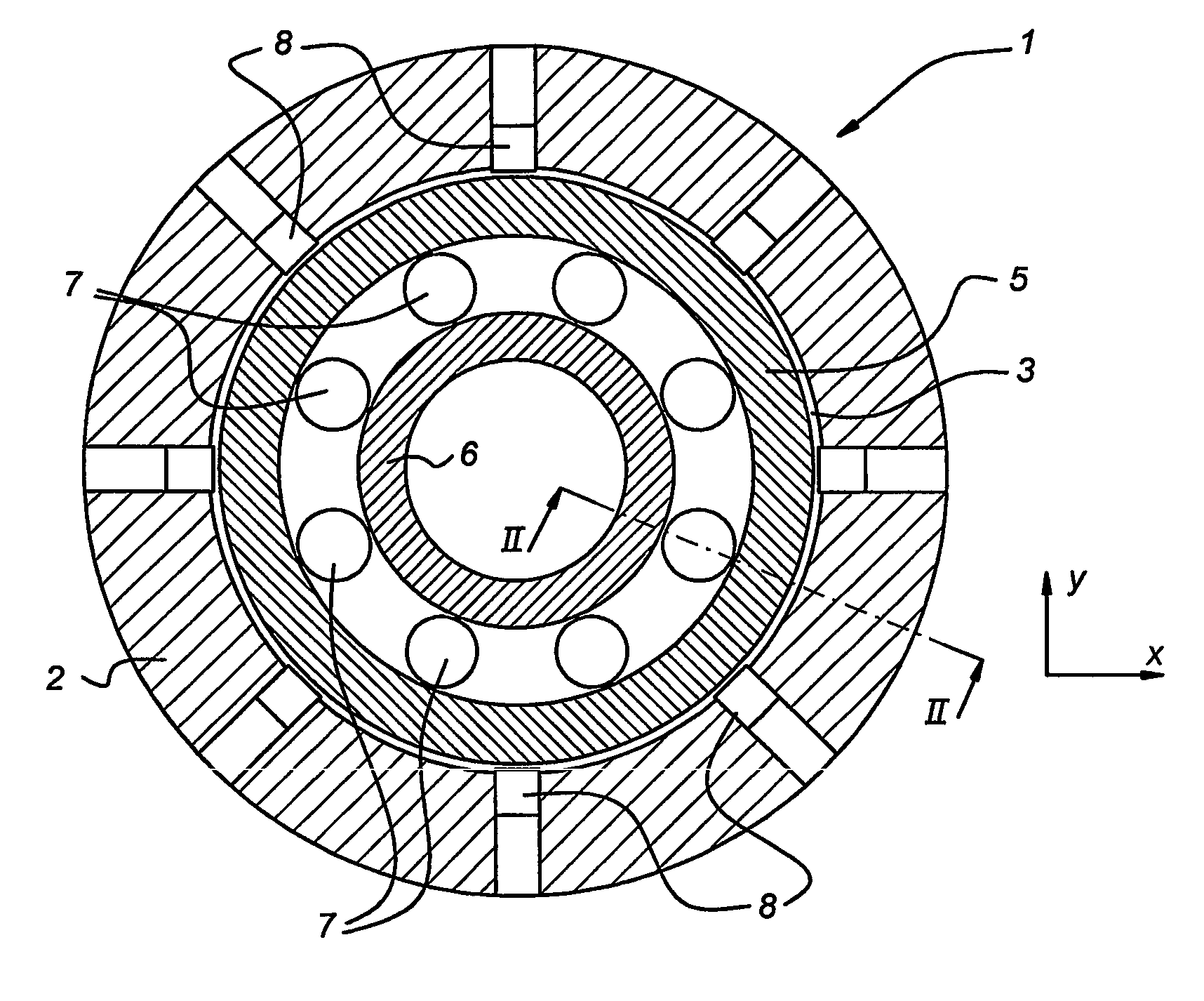
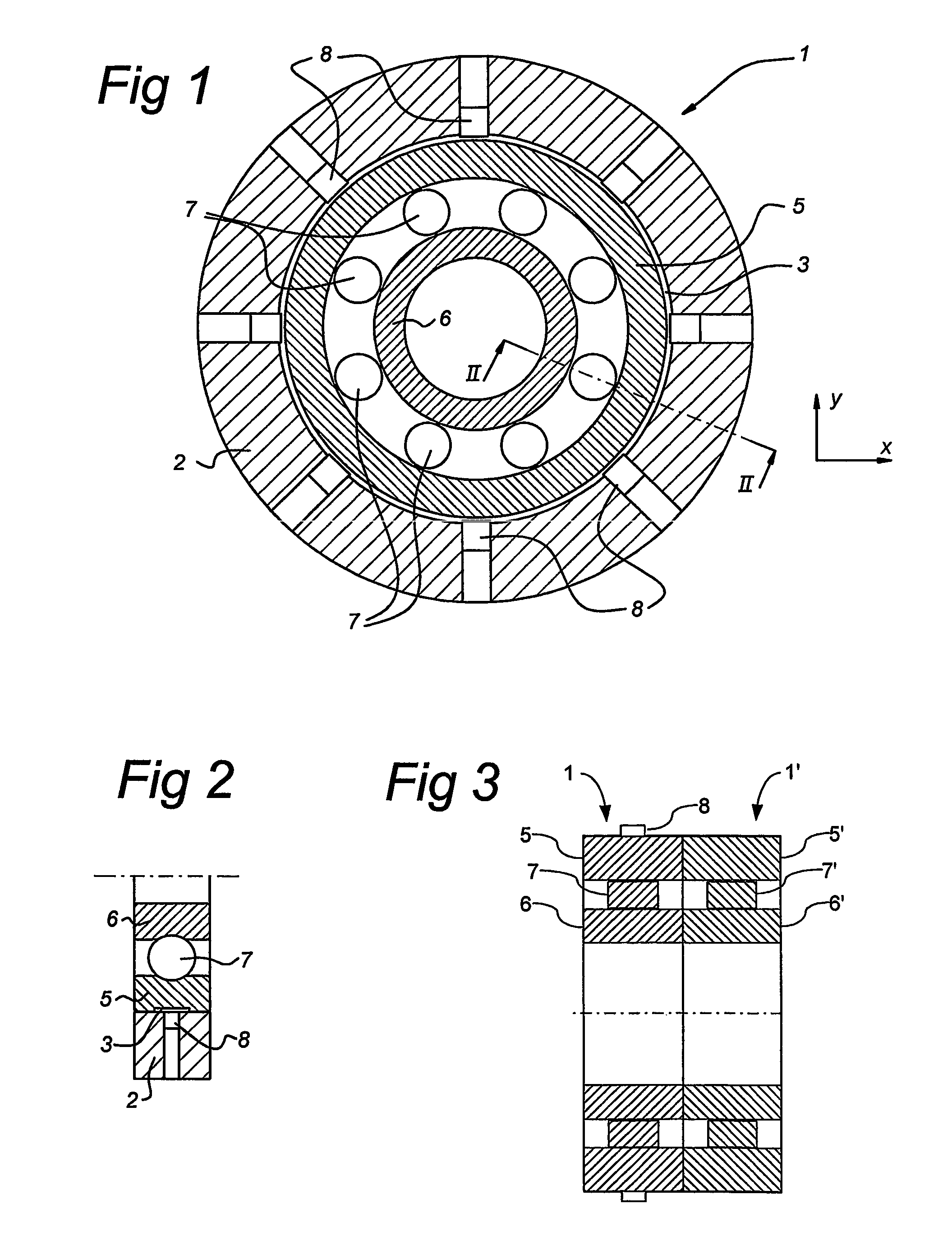
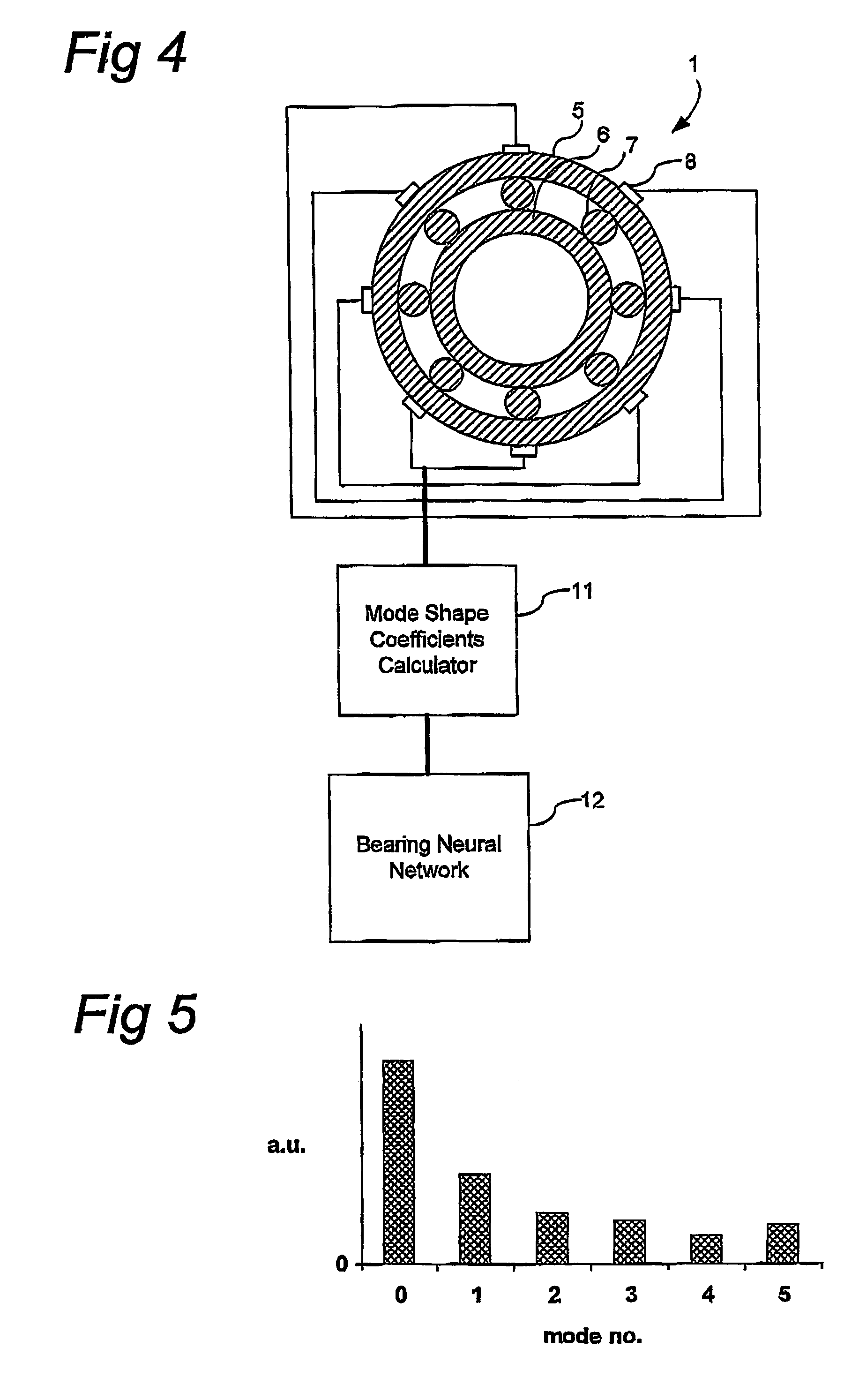
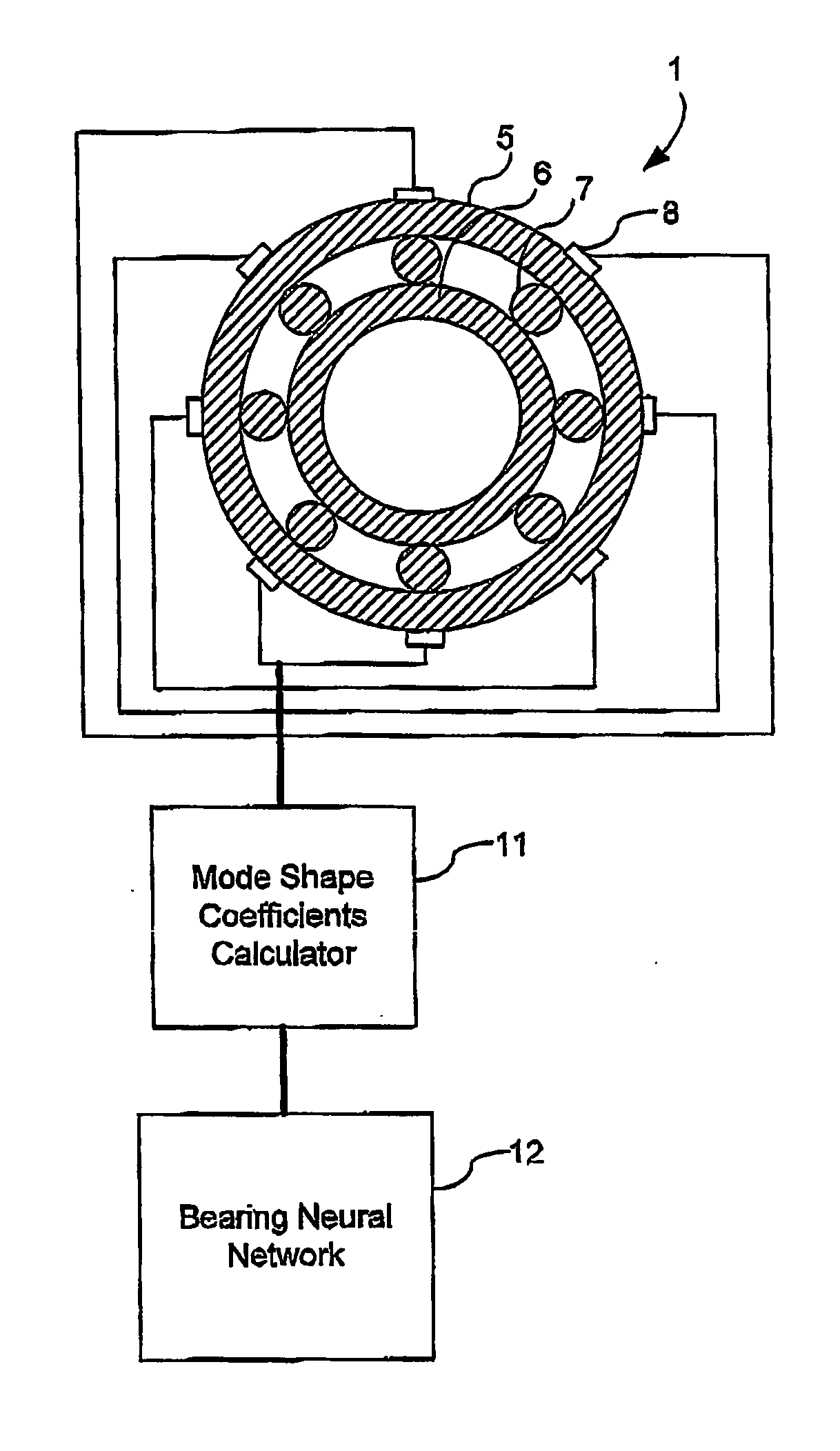
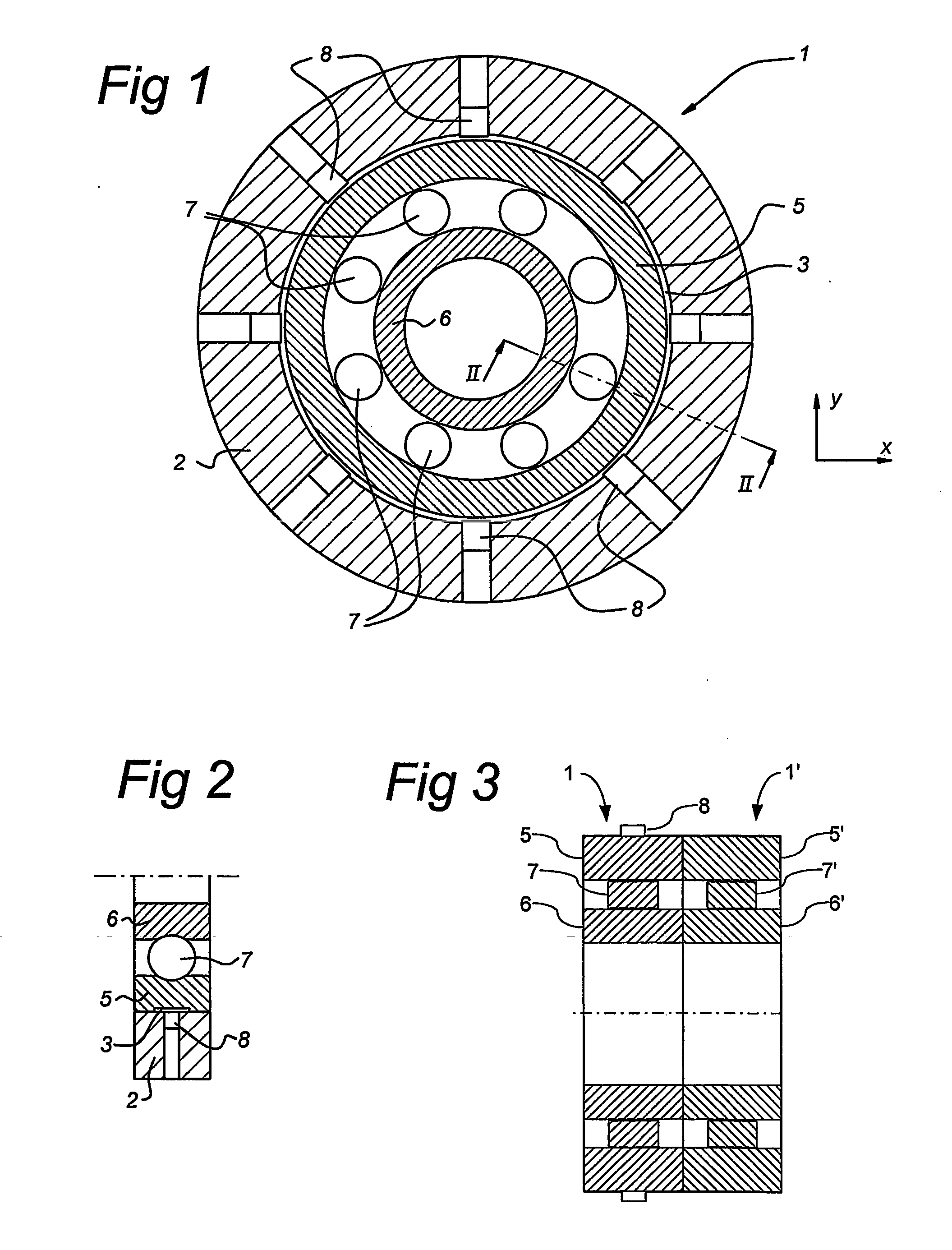
Method and sensor arrangement for determining a load vector acting on a rolling element bearing (1) in operation. A plurality of N sensors (8) are provided which measure displacement and / or strain for determining displacement and / or strain in one of the elements (5, 6, 7) of the rolling element bearing (1). Furthermore, a mode shape coefficients calculator (11) is provided, connected to the plurality of N sensors (8), for determining a deformation of the element (5, 6, 7) by calculating amplitude and phase of N / 2 Fourier terms representing at least one radial mode shape of the ring shape element (5, 6, 7). Also, a bearing neural network (12) is present, connected to the mode shape coefficients calculator (11), the bearing neural network (12) being trained to provide the load vector on the rolling element bearing (1) from the N / 2 Fourier terms.
Owner:AB SKF
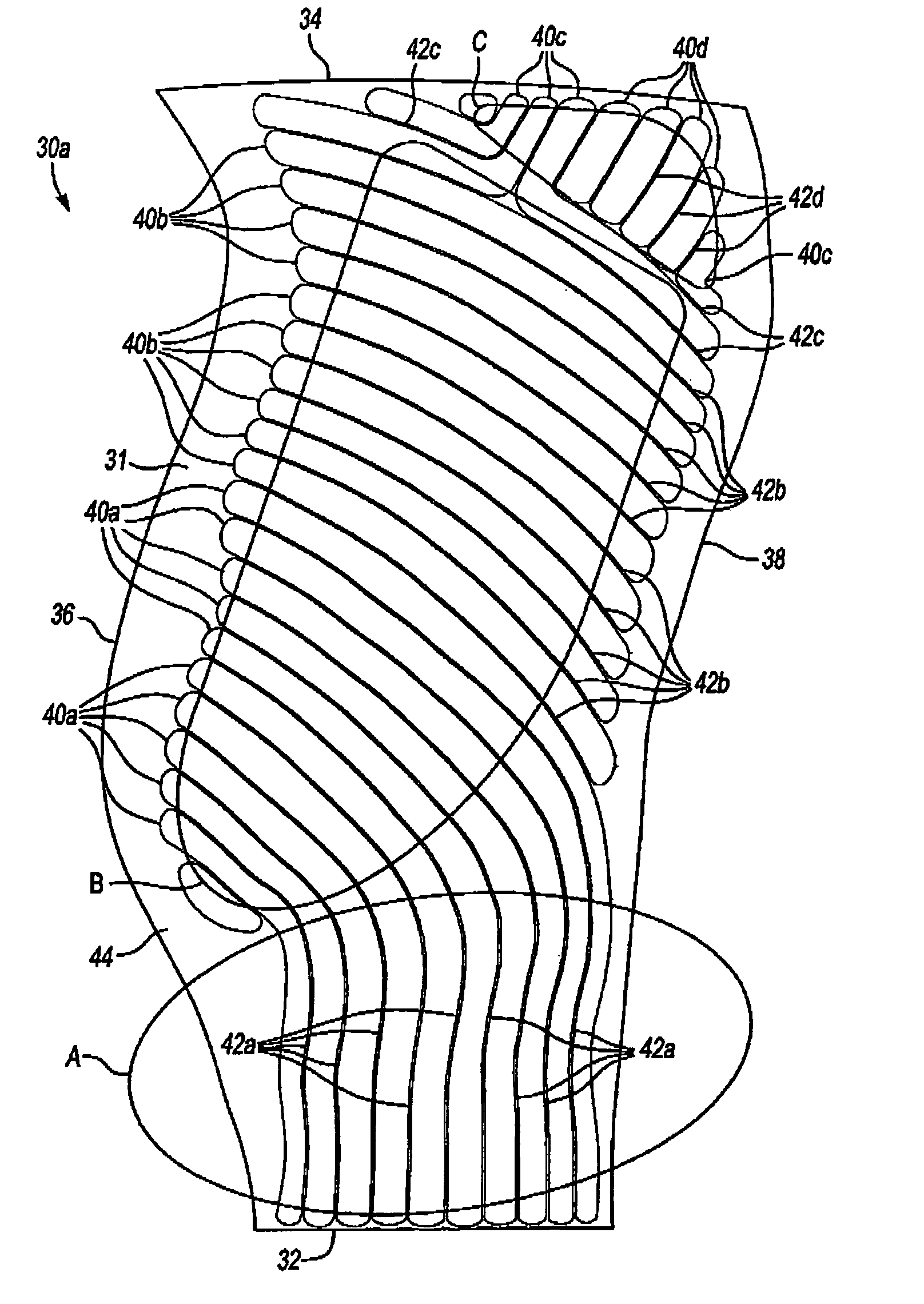
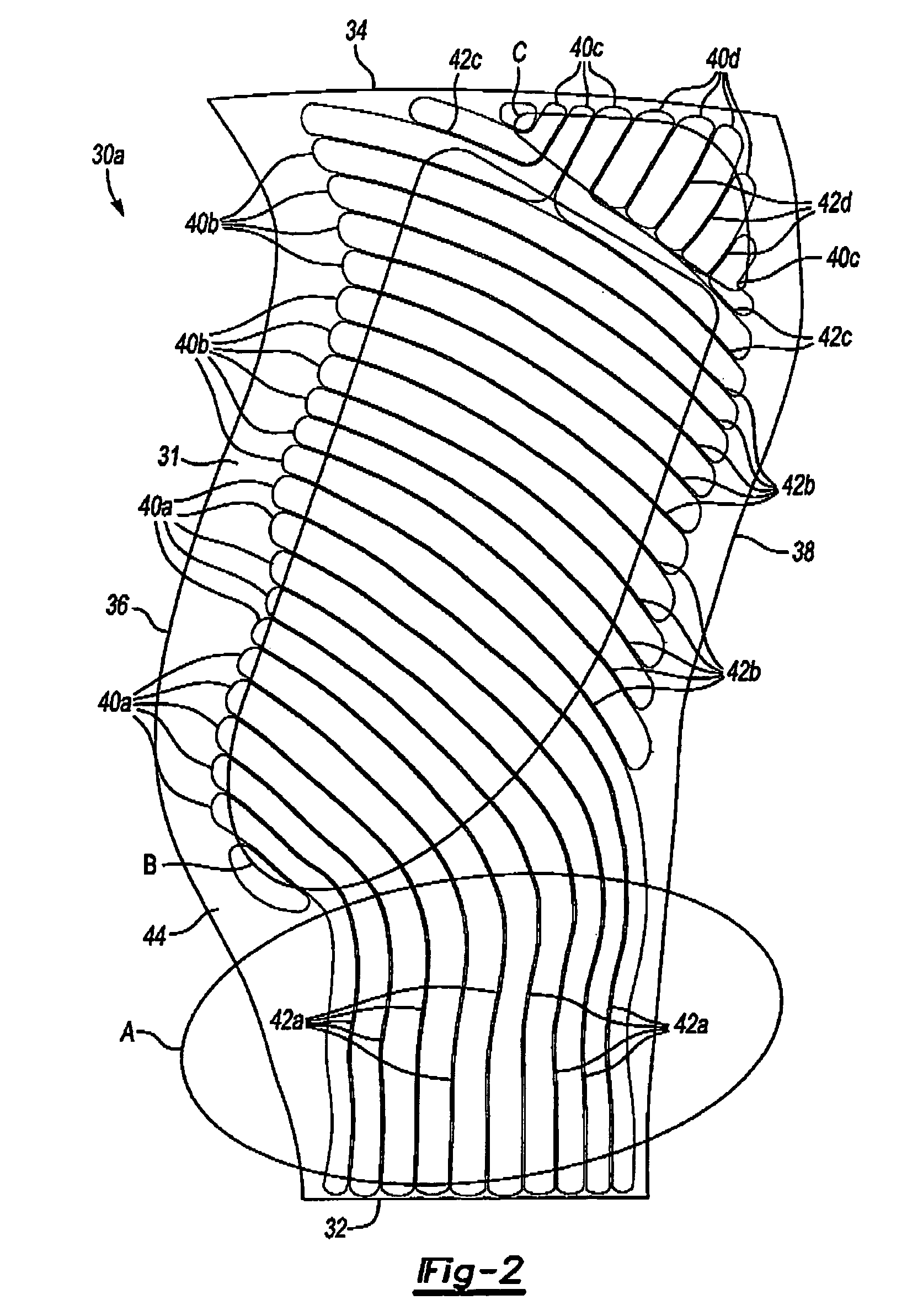
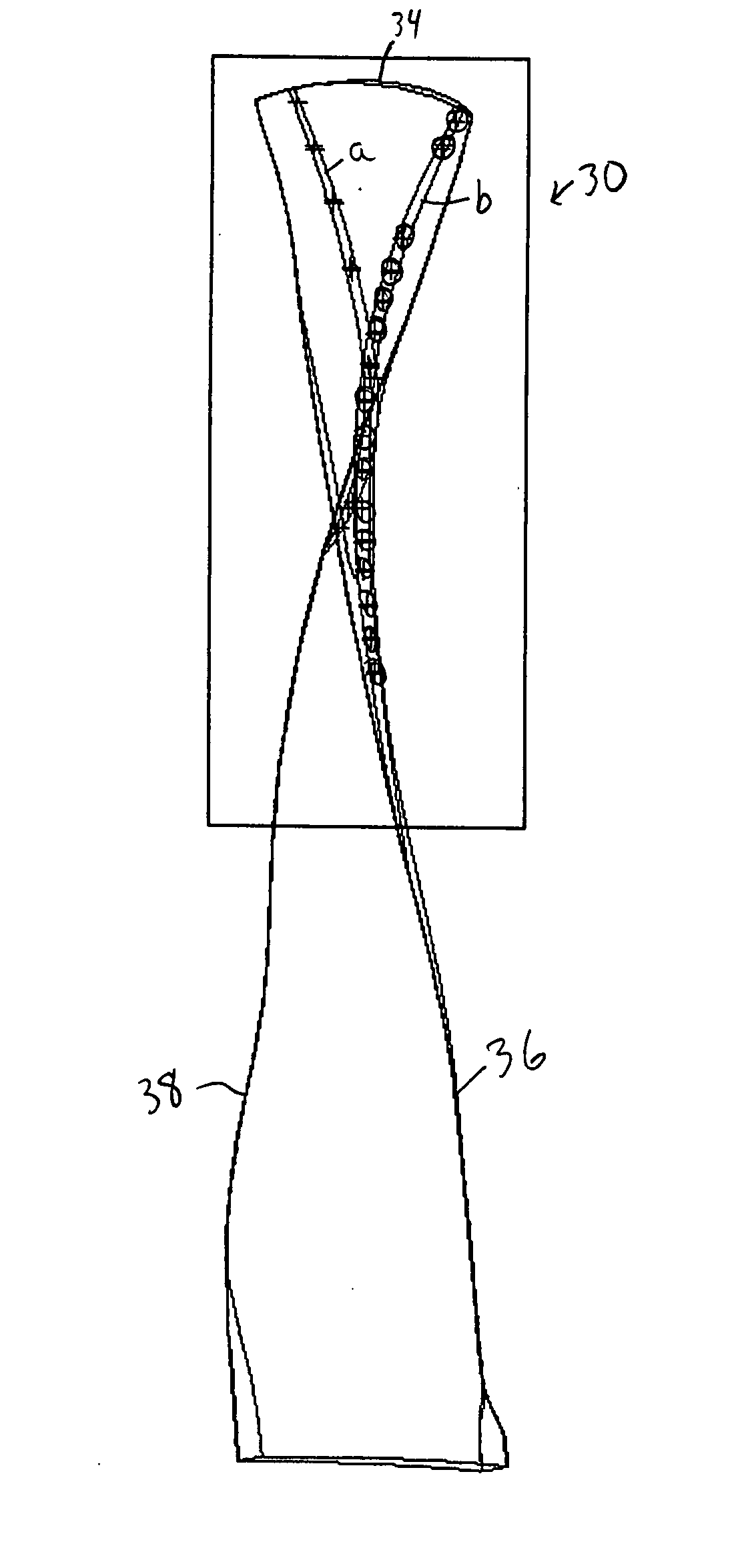
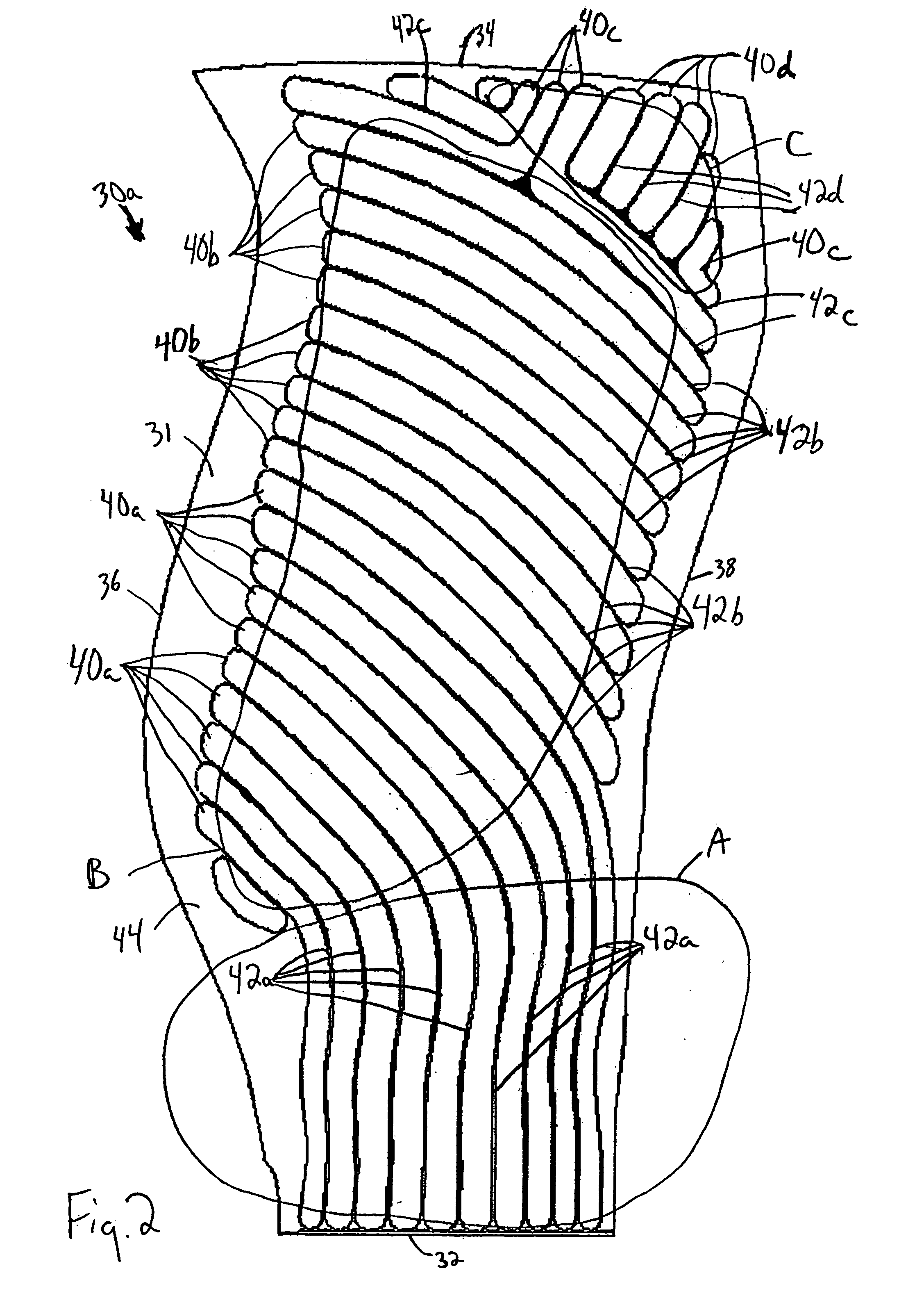
Hollow fan blade for gas turbine engine
A hollow fan blade for turbo fan gas turbine engines is formed of two separate detail halves. Each detail half has a plurality of cavities and ribs machined out to reduce weight. These detail halves are subsequently bonded and given an airfoil shape in the forming operation. The present invention provides a hollow fan blade with internal cavity and rib geometry with improved durability that permits the bonding and forming to be performed without the need for gas pressurization. The ability to form the hollow fan blade of the present invention without gas pressurization is a result of the cavity and rib geometry and the orientation of the ribs. The ribs are tapered and transition into a compound radius of the floor that simulates the classical arch design element. The orientation of the ribs is generally in a parallel plane with the load vector that results from forming loads during the pre-form and final form operations. This orientation provides compressive stress transfer into the ribs and away from the concave and convex skins. The rib spacing is controlled where ribs can not be held in a parallel plane with the load vector.
Owner:RTX CORP
Hollow fan blade for gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20050163620A1Increased durabilityReduce manufacturing costPropellersRotary propellersEngineeringFan blade
A hollow fan blade for turbo fan gas turbine engines is formed of two separate detail halves. Each detail half has a plurality of cavities and ribs machined out to reduce weight. These detail halves are subsequently bonded and given an airfoil shape in the forming operation. The present invention provides a hollow fan blade with internal cavity and rib geometry with improved durability that permits the bonding and forming to be performed without the need for gas pressurization. The ability to form the hollow fan blade of the present invention without gas pressurization is a result of the cavity and rib geometry and the orientation of the ribs. The ribs are tapered and transition into a compound radius of the floor that simulates the classical arch design element. The orientation of the ribs is generally in a parallel plane with the load vector that results from forming loads during the pre-form and final form operations. This orientation provides compressive stress transfer into the ribs and away from the concave and convex skins. The rib spacing is controlled where ribs can not be held in a parallel plane with the load vector.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
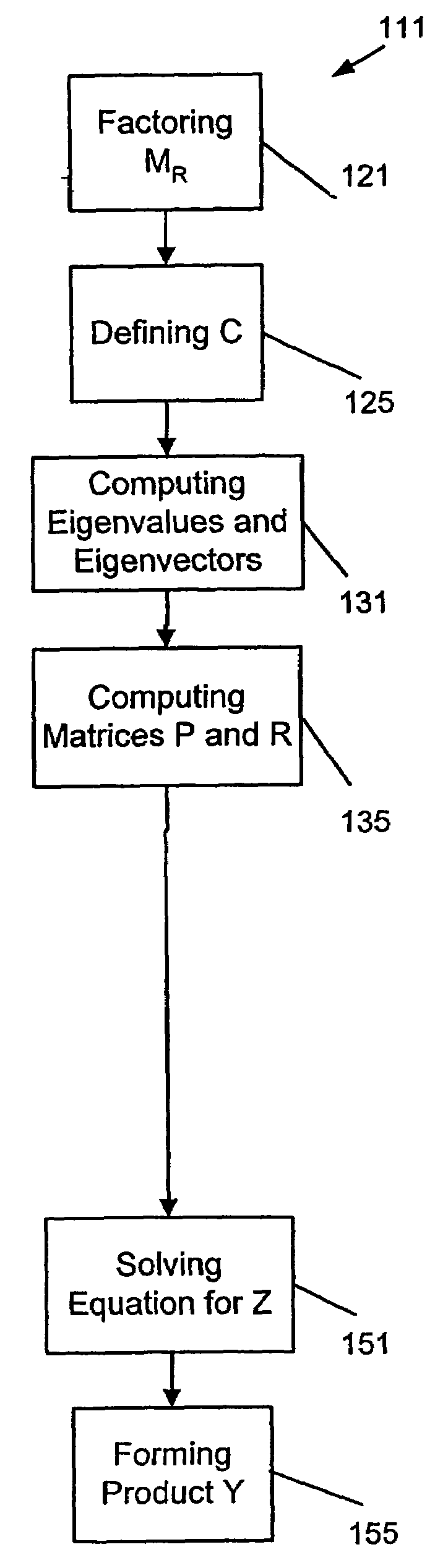
Damped frequency response apparatus, systems, and methods
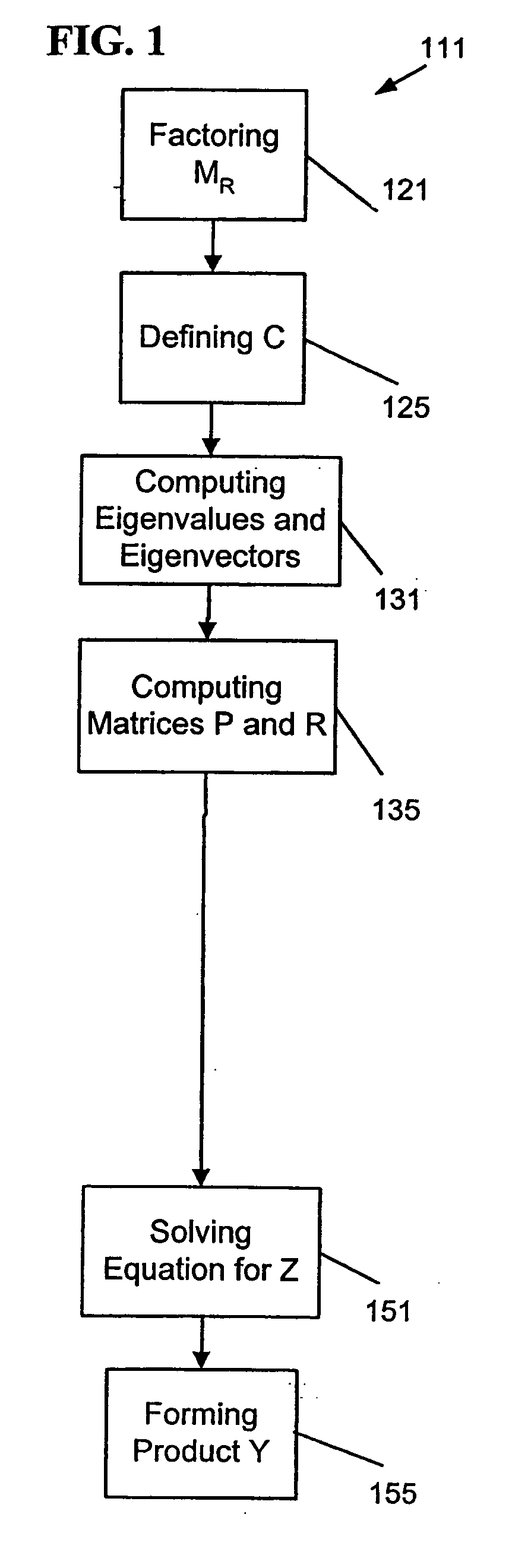
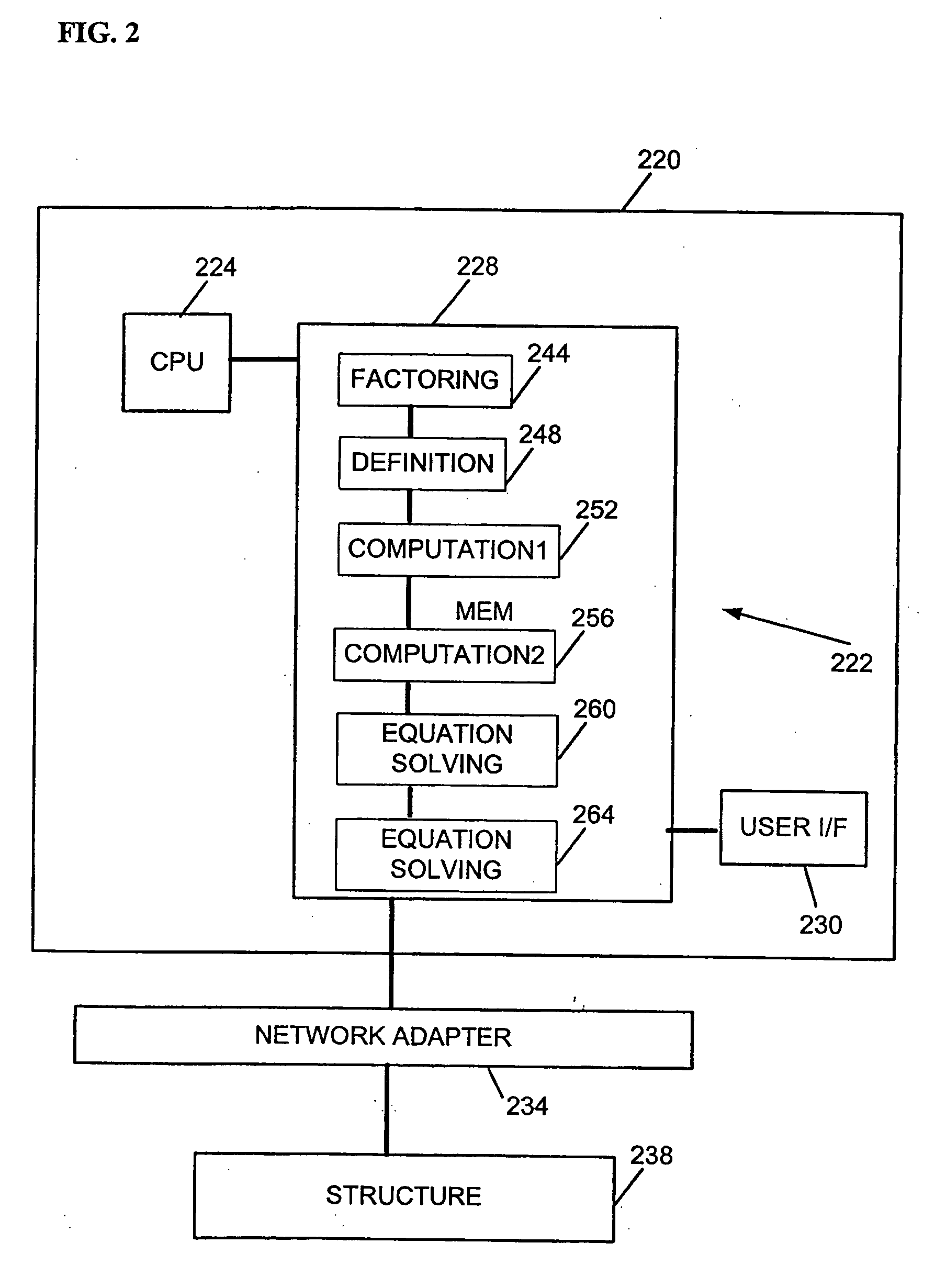
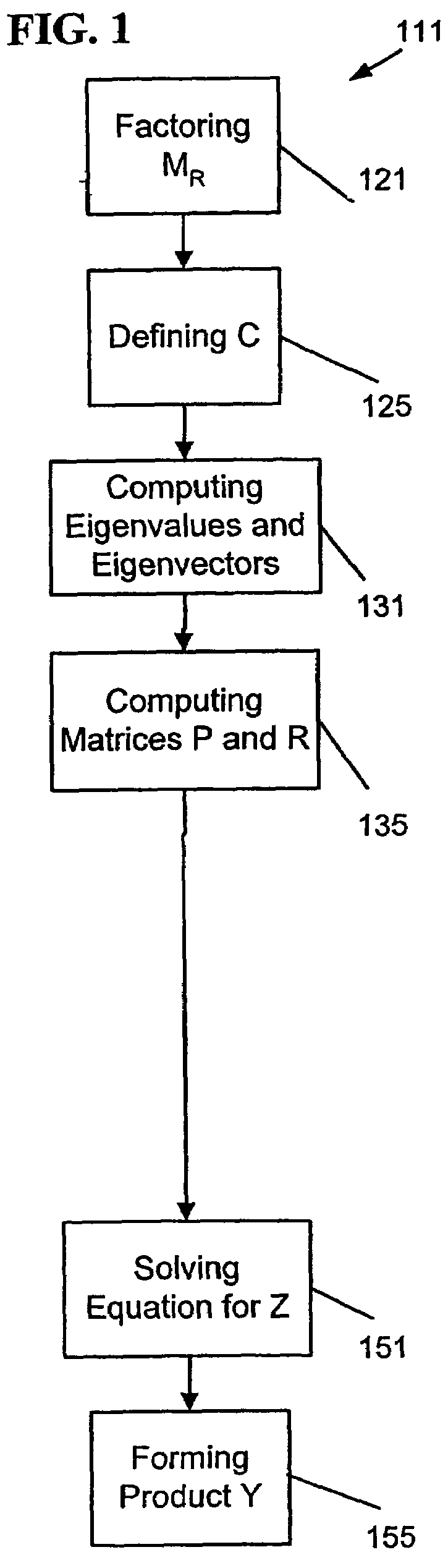
ActiveUS20050171742A1Vibration measurement in solidsForce measurementEigenvalues and eigenvectorsProduct formation
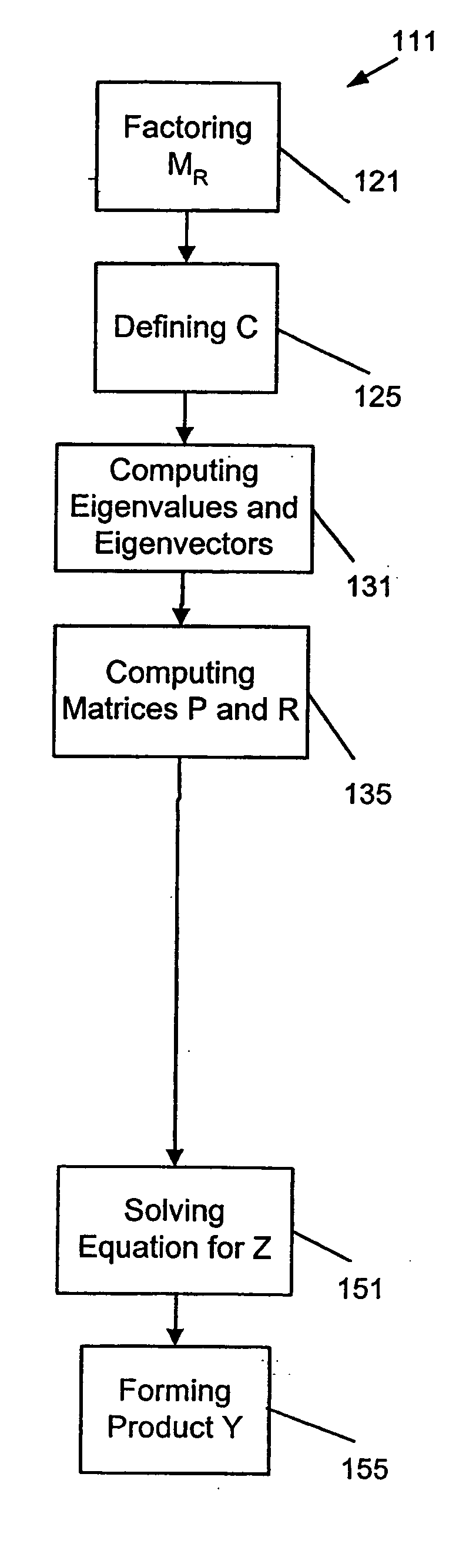
An apparatus, system, and method may operate to solve a first equation associated with a structure of the form {−ω2MR+iωBR+[(1+iγ)KR+i(K4R)]}Y=FR. The apparatus and system may include a definition module to define an intermediate matrix C=(1+iγ)LM−1KRLM−T+iLM−1K4RLM−T, a first computation module to compute a plurality of eigenvalues and eigenvectors for a second equation CΦC=ΦCΛC, a second computation module to compute a matrix P=ΦCTLM−1UR and a matrix R=VRTLM−TΦC, an equation solving module to solve a third equation of the form (D(ω)+PQ(ω)R)Z=ΦCTLM−1FR for Z, wherein D(ω)=−ω2I+ΛC and Q(ω)=iωΣR, and a product formation module to form a product Y=LM−TΦCZ, wherein the product Y is a matrix having a plurality of vectors corresponding to the plurality of load vectors acting on the structure and included in the matrix F.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
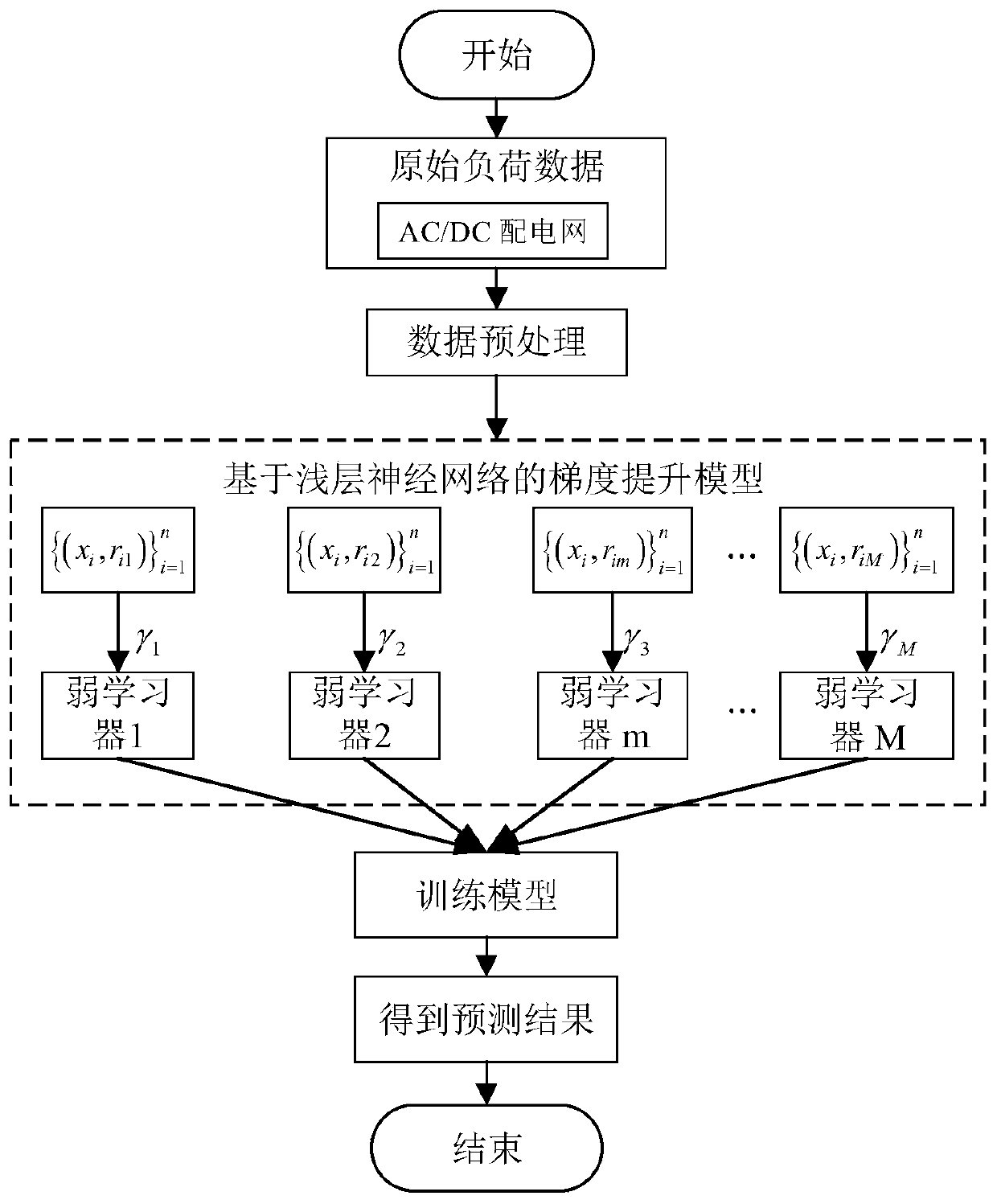
Short-term load prediction method based on GBDT (gradient boosting decision tree)
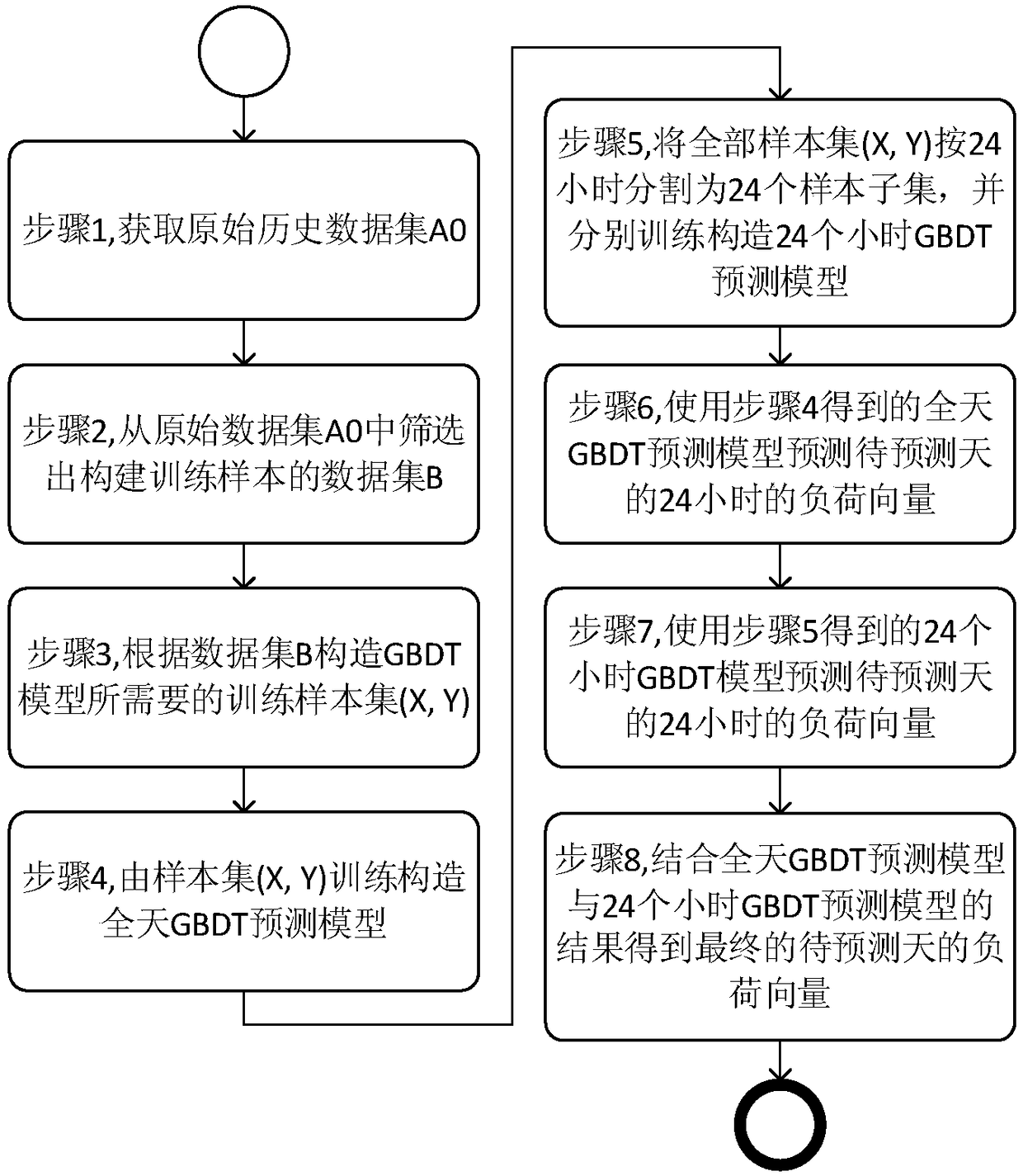
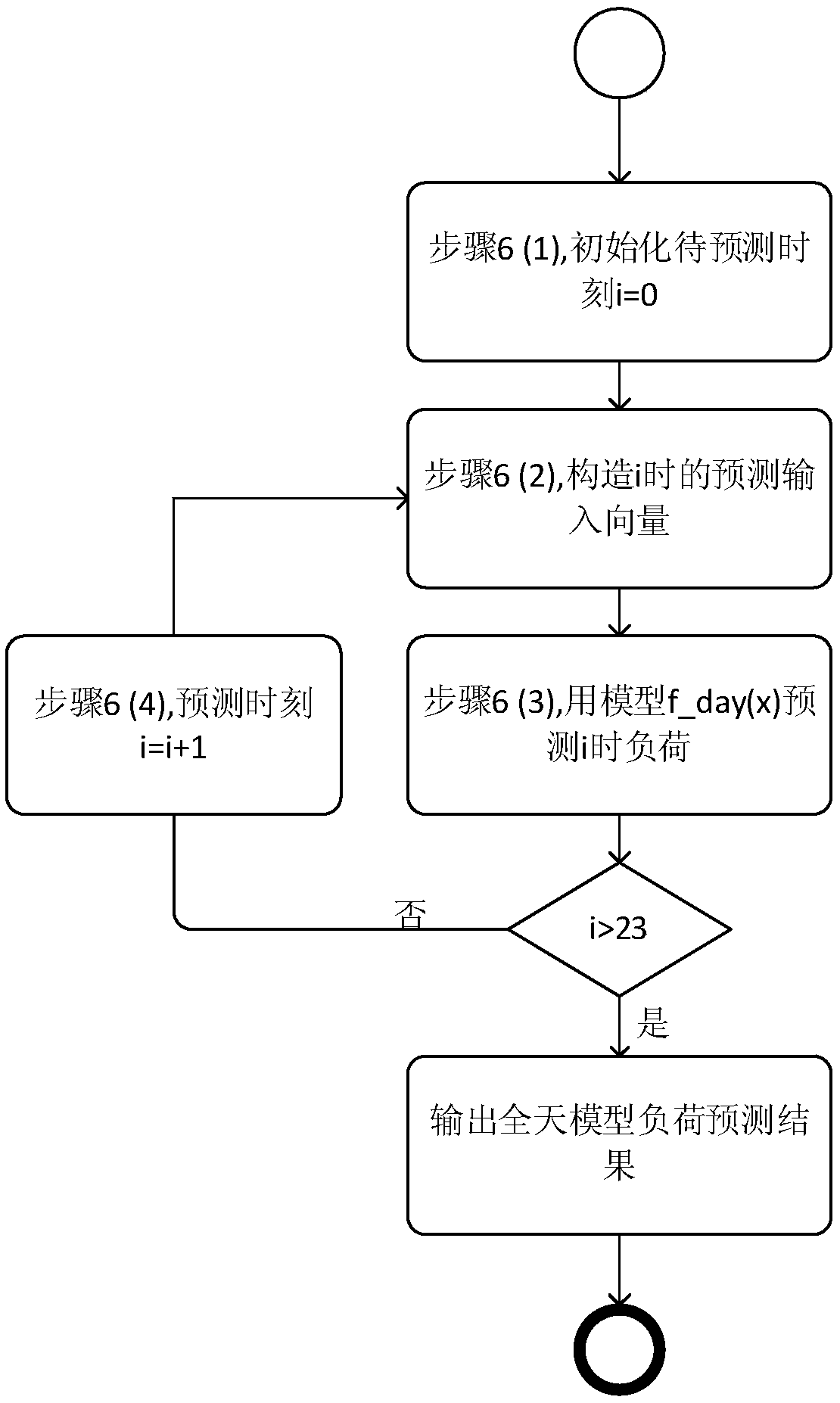
ActiveCN108539738AHigh precisionGeneralization error is controllableLoad forecast in ac networkData setOriginal data
An embodiment of the invention discloses a short-term load prediction method based on a GBDT (gradient boosting decision tree). The method comprises the following steps: acquiring historical load dataof N days before the prediction-waiting day, and forming an original data set A0; screening a data set B for constructing training samples from the original data set A0; constructing total sample set(X, Y) required for constructing a GBDT prediction model by the data set B; training and constructing a whole-day GBDT prediction model by the total sample set (X, Y), and prediction whole-day load vector of the prediction-waiting day according to the whole-day GBDT prediction model; segmenting the total sample set (X, Y) into 24 sample subsets by the hour, training and constructing hour GBDT prediction models respectively, and predicting 24-hour load vectors of the prediction-waiting day according to the hour GBDT prediction models; predicting the final load vector of the prediction-waitingday according to combination of the whole-day load vector and the 24-hour load vectors. The short-term load prediction precision is improved by sufficiently mining characteristics in the historical load data and constructing the different GBDT models.
Owner:国网山东省电力公司营销服务中心(计量中心) +2
System design method for minor fault detection and position of electrical traction system
ActiveCN108490923AMeet real-time requirementsEffective Early Failure DetectionProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringSystems designPerformance index
The invention discloses a system design method for minor fault detection and position of an electrical traction system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing an off-line data model: collecting sensor steady-state operation data of the electrical traction system and carrying out pretreatment on the off-line data; calculating values of a principal component and a residual component in different layers of subspaces of the data obtained after pretreatment and a load vector; determining and calculating a performance index and a probability density function of a principle component analysis method and a fault detection threshold; and 2) on-line fault diagnosis: processing online data; calculating a performance index of the principal component and the residual component in different layers of subspaces; and through the obtained fault detection threshold, constructing a probability matrix and carrying out fault diagnosis through Bayesian reasoning. The method can carry outeffective multi-feature description on tiny signals of an electrical drive device before occurrence of a fault, and can also carry out real-time online fault diagnosis under the condition that the model and parameters of the electrical drive system are unknown.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
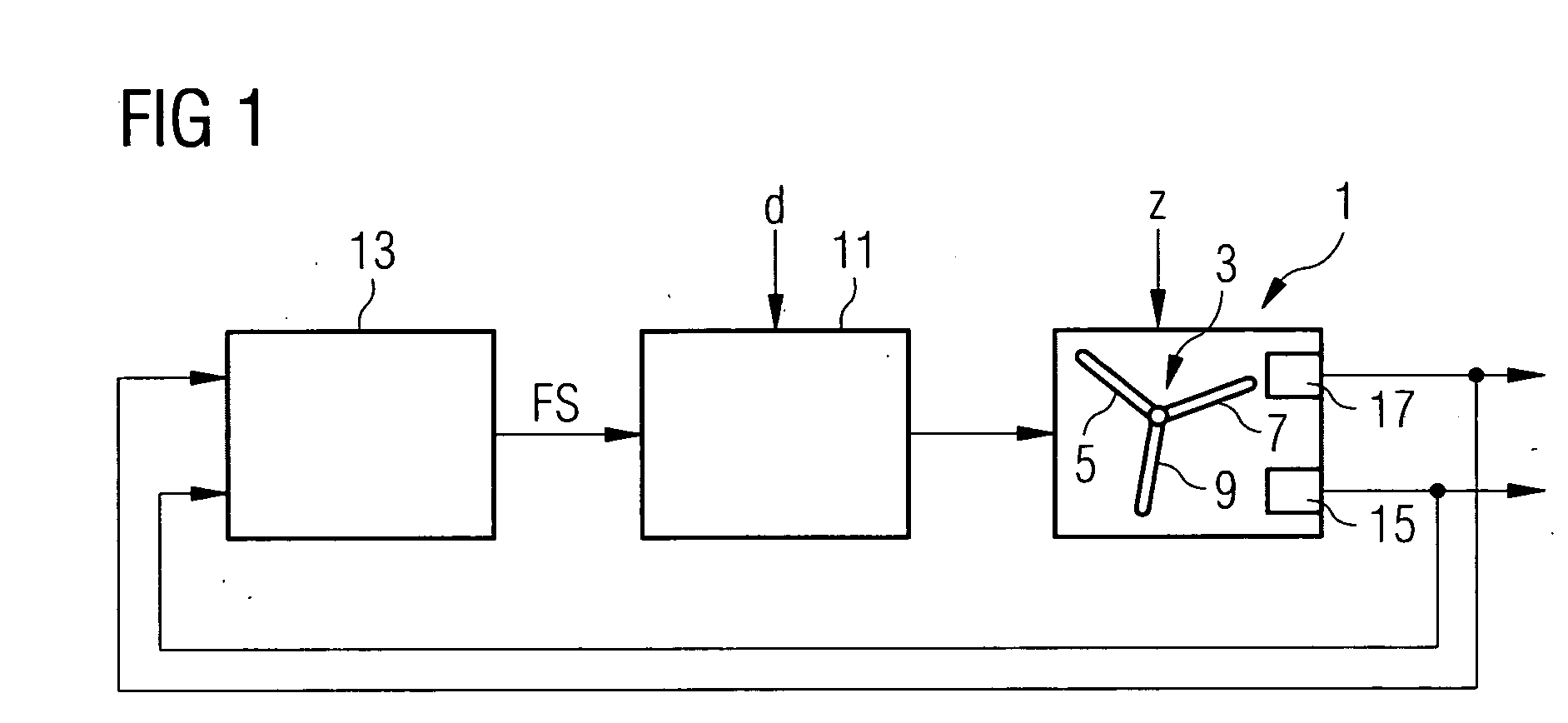
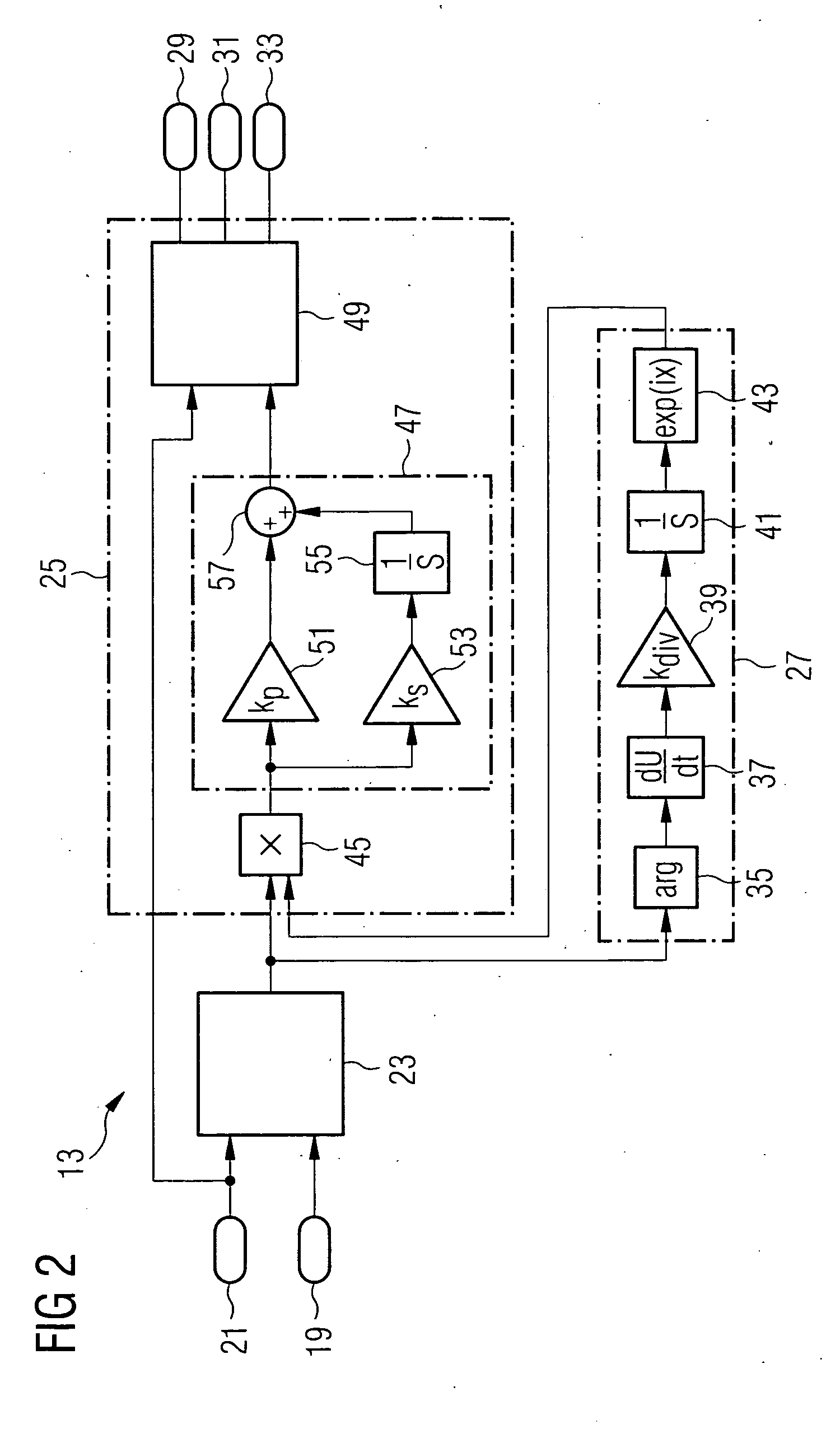
Method and device for controlling load reduction for a wind turbine rotor
A method for controlling load reduction for a wind turbine rotor with rotor blades comprising an aerodynamic active element responsive to a control signal for modifying its setting is provided. The loads acting on the rotor blades in relation to the rotor's azimuth are detected and individual control signals based on a PI control system are established. Each individual control signal is a complex number containing an amplitude defining the degree of modification of the respective setting and an angle defining the phase of the modification of the respective setting with respect to the rotor's azimuth. The angle of the complex number is corrected by a phase correction factor. The elements are provided with the individual control signals. The input to the PI-control system is a complex load vector.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
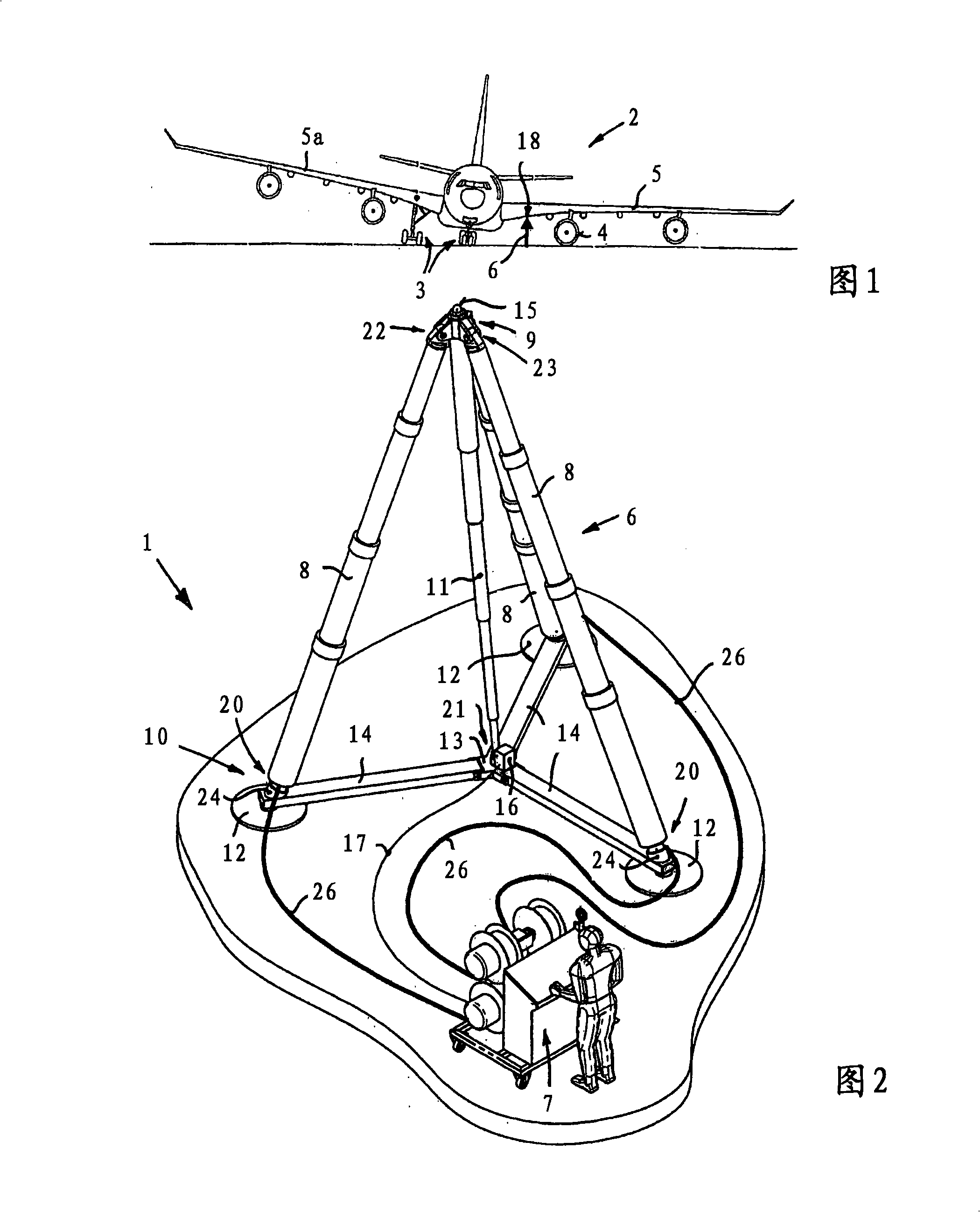
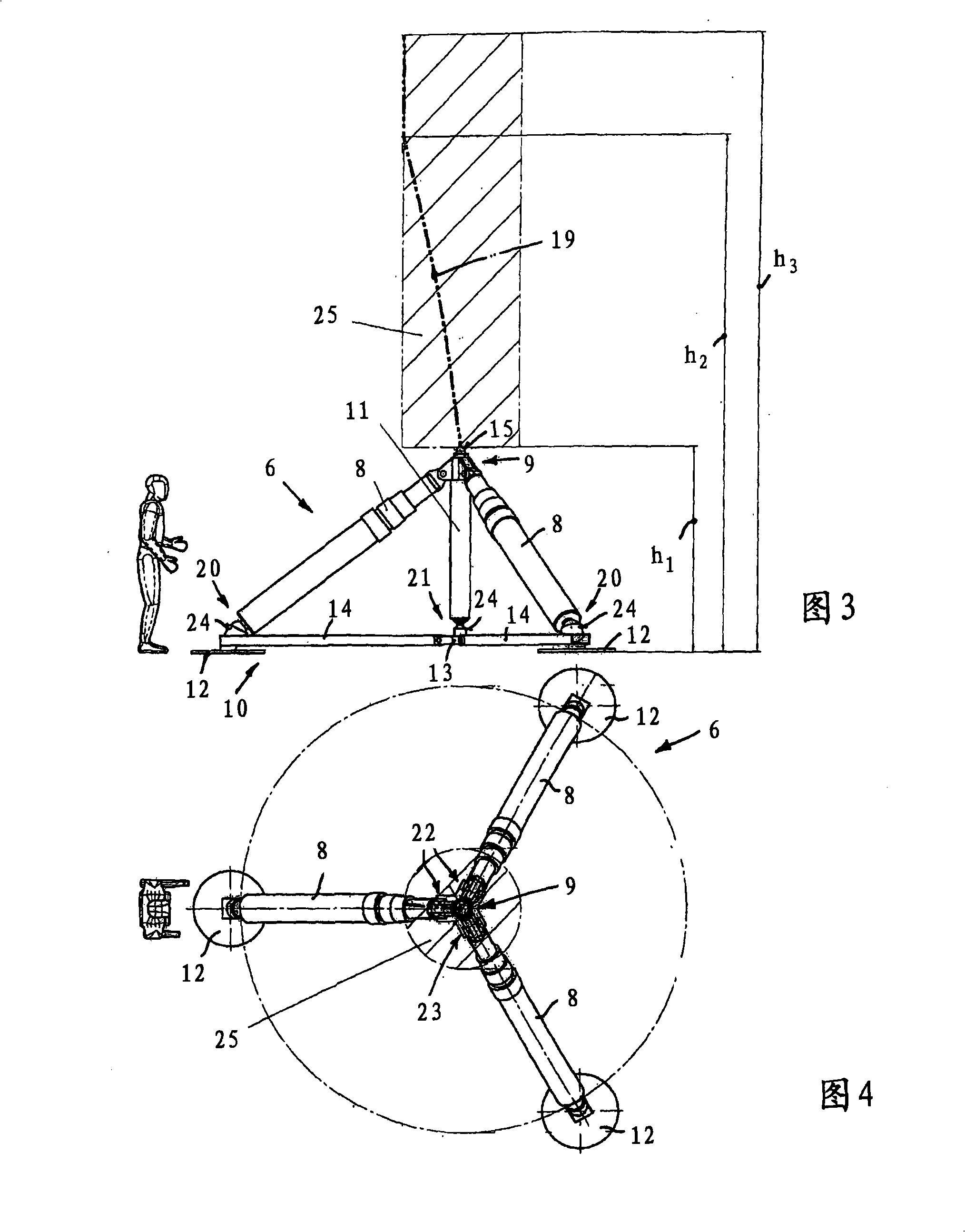
Lifting system
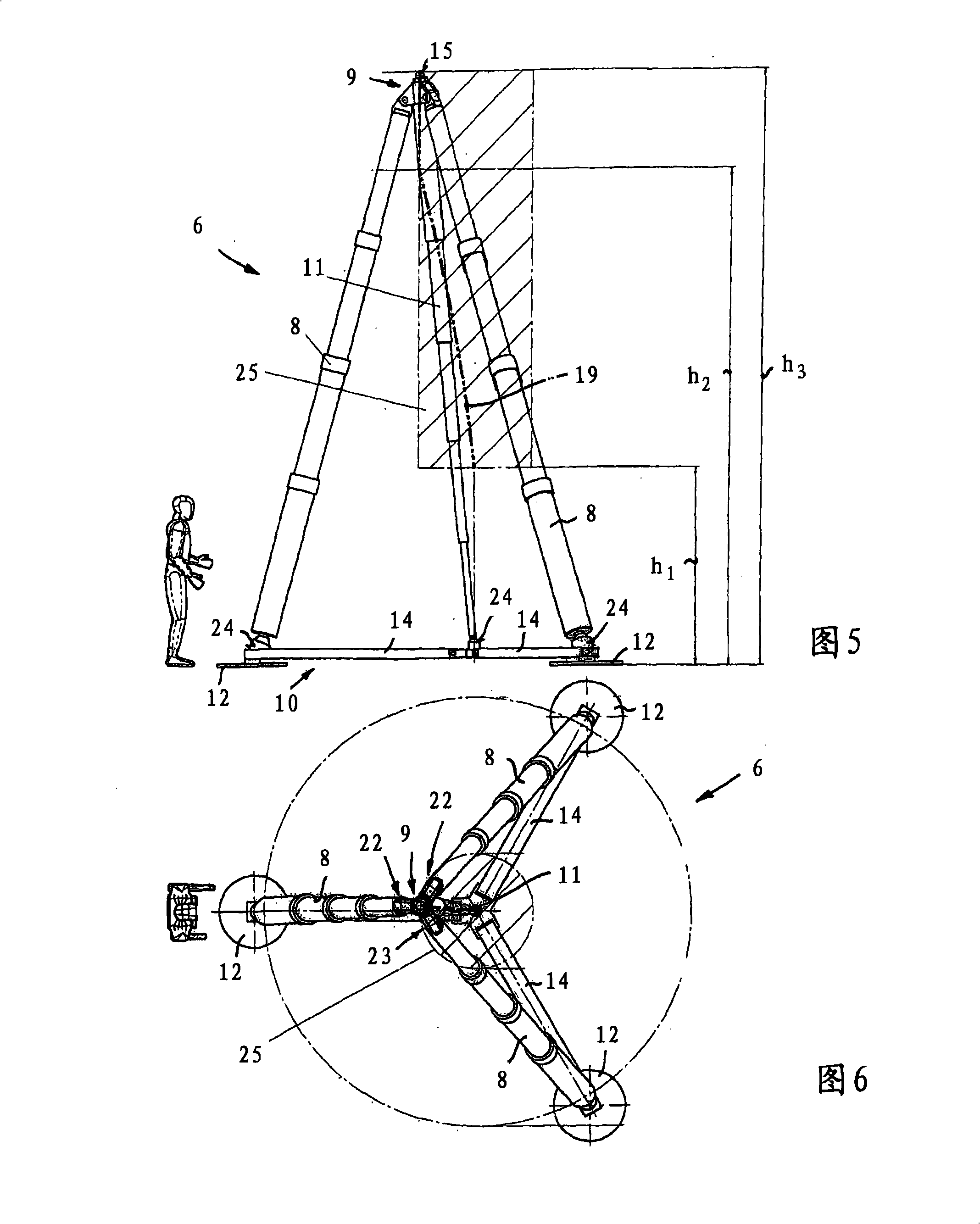
InactiveCN101309851AFree positioningLateral force balanceLifting framesGround installationsDisplacement controlMovement control
A lifting system (1) is used for lifting loads, for example for lifting and recovering an aircraft (2) following an accident, and has a lift (6) which can be positioned underneath a load, in particular underneath a mainplane (5) of an aircraft. The lift (6) has at least three lifting cylinders (8) or similar lifting elements and a docking head (9) for coupling to a load holding point. A measurement system is provided in order to detect the position of the docking head (9) and to measure the load vector that occurs at the docking head (9). A control device is connected to the measurement system, for mutually independent, load-controlled or movement-controlled confirmation of the individual lifting cylinder drives.
Owner:海德罗器械(升降机)有限及两合公司
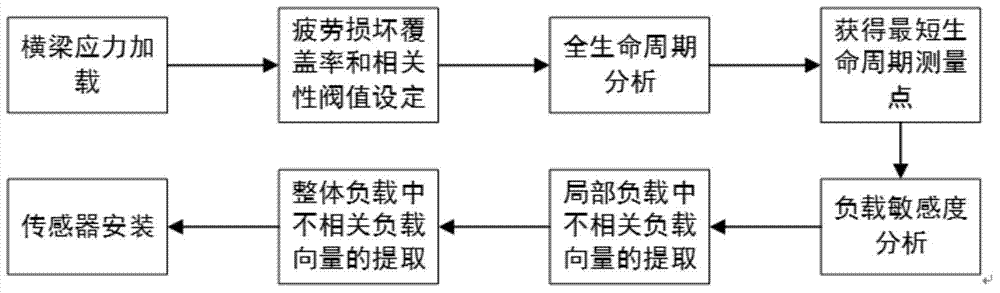
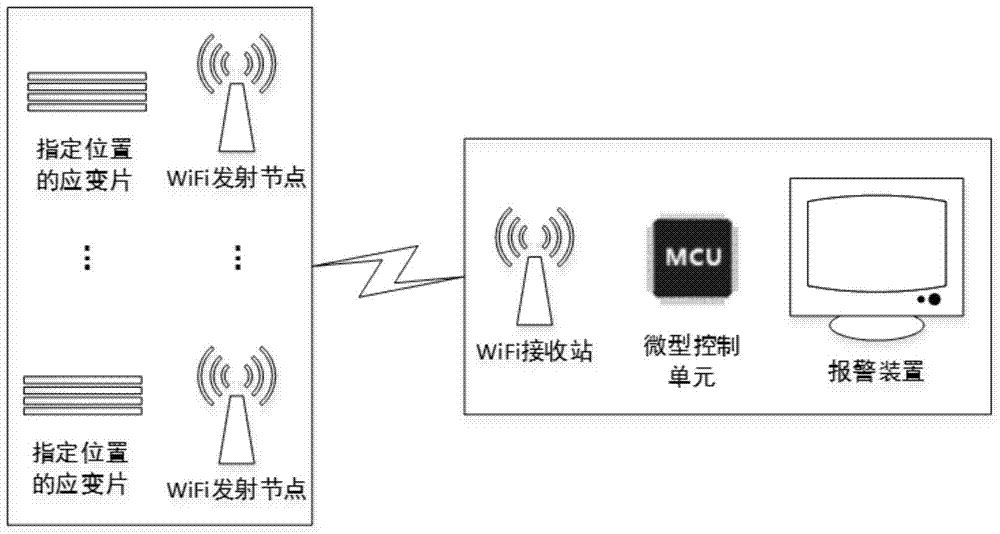
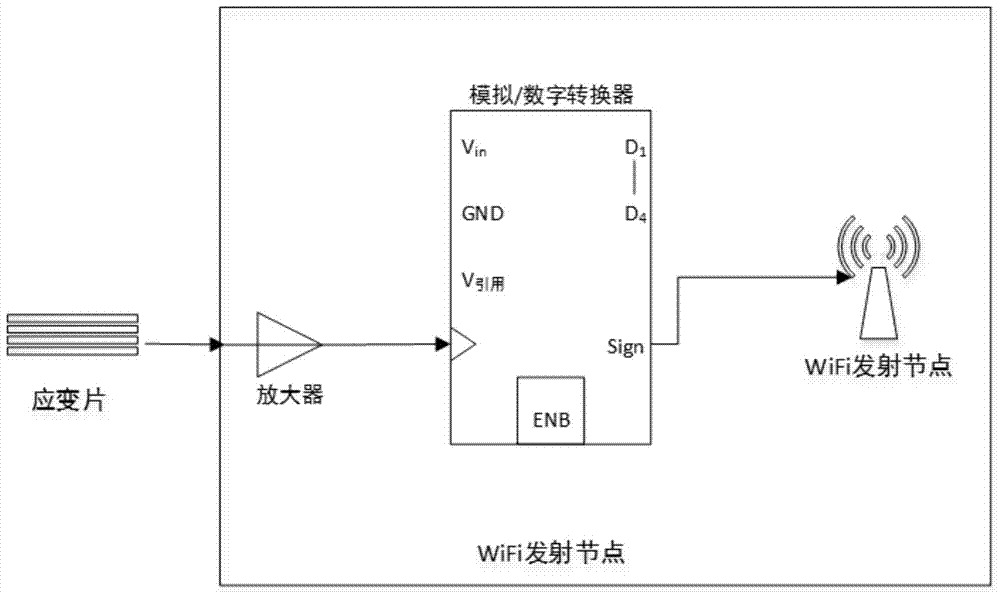
Online crane beam stress monitoring and fault diagnosis system and method
InactiveCN104748960AReal-time monitoring of dynamic stress stateNo fatigue damageMachine part testingTransmission systemsFatigue damageEngineering
The invention provides an online crane beam stress monitoring and fault diagnosis system which comprises a plurality of stress sensors and wireless transmitting nodes which are all arranged on a crane beam, a wireless receiving station and a remote microprocessor. The stress sensors transmit collected stress signals to the corresponding wireless transmitting nodes the wireless transmitting nodes transmit the stress signals to the wireless receiving station, the wireless receiving station then transmits the stress signals to the remote microprocessor, and the stress signals collected by the stress sensors are compared with corresponding stress thresholds; position distribution of the stress sensors are acquired through rain-flow counting method fatigue life analysis, load sensitivity analysis and independent fatigue damage model based uncorrelated load vectors under local load and overall load. Implicit leak detection of the crane beam under the condition of variable load of width of a complicated production field and signal interference and attenuation during wire transmission are avoided, fatigue damage is ensured not to occur to the beam under the conditions of full life circle and full load, and safe production is guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
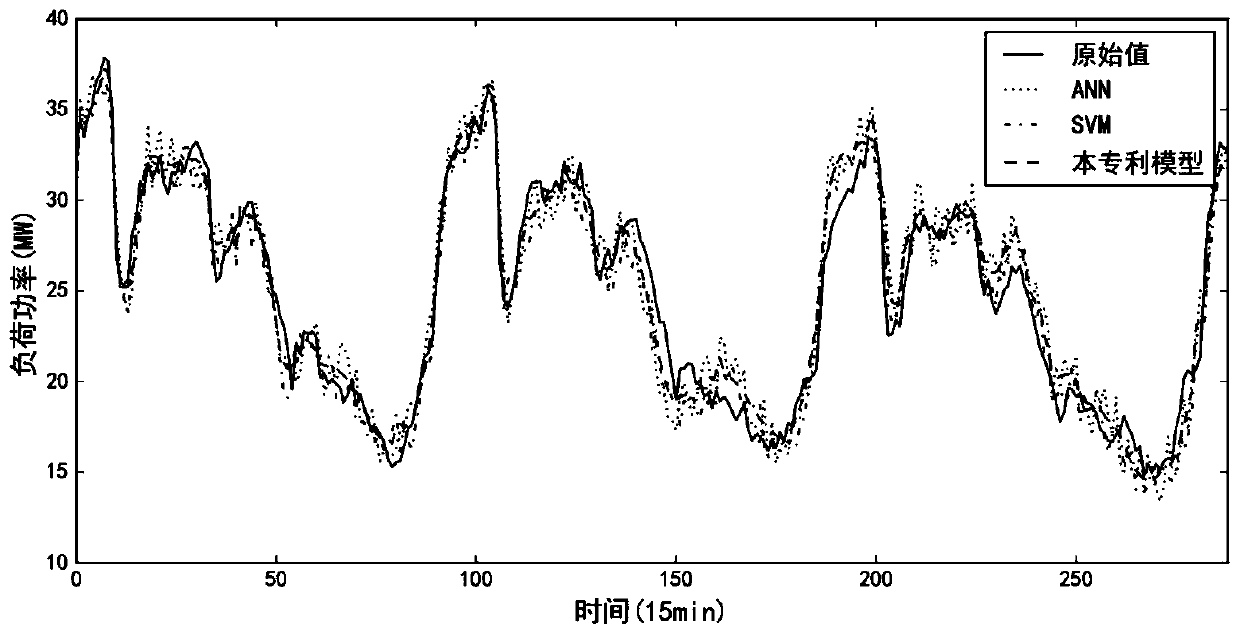
AC-DC power distribution network load prediction method based on ensemble learning
ActiveCN110707763AReduce generalization errorHigh precisionInformation technology support systemAc network circuit arrangementsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses an AC / DC power distribution network load prediction method based on ensemble learning, and the method comprises the steps of carrying out the load data filling and normalization on the original load data, sampling a load sample input vector and a sample label through a sliding time window, and constructing a training data set; establishing a gradient lifting model, settingthe number of weak learners, and establishing a plurality of shallow neural networks to fit the negative gradient of the gradient lifting algorithm to obtain a combined prediction model; and selectinga load vector before a to-be-predicted time point as an input vector by using the sliding time window, and determining a load prediction value in combination with an ensemble learning model. According to the invention, the load prediction is carried out by fusing the strong learners of multiple models, so that the precision of load prediction is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
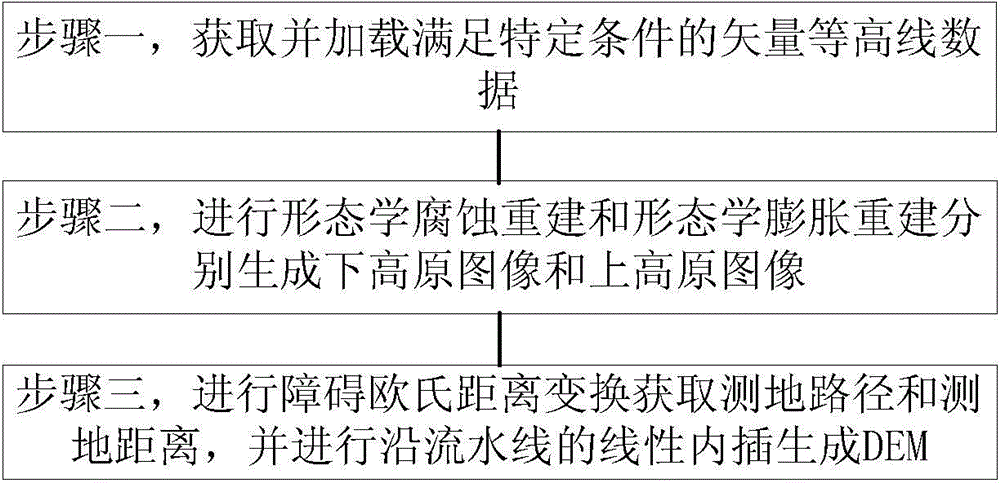
Interpolation method for DEM (Digital Elevation Model) generated by contour lines
The invention discloses an interpolation method for a DEM (Digital Elevation Model) generated by contour lines. The interpolation method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring and loading vector contour line data meeting specific conditions, wherein the specific conditions are: each contour line is spatially and continuously distributed and cannot be interrupted, and odd contour lines and even contour lines exist at intervals; 2, performing morphological corrosion reconstruction and morphological expansion reconstruction to generate a lower plateau image and an upper plateau image respectively; 3, performing obstacle Euclidean distance conversion to acquire a geodesic path and a geodesic distance, and performing pipelined linear interpolation to generate the DEM. The generated DEM has the characteristics of high accuracy and high fidelity and is generated by using the linear interpolation method, the DEM accuracy obtained under the condition that only contour line data are used is equal to or higher than the DEM accuracy obtained by using a map algebra method, manual intervention is not needed, the DEM is not limited by iterations, an adaptive algorithm is truly achieved, and the interpolation method can be applied to various industries.
Owner:SHANDONG LINYI TOBACCO
Damped frequency response apparatus, systems, and methods
InactiveUS7188039B2Vibration measurement in solidsForce measurementViscous dampingFrequency response
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and system for analyzing test vectors to determine toggle counts
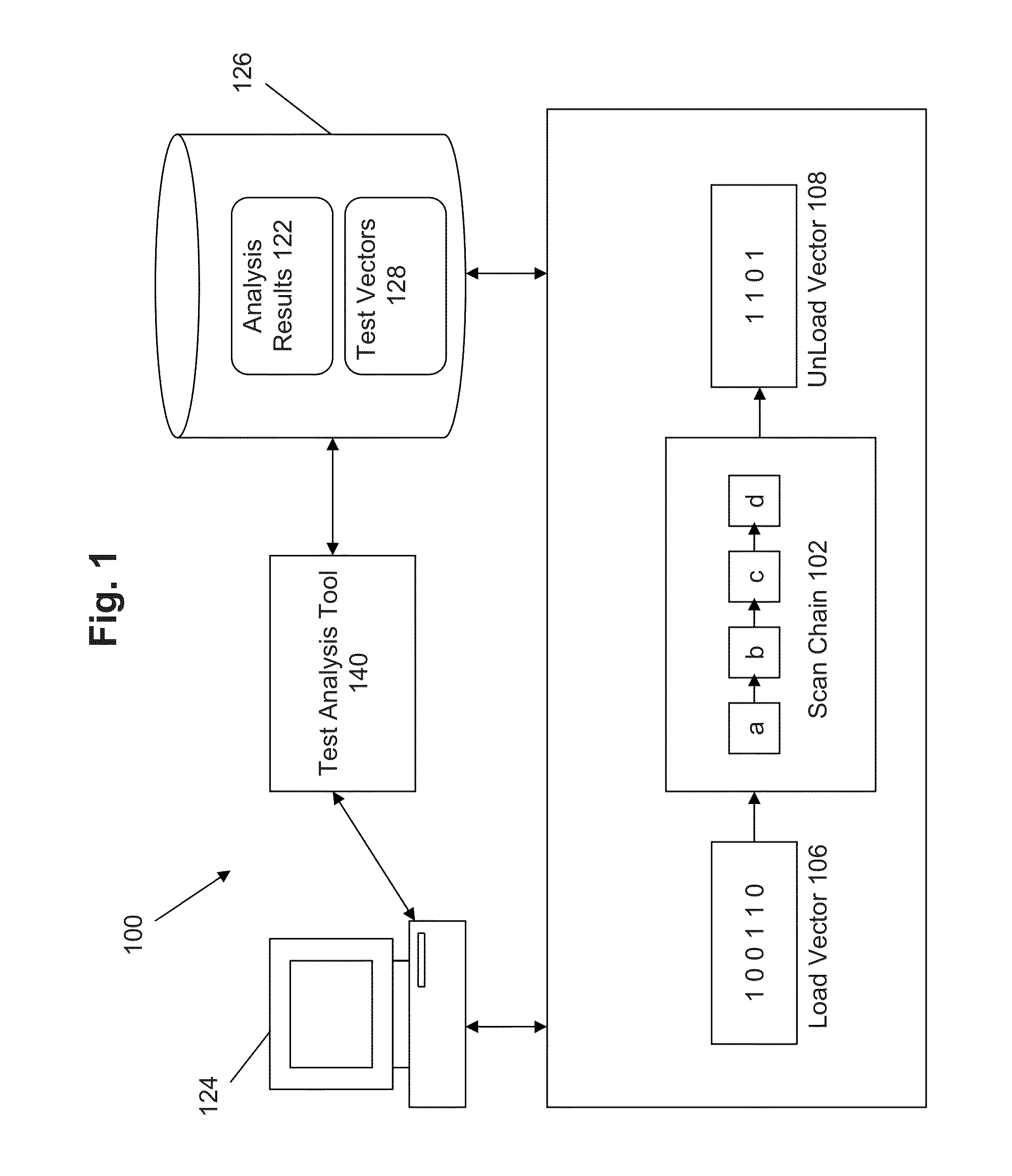
ActiveUS8615692B1High average test powerDissipating powerElectric devicesElectronic circuit testingComputer scienceTest vector
A system, method, and computer program product is disclosed that recycle digital assertions for analyzing the test vectors to quickly and accurately calculate the switching activity at each test clock pulse or scan cycle. According to some approaches, load vector data and unload vector data are analyzed to determine toggle counts and switching activity, without requiring simulation to be performed.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method and device for generating multi-energy demand typical scenes of comprehensive energy system
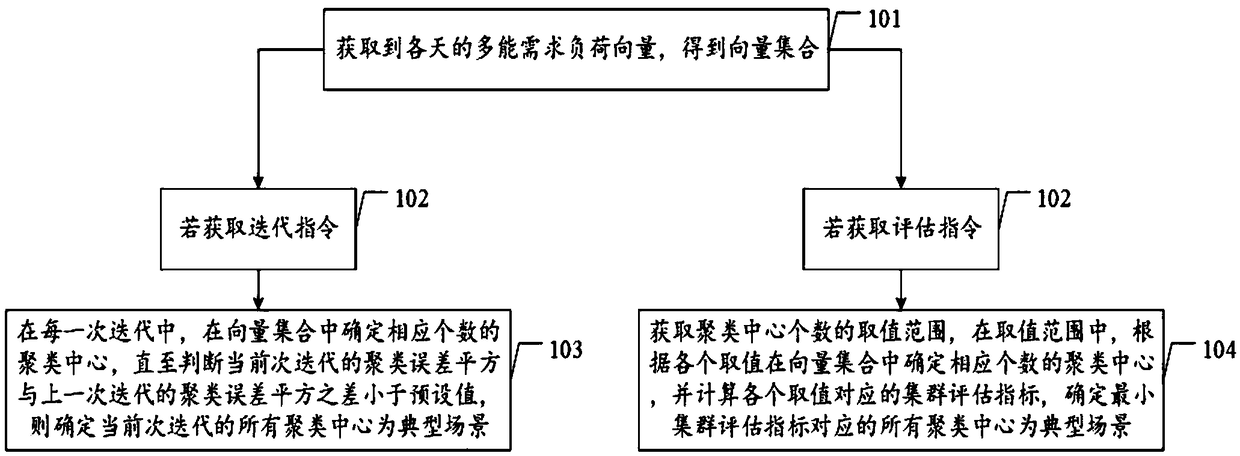
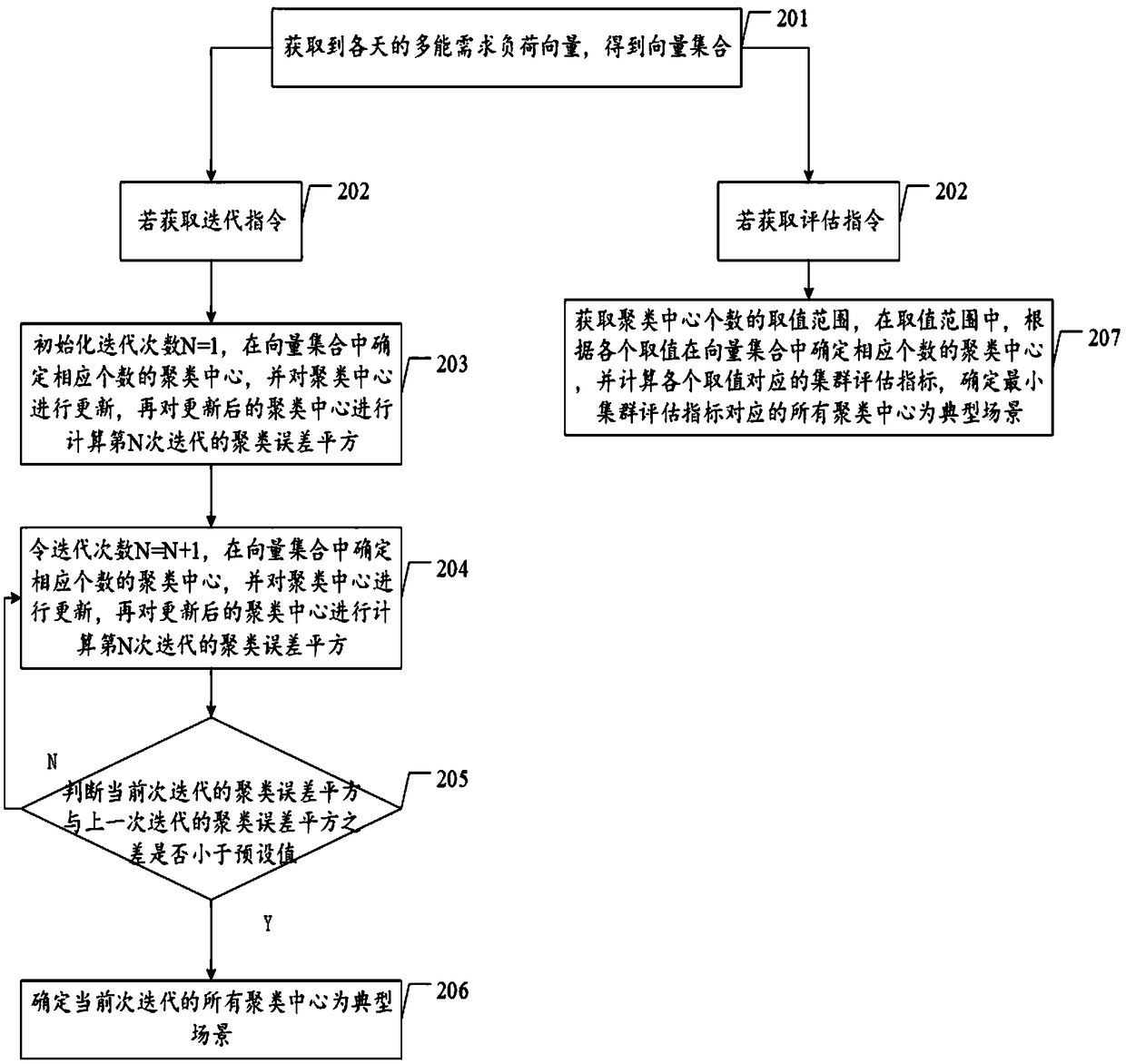
InactiveCN108764335AEasy to analyzeAccurate analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesMachine learningEnergy system
The invention discloses a method and a device for generating multi-energy demand typical scenes of a comprehensive energy system. The method comprises the following steps of S1, acquiring multi-energydemand load vectors of all the days to obtain a vector set; S2, if an iterative instruction is acquired, executing S3, and if an evaluation instruction is acquired, executing S4; S3, during each iteration, determining a clustering center of the corresponding number in the vector set until a difference between a clustering error square of the current iteration and a clustering error square of thelast iteration is judged to be smaller than a preset value, and determining all clustering centers of the current iteration to be typical scenes; and S4, acquiring a value range of the number of the clustering centers, determining the clustering centers of the corresponding number in the vector set according to the values in the value range, computing a cluster evaluation index corresponding to each value, and determining all clustering centers corresponding to the minimum cluster evaluation index to be the typical scenes. Through the typical scenes generated by the method of the method, the comprehensive energy system can be comprehensively and accurately analyzed.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
Methods for detecting and classifying loads on AC lines
InactiveUS7701196B2Current/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase angleRelative magnitudeRelative phase
Methods for detecting and classifying loads on alternating current (AC) lines are provided. One such method includes the steps of placing an AC field sensor in AC electric and magnetic fields generated by an AC line, generating an electric field signal representative of the AC electric field received by the AC field sensor, generating a magnetic field signal representative of the AC magnetic field received by the AC field sensor, generating a relative phase signal representative of relative phase changes between the electric and magnetic fields, and processing the relative phase signal to detect and classify loads on the AC line. In another method, relative load vector signals representative of relative magnitude and phase changes in the magnetic field are generated and processed to detect and classify loads on the AC line.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com