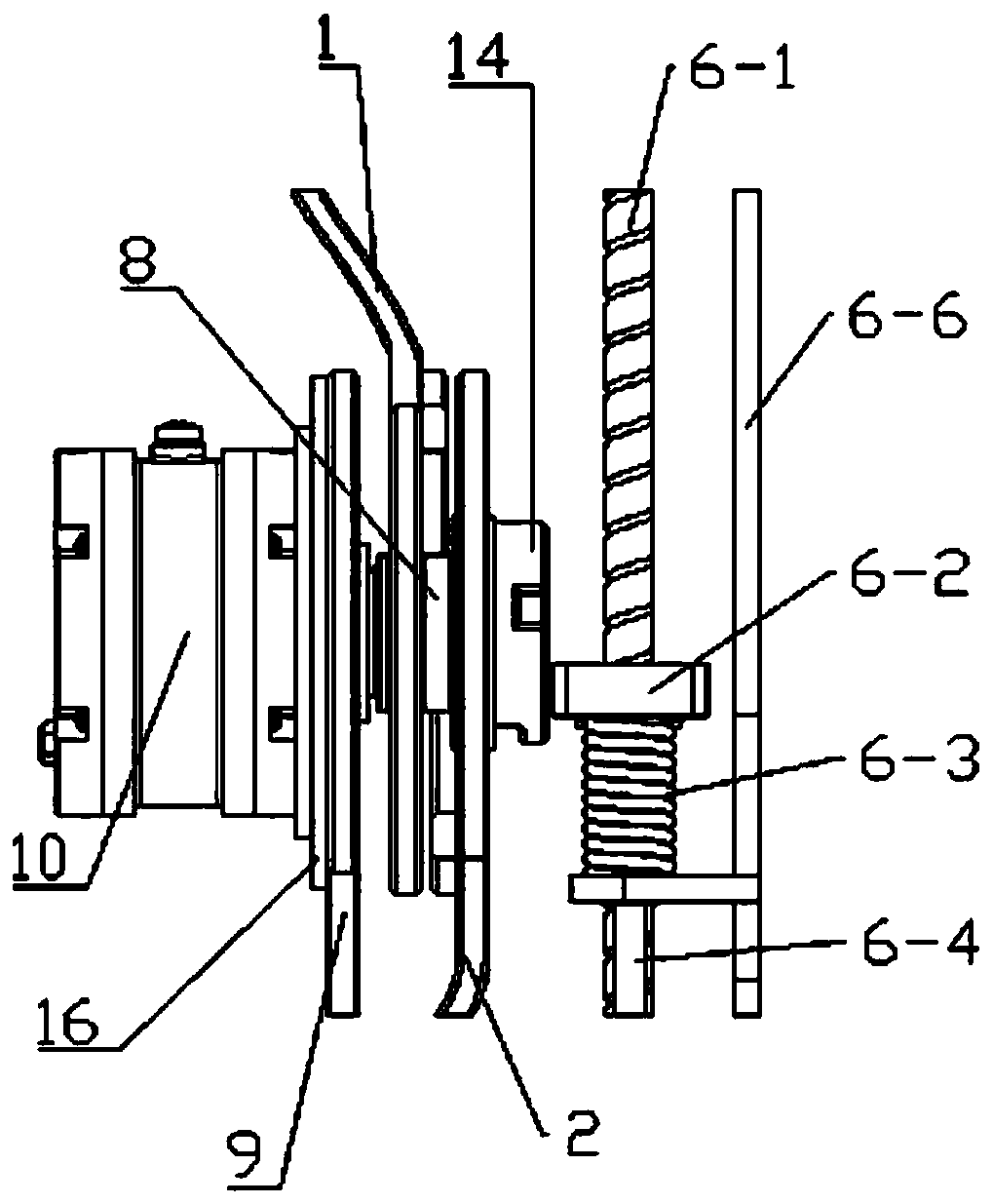
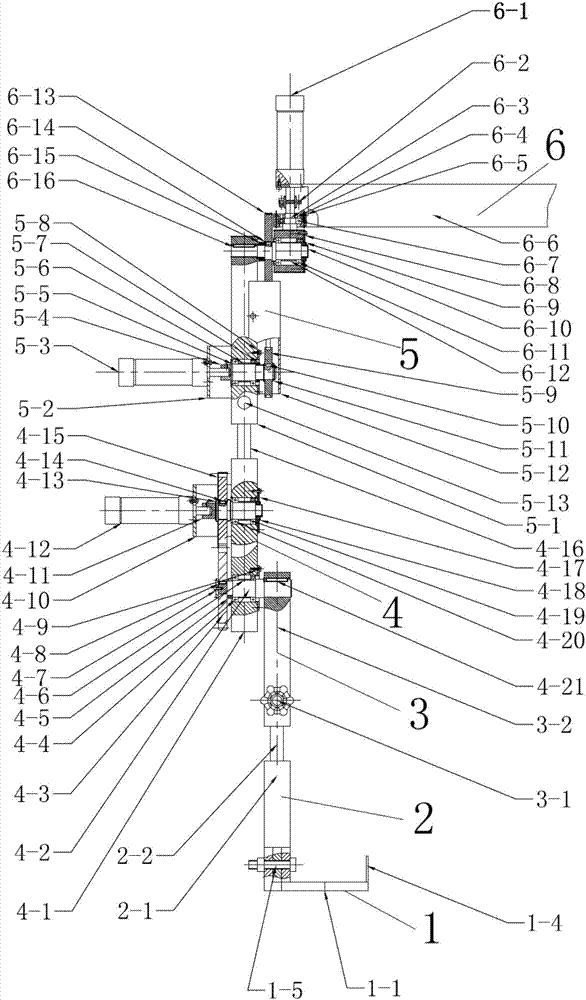
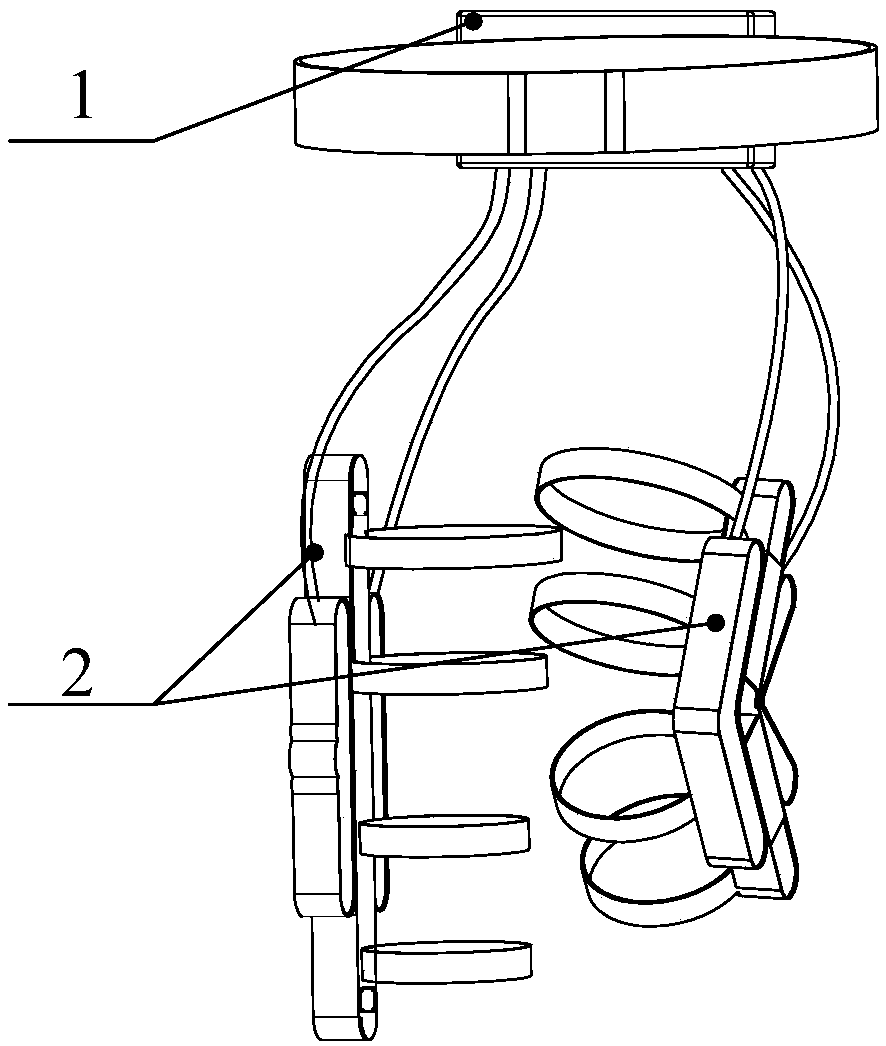
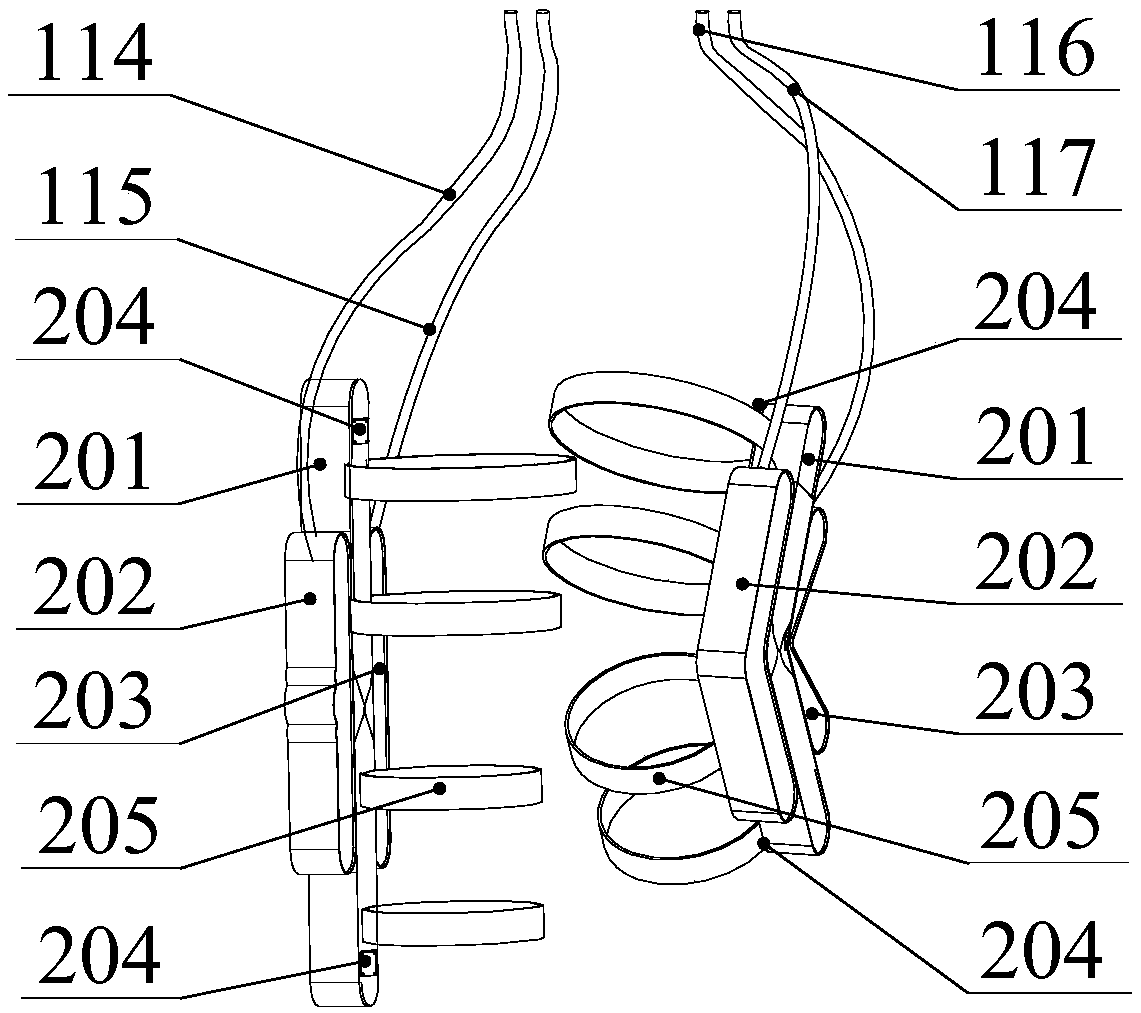
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
190 results about "Knee joint movement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
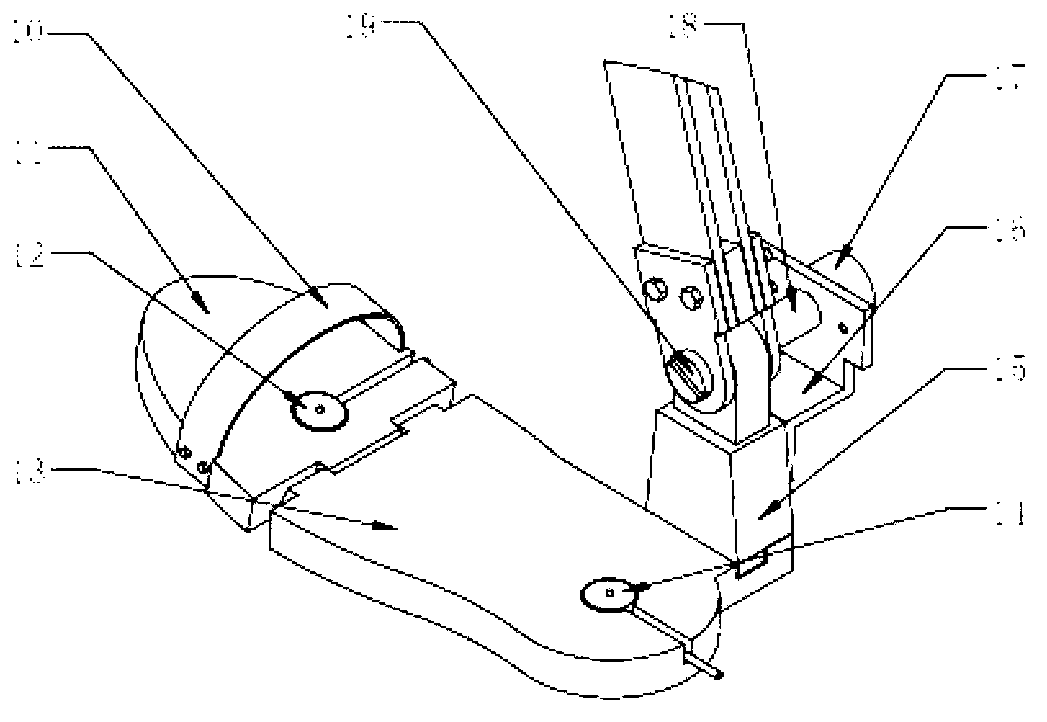
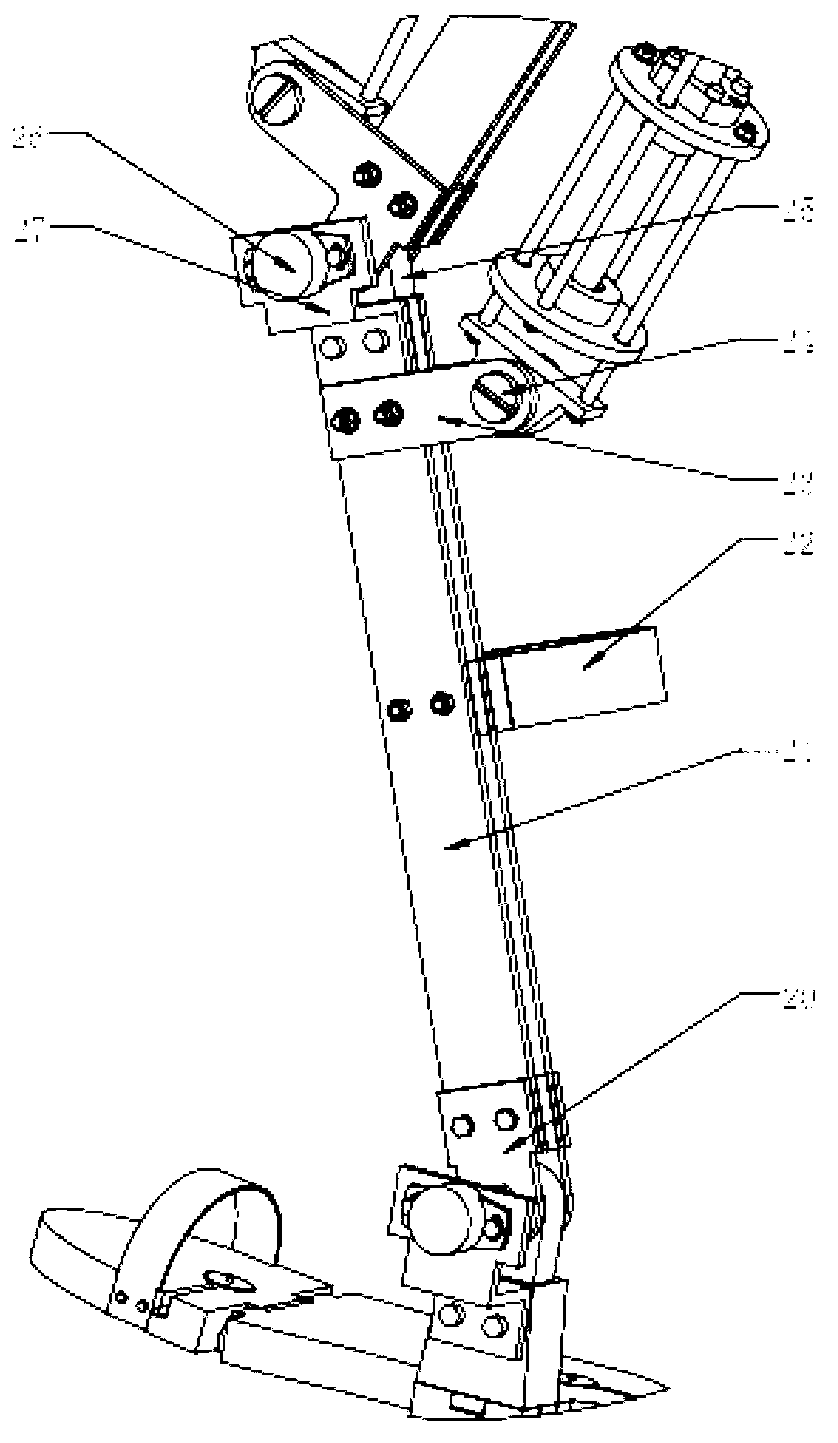
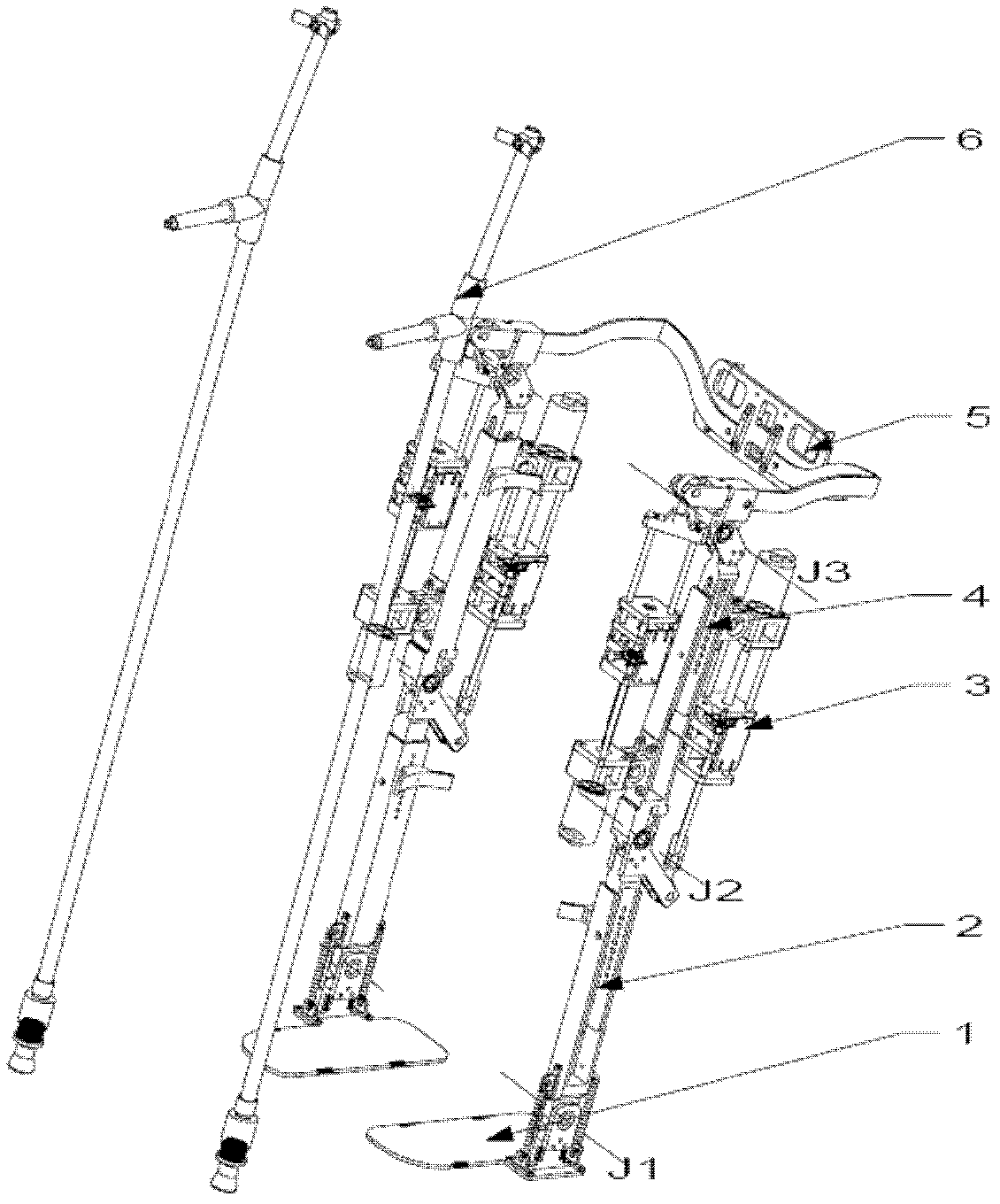
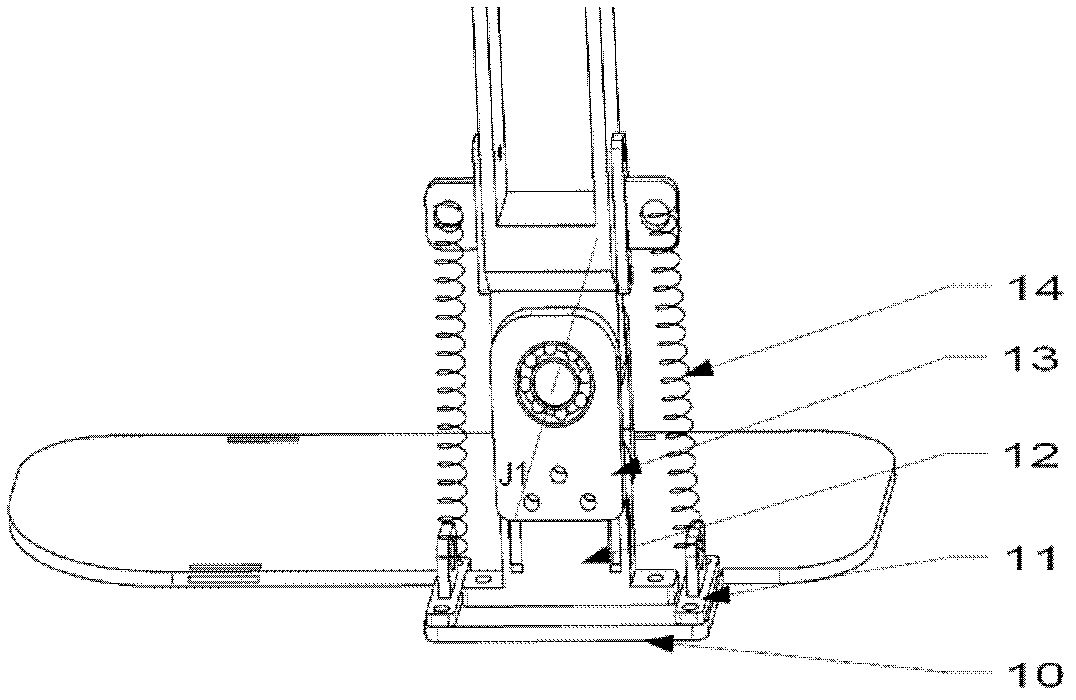
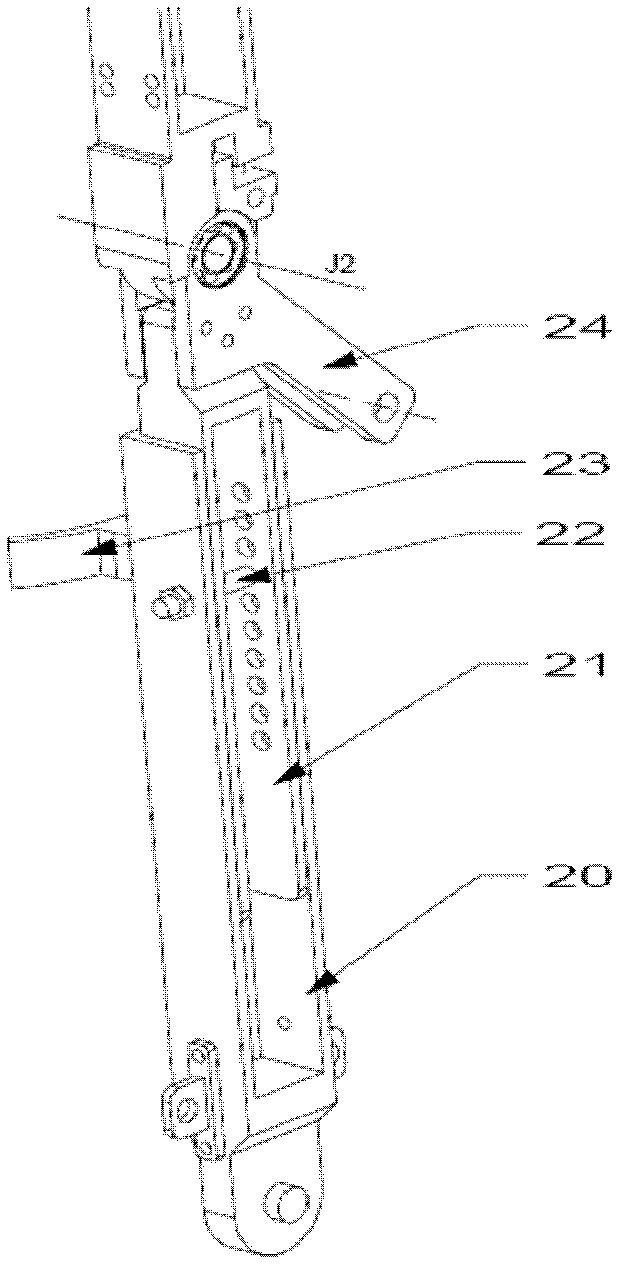
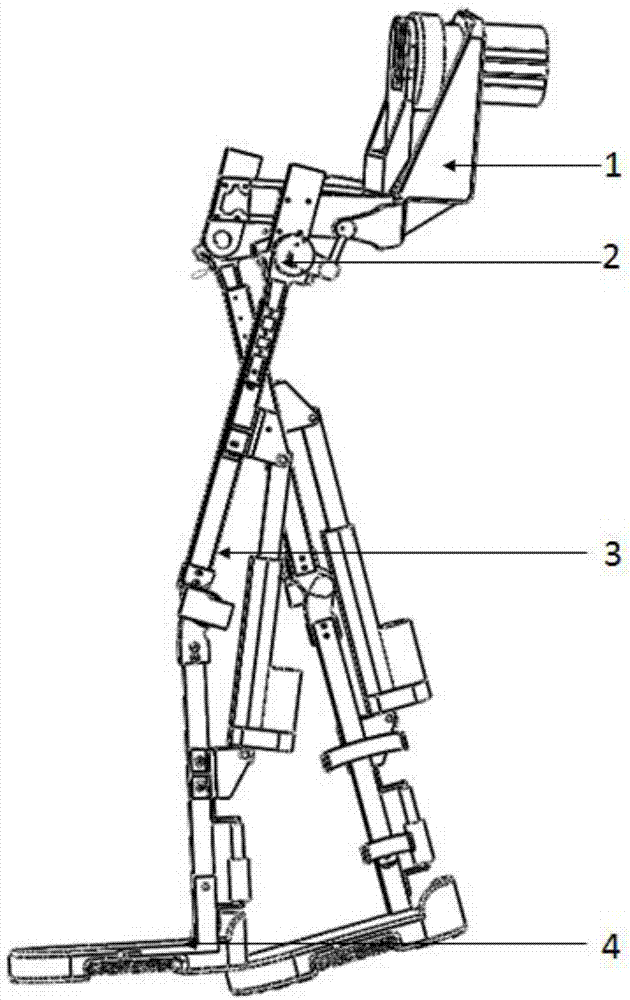
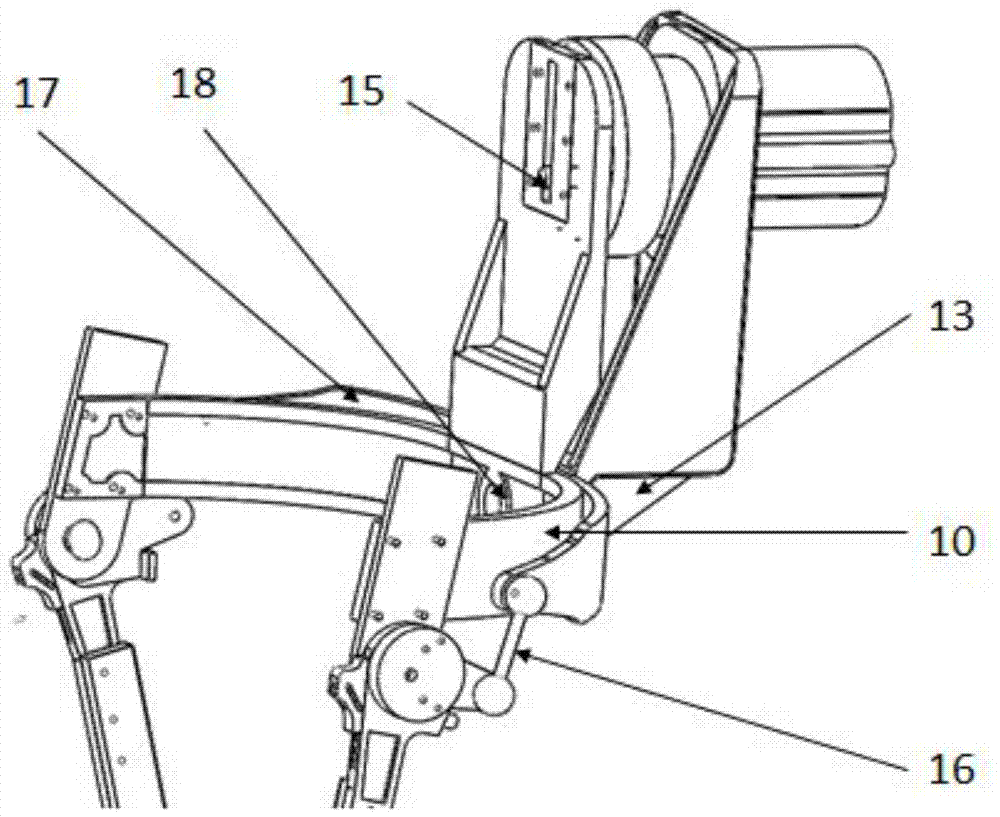
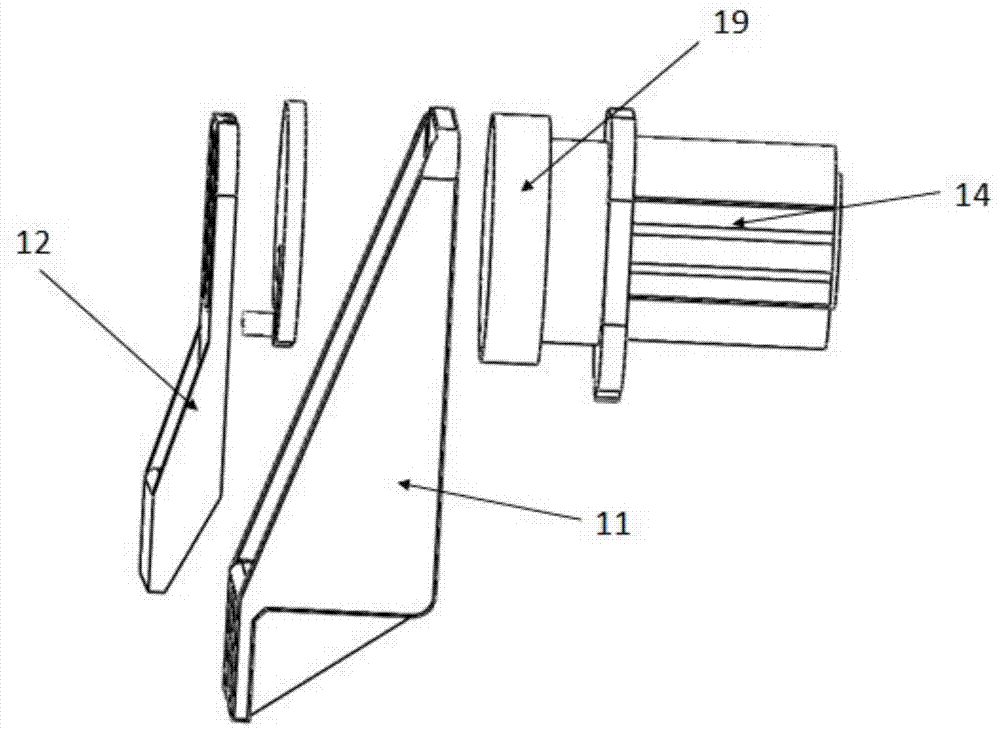
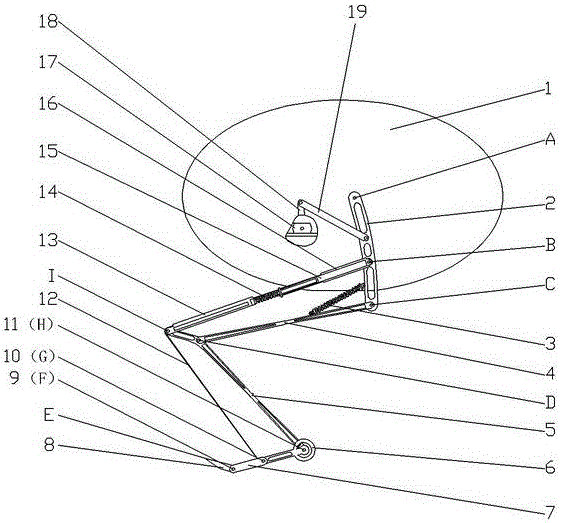
Device and Method for Knee Rehabilitation
InactiveUS20140094721A1Function increaseIncrease muscle strengthElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesStretch exerciseKnee rehabilitation
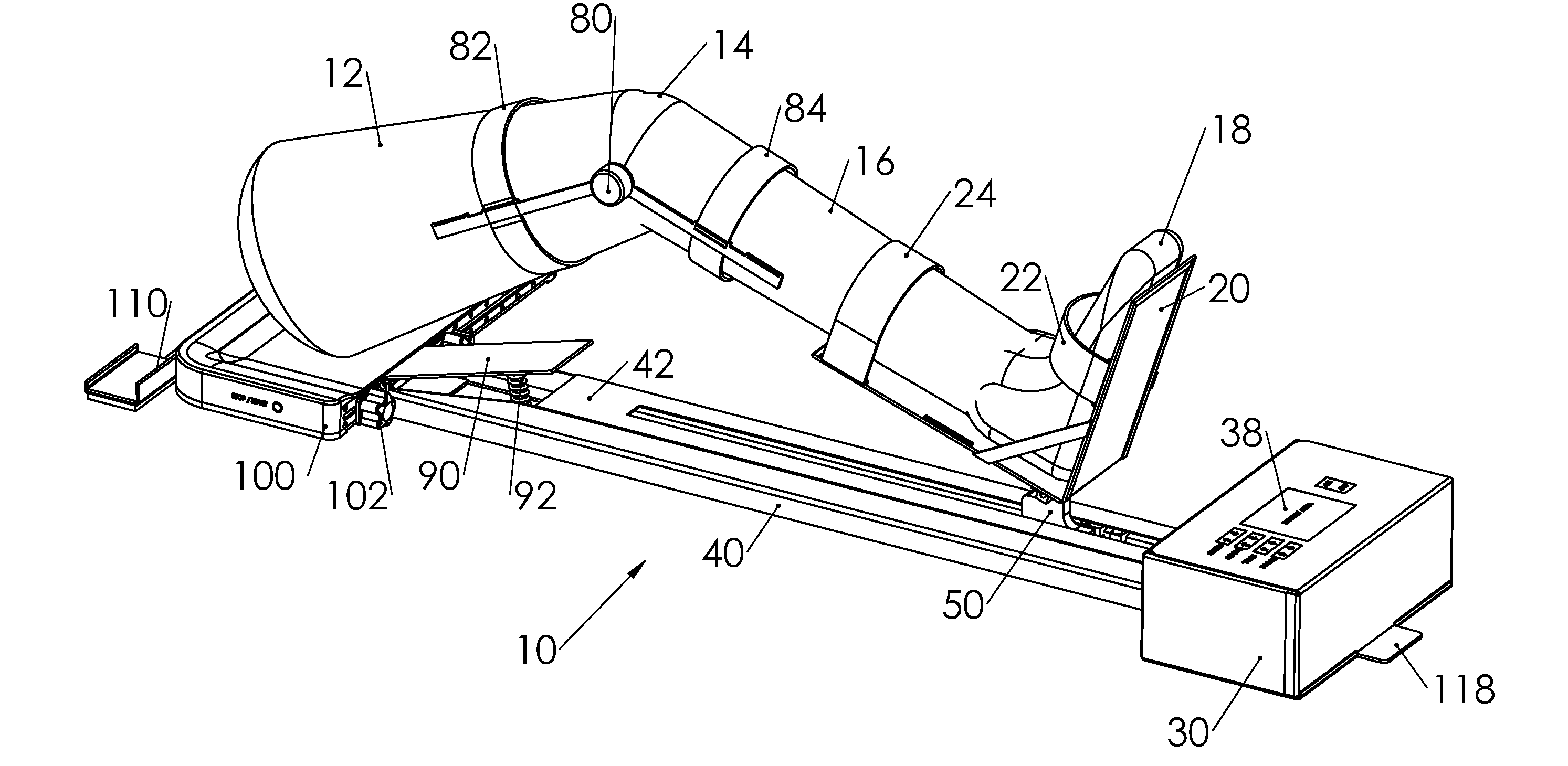
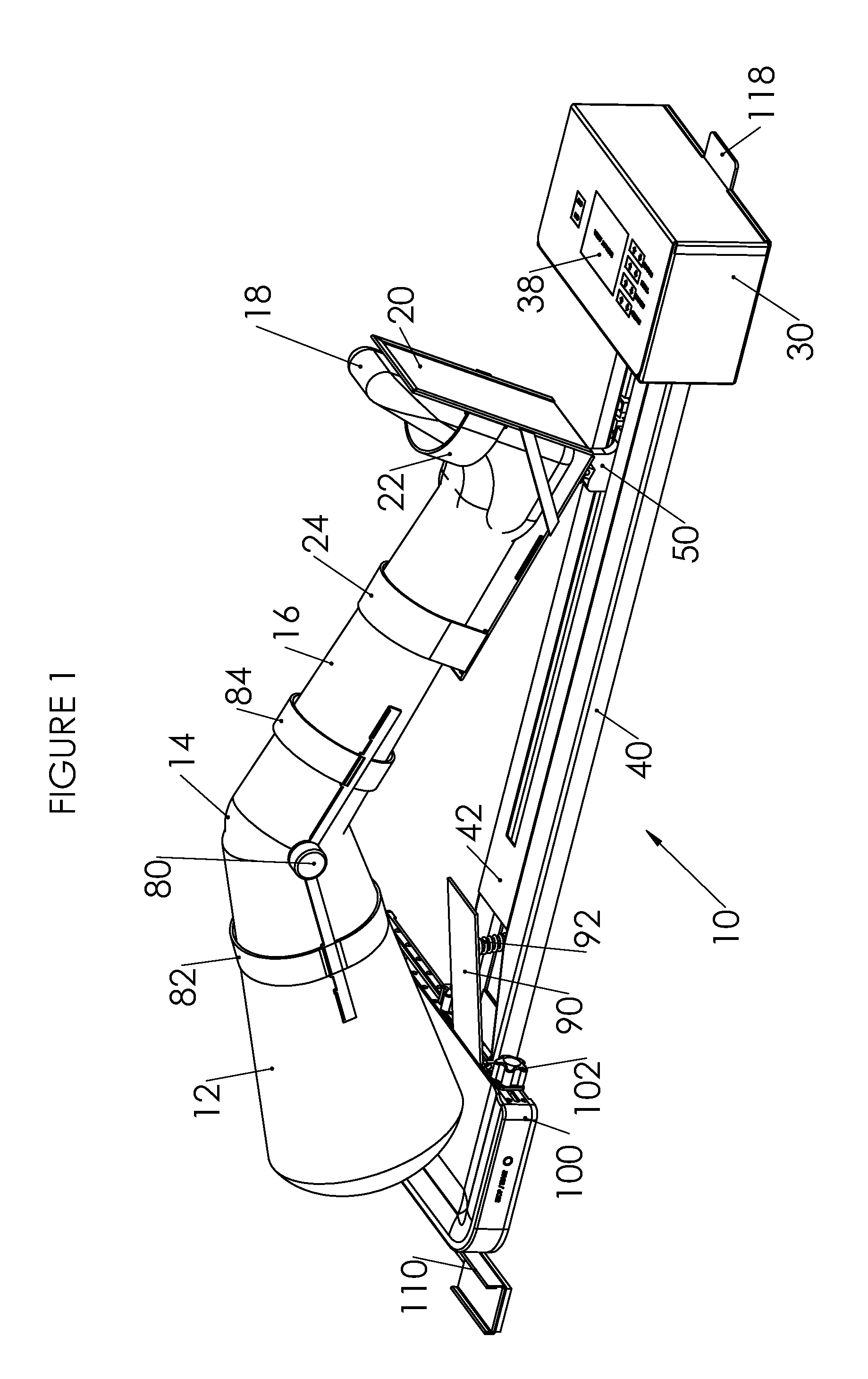
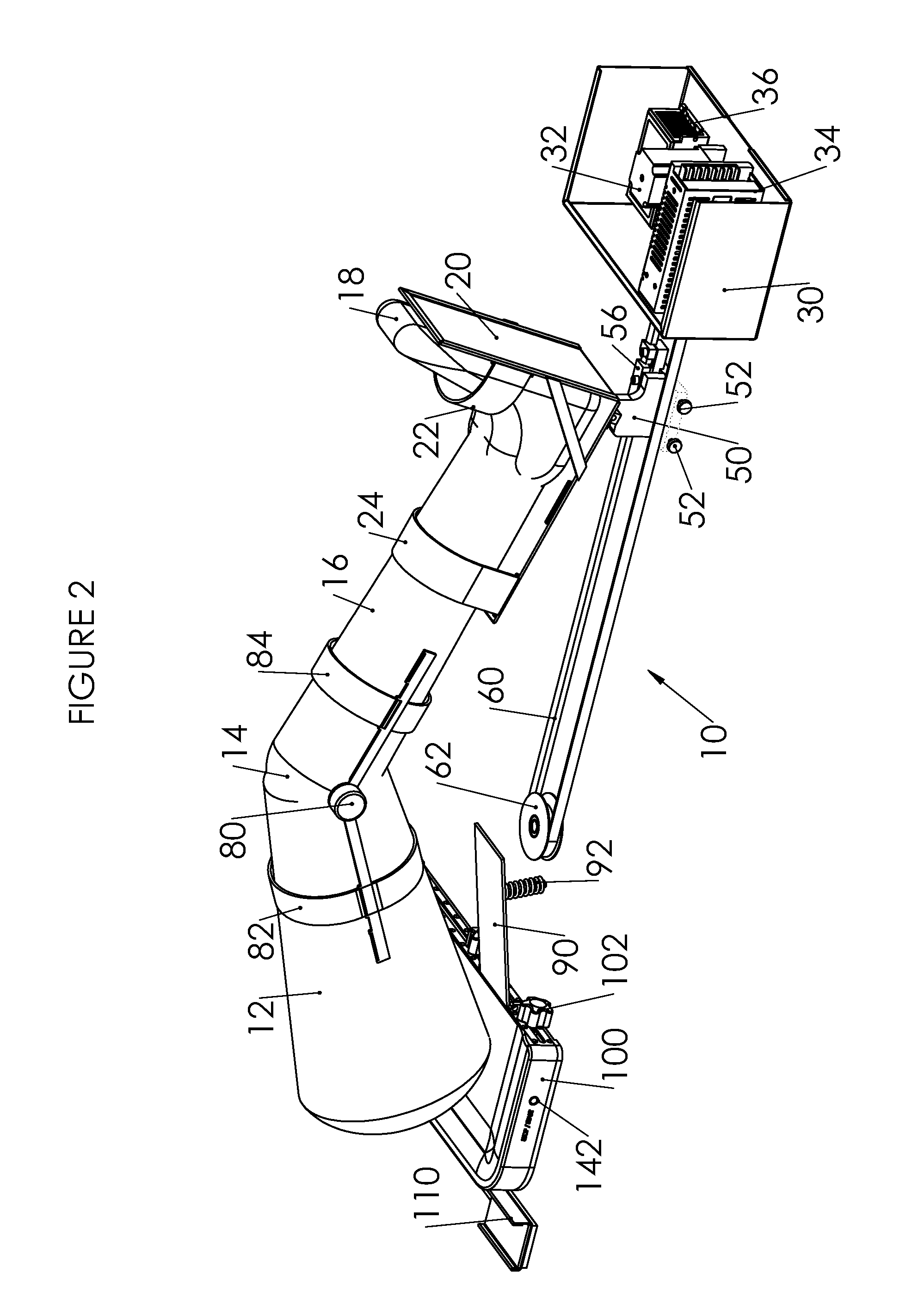
A device for increasing the range of motion of a patient's knee joint comprising of a longitudinal track frame, having a sitting platform at one end and a movable leg and foot platform at the other end, driven back and forth by a foot actuation mechanism in a flexion-extension motion, linearly along the longitudinal track by an electronically controlled motor in accordance with user defined settings and operable in a passive, active or resistive mode in either a supine or sitting position.
Owner:DIALLO IBRAHIMA
Wearable lower limb exoskeleton walking-assisted robot
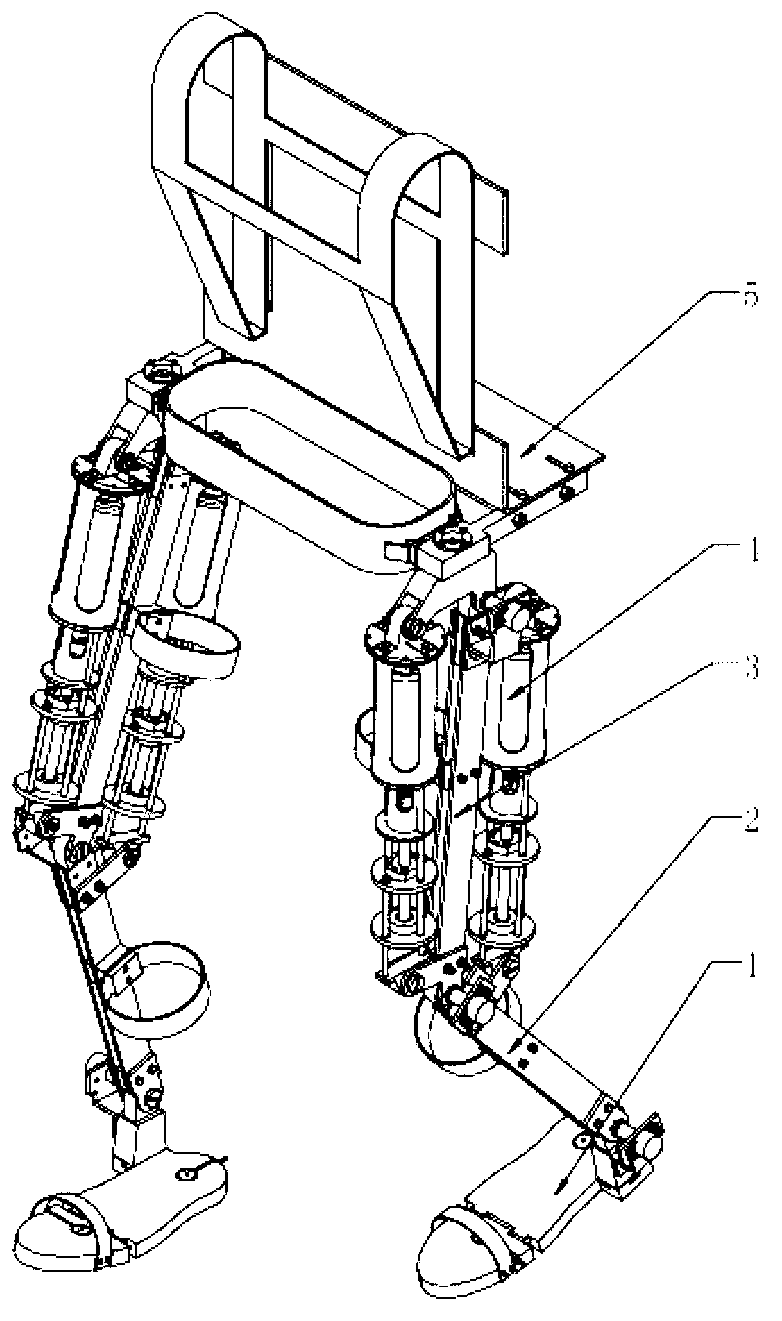
The invention discloses a wearable lower limb exoskeleton walking-assisted robot, which comprises an ankle joint motion module, a knee joint motion module, a hip joint motion module, a drive module and a waist and supporting frame module, wherein the knee joint motion module is connected with the ankle joint motion module and the hip joint motion module respectively; the drive module is connected with the knee joint motion module and the ankle joint motion module respectively; and the hip joint motion module is connected with the waist and supporting frame module. During the walking period of the robot, the consistency of hip joint motion and human body motion is good, the coaxiality and the position deviation of the knee joints of a human body and the robot are small, and the ankle joint is compact in structure.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Lower limb exoskeleton walking rehabilitation robot
ActiveCN102499859AImprove comfortImprove reliabilityWalking aidsArtificial legsMedical equipmentExoskeleton
The invention discloses a lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot in the technical field of medical equipment. The lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot comprises an ankle joint motion module, a knee joint motion module, a hip joint motion module, a hip and support module and a crutch module, wherein one end of the knee joint motion module is connected with the ankle joint motion module, and the other end of the knee joint motion module is connected with the hip joint motion module; the hip and support module is connected with the hip joint motion module; and the crutch module is independent of an exoskeleton body. The lower limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot can help patients who suffer from paraplegia stand up and walk, and the bend and stretch motion of a knee joint and a hip joint is controlled by collecting contact information of a crutch and the ground so as to help the patients to stride; and an oppositely-pulled spring of the knee joint can help to reduce impact from the ground, so that patients can walk comfortably, and the efficiency of rehabilitation training is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
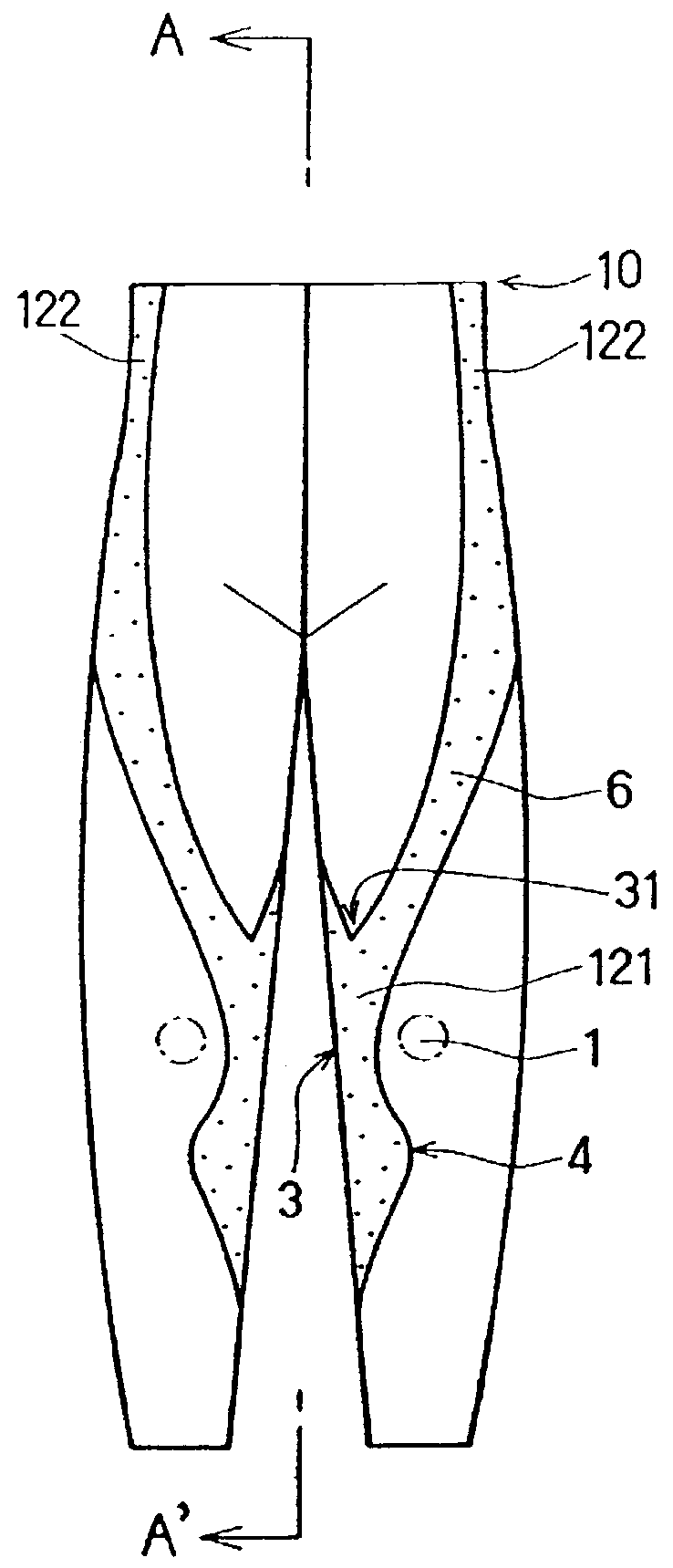
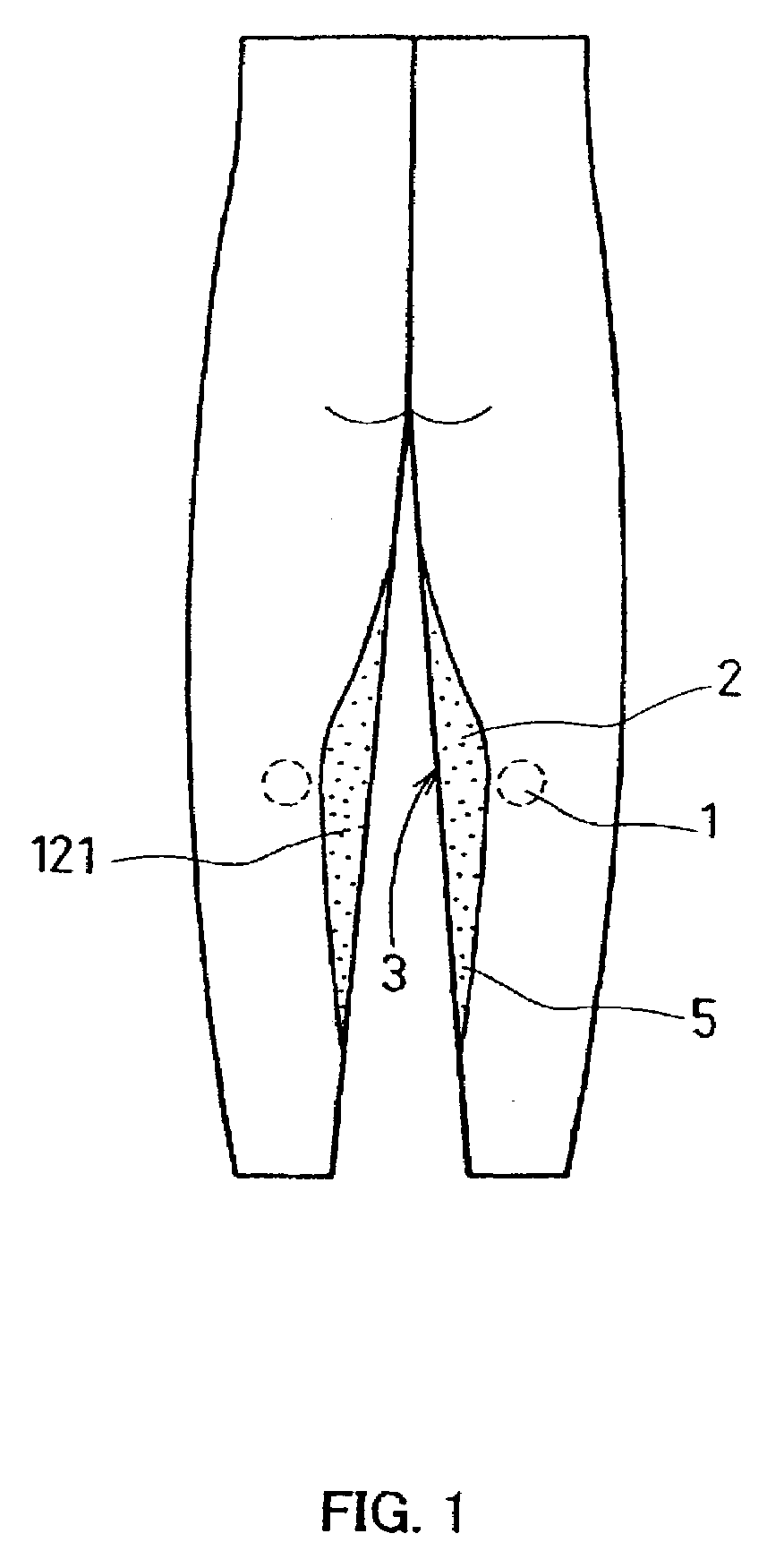
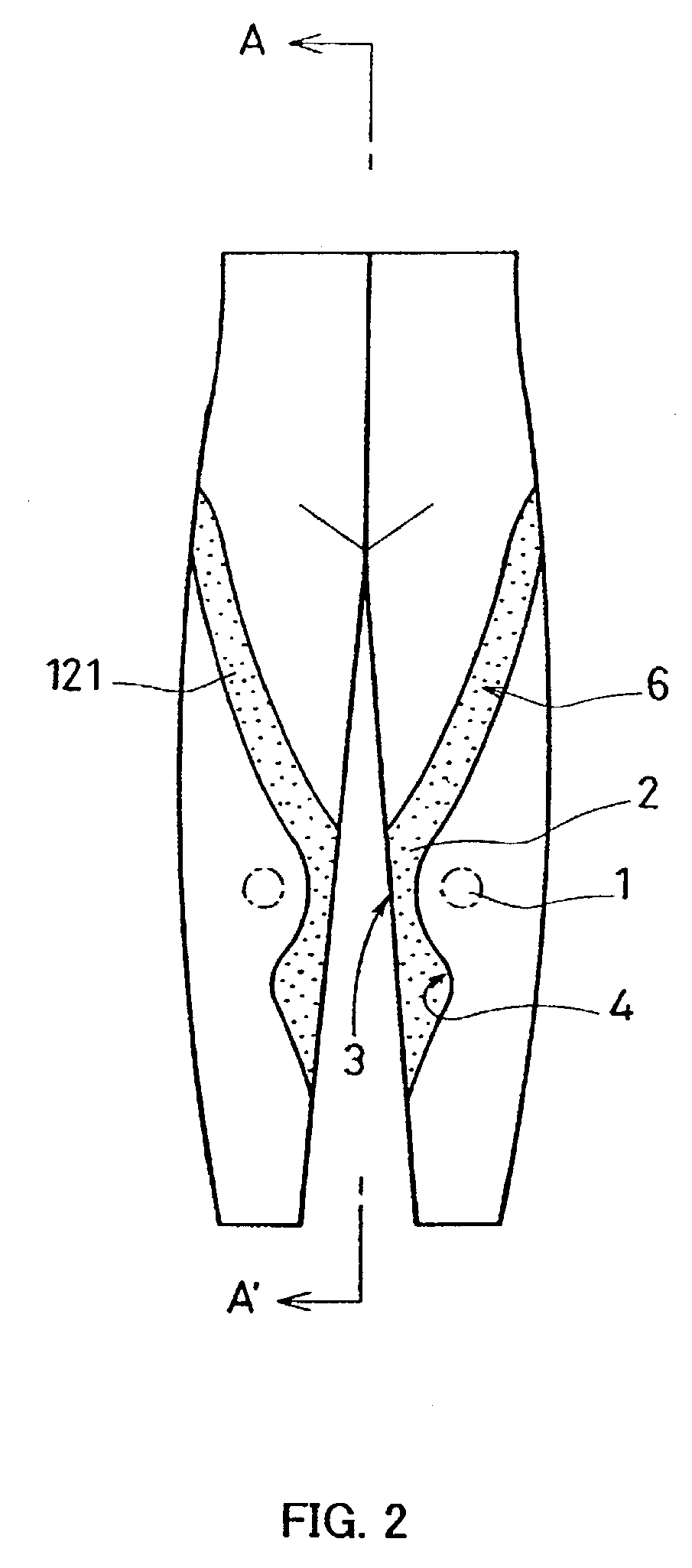
Tights-type leg support garment
A leg support garment of a tights type that has stretchability and is applied in close contact with the human body so as to support the legs is provided with a stretchable part having a relatively great straining force. The stretchable part having a relatively great straining force includes a stretchable portion (A) having a relatively great straining force that substantially covers the ligamentum collateralle on a medial side of the knee joint of the human body, and on a superior side of the knee joint, extends through a length of not less than ¼ of that of the thigh, along at least one selected from the musculus group consisting of the musculus sartorius, the musculus semitendinosus, the musculus semimembranosus, and the musculus gracilis. Thus, it is possible to provide a leg support garment that is capable of effectively protecting the knees and stably maintaining the knee joints without decreasing the degree of freedom of the movement of the knee joints, that provides a good feeling when worn, and that is useful for preventing and reducing gonalgia of the knees, and further, for preventing injuries to the ligamentum collateralle medialis caused by sports or the like.
Owner:WACOAL
Human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot
InactiveCN104490568AImprove comfortImprove reliabilityChiropractic devicesWalking aidsExoskeleton robotCoxal joint
A human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot belongs to the technical field of medical rehabilitation equipment, and comprises a lower back movement module, a hip joint movement module, a knee joint movement module and an ankle joint movement module, wherein a back servo motor drives a hip joint to move through a crank and rocker mechanism and a space four-links mechanism; an electric knee push rod drives a knee joint to move; an electric ankle push rod drives an ankle joint to move. The human lower extremity exoskeleton walking aid rehabilitation robot helps a patient with lower limb paralysis to stand and walk, and the flexion and extension movement of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint is controlled by acquiring pressure signals of soles of feet, so that the patient is helped to stride; the construction and model design of the ankle joint inversion and eversion passive driving degree of freedom can help to reduce impact from the ground, is conductive to reducing the burden of a user keeping balance of the self and the exoskeleton robot in a frontal plane, is beneficial for the patient to walk comfortably, and improves the rehabilitation training efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Patellar Components
ActiveUS20080300689A1Reduce and minimize shear forceLessen anterior knee painJoint implantsKnee jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAnterior knee pain
Embodiments of the present invention provide patellar component designs that are optimally shaped to help reduce shear force and accommodate slight implantation error. Further, they help lessen anterior knee pain, particularly during deep-flexion activities and help ease the transition during the range of knee movement in a controlled way.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
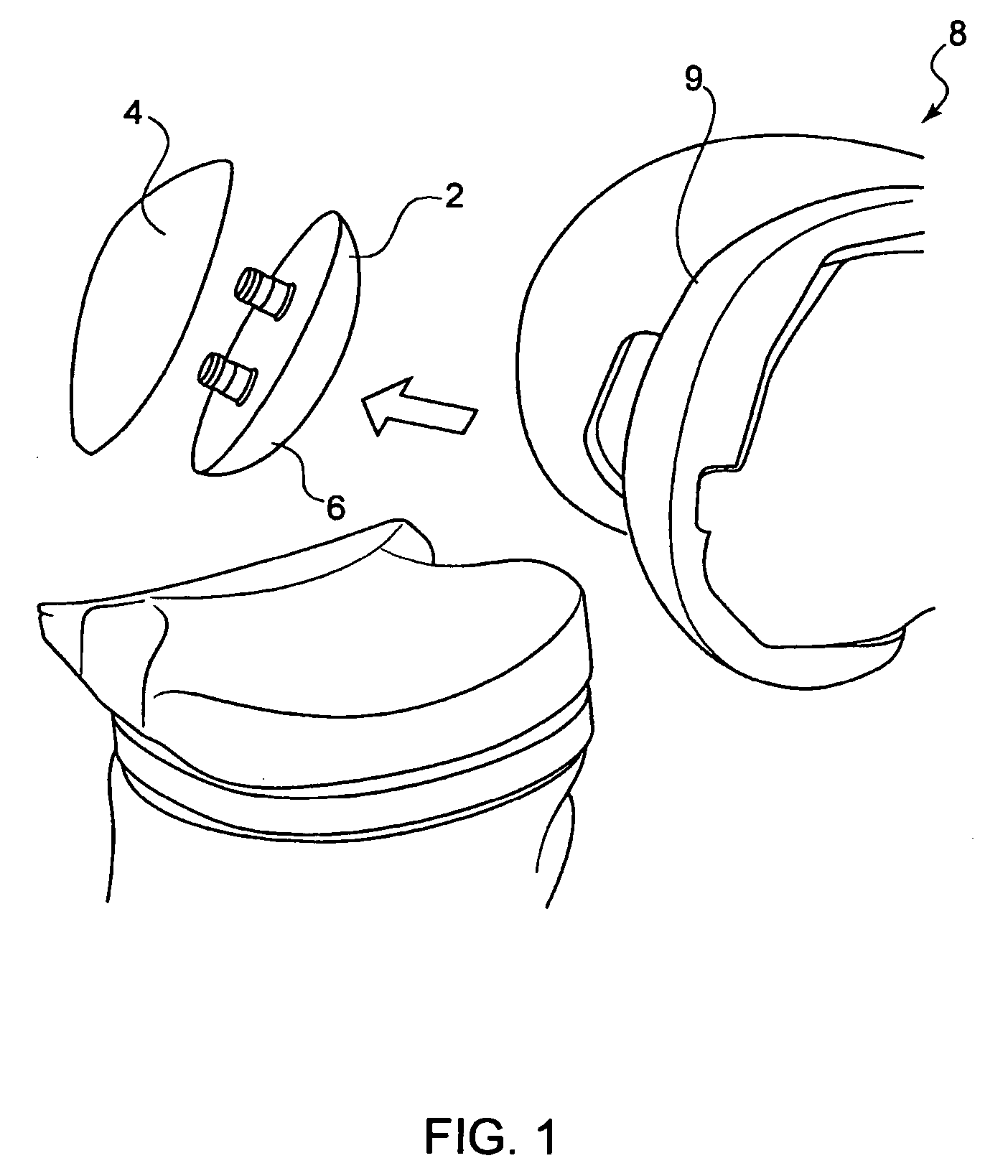
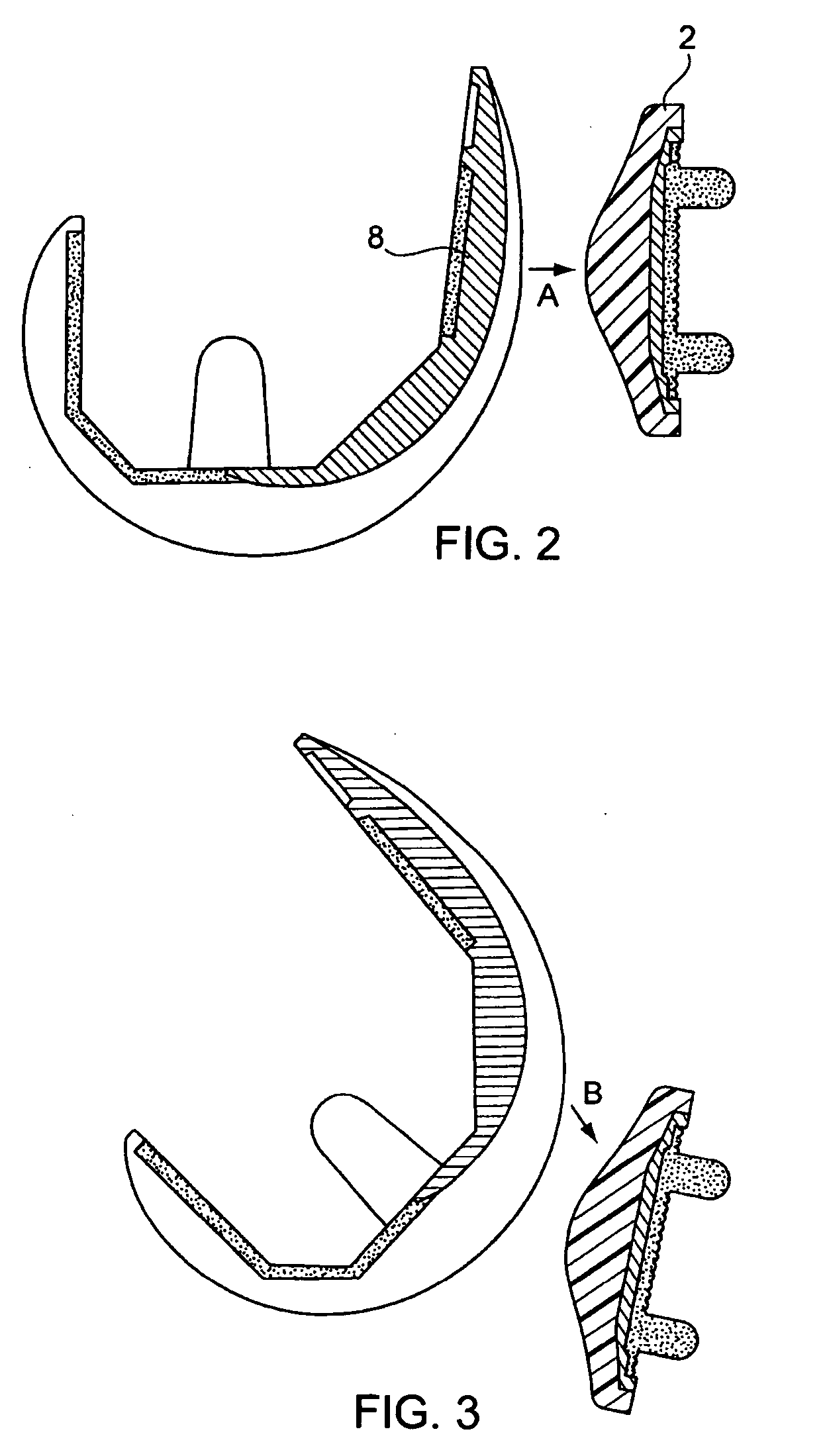
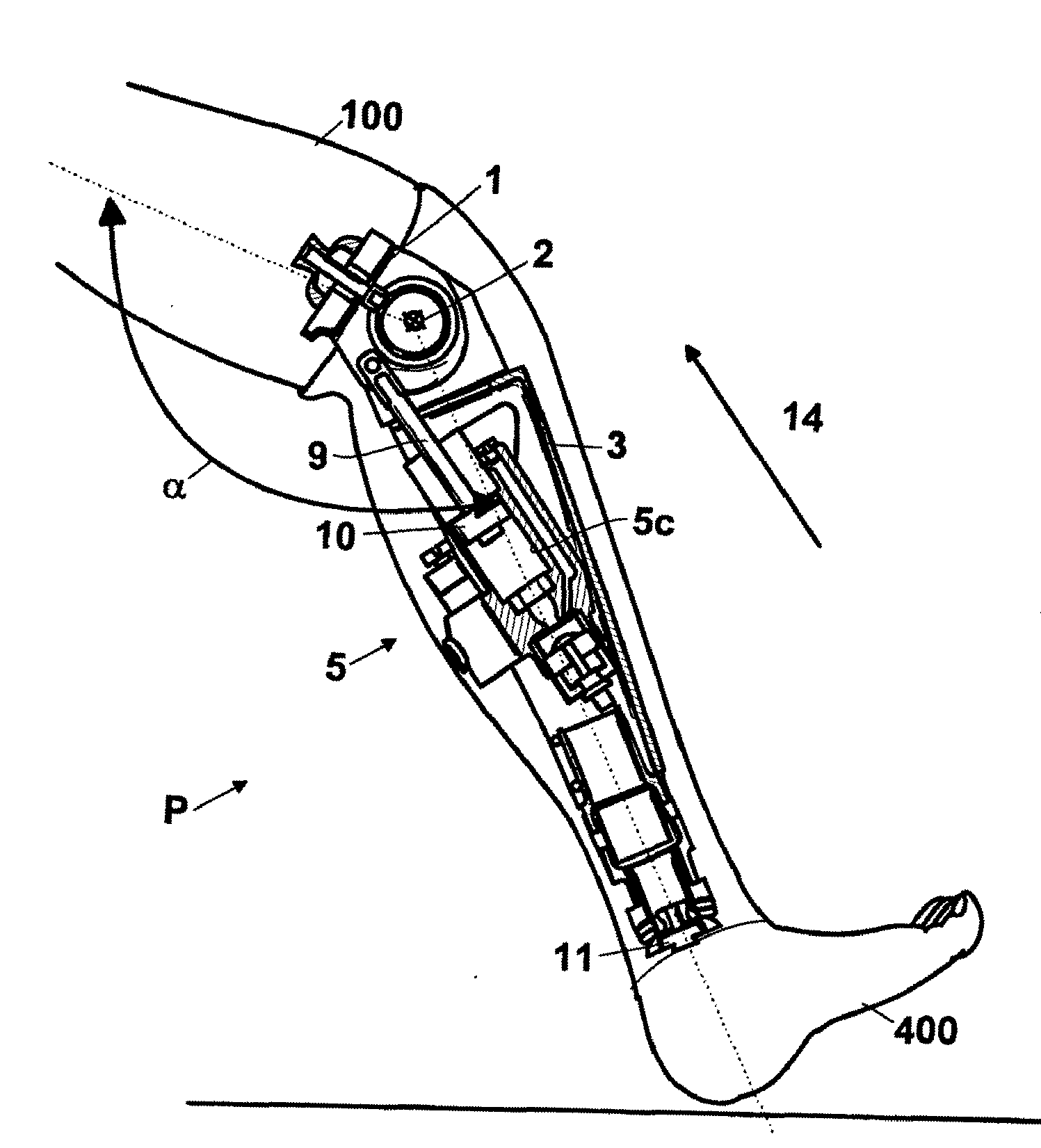
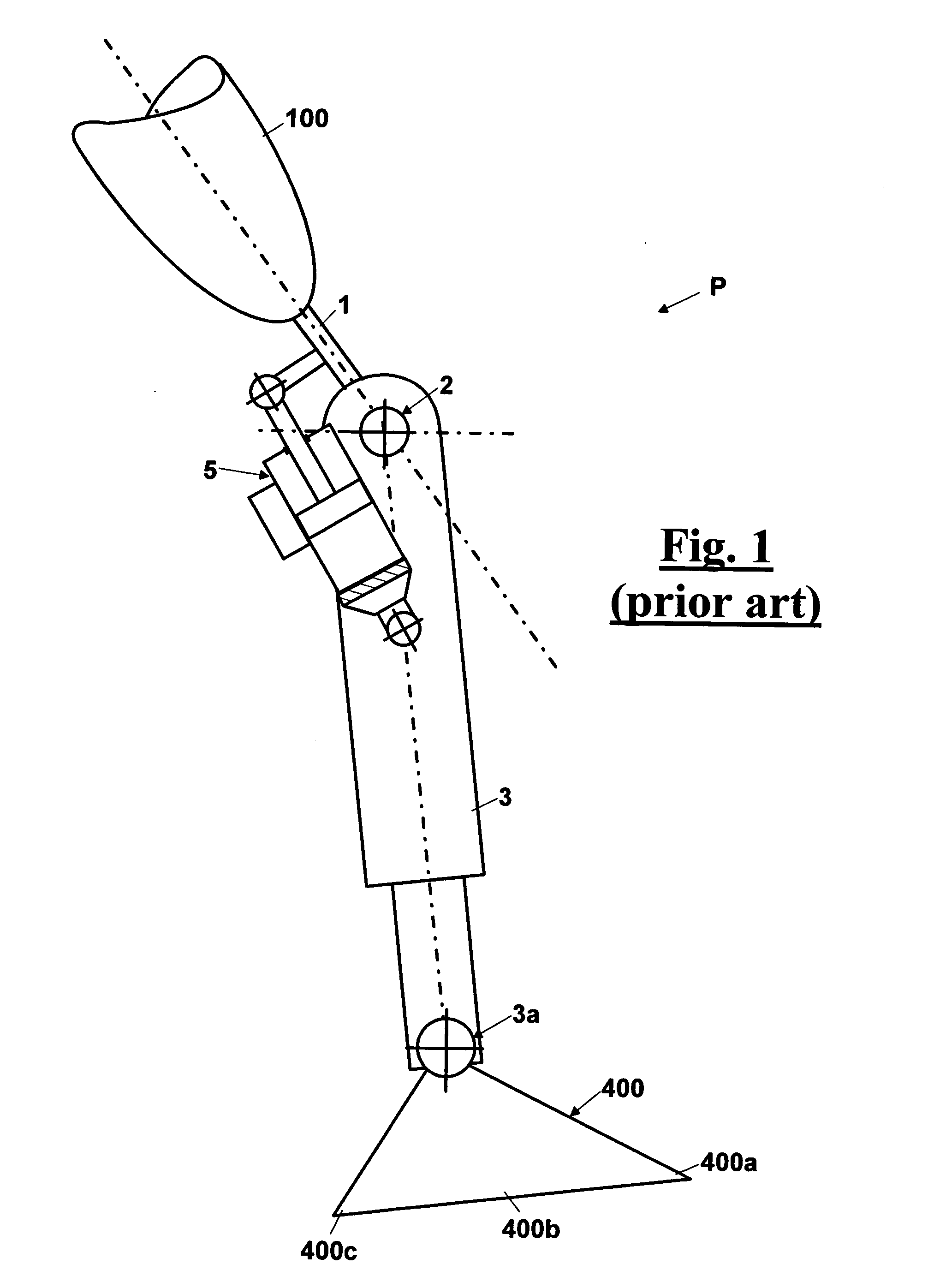
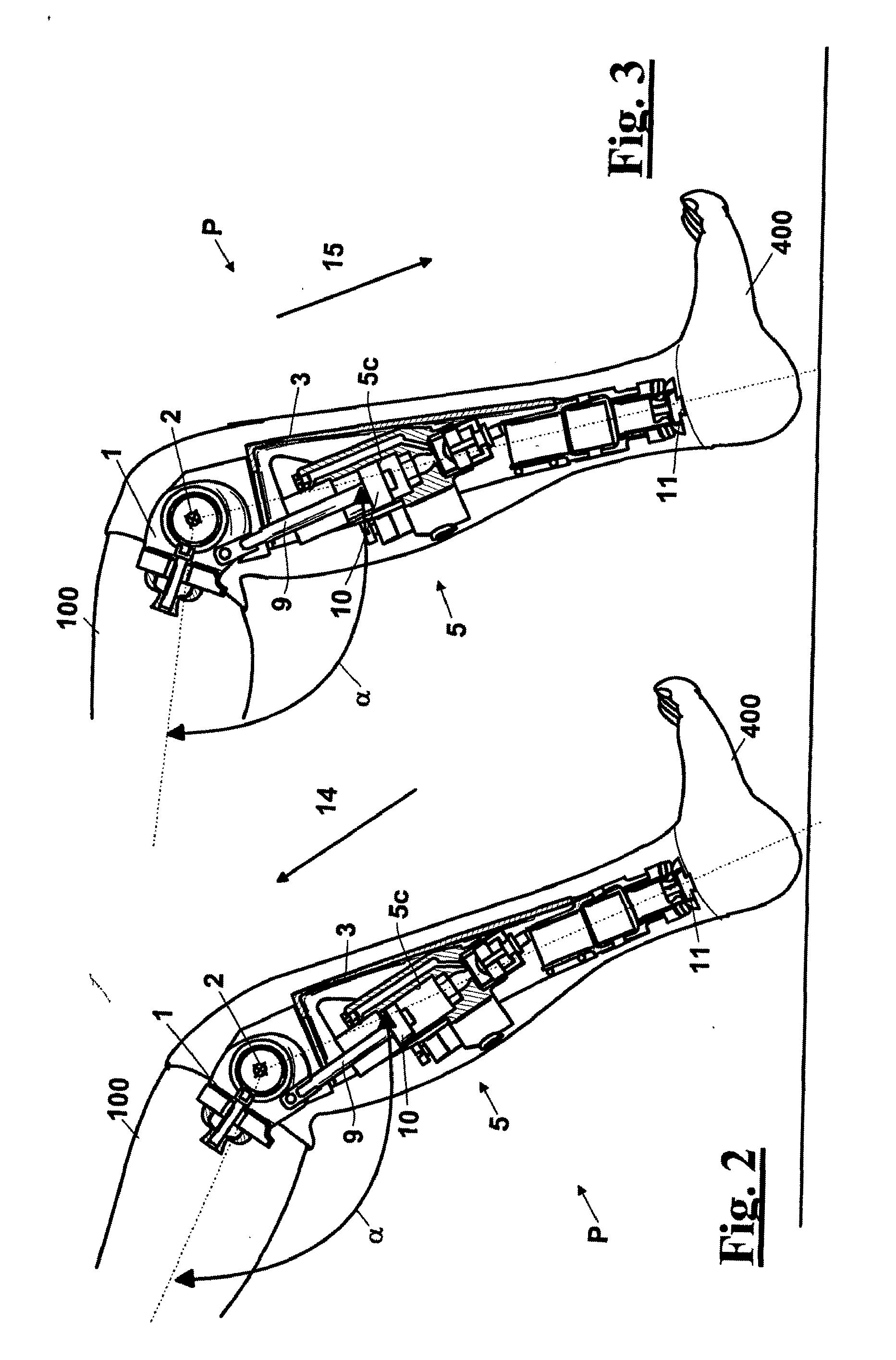
Automatic prosthesis for above-knee amputees
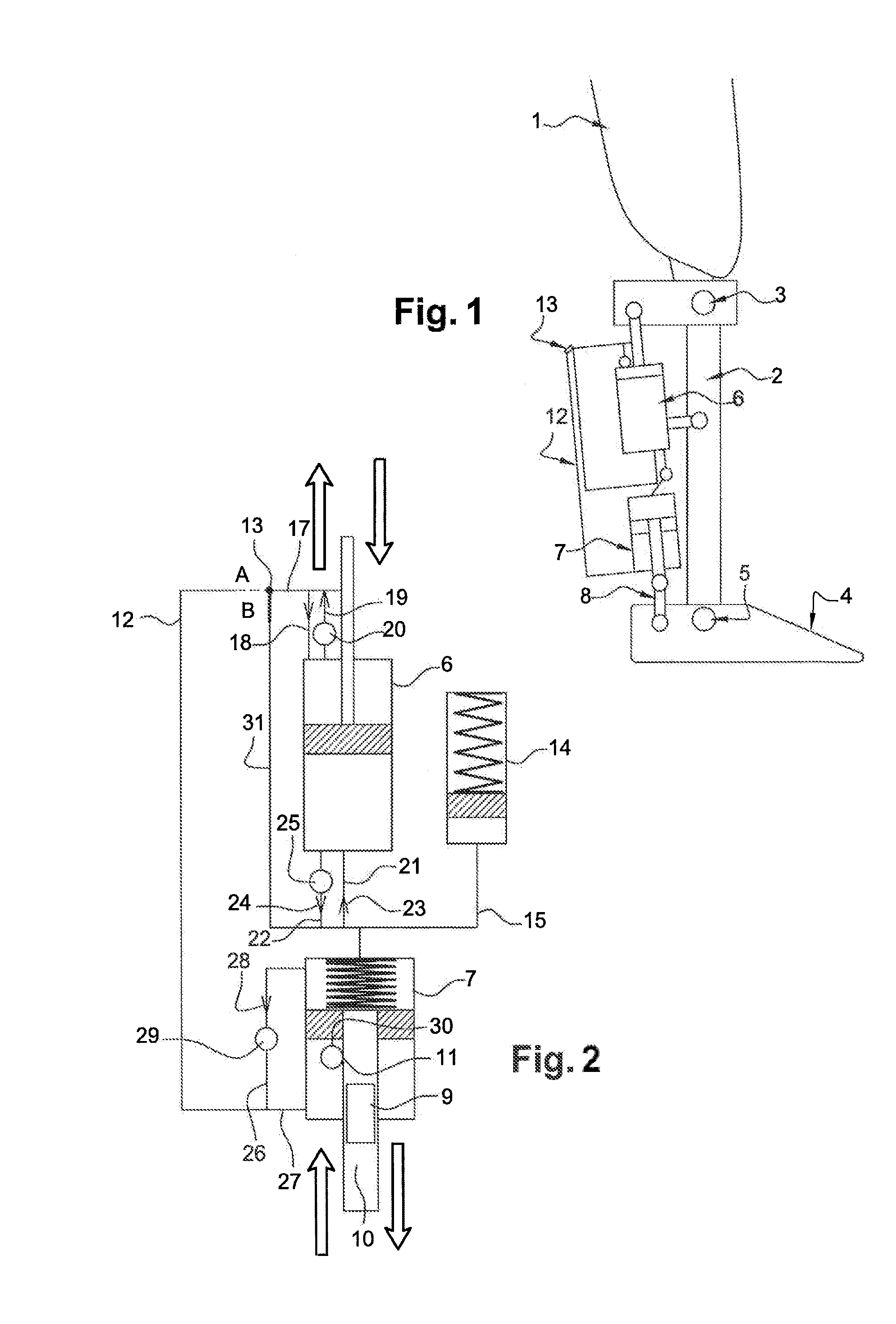
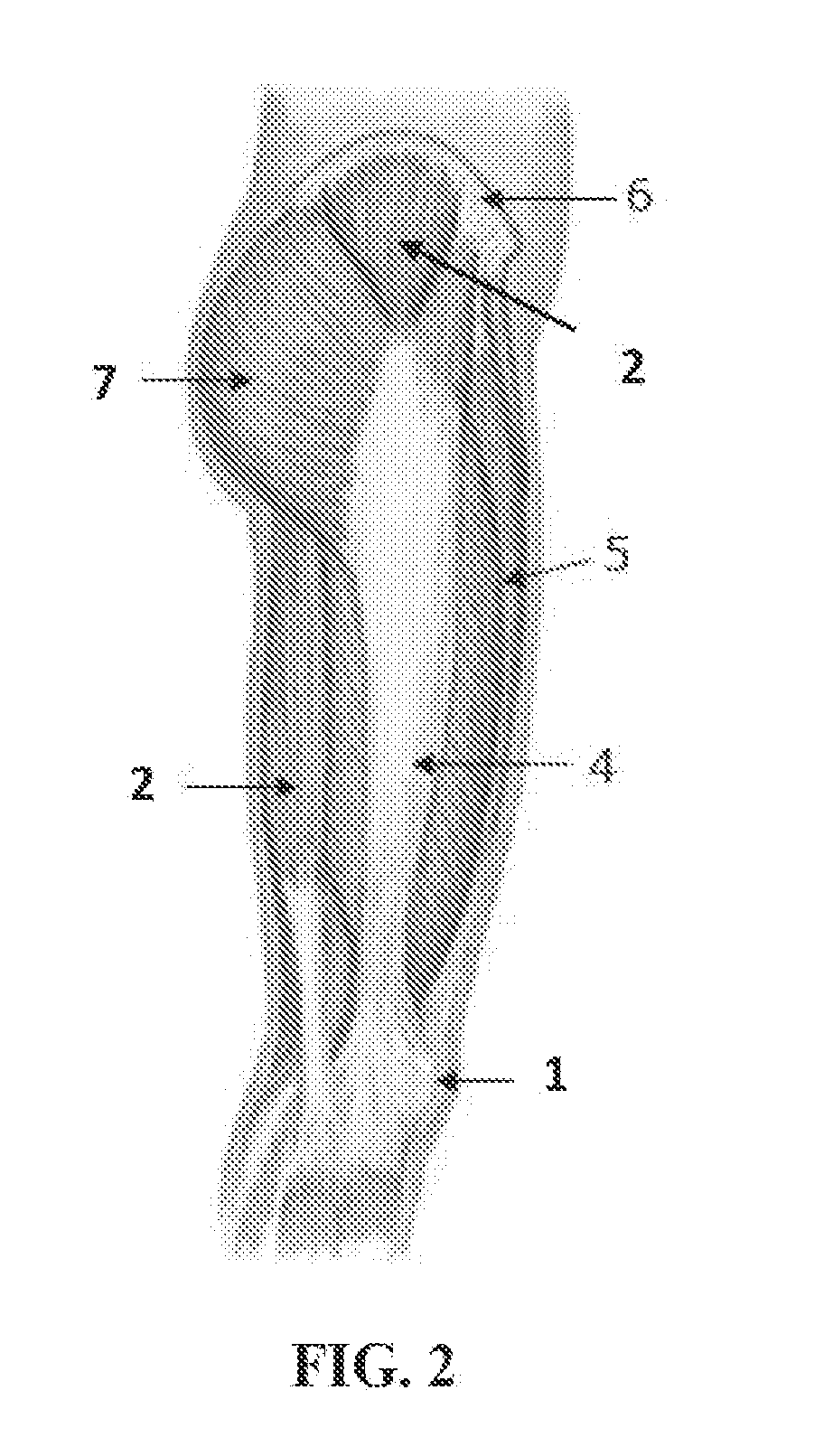
A above knee prosthesis (P) applied to femoral connection (100) of an amputee that comprises a upper hinge (1) connected to femoral connection of the patient, an articulation axis (2) with the function of reproducing the knee movements, a tibia-calf muscle unit (3) pivotally connected to the femoral•segment and a damper (5) that reproduces some functions of the calf muscle and ensures to the prosthesis to brake and to allow the sequential swing and stance phases typical of the gait. The damper comprises a cylinder (5c) wherein a piston (10) and a stem (9) act connected to each other and adapted to carry out a damping reaction of said damper responsive to the forces loaded on the prosthesis. In particular, a force transducer is provided in the damper arranged, in particular, in the stem with a microprocessor that receives a force signal from the transducer and operates means for adjusting the reaction of the damper responsive to the detected force signal.
Owner:OFFICINE ORTOPEDICHE RIZZOLI SRL
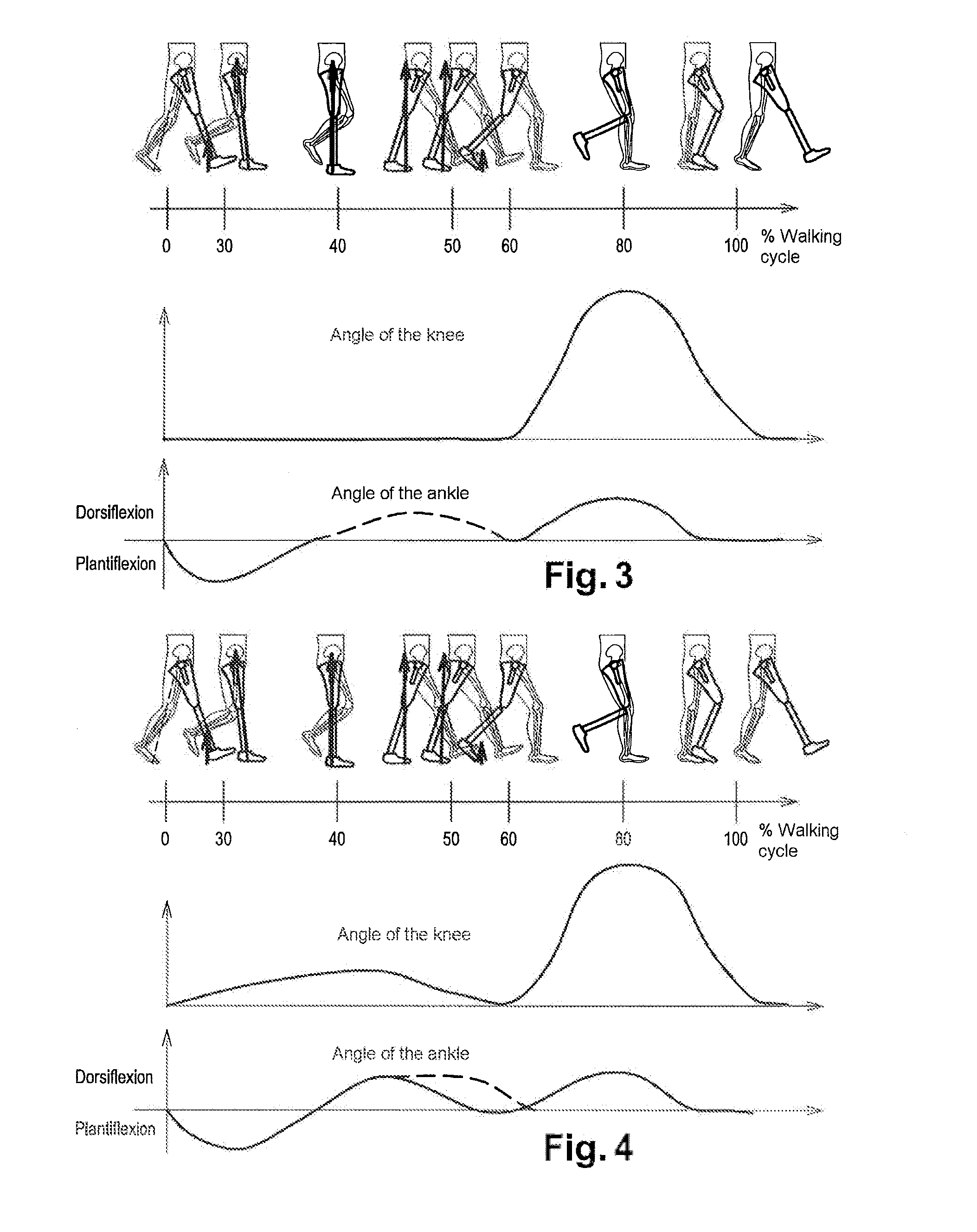
Rehabilitation evaluation method and system based on wearable sensor
ActiveCN112603295AAddressing Home Rehabilitation Assessment QuestionsSensorsMuscle exercising devicesMuscle strengthEngineering
The invention discloses a rehabilitation evaluation method and system based on a wearable sensor. The method comprises the steps that: for a to-be-detected person, an inertia measurement unit is used for collecting knee joint posture information and calculating the knee joint movement range in the walking process; gait parameters during walking are obtained, and a gait function is estimated; supine straight leg lifting time and prone straight leg lifting time are acquired, and muscle strength information is estimated; and the rehabilitation condition of the to-be-detected person is evaluated on the basis of the knee joint movement range, the gait function and the muscle strength information. According to the rehabilitation evaluation method and system based on the wearable sensor of the invention, a patient can complete rehabilitation evaluation at home; the practicability and reliability of the method and system are high, and the economic burden of the patient is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
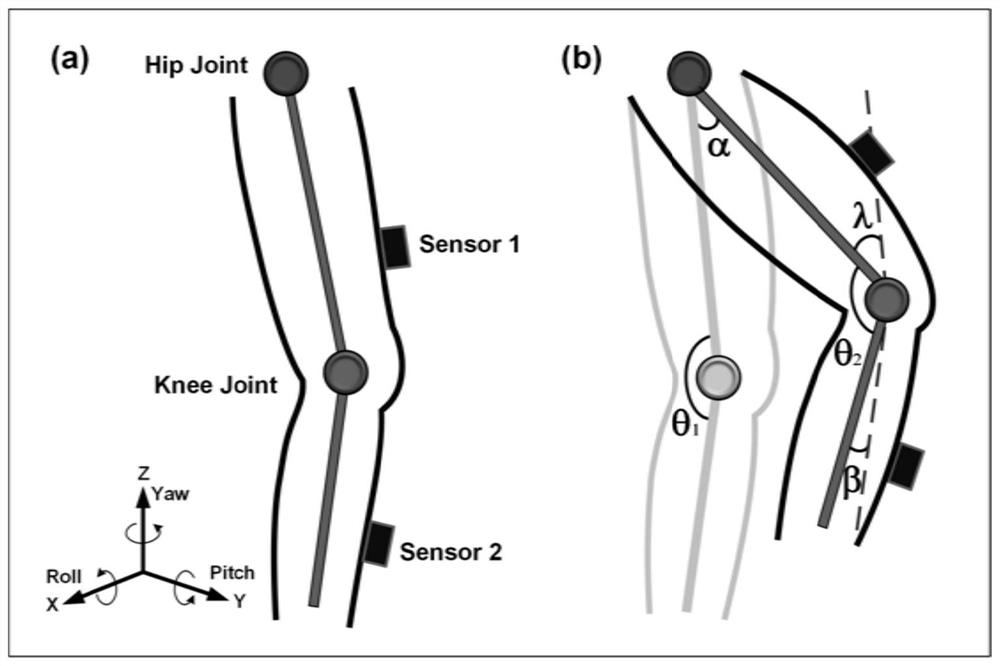
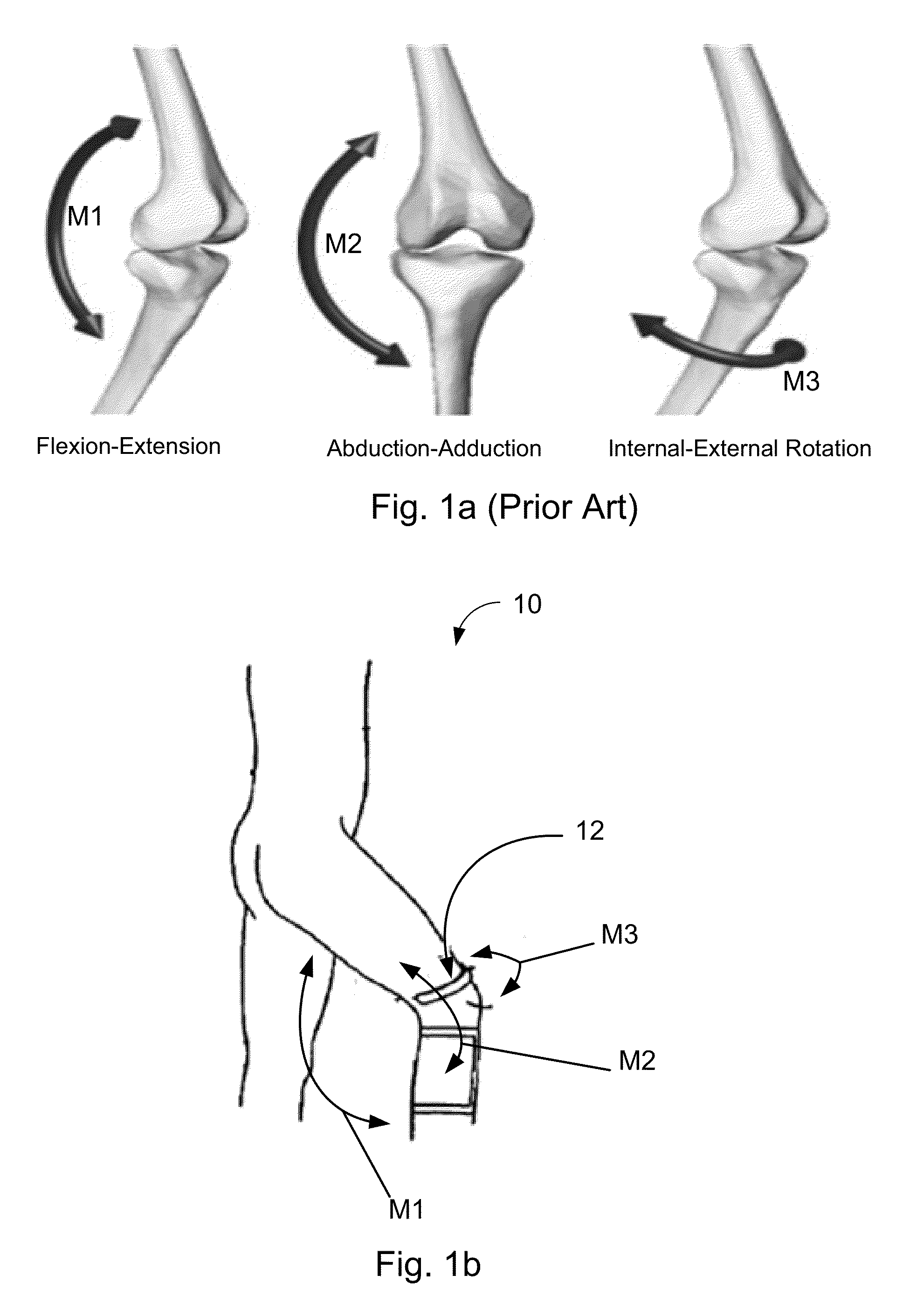
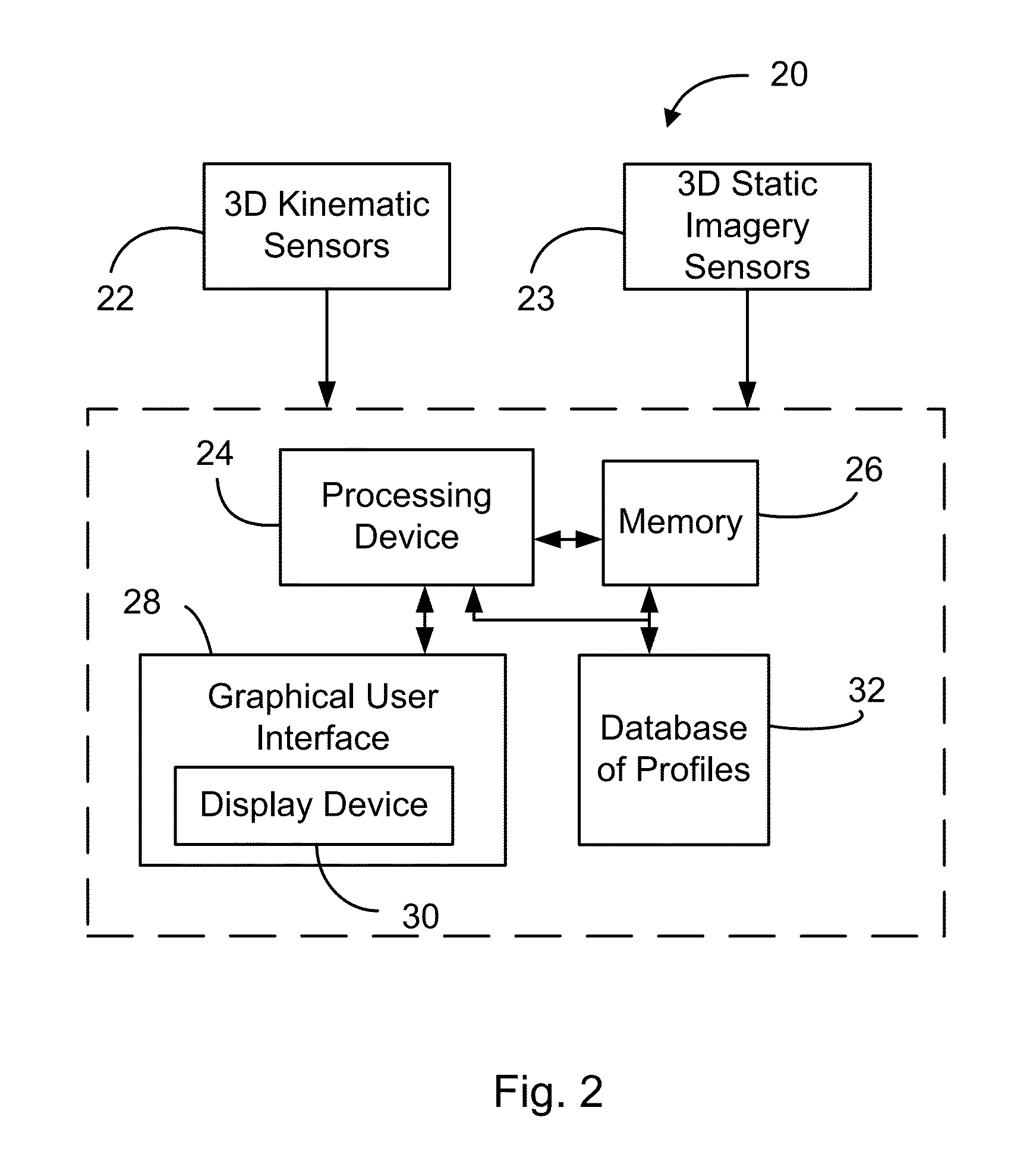
System for the analysis of 3D kinematic of the knee
InactiveUS7291119B1Accurate measurementAccurate analysisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPerson identificationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationBody of femur
A harness for attachment about a knee femur and comprised of a rigid and non-flexible frame support two resiliently mounted clamping means and sensors is described for the non-invasive measurement of knee motion and its analysis in 3-D is described. The clamping means elements are urged under pressure outwardly for application against a skin outer surface at predetermined medial and lateral sites relative to a femur. A non-resilient adjustable stabilizing element is connected to the rigid frame and disposed at a predetermined location with respect to the medial clamping element in spaced relationship therewith and adjustable for clamping contact on a skin outer surface and in alignment with the center of a medial condyle of the femur whereby to stabilize the rigid frame about a knee. An attachment rod is secured to the harness and has straps for securing the rod above the knee.
Owner:POLYVALOR S E C +2
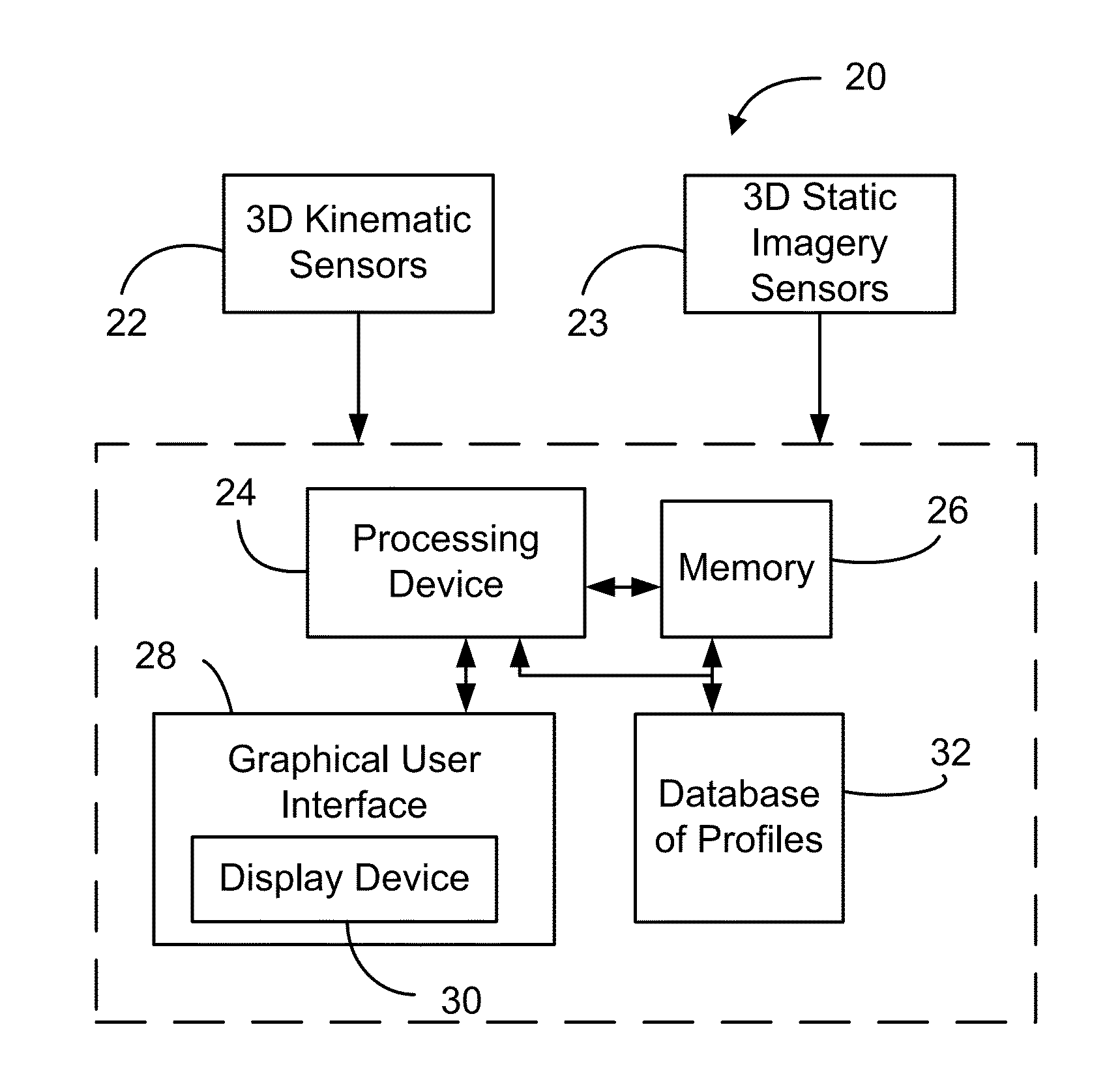
Method and system for human joint treatment plan and personalized surgery planning using 3-d kinematics, fusion imaging and simulation
ActiveUS20130185310A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPersonalizationProgram planning
The present document describes a method for producing a knee joint treatment plan and / or surgery plan for a patient, the method comprising: obtaining 3D kinematic data of the knee joint in movement; determining, from the 3D kinematic data, scores characterising the joint function of the patient, the one or more scores being relative to one or more criteria; and comparing the scores to data in a database which characterize a plurality of treatment plans and / or surgery plans to generate the list of one or more treatment plans and / or surgery plans which match the scores.
Owner:EMOVI
Wearable lower limb rehabilitation training device
InactiveCN103622796AImprove comfortImprove the effect of rehabilitation trainingChiropractic devicesWalking aidsThighLeg length
The invention provides a wearable lower limb rehabilitation training device which comprises a base, a column, a waist bracket, knee-joint motion control units and hip joint motion control units, wherein the column is installed on the base, the waist bracket is installed at the top of the column and is provided with two protective frames, each protective frame is provided with the hip joint motion control unit and the knee-joint motion control unit, each hip joint motion control unit comprises a hip joint motor, a thigh rod, a thigh connecting rod, a thigh driving rod and a thigh layer board, and each knee-joint motion control unit comprises a knee-joint motor, a shank rod, a shank connecting rod, a shank driving rod and a pedal. The upper end of the shank rod is connected with the thigh rod through a thigh joint shaft. The device can realize lower limb rehabilitation training of patients or the old, improve a training effect, and further improve the comfort level of a user. Meanwhile, the device can be suitable for crowds in different body types by adopting a leg length, height and width adjusting mechanism.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for controlling movement of knee joints of artificial limbs
ActiveCN102512270AEnsure safetySimplify detection difficultyProsthesisPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMulti axis
The invention relates to a method for controlling movement of knee joints of artificial limbs, which relates to knee joints of artificial limbs. Steps of the method include that a control component for a knee joint of an artificial limb is mounted and comprises a four-bar linkage on-knee artificial limb knee joint body and a sensor, a Hall sensor is mounted at a boundary position at which a piston of a cylinder moves from a supporting phase to a swinging phase, the piston of the cylinder can move to an artificial limb knee joint locking position, and another Hall sensor is mounted at the artificial limb knee joint locking position; a microcontroller detects the tread period of an artificial limb wearer so as to judge stepping speed, the Hall sensors judge a tread time phase, the microcontroller controls opening of a needle valve of an air cavity, and damping generated in a cylinder body of the cylinder is adjusted so as to adjust the stepping speed; finally, the artificial limb wearer walks normally, when at the swinging phase, the needle valve of the air cavity moves according to an opening value corresponding to the stepping speed, after being in the supporting phase, the needle valve of the air cavity is closed completely, the value of the damping maximizes, and then the knee joint of the artificial limb is locked; and shortcomings that the prior art is lack of a method for controlling movement of a knee joint of a multi-axis artificial limb.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
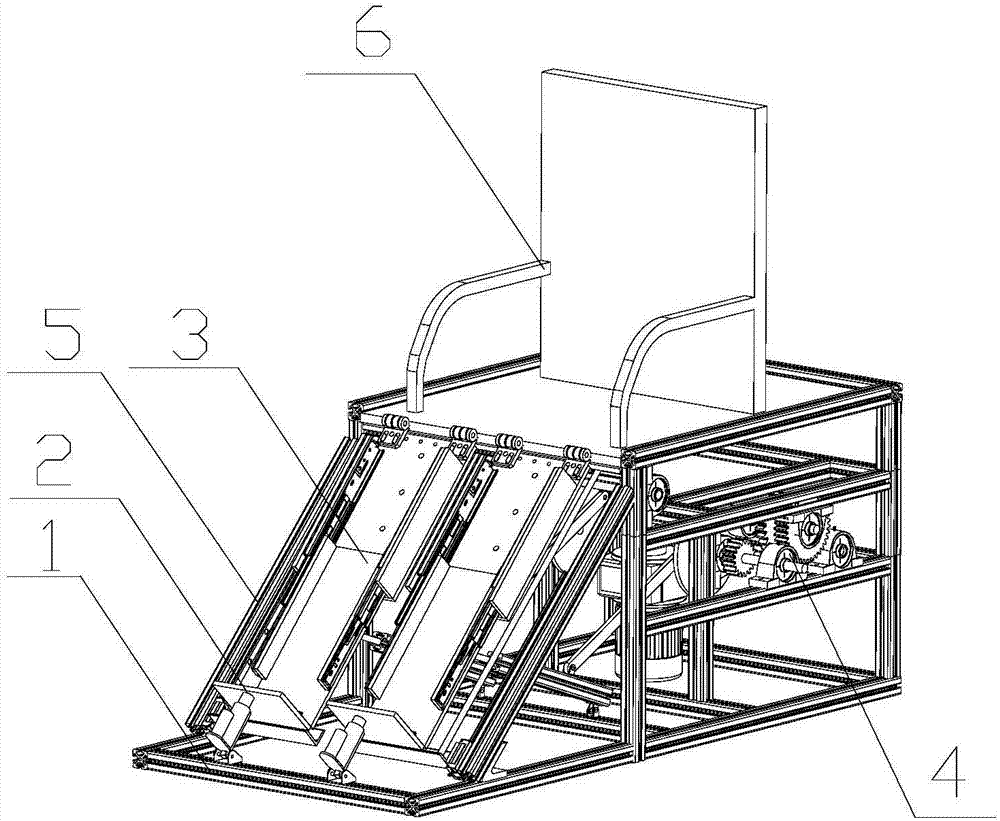
Knee range of motion device utilizing tangential joint translation and distraction
A knee range of motion device utilizing tangential joint translation and distraction is disclosed. The device includes a carriage connected to a base, the carriage having a base attachment section; a thigh support section pivotally attached to the base attachment section; and a lower leg support section pivotally connected to the thigh support section. The device further including a carriage support extending between the thigh support section and the base, the carriage support pivotally connected to the thigh support section and adapted to slide in slots on the base; a first actuator connected to the lower leg support section to extend and retract the lower leg support section, thereby causing a foot support connected to the lower leg section to move; and a second actuator connected to the lower leg support section to raise and lower a calf support, causing an anterior and posterior tibial translation.
Owner:STEWART RICHARD
Hydraulic system for a knee-ankle assembly controlled by a microprocessor
The present invention pertains to a femoral knee-ankle prosthesis intended for persons who are lower-limb amputees but still have a segment suitable for a femoral connection and a tibial connection connected to the femoral segment based on an articulation which reproduces the movements of the knee, the said tibial segment being articulated on one foot based on an articulation reproducing the movements of the ankle, an initial damper the ends of which are joined respectively with the femoral and tibial segments, and another hydraulic damper of which the ends are joined respectively with the tibial and foot segment; the said prosthesis is remarkable in that the chamber of the first hydraulic damper is connected to the chamber of the second hydraulic damper and in that it consists of the means of controlling the first and / or second hydraulic damper depending on the phase of the walking cycle such as the stance phase or the swing phase and / or real-life situations such as stairs, slopes or standing, etc., in such a manner that the flexion of the knee allows the dorsiflexion of the ankle in proportion to the movement of the knee during the stance phase and such that the flexion of the knee results in the dorsiflexion of the ankle during the swing phase.
Owner:PROTEOR
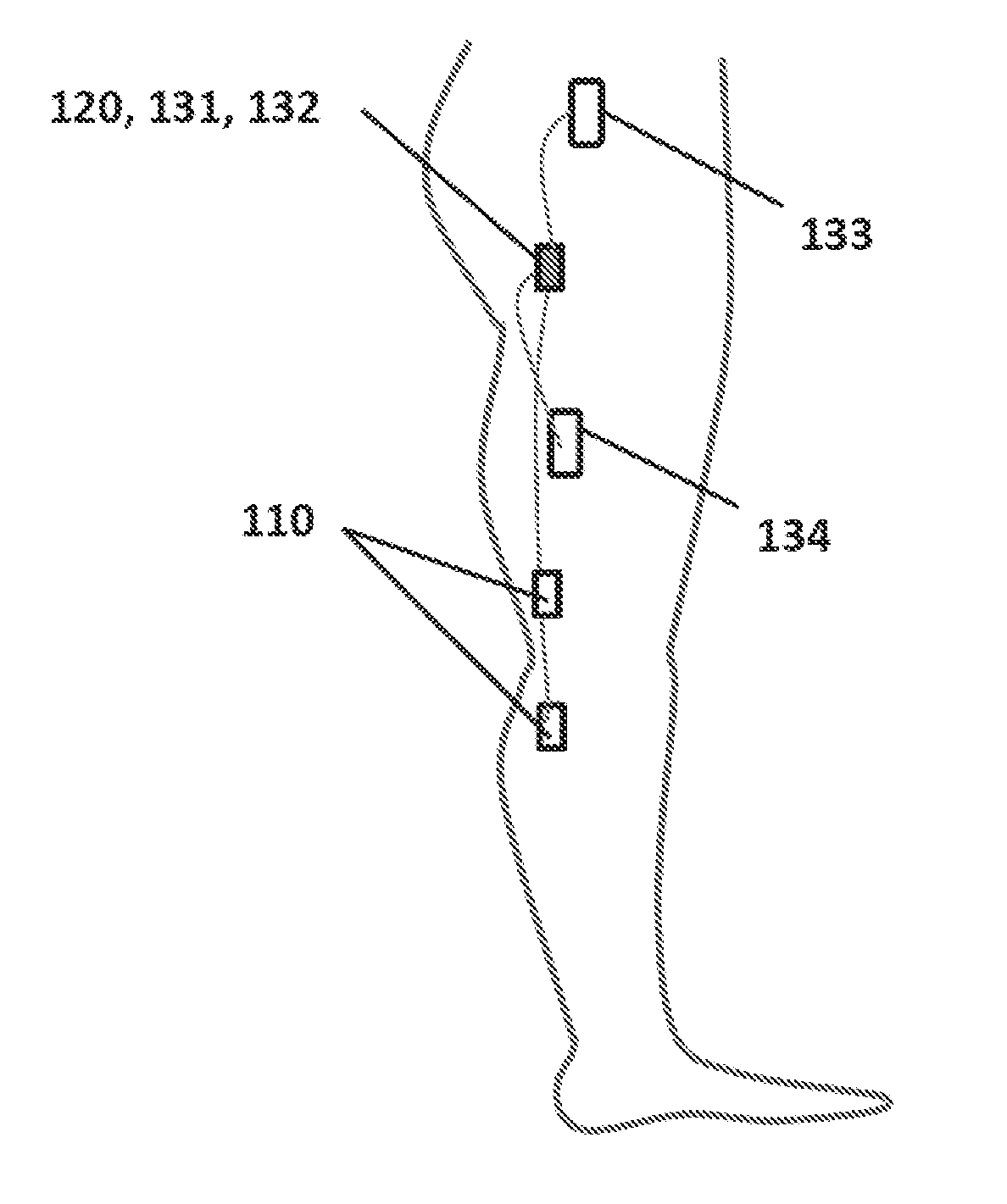
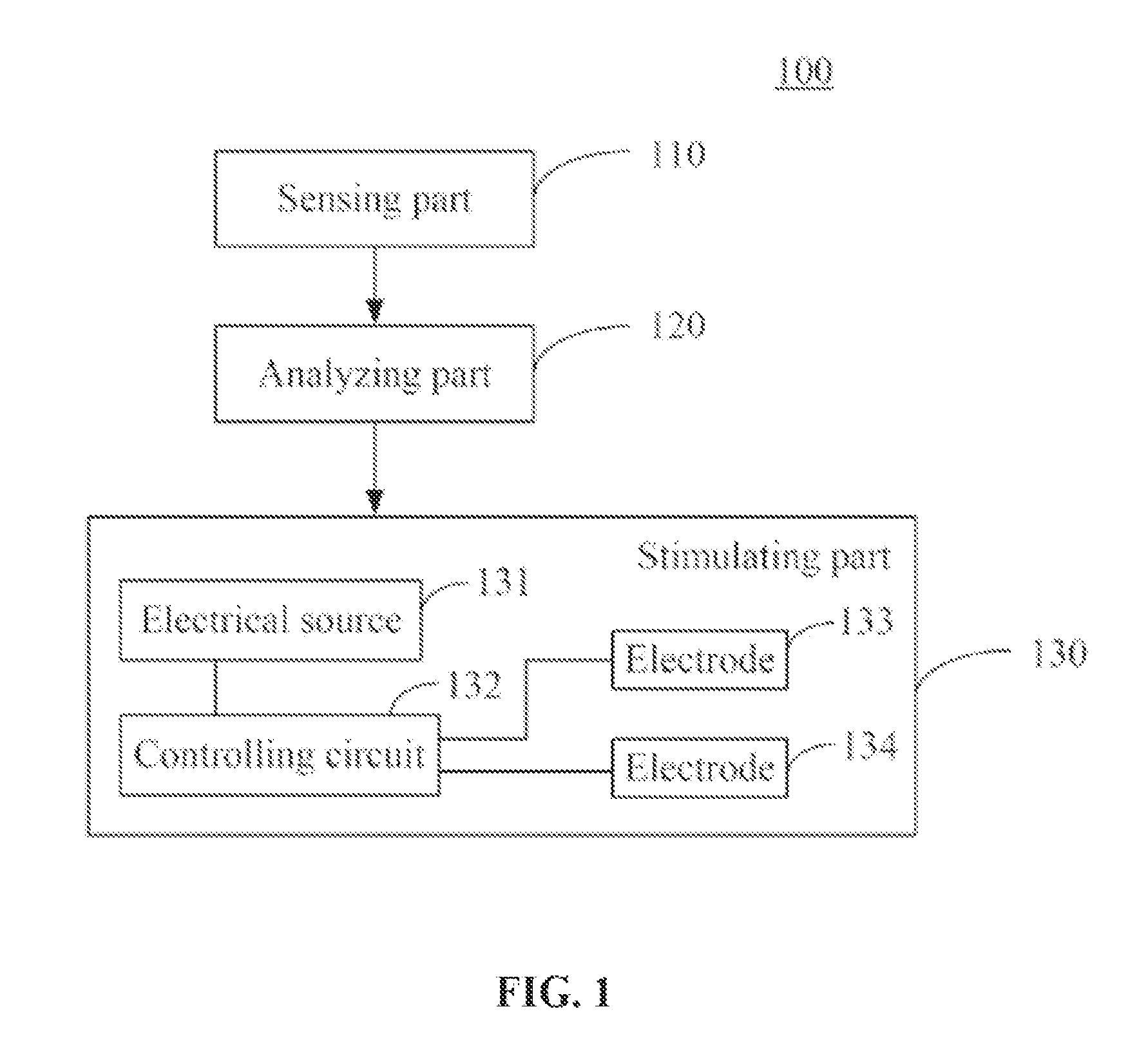
Device and methods for preventing knee sprain injuries
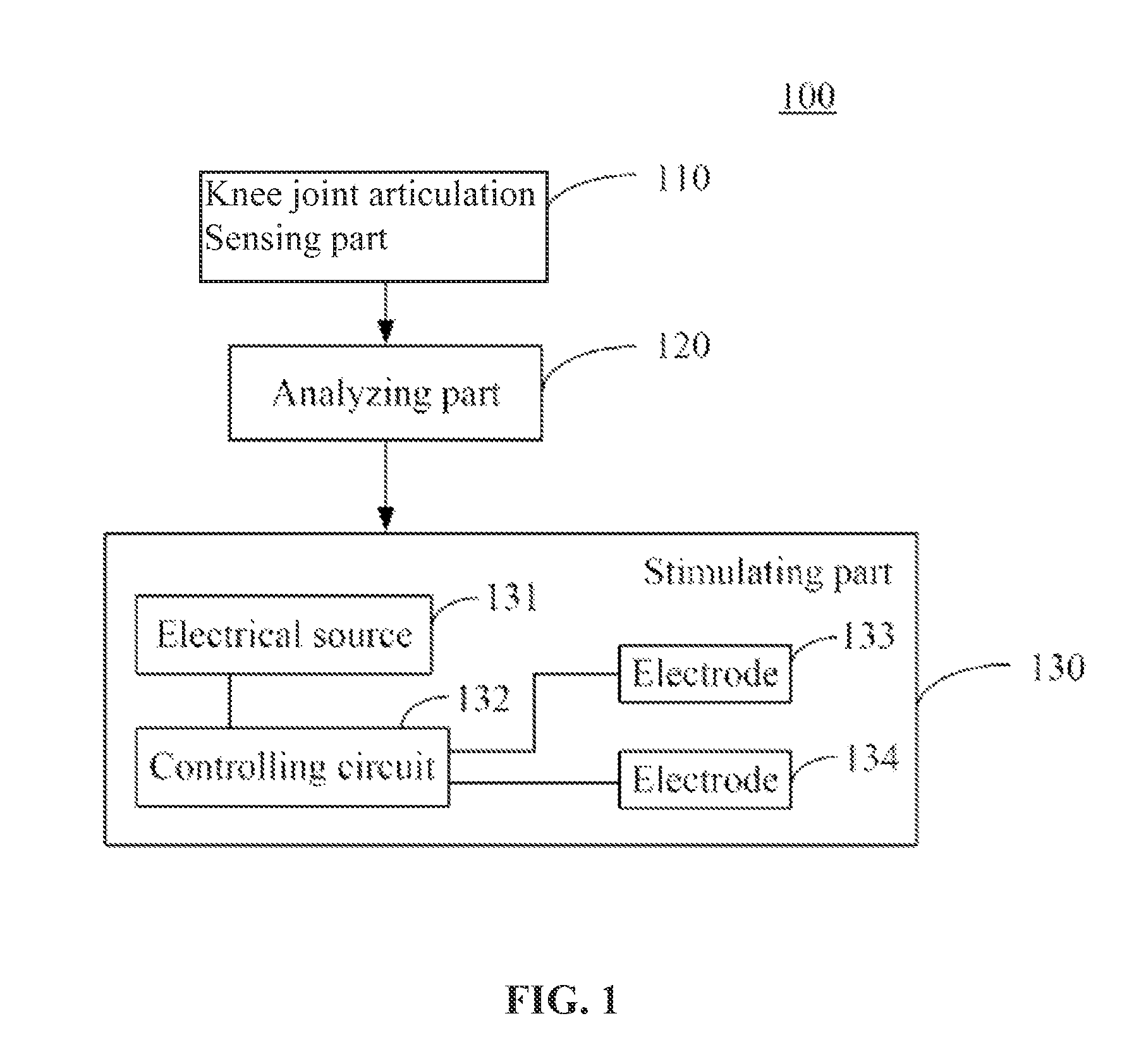
ActiveUS20140277271A1Avoid injuryImprove pronunciationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSensing dataPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Devices and methods for preventing knee sprain injuries. To protect the knee joint from knee sprain injuries, the device comprises a sensing part configured to sense data associated with knee motion; an analyzing part configured to analyze the knee motion data to determine a knee articulation; and a stimulating part configured to stimulate one or more lower limb muscles to initiate an earlier muscle reaction than would naturally occur in response to the determined knee joint articulation. The determined knee joint articulation may include knee joint articulation or a particular type of articulation such as a knee sprain movement associated with knee sprain. The methods involve sensing data associated with knee joint motion, analyzing the data to determine a knee joint articulation; and stimulating one or more lower limb muscles to initiate an early muscle reaction within the determined knee joint articulation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Robot for lower-limb rehabilitation training
ActiveCN105919775ASimple control principleEasy to operateChiropractic devicesManipulatorRange of motionReduction drive
The invention discloses a robot for lower-limb rehabilitation training. The robot comprises a control panel, a case body assembly as well as a drive part assembly, a drive arm assembly, a driven arm assembly, an ankle joint assembly and a shank assembly which are sequentially connected, wherein the drive part assembly comprises a hip joint motor and a speed reducer and is used for driving the drive arm assembly to control the hip joint to move; the drive arm assembly comprises a drive arm, one end of the drive arm is connected with an output shaft of the speed reducer, and the other end of the drive arm is rotationally connected with the driven arm assembly; a driven arm assembly body I used for driving the driven arm assembly to control the knee joint to move, a driven arm assembly body II used for driving the ankle joint assembly to control the ankle joint to stretch or bend and a driven arm assembly body III used for driving the shank assembly to control the shank to move are arranged in the driven arm assembly. The robot for lower-limb rehabilitation training is used for rehabilitation training on the range of motions, coordination of joints and the like, is easy to operate and suitable for wide occasions and can be used for training in different modes according to different rehabilitation stages, and the control principle is simple.
Owner:GUANGDONG YISHENG IND CO LTD
Lower limb rehabilitation training machine
The invention relates to a lower limb rehabilitation training machine. The lower limb rehabilitation training machine comprises an outer frame, two ankle exercising mechanisms, two parallelly arranged leg extension mechanisms, two knee joint exercising mechanisms, two hip joint exercising mechanisms, an adjustable backrest mechanism and a controller, wherein the ankle exercising mechanisms, the leg extension mechanisms, the knee joint exercising mechanisms and the hip joint exercising mechanisms are in one-to-one correspondence; each ankle exercising mechanism is connected with the lower portion of the corresponding leg extension mechanism, and the upper portion of each leg extension mechanism is hinged to the front edge of the seat plate of the adjustable backrest mechanism; the knee joint exercising mechanisms are mounted on the outer frame, and the power output end of each knee joint exercising mechanism is connected with the corresponding leg extension mechanism; the two hip joint exercising mechanisms are mounted on the outer frame; the ankle exercising mechanisms, the knee joint exercising mechanisms and the hip joint exercising mechanisms are electrically connected the corresponding pins of the controller. The lower limb rehabilitation training machine has the advantages that labor input is reduced, and the three joints of legs can be passively and safely exercised at home.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Device and methods for preventing knee sprain injuries
ActiveUS9008784B2Avoid injuryImprove pronunciationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSensing dataPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Devices and methods for preventing knee sprain injuries. To protect the knee joint from knee sprain injuries, the device comprises a sensing part configured to sense data associated with knee motion; an analyzing part configured to analyze the knee motion data to determine a knee articulation; and a stimulating part configured to stimulate one or more lower limb muscles to initiate an earlier muscle reaction than would naturally occur in response to the determined knee joint articulation. The determined knee joint articulation may include knee joint articulation or a particular type of articulation such as a knee sprain movement associated with knee sprain. The methods involve sensing data associated with knee joint motion, analyzing the data to determine a knee joint articulation; and stimulating one or more lower limb muscles to initiate an early muscle reaction within the determined knee joint articulation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Automatic prosthesis for above-knee amputees
A above knee prosthesis (P) applied to femoral connection (100) of an amputee that comprises a upper hinge (1) connected to femoral connection of the patient, an articulation axis (2) with the function of reproducing the knee movements, a tibia-calf muscle unit (3) pivotally connected to the femoral•segment and a damper (5) that reproduces some functions of the calf muscle and ensures to the prosthesis to brake and to allow the sequential swing and stance phases typical of the gait. The damper comprises a cylinder (5c) wherein a piston (10) and a stem (9) act connected to each other and adapted to carry out a damping reaction of said damper responsive to the forces loaded on the prosthesis. In particular, a force transducer is provided in the damper arranged, in particular, in the stem with a microprocessor that receives a force signal from the transducer and operates means for adjusting the reaction of the damper responsive to the detected force signal.
Owner:OFFICINE ORTOPEDICHE RIZZOLI SRL
Knee-joint exoskeleton system integrating functional electric stimulation
ActiveCN103655122AConvenient force controlKnee joint rehabilitation trainingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesElectricityPull force
The invention provides a knee-joint exoskeleton system integrating functional electric stimulation. A direct current servo motor driver is connected with a knee-joint exoskeleton. A controller and the direct current servo motor driver are connected with a multi-passage functional electric stimulator. The controller controls the knee-joint exoskeleton through the direct current servo motor driver and controls the multi-passage functional electric stimulator. The knee-joint exoskeleton and the multi-passage functional electric stimulator work in a coordination mode, and the synchronism of the knee-joint exoskeleton and the multi-passage functional electric stimulator is controlled by the controller. According to the knee-joint exoskeleton system, independent power of patient muscles are developed through the functional electric stimulation, a rehabilitation robot plays an auxiliary role, the independent power of the patient muscles and the rehabilitation robot work together, so that best knee-joint rehabilitation training is provided for paralytics. The synchronism of the knee-joint exoskeleton and the multi-passage functional electric stimulator is ensured by the controller. The knee-joint exoskeleton is drawn by a steel wire to drive a knee joint to move, and the steel wire is connected with a tension sensor, so that better force control is provided, and possibility for active rehabilitation motion control is offered.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Mechanical leg imitating ostrich hind limb
The invention discloses a bionic mechanical leg imitating the motion function characteristic of an ostrich hind limb. The mechanical leg comprises a body, a hip joint motion mechanism, a knee joint motion mechanism and an ankle joint motion mechanism. The hip joint motion mechanism is composed of a motor and a crank-rocker mechanism, wherein the crank-rocker mechanism comprises a crank, a femur and a connecting rod. The knee joint motion mechanism comprises the femur, a first spring, a tibia, a metatarsus, a brake cable, a lower fibula, a second spring, an air cylinder and an upper fibula. The ankle joint motion mechanism comprises the metatarsus, a first apotelus bone, a second apotelus bone, a third apotelus bone, a third torsional spring, a second torsional spring and a first torsional spring. The ostrich hind limb capable of efficiently moving serves as the bionic prototype, through combination of testing on hind limb motion parameters during running of an ostrich and biological anatomic analysis, the mechanical leg imitating the ostrich hind limb is obtained through optimization design according to the tendon-bone and muscle-tendon interaction mechanism of the ostrich, and the mechanical leg is simple in structure, safe, reliable, low in vibration, and capable of efficiently saving energy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
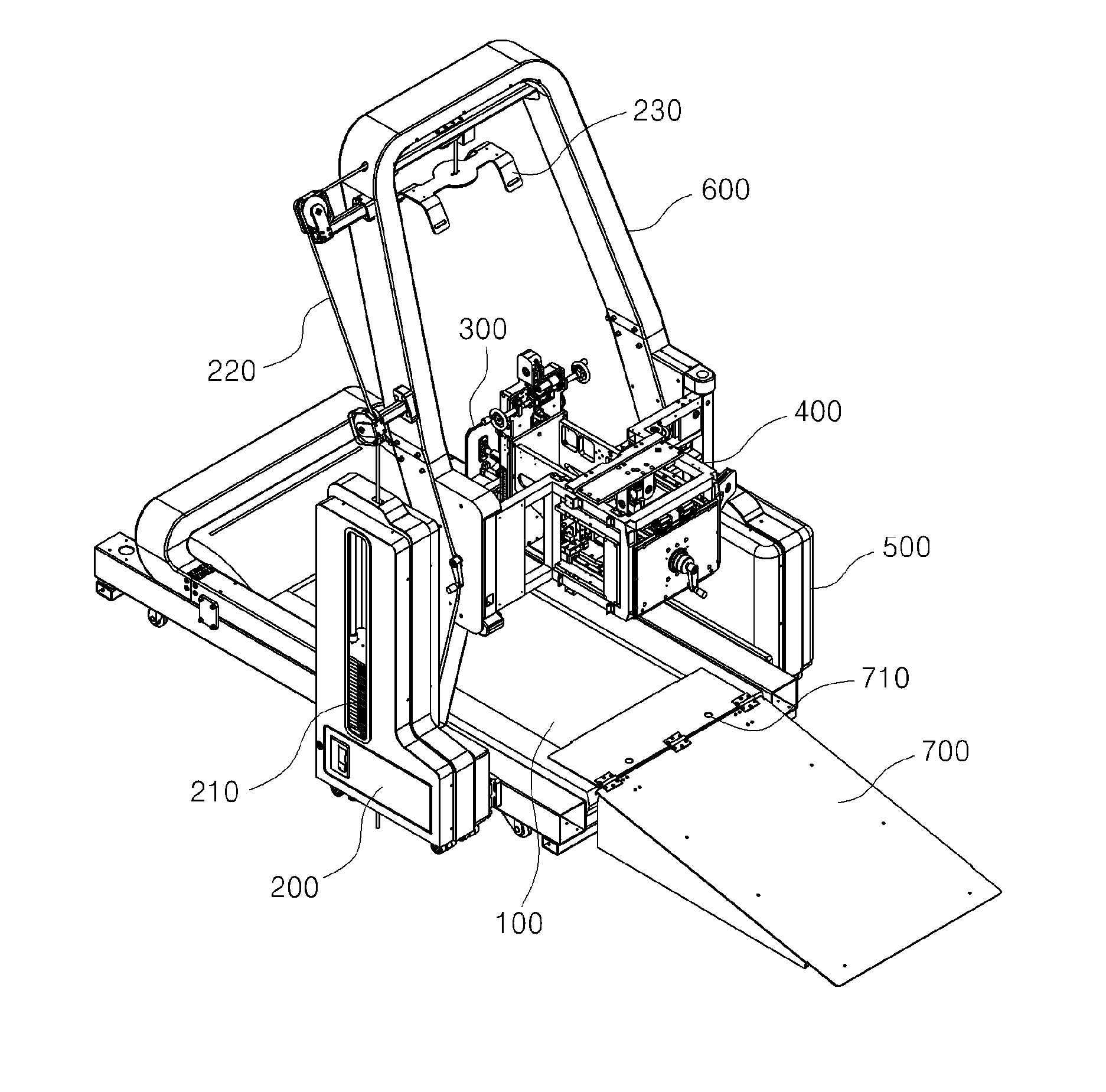
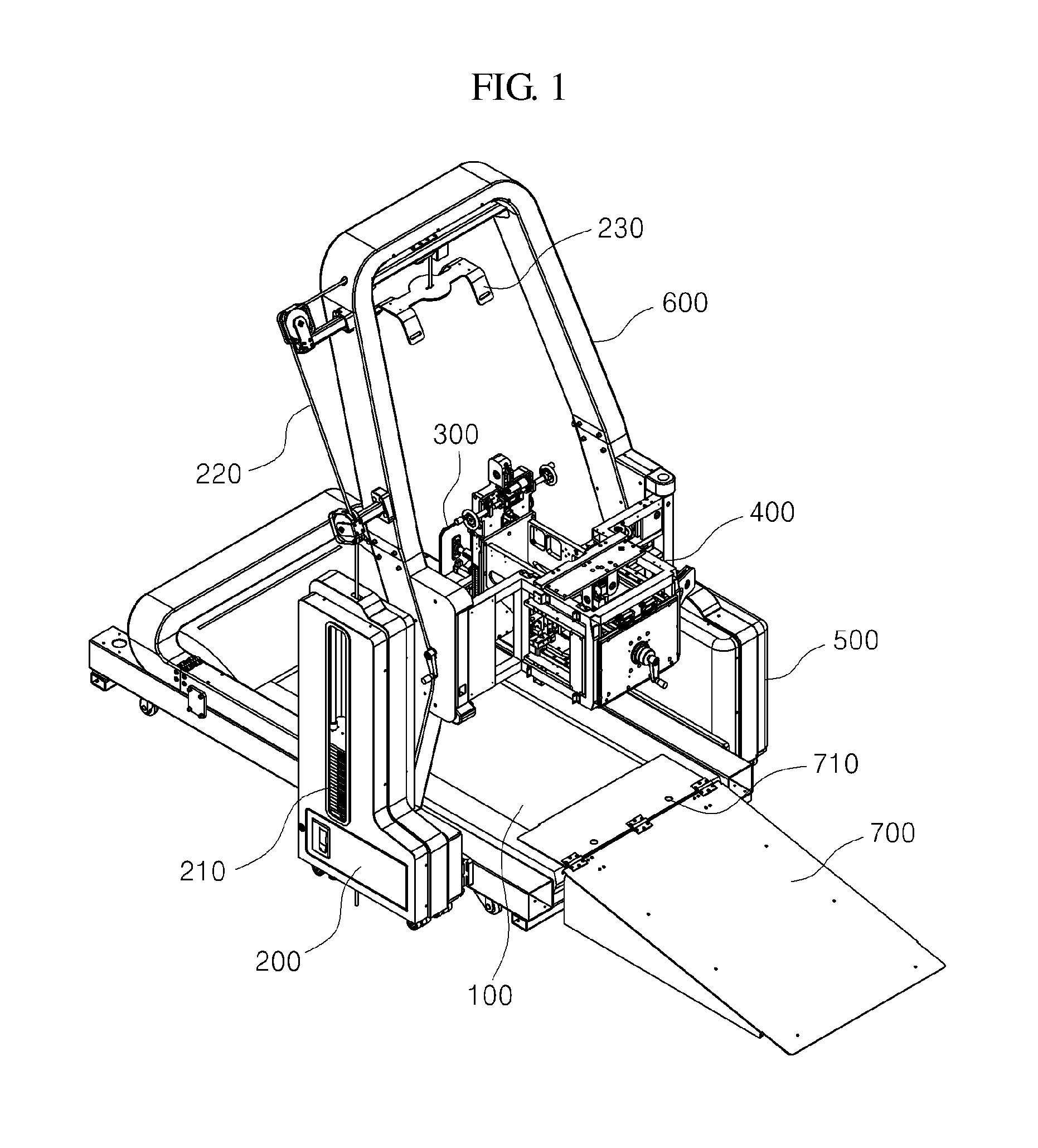
Walking training apparatus
ActiveUS20140378279A1Reduce fatigueMaximize efficiencyChiropractic devicesWalking aidsControl signalEngineering
The present invention relates to a walking training apparatus. The walking training apparatus includes: a treadmill providing a bottom surface to allow a user who is training to walk to do so in a stationary position; a user counterweight unit including a counterweight, a wire, and a harness jacket, wherein the user counterweight unit lifts the user's body upward in order to reduce the load from the user's weight; a joint motion robot worn on one lower leg of the walker, wherein the joint motion robot is constituted by a hip-joint motion part, a knee-joint motion part, and an ankle-joint motion part; a joint motion robot support part supporting and coupled to the joint motion robot to reduce the load of the weight of the joint motion robot, wherein the joint motion robot support includes a horizontal movable part and a vertical movable part for moving the joint motion robot; and a control unit linked with at least one of the treadmill, the user counterweight unit, the joint motion robot, and the joint motion robot support in order to generate a customized control signal according to the user and to transmit the signal.
Owner:P&S MECHANICS
Knee joint exoskeleton based on rope variable-rigidity multifunctional driver and control method
ActiveCN111481402AControllable walking assist torqueImplementation driveGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationGait analysis
The invention discloses a knee joint exoskeleton based on a rope variable-rigidity multifunctional driver and a control method, the knee joint exoskeleton comprises a leg structure, the multifunctional driver, a sensing and control system and a waist control box, and the multifunctional driver is composed of a motor element, a length adjusting mechanism, a rigidity adjusting mechanism and a jointmagneto-rheological brake. According to the control method, on the basis of gait analysis and requirements of a user and the functions of driving, braking, hybrid braking, rigidity adjusting and the like of the multifunctional driver, expected auxiliary torque and movement are output, and a patient suffering from knee joint dyskinesia is helped to do exercise rehabilitation; the knee joint exoskeleton is high in energy efficiency, large in output torque, adjustable in rigidity, convenient to wear and suitable for assisting walking of old people and postoperative rehabilitation training of kneejoint injury patients.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Power-assisted walking robot adapted to medical rehabilitation, correction or training
ActiveCN107049715ASimple structureCompact and reasonable layoutProgramme-controlled manipulatorWalking aidsEngineeringBilateral symmetry
The invention discloses a power-assisted walking robot adapted to medical rehabilitation, correction or training. The power-assisted walking robot comprises a left lower limb, a right lower limb, a waist support board, left and right connecting blocks. The waist support board has a radian and is horizontally placed. The concave surface of the waist support board faces forward. The left and right ends of the waist support board are integrally connected with the left lower limb and the right lower limb through the left and right connecting blocks. The left and right connecting blocks are of integral shaft-hole structures with shafts in the vertical direction and holes in horizontal directions. The perpendicular bisector of the longitudinal center line of the waist support board is a symmetrical shaft. The power-assisted walking robot is composed of a left half part and a right half part, both of which are in bilateral symmetry. The power-assisted walking robot adapted to medical rehabilitation, correction or training has the following beneficial effects: the robot is simple in structure and compact and reasonable in layout and has three active degrees of freedom including two motion of the hip joint and one knee joint motion and one passive degree of freedom including ankle joint motion; and all components of the robot are good in coordination, high in running precision, flexible in control and adjustable in leg length and convenient to use.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Flexible walking-aid exoskeleton
The invention discloses a flexible walking-aid exoskeleton. The exoskeleton includes a portable control box, wearable flexible actuators and the like. A wearable inertial measurement unit module is used for acquiring a lower-limb movement picture in real time, and a core signal source is provided for a drive and control module. Under the excitation of the signal source, the drive and control module is used for understanding, judgment, decision making and anomaly detection of the human-body lower-limb movement picture, the output flow of a micro inflatable pump is controlled in real time, and asolenoid valve component is controlled for switching of air channels. Based on the real-time movement state of the lower limbs of a user, pressure control is conducted on corresponding air bags of the wearable flexible actuators on the left leg and the right leg, in the walking process, torque for aiding the knee joint in bending and stretching is provided for the left leg and the right leg, andthe purpose of providing flexible walking aid for the elderly with knee-joint sport injuries and weak walking ability is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Cylinder fixation type four-bar mechanism intelligent artificial limb knee joint
An intelligent prosthetic limb knee joint with a cylinder stationary type four-bar mechanism belongs to the fields of biological medicine engineering and rehabilitation assistant devices. The intelligent prosthetic limb knee joint with a cylinder stationary type four-bar mechanism includes a above-knee prosthesis part, a knee joint antebrachium, a knee joint postbrachium, a below-knee prosthesis part, a cylinder part, and a linear motor and a needle valve used for providing intelligent driving. The cylinder part is fixed on the below-knee prosthesis part through positioning pins; a pendulum bar is additionally disposed between the upper end of a piston rod and the above-knee prosthesis part, and a torsional spring is assembled on the upper shaft of the pendulum bar. During the knee joint movement, the product of the invention moves following the below-knee prosthesis only and does not swing itself, thus, during the knee joint movement, the influence of large space occupation and great additional rotary inertia caused by relative swing of the cylinder body on pace control are avoided. At the same time, the linear motor and the needle valve are assembled at the lower end of the cylinder body, the intermediate parts are reduced, the costs for manufacture and maintenance are lowered and the operation accuracy and operation efficiency are enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
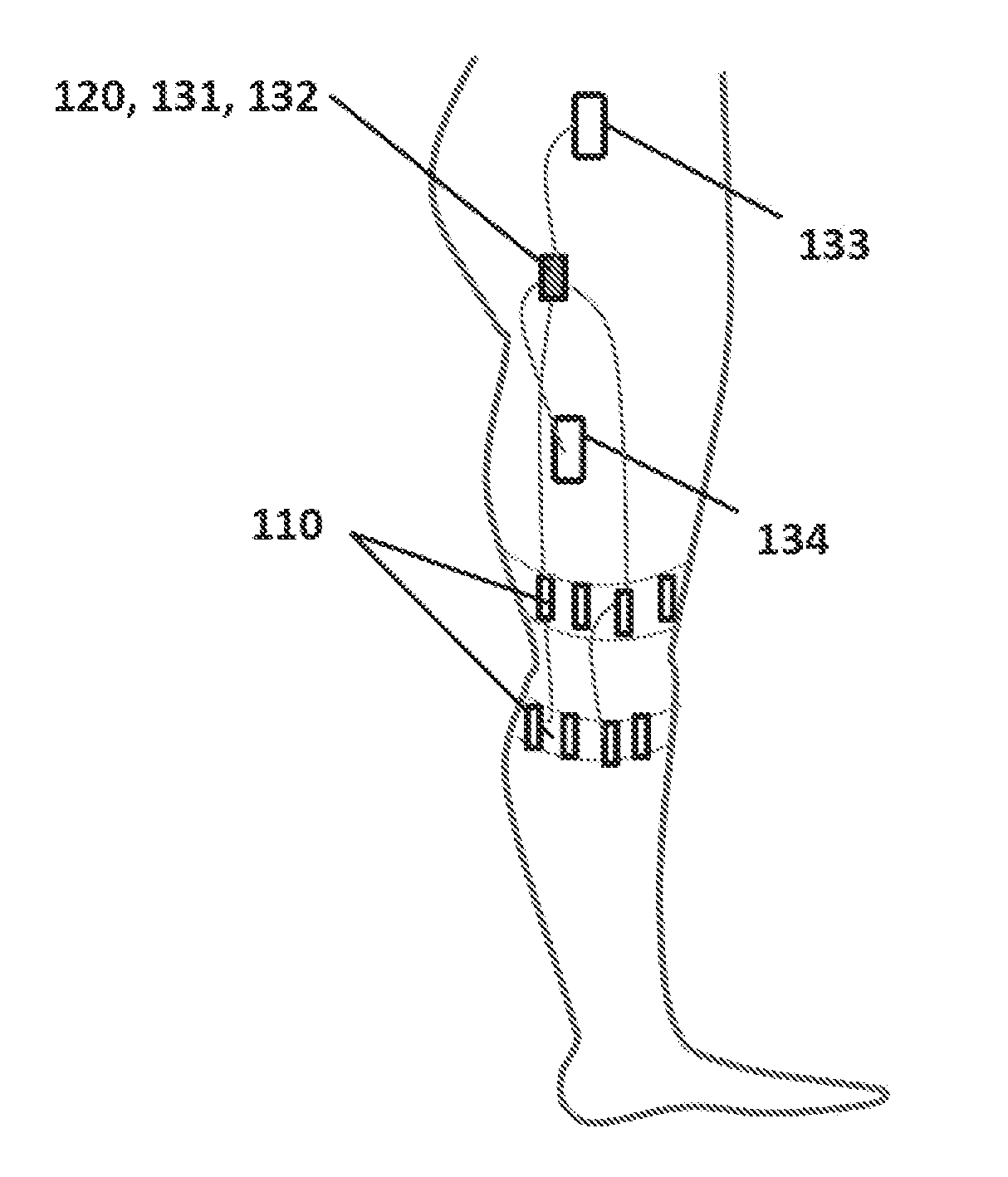
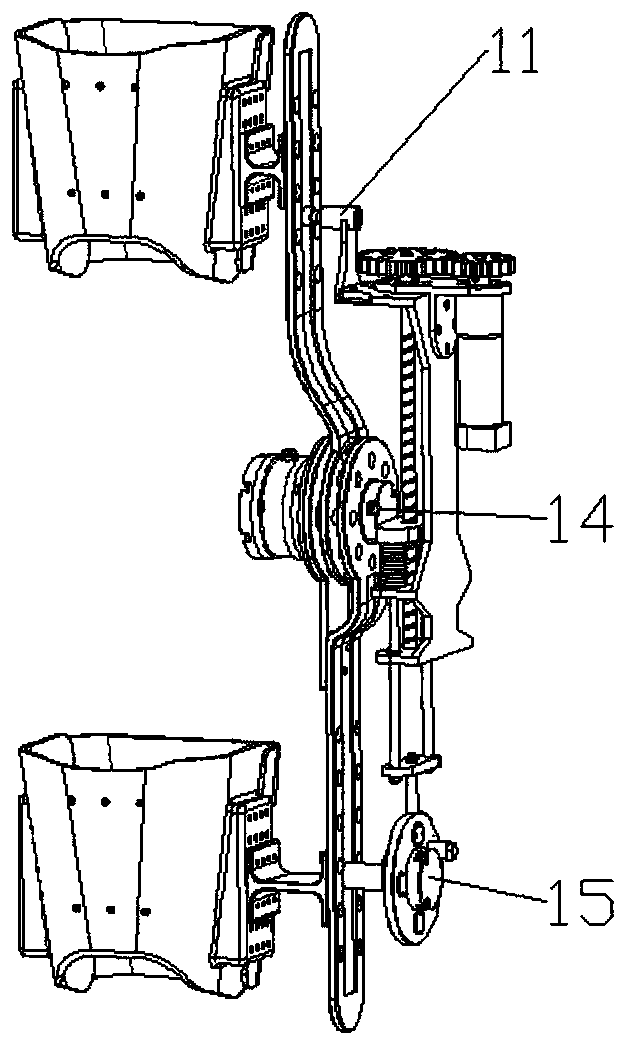
Flexible fabric sensor for measuring human body knee joint movement and method thereof
ActiveCN106889991AComfortable to wearImprove performanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of wearable sensors, and particularly discloses a novel flexible fabric sensor for measuring human body knee joint movement and a method thereof. The current bending angle, formed when a user walks and does movement training, of the knee joint can be measured and output in real time. Common cloth is combined with conductive yarn, a sensitive unit of the flexible fabric sensor is developed, after the sensor is calibrated through a designed method, bending movement of the knee joint is converted into stretching movement of the flexible fabric sensor through a certain wearing mode, the problem that a rotating shaft moves when the knee joint rotates is effectively solved, and the current bending angle of the knee joint of the user is calculated and output. The flexible fabric sensor is convenient to use, low in cost and capable of being not limited by a field and measuring the bending angle of the knee joint of the user in a comfortable mode in real time and has high reliability and a good popularization prospect.
Owner:NANJING ZHELI INTELLIGENT MFG RES INST CO LTD
Energy collection device
PendingCN110311531AHigh outputImprove power generation efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHuman bodyElectromagnetic generator
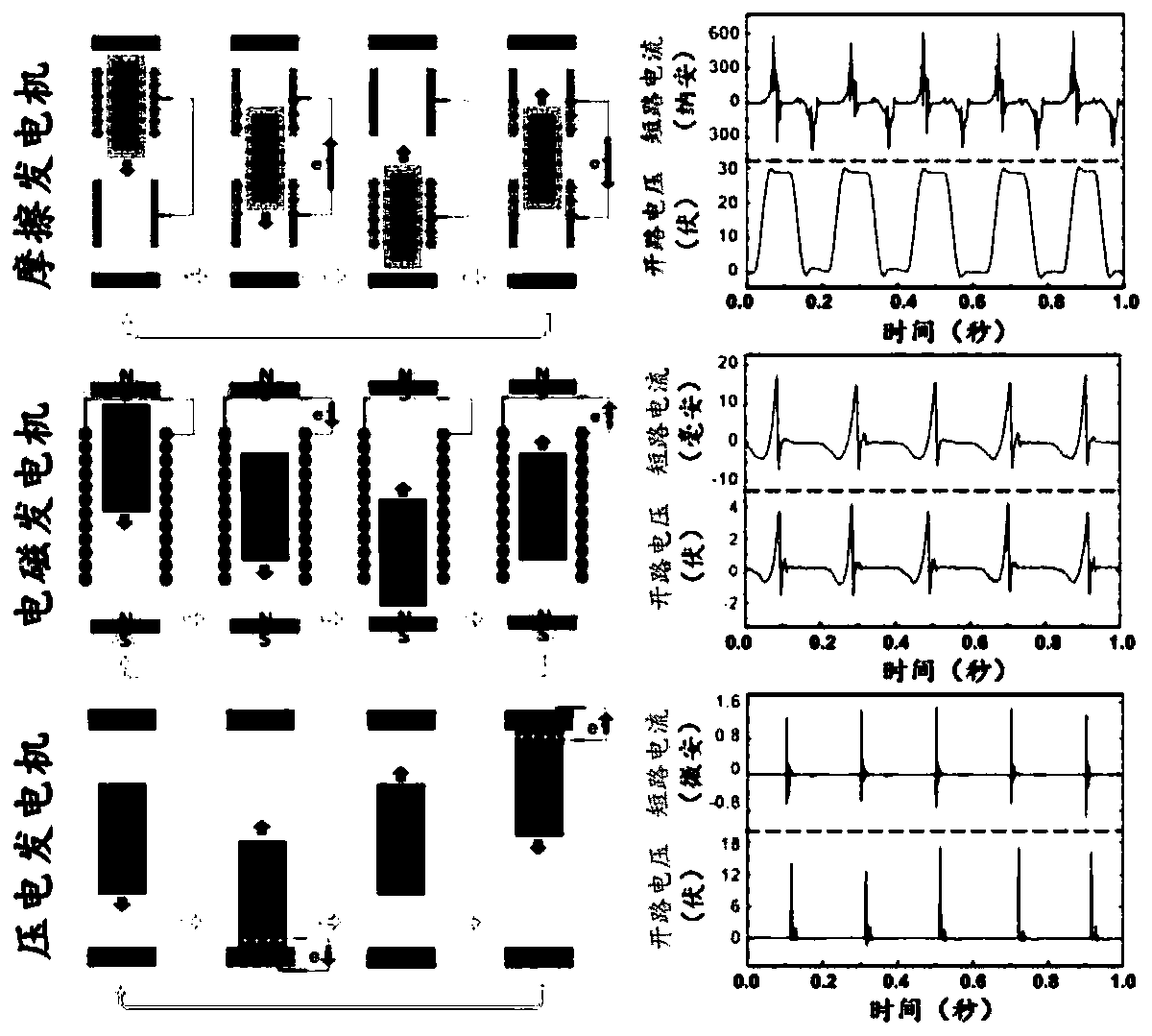
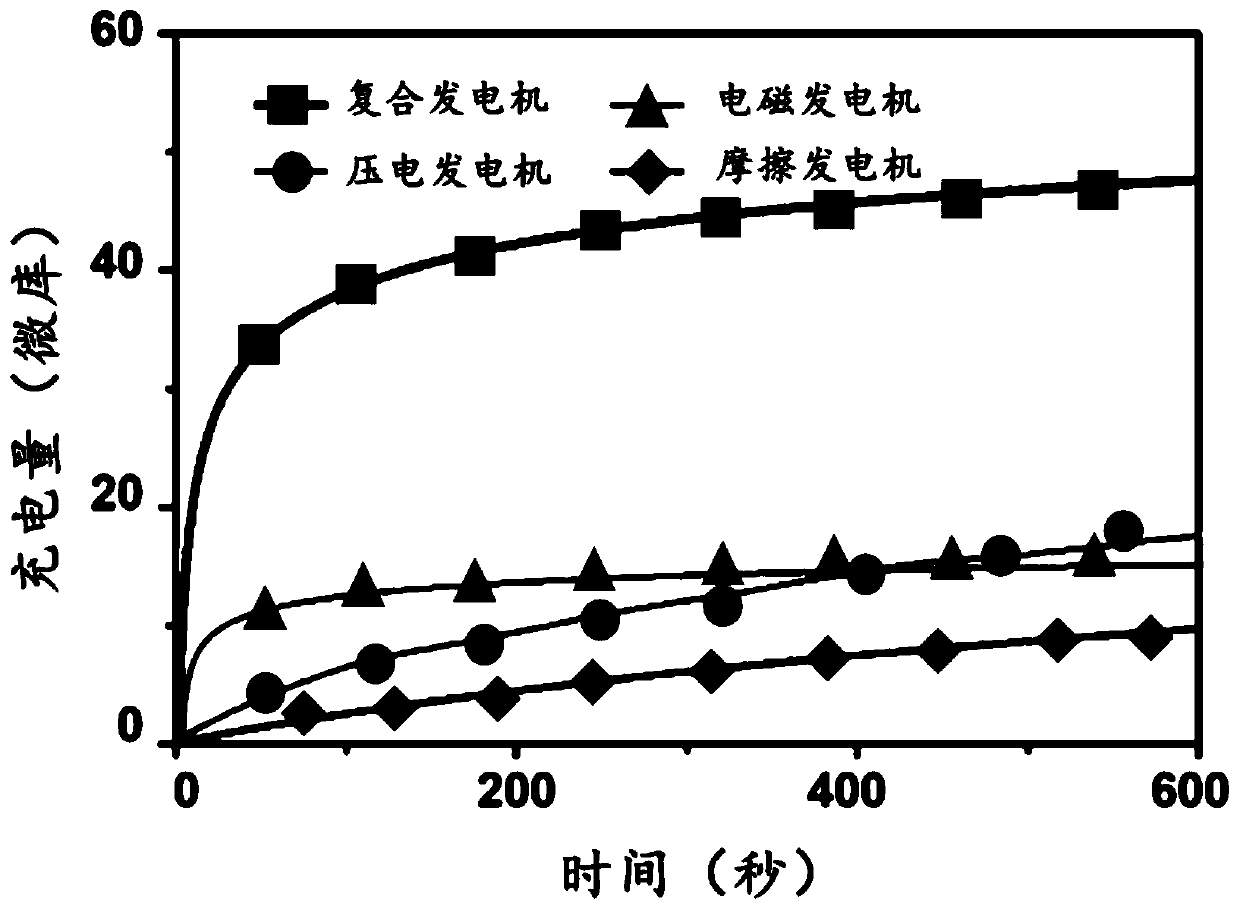
The invention provides an energy collection device which can collect energy during human motion to supply energy for electronic equipment and realize long-term endurance of the electronic equipment. An electromagnetic generator, a friction generator and a piezoelectric generator are integrated to construct a composite generator for collecting the energy during human motion. The composite generatorcan improve the output and greatly expand the scope of generator application. Meanwhile, a wearable general energy collection device is designed according to the human motion scenes. The device can be worn on the arms, elbows, legs, knees, waists and other parts. When the human body is moving (walking, running, jumping, etc.), arm swinging, leg movement, knee movement, etc. will drive the systemto shake and realize the conversion of mechanical energy to electric energy in the process of human movement, and thus the energy collection device has a good application prospect.
Owner:广东心科医疗科技有限公司
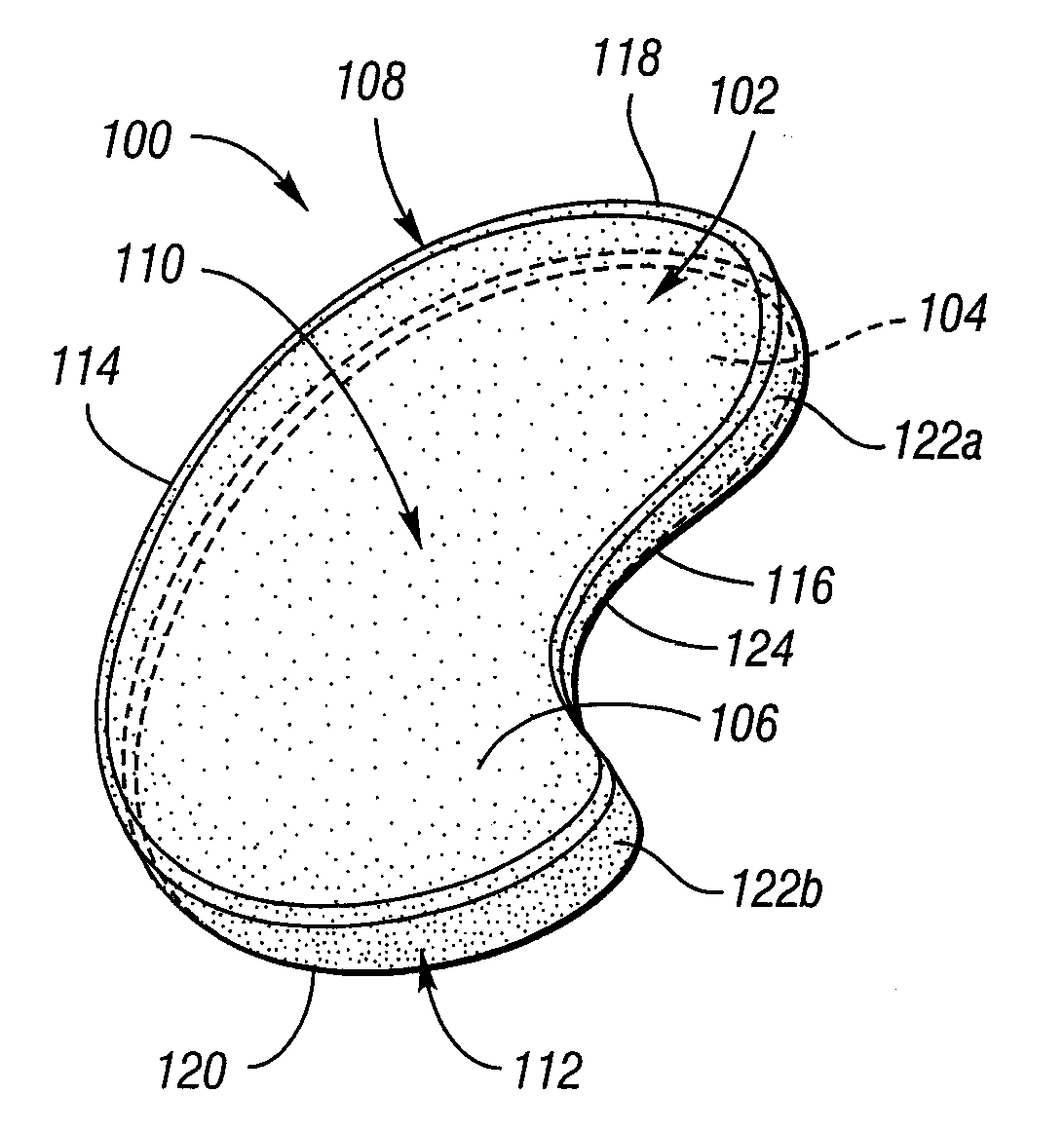
Surgically Implantable Knee Prosthesis
A prosthesis is provided for implantation into a knee joint compartment between a femoral condyle and its corresponding tibial plateau. The prosthesis is configured to be translatable with respect to the tibial plateau during knee articulation, and includes a body having a generally elliptical shape in plan and a pair of opposed surfaces including a substantially flat bottom surface and an opposed top surface.
Owner:FELL BARRY M +1
Knee joint biomechanical characteristic measuring device and measuring method based on body surface images
InactiveCN101999904ATo achieve the purpose of changing the strain with timeAvoid restrictionsImage analysisMuscle exercising devicesMeasurement deviceGear drive
The invention discloses a knee joint biomechanical characteristic measuring device and measuring method based on body surface images. The measuring device comprises a track, a transmission gear, a movable sliding block, a movable clamp, a fixed clamp, a camera and the like, wherein the transmission gear drives the movable sliding block to reciprocate along the track; and the movable sliding block can be respectively provided with a movable rod or pedal with the movable clamp to drive an in-vitro or in-vivo knee joint to make a flexion movement. The measuring method comprises the following steps: fixing a knee joint to be tested by using the measuring device, making a mark point array on a body surface test zone, shooting to record the time sequence images of the mark point array along the flexion movement of the knee joint, and extracting the relative movement of each point of the mark point array by using the image technology, thereby obtaining the strain distribution information, flexion information and relationship of the corresponding zone of the knee joint. The invention can be used for measuring the knee joint movement and the corresponding tissue strain in real time in a noninvasive, harmless, non-contact, quick, accurate and simple way without complex three-dimensional computation, ray scanning and the like, and offers greater degree of freedom to the test motion.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com