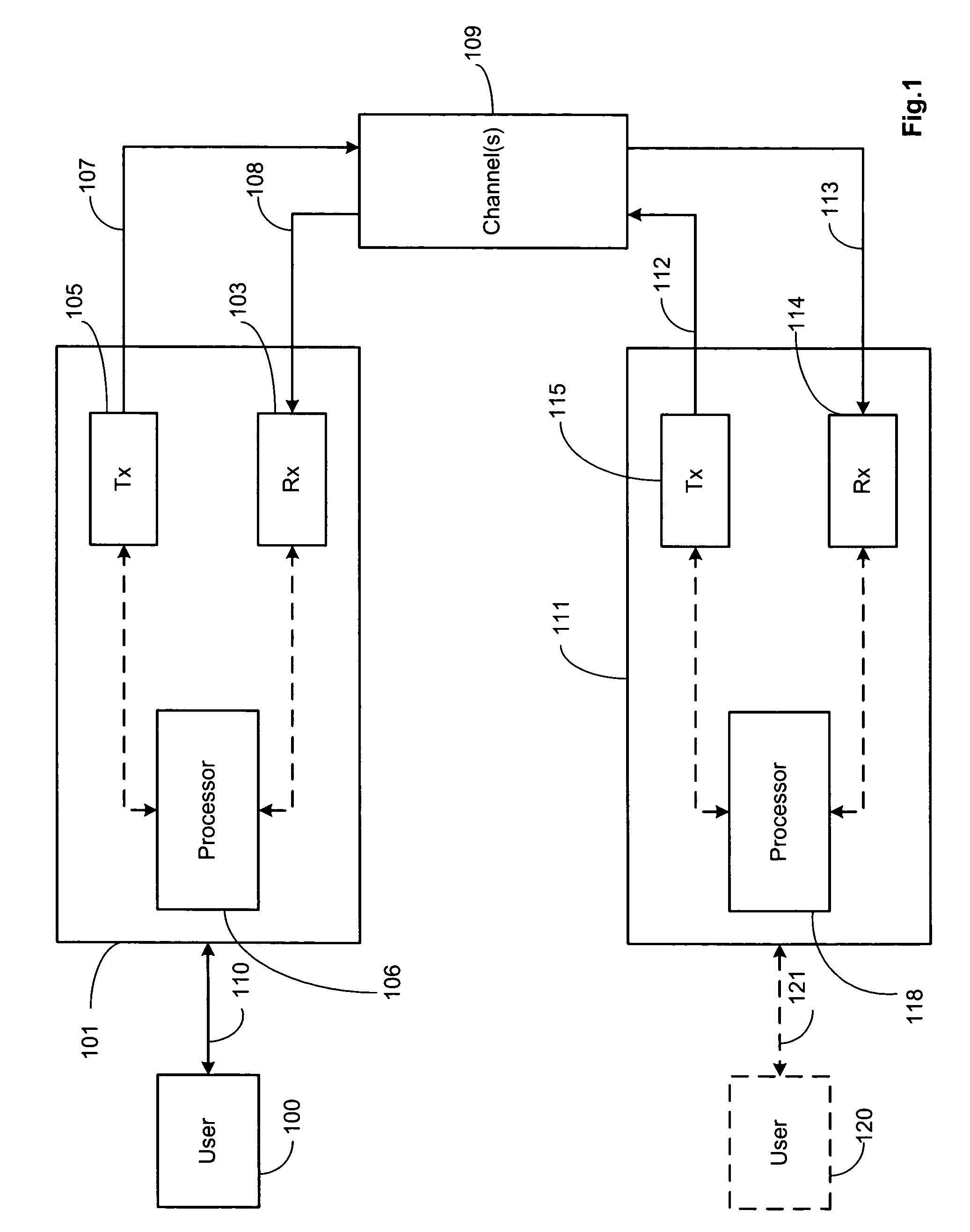
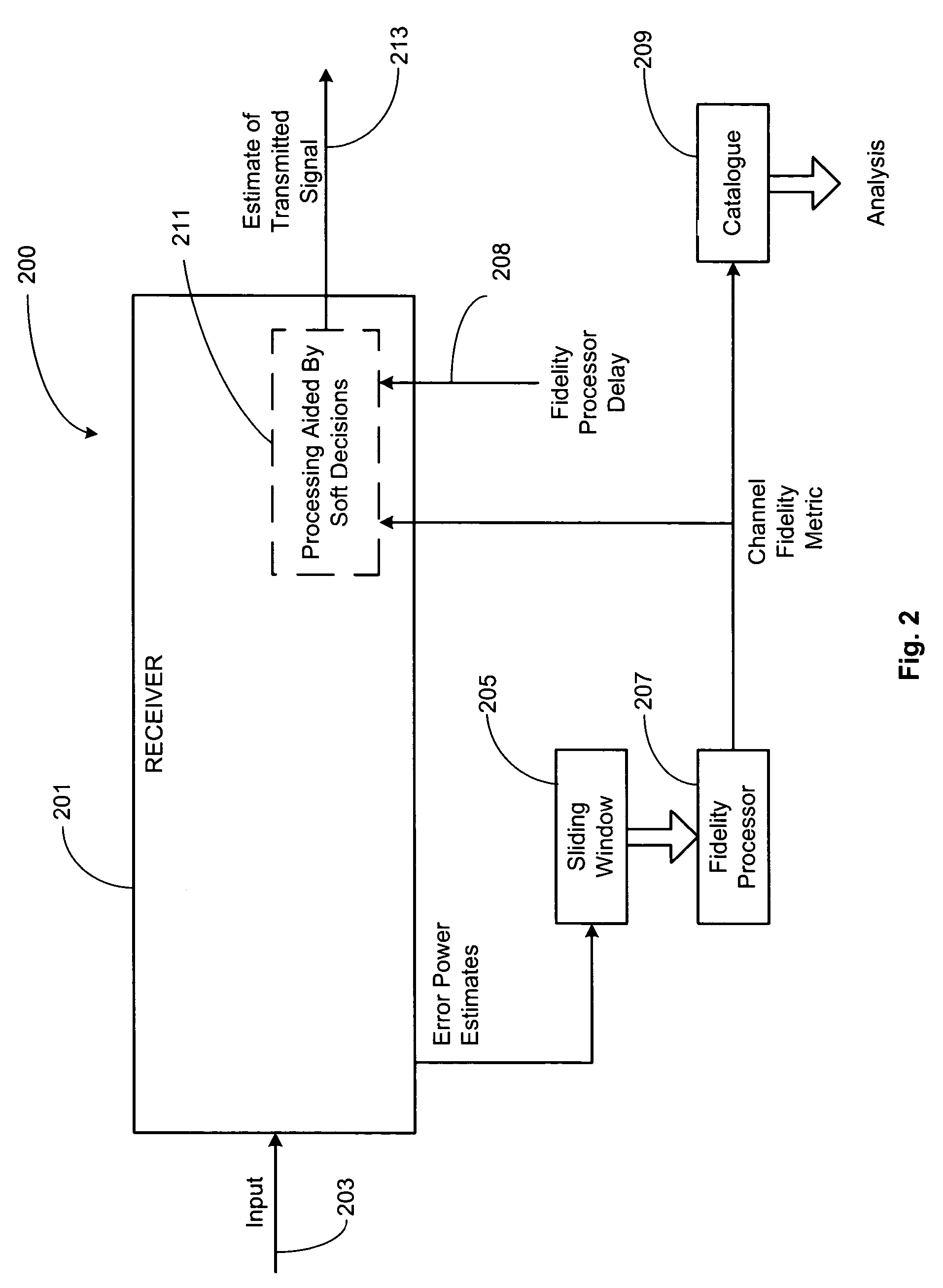
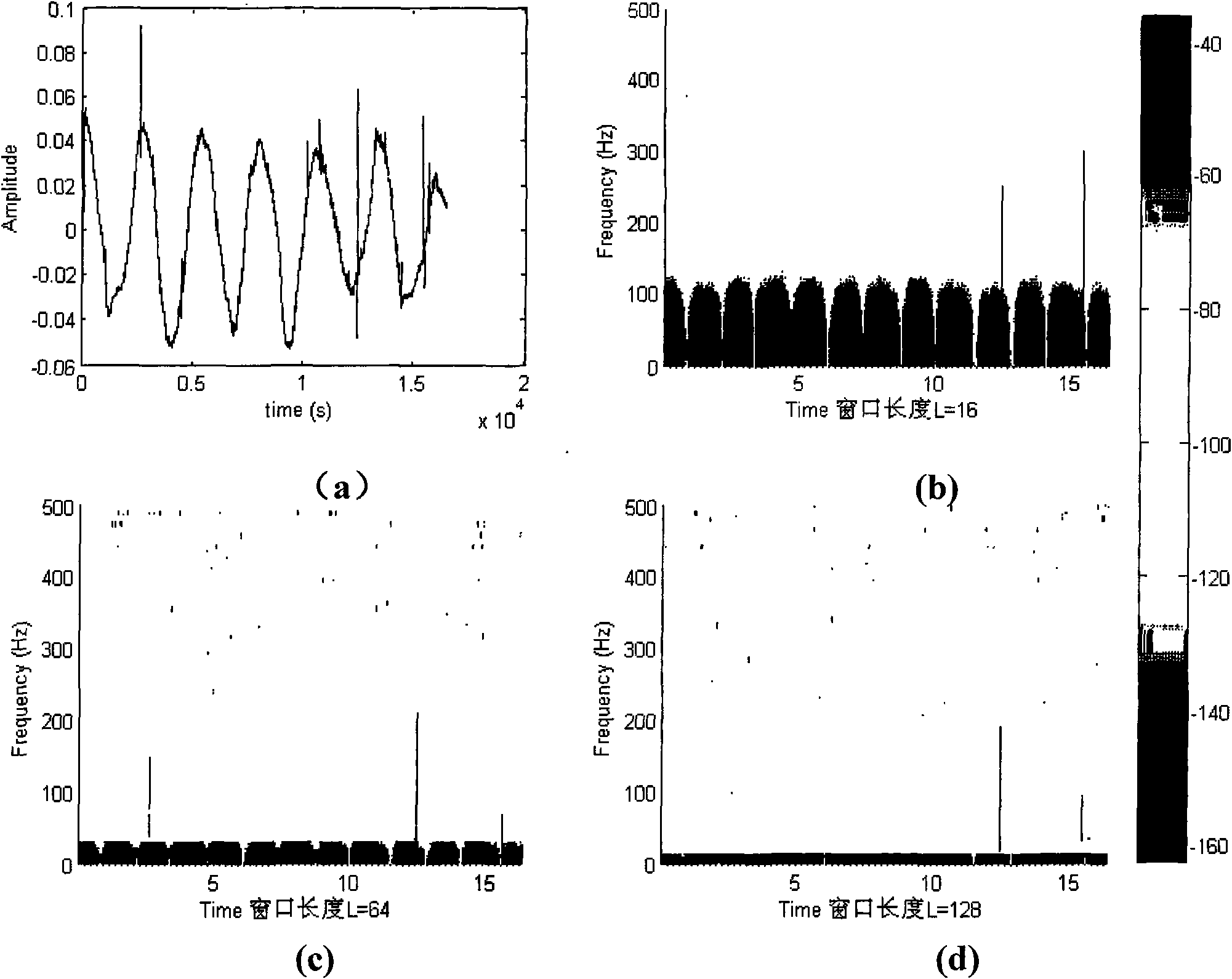
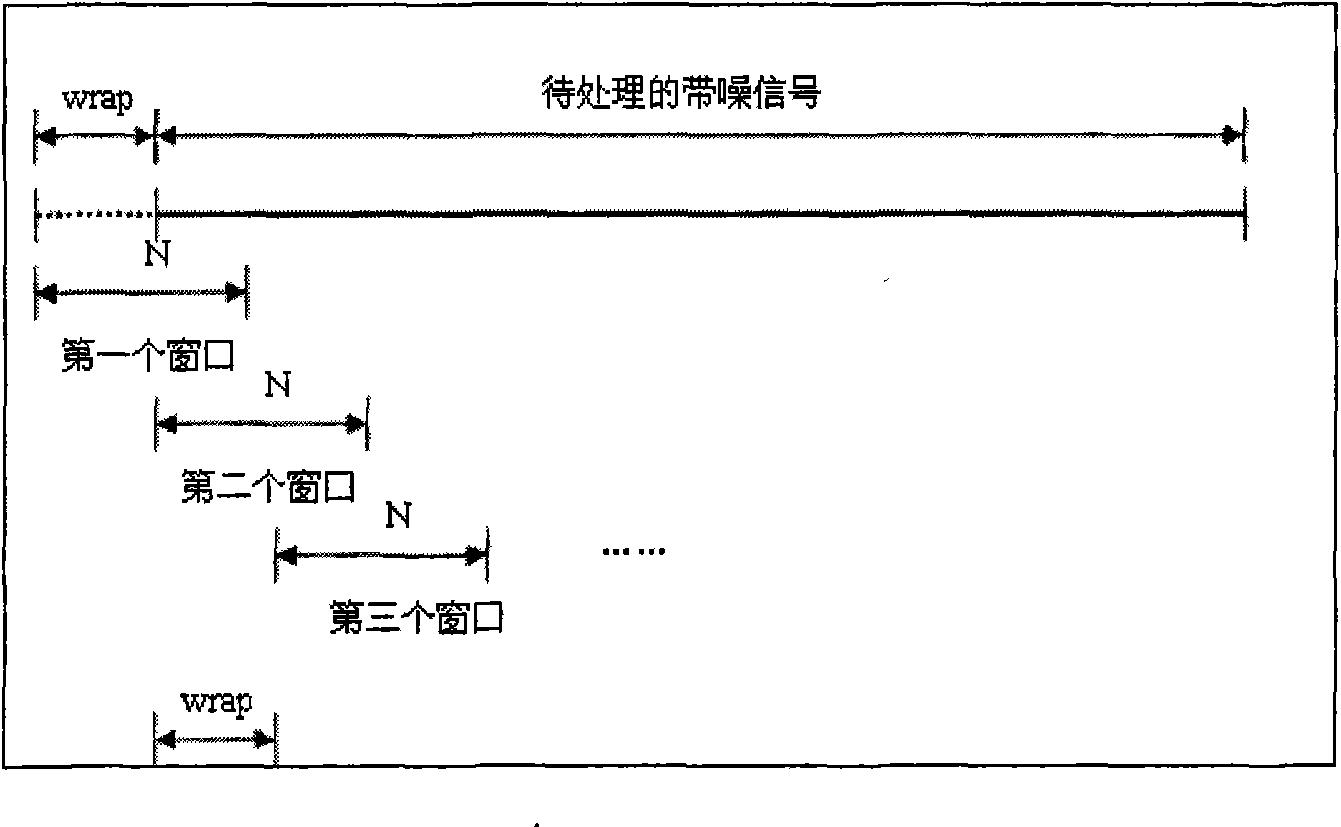
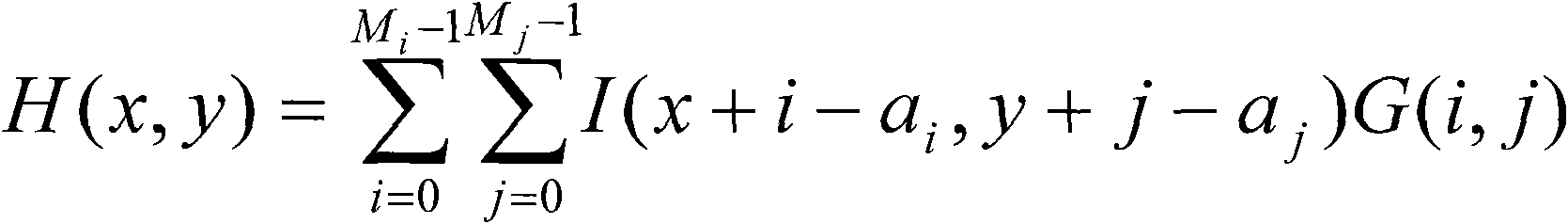Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Impulse noise detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
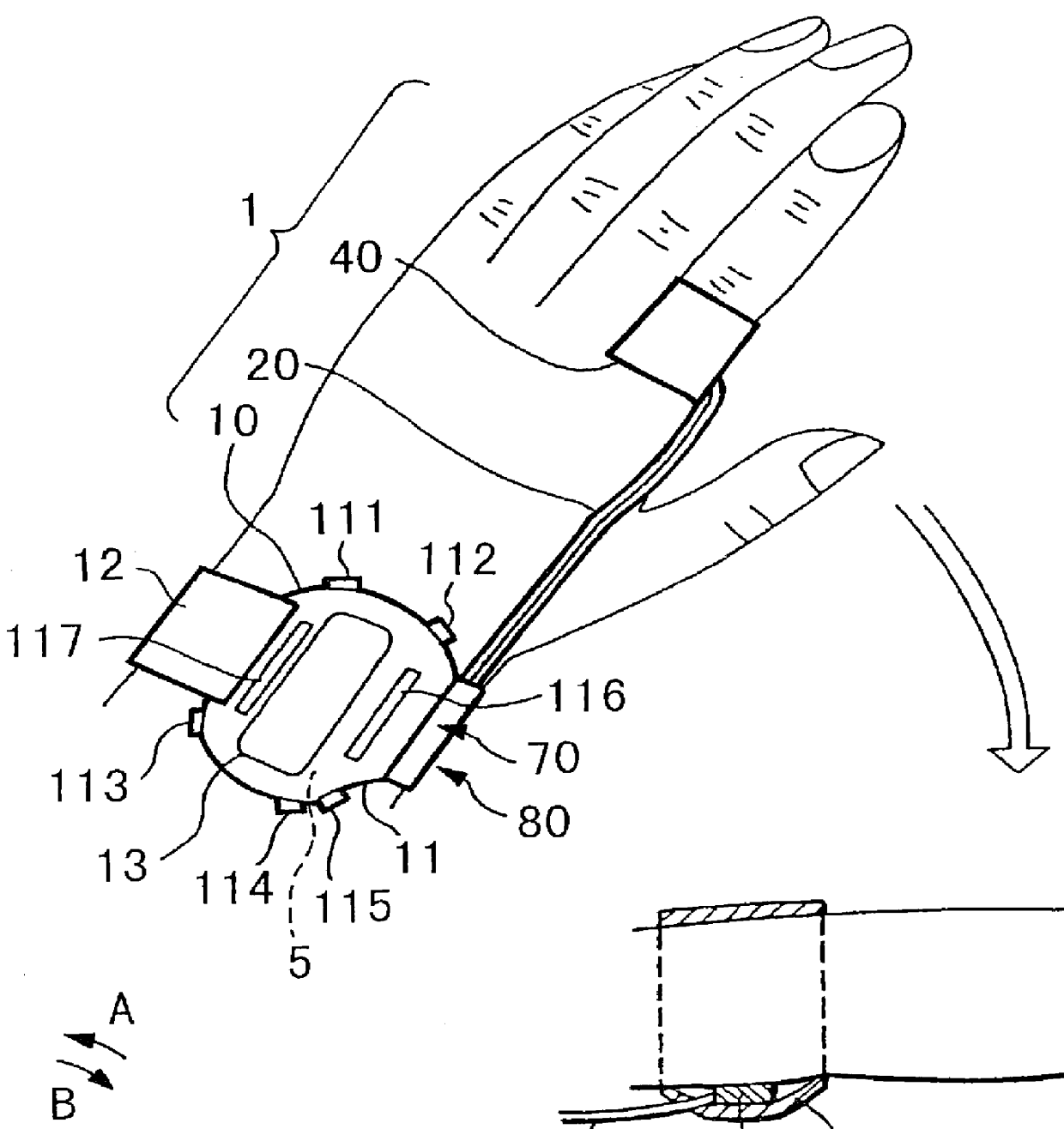
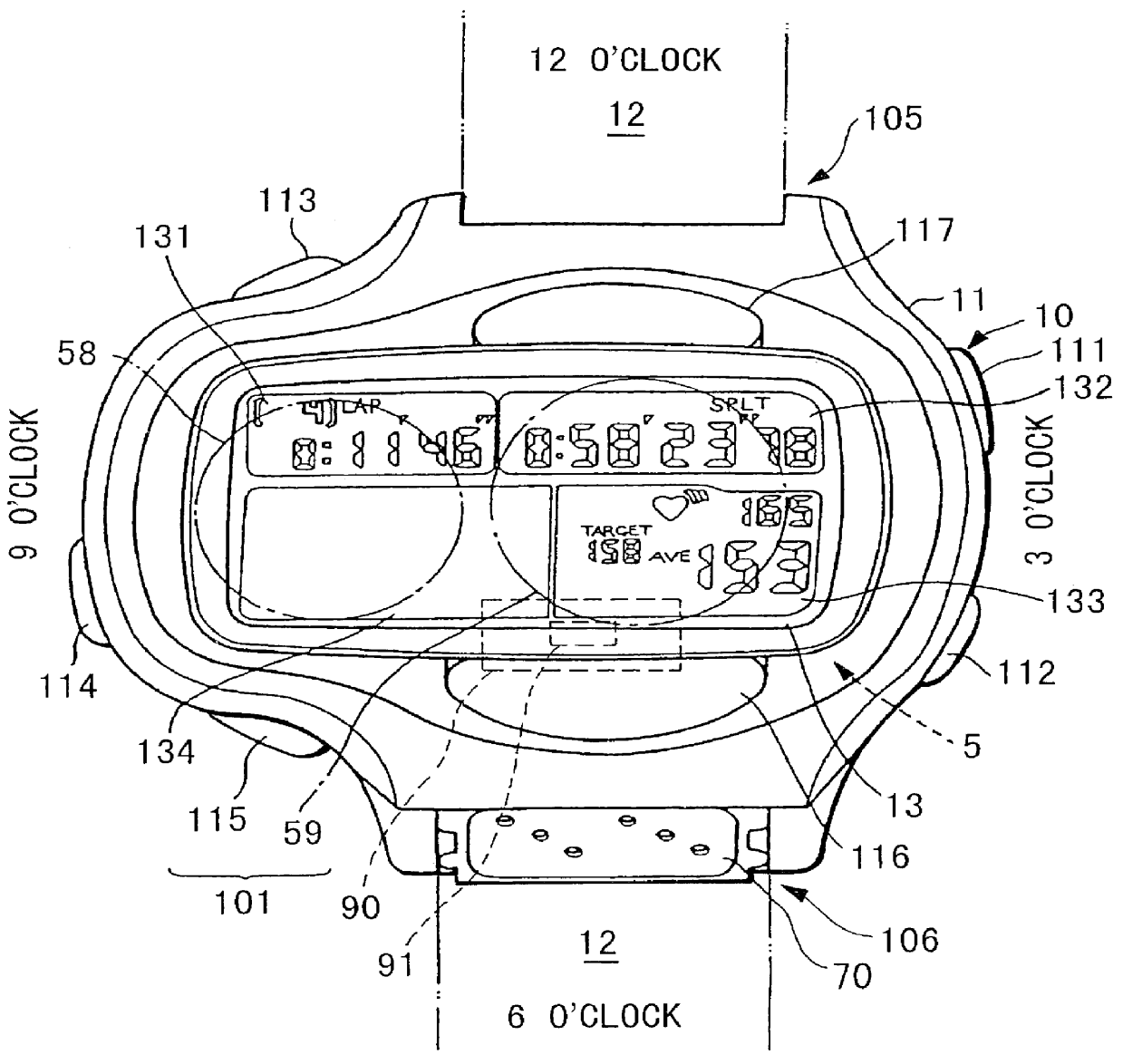
Pulse wave detecting device and pulse measurer
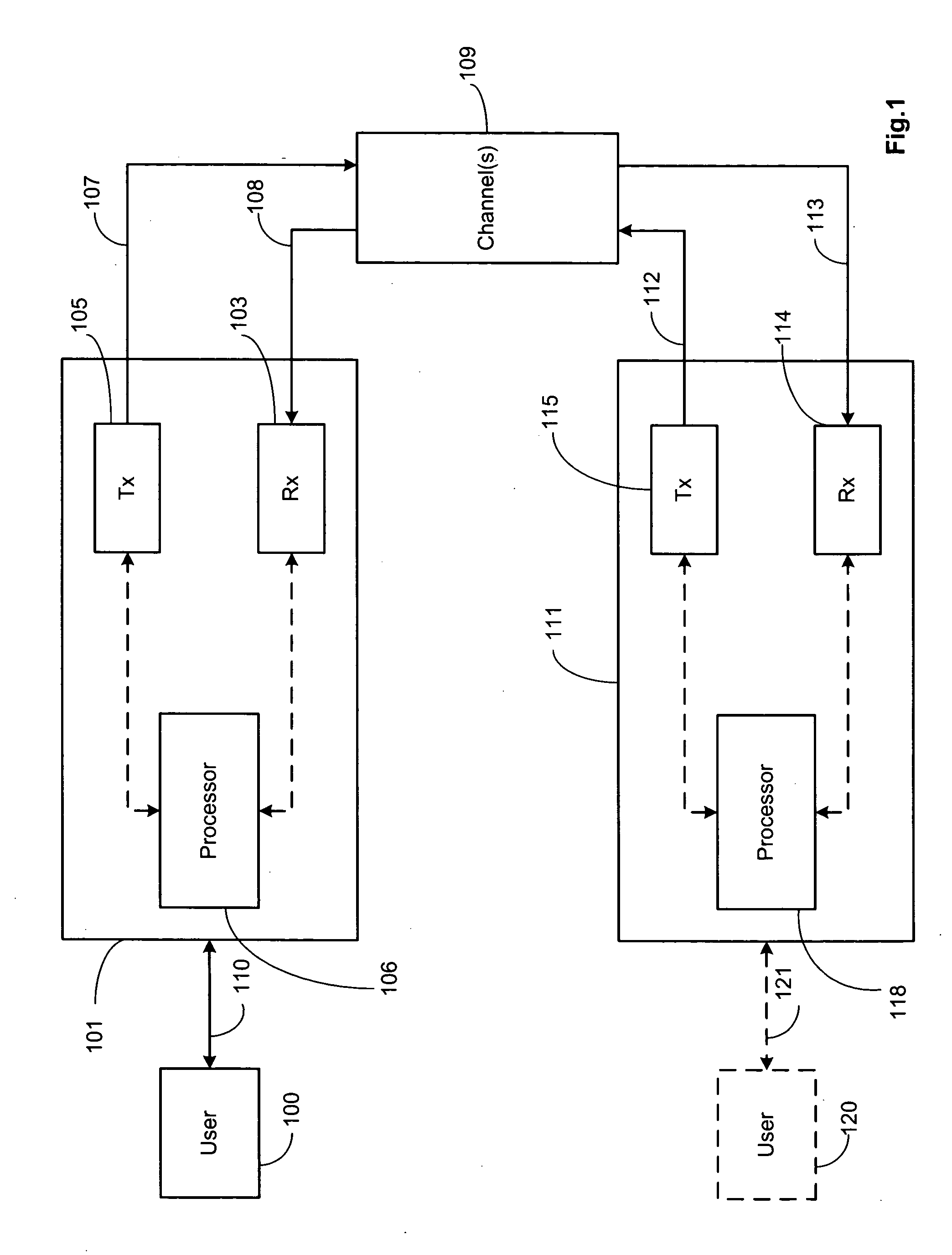
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 01128 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 4, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 4, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 17, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 41143 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 24, 1998The present invention relates to a pulse wave detecting device for detecting pulse waves, and to a pulse measurer employing this pulse wave detecting device. The present invention addresses the problem of obtaining a pulse wave signal in which the noise components have been suitably removed from a pulse waveform, and of determining the pulse rate with high accuracy based on this pulse wave signal. The method for deriving the pulse wave signal and pulse rate is as follows. The pulse wave signal from pulse wave detecting sensor unit (30) is temporarily stored in buffer (503). When impulse noise is detected in the pulse wave signal in buffer (503) by impulse noise detecting means (505), the band pass for first digital filter (506) becomes a hill-shaped curve centered on the frequency corresponding to the preceding pulse rate, and impulse noise in the pulse wave signal output from buffer (503) is decreased. Thereafter, overall noise and body movement components are decreased in the pulse wave signal by means of second digital filter (507) and third digital filter (508). The signal is then subjected to frequency analysis by frequency analyzer (509), and the pulse rate is calculated from the results of this analysis.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
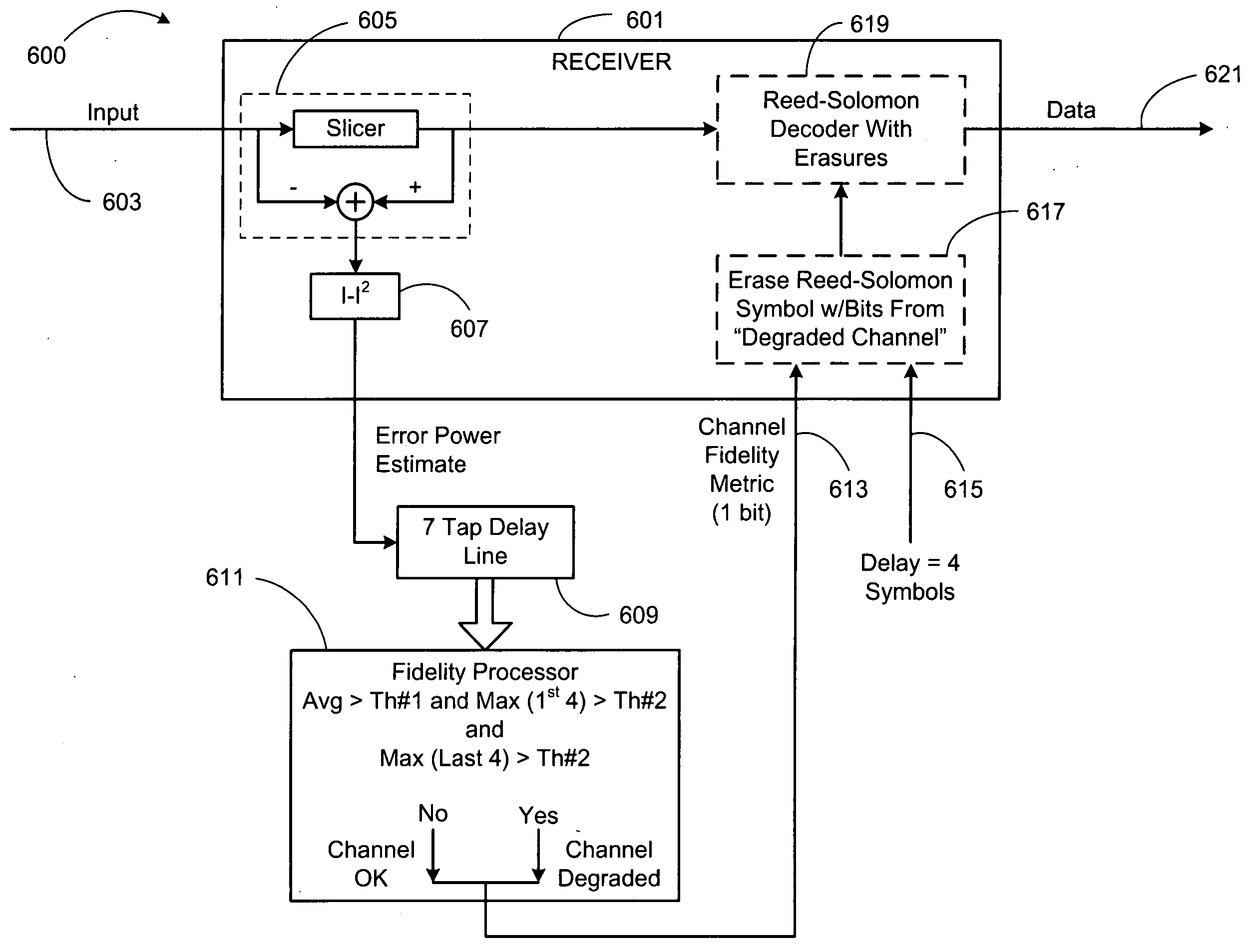
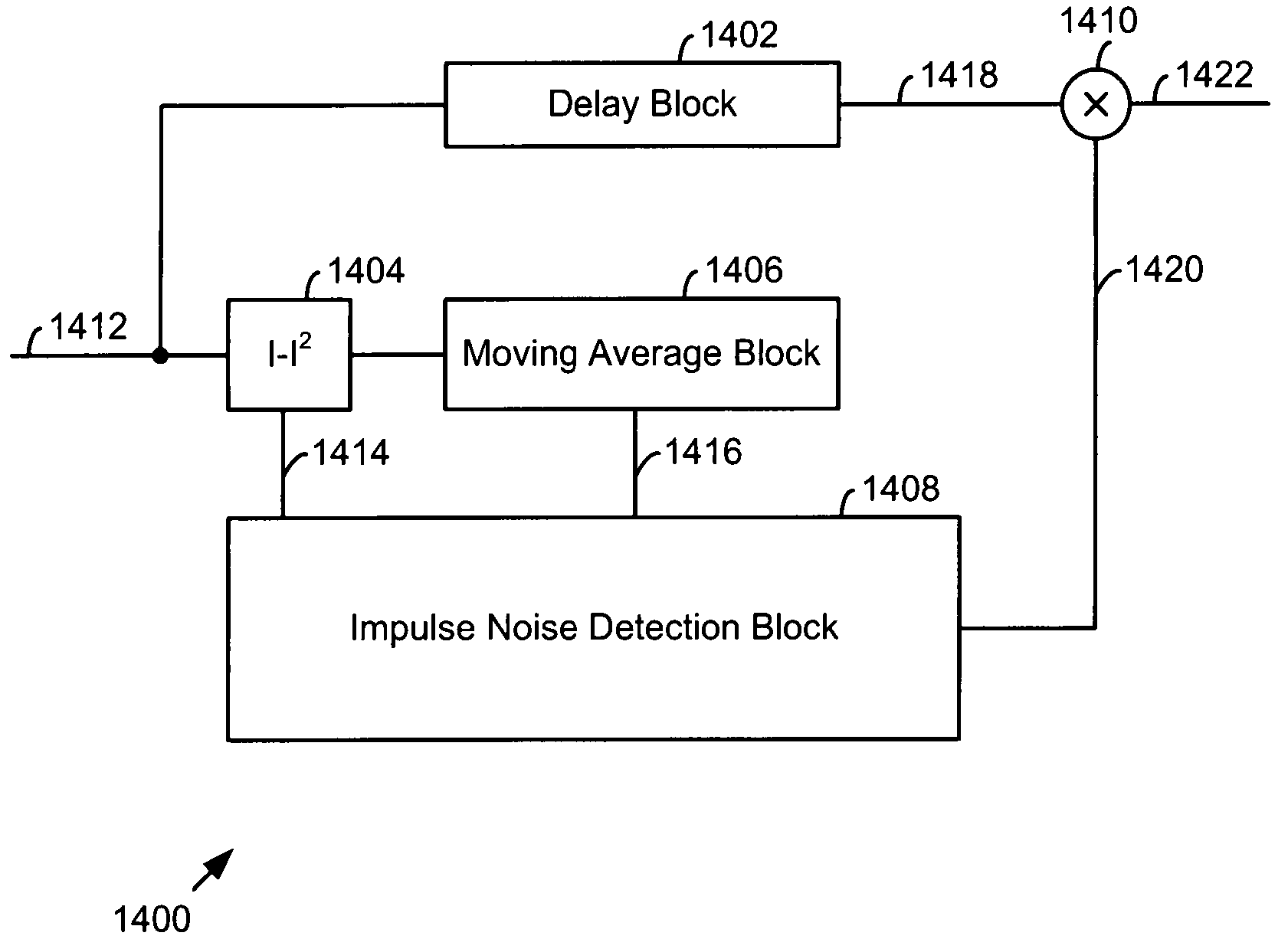
Chip blanking and processing in SCDMA to mitigate impulse and burst noise and/or distortion
InactiveUS20050047489A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMoving averageCommunications system
A system for mitigating impairment in a communication system includes a delay block, a signal level block, a moving average window block, an impulse noise detection block, and a combiner. The delay block receives and delays each chip of a plurality of chips in a spreading interval. The signal level block determines a signal level of each chip of the plurality of chips in the spreading interval. The moving average window block determines a composite signal level for a chip window corresponding to the chip. The impulse noise detection block receives the signal level, receives the composite signal level, and produces an erasure indication for each chip of the plurality of chips of the corresponding chip window. The combiner erases chips of the plurality of chips of the spreading interval based upon the erasure indication.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Receiver and method of receiving
InactiveUS20100246726A1Computationally effectiveComputationally efficientError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionNoise levelFourier transform on finite groups
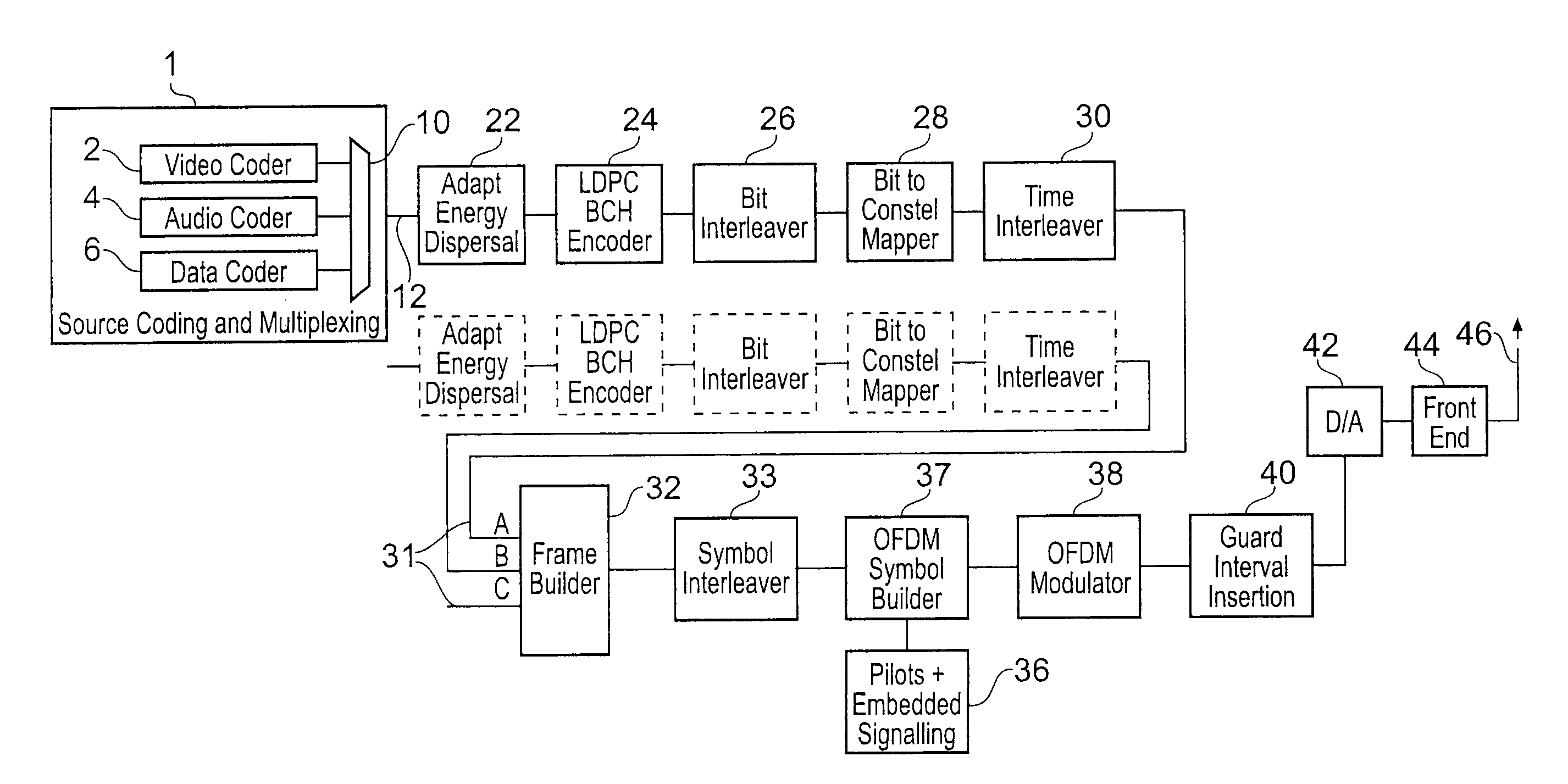
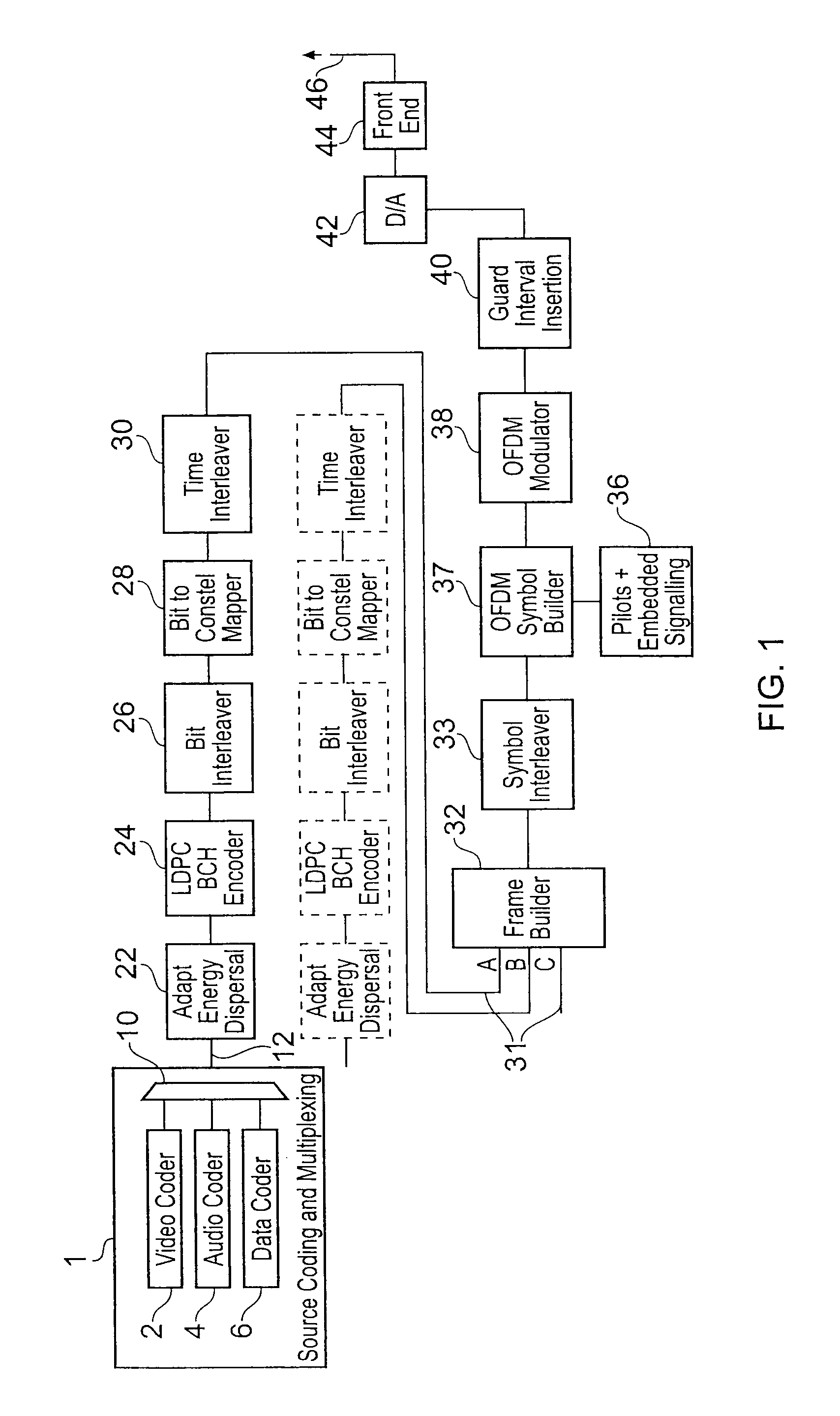
A receiver recovers data from Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbols, the OFDM symbols including sub-carrier symbols carrying data symbols and sub-carrier signals carrying pilot symbols. The receiver includes a Fourier transform processor arranged in operation to receive a time domain digital version of the OFDM symbols and to form a frequency domain version of the OFDM symbols, from which the pilot symbol sub-carriers and the data symbol bearing sub-carriers can be recovered, and a detector arranged in operation to recover the data symbols from the data bearing sub-carriers of the OFDM symbols. The receiver includes a noise estimator arranged in operation to generate a long term estimate of noise power in the frequency domain version of the OFDM symbols at a plurality of frequencies, by accumulating an average noise power at the plurality of frequencies from a plurality of the OFDM symbols, and for generating an estimate of a current level of the noise power in the frequency domain version of a current one of the OFDM symbols at the plurality of frequencies. An impulsive noise detector detects the presence of an impulse of noise in the current OFDM symbol, by comparing the noise power in the current OFDM symbol with the long term noise power at the plurality of frequencies, and to generate an impulse noise flag to indicate that the current OFDM symbol is affected by an impulse of noise if the comparison indicates the presence of an impulse of noise. Impulsive noise in the time domain will generate an increase in noise level across the frequency bandwidth of the OFDM symbols. If all frequencies experience an increase then an impulse of noise can be detected. Thereafter the detector can conceal the effect of the impulse noise on the recovering of the data symbols from the data bearing sub-carriers, for example by adapting channel state information for use in de-mapping modulated symbols into data symbols.
Owner:SONY CORP
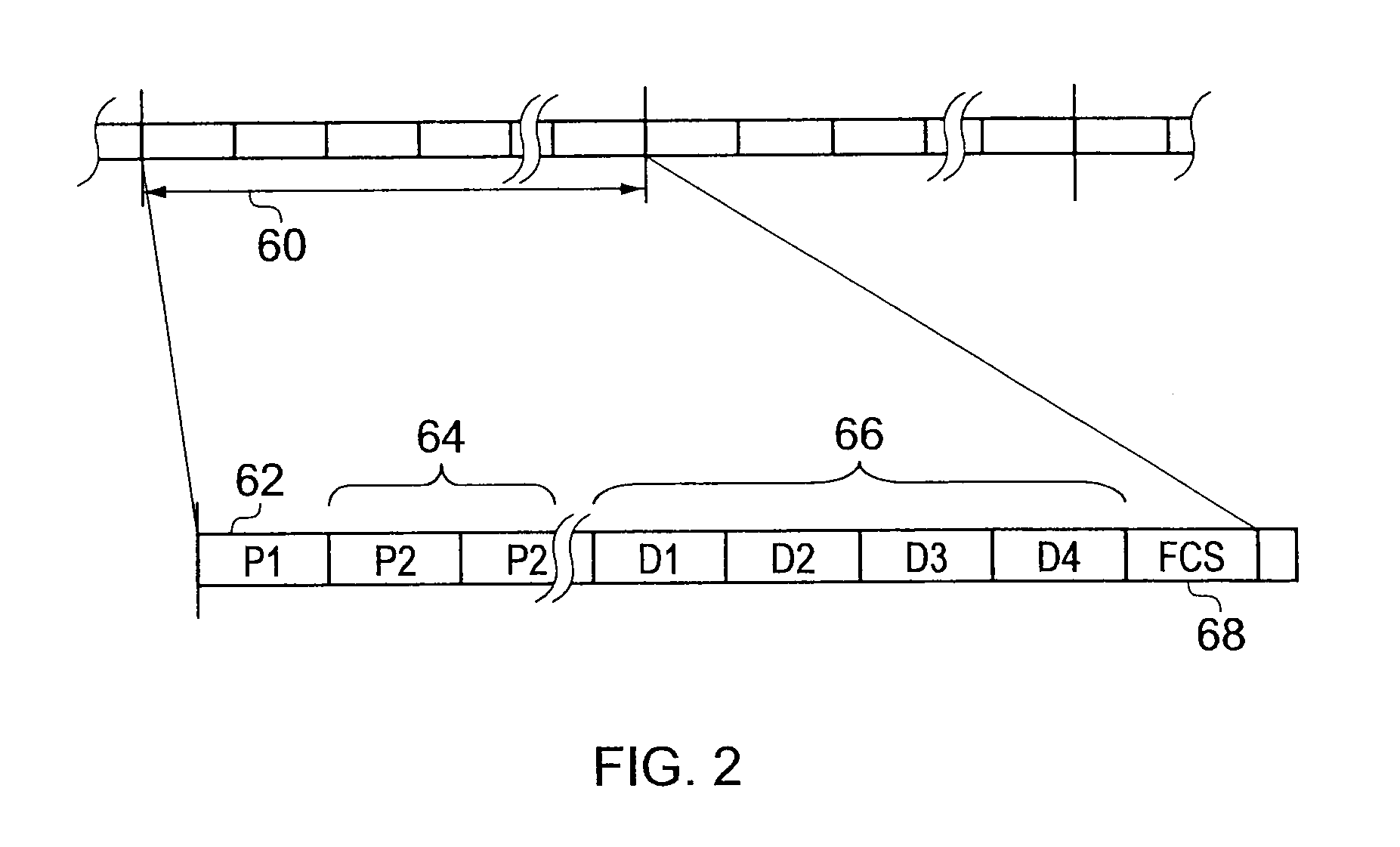
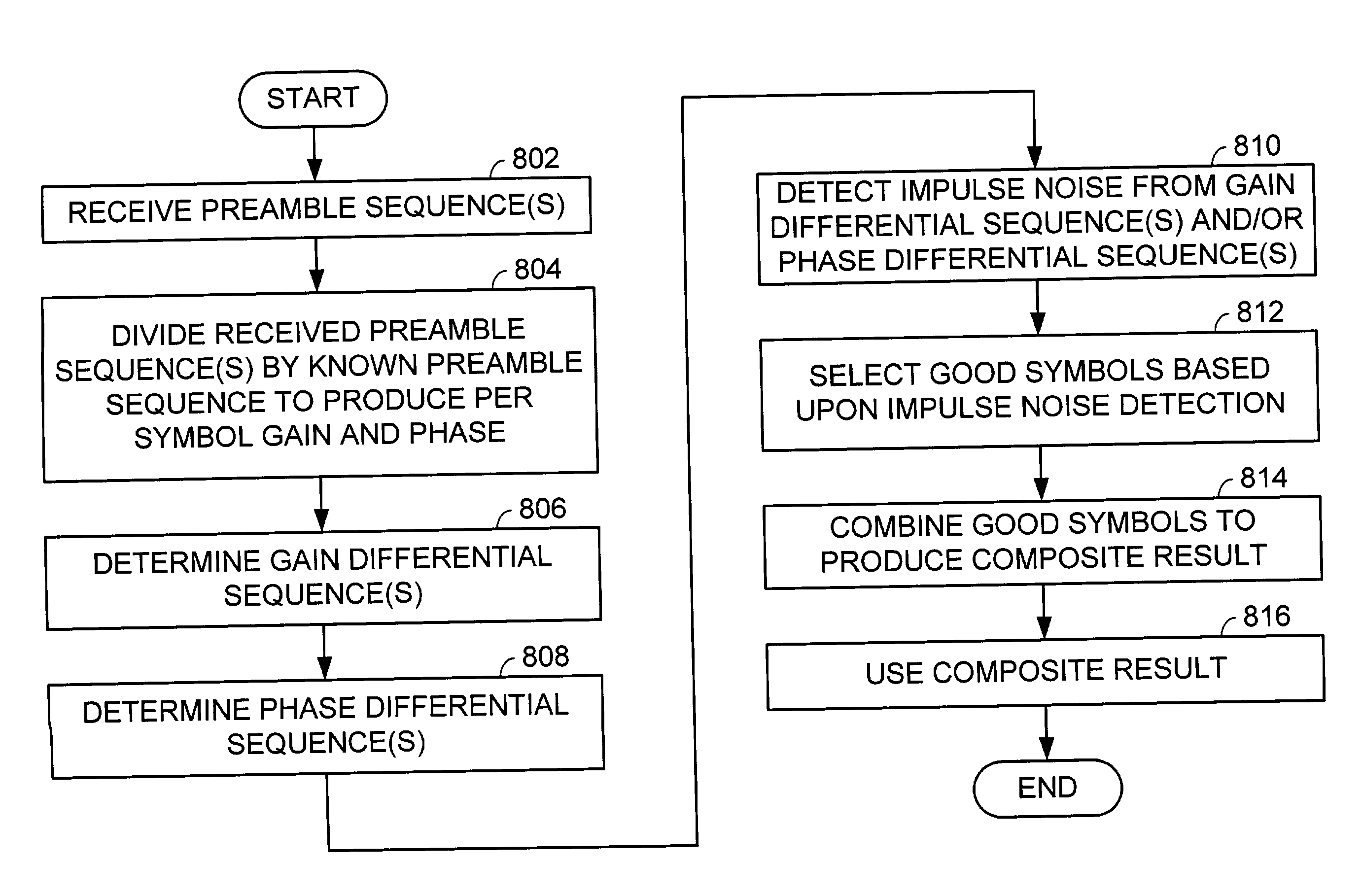
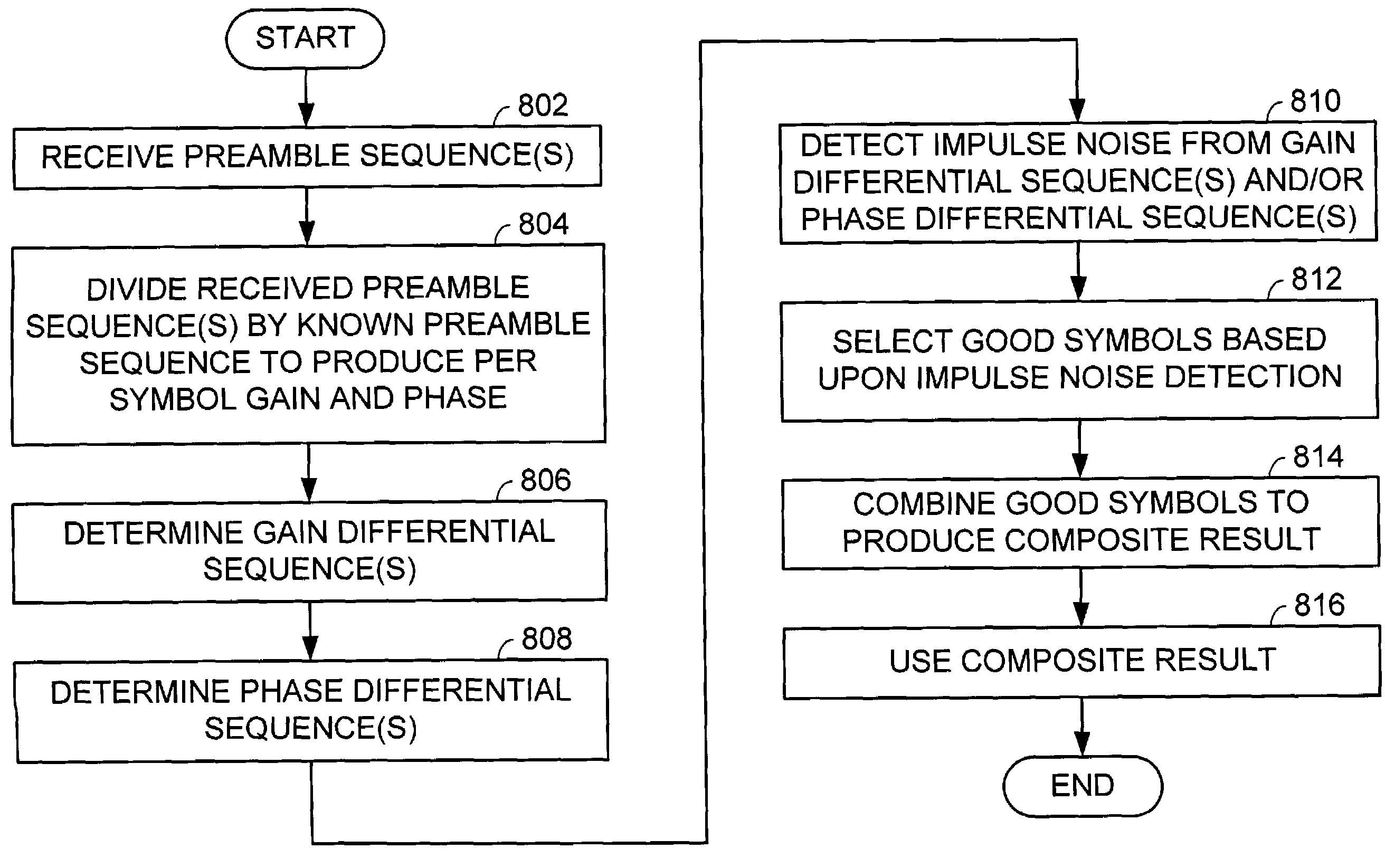
Impulse noise detection from preamble symbols
InactiveUS20040066865A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTelecommunicationsCommunication device
A communication device constructed according to the present invention detects impulse noise in a preamble sequence. In detecting impulse noise in the preamble sequence the communication device first receive a preamble sequence that includes a plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device then divides the plurality of preamble symbols by at least one known preamble symbol to produce a plurality of preamble gains and / or a plurality of preamble phases corresponding to the plurality of preamble symbols. Finally, the communication device determines, based upon the plurality of preamble gains and / or the plurality of preamble phases, that at least one preamble symbol has been adversely affected by impulse noise. The communication device may discard at least one preamble symbol that has been adversely affected by impulse noise from the plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device may combine non-discarded preamble symbols of the plurality of preamble symbols of the preamble sequence to produce a composite result.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Impulse noise detection from preamble symbols
A communication device constructed according to the present invention detects impulse noise in a preamble sequence. In detecting impulse noise in the preamble sequence the communication device first receive a preamble sequence that includes a plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device then divides the plurality of preamble symbols by at least one known preamble symbol to produce a plurality of preamble gains and / or a plurality of preamble phases corresponding to the plurality of preamble symbols. Finally, the communication device determines, based upon the plurality of preamble gains and / or the plurality of preamble phases, that at least one preamble symbol has been adversely affected by impulse noise. The communication device may discard at least one preamble symbol that has been adversely affected by impulse noise from the plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device may combine non-discarded preamble symbols of the plurality of preamble symbols of the preamble sequence to produce a composite result.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
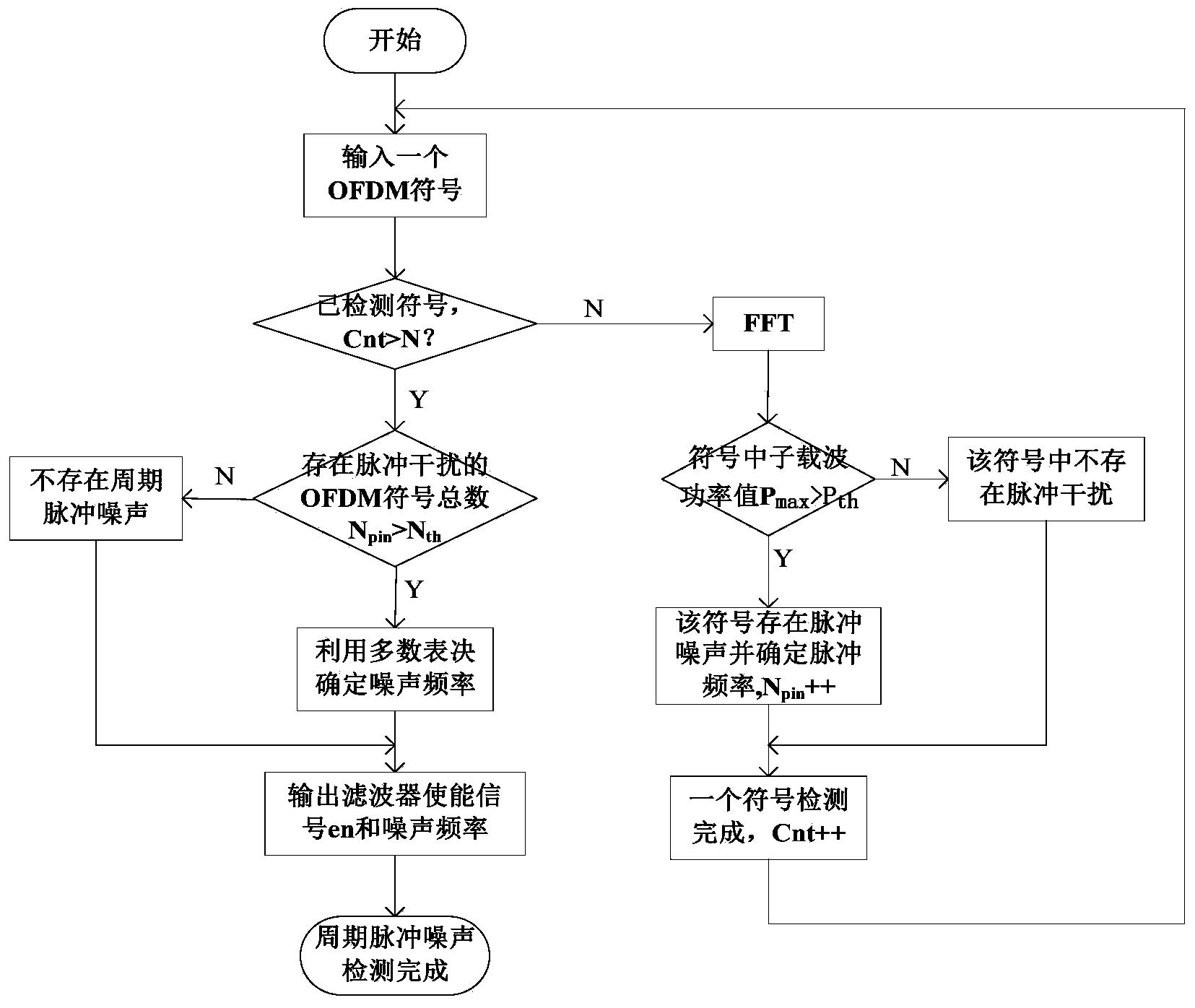
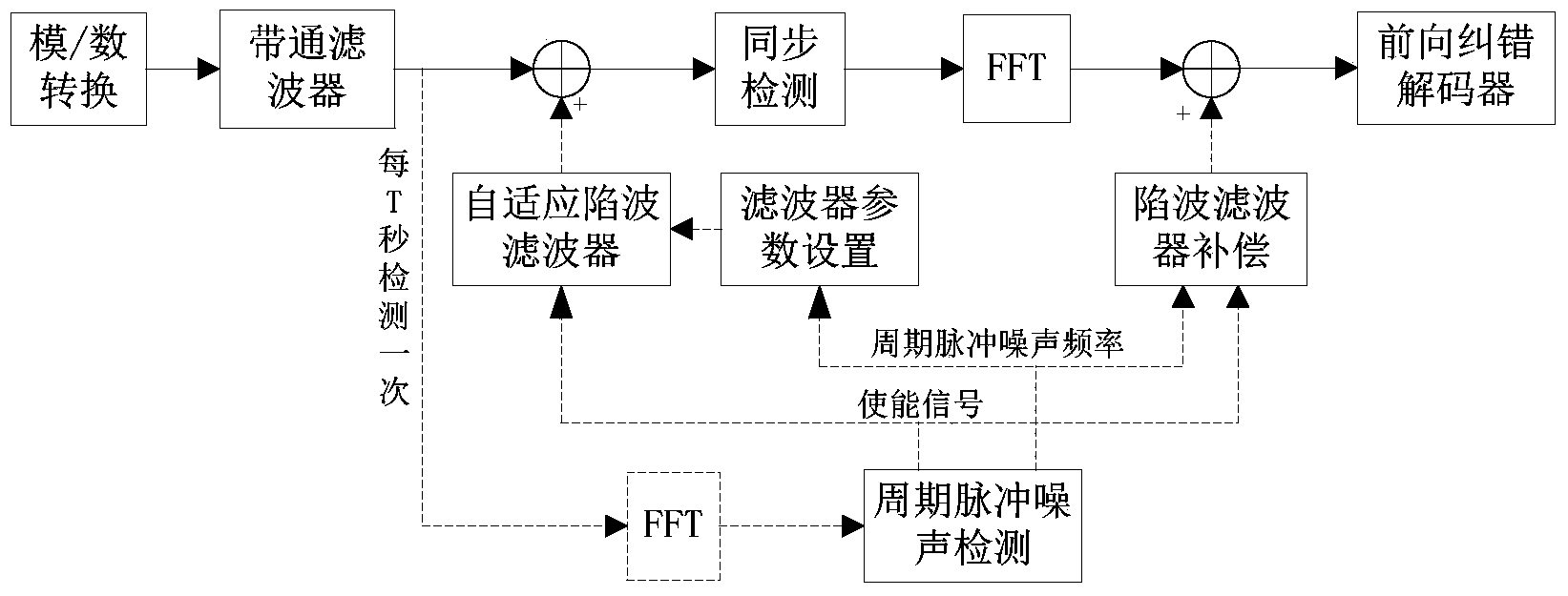
Power line carrier periodic impulse noise detecting and restraining method based on OFDM
ActiveCN104301280AReduce complexityImprove accuracyPower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalEngineering
A power line carrier periodic impulse noise detecting and restraining method based on the OFDM includes the steps of firstly, judging whether periodic impulse noise exists or not, conducting statistic positioning on the frequency band of the periodic impulse noise, modulating a filter again, and restraining the periodic impulse noise in a targeted mode. The complexity of a traditional noise restraining method is remarkably lowered; meanwhile, the restraining effect is remarkably improved, and the signal accuracy is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
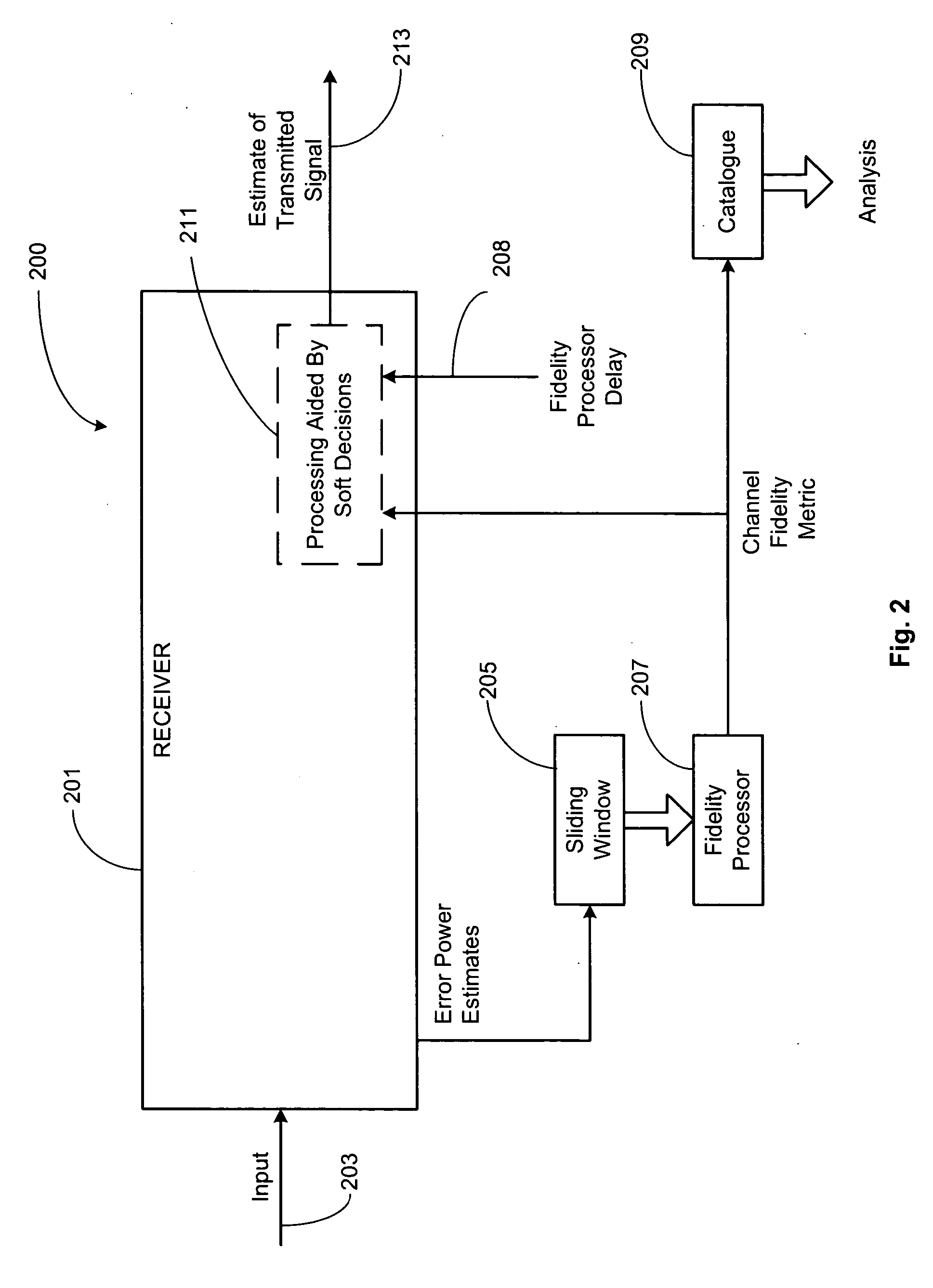
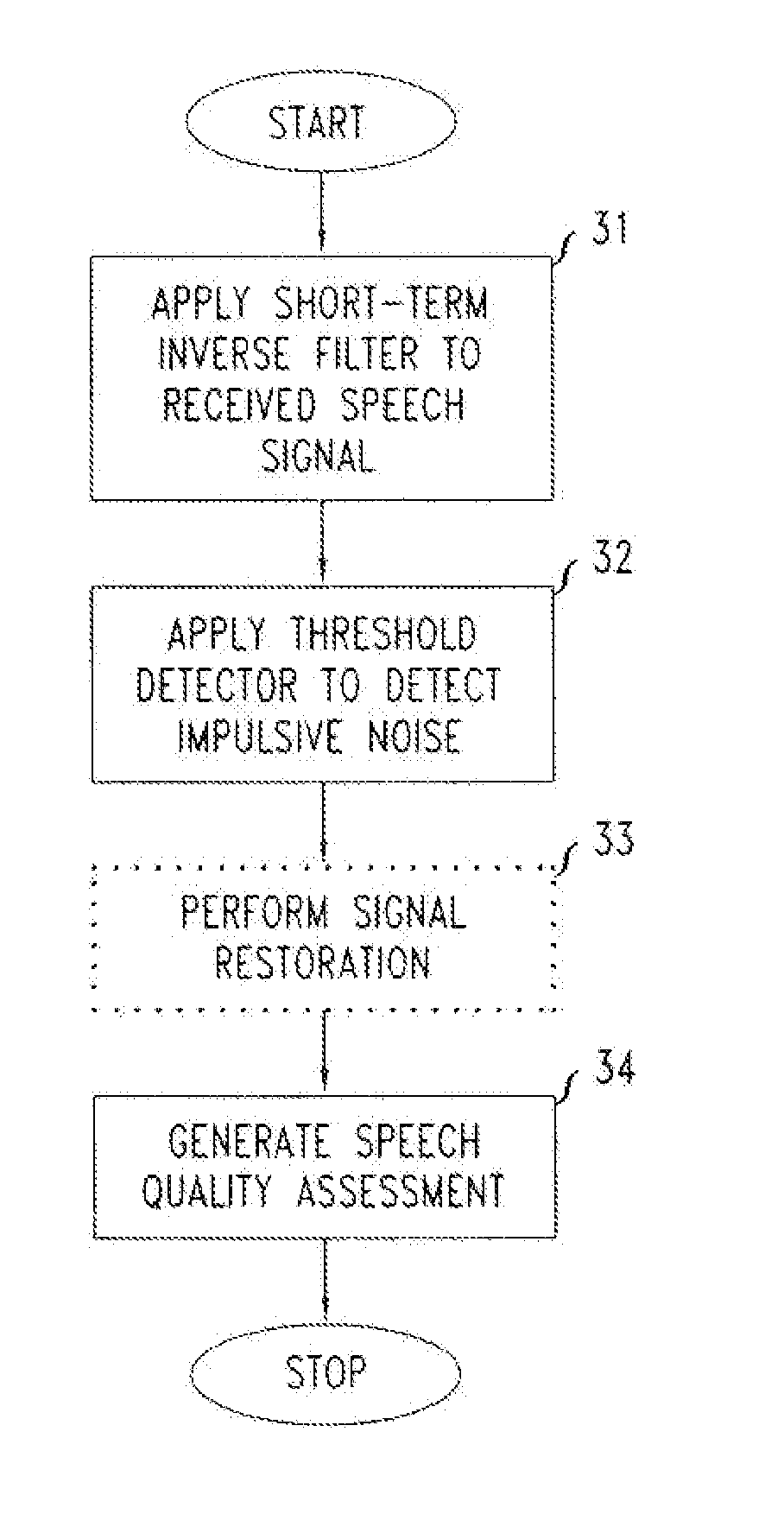
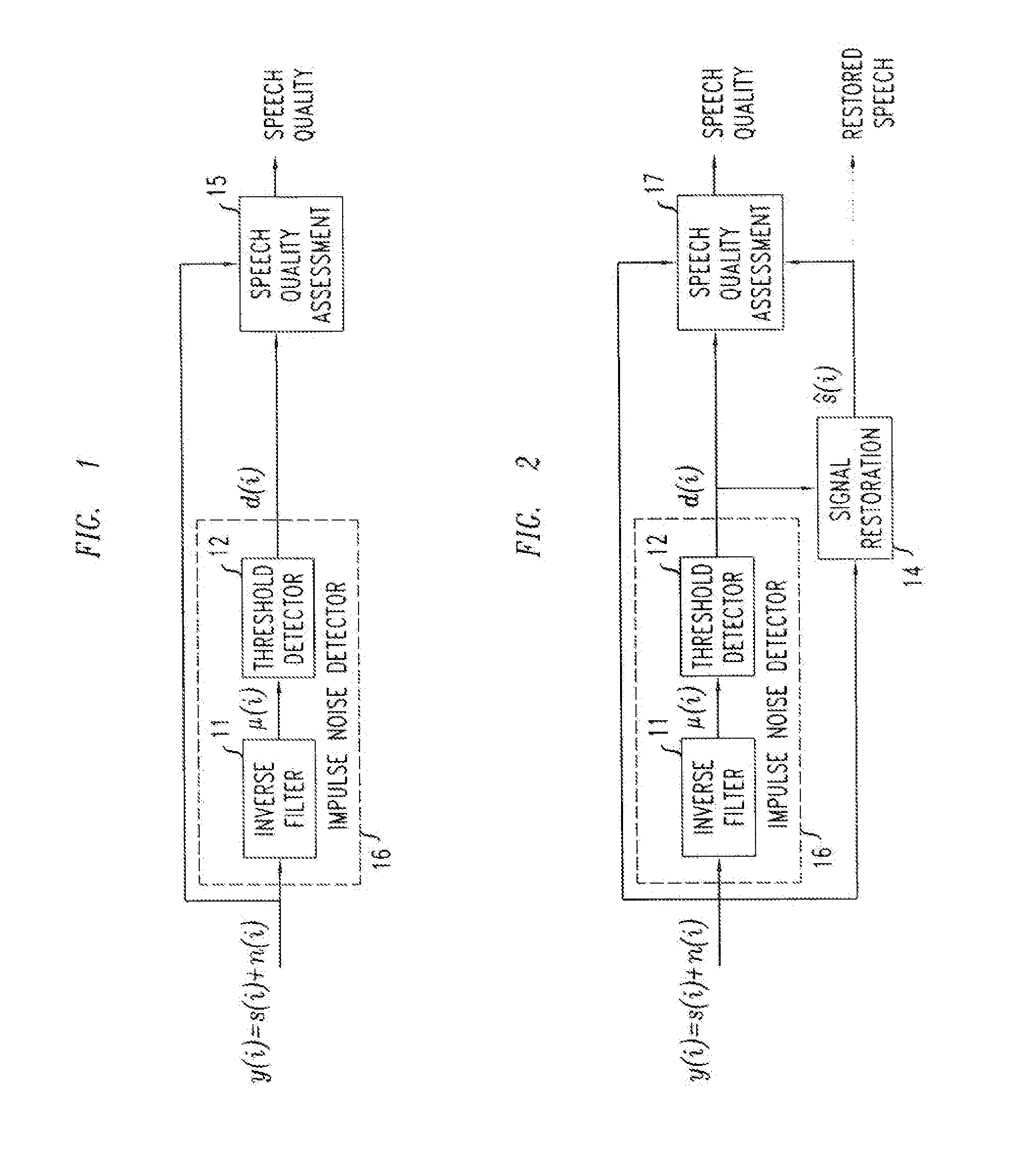
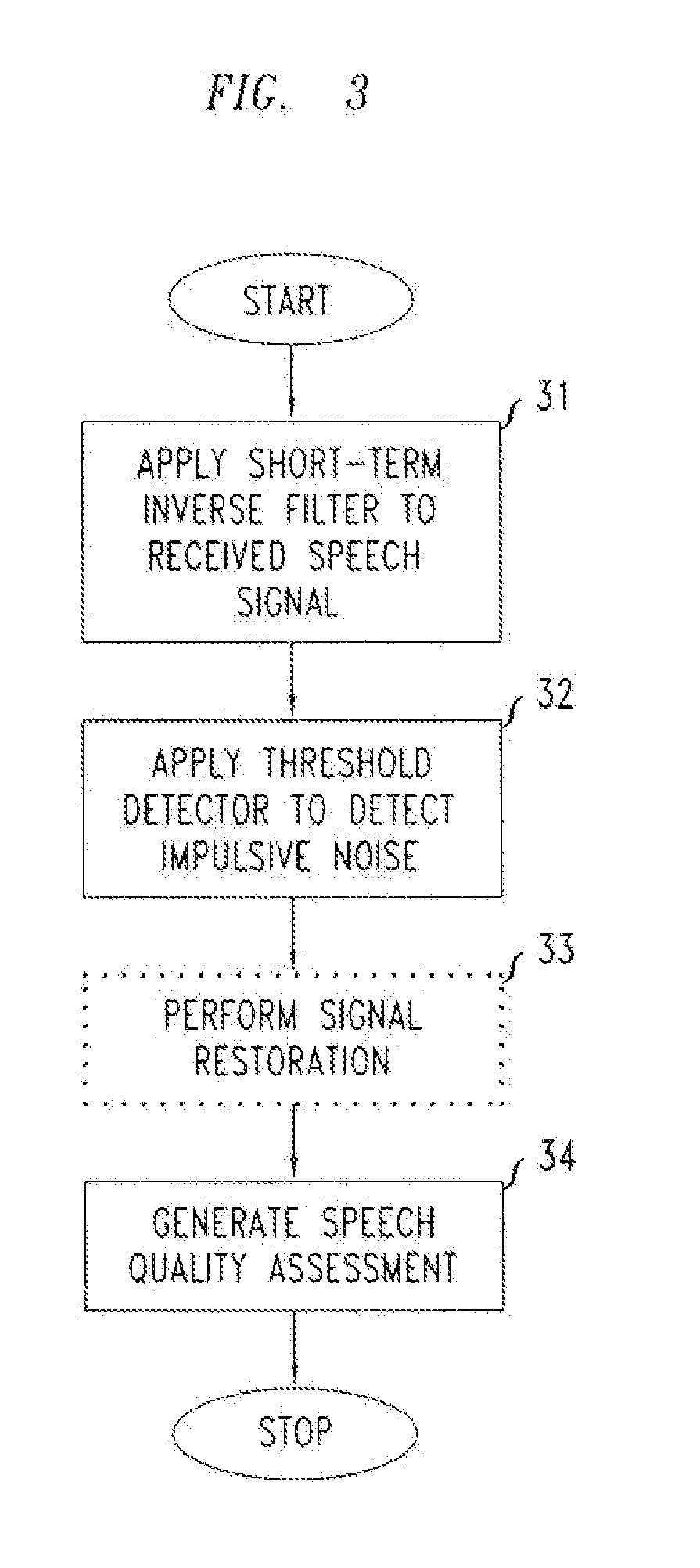
Method And Apparatus For The Detection Of Impulsive Noise In Transmitted Speech Signals For Use In Speech Quality Assessment
InactiveUS20110153313A1Improve voice qualityProvide goodSpeech recognitionCommunications systemStatistical analysis
A method and apparatus for performing speech quality assessment in a speech communication system (such as, for example, a VoIP communication system) which detects and measures the presence of impulsive noise is provided. Specifically, in one illustrative embodiment, an autoregressive (AR) model of speech (and, in particular, of the excitation of the vocal tract) is advantageously employed to estimate a short-term variance of the speech excitation, and the standard deviation of the speech excitation (i.e., the square root of the variance) is then advantageously compared to a predetermined threshold to identify whether impulsive noise is present. Then, based on a statistic analysis of any such identified impulsive noise, a speech quality assessment is generated.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
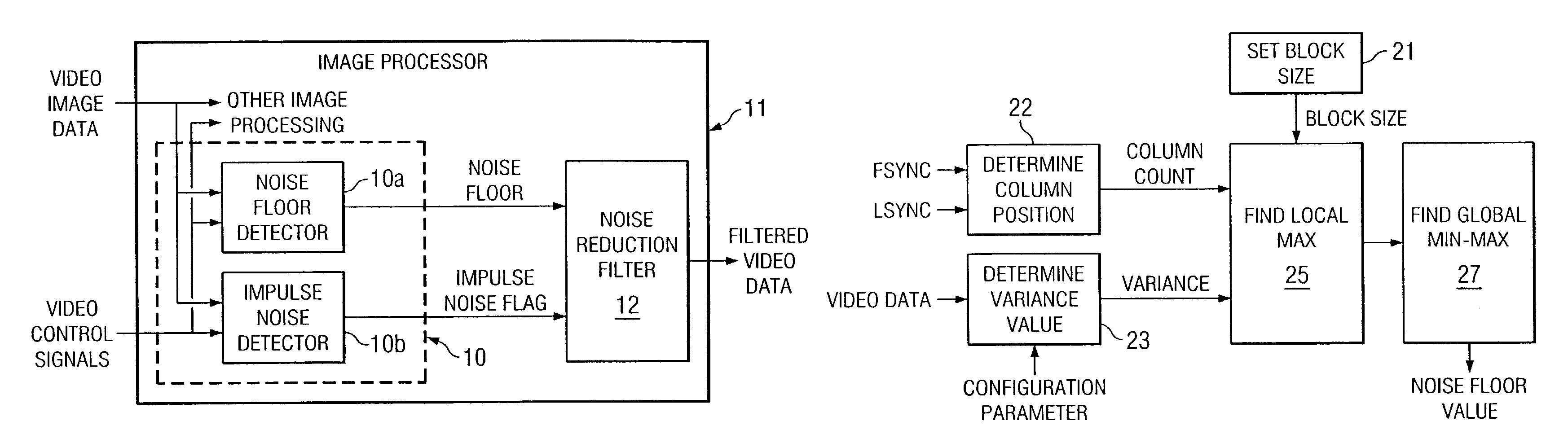
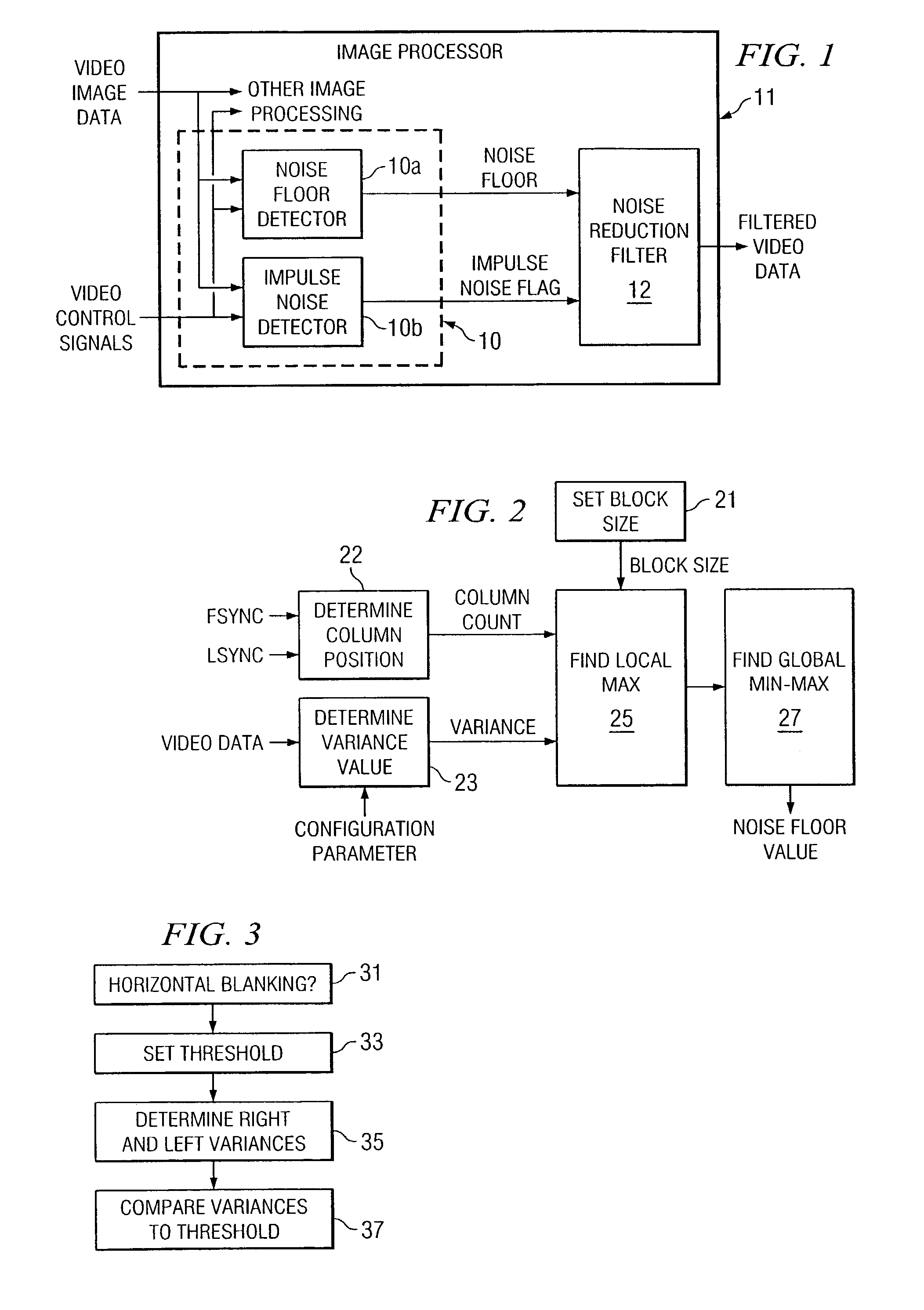
Video noise floor estimator with impulse noise detection
ActiveUS7139035B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsEngineeringNoise reduction
A method of detecting both linear and non linear noise in video data. Linear noise is detected on a line-by-line basis, by blocks within each line. Non linear noise is detected during horizontal blanking periods. The method provides a noise floor value for linear noise and an impulse noise flag for non linear noise, both of which are delivered to a noise reduction filter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Chip blanking and processing in SCDMA to mitigate impulse and burst noise and/or distortion
InactiveUS7366258B2Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMoving averageCommunications system
A system for mitigating impairment in a communication system includes a delay block, a signal level block, a moving average window block, an impulse noise detection block, and a combiner. The delay block receives and delays each chip of a plurality of chips in a spreading interval. The signal level block determines a signal level of each chip of the plurality of chips in the spreading interval. The moving average window block determines a composite signal level for a chip window corresponding to the chip. The impulse noise detection block receives the signal level, receives the composite signal level, and produces an erasure indication for each chip of the plurality of chips of the corresponding chip window. The combiner erases chips of the plurality of chips of the spreading interval based upon the erasure indication.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Historical voice frequency noise detection and elimination method
InactiveCN101882442AImprove restoration qualityReduce FRPSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumPhase noise
The invention discloses a historical voice frequency noise detection and elimination method. The existing historical voice frequency noise elimination method has high complexity, depends on the veracity of predicting model coefficients, has a complex algorithm and low efficiency and needs to estimate the statistical property of the noise in advance. The method of the invention comprises: (1) sound modeling: a sound signal can be described with the following method: y(k)=x(k)+j(k)*d(k); (2) short time discrete Fourier transform and spectrogram: an analysis window sliding along time is adopted for windowing and cutting off a non-stable signal so as to decompose the non-stable signal into a series of approximatively stable short signal, and Fourier transform is adopted to analyze the frequency spectrum of each stable short signal; (3) pulse noise detection; (4) pulse noise detection performance analysis; (5) signal repair and reconstruction; and (6) experiment result and analysis. The invention is used for removing the pulse noise in the audio data.
Owner:SHANGHAI CONSERVATORY OF MUSIC +1
Noise removal apparatus and an FM receiver
InactiveUS6993309B2Reduce distortion problemsCancel noiseTransmission monitoringTransmission noise suppressionPhase noiseNoise removal
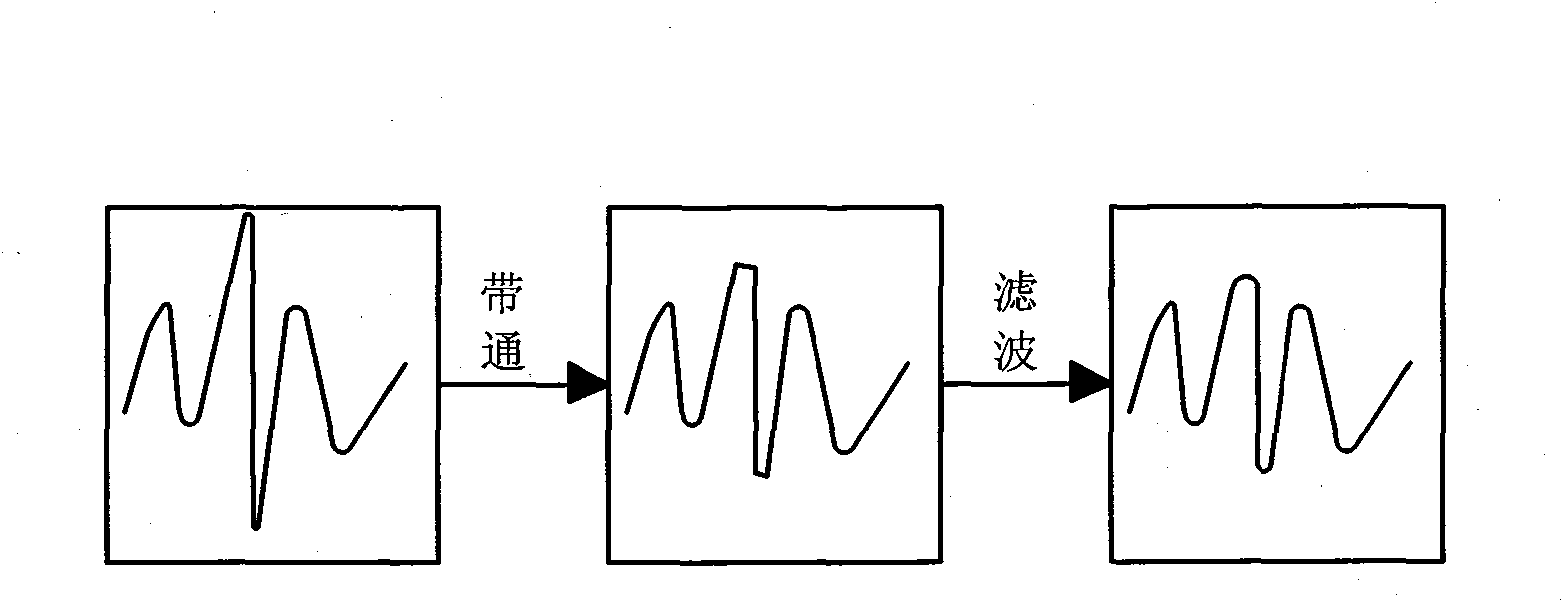
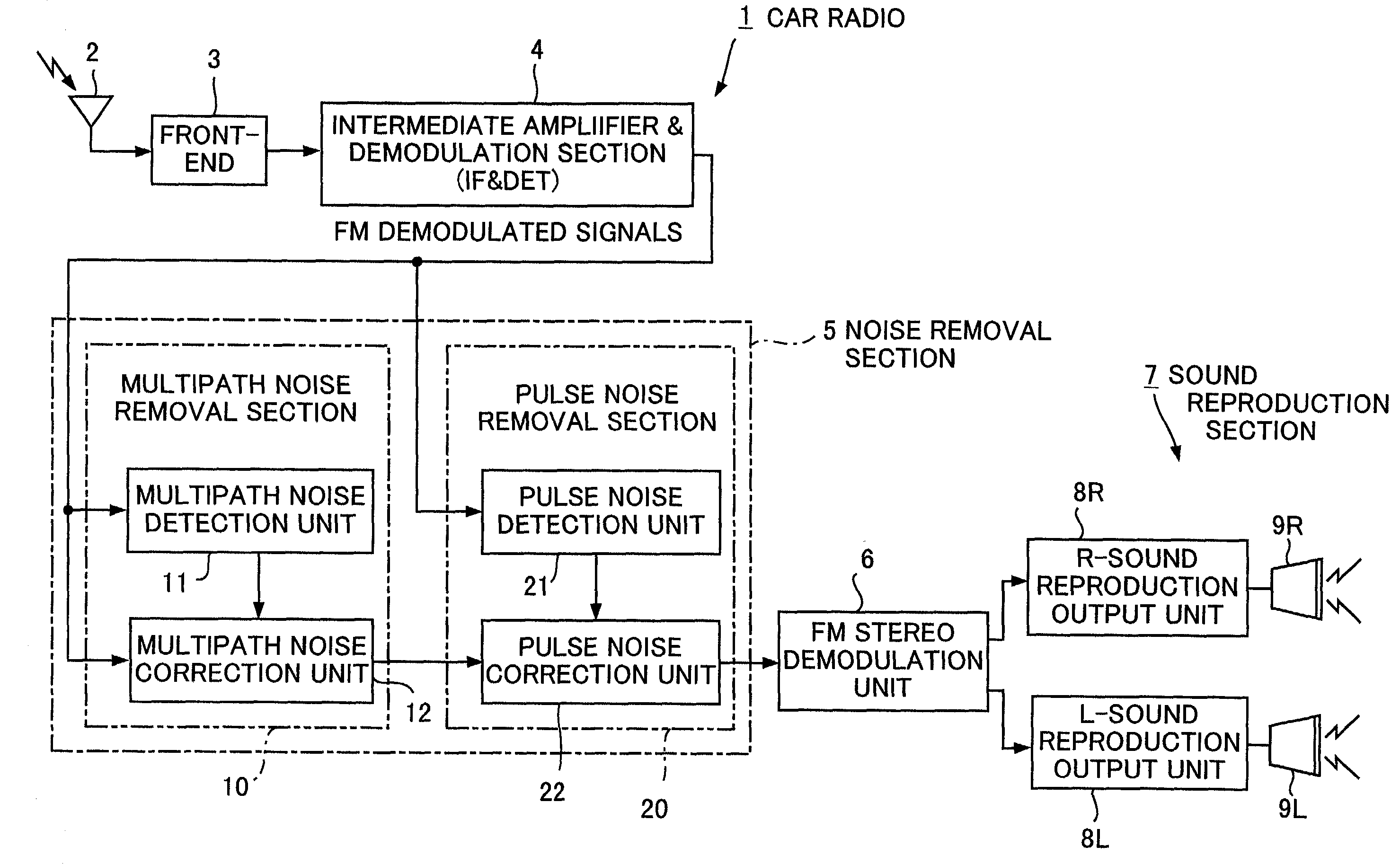
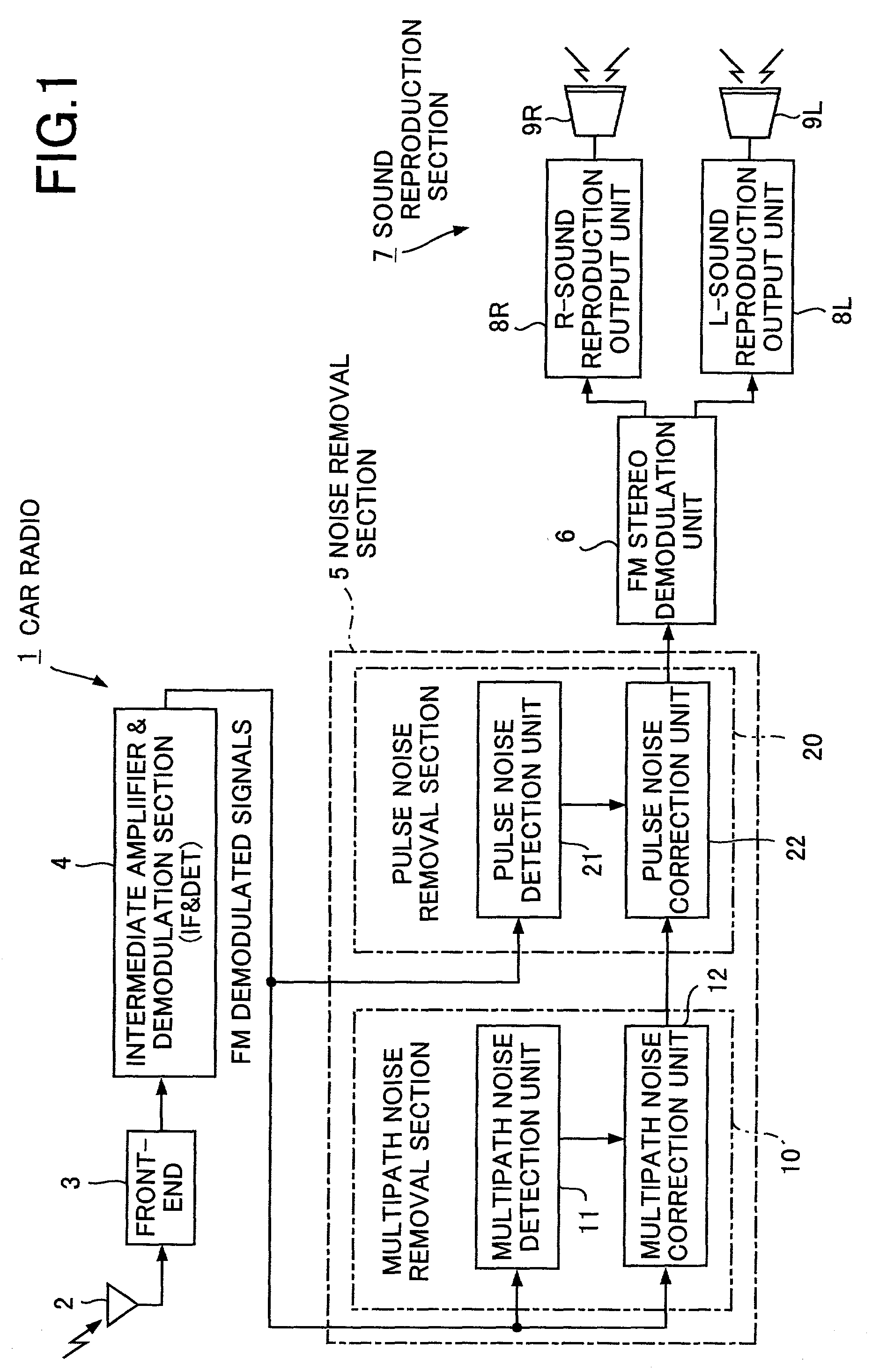
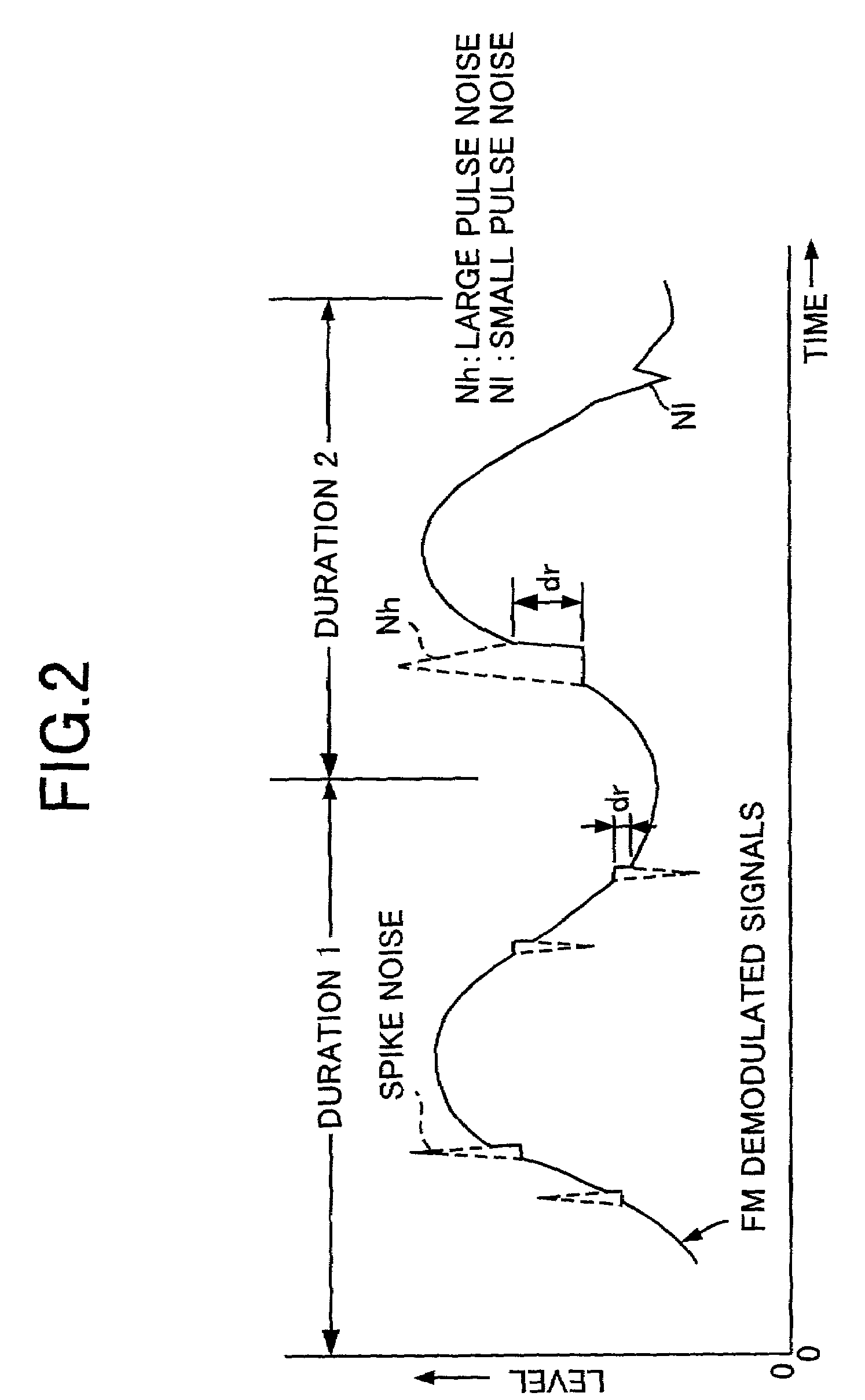
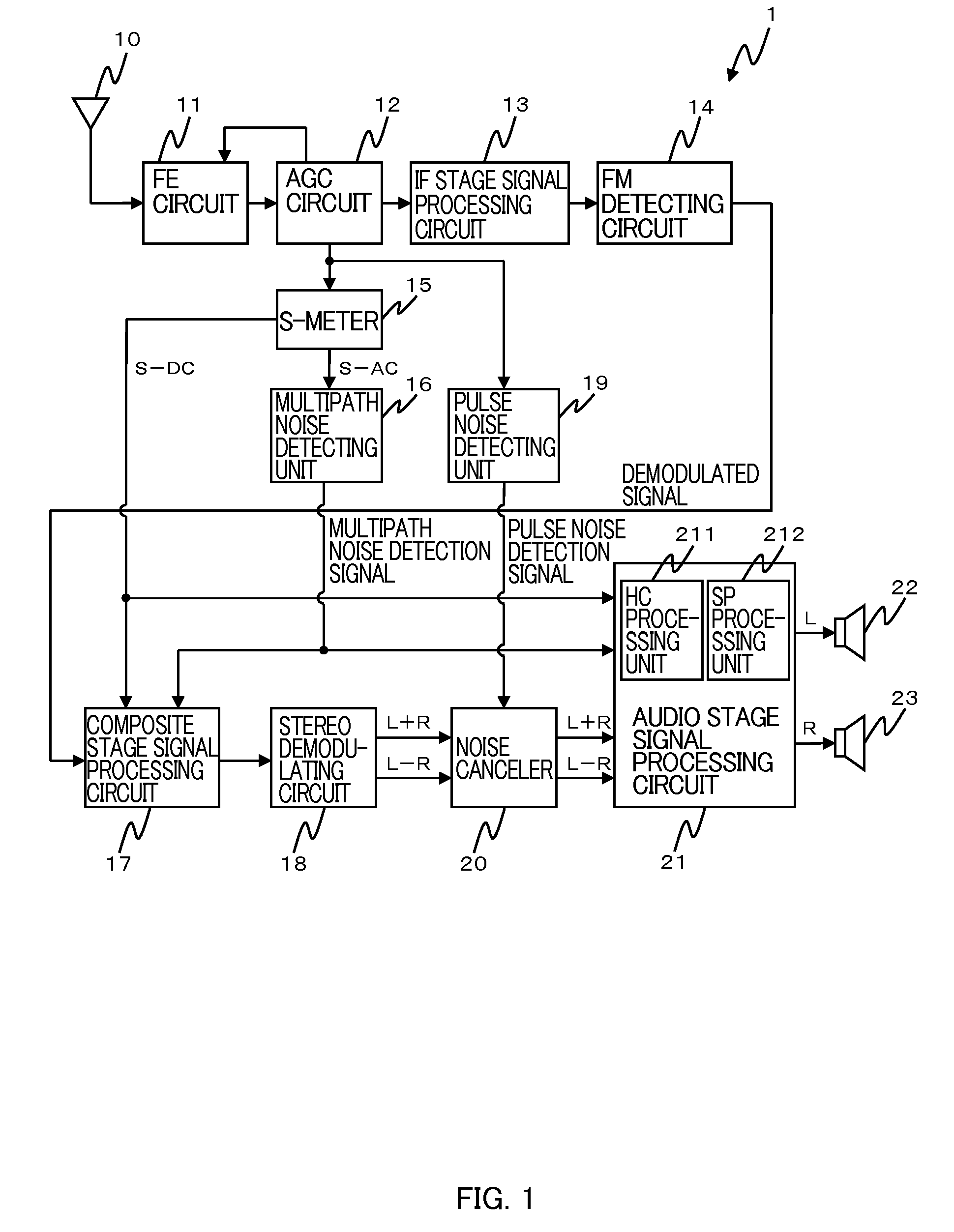
A noise removal unit mounted on a car radio according to the invention removes multipath noise and pulse noise from FM demodulated signals. At this time, the noise removal unit removes all of the multipath noise. Also, in case where the generation density of noise is high, the noise removal unit reduces the detection sensitivity so as not to detect pulse noise, particularly of small level, as noise. Comparing to multipath noise, pulse noise is noise rendering a large correction error than multipath noise. Therefore, in case where the generation density of pulse noise is high, by adapting the unit not to remove pulse noise of small level, it is made possible to reduce distortion of the FM demodulated signals to a minimum. Accordingly, it is made to reduce deterioration of the quality of FM voices to a minimum.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
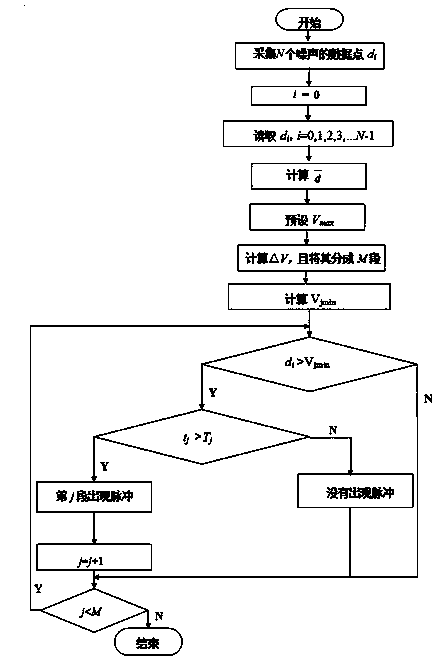
A low-voltage power line communication channel impulse noise detection method based on an amplitude and a width
InactiveCN103647610AImprove recognition accuracyPower distribution line transmissionTransmission monitoringNoise detectionLow voltage
The invention relates to a low-voltage power line communication channel impulse noise detection method based on an amplitude and a width, and belongs to the technical field of noise detection. The invention low-voltage power line communication channel impulse noise detection method based on the amplitude and the width comprises the following steps: S1, sampling is carried out on power line communication channel noises; S2, an absolute value mean value of the sampled noises is calculated; S3, a pulse highest amplitude threshold value is preset; S4, a difference value between the absolute value mean value and the highest threshold value is calculated; S5, the difference value is segmented uniformly; S6, the sampled noises are compared with the a segment of pulse amplitude lowest threshold value; if noise data which is greater than the amplitude lowest threshold exists in the sampled data, the present step is turned to a step S7; and otherwise, the present step is turned to a step S8; S7, whether a continuous time of the noise data of one segment of pulse amplitude lowest threshold value is greater than the segment of preset impulse continuous time threshold value; and S8, whether the comparison of all the segments is finished is determined. According to the invention, the impulse noises can be detected and identified, and the identification accuracy of the impulse noises is raised.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
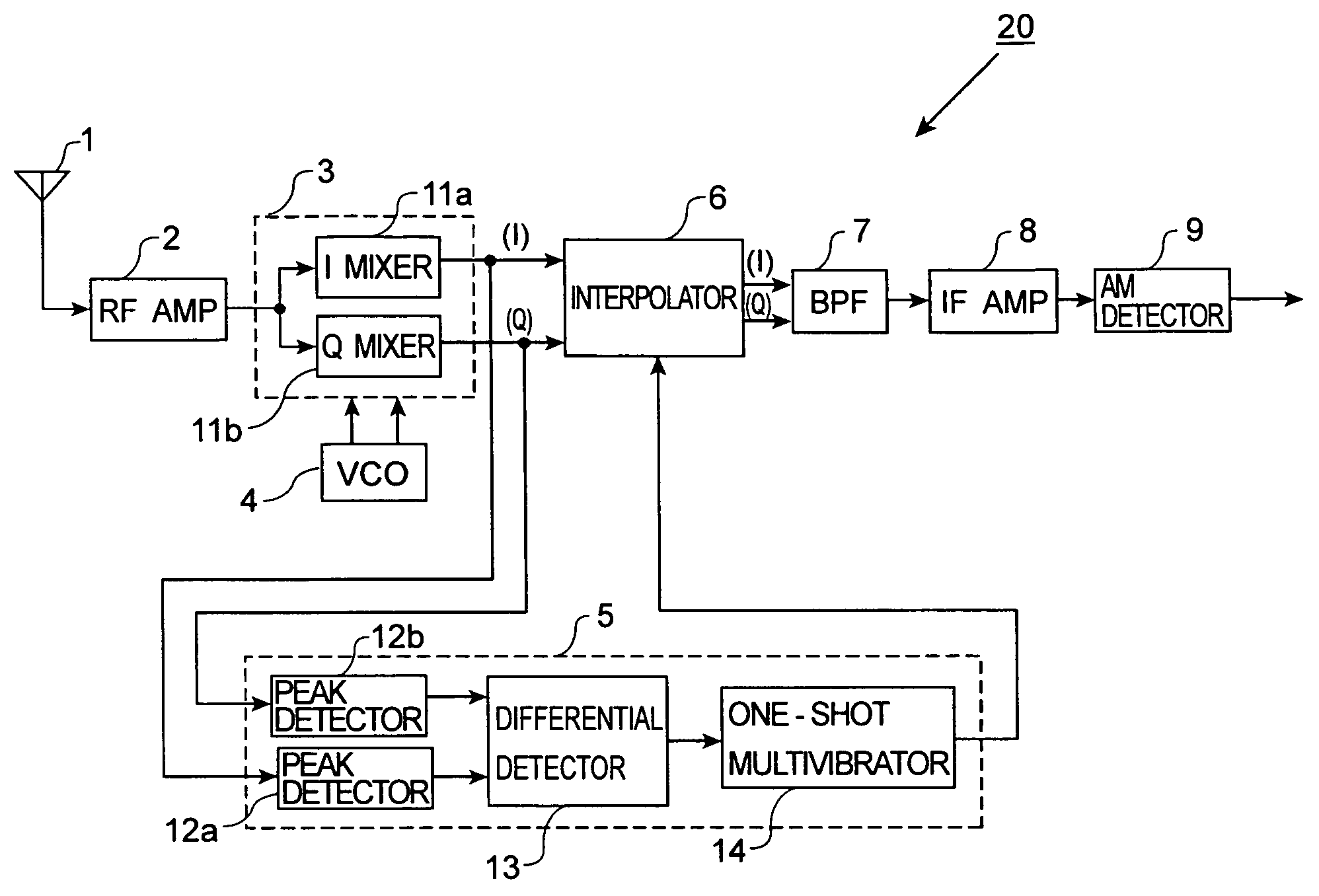
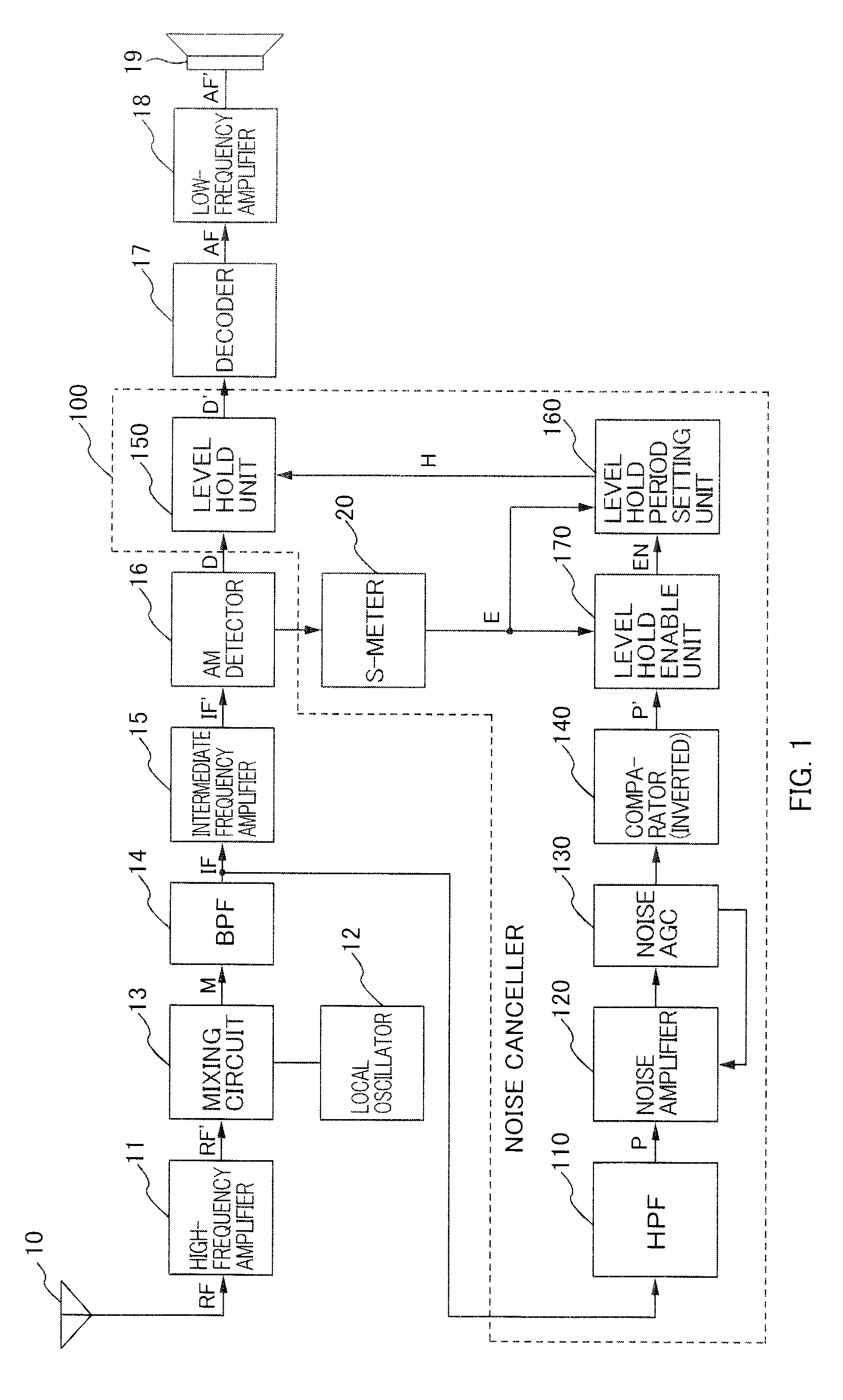
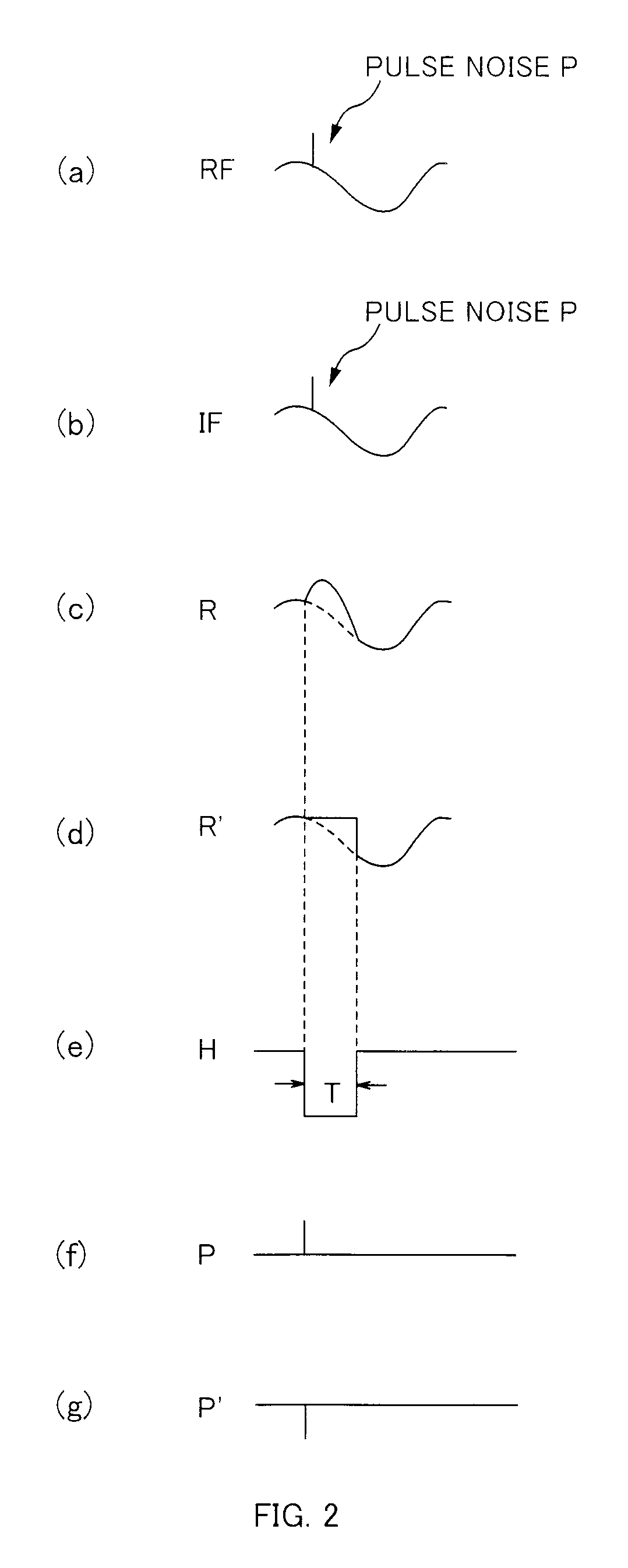
Receiver
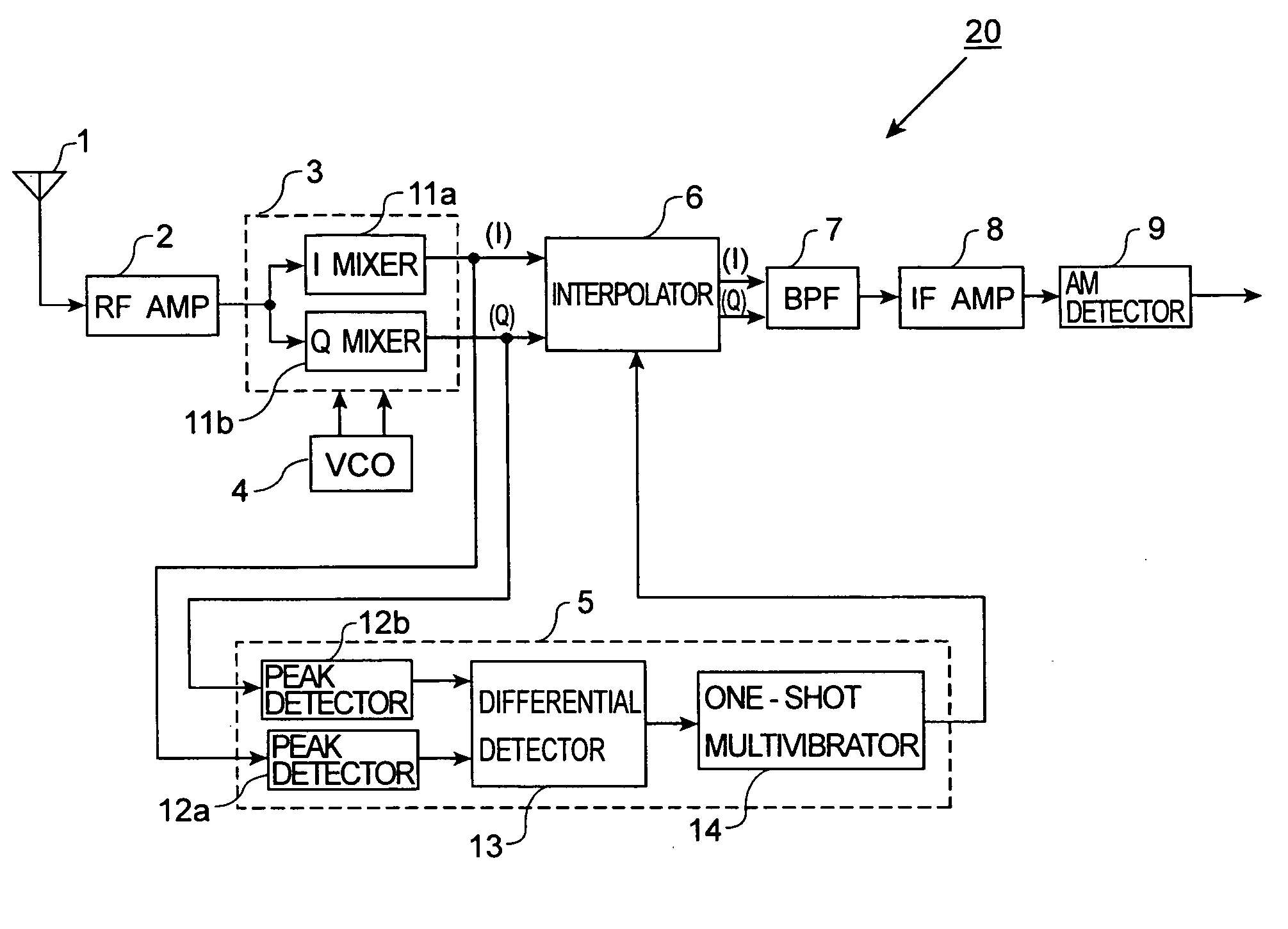
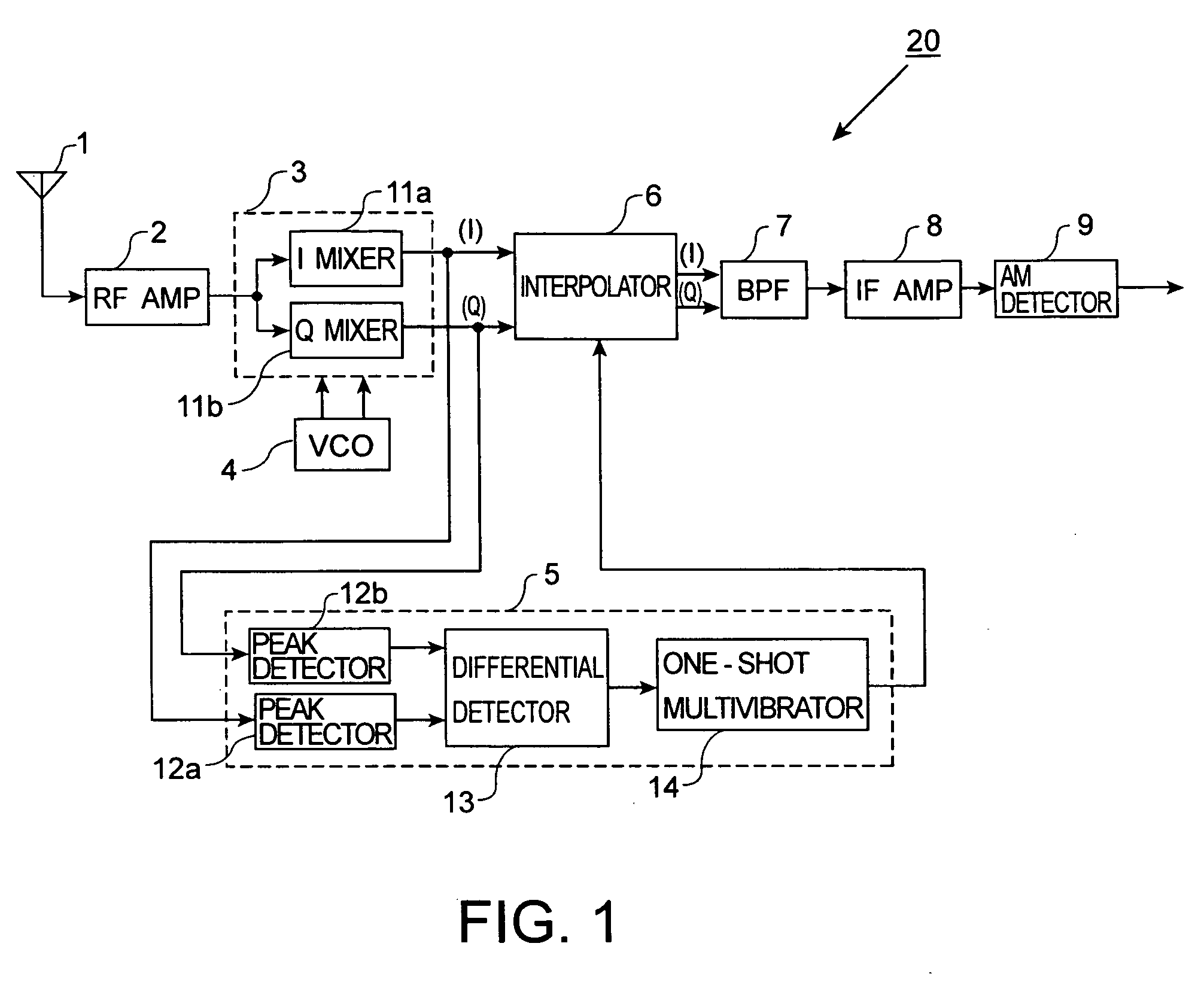
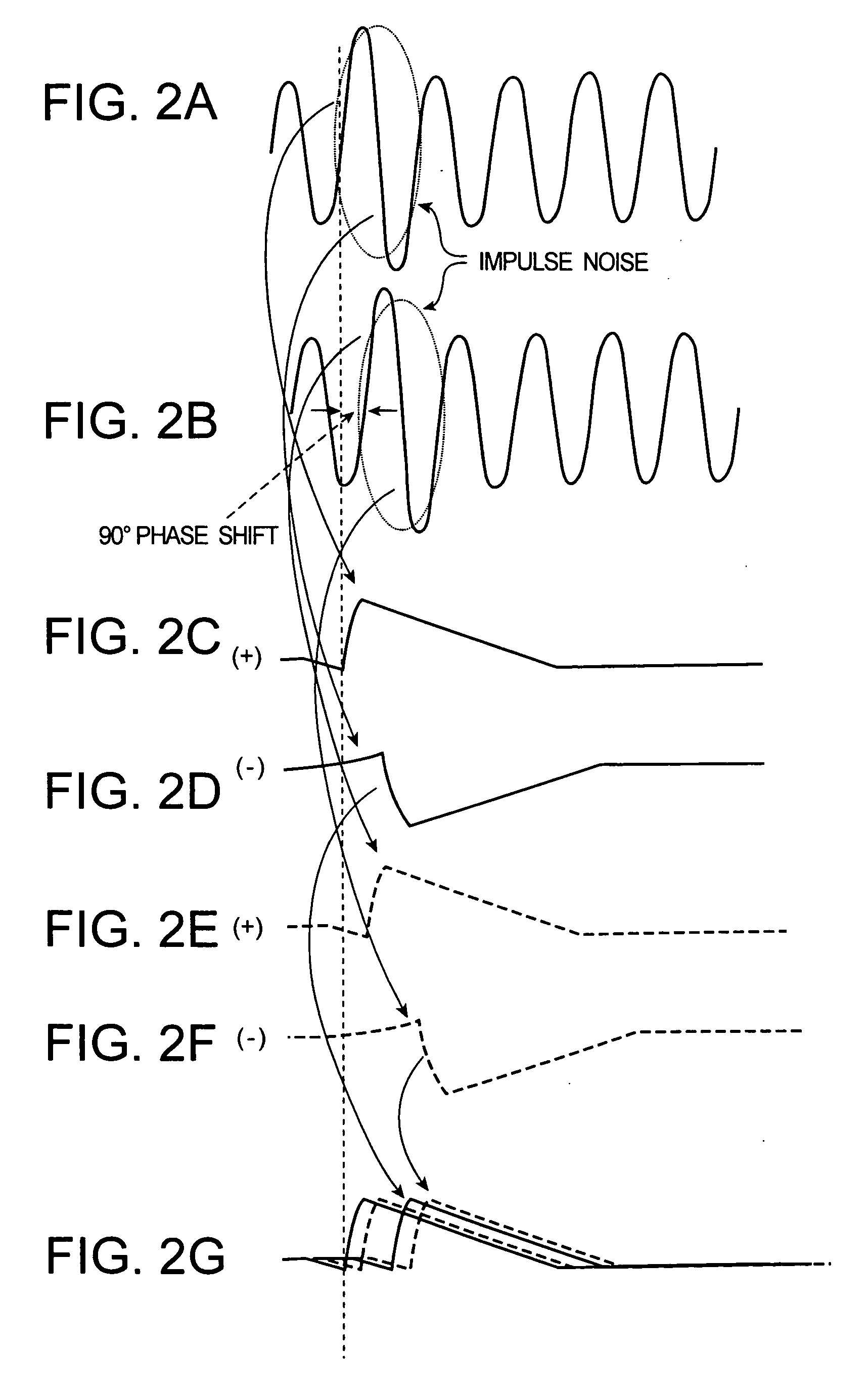
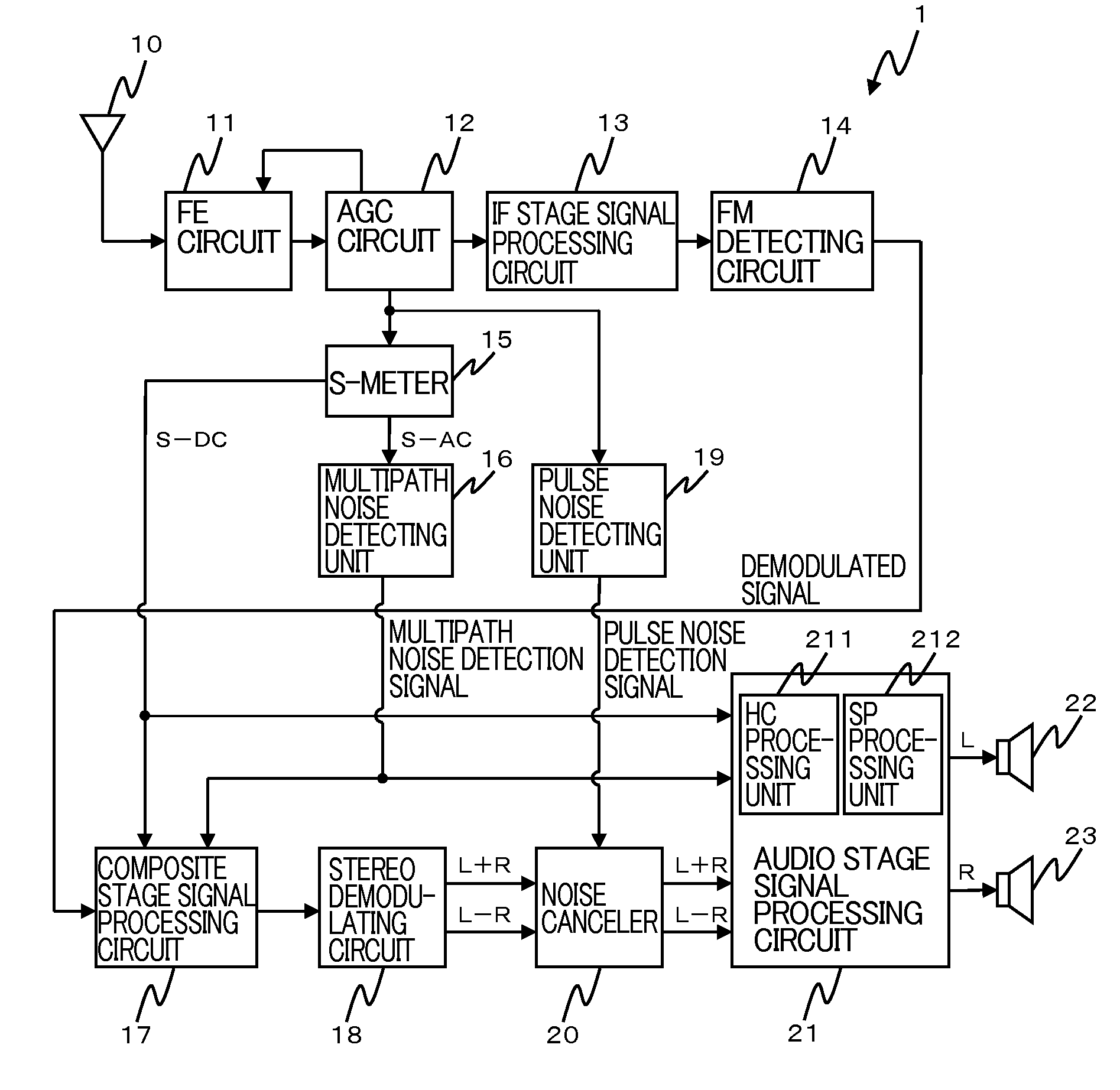
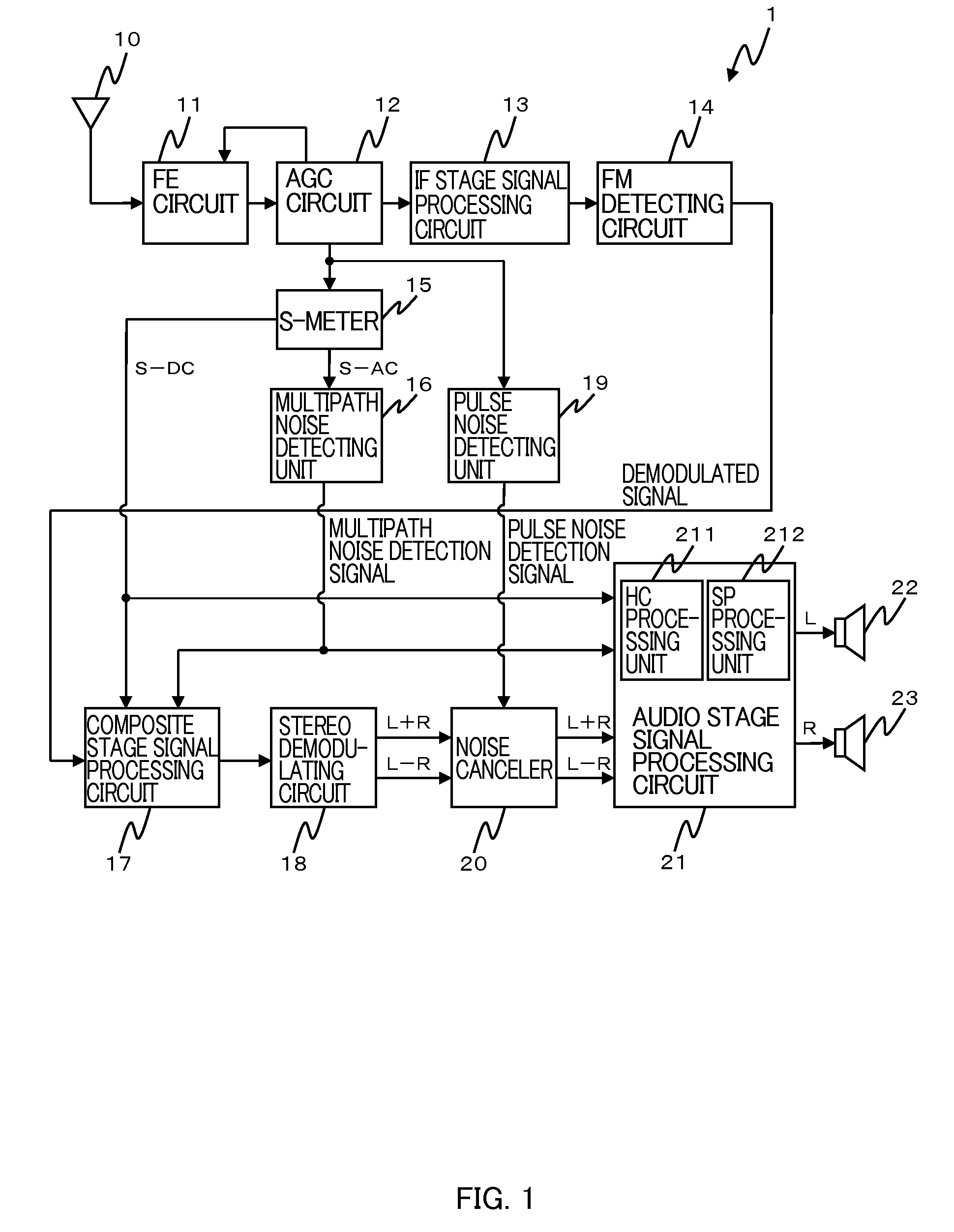
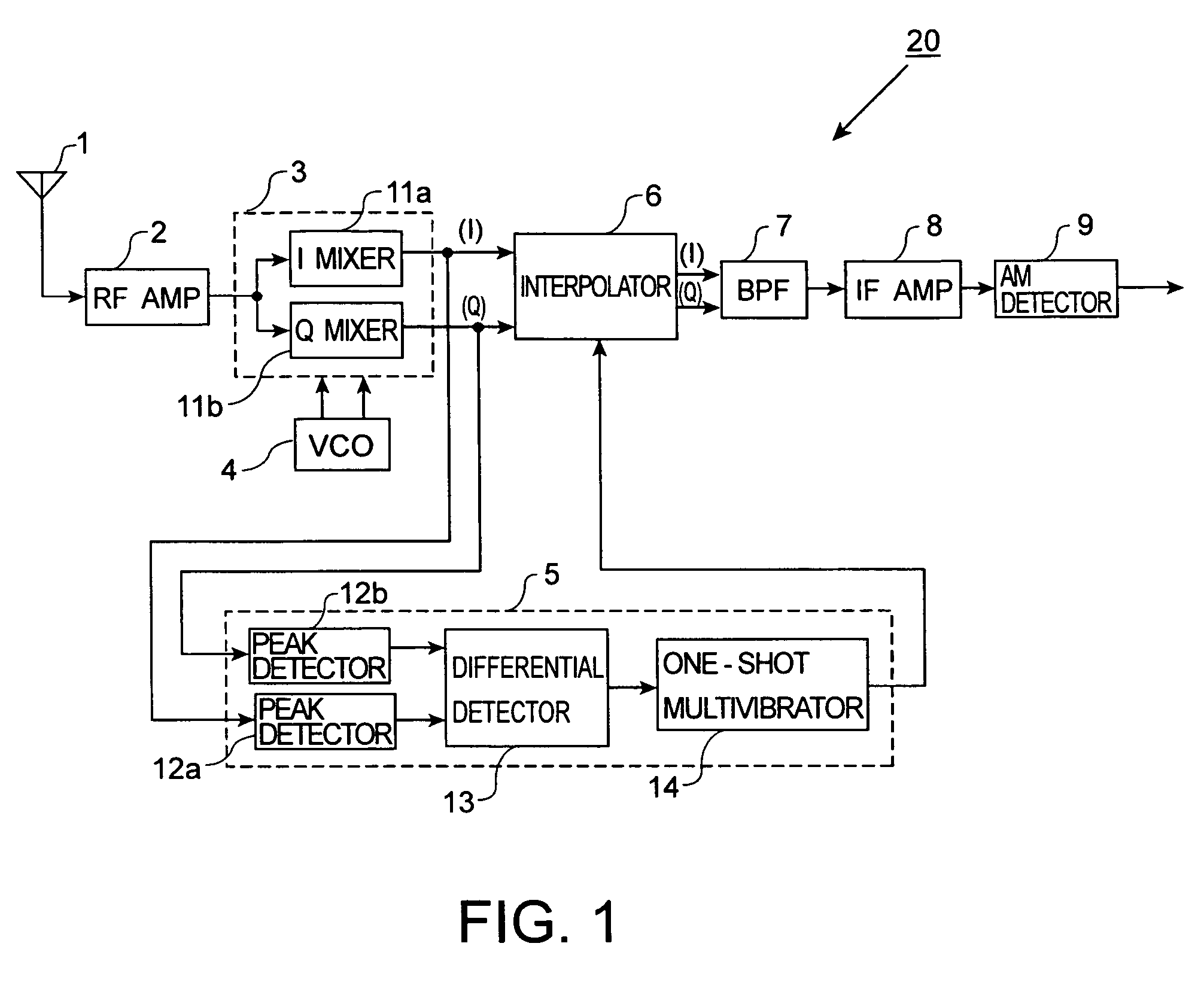
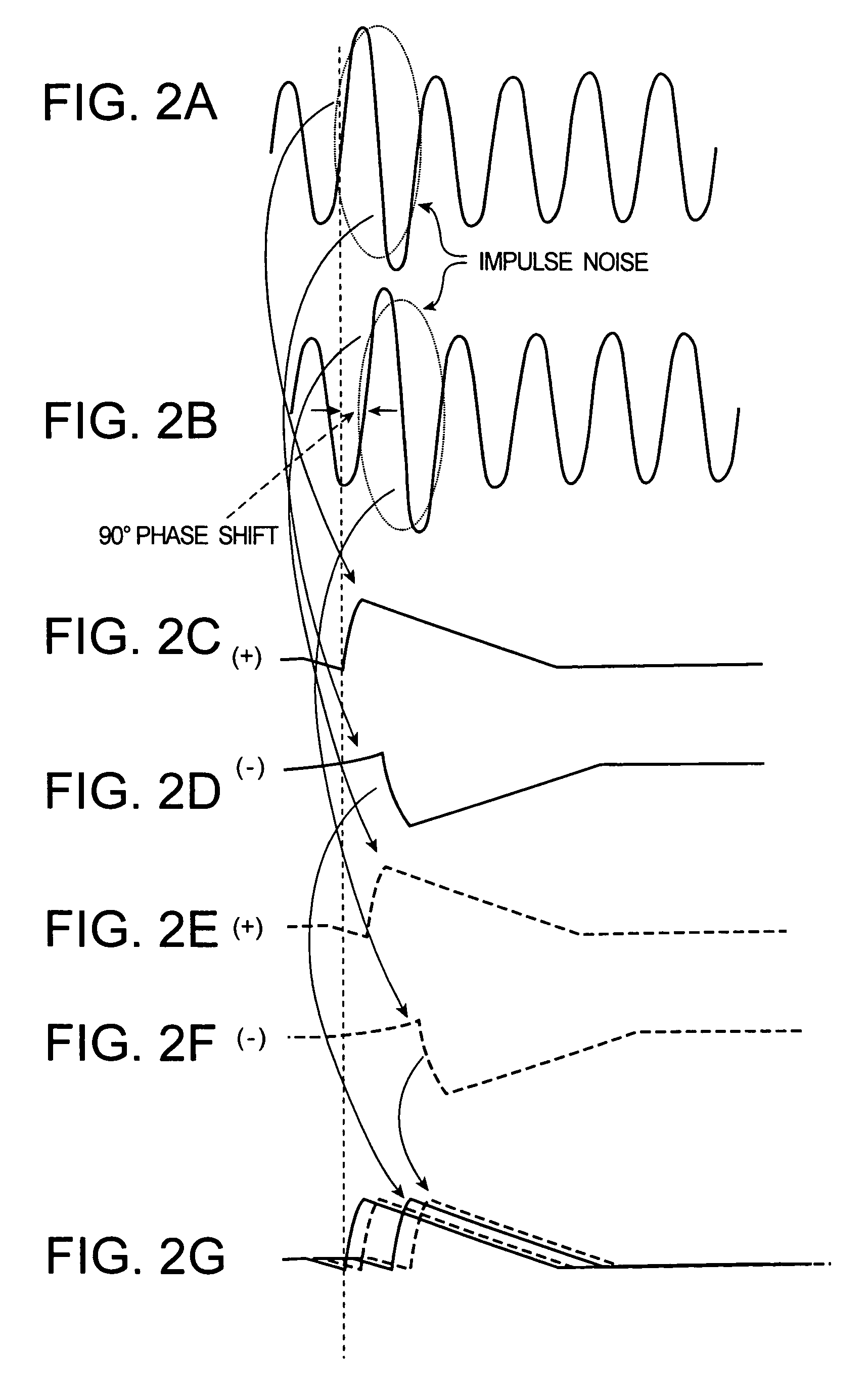
AM receiver 20 is provided with antenna 1, RF amplifier 2, I / Q mixer 3, VCO 4, impulse noise detector 5, interpolator 6, BPF 7, IF amplifier 8 and AM detector 9. I / Q mixer 3 is composed of I mixer 11a as an in-phase mixer and Q mixer 11b as an orthogonal mixer. Impulse noise detector 5 generates an interpolation signal from in-phase and orthogonal output signals from I / Q mixer 3. Interpolator 6 carries out shaping of waveforms of the output signals from I / Q mixer 3 in response to the interpolation signal and eliminates impulse noises from the output signals from I / Q mixer 3.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
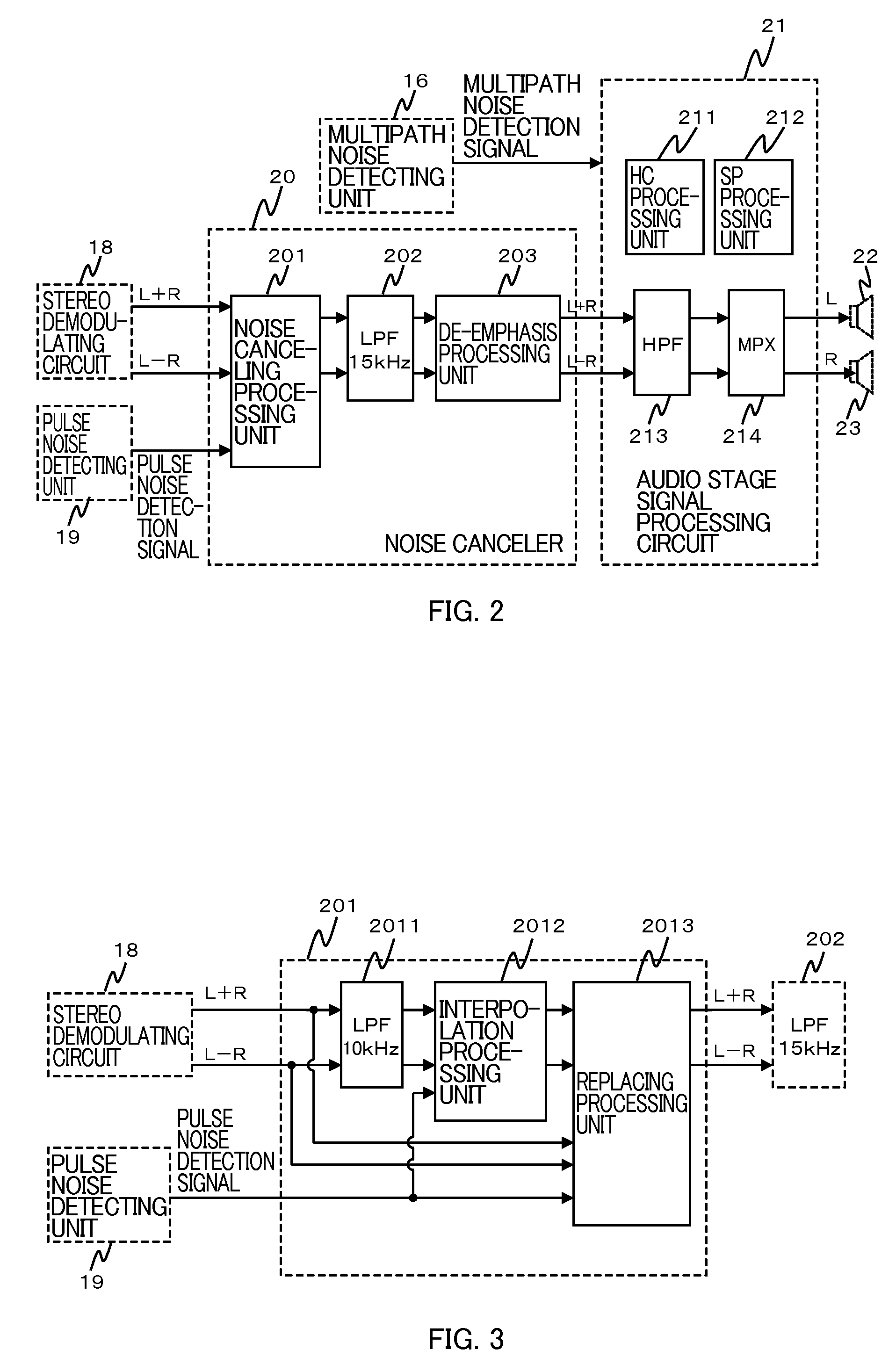
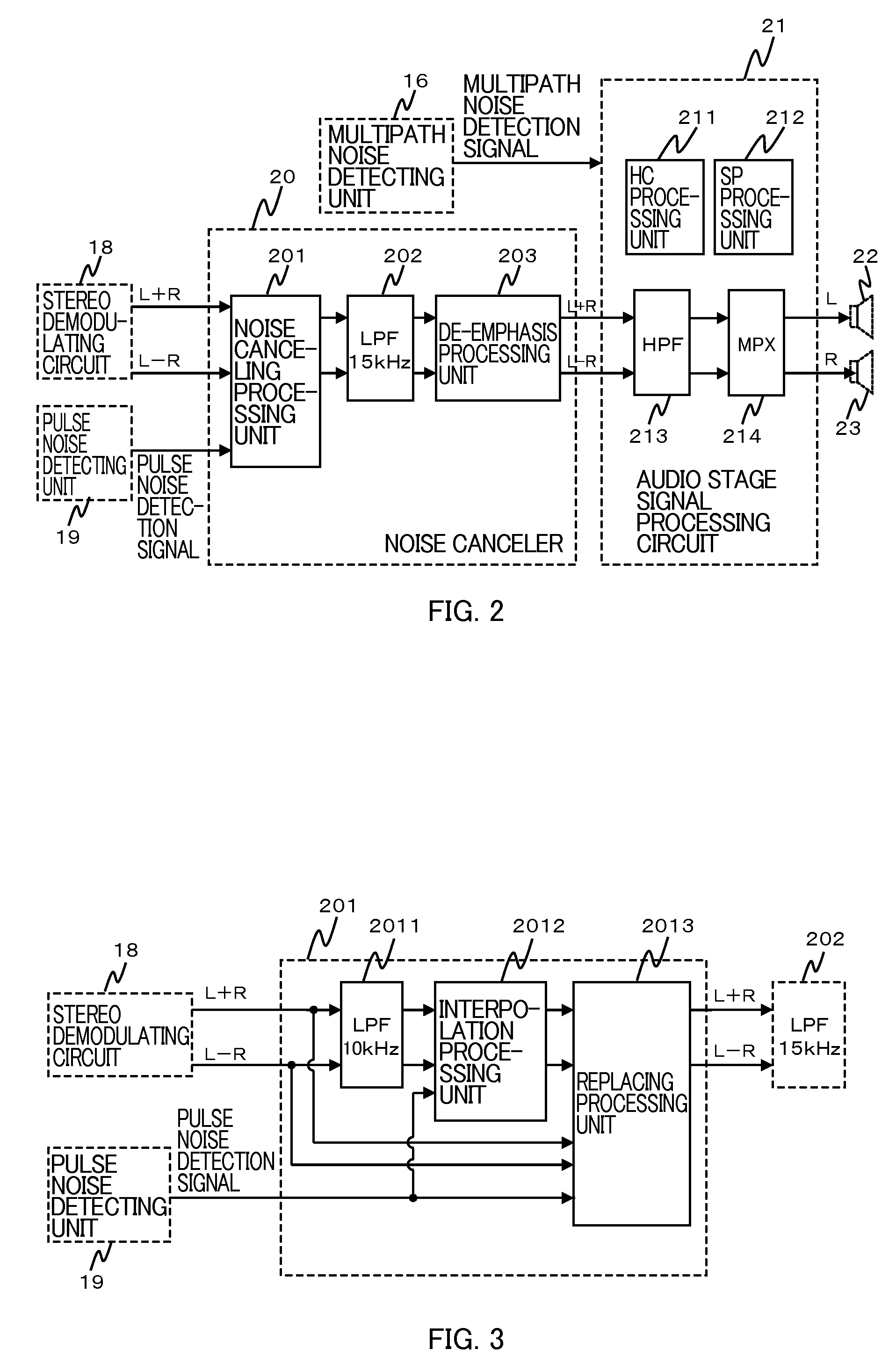
Noise Canceler and Receiving Apparatus Using the Same
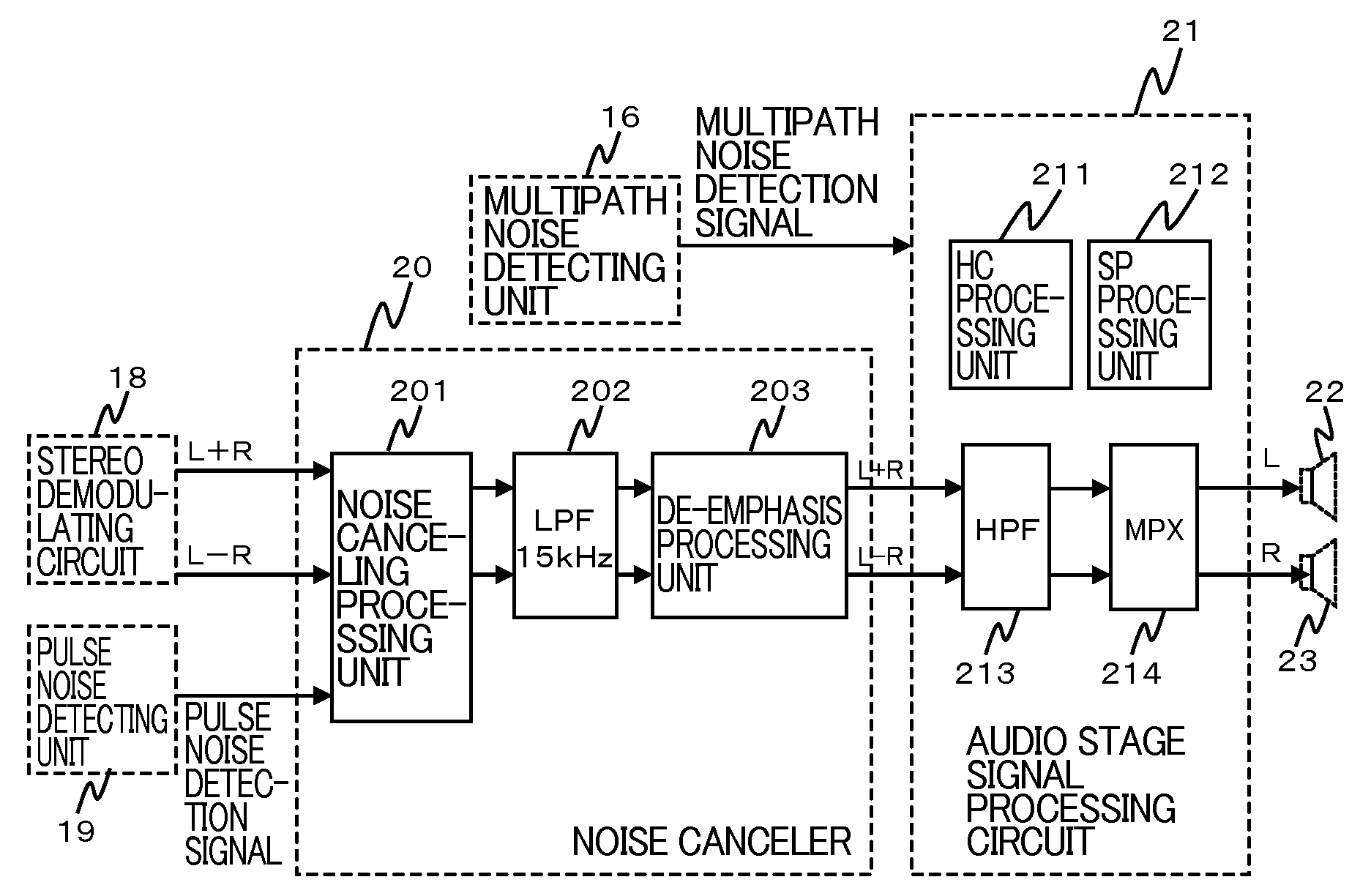
InactiveUS20070297622A1Improve signal qualityRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionLow-pass filterPulse noise
A noise canceler comprising: a first low-pass filter that a demodulated signal is to be input to; an interpolation processing unit that the demodulated signal after passing through the first low-pass filter and a pulse noise detection signal indicating presence of a pulse noise, are to be input to, the interpolation processing unit configured to perform interpolation processing on a demodulated signal present during a period determined by the pulse noise detection signal, out of the input demodulated signal, based on the input demodulated signal; a replacing processing unit that the demodulated signal subjected to the interpolation processing, the pulse noise detection signal, and the demodulated signal before passing through the first low-pass filter, are to be input to, the replacing processing unit configured to output a signal obtained by replacing a demodulated signal present during the period, out of the demodulated signal before passing through the first low-pass filter, with the demodulated signal subjected to the interpolation processing, wherein the demodulated signal is present during the period; and a second low-pass filter that the signal output from the replacing processing unit is to be input to, the second low-pass filter including a cut-off frequency higher than that of the first low-pass filter.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
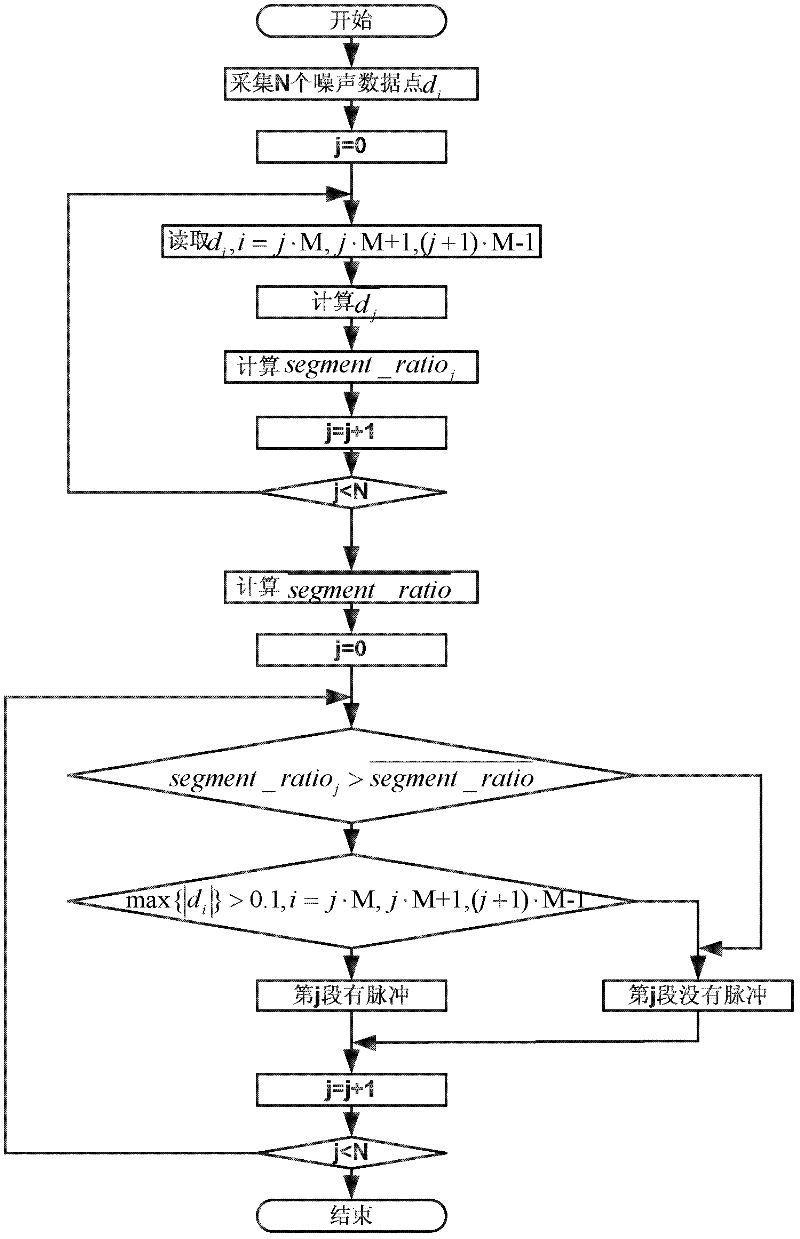
Pulse noise detection method of power line communication channel
ActiveCN102347811AImprove recognition accuracyPower distribution line transmissionTransmission monitoringPhase noiseComputer science
The invention discloses a pulse noise detection method of a power line communication channel, comprising the following steps of: S1, sampling noise of the power line communication channel; S2, segmenting continuous sampling points; S3, computing the average value of absolute values of all segments; S4, computing the average ratio of absolute variances of all the segments; S5, computing the average value of average ratios of the absolute variances; S6, comparing the average ratio of the absolute variances with the average value; if the average value of the absolute variances of a segment is larger than the average value, turning to step S7; otherwise, turning to step S8; S7, judging whether noise data amplitude in the segment exceeds a preset noise threshold; if so, judging that the segment appears the pulse noise once; otherwise, judging that the segment has no pulse noise; judging whether the comparison is over; if so, returning results; otherwise, turning to the step S6 and continuing to compare. Recognition accuracy of pulse noise is improved by using the method.
Owner:兆讯恒达科技股份有限公司
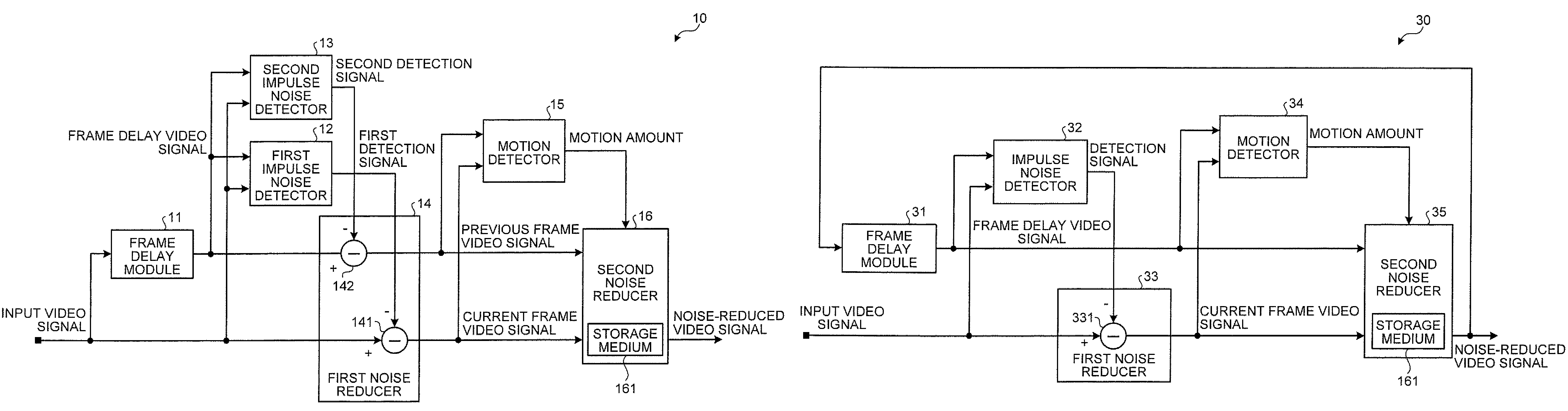
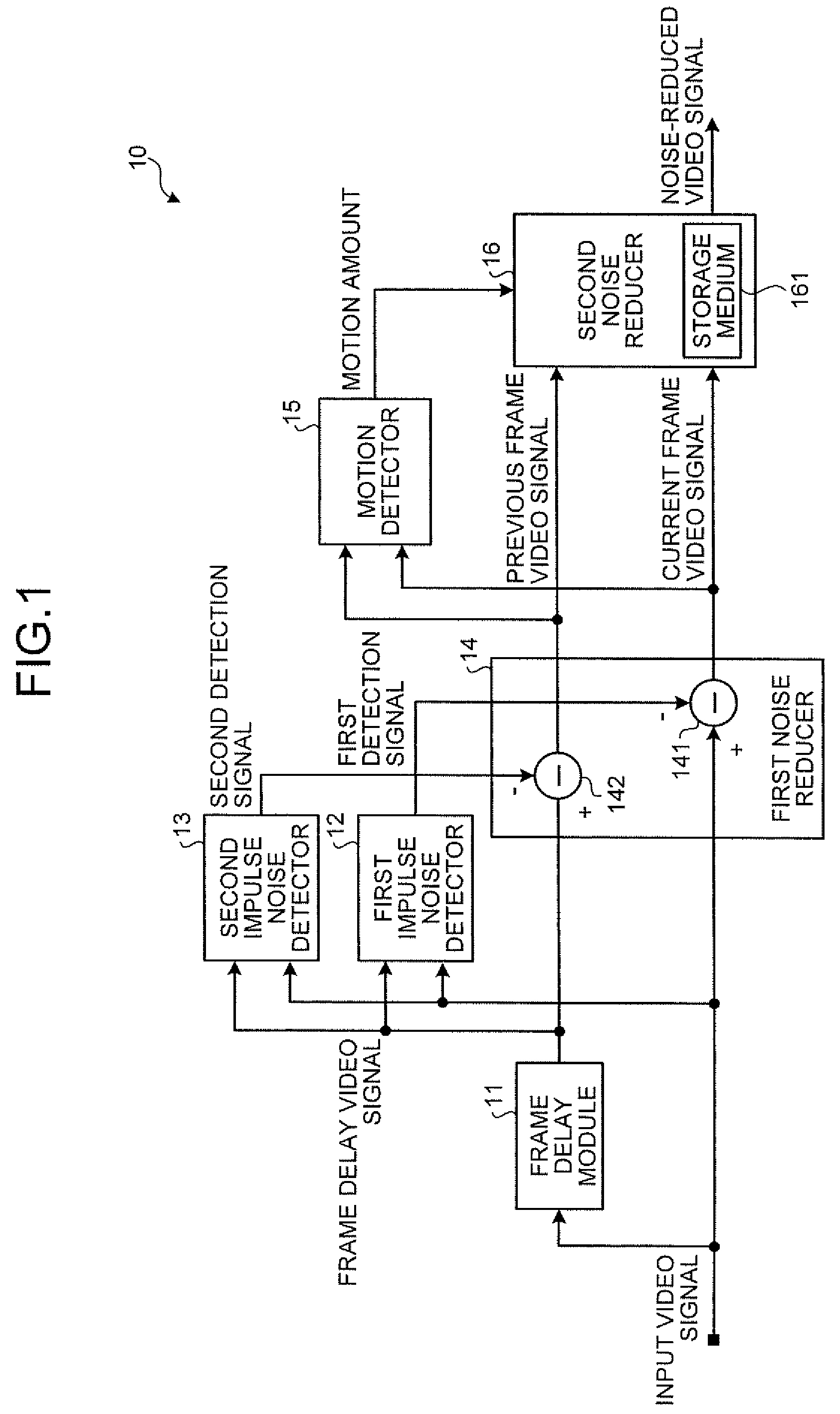
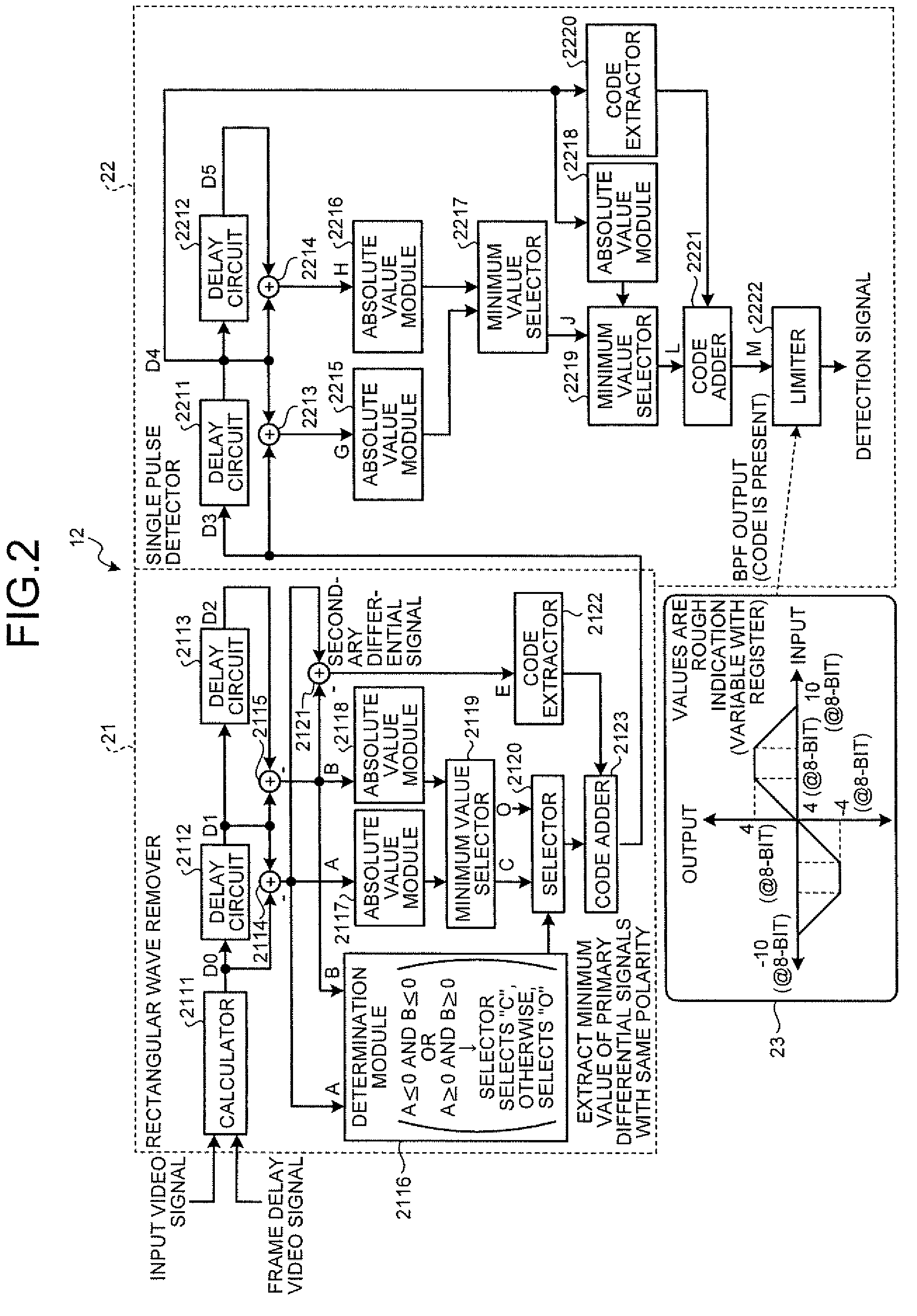
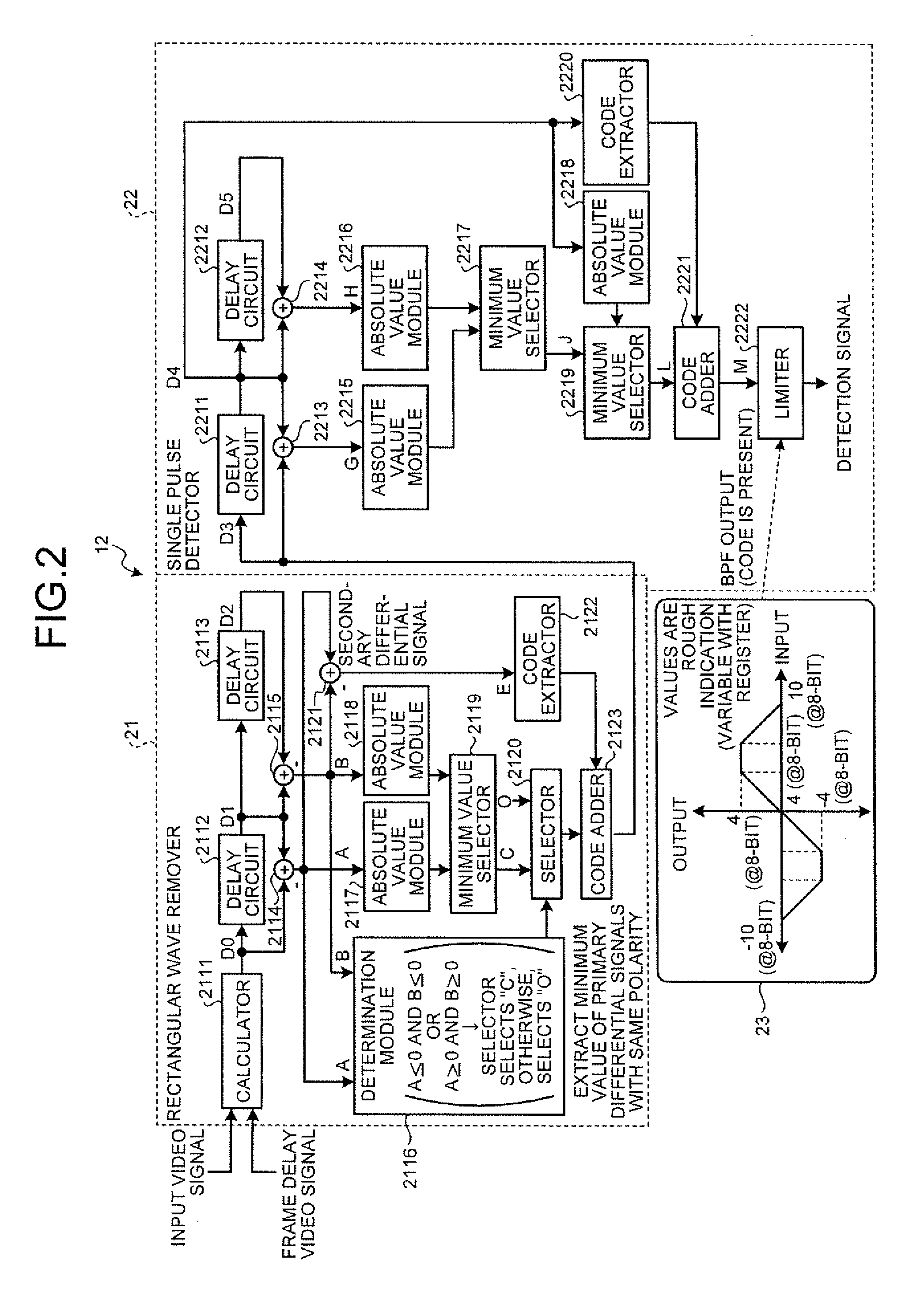
Noise reduction apparatus and noise reduction method
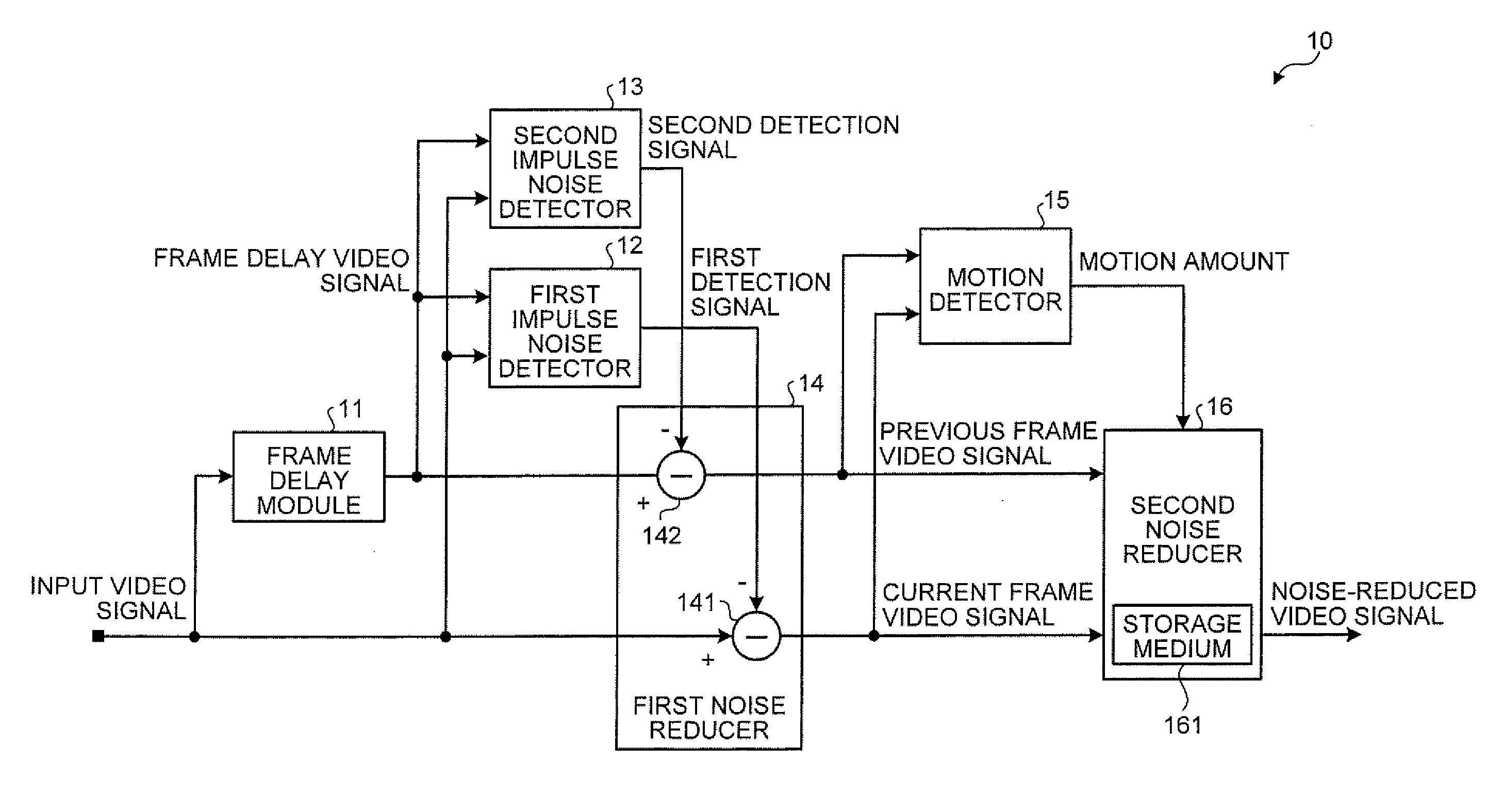
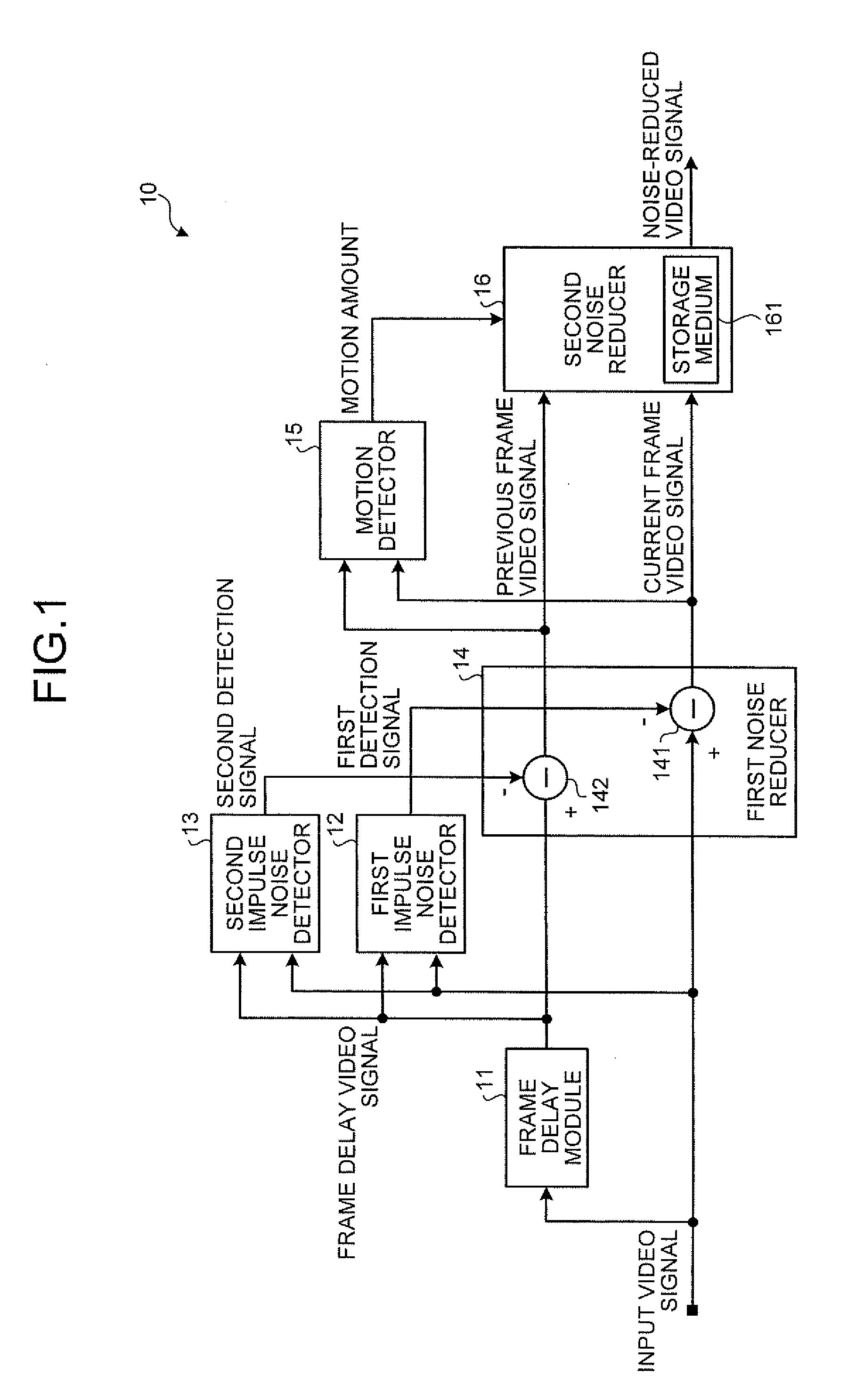
According to one embodiment, a noise reduction apparatus includes a frame delay module, first and second impulse noise detectors, first and second impulse noise reducers, a motion detector, and a noise reducer. The frame delay module delays a video signal by one frame to obtain a frame delay video signal. The first and second impulse noise detectors detect impulse noise in the video signal and the frame delay video signal. The first impulse noise reducer generates a current frame video signal by reducing the impulse noise in the video signal. The second impulse noise reducer generates a previous frame video signal by reducing the impulse noise in the frame delay video signal. The motion detector detects motion amount from the current and previous frame video signals. The noise reducer reduces noise other than the impulse noise in the current frame video signal based on the motion amount.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and device for eliminating impulse noise
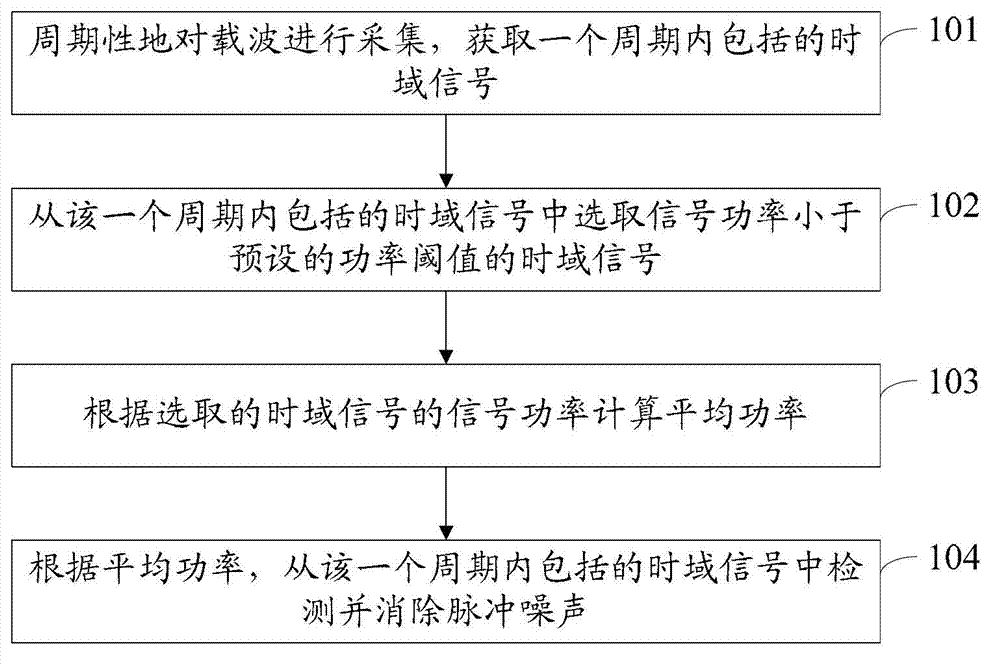
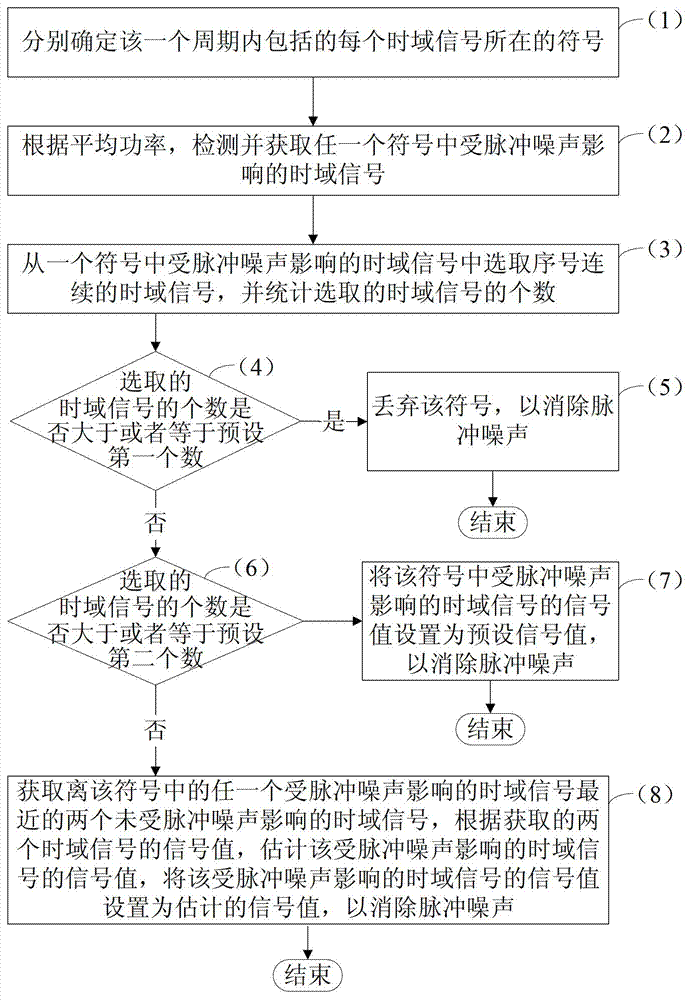
InactiveCN103209006AEliminate the effects ofImprove accuracyPower distribution line transmissionLine-transmission monitoring/testingTime domainComputer module
The invention discloses a method and a device for eliminating impulse noise, and belongs to the field of communication. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a carrier wave periodically to acquire time-domain signals which are included within a period; selecting a time-domain signal of which the signal power is smaller than a preset power threshold value from the time-domain signals which are included within the period; calculating average power according to the signal power of the selected time-domain signal; and detecting and eliminating the impulse noise in the time-domain signals which are included within the period according to the average power. The device comprises an acquisition module, a first selection module, a first calculation module and a first elimination module. According to the method and the device, the average power is calculated according to the selected time-domain signal of which the signal power is smaller than the preset power threshold value; and the impulse noise in the time-domain signals is detected and eliminated according to the average power to improve the accuracy of detecting the impulse noise, so that the influence of the impulse noise on the time-domain signals can be eliminated better.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wide band noise early detection and protection architecture for a frequency domain equalizer
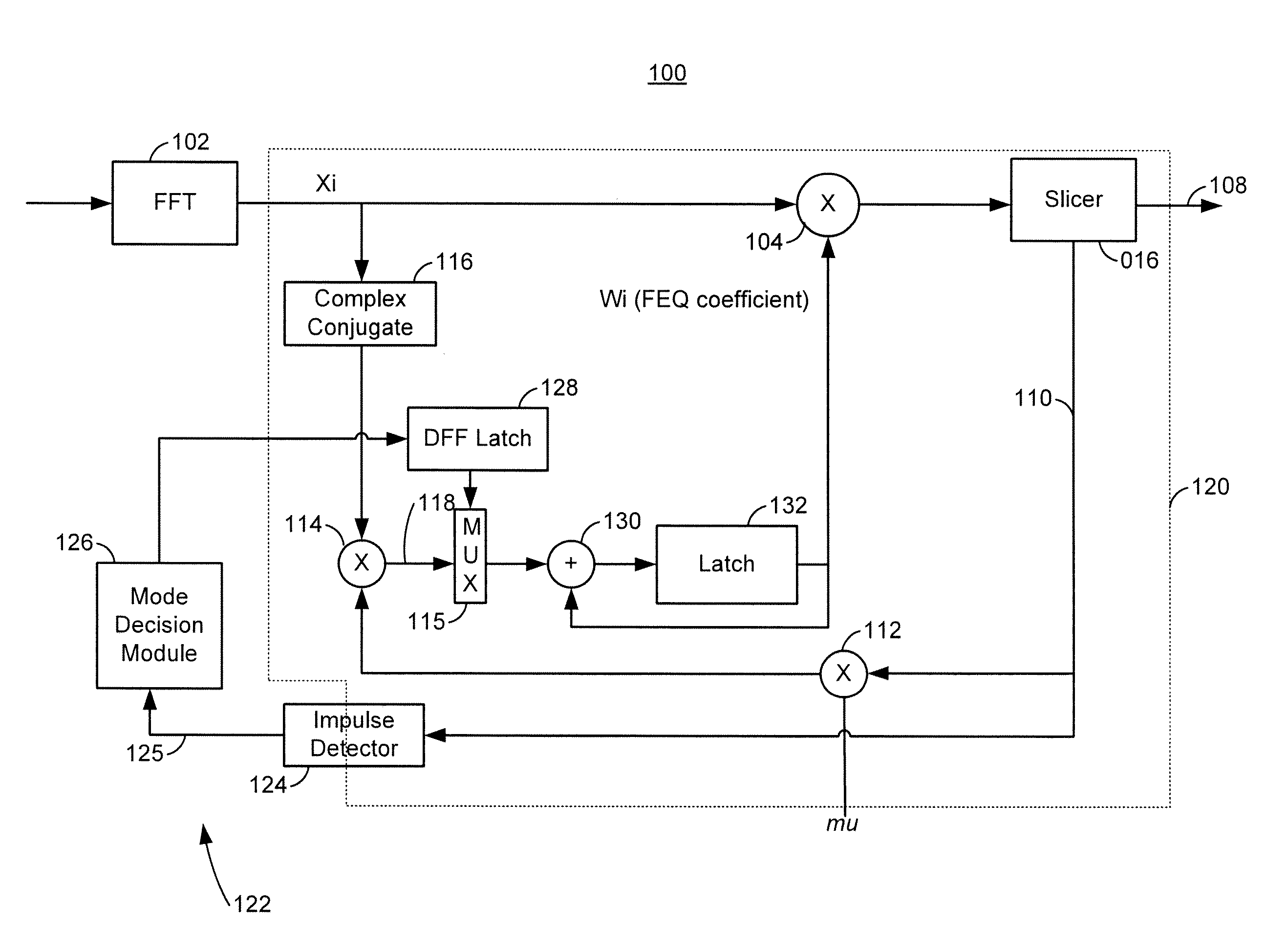
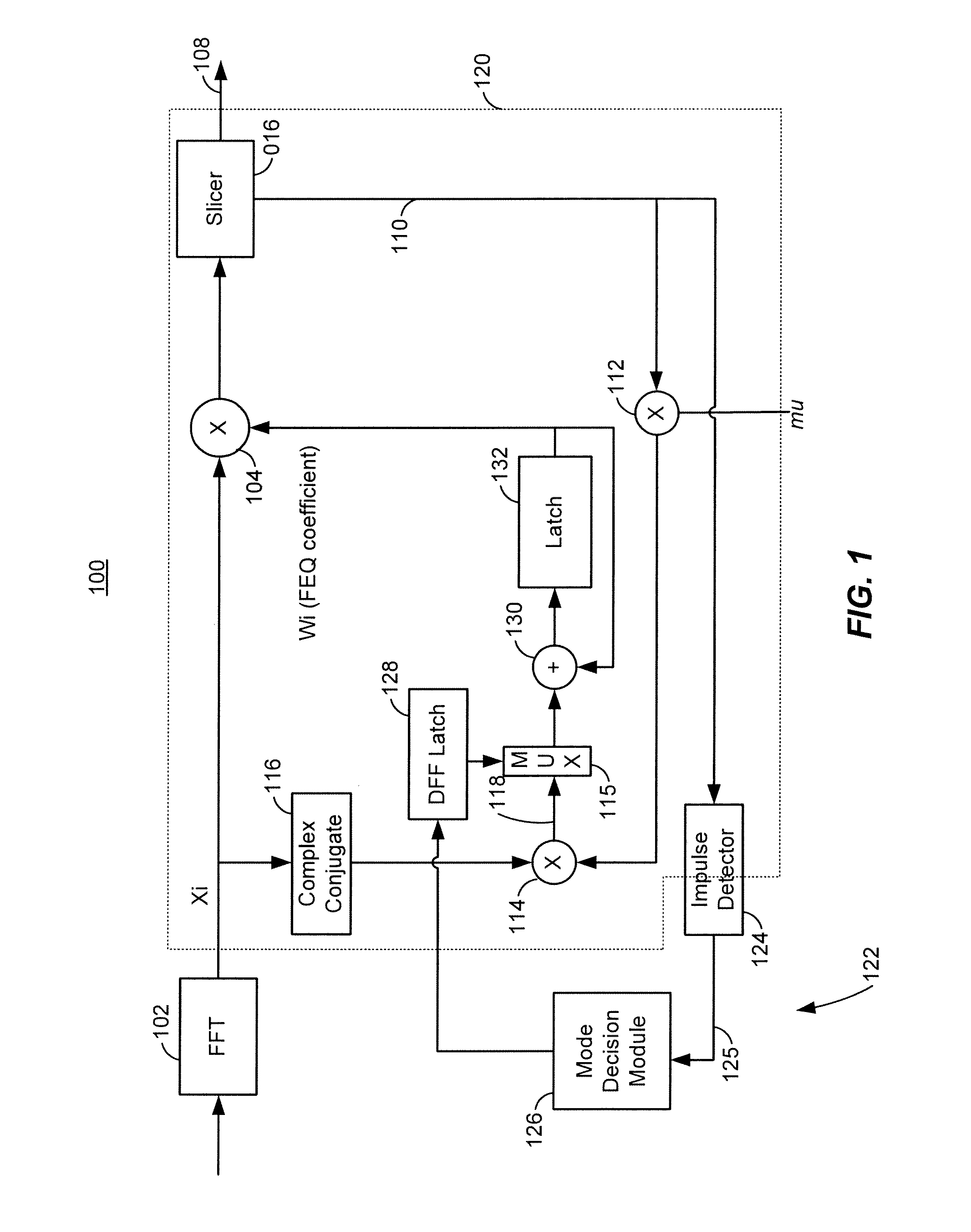
Apparatus and methods are described for detecting an impulse noise and for controlling frequency domain equalizer (FEQ) coefficient updating in response to impulse noise detection. Upon detection of the impulse noise, FEQ coefficient updating may immediately be frozen to prevent the FEQ coefficients from being corrupted by the impulse noise. The FEQ coefficient updating may be resumed after the impulse has ended, allowing for normal operation and channel detection.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Noise canceler and receiving apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7689192B2Improve signal qualityRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionLow-pass filterPulse noise
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Receiver
AM receiver 20 is provided with antenna 1, RF amplifier 2, I / Q mixer 3, VCO 4, impulse noise detector 5, interpolator 6, BPF 7, IF amplifier 8 and AM detector 9. I / Q mixer 3 is composed of I mixer 11a as an in-phase mixer and Q mixer 11b as an orthogonal mixer. Impulse noise detector 5 generates an interpolation signal from in-phase and orthogonal output signals from I / Q mixer 3. Interpolator 6 carries out shaping of waveforms of the output signals from I / Q mixer 3 in response to the interpolation signal and eliminates impulse noises from the output signals from I / Q mixer 3.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Noise reduction apparatus and noise reduction method
InactiveUS20100026896A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion detectorReducer
According to one embodiment, a noise reduction apparatus includes a frame delay module, first and second impulse noise detectors, first and second impulse noise reducers, a motion detector, and a noise reducer. The frame delay module delays a video signal by one frame to obtain a frame delay video signal. The first and second impulse noise detectors detect impulse noise in the video signal and the frame delay video signal. The first impulse noise reducer generates a current frame video signal by reducing the impulse noise in the video signal. The second impulse noise reducer generates a previous frame video signal by reducing the impulse noise in the frame delay video signal. The motion detector detects motion amount from the current and previous frame video signals. The noise reducer reduces noise other than the impulse noise in the current frame video signal based on the motion amount.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
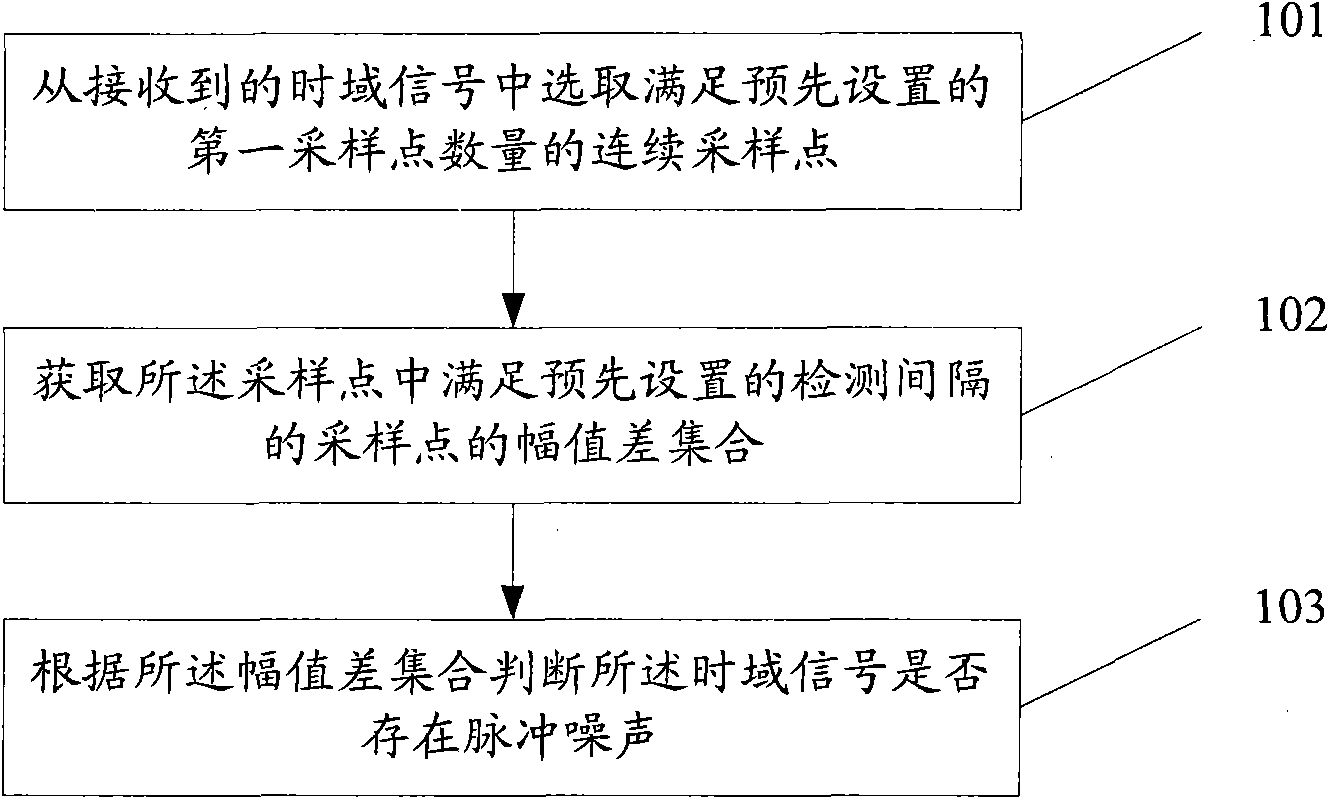
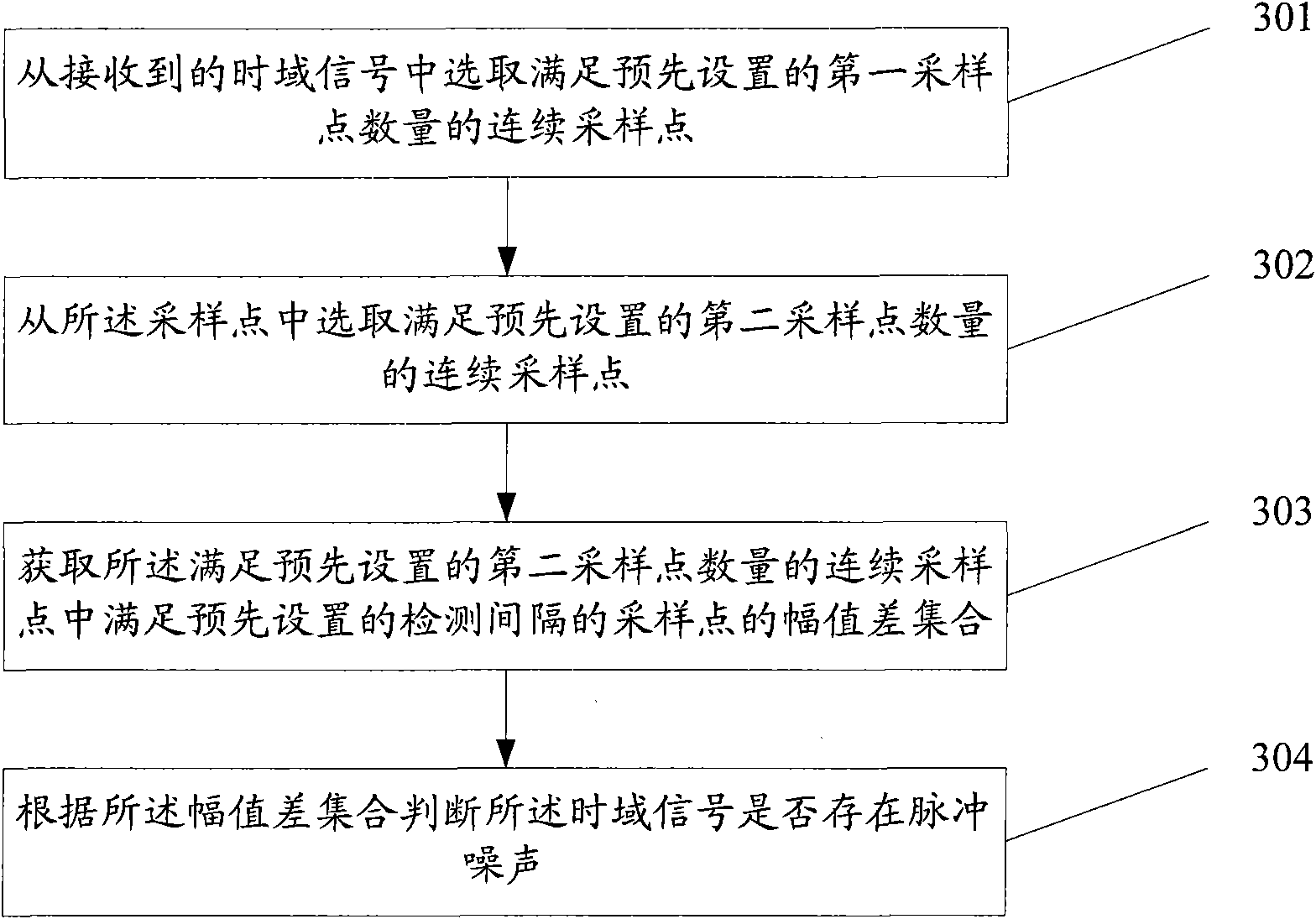
Method, device and system for detecting pulse noise
ActiveCN102098115AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityTransmission monitoringDigital subscriber lineTime domain
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, device and system for detecting pulse noise, relating to the field of communication, and aiming to solve the problems that the pulse noise detection method is complex and has lower detection accuracy and sensitivity in the prior art. The technical scheme provided by the invention comprises the following steps: selecting continuous sampling points in accordance with the number of preset first sampling points from received time domain signals; acquiring an amplitude difference set of sampling points in accordance with preset detection intervals in the sampling points; and judging whether the time domain signals have pulse noise according to the amplitude difference set. The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention can be applied to a pulse noise detection technique of various digital signal processing systems such as DSL (digital subscriber line), Cable and other wired access modes, wireless access, WIFI (wireless fidelity) or 3G (the 3rd generation telecommunication) and the like.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A method and system for filtering coherent noise
InactiveCN109145825AAvoid disadvantagesEliminate the effects ofCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal varianceBackground noise
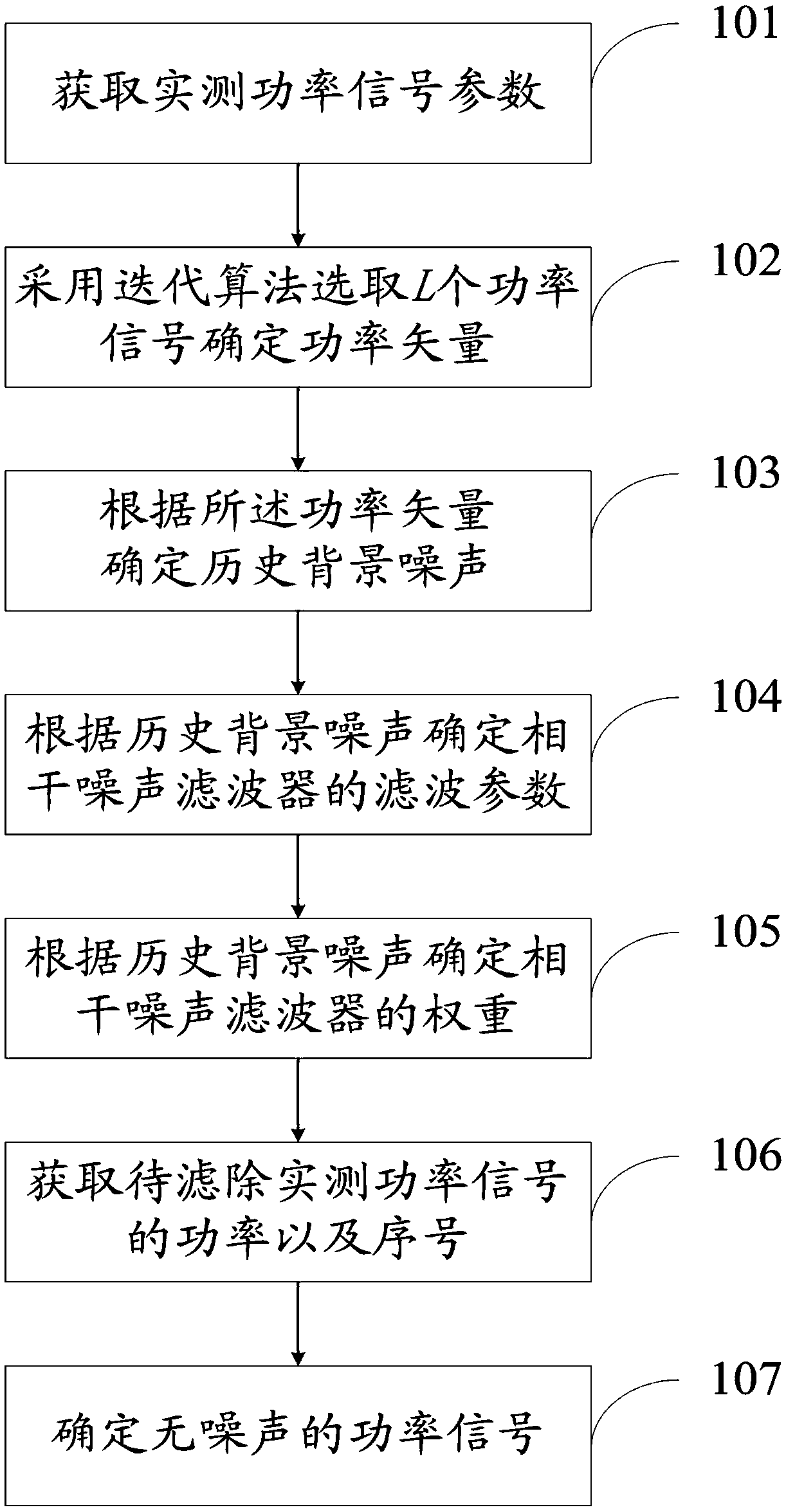
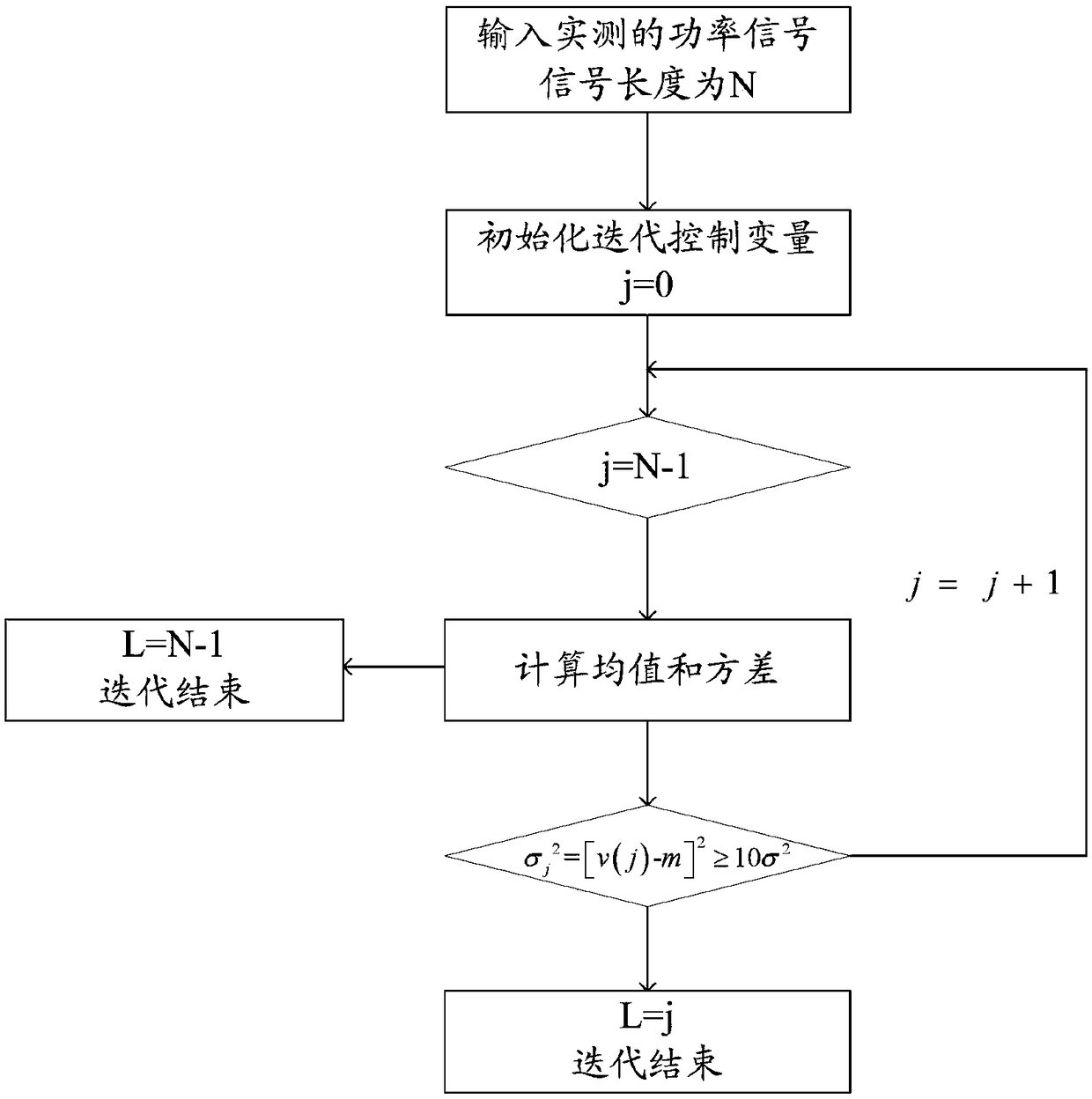
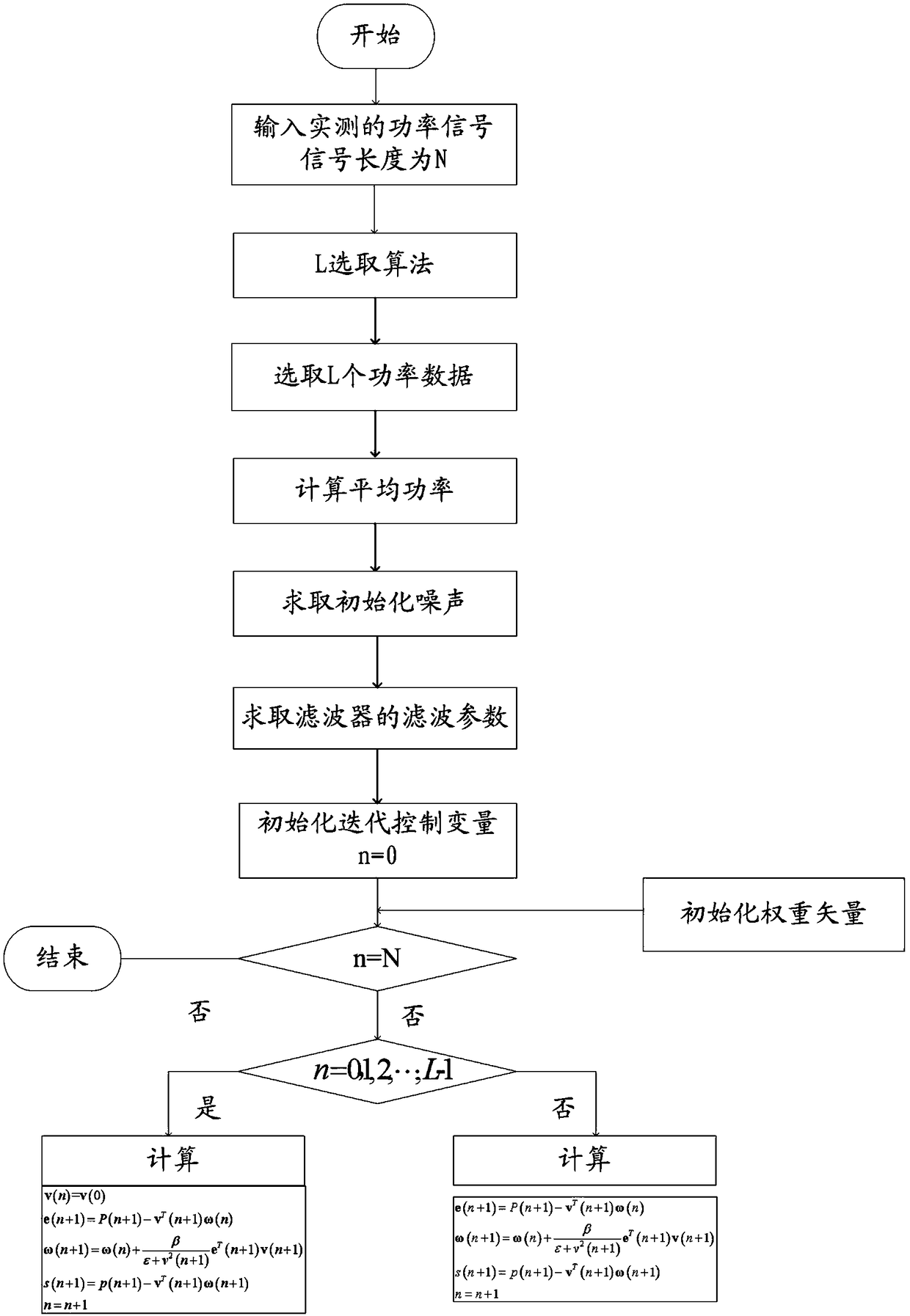
The invention discloses a coherent noise filtering method and a system. The filtering method comprises the following steps: obtaining measured power signal parameters; starting from the first measuredpower signal of the measured power signal sequence, an iterative algorithm being used to select L power signals to determine the power vector; determining a historical background noise according to the power vector; determining a filter parameter of a coherent noise filter according to the historical background noise; determining a weight of the coherent noise filter according to the historical background noise using an optimization criterion of minimizing signal variance; obtaining the power and the serial number of the measured power signal to be filtered out; according to the historical background noise, the filtering parameter, the weight, the power and the serial number of the measured power signal to be filtered, filtering the background noise of the measured power signal to be filtered, and determining a noise-free power signal. The filtering method and the system provided by the invention can improve the impulse noise detection accuracy and the coherent noise filtering accuracy.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
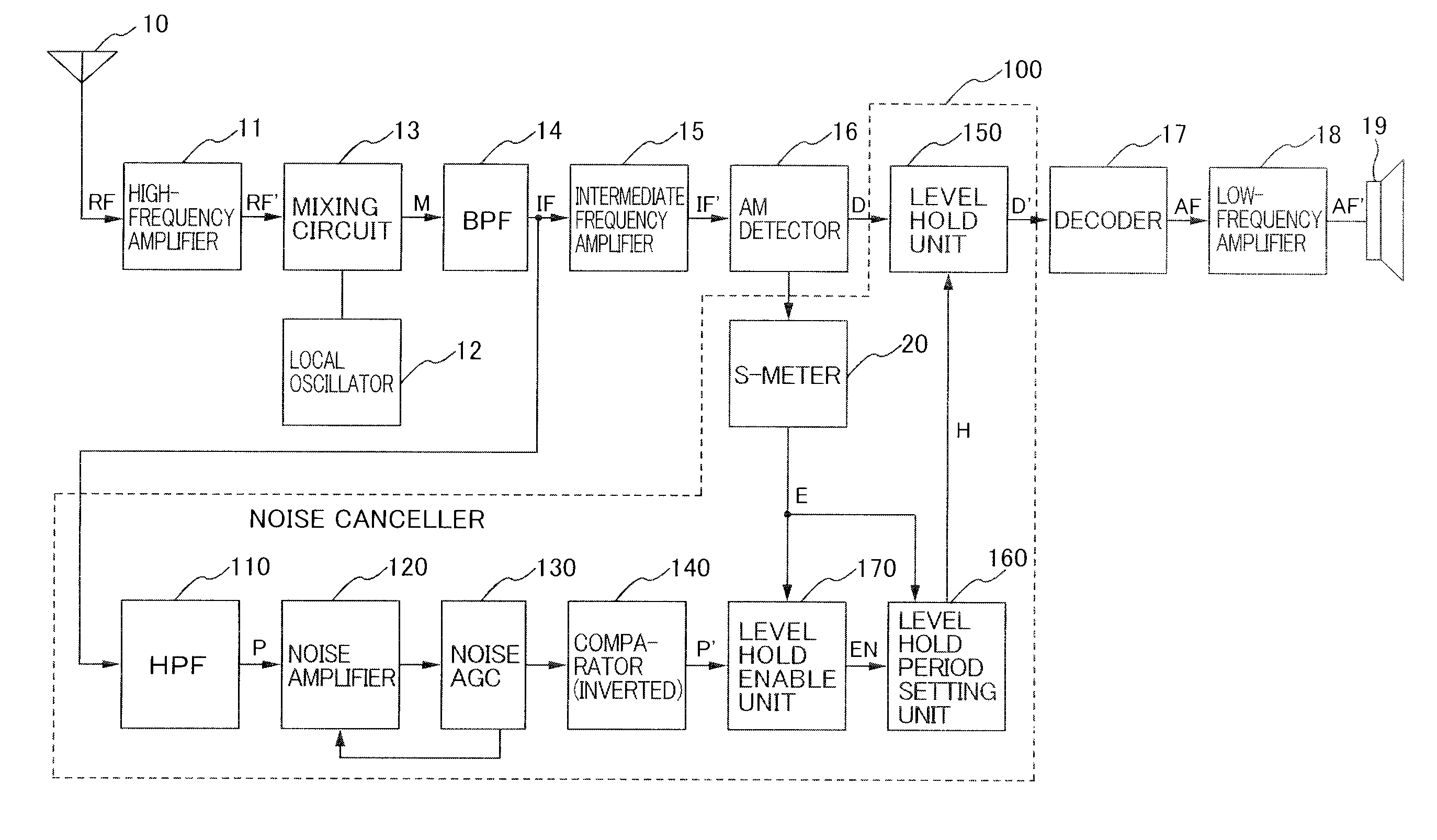
Noise Canceller and AM Receiving Apparatus Using the Same
A noise canceller that a receiving signal received by a receiving antenna is input to, the noise canceller removing a pulse noise superimposed on the receiving signal to output the signal, the noise canceller comprising: a pulse noise detecting unit that detects the pulse noise superimposed on the receiving signal; a reception level detecting unit that detects the level of the receiving signal; a level hold unit that is triggered by the detection of the pulse noise with the pulse noise detecting unit to hold the level of the receiving signal in a process on the preceding stage of the output; and a level hold period setting unit that sets the level hold period when the level is held in the level hold unit in accordance with the level of the receiving signal detected by the reception level detecting unit.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Detection of impulse noise using unused spreading codes
Owner:ARRIS INT IP LTD
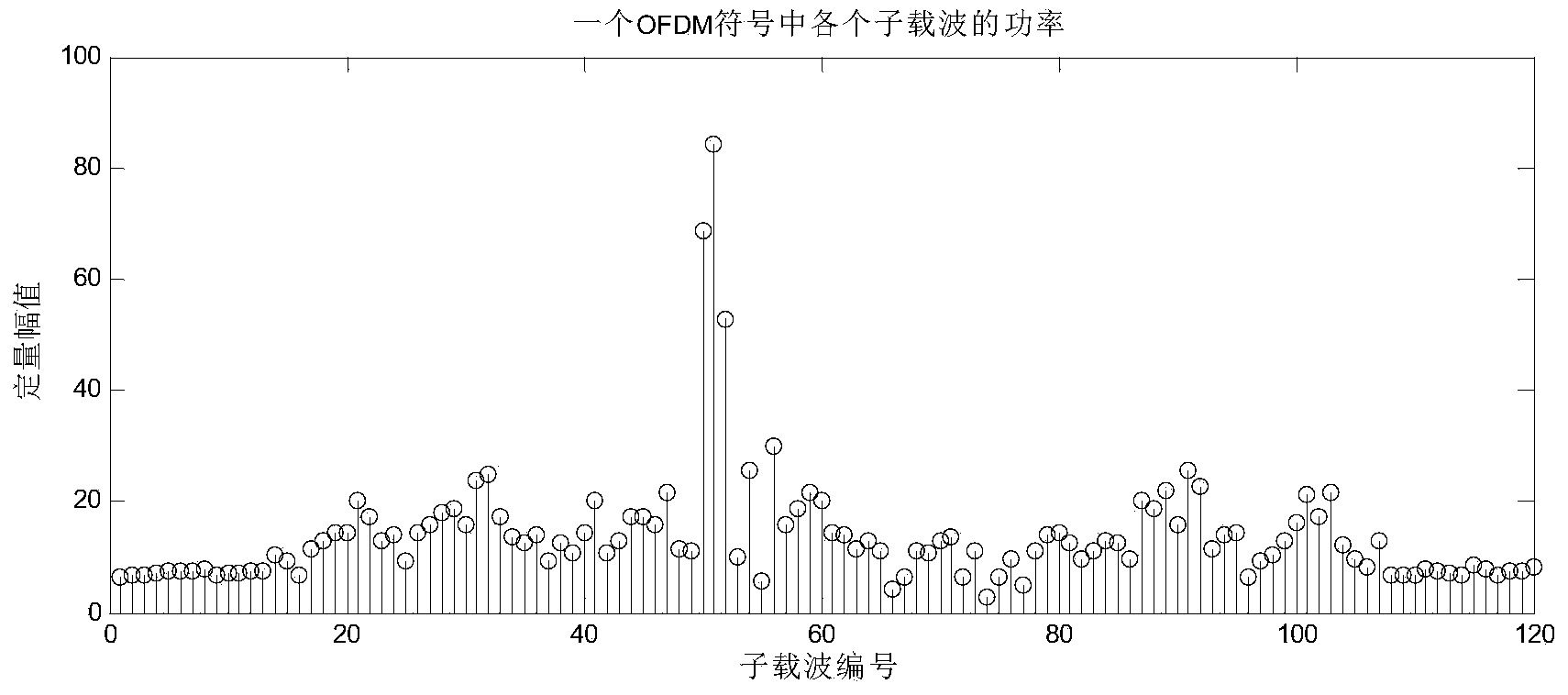
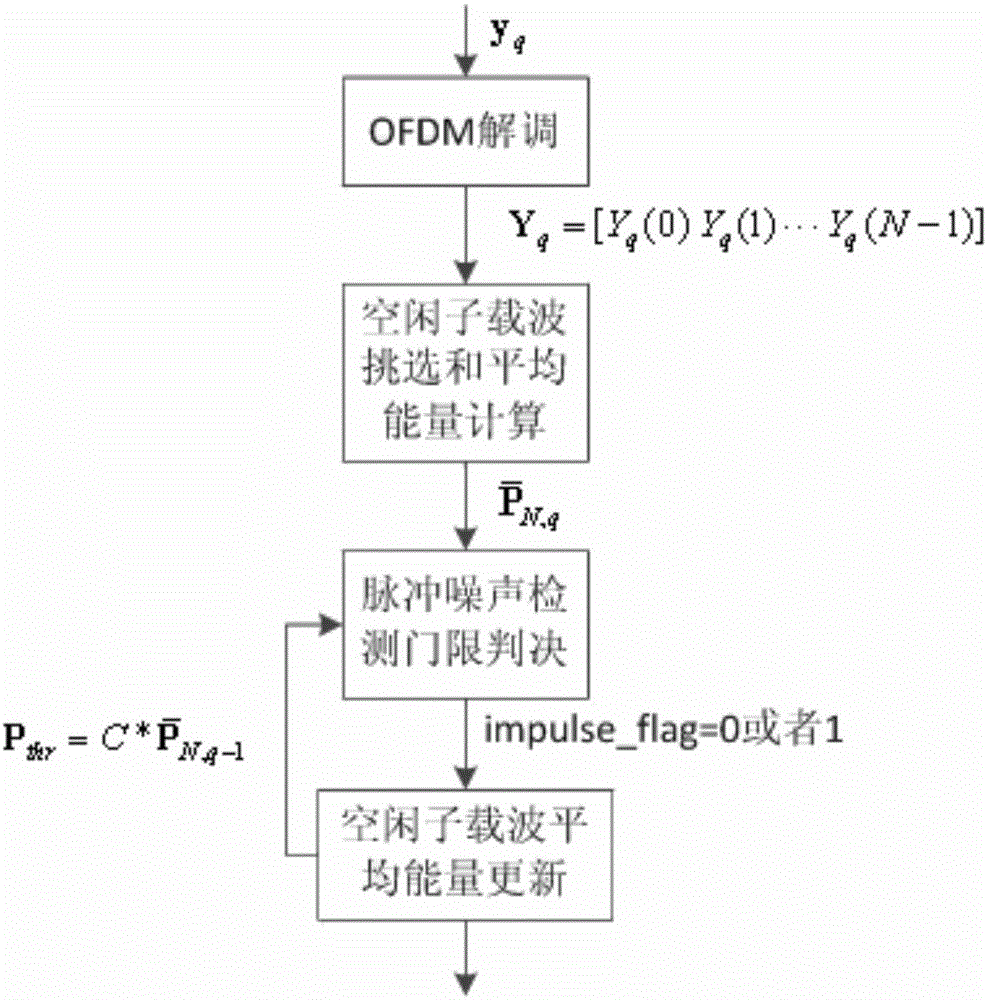
Impulse noise detection method in OFDM communication system
ActiveCN105897630AImprove accuracyGaussian overcomingDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransmission monitoringCarrier signalEngineering
The invention provides an impulse noise detection method in an OFDM communication system, comprising the following steps: setting a judgment threshold based on the average energy of the null subcarriers of at least one OFDM symbol in an OFDM communication system; estimating the average energy of the null subcarriers of subsequent OFDM symbols, comparing the average energy with the judgment threshold, and judging whether there is impulse noise; and updating the judgment threshold according to the comparison result, and giving an instruction on whether there is impulse noise detected. Impulse noise is detected based on the fact that data is not modulated on the null subcarriers in an OFDM communication system, energy mainly comes from leaked energy of Gaussian noise and adjacent subcarriers, and the energy of impulse noise is usually significantly higher than that of Gaussian noise.
Owner:BEIJING HANNUO SEMICON TECH CO LTD
PLC channel impulse noise detection method and system using square exponential kernel
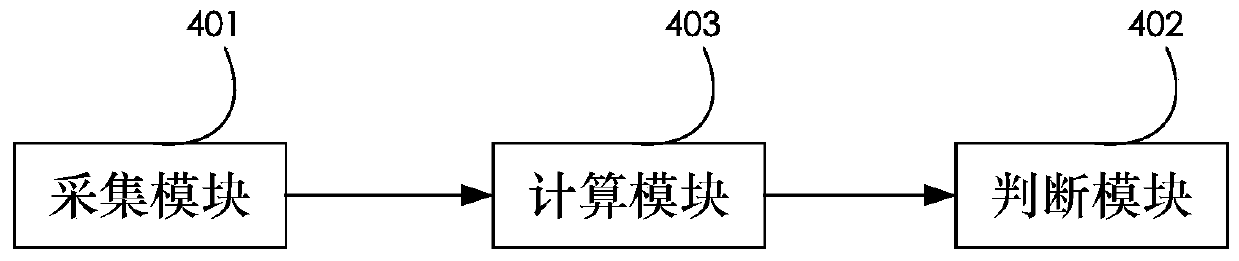
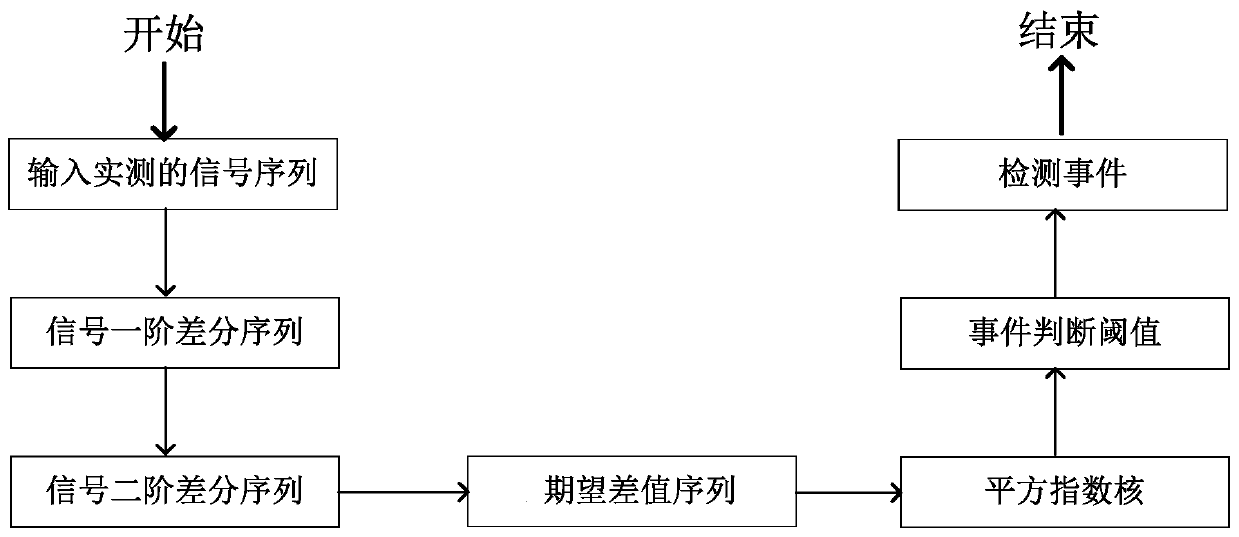
InactiveCN110719121AApparent non-stationarityObvious featuresPower distribution line transmissionLine-transmission monitoring/testingExponential kernelProgrammable logic controller
The embodiment of the invention discloses a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) channel impulse noise detection method and system by utilizing a square exponential kernel. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, inputting an actually measured signal sequence S; and step 2, detecting the PLC channel impulse noise according to the square exponential kernel property. The method specificallycomprises the following steps: if a square exponent kernel HK of a Kth window meets a judgment condition that | HK | is greater than or equal to e0, detecting impulse noise at a Kth point of a signalsequence S; otherwise, determining that the impulse noise is not detected, wherein e0 is an impulse noise judgment threshold value.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
Pulse noise detection method based on local extremum value
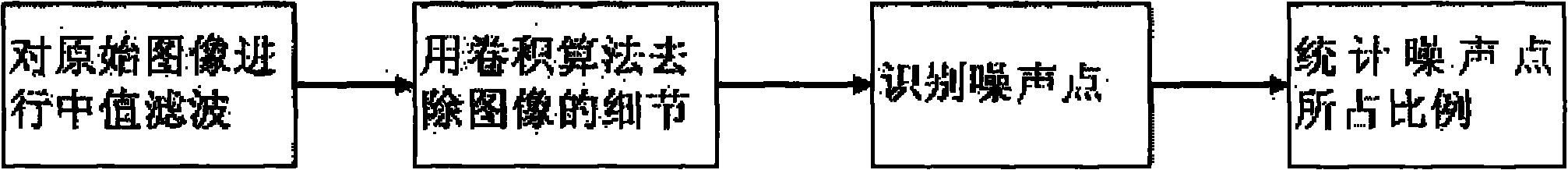
InactiveCN102005032AAvoid misjudgmentImprove accuracyImage enhancementPattern recognitionPhase noise
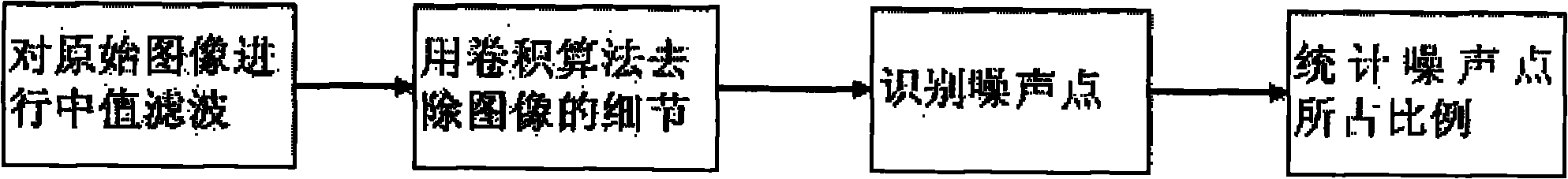
The invention provides a pulse noise detection method based on a local extremum value and application of the pulse noise detection method to a video fault diagnosis system. By using the method, pulse noise in an image can be effectively and accurately detected and the false detection on the detailed information in the image can be avoided, thereby the intelligent video fault diagnosis and analysis can be realized.
Owner:PCI TECH GRP CO LTD
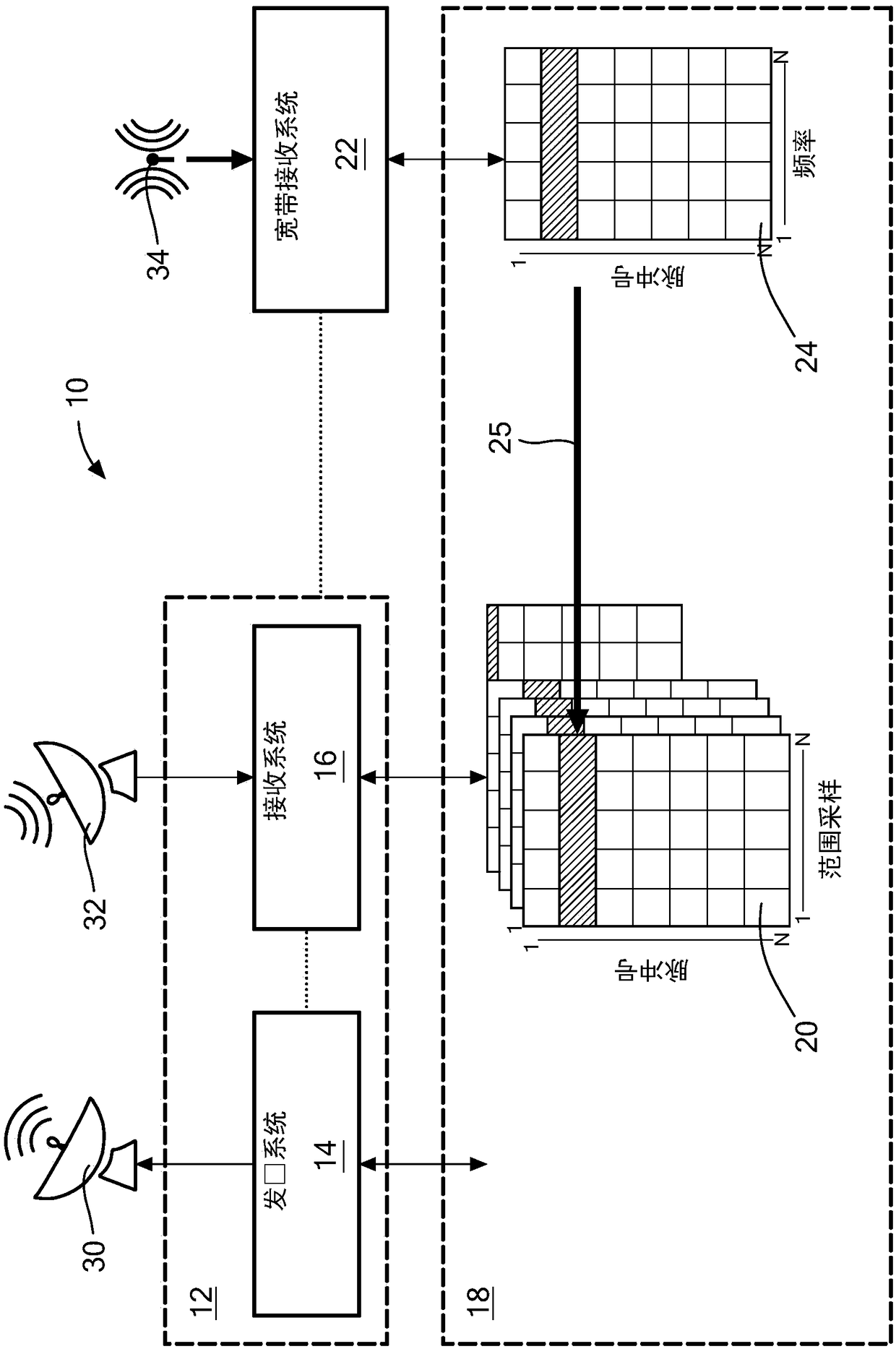
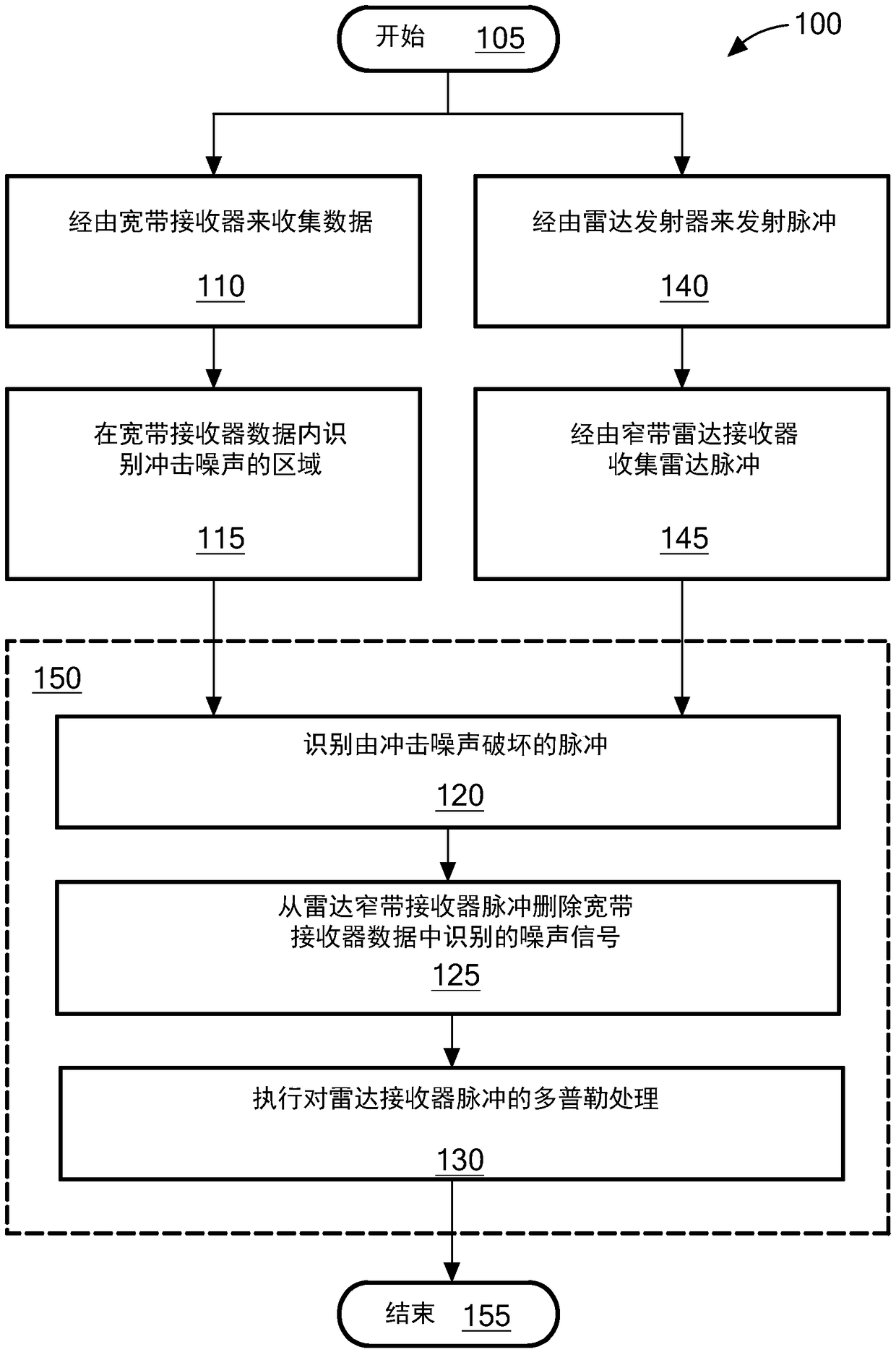
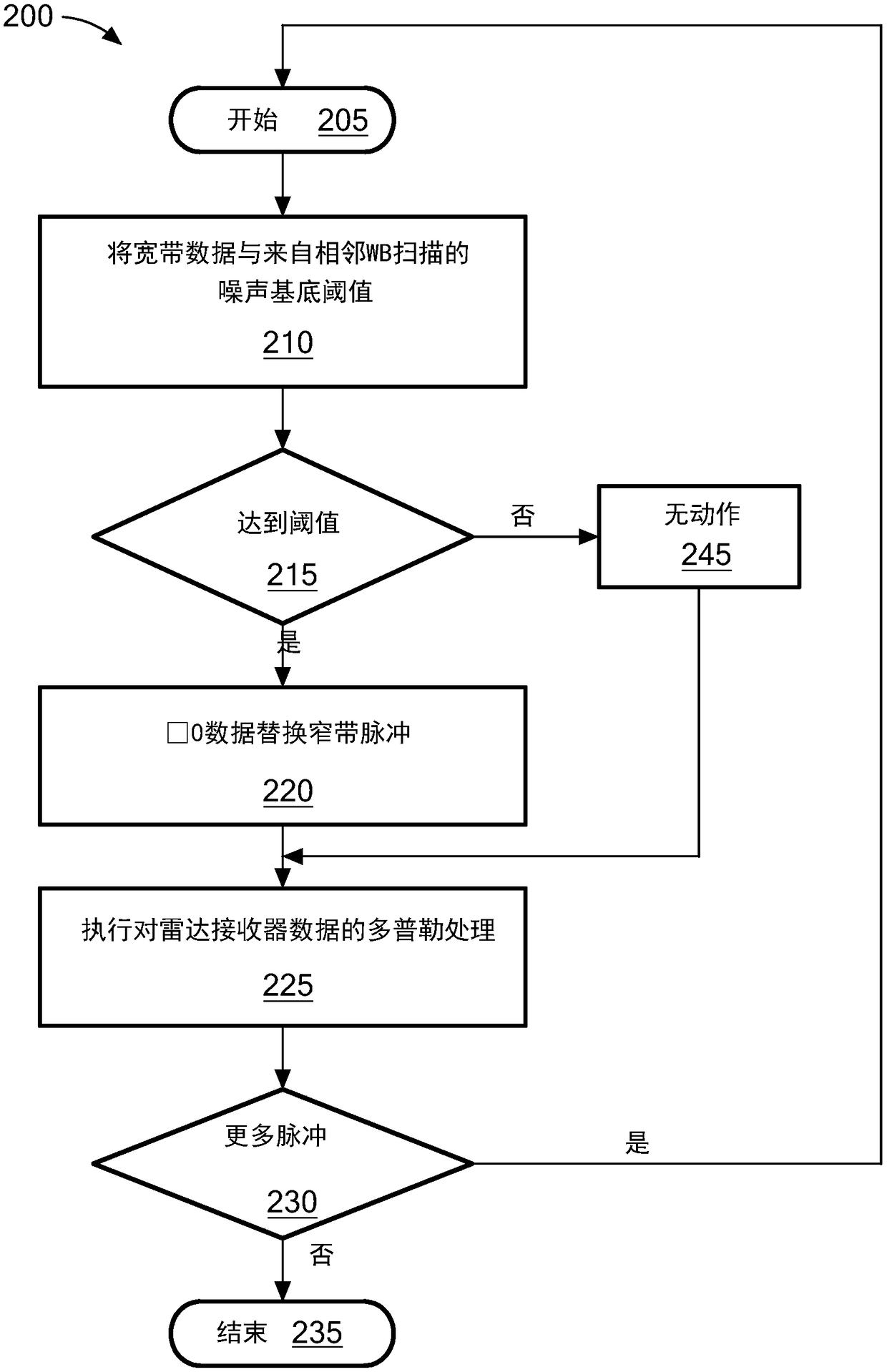
Impulse noise detection and removal for radar and communication systems
A radar system including a narrowband radar receiver configured to receive pulsed radar return signals and a wideband receiver configured for receiving wideband signals. A noise data processor is configured to identify impulse noises by analyzing wideband signals received by the wideband receiver and a radar processor is configured to cancel the identified impulse noises from pulse signals received by the radar receiver. The wideband impulse noises utilized to cancel noise from the pulse signals corresponds to the same time period sweep of detection as that of the pulse signals.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
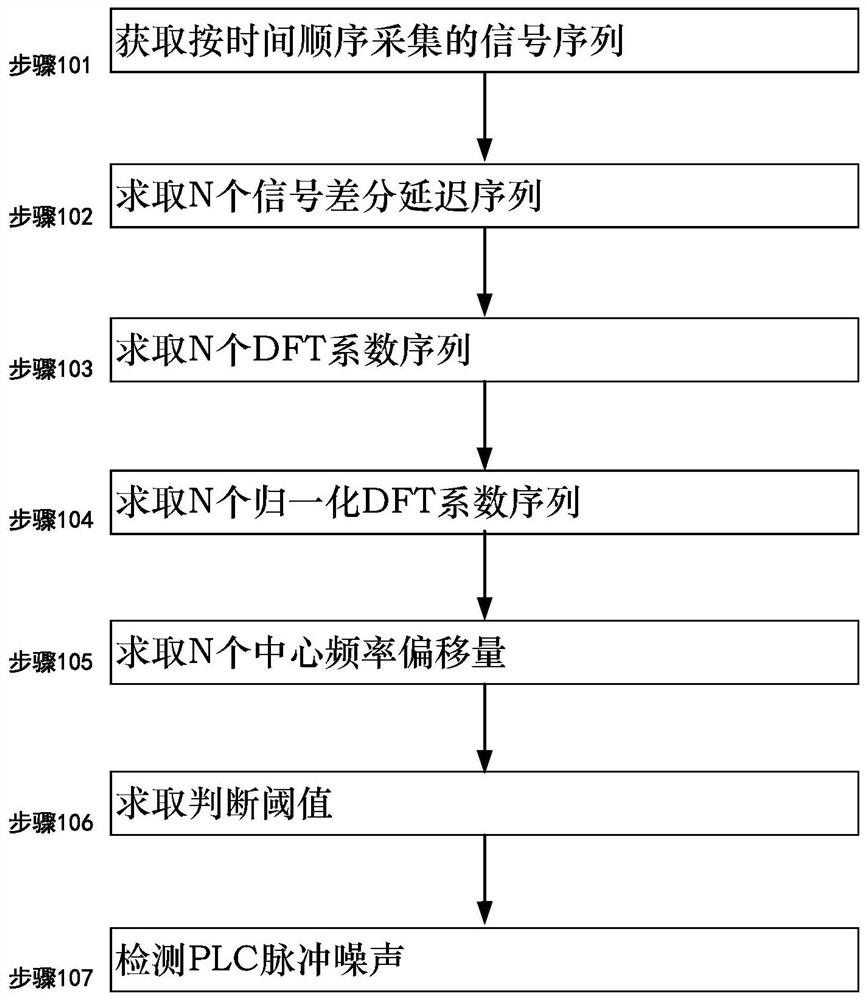
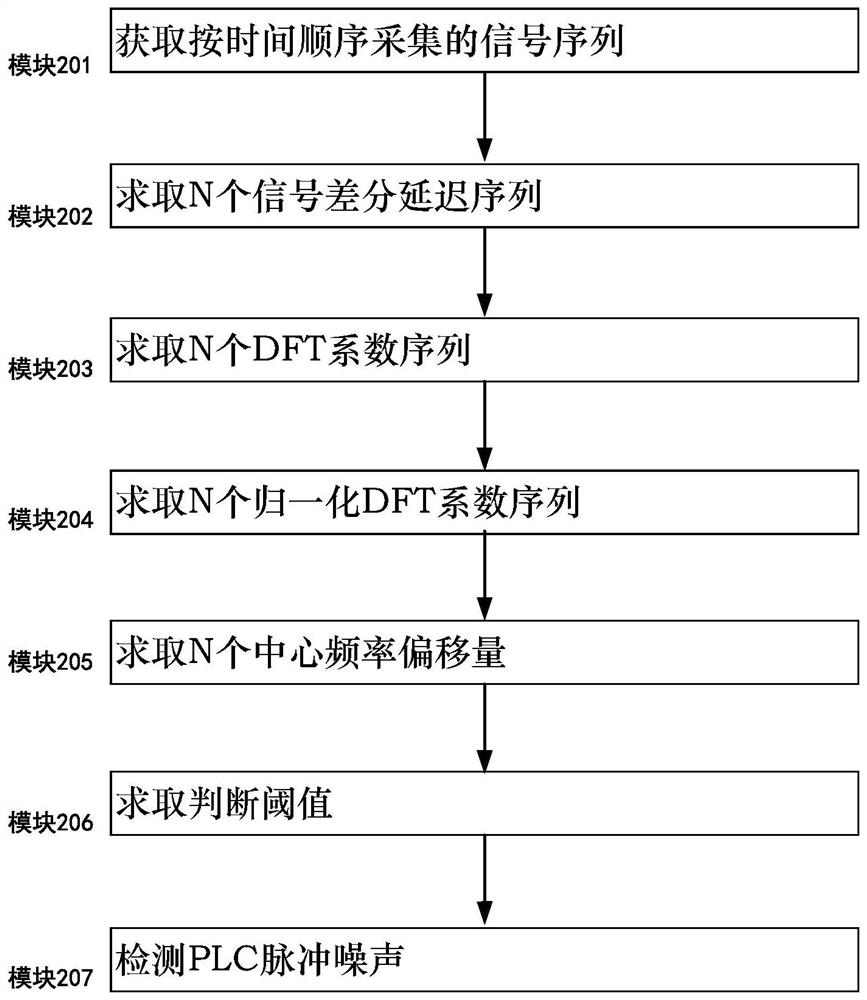
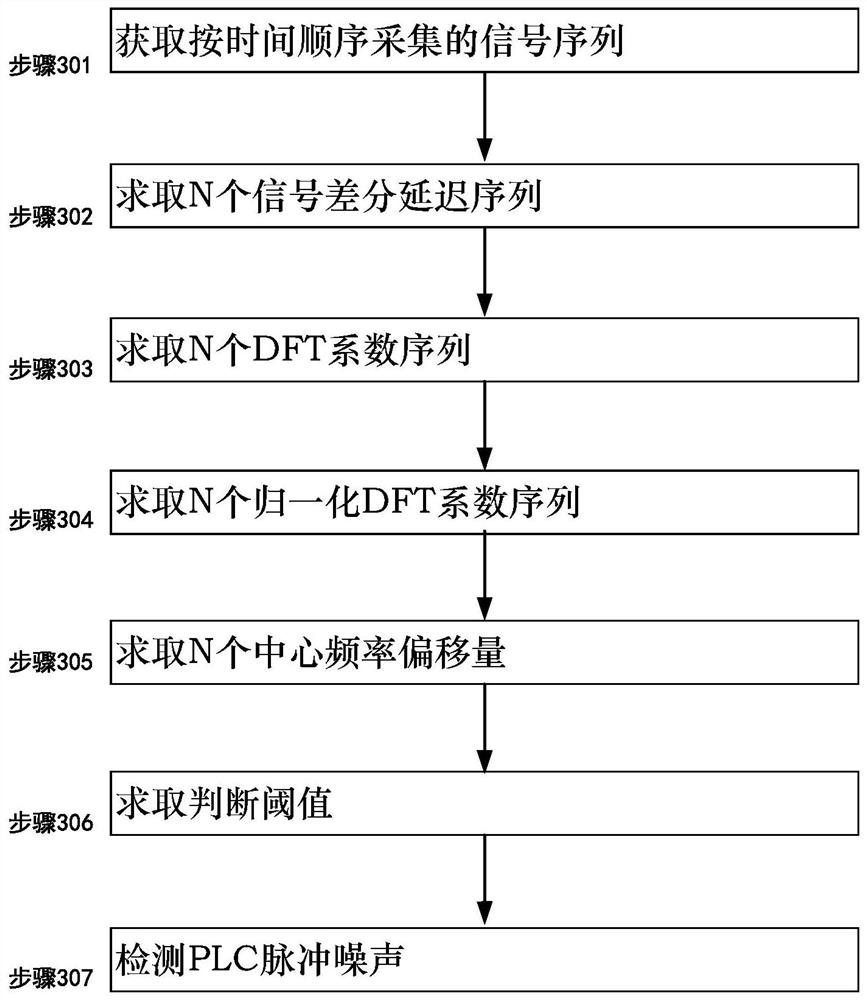
PLC channel impulse noise detection method and system using offset
InactiveCN111756456AApparent non-stationarityObvious featuresTransmission monitoringEngineeringCenter frequency
The embodiment of the invention discloses a PLC channel impulse noise detection method and system using offset. The method comprises the steps: 101, acquiring a signal sequence S collected according to the time sequence; 102, solving N signal differential delay sequences; 103, solving N DFT coefficient sequences; 104, solving N normalized DFT coefficient sequences; 105, solving N central frequencyoffsets; 106, solving a judgment threshold value; 107, detecting the PLC impulse noise.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com