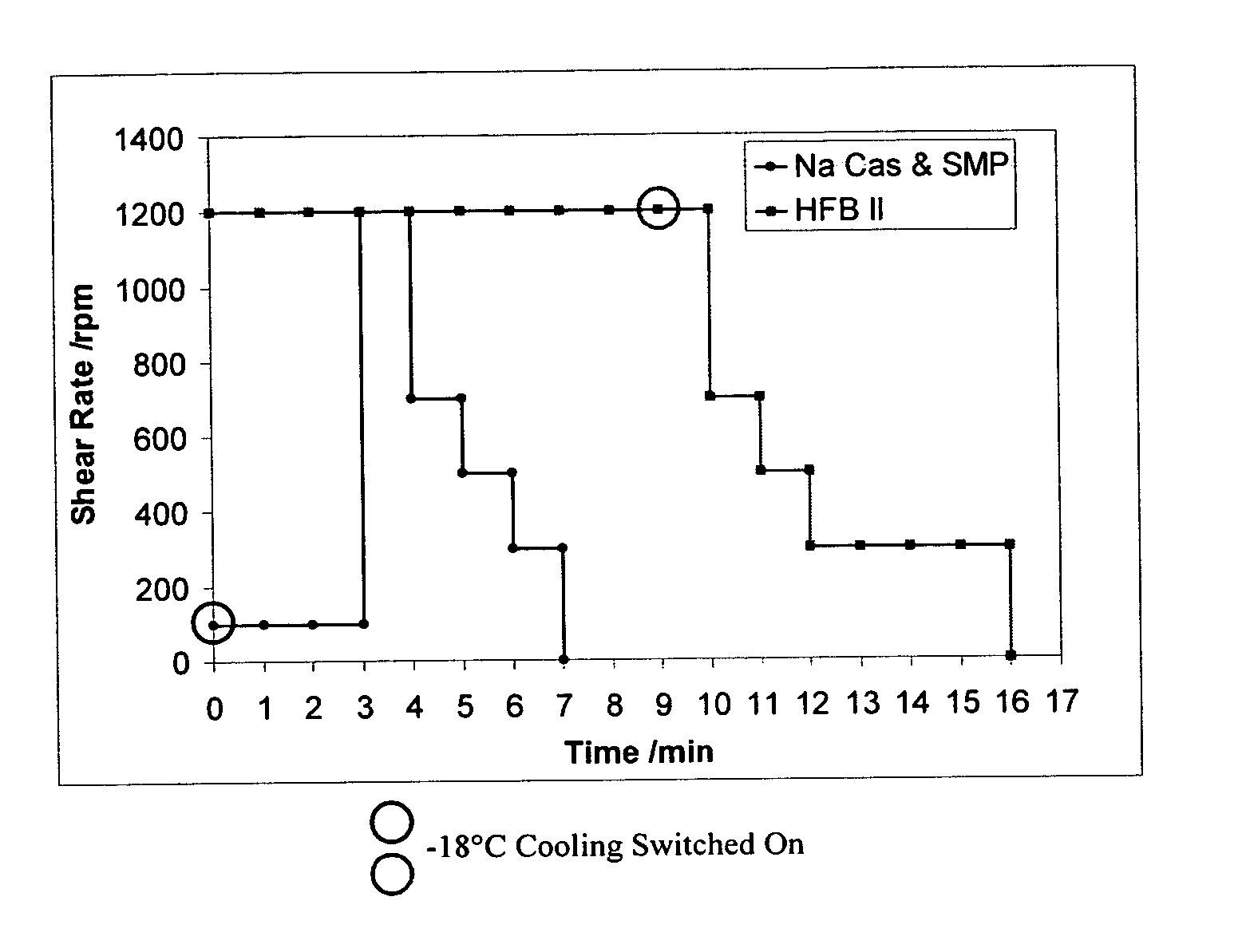
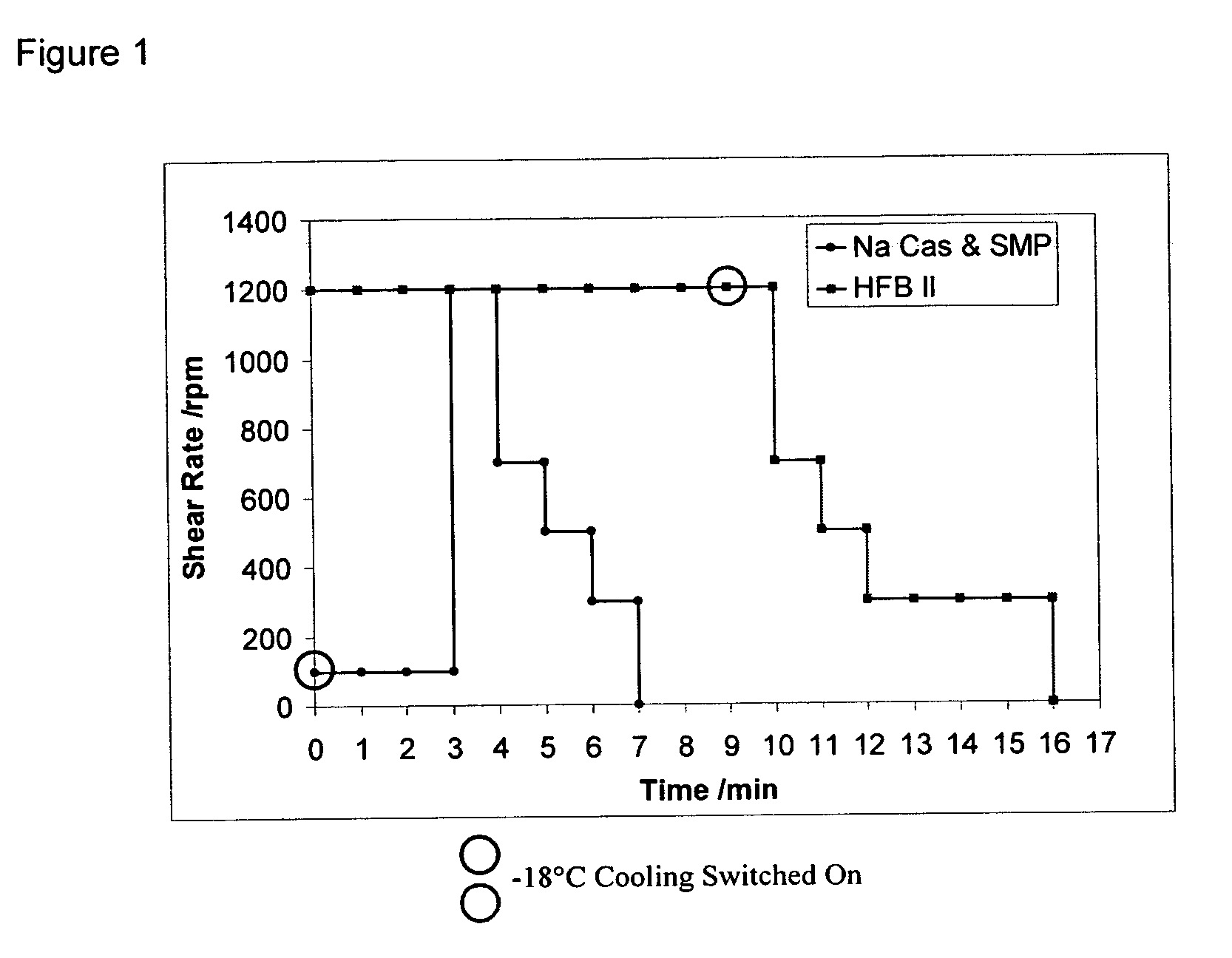
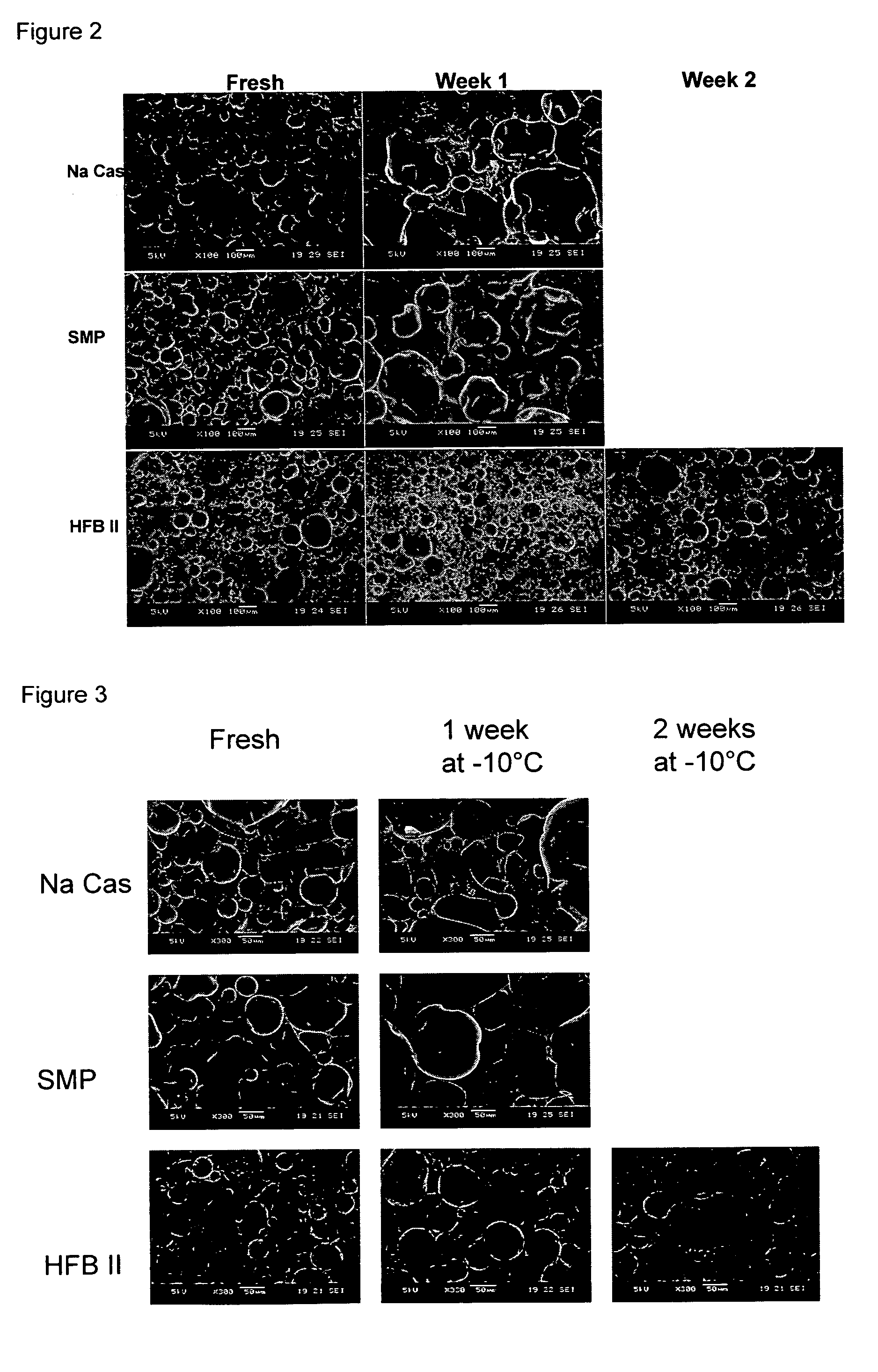
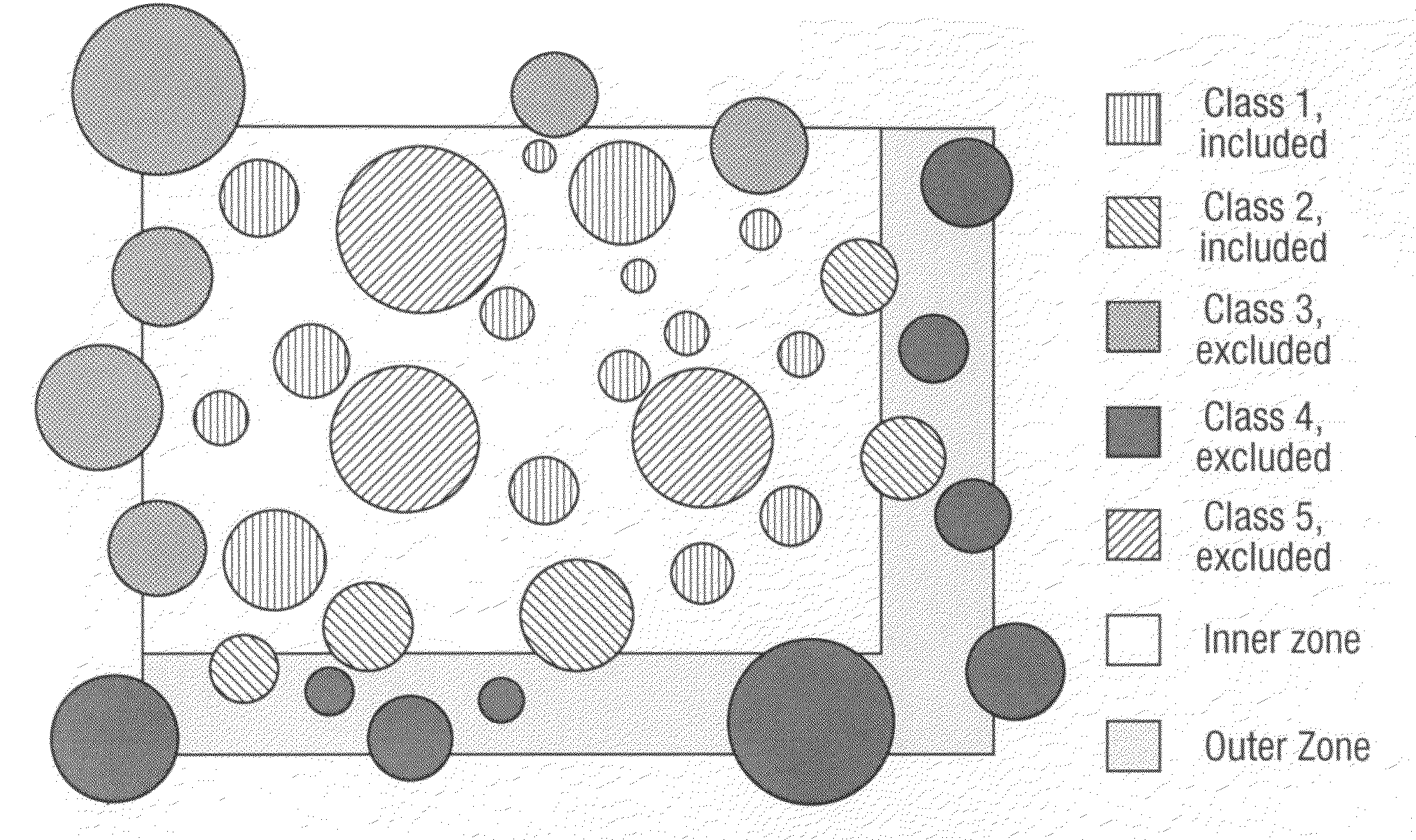
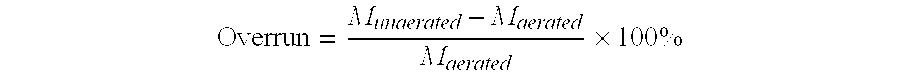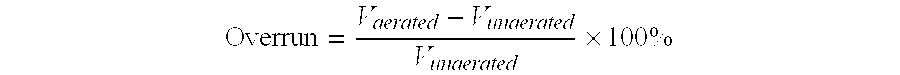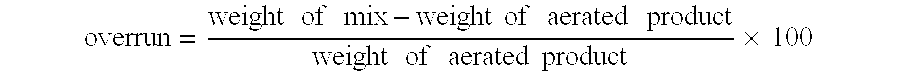Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
139 results about "Hydrophobin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
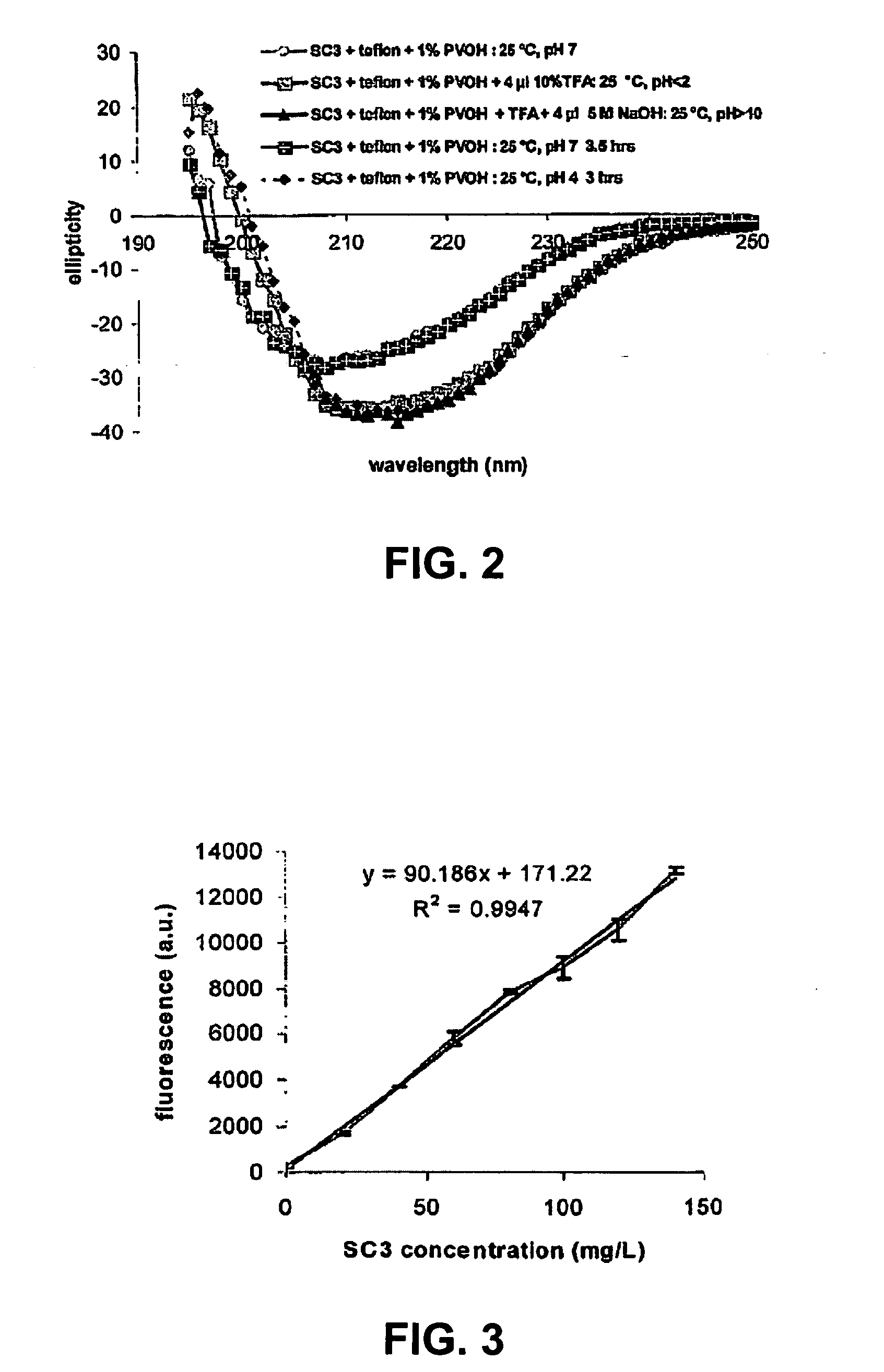
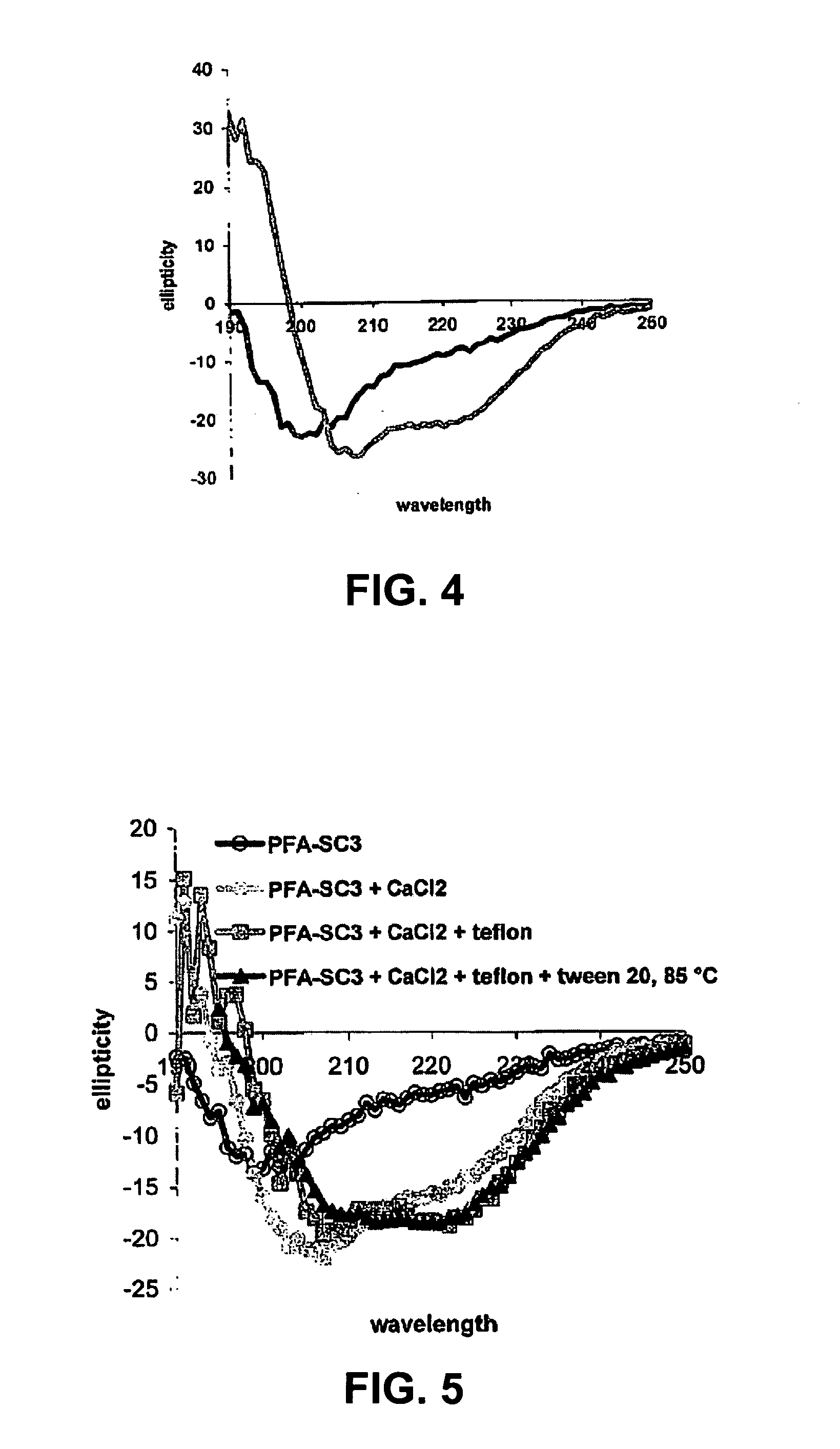
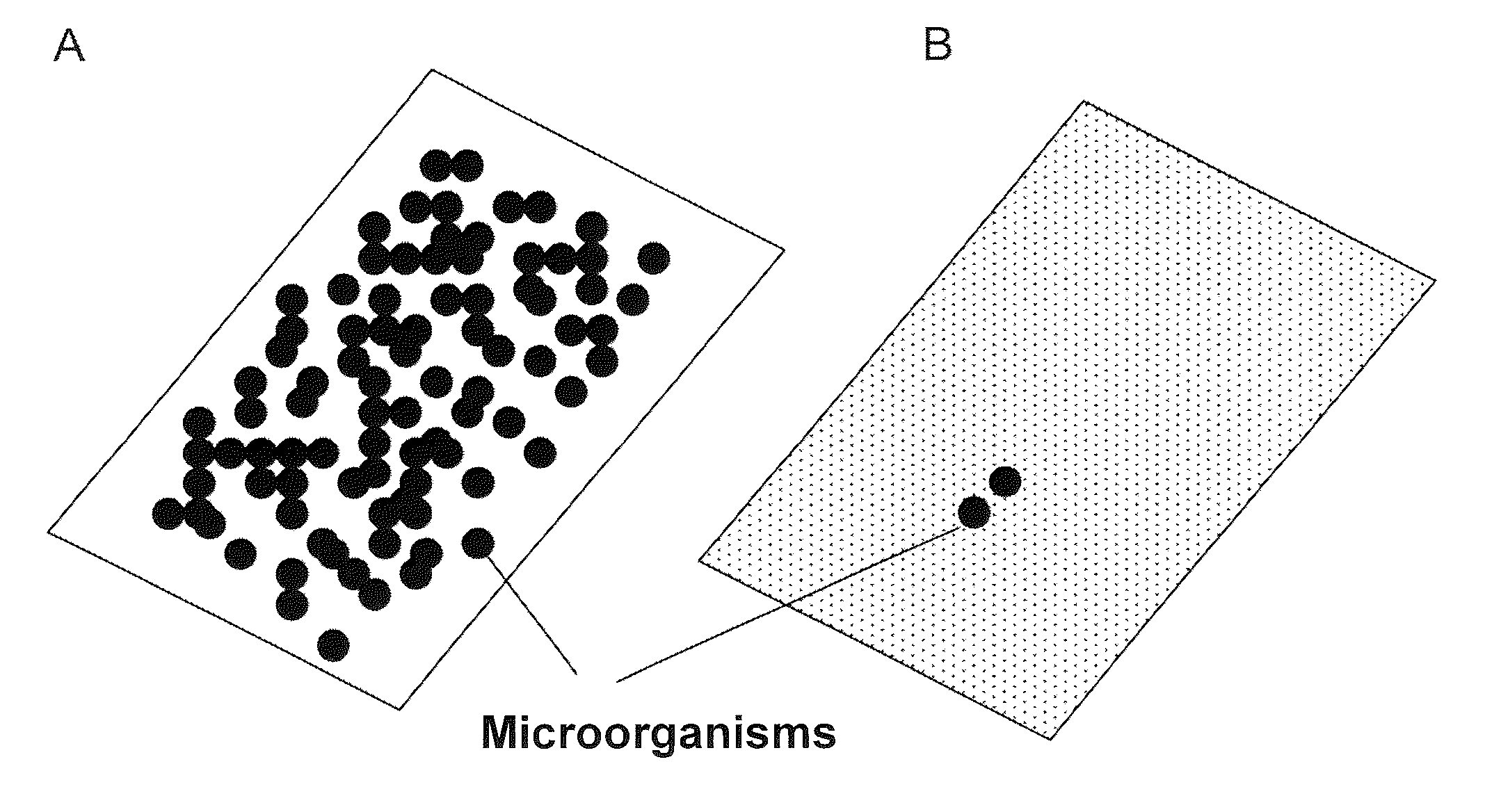
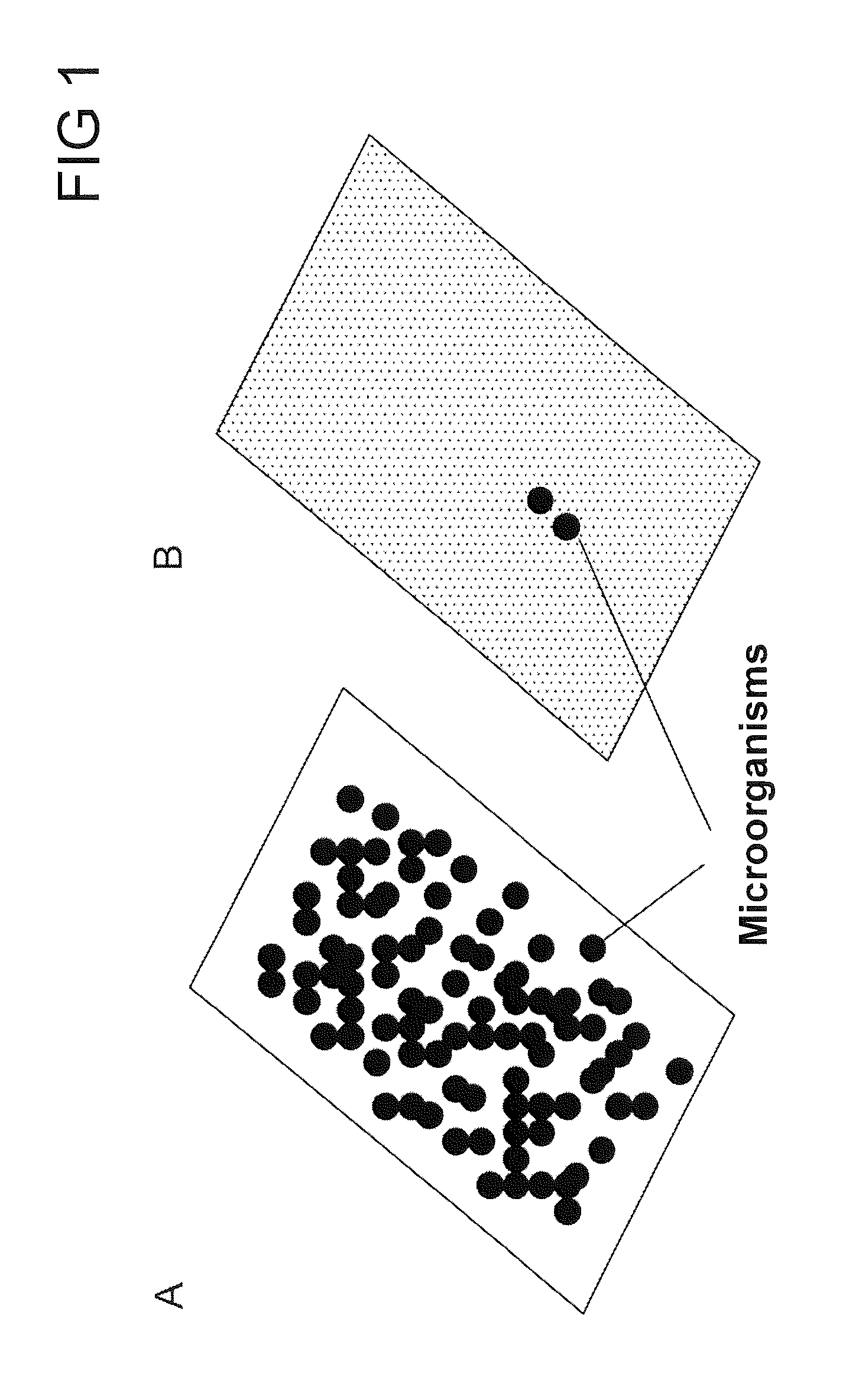
Hydrophobins are a group of small (~100 amino acids) cysteine-rich proteins that are expressed only by filamentous fungi. They are known for their ability to form a hydrophobic (water-repellent) coating on the surface of an object. They were first discovered and separated in Schizophyllum commune in 1991. Based on differences in hydropathy patterns and biophysical properties, they can be divided into two categories: class I and class II. Hydrophobins can self-assemble into a monolayer on hydrophilic:hydrophobic interfaces such as a water:air interface. Class I monolayer contains the same core structure as amyloid fibrils, and is positive to Congo red and thioflavin T. The monolayer formed by class I hydrophobins has a highly ordered structure, and can only be dissociated by concentrated trifluoroacetate or formic acid. Monolayer assembly involves large structural rearrangements with respect to the monomer.
Use of Hydrophobin-Polypeptides and Conjugates From Hydrophobin-Polypeptides Having Active and Effect Agents and the Production Thereof and Use Thereof In the Cosmetic Industry
InactiveUS20090136433A1Feel goodGood skin compatibilityCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineCosmetic industry
Cosmetic composition for the treatment of keratin-containing materials, mucosa and teeth, comprising at least one hydrophobin polypeptide sequence (i)(I)Xn-C1-X1-50-C2-X0-5-C3-Xp-C4-X1-100-C5-X1-50-C6-X0-5-C7-X1-50-C8-Xm
Owner:BASF AG
Thermophilic hydrophobin proteins and applications for surface modification
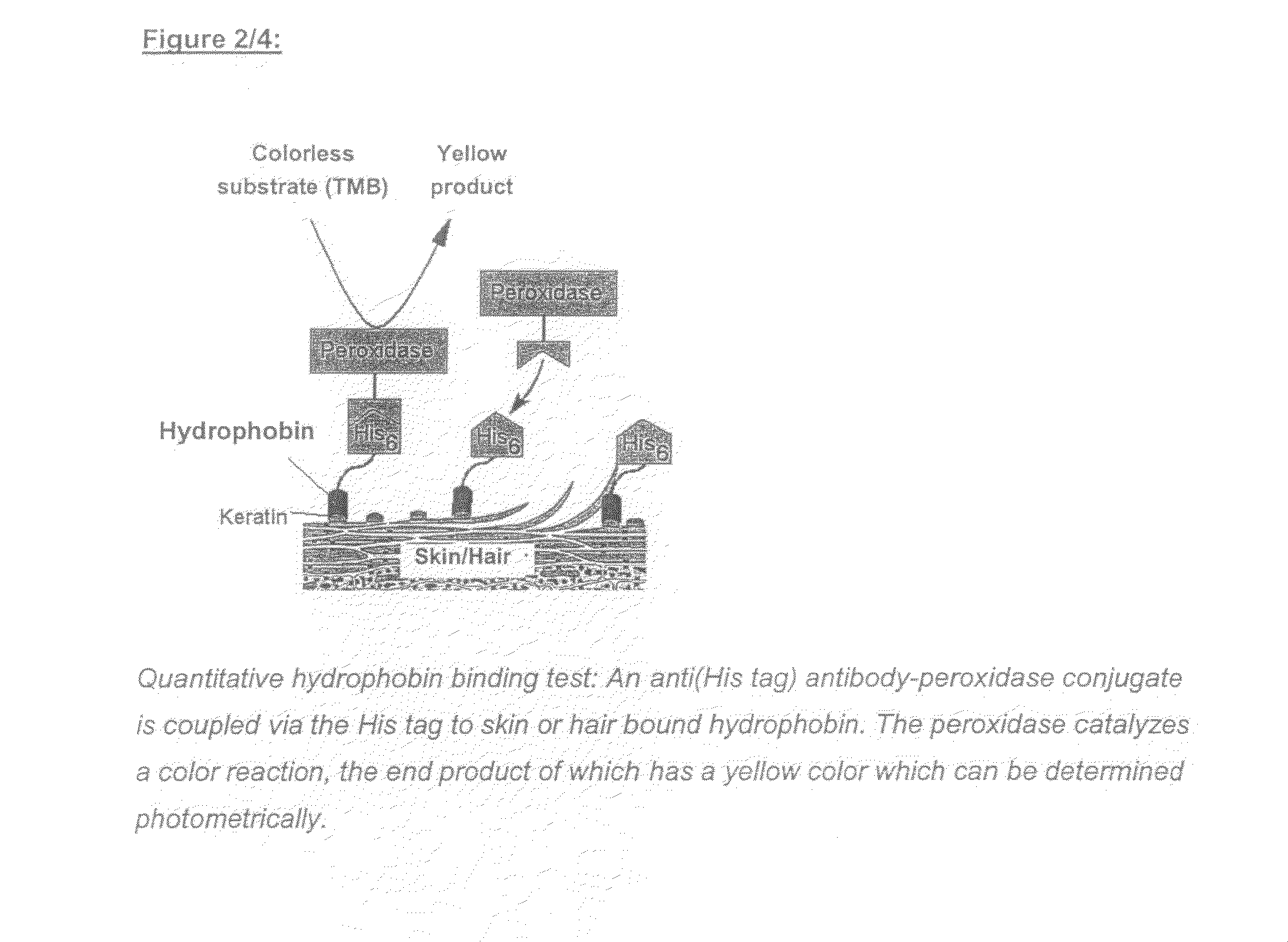
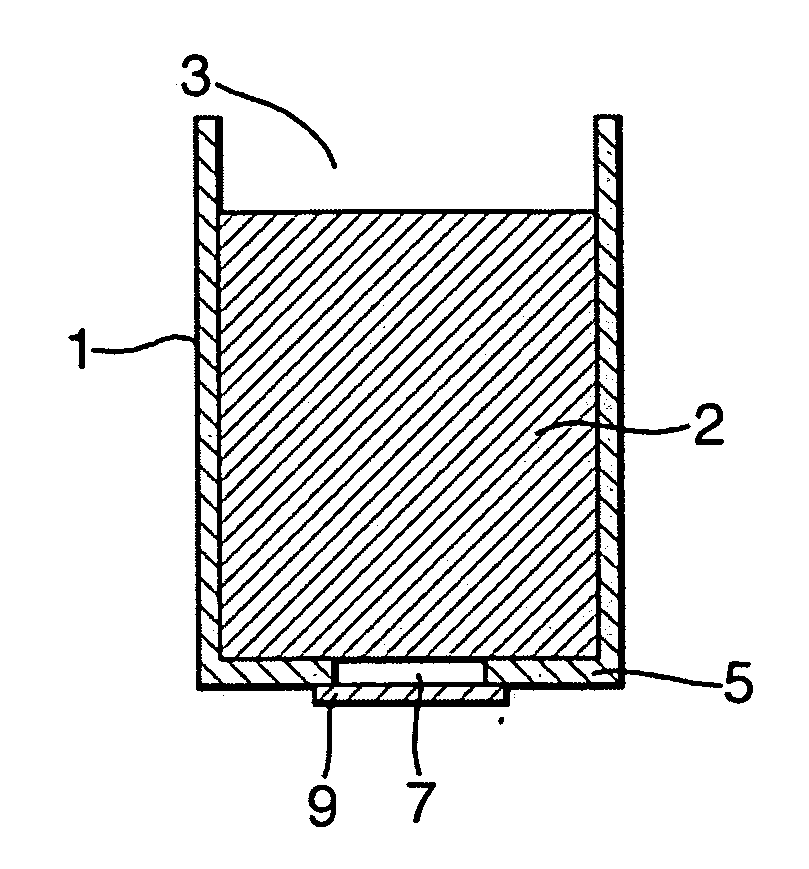
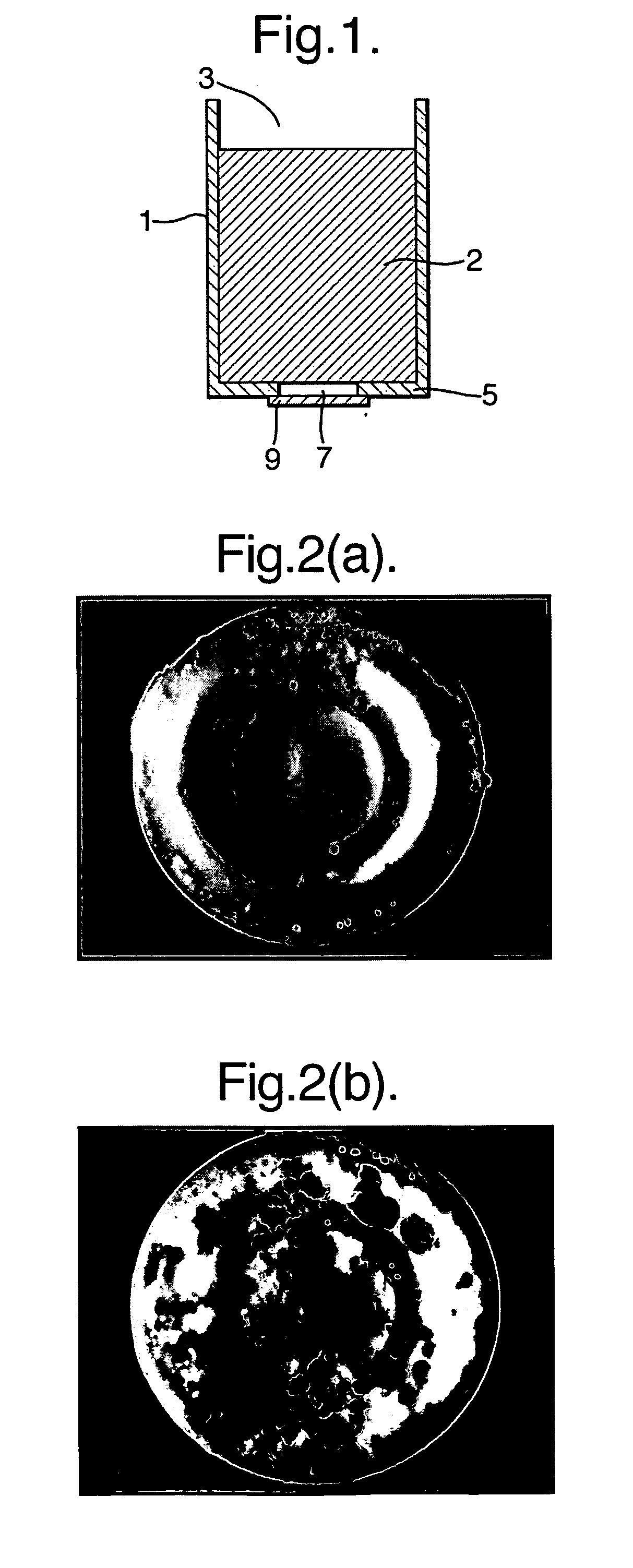
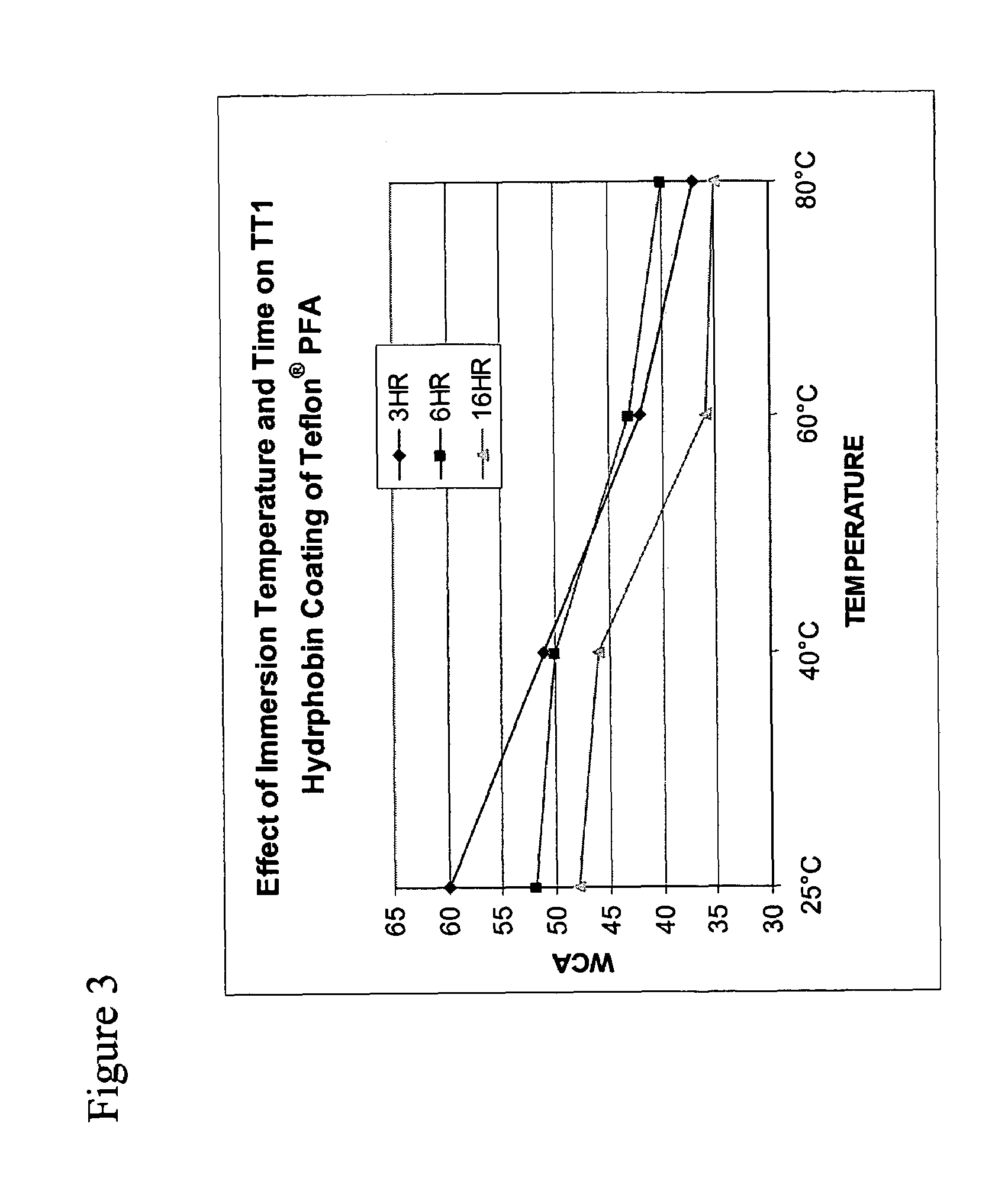
The present invention relates to a thermophilic hydrophobin, TT1, or a protein or polypeptide substantially similar thereto, derived from the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. The invention further relates to a polynucleotide encoding such hydrophobin, as well as to materials coated with such hydrophobin.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Aerated fat-continuous products
InactiveUS20090142467A1Light colorLow calorie contentMilk preservationCocoaBiotechnologyBiochemical engineering
An aerated fat-continuous product comprising hydrophobin is provided. Processes for producing the product are also provided.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Process for producing a frozen aerated composition
A process for producing a frozen aerated composition is provided, the process comprising aerating an aqueous mixture, followed by quiescently freezing the aerated mixture, characterized in that the mixture comprises hydrophobin.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Frozen products
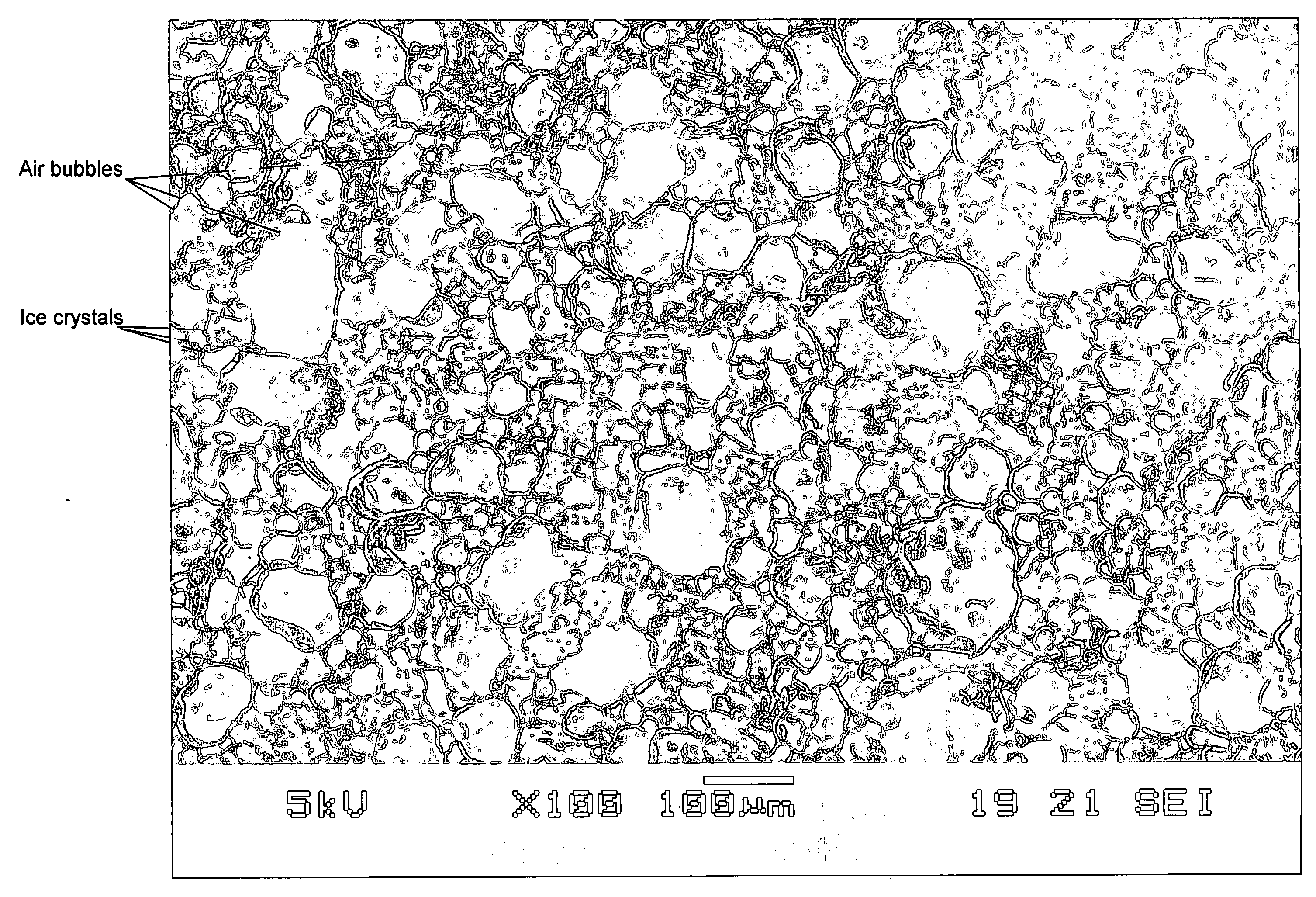
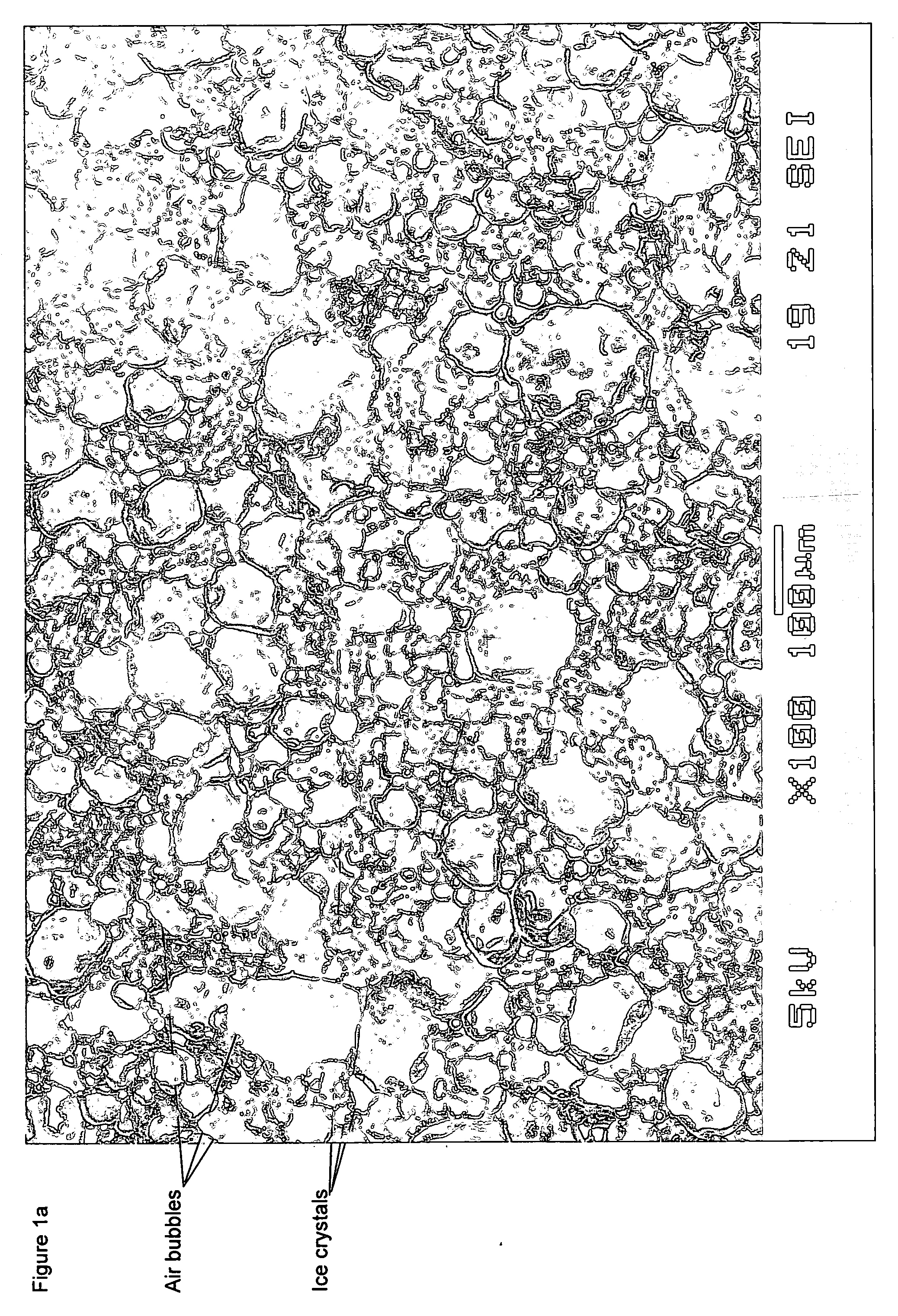
InactiveUS20060024419A1Reduce volumeExtended shelf lifeMilk preparationFrozen sweetsHydrophobinIce crystals
A frozen composition is provided which includes hydrophobin. Also provided is the use of hydrophobin in inhibiting ice crystal growth and / or modifying ice crystal habit in frozen food products.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Aerated food products and methods for producing them
InactiveUS20080213453A1Low efficacyEffectivenessMilk preparationFrozen sweetsSURFACTANT BLENDHydrophobin
An aerated food product comprising hydrophobin and a surfactant is provided, the aerated food product containing a population of gas bubbles, wherein at least 65% of the gas bubbles have a diameter of less than 20 μm. Processes for producing such an aerated food product are also provided.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Aerated compositions
InactiveUS20080175972A1Clean flavorHigh poly-unsaturated fat contentFrozen sweetsConfectioneryHydrophobinChemistry
An aerated composition having an overrun of at least 10% and comprising water and an emulsified fat phase wherein at least 50% of the fat is liquid at 5° C. is provided, characterized in that the composition comprises hydrophobin. An aeratable composition is also provided.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
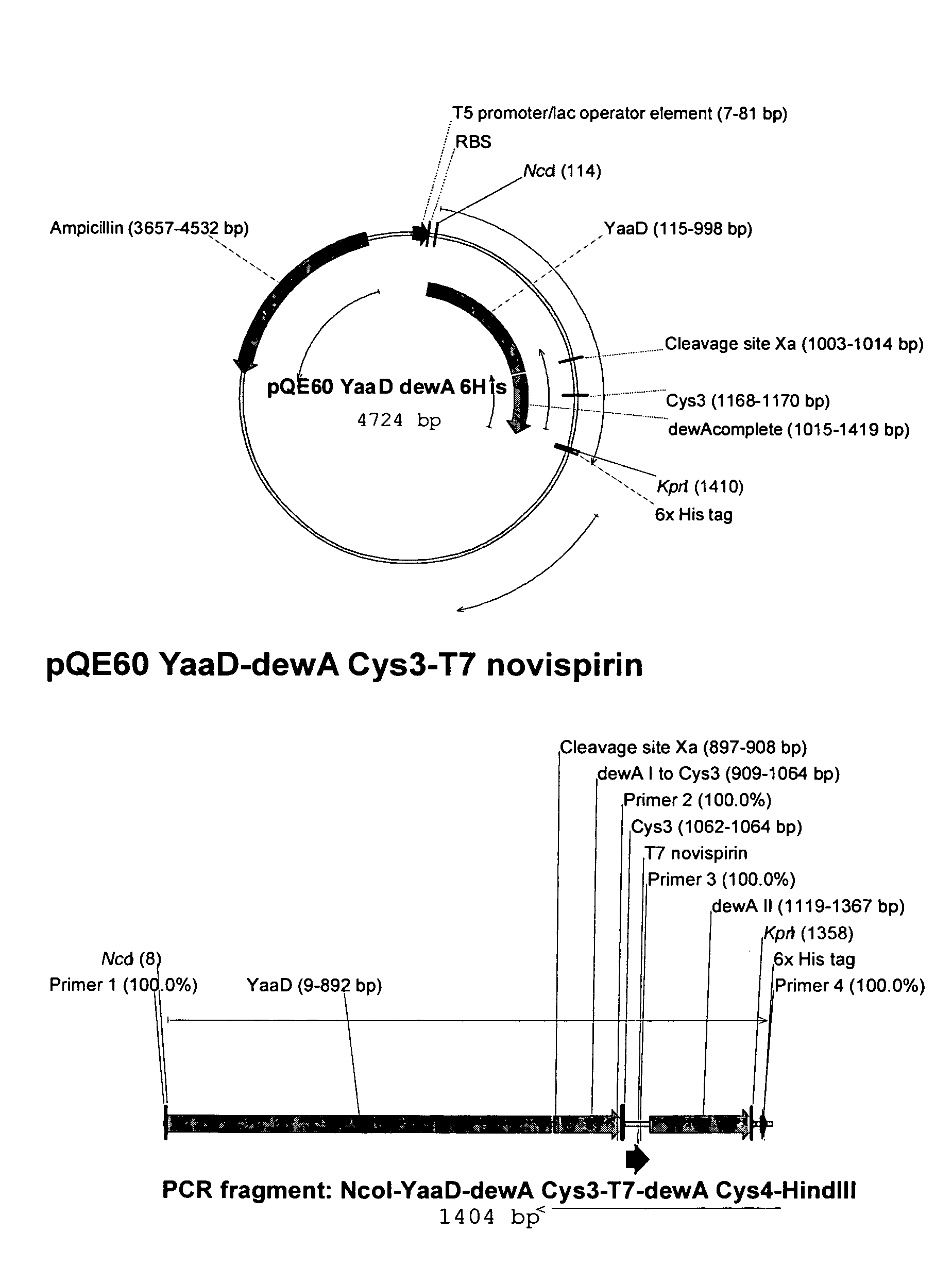
Novel Hydrophobin Fusion Products, Production and Use Thereof
Polypeptides of the general structural formula (I)Xn—C1—X1-50—C2—X0-5—C3—X1-100—C4—X1-100—C5—X1-50—C6—C0-5—C7—X1-50—C8—Xm (I)production and use thereof.
Owner:BASF AG
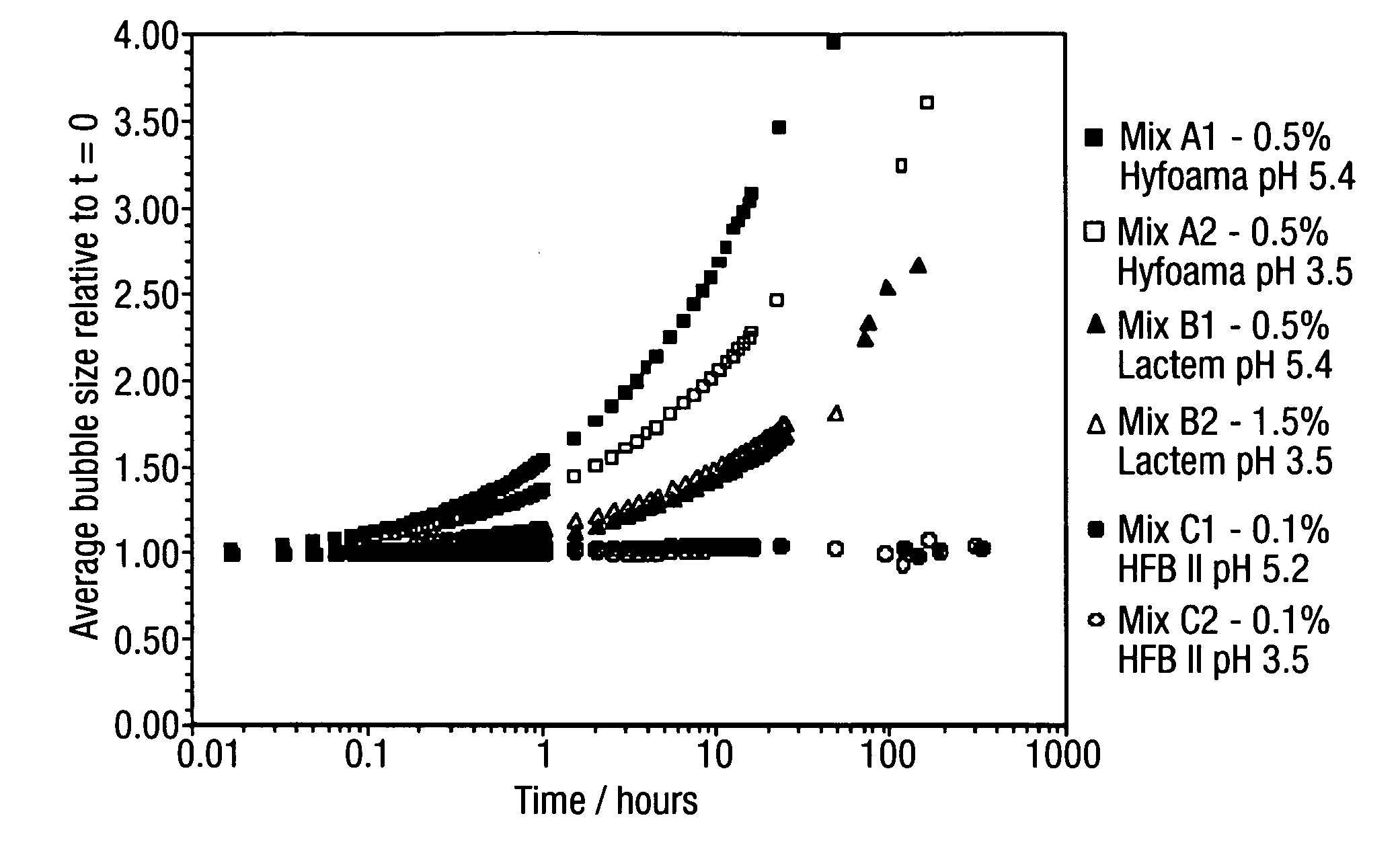
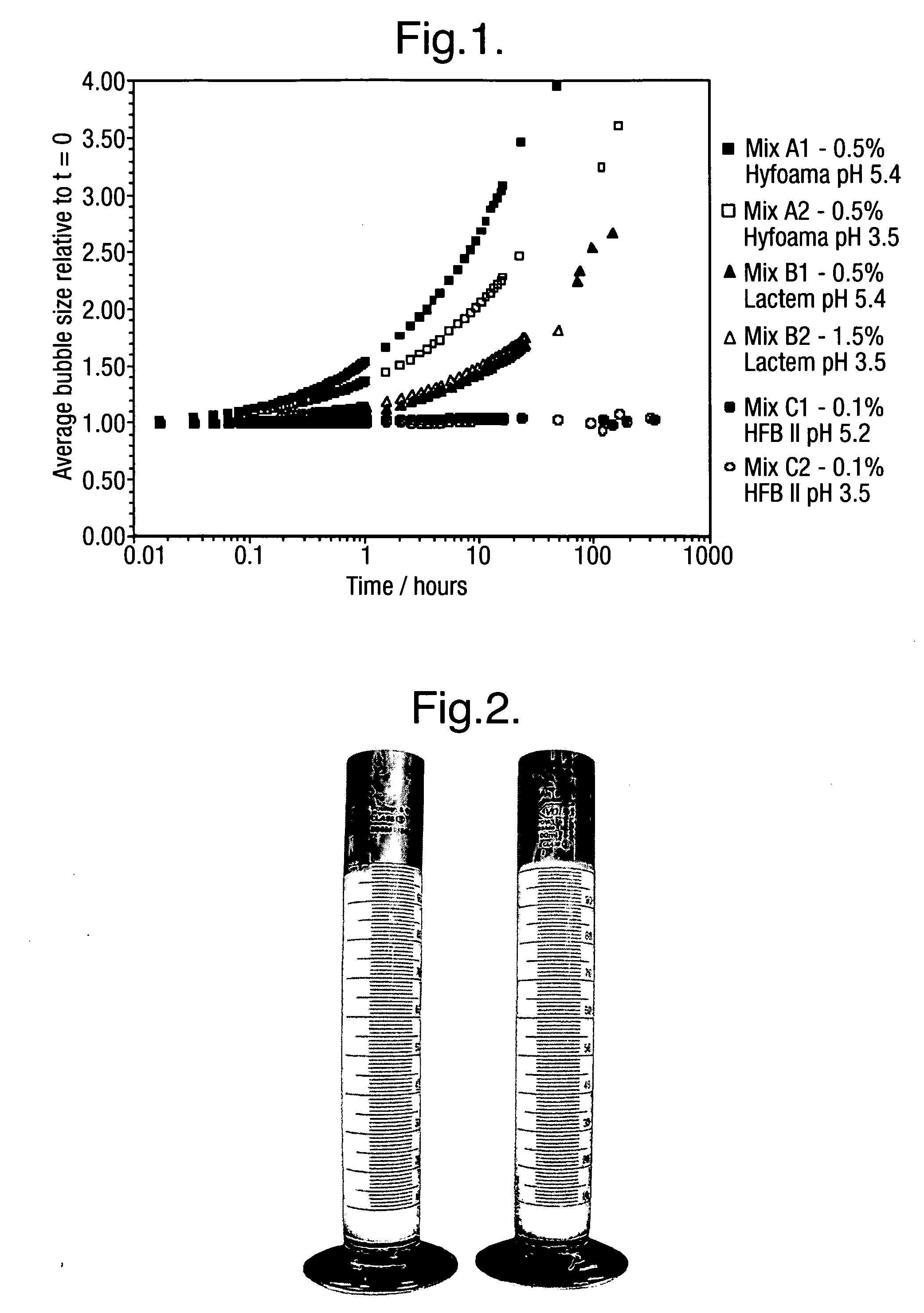
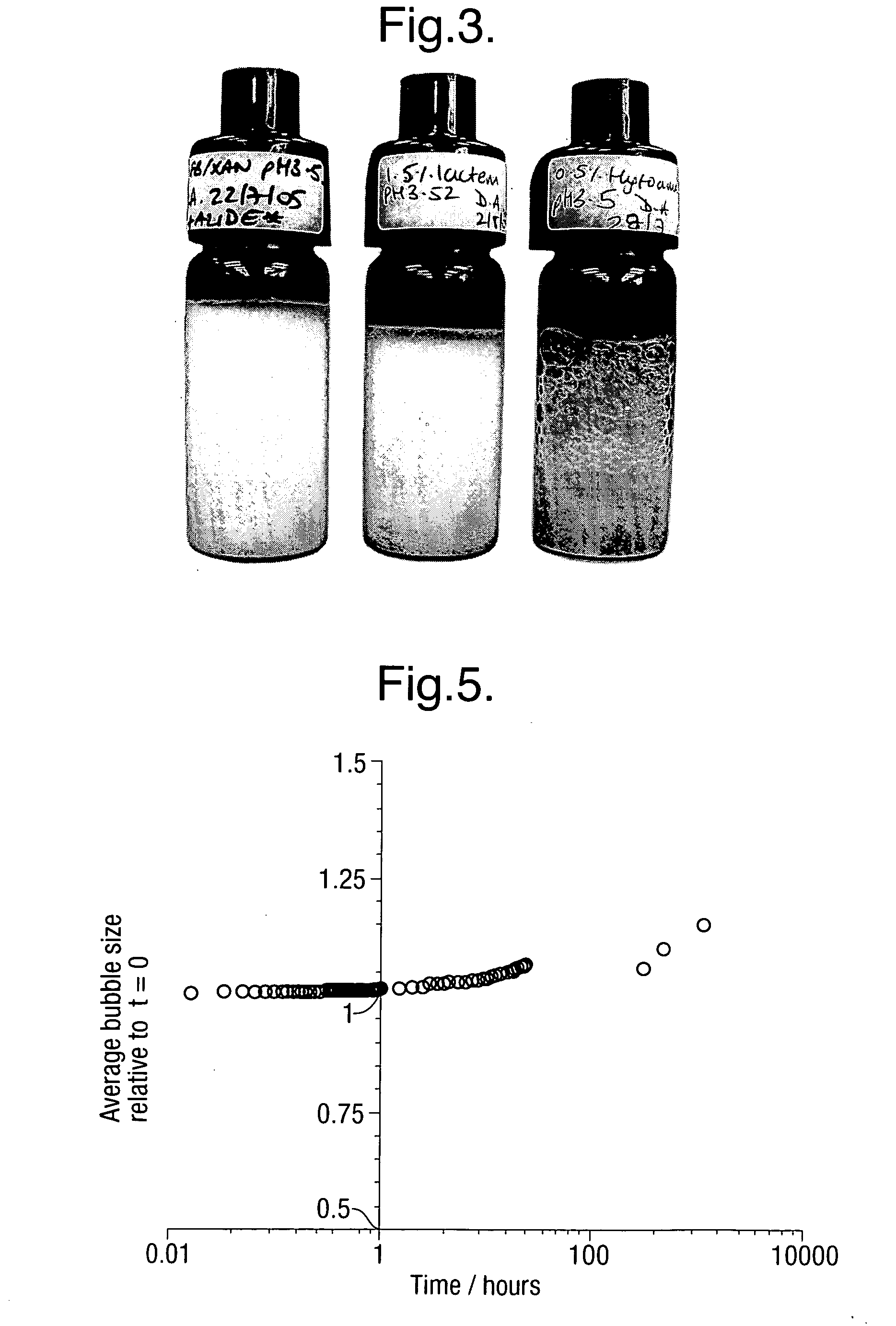
Low pH aerated products
An aerated composition having a pH of less than 5.5 is provided, which composition comprises hydrophobin.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
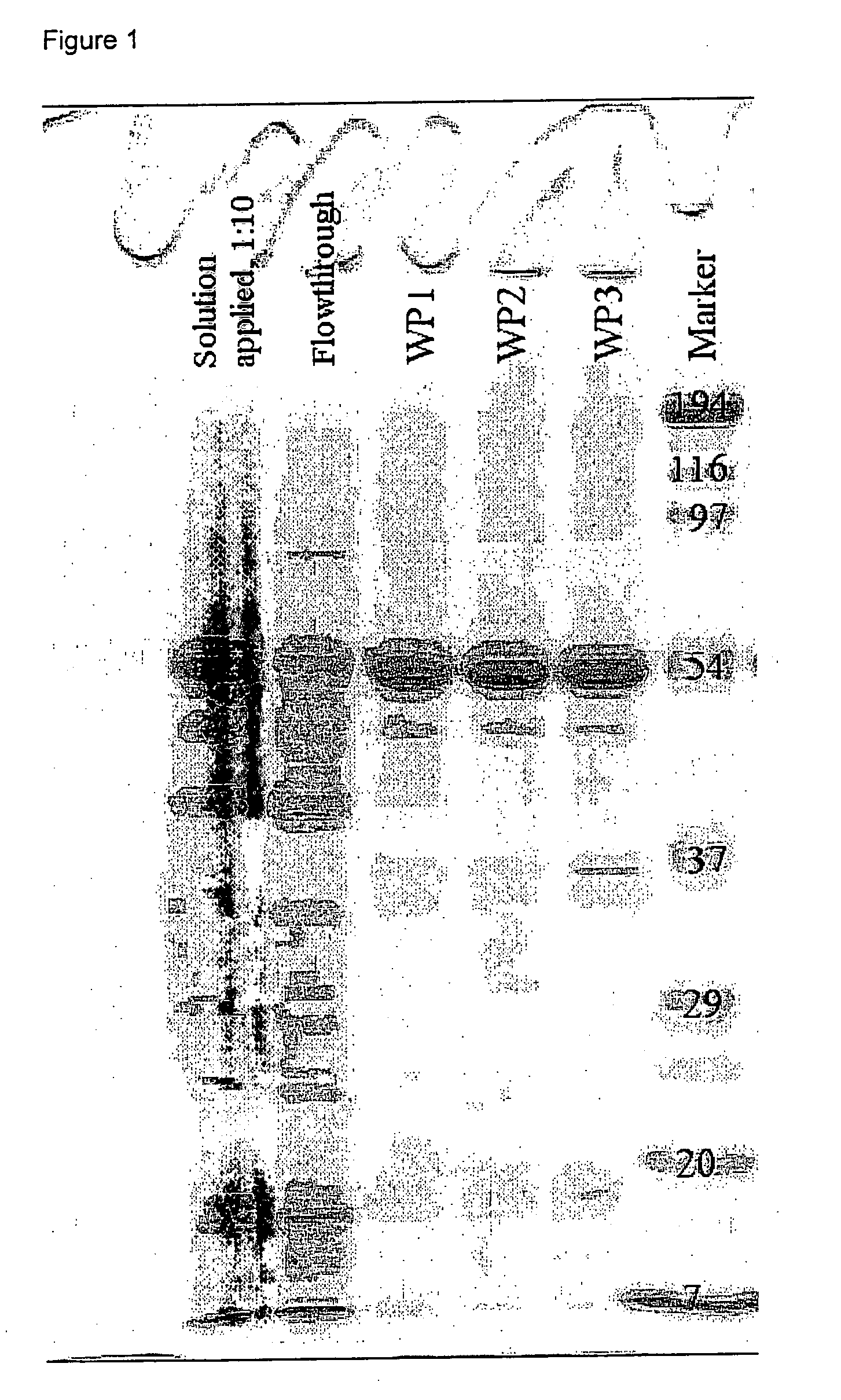
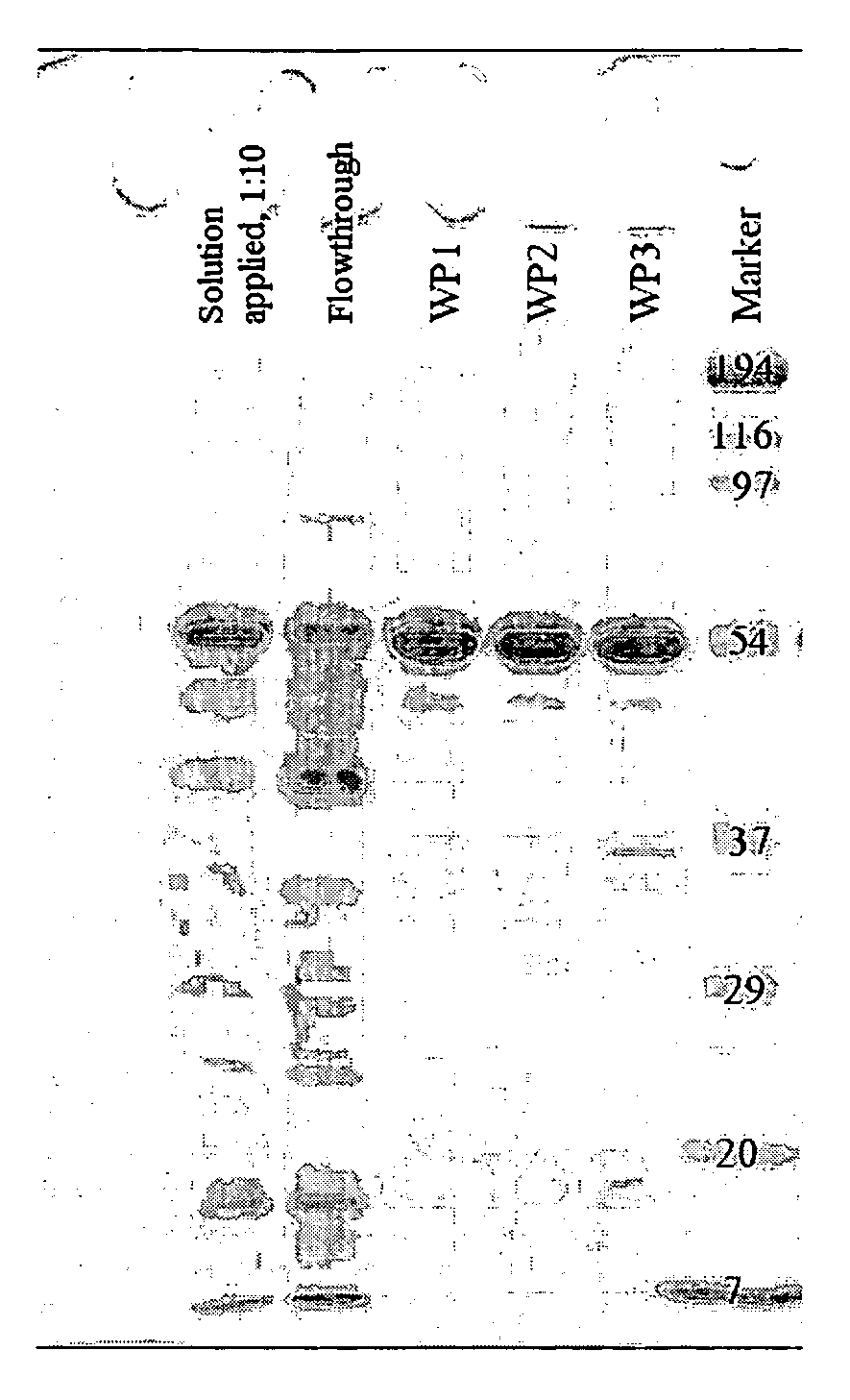
Method for extracting hydrophobin from a solution
Process for extracting hydrophobin from a solution wherein carrageenan is added to the solution and the pH of the solution is brought below 3.5, and the ionic strength of the solution is below 0.5.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Novel cysteine-depleted hydrophobin fusion proteins, their production and use thereof
InactiveUS20090136996A1Produced economicallySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsStructural formulaHydrophobin
Polypeptides of the general structural formula (I)Xn—C1—X1-50—C2—X0-5—C3—Xp—C4—X1-100—C5—X1-50—C6—X0-5—C7—X1-50—C8—Xm (I),production and use thereof.
Owner:BASF AG
Frozen aerated confection
InactiveUS20070141206A1Improve stabilityCoarsening of both the air bubbles and ice crystals is reducedFrozen sweetsConfectioneryHydrophobinFood science
A frozen aerated confection comprising an ice structuring protein (ISP) and a hydrophobin is provided.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Cleavable surfactants and methods of use thereof
Owner:CAPRIOLI RICHARD M +2
Baked products
A method of maintaining softness in a cookie or cake, the method comprising: preparing a dough comprising 20-55% flour having a gluten content of less than 12 wt %, 10-50% sugar, 2-20% fat, 0-10% egg and / or milk solids, 5-30% water and a hydrophobin, and then baking the dough to form the cookie or cake is provided. The use of a hydrophobin for maintaining softness in a cookie or cake comprising flour having a gluten content of less than 12 wt % is also provided.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Use of hydrophobin as a spreading agent
InactiveUS20110312497A1Increases intensity and resistanceExtended stayBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineTopical uses
The present invention relates to the use of hydrophobin as a spreading agent, in particular in cosmetic or pharmaceutical compositions. The invention further relates to compositions for treating surfaces, in particular cosmetic or pharmaceutical compositions for topical use, that contain hydrophobin as a spreading agent.
Owner:BASF AG
Aerated product
A product comprising a container which contains an aerated composition is provided, the container having a dispensing aperture through which the aerated composition can be dispensed, characterized in that the aerated composition comprises hydrophobin.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
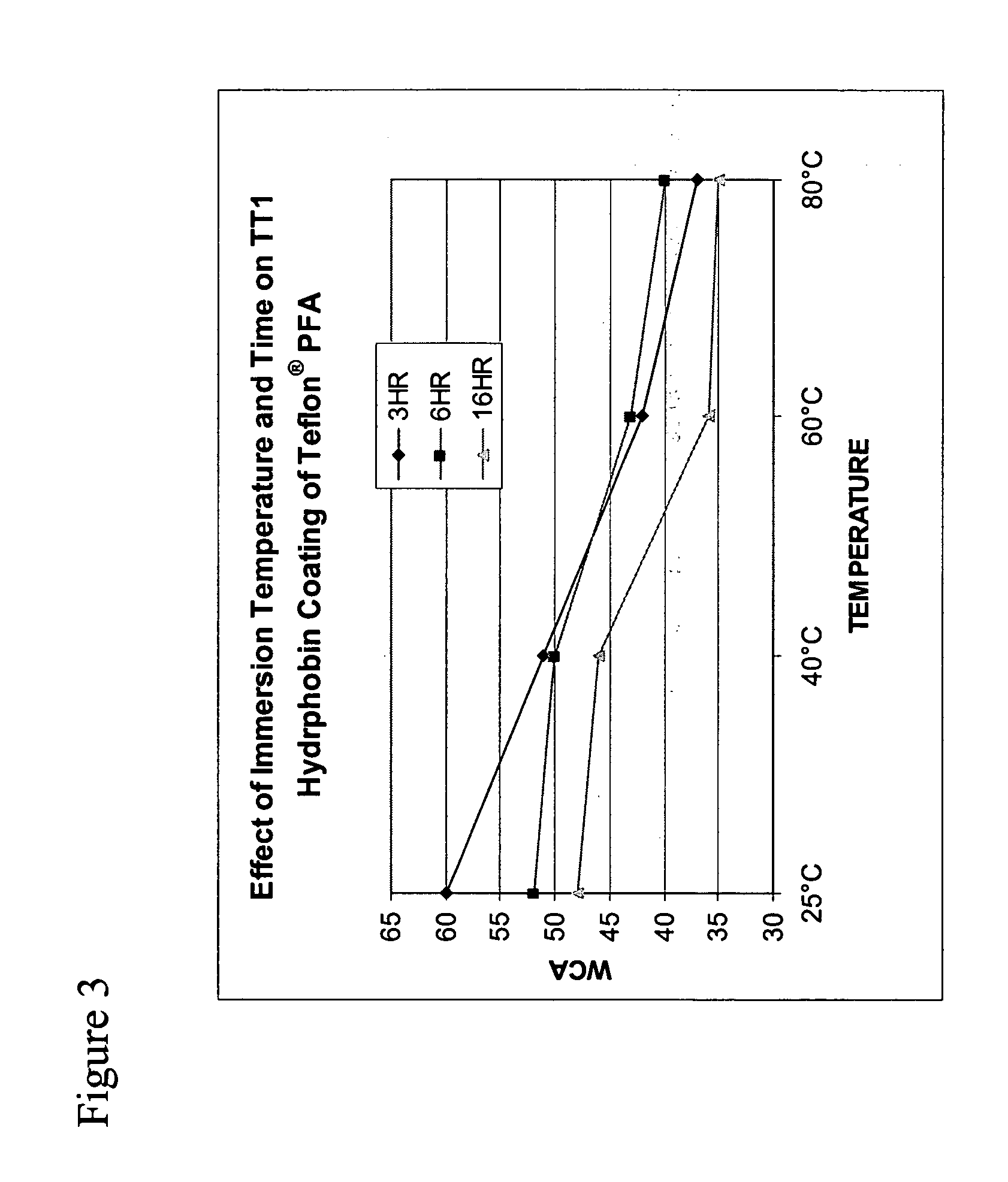
Thermophilic hydrophobin proteins and applications for surface modification
The present invention relates to a thermophilic hydrophobin, TT1, or a protein or polypeptide substantially similar thereto, derived from the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. The invention further relates to a polynucleotide encoding such hydrophobin, as well as to materials coated with such hydrophobin.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Method of binding a compound to a surface
InactiveUS20050238685A1Low mass production costIncrease storage spaceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound (substance)Hydrophobin
The present invention relates to a method of binding a compound to at least a part of a surface of an object, the method comprising the step of adsorbing a hydrophobin-like substance to the surface. The invention provides a method of providing a surface of an object with a reactive compound comprising the steps of coating at least a part of the surface of the object with a coating of a hydrophobin-like substance and contacting the compound with the coated hydrophobin-like substance to form a non-covalent bond between the hydrophobin-like substance and the compound.
Owner:HEKTOR HARM JAN +5
Aerated food products being warm containing soluble and/or insoluble solids and methods for producing them
An aerated food product having an overrun of at least 20%, comprising 40-97% water, 3-50% soluble and / or insoluble solids and hydrophobin, wherein the aerated food product has a temperature of at least 50° C.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Method for coating an object with hydrophobin at low temperatures
InactiveUS20070166346A1Increase contact angleLower contact anglePharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesBiological bodyRoom temperature
The invention relates to methods for coating objects with hydrophobins. Provided is a method for providing the surface of an object with a hydrophobin coating, comprising contacting at least a part of an object with a hydrophobin-containing solution to form a hydrophobin layer on the surface of the object and exposing the layer to a pH below 7, preferably below 4, more preferably below 2, optionally in the presence of a detergent. Contacting can be performed at around room temperature and the hydrophobin-containing solution can be a supernatant of a culture medium of an organism that secretes a hydrophobin.
Owner:APPLIED NANOSYST
Frozen products
InactiveUS8206770B2Reduce volumeExtended shelf lifeMilk preparationFrozen sweetsIce crystalsHydrophobin
A frozen composition is provided which includes hydrophobin. Also provided is the use of hydrophobin in inhibiting ice crystal growth and / or modifying ice crystal habit in frozen food products.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
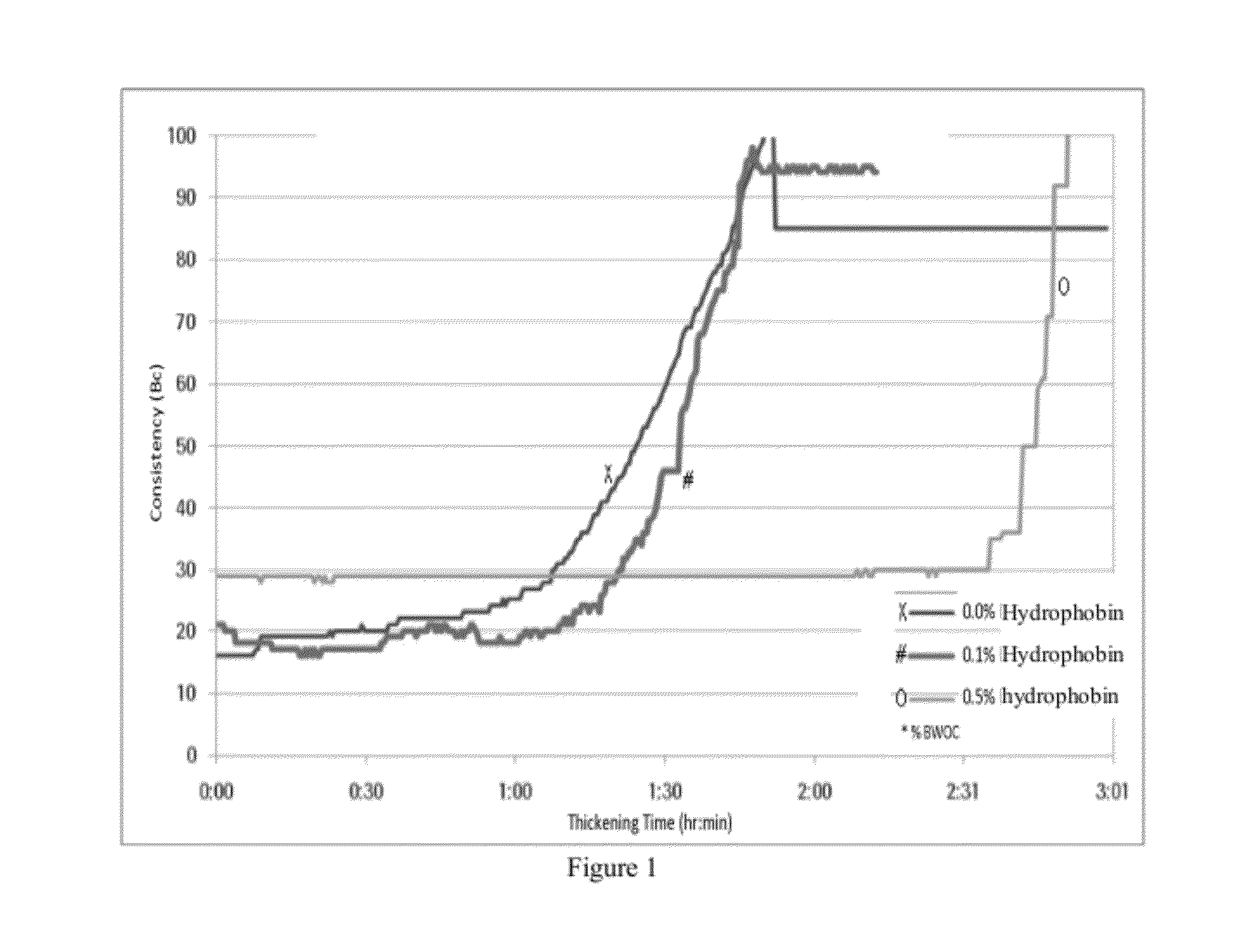
Compositions and methods for well completions
Cement retarders for well cements are based on hydrophobins. Hydrophobins are proteins or polypeptides that form hydrophobic coatings on surfaces. The size of the hydrophobins is preferably between about 100 and 350 amino acids, and the preferred hydrophobin concentration is between about 0.001% and 1.0% by weight of cement. Portland cement is the preferred well cement. Cement slurries containing hydrophobins are useful for both primary and remedial cementing applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for the immobilization of cationic active ingredients on surfaces
InactiveUS20120094007A1Prevent surface from slippingImprove antibacterial propertiesBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTSolvent
A method and composition for immobilizing an antimicrobial active ingredient on a surface of a substrate, in which the surface of the substrate is treated with a composition comprising(i) a solvent,(ii) a hydrophobin,(iii) a cationic antimicrobial active ingredient,(iv) optionally additives or auxiliary components,which permits a long-lasting antimicrobial finishing of the substrate surface.
Owner:BASF AG
Aerated food products being warm or having been heated up and methods for producing them
An aerated food product having an overrun of at least 20%, comprising 40-95% water, 5-55% fat, and hydrophobin, wherein the aerated food product has a temperature of at least 50° C.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Use of a synergistic mixture of water-soluble polymers and hydrophobins for thickening aqueous phases
Owner:BASF AG
Method for the isolation of hydrophobic proteins
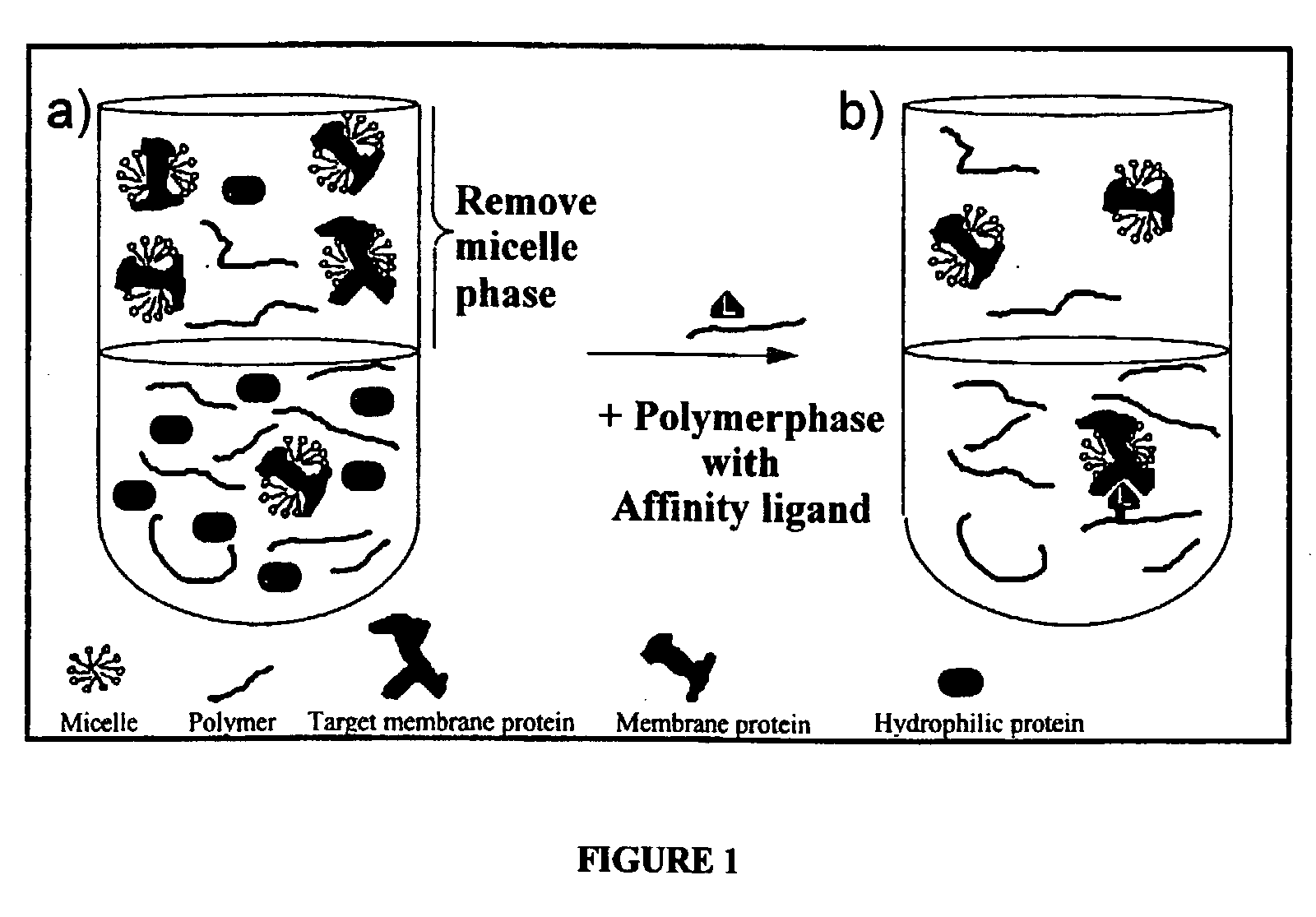
InactiveUS20030049819A1High selectivityHigh resolutionDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCrystallographyIntegral membrane protein
A method for separating one or more hydrophobic proteins, for instance membrane proteins such as integral membrane proteins, from a mixture of proteins. The method is characterized in that said mixture is partitioned in a phase system comprising a micelle-enriched aqueous phase (micelle-phase) and a polymer-enriched aqueous phase (polymer phase). At least part of the polymer of the polymer phase carries an affinity ligand that is capable of binding to an affinity structure on at least one of said one or more hydrophobic proteins.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Method for loading bioactive protein on hydrophobic stent material
The invention discloses a method for loading a bioactive protein on a hydrophobic stent material. Through the effect of bonding with the hydrophobic end of an amphiphilic protein HFBI, the bioactive protein is loaded onto the degradable aliphatic polyester porous fiber stent material, the bioactive protein is then bonded with the hydrophobic end of a hydrophobin, and thereby a novel bioactive protein-loaded tissue engineering stent material is prepared. The stent material remarkably improves the hydrophilic property of hydrophobic materials, the biocompatibility is good, and the invention proves that the stent material has the effect of promoting cell migration and vascularization. The method can be used for loading a macromolecular protein on the surface of a hydrophobic material, and while the biocompatibility of the material is improved, the activity of the loaded protein is kept, so that the hydrophobic material can play a corresponding biological role.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Oral care compositions
InactiveUS20130084254A1Improve foamabilityGood storage stabilityCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCleansing AgentsDentistry
The invention provides a non-aerated, foamable oral care composition comprising less than 1.5% anionic surfactant (by total weight anionic surfactant based on the total weight of the composition), abrasive cleaning agent and hydrophobin. The composition is mild to oral mucosa yet exhibits excellent foamability, texture and storage stability.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Dyeing liquid for preparing zirconia false tooth ceramic blank in gradient color
The invention discloses a dyeing liquid for preparing a zirconia false tooth ceramic blank in a gradient color. The dyeing liquid includes a solvent, a colorant, a surfactant, a permeation fortifier,an inorganic additive and an antibacterial agent, wherein the mass ratio of the solvent to the colorant to the permeation fortifier to the inorganic additive is (5-10):(2-3):1:(0.5-1), and the permeation fortifier is a mixture of an alcohol ether ester solvent, propylene glycol carbonate, acyl alaninate and hydrophobin. The coloring permeation depth of the dyeing liquid on the zirconia false toothceramic blank is greater than 5mm, the permeation time is short, and permeation on the surface of a ceramic or in the vertical direction of the ceramic is uniform; by adding the natural antibacterialagent into the dyeing liquid, the probability of inflammation of false tooth gingiva can be reduced; by adding inorganic ions into the dyeing liquid, the optical effect of the false tooth ceramic blank is obviously improved, and the transparency of the false tooth ceramic blank is enhanced.
Owner:湖南鹏登生物科技股份有限公司
Environmentally Friendly and Aerated Topical Benefit Composition
Environmentally friendly and aerated topical benefit compositions are described. The compositions are emulsified with hydrophobin and upon topical application deliver excellent sensory and absorption characteristics along with consumer desirable drying times.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com