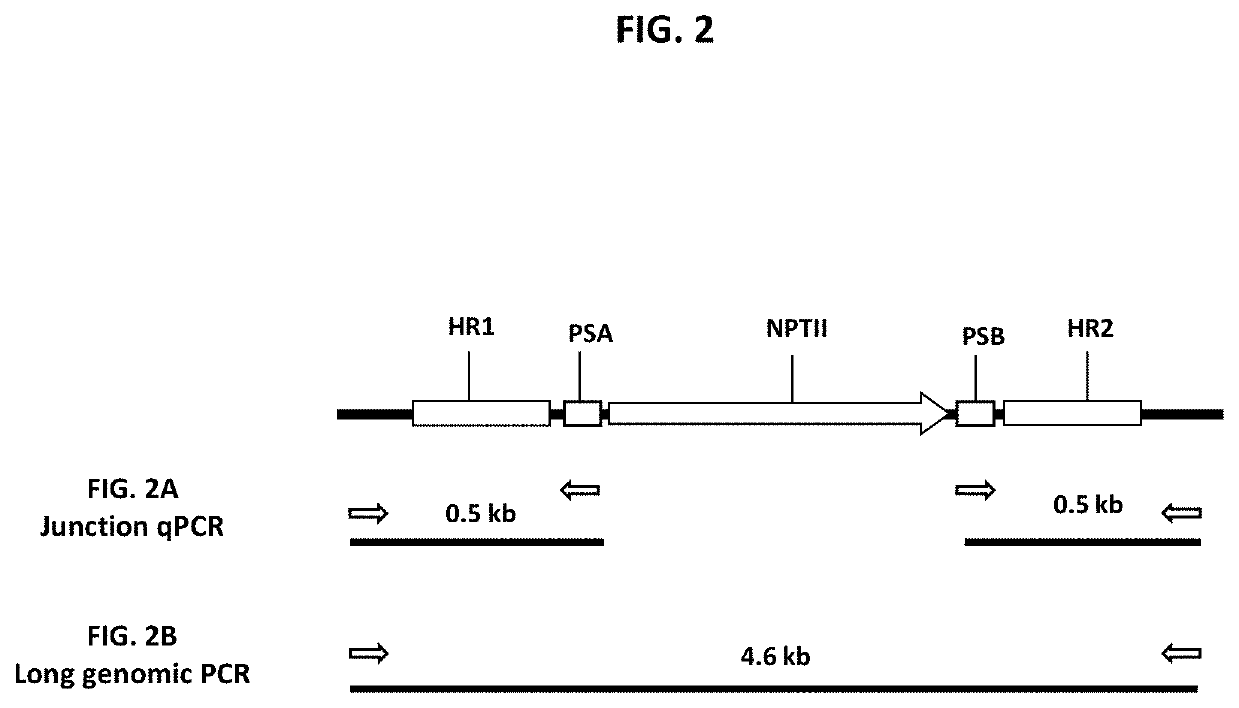
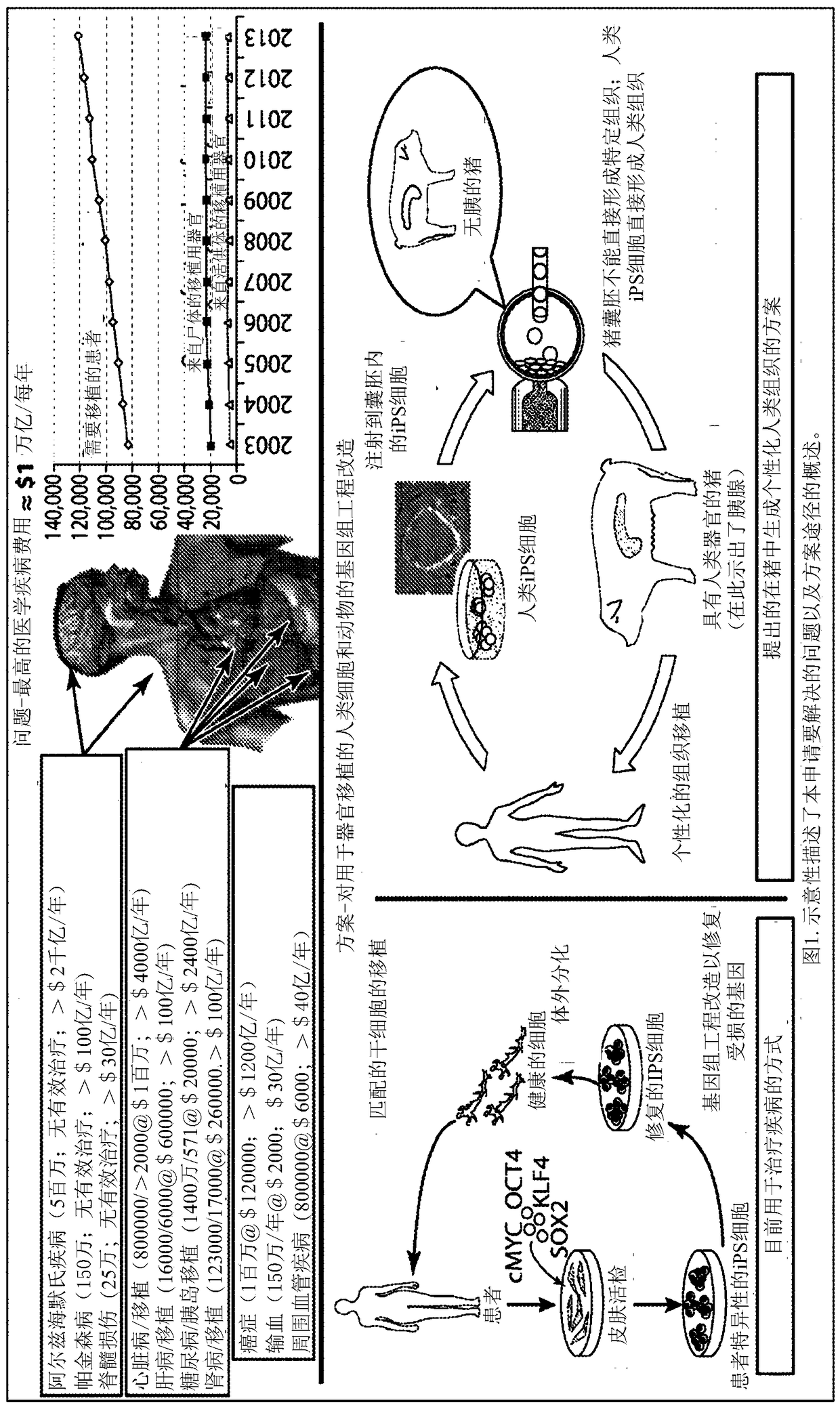
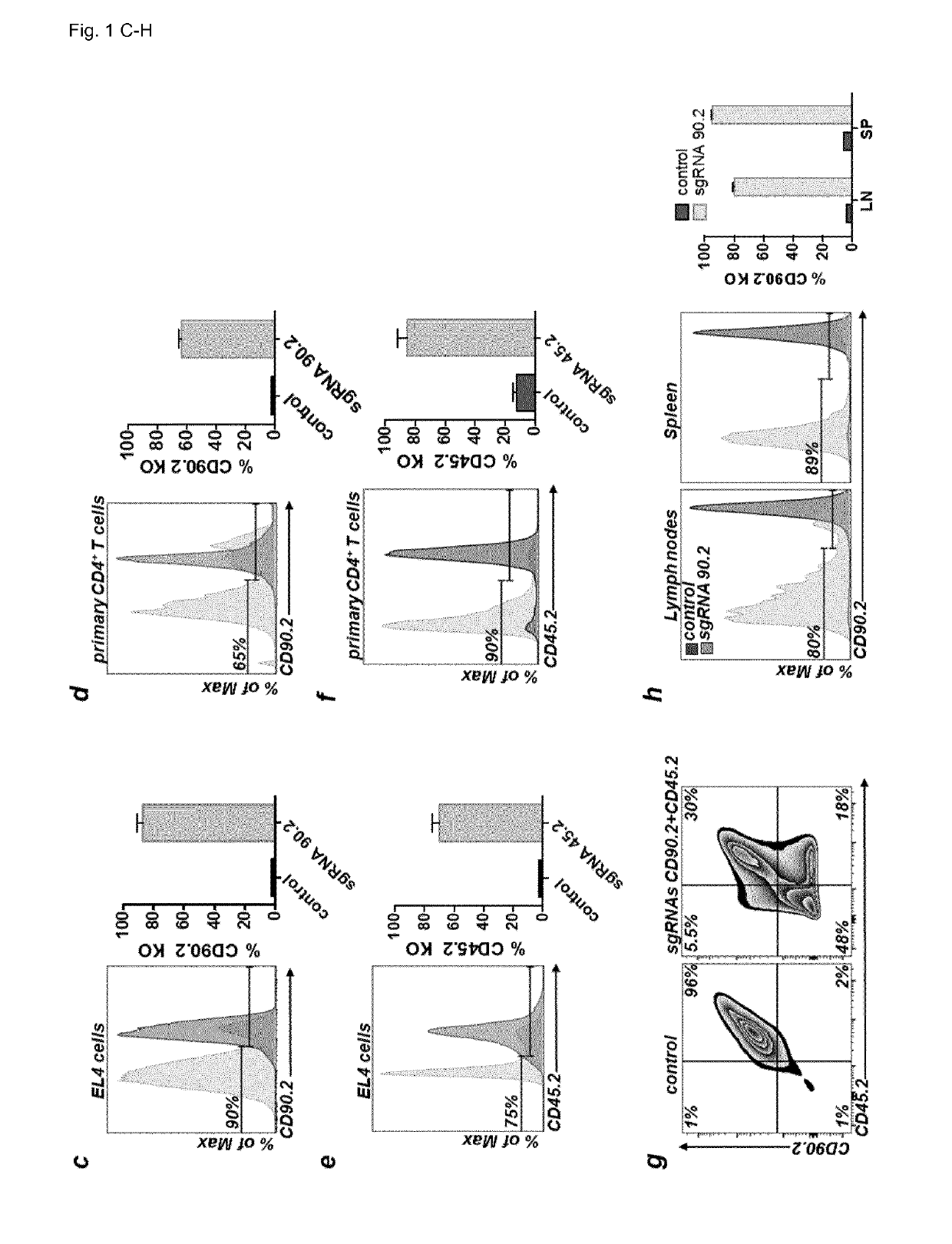
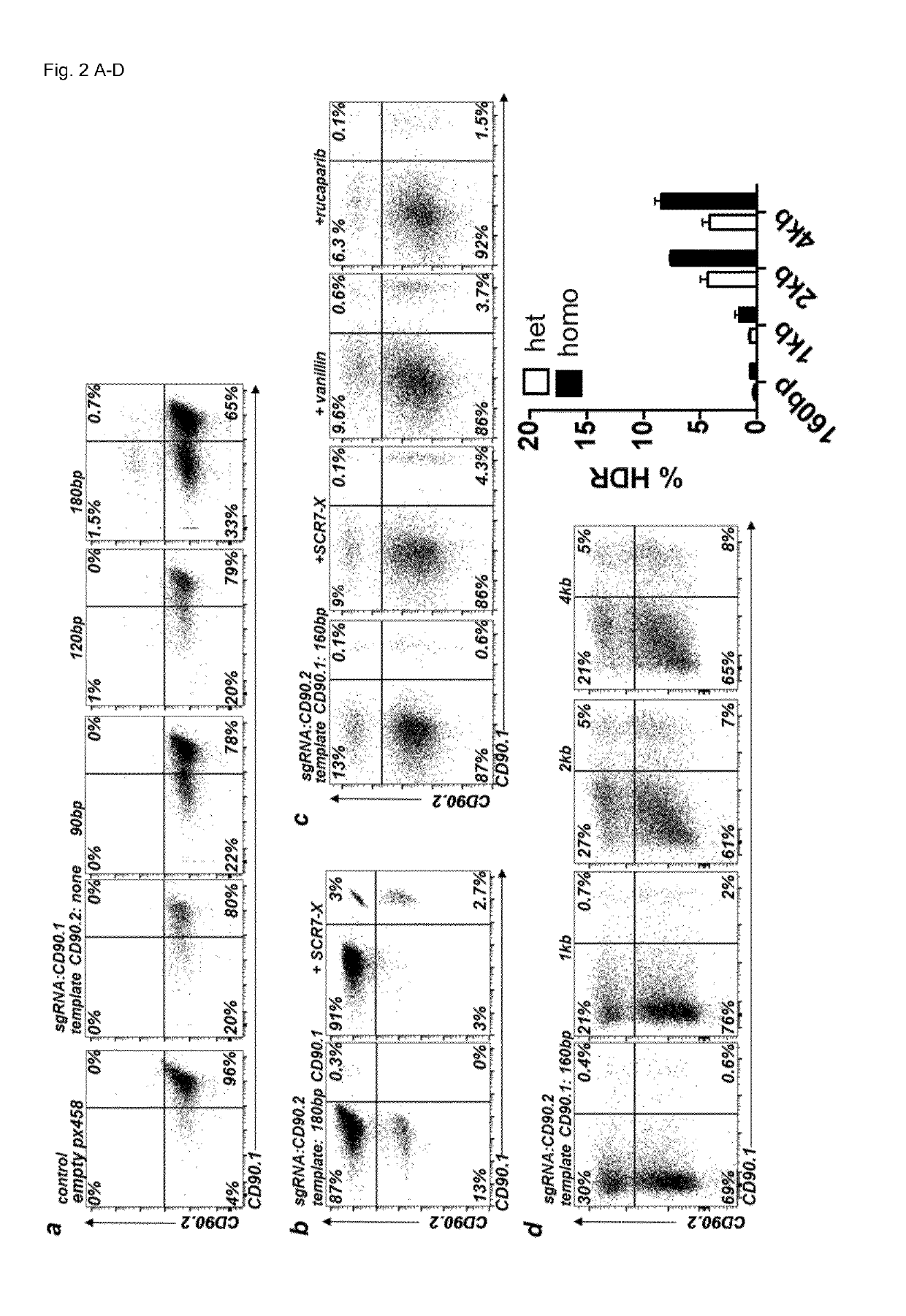
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Homology directed repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
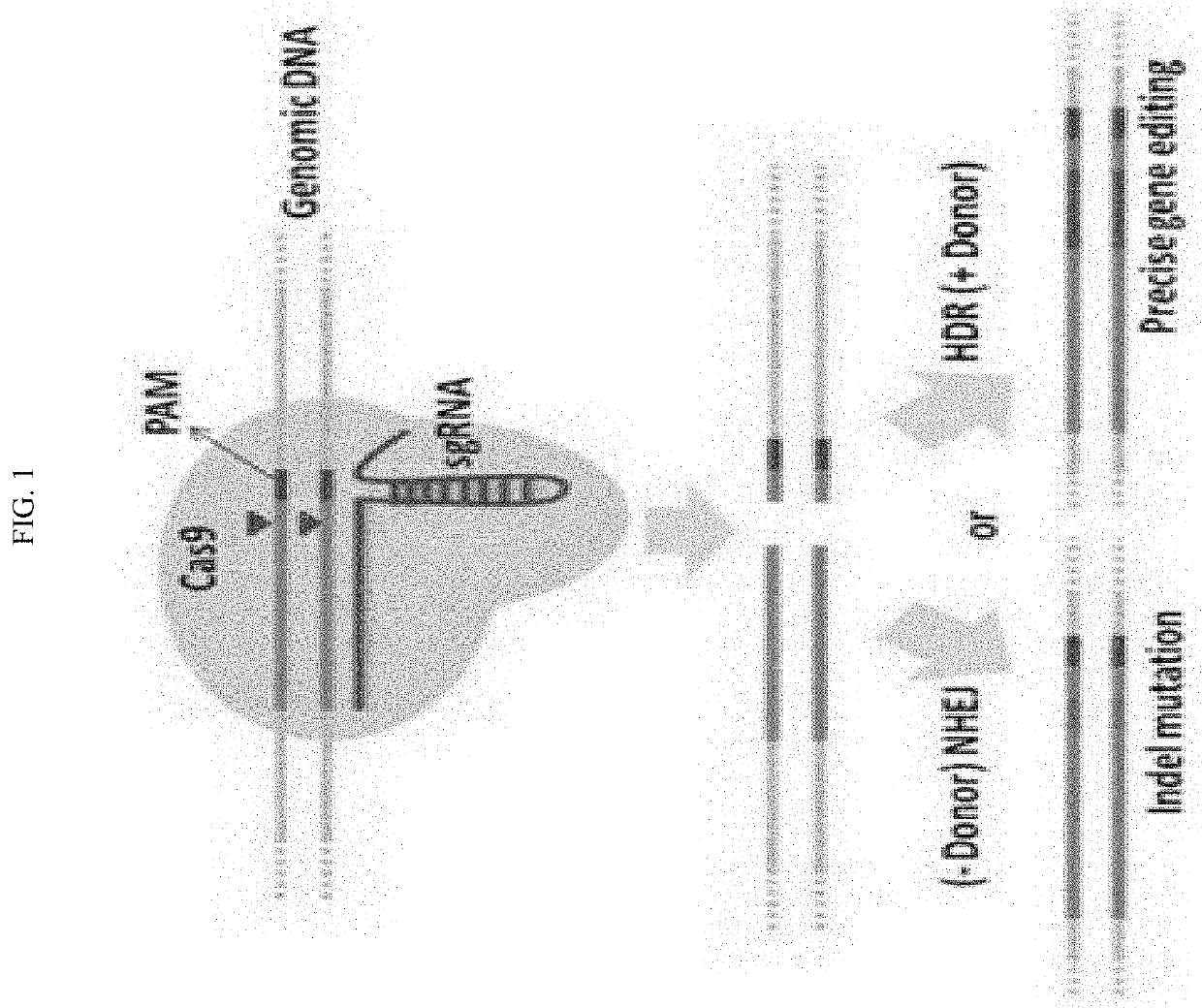
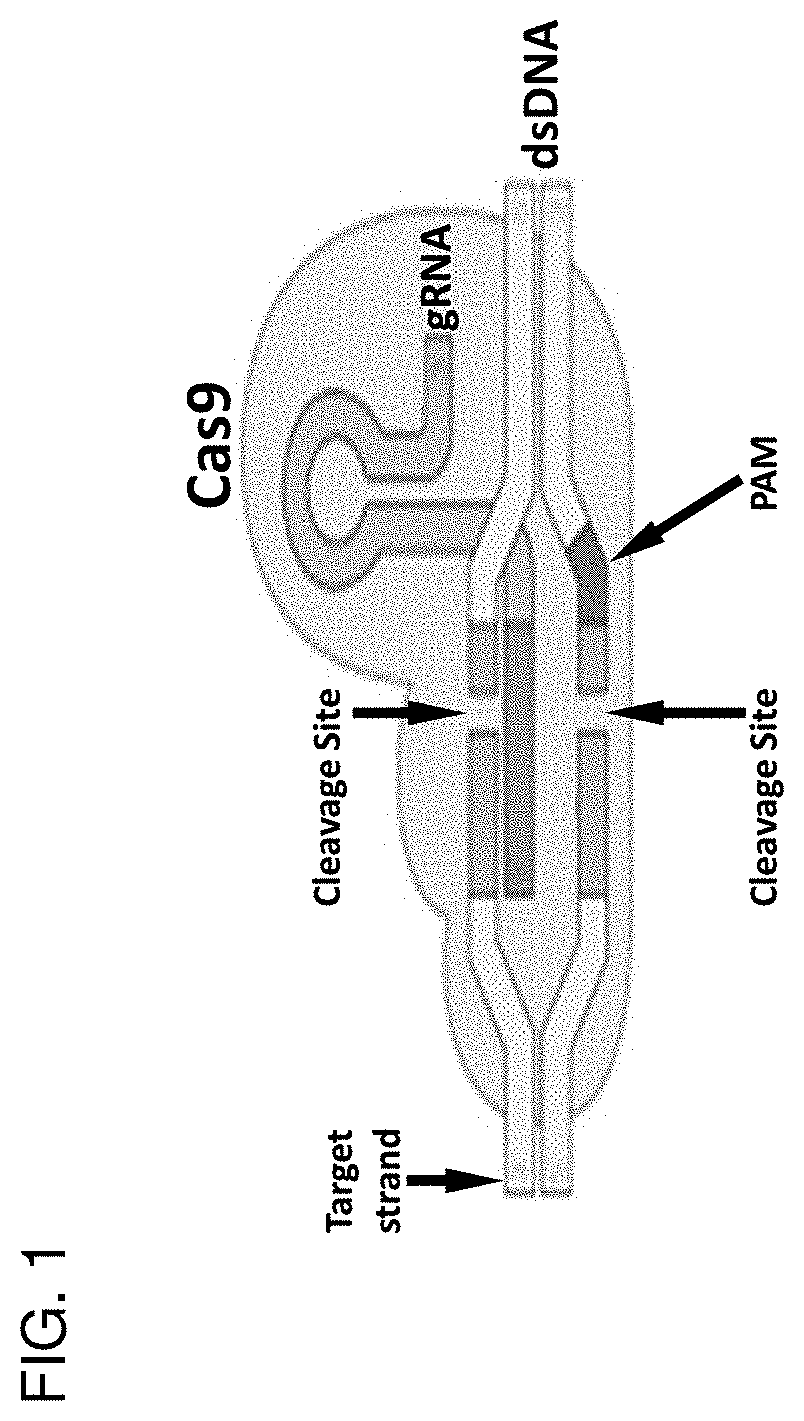
Homology directed repair (HDR) is a mechanism in cells to repair double-strand DNA lesions. The most common form of HDR is homologous recombination. The HDR mechanism can only be used by the cell when there is a homologous piece of DNA present in the nucleus, mostly in G2 and S phase of the cell cycle. Other examples of homology-directed repair include single-strand annealing and breakage-induced replication. When the homologous DNA is absent, another process called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) takes place instead.
Methods and materials for assessing loss of heterozygosity
InactiveUS20120015050A1Raise the possibilityReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellRegimen
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing samples (e.g., cancer cells) for the presence of a loss of heterozygosity (LOH) signature. For example, methods and materials for determining whether or not a cell (e.g., a cancer cell) contains an LOH signature are provided. Materials and methods for identifying cells (e.g., cancer cells) having a deficiency in homology directed repair (HDR) as well as materials and methods for identifying cancer patients likely to respond to a particular cancer treatment regimen also are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS +1
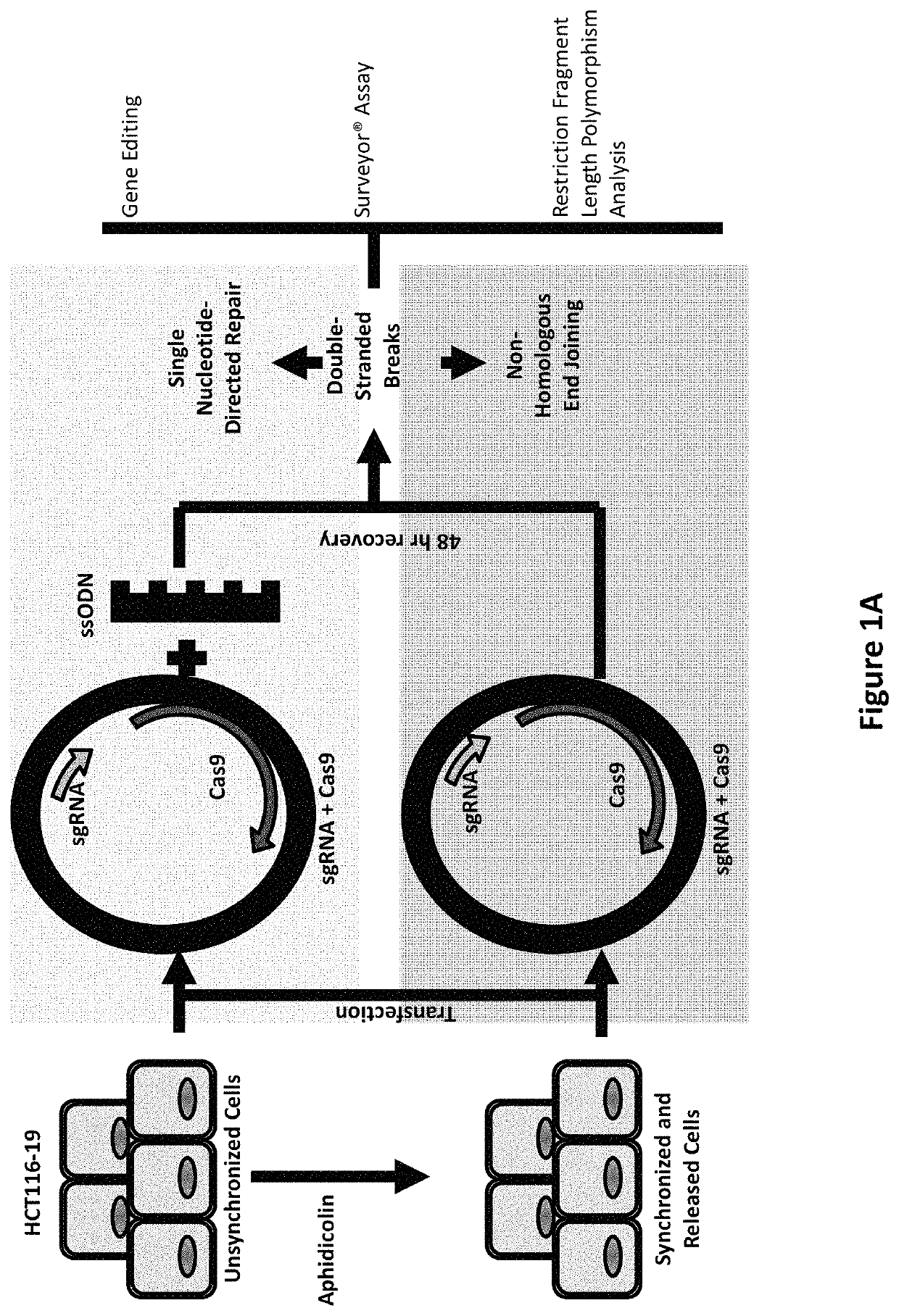
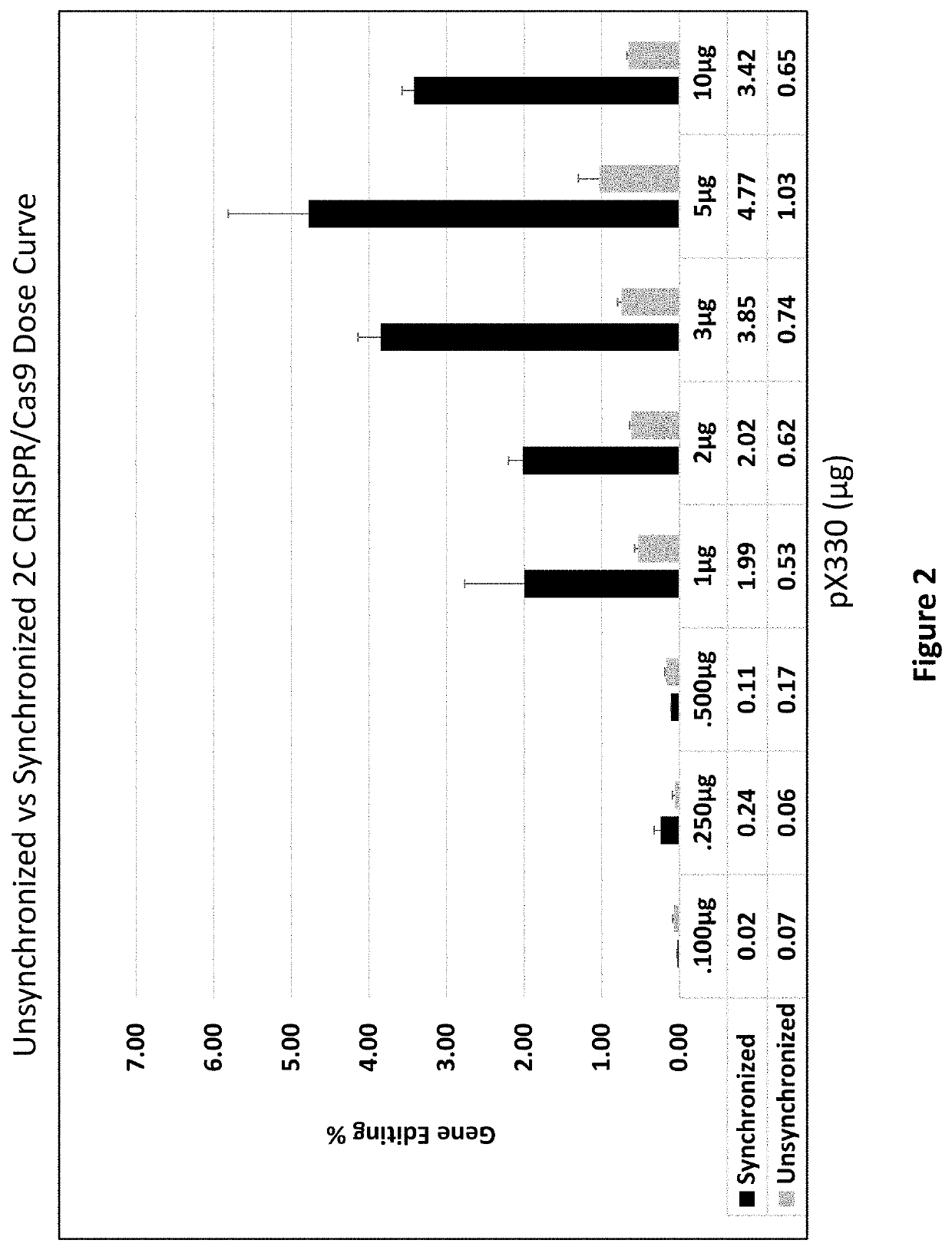
Compositions and Methods for Improving Homogeneity of DNA Generated Using a CRISPR/Cas9 Cleavage System
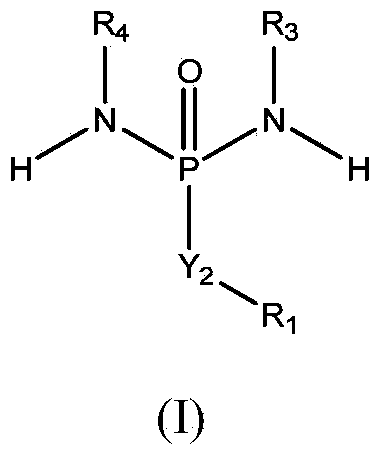
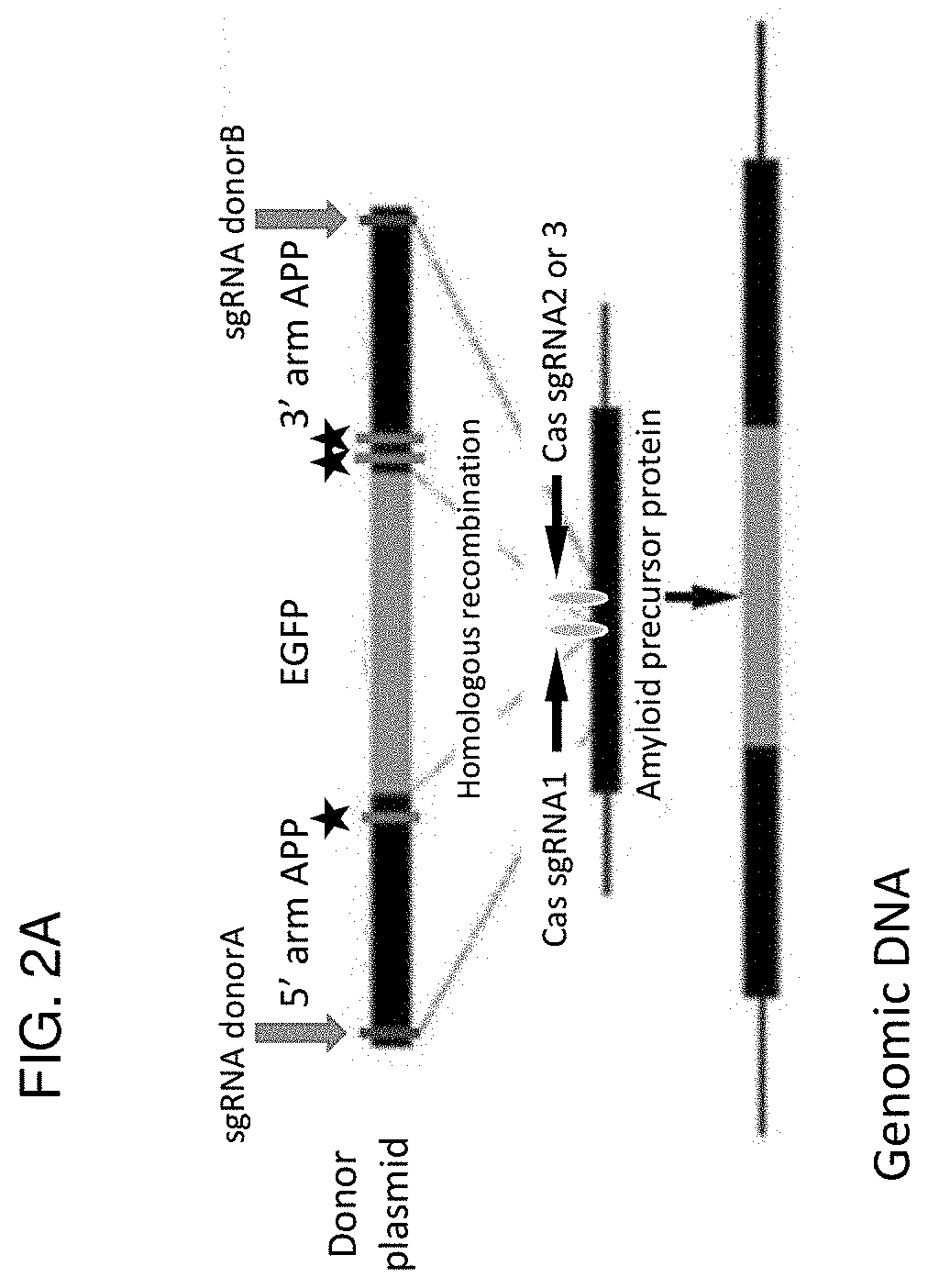
The invention relates to the unexpected discovery of a system and methods for precise homology directed repair after CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage. The invention includes a DNA cleavage and repair system comprising a CRISPR / Cas9 system and an oligonucleotide 100% complementary to cleaved DNA to promote homology directed DNA repair. The invention further includes methods for inducing homology directed repair of cleaved DNA and repairing a CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage.
Owner:CHRISTIANA CARE HEALTH SERVICES INC
Methods and materials for assessing loss of heterozygosity
InactiveUS20150080260A1Raise the possibilityReduce in quantityTherapiesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellRegimen
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing samples (e.g., cancer cells) for the presence of a loss of heterozygosity (LOH) signature. For example, methods and materials for determining whether or not a cell (e.g., a cancer cell) contains an LOH signature are provided. Materials and methods for identifying cells (e.g., cancer cells) having a deficiency in homology directed repair (HDR) as well as materials and methods for identifying cancer patients likely to respond to a particular cancer treatment regimen also are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS +1
Methods and materials for assessing homologous recombination deficiency
InactiveUS20140363521A1Raise the possibilityHeavy metal active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementRegimenCancer cell
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing samples (e.g., cancer cells) for the presence of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) or an HRD signature. For example, methods and materials for determining whether or not a cell (e.g., a cancer cell) contains an HRD signature are provided. Materials and methods for identifying cells (e.g., cancer cells) having a deficiency in homology directed repair (HDR) as well as materials and methods for identifying cancer patients likely to respond to a particular cancer treatment regimen also are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Methods for increasing cas9-mediated engineering efficiency
ActiveUS20160257973A1Reduce the binding forceReducing cleavageHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsHomology directed repairDouble strand
Methods for use with Type II CRISPR-Cas9 systems for increasing Cas9-mediated genome engineering efficiency are disclosed. The methods can be used to decrease the number of off-target nucleic acid double-stranded breaks and / or to enhance homology-directed repair of a cleaved target nucleic acid.
Owner:CARIBOU BIOSCI
Methods and materials for assessing homologous recombination deficiency
InactiveUS20180030544A1Heavy metal active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementRegimenCancer cell
This document provides methods and materials involved in assessing samples (e.g., cancer cells) for the presence of homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) or an HRD signature. For example, methods and materials for determining whether or not a cell (e.g., a cancer cell) contains an HRD signature are provided. Materials and methods for identifying cells (e.g., cancer cells) having a deficiency in homology directed repair (HDR) as well as materials and methods for identifying cancer patients likely to respond to a particular cancer treatment regimen also are provided.
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS
Methods for increasing the efficiency of homology directed repair (HDR) in the cellular genome
PendingCN110300803AImprove Homology Directed Repair (HDR) EfficiencyHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsHomology directed repairNuclease
In certain embodiments, the disclosure provides a method for increasing the efficiency of homology directed repair (HDR) in the genome of a cell, comprising: (a) introducing into the cell: (i) a nuclease; and (ii) a donor nucleic acid which comprises a modification sequence to be inserted into the genome; and (b) subjecting the cell to a temperature shift from 37 DEG C to a lower temperature; wherein the nuclease cleaves the genome at a cleavage site in the cell, and the donor nucleic acid directs the repair of the genome sequence with the modification sequence through an increased rate of HDR.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Methods for treating cancer
ActiveCN103458896ADipeptide ingredientsPhosphorous compound active ingredientsHypoxia activated prodrugOncology
Administration of TH-302 or another hypoxia activated prodrug in combination with a pharmacological agent that down-regulates or inhibits homology directed repair (HDR) is useful for treating cancer.
Owner:分子模板有限公司
Methods for increasing CAS9-mediated engineering efficiency
ActiveUS9970030B2Reducing off-targeting nuclease cleavageBinding and/or cleavage of the first complex to the off-target nucleic acid is reducedSugar derivativesHydrolasesHomology directed repairDouble strand
Methods for use with Type II CRISPR-Cas9 systems for increasing Cas9-mediated genome engineering efficiency are disclosed. The methods can be used to decrease the number of off-target nucleic acid double-stranded breaks and / or to enhance homology-directed repair of a cleaved target nucleic acid.
Owner:CARIBOU BIOSCI
Multiplex production and barcoding of genetically engineered cells
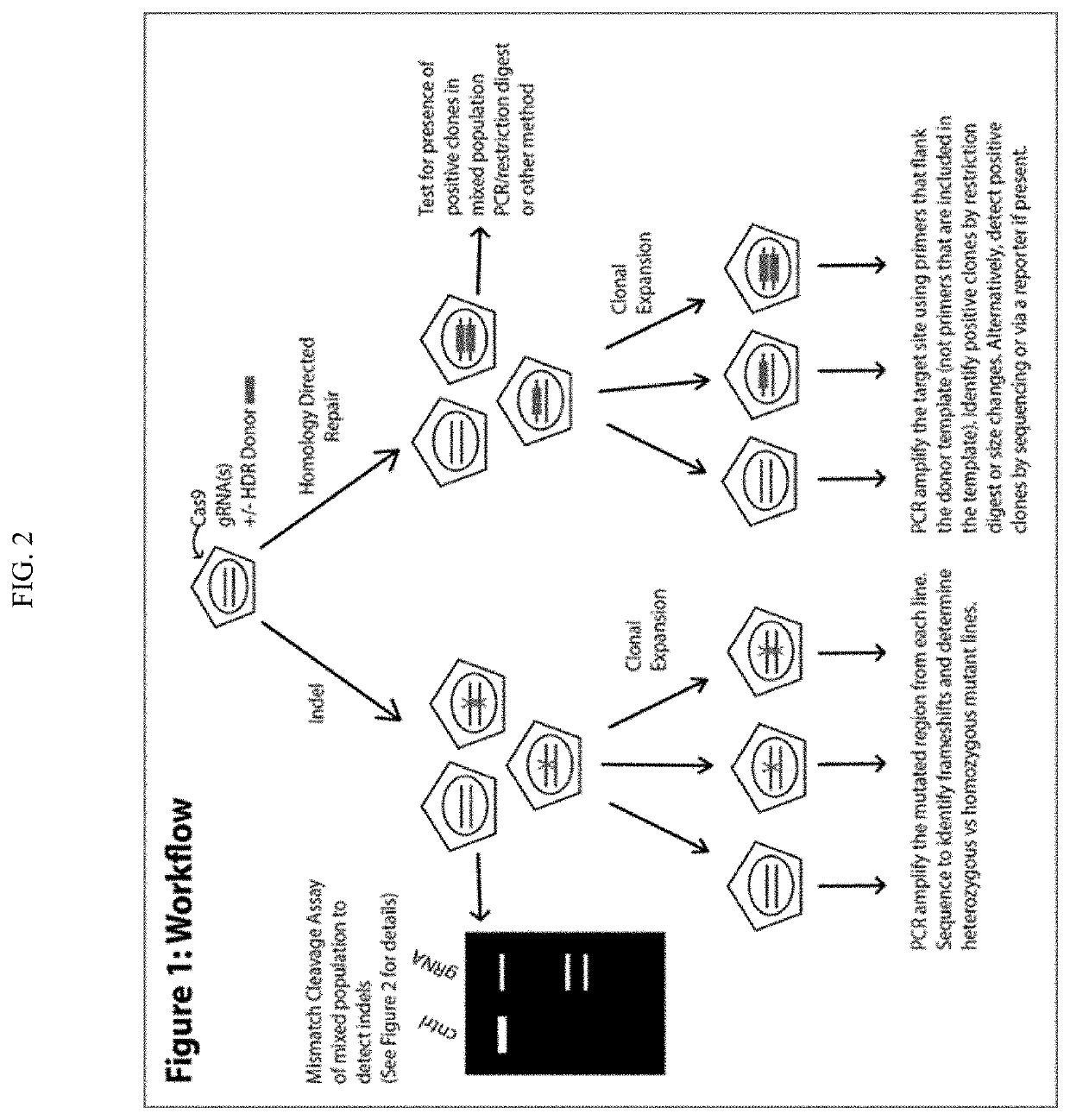
The present disclosure relates to the multiplex production and phenotyping of genetically engineered cells by using RNA-guided nucleases and genomic barcoding. In particular, the high-throughput multiplex genome editing is achieved by utilizing a system that facilitates the precise genome editing at desired target chromosomal loci by homology directed repair. The integration of guide RNA and donorDNA sequences as a genomic barcode at a separate chromosomal locus allows identification, isolation, and massively-parallel validation of individual variants from a pool of transformants. Strains canbe arrayed according to their precise genetic modifications, as specified by donor DNA incorporation in heterologous or native genes. The present disclosure further relates to a method of editing codons outside of canonical guide RNA recognition regions, which enables the complete saturation mutagenesis of protein-coding genes, a marker-based internal cloning method which removes background due to oligonucleotide synthesis errors and incomplete vector backbone cleavage, and a method of enhancing homology directed repair by the active donor recruitment.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Engineering of humanized by geneti complementation
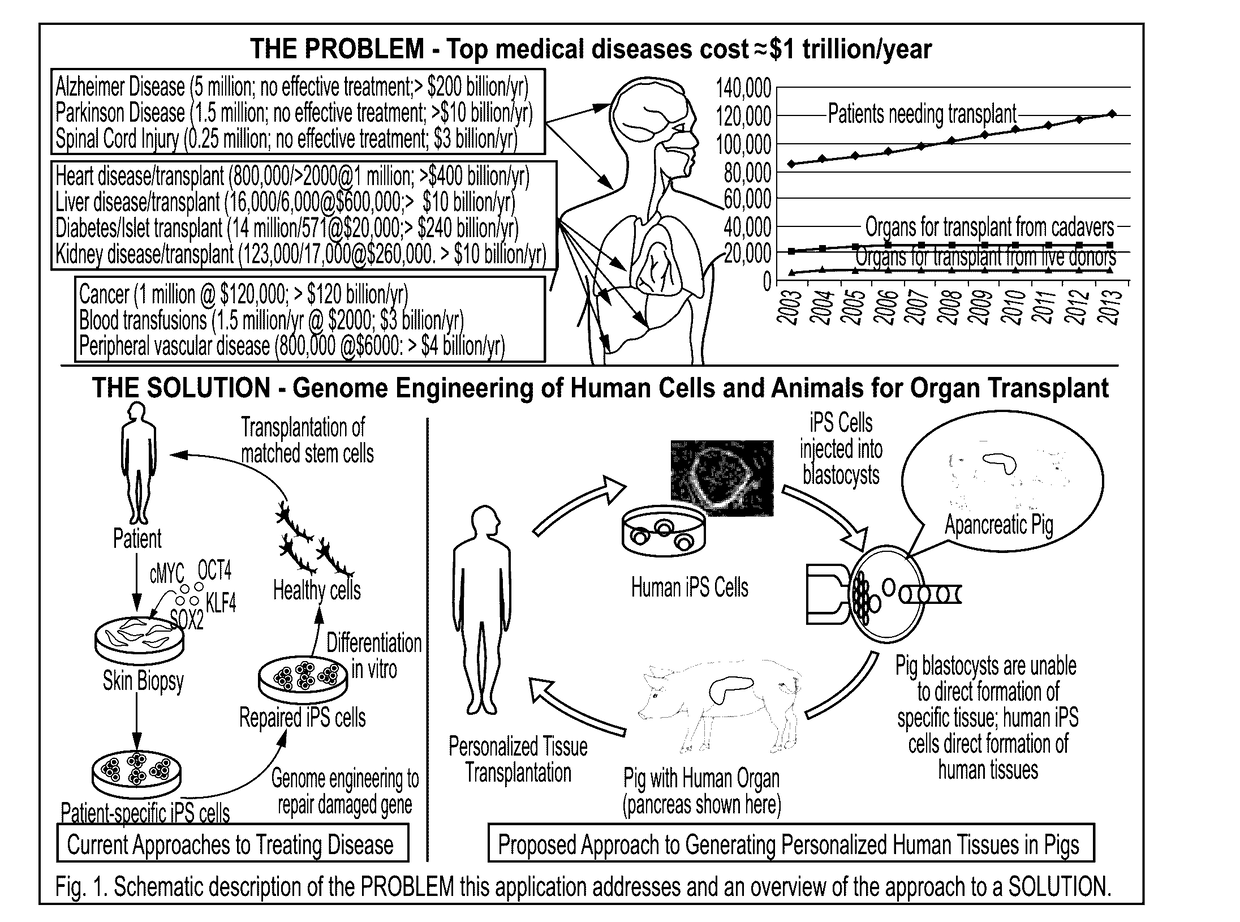
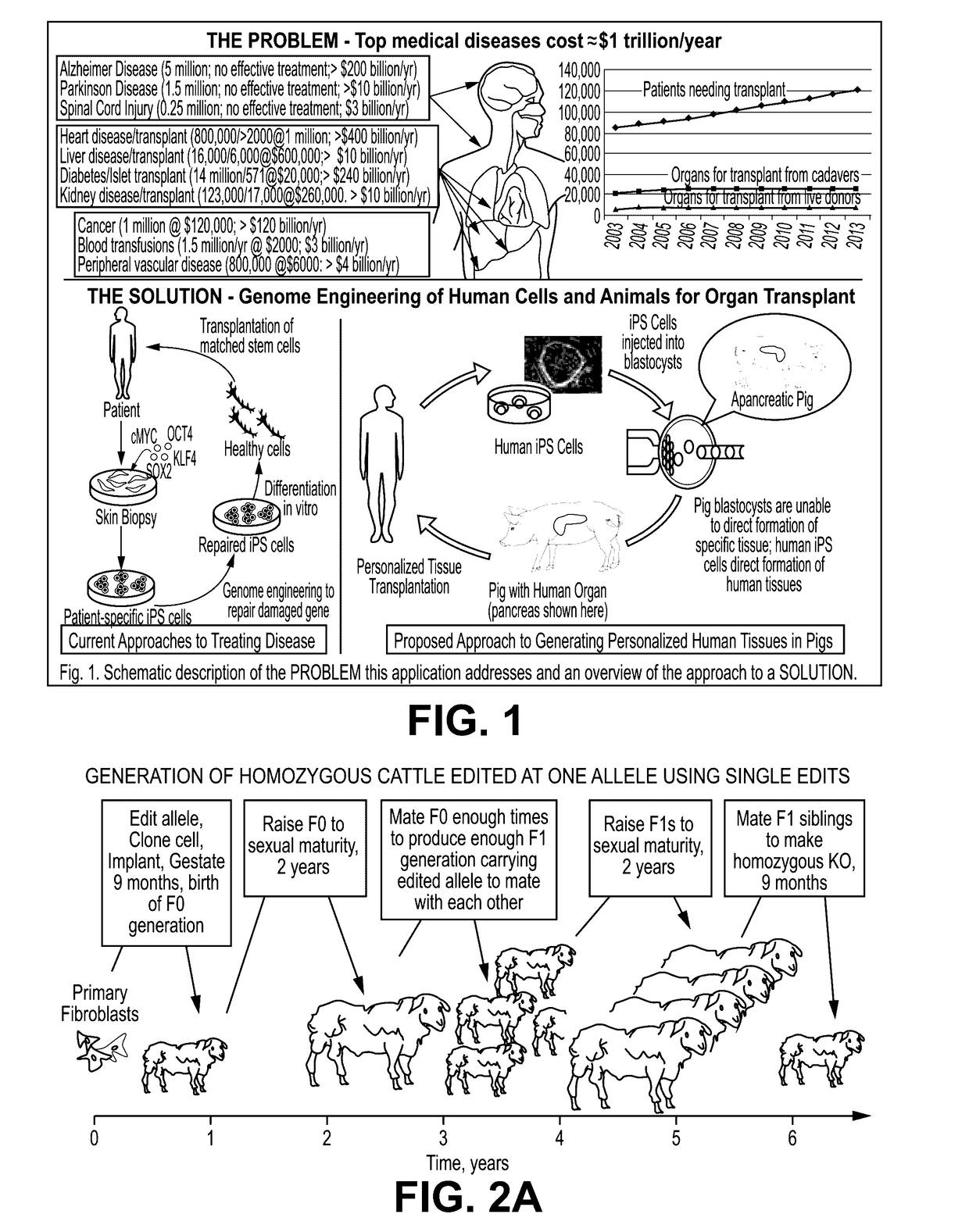
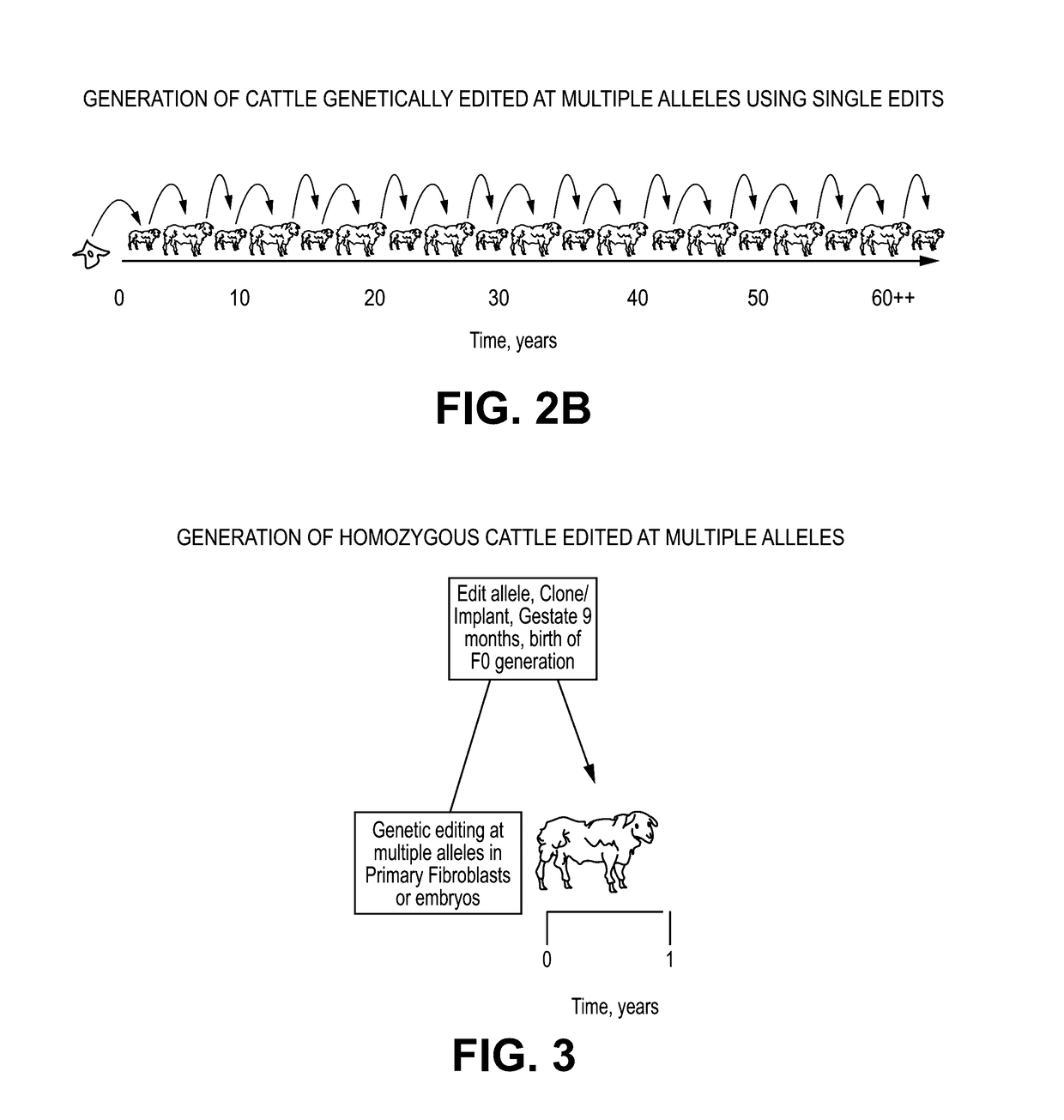
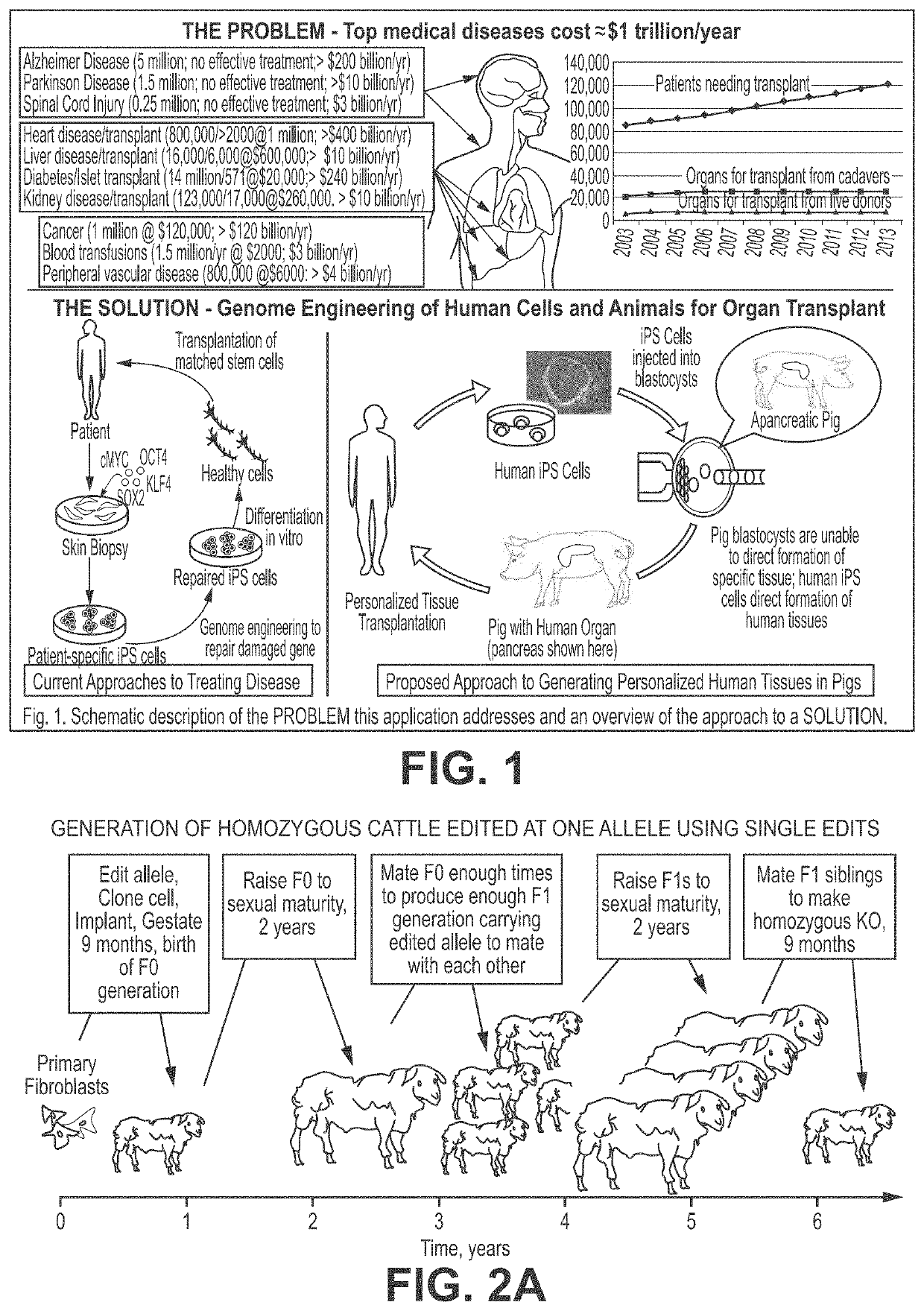
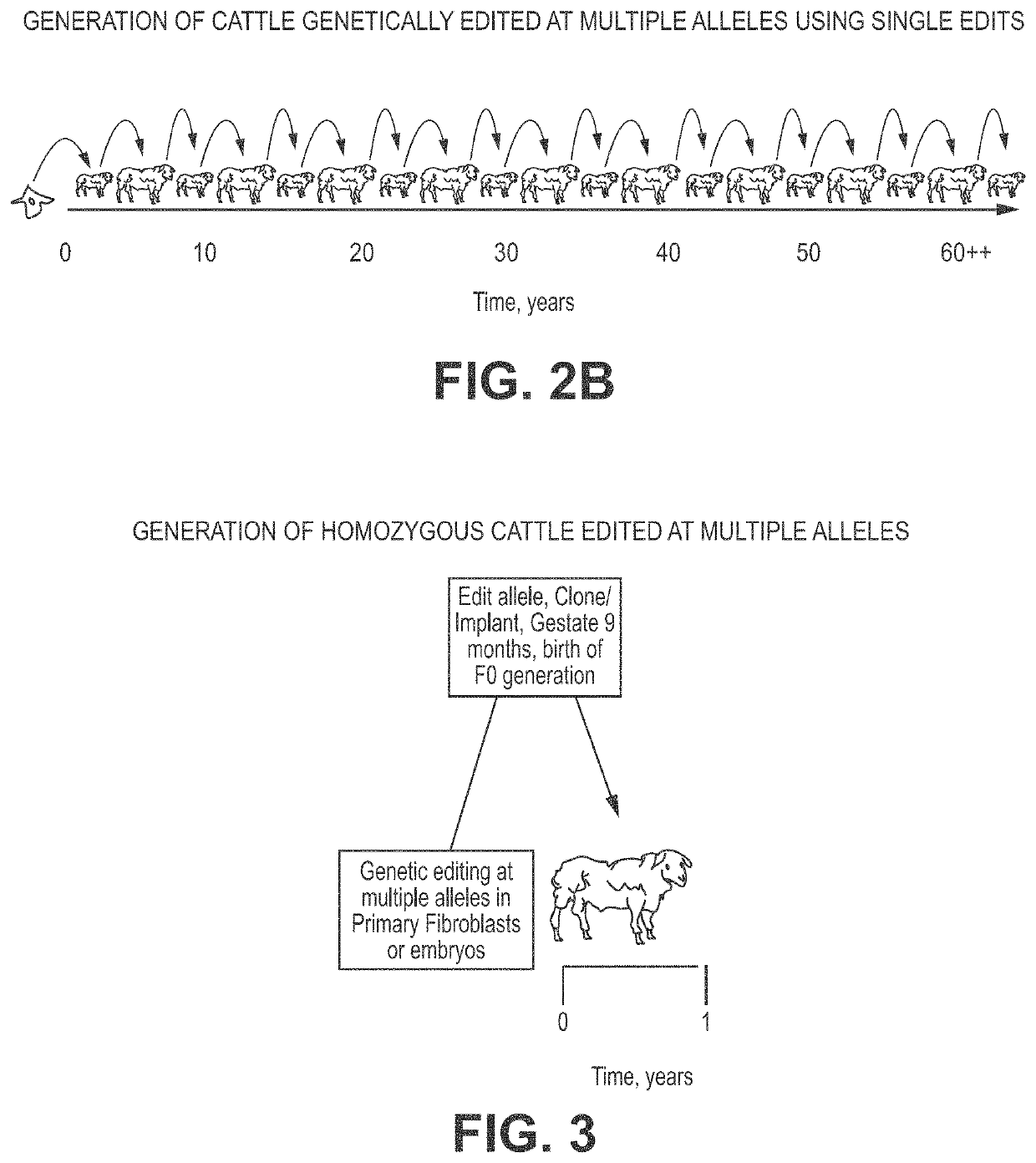
Provided here are methods for editing of a host genome to knock out or debilitate genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stagewith donor stem cells to complement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a 'niche"' for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +2
Methods and compositions for homology directed repair of double strand breaks in plant cell genomes
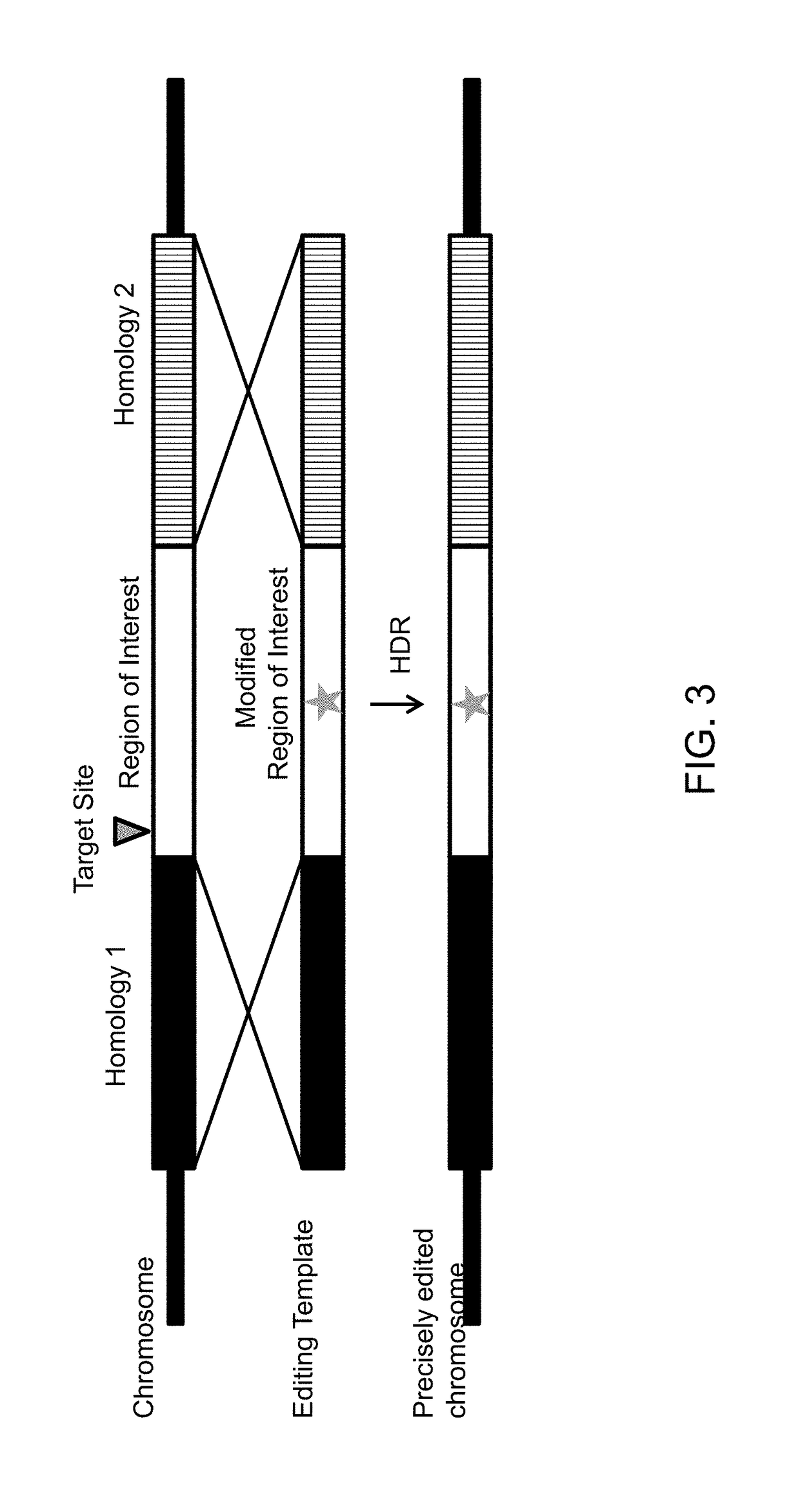
Methods and compositions are provided for the improvement of homology-directed repair of a double strand break in a plant cell, via the use of a polynucleotide comprising sequences homologous to the target site. In some aspects, the double strand break is created by an RNA-guided Cas endonuclease. The homology-directed repair of the double-strand break may include incorporation of a heterologous polynucleotide, for example a gene encoding a trait of agronomic importance. The homology-directed repair of the double-strand break may occur as a result of template-directed repair using a polynucleotide repair template.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method to enhance screening for homologous recombination in genome edited cells using recombination-activated fluorescent donor delivery vector
PendingUS20200157531A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHomology directed repairBioinformatics
Constructs, vectors, and methods for enhancing homology directed repair using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing platform are disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Engineering of humanized car t-cell and platelets by genetic complementation
Human or humanized tissues and organs suitable for transplant are disclosed herein. Gene editing of a host animal provides a niche for complementation of the missing genetic information by donor stem cells. Editing of a host genome to knock out or disrupt genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stage with donor stem cells to complement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a “niche” for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RECOMBINETICS INC +1
Compositions and methods for improving homogeneity of DNA generated using a CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage system
The invention relates to the unexpected discovery of a system and methods for precise homology directed repair after CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage. The invention includes a DNA cleavage and repair system comprising a CRISPR / Cas9 system and an oligonucleotide 100% complementary to cleaved DNA to promote homology directed DNA repair. The invention further includes methods for inducing homology directed repair of cleaved DNA and repairing a CRISPR / Cas9 cleavage.
Owner:CHRISTIANA CARE HEALTH SERVICES INC
Methods and compositions for homology directed repair of double strand breaks in plant cell genomes
PendingUS20210238614A1Improve water efficiencyImprove nitrogen utilizationHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyHeterologous
Methods and compositions are provided for the improvement of homology-directed repair of a double strand break in a plant cell, via the use of a polynucleotide comprising sequences homologous to the target site. In some aspects, the double strand break is created by an RNA-guided Cas endonuclease. The homology-directed repair of the double-strand break may include incorporation of a heterologous polynucleotide, for example a gene encoding a trait of agronomic importance. The homology-directed repair of the double-strand break may occur as a result of template-directed repair using a polynucleotide repair template.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Methods for increasing cas9-mediated engineering efficiency
InactiveUS20180171360A1Reducing off-targeting nuclease cleavageBinding and/or cleavage of the first complex to the off-target nucleic acid is reducedHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsHomology directed repairDouble stranded
Methods for use with Type II CRISPR-Cas9 systems for increasing Cas9-mediated genome engineering efficiency are disclosed. The methods can be used to decrease the number of off-target nucleic acid double-stranded breaks and / or to enhance homology-directed repair of a cleaved target nucleic acid.
Owner:CARIBOU BIOSCI
Methods and materials for assessing loss of heterozygosity
ActiveUS20170022569A1Raise the possibilityHeavy metal active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellOncology
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS +1
Compositions and methods for chimeric embryo-assisted organ production
Human or humanized tissues and organs suitable for transplant are disclosed herein. Gene editing of a host animal provides a niche for complementation of the missing genetic information by donor stemcells. Editing of a host genome to knock out or disrupt genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stage with donor stem cells tocomplement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a 'niche' for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
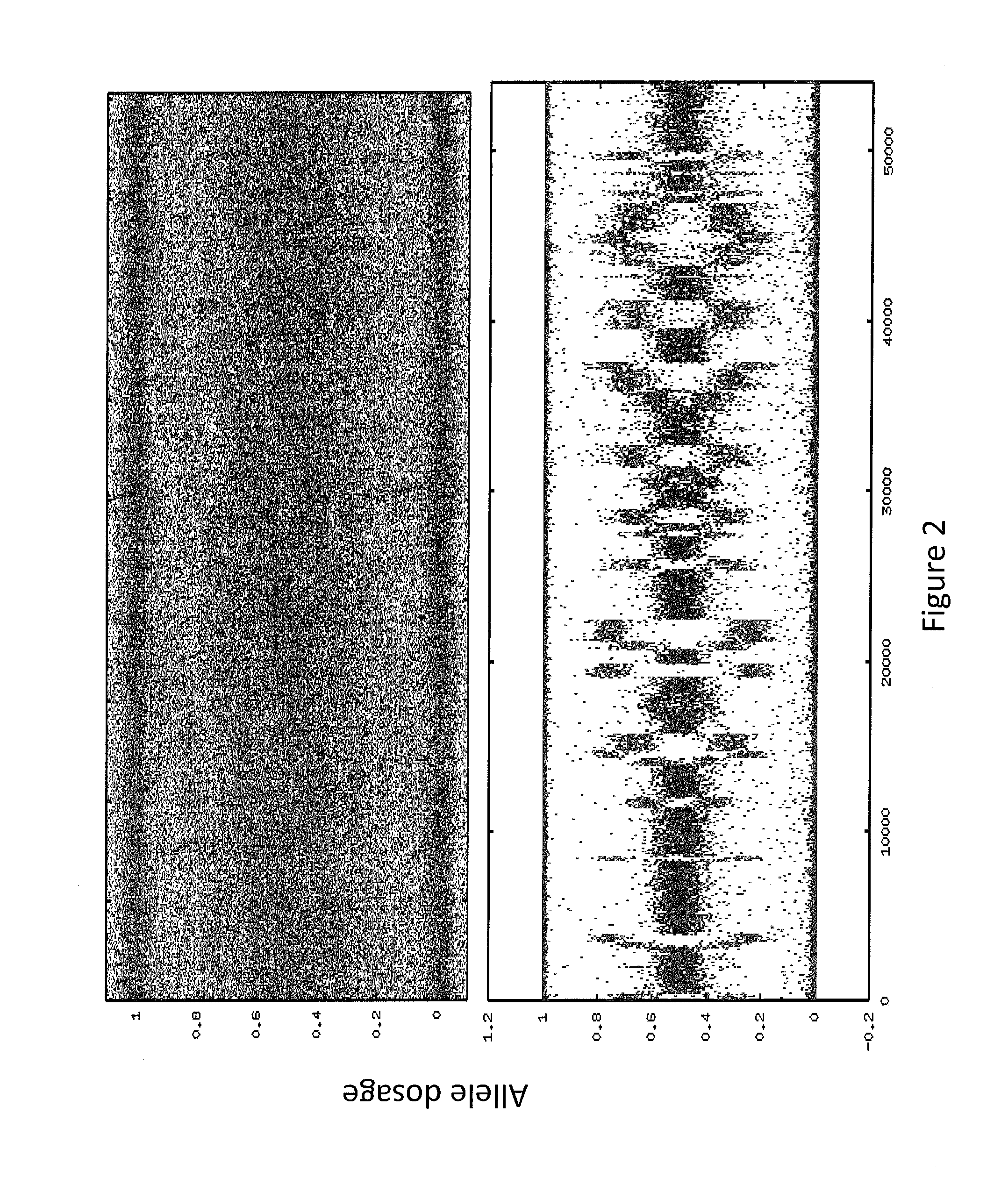
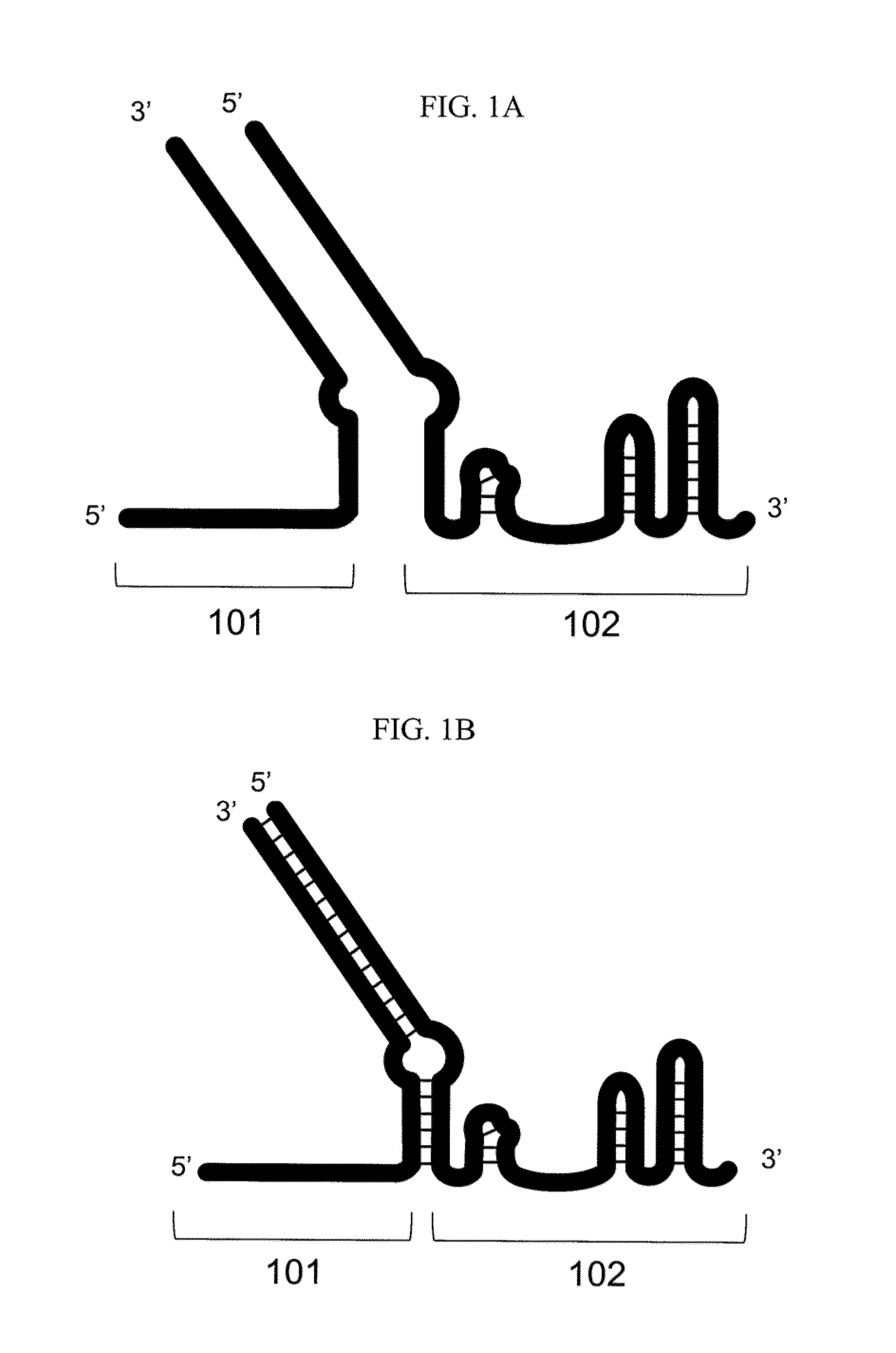
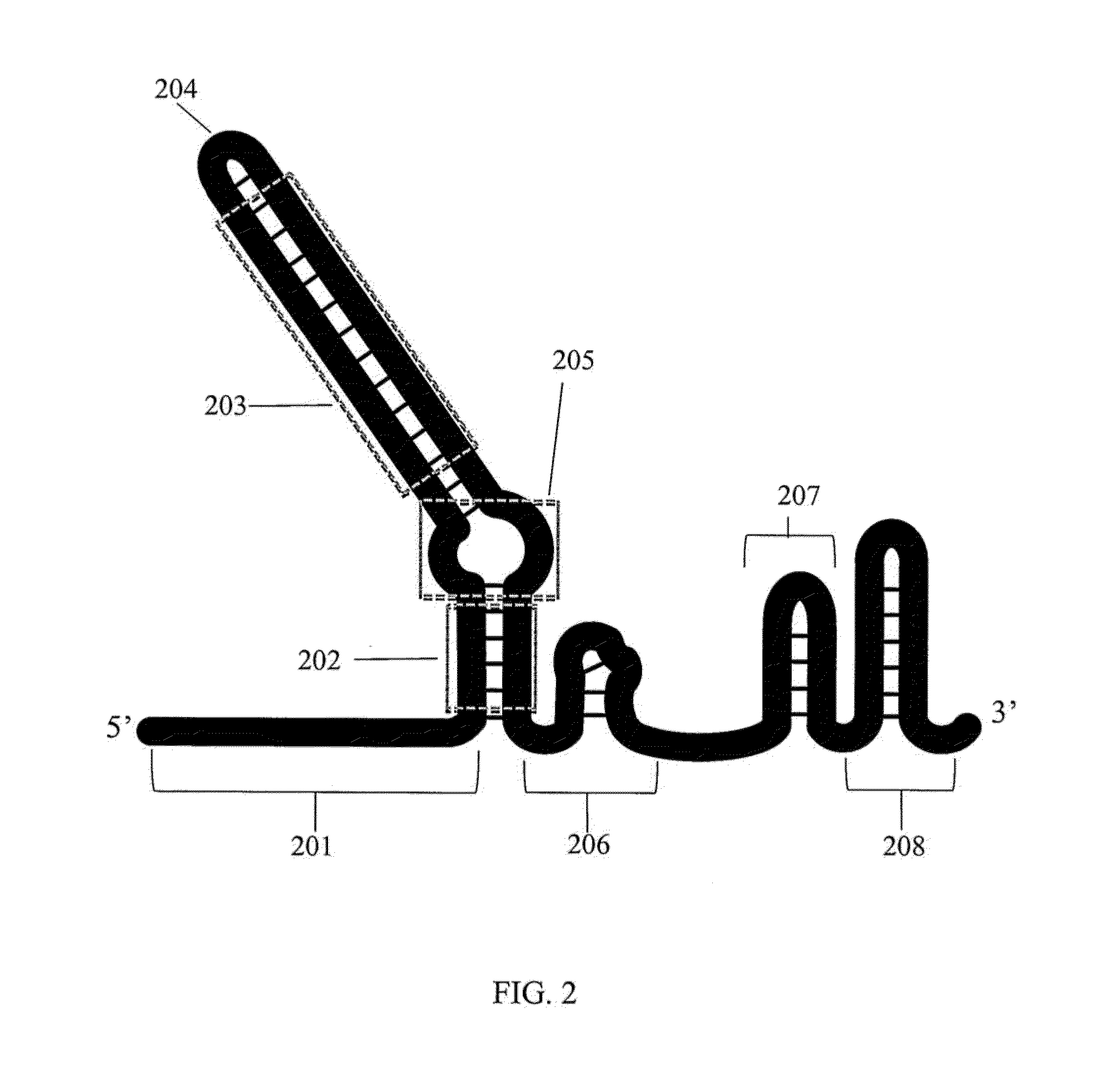
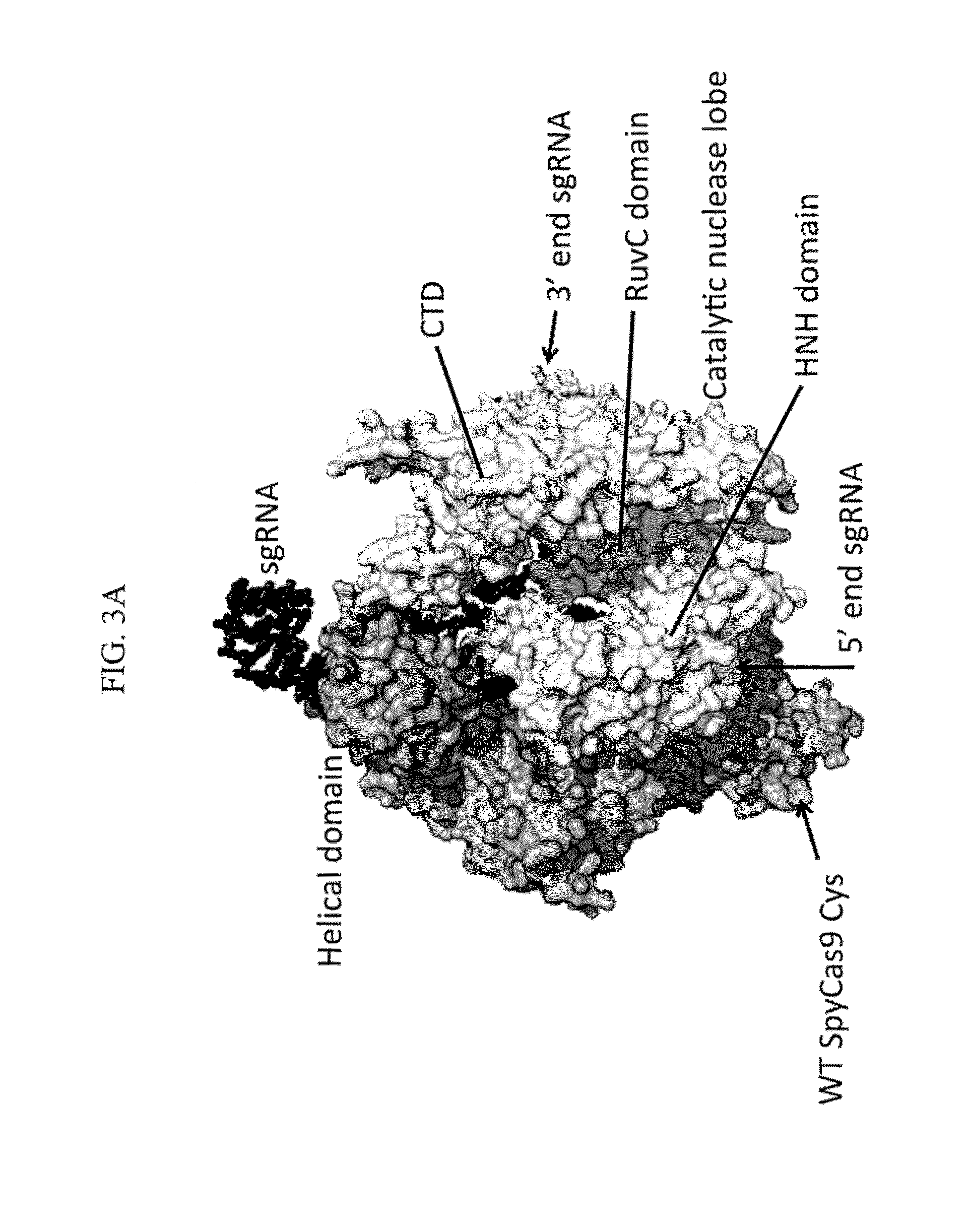
Allele editing and applications thereof
ActiveUS20190136263A1Low efficiencyMinimize possible side effectStable introduction of DNAMammal material medical ingredientsDNA constructAllele
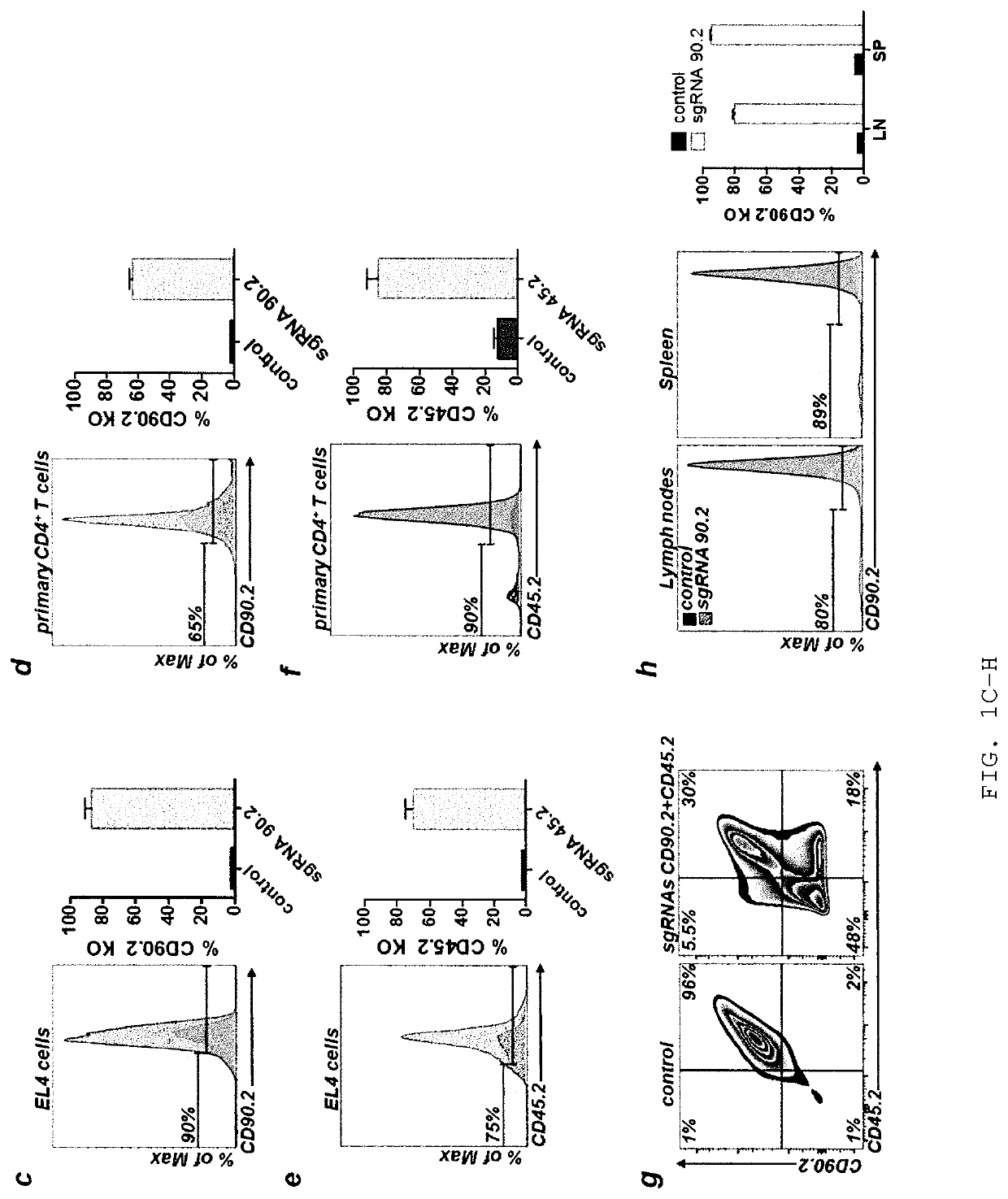
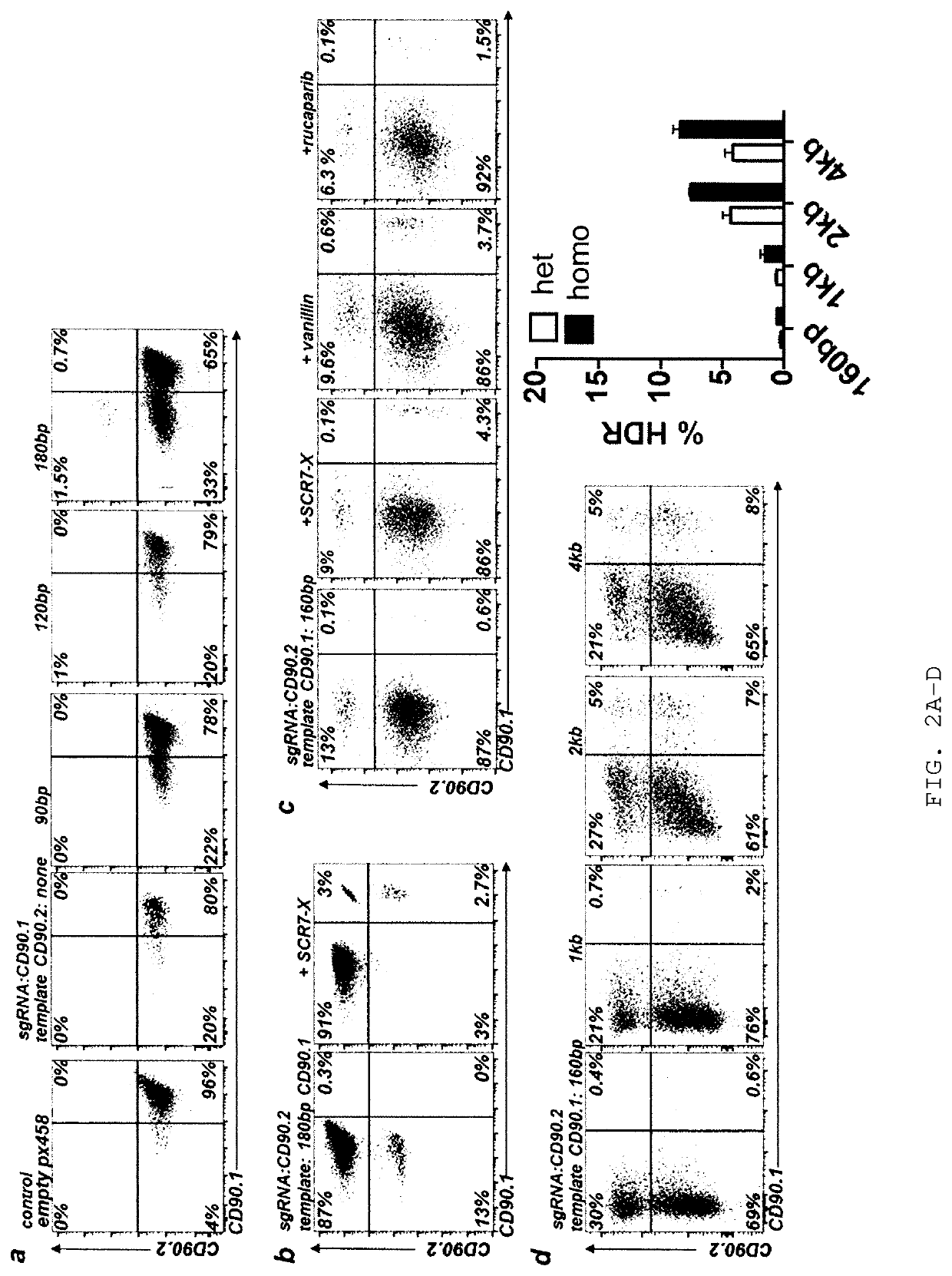
The invention relates to a method to determine a homology directed repair (HDR) event within a eukaryotic cell, wherein the cell expresses a first isoform of a surface protein, which is different from a second isoform of said surface protein with regard to an amino acid marker. The method comprises the steps of inducing a DNA double strand break, providing a HDR template DNA construct comprising the amino acid marker corresponding to the second isoform of the surface protein and subsequently determining the expression of the first or second isoform of said surface protein on said cell, wherein expression of the second isoform indicates a successful HDR event. The invention also relates to a method for editing a genomic location of interest within a eukaryotic cell, and to a method of selectively depleting or enriching an edited cell in a composition of non-edited and edited cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
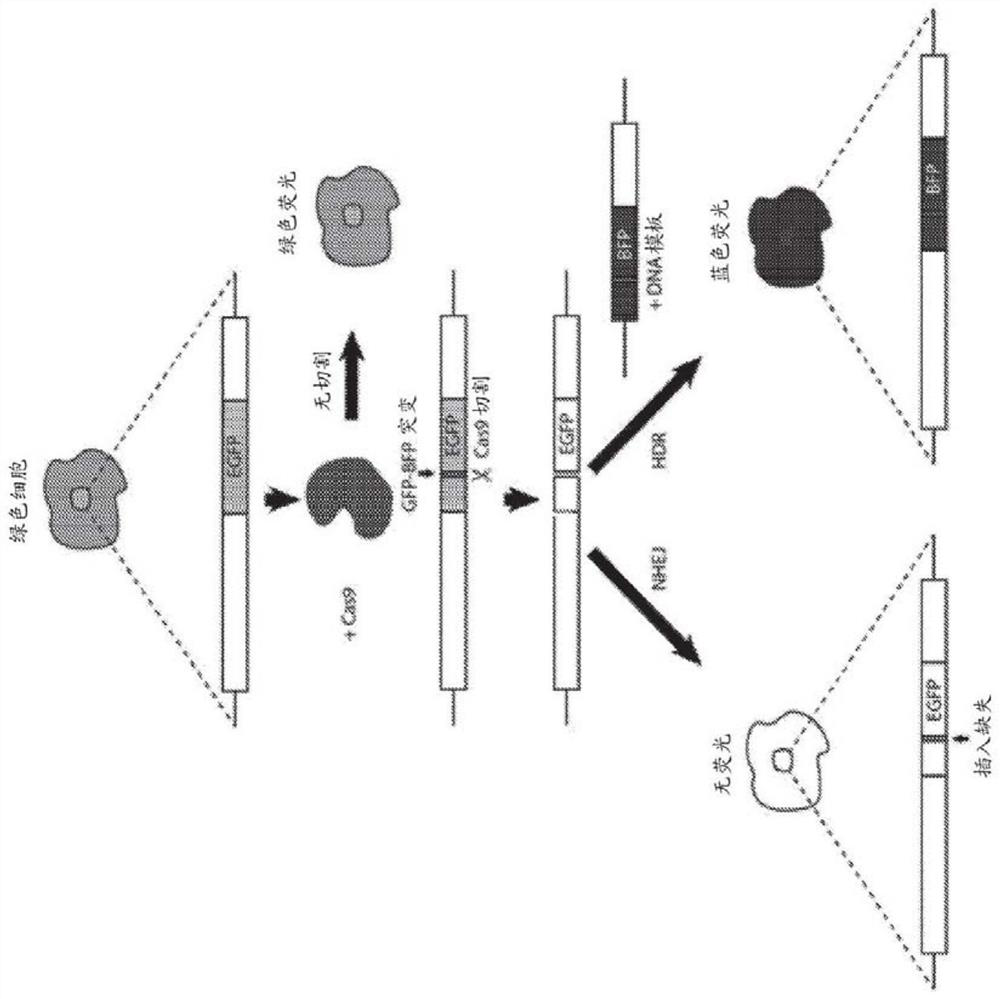
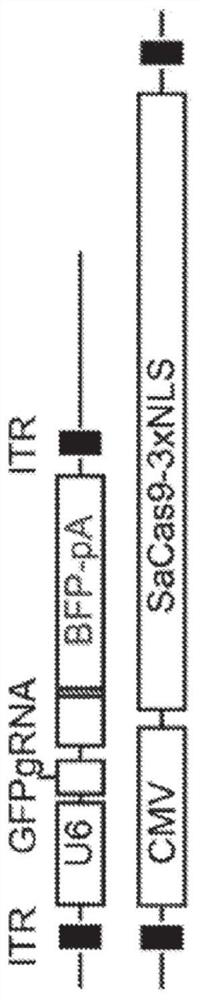
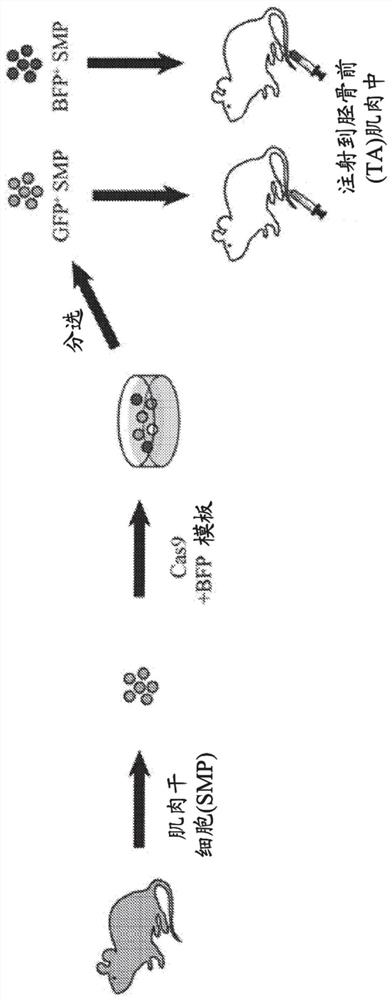
In vivo homology directed repair in heart, skeletal muscle, and muscle stem cells
PendingCN112512595AEasy to understandHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsCardiac muscleMuscle stem cell
Disclosed are methods of genomic modification of skeletal and cardiac muscle using sequence-targeting nucleases and a donor sequence delivered via a virus.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE 17 Q
Engineering of Humanized Kidney by Genetic Complementation
InactiveUS20190254266A1Animal reproductionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsEmbryoGenotype
Human or humanized tissues and organs suitable for transplant are disclosed herein. Gene editing of a host animal provides a niche for complementation of the missing genetic information by donor stem cells. Editing of a host genome to knock out or debilitate genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stage with donor stem cells to complement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a “niche” for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +2
Methods and materials for assessing loss of heterozygosity
ActiveUS9388472B2Raise the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsCancer cellRegimen
Owner:MYRIAD GENETICS +1
Compositions and methods for modifying a target nucleic acid
PendingUS20220017882A1Reduce deliveryImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainA-DNAAnionic polymers
The disclosure provides compositions and methods for modifying a target nucleic acid. In some embodiments, a composition can include a targetable nuclease, a DNA-binding protein, and a donor template comprising a homology directed repair (HDR) template and one or more DNA-binding protein target sequences. In some embodiments, a composition can include a Cas protein, one or more single guide RNAs (sgRNAs), and an anionic polymer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for performing and measuring homologous chromosome template repair
PendingUS20220325338A1Increase chanceEliminate riskHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHomologous chromosomeHomology directed repair
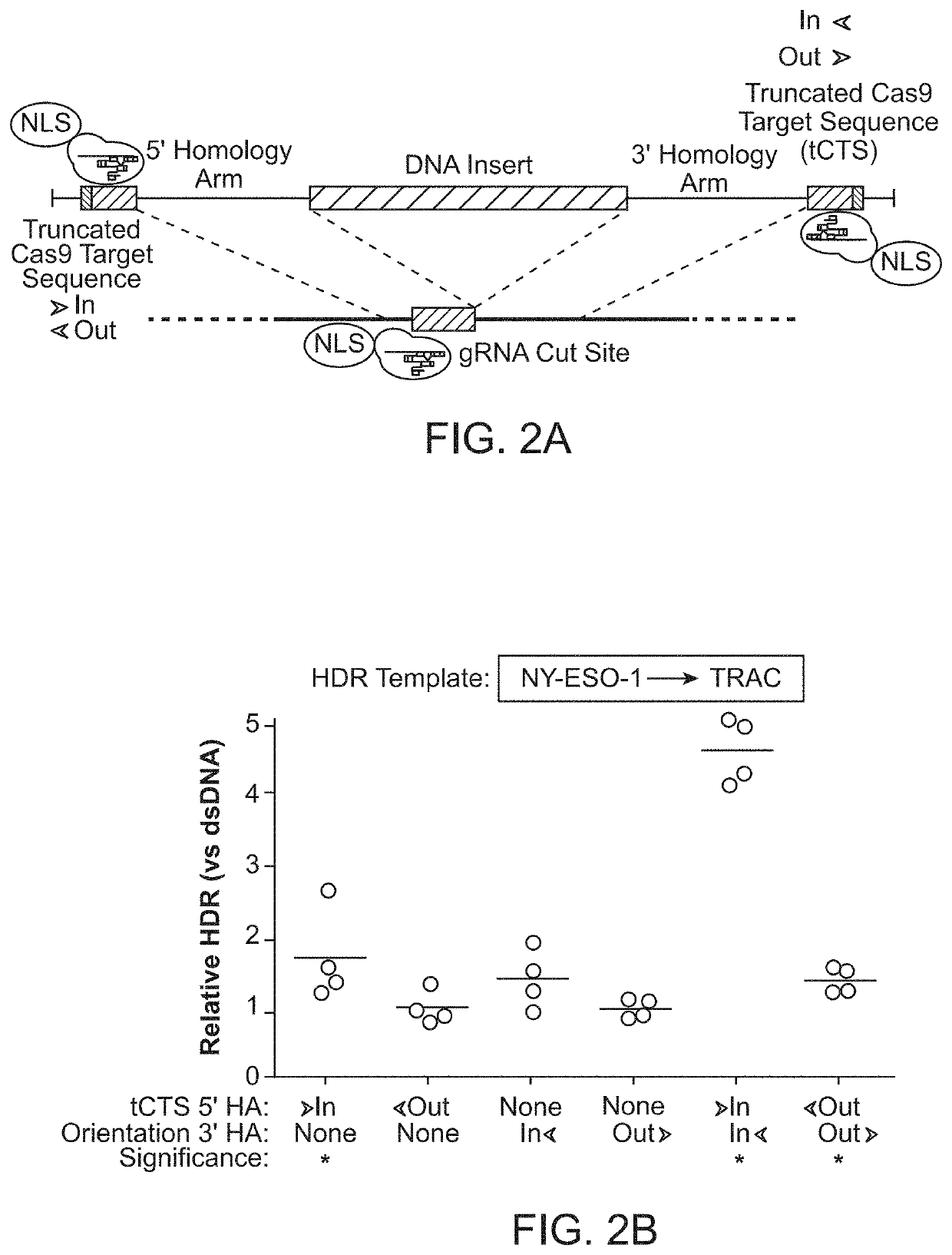
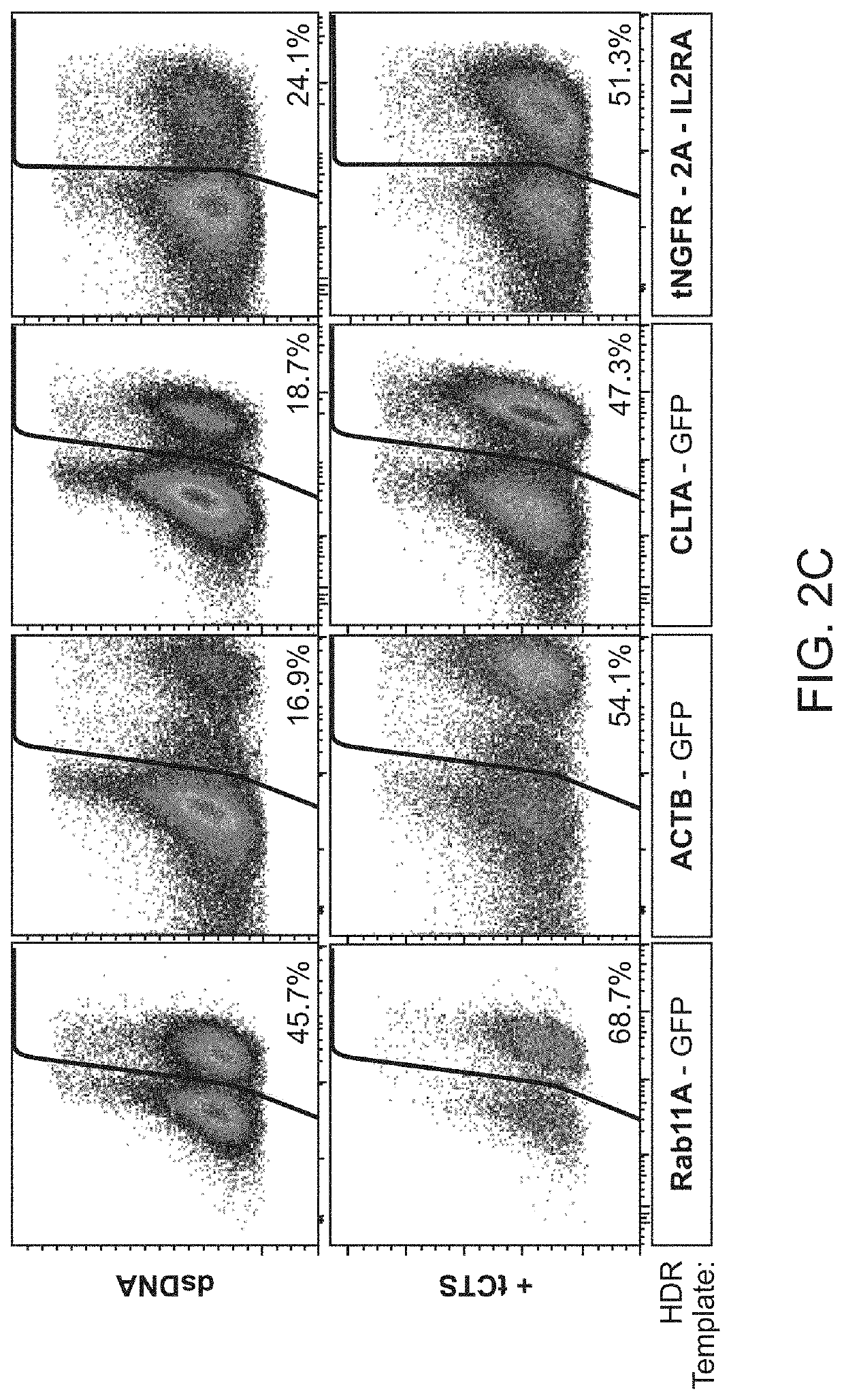
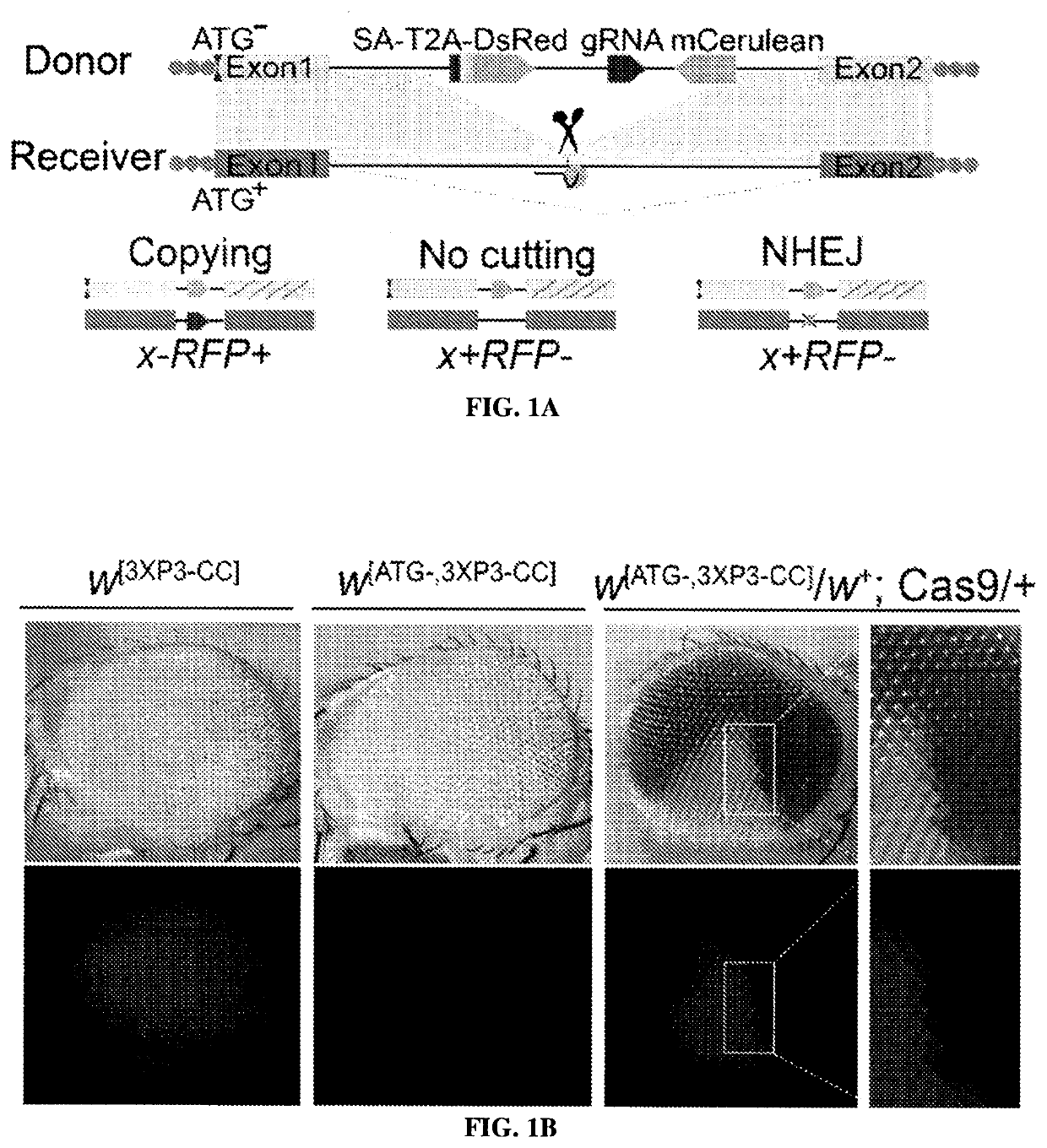
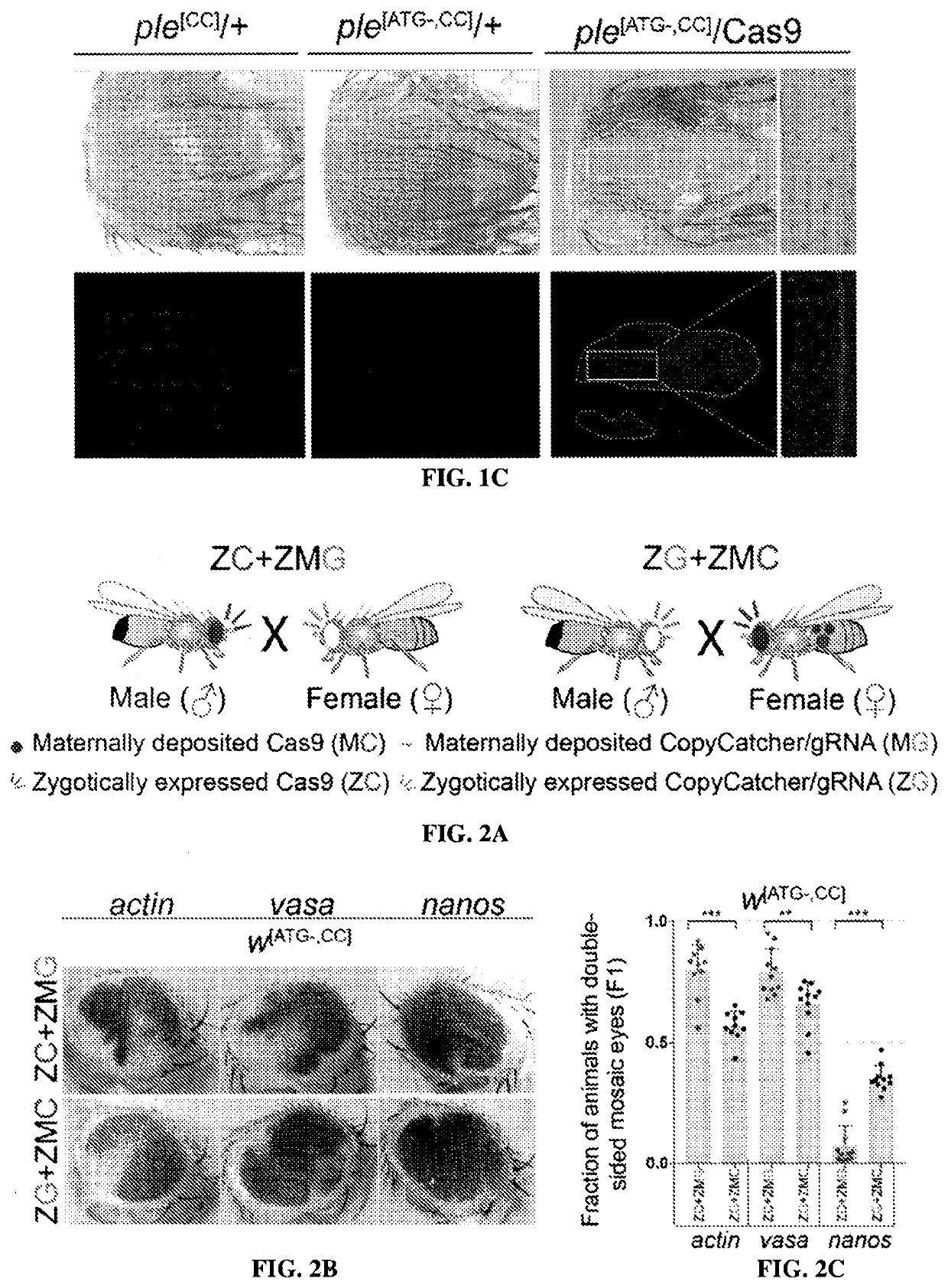
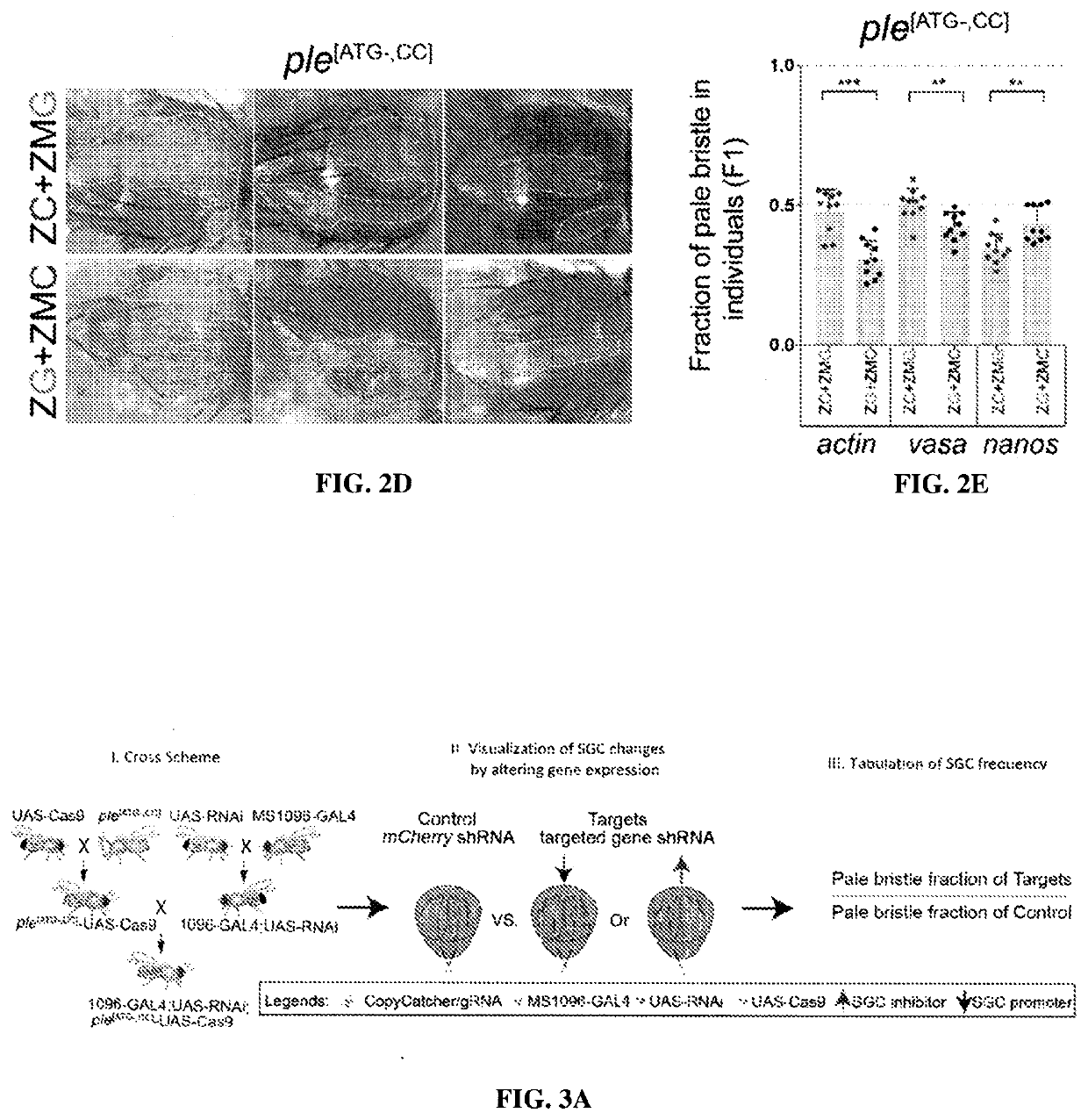
Provided herein are systems and methods for performing repair of mutant chromosomes in cells by using the homologous chromosome as a template for homology directed repair. Also provided herein are CopyCatcher systems, methods, and organisms for the study and measurement of homologous chromosome template repair and related mechanisms in cells and organisms.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for homology directed repair
Described are methods of homology directed repair (e.g., for treating a disease or disorder) and fusion proteins, polynucleotides (e.g., guide polynucleotides (e.g., guide RNAs) and polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins), vectors containing the polynucleotides, viral or non-viral delivery vehicles containing the vectors, and compositions (e.g., pharmaceutical compositions) containing the same for use in methods of homology directed repair.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Compositions for genome editing
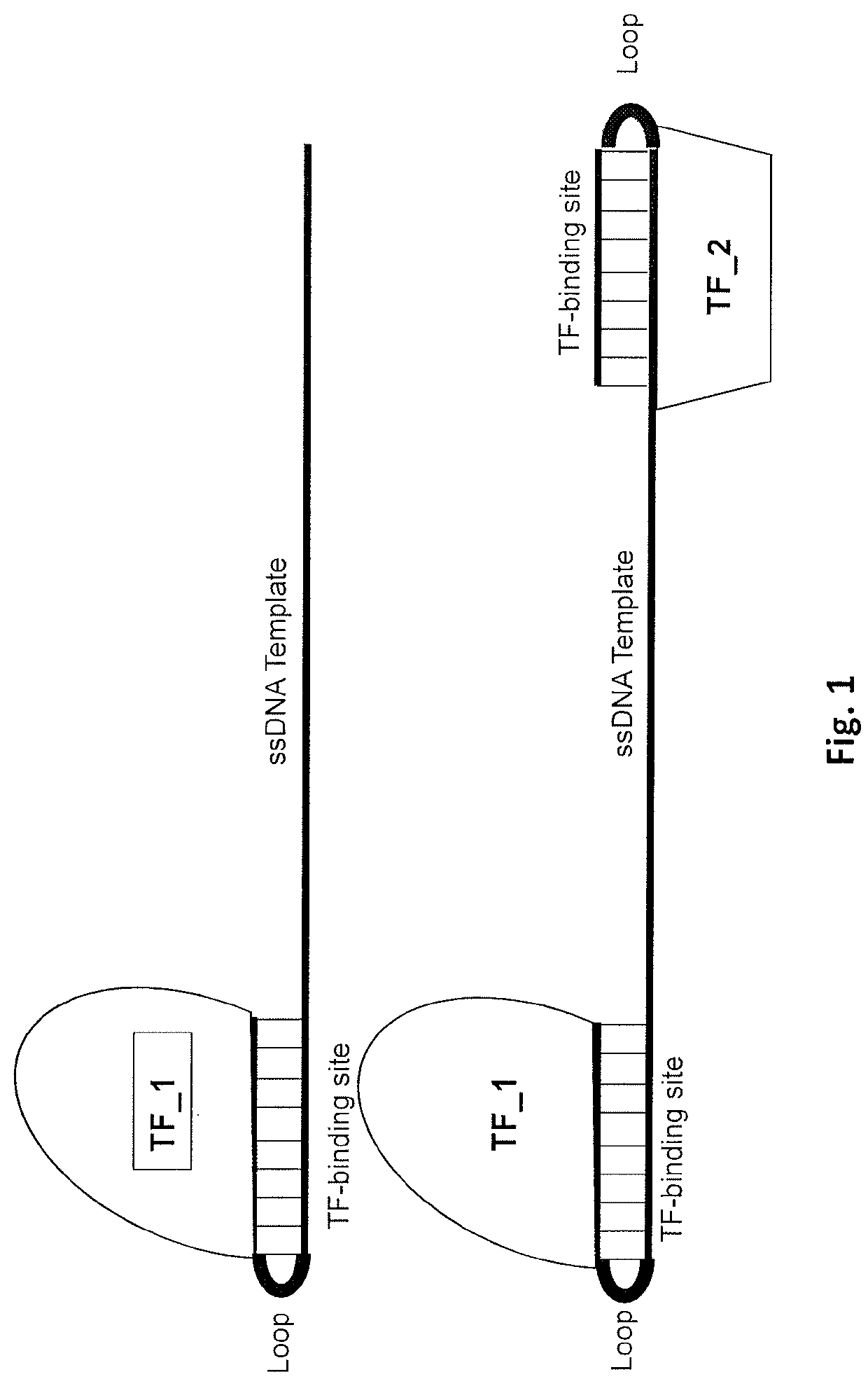
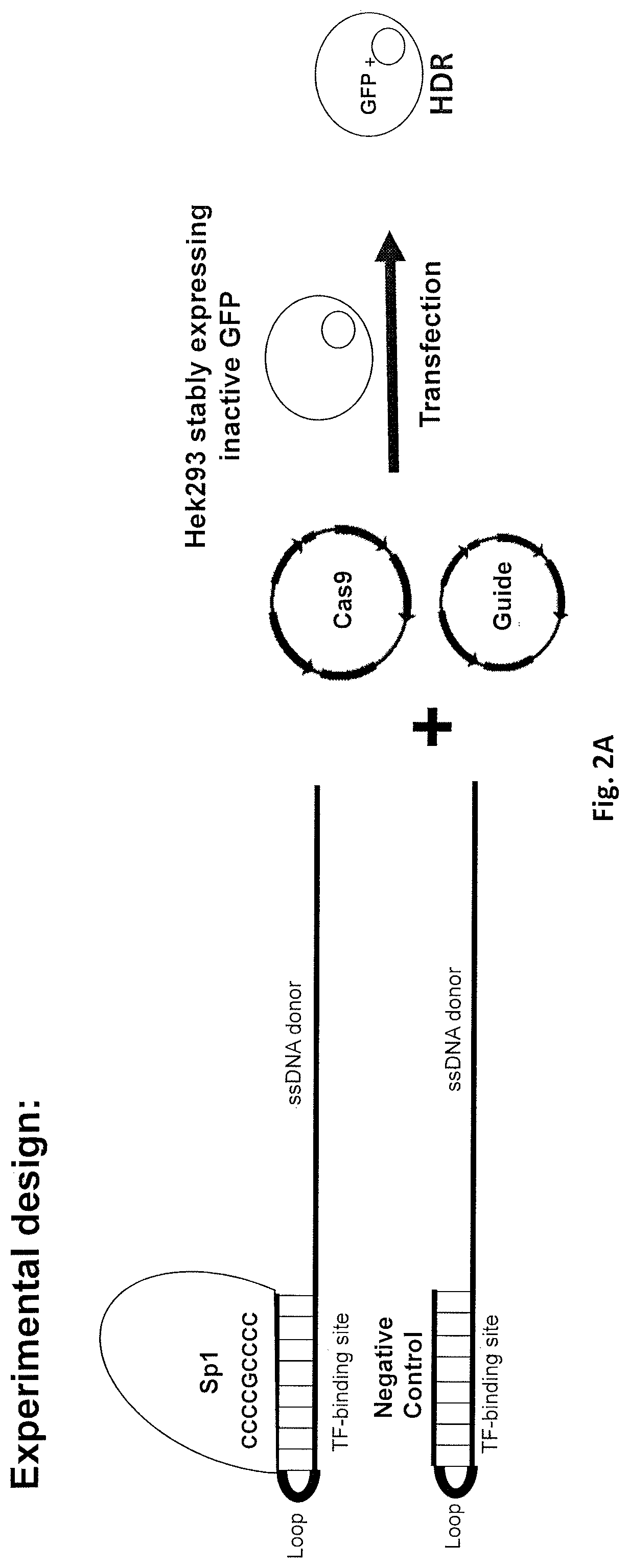
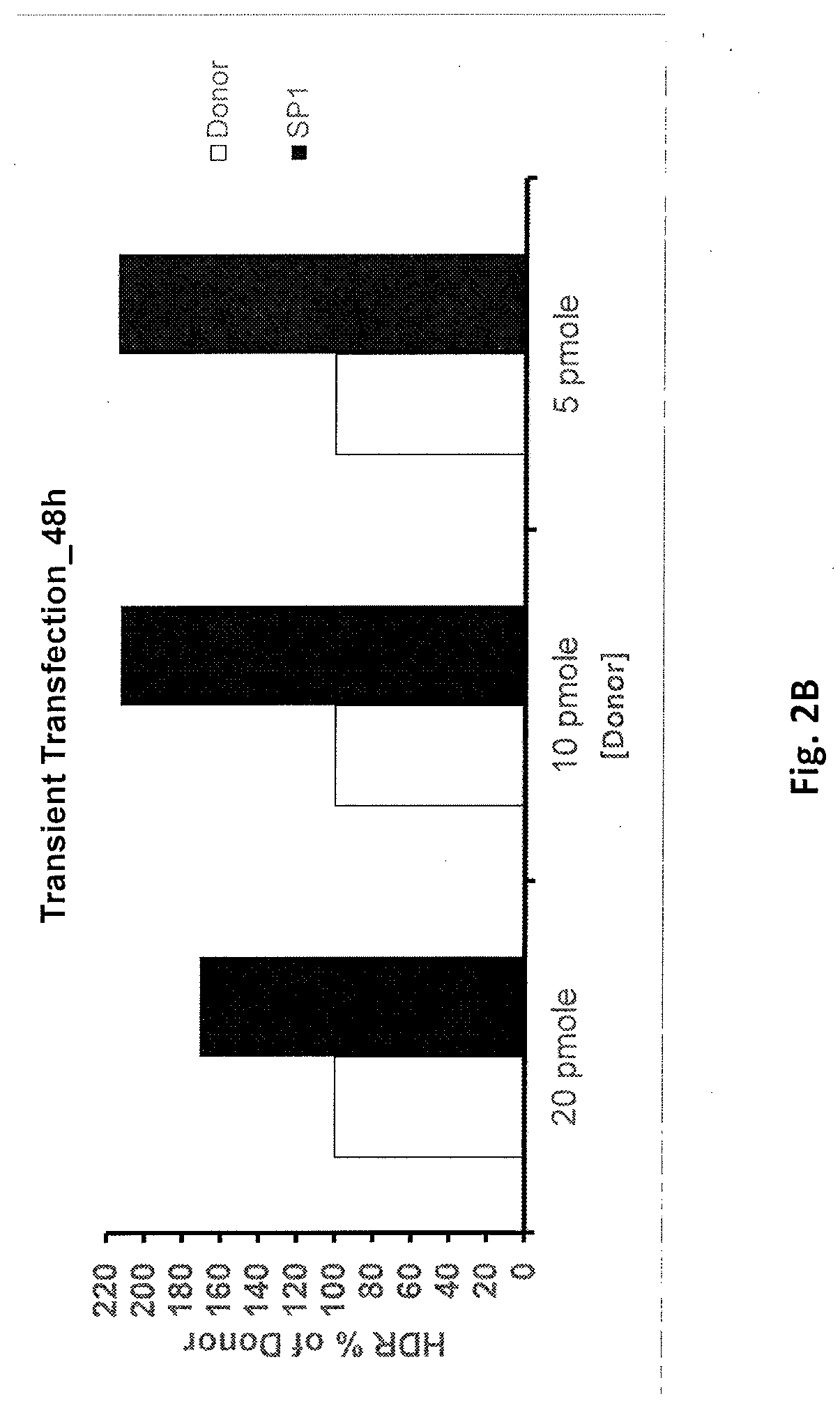
PendingUS20210371857A1Improve efficiencyPromote elevated HDR repair rateHydrolasesPeptidesGenome editingBinding site
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for increasing the rate of site specific insertion of a donor DNA sequence to the genome. More specifically, the method introduces a donor DNA template containing at least one transcription factor binding site to a cell in order to favor specific insertion of a donor template sequence at a target site by homology directed repair (HDR).
Owner:EMENDOBIO INC
Allele editing and applications thereof
ActiveUS11499168B2Low efficiencyMinimize possible side effectGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNADNA constructHomology directed repair
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Methods and compositions for enhanced nuclease-mediated genome modification and reduced off-target site effects
InactiveUS20180362961A1Microbiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGeneticsHomology directed repair
Compositions and methods are provided for editing nucleotides or altering target sites in the genome of a cell. The methods and compositions employ a guide RNA / Cas endonuclease system and at least one component selected from the group consisting of (i) an inhibitor of end joining (NHEJ), (ii) an activator of homology-directed repair (HDR) or (iii) any one combination of (i) and (ii), to provide an effective system for editing nucleotides or altering target sites within the genome of a cell. The present disclosure also describes methods for editing a nucleotide sequence in the genome of a microbial cell employing a guide RNA / Cas endonuclease system and at least one component selected from the group consisting of (i) an inhibitor of NHEJ, (ii) an activator of HDR, or (iii) any one combination of (i) and (ii), wherein said microbial cell has reduced or no off-target site effects.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Engineering of humanized car t-cell and platelets by genetic complementation
Human or humanized tissues and organs suitable for transplant are disclosed herein. Gene editing of a host animal provides a niche for complementation of the missing genetic information by donor stem cells. Editing of a host genome to knock out or disrupt genes responsible for the growth and / or differentiation of a target organ and injecting that animal at an embryo stage with donor stem cells to complement the missing genetic information for the growth and development of the organ. The result is a chimeric animal in which the complemented tissue (human / humanized organ) matches the genotype and phenotype of the donor. Such organs may be made in a single generation and the stem cell may be taken or generated from the patient's own body. As disclosed herein, it is possible to do so by simultaneously editing multiple genes in a cell or embryo creating a “niche” for the complemented tissue. Multiple genes can be targeted for editing using targeted nucleases and homology directed repair (HDR) templates in vertebrate cells or embryos.
Owner:RECOMBINETICS INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com