Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "First tarsal bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
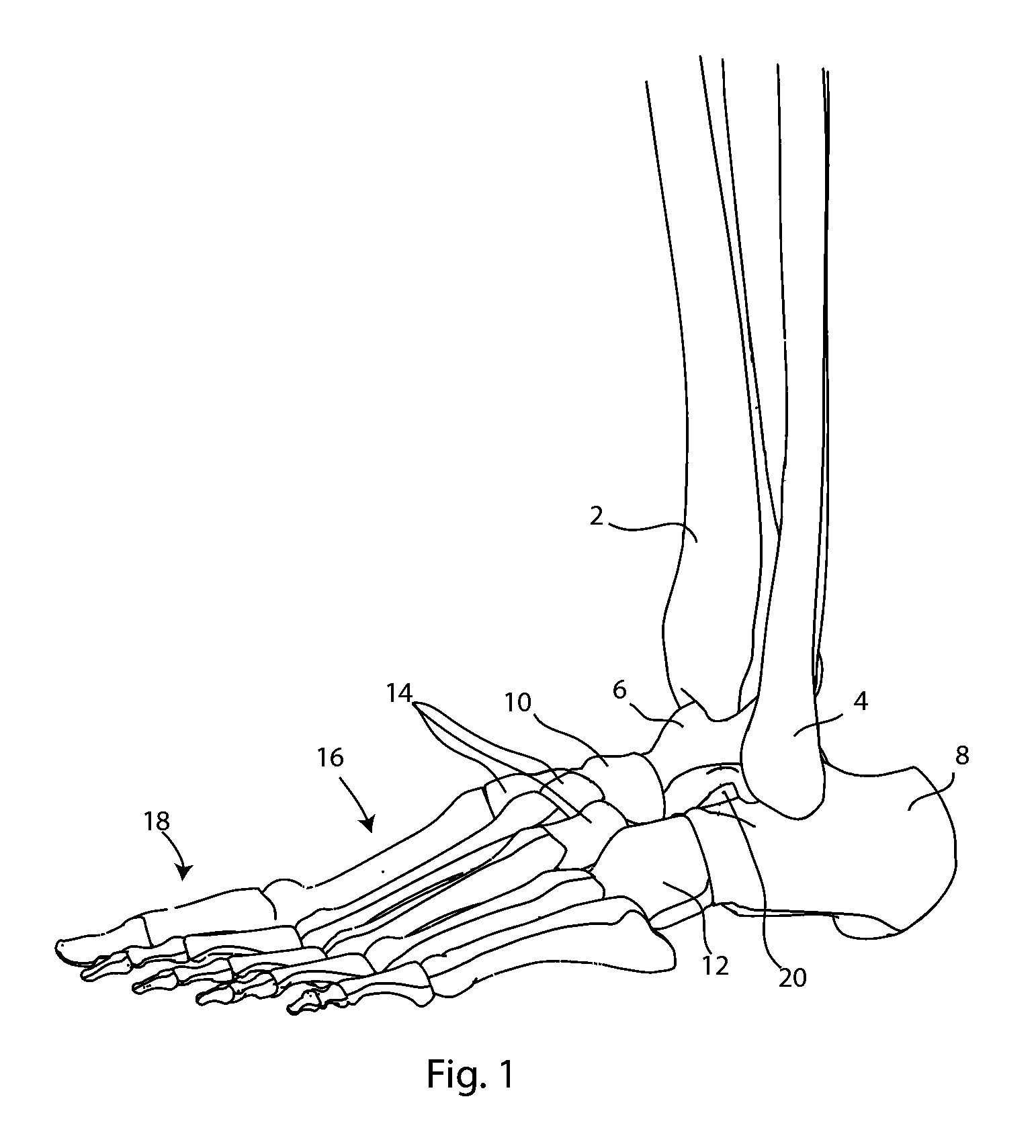
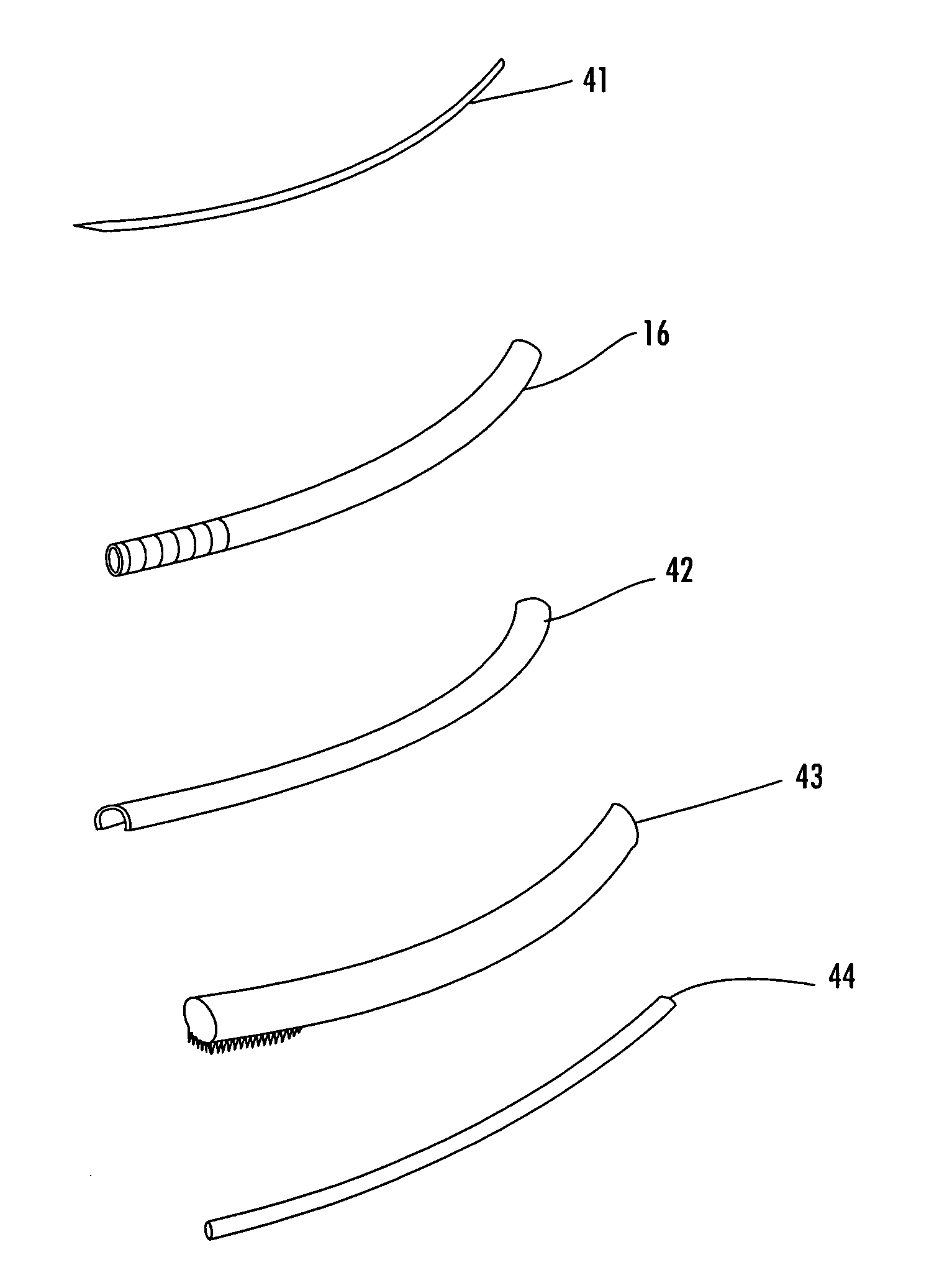
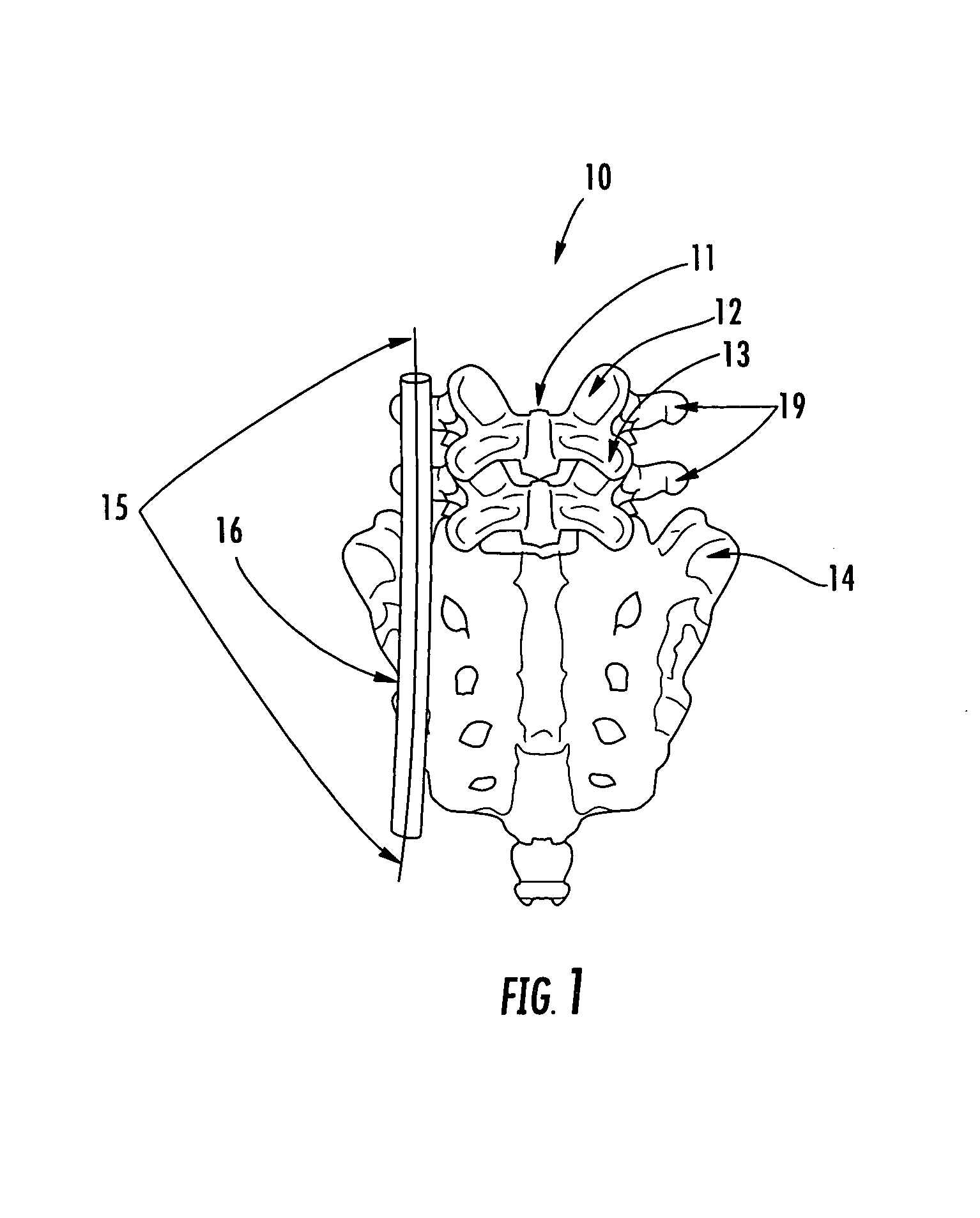
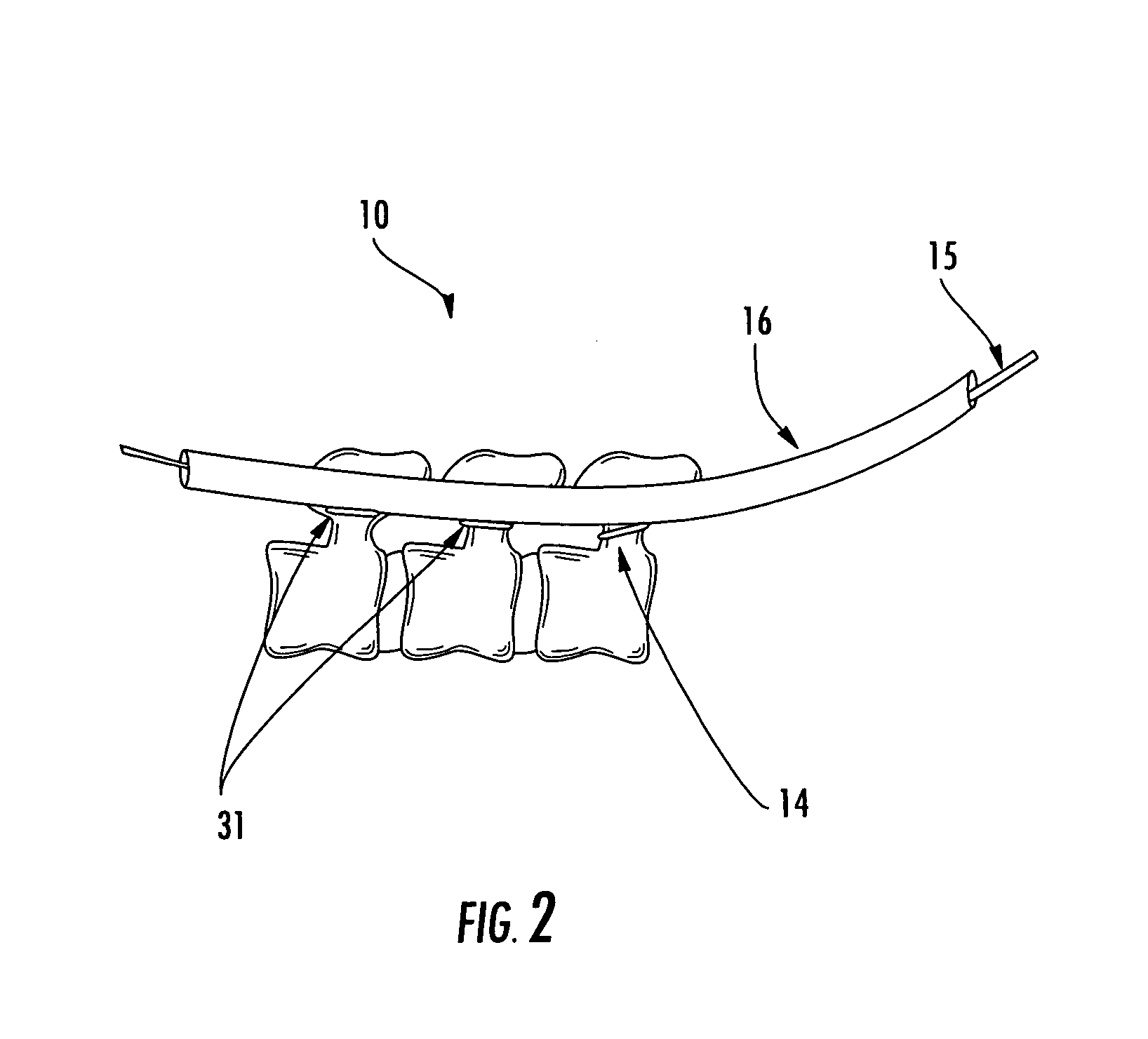
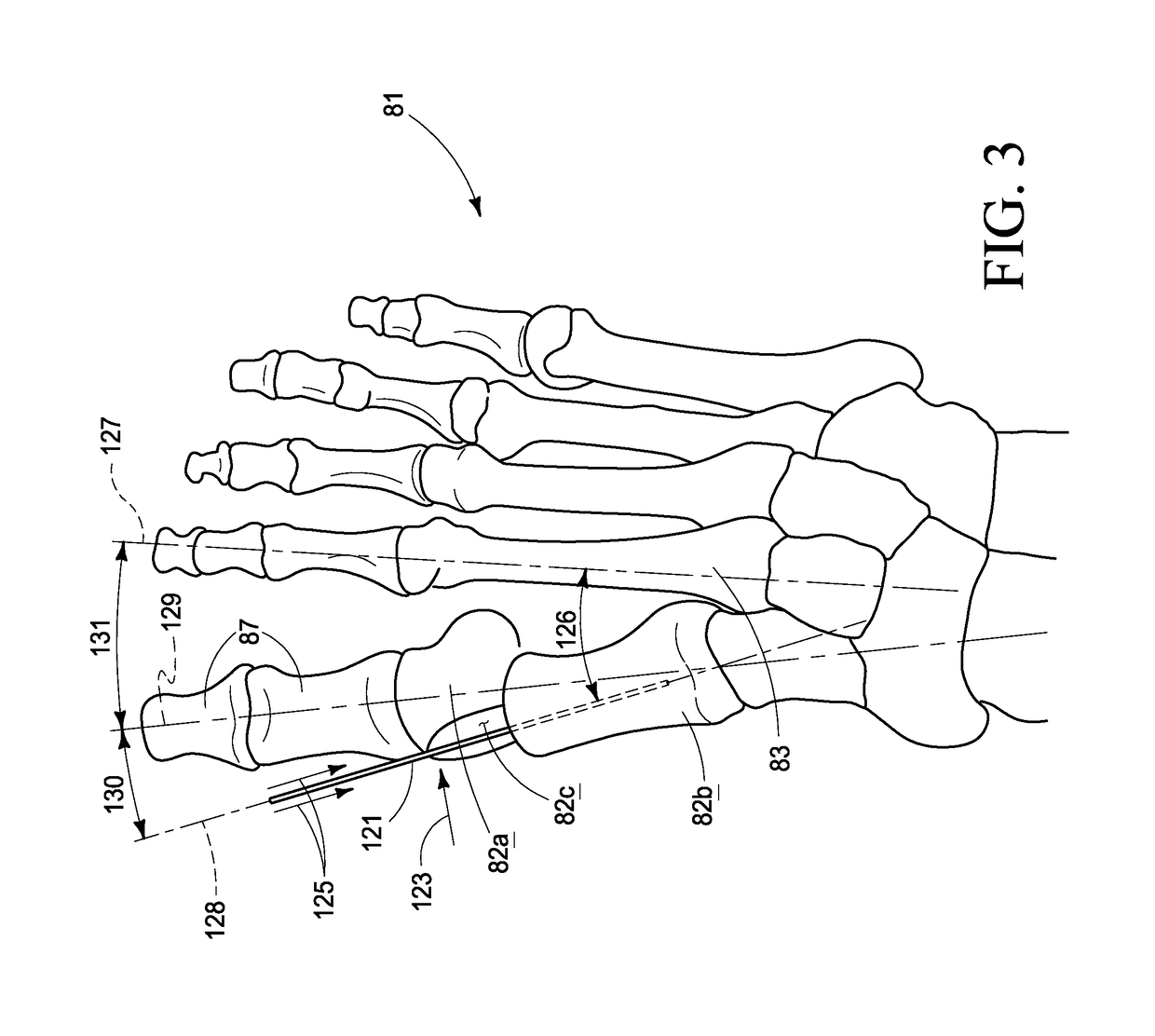
The base of each of the metatarsal bone articulates with some of the tarsal bones, while the head articulates with the first row of Phalanges. The bone in the foot just behind the big toe is the 1st metatarsal bone. It is the shortest but the thickest among the group of metatarsal bones.
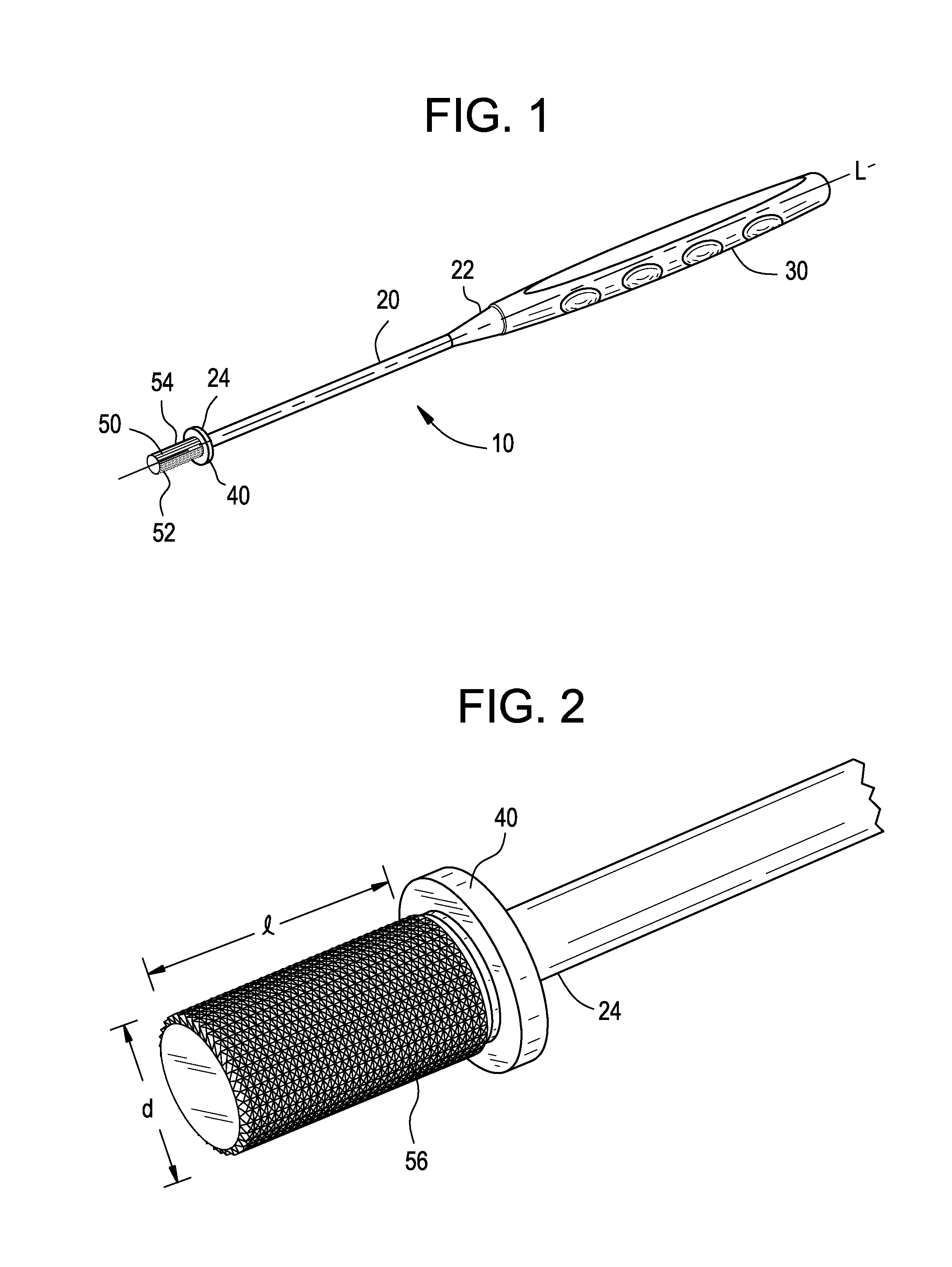
Hammertoe implant
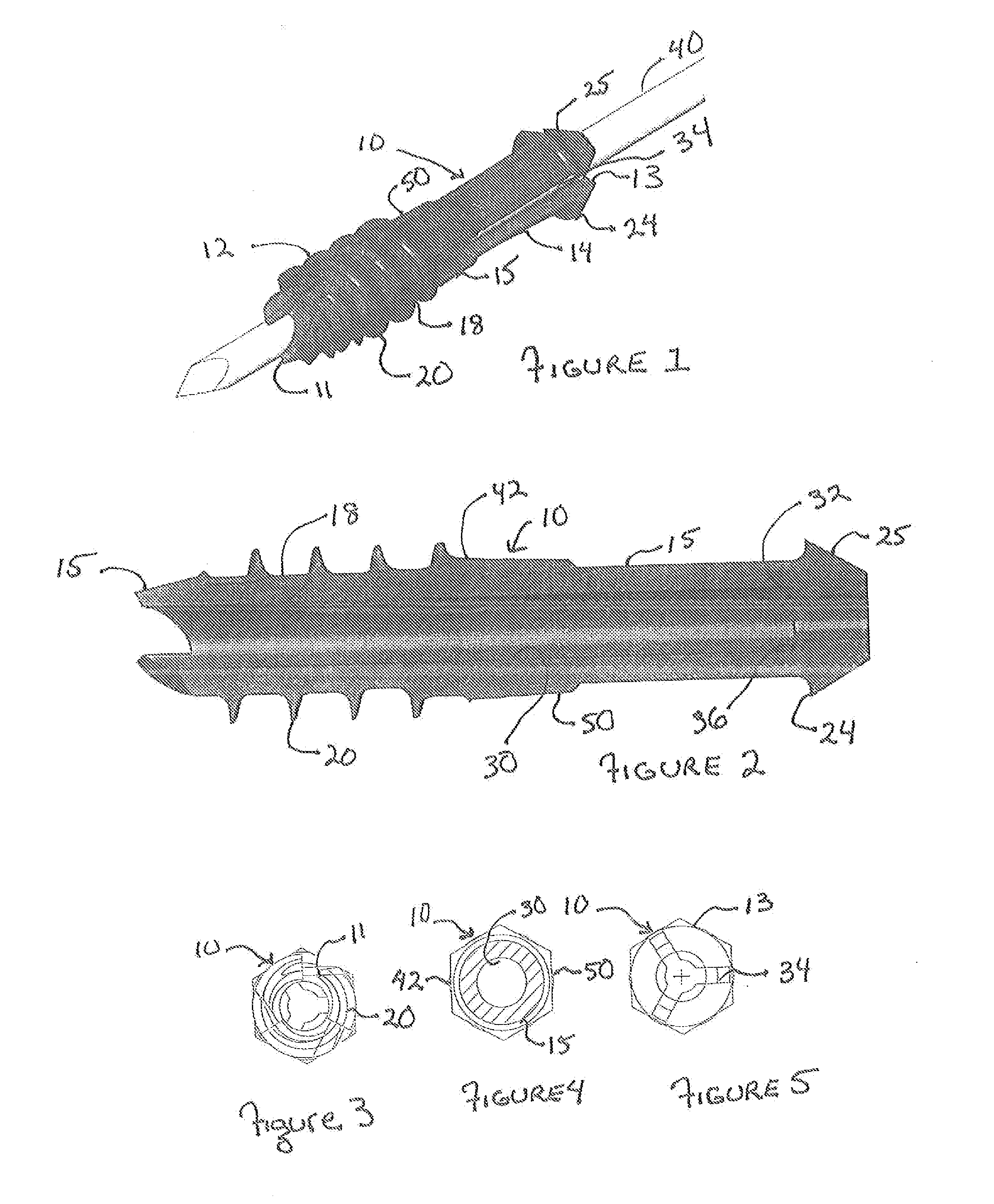
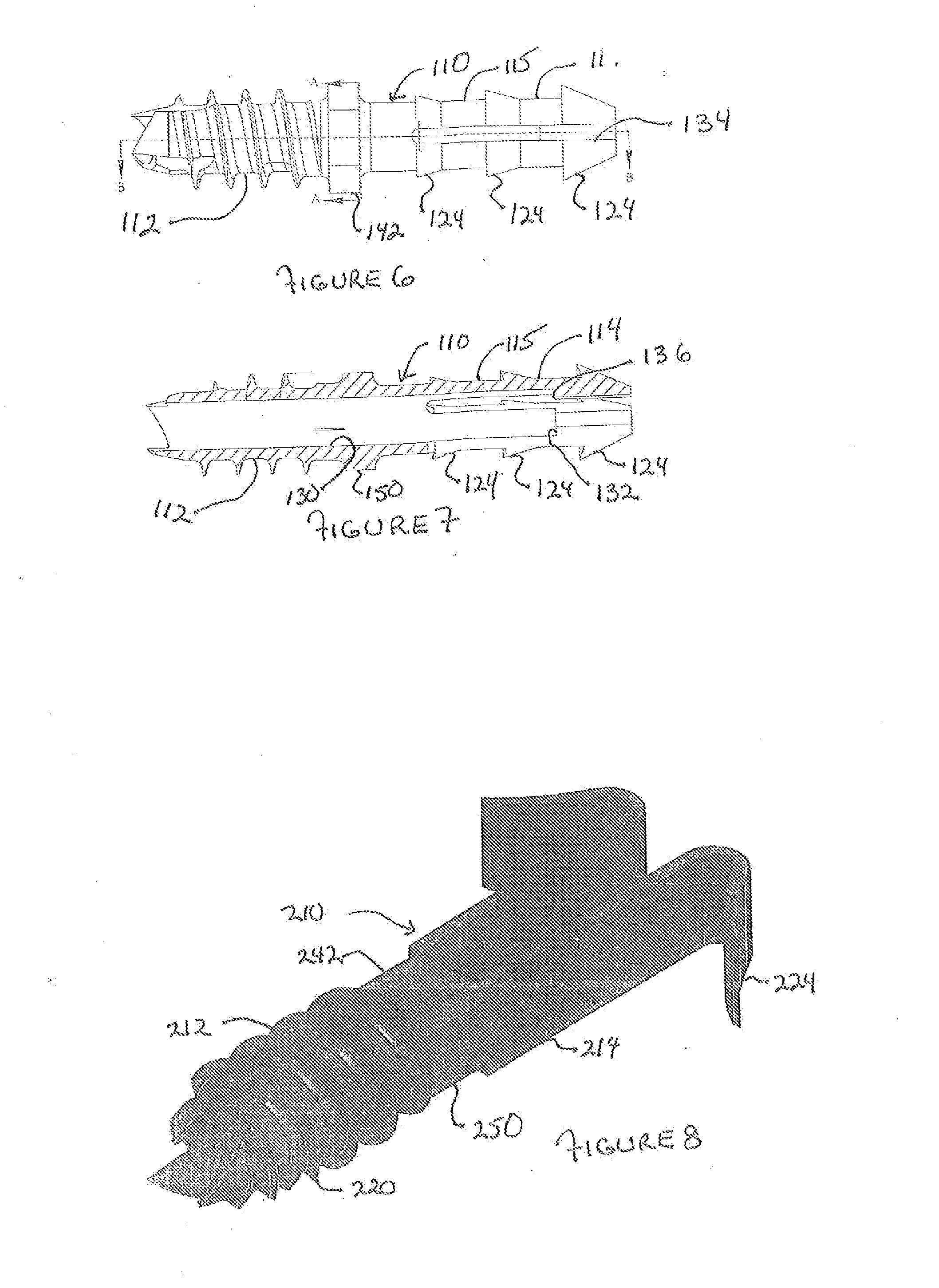
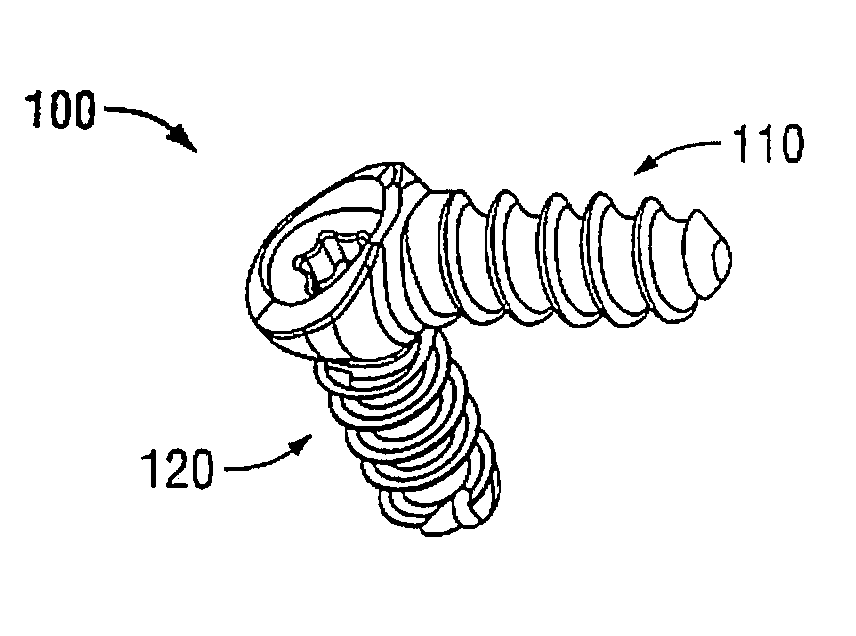
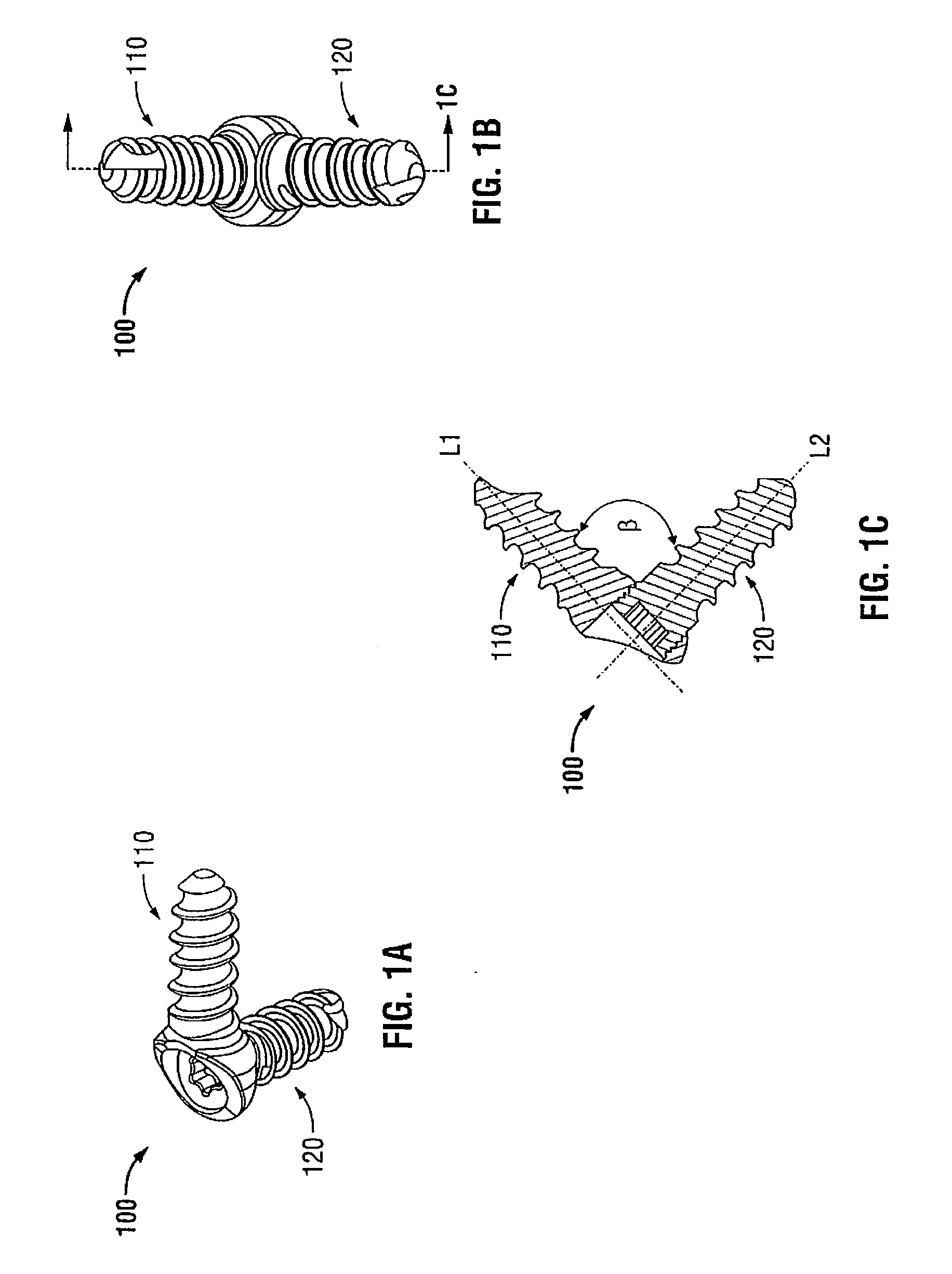
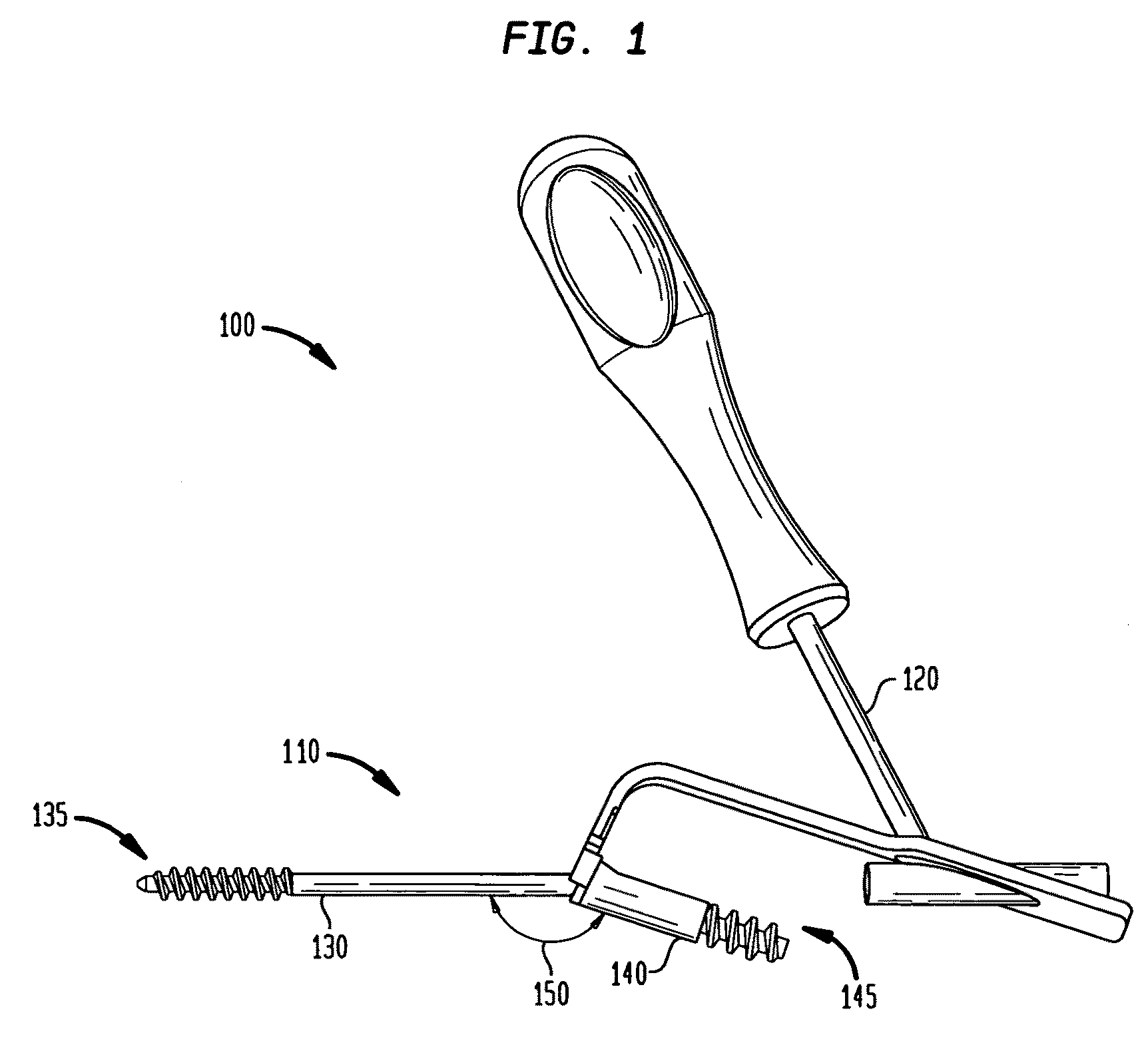
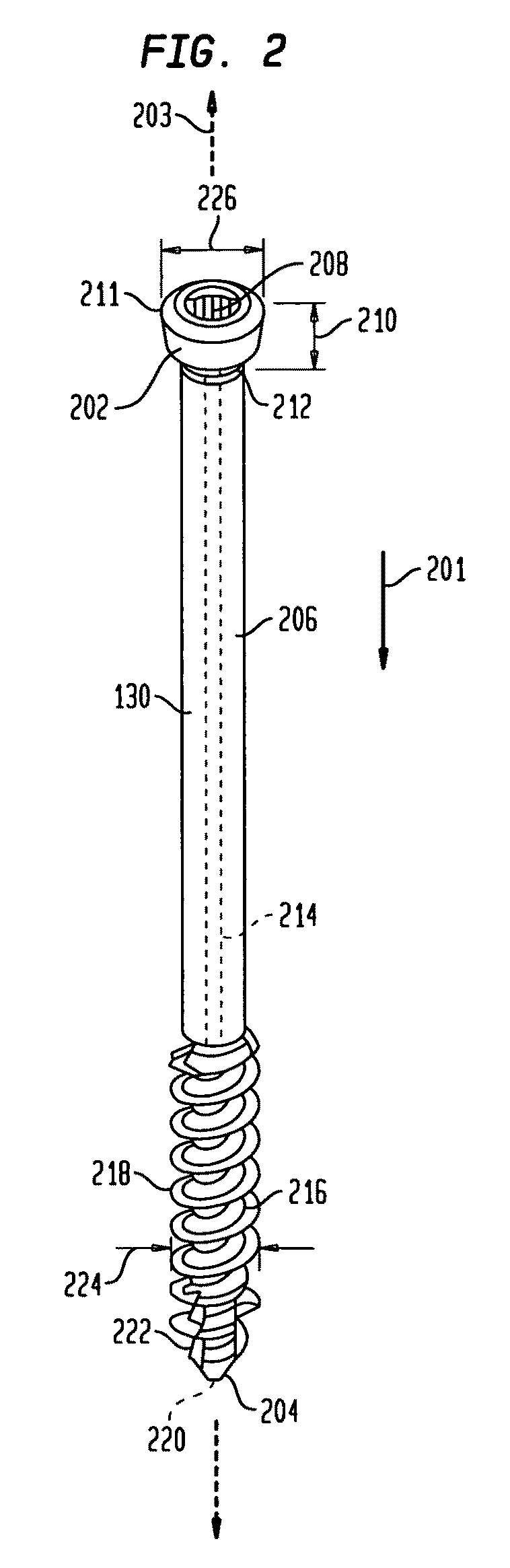
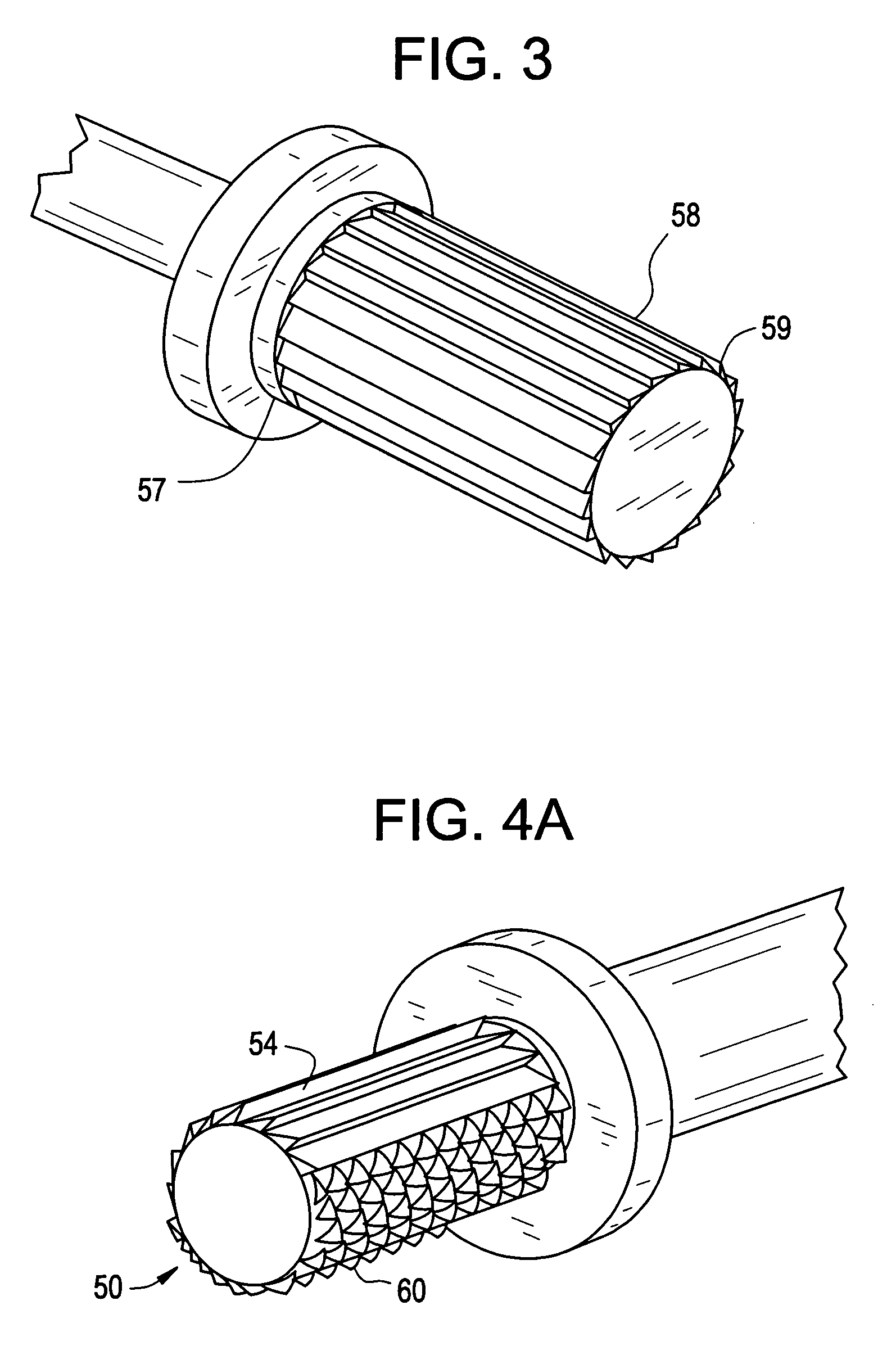
The invention comprises an implant having a first end section and a second end section, where the first end has a cancellous thread for implantation in a first section of bone and the second end includes expansion slots and barbs or wings, that that resist movement out of a second section of bone. These anchors expand outwardly when a rigid wire, such as a k-wire is fed through a central cannulation in the implant and either the wire expands in diameter or the cannulation decreases in diameter. The implant also includes a collar intermediate to the first and second section which includes one or more surfaces to allow the first section to be screwed into a first bone section.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
Joint Arthrodesis and Arthroplasty
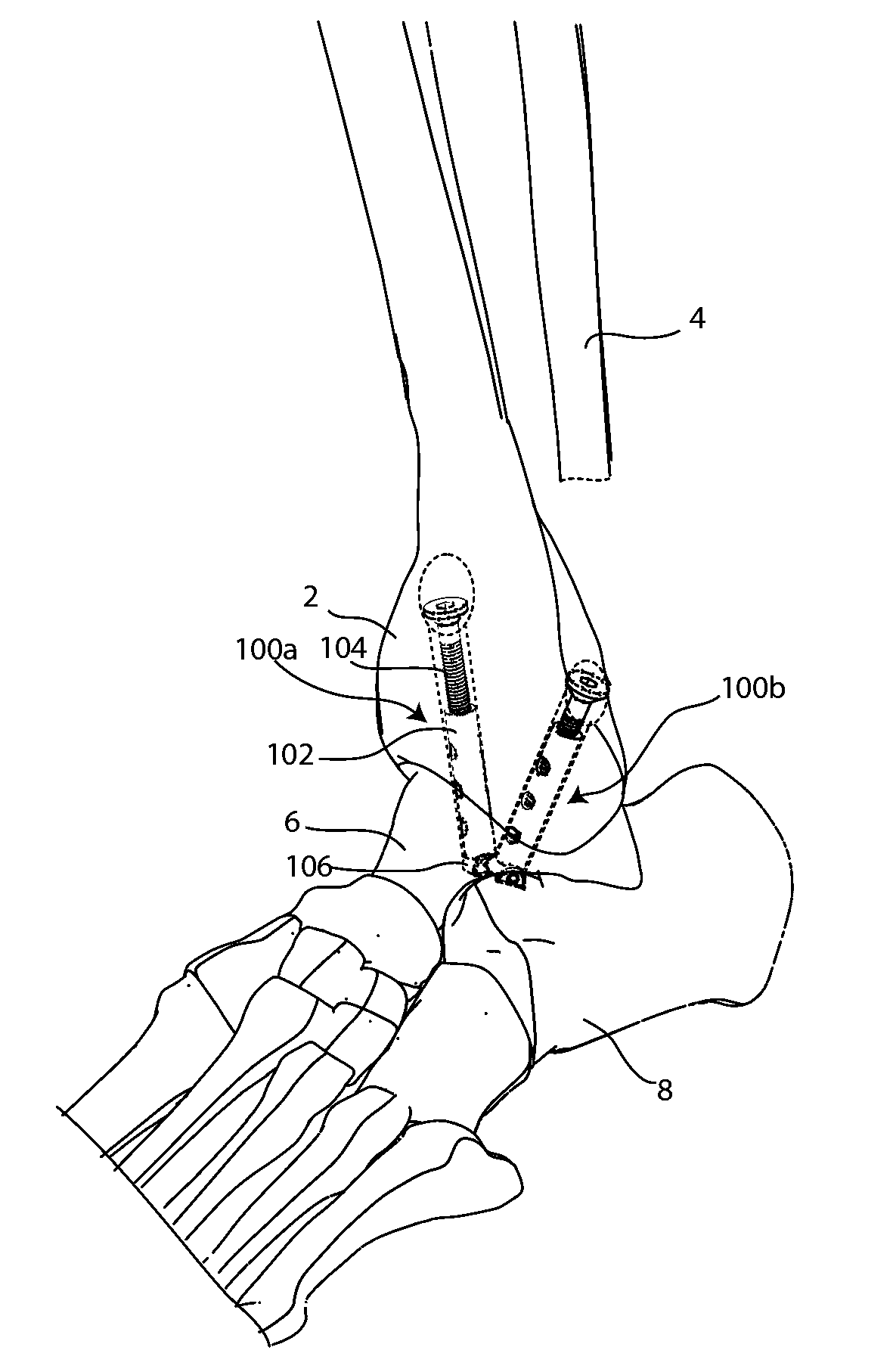
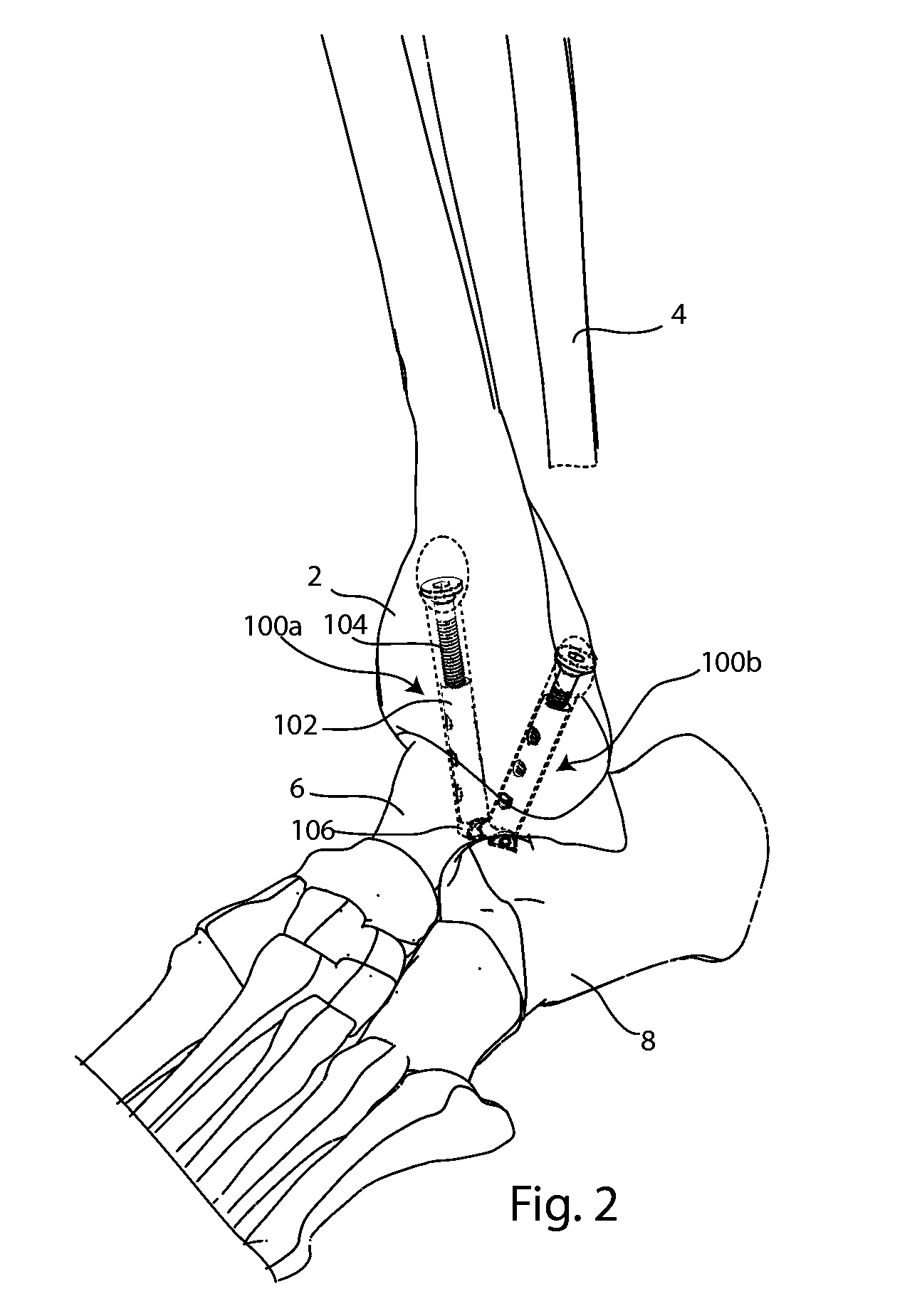
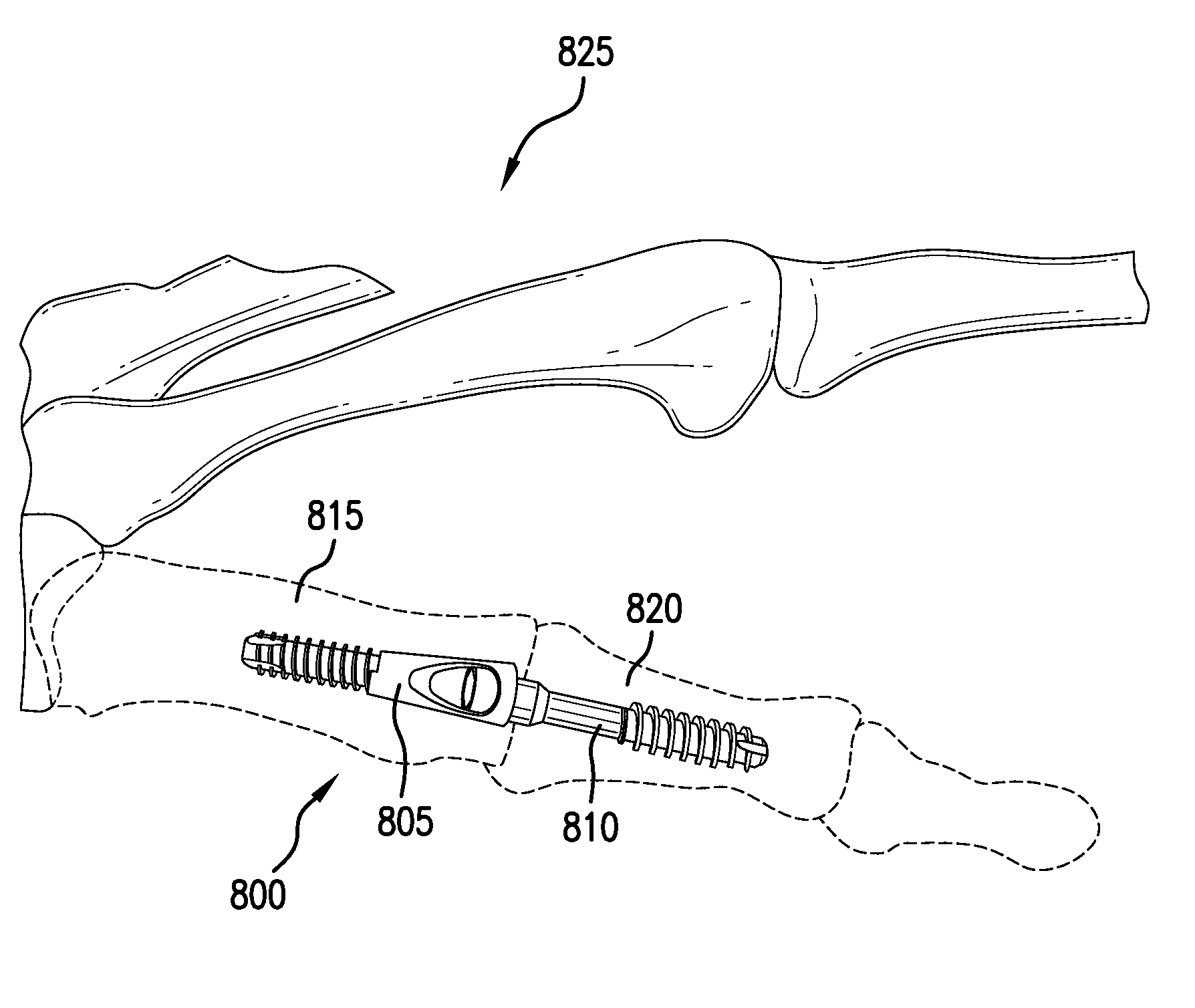
An implantable fixation system for fusing a joint between a first bone and a second bone. The system may include an anchor, standoff, bolt, and cortical washer. The system may be implanted across the joint along a single trajectory, the length of the system adjustable to provide compressive force between the anchor and the cortical washer. The system may be implanted across a tibiotalar joint with the anchor positioned in the sinus tarsi. A spacing member may be inserted between the two bones and the fixation system implanted to extend through an opening in the spacing member. The spacing member may be anatomically shaped and / or provide deformity correction. An ankle arthroplasty system may include a tibial plate, a talar plate, and a bearing insert. The plates may be anchored to the tibia and talus along a single trajectory. The ankle arthroplasty system may be revisable to a fusion system.
Owner:MEDICINELODGE +1
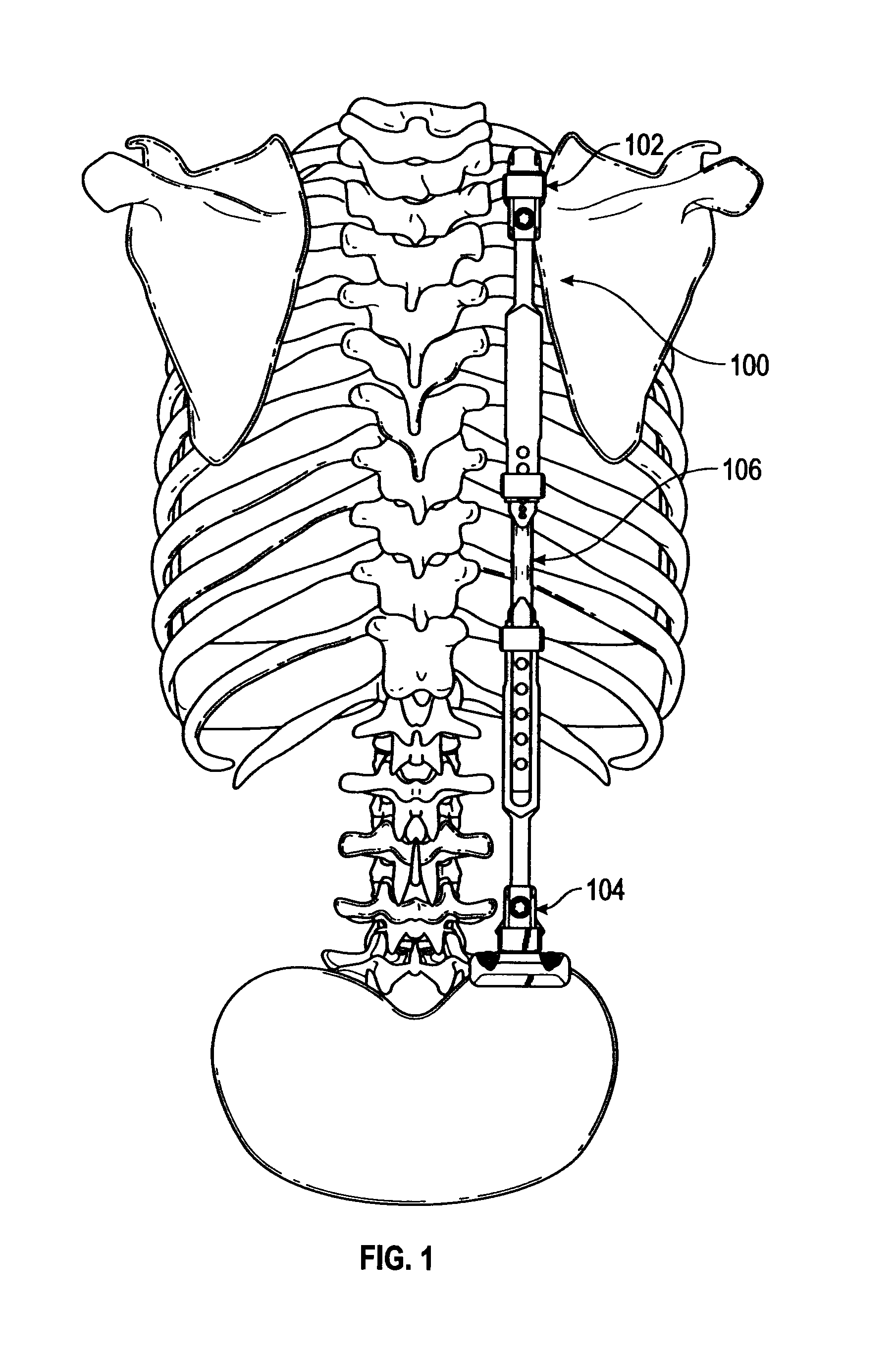
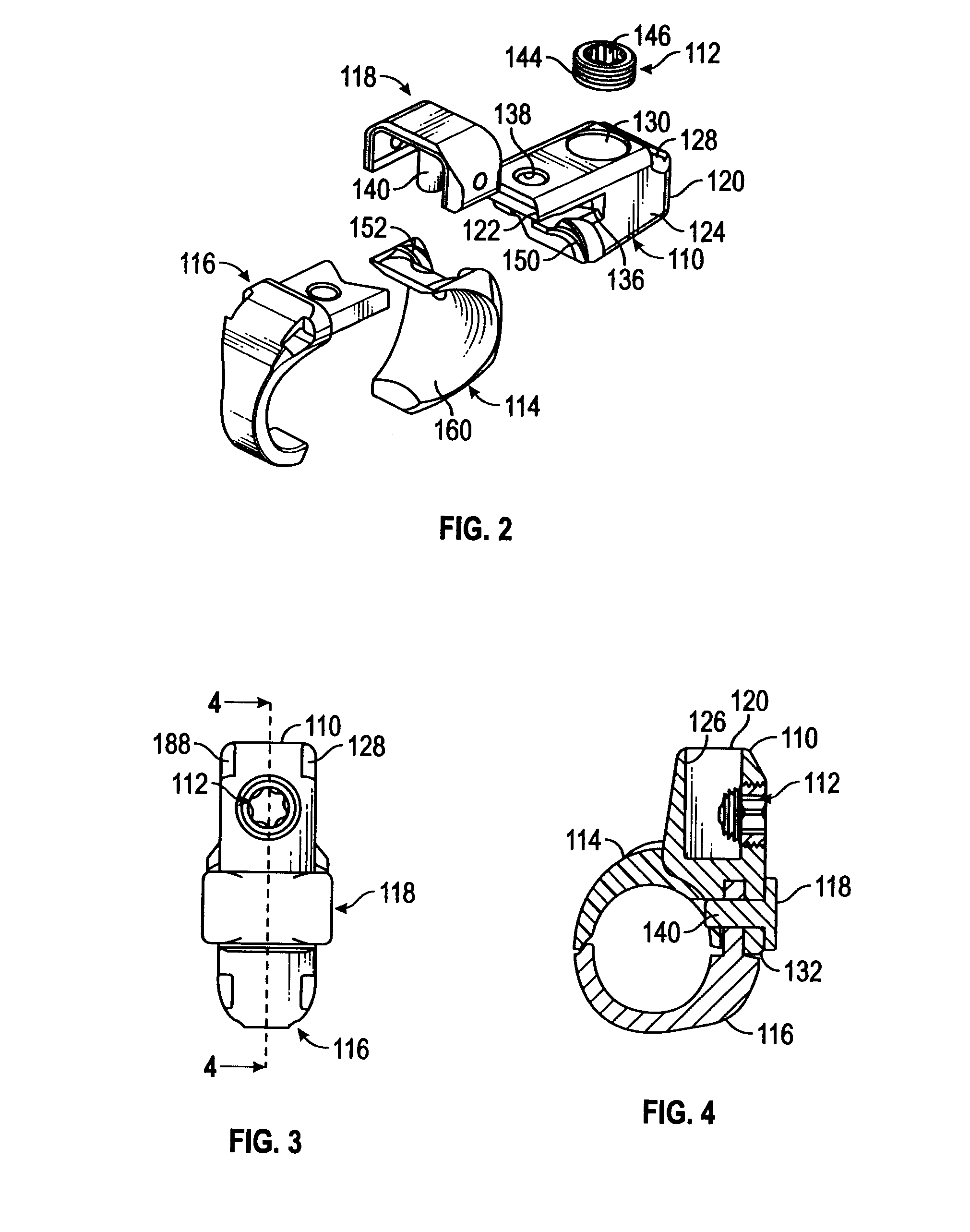
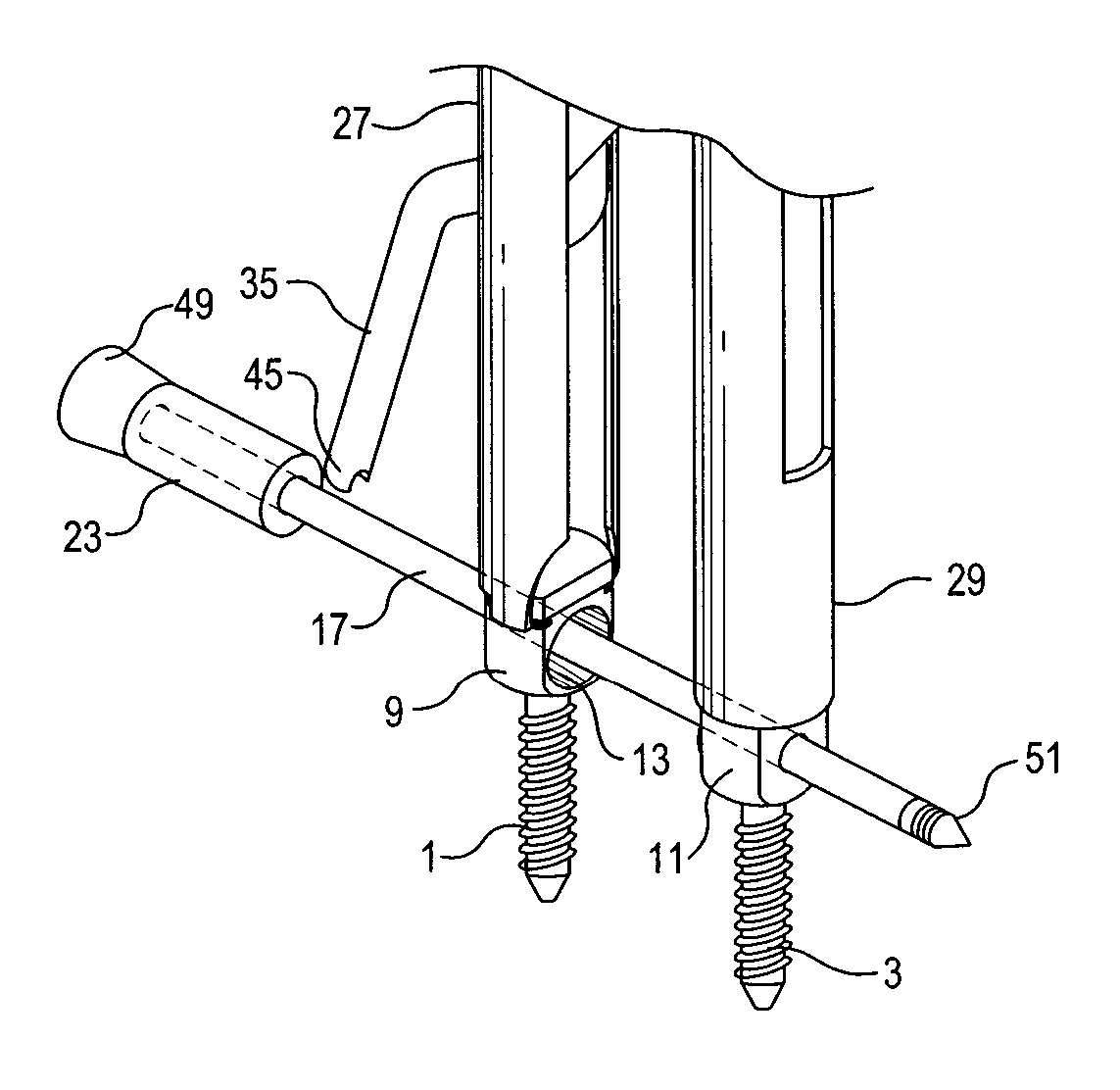
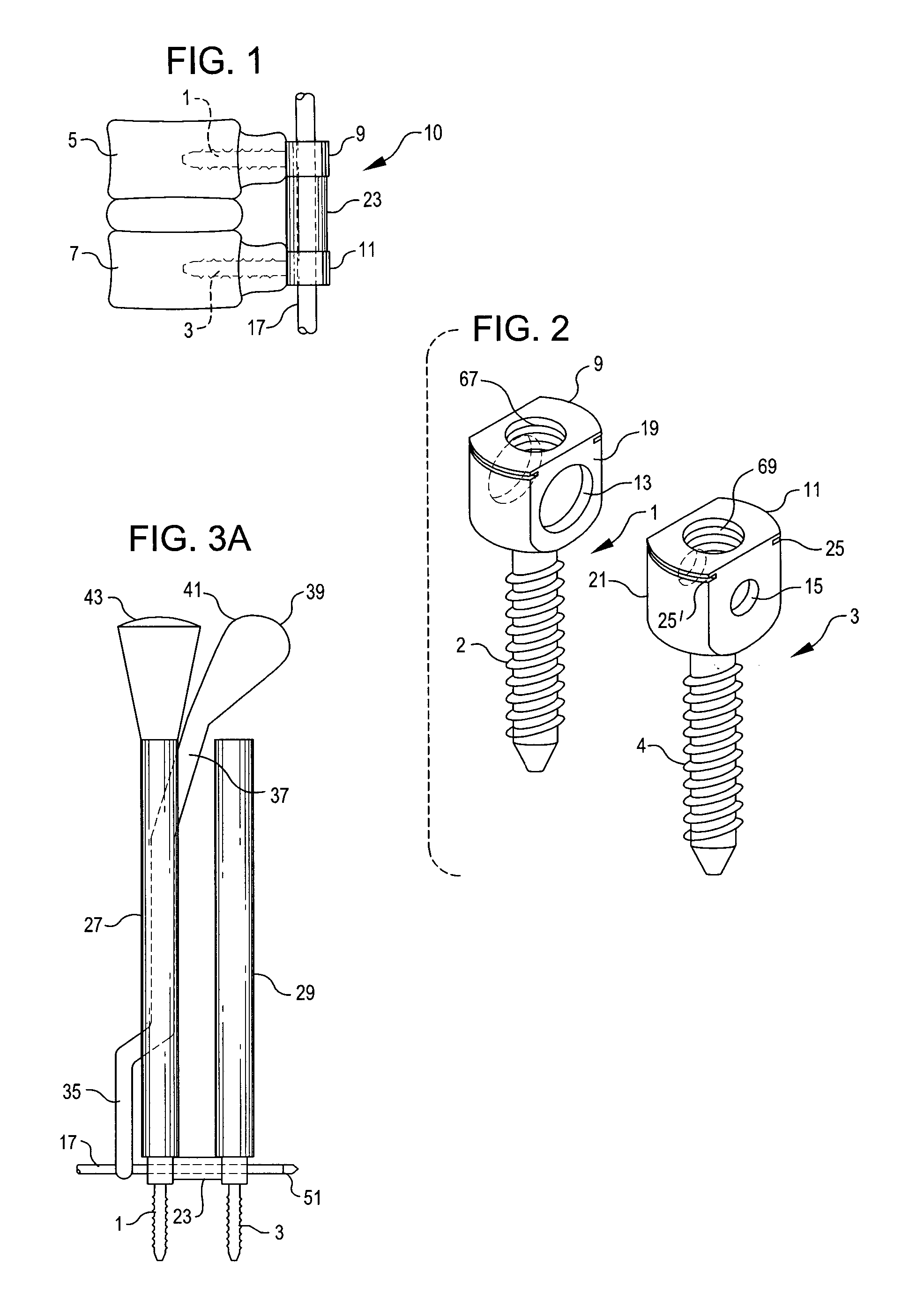
Bone screw assembly
A bone screw assembly includes a first bone screw, second bone screw, and a coupler. The first bone screw defines a first axis and the second bone screw defines a second axis. The coupler is operably associated with the first bone screw and the second bone screw. The coupler is adapted to mount the first bone screw and the second bone screw to adjacent bone structures. The first axis of the first bone screw and the second axis of the second bone screw define an angle therebetween. The first bone screw and the second bone screw are securable to each other.
Owner:GOREK JOSEF
Hammertoe implant
The invention comprises an implant having a first end section and a second end section, where the first end has a cancellous thread for implantation in a first section of bone and the second end includes expansion slots and barbs or wings, that that resist movement out of a second section of bone. These anchors expand outwardly when a rigid wire, such as a k-wire is fed through a central cannulation in the implant and either the wire expands in diameter or the cannulation decreases in diameter. The implant also includes a collar intermediate to the first and second section which includes one or more surfaces to allow the first section to be screwed into a first bone section.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
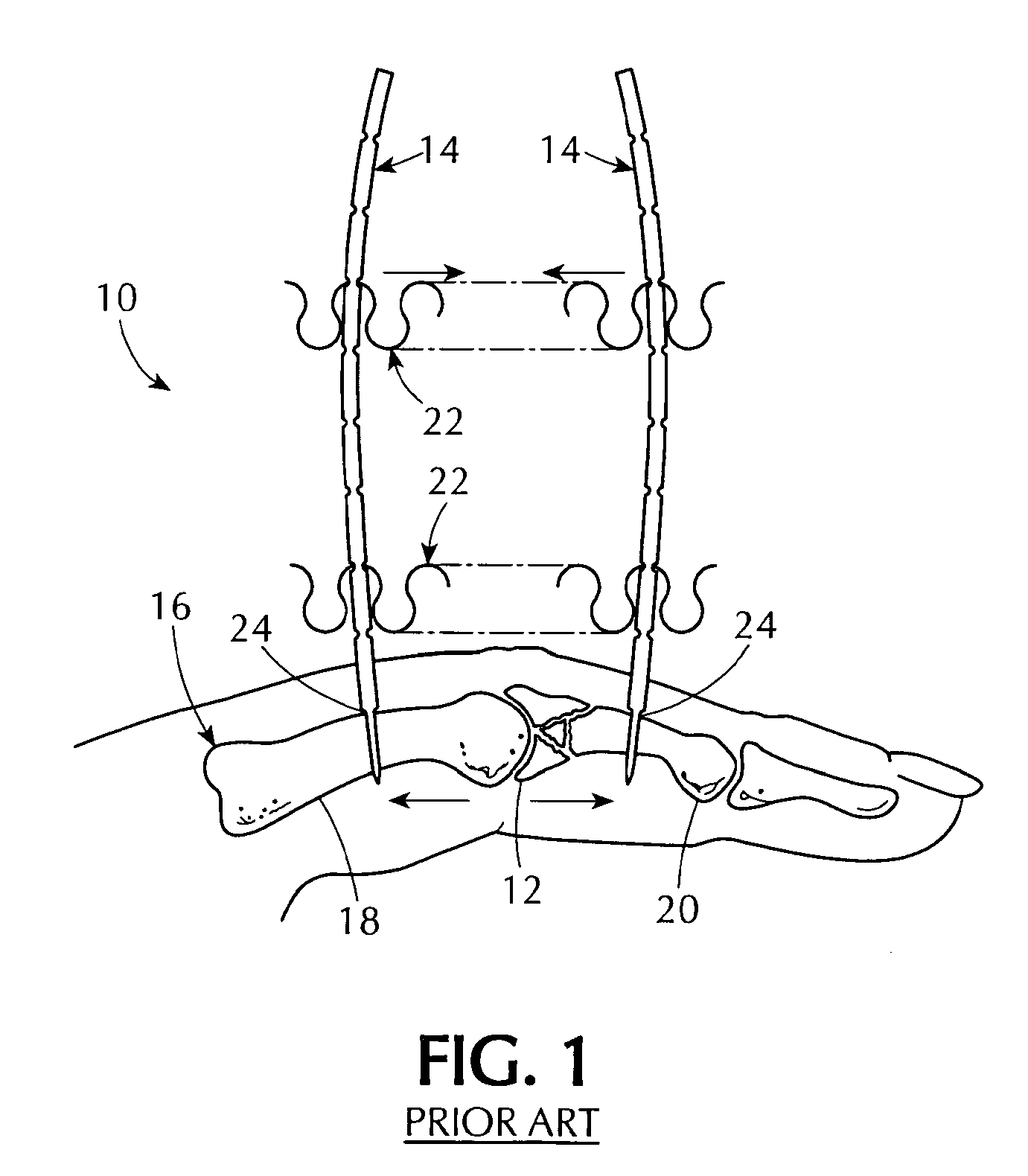
Unilateral fixator
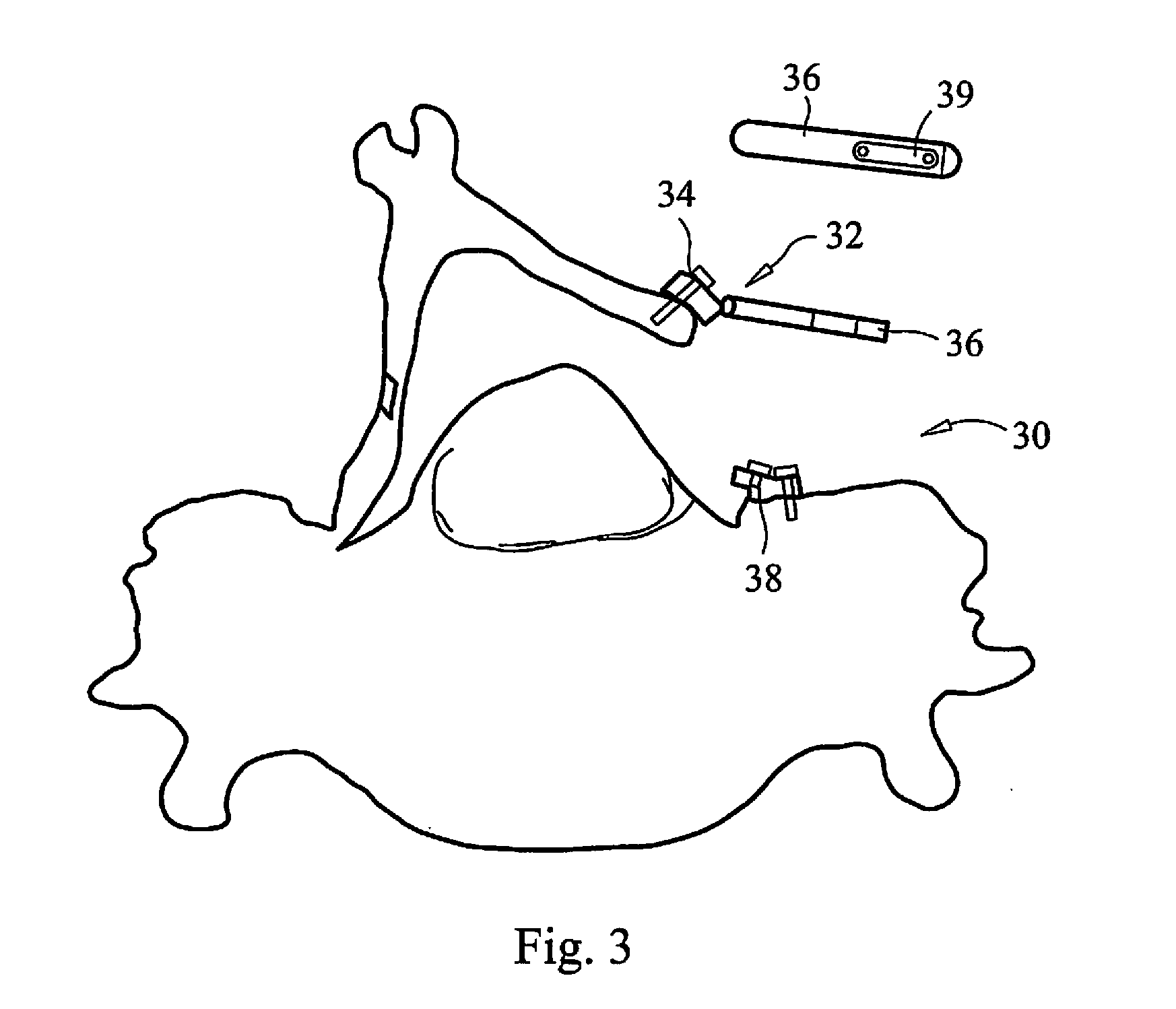
ActiveUS8388619B2Great advantageDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingBone clampFirst tarsal bone
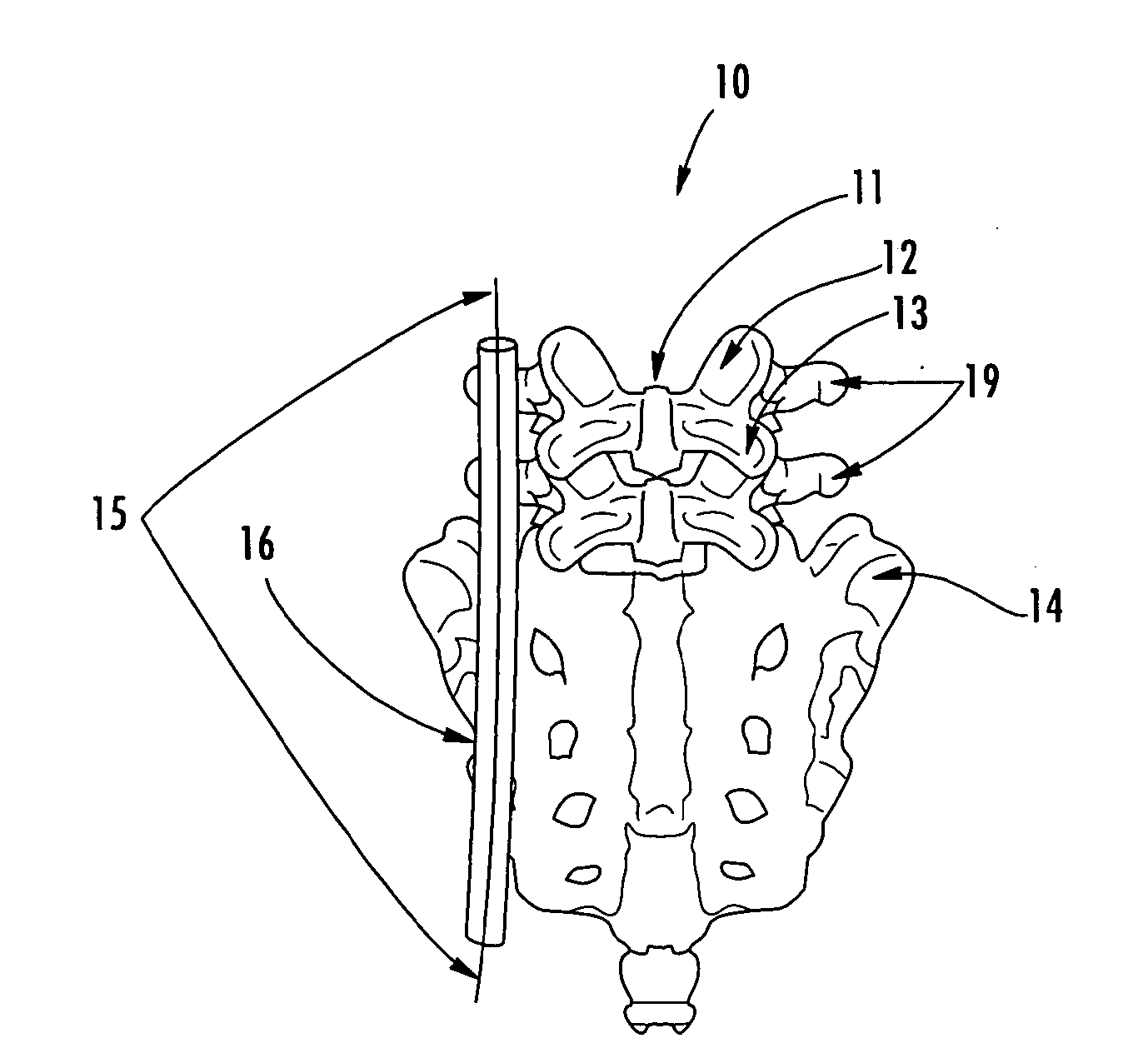
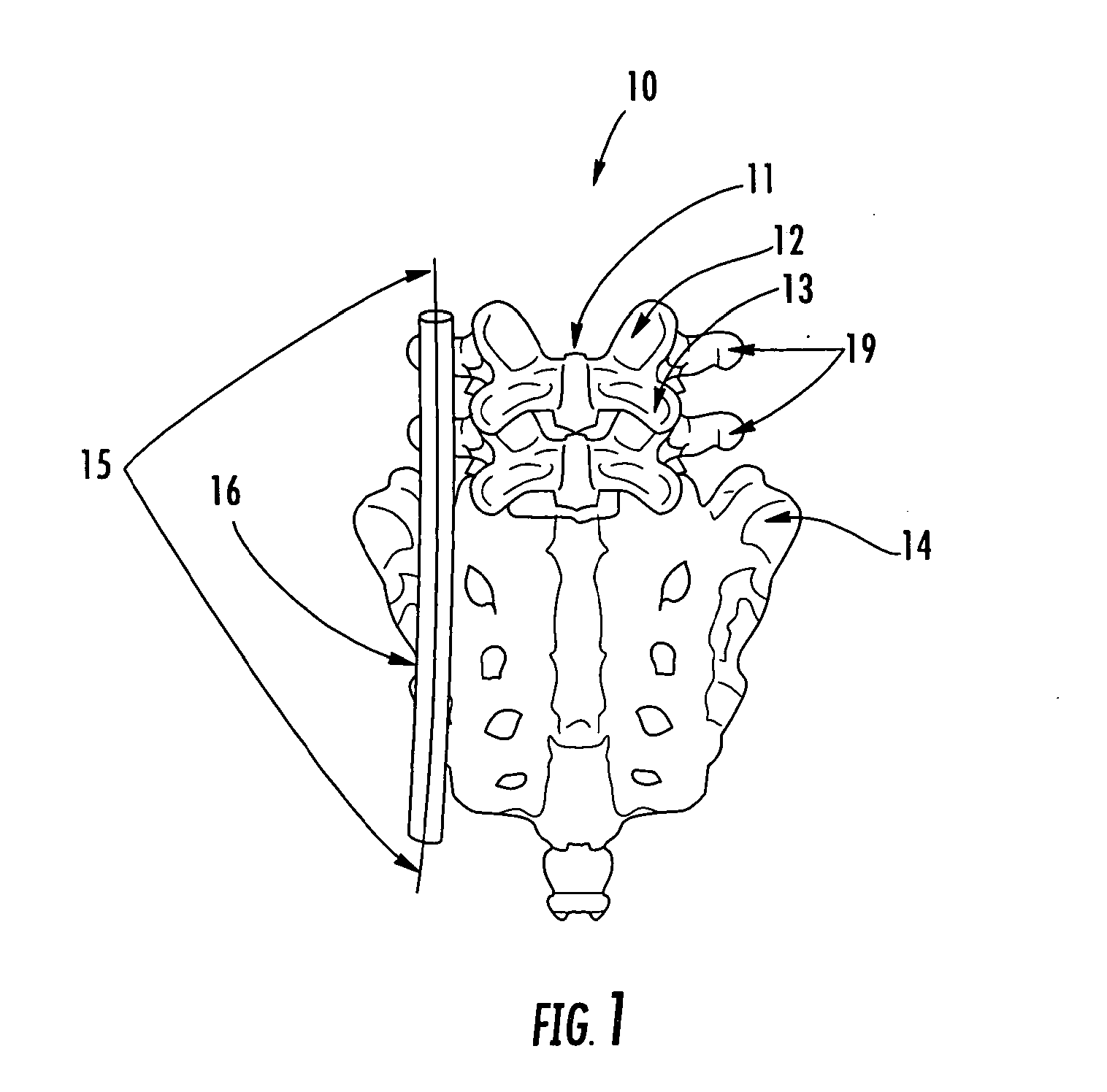
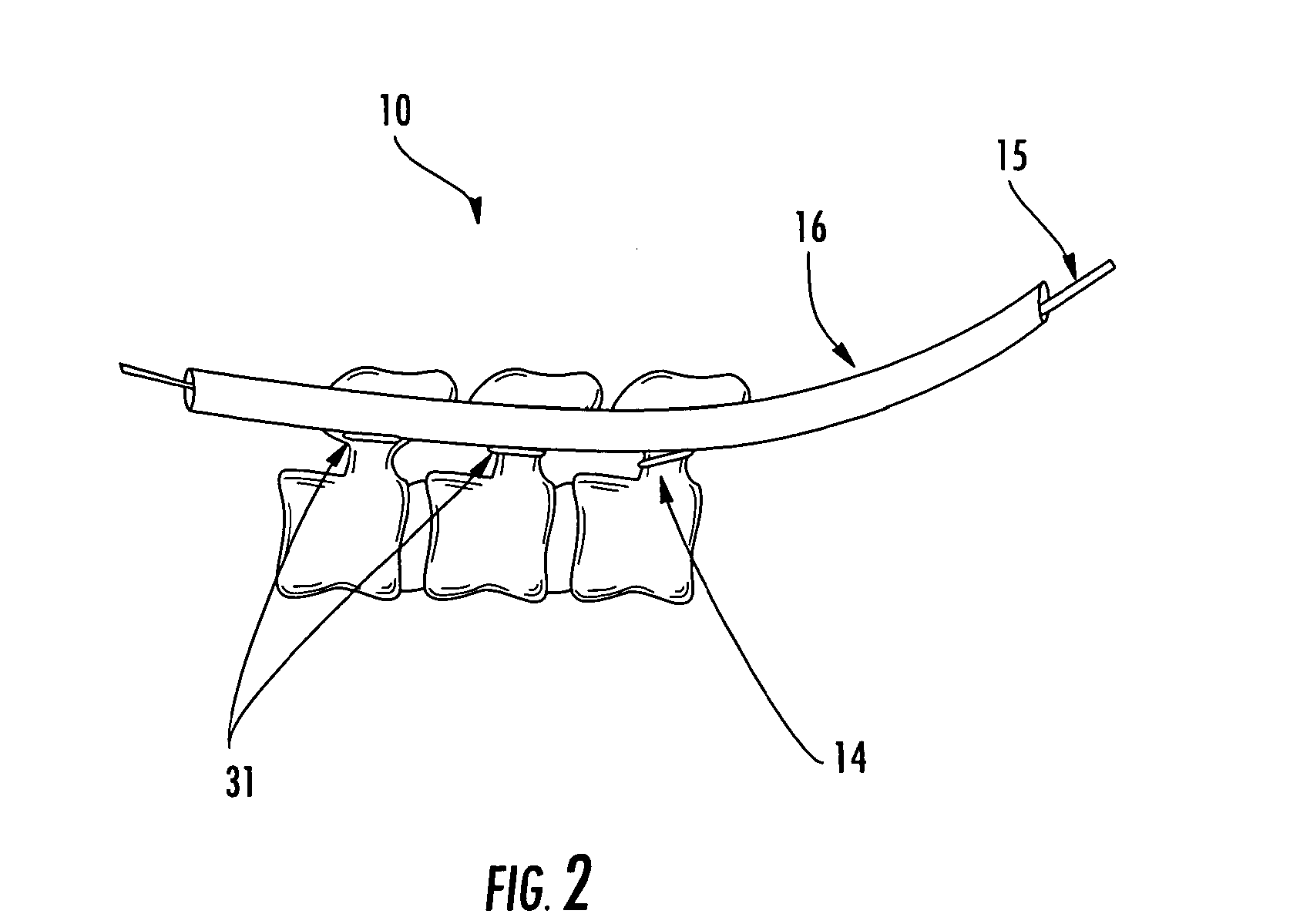
A unilateral fixator for adjustment of a first bone portion relative to a second bone portion. The fixator includes a telescopically adjustable strut having first and second ends and a strut axis, and first and second compound joints. The first compound joint is coupled to the first end of the strut and to a first bone clamp, and includes a first gear mechanism controlling linear and rotational motion of the first bone clamp relative to first and second axes while the first bone clamp is engaged with the first bone portion. The first and second axes are generally orthogonal to one another and to the strut axis. The second compound joint is coupled to the second end of the strut and to a second bone clamp and includes a second gear mechanism controlling linear and rotational adjustment of the second bone clamp. The first compound movable joints can rotate about the strut axis.
Owner:ARTHREX INC
Devices and methods for bone anchoring
InactiveUS20160038186A1Successfully addressSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisForce constantBone tissue
A device for fixation of bone tissue and methods of using same are provided. The device includes a first anchor positionable within a first bone region, a second anchor positionable within a second bone region and a wire interconnecting the first and second anchors. The wire is attached to the first anchor via an elastically deformable element having a force constant (K) of 20-80 N / mm along a longitudinal axis of the first anchor.
Owner:CYCLA ORTHOPEDICS
Intramedullary fixation assembly and method of use
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
Bone support apparatus
A bone support apparatus includes a first bone connector with a first bone cradle insert configured to contact a patient's bone and constructed of a resilient material, a second bone connector configured to contact a patient's bone, and an adjustable rod assembly having a first end connected to the first bone connector and a second end connected to the second bone connector. The adjustable rod assembly has a first elongated member, a second elongated member, and an expansion member with a first end adjustably connected to the first elongated member and a second end adjustably connected to the second elongated member. The distance between the first bone connector and the second bone connector is adjustable by moving at least one of the first end and the second end relative to the first and second elongated member.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Percutaneous system for dynamic spinal stabilization
ActiveUS9526525B2Effective and stableReduce the amount requiredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFirst tarsal boneSecond tarsal bone
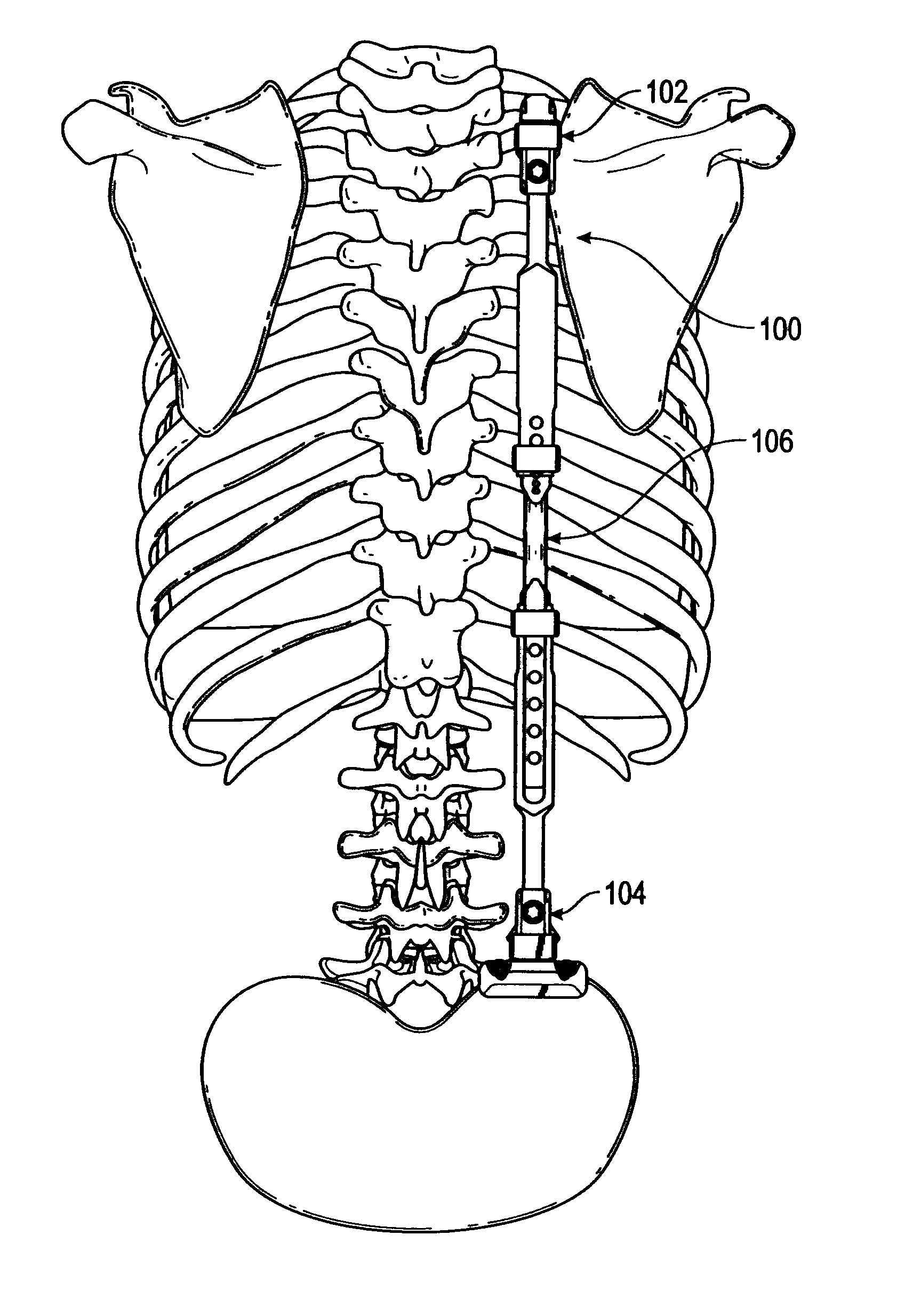
A minimally invasive, percutaneous system that allows for dynamic stabilization of the spine is provided, together with methods of using the system. The system comprises a first bone anchoring member that is anchored in a first vertebra, and a second bone anchoring member that is anchored in a second, adjacent, vertebra. The first and second bone anchoring members include a first head portion and second head portion, respectively, that are designed to hold first and second ends of a flexible, elongated member, or cord. In certain embodiments, the cord is provided with a stiffened, relatively inflexible, end portion that is fixedly attached to the cord and that facilitates threading of the cord through the first and second head portions.
Owner:NEUROPRO TECH
Bone alignment implant and method of use
A bone alignment implant includes a first bone fastener with a first bone engager that is adapted for fixation into the metaphyseal bone and a second bone fastener with a second bone engager that is adapted for fixation into the diaphyseal bone. A link connecting the two fasteners spans across the physis. Alternatively, the bone alignment implant is adapted for fixation into the diaphyseal sections of two adjoining vertebral bodies. These implants act as a flexible tethers between the metaphyseal and the diaphyseal sections of bone during bone growth. These implants are designed to adjust and deform during the bone realignment process. When placed on the convex side of the deformity, the implant allows the bone on the concave side of the deformity to grow. During the growth process the bone is then realigned. A similar procedure is used to correct torsional deformities.
Owner:AMEI TECH
Ligament reestablishing system
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments and discloses a ligament reestablishing system. After a ligament is reestablished for the first time by using the ligament reestablishing system, the ligament can be quickly replaced through a small incision outside a joint without using an arthroscope if a revision surgery needs to be carried out on the ligament. Because the technology has the character of quick revision, a ligament substitute material is not needed to be firmly combined with a bone channel any longer, so the ligament reestablishing system provides possibilities for reliable use of artificial materials except autologous / allogenic tendons. Moreover, the difficulty and cost of the revision surgery are reduced, the hospital time is reduced, and the indication of ligament reestablishment is expanded. The ligament reestablishing system comprises a first endosteal hollow channel, a second endosteal hollow channel, a ligament substitute, a first fixing piece and a second fixing piece. A bone penetrating through the near end of the joint and a bone penetrating through the far end of the joint are implanted into the first endosteal hollow channel and the second endosteal hollow channel respectively. The ligament substitute is placed into the first endosteal hollow channel and the second endosteal hollow channel.
Owner:叶维光
Bone removal tool
ActiveUS8273088B2Efficient and precise preparationDiagnosticsJoint implantsFirst tarsal boneBiomedical engineering
A bone preparation device for preparing a bone surface for receiving an implant is disclosed, as is a method of using the device, wherein the device contains a gripping element for gripping a first bone surface and a abrading element for abrading an opposing bone surface.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Ligament reconstruction system
A system for ligament reconstruction includes placing a first jig having a first plurality of drill guide holes on a first bone of the joint, forming two intersecting holes in the first bone using the first plurality of drill guide holes, placing a second jig having a second plurality of drill guide holes on a second bone of the joint, forming a tunnel and a first branch hole and a second branch hole in the second bone using the second plurality of drill guide holes, placing a tendon having sutured ends through the two intersecting holes, extending the sutured ends through the tunnel and through the first and second branch holes so that the first and second ends of the tendon are positioned within the tunnel, and affixing the tendon within the tunnel. The apparatus of this system has specially formed jigs placed over bones.
Owner:COLLINS EVAN D
Orthopedic external fixator and method of use
An orthopedic apparatus is provided for bridging a first bone unit to a second bone unit. The apparatus is demonstrated on a finger joint, wherein one of the bones and / or ligaments and / or tendons of the joint is / are injured. A method for implanting and using the apparatus also is presented. The apparatus includes a reformably deformable span portion which is generally circular and preferably rhombic. By deforming or reforming the span portion, it can be repositioned laterally, and / or it can be rotated to allow range of rotary motion so as to promote healing.
Owner:VIRAK ORTHOPEDIC RES +1
Floating patella sensor, knee stabilizer with same and robotic knee testing apparatus with same
ActiveUS20170143250A1Accurate objective reliable reproducible measureEasy to measureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsJoint manipulationKnee Joint
Owner:ERMI
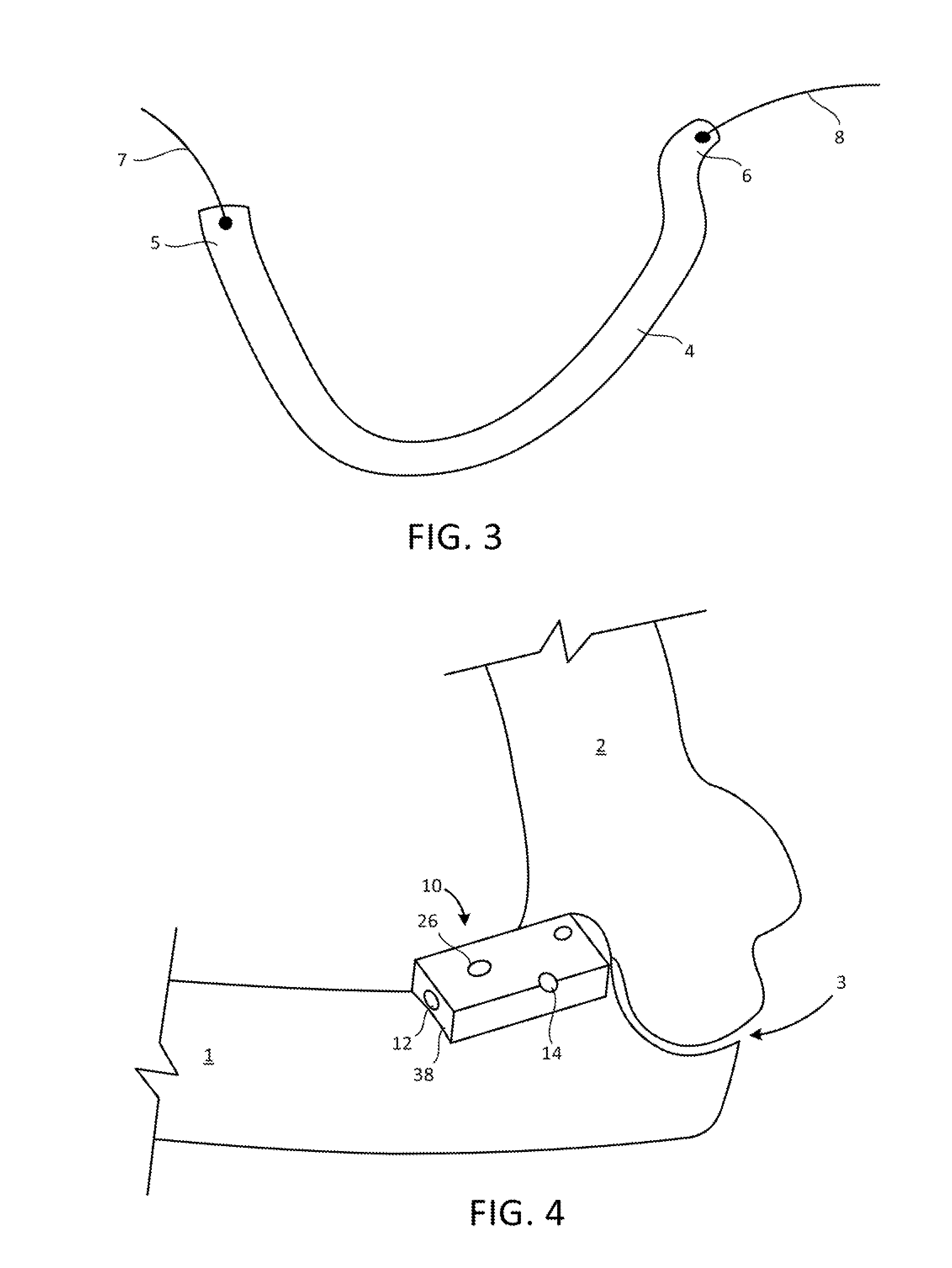
Implant for a bone joint
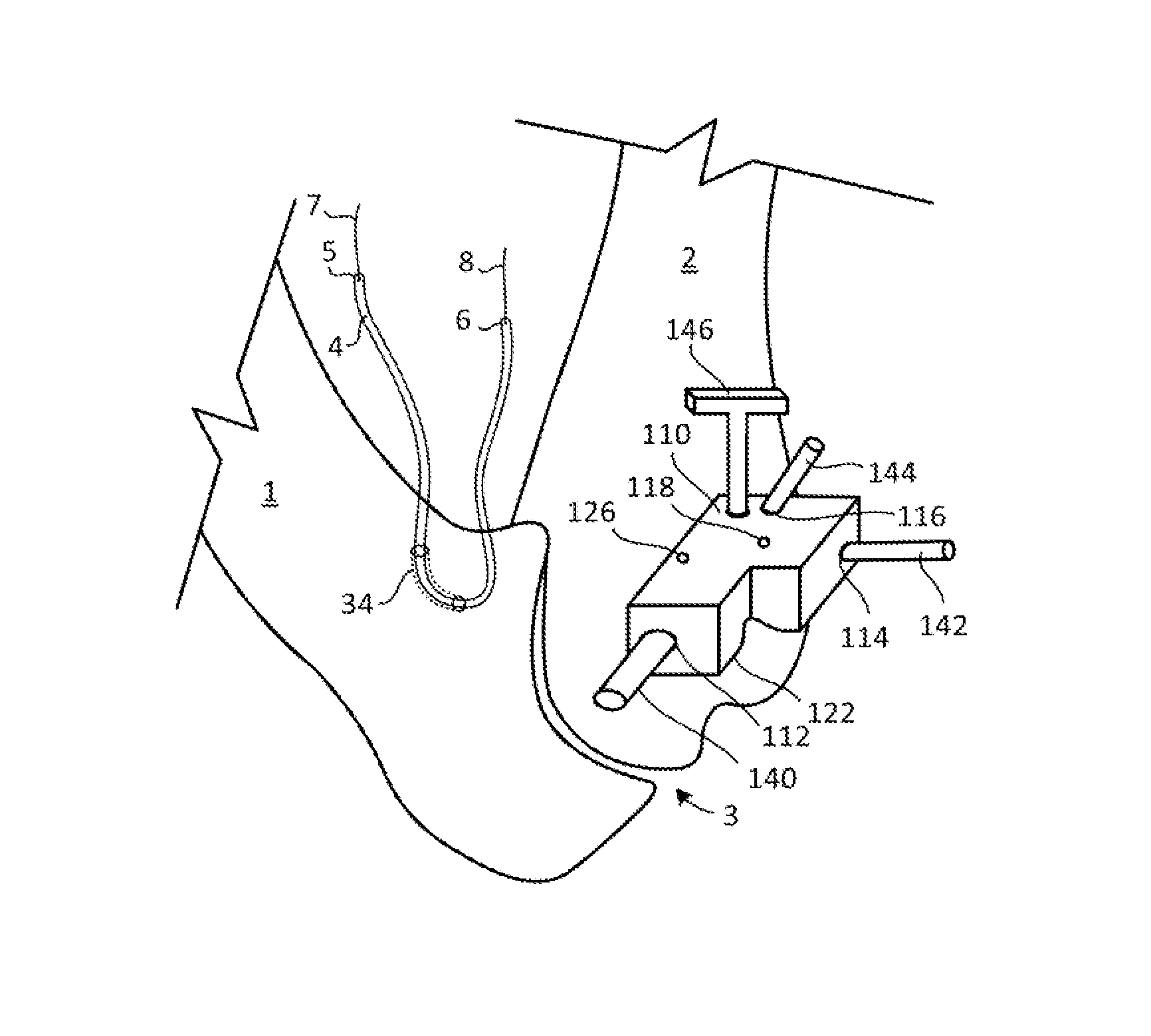
ActiveUS20170224499A1Great degree of articulationAvoid complicationsFinger jointsAnkle jointsCouplingBones joints
An implant (30) for a mammalian bone joint (3) for spacing a first bone (2) of the joint from a second bone (1) of the joint while allowing translational movement of the second bone in relation to the first bone is described. The implant comprises (a) a distal part (31) configured for intramedullary engagement with an end of the second bone, (b) a proximal part (34) having a platform (15) configured for non-engaging abutment of an end of the first bone and translational movement thereon, and (c) an articulating coupling (10, 16) provided between the distal and proximal ends allowing controlled articulation of the first and second bones. The bone-abutting platform is shaped to conform to and translate upon the end of the first bone. A kit for assembly to form the implant of the invention, and the use of the implant to treat osteoarthritis in a bone joint, are also described.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY
Laminoplasty fixation devices
Devices and methods for treating degenerative conditions of the spine or for alleviating pain or discomfort associated with the spinal column are disclosed. In particular, laminoplasty fixation devices and methods are disclosed. Also disclosed, is a vertebral implant comprising a first bone engaging portion configured for securing to a first cut portion of a vertebra and a second bone engaging portion configured for securing to a second cut portion of the vertebra. A body portion is provided for associating the first and second bone engaging portions at a preselected spacing from each other, wherein the implant is adjustable to select said spacing.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Percutaneous posterolateral spine fusion
A method, tools, and system for performing a percutaneous or minimally invasive spine fusion procedure are provided. A trocar and then dilator are used to create a channel for a hollow and longitudinally slit delivery tube. The method includes inserting a decorticator, such as a rasp, via a delivery tube, decorticating a first region of a first bone associated with a spine, and pushing a bone fusion substance via the delivery tube to the region to fuse the first region with a second region of a second bone associated with the spine. The spine fusion may be a posterolateral fusion and the first region may be a transverse process region of a lumber spine. The bone fusion substance may be pushed using a pusher instrument inserted into the delivery tube, and the delivery tube may be removed while the pusher instrument is held in place to direct the bone fusion substance.
Owner:KORNEL EZRIEL E
Methods, instruments and implants for scapho-lunate reconstruction
A method for bone reconstruction includes aligning a first hone with a second bone using a plurality of guidewires to correct rotational deformity of the first and second bones. A first module of a targeting apparatus is positioned in proximity to the first bone. A tip of the first module is engaged with the first bone. A second module of the targeting apparatus is positioned in proximity to the second bone. A tip of the second module is engaged with the second bone. Alignment of the first module and the second module is secured. The alignment is verified using a guidewire, the guidewire wire is inserted through a passage extending through the second module. A length between the first bone and the second bone is determined using a depth gauge. An implant is selected based on the determined length for delivery along the passage extending through the second module.
Owner:ACUMED
Combined intramedullary-extramedullary bone stabilization and alignment system
Disclosed is a combined intramedullary and extramedullary bone stabilization and alignment system, which includes both methods and apparatuses for the alignment and stabilization of a first bone or piece of bone to a second bone or piece of bone. Embodiments of the system may include an implant device which has an elongated framework within intramedullary portion and an extramedullary portion which are cannulated. The cannulated aspect of the framework includes a wire aperture through both the intramedullary portion and the extramedullary portion.
Owner:LUNDQUIST ANDREW +1
Percutaneous posterolateral spine fusion
A method, tools, and system for performing a percutaneous or minimally invasive spine fusion procedure are provided. A trocar and then dilator are used to create a channel for a hollow and longitudinally slit delivery tube. The method includes inserting a decorticator, such as a rasp, via a delivery tube, decorticating a first region of a first bone associated with a spine, and pushing a bone fusion substance via the delivery tube to the region to fuse the first region with a second region of a second bone associated with the spine. The spine fusion may be a posterolateral fusion and the first region may be a transverse process region of a lumber spine. The bone fusion substance may be pushed using a pusher instrument inserted into the delivery tube, and the delivery tube may be removed while the pusher instrument is held in place to direct the bone fusion substance.
Owner:KORNEL EZRIEL E
Osteosynthesis device
ActiveUS20130274746A1High deformationEasy to introduceFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisFirst tarsal bone
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
System and method for assessing, measuring, and correcting an anterior-posterior bone cut
ActiveUS20140276860A1Musculoskeletal system evaluationSurgical navigation systemsRemote systemProsthesis
A system and method is disclosed herein for measuring anterior-posterior slope of a bone to set a cutting jig coupled to the muscular-skeletal system. The system comprises a sensored module that can be placed within a prosthetic component to measure anterior-posterior slope. The system further includes a remote system for receiving, processing, and displaying quantitative measurements from the sensors. A first bone and a second bone are placed in extension. A sensored module is referenced to a bone landmark of the first bone. The sensored module includes a three-axis accelerometer that is configured to measure position, tilt, and rotation. A bone cutting jig is coupled to the first bone. The sensored insert is coupled to the bone cutting jig. The accelerometer in the sensored insert is used to measure the anterior-posterior slope. The bone cutting jig is then adjusted to a predetermined anterior-posterior slope as measured by the sensored insert.
Owner:ORTHOSENSOR
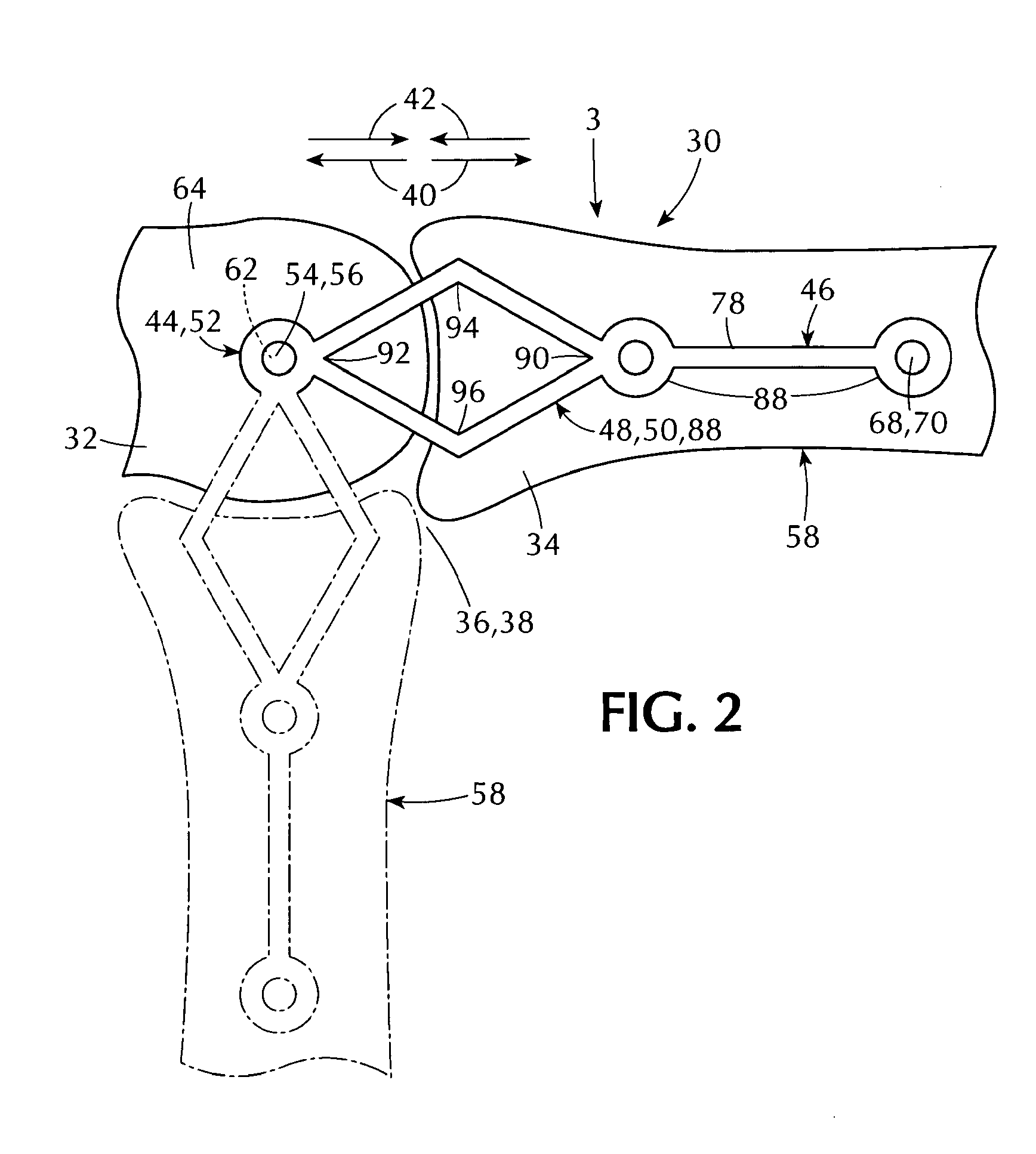
Orthopedic apparatus for correcting rotational bone deformities and method for using the orthopedic apparatus
ActiveUS9877755B2Promote growthCorrect angular deformationBone platesOrthopedic devicesOrthopedic apparatus
Embodiments of an orthopedic apparatus and method for using the orthopedic apparatus to correct rotational bone deformities are disclosed. Embodiments of the orthopedic apparatus include a stationary segment having a fixed portion engaged to a first bone portion and a track portion engaged to a mobile segment that is engaged to a second bone portion separated by the first bone portion by a growth plate such that the mobile segment migrates over time from a first position along the stationary segment to a second position along the stationary segment in such a way that torsional growth and correction of an angular deformity are promoted.
Owner:PEGA MEDICAL
Method for forming a bioresorbable composite implant in a bone
InactiveUS7959684B2High compressive strengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantCompressive strengthFirst tarsal bone
A method for forming a composite implant in a bone cavity is disclosed, which includes i) forming a first bone filler in a bone cavity; and ii) inserting a second bone filler into an unfilled space in the bone cavity, wherein the first bone filler has a higher compressive strength and slower bioresorption rate in comparison with the second bone filler.
Owner:JOY MEDICAL DEVICES CORP
Flexible artificial intervertebral disc
PendingCN110368148AEasy to useMeet physical activity needsJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral discPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention provides a flexible artificial intervertebral disc. The flexible artificial intervertebral disc comprises a first bone trabecula layer, a second bone trabecula layer, a flexible part anda supporting part, wherein the first bone trabecula layer and the second bone trabecula layer are arranged at an interval, one side of the flexible part is connected with the first bone trabecula layer, the other side of the flexible part is connected with the second bone trabecula layer, the flexible part is made of a polymer material, and an accommodating cavity is formed in the flexible part;the supporting part is arranged in the accommodating cavity of the flexible part, and the hardness of the supporting part is greater than that of the flexible part. Since the flexible part is made ofthe polymer material and supported by the relatively hard supporting part, elastic deformation at different positions is facilitated, the physiological activity requirement of a patient can be met, and the movement amplitude can be controlled conveniently. Moreover, due to the arrangement of the supporting part, the intervertebral space restenosis caused by height loss can be prevented, and the artificial intervertebral disc can be reliably used for a long time.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
High-frequency serial humanoid four-degree-of-freedom mechanical foot
ActiveCN105564531BAchieve high-frequency response characteristicsReasonable structureVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot comprises a tarsal bone board, a metatarsal bone board, a toe, an ankle joint connecting the tarsal bone board with a mechanical crus, a tarsal bone joint connecting the tarsal bone board with the metatarsal bone board and a toe joint connecting the metatarsal bone board with the toe; the ankle joint comprises a first ankle gear shaft, a second ankle gear shaft, a first U-shaped frame, a first motor, an ankle rotation shaft, a bearing frame, a bolt and a fourth motor; the first ankle gear shaft is perpendicular to the ankle rotation shaft; the tarsal bone joint comprises a first tarsal bone gear shaft, a second tarsal bone gear shaft and a second motor; the first tarsal bone gear shaft is in mesh transmission with the second tarsal bone gear shaft, and an output shaft of the second motor is connected with one end of the first tarsal bone gear shaft; the toe joint comprises a first toe gear shaft, a second toe gear shaft, a third U-shaped frame and a third motor. The humanoid robot foot is reasonable in structure and better in humanoid effect and has four freedom degrees, the high-frequency motion characteristic and the series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Intervertebral Interference Implants and Instruments
An implant includes an implant body sized and shaped for insertion into a sacro-iliac joint, the implant including a first bone fixation element receiving channel extending through a portion thereof along a first central axis oriented so that, when the implant body is received within the sacro-iliac joint in a desired configuration, a bone fixation element inserted into the first bone fixation element receiving channel will extend into a first one of the bones forming the joint.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
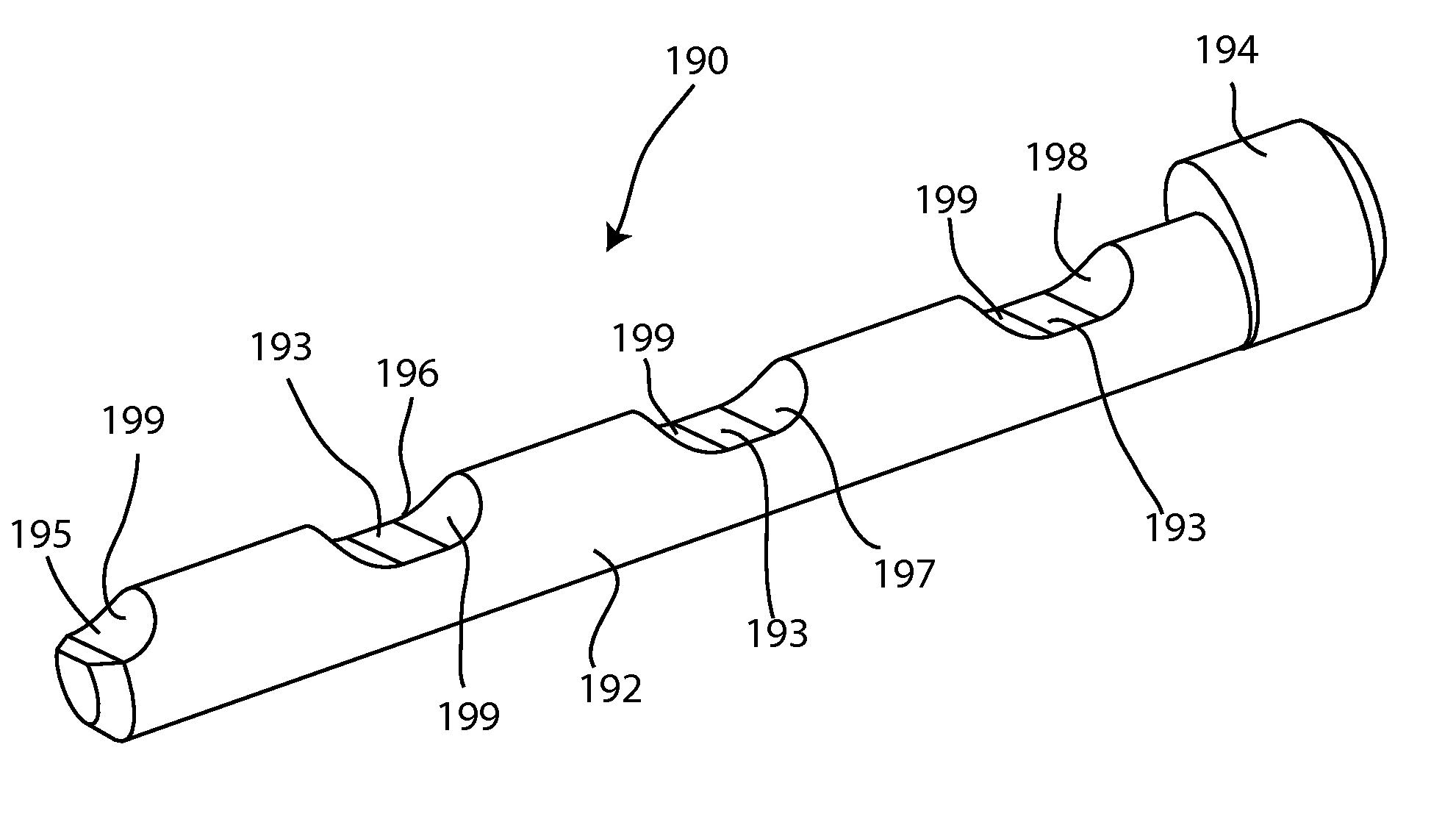
Bone fixation member systems and methods of use
A bone fixation member can be configured to secure first and second bone segments of a target bone together in a compressed approximated position. The bone fixation member can include a strap made of a first material, a locking head extending from a proximal end of the strap, and a leader portion extending from a distal end of the strap. The locking head can have a housing and a strap receiving slot that extends through the housing, slot is configured to receive a distal end of the strap. The housing can be tapered such that a distal end of the housing has a thickness that is greater than the thickness of a proximal end of the housing. The leader portion can be configured to be more flexible than the strap. The leader portion can be made of a second material that is different than the first material.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
High-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot
ActiveCN105564531AAchieve high-frequency response characteristicsReasonable structureVehiclesFirst tarsal boneSacroiliac joint
The invention discloses a high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot comprises a tarsal bone board, a metatarsal bone board, a toe, an ankle joint connecting the tarsal bone board with a mechanical crus, a tarsal bone joint connecting the tarsal bone board with the metatarsal bone board and a toe joint connecting the metatarsal bone board with the toe; the ankle joint comprises a first ankle gear shaft, a second ankle gear shaft, a first U-shaped frame, a first motor, an ankle rotation shaft, a bearing frame, a bolt and a fourth motor; the first ankle gear shaft is perpendicular to the ankle rotation shaft; the tarsal bone joint comprises a first tarsal bone gear shaft, a second tarsal bone gear shaft and a second motor; the first tarsal bone gear shaft is in mesh transmission with the second tarsal bone gear shaft, and an output shaft of the second motor is connected with one end of the first tarsal bone gear shaft; the toe joint comprises a first toe gear shaft, a second toe gear shaft, a third U-shaped frame and a third motor. The humanoid robot foot is reasonable in structure and better in humanoid effect and has four freedom degrees, the high-frequency motion characteristic and the series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com