Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
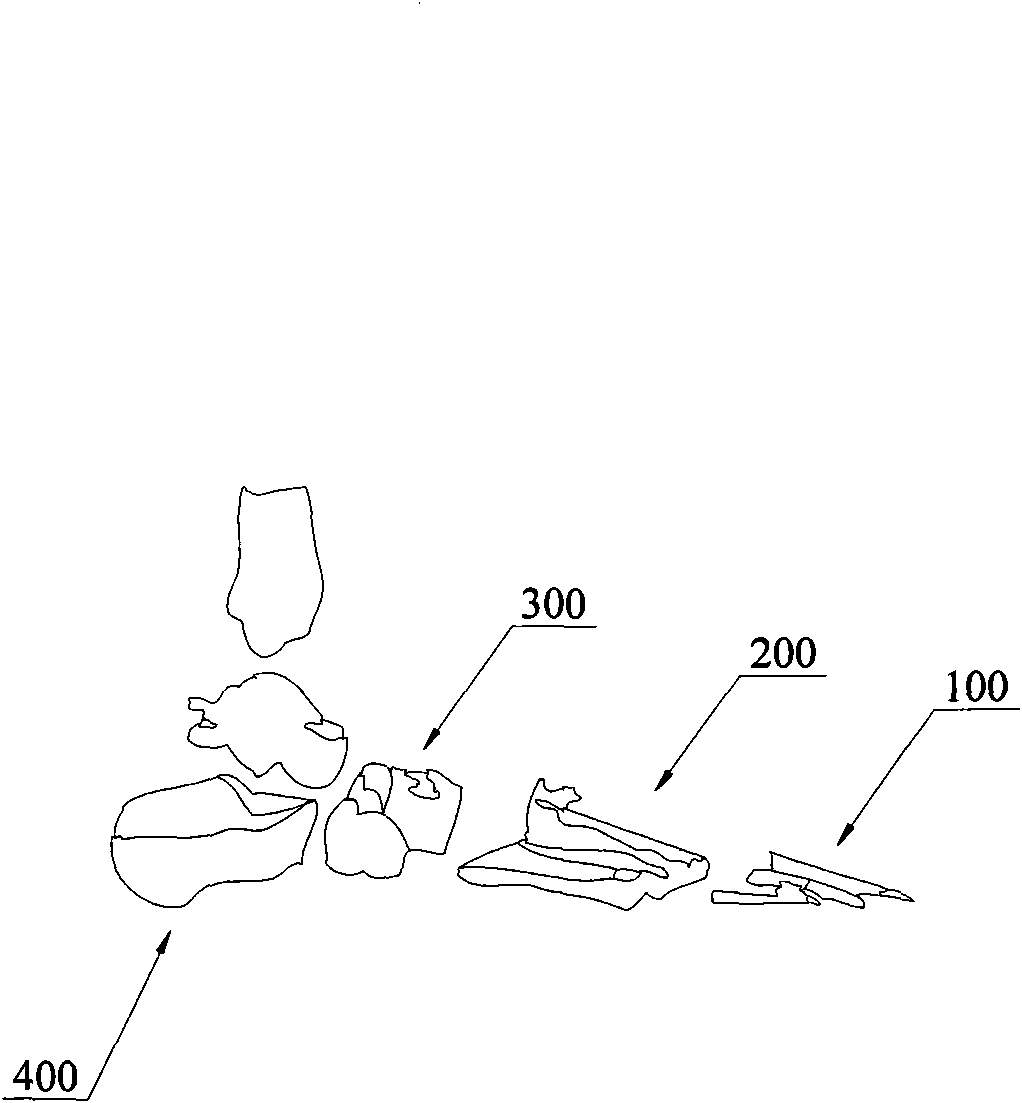
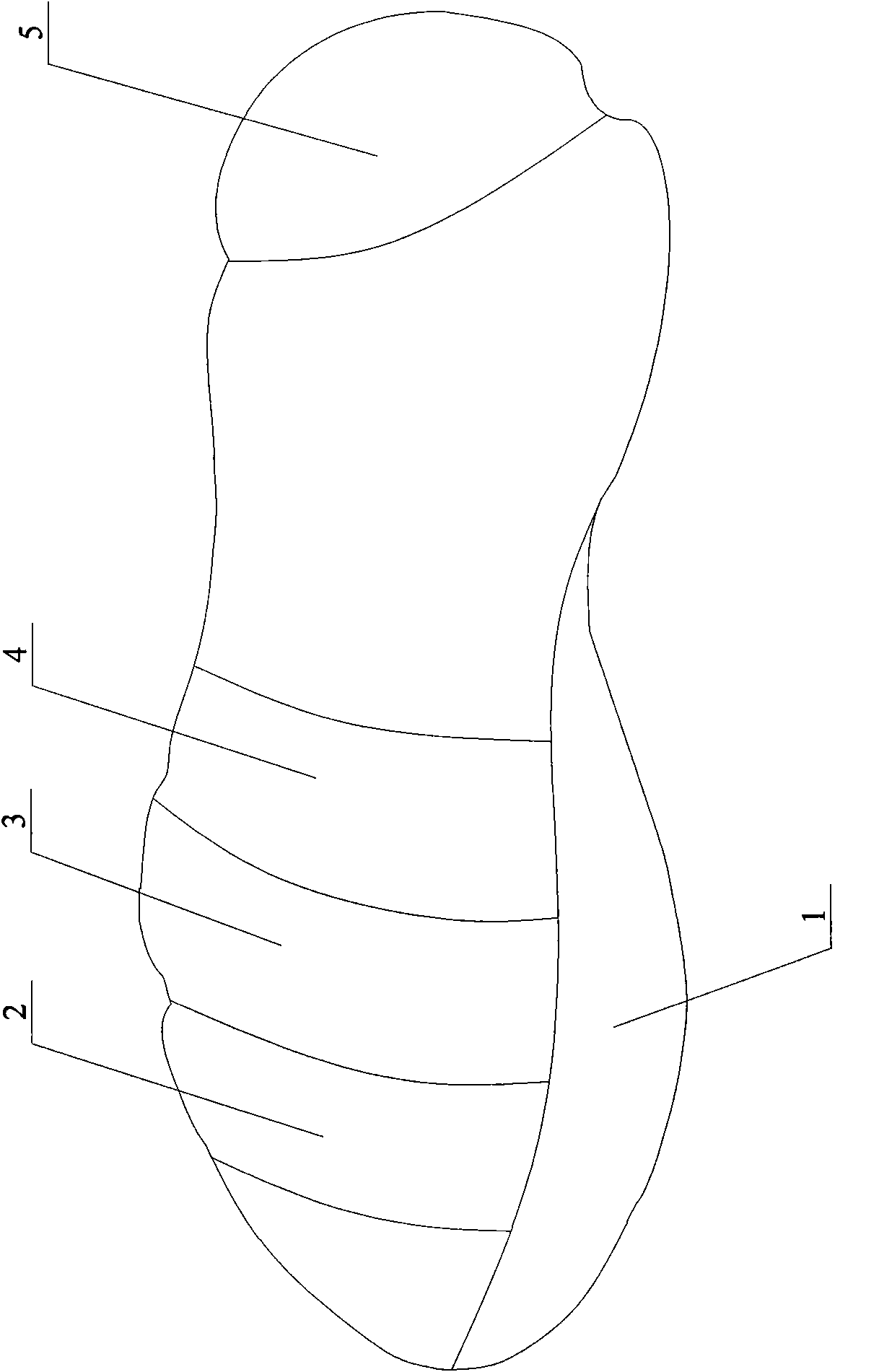
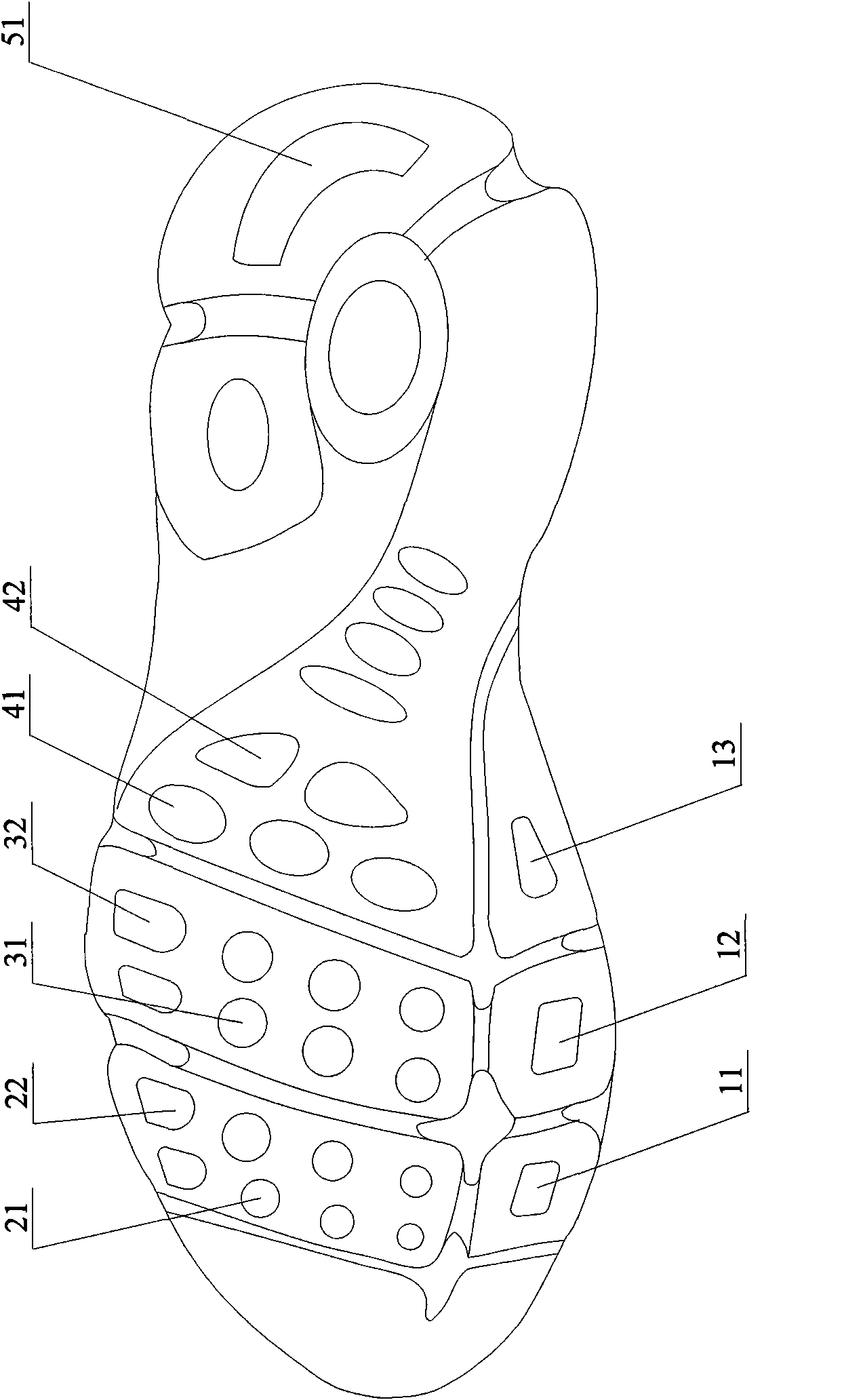
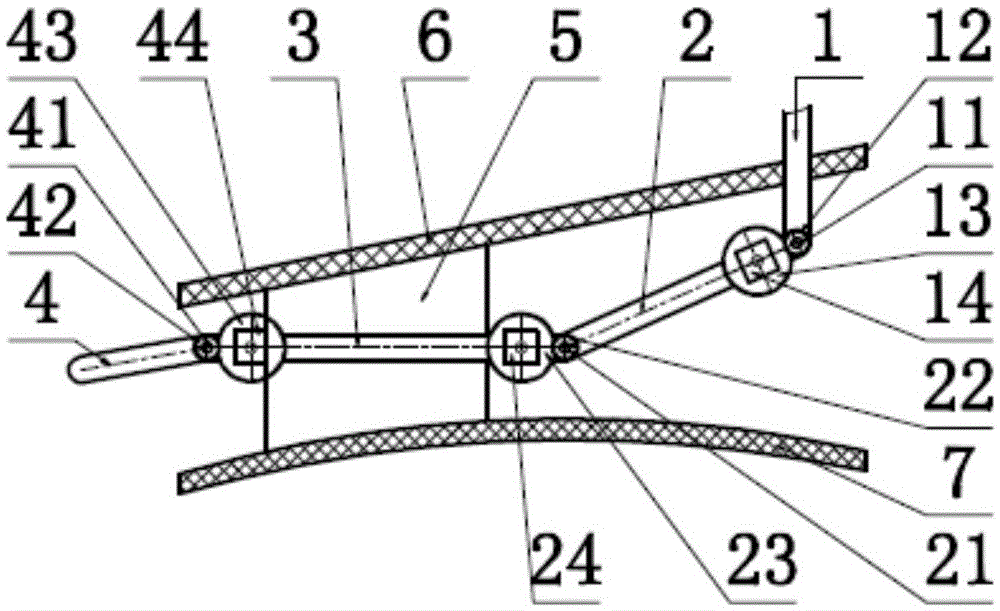
60 results about "Tarsal Bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any of the short bones between the tibiotarsal joint and the tarsometatarsal joint.
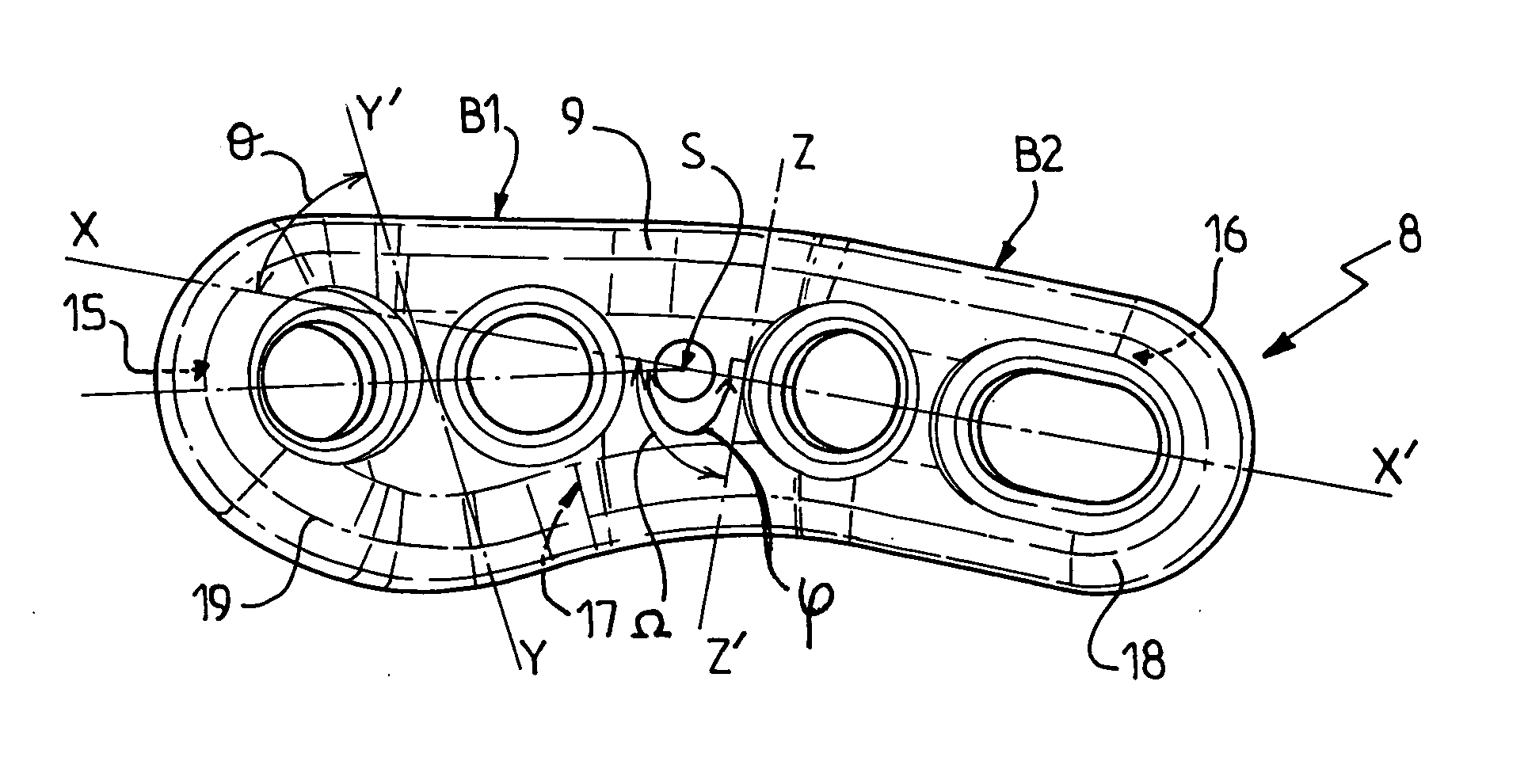
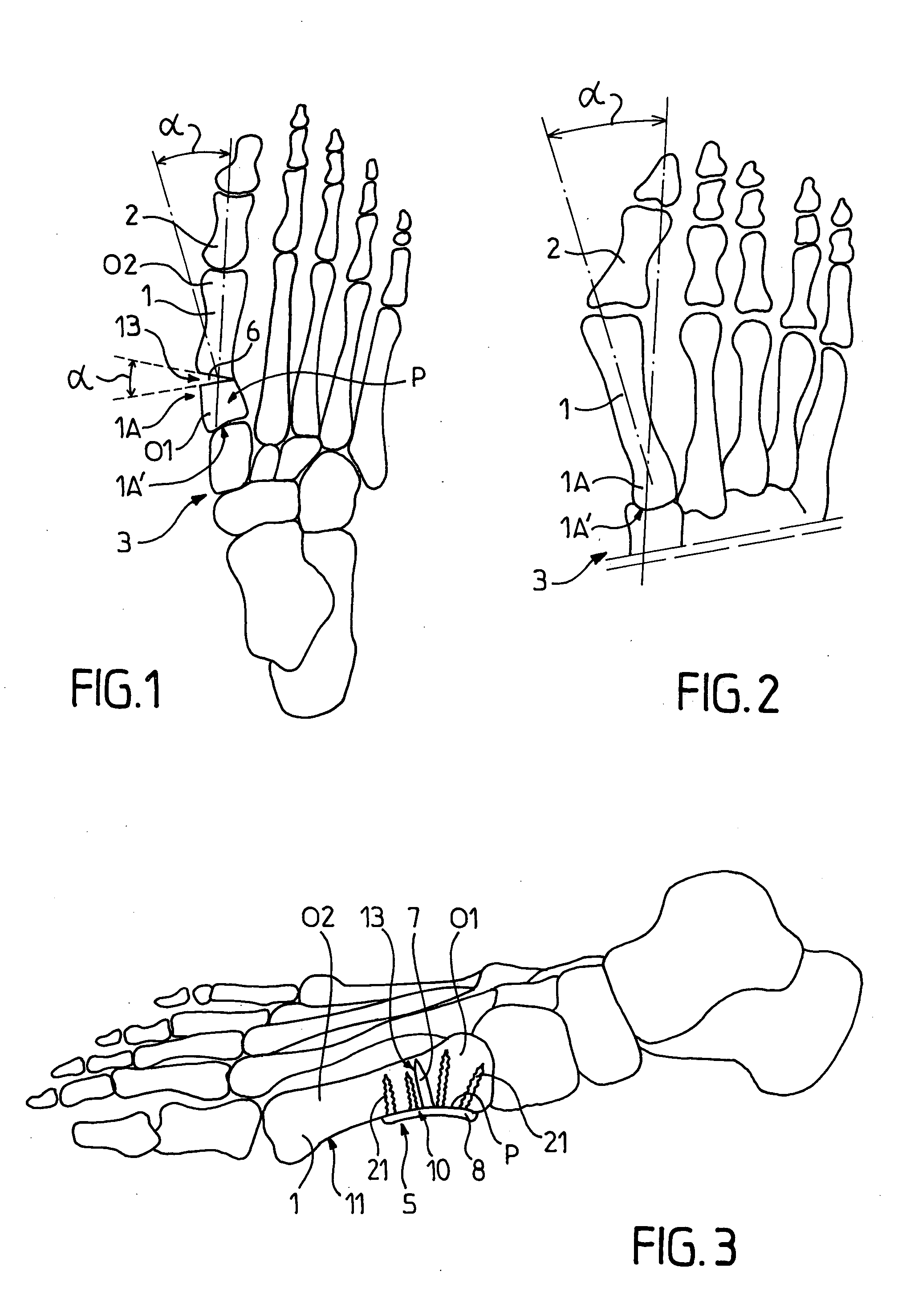
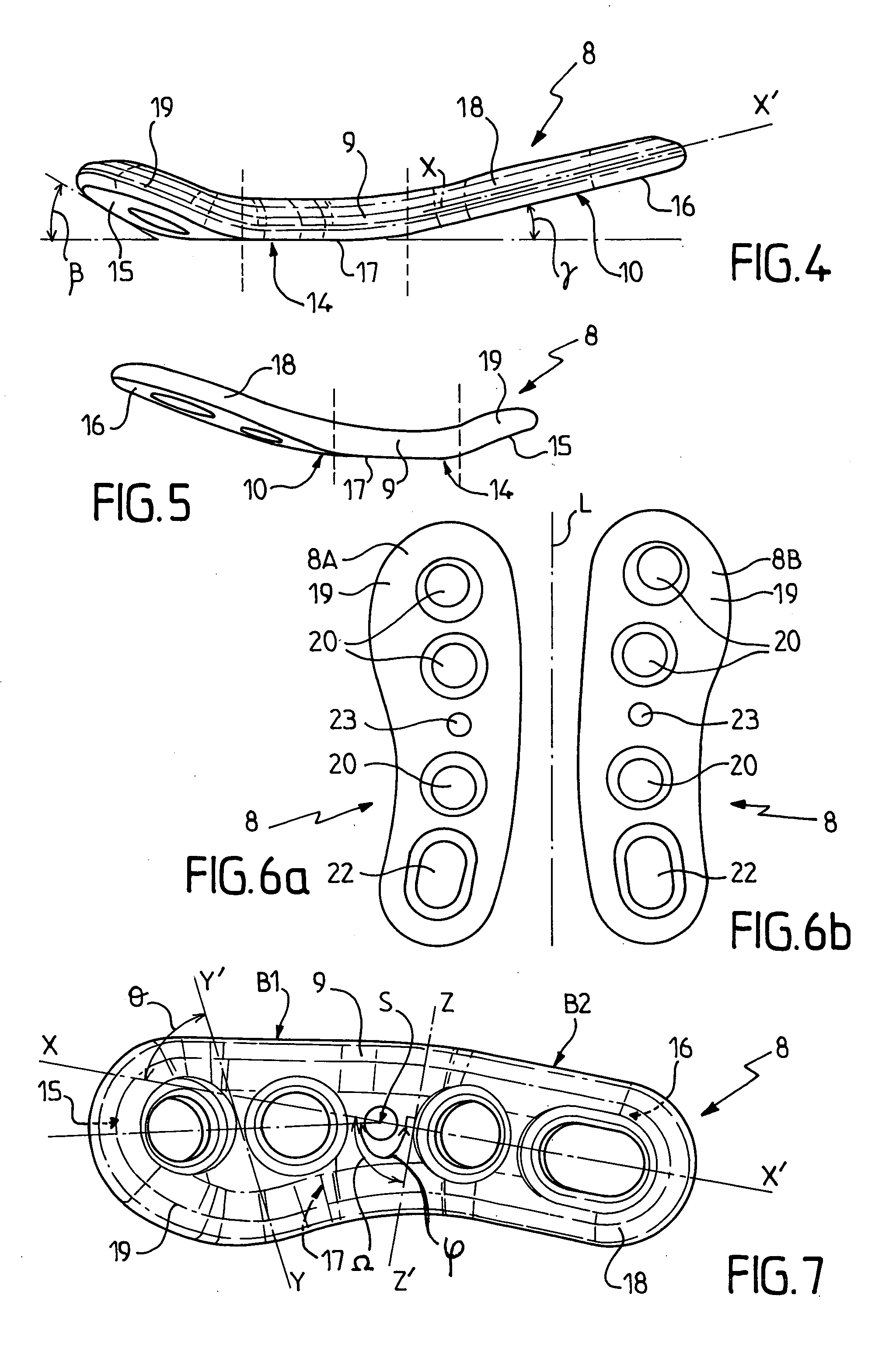
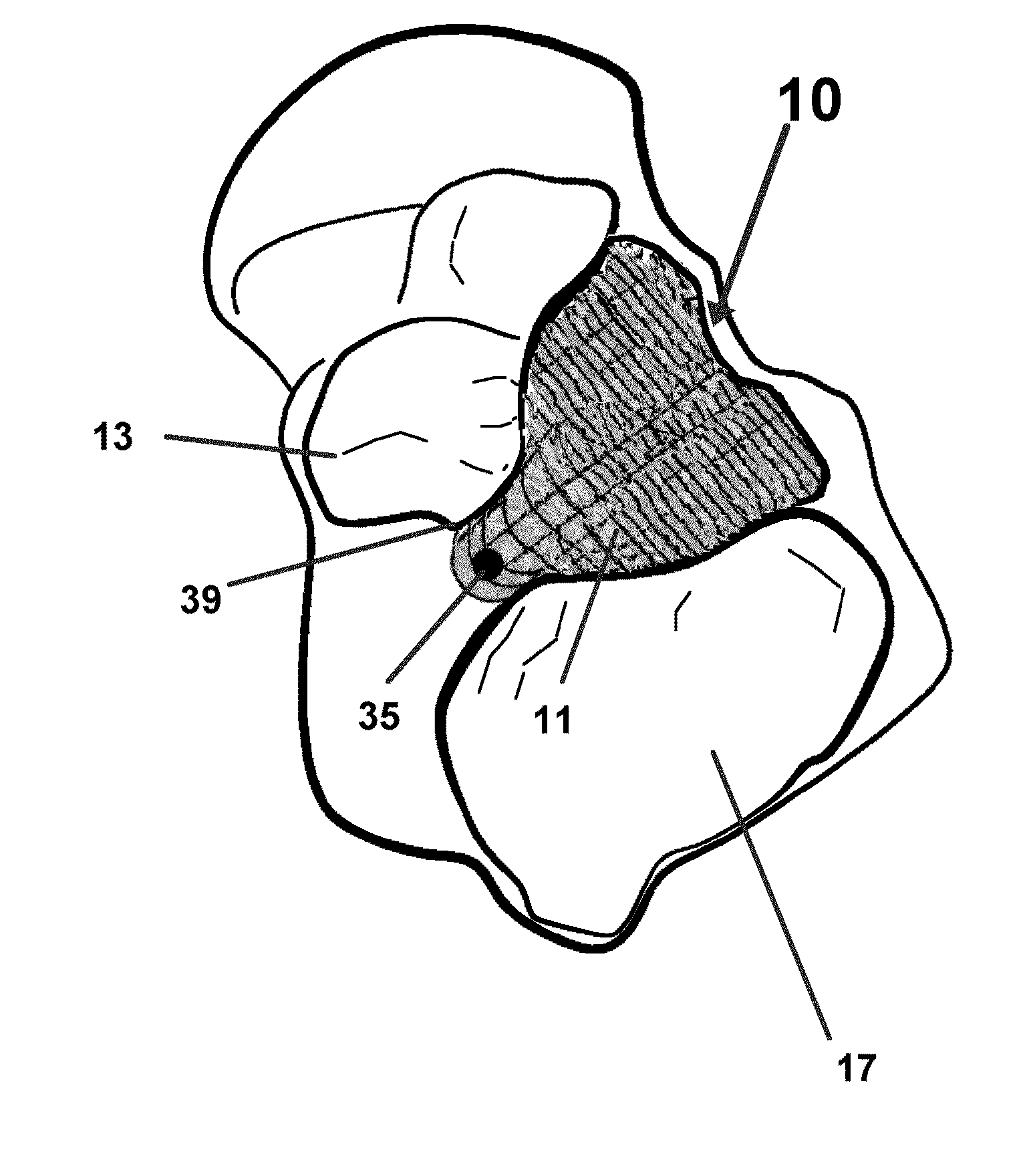
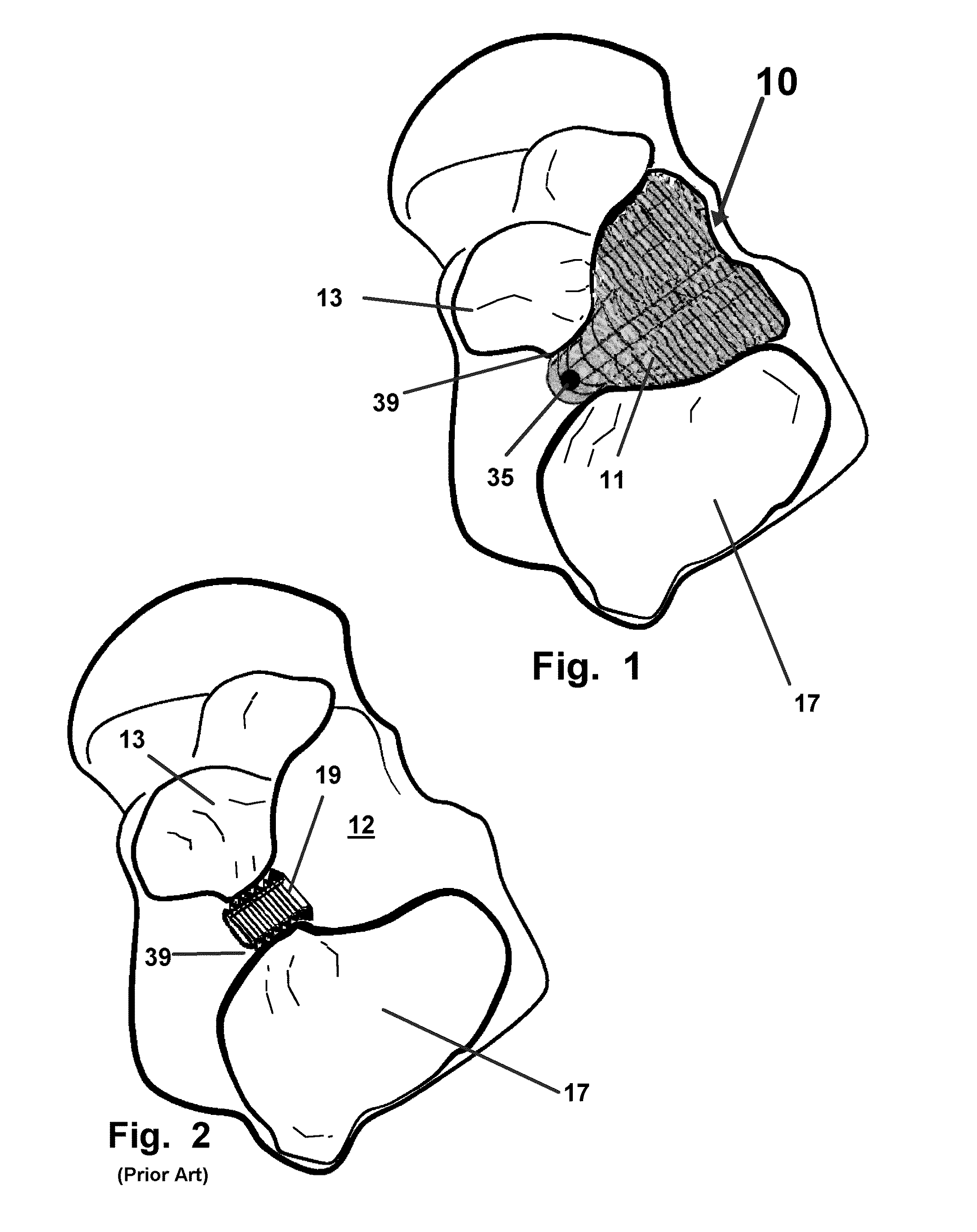
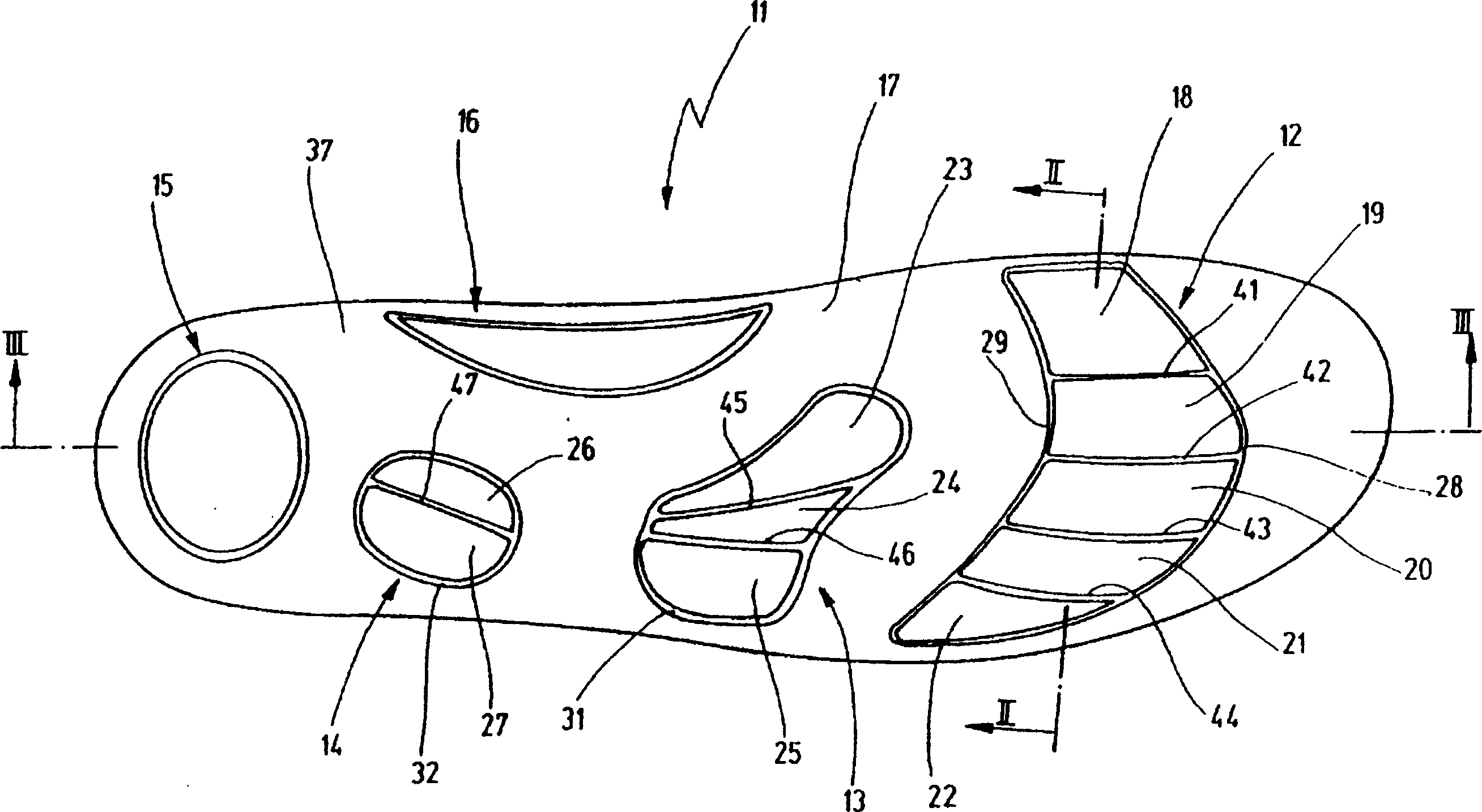
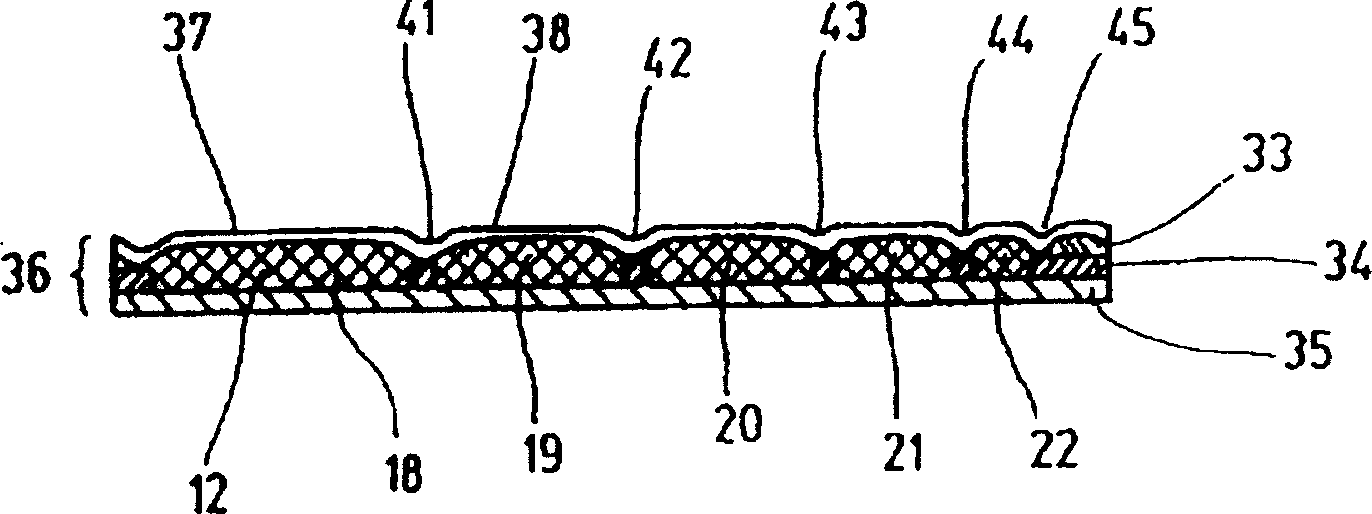
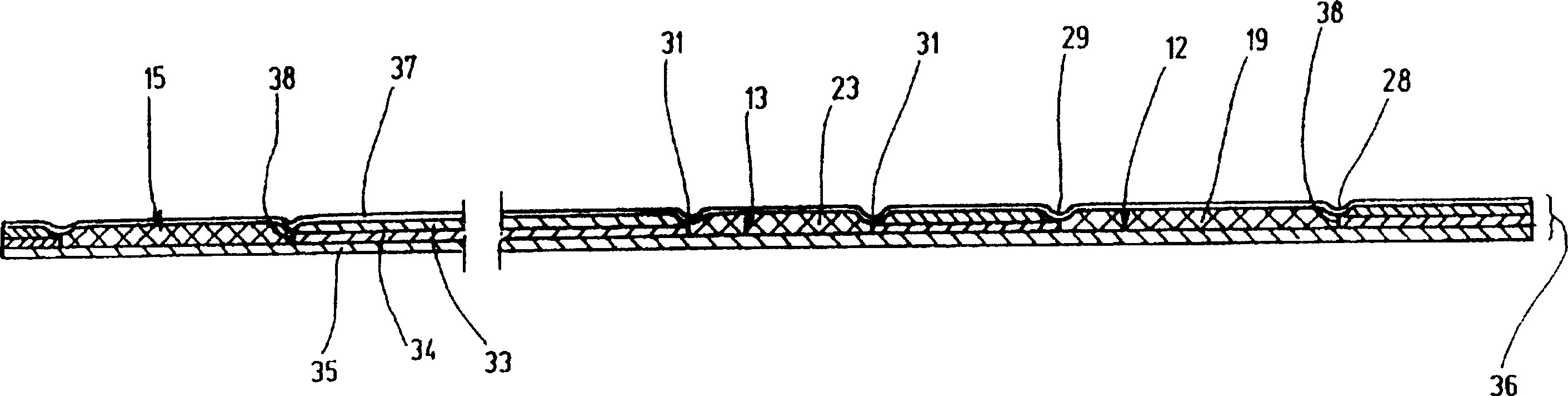
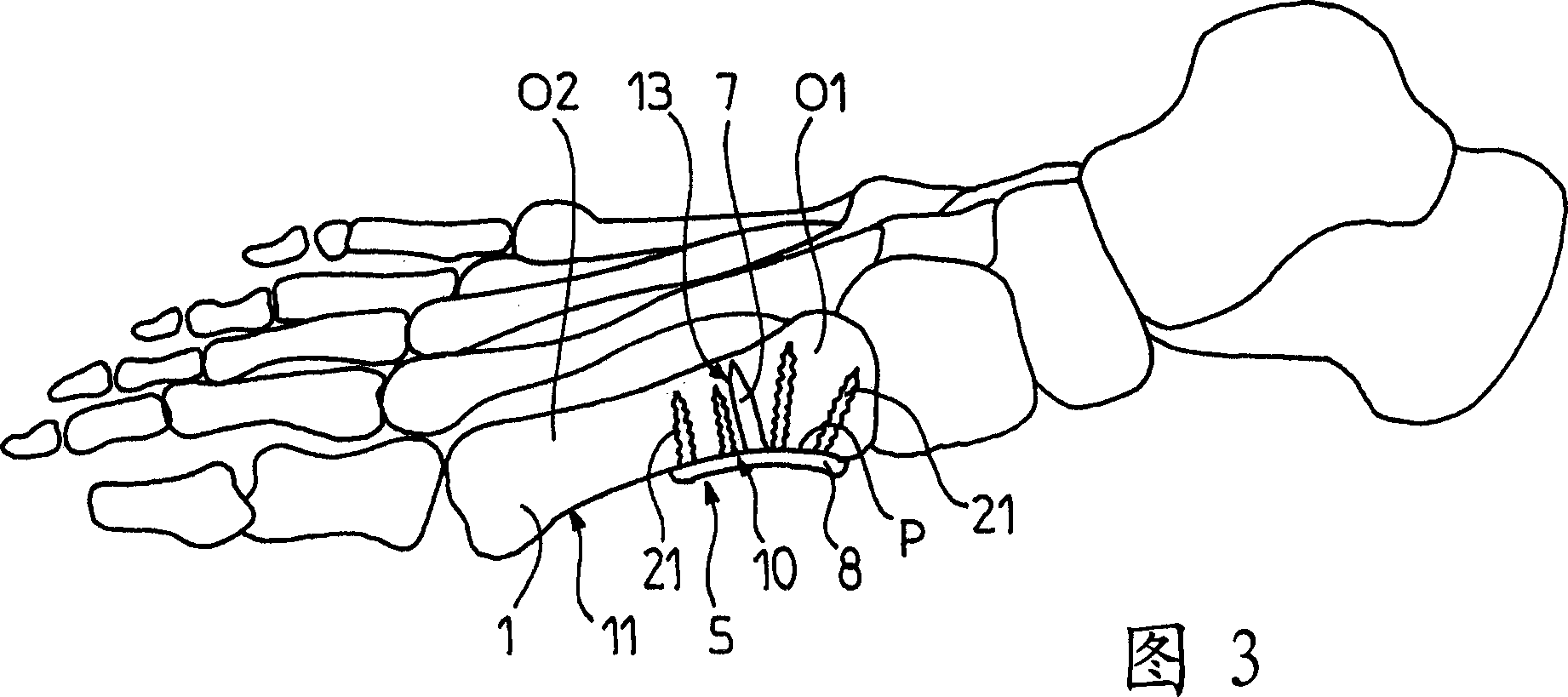
Fastener implant for osteosynthesis of fragments of a first metatarsal bone that is broken or osteotomized in its proximal portion and a corresponding osteosynthesis method
InactiveUS20060015102A1Easy to put into placeEasy to position properlyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPlantar surfaceBone splinters
The invention provides a fastener implant for osteosynthesis of fragments of the first metatarsal bone in its proximal portion situated towards the tarsal bone, the implant comprising at least a fastener element for fastening via a fastener face on or against the outside surface of the first metatarsal bone in order to hold the bone fragments together, wherein said fastener face includes at least one anatomical surface portion of shape that is substantially complementary to the shape of the plantar surface of the proximal portion of the first metatarsal bone.
Owner:NEWDEAL
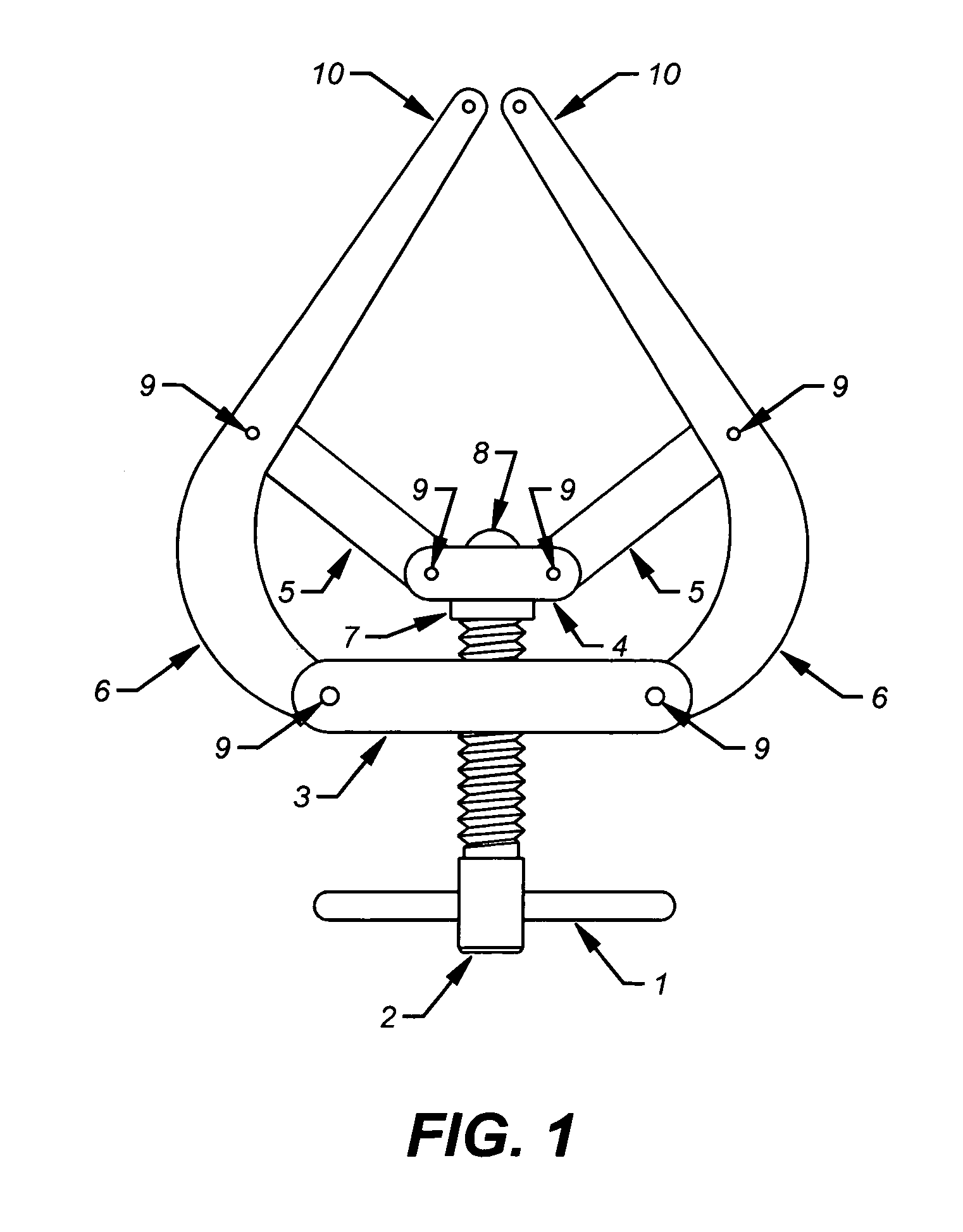
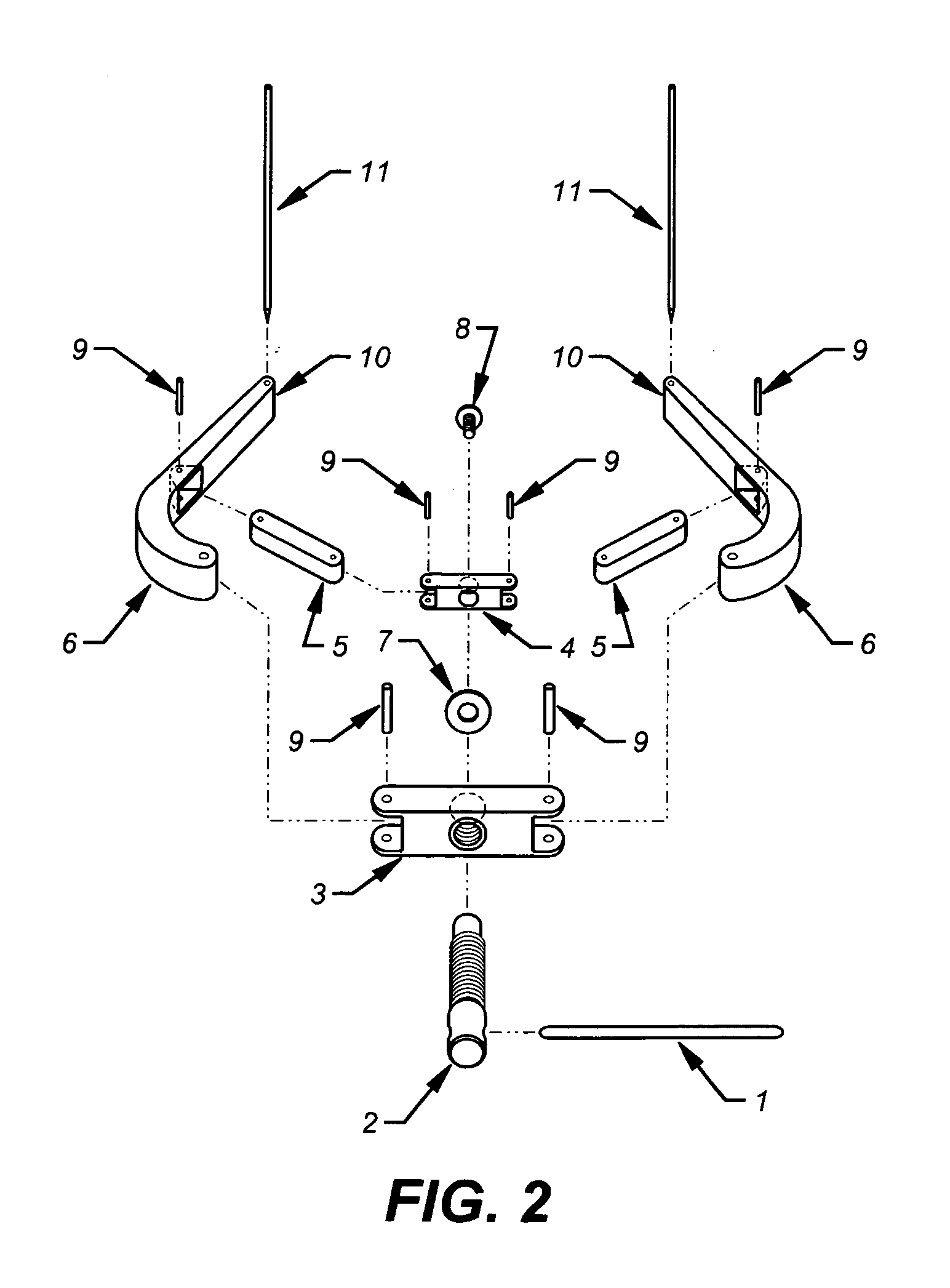
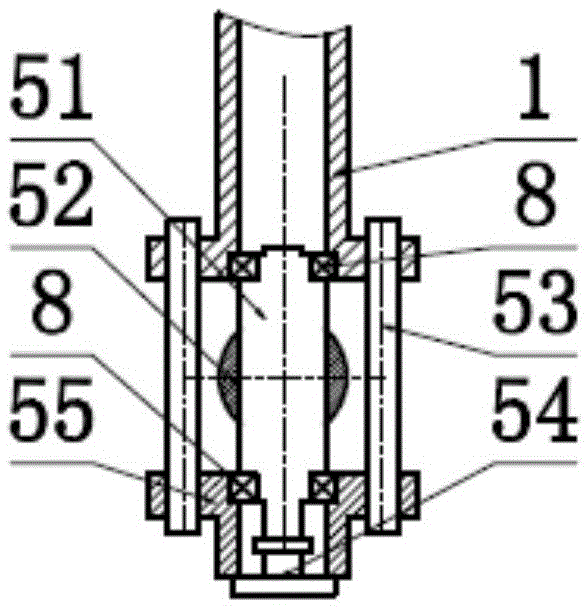
Tarsal joint space distractor
InactiveUS7097647B2Easy to useAbility to efficientlyProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesDistractionMedicine
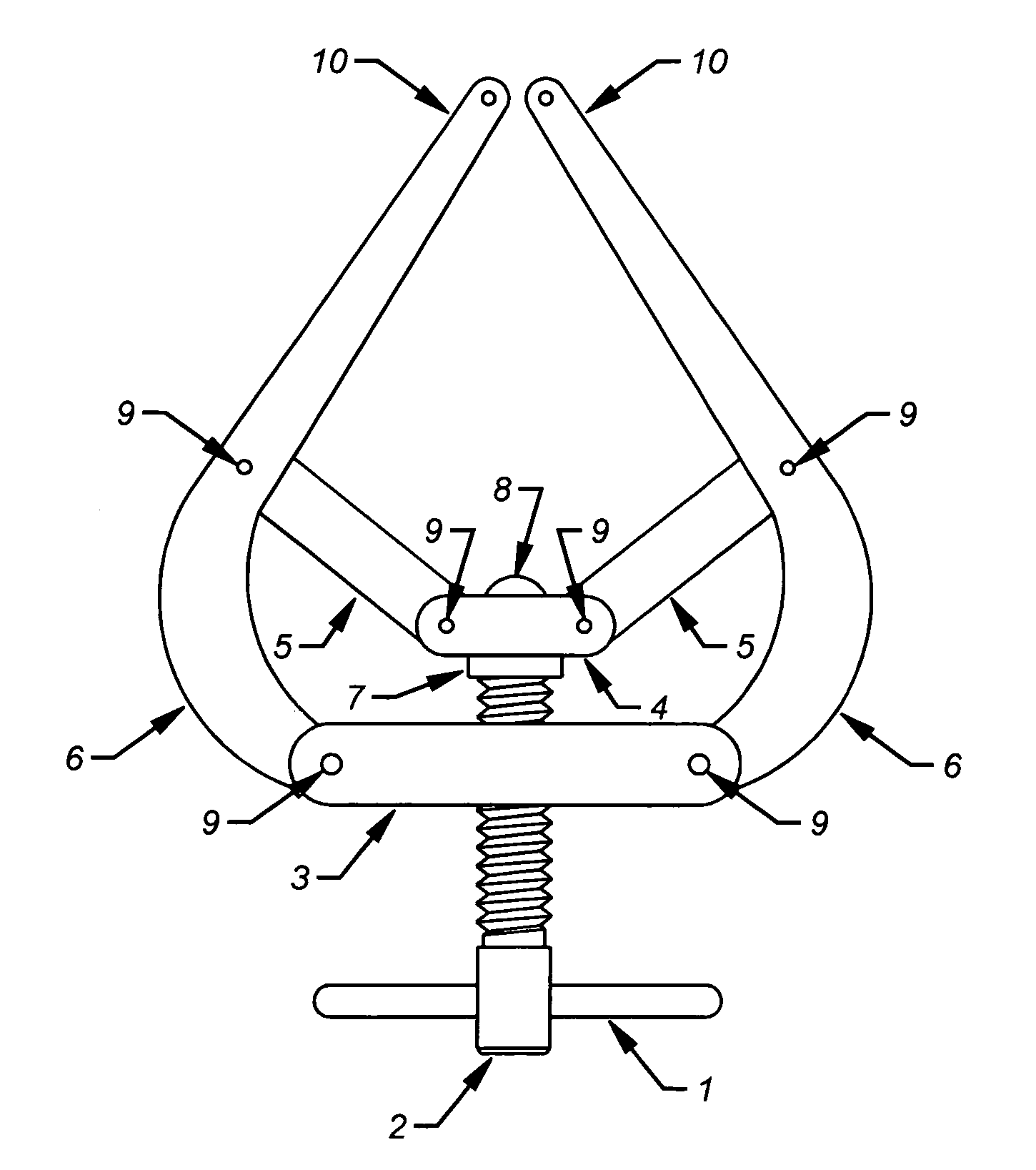
This disclosure relates to an improved dual axis surgical retractor for use by orthopedic or podiatric surgeons for controlled distraction of tarsal joints or compression of osseus fragments. This retractor generally consists of a pair of screw actuated retractor arms, the tips of which each have apertures for receiving and facilitating temporary pin fixation of the respective tarsal bones to be retracted or osseus fragments to be compressed.
Owner:SEGLER CHRISTOPHER PAIGE
Subtalar implant and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20070173954A1Facilitate proper positioningAnkle jointsJoint implantsAnatomical structuresSacroiliac joint
The present invention provides a subtalar implant as well as methods of use thereof for the purpose of correcting podiatric disorders such as various types of flat foot conditions relating to the subtalar joint. The subtalar implant is capable of threaded engagement with a positioning element used to position and manipulate the implant during surgical implantation in the sinus tarsi of the foot. The implant is cannulated to receive a guide rod to facilitate final positioning of the implant. Once implanted, the subtalar implant provides anatomical fit with the subtalar joint anatomical structure without the need for indentations to receive osseous tissue growth to anchor the subtalar implant.
Owner:VILEX LLC
Foot support
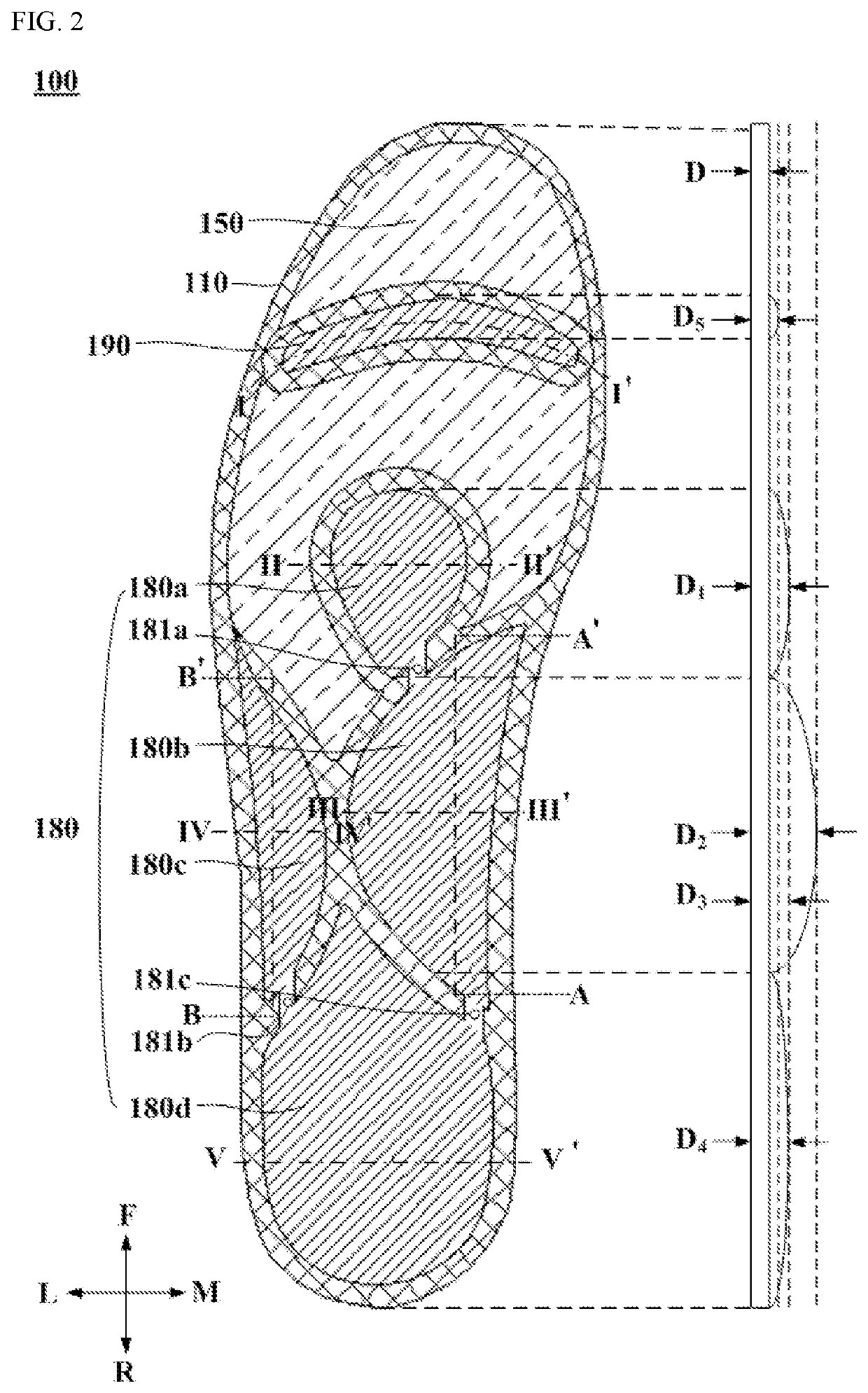
A foot support includes a base material having an area approximately a size of a foot, a deepened heel cup in an upper portion of a heel portion of the base material, a heel skive in a lower portion of the base material in a heel portion of the base material, and a top cover configured to cover substantially all of an upper surface of the base material. The heel skive is configured to add additional stability to the mid-tarsal and sub-talor joints by inverting them.
Owner:WEISS ALLAN G
Subtalar arthroereisis implant apparatus and treatment method
ActiveUS20110208317A1Precise positioningPerformance maximizationAnkle jointsJoint implantsCalcaneusBone structure
A device and method of manufacturing and implanting a custom subtalar arthroereisis implant having side surfaces which are mirrored in topography with the sinus tarsi of a patient. The implant is formed using images of the patient standing in a weight bearing position with their sinus tarsi and the surrounding bone structure in an anatomically correct alignment. Once implanted, the implant urges and maintains the anatomically correct alignment thereby minimizing any patient tendency for abnormal motion between said patent's talus and calcaneus.
Owner:FELDMAN KENT A
Foot shape data acquisition method based on pictures
InactiveCN106127773AEasy extractionImprove online shoe shopping experienceImage enhancementImage analysisCouplingData acquisition
The invention discloses a foot shape data acquisition method based on pictures. The method comprises five steps of picture shooting, picture pretreatment, foot length and width calculation, tarsus height calculation and shoes selecting and coupling. Firstly, two foot shape pictures are shot and pretreated to extract foot shape contour data; according to two sets of the foot shape contour data, the foot length, the foot width and the front tarsal bone bump height are calculated respectively to obtain corresponding foot shape parameters; and finally, according to data of the gender, age and foot shape parameters of a user, coupling with the brand and pattern of some pair of shoes on an online mart is conducted to recommend the optimal size for the user. The invention can conveniently and rapidly extract the foot shape data, can accurately perform size coupling of shoes of different brands and types according to the foot shape data, and can greatly improve the online shoes purchasing experience and reduce the rate of returns as the user selects unsuitable sizes in online shopping. The method is advantaged by simple operation, convenient usage and low cost.
Owner:BEIJING 3DWORLD SCI & TECH CO LTD
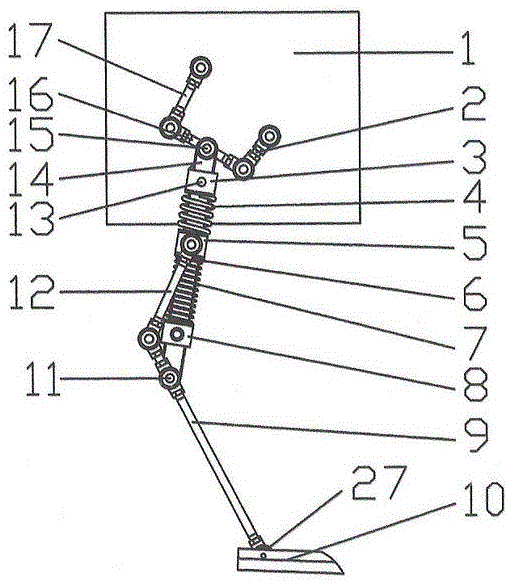
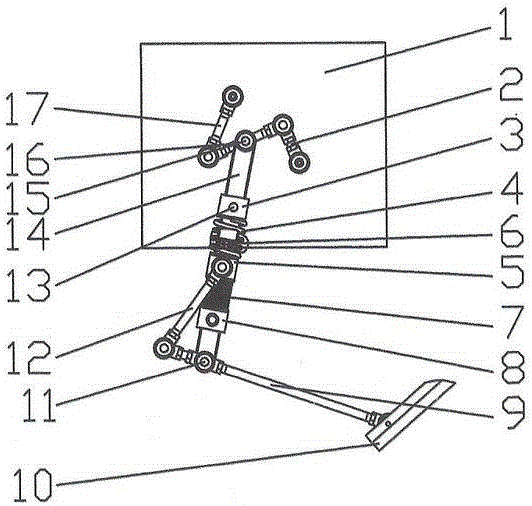
Energy-saving walking leg mechanism simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic
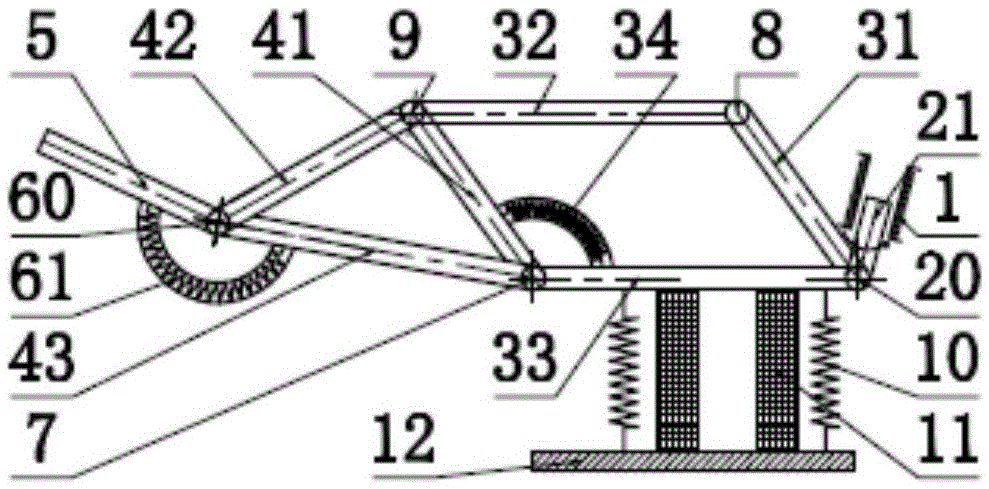
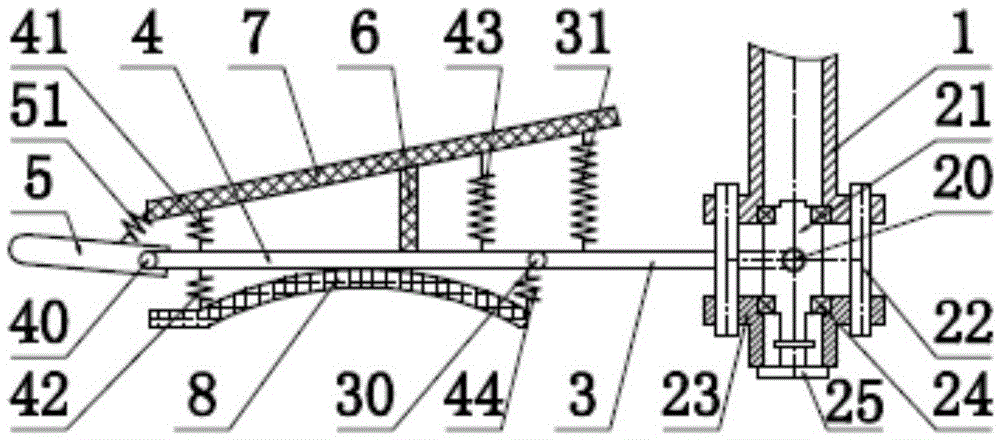
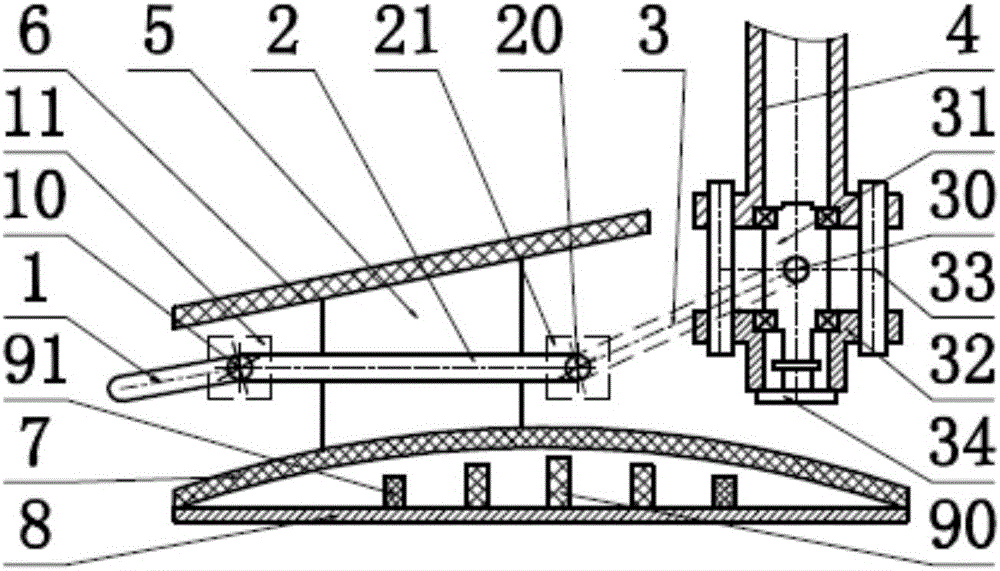
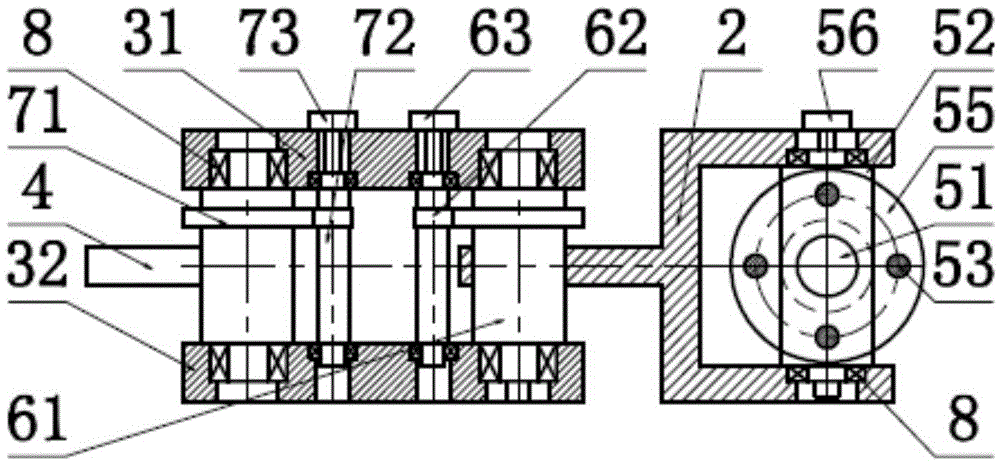
The invention discloses an energy-saving walking leg mechanism simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic. The energy-saving walking leg mechanism comprises a rack, a crank connection rod mechanism, a rebounding mechanism and a toe, wherein the crank connection rod mechanism comprises a crank, a thigh and a rocking rod; the rebounding mechanism comprises a fixed sliding block, a crus, a movable sliding block, a connection rod, a spring, a baffle plate, a ratchet mechanism, a brake cable, an angle limiter and metatarsal bones. The energy-saving walking leg mechanism is designed on the basis of the size parameters of the ostrich hindlimb and the rebounding characteristics of joints between ostrich tarsal bones; an energy-saving and efficient walking leg is designed by simulating the ostrich hindlimb movement; the metatarsal bones automatically stretch by using the rebounding force generated by compressing the spring, so that the energy loss is reduced; the energy-saving and efficient walking leg simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic can achieve the energy-saving and efficient purpose.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
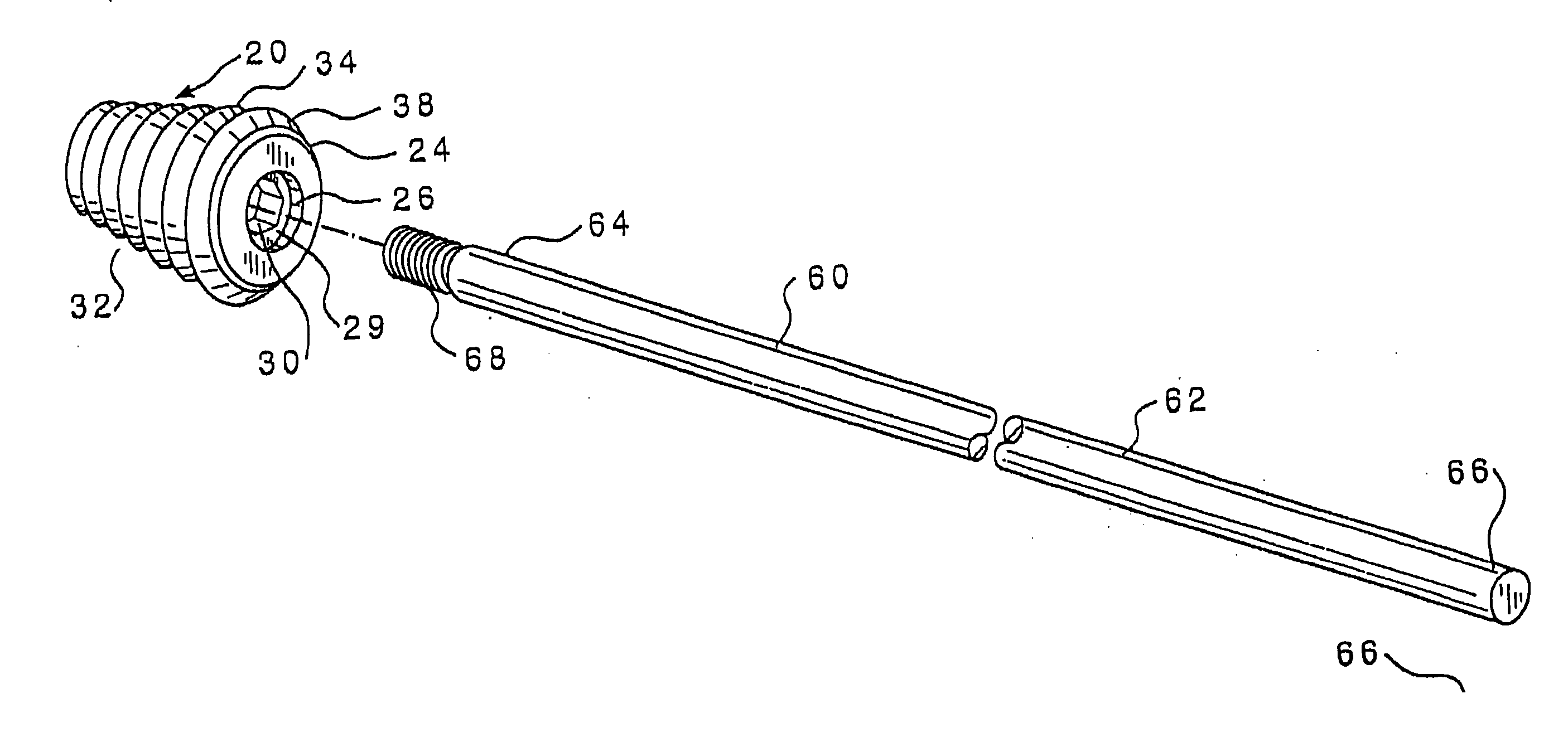
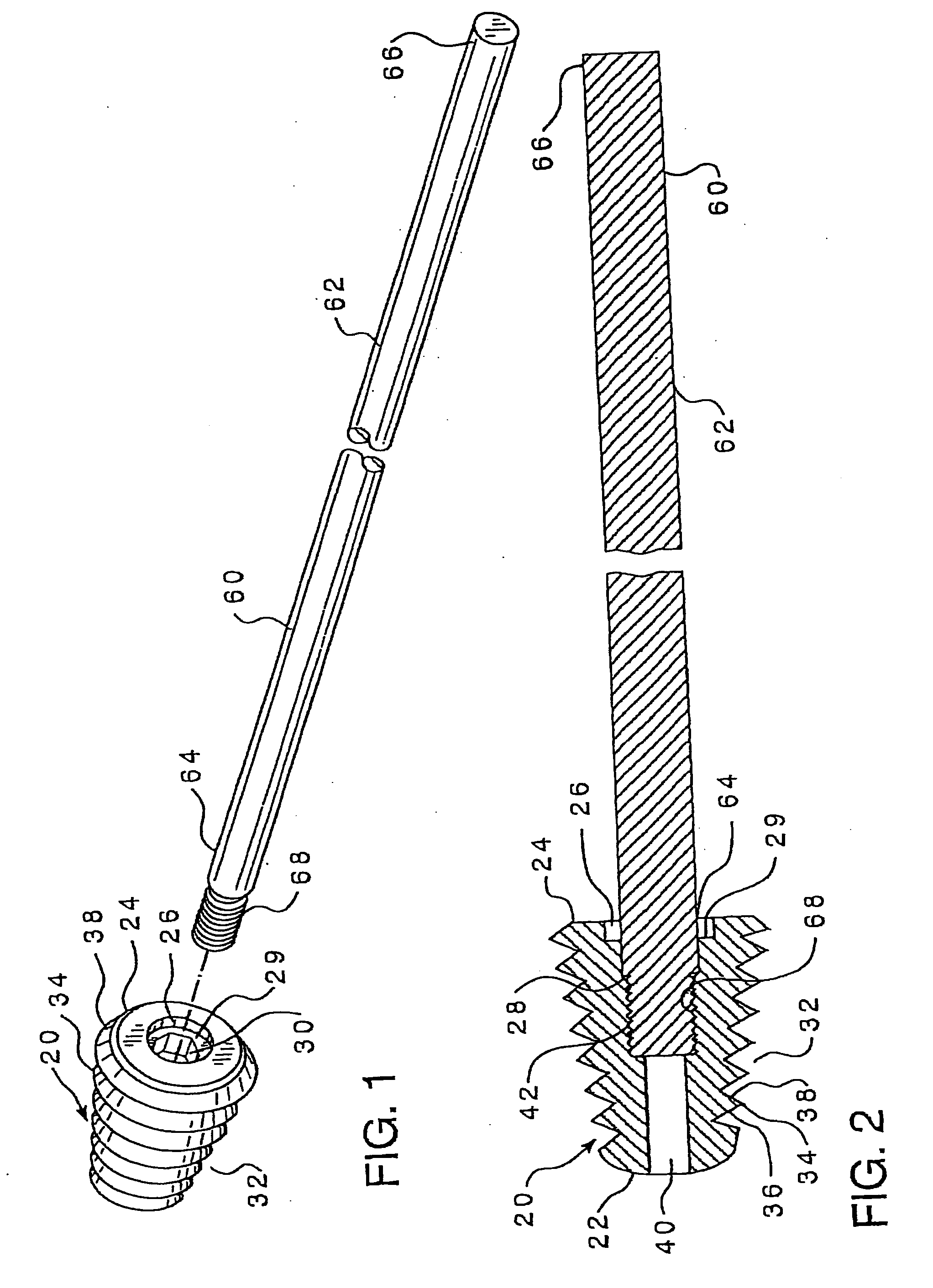
Percutaneous Metatarsal Fixation Guide and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20190117238A1Reduce riskPrecise alignmentInternal osteosythesisFastenersLong axisFracture sites
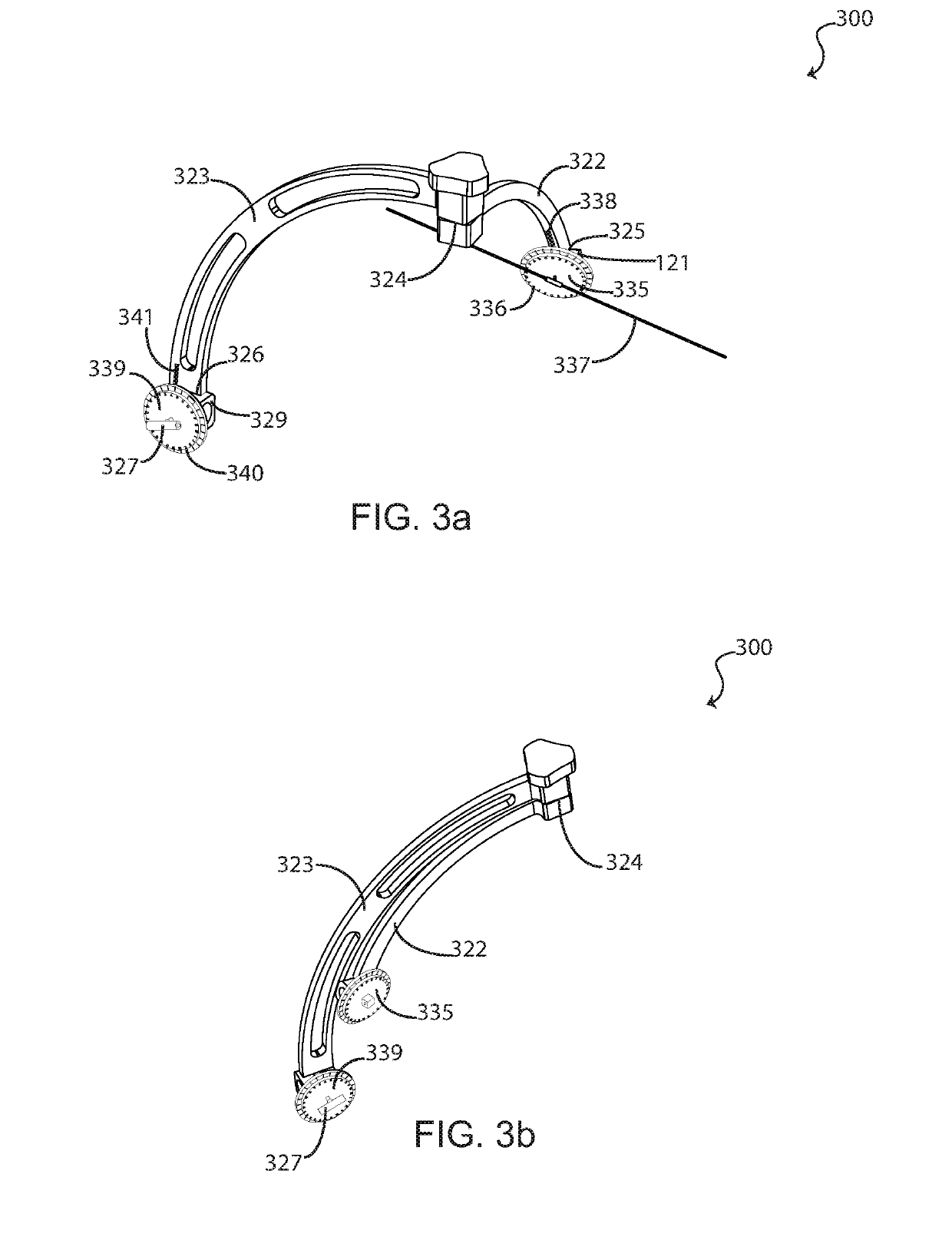
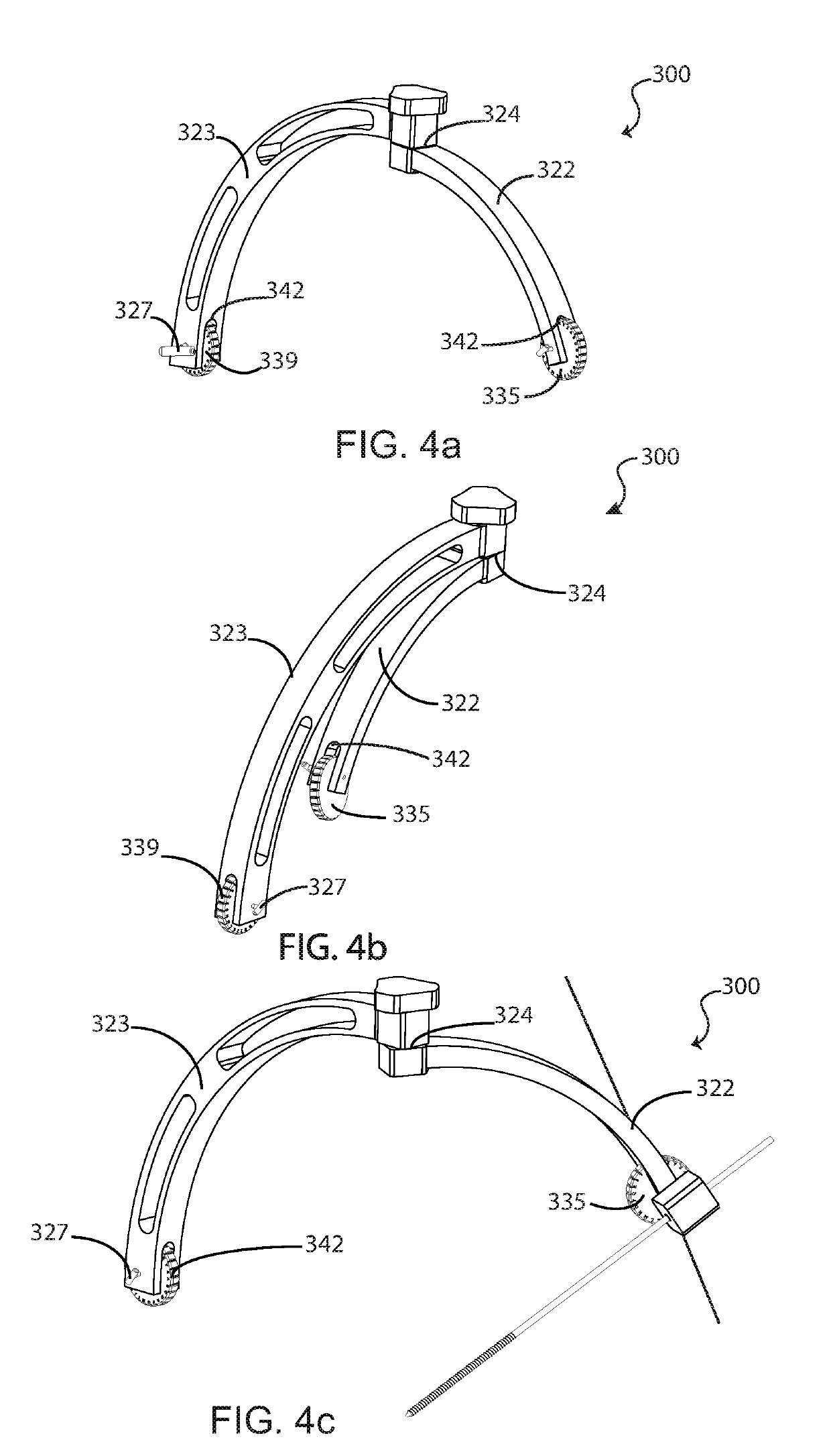
A percutaneous metatarsal fixation guide, including methods of use, is provided. The percutaneous metatarsal fixation guide includes a means for aligning a drill guide bearing a drill sleeve with the central longitudinal axis of a fractured metatarsal, metacarpal, or similar bone. Precise radiographic alignment of the drill sleeve with the long axis of the fractured bone facilitates accurate placement of fixation hardware across the fracture site, allowing for healing in alignment. The fixation bearing two corresponding index wheels is rigidly mounted to a tarsal bone via a temporary threaded K-wire, wherein an index marking on a second index wheel coupled to a drill sleeve may be positioned to correspond with an index marking on first index wheel coupled to an alignment guide, such that the drill sleeve is aligned with the fractured metatarsal. This allows precise placement of fixation hardware, compared to using a conventional “free-hand” technique.
Owner:LEVITT ANDREW
Four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel impact resistant mechanical foot for humanoid robot
The invention discloses a four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel impact resistant mechanical foot for a humanoid robot, which belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel impact resistant mechanical foot for the humanoid robot comprises a mechanical shank, a tarsal skeleton, an ankle shaft A, an ankle shaft B, a metatarsal skeleton, a toe, a toe joint, a sole, two compression resistant rubber columns, two tensile springs, a torsion spring B and a torsion spring A, wherein the toe joint is used for connecting the toe with the metatarsal skeleton; the torsion spring B is mounted between the toe and a metatarsal bone rod C; the torsion spring A is mounted between a tarsal bone rod C and a metatarsal bone rod A; the tarsal skeleton comprises a tarsal bone rod A, a tarsal bone rod B and a tarsal bone rod C; the metatarsal skeleton comprises a metatarsal bone rod A, a metatarsal bone rod B and a metatarsal bone rod C; the two tensile springs are mounted on the external sides of the two compression resistant rubber columns and always in a tensile and stressed state; the mechanical shank can rotate around the ankle shaft A; the ankle shaft B is orthogonal to the ankle shaft A; and the mechanical shank can realize twisting motion around the ankle shaft B. The invention is the humanoid robot foot with reasonable structure, impact resistance and four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Shock-resistant four-degree-of-freedom parallel humanoid mechanical foot
The invention discloses a shock-resistant four-degree-of-freedom parallel humanoid mechanical foot and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The shock-resistant four-degree-of-freedom parallel humanoid mechanical foot comprises a mechanical shank, an orthogonal ankle joint shaft, a tarsal bone rod, a metatarsal bone rod arranged at the left end of the tarsal bone rod through a tarsal and metatarsal hinge, toes arranged on the metatarsal bone rod through a metatarsal and toe hinge, an arch-shaped sole board arranged at the bottom of the metatarsal bone rod, an instep face and a rubber strut with the two ends connected with the instep face and the metatarsal bone rod 4. The orthogonal ankle joint shaft comprises a main shaft frame, a main ankle shaft A, a main ankle shaft B, bolts and a motor. A toe spring is arranged between the toes and the metatarsal bone rod. An upper metatarsal bone spring A and an upper metatarsal bone spring B are arranged between the instep face and the metatarsal bone rod. The right end of the instep face is connected with the tarsal bone rod through a tarsal bone spring. The left end and the right end of the arch-shaped sole board are connected with the metatarsal bone rod through a lower metatarsal bone spring A and a lower metatarsal bone spring B. The shock-resistant four-degree-of-freedom parallel humanoid mechanical foot is reasonable in structure and stable in operation, has four degrees of freedom and the shock resistant function and is in a parallel mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
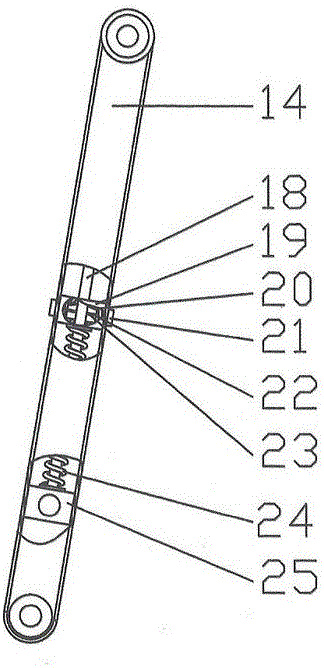
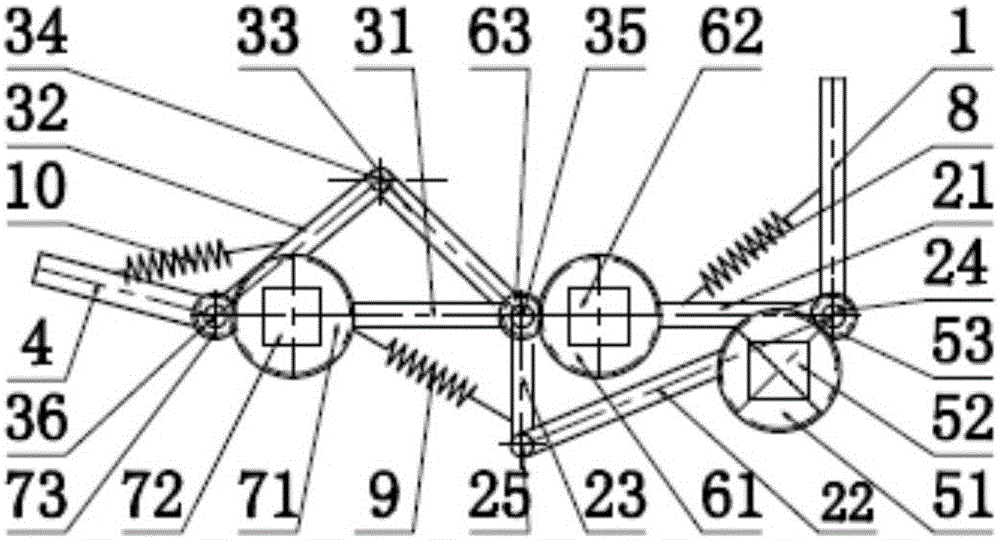
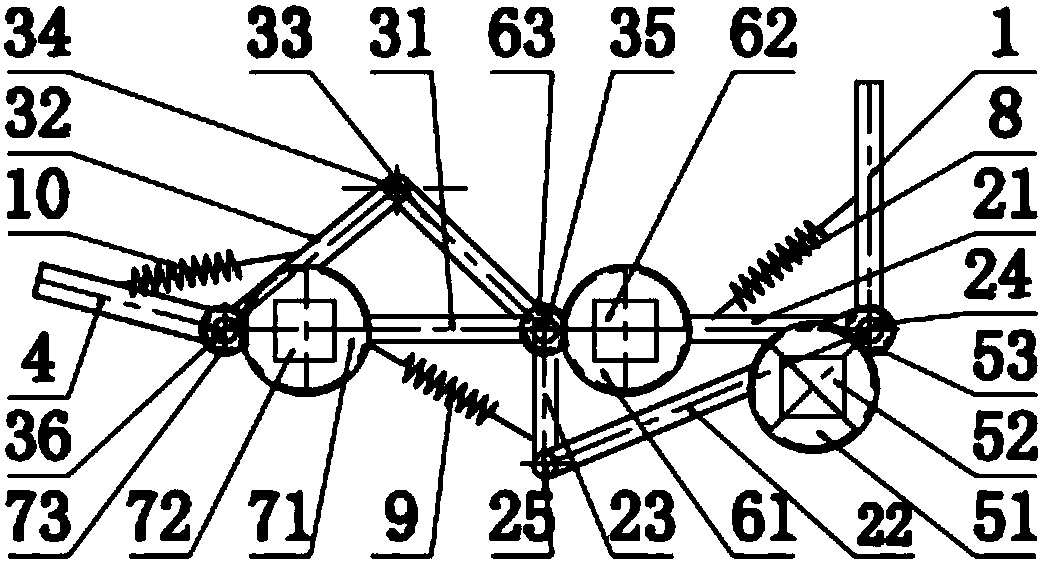
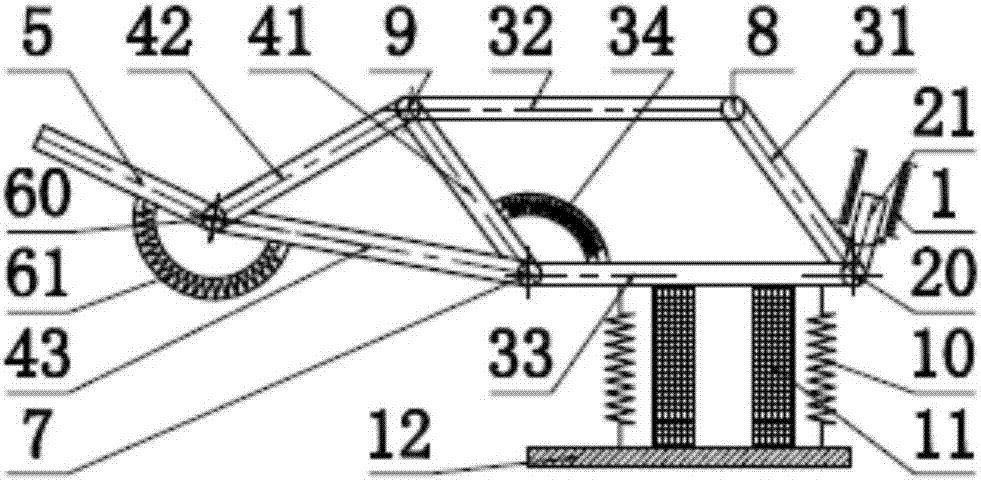
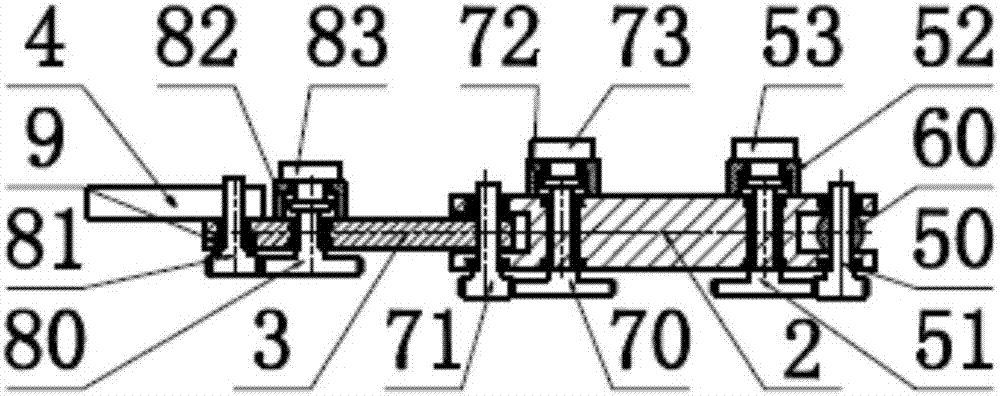
Bionic passive rebound mechanical leg
The invention discloses a bionic passive rebound mechanical leg which comprises a body, a crank connecting rod mechanism, a passive rebound mechanism and a foot end, wherein the crank connecting rod mechanism comprises a crank, a thigh bone and a rocker; the passive rebound mechanism comprises a fixed slide block, a shin bone, an upper outer spring, a pulley, a movable slide block, a splinter bone, a lower outer spring, a stopper, a metatarsal bone, a pin shaft and an inner spring mechanism; the inner spring mechanism comprises a base, an inner shaft, a compressed spring plate, a compressed spring plate base, a baffle, a small spring, a small spring guide rod and a brake cable; the foot end comprises a torsional spring and toes; the toes are made from flexible storage energy materials. According to the bionic passive rebound mechanical leg, based on the dimension parameters of ostrich hind limbs and passive rebound characteristics of joints among ostrich tarsal bones, the passive rebound function of the joints among the tarsal bones of bionic ostrich hind limbs is realized by utilizing the passive rebound mechanism, so that the energy consumption can be reduced, the ground impact force can be absorbed at initial contact by utilizing an elastic element, and the buffering and damping effects are achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Series-parallel damping humanoid three-freedom-degree mechanical foot
ActiveCN105730549AAchieve relative motionRealize simulationVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDamping function
The invention discloses a series-parallel damping humanoid three-freedom-degree mechanical foot and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The series-parallel damping humanoid three-freedom-degree mechanical foot comprises a mechanical shank, a tarsal bone rod A, a tarsal bone rod B, a tarsal bone rod C, a metatarsal bone rod A, a metatarsal bone rod B, a metatarsal bone rod C, a mechanical toe, a shank spring connecting the mechanical shank with the tarsal bone rod A, an ankle large gear, an ankle motor, an ankle small gear, a tarsal bone large gear, a tarsal bone motor, a tarsal bone small gear, an ankle shaft, a tarsal bone hinge, a metatarsal bone shaft, a toe shaft, a tarsal and metatarsal spring, a toe spring, a toe large gear, a toe small gear and a toe motor, wherein the ankle large gear, the ankle motor and the ankle small gear are arranged on the tarsal bone rod B. The ankle shaft is fixedly combined with the mechanical shank and provided with the ankle small gear. The metatarsal bone shaft is fixedly combined with the metatarsal bone rod A and provided with the ankle small gear. The toe shaft is fixedly combined with the mechanical toe and provided with the toe small gear. The mechanical foot is a humanoid mechanical foot which is simple in structure, has the three freedom degrees and a damping function and is in a series-parallel mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Inner sole for shoe
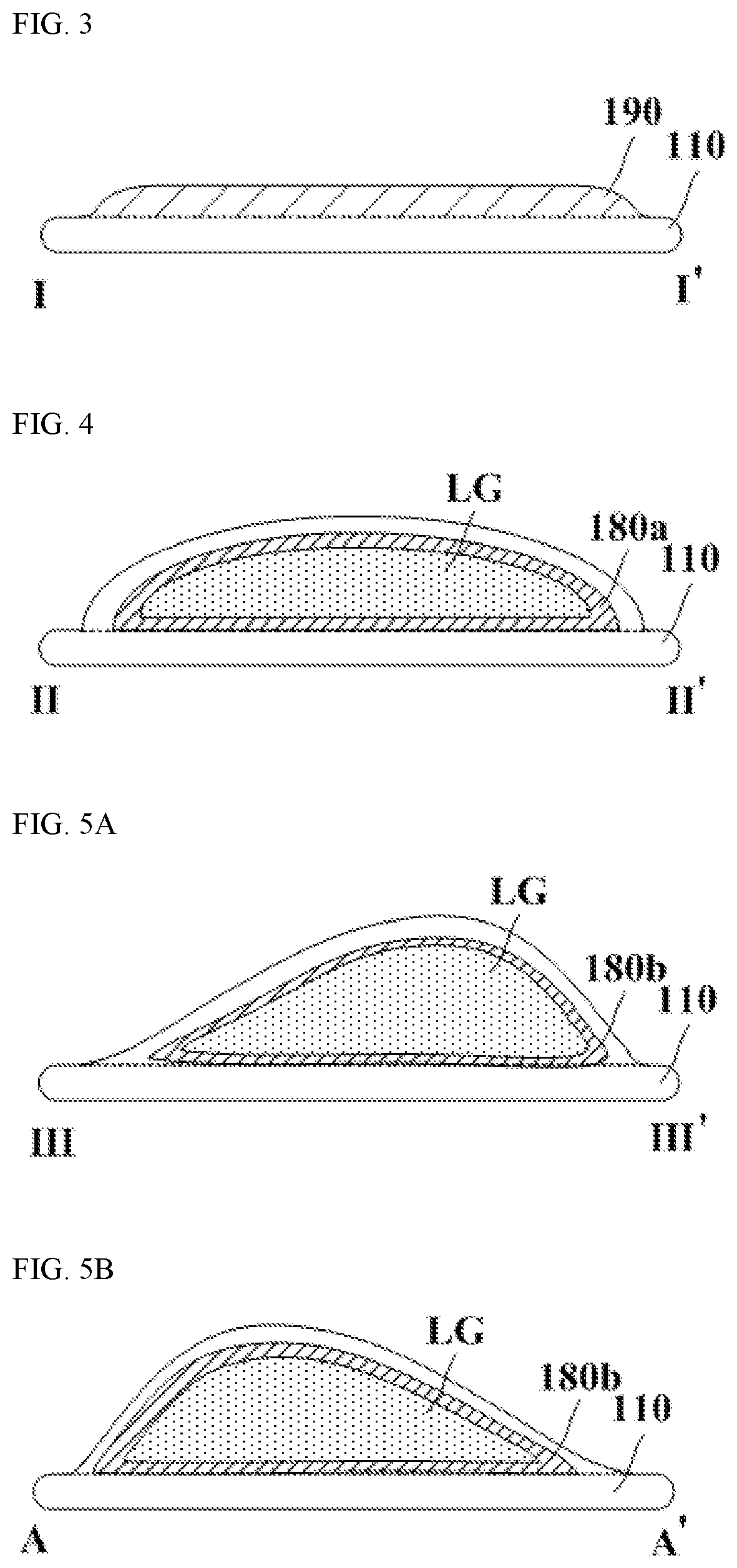
A shoe insole, including a sole base, a sole covering layer and several pillow-type layers distributed on the surface of the sole, wherein these layers are arranged in the support area that affects the contraction of the foot muscles, and the first pillow-type layer is located at the forefoot joint area, the second pillow layer is located in the metatarsal / tarsal transition zone, and the third pillow layer is located in the metatarsal / heel transition zone. Each pillow layer itself is divided into discrete layers that are arranged laterally on the sole surface and are separated from each other. The convex disk-shaped block, and the pillow-type layer forms a plane with the surface of the sole base. The fourth pillow-type layer is located in the heel area and is convex disk-shaped. It is best to be approximately elliptical in the transverse direction of the sole and is in contact with the surface of the sole base. Forming a plane, the fifth occipital layer is sickle-shaped and is located in the arch area. Alternatively, the surface of the pillow layers is raised relative to the plane of the surface of the sole base, and the fourth pillow layer and the fifth pillow layer are raised above the plane of the shoe base and the latter are located in the arch area .
Owner:汉斯塞特
Fastener implant for osteosynthesis of fragments of a first metatarsal bone that is broken or osteotomized in its proximal portion
InactiveCN1732862ARapid return to daily physical activityAvoid separationInternal osteosythesisBone implantPlantar surfaceBone fragment
The invention provides a fastener implant for osteosynthesis of fragments of the first metatarsal bone in its proximal portion situated towards the tarsal bone, the implant comprising at least a fastener element for fastening via a fastener face on or against the outside surface of the first metatarsal bone in order to hold the bone fragments together, wherein said fastener face includes at least one anatomical surface portion of shape that is substantially complementary to the shape of the plantar surface of the proximal portion of the first metatarsal bone.
Owner:NEWDEAL
Alpha adrenergic receptor agonists for treatment of inflammatory diseases
Effective treatments of pain and / or inflammation from tendonitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, tarsal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis, bursitis and / or an oral-facial disease are provided. Through the administration of an effective amount of at least one alpha adrenergic agonist at or near a target site, one can reduce, prevent or treat pain and / or inflammation from tendonitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, tarsal tunnel syndrome, osteoarthritis, bursitis and / or an oral-facial disease.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC +1
Sole structure of sports shoes
The invention relates to a sole which is a sole structure of sports shoes, wherein the bottom surface of the sole structure is divided into a phalange section, a big toe section, a first metatarsus section, a second metatarsus section, a tarsal bone section and an external calcaneus section, corresponding to phalange, metatarsus, tarsal bone and calcaneus of human foot. The phalange section, the big toe section, the first metatarsus section, the second metatarsus section, the tarsal bone section and the external calcaneus section are respectively provided with a plurality of sucking discs which are provided with concave sucking disc bodies in an embedding manner. The inner concave surfaces of the sucking disc bodies are provided with a bulge respectively. The sole structure is designed on basis of an octopus sucking disc structure and a plurality of sucking discs are internally embedded at the phalange section, the big toe section, the first metatarsus section, the second metatarsus section, the tarsal bone section and the external calcaneus section respectively so as to ensure that the sucking discs can firmly adsorb on the ground of a place by means of differences of inside and outside atmospheric pressures of the sucking disc, thus providing stronger adsorption force to the ground and stability.
Owner:吴荣光
Three-degrees-of-freedom series high-frequency mechanical foot for humanoid robot
ActiveCN105620580AAchieve high frequency motion responseSimple structureVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationThree degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a three-degrees-of-freedom series high-frequency mechanical foot for a humanoid robot, which belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The three-degrees-of-freedom series high-frequency mechanical foot for the humanoid robot comprises an instep surface, a sole, a tarsal bone, a metatarsal bone, a metatarsal skeleton, a toe, an ankle shaft, an ankle gear A, an ankle gear B, an ankle motor, a tarsal bone shaft, a tarsal bone gear A, a tarsal bone gear B, a tarsal motor, a toe shaft, a toe gear A, a toe gear B and a toe motor, wherein the ankle gear B and the ankle gear A are respectively mounted on the tarsal bone and a mechanical shank; the tarsal bone gear B and the tarsal bone gear A are respectively mounted on the metatarsal bone and the tarsal bone; the toe gear B and the toe gear A are respectively mounted on the metatarsal bone and the toe; output shafts of the ankle motor, the tarsal motor and the metatarsal motor are respectively connected with the ankle gear B, the tarsal bone gear B and the toe gear B; the upper and lower ends of the metatarsal skeleton are respectively provided with the instep and the sole; and the metatarsal bone is mounted on the metatarsal skeleton. The invention is a humanoid robot foot with reasonable structure, three-degrees-of-freedom and high frequency response characteristic and series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Three-freedom-degree series vibration-reducing mechanical humanoid robot foot
InactiveCN105752193AReasonable structureVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMechanical equilibrium
The invention discloses a three-freedom-degree series vibration-reducing mechanical humanoid robot foot, and belongs to the field of humanoid robots.The foot comprises toes, a metatarsal bone, a tarsal bone, a toe joint, a first torsion spring, a tarsometatarsal joint, a second torsion spring, an ankle joint, a third torsion spring, a tarsal skeleton, an instep and an arch-shaped foot sole; the arch-shaped foot sole is installed on the lower surface of the tarsal skeleton; the metatarsal bone is installed in front of the middle of the tarsal skeleton; when the second torsion spring is located in a mechanical balance state, the included angle between the metatarsal bone and the tarsal bone is 150 degrees; when the third torsion spring is located in a mechanical balance state, a shank bone is in a vertical state and forms a 120-degree included angle with the tarsal bone; the toes and the metatarsal bone can freely rotate with the help of the toe joint; the metatarsal bone and the tarsal bone can freely rotate with the help of the tarsometatarsal joint; the shank bone can freely rotate relative to the tarsal bone around the ankle joint.The humanoid robot foot is simple in structure, has three motion freedom degrees and a vibration reducing function and is in a series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
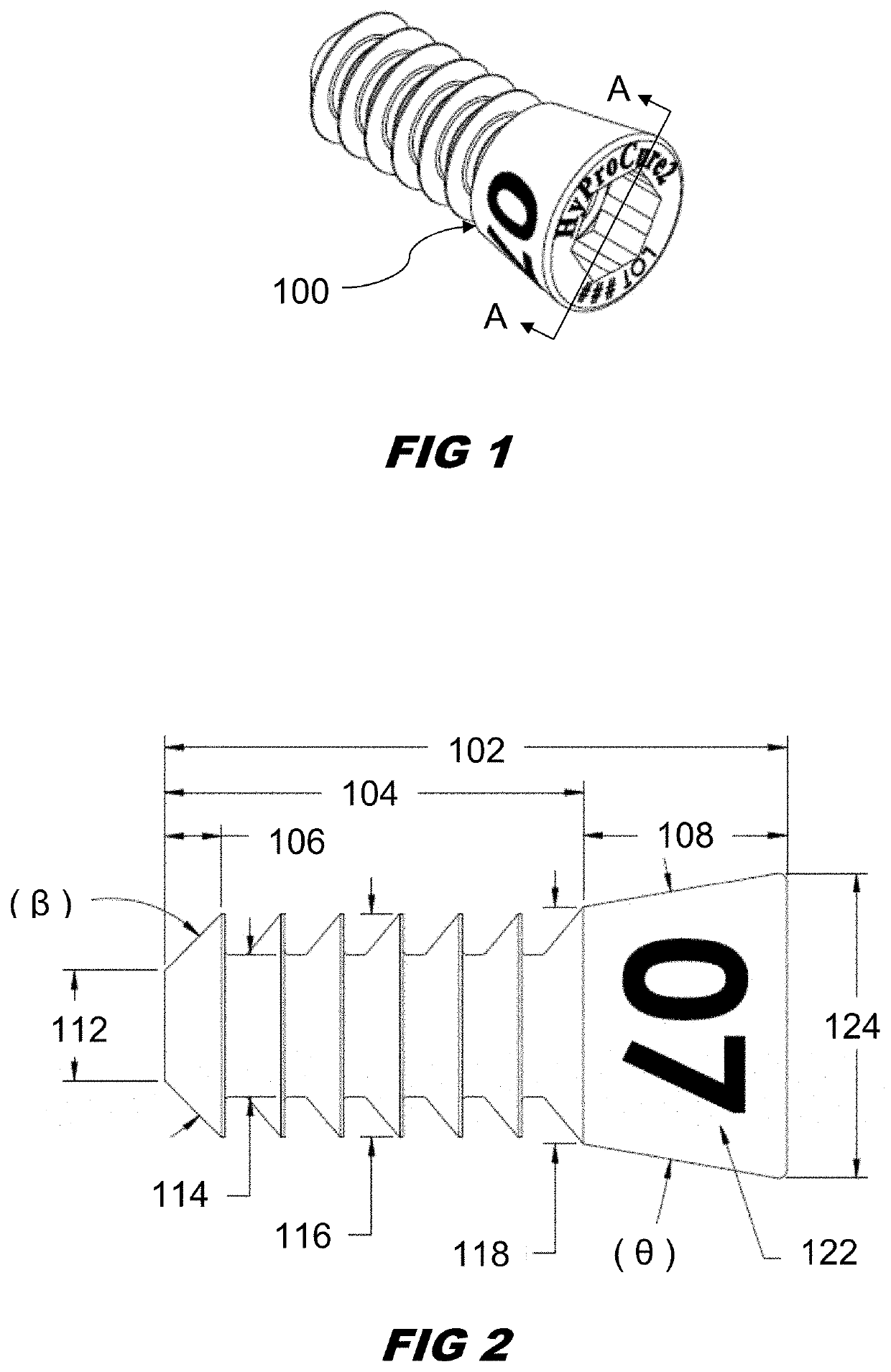
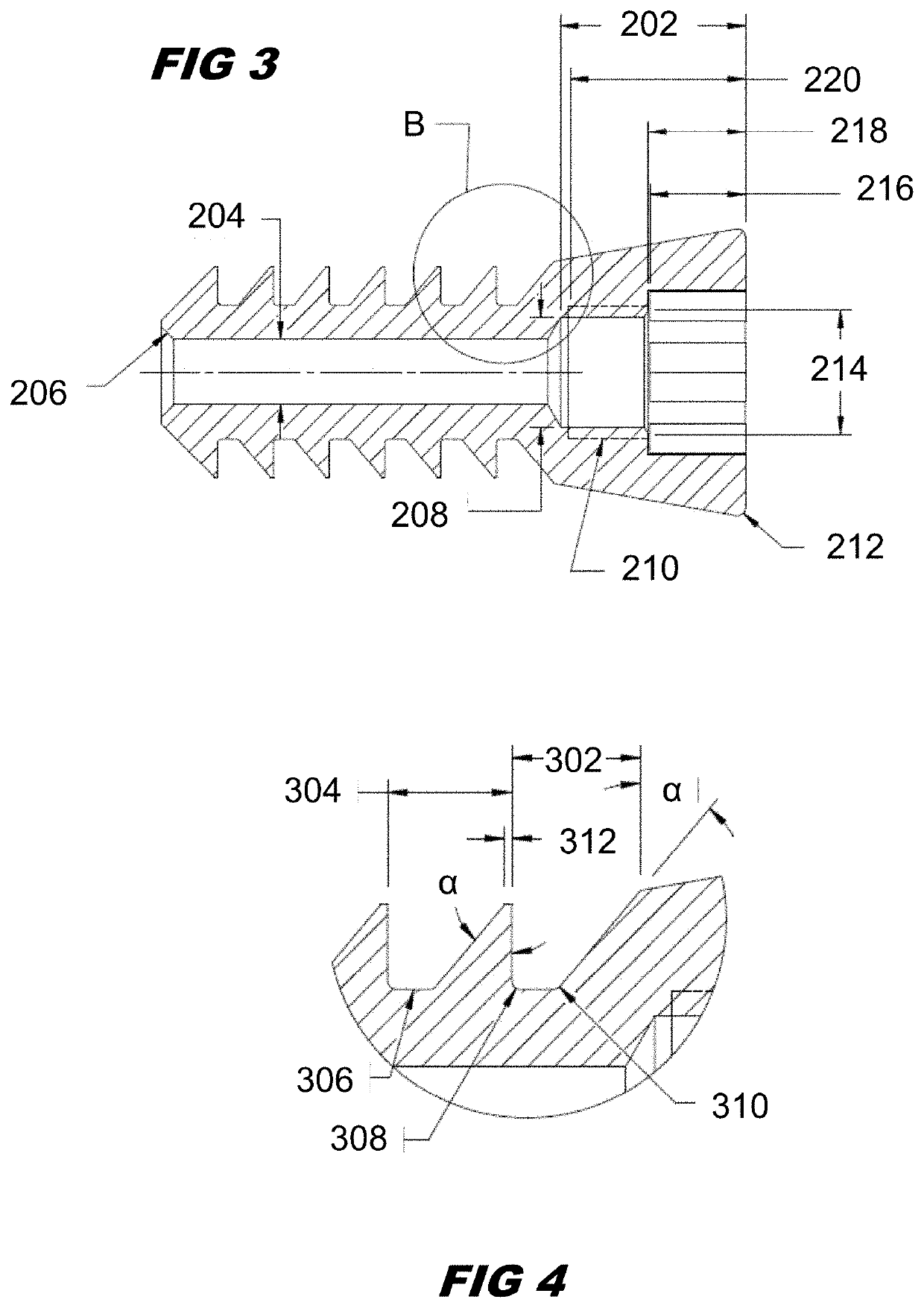
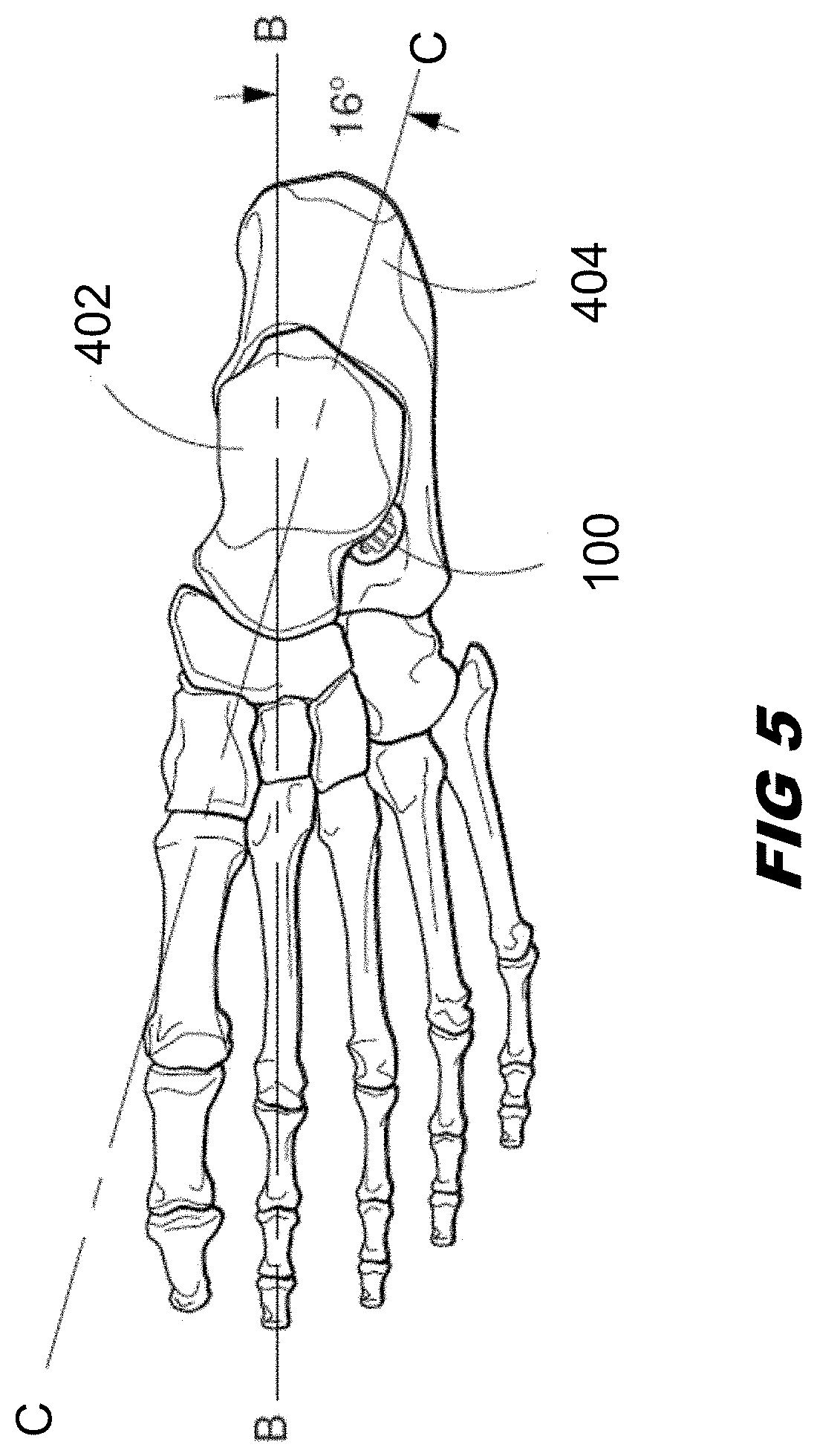
Sinus tarsi implant
PendingUS20210128313A1Increase mechanical retentionPrecise positioningAnkle jointsSurgeryTarsal canalTitanium alloy
A sinus tarsi implant for the purpose of stabilizing and restoring motion between the talus and calcaneus while allowing normal motion and alignment. In a preferred embodiment, the implant is composed of a titanium alloy that is a combination of a cylindrical portion and an axially connected conical portion. The cylindrical portion has a surface with multiple parallel grooves that are each parallel to the transverse axis of the cylinder. The grooves are uniquely shaped with a perpendicular medial side and an angled lateral side. The implant is cannulated to enable use of a guide wire that insures proper alignment during insertion.
Owner:GRAHAM MICHAEL
Anti-impact in-series four-freedom-degree human-simulated mechanical foot
ActiveCN105752190AAchieve impact resistanceRealize simulationVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAnkle
The invention discloses an anti-impact in-series four-freedom-degree human-simulated mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of human-simulated robots. The mechanical foot comprises a sole plate, an arch-shaped skeleton, a tarsal bone plate, a metatarsal bone rod, a toe, a tarsal bone rod and an ankle joint power device, wherein the arch-shaped skeleton and the tarsal bone plate are installed on the sole plate, the metatarsal bone rod is installed in the middle of the tarsal bone plate, the toe is connected with the left end of the metatarsal bone rod through a toe shaft, the tarsal bone rod is installed at the right end of the metatarsal bone rod through a tarsometatarsal shaft, and the ankle joint power device is used for connecting the metatarsal bone rod and a mechanical shank. The toe shaft is connected with an output shaft of a motor A, and the tarsometatarsal shaft is connected with an output shaft of a motor B; long rubber pillars and short rubber pillars are sequentially installed from middle to outer side between the arch-shaped skeleton and the sole plate; certain gaps are reserved between the upper portions of the long rubber pillars and the upper portions of the short rubber pillars and the lower bottom surface of the arch-shaped skeleton; the ankle joint power device comprises an ankle shaft A, an ankle shaft B, a flange plate, a motor C and screws. The anti-impact in-series four-freedom-degree human-simulated mechanical foot is reasonable in structure, has four motion freedom degrees and an anti-impact function, and is in a series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Hybrid insole with multi-shock absorbing pad and method for fabricating thereof
Provided are a hybrid insole with a multi-shock absorbing pad and a method for fabricating the hybrid insole. The hybrid insole includes an insole body including at least one sheet layer that is formed of an elastic material and has a shape of a human sole; a first absorbing pad means including first to fourth absorbing pad portions attached to the insole body corresponding to a metatarsal region, a tarsal bone region, and a calcaneus region of the human foot, and first to third connecting portions selectively connecting the first to fourth absorbing pad portions; and a second absorbing pad means including a fifth absorbing pad portion attached to the insole body corresponding to the metatarsal region and a phalange region of the human foot.The hybrid insole is configured such that absorbing pads of different structures are disposed to correspond to the bone structure for each region of the foot and the shape of an arch, thus distributing and absorbing the weight load of the human body.
Owner:KANG JOON HAN
Four-freedom-degree parallel human-simulated low-frequency mechanical foot
ActiveCN105539629ARealize the simulation of human foot movement postureAchieve decelerated low-frequency response characteristicsVehiclesPinionSacroiliac joint
The invention discloses a four-freedom-degree parallel human-simulated low-frequency mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of human-simulated robots. The four-freedom-degree parallel human-simulated low-frequency mechanical foot comprises a tarsal bone frame, a tarsal bone plate A, a tarsal bone plate B, a toe, a pinion shaft B, a large gear shaft A, a pinion shaft A, a stepper motor A, a stepper motor B, an ankle motor B and an orthogonal ankle joint, wherein the tarsal bone plate A and the tarsal bone plate B are mounted in parallel; the toe is mounted on a large gear shaft B; the stepper motor A and the stepper motor B are mounted on the tarsal bone plate A; the ankle motor B and the orthogonal ankle are mounted on the tarsal bone frame; an output shaft of the tarsal bone motor B is connected with one end of an orthogonal ankle shaft A; an output shaft of the stepper motor A is connected with one end of the pinion shaft A; an output shaft of the stepper motor B is connected with one end of the pinion shaft B; the orthogonal ankle joint comprises the orthogonal ankle shaft A, an orthogonal ankle shaft B, an ankle shaft A frame, bolts and an ankle motor A in an orthogonal manner. The four-freedom-degree parallel human-simulated low-frequency mechanical foot is a human-simulated robot foot which is reasonable in structure and relatively good in simulation effect and has the characteristic of low-frequency movement and a four-freedom-degree parallel mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Hybrid shock-absorbing humanoid three-degree-of-freedom mechanical foot
ActiveCN105730549BAchieve relative motionRealize simulationVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDamping function
The invention discloses a series-parallel damping humanoid three-freedom-degree mechanical foot and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The series-parallel damping humanoid three-freedom-degree mechanical foot comprises a mechanical shank, a tarsal bone rod A, a tarsal bone rod B, a tarsal bone rod C, a metatarsal bone rod A, a metatarsal bone rod B, a metatarsal bone rod C, a mechanical toe, a shank spring connecting the mechanical shank with the tarsal bone rod A, an ankle large gear, an ankle motor, an ankle small gear, a tarsal bone large gear, a tarsal bone motor, a tarsal bone small gear, an ankle shaft, a tarsal bone hinge, a metatarsal bone shaft, a toe shaft, a tarsal and metatarsal spring, a toe spring, a toe large gear, a toe small gear and a toe motor, wherein the ankle large gear, the ankle motor and the ankle small gear are arranged on the tarsal bone rod B. The ankle shaft is fixedly combined with the mechanical shank and provided with the ankle small gear. The metatarsal bone shaft is fixedly combined with the metatarsal bone rod A and provided with the ankle small gear. The toe shaft is fixedly combined with the mechanical toe and provided with the toe small gear. The mechanical foot is a humanoid mechanical foot which is simple in structure, has the three freedom degrees and a damping function and is in a series-parallel mode.
Owner:上海韦航装备科技有限公司
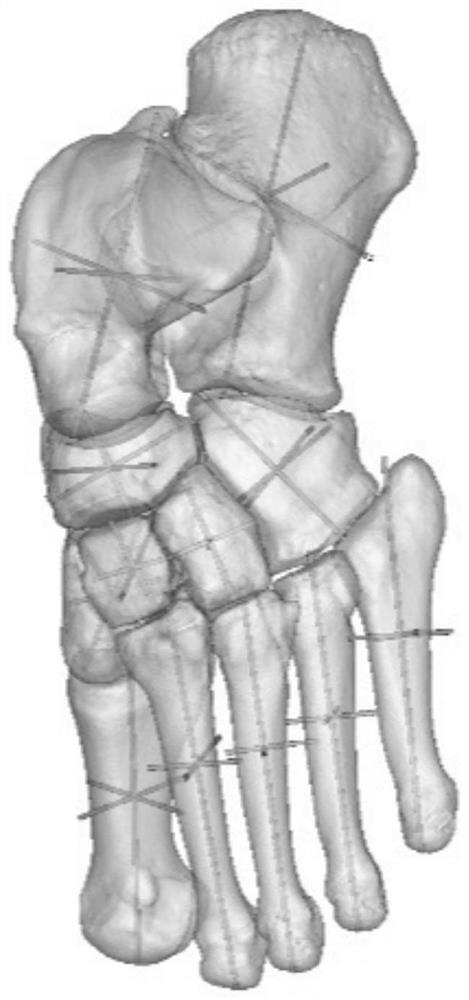
A method for constructing arch-rod structure based on the principal axis of the living bone inertia of the arch of the foot
ActiveCN107945877BReduce frictionSmooth rotationMedical simulationRectangular coordinatesMechanical models
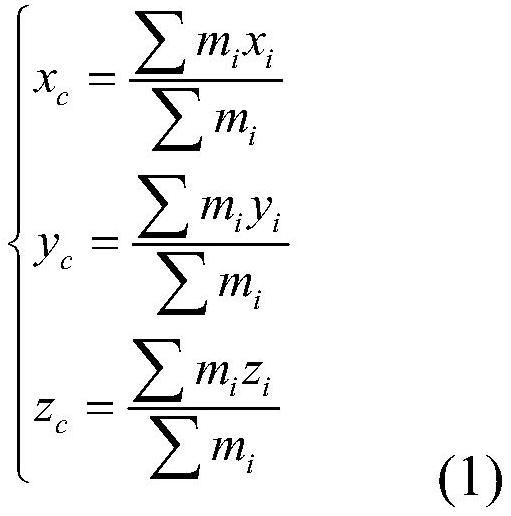
The invention provides a method for constructing the arch rod structure based on the main axis of inertia of the living arch of the foot bone. Based on the center of mass of the living arch of the foot bone, the main axis of inertia of the living bone is solved according to a specific rotation sequence; Three-dimensional rectangular coordinate system; select six maximum and minimum marked points along the three coordinate axes in the established three-dimensional rectangular coordinate system; reverse the six marked points in the reverse order of specific rotation; connect the six points to form a living arch The rod structure of the bone; the rod structure connecting 7 tarsal bones and 5 metatarsals constitutes the arch rod system; a new method for foot statics, dynamics analysis and optimal calculation of the foot wear structure is formed, with the rod structure With a sufficient mechanical model, mechanical analysis can be carried out as needed.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Three-degrees-of-freedom parallel-connection impact-resistant humanoid mechanical foot
ActiveCN105667627AEffective absorptionAchieve relative motionVehiclesThree degrees of freedomHumanoid robot
The invention discloses a three-degrees-of-freedom parallel-connection impact-resistant humanoid mechanical foot and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The three-degrees-of-freedom parallel-connection impact-resistant humanoid mechanical foot comprises a mechanical shank, a tarsal bone rod, a metatarsal bone rod, a toe, a tarsal bone impact pad, a tarsal bone spring, an arch-shaped sole plate, an instep face, a metatarsal bone upper spring A, a rubber column A and a rubber column B. The mechanical shank is connected with the tarsal bone rod through an ankle hinge. The two ends of the arch-shaped sole plate are connected with the two ends of a metatarsal bone plate through a metatarsal bone lower spring A and a metatarsal bone lower spring B correspondingly. The instep face is connected with the upper portion of the metatarsal bone rod through the metatarsal bone upper spring A and a metatarsal bone upper spring B. The tarsal bone impact pad is arranged at the bottom of the tarsal bone rod. The toe is connected with the left end of the instep face through a toe spring. The arch-shaped sole plate is an upward-convex type elastic thin plate. The two ends of the arch-shaped sole plate and the tarsal bone impact pad are in the same horizontal plane. The three-degrees-of-freedom parallel-connection impact-resistant humanoid mechanical foot is a parallel-connection mode humanoid robot foot which is reasonable in structure and has three degrees of freedom of motion and impact resistance.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Humanoid robot four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel-connection low-frequency mechanical foot
ActiveCN105667629AAchieve a high degree of imitationProlong exercise lifeVehiclesDegrees of freedomControl theory
The invention discloses a humanoid robot four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel-connection low-frequency mechanical foot and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The humanoid robot four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel-connection low-frequency mechanical foot comprises a U-shaped tarsal bone frame, an ankle joint shaft A, a shank rotary power device, a rotary shaft, a low-frequency power device B, a metatarsal bone plate, a low-frequency power device A, a stepping motor A, a toe shaft and a parallel connection toe. The structure of the low-frequency power device A is completely the same as that of the low-frequency power device B. The low-frequency power device A and the low-frequency power device B each comprises a worm bracket B, a worm bracket A, a worm, a U-shaped frame, a stepping motor B and worm wheel. The worm wheel in the low-frequency power device A is arranged on the rotary shaft. The worm wheel in the low-frequency power device B is arranged on the ankle joint shaft A. The shank rotary power device comprises an ankle joint shaft B, an ankle motor A, a flange plate and a bolt. The ankle joint shaft A perpendicularity passes through the ankle joint shaft B. The humanoid robot four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel-connection low-frequency mechanical foot is a series-parallel-connection mode humanoid mechanical foot which is reasonable in structure and highly human-simulated, and has four degrees of freedom of motion and low-frequency motion performance.
Owner:爱豆贝思(江苏)人工智能科技有限公司
Alpha adrenergic receptor agonists for treatment of inflammatory diseases
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC +1
Four-degree-of-freedom hybrid shock-resistant mechanical foot for humanoid robot
The invention discloses a four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel impact resistant mechanical foot for a humanoid robot, which belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel impact resistant mechanical foot for the humanoid robot comprises a mechanical shank, a tarsal skeleton, an ankle shaft A, an ankle shaft B, a metatarsal skeleton, a toe, a toe joint, a sole, two compression resistant rubber columns, two tensile springs, a torsion spring B and a torsion spring A, wherein the toe joint is used for connecting the toe with the metatarsal skeleton; the torsion spring B is mounted between the toe and a metatarsal bone rod C; the torsion spring A is mounted between a tarsal bone rod C and a metatarsal bone rod A; the tarsal skeleton comprises a tarsal bone rod A, a tarsal bone rod B and a tarsal bone rod C; the metatarsal skeleton comprises a metatarsal bone rod A, a metatarsal bone rod B and a metatarsal bone rod C; the two tensile springs are mounted on the external sides of the two compression resistant rubber columns and always in a tensile and stressed state; the mechanical shank can rotate around the ankle shaft A; the ankle shaft B is orthogonal to the ankle shaft A; and the mechanical shank can realize twisting motion around the ankle shaft B. The invention is the humanoid robot foot with reasonable structure, impact resistance and four-degrees-of-freedom series-parallel mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
High-frequency serial humanoid four-degree-of-freedom mechanical foot
ActiveCN105564531BAchieve high-frequency response characteristicsReasonable structureVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The high-frequency series humanoid four-freedom-degree mechanical foot comprises a tarsal bone board, a metatarsal bone board, a toe, an ankle joint connecting the tarsal bone board with a mechanical crus, a tarsal bone joint connecting the tarsal bone board with the metatarsal bone board and a toe joint connecting the metatarsal bone board with the toe; the ankle joint comprises a first ankle gear shaft, a second ankle gear shaft, a first U-shaped frame, a first motor, an ankle rotation shaft, a bearing frame, a bolt and a fourth motor; the first ankle gear shaft is perpendicular to the ankle rotation shaft; the tarsal bone joint comprises a first tarsal bone gear shaft, a second tarsal bone gear shaft and a second motor; the first tarsal bone gear shaft is in mesh transmission with the second tarsal bone gear shaft, and an output shaft of the second motor is connected with one end of the first tarsal bone gear shaft; the toe joint comprises a first toe gear shaft, a second toe gear shaft, a third U-shaped frame and a third motor. The humanoid robot foot is reasonable in structure and better in humanoid effect and has four freedom degrees, the high-frequency motion characteristic and the series mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
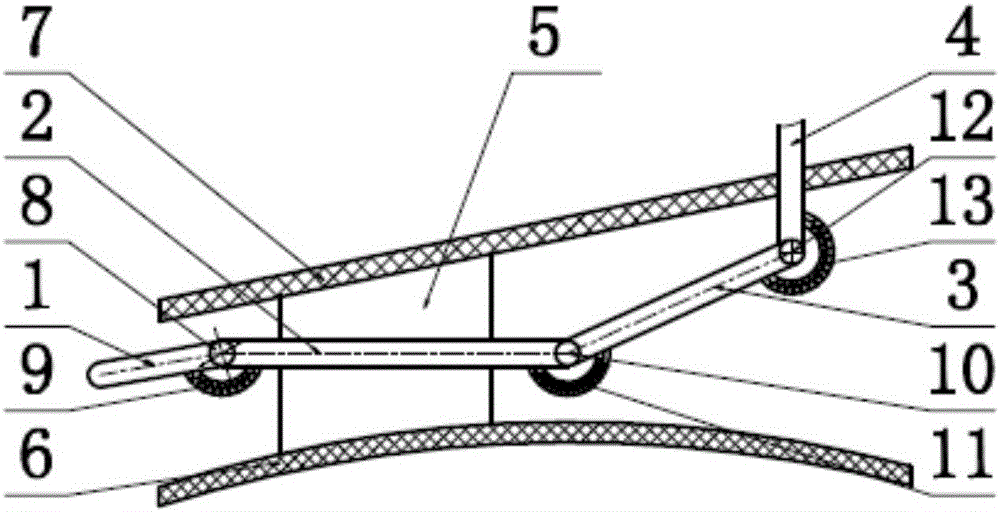
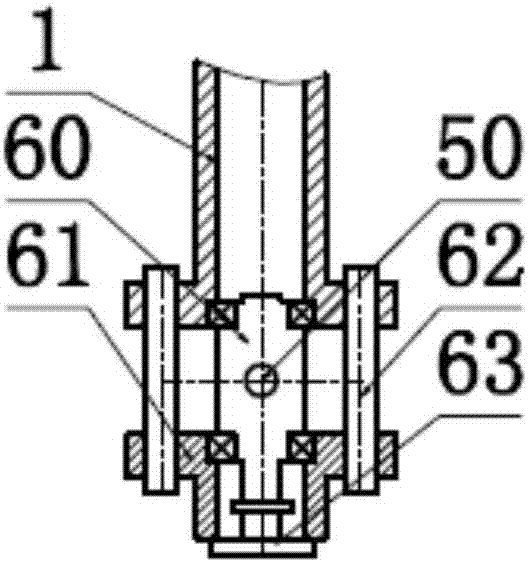
Tarsal sinus stabilizer for talus turning
The tarsal sinus stabilizer comprises a main nail body, a cylindrical through cavity is formed in the axis of the main nail body, the two ends of the cylindrical through cavity expand outwards to form a first circular truncated cone cavity and a second circular truncated cone cavity respectively, and the tarsal sinus stabilizer further comprises a first nail body and a second nail body; the first nail body comprises a first circular truncated cone body and a first screw rod which are connected with each other, the second nail body comprises a second circular truncated cone body and a second screw rod which are connected with each other, the side wall of the first circular truncated cone body is attached to the inner wall of the first circular truncated cone cavity, and the side wall of the second circular truncated cone body is attached to the inner wall of the second circular truncated cone cavity; the first screw rod and the second screw rod are respectively inserted from two ends of the cylindrical through cavity, the second screw rod is inserted into an axis through cavity formed by the first screw rod, and the outer wall of the second screw rod is in threaded connection with the inner wall of the axis through cavity. The threads of the two screw rods are continuously tightened, and the main nail body is expanded to the required diameter.
Owner:SUZHOU IDEAL MEDICAL APPLIANCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com