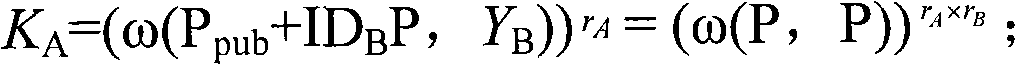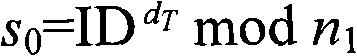Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Encrypted key exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
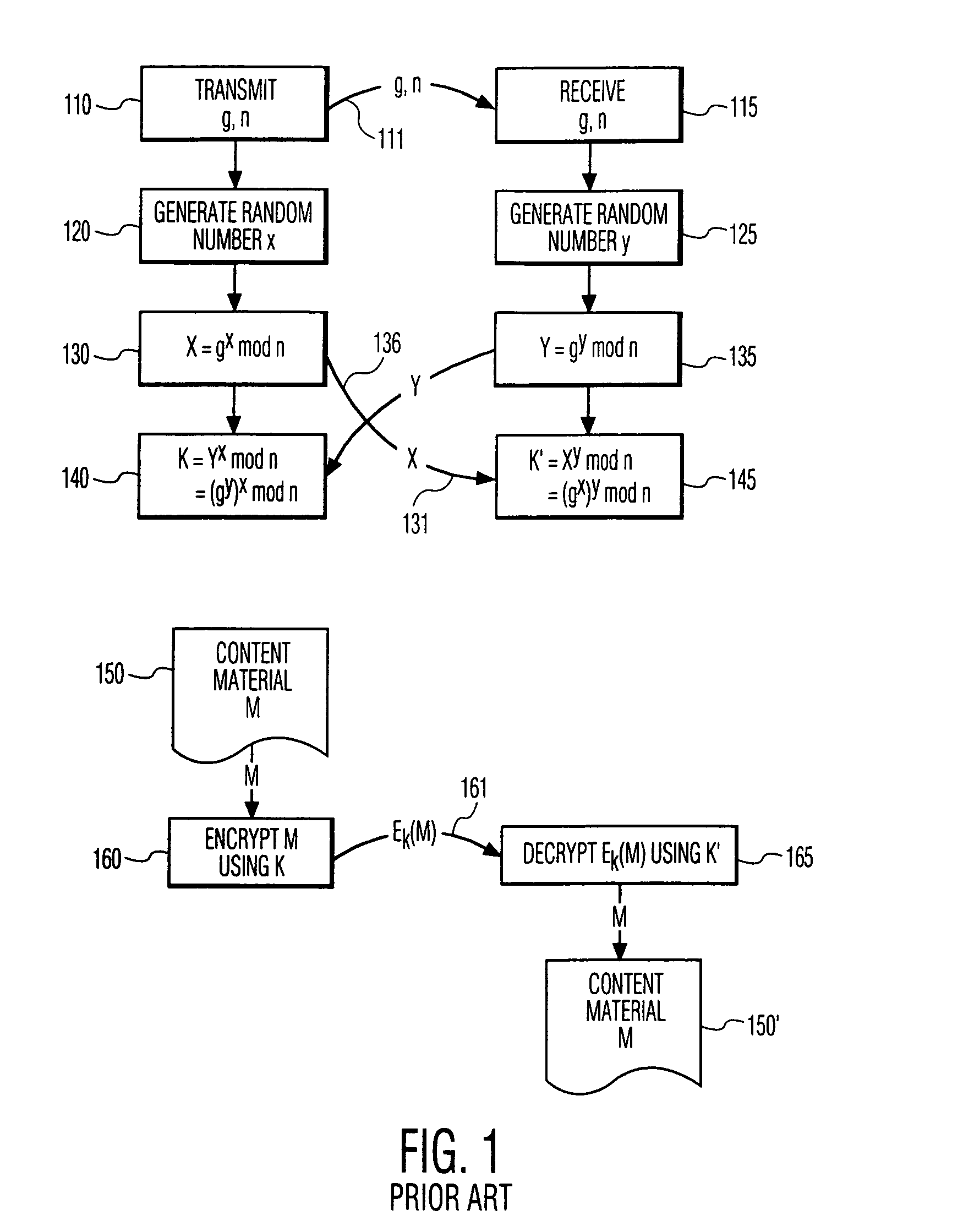
Encrypted Key Exchange (also known as EKE) is a family of password-authenticated key agreement methods described by Steven M. Bellovin and Michael Merritt. Although several of the forms of EKE in this paper were later found to be flawed, the surviving, refined, and enhanced forms of EKE effectively make this the first method to amplify a shared password into a shared key, where the shared key may subsequently be used to provide a zero-knowledge password proof or other functions.
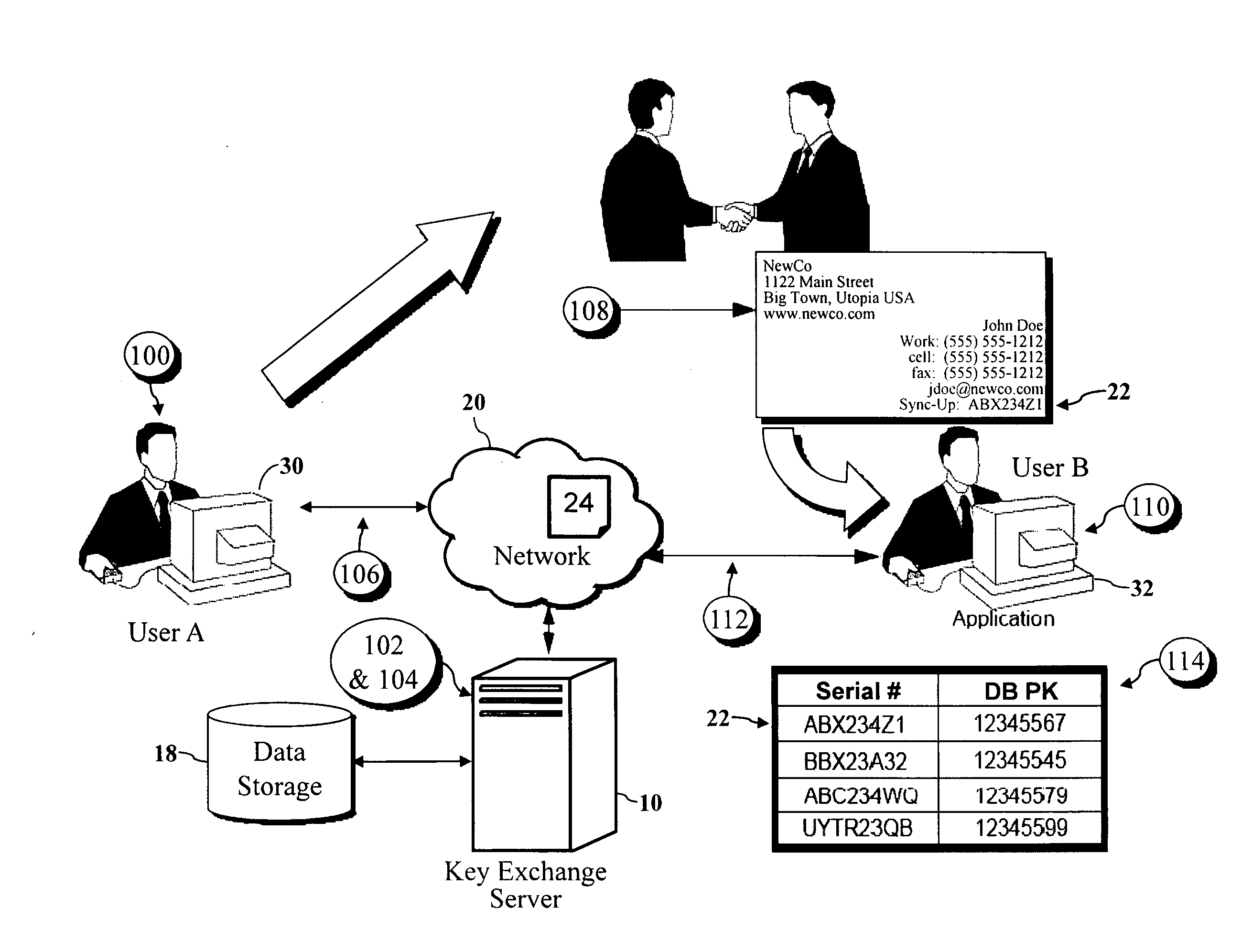
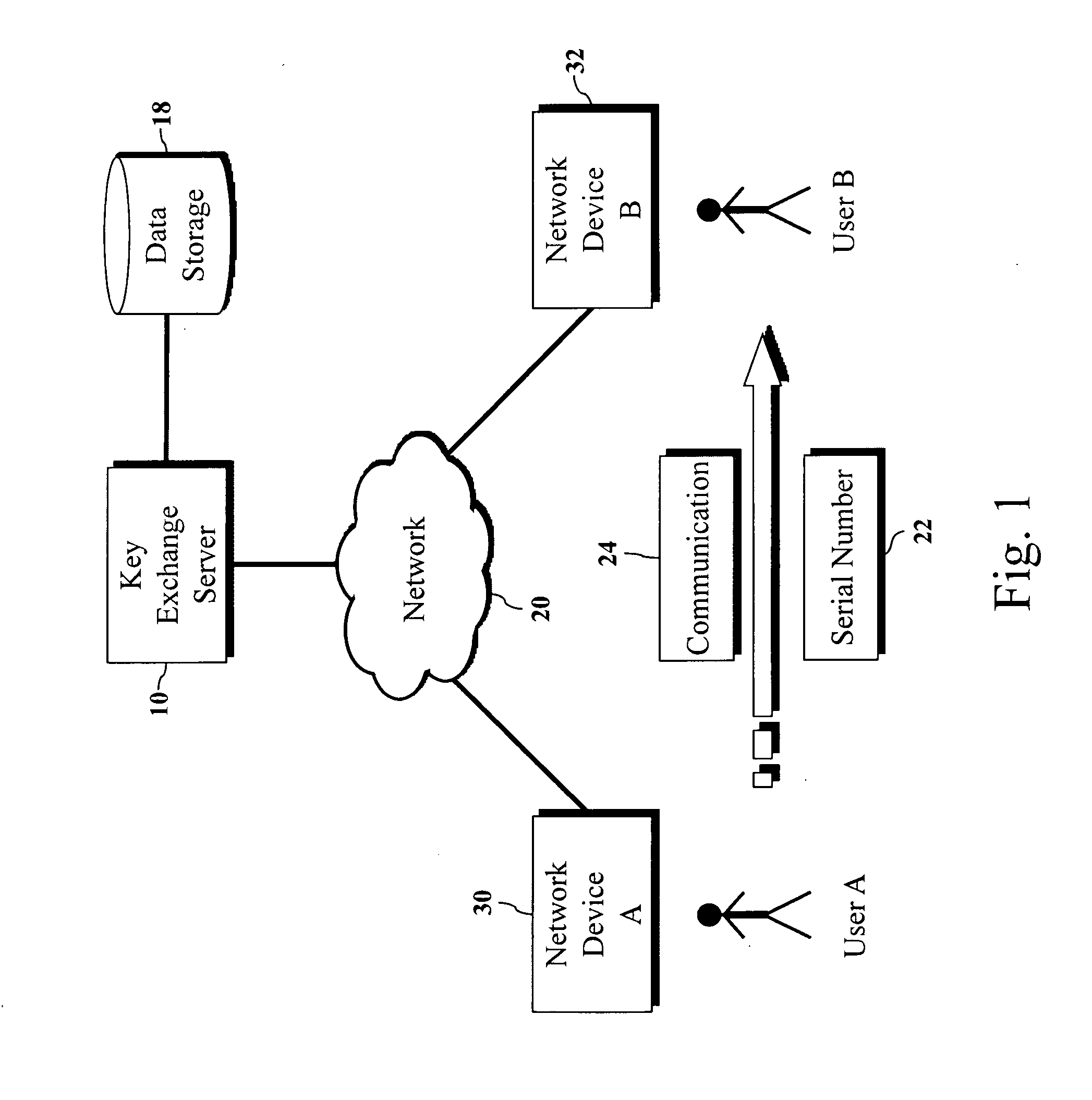
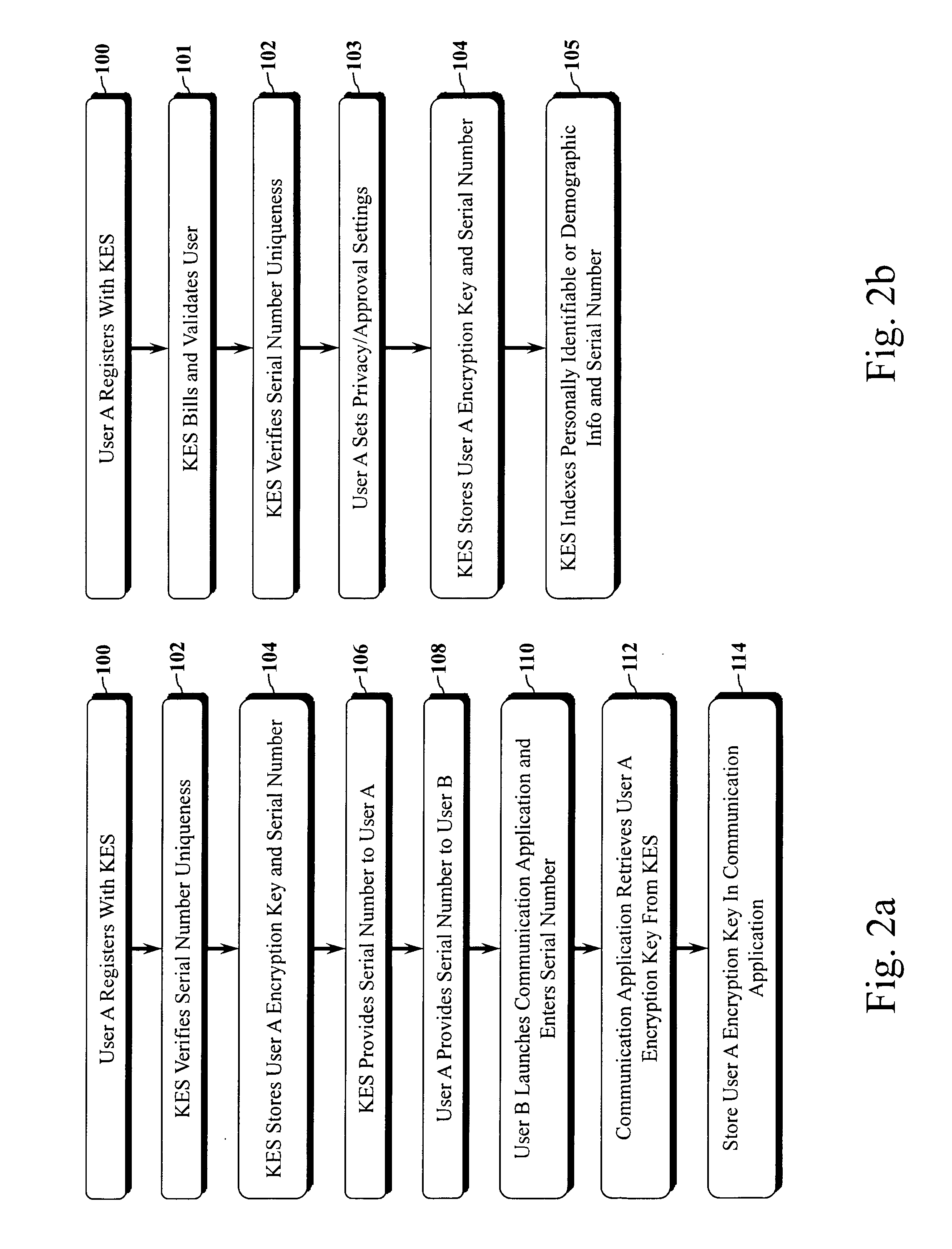
Encryption key exchange system and method
InactiveUS20120204032A1Improve usabilityUser identity/authority verificationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsUsabilityEncryption
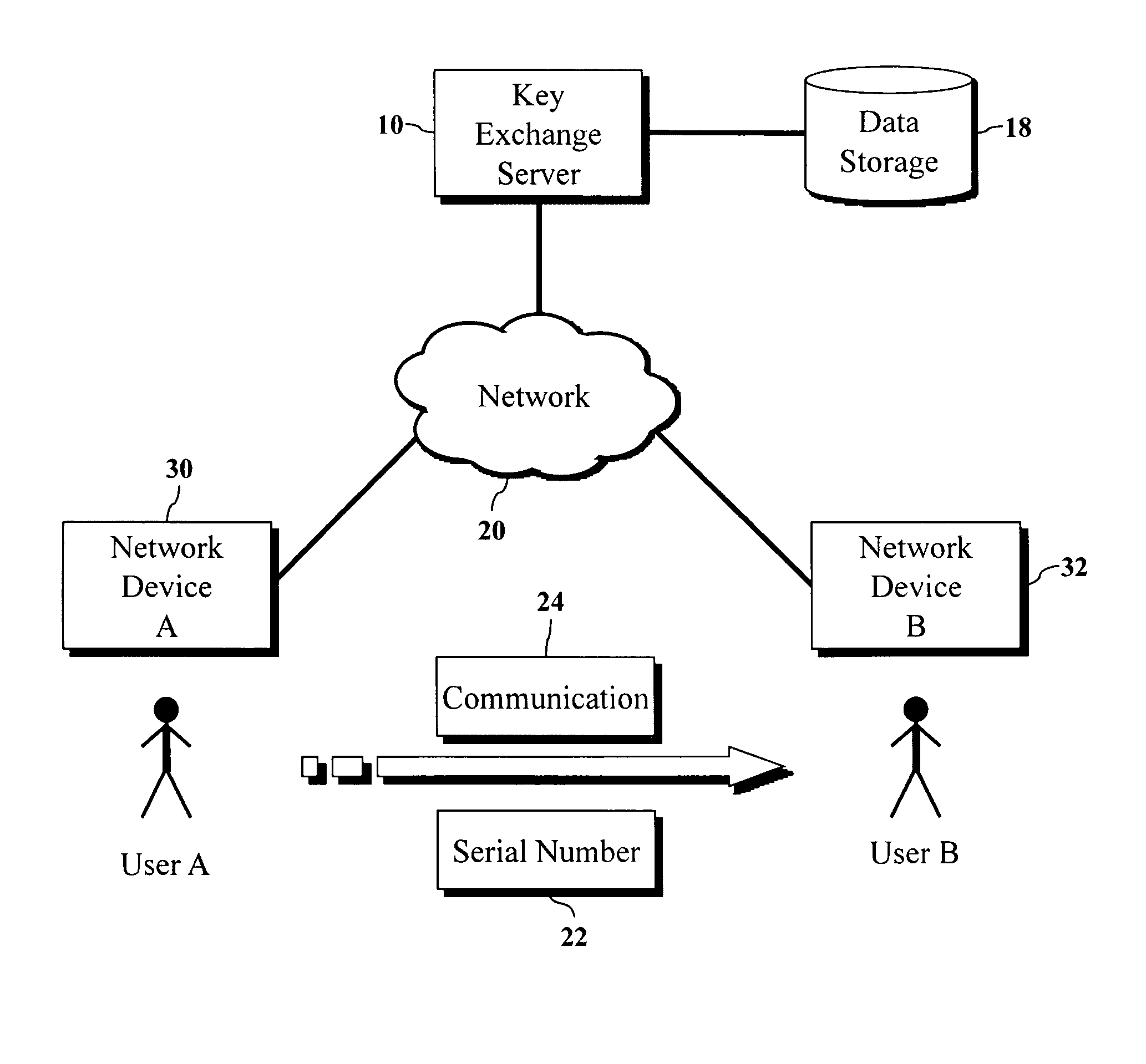
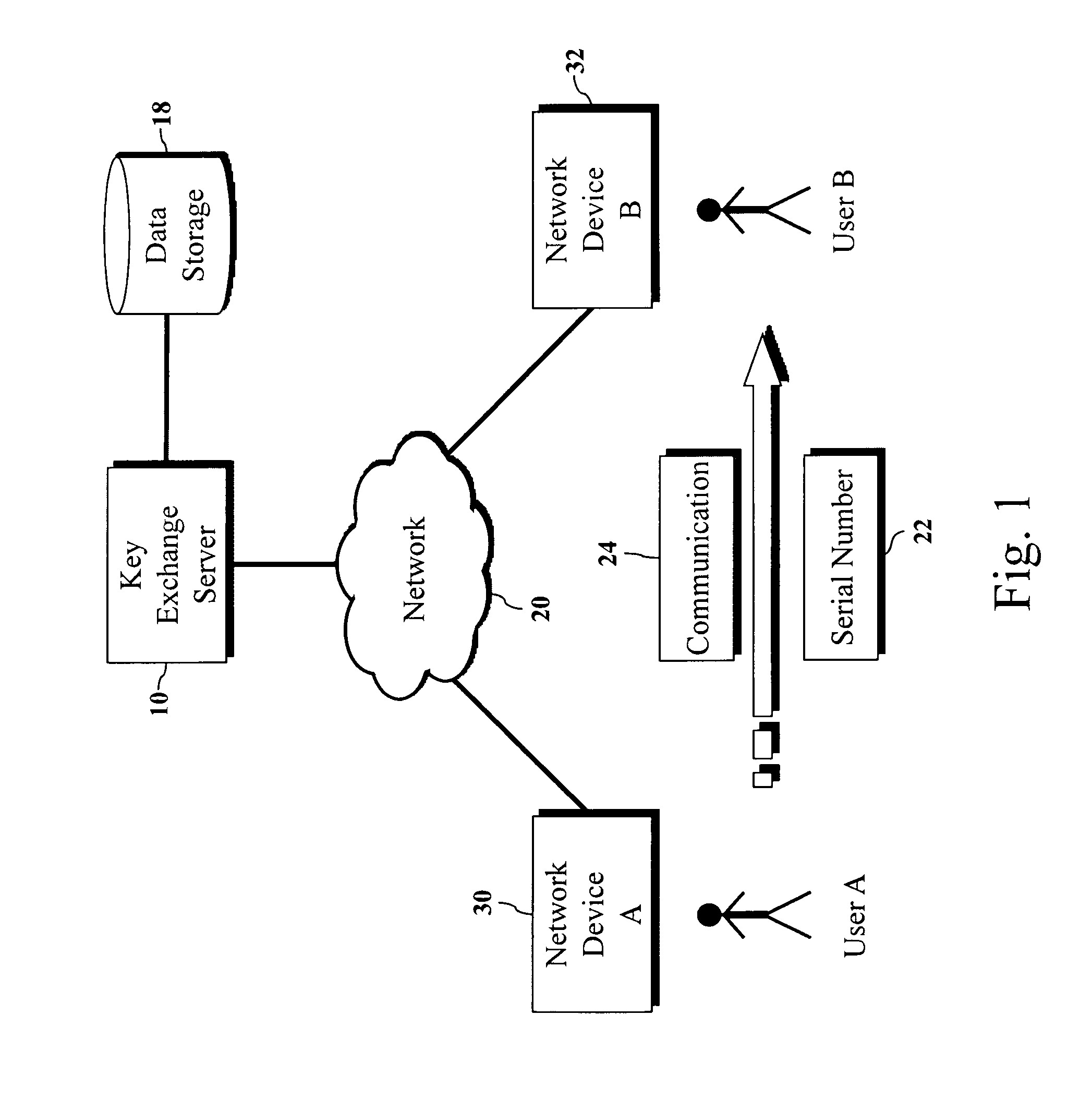
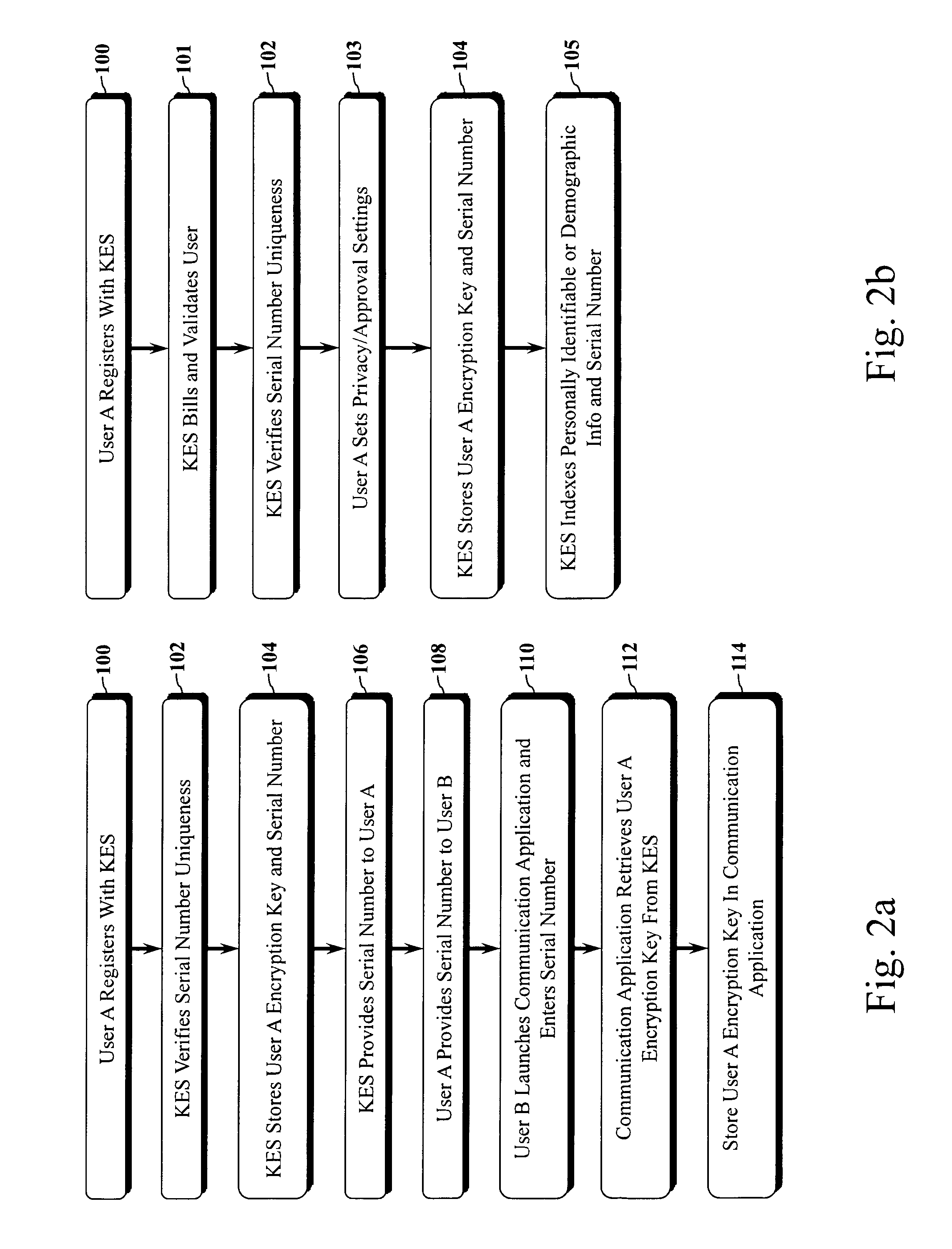
The present invention is a computer-implemented key exchange system and methods for improving the usability of encryption technologies such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). One aspect of the present invention includes registering users, verifying user identity, and classifying users such that the users may send a communications such that communication recipients can verify the user identity and classification of the communication sender. Another aspect of the present invention includes users initiating relationships with other users, approving the establishment of relationships, and exchanging encryption keys between users after the establishment of a relationship.
Owner:SYNC UP TECH
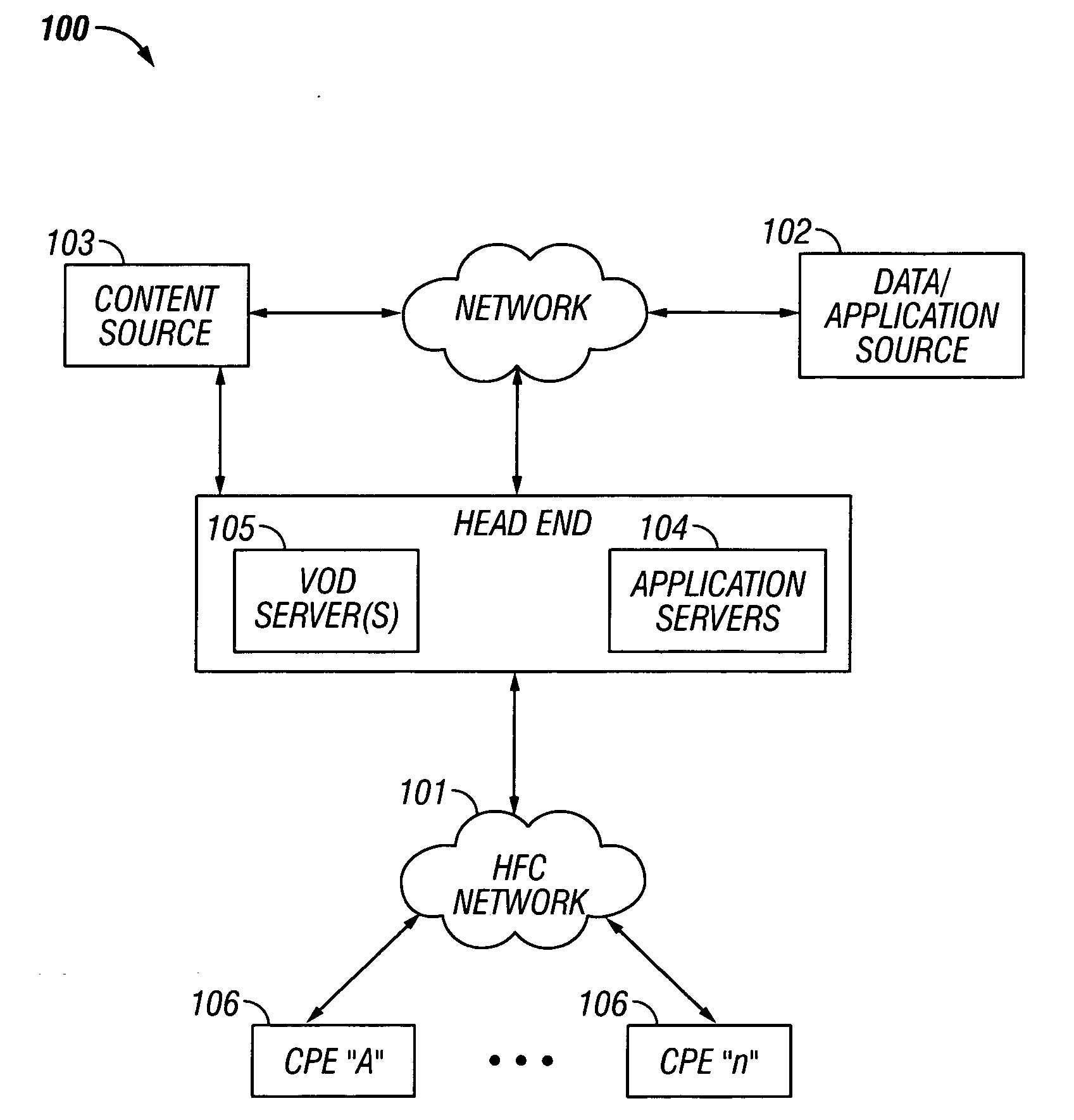
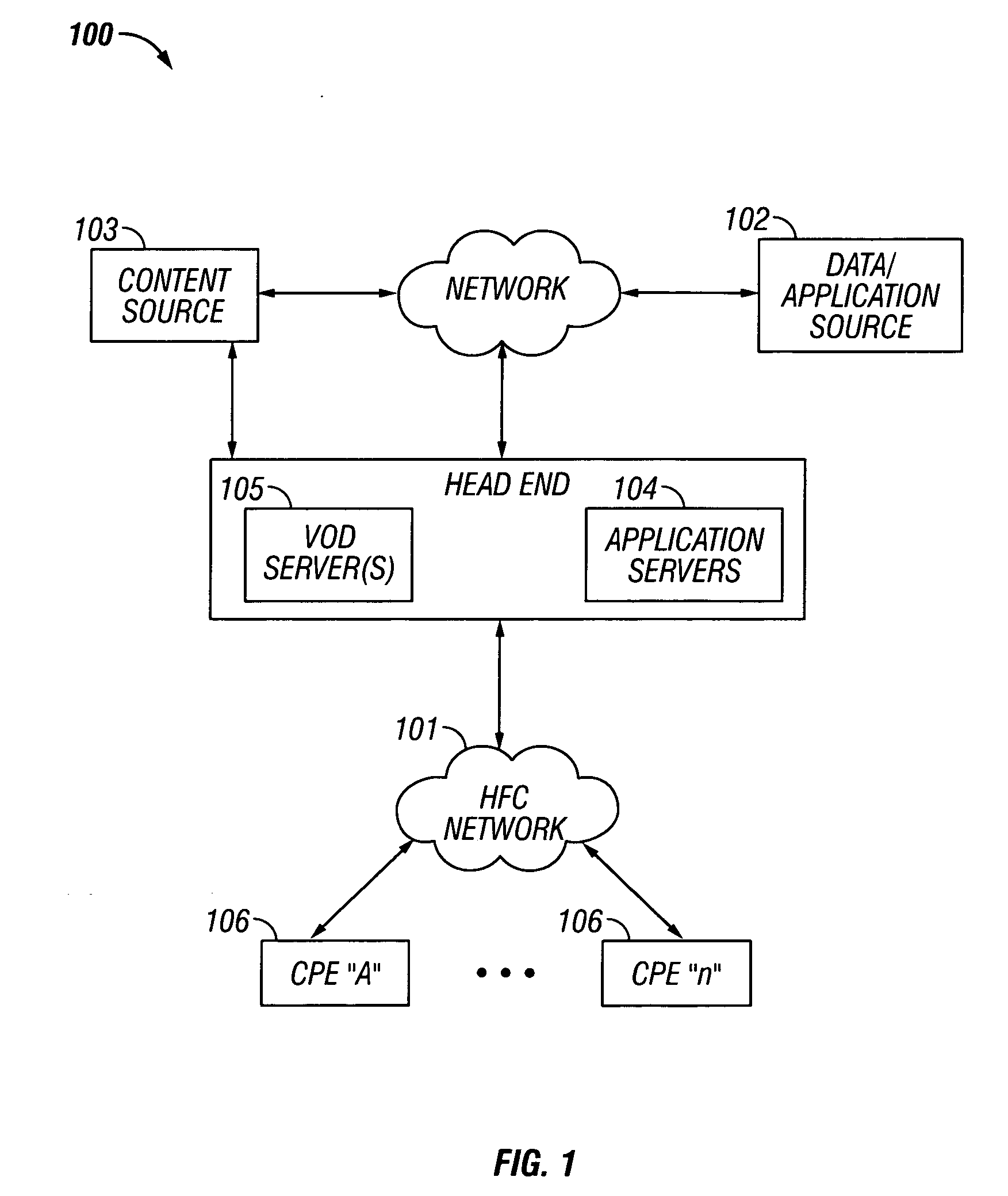
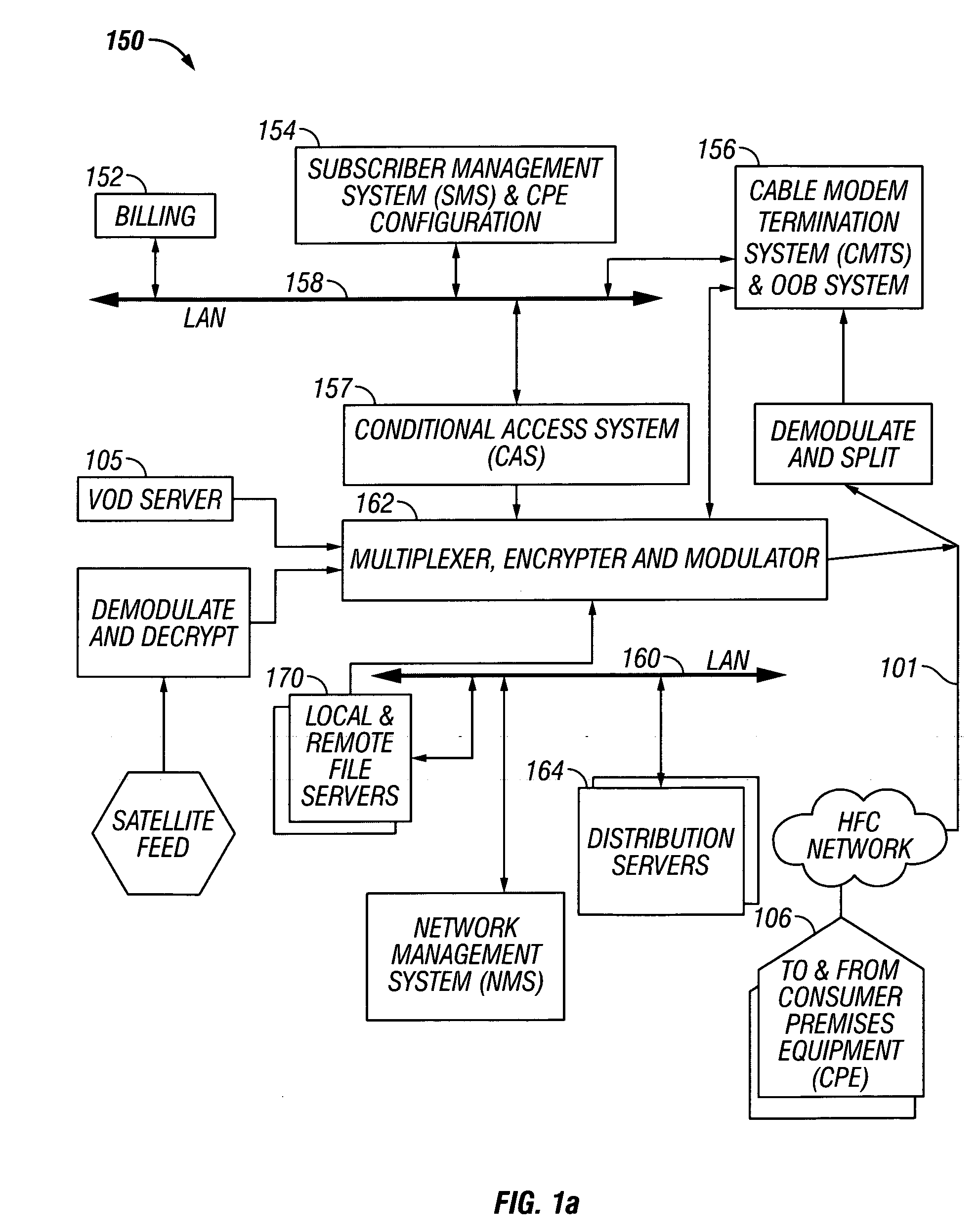
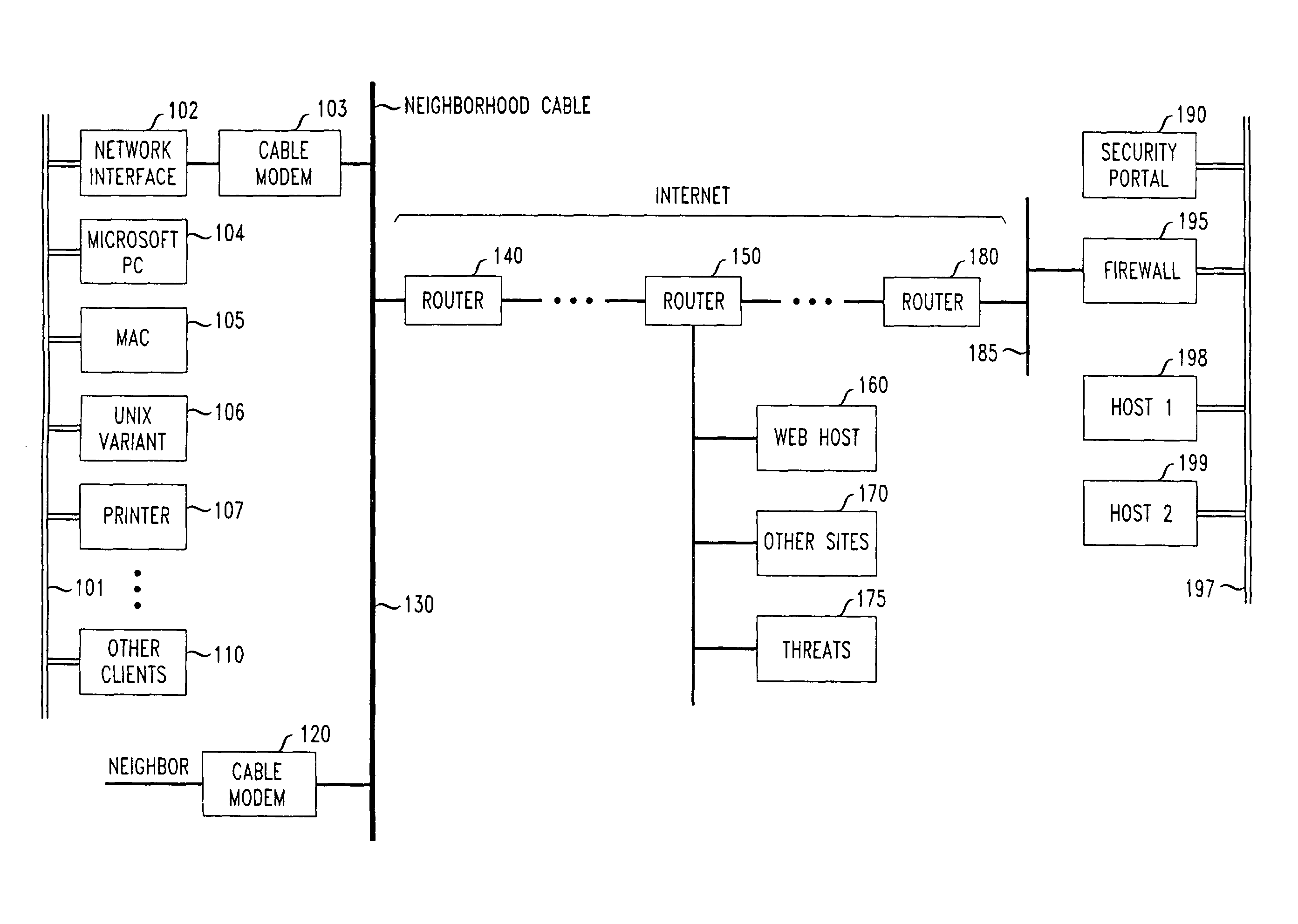
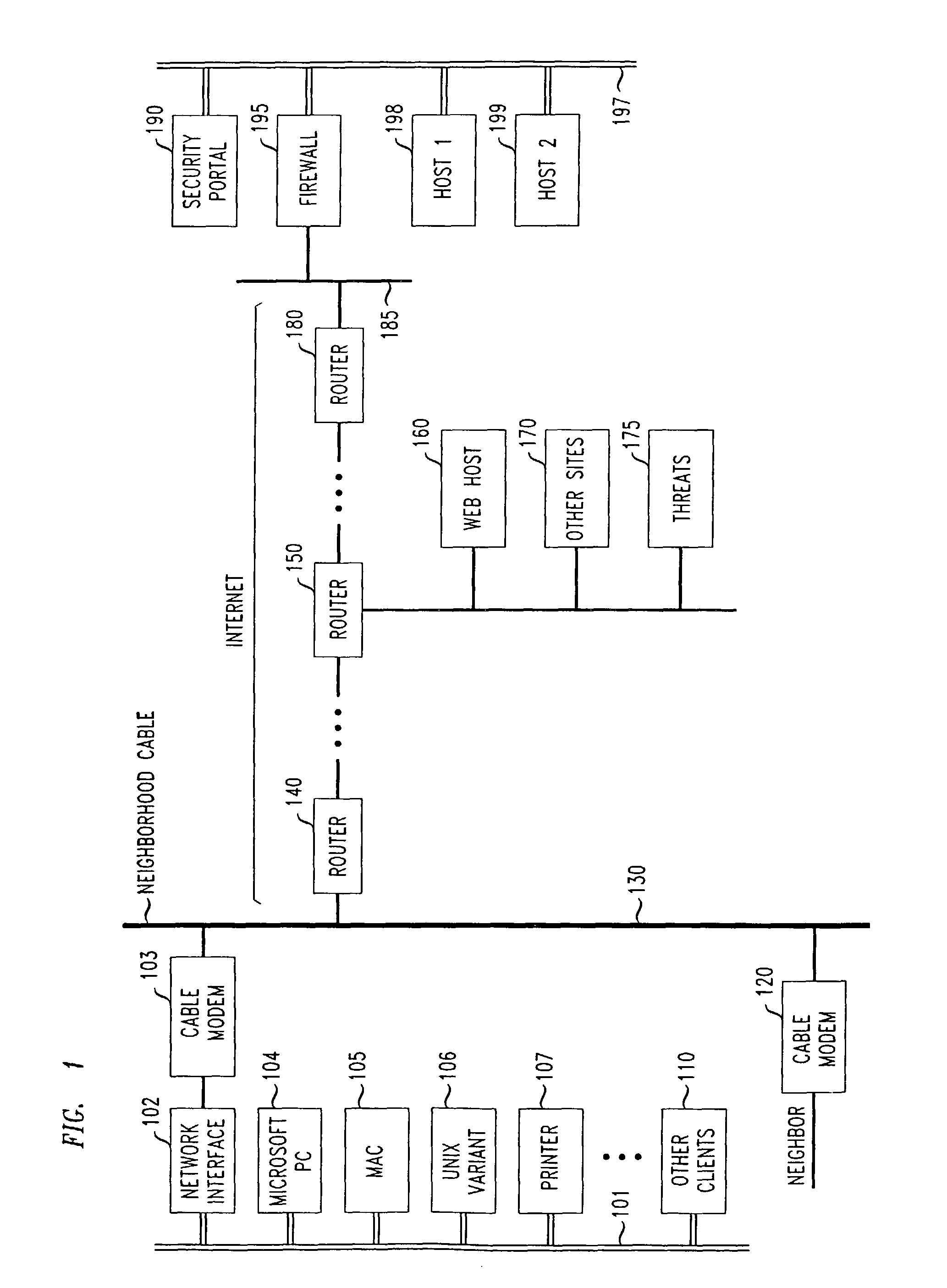
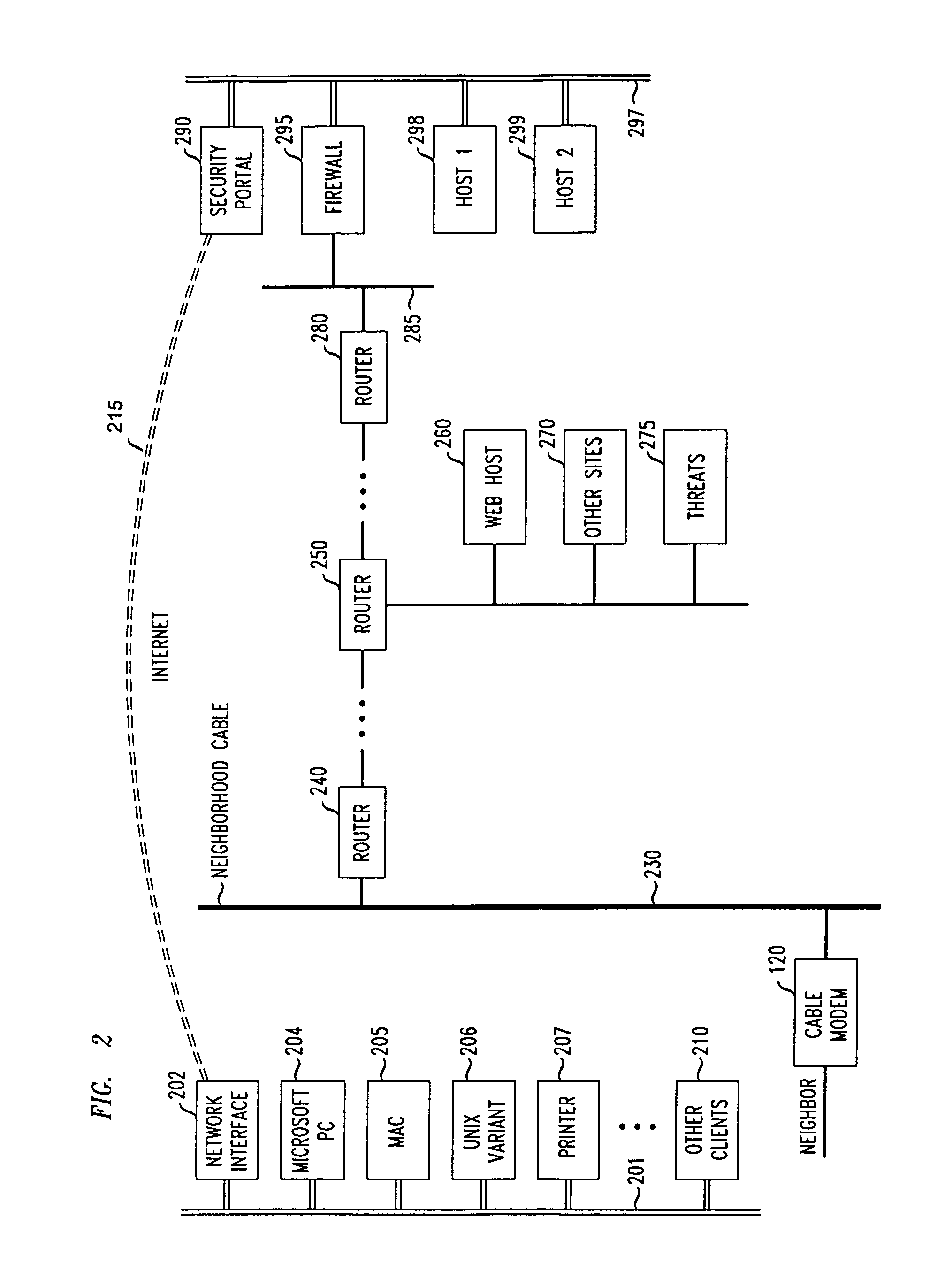
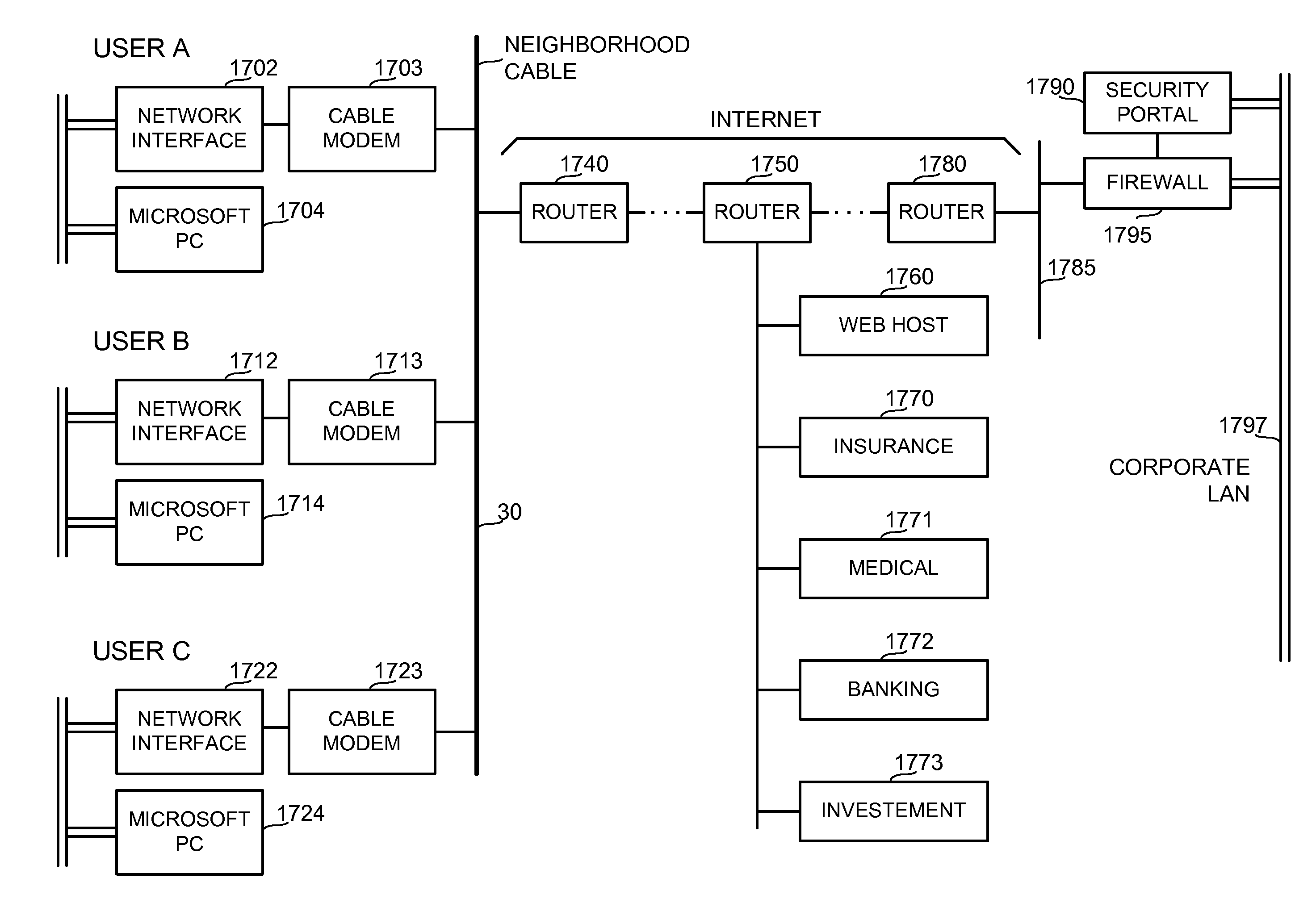
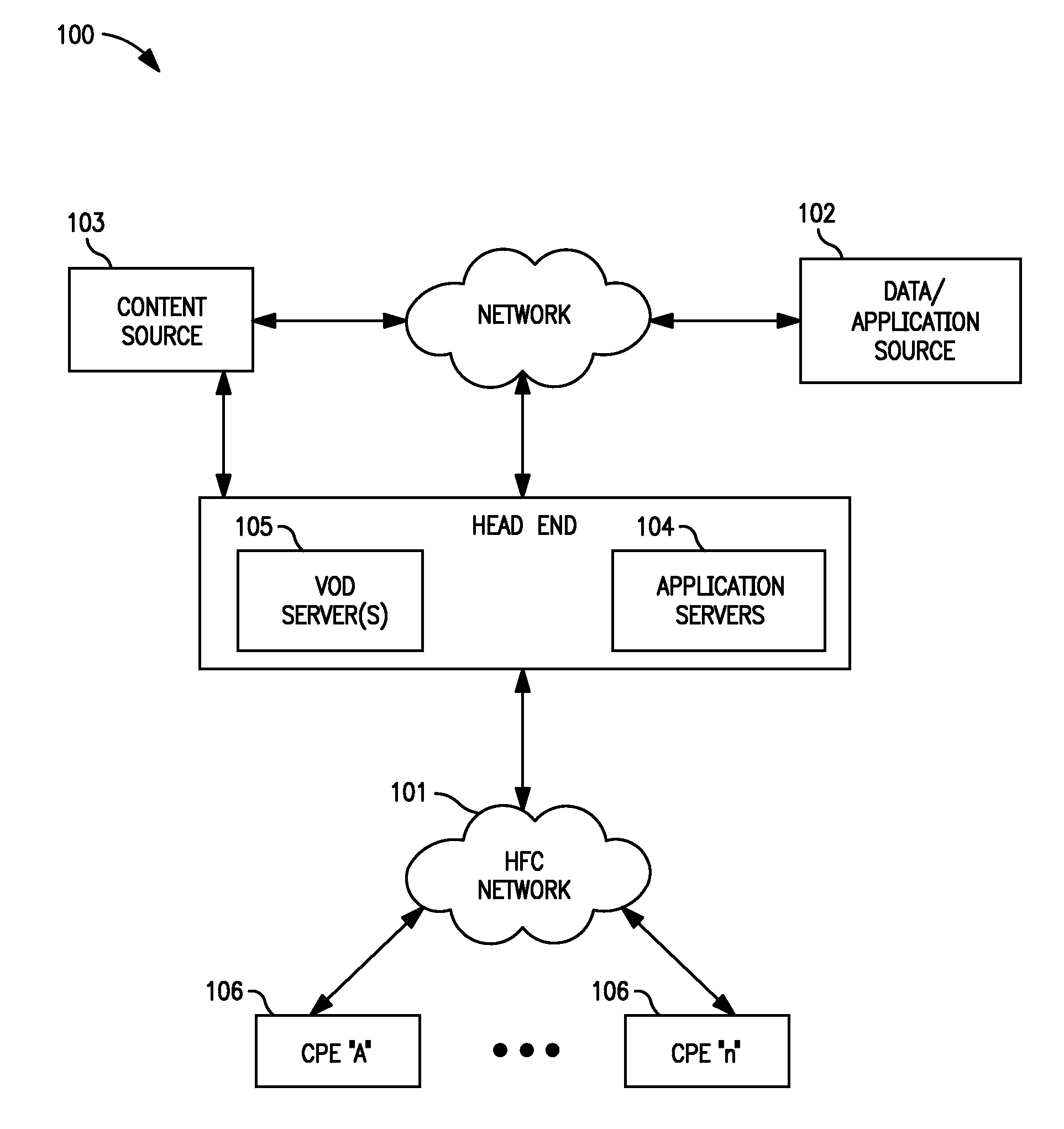
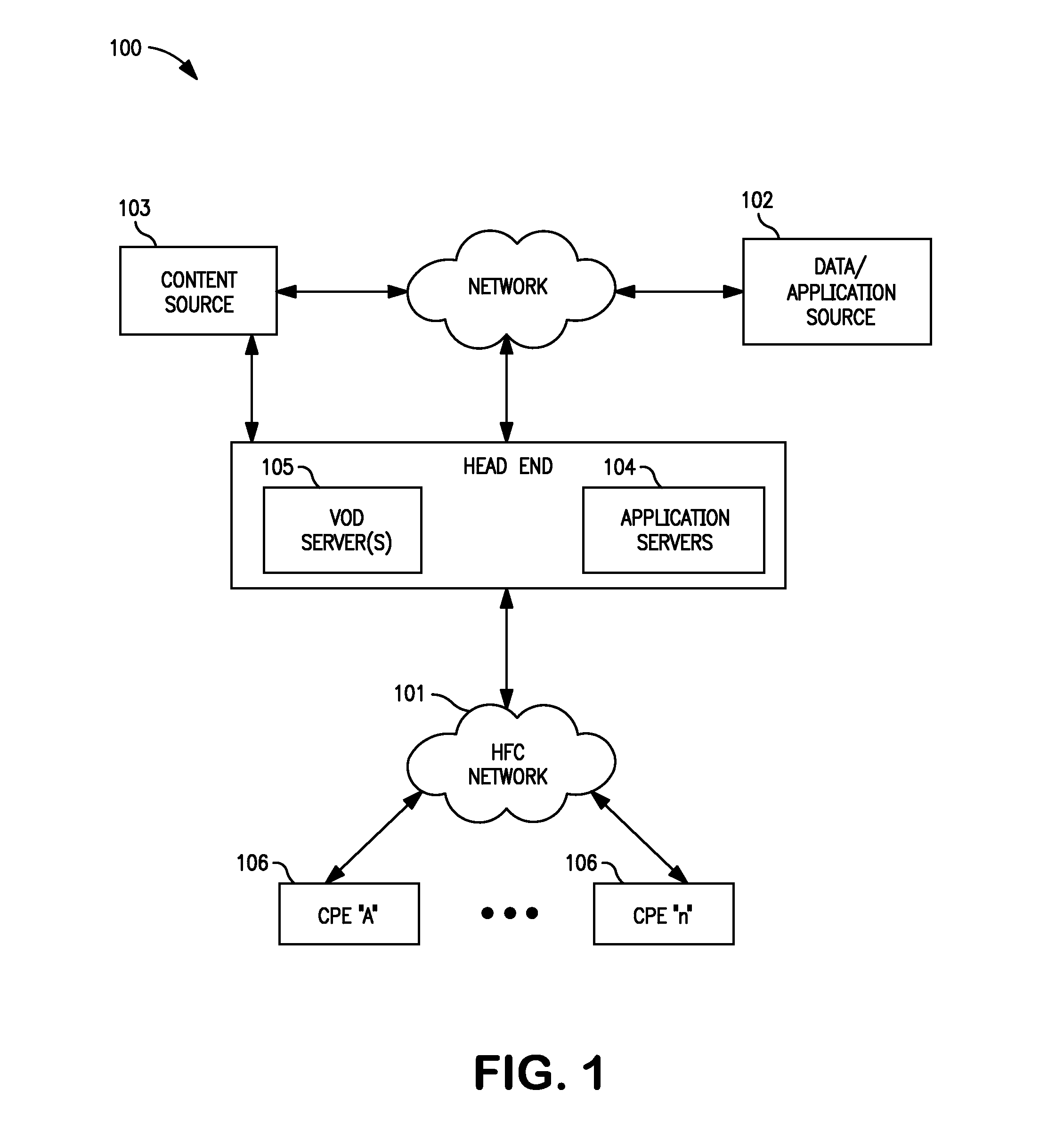
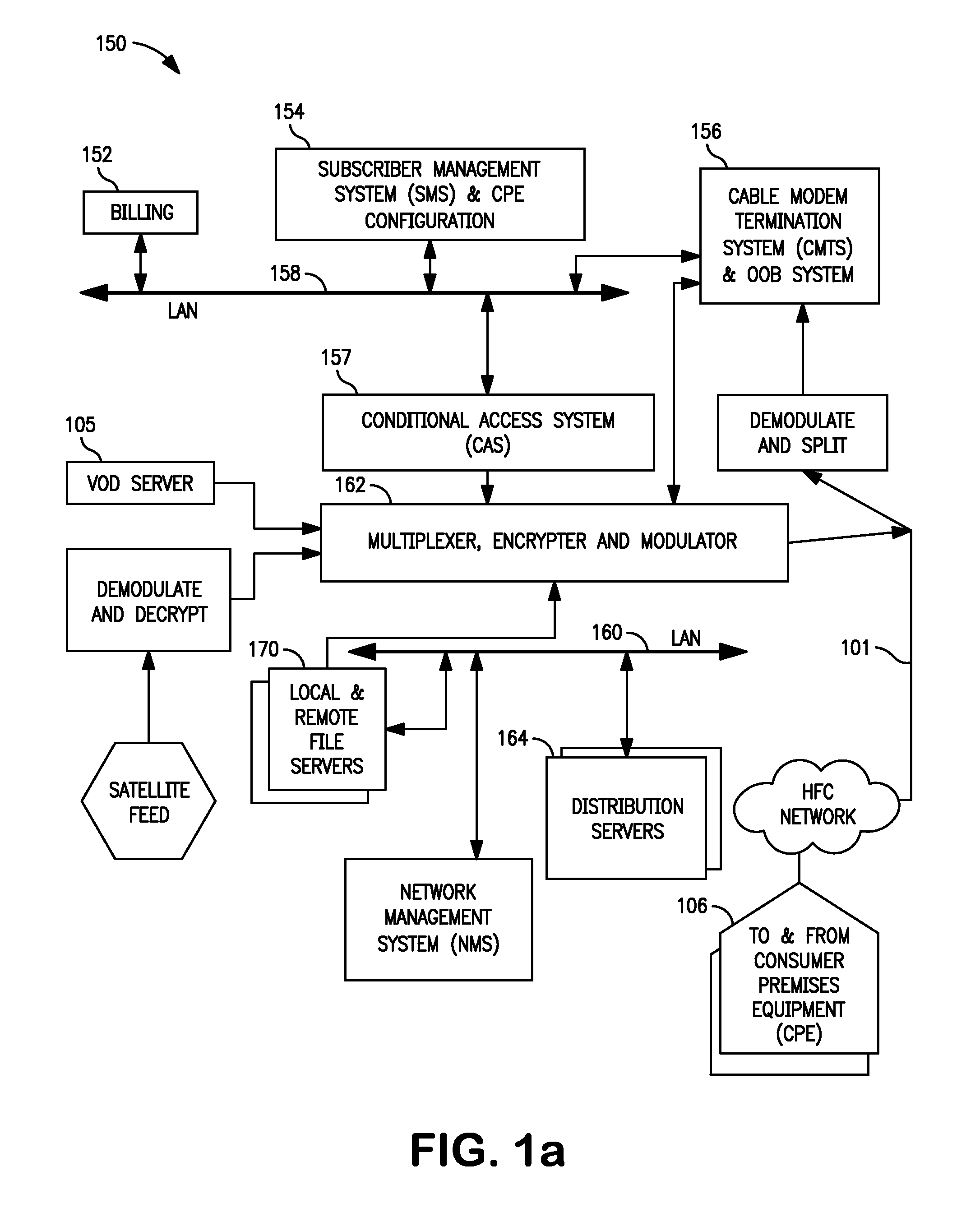
Methods and apparatus for premises content distribution
Apparatus and methods for protected content access, browsing and transfer over a network. In one embodiment, the network comprises a premises (e.g., residential) LAN, and the apparatus comprises a server and renderer consumer premise equipment (CPE). The renderer CPE scans the network to search for a server CPE that implement a compatible security framework. The renderer authenticates itself with the server, and the server allows content browsing and selection access only to an authorized and authenticated renderer. A negotiation and exchange protocol comprises messages exchanged between the renderer and the server that include one or more of device identification, encryption key exchange, digital certificates and information regarding security package used by each CPE.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
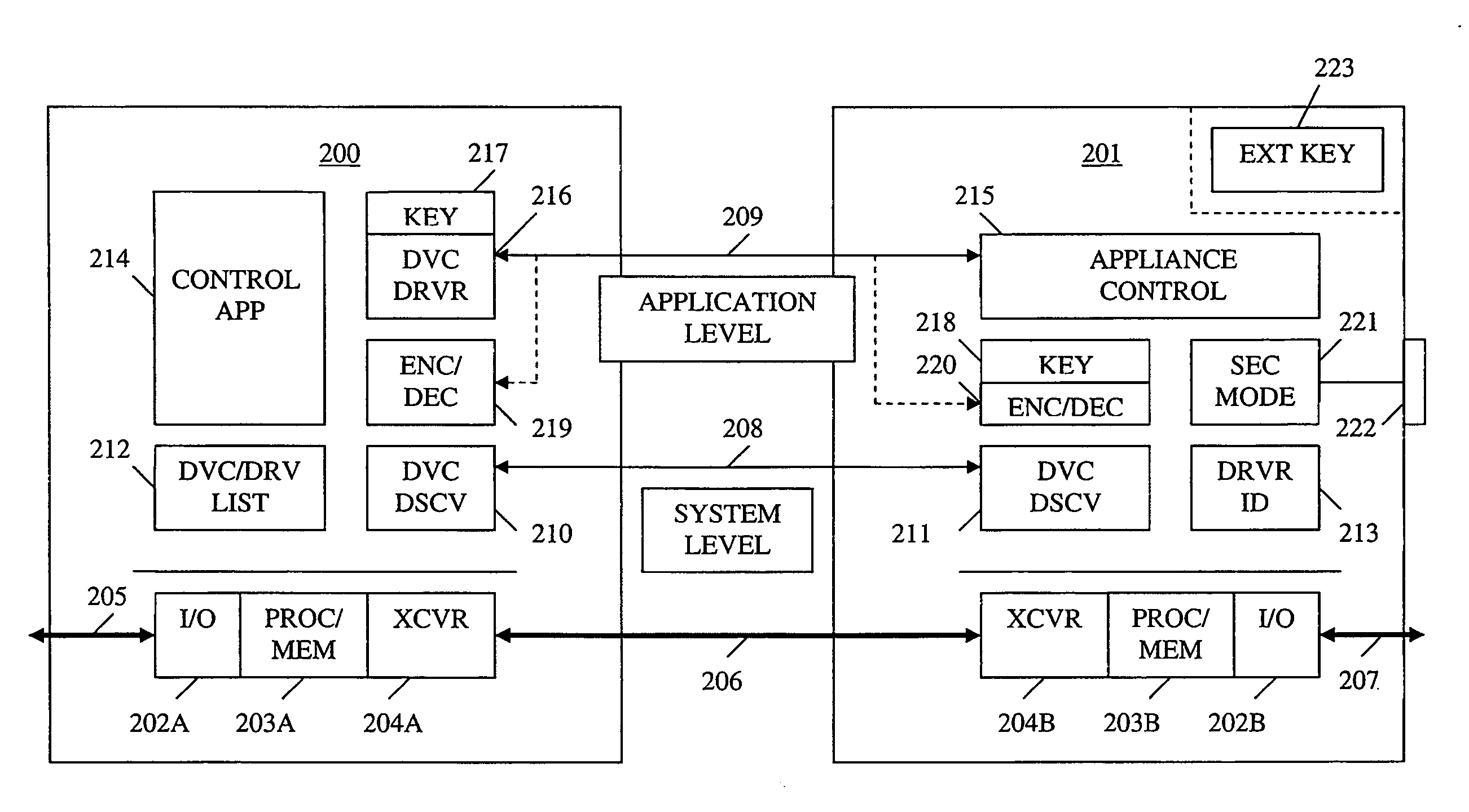
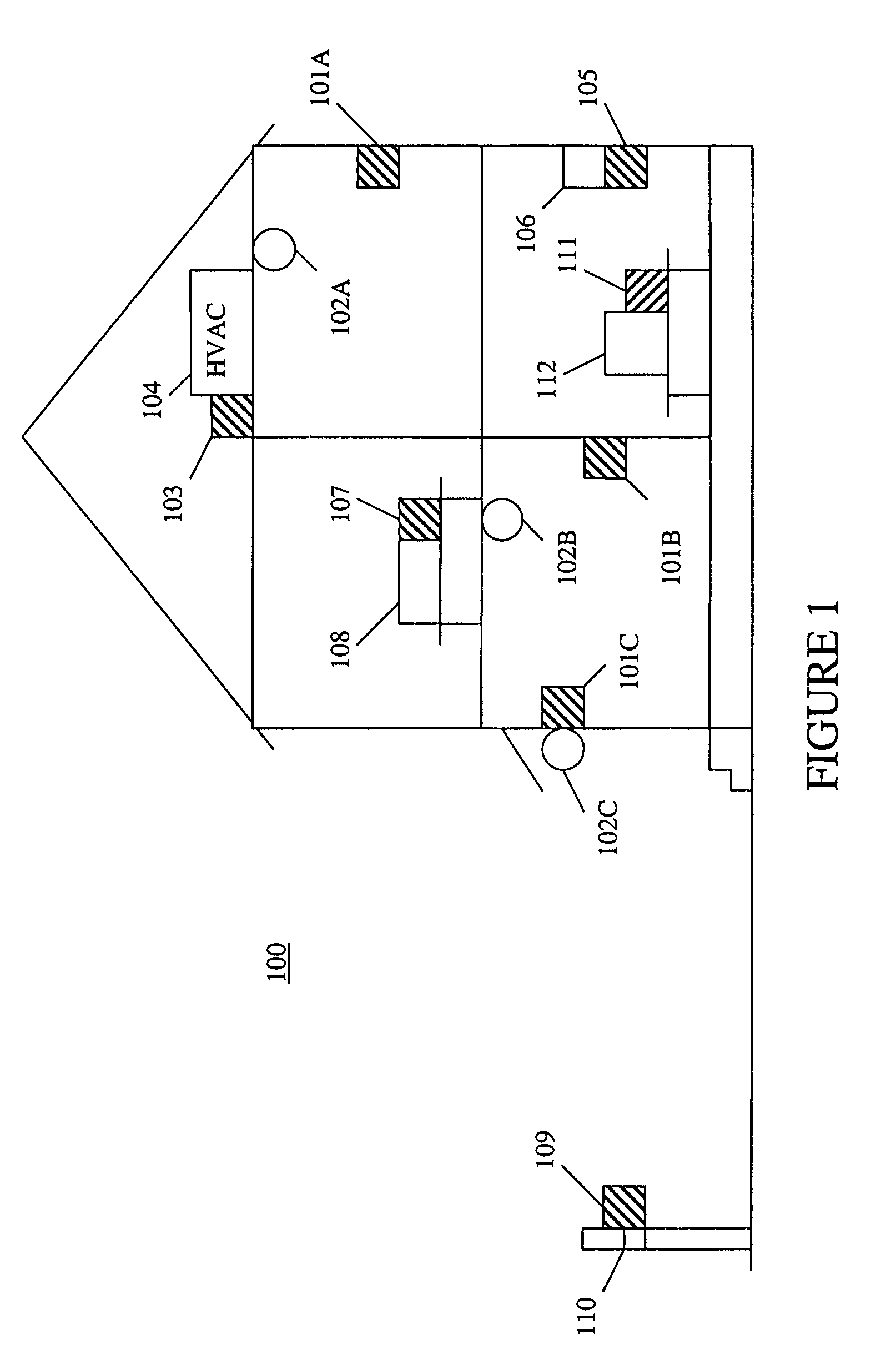
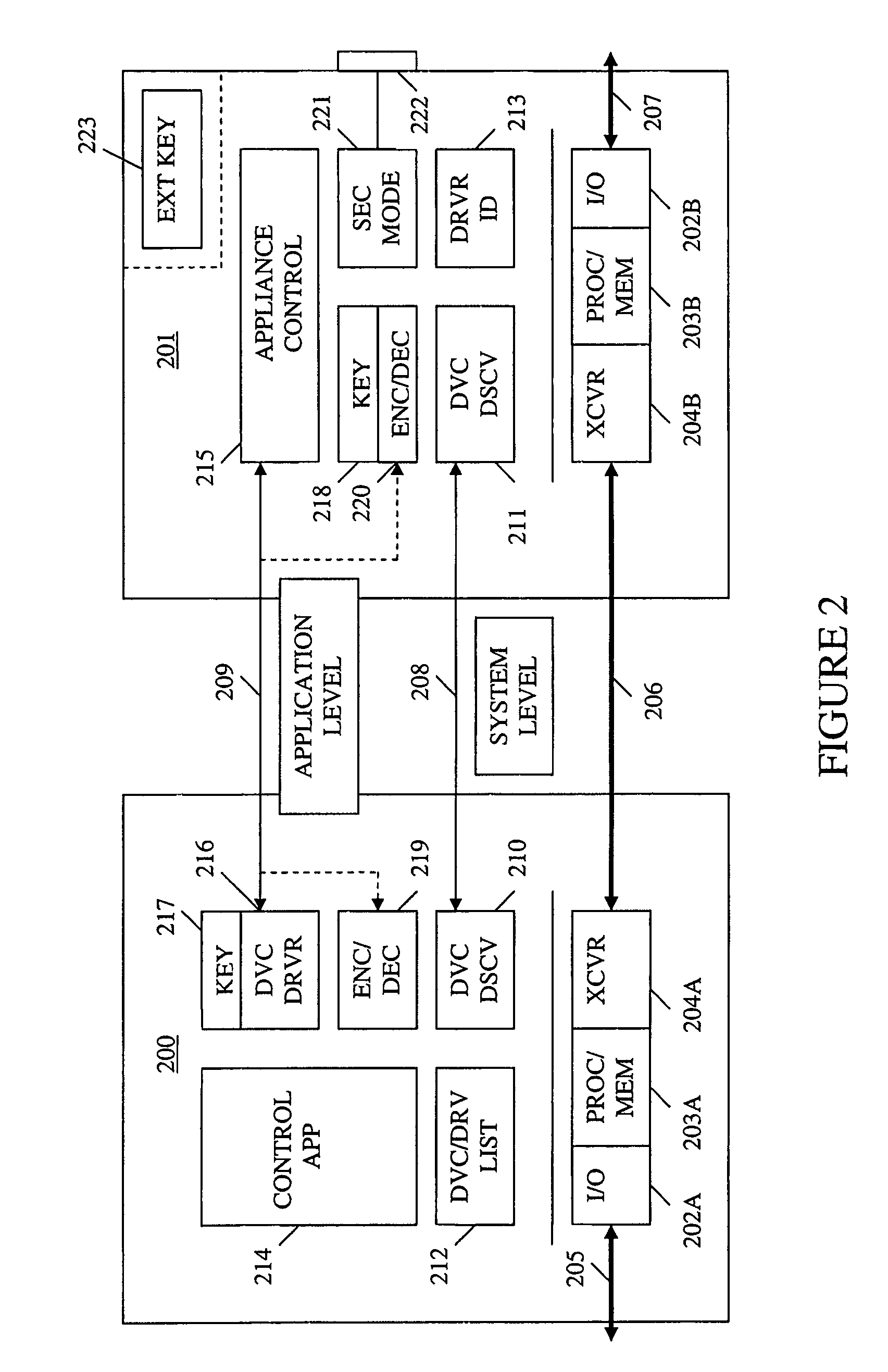
Method and apparatus for device detection and multi-mode security in a control network
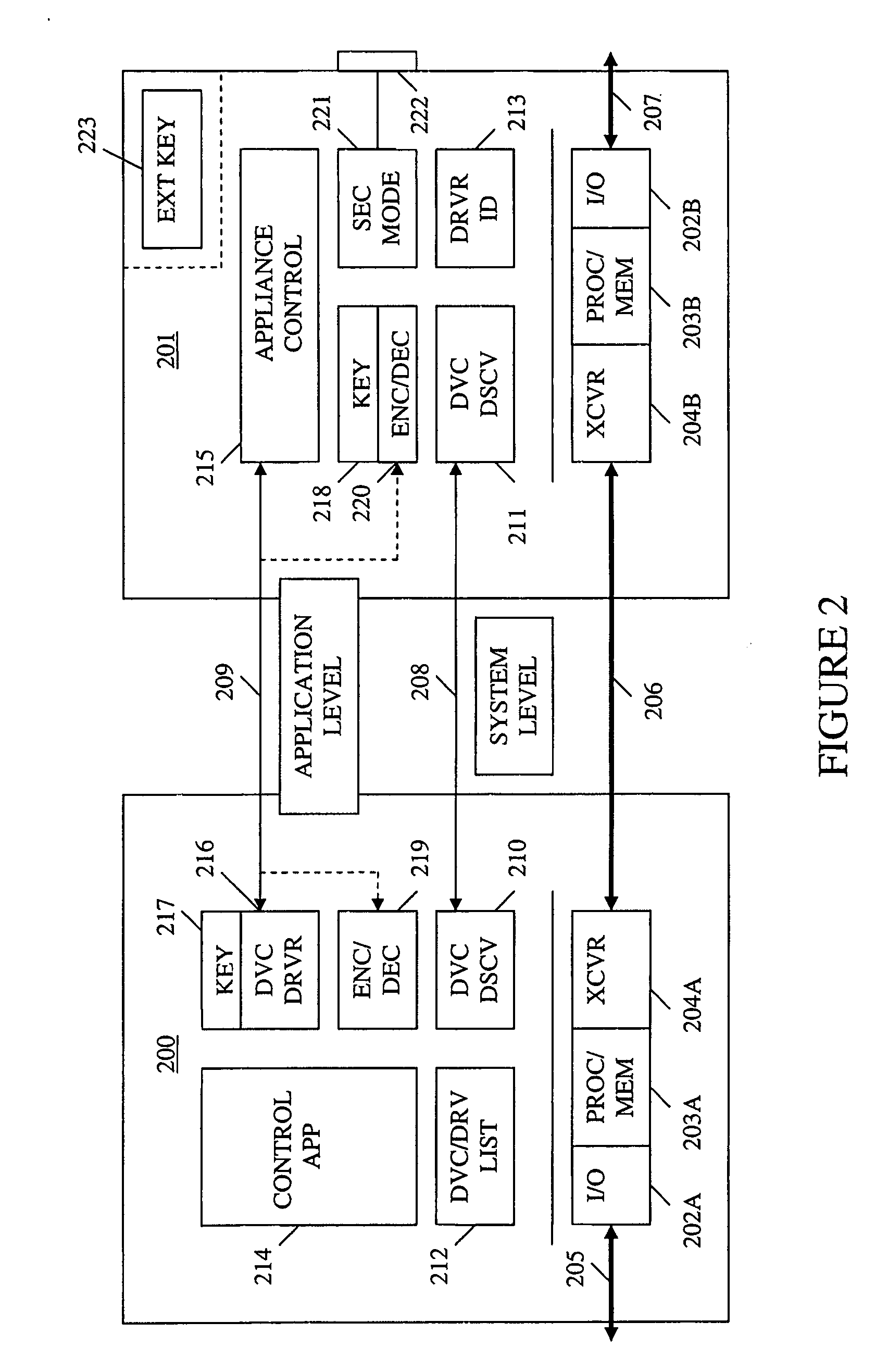
ActiveUS20060174102A1Facilitate key exchangeAvoid reconfigurationSecurity arrangementSecuring communicationWireless controlUser management
A method and apparatus for device discovery and multi-mode security in a wired and / or wireless control network are described. A controlled device is configured with discovery-level instructions and application-level control instructions. The controlled device includes a user-configurable parameter for selecting between multiple security modes. In one or more security modes, the controlled device may ignore application-level messages until encrypted communications are established with a controller. In one mode, the encrypted communication is established with an encryption key exchange using a predetermined security key. In another mode, a specific key is manually entered into the controller by the user / administrator to facilitate the encryption key exchange. Additionally, for control applications where security is not important, an unencrypted security mode may be implemented. A driver ID provided by the controlled device facilitates loading of a preferred device driver by the controller.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
Encryption key exchange system and method
InactiveUS9002018B2Improve usabilityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationUsabilityEncryption
Owner:SYNC UP TECH
Method and system for performing perfectly secure key exchange and authenticated messaging
InactiveUS20060034456A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationBusiness processExchange of information
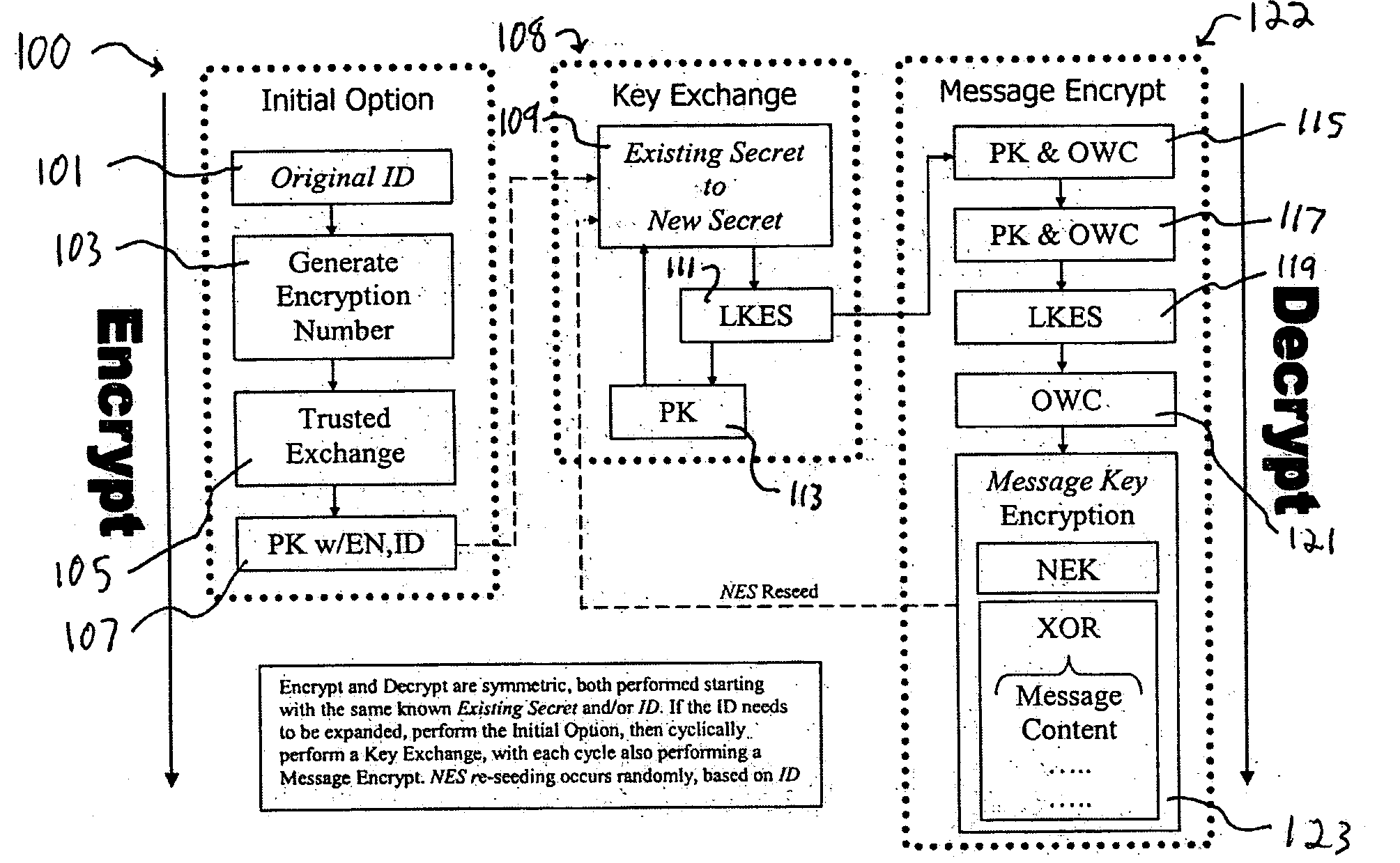
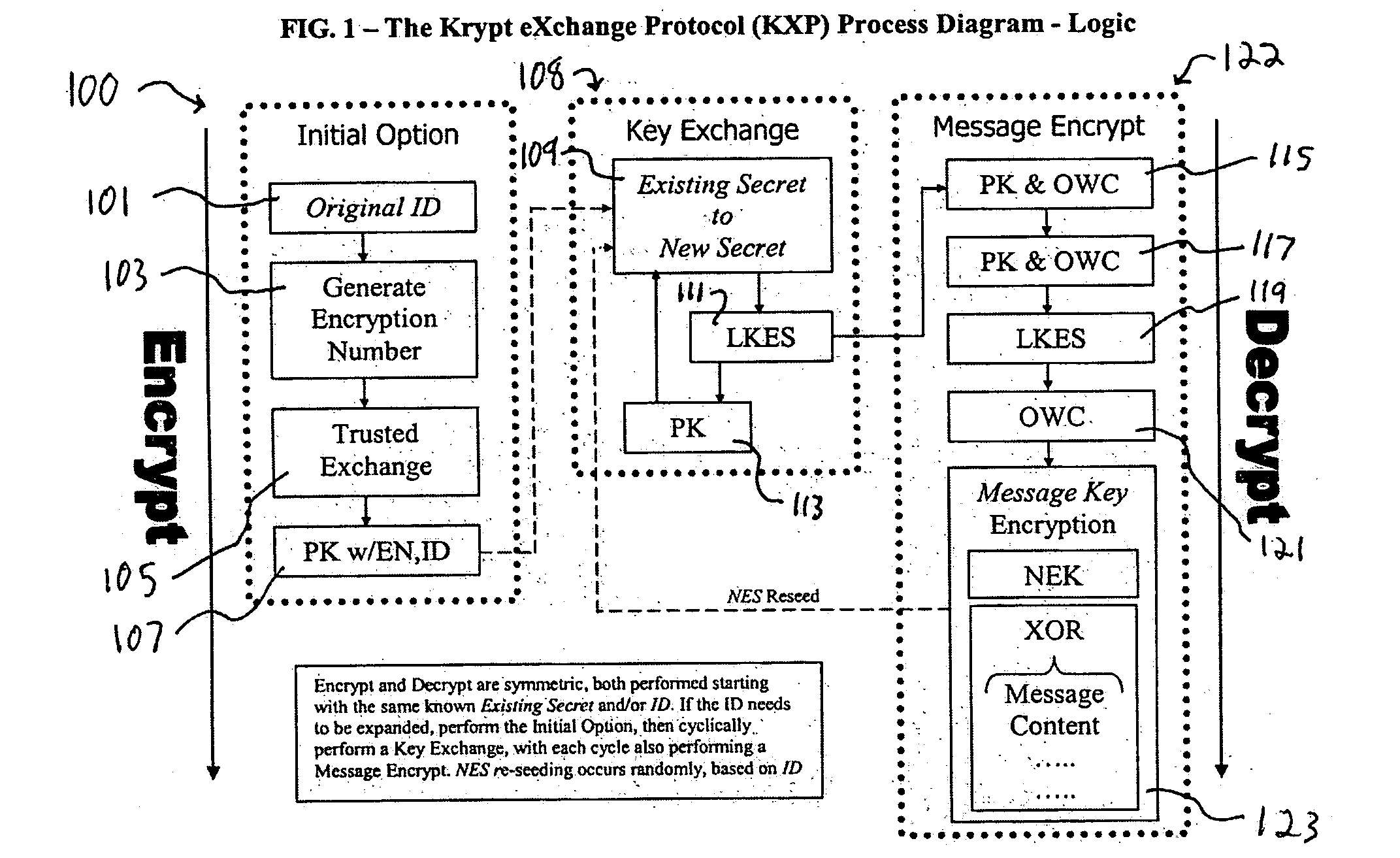
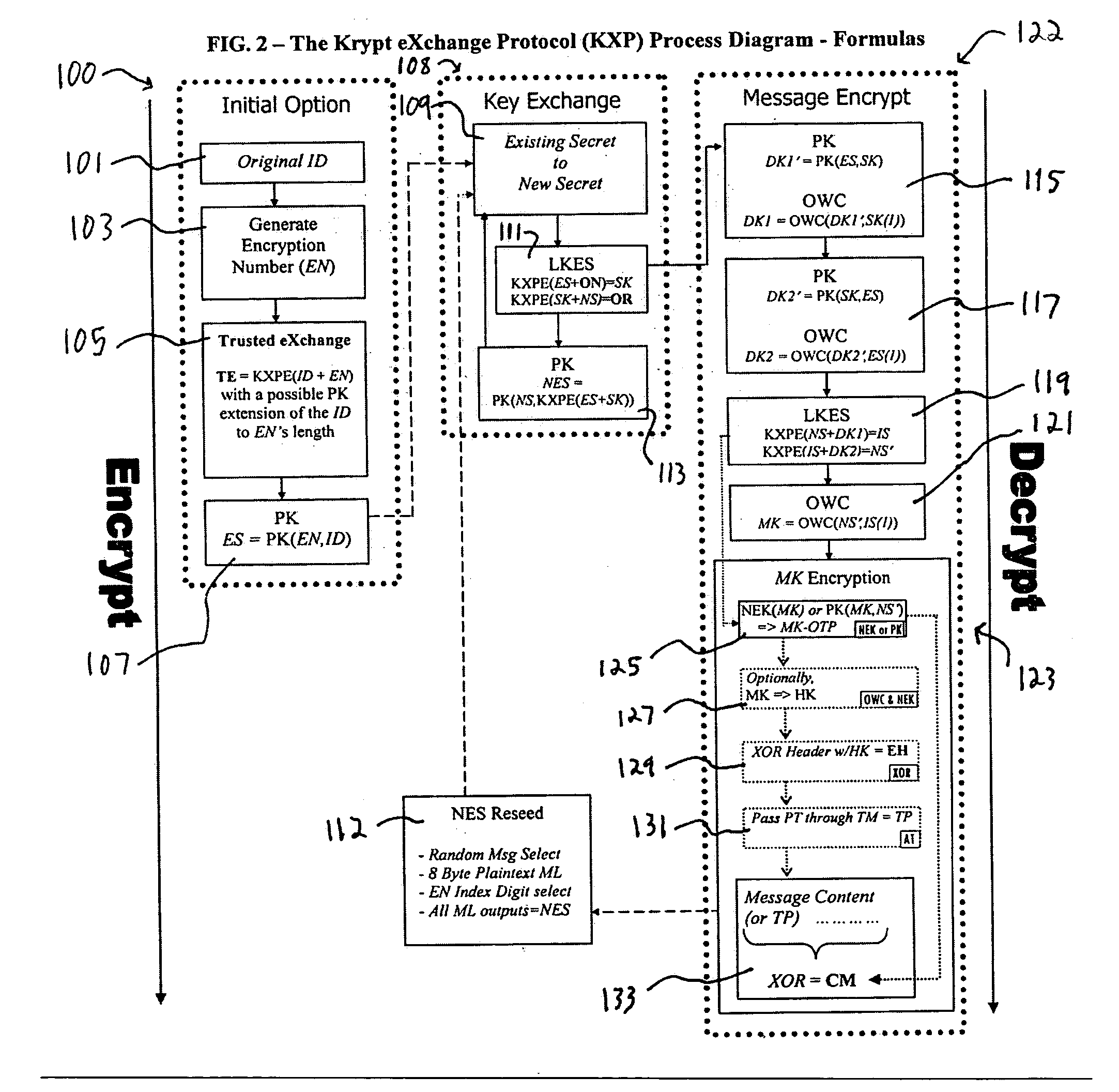
A system and method for the cryptographic exchange of information is provided which affords maximum security, process simplicity and participant convenience to any software application, business process or device used to communicate messages. The system provides the ability to openly exchange encryption keys for each communication between participants in a totally secure fashion. Along with the key exchange, the system and method can be used to secure all accompanying message content with a derived message key. The system and method derives the message key in such a manner that the original encryption key cannot positively be determined from a discovered message key. The system and method additionally provide a technique for authenticated exchange of new encryption keys such that the new key is completely dissimilar from any previous key, effectively eliminating any chained key knowledge.
Owner:RELEVANT SECURITY
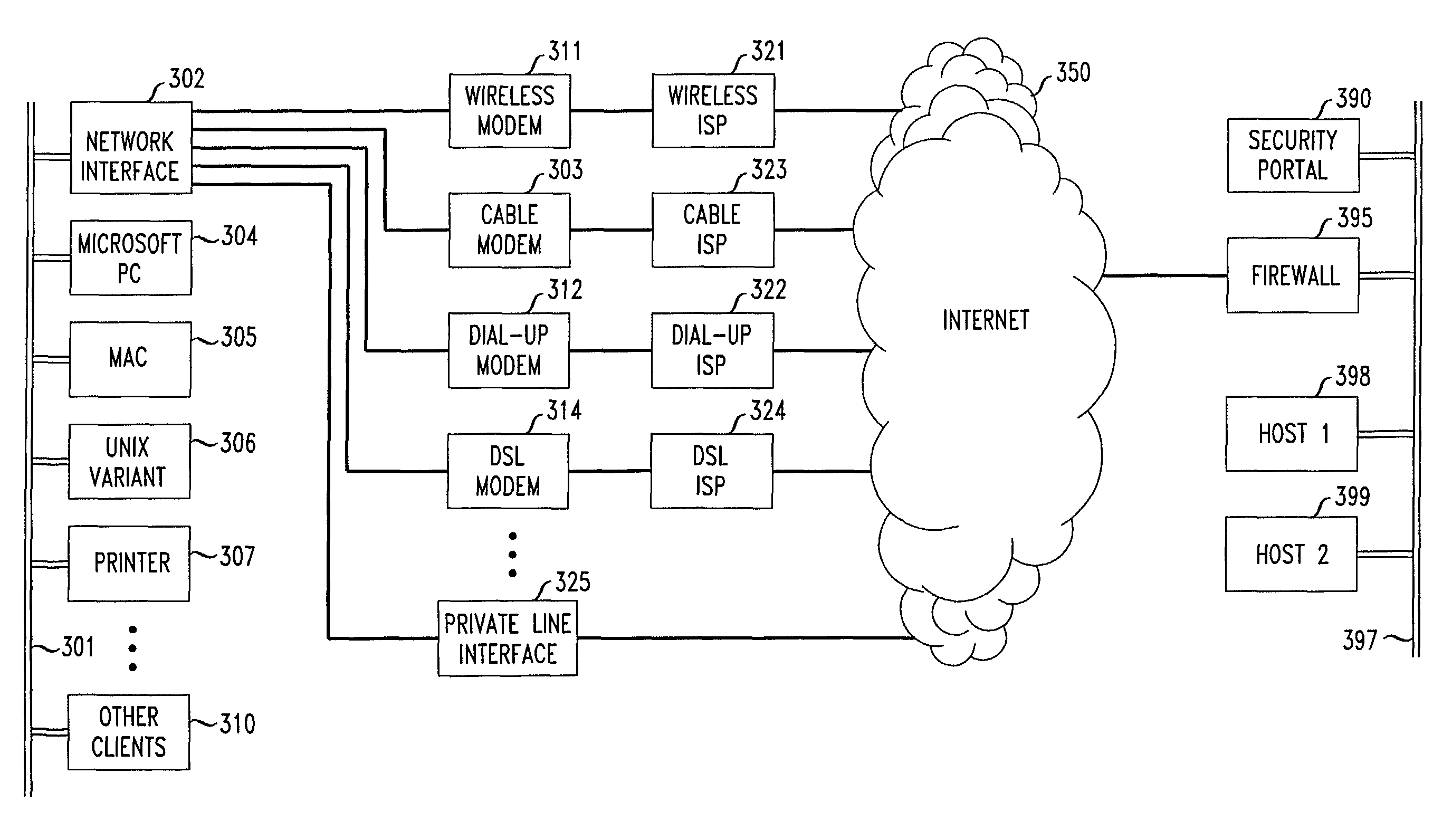
Flexible automated connection to virtual private networks
InactiveUS20060080441A1Quickly and efficiently configuredUnified interfaceDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkEncryption decryption
A network interface unit is provided for use intermediate a LAN and a public or private network, or a combination of both, for establishing secure links to a VPN gateway. Login by a LAN client with the network interface unit, addressing, authentication, and other configuration operations achieved using a web page-based GUI are applied in establishing tunnels from LAN clients to desired VPN destinations. Illustrative network interface units include a DHCP server and provide encryption-decryption and encapsulation-decapsulation of data packets for communication with VPN nodes. Configuration and connection of a client are further enhanced by a built-in DNS server and other functional servers to provide a high degree of autonomy in establishing connections to a desired VPN gateway via an ISP or other public and / or private network links to. The interface unit then performs required authentication exchanges, and required encryption key exchanges.
Owner:CHEN YIHSIU +6
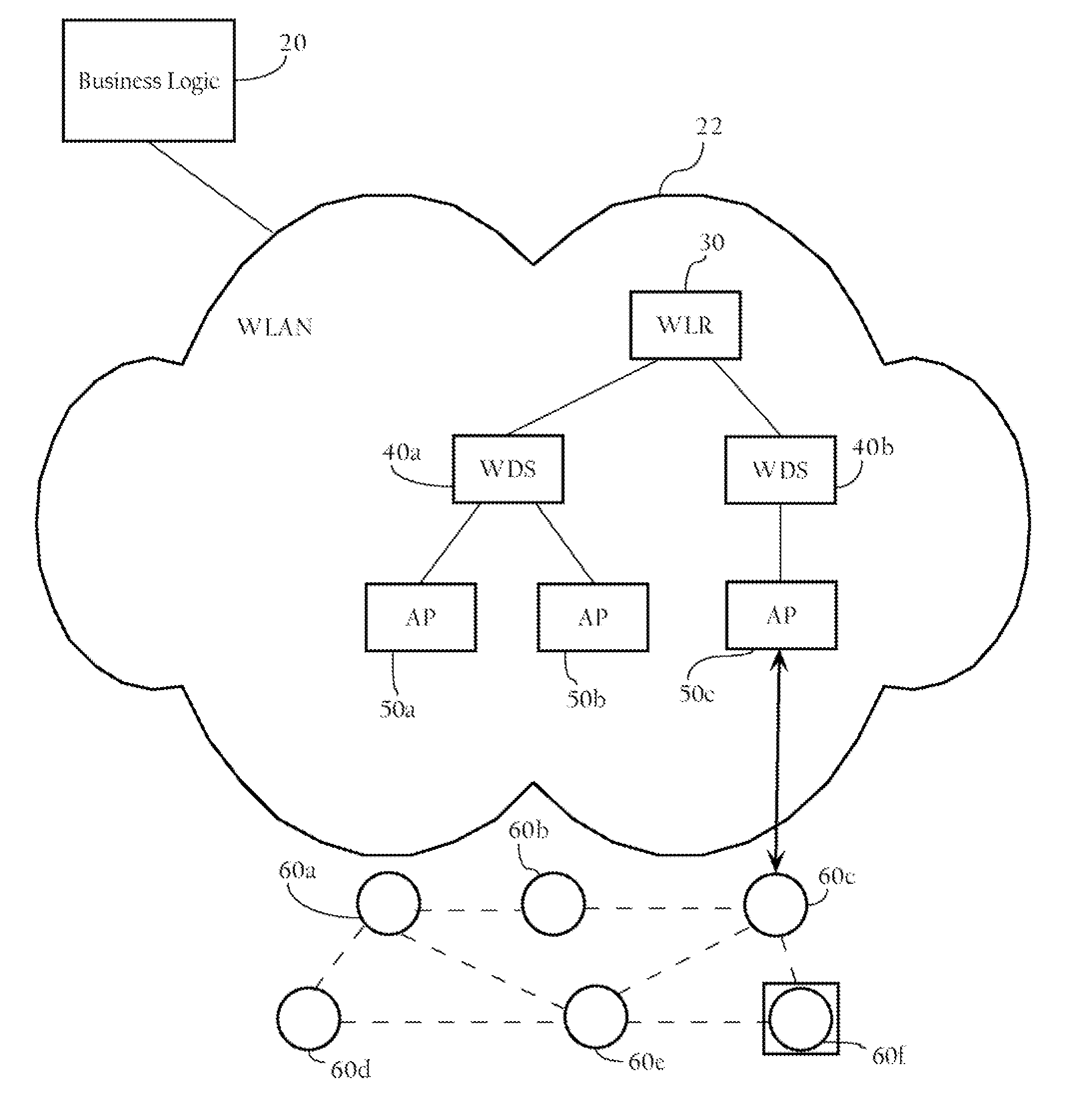
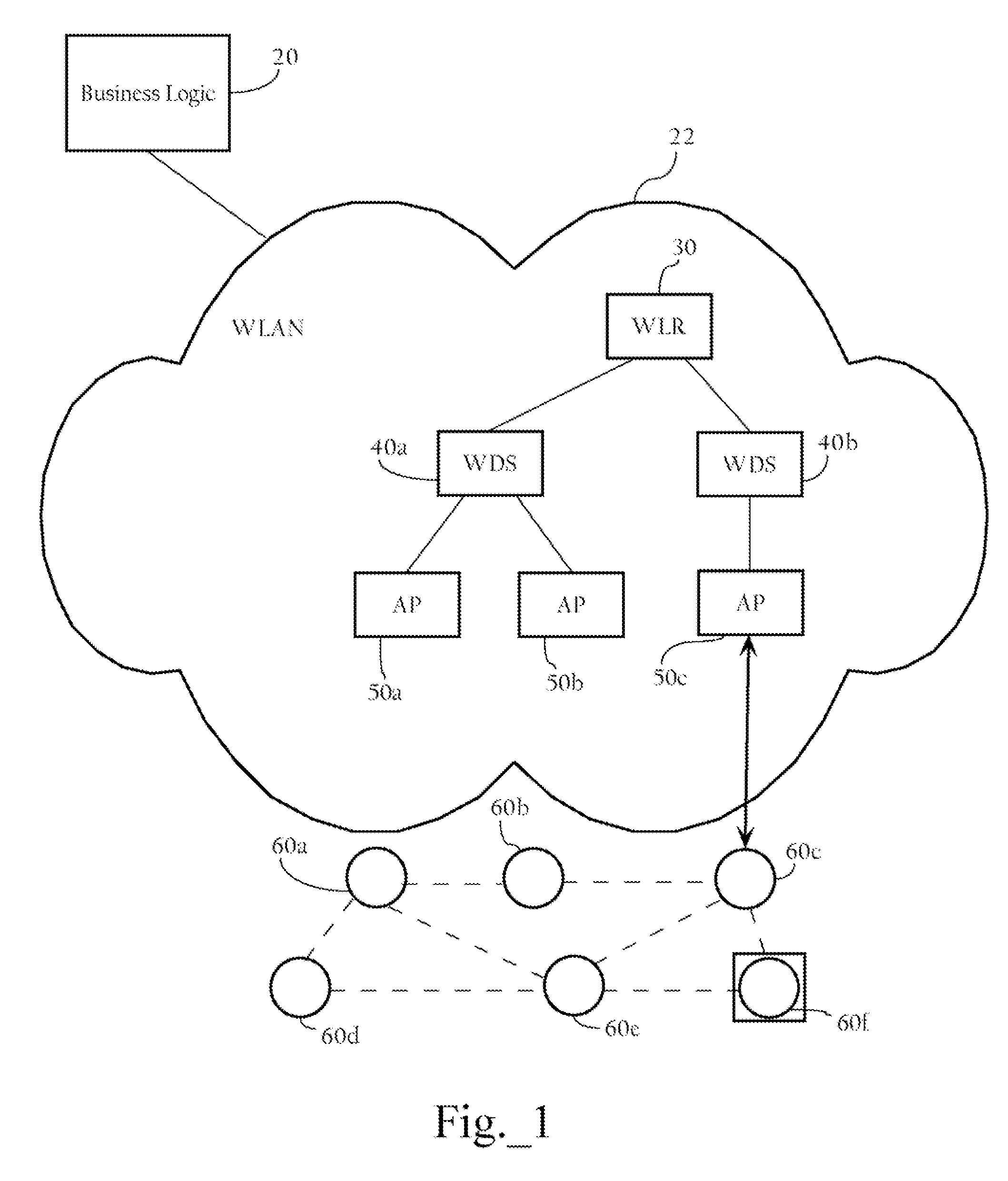
Intelligent association of nodes with PAN coordinator
InactiveUS20060116170A1Broadcast with distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementSensor nodeComputer science
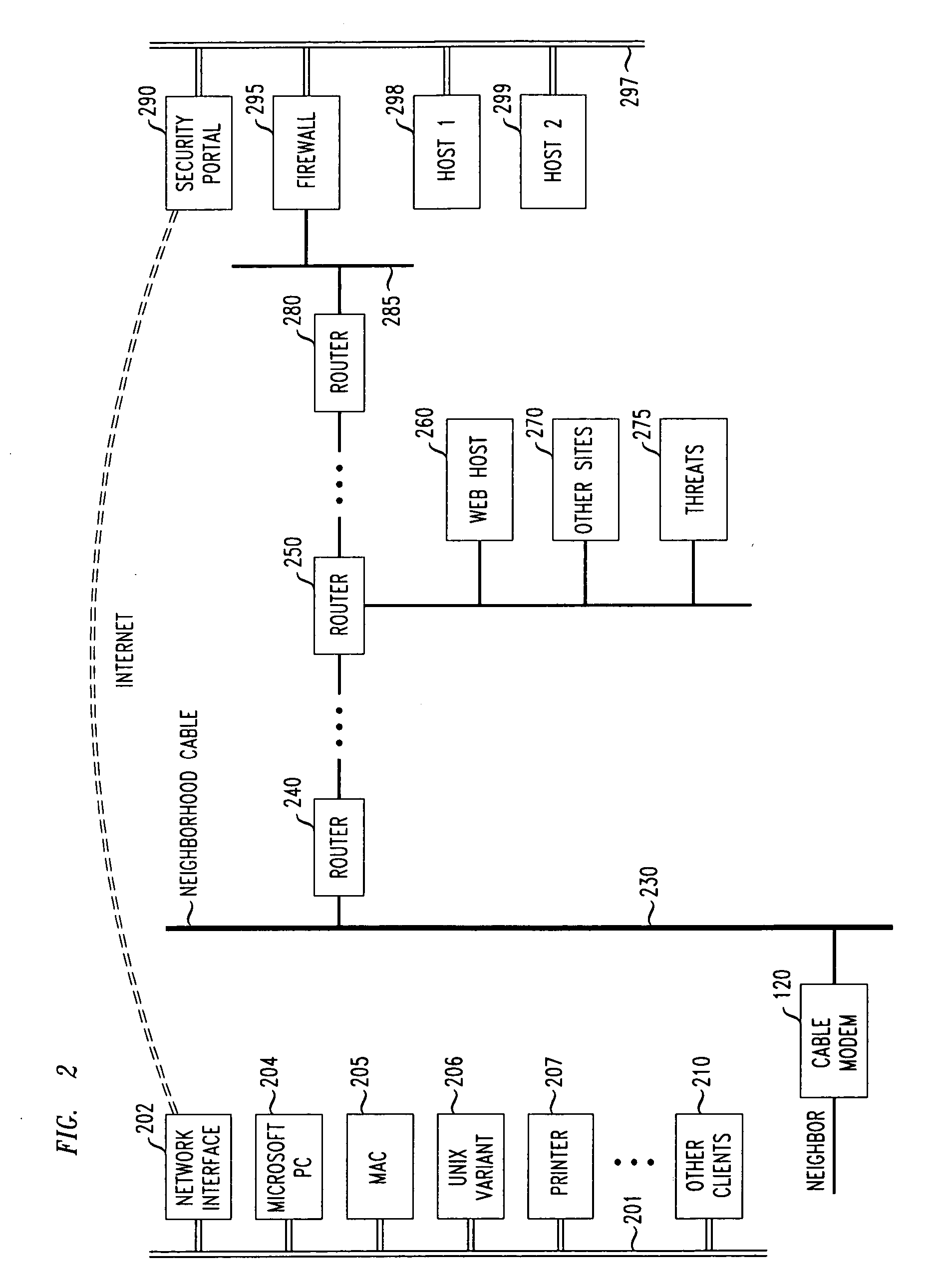
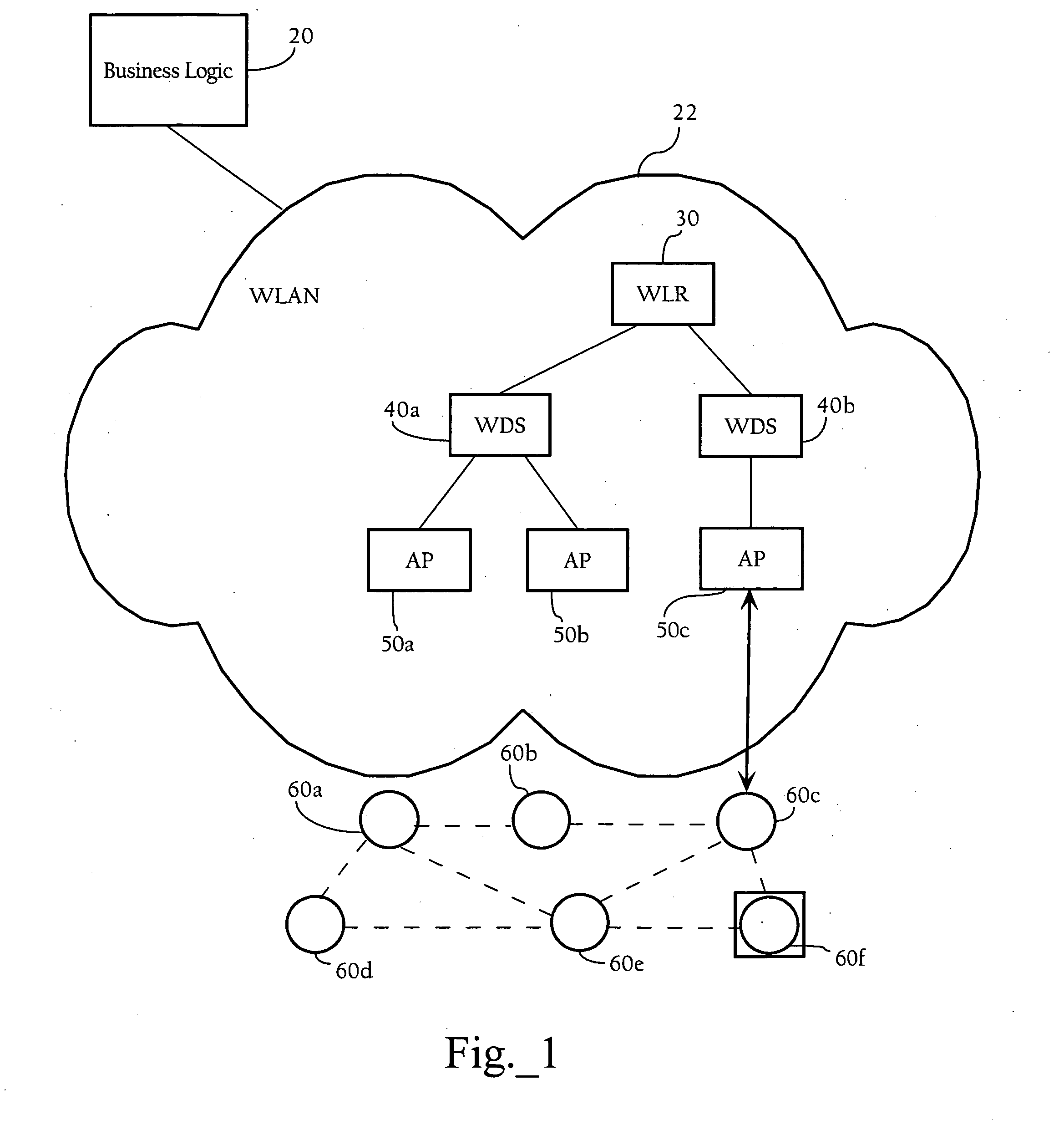
Methods, apparatuses, and systems directed to managing wireless node access to one or more wireless networks. According to one implementation of the present invention, a business logic application may function as a package tracking application to manage access to wireless access points in different WLANs along the route. A sensor node is initialized and configured with one or more connection parameter sets allowing it to associate with a given wireless network implemented by one or more access points. In one implementation, the sensor node is configured only to accept received wireless frames that it can properly decrypt using the currently-stored encryption key. Accordingly, until the sensor node comes within radio contact of a wireless access point or other wireless node configured with the same encryption key, it does not establish a wireless connection. When the sensor node and such a wireless access point associate, they may exchange encrypted information (e.g., data regarding the package) using an encryption key. Before the sensor node disassociates with the wireless access point, the wireless access point transmits a new connection parameter set to the sensor node. This new connection parameter set includes a network ID for another wireless network. In addition, the new connection parameter set also includes an encryption key and a frequency identifier. In one implementation, the sensor node re-initializes itself using the new connection parameter set information. This process may continue until the sensor node arrives at its final destination and, in this manner, the wireless networks with which the sensor node associates may be controlled.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Encryption communication system, apparatus, method, and program
InactiveUS20080098226A1Avoid it happening againUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareCommunications system
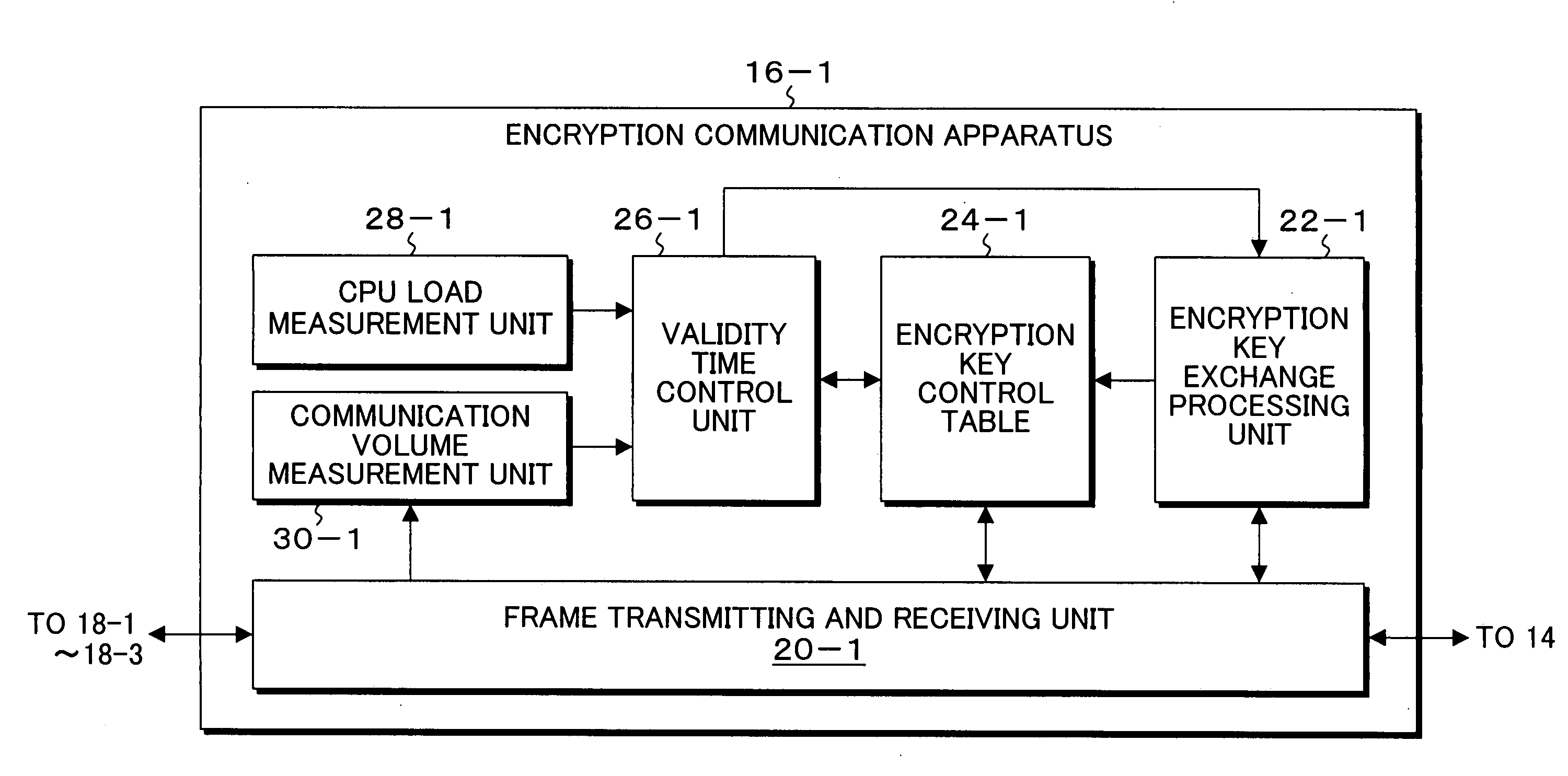
A plurality of encryption communication apparatuses to which terminal apparatuses are connected are connected via a network, data received from the terminal apparatus which is a transmission source is encrypted by the encryption communication apparatus and transmitted to the other encryption communication apparatus, and data received from the other encryption communication apparatus is decrypted and transmitted to the terminal apparatus which is a transmission destination. Upon initiation of first communication with the other encryption communication apparatuses, the encryption communication apparatus generates and exchange encryption keys according to an encryption key exchange protocol, records them in the encryption key control table and, and sets validity time so as to control that. The encryption key is subjected to encryption key update when validity time is close; however, even during validity time period, when the state that CPU load is low is determined, the encryption key of the encryption communication apparatus which is a counterpart having a small communication volume is searched, and the encryption key is updated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for connection to virtual private networks for secure transactions
ActiveUS8239531B1Quickly and efficiently configuredUnified interfaceData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationTelecommunications link
A system and method are provided for use in establishing secure end-to-end communication links over a VPN gateway via a network interface unit. Illustrative embodiments include establishing and providing secure communication relationships between users (customers) and companies for e-commerce and other business purposes. Each company's data and linkage to users remaining private and secure from the other participating companies as well as from the general public over the Internet. Login by user with network interface units, addressing, authentication, and other configuration operations achieved using a web page-based GUI are applied in establishing tunnels from LAN clients to desired VPN destinations. Required authentication exchanges and required encryption key exchanges facilitate the secure communications. Financial arrangements regarding the provisioning and use of network interface units are also disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
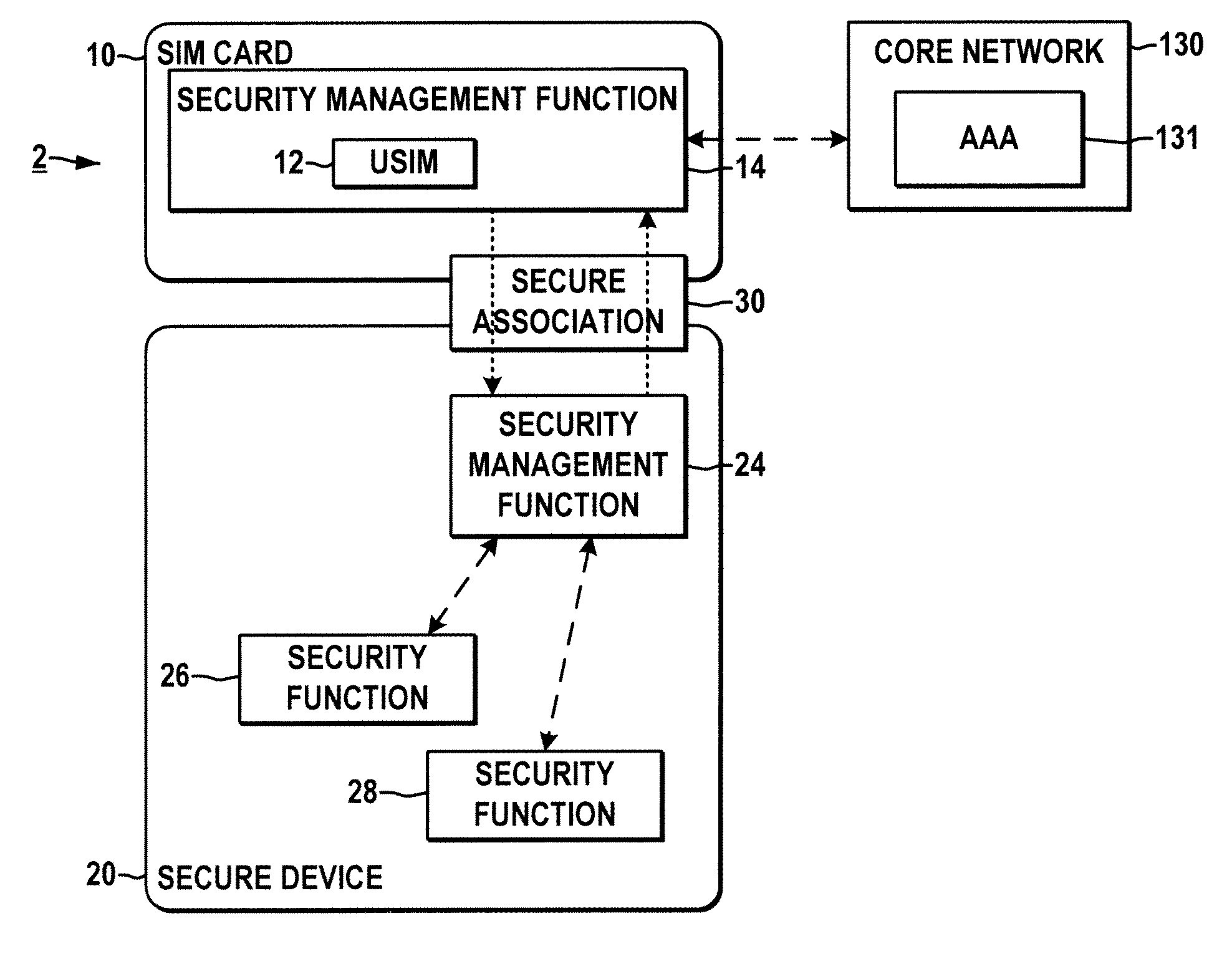
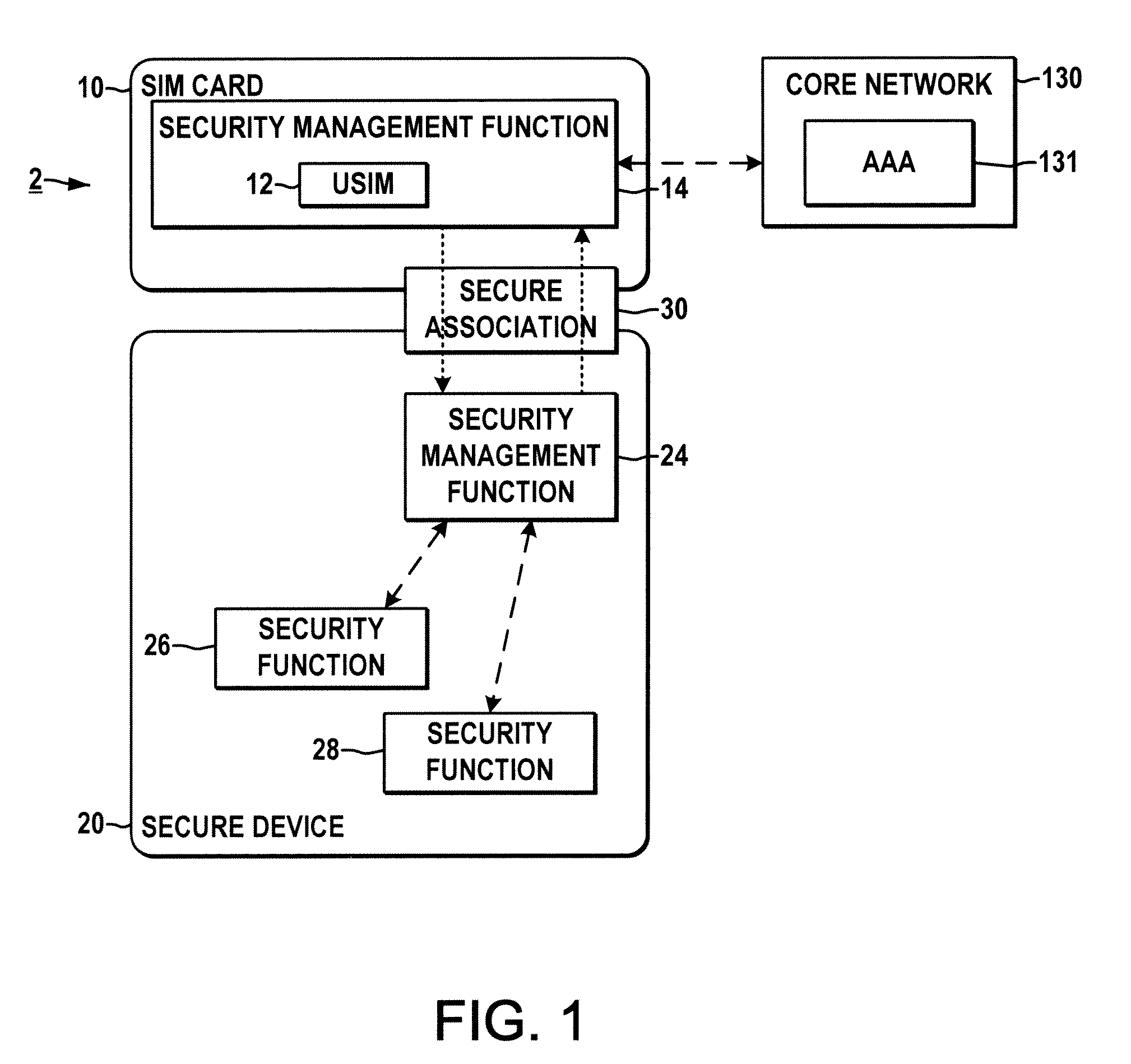
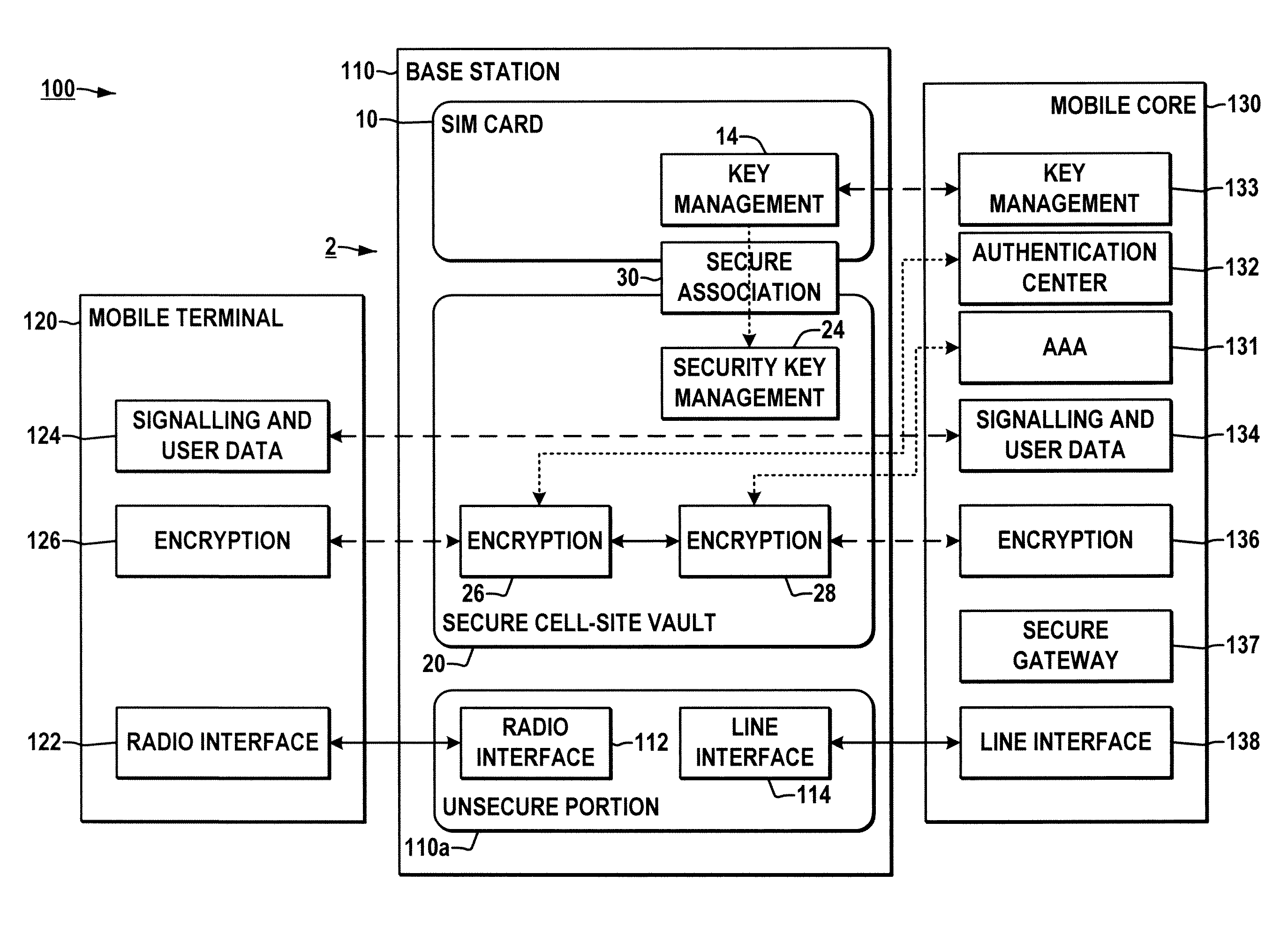
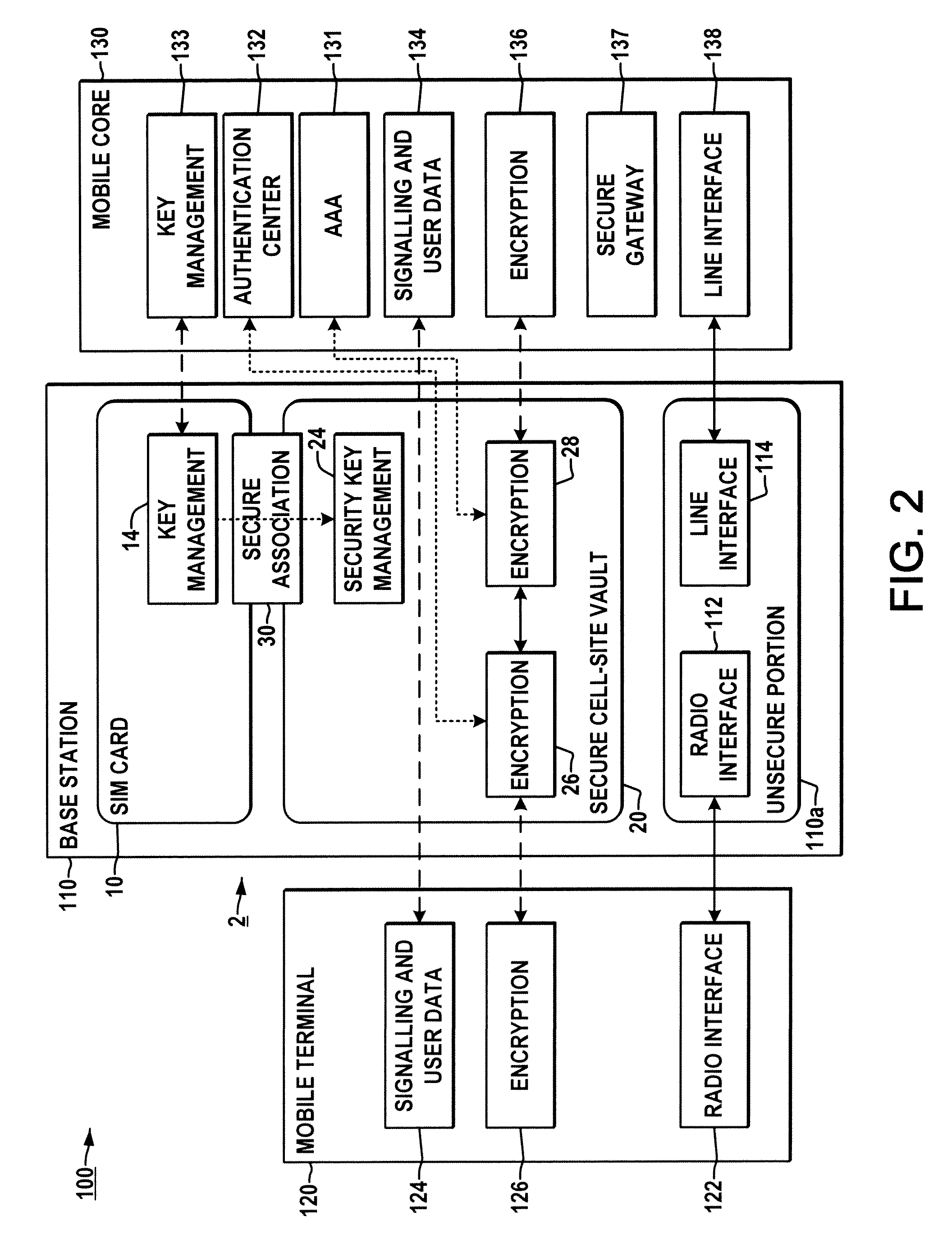
System and method for securing a base station using SIM cards
ActiveUS20090227234A1Promote generationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsEngineeringEncryption
Methods and systems are provided for securing integrated base stations, such as base station routers (BSRs), in which a SIM card is operatively coupled with a secured portion of a base station and a secure association is established therebetween to facilitate encryption key exchange between the secured portion of the base station and a core network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
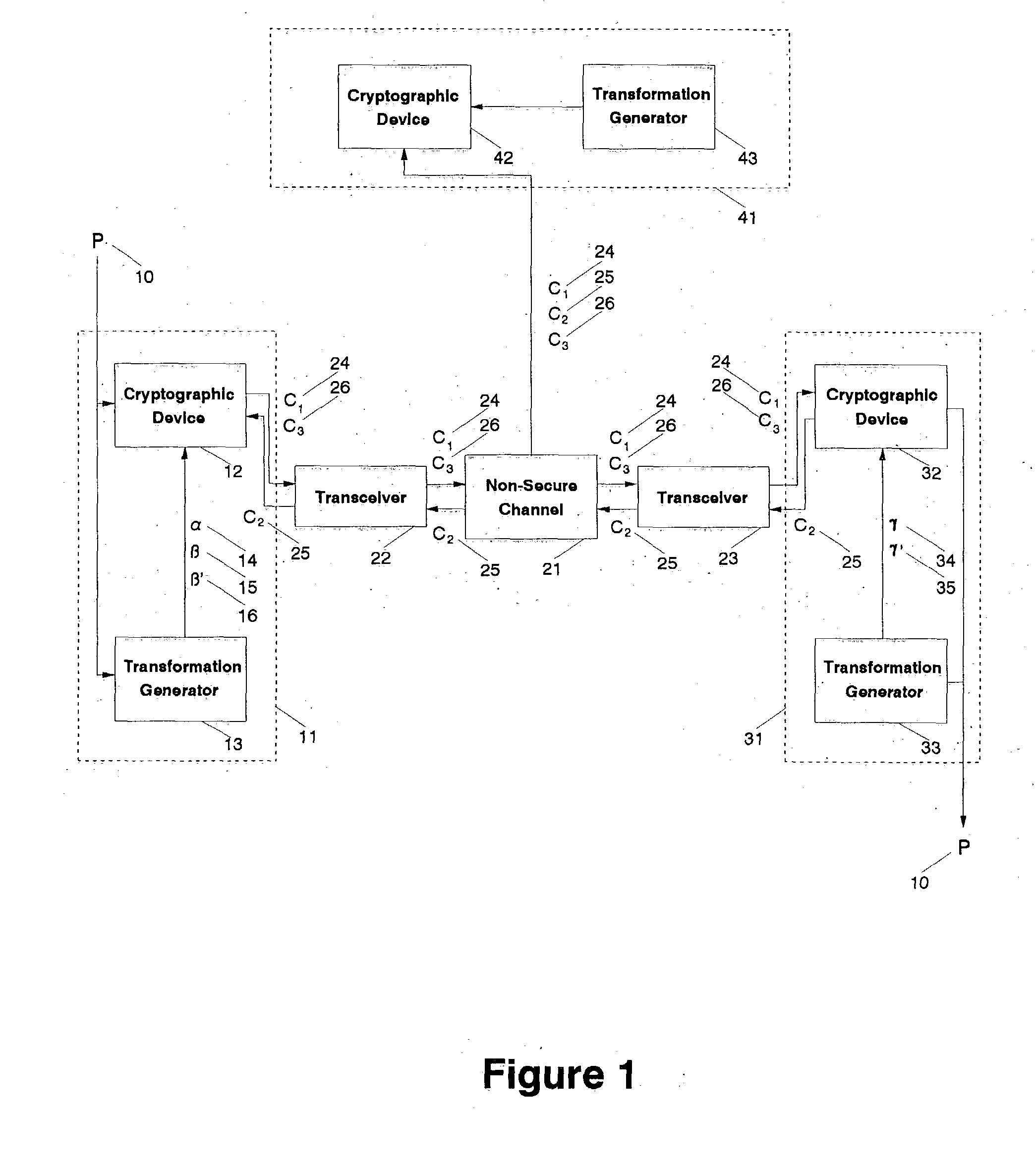
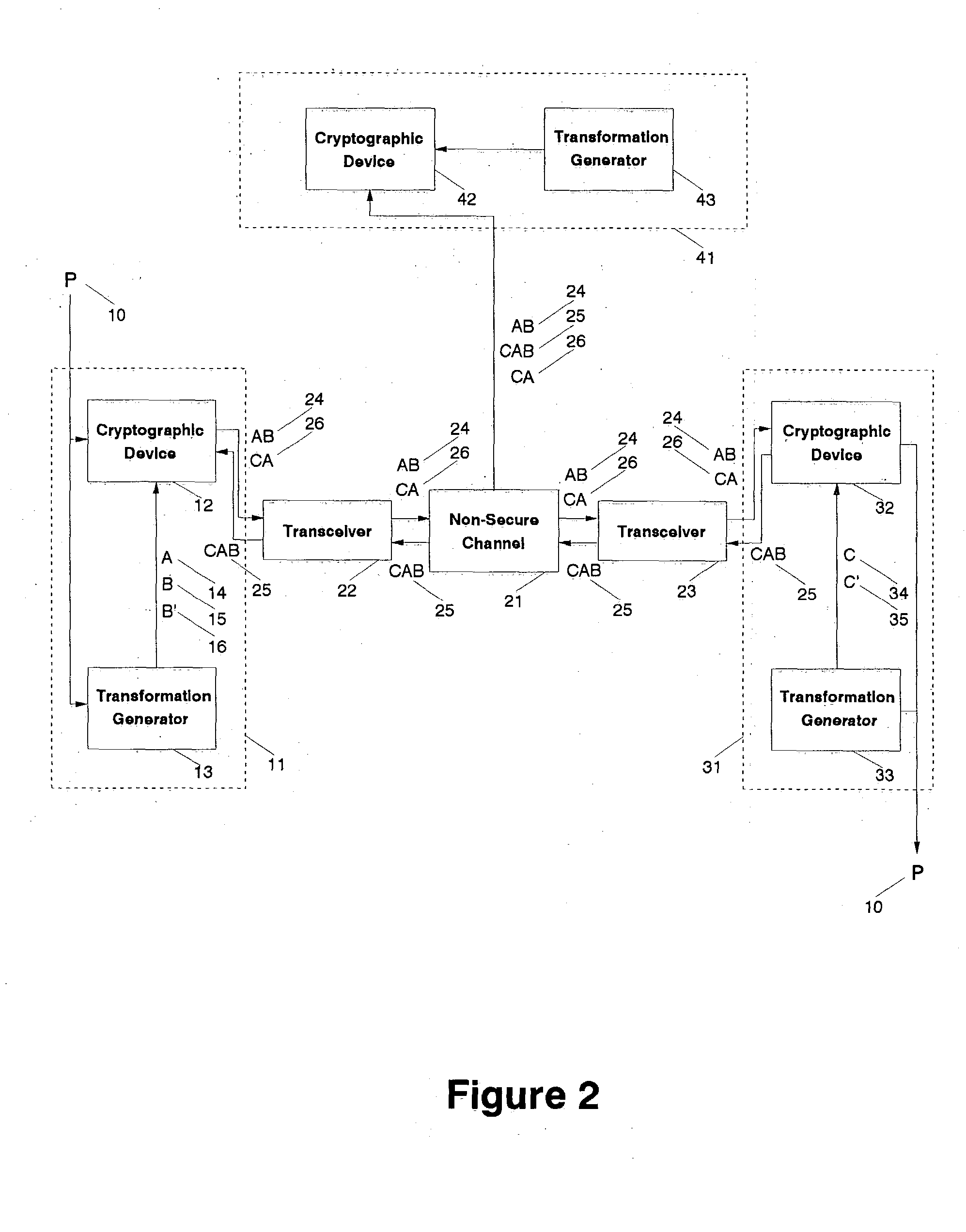
Fully secure message transmission over non-secure channels without cryptographic key exchange
InactiveUS20050002533A1Impossible to determineKey distribution for secure communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresComputer hardwareSecure communication
A cryptographic system transmits a fully secure cryptographic message over a non-secure communication channel without prior exchange of cryptographic keys using a three-pass protocol. The transmitting agent initiating the communication embodies the message for the designated receiving agent in the composite output of two distinct transformations such that a generalized reversal of the combined transformations cannot be determined from that output. That output is transmitted as a first-pass over a non-secure channel to the receiving agent. The receiving agent generates a second composite output by transforming the received message such that a generalized reversal of this second combined transformation cannot be determined from that resulting output. That second output is transmitted as a second-pass over a non-secure channel to the initial transmitting agent. The initial agent generates a third composite output from the returned message by reversing one of the two initial transformations such that a generalized reversal of this third composite transformation cannot be determined from that resulting output. The third output is transmitted as a third-pass over a non-secure channel to the receiving agent. The receiving agent uses a reversal of the second transformation applied to the final message to extract the initial message. The transformations (or keys) used by either party need not be known by the other, making this an independent-key cryptographic process. It is technically impossible for any eavesdropping agent, even one who captures all transmissions between the transmitting and receiving agents, to directly recreate the initial message from the observed transmissions.
Owner:LANGIN HOOPER JERRY JOE +1
Method and apparatus for connection to virtual private networks for secure transactions
InactiveUS20130163757A1Quickly and efficiently configuredUnified interfaceKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsSecure communicationTelecommunications link
A system and method are provided for use in establishing secure end-to-end communication links over a VPN gateway via a network interface unit. Illustrative embodiments include establishing and providing secure communication relationships between users (customers) and companies for e-commerce and other business purposes. Each company's data and linkage to users remaining private and secure from the other participating companies as well as from the general public over the Internet. Login by user with network interface units, addressing, authentication, and other configuration operations achieved using a web page-based GUI are applied in establishing tunnels from LAN clients to desired VPN destinations. Required authentication exchanges and required encryption key exchanges facilitate the secure communications. Financial arrangements regarding the provisioning and use of network interface units are also disclosed.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Intelligent Association of Nodes with PAN Coordinator
ActiveUS20070171859A1Network traffic/resource managementUser identity/authority verificationSensor nodeWireless access point
Methods apparatuses, and systems directed to managing wireless node access to one or more wireless networks. According to one implementation of the present invention, a business logic application may function as a package tracking application to manage access to wireless access points in different WLANs along the route. A sensor node is initialized and configured with one or more connection parameter sets allowing it to associate with a given wireless network implemented by one or more access points. In one implementation, the sensor node is configured only to accept received wireless frames that it can properly decrypt using the currently-stored encryption key. Accordingly, until the sensor node comes within radio contact of a wireless access point or other wireless node configured with the same encryption key, it does not establish a wireless connection. When the sensor node and such a wireless access point associate, they may exchange encrypted information (e.g., data regarding the package) using an encryption key. Before the sensor node disassociated with the wireless access point, the wireless access point transmits a new connection parameter set to the sensor node. This new connection parameter set includes a network ID for another wireless network. In addition, the new connection parameter set also includes an encryption key and a frequency identifier. In one implementation, the sensor node re-initializes itself using the new connection parameter set information. This process may continue until the sensor node arrives at its final destination and, in this manner, the wireless networks with which the sensor node associates may be controlled.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
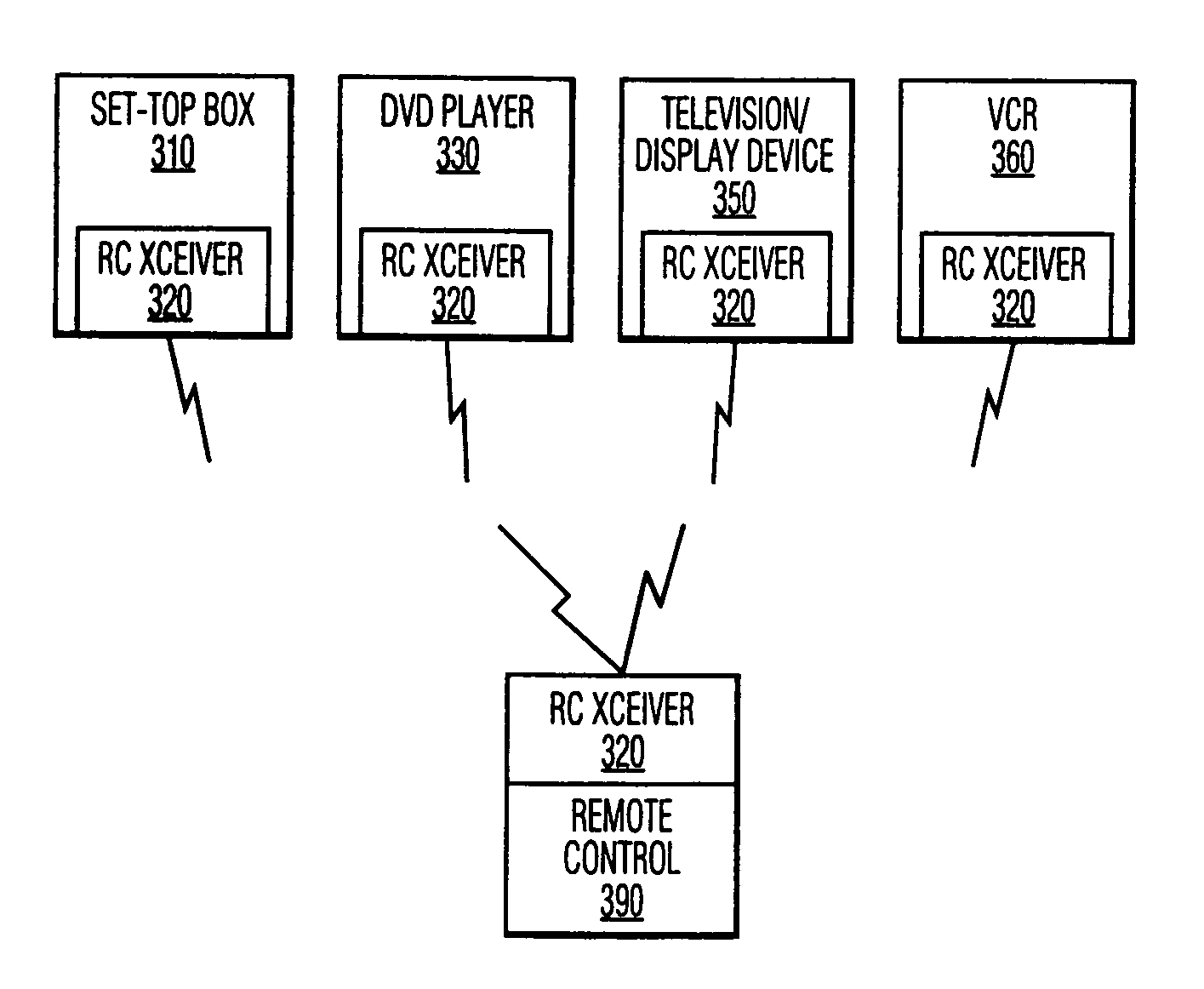
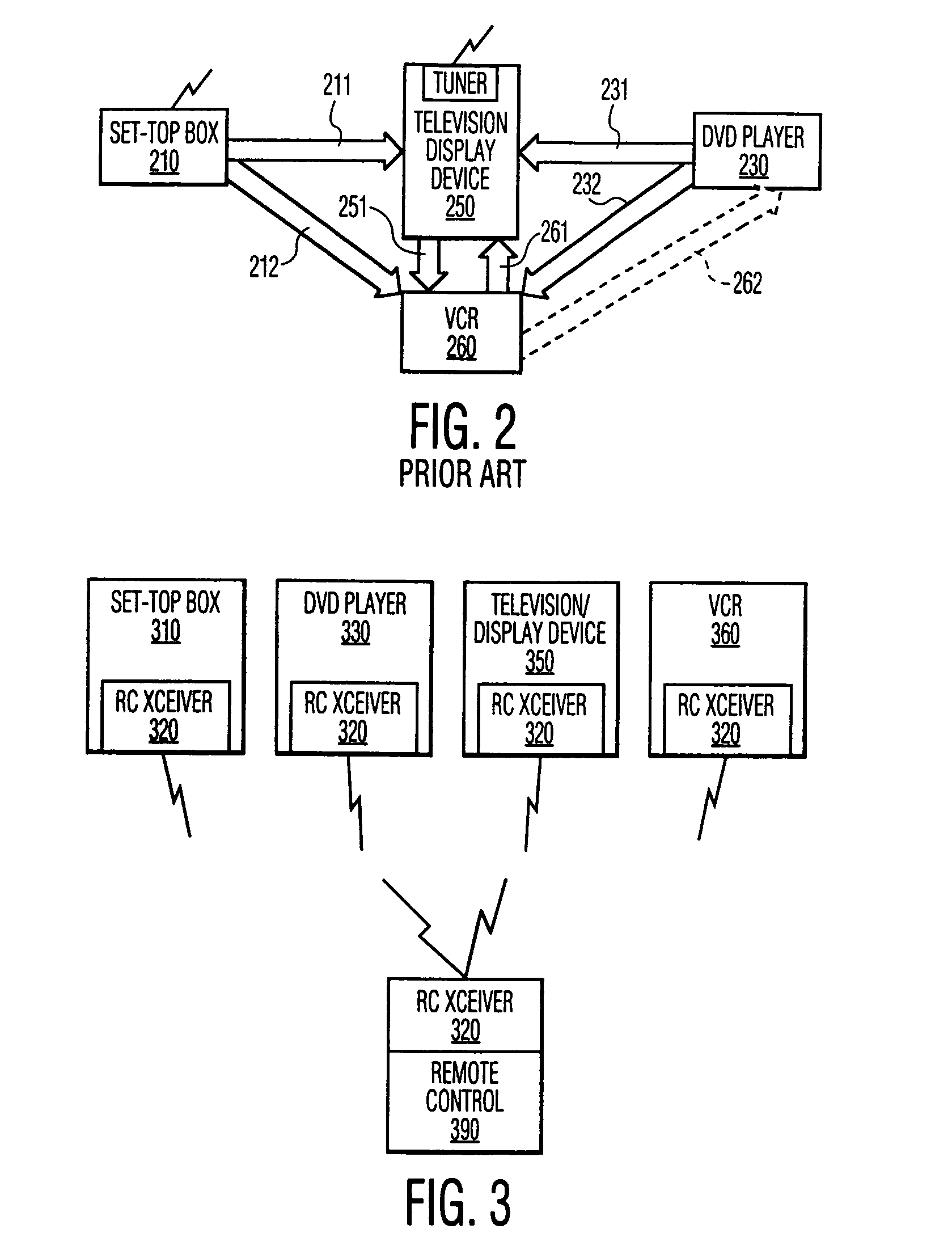
Key exchange via a portable remote control device
InactiveUS6993134B1Television system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationTransceiverRemote control
The communications means that are commonly provided for the remote control of electronic components are utilized to effect an exchange of parameters to facilitate a cryptographic key exchange. The bidirectional remote control transceivers, typically infrared transceivers, that are commonly used to communicate commands from the remote control device and to communicate feedback to the remote control device are configured to communicate parameters between a pair of consumer devices that are controllable by the remote control device. In a preferred embodiment of this invention the remote control device contains the control means to effect the transfer of these parameters between the consumer devices.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
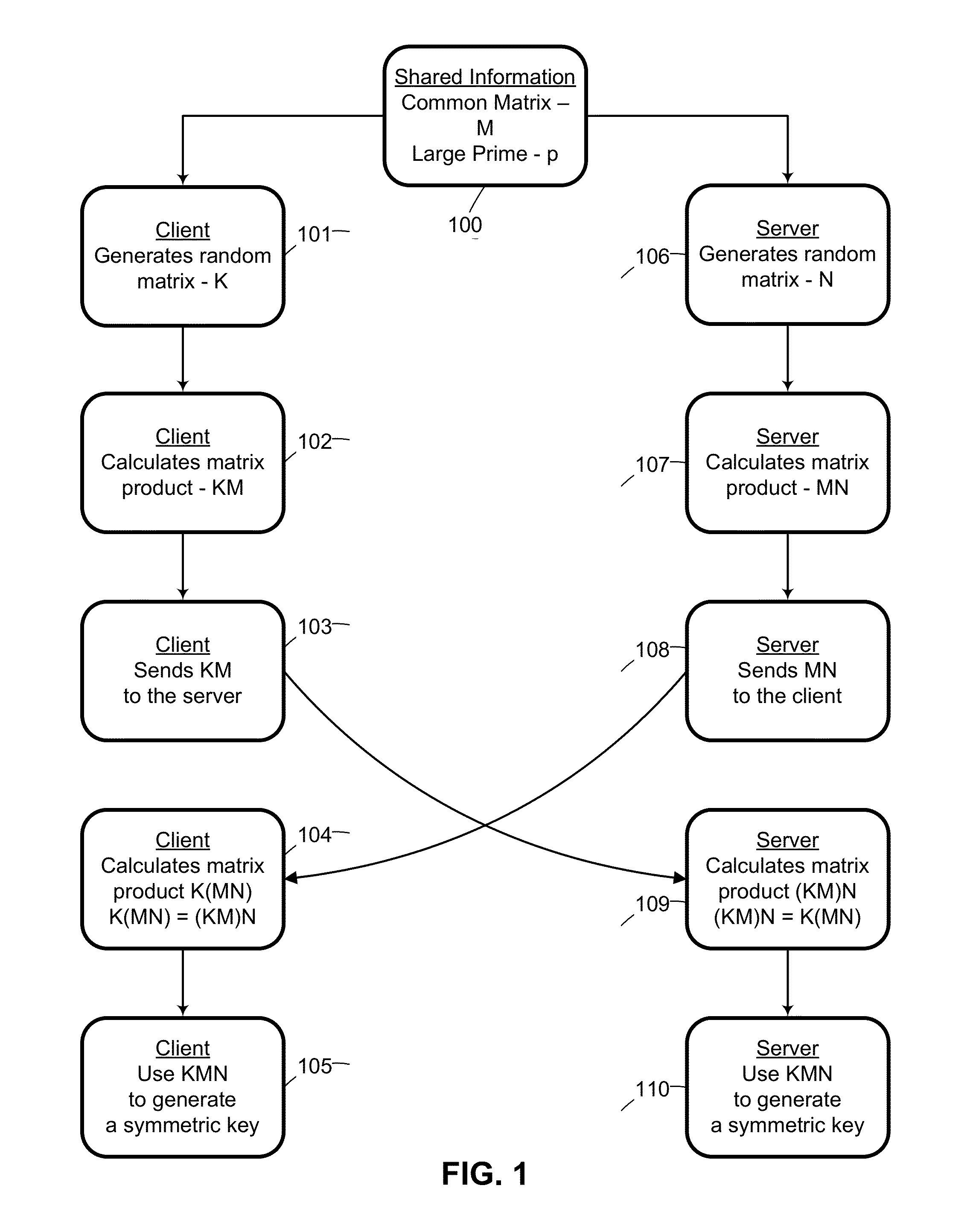
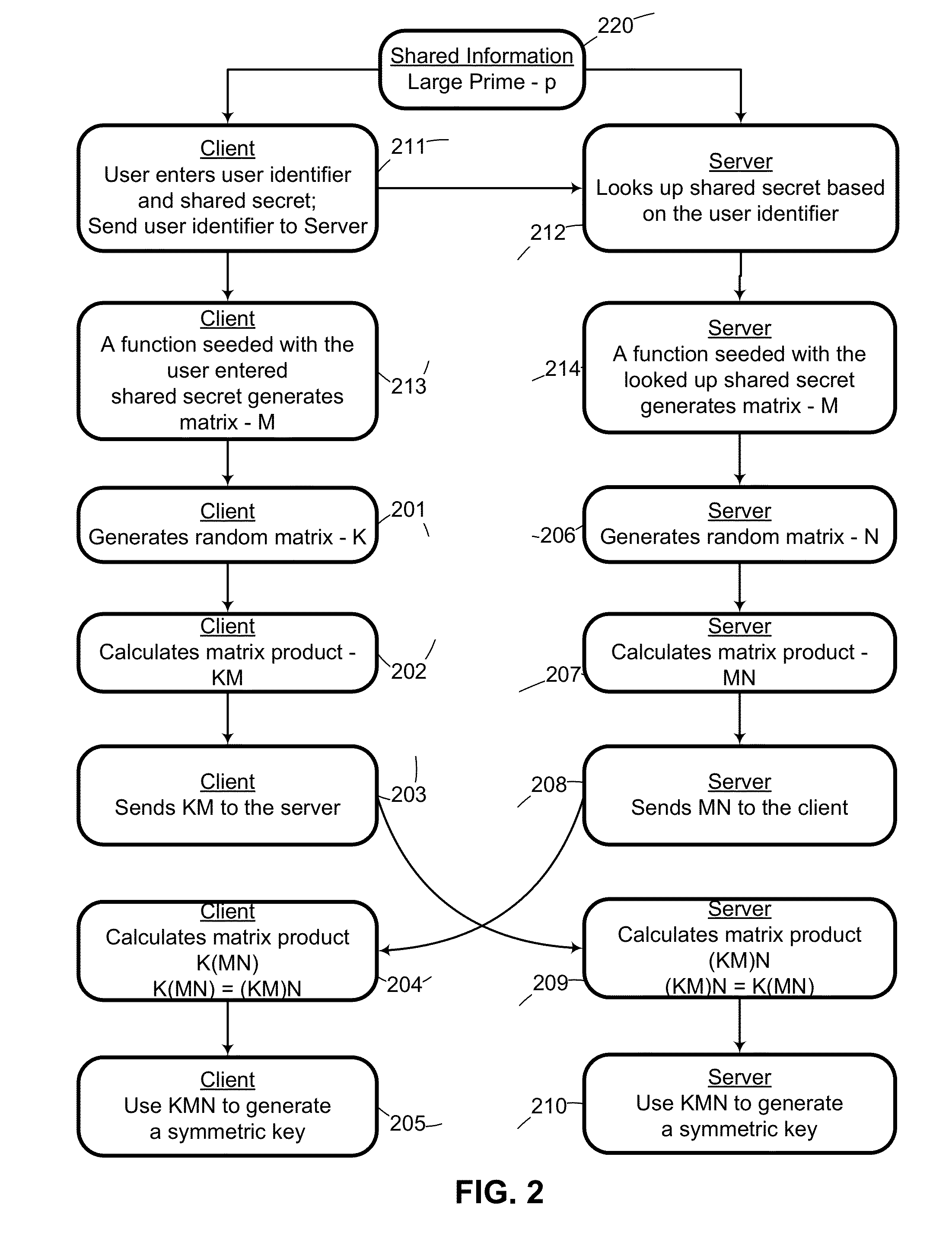
System and method for cryptographic key exchange using matrices
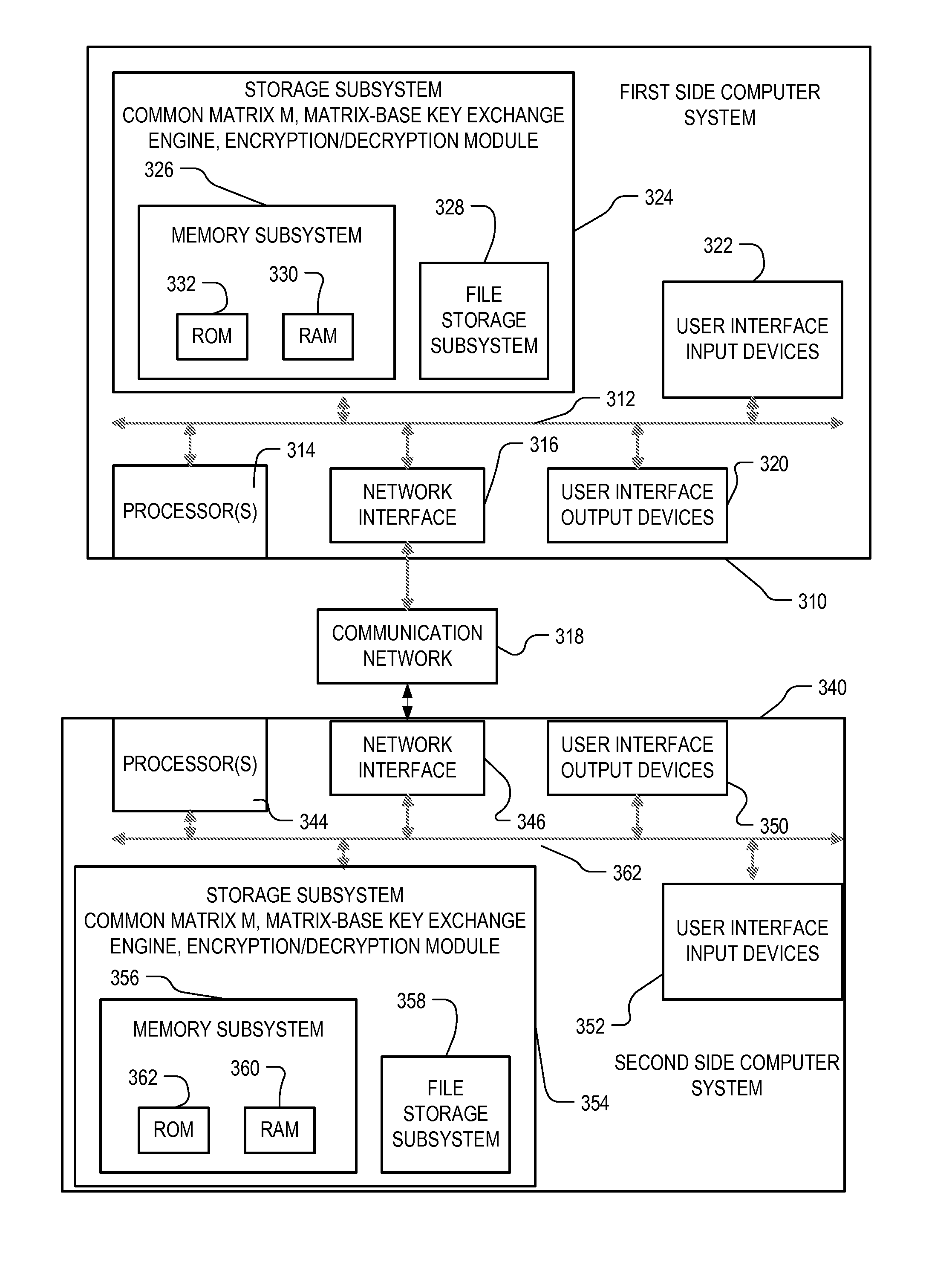
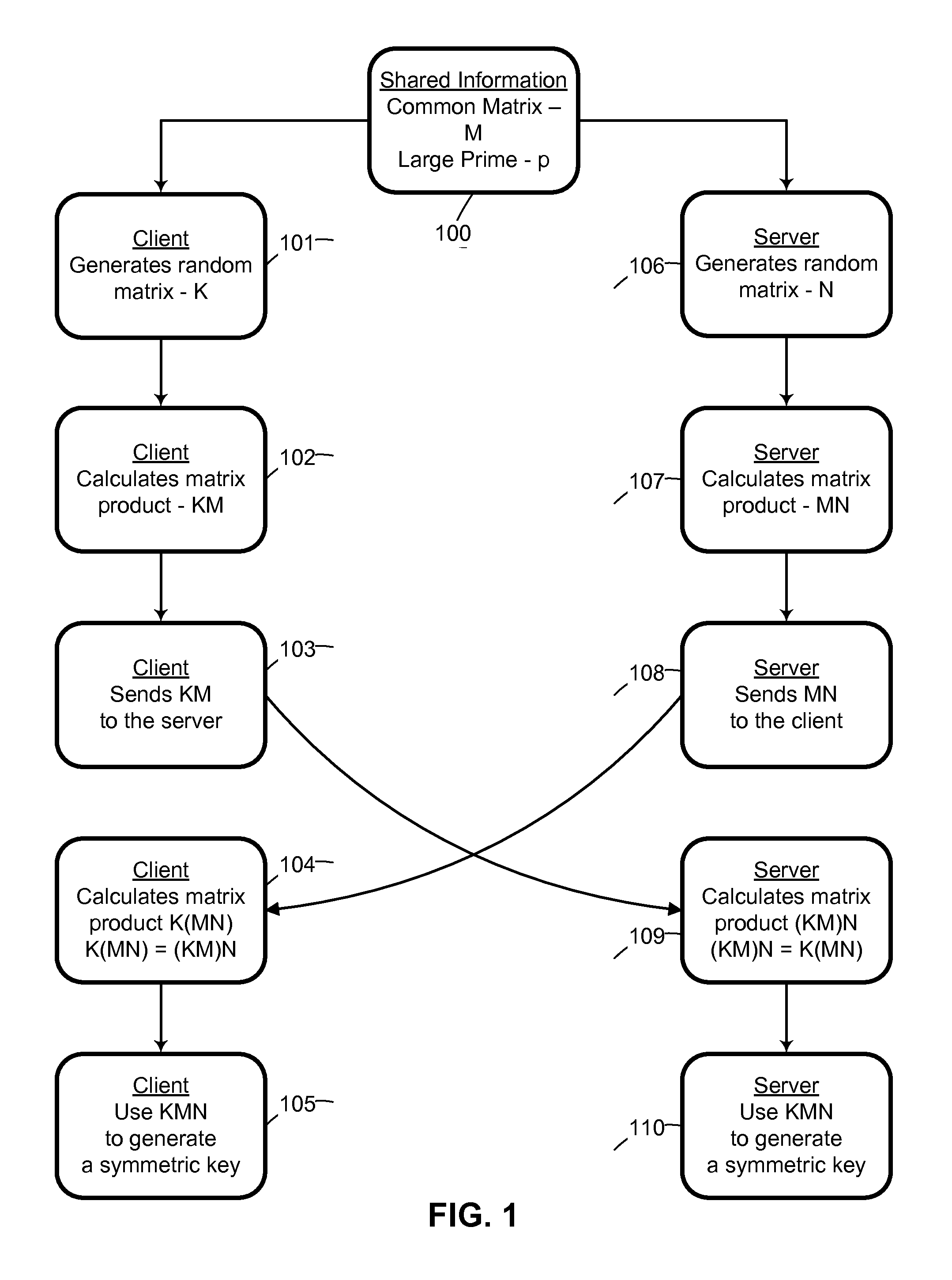
ActiveUS20120166809A1Improve performanceUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationThird partySecure communication
Two parties can establish a cryptographic key using a matrix based key exchange protocol, for secure communications without any prior distribution of secret keys or other secret data, and without revealing said key to any third party who may have access to all of the transmissions between them. A common matrix M, shared in advance, is multiplied by a random matrix K on the sending side, and a different random matrix N on the receiving side. The matrix product KM is sent from the sending side to the receiving side, and the matrix product MN is sent from the receiving side to the sending side. Both sides produce the common matrix product KMN, and use it for producing a symmetric key for encrypted communications.
Owner:AUTHERNATIVE INC
Encryption key exchange process using access device
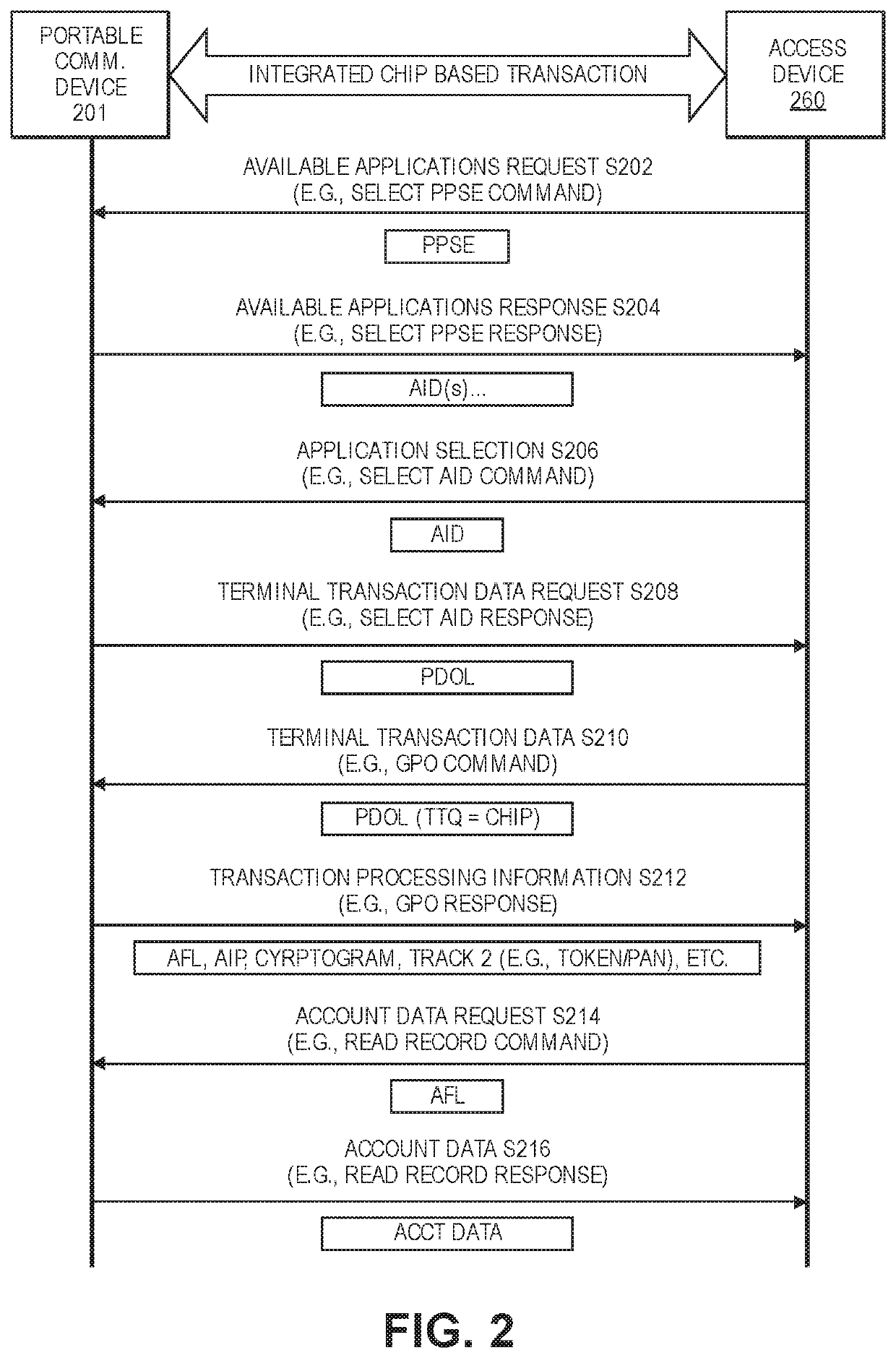
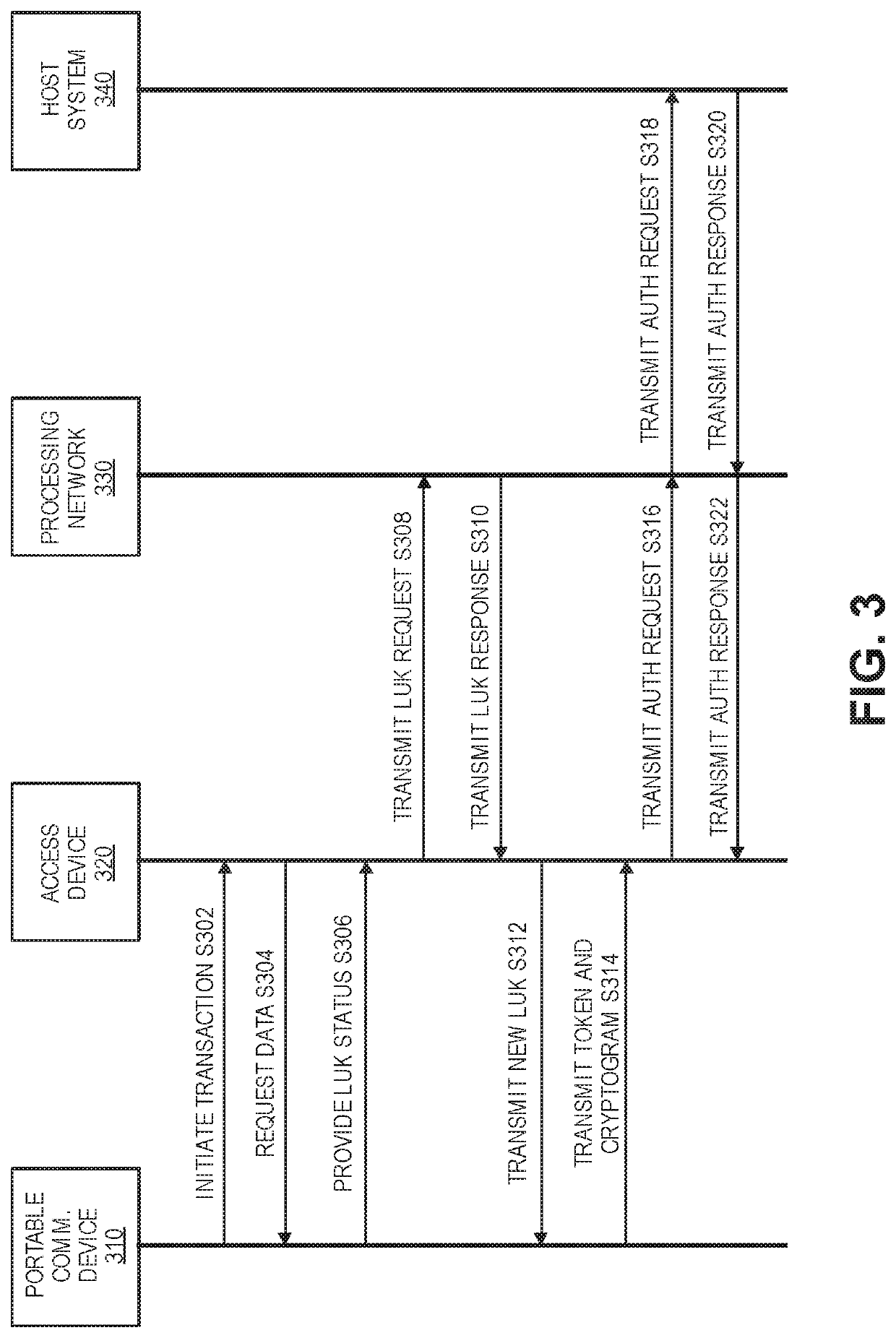
ActiveUS20200314644A1No longerImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionEngineeringCryptogram
Encryption key exchange processes are disclosed. A disclosed method includes initiating communication between a portable communication device including a token and a first limited use encryption key, and an access device. After communication is initiated, the portable communication device receives a second limited use key from a remote server via the access device. The portable communication device then replaces the first limited use key with the second limited use key. The second limited use key is thereafter used to create access data such as cryptograms that can be used to conduct access transactions.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Methods and apparatus for premises content distribution
ActiveUS8732854B2Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsEngineeringExchange protocol
Apparatus and methods for protected content access, browsing and transfer over a network. In one embodiment, the network comprises a premises (e.g., residential) LAN, and the apparatus comprises a server and renderer consumer premise equipment (CPE). The renderer CPE scans the network to search for a server CPE that implement a compatible security framework. The renderer authenticates itself with the server, and the server allows content browsing and selection access only to an authorized and authenticated renderer. A negotiation and exchange protocol comprises messages exchanged between the renderer and the server that include one or more of device identification, encryption key exchange, digital certificates and information regarding security package used by each CPE.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
System for automated connection to virtual private networks related applications
ActiveUS7827278B2Quickly and efficiently configuredUnified interfaceMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlPrivate networkEncryption decryption
A network interface unit is provided for use intermediate a LAN and a public or private network, or a combination of both, for establishing secure links to a VPN gateway. Login by a LAN client with the network interface unit, addressing, authentication, and other configuration operations achieved using a web page-based GUI are applied in establishing tunnels from LAN clients to desired VPN destinations. Illustrative network interface units include a DHCP server and provide encryption-decryption and encapsulation-decapsulation of data packets for communication with VPN nodes. Configuration and connection of a client are further enhanced by a built-in DNS server and other functional servers to provide a high degree of autonomy in establishing connections to a desired VPN gateway via an ISP or other public and / or private network links to. The interface unit then performs required authentication exchanges, and required encryption key exchanges.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
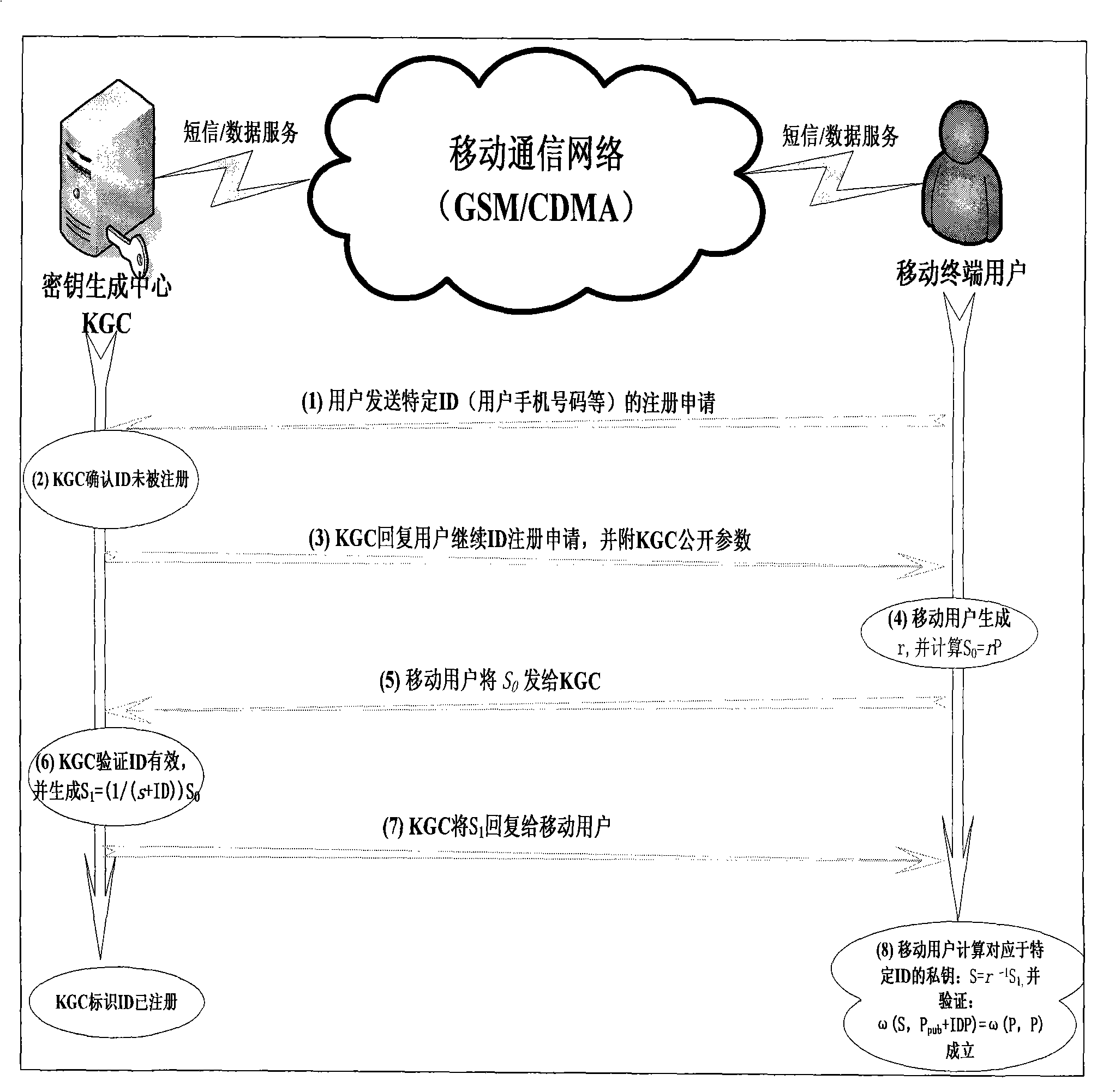
Method for ciphering wireless mobile terminal communication
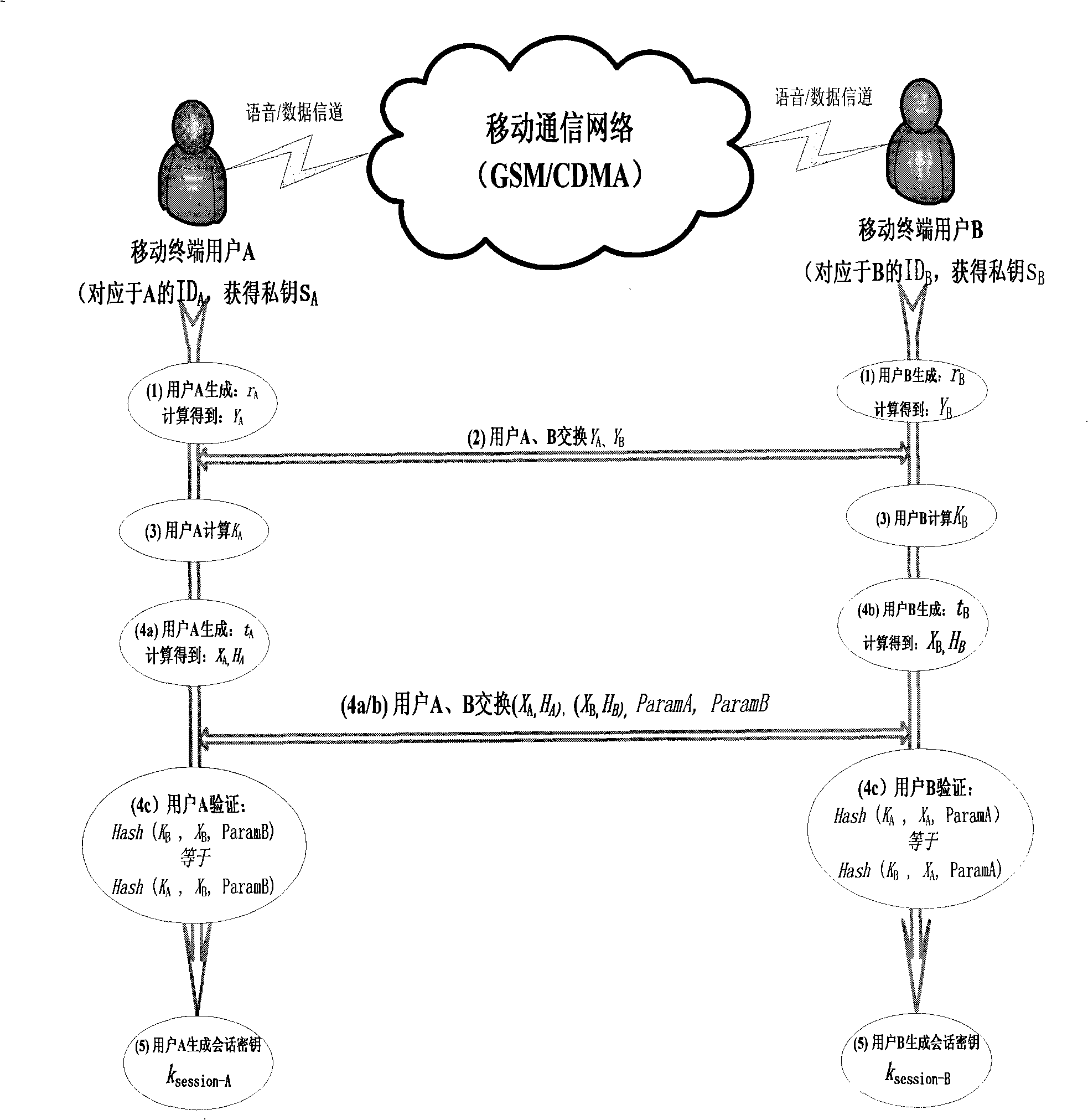
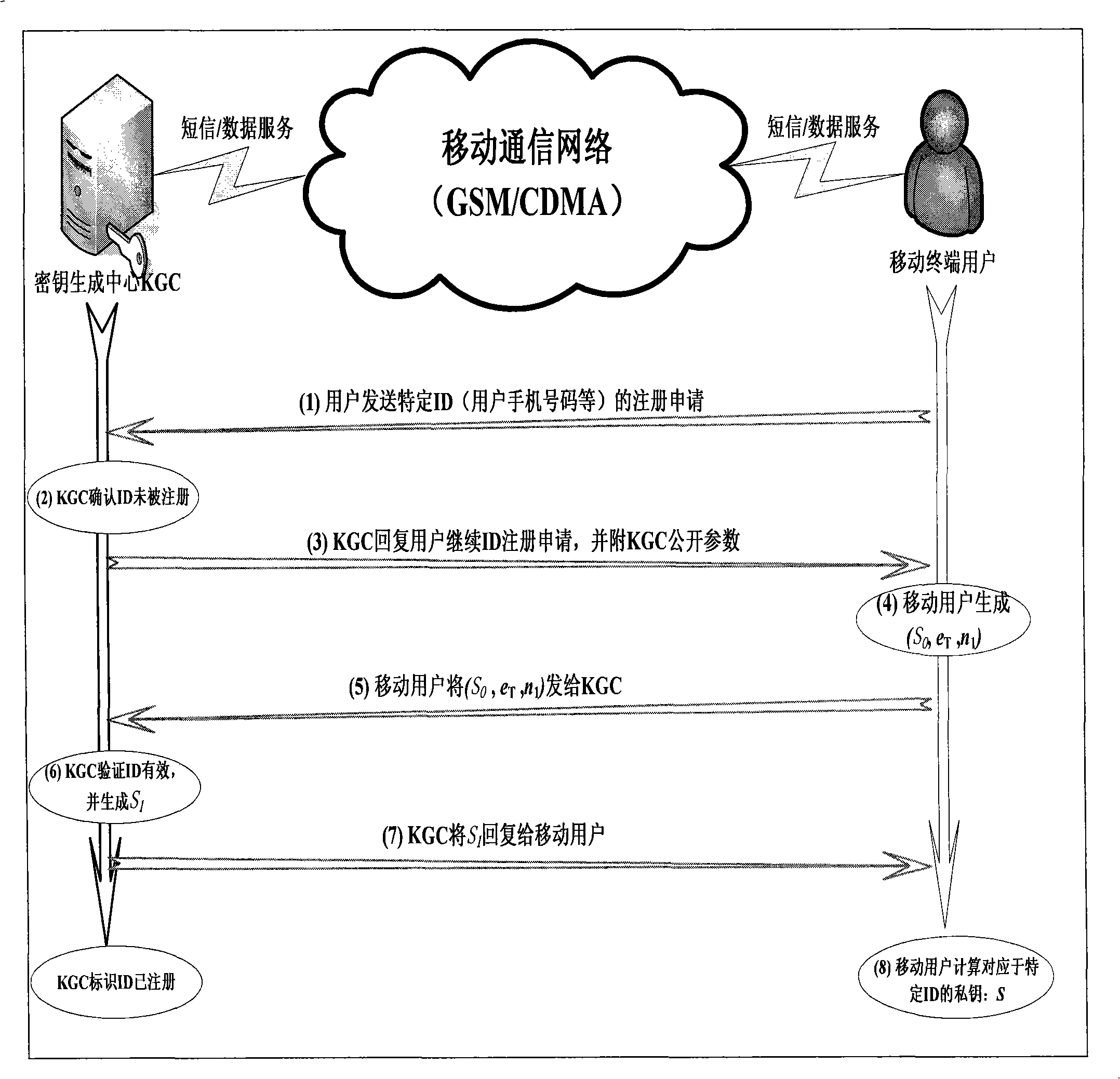
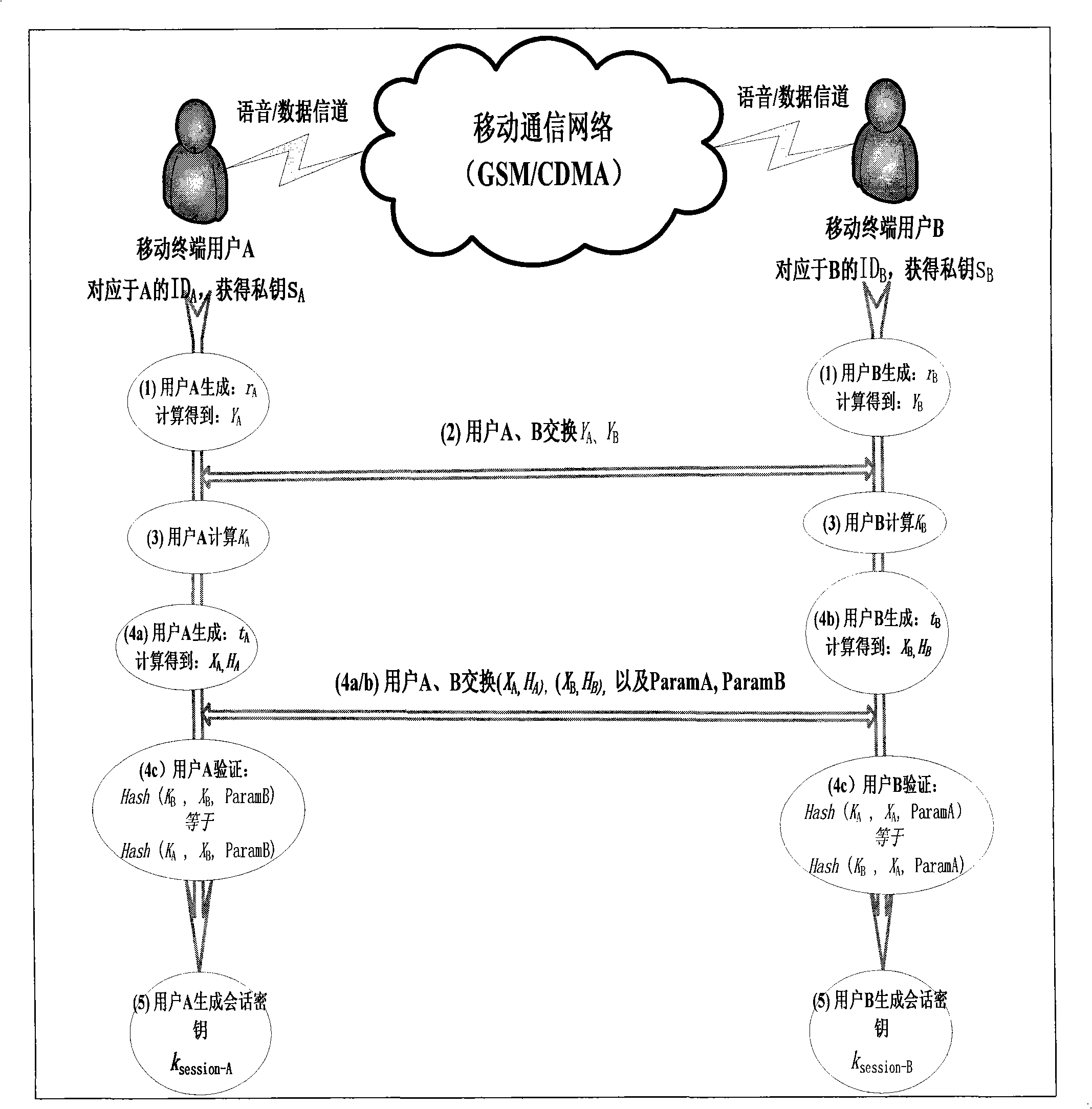
ActiveCN101277513AOccupies less bandwidthThe overall calculation is smallRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsExchange protocolSession key
The present invention provides a method of secure communication for a wireless mobile terminal. In the invention, the wireless mobile communication user realizes secure information exchange of terminal to terminal based on the guarantee reliability identity authentication without bearing deployment, maintenance and complex operation of public key infrastructure, without the participation of telecom operator, without replacing or impacting telecom signaling exchange protocol. The mobile communication user uses mobile terminal identity mark as identity, introducing a credible thirst party, named for key generation center, the main function is to help user to generate key according to the identity of user. The user acquires a key corresponding to the identity from the credible third party by mobile phone message or data service. The key guarantees the encryption key exchange and safety parameter between users to negotiate and resist active attack, session key between mobile users is independent to the KGC random generation, realizing the safety communication of terminal to terminal.
Owner:北京合众思壮时空物联科技有限公司
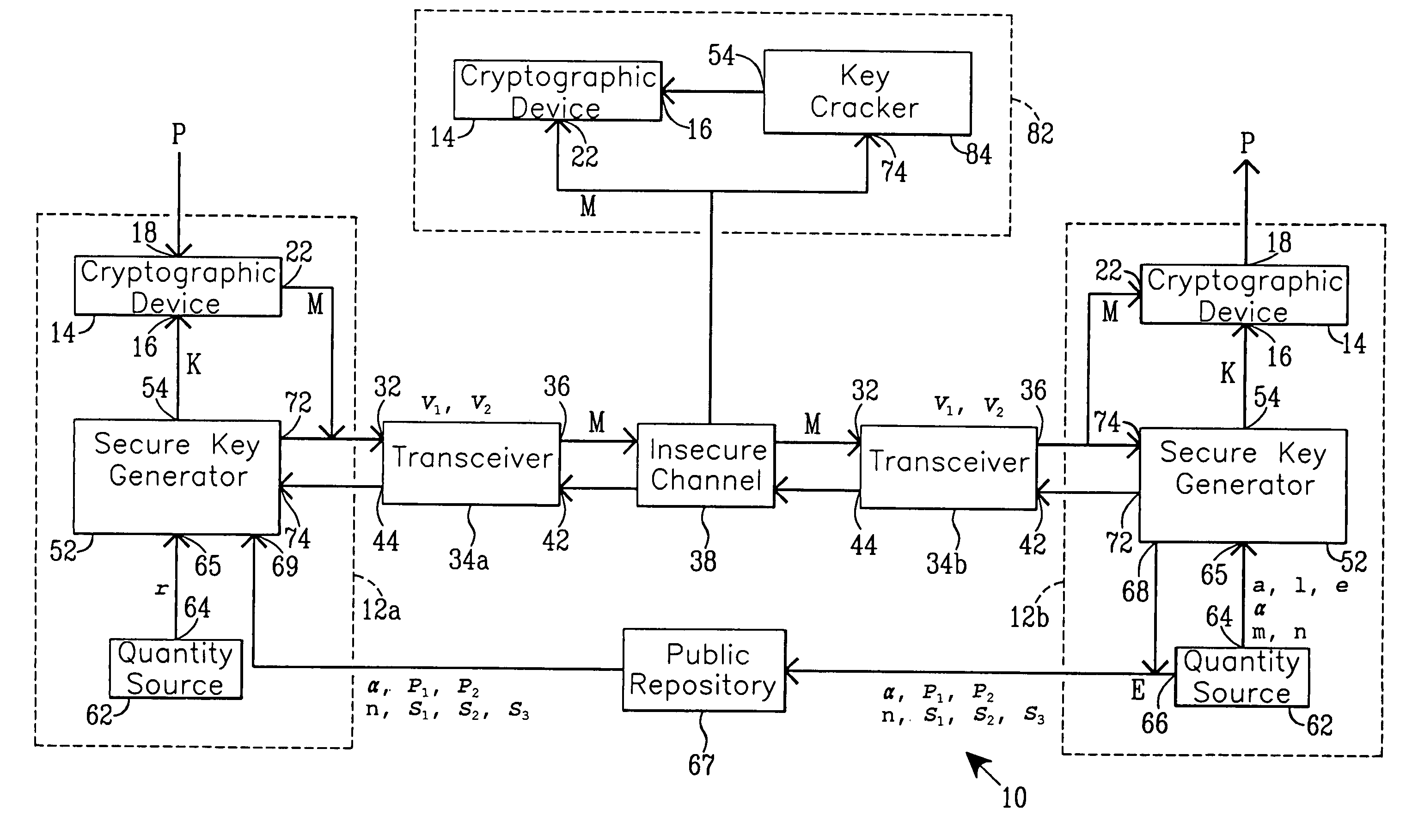
Simplified secure, swift cryptographic key exchange
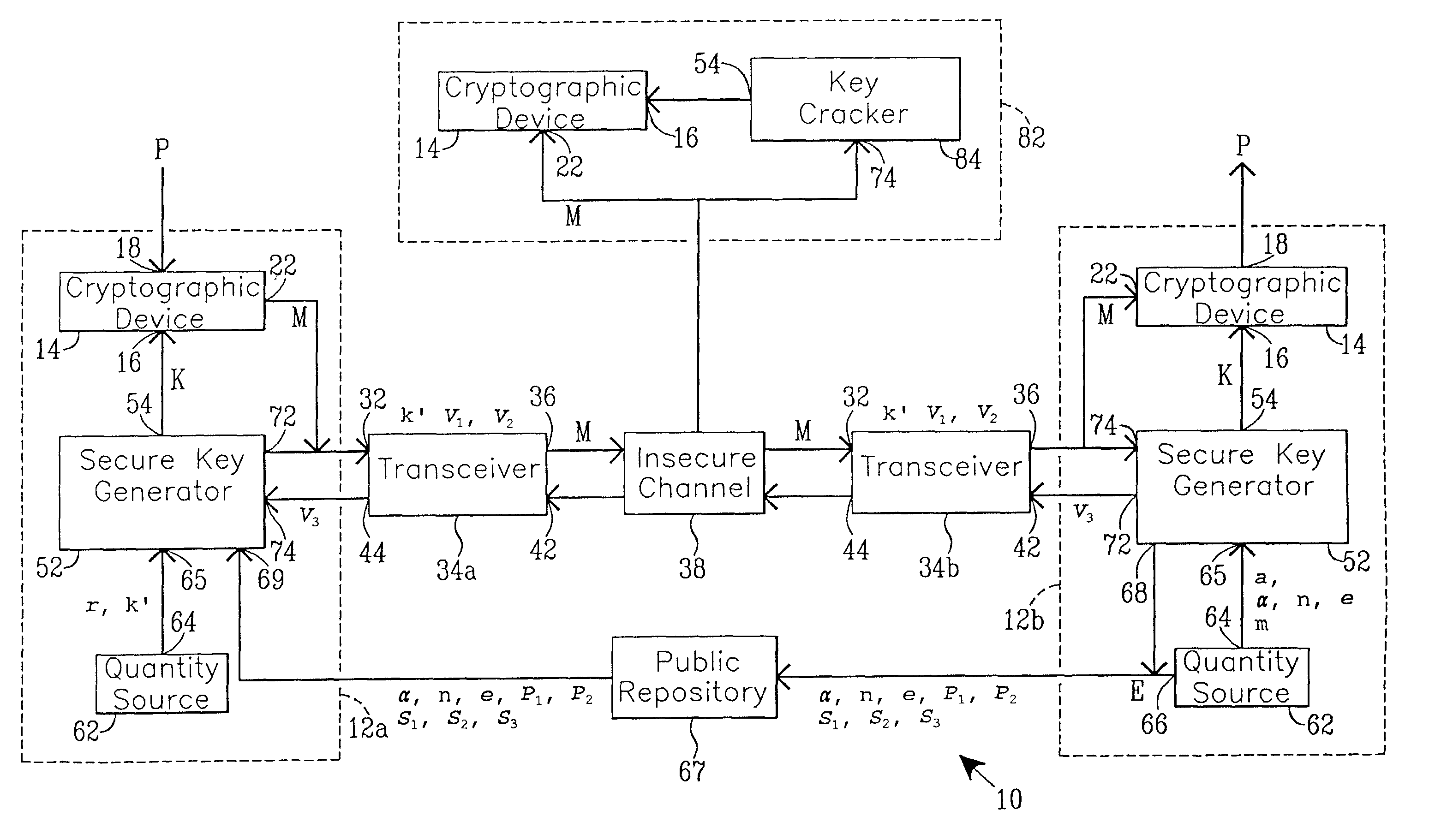
InactiveUS7020282B1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationDigital signaturePublic repository
One aspect of the present invention establishes a session key by a receiving unit R transmitting a plurality of quantities for storage in a public repository. A sending unit S:1. retrieves the plurality of quantities; and2. computes and transmits to the unit R a plurality of sender's quantities.The unit R then:1. computes and transmits to the unit S at least one receiver's quantity; and2. computes the session key.The unit S, using the receiver's quantity, computes the session key.Another aspect provides a digital signature. Before transmitting a signed message, the unit S stores a plurality of quantities in the public repository. A unit R, that receives the message and the digital signature, verifies their authenticity by:1. retrieving the quantities from the repository;2. using the digital signature and the quantities, evaluates expressions in at least two (2) different relationships; and3. verifies the digital signature upon finding equality between evaluation results.
Owner:CHANG CHUNG NAN
Method for ciphering wireless mobile terminal communication
ActiveCN101277512AUser identity/authority verificationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsExchange protocolSecurity parameter
The present invention provides a method of communication encryption for a wireless mobile terminal. In the invention, the wireless mobile communication user realizes security information exchange of terminal to terminal based on the guarantee reliability identity authentication without bearing deployment, maintenance and complex operation of public key infrastructure, without the participation of telecom operator, without replacing or impacting telecom signaling exchange protocol. The mobile communication user uses mobile terminal identity mark as identity, introducing a credible thirst party, named for key generation center, the main function is to help user to generate key according to the identity of user. The user acquires a key corresponding to the identity from the credible third party by mobile phone message or data service. The key guarantees the encryption key exchange and safety parameter between users to negotiate and resist active attack, session key between mobile users is independent to the KGC random generation, realizing the safety communication of terminal to terminal.
Owner:北京合众思壮时空物联科技有限公司
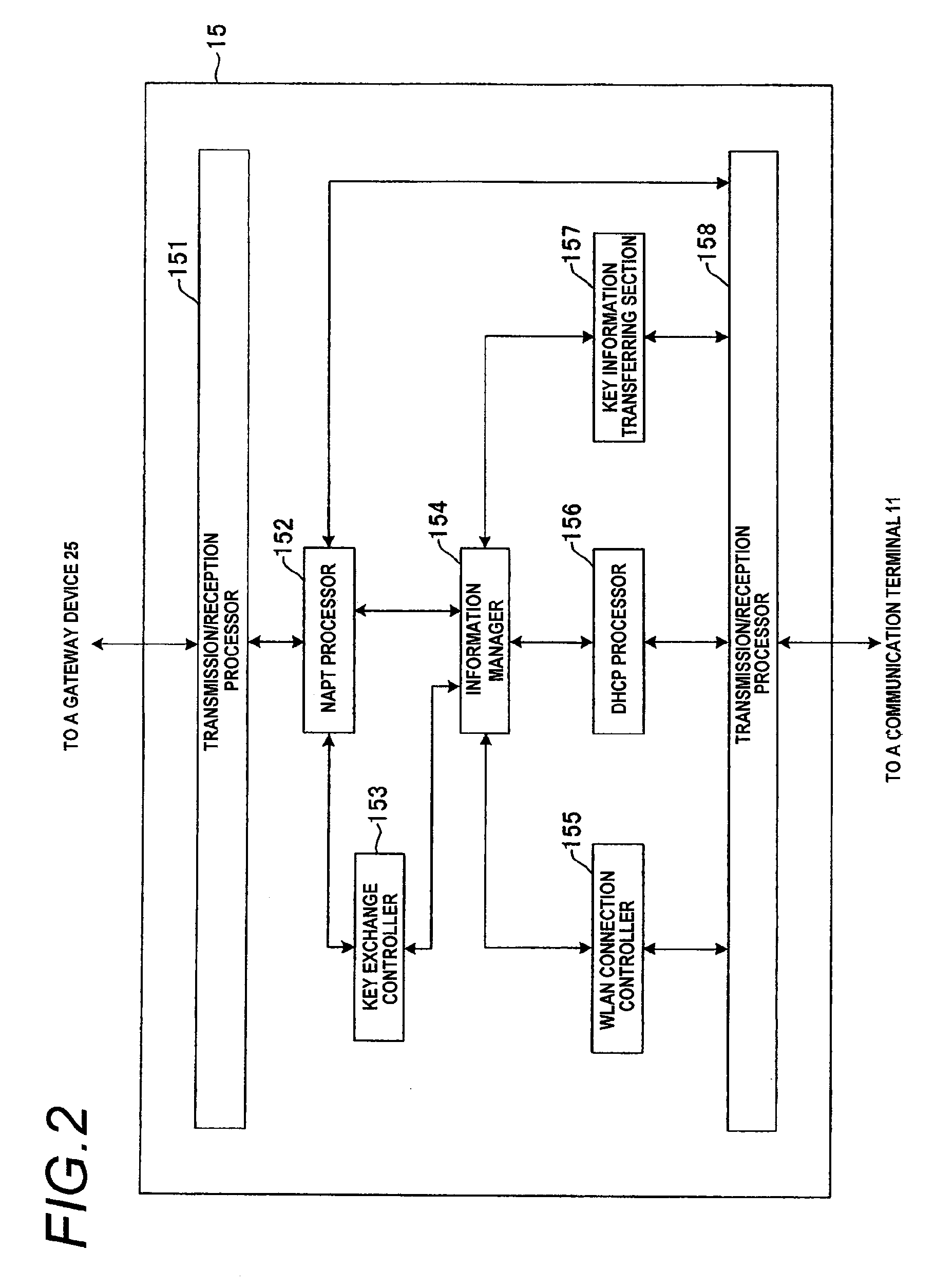
Network relay device, communication terminal, and encrypted communication method
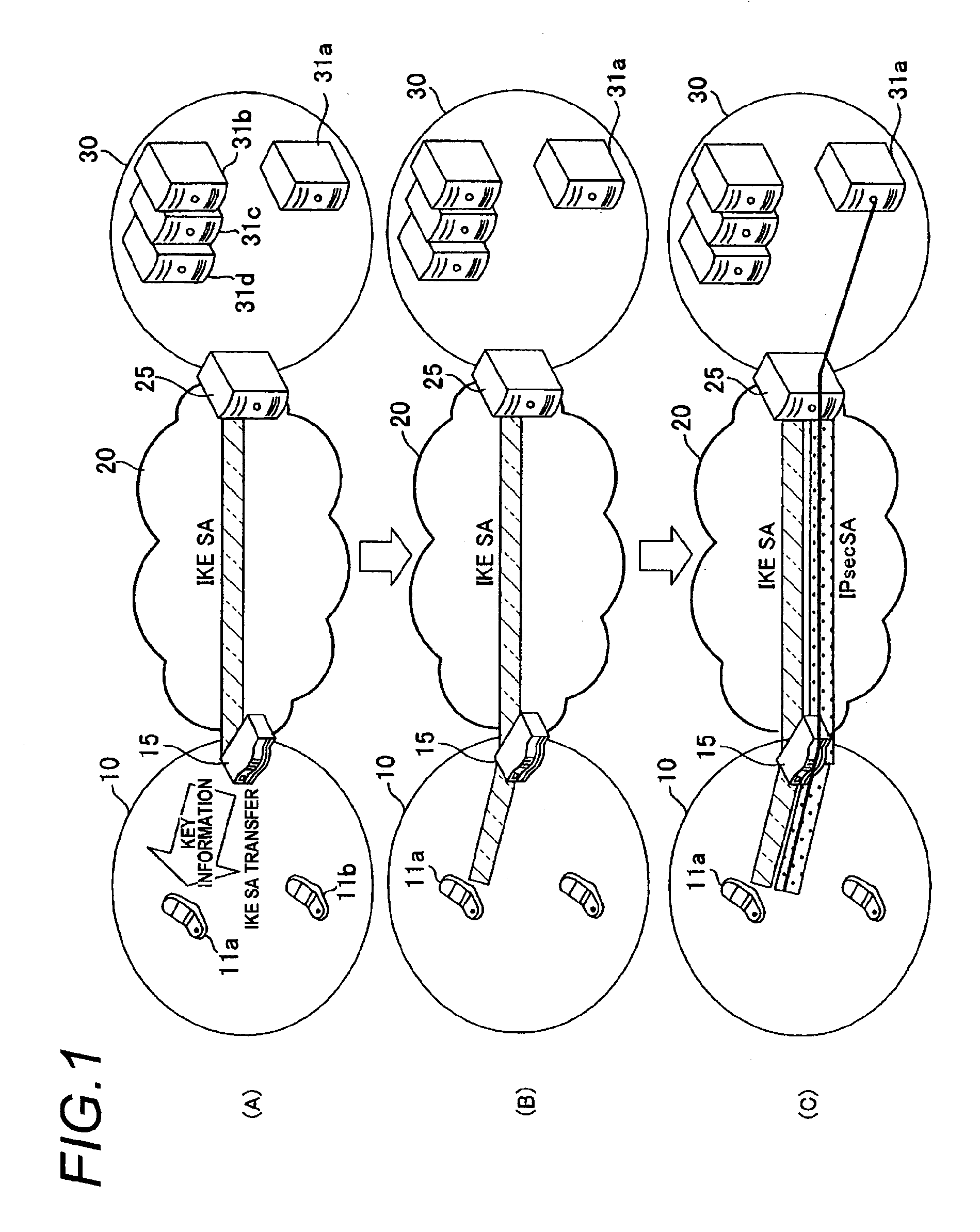
InactiveUS20100119069A1Shorten the timeKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationIPsecEncrypted key exchange
A time required for actually starting encrypted communication after a trigger of an encrypted communication is shortened. When a key exchanging process is to be applied in order to exchange key information upon encrypting a communication performed between a communication terminal 11 and a gateway device 25, a network relay device 15 relays the key information, contents of the key exchanging process are divided into a former-half process and a later-half process, and the network relay device 15 executes the former-half process substitute for the communication terminal 11 to establish “IKE SA”. Then, information obtained as the result of the former-half process is transferred from the network relay device 15 to the communication terminal 11. Then, the later-half process of the key exchange process is executed between the communication terminal 11 and the gateway device 25, the communication terminal 11 and the gateway device 25 share common key information with each other to establish “IPsec SA”, and an encrypted communication is performed by using this key information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
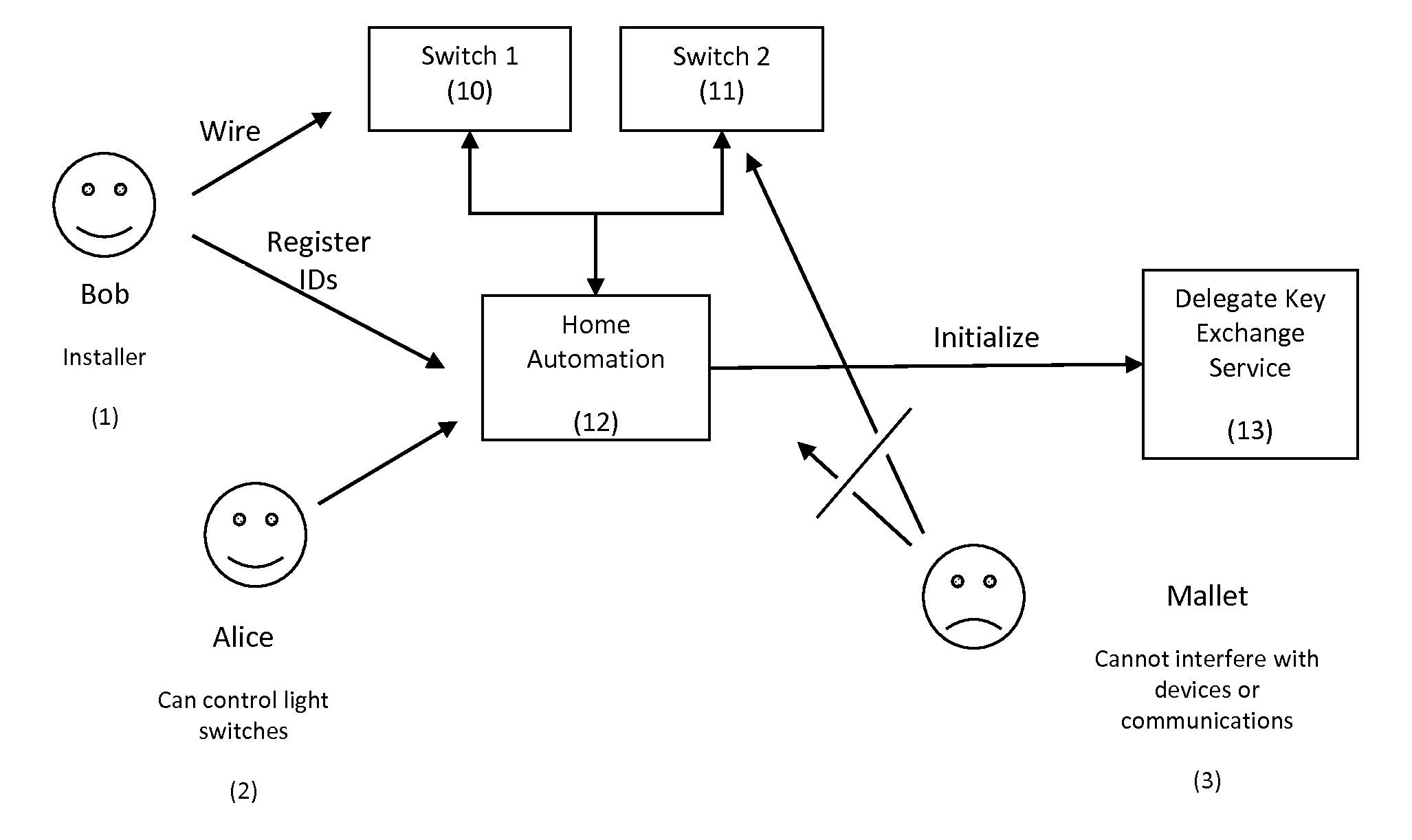
Delegated Key Exchange System and Method of Operation
A cryptographic key exchange protocol that enables a device that does not have the capability to perform public key operations to securely establish a shared key with a host device without any information disclosing the key being revealed to the delegate key service.
Owner:HALLAM BAKER PHILLIP MARTIN
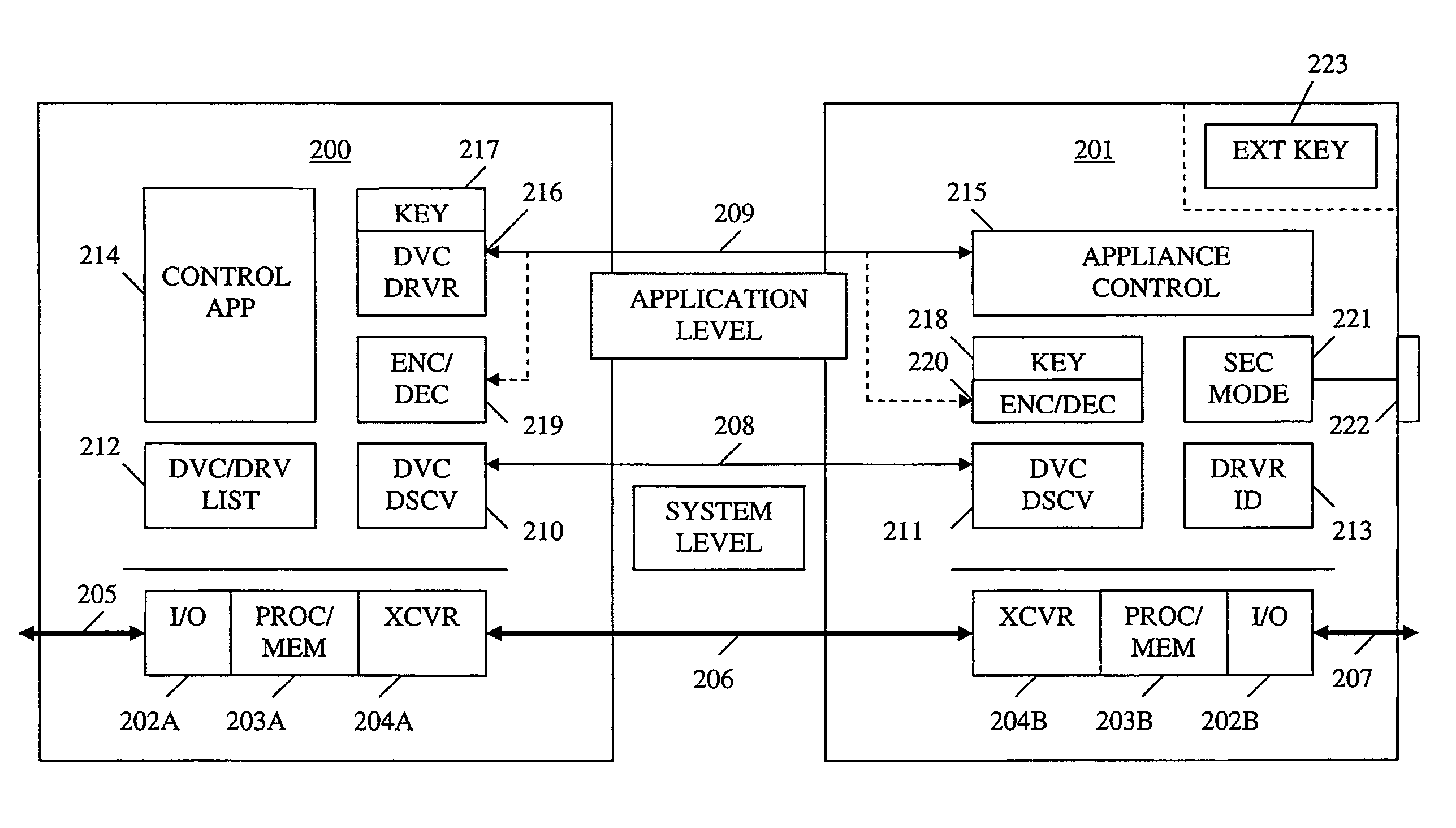
Method and apparatus for device detection and multi-mode security in a control network
A method and apparatus for device discovery and multi-mode security in a wired and / or wireless control network are described. A controlled device is configured with discovery-level instructions and application-level control instructions. The controlled device includes a user-configurable parameter for selecting between multiple security modes. In one or more security modes, the controlled device may ignore application-level messages until encrypted communications are established with a controller. In one mode, the encrypted communication is established with an encryption key exchange using a predetermined security key. In another mode, a specific key is manually entered into the controller by the user / administrator to facilitate the encryption key exchange. Additionally, for control applications where security is not important, an unencrypted security mode may be implemented. A driver ID provided by the controlled device facilitates loading of a preferred device driver by the controller.
Owner:SNAP ONE LLC
Managed Access Point Protocol
ActiveUS20090158042A1Facilitating deployment and configurationFacilitates deployment and configurationAssess restrictionUser identity/authority verificationNetworked systemRadio access point
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating deployment and configuration of managed access points in hierarchical wireless network systems. An embodiment of the invention facilitates deployment and configuration of conventional, substantially autonomous access points operating in connection with a central management node, such as a server or appliance. In another embodiment, the present invention facilitates deployment and configuration of light-weight access points in a hierarchical wireless network system. In one embodiment, the present invention also provides a streamlined encryption key exchange protocol adapted to hierarchical wireless network system architectures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
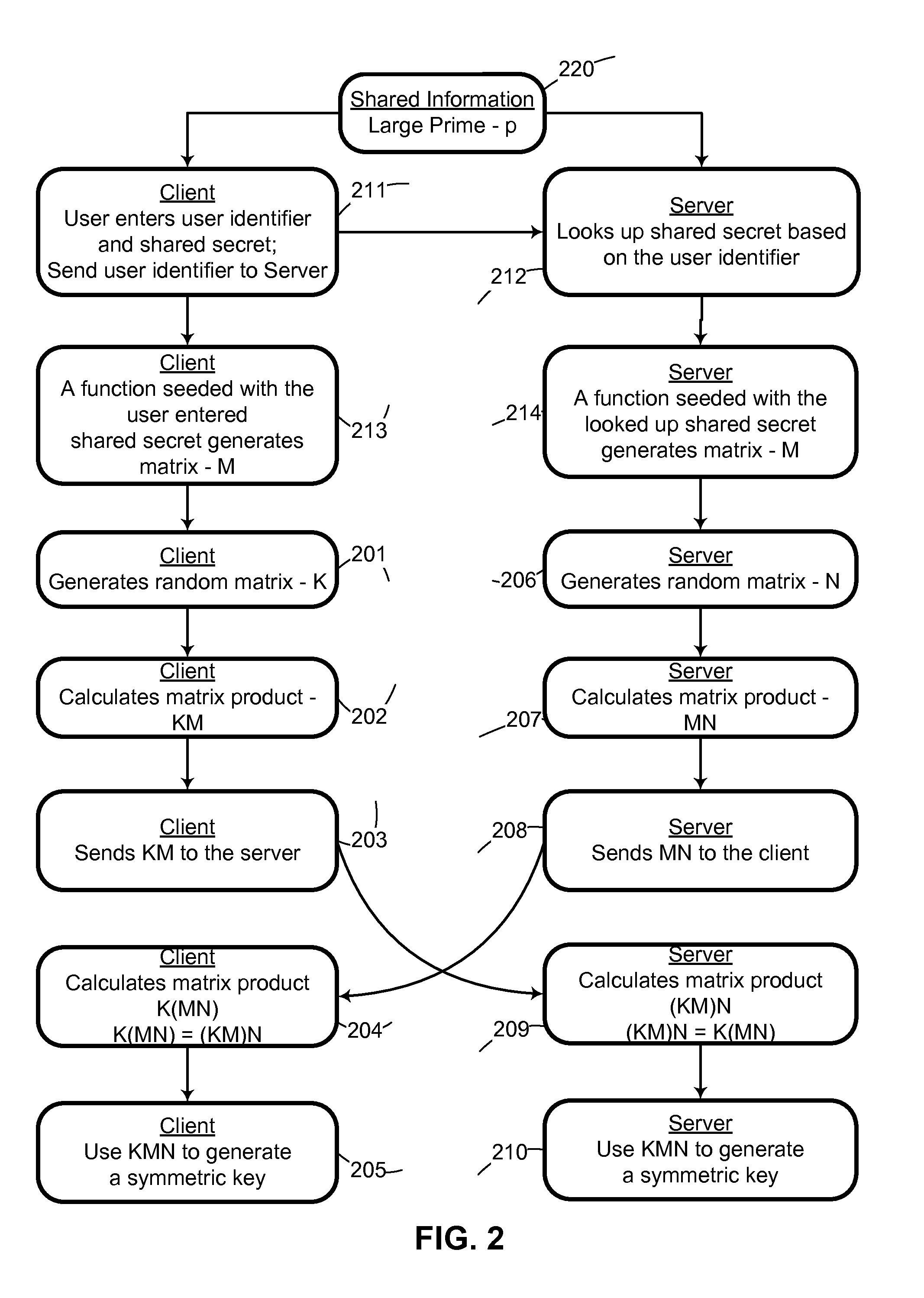
System and method for mutually authenticated cryptographic key exchange using matrices
ActiveUS8656484B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationThird partySecure communication
Two parties can establish a cryptographic key using a matrix based key exchange protocol, for secure communications without any prior distribution of secret keys or other secret data, and without revealing said key to any third party who may have access to all of the transmissions between them. The two parties use a shared secret to produce a common matrix M. The common matrix M, is multiplied by a random matrix K on the sending side, and a different random matrix N on the receiving side. The matrix product KM is sent from the sending side to the receiving side, and the matrix product MN is sent from the receiving side to the sending side. Both sides produce the common matrix product KMN, and use it for producing a symmetric key for encrypted communications, after mutually authenticating one another over an insecure network.
Owner:AUTHERNATIVE INC
Secure cryptographic key exchange and verifiable digital signature
InactiveUS7327846B1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signaturePublic repository
One aspect of the present invention establishes a session key by a receiving unit R transmitting a plurality of quantities for storage in a public repository. A sending unit S:1. retrieves the plurality of quantities; and2. computes and transmits to the unit R a plurality of sender's quantities; and3. using at least one of the plurality of public quantities, computes the session key K.The unit R, using the sender's quantities:1. computes and transmits to the unit S at least one receiver's quantity; and2. computes the session key.Another aspect provides a digital signature. Before transmitting a signed message, the unit S stores a plurality of quantities in the public-repository. A unit R, that receives the message and the digital signature, verifies their authenticity by:1. retrieving the quantities from the repository;2. using the digital signature and the quantities, evaluates expressions in at least two (2) different relationships; and3. verifies the digital signature upon finding equality between evaluation results.
Owner:ONE LINE POST
Flexible automated connection to virtual private networks
ActiveUS7827292B2Quickly and efficiently configuredUnified interfaceMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkEncryption decryption
A network interface unit is provided for use intermediate a LAN and a public or private network, or a combination of both, for establishing secure links to a VPN gateway. Login by a LAN client with the network interface unit, addressing, authentication, and other configuration operations achieved using a web page-based GUI are applied in establishing tunnels from LAN clients to desired VPN destinations. Illustrative network interface units include a DHCP server and provide encryption-decryption and encapsulation-decapsulation of data packets for communication with VPN nodes. Configuration and connection of a client are further enhanced by a built-in DNS server and other functional servers to provide a high degree of autonomy in establishing connections to a desired VPN gateway via an ISP or other public and / or private network links to. The interface unit then performs required authentication exchanges, and required encryption key exchanges.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P A NEVADA LIMITED PARTERSHIP
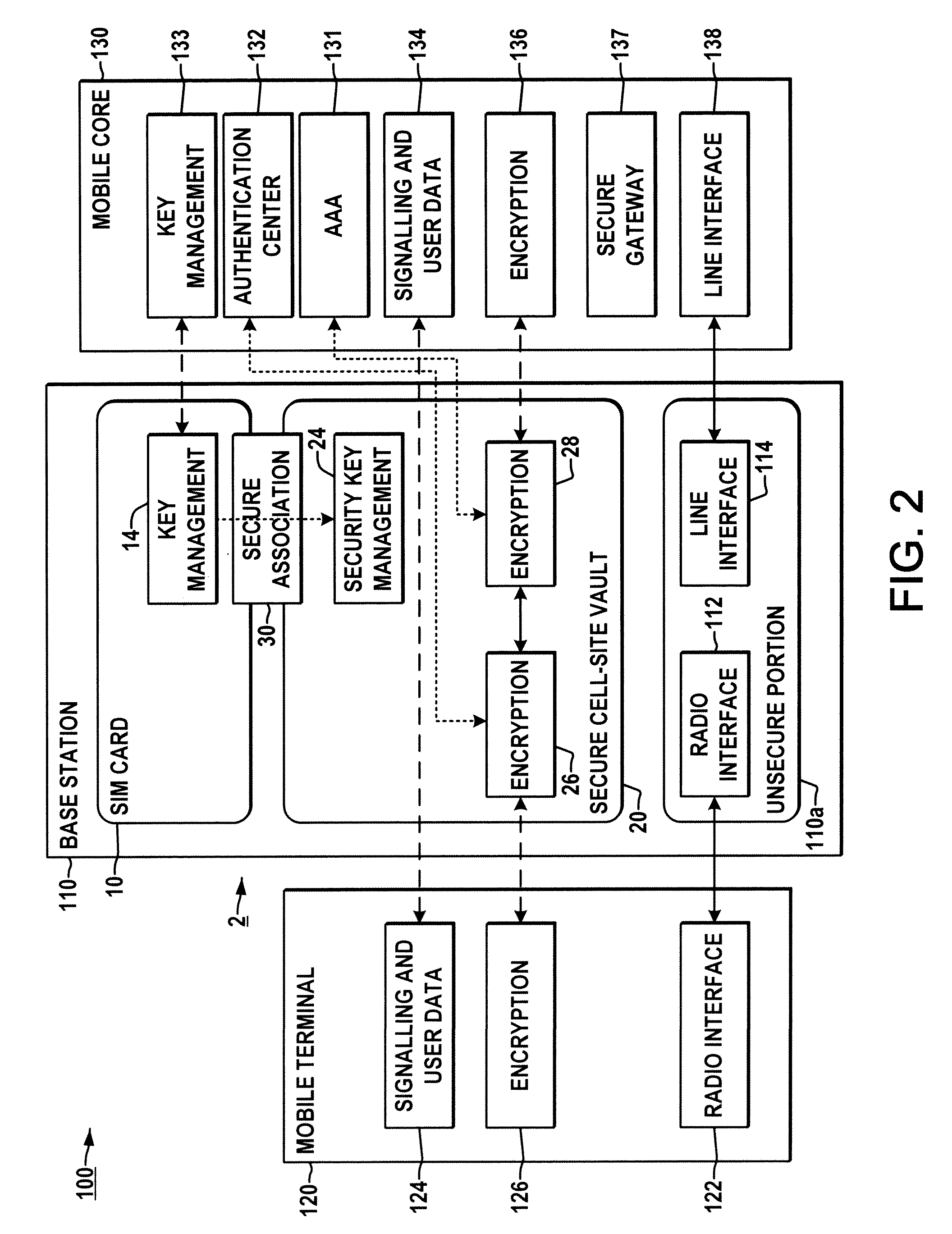
System and method for securing a base station using SIM cards
ActiveUS8249553B2Promote generationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsEngineeringRadio Base Station
Methods and systems are provided for securing integrated base stations, such as base station routers (BSRs), in which a SIM card is operatively coupled with a secured portion of a base station and a secure association is established therebetween to facilitate encryption key exchange between the secured portion of the base station and a core network.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
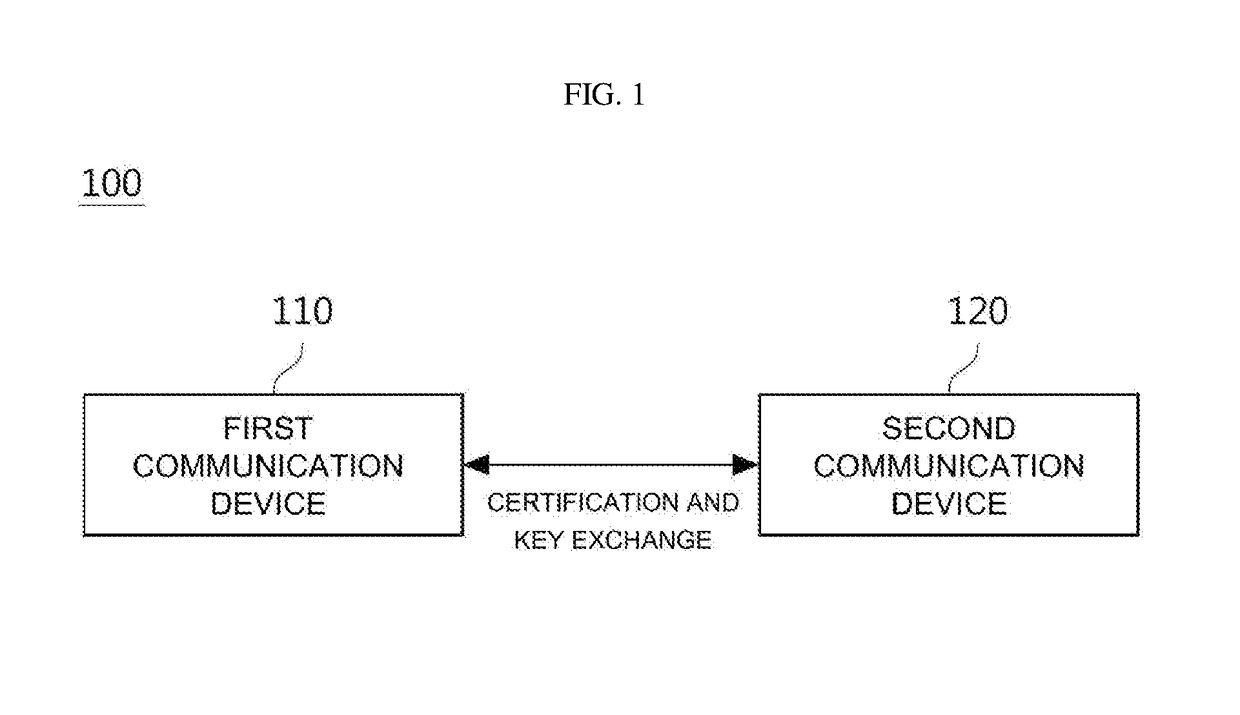
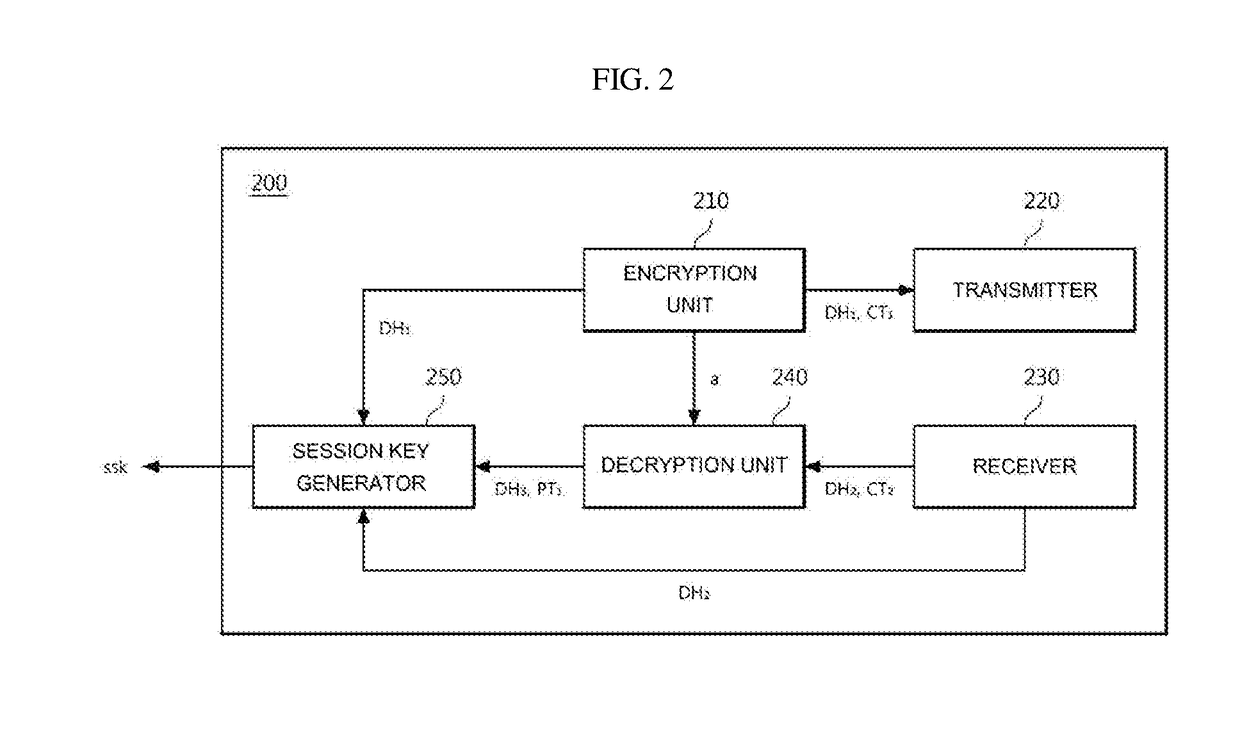
Apparatus and method for exchanging encryption key
InactiveUS20170085543A1Improve securityEfficient encryption key exchangeKey distribution for secure communicationCommunication deviceTransmitter
Disclosed herein are an apparatus and method for exchanging an encryption key. According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, an encryption key exchange apparatus includes an encryption unit to generate a first Diffie-Hellman value and a first secret key using a first random integer and a public key of a second communication device and to encrypt certification data by a symmetric key cryptography using the first secret key, a transmitter to transmit the first Diffie-Hellman value and the encrypted certification data to the second communication device, a receiver to receive, from the second communication device, a second Diffie-Hellman value generated using a second random integer selected by the second communication device, and an acknowledgement message encrypted by the symmetric key cryptography using a second secret key generated from the second random integer and the first Diffie-Hellman value, and a decryption unit to generate the second secret key using the first random integer and the second Diffie-Hellman value and to decrypt the encrypted acknowledgement message using the generated second secret key.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD SINCHEON DONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com