Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
184 results about "Content centric networking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
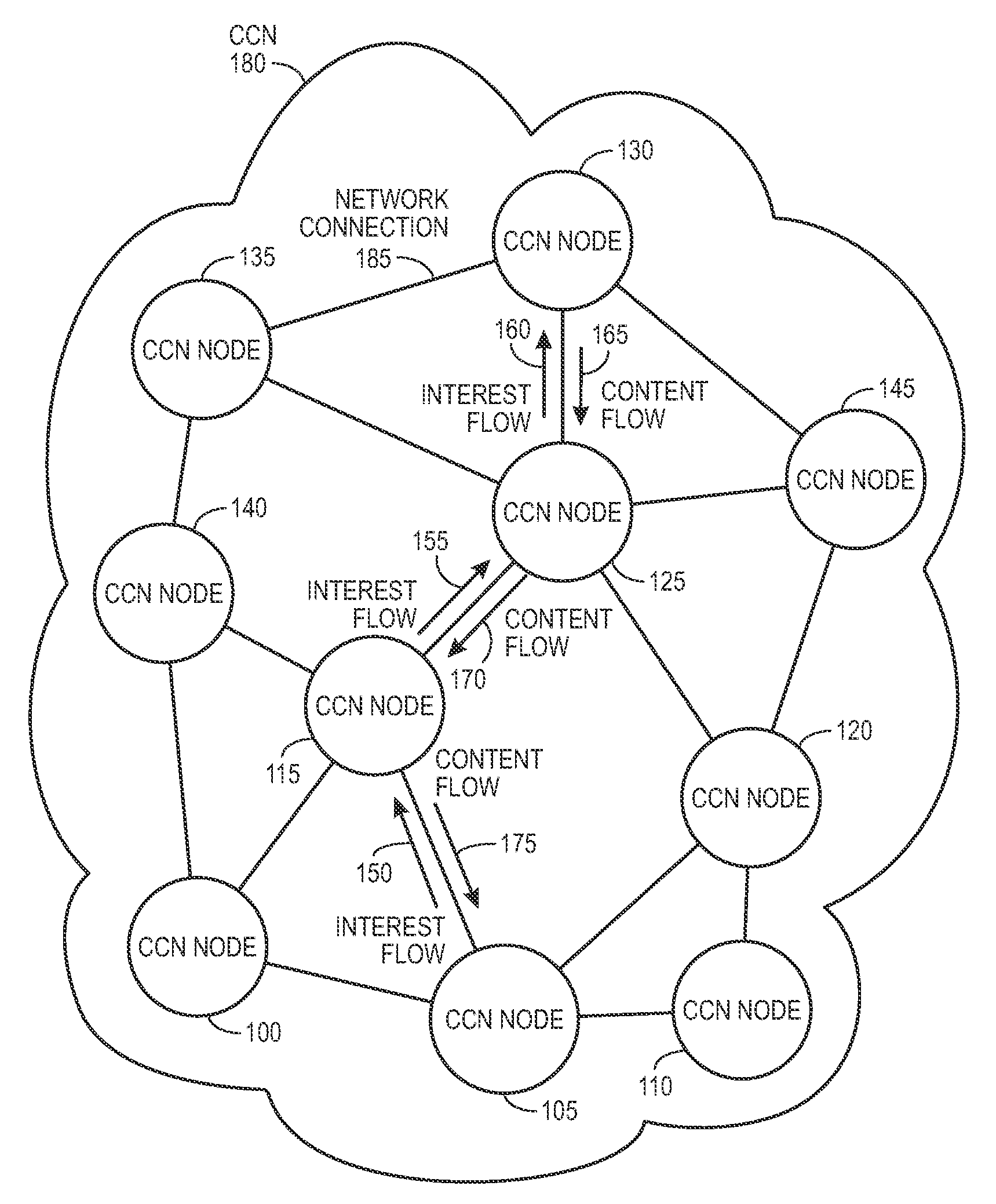
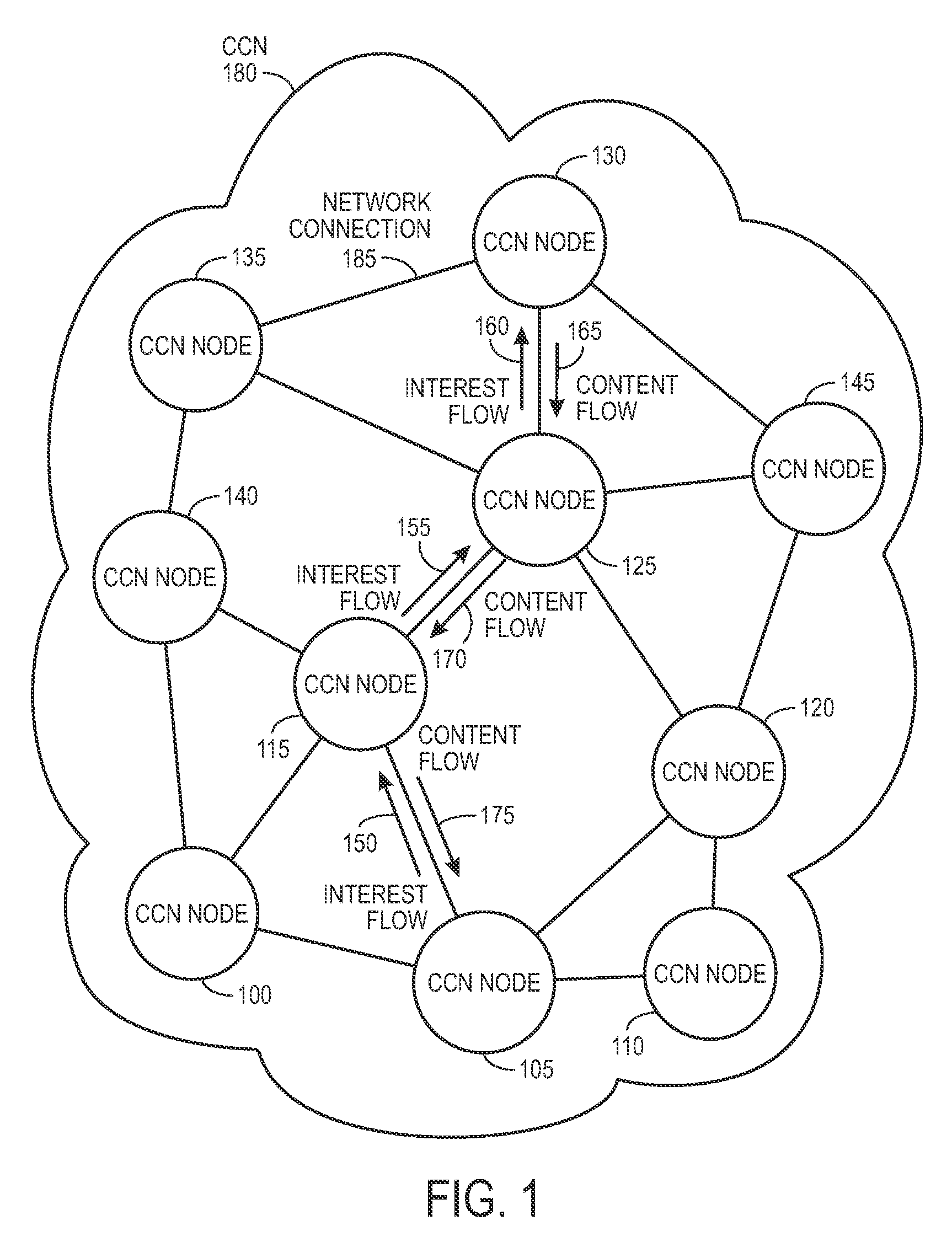
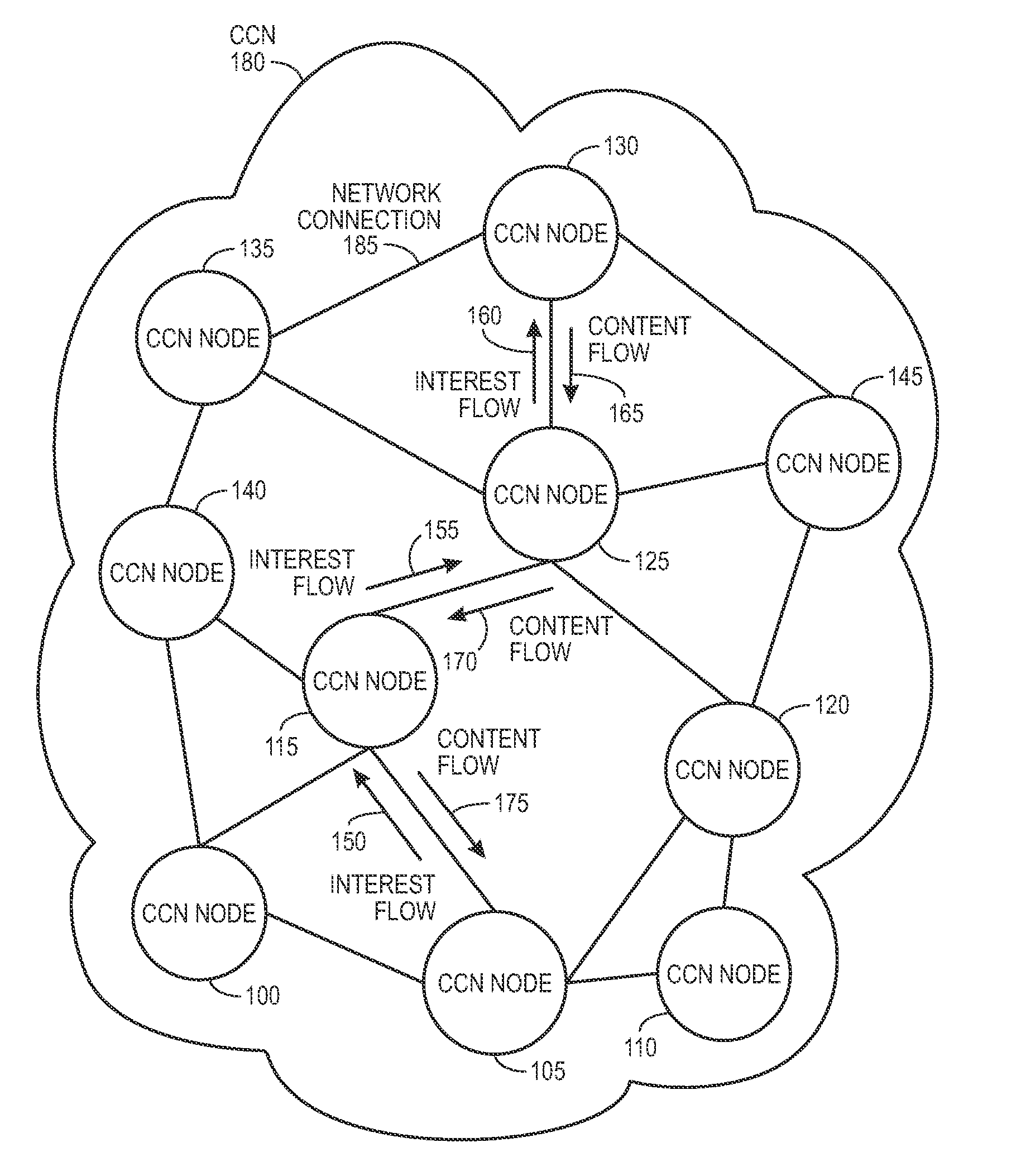
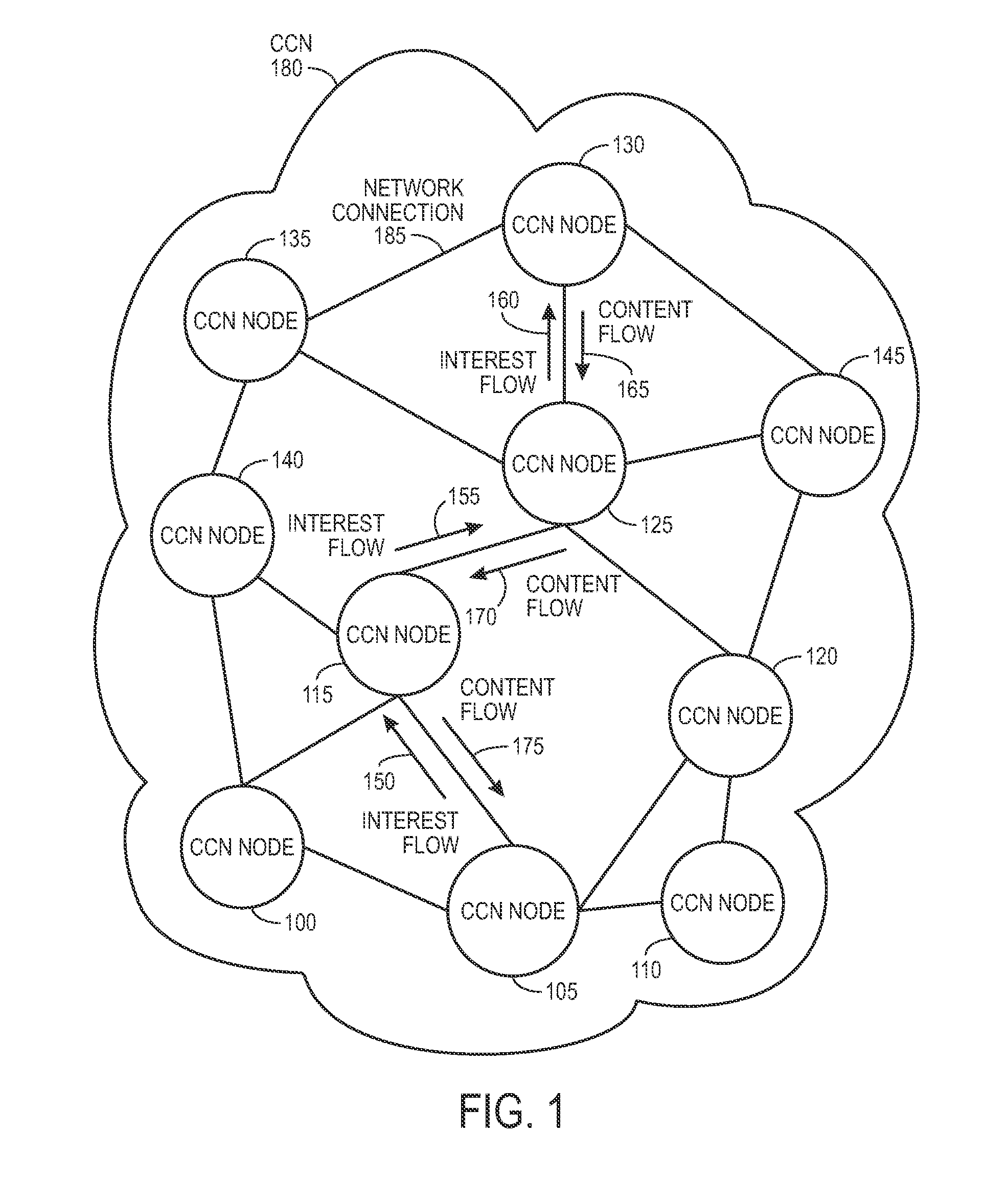
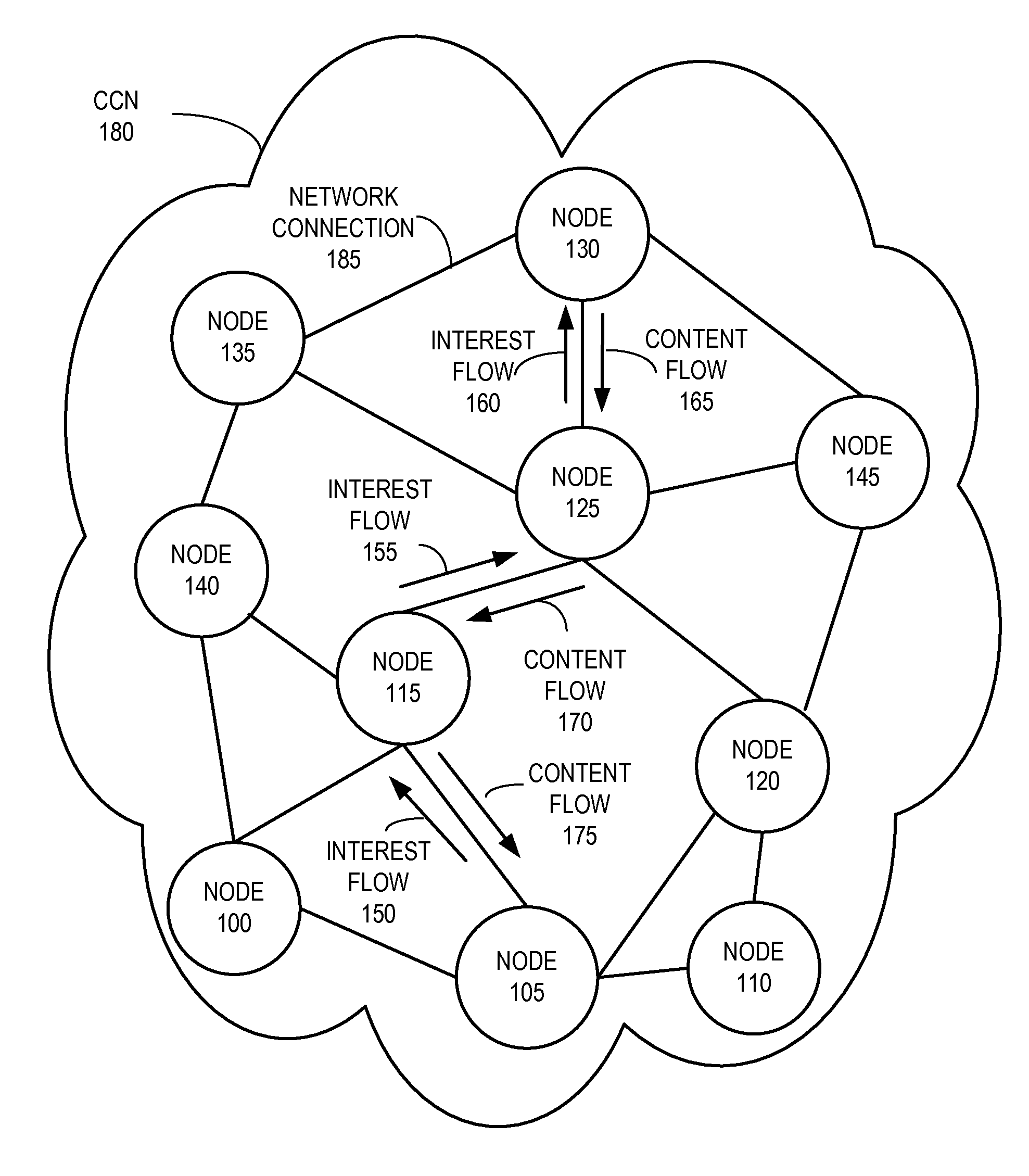
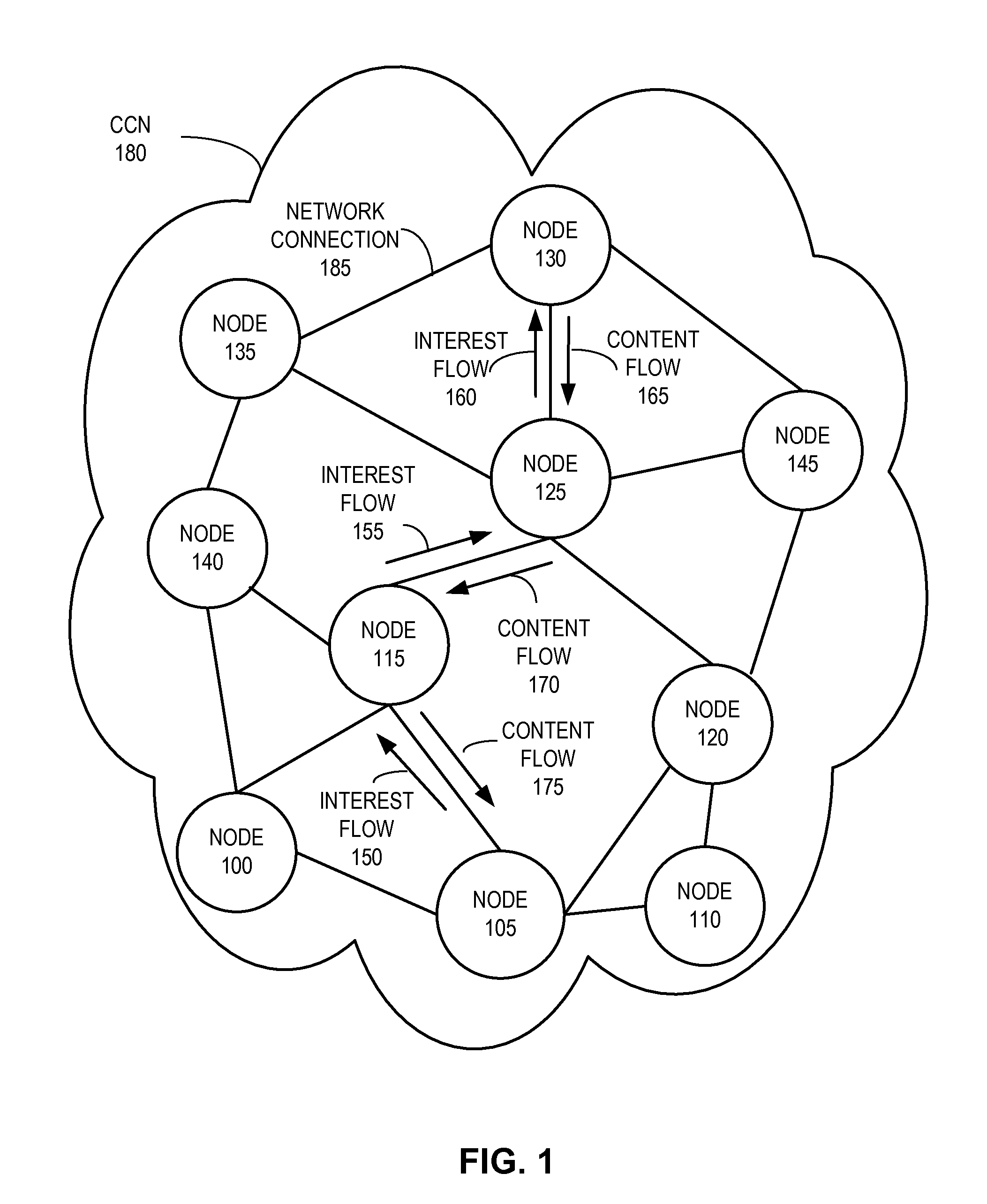
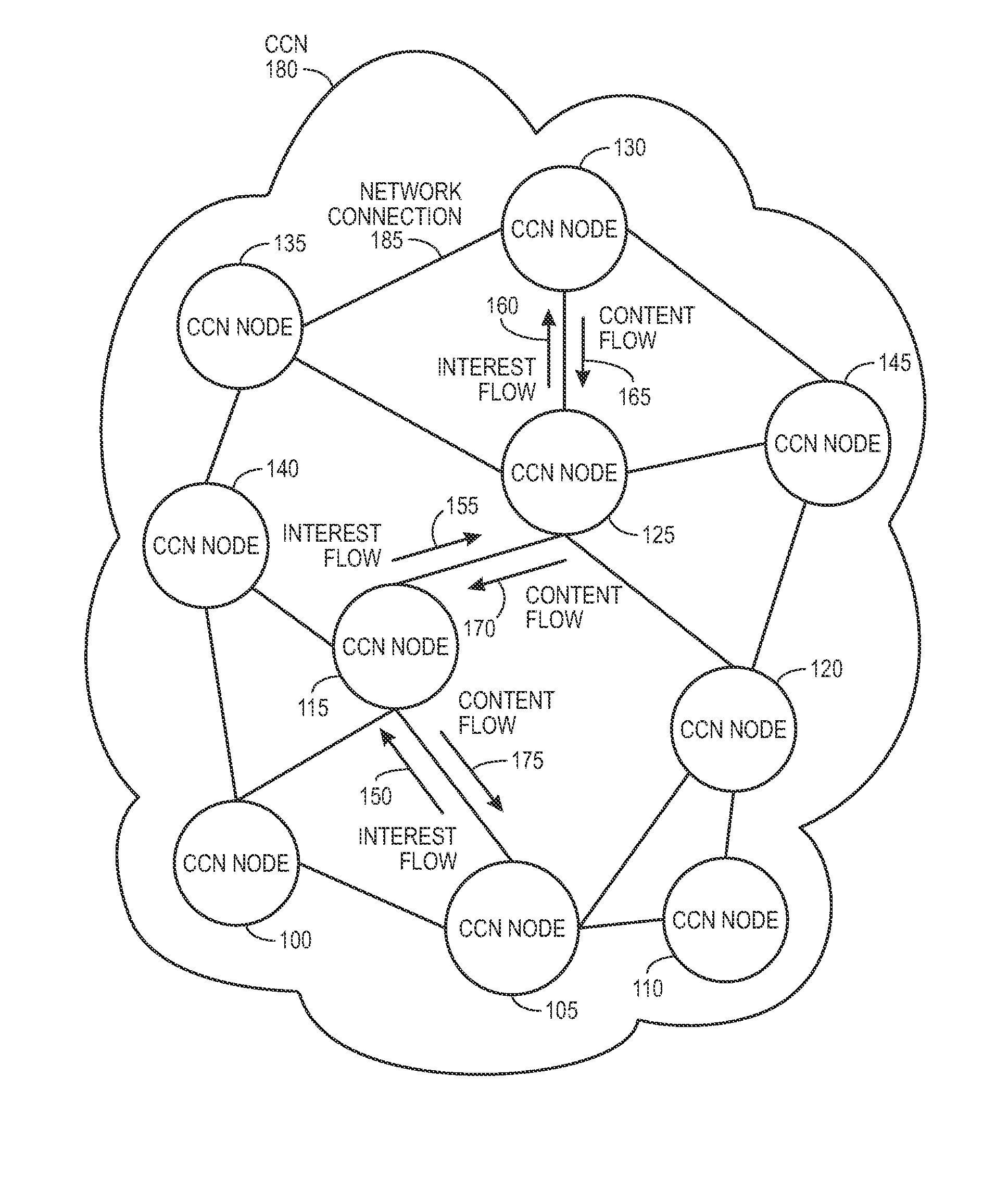
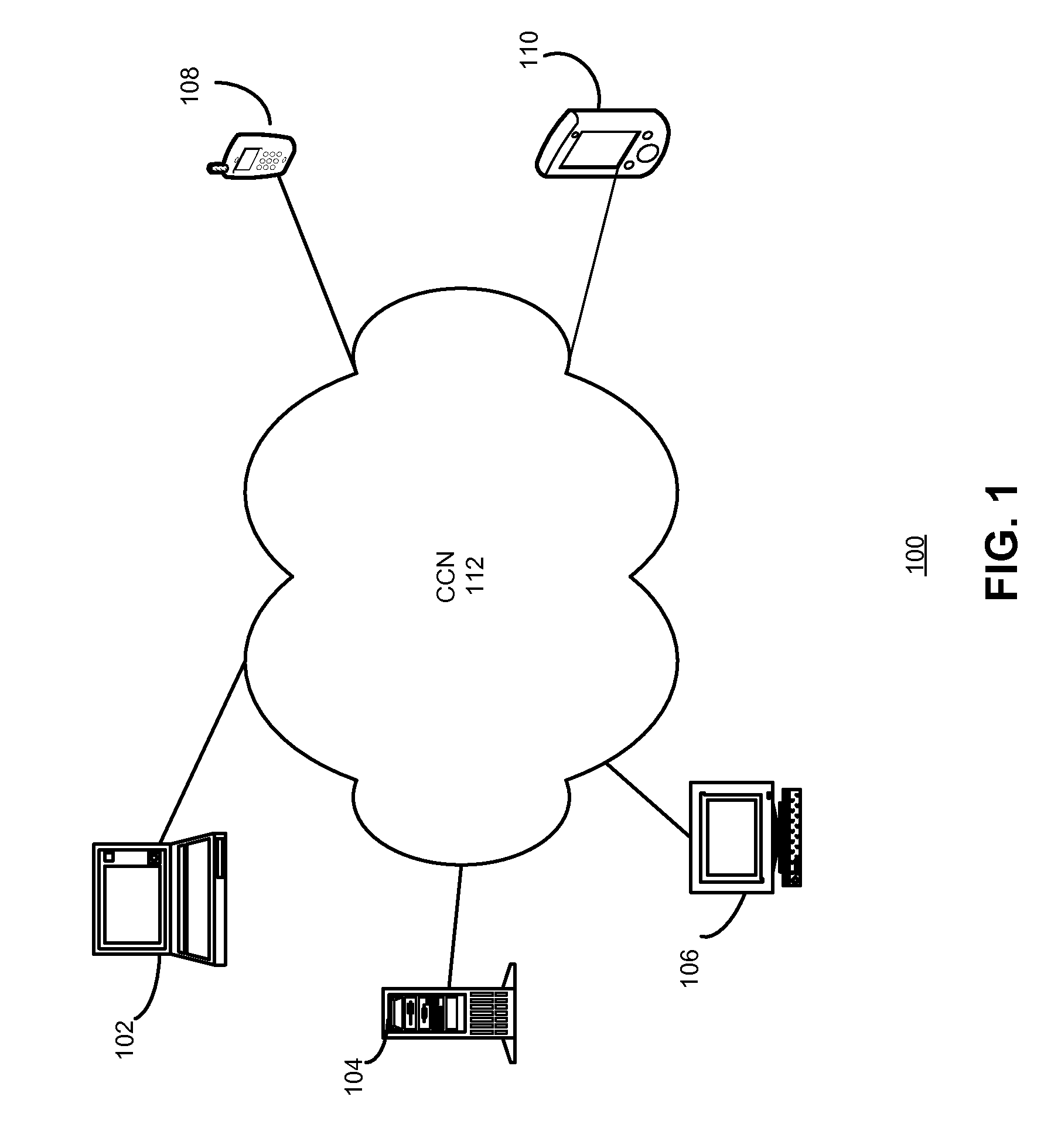
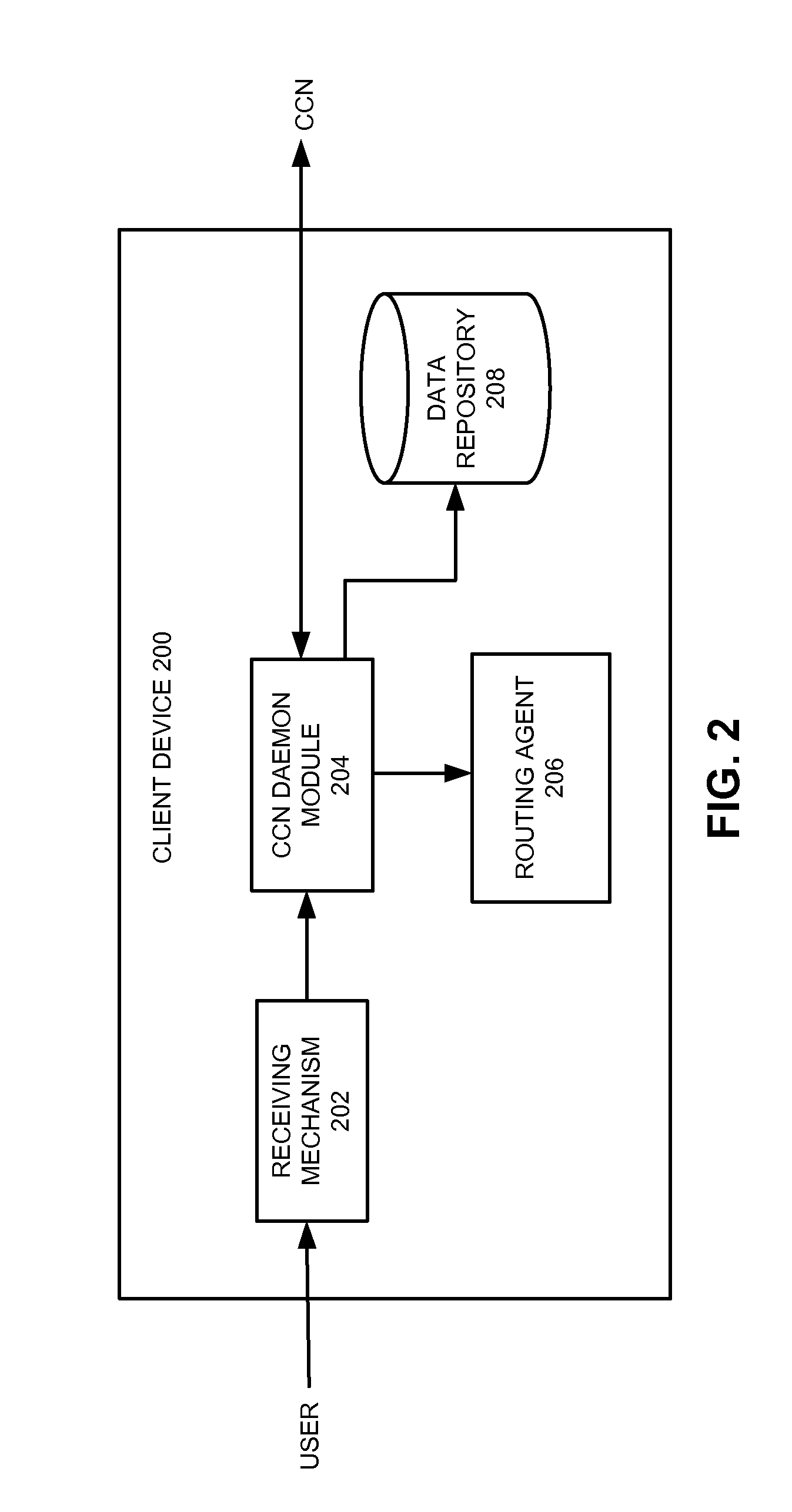
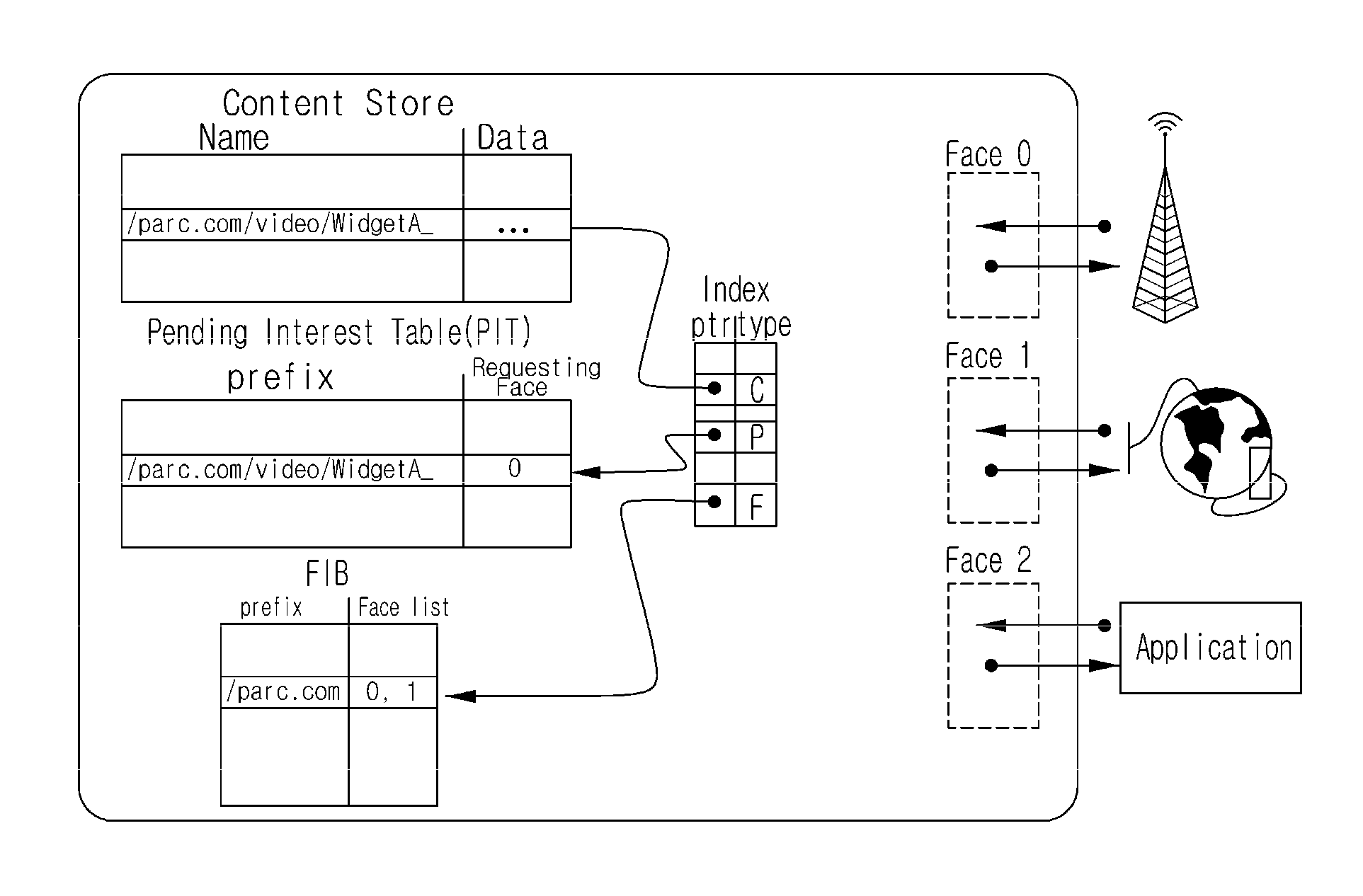
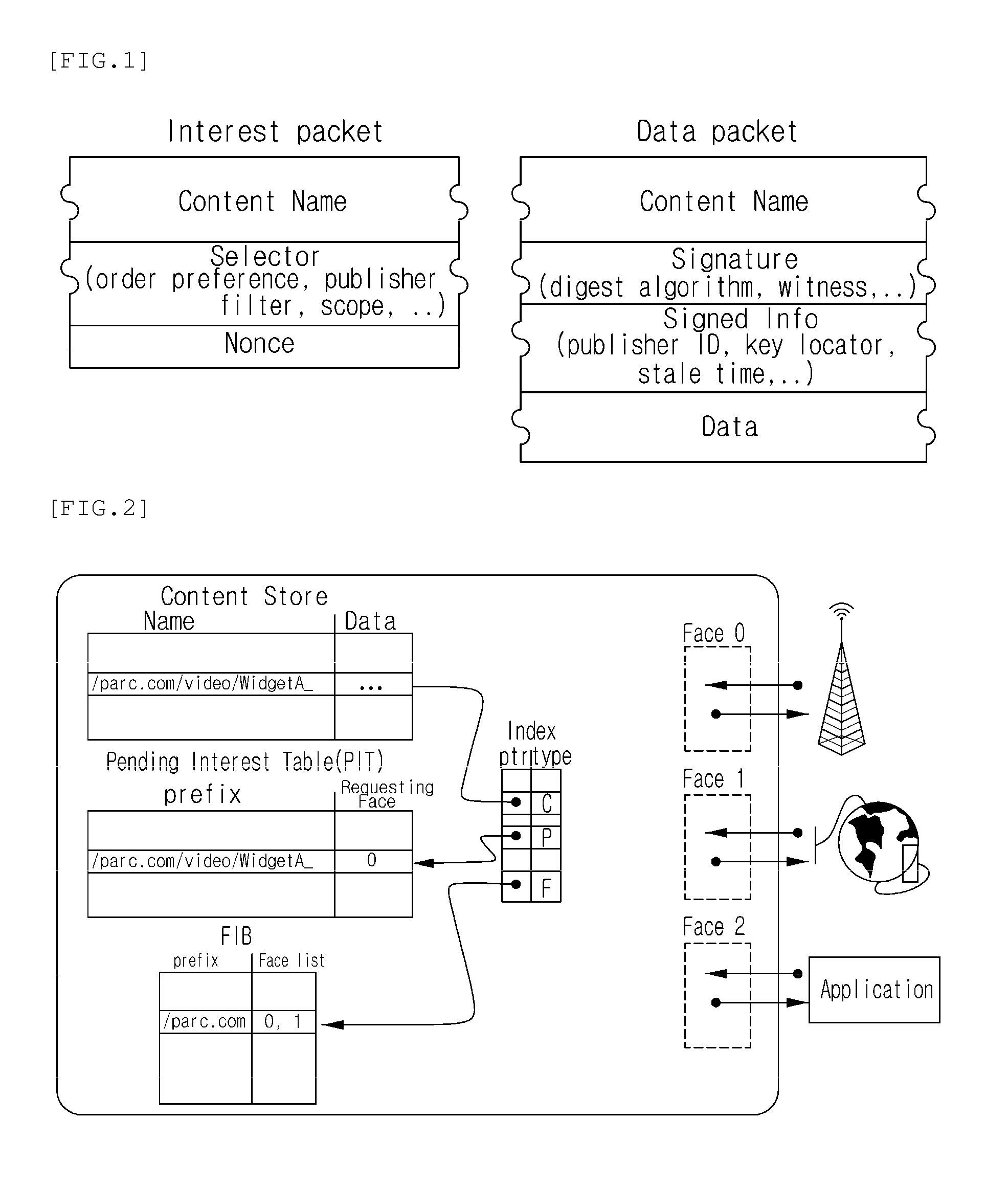
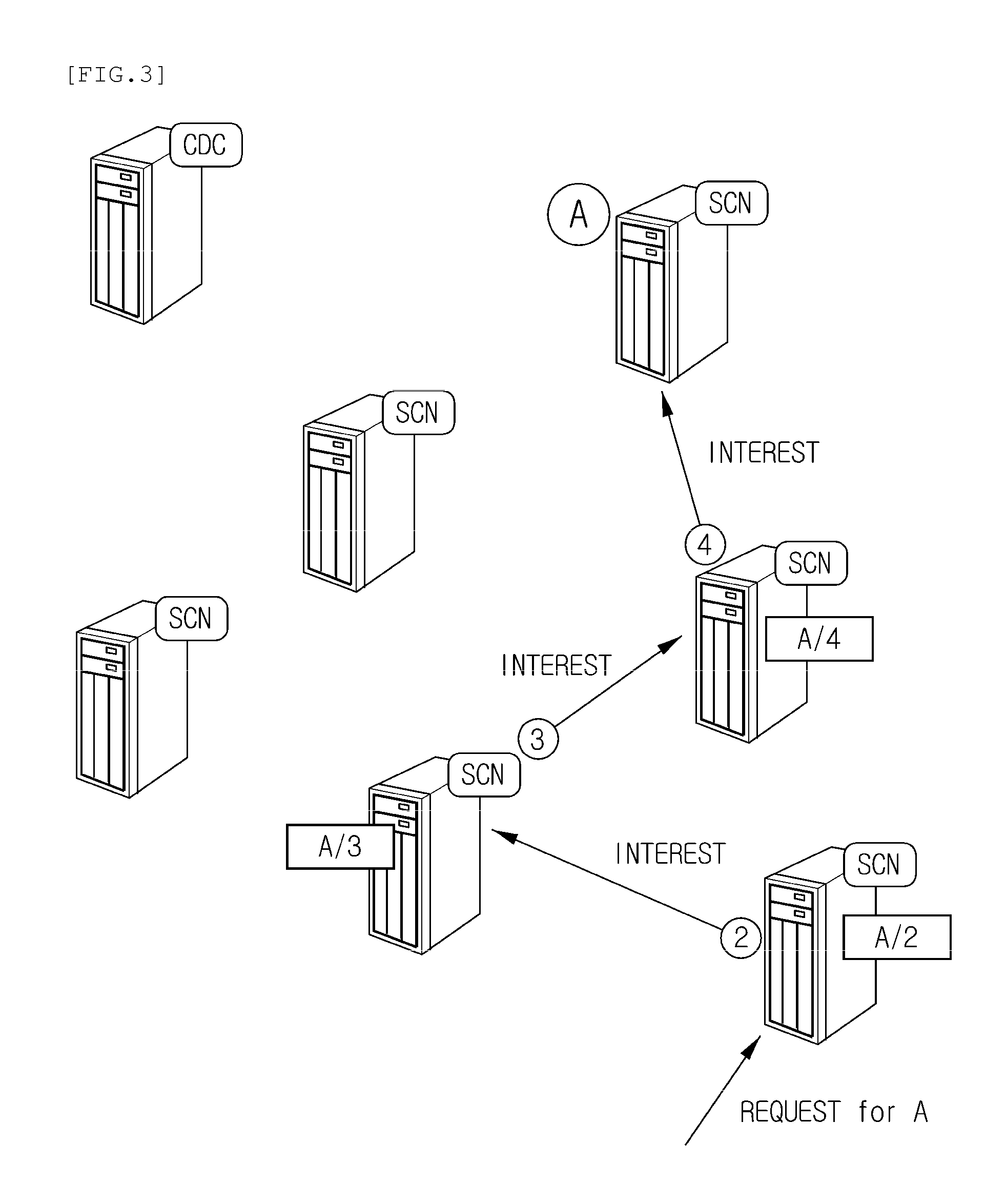
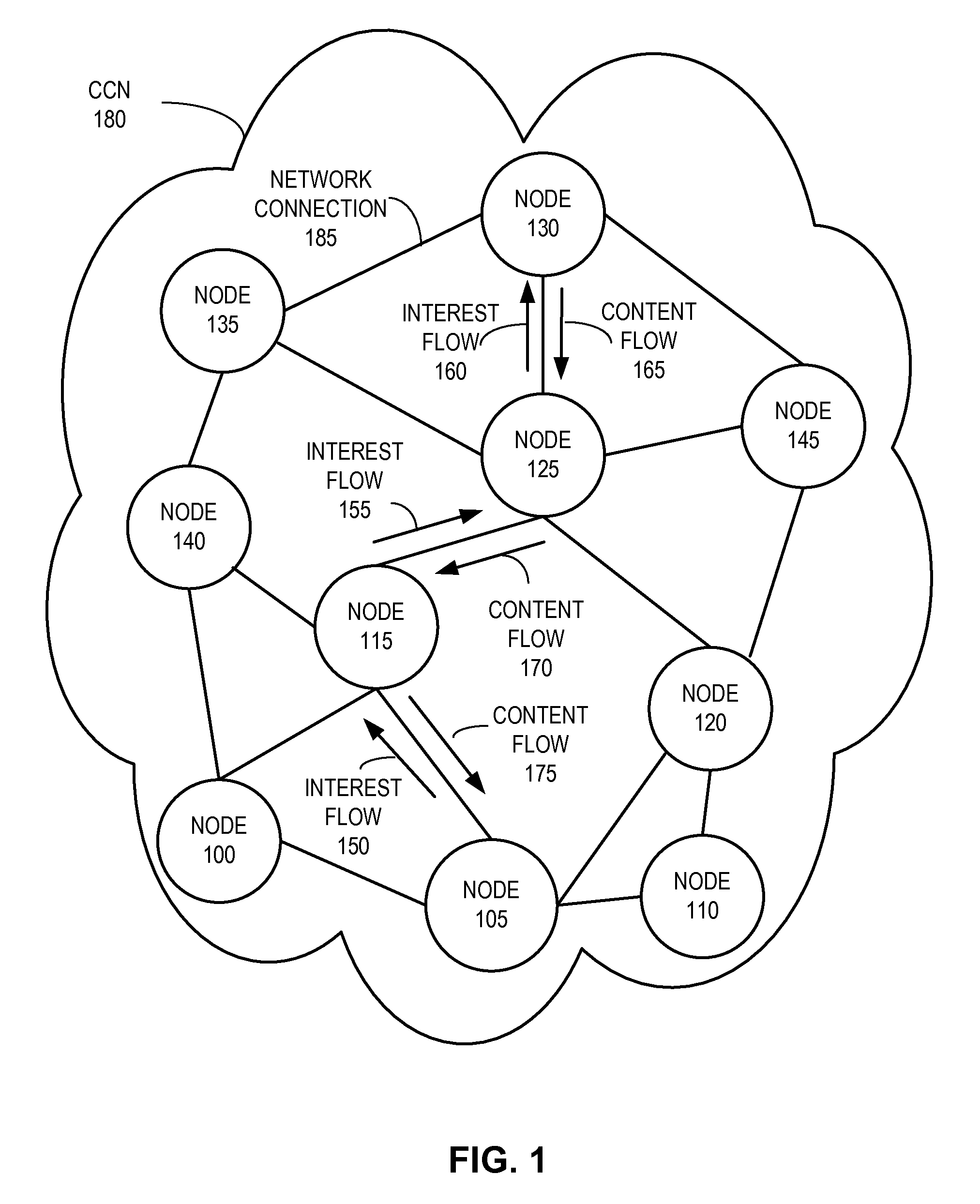
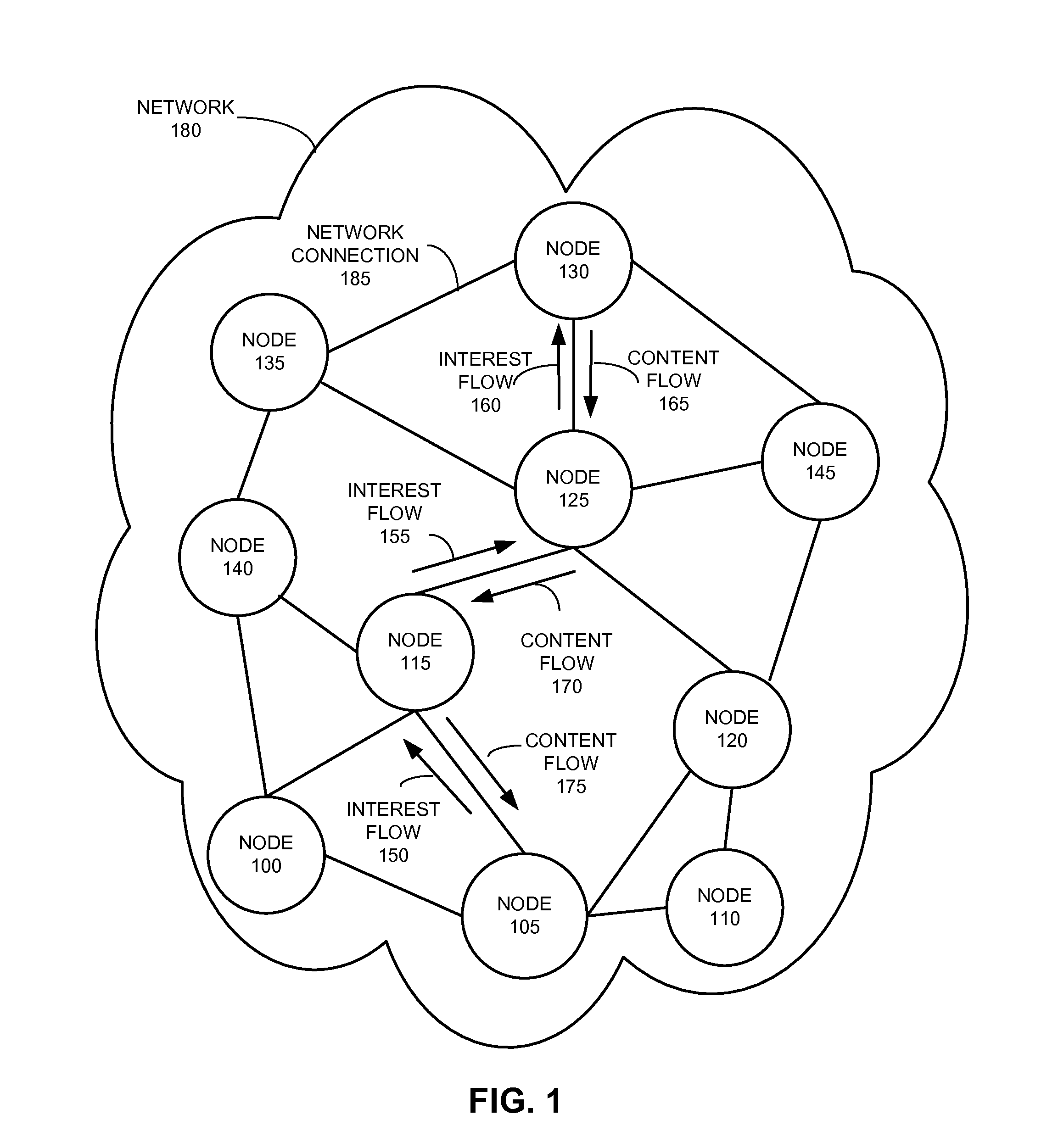
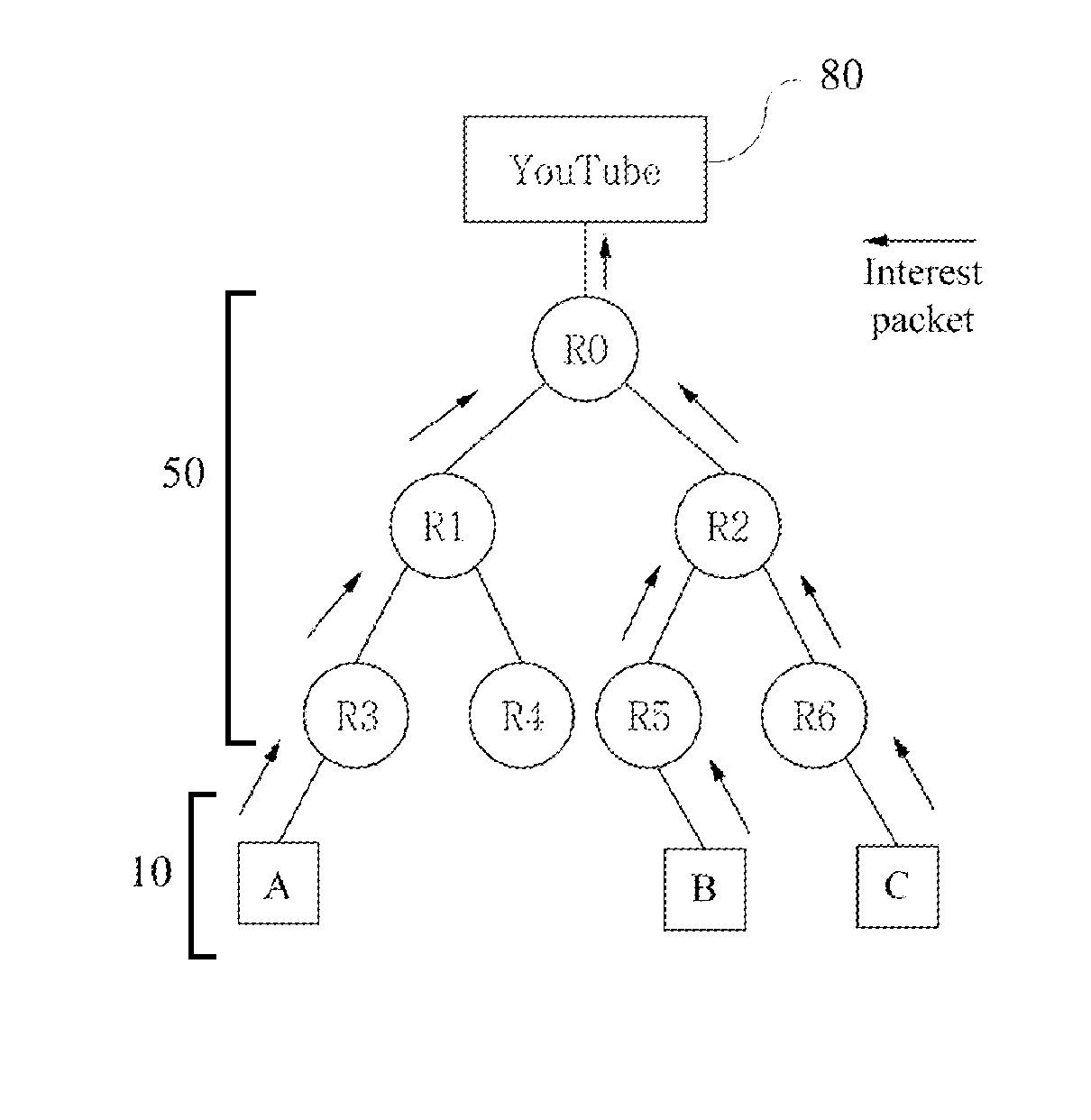
In contrast to IP-based, host-oriented, Internet architecture, content centric networking (CCN) emphasizes content by making it directly addressable and routable. Endpoints communicate based on named data instead of IP addresses. CCN is characterized by the basic exchange of content request messages (called "Interests") and content return messages (called "Content Objects"). It is considered an information-centric networking (ICN) architecture.
Controlling the spread of interests and content in a content centric network
ActiveUS20090288163A1Easy flow controlExpected levelMemory loss protectionMultiple keys/algorithms usageContent centricSystem maintenance
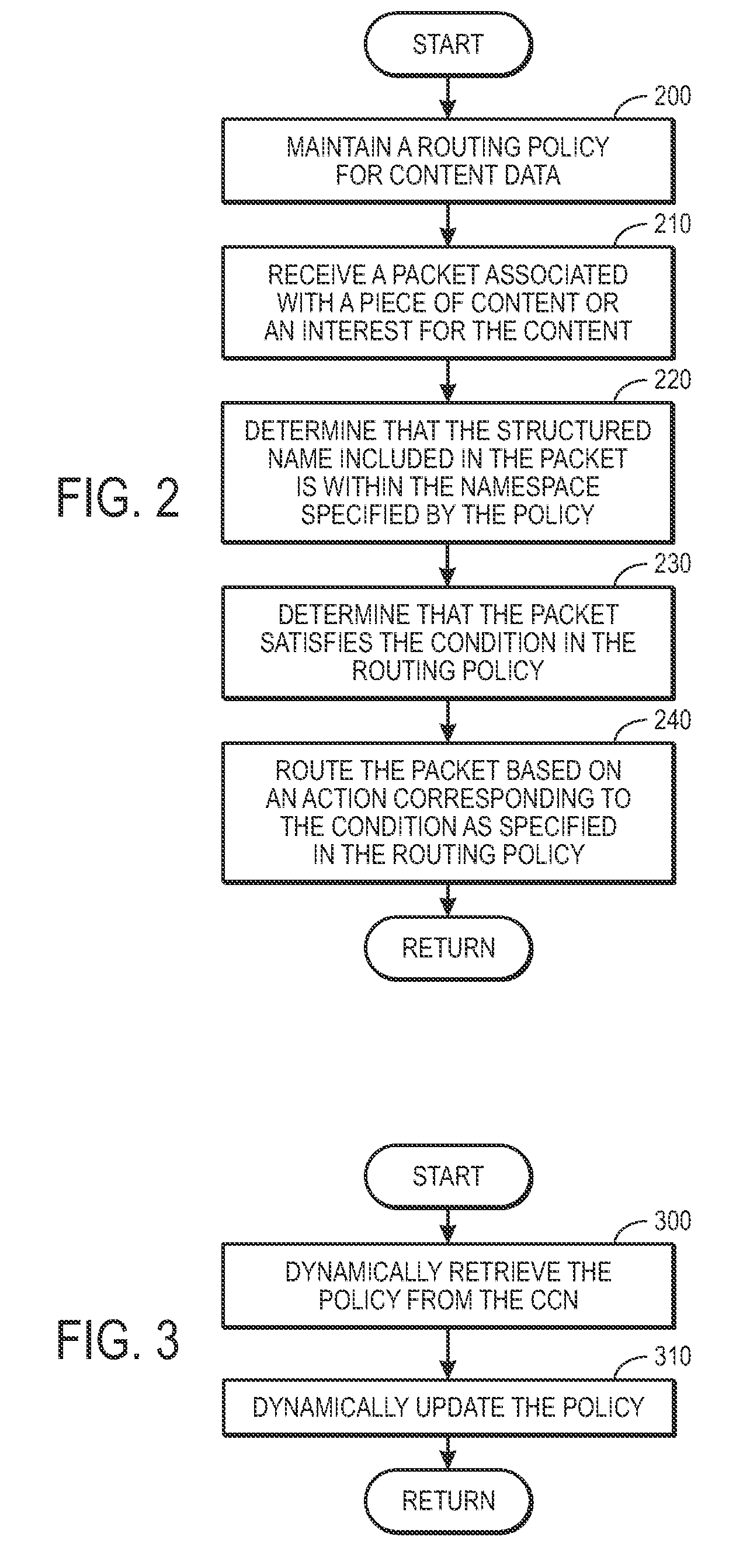
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for controlling the spread of interests and content in a content centric network (CCN). During operation, the system maintains a routing policy for content data. The system also receives a packet associated with a piece of content or an interest for the content. Next, the system determines that the structured name included in the packet is within the namespace specified in the routing policy. The system further determines that the packet satisfies the condition in the routing policy. Subsequently, the system routes the packet based on in part the action corresponding to the condition as specified in the routing policy.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
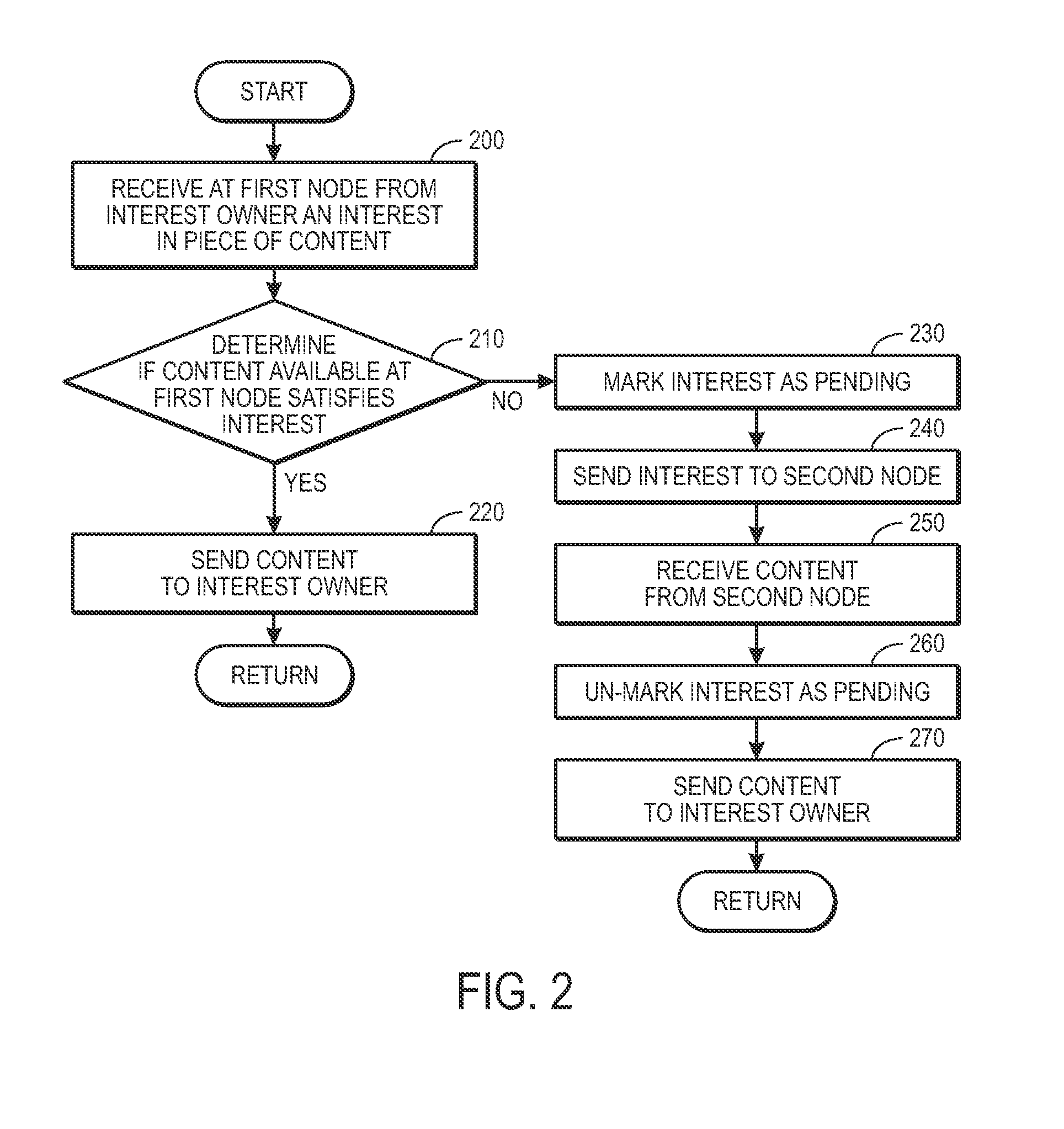
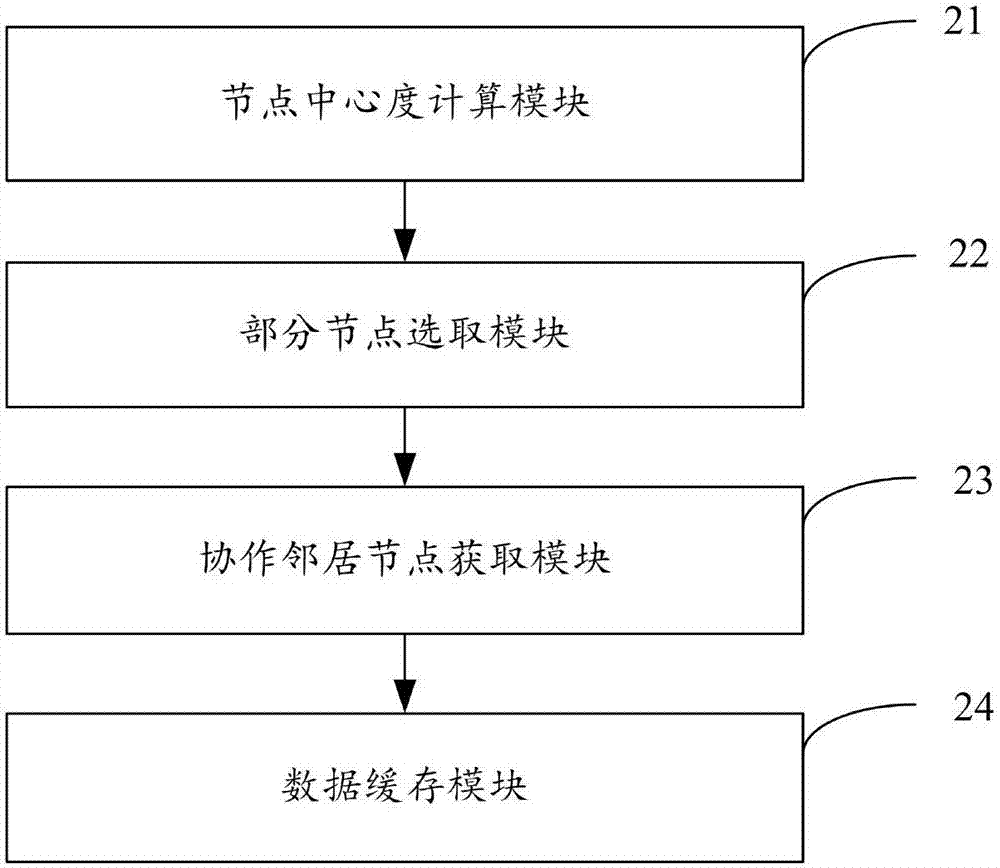
Method and apparatus for facilitating communication in a content centric network
ActiveUS20090287835A1Easy flow controlMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent centricWorld Wide Web
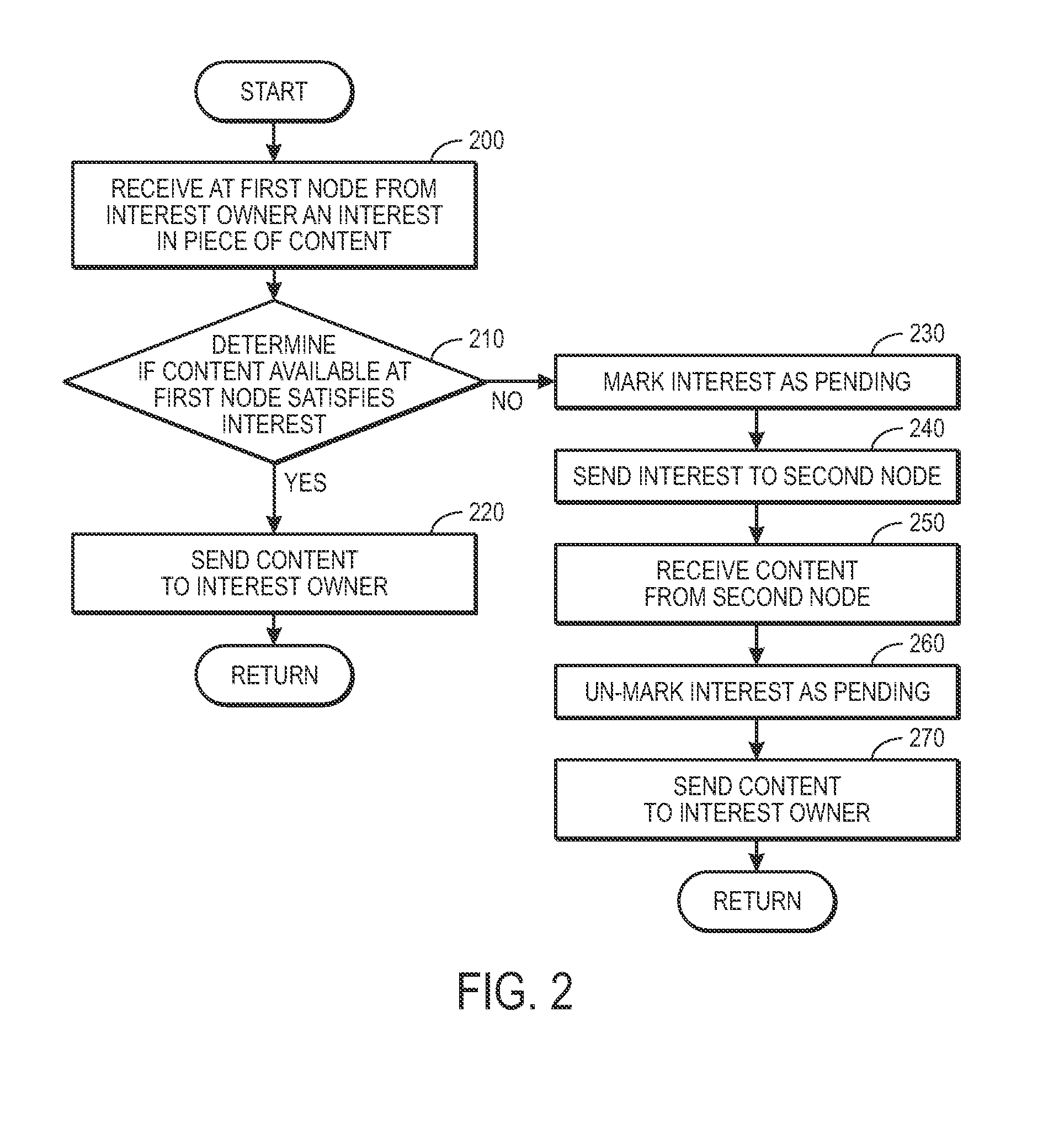
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating communication in a content centric network (CCN). During operation, the system receives at a first node from an interest owner an interest in a piece of content. The interest indicates a structured name for the content. Furthermore, the name is unique and persistent with respect to the content, and where the name includes authentication information for the content. Next, the system determines whether content available at the first node satisfies the interest. If so, the system sends the content to the interest owner. Otherwise, the system marks the interest as pending, and forwards the interest to a second node in the network based on the interest. After receiving content from the second node in response to the forwarded interest, the system un-marks the interest as pending and sends the content to the interest owner.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for facilitating forwarding a packet in a content-centric network
ActiveUS20100195655A1Good for forwardingData switching by path configurationContent centricVariable length
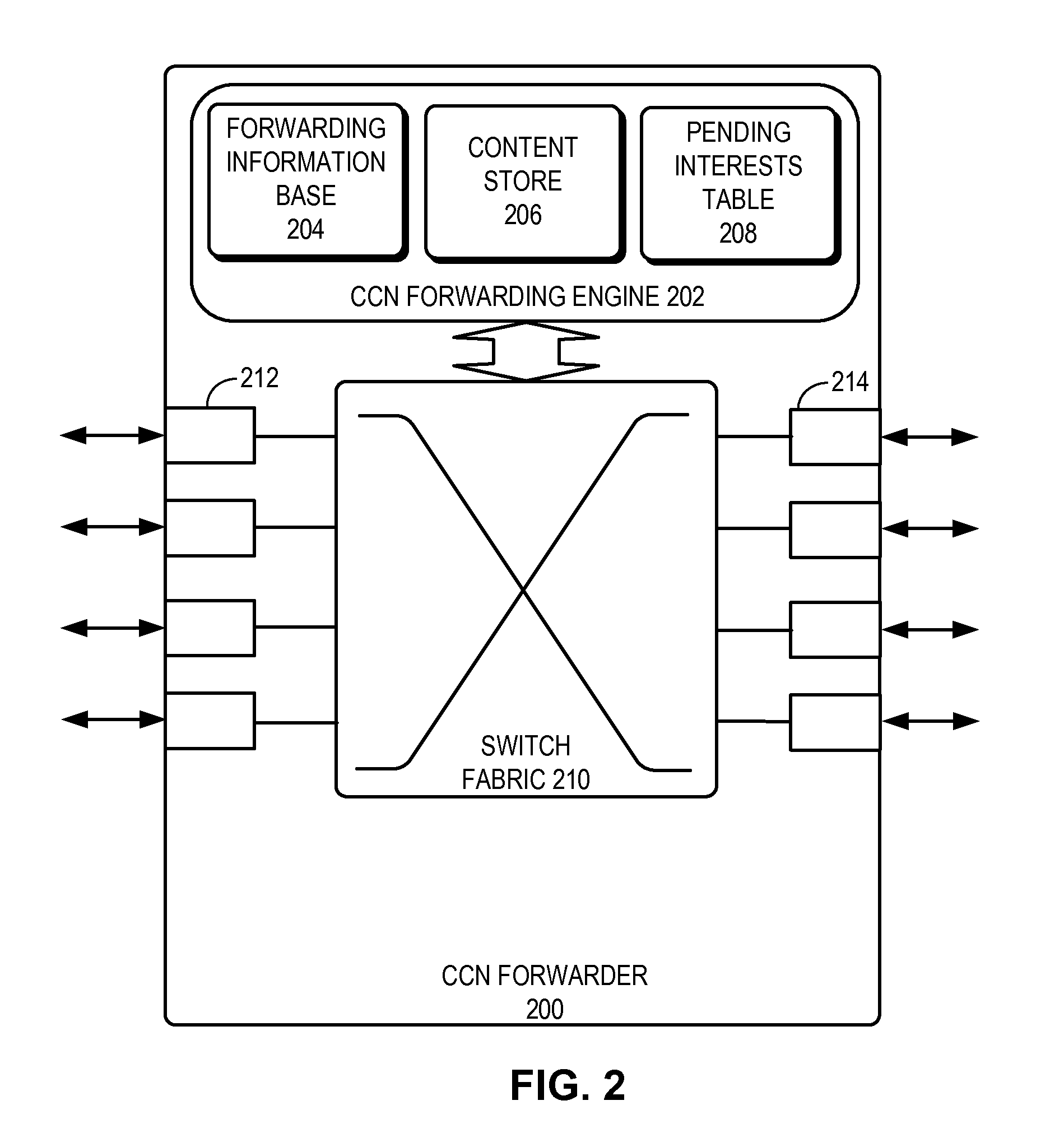
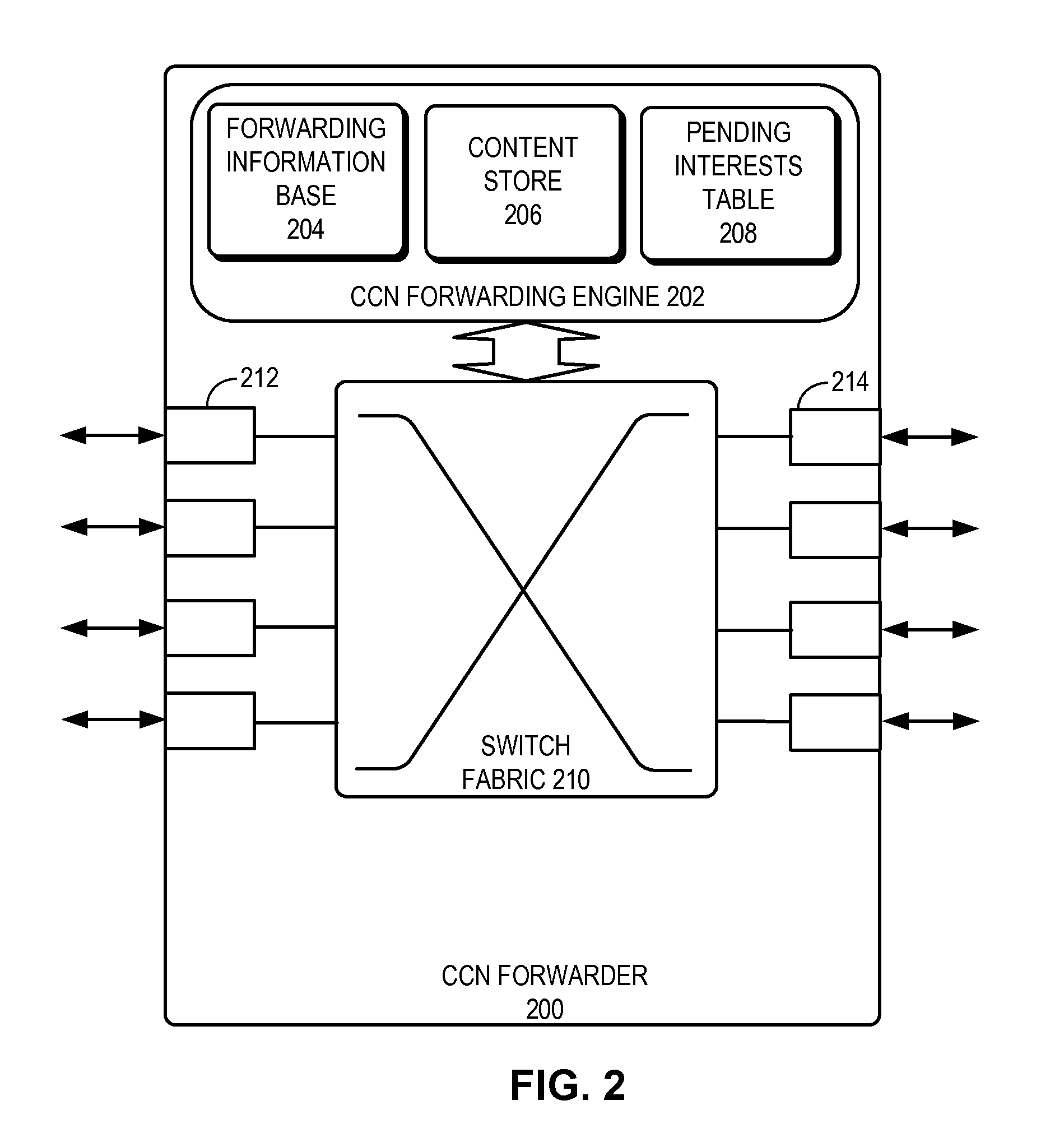
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates forwarding a packet. During operation, the system receives a packet with a hierarchically structured variable-length identifier (HSVLI). The system then performs a lookup at a forwarding engine based at least on the packets HSVLI. The system further makes a forwarding decision based on the lookup.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Session migration over content-centric networks
ActiveUS20110265174A1Facilitating session migrationFacilitating sessionComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsSession fixationContent centric
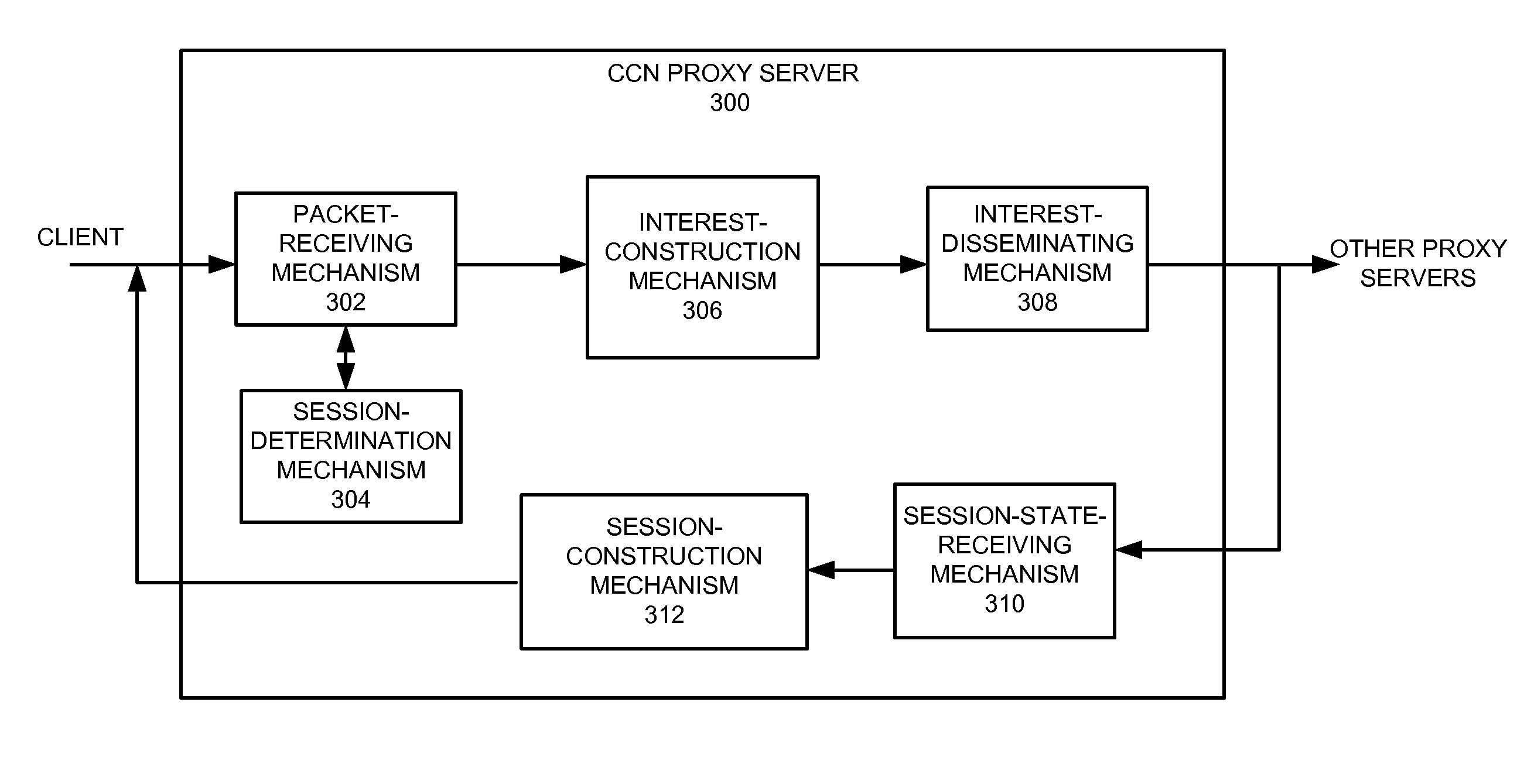
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating session migration. During operation, the system receives a communication packet from a client destined to a remote server. The system determines whether the communication packet belongs to a pre-existing communication session, and whether session state information associated with the session is available locally. In response to the communication packet belonging to a pre-existing communication session and the session state information being unavailable locally, the system constructs an interest requesting the session state information, disseminates the interest over a network, and receives the session state information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for facilitating communication in a content centric network
ActiveUS8386622B2Easy flow controlMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent centricWorld Wide Web
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating communication in a content centric network (CCN). During operation, the system receives at a first node from an interest owner an interest in a piece of content. The interest indicates a structured name for the content. Furthermore, the name is unique and persistent with respect to the content, and where the name includes authentication information for the content. Next, the system determines whether content available at the first node satisfies the interest. If so, the system sends the content to the interest owner. Otherwise, the system marks the interest as pending, and forwards the interest to a second node in the network based on the interest. After receiving content from the second node in response to the forwarded interest, the system un-marks the interest as pending and sends the content to the interest owner.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
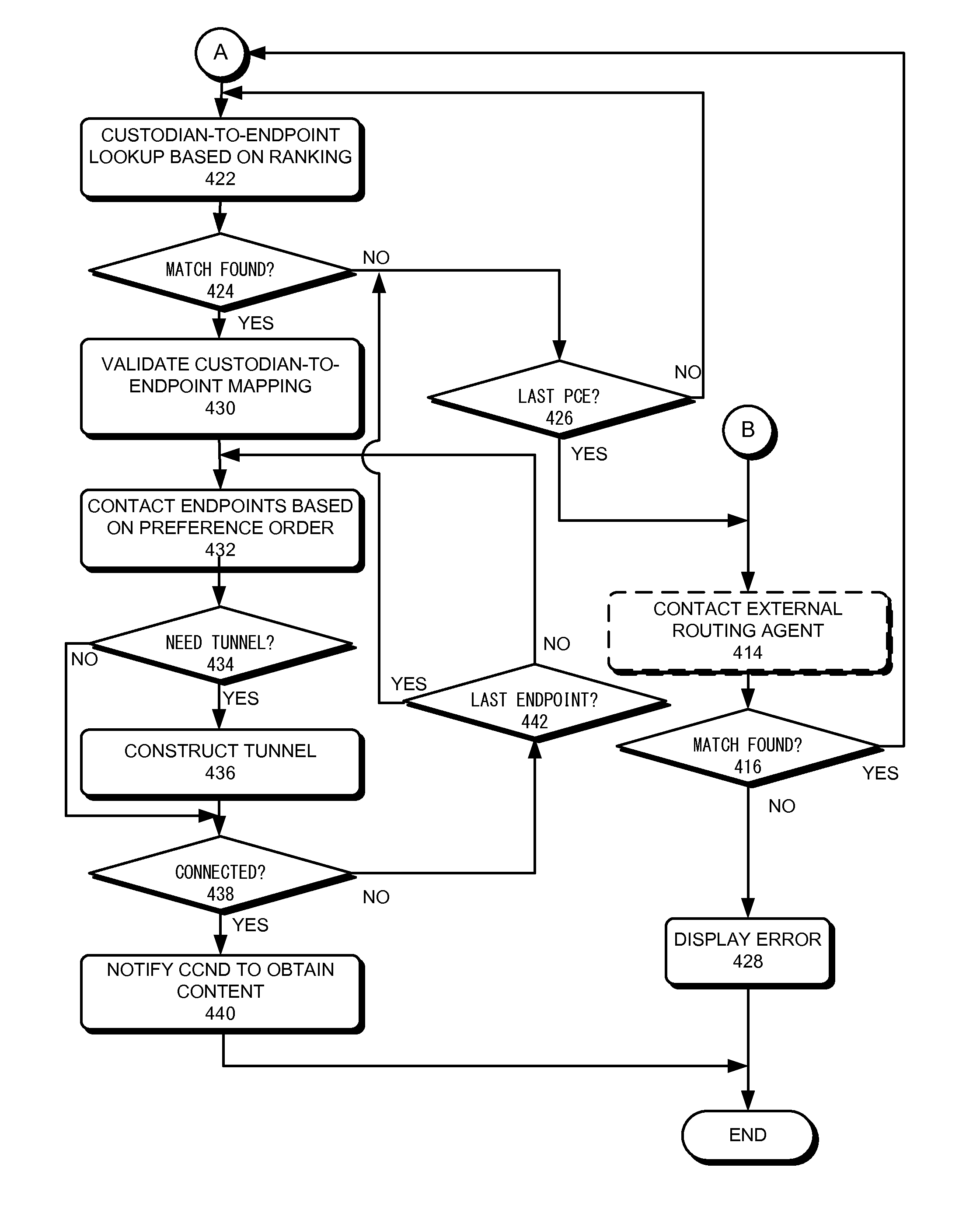
Custodian-based routing in content-centric networks
ActiveUS20120158973A1Easy to optimizeFacilitating custodian-based routingData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunication endpointComputer network
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating custodian-based routing. During operation, the system receives, at a computing device, a request for a piece of content from a user, and determines whether the content is available locally. In response to the content not being available locally, the system identifies a remote custodian device that stores the content. The custodian device is not identified by its physical address. The system then identifies a communication endpoint associated with the identified custodian device, and maps a physical address corresponding to the identified communication endpoint. The system establishes a connection to the communication endpoint using the mapped physical address to obtain the requested content.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Routing method in content-centric network
InactiveUS20130111063A1Avoid network bottlenecksFlexibly solving network congestionDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryTraffic capacity
Disclosed is a centralized controlling method of the process of delivering a routing packet for content transmission in a content-centric network (CCN). The routing method in a content centric network according to the present invention includes: a content distribution controller in the content centric network receiving a request for specific-content distribution from a user, determining locations of routers storing the content, and finding one of the routers to which the request from the user will be transmitted; and the content distribution controller finding an optimal path in consideration of a traffic distribution status and then transmitting a forwarding information base (FIB) to routers included in the optimal path.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method of implementing content-centric network (CCN) using internet protocol (IP)-based network in gateway, and gateway
ActiveUS20130173822A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
A method of implementing a Content-Centric Network (CCN) using an Internet Protocol (IP)-based network, and a gateway that may implement such a method, are provided. A method of implementing a CCN using an IP-based network may involve: determining an application protocol and a packet type corresponding to the application protocol of an IP-based network, the application protocol being included in an IP packet of an IP-based network, and generating a content name corresponding to the IP packet, based on the application protocol and the packet type.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for facilitating forwarding a packet in a content-centric network
ActiveUS8204060B2Data switching by path configurationContent centricStructure of Management Information
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates forwarding a packet. During operation, the system receives a packet with a hierarchically structured variable-length identifier (HSVLI). The system then performs a lookup at a forwarding engine based at least on the packets HSVLI. The system further makes a forwarding decision based on the lookup.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Network apparatus based on content name, method of generating and authenticating content name
ActiveUS20130074155A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationA domainAuthentication information
A method of generating and authenticating a content name in content-centric networking (CCN) and a network apparatus are provided. A content name generation method includes generating authentication information using a secret key shared by network apparatuses that belong to a domain in content-centric networking (CCN); and generating a content name that includes the authentication information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for managing devices over a content centric network
ActiveUS20150381546A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksContent centricLongest prefix match
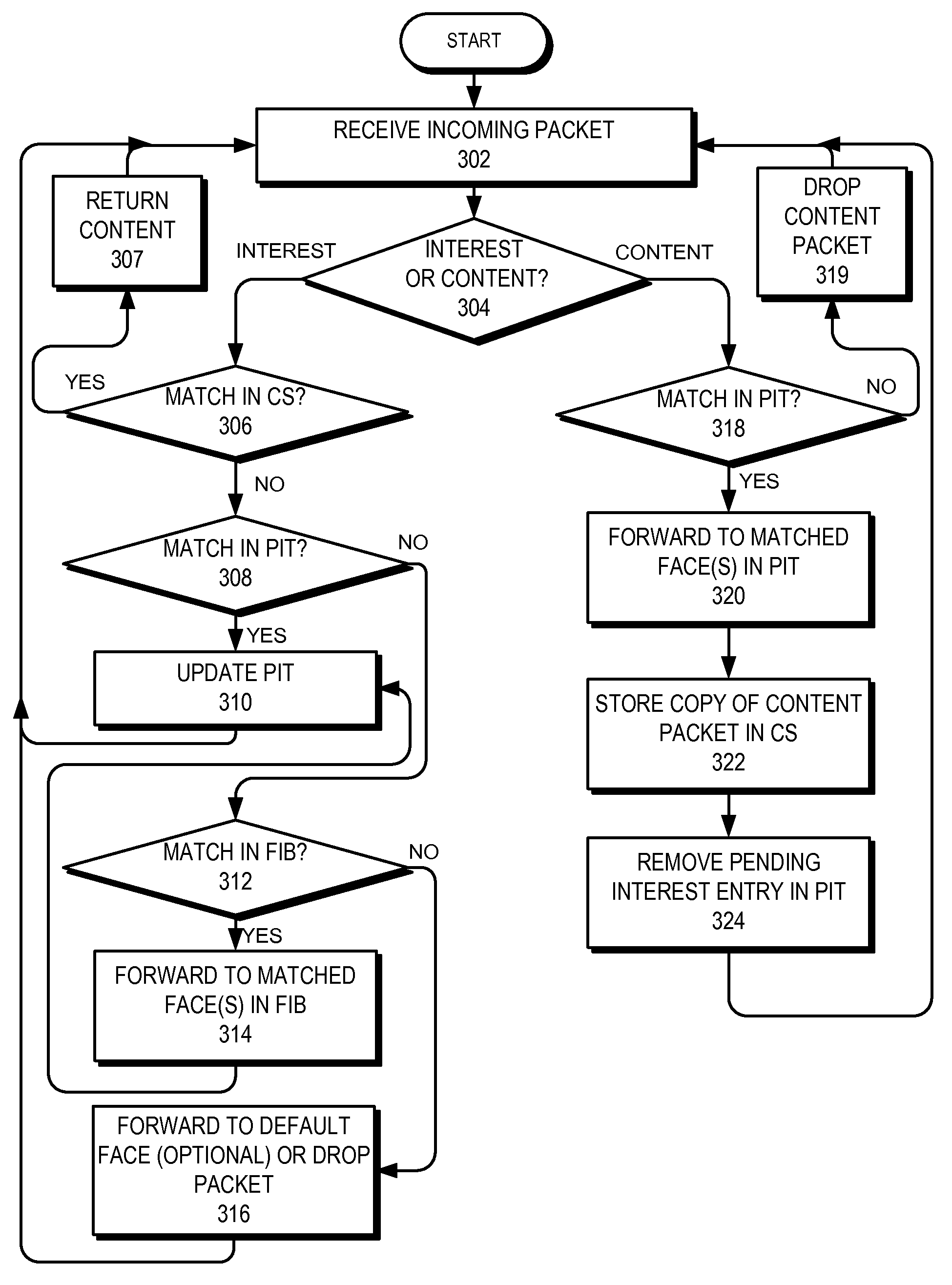
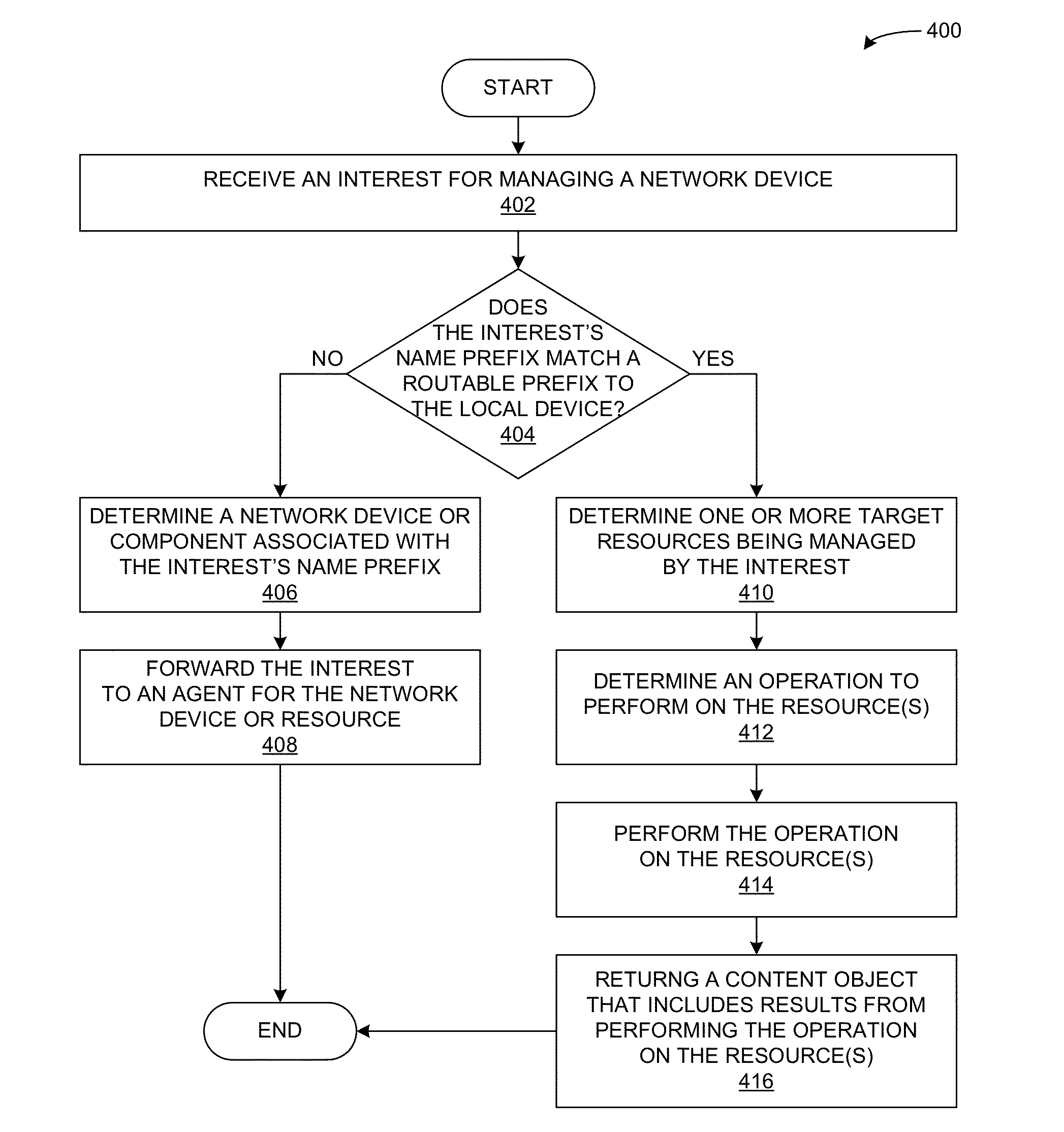
A device can process commands from a remote device that manages the local device over a content centric network. During operation, the device can receive an Interest for managing a device resource, such that the Interest's name includes a name or a name prefix associated with the device resource, and includes a command for managing the resource. If the device determines that the name prefix corresponds to the local device, the device analyzes the Interest's command to determine a device resource and performs the resource-managing operation on the device resource. If the name prefix does not correspond to the local device, the device performs a longest-prefix-matching lookup using the Interest's name prefix to determine a destination for the Interest. If the Interest's destination corresponds to a component of the local device, the device forwards the Interest to the component or a local agent for the component.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for circular link resolution with computable hash-based names in content-centric networks
ActiveUS20150349961A1For easy referenceUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionSelf certifiedContent centric
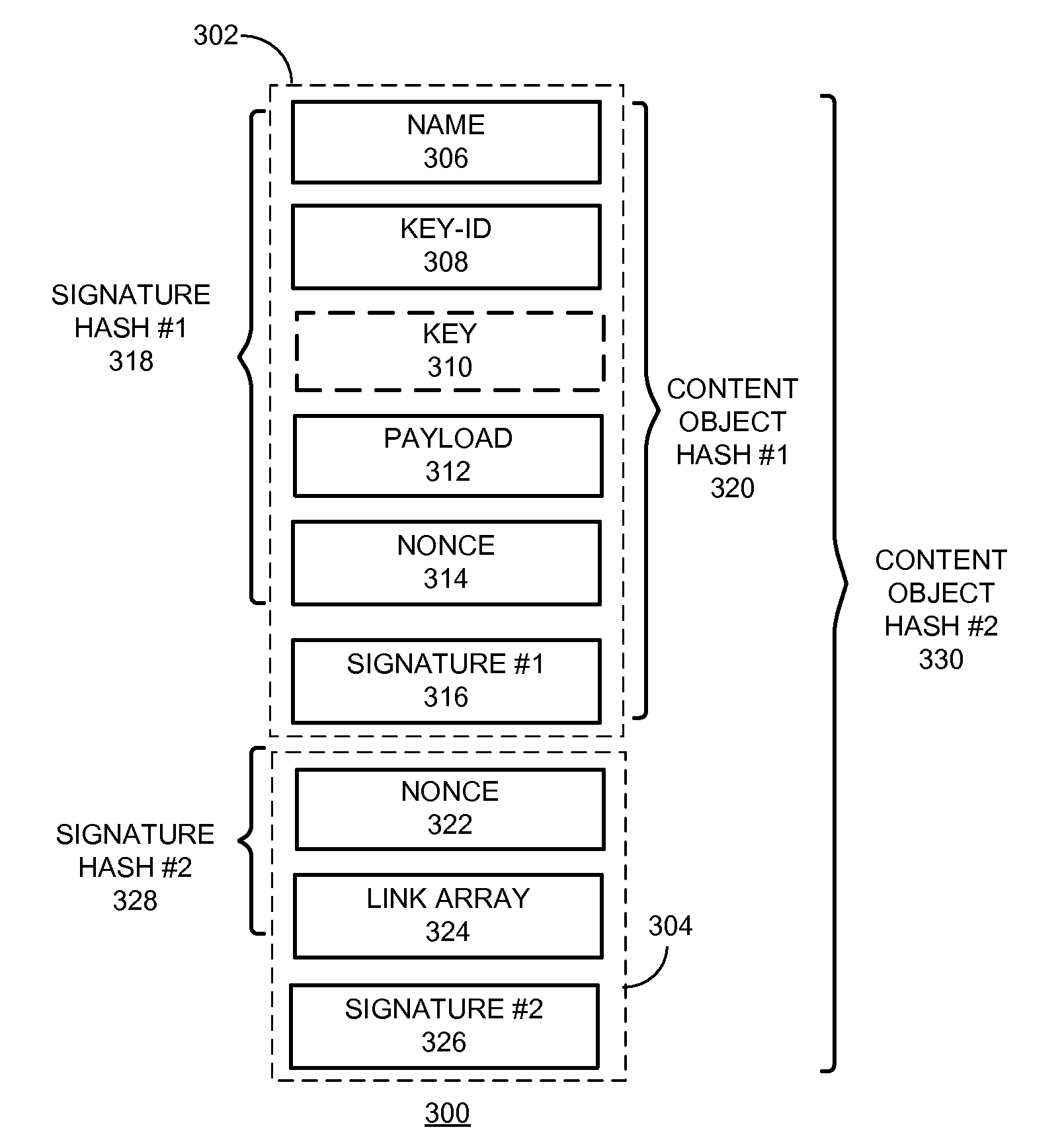
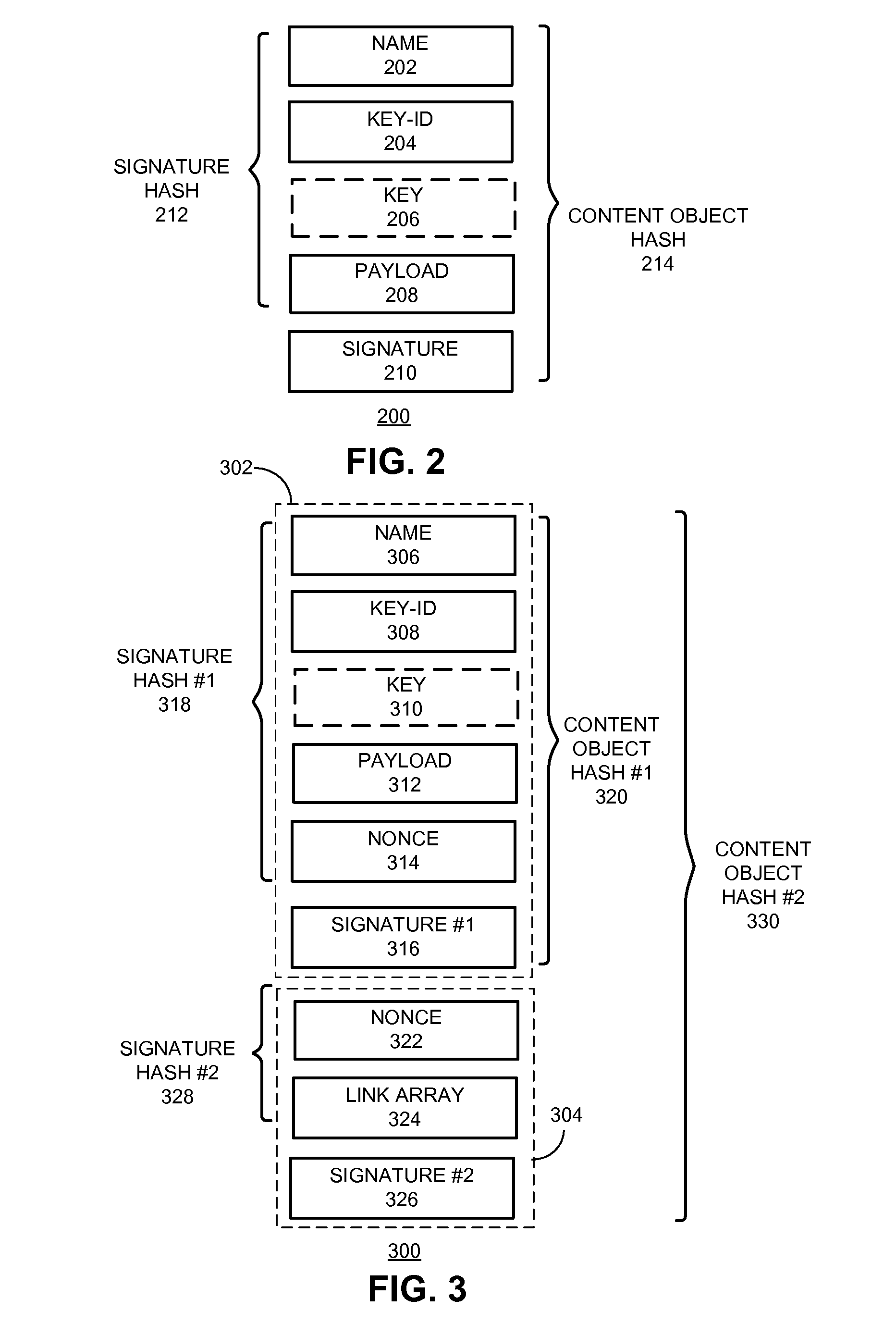
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for constructing a linked object. During operation, the system constructs a first portion of the linked object. The first portion includes at least one or more data items and a computable identifier calculated based on the one or more data items, and the first portion is referenced by a self-certified name associated with the linked object. The system constructs a second portion of the linked object. The second portion includes at least the computable identifier and an external link that references a second linked object using a self-certified name associated with the second linked object.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
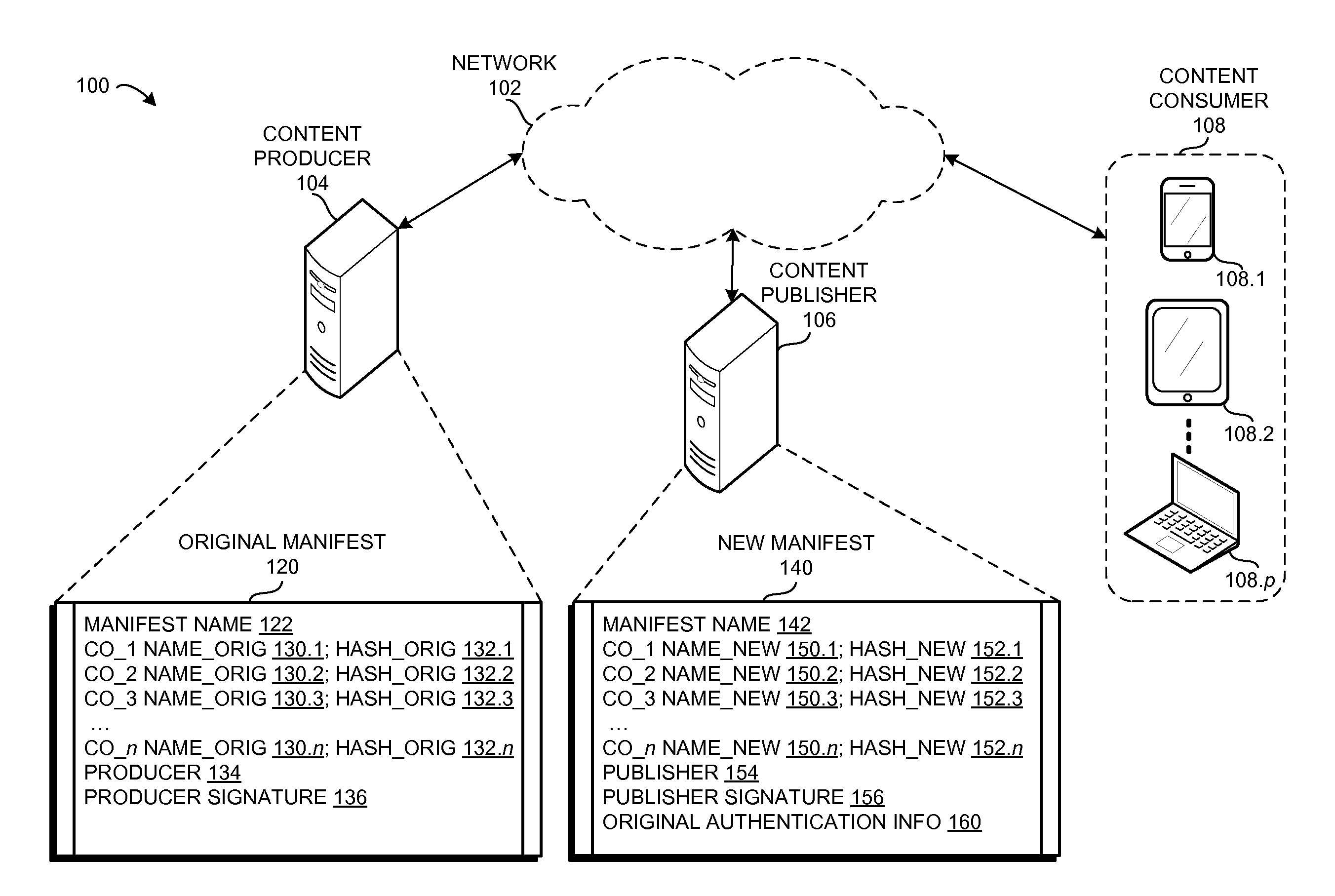
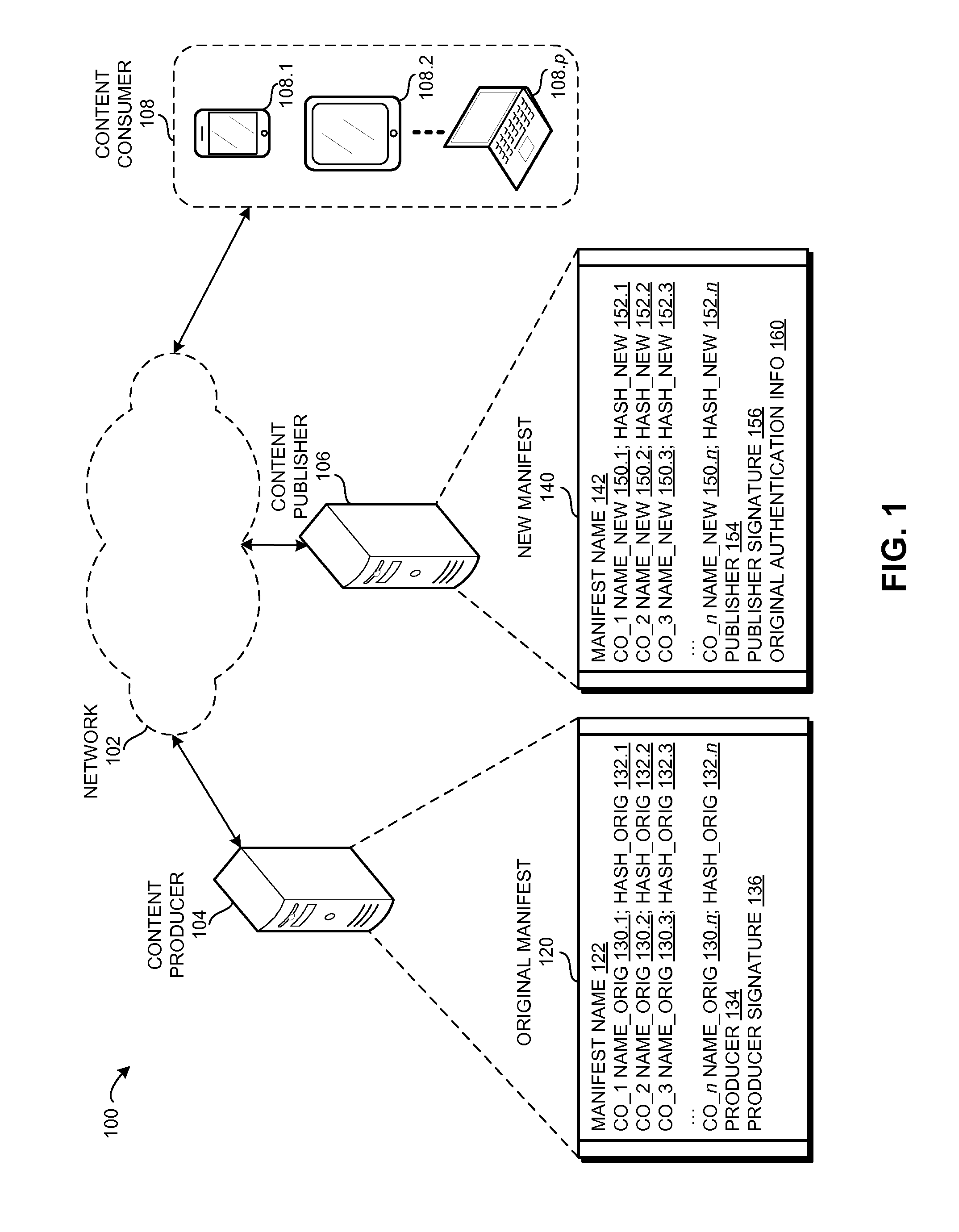
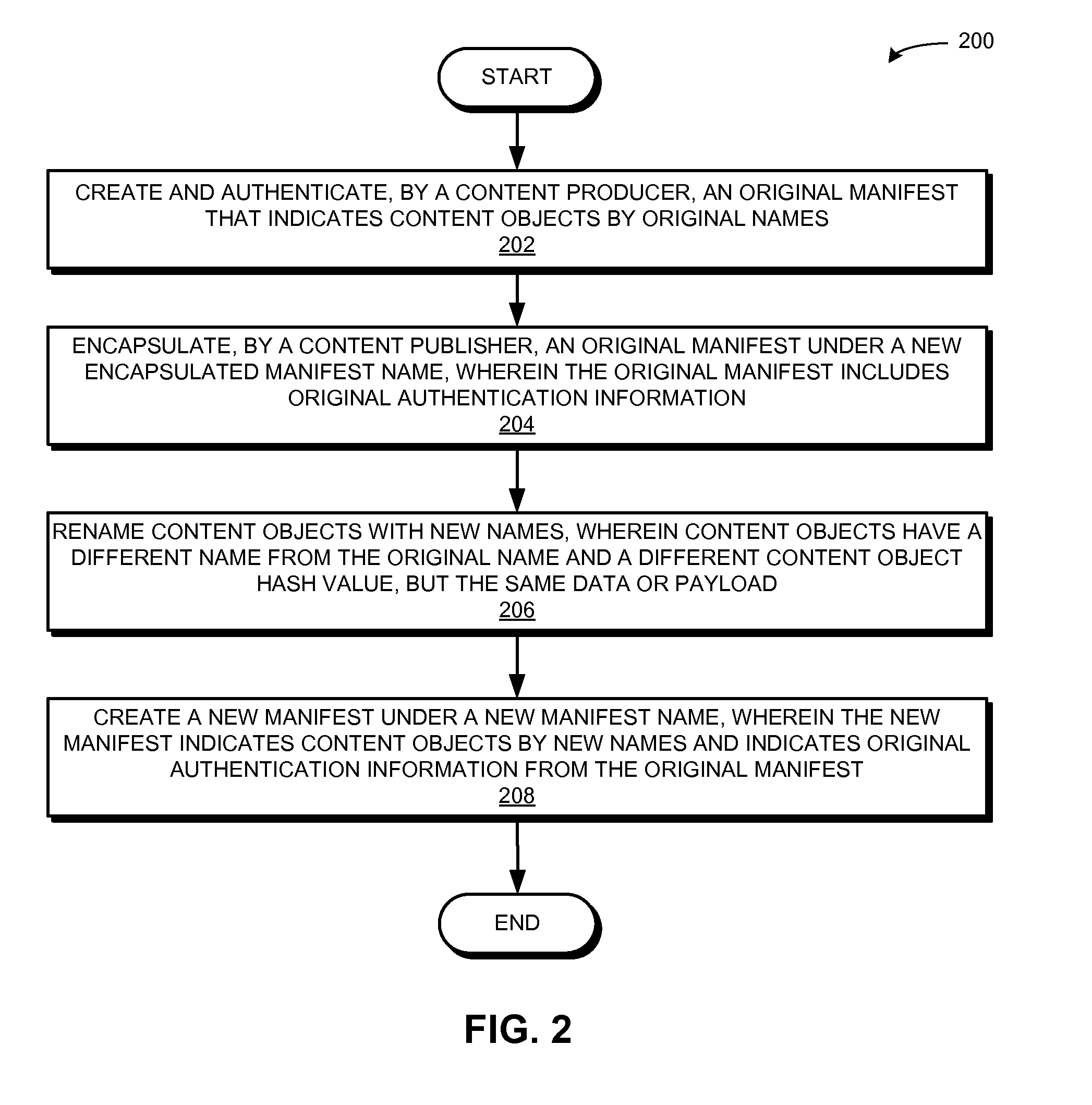
Method and system for verifying renamed content using manifests in a content centric network
ActiveUS20160171184A1Promote redistributionDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionInternet privacyContent centric
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates redistribution of content objects with a different name without requiring re-computation of the original authentication information. During operation, the system determines, by a content producing device, an original manifest which indicates at least an original name associated with a content object, wherein the name is a hierarchically structured variable length identifier (HSVLI) which comprises contiguous name components ordered from a most general level to a most specific level. The system renames the content object with a new name. The system also creates a new manifest which indicates the new name, wherein the new manifest includes original authentication information associated with the original manifest.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Aggregate signing of data in content centric networking
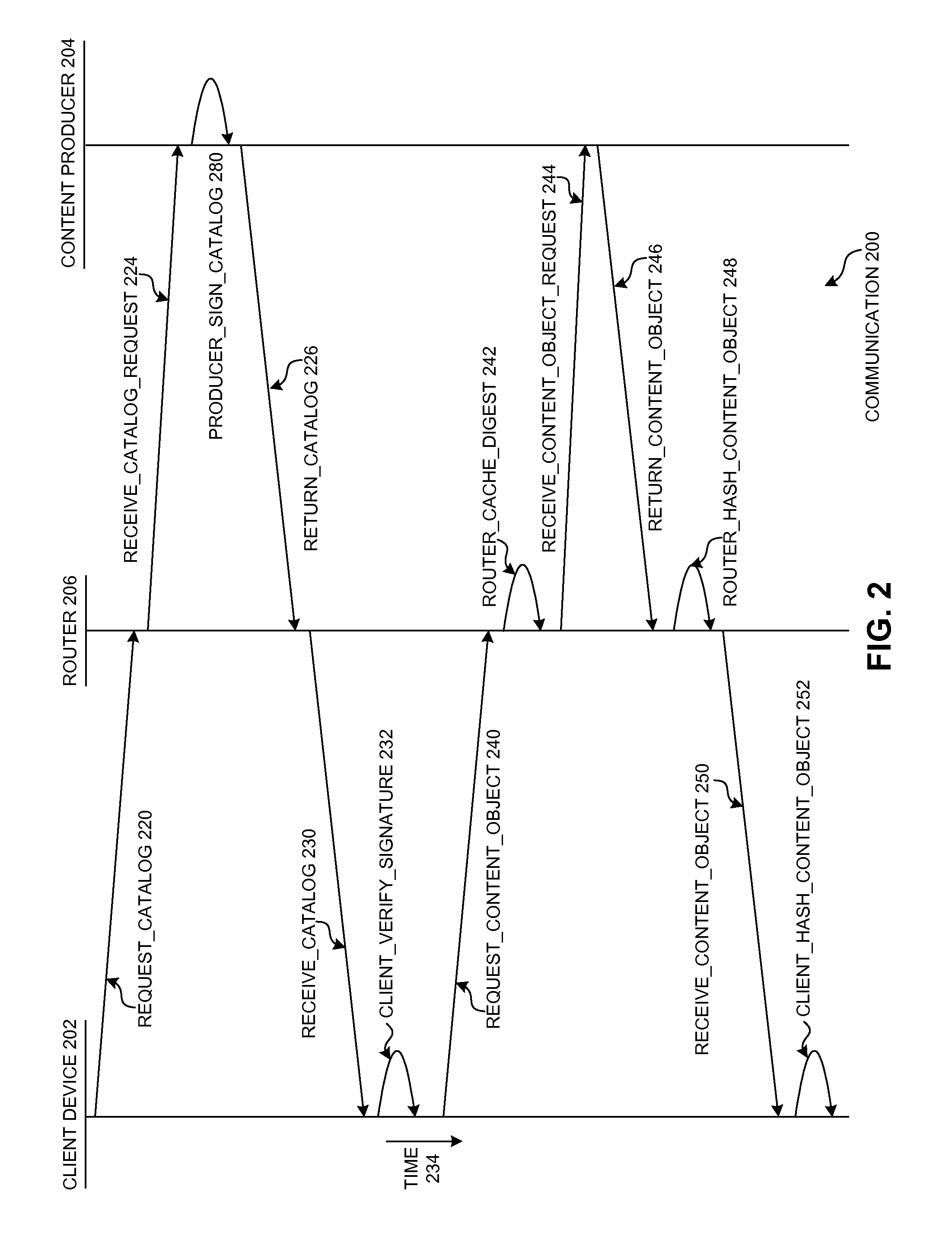
ActiveUS20150280918A1Facilitates routers in verifying content objectsData processing applicationsPublic key for secure communicationIndication of interestDigital signature
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates routers in verifying content objects in a cost-effective manner by aggregating content objects into a secure content catalog. During operation, a client computing device receives a secure content catalog, which indicates a set of content objects and their corresponding digests. The catalog is digitally signed with the private key of a producer of the catalog. The client computing device constructs an interest for a content object, where the interest indicates a name for the content object and the corresponding digest for the content object, which is based on the secure content catalog. The name for the request content object is a hierarchically structured variable length identifier (HSVLI) which comprises name components ordered from a most general level to a most specific level.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Content-centric networking multi-interest package compression sending and processing method
InactiveCN103095724AReduce the numberFix compression issuesTransmissionDistributed computingContent centric networking
The invention discloses a content-centric networking multi-interest packet compression sending and processing method. The method comprises that compression interest packets are added, a content name part of each of the compression interest packets is divided into common prefixes of various interest content names and suffixes of the various interest content names, multiple interest packets which have a common prefix are compressed to be compression interest packet request data, when a network node receives the compression interest packets, the common interest prefix and the interest suffix are sliced to be an integrated content name, searching is carried out in content caching, a undetermined interest table and forwarding information table, forwarding interfaces are determined, for each interface, the common prefixes of the content names in all the interests to be sent are extracted, and the common prefixes and the surplus suffixes of the content names are combined to form a compressed interest packet which is sent.. The method effectively reduces the number of the interest packets in the network, and consumption of bandwidth is reduced, the compression problem of the multiple interest packets which have the same name prefix in the content center network is solved, and the content-centric networking multi-interest packet compression sending and processing method has stronger popularization and application value.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Content centric networking system providing differentiated service and method of controlling data traffic in content centric networking providing differentiated service
ActiveUS20150281083A1Low priorityReduce in quantityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesNetworked system
There is provided a content centric networking system providing a differentiated service that includes a client device that creates an interest packet, an edge router directly connected to the client device in the content centric networking system, that determines a traffic class for an interest packet on the basis of the information included in an interest packet received from the client device, and marks the determined traffic class information in association with the interest packet; and a differentiated service router, which when receiving the interest packet added with the traffic class information, stores the traffic class information in a pending interest table (PIT) and differentially transmits the data requested by the interest packet in accordance with the traffic class information.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Multi-layer encryption privacy protection method used for content-centric networking
InactiveCN106254069APrivacy protectionResistance to snoopingKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationContent centric networkingPrivacy protection
The invention discloses a multi-layer encryption privacy protection method used for content-centric networking. The multi-layer encryption privacy protection method comprises the steps that: a requester sends an interest package used for creditability validation to a publisher of content, and the publisher responds to the requestor; the requestor sequentially uses a publisher public key and a router public key for encrypting the requested interest packet, and sends the requested interest packet to a router; the router decrypts the requested interest packet by using a private key to obtain information it needs, and then forwards the requested interest packet to the next-layer router until the requested interest packet is sent to the publisher; the publisher decrypts the requested interest packet by using a publisher private key, validates the creditability of the requester, responds to the requested interest packet when the validation passes, and sends data to the router; and the router decrypts a data packet by using a private key to obtain response data, and forwards the response data to the next-level router until the response data is forwarded to the requester. The multi-layer encryption privacy protection method adopts the public keys for encryption, is relatively high in security, and can protect the privacy of the requestor and the publisher to a greater extent.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Content classification based category popularity cache replacement method in oriented content-centric networking
ActiveCN104253855AAvoid going it aloneEasy to manageTransmissionExponentially weighted moving averageData content
The invention relates to a content classification based category popularity cache replacement method in an oriented content-centric networking. The content classification based category popularity cache replacement method comprises the following steps: firstly determining whether a remaining cache space of a node can accommodate new data content or not; caching the new data content if the cache space is enough; calculating the popularity of all content categories in standard computing nodes according to an exponentially weighted moving average method, and selecting the content category with the smallest popularity; removing a content item with the fewest request times in predefined time in the content category with the smallest popularity out of a node cache; extracting name character string characteristics of the new data content and classifying; storing the newly arrived data content item into corresponding content category in the node, and updating a category heat table and a log. The cache of nodes in CCN (content-centric networking) can be better managed according to the content name category, so that the content can be found and replaced from the name of the content in the communication process in the networking, the diversity of the content in the node cache is balanced, and the efficiency of cache replacement is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
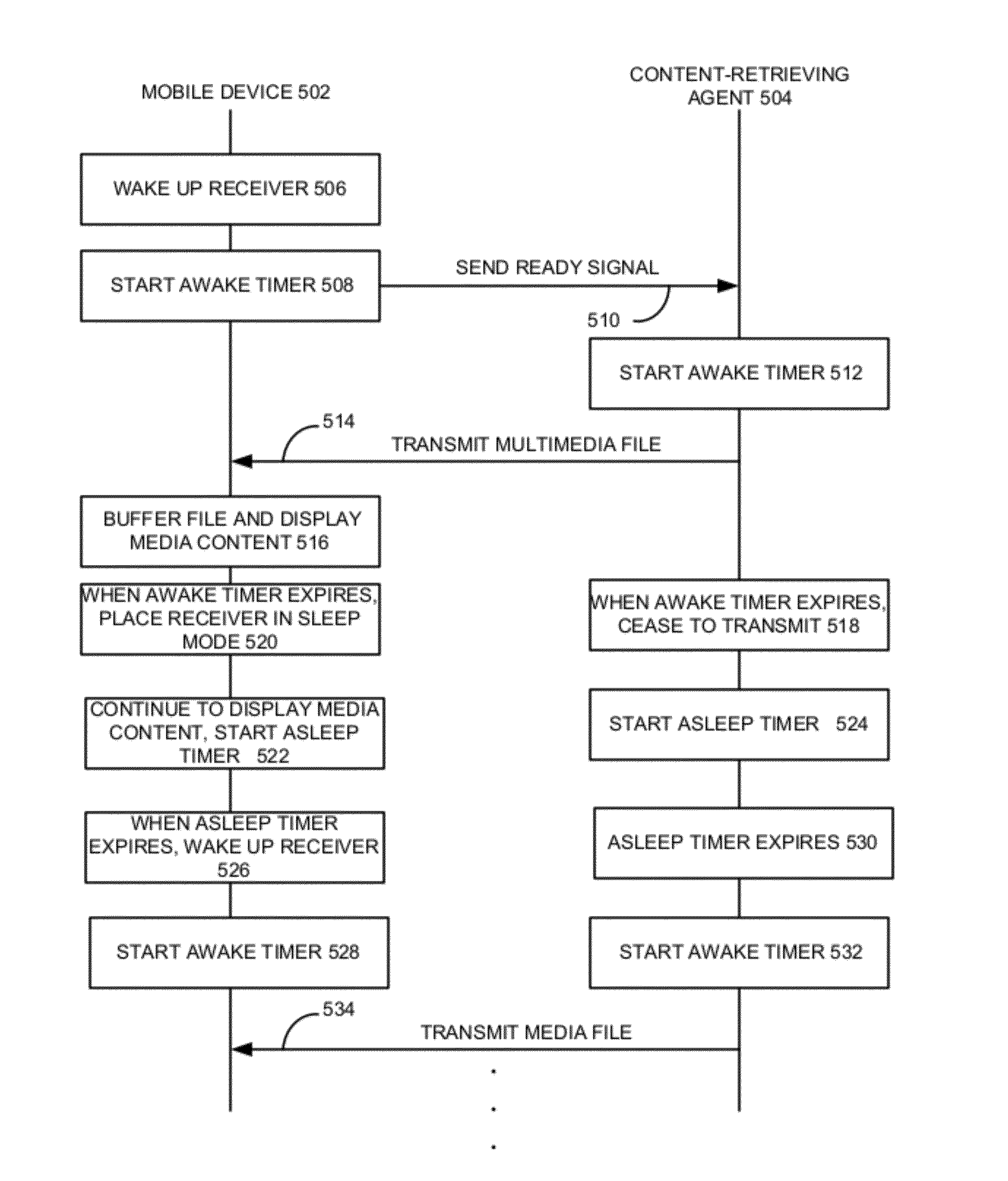
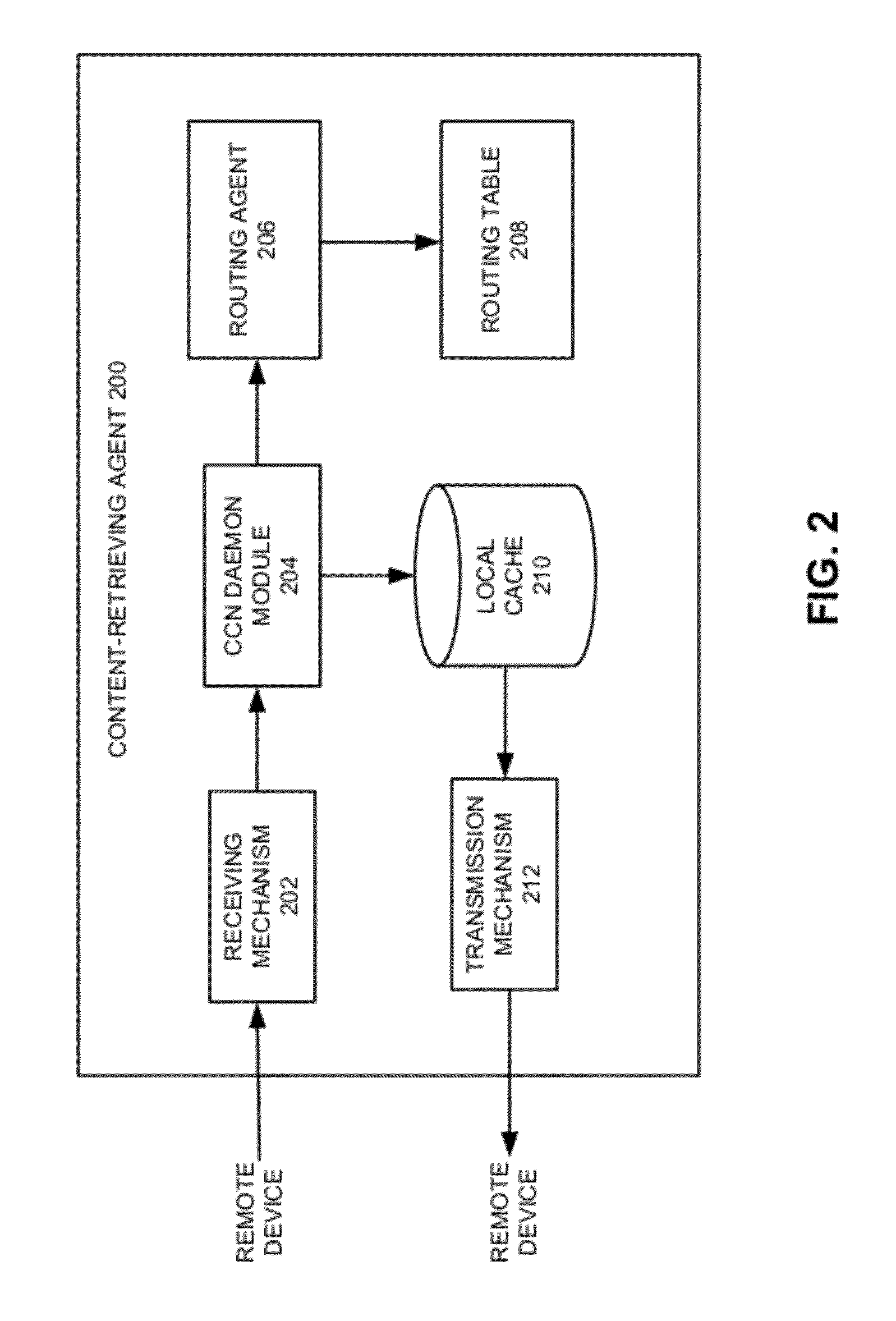
Energy-efficient content retrieval in content-centric networks
ActiveUS20120155348A1Easy to optimizeEasy retrievalPower managementTransmission systemsContent centricContent retrieval
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system including a mobile device and a content-retrieving agent for facilitating energy-efficient content retrieval. During operation, the mobile device receives a request for a piece of content from a user. In response to the request, the mobile device forwards the request to the content-retrieving agent which is configured to obtain the requested content from a remote device on behalf of the mobile device. The system allows the mobile device's receiver to be placed in an energy-saving sleep mode when the content-retrieving agent is obtaining the requested content for the mobile device and is not transmitting the content to the mobile device. The system allows the mobile device's receiver to wake up when the content-retrieving agent is transmitting the content to the mobile device. The mobile device receives the content from the content-retrieving agent.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Energy-efficient content caching with custodian-based routing in content-centric networks
ActiveUS20120158912A1Easy to optimizeFacilitating custodian-based routingEnergy efficient ICTData processing applicationsContent centricPhysical address
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for facilitating custodian-based routing. During operation, the system receives, at a computing device serving as a backup custodian to one or more mobile devices, a request for a piece of content from a requesting device, which has mapped the content to the computing device based on the content's name without using the computing device's physical address. The system determines whether the content is available on the computing device. In response to the content not being available on the computing device, the system identifies a mobile device that stores the content, and obtains the content from the identified mobile device. The system then caches the content on the computing device, thereby enabling the computing device to provide the content in response to subsequent requests without connecting to the identified mobile device, and provides the content to the requesting device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Content routing system of network layer based on software defined networking (SDN) technology and content-centric networking (CCN) frame and working mode thereof
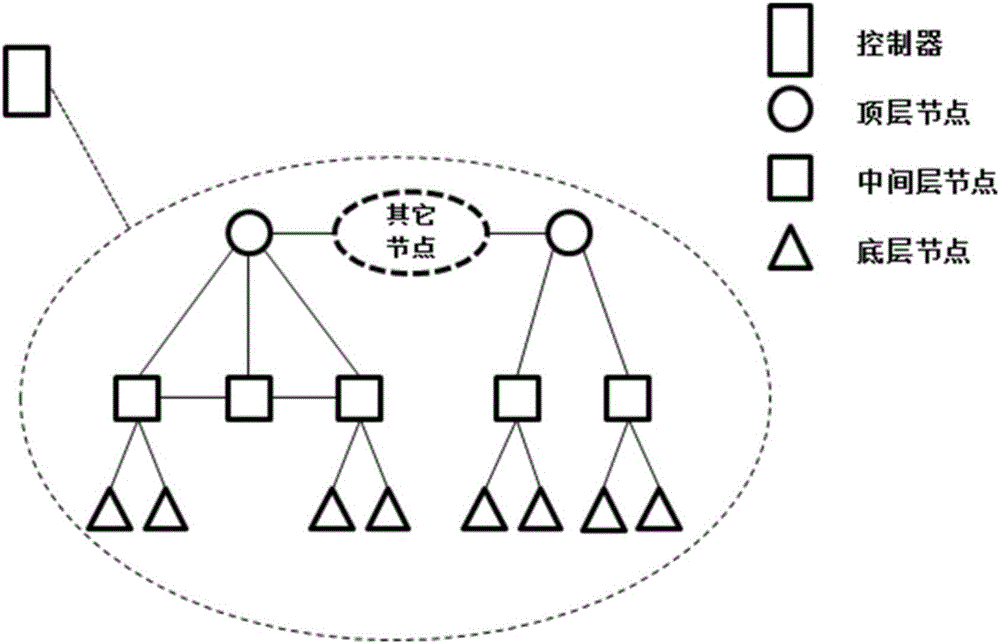
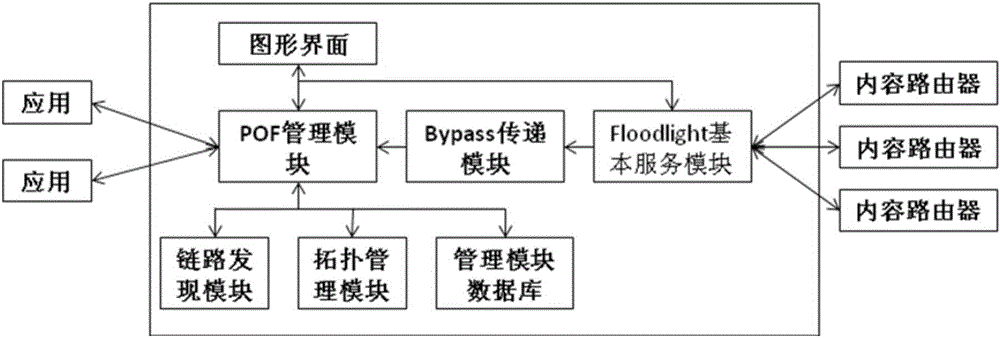
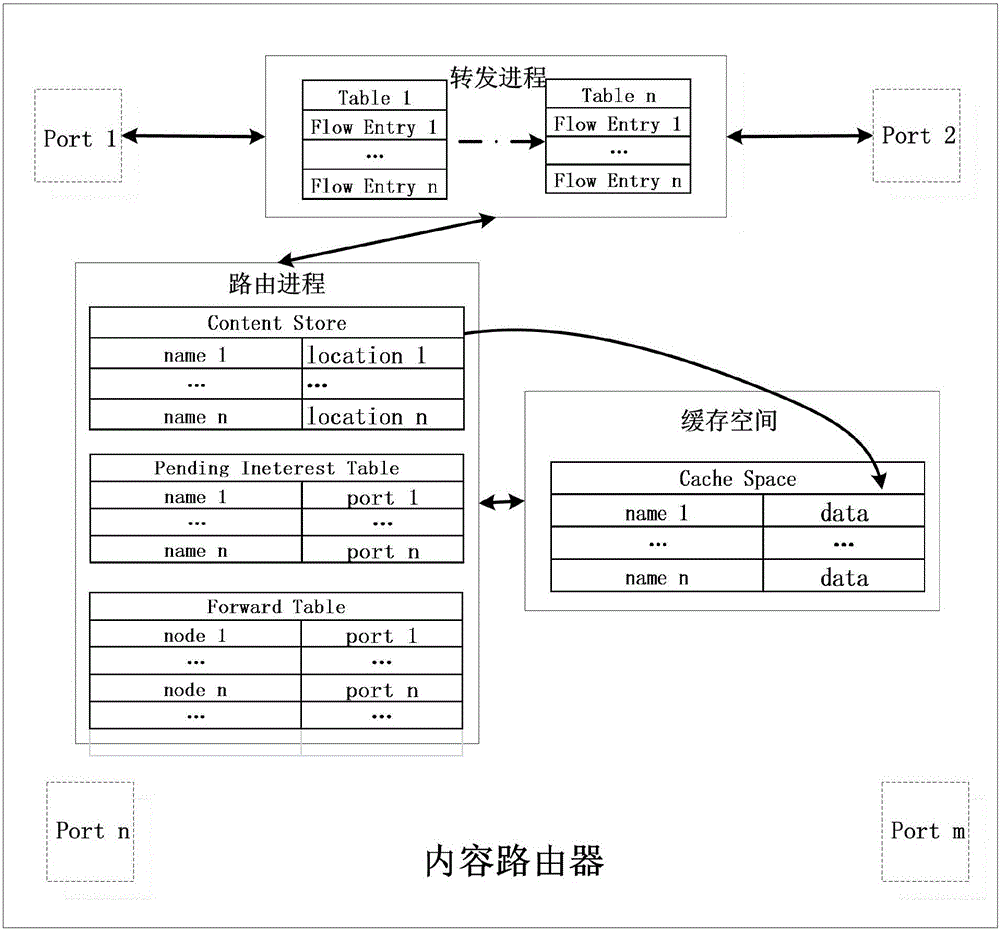
The present invention discloses a content routing system of a network layer based on an SDN technology and a CCN frame and a working mode thereof. The system is characterized by comprising a protocol oblivious forwarding (POF) controller and n content routers, wherein the POF controller comprises a link discovery module and a topology management module, and the content routers are used for operating a POFSwitch forwarding process and a POF-CCN routing process. According to the present invention, a hard coupling relationship of the content names and the positions thereof is removed in the system network layer, thereby being able to directly route to the content sources according to the content names, and realizing a content obtaining function of the network layer.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for load balancing of content-centric network
InactiveUS20130097277A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityContent centric
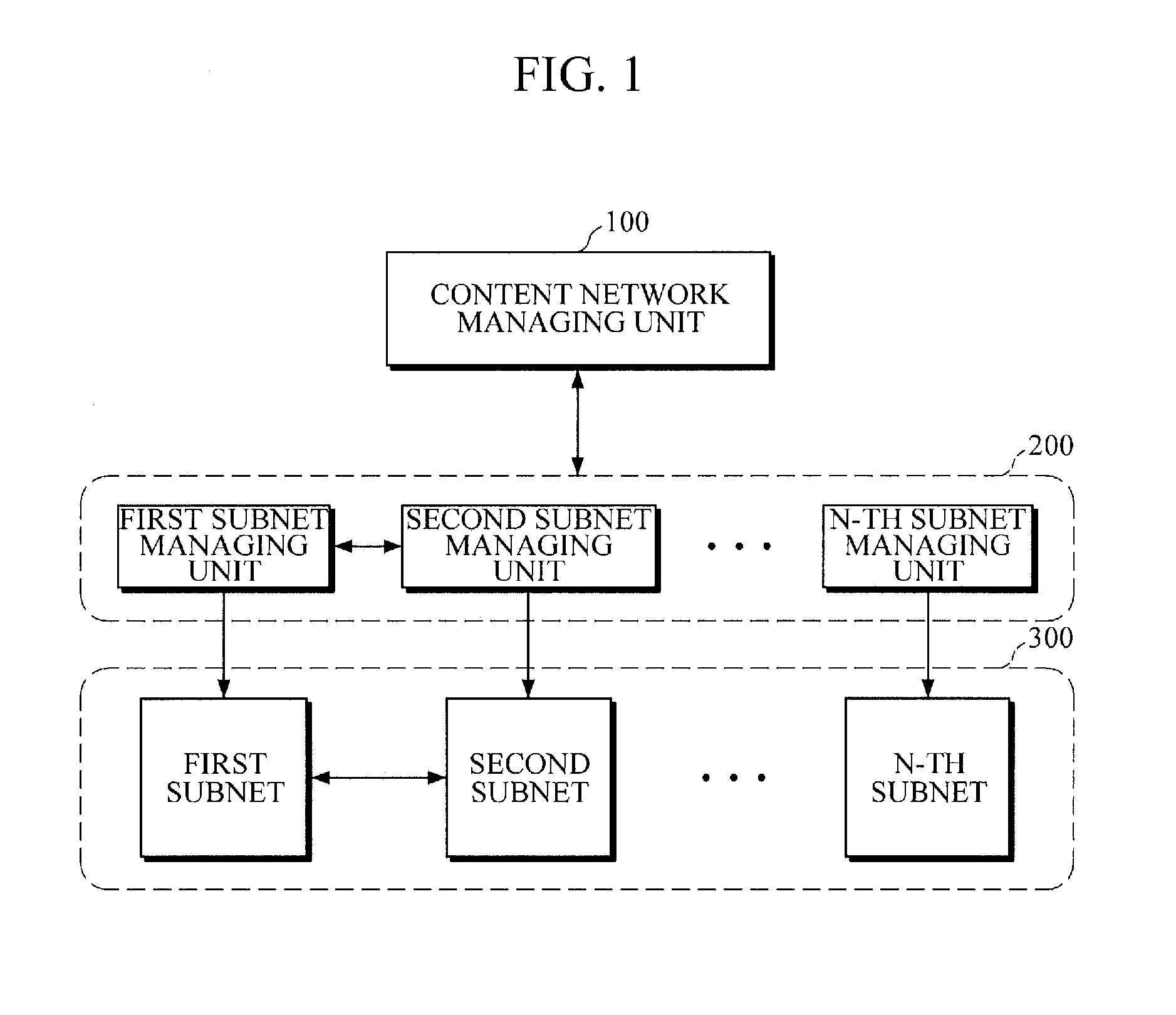
An apparatus and a method for load balancing of a content-centric network for optimally delivering content requested by a user are provided. The apparatus includes two or more subnet managing units divided according to physical distance or service providers and a content network managing unit configured to manage and connect subnets. In addition, the method includes searching for two or more subnets containing content; in response to two or more subnets being found according to the search result, selecting a subnet delivering a requested content from among the two or more found subnets according to a network state and selecting nodes included in the subnet; and delivering the content. Accordingly, an optimal server node is selected on the network in the middle of content delivery from a content server to the user so that traffic efficiency may be enhanced and a higher-quality real-time streaming service may be provided.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System and method for distance-based interest forwarding
ActiveUS20160173386A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksIndication of interestContent centric
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for correctly processing an interest in a content-centric network (CCN). During operation, a first node in the CCN receives an interest for a piece of content from a second node. The interest indicates a name of the piece of content and a hop count from the second node to a destination node advertising the piece of content. The system determines, based on forwarding information and information associated with pending interests stored on the first node, whether a distance-based forwarding condition is met; and in response to the distance-based forwarding condition being met, accepts the interest.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
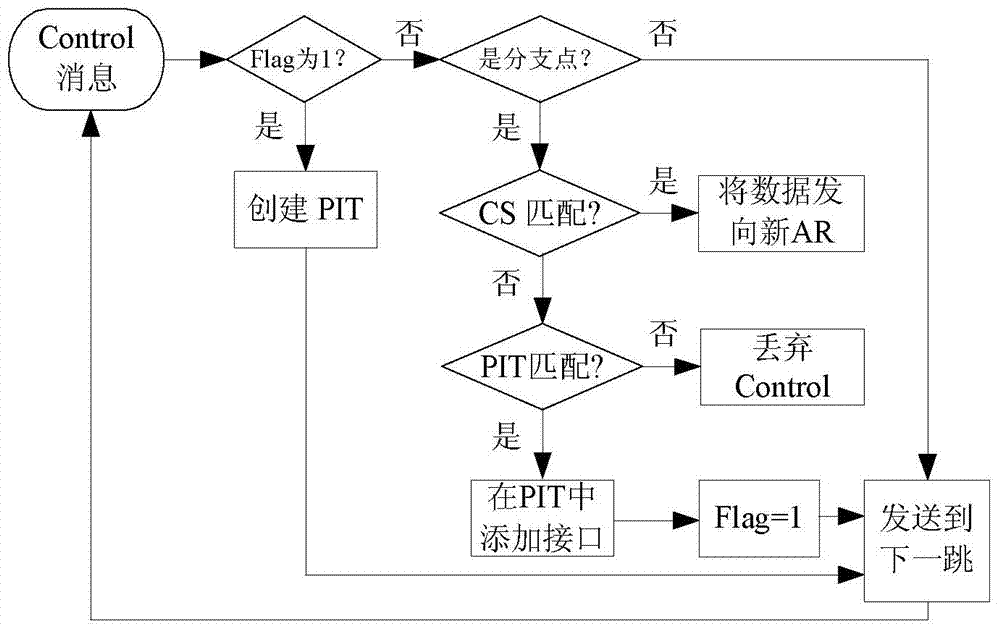
Distributed mobile data transmission method for CCN (Content-Centric Networking)
The invention discloses a distributed mobile data transmission method for CCN (Content-Centric Networking). The method includes the following steps: 1) when moving from an access router AR1 to the overlapping area of the AR1 and a router AR2, a receiver sends a message HI containing the identification information of the AR2 to the AR1; 2) when receiving the HI, the AR1 searches the content name corresponding to the receiver in a request table PIT (Pending Interest Table), builds a signaling message by using the content name and the identification of the AR2, and deletes the corresponding PIT entry; 3) the AR1 sends the signaling message along a reverse path corresponding to the content name, and identifies a branch node; the branch node directs the corresponding entry in the PIT to the AR2 and continues to forward the signaling message, and a subsequent router builds a PIT entry corresponding to the content name and directs a next-hop interface to the AR2; 4) an intermediate router between the branch node and the AR2 builds a PIT entry corresponding to the content name. The invention avoids handoff delay and enormous network expenses.
Owner:CHINA INTERNET NETWORK INFORMATION CENTER
Dynamic interest forwarding mechanism for information centric networking
InactiveUS20160156737A1Improve end-user performanceReduce networking costsDigital computer detailsData switching networksMinimum timeInformation-centric networking
A method for managing packets over interfaces of a Content Centric Networking node, the method comprising the following stepsreceiving over an interface of the node at least a request for a data packet;if the data packet is stored by the node, forwarding the data packet over the interface of the received request;otherwiseperforming an exploration step, byselecting randomly at least an interface towards a neighboring node;forwarding the request over the selected interface;receiving in response over the randomly selected interface, the data packet with associated minimum time delivery value estimated by the neighboring node;identifying an interface providing the minimum data packet delivery time value based on exploration step results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Explicit content deletion commands in a content centric network
One embodiment provides a system that deletes cached content. During operation, the system generates, by a content producing device, a content object packet that includes a name for the content object and a deletion identifier that is used to verify a subsequent deletion command. The system receives a notification message that includes a routable prefix for a router and indicates that the router has cached the content object packet. The system stores in a data structure a mapping between the routable prefix, the name, and a previously generated deletion token which is used as a pre-image of the deletion identifier. In response to determining a condition to delete the cached content object packet, the system transmits a deletion command based on the routable prefix, wherein the deletion command includes the deletion token and the name for the cached copy of the content object packet to be deleted.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Content-centric networking cache judgment method based on node importance degrees
ActiveCN103312725AIncrease storage ratioProlong survival timeData switching networksCache hit rateOperating system
The invention discloses a content-centric networking cache judgment method based on node importance degrees. According to the method, importance degrees of nodes on return paths are considered, reasonable distribution of network cache resources is further improved, and the cache hit rate is increased, so that performances of a content-centric networking are improved on the whole. The method is applicable to deployment of the content-centric networking.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Caching method and device for content centric networking (CCN)
ActiveCN106982248AReduce redundancyReduce overheadTransmissionContent based networkingDistributed computing
The invention is applicable to the technical field of computers, and provides a caching method and device for content centric networking (CCN). The method comprises the following steps: according to a preset node centricity calculation formula, generating the node centricity of each node in the CCN; according to the centricities of all the nodes, selecting a part of the nodes; calculating the number of collaborative neighbor nodes corresponding to each node in the part of the nodes, and acquiring the collaborative neighbor nodes corresponding to each node in the part of the nodes according to the number of the collaborative neighbor nodes; and when one of the collaborative neighbor nodes receives data to be cached, determining a caching node corresponding to the data among the collaborative neighbor nodes, and caching the data in the caching node. The method and device provided by the invention has the advantages that the redundancy of cached contents in the CCN is effectively reduced, the variety of the cached contents is improved, and expenses for collaborative communication among the nodes in the CCN are effectively reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Content centric networking edge node potential enhanced routing method
The invention relates to a content centric networking edge node potential enhanced routing method and belongs to the field of the Internet. For the problem that the routing efficiency is low due to the fact that a content centric networking cannot sense cache content, the ENPER (Edge Node Potential-enhanced Routing) based on potential is provided. A potential model of nodes is established and through enhancement of the potential of edge nodes, interest packets are attracted to nearby cache nodes for response, so the forwarding time of the interest packets is reduced and a cache hit rate is improved. According to the ENPER, statistics and prediction are carried out on the popularity of content through the edge nodes, and through combination of a size of the networking, potential notification ranges of the content with different popularity are distinguished, thereby reducing the network overhead. According to the method, the load and cache notification overhead of an issuer server are effectively reduced, and compared with Best-routing, the ENPER has the advantage that the average request time delay of the content is reduced by 43%.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Interest return control message
ActiveUS20160019110A1Easy to processNon-redundant fault processingData switching networksContent centricStructure of Management Information
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates processing of error-condition information associated with a content-centric network (CCN) message transmitted over a network. During operation, the system receives, by a first node, a packet that corresponds to a CCN message, where a name for the CCN message is a hierarchically structured variable length identifier (HSVLI) which comprises contiguous name components ordered from a most general level to a most specific level. Responsive to determining that the CCN message triggers an error condition, the system generates an interest return message by pre-pending a data structure to the CCN message, where the data structure indicates the error condition. The system transmits the interest return message to a second node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com