Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Combustion kinetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
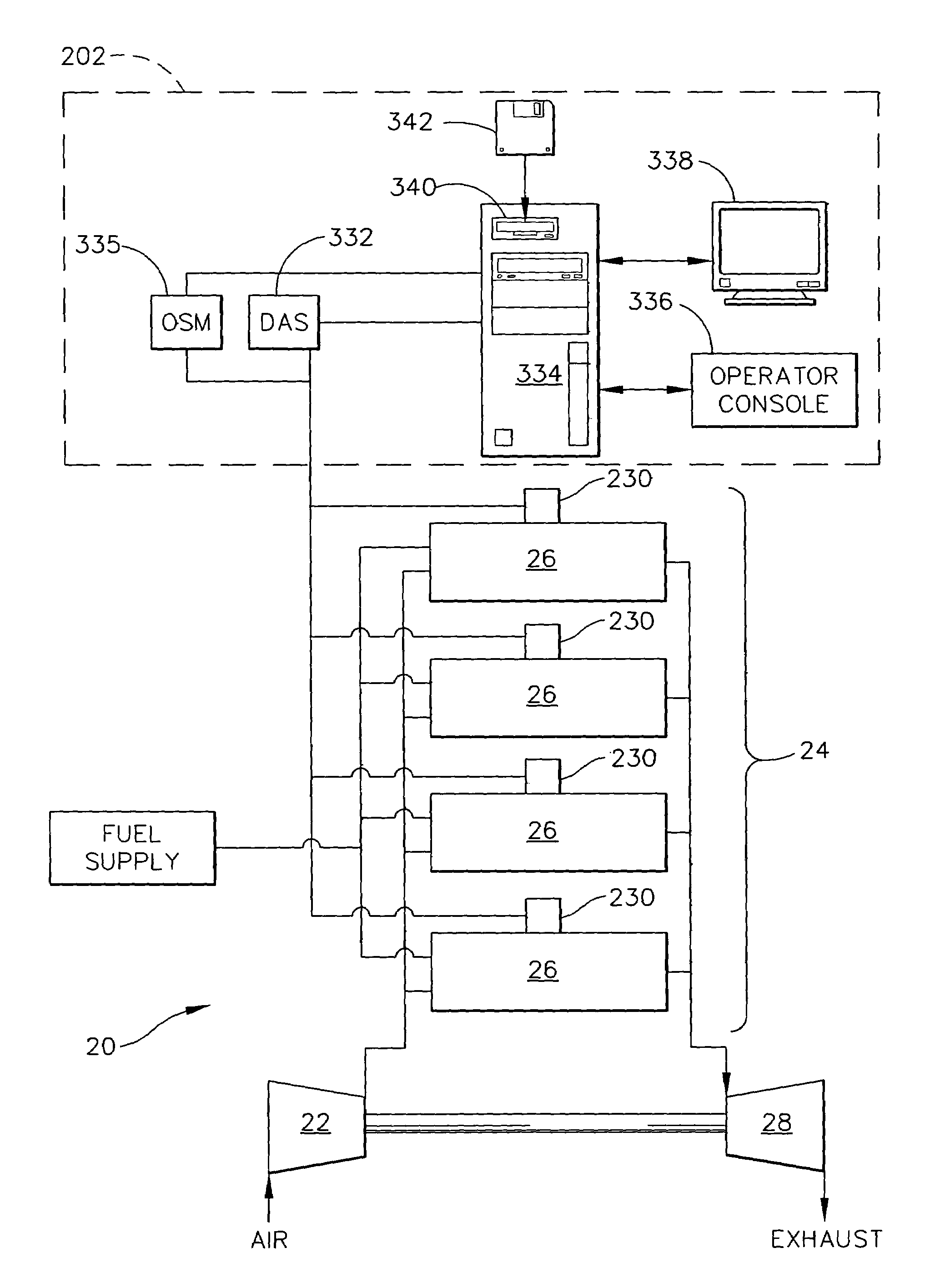
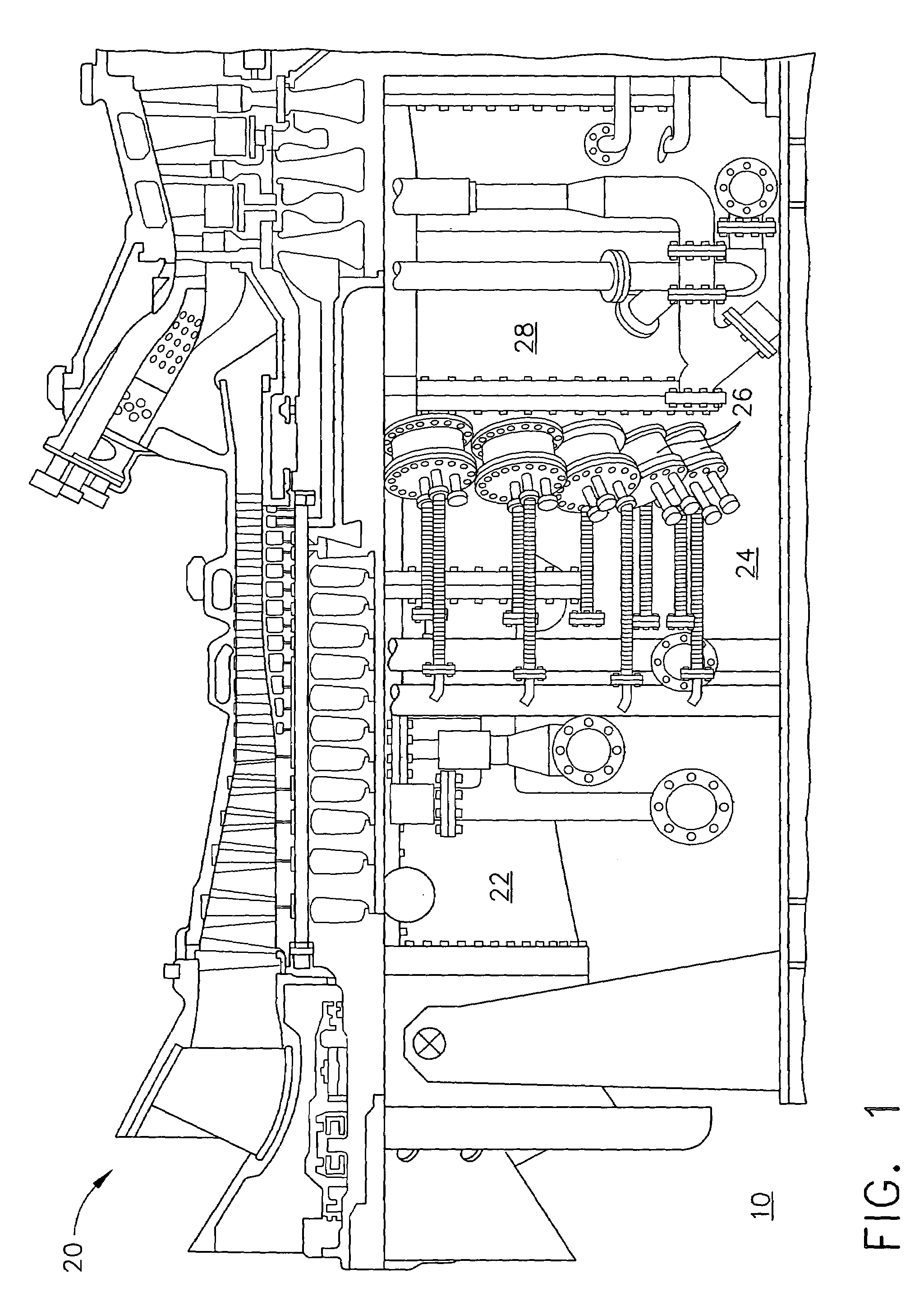
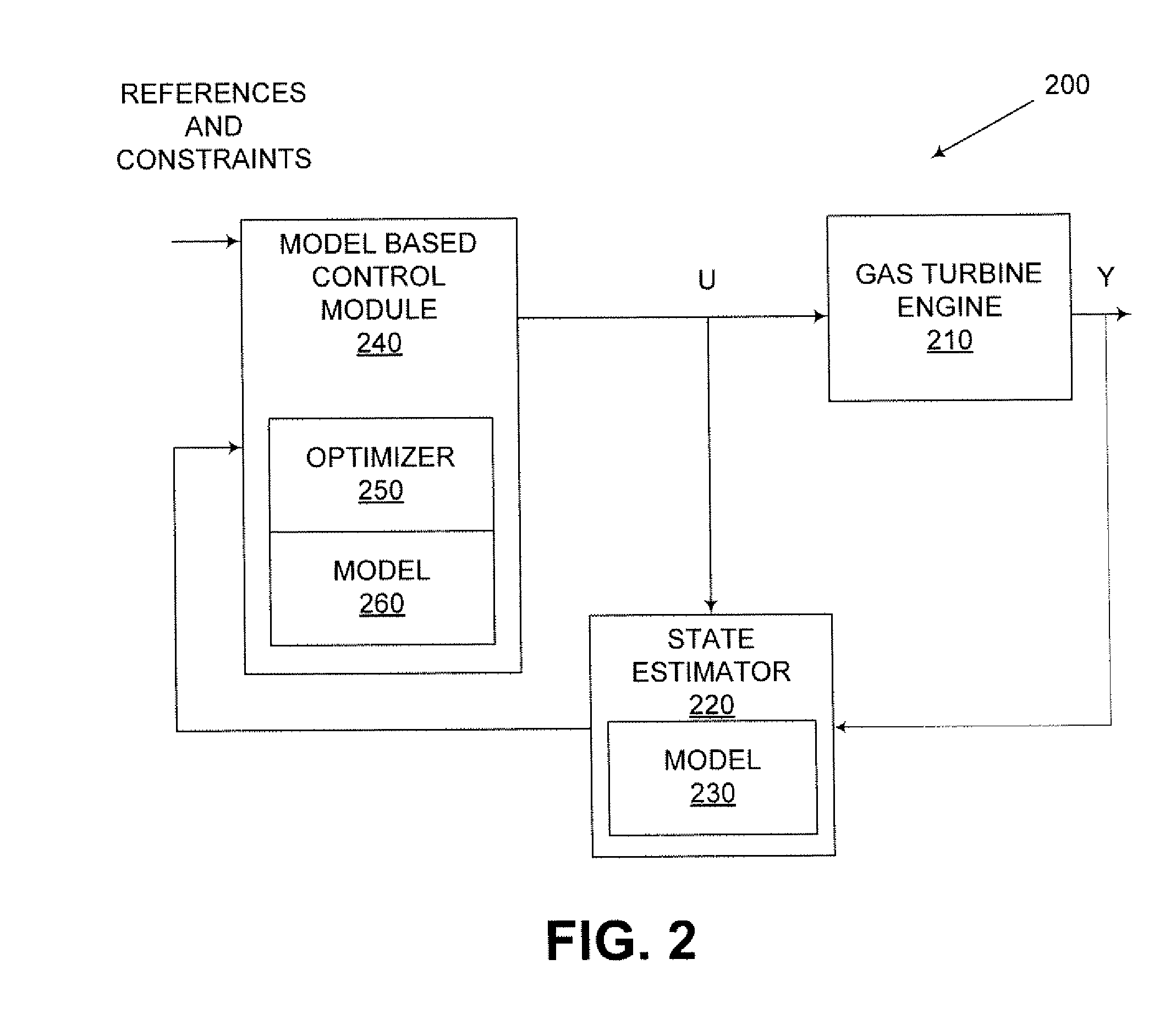
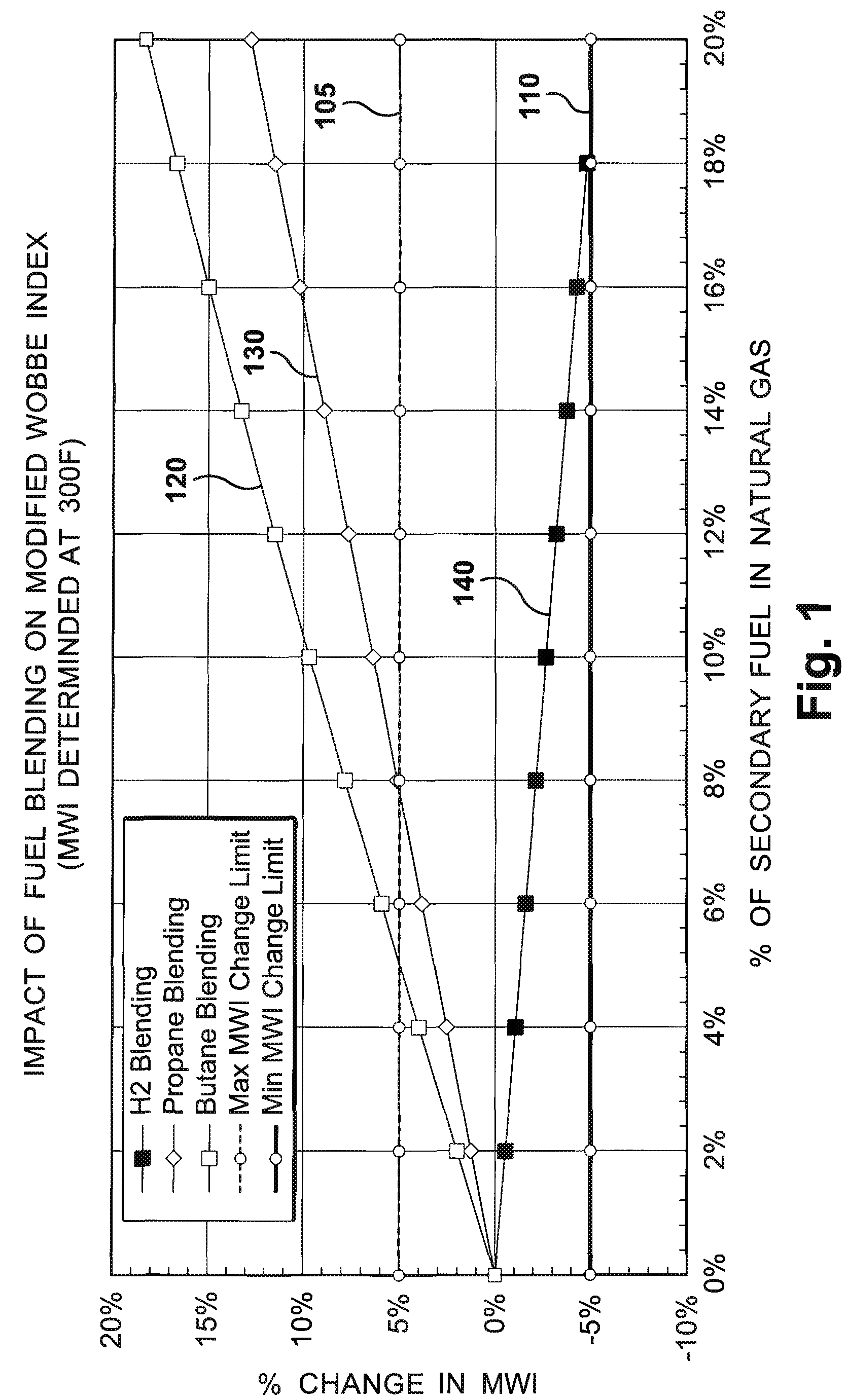
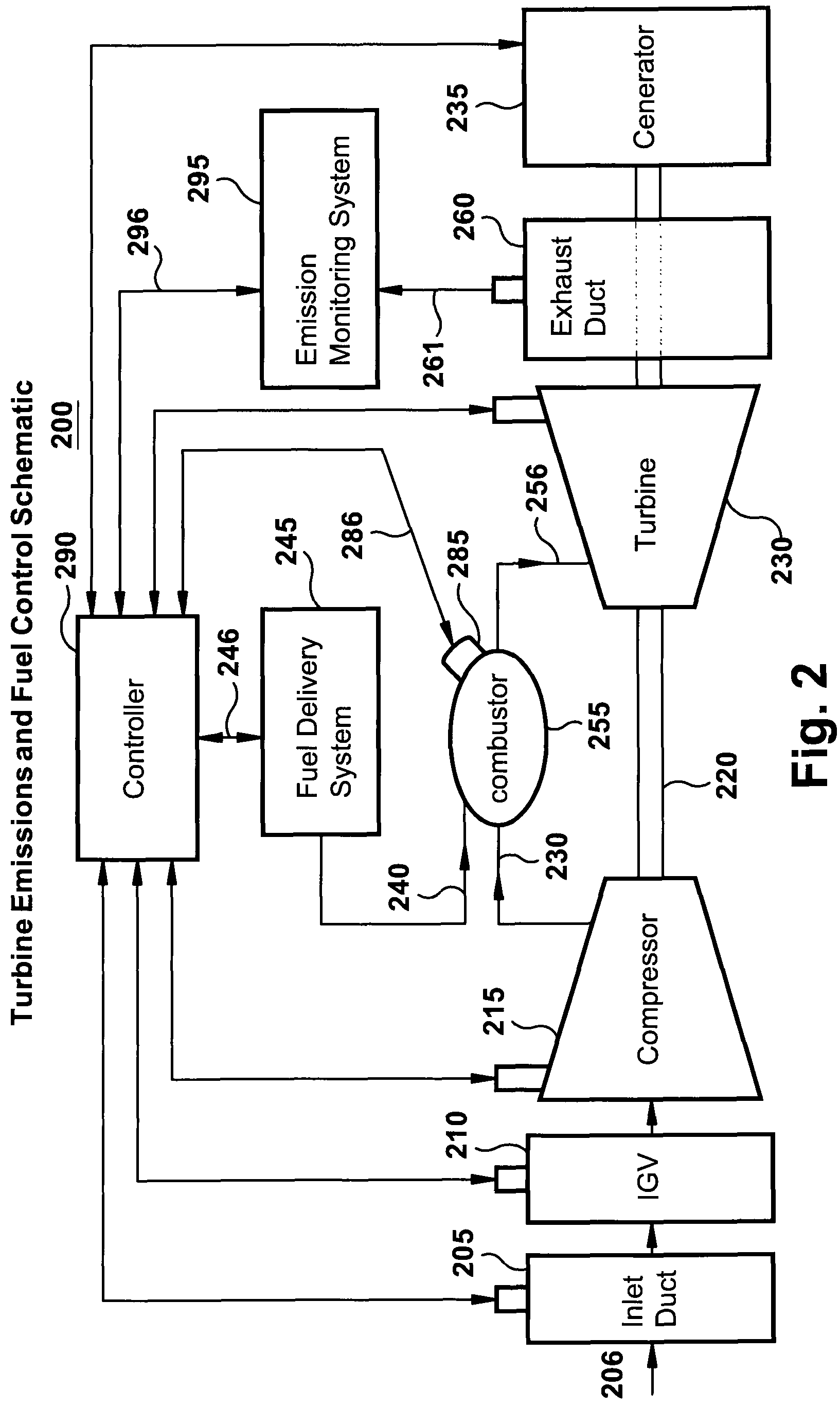
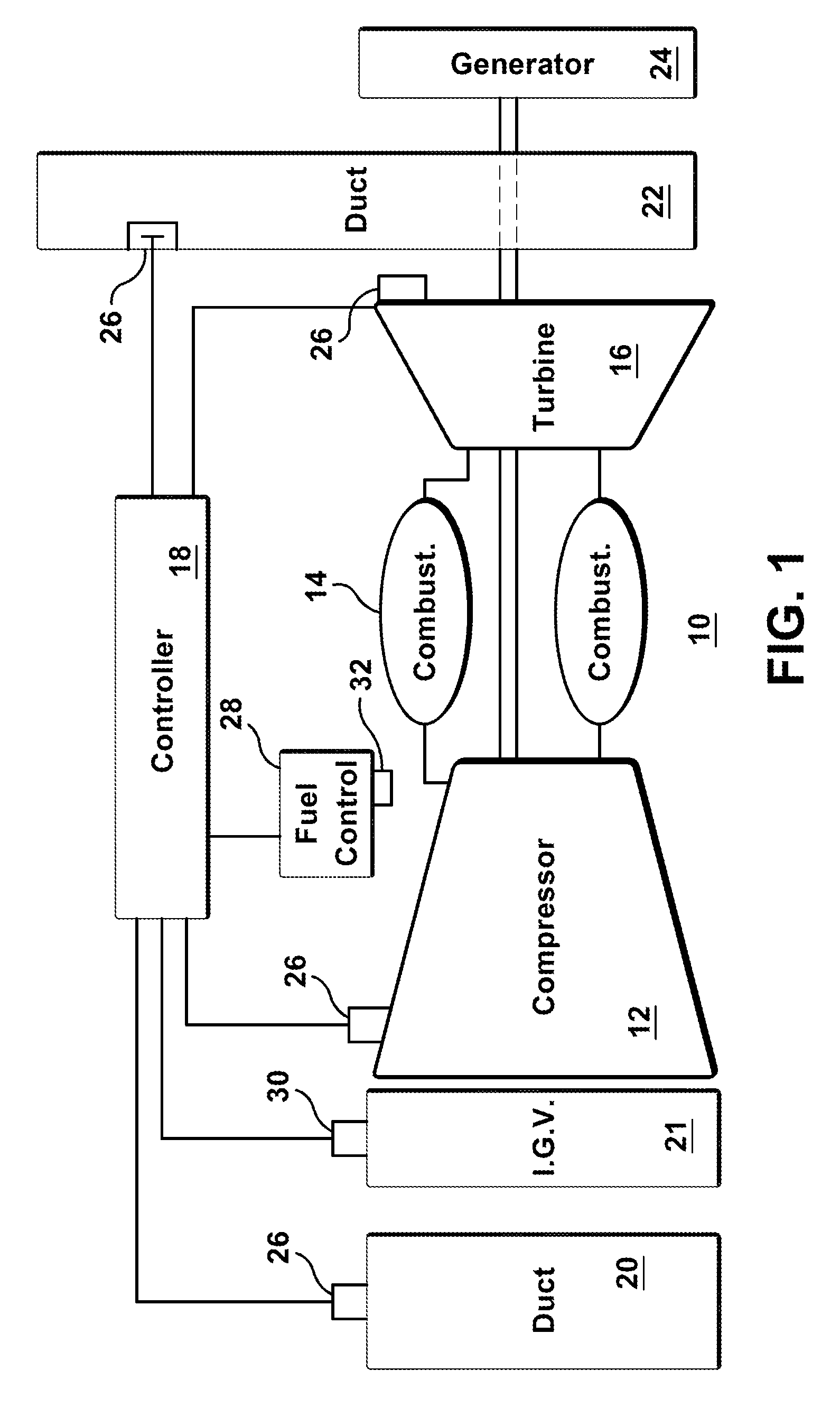
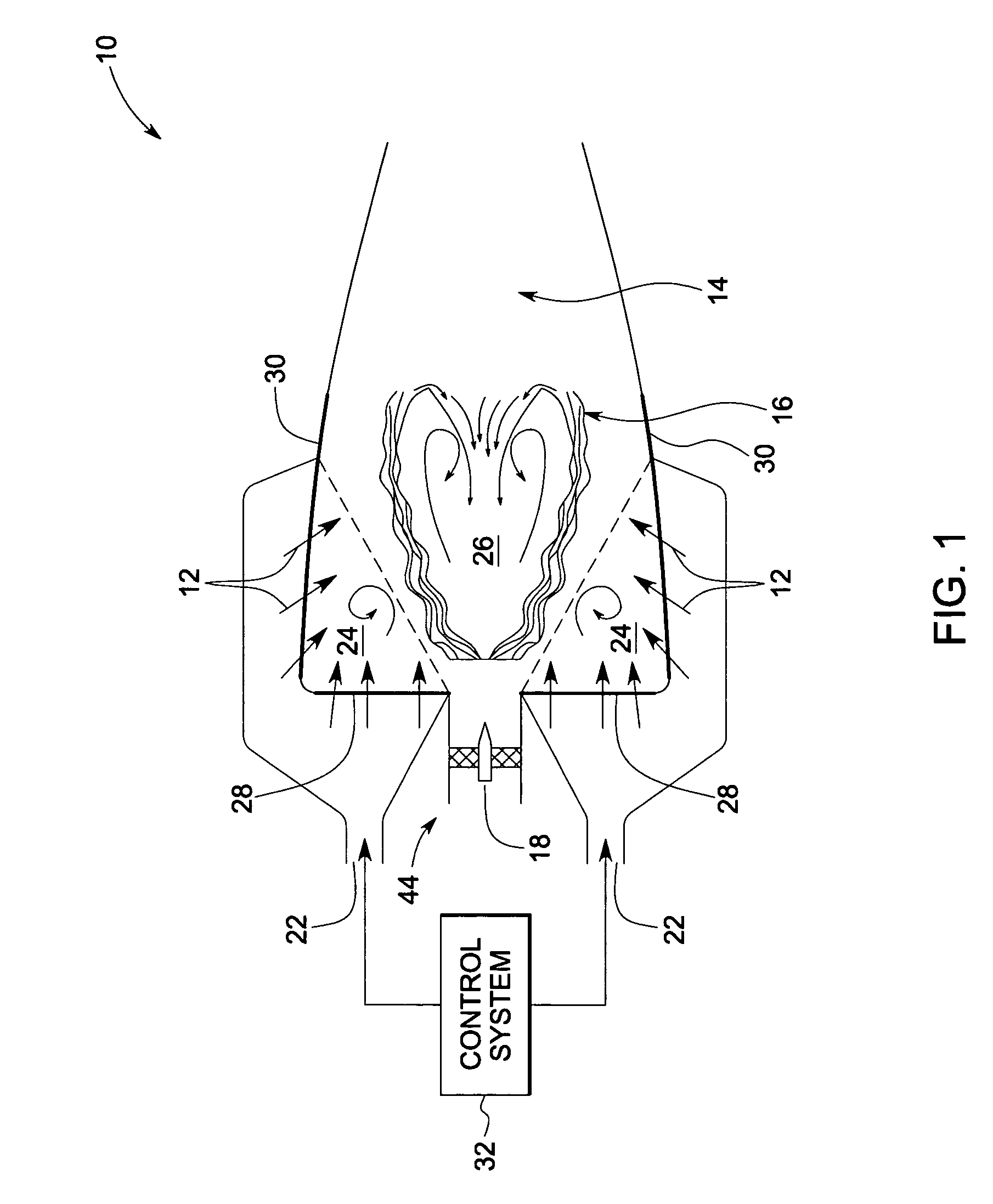
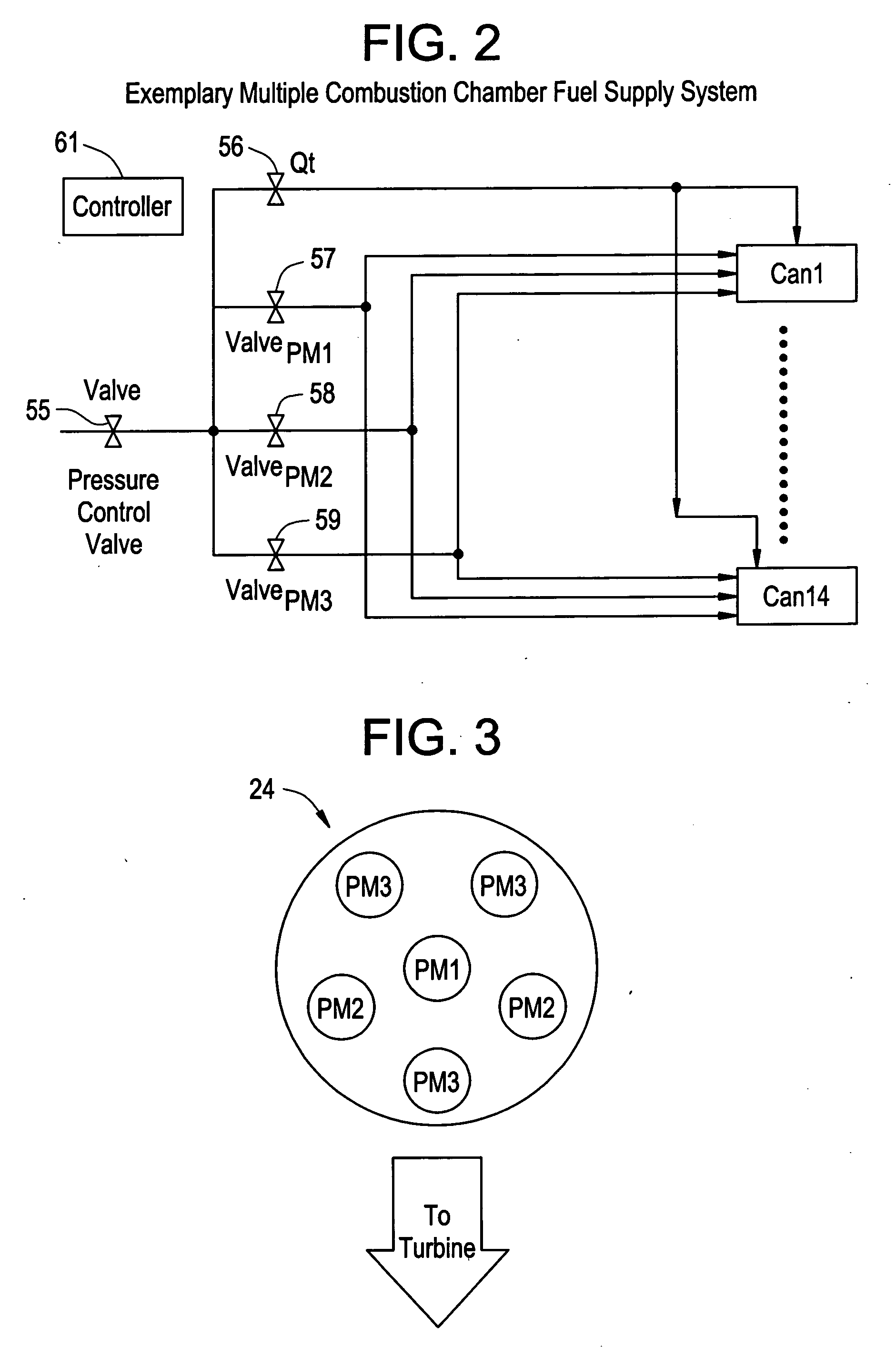
System and method for automatic fuel blending and control for combustion gas turbine
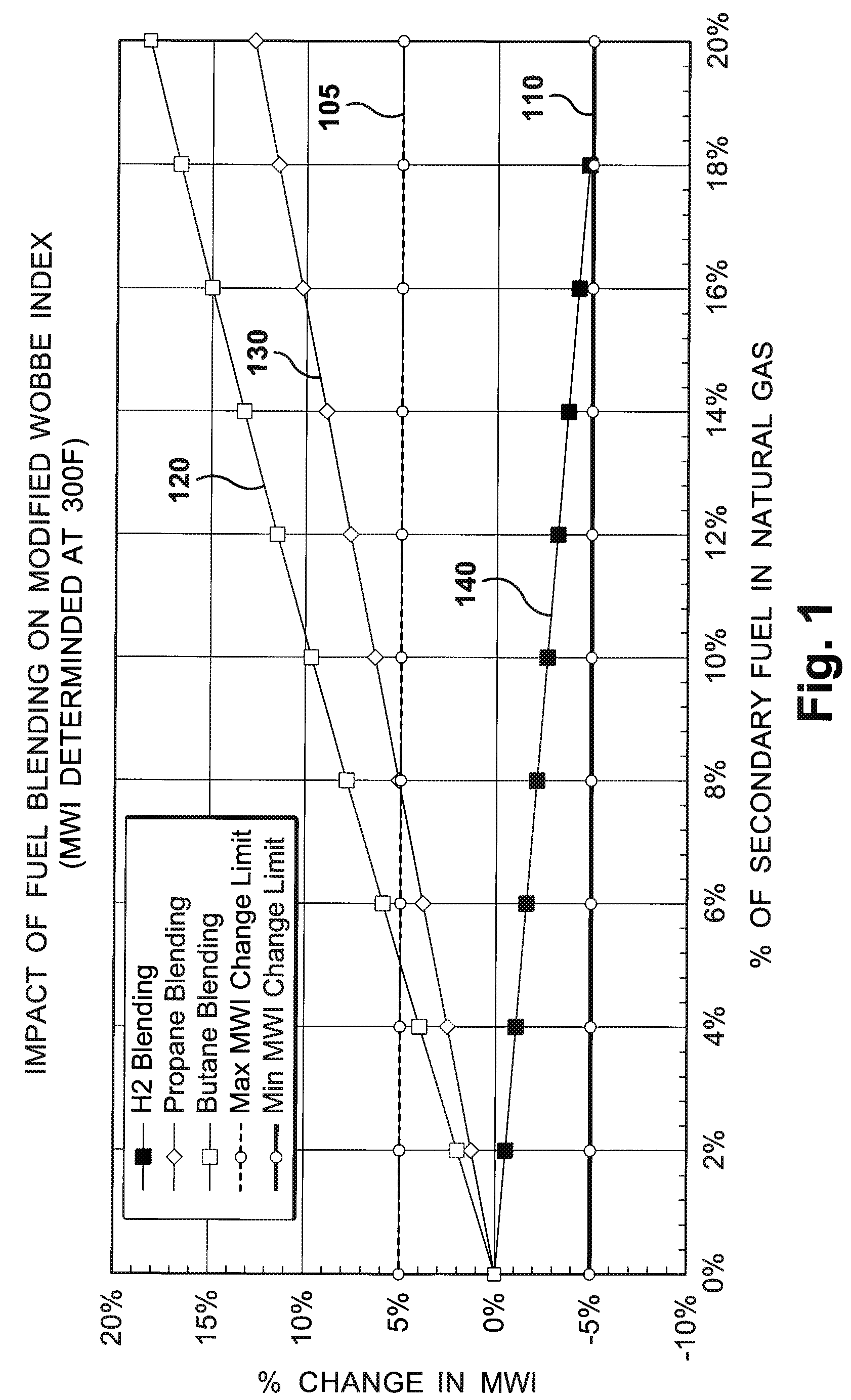
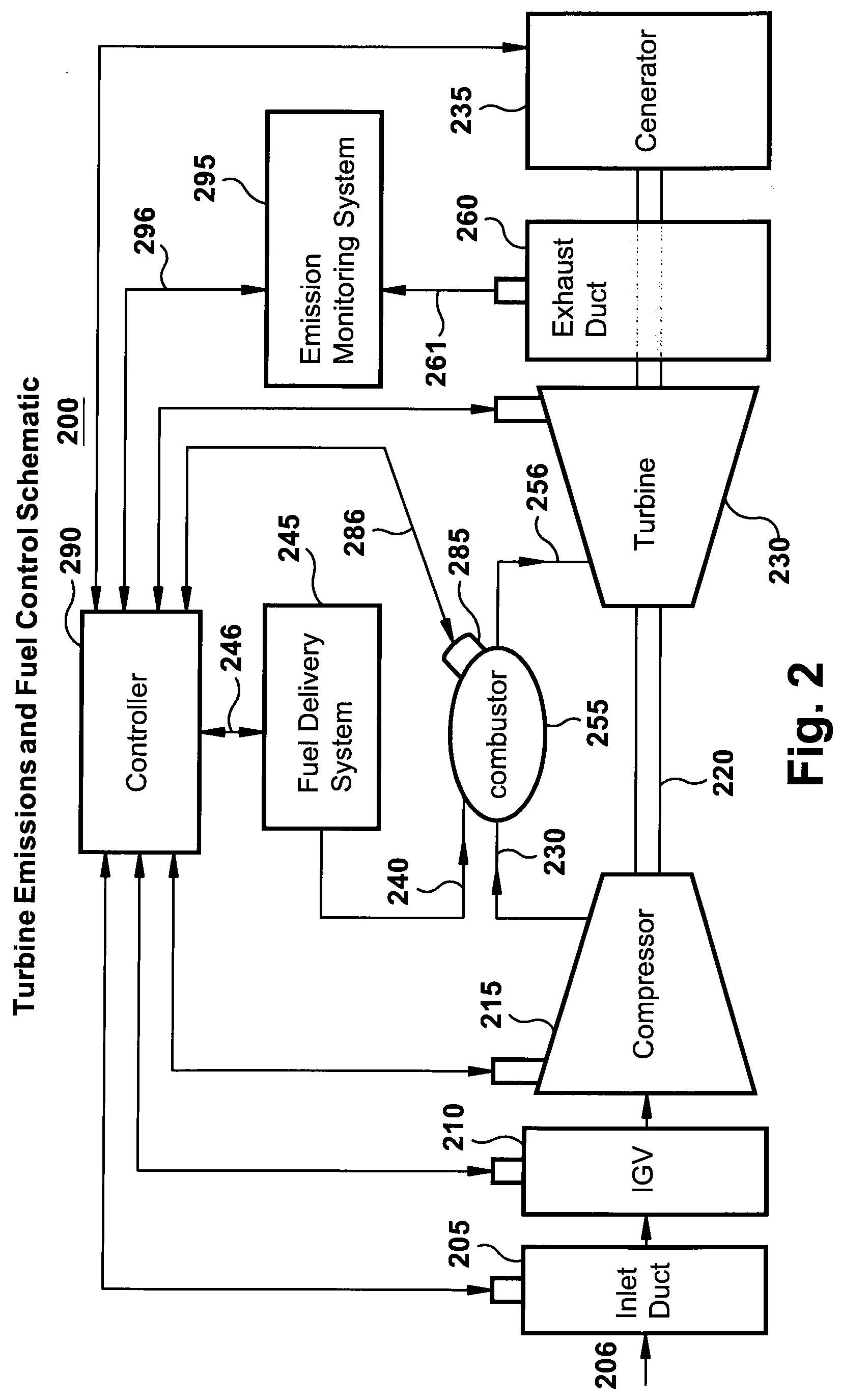
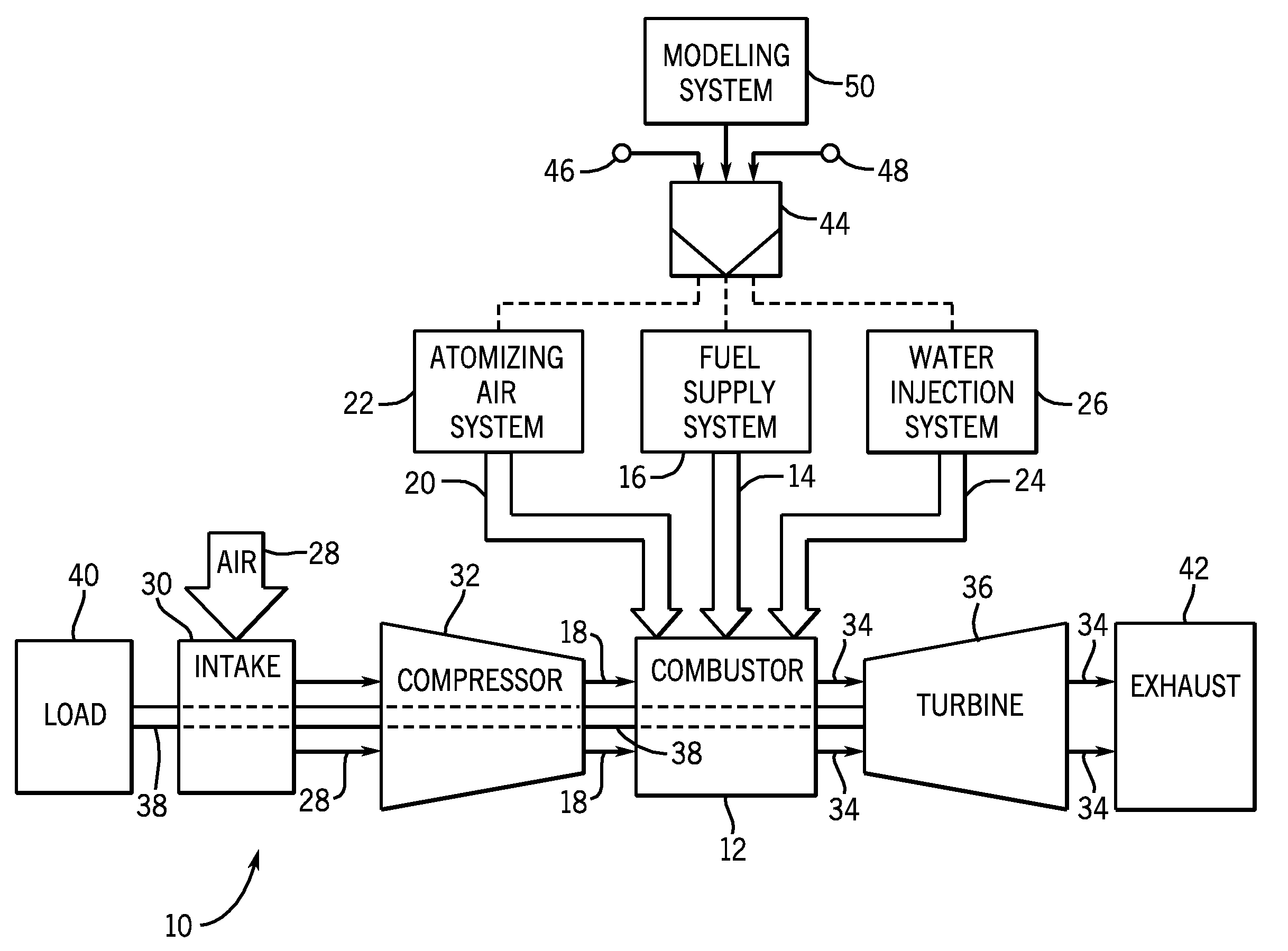
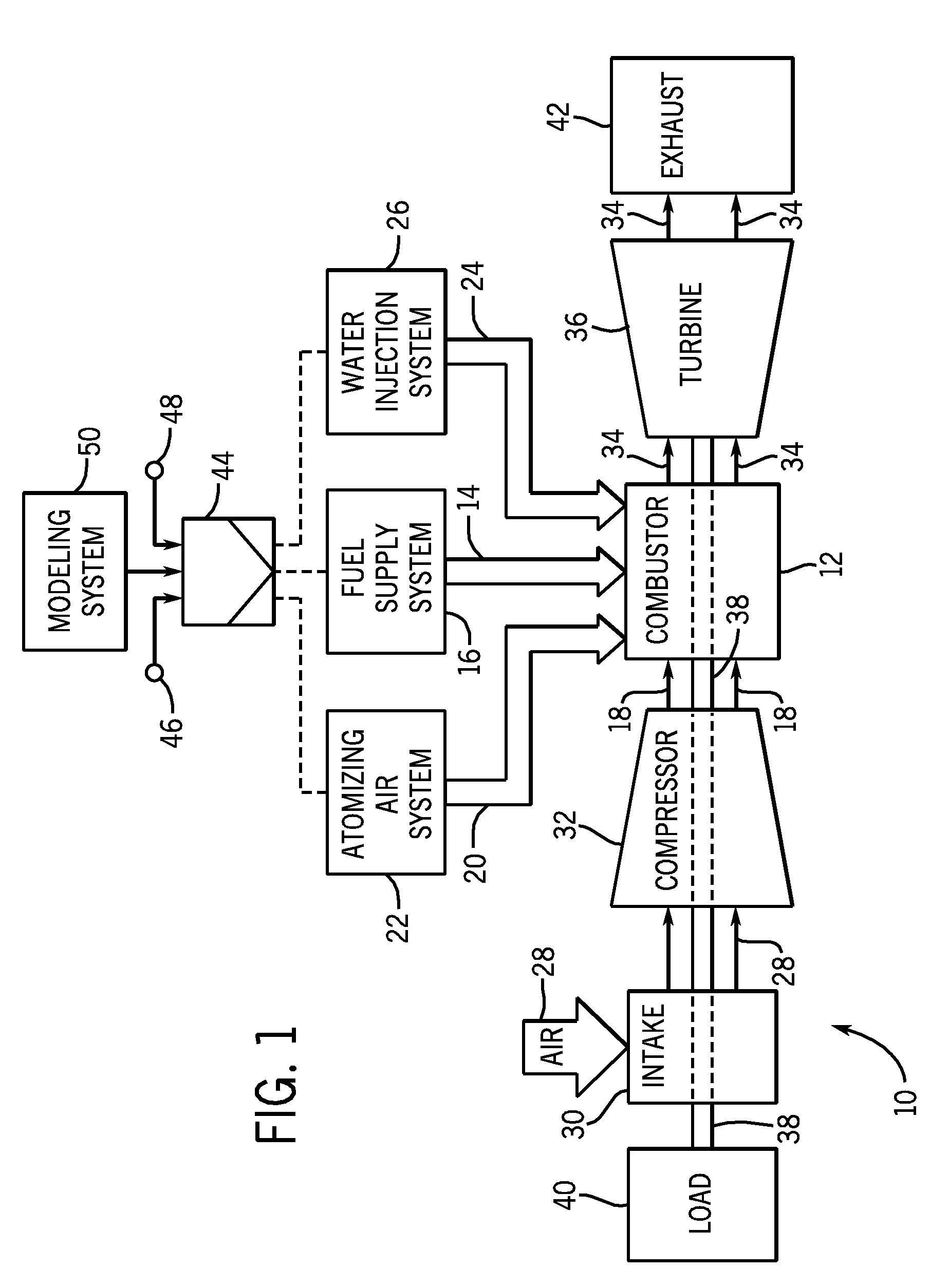
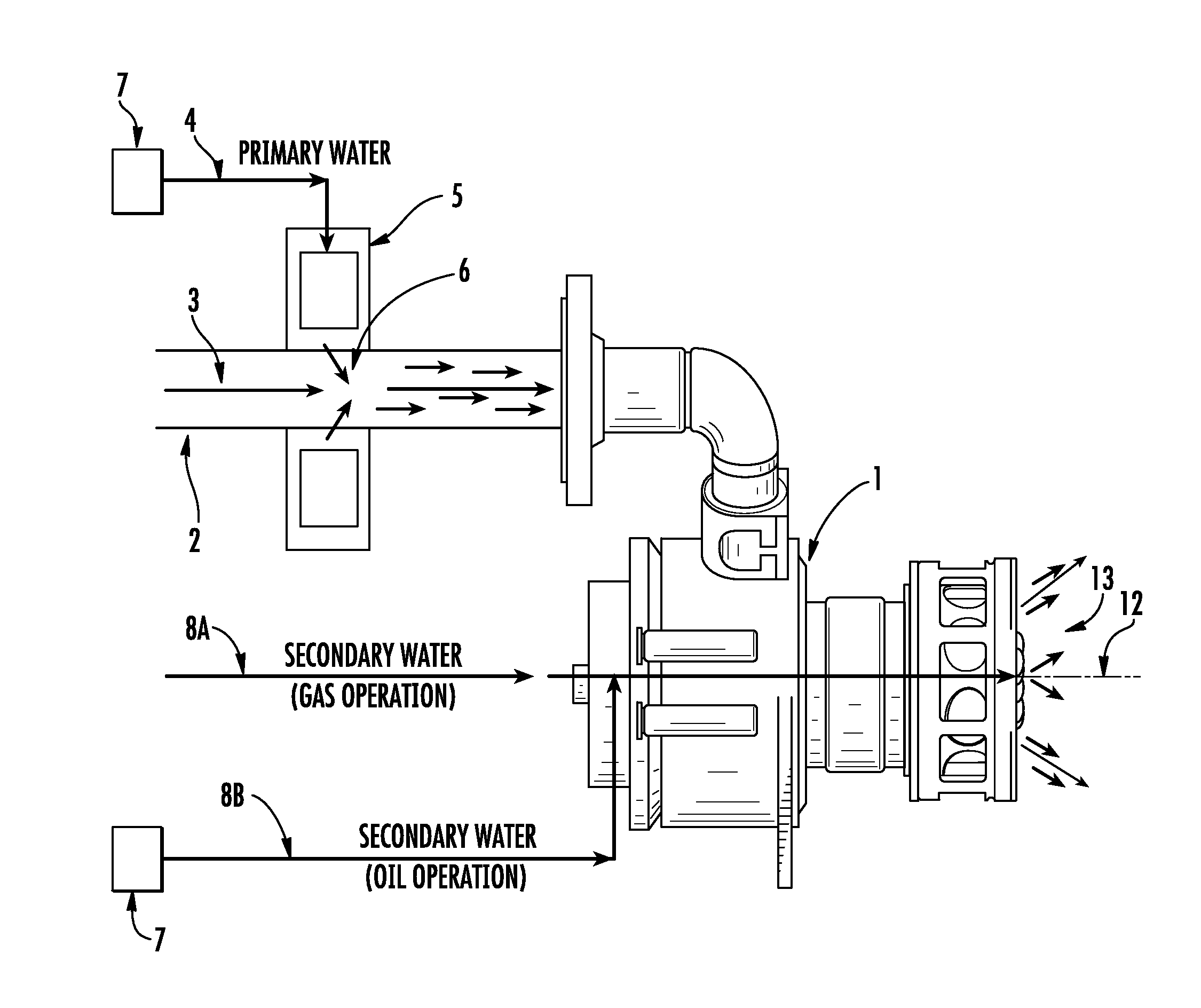
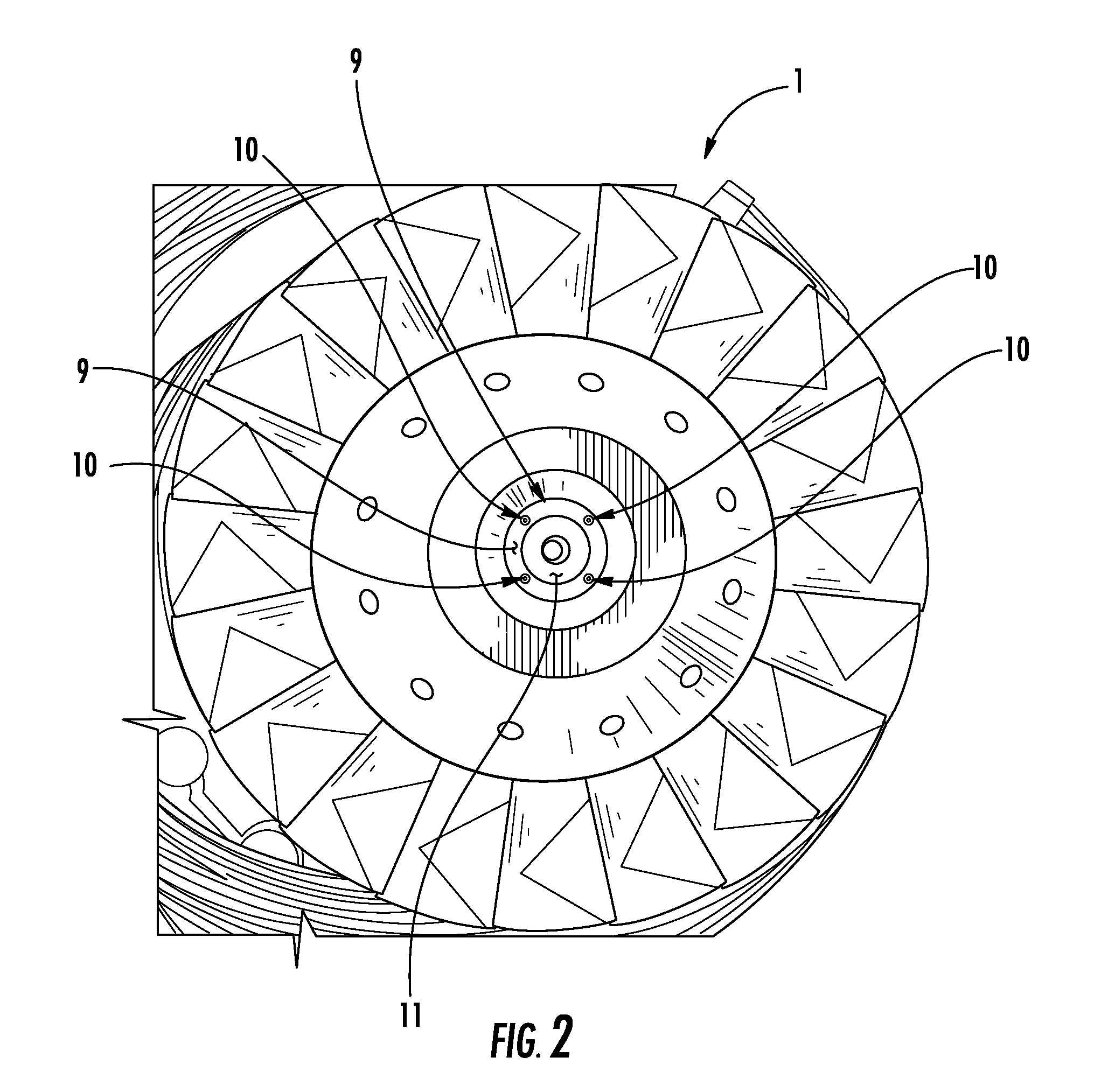
A flexible and automatic system and method for blending an inexpensive secondary gas with a primary gas fuel for operation of a Dry Low NOx gas turbine. The secondary gas may be a gas fuel such as hydrogen, ethane, butane, propane and liquefied natural gas or an inert gas. Combustion dynamics are avoided by controlling the blended fuel within a permissible range for a Modified Wobbe Index. Combustion dynamics and gas turbine exhaust emissions may also be monitored to maintain safe combustion with the blended fuel. A gas turbine control system may adjust the blend and temperature of the primary gas fuel and the secondary gas to promote desired combustion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
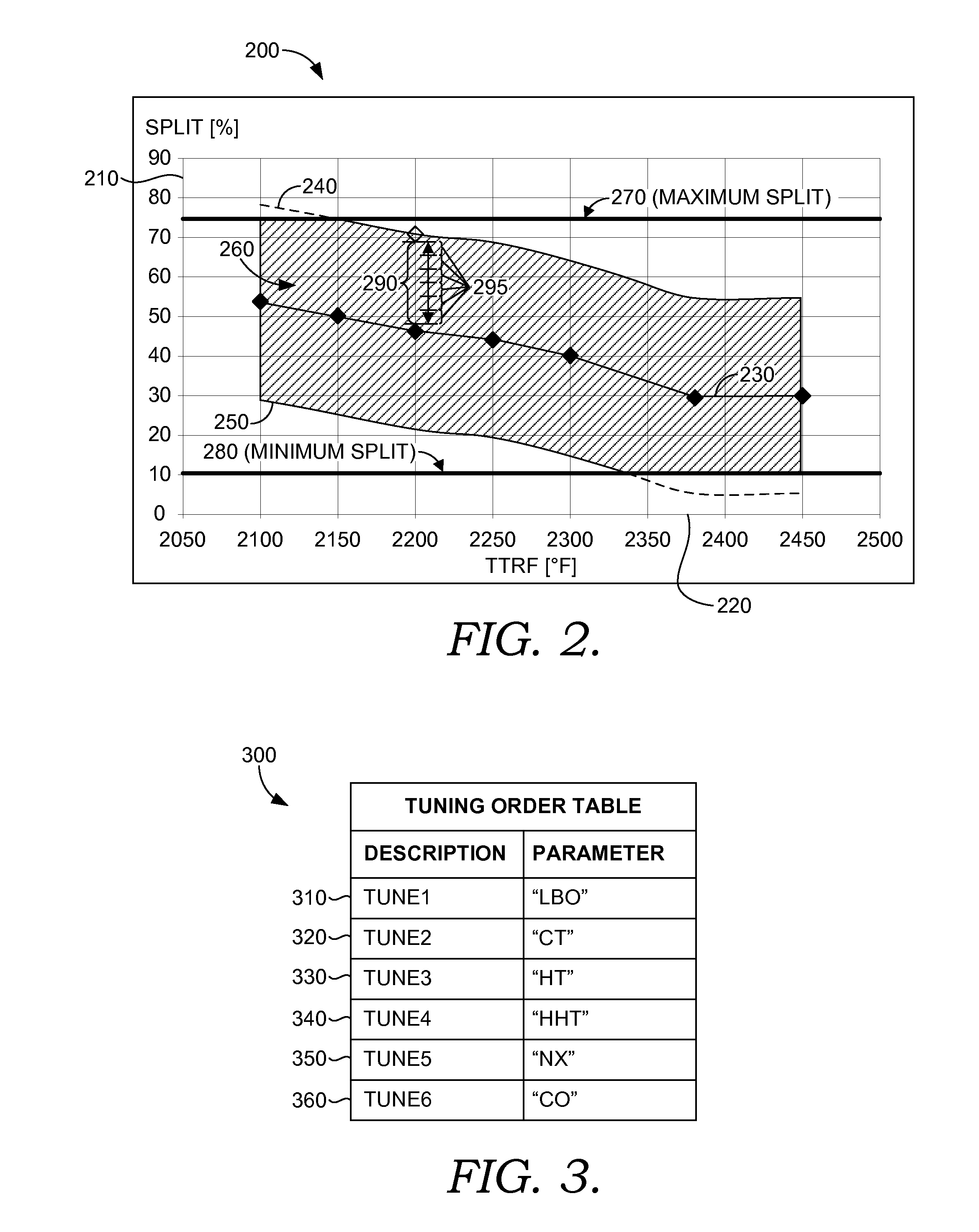
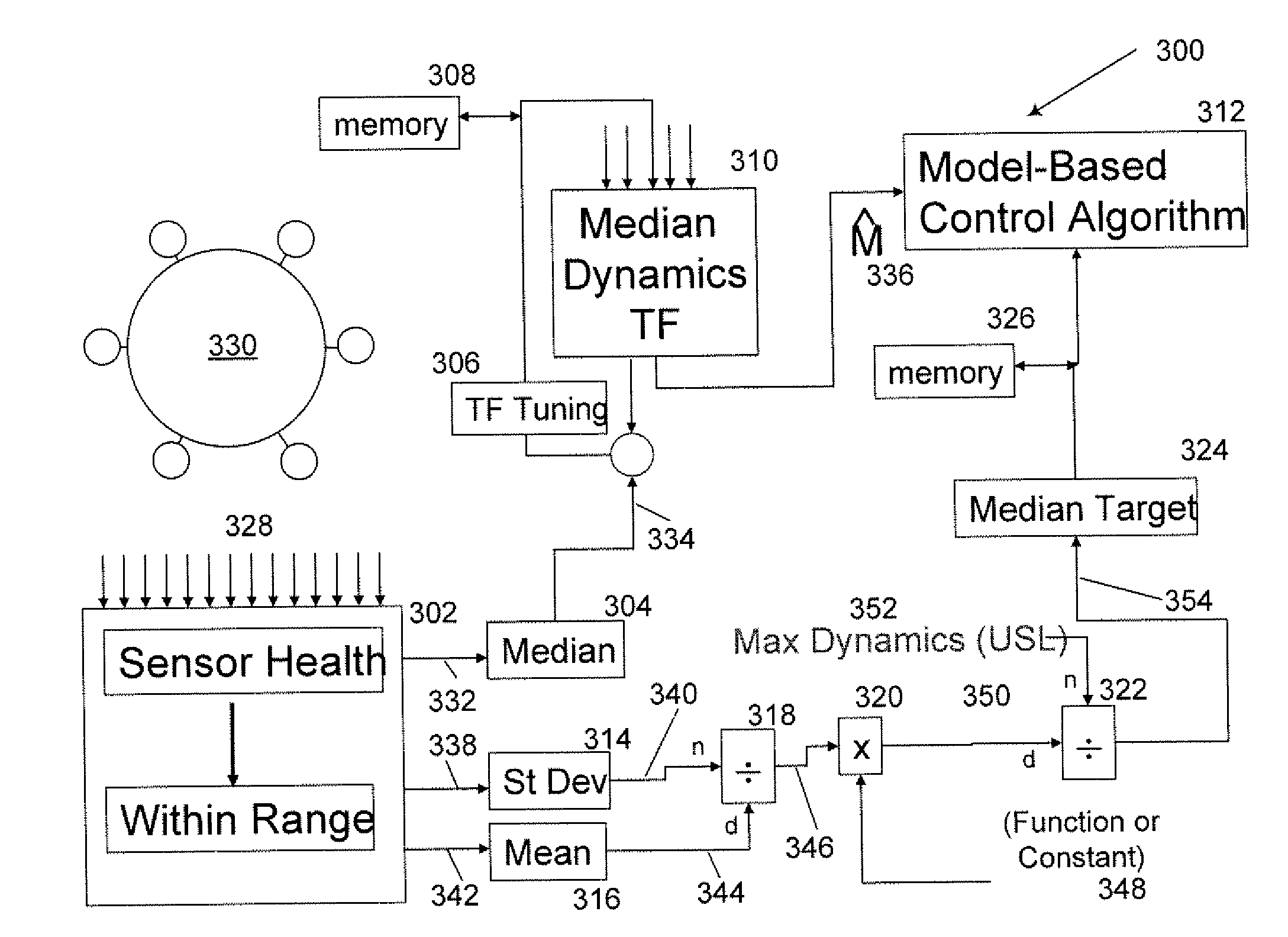
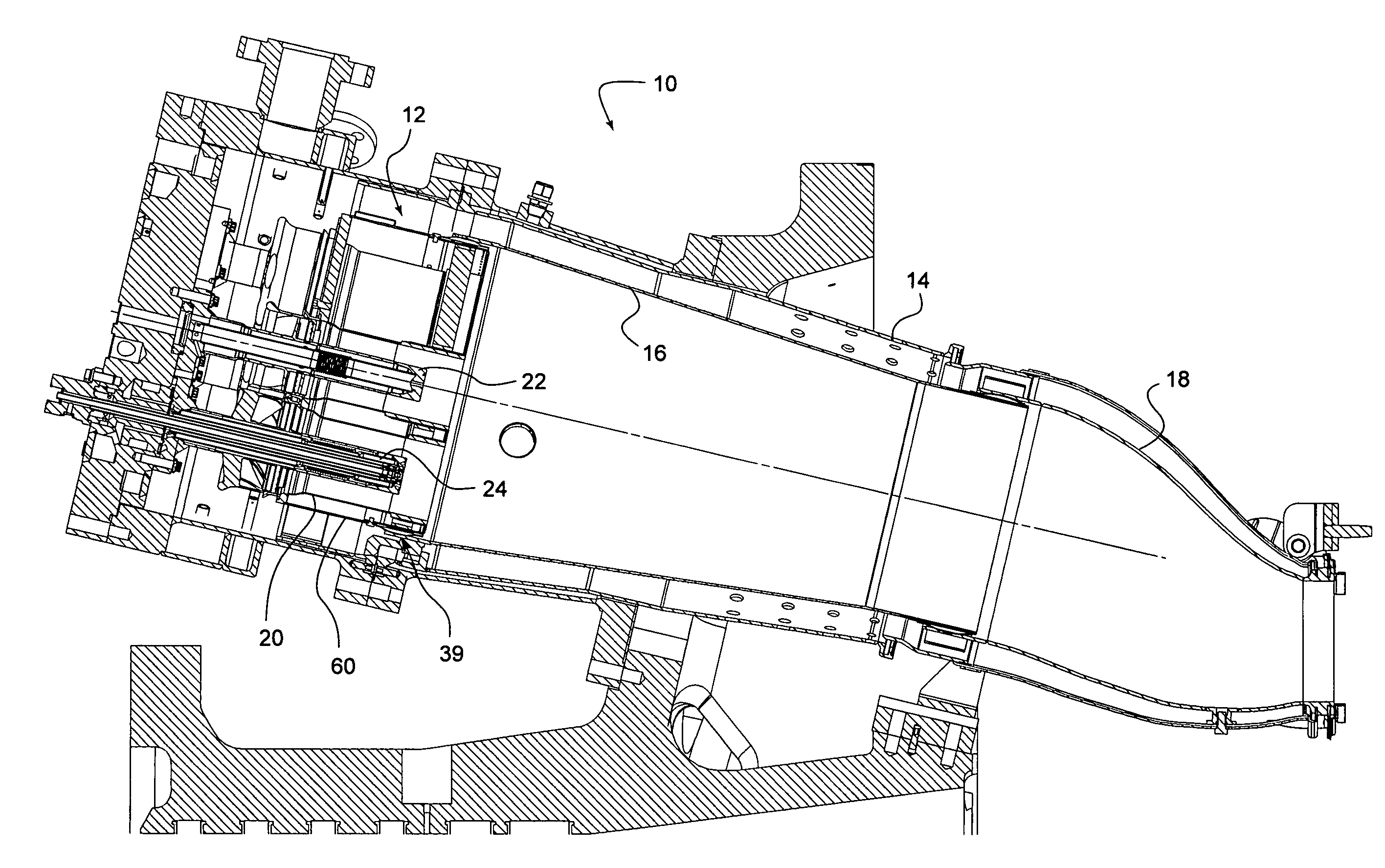
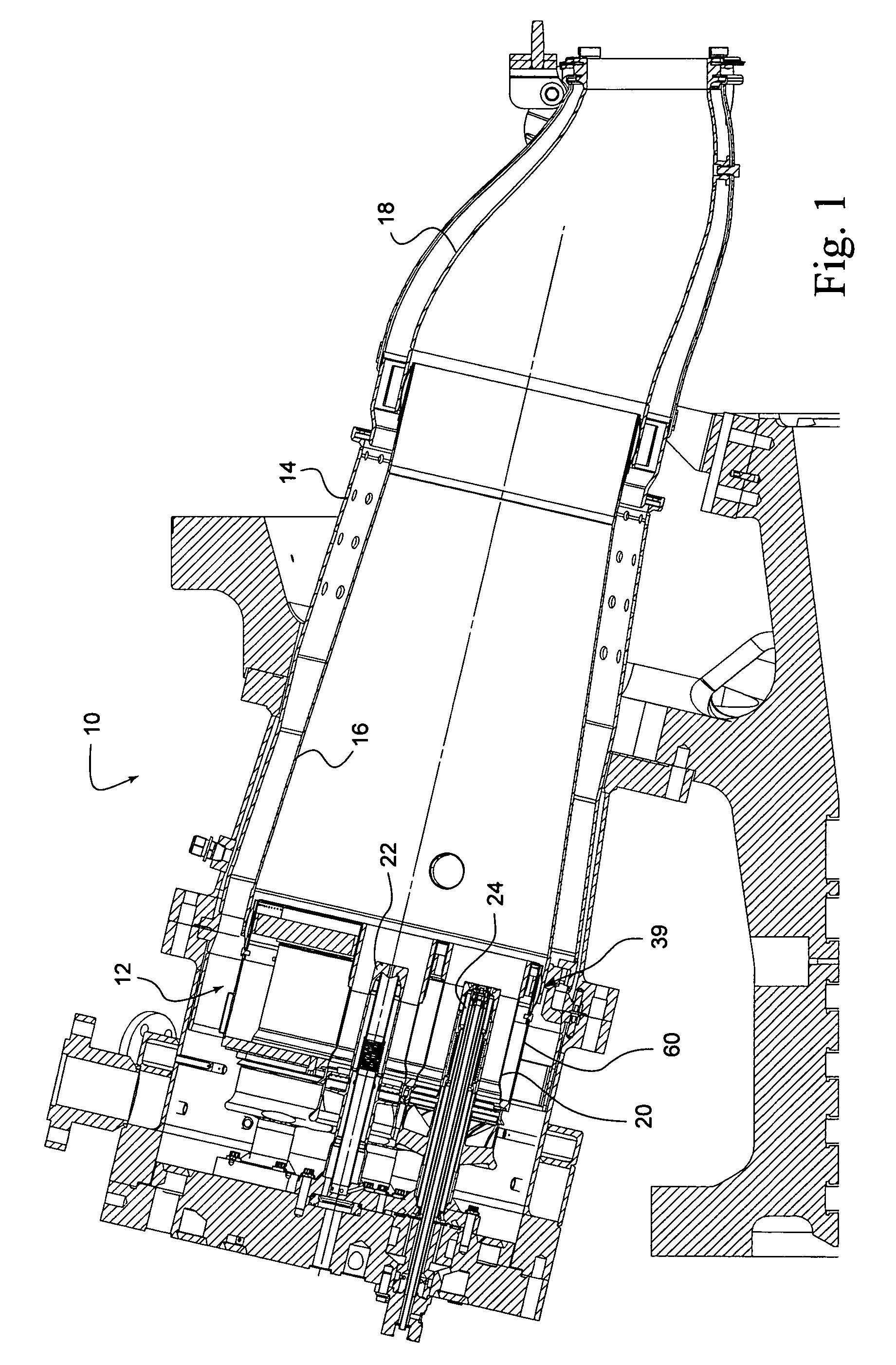
Dynamically Auto-Tuning a Gas Turbine Engine
ActiveUS20110265487A1Save processing timeImprove errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel supply regulationEngineeringCombustion kinetics
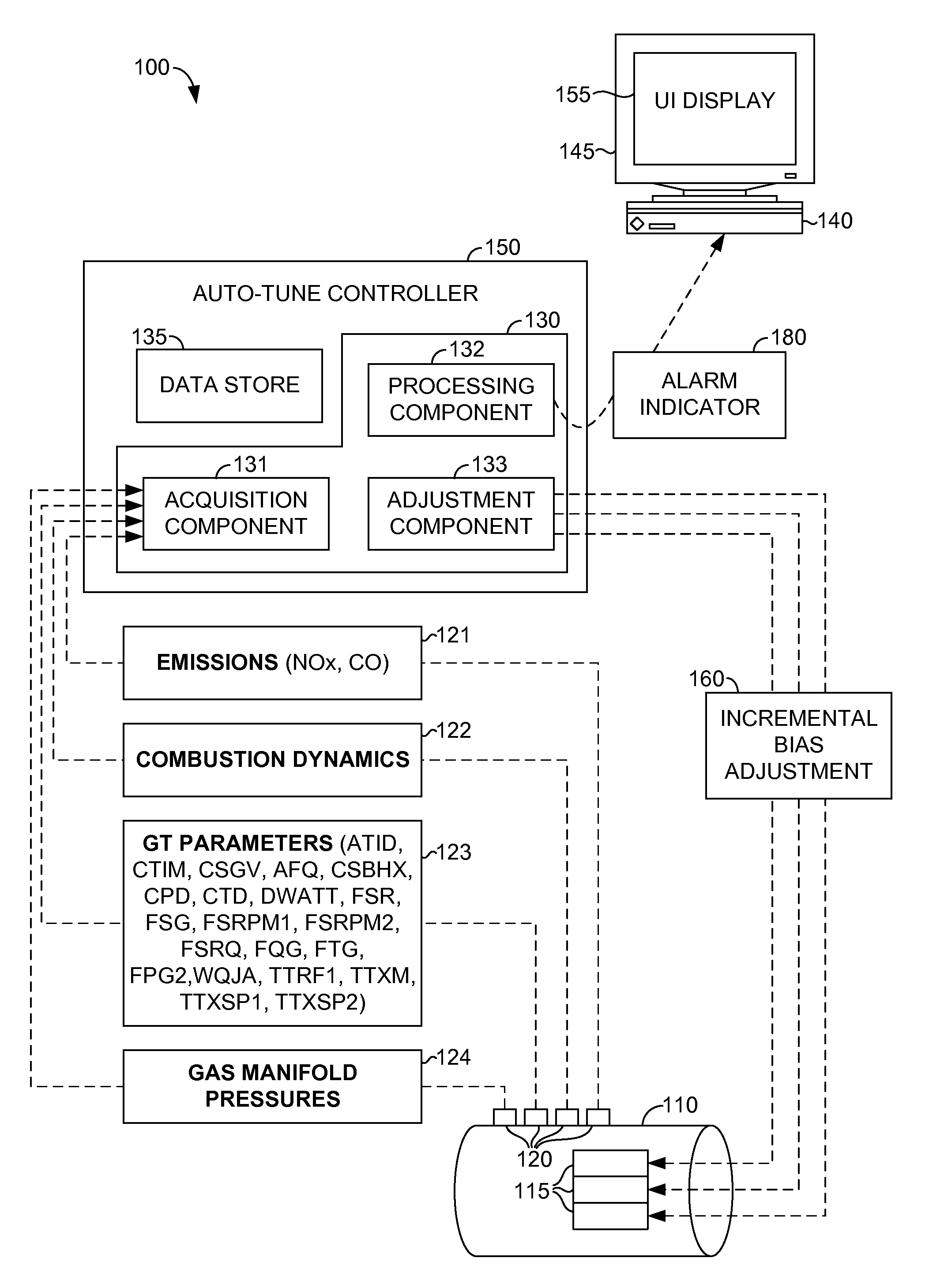
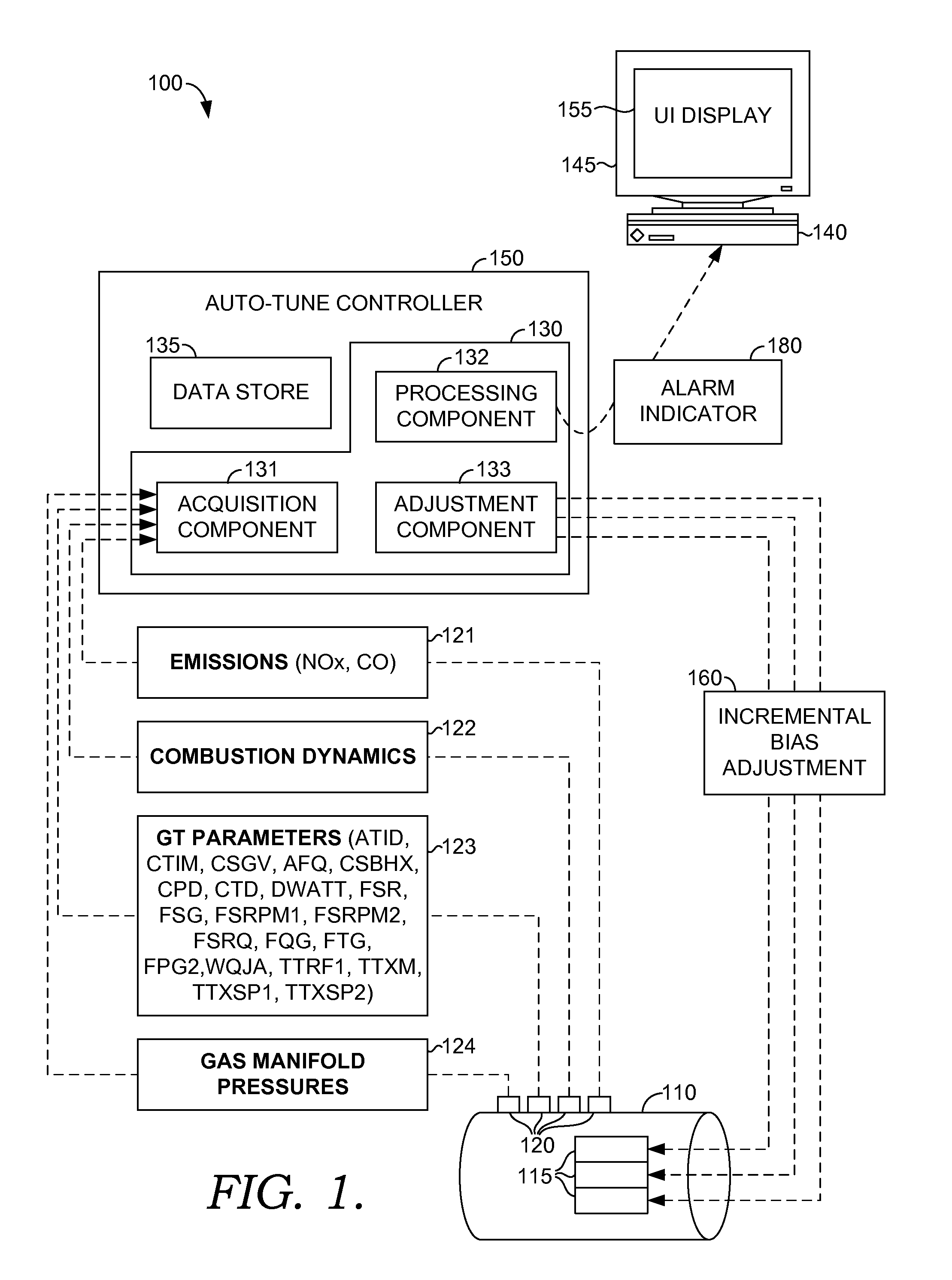
Tuning processes implemented by an auto-tune controller are provided for measuring and adjusting the combustion dynamics and the emission composition of a gas turbine (GT) engine via a tuning process. Initially, the tuning process includes monitoring parameters, such as combustion dynamics and emission composition. Upon determining that one or more of the monitored parameters exceed a critical value, these “out-of-tune” parameters are compared to a scanning order table. Upon comparison, the first out-of-tune parameter that is matched within the scanning order table is addressed. The first out-of-tune parameter is then plotted as overlaid slopes on respective graphs, where the graph represents a fuel-flow split. Typically, the slopes are plotted as a particular out-of-tune parameter against a particular fuel-flow split. The slopes for each graph are considered together by taking into account the combined impact on each out-of-tune parameter when a fuel-flow split is selected for adjustment.
Owner:H2 IP UK LTD
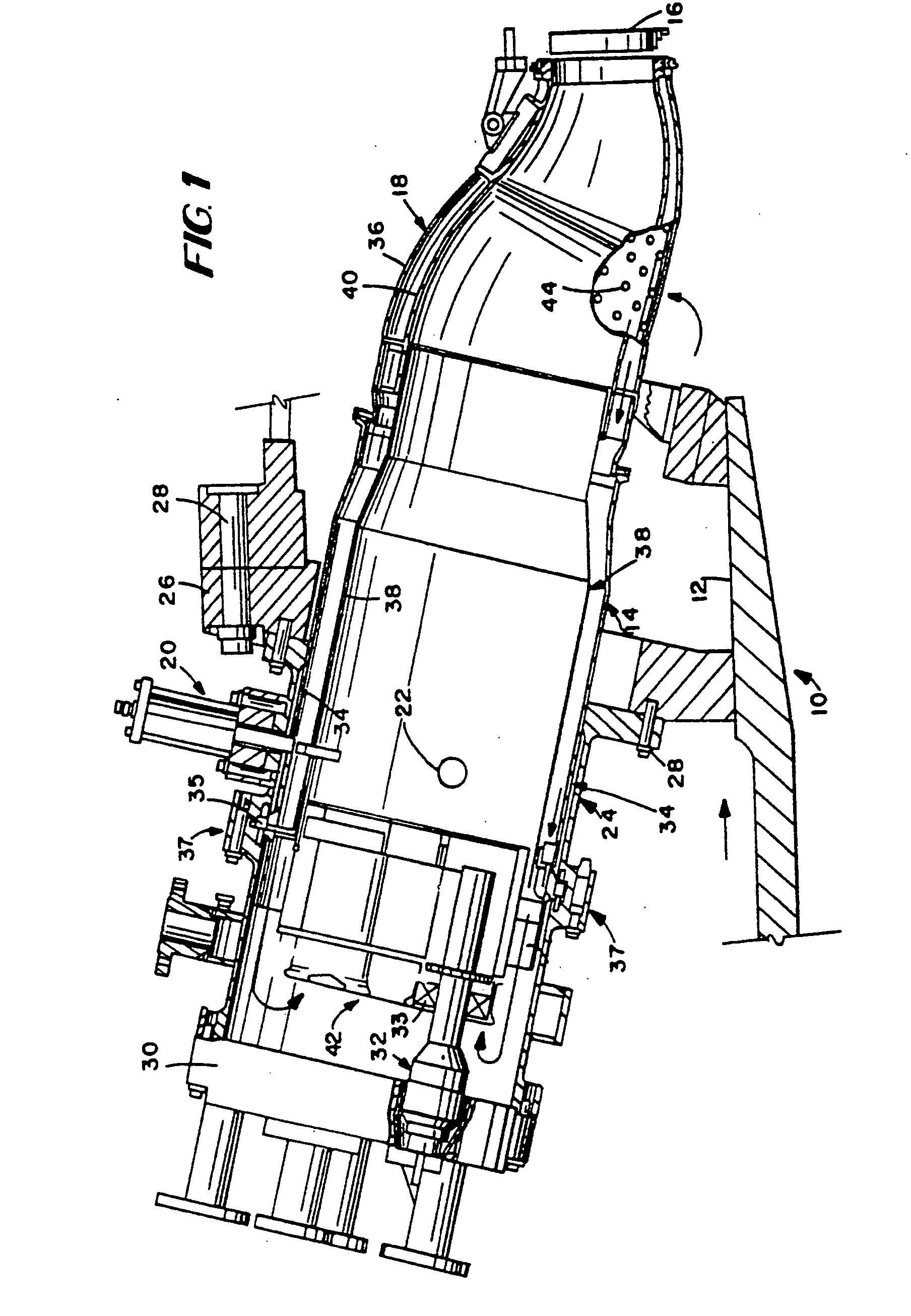
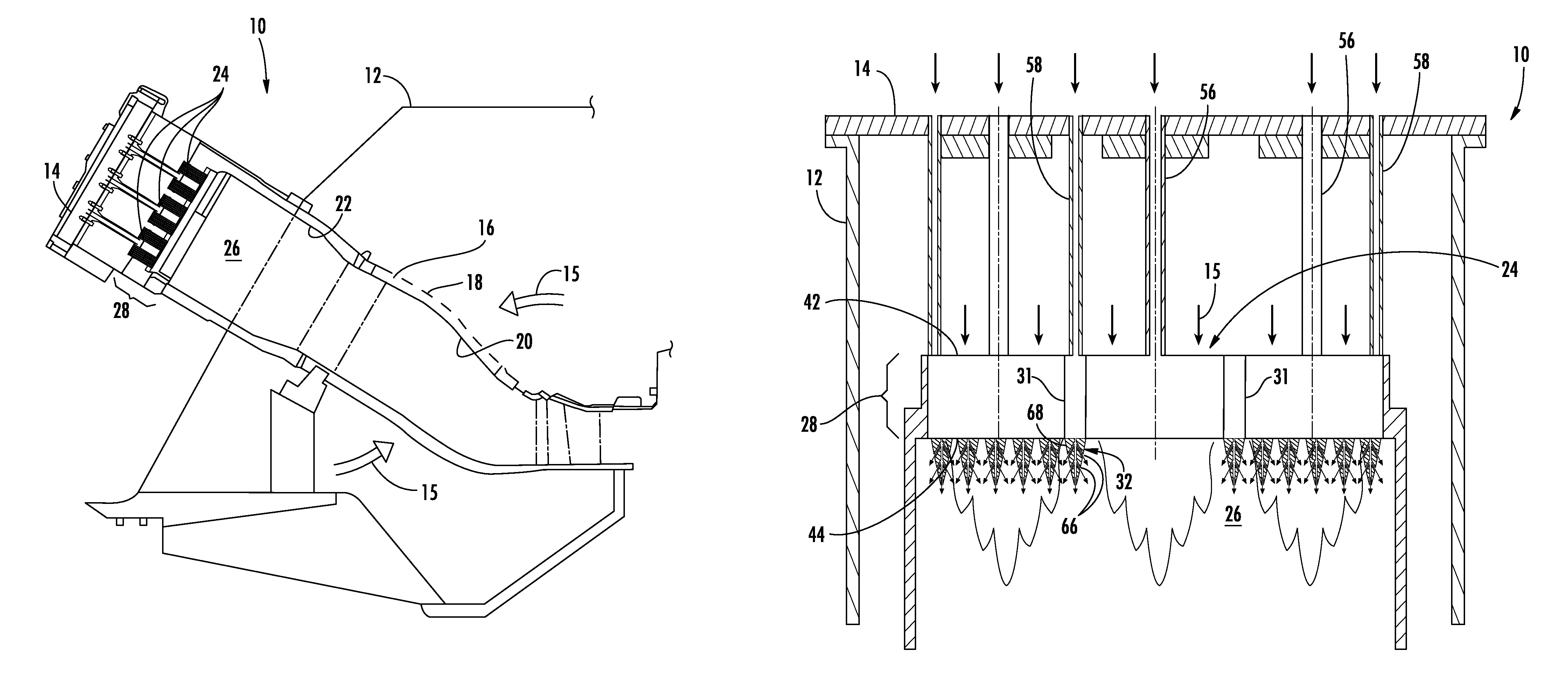
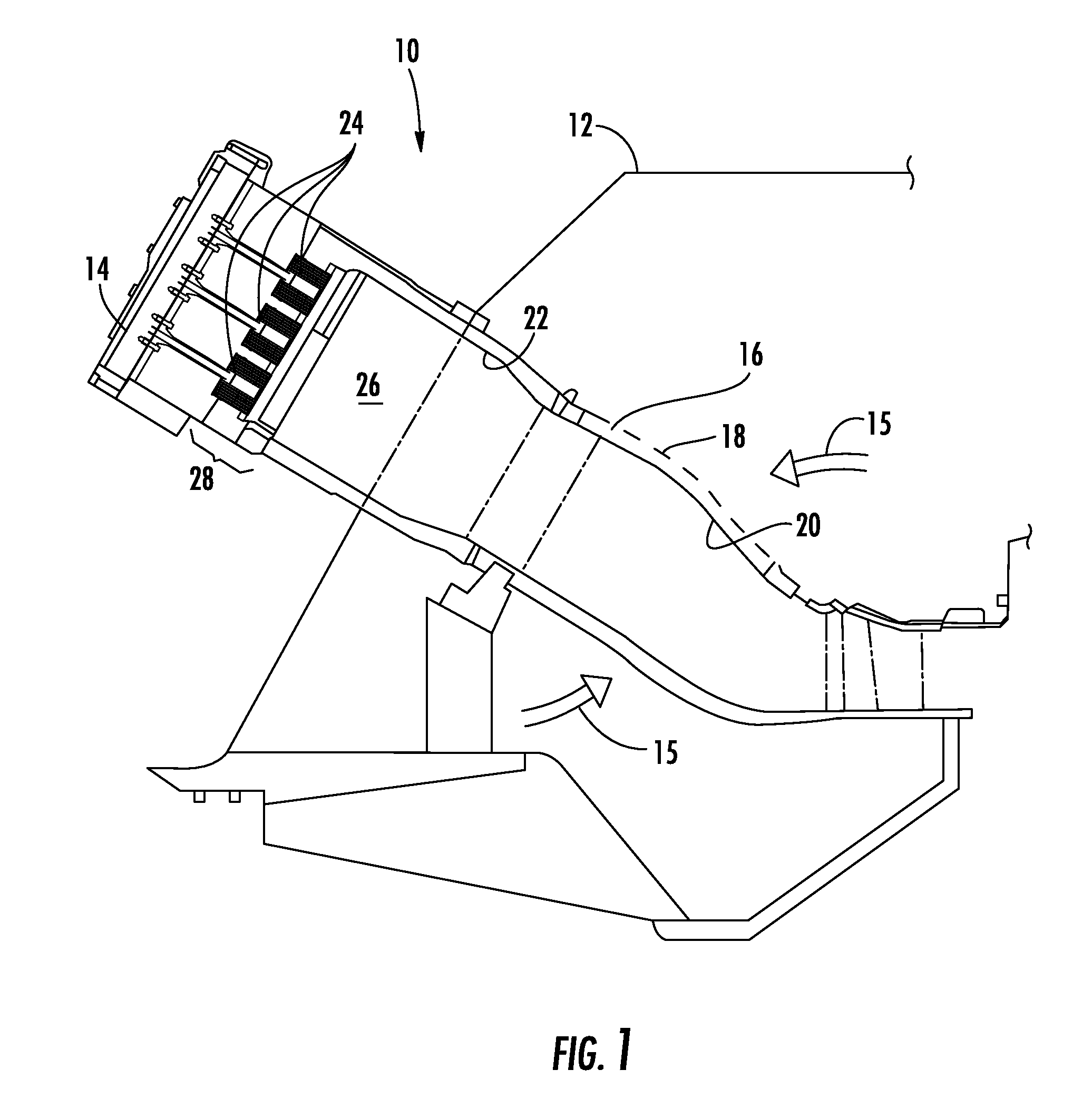
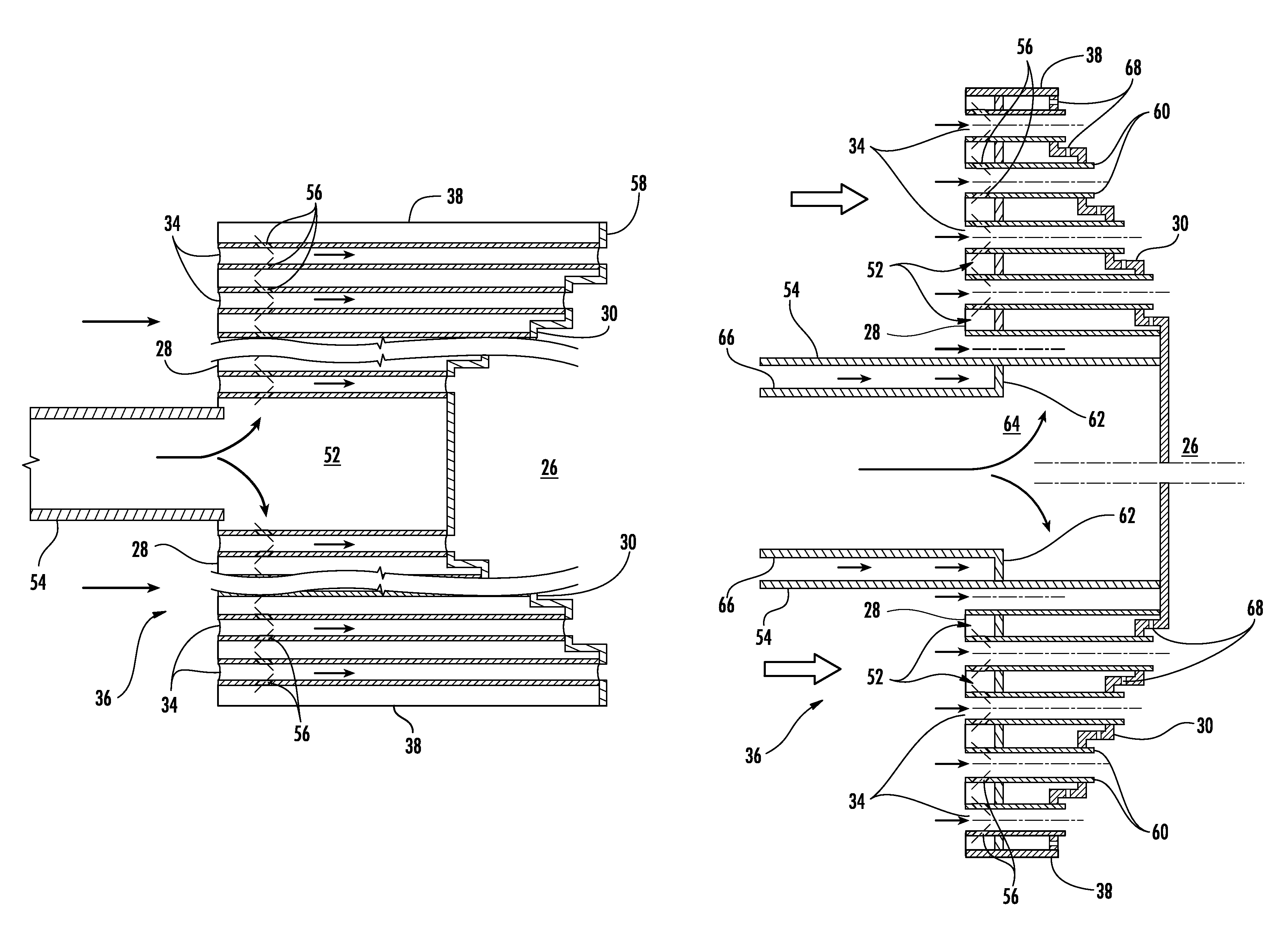
Combustion liner cap assembly for combustion dynamics reduction
A combustion liner cap assembly includes a cylindrical outer sleeve supporting internal structure therein and a plurality of fuel nozzle openings formed through the internal structure. A first set of circumferentially spaced cooling holes is formed through the cylindrical outer sleeve, and a second set of circumferentially spaced cooling holes is formed through the cylindrical outer sleeve. The second set of cooling holes is axially spaced from the first set of cooling holes. The resulting construction serves to decrease combustion dynamics in a simplified manner that is retrofittable to current designs and reversible without impacting the original configuration. The reduction in combustion dynamics improves hardware life, which leads to reduced repair and replacement costs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for gas turbine engine lean blowout avoidance
A method of monitoring and controlling the combustion dynamics of a gas turbine engine system is provided. The system includes at least one gas turbine that includes at least one combustor can. The method includes receiving a signal from a gas turbine engine sensor that is indicative of combustion dynamics in at least one of the combustor cans, processing the received signal to determine a probability of lean blowout for at least one combustor can, and controlling the gas turbine engine system to facilitate reducing a probability of a lean blowout (LBO) event using the determined probability of lean blowout.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and Methods for Using a Combustion Dynamics Tuning Algorithm with a Multi-Can Combustor
ActiveUS20090005952A1Analogue computers for vehiclesContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCombustion kinetics
Embodiments of the invention can provide systems and methods for using a combustion dynamics tuning algorithm with a multi-can combustor. According to one embodiment of the invention, a method for controlling a gas turbine engine with an engine model can be implemented for an engine comprising multiple cans. The method can include obtaining operating frequency information associated with multiple cans of the engine. In addition, the method can include determining variation between operating frequency information of at least two cans. Furthermore, the method can include determining a median value based at least in part on the variation. Moreover, the method can include determining whether the median value exceeds at least one operating threshold. The method can also include implementing at least one engine control action to modify at least one of the operating frequencies if at least one operating threshold is exceeded.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
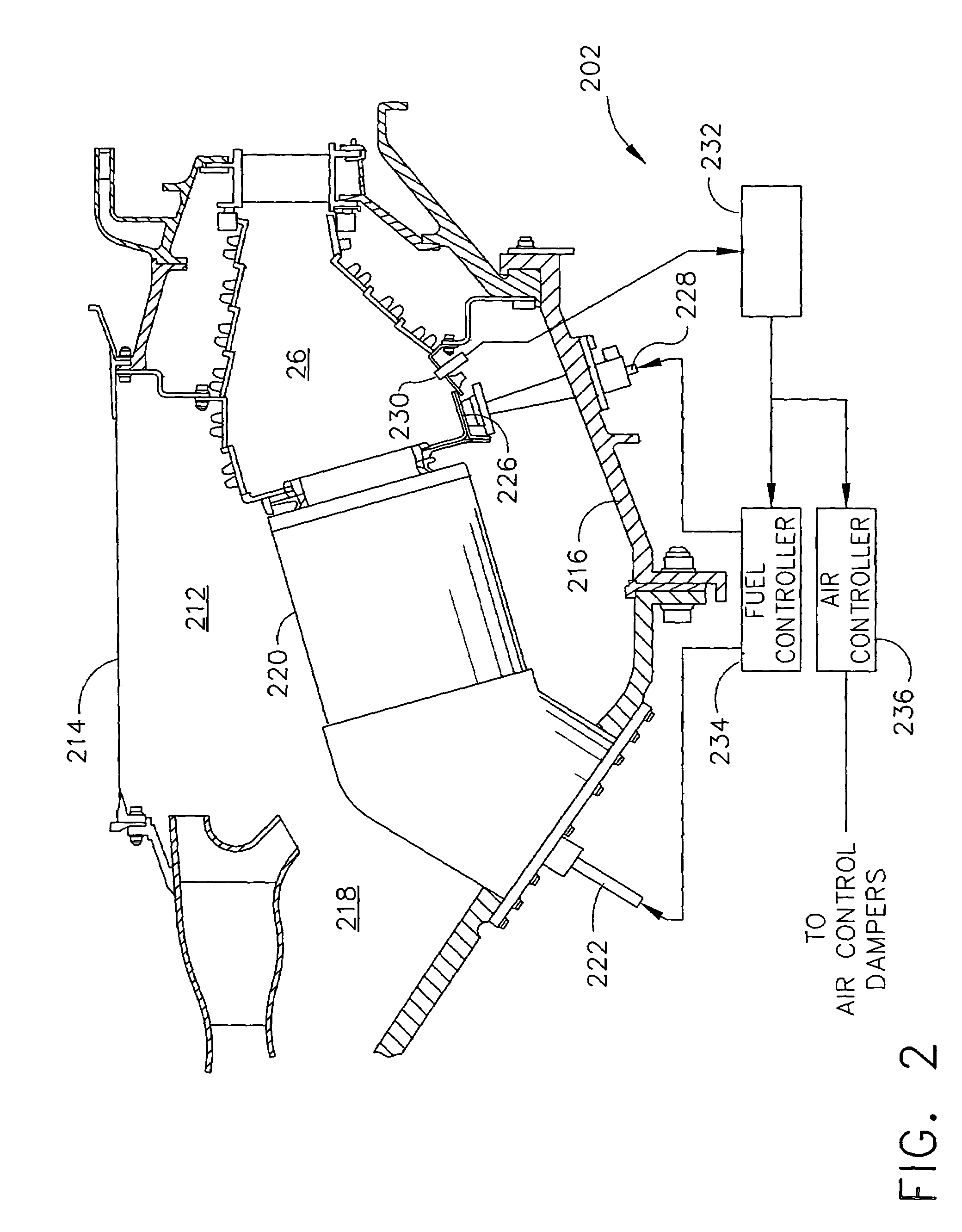
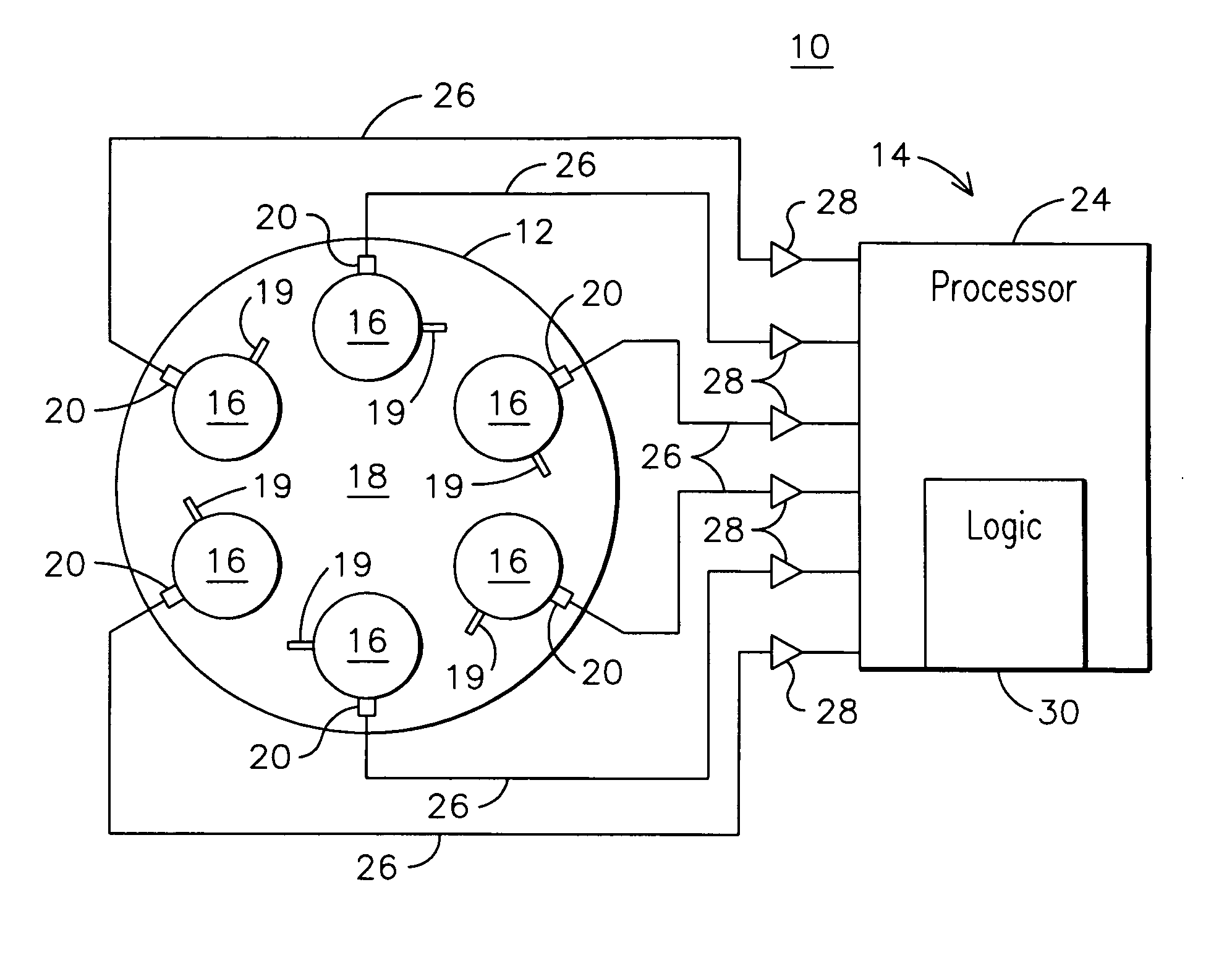
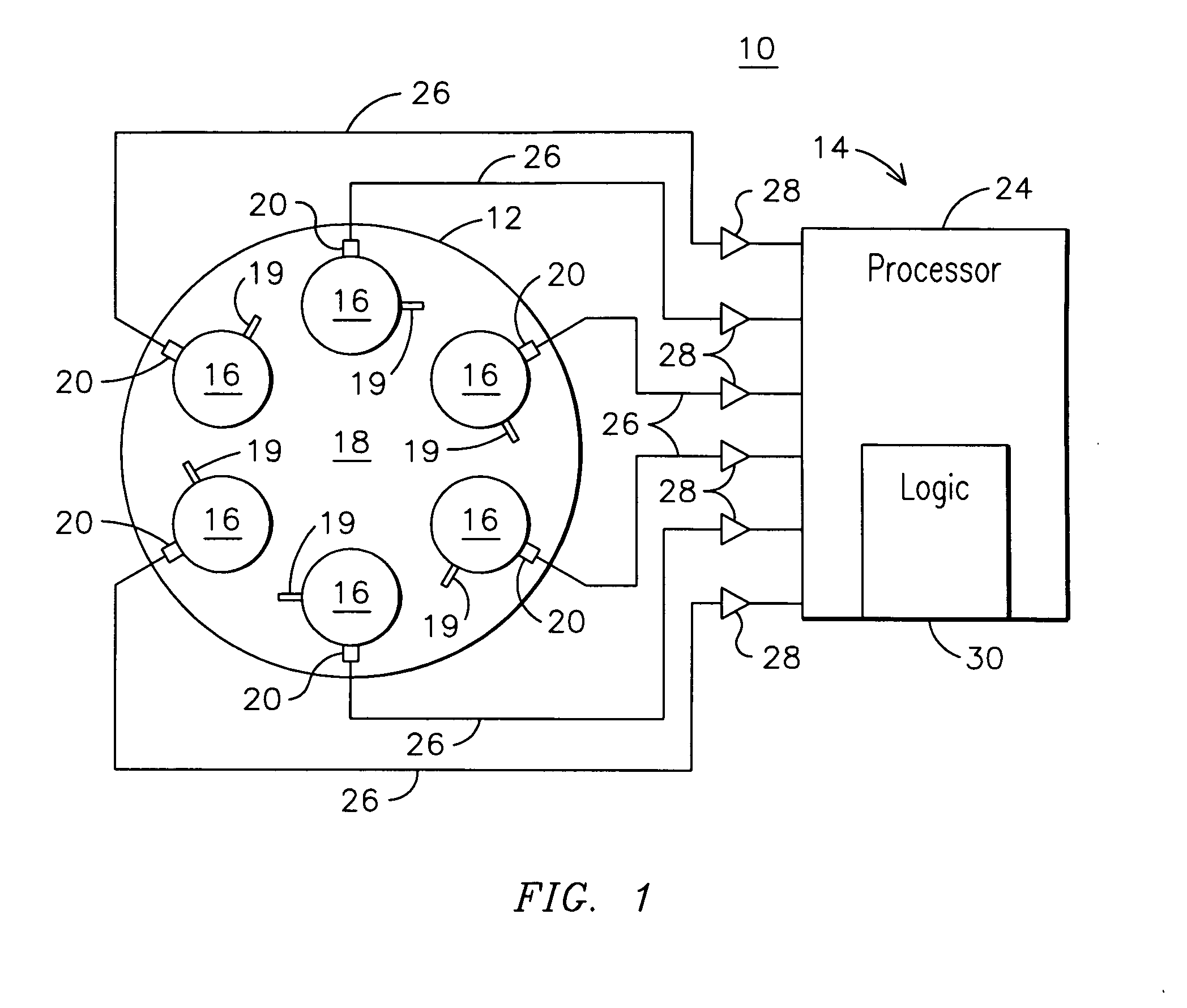
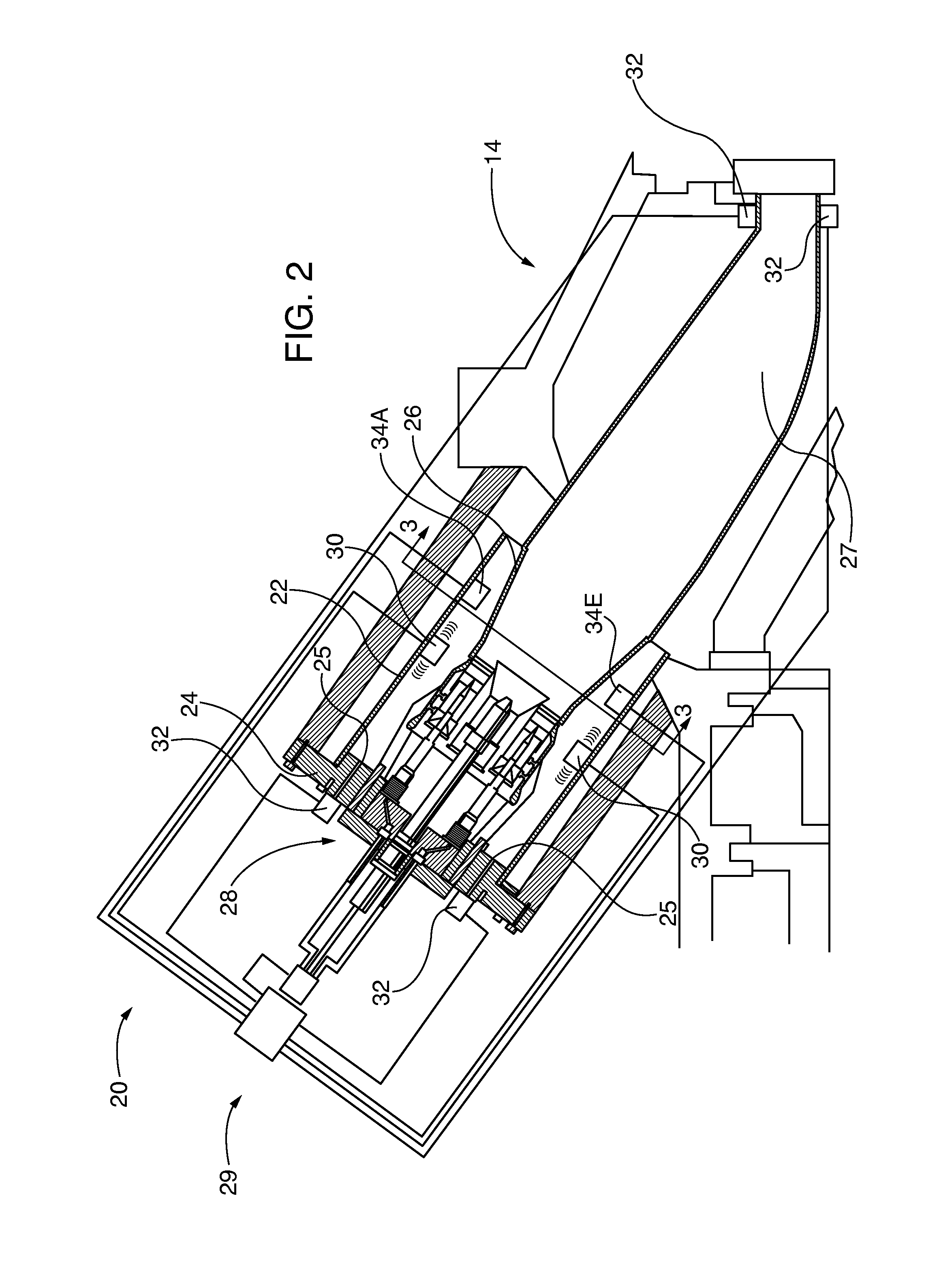
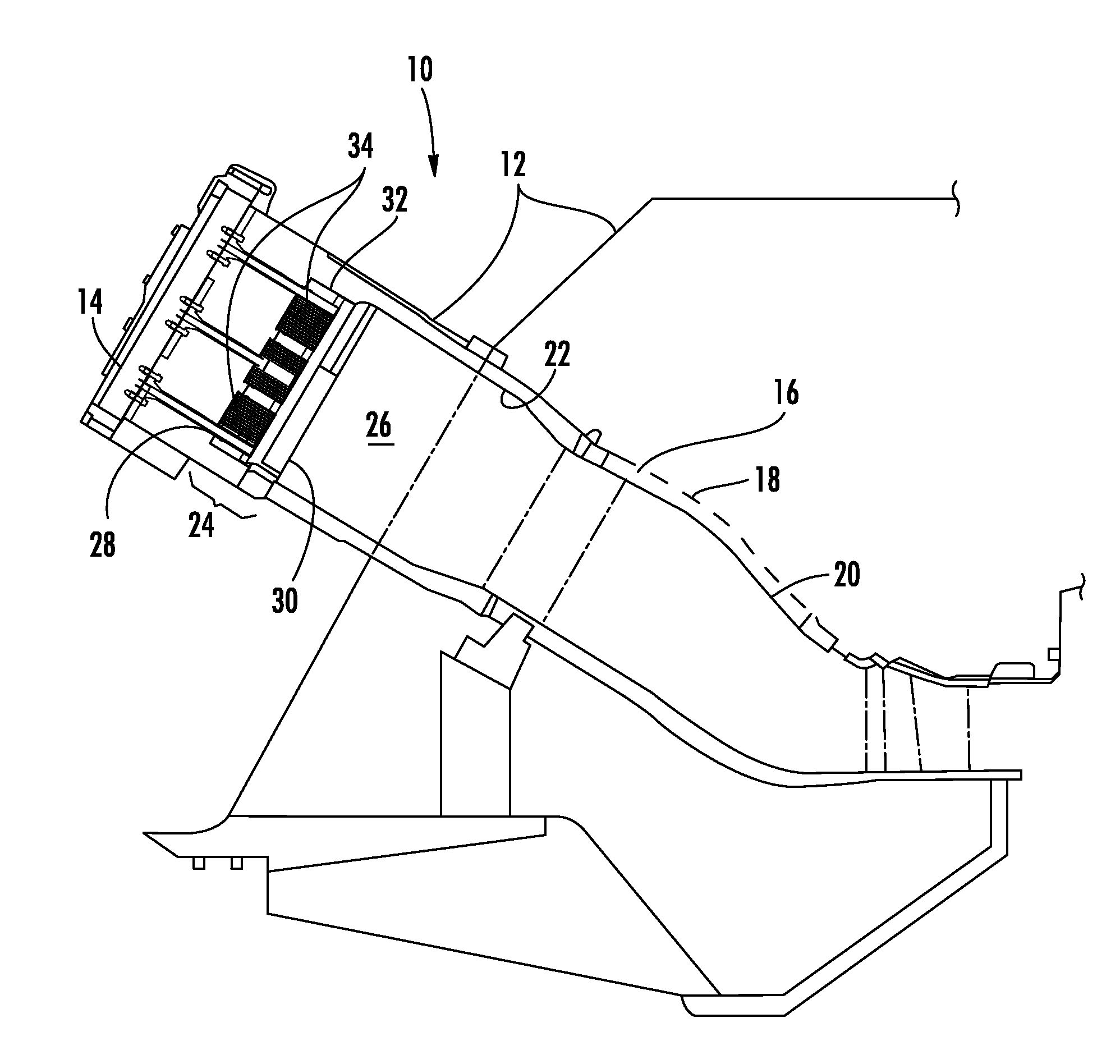
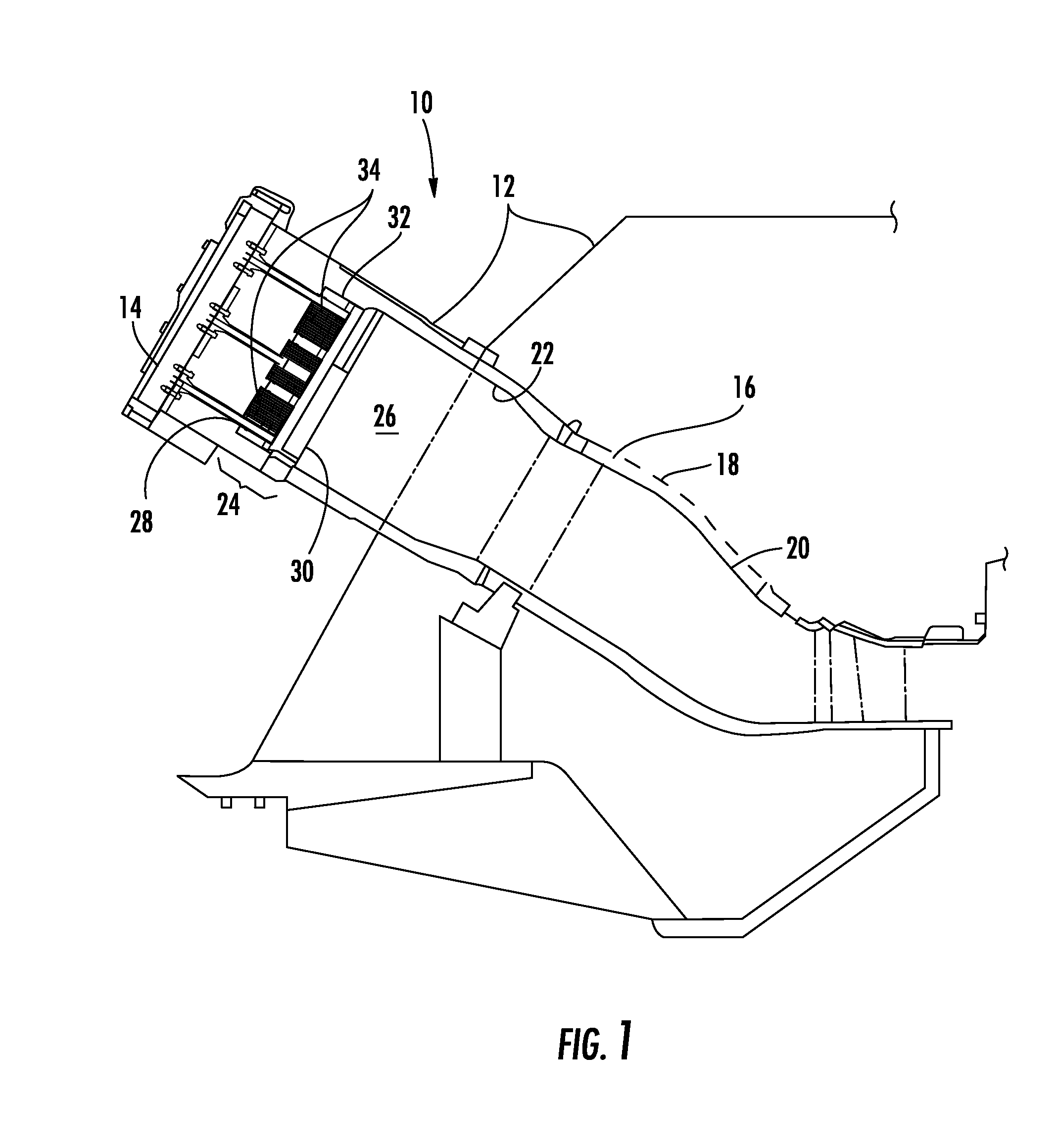
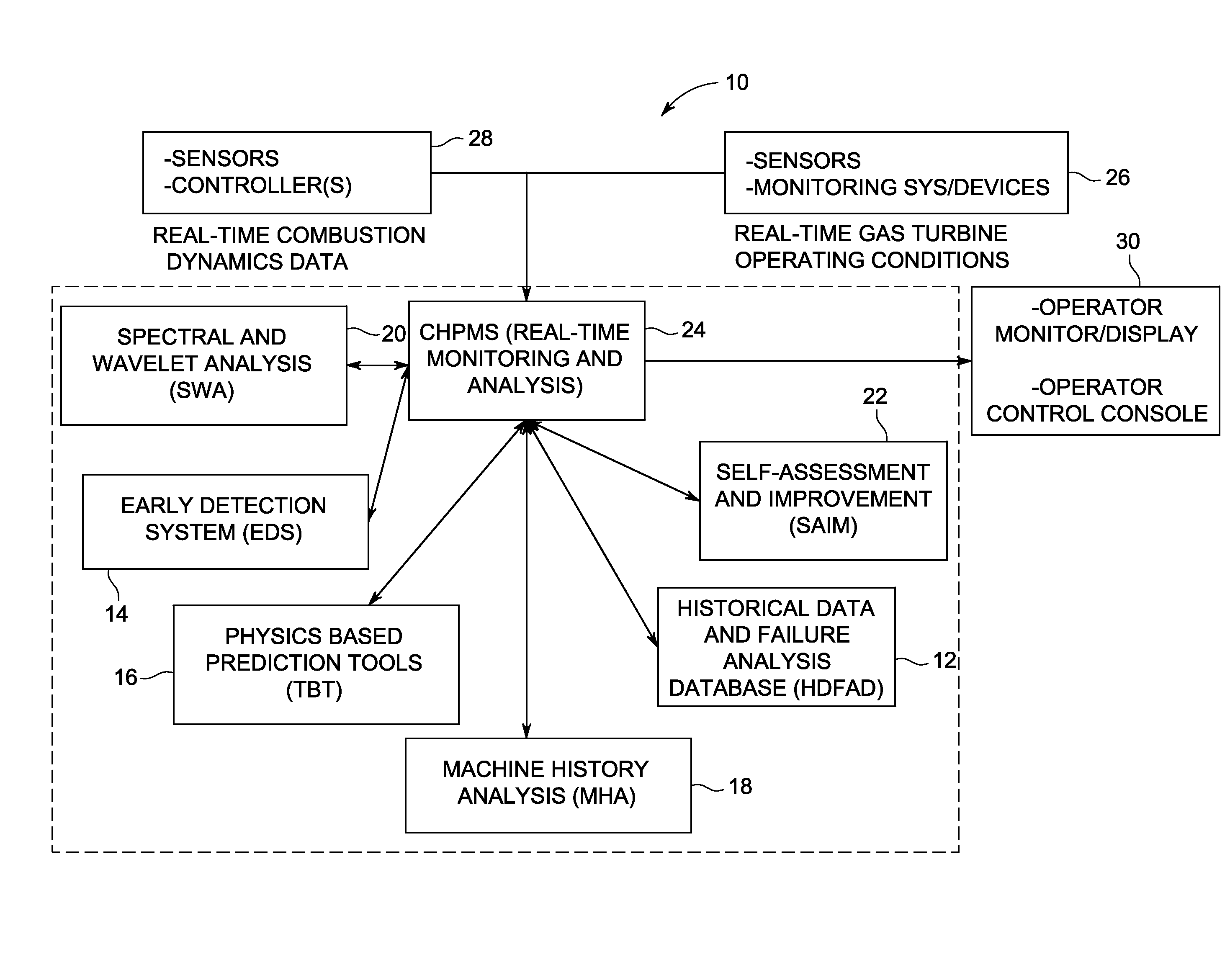
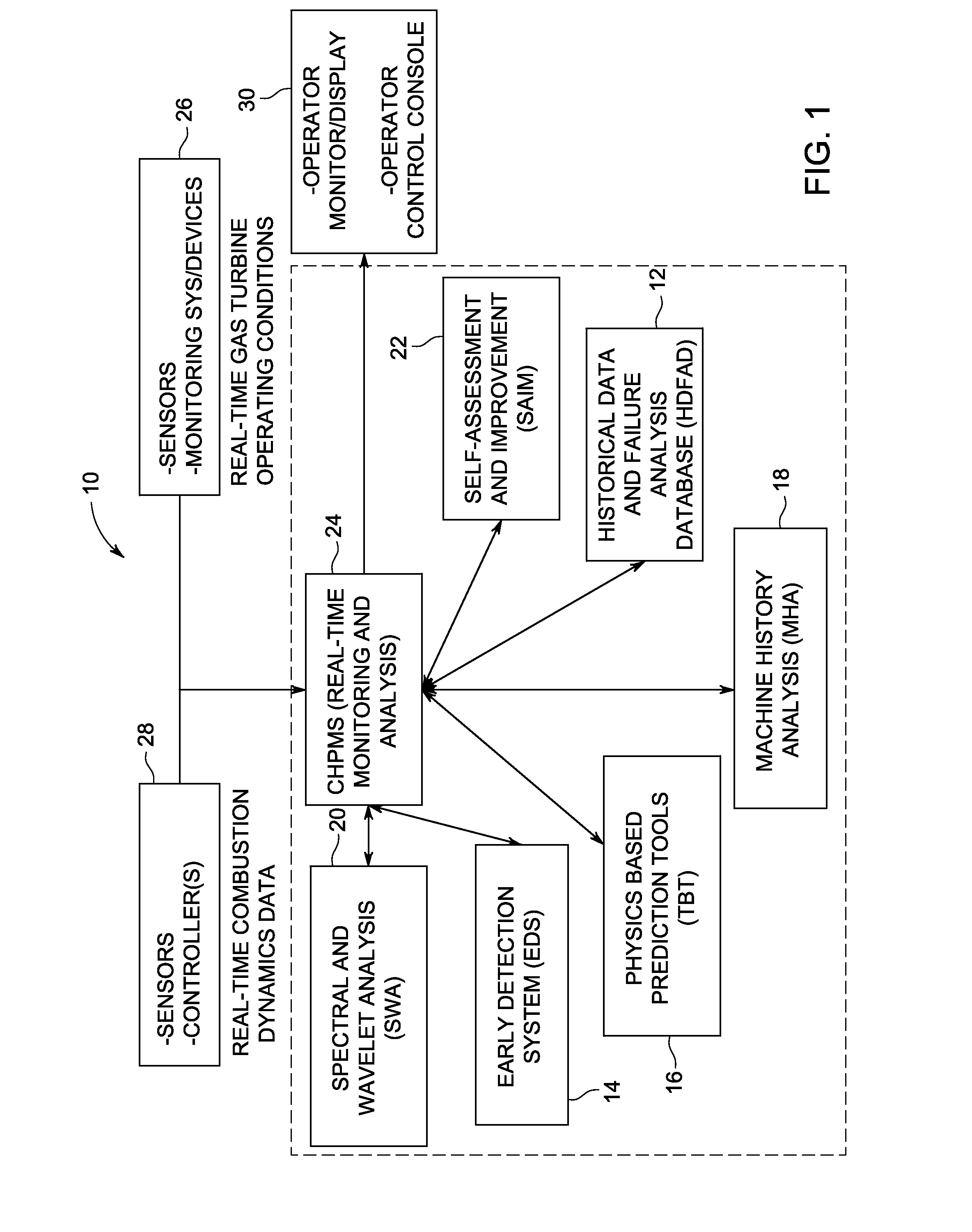
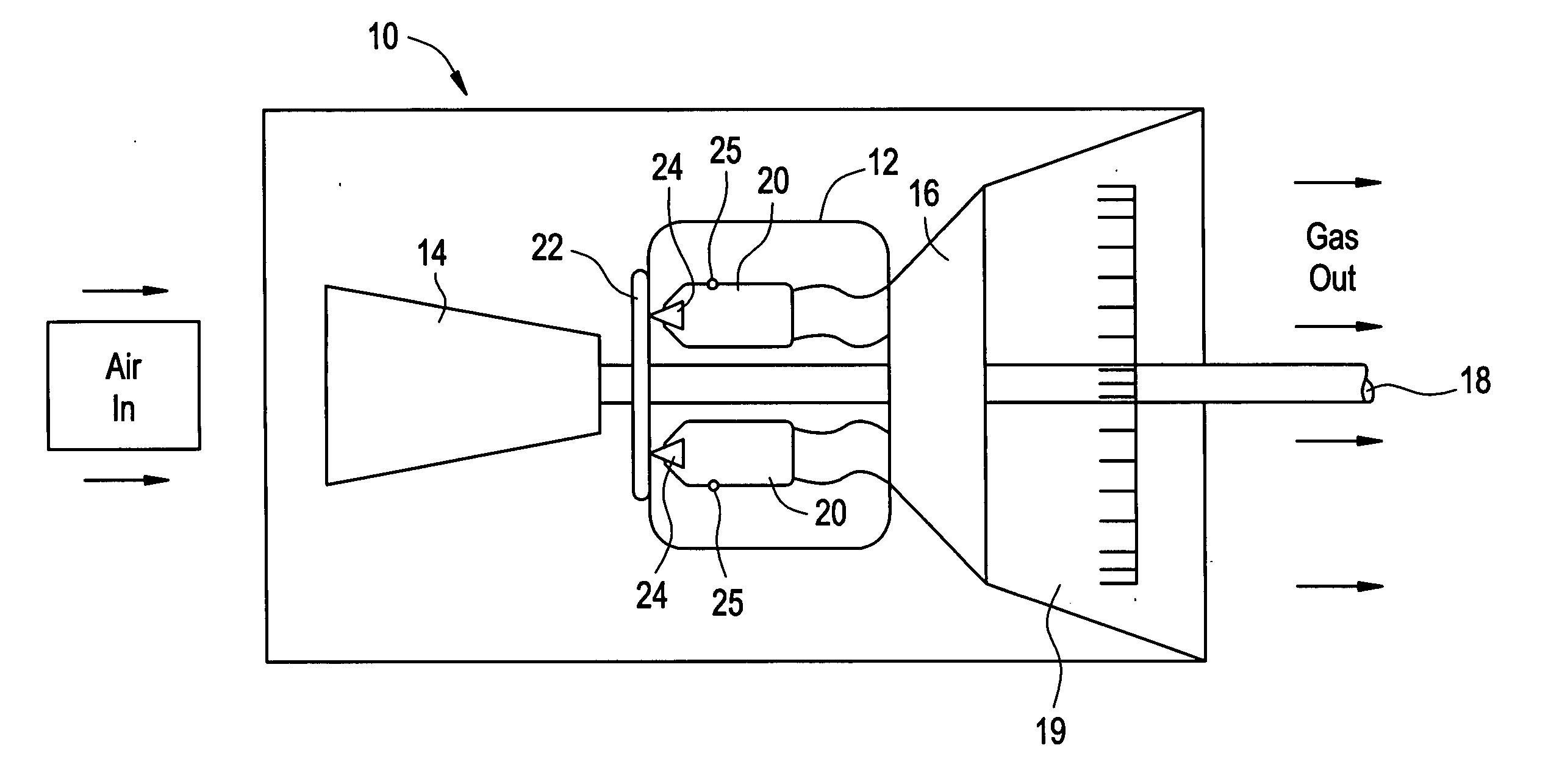
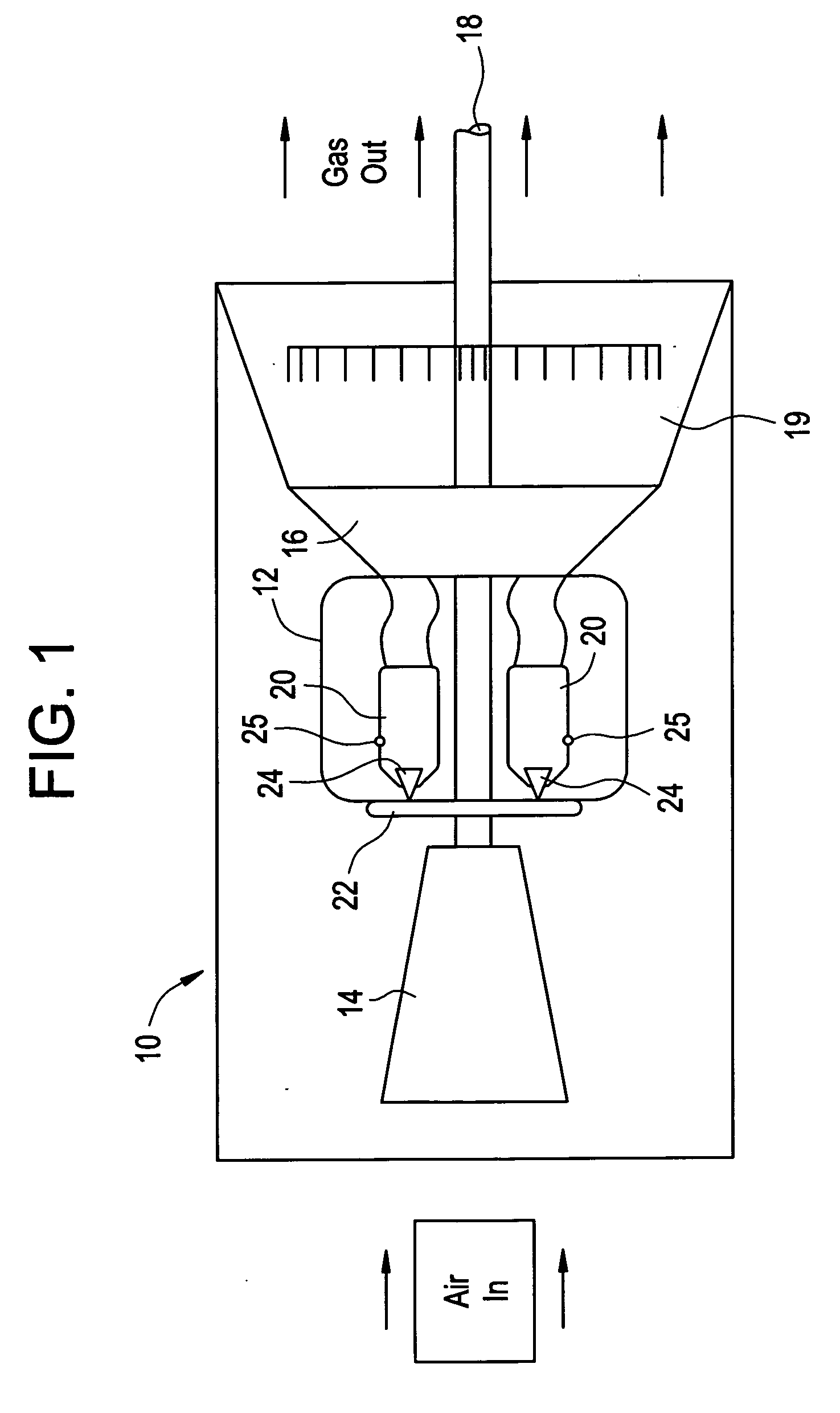
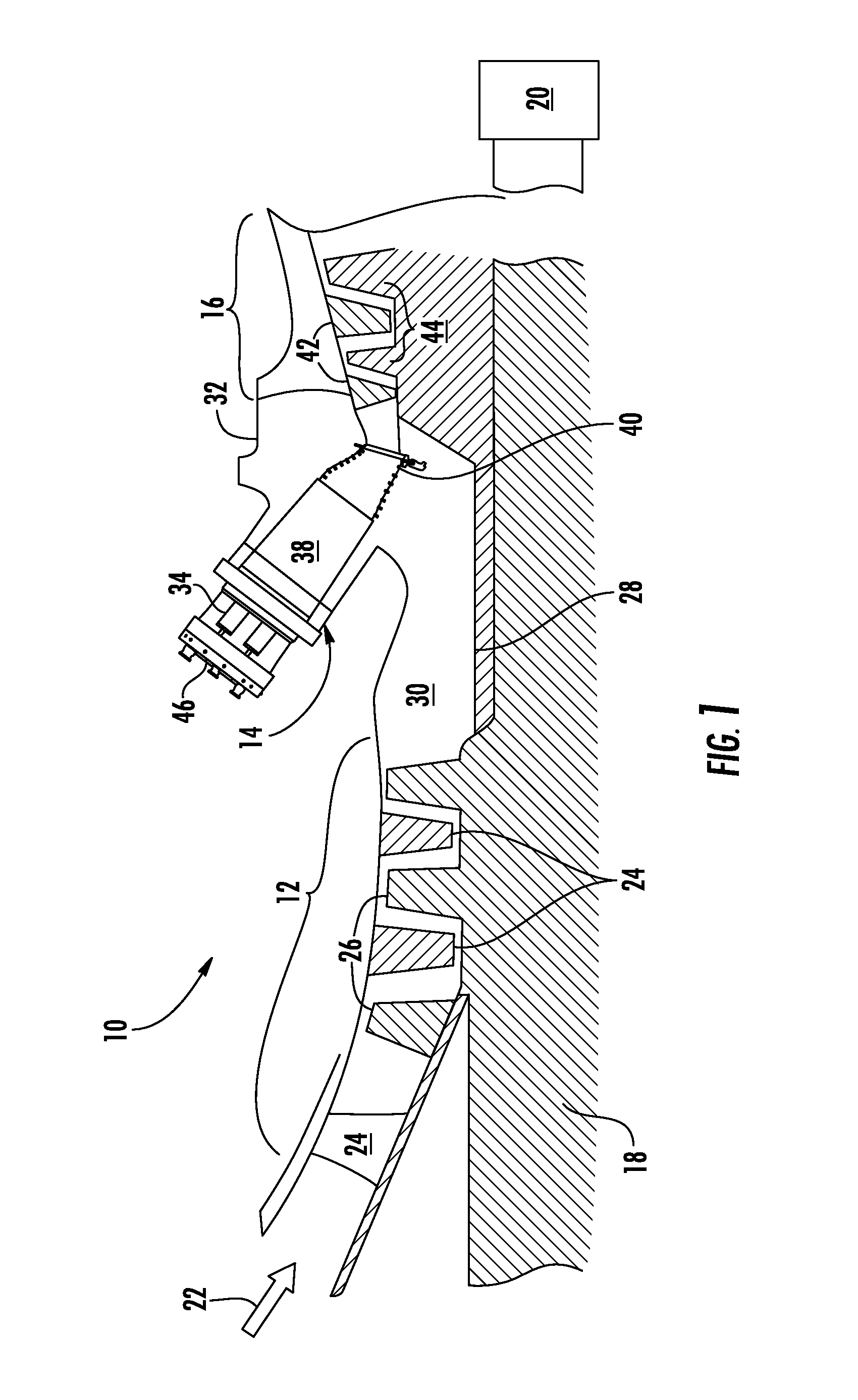
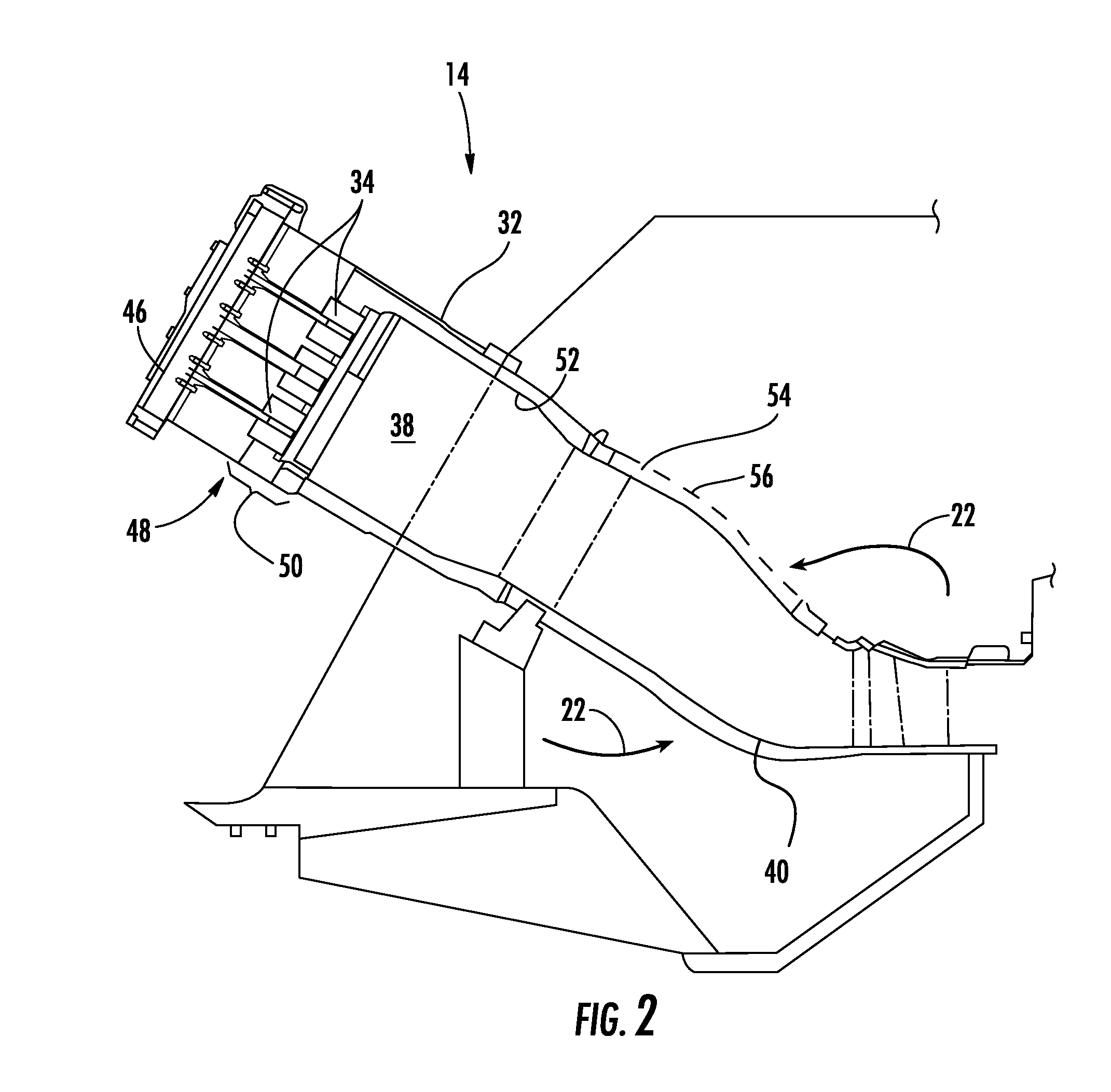
Monitoring health of a combustion dynamics sensing system
A method and system (14) for monitoring a health of a combustion dynamics sensing system (10) includes monitoring respective dynamic conditions of at least two combustor cans (16) of a can annular combustor (12) of a gas turbine engine with respective dynamic condition sensors (20) associated with each of the cans. The method also includes establishing a baseline relationship between the respective dynamic conditions and then identifying a variance from the baseline relationship indicative of a degraded signal quality provided by a dynamic condition sensor associated with at least one of the cans.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Methods and systems for inducing combustion dynamics
InactiveUS20100287943A1Increase combustion dynamicReduce combustion dynamicPulsating combustionEngine fuctionsDynamic methodCombustion
Methods and systems are provided for inducing combustion dynamics within turbine engines to remove combustion deposits within the turbine engine during operation of the turbine engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
SYSTEM FOR REDUCING COMBUSTION DYNAMICS AND NOx IN A COMBUSTOR
A combustor includes an end cap that extends radially across at least a portion of the combustor. The end cap includes an upstream surface axially separated from a downstream surface. A plurality of tubes extend from the upstream surface through the downstream surface of the end cap to provide fluid communication through the end cap. Each tube in a first set of the plurality of tubes has an inlet proximate to the upstream surface and an outlet downstream from the downstream surface. Each outlet has a first portion that extends a different axial distance from the inlet than a second portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for gas turbine engine lean blowout avoidance
InactiveUS20060042261A1Reduce probabilityPromote lowerEngine fuctionsEfficient propulsion technologiesCombustorTurbine
A method of monitoring and controlling the combustion dynamics of a gas turbine engine system is provided. The system includes at least one gas turbine that includes at least one combustor can. The method includes receiving a signal from a gas turbine engine sensor that is indicative of combustion dynamics in at least one of the combustor cans, processing the received signal to determine a probability of lean blowout for at least one combustor can, and controlling the gas turbine engine system to facilitate reducing a probability of a lean blowout (LBO) event using the determined probability of lean blowout.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for monitoring gas turbine combustion dynamics
InactiveUS6976351B2Verify accuracyGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsCombustorCombustion kinetics
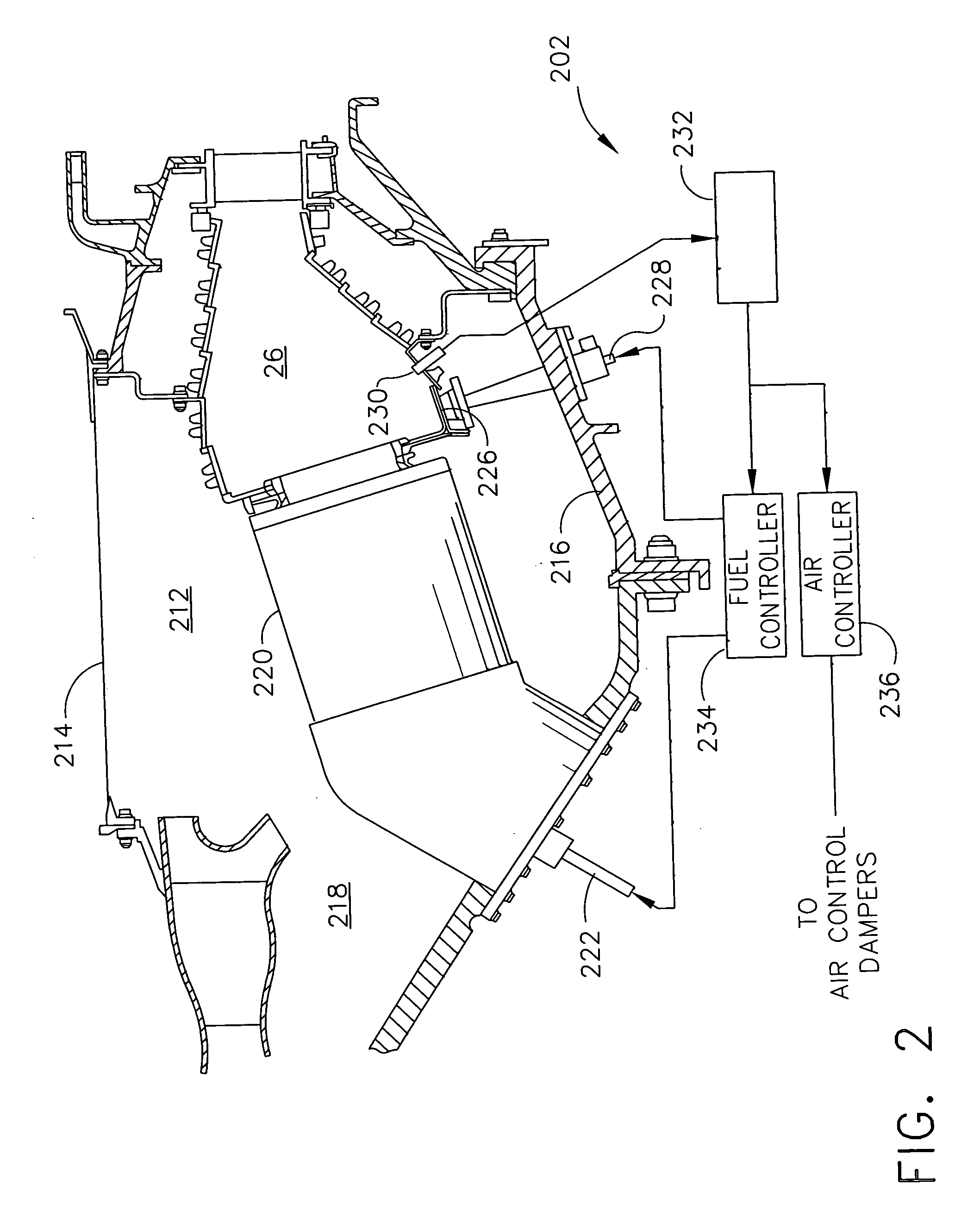
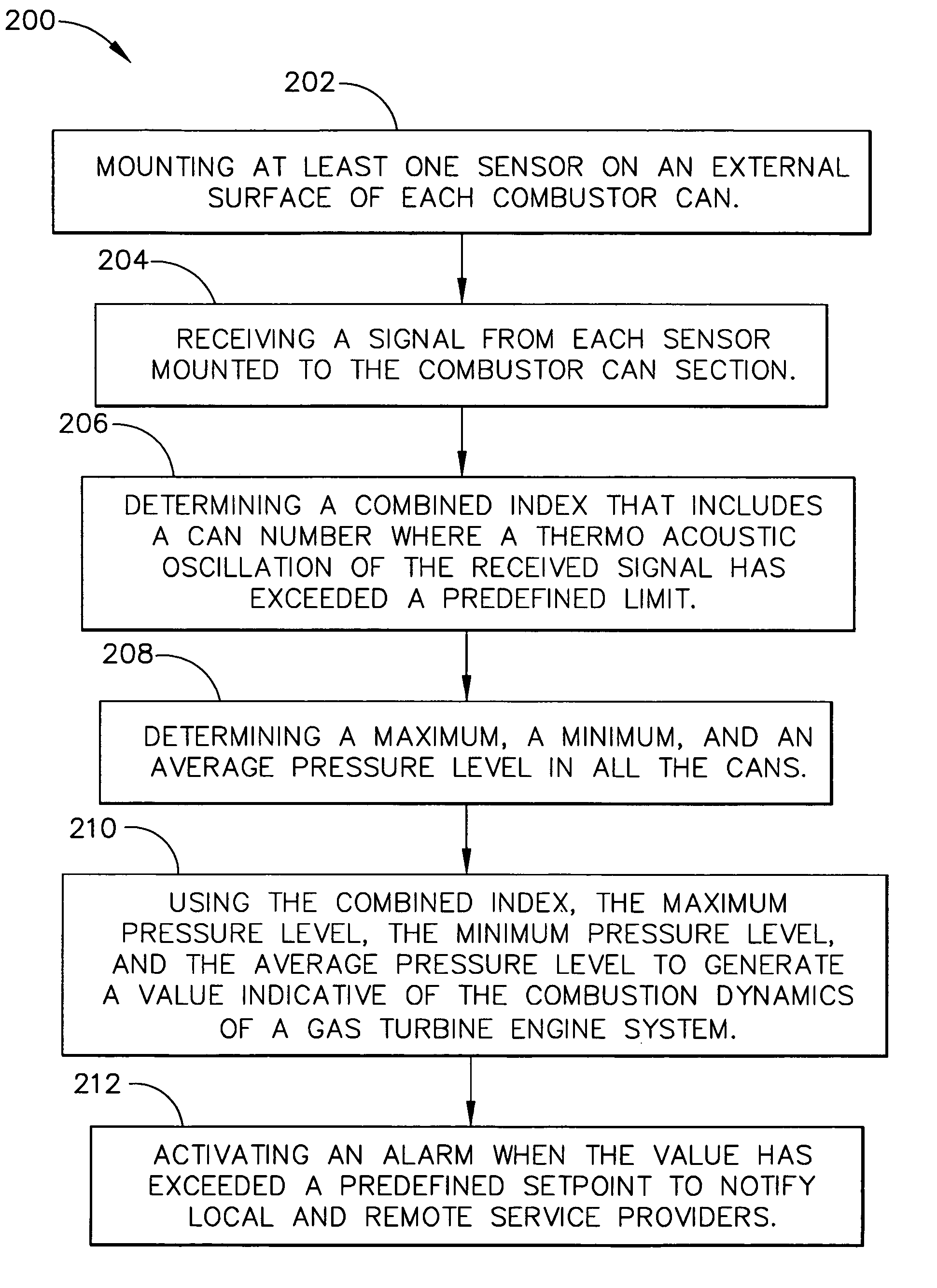
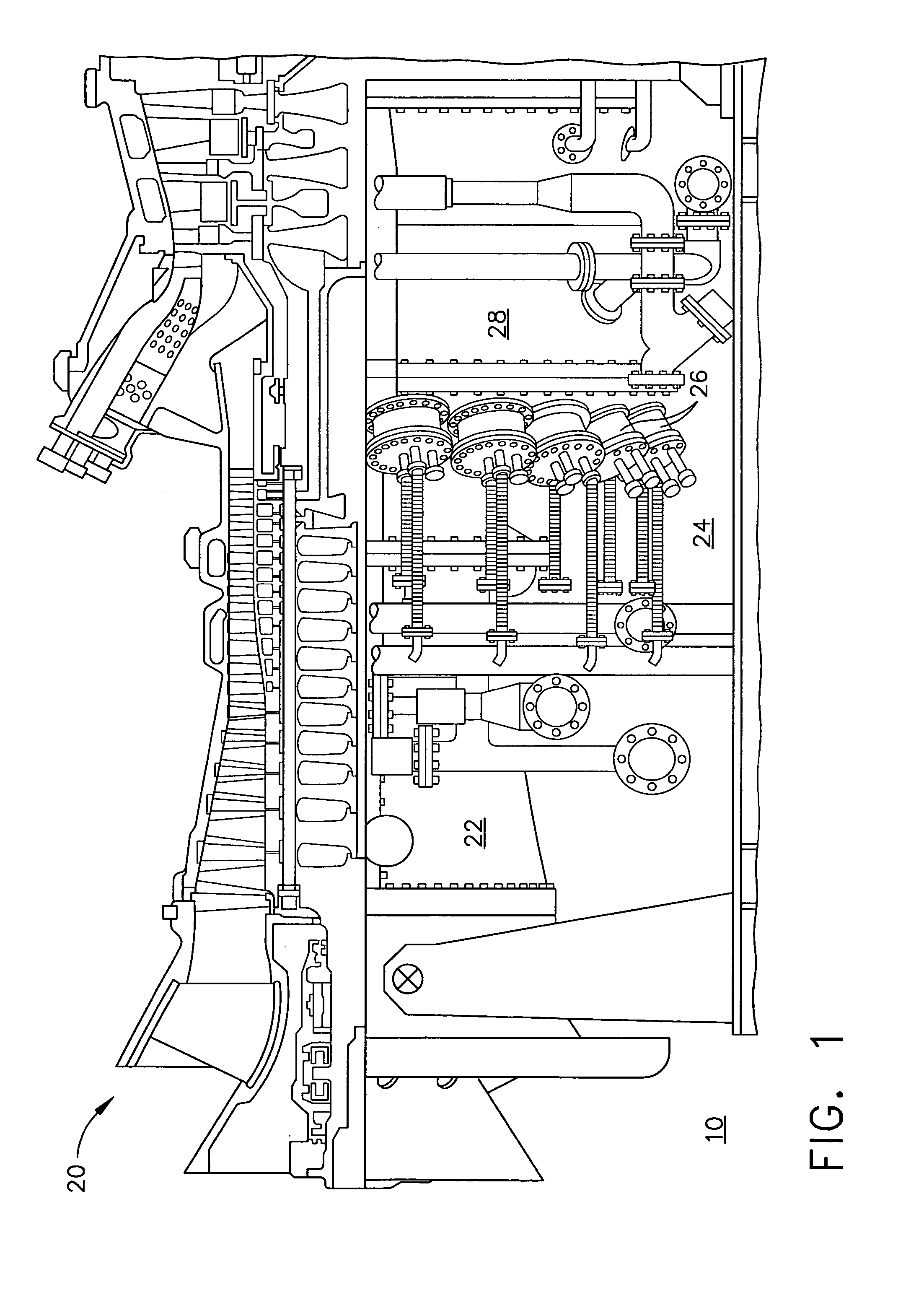
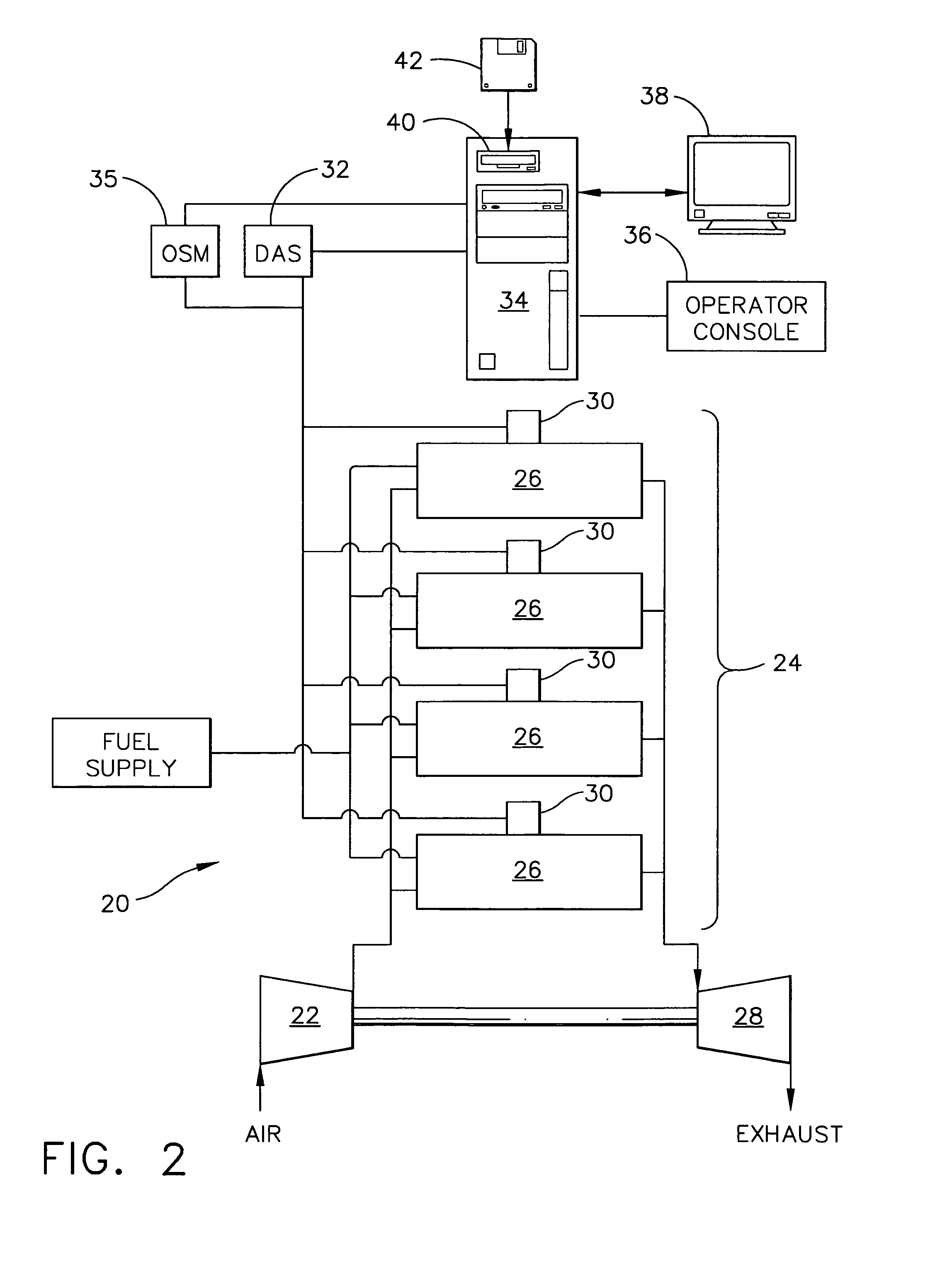
A method for monitoring and diagnosing the combustion dynamics of a gas turbine engine system includes mounting at least one sensor on an external surface of at least one combustor can, receiving a signal from the sensor mounted to the combustor can, validating an accuracy of the signal from the sensors, determining the combustion dynamics of the can based on the received signals, and generating an indication when a combustion dynamic threshold has been exceeded.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for automatic fuel blending and control for combustion gas turbine
A flexible and automatic system and method for blending an inexpensive secondary gas with a primary gas fuel for operation of a Dry Low NOx gas turbine. The secondary gas may be a gas fuel such as hydrogen, ethane, butane, propane and liquefied natural gas or an inert gas. Combustion dynamics are avoided by controlling the blended fuel within a permissible range for a Modified Wobbe Index. Combustion dynamics and gas turbine exhaust emissions may also be monitored to maintain safe combustion with the blended fuel. A gas turbine control system may adjust the blend and temperature of the primary gas fuel and the secondary gas to promote desired combustion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
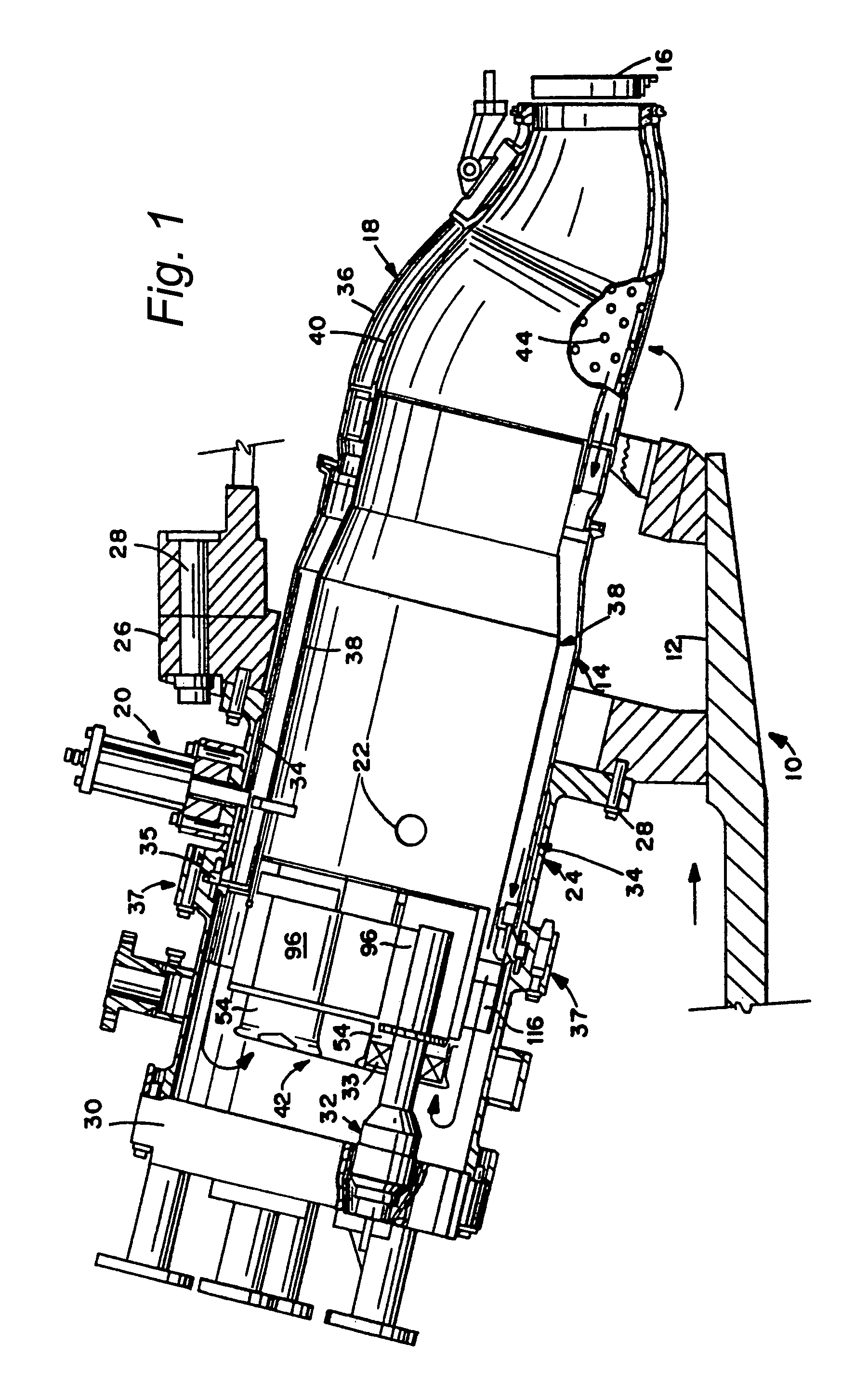
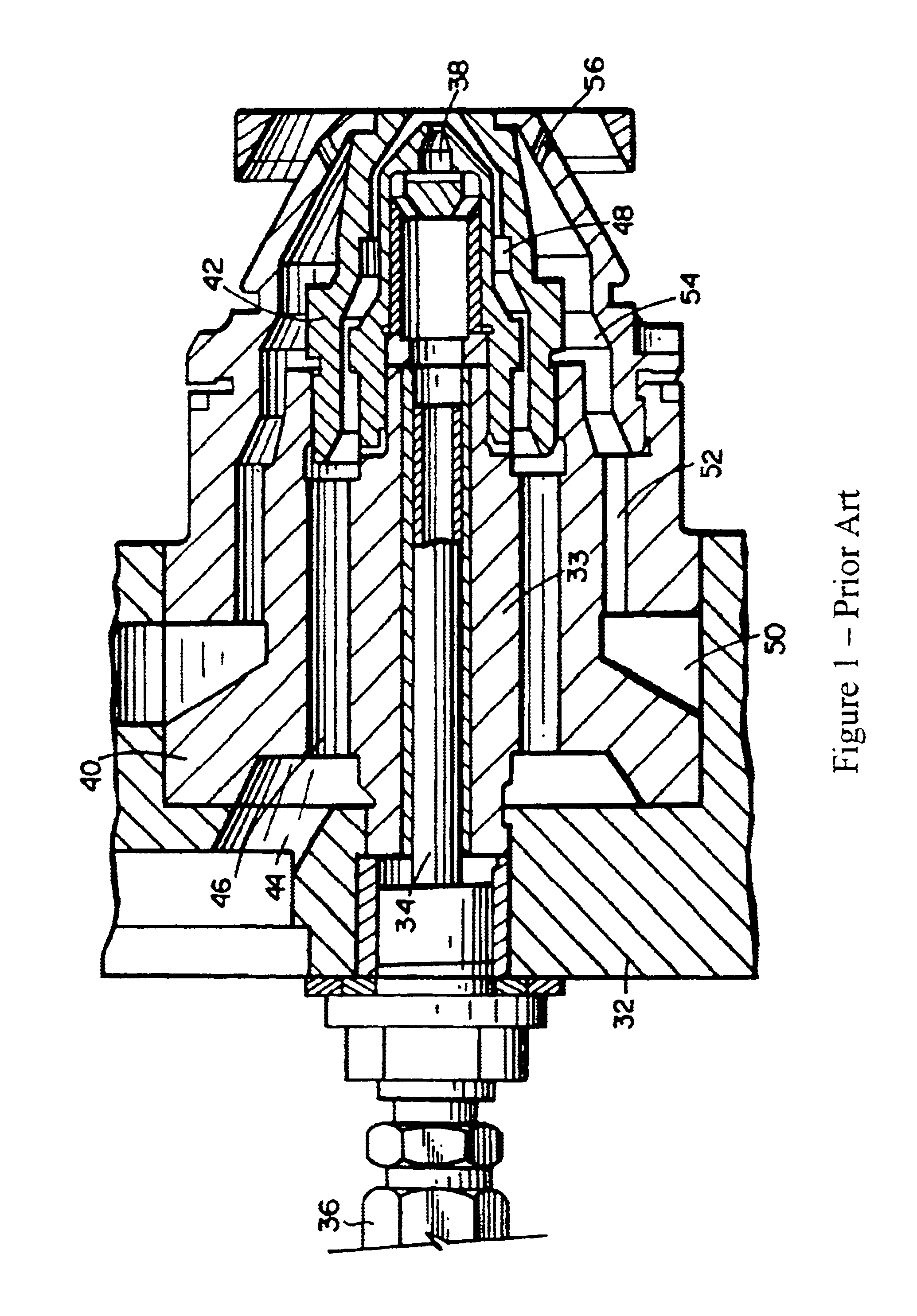
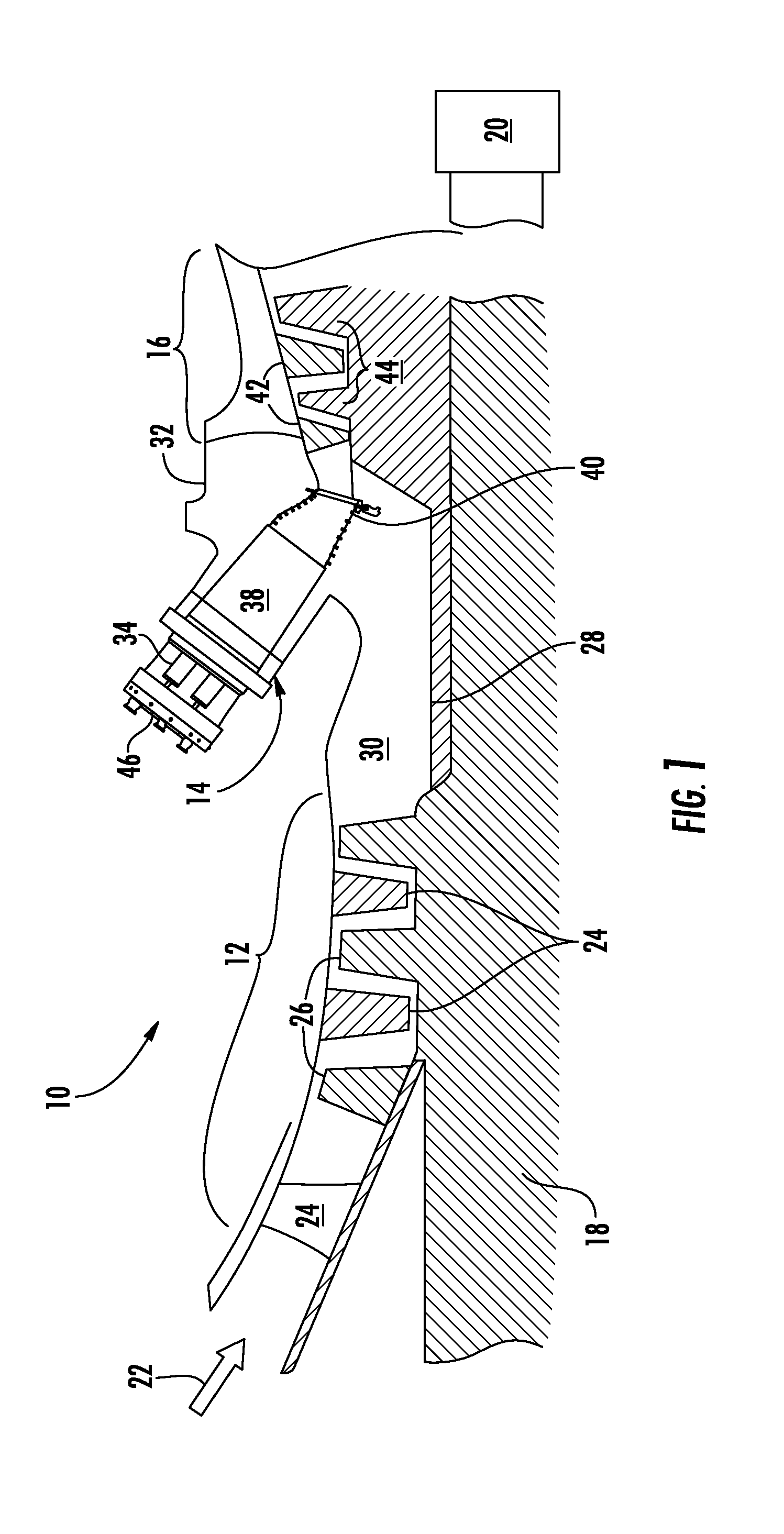
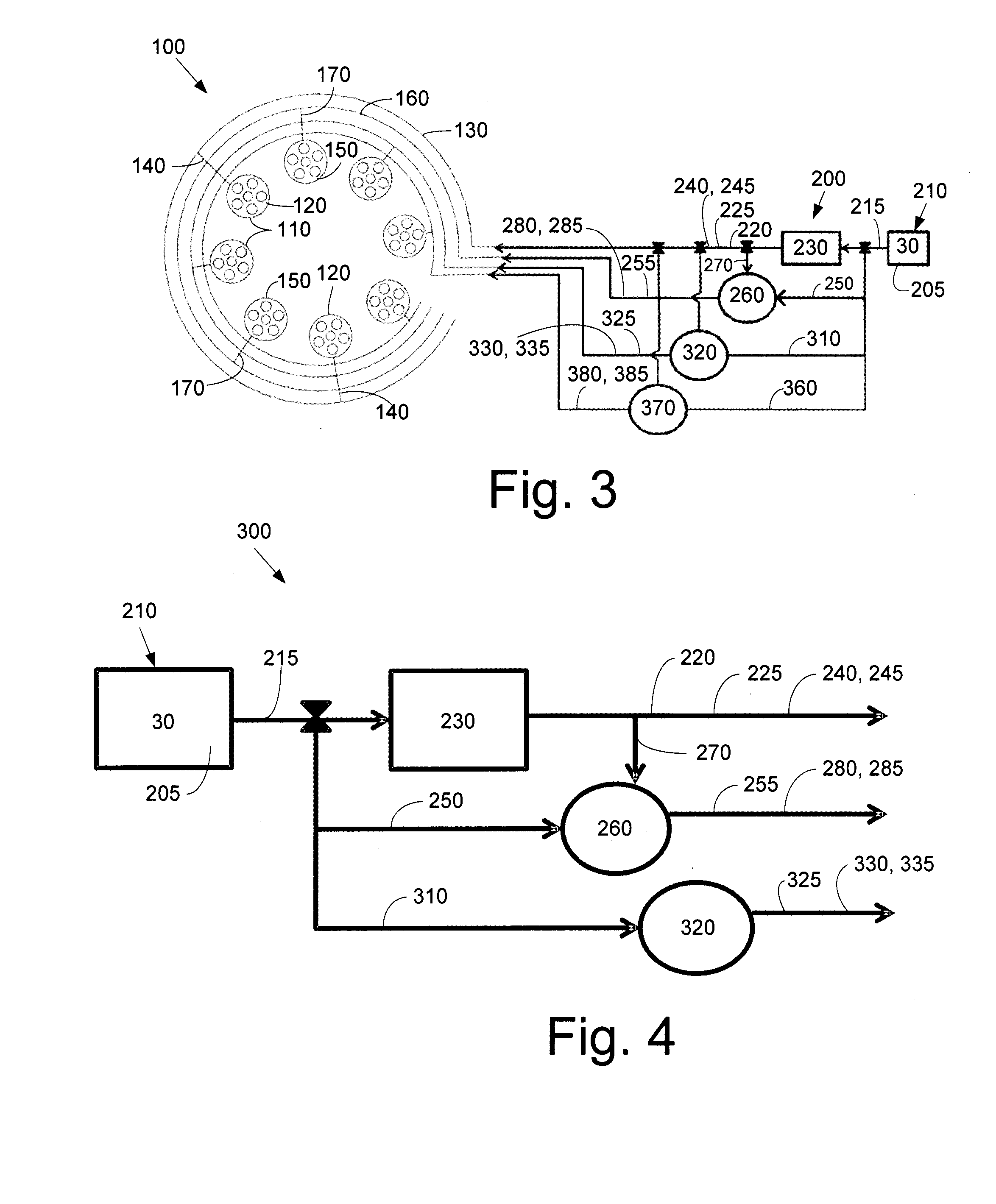
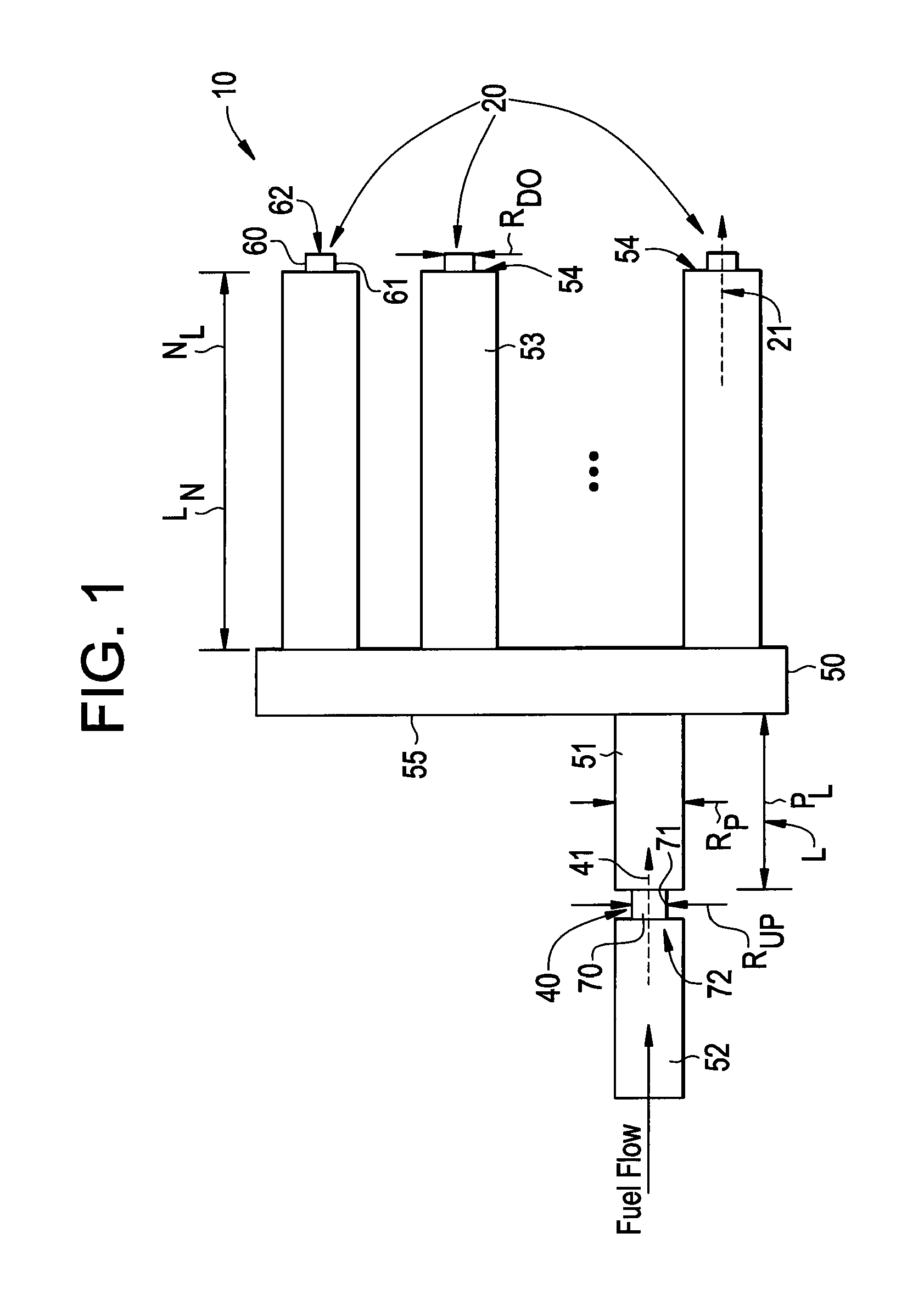
Method of fuel nozzle sizing and sequencing for a gas turbine combustor
InactiveUS6883329B1Uniform flame temperature distributionReduced pressure levelTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorProduct gas
A method for providing a gas turbine engine and a combustor having a more uniform fluid flow is disclosed. For a combustor end cover, individual nozzle flow rates are determined and nozzles positioned on an end cover such that each nozzle injects substantially the same amount of fluid as an adjacent nozzle. As a result, gas temperature variations within the combustor are reduced and combustion dynamics lowered. For a gas turbine engine utilizing a plurality of combustors, individual end cover flow rates are determined and end covers positioned on each combustor relative to the supply inlet of the engine such that each end cover is supplied with a substantially similar flow rate. Other factors including pressure loss and fluid temperature changes are taken into consideration when determining nozzle and end cover positions.
Owner:H2 IP UK LTD
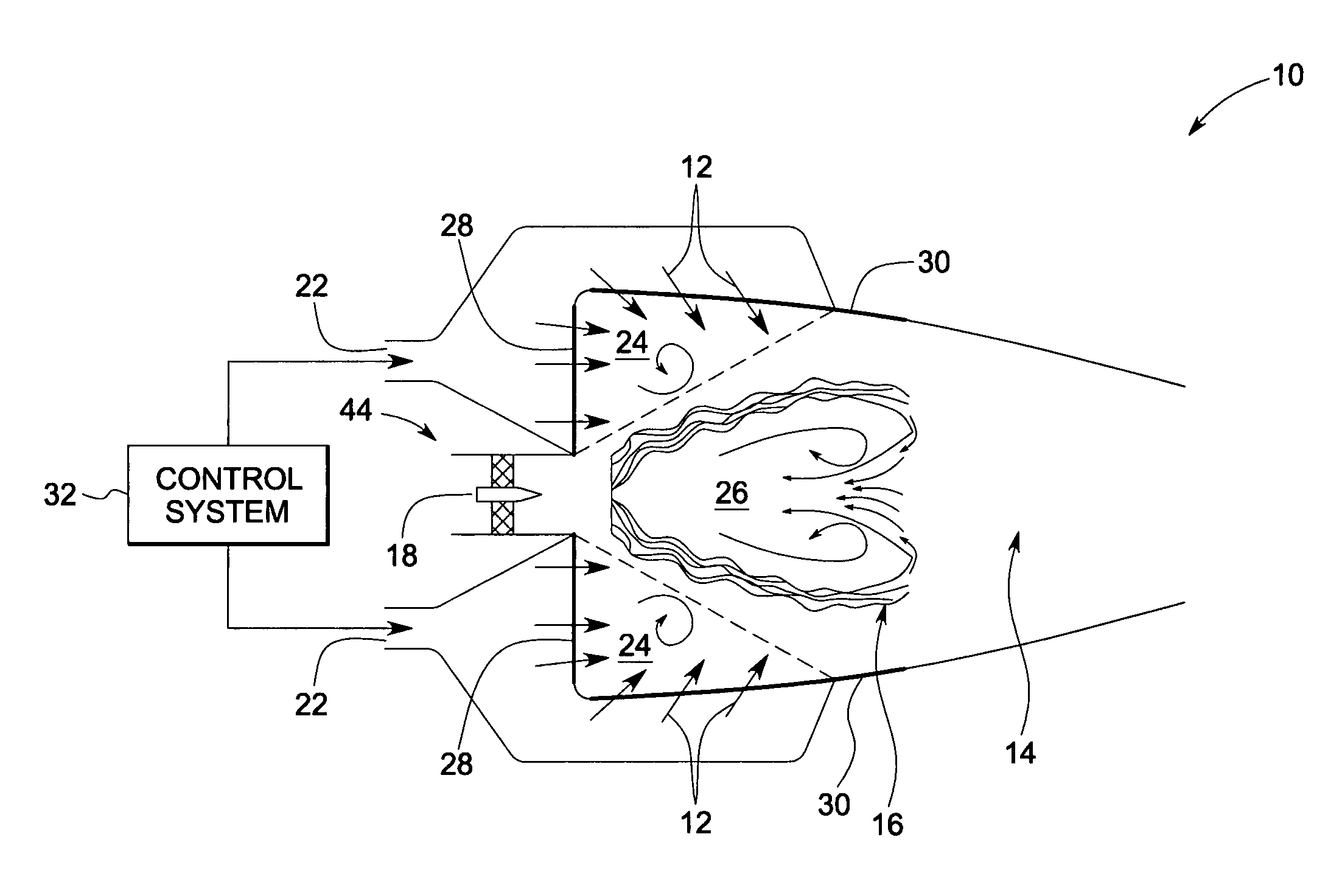
Multi functional sensor system for gas turbine combustion monitoring and control
ActiveUS20150168228A1Optimizing engine controlImprove performanceContinuous combustion chamberGas-turbine engine testingCombustion chamberEngineering
Thermoacoustic sensors, such as dynamic pressure sensors, in the combustor measure vibratory responses of the combustor. An integrated monitoring and control system controller correlates sensor readings with combustion thermoacoustic properties in order to identify combustion anomalies by wavelet or Fourier analysis techniques; determine bulk temperature characteristics within the combustor with dominant mode frequency analysis techniques; and optionally determines absolute active path temperatures within the combustor with acoustic pyrometry transmission and time-of-flight analysis techniques. In some embodiments all of the monitoring functions are performed with a commonly shared array of thermoacoustic sensors that function as both combustion dynamics thermoacoustic vibration / wave receivers and acoustic transmitters. The monitored combustion properties are used for controlling gas turbine combustion.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
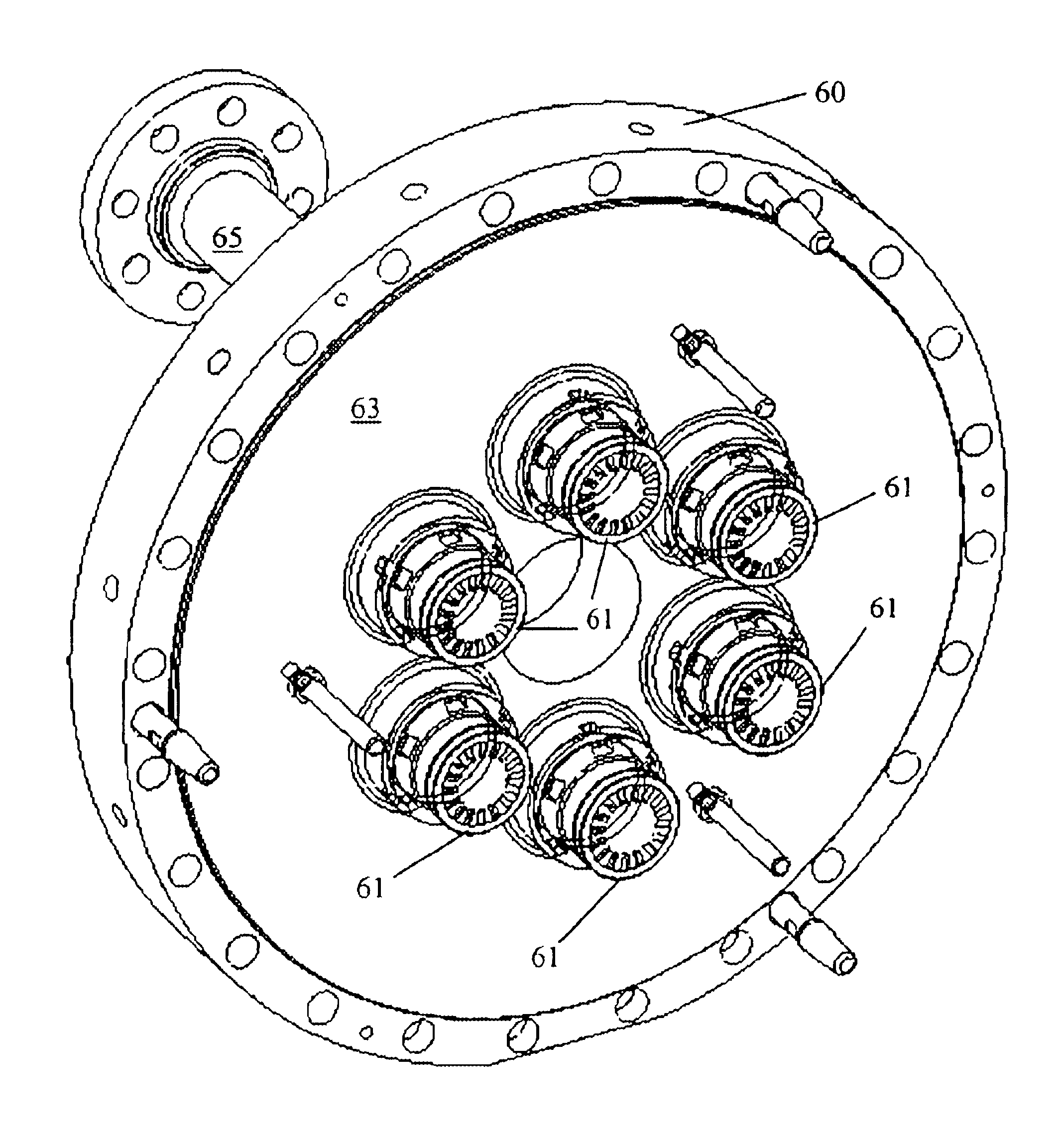
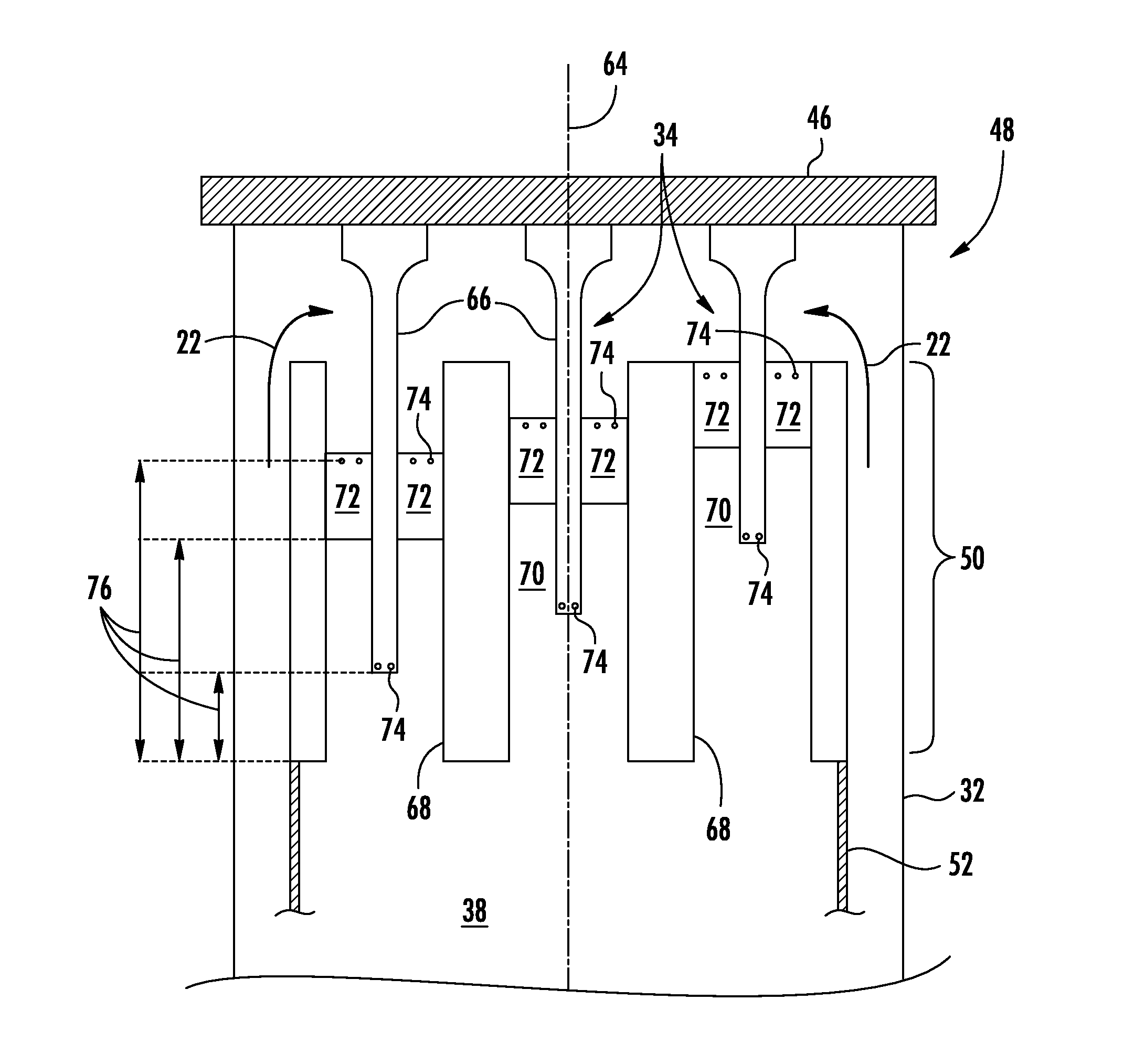
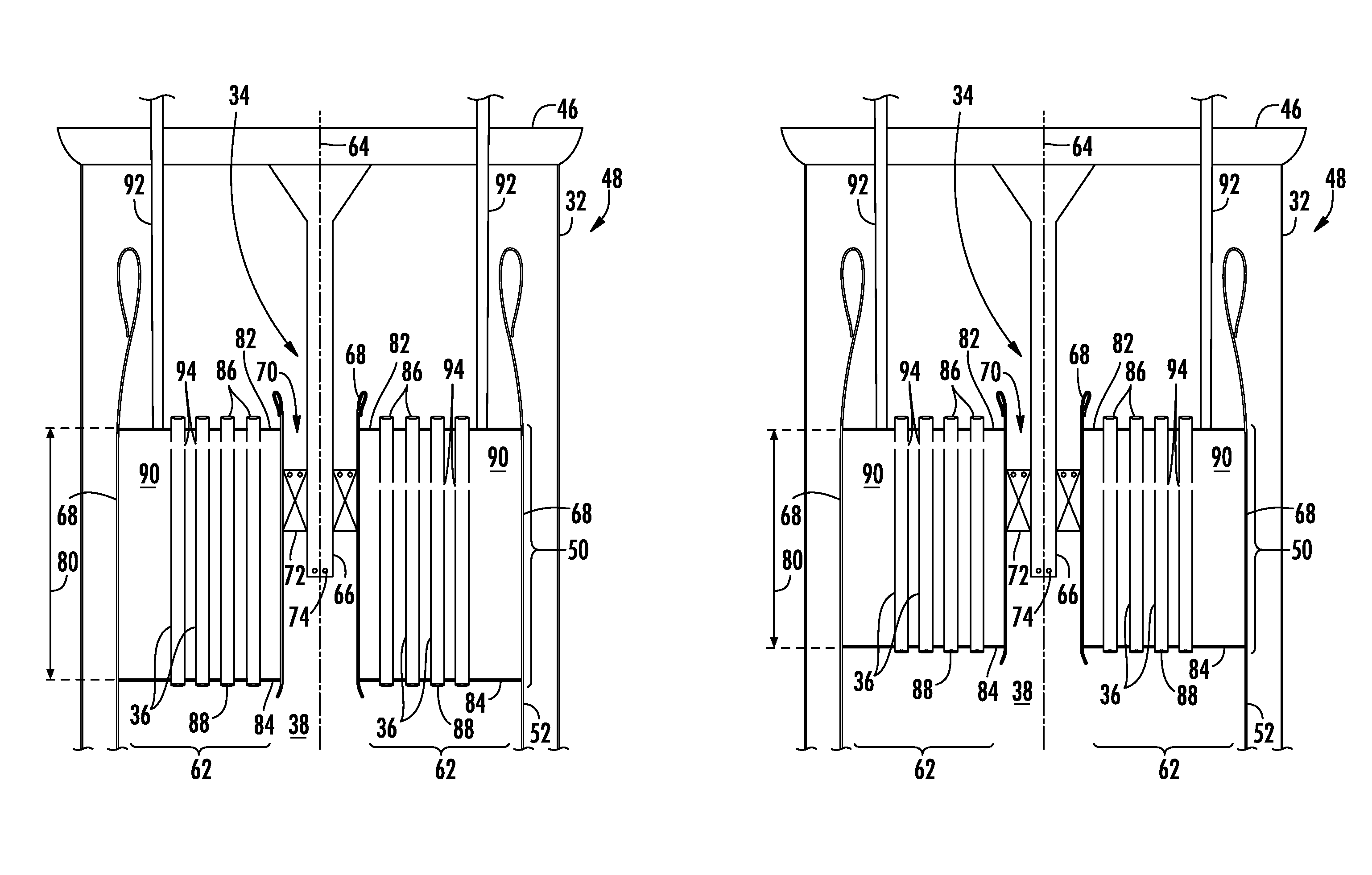
System and method for reducing combustion dynamics
ActiveUS20140245738A1Reduce combustion dynamicContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustion chamberCombustor
A system and method for reducing combustion dynamics includes first and second combustors arranged about an axis, and each combustor includes a plurality of tubes that extend axially through at least a portion of the combustor and a combustion chamber downstream from the plurality of tubes. A fuel injector extends through each tube to provide fluid communication into each tube at a fourth axial distance from the combustion chamber. The fourth axial distance in the first combustor is different than the fourth axial distance in the second combustor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
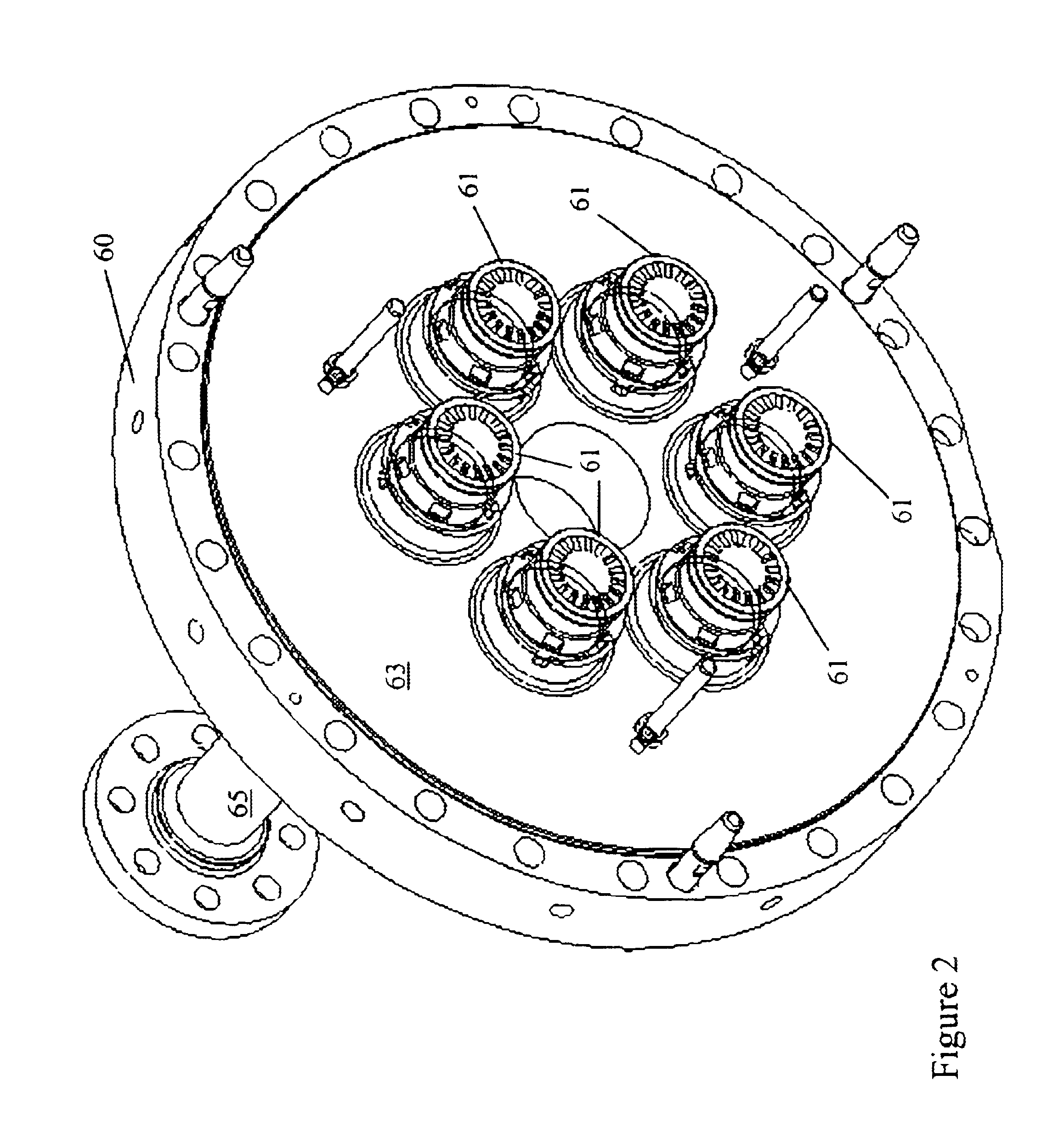
System and method for reducing combustion dynamics and NOX in a combustor
ActiveUS20130104556A1Reduce combustion dynamicBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustorWorking fluid
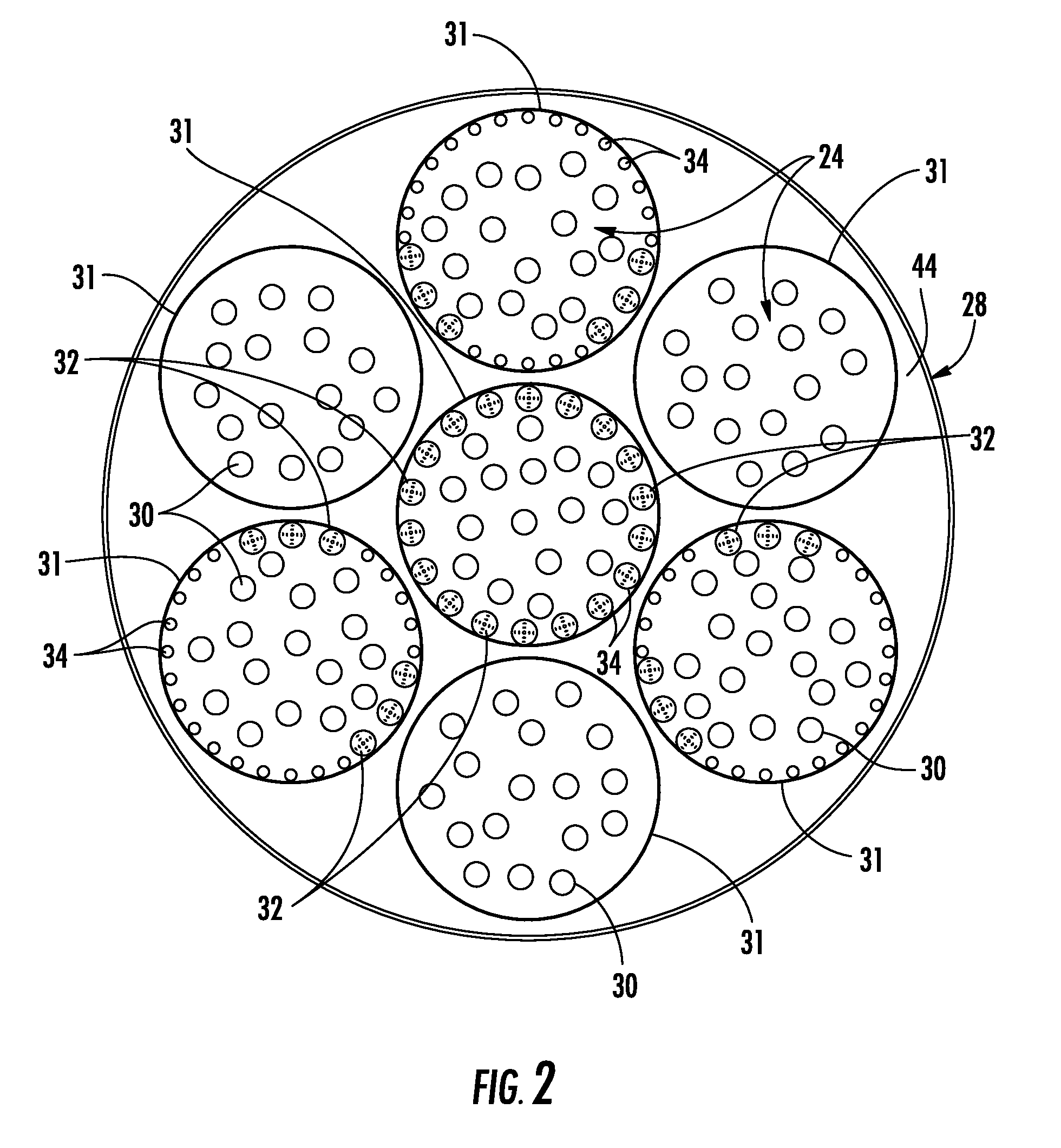
A system for reducing combustion dynamics and NOx in a combustor includes a tube bundle that extends radially across at least a portion of the combustor, wherein the tube bundle comprises an upstream surface axially separated from a downstream surface. A shroud circumferentially surrounds the upstream and downstream surfaces. A plurality of tubes extends through the tube bundle from the upstream surface through the downstream surface, wherein the downstream surface is stepped to produce tubes having different lengths through the tube bundle. A method for reducing combustion dynamics and NOx in a combustor includes flowing a working fluid through a plurality of tubes radially arranged between an upstream surface and a downstream surface of an end cap that extends radially across at least a portion of the combustor, wherein the downstream surface is stepped.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
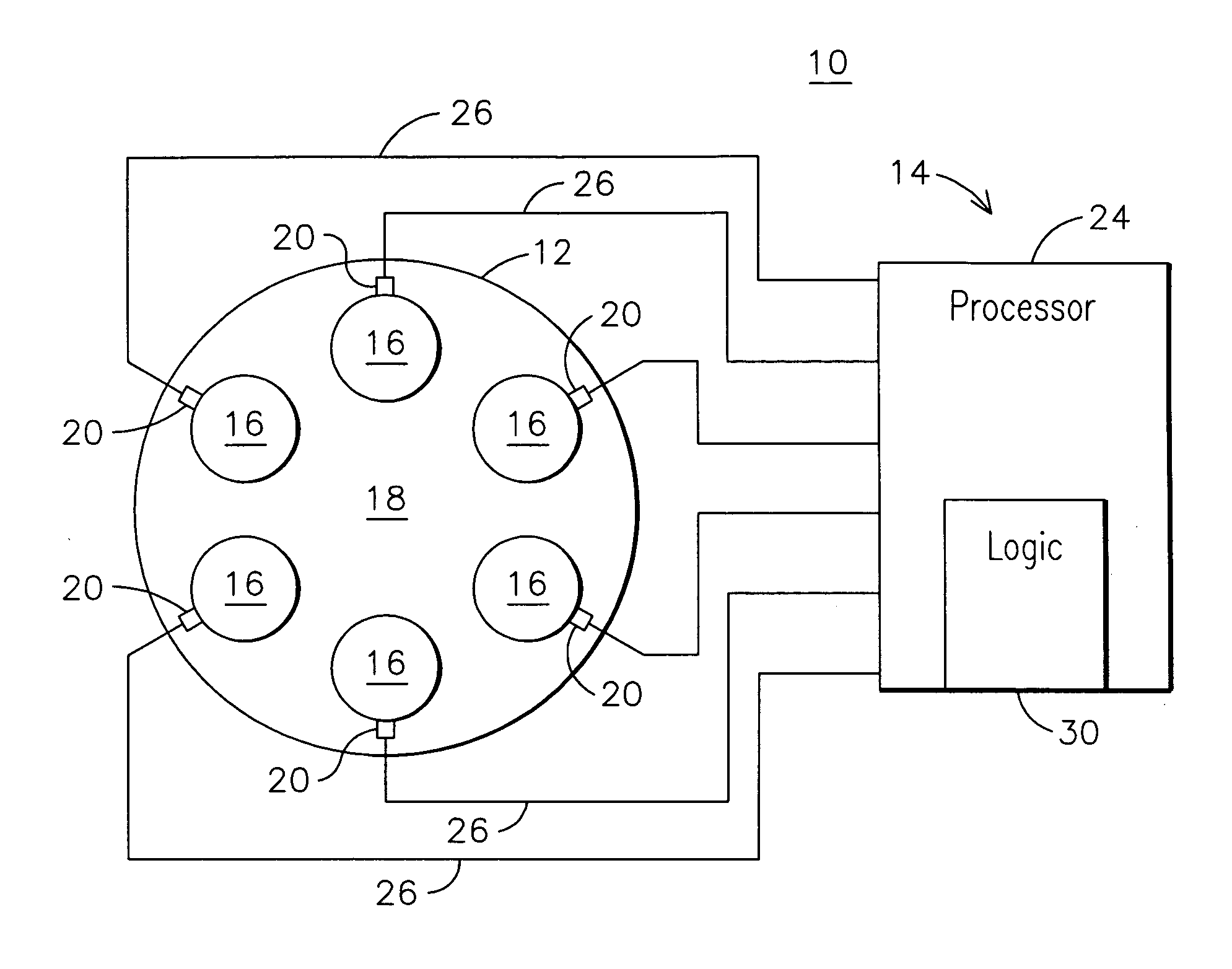
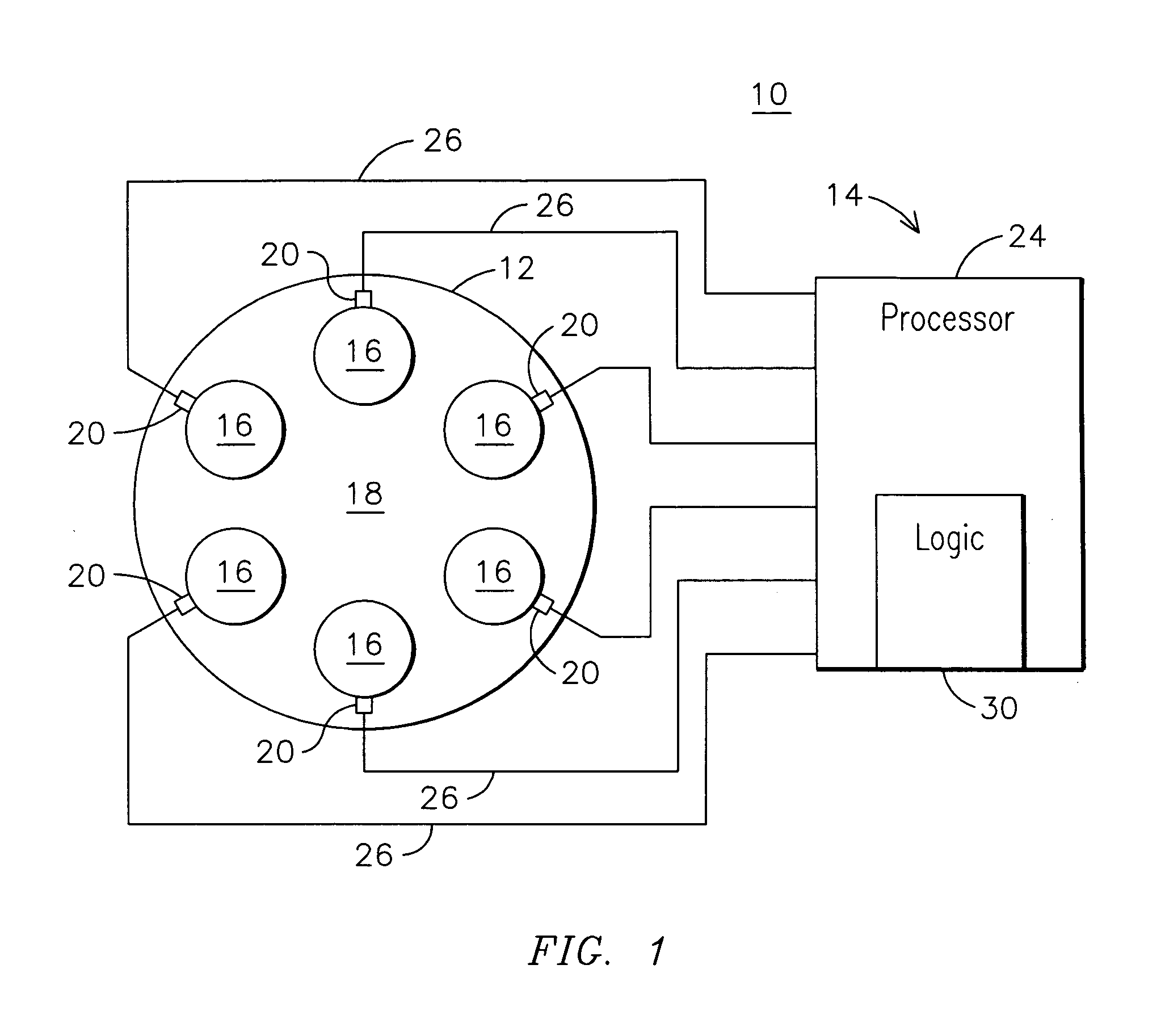
Combustion dynamics monitoring
InactiveUS20070214797A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCombustorEngineering
A method for monitoring combustion dynamics of a can annular combustor (12) of a gas turbine engine includes monitoring respective dynamic operating conditions of cans (16) of the can annular combustor with respective dynamic operating condition sensors (20) associated with each of the cans. The method also includes grouping the cans into two or more groups according to their respective dynamic operating conditions and identifying a sensor providing an anomalous dynamic operating condition reading for at least one of the cans. The method further includes determining a need to service the identified sensor according to the associated can's group membership.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
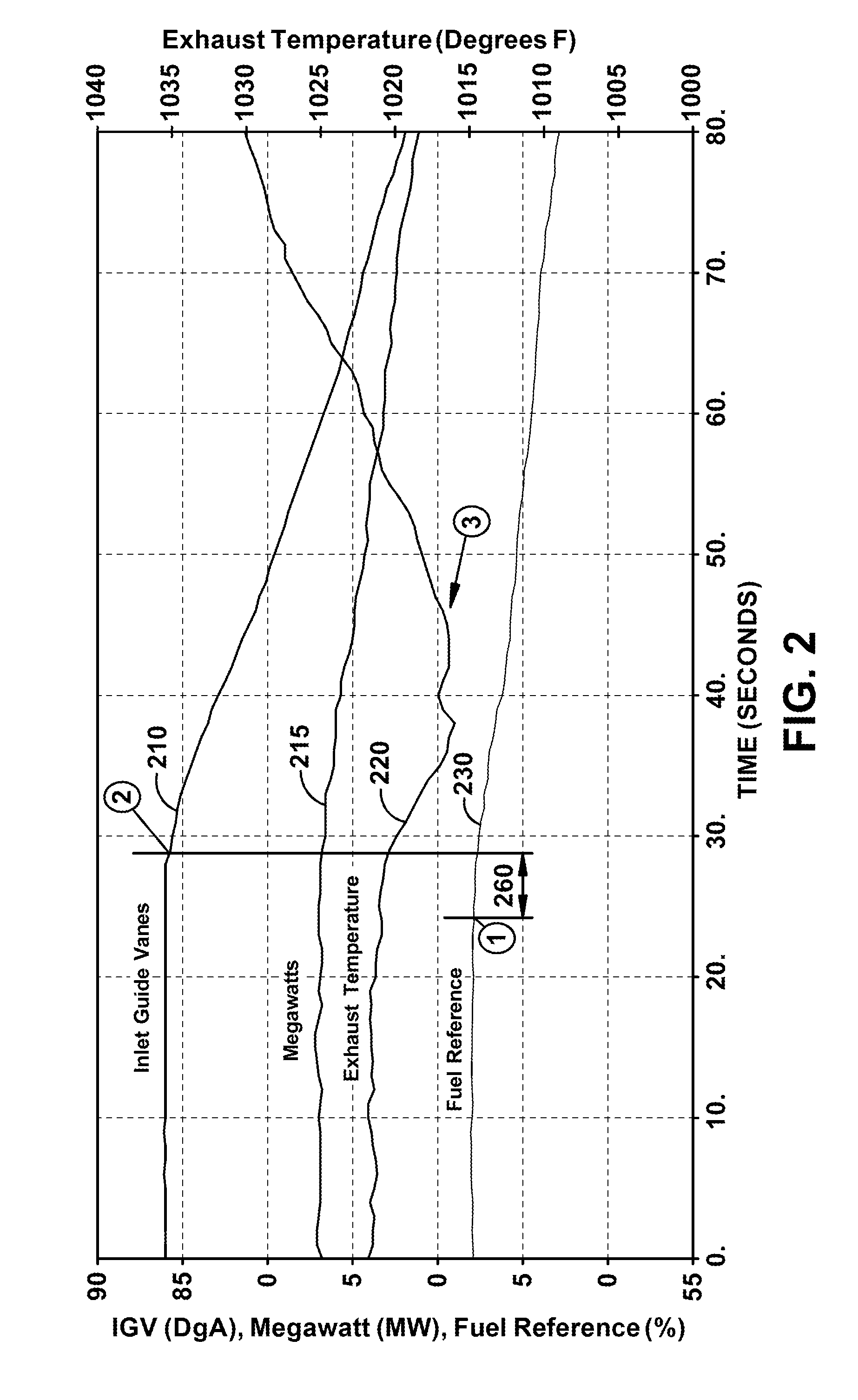
Method Of Mitigating Undesired Gas Turbine Transient Response Using Event Based Actions
A method of managing transient events regularly seen during gas turbine operation that may cause undesirable operation and hardware damage. During certain transient operations, a lag may be seen between reference exhaust temperature and actual turbine exhaust temperature. This lag can result in an under-fired condition within the combustion system of variable magnitude and duration. Either fuel split schedules or a control algorithm can be positioned during these transients to prevent combustion dynamics or loss of flame. Combustion dynamics are known to cause damage that may require hardware replacement. Once the transient has completed, normal control operation is resumed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for controlling combustion dynamics and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20100223933A1Working fluid for enginesEfficient propulsion technologiesCombustion systemCombustion chamber
A method for controlling combustion dynamics is provided. The method includes providing a flow of partially premixed, premixed, or lean premixed fuel-air into a combustion chamber. The method also includes monitoring the combustion system for combustion dynamics. The method further includes actuating a system to control and abate combustion dynamics.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustor can temperature control system
ActiveUS20140238041A1Reduce coherenceReduced dynamicsTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsEngine fuctionsTemperature controlCombustor
The present application provides a fuel delivery system for a combustor with reduced coherence and / or reduced combustion dynamics. The combustor can assembly may include a first manifold for delivering a first flow of fuel to a first set of fuel injectors and a second manifold for delivering a second flow of fuel to a second set of fuel injectors. The first flow of fuel may have a first temperature and the second flow of fuel may have a second temperature. The first temperature may be higher than the second temperature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustor and cap assemblies for combustors in a gas turbine
The cap assembly of a turbine combustor includes a plurality of burner tubes sealed against fuel nozzles extending in the tubes. These piston seals are coated with a high velocity oxygen fuel coating to extend their service life. The outer cap body assembly includes concentric seal rings each with cantilevered convex fingers circumferentially offset from one another to seal between the cap assembly casing and the inner liner. The cap assembly casing is provided with a plurality of holes at predetermined locations about the casing to minimize or eliminate response to combustion dynamics.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
FUEL SYSTEM ACOUSTIC FEATURE TO MITIGATE COMBUSTION DYNAMICS FOR MULTI-NOZZLE DRY LOW Nox COMBUSTION SYSTEM AND METHOD
A dry low NOx (DLN) fuel nozzle of a fuel system is provided and includes one or more downstream orifices formed to define a first fluid path along which fluid is directed to flow, an upstream orifice, located upstream from the one or more downstream orifices, formed to define a second fluid path along which the fluid is directed to flow and connecting passages disposed to fluidly couple the first and second fluid paths of the downstream and upstream orifices, respectively, to one another. At least one of a radial size and an axial location of the upstream orifice is set to cooperatively detune an acoustic impedance of the fuel system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustion liner cap assembly for combustion dynamics reduction
ActiveUS20050044855A1Reduce combustion dynamicContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustionEngineering
A combustion liner cap assembly includes a cylindrical outer sleeve supporting internal structure therein and a plurality of fuel nozzle openings formed through the internal structure. A first set of circumferentially spaced cooling holes is formed through the cylindrical outer sleeve, and a second set of circumferentially spaced cooling holes is formed through the cylindrical outer sleeve. The second set of cooling holes is axially spaced from the first set of cooling holes. The resulting construction serves to decrease combustion dynamics in a simplified manner that is retrofittable to current designs and reversible without impacting the original configuration. The reduction in combustion dynamics improves hardware life, which leads to reduced repair and replacement costs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
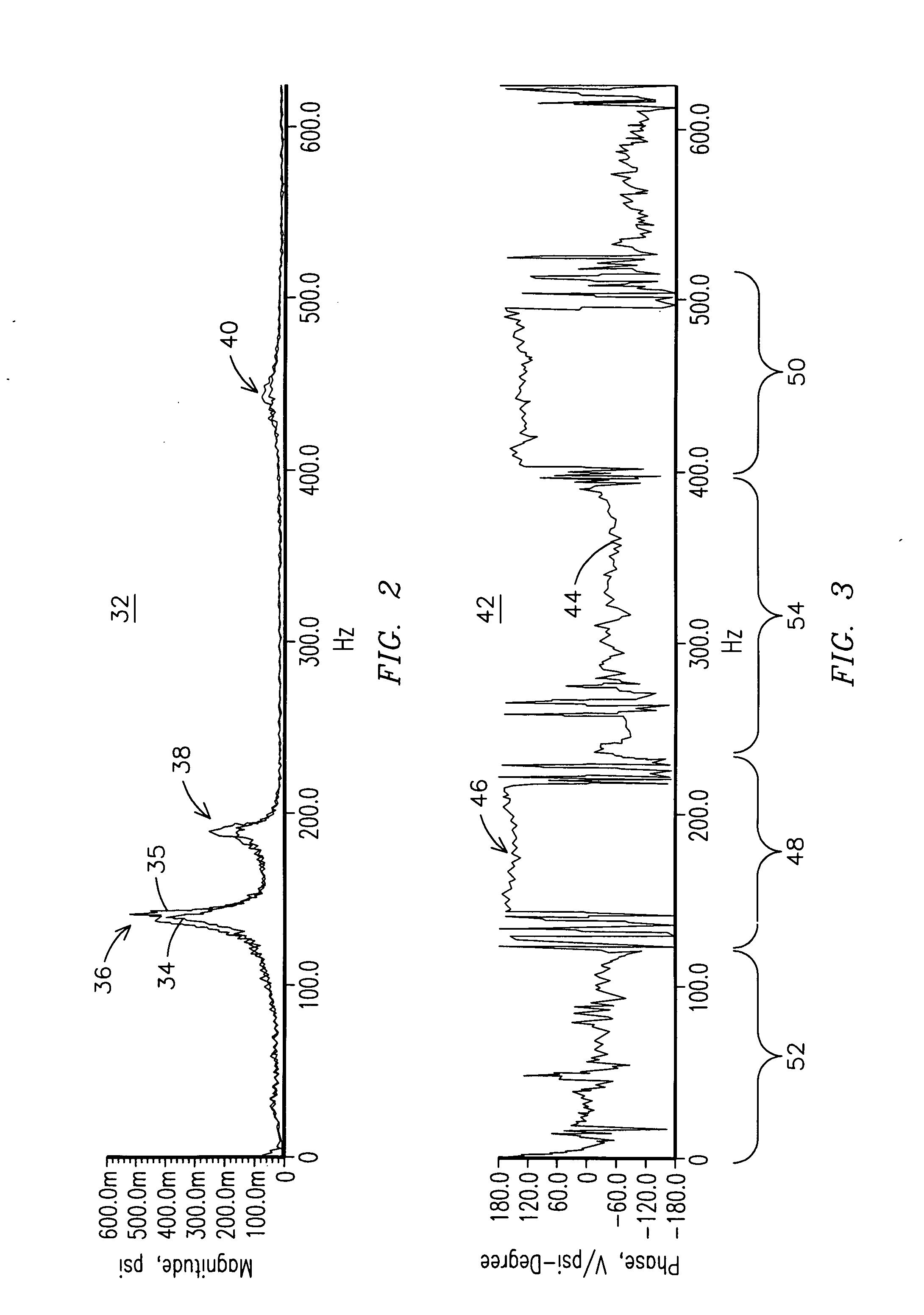
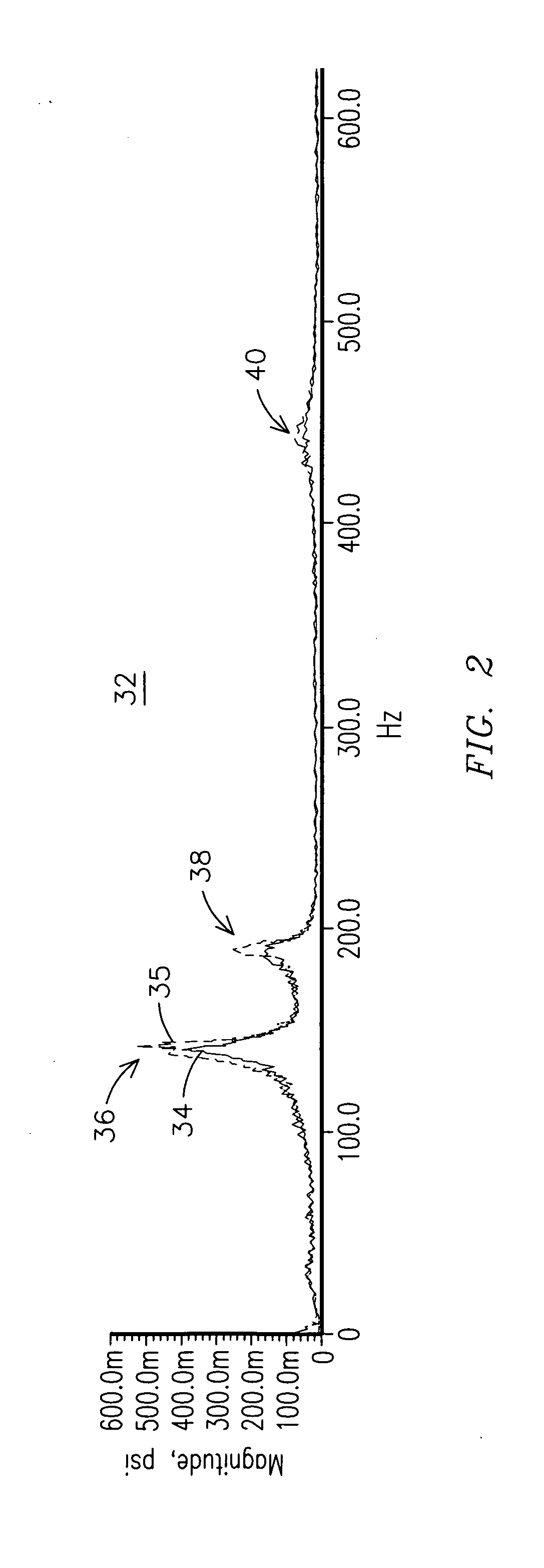
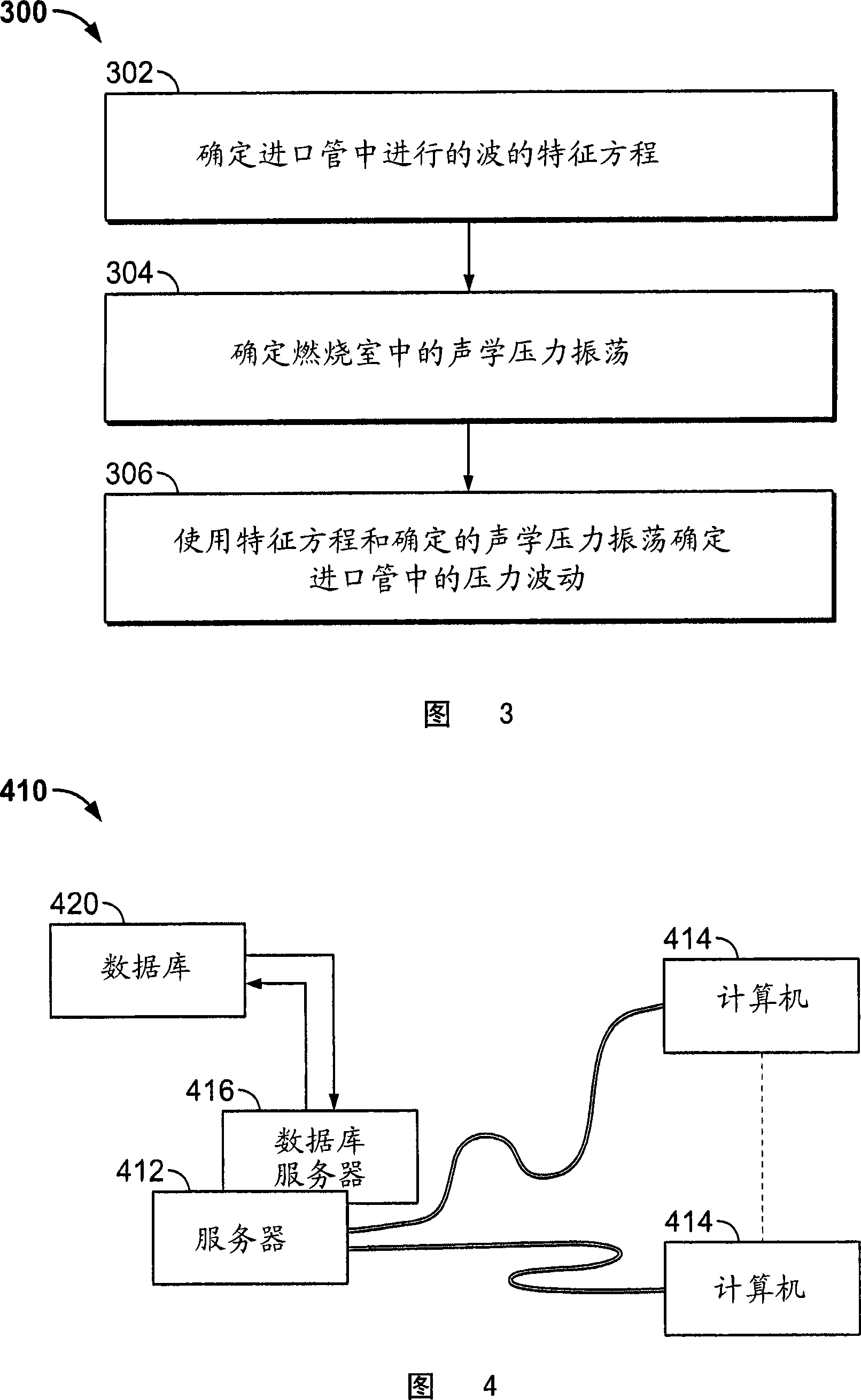
Methods and systems for analysis of combustion dynamics in the time domain
Methods and systems for analyzing combustion dynamics of a combustor system in the time domain are provided. The combustor system includes an inlet pipe coupled in flow communication with a combustion chamber. The method includes determining a characteristic equation of a wave traveling in the inlet pipe, determining an acoustic pressure oscillation in the combustion chamber, and determining a pressure fluctuation in the inlet pipe using the characteristic equation and the determined acoustic pressure oscillation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for reducing combustion dynamics in a combustor
InactiveUS8511086B1Reduce combustion dynamicContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberCombustor
A system for reducing combustion dynamics in a combustor includes an end cap having an upstream surface axially separated from a downstream surface, and tube bundles extend through the end cap. A diluent supply in fluid communication with the end cap provides diluent flow to the end cap. Diluent distributors circumferentially arranged inside at least one tube bundle extend downstream from the downstream surface and provide fluid communication for the diluent flow through the end cap. A method for reducing combustion dynamics in a combustor includes flowing fuel through tube bundles that extend axially through an end cap, flowing a diluent through diluent distributors into a combustion chamber, wherein the diluent distributors are circumferentially arranged inside at least one tube bundle and each diluent distributor extends downstream from the end cap, and forming a diluent barrier in the combustion chamber between at least one pair of adjacent tube bundles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Secondary water injection for diffusion combustion systems
InactiveUS20110314831A1Easy to controlReduce wearTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion systemEngineering
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Methods and systems for analysis of combustion dynamics in the time domain
InactiveUS20080091379A1Inflated body pressure measurementVolume/mass flow measurementTime domainCombustor
Methods and systems for analyzing combustion dynamics of a combustor system in the time domain are provided. The combustor system includes an inlet pipe coupled in flow communication with a combustion chamber. The method includes determining a characteristic equation of a wave traveling in the inlet pipe, determining an acoustic pressure oscillation in the combustion chamber, and determining a pressure fluctuation in the inlet pipe using the characteristic equation and the determined acoustic pressure oscillation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustor health and performance monitoring system for gas turbines using combustion dynamics
A system and method each utilize combustion dynamics data to monitor and assess gas turbine combustor health and performance. The system and method each employ a physics-based model to differentiate changes in the spectral features attributable to variations in the operating conditions from differences caused from changes in the hardware.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
NOx ADJUSTMENT METHOD FOR GAS TURBINE COMBUSTORS
ActiveUS20060260319A1Engine manufactureTurbine/propulsion fuel flow conduitsCombustorCombustion chamber
An embodiment may comprise a system for controlling NOx emissions from a turbine having combustion chambers. The system may comprise a center fuel flow and a plurality of outer fuel flows for each of a plurality of combustion chambers. An outer fuel flow is set to achieve a desired level of combustion dynamics for at least one of the plurality of combustion chambers. A delta adjustment value is determined for the center fuel flow that will result in a desired level of NOx emissions from the turbine, and for adjusting the center fuel flow according to the determined delta adjustment value to obtain the desired level of NOx emissions from the turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System for reducing combustion dynamics
A system and method for reducing combustion dynamics includes first and second combustors arranged about an axis, and each combustor includes a cap assembly that extends radially across at least a portion of the combustor and a combustion chamber downstream from the cap assembly. Each cap assembly includes a plurality of tubes that extend axially through the cap assembly to provide fluid communication through the cap assembly to the combustion chamber and a fuel injector that extends through each tube to provide fluid communication into each tube. Each cap assembly has an axial length, and the axial length of the cap assembly in the first combustor is different than the axial length of the cap assembly in the second combustor.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
System and method for reducing combustion dynamics and NOx in a combustor
ActiveUS9188335B2Reduce combustion dynamicBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustorWorking fluid
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com