Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Cognitive load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
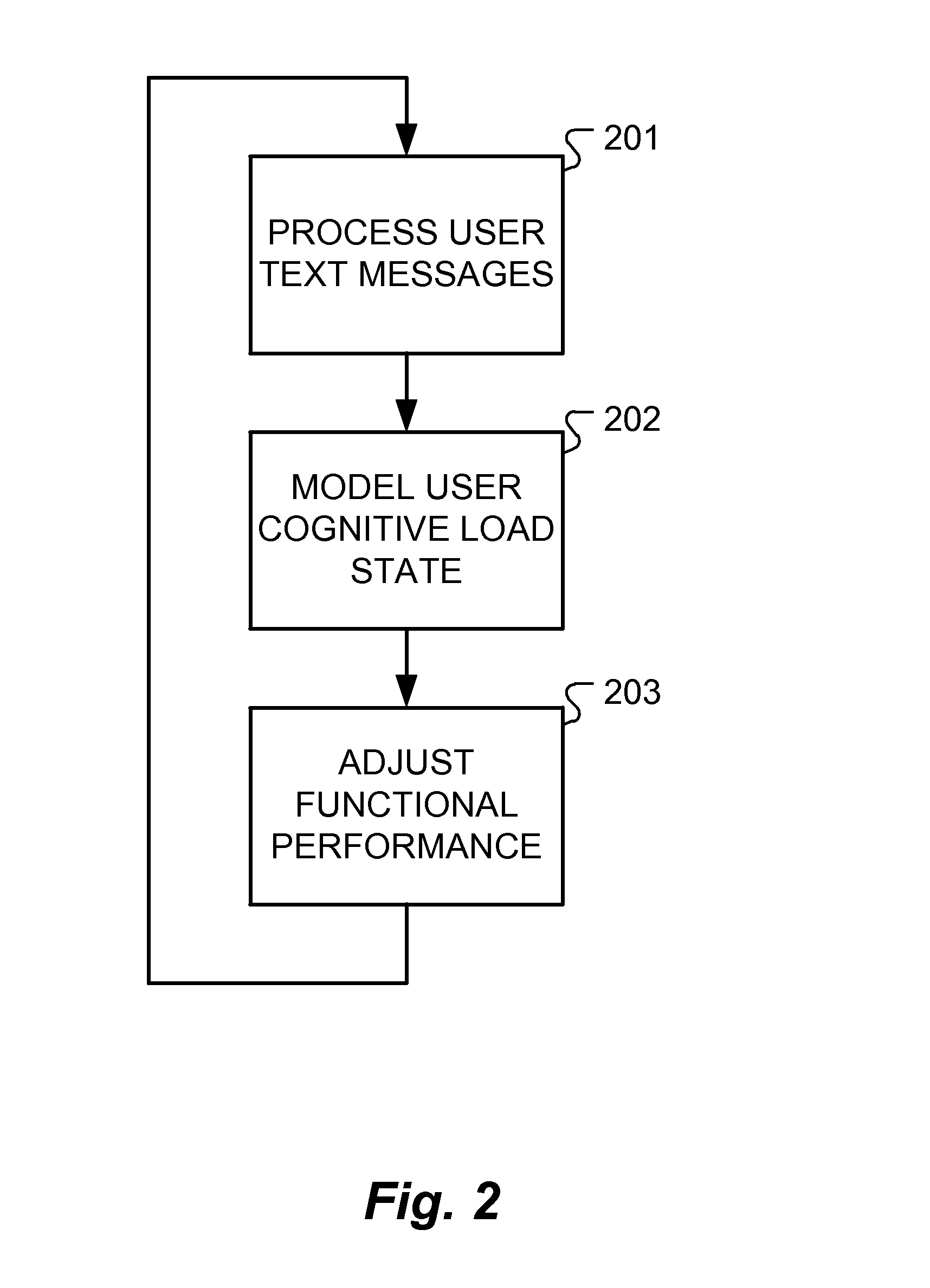
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load refers to the used amount of working memory resources. Cognitive load theory differentiates cognitive load into three types: intrinsic, extraneous, and germane.
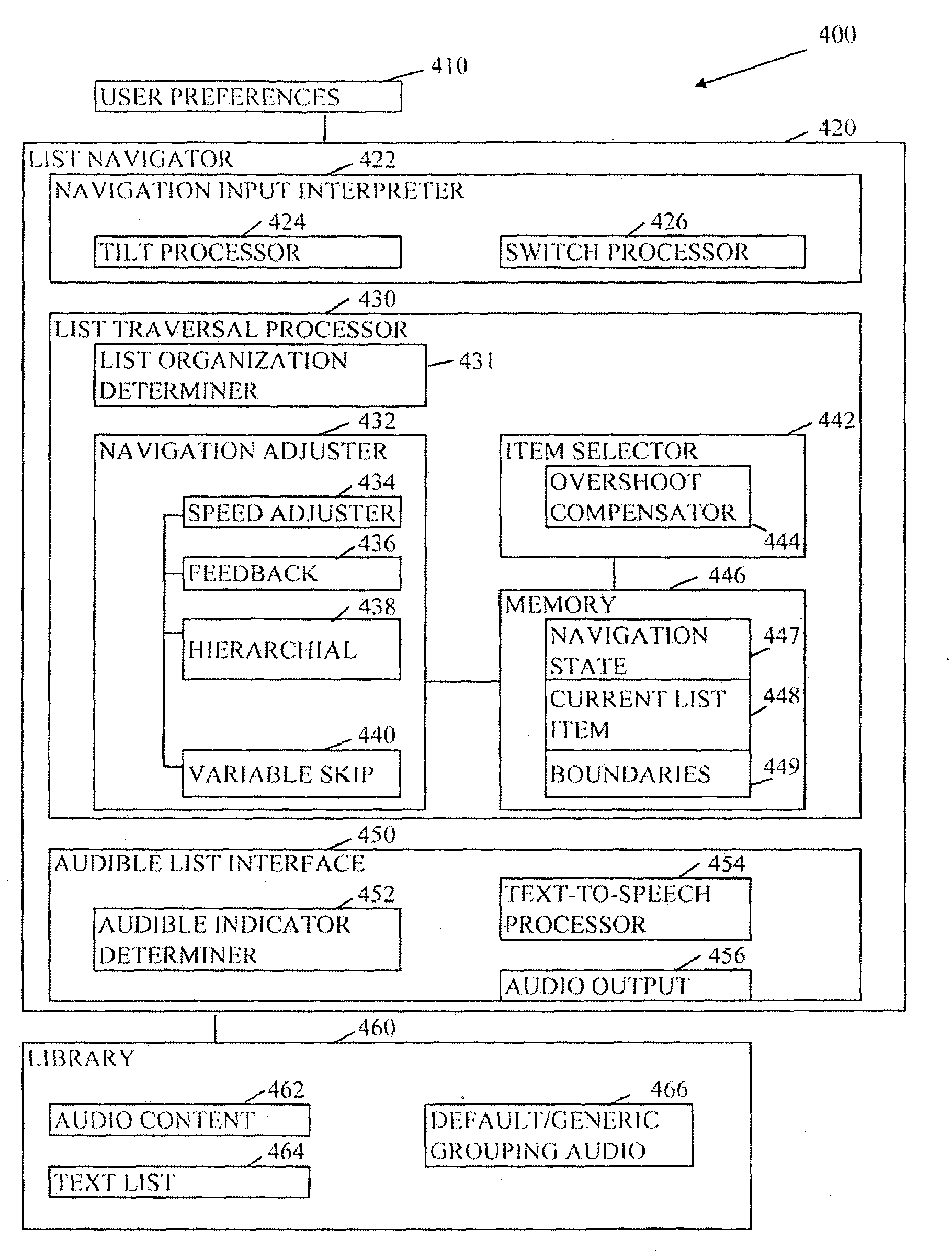
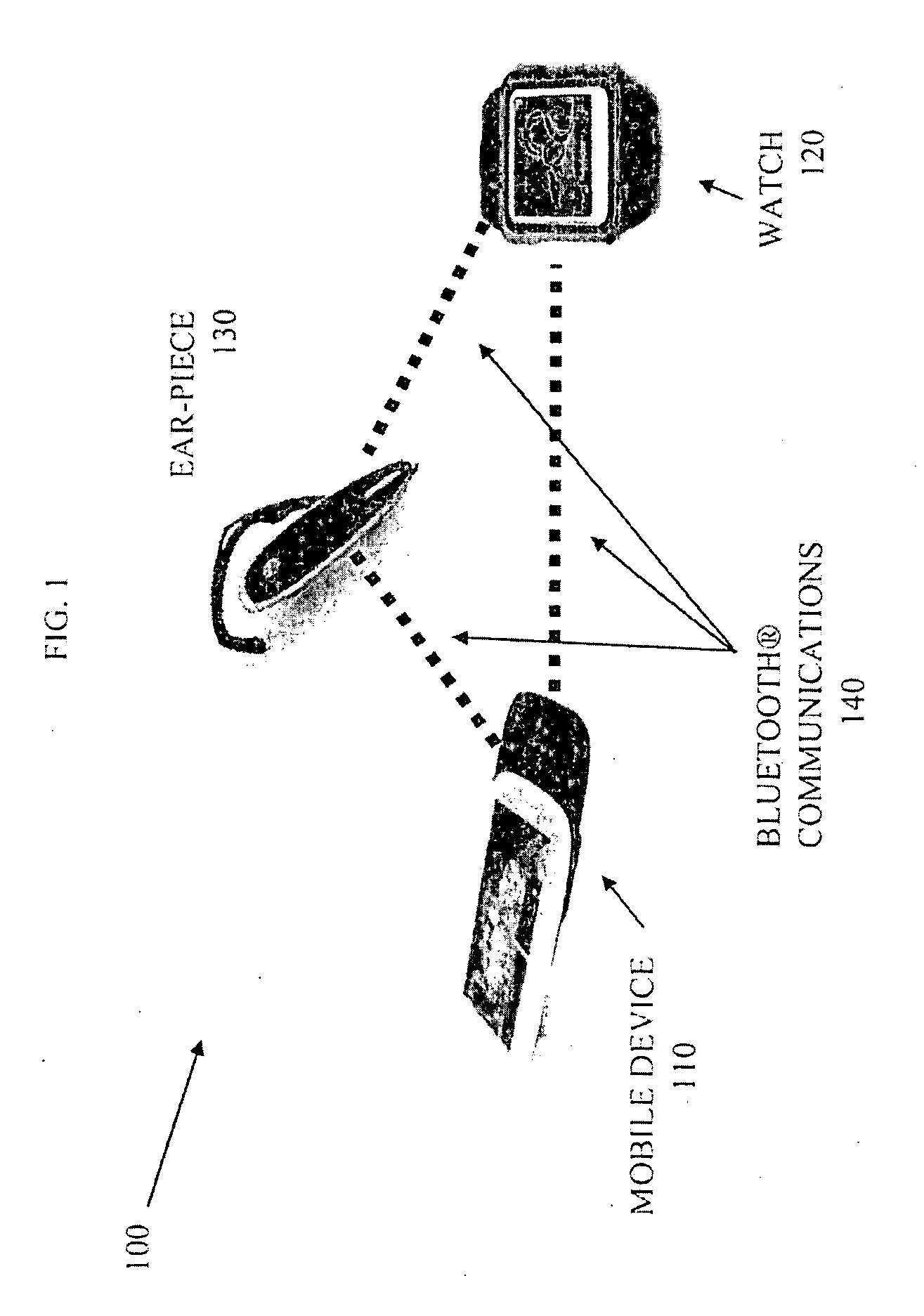
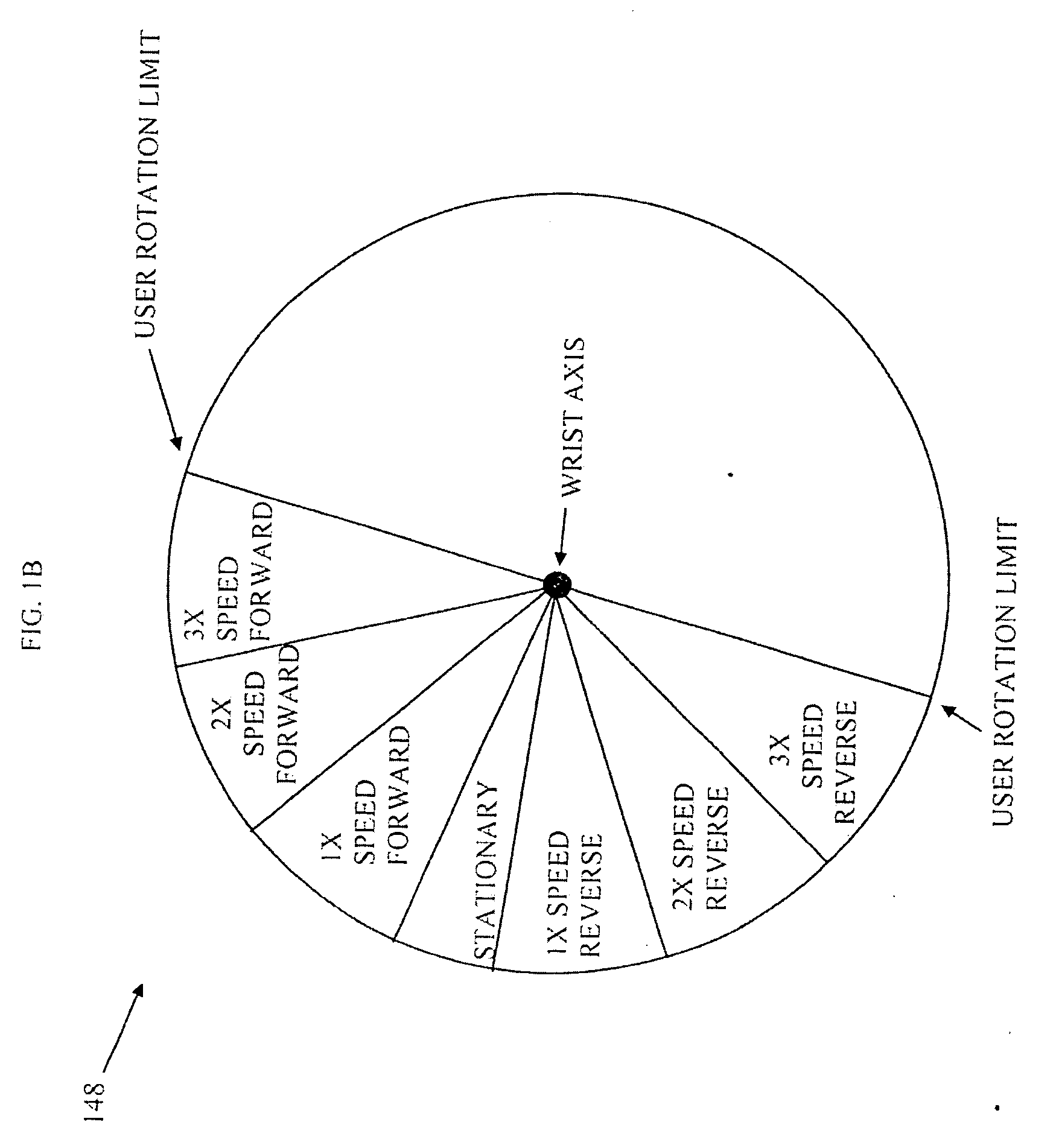
Audible list traversal
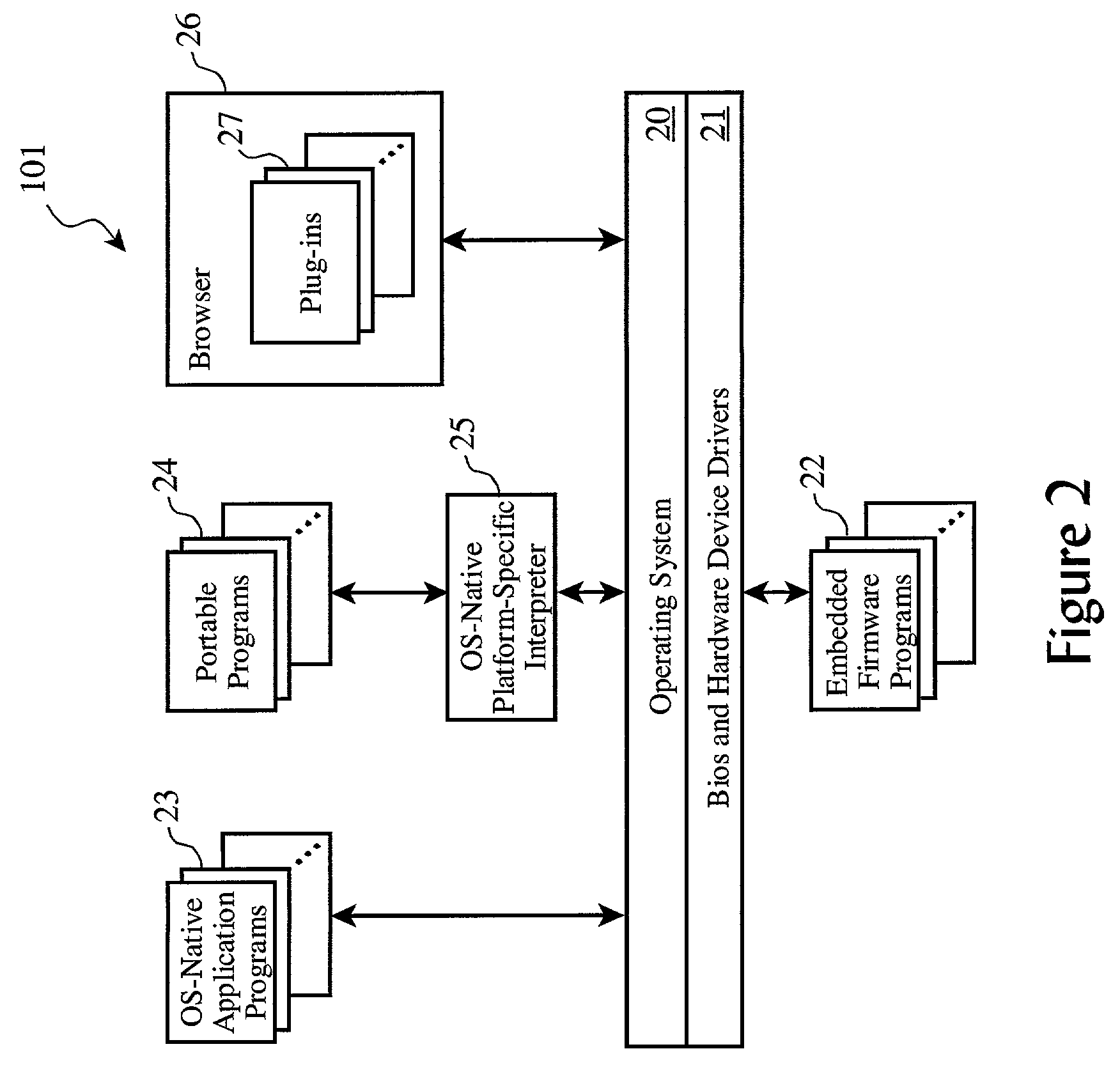
Many embodiments may comprise logic such as hardware and / or code to implement user interface for traversal of long sorted lists, via audible mapping of the lists, using sensor based gesture recognition, audio and tactile feedback and button selection while on the go. In several embodiments, such user interface modalities are physically small in size, enabling a user to be truly mobile by reducing the cognitive load required to operate the device. For some embodiments, the user interface may be divided across multiple worn devices, such as a mobile device, watch, earpiece, and ring. Rotation of the watch may be translated into navigation instructions, allowing the user to traverse the list while the user receives audio feedback via the earpiece to describe items in the list as well as audio feedback regarding the navigation state. Many embodiments offer the user a simple user interface to traverse the list without visual feedback.
Owner:INTEL CORP
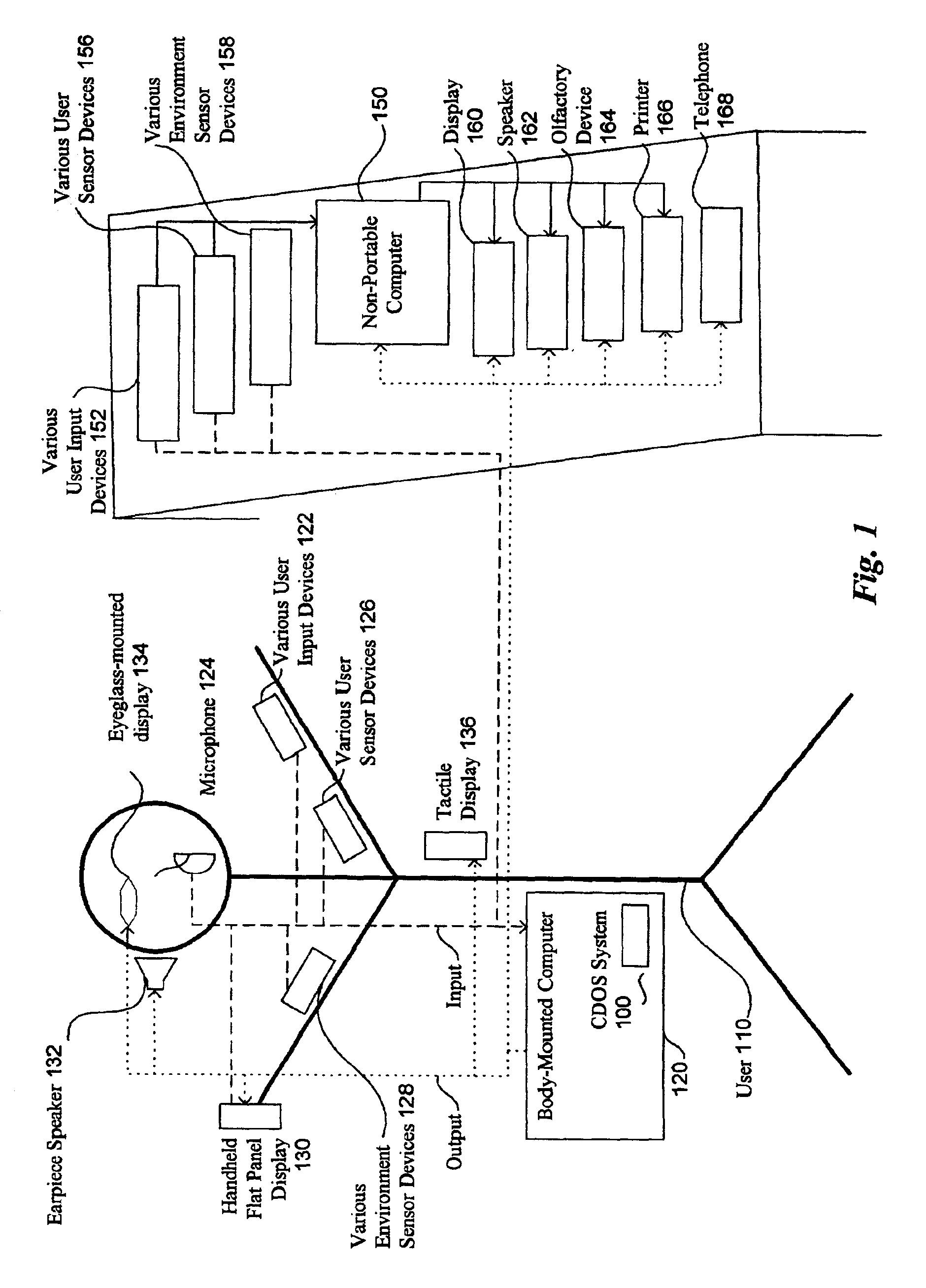
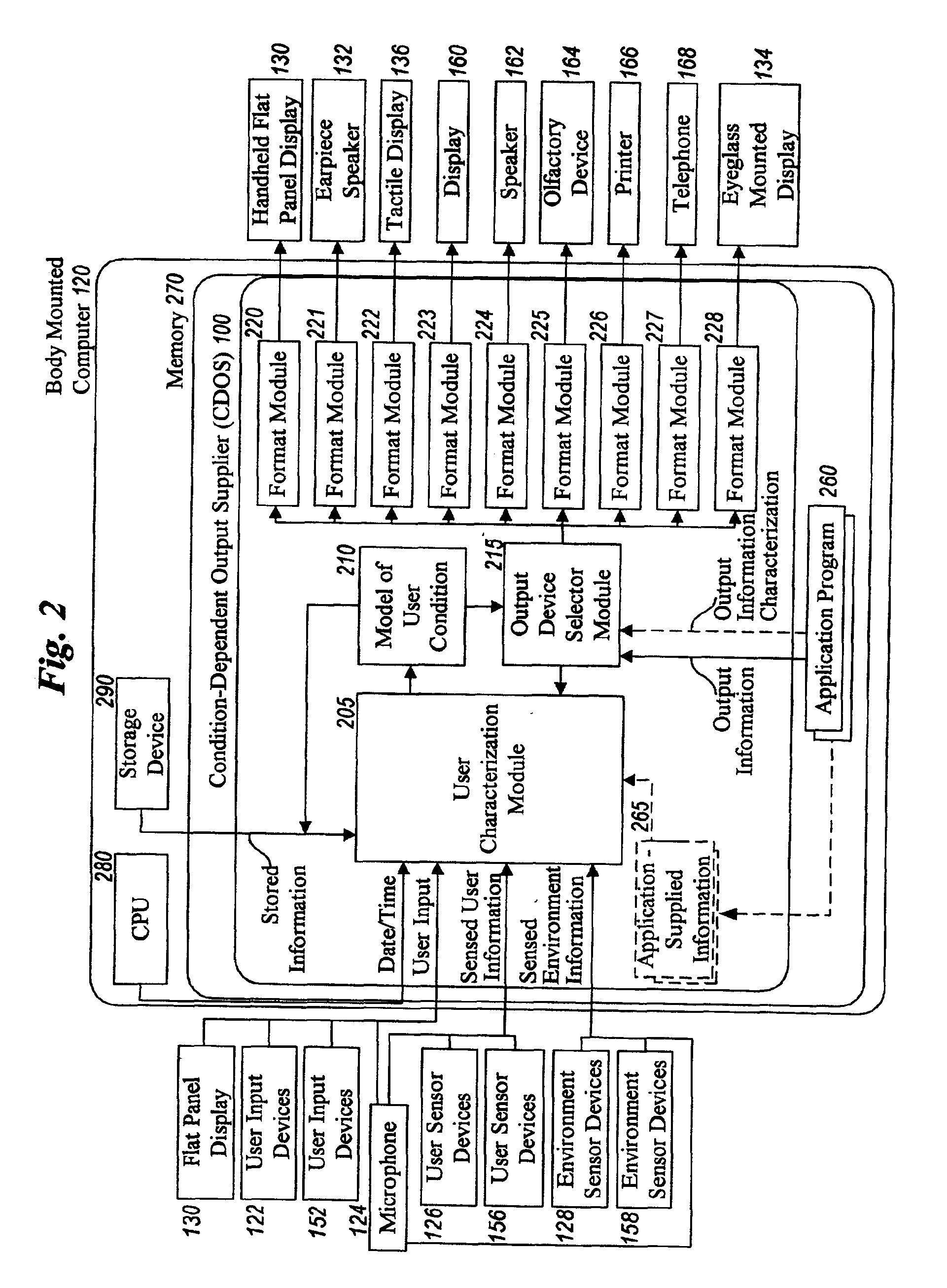
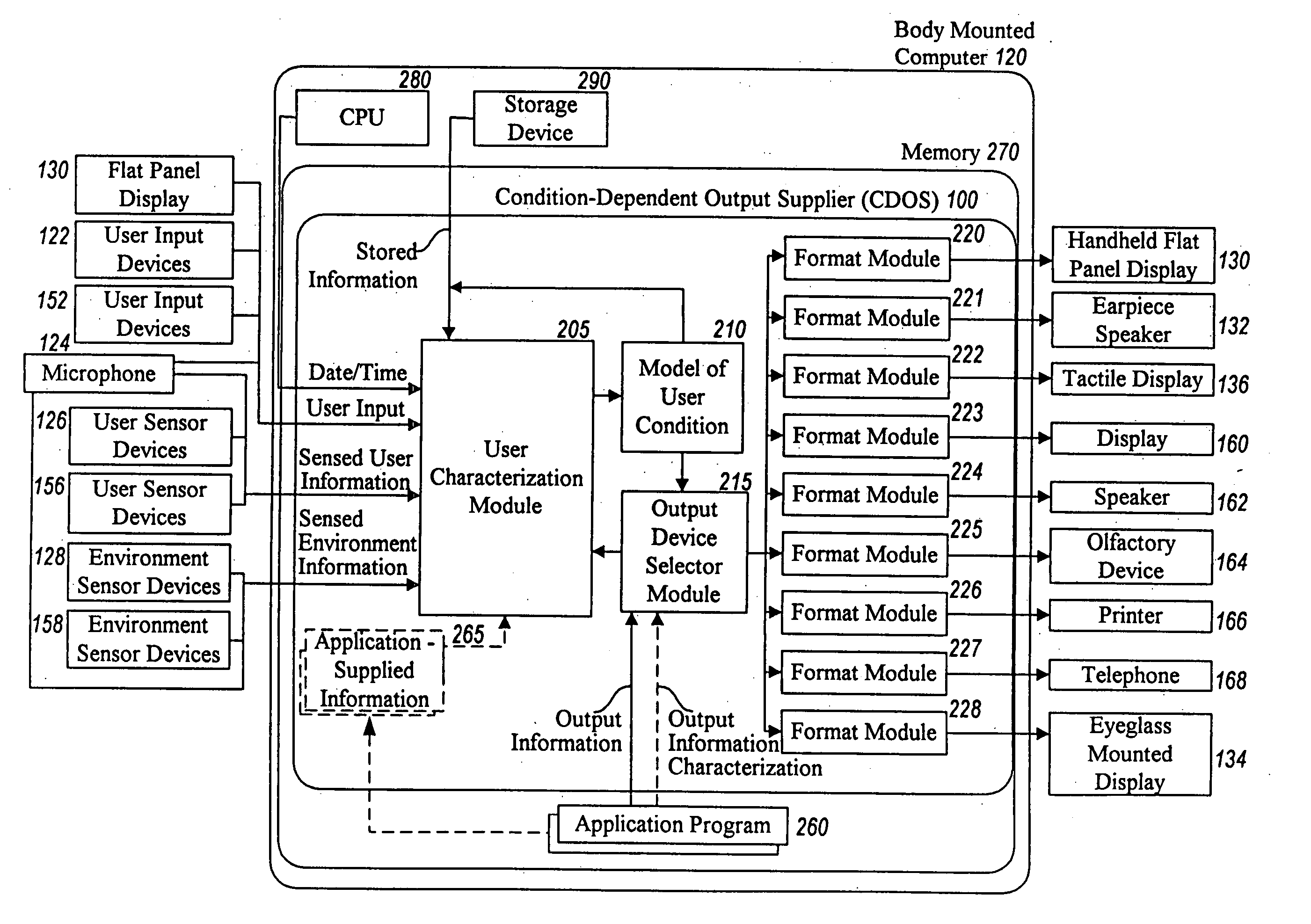
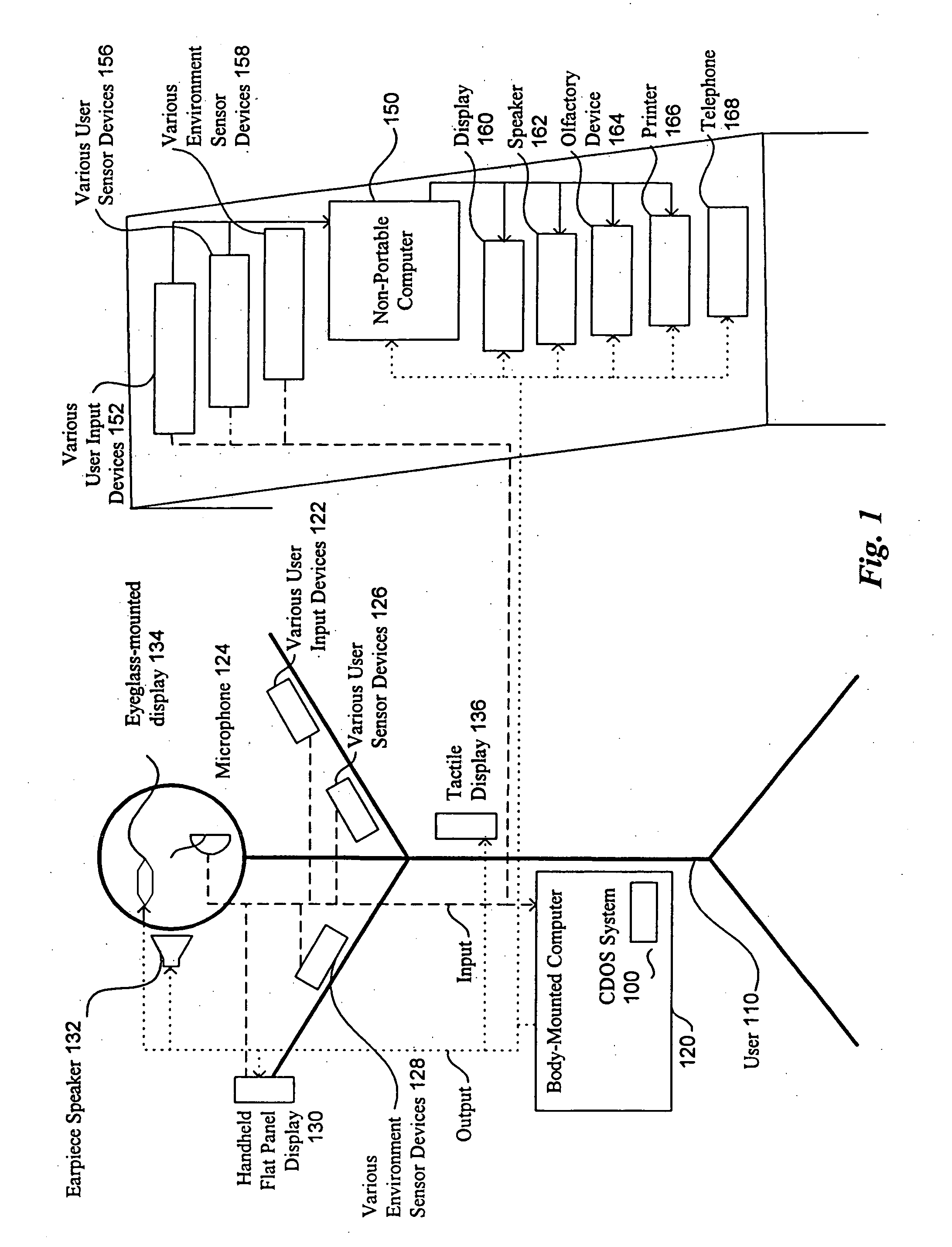
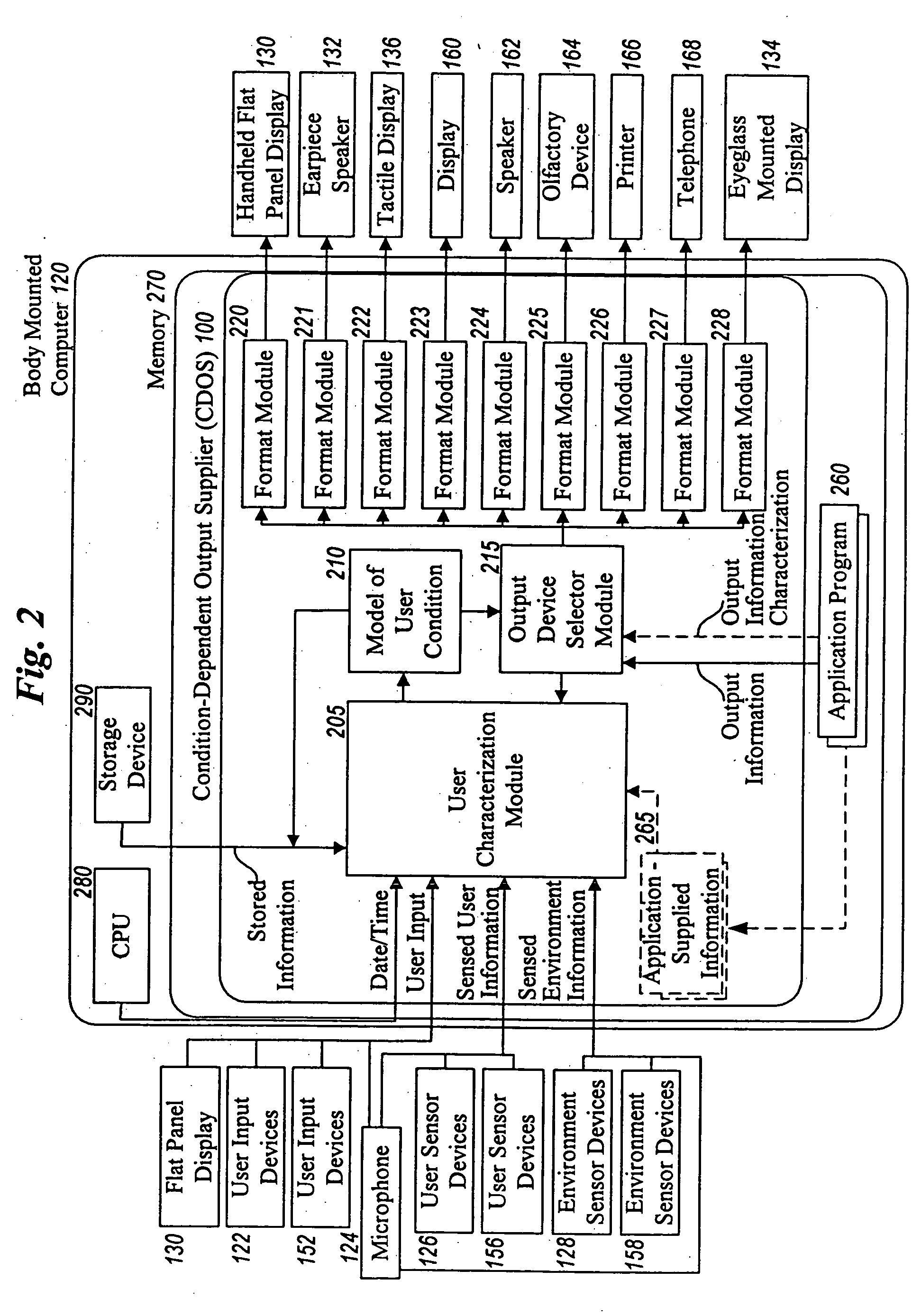
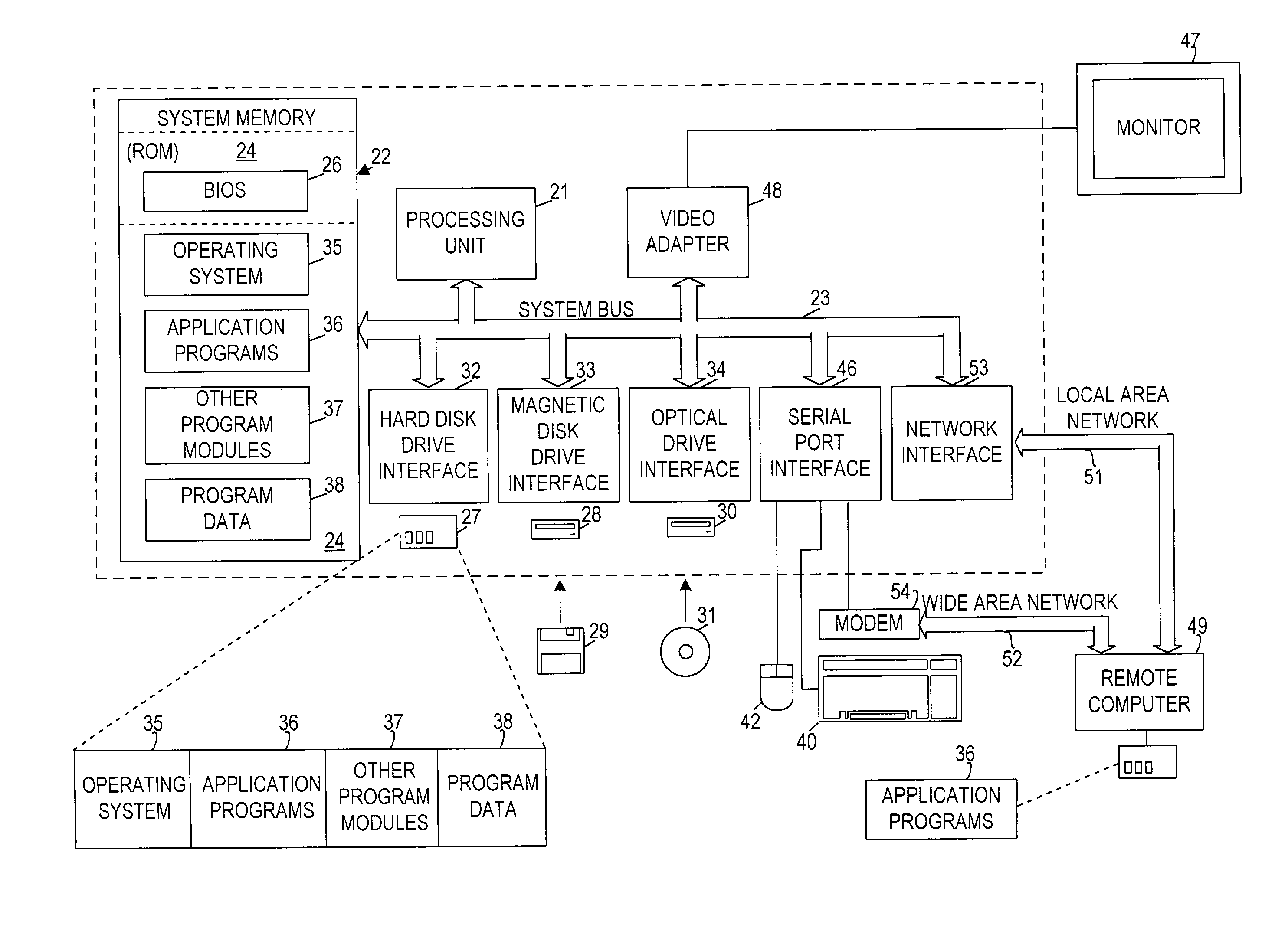
Method and system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user's condition
InactiveUS6874127B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsAbstract conceptDisplay device
A system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user's current condition. In particular, the system monitors the user and the user's environment, and creates and maintains an updated model of the current condition of the user. The user condition can include a variety of condition variables, including abstract concepts such as the user's current cognitive load, desired level of privacy for output information, and desired scope of audience for output information. Upon receiving output information to be presented to the user (e.g., from an application program), the system determines an appropriate output device and an appropriate format with which to present the information to the user, and then presents the output information. The system can also receive description information about the output information that describes relevant factors for determining when and how to present the output information (e.g., the importance and urgency of the output information, the consequences of the user not receiving or ignoring the output information, etc.). Some versions of the system execute on a wearable computer having a variety of available output display devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
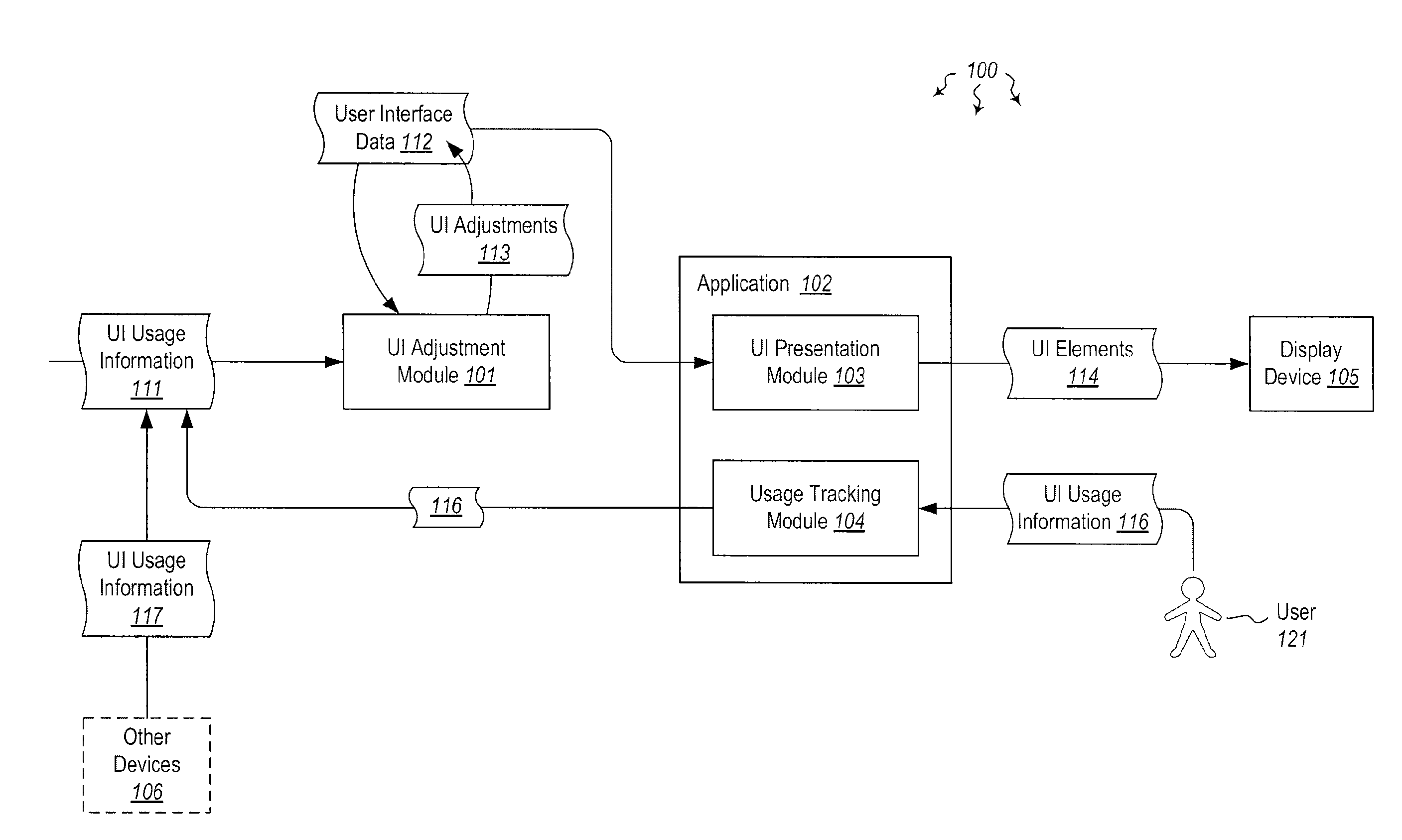
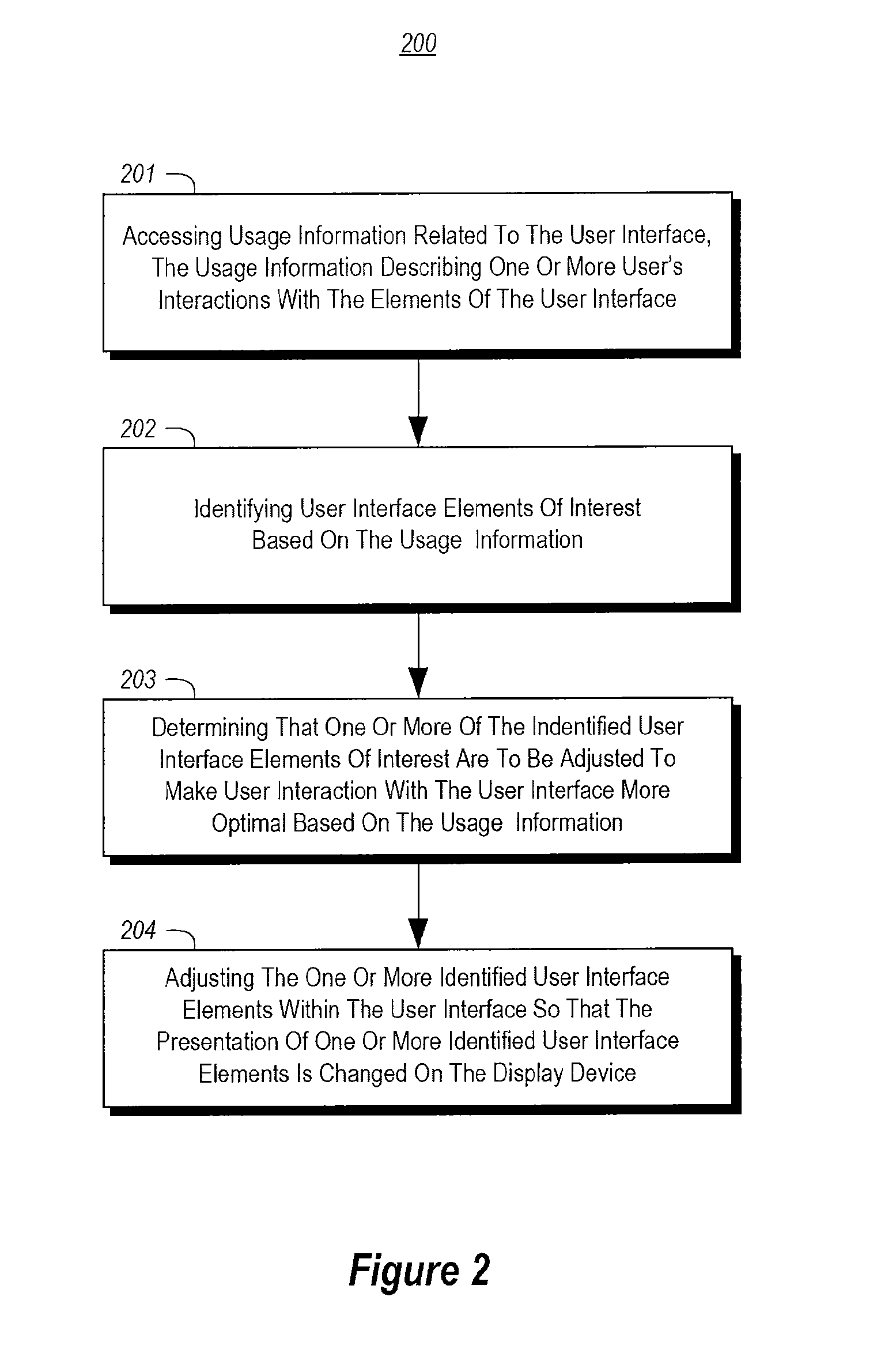
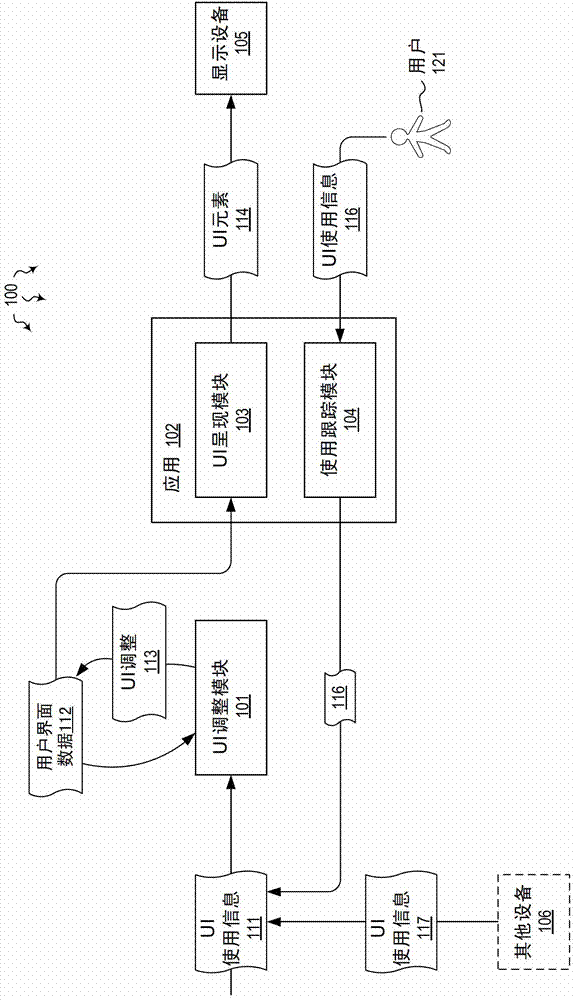
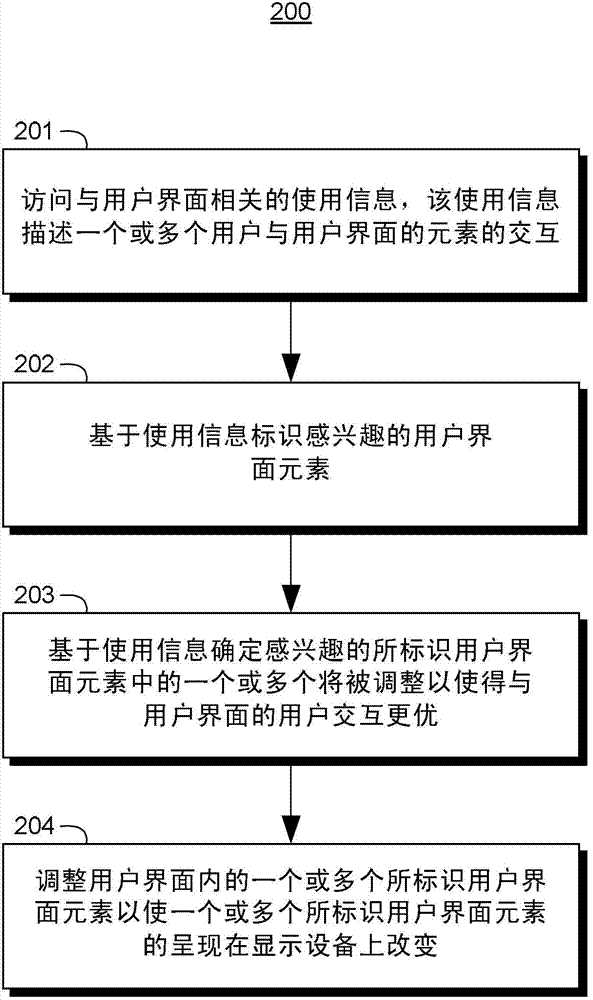
Adjusting user interface elements
InactiveUS20130152001A1Enhanced interactionSubstation equipmentExecution for user interfacesMobile vehicleHuman–computer interaction
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for adjusting user interface elements. Embodiments of the invention can adjust the size, shape, and position of user interface elements and whitespace based on historical usage data. Adjustments can reduce the cognitive load associated with selecting some user interface elements. In dangerous environments, such as, for example, a moving vehicle, reducing the cognitive load allows a user to pay attention to other matters, such as, for example, safely operating the moving vehicle. Historical usage data can originate from one or more users and one or devices. Adjustment limits can be used to insure user interfaces remain appropriately usable. User interface element adjustments can be used to optimize a user interface and / or influence user interactions with a user interface.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
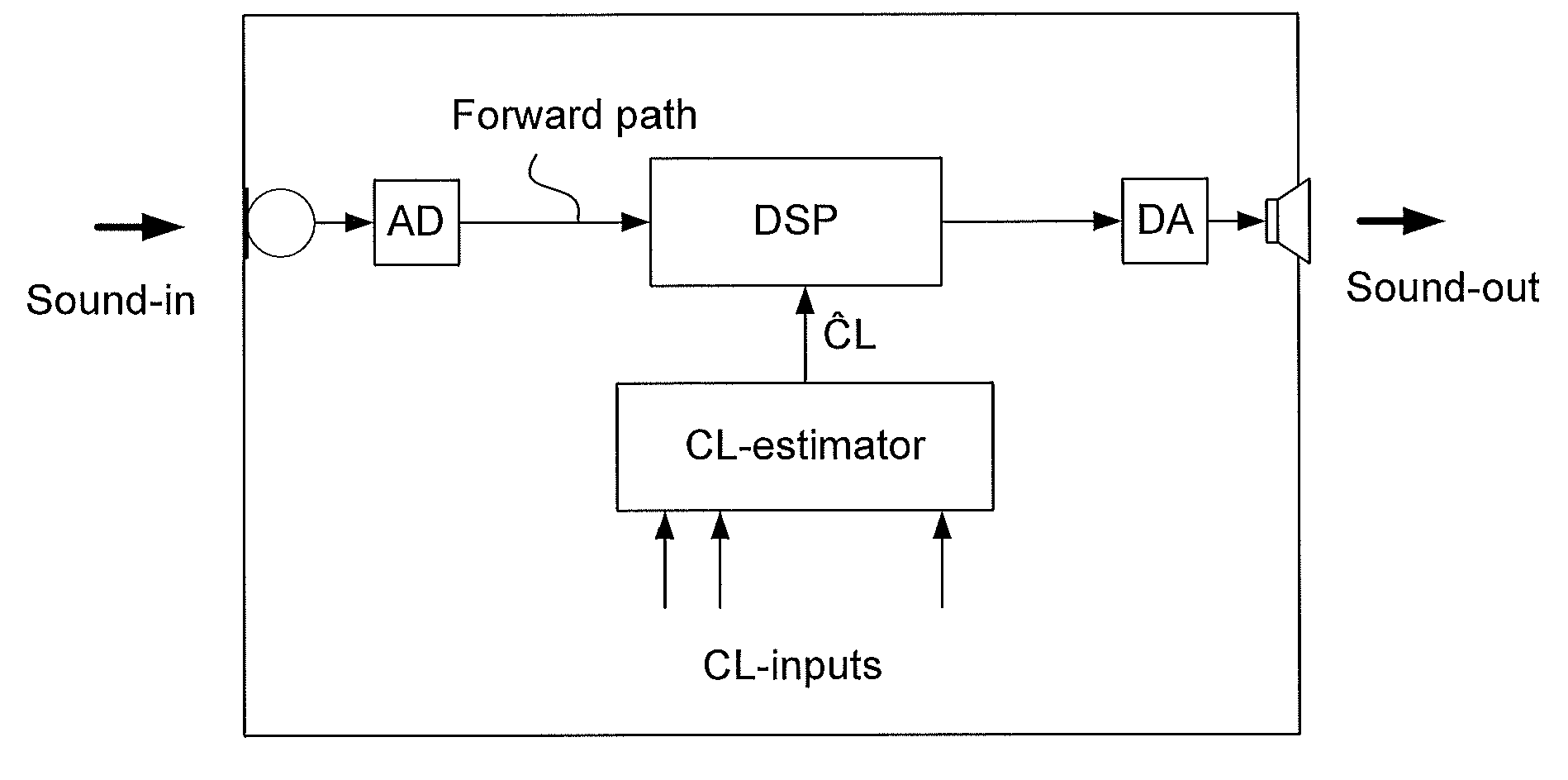
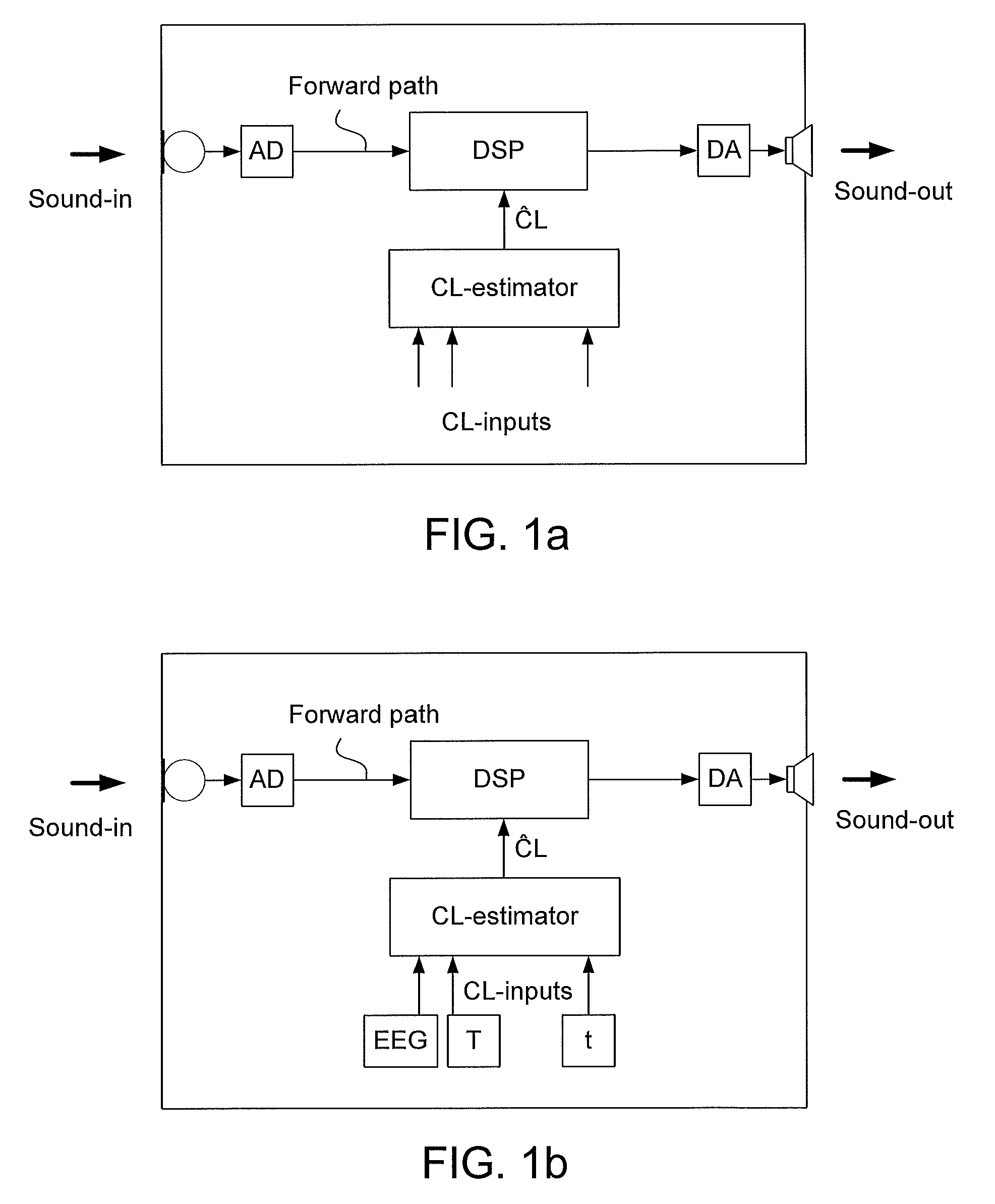
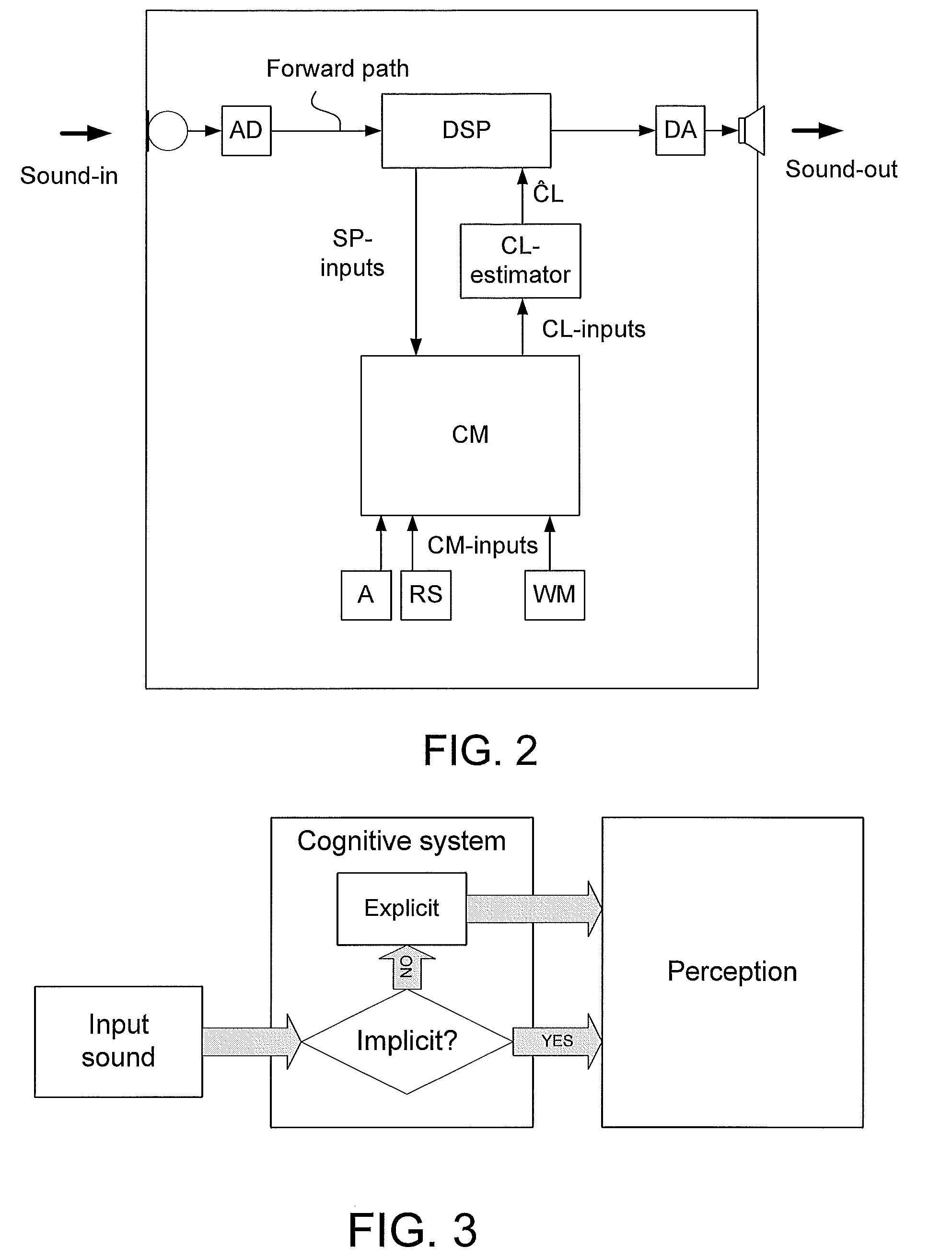
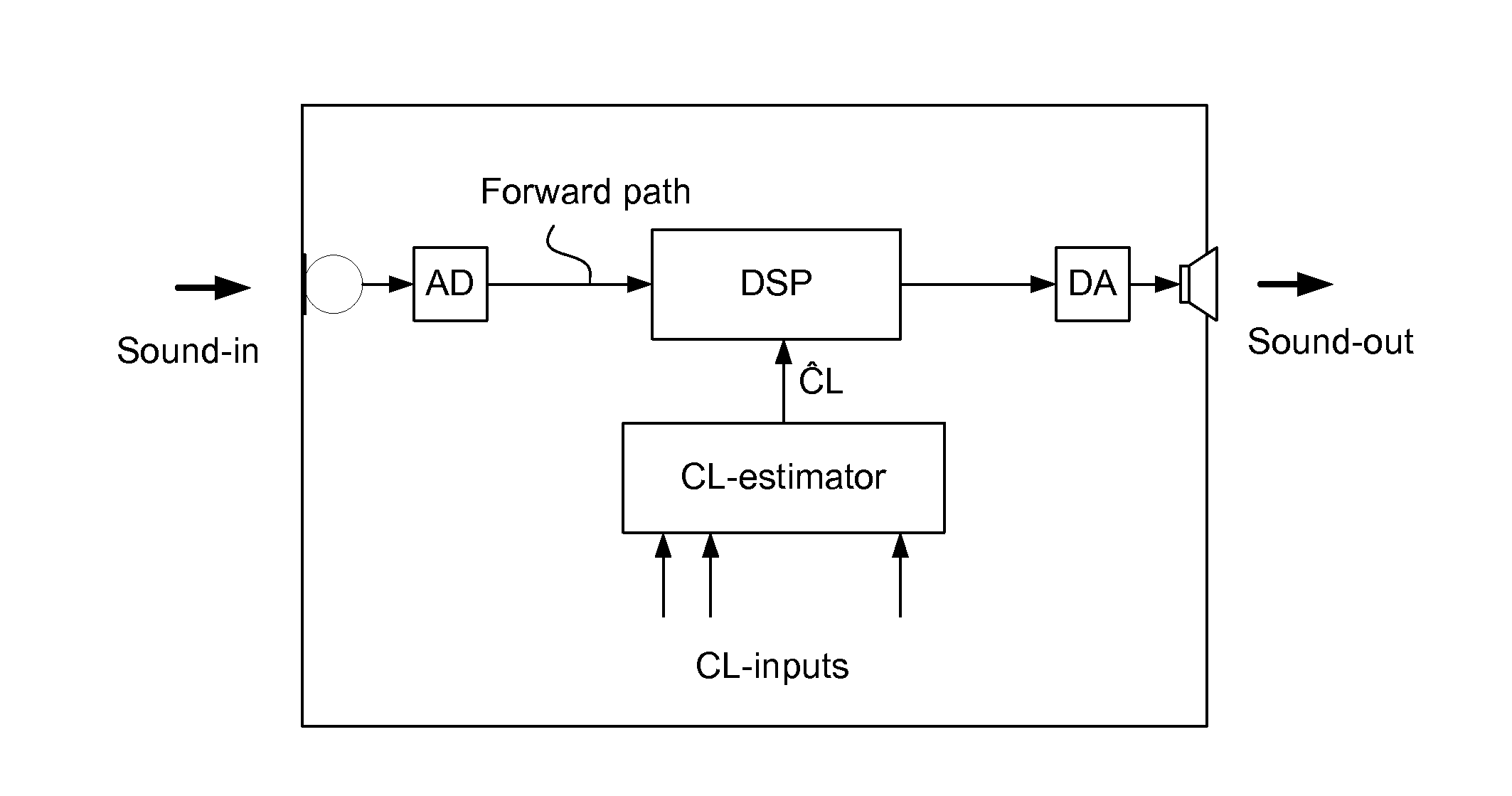
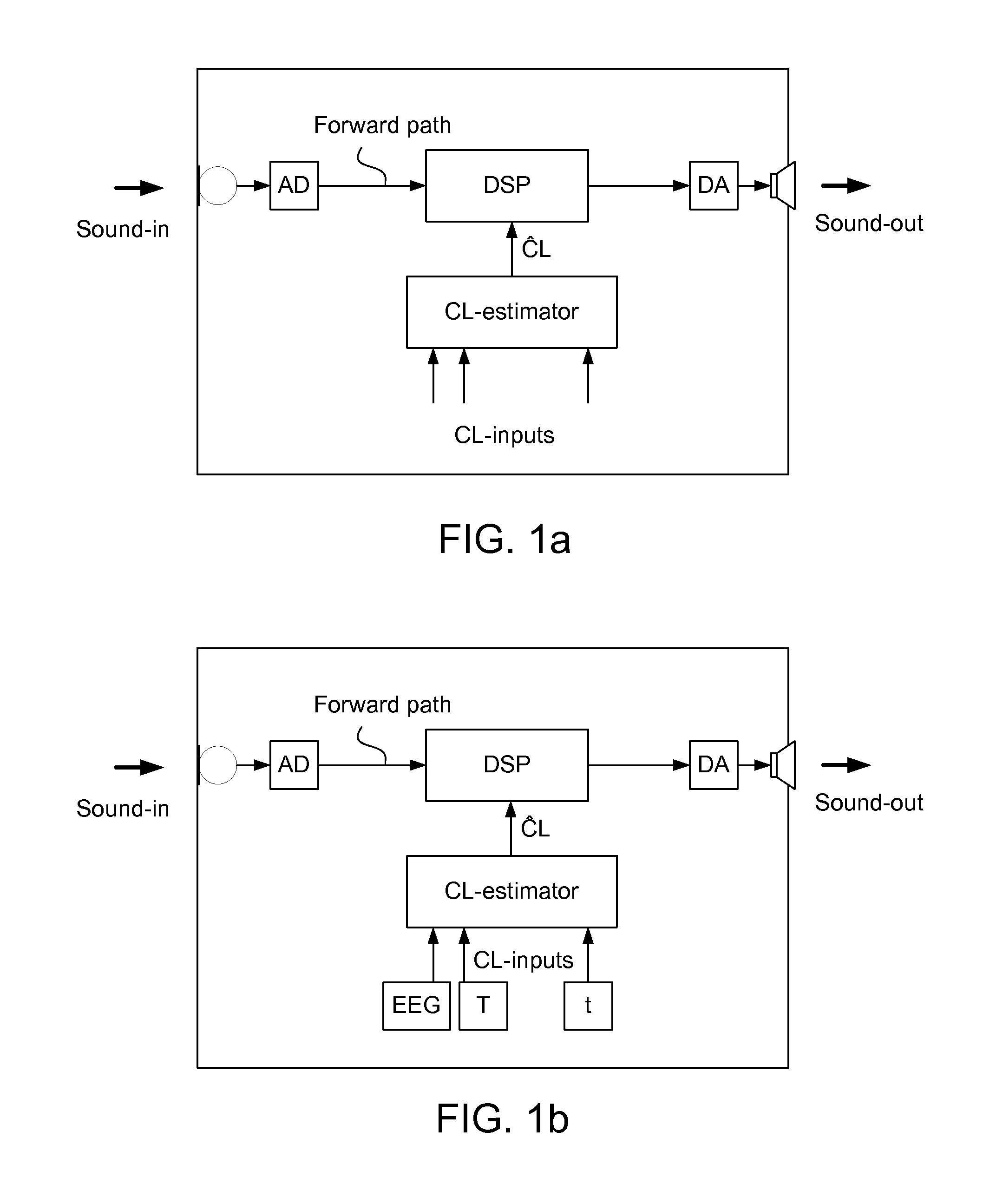
Method of operating a hearing instrument based on an estimation of present cognitive load of a user and a hearing aid system
ActiveUS20100196861A1Easy to customizeImprove comfortElectronic input selection/mixingTeaching apparatusData processing systemHearing aid
A method of operating a hearing instrument for processing an input sound and to provide an output stimulus according to a user's particular needs, and related system, computer readable medium and data processing system. An object is to provide an improved customization of a hearing instrument. The method includes the steps a) providing an estimate of the present cognitive load of the user; b) providing processing of an input signal originating from the input sound according to a user's particular needs; and c) adapting the processing in dependence of the estimate the present cognitive load of the user. The estimate of the present cognitive load of a user is produced by in-situ direct measures of cognitive load (e.g. based on EEG-measurements, body temperature, etc.) or by an on-line cognitive model in the hearing aid system whose parameters have been preferably adjusted to fit to the individual user.
Owner:OTICON
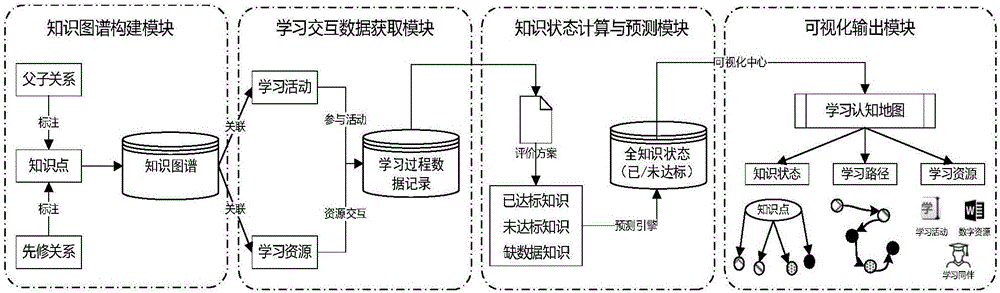
Online learning cognitive map generation system and method for representing knowledge learning mastering state of leaner in specific field
The invention discloses an online learning cognitive map generation system and method for representing the knowledge learning mastering state of a leaner in a specific field. The system comprises an intelligent terminal and a server. The intelligent terminal is used for online learning interaction. The online learning cognitive map generation system runs in the server comprising a knowledge graph construction module, a learning interaction data acquisition module, a knowledge state calculation and prediction module and a visual output module. The online learning cognitive map generation system and method are suitable for a common online learning platform and can simulate the cognitive structure of the learner and diagnose the learning defect of the leaner to provide personalized learning resources and social network services for the learner, so that learning confusion is reduced, cognitive loads are reduced, and learning pertinency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
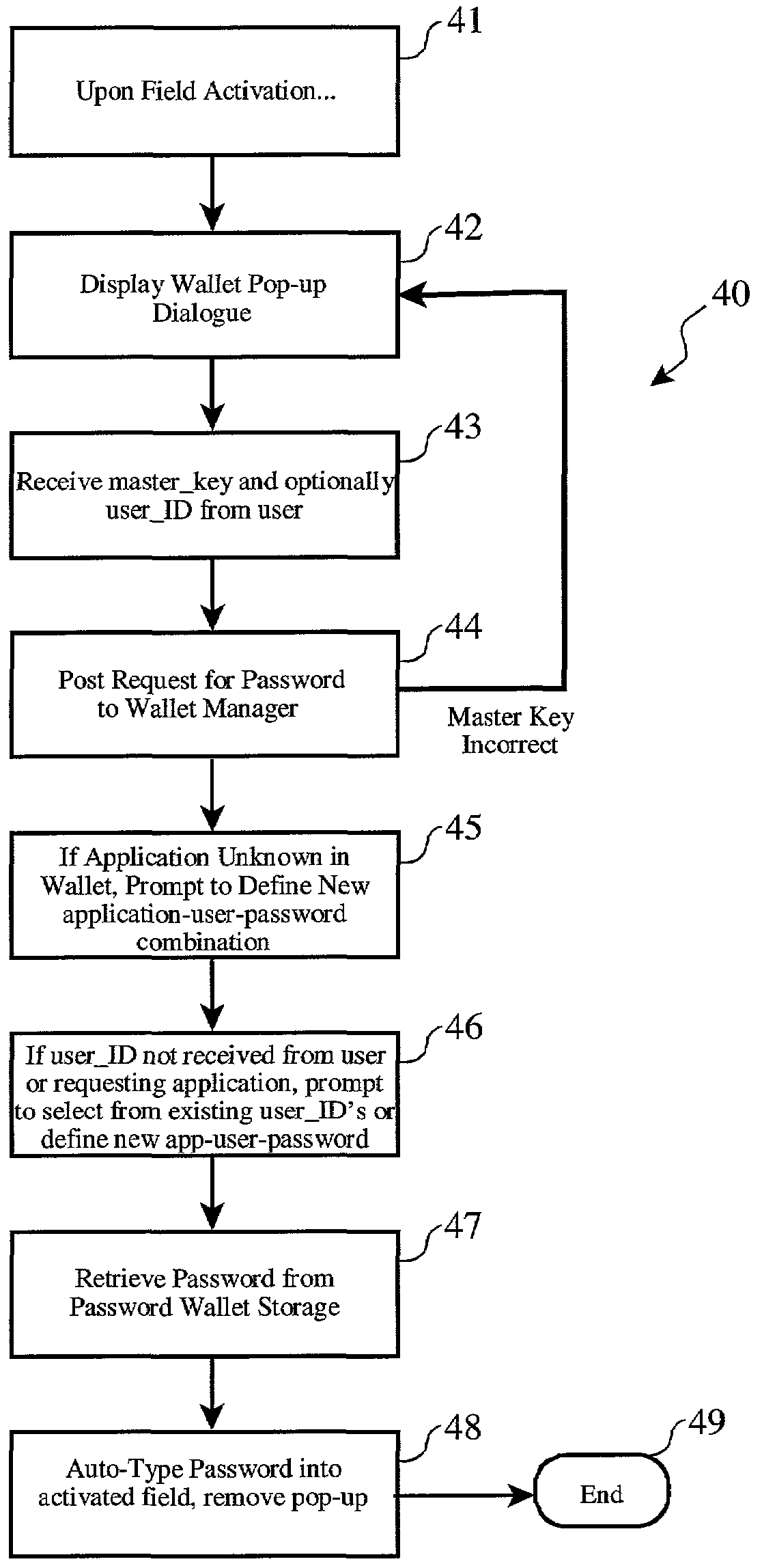
Electronic password wallet
InactiveUS7136490B2Easy and fast accessKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsWeb siteDisplay device
A convenient and secure system and method for access to any number of password-protected computer applications, web sites and forms without adding to the user cognitive load and without circumventing the inherent security of such password-protection schemes. An existing password field on a device display is overlaid with password wallet pop-up field which allows a wallet “master” key to unlock the wallet. An application-specific and / or user-specific password is automatically retrieved from the wallet and entered into the password field with no other user action required.
Owner:LINKEDIN
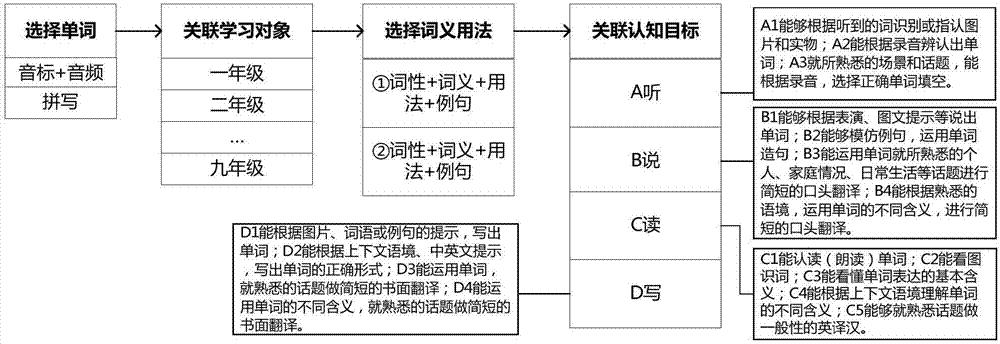
Word cognitive state model-based adaptive learning system and method
ActiveCN106897950AExpansion of learning resourcesMeet learning needsData processing applicationsSpeech recognitionAdaptive learningState model
The invention relates to a word cognitive state model-based adaptive learning system and method. The system comprises a mobile terminal, a computer terminal and a server end; the system further comprises a domain knowledge and extension resource module, a cognitive objective introduction module, a cognitive state analysis module, an adaptive learning module and a background database. The method comprises the steps of domain knowledge and extension resource structuralization, cognitive objective introduction and learning activity design, word learning and breakthrough making, learner cognitive state analysis and adaptive content recommendation. The word cognitive state model-based adaptive learning system and method of the invention are applicable to students who can learn English, can analyze the interactive data of the learners, evaluate the cognitive states of the learners, provide accurate recommendations which are suitable for the cognitive states and capacities of the learners in word learning, and minimize the cognitive burden brought by vocabularies which have been already mastered by the learners or vocabularies which are excessively difficult so as to reduce learning burden and improve learning efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
System and Method for Improving Student Learning by Monitoring Student Cognitive State
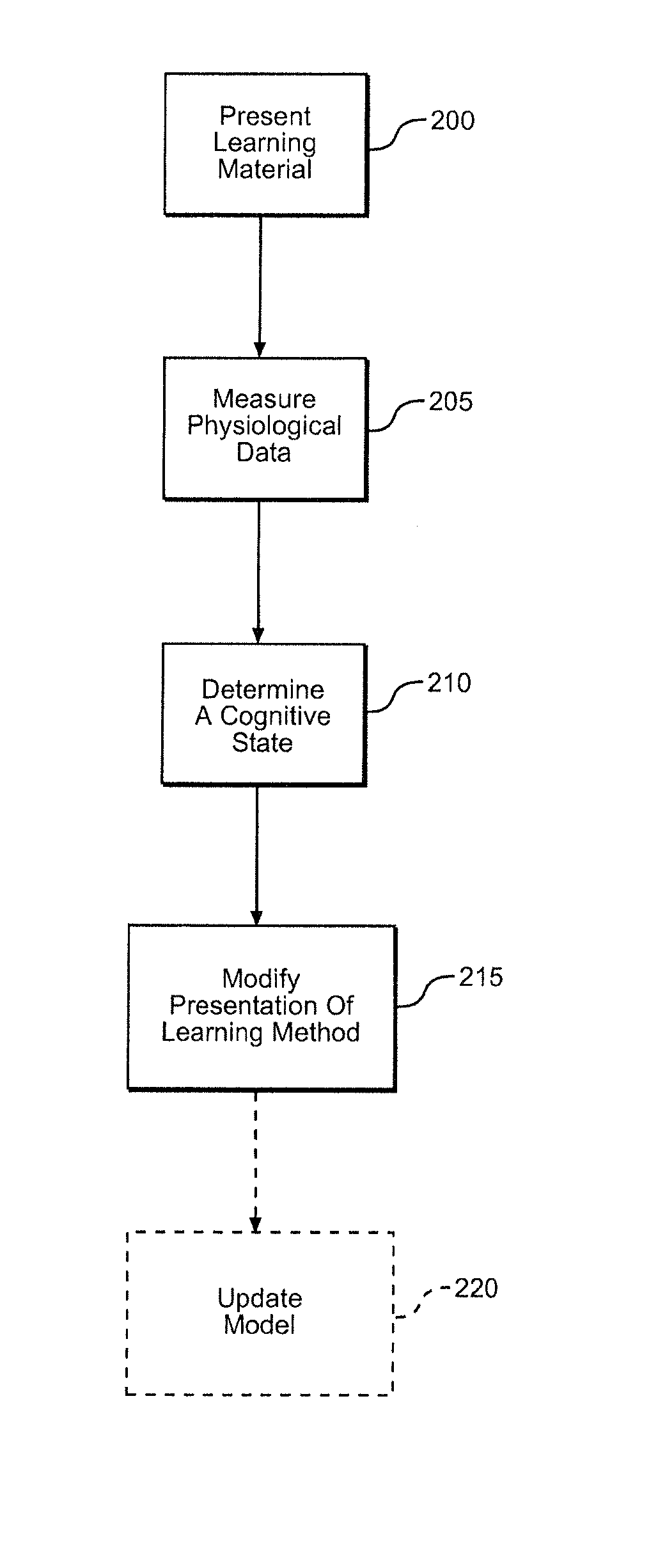
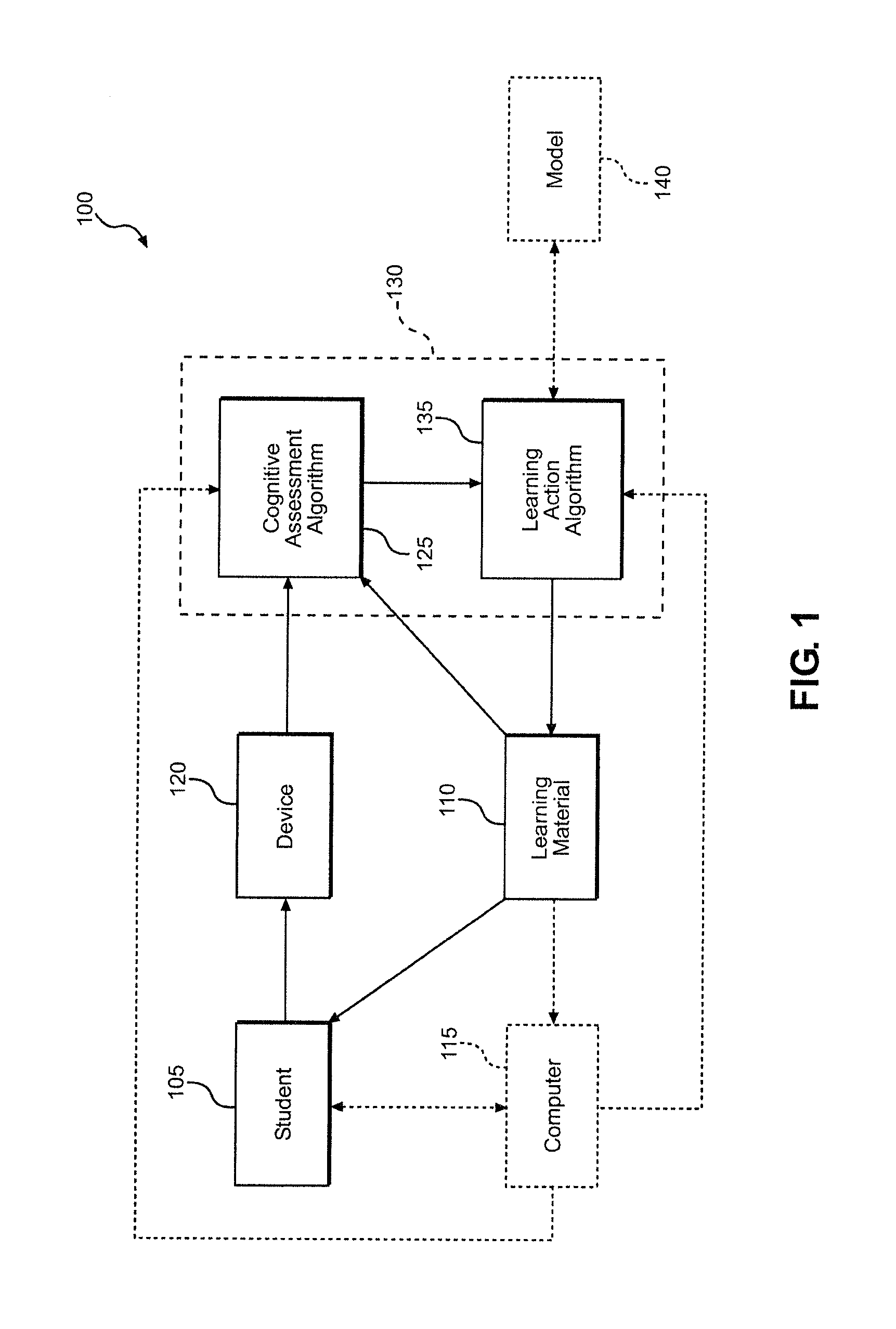
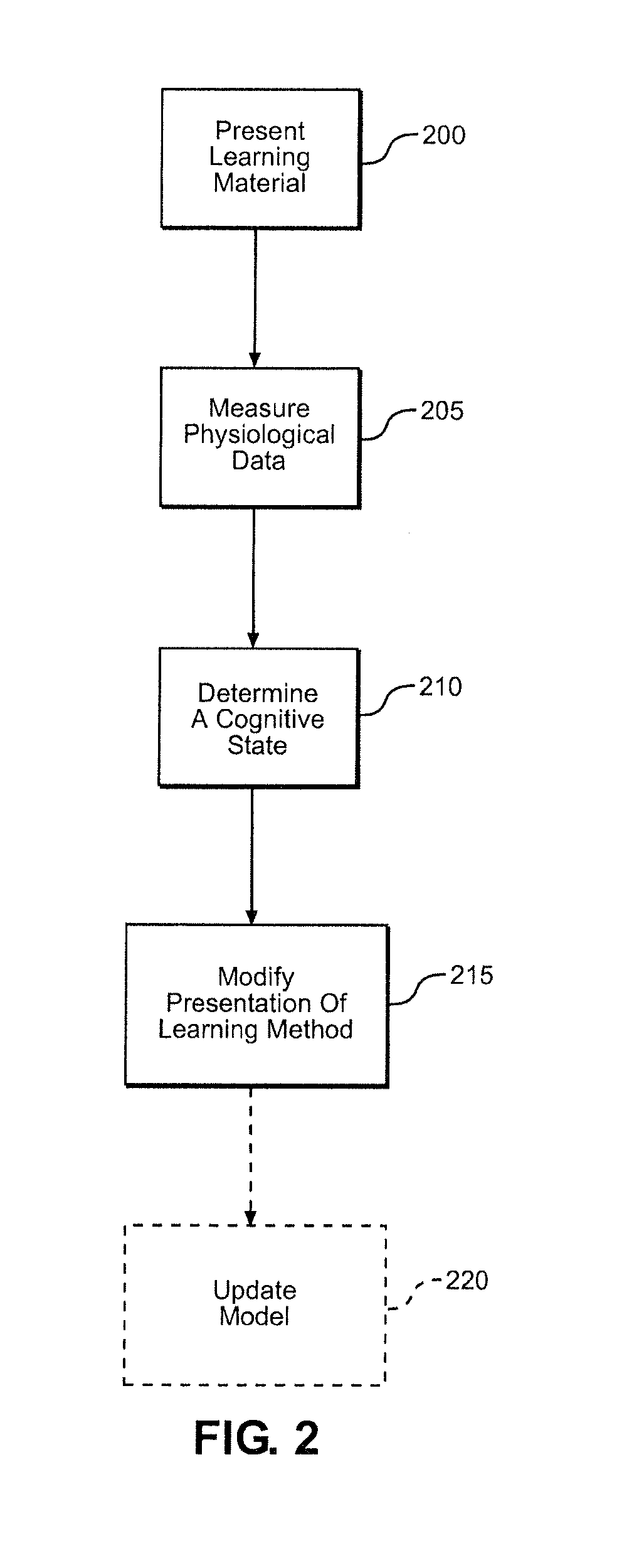
ActiveUS20160203726A1Changing complexityComplexity rateElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyCognitive appraisalCognitive status
A system and method for improving student learning includes learning material that is presented to a student and a device that is used to acquire physiological data from the student in real time during a learning session. A cognitive assessment algorithm determines a cognitive state of the student using the physiological data, and a learning action algorithm modifies the presentation of the learning material in response to the student's cognitive state. The learning material can include lectures, questions asked of the student or problems or activities being completed by the student. In one embodiment, the device directly measures the brain activity of the student to determine the student's cognitive state. The cognitive state of the student can include the student's cognitive load, engagement or fatigue.
Owner:QUANTUM APPLIED SCI & RES
Method and system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user's condition
InactiveUS20060053377A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDigital computer detailsAbstract conceptDisplay device
A system for controlling presentation of information to a user based on the user's current condition. In particular, the system monitors the user and the user's environment, and creates and maintains an updated model of the current condition of the user. The user condition can include a variety of condition variables, including abstract concepts such as the user's current cognitive load, desired level of privacy for output information, and desired scope of audience for output information. Upon receiving output information to be presented to the user (e.g., from an application program), the system determines an appropriate output device and an appropriate format with which to present the information to the user, and then presents the output information. The system can also receive description information about the output information that describes relevant factors for determining when and how to present the output information (e.g., the importance and urgency of the output information, the consequences of the user not receiving or ignoring the output information, etc.). Some versions of the system execute on a wearable computer having a variety of available output display devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
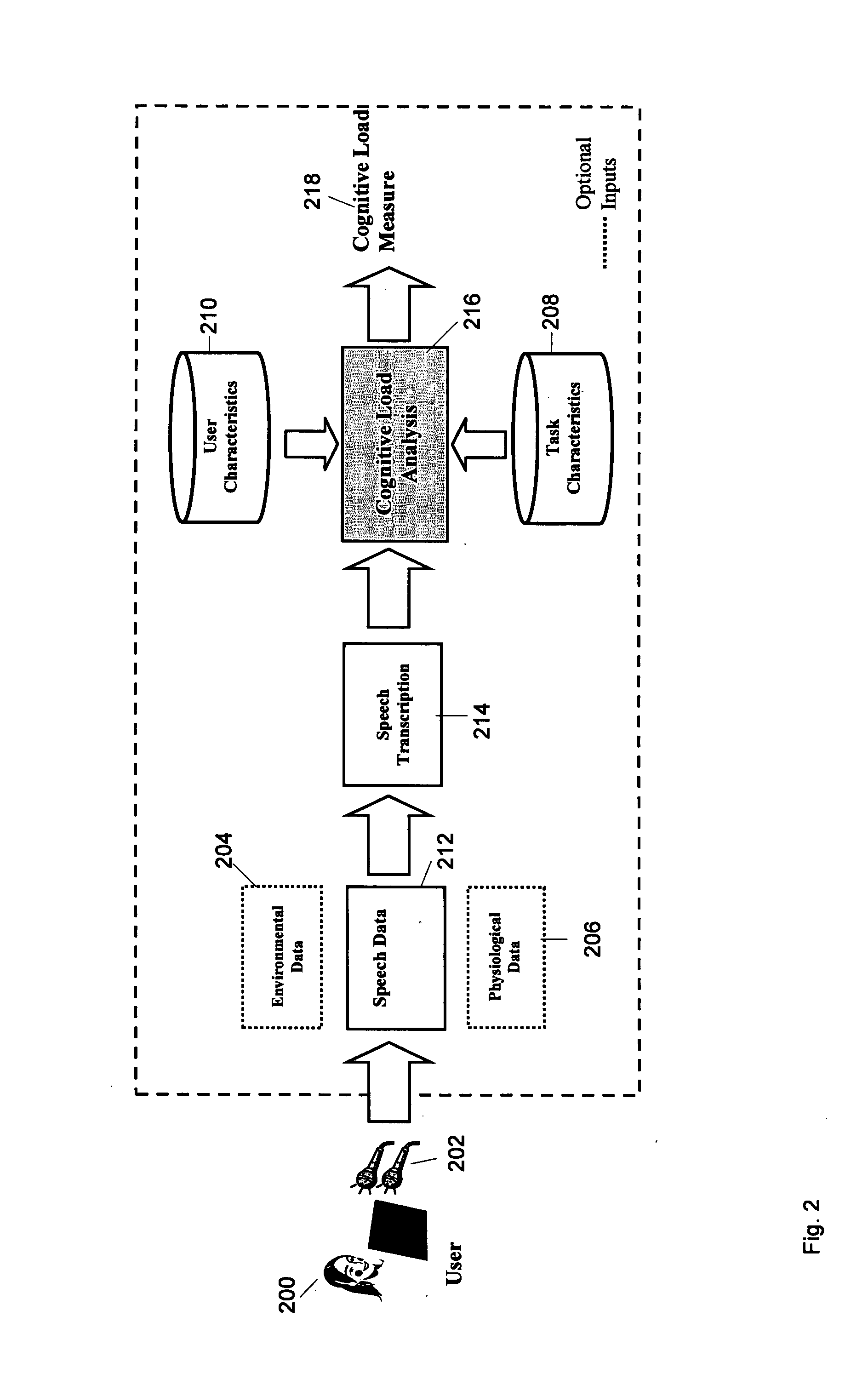
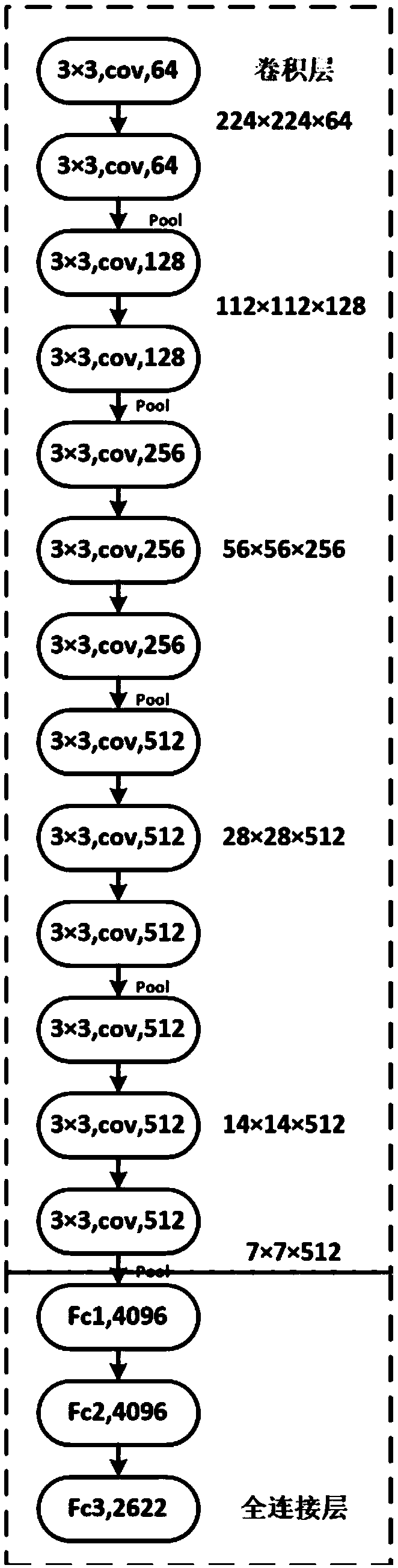
Systems and methods for estimating and integrating measures of human cognitive load into the behavior of computational applications and services
InactiveUS6999955B1Facilitate cognitive processingLower capability requirementsKernel methodsProbabilistic networksGraphicsAnimation
The present invention relates to a system and methodology for extending and making more appropriate the interactive decisions made by automated services by taking into consideration estimates of the time required by users for the cognitive processing of problems, visualizations, and content based on several factors, including the competency and familiarity of the user with the output and nature of the sequences of output, the complexity of the output and overall tasks being considered, and the context of the user. The methods allow automated applications to control the rate at which the applications interact with users. Portions of automated services are controlled in view of limited human processor capabilities in design / operation of such services, and / or visualizations / output from the services (e.g., amount of dwell time provided / considered before a next automated sequence is displayed / invoked). Models can be formulated and utilized in conjunction with automated services such as automatically determining and pausing a period of time before a next sequence in a service is enabled or disabled. The models can also be employed to determine multiple dwells for comprehension, as a function of complexity of graphical / conceptual relationships, at different phases of an animation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
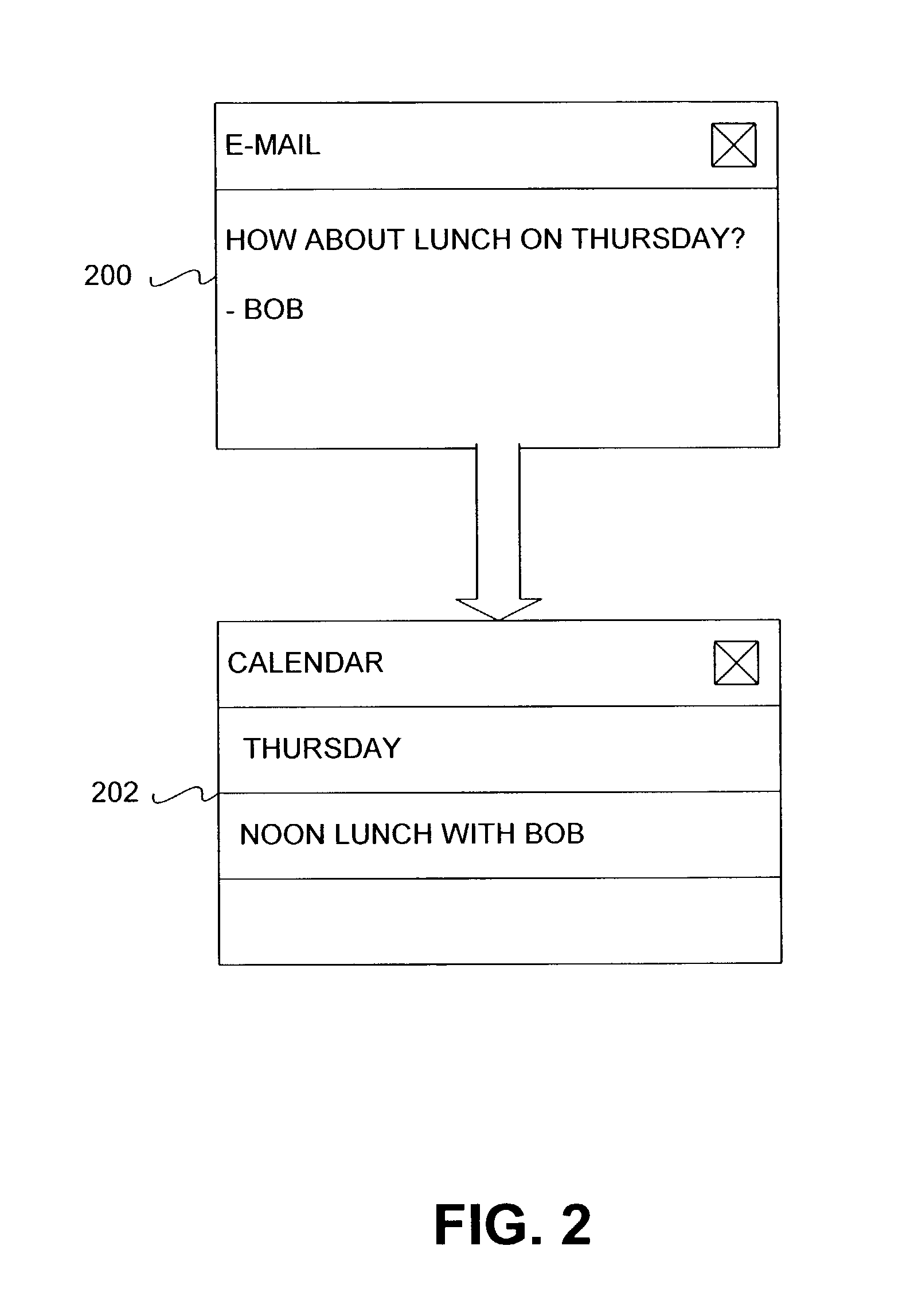
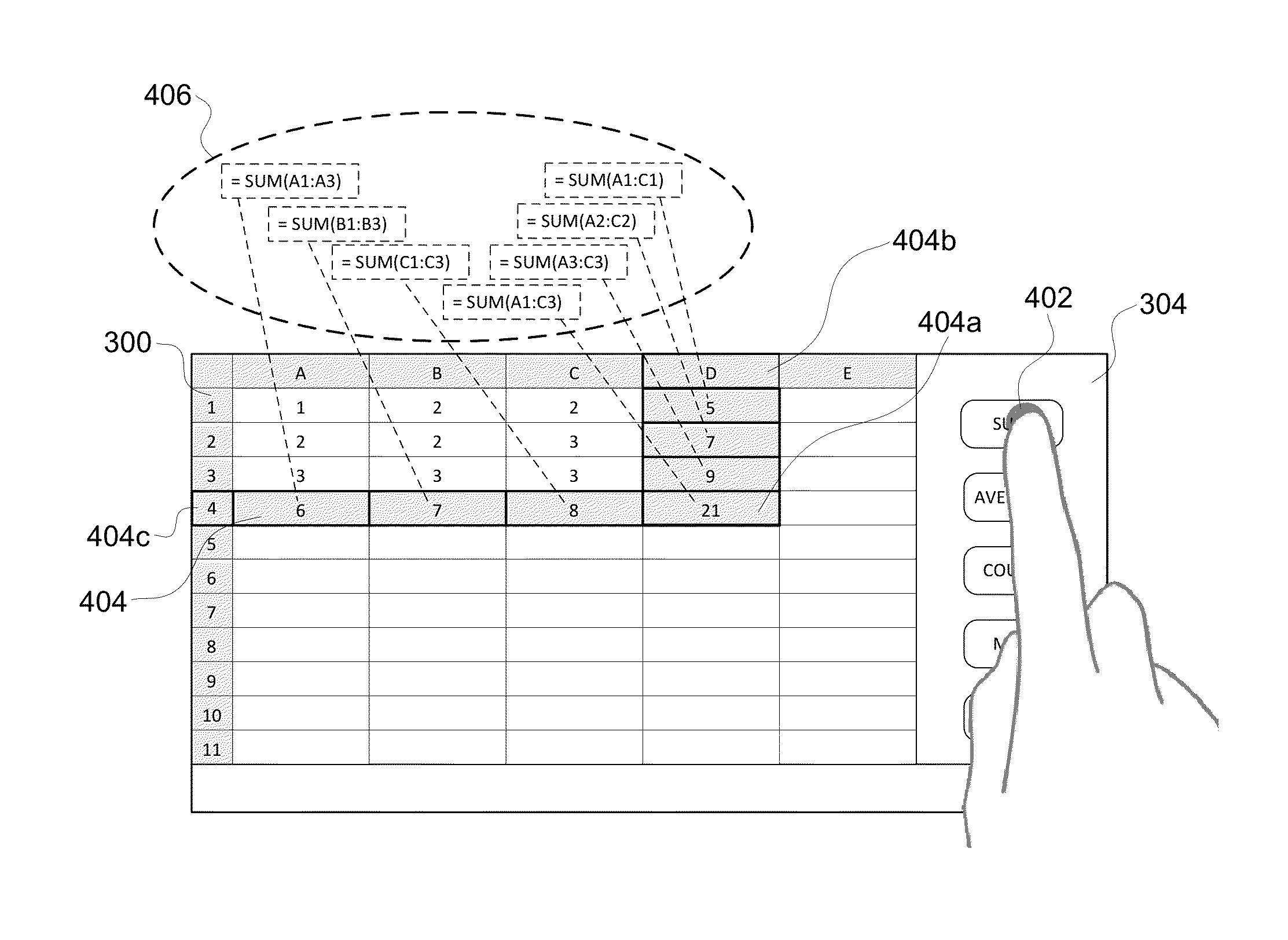
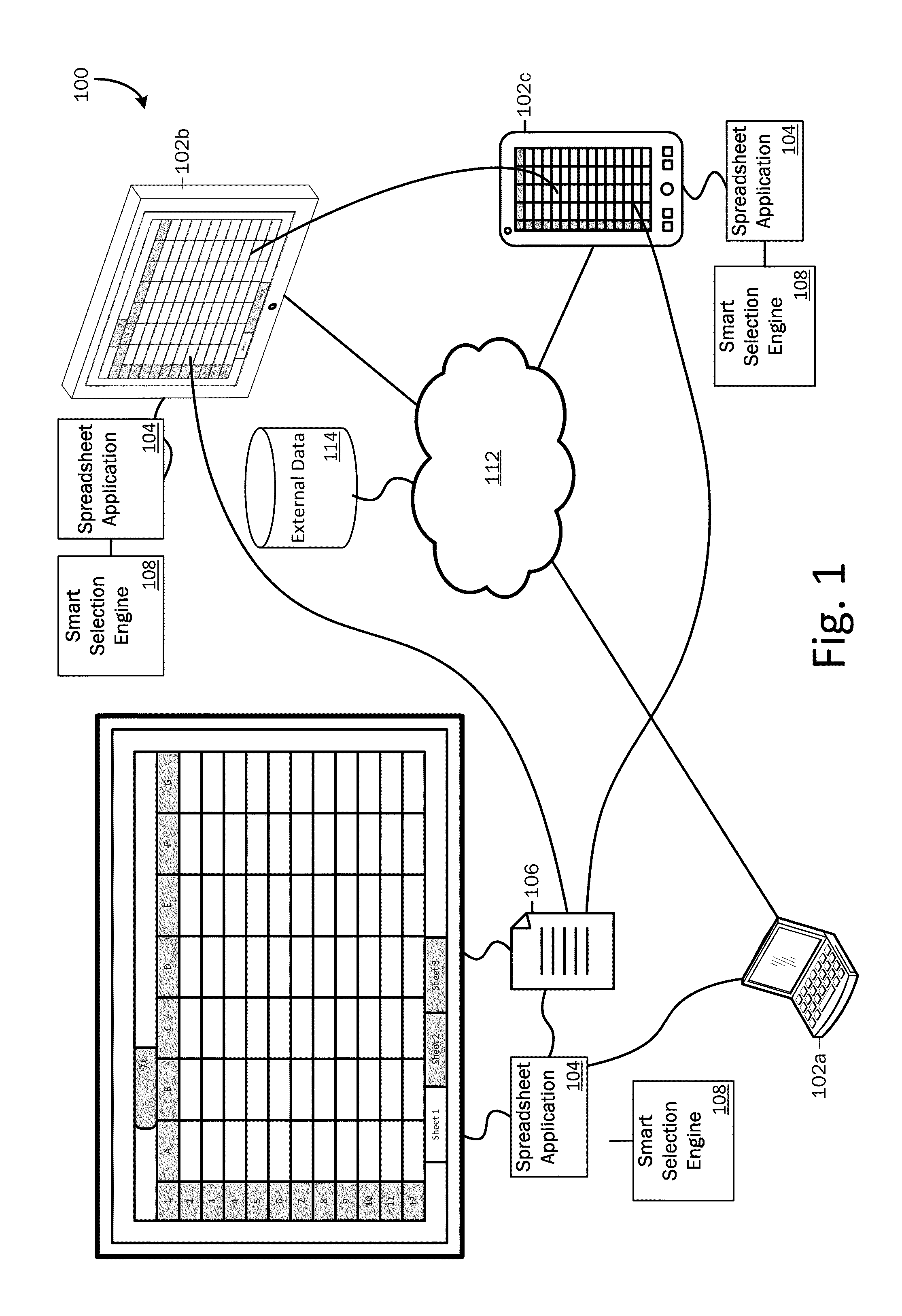
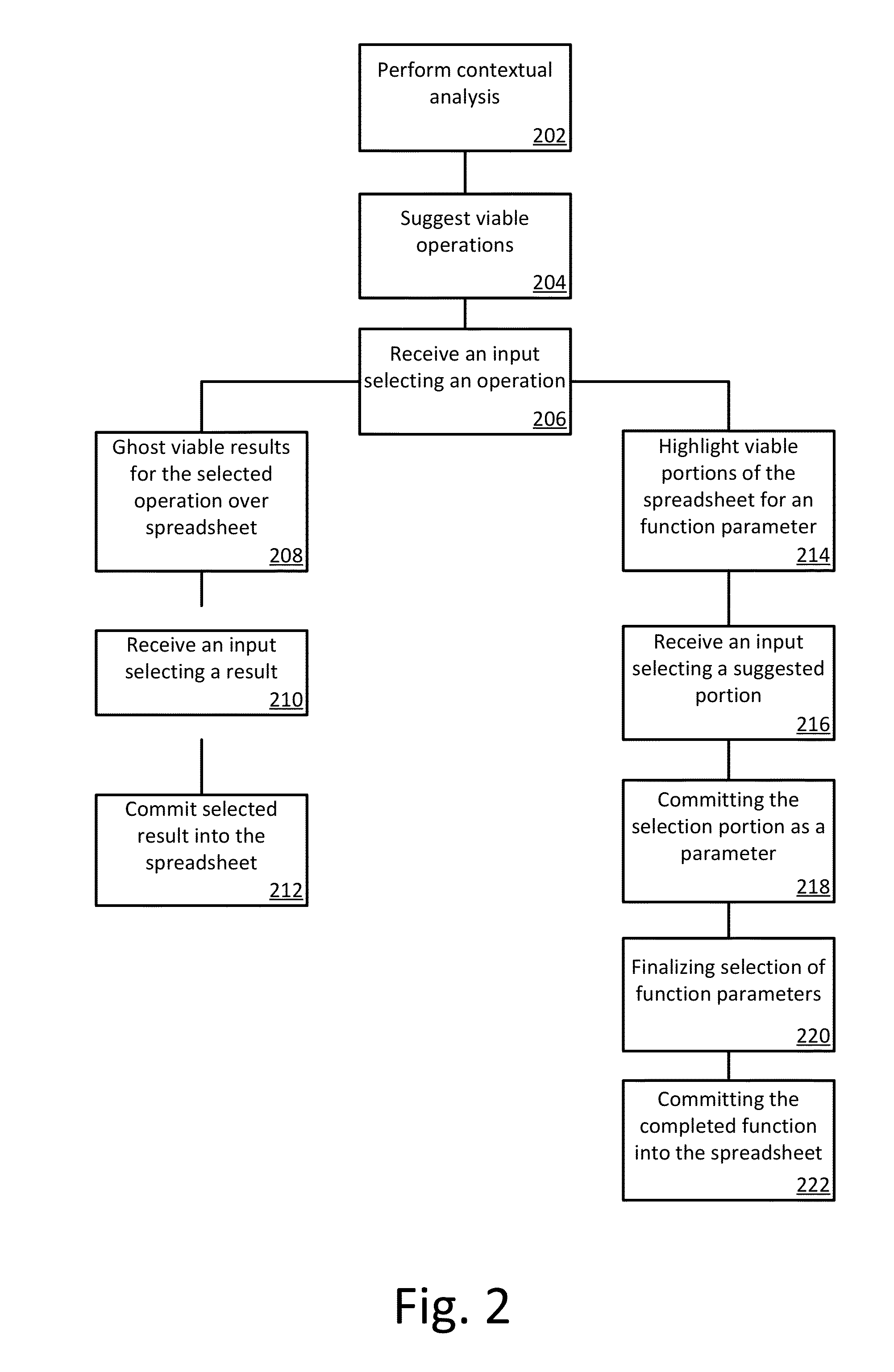
Smart Selection Engine
ActiveUS20140372854A1Reduces cognitive load and complexityEasy to understandText processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A smart selection engine is provided. The smart selection engine may run in the context of a spreadsheet application on any device, service, or general endpoint capable of running the spreadsheet application. The smart selection engine reduces the cognitive load and complexity for performing spreadsheet operations by clearly presenting the user with easy to use and understand options that are big, simple, and lend themselves nicely to natural user interfaces, touch enabled devices, and devices with small displays as well as with graphical user interfaces, larger displays, and traditional input devices. By making contextually based suggestions, the smart selection engine reduces or eliminates the need for the user to be aware of the available operations or how to perform the operations. Further, the smart selection engine improves the consistency and efficiency of working with a spreadsheet.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
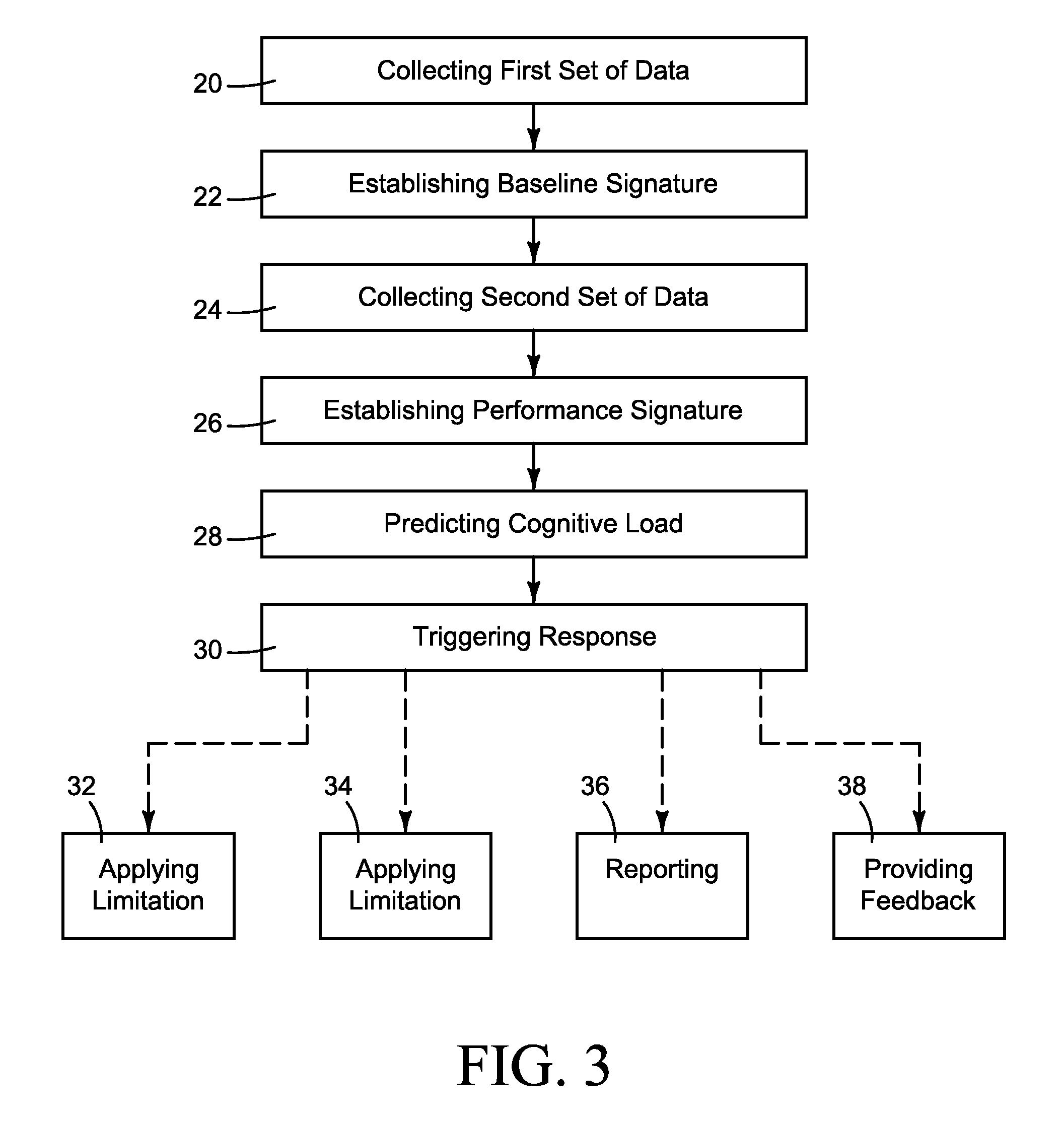
Apparatuses and methods of determining if a person operating equipment is experiencing an elevated cognitive load
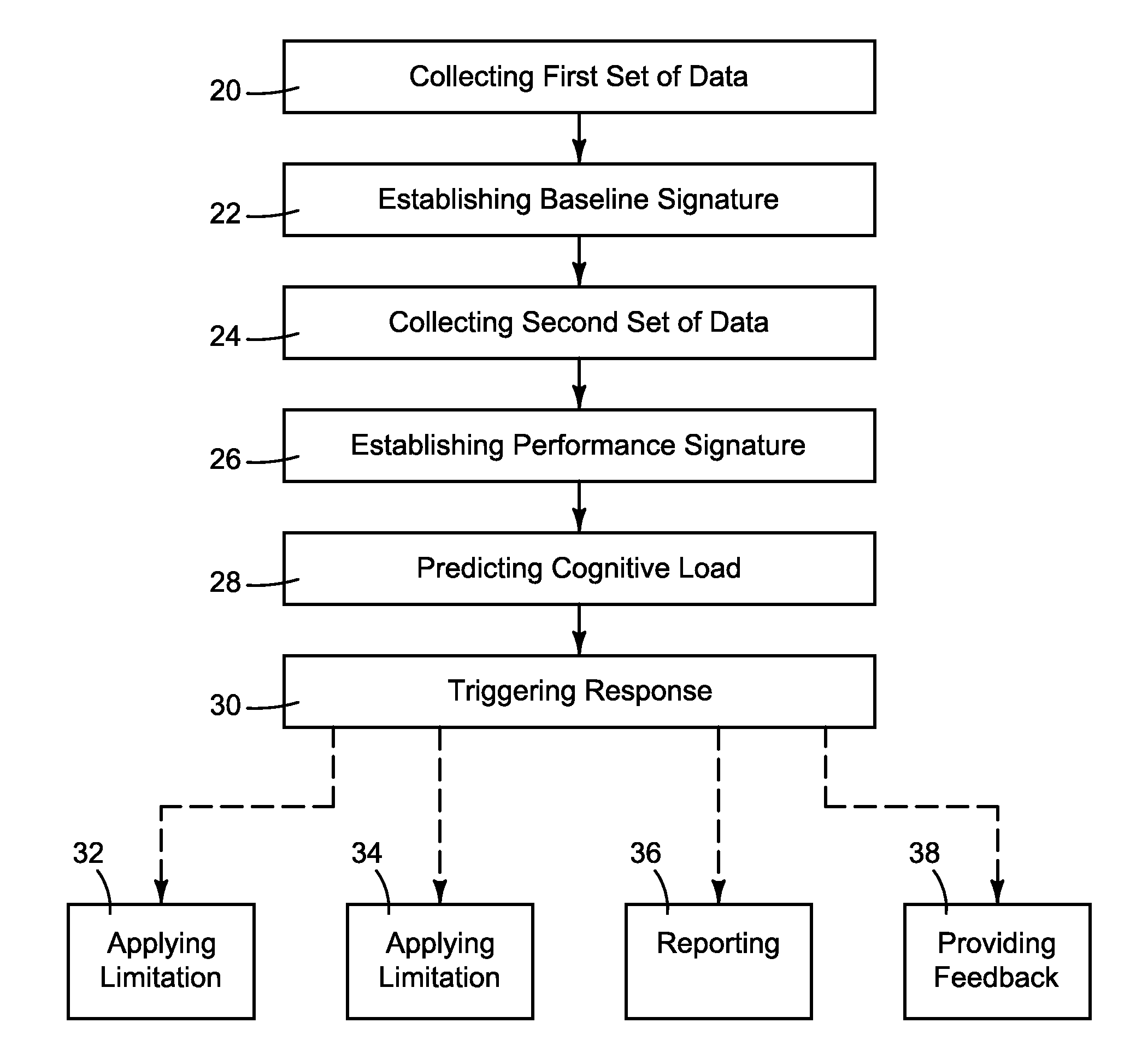
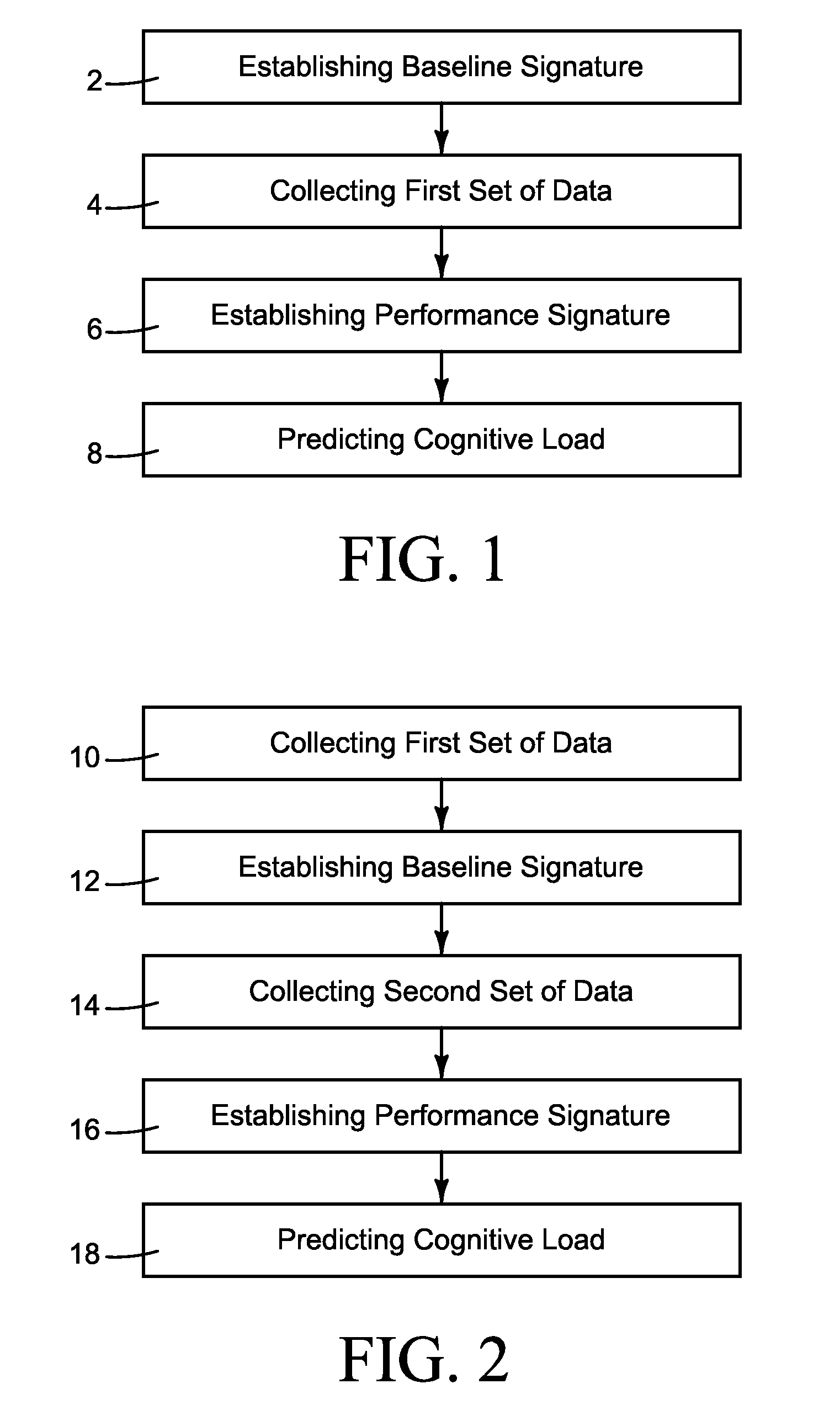
ActiveUS20120235819A1Increase cognitive loadIncrease awarenessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCognitive loadComputer science
A method of, and apparatus for, determining if a person operating equipment is experiencing an elevated cognitive load, wherein the person's use of a device at a first time is monitored so as to set a baseline signature. Then, at a later time, the person's use of the device is monitored to determine the person's performance at the second time, as represented by a performance signature. This performance signature can then be compared against the baseline signature to predict whether the person is experiencing an elevated cognitive load.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
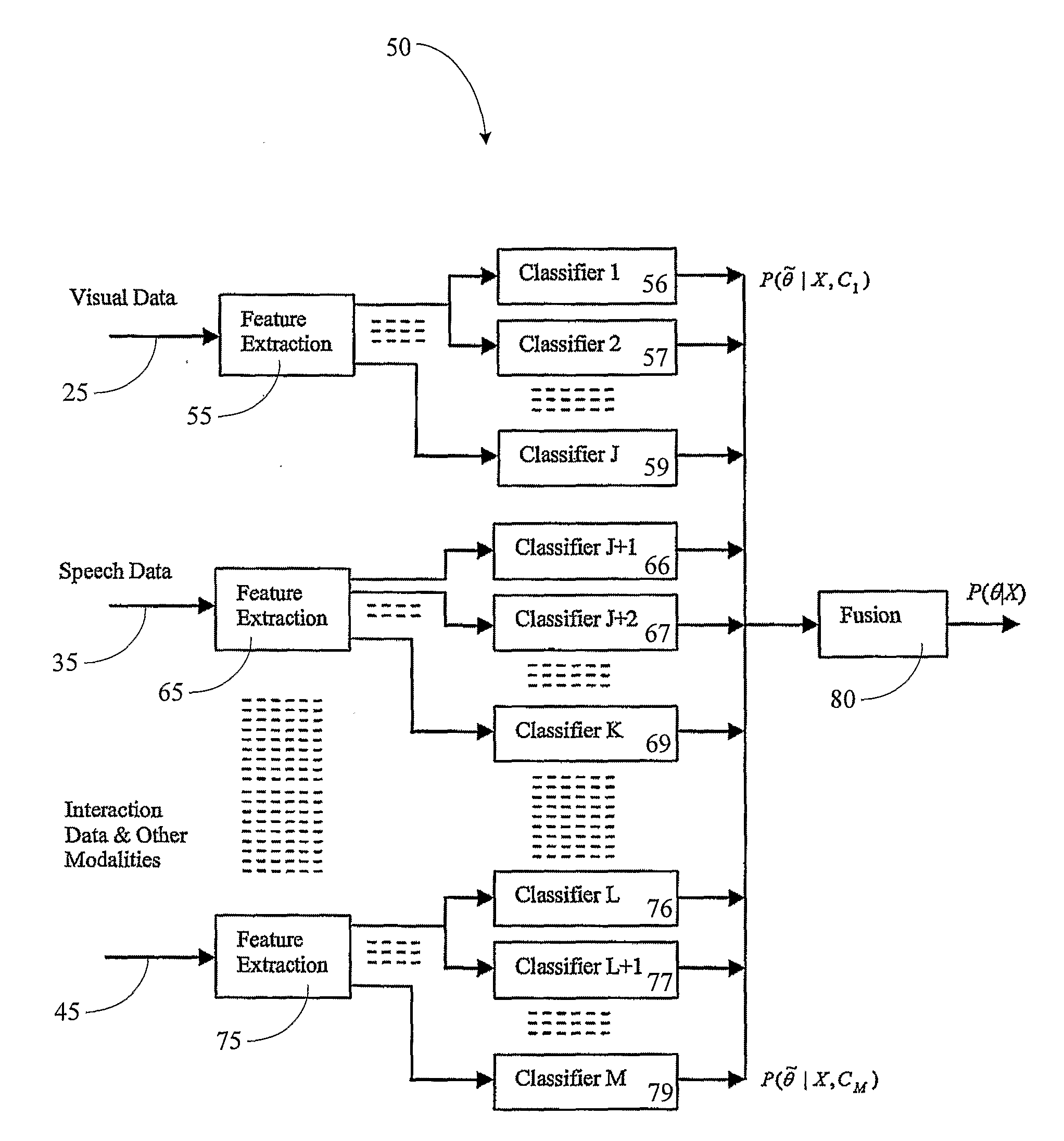
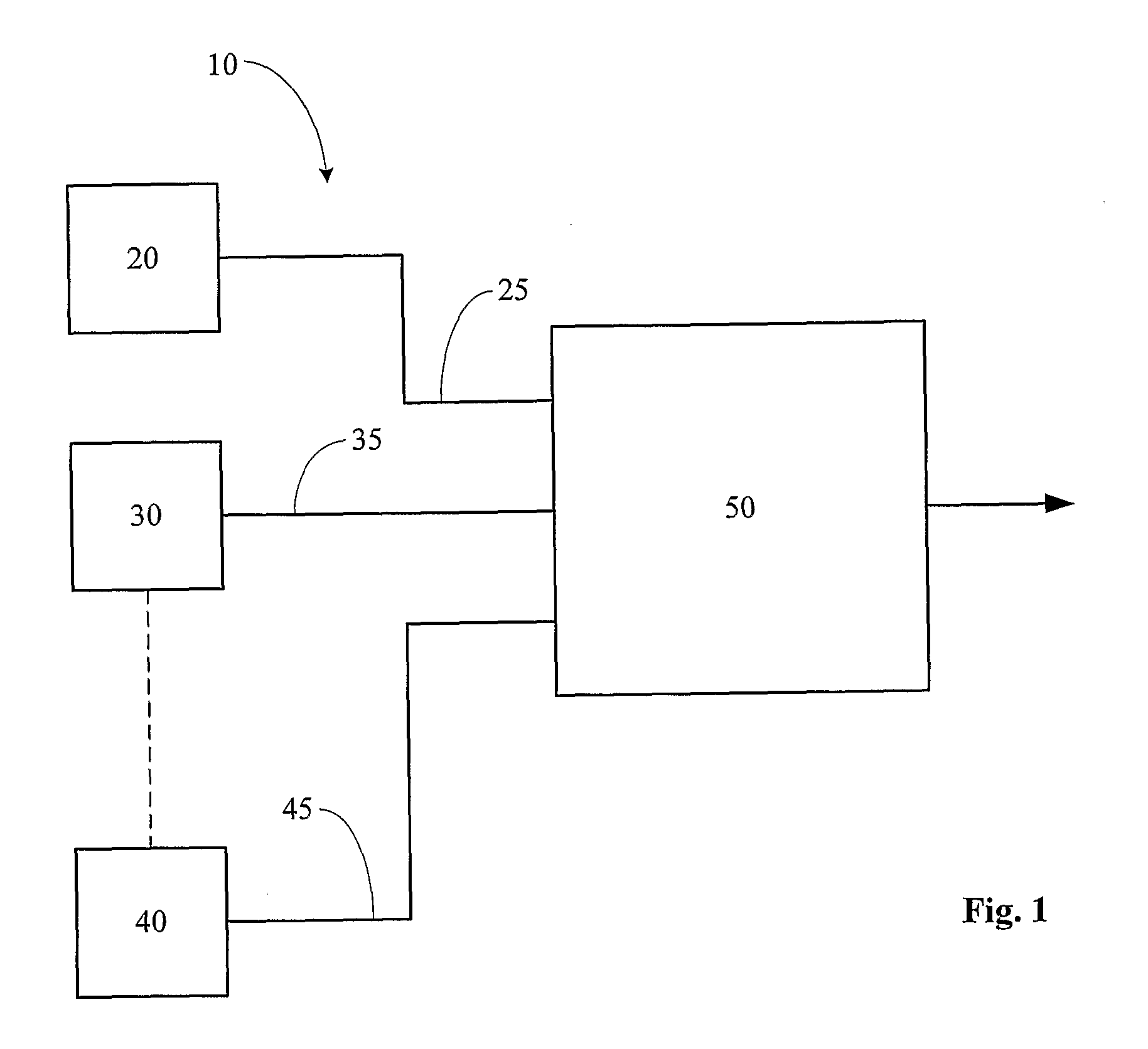
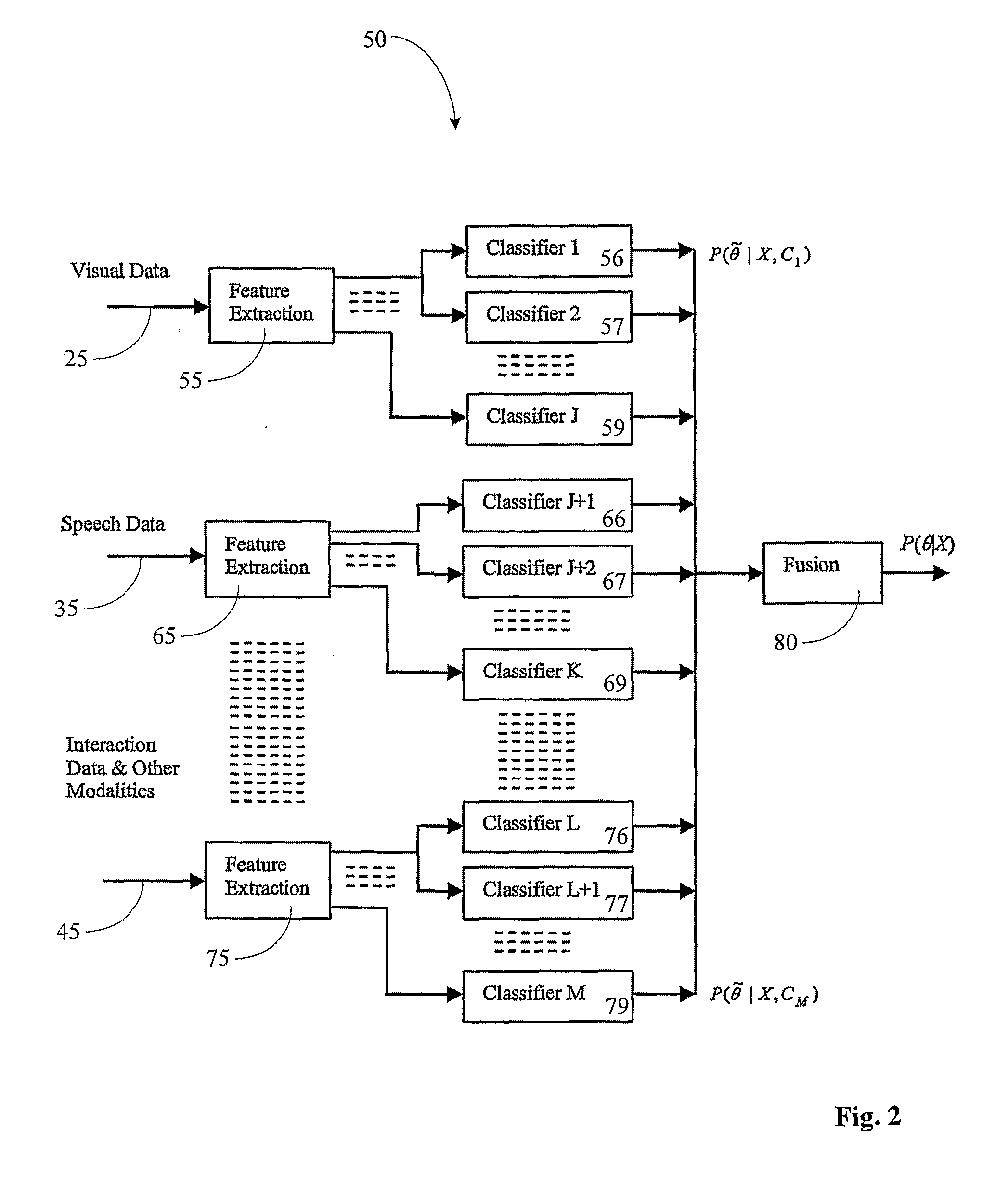
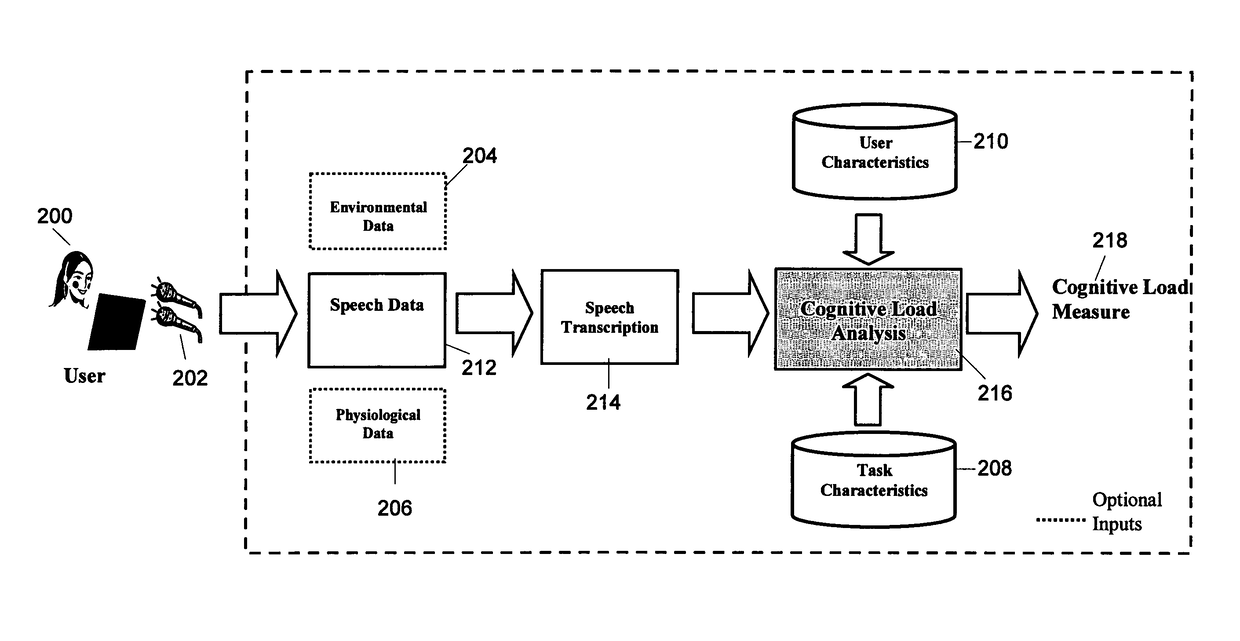
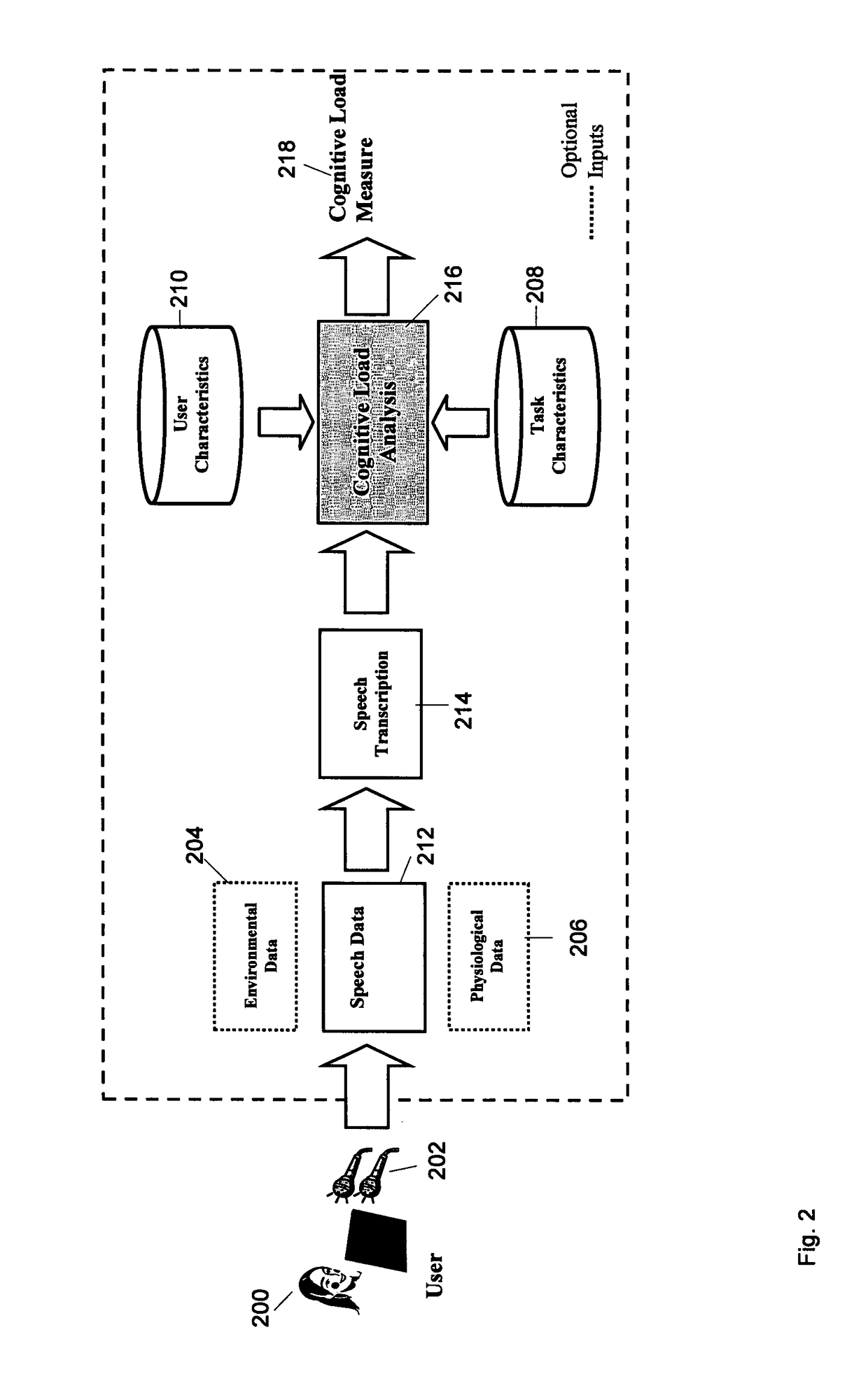
Measuring cognitive load
ActiveUS20100217097A1Weight featureImprove individual classificationMedical automated diagnosisMental therapiesData signalOutput device
This invention concerns a method for measuring cognitive load of a person in performing a task. In other aspects the invention can be expressed as a computer and as software that are used to perform the method. The computer (50) has an interface having a plural number of unimodal input (20, 30 to 40) and output devices, and a cognitive load analyzer (50). The analyzer comprises a receiver to receive input data signal streams (25, 35 and 45) from respective devices (20, 30 and 40). A classifier (56 to 59), (66 to 69) and (76 to 79) is also provided to identify predetermined “meta-interaction patterns” from the streams (25, 35 and 45), and to weight the identified predetermined “meta-interaction patterns” to produce respective weighted outputs. A combiner (80) to fuse the outputs to produce a measure indicating the person's cognitive load.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
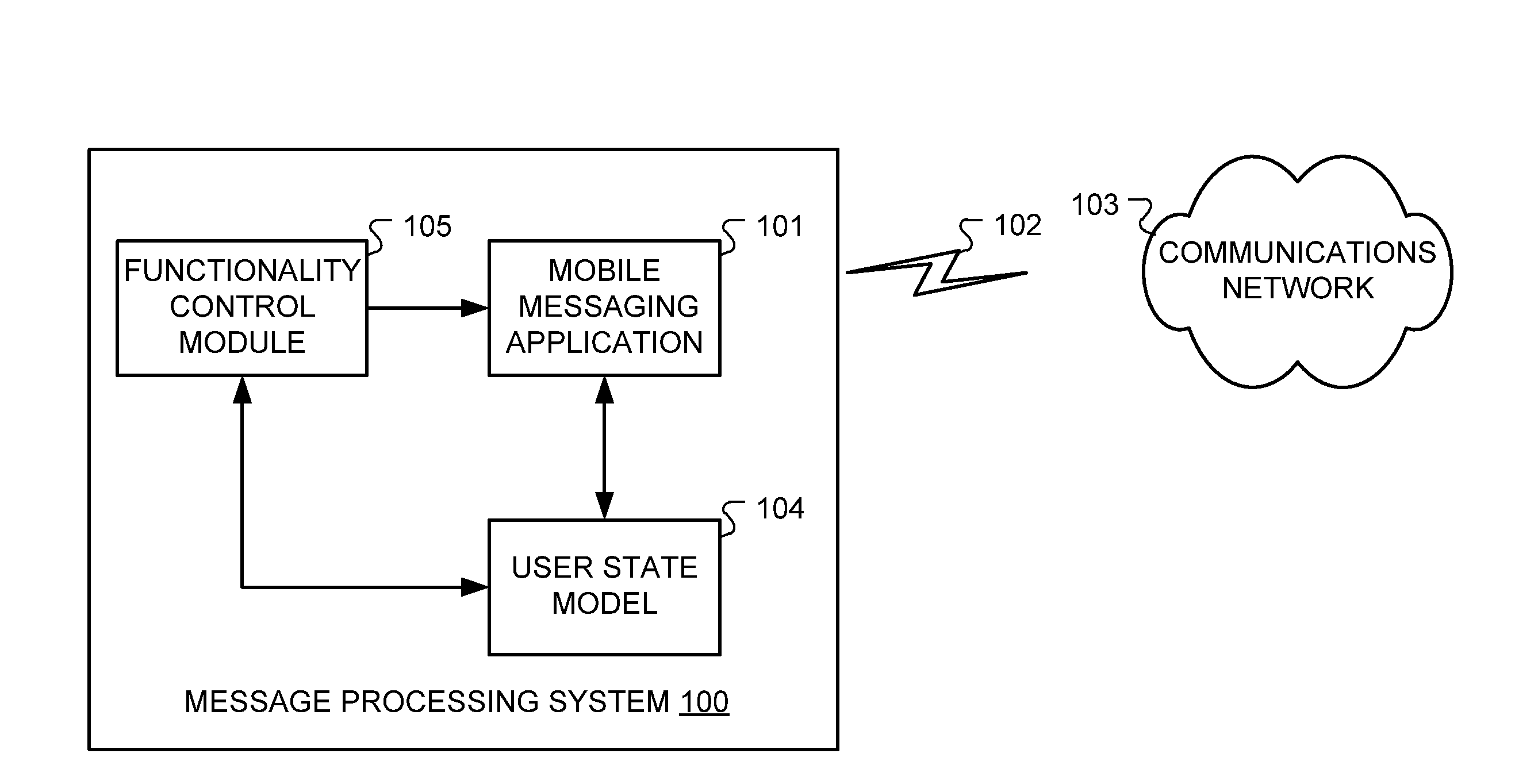
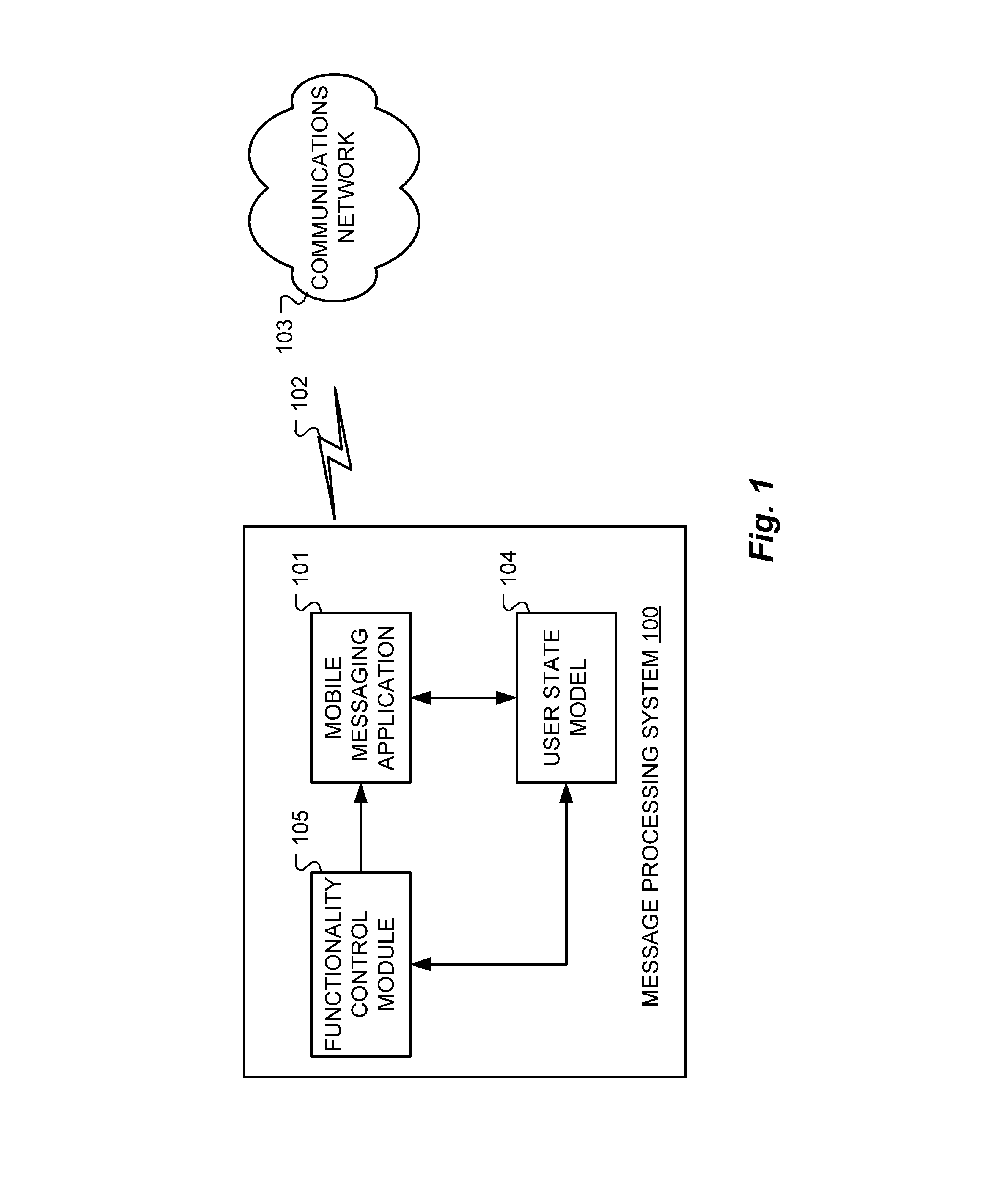
Situation-Aware Message Presentation For Automotive Messaging
ActiveUS20130165165A1Assess restrictionMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsMobile contextApplication software
A text message processing arrangement is described for use in a mobile environment. A mobile messaging application processes user text messages during a user messaging session. A user state model reflects situational parameters to characterize user cognitive load. A functionality control module adjusts functional performance of the mobile messaging application based on the user state model.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
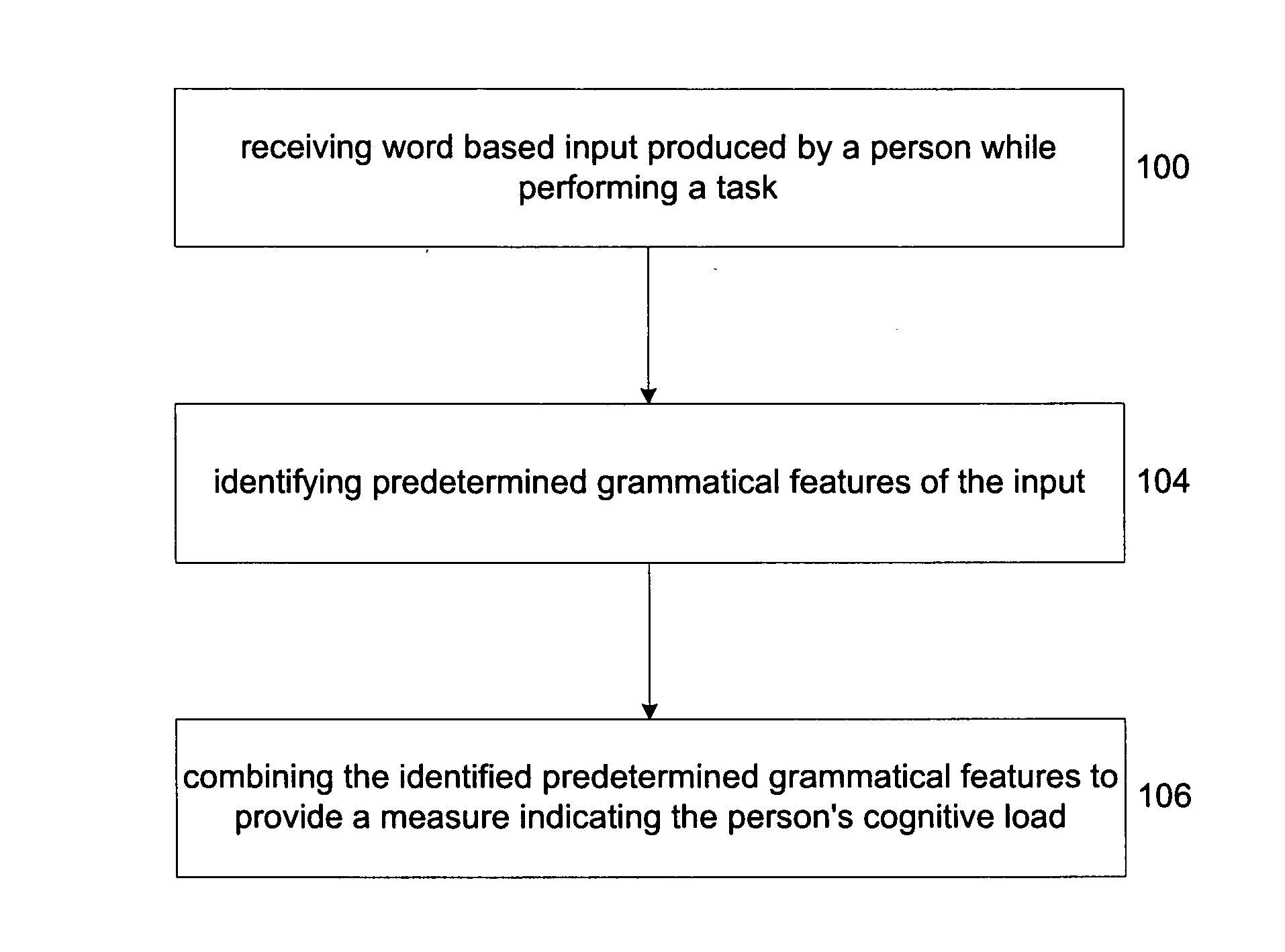
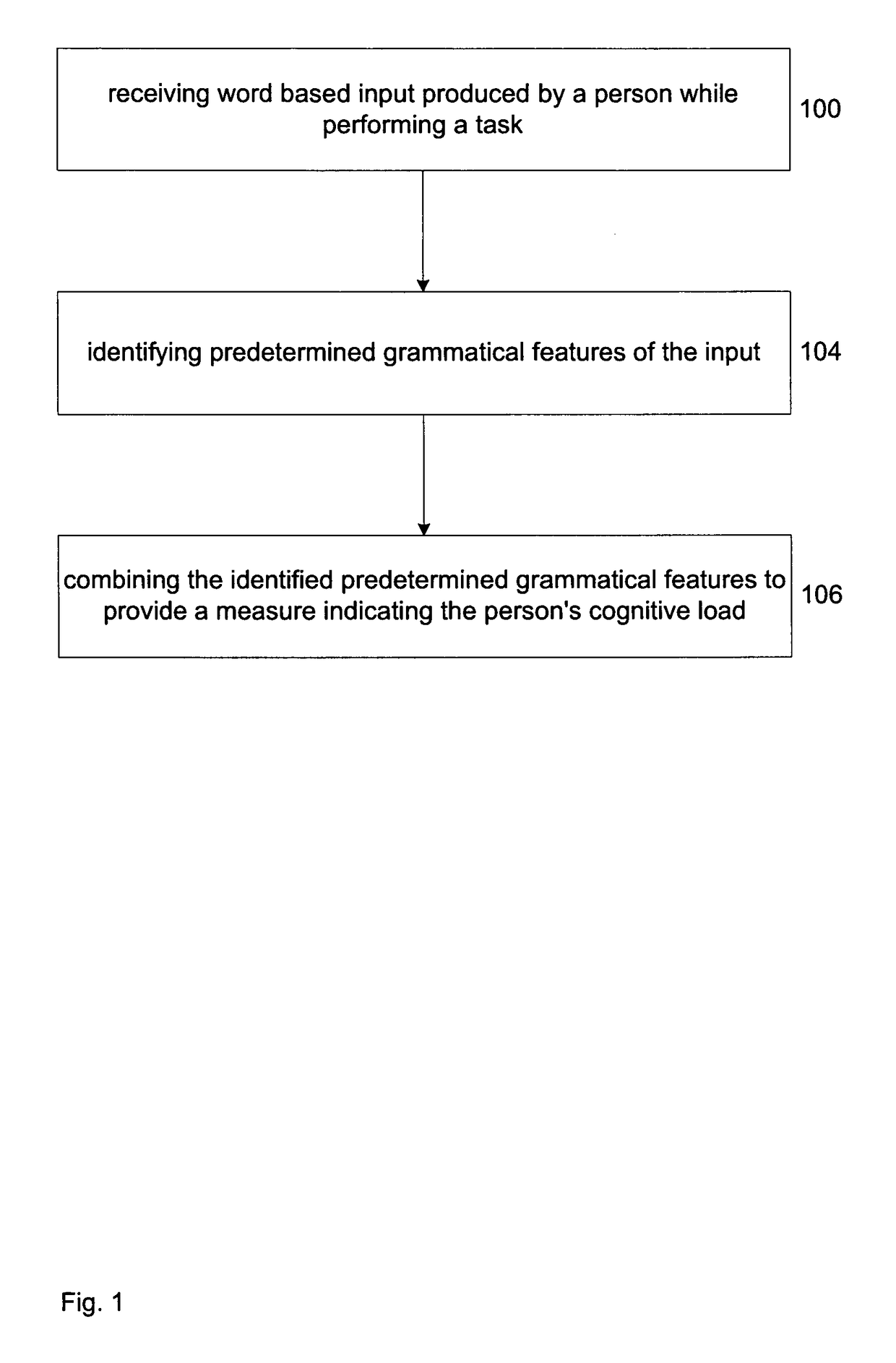
Measuring cognitive load
ActiveUS20110207099A1Accurate load measurementAccurate measurementMedical automated diagnosisSensorsComputerized systemPhysical therapy
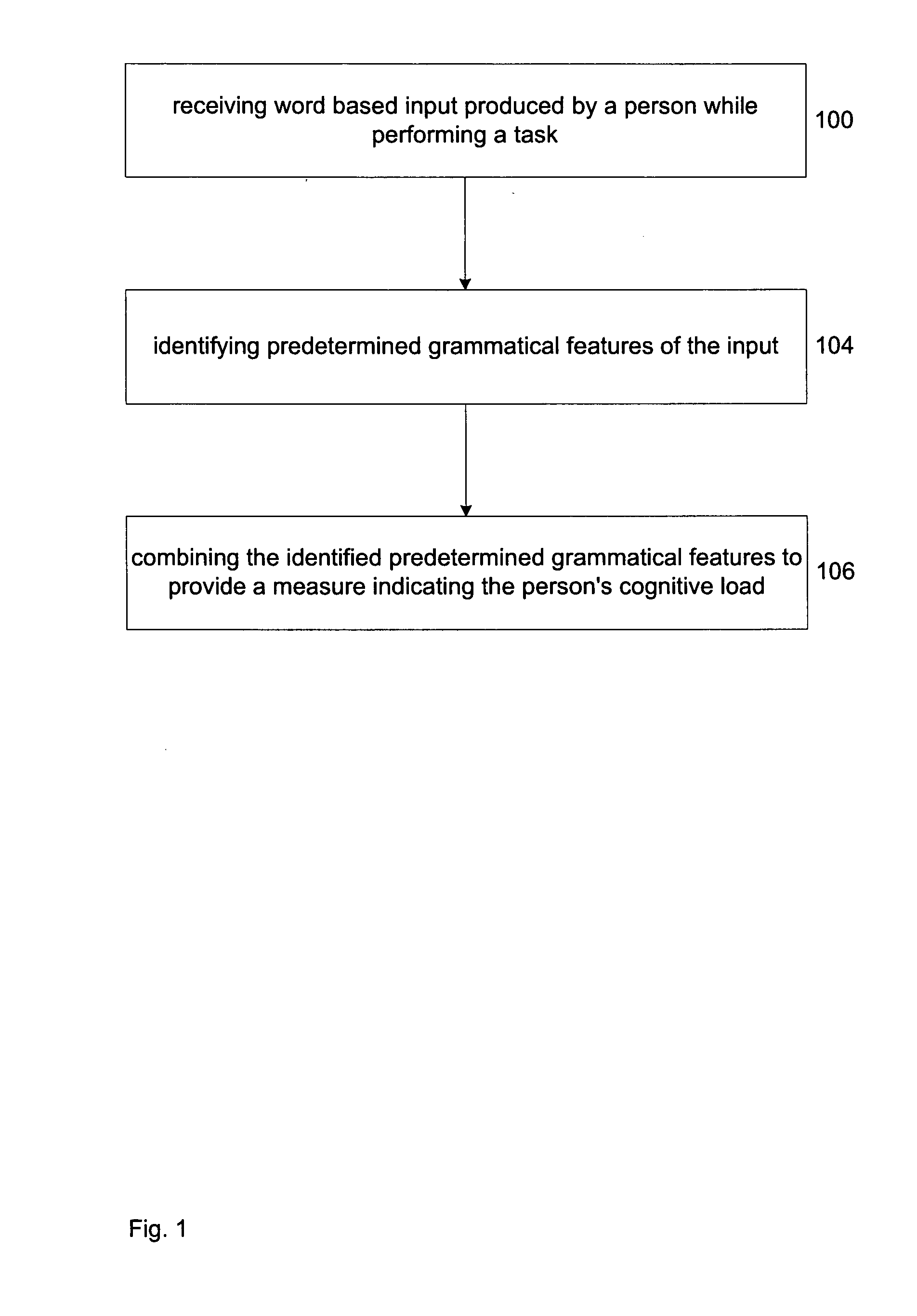
This invention concerns measuring cognitive load. A word based input is produced by a person while performing a task (100). Predetermined grammatical features of the word based input are identified (104). Then, the identified grammatical features are weighted and combined to provide a measure indicating the person's cognitive load (106). The use of grammatical features represents a divergence from the known methods of providing a measure of a person's cognitive load. It is an advantage of the invention that by concentrating on the grammatical features it is able to provide an objective, non-intrusive measure of the person's cognitive load. Aspects the invention include a method, a computer system and software that are used to perform the method.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Interactive vision therapy board
InactiveUS20110184498A1Extension of timeEye exercisersDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringTherapeutic intent
A light board machine useful for visual training and therapy purposes includes a planar backboard having an array of light locations having two colored lights (red and green), a microprocessor controller for controlling the operation, sequencing and timing of the lights, and a user-feedback device, such as a touch-activated panel, which cooperate to provide visual training and therapy functions. The present invention includes the option to use red (lights) only, green only or red and green in a random order. The present invention also includes letters and numbers behind some of the lights (e.g. 80 of the 120 lights), and has a sequential pattern option of 30, 60, 90 or 120 lights. This invention is compatible with the use of red / green glasses to accommodate training of binocularity and depth. This invention is used in a therapy setting and will helps to enhance eye hand coordination, response / reaction time, peripheral vision / awareness, localization, awareness of space and depth perception, eye tracking (saccades and occulomotor), sequential movement and processing, as well as a cognitive loading component that therapists use in a variety of ways for individual patients and specific therapy modalities.
Owner:DONLEY ROBIN LYNN
Adjusting user interface element
The invention relates to a method of adjusting user interface element, a system and computer program products. In each embodiment of the invention, the user interface elements and the size, shape and position of a vacant zone can be adjusted based on a using data history. The adjustment can reduce cognitive loads related to selected user interface elements. For example, in a vehicle moving dangerous condition, the reduction of cognitive loads allows a user to focus on safe operations of the moving vehicle. The historic using data can be traced back to one or more users and one or more equipments. The limit value adjustment can be used for ensuring the user interface is properly kept valid. The adjustment on the user interface element can be used for optimizing user interfaces and / or influencing user interaction with user interfaces.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Compact Stylus-Based Input Technique For Indic Scripts
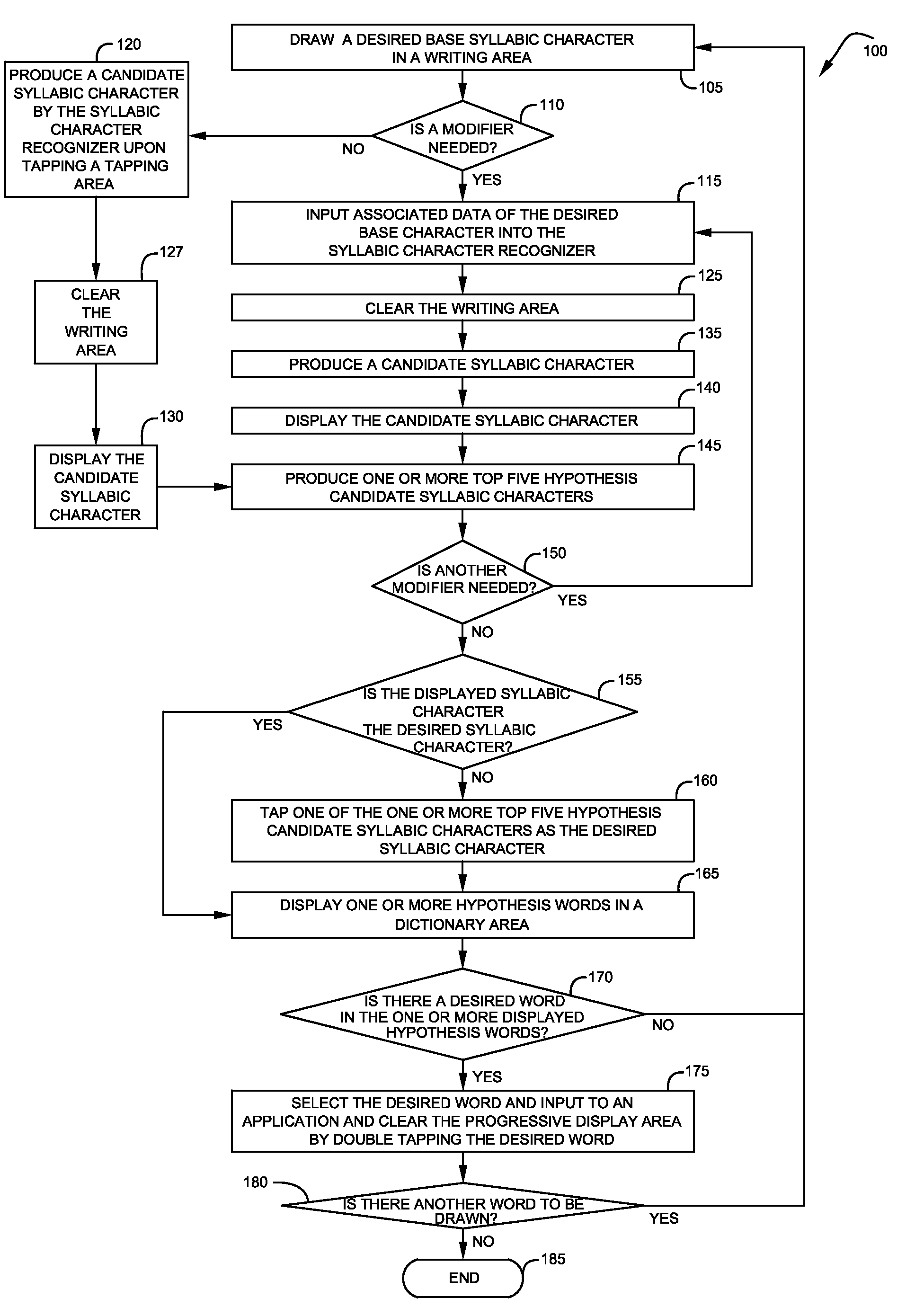
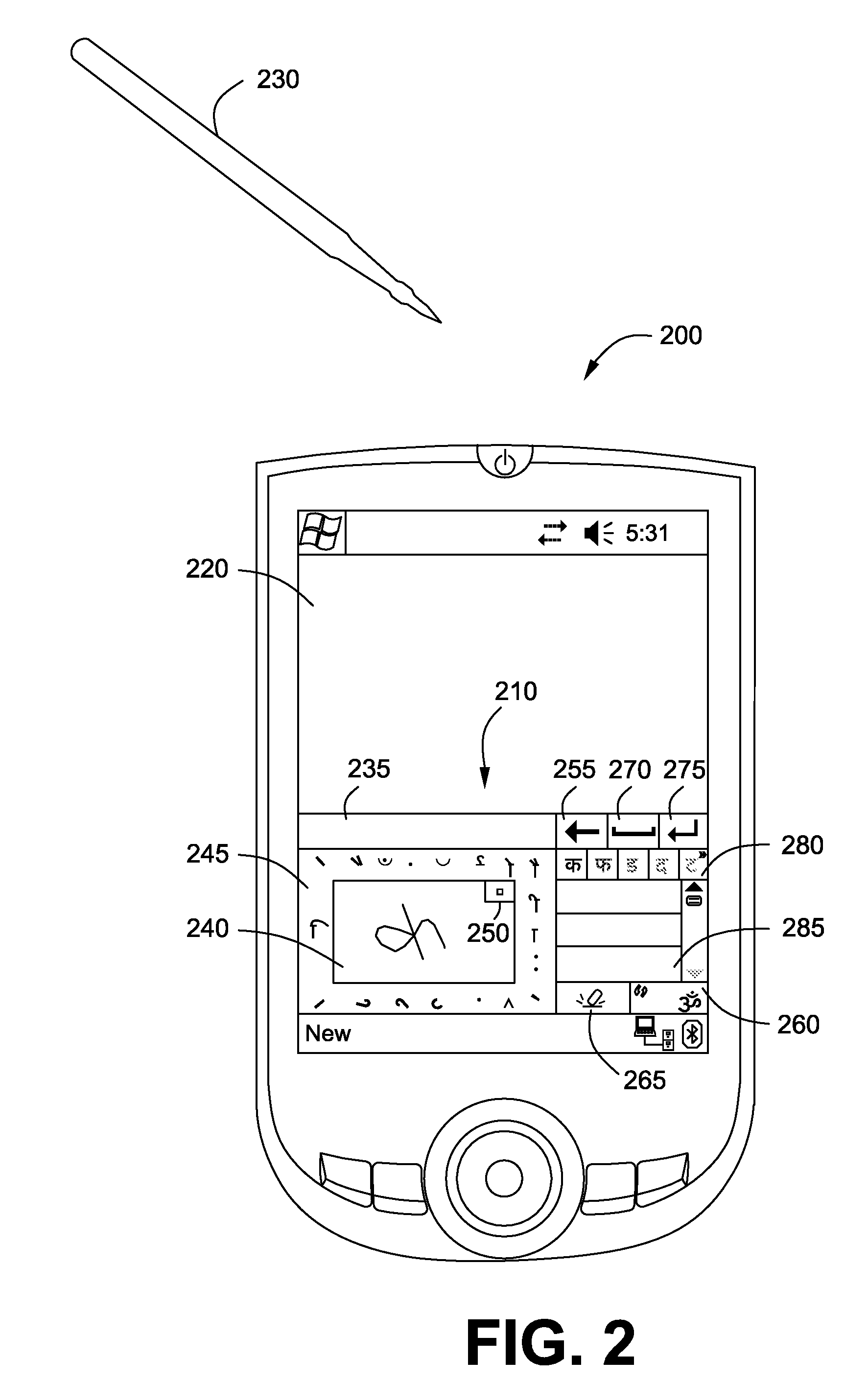
A technique for stylus-based syllabic input that is fast and easy and does not require any additional hardware and can be deployed on a handheld device is described. In one example embodiment, this is accomplished by writing a base syllabic character consisting of a vowels or consonant in a writing area. One or more modifiers that are displayed as icons substantially around the writing area of a syllabic level user interface are then selected to form a desired syllabic character. The one or more modifiers are arranged at familiar / natural positions around the base character's writing area to facilitate entry / selection of modifiers and to reduce eye movement / cognitive load on the user. The syllabic characters are then accumulated locally until a desired word is formed, to reduce visual disconnect between the input interface and the end application, and to provide context for formation of the desired word. Further, one or more hypothesis words are then presented to speed up the formation and inputting of a desired word. The formed desired word is then cleared from the display area and sent to an application display area by tapping a space button provided in the syllabic character input user interface.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Peripheral vision in a human-machine interface
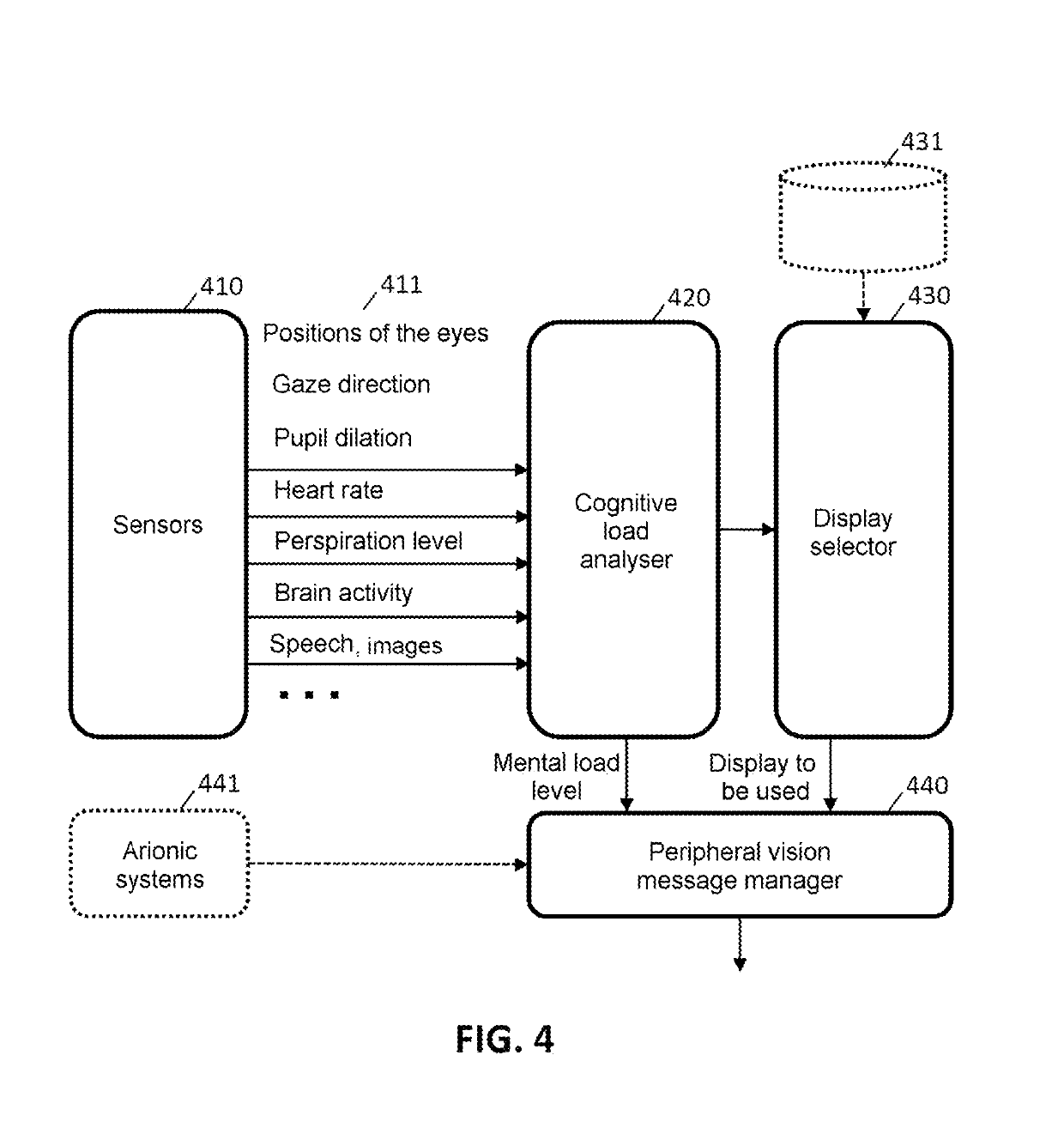
ActiveUS20190250408A1Simplify human-machine interactionRelieve pilotAircraft componentsInput/output for user-computer interactionAviationGraphics
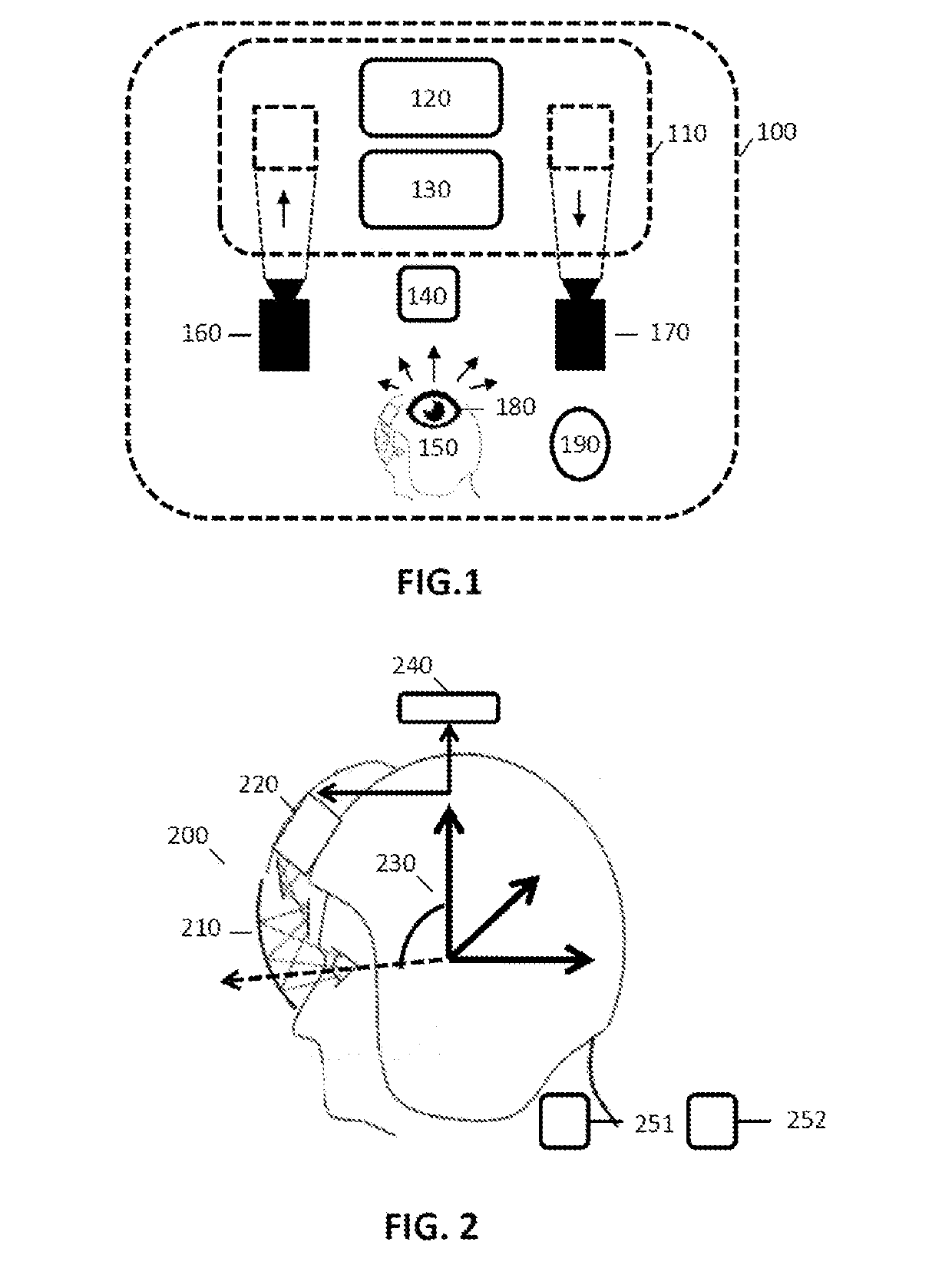
A computer-implemented method for managing a graphical human-machine interface, includes the steps of receiving information relating to the position of the eyes and the gaze direction of a user at the interface; receiving physiological information of the user; determining a level of cognitive load on the basis of the received physiological information; adjusting the display of the interface on the basis of the gaze direction and / or of the determined level of cognitive load. Some developments describe the management of the display zones (foveal zone and peripheral zones), the selection of one or more displays, the management of the distance from the message display to the current gaze location, the management of the criticality of the messages, various graphical techniques for attracting attention, the management of the flight context in the avionic case, the management of visual density, etc. Some system aspects are described (virtual and / or augmented reality).
Owner:THALES SA
Emotional stability comprehensive evaluation system and information processing method
InactiveCN107212896AEffective trainingSensorsPsychotechnic devicesInformation processingFeature extraction
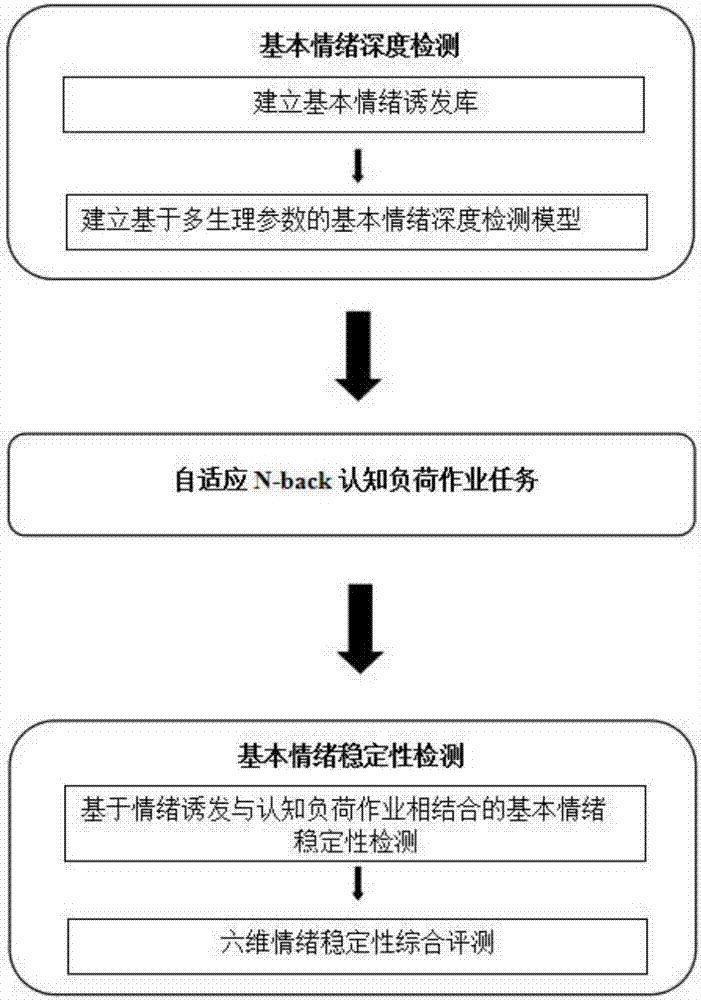
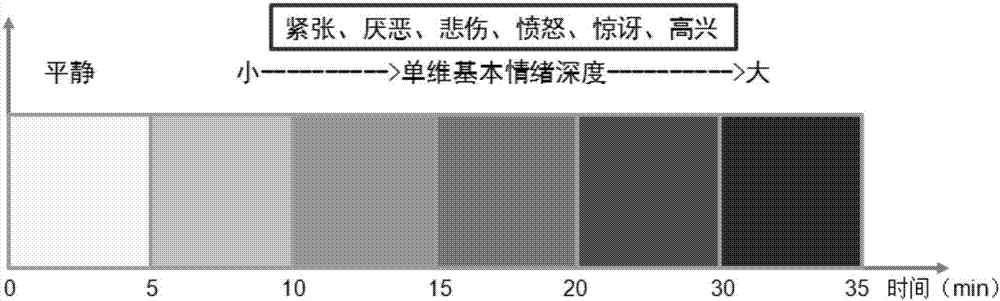
The invention belongs to the field of emotional stability evaluation and particularly relates to an emotional stability comprehensive evaluation system and an information processing method. The method includes the steps of basic emotion depth detection; adaptive N-back cognitive load job tasks; basic motion stability detection. The step of basic emotion depth detection includes the processes that a basic emotion elicitation library is established; a basic emotion depth detection model based on multiple physiological parameters is established. The emotion elicitation library refers to a video material library for eliciting emotions, emotion theme related video materials are obtained, screened and classified, the basic emotion elicitation library is formed, multiple people perform one-dimensional emotion elicitation depth scoring on all emotion elicitation materials, and the average score of each segment of elicitation material serves as the one-dimensional emotion elicitation depth score of the materials. The emotional stability comprehensive evaluation system and the information processing method have the advantages that through subjective detection and fusion analysis of multi-mode physiological signals, the optimum physiological representation in different-type emotion stress states is screened out, and the basic emotion depth is automatically sorted through feature extraction and mode classification algorithms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
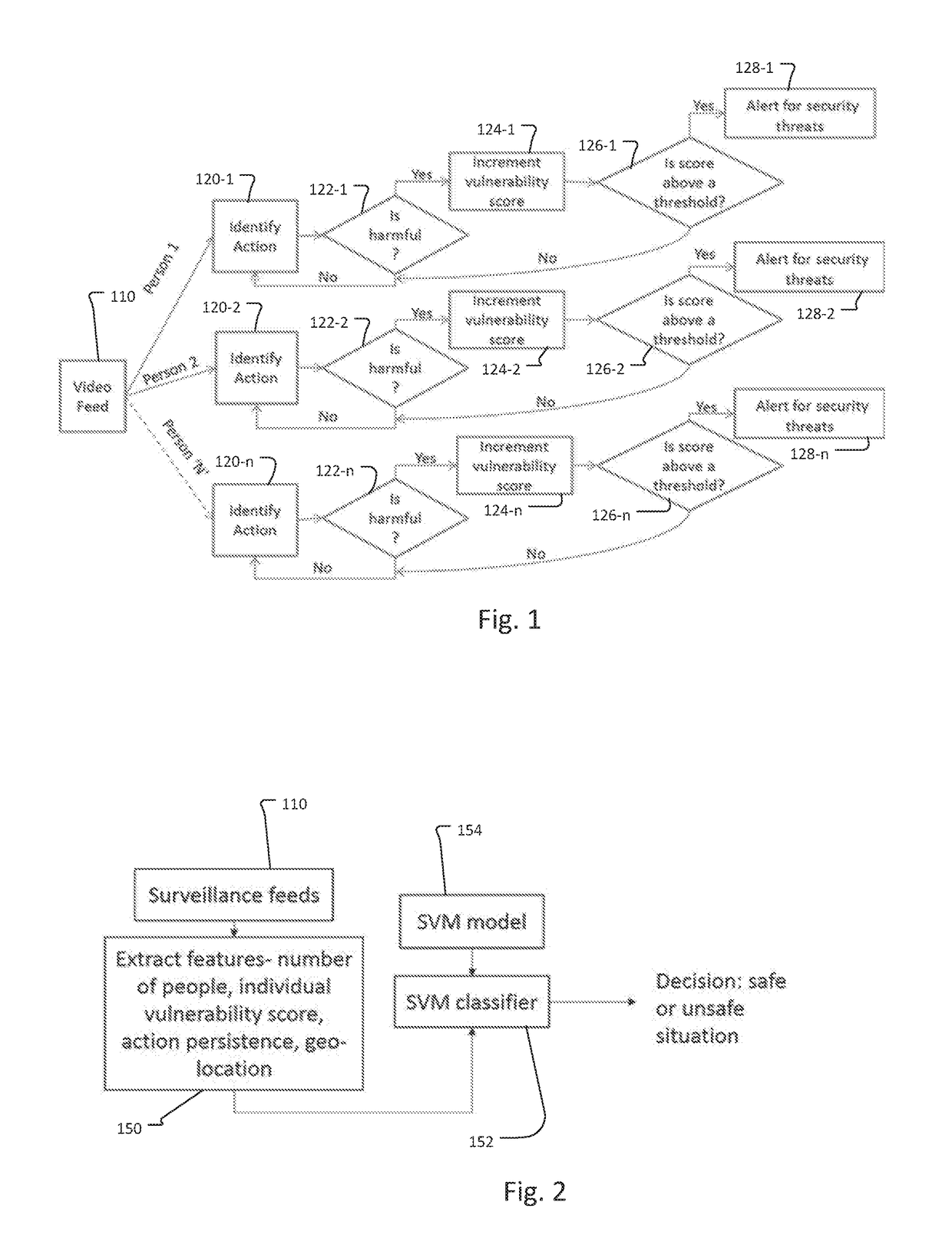
Surveillance System with Human Behavior Prediction by Human Action Recognition
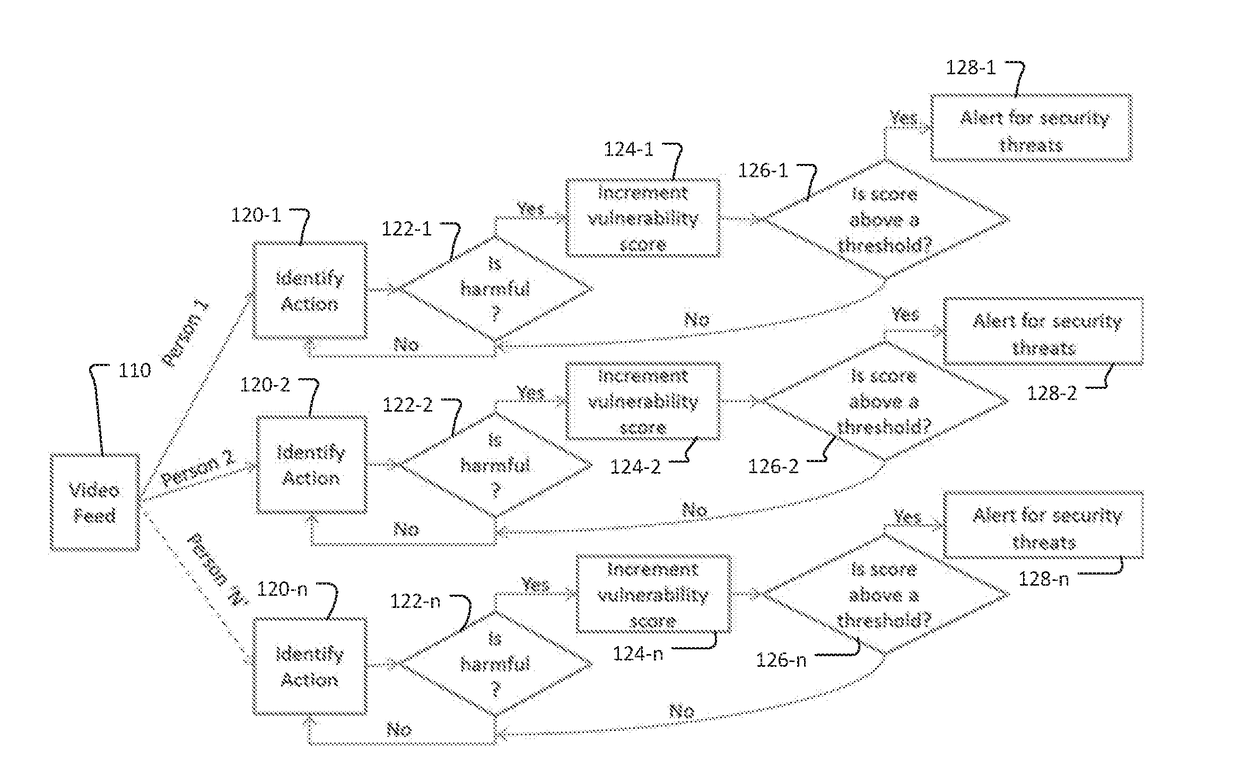
ActiveUS20180314897A1Reduce cognitive loadImprove system efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsHuman behaviorMonitoring system
The present invention concerns surveillance systems that flag the potential threats automatically using intelligent systems. It can then notify or automatically alert the security personnel of impending dangers. Such a system can lower the cognitive load on the security personnel and can assist them to bring to prioritize their attention to potential threats and thereby improve the overall efficiency of the system. There could also be savings in labor cost.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
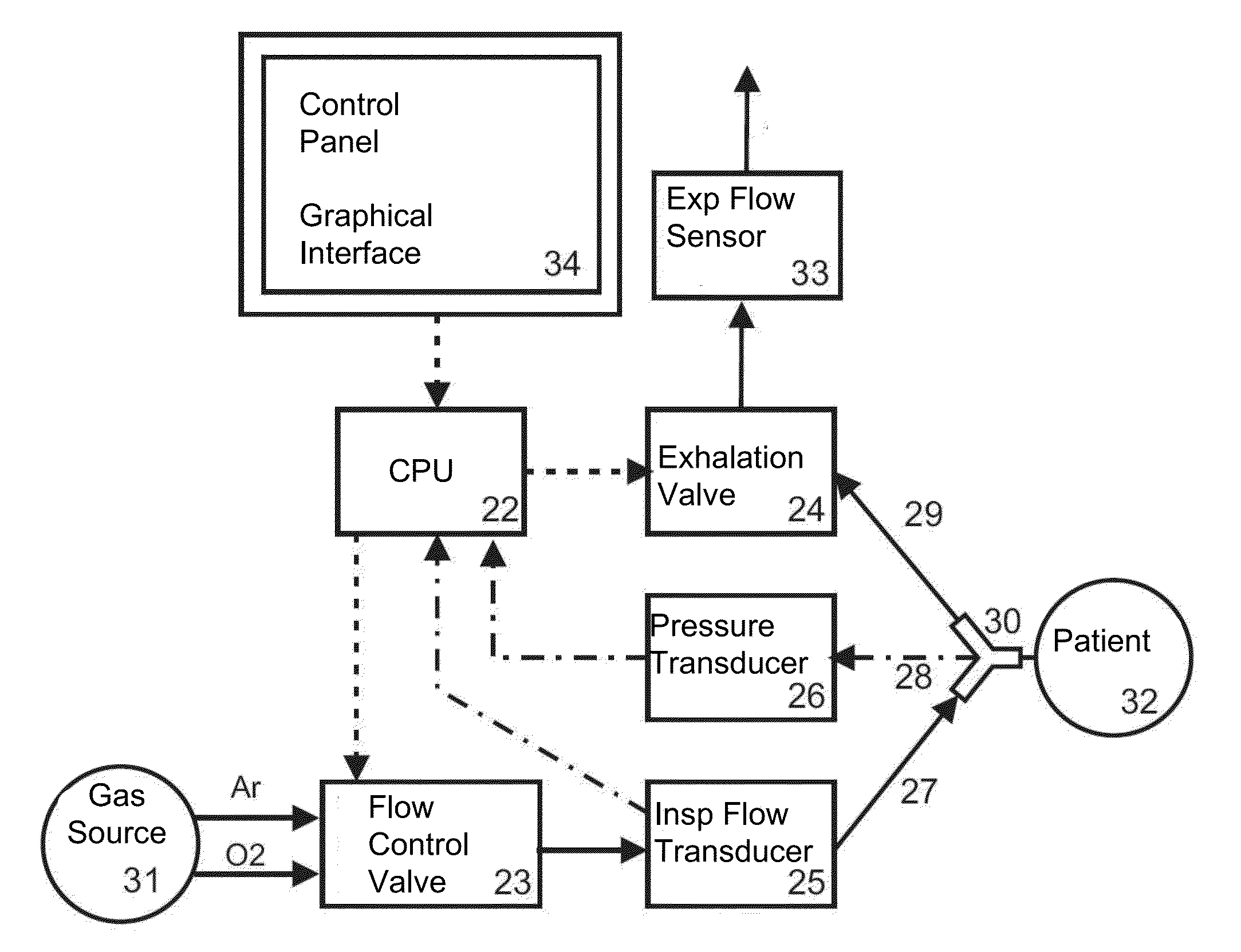
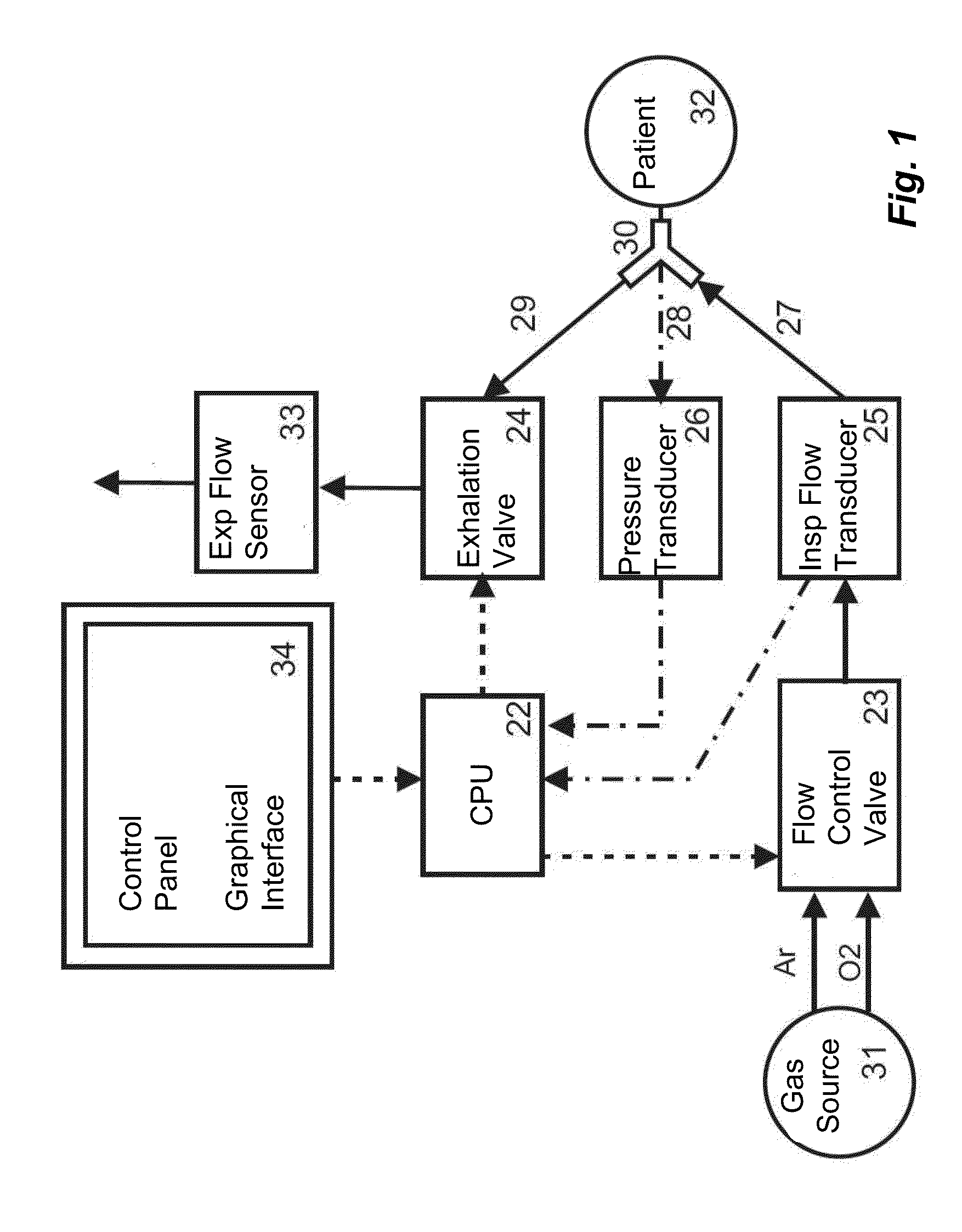
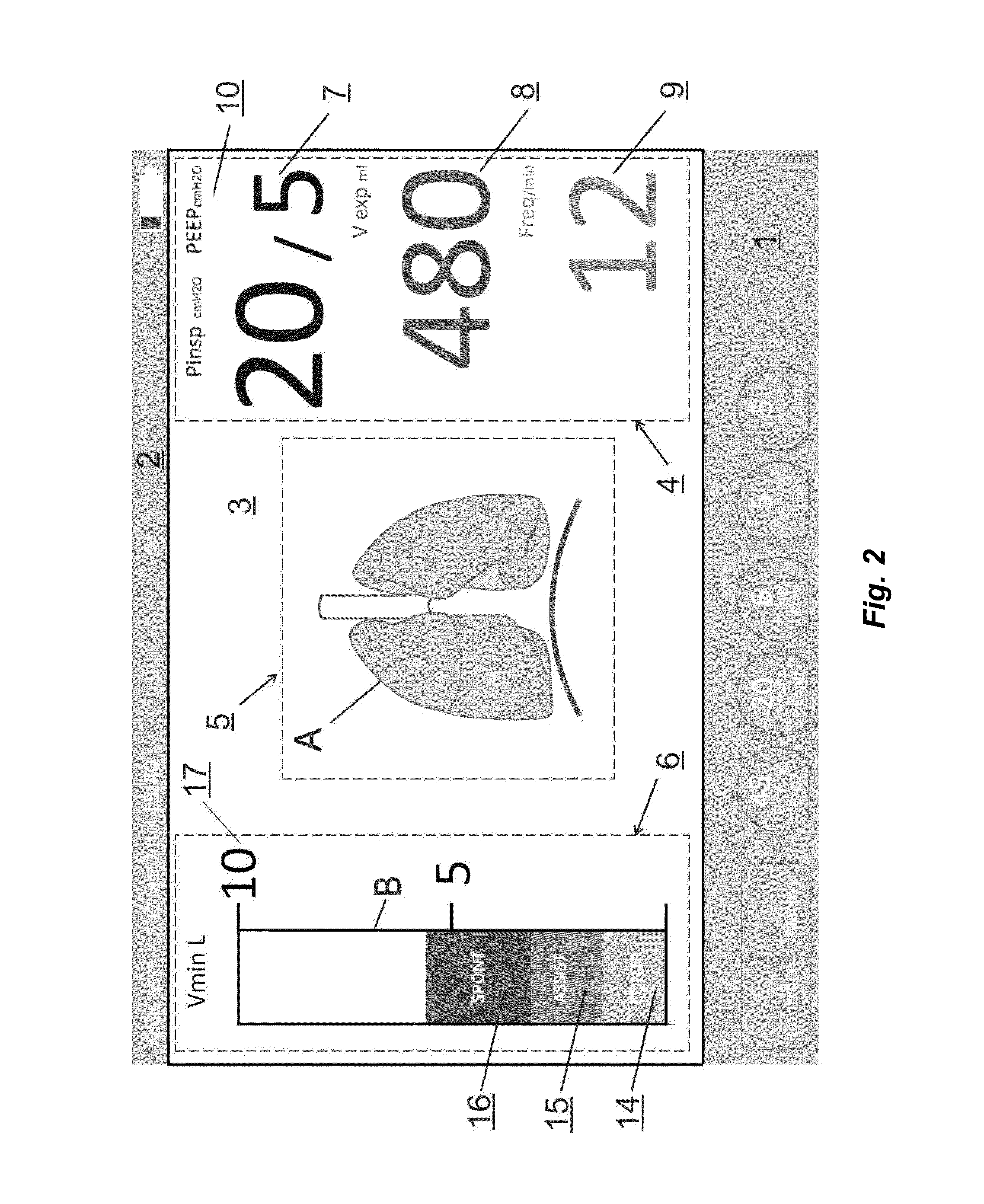
Lung ventilation device
InactiveUS20130125883A1Effective limitEfficiently problemsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGraphical user interfaceIntensive care medicine
The present invention refers to a lung ventilation device fitted with a patient monitoring and surveillance graphical interface comprising technical and functional characteristics that can reduce the cognitive load of the medical staff members in environments whose monitored beds require safe and efficient surveillance, principally for the identification and detection of parameters that are monitored at distance. More particularly, the present invention comprises a graphical interface whose configuration allows visualization at distance and interpretation of the main parameters associated with the patient, as well as includes means for facilitating the detection of the occurrence of critical alarms, even by an operator away from the patient.
Owner:INTERMED EQUIPAMENTO MEDICO HOSPITALAR
Measuring cognitive load
ActiveUS9737255B2Accurate measurementMedical automated diagnosisSensorsComputerized systemPhysical therapy
This invention concerns measuring cognitive load. A word based input is produced by a person while performing a task (100). Predetermined grammatical features of the word based input are identified (104). Then, the identified grammatical features are weighted and combined to provide a measure indicating the person's cognitive load (106). The use of grammatical features represents a divergence from the known methods of providing a measure of a person's cognitive load. It is an advantage of the invention that by concentrating on the grammatical features it is able to provide an objective, non-intrusive measure of the person's cognitive load. Aspects the invention include a method, a computer system and software that are used to perform the method.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
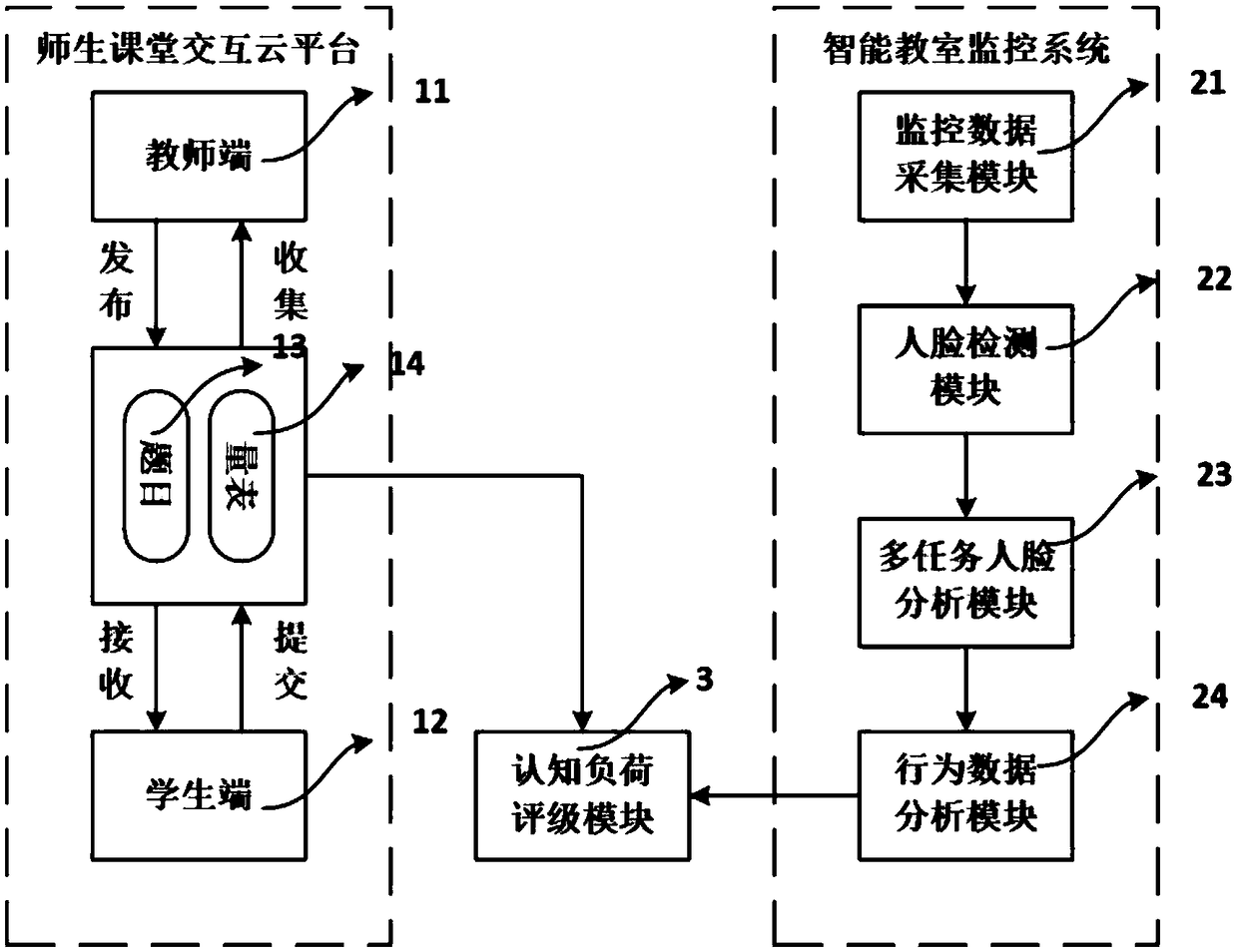
System for measuring cognitive load of classroom teaching
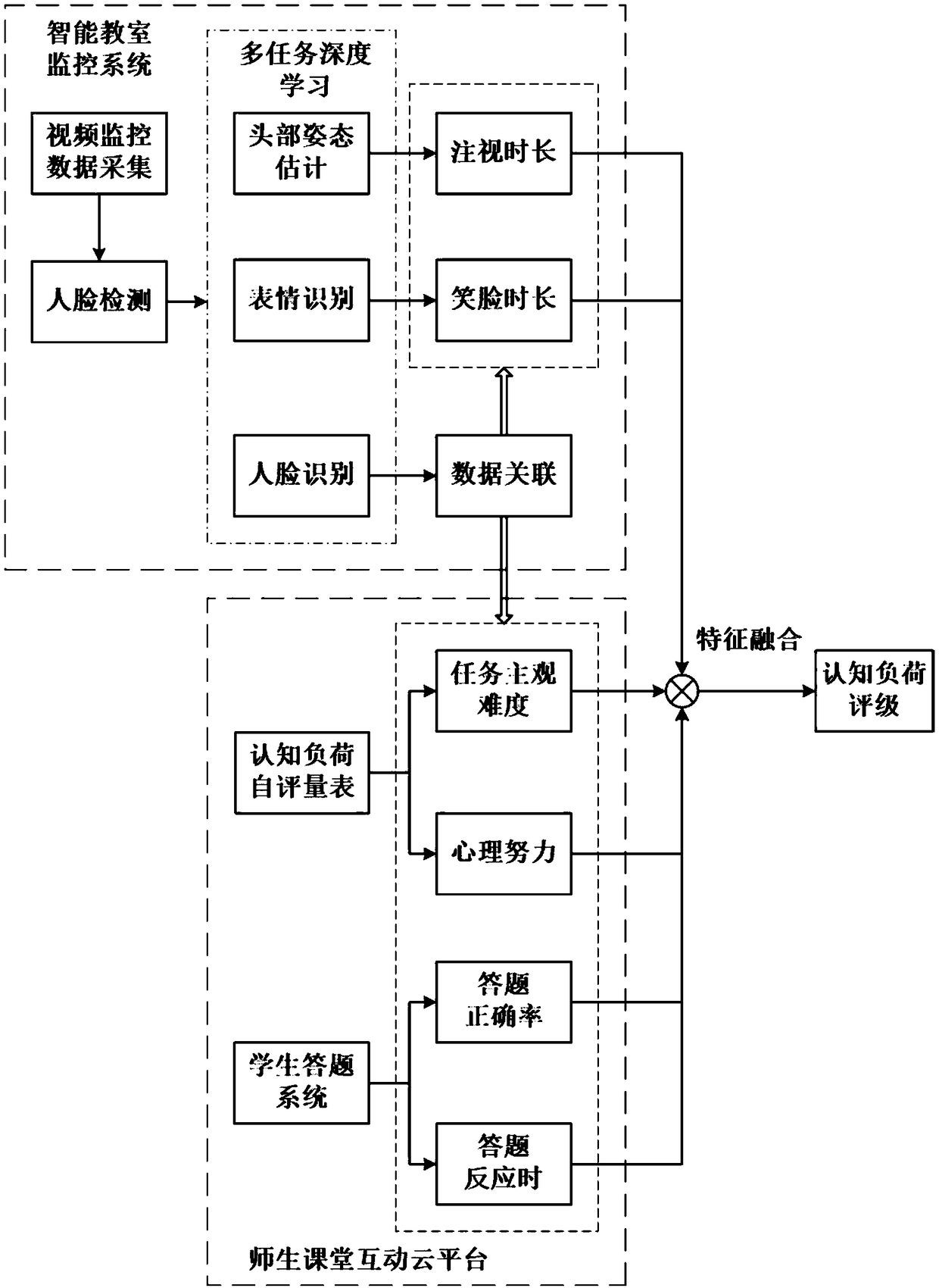
ActiveCN109117731ACognitive load objectiveCognitive load is rated objectivelyData processing applicationsElectrical appliancesTask completionFeature vector
The invention provides a classroom cognitive load detection system, which belongs to the field of education informatization. The system comprises a task completion degree feature acquisition module, which is used for recording the correct rate of answering questions when the students complete the task; a cognitive load self-assessment module, which is used to quantitatively analyze the students' psychological effort degree and the subjective difficulty of the task; the expression and attention feature acquisition module is used for collecting the video of students' classroom performance, and counting the smiling face duration and fixation duration according to the video analysis result; a feature fusion module, configured to fuse the six indexes into feature vectors; the cognitive load judging module being configured to send the feature vector into the classifier to identify the class cognitive load level of the students. The invention can objectively, quickly and accurately rate the cognitive load of students in the classroom, help the teaching teacher to improve the organization and presentation mode of the learning materials, reduce the external cognitive load caused thereby, and thus improve the teaching effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
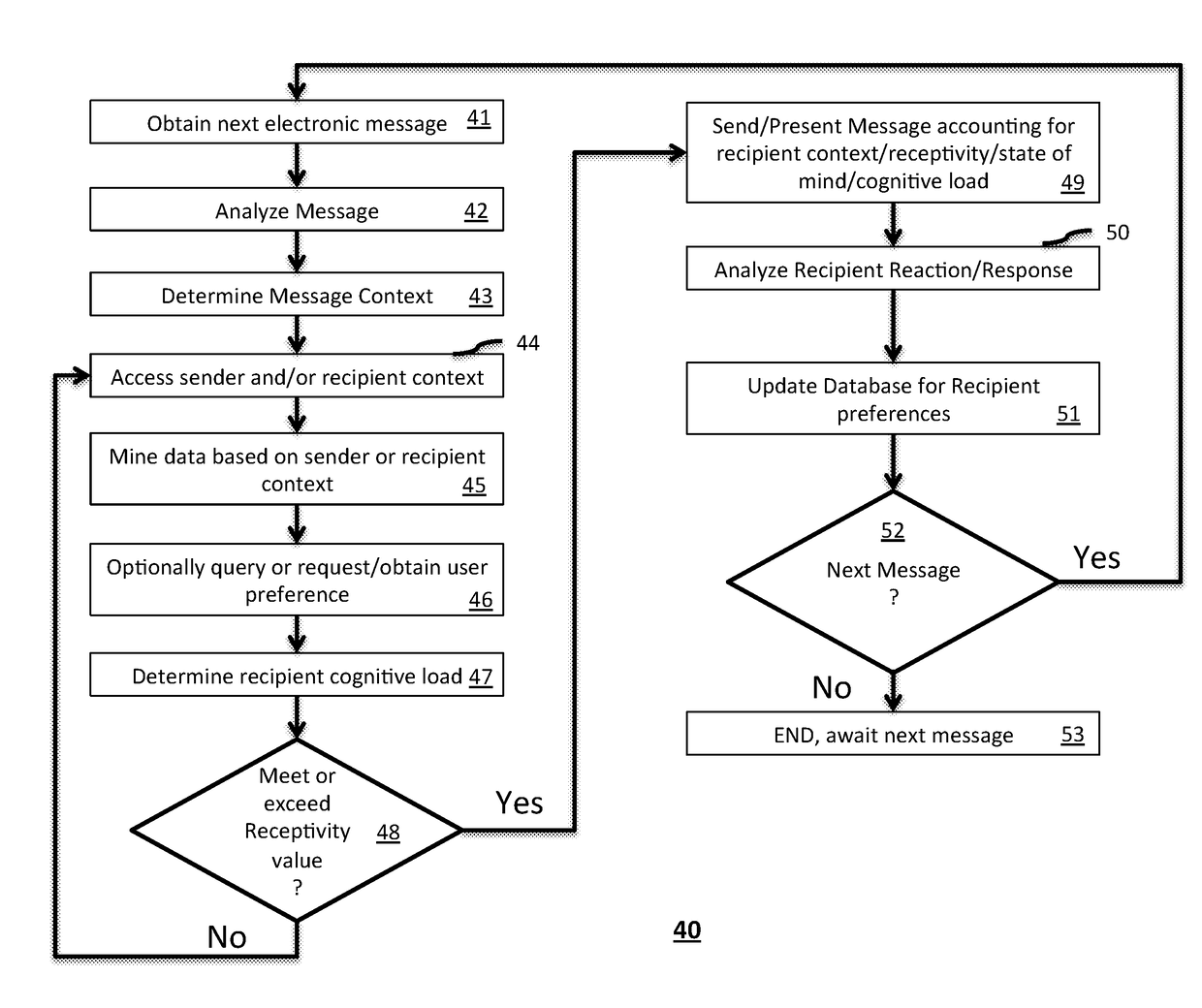
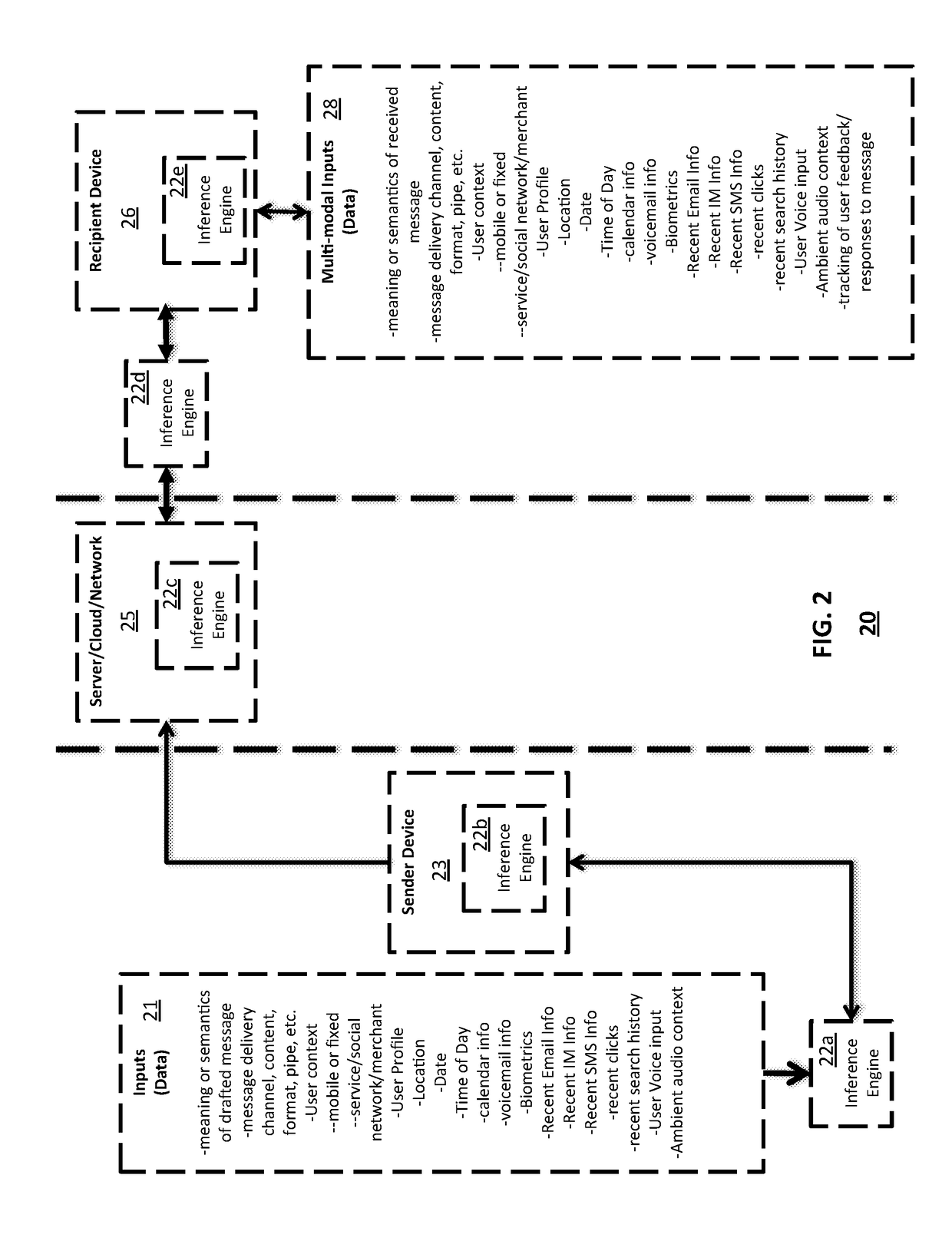
Message delivery and presentation methods, systems and devices using receptivity
A method, system or device includes one or more sensors for measuring a multimodal metric, a memory having computer instructions, and one or more processors operatively coupled to the one or more sensors and the memory. The one or more processors when executing computer instructions cause the one or more processors to perform operations such as analyzing the multimodal metric to provide an analysis and determine a receptivity to a message, and delivering or receiving or presenting the message at a period of time when the receptivity is over a predetermined threshold based on the analysis. Receptivity to a message can be measured in many different ways including the use of the one or more sensors such one or more microphones used for determining a cognitive load of a recipient.
Owner:STATON TECHIYA LLC
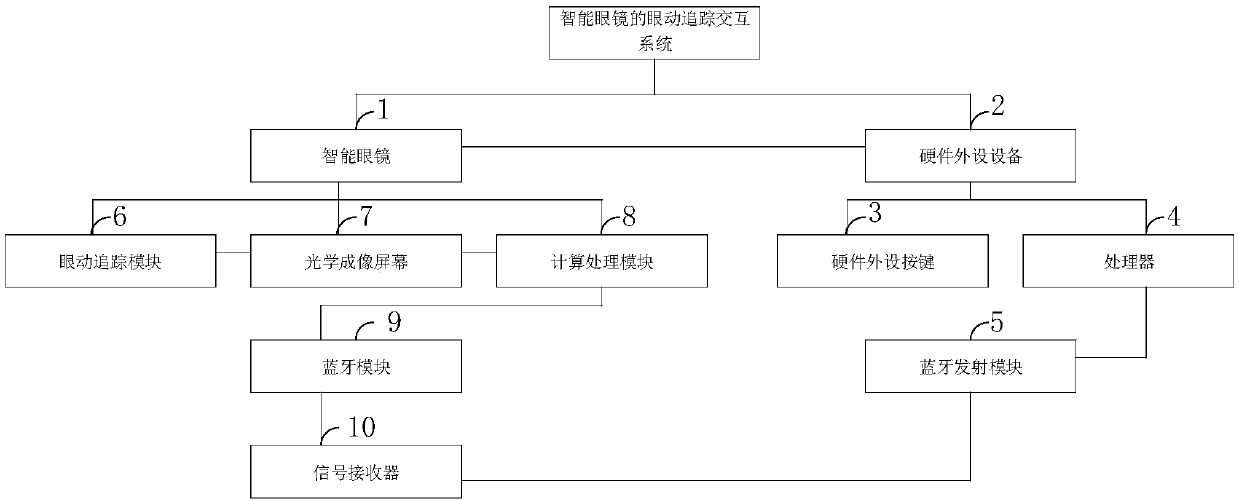
An eye movement tracking interaction method and system of near-to-eye display equipment
InactiveCN109597489AImprove interactive experienceReduce concentrationInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInteraction controlSubjective consciousness
The invention belongs to the technical field of near-to-eye display equipment application, and discloses an eye movement tracking interaction method and system for near-to-eye display equipment. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the sight line tracking through an eye movement tracking module on the near-to-eye display equipment, carrying out the calculation of the obtained eye movementinformation, and mapping the eye movement information to the coordinate position of an optical imaging screen button of the near-to-to-eye display equipment; clicking the imaging screen button, and executing the interaction function program after interaction succeeds. Compared with blink selection of existing eye movement interaction, attention of a user in the interactive control process througheyeballs is greatly reduced, meanwhile, cognitive loads in subjective consciousness are reduced, and discomfort caused by inharmonious control over monocular blink muscles is avoided; Compared with gesture recognition interaction control, the method has the advantages that the concealment is high, the operation is convenient and fast, and the method is suitable for application scenarios with privacy requirements.
Owner:幻蝎科技(武汉)有限公司
Application-launching interface for multiple modes
ActiveCN102566917AProgram loading/initiatingExecution for user interfacesMultiple modesHuman–computer interaction
The invention describes techniques and apparatuses enabling an application-launching interface for multiple modes. This interface enables a user to quickly and easily select to launch applications associated with different modes. A user may avoid wading through multiple interfaces, making multiple selections, and / or a cognitive load associated with deciding on a mode with which to interact.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
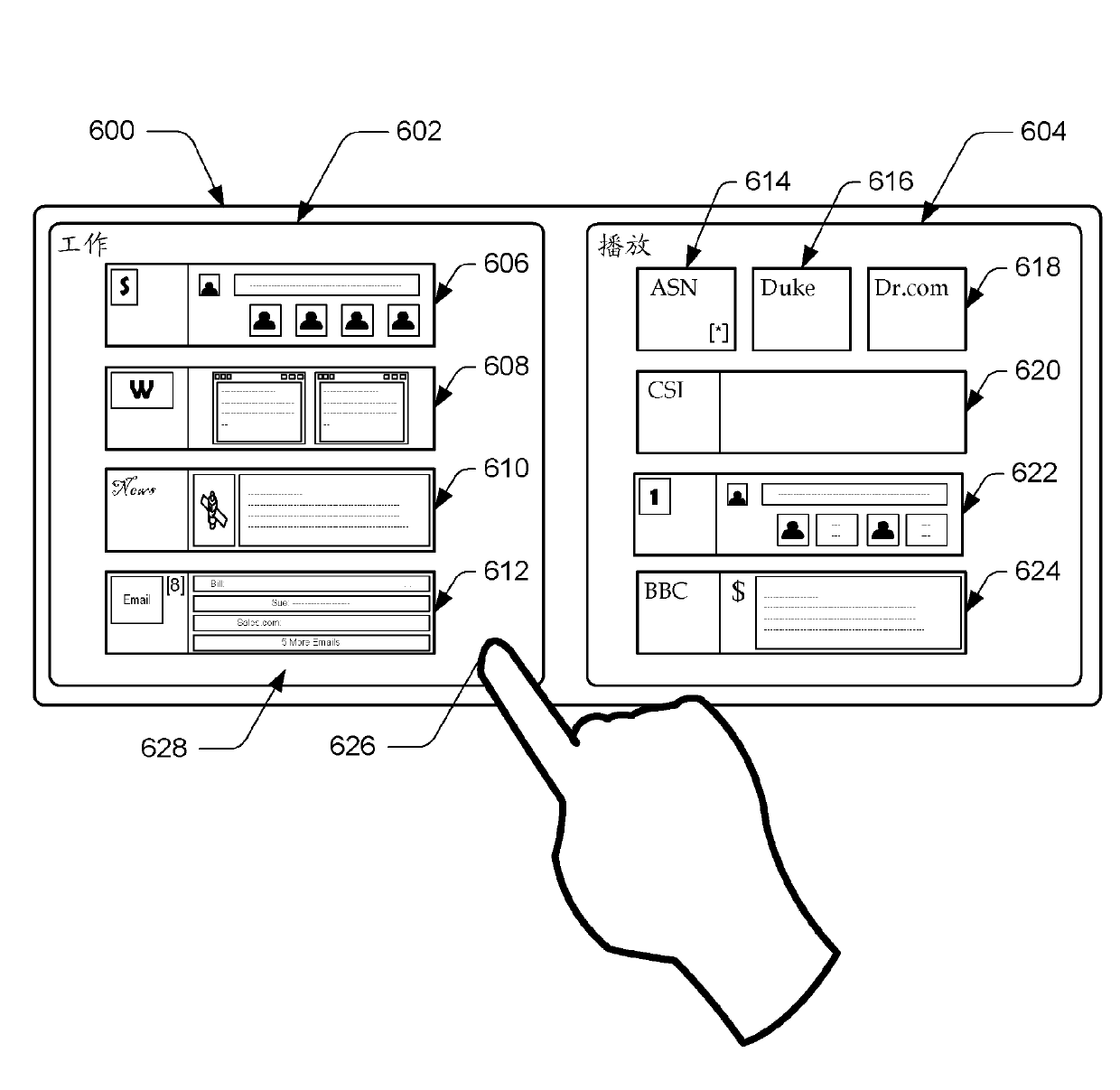
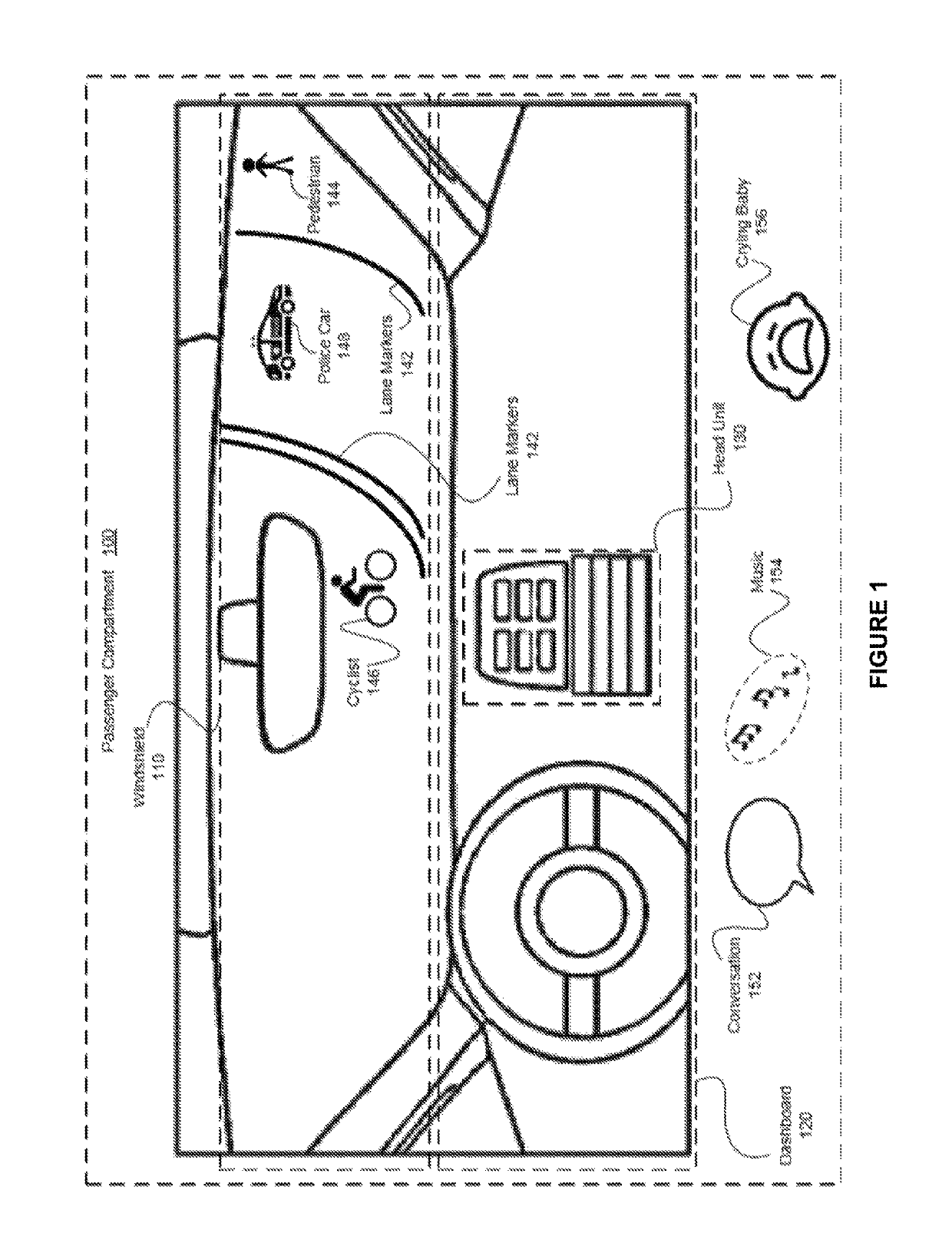
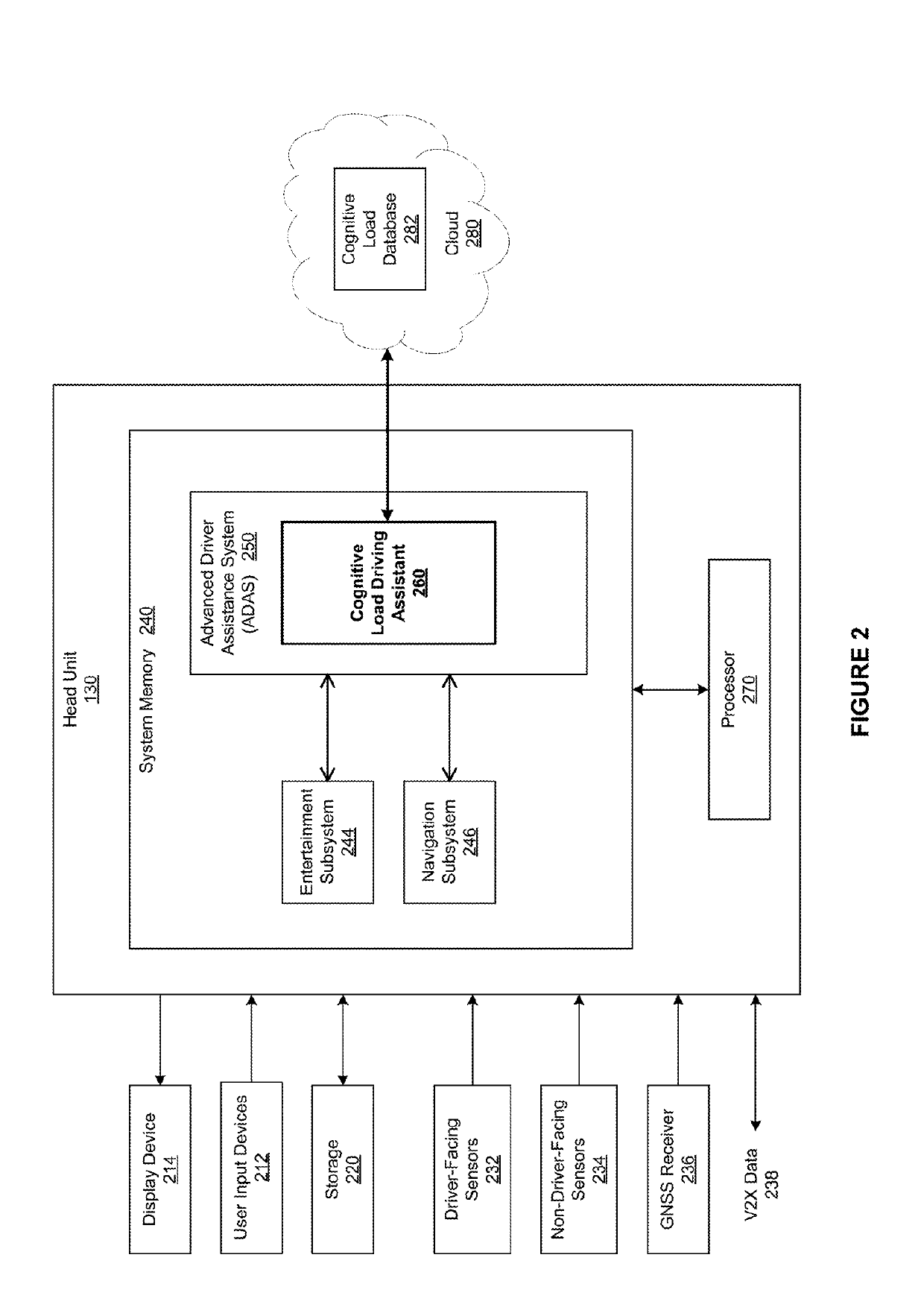
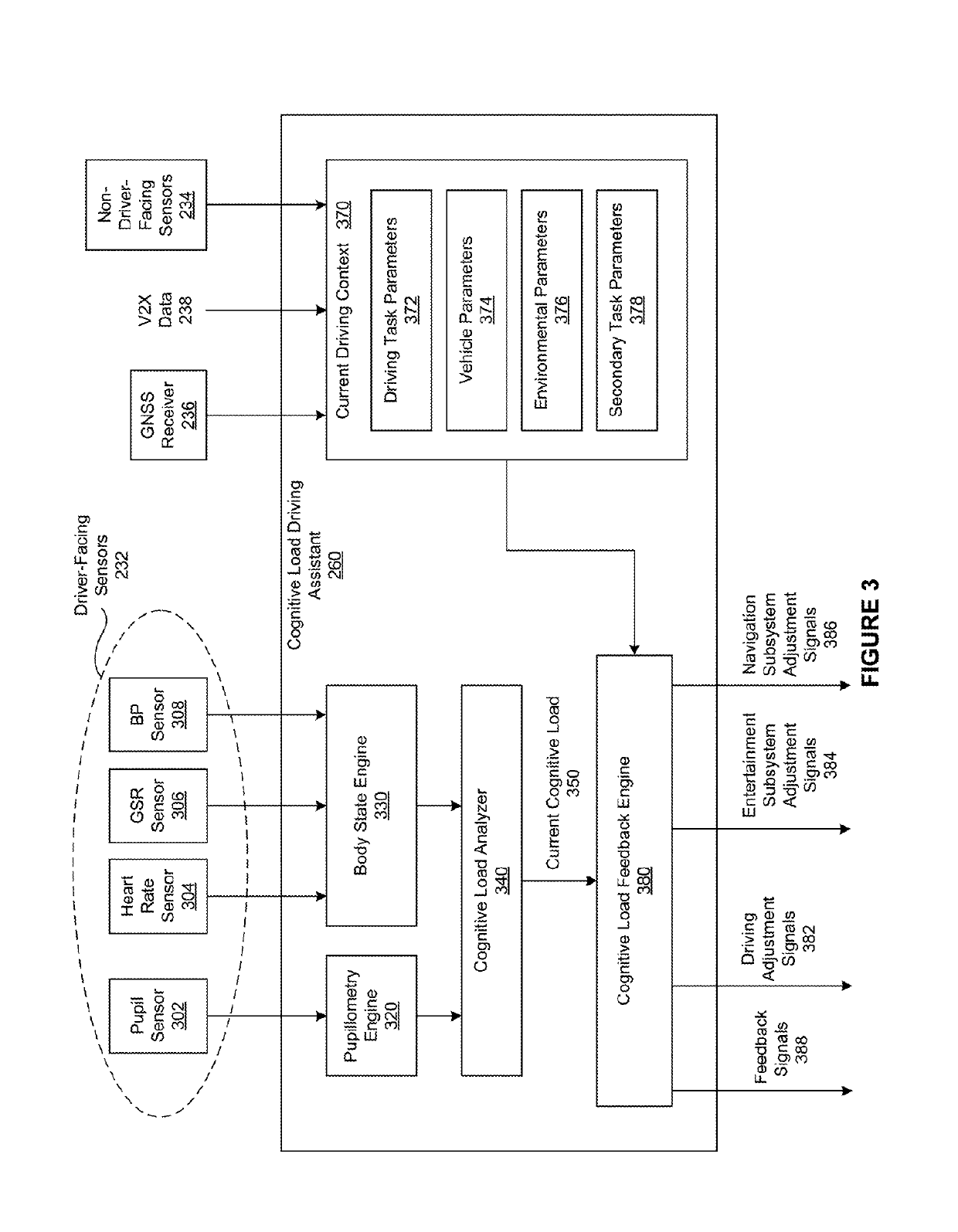
Cognitive load driving assistant
ActiveUS10399575B2Reduce cognitive loadReduce complexityInstruments for road network navigationDetection of traffic movementEngineeringCognitive load
In one embodiment, a cognitive load driving assistant increases driving safety based on cognitive loads. In operation, the cognitive load driving assistant computes a current cognitive load of a driver based on sensor data. If the current cognitive load exceeds a threshold cognitive load, then the cognitive load driving assistant modifies the driving environment to reduce the cognitive load required to perform the primary driving task and / secondary task(s), such as texting via a cellular phone. The cognitive load driving assistant may modify the driving environment indirectly via sensory feedback to the driver or directly through reducing the complexity of the primary driving task and / or secondary tasks. In particular, if the driver is exhibiting elevated cognitive loads typically associated with distracted driving, then the cognitive load driving assistant modifies the driving environment to allow the driver to devote appropriate mental resources to the primary driving task, thereby increasing driving safety.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Method of operating a hearing instrument based on an estimation of present cognitive load of a user and a hearing aid system
InactiveUS20160080876A1Easy to customizeImprove comfortPsychotechnic devicesElectronic input selection/mixingData processing systemHearing aid
A method of operating a hearing instrument for processing an input sound and to provide an output stimulus according to a user's particular needs, and related system, computer readable medium and data processing system. An object is to provide an improved customization of a hearing instrument. The method includes the steps a) providing an estimate of the present cognitive load of the user; b) providing processing of an input signal originating from the input sound according to a user's particular needs; and c) adapting the processing in dependence of the estimate the present cognitive load of the user. The estimate of the present cognitive load of a user is produced by in-situ direct measures of cognitive load (e.g. based on EEG-measurements, body temperature, etc.) or by an on-line cognitive model in the hearing aid system whose parameters have been preferably adjusted to fit to the individual user.
Owner:OTICON
Method and apparatus for context adjusted consumer capture
InactiveCN103218728AParticular environment based servicesAnti-theft devicesData miningCognitive load
In a first illustrative embodiment, a computer implemented method includes obtaining the identities of one or more vehicle occupants. The method also includes obtaining data relating to a current vehicle environment. The method further includes selecting an advertisement for delivery based at least in part on data retrieved respective to identified occupants and data relating to the vehicle environment. Also, the illustrative method includes evaluating a driver cognitive load. The method additionally includes providing the selected advertisement for delivery based on the driver cognitive load being below a suitable threshold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com