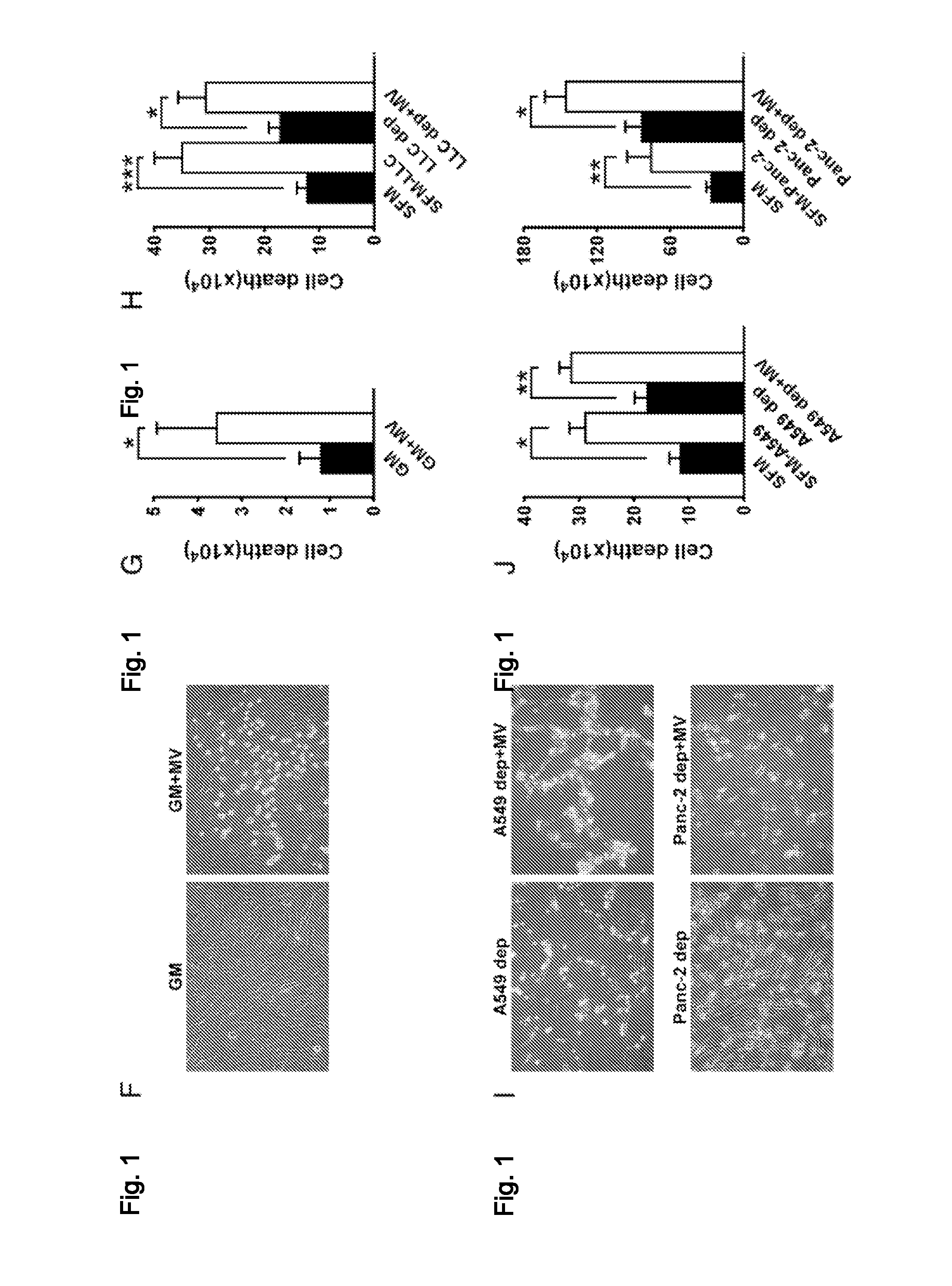
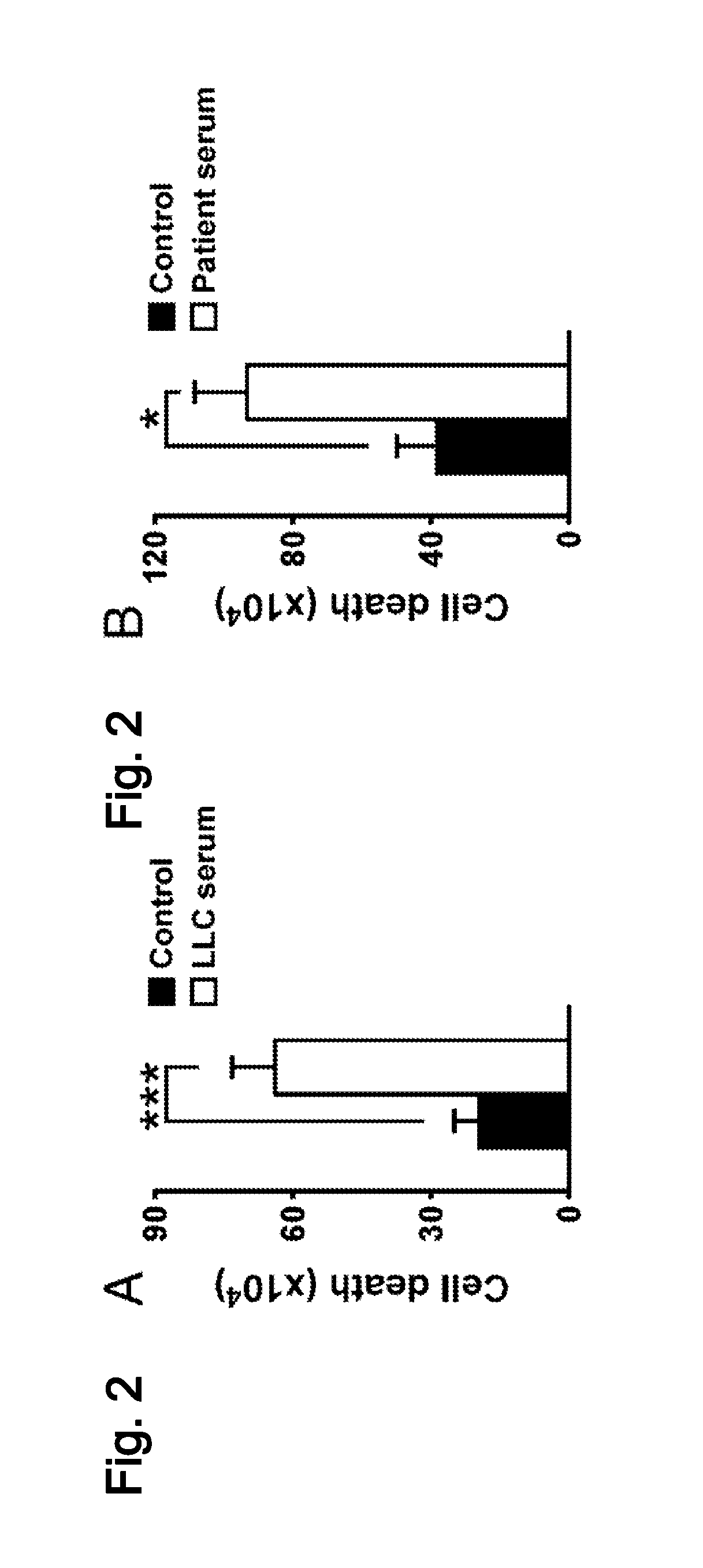
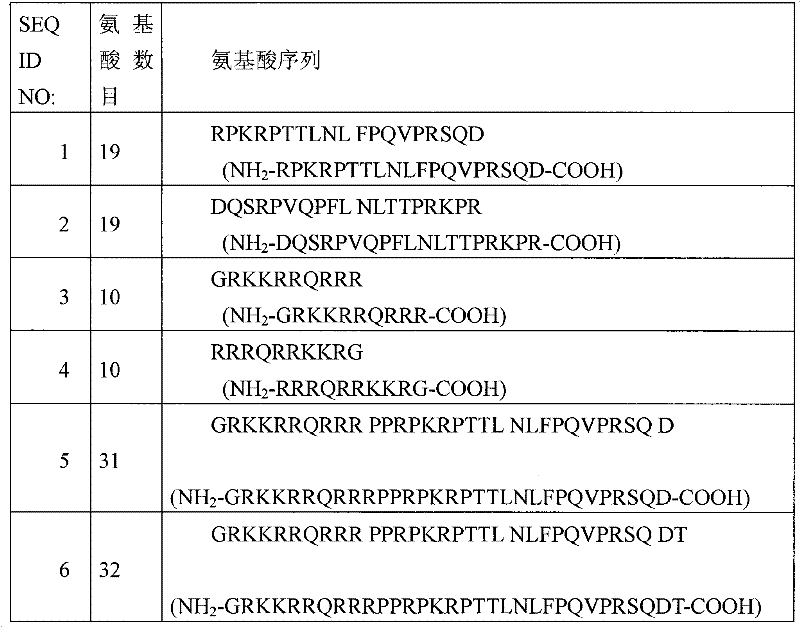
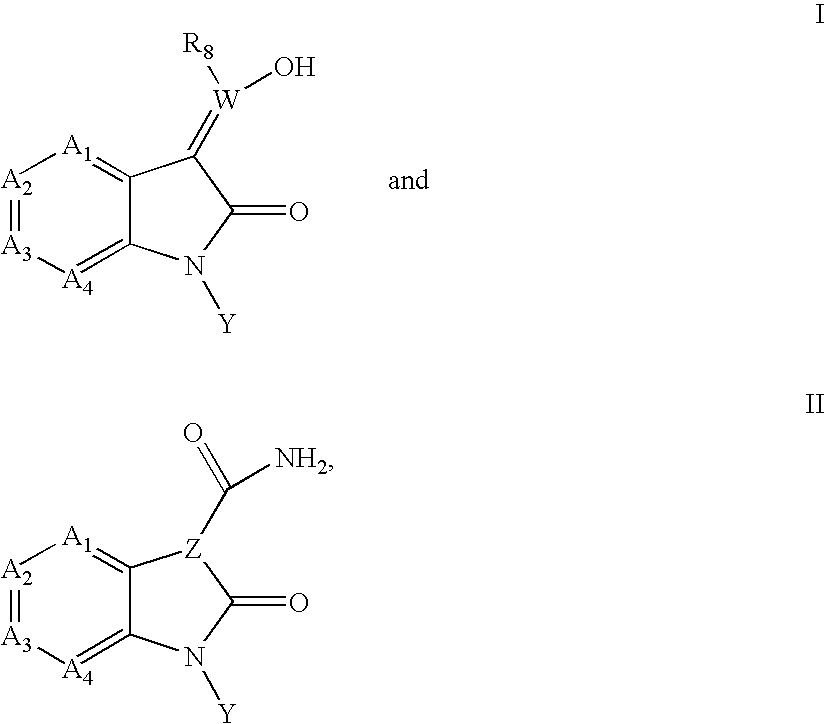
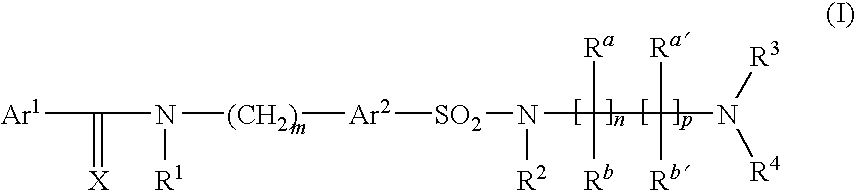Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "C-Jun N-terminal kinases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
C-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), were originally identified as kinases that bind and phosphorylate c-Jun on Ser-63 and Ser-73 within its transcriptional activation domain. They belong to the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, and are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock. They also play a role in T cell differentiation and the cellular apoptosis pathway. Activation occurs through a dual phosphorylation of threonine (Thr) and tyrosine (Tyr) residues within a Thr-Pro-Tyr motif located in kinase subdomain VIII. Activation is carried out by two MAP kinase kinases, MKK4 and MKK7, and JNK can be inactivated by Ser/Thr and Tyr protein phosphatases. It has been suggested that this signaling pathway contributes to inflammatory responses in mammals and insects.
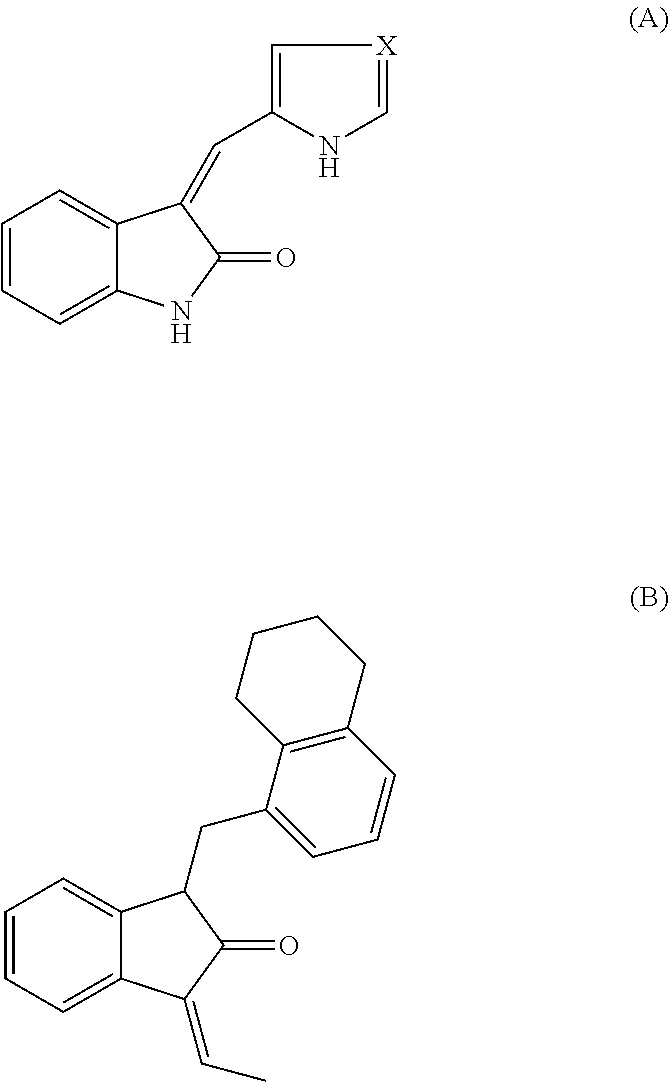
Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) and other protein kinases
InactiveUS6949544B2Effective inhibitorAvoid cell deathBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseProtein kinase domain
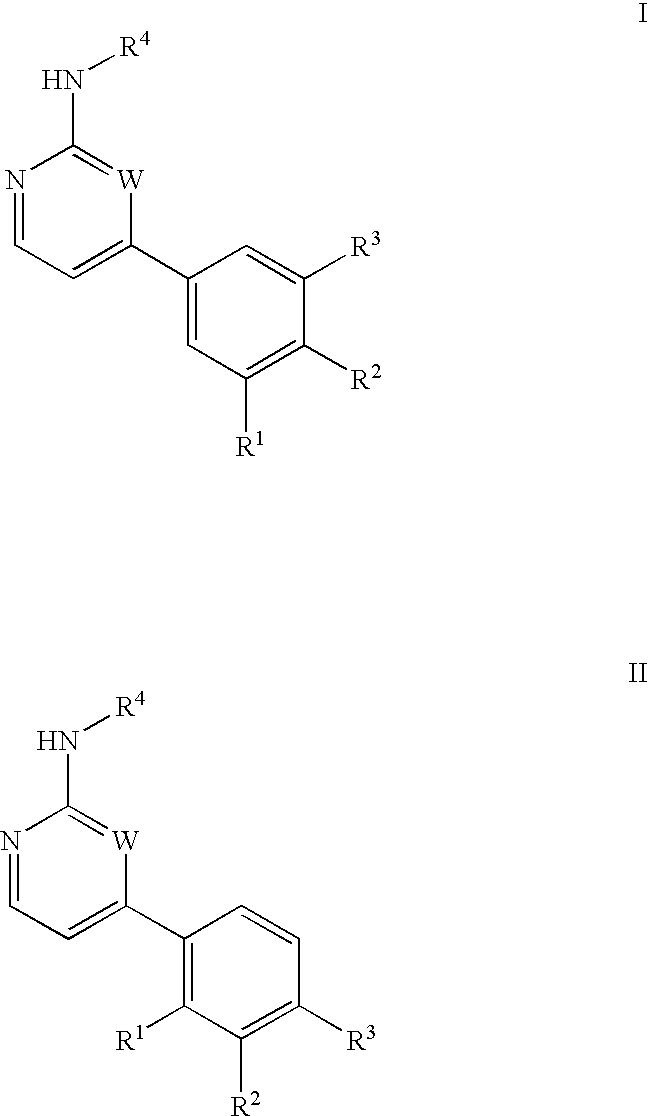
The present invention provide a compound of formula I or II: or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as described in the specification. These compounds are inhibitors of protein kinase, particularly inhibitors of JNK, a mammalian protein kinase involved cell proliferation, cell death and response to extracellular stimuli; and Src-family kinases, especially Src and Lck kinases. These compounds are also inhibitors of GSK3 and CDK2 kinases. The invention also relates to methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors of the invention and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases
The present invention relates to compounds that are inhibitors of c-jun N-terminal kinase 1, 2, or 3 (JNK1, JNK2, or JNK3), compositions containing the compounds and the use of the compounds in the prevention or treatment of disorders regulated by the activation of JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Novel fused heterocyclic compound and use thereof
The compound represented by the general formula (I): wherein, a fused ring AB represents a 5- to 10-membered fused heterocyclic ring; R1 represents (1) a hydrogen atom, (2) a halogen atom, (3) a cyano group, (4) an oxo group, (5) an optionally protected hydroxyl group, (6) an optionally protected carboxyl group, (7) an optionally protected amino group, (8) a cyclic group which may have a substituent (s), (9) an aliphatic hydrocarbon group which may have a substituent (s), or (10) an optionally protected thiol group; n represents 0 or an integer of 1 to 8; provided that n represents an integer of not less than 2, plural R1 are the same or different; a salt thereof, a solvate thereof or a prodrug thereof has a kinase (especially c-Jun N-terminal kinase) inhibitory activity and an inhibitory activity of a function of AP-1 as a transcription factor, it is useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for a for example, a diabetes of metabolic disease, etc., a rheumatoid arthritis of inflammatory, etc.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) and other protein kinases
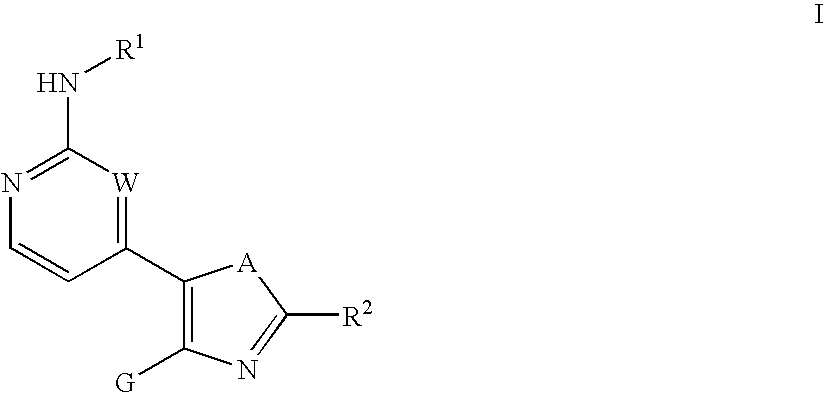
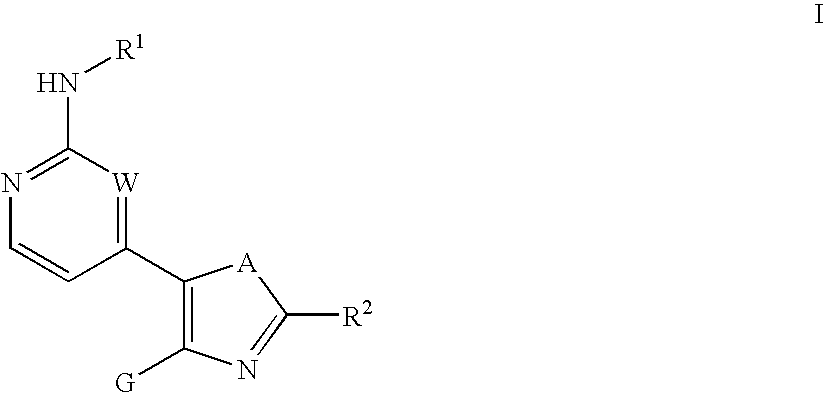
The present invention provides compounds of formula I:or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof, wherein R1, R2, A, G, and W are as described in the specification. These compounds are inhibitors of protein kinase, particularly inhibitors of JNK, a mammalian protein kinase involved cell proliferation, cell death and response to extracellular stimuli, Lck, Src, and Aurora kinases. The invention also relates to methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors of the invention and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Inhibitors of c-jun-n-terminal kinase (JNK)
ActiveUS20140309249A1Reduce tumor burdenStop growthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideKinase activityNeuro-degenerative disease
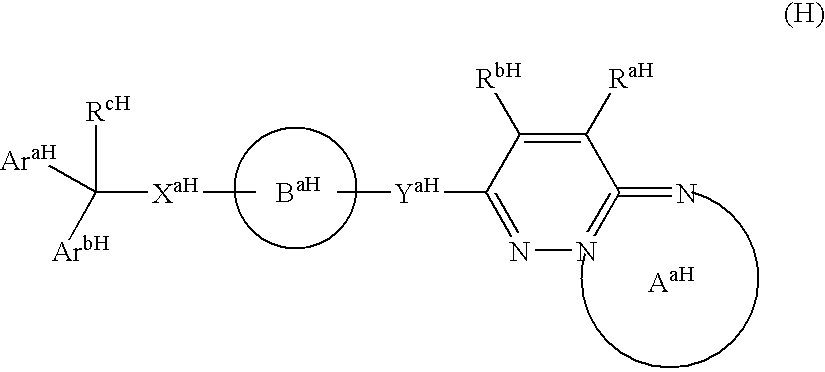
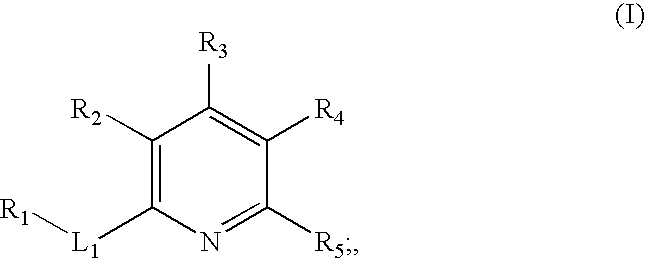
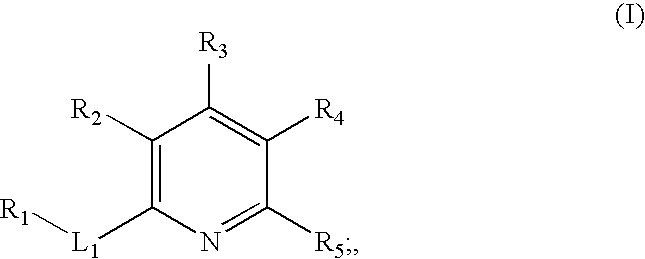
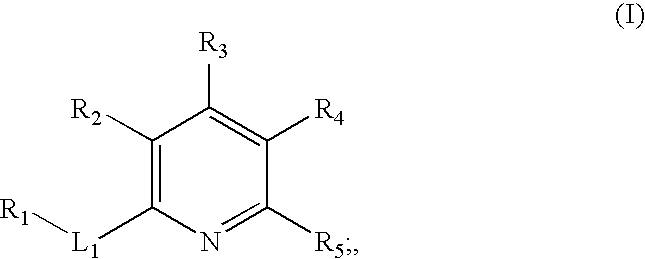
The present invention provides novel compounds according to Formula (I): where Ring A, Ring B, X, L1, L2, RA, RC, RD, RE, m, n, and p are as defined herein. Compounds of the present invention are contemplated useful for the prevention and treatment of a variety of human diseases associated with kinase activity, for example, proliferative diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Inhibitors of c-Jun N terminal kinases (JNK) and other protein kinases
InactiveUS7169798B2Avoid cell deathTreat and prevent reperfusion/ischemiaBiocideNervous disorderProtein kinase domainExtracellular stimulation
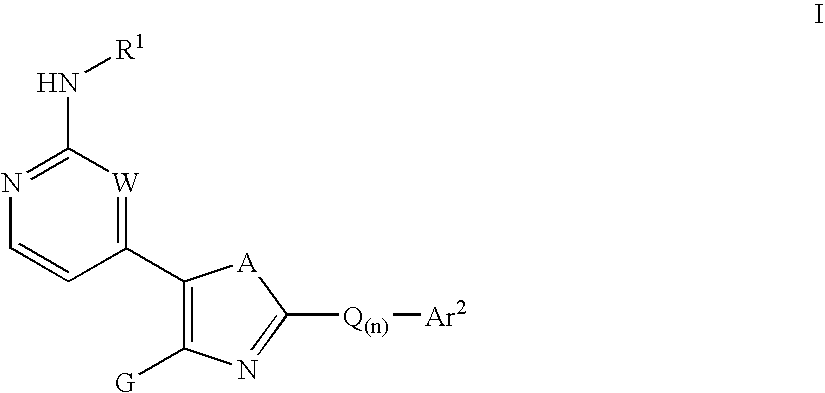
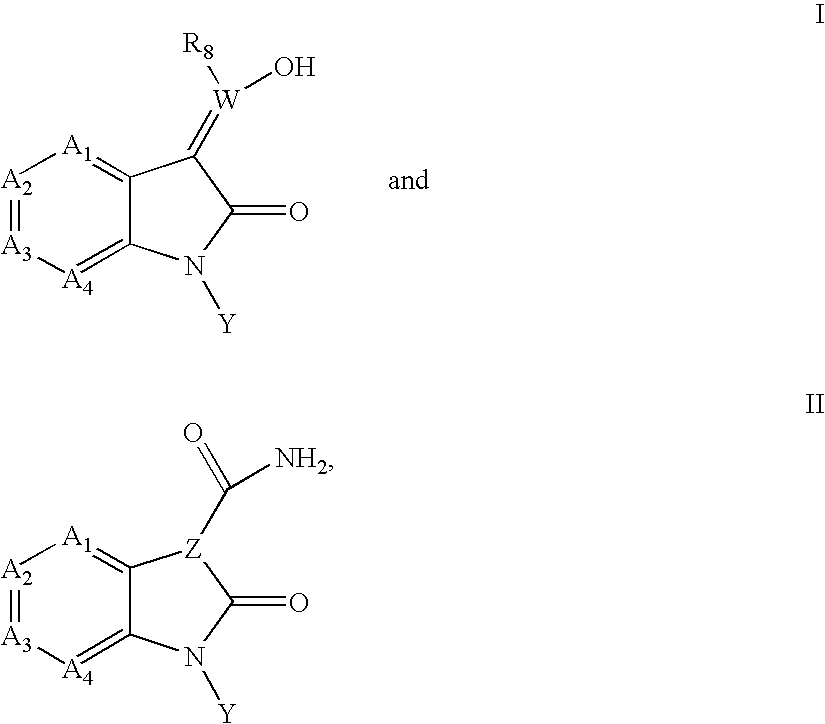
The present invention provides compounds of formula I:where R1 is H, CONH2, T(n)-R, or T(n)-Ar2, n may be zero or one, and G, XYZ, and Q are as described below. These compounds are inhibitors of protein kinase, particularly inhibitors of JNK, a mammalian protein kinase involved cell proliferation, cell death and response to extracellular stimuli. The invention also relates to methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors of the invention and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
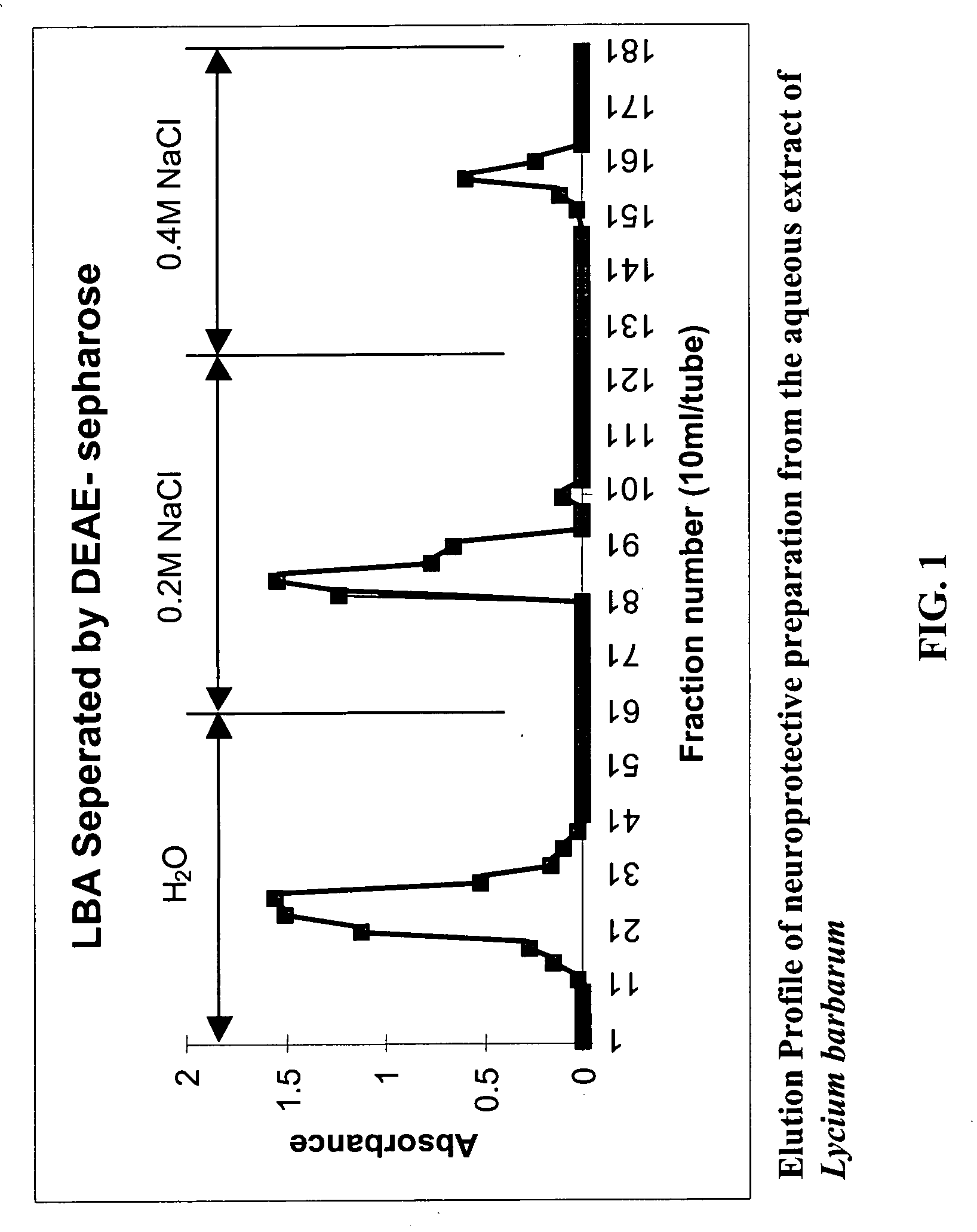
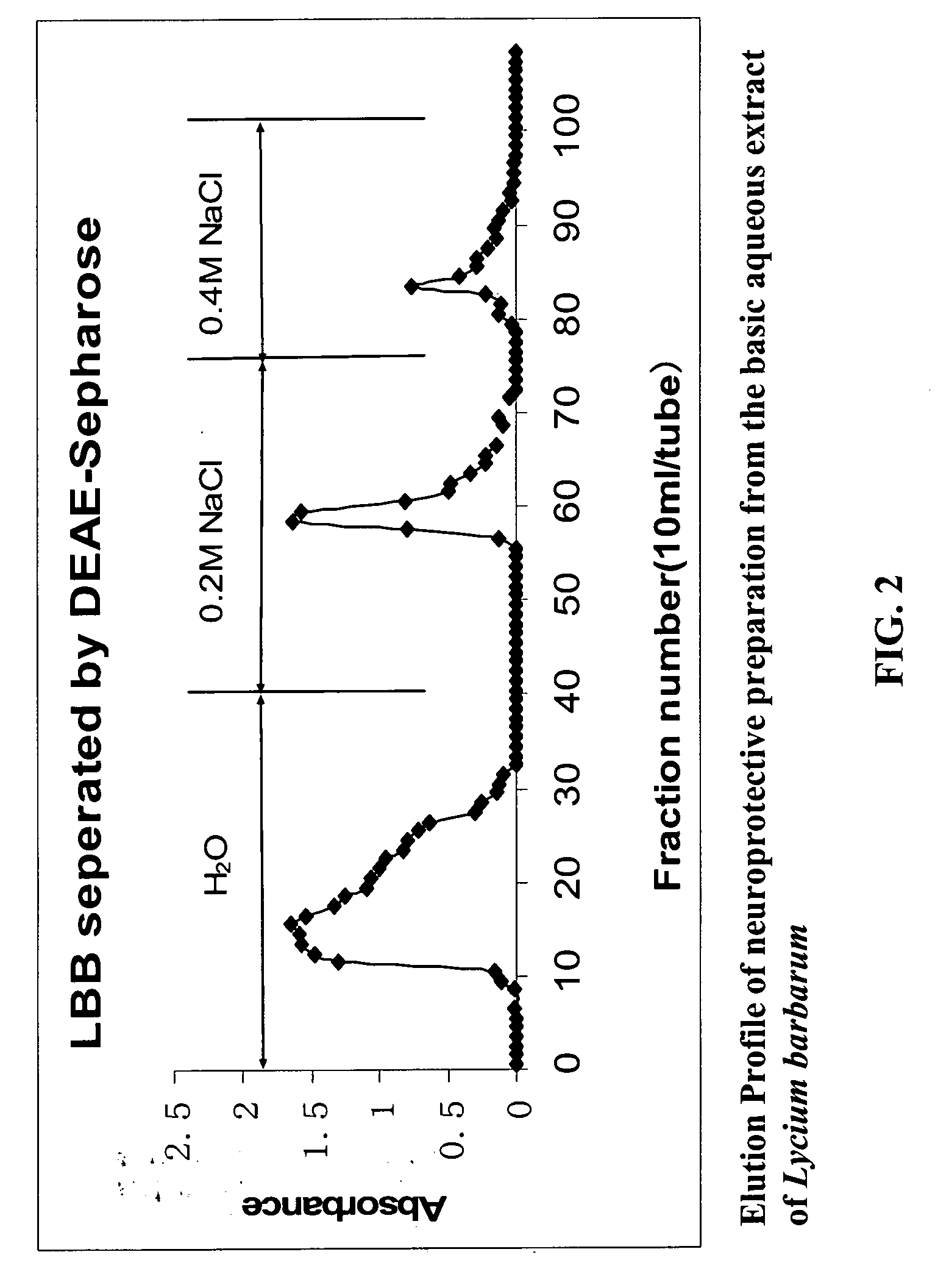
Polysaccharide extract from Lycium barbarum as neuroprotective agent against beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity
InactiveUS20050170028A1Prevent neuronal deathOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseΒ amyloid peptide
Extracts of Lycium barbarum serve as a neuroprotective agent against β-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity which thus permits their use for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and for the prevention of neuronal loss in aging against the accumulation of β-amyloid peptide in the brain. Stress kinases (c-Jun N-terminal kinase and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase) are used as a technological platform for screening neuroprotective drugs.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
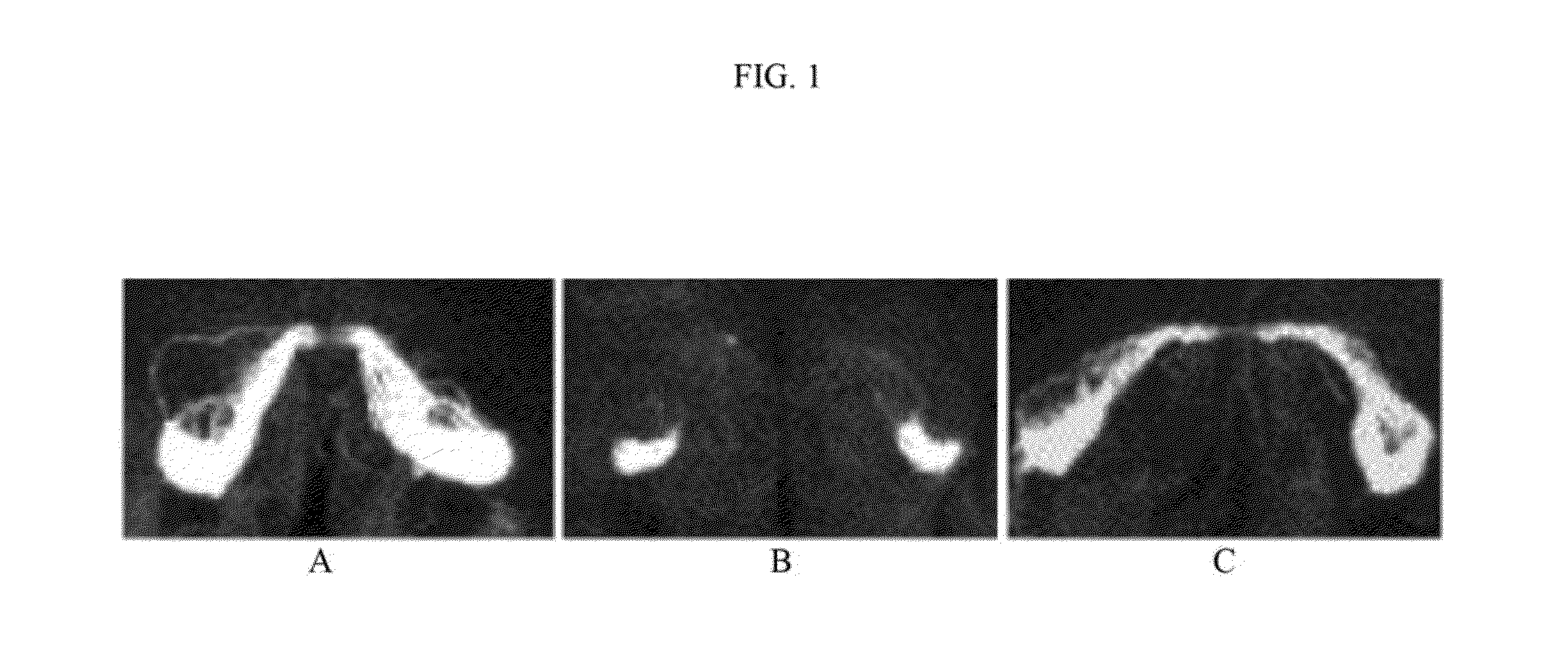
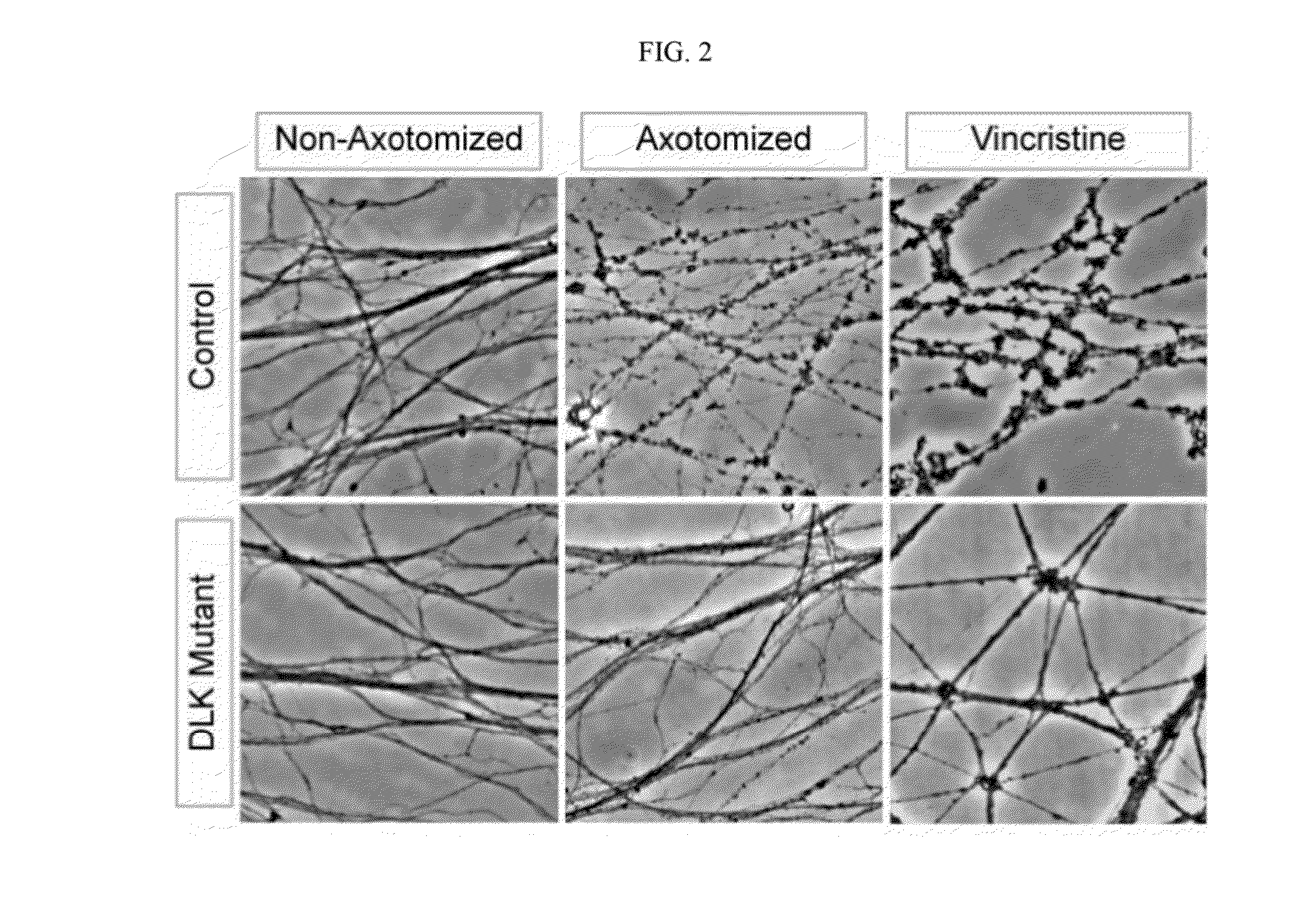
Methods and compositions for inhibition of axonal degeneration by modulation of the dlk/jnk pathway
InactiveUS20100056609A1Shorten the progressInhibit axonal degenerationCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsWallerian degenerationAxon degeneration
Methods of reducing Wallerian degeneration are disclosed. These methods comprise inhibiting expression or activity of a mixed lineage kinas such as a dual leucine-zipper-bearing kinase (DLK), inhibiting expression or activity of a molecule acting downstream from DLK, such as a c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), or a combination thereof. Further disclosed are methods of screening candidate compounds for DLK inhibition activity. These methods comprise providing a neuronal culture comprising a plurality of axons; contacting the culture with a candidate compound and with an axon degeneration-triggering agent; and comparing axonal degeneration in the culture to a control culture comprising the axon degeneration-triggering agent but not the candidate compound.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Inhibitors of c-jun N terminal kinases (JNK) and other protein kinases
InactiveUS20050026967A1Avoid cell deathTreat and prevent reperfusion/ischemiaBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseProtein kinase domain
The present invention provides compounds of formula I: where R1 is H, CONH2, T(n)—R, or T(n)—Ar2, n may be zero or one, and G, XYZ, and Q are as described below. These compounds are inhibitors of protein kinase, particularly inhibitors of JNK, a mammalian protein kinase involved cell proliferation, cell death and response to extracellular stimuli. The invention also relates to methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors of the invention and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
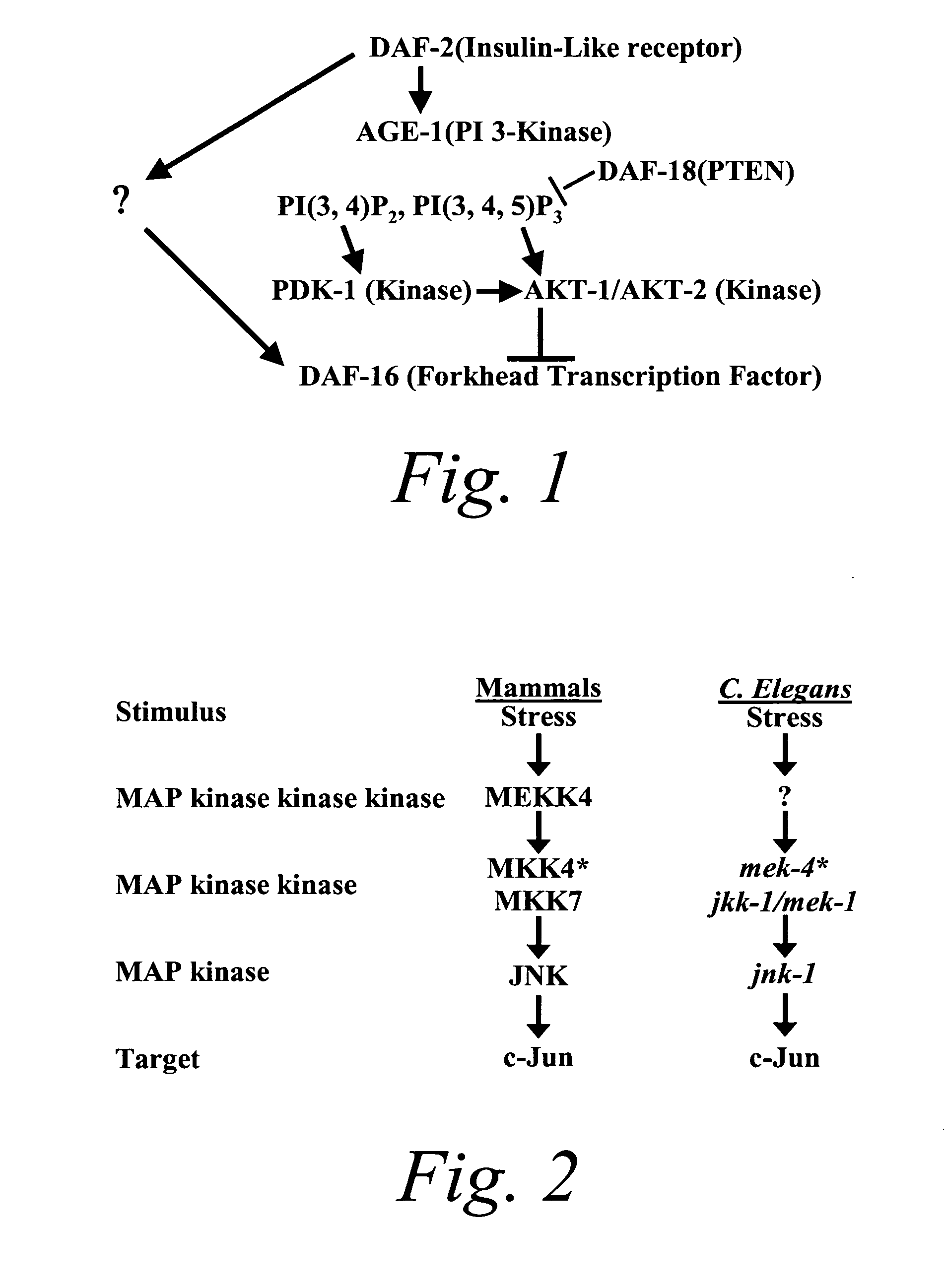
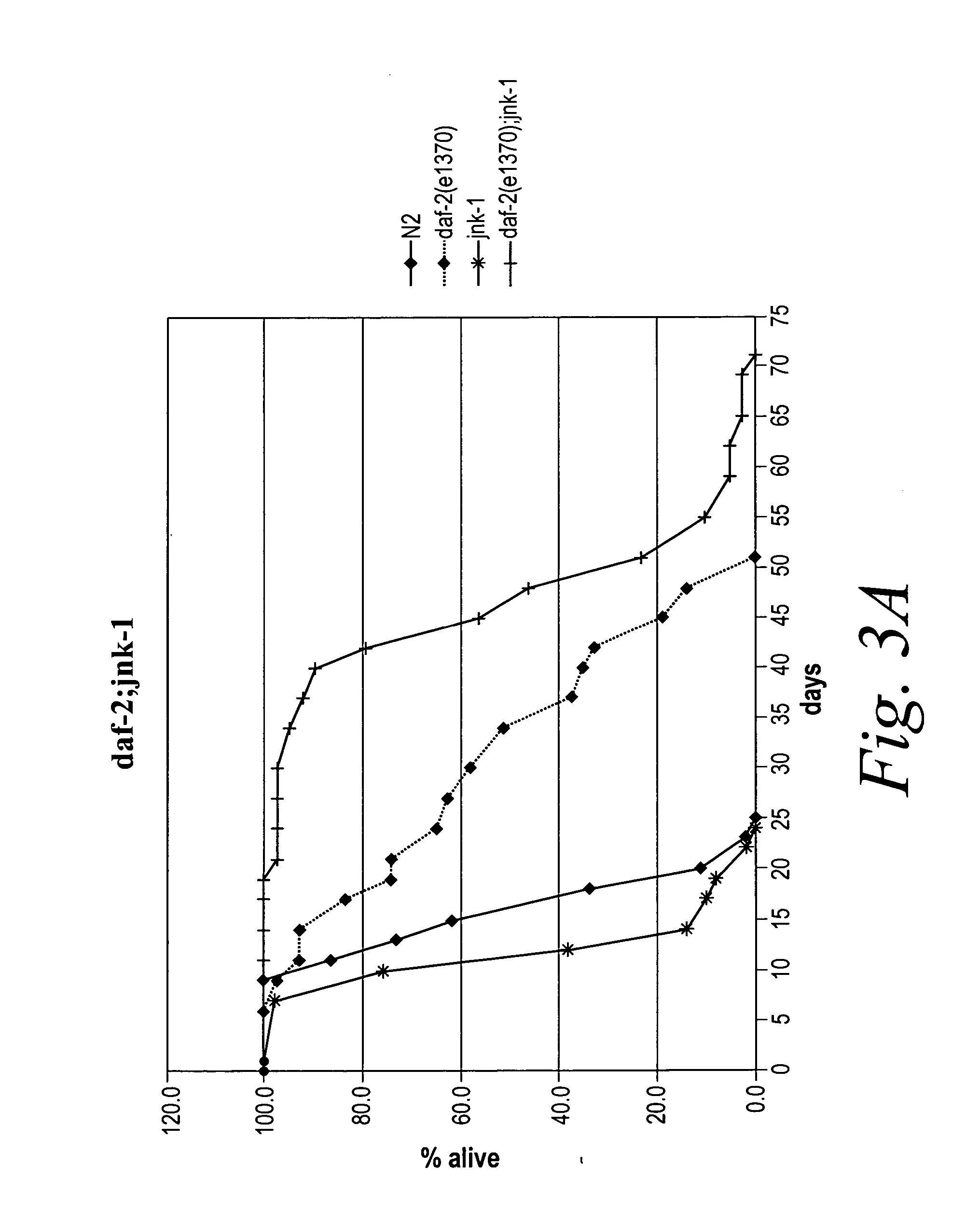
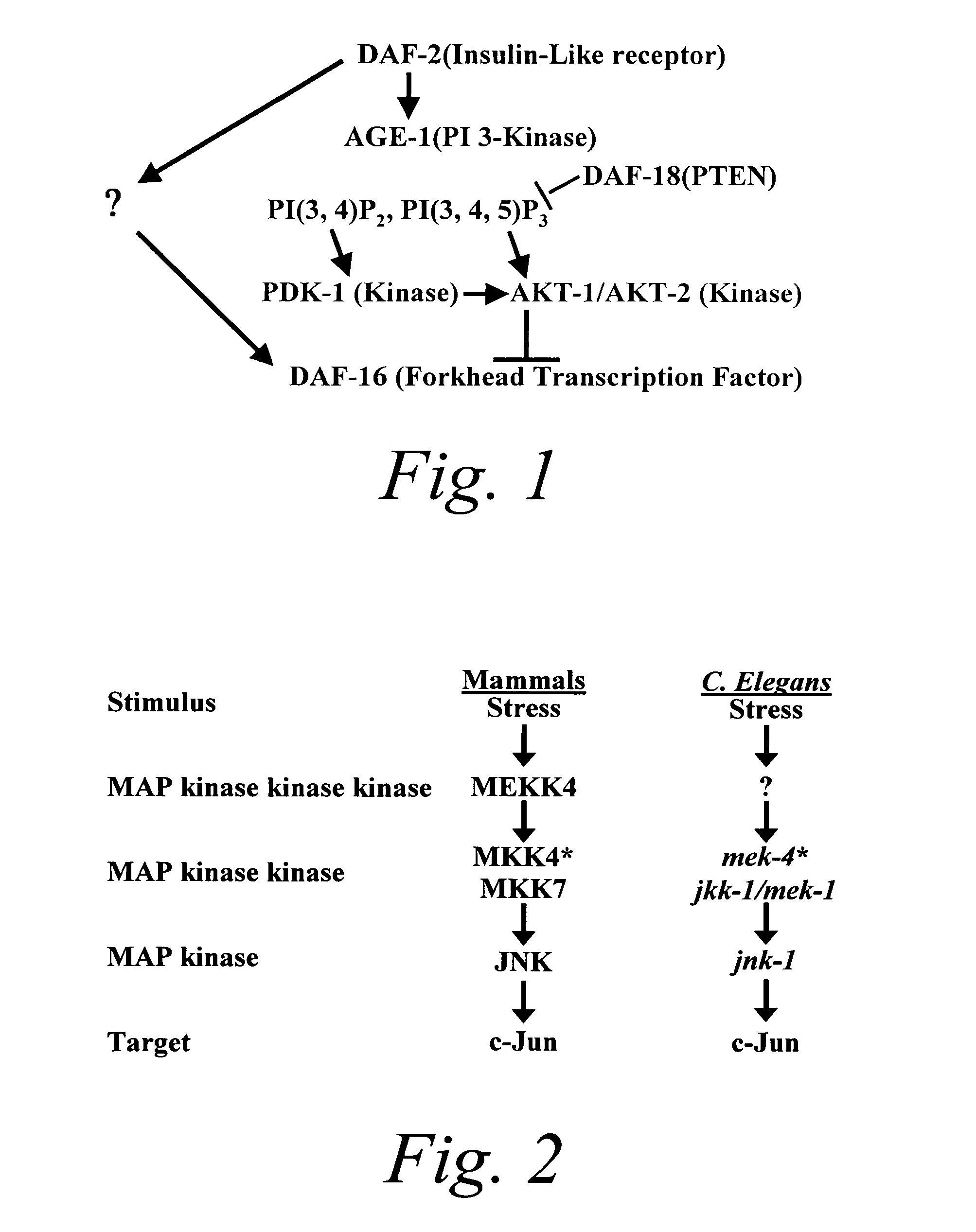
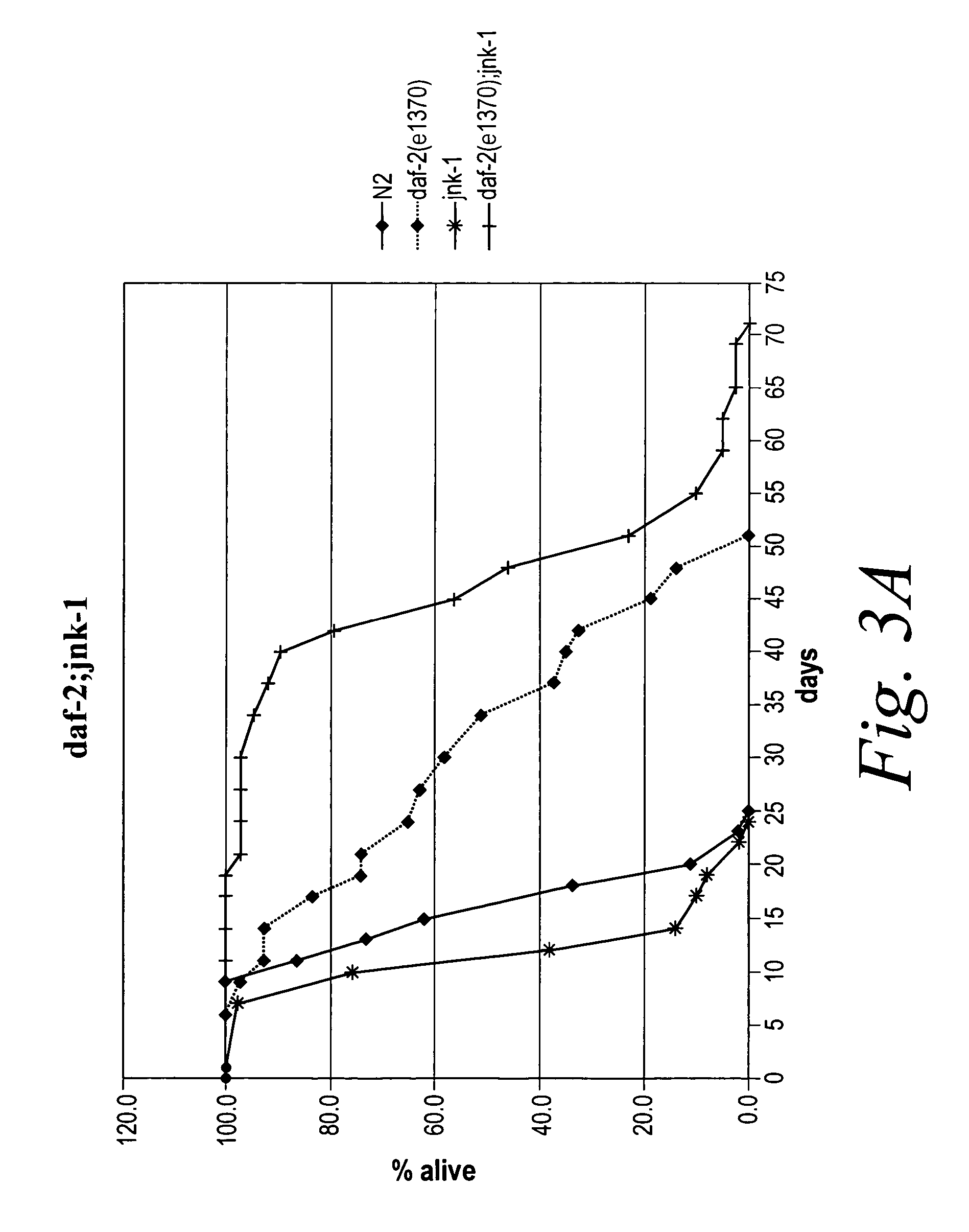
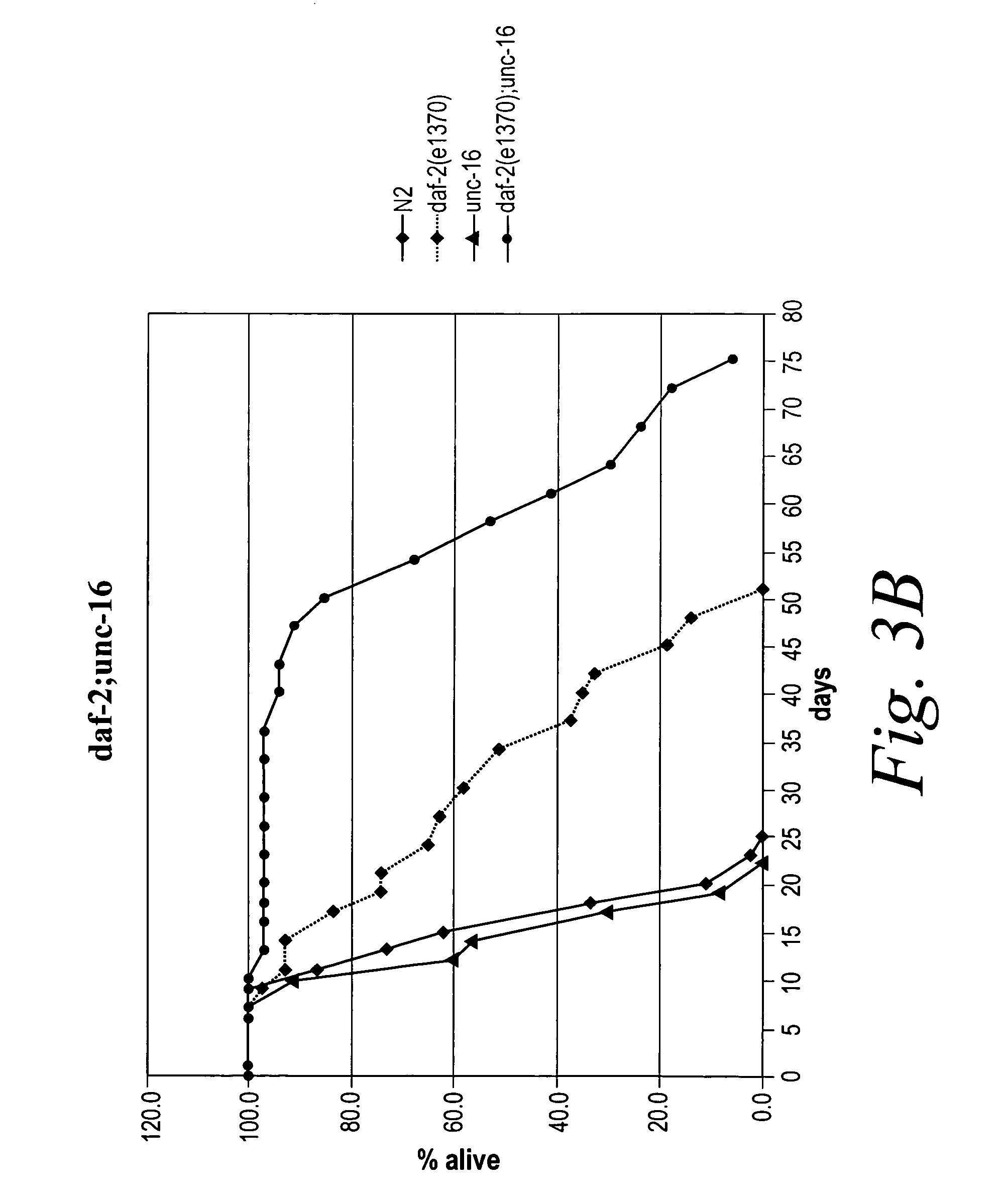
Methods of identifying longevity modulators and therapeutic methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060272039A1Extend your lifeReduced lifespanPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBiological bodyInsulin signalling
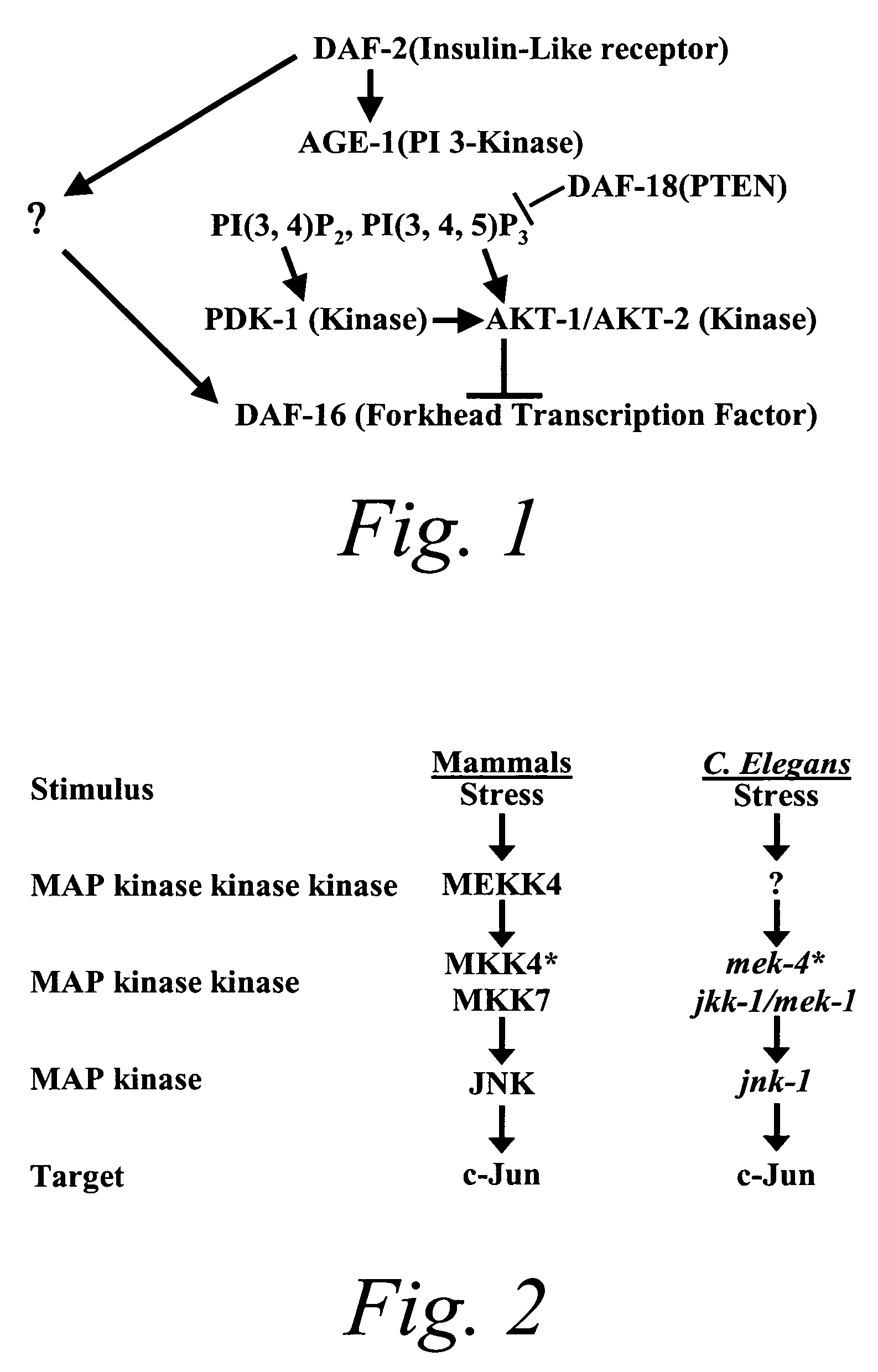
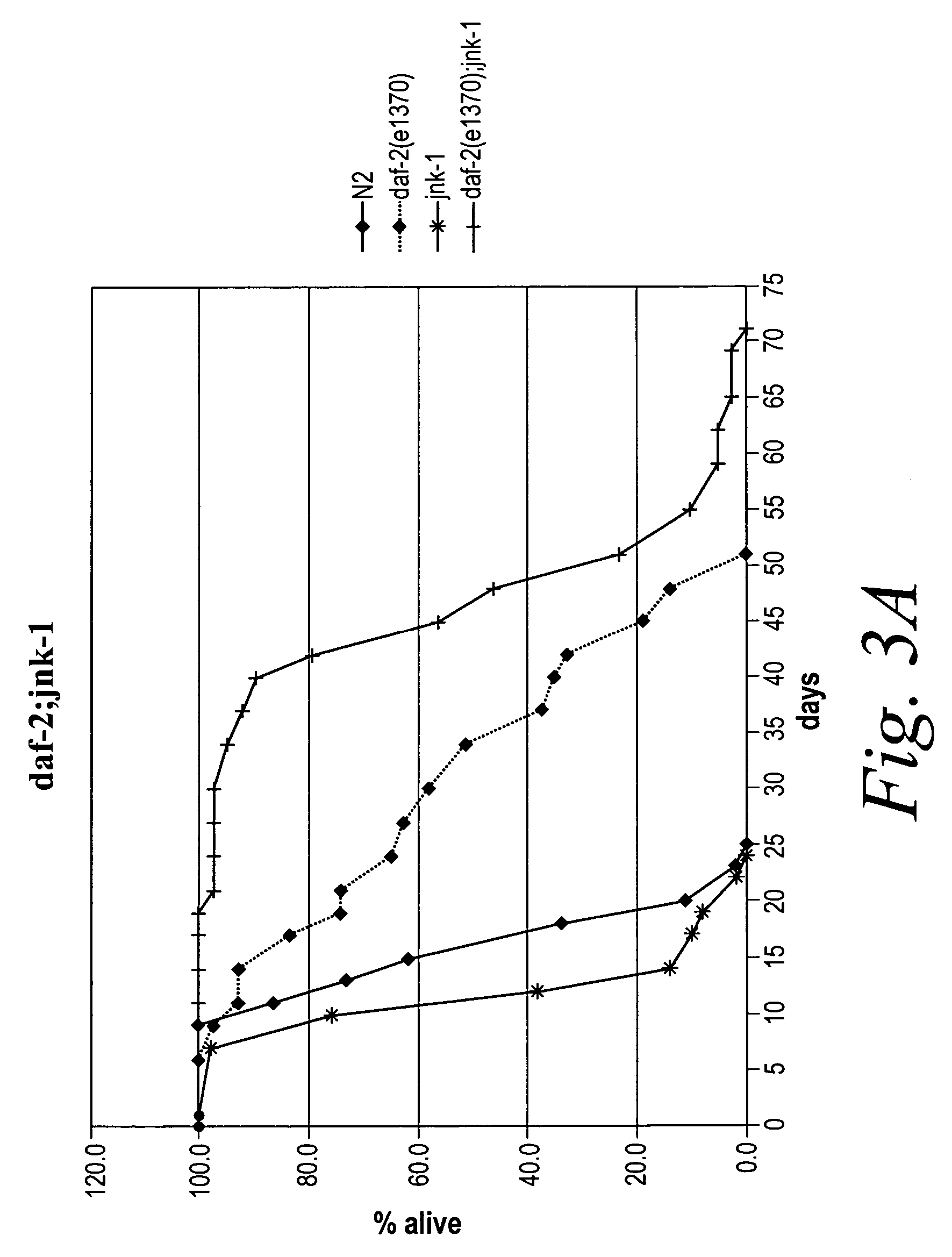
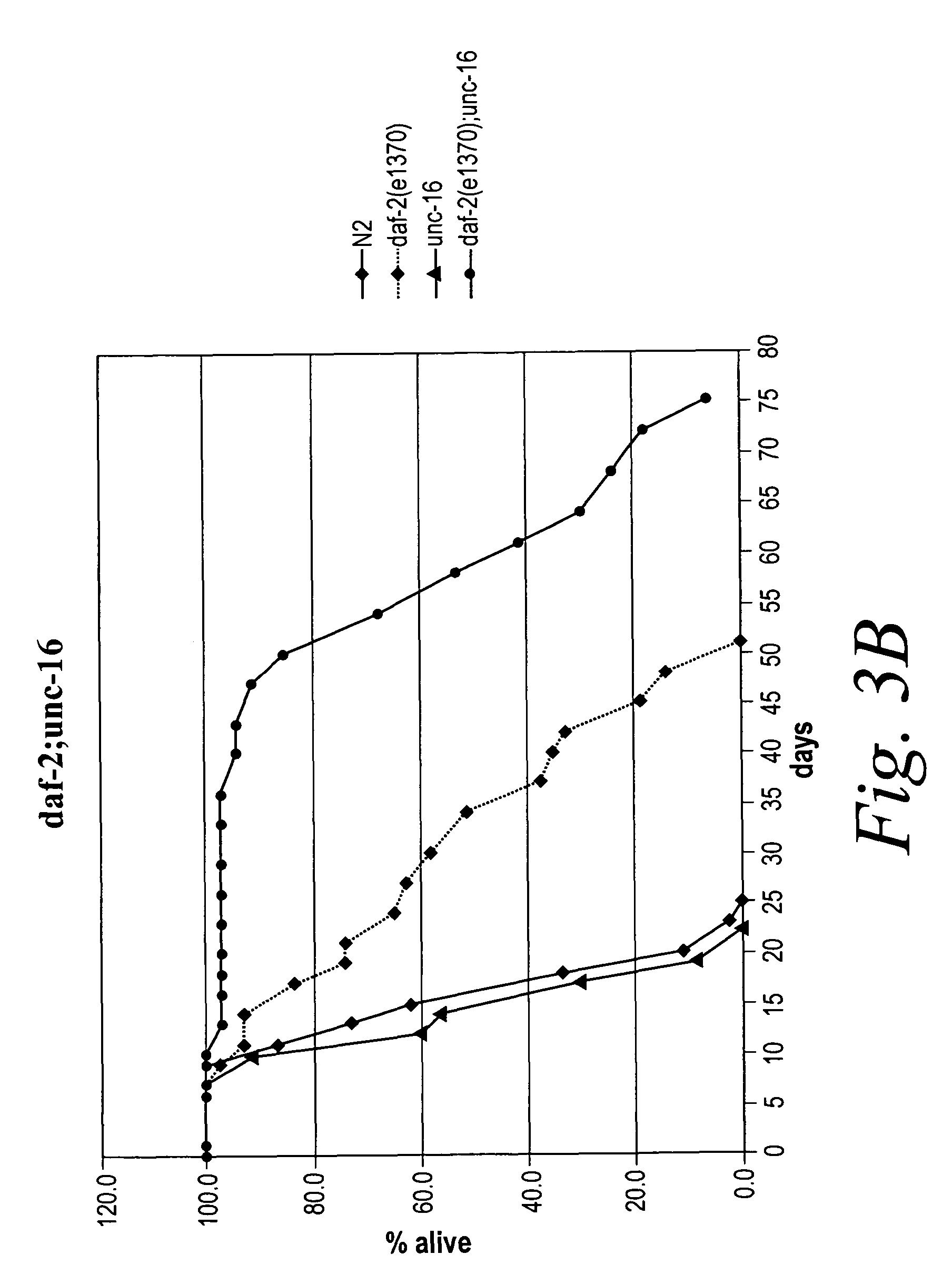
The present invention is based at least in part on the discovery of a role for the JNK signaling pathway in longevity. In particular, the present inventors have shown that overexpression of c-jun N-terminal kinase 1 (jnk-1) extends lifespan and that said extended lifespan is associated with DAF-16 phosphorylation by JNK-1 and the consequent DAF-16 localization to the nucleus. Accordingly, the present invention features methods of identifying modulators of longevity in assays featuring organisms and / or cells having a JNK signaling pathway and, optionally, an IR signaling pathway. Also featured is an in vitro method of identifying an agent capable of enhancing longevity featuring an assay composition having a JNK signaling pathway molecule and insulin signaling pathway molecule. Further featured are therapeutic methods for the use of JNK signaling pathway modulators to enhance longevity, to prevent or reduce obesity and to prevent or treat type II diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Inhibitors of c-jun N-terminal kinases
Owner:ABBVIE INC
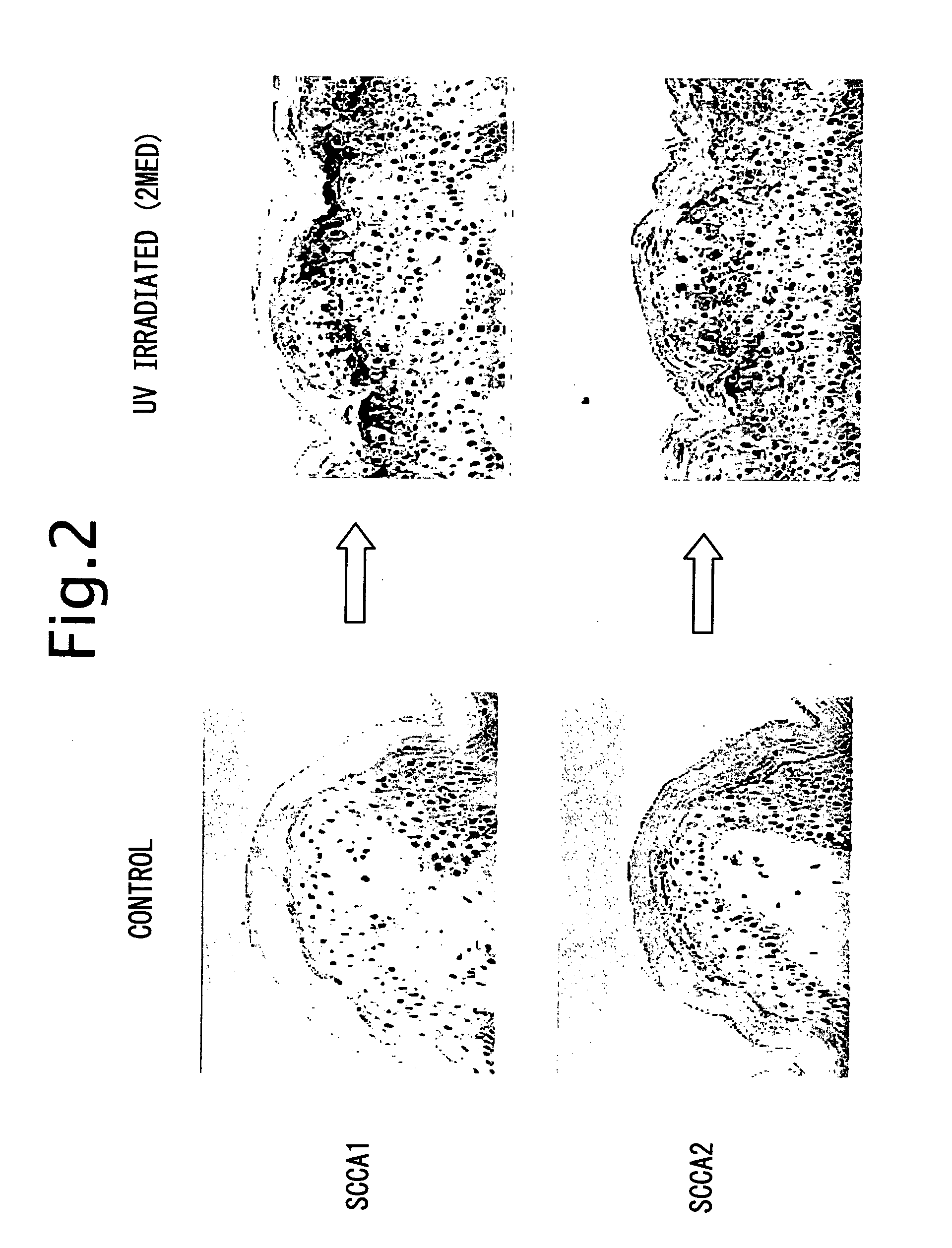
Method for inhibiting jnk-1 kinase activity by SCCA
InactiveUS20050215509A1Novel and effective anti-apoptosisCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsKinase activityAntigen
The present invention provides a method and composition that inhibit the kinase activity of JNK-1 (c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1) in cells by increasing the expression of squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) in cells.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
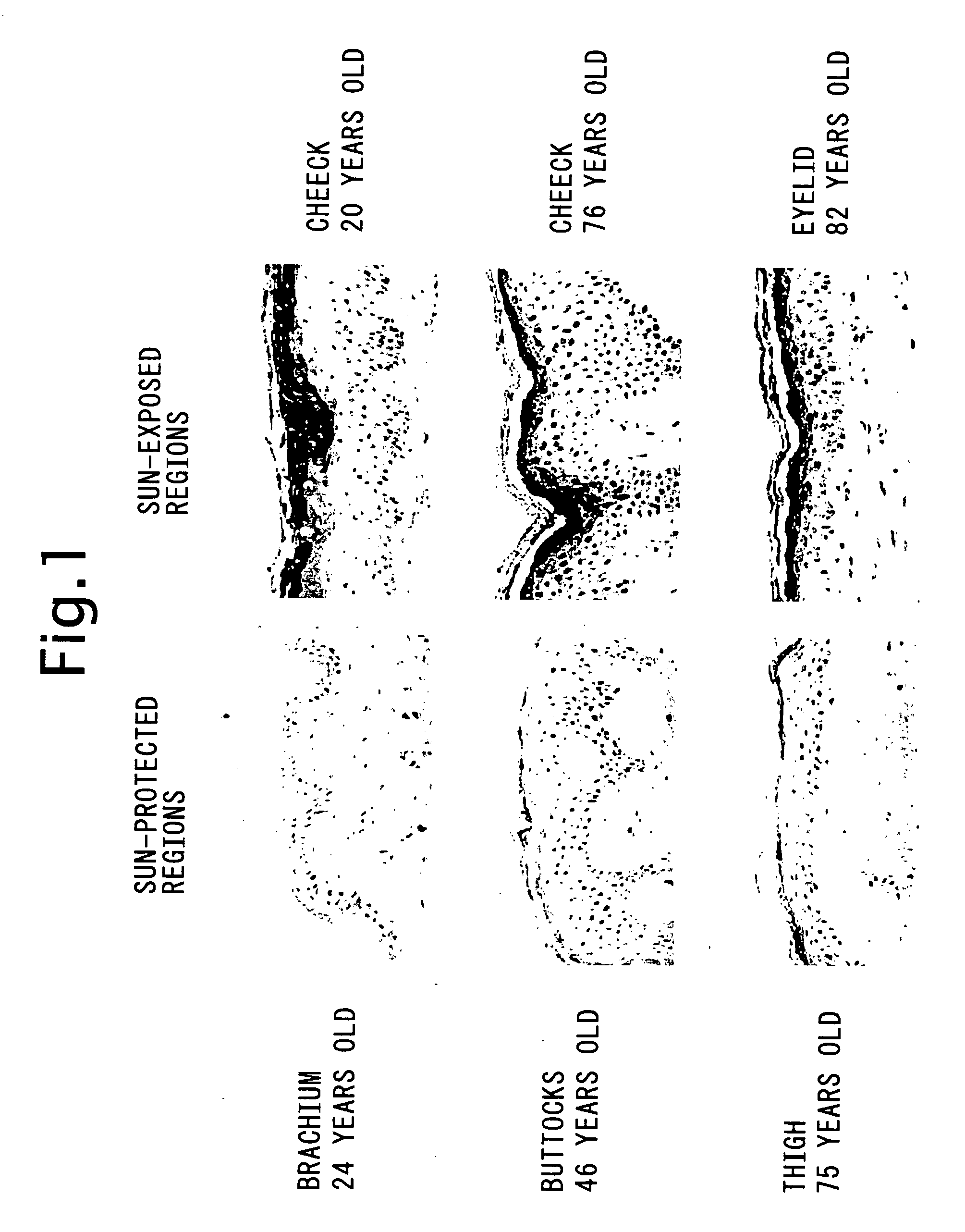
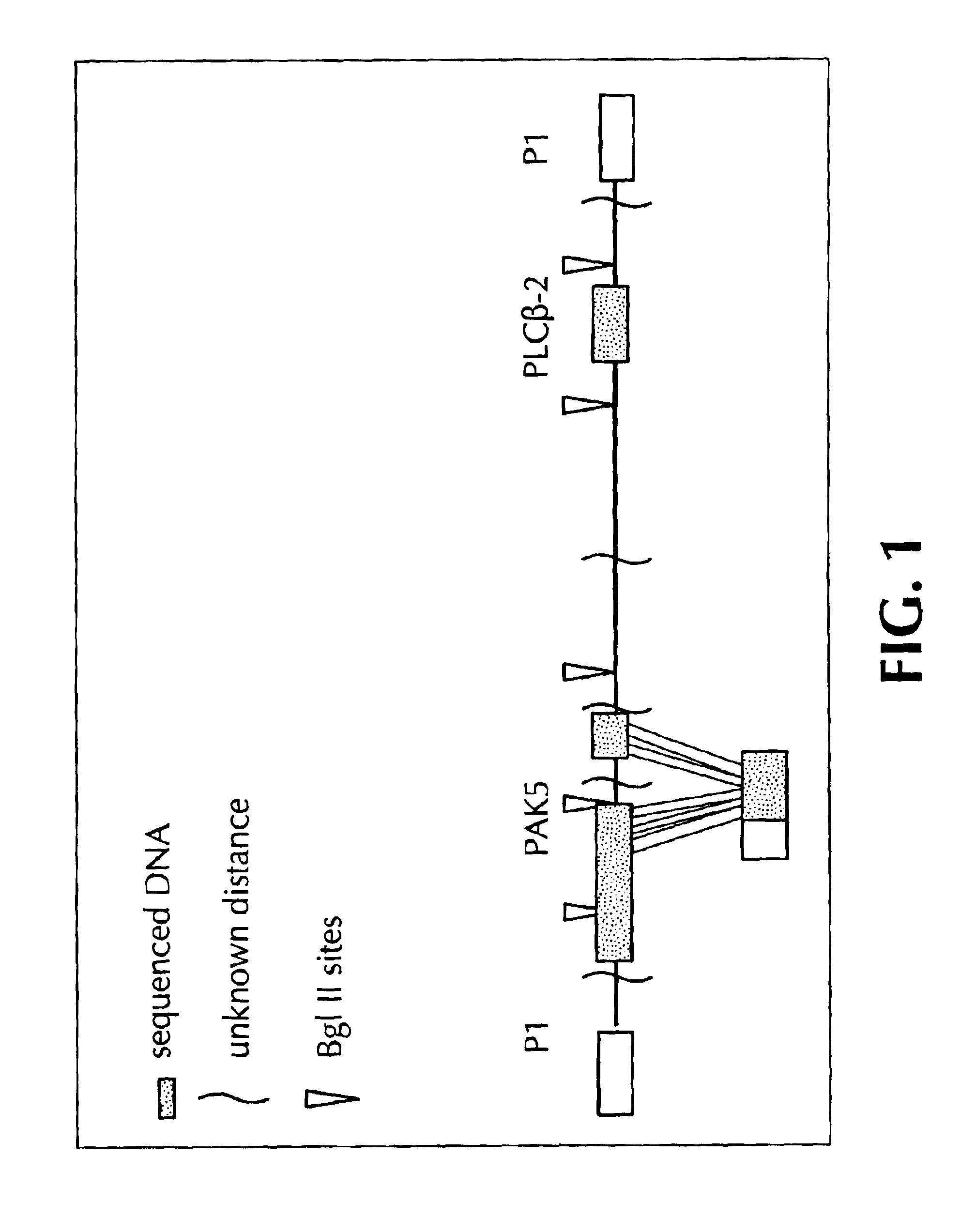
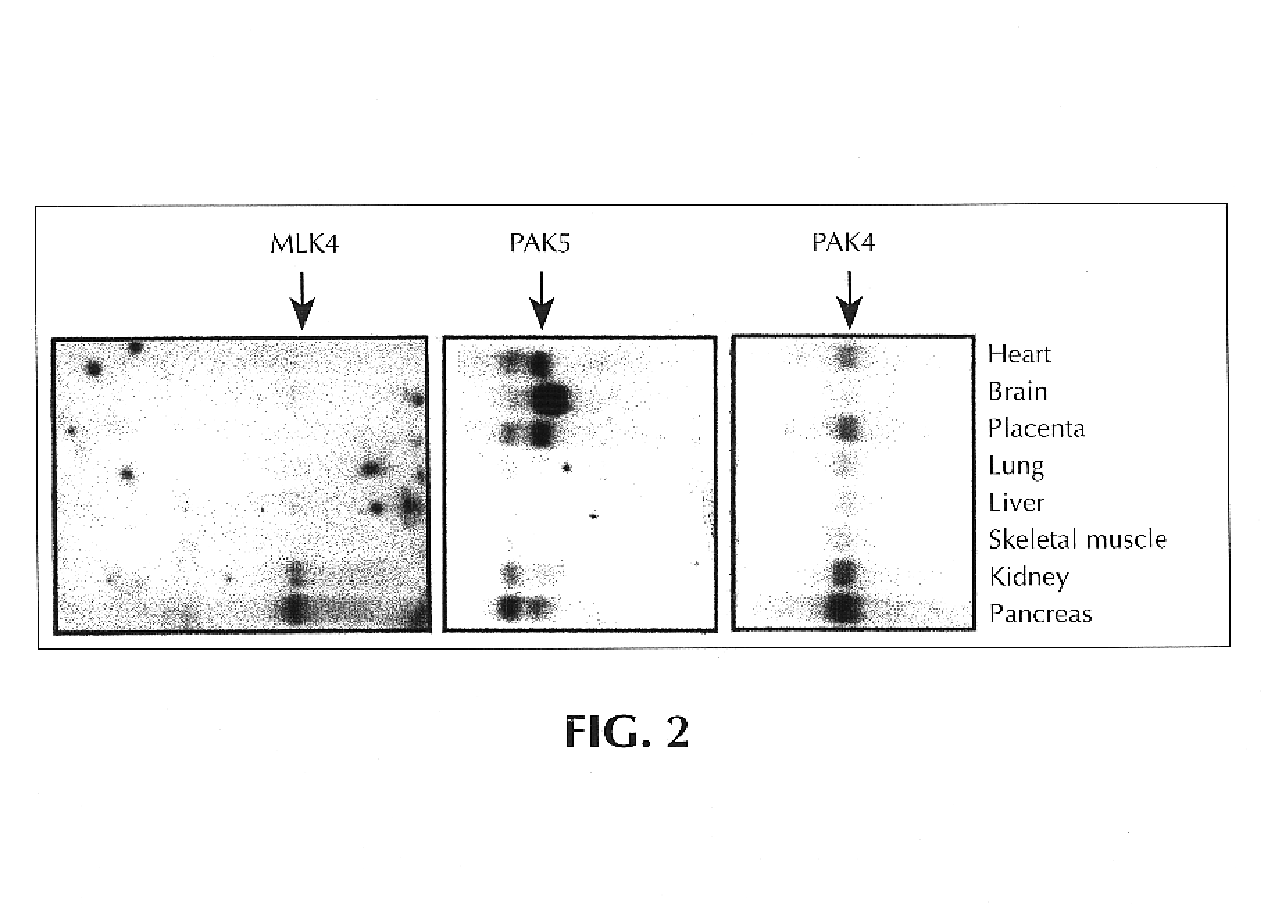
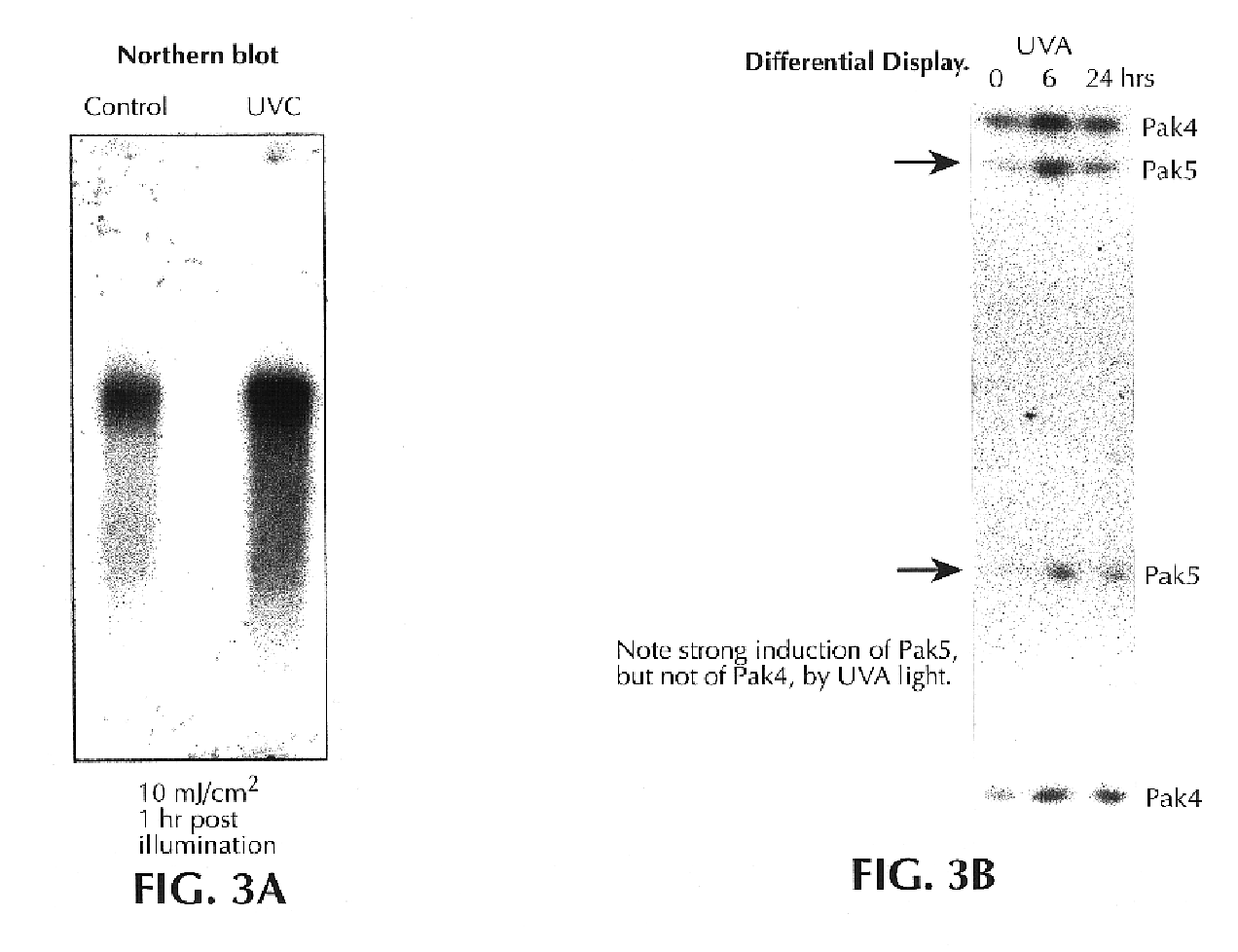
Genes and polynucleotides associated with ultraviolet radiation-mediated skin damage and uses thereof
The invention relates to novel polynucleotides and their encoded gene products that are expressed in skin cells, particularly keratinocytes, and methods of using the same. Specifically, the present invention provides polynucleotides encoding several novel protein kinases that are c-Jun N-terminal kinase kinase kinases, i.e., MLK4, PAK4, PAK5 and YSK2. In addition, the invention provides methods of using the disclosed polynucleotides and their gene products in drug discovery, particularly in screening for drugs that can reduce ultraviolet light-induced damage of the skin, inflammation and psoriasis, and drugs that can enhance wound healing.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Methods and compositions for inhibition of axonal degeneration by modulation of the dlk/jnk pathway
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
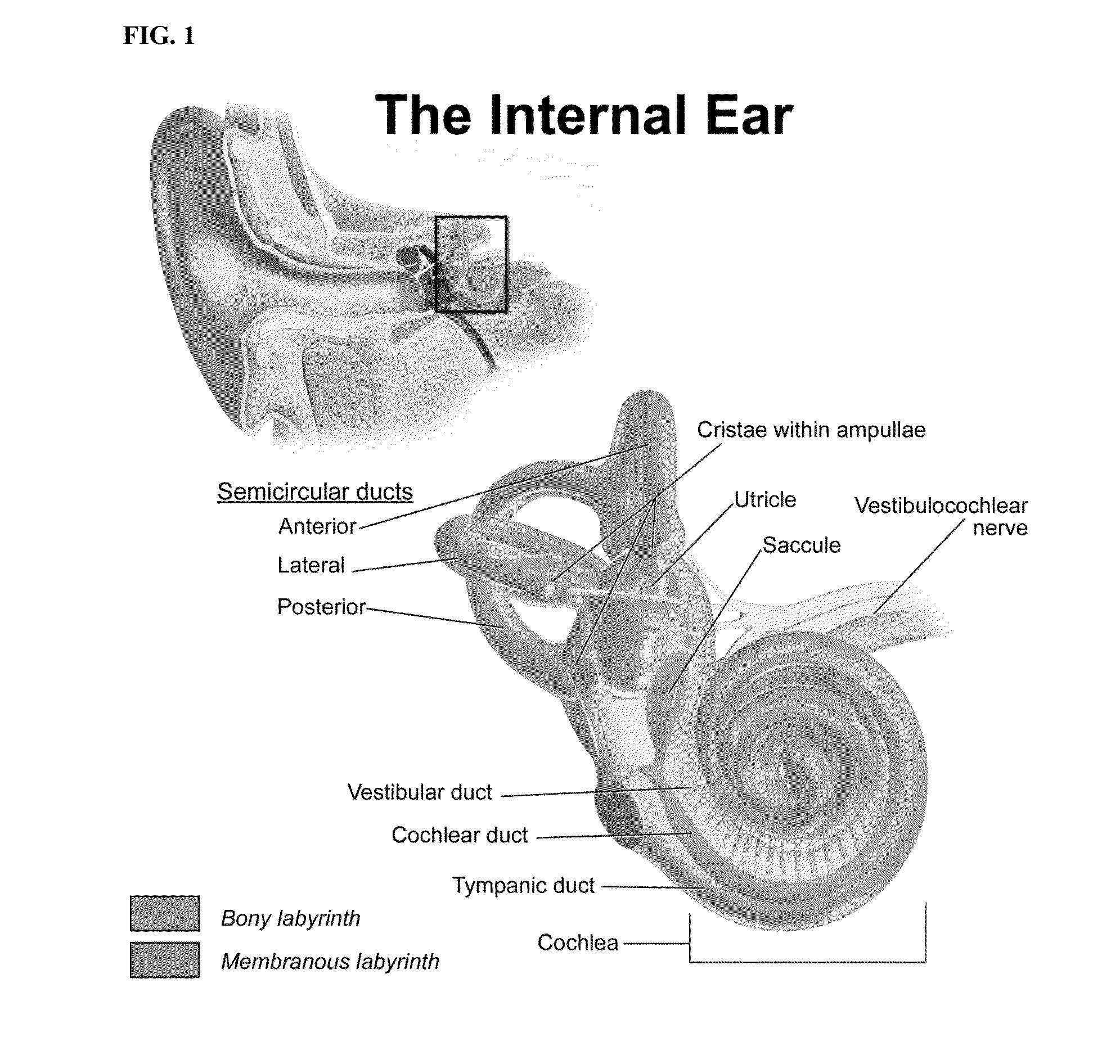
Pharmacologic treatments of meniére's disease
InactiveUS20150374779A1Attenuating long-term outcomeEffective attenuationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseasePharmacologic therapy
The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating Meniére's Disease. In particular, the invention provides a method for treating Meniére's Disease in a subject in need thereof by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Owner:AURIS MEDICAL AG
Compositions and methods for treating cachexia
The present invention relates, in various embodiments, to methods of treating cachexia (e.g., cancer cachexia) in a patient. The methods comprise administering at least one compound for inhibiting, in alternative embodiments, the expression or activity of a microRNA that is present in microvesicles secreted from cancer cells in the patient (e.g., a miR-21 gene product), the expression or activity of a Toll-like receptor (e.g., TLR7, TLR8), the expression or activity of a c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), the secretion of microvesicles from cancer cells, or the fusion of microvesicles from cancer cells with muscle cells or adipocytes. The present invention also relates, in certain embodiments, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising at least two compounds useful in the practice of the methods of the invention described herein.
Owner:CROCE CARLO M +1
Agent for controlling circadian rhythm disorder
InactiveUS20050037449A1Inhibit phosphorylationInhibition of transcriptional activityCompound screeningBiocidePhosphorylation InhibitionCircadian Rhythm Disorders
A method for controlling circadian rhythm disorders is described, characterized by inhibiting the phosphorylation of BMAL1 by c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 (JNK3) due to the interaction between JNK3 and BMAL1; a method for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by circadian rhythm disorders; and a method for identifying a compound that inhibit phosphorylation of BMAL1 by JNK3. Also provided are: an agent for controlling circadian rhythm disorders, having the above characteristics; an agent for treating and / or preventing diseases caused by circadian rhythm disorders; a compound obtained by the identification method described above; an agent for inhibiting the phosphorylation of BMAL1 by JNK3, containing the compound; an agent for recovering the suppressed transcriptional activity of the complexes containing BMAL1 and CLOCK and for inhibiting the phosphorylation the same, containing an agent for inhibiting the expression and / or function of JNK3; and a pharmaceutical composition containing one of these.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
Prophylactic or therapeutic agent for retinal diseases and method for preventing or treating retinal diseases, each comprising jnk (c-jun n-terminal kinase)-inhibiting peptide, and use of the peptide
InactiveCN102365093AEffective treatmentSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBlood vessel
The intravitreal administration of a JNK-inhibiting peptide which comprises (a) at least either one of the JNK-inhibiting sequences depicted in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2 and (b) at least either one of the transfer sequences depicted in SEQ ID NO:3 and SEQ ID NO:4 and has a length shorter than 150 amino acid residues wherein at least one amino acid residue is a D-amino acid residue can prevent the occurrence of spermidine-induced damage of retinal pigment epitheliums, tunicamycin-induced visual cell injury, and laser-induced choroidal neovascularization. Therefore, the JNK-inhibiting peptide is useful for the prevention or treatment of retinal diseases. By using the JNK-inhibiting peptide, it becomes possible to provide a medicinal agent and a method both of which can prevent or treat retinal diseases through topical administration in eyes. It also becomes possible to provide use of the JNK-inhibiting peptide for the production of the medicinal agent.
Owner:SANTEN PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for treating and preventing tinnitus
InactiveUS20150306178A1Ameliorating and reducing occurrenceSenses disorderOintment deliveryDiseaseInner Ear Disorder
The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating inner ear disorders. In particular, the invention provides a method for treating and / or preventing acute inner ear tinnitus in a subject in need thereof by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Owner:AURIS MEDICAL AG
Inhibitors of c-JUN N-terminal kinases (JNK)
The present invention relates to inhibitors of JNK, a mammalian protein kinase involved cell proliferation, cell death and response to extracellular stimuli. The invention also relates to methods for producing these inhibitors. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the inhibitors of the invention and methods of utilizing those compositions in the treatment and prevention of various disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Arylsulfonamide derivatives as C-Jun-N-Terminal Kinases (JNK's) inhibitors
InactiveUS7683078B2Using treatment methodBiocideSenses disorderAutoimmune diseasePharmaceutical formulation
The present invention relates to sulfonamide derivatives of formula (I) notably for use as pharmaceutically active compounds, as well as to pharmaceutical formulations containing such sulfonamide derivatives. Said sulfonamide derivatives are useful in the treatment of neuronal disorders, autoimmune diseases, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, said sulfonamide derivatives are efficient modulators of the JNK pathway, they are in particular efficient and selective inhibitors of JNK2 and -3. The present invention is furthermore related to novel sulfonamide derivatives as well as to methods of their preparation. Formula (I) IAr1 is a substituted or unsubstituted aryl or heteroaryl group; X is O or S, preferably O; Ar2 a substituted or unsubstituted arylene or heteroarylene group; R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and a C1-C6-alkyl group.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
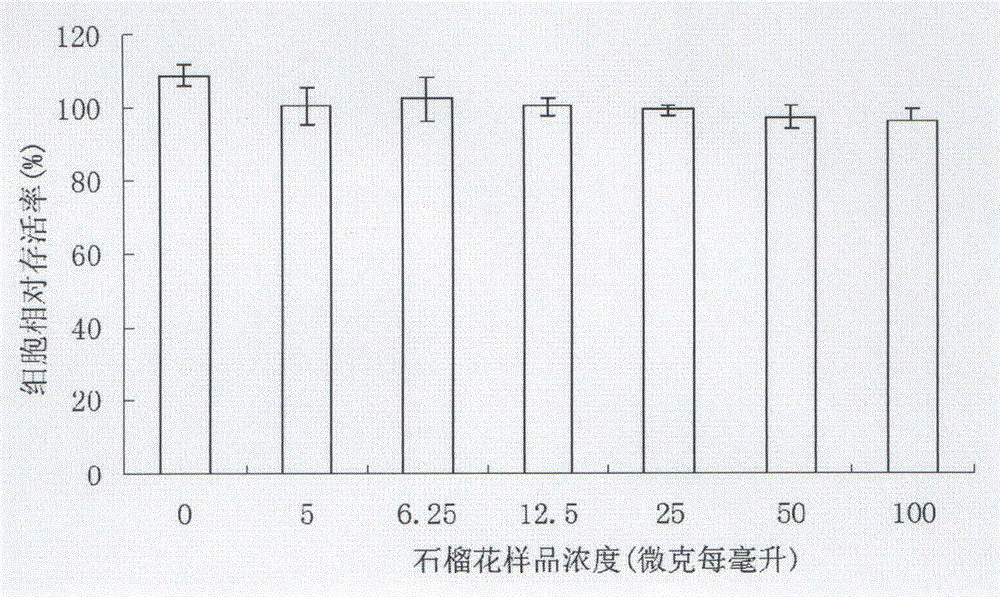
Anti-inflammatory application of pomegranate flower polyphenol
InactiveCN104825504AGood anti-inflammatory activityInhibition of excess releaseAntipyreticAnalgesicsInterleukin 6Protein C
The invention relates to an anti-inflammatory application of pomegranate flower polyphenol. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology is adopted to analyze the influence of pomegranate flower polyphenol on the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response of mouse macrophage (RAW264.7), and the results show that pomegranate flower polyphenol can prominently inhibit the excess releasing of inflammatory mediator namely nitrogen monoxide (NO) and excess secretion of inflammation inhibiting factor namely interleukin 6, interleukin 1[beta], and tumor necrosis factor [alpha]. The western blotting shows that pomegranate flower polyphenol can inhibit the excess expression of the following three key enzymes in the inflammation signal path: extracelluar regulated protein kinase, C-JUN N-terminal kinase, and epoxidase 2. So the pomegranate flower polyphenol has a very good anti-inflammatory activity, can be used as the lead compound of anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent or treat inflammation caused by excess of nitrogen monoxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor [alpha] (TNF-[alpha]), interleukin 6 (IL-6) or interleukin 1[beta] (IL-1[beta]).
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
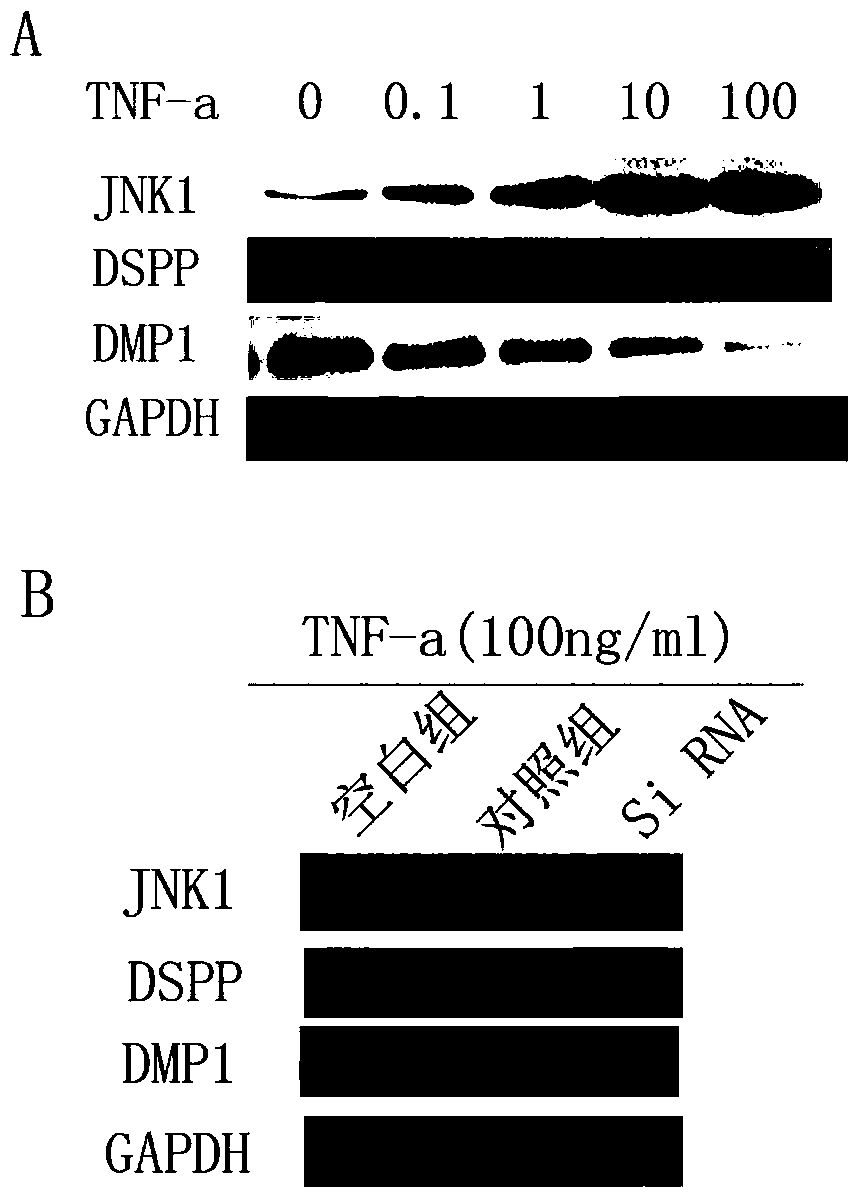
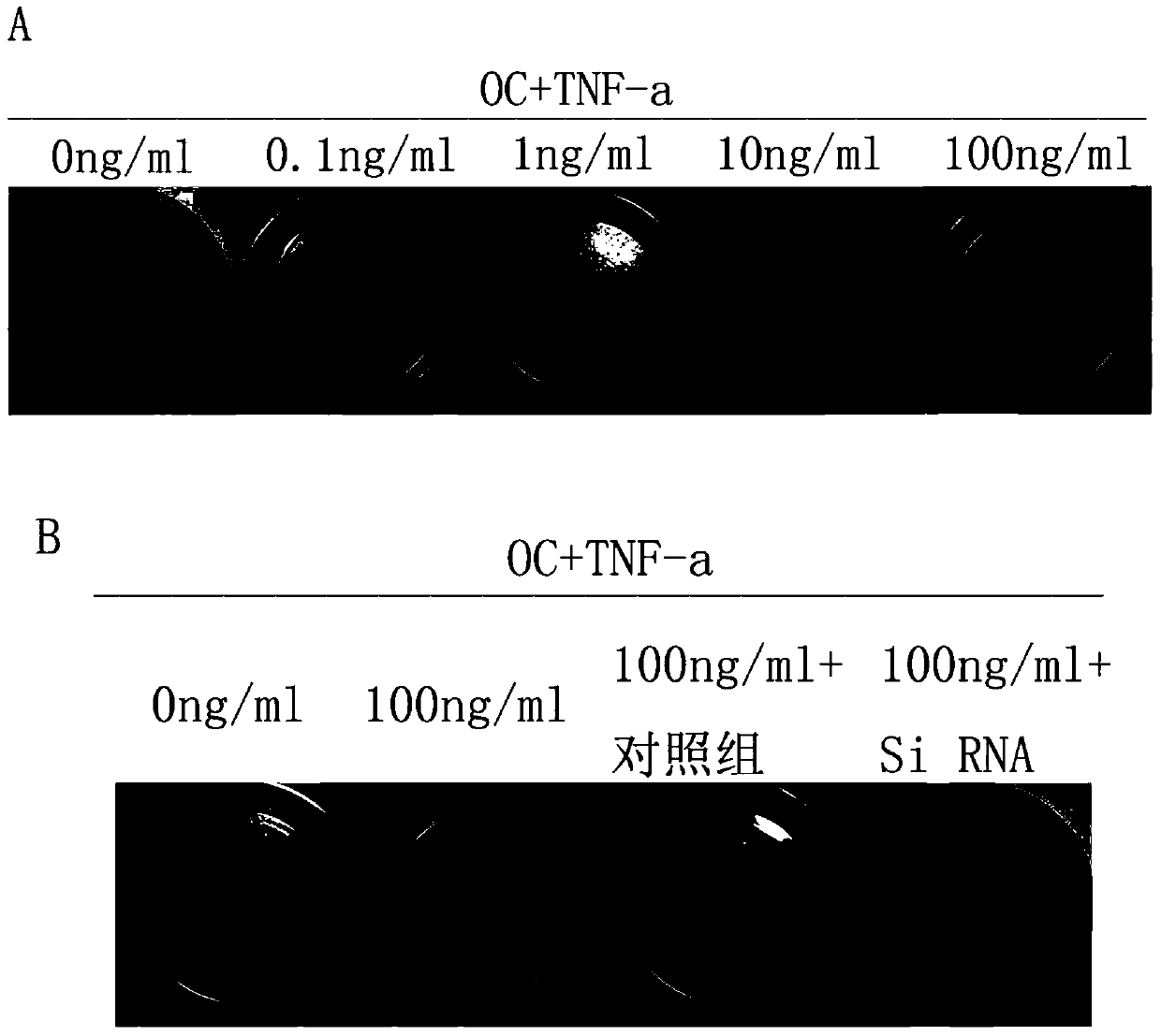
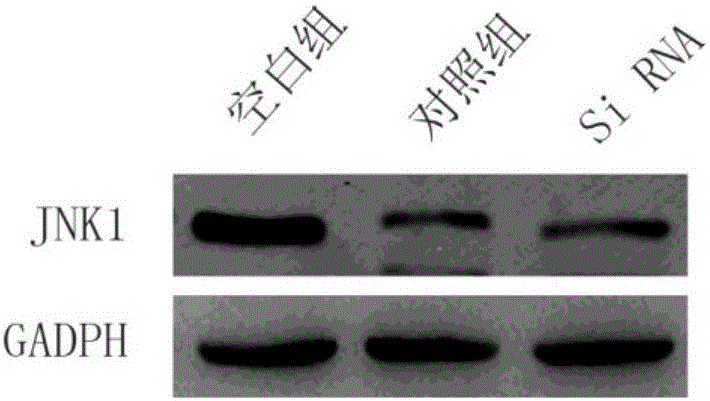
Small interfering RNA targeting human jnk1 gene and its application
ActiveCN106047908BDecreased expression of p-JNKReduce apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemNucleotideApoptosis
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a human JNK1 (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) gene targeting small interfering RNA (ribonucleic acid) and application thereof. The small interfering RNA comprises a sense strand and an anti-sense strand, a nucleotide sequence of the sense strand is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and a nucleotide sequence of the anti-sense strand is as shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The sequences of the small interfering RNA are not publically reported yet, interference after transcription of the JNK1 gene can be realized to reduce expression of p-JNK in inflamed dental pulp stem cells, apoptosis of the dental pulp stem cells can be specifically reduced, odontoblast differentiation of the dental pulp stem cells is promoted, and a novel treatment scheme is provided for pulpitis.
Owner:江苏国辰医疗科技有限公司
Arylsulfonamide derivatives as c-jun-n-terminal kinases (jnk's) inhibitors
The present invention relates to sulfonamide derivatives of formula I notably for use as pharmaceutically active compounds, as well as to pharmaceutical formulations containing such sulfonamide derivatives. Said sulfonamide derivatives are useful in the treatment of neuronal disorders, autoimmune diseases, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, said sulfonamide derivatives are efficient modulators of the JNK pathway, they are in particular efficient and selective inhibitors of JNK2 and -3. The present invention is furthermore related to novel sulfonamide derivatives as well as to methods of their preparation.Ar1 is a substituted or unsubstituted aryl or heteroaryl group;X is O or S, preferably O;Ar2 a substituted or unsubstituted arylene or heteroarylene group;R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen and a C1-C6-alkyl group;
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Methods of identifying longevity modulators and therapeutic methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7858327B2Extend your lifeReduced lifespanBiological testingIn-vivo testing preparationsBiological bodyInsulin signalling
The present invention is based at least in part on the discovery of a role for the JNK signaling pathway in longevity. In particular, the present inventors have shown that modulation of the c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway in an organism, optionally in combination with modulation of the insulin receptor (IR) signaling pathway, can enhance longevity in an organism. Accordingly, the present invention features methods of identifying modulators of longevity in assays featuring organisms and / or cells having either a functional or deregulated JNK signaling pathway and, optionally, a functional or deregulated IR signaling pathway. Also featured is an in vitro method of identifying an agent capable of enhancing longevity featuring an assay composition having a JNK signaling pathway molecule and insulin signaling pathway molecule. Further featured are therapeutic methods for the use of JNK signaling pathway modulators to enhance longevity.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
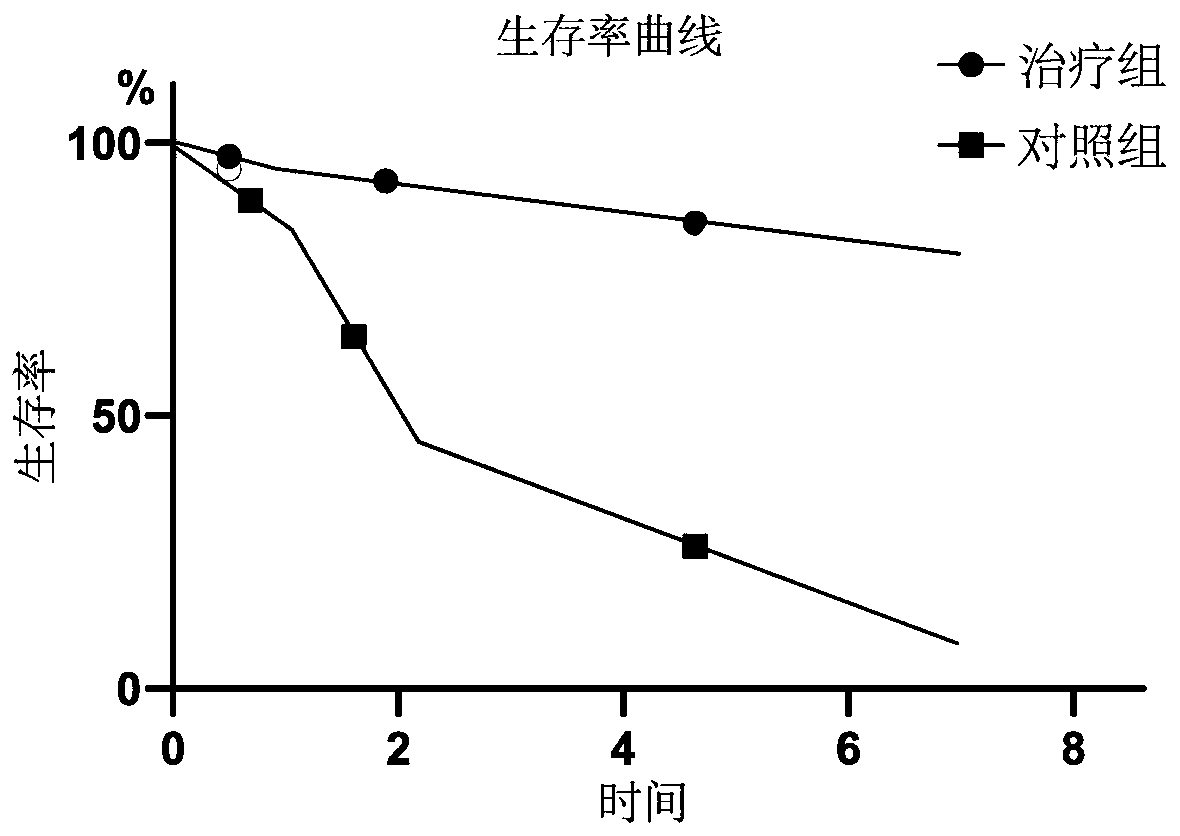
Application of CTSG (cathepsin G) cell factor in preparation of medicaments to treat hepatic failure
InactiveCN110201149ASuppress deathInhibit apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemUpper gastrointestinalCathepsin G
The invention discloses application of a CTSG (cathepsin G) cell factor in the preparation of medicaments to treat hepatic failure. Death of mass hepatic cells occurs during the course of hepatic failure; the CTSG cell factor helps overcome the aforementioned problem. CTSG JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) is one of MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) family members; JNK pathway can inhibit apoptosis of hepatic cells by regulating the expression of CTSG. The CTSG cell factor can be applied to the preparation of medicaments to treat hepatic failure to significantly increase biochemical indexesof a patient, reduce bilirubin level, lower aminotransferase, improve the coagulation function, inhibit cell apoptosis, promote the regeneration of hepatic cells and bile duct cells, prevent occurrence of fatal complications, such as massive alimentary tract bleeding, severe hepatic encephalopathy and hepatorenal syndrome, extend the survival time of the patient significantly, and increase the survival rate.
Owner:杭州笙源生物科技有限公司
Methods of identifying longevity modulators and therapeutic methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7932049B2Extend your lifeReduced lifespanPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInsulin signallingPhosphorylation
The present invention is based at least in part on the discovery of a role for the JNK signaling pathway in longevity. In particular, the present inventors have shown that overexpression of c-jun N-terminal kinase 1 (jnk-1) extends lifespan and that said extended lifespan is associated with DAF-16 phosphorylation by JNK-1 and the consequent DAF-16 localization to the nucleus. Accordingly, the present invention features methods of identifying modulators of longevity in assays featuring organisms and / or cells having a JNK signaling pathway and, optionally, an IR signaling pathway. Also featured is an in vitro method of identifying an agent capable of enhancing longevity featuring an assay composition having a JNK signaling pathway molecule and insulin signaling pathway molecule. Further featured are therapeutic methods for the use of JNK signaling pathway modulators to enhance longevity, to prevent or reduce obesity and to prevent or treat type II diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Drug eluting stent and therapeutic methods using C-JUN N-terminal kinase inhibitor
InactiveCN101130115AReduce concentrationSmall doseStentsSurgeryLipid formationPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to a system and device for preventing stenosis and / or restenosis after an invasive procedure in a body vessel or cavity having an inner wall surface, the system comprising inserting a device coated with a growth arresting, lipid-derived, bioactive substance at a desired location along the inner wall surface of the body vessel or cavity. The present invention provides for the use of c-Jun aminoterminal kinase inhibitor (''JNK Inhibitor'') and certain analogs as restenosis inhibitors, incorporated into a stent.
Owner:杨笕春
Human JNK1 (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) gene targeting small interfering RNA (ribonucleic acid) and application thereof
ActiveCN106047908ADecreased expression of p-JNKReduce apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemNucleotideApoptosis
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a human JNK1 (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) gene targeting small interfering RNA (ribonucleic acid) and application thereof. The small interfering RNA comprises a sense strand and an anti-sense strand, a nucleotide sequence of the sense strand is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and a nucleotide sequence of the anti-sense strand is as shown in SEQ ID NO:3. The sequences of the small interfering RNA are not publically reported yet, interference after transcription of the JNK1 gene can be realized to reduce expression of p-JNK in inflamed dental pulp stem cells, apoptosis of the dental pulp stem cells can be specifically reduced, odontoblast differentiation of the dental pulp stem cells is promoted, and a novel treatment scheme is provided for pulpitis.
Owner:江苏国辰医疗科技有限公司
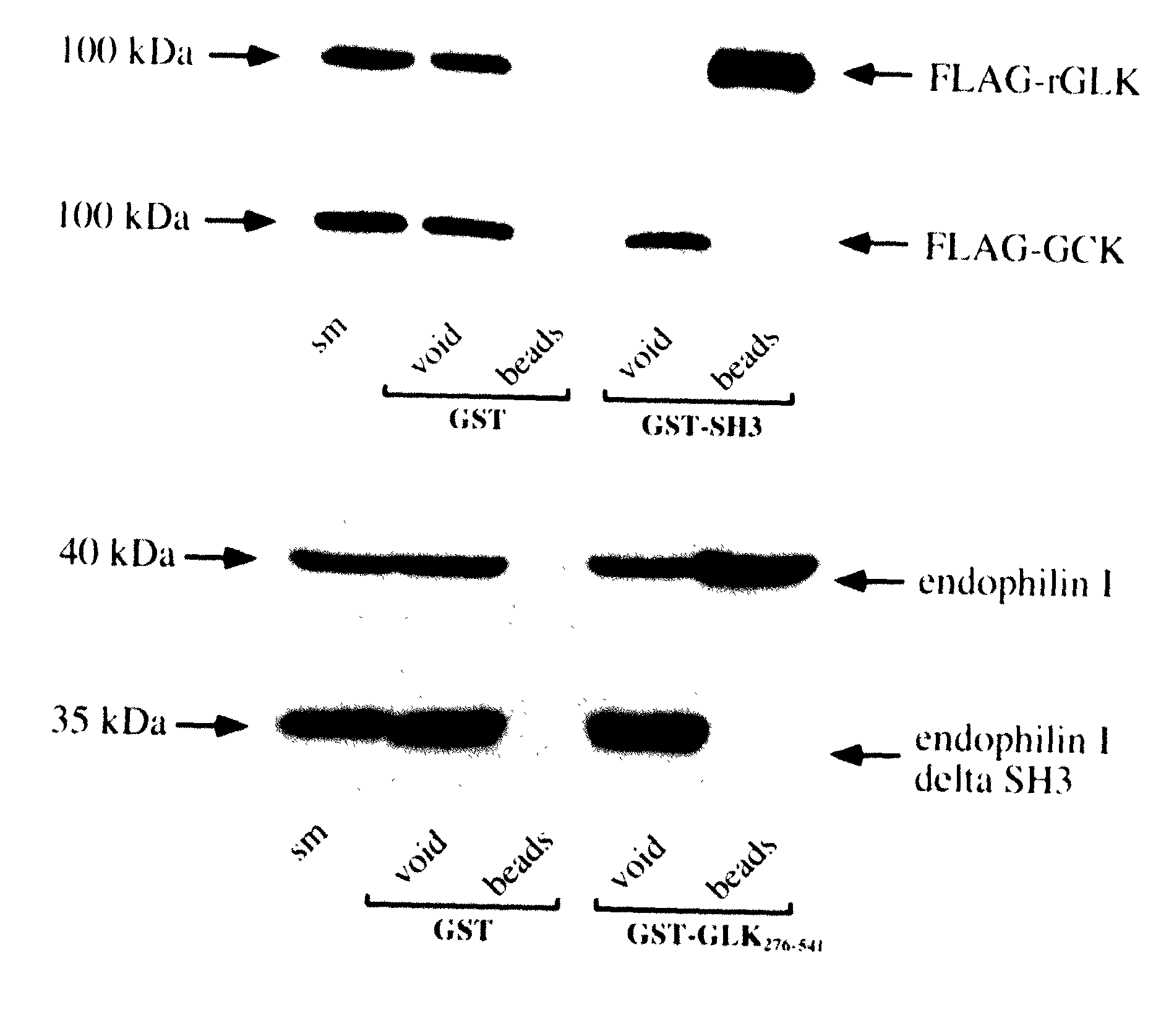
Regulation of JNK activity by modulation of the interaction between the endocytic protein endophilin and the germinal center kinase-like kinase
InactiveUS20020164672A1Alter abilityAltering abilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHuntingtons choreaEndophilin I
Endophilin I is a brain-specific protein functioning in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. The present invention is based on the finding that the rat germinal center kinase-like kinase (rGLK), a member of the germinal center kinase (GCK) family of c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activating enzymes, is a novel endophilin I-binding partner. In a first aspect of the present invention, the novel interaction between endophilin I and rGLK is put to use in a novel screening assay. In a second aspect of the present invention, the interaction between endophilin I and GLK is modulated for therapeutic purposes, namely for the prevention and / or curtailment of neurological disorders associated with the JNK pathway. JNK-mediated neuronal cell death is believed to play an important role in injuries and diseases involving neuronal degeneration, such as Huntington's disease.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com