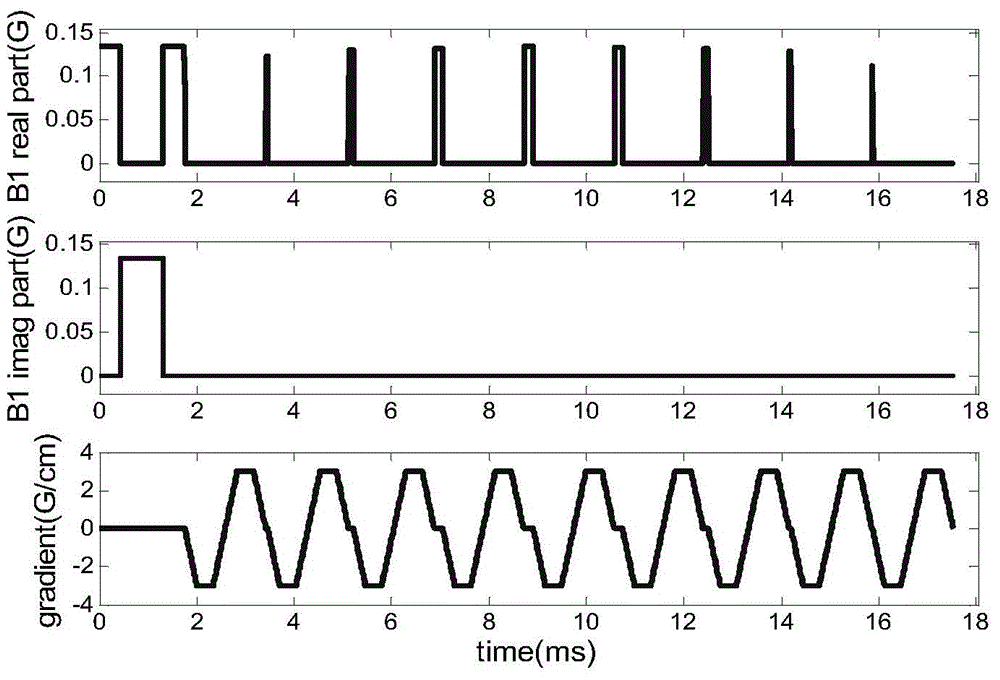
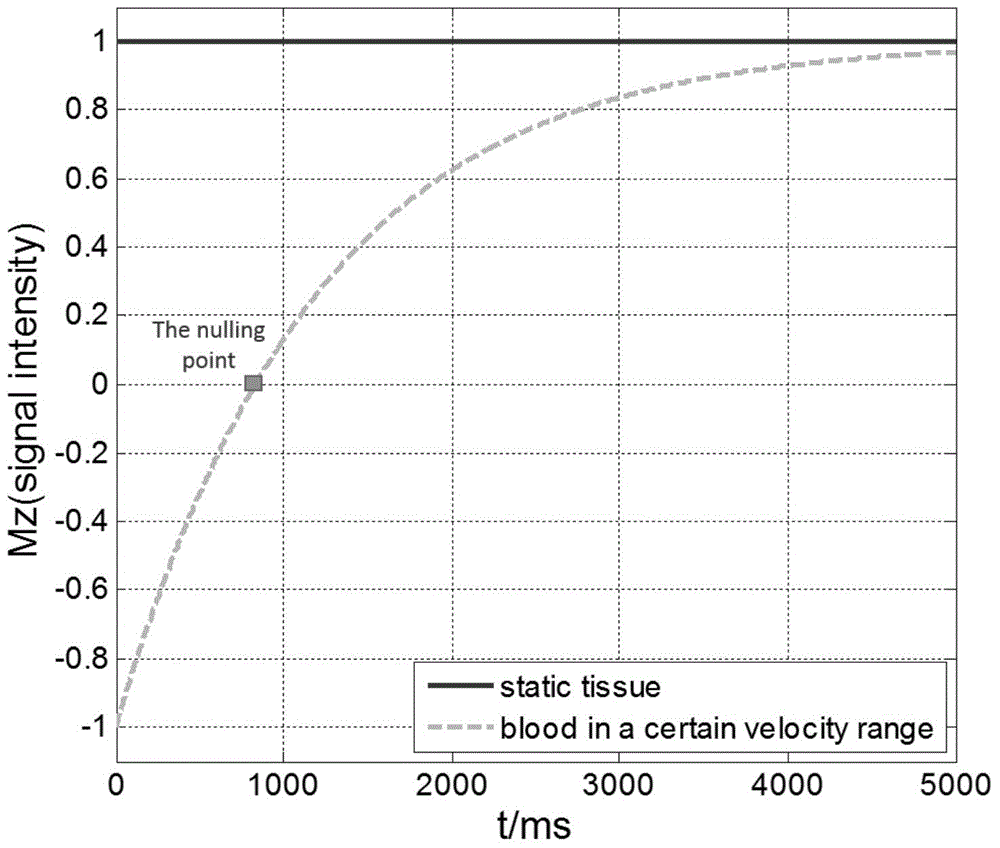
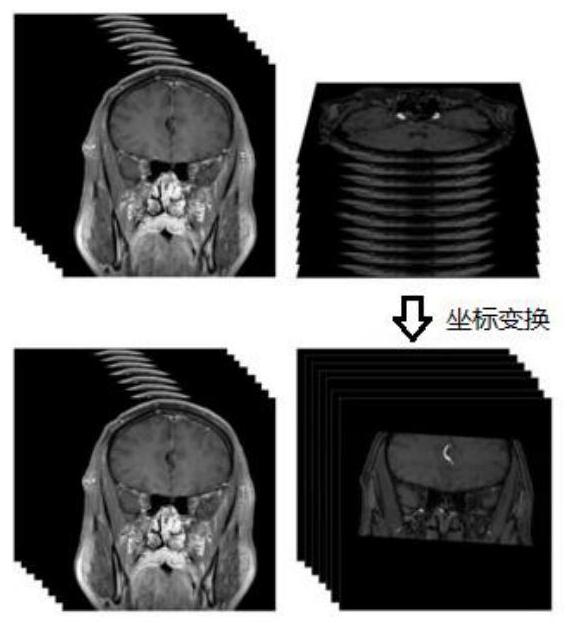
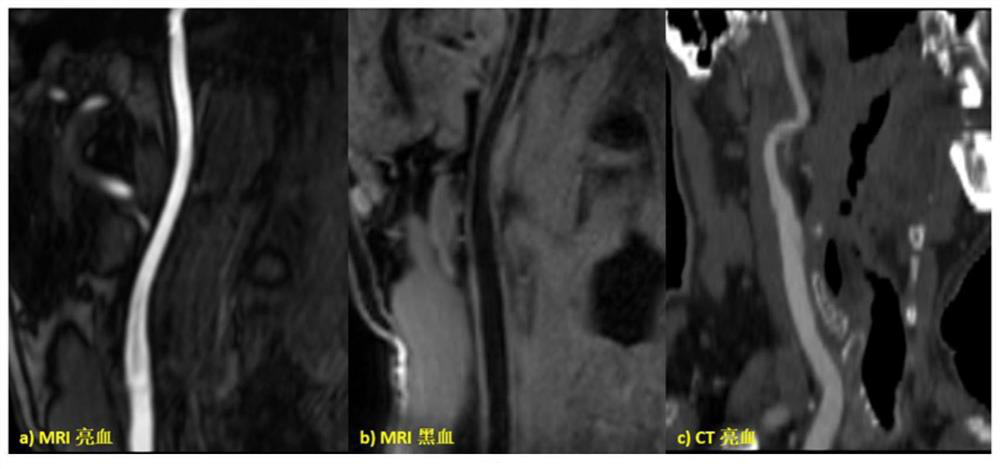
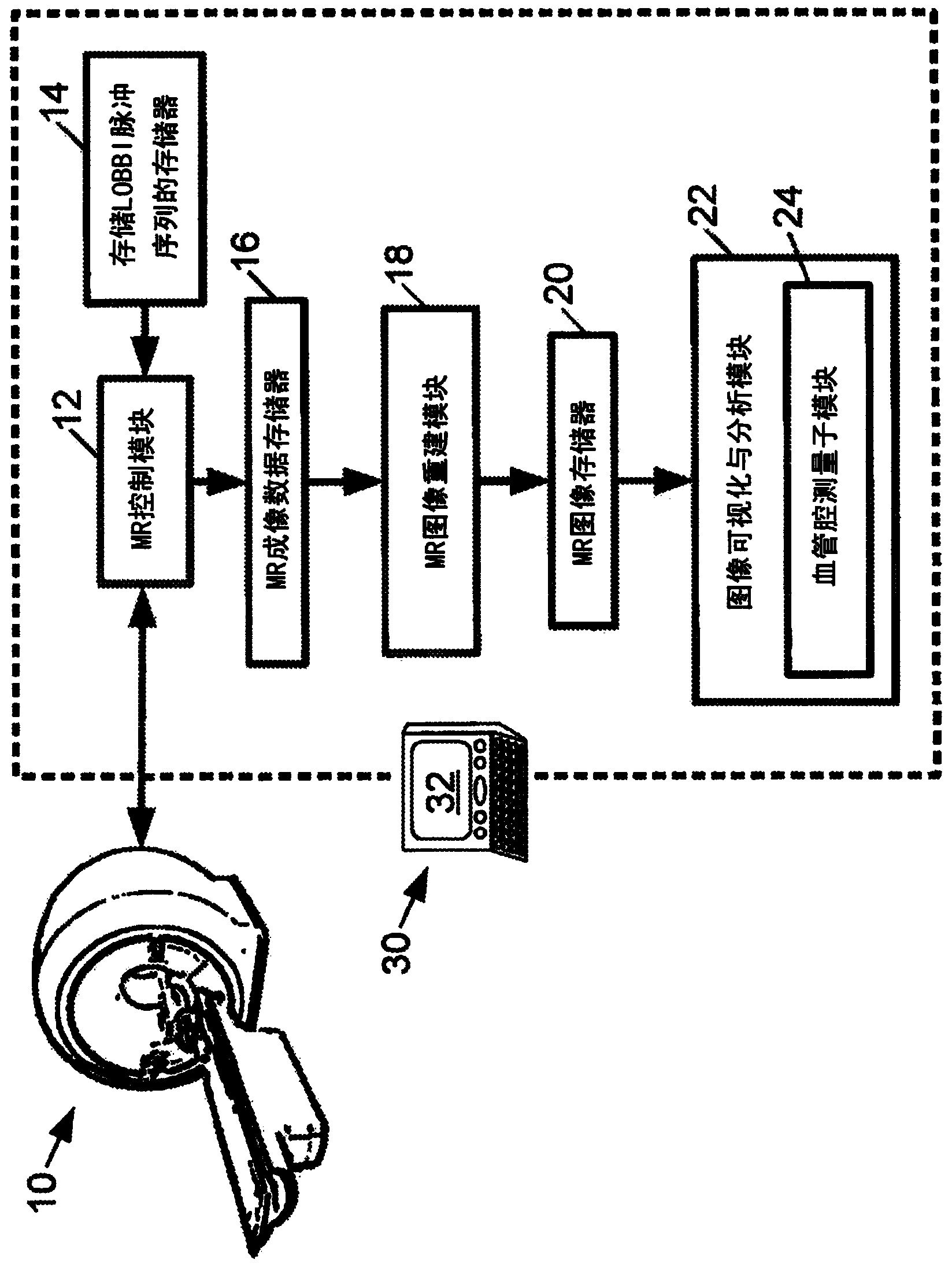
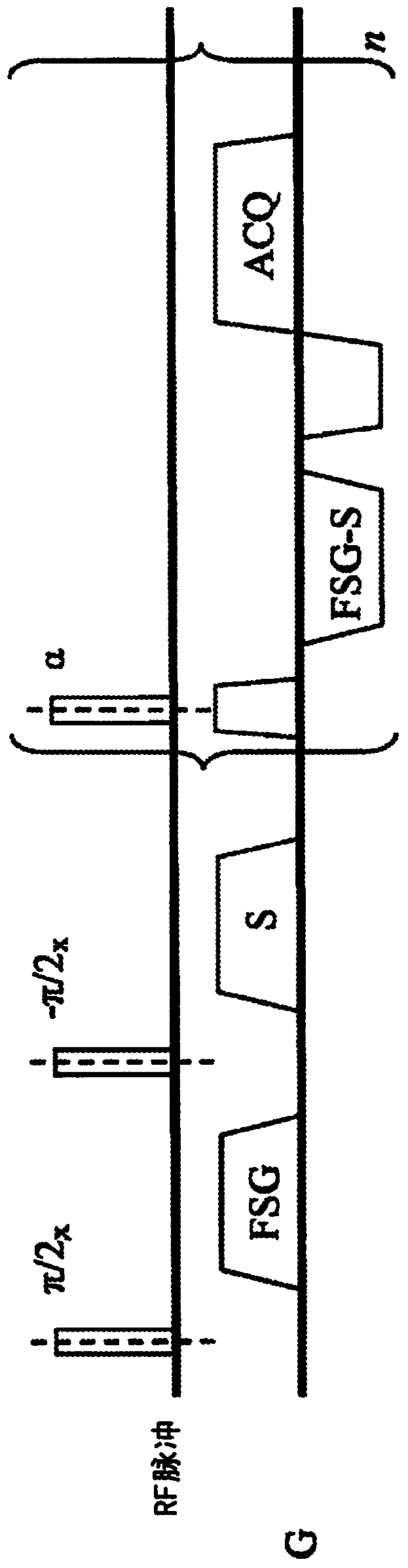
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Black blood" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
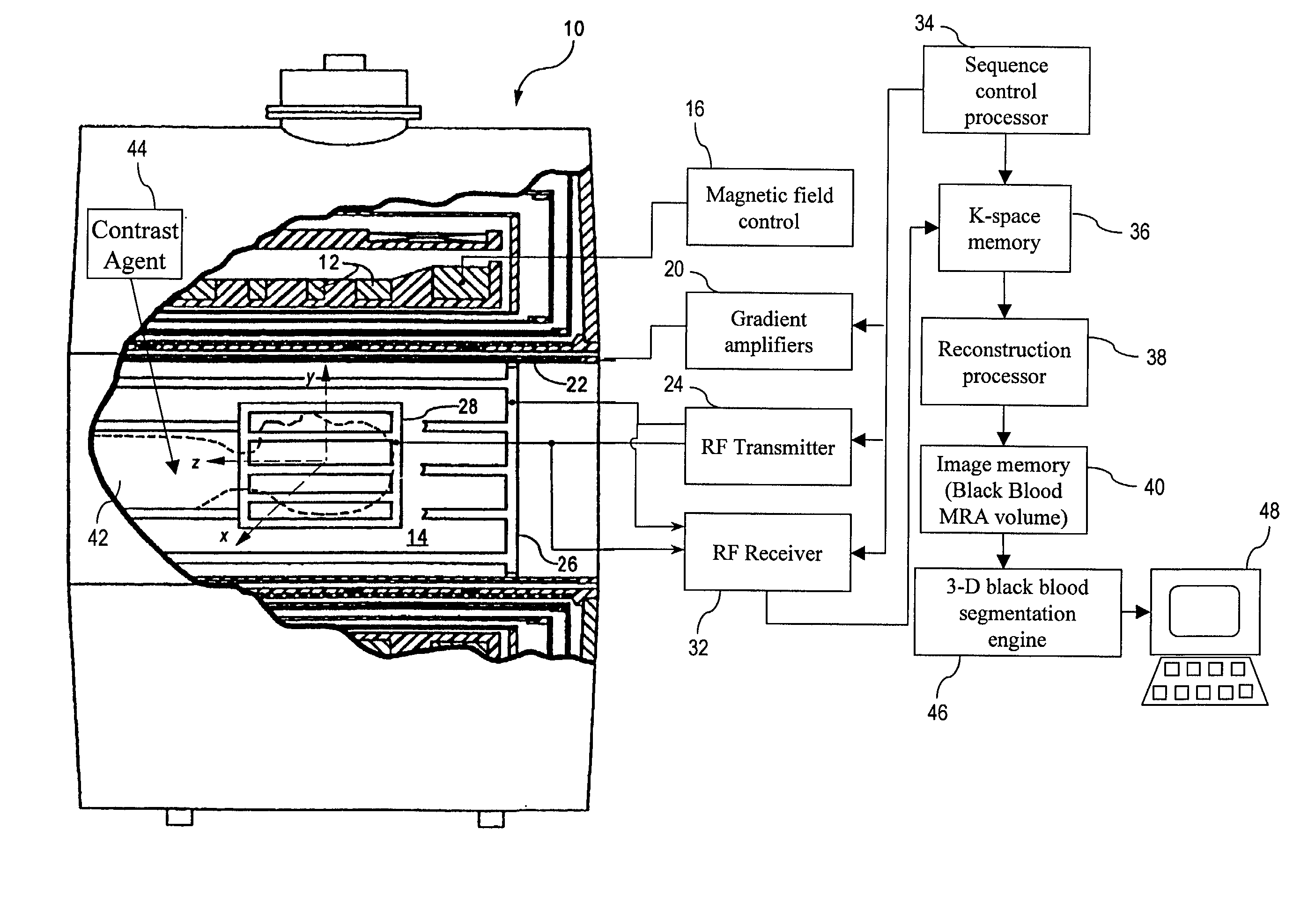
Black blood angiography method and apparatus
InactiveUS7020314B1Structural interferenceRemove non-vascular contrastImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionBlack bloodBlood Vessel Tissue
To produce a black body angiographic image representation of a subject (42), an imaging scanner (10) acquires imaging data that includes black blood vascular contrast. A reconstruction processor (38) reconstructs a gray scale image representation (100) from the imaging data. A post-acquisition processor (46) transforms (130) the image representation (100) into a pre-processed image representation (132). The processor (46) assigns (134) each image element into one of a plurality of classes including a black class corresponding to imaged vascular structures, bone, and air, and a gray class corresponding to other non-vascular tissues. The processor (46) averages (320) intensities of the image elements of the gray class to obtain a mean gray intensity value (322), and replaces (328) the values of image elements comprising non-vascular structures of the black class with the mean gray intensity value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
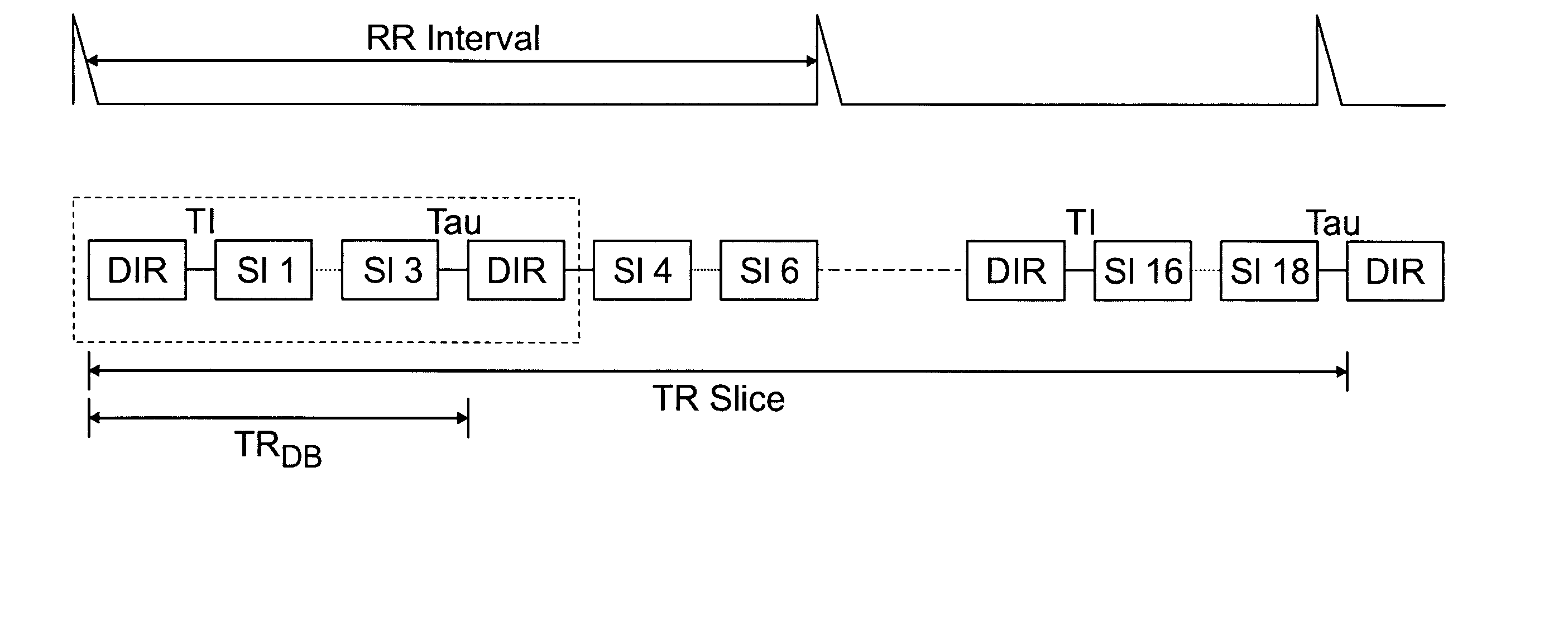
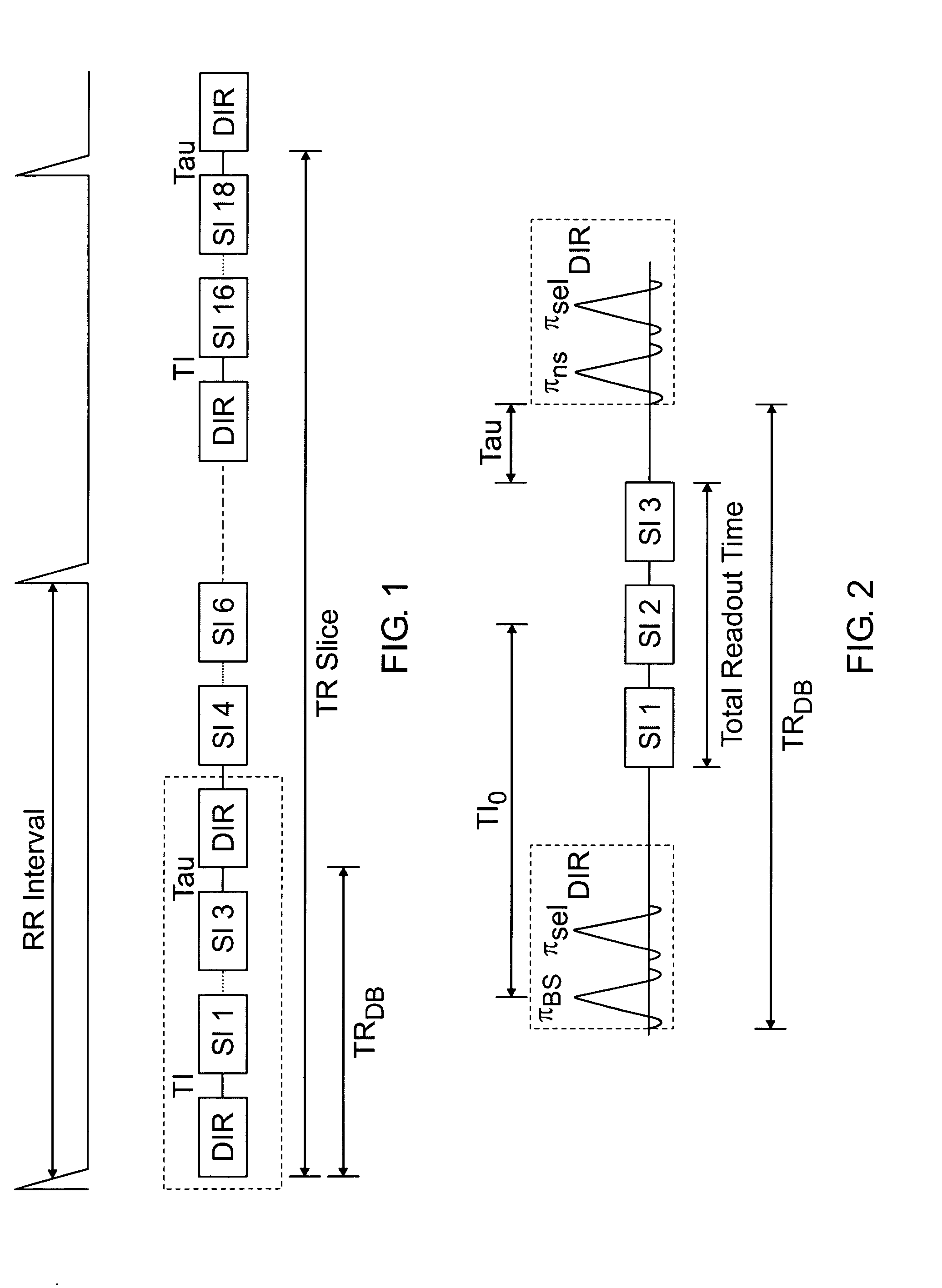
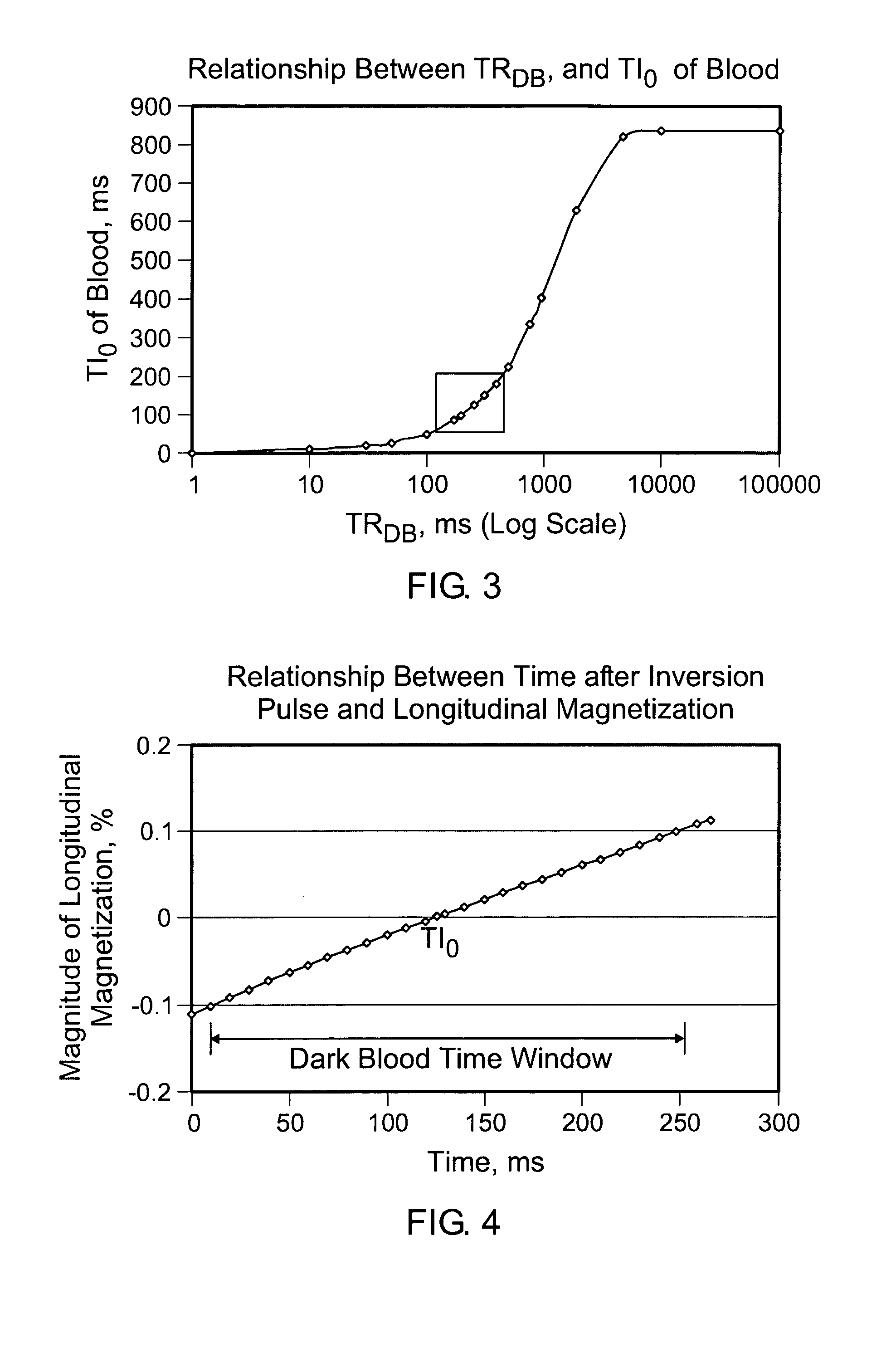
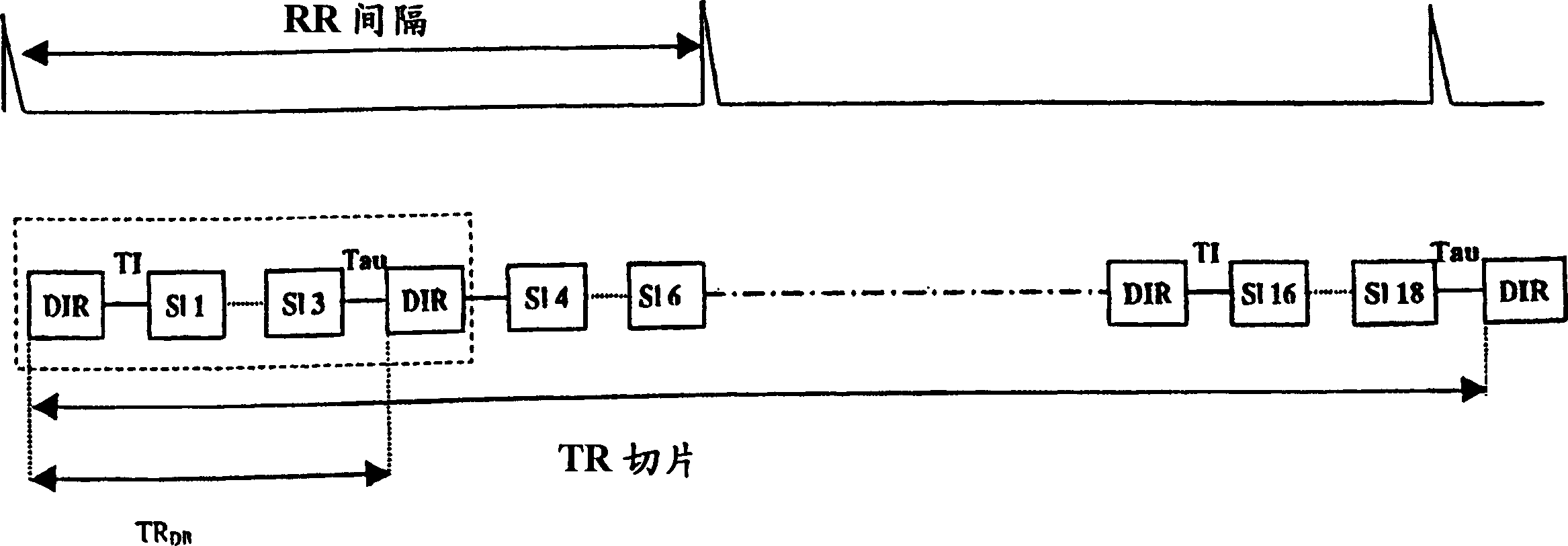
Rapid multislice black blood double-inversion recovery technique for blood vessel imaging
ActiveUS20050010104A1Fast image acquisitionAcceptable image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodRR interval
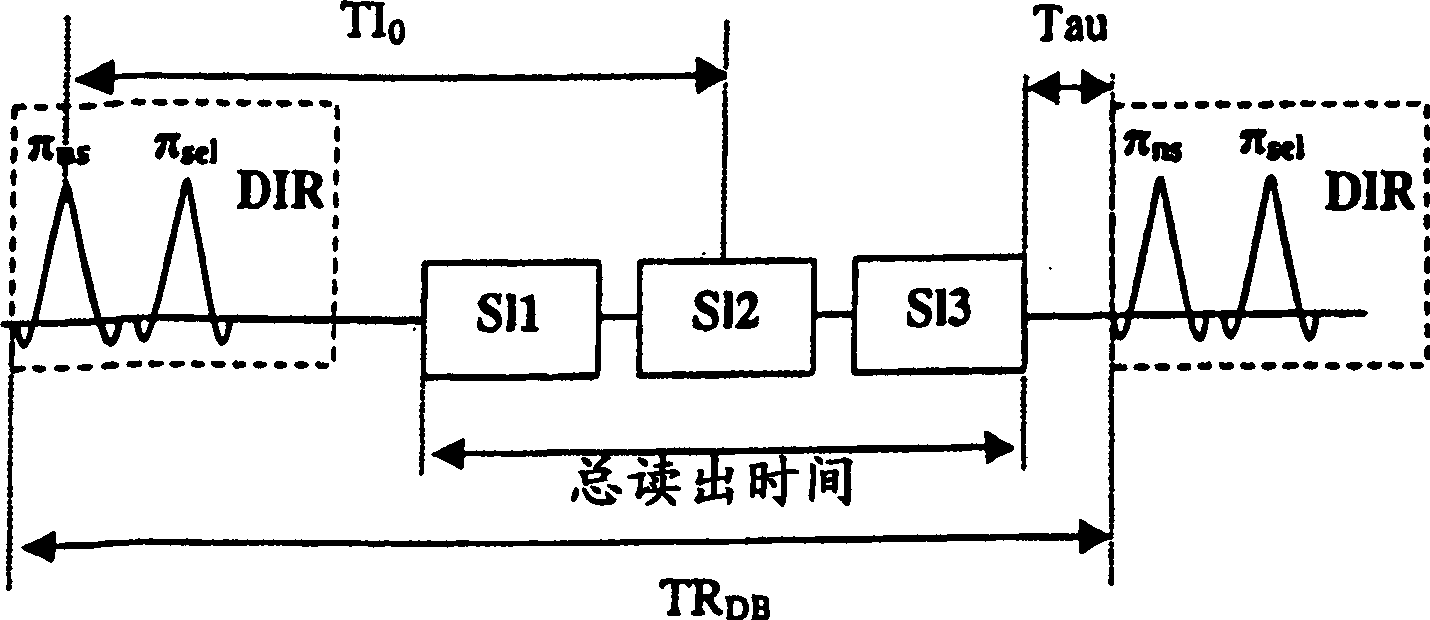
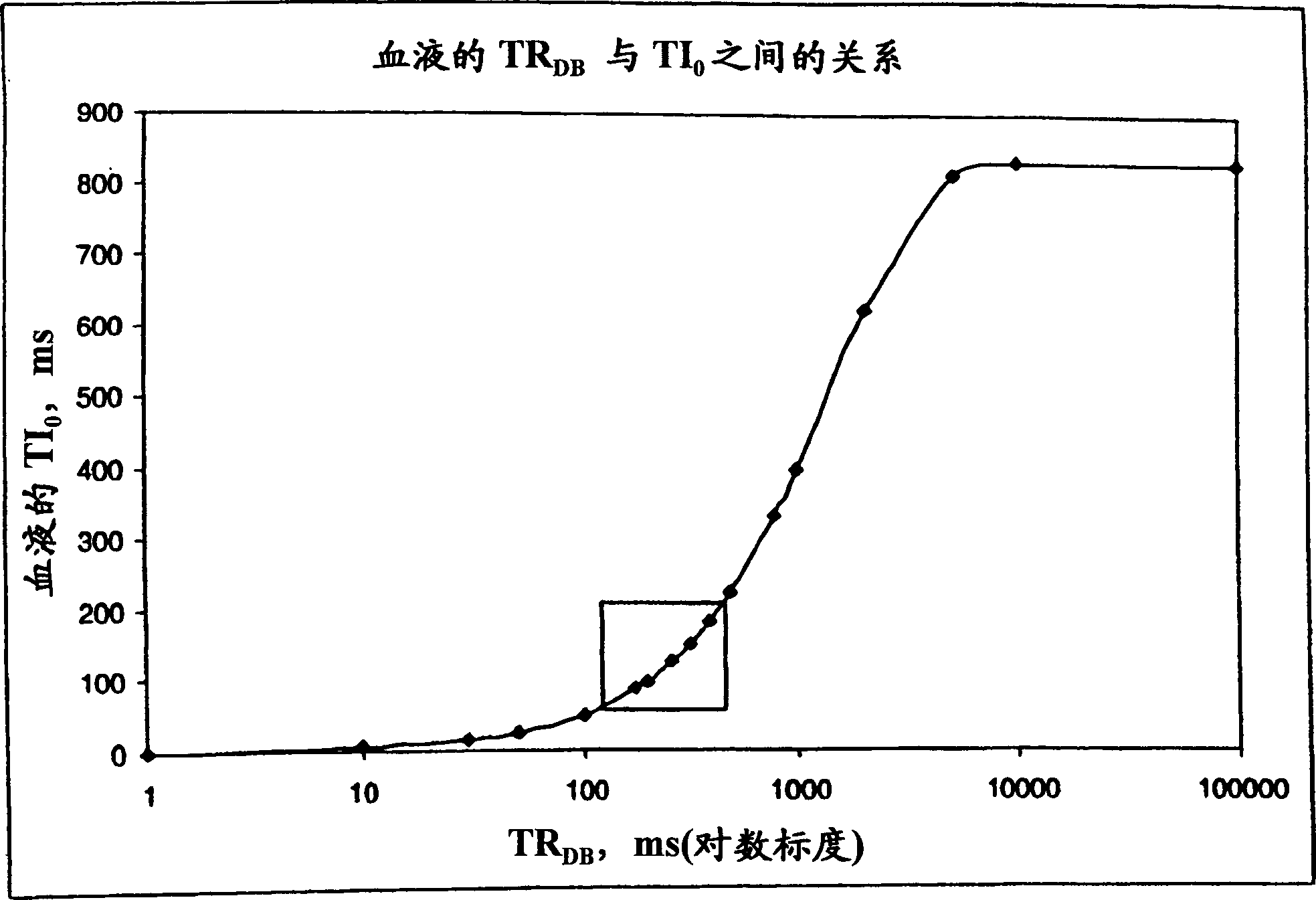
DIR imaging of blood vessels by administering a series of DIR preparation pulse modules at a repetition interval short enough that at least two DIR preparation pulse modules generally occur within each RR interval, and by acquiring image data for a plurality of slices following each DIR module.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
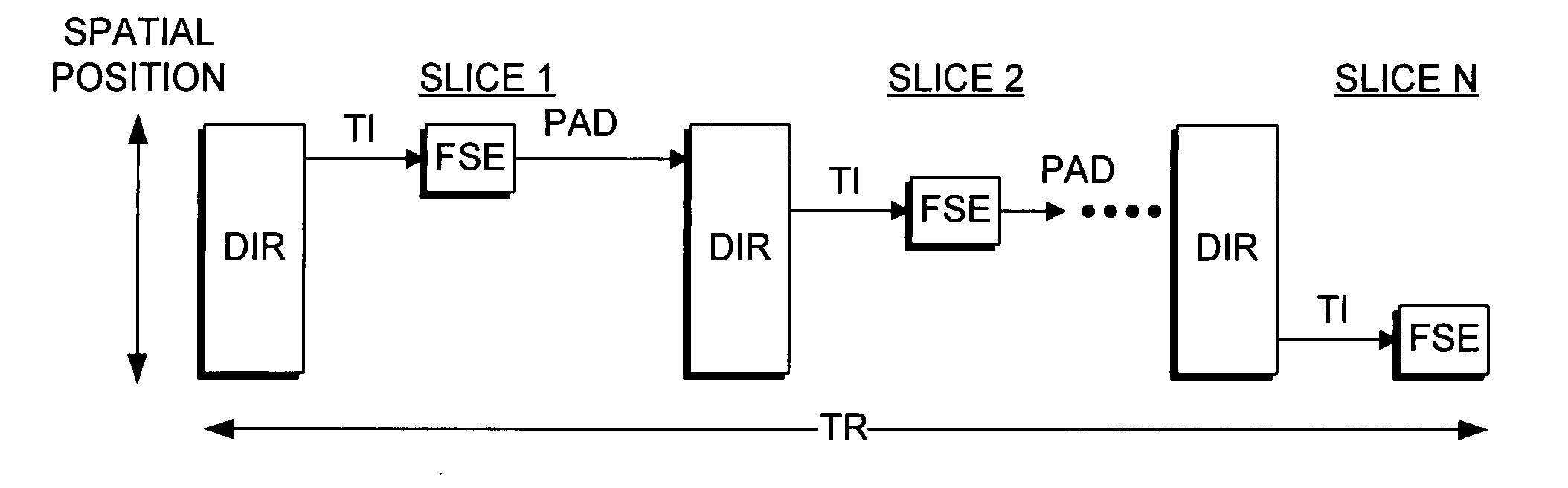
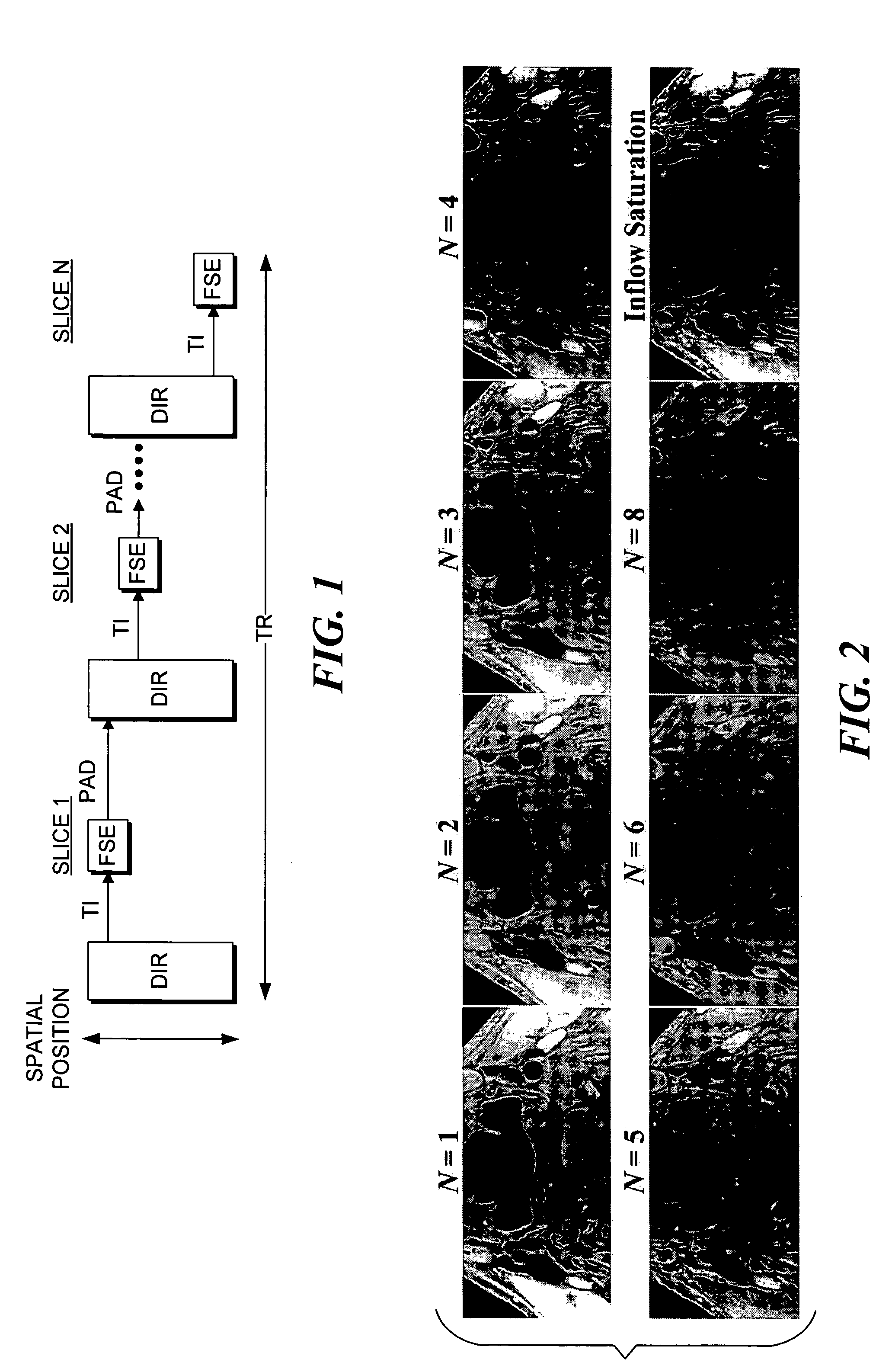
Multi-slice double inversion-recovery black-blood imaging with simultaneous slice re-inversion
ActiveUS7315756B2Enabling visual evaluationClearly visibleDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodMulti slice
A multi-slice double inversion recovery (DIR) pulse sequence with read out of a signal for imaging successive slices implemented on a magnetic resonance image scanner. In the method, when the DIR pulse sequence is applied before imaging each slice, a slab-selective inversion re-inverts the entire slab that includes all of the slices. All slices are imaged within a predefined repetition time (TR). The number, N, of slices acquired per TR controls the inversion time to execute the read out of the signal for imaging each slice at a zero-crossing point of blood. In a test, multi-slice DIR images of carotid arteries were obtained with N ranging from 2-8, for four subjects. The results were compared with those for both standard single-slice DIR, and inflow saturation techniques. Multi-slice DIR with N=2-6 provided blood flow suppression in carotid arteries similar to that of single-slice DIR, and significantly better than inflow saturation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Rapid multislice black blood double-inversion recovery technique for blood vessel imaging
InactiveCN1575748ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBlack bloodInversion recovery
DIR imaging of blood vessels by administering a series of DIR preparation pulse modules at a repetition interval short enough that at least two DIR preparation pulse modules generally occur within each RR interval, and by acquiring image data for a plurality of slices following each DIR module.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Magnetic resonance imaging needing a long waiting time between pre-pulses and imaging pulse train
InactiveUS7623901B2Improve image qualityReduce artifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSystole
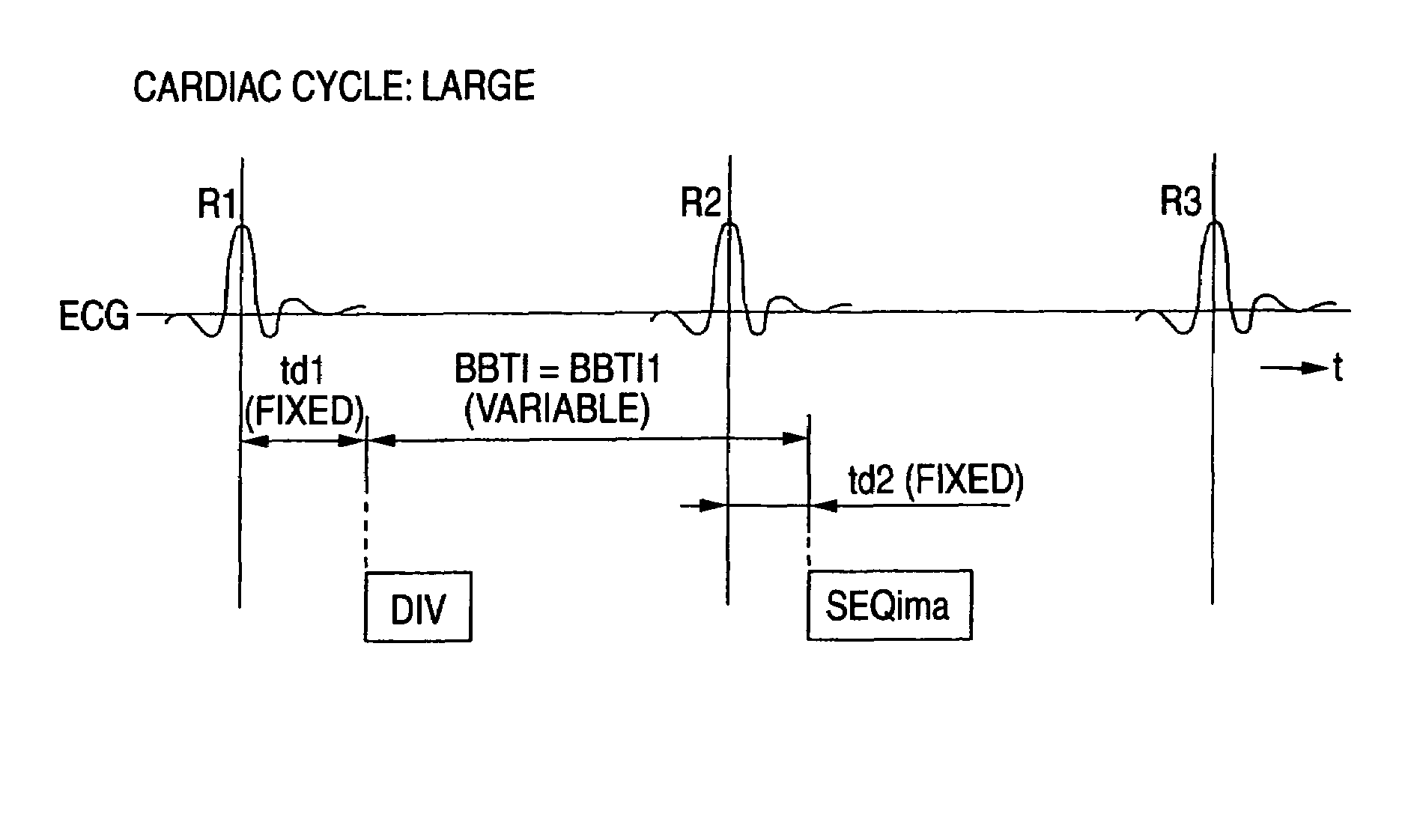
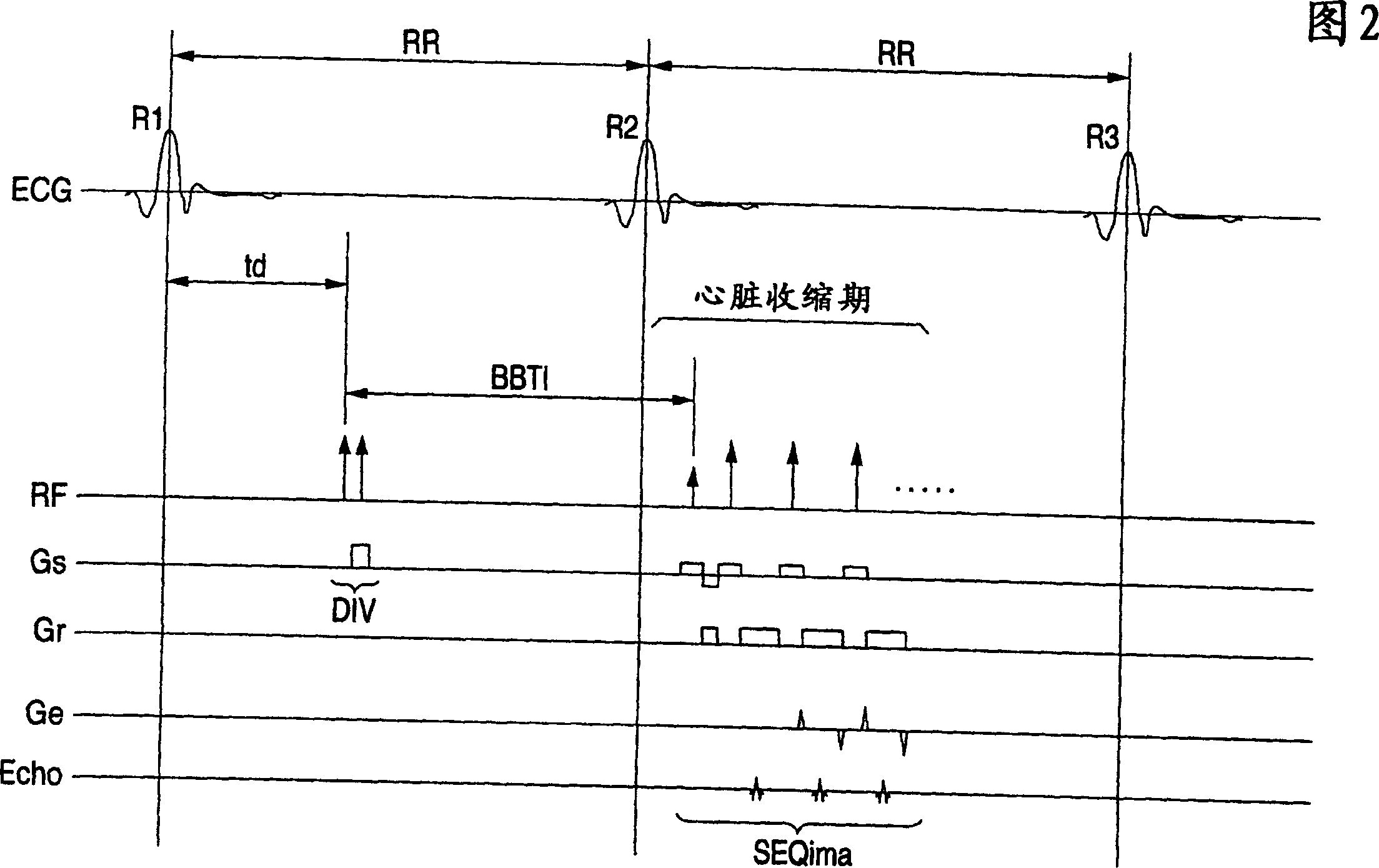
In the black blood method using a double inversion pulse, images in the systole of the cardiac cycle can be captured in a reliable manner even in the presence of a cycle-to-cycle variance in the heart beat cycle. A pulse sequence of the black blood method composed of a double inversion pulse DIV and an imaging pulse train SEQima is used. This sequence is applied in sync with an ECG signal of a subject to be imaged, and magnetic resonance imaging is thereby performed. The double inversion DIV is applied in sync with an R-wave:R1 appearing on the ECG signal at a given timing, with a first delay time td1 (fixed value), and the imaging pulse train SEQima is applied in sync with the following R-wave:R2 with a second delay time td2 (fixed value: set in accordance with the systole). A variance of the cardiac cycle is absorbed in an inversion time BBTI.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance machine requiring long waiting time between pre-pulses and imaging pulse train
InactiveCN1543326AReliable captureImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalBlack blood
In the black blood method using a double inversion pulse, images in the systole of the cardiac cycle can be captured in a reliable manner even in the presence of a cycle-to-cycle variance in the heart beat cycle. A pulse sequence of the black blood method composed of a double inversion pulse DIV and an imaging pulse train SEQima is used. This sequence is applied in sync with an ECG signal of a subject to be imaged, and magnetic resonance imaging is thereby performed. The double inversion DIV is applied in sync with an R-wave:R1 appearing on the ECG signal at a given timing, with a first delay time td1 (fixed value), and the imaging pulse train SEQima is applied in sync with the following R-wave:R2 with a second delay time td2 (fixed value: set in accordance with the systole). A variance of the cardiac cycle is absorbed in an inversion time BBTI.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging system and method
InactiveUS20060074291A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringBlack bloodInversion recovery
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system using a double inversion recovery (DIR) imaging pulse sequence for acquiring black-blood images for obtaining a first level of nulling of a blood signal from acquired imaging slices is provided. The MRI system comprises an image processor configured changing a respective time order of the imaging slices at a selected point or points during the pulse sequence to obtain a second level of nulling of the residual blood signal from the imaging slices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
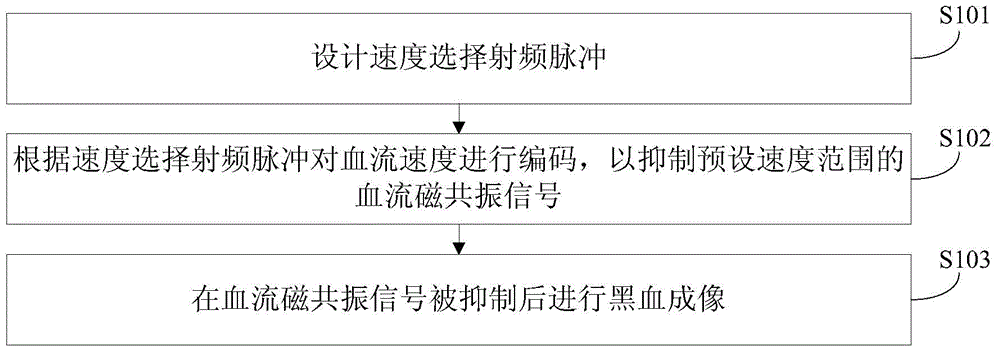
Speed selection radiofrequency pulse-based magnetic resonance black blood imaging method and system
InactiveCN104305959AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh Contrast to Noise RatioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodImaging quality
The invention discloses a speed selection radiofrequency pulse-based magnetic resonance black blood imaging method, comprising the following steps of designing a speed selection radiofrequency pulse; according to the speed selection radiofrequency pulse, coding a blood flow speed to inhibit a blood flow magnetic resonance signal in a preset speed range; performing black blood imaging after the blood flow magnetic resonance signal is inhibited. According to the black blood imaging method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the blood flow speed is coded by designing the speed selection radiofrequency pulse and according to the speed selection radiofrequency pulse, so the blood flow magnetic resonance signal in the specific speed range is inhibited, the black blood imaging is realized, the blood flow magnetic resonance signal is effectively inhibited, the imaging quality is improved, and the magnetic resonance signal of a static tissue is prevented from being influenced by the blood flow inhibition radiofrequency pulse. The invention also discloses a speed selection radiofrequency pulse-based magnetic resonance black blood imaging system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
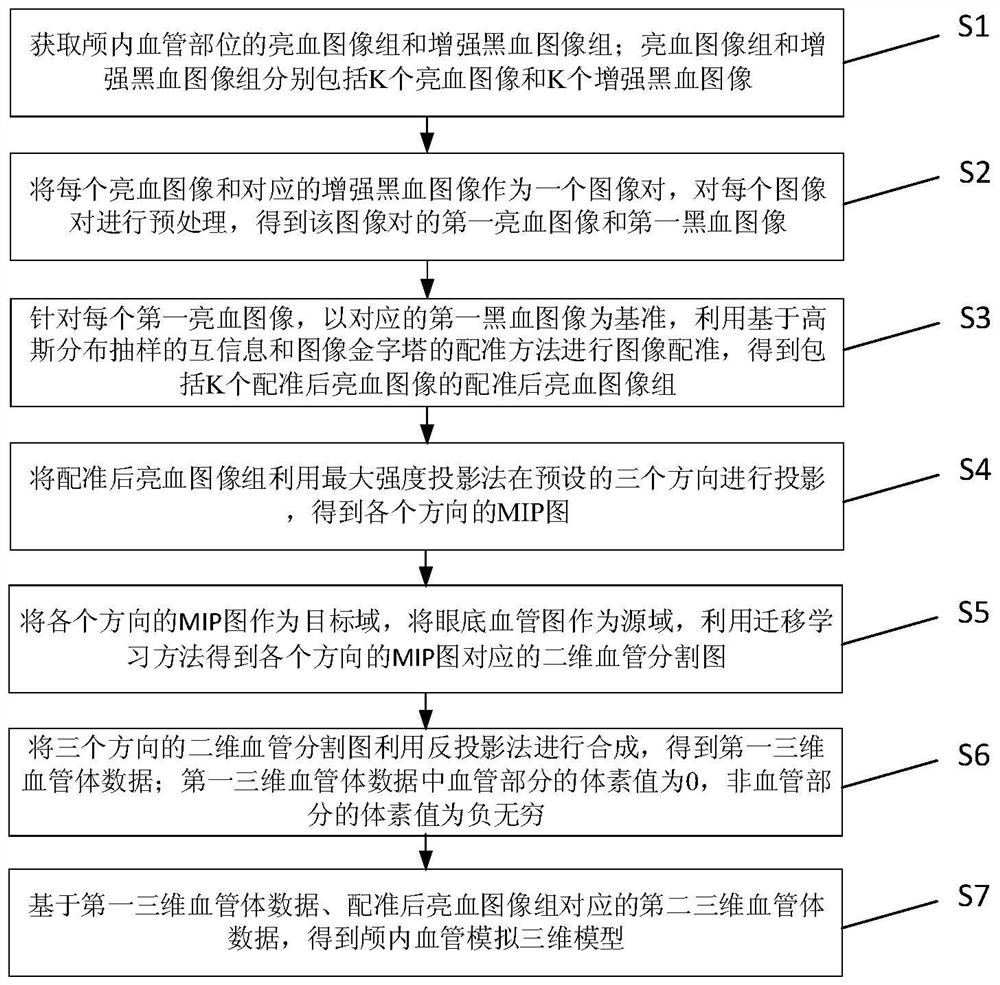
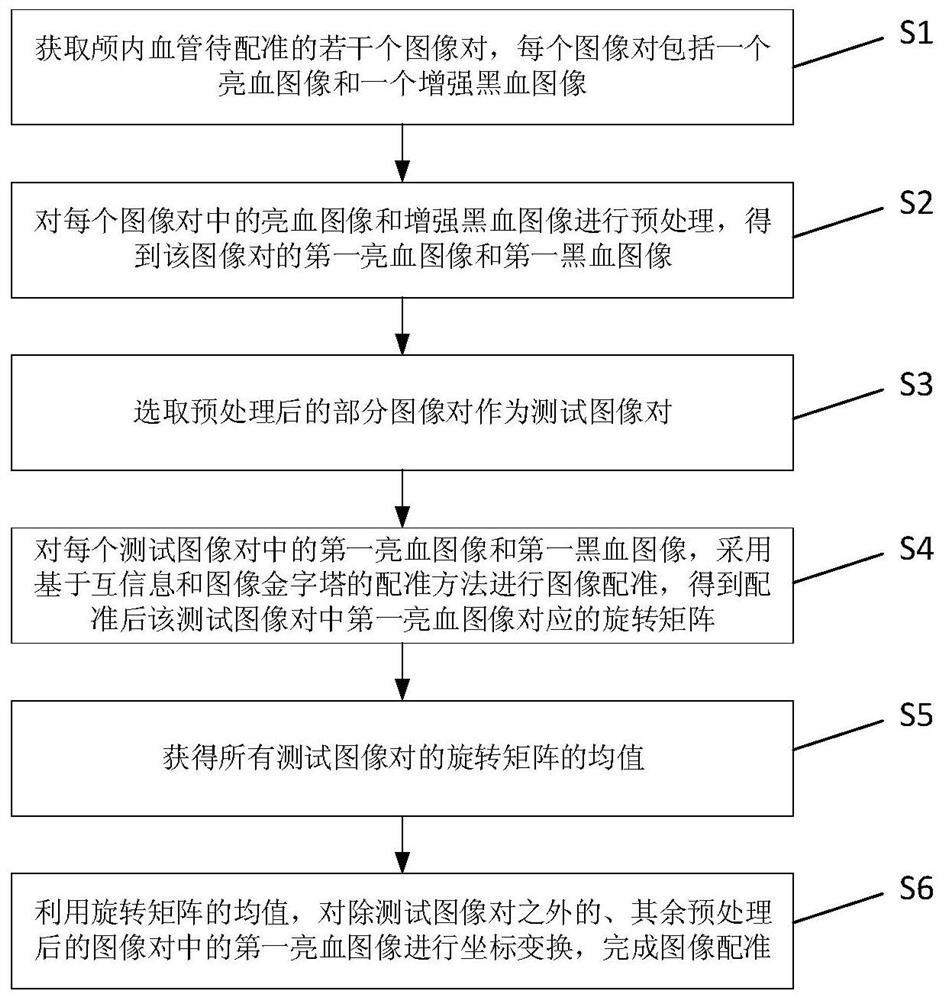
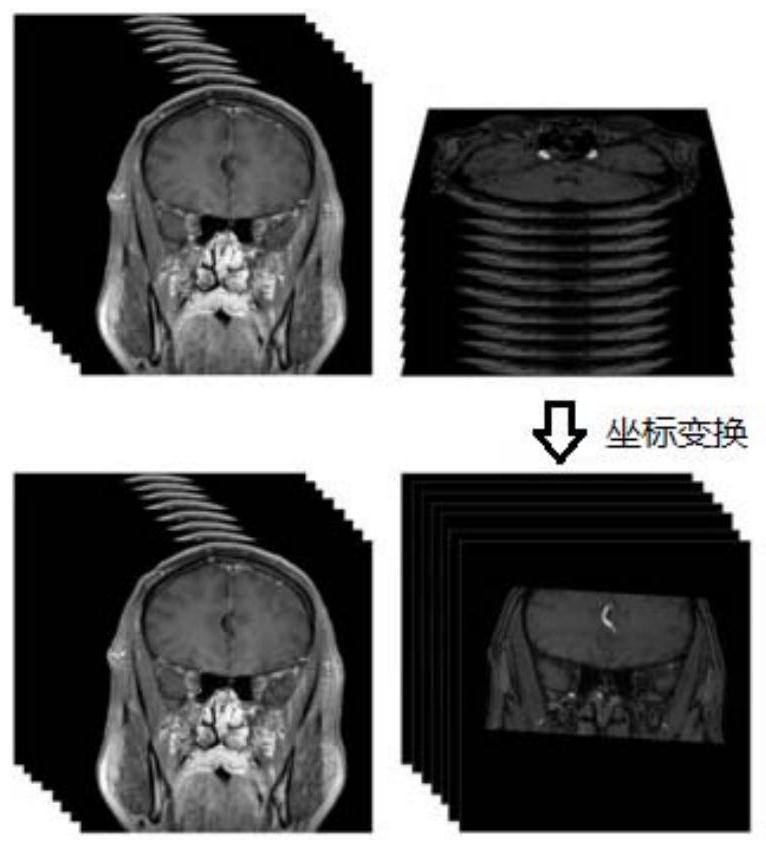
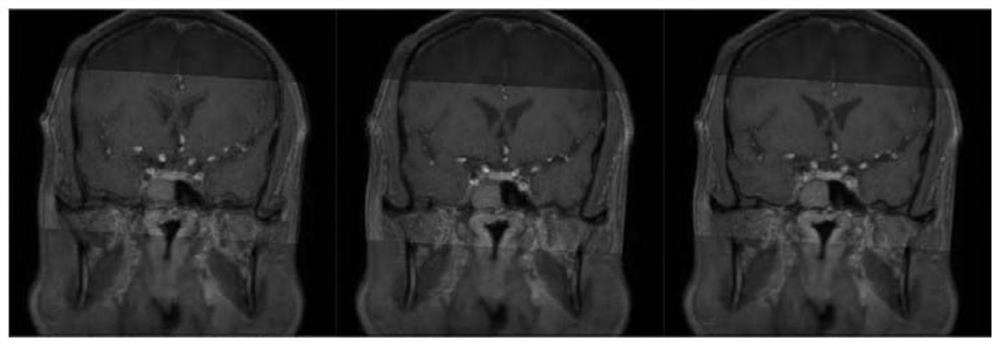
Method for establishing intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional stenosis model based on transfer learning
InactiveCN112598619APrecise Segmentation EffectPrecise positioningImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionVascular bodyBlack blood
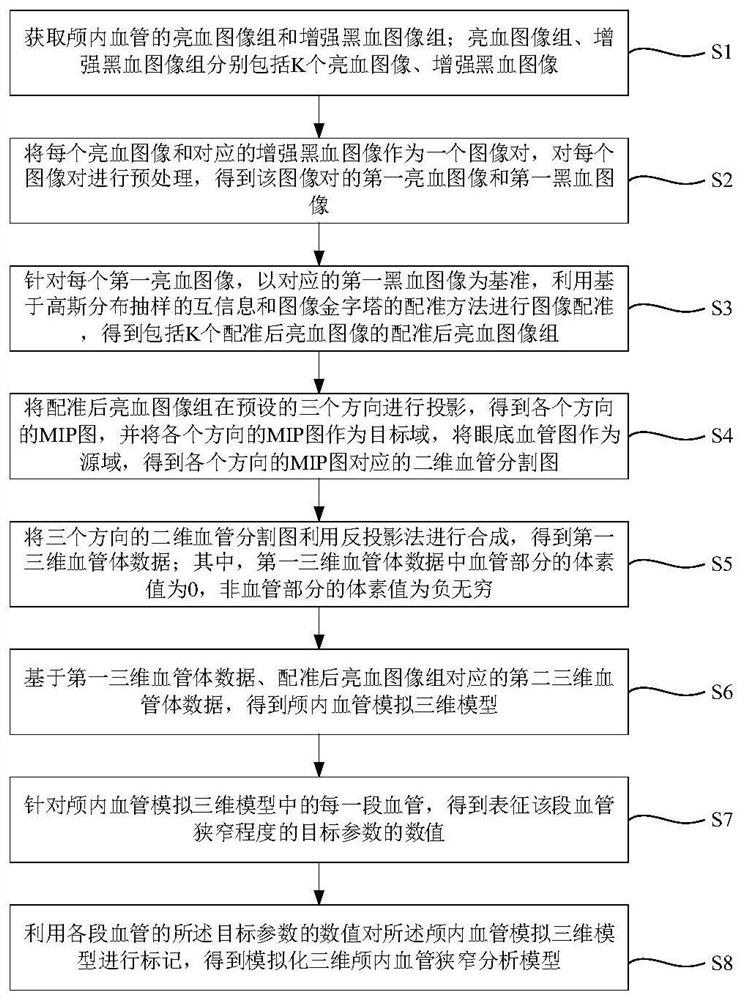
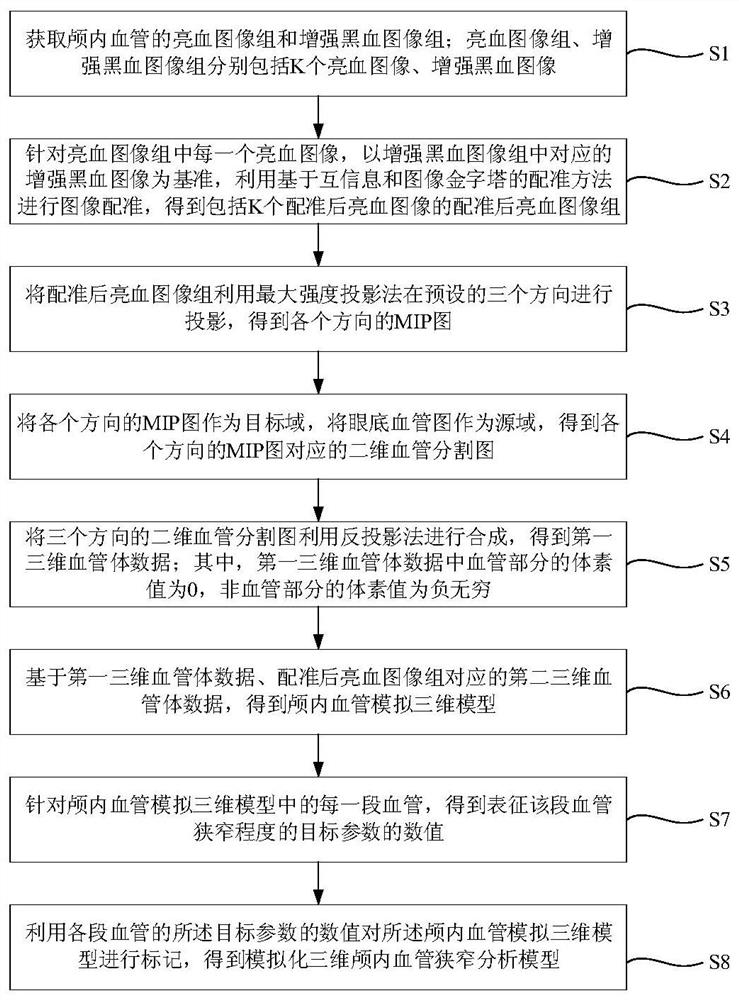
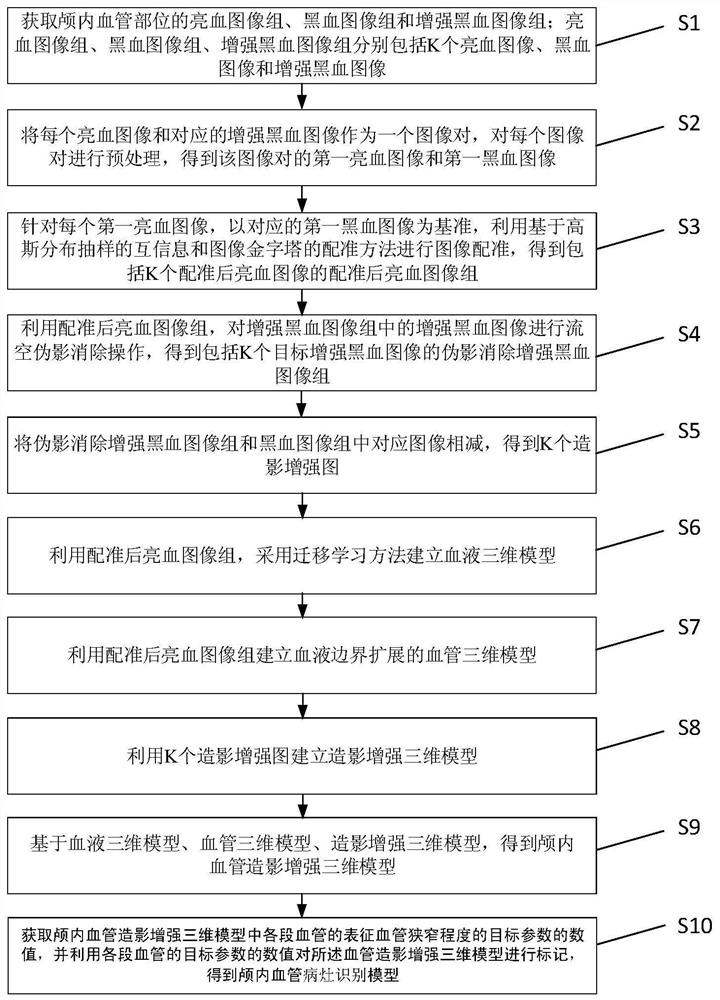
The invention discloses a method for establishing an intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional stenosis model based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial vessel; preprocessing each bright blood image and the corresponding enhanced black blood image to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; performing image registration by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid; groupingthe registered bright blood images to obtain MIP images in all directions; obtaining a two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image based on the MIP image and the fundus blood vessel image; performing back projection synthesis on the two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image to obtain first three-dimensional blood vessel body data, and obtaining an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the second three-dimensional blood vessel body data; and for each section of blood vessel in the model, obtaining a numerical value of a target parameter representingthe stenosis degree of the section of blood vessel, and marking the intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the numerical value of the target parameter to obtain a simulated three-dimensional intracranial blood vessel stenosis analysis model.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
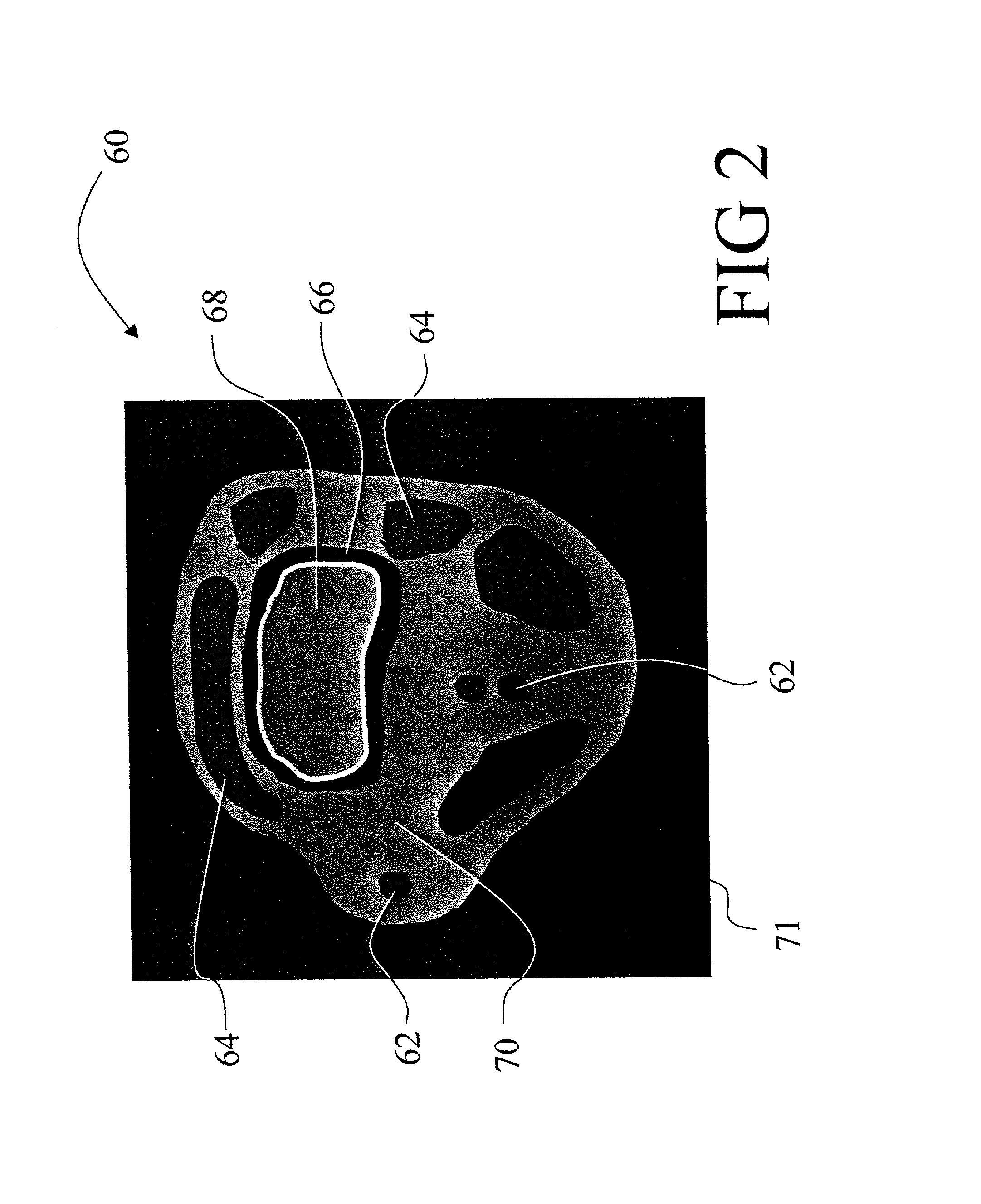
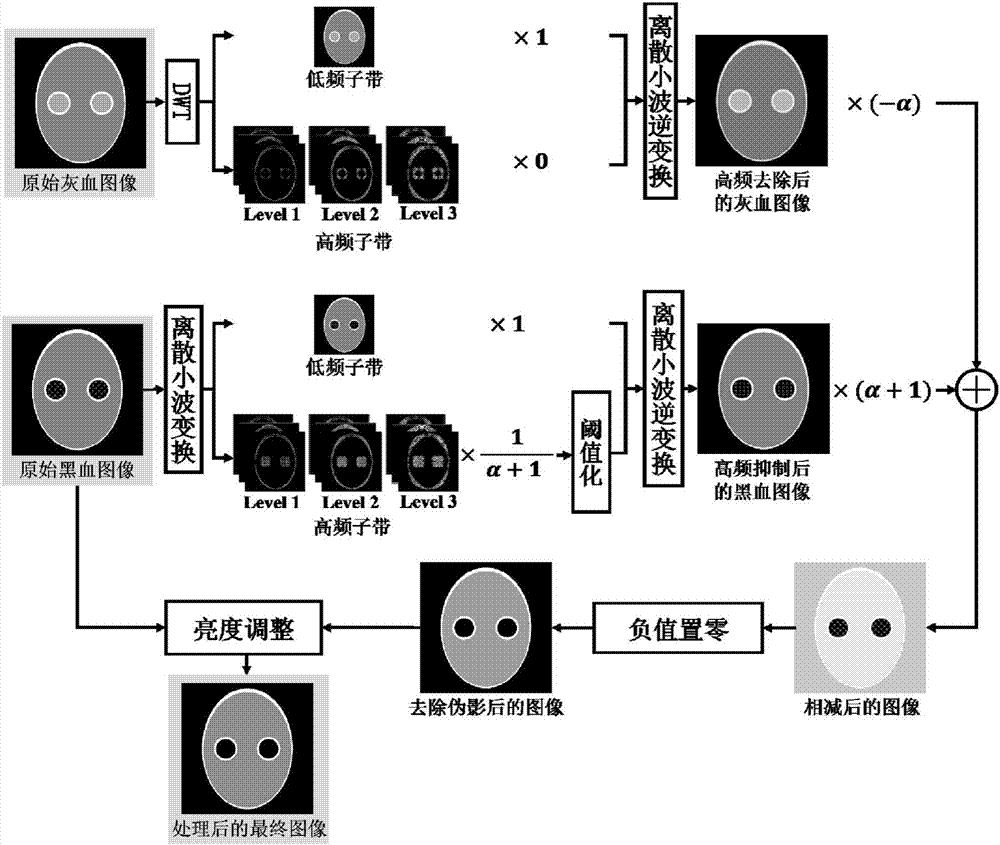
Blood flow artifact removing method for carotid magnetic resonance blood vessel wall imaging
ActiveCN107154025ARemove completelyReduce signal to noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisBlack bloodLightness
The invention discloses a blood flow artifact removing method for carotid magnetic resonance blood vessel wall imaging. The method comprises steps of firstly, black blood and gray blood images are obtained by using the black-gray blood double contrast imaging technique, and then the images are pretreated based on the two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform to suppress the high frequency subband; different pre-emphases are adopted to process the black blood and gray blood images, and the black blood image after the pre-emphasis is subtracted from the black blood image after the pre-emphasis, so as to obtain a subtracted image; and the brightness of the subtracted image is adjusted so that the average brightness of the subtracted image is equal to the average brightness of the initial black blood image, and the blood vessel wall magnetic resonance image of which the blood flow artifact is removed is obtained. The method can reduce the signal-to-noise ratio of the lumen, improve the wall-to-cavity differential noise ratio, and more completely remove the blood flow artifacts in the original black blood imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
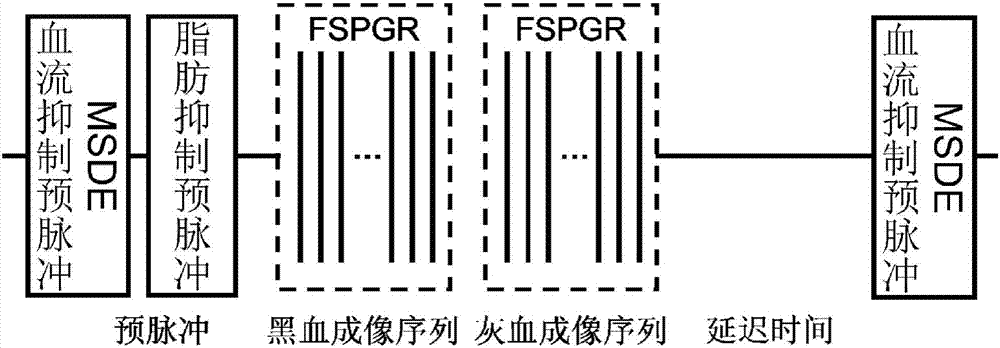
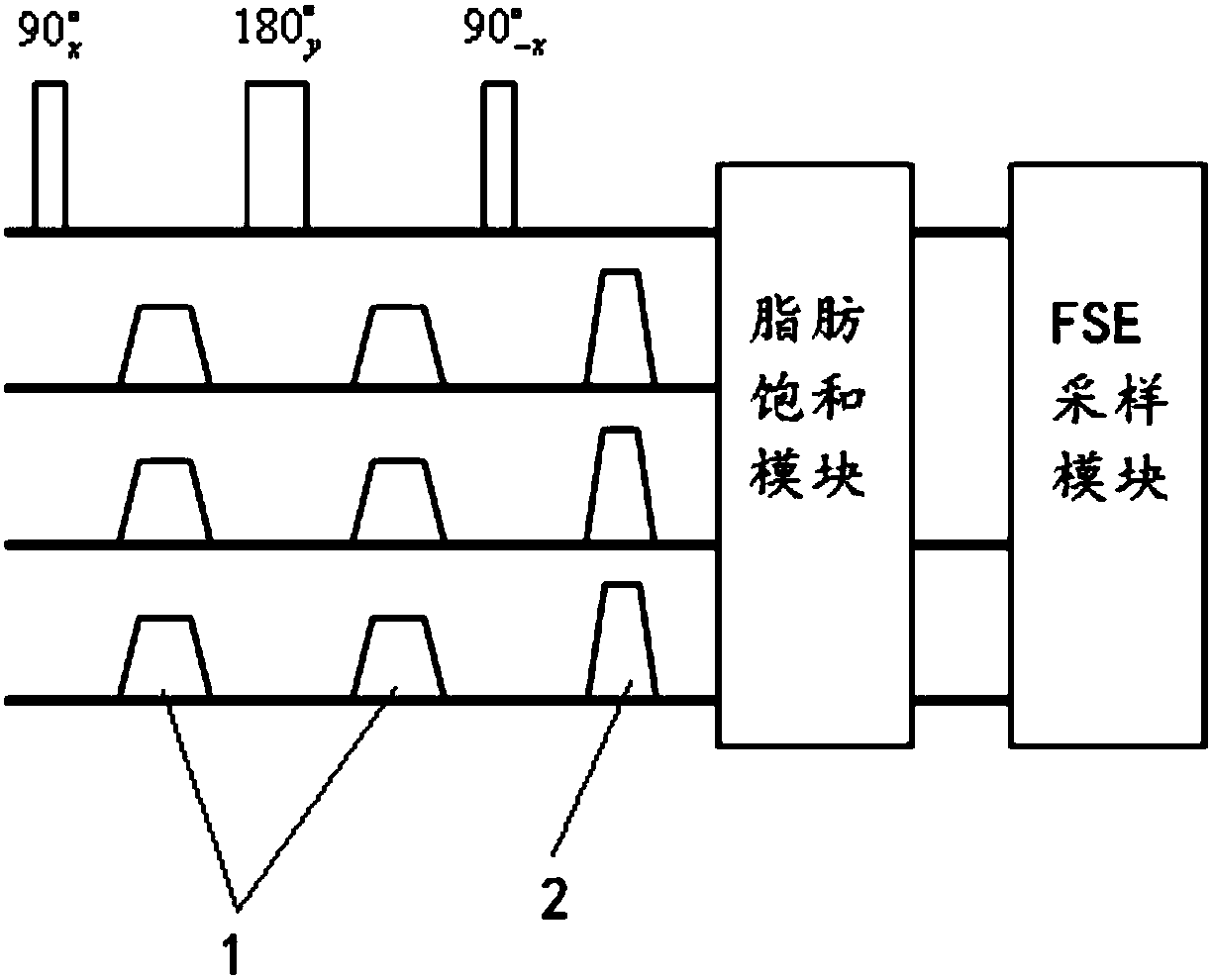
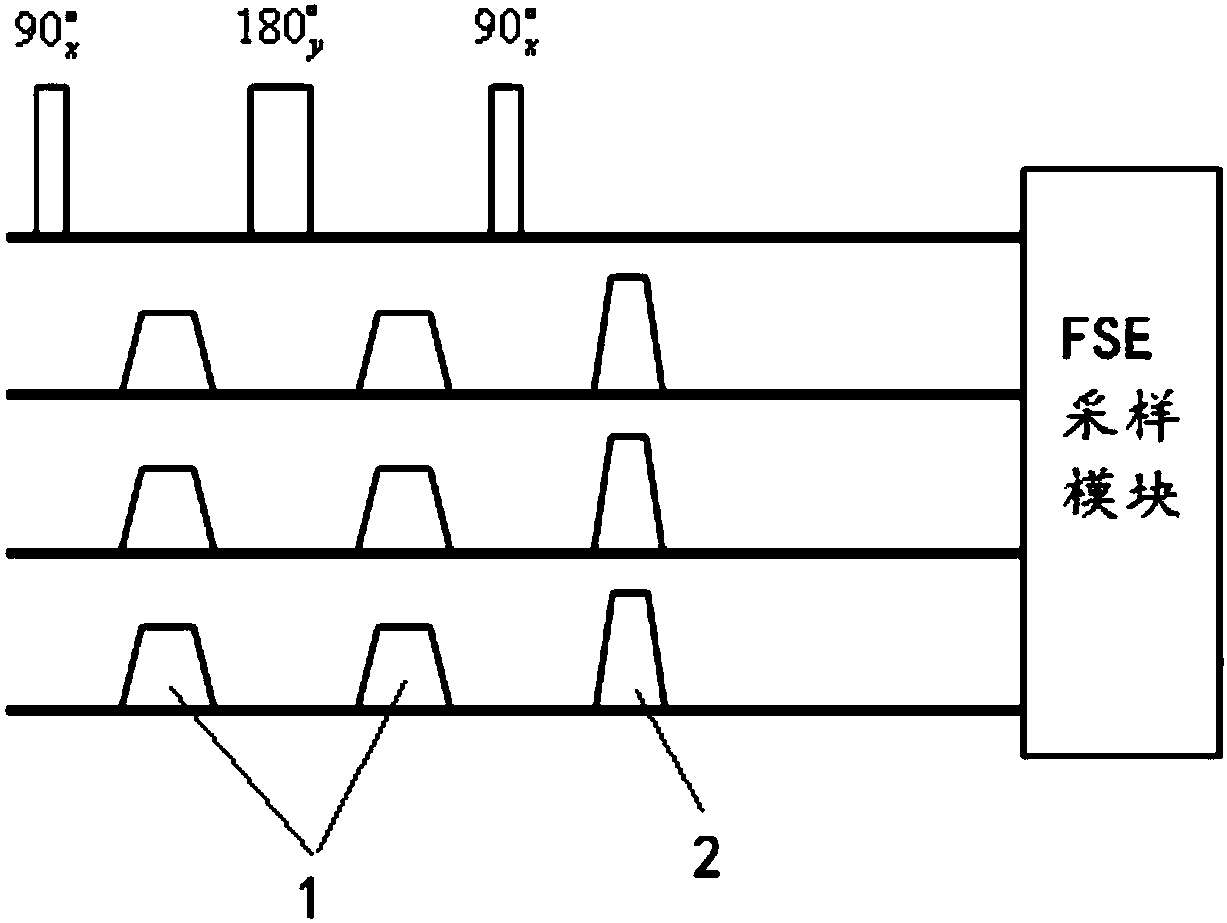
Fat-suppressed black blood magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveCN108363026ASuppression achievedLower specific absorption rateDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBlack bloodPulse sequence
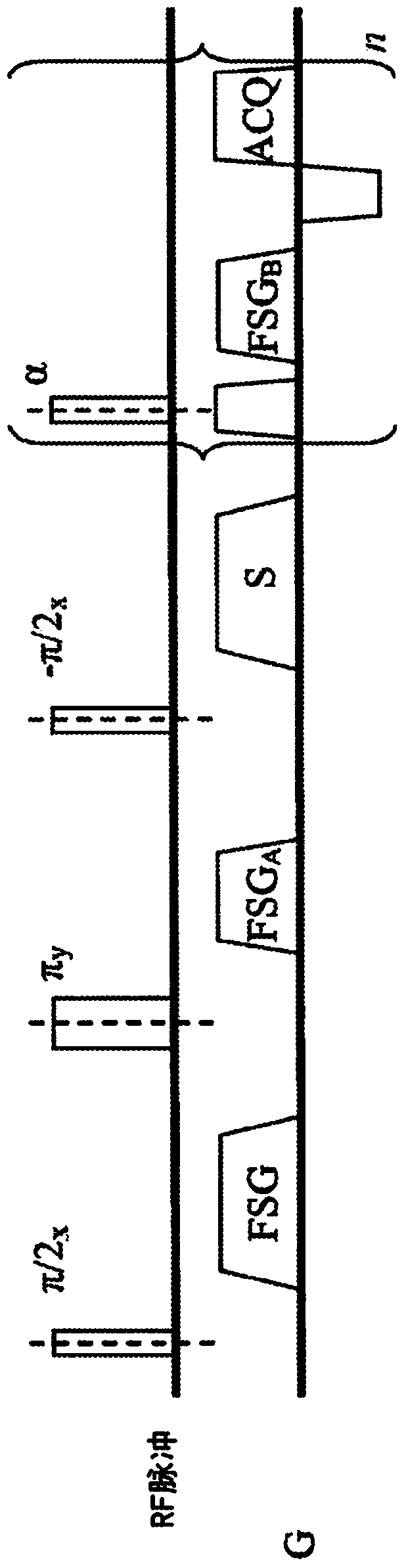
The present invention discloses a fat-suppressed black blood magnetic resonance imaging method. The method comprises the steps of: emitting excitation signals comprising a 90<o>x, 180<o>y and 90<o>x radio-frequency pulse impulse sequence, two same motion sensitivity gradient magnetic fields and a noise filtering gradient magnetic field, wherein one of the motion sensitivity gradient magnetic fields is loaded between the first 90<o>x pulse and the 180<o>y pulse, the other one of the motion sensitivity gradient magnetic fields is loaded between the 180<o>y pulse and the second 90<o>x pulse, thetwo motion sensitivity gradient magnetic fields are symmetrically loaded around the 180<o>y, and the noise filtering gradient magnetic field is loaded behind the 90<o>x, 180<o>y and 90<o>x radio-frequency pulse impulse sequence; setting delay after the 90<o>x, 180<o>y and 90<o>x radio-frequency pulse impulse sequence to a signal zeroing point of a fat tissue; and collecting electromagnetic wave signals. The fat-suppressed black blood magnetic resonance imaging method can reduce the sensibility for magnetic field bump so as to improve the fat suppressing effect and reduce the specific absorption rate of an MSDE (Motion-Sensitized Driven-Equilibrium) pulse sequence.
Owner:ALLTECH MEDICAL SYST
Blood vessel center line determination method and device, computer equipment and readable storage medium
PendingCN114299055AQuick and accurate determinationImprove accuracyImage analysisImage extractionBlack blood
The invention relates to a blood vessel center line determination method and device, computer equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a black blood medical image and a bright blood medical image; performing blood vessel identification processing on the black blood medical image and the bright blood medical image to obtain a black blood vessel identification image and a bright blood vessel identification image, and performing registration and fusion processing on the black blood vessel identification image and the bright blood vessel identification image to obtain a fused blood vessel identification image; and extracting the segment center line of each segment of blood vessel in the fused blood vessel identification image, and determining the center line of the blood vessel in the black blood medical image or the bright blood medical image according to the segment center line of each segment of blood vessel. The blood vessel center line determination method provided by the invention can improve the accuracy of extracting the blood vessel center line.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
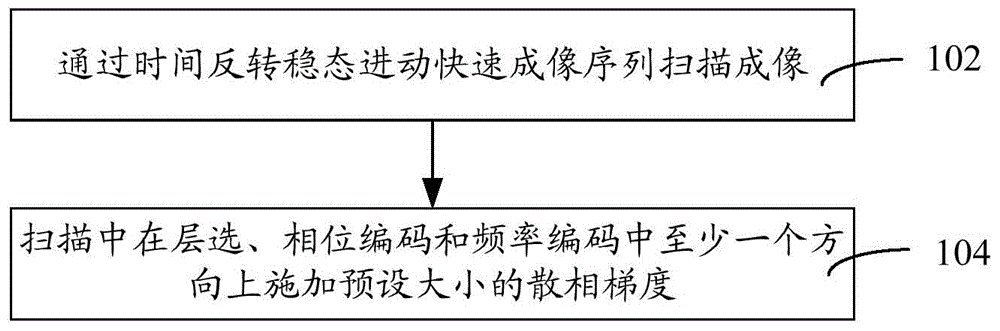
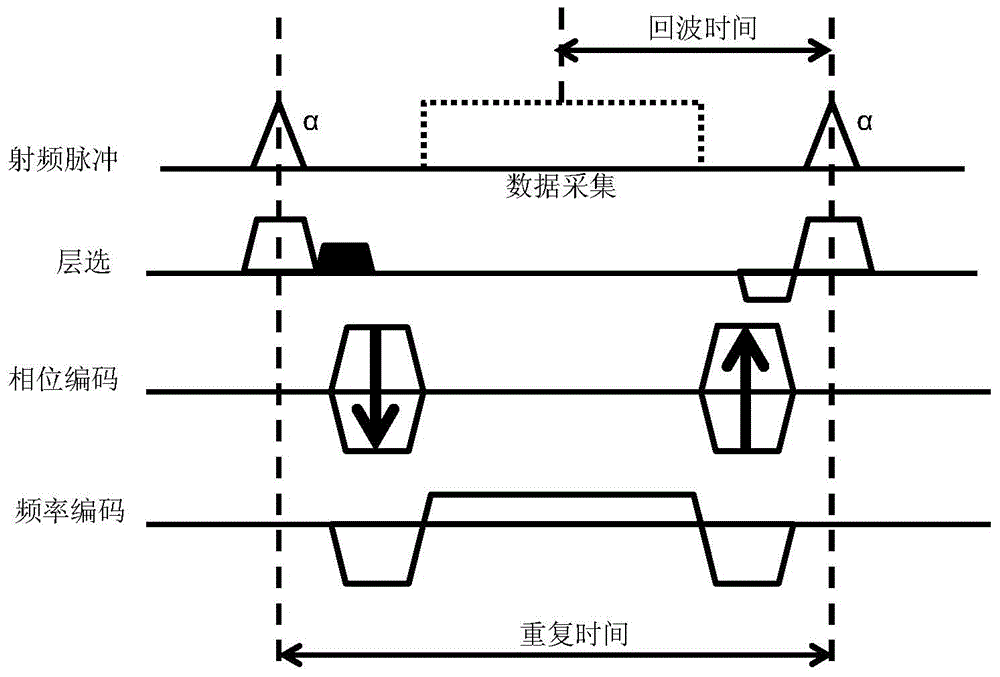
Method and system for controlling black blood in time-reversal steady state free precession quick imaging sequence
ActiveCN104644172ASignal does not affectEnhanced inhibitory effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodPhase gradient
The invention relates to method and system for controlling black blood in a time-reversal steady state free precession quick imaging sequence. The method comprises the steps of scanning and imaging through the time-reversal steady state free precession quick imaging sequence; applying dispersed phase gradient with preset size in at least one of the layer selection direction, phase encoding layer and frequency encoding layer during scanning. According to the method and system for controlling black blood in the time-reversal steady state free precession quick imaging sequence, the dispersed phase gradient is applied in at least one of the layer selection direction, phase encoding layer and frequency encoding layer during scanning, so that the blood signal inhibition effect in an area in which blood flows slowly can be improved, and as a result, the quality of the imaged image can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
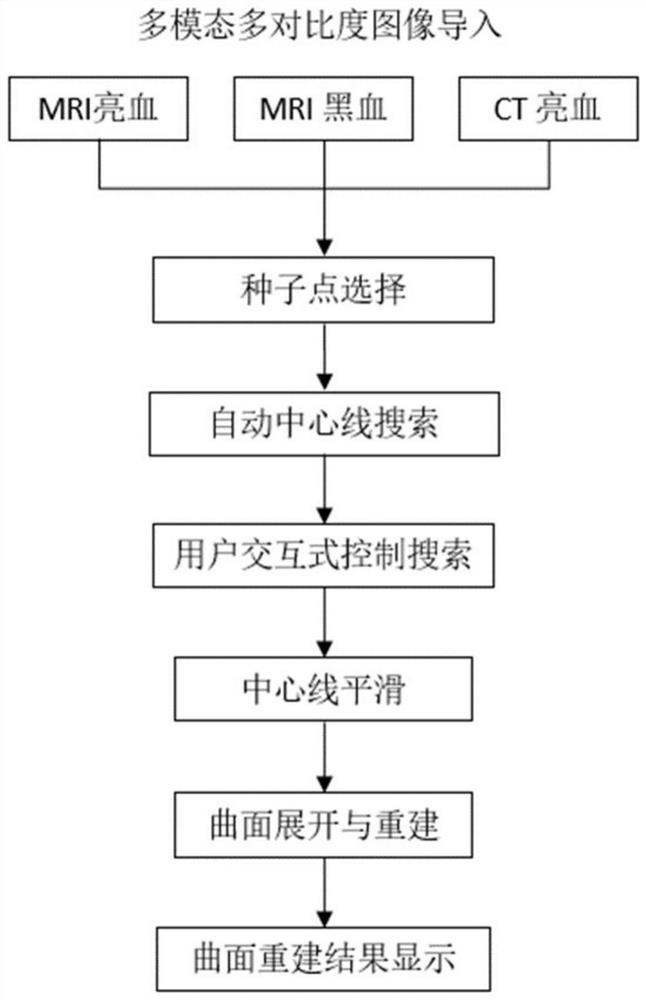
Fast curved surface reconstruction method for multi-modal multi-contrast medical image and storage medium
PendingCN113538618AProcessing speedReduce Resampling DistortionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBlack bloodRadiology
The invention discloses a fast curved surface reconstruction method for a multi-modal multi-contrast medical image and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: importing a multi-modal multi-contrast image; selecting two adjacent points as initial seed points for the target blood vessel segment in the image; performing automatic center line search; in the searching process, taking the first initial seed point as a starting point, controlling the searching direction through the second initial seed point, and conducting point-by-point searching on the center line of the target blood vessel segment; smoothening the center line; scanning the smoothed center line along a user-defined direction to obtain an original curved surface required by curved surface reconstruction; and unfolding the original curved surface to obtain a curved surface reconstruction result. According to the method, the center lines of multiple contrast images such as a CT blood vessel image, an MRI bright blood image and an MRI black blood image can be rapidly extracted. In addition, according to the method, a new data structure is adopted to display a two-dimensional plane image, and resampling distortion of a curved surface image is avoided.
Owner:脑玺(苏州)智能科技有限公司
Black blood mri using a stimulated echo pulse sequence with flow sensitization gradients
ActiveCN103502832AEffective Black Blood ImagingConvenient black blood imagingMeasurements using magnetic resonanceBlack bloodStimulated echo
A black blood magnetic resonance imaging sequence is performed using a magnetic resonance scanner. The sequence includes: applying a first flow sensitization gradient; applying a spoiler gradient after applying the first flow sensitization gradient; applying a second flow sensitization gradient after applying the spoiler gradient wherein the second flow sensitization gradient has area equal to the first flow sensitization gradient but of opposite polarity; applying a slice-selective radio frequency excitation pulse after applying the spoiler gradient; and performing a magnetic resonance readout after applying the second flow sensitization gradient and after applying the slice selective radio frequency excitation. The readout acquires magnetic resonance imaging data having blood signal suppression in the region excited by the slice-selective radio frequency excitation pulse. The magnetic resonance imaging data is suitably reconstructed to generate a black blood image that may be displayed.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Method for quickly establishing intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning
PendingCN112562058ARealize 3D visualizationImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisVascular bodyBlack blood
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a bright blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial blood vessel part; preprocessing each bright blood image and the corresponding enhanced black blood image to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; performing image registration on the first bright blood image by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid; utilizing a maximum intensity projection method to obtain MIP images in all directions from the registered bright blood image groups; taking the MIP image as atarget domain, taking the fundus blood vessel image as a source domain, and obtaining a two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image by using a transfer learning method; performing back projectionsynthesis on the two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation images in the three directions to obtain first three-dimensional blood vessel body data; and obtaining an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the second three-dimensional blood vessel body data corresponding to the registered bright blood image group. According to the method, the whole state of the intracranial blood vessel can be simply, conveniently, quickly and visually obtained clinically.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
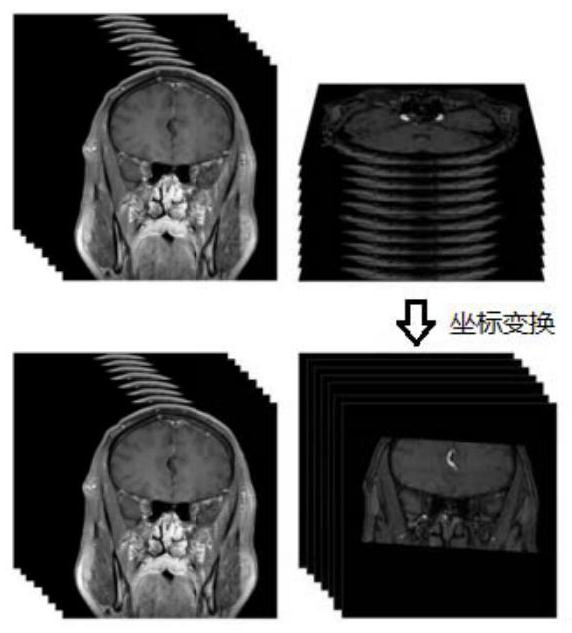
Intracranial blood vessel image fusion method and computer readable storage medium
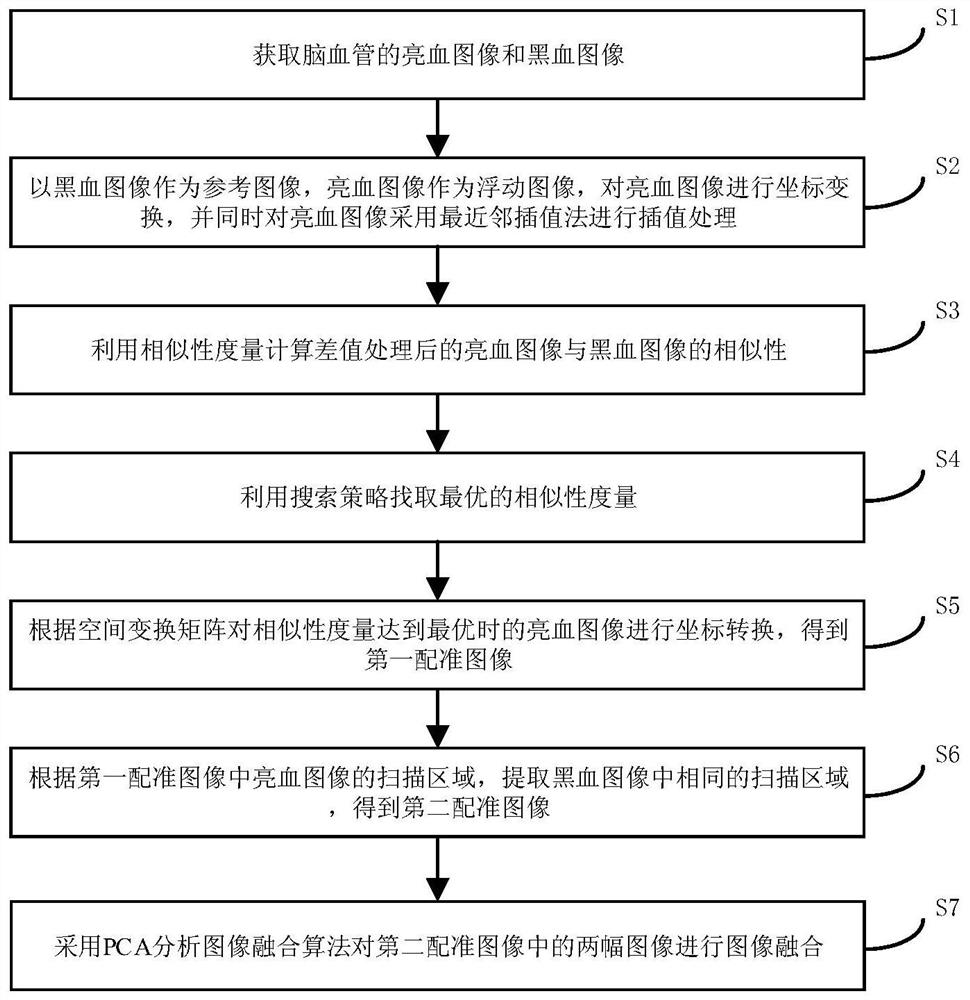
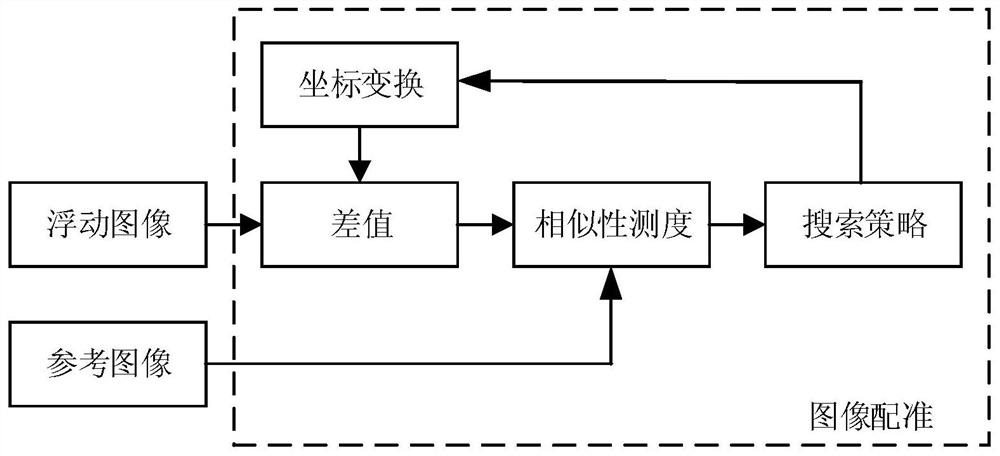
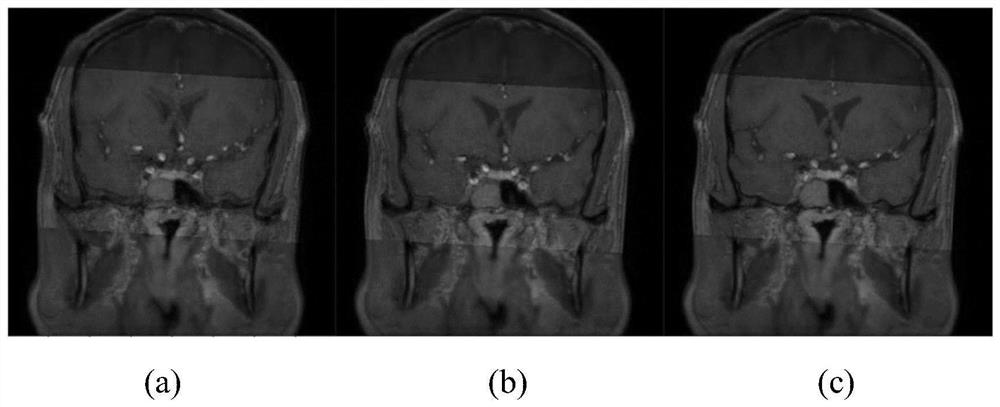
InactiveCN112508869AAccurate intracranial disease diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisBlack bloodImage fusion algorithm
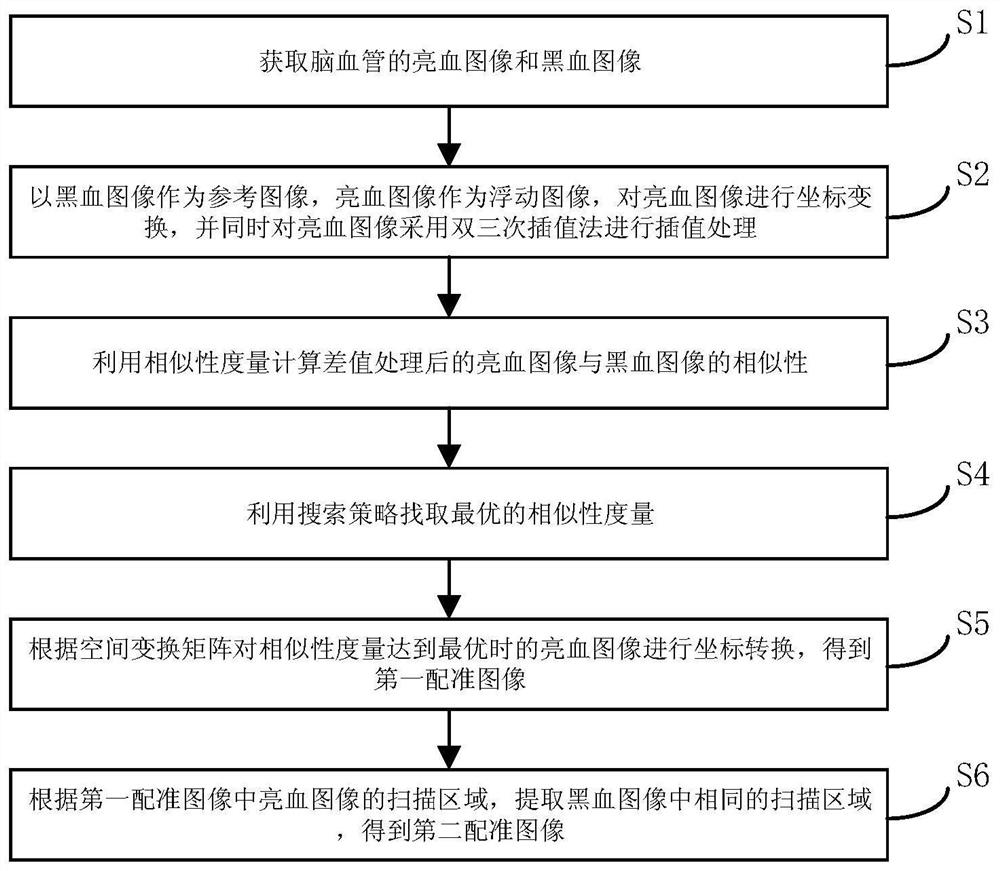
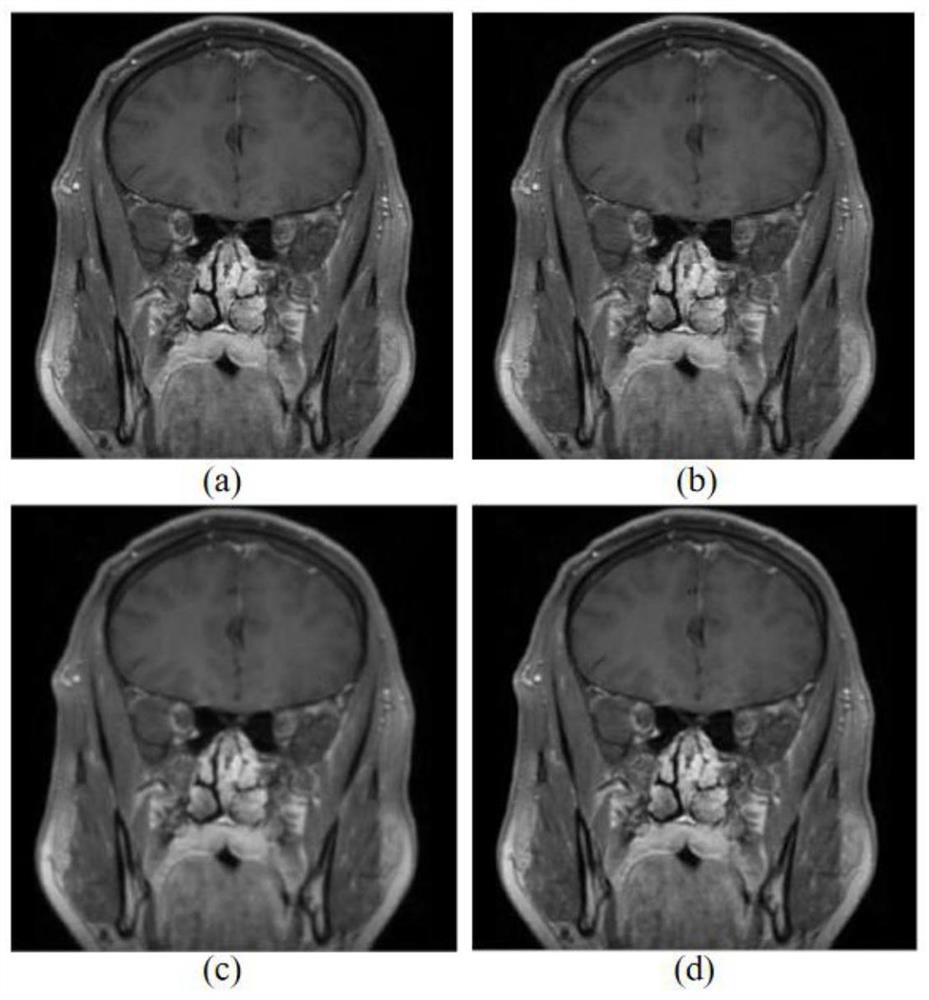
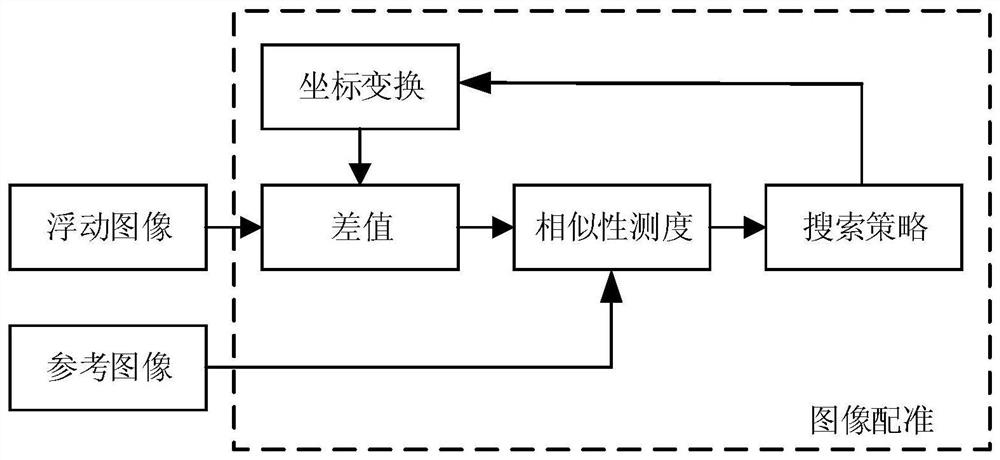
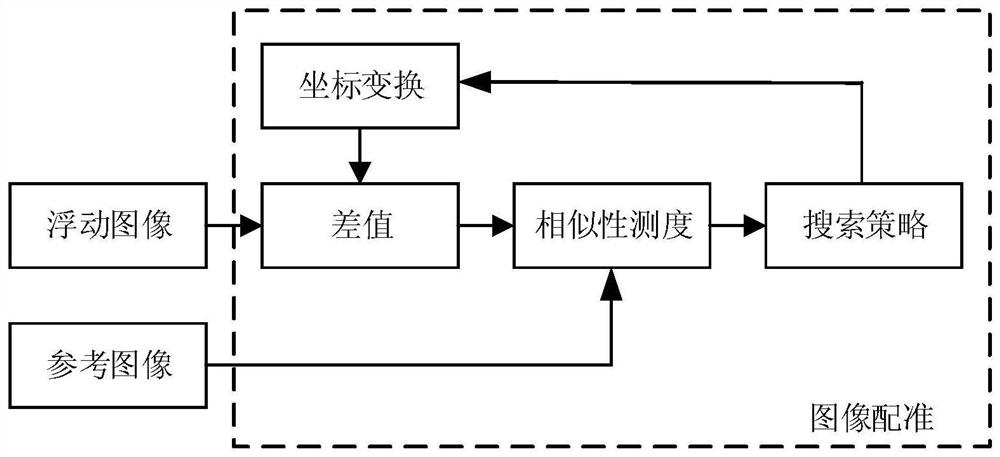
The invention discloses an intracranial blood vessel image fusion method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright blood image and a black blood image of an intracranial blood vessel; taking the black blood image as a reference image and the bright blood image as a floating image, performing coordinate transformation on the bright blood image, and performing interpolation processing on the bright blood image by adopting a nearest neighbor interpolation method; calculating the similarity between the bright blood image and the black blood image after interpolation processingby using similarity measurement; finding the optimal similarity measurement by using a search strategy, and stopping iteration when the similarity measurement is optimal; according to the space transformation matrix, carrying out coordinate transformation on the bright blood image when similarity measurement is optimal, and obtaining a first registration image; extracting the same scanning area inthe black blood image according to the scanning area of the bright blood image in the first registration image to obtain a second registration image; and adopting a PCA analysis image fusion algorithm to perform image fusion on the two images in the second registration image. According to the scheme, a doctor can be assisted in accurate intracranial disease diagnosis.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
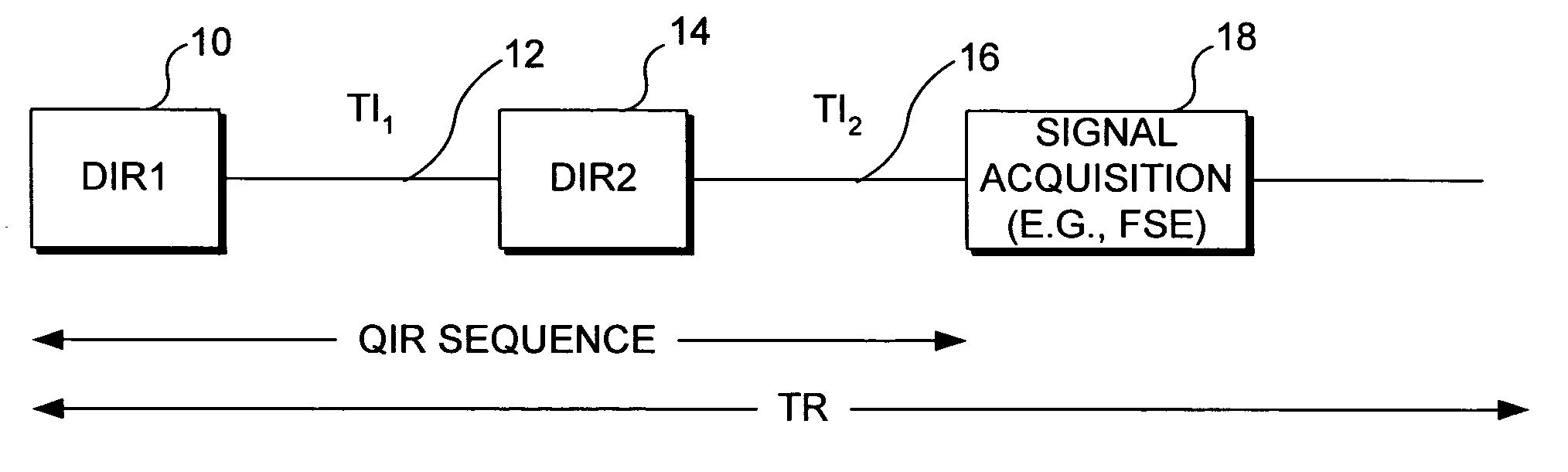
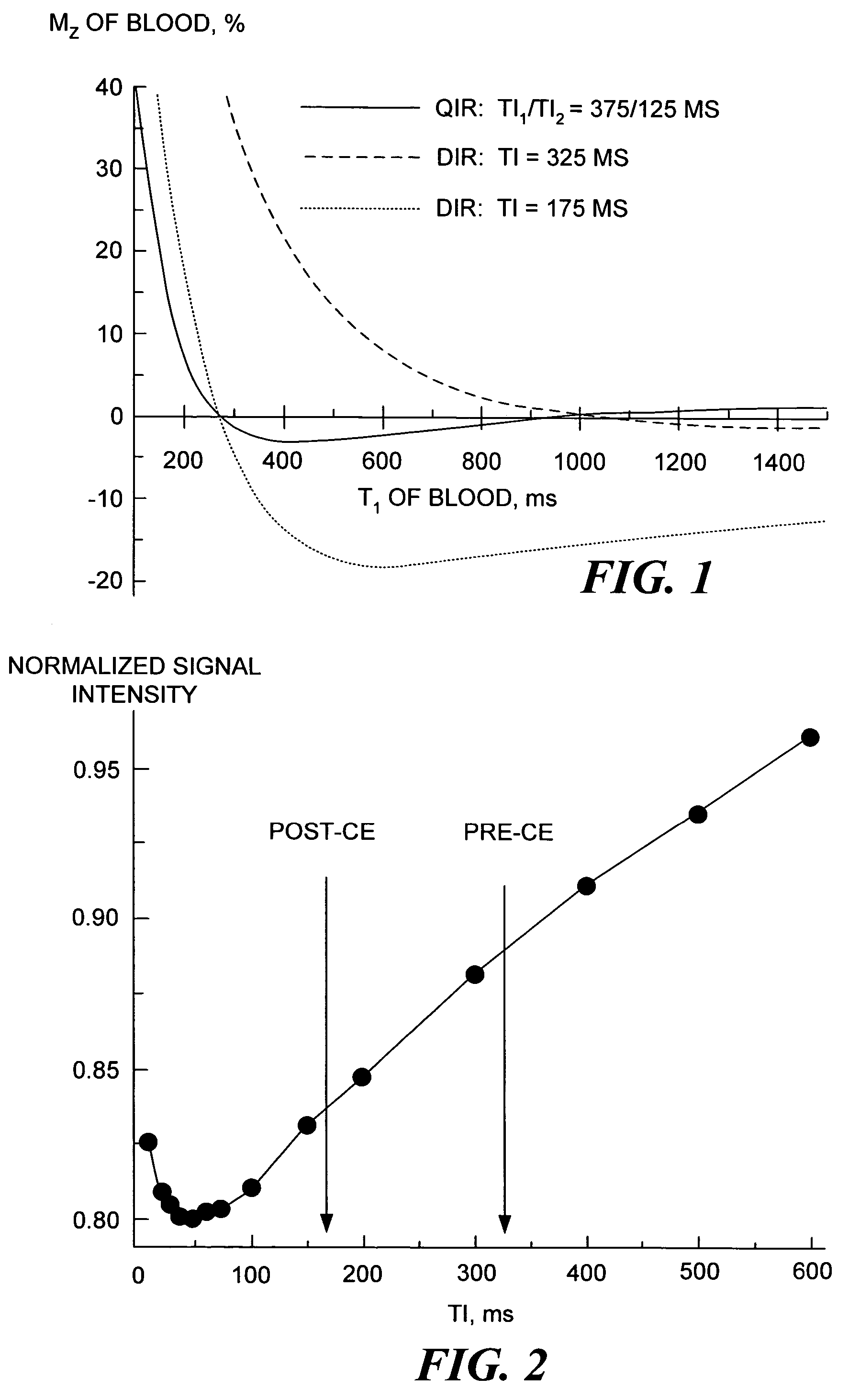
Quadruple inversion recovery for quantitative contrast-enhanced black blood imaging
InactiveUS7715900B2Inhibition is effectiveIncrease contrastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodInversion recovery
A contrast enhancement (CE) agent is infused into blood flowing through a site that is to be imaged with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Two double inversion procedures are carried out, forming a quadruple inversion recovery (QIR) pulse sequence. Each double inversion procedure comprises a non-selective and slice-selective inversion RF pulse. The first double inversion procedure is followed by a first predefined inversion delay period, TI1, and the second procedure by a second predefined inversion delay period, TI2. A black-blood image can thus be produced in which blood appears consistently black and tissues surrounding the blood, such as a vessel wall, heart, atherosclerotic plaque, or thrombus, are clearly visible. Unlike the prior art black-blood imaging technique, the QIR method does not require a precise knowledge of the T1 of the blood carrying the CE agent in order to suppress the signal and artifacts caused by the blood flowing through the site.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
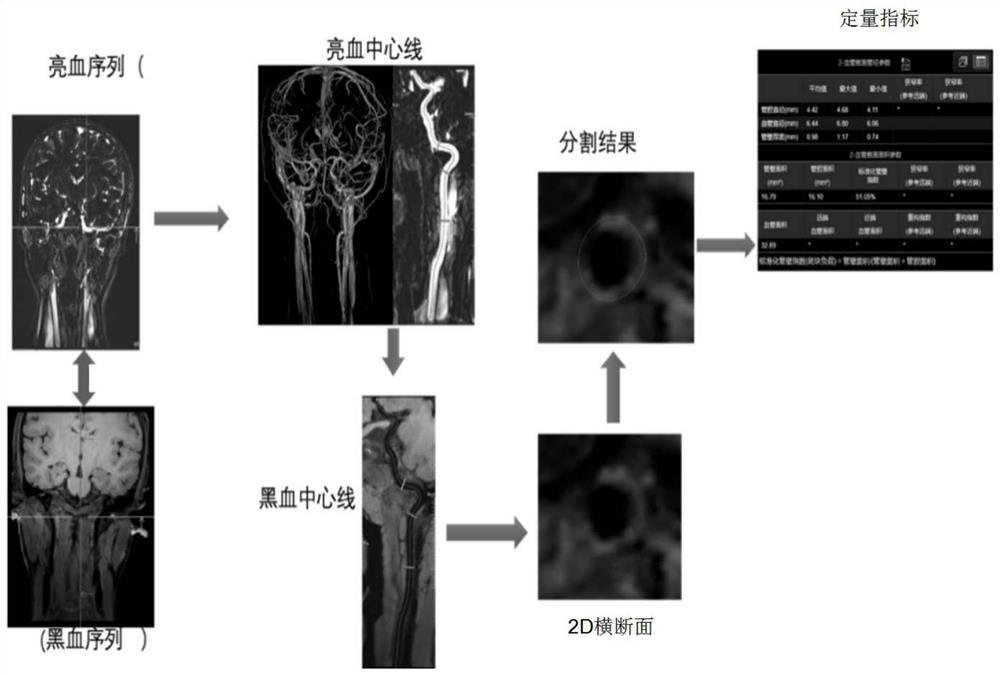
Magnetic resonance blood vessel wall image analysis method and system and computer readable medium
PendingCN112561781AEfficient and accurate segmentation resultsImage enhancementImage analysisBlack blood3d image
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance blood vessel wall image analysis method. The method comprises the steps: reading a 3D image; acquiring a bright blood sequence of the 3D image, and automatically extracting blood vessels based on a central line of the bright blood sequence; acquiring a black blood sequence of the 3D image, and registering the center line of the bright blood sequence tothe black blood sequence; reconstructing a whole blood vessel according to the center line of the black blood sequence; obtaining a reconstructed 2D cross section; building a new training model, and training the training model according to the reconstructed lumen and wall characteristics of the 2D cross section; and importing a given blood vessel wall image into the trained training model to predict a lumen and a vessel wall. The invention further discloses a magnetic resonance blood vessel wall image analysis system and a computer readable medium. The blood vessel is reconstructed by matchingthe center line of the bright blood sequence of the 3D image with the black blood sequence, then the characteristics of the lumen and the wall of the tube are automatically obtained through deep learning and learning of a large number of samples, the method does not need to seriously depend on experience of doctors any more, and the segmentation result can be efficiently and accurately obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
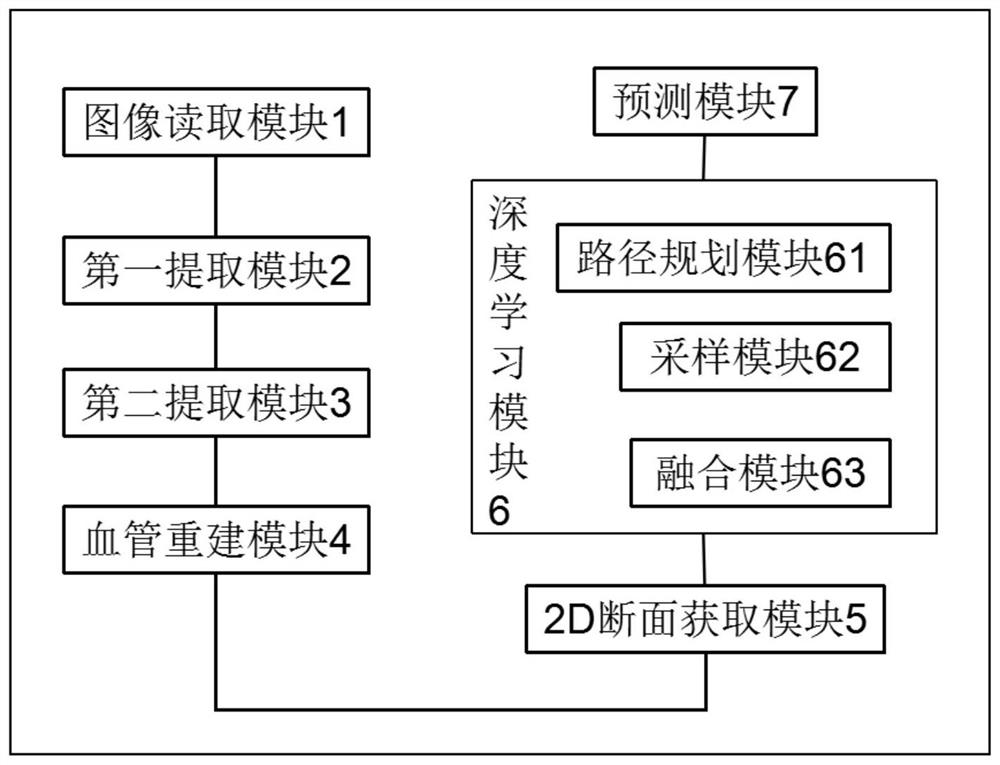
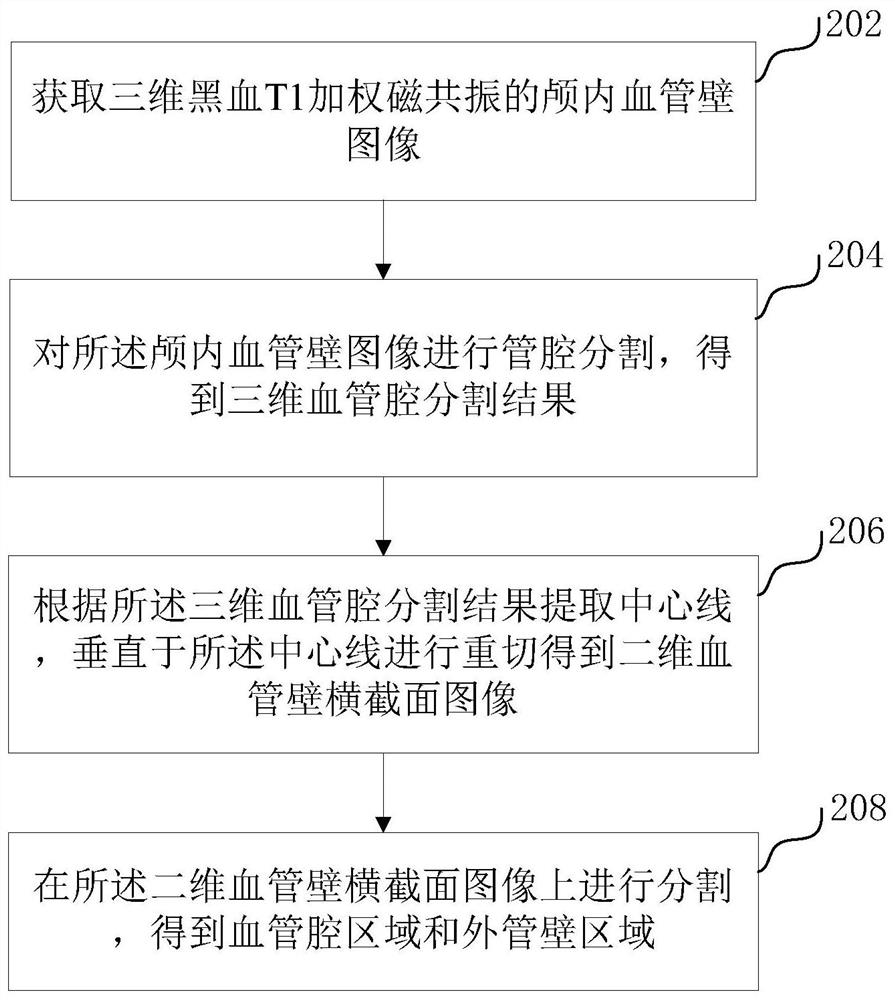
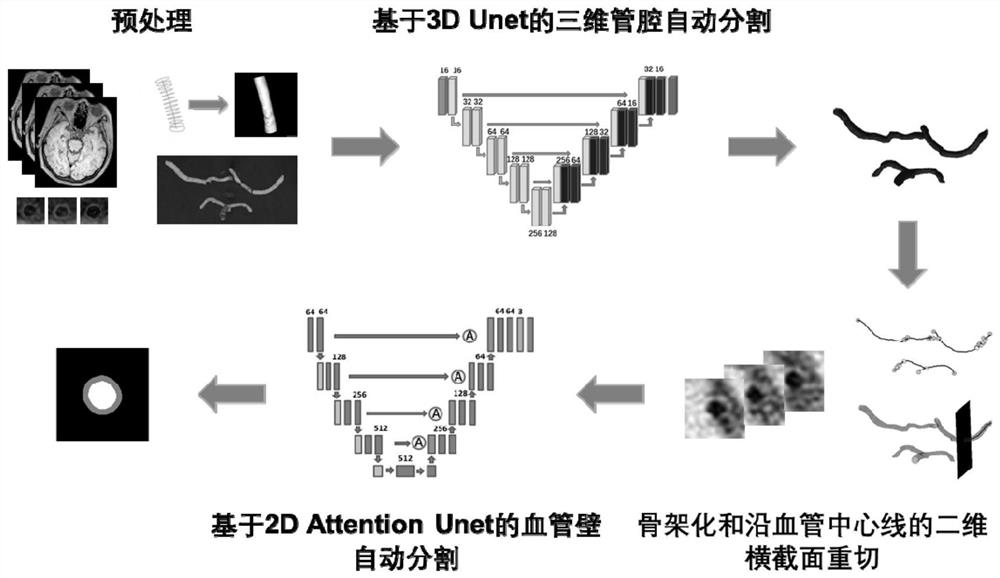
Blood vessel wall image segmentation method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN113223015AImprove accuracyImprove segmentation efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisBlack bloodLumen segmentation
The invention relates to a blood vessel wall image segmentation method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an intracranial blood vessel wall image of three-dimensional black blood T1 weighted magnetic resonance; performing lumen segmentation on the intracranial vascular wall image to obtain a three-dimensional vascular lumen segmentation result; extracting a center line according to the three-dimensional blood vessel cavity segmentation result, and carrying out re-cutting perpendicular to the center line to obtain a two-dimensional blood vessel wall cross section image; and segmenting the two-dimensional blood vessel wall cross section image to obtain a blood vessel cavity area and an outer tube wall area. The three-dimensional lumen in the magnetic resonance image is firstly segmented, then the two-dimensional lumen is segmented on the two-dimensional blood vessel wall cross section image according to the three-dimensional lumen segmentation result, and the accuracy and the segmentation efficiency of blood vessel wall image segmentation are improved through accurate segmentation of the lumen and the lumen.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
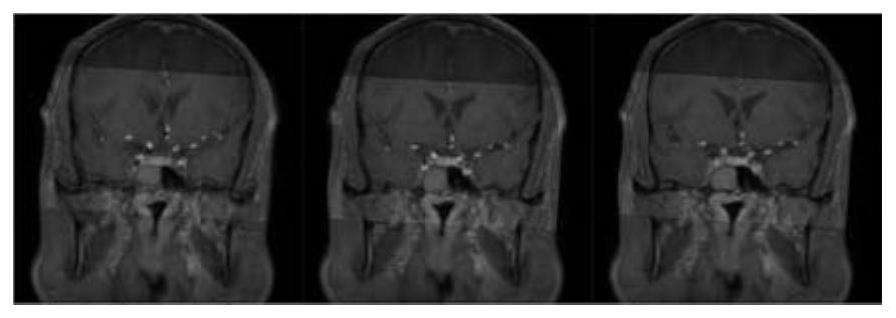
Intracranial blood vessel comprehensive image generation method
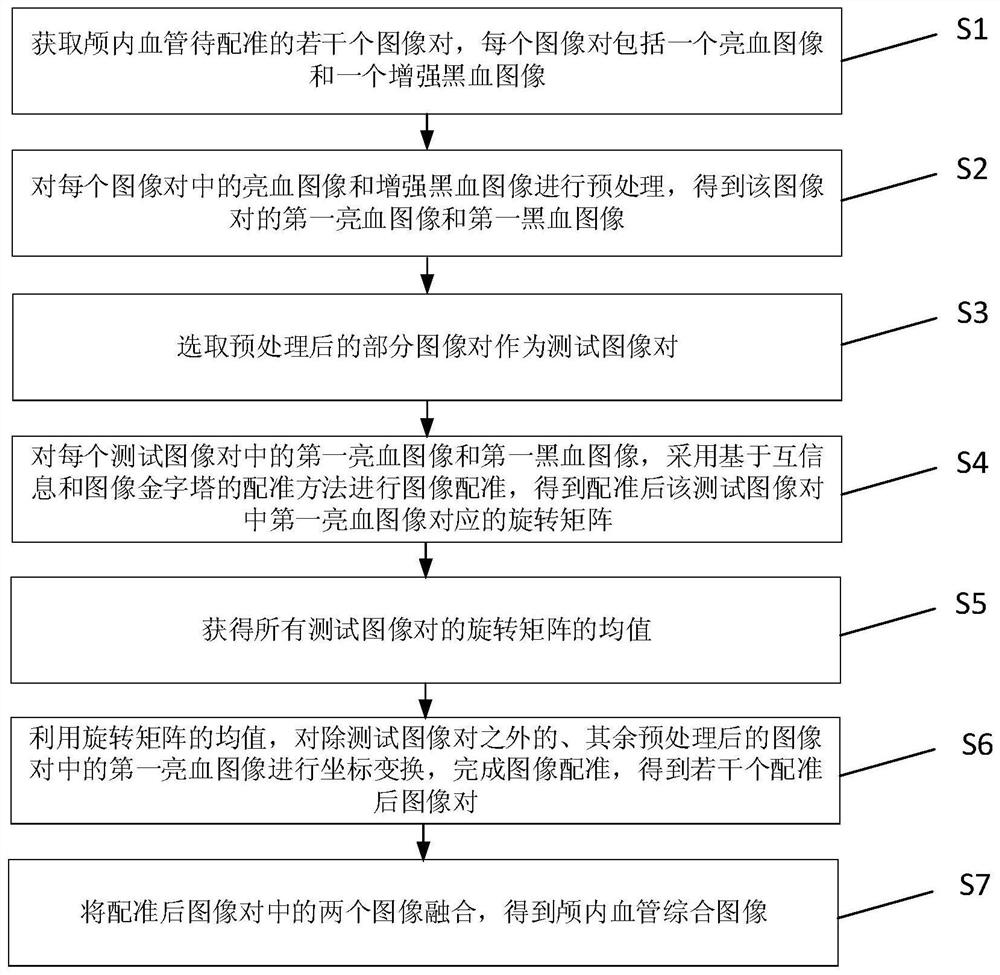
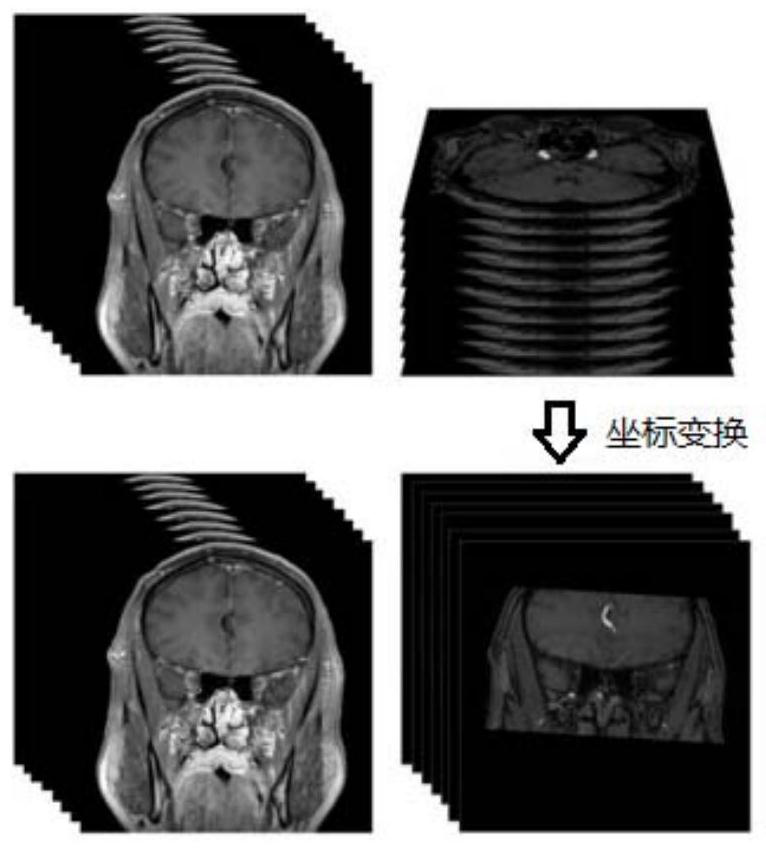
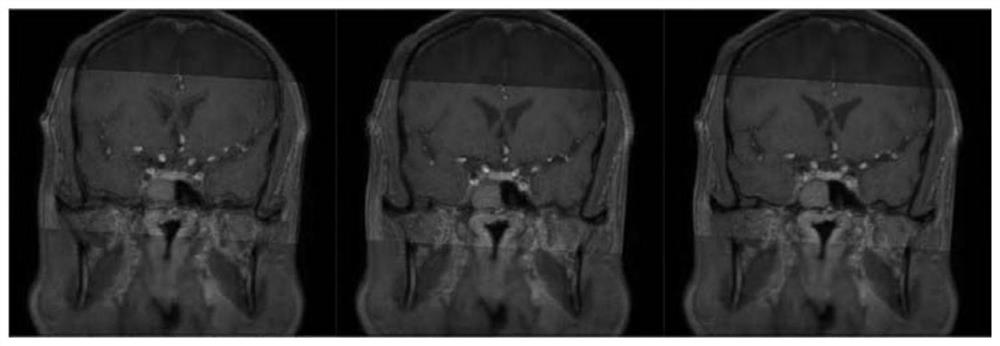
InactiveCN112508868ASpeed up the registration processIncreased complexityImage enhancementImage analysisBlack bloodImage pair
The invention discloses an intracranial blood vessel comprehensive image generation method, which comprises the steps of obtaining a plurality of image pairs to be registered of intracranial blood vessels, and preprocessing a bright blood image and an enhanced black blood image in each image pair to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image of the image pair; selecting a partof preprocessed image pairs as test image pairs; performing image registration on the first bright blood image and the first black blood image in each test image pair by adopting a registration method based on mutual information and an image pyramid to obtain a rotation matrix corresponding to the first bright blood image in the test image pair after registration; obtaining the mean value of therotation matrixes of all the test image pairs; utilizing the mean value of the rotation matrix to perform coordinate transformation on the first bright blood images in other preprocessed image pairs except the test image pair, and finishing image registration to obtain a plurality of registered image pairs; and fusing the two images in the registered image pair to obtain an intracranial vessel comprehensive image.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Method for establishing intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional stenosis model based on transfer learning
InactiveCN112508873ARealize 3D visualizationImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionVascular bodyBlack blood
The invention discloses a method for establishing an intracranial vessel simulation three-dimensional stenosis model based on transfer learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial vessel; performing image registration by using a registration method based on mutual information and an image pyramidto obtain a registered bright blood image group; utilizing the registered bright blood image group to obtain an MIP image in each direction; obtaining a two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation image based on the MIP image as a target domain and a fundus blood vessel image; synthesizing the two-dimensional blood vessel segmentation images in the three directions by using a back projection methodto obtain first three-dimensional blood vessel body data; obtaining an intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the second three-dimensional blood vessel body data corresponding to the registered bright blood image group; and for each section of blood vessel in the model, obtaining a numerical value of a target parameter representing the stenosis degree of the section of blood vessel, and marking the intracranial blood vessel simulation three-dimensional model by utilizing the numerical value of the target parameter to obtain a simulated three-dimensional intracranial vessel stenosis analysis model.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Method for establishing enhanced three-dimensional model for intracranial angiography
InactiveCN112634197AImprove registration efficiencyImprove registration accuracyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBlack bloodContrast enhancement
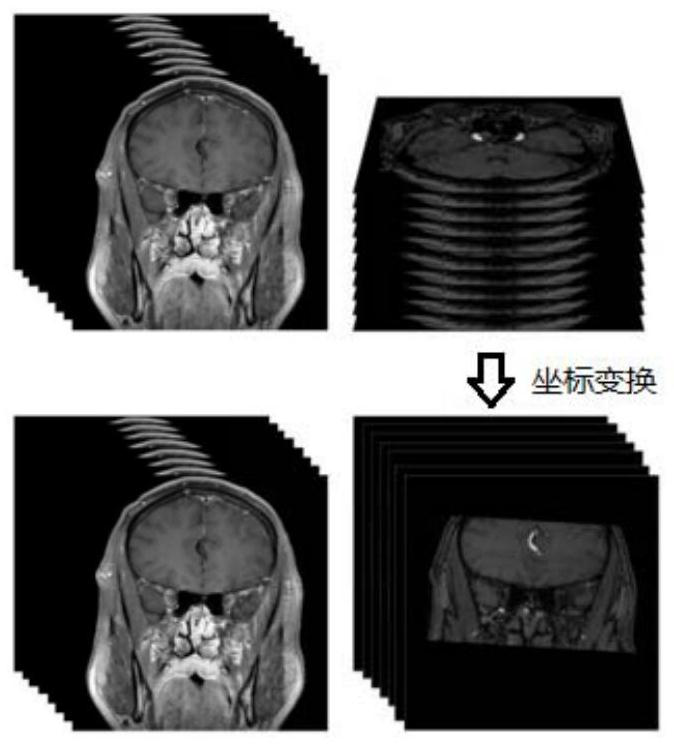
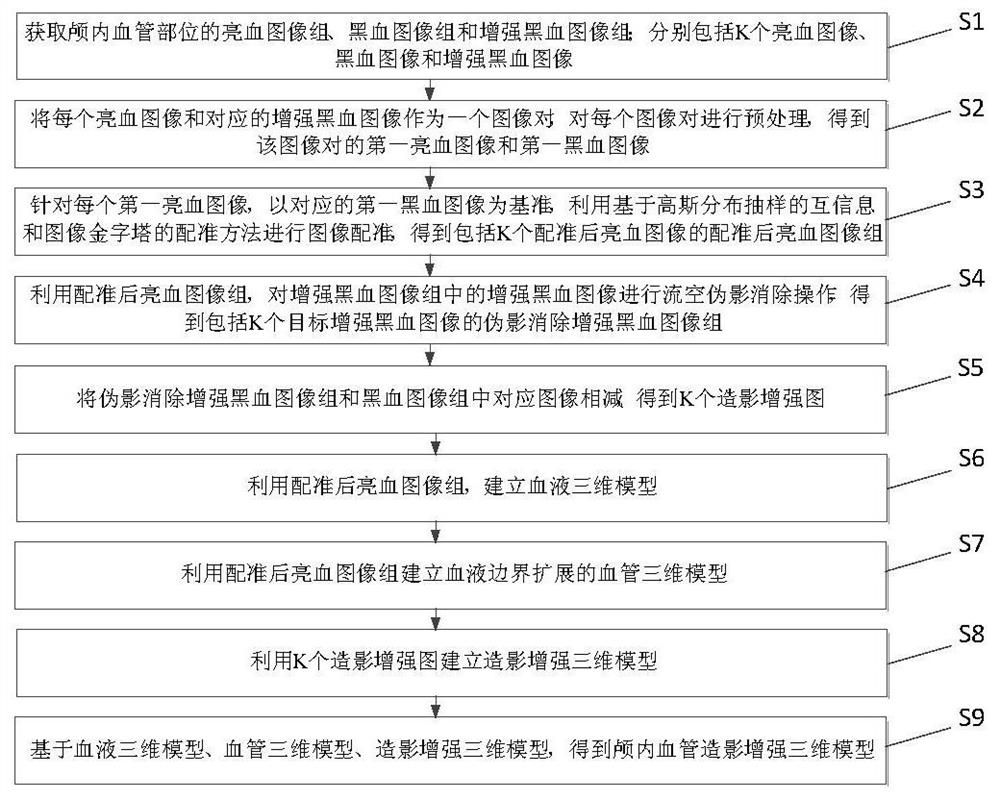
The invention discloses a method for establishing an enhanced three-dimensional model for intracranial angiography. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright blood image group, a black blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group of an intracranial blood vessel part; preprocessing each image pair to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; for each first bright blood image, taking the corresponding first black blood image as a reference, and performing image registration by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid to obtain a registered bright blood image group; carrying out flow empty artifact elimination operation to obtain an artifact elimination enhanced black blood image group; subtracting corresponding images in the artifact elimination enhanced black blood image group and the black blood image group to obtain K contrast enhanced images; establishing a blood three-dimensional model and a blood vessel three-dimensional model of blood boundary expansion by using the registered bright blood image group; establishing a contrast enhancement three-dimensional model by utilizing the K contrast enhancement images; obtaining an intracranial angiography enhanced three-dimensional model based on the blood three-dimensional model, the blood vessel three-dimensional model and the angiography enhanced three-dimensional model.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Intracranial vascular focus identification method based on transfer learning
InactiveCN112669257AQuick eliminationImprove registration efficiencyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBlack bloodComputer vision
The invention discloses an intracranial vascular focus recognition method based on transfer learning. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a bright blood image group, a black blood image group and an enhanced black blood image group; preprocessing to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image; taking the corresponding first black blood image as a reference for each first bright blood image, and obtaining a registered bright blood image group by using mutual information based on Gaussian distribution sampling and a registration method of an image pyramid; performing flow empty artifact elimination to obtain an artifact-eliminated enhanced black blood image group; subtracting corresponding images in the artifact elimination enhanced black blood image group and the black blood image group to obtain K contrast enhanced images; and establishing a blood three-dimensional model by utilizing the registered bright blood image group and adopting a transfer learning method, and establishing a blood vessel three-dimensional model of blood boundary expansion by utilizing the registered bright blood image group. The focus area of the intracranial blood vessel can be simply, conveniently, quickly and visually recognized clinically.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Intracranial blood vessel image registration method, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
InactiveCN112508880AEffective Auxiliary Diagnostic InformationSpecial structureImage enhancementImage analysisBlack bloodReference image
The invention discloses an intracranial blood vessel image registration method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a bright blood image and a black blood image of an intracranial blood vessel; taking the black blood image as a reference image and the bright blood image as a floating image, performing coordinate transformation on the bright blood image, and performing interpolationprocessing on the bright blood image by adopting a bicubic interpolation method; calculating the similarity between the bright blood image and the black blood image after interpolation processing byusing similarity measurement; finding out the optimal similarity measurement by utilizing a search strategy; according to the space transformation matrix, carrying out coordinate transformation on thebright blood image when similarity measurement is optimal, and obtaining a first registration image; and according to the scanning area of the bright blood image, extracting the same scanning area inthe black blood image to obtain a second registration image. According to the scheme, a doctor can be assisted in accurate intracranial disease diagnosis.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Slow thawing method for beef
InactiveCN105875797ANo black borderFresh meatMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingBlack bloodElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for slowing down and thawing beef. The original meat temperature is minus 16 degrees Celsius, and enters a transfer fresh-keeping warehouse through an electric pulley; the fresh-keeping warehouse is provided with an electrolytic water spray head, and the electrolyzed water is mainly acidic water. The water temperature is kept at room temperature, and the beef is sprayed in the fresh-keeping warehouse for 4 hours. After the raw meat is sprayed, it will leave the fresh-keeping warehouse through the electric pulley. The package is then transferred to the water circulation system through the electric pulley frame for immersion. The temperature of the water is kept at 4 degrees Celsius to 6 degrees Celsius, and the water circulation is used to soak for 24 hours to 36 hours for relaxation. The lower part of the pool of the water circulation system is equipped with volcanic stones, and the lower part of the pool is provided with a filter screen, through which the circulating water filters impurities and is then pumped into the pool by an electric water pump. Edge phenomenon, remove black blood.
Owner:无锡市馥润食品有限公司
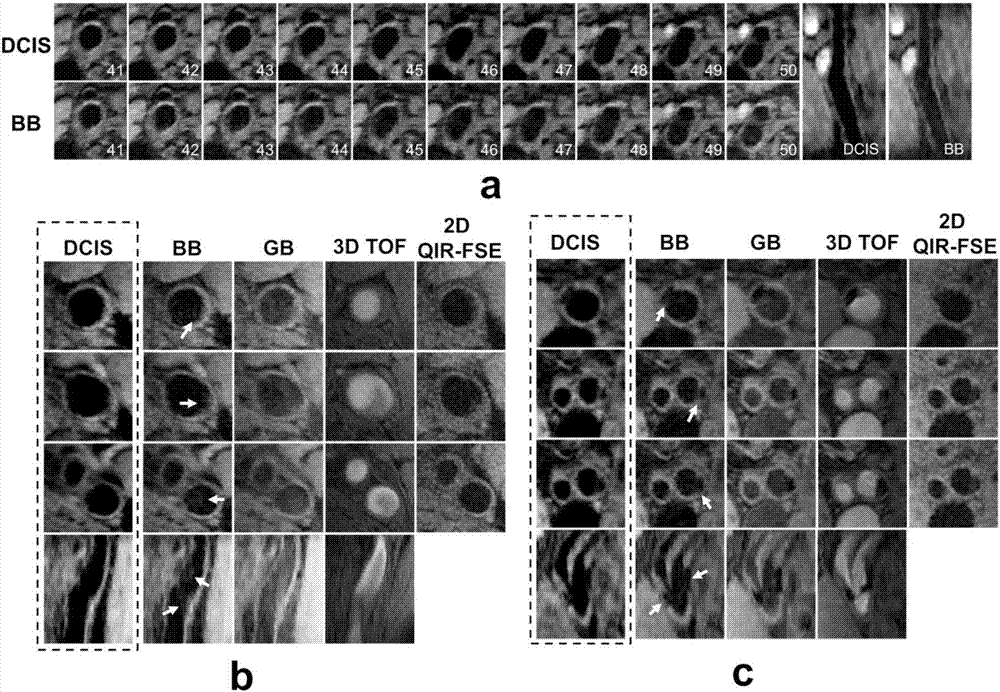
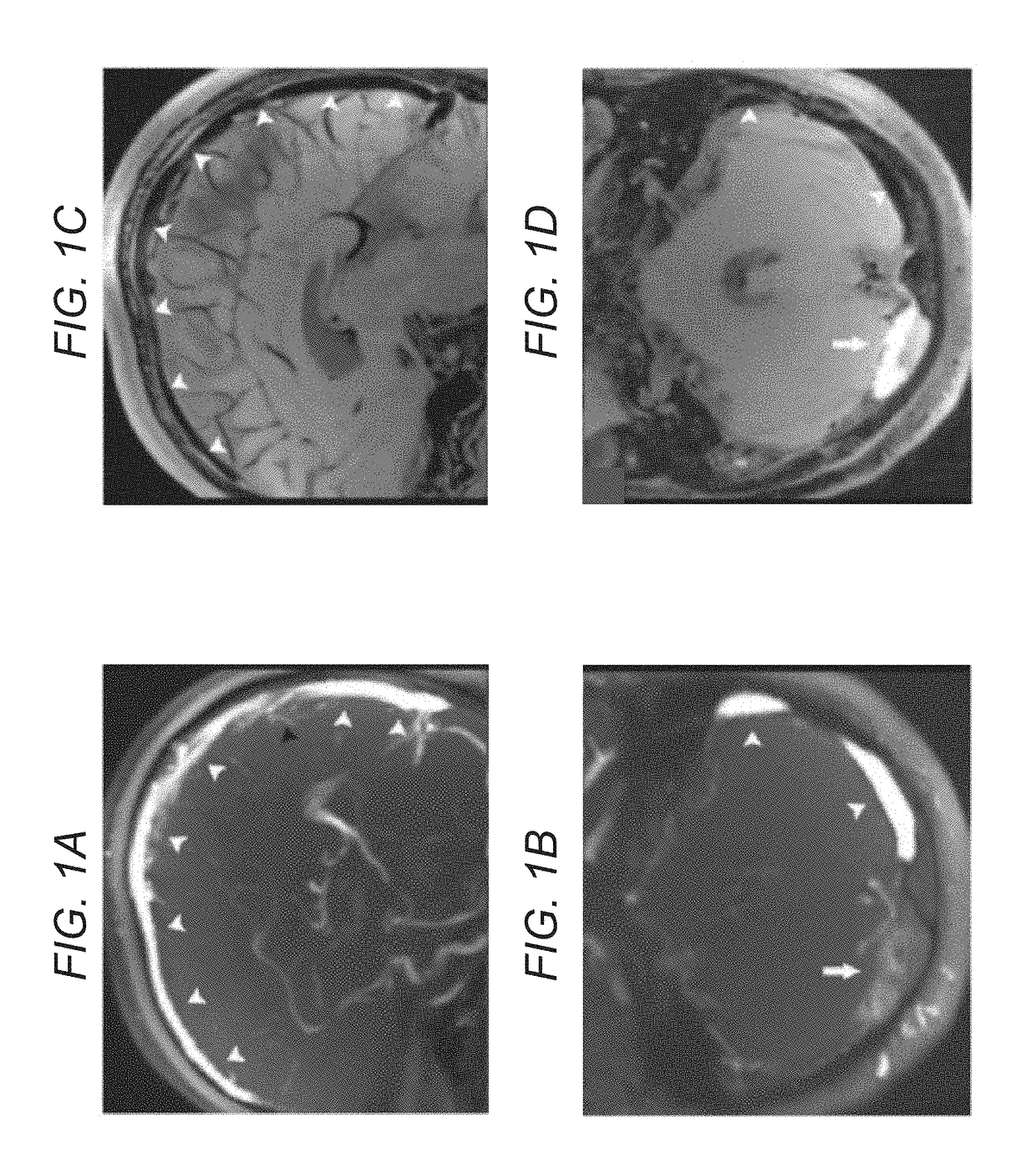
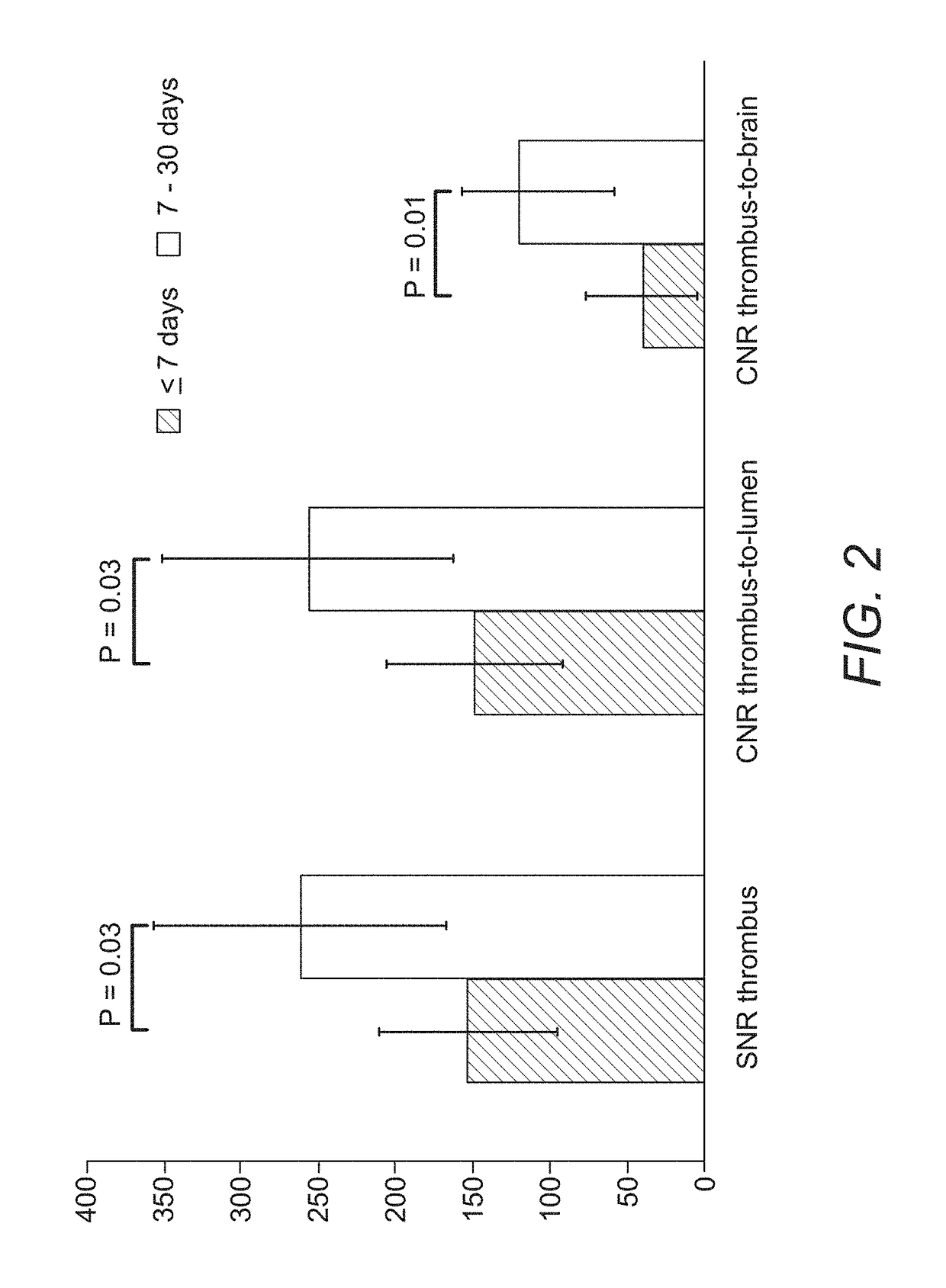
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance black-blood thrombus imaging in detection of cerebral venous thrombosis
InactiveUS20170224217A1Increase imaging speedMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsContrast levelBlack blood
In various embodiments, the present invention teaches systems and methods for using T1-weighted black-blood MR imaging, with which a CVT can be well isolated from the surrounding tissues due to the signal suppression of flowing blood. In some embodiments, the invention teaches using black-blood imaging (3D variable-flip-angle turbo spin-echo acquisition) to directly visualize thrombi. In certain embodiments, the invention teaches using T1 weighted image contrast and isotropic sub-millimeter spatial resolution for accurate detection and staging of thrombi. In various embodiments, the invention allows for the detection of chronic thrombosis recanalization.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Intracranial blood vessel image registration method
InactiveCN112508881AEasy to handleSpeed up the registration processImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBlack bloodImage pair
The invention discloses an intracranial blood vessel image registration method which comprises the steps of acquiring a plurality of image pairs to be registered of intracranial blood vessels, whereineach image pair comprises a bright blood image and an enhanced black blood image; preprocessing the bright blood image and the enhanced black blood image in each image pair to obtain a first bright blood image and a first black blood image of the image pair; selecting a part of preprocessed image pairs as test image pairs; performing image registration on the first bright blood image and the first black blood image in each test image pair by adopting a registration method based on mutual information and an image pyramid to obtain a rotation matrix corresponding to the first bright blood imagein the test image pair after registration; obtaining the mean value of the rotation matrixes of all the test image pairs; and performing coordinate transformation on the first bright blood images inother preprocessed image pairs except the test image pair by using the mean value of the rotation matrix to complete image registration. The method provided by the invention can improve the registration precision and registration speed of the intracranial blood vessel image.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Magnetic resonance black blood imaging method and system
PendingCN113945877AReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBlack bloodInversion Time
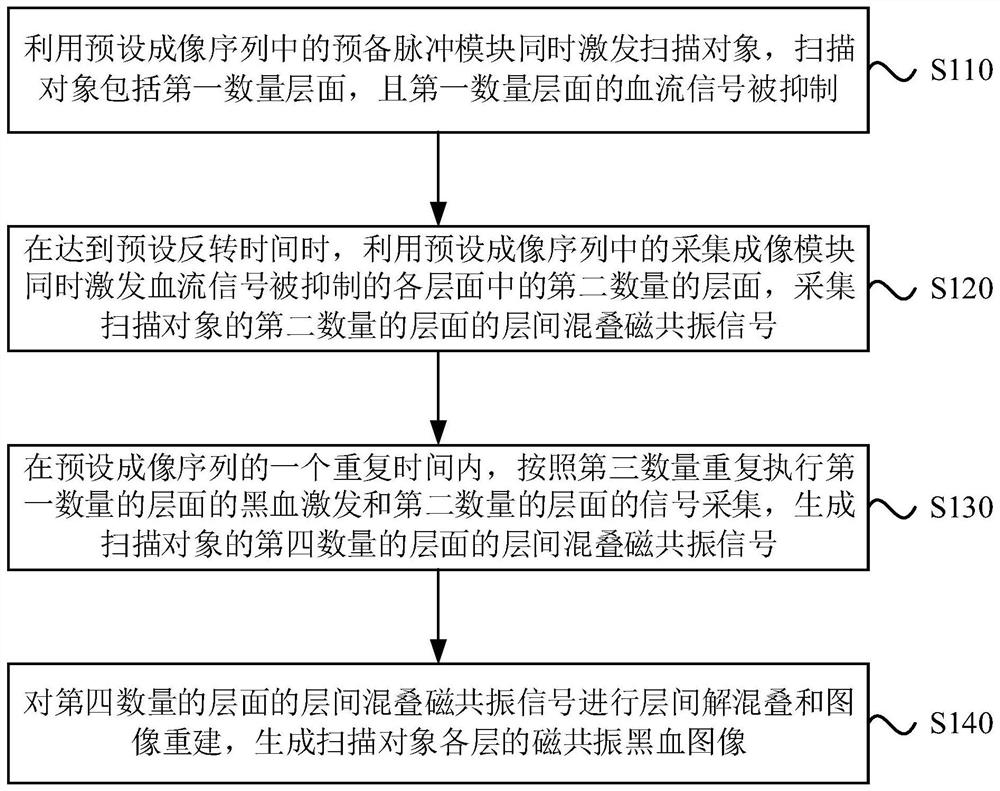
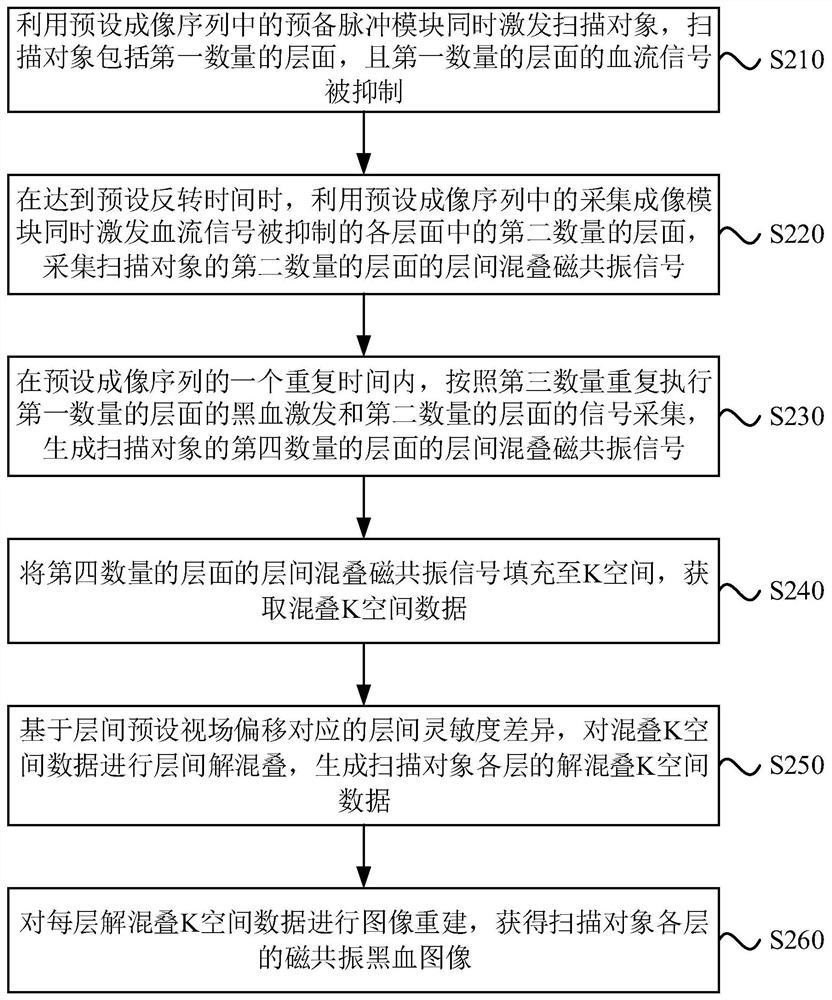
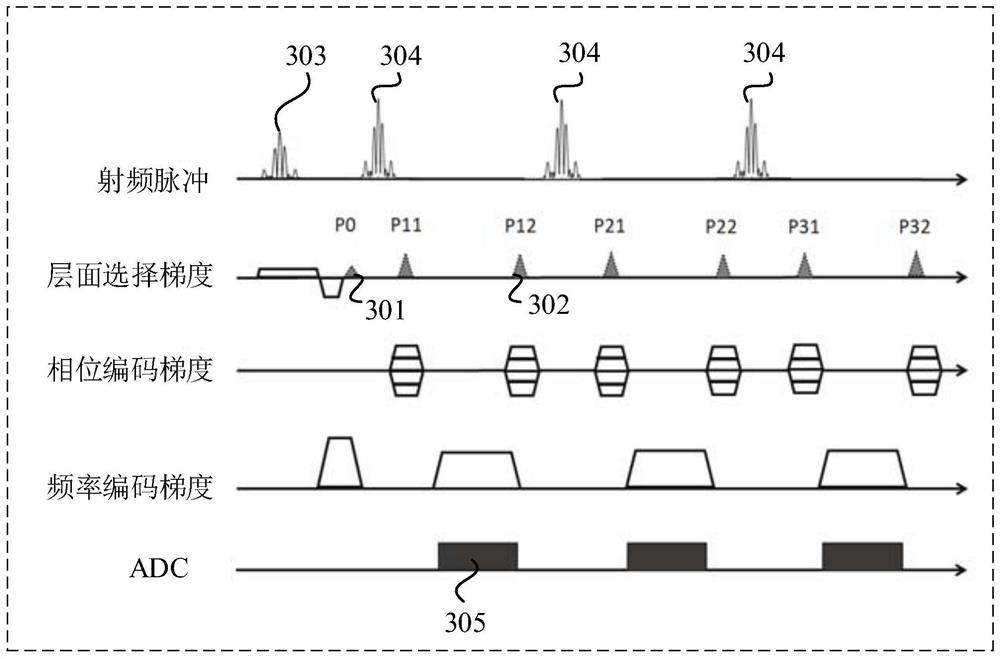
The embodiment of the invention discloses a magnetic resonance black blood imaging method and system. The method comprises the steps that a preparation pulse module in a preset imaging sequence is utilized to excite a scanning object at the same time, and the scanning object comprises a first number of layers where blood flow signals are restrained; when the preset inversion time is reached, a second number of layers in the layers of which the blood flow signals are restrained are simultaneously excited by utilizing an acquisition imaging module in the preset imaging sequence, and interlayer aliasing magnetic resonance signals of the second number of layers are acquired; in a repetition time of the preset imaging sequence, black blood excitation and signal acquisition are repeatedly executed according to a third number, and interlayer aliasing magnetic resonance signals of a fourth number of layers are generated; and interlayer de-aliasing and image reconstruction are conducted on the interlayer aliasing magnetic resonance signals of the fourth number of layers to generate a magnetic resonance black blood image of each layer. By means of the technical scheme, collection of magnetic resonance signals in which multiple layers of blood flow signals are completely inhibited at the same time is achieved, and the magnetic resonance black blood imaging speed is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Cerebrovascular image flow void artifact elimination method and system
InactiveCN112509085AFacilitate eliminationEffective Auxiliary Diagnostic InformationImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionBlack bloodRadiology
The invention discloses a cerebrovascular image flow void artifact elimination method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a bright blood image and an enhanced black blood image of the brain blood vessel; taking the enhanced black blood image as a reference image and the bright blood image as a floating image, performing coordinate transformation on the bright blood image, and performing interpolation processing on the bright blood image by adopting a bilinear interpolation method; calculating the similarity between the bright blood image after interpolation processing and the enhancedblack blood image by using similarity measurement; finding out the optimal similarity measurement by utilizing a search strategy; carrying out coordinate transformation on the bright blood image whenthe similarity measurement is optimal, and obtaining a first registration image; extracting the same scanning area in the enhanced black blood image according to the scanning area of the bright bloodimage in the first registration image to obtain a second registration image; and carrying out flow void artifact elimination on the second registration image. According to the scheme of the invention, the flow void artifact can be quickly eliminated, more accurate and comprehensive blood vessel images can be displayed, and doctors can be assisted in accurate intracranial disease diagnosis.
Owner:XIAN CREATION KEJI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com