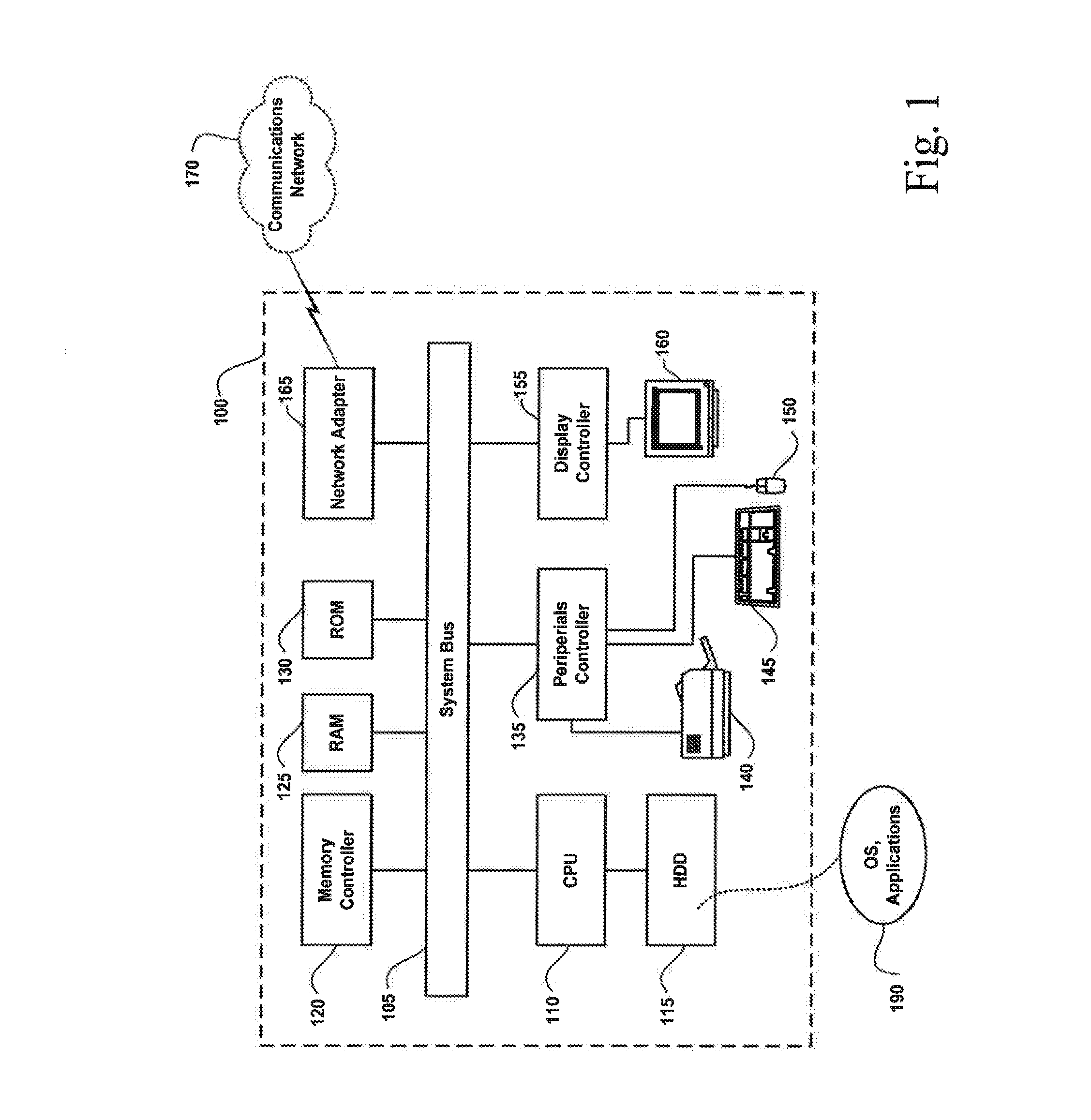
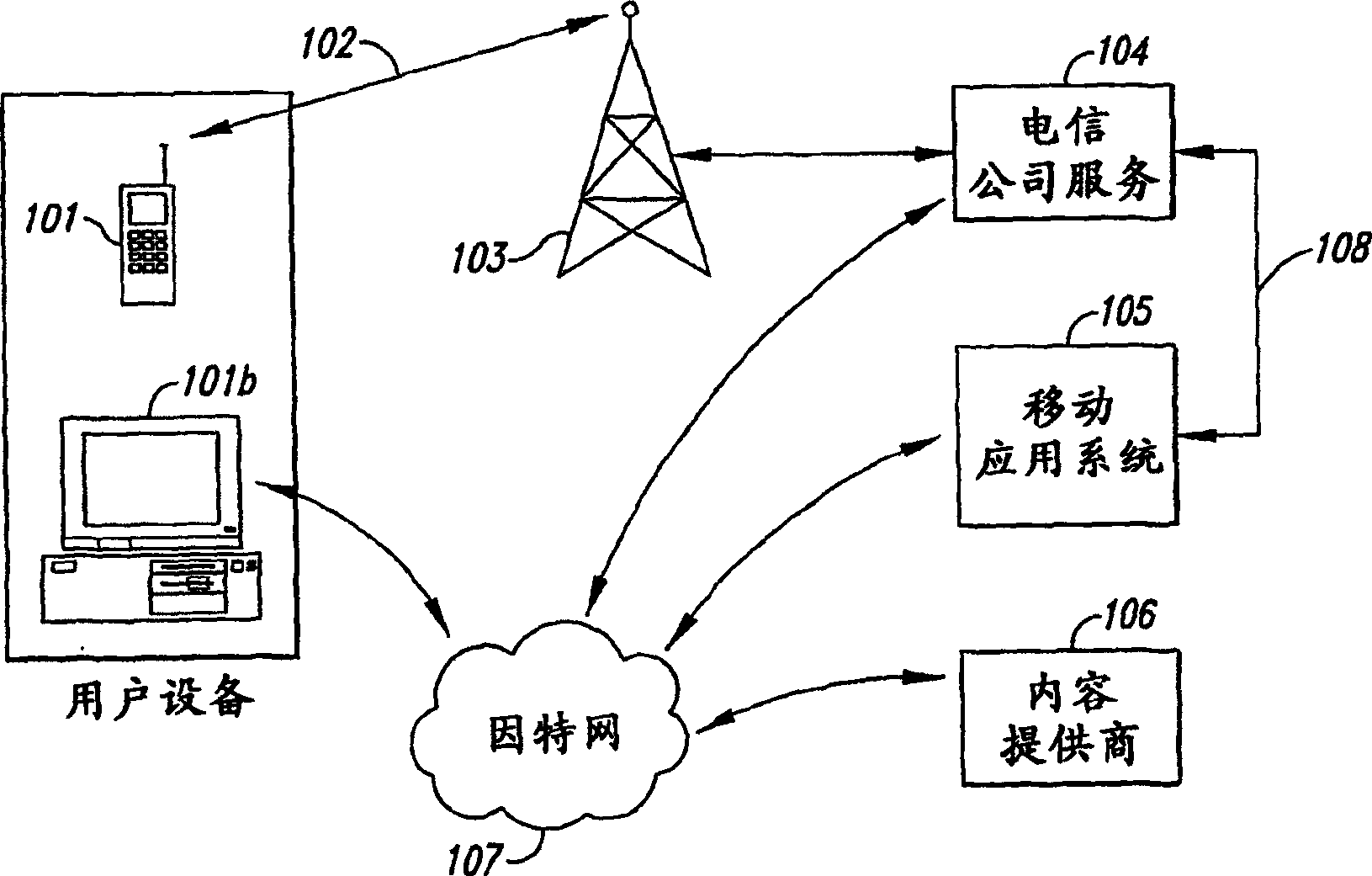
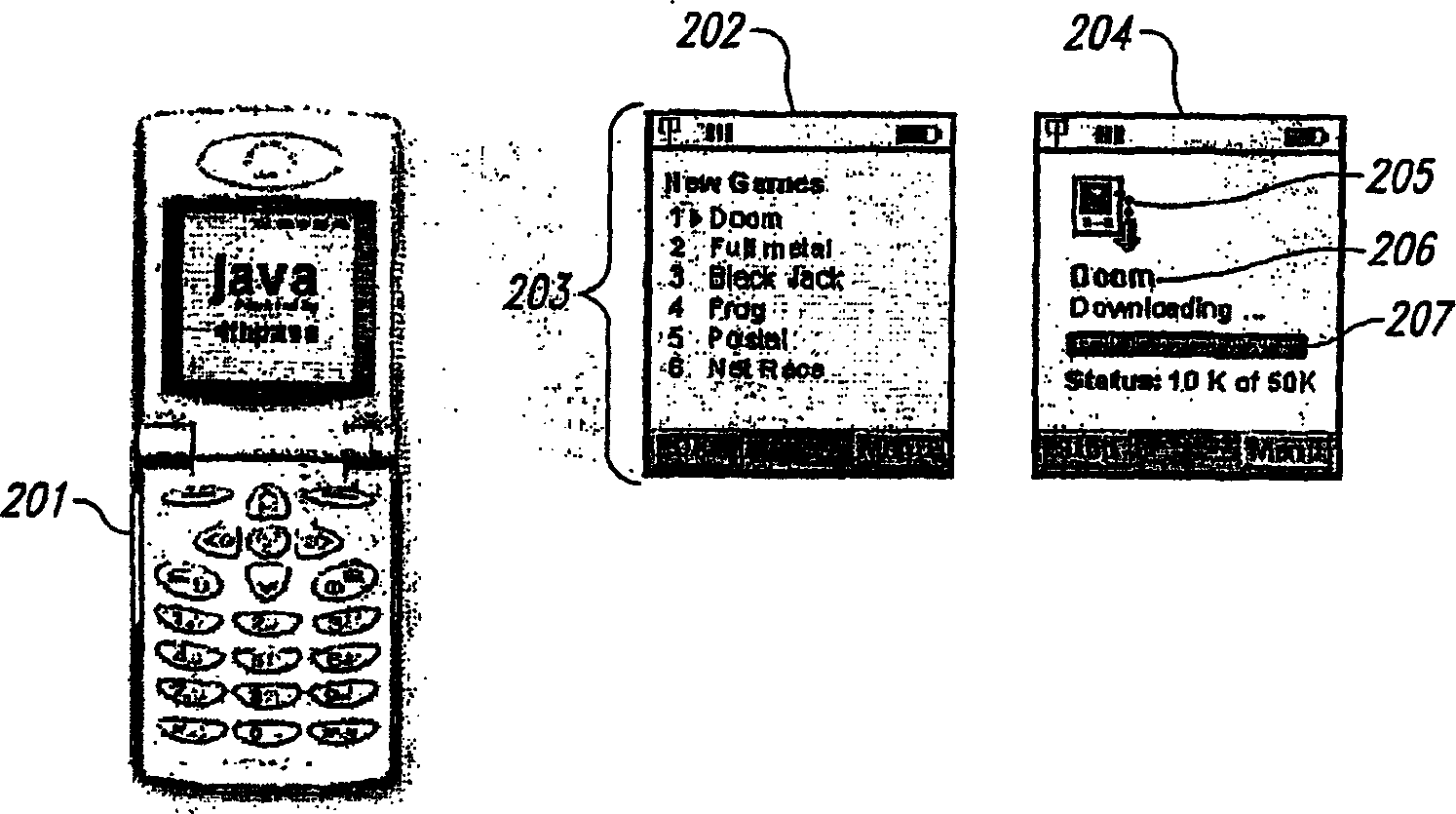
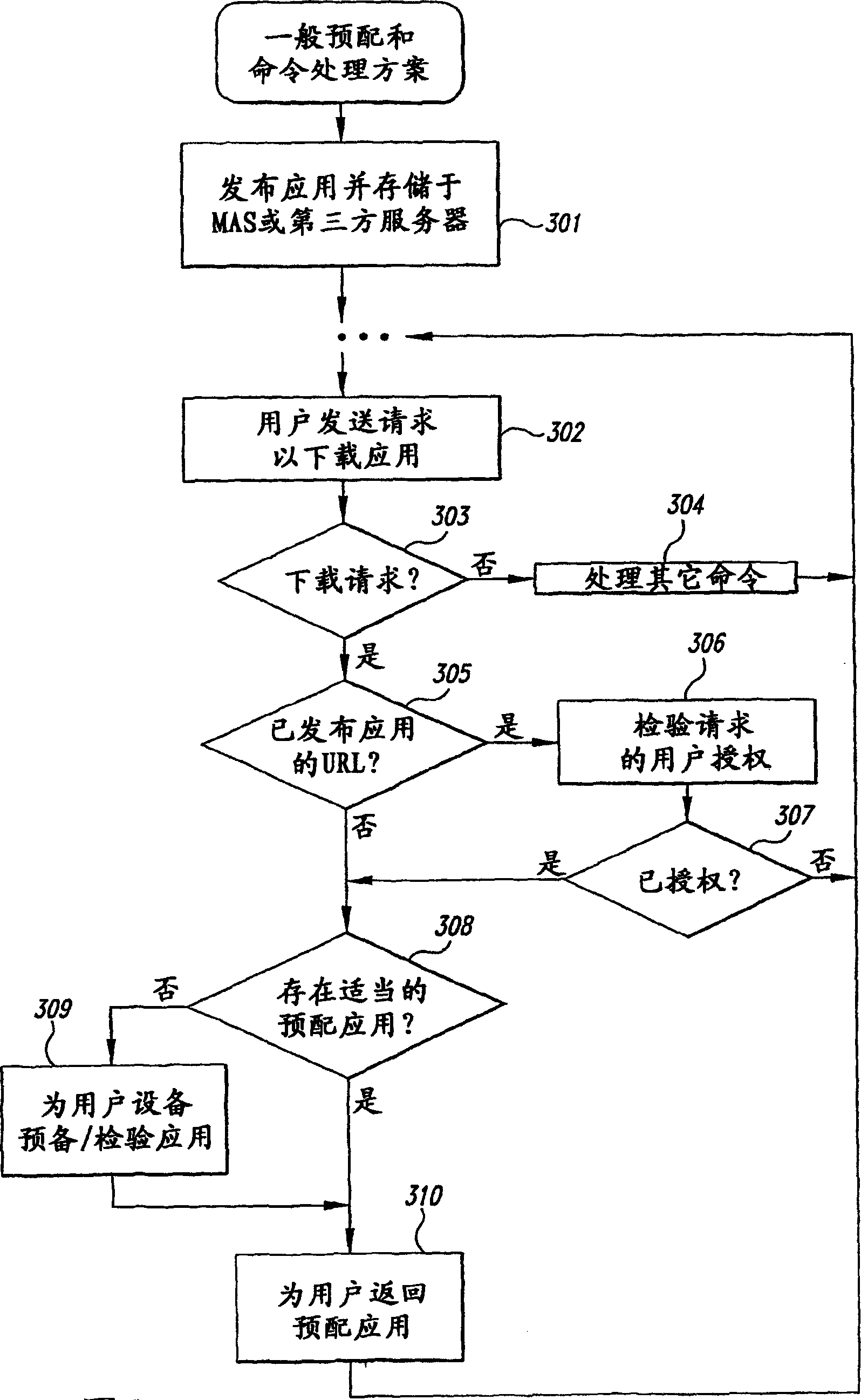
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
208 results about "Application computers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A: Types of computer applications include word processing software, database software, spreadsheet software, presentation software, multimedia software, enterprise software, information worker software, simulation software, educational software, content access software, and software that enables the development or engineering of products.
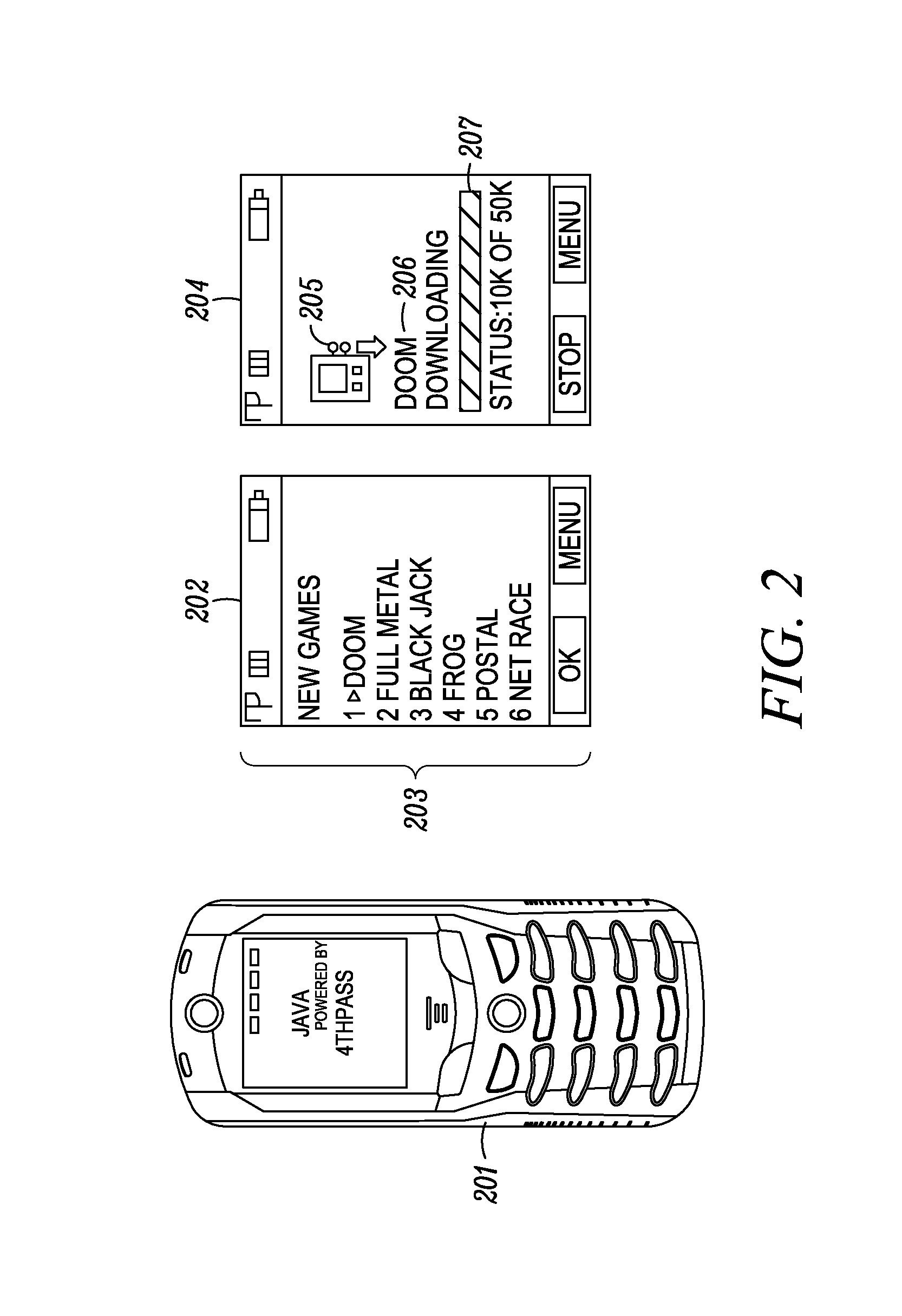
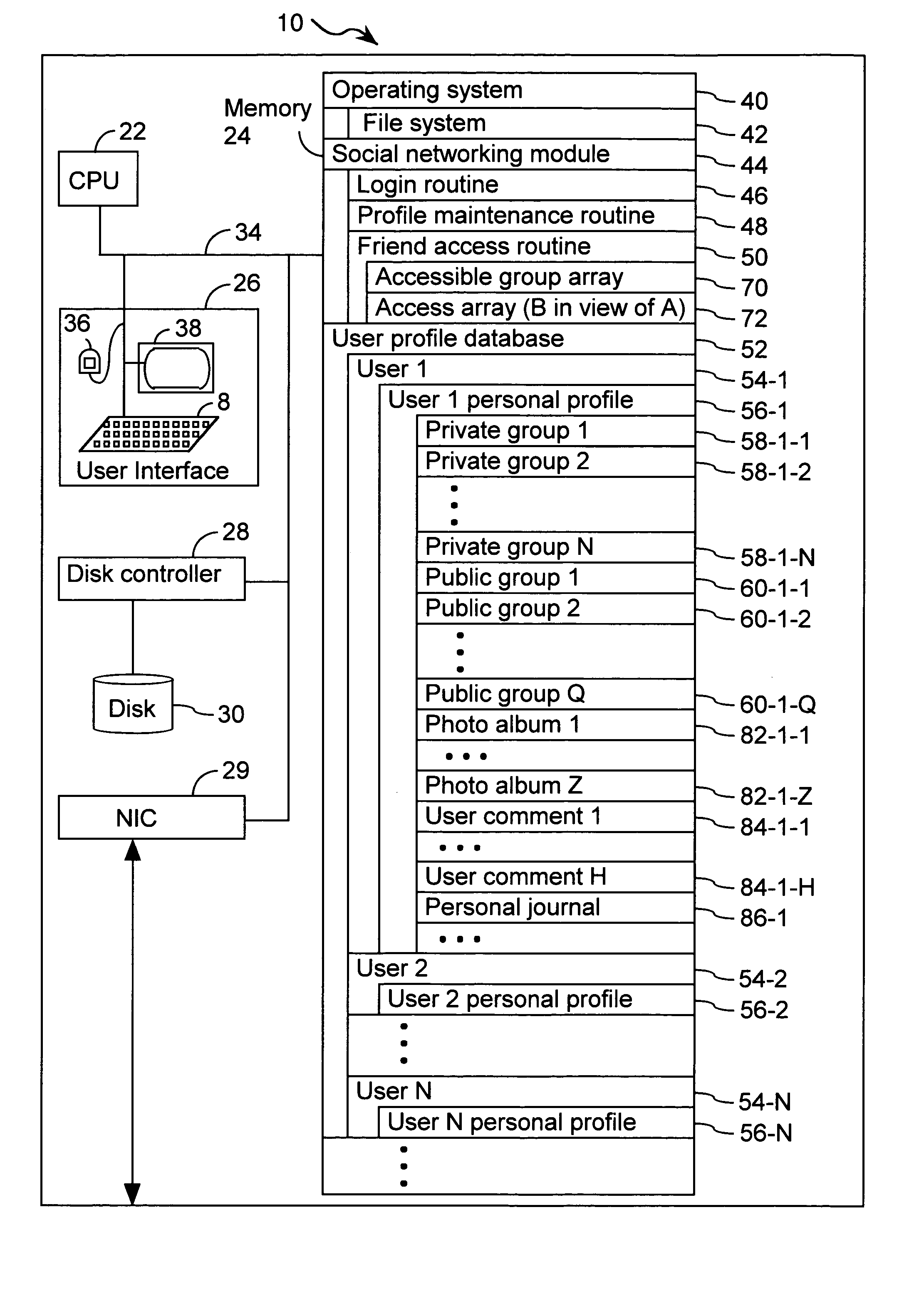
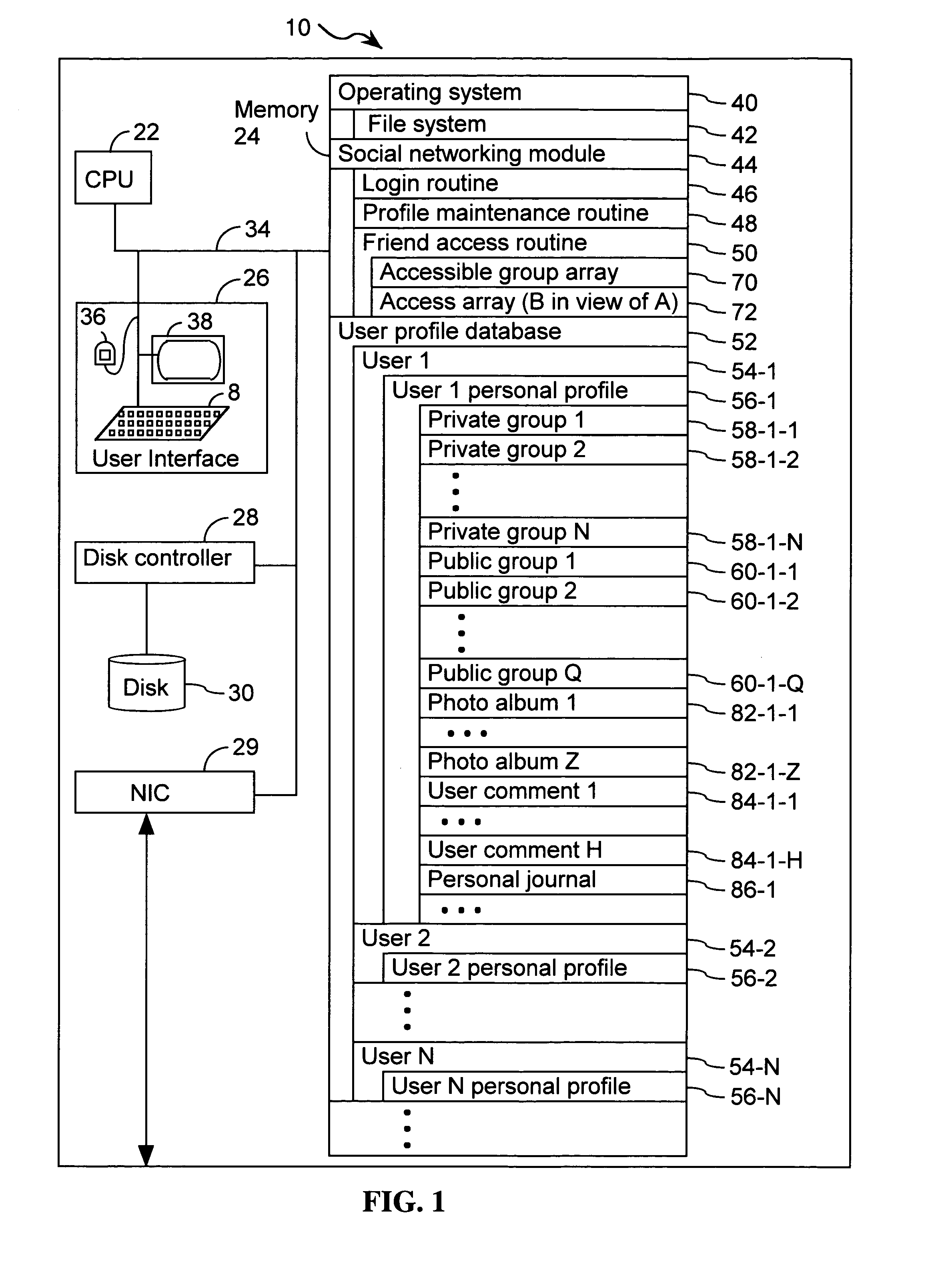
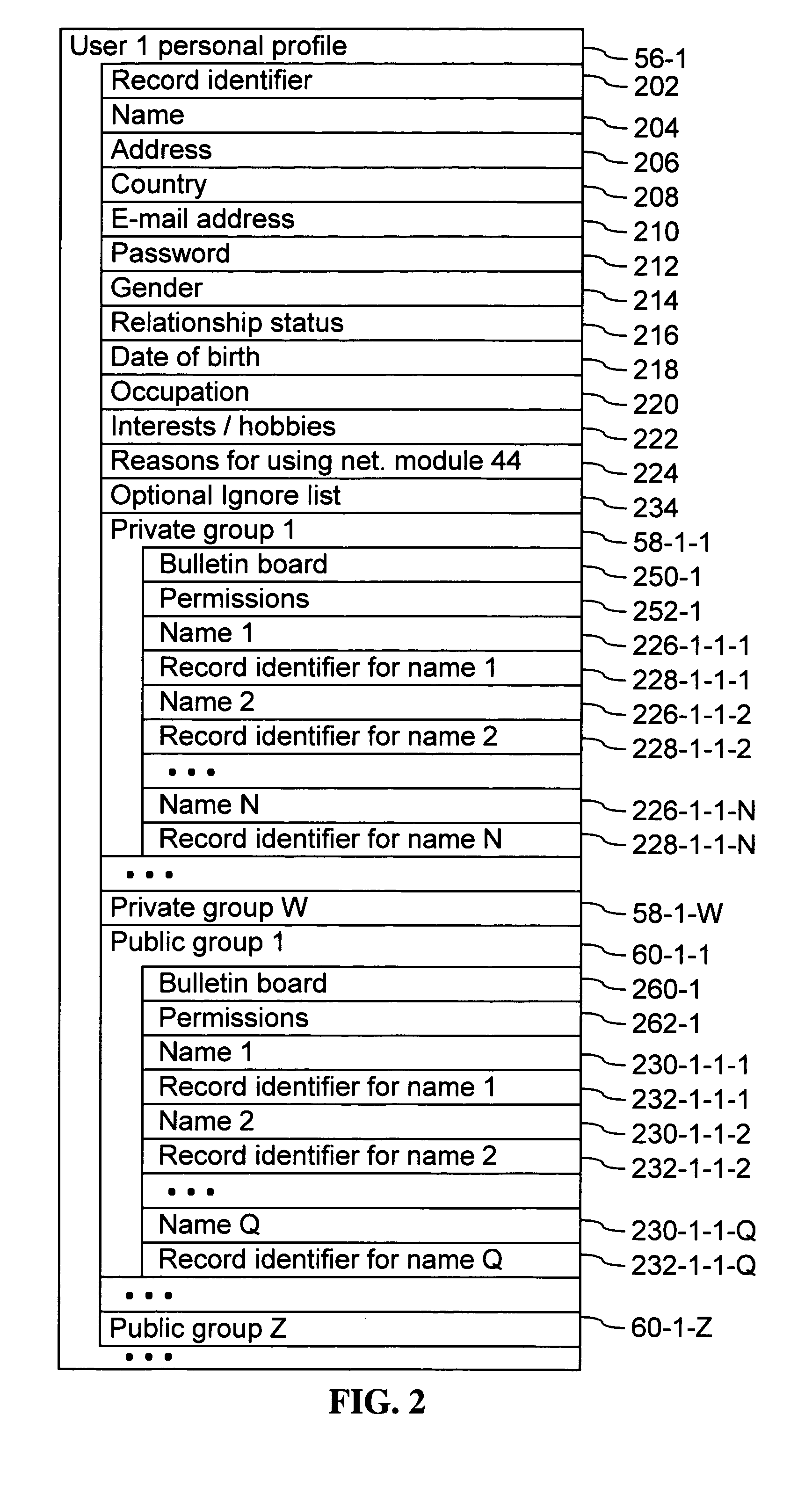
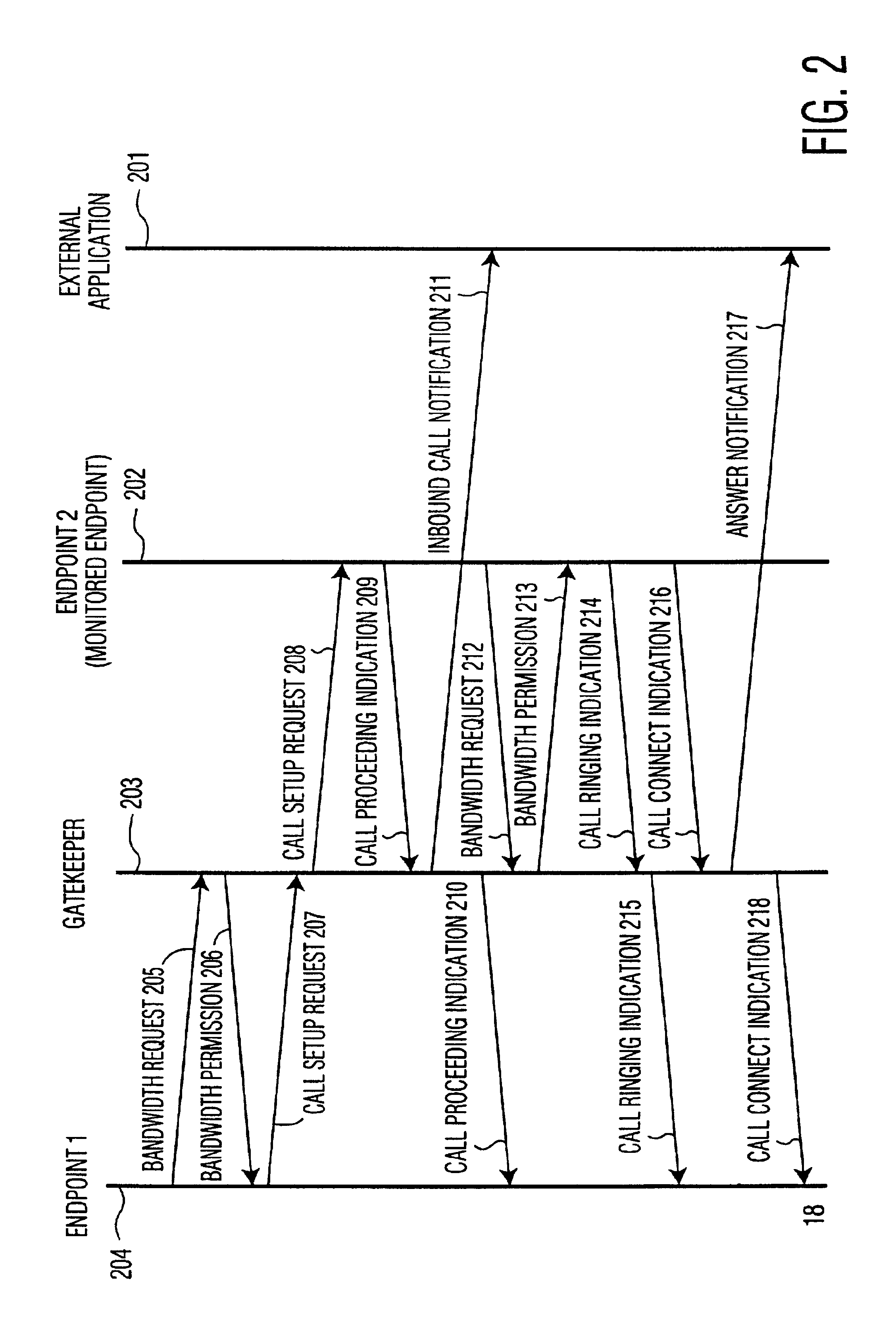
Systems and methods for class designation in a computerized social network application
InactiveUS20050210409A1Digital data processing detailsTransmissionApplication computersPersonal details
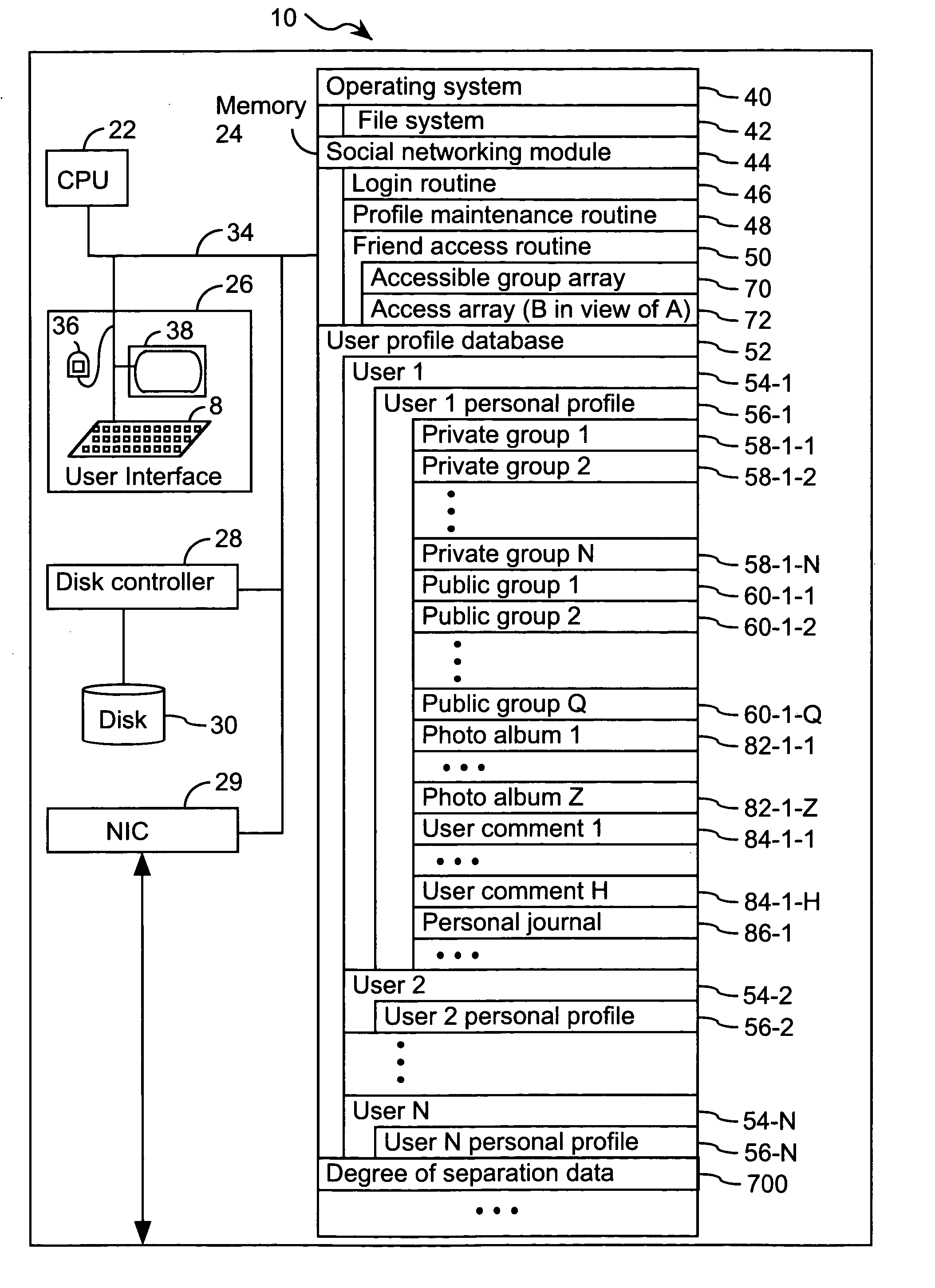
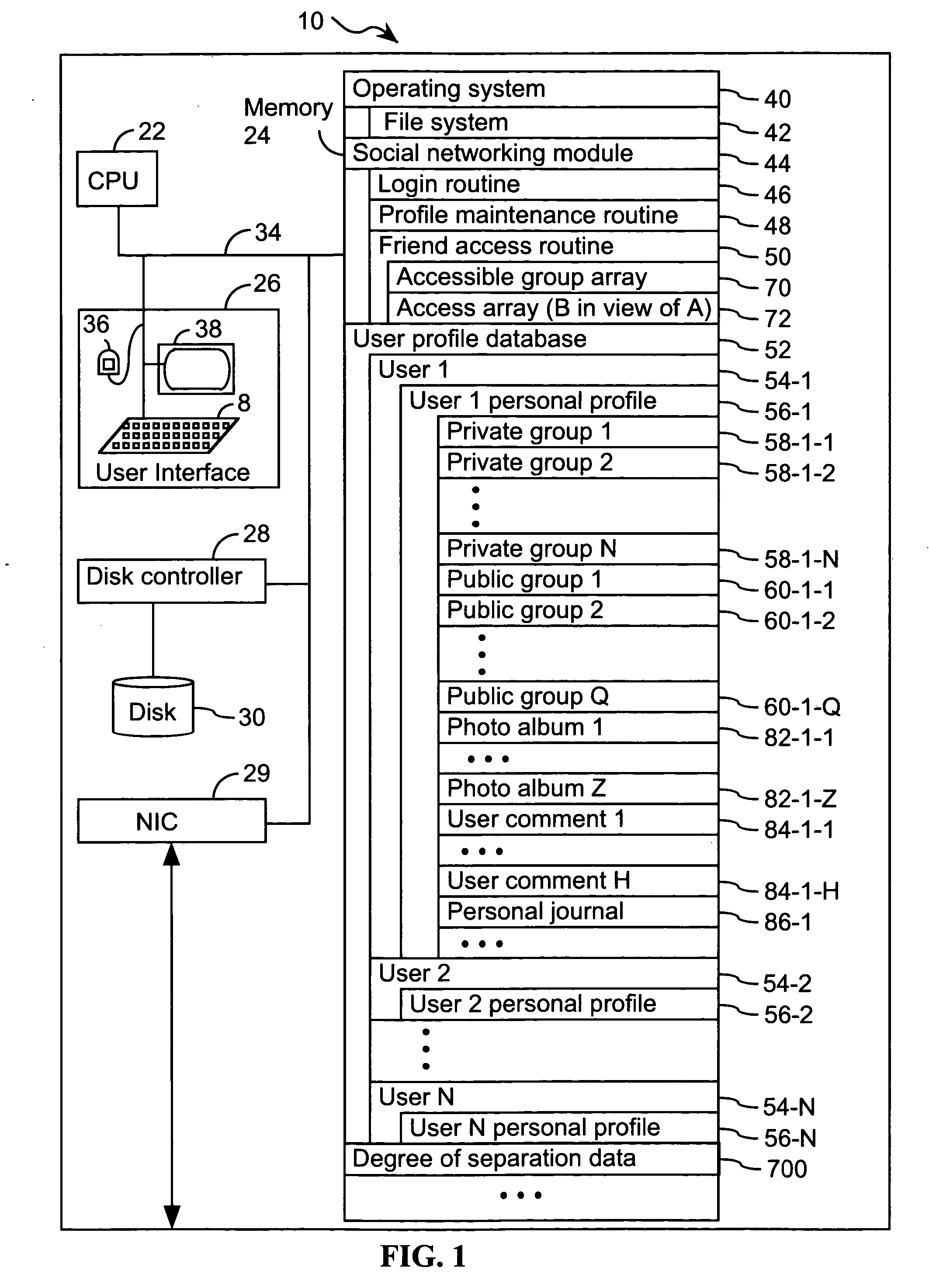
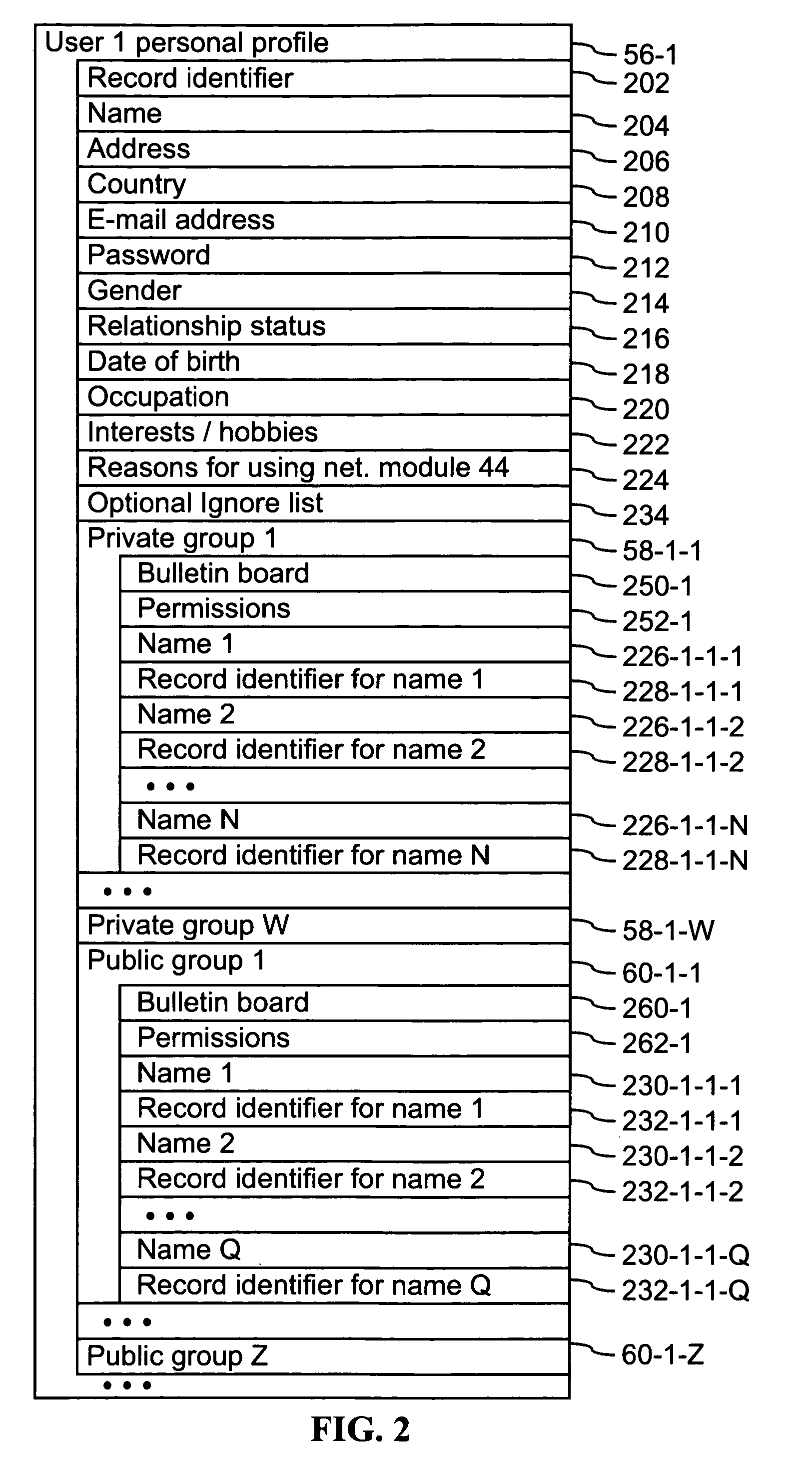
Computer program products, methods, and systems for facilitating a computerized social network are provided. The invention includes a user profile database having a plurality of personal profiles, each corresponding to a user in the social network. Each personal profile includes an identity of at least one user of the network other than the user represented by the personal profile. Each respective personal profile includes a capability of organizing each of the at least one users into one or more groups associated with the user corresponding to the respective personal profile. A friend access routine includes instructions for receiving a request from a first user to access users in the personal profile of a second user. The friend access routine determines which of the users in the personal profile of the second user can be accessed by the first user.
Owner:JOU KENNY
Method and System for Maintaining and Distributing Wireless Applications
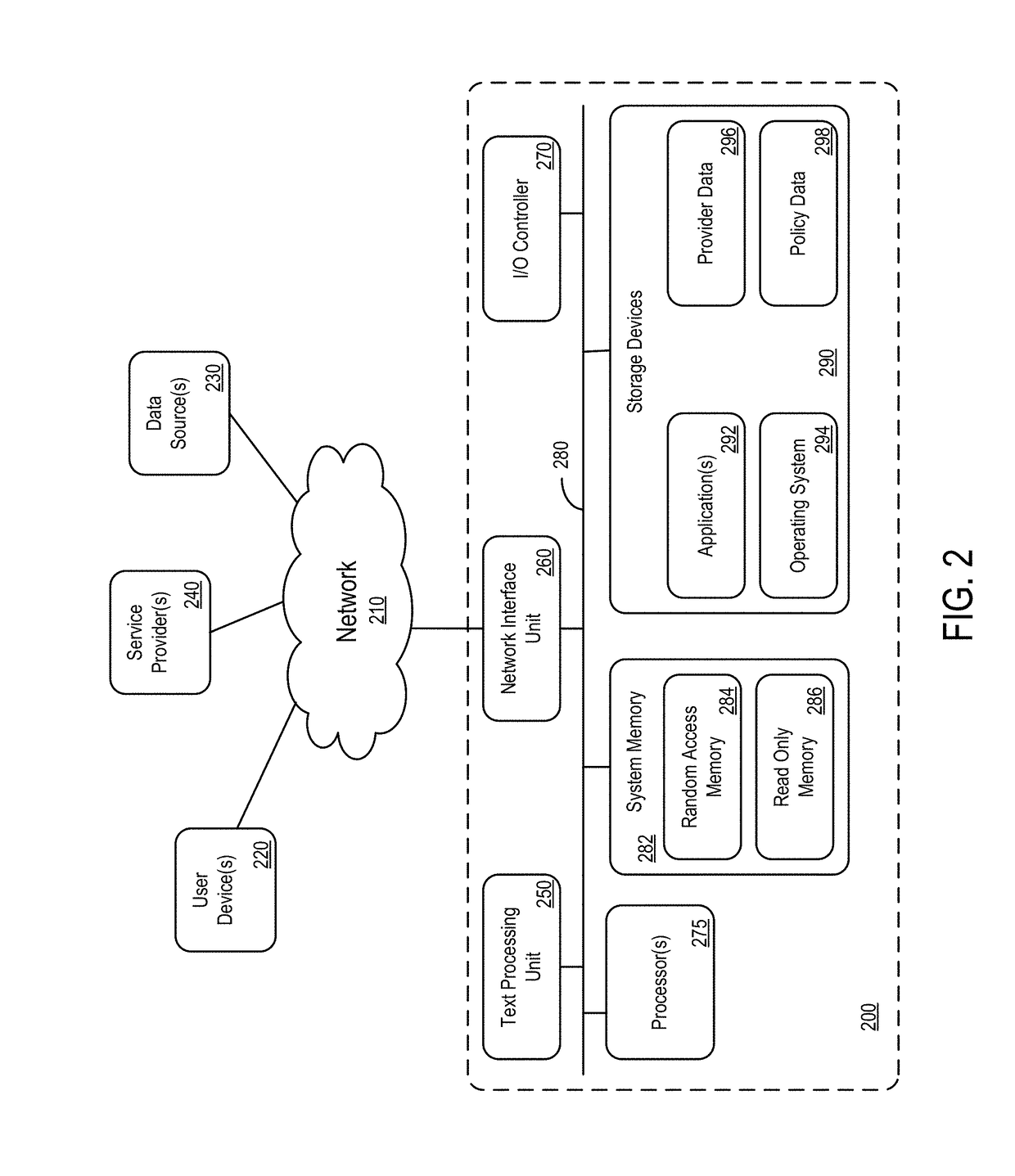
InactiveUS20080301231A1Greater assurance of their ability to successfully executeRaise the possibilityAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementSupply managementApplication computers
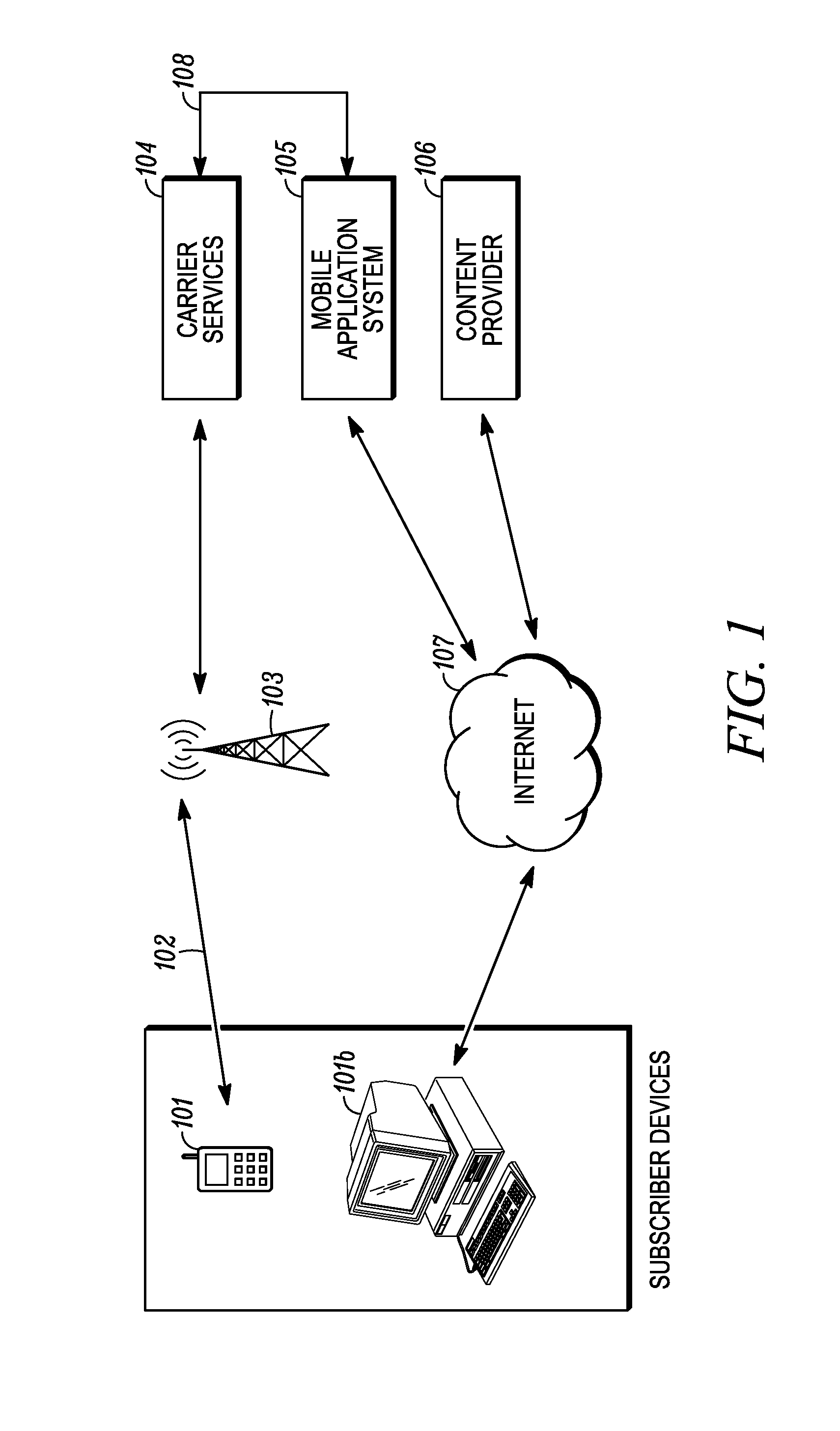
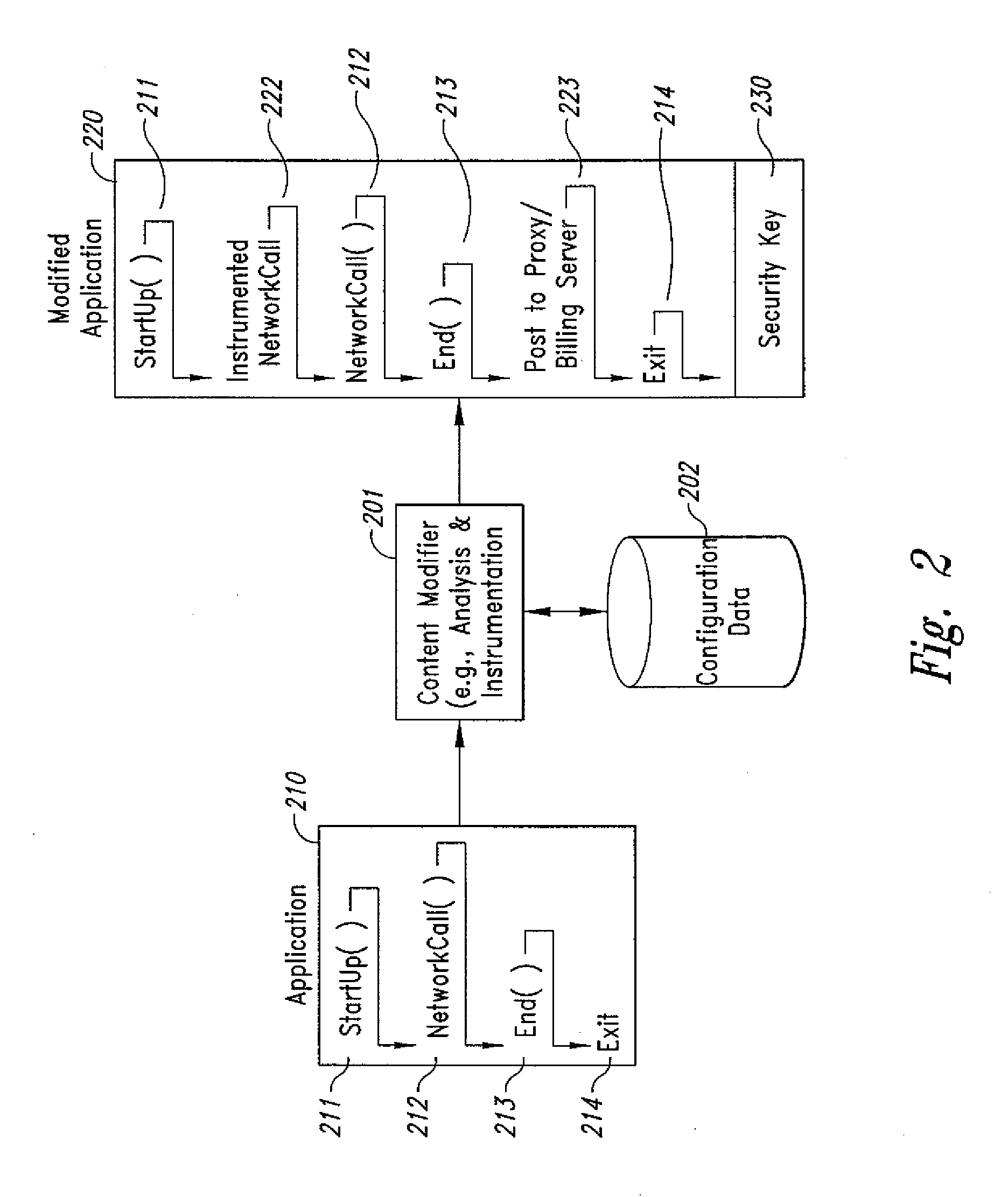
Computer- and network-based methods and systems for maintaining and provisioning wireless applications are provided. Example embodiments provide a Mobile Application System (MAS), which is a collection of interoperating server components that work individually and together in a secure fashion to provide applications and resources to mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to deploy applications and resources for wired subscriber devices. Application, resources, and other content is provisioned and verified by the MAS for authorized access by the subscriber, compatibility with a requesting subscriber device, and the security and billing policies of the carrier and system administrators of the MAS. In this manner, applications, resources, and other content can be downloaded to devices, such as wireless devices, with greater assurance of their ability to successfully execute. In one embodiment, content is provisioned by one or more of the steps of inspecting the content for malicious or banned code, optimizing the content for smaller size and greater speed, instrumentation of code that implements security, billing, and other carrier policies, and packaging of code for the intended subscriber device. Additional security is provided through application filters that are used to prevent applications that contain designated API from being downloaded to a subscriber's device. In one embodiment, the MAS includes a Protocol Manager, Provisioning Manager, Cache, Deployment Manager, Billing Manager, Logging Manager, Administrator, and Heartbeat Monitor, which interoperate to provide the provisioning functions.
Owner:MEHTA SAMIR NARENDRA +2
Systems and methods for class designation in a computerized social network application
InactiveUS20050209999A1Digital data processing detailsServices signallingApplication computersPersonal details
Computer program products, methods, and systems for facilitating a computerized social network. The computer program products and systems include a user profile database and a social networking module. The user profile database comprises a plurality of personal profiles. Each respective personal profile in the plurality of personal profiles corresponds to a respective user in the computerized social network. Further, each respective personal profile in the plurality of personal profiles includes an identity of at least one user of the computerized social network other than the user represented by the respective personal profile. In addition, each respective personal profile in the plurality of personal profiles includes a capability to organize each of the at least one users into one or more groups associated with the user corresponding to the respective personal profile. The social networking module has a friend access routine that includes instructions for receiving a request from a first user to access users in the personal profile of a second user. The friend access routine further includes instructions for determining which of the users in the personal profile of the second user can be accessed by the first user.
Owner:JOU KENNY
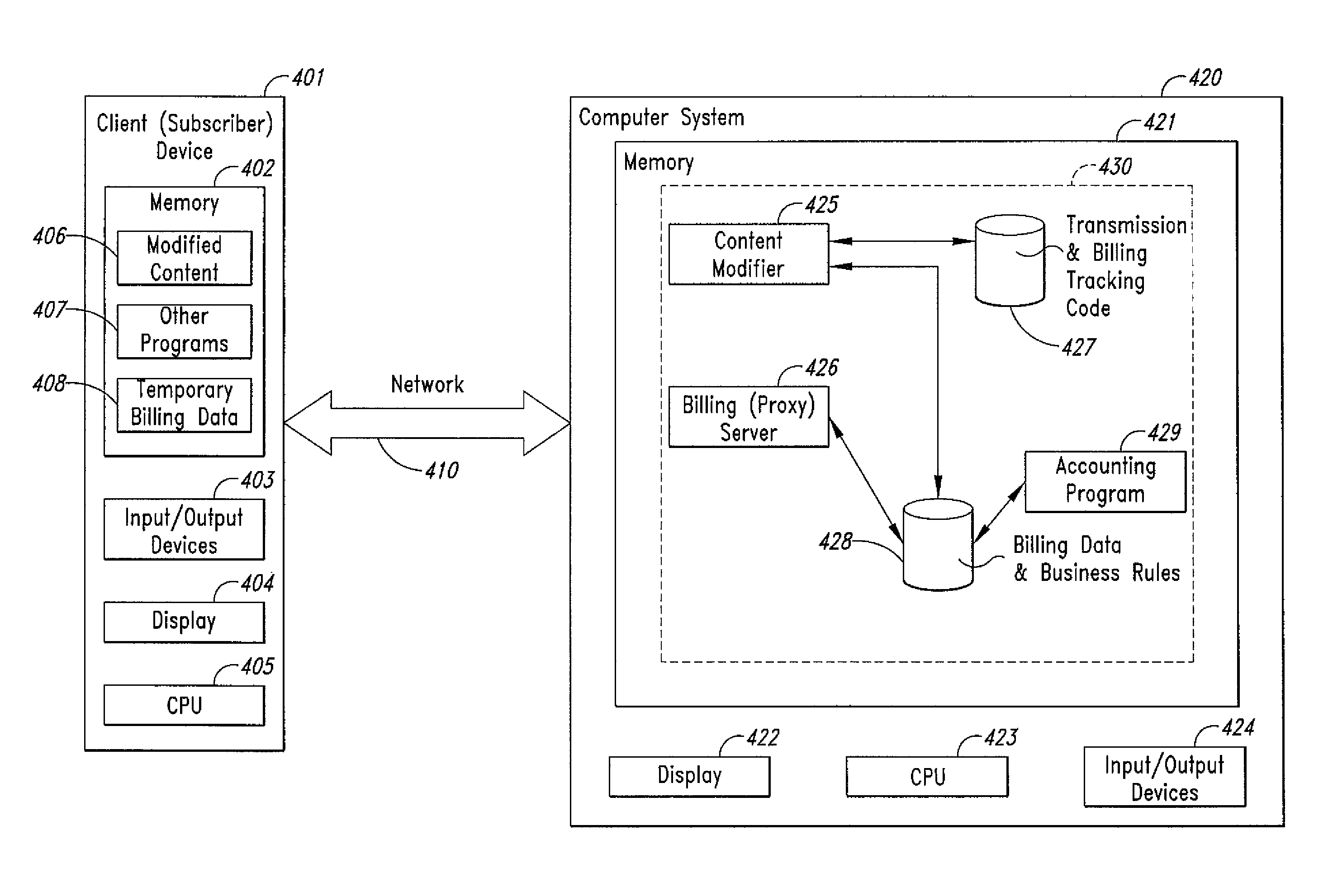
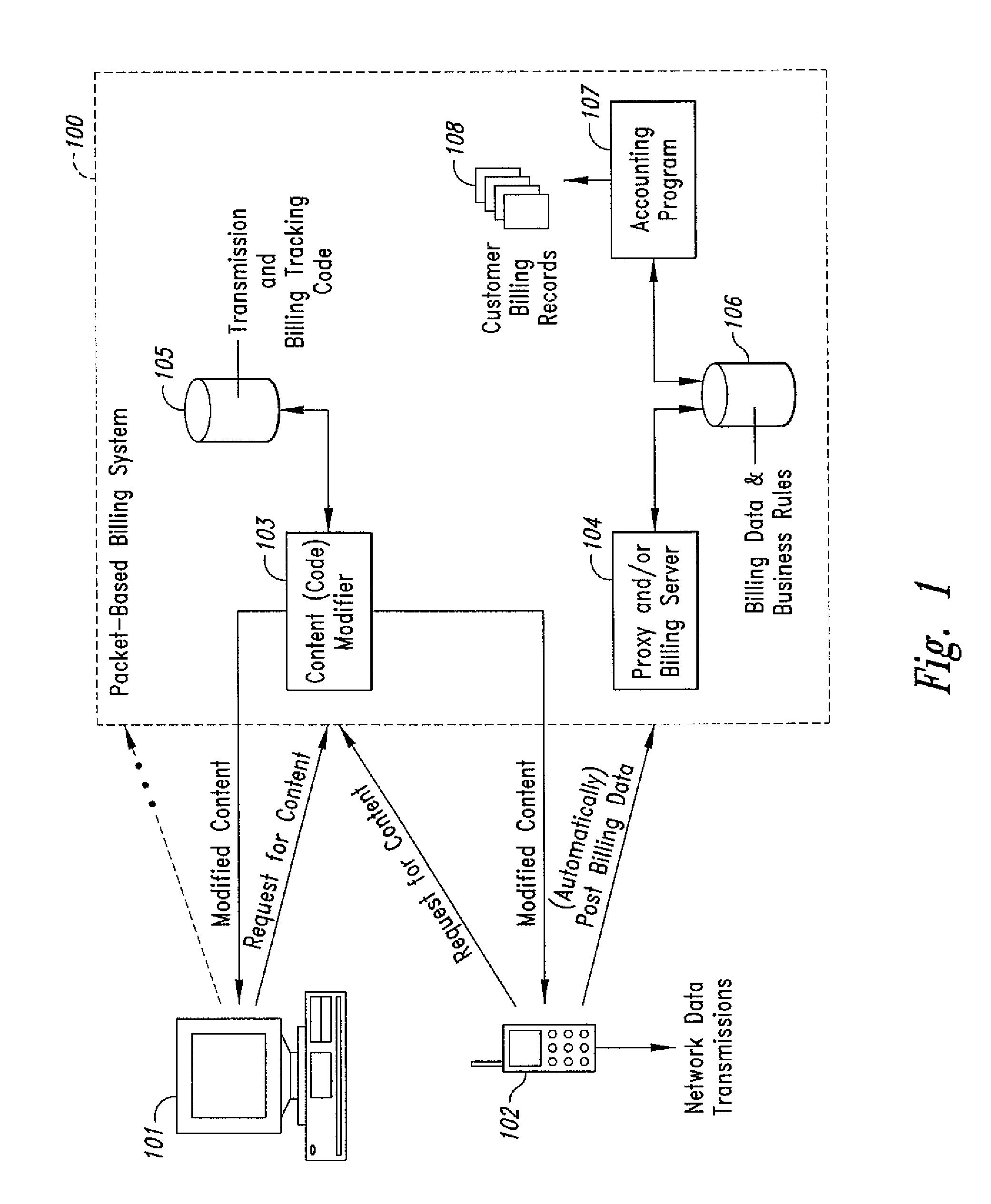
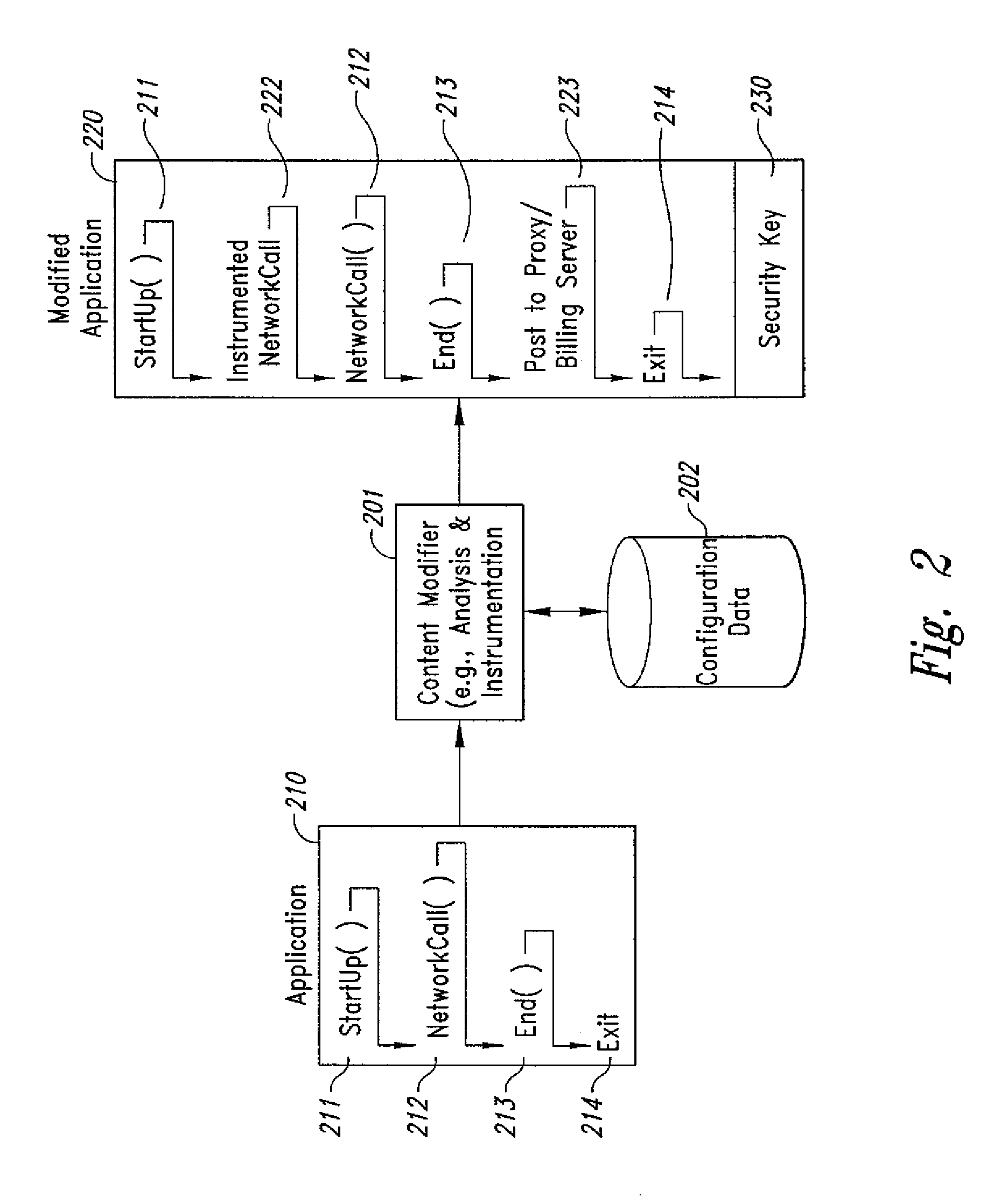
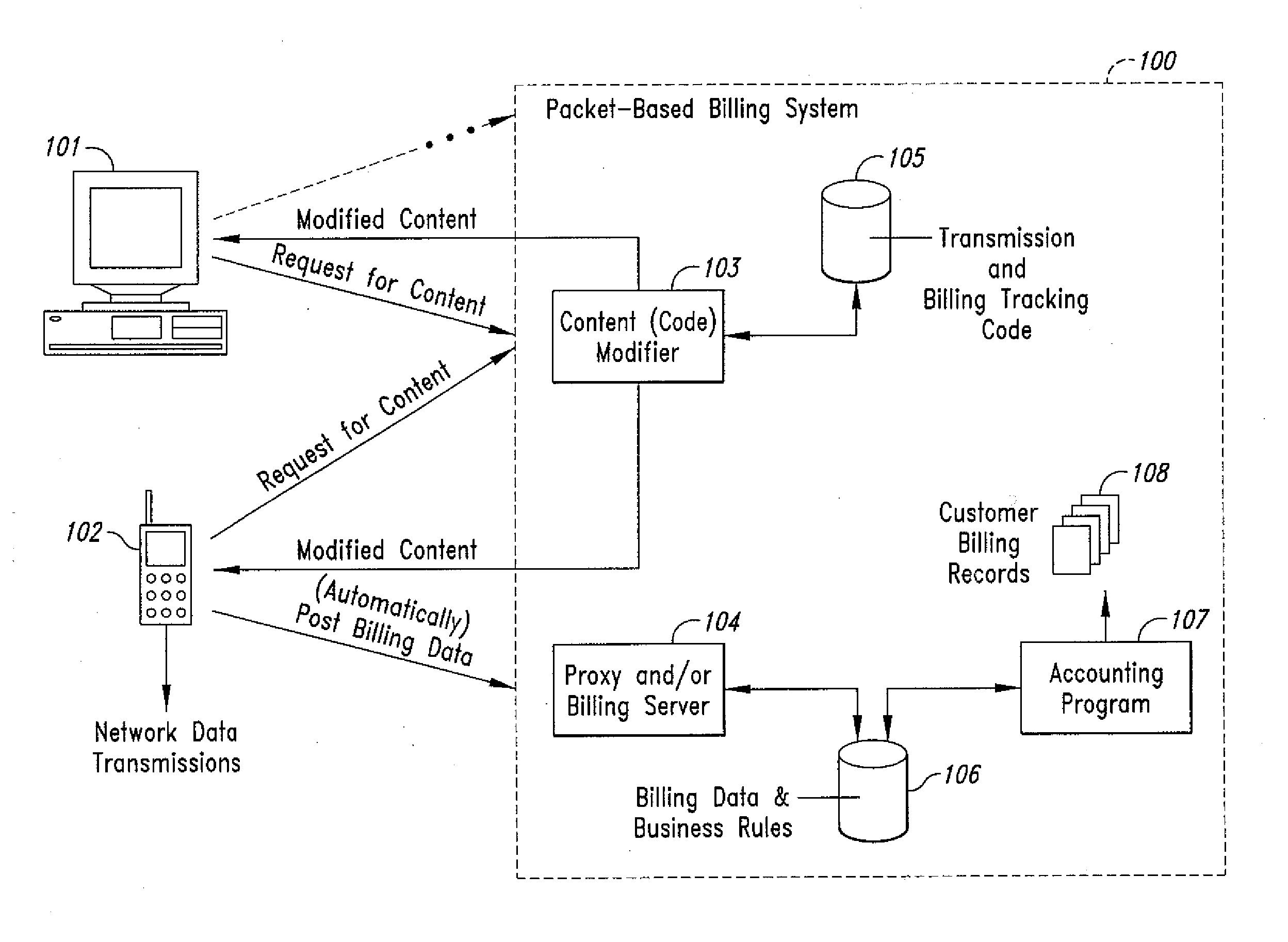
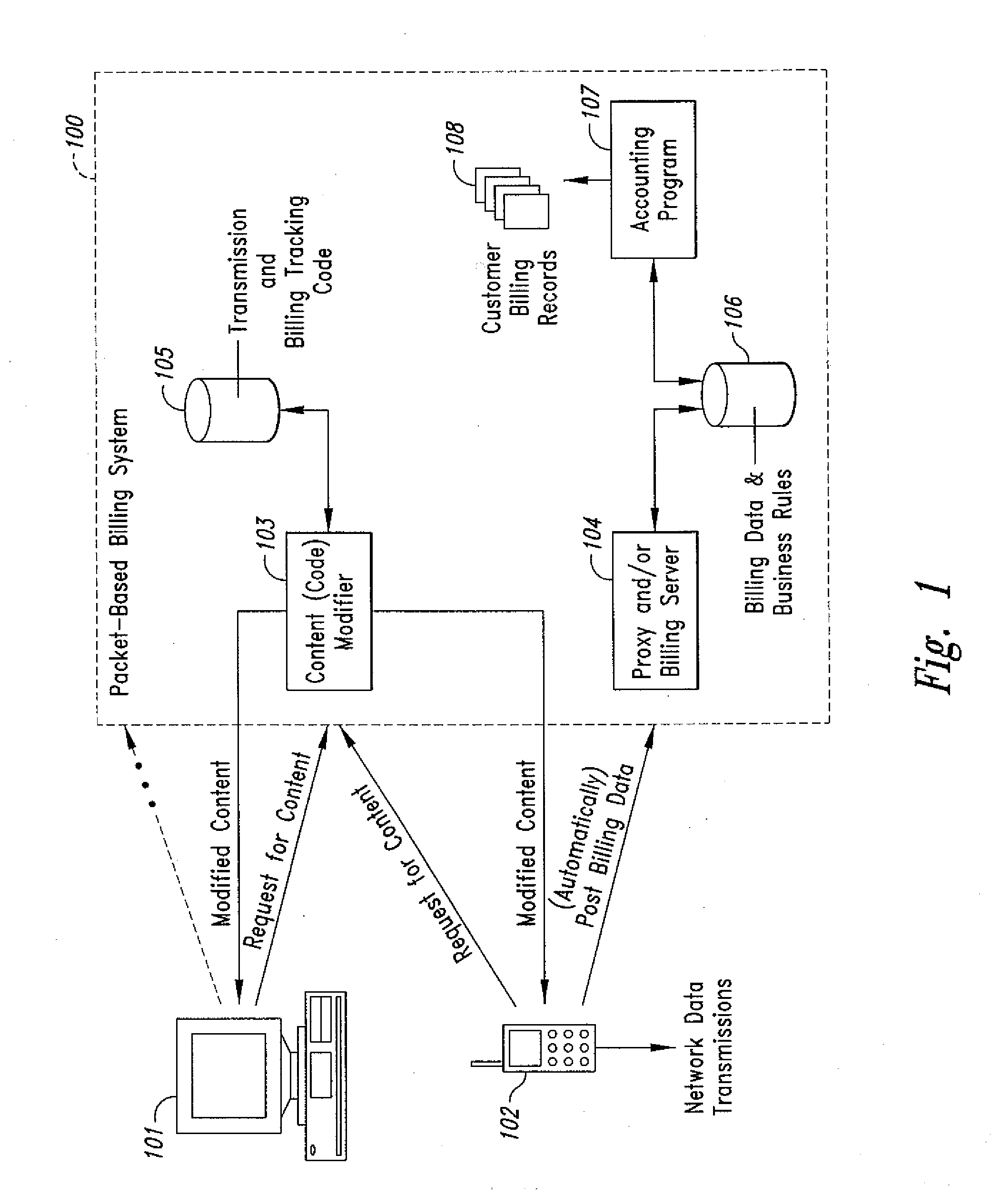
Method and system for transmission-based billing of applications
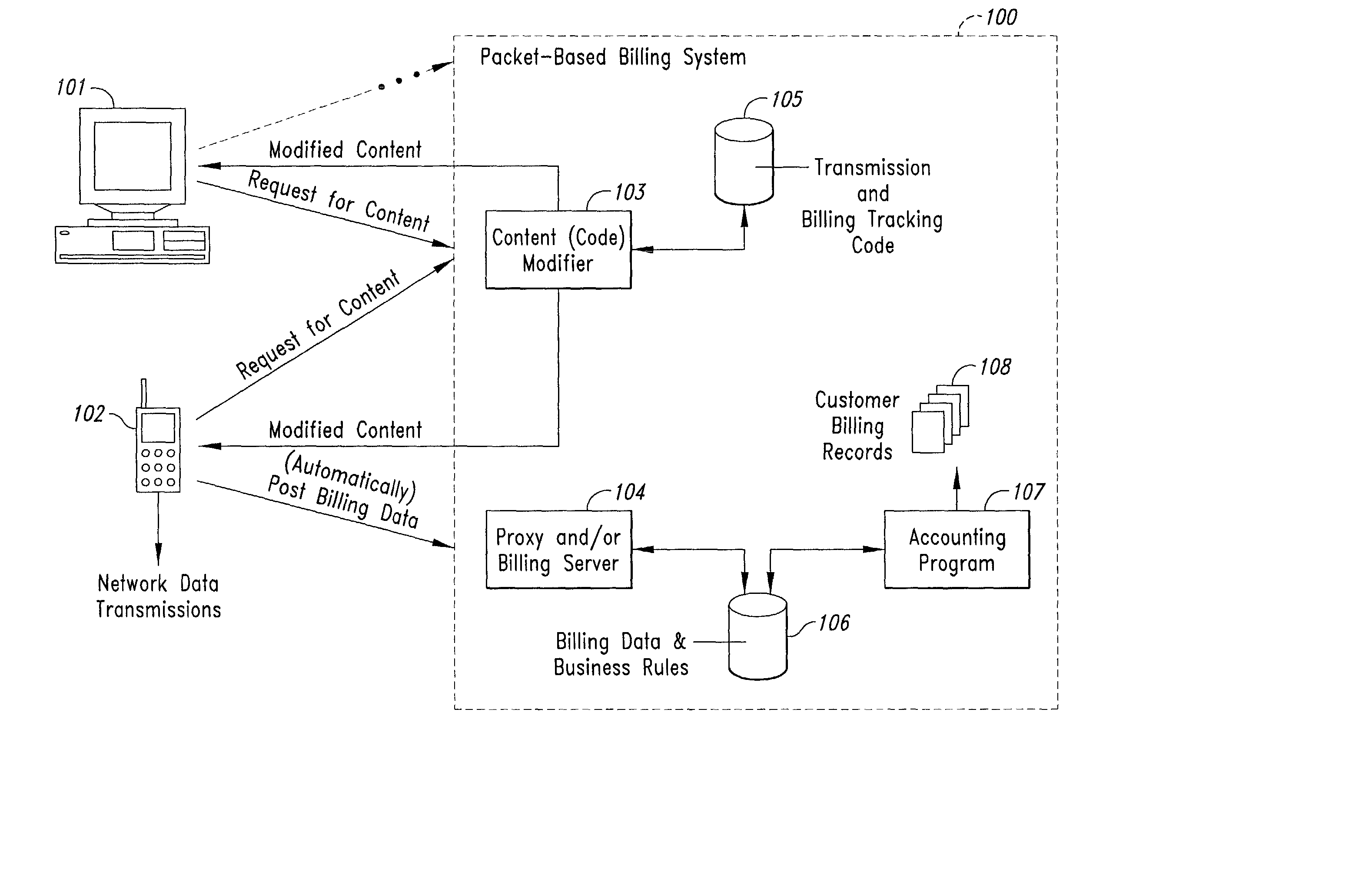
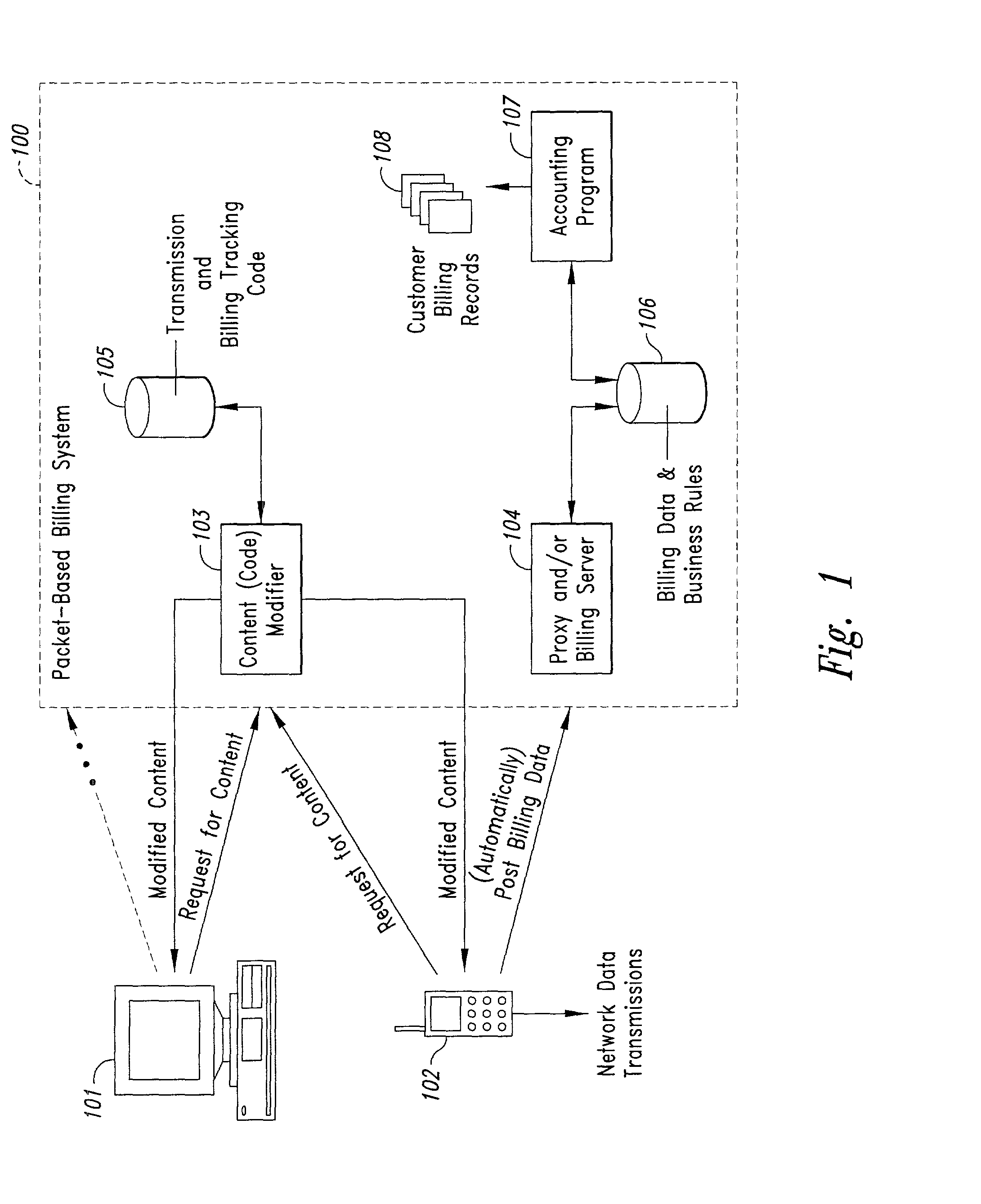
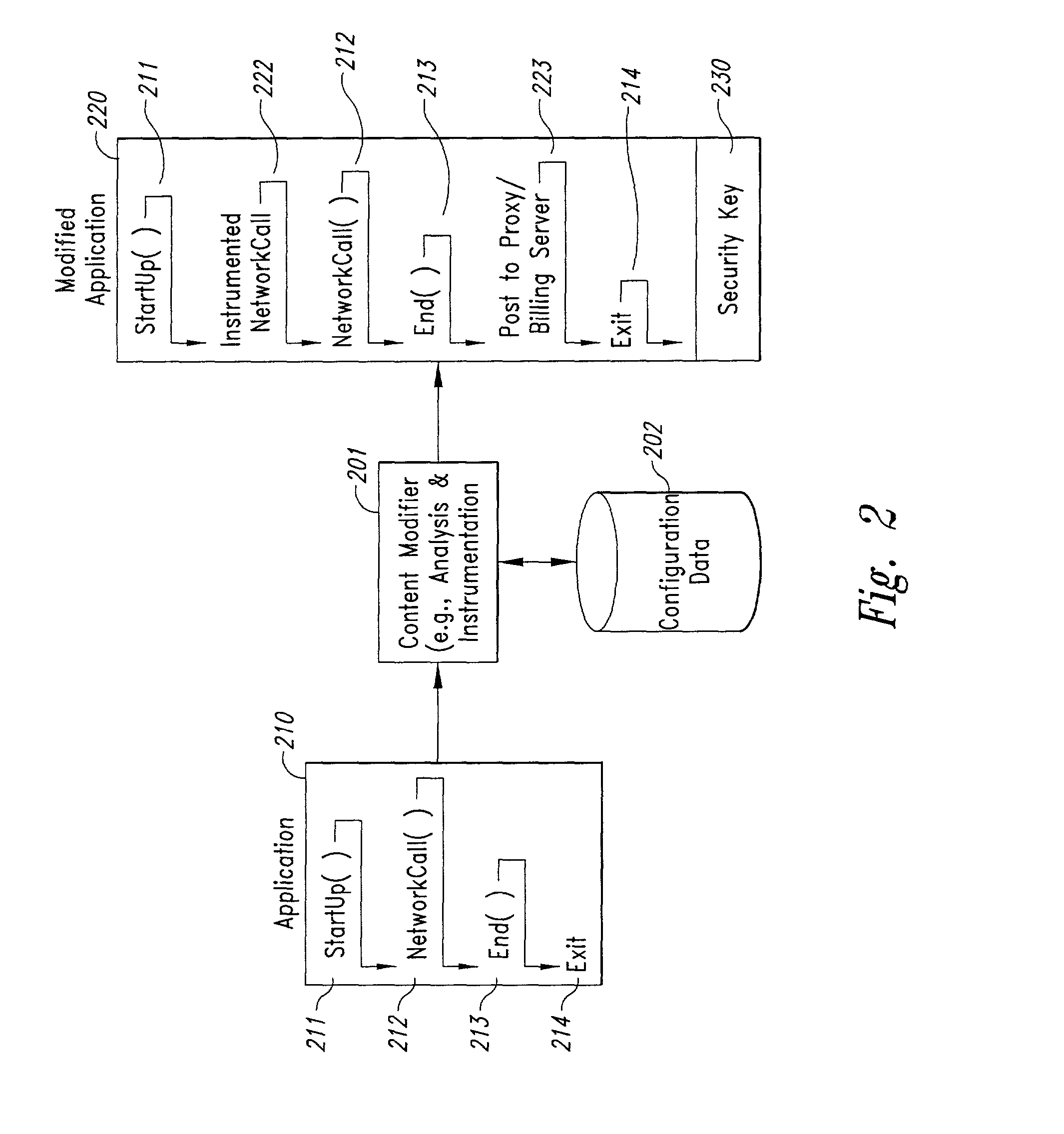
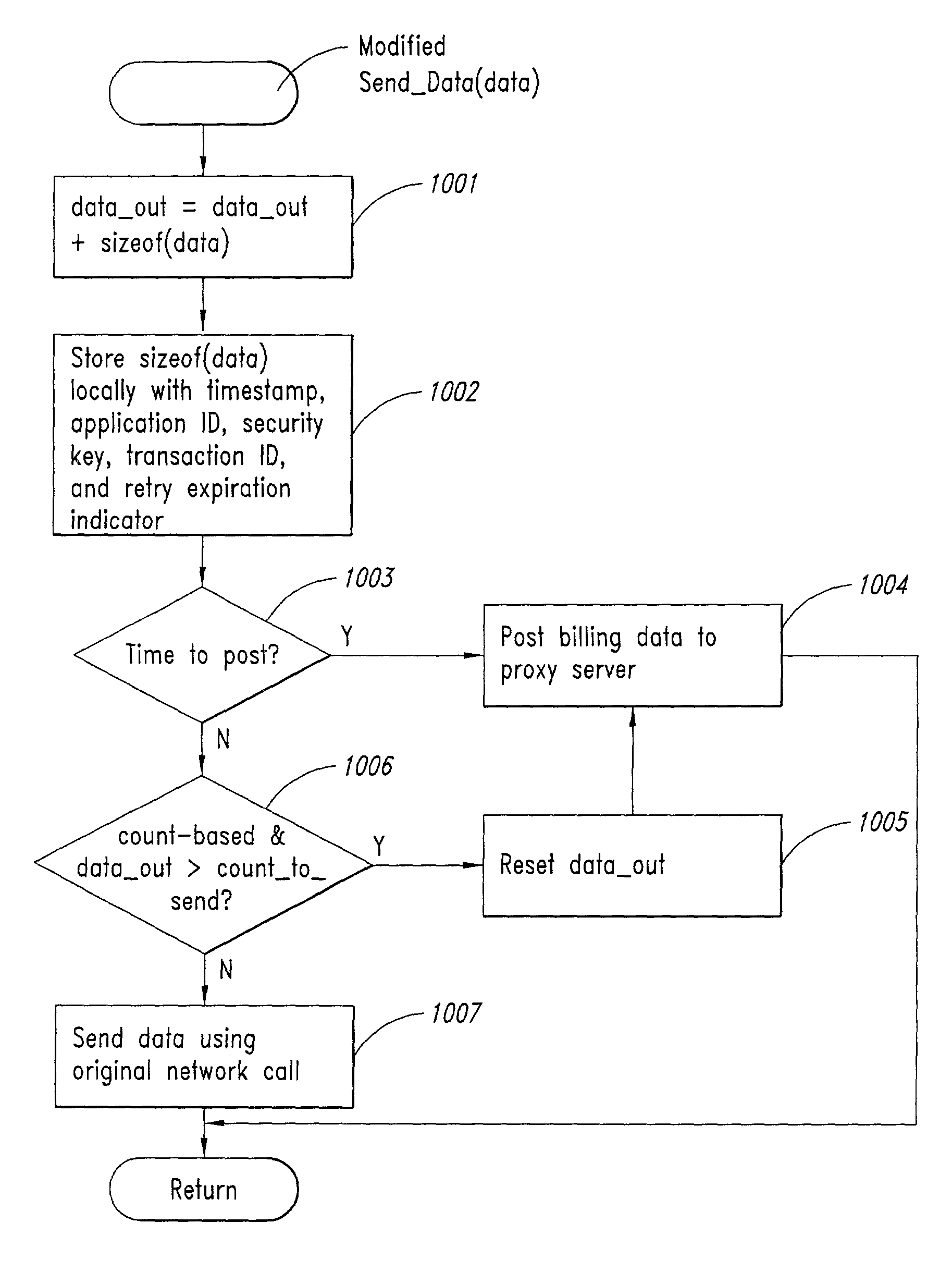
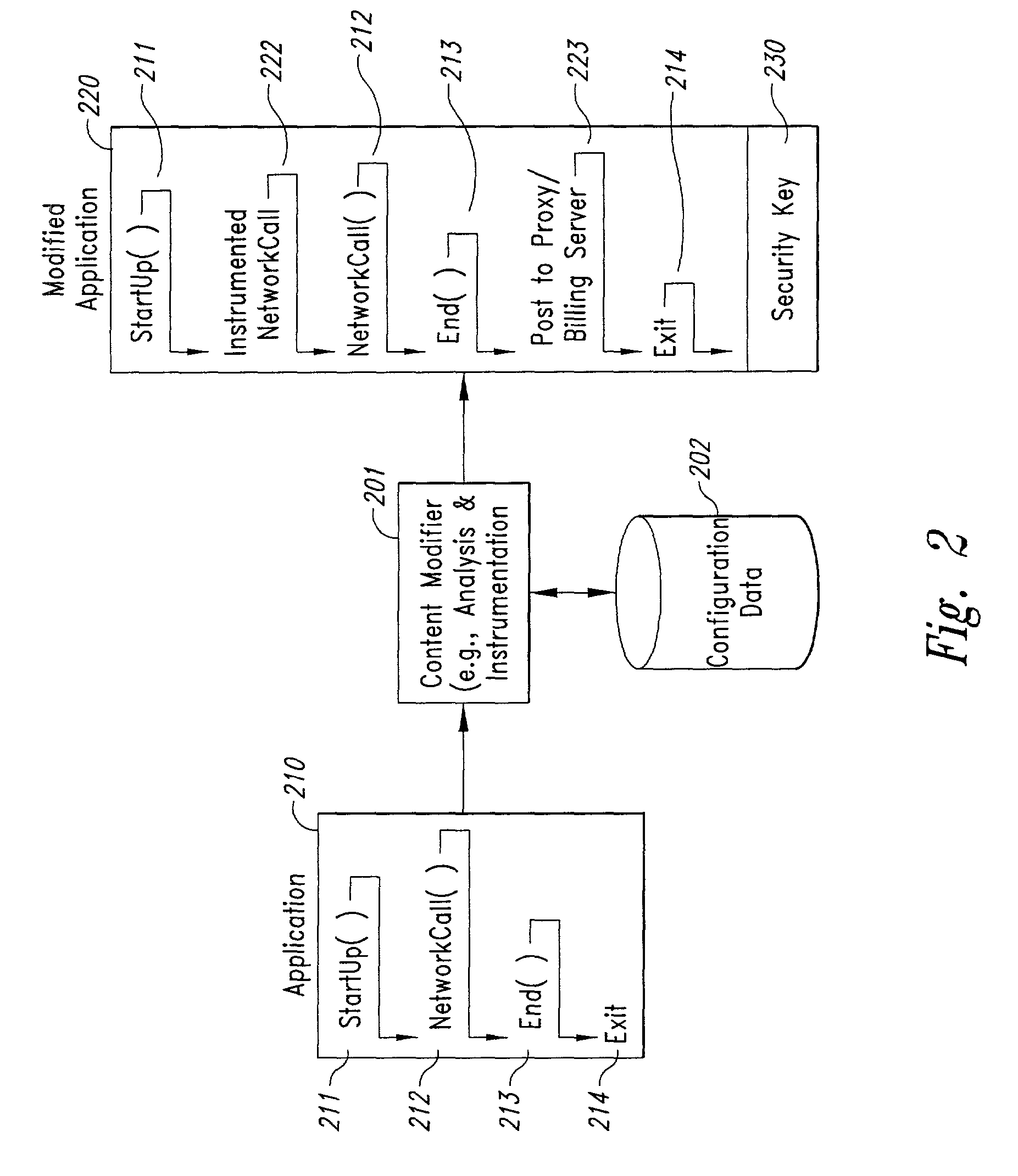
InactiveUS20020128984A1Short response timeImprove efficiencyMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesApplication computersApplication software
Computer-and network-based methods and systems for transmission-based billing are provided. Example embodiments provide a Packet-Based Billing System ("PBBS"), which enables application providers, such as carriers and content providers, to bill subscribers for the use of content on mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices, on a per-application, per-user basis based upon the extent of the usage. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to bill subscribers for the use of content on a per-application, per-user basis for wired subscriber devices as well, using the same techniques. In operation, the PBBS provides modified content by inserting billing and tracking code into content returned to a requesting device. The modified content, when executed, tracks the amount of data sent and received between the content and a network and posts the accumulated data to a proxy / billing server according to business rules for an interval / frequency to post such data. The proxy / billing server stores the raw billing data and an accounting program retrieves the billing data to generate customer (call) data records. Business rules that specific different charges for different content or users can be incorporated into the system.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
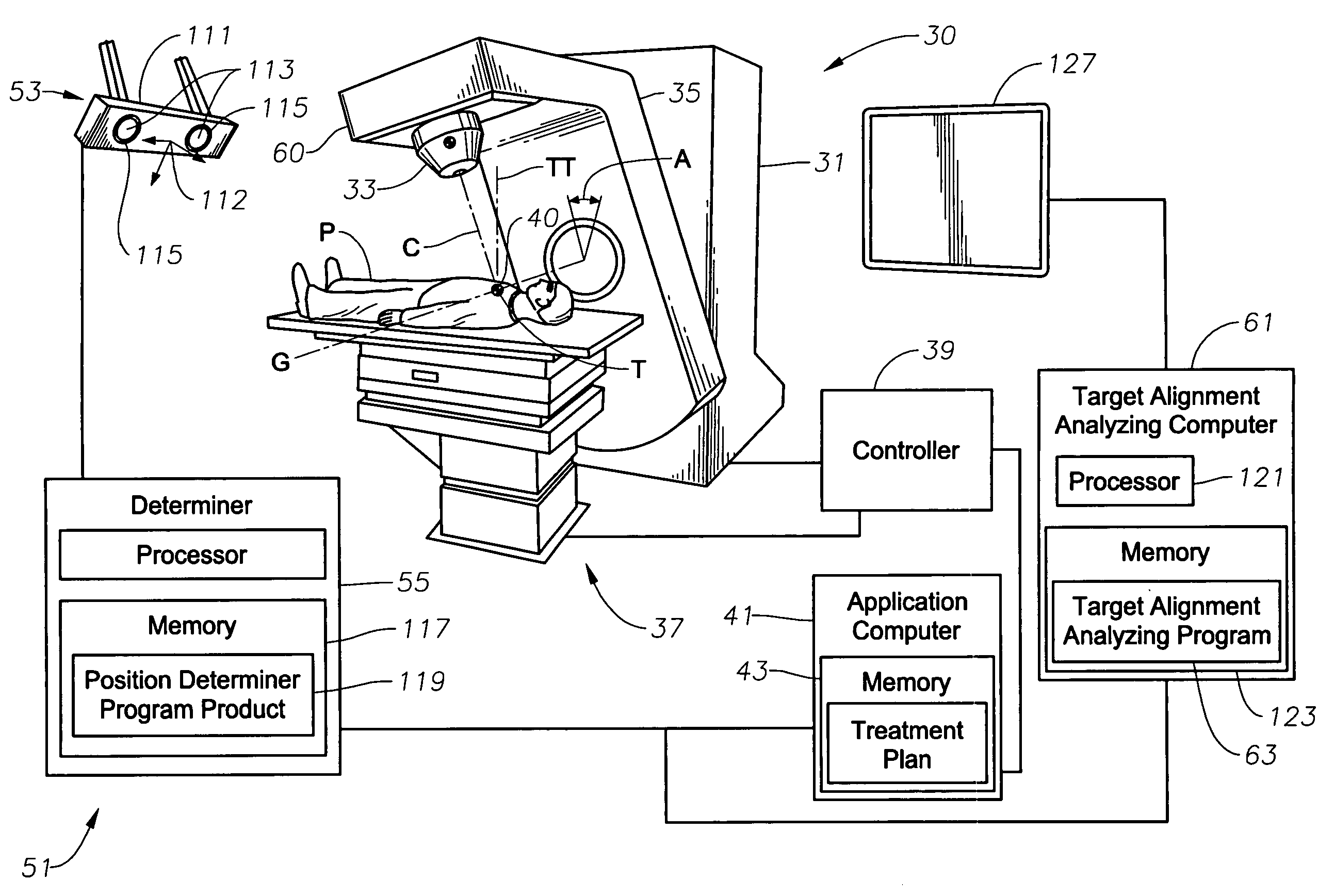
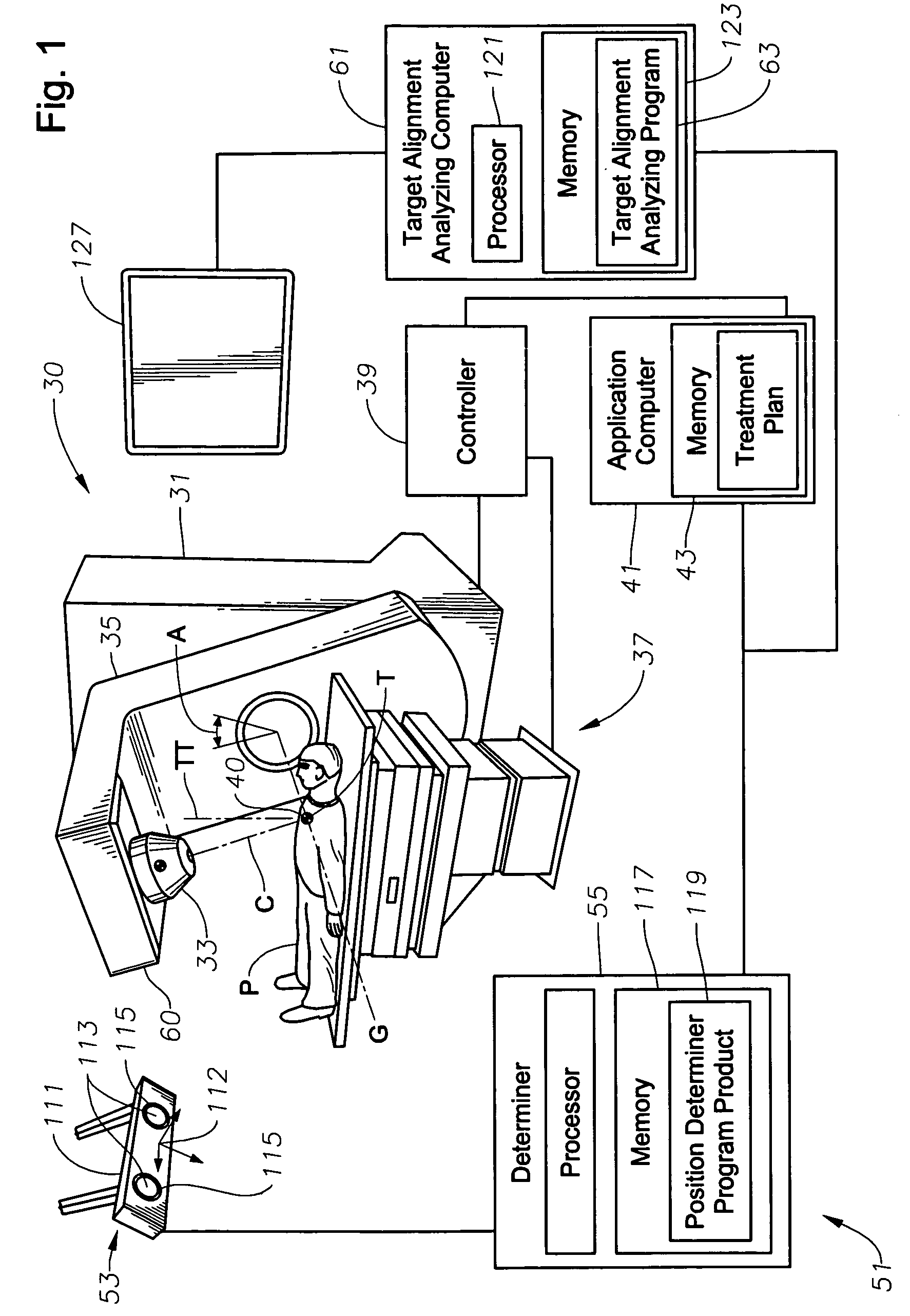
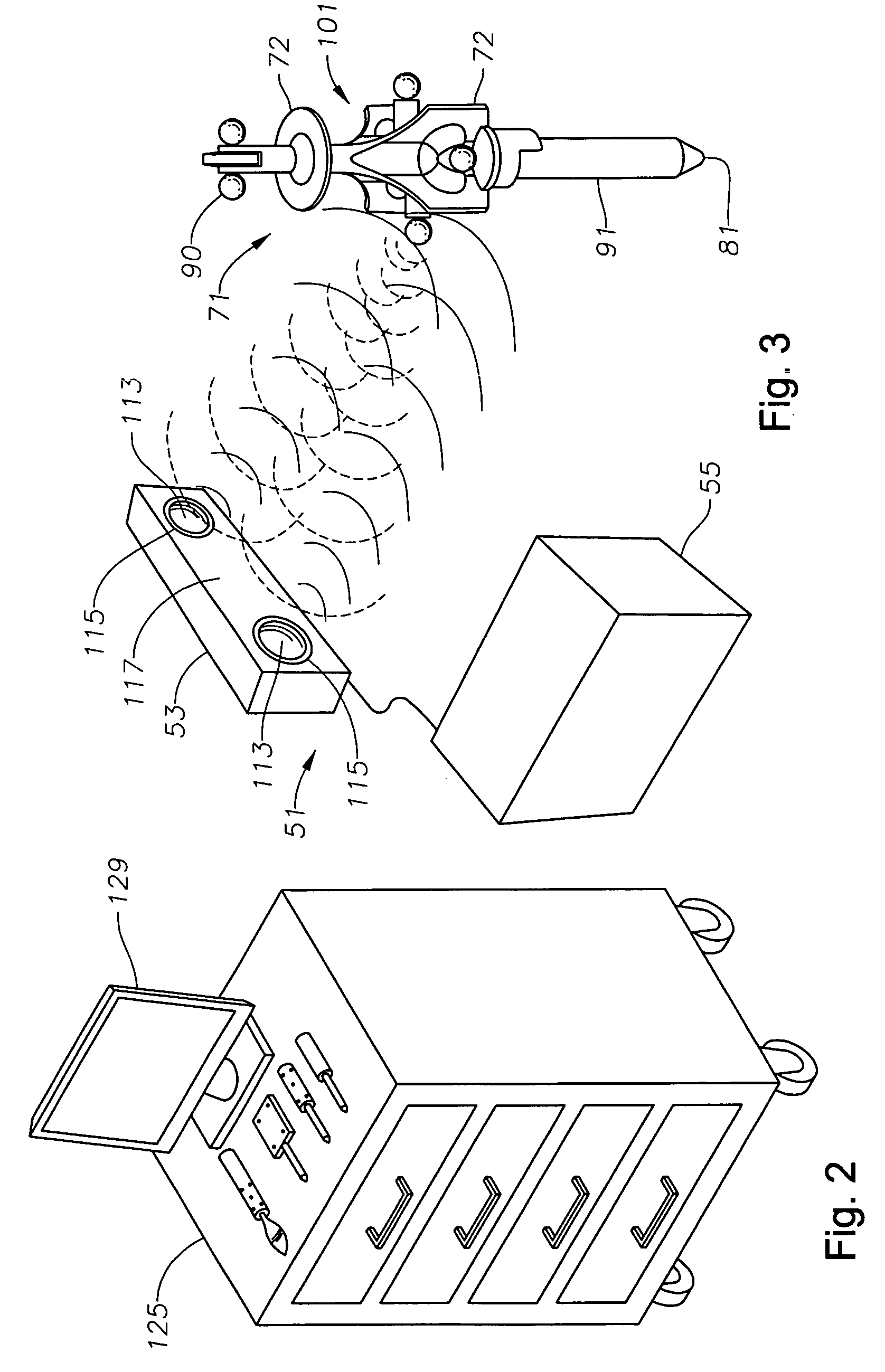
System, tracker, and program product to facilitate and verify proper target alignment for radiation delivery, and related methods
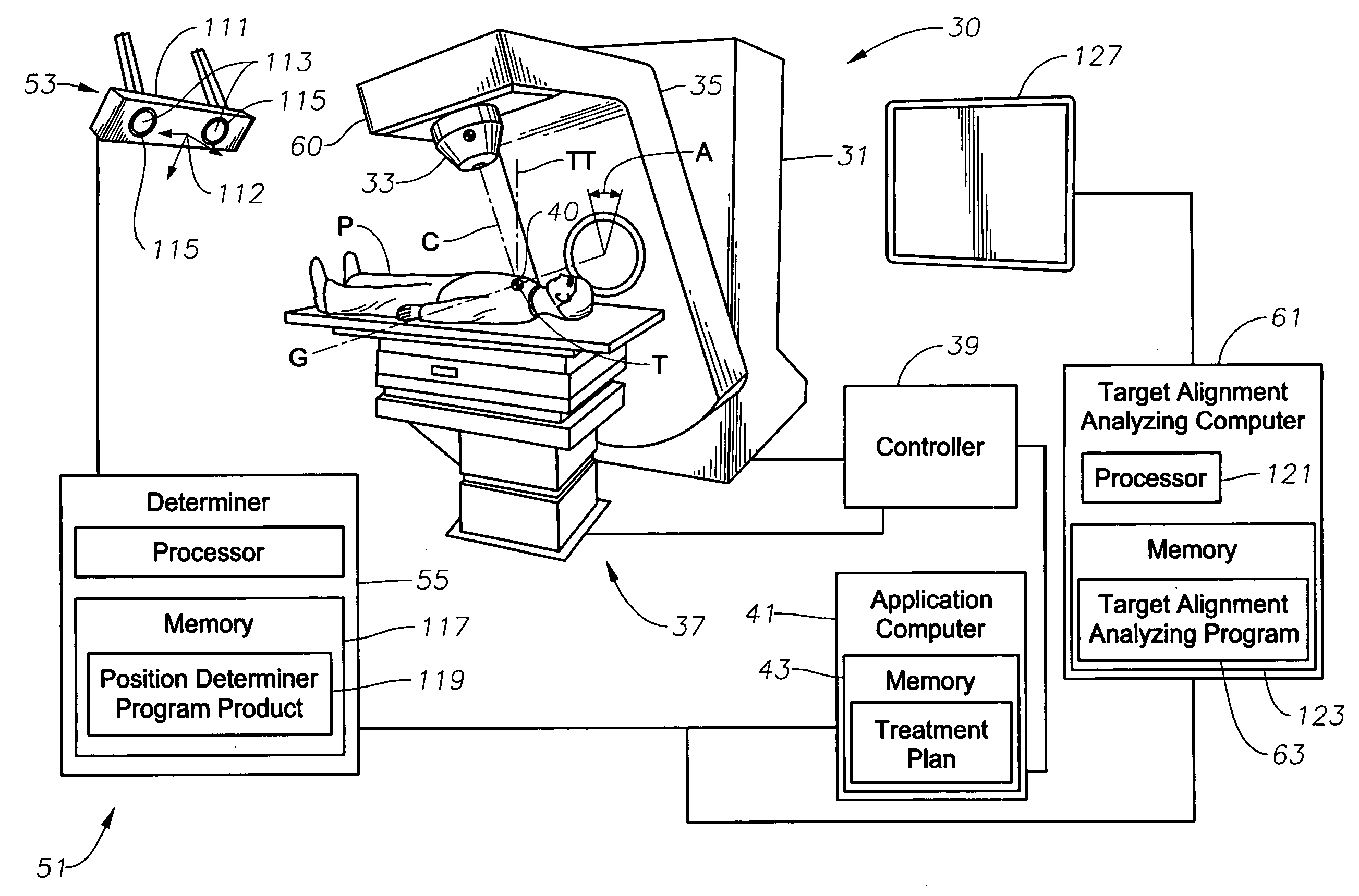
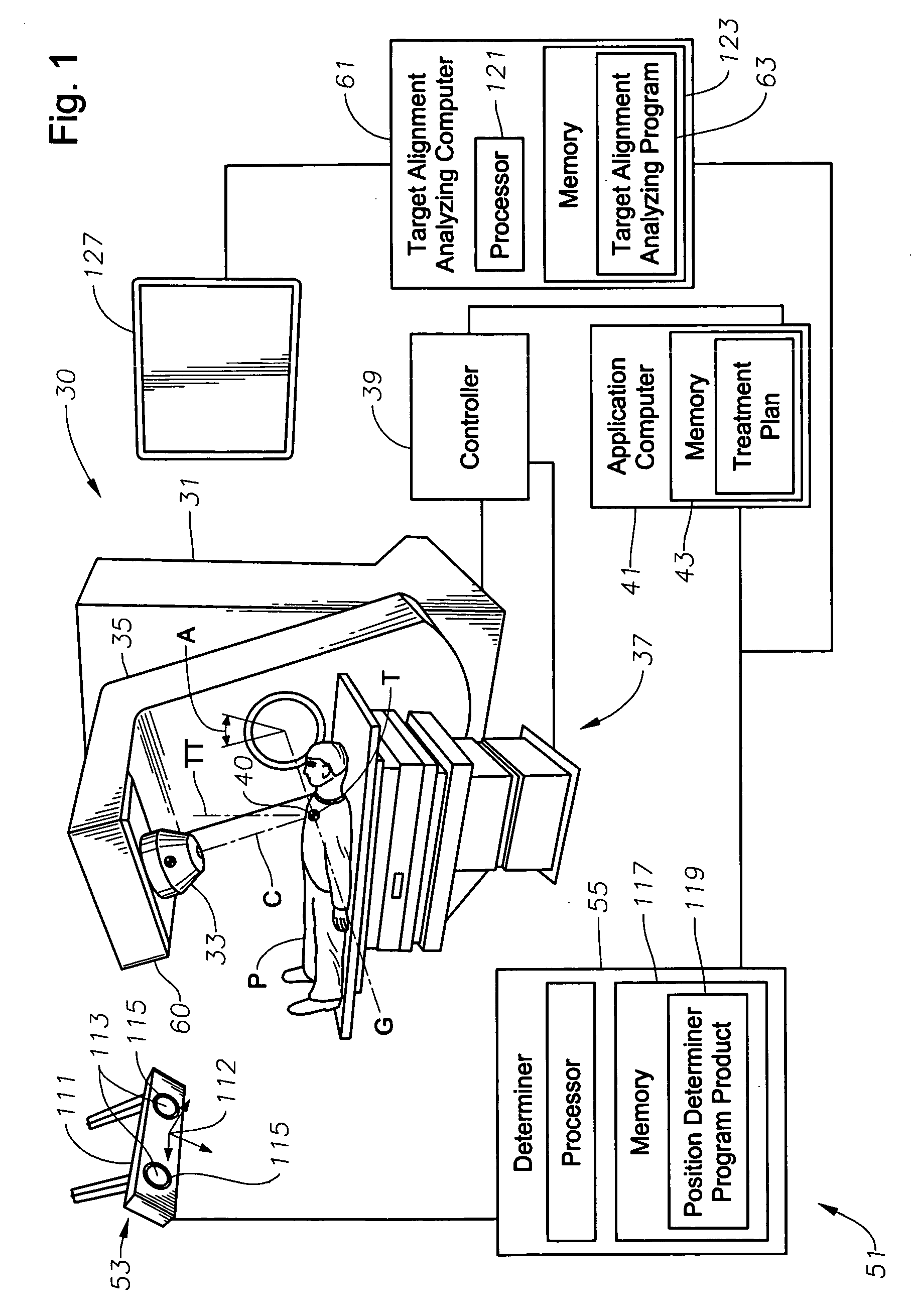
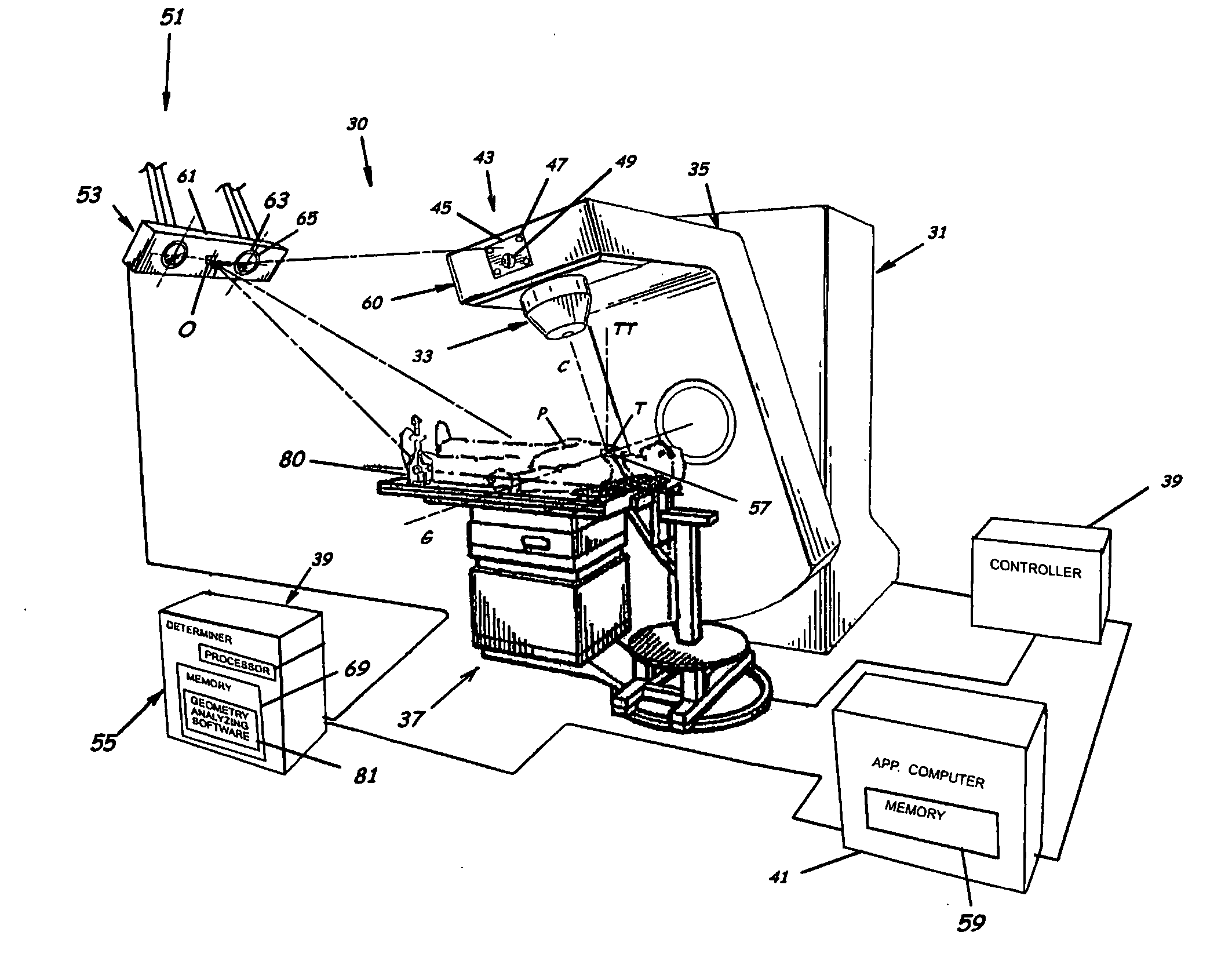
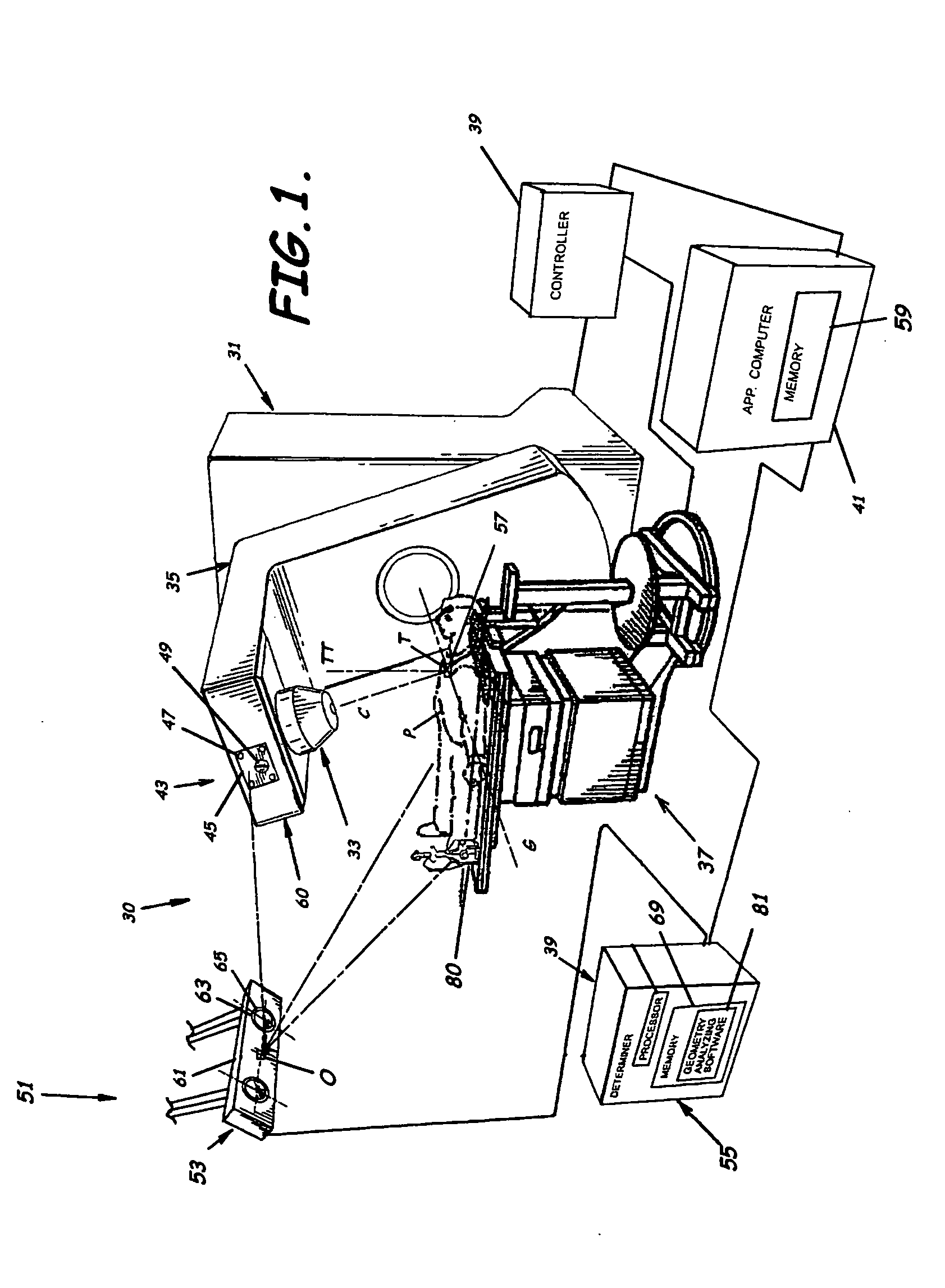
ActiveUS20060285641A1Simple quick applicationEasy to implementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTreatment deliveryApplication computers
A system, tracker, program product, and methods to facilitate and verify proper target alignment for radiation delivery are provided. The system includes a radiation delivery apparatus having a radiation emitter, a rotating assembly controlled by a controller, and an application computer which provides treatment delivery instructions to the controller. The system also includes a trackable body having a trackable body reference point to be positioned adjacent a surface point of a patient to determine a position of such surface point. The system also includes an apparatus to track a trackable body which has a trackable body detector to detect a position of indicators carried by the trackable body and a trackable body determiner to determine a position of the trackable body reference point. The system also includes a target alignment analyzing computer having memory and target alignment analyzing program product stored therein to aid a user of the system to make and display various patient body-surface related measurements.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Circuit arrangement and method for starting up a circuit arrangement
InactiveUS20080082828A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsApplication computersStart up
A circuit arrangement has a crypto unit which provides at least one cryptographic function. An access monitoring interface is also provided in order to check an access request from an application computer program to a cryptographic function of the crypto unit. The access monitoring interface is designed such that it checks whether the application computer program is authorized to access the cryptographic function, and the cryptographic function is called only if it is authorized to do so.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Automated service management system with rule-based, cascading action requests
InactiveUS20170220998A1Faster and efficient performanceFacilitate communicationFinanceOffice automationService product managementIT service management
A system may generate action requests for a service management system. A user preference data store may contain electronic records for a set of users, including, for example, at least one user preference value. A back-end application computer server may receive, from a remote user mobile device, an indication associated with an event. The server may then determine at least one location coordinate associated with the event and select a sub-set of service providers from a service provider data store based on the location and at least one user preference value. The server may generate an action request for a designated one of the sub-set of service providers in accordance with logic based rules and transmit information about the action request to the designated service provider and the remote user mobile device. The server may receive an action request update and transmit a modified action request to another service provider.
Owner:HORN GREGORY WILLIAM +1
Method and system for transmission-based billing of applications
InactiveUS7436816B2Avoid dataAvoid misappropriationSpecial service provision for substationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsApplication computersApplication software
Computer- and network-based methods and systems for transmission-based billing are provided. Example embodiments provide a Packet-Based Billing System (“PBBS”), which enables application providers, such as carriers and content providers, to bill subscribers for the use of content on mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices, on a per-application, per-user basis based upon the extent of the usage. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to bill subscribers for the use of content on a per-application, per-user basis for wired subscriber devices as well, using the same techniques. In operation, the PBBS provides modified content by inserting billing and tracking code into content returned to a requesting device. The modified content, when executed, tracks the amount of data sent and received between the content and a network and posts the accumulated data to a proxy / billing server according to business rules for an interval / frequency to post such data. The proxy / billing server stores the raw billing data and an accounting program retrieves the billing data to generate customer (call) data records. Business rules that specific different charges for different content or users can be incorporated into the system.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
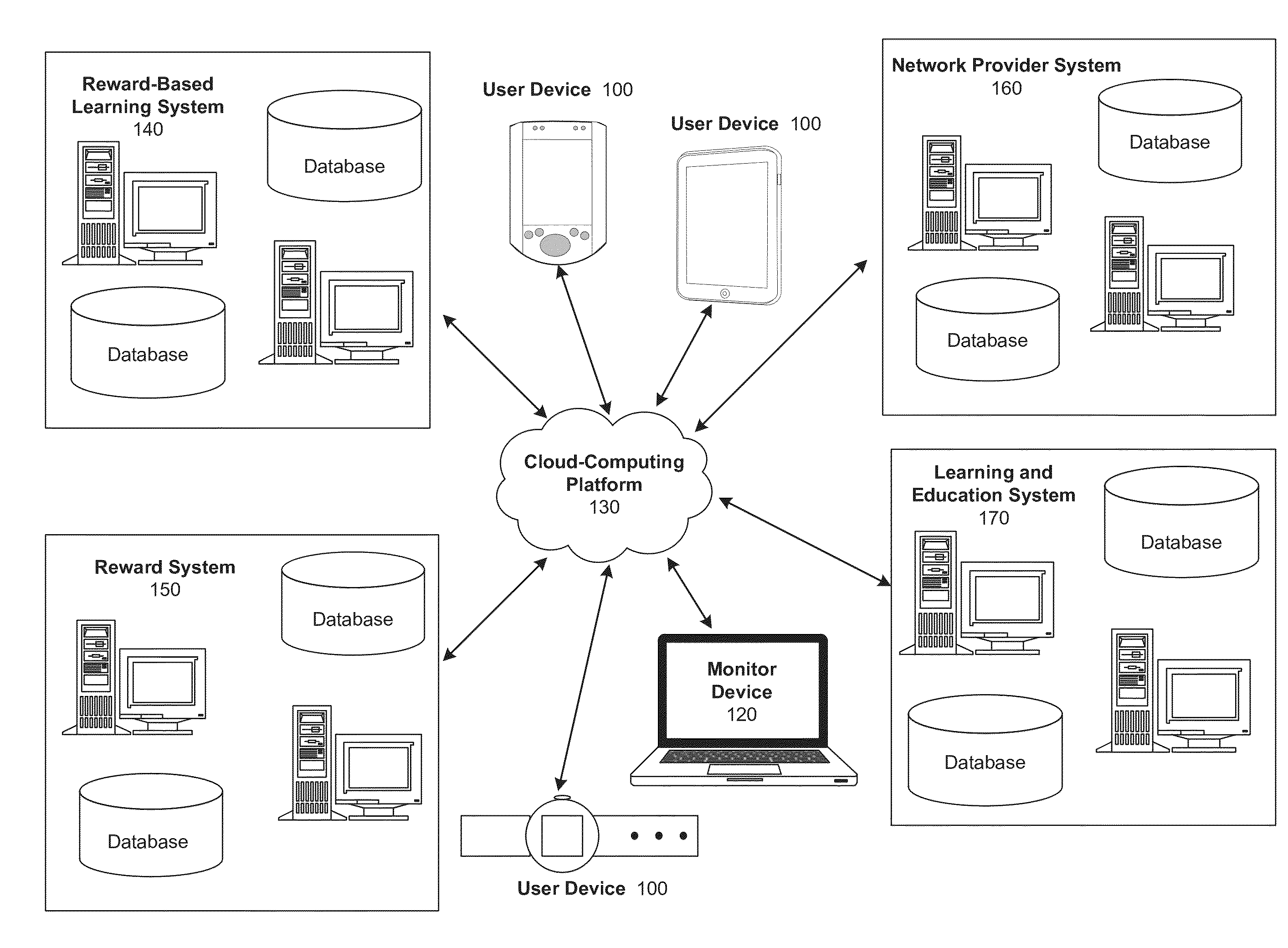
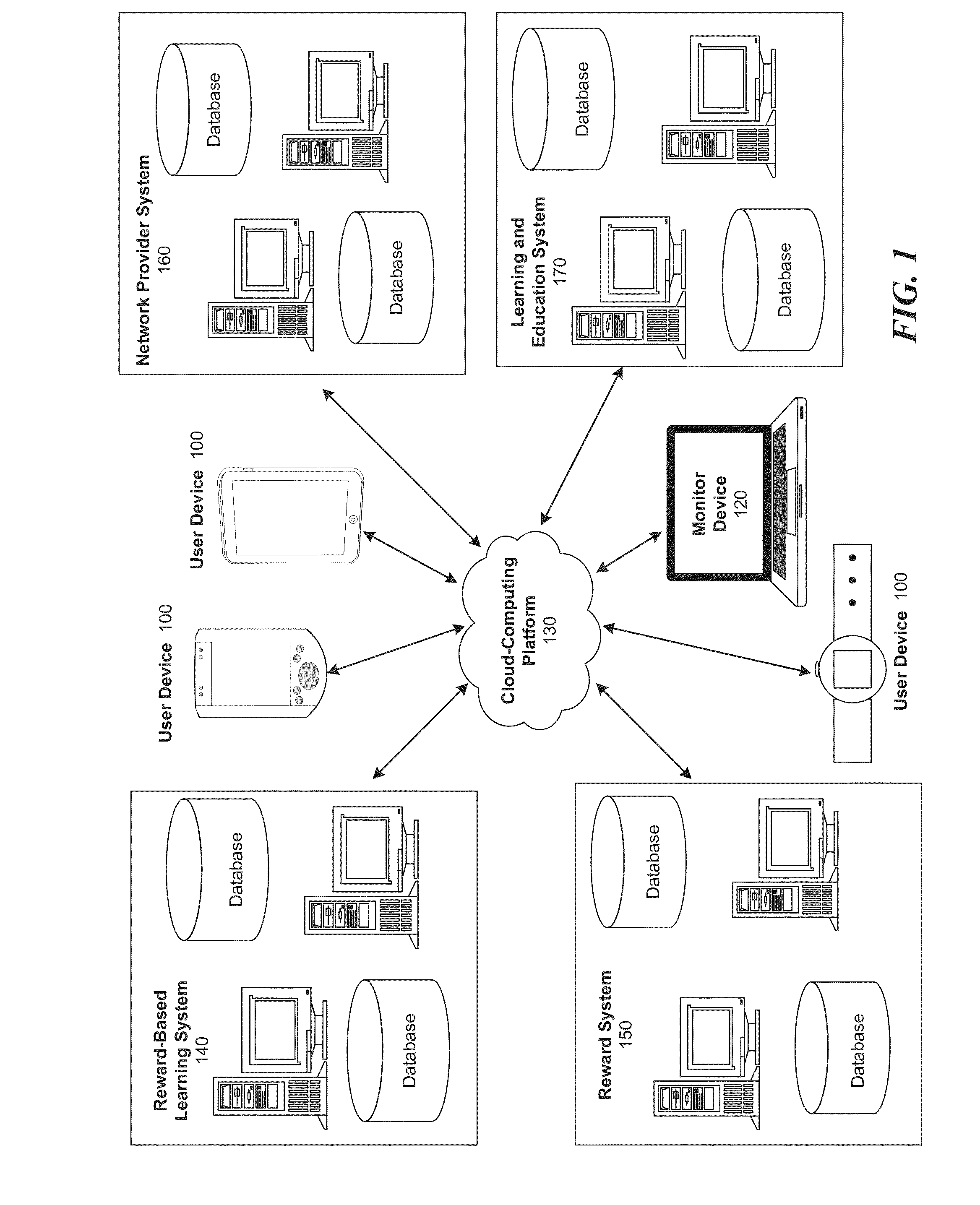
Method and system for integrated reward system for education related applications
InactiveUS20140272847A1Improve performanceDesirable levelDiscounts/incentivesElectrical appliancesApplication computersReward system
Computer implemented systems, methods and computer program products for assessing and designing customized reward-based learning sessions. These technologies involve determining factors for a student's peak academic performance, such as: 1) their preferred type of reward trigger; 2) their preferred timing of the learning objective relative to the reward; and, 3) the nature of the reward (time to use an electronic device, cash, store credit). The reward trigger is the type of event that most motivates a student to learn, such as achieving an academic milestone, demonstrating effort and improvement in lessons, and random rewards for participating in educational sessions. The timing of the learning objective relative to the reward may be measured as the time at which the user initiates operation of an electronic device, the time at which the user engages in a learning or testing exercise, or the time at which the user receives the reward.
Owner:EDULOCK
System, tracker, and program product to facilitate and verify proper target alignment for radiation delivery, and related methods
ActiveUS7613501B2Facilitate and verify proper target alignmentPrecise applicationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTreatment deliveryApplication computers
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
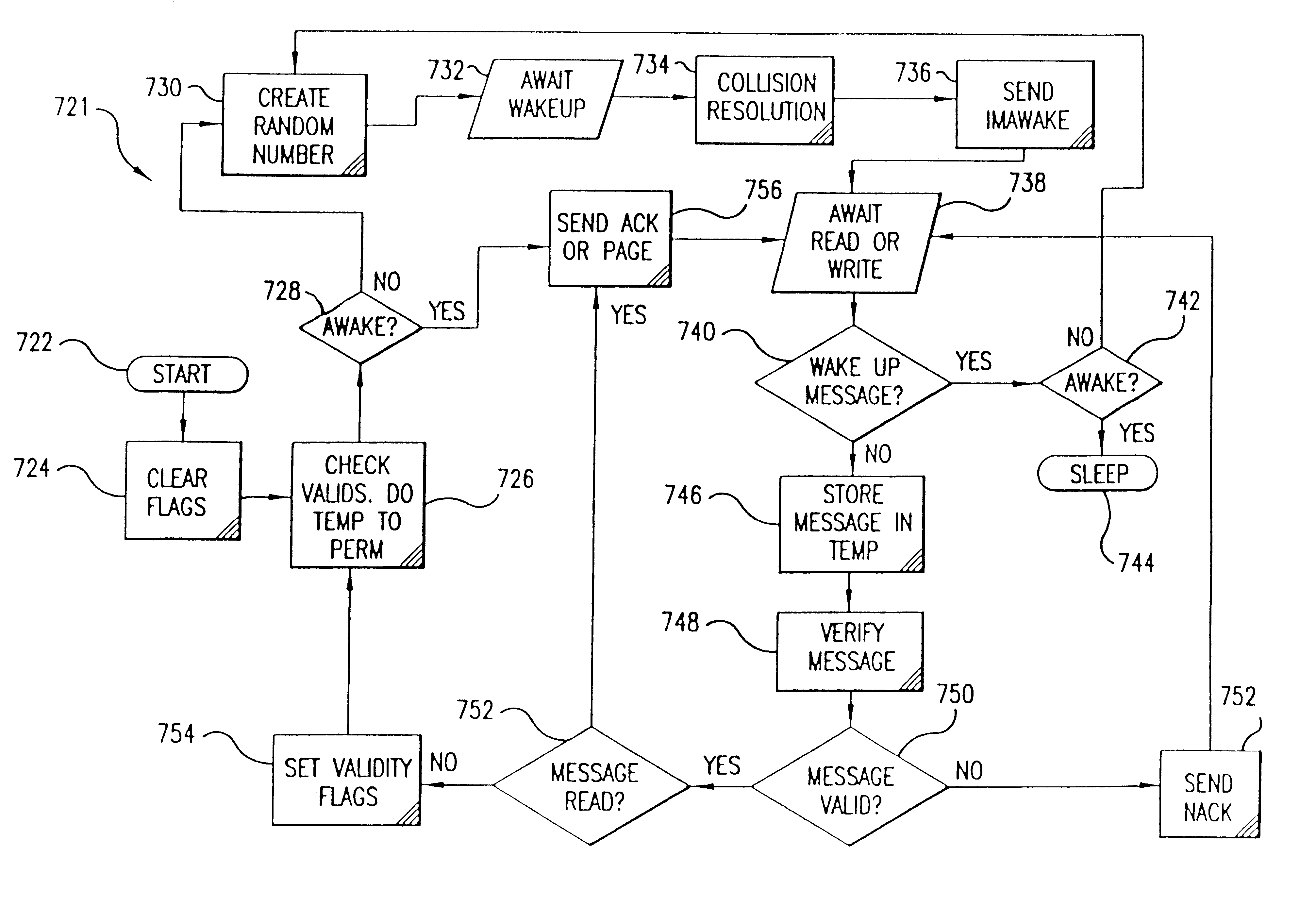
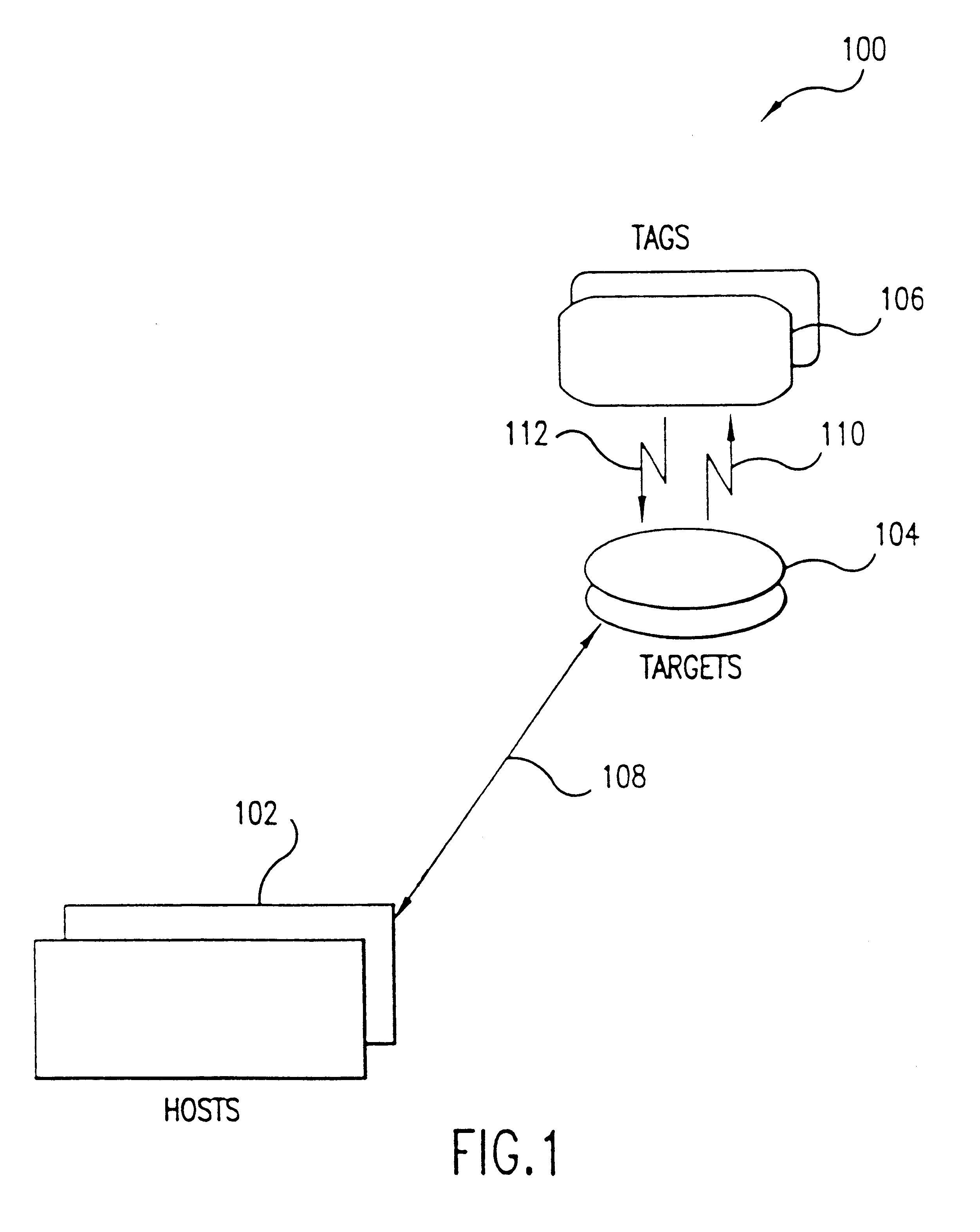
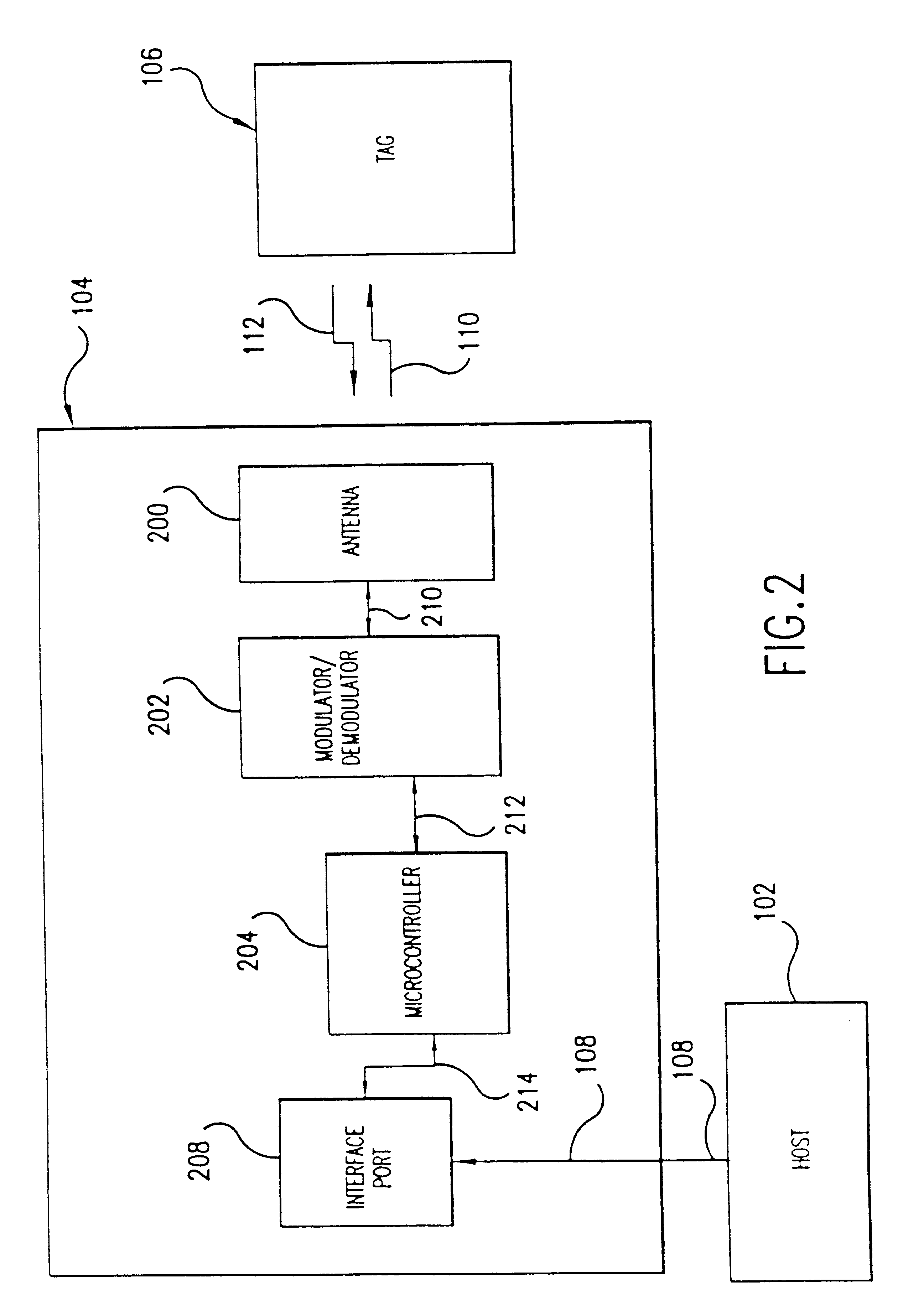
Anti-tear protection for smart card transactions
InactiveUS6727802B2Avoid collisionShorten transaction timeMemory record carrier reading problemsUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation processingProduct system
A fast data transfer collection system using message authentication and contactless RF proximity card technology in non-contact storage and retrieval applications. The system is generally comprised of Host computers (application computer systems), Target radio frequency (RF) terminals, and a plurality of portable Tags ("smart" or "proximity" cards). A Host provides specific application functionality to a Tag holder, with a high degree of protection from fraudulent use. A Target provides control of the RF antenna and resolves collisions between multiple Tags in the RF field. A Tag provides reliable, high speed, and well authenticated secure exchanges of data / information with the Host resulting from the use of a custom ASIC design incorporating unique analog and digital circuits, nonvolatile memory, and state logic. Each Tag engages in a transaction with the Target in which a sequence of message exchanges allow data to be read(written) from(to) the Tag. These exchanges establish the RF communication link, resolve communication collisions with other Tags, authenticate both parties in the transaction, rapidly and robustly relay information through the link, and ensure the integrity and incorruptibility of the transaction. The system architecture provides capabilities to ensure the integrity of the data transferred thus eliminating the major problem of corrupting data on the card and in the system. The architecture and protocol are designed to allow simple and efficient integration of the transaction product system into data / information processing installations.
Owner:KELLY GUY M +3
Method and system for transmission-based billing applications
InactiveUS8310943B2Avoid dataAvoid misappropriationSpecial service provision for substationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsApplication computersDatabase
Computer- and network-based methods and systems for transmission-based billing are provided. Example embodiments provide a Packet-Based Billing System (“PBBS”), which enables application providers, such as carriers and content providers, to bill subscribers for the use of content on mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices, on a per-application, per-user basis based upon the extent of the usage. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to bill subscribers for the use of content on a per-application, per-user basis for wired subscriber devices as well, using the same techniques. In operation, the PBBS provides modified content by inserting billing and tracking code into content returned to a requesting device. The modified content, when executed, tracks the amount of data sent and received between the content and a network and posts the accumulated data to a proxy / billing server according to business rules for an interval / frequency to post such data. The proxy / billing server stores the raw billing data and an accounting program retrieves the billing data to generate customer (call) data records. Business rules that specific different charges for different content or users can be incorporated into the system.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Remote application publication and communication system
InactiveUS7587459B2Web data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemProcedure calls
The invention is a system and method for publishing distributed applications accessible over a distributed network without having publishing computer to accept remote procedure calls from clients, and also allow integration between such distributed applications. In one embodiment, the invention includes a remote application computer having a service agent, translation file, and published software application thereon. The service agent provides the ability to identify the remote application computer and communicate with the distributed network, the translation file provides parameters to the service agent for interpreting the data i / o format of the published application, and the published application monitors and reports on conditions of a building or structure's environmental, security, and occupancy status.
Owner:EUTECH CYBERNETICS PTE
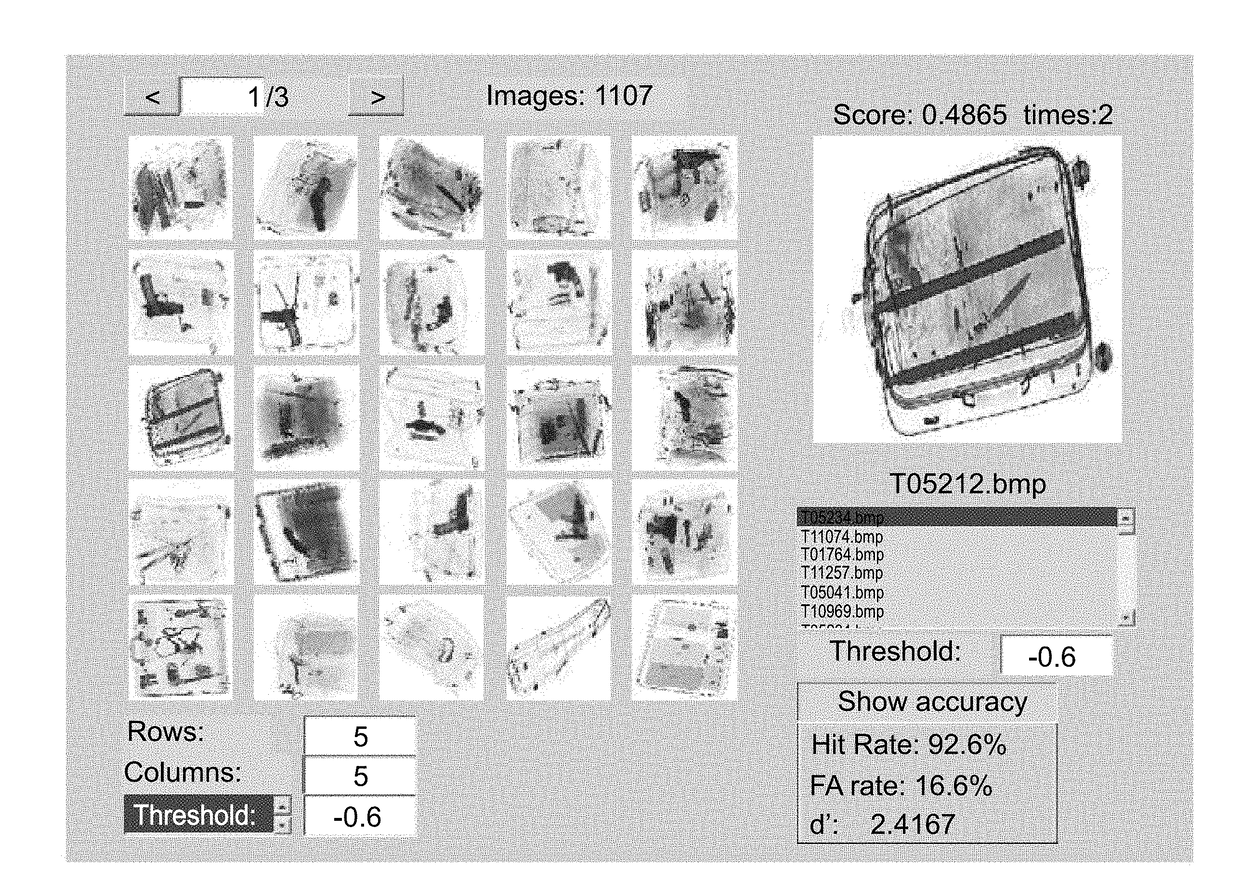
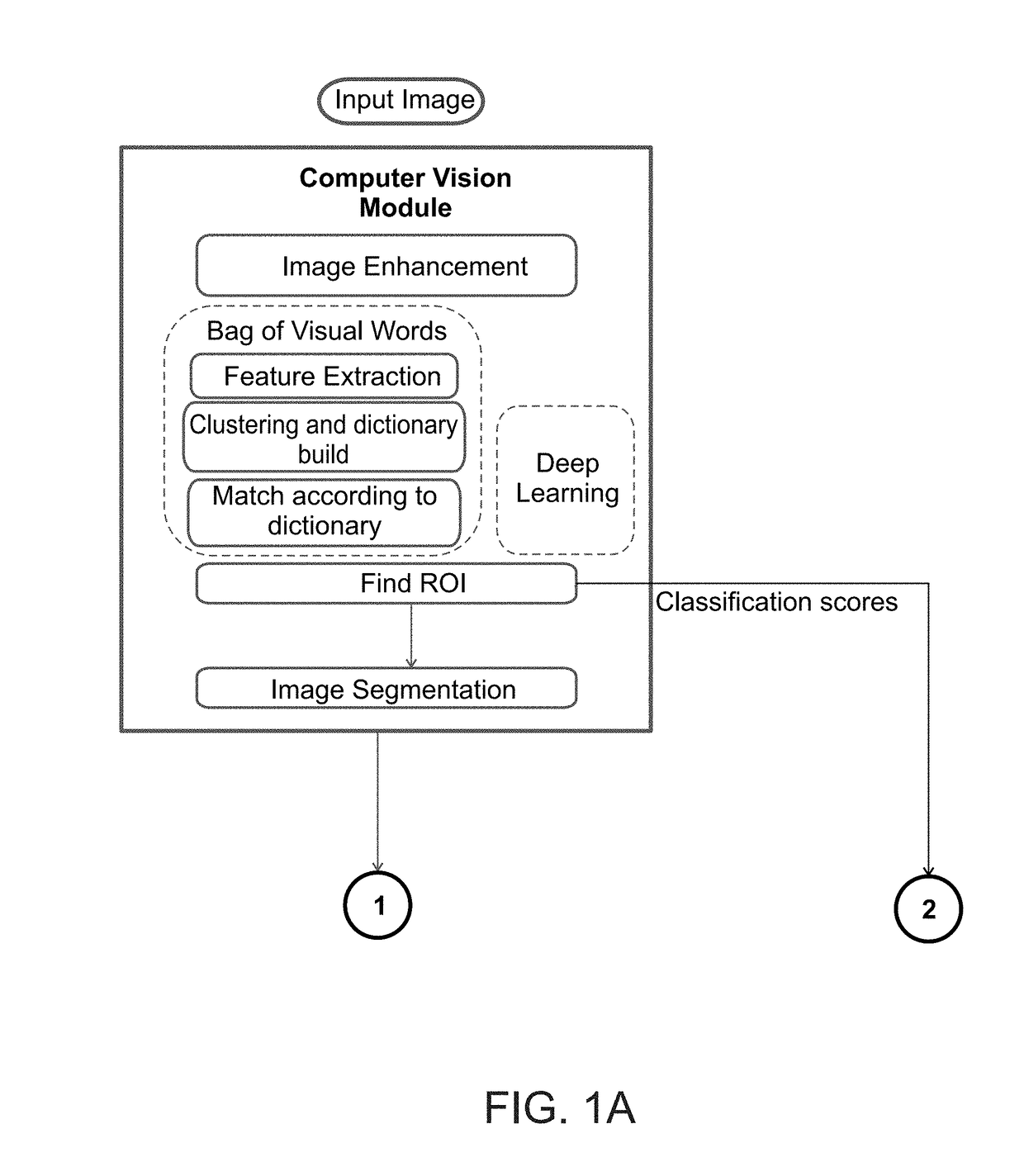
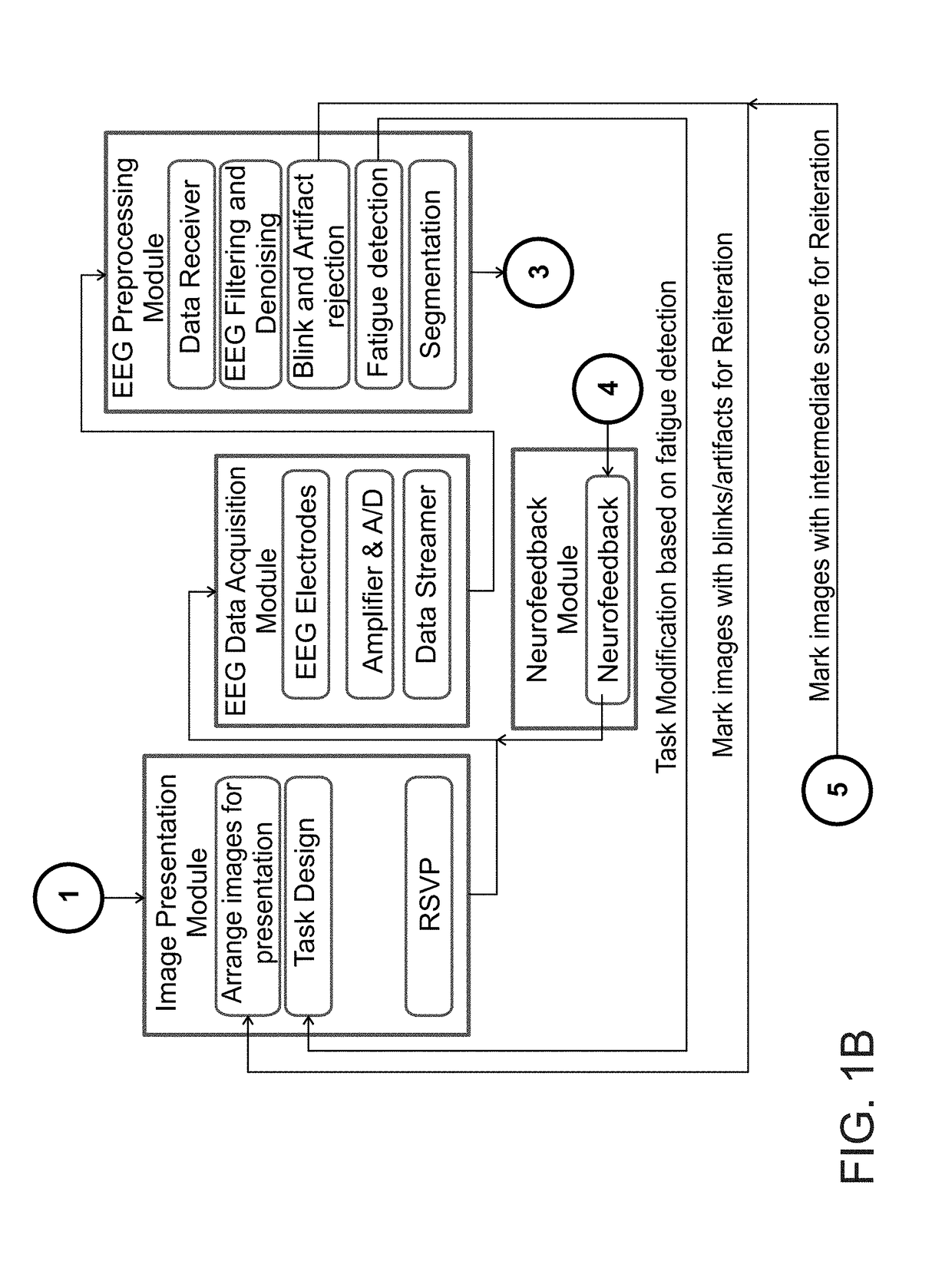
Image classification by brain computer interface
ActiveUS20180089531A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectroencephalographyBrain computer interfacingApplication computers
A method of classifying an image is disclosed. The method comprises: applying a computer vision procedure to the image to detect therein candidate image regions suspected as being occupied by a target; presenting to an observer each candidate image region as a visual stimulus, while collecting neurophysiological signals from a brain of the observer; processing the neurophysiological signals to identify a neurophysiological event indicative of a detection of the target by the observer; and determining an existence of the target in the image is based, at least in part, on the identification of the neurophysiological event.
Owner:INNEREYE
Web-based enterprise management with multiple repository capability
InactiveUS6976262B1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb-Based Enterprise ManagementResource information
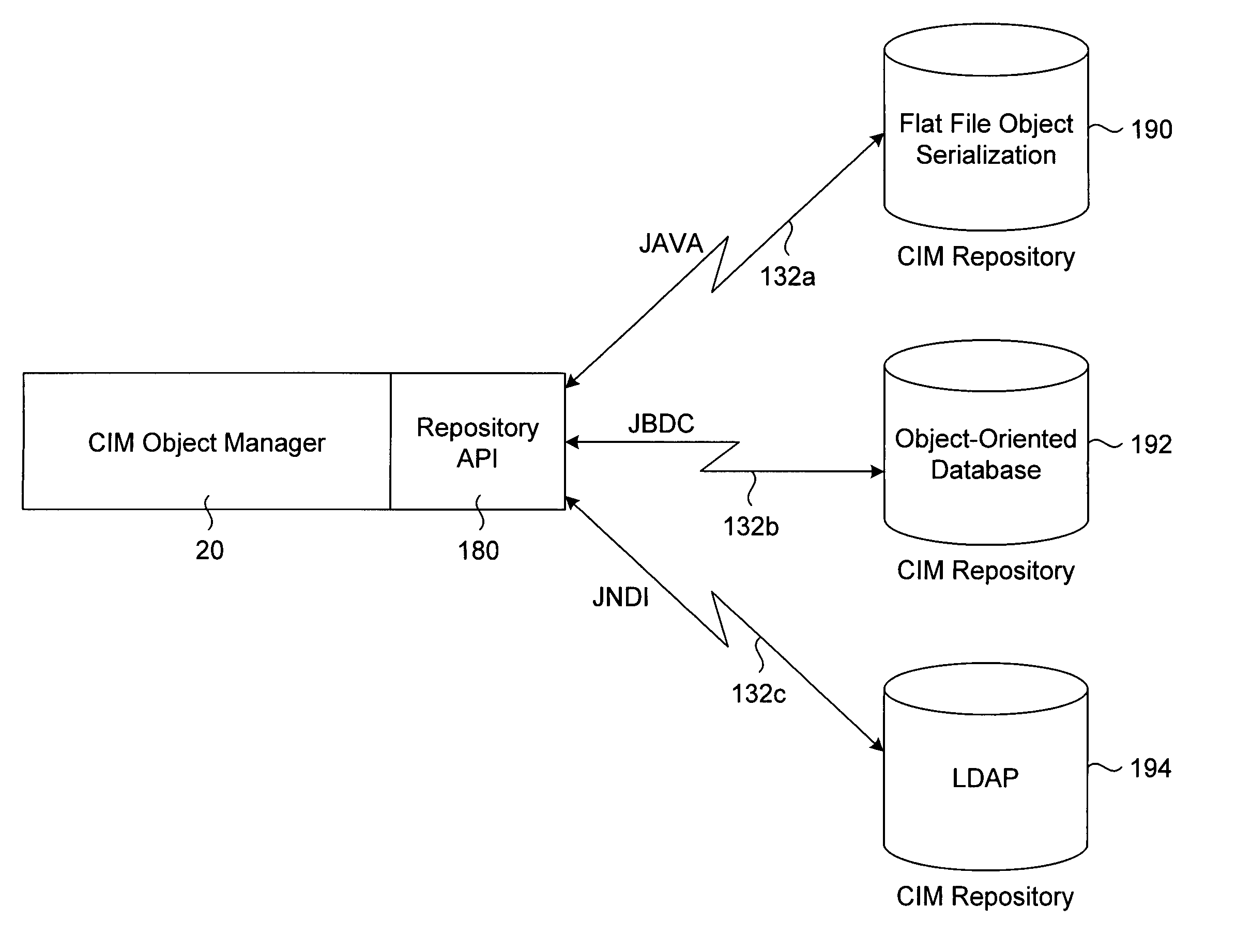
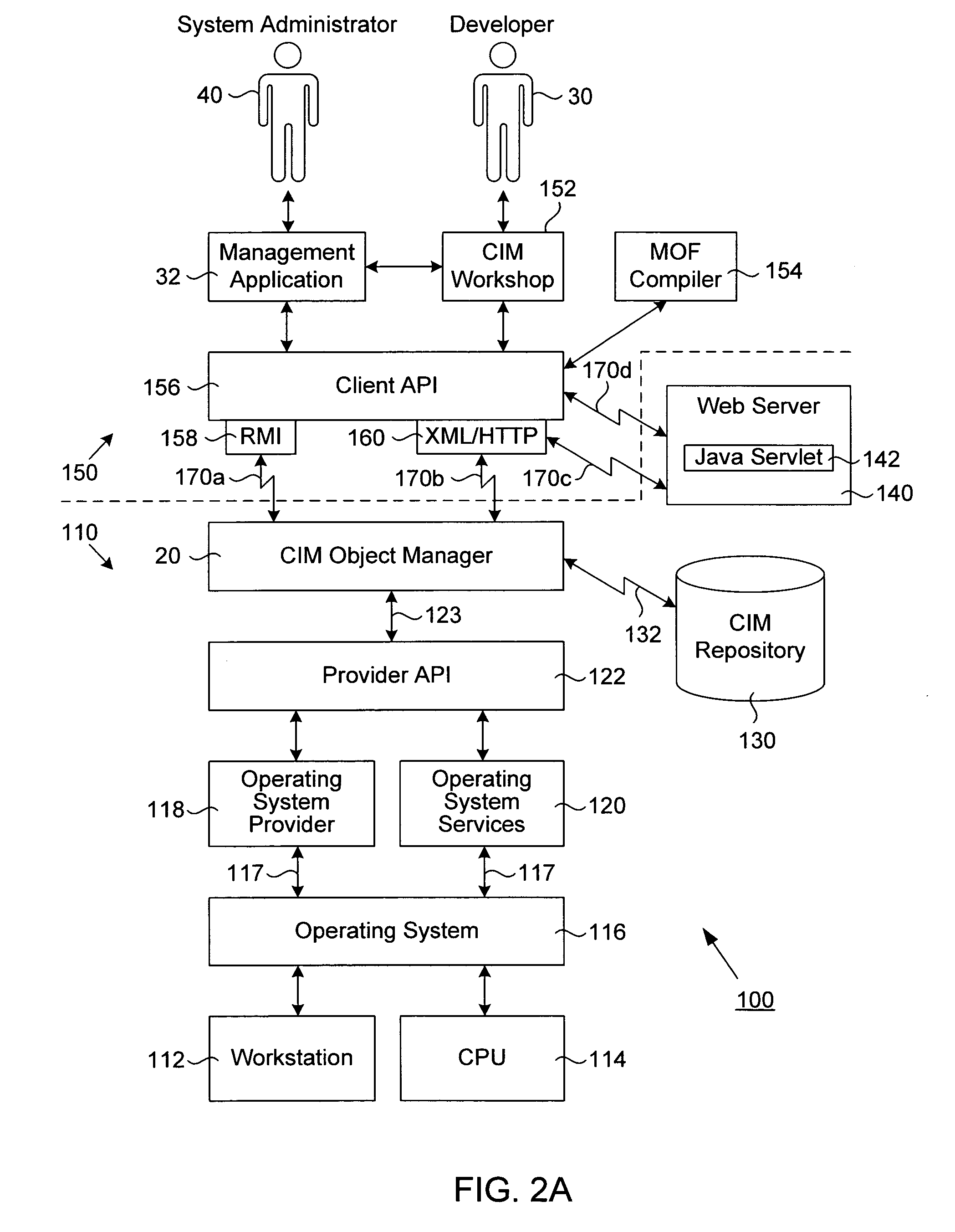
A transport neutral technique allows an object manager to communicate with a CIM repository using any of a variety of protocols. The object manager software is independent of the transport mechanism used and need not be changed if the transport mechanism changes. A computer system to be managed includes a CIM object manager and any number of provider APIs that provide resource information about the computer system. A CIM repository stores classes and instances used by the object manager. A remote application computer runs a software management application that communicates with the object manager of the computer system using a local client API. A Repository API of the object manager includes an interface definition defining all methods called by the object manager. Also included is a protocol-specific class that implements the interface definition; there is a protocol-specific class for each protocol desired to be supported. Each class implements methods using a specific protocol. A factory class is executed when the object manager invokes a method call passing in a desired protocol parameter. The factory class creates a protocol-specific object of one of the protocol-specific classes depending on the protocol parameter. The object is returned to the object manager which executes one of its protocol-specific methods thus allowing communication to a repository using a protocol independent of the object manager.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Processing system for data elements received via source inputs
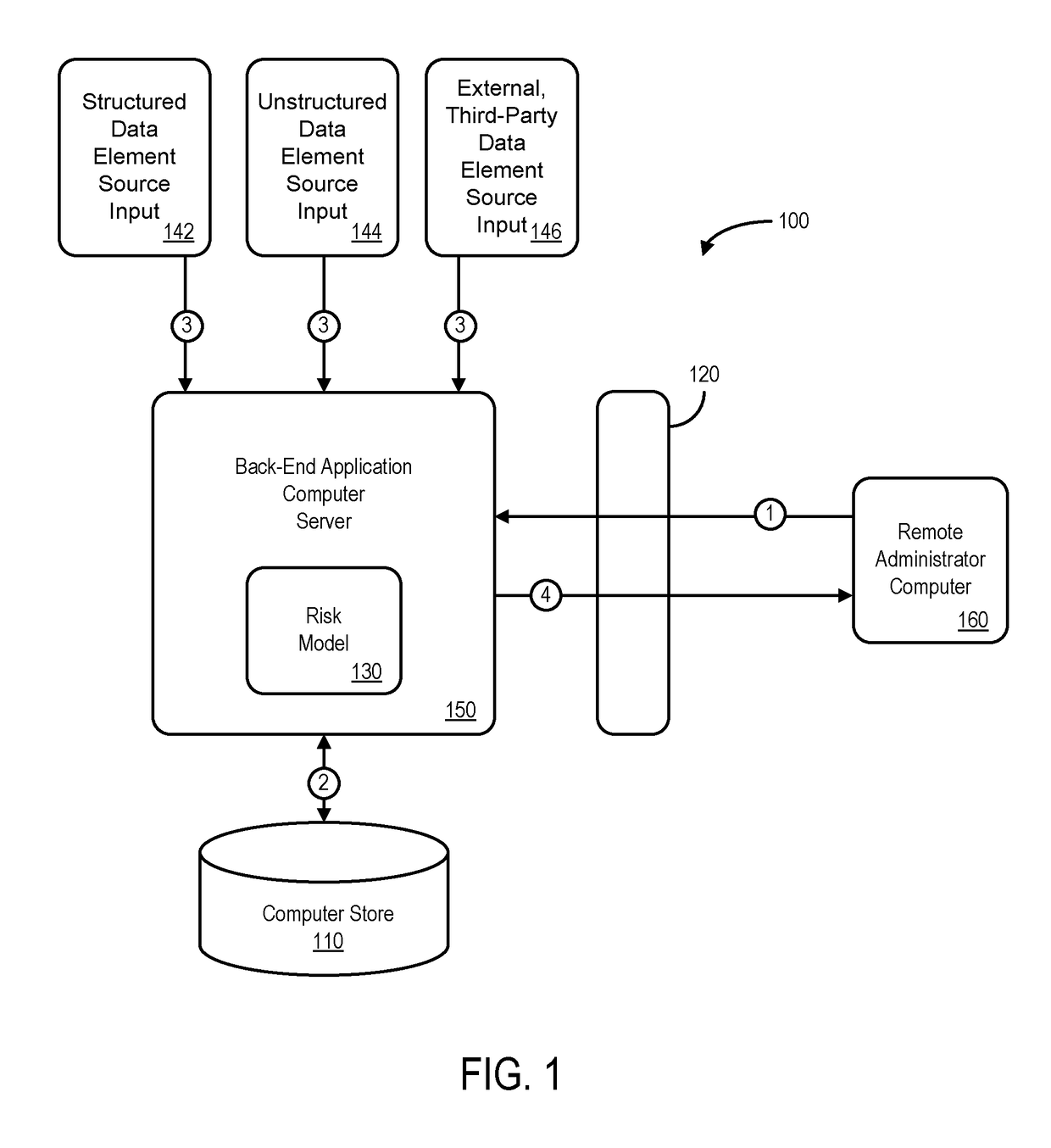
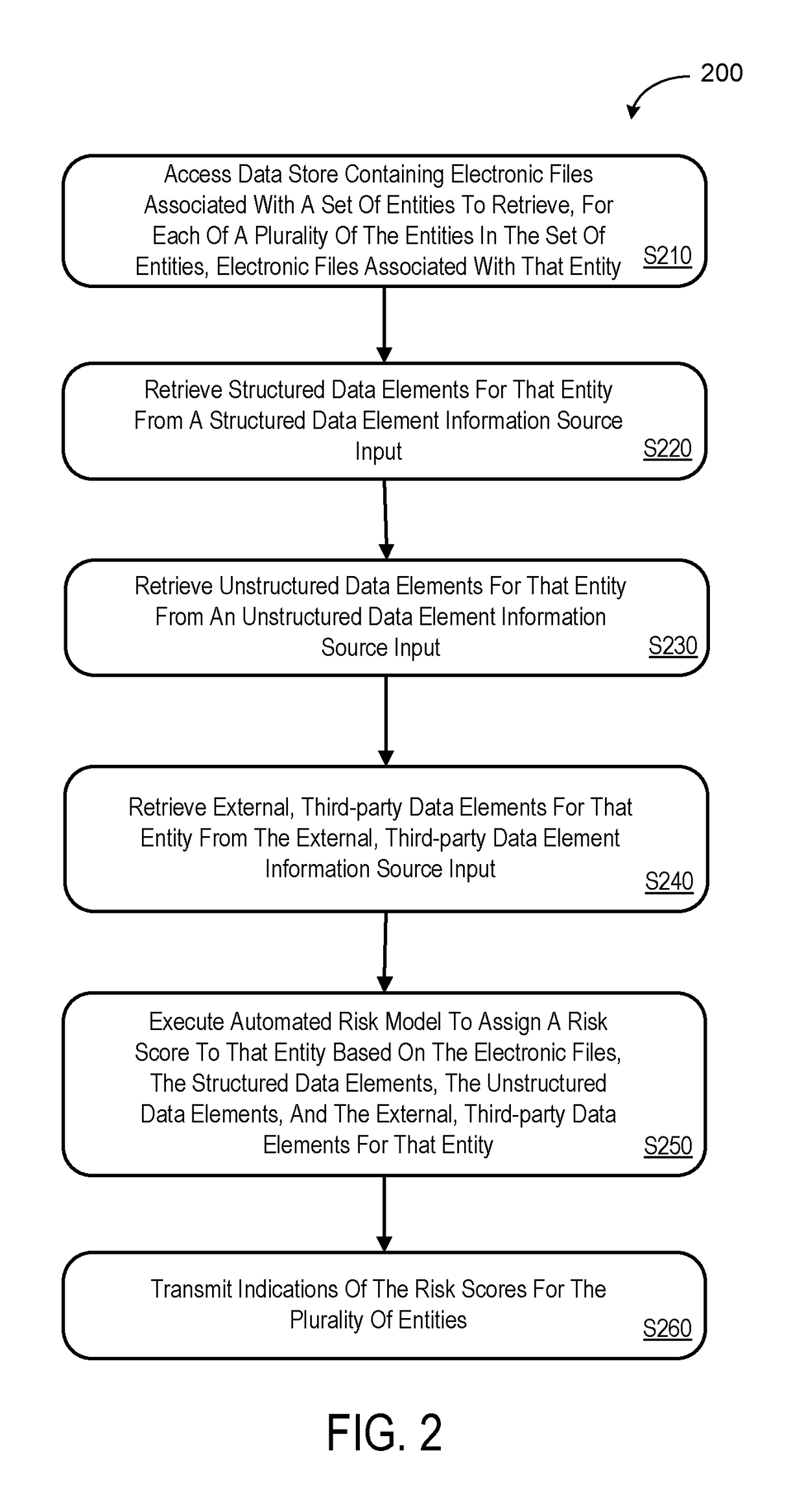
ActiveUS20170154382A1Faster and accurate resultFast and accurate resultFinanceThird partyApplication computers
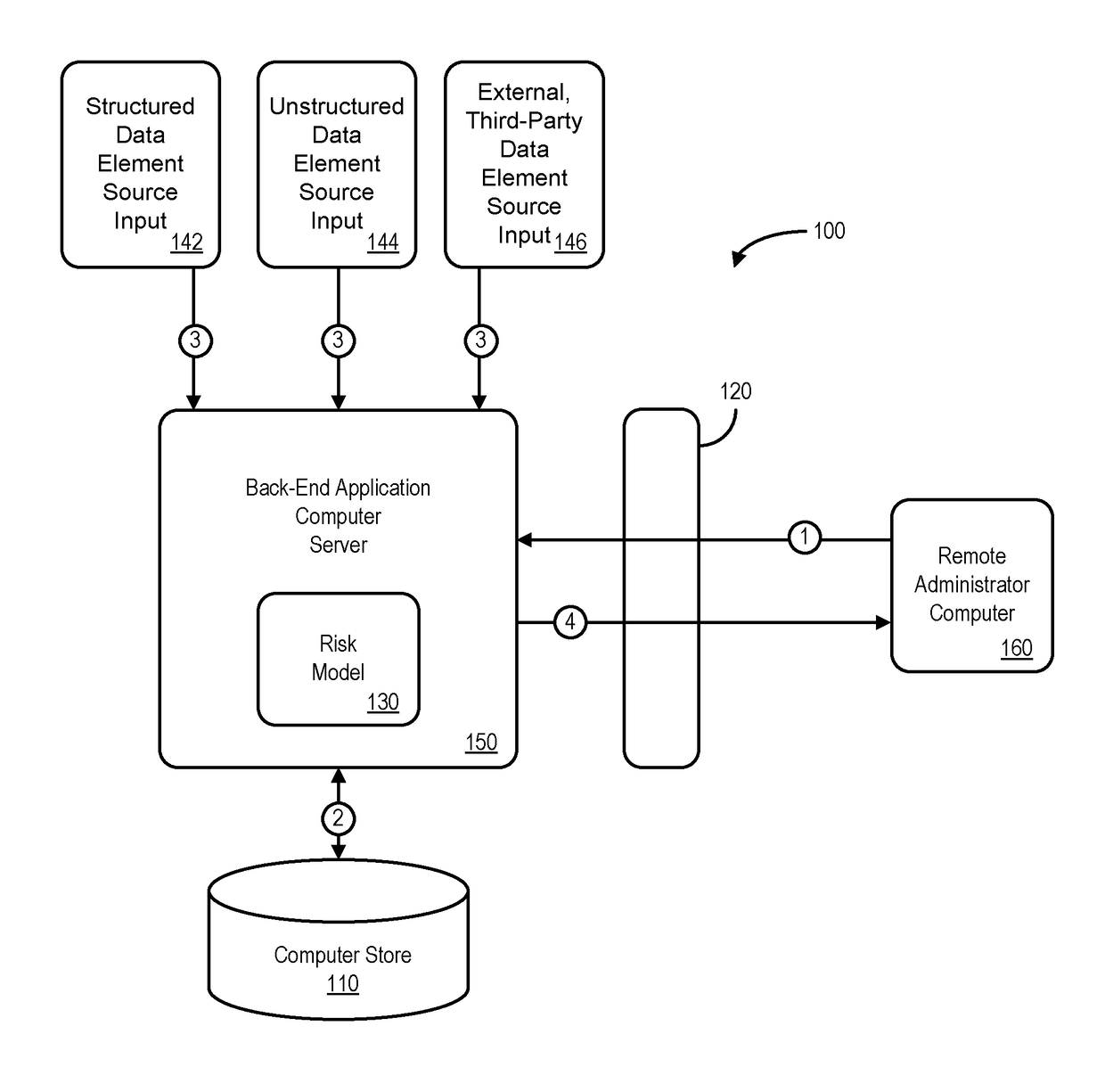
Mediums, apparatus, computer program code, and means may be provided to evaluate relative risks based at least in part on source inputs received via a distributed communication network by an automated back-end application computer server. According to some embodiments, the server may access a data store containing electronic files associated with a set of entities to retrieve, for each of a plurality of the entities in the set of entities, electronic files associated with that entity. The server may also retrieve structured data elements, unstructured data elements, and external, third-party data elements for that entity. The server may then execute an automated risk model to assign a risk score to that entity based on the electronic files, the structured data elements, the unstructured data elements, and the external, third-party data elements for that entity and transmit indications of the risk scores for the plurality of entities.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
Terminal device, display method, and application computer program product
InactiveUS20110298826A1Reduce power consumptionNecessary electrical powerEnergy efficient ICTCathode-ray tube indicatorsApplication computersTerminal equipment
Owner:SONY CORP +1
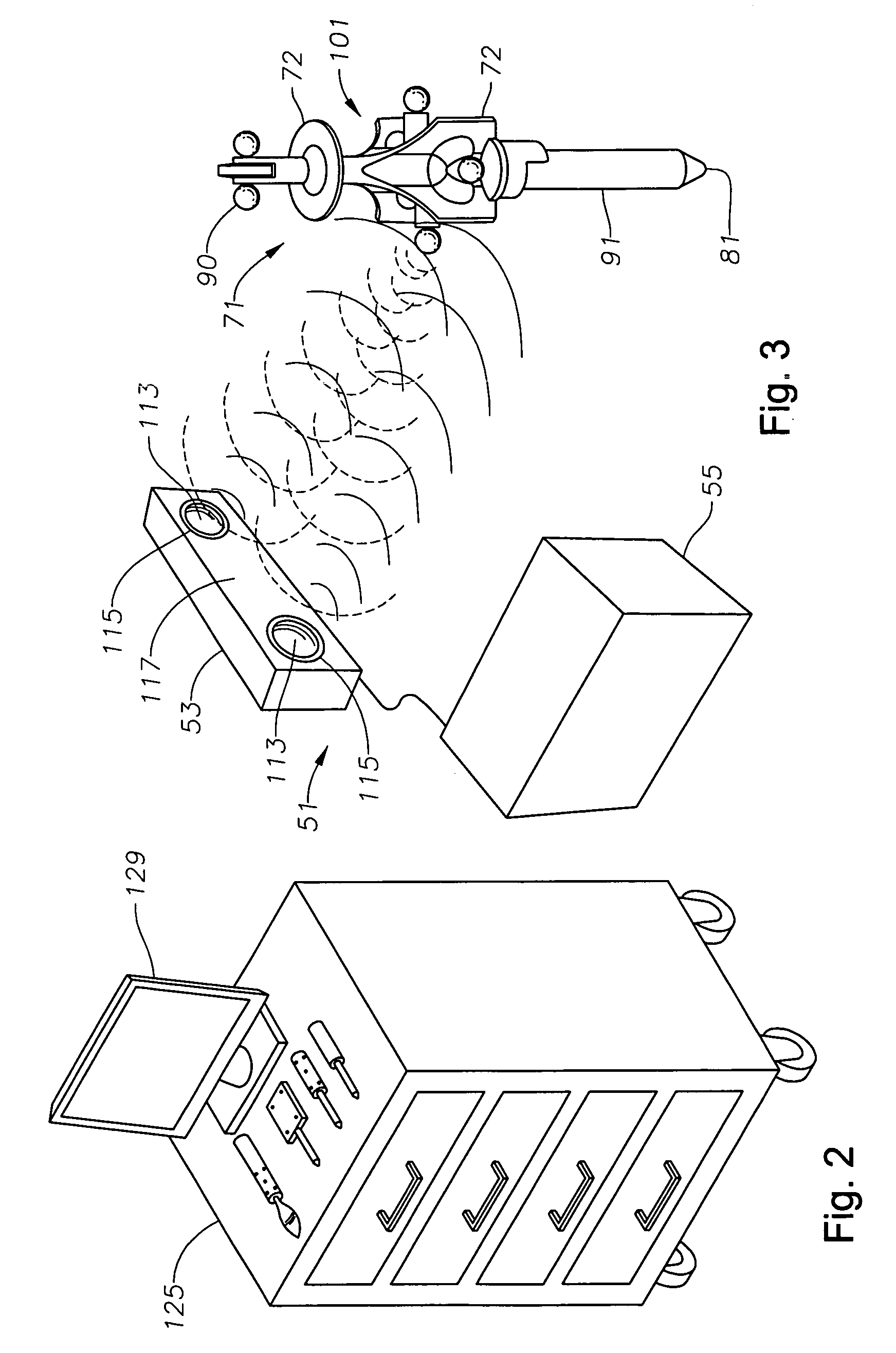
System for monitoring the geometry of a radiation treatment apparatus, trackable assembly, program product, and related methods
ActiveUS20060215813A1Accurate CalibrationPrecise applicationRadiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment deliveryApplication computers
A system to monitor a geometry of a treatment apparatus, an apparatus, a trackable assembly, program product, and methods are provided. The system includes a treatment apparatus having a radiation emitter, a rotating assembly controlled by a controller, and an application computer, which provides treatment delivery instructions to the controller. The system can also include a trackable assembly connected to the rotating assembly and having a fixedly connected first trackable body which functions as a reference fixture and a pivotally connected second trackable body which provides data used to determine a rotation angle of the rotating assembly. The system also includes an apparatus to track a trackable body which has a trackable body detector to detect a position of the indicators carried by the first and the second trackable bodies and a determiner to determine and verify the location of the origin of an isocenter coordinate system and to determine rotational path data about the rotating assembly.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Pre-boot security controller
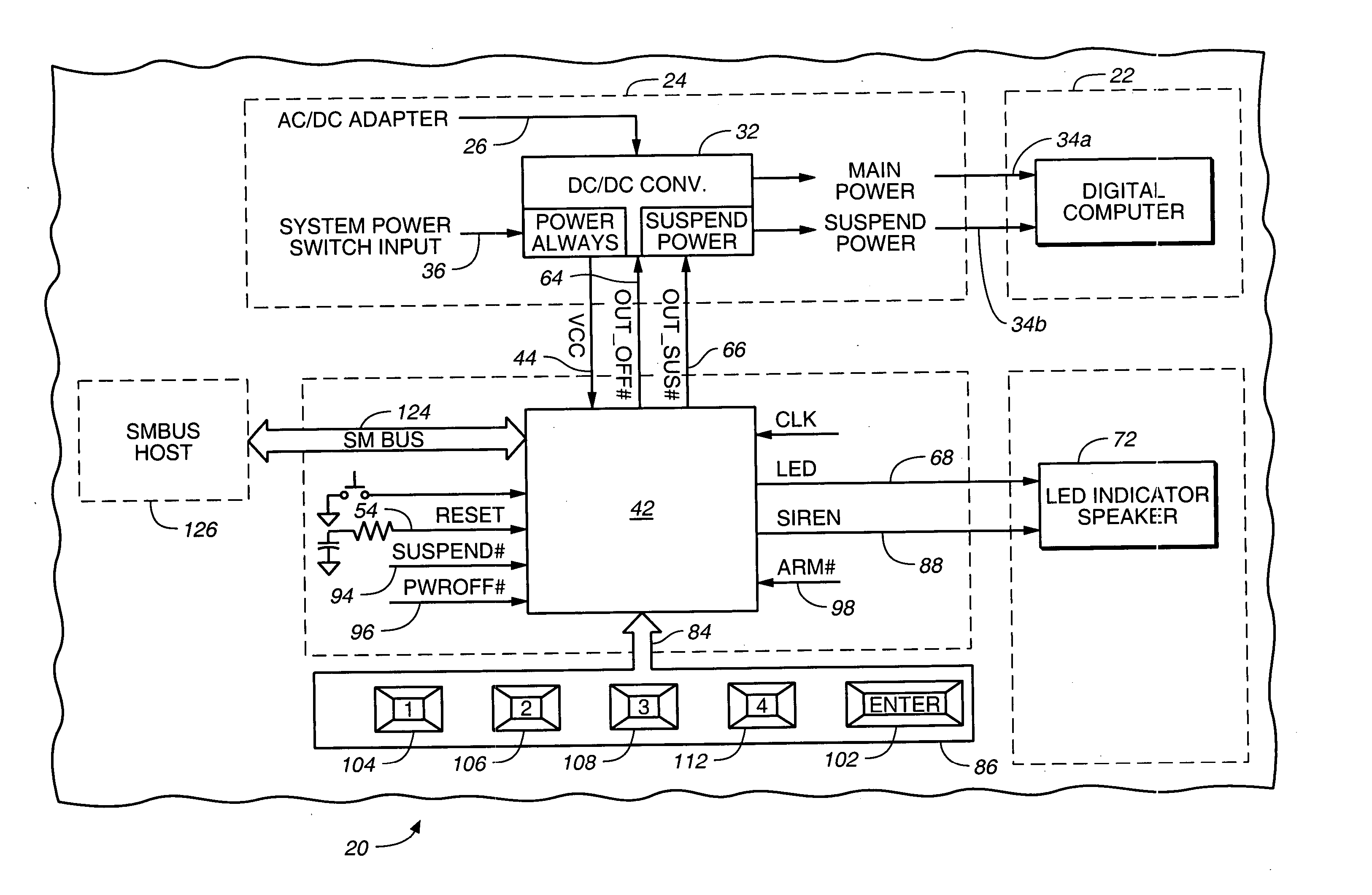
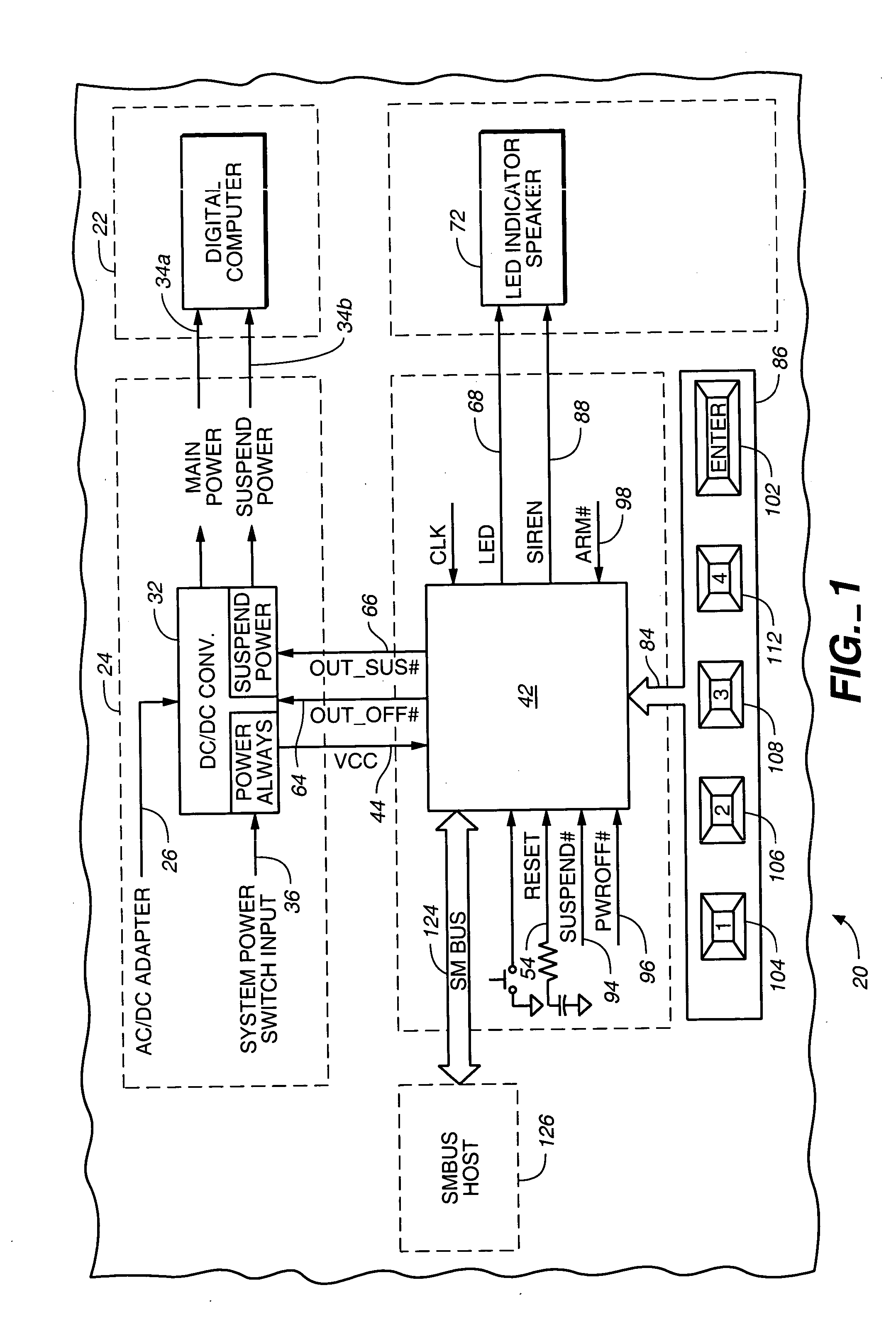
InactiveUS20050081071A1Well as to enablePrevent theftVolume/mass flow measurementUnauthorized memory use protectionApplication computersPassword
A pre-boot security controller in an electronic device is energized even though a power subsystem does not energize operation of a digital computer in the device. The security controller stores supervisor and user passwords in a non-volatile password memory for comparison with a password entered using a security keypad. While the security controller is in a security operating mode, an output signal from the securing controller indicates the existence of that operating mode. Upon entry of a matching password, the security controller enables the power subsystem to energize operation of the digital computer, disables the output signal that indicates the existence of the security operating mode, and the security controller transitions from the security to an application operating mode. In the application operating mode, the pre-boot security controller preserves data about pressings of the security keypad. A computer program executed by the digital computer may respond to recorded keypad pressing by initiating execution of a specific application computer program that a user associates with a specific key on the security keypad.
Owner:MAISHI ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) LTD
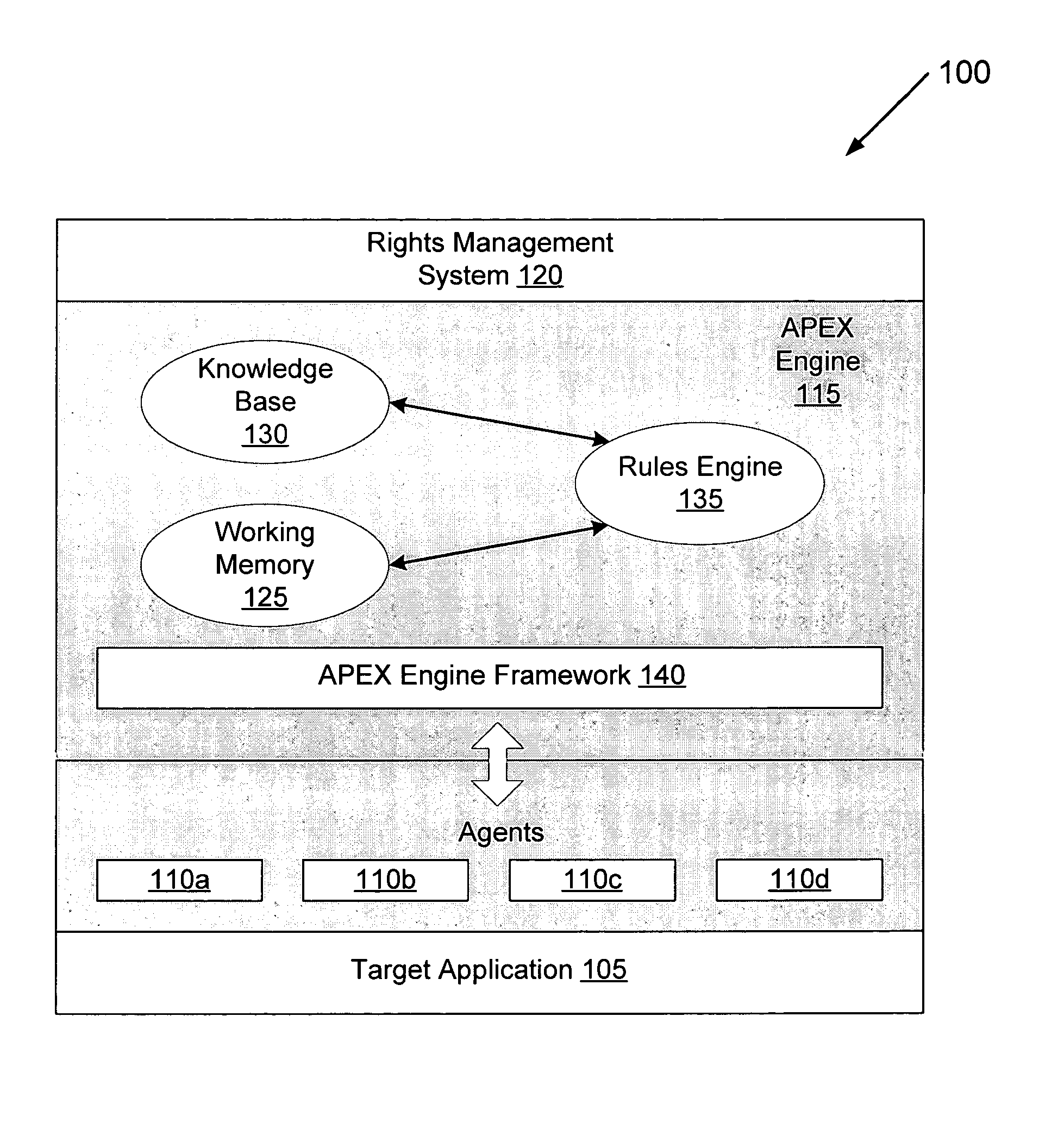
Method and system for using a rules engine for enforcing access and usage policies in rights-aware applications
InactiveUS7984513B1Improves robustness and testabilitySimplify the development processMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsApplication computersSoftware engineering
Computer system and method enforces control policies including access and usage policies. A rules-based engine member or assembly is coupled between a rights-management (or similar) system and one or more target applications. The rules-based engine member centralizes data security determinations for the target applications. One or more agents are responsive to the rules-based engine member and target applications, and handle low-level details in interactions between the rules-based engine member and target applications. A generic engine framework serves as a normalizing factor and enables scalability.
Owner:LIQUID MACHINES
Mapping protocol endpoints to networked devices and applications based on capabilities
ActiveUS20130191524A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksApplication computersUser interface
In an embodiment, a non-transitory computer readable storage medium storing instructions which cause processors to perform: collecting, at a management computer located separately with respect to a networked plurality of devices, device information about each of the devices; for each particular device: determining matches between the device capabilities for the particular device, and features of software applications; for a particular match: determining a particular software application that is configured to control the particular device; based at least in part on the device information for the particular device, determining a particular protocol endpoint from protocol endpoints that is configured to communicate control instructions from the particular software application to the particular device; creating data comprising a mapping between the particular software application, the particular protocol endpoint and the particular computing device; configuring an application computer program to use the mapping and a user interface computer program to manage the particular device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and System for Transmission-Based Billing Applications
InactiveUS20070189514A1Short response timeImprove efficiencyMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionServer agentApplication computers
Computer- and network-based methods and systems for transmission-based billing are provided. Example embodiments provide a Packet-Based Billing System (“PBBS”), which enables application providers, such as carriers and content providers, to bill subscribers for the use of content on mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices, on a per-application, per-user basis based upon the extent of the usage. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to bill subscribers for the use of content on a per-application, per-user basis for wired subscriber devices as well, using the same techniques. In operation, the PBBS provides modified content by inserting billing and tracking code into content returned to a requesting device. The modified content, when executed, tracks the amount of data sent and received between the content and a network and posts the accumulated data to a proxy / billing server according to business rules for an interval / frequency to post such data. The proxy / billing server stores the raw billing data and an accounting program retrieves the billing data to generate customer (call) data records. Business rules that specific different charges for different content or users can be incorporated into the system.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
System and method for controlled sharing and synchronizing information across a plurality of mobile client application computers
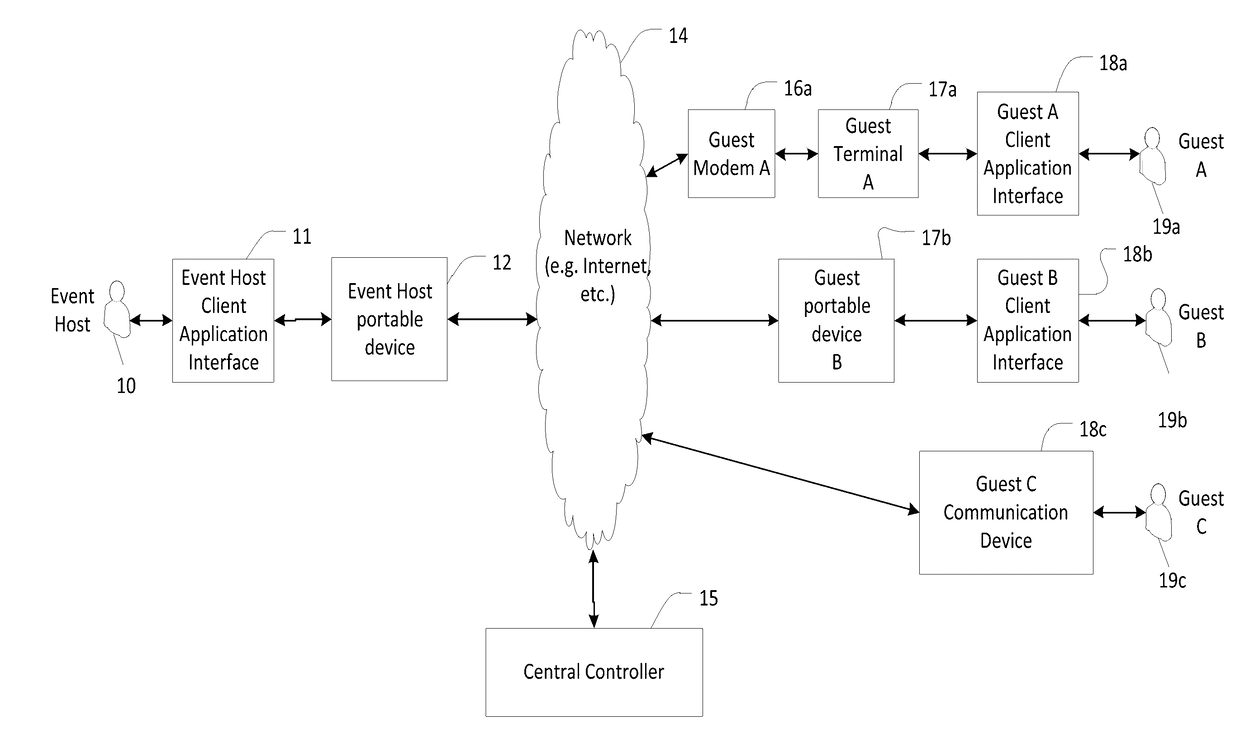
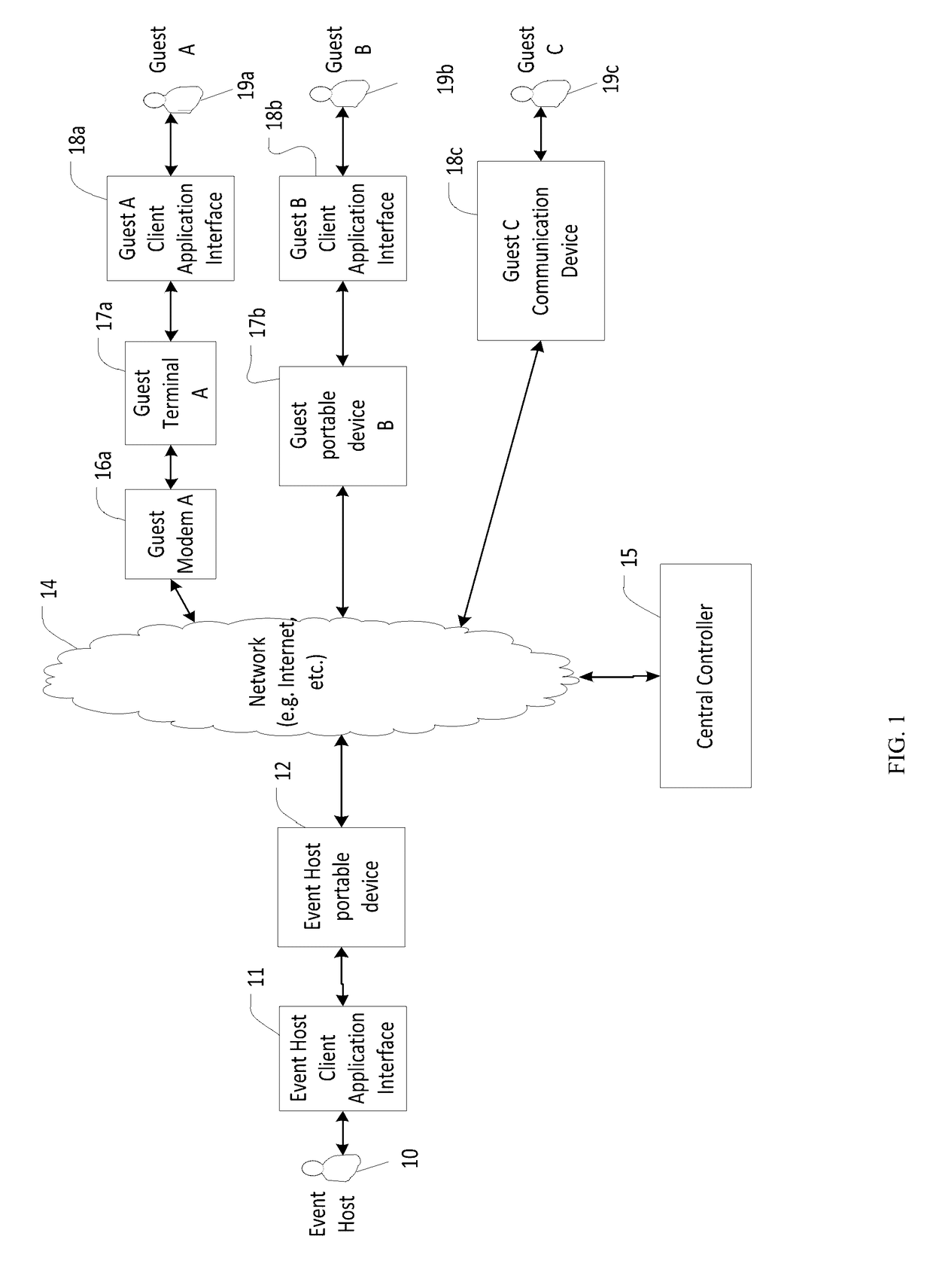
InactiveUS20170118165A1Effective informationData switching networksSecurity arrangementInformation sharingApplication computers
A system and method for interactively sharing and synchronizing information by providing controlled information sharing among a plurality of users with different electronic contact types using network-based communication between a plurality of client applications on a plurality of mobile devices and a central controller computer, are described. In an exemplary embodiment, an information context is established and associated with an action initiated by a first client application. A plurality of client applications may then share information within the information context whereby the plurality of client applications participate in the information context based on associated contact information. A method for synchronization allows for shared information on different client devices to be controlled and automatically synchronized by the central controller. Messages, data structures, communications, and protocols between clients and the central controller allowing participant clients to have different permissions and privileges to at least create, update, view and delete information data are described.
Owner:KUMAR ASHISH
Apparatus, system, and method for obfuscation and de-obfuscation of digital content
InactiveUS20160224766A1Reduced Clarity RequirementsReduce understandabilityProgram/content distribution protectionObfuscationApplication computers
Computer-implemented apparatus, system, and method of generating digital content with various degrees of obfuscation applied. A publisher of content, such as a private or commercial publisher of digital content, may set access restrictions to the content, such as to obfuscate and / or de-obfuscate the content based on select criteria.
Owner:STEELBERG CHAD +3
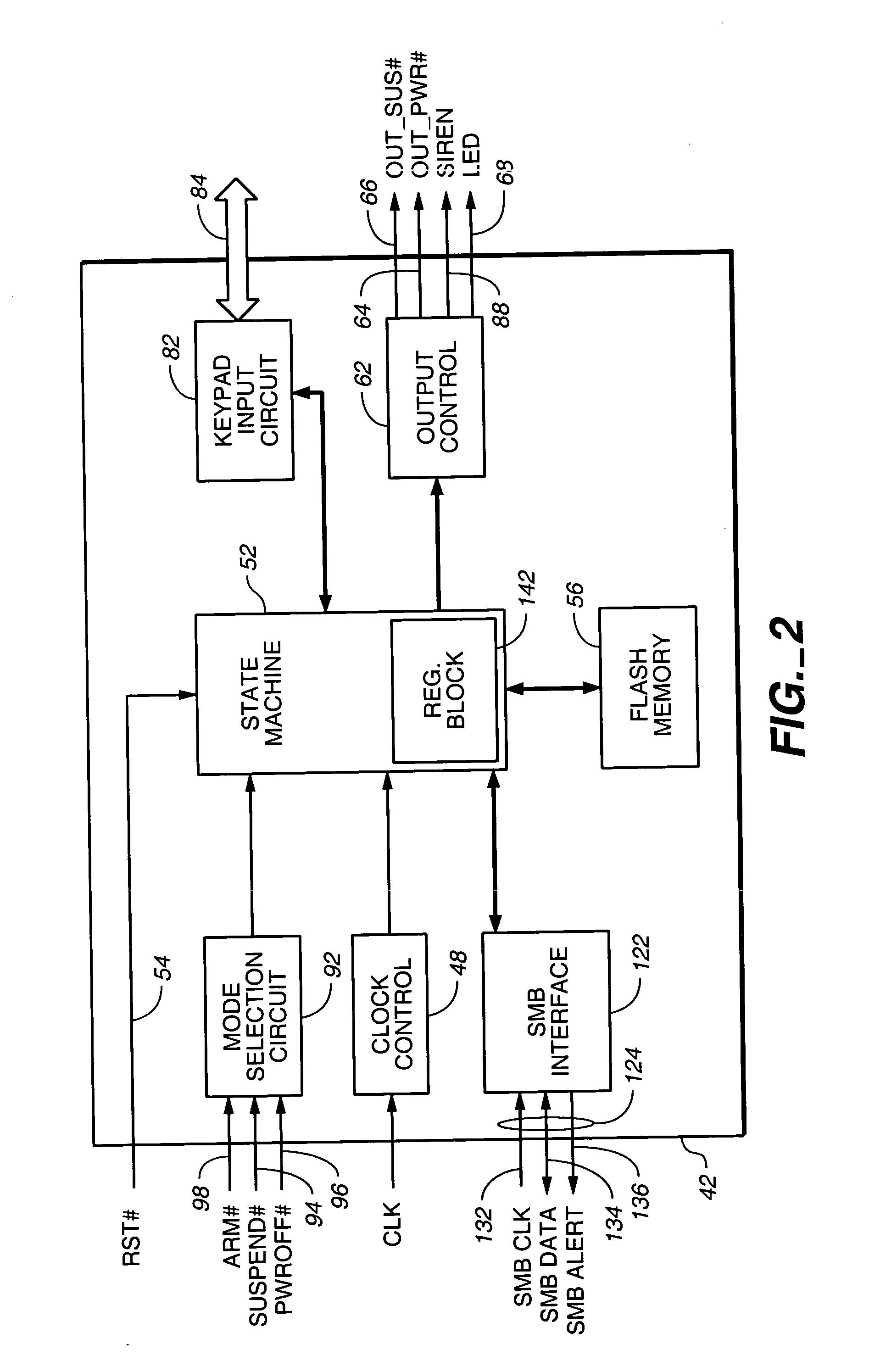
Method and system for maintaining and distributing wireless applications
InactiveCN1489736AMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesWireless Application ProtocolApplication computers
Computer- and network-based methods and systems for maintaining and provisioning wireless applications are provided. Example embodiments provide a Mobile Application System (MAS), which is a collection of interoperating server components that work individually and together in a secure fashion to provide applications and resources to mobile subscriber devices, such as wireless devices. Embodiments of the present invention can also be used to deploy applications and resources for wired subscriber devices. Application, resources, and other content is provisioned and verified by the MAS for authorized access by the subscriber, compatibility with a requesting subscriber device, and the security and billing policies of the carrier and system administrators of the MAS. In this manner, applications, resources, and other content can be downloaded to devices, such as wireless devices, with greater assurance of their ability to successfully execute. In one embodiment, content is provisioned by one or more of the steps of inspecting the content for malicious or banned code, optimizing the content for smaller size and greater speed, instrumentation of code that implements security, billing, and other carrier policies, and packaging of code for the intended subscriber device. Additional security is provided through application filters that are used to prevent applications that contain designated API from being downloaded to a subscriber's device. In one embodiment, the MAS includes a Protocol Manager, Provisioning Manager, Cache, Deployment Manager, Billing Manager, Logging Manager, Administrator, and Heartbeat Monitor, which interoperate to provide the provisioning functions.
Owner:4THPASS INC
Methods and systems for consistent concurrent operation of a plurality of computer-aided design applications
InactiveUS8892404B2Improve user experienceCAD network environmentSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignApplication computers
Owner:PARAMETRIC TECH CORP
Method and system for storing java objects in devices having a reduced support of high-level programming concepts
InactiveUS6754886B1Improve efficiencyHandling of simpler and flexibleInterprogram communicationProgram loading/initiatingArray data structureApplication computers
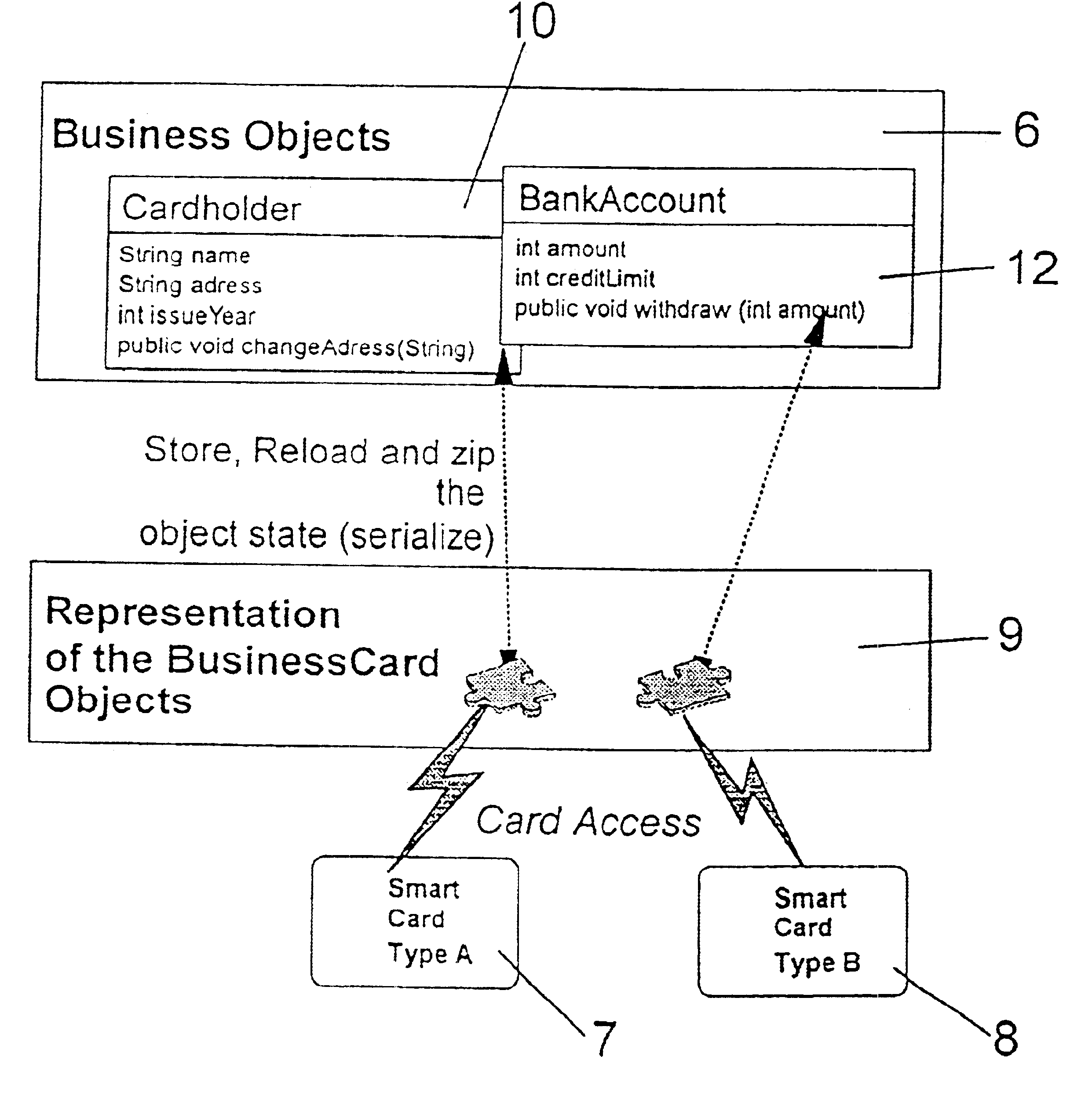
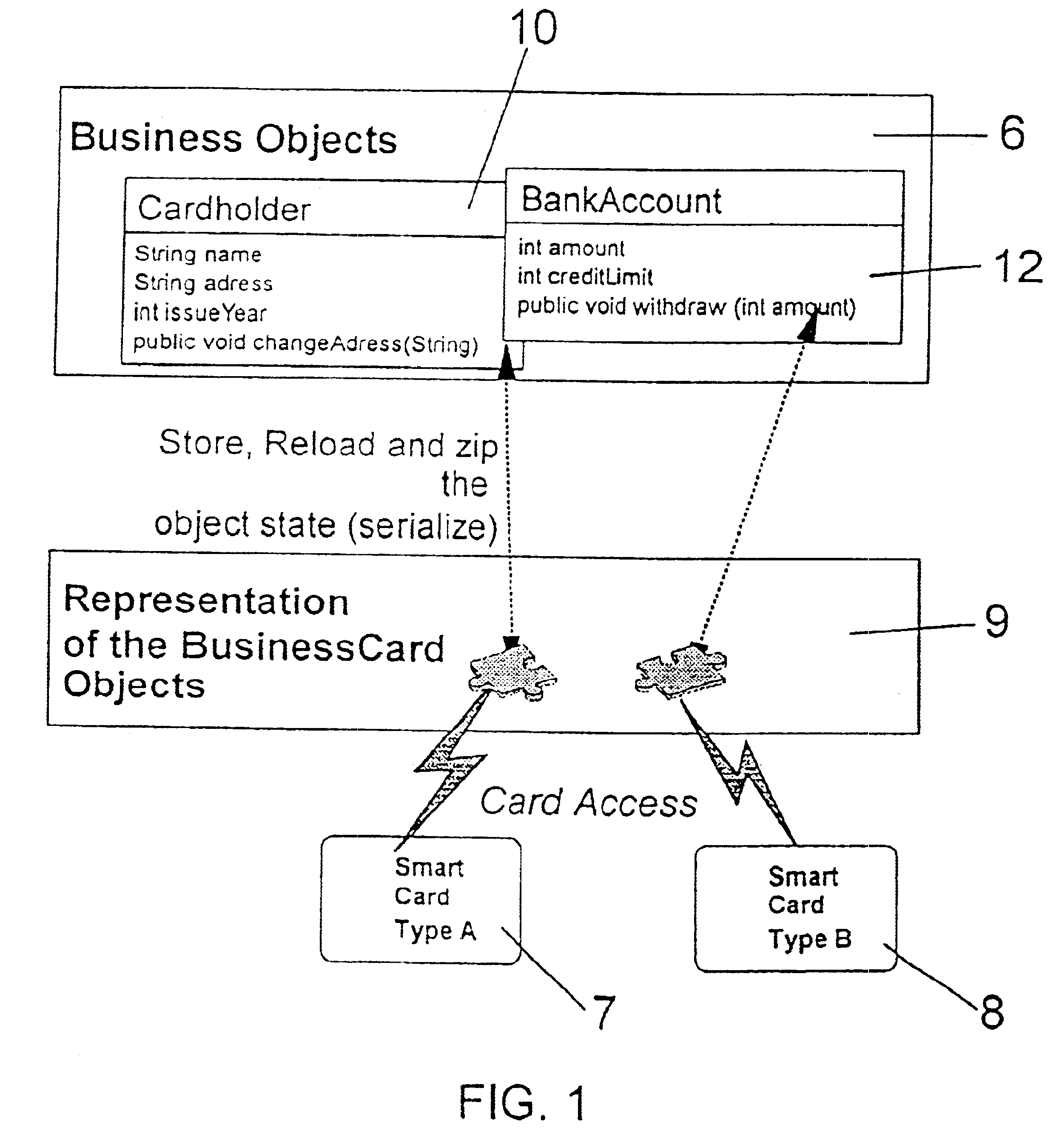
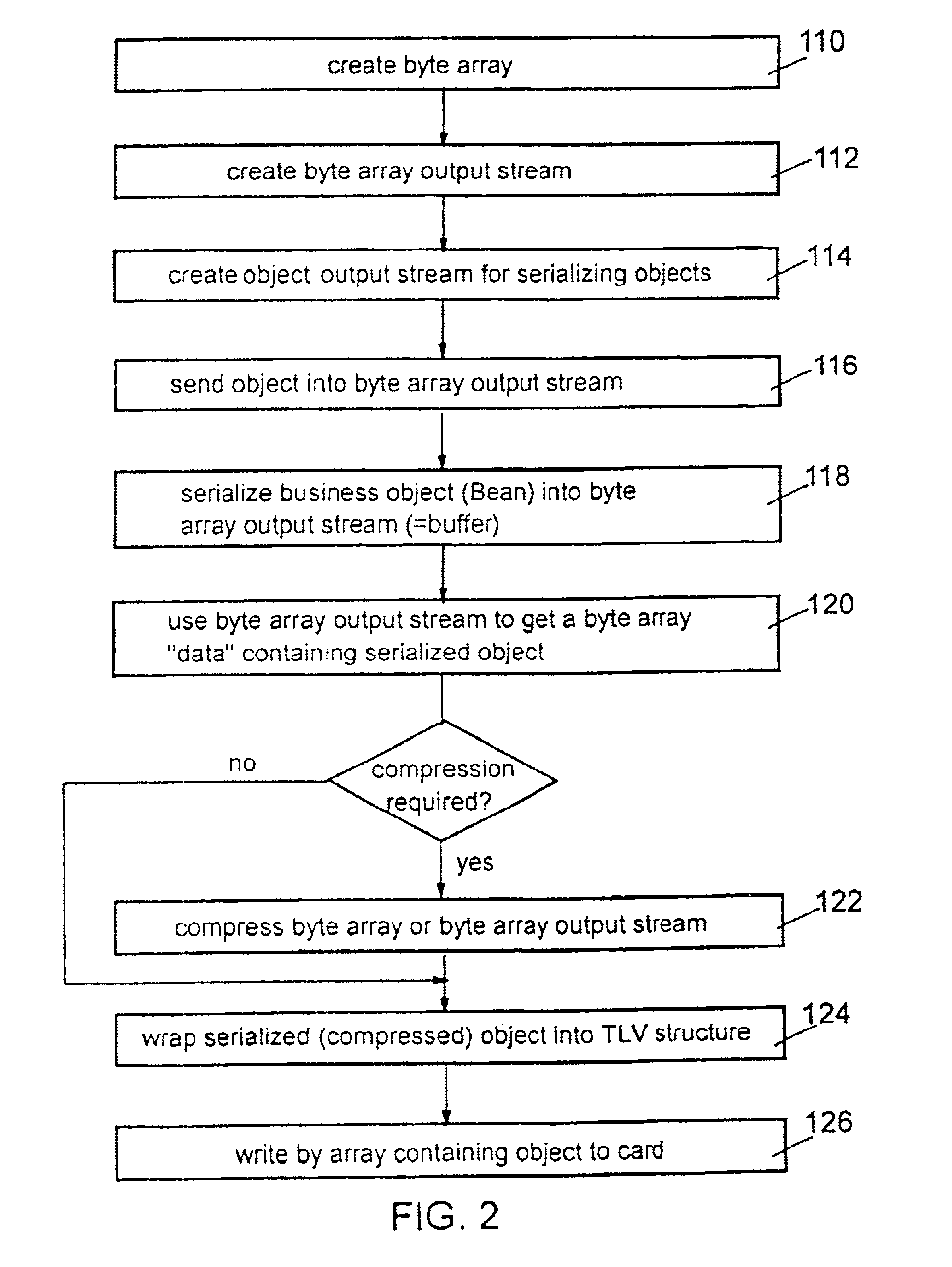
The objects to be stored on a SmartCard or on a similar device are output from the host application computer in a form adapted to the device, particularly in form of a byte array which can easily be stored on such a SmartCard. That serialization comprises to convert any particular object into a sequence of bytes representing the object and its current status by storing all attributes, the name of them and all further objects which are referenced by the object which is subject to that serialization step. With the total of that information that object can be recovered in an unchanged form after any reset or interruptions which can possibly take place during usage of the SmartCard in a respective SmartCard terminal. The recover procedure is performed in analogous form: the object as well as all further objects being referenced by that object is instantiated and is initialized with the data read out from the SmartCard. The byte array representing that object can be stored both on common file system oriented SmartCards and on JavaCards, too, without being confronted to any specific further problem.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for computer telephone integration in packet switched telephone networks
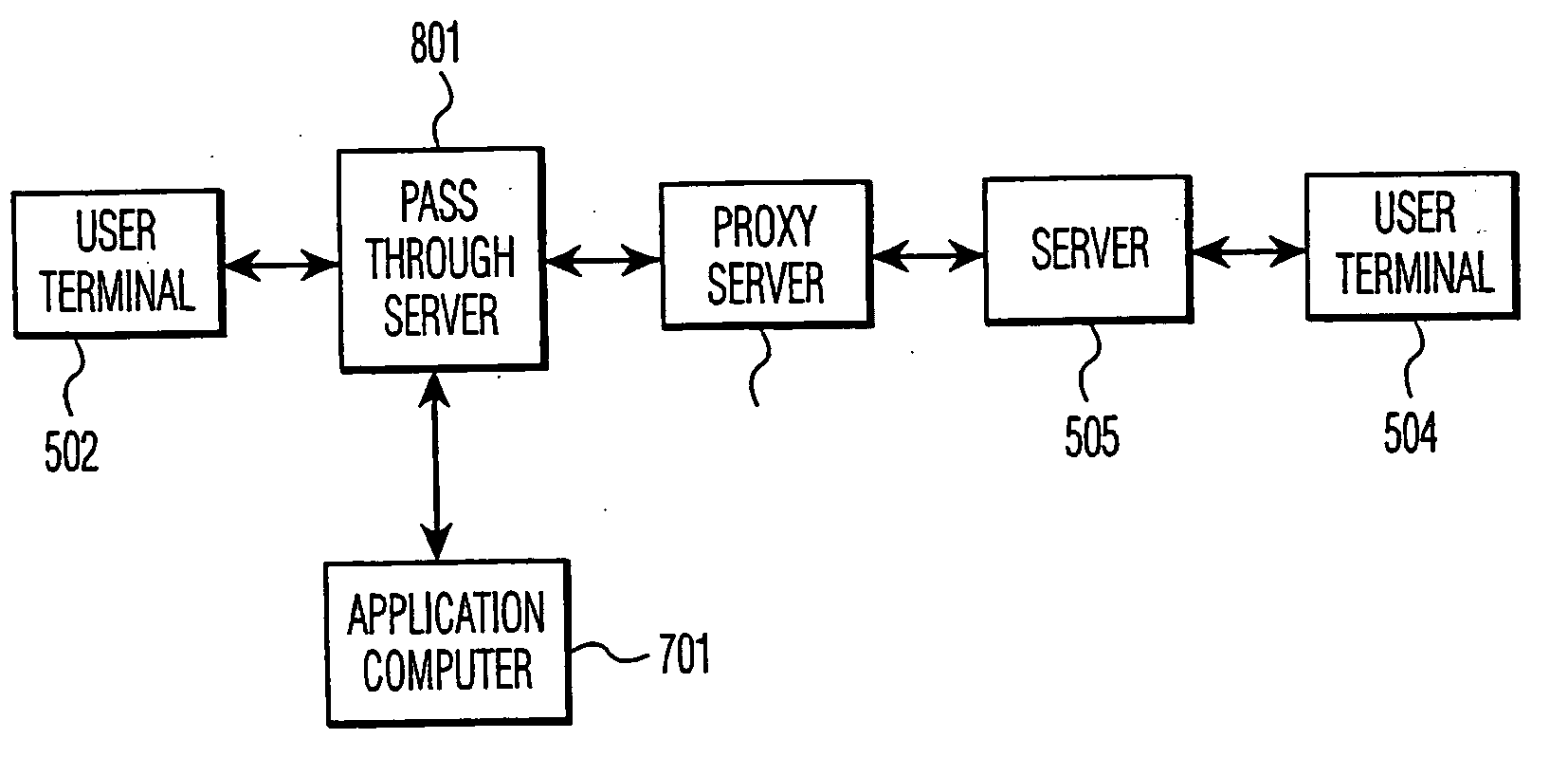
InactiveUS20050122964A1Application programming interface detailsSpecial service for subscribersSession Initiation ProtocolApplication computers
A computer telephony interface (CTI) applications computer interfaces to a Internet telephony system which utilizes, preferably, the session initiation protocol (SIP). In one preferred technique, an additional pass through server is added to connect end users to their associated SIP proxy server, and to connect a CTI applications computer to the system.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for computer telephone integration in packet switched telephone networks
InactiveUS6856618B2Application programming interface detailsSpecial service for subscribersSession Initiation ProtocolApplication computers
A computer telephony interface (CTI) applications computer interfaces to a Internet telephony system which utilizes, preferably, the session initiation protocol (SIP). In one preferred technique, an additional pass through server is added to connect end users to their associated SIP proxy server, and to connect a CTI applications computer to the system.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Rollover solutions
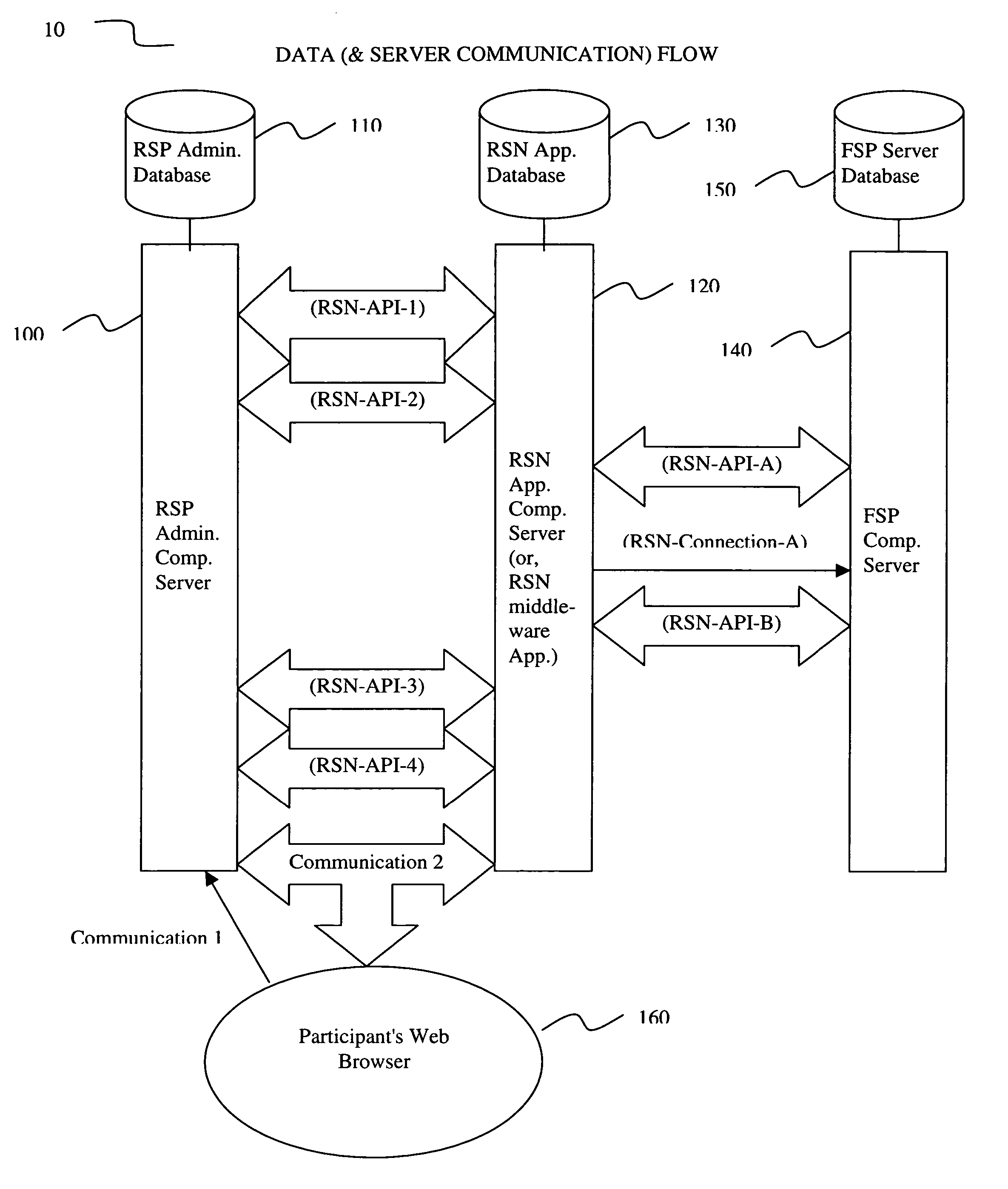
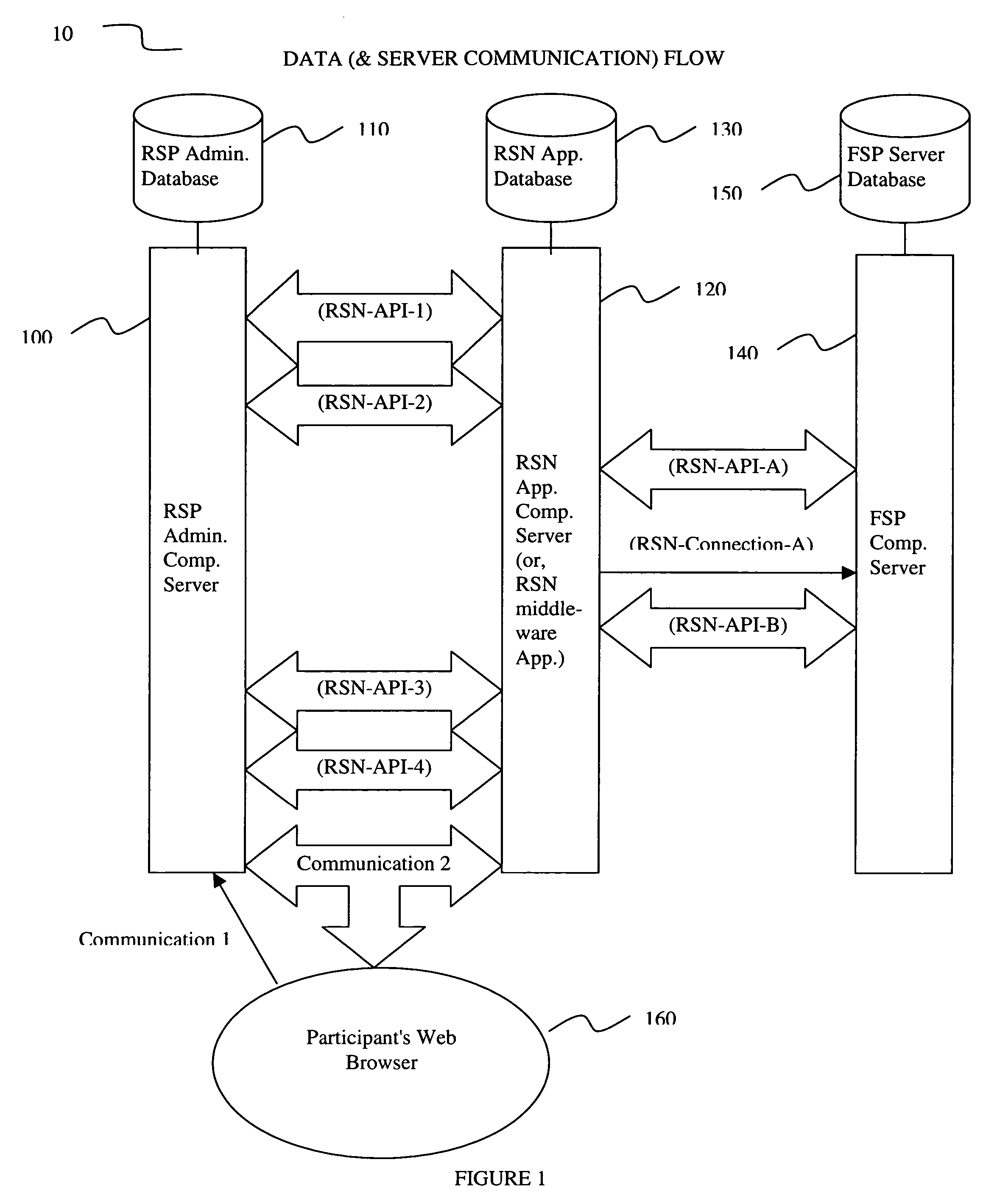
InactiveUS20060293984A1Facilitate communicationFacilitates real time account openingFinanceRolloverCommunication interface
An apparatus for and a method of an electronic middleware interface consisting of communication interfaces designed to transfer data between financial record keeping systems and new account opening applications is presented. A retirement savings plan (RSP) administrator computer server communicates via the electronic middleware communication interfaces to a Rollover Solutions Network (RSN) application computer server to communicate financial savings plan participant data. The RSN application computer server utilizes the participant data to contact a financial service provider (FSP) computer server to identify the participant retirement accounts for rollover purposes. Alternatively, the RSN application computer server can contact the FSP computer server to open a new retirement account. Utilizing either the established retirement account or the new retirement account the RSN application computer server instructs the RSP administrator computer server to initiate rollover of the participants retirement account funds to the FSP.
Owner:WEALTH MANAGEMENT SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com