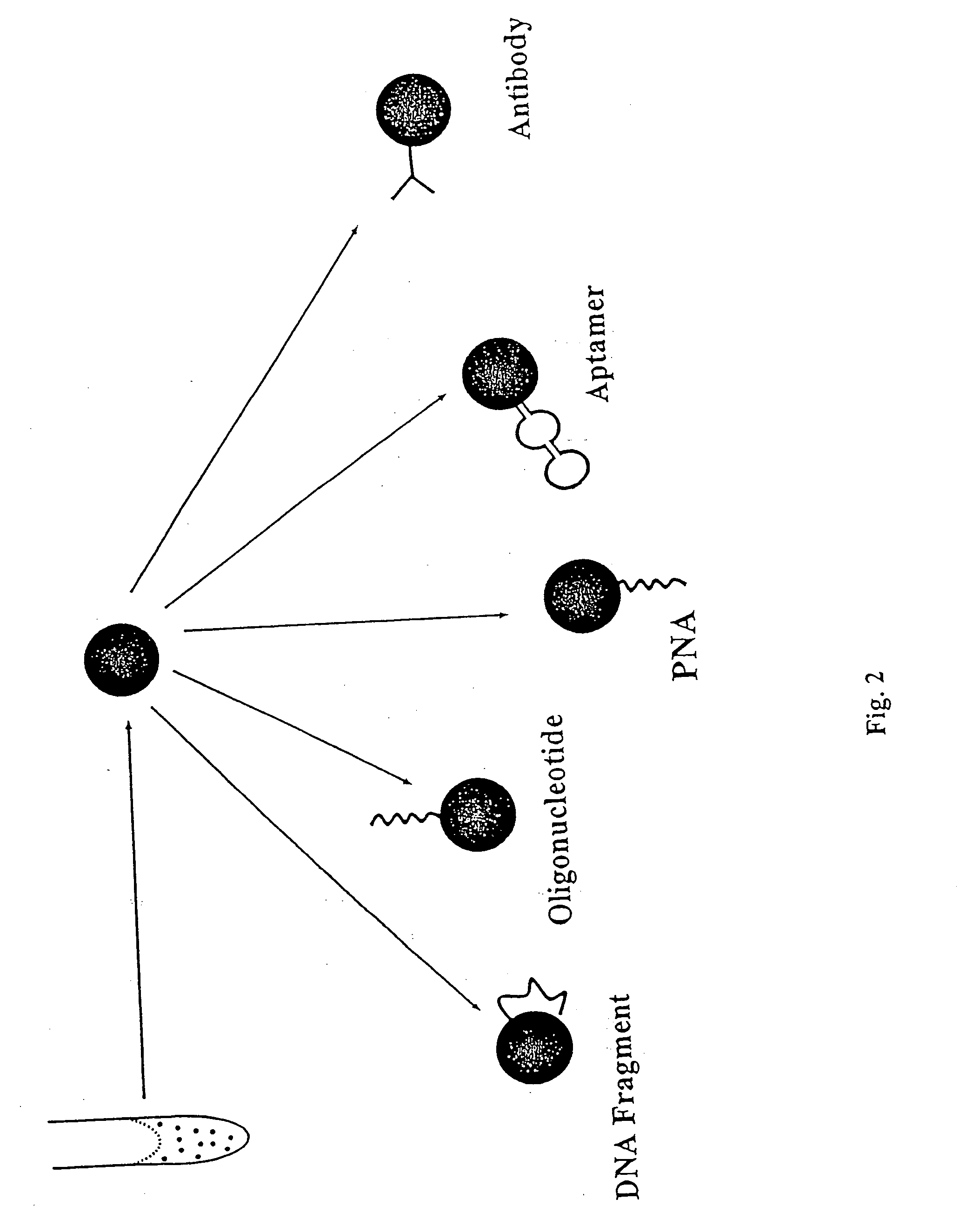
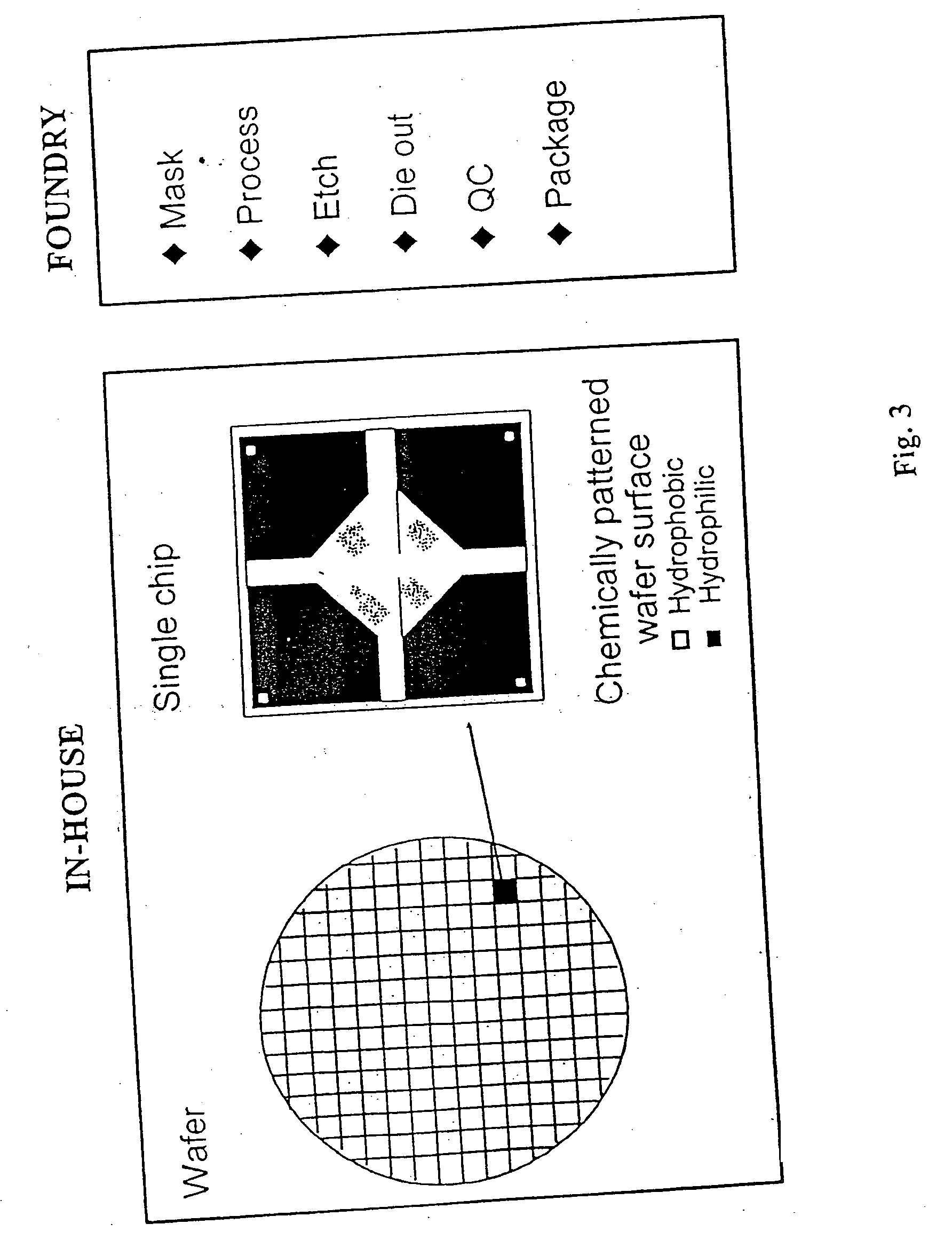
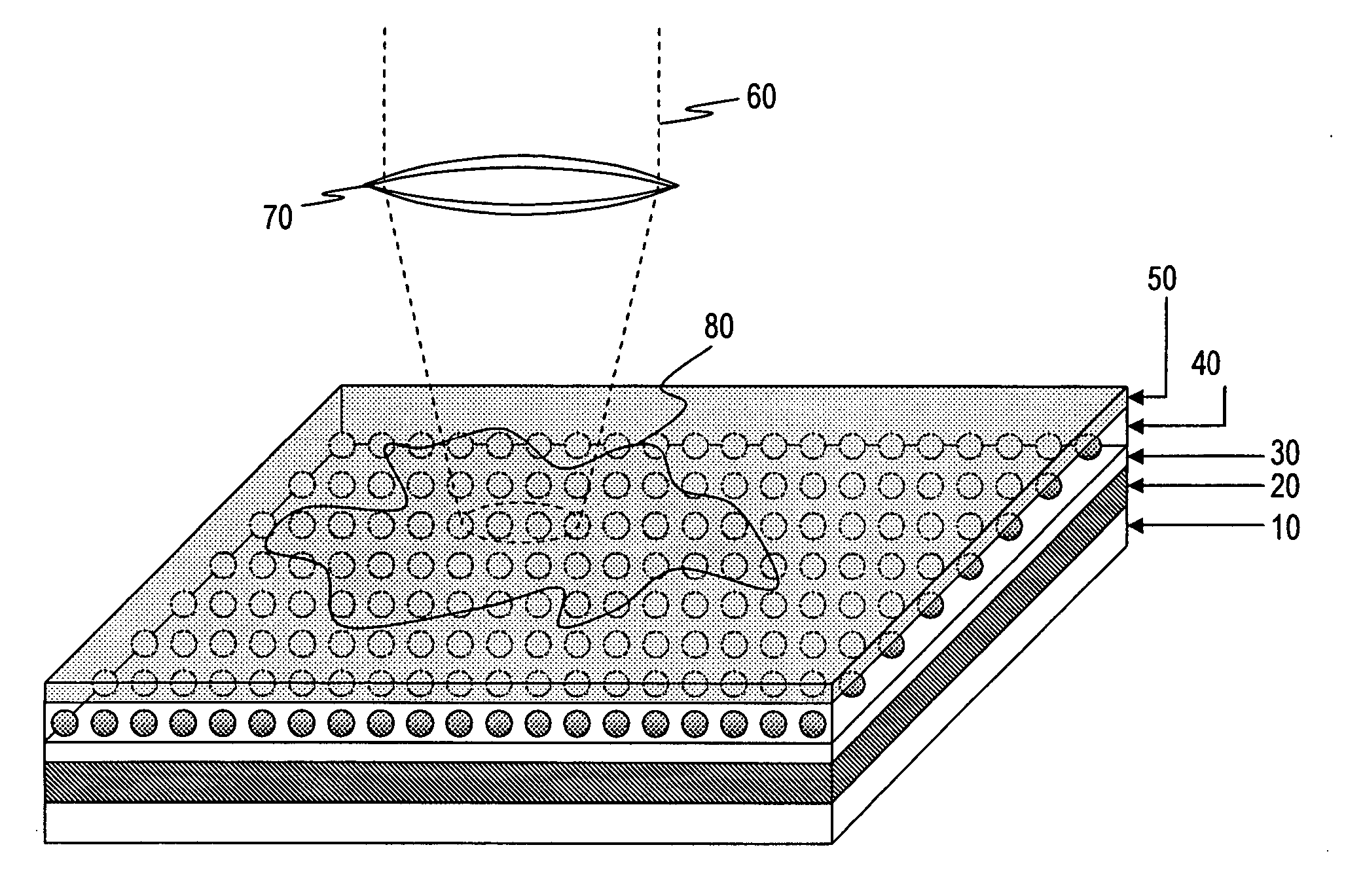
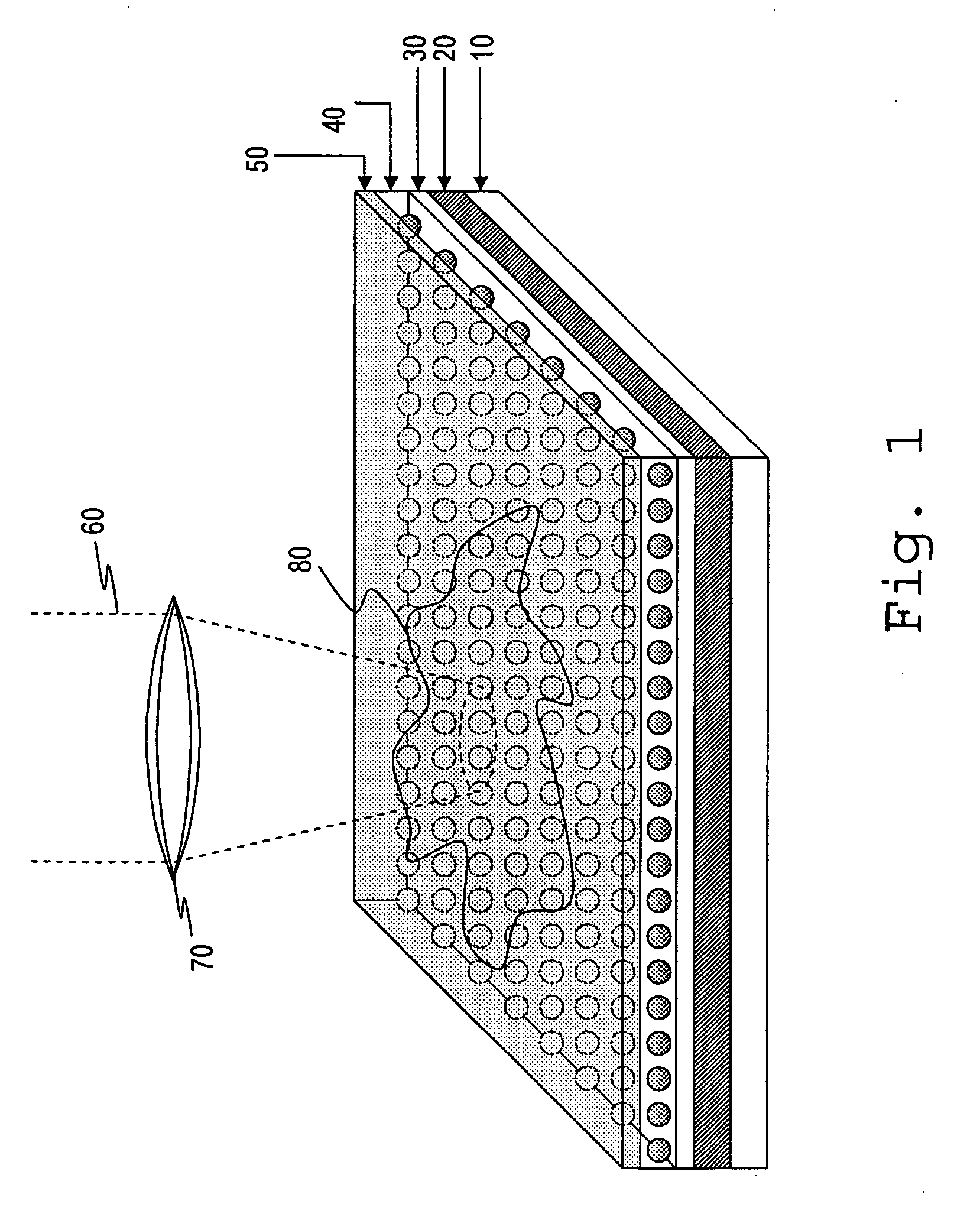
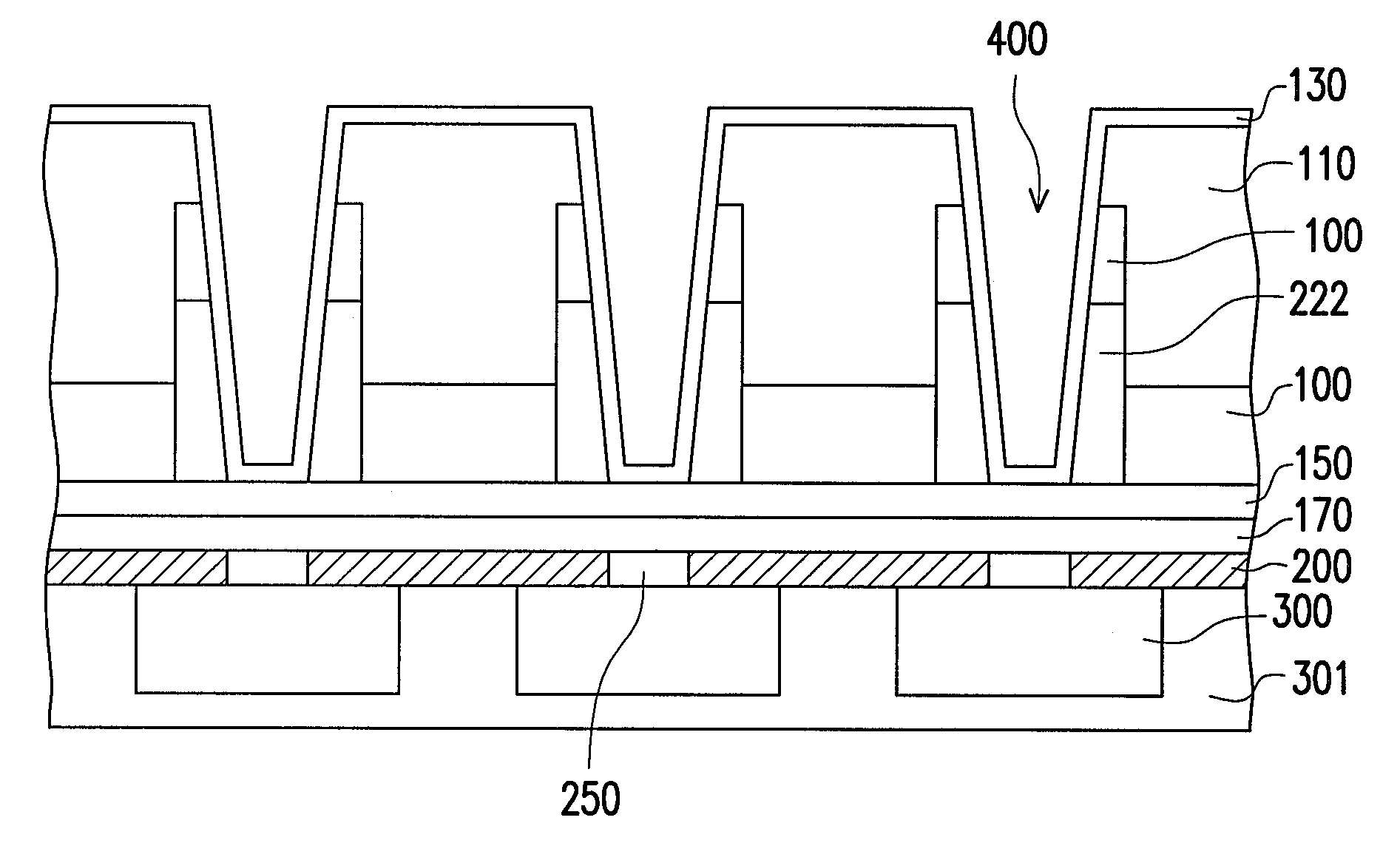
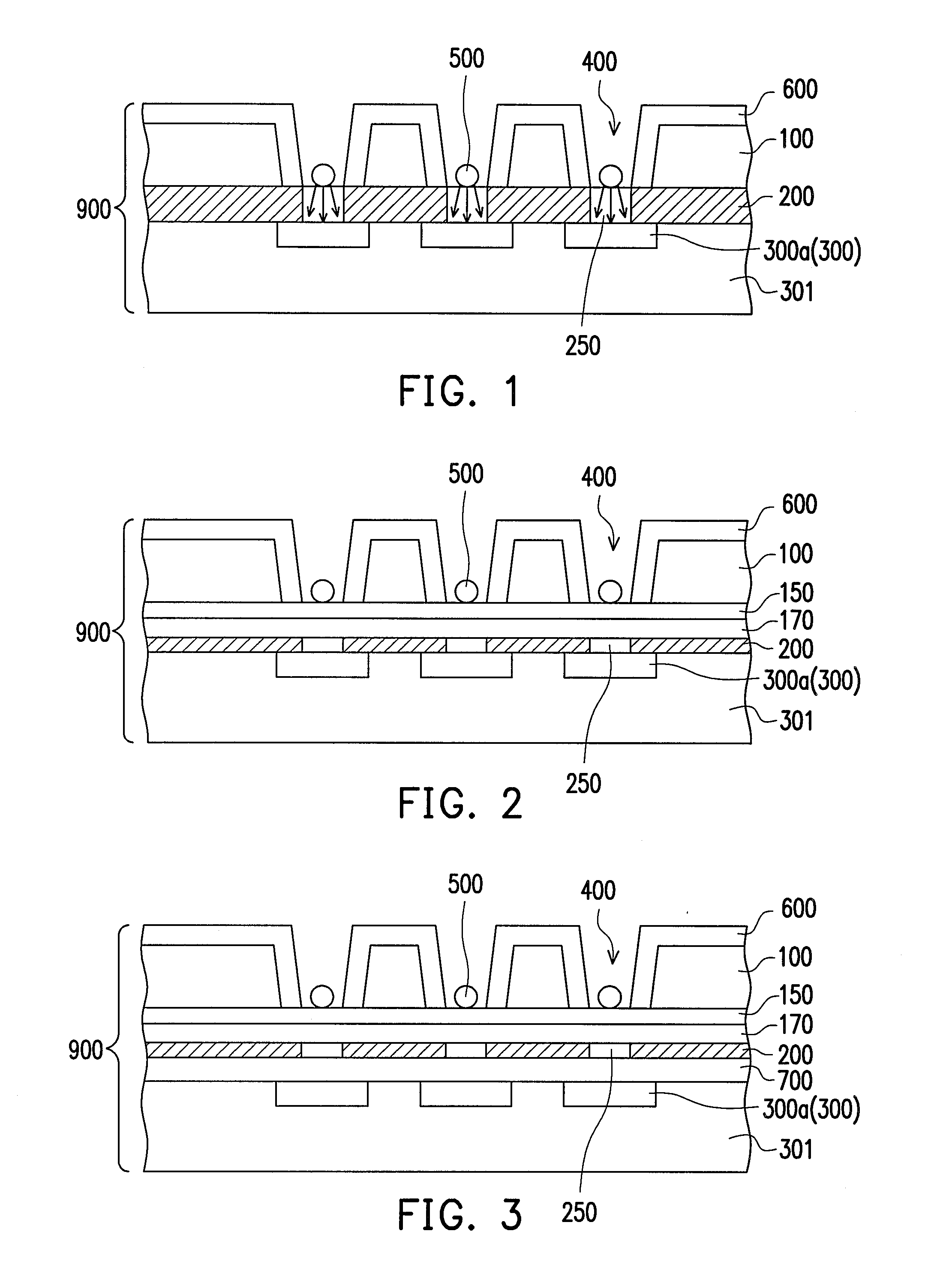
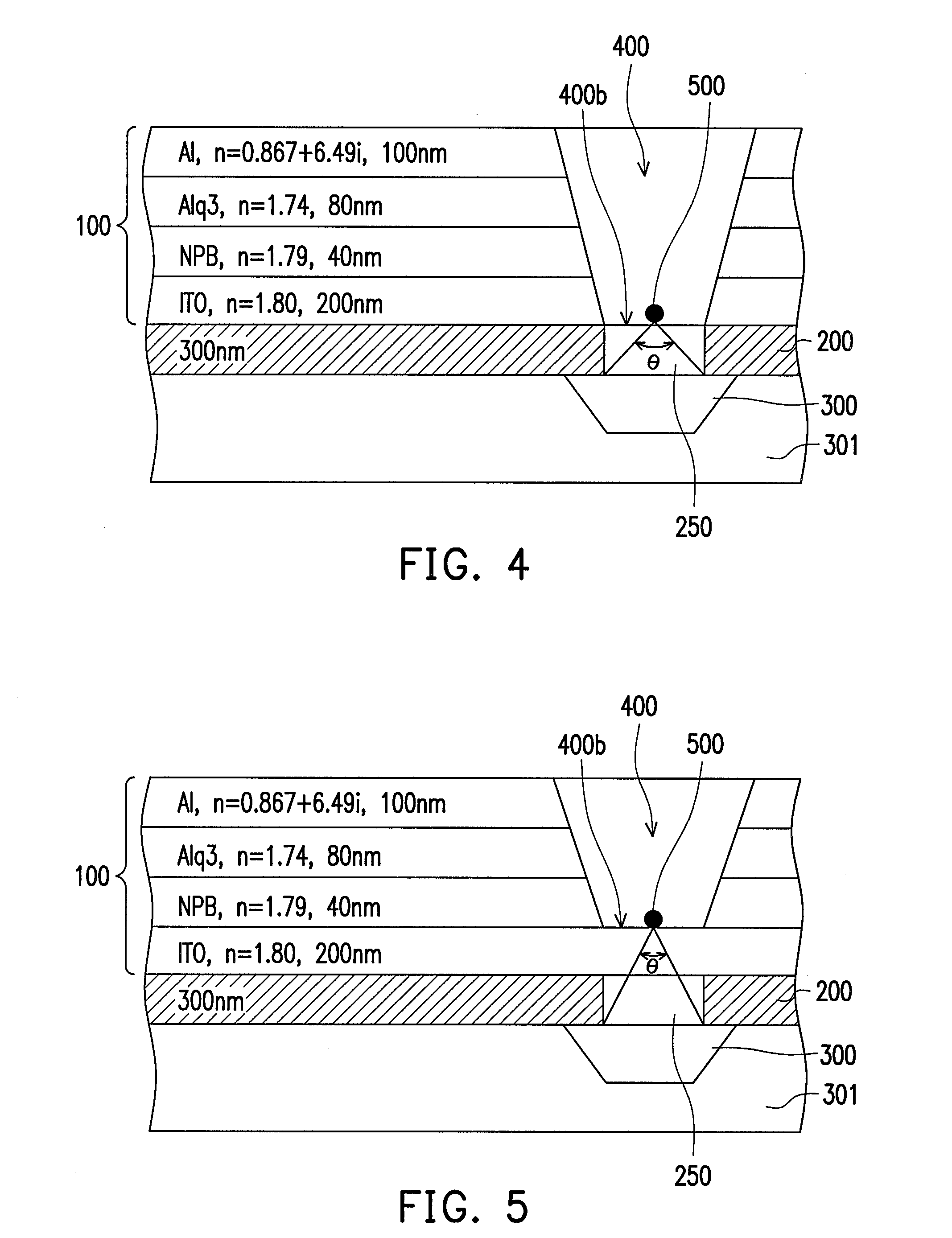
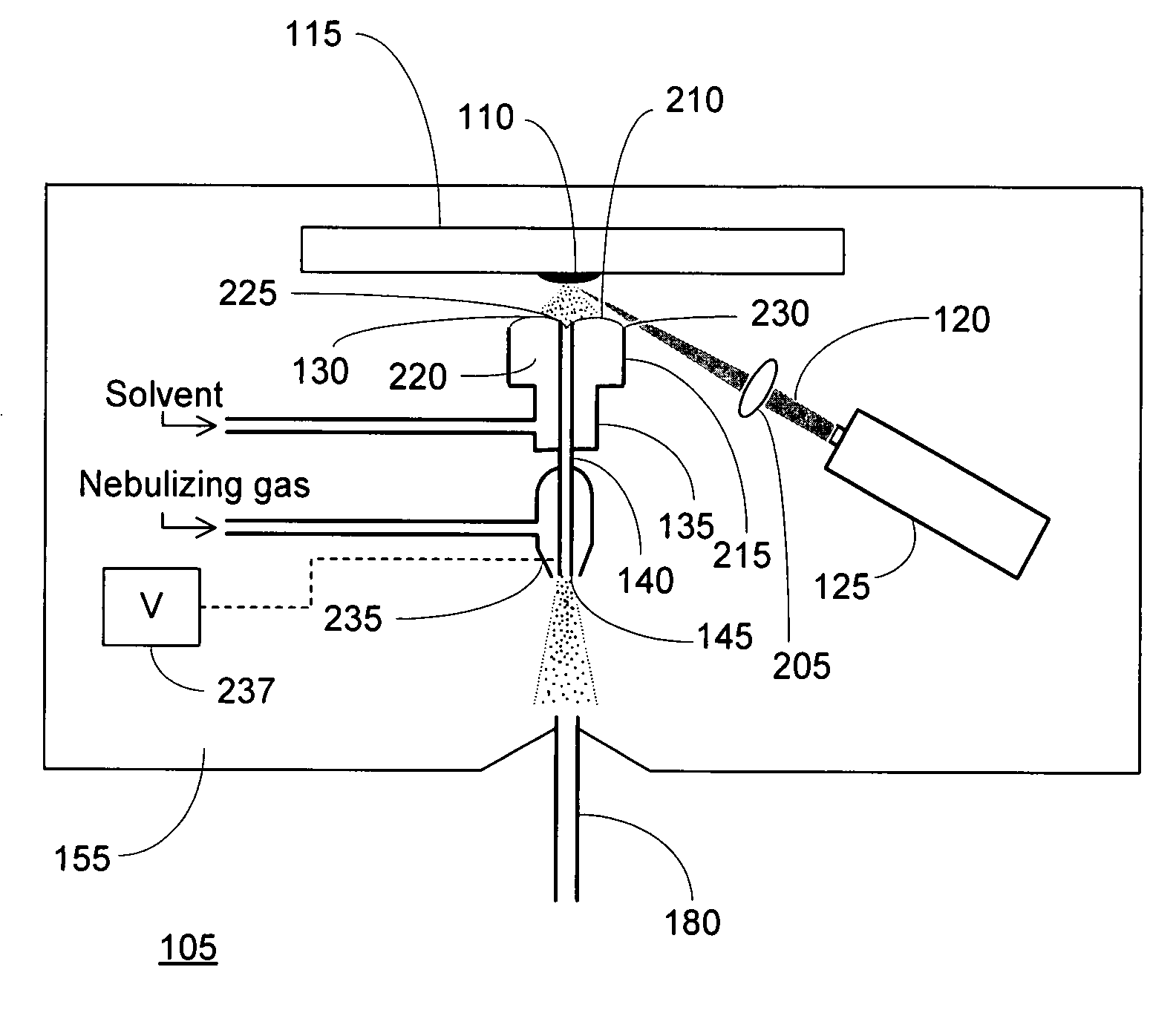
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
253 results about "Analyte molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
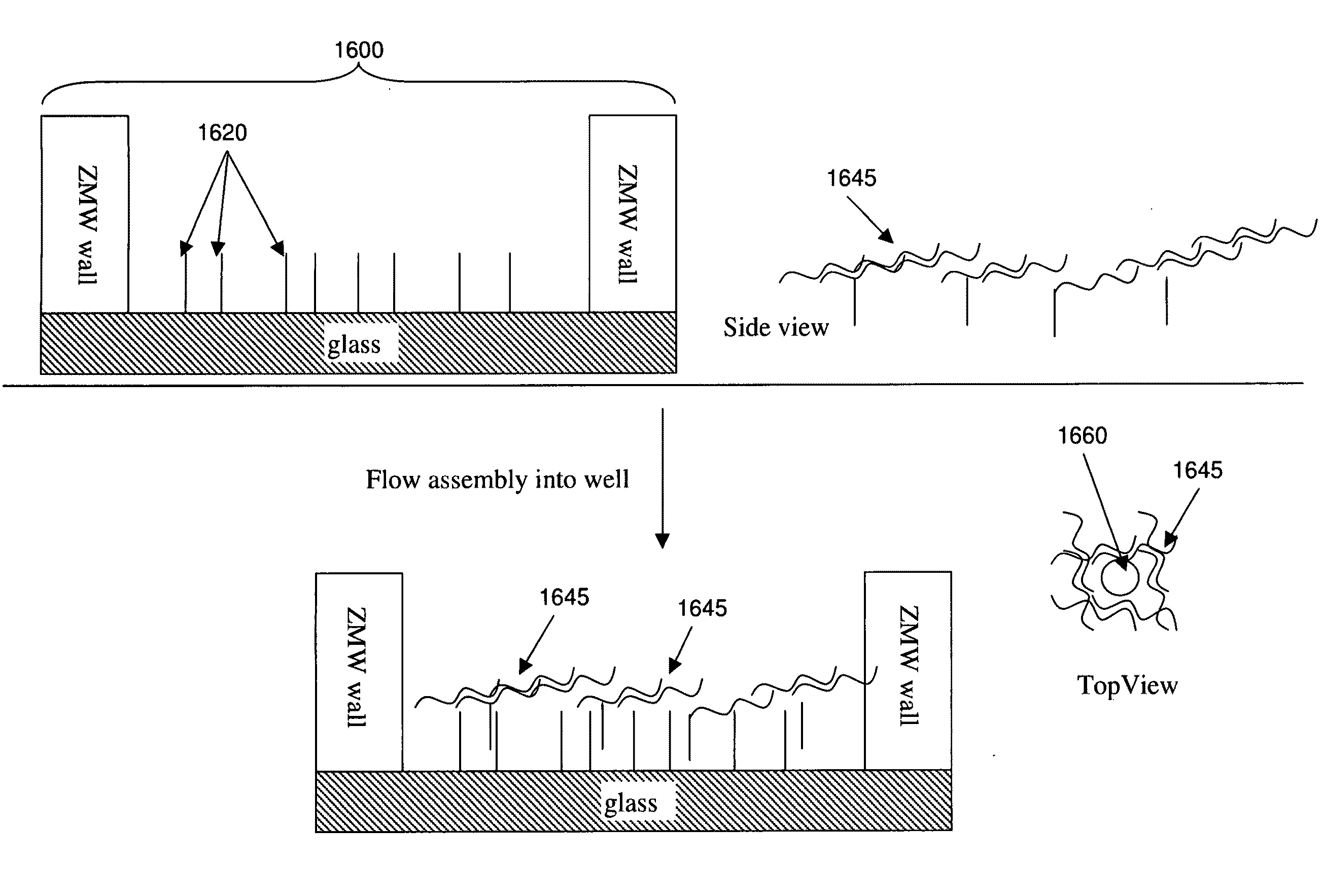
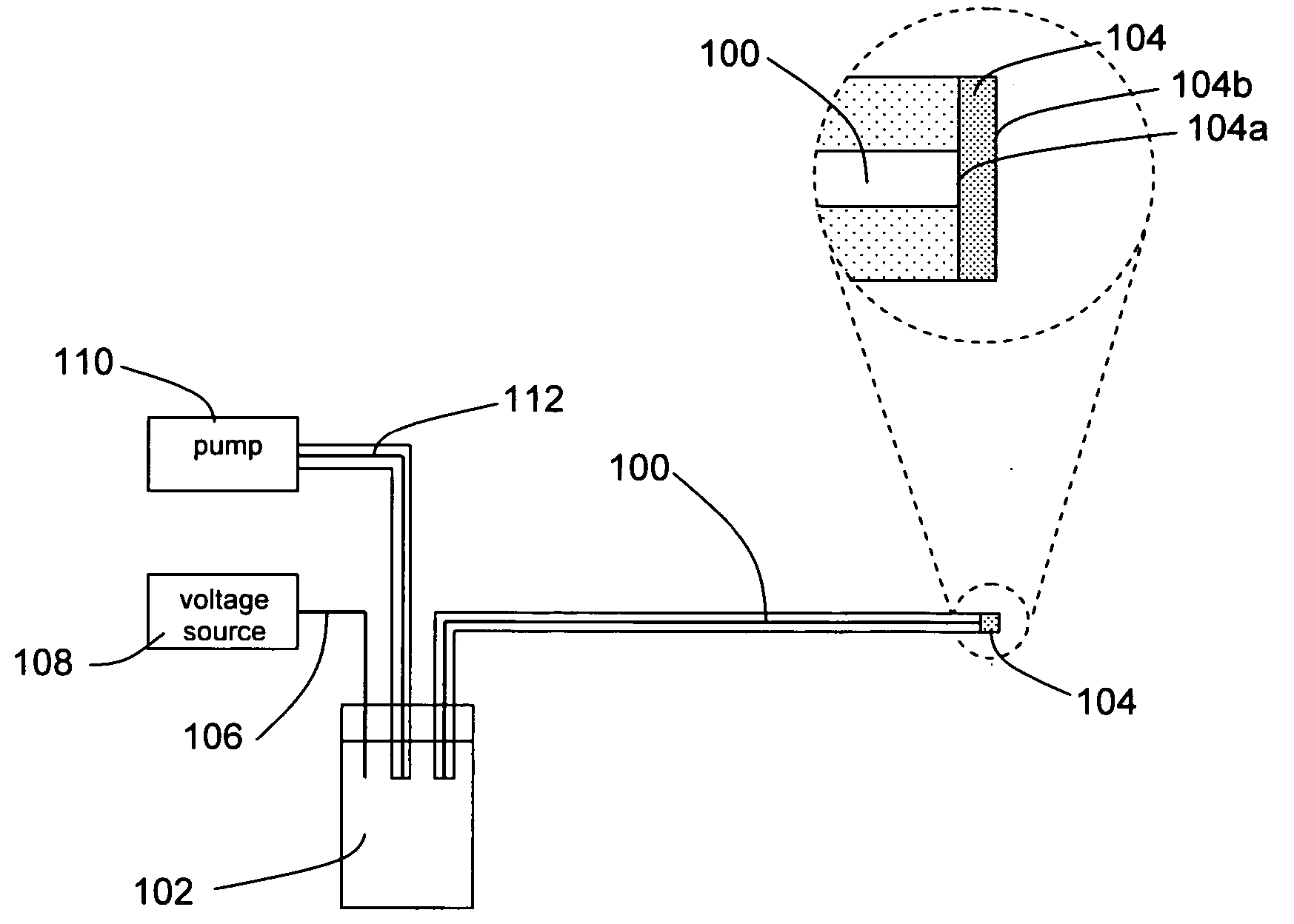
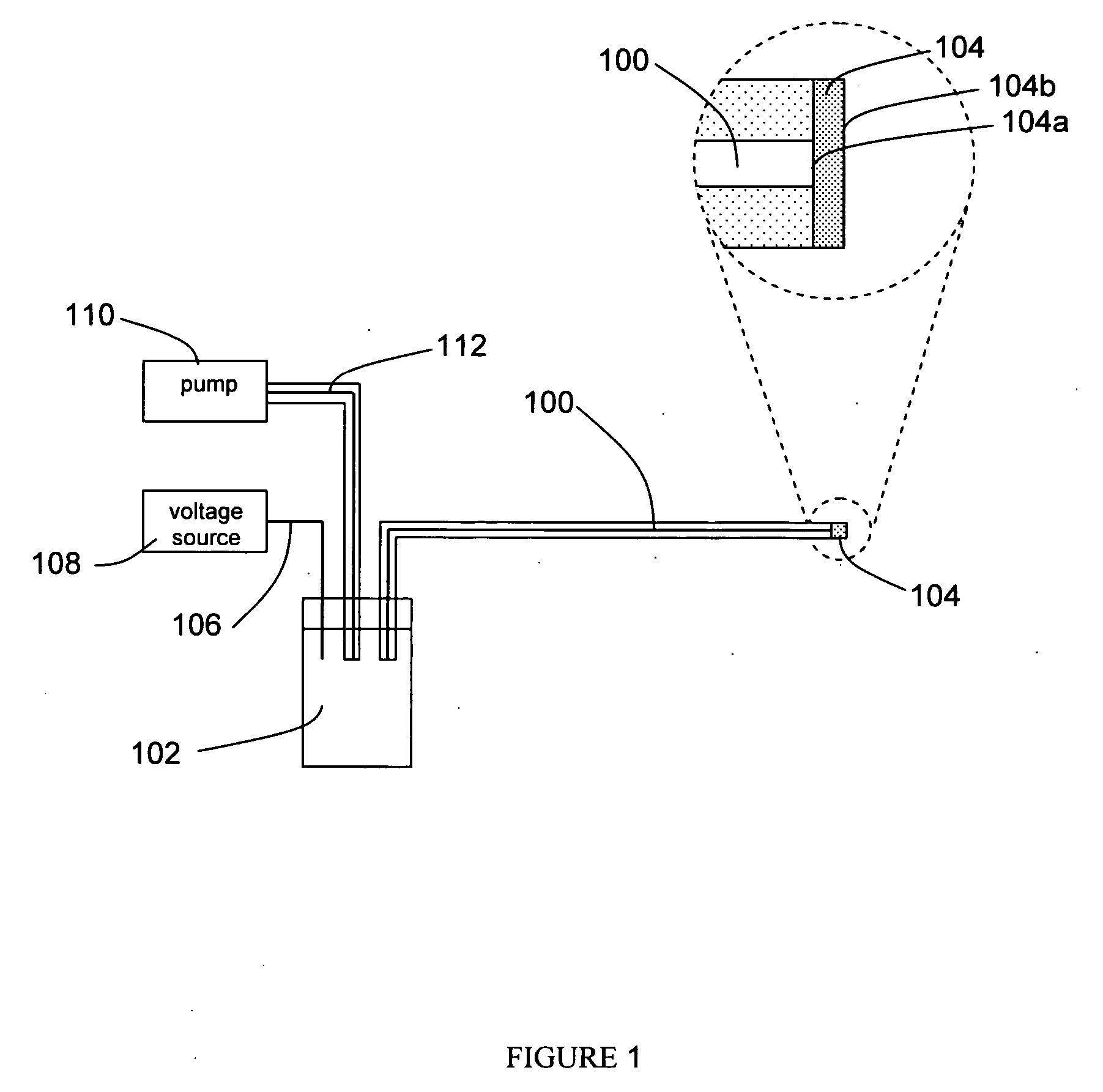
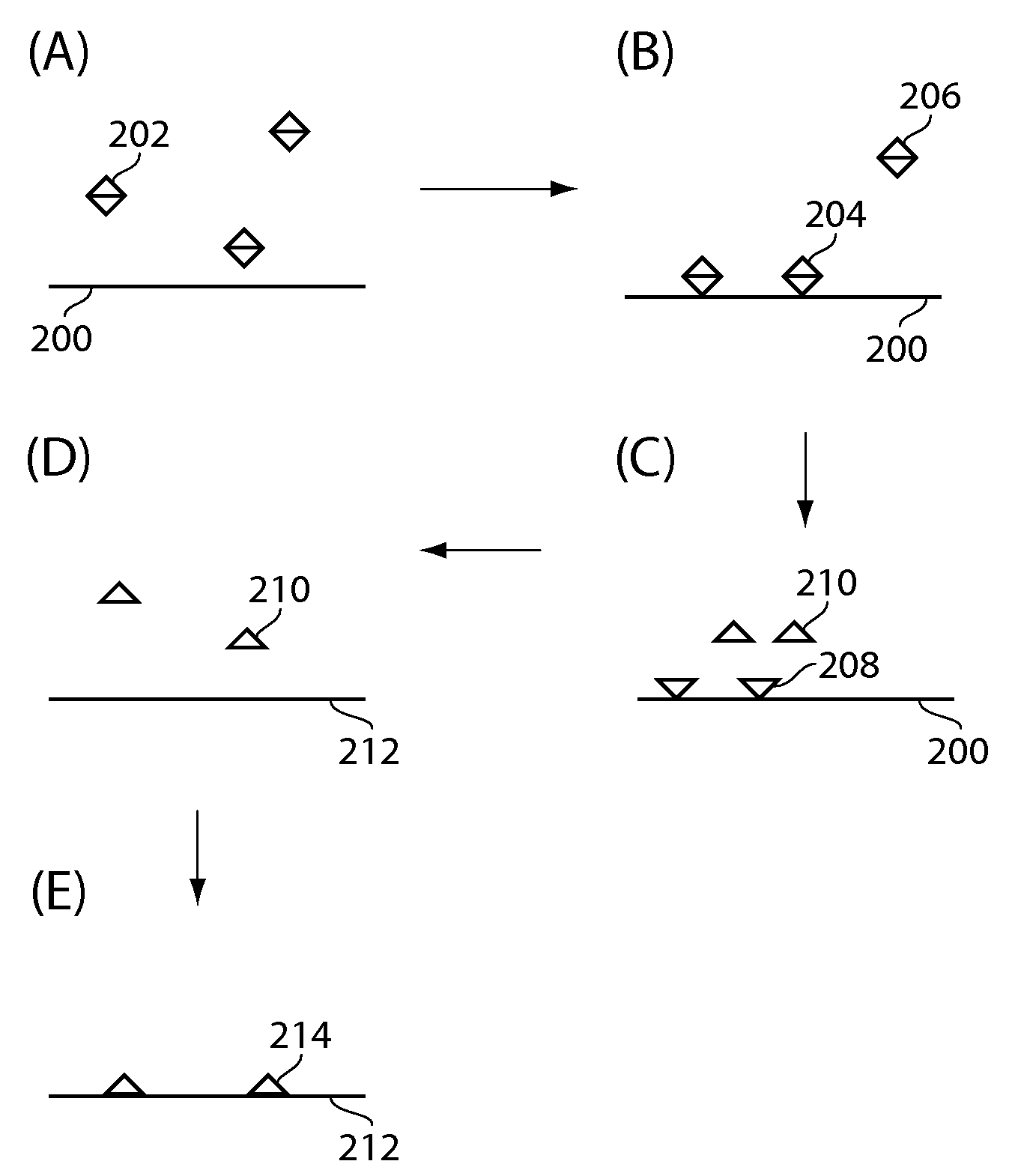
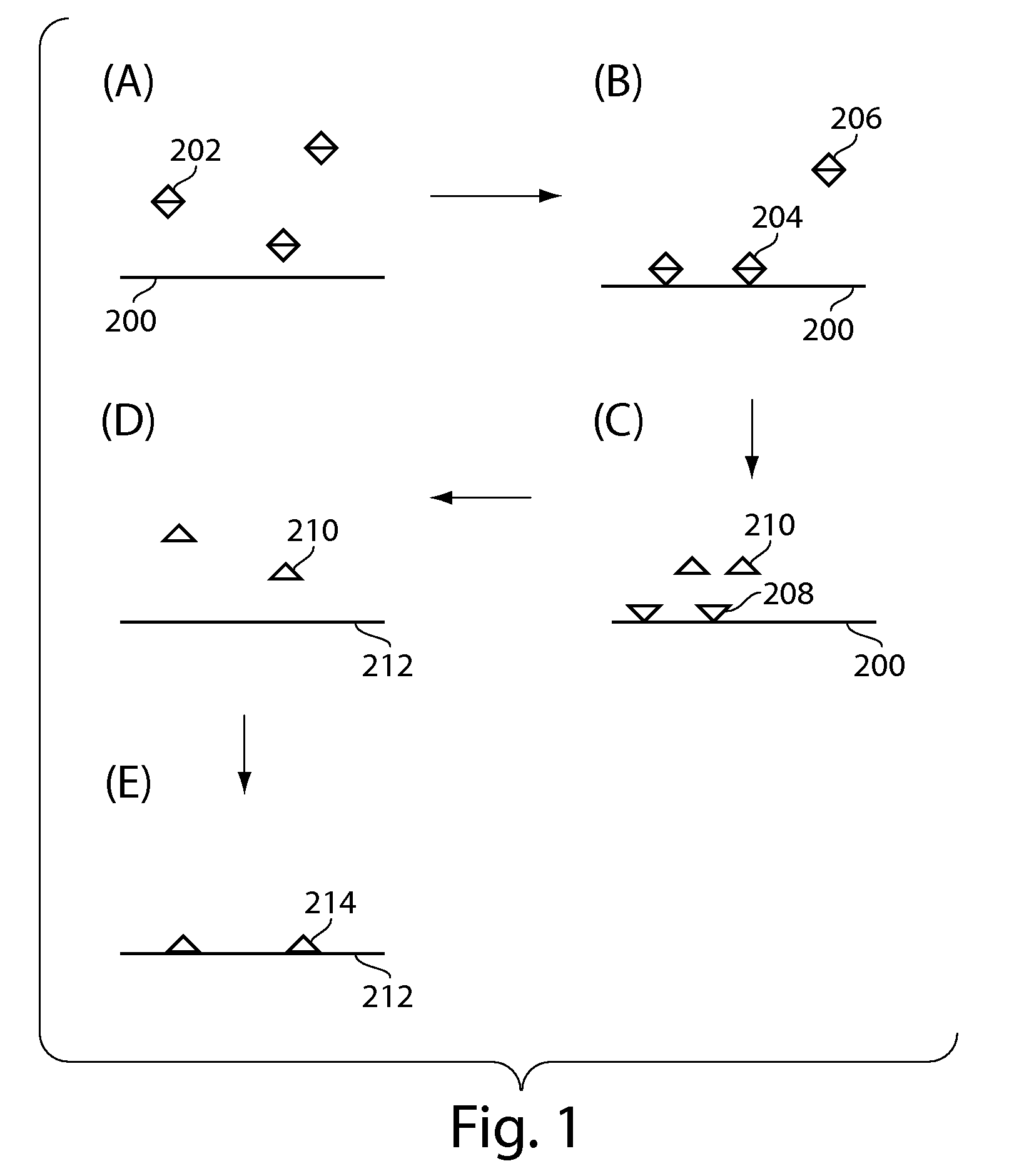
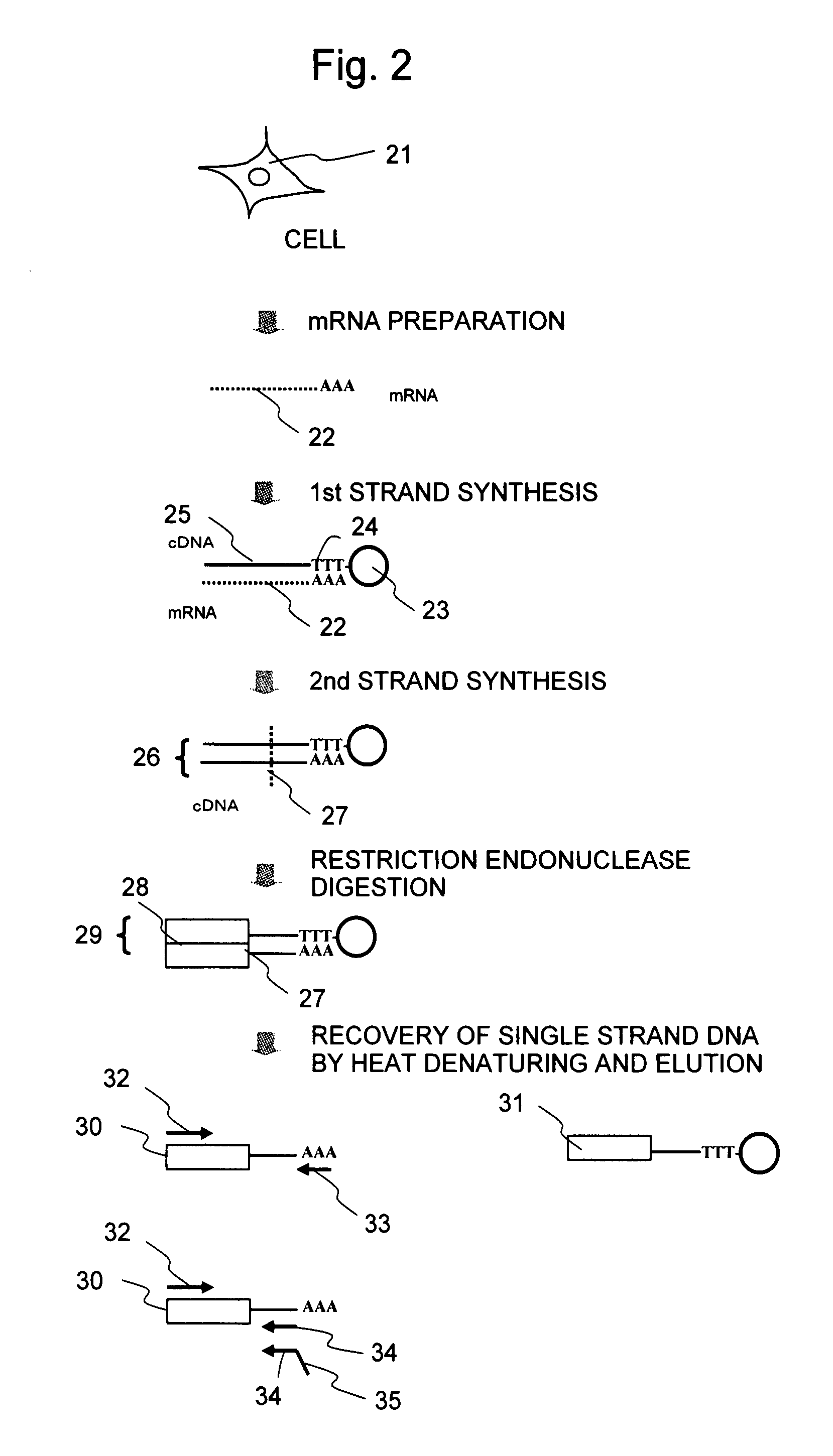
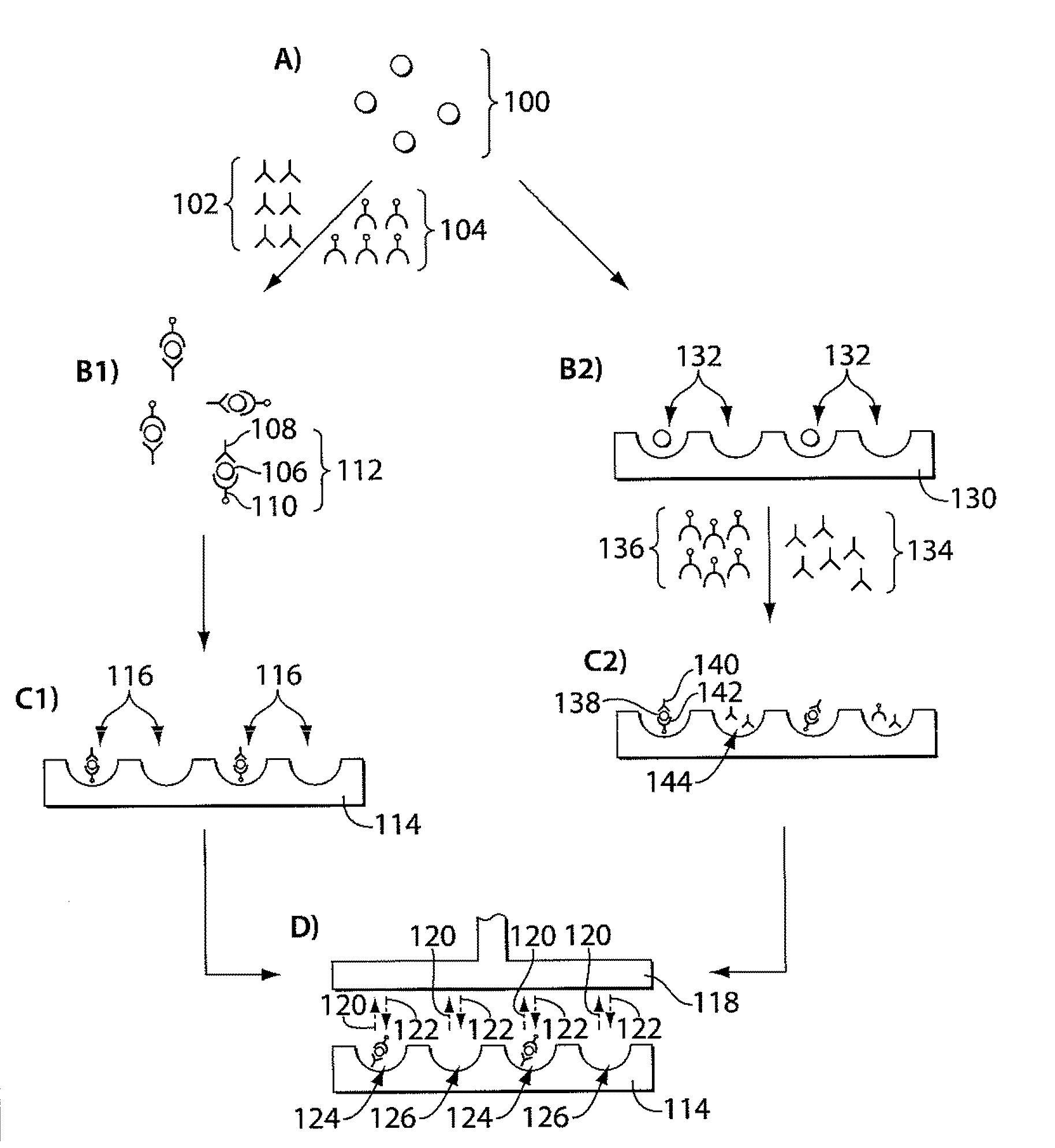
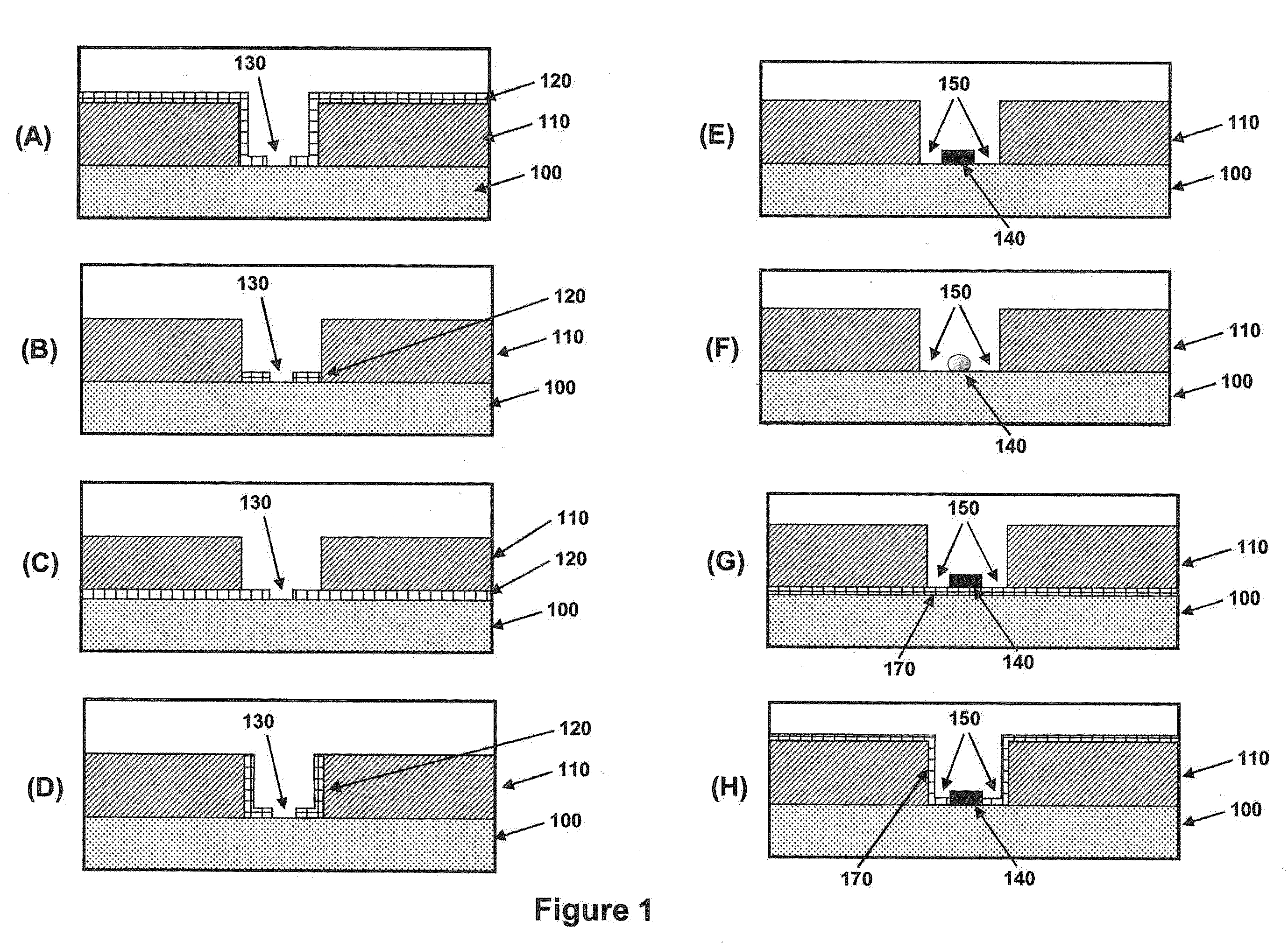
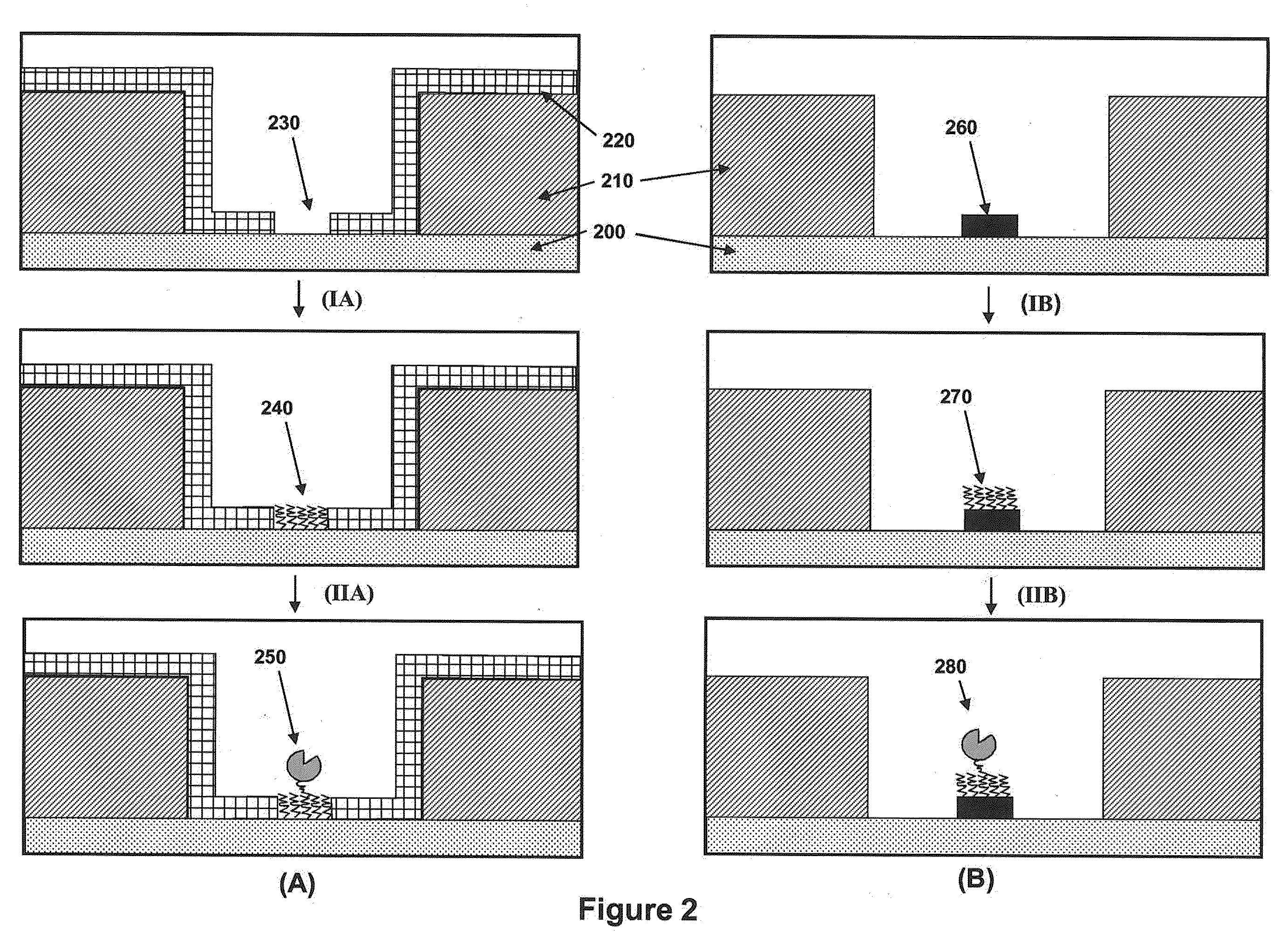
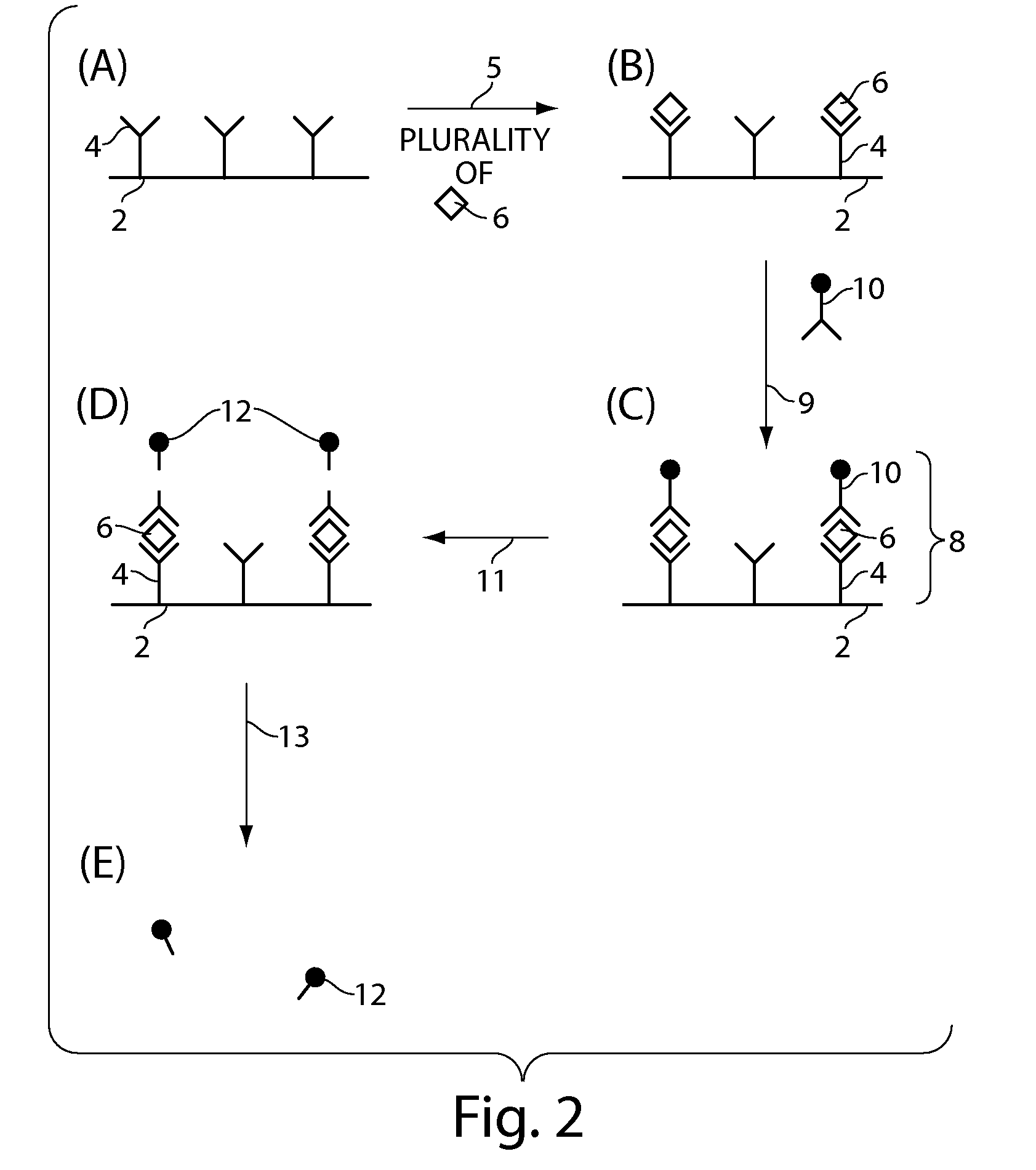
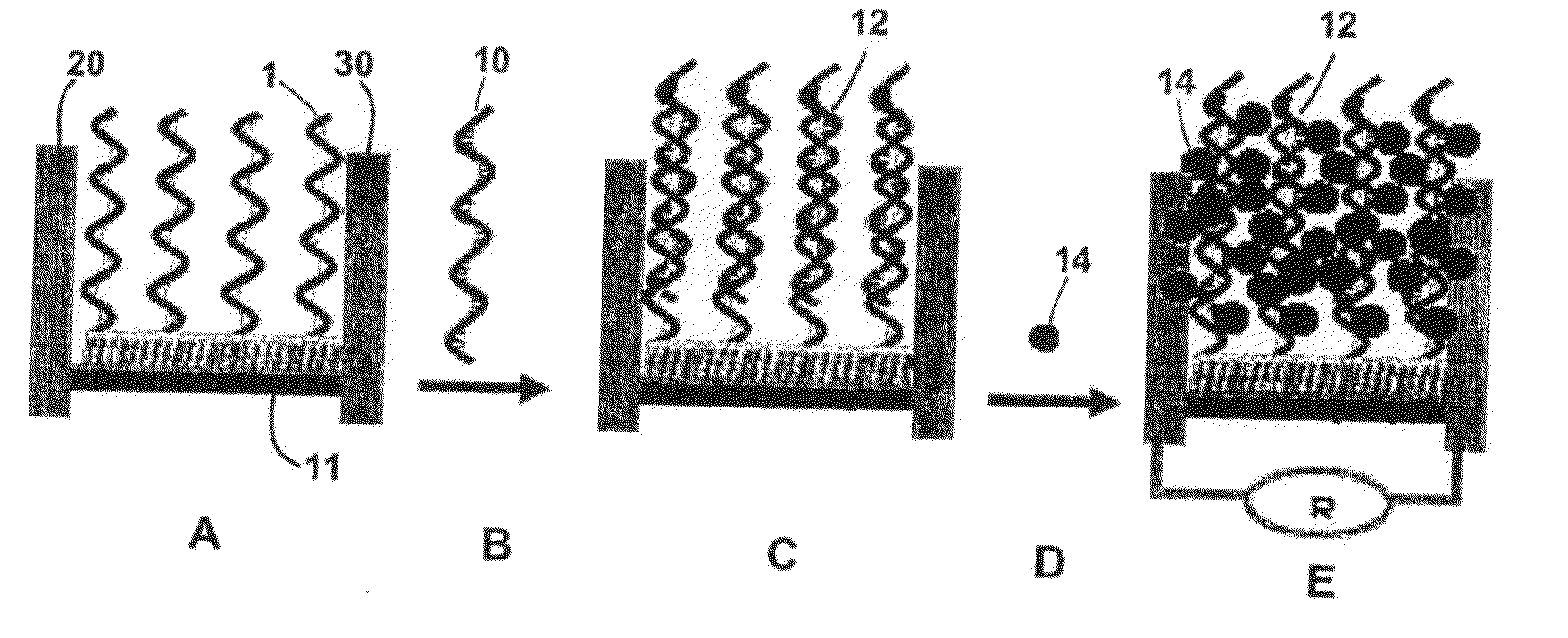
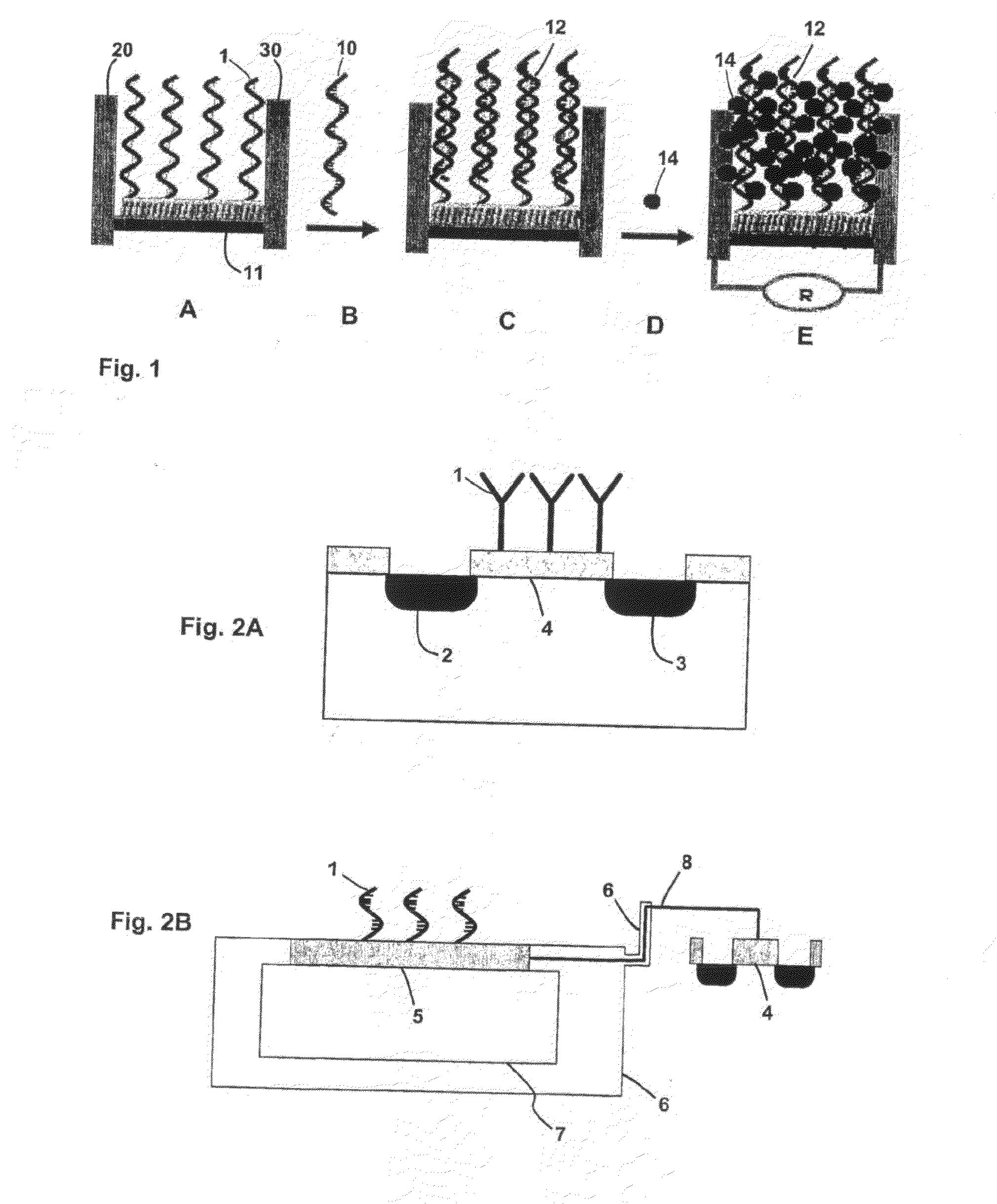
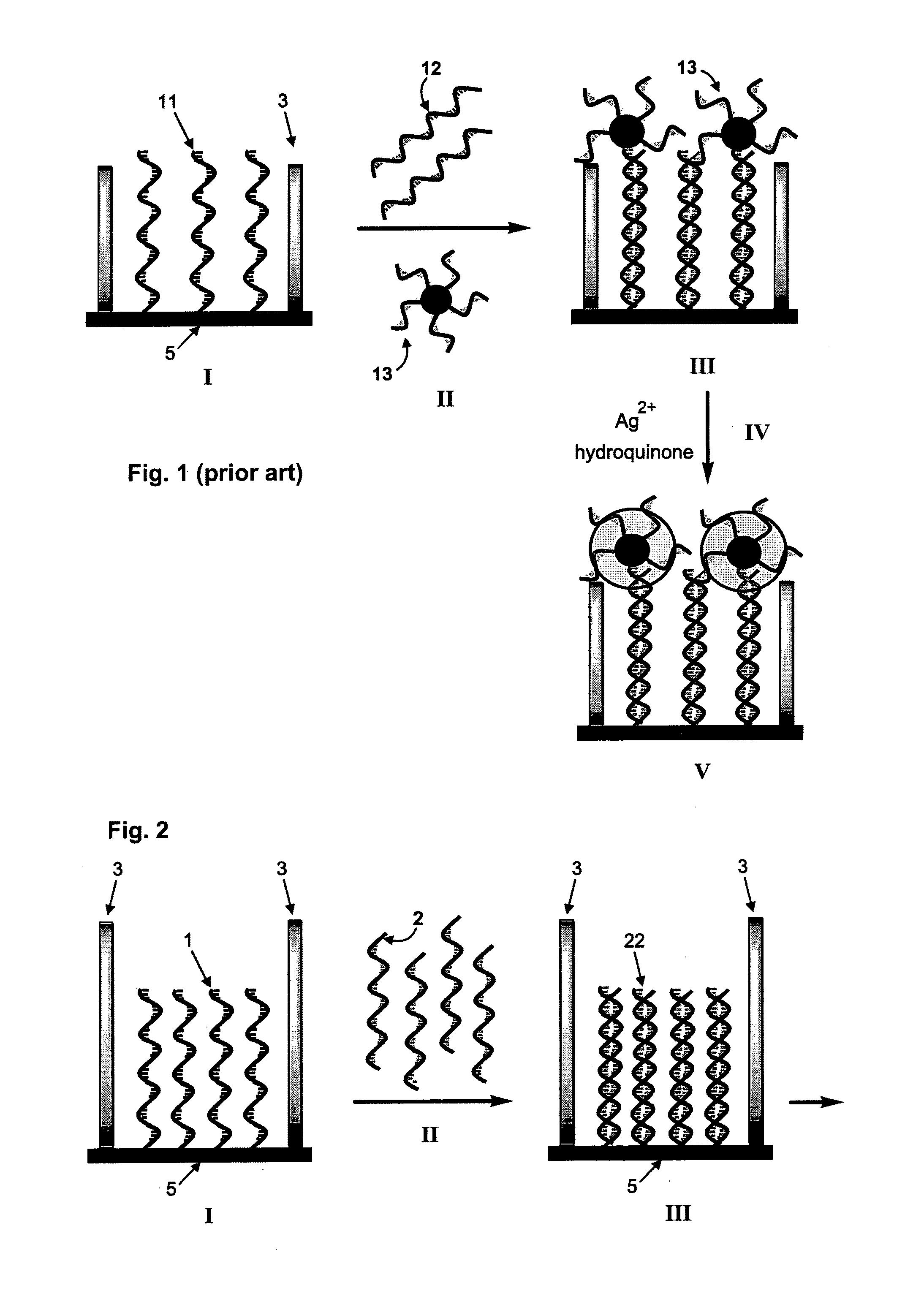
Single molecule loading methods and compositions
ActiveUS20100009872A1Improve throughputImprove efficiencySequential/parallel process reactionsNucleotide librariesAnalyte moleculeMolecular physics
Methods, compositions and arrays for non-random loading of single analyte molecules into array structures are provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Assembly of arrays on chips segmented from wafers
InactiveUS20050244850A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMagnetite NanoparticlesAnalyte molecule
The present invention provides a method for the generation of novel libraries of encoded magnetic particles from sub-libraries of by the generation of novel sub-libraries of magnetic nanoparticles and encoded particles. The sub-libraries are functionalized on demand are useful in the formation of arrays. The present invention is especially useful for performing multiplexed (parallel) assays for qualitative and / or quantitative analysis of binding interactions of a number of analyte molecules in a sample.
Owner:HUANG HIU +1
Optical sensor with layered plasmon structure for enhanced detection of chemical groups by SERS
InactiveUS20060034729A1Produced in advanceRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementExcitation beamLight excitation
An optical sensor and method for use with a visible-light laser excitation beam and a Raman spectroscopy detector, for detecting the presence chemical groups in an analyte applied to the sensor are disclosed. The sensor includes a substrate, a plasmon resonance mirror formed on a sensor surface of the substrate, a plasmon resonance particle layer disposed over the mirror, and an optically transparent dielectric layer about 2-40 nm thick separating the mirror and particle layer. The particle layer is composed of a periodic array of plasmon resonance particles having (i) a coating effective to binding analyte molecules, (ii) substantially uniform particle sizes and shapes in a selected size range between 50-200 nm (ii) a regular periodic particle-to-particle spacing less than the wavelength of the laser excitation beam. The device is capable of detecting analyte with an amplification factor of up to 1012-1014, allowing detection of single analyte molecules.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
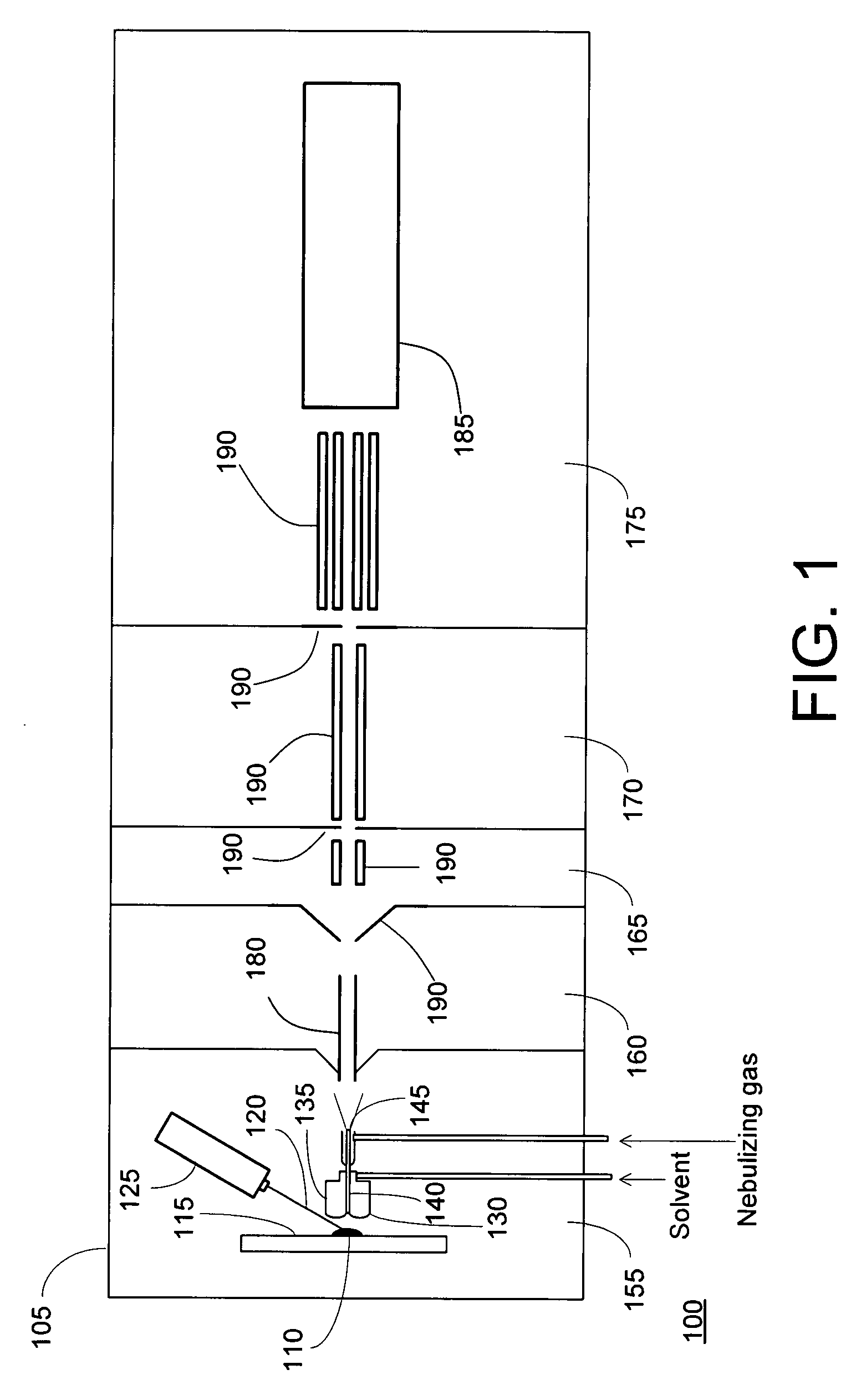
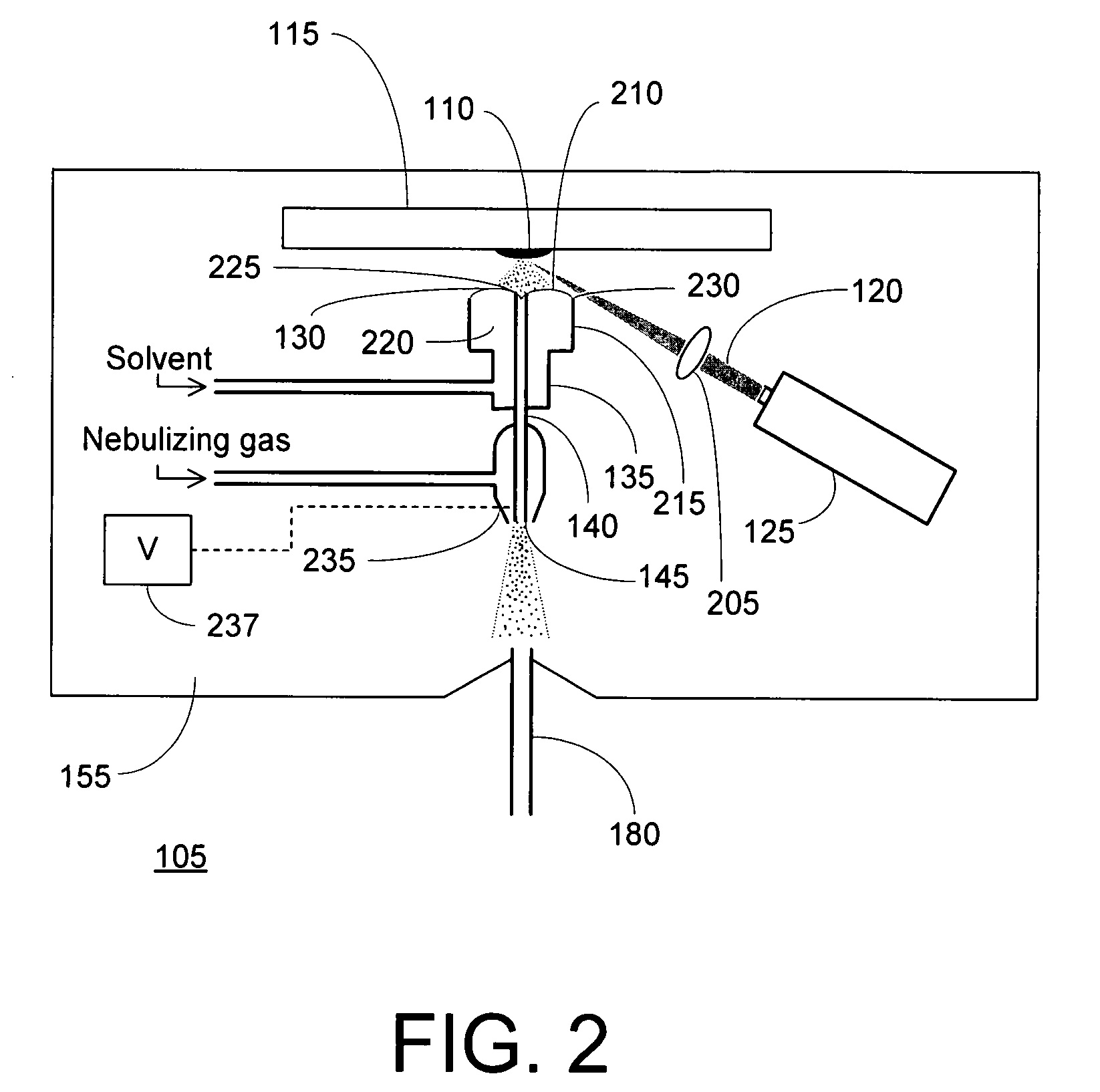
Ionization by droplet impact
ActiveUS20060108539A1Minimize the numberIncrease kinetic energySamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermal energyMass spectrometric
The invention relates to methods and instruments for ionizing analyte molecules, preferably biomolecules, which are dissolved in liquids or firmly adsorbed on surfaces. Liquids are nebulized at atmospheric pressure by electrospraying. Highly charged microdroplets, which enter the vacuum of the mass spectrometer through the inlet capillary, strike an impact plate when energy is fed in. The repulsive Coulomb force of the charges, the absorption of additional thermal energy and / or the conversion of their kinetic energy into thermal energy cause the microdroplets to burst and evaporate. Analyte molecules which are located in the nebulized liquid or on the impact plate are released in charged form and can be fed to the mass spectrometer for analysis by the extraction and collection effect of an ion funnel operated with RF and DC voltages.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus for single molecule detection and method thereof
InactiveUS20120156100A1Analysis by electrical excitationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceDetector array
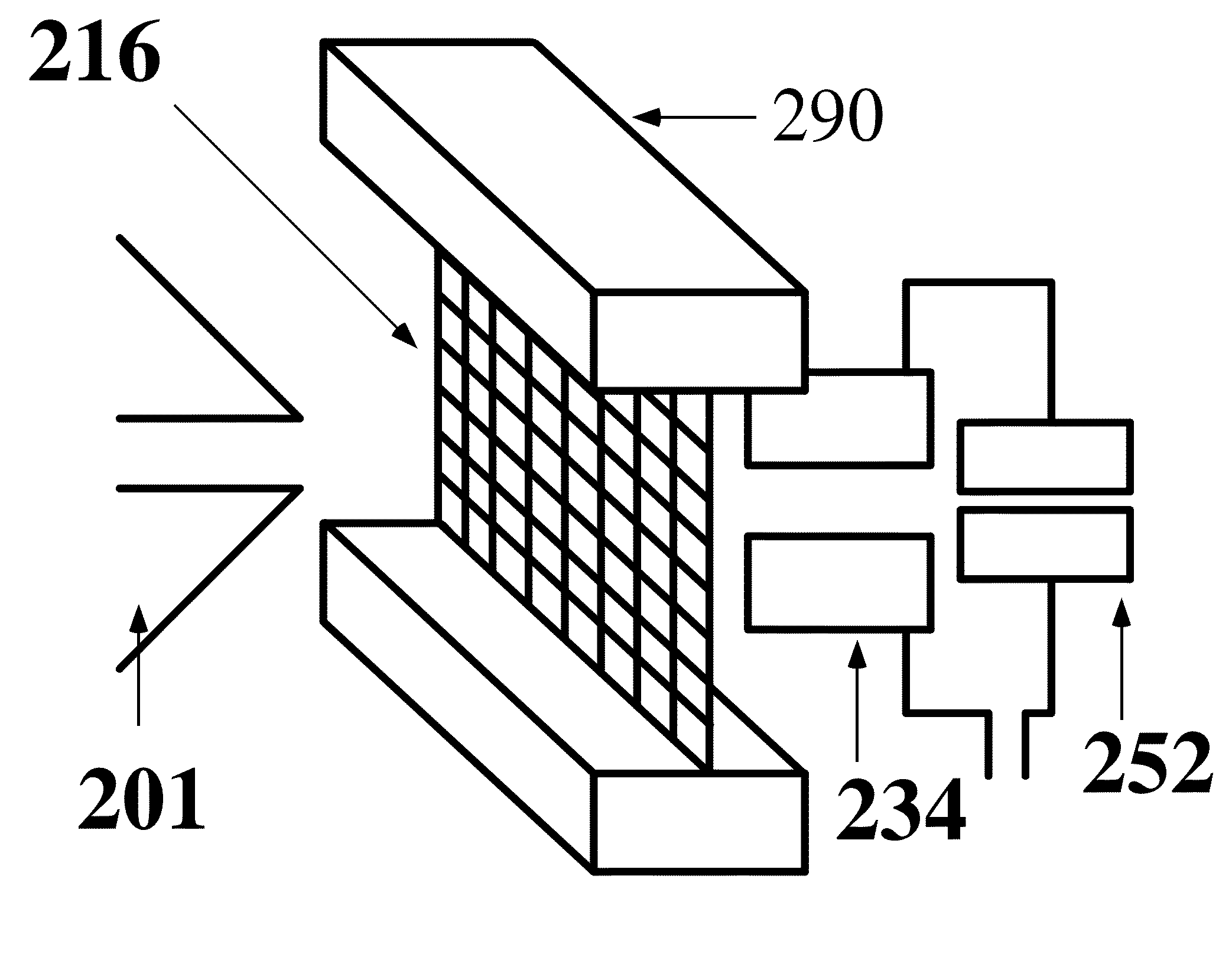
The present invention directs to a detection apparatus for detecting the fluorescence signal emitting from a single and individual analyte molecule. By integrating the excitation light source, the detector array and the nanowell array all together within the detection apparatus, the single analyte molecule trapped in the nanowell can be excited by the light source and emits fluorescence signal to the detector array.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Laser desorption - electrospray ion (ESI) source for mass spectrometers
InactiveUS20080272294A1Minimize dilutionMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsDesorptionElectrospray ionization
An ion source is disclosed for forming multiply-charged analyte ions from a solid sample. A beam of pulsed radiation is directed onto a portion of the sample to desorb analyte molecules. A retaining structure holding a solvent volume is positioned proximate the sample. Desorbed analyte molecules contact a free surface of the solvent and pass into solution. The solution is then conveyed through an outlet passageway to an electrospray apparatus, which introduces a spray of charged solvent droplets into an ionization chamber.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Optical sensor with layered plasmon structure for enhanced detection of chemical groups by SERS
InactiveUS7351588B2Produced in advanceRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification factorPhysics
An optical sensor and method for use with a visible-light laser excitation beam and a Raman spectroscopy detector, for detecting the presence chemical groups in an analyte applied to the sensor are disclosed. The sensor includes a substrate, a plasmon resonance mirror formed on a sensor surface of the substrate, a plasmon resonance particle layer disposed over the mirror, and an optically transparent dielectric layer about 2-40 nm thick separating the mirror and particle layer. The particle layer is composed of a periodic array of plasmon resonance particles having (i) a coating effective to binding analyte molecules, (ii) substantially uniform particle sizes and shapes in a selected size range between 50-200 nm (ii) a regular periodic particle-to-particle spacing less than the wavelength of the laser excitation beam. The device is capable of detecting analyte with an amplification factor of up to 1012-1014, allowing detection of single analyte molecules.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
Methods and apparatus for porous membrane electrospray and multiplexed coupling of microfluidic systems with mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060192107A1Stable electrosprayReduce pressureParticle separator tubesComponent separationTarget surfaceCoupling
Disclosed are an apparatus, system, and method for performing electrospray of biomolecules, particularly peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. The apparatus comprises at least (1) a microfluidic substrate for containing an electrospray microchannel for delivering analyte molecules to a side edge of the substrate, and (2) a porous membrane attached to the side edge for performing electrospray from the exposed membrane surface. In one preferred embodiment, the exposed membrane surface is positioned above a target surface for depositing analyte molecules onto the target surface by electrospray. In another preferred embodiment, a proteolytic enzyme is bound to the porous membrane for performing protein digestion during electrospray.
Owner:DEVOE DONALD L +3
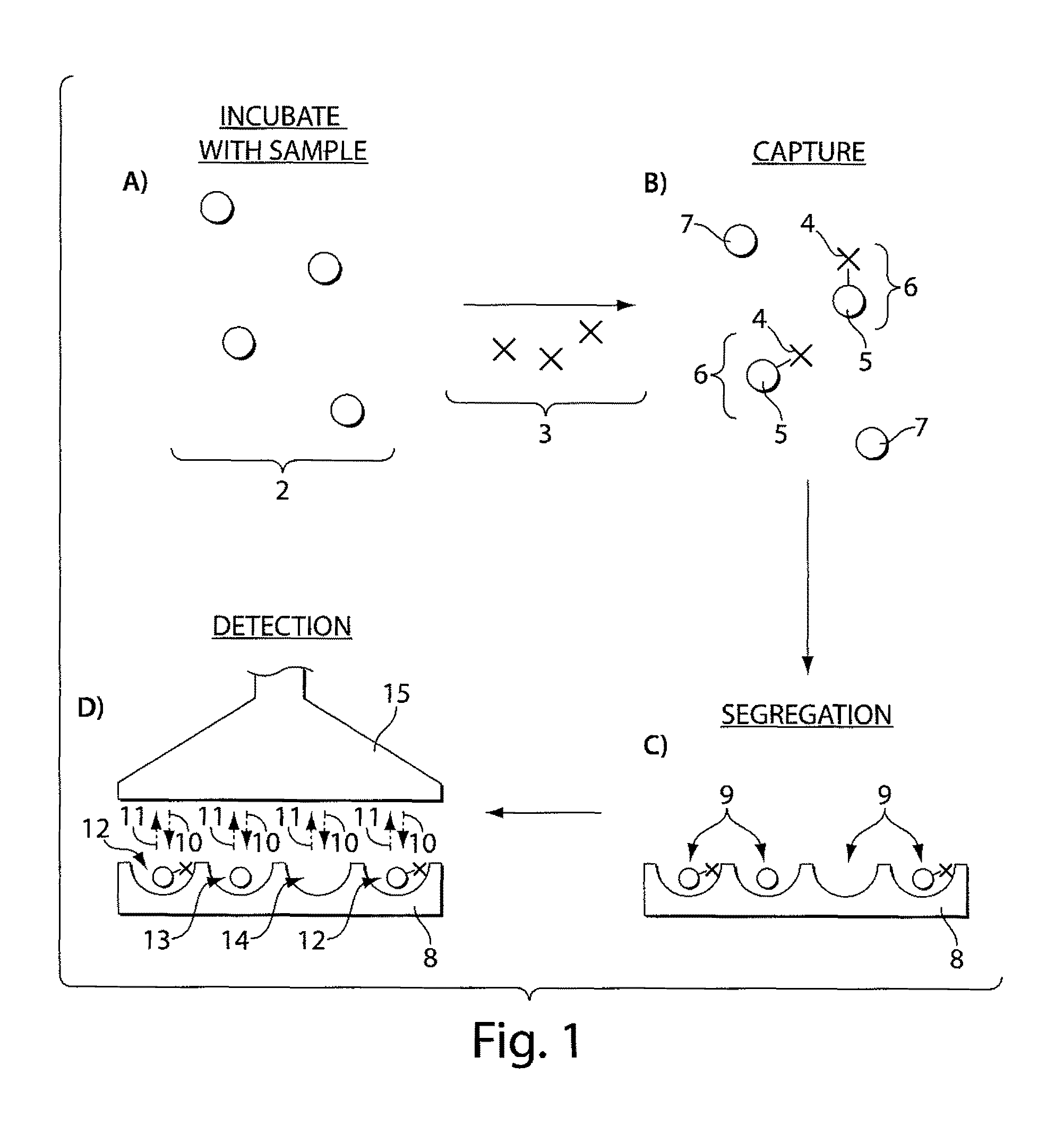
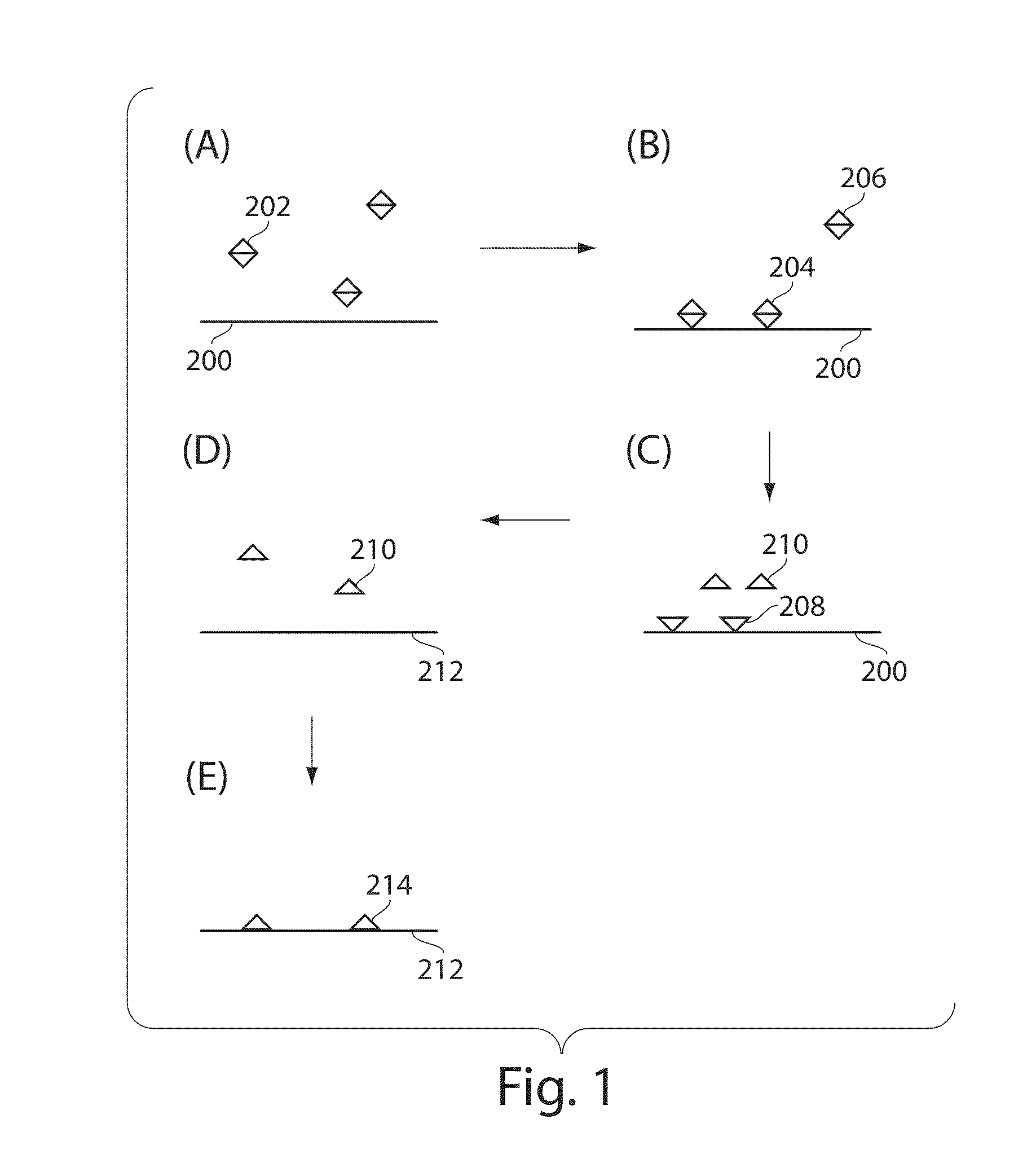
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules or particles using beads or other capture objects
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules or particles using beads or other capture objects
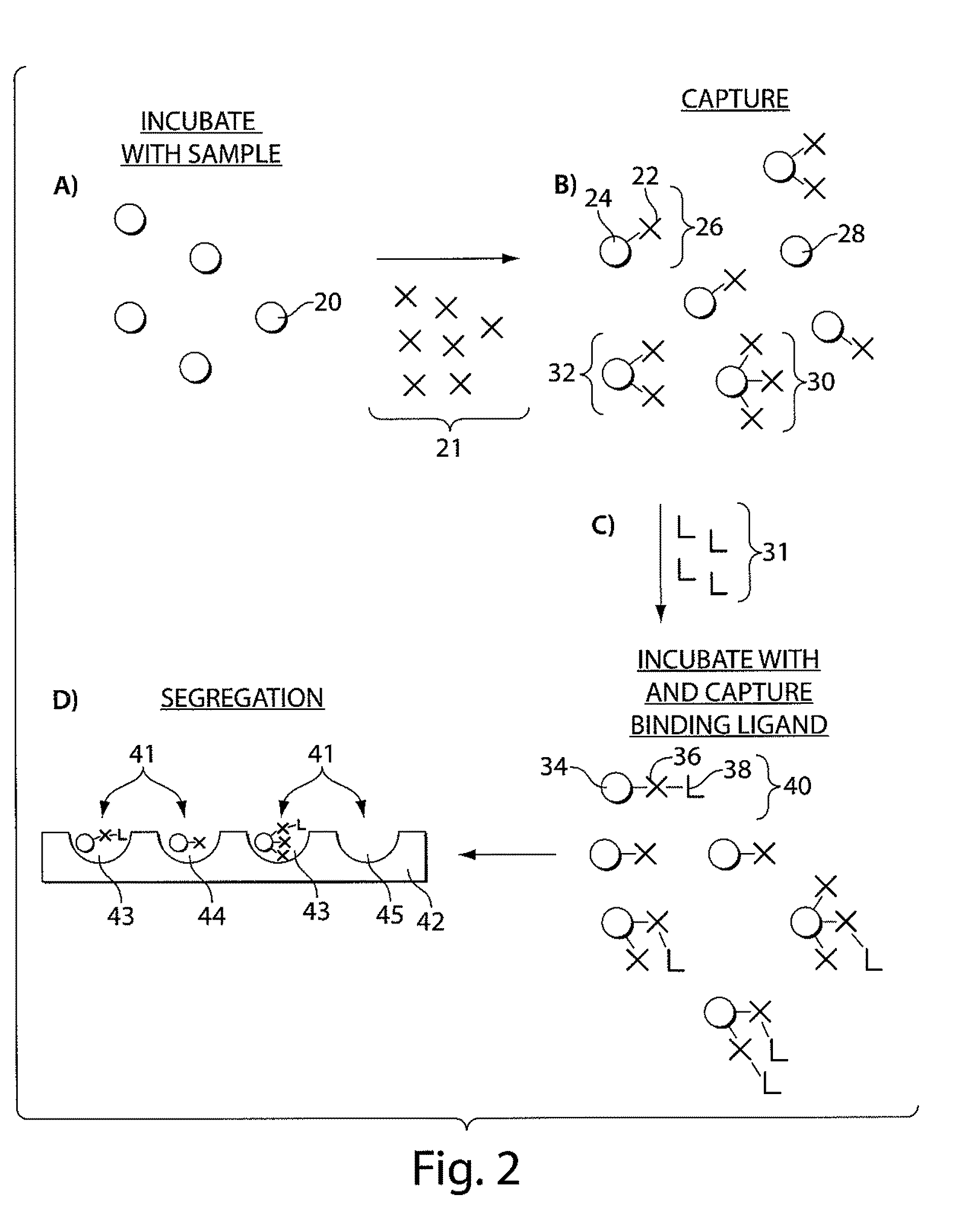
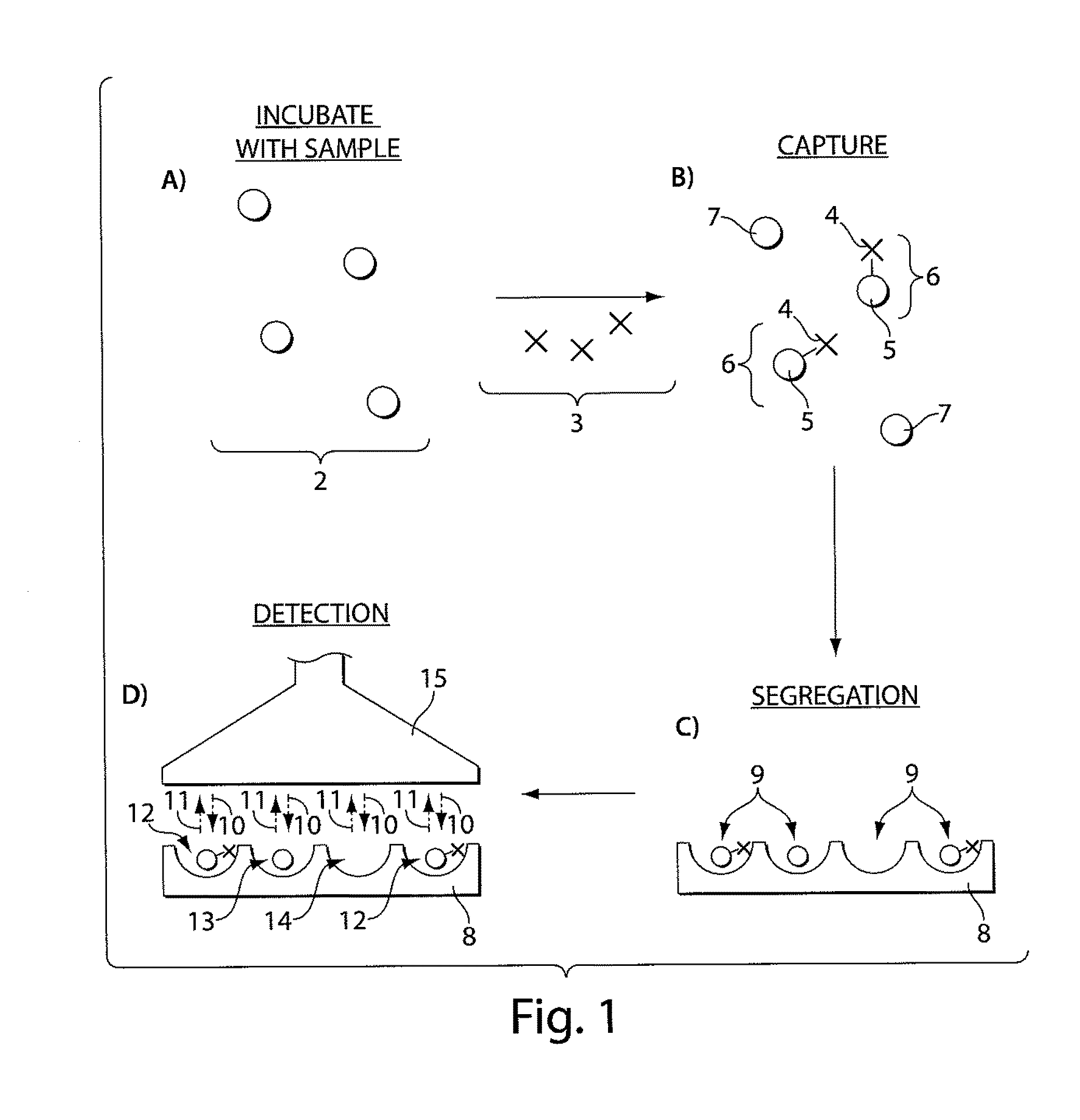
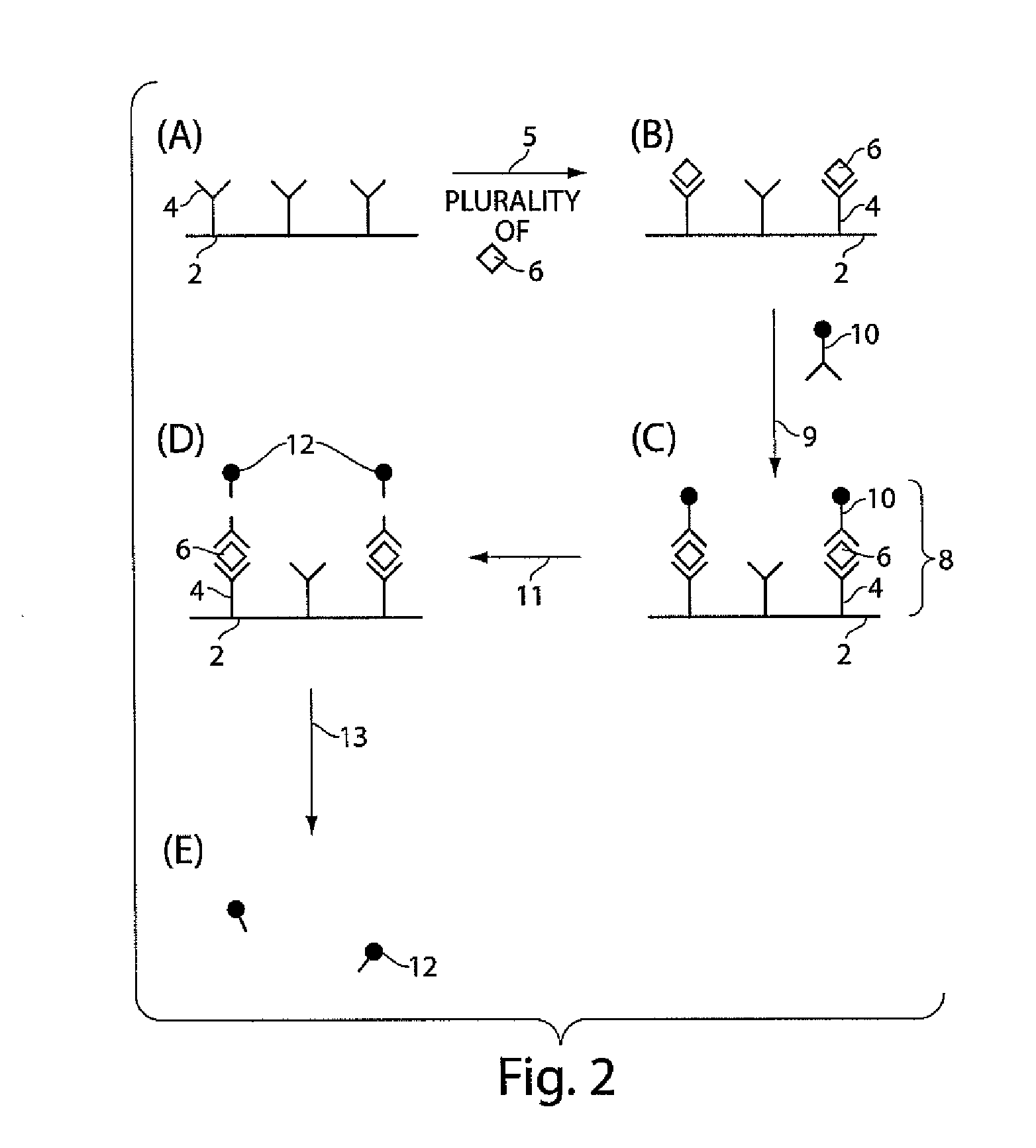
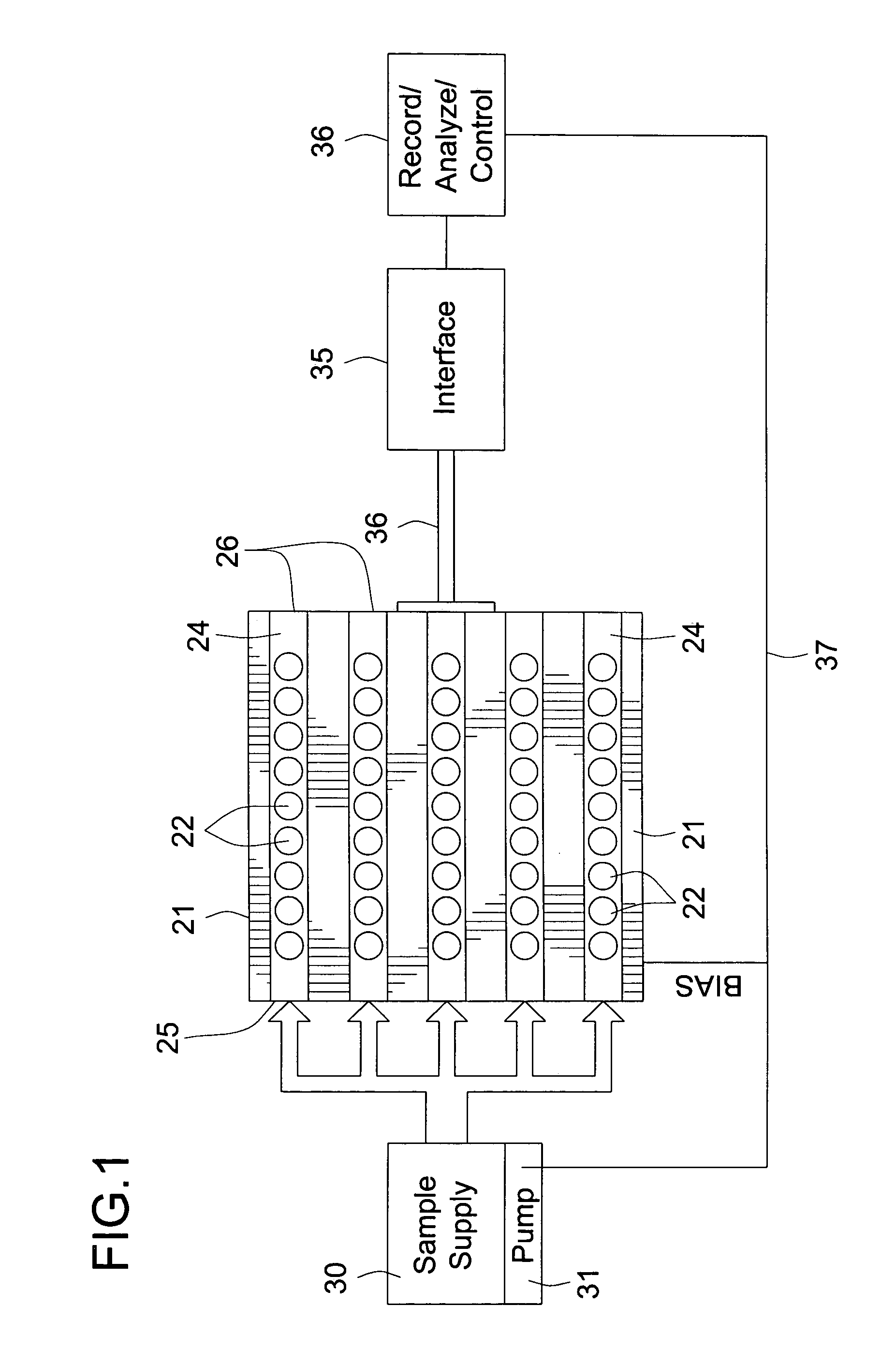
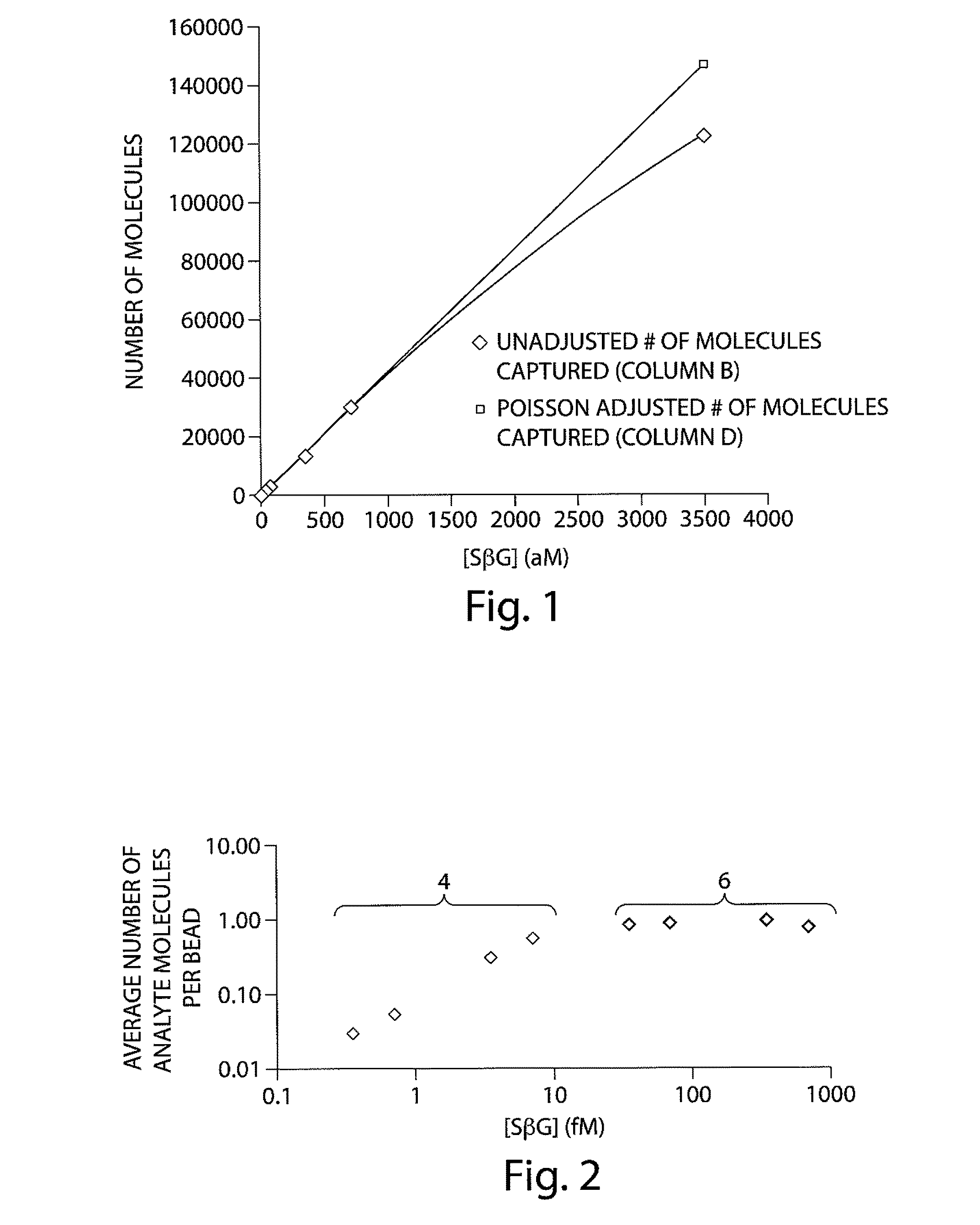
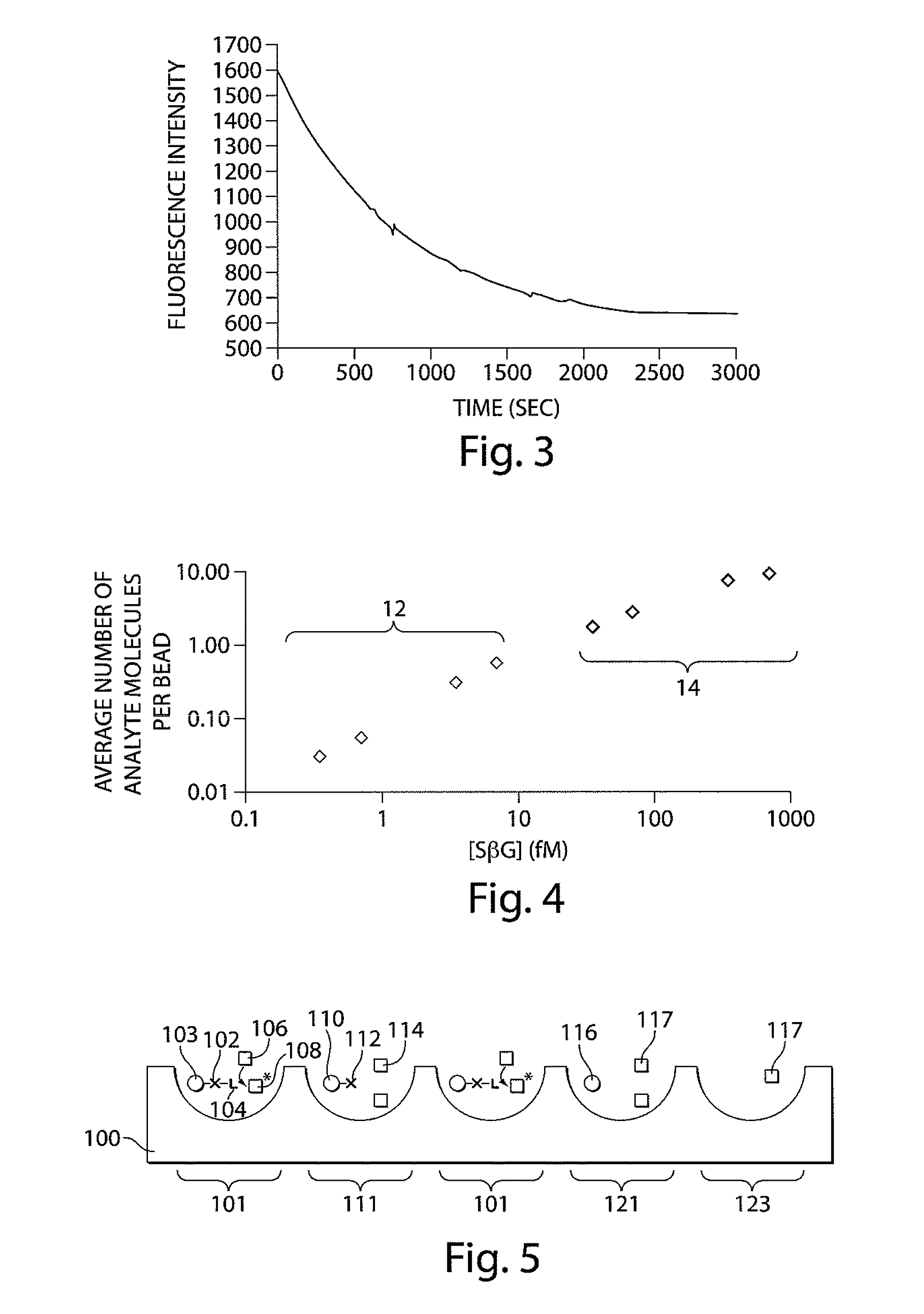
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample and in some cases, determining a measure of the concentration of the molecules or particles in the fluid sample. Methods of the present invention may comprise immobilizing a plurality of analyte molecules or particles with respect to a plurality of capture objects. At least a portion of the plurality of capture objects may be spatially separated into a plurality of locations. A measure of the concentration of analyte molecules in a fluid sample may be determined, at least in part, on the number of reaction vessels comprising an analyte molecule immobilized with respect to a capture object. In some cases, the assay may additionally comprise steps including binding ligands, precursor labeling agents, and / or enzymatic components.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
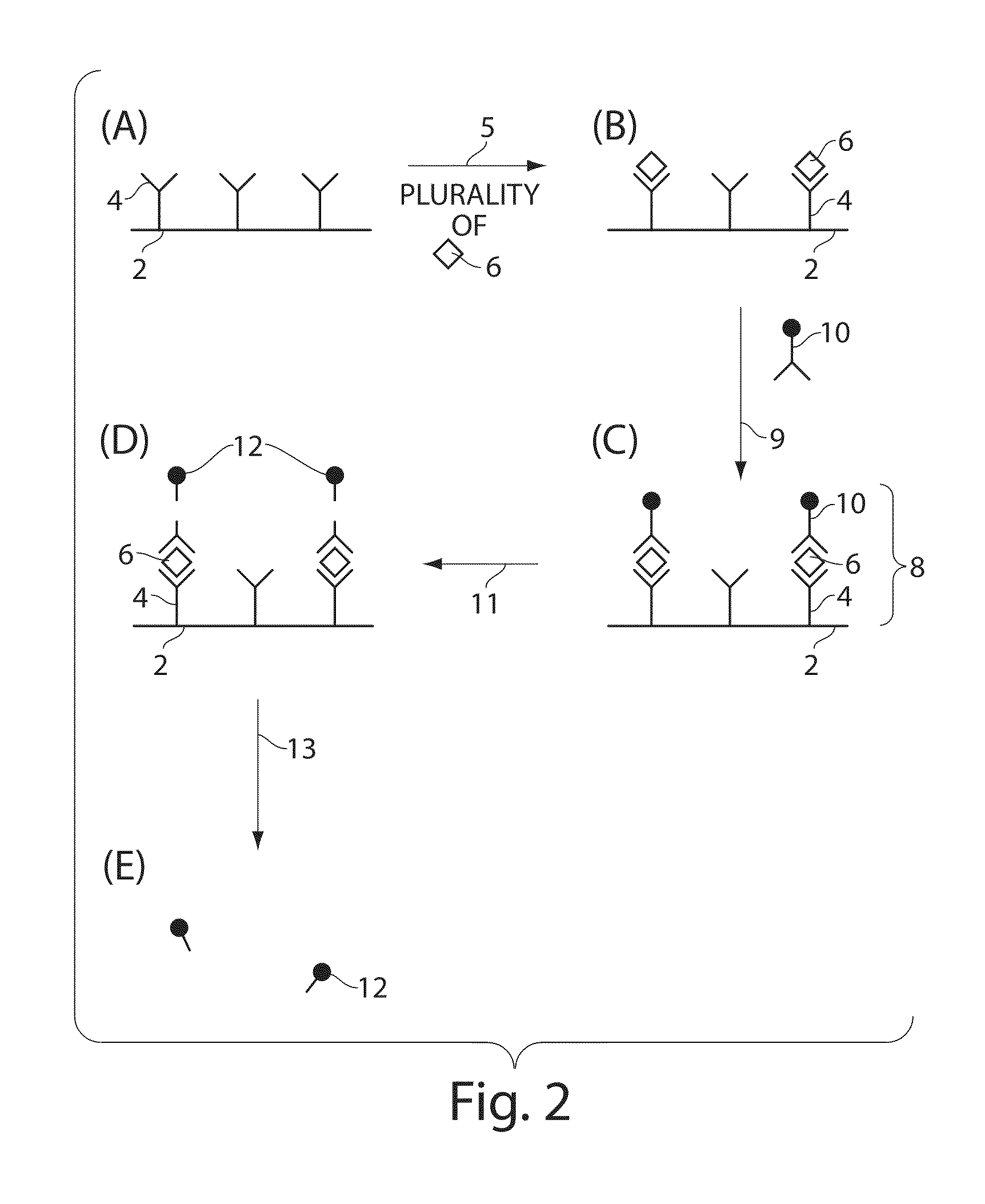
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules on single molecule arrays
ActiveUS20100075407A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyte moleculeUltra sensitive
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample and in some cases, determining a measure of the concentration of the molecules or particles in the fluid sample. Methods of the present invention may comprise immobilizing a plurality of analyte molecules or particles to form a plurality of complexes, releasing at least a portion of some of the plurality of complexes, determining at least a portion of the plurality of complexes released, and determining a measure of the concentration of the analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
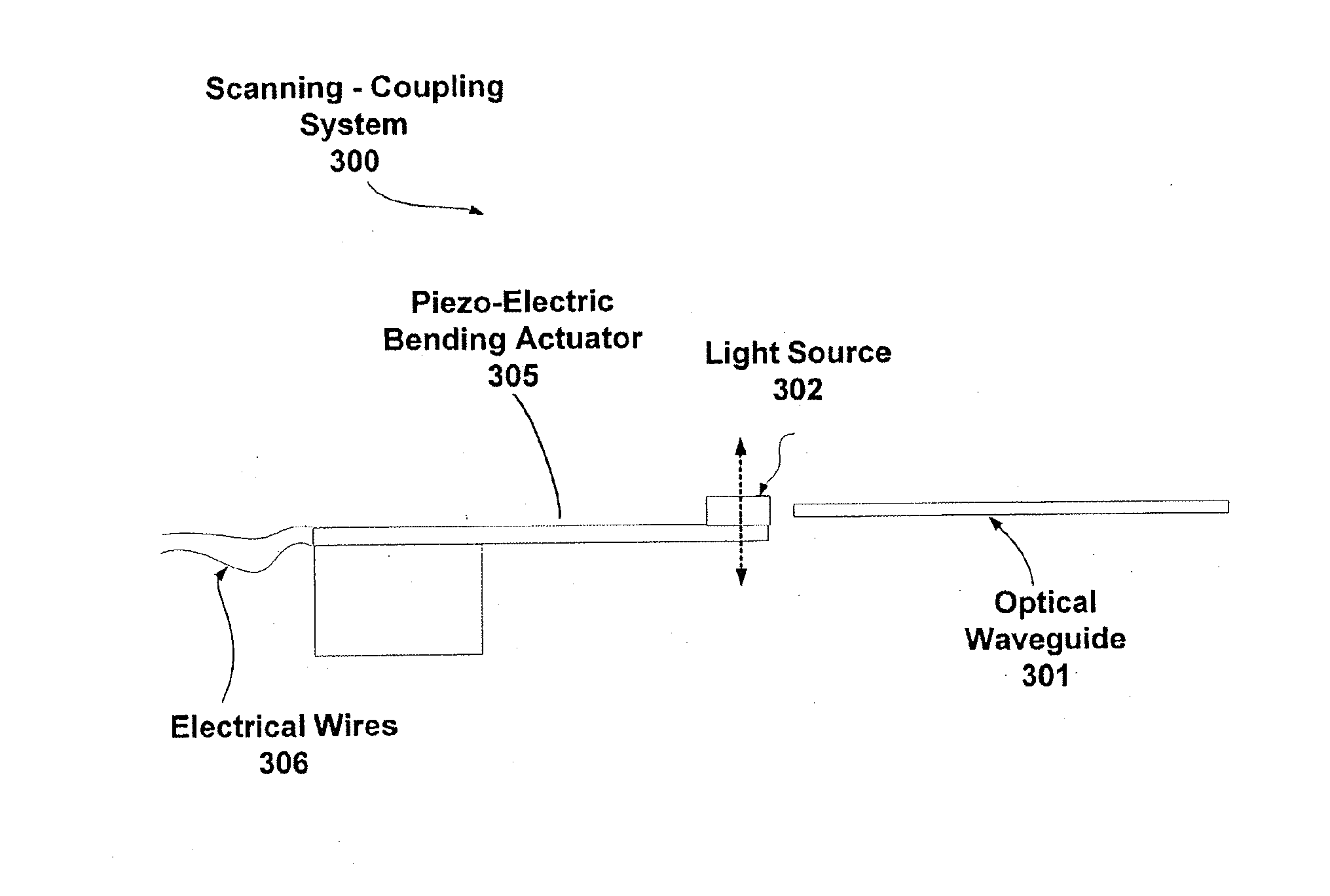
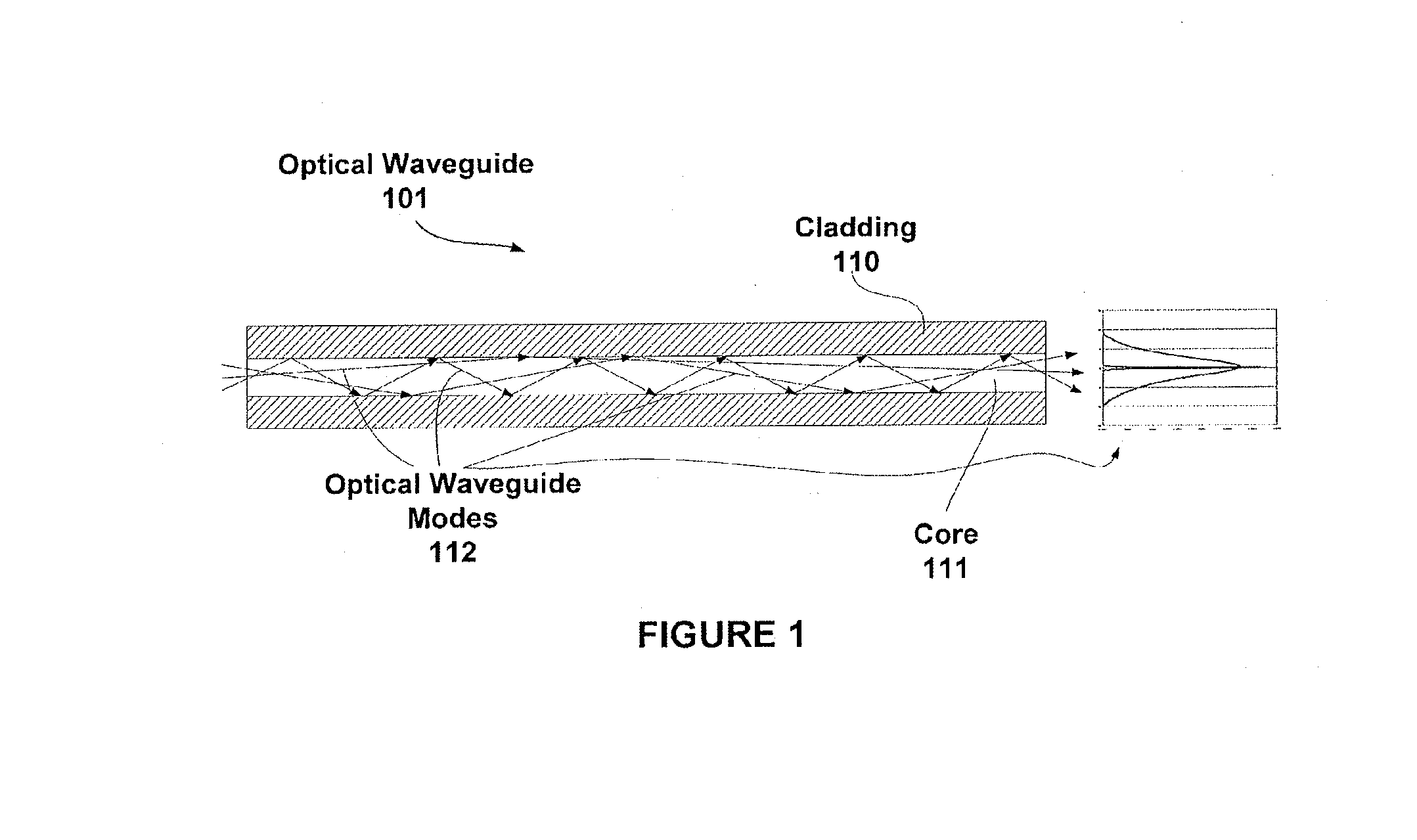
Waveguide-based detection system with scanning light source
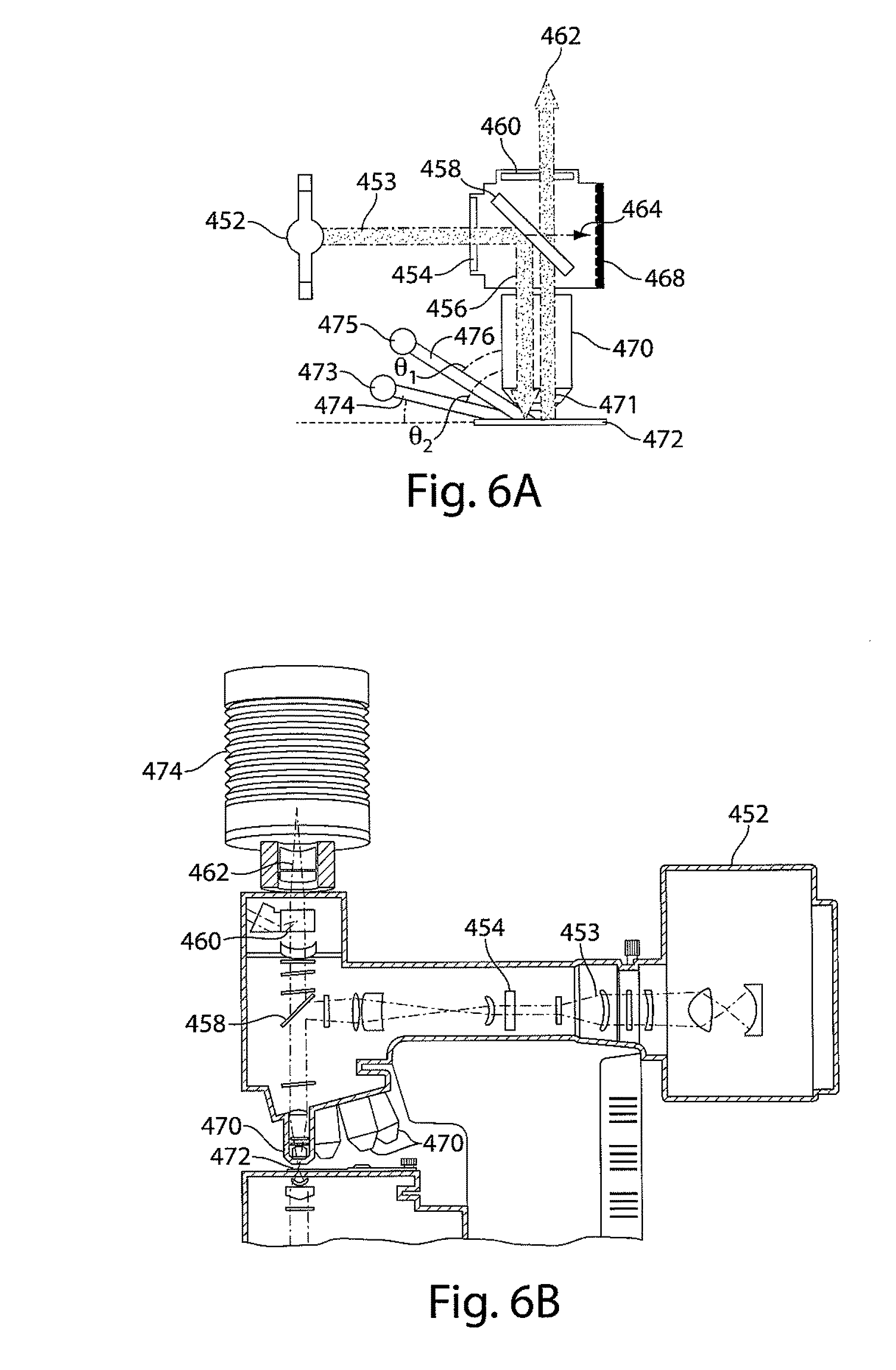
ActiveUS20140178861A1Simple and cost-effectiveEnhanced couplingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCouplingLight beam
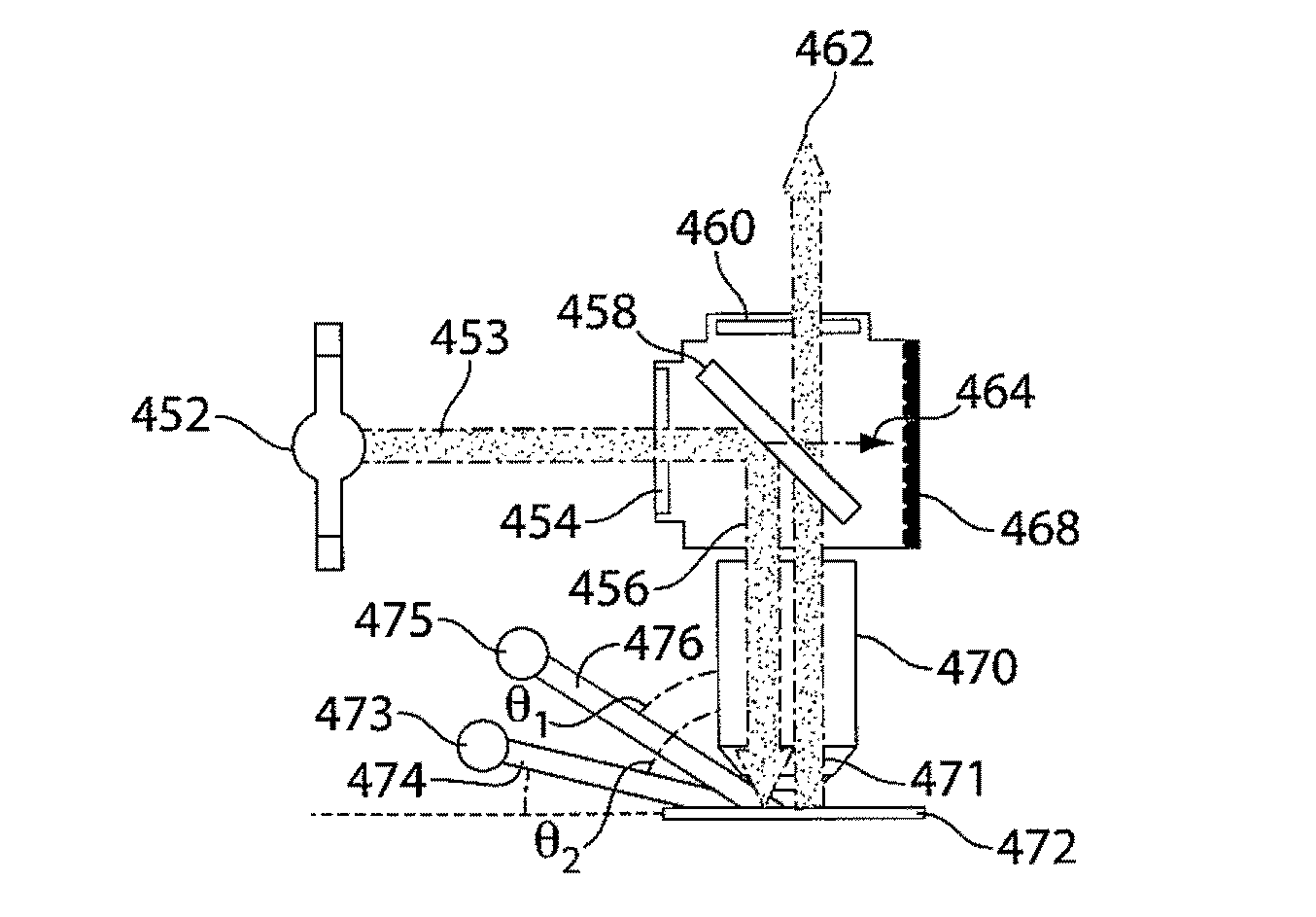
The invention provides methods and devices for generating optical pulses in one or more waveguides using a spatially scanning light source. A detection system, methods of use thereof and kits for detecting a biologically active analyte molecule are also provided. The system includes a scanning light source, a substrate comprising a plurality of waveguides and a plurality of optical sensing sites in optical communication with one or more waveguide of the substrate, a detector that is coupled to and in optical communication with the substrate, and means for spatially translating a light beam emitted from said scanning light source such that the light beam is coupled to and in optical communication with the waveguides of the substrate at some point along its scanning path. The use of a scanning light source allows the coupling of light into the waveguides of the substrate in a simple and cost-effective manner.
Owner:LDIP LLC
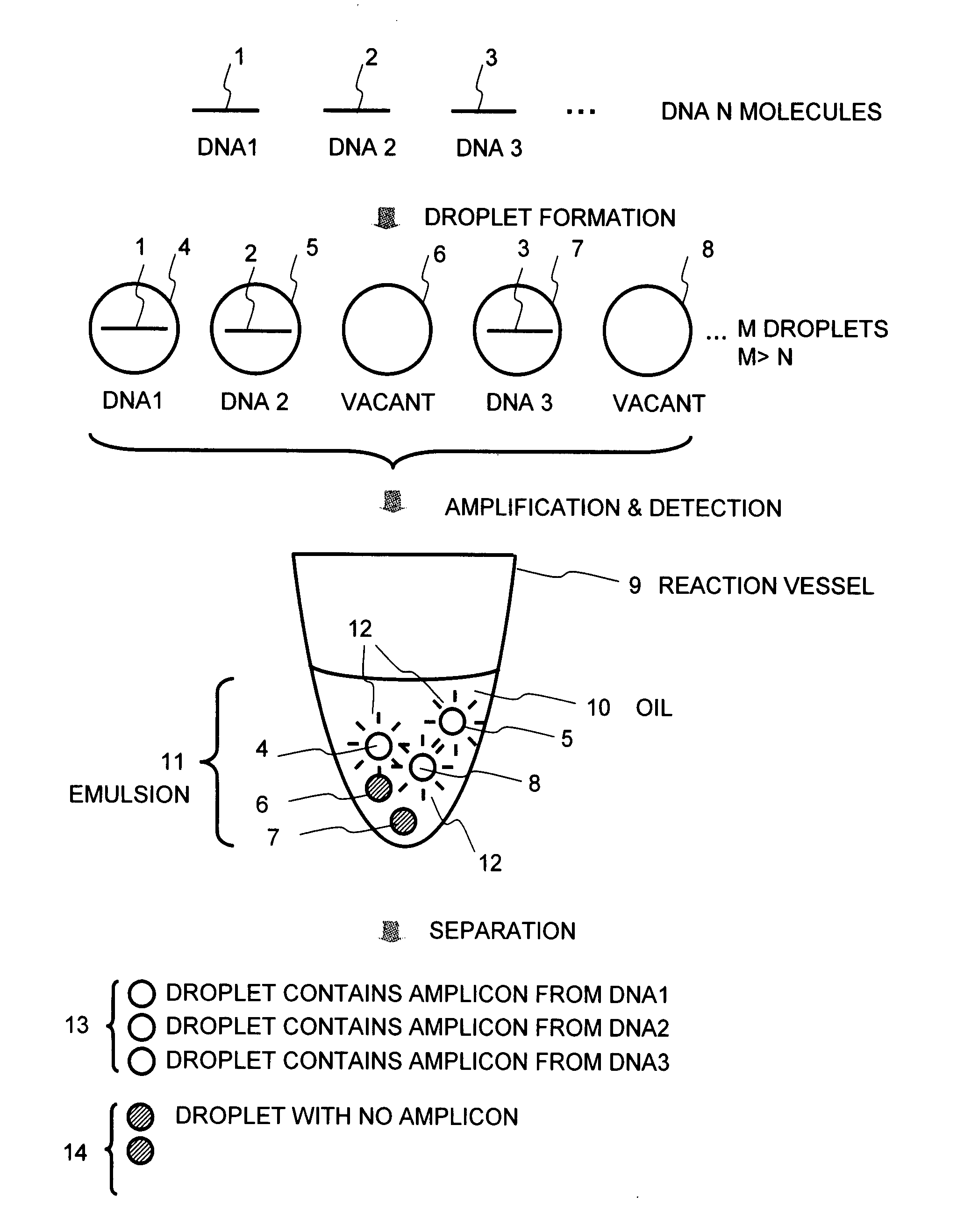
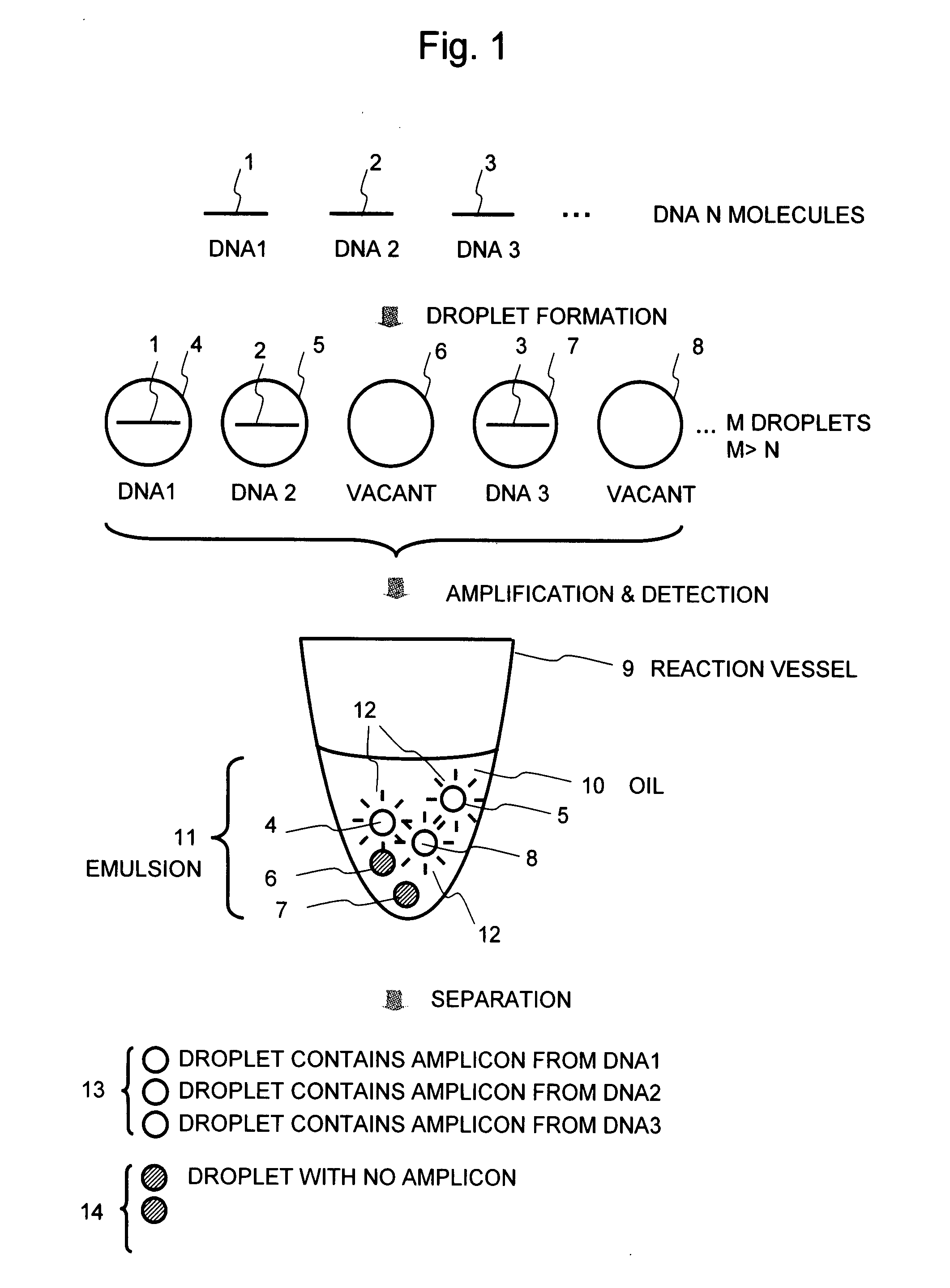
Method and apparatus for sample preparation
InactiveUS20080241841A1Low costPurpose savedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyte moleculeDNA
A method of the present invention comprises fractionating a sample solution containing analyte DNA molecules into small droplets, wherein the number M of the droplets is greater than the total number N of the DNA molecules, subjecting an emulsion containing the droplets to, for example, PCR amplification, and detecting the presence or absence (amount) of an amplicon obtained in each droplet by fluorescent detection using an intercalator or the like.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
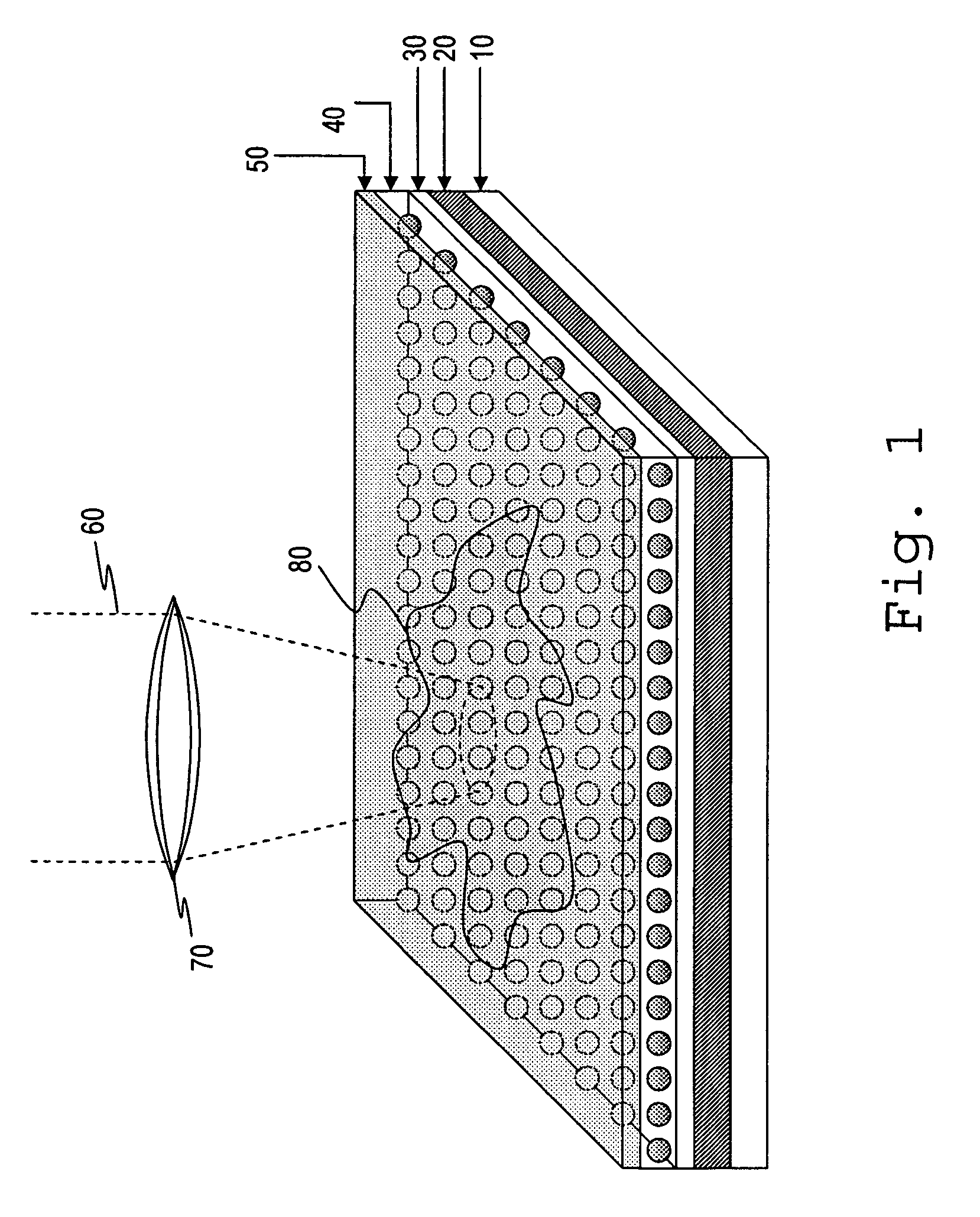
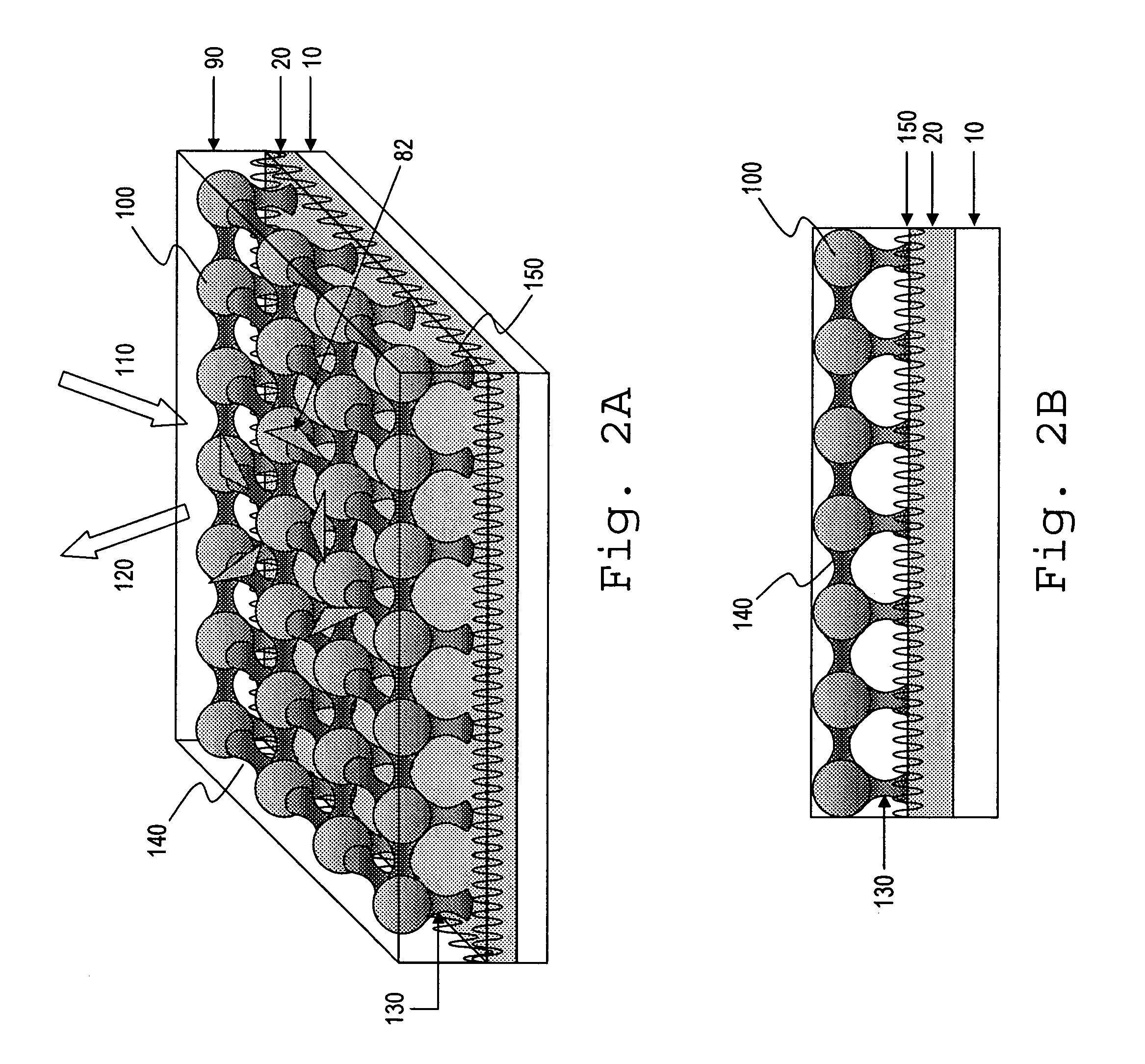
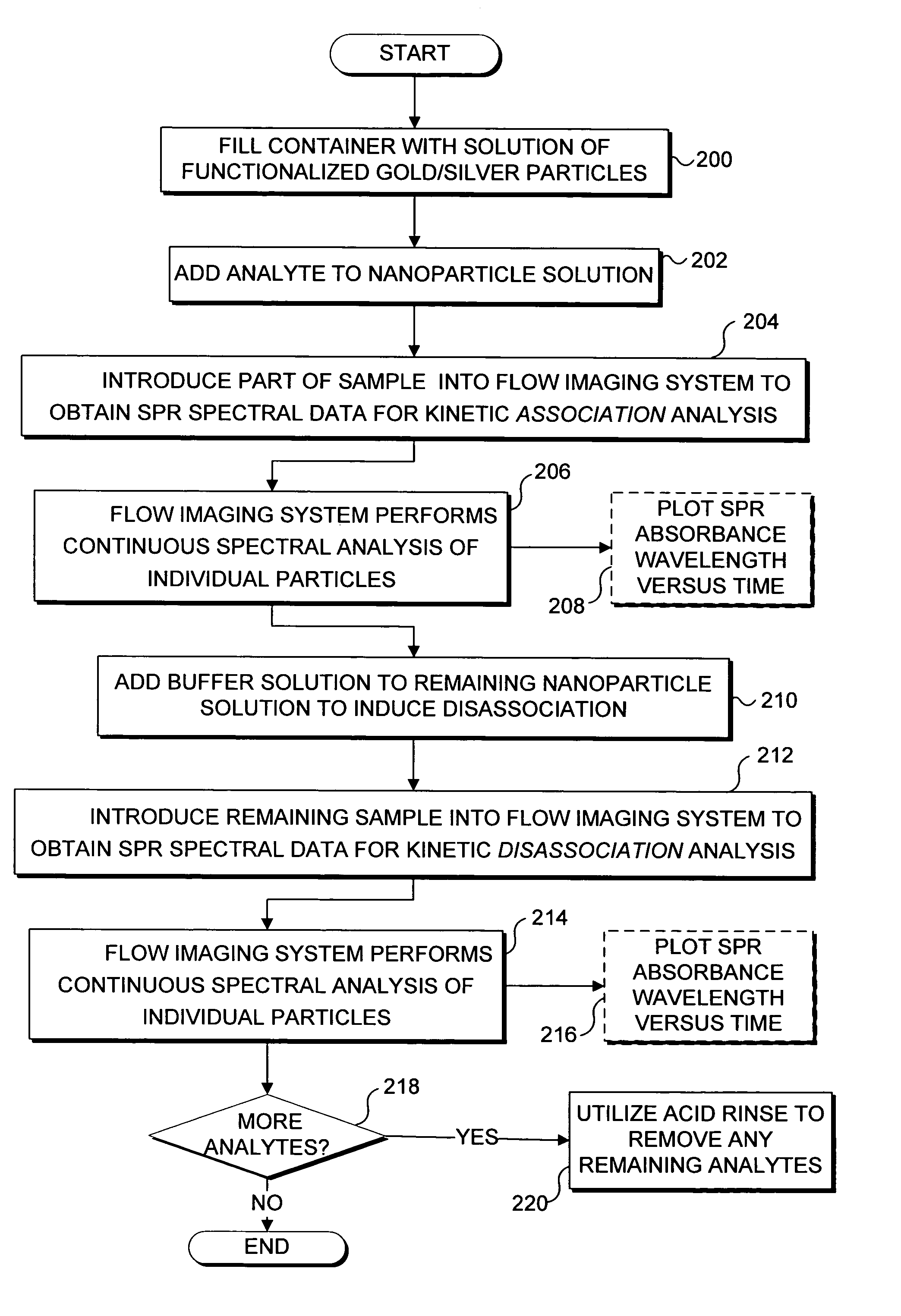
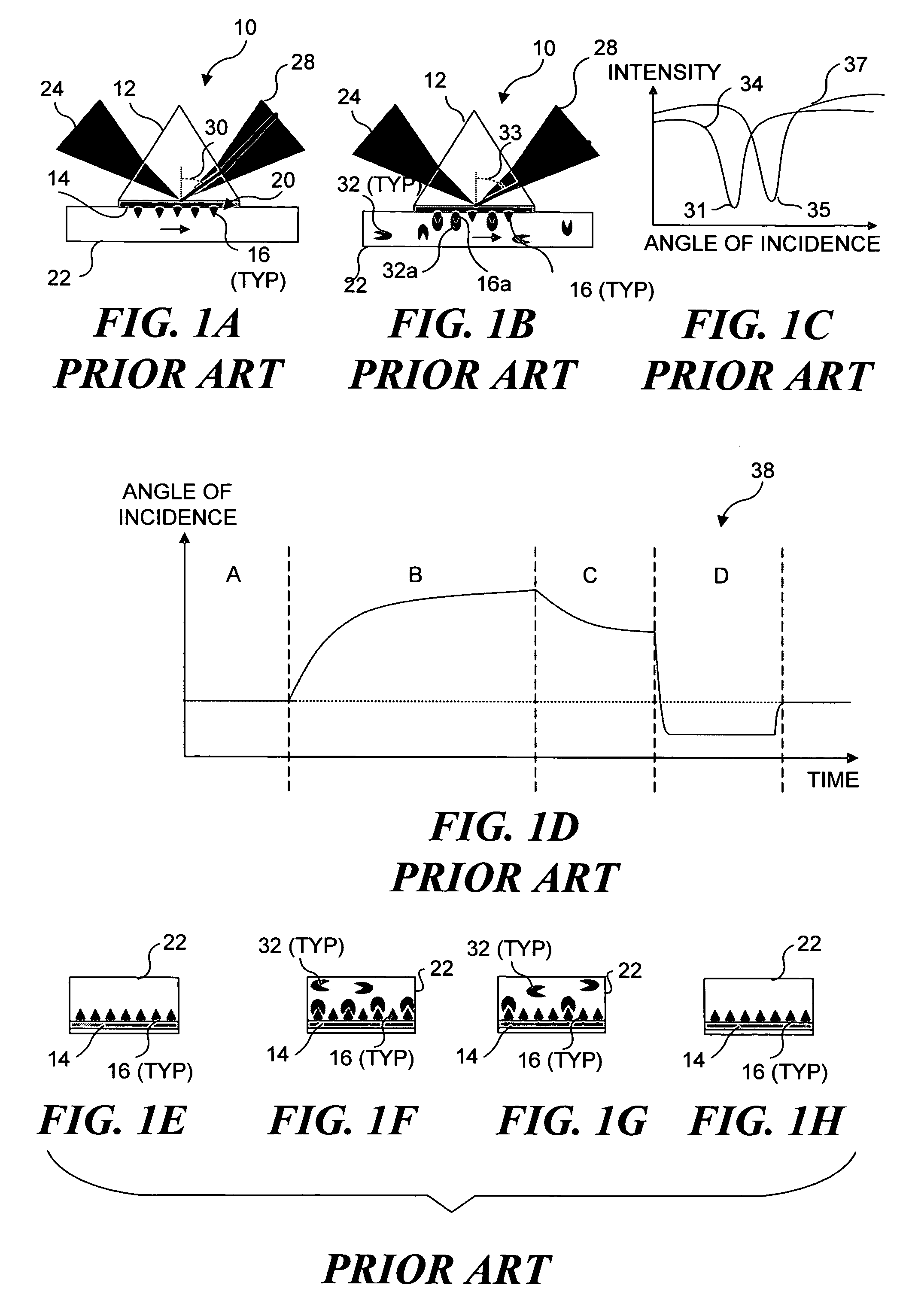
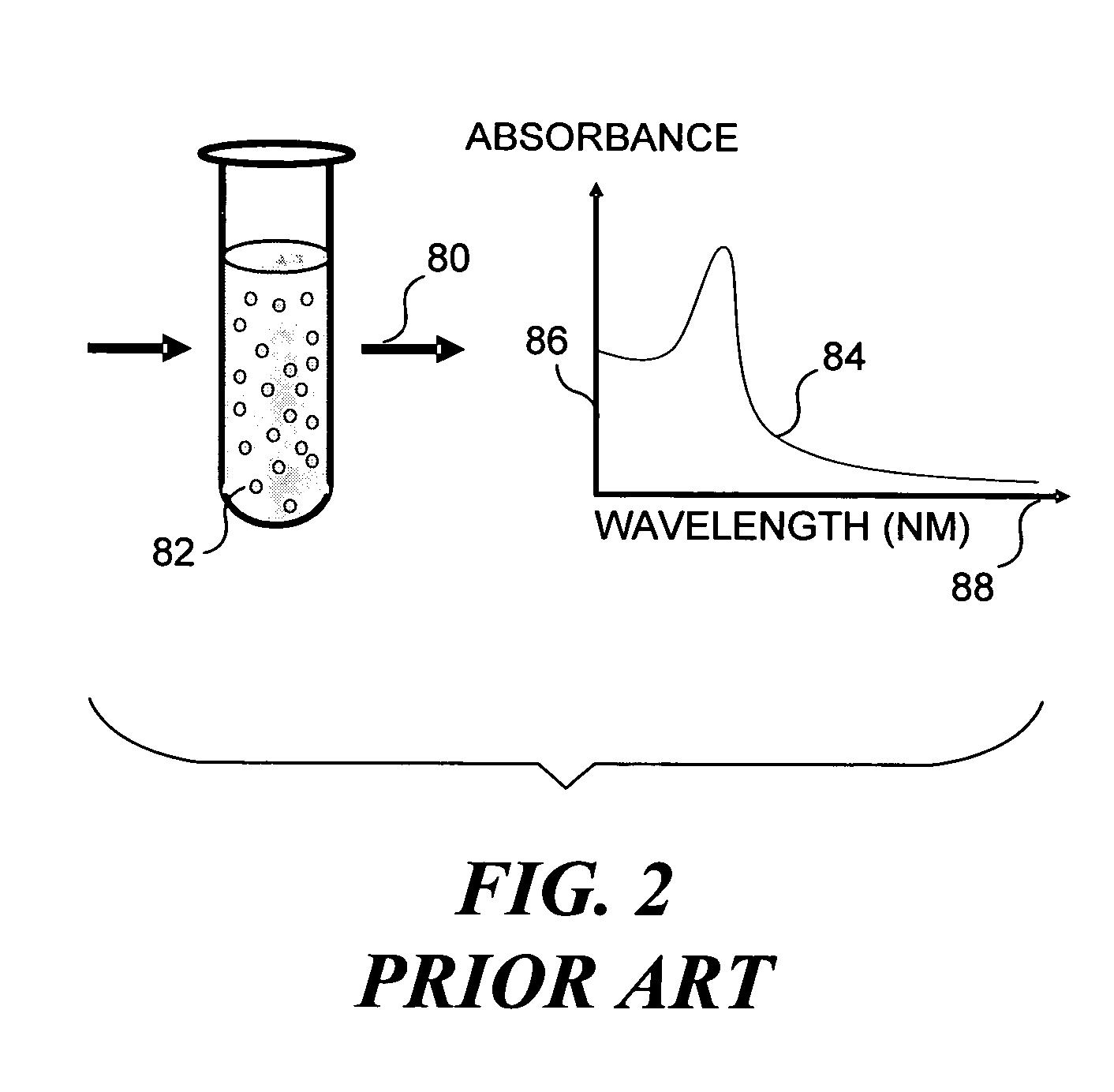
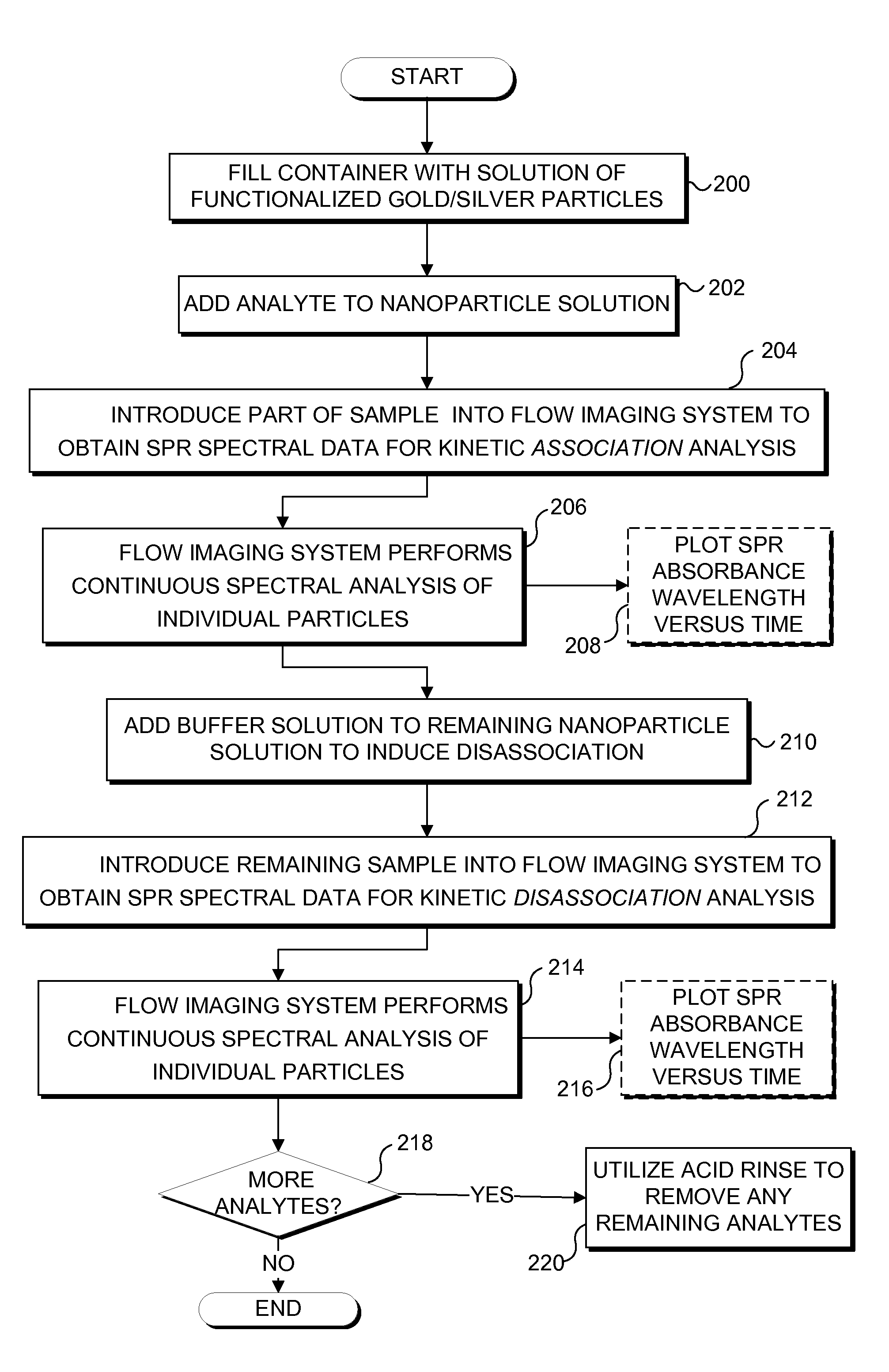
Imaging platform for nanoparticle detection applied to SPR biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS7057732B2Increase curve 's linearityAccurate CalibrationSpectrum investigationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsSurface plasmonic resonanceAnalyte molecule
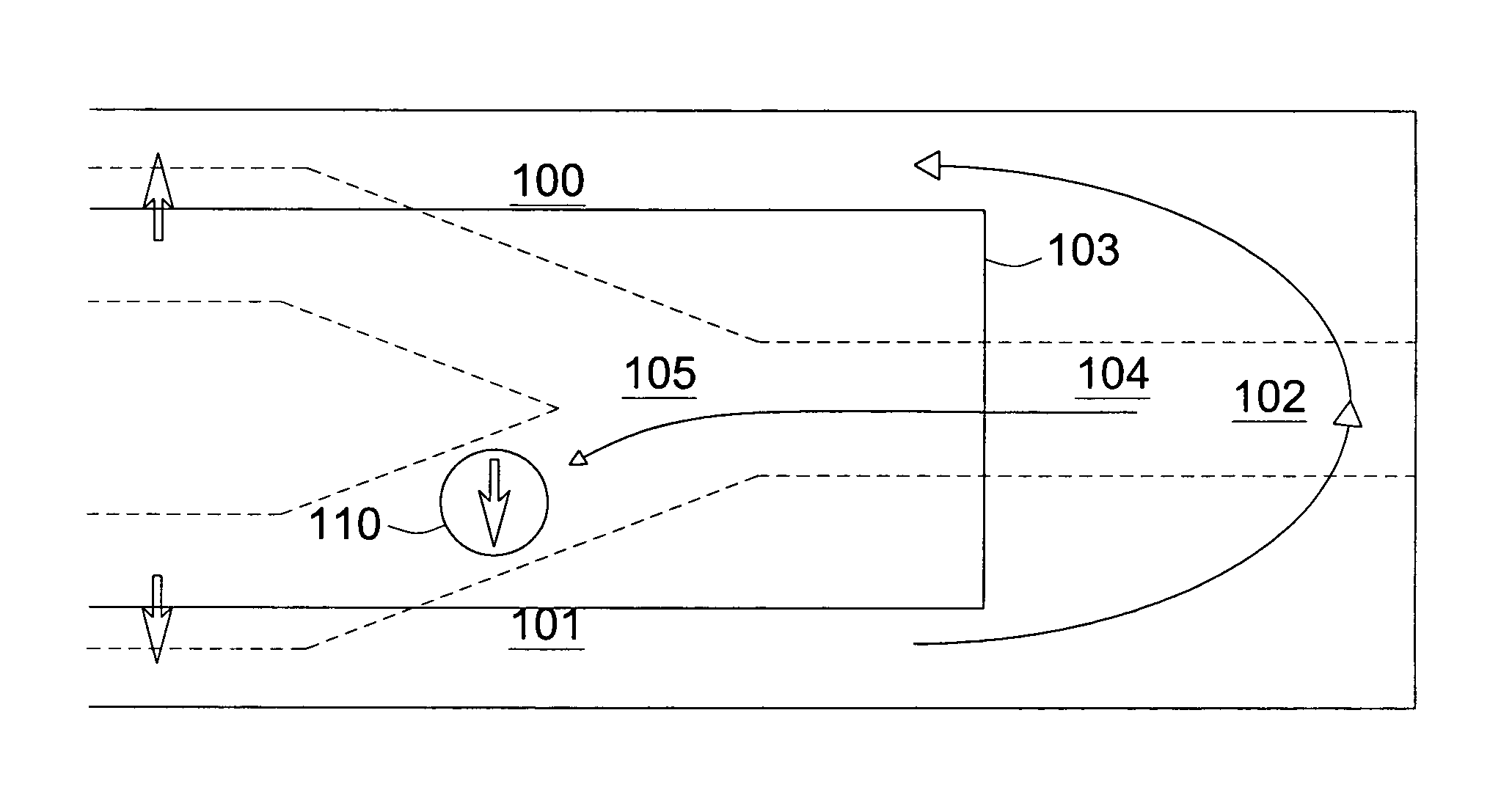
A flow imaging system is used to implement surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detection to study bio-molecular interactions. The flow imaging system is used to capture SPR absorption spectra of large numbers of objects, where each object includes both a metal film capable of exhibiting SPR, and detecting molecules. Analyte molecules are added to a solution of such objects, and the result is introduced into the flow imaging system which collects full SPR spectral data from individual objects. The objects can be nanoparticles or larger particles that support metal island films. The SPR spectral data can be used to determine specificity, kinetics, affinity, and concentration with respect to the interactions between the detecting molecules and the analyte molecules.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
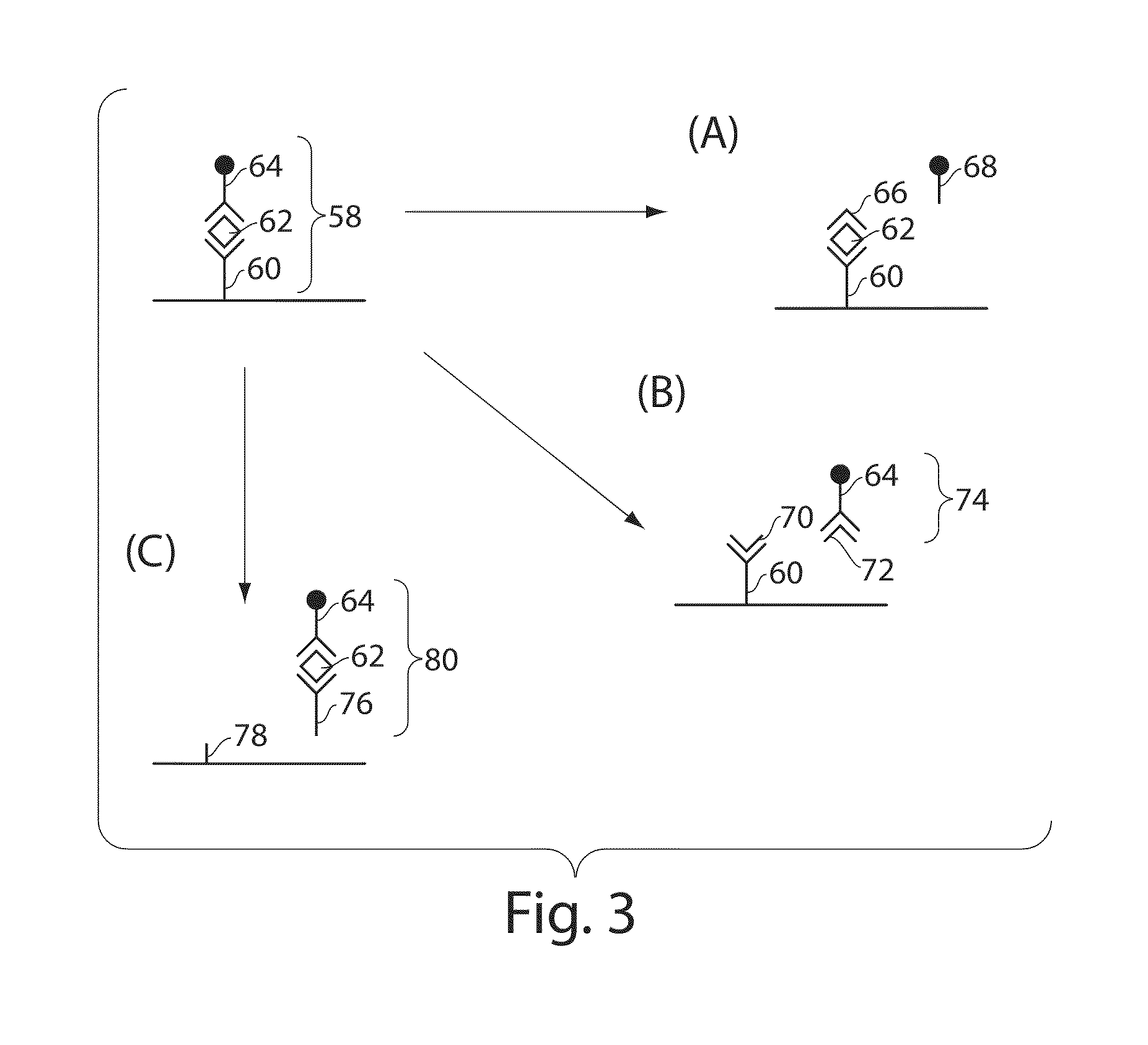
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules using dual detection methods
ActiveUS20110212462A1Reduce and limit negative effectBiological testingAnalyte moleculeUltra sensitive
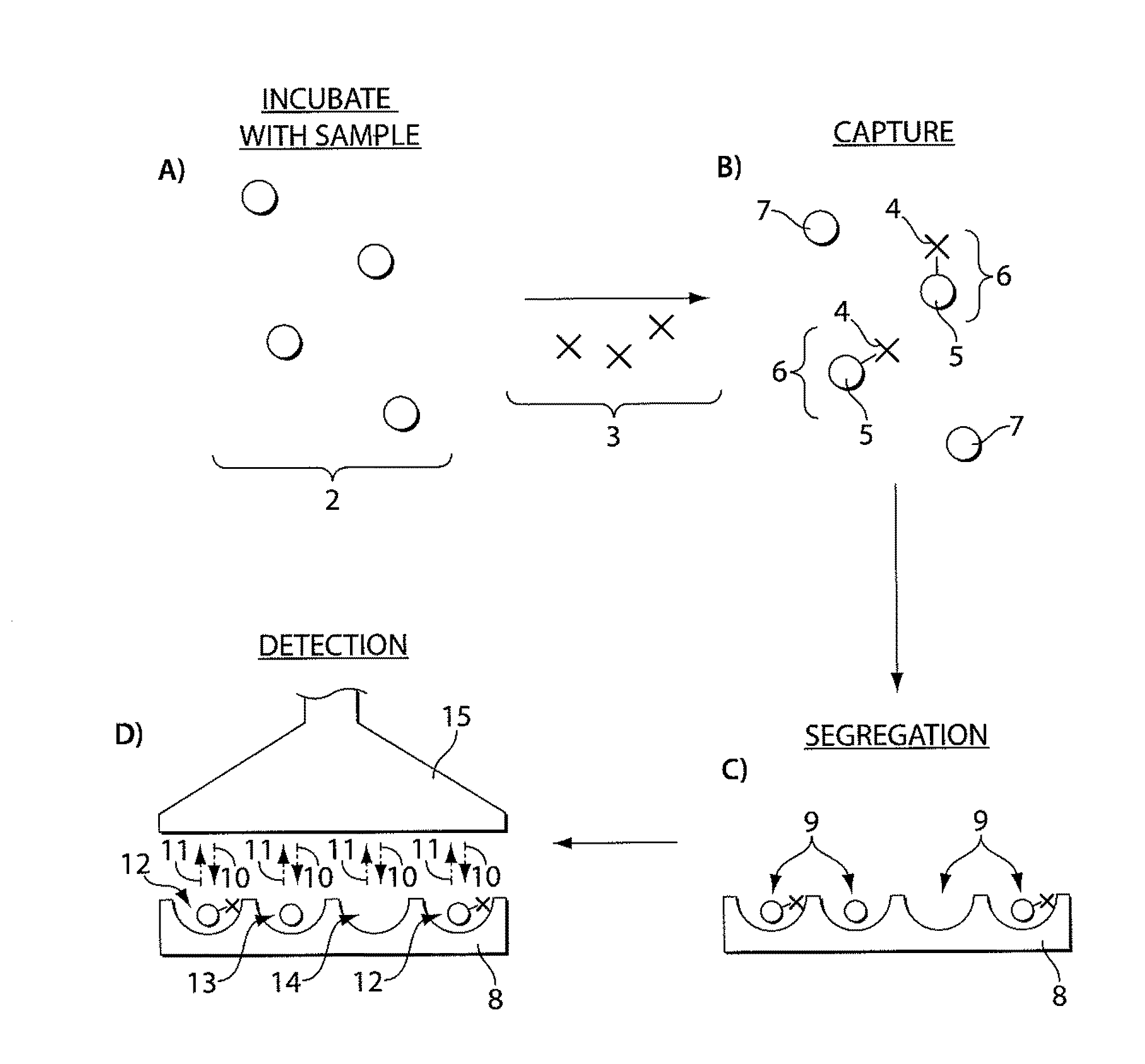
Described herein are systems and methods for the detection of and / or determination of a measure of the concentration of analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample. In some cases, the systems and methods employ techniques to reduce or limit the negative effects associated with non-specific binding events. Certain methods of the present invention involve associating the analyte molecules at least a first type of binding ligand and at least a second type of binding ligand, and spatially segregating the analyte molecules into a plurality of locations on a surface. The presence of an analyte molecule at or in a location may be determined by determining the presence of both the first type of binding ligand and the second type of binding ligand.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules on single molecule arrays
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample and in some cases, determining a measure of the concentration of the molecules or particles in the fluid sample. Methods of the present invention may comprise immobilizing a plurality of analyte molecules or particles to form a plurality of complexes, releasing at least a portion of some of the plurality of complexes, determining at least a portion of the plurality of complexes released, and determining a measure of the concentration of the analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
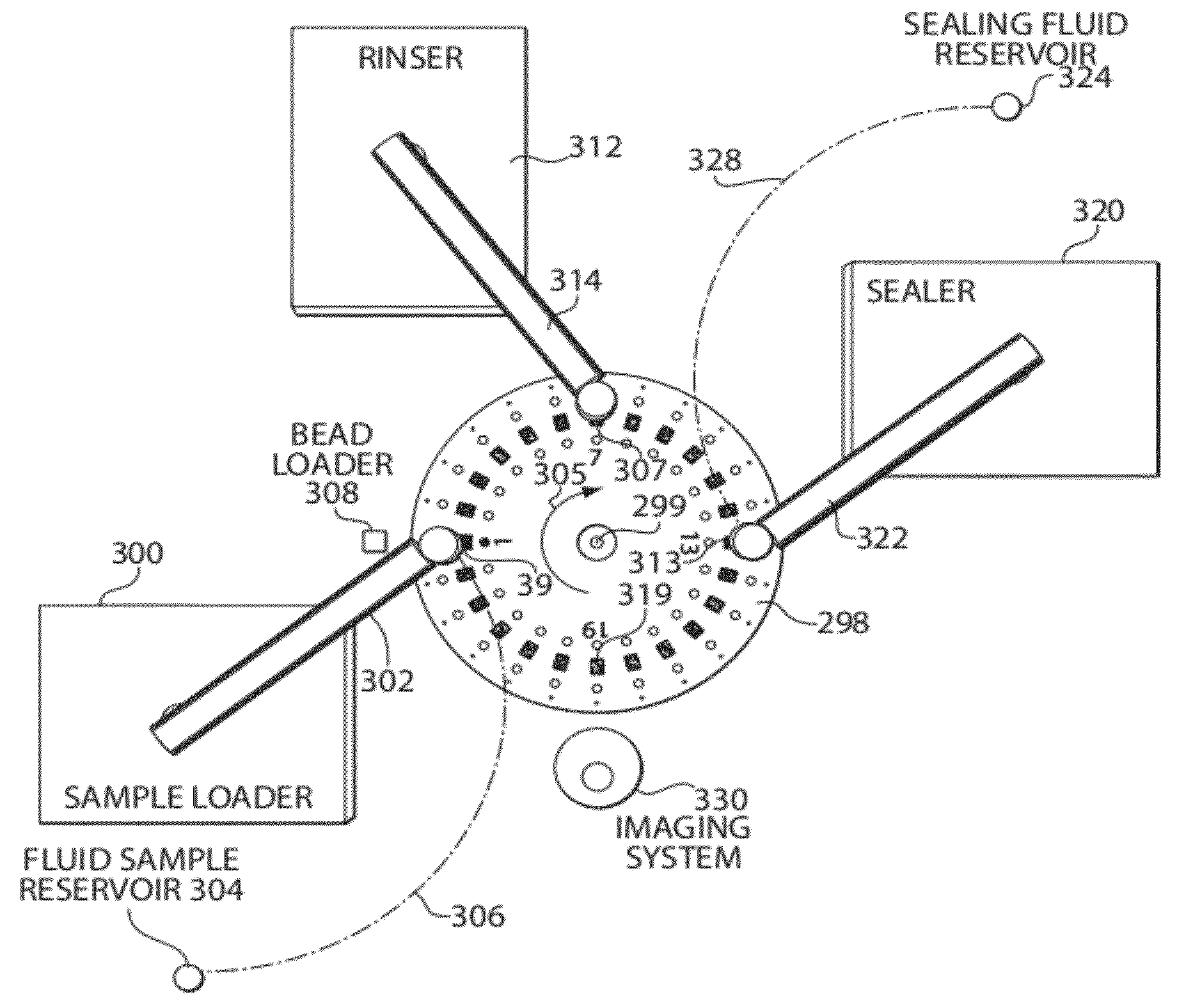
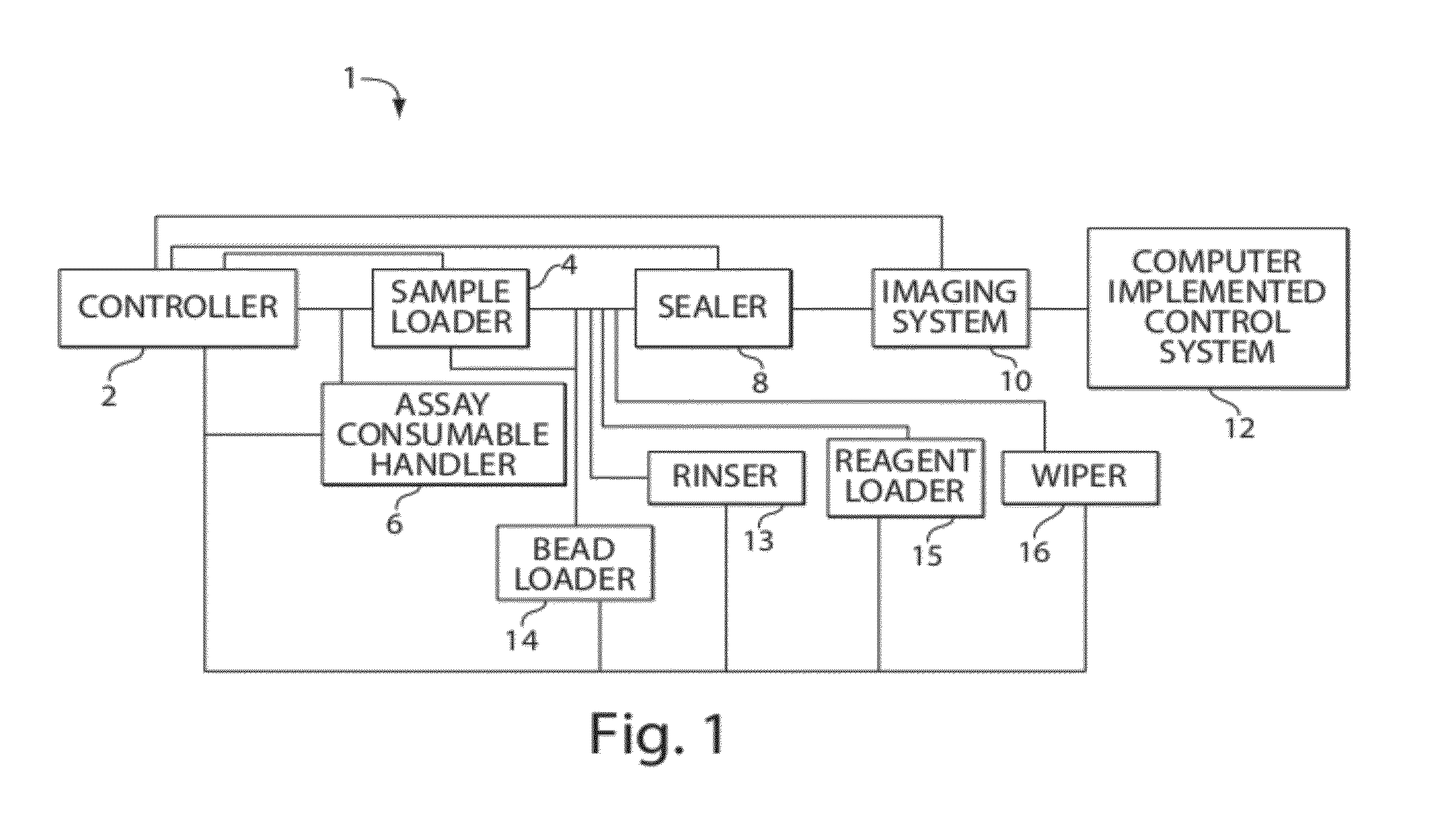
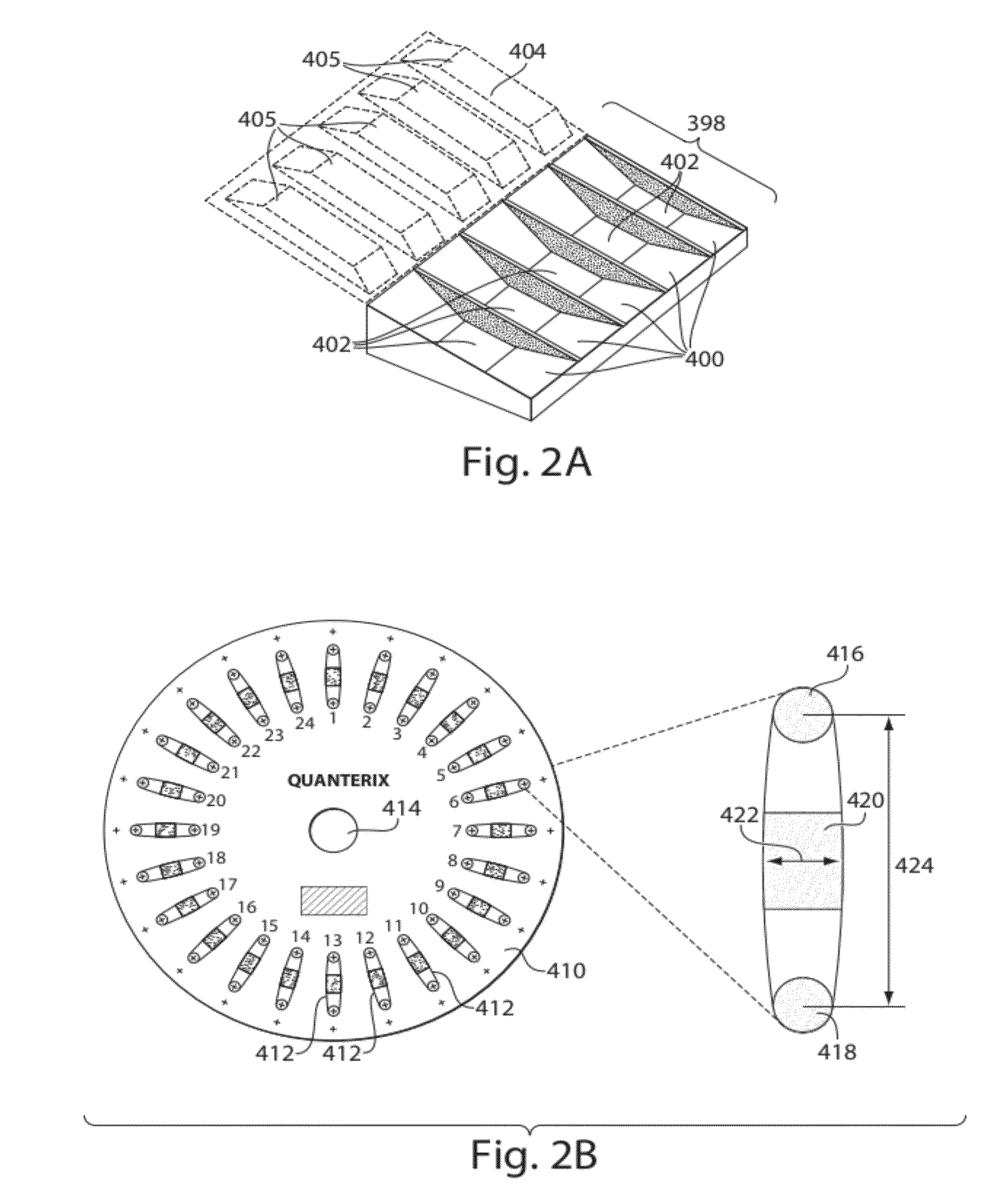
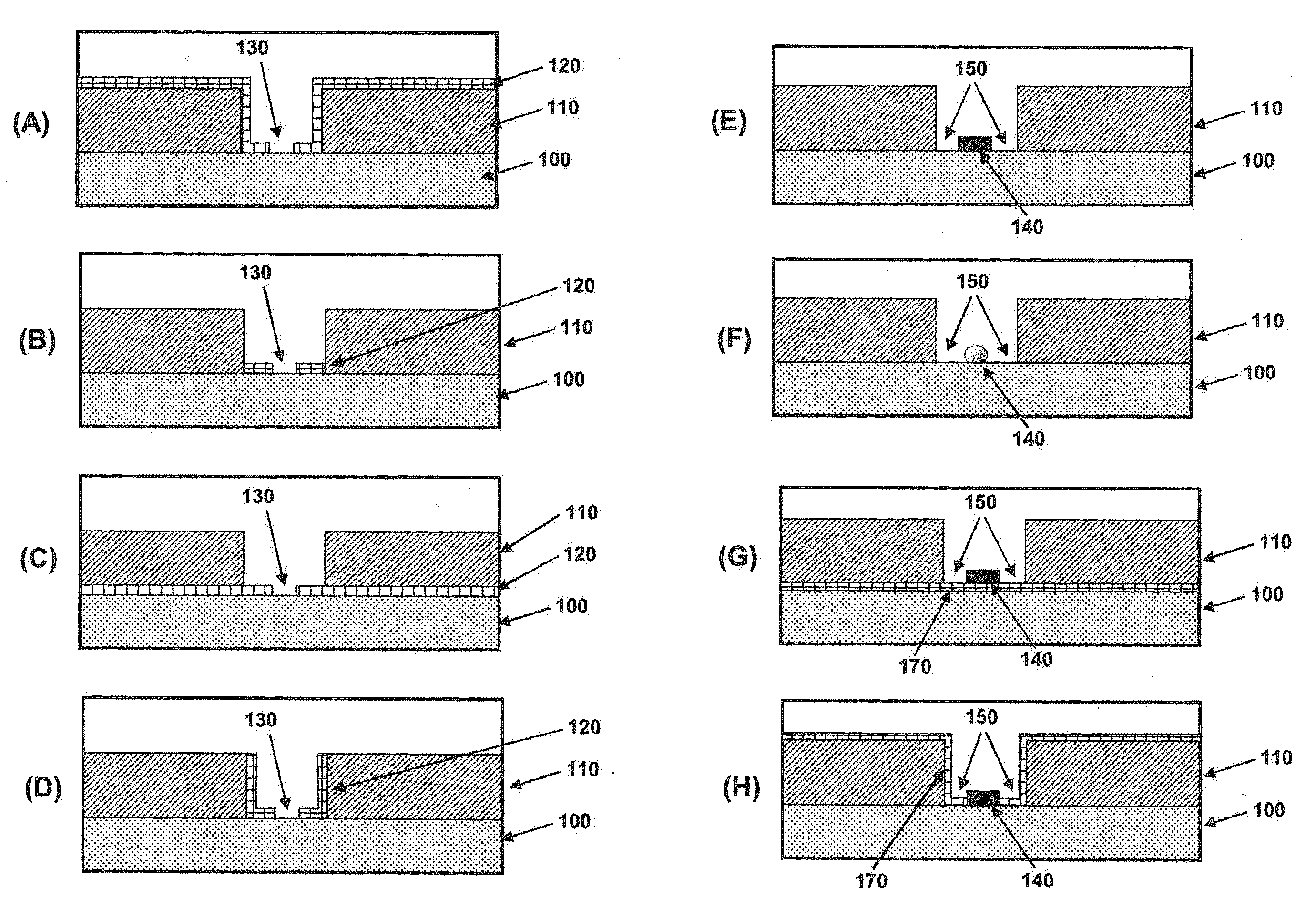
Systems, devices, and methods for ultra-sensitive detection of molecules or particles
ActiveUS20120196774A1Hollow inflatable ballsHollow non-inflatable ballsAnalyte moleculeUltra sensitive
Described are systems, devices, and methods which related to various aspects of assays for detecting and / or determining a measure of the concentration of analyte molecules or particles in a sample fluid. In some cases, the systems employ an assay consumable comprising a plurality of assay sites. The systems, devices, and / or methods, in some cases, are automated. In some cases, the systems, devices, and / or methods relate to inserting a plurality of beads into assay sites, sealing assay sites, imaging assay sites, or the like.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Nanoscale apertures having islands of functionality
ActiveUS20110257040A1Inhibit bindingIncreasing throughput and efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesAnalyte moleculeChemistry
Methods, compositions and arrays for non-random loading of single analyte molecules into array structures are provided. Arrays of confined regions are produced wherein each confined region comprises a single island within the confined region. The island can be selectively functionalized with a coupling agent to couple a single molecule of interest within the confined region.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Ultra-sensitive detection of molecules by capture-and-release using reducing agents followed by quantification
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample and in some cases, determining a measure of the concentration of the molecules or particles in the fluid sample. Methods of the present invention may comprise immobilizing a plurality of analyte molecules or particles to form a plurality of complexes, releasing at least a portion of some of the plurality of complexes, determining at least a portion of the plurality of complexes released, and determining a measure of the concentration of the analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
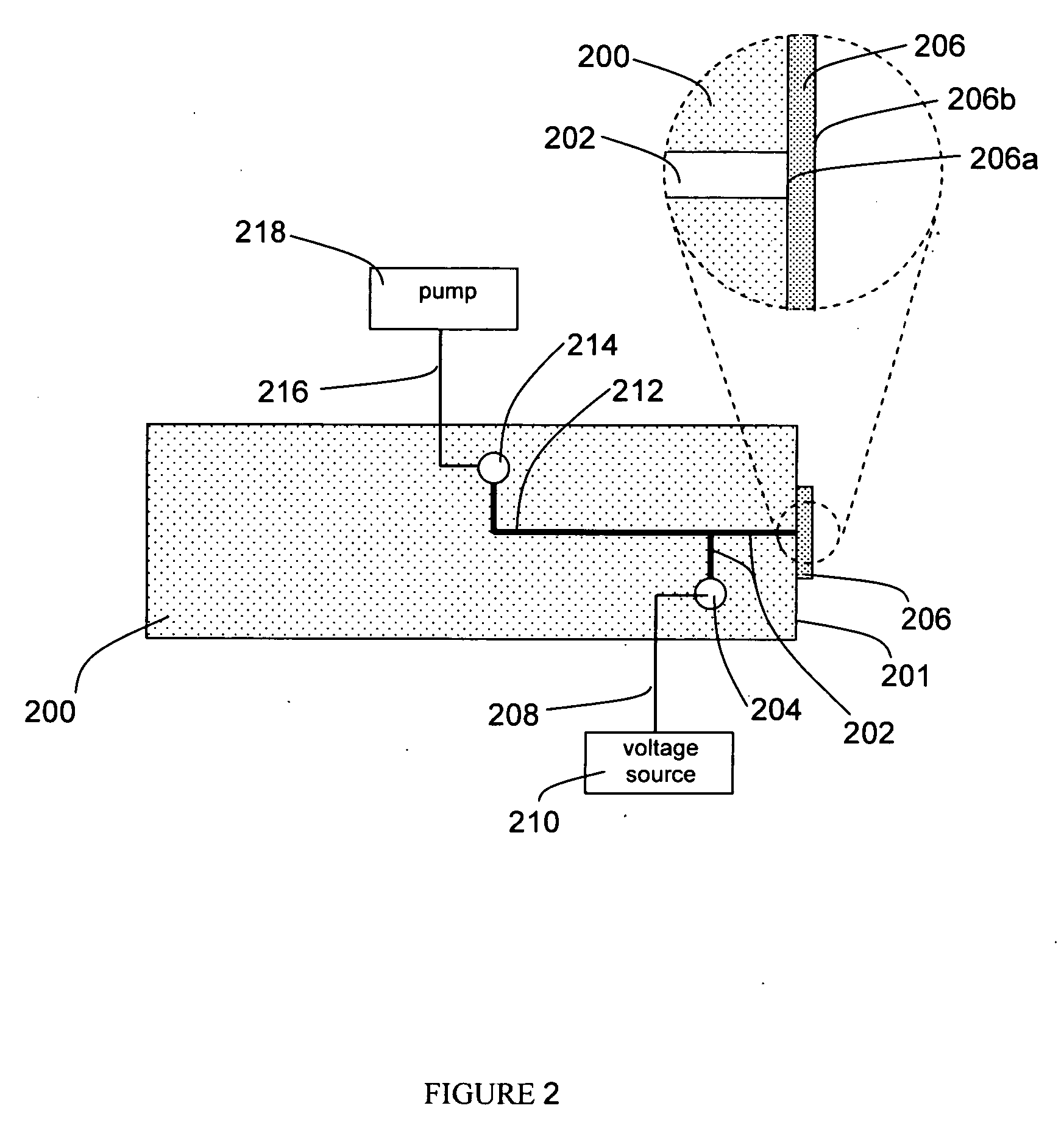
Method of electrically detecting a biological analyte molecule
InactiveUS20100194409A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityNanoparticle
The invention provides a method of electrically detecting a biological analyte molecule by means of a pair of electrodes. The electrodes are arranged at a distance from one another within a sensing zone. A capture molecule, which has an affinity to the analyte molecule and which is capable of forming a complex with the analyte molecule, is immobilised on an immobilisation unit. The immobilisation unit is contacted with a solution suspected to comprise the analyte molecule. The analyte molecule is allowed to form a complex with the capture molecule. The invention also provides a probe defined by a nanoparticulate tag that comprises or consists of electrically conducting matter that is capable of chemically interacting with the analyte molecule. In the method of the invention the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag is added. Thereby the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag is allowed to associate to the complex formed between the capture molecule and the analyte molecule. The presence of the analyte molecule is determined based on an electrical characteristic, influenced by the electrically conducting nanoparticulate tag, of a region in the sensing zone.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
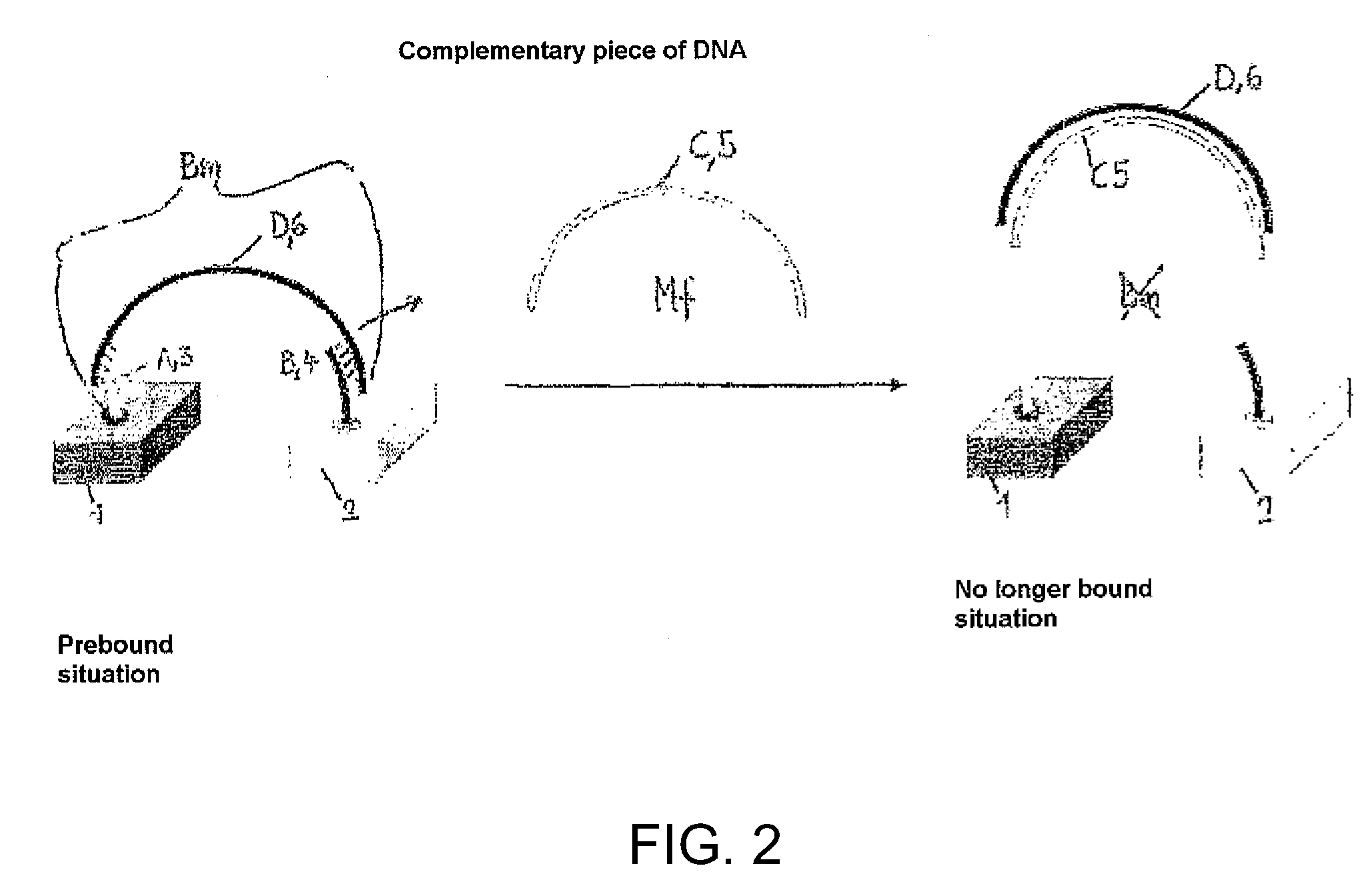
Method for Identifying and Quantifying Organic and Biochemical Substances
InactiveUS20100184062A1Improve cross-linking efficiencyReduce detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBinding siteAnalyte molecule
The invention relates to a method for identifying organic or biochemical substances and for determining their concentration in a fluid medium using a nanogap sensor that comprises at least two electrodes. The invention is characterized in that: a nanogap sensor) with electrodes of different materials is used, a respective probe molecule is bonded to each surface of the two electrodes of the sensor and the free remainder of the probe molecules have at least one bondable group with specificity for bonding to a sought substance or to an analyte molecule in the fluid medium. The analyte molecule has at least two binding sites and passes selectively out of the fluid medium in which it is contained, binds to the free ends of the probe molecules, forming a bridge with the probe molecule, and modifies the resulting impedance between the electrodes. The concentration of the substance in the fluid medium can be determined as a result of the modification.
Owner:ROSWELL BIOTECH INC +1
Imaging platform for nanoparticle detection applied to SPR biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS7221457B2Spectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsAnalyte moleculeLarge particle
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
Ultra-sensitive detection of enzymes by capture-and-release followed by quantification
InactiveUS20100075355A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAnalyte moleculeUltra sensitive
The present invention relates to systems and methods for detecting analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample and in some cases, determining a measure of the concentration of the molecules or particles in the fluid sample. Methods of the present invention may comprise immobilizing a plurality of analyte molecules or particles to form a plurality of complexes, releasing at least a portion of some of the plurality of complexes, determining at least a portion of the plurality of complexes released, and determining a measure of the concentration of the analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Methods and systems for extending dynamic range in assays for the detection of molecules or particles
ActiveUS20110212537A1Improve dynamic rangeAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingAnalyte moleculeAnalysis method
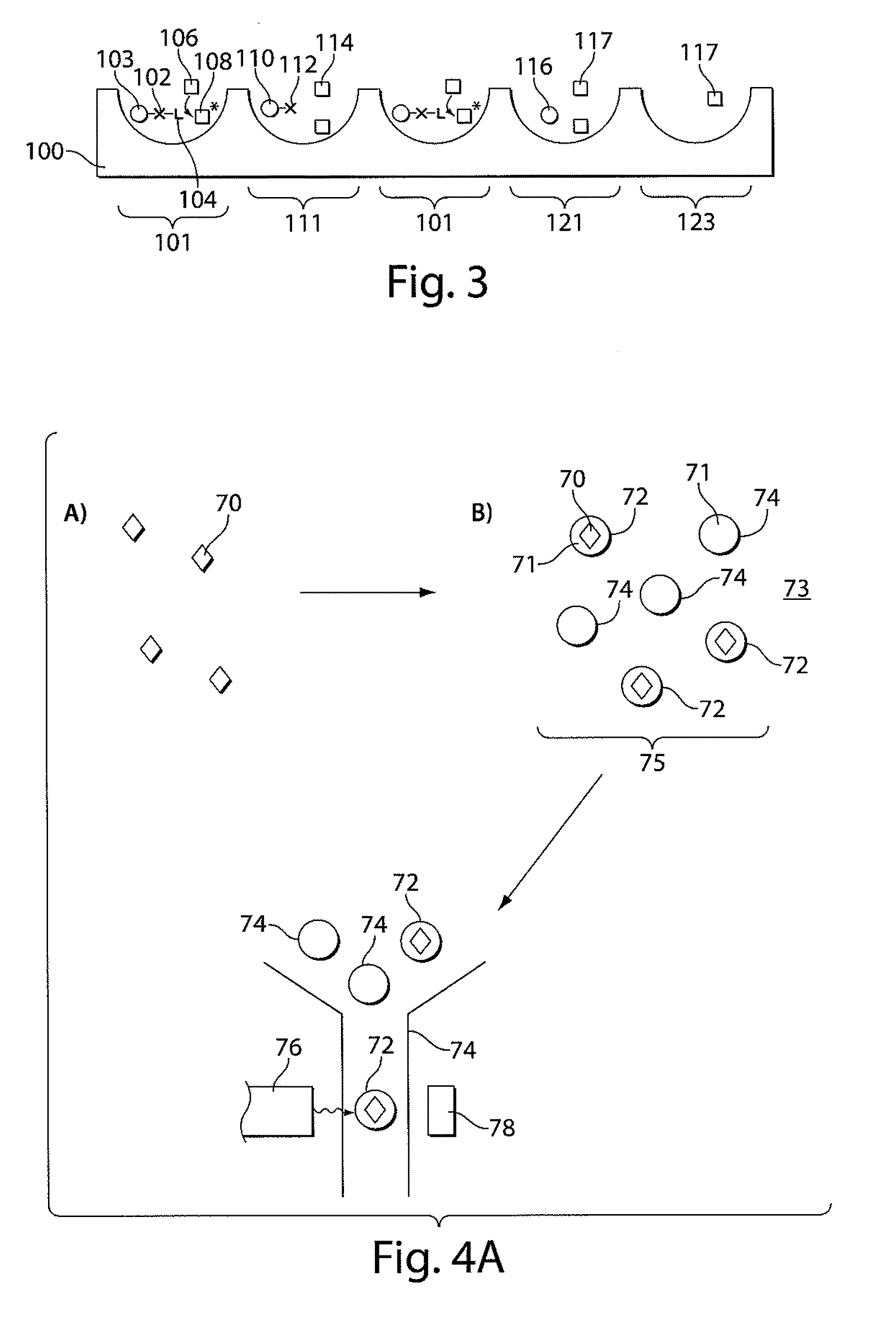
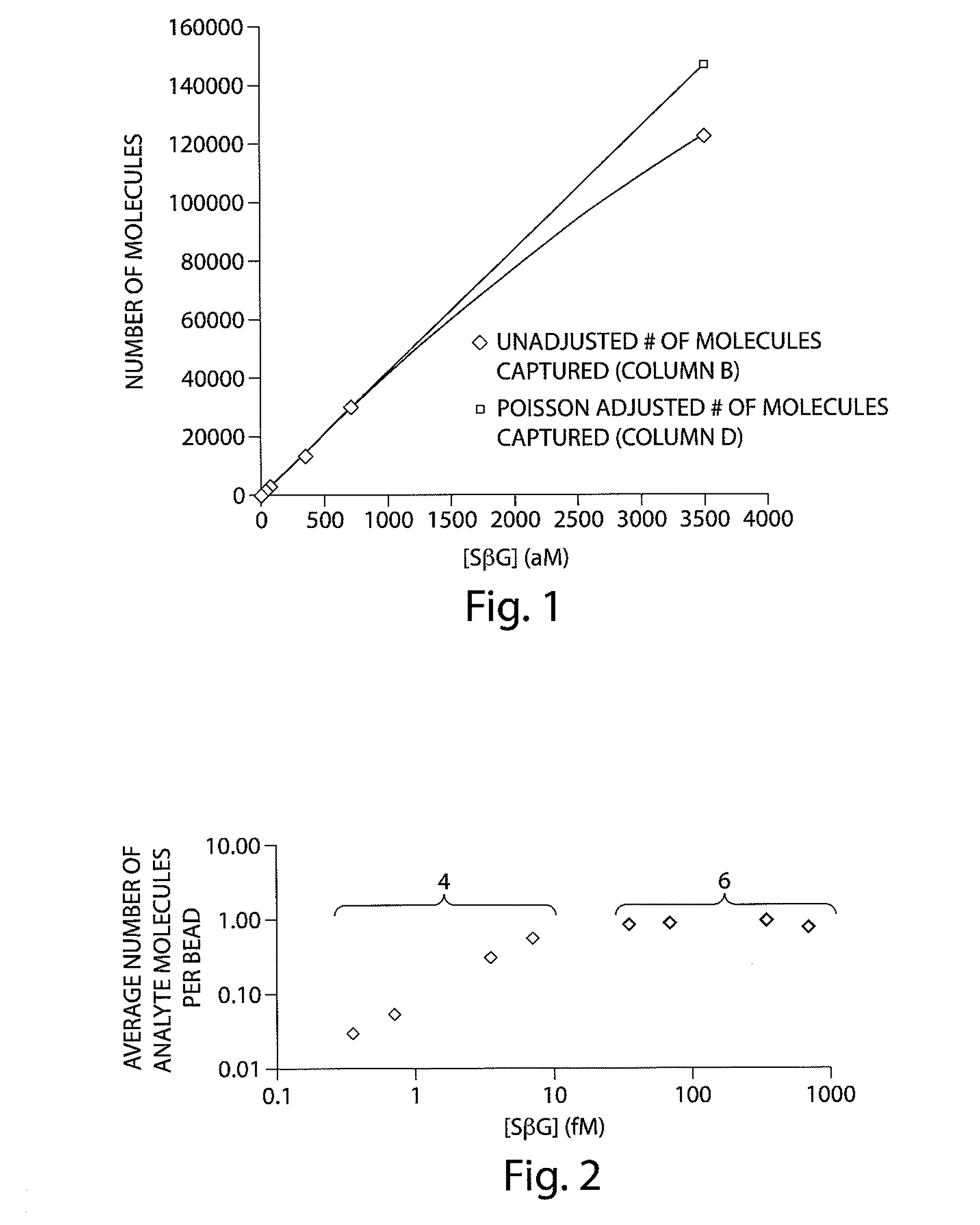
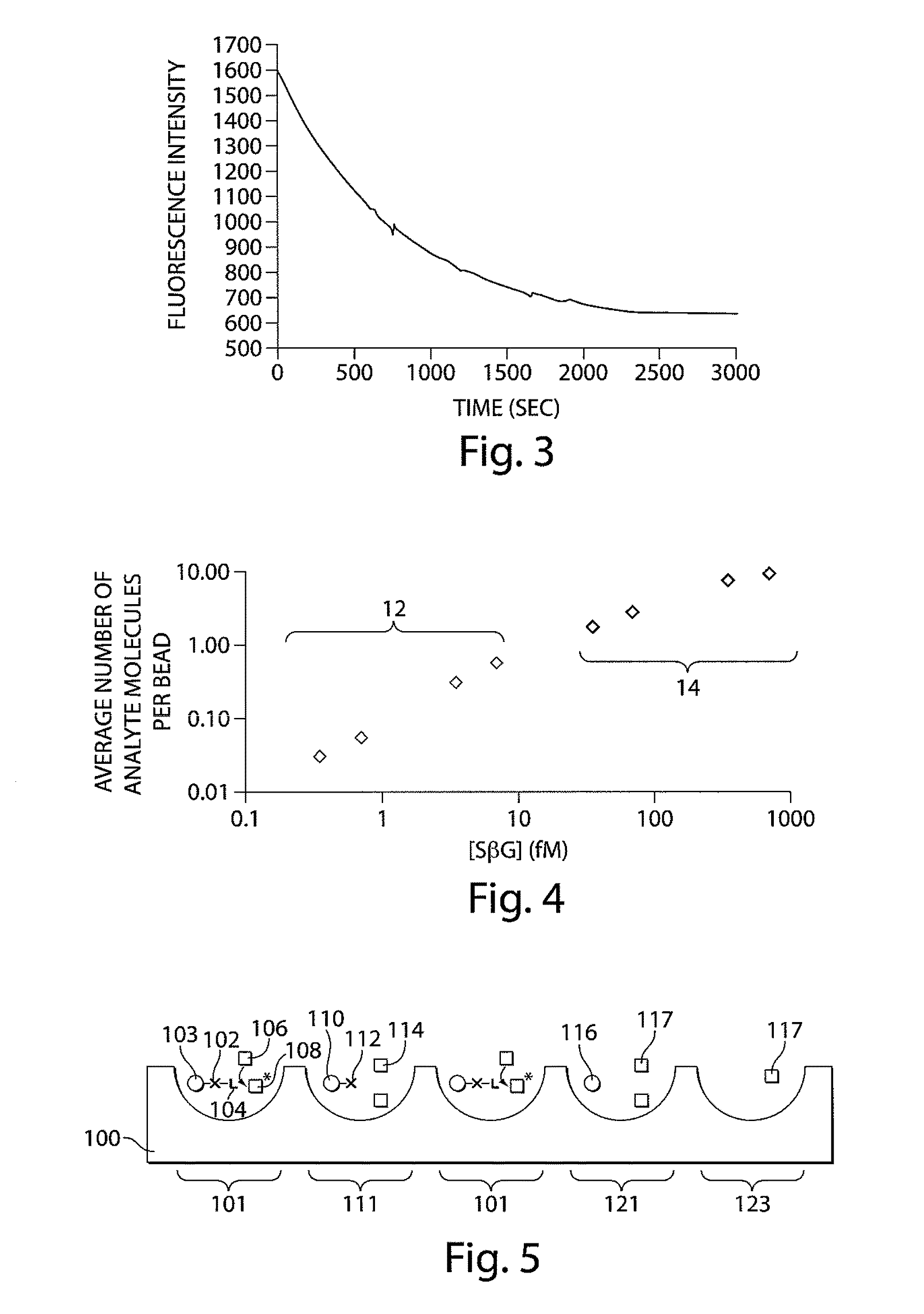
Described herein are systems and methods for extending the dynamic range of assay methods and systems used for determining the concentration of analyte molecules or particles in a fluid sample. In some embodiments, a method comprises spatially segregating a plurality of analyte molecules in a fluid sample into a plurality of locations. At least a portion of the locations may be addressed to determine the percentage of said locations containing at least one analyte molecule. Based at least in part on the percentage, a measure of the concentration of analyte molecules in the fluid sample may be determined using an analog, intensity-based detection / analysis method / system and / or a digital detection / analysis method / system. In some cases, the assay may comprise the use of a plurality of capture objects.
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Virtual reads for readlength enhancement
InactiveUS20090118129A1Easy to assembleReduce the amount requiredSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementContigGeolocation
Methods arrays and systems that facilitate contig assembly during nucleic acid sequencing are provided. Geographical locations of analyte molecules on an array are correlated with subsequence relationships within larger nucleic acids.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Apparatus and method for thermal assisted desorption ionization systems
ActiveUS8754365B2Raise transfer toHigh resolutionSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas phaseDesorption
The present invention is directed to a method and device to desorb an analyte using heat to allow desorption of the analyte molecules, where the desorbed analyte molecules are ionized with ambient temperature ionizing species. In various embodiments of the invention a current is passed through a mesh upon which the analyte molecules are present. The current heats the mesh and results in desorption of the analyte molecules which then interact with gas phase metastable neutral molecules or atoms to form analyte ions characteristic of the analyte molecules.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Method and apparatus for magnetoresistive monitoring of analytes in flow streams
InactiveUS7179383B1High sensitivityMaterial thermal conductivityVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityStream flow
Method and apparatus for manipulating and monitoring analyte flowing in fluid streams. A giant magnetoresistive sensor has an array of sensing elements that produce electrical output signals which vary in dependence on changes in the magnetic field proximate the sensing elements. The analyte is included in a stream, such that the stream has a magnetic property which is dependent on the concentration and distribution on the analyte therein. The stream is flowed past the giant magnetoresistive sensor and in sufficiently close proximity to cause the magnetic properties of the stream to produce electrical output signals. The electrical output signals are monitored as an indicator of analyte concentration or distribution in the stream flowing past the GMR sensor. Changes in the magnetic field produced by the background stream are introduced by analyte molecules, whose presence in the flow past the GMR will effect the output reading.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Methods and systems for extending dynamic range in assays for the detection of molecules or particles
ActiveUS8415171B2Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingAnalyte moleculeAnalysis method
Owner:QUANTERIX CORP
Method of electrically detecting a nucleic acid molecule
InactiveUS20100285601A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNucleotideBiological activation
The method is performed by means of a pair of electrodes that are arranged at a distance and within a sensing zone. A nucleic acid capture molecule with an uncharged backbone and a nucleotide sequence that is at least partially complementary to at least a portion of a strand of the target nucleic acid molecule, is immobilised on an immobilisation unit. The immobilisation unit, which is arranged within the sensing zone, is contacted with a solution suspected to comprise the target nucleic acid molecule, which hybridizes to the nucleic acid capture molecule. An activation agent is added, which has an electrostatic net charge complementary to the net charge of the target nucleic acid molecule. It associates to the complex of nucleic acid capture molecule and target nucleic acid molecule. Added is a water soluble polymer with at least one polymer strand and with an electrostatic net charge that is complementary to the net charge of the activation agent. Thus the polymer associates to the activation agent. A metal salt is added, which can act as an oxidant and the metal ions of which have an electrostatic net charge complementary to the net charge of the polymer. The metal ions associate to the polymer. Upon adding a reducing agent, the latter reduces the metal ions, forming a metal wire. The presence of the analyte molecule is determined based on an electrical characteristic of a region in the sensing zone that is affected by the metal wire.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
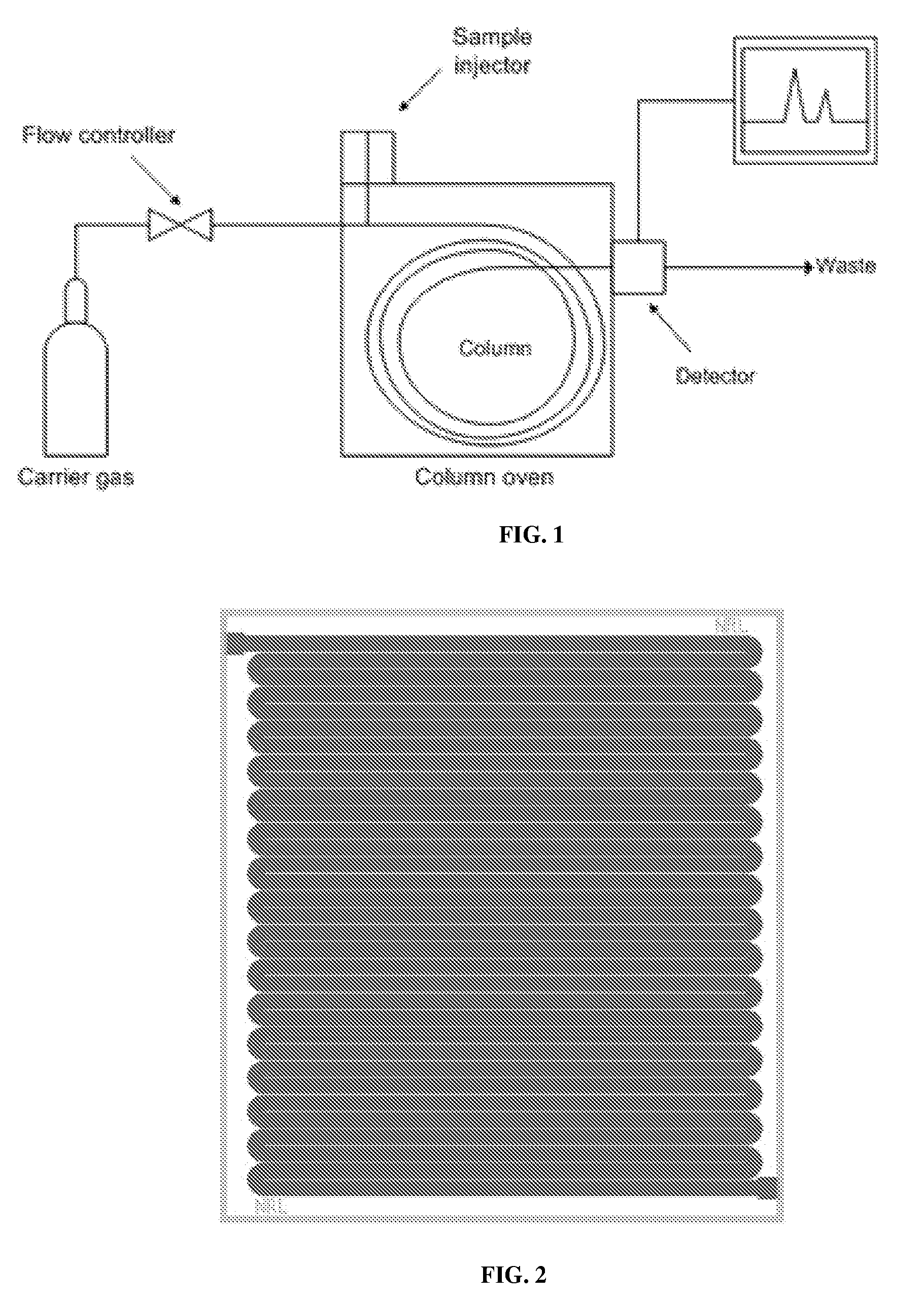
Microfabricated gas chromatograph
ActiveUS20090272270A1Mitigate band broadeningMitigate tailing problemLamination ancillary operationsComponent separationStationary phaseContinuous flow
The present invention is generally directed to a microfabricated gas chromatograph column having two patterned substrates, each optionally having a stationary phase material coating, bonded together to provide a continuous flow channel. The flow channel can have a serpentine arrangement or a modified serpentine arrangement comprising alternating series of consecutive turns in one direction where each series has enough turns to move carrier gas and analyte molecules from the center of the column cross section to an outer wall of the channel or from one outer wall of the channel to the opposite outer wall. Different portions of the substrates can be coated with differing thicknesses of stationary phase material and / or with different stationary phase materials. The column can have a circular cross-section or a semi-circular cross-section where the flat portion of the cross-section has grooves. Also disclosed is the related method of making the microfabricated gas chromatograph column.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com