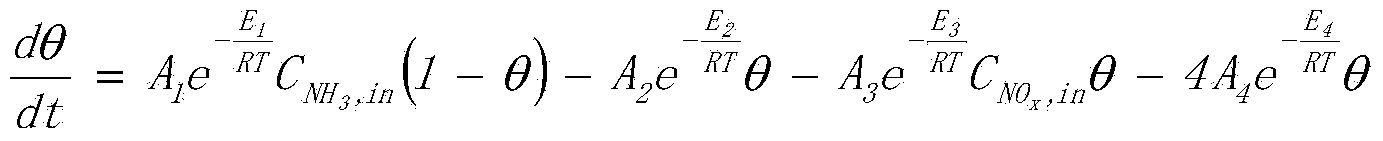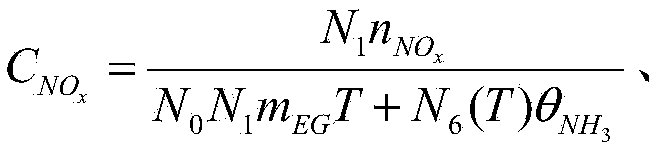Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
462 results about "Ammonia storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
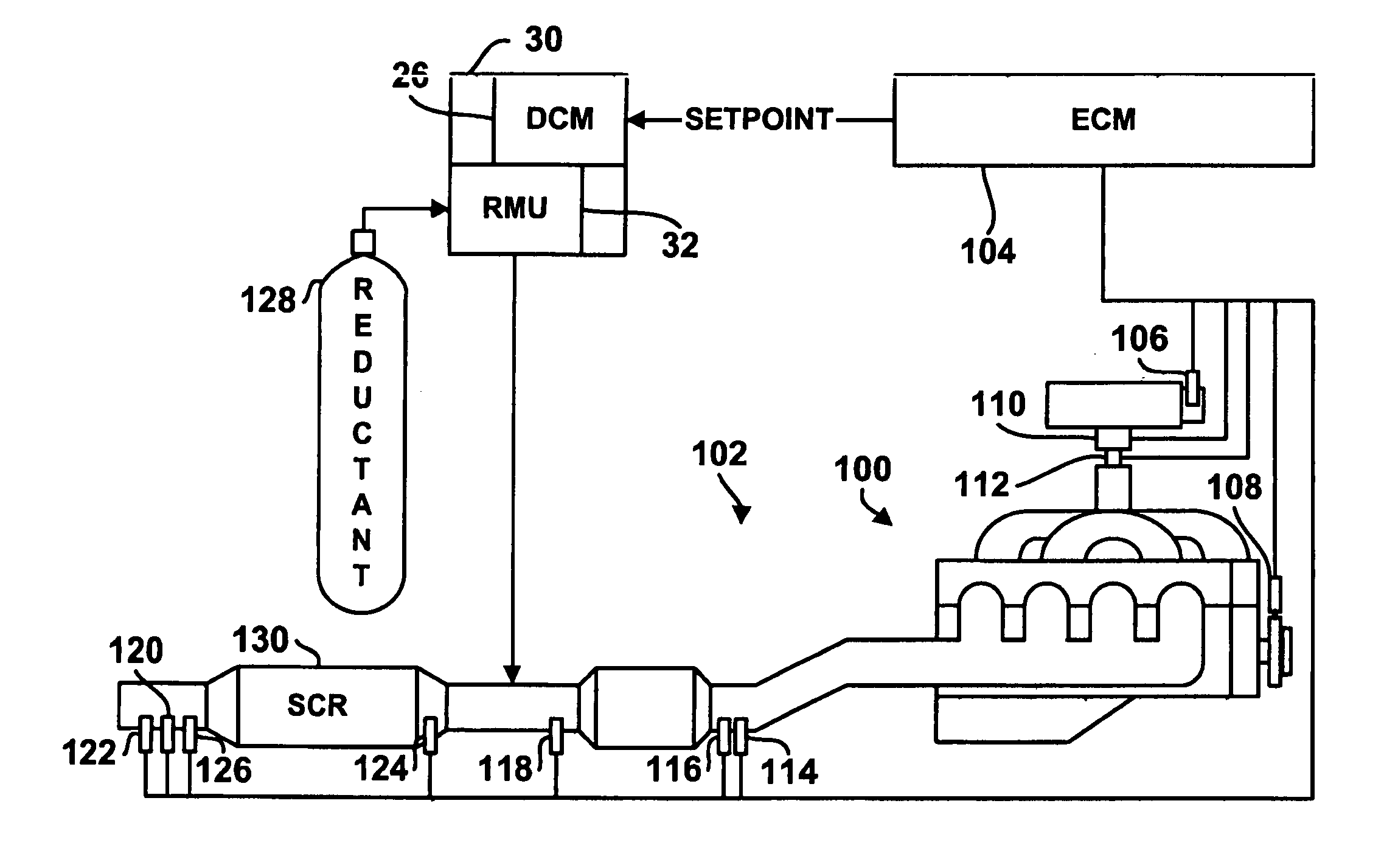
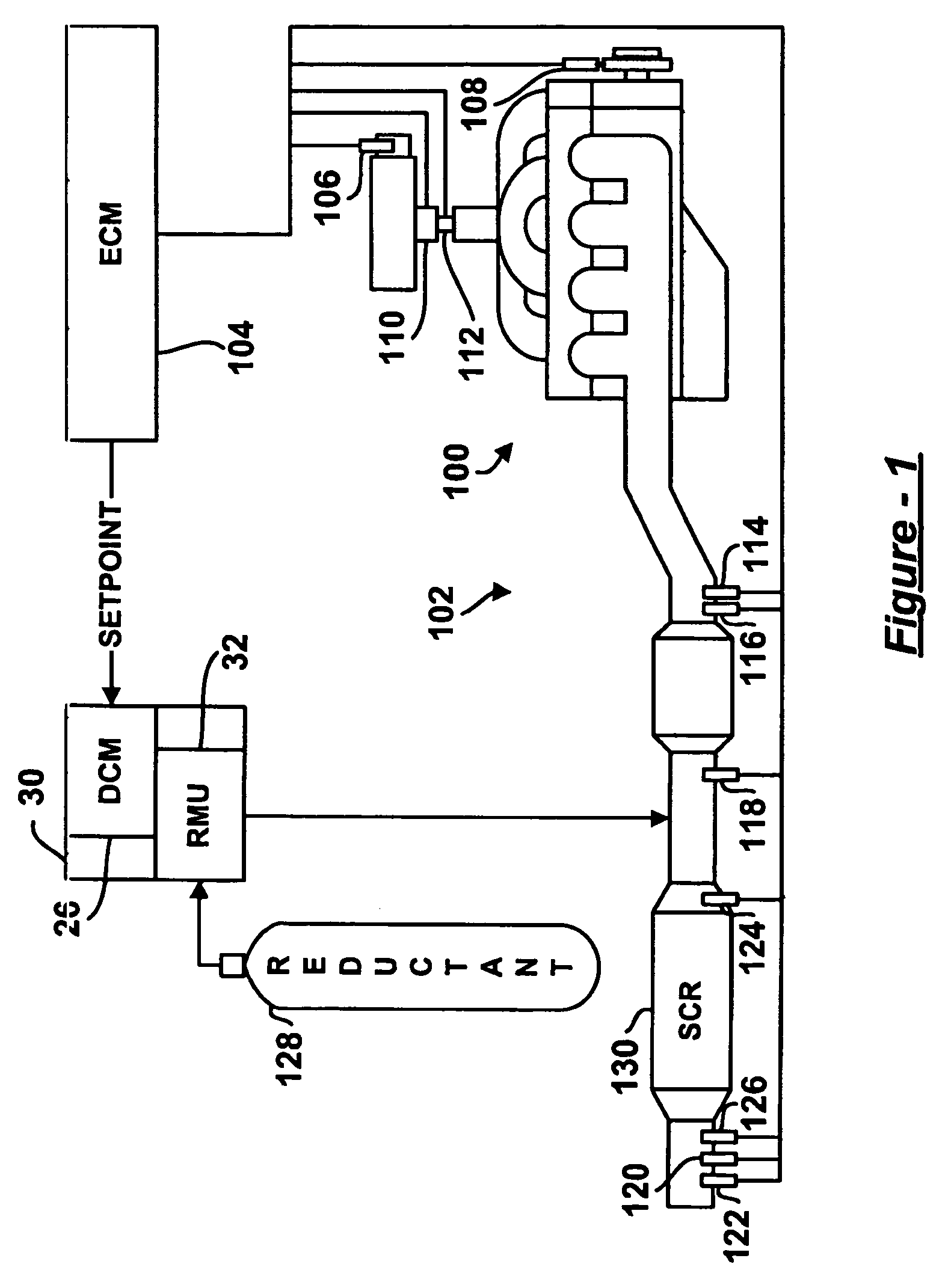
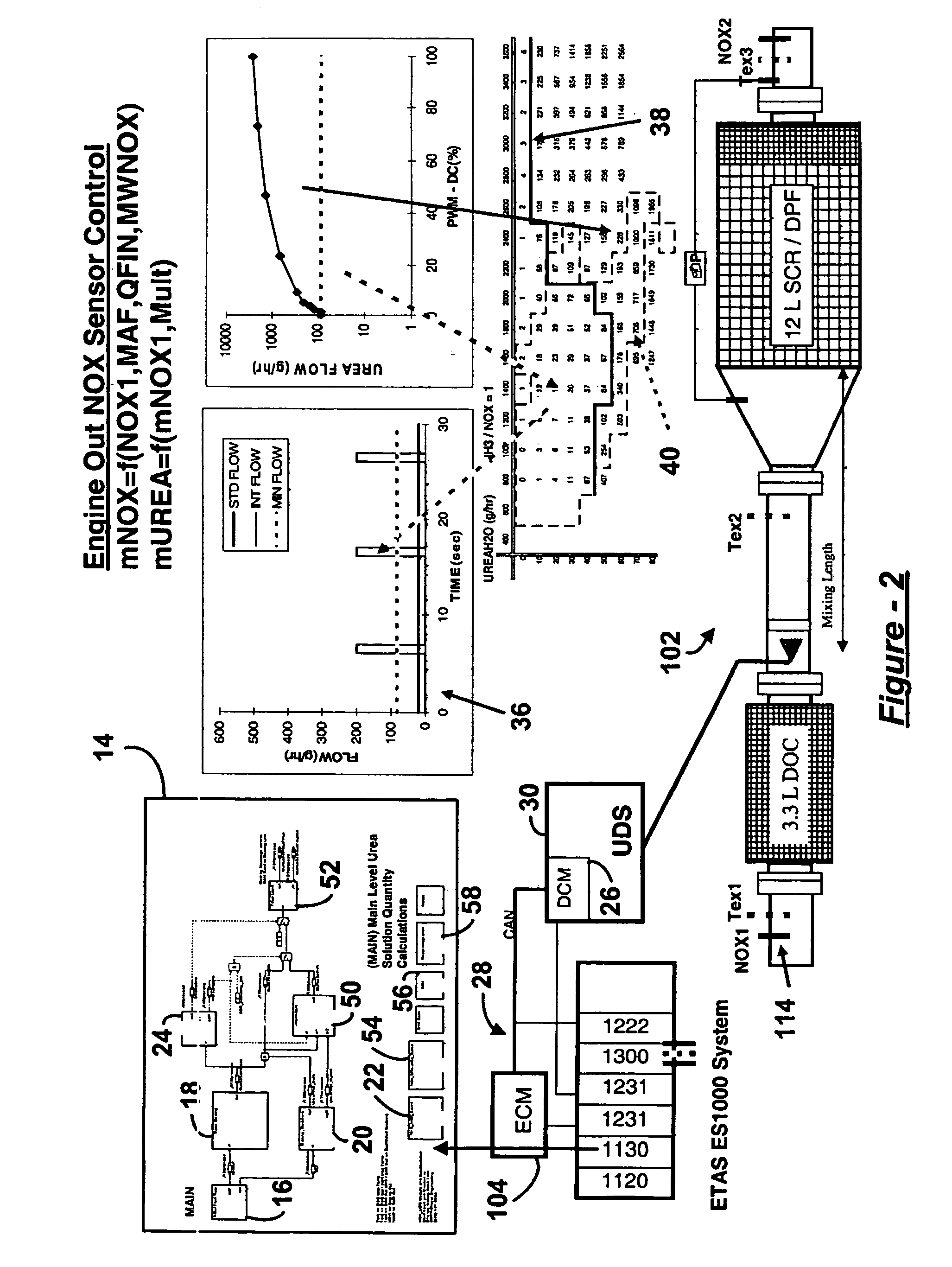
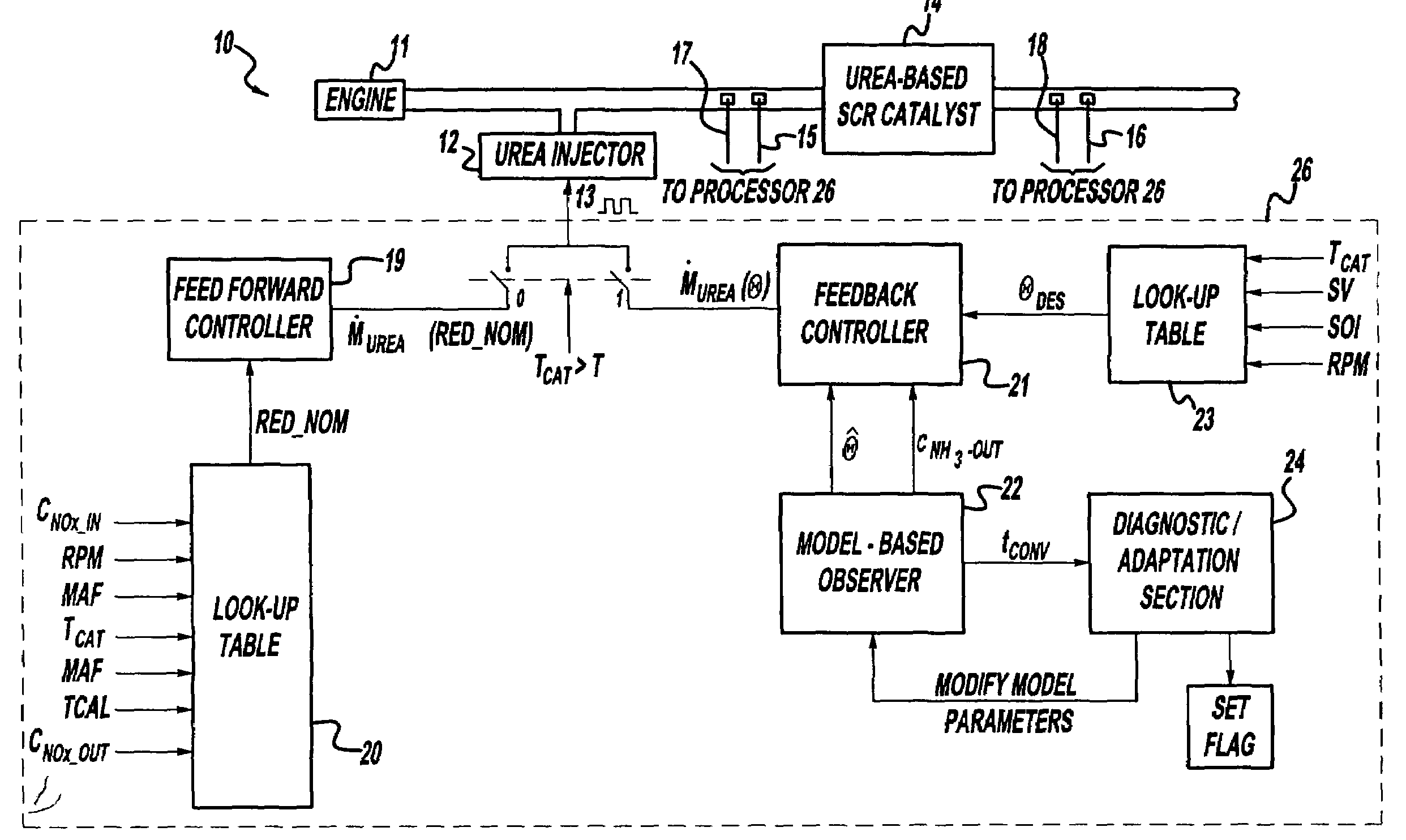
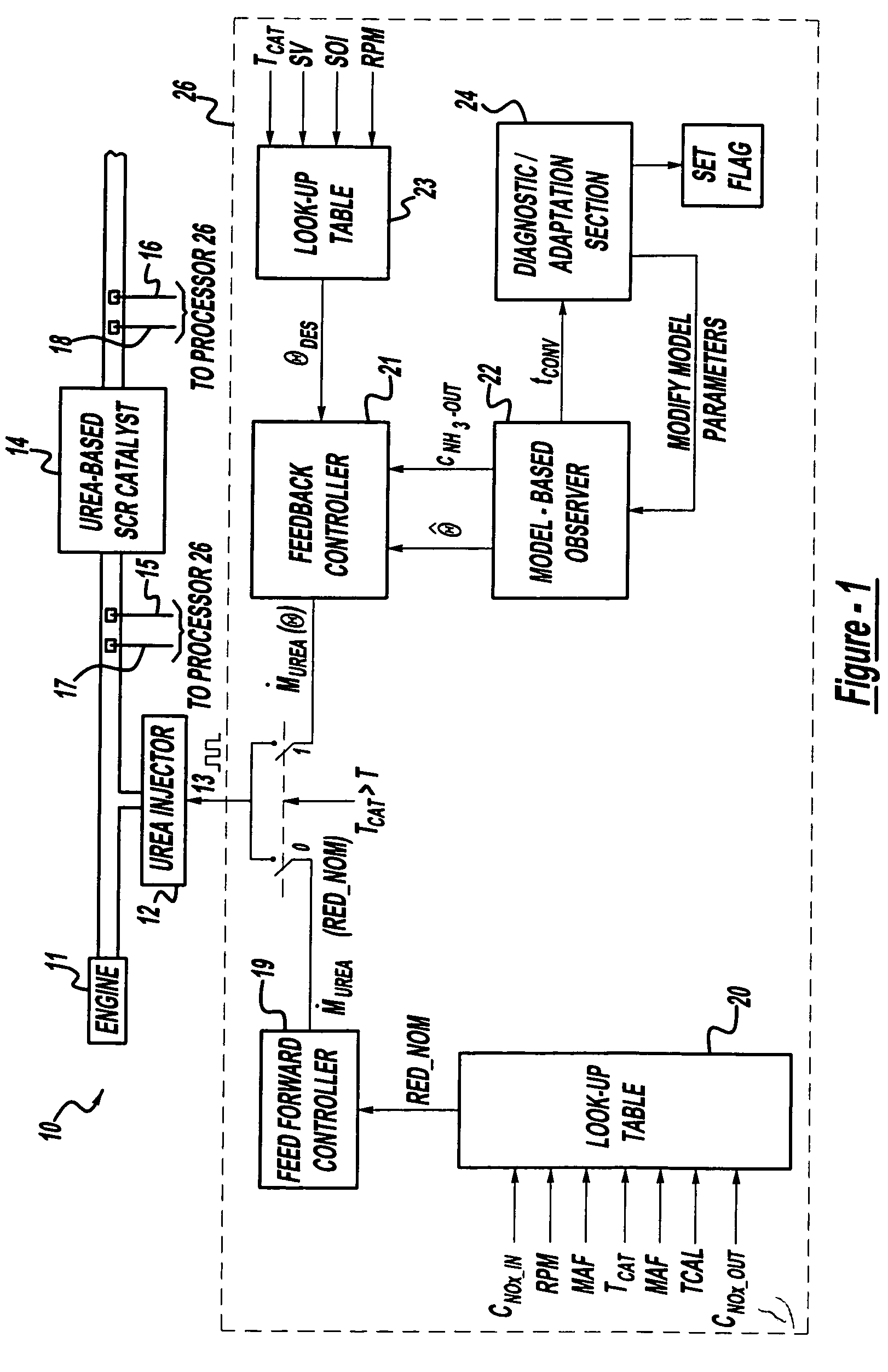
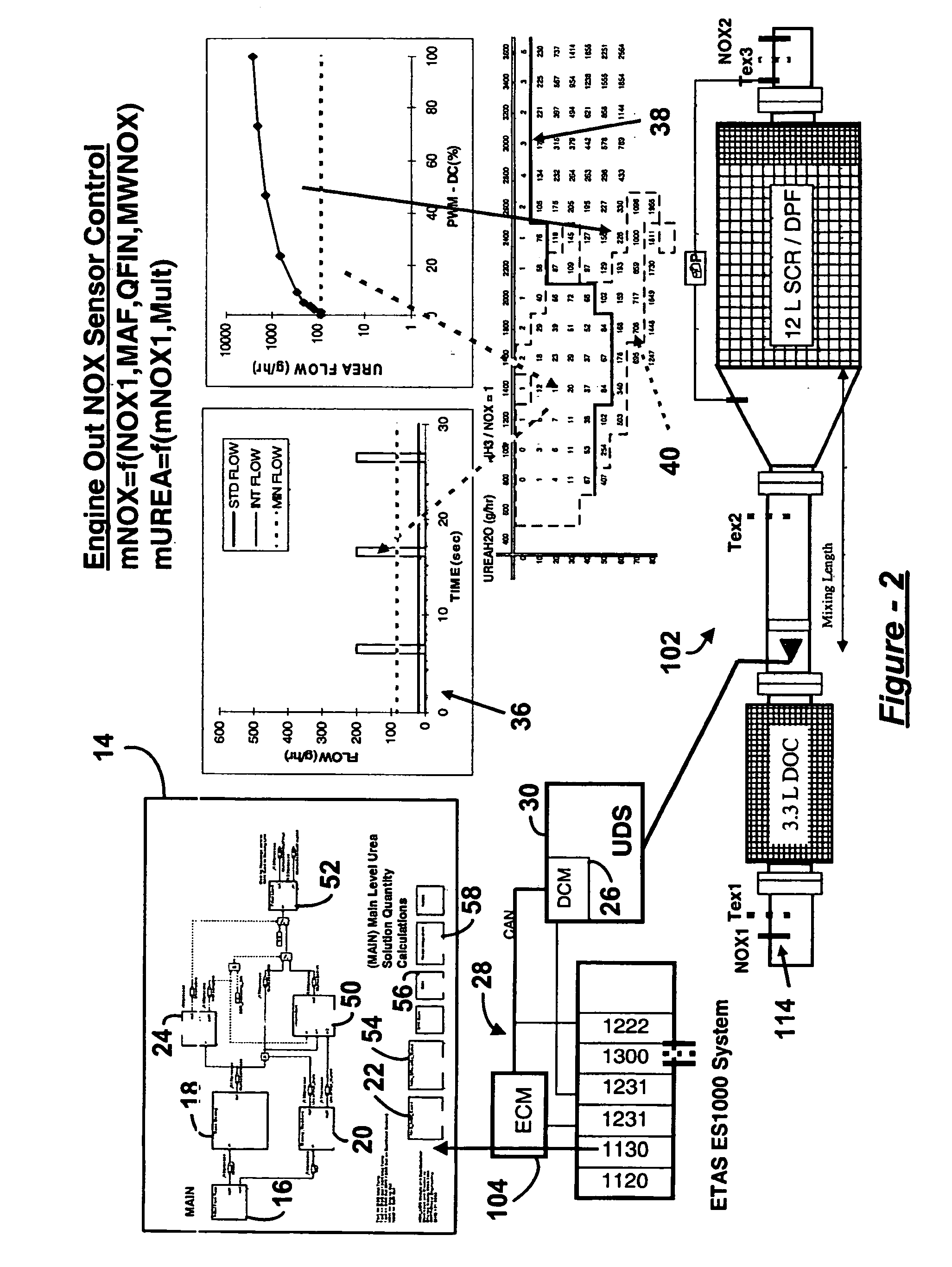
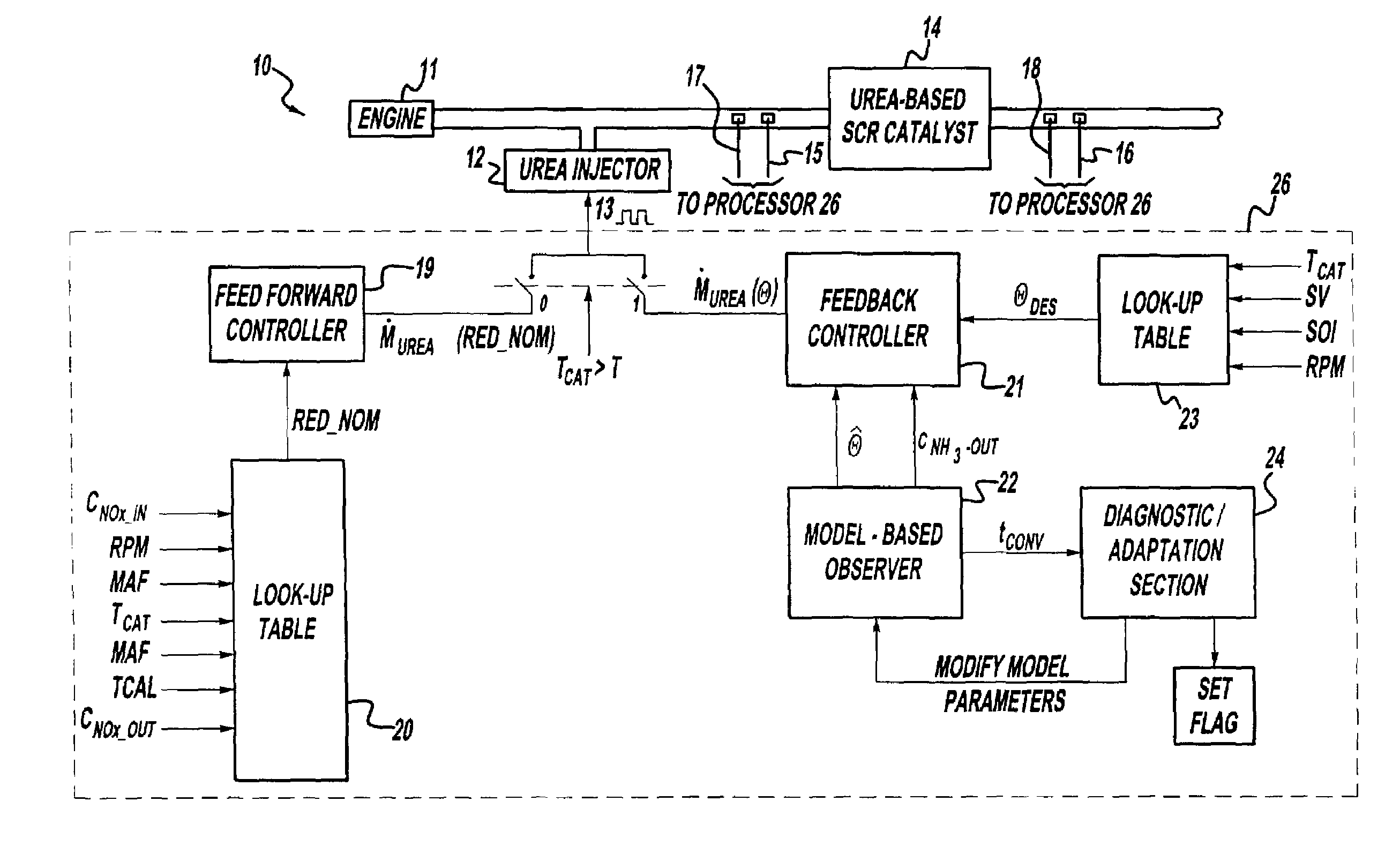
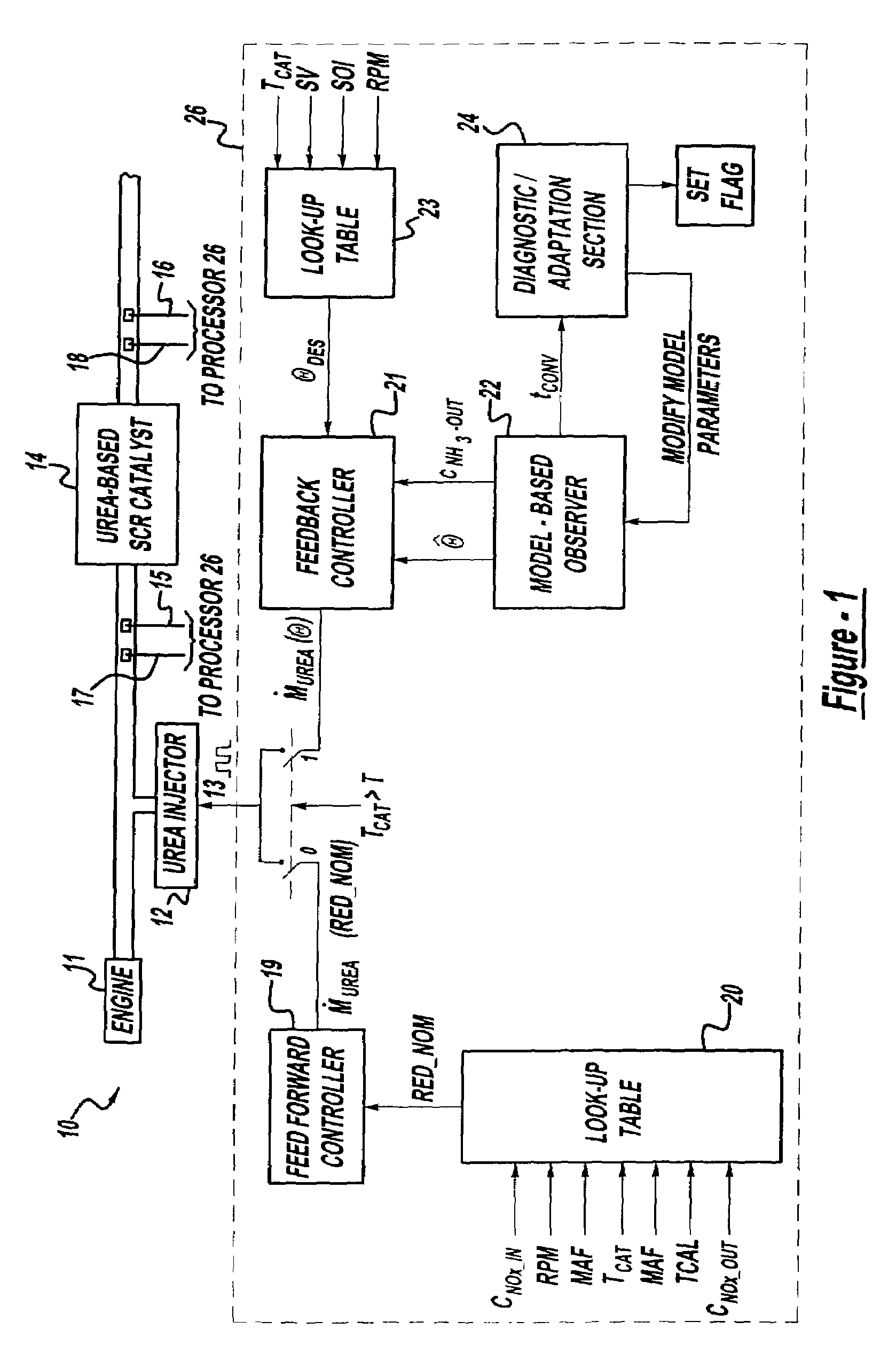
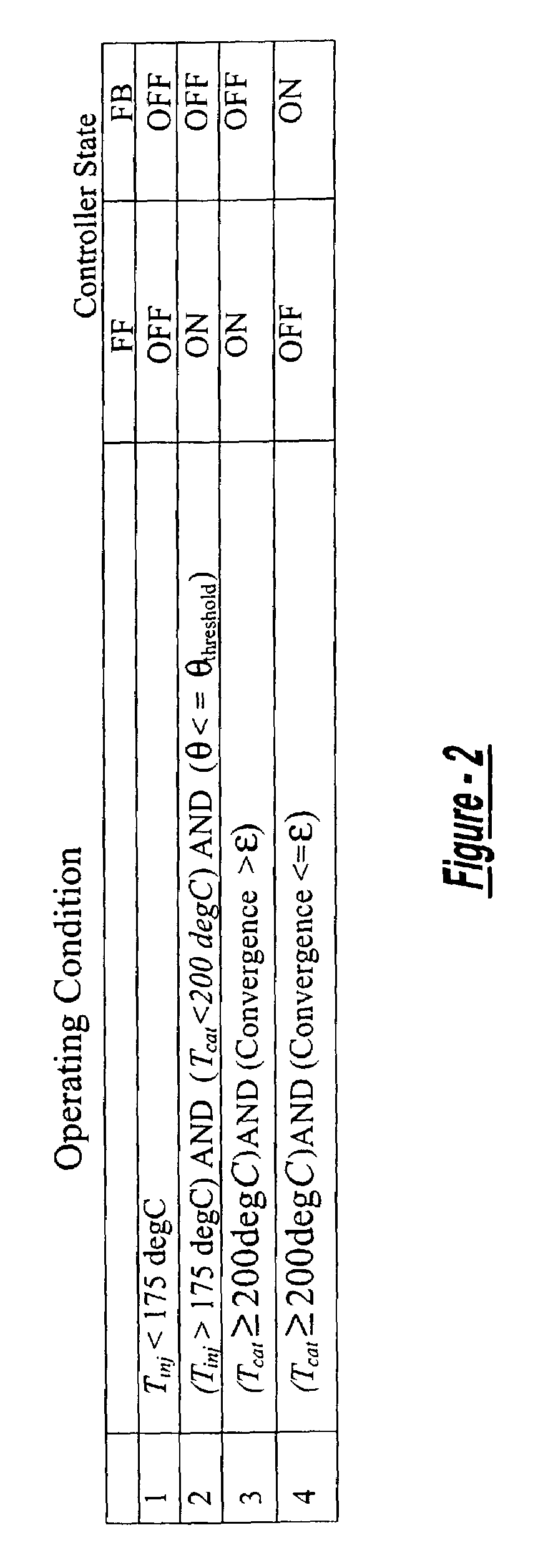
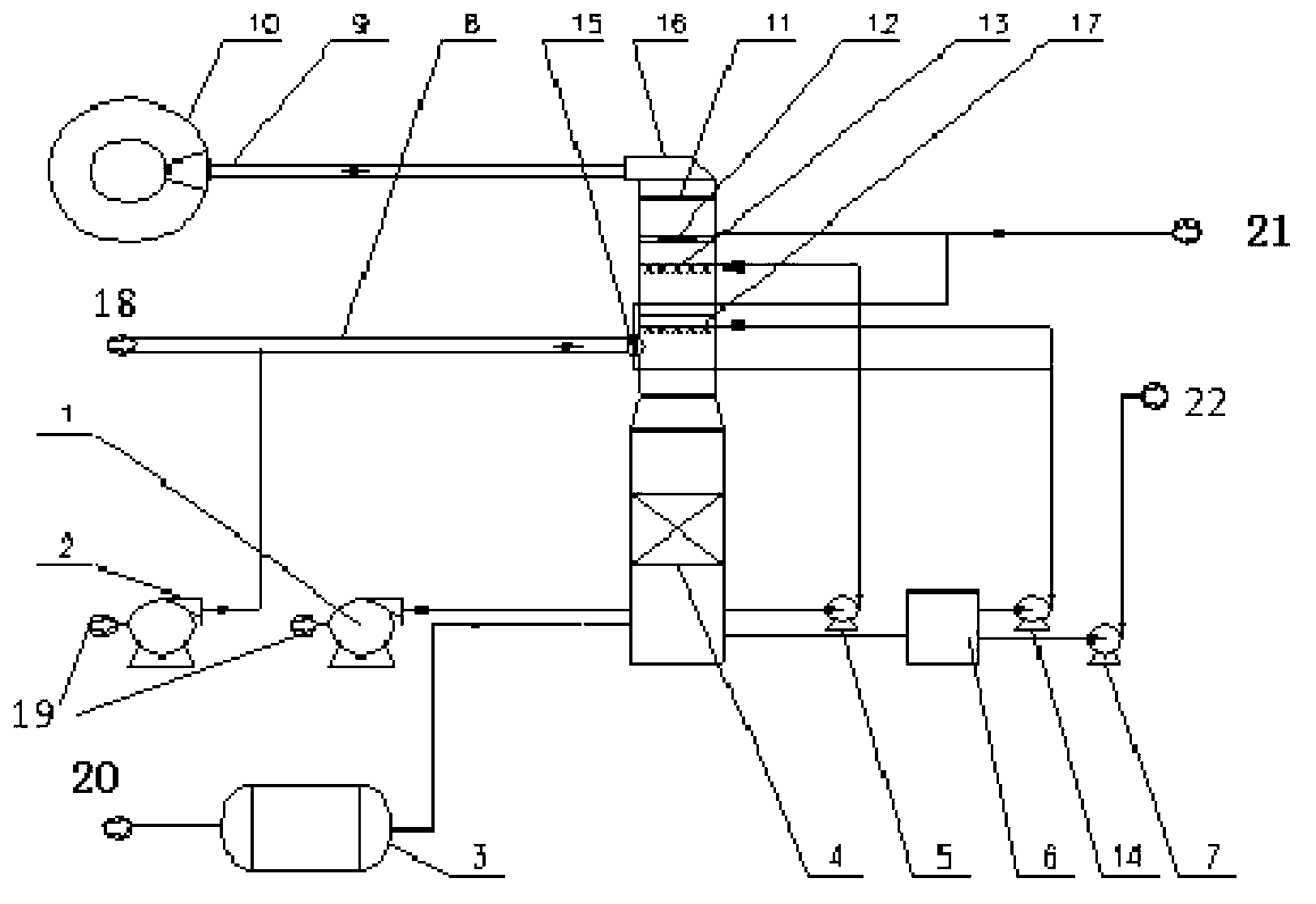
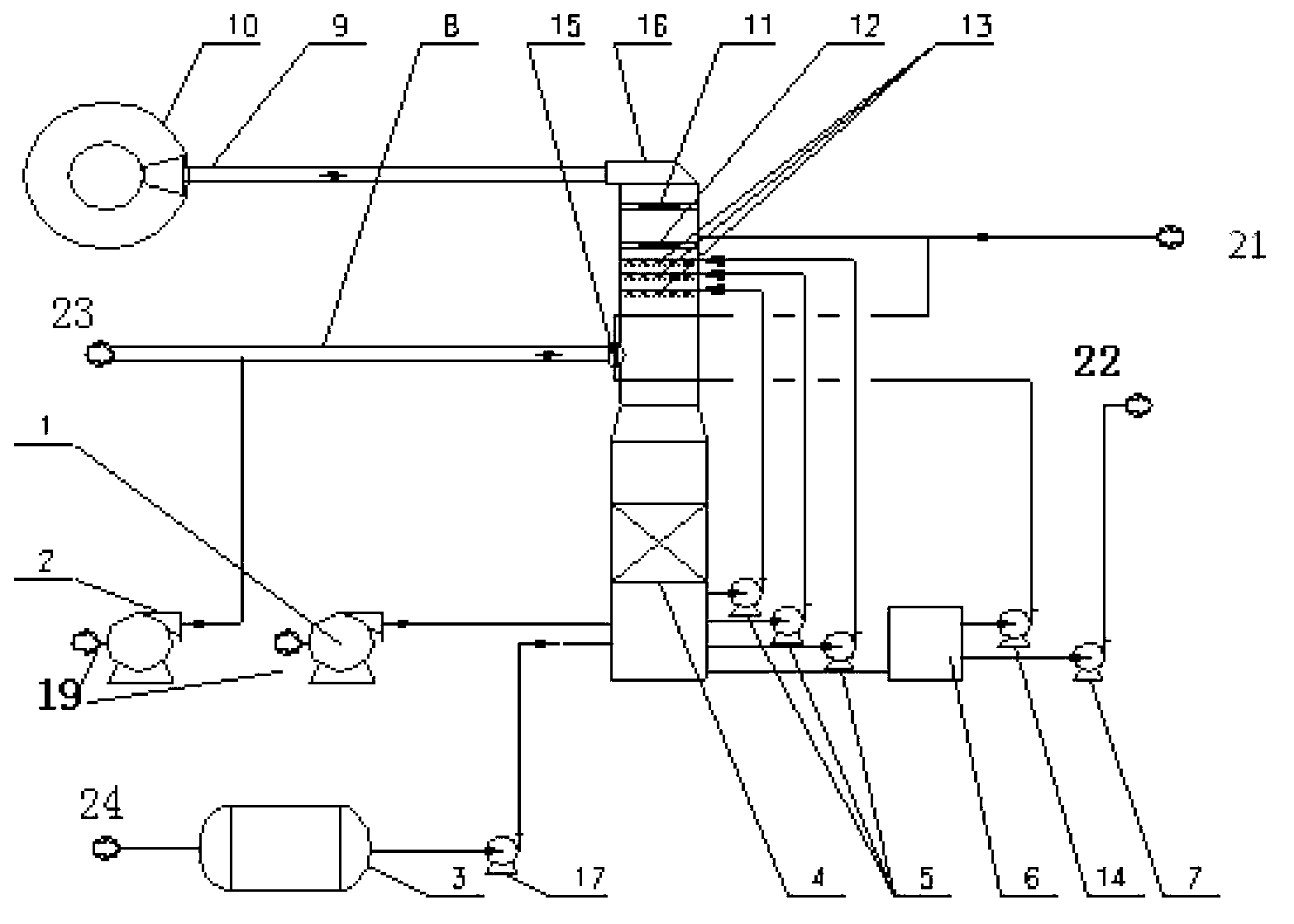
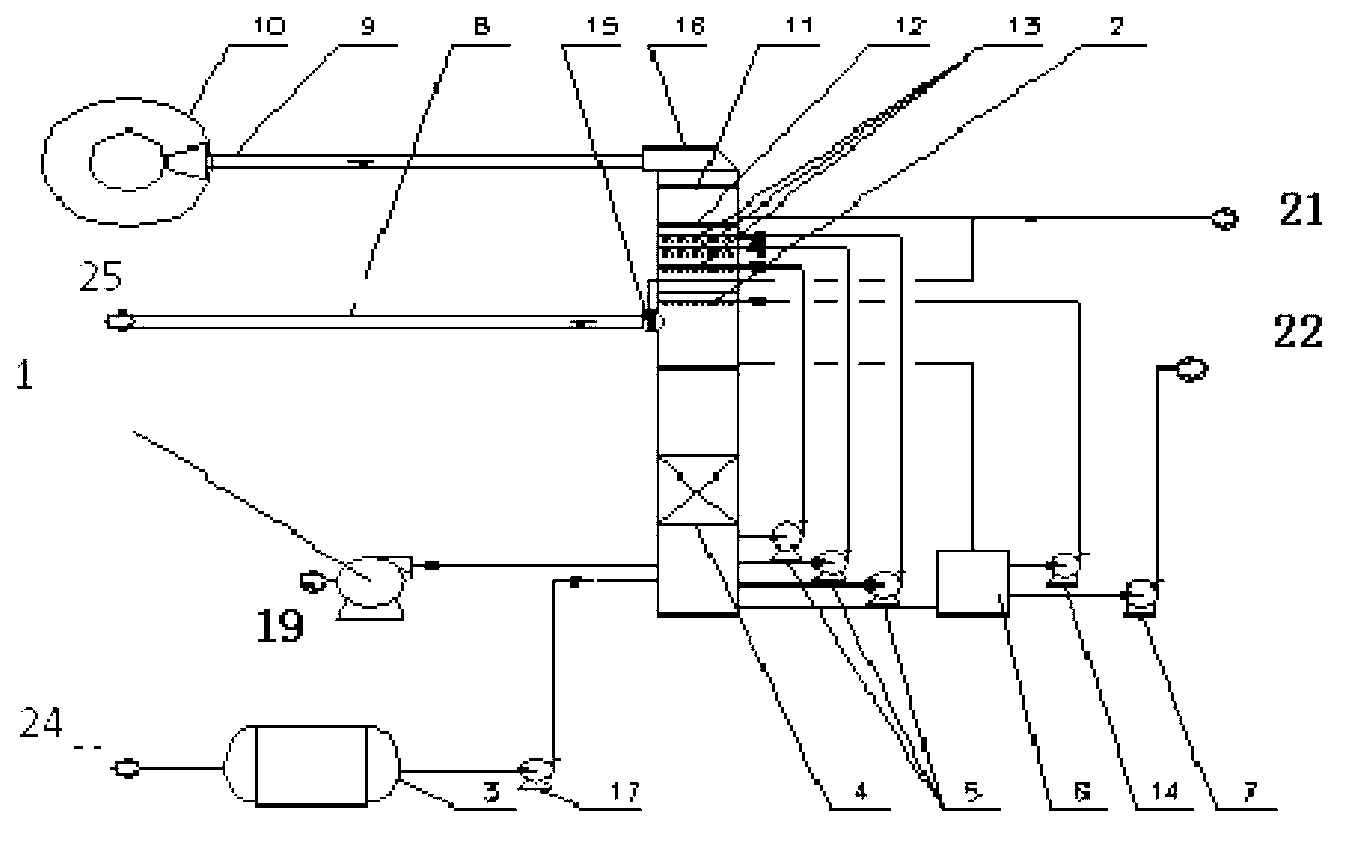
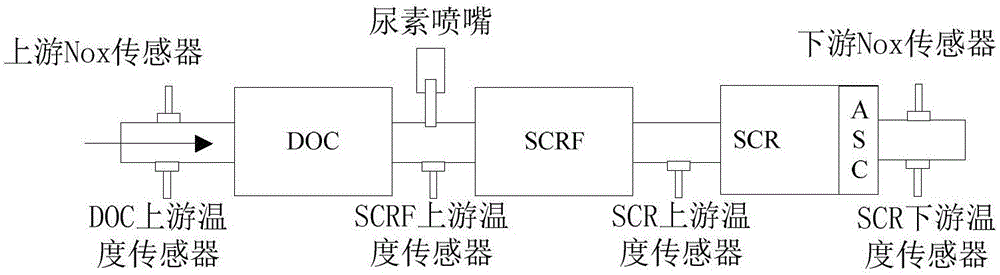
System for controlling the urea supply to SCR catalysts
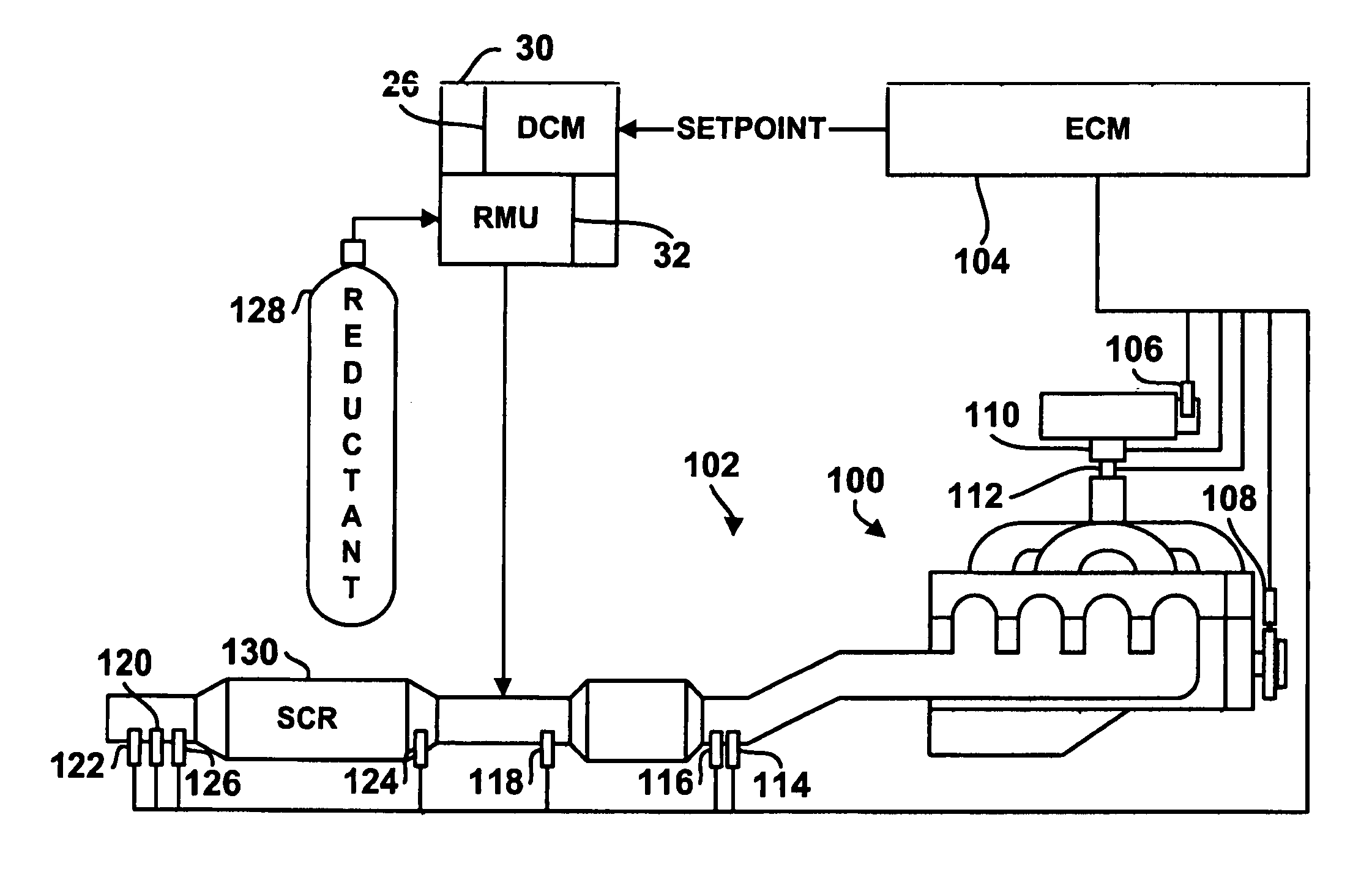
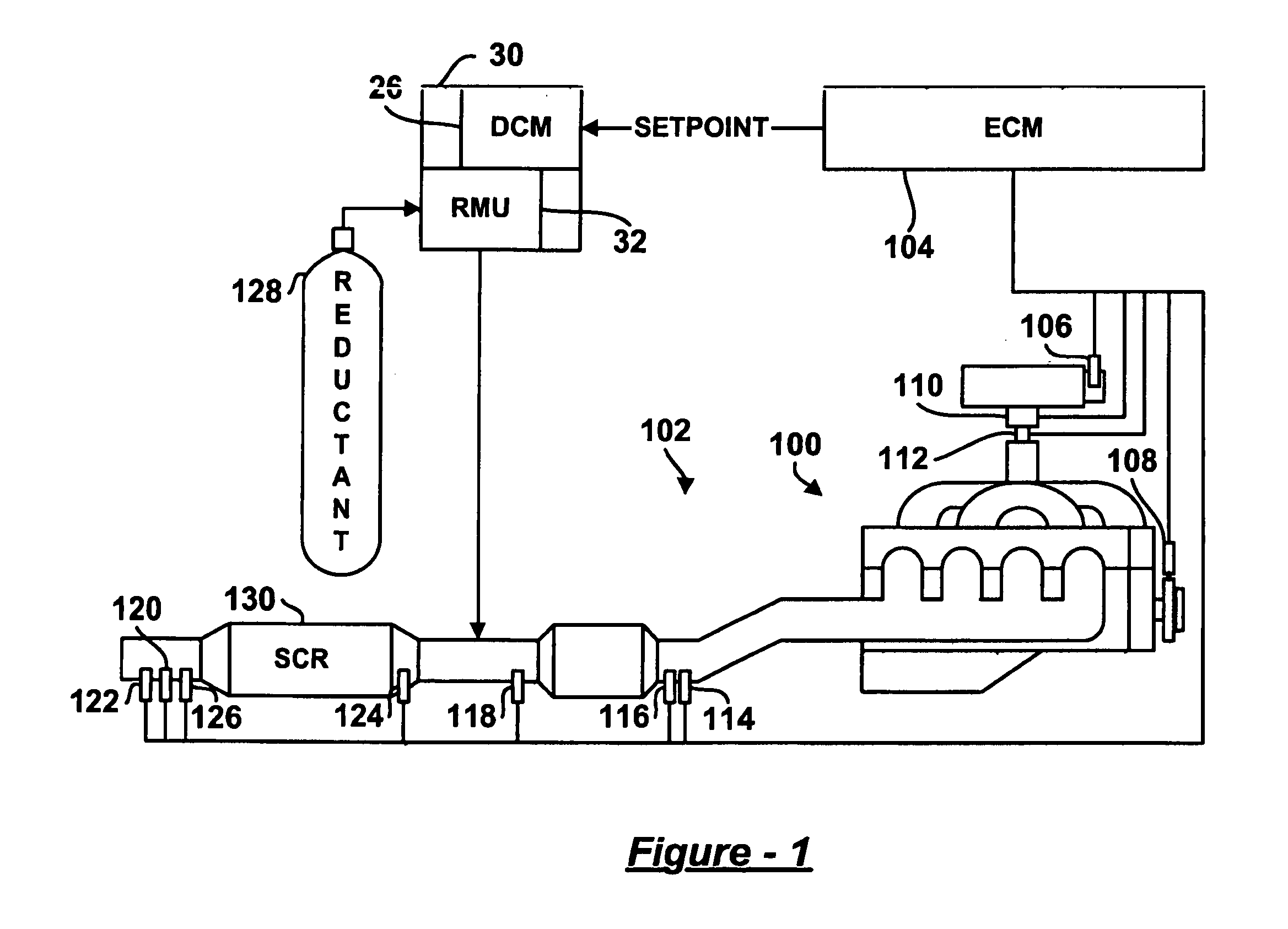
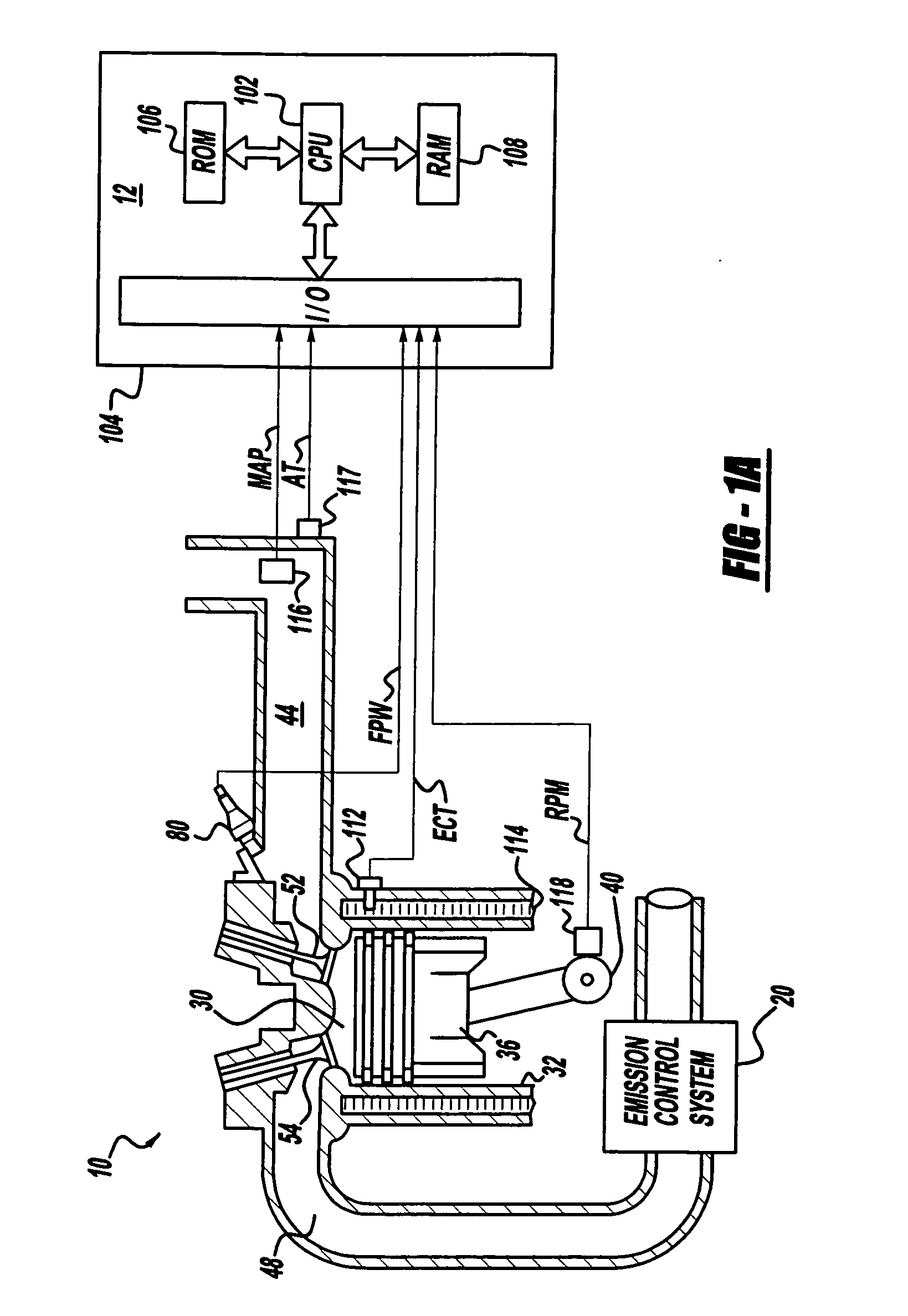
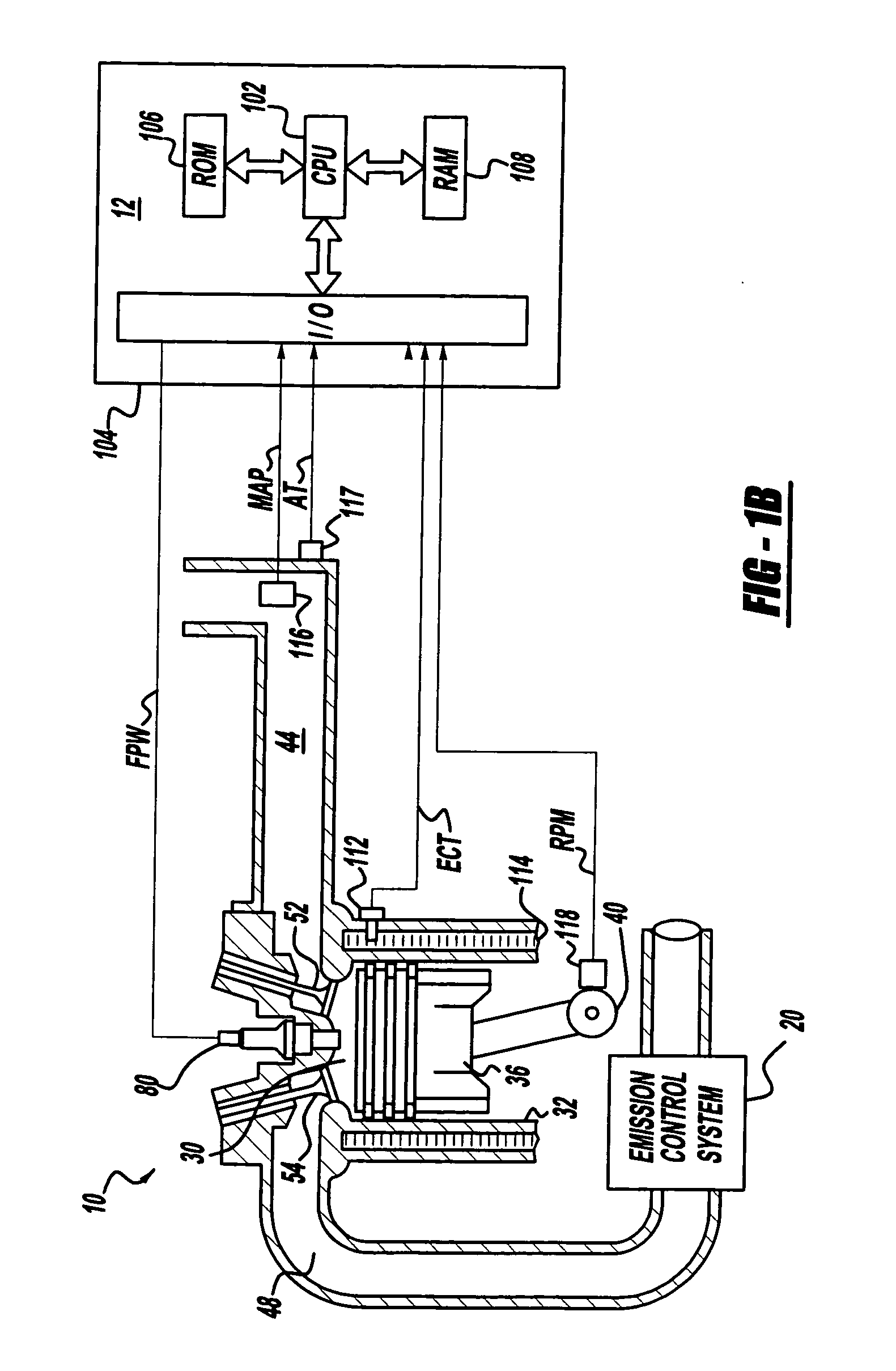
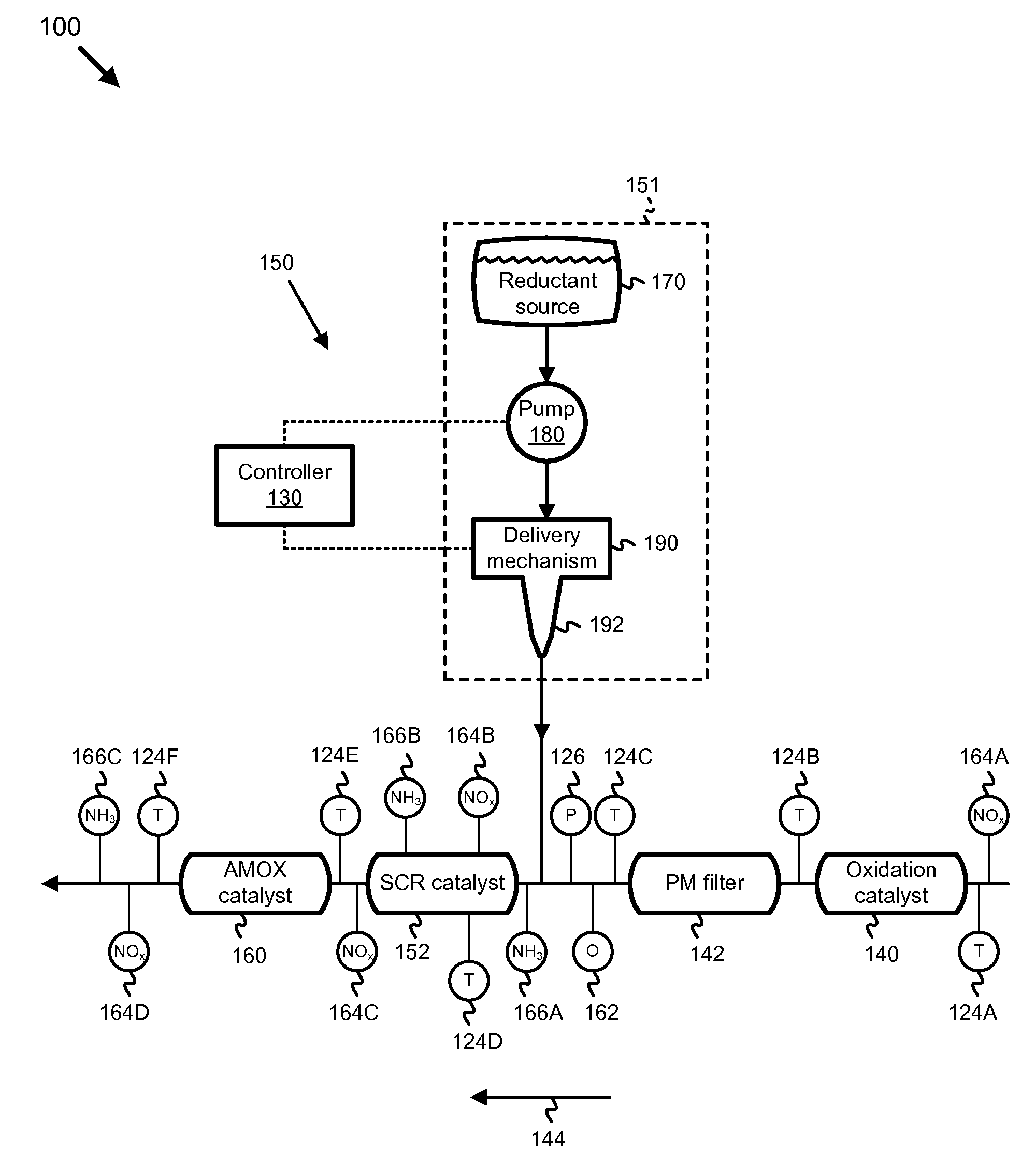
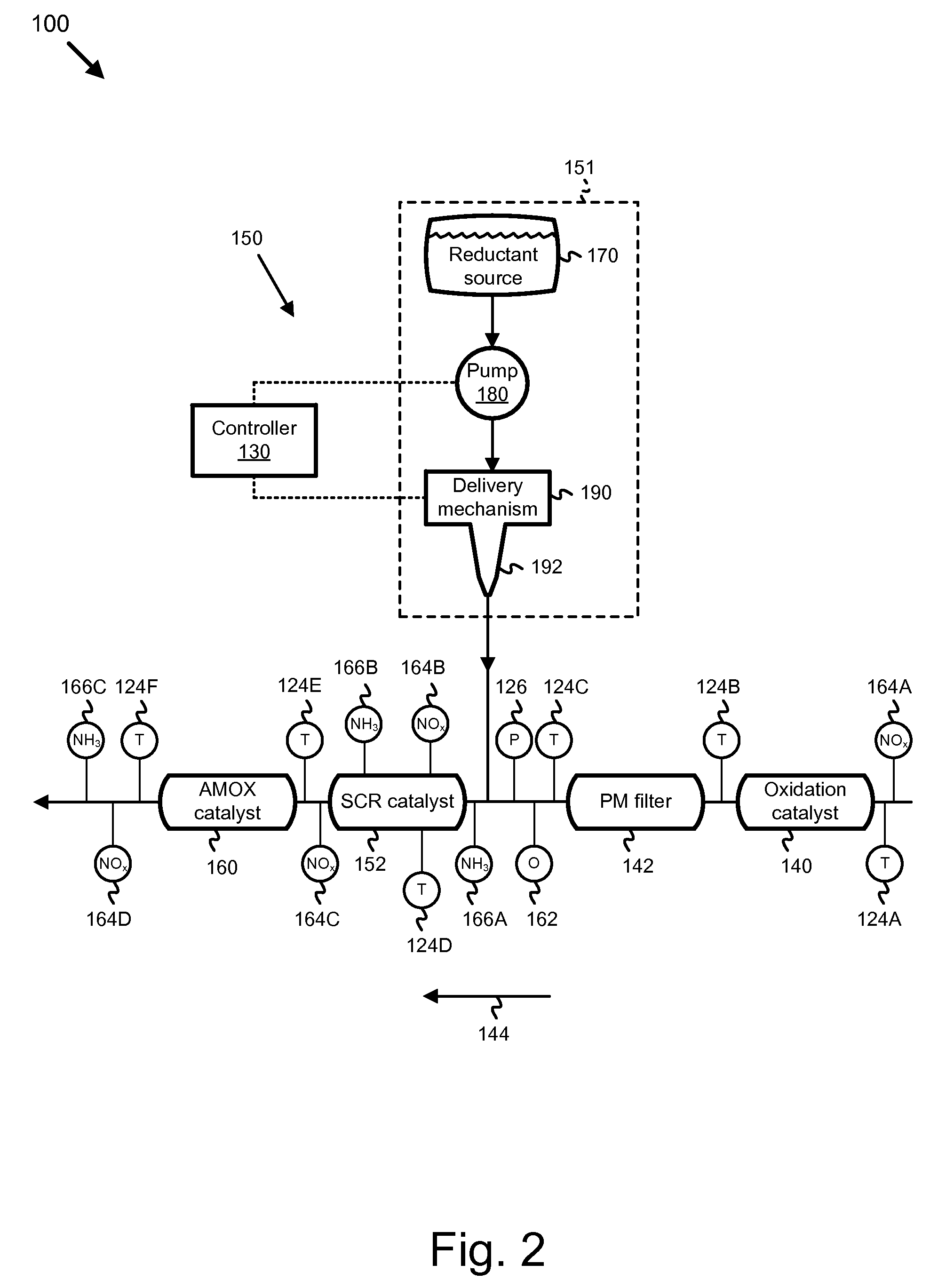
A reductant dosing control system, for use in a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system of a motor vehicle includes an input receiving a NOx feedback signal from an NOx sensor provided to the SCR system. A base dosing module calculates a required quantity of reductant to inject in front of a SCR catalyst of the SCR system based on the NOx feedback signal. The SCR catalyst has ammonia storage properties. An output signals a reductant metering mechanism to periodically or continuously inject excess reductant based on the required quantity of reductant.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
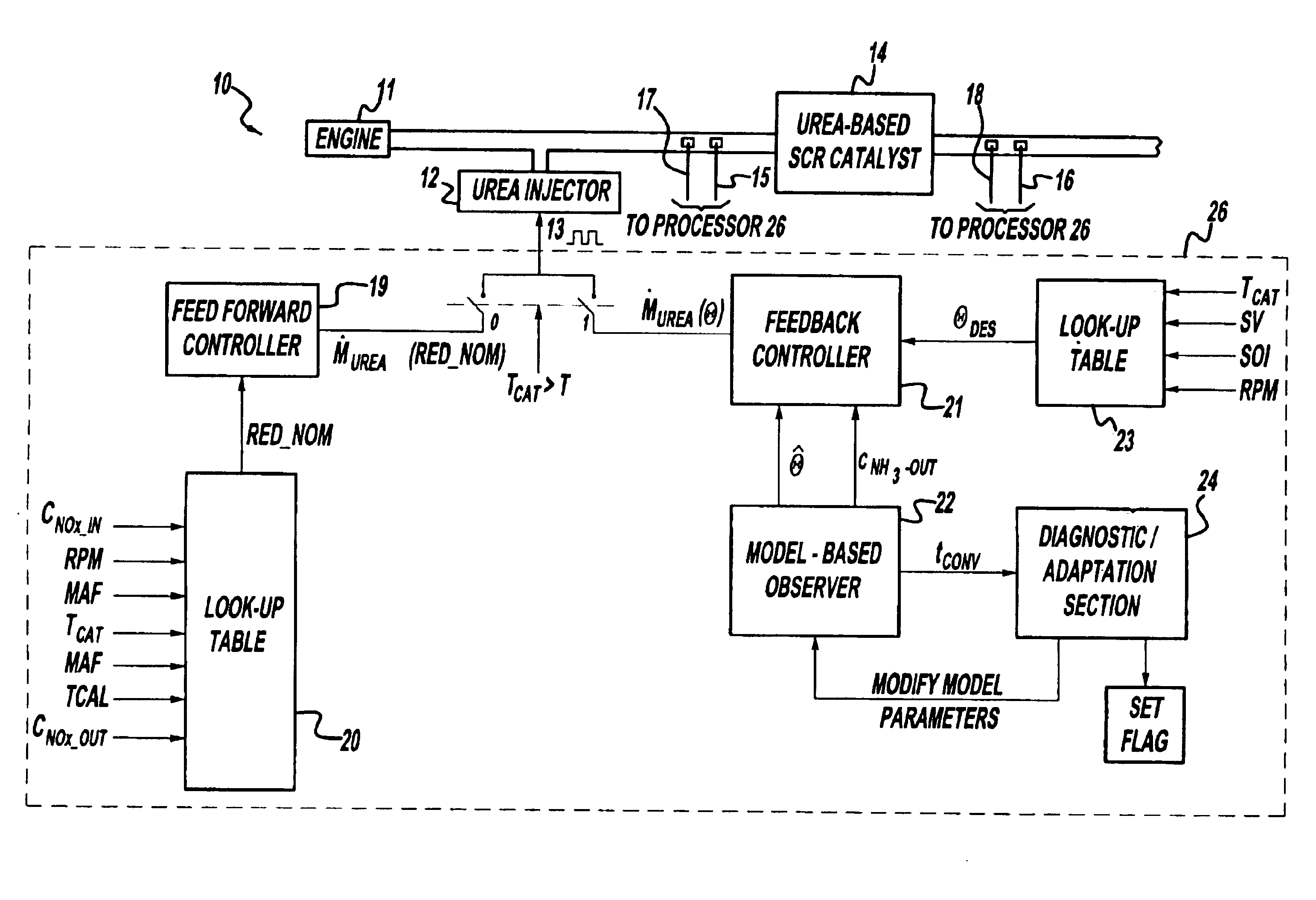
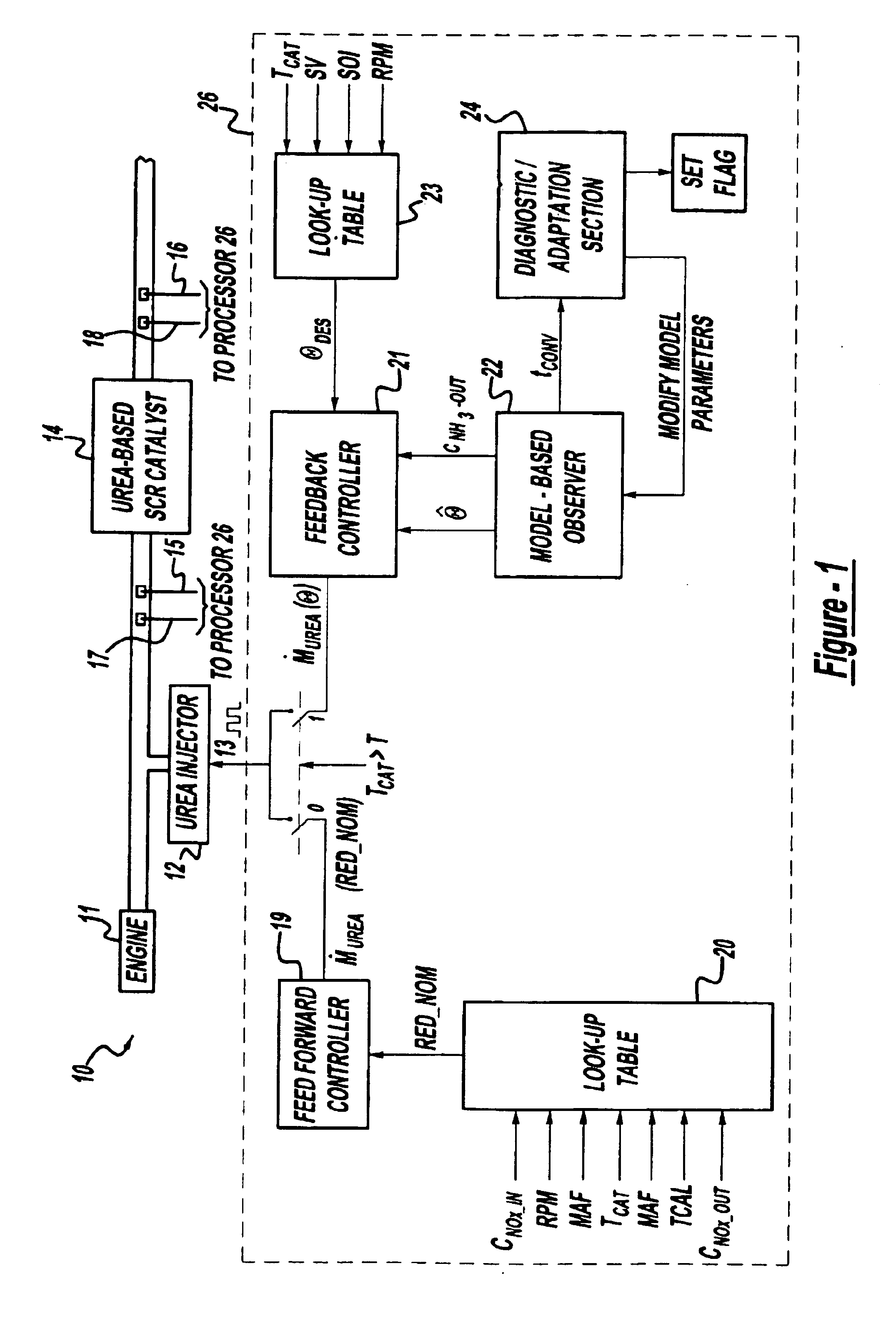
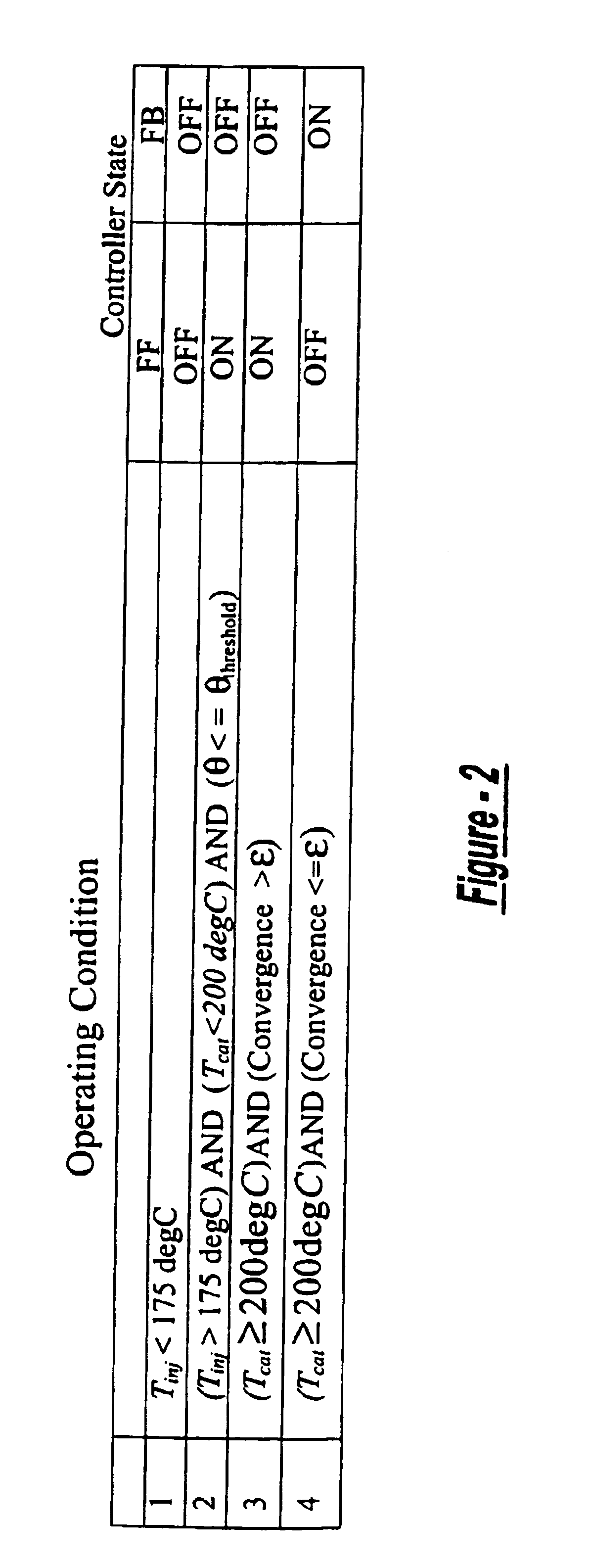
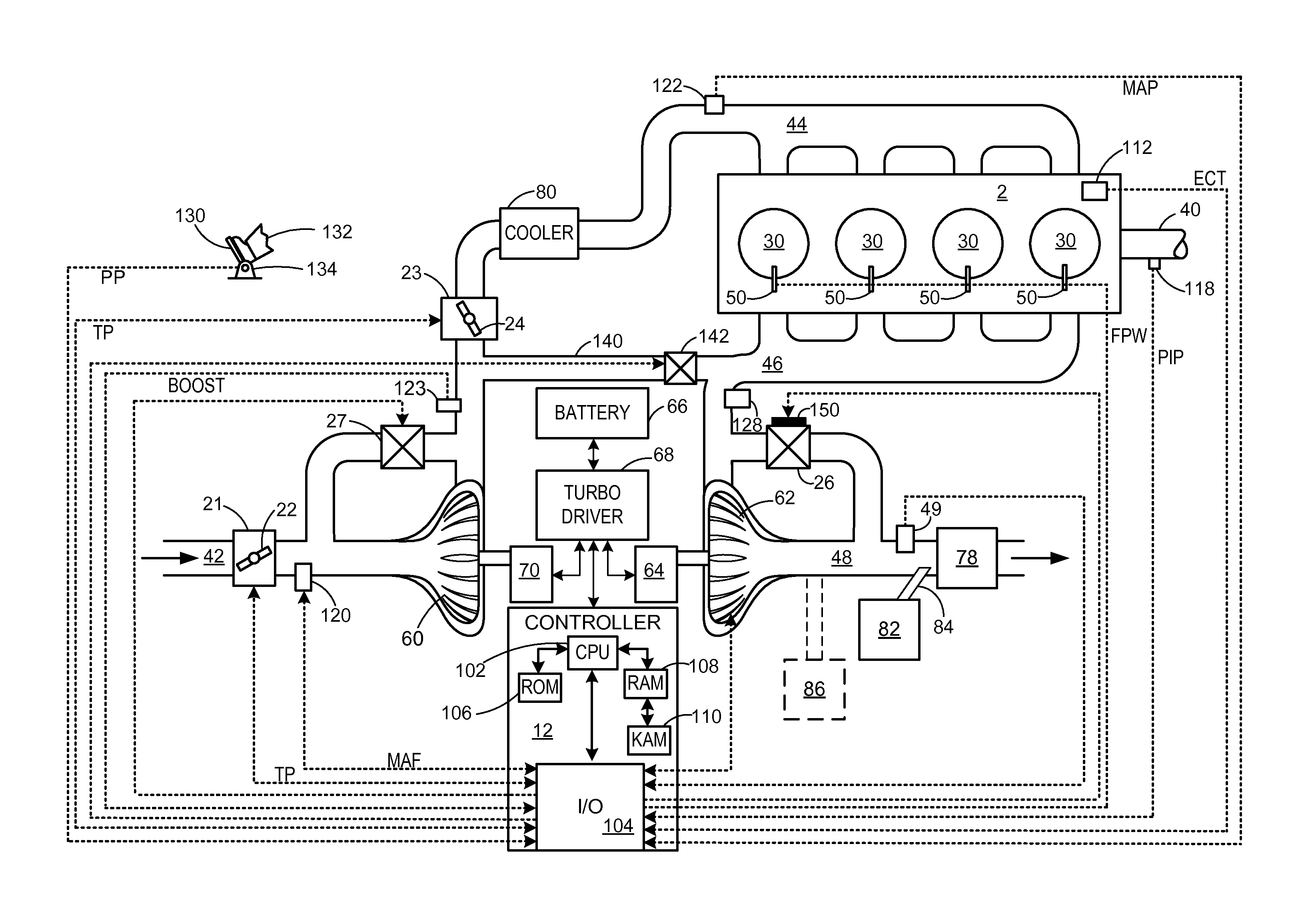
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS7093427B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesAuxillariesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as sulfur poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System for controlling the urea supply to SCR catalysts
ActiveUS20060130458A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusControl systemAmmonia storage
A reductant dosing control system, for use in a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system of a motor vehicle includes an input receiving a NOx feedback signal from an NOx sensor provided to the SCR system. A base dosing module calculates a required quantity of reductant to inject in front of a SCR catalyst of the SCR system based on the NOx feedback signal. The SCR catalyst has ammonia storage properties. An output signals a reductant metering mechanism to periodically or continuously inject excess reductant based on the required quantity of reductant.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6993900B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageDynamic models
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS6981368B2Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesDynamic modelsAmmonia storage
A method is presented for estimating an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a dynamic model of the catalyst. The model takes into account chemical and physical properties of the catalyst, such as catalyst volume, the number of available ammonia storage cites, adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as poisoning, thermal aging, and different catalyst operating temperatures, and generates the estimate based on a measured or estimated amount of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture upstream of the catalyst, an amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to facilitate NOx reduction, and on a measured value of NOx in an exhaust gas mixture downstream of the catalyst. The estimated ammonia storage amount is then used to control the amount of reductant injected into the catalyst to maintain desired ammonia storage amount such that maximum NOx conversion efficiency coupled with minimum ammonia slip are achieved.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas aftertreatment systems
InactiveUS20070137181A1Accurate estimateImprove NOx conversion efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAmmonia storageExhaust fumes
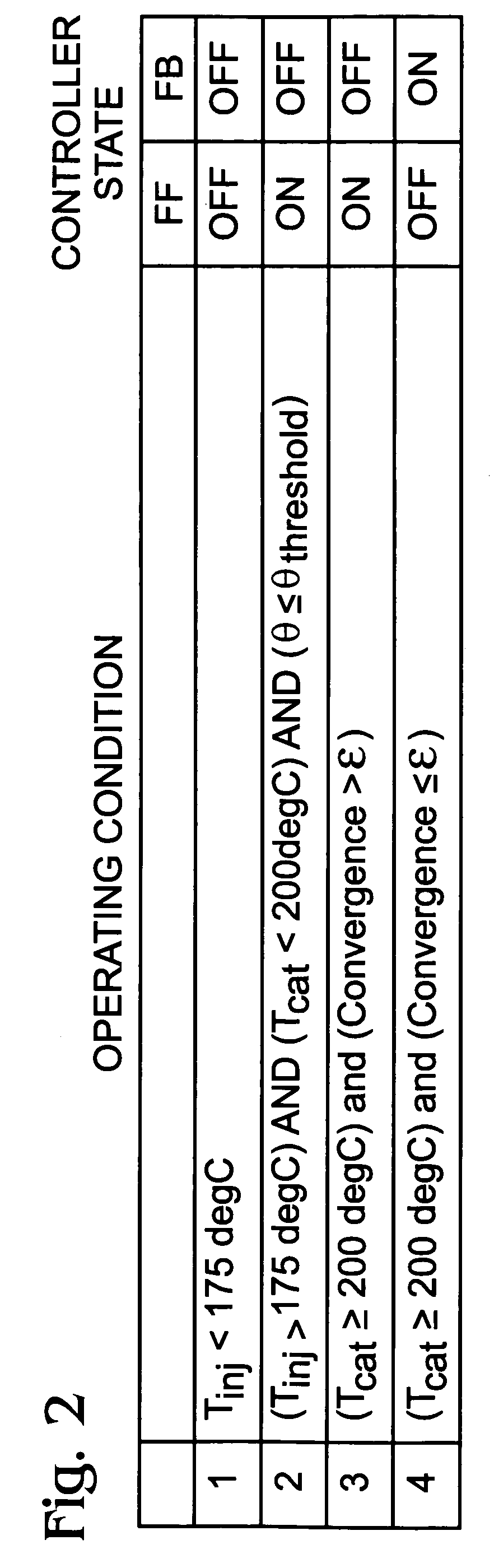
A method are presented for monitoring an amount of ammonia stored in a urea-based SCR catalyst based on a response of a sensor coupled downstream of the catalyst to a periodic desorbtion of a small amount of ammonia. The sensor could be an ammonia sensor, or a NOx sensor whose signal is sensitive to presence of both NOx and ammonia. The method can be performed at engine start to establish initial ammonia storage amount, or, alternatively, to adjust ammonia storage amounts or diagnose degradation when NOx conversion efficiency of the catalyst is below a predetermined value.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
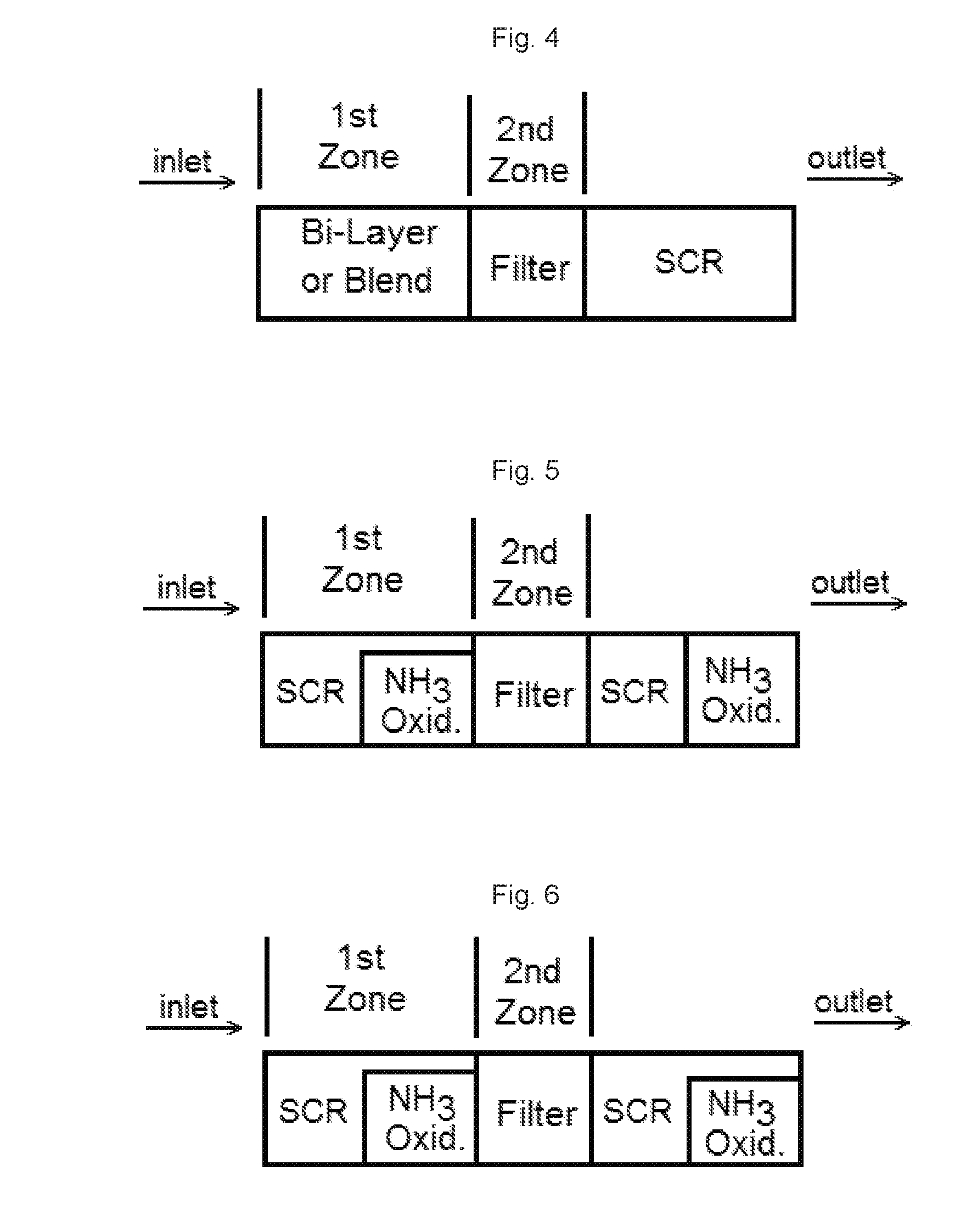
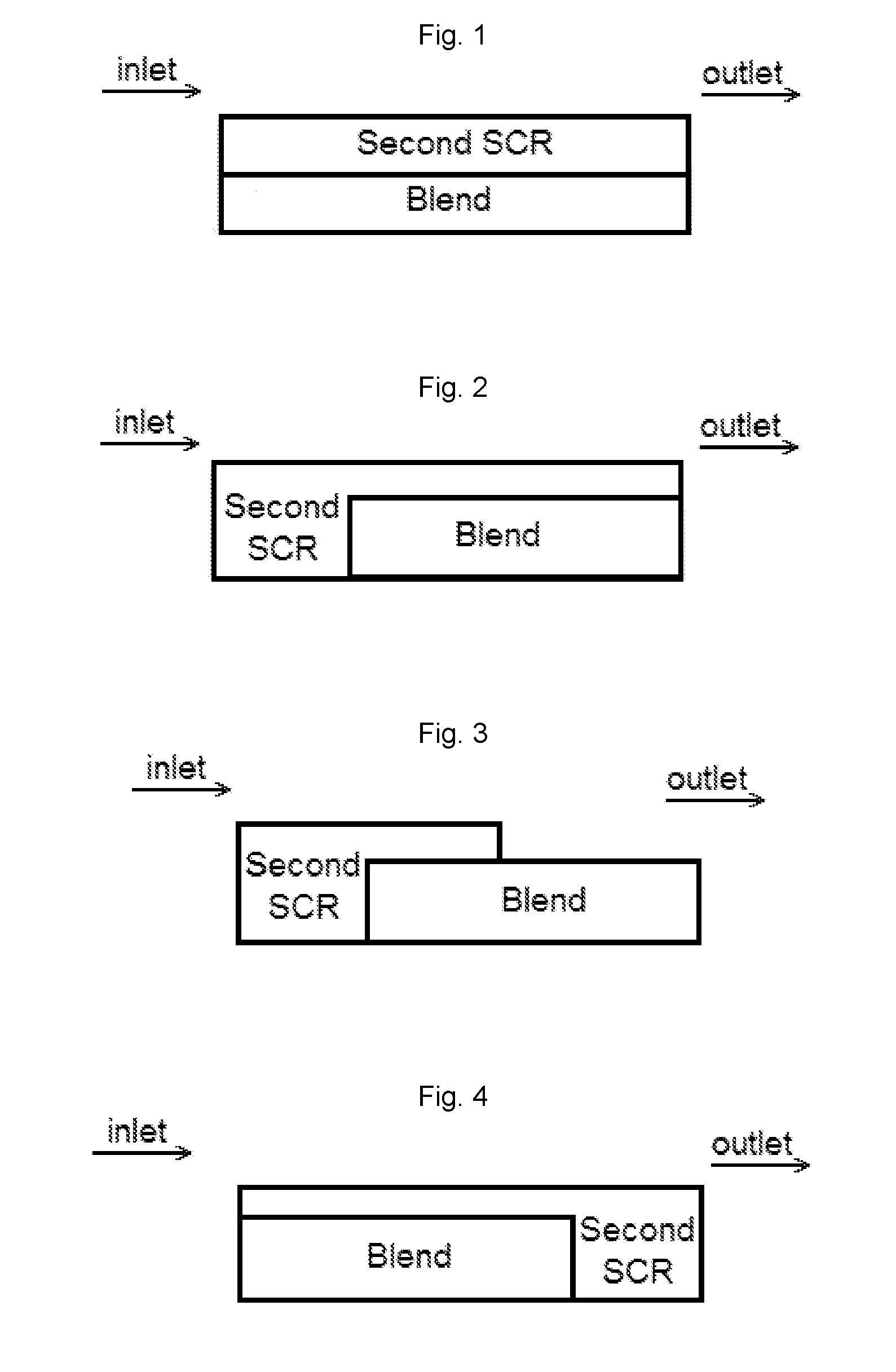
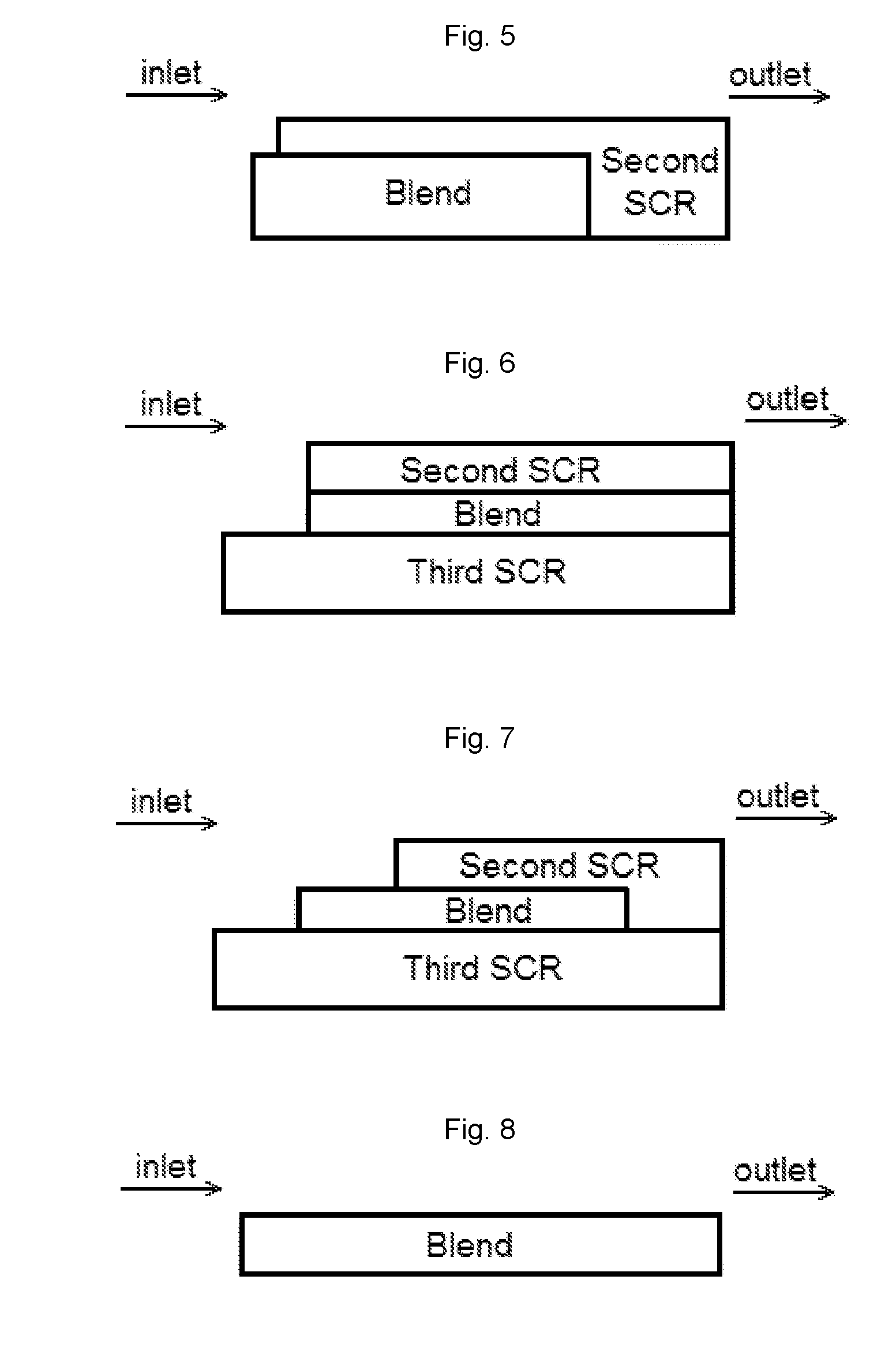
Ammonia slip catalyst designed to be first in an scr system
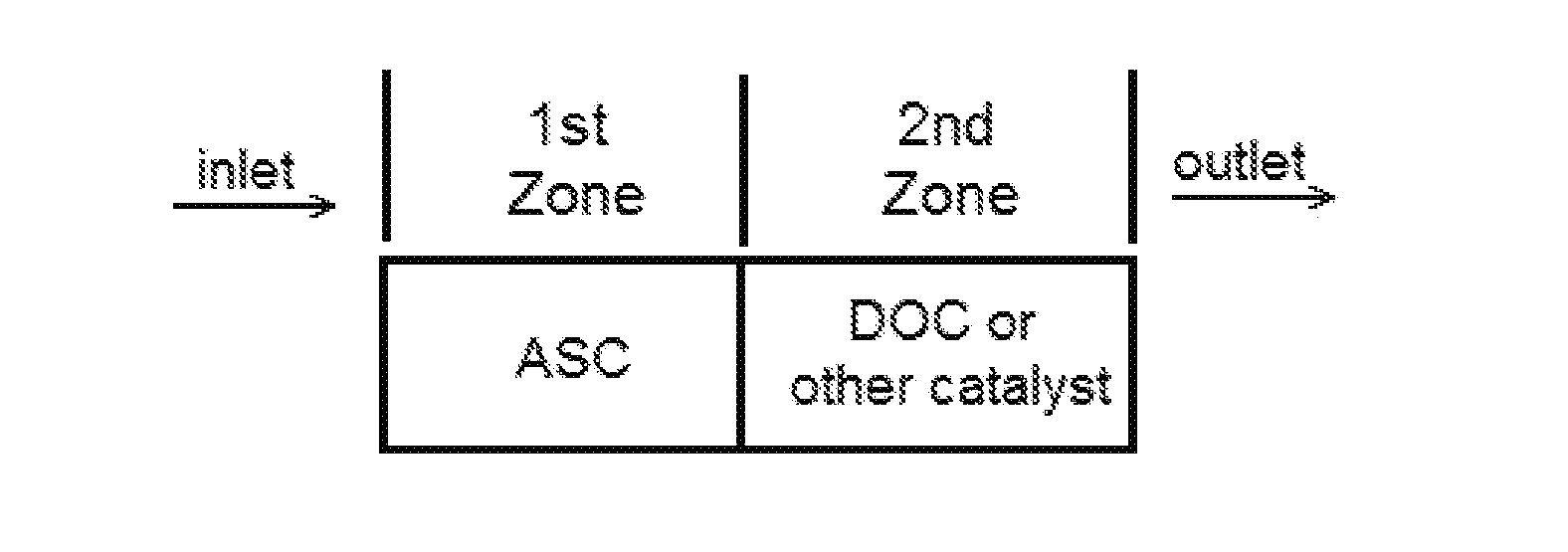
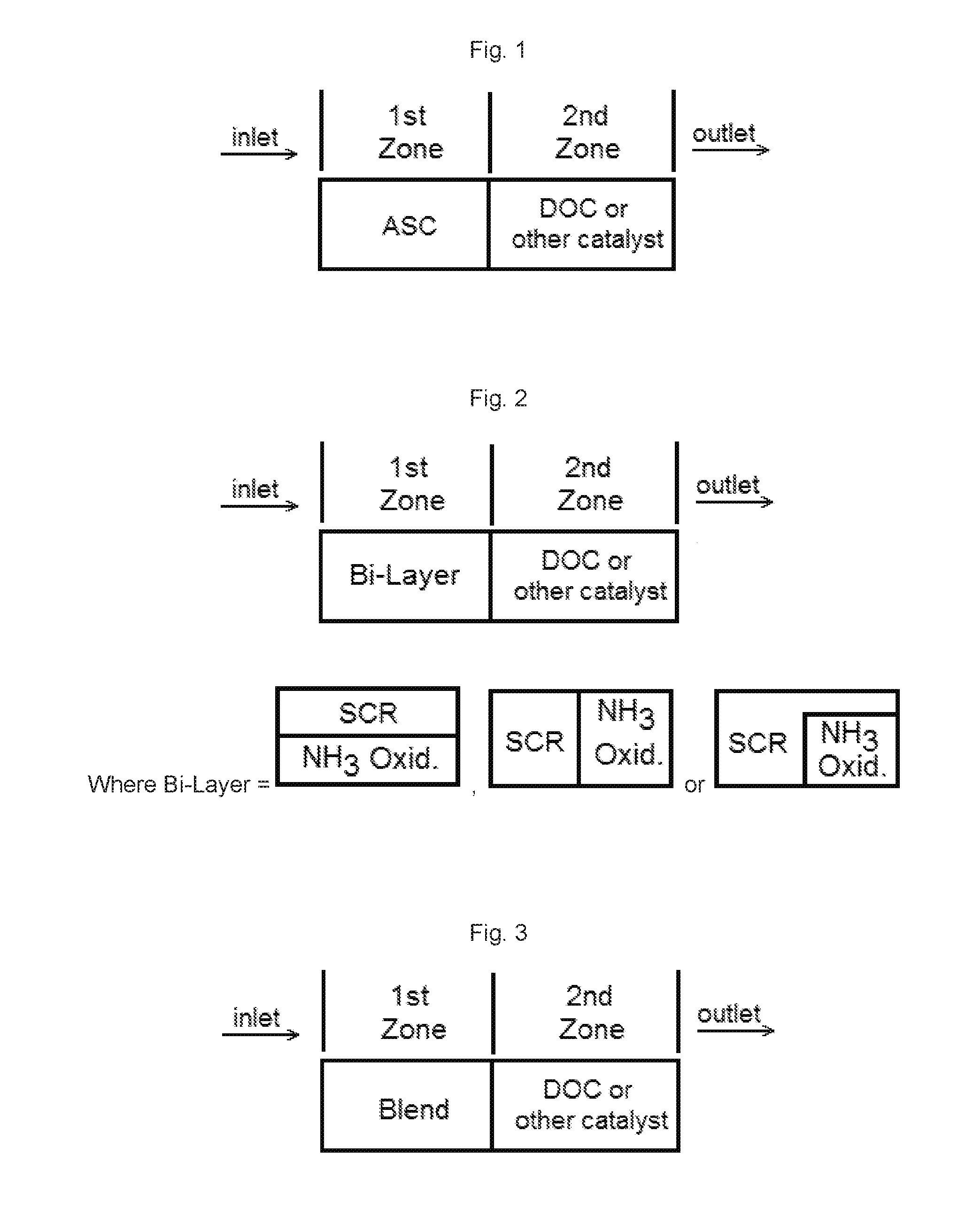
Catalyst articles having an ammonia slip catalyst (ASC) comprising a blend of platinum on a support with low ammonia storage and a first SCR catalyst, and a second catalyst, such as a diesel oxidation catalyst, a diesel exotherm catalyst (DEC), a NOx absorber, a selective catalytic reduction / passive NOx adsorber (SCR / PNA), a cold-start catalyst (CSC) or a three-way catalyst (TWC) are disclosed. The catalyst articles can also contain one or two additional SCR catalysts. The catalysts can be present in one of various configurations. The catalytic articles are useful for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx in exhaust gases and in reducing the amount of ammonia slip. Methods of using the catalytic articles in an SCR process, where the amount of ammonia slip is reduced, are also described.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Ammonia process flue gas treatment method for acidic tail gas and device
ActiveCN103223292AIncreased self-concentrationGood desulfurization absorptionDispersed particle separationAmmonium sulfatesEnvironmental resistanceAmmonia storage
The invention relates to an ammonia process flue gas treatment method for acidic tail gas. The method includes the steps of: 1) controlling the sulfur dioxide concentration of tail gas entering an absorption tower at a level of less than or equal to 30000mg / Nm<3>; 2) arranging process water in an absorption tower entrance flue or in the absorption tower or cooperating with a ammonium sulphate solution to perform spray cooling; 3) disposing an oxidation section in the absorption tower, setting an oxidation distributor at the oxidation section to achieve oxidation of a desulfurized absorption liquid; 4) arranging an absorption section in the absorption tower, utilizing an absorption liquid distributor in the absorption section to realize desulfurization spray absorption by an ammonia-containing absorption liquid, which is fed through an ammonia storage groove; 5) arranging a water washing layer at an absorption section upper part in the absorption tower, washing the absorption liquid in the tail gas by the water washing layer and reducing the absorption liquid escape; and 6) setting a demister at the upper part of the water washing layer in the absorption tower to control the mist drop content in the purified tail gas. Employment of the Claus sulfur recovery and ammonia process desulfurization integrated desulfurization technology in the coal chemical industry can reduce the investment cost of after-treatment, the process can be simpler, and factory environmental protection treatment can form an intensive advantage.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW CENTURY JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
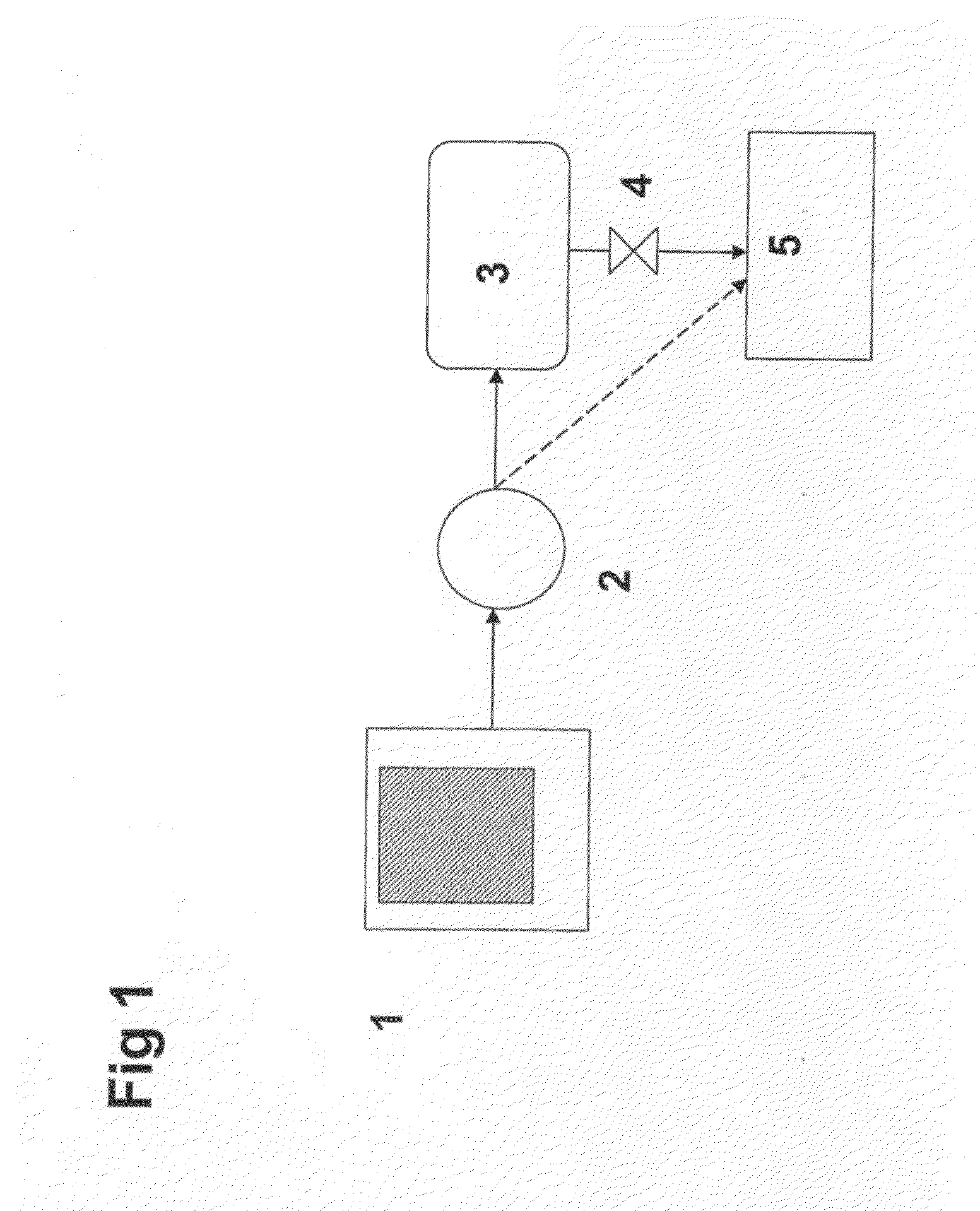
Adsorption based ammonia storage and regeneration system
One aspect of the invention relates to a device for storing ammonia for use in SCR on board a vehicle. The device comprises an adsorption bed with a high capacity for storing ammonia. The device can be designed to hold a long-lasting charge of ammonia comparable to a urea tank, but will not release substantial amounts of ammonia into the environment even if the device is accidentally ruptured. In one embodiment, the devices are charged at stationary locations. In another embodiment, the devices are charged by vehicle-mounted ammonia synthesis plants. The device facilitate the use of small ammonia synthesis plants that operate at low pressures and give low conversions. Preferably, the devices are operated through temperature swing adsorption.
Owner:EATON CORP
APPARATUS, SYSTEM, AND METHOD FOR REDUCING NOx EMISSIONS ON AN SCR CATALYST USING AMMONIA STORAGE AND SLIP CONTROL
ActiveUS20090272104A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageProcess engineering
Various embodiments of an apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for reducing NOx emissions using ammonia storage on an SCR catalyst. For example, according to one representative embodiment, an apparatus for reducing NOx emissions in an engine exhaust includes a NOx reduction target module that is configured to determine a NOx reduction requirement. The apparatus also includes an ammonia storage module that is configured to determine an ammonia storage modifier. An ammonia target module of the apparatus is configured to determine an ammonia addition requirement. The ammonia target module is communicable in data receiving communication with the ammonia storage module to receive the ammonia storage modifier, which is added to the ammonia addition requirement. The apparatus also includes a reductant target module that is configured to determine a reductant injection requirement that includes an amount of reductant added to the exhaust gas stream to achieve the ammonia addition requirement.
Owner:CUMMINS INTPROP INC
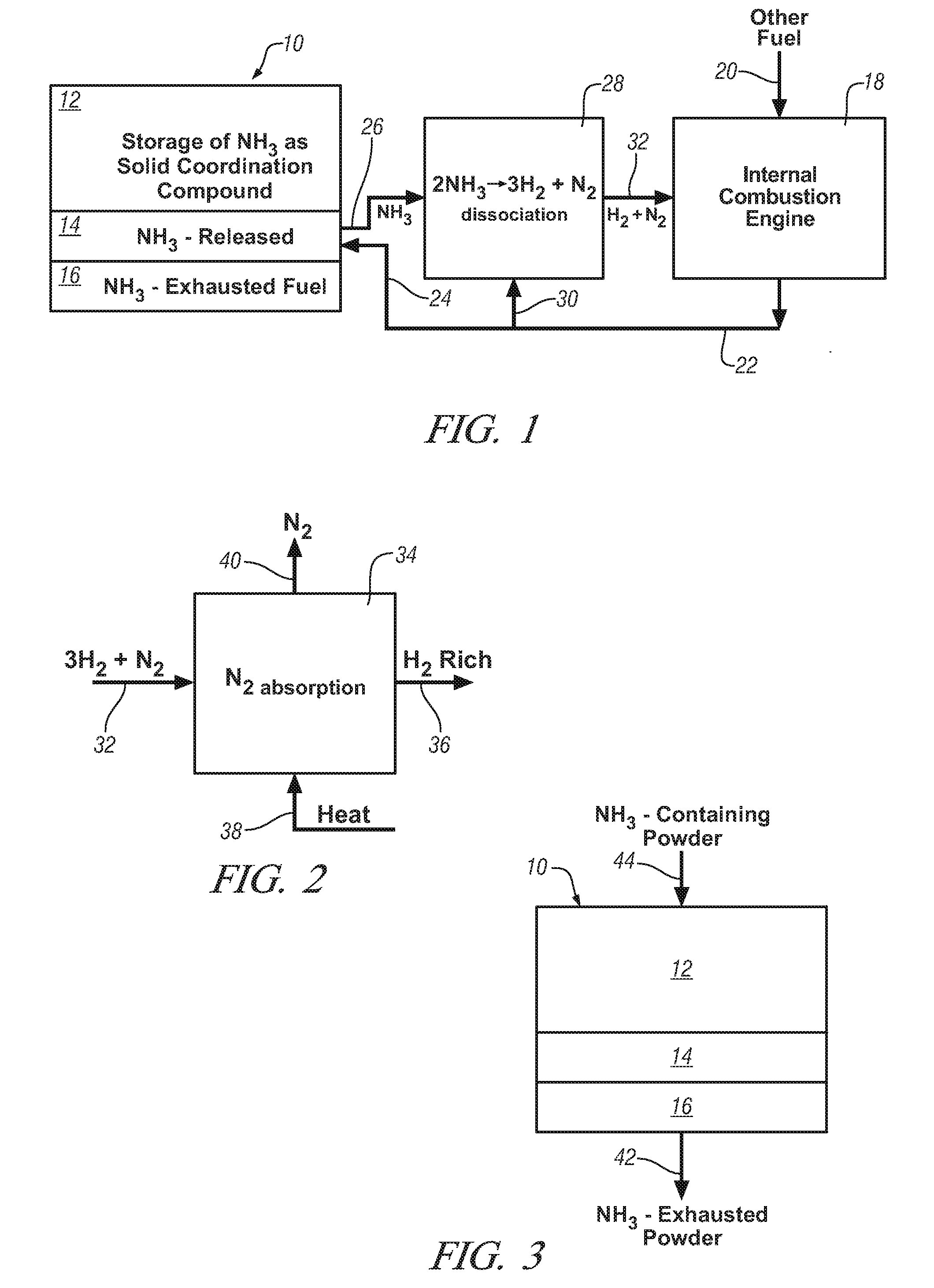
Use of an ammonia storage device in production of energy
An electric power generating unit comprising (i) an ammonia storage device in the form of a container comprising an ammonia absorbing and releasing salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals such as Li, K, Mg, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu or Zn, X is one or more anions selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, thiocyanate, sulphate, molybdate, phosphate, and chlorate ions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, Z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and n is the coordination number of 2 to 12. (ii) means for heating said container and ammonia absorbing and releasing salt for releasing ammonia gas and (iiia) a fuel cell for converting ammonia directly into electric power; or (iiib1) a reactor for dissociating ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen and (iiib2) a fuel cell for converting hydrogen into electric power.
Owner:AMMINEX
Flue gas-treating method and apparatus for treating acidic tail gas by using ammonia process
ActiveUS9370745B2Improve desulfurization efficiencyEffectively control the ammonia slip and the aerosol generationGas treatmentDispersed particle separationFlue gasAmmonia storage
Owner:JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION GRP INC
Ammonia storage for on-vehicle engine
InactiveUS20080241033A1Efficient and reversible processCobalt ammonia complexesCyanogen compoundsAmmonia storageExternal combustion engine
Ammonia is used as precursor source of hydrogen fuel in an on-vehicle internal combustion engine. Ammonia is stored as, for example, a ligand in an on-vehicle transition metal composition. Upon demand for hydrogen by the vehicle's engine control system, ammonia is expelled as a gas from some of the composition and the ammonia gas is dissociated into a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen and delivered as a fuel-containing mixture to the engine. In a preferred embodiment, the hydrogen is used as a supplement to gasoline as a fuel for engine operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Use Of An Ammonia Storage Device In Production Of Energy
InactiveUS20070207351A1Reactant parameters controlMagnesium halidesAlkaline earth metalAmmonia storage
An electric power generating unit comprising (i) an ammonia storage device in the form of a container comprising an ammonia absorbing and releasing salt of the general formula: Ma(NH3)nXz, wherein M is one or more cations selected from alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and transition metals such as Li, K, Mg, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu or Zn, X is one or more anions selected from fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, thiocyanate, sulphate, molybdate, phosphate, and chlorate ions, a is the number of cations per salt molecule, Z is the number of anions per salt molecule, and n is the coordination number of 2 to 12. (ii) means for heating said container and ammonia absorbing and releasing salt for releasing ammonia gas and (iiia) a fuel cell for converting ammonia directly into electric power; or (iiib1) a reactor for dissociating ammonia into hydrogen and nitrogen and (iiib2) a fuel cell for converting hydrogen into electric power is useful for large stationary energy producing facilities, but also for use for is useful for large stationary energy producing facilities, but also for use for small rechargeable and / or replaceable power supply units for micro-fabricated or miniaturized ammonia decomposition reactors for use in mobile units and portable devices may be used for large energy producing facilities, and by use of small rechargeable and / or replaceable ammonia storage decomposition reactors, it is also possible to provide energy for mobile units and portable devices.
Owner:AMMINEX
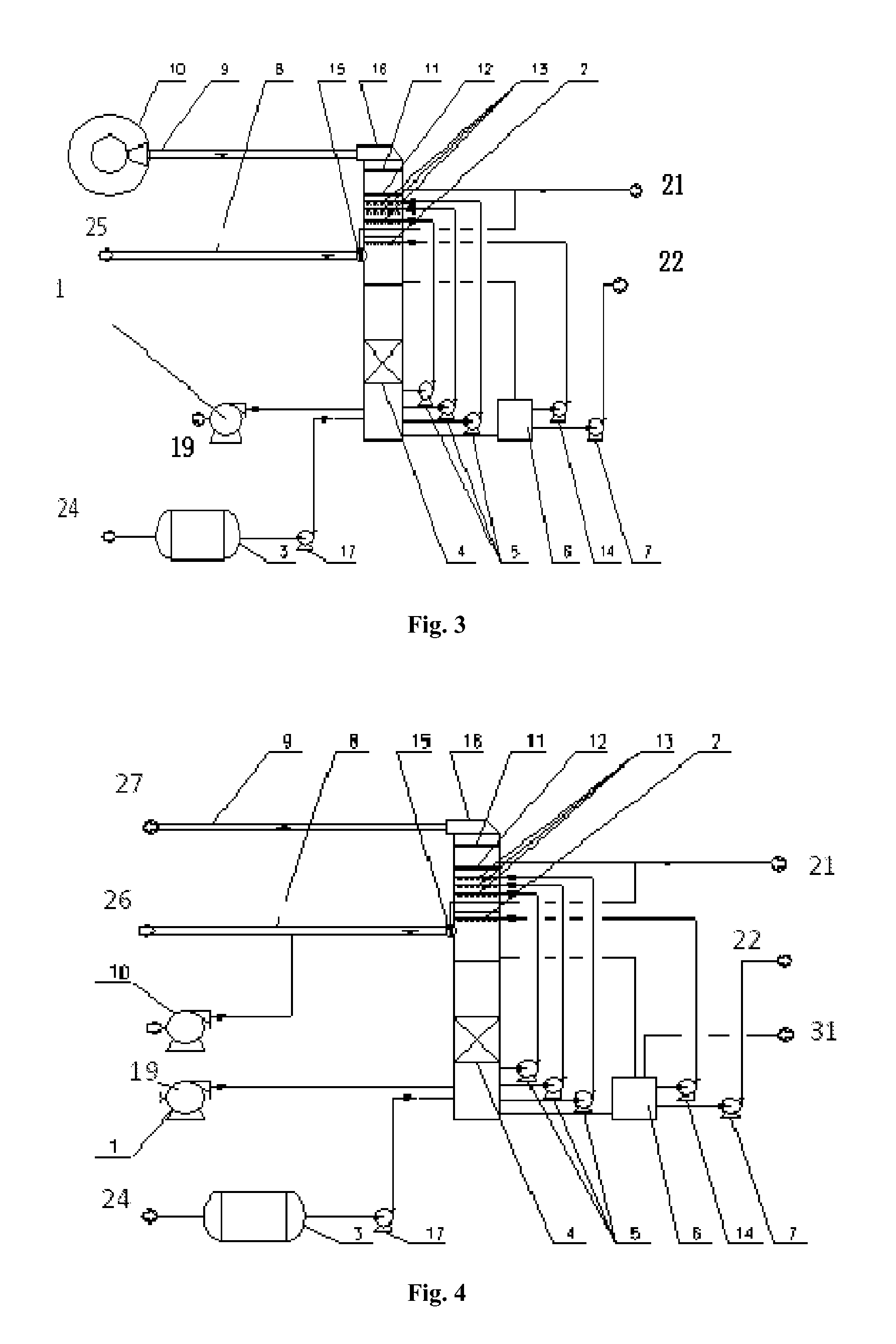
Method and device for ammonia storage and delivery using in situ re-saturation of a delivery unit
InactiveUS20100062296A1Partially be recoveredInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageAbsorbent material
Disclosed is a method for storing and delivering ammonia, wherein a first ammonia adsorbing / absorbing material having a higher vapor pressure at a given temperature than a second ammonia adsorbing / absorbing material is used as an ammonia source for said second ammonia adsorbing / absorbing material when said second adsorbing / absorbing material is depleted of ammonia by consumption, and a device for performing the method.
Owner:AMMINEX
Selective NOx catalytic reduction system including an ammonia sensor
InactiveUS20090133383A1Reduce hysteresisRapid responseInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageProcess engineering
An improved SCR system for controlling NOx levels in internal combustion engine exhaust, comprising a least one ammonia sensor disposed at an intermediate longitudinal location in an SCR catalyst and in communication with a System Control Module (SCM). The ammonia measurement permits calculation of ammonia storage on catalyst sites via a stored SCM algorithm. Locating the ammonia sensor midway in the catalyst allows for optimum control of NOx reduction and permits the portion of the catalyst downstream of the sensor to be treated as a slip catalyst, thus minimizing or eliminating the need for a second slip catalyst and housing, and reducing the size, volume, complexity, and cost of an SCR system. In-brick ammonia sensor permits the system to manage engine exhaust to a desired NOx conversion level and ammonia slip target value, thus minimizing the rate of consumption of ammonia while meeting required limits for NOx emissions.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
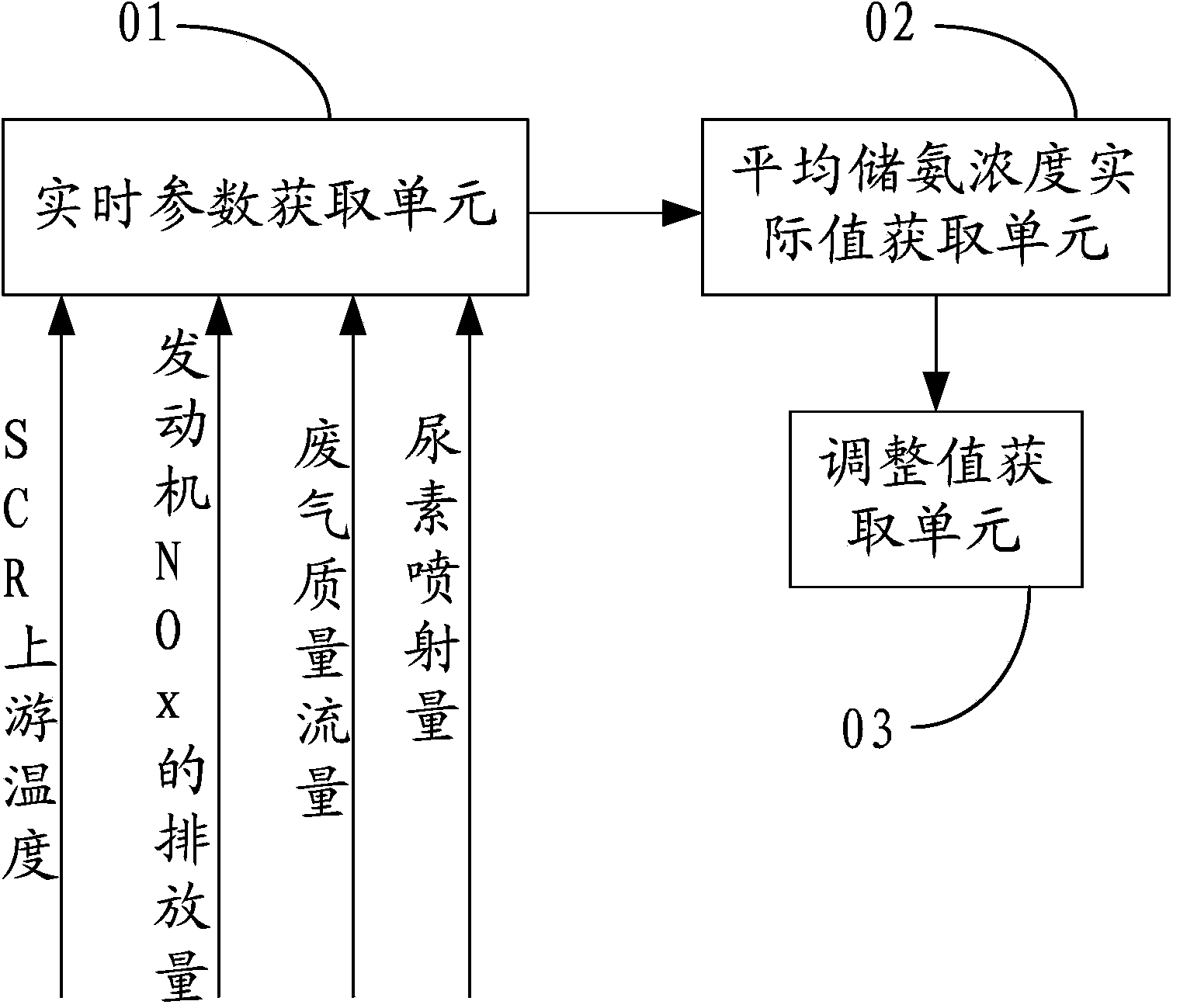
Urea injection control method based on real-time ammonia storage amount management for catalytic reduction of diesel
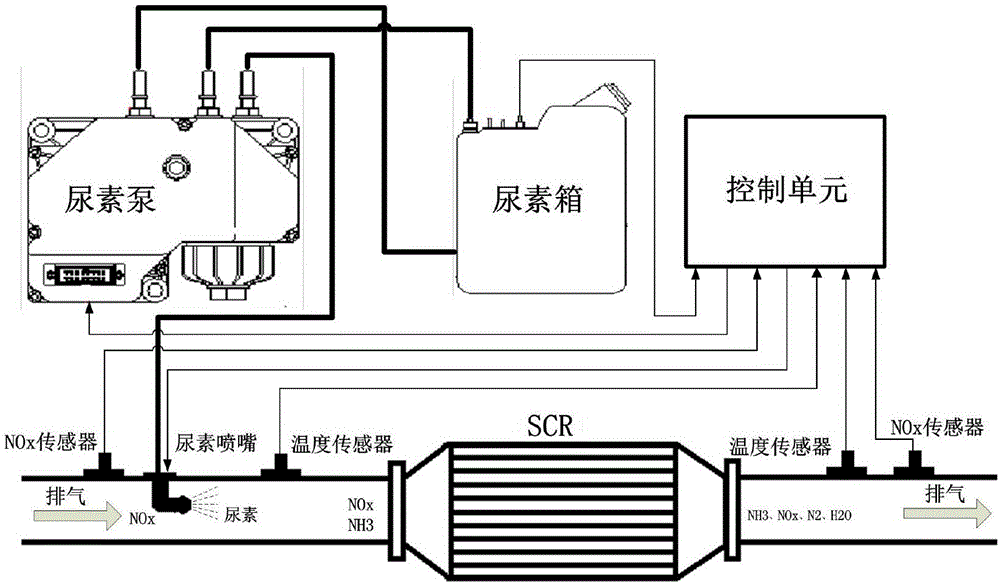
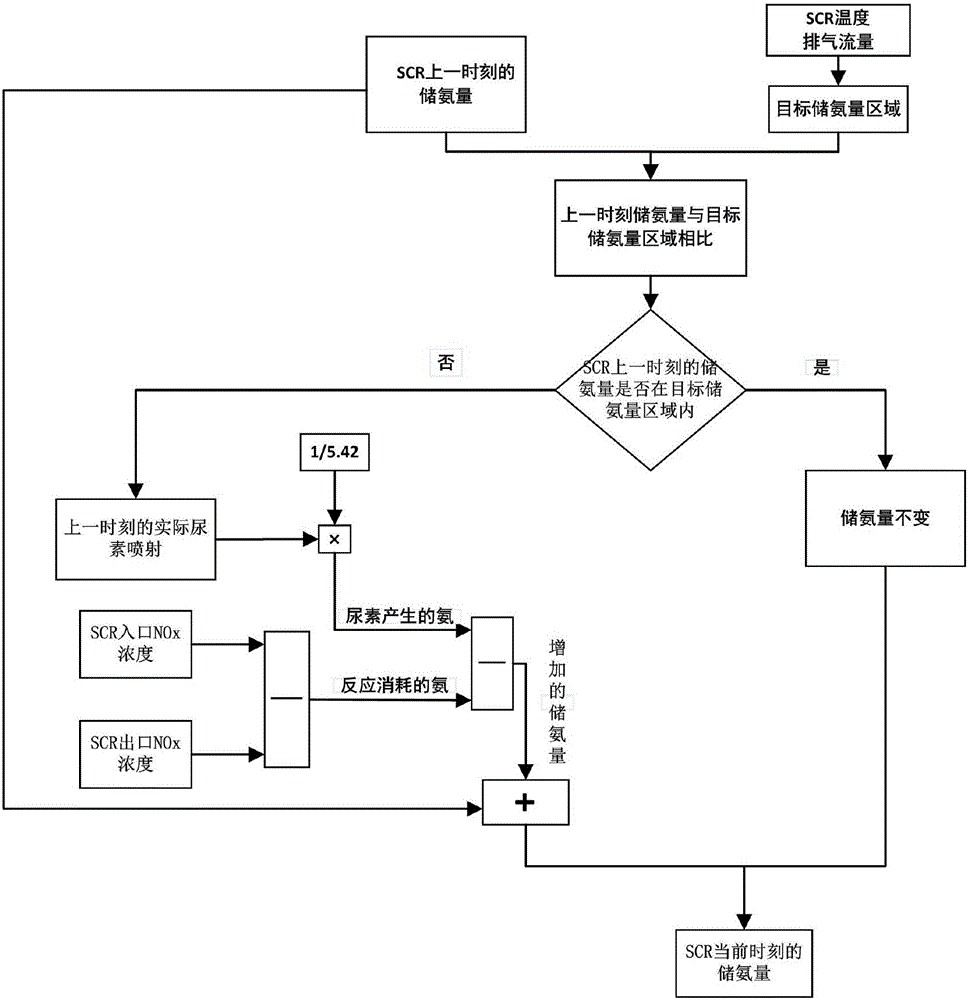
ActiveCN106837497AImprove conversion efficiencyEmission reductionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageRelease time
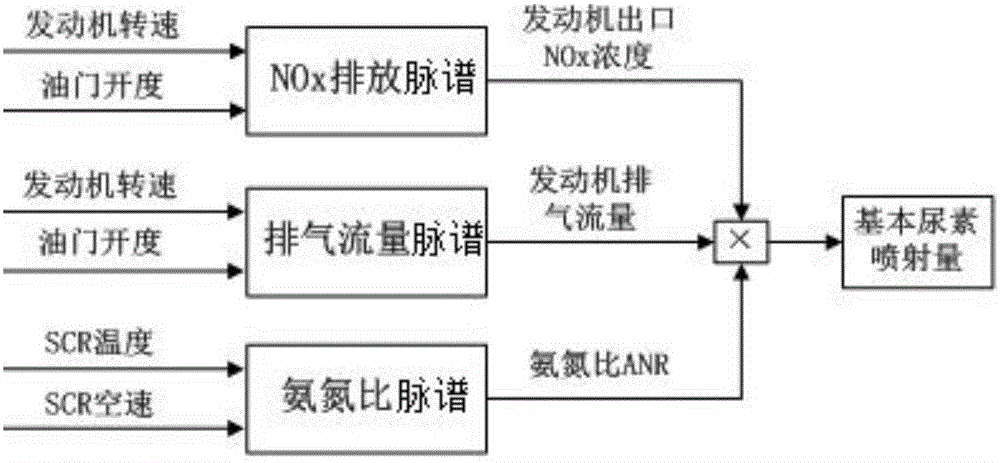
The invention discloses a urea injection control method based on real-time ammonia storage amount management for catalytic reduction of diesel. The method comprises the following steps: an ammonia storage amount calculation model is established according to ammonia mass conservation of an SCR system, and ammonia storage amount of SCR at the current moment in actual working condition is calculated; NOx emission map, an exhaust mass flow map and an ammonia-nitrogen ratio map of an engine are calibrated on the basis of steady-state experiments, and basic urea injection amount is calculated; a target ammonia storage amount area, an ammonia adsorption time constant and an ammonia release time constant are experimentally calibrated, and modified urea injection amount is calculated; urea injection is controlled in the actual working condition on the basis of the sum of the basic urea injection amount and the modified urea injection amount, and slow urea injection and injection stopping are used for assistance under the working condition of sudden increase of exhaust temperature, so that the ammonia storage amount of the SCR at the current moment approaches the target ammonia storage amount area. NOx conversion efficiency in all working conditions of the SCR in aftertreatment of the diesel can be increased, and urea consumption and ammonia leakage are reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
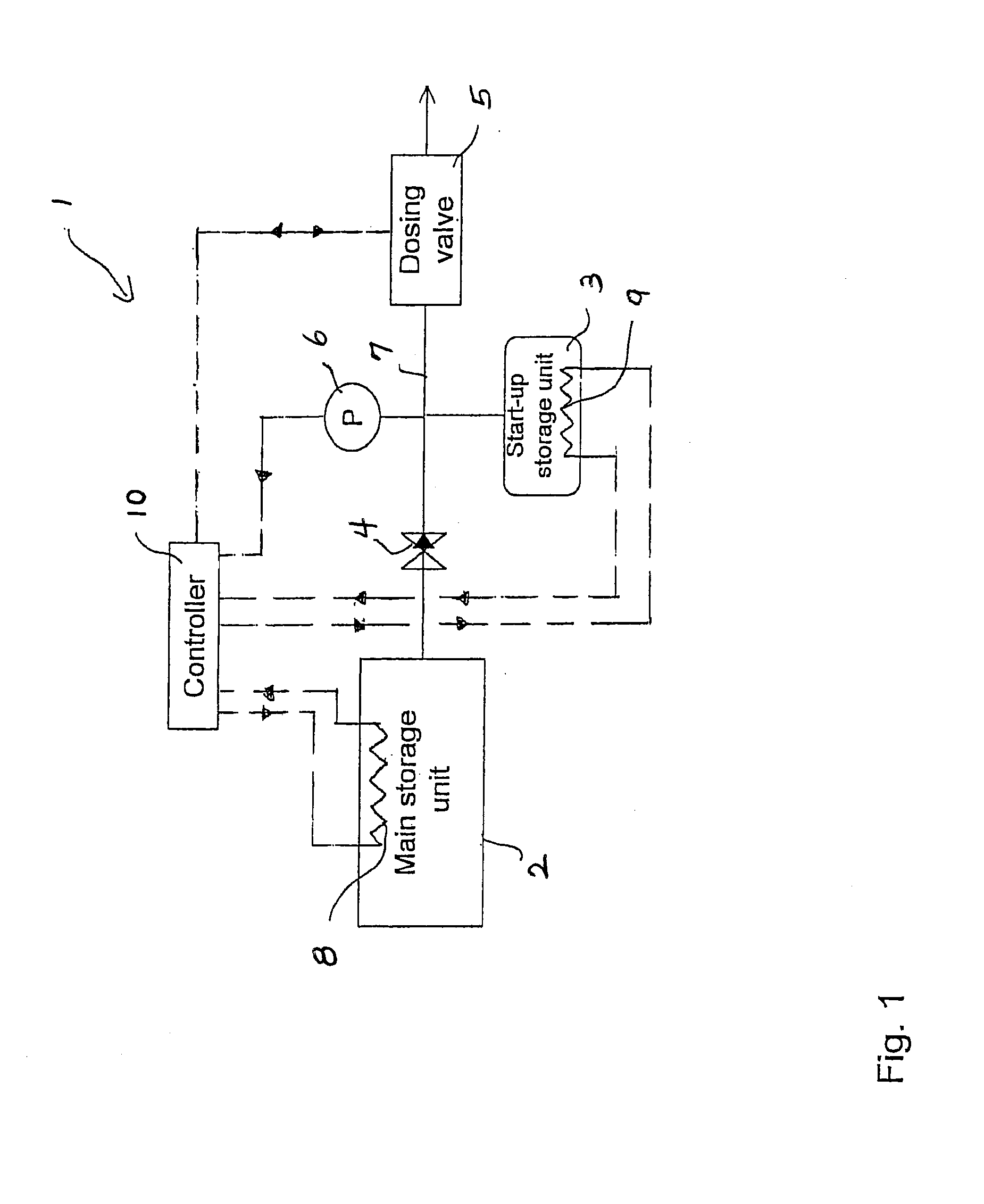
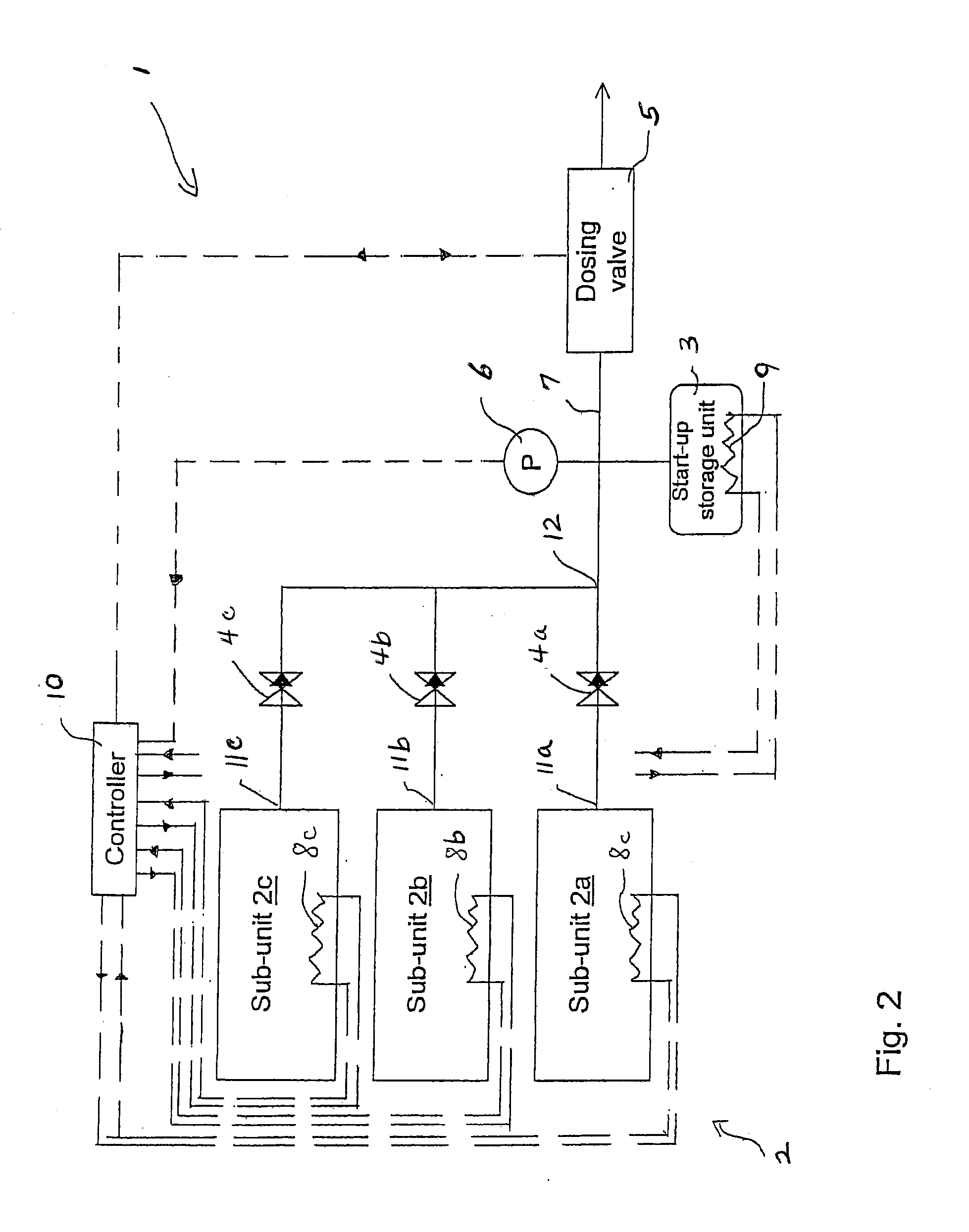
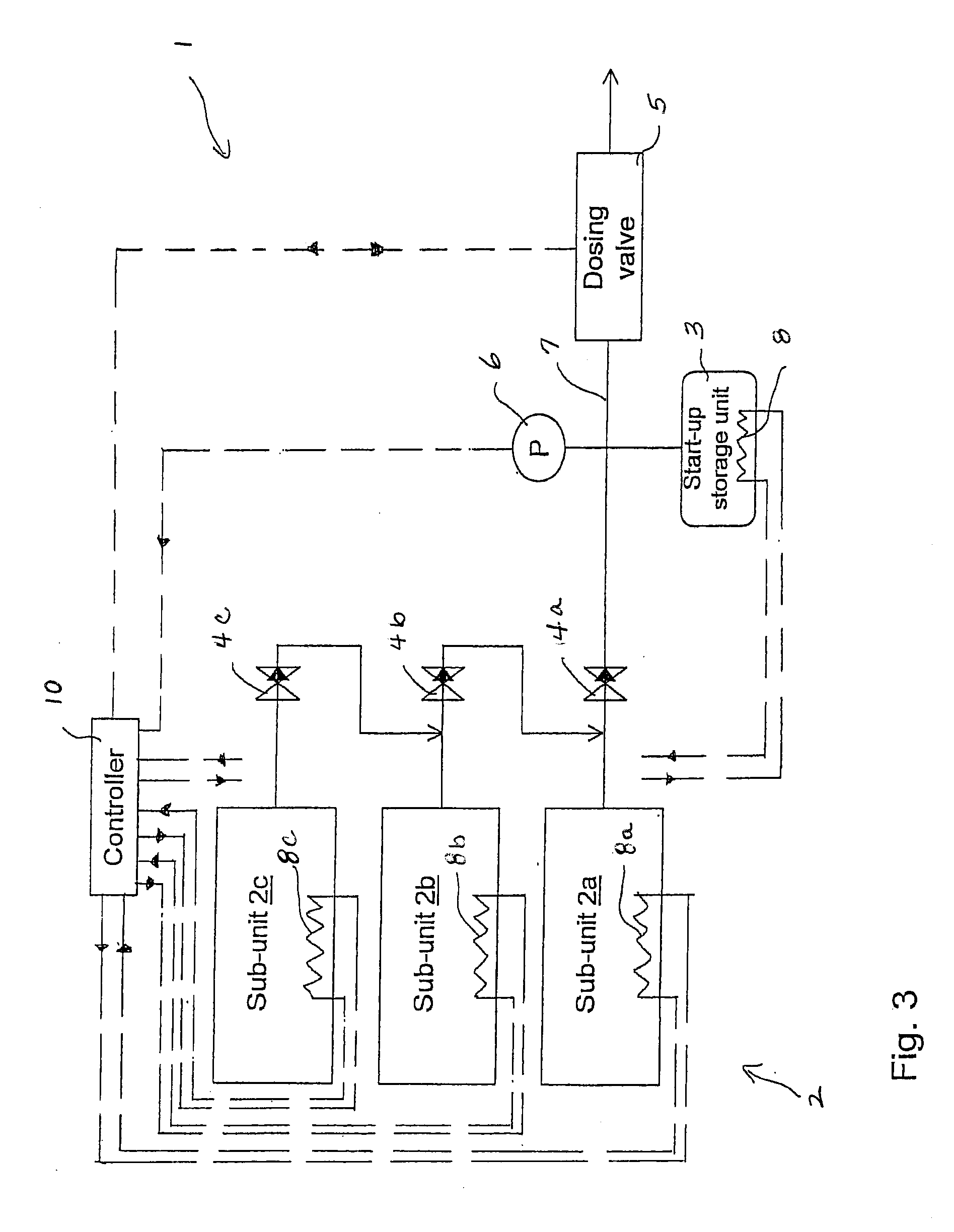
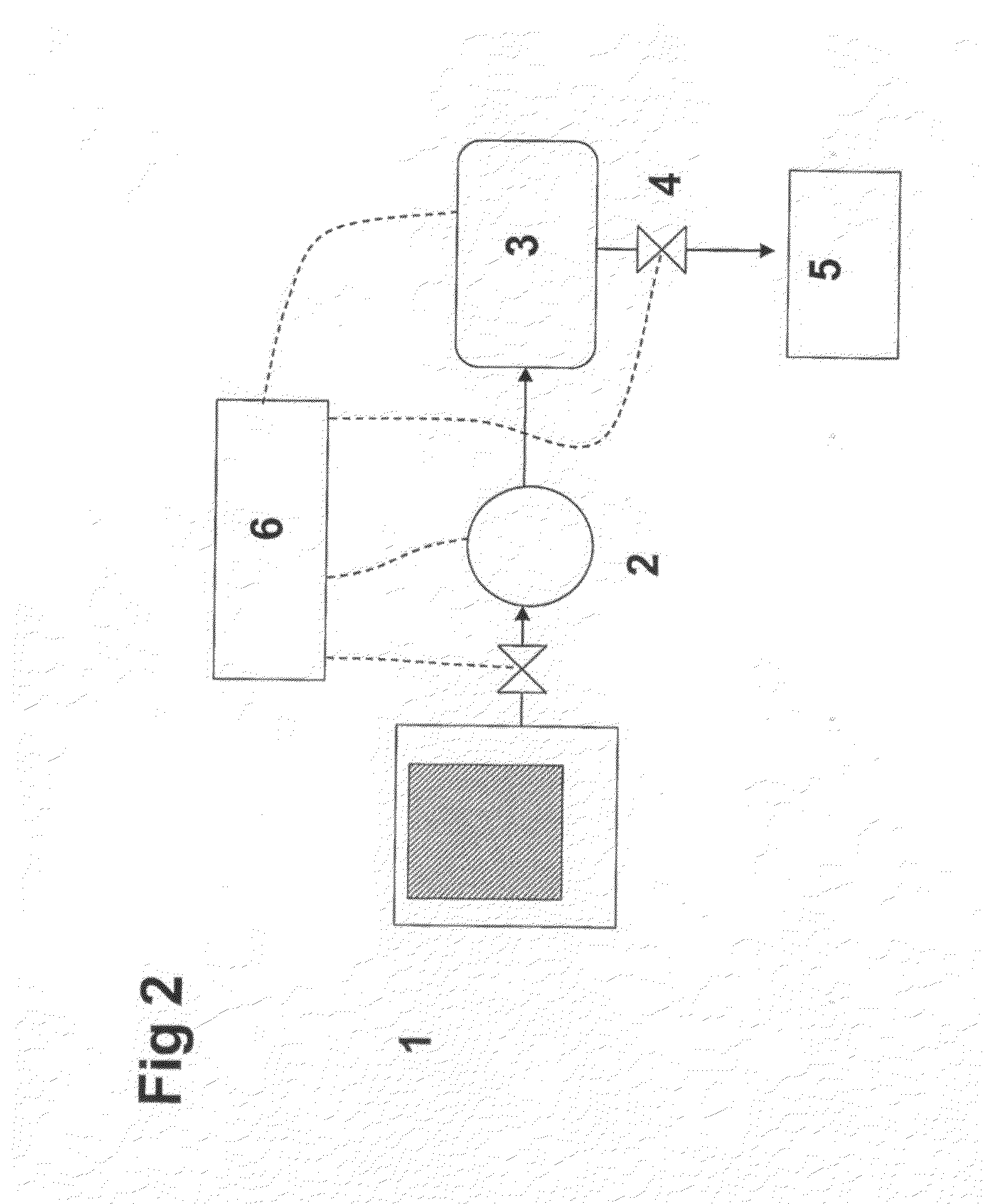
Release of Stored Ammonia at Start-Up
ActiveUS20100086467A1Demand for it variesPrevent backflowInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageGaseous ammonia
A system for storage and dosing of ammonia, including a solid ammonia storage material capable of binding and releasing ammonia reversibly by adsorption / absorption. The system is able to release ammonia gradually according to a demand that can vary over time with intermediate periods of no ammonia demand. A main storage unit and a start-up storage unit are provided. The storage units hold ammonia storage material. At least one one-way valve is provided via which the one main storage unit is in communication with the start-up storage unit. The one-way valve prevents any back-flow of ammonia from the start-up storage unit to the main storage unit. Heating devices are arranged to heat the main storage unit and the start-up storage unit separately to generate gaseous ammonia by thermal desorption from the solid storage material. A controller controls the heating power of the main storage unit and the start-up storage unit, thereby enabling ammonia release from at least one of the start-up and / or the main storage unit. A dosing valve controls ammonia flow from the storage units according to a demand.
Owner:AMMINEX EMISSIONS TECH
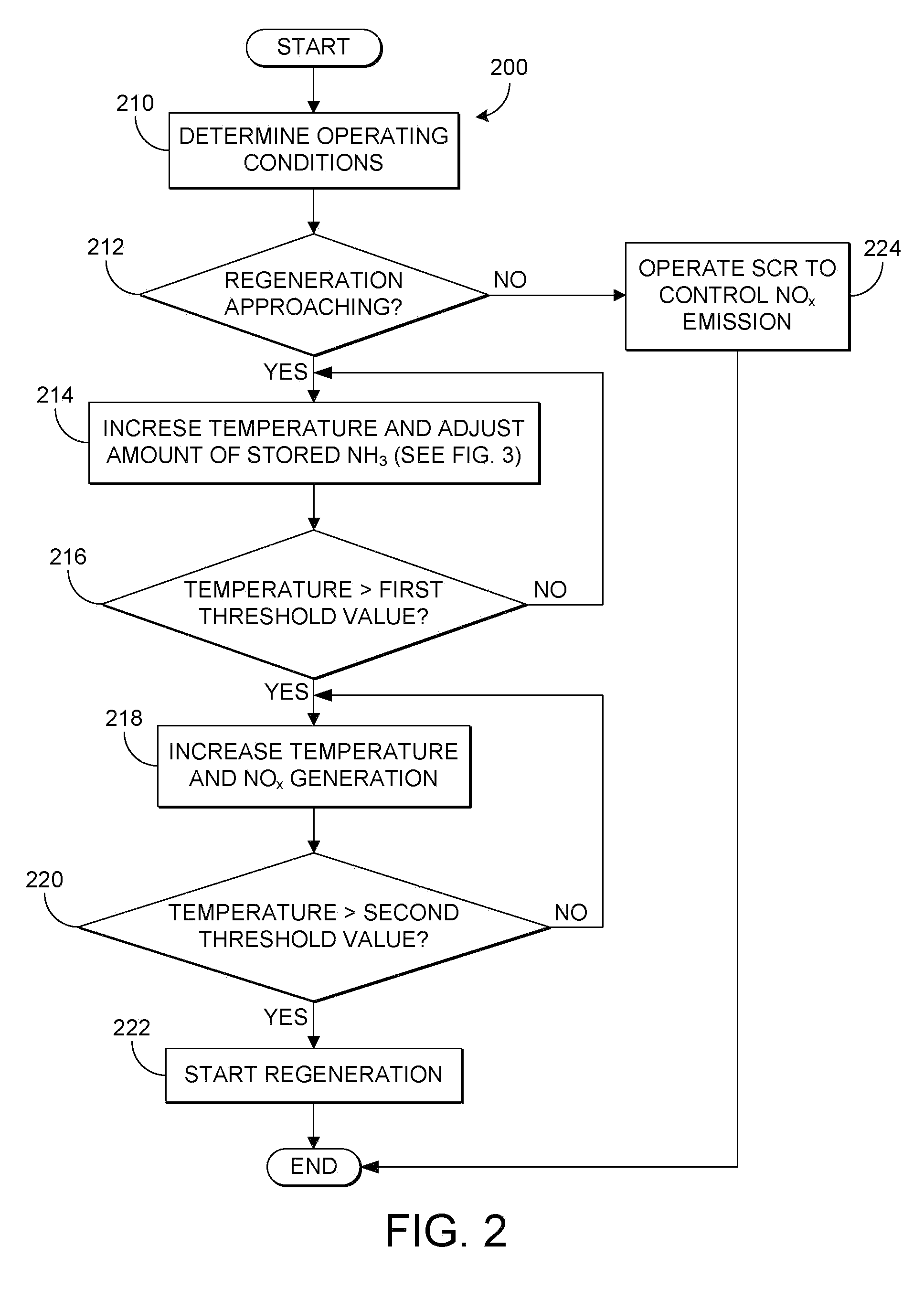
Scr catalyst heating control
ActiveUS20110023462A1Increase temperatureAccelerate emissionsElectrical controlSamplingAmmonia storageProcess engineering
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
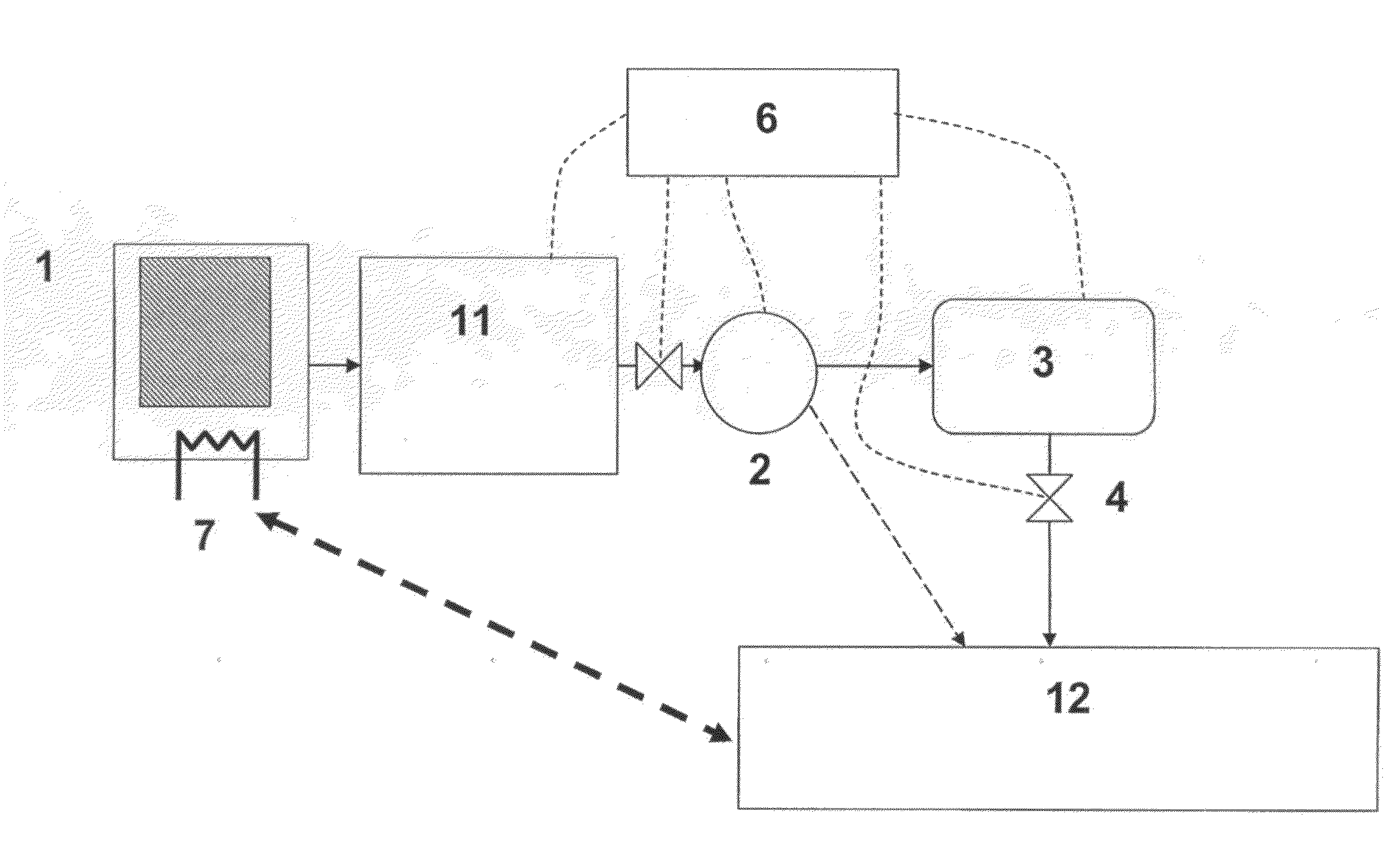
Method and device for safe and controlled delivery of ammonia from a solid ammonia storage medium
InactiveUS20100293927A1Facilitated releaseReduce the temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusGas phaseDesorption
Solid metal ammine complexes are applied for safe and high-density storage of ammonia to be released for use as reducing agent in selective catalytic reduction of NOx in exhaust gases. The compositional formula of the metal ammine complexes is M(NH3)nXz, where MZ+ represents one or more metal ions capable of binding ammonia, X represents one or more anions, n is the coordination number (from 2 to 12), and z the valency of the metal ion (and thus the total number of compensating anion charges). Ammonia is released by generating a reduced gas-phase pressure of ammonia inside the container, which is below the equilibrium desorption pressure of ammonia at the operating temperature of the storage material thus enabling the unit to be operated is a safe manner with lower operating temperature and pressure.
Owner:AMMINEX
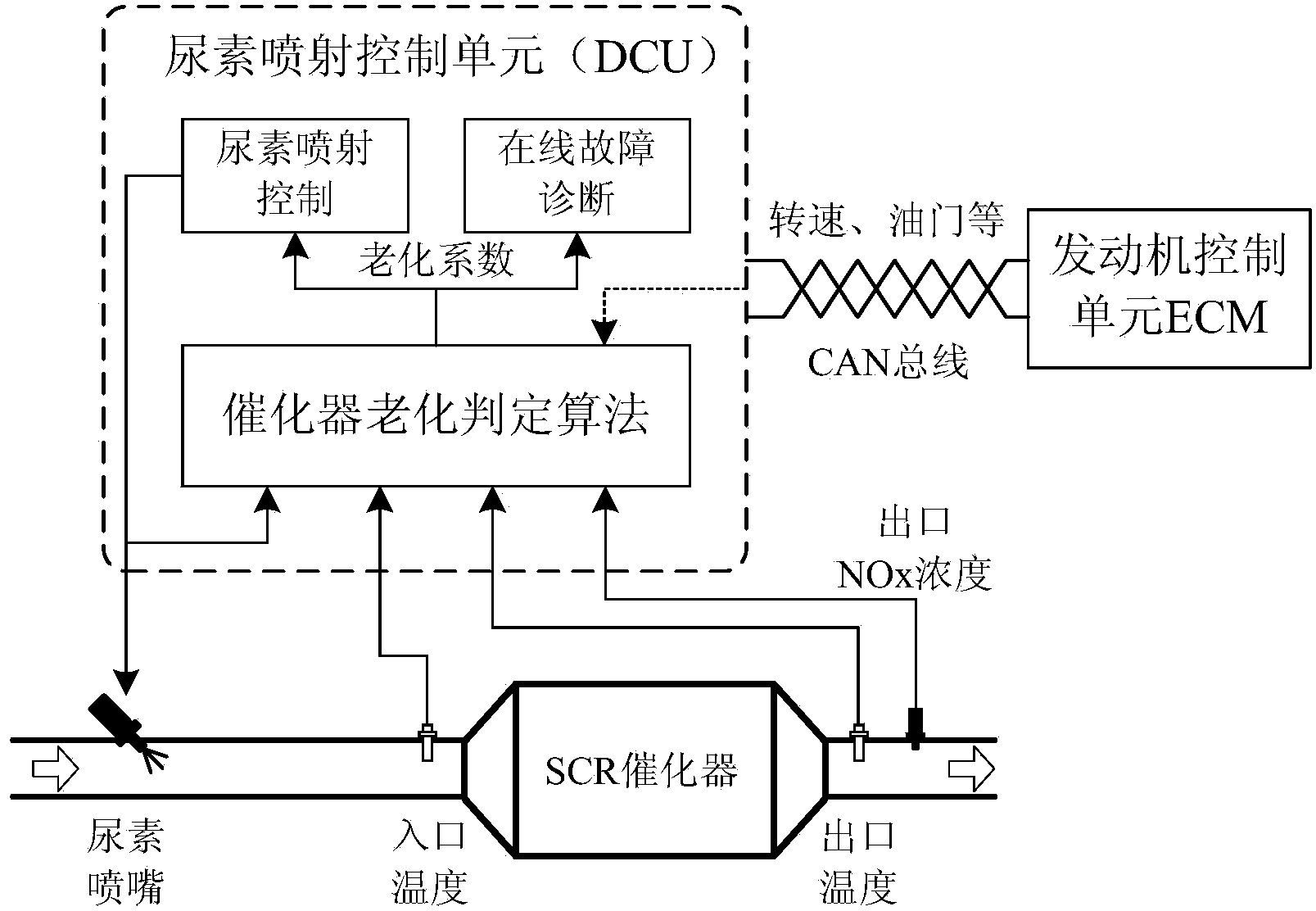
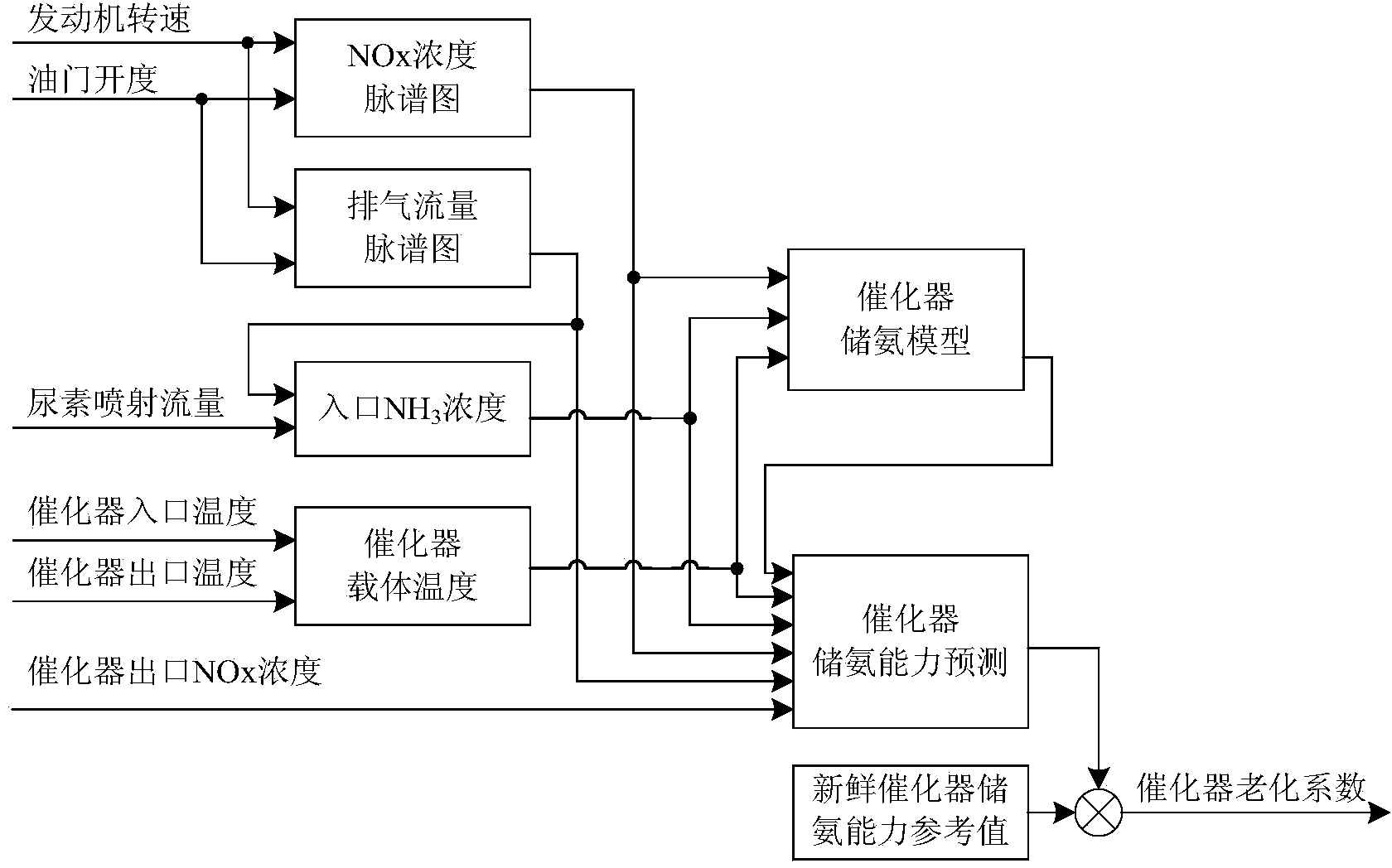
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst aging judgment method based on NOx feedback and ammonia storage prediction
ActiveCN104234802AInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust treatment electric controlAfter treatmentControl signal
The invention discloses an SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst aging judgment method based on NOx feedback and ammonia storage prediction. On the basis of the existing sensor and control signal of a Chinese Emission Standard IV / European Emission Standard IV diesel engine SCR tail gas after-treatment system, by predicting the theoretical ammonia storage level of an SCR catalyst in real time through acquired signals, obtaining the actual ammonia storage capacity prediction value(active coating surface active site density) of the catalyst in combination with catalyst outlet NOx feedback signals and comparing the prediction value with the theoretical reference value of a fresh catalyst, a quantized aging coefficient capable of measuring the aging degree of the catalyst is obtained. Catalyst aging degree judgment results can be directly used for urea water injection amount control of a urea injection unit and catalyst-related OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) fault diagnosis of an SCR system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ammonia slip catalyst with low n2o formation
PendingUS20160367975A1Improvement in N yieldImproving N yieldNitrous oxide captureMolecular sieve catalystsPlatinumAmmonia storage
Catalysts having a blend of platinum on a support with low ammonia storage with an SCR catalyst are disclosed. The catalysts can also contain one or two additional SCR catalysts. The catalysts can be present in one of various configurations. Catalytic articles containing these catalysts are disclosed. The catalytic articles are useful for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx in exhaust gases and in reducing the amount of ammonia slip. Methods for producing such articles are described. Methods of using the catalytic articles in an SCR process, where the amount of ammonia slip is reduced, are also described.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Method for metering ammonia into the exhaust-gas region of an internal combustion engine and device for implementing the method
InactiveUS20050198943A1Increase motivationEasy to openElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCatalytic transformationNitrogen oxides
A method for metering ammonia into the exhaust-gas region of an internal combustion engine and a device for implementing the method. The ammonia storage capacity of an SCR catalytic converter situated in the exhaust-gas region of the internal combustion engine is utilized. After the internal combustion engine has been switched off, ammonia is introduced into the exhaust-gas region in front of the SCR catalytic converter. Thus, following a renewed start-up of the internal combustion engine, the ammonia required in the SCR catalytic converter for reducing the nitrogen oxides contained in the exhaust gas of the internal combustion engine are already available before an ammonia source is ready for operation. The procedure eliminates the need for a pressure storage of ammonia in the switched-off state of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Model-based urea emitting amount control method and aftertreatment control system
ActiveCN106837480AJet Precise ControlStrong control adaptabilityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCycle controlAmmonia storage
The invention relates to a model-based urea emitting amount control method. The method includes the following steps that S1, according to the actual urea emitting amount, based on an SCRF model, a first ammonia storage value in an SCRF is calculated; S2, based on an SCR model, a second ammonia storage value in an SCR is calculated; S3, the first ammonia storage value obtained in the step S1 and the second ammonia storage value obtained in the step S2 are subject to weighted treatment to obtain an actual ammonia storage value; S4, a difference is obtained from the actual ammonia storage value obtained in the step S3 and an actual storage setting value, and a closed-cycle correction ammonia nitrogen ratio is obtained through a PID controller; and S5, the sum of the closed-cycle correction ammonia nitrogen ratio obtained in the step S4 and a feedforward ammonia nitrogen ratio is obtained to be finally converted into the needed urea emitting amount. According to the model-based urea emitting amount control method, a model-based closed-cycle control strategy is adopted, accurate control over urea emitting can be achieved, the engine emission requirements can be met, standardization work can be reduced, and the problem about crystallization can be solved.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
Ammonia storage control
Various methods for controlling ammonia levels stored in a catalyst by controlling exhaust gas temperatures are provided. In one embodiment, a temperature of a catalyst in an internal combustion engine is determined. If the temperature of the catalyst exceeds a first threshold at which an ammonia capacity of the catalyst for the temperature is below a current stored ammonia level in the catalyst, a load of the engine is reduced including adjusting a torque output of a motor operatively coupled to the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Zoned Catalyst for Treating Exhaust Gas
ActiveUS20160038878A1Reduce undesirable production of N2OLow ammonia storage capacityCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsMolecular sieveAmmonia storage
Provided is a system for treating an exhaust gas comprising a first SCR catalyst zone comprising an iron loaded medium- or large-pore molecular sieve having a first ammonia storage capacity; and a second SCR catalyst zone comprising a copper loaded small-pore molecular sieve having a second ammonia storage capacity, wherein the first SCR catalyst zone is disposed upstream of the second SCR catalyst zone with respect to normal exhaust gas flow through the system and wherein the second ammonia storage capacity is greater than the first ammonia storage capacity. Also provided is a method for using the system to treat exhaust gas.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Flue gas-treating method and apparatus for treating acidic tail gas by using ammonia process
ActiveUS20150352486A1Improve efficiencyReduce investmentCombination devicesGas treatmentAmmonia storageFlue gas
A flue gas-treating method for treating acid tail gas by using an ammonia process, comprising the following steps of: 1) controlling the concentration of sulfur dioxide in an acid tail gas entering an absorber to be ≦30,000 mg / Nm3; 2) spraying and cooling with a process water or / and an ammonium sulfate solution in the inlet duct of the absorber or inside the absorber; 3) providing an oxidation section in the absorber, wherein the oxidation section is provided with oxidation distributors for oxidizing the desulfurization absorption solution; 4) providing an absorption section in the absorber wherein the absorption section achieves desulfurization spray absorption by using absorption solution distributors via an absorption solution containing ammonia; the absorption solution containing ammonia is supplied by an ammonia storage tank; 5) providing a water washing layer above the absorption section in the absorber, wherein the water washing layer washes the absorption solution in the tail gas to reduce the slip of the absorption solution; 6) providing a demister above the water washing layer inside the absorber to control the concentration of mist droplets contained in the cleaned tail gas. In the coal chemical industry, the integration of the Claus sulfur recovery process and the ammonia desulfurization technology can reduce the investment of the post-treatment and simplify the operation process, and provide intensive advantages to the environmental control of plants.
Owner:JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION GRP INC
System for controlling the urea supply to SCR catalysts
A reductant dosing control system, for use in a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) system of a motor vehicle includes an input receiving a NOx feedback signal from an NOx sensor provided to the SCR system. A base dosing module calculates a required quantity of reductant to inject in front of a SCR catalyst of the SCR system based on the NOx feedback signal. The SCR catalyst has ammonia storage properties. An output signals a reductant metering mechanism to periodically or continuously inject excess reductant based on the required quantity of reductant.
Owner:GENERAL MOTORS CORP
SCR (selective catalytic reduction) feed-forward control method and device
InactiveCN104314650APrevent leakageExcellent transient control effectInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusAmmonia storageProcess engineering
The invention discloses an SCR (selective catalytic reduction) feed-forward control method and device. The SCR feed-forward control method comprises the following steps: acquiring SCR upstream temperature, the NOx emission of an engine, exhaust gas mass flow and urea spraying rate in real time; calculating an actual average ammonia storage concentration value according to the SCR upstream temperature, the NOx emission of the engine, the exhaust gas mass flow and the urea spraying rate; generating a regulation value for regulating the urea spraying rate according to a preset urea spraying regulation algorithm by taking a difference between a set average ammonia storage concentration value and the actual average ammonia storage concentration value as a parameter. According to the method and the device, required urea spraying rate can be calculated in real time according to a current working condition of the engine without waiting for the variation of residual NH3 at the rear end of an SCR catalytic converter; the lag of regulation of the urea spraying rate for the variation of the residual NH3 is avoided, so that the transient control effect is better, and the leakage of NH3 can be effectively avoided.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
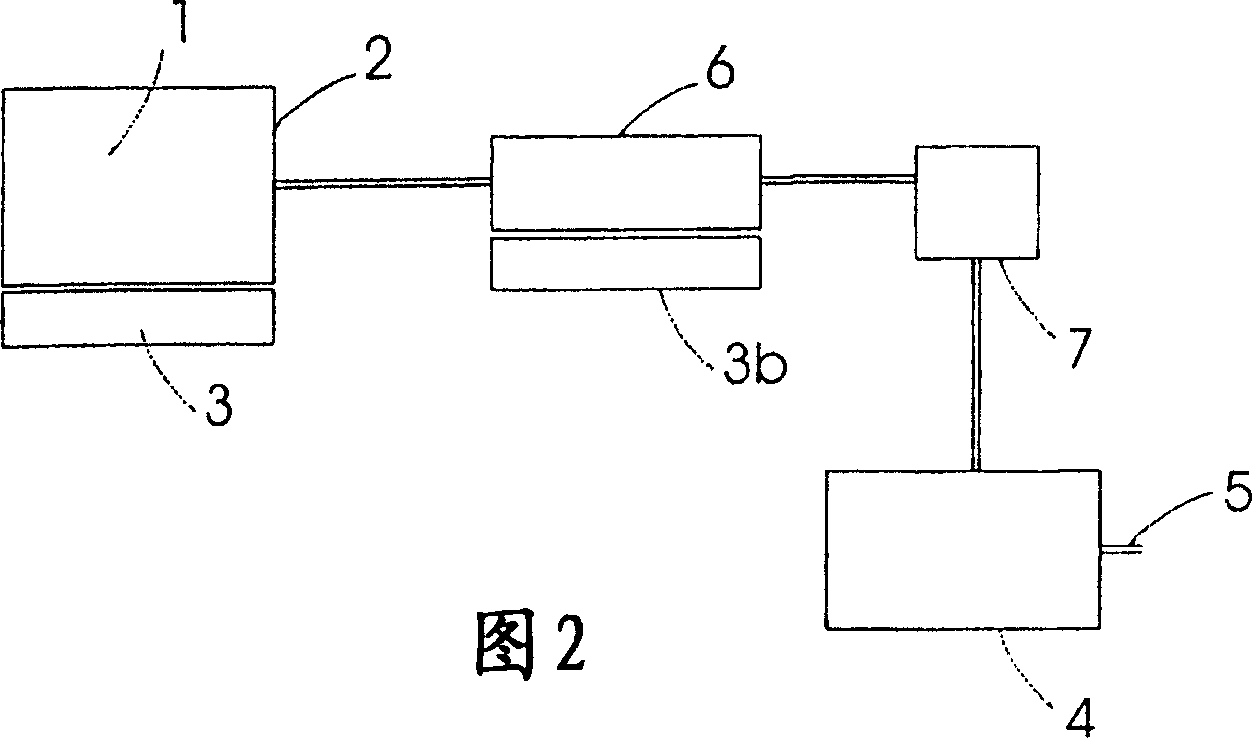
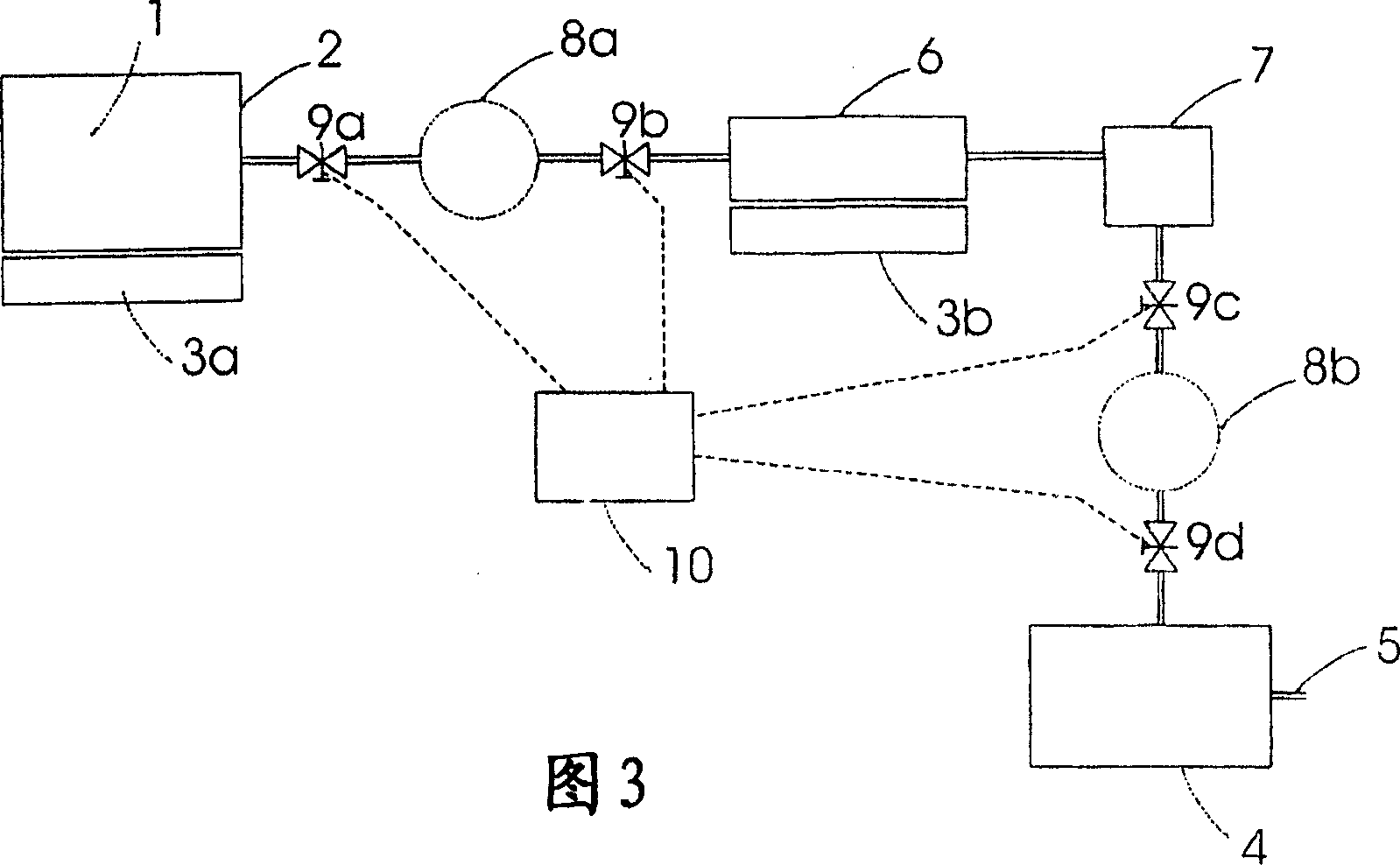
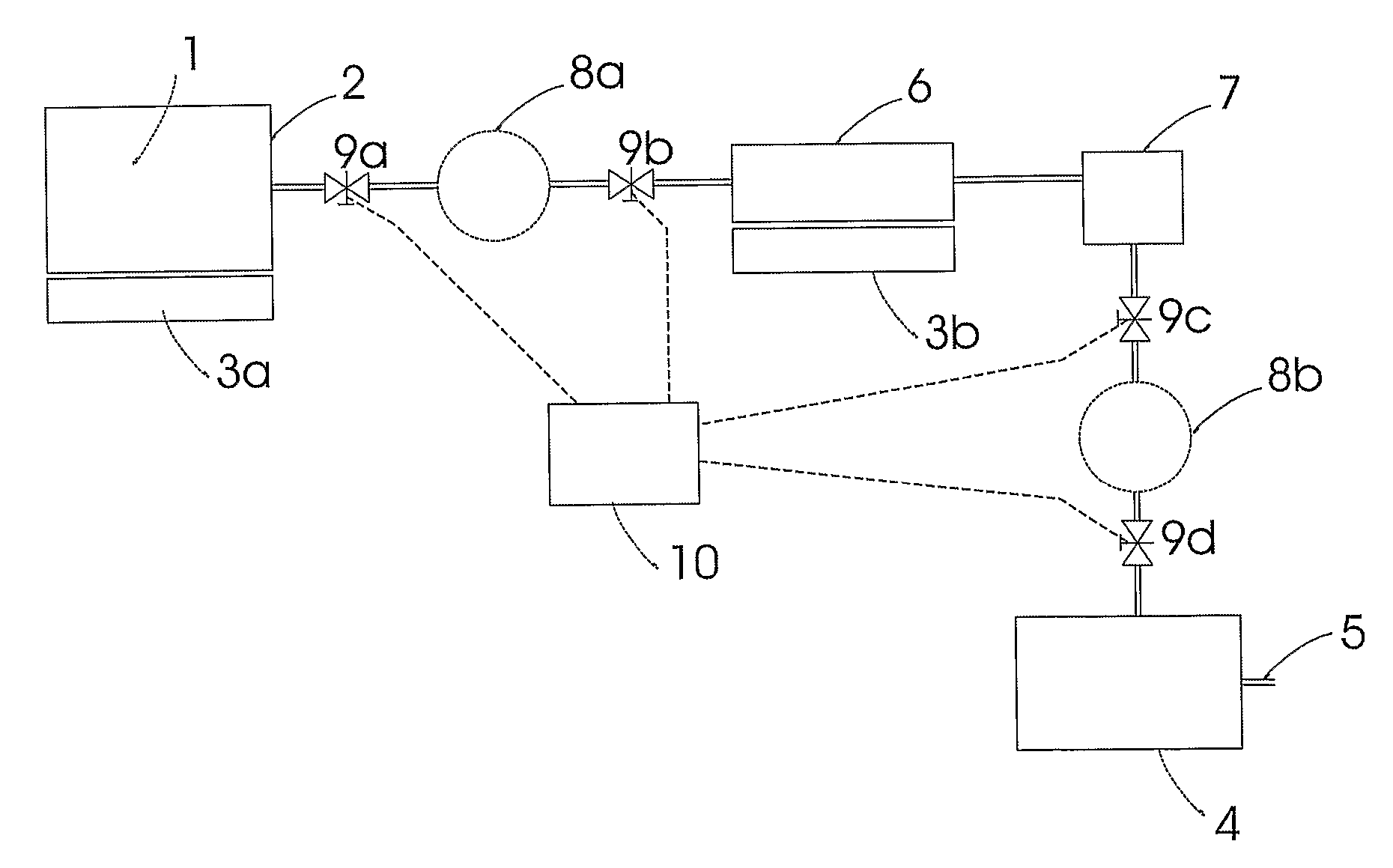
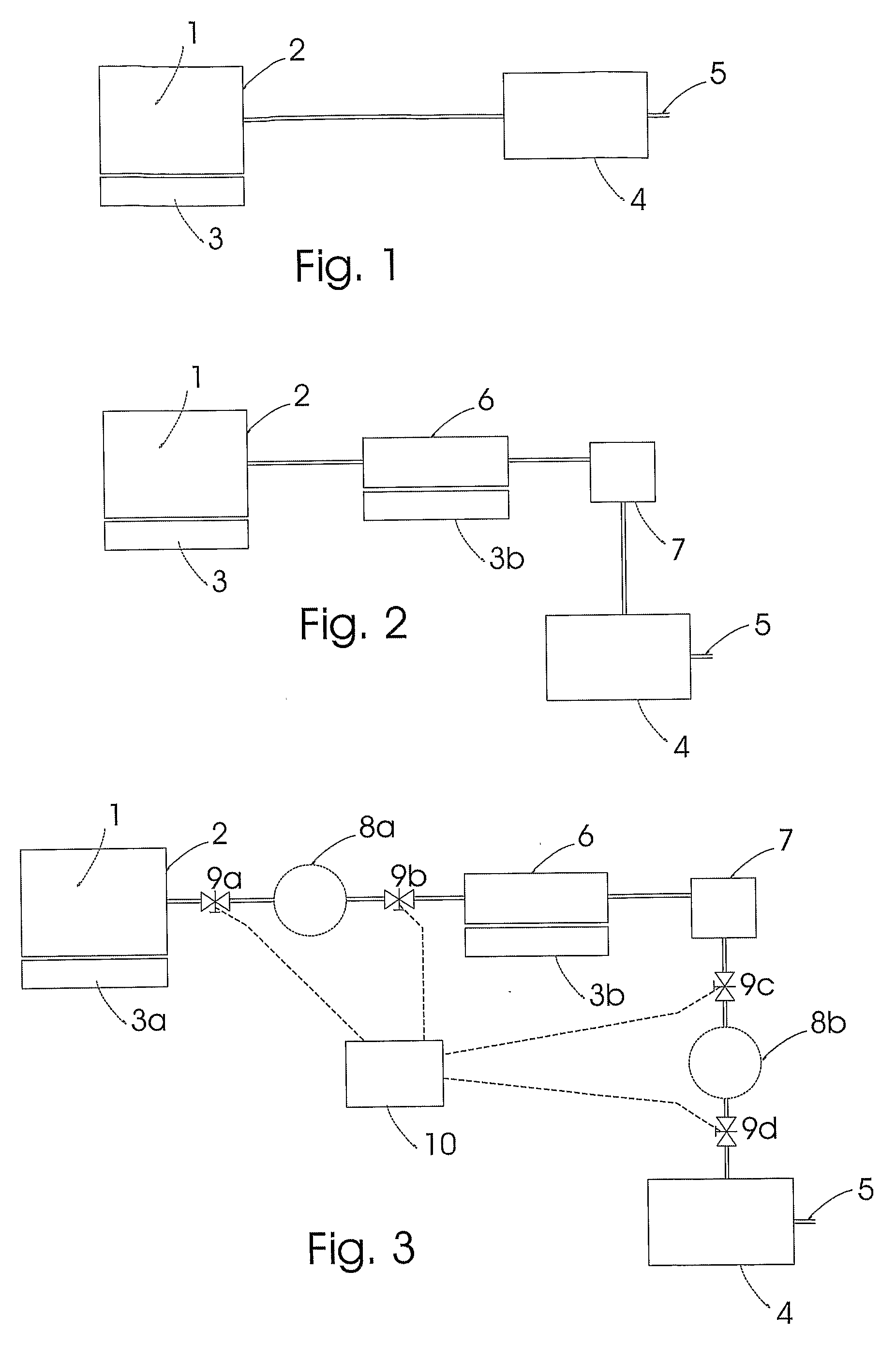
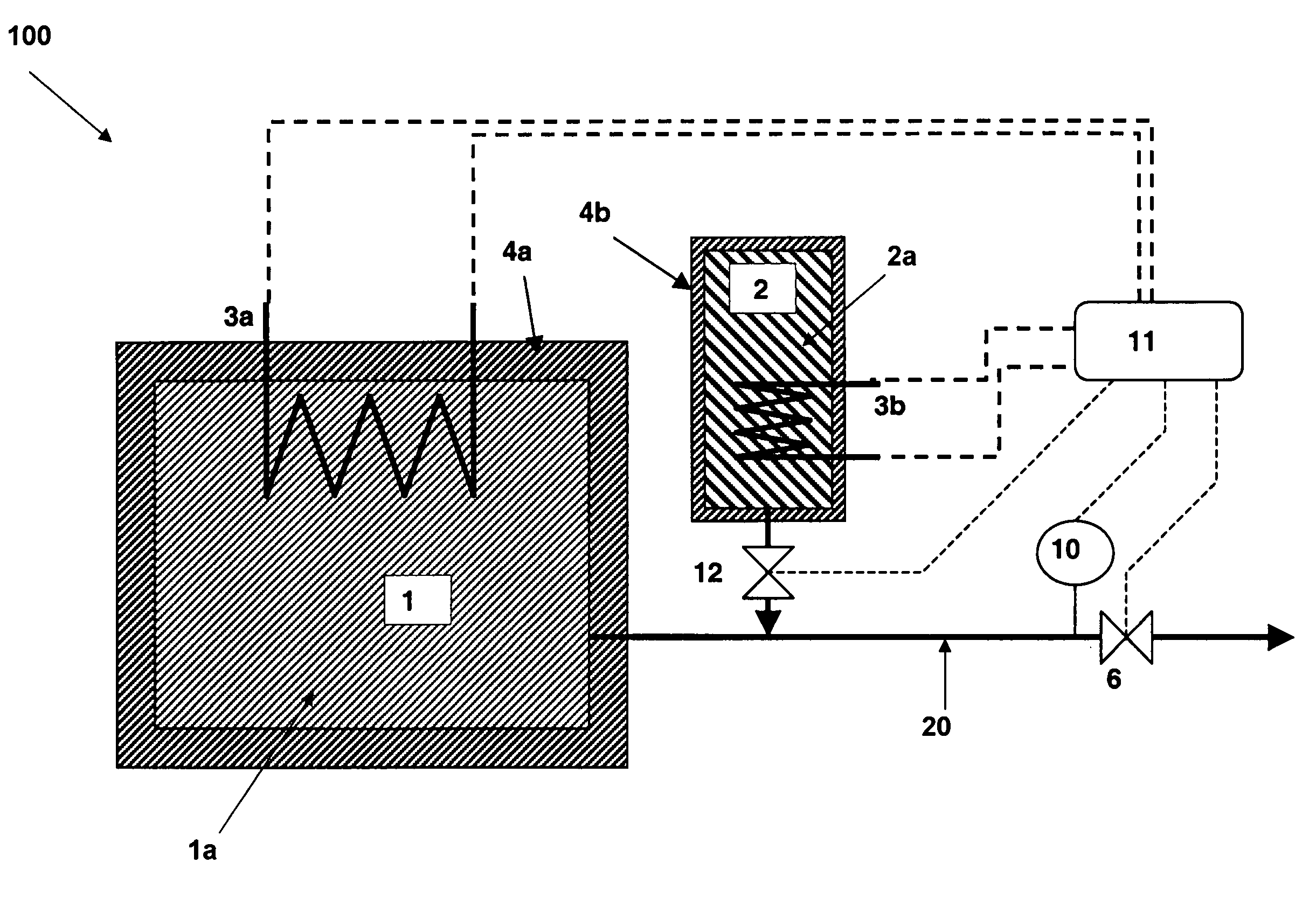
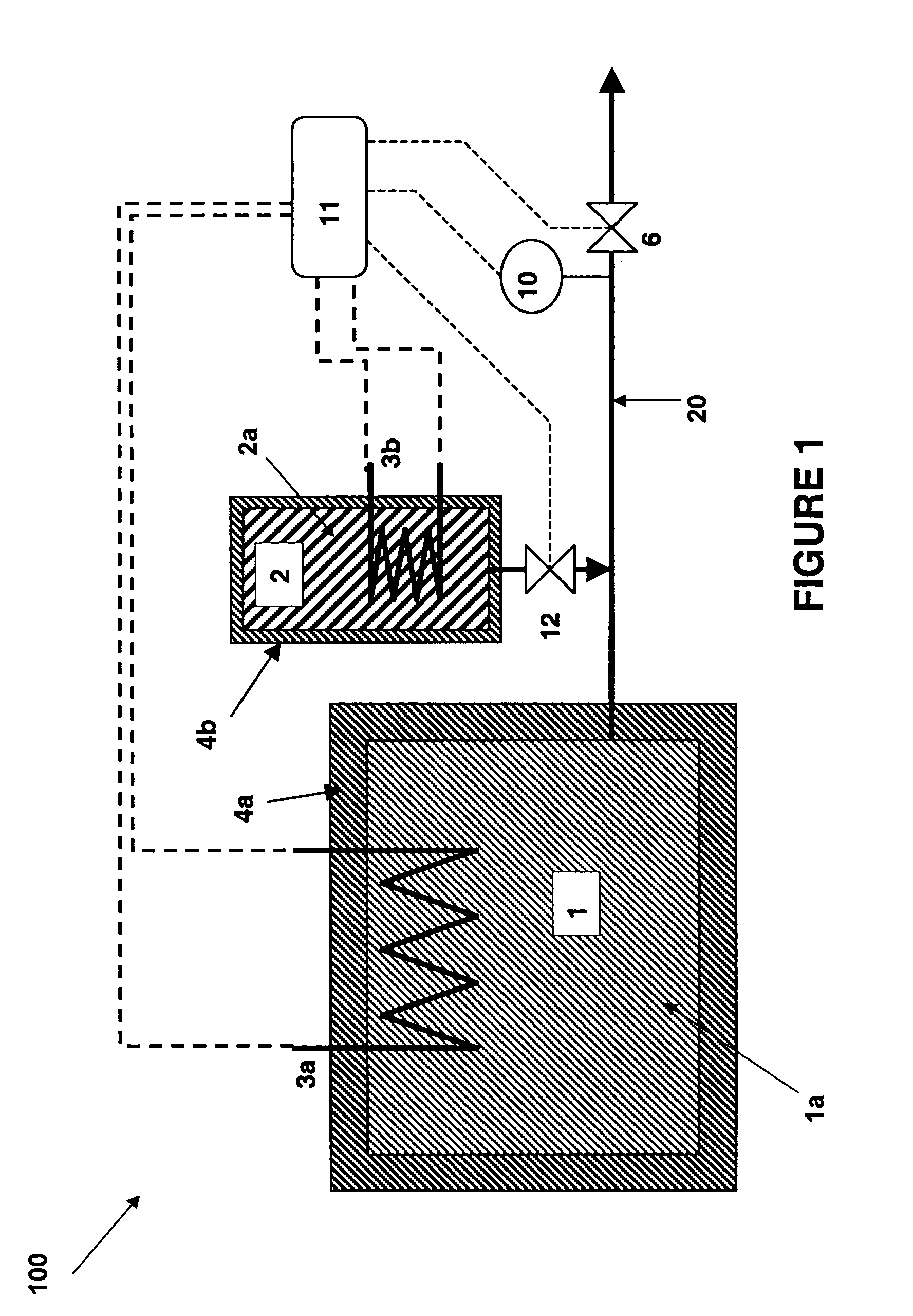
Method and Device for Safe Storage and Use of Volatile Ammonia Storage Materials
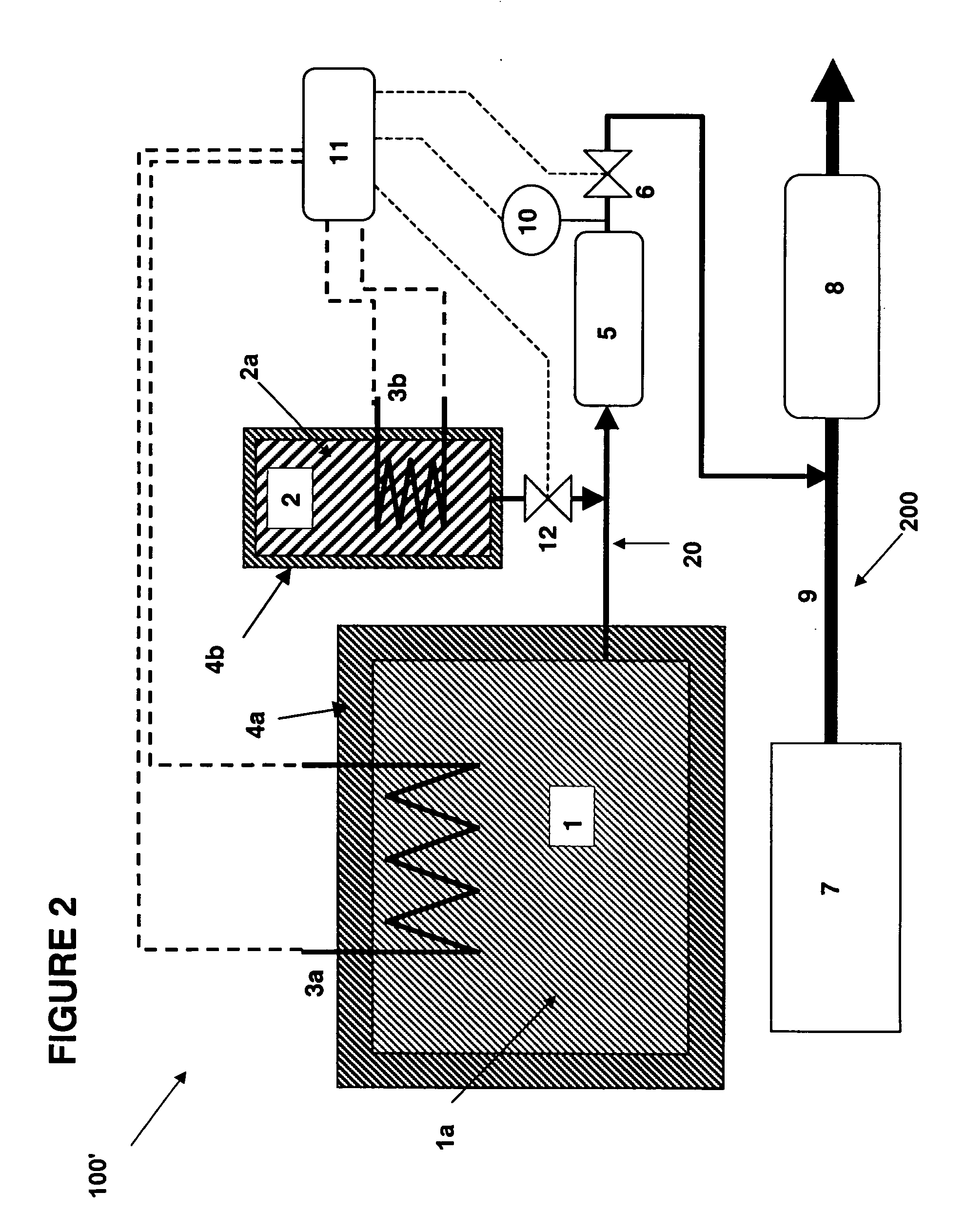
There is described a method and apparatus (100, 100′) for storing and delivering ammonia wherein at least two ammonia storage materials (1a, 2a) capable of reversibly adsorbing or absorbing ammonia having different ammonia vapor pressures are used. Ammonia storage material (2a) having a lower vapor pressure, which is only partially saturated with ammonia or void of ammonia, is brought into fluid communication with ammonia storage material (1a) having a higher ammonia vapor pressure to adsorb or absorb ammonia released from the ammonia storage material (1a) having a higher ammonia vapor pressure when the latter is higher than a pressure threshold. An automotive NOx treatment system (200) comprising such apparatus (100, 100′) is also described.
Owner:AMMINEX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com