Attenuated parainfluenza virus (PIV) vaccines
a technology vaccine, which is applied in the field of attenuated parainfluenza virus (piv) vaccine, can solve the problems of no approved vaccine agent for any hpiv strain, no cure agent for hpiv related illnesses, and substantial morbidity in children
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Construction of Plasmid p218(131)
Encoding Negative Sense PIV Genomic RNA
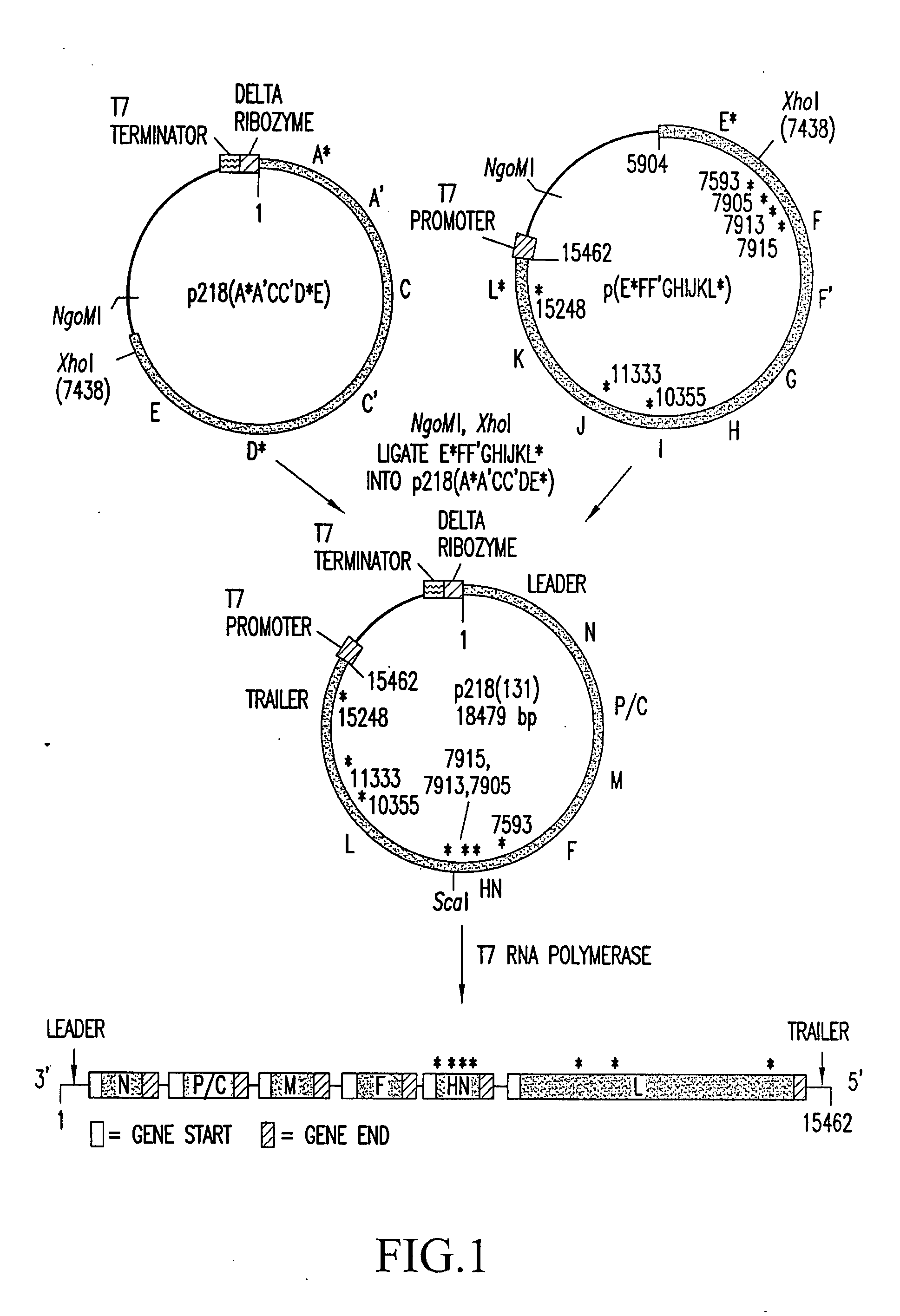
[0368] A full cDNA clone designated p218(131) (FIG. 1; SEQ ID NO: 71) (deposited under the terms of the Budapest Treaty with the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) of 12301 Parklawn Drive, Rockville, Md. 20852, U.S.A., and granted the designation 97991) was constructed to encode the complete 15462 nt genomic sequence of HPIV3 JS strain (SEQ ID NO: 180). A hepatitis delta ribozyme was placed abutting the 3′ end of the genomic sequence such that self-cleavage would yield the 3′ end of HPIV3 (Perrotta and Been, Nature 350: 434-436, (1991), incorporated herein by reference in its entirety). A T7 transcription terminator was placed following the delta ribozyme. The T7 promoter was placed adjacent to the 5′ end of the genomic sequence such that the 5′ terminal nucleotide of the HPIV3 genome was the first nucleotide synthesized. In this configuration, the cDNA encodes a complete negative-sense copy of PIV3 genom...
example ii
Transcription and RNA Replication System for HPIV3
[0376] The present example describes compositions and methods for producing a reconstituted transcription and RNA replication system for human parainfluenza virus type 3 (HPIV3). This exemplary system was developed using components expressed intracellularly from transfected plasmids driven by a T7 RNA polymerase supplied by a vaccinia virus recombinant. The system is based on a negative-sense analog of HPIV3 genomic RNA in which the viral genes were deleted and replaced with a polynucleotide encoding bacterial chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT). The N, P and L proteins are expressed from cotransfected plasmids so as to direct efficient transcription and RNA replication. Transcription according to this example yields subgenomic polyadenylated mRNA, which can be readily isolated, e.g., by oligo(dT) chromatography. RNA replication according to this example yields mini-antigenome and progeny minigenome, which are shown to be encap...
example iii
Construction and Expression of Modified PIV3 Minigenomes
[0389] In the present example, a panel of cDNAs was constructed to encode PIV3 minigenomes which differed in length by single nucleotide increments. Transcription and RNA replication in this reconstituted system were the most efficient for the minigenome whose length was an even multiple of six. In this context, members of the Paramyxovirus and Morbillivirus genera typically abide by a “rule of six,” i.e., genomes (or minigenomes) replicate efficiently only when their nucleotide length is a multiple of six (thought to be a requirement for precise spacing of nucleotide residues relative to encapsidating NP protein). However, the present findings illustrate that minigenomes whose lengths were one nucleotide greater than or less than an even multiple of six were surprisingly active, especially in RNA replication.
[0390] A panel of seven cDNAs was constructed to encode seven PIV3-CAT minigenomes, called PIV3-CAT 0 to +6, that diff...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com