Producing method of high steam pressure chalcogen alloy block
A technology of chalcogen and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the manufacturing field of high vapor pressure chalcogen alloy bulk material, can solve the problems of the difference between concentration and target composition, reduce the reliability of the alloy, corrosion, etc., so as to improve the volatilization and dissipation of low-melting point metals. , the effect of reducing manufacturing costs and increasing process stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The purpose of the present invention and its advantages in structure and function will be described according to the structure shown in the accompanying drawings, together with specific embodiments, in order to enable people to have a deeper and more specific understanding of the present invention.
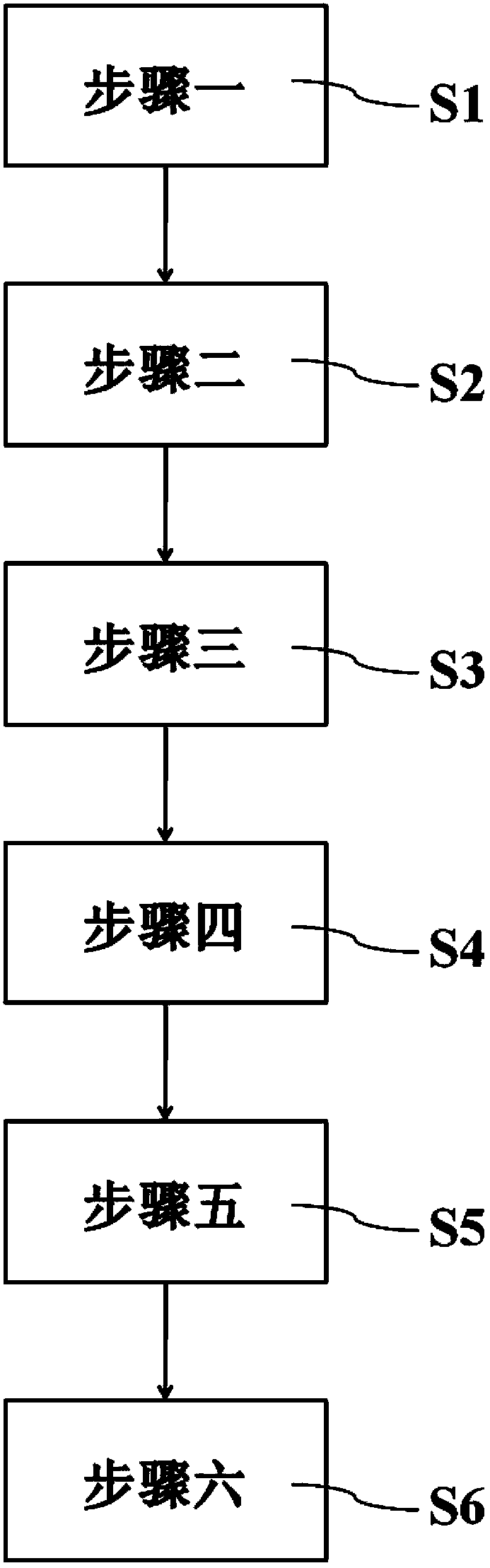
[0030] First, please refer to figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of the steps of a preferred embodiment of the manufacturing method of the high vapor pressure chalcogen alloy bulk material of the present invention, which mainly includes the following steps:
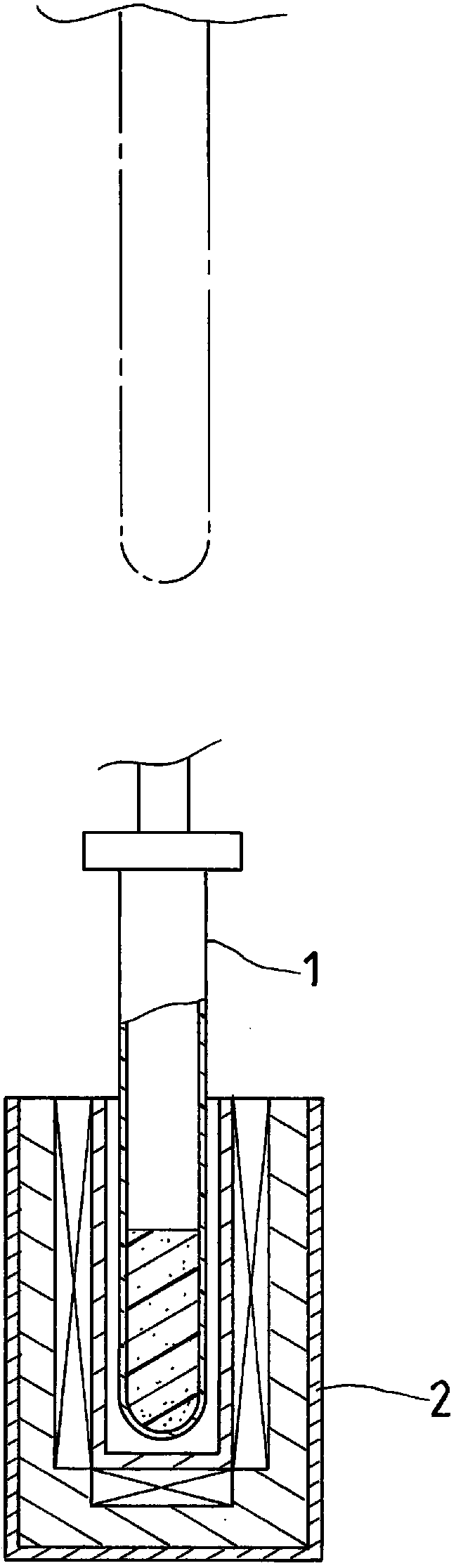
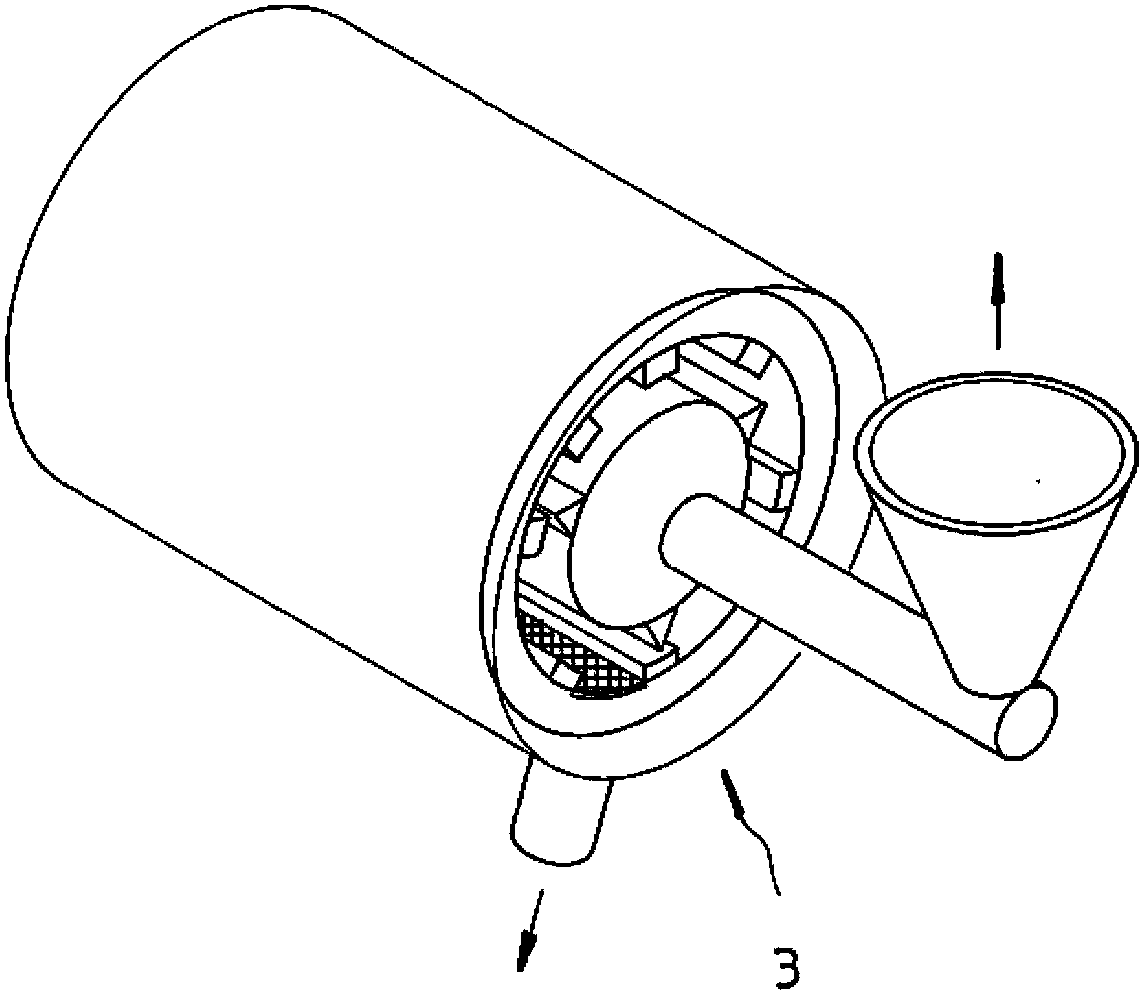
[0031] Step 1 S1: Calculated based on the atomic percentage of 100% of the total raw material composition, the preparation includes 0.5-30 atomic percentage of chalcogen elements, the chalcogen elements are gallium, indium, thallium, germanium, tin, lead, antimony, bismuth, selenium , one of tellurium or polonium elements, and the metal element raw material of the remaining atomic percentage; wherein, the purity of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com