Organic solvent resisting lipase, application thereof and bacteria for producing same
A technology resistant to organic solvents and lipases, applied in applications, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low tolerance to organic solvents, low enzyme production, and difficult purification, etc., to achieve strong tolerance, wide pH range, and easy The effect of purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] This experiment illustrates the screening procedure for natural strains producing organic solvent-resistant lipase.
[0025] The following method was used for the initial screening: use different concentrations of cyclohexane, toluene, DMSO and other organic solvents as the screening pressure to obtain organic solvent-resistant extremophiles from oily soil samples, and then use olive oil rhodamine B plates to screen out 6 strains of fat Enzyme-producing strains. The specific formula of olive oil rhodamine B plate is: yeast extract 1g / L, corn steep liquor 5mL / L, K 2 HPO 4 1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L, olive oil 60mL / L, Rhodamin B 0.024g / L.
[0026] In order to obtain excellent organic-solvent-resistant lipase-producing bacteria, the above-mentioned 6 strains were re-screened by testing the enzyme-producing ability of shake flasks and the stability of lipase in organic solvents. Inoculate 6 strains into the enzyme-producing fermentation medium, the specific formula i...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This experiment illustrates the biological properties, identification and enzyme production conditions of the organic solvent-resistant lipase-producing strain LX1.
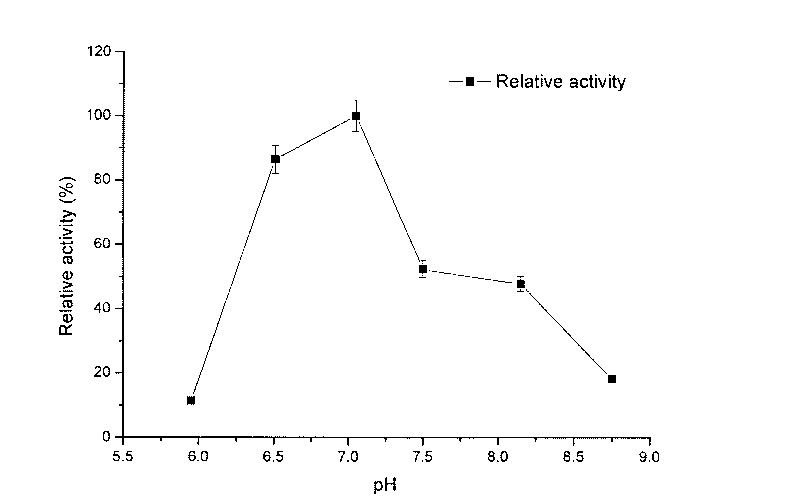
[0031] Biological properties of the strain LX1: Gram staining showed that the strain was a Gram-negative strain without spores. After growing in broth medium for 24 hours, the colony size and diameter are 1.5mm-2mm, the growth temperature range is 24°C-37°C, the optimum growth temperature is 27°C, the growth pH range is 6.0-11.0, and the optimum growth pH is 8.0, its physiological and biochemical characteristics are manifested in that the results of catalase reaction, oxidase reaction, nitric acid reduction reaction and gelatin reaction are positive, and it grows under aerobic conditions.
[0032] Species identification of strain LX1: BIOLOG automatic bacterial identification instrument and 16S rDNA sequence analysis showed that the strain was Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and named it Pseudomonas aeruginosa LX1...
Embodiment 3
[0035] This experiment illustrates the purification procedure for organic solvent-resistant LX1 lipase.
[0036] After culturing Pseudomonas aeruginosa LX1 in the enzyme-producing medium for 30 hours, the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm and 4°C for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken as the crude enzyme solution; Ammonium sulfate was precipitated, and the supernatant was taken after centrifugation, and then precipitated with 50% saturated ammonium sulfate, and the precipitate was dissolved with 0.01M Tris-HCl buffer solution of pH 7.10, and dialyzed to remove salt. Purify the enzyme solution obtained from the above treatment with a DEAE-Sepharose FF ion-exchange chromatography column, elute with 0.01M Tris-HCl (pH 7.10, NaCl content is 1mol / L) buffer, and collect the lipase activity peak . By SDS-PAGE electrophoresis ( figure 1 ), found that the two-step purified organic solvent-resistant lipase (named as organic solvent-resistant LX1 lipase) had reach...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com