Magnetic recording medium based on multiferroic film and write-in method thereof
A magnetic recording medium, multiferroic technology, applied in recording/reproducing/deleting methods, magnetic recording, data recording, etc., to achieve the effect of great application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
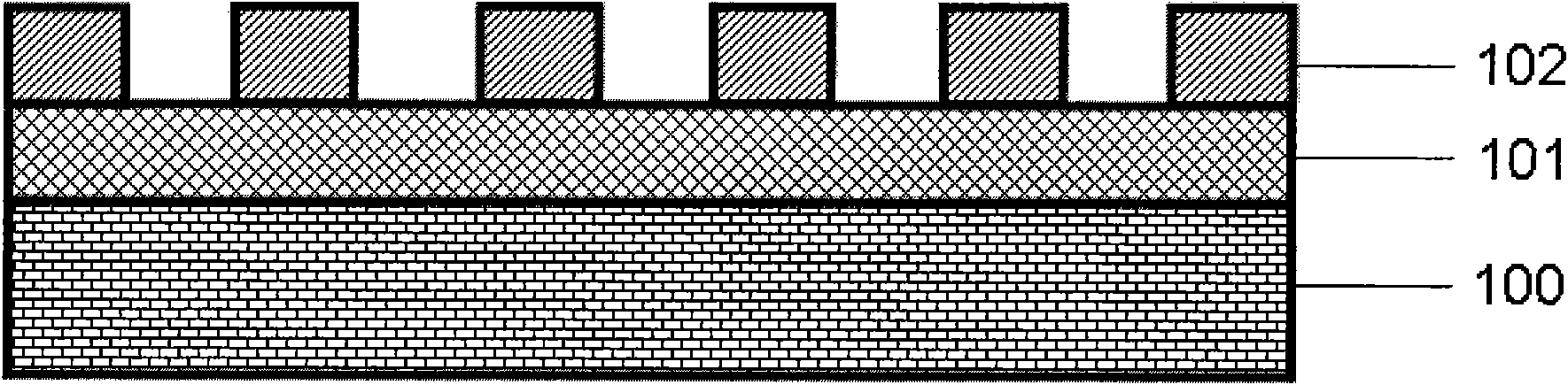
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, niobium-doped strontium titanate (Nb:SrTiO 3 ) as the substrate 100, grown by the ferroelectric material Ba by magnetron sputtering or pulsed laser deposition 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 The ferroelectric structural unit 101 and the ferromagnetic material La 0.67 Sr 0.33 MnO 3 The formed ferromagnetic layer is then etched by an electron beam to obtain a ferromagnetic structural unit 102 .
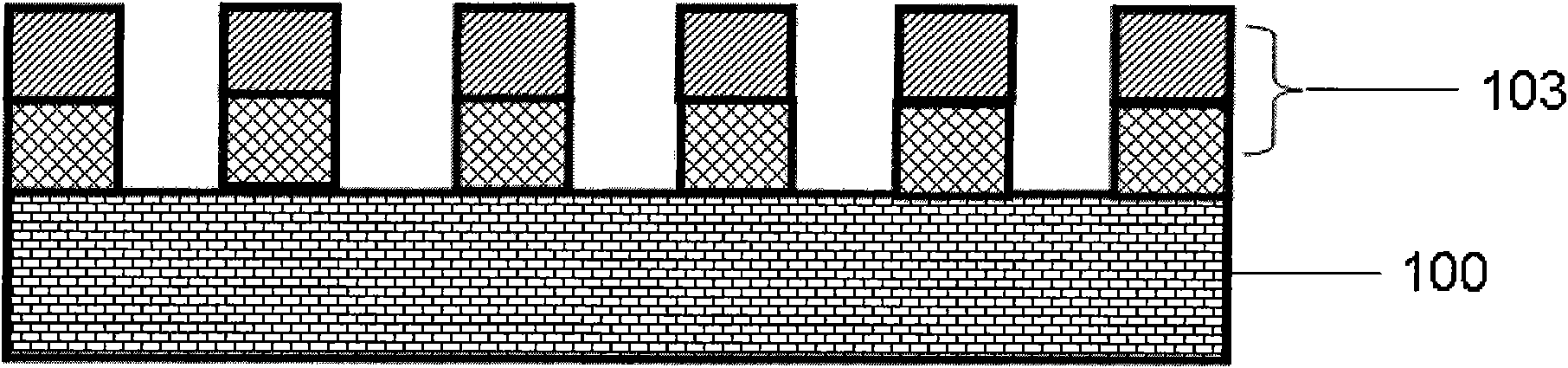
[0038] The writing method of the above-mentioned magnetic recording medium based on the multiferroic thin film is as follows Figure 7 As shown, the signal source 200 generates a pulse electric signal, generates an electric field through the electrode 201, and the voltage is applied to the ferroelectric structural unit 203, thereby causing the ferroelectric structural unit 203 to generate electrical polarization, and the ferroelectric structural unit 203 and the ferromagnetic structural unit 202 The magnetoelectric coupling effect controls the magnetization dir...
Embodiment 2
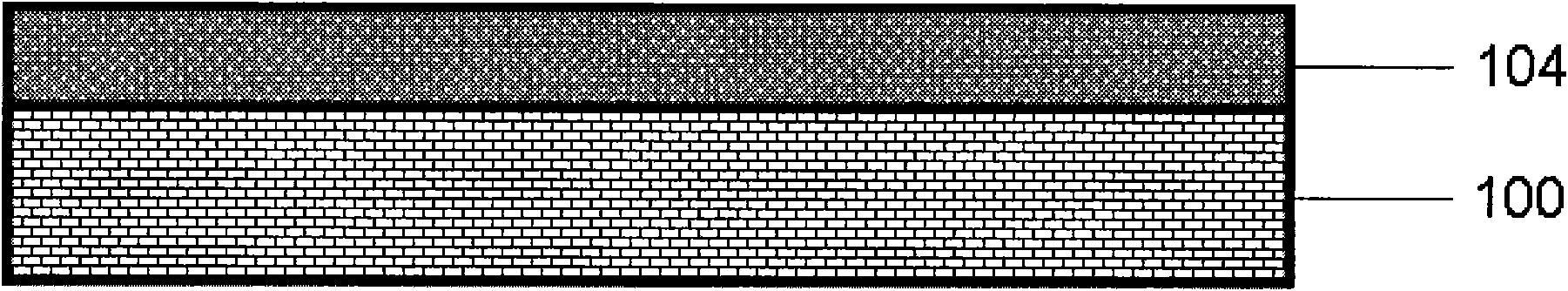
[0046] Such as image 3 with Figure 4 The shown magnetic recording media based on multiferroic thin films, in Pt / Ti / SiO 2 / Si substrate, the single-phase multiferroic material BiFeO was prepared by magnetron sputtering or pulsed laser deposition 3 The formed dielectric layer 104 can be obtained by electron beam etching, ion beam etching and other methods such as Figure 4 The unit structure 105 .
[0047] The data writing method is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0048] Single-phase multiferroic materials can also use doped bismuth ferrite (BiFeO 3 ), such as: doped potassium (K), calcium (Ca), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) , copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), yttrium (Y), niobium (Nb), lead (Pb), lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr) , neodymium (Nd), samarium (Sm), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb) or ytterbium (Yb).
Embodiment 3
[0050] Such as Figure 5 The magnetic recording medium based on the multiferroic thin film shown, on the niobium-doped strontium titanate substrate 100, the multiferroic thin film magnetic film with the 1-3 type structure is grown uniformly at intervals by the method of pulsed laser deposition and self-assembly. Recording medium (cobalt ferrite nanopillars 106 embedded in bismuth ferrite ferroelectric matrix 107).
[0051] All the other parts are identical with embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com