Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "Signal delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
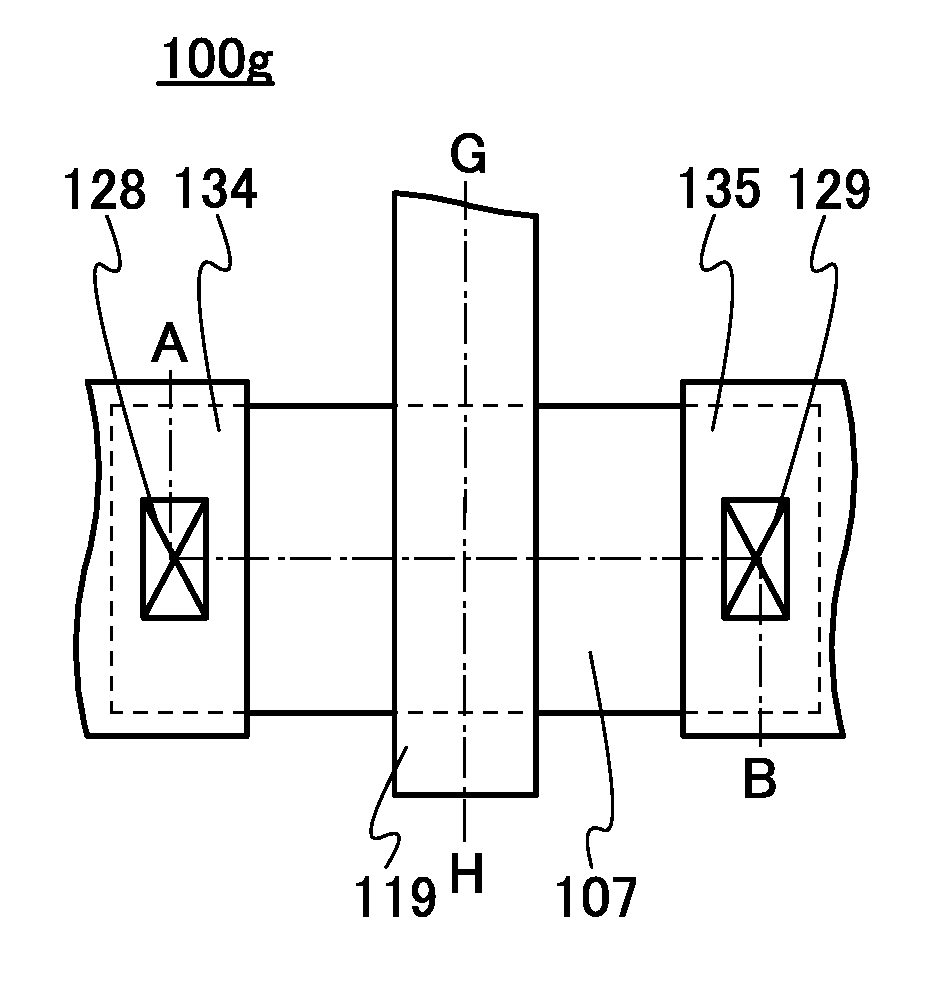
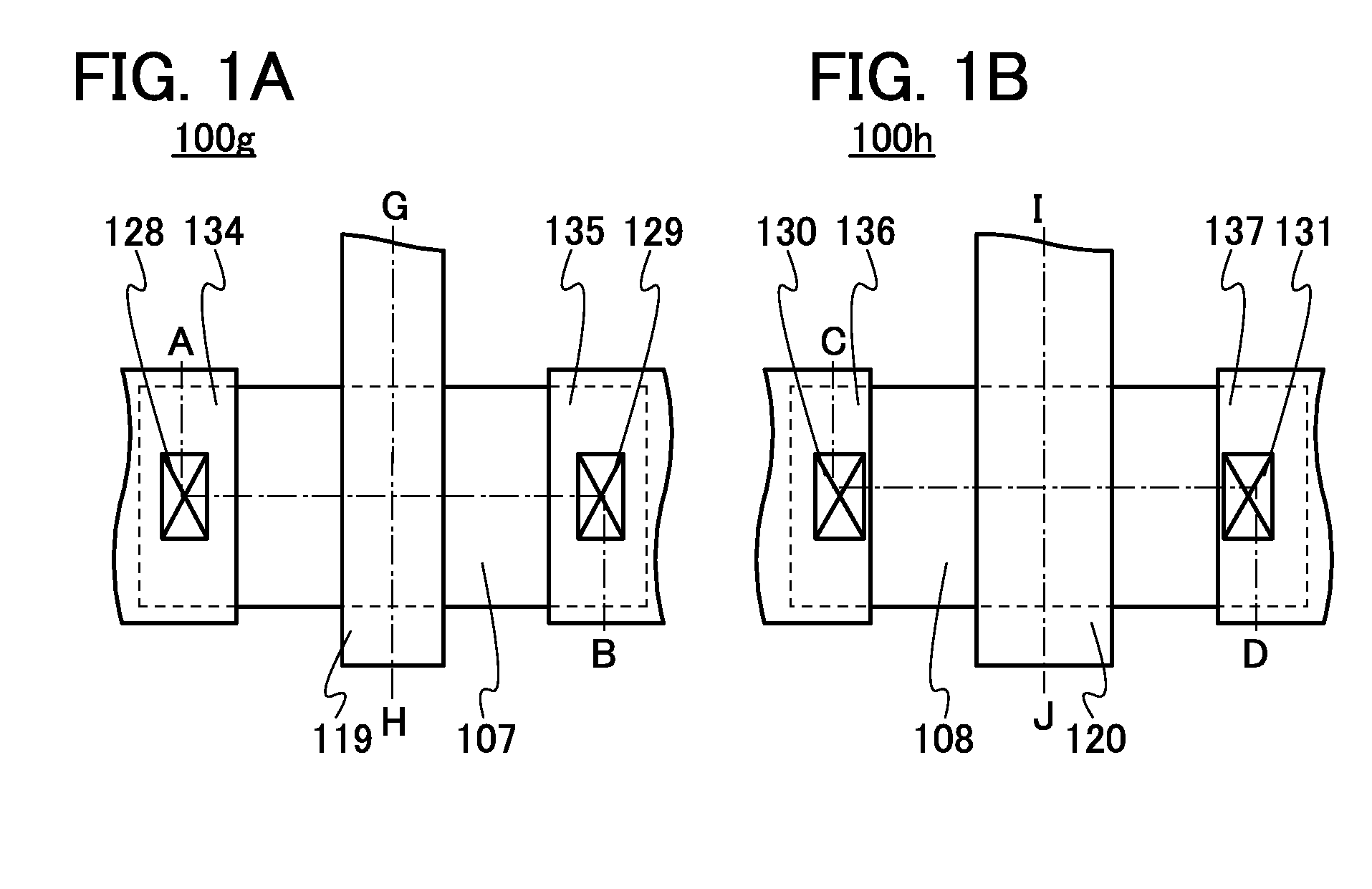
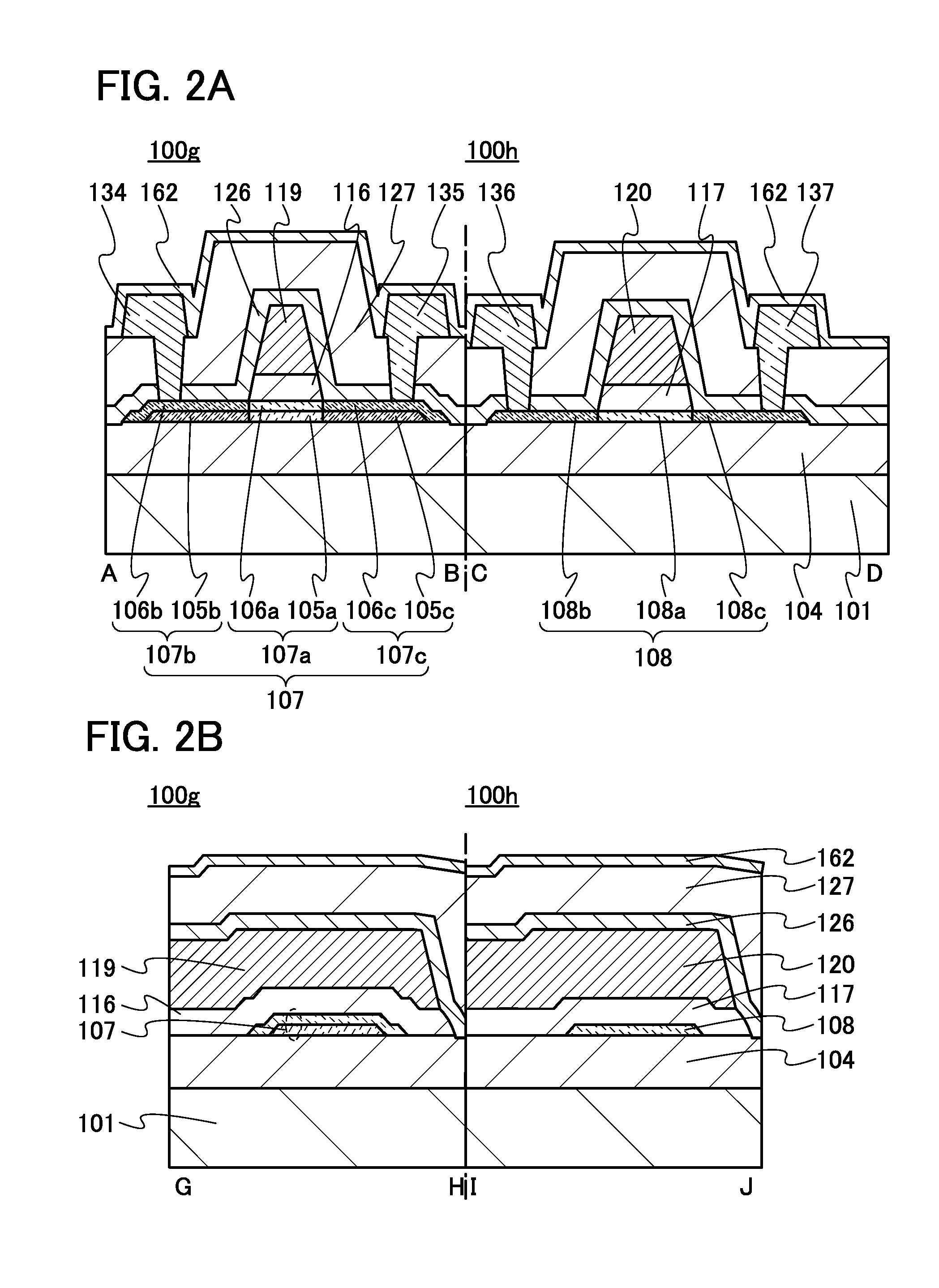
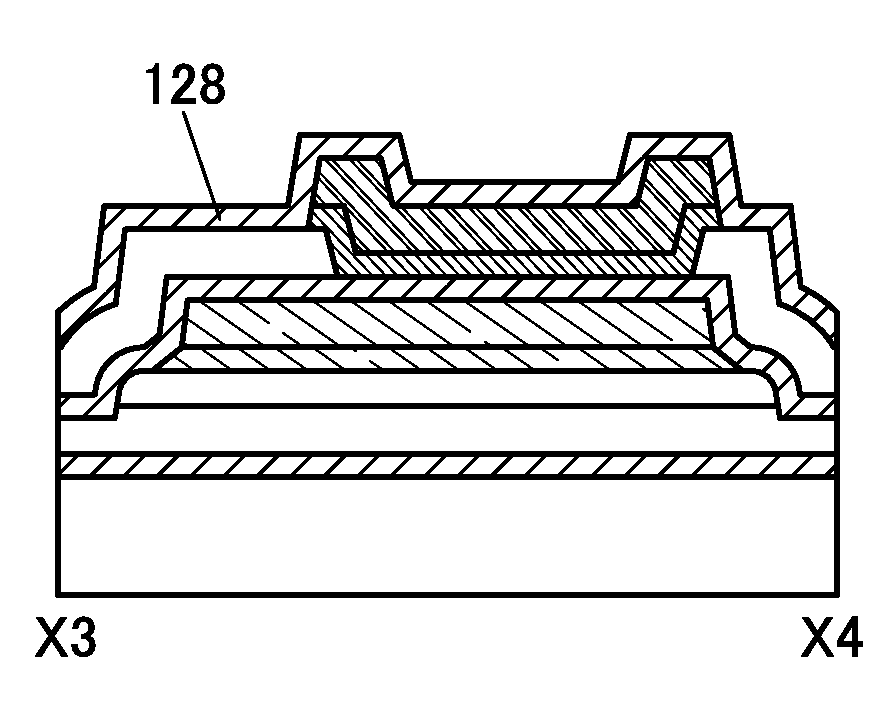
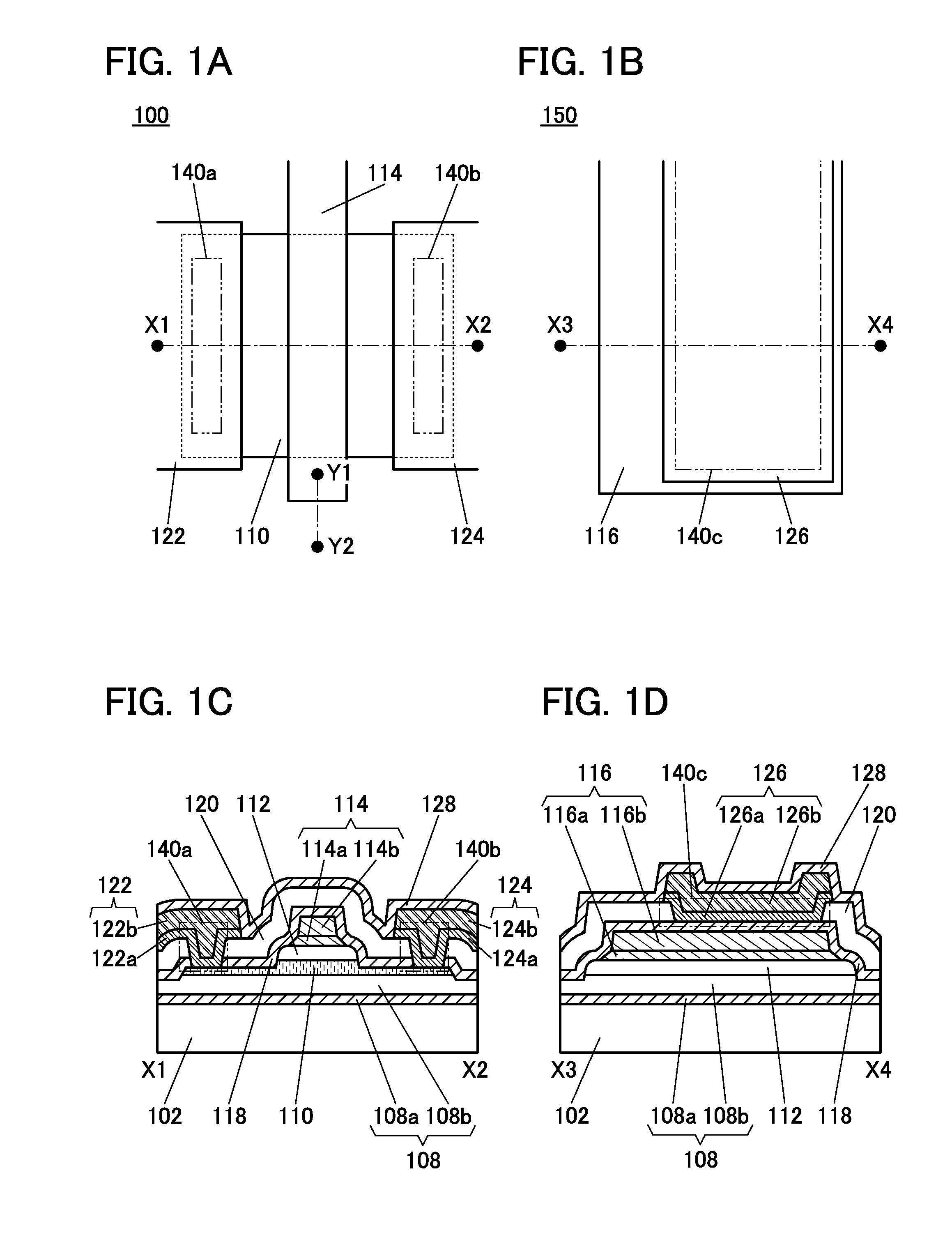
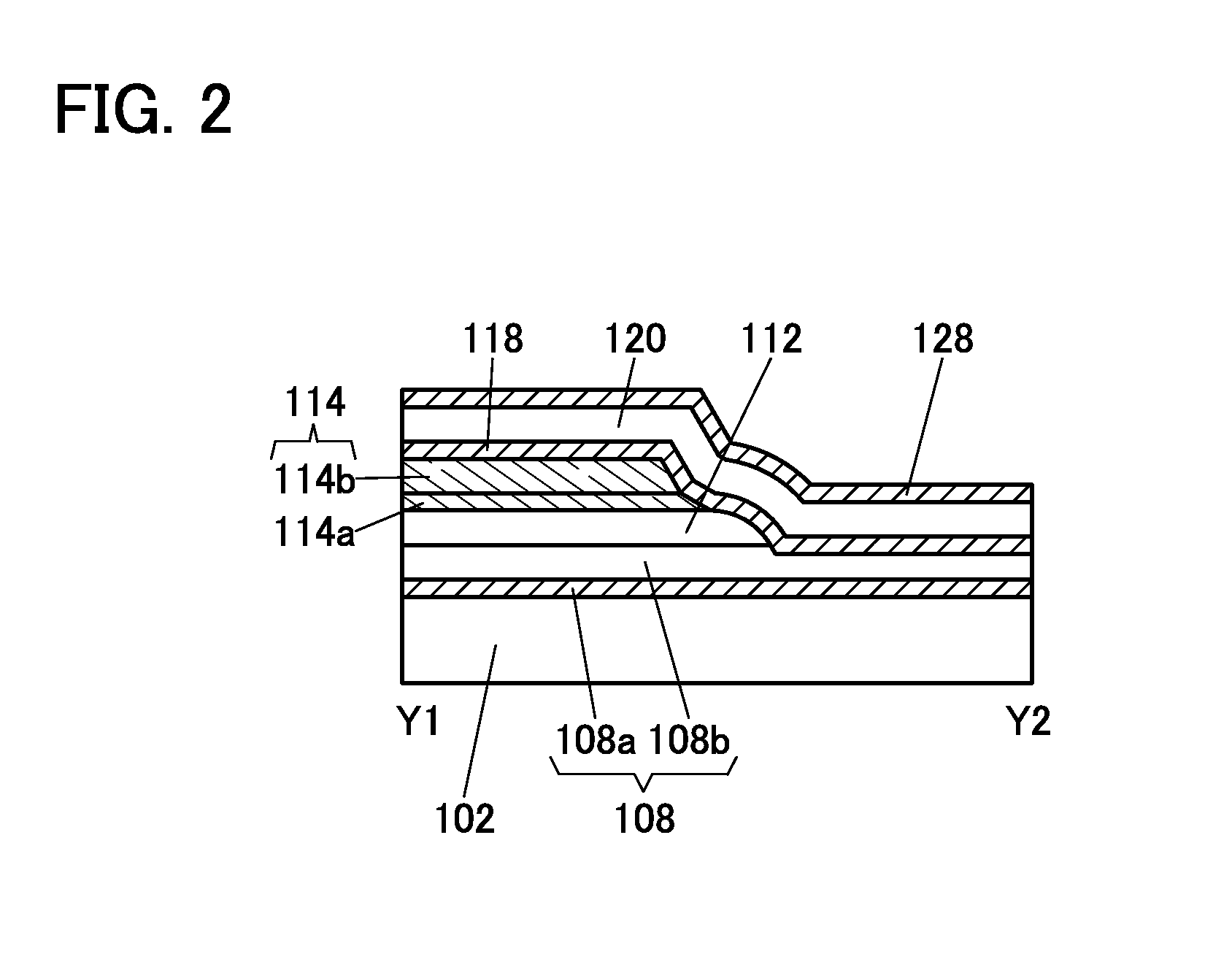
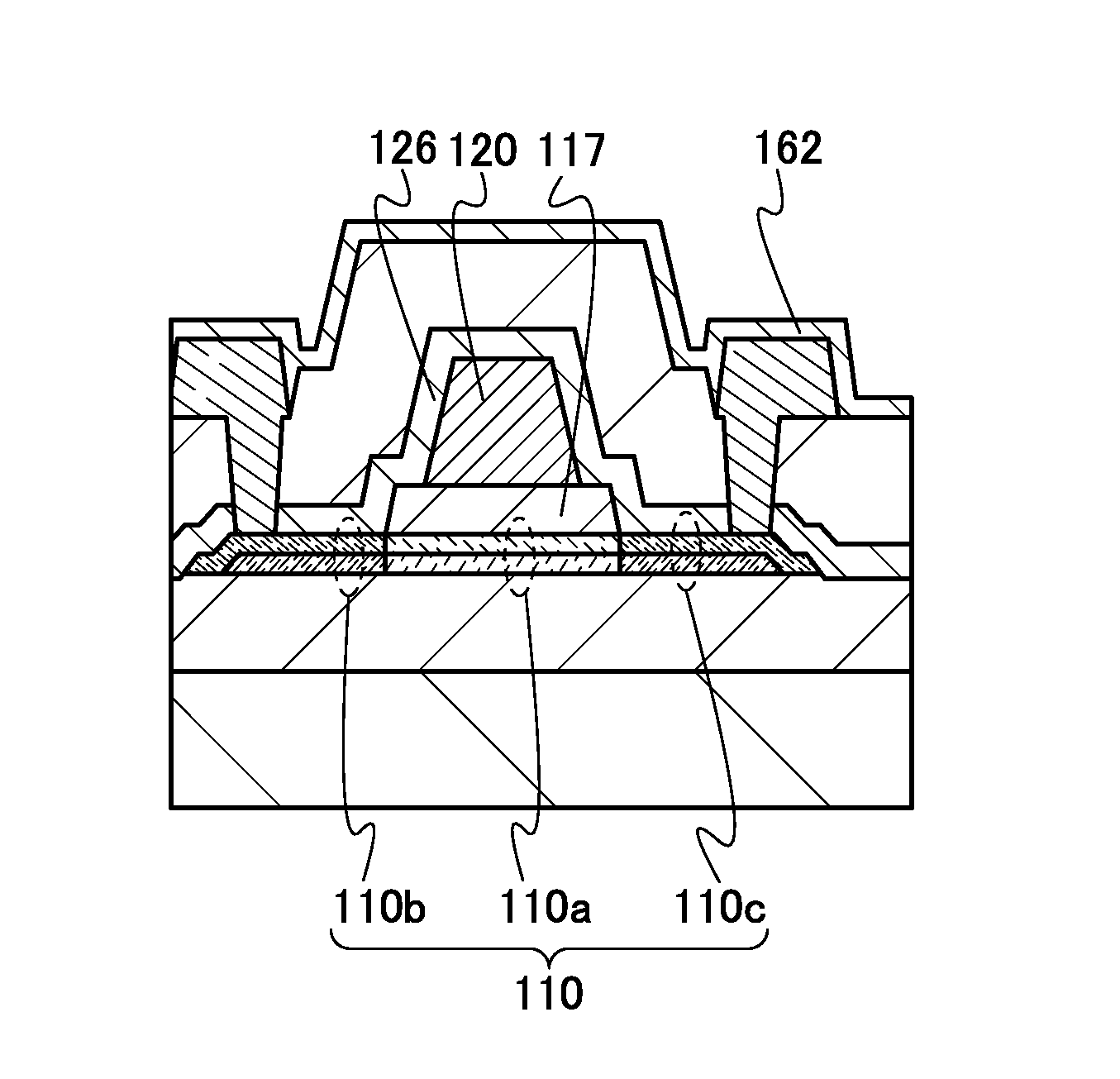
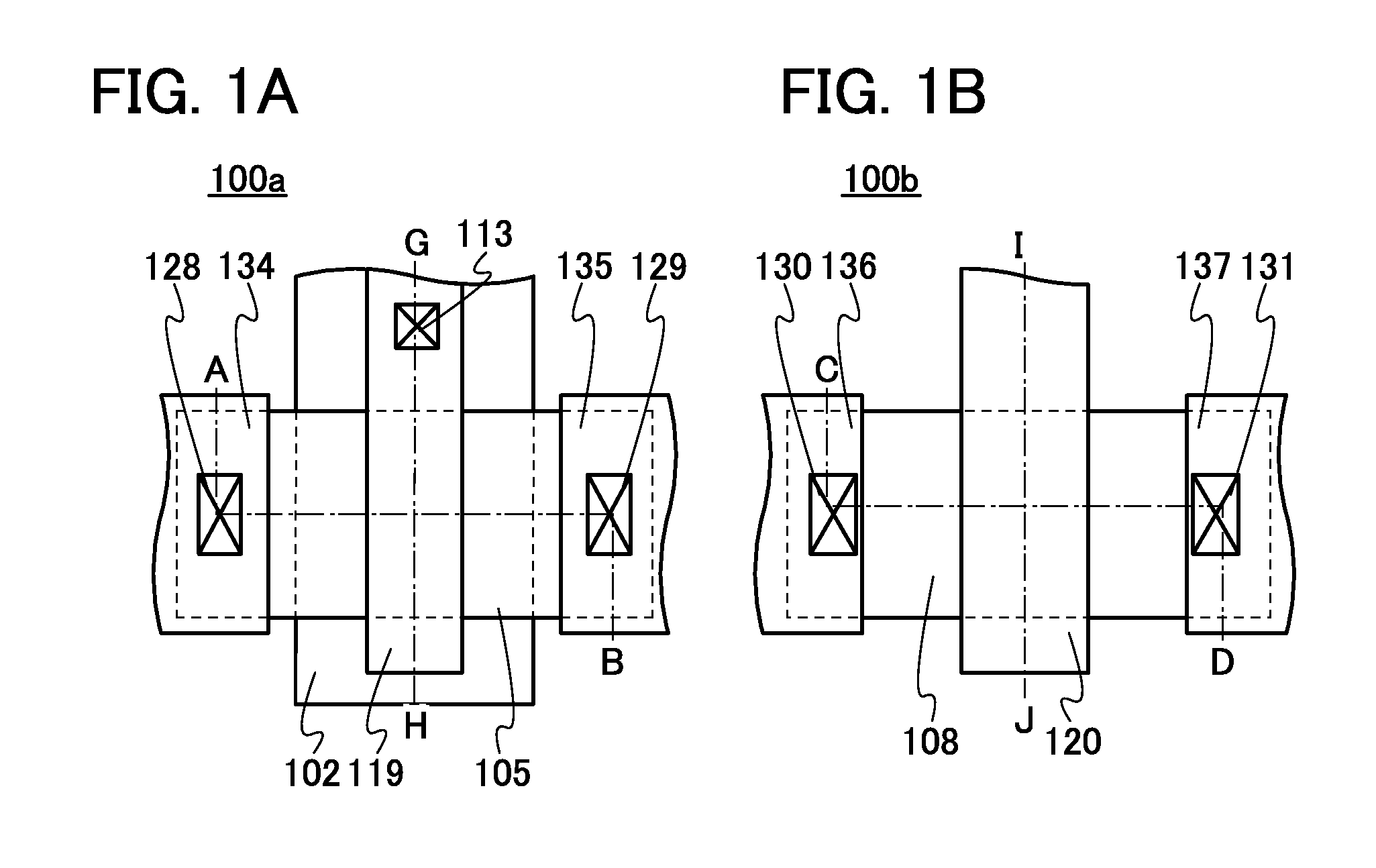
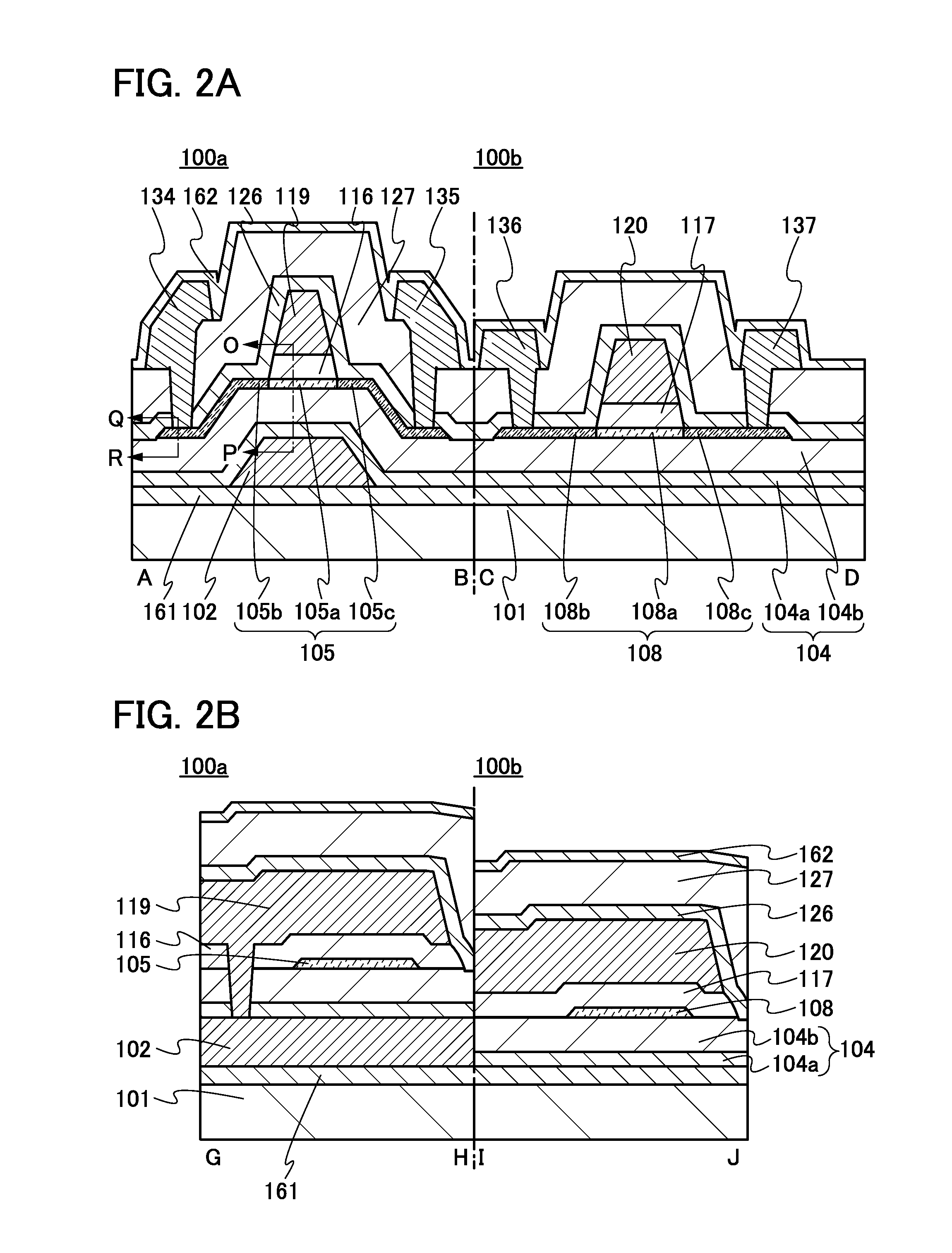
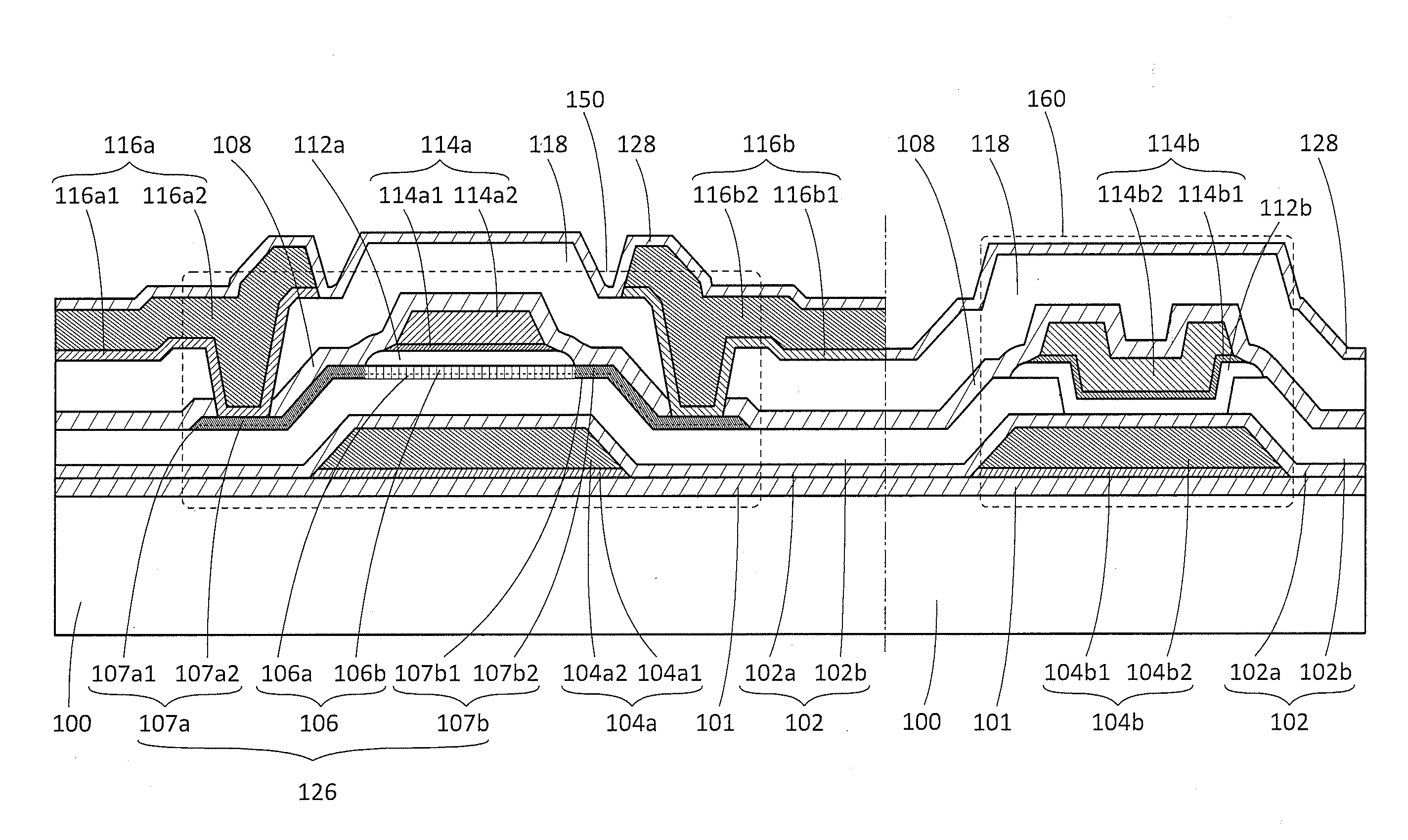
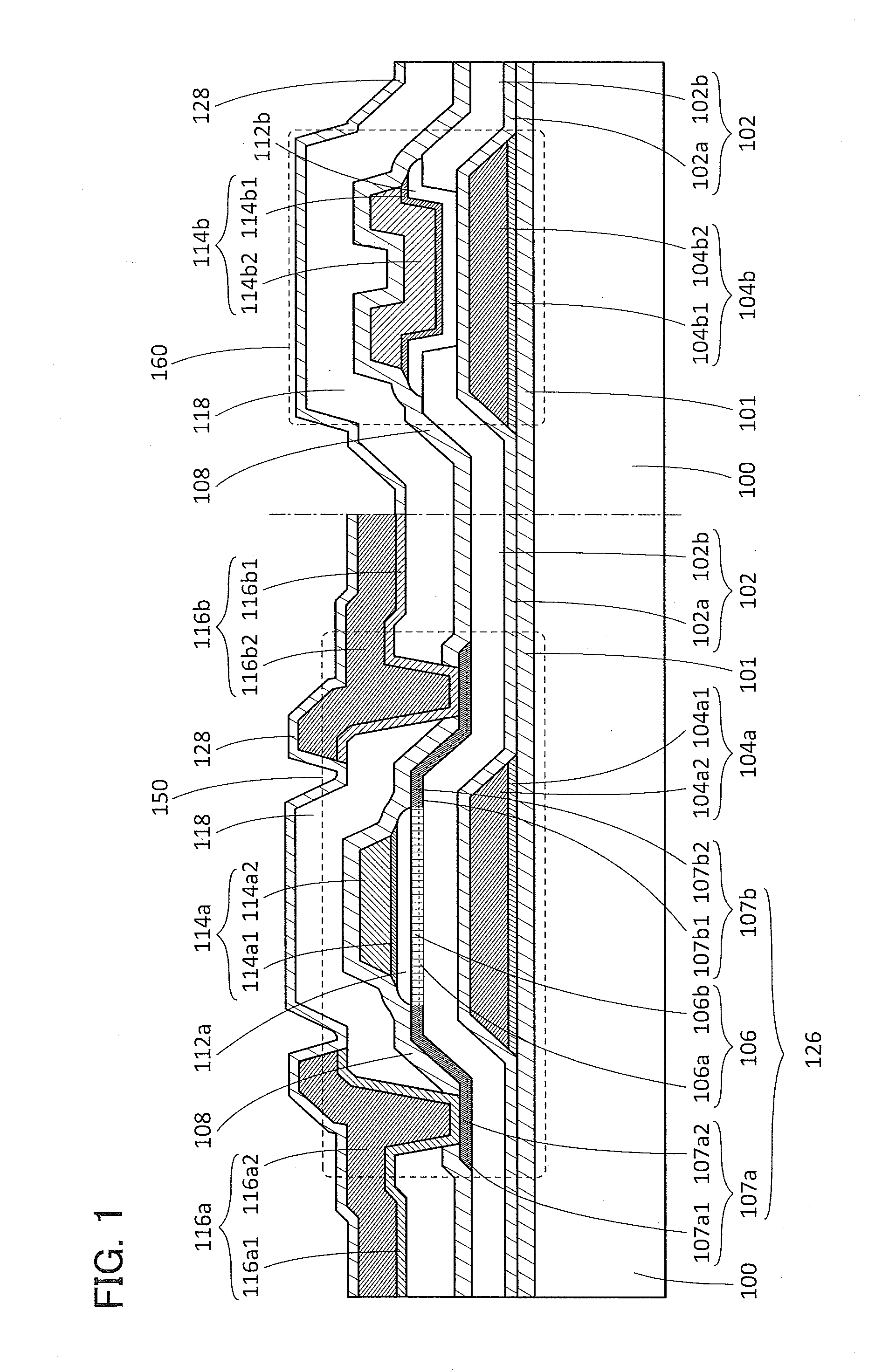
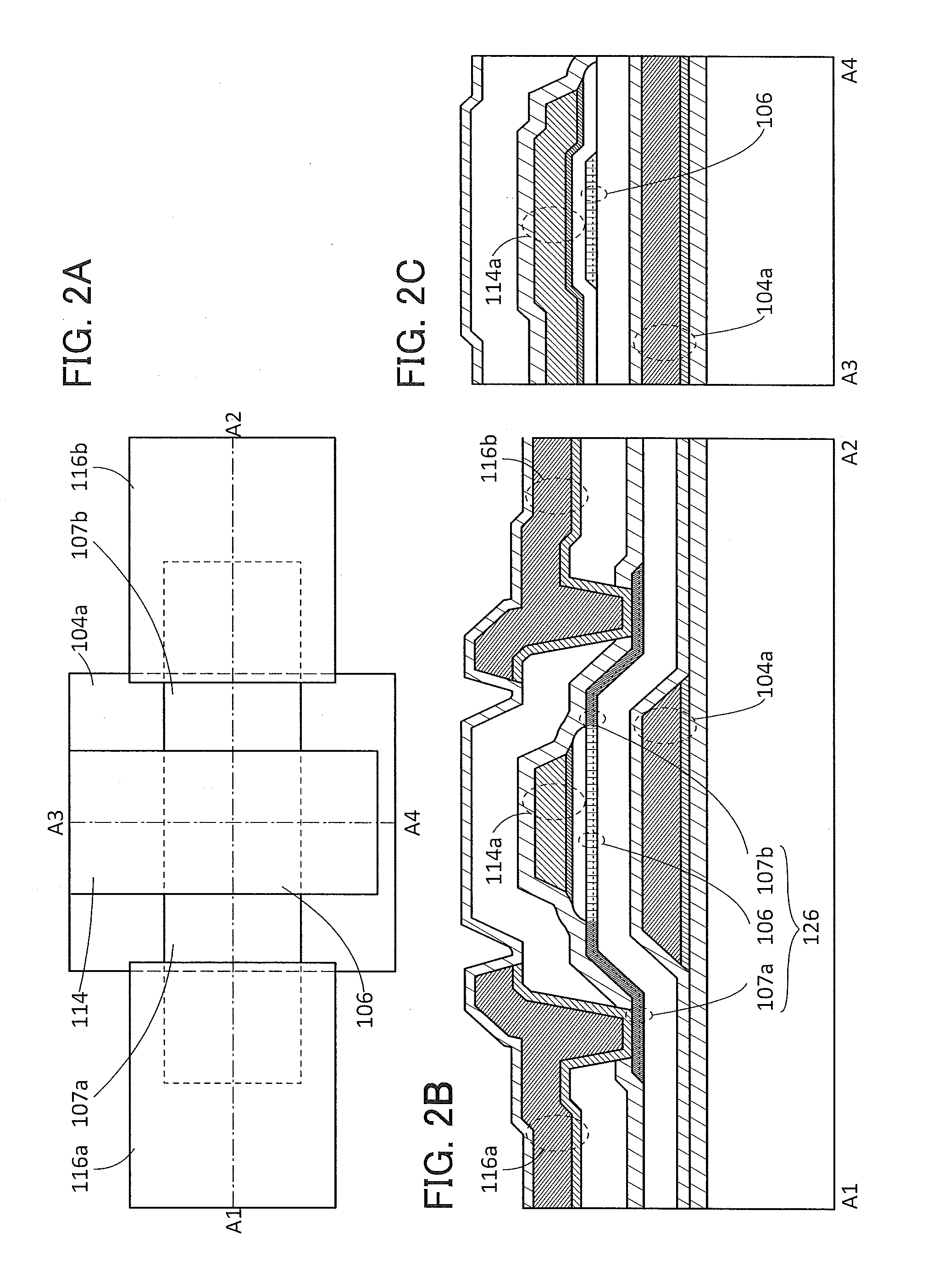
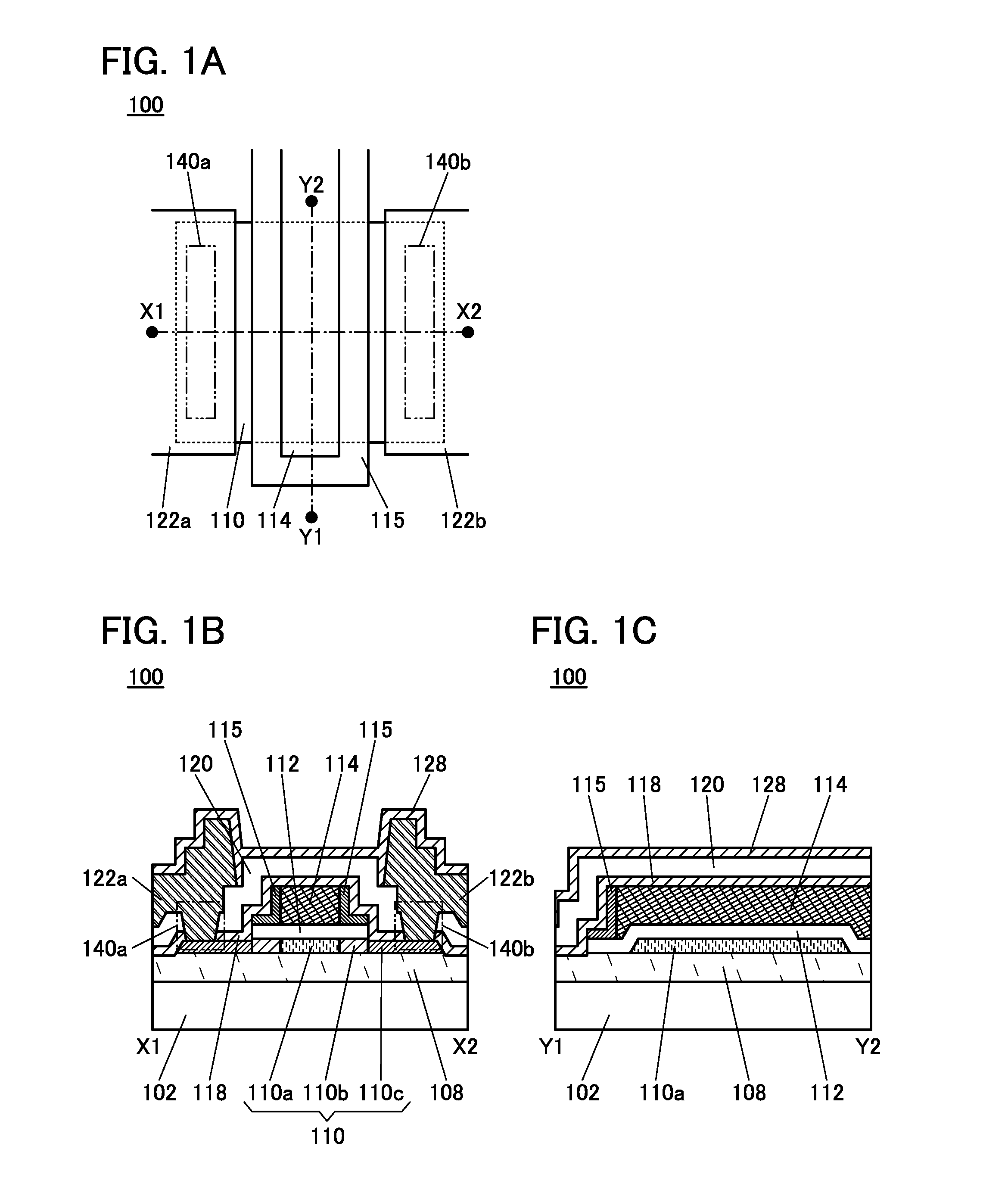
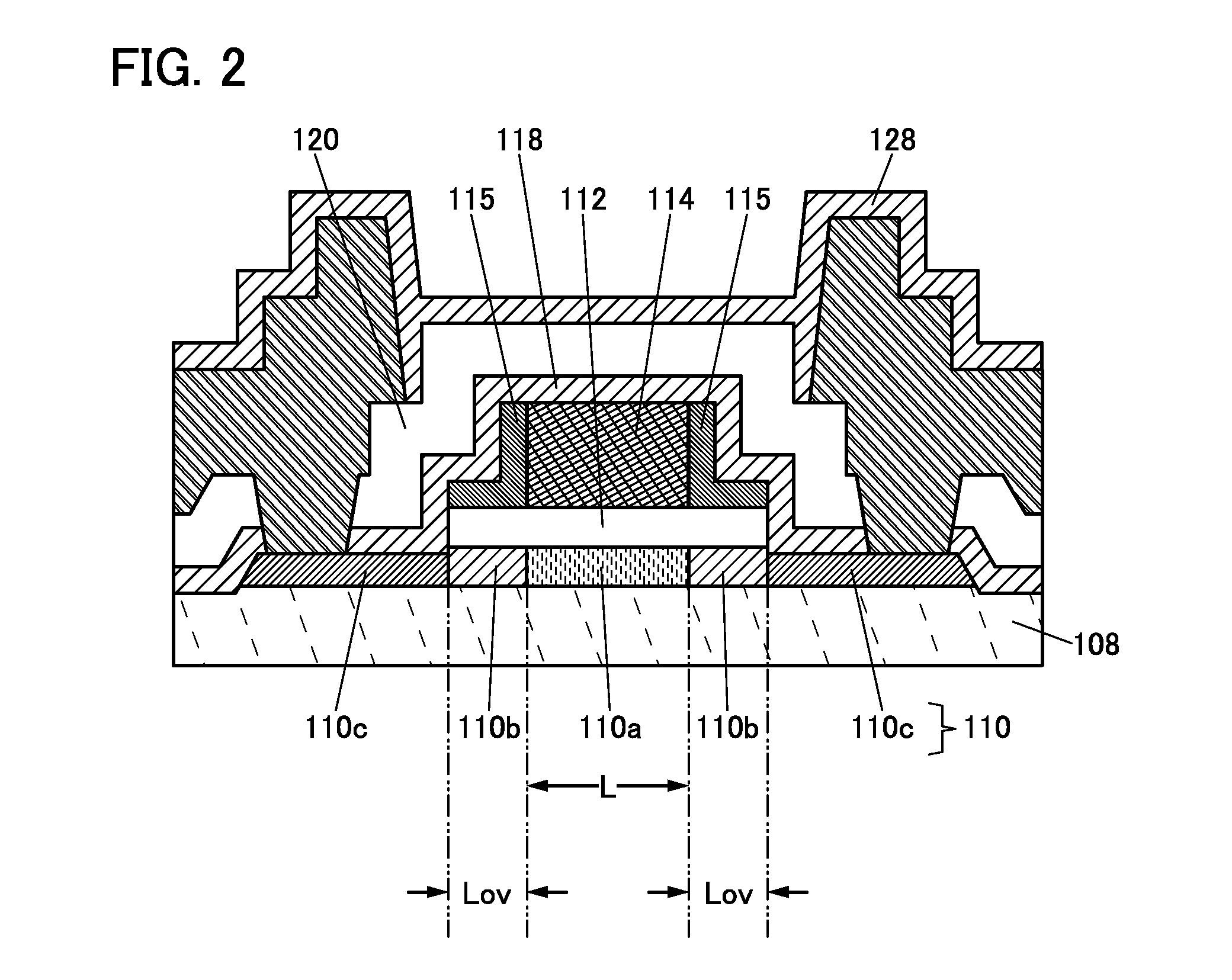
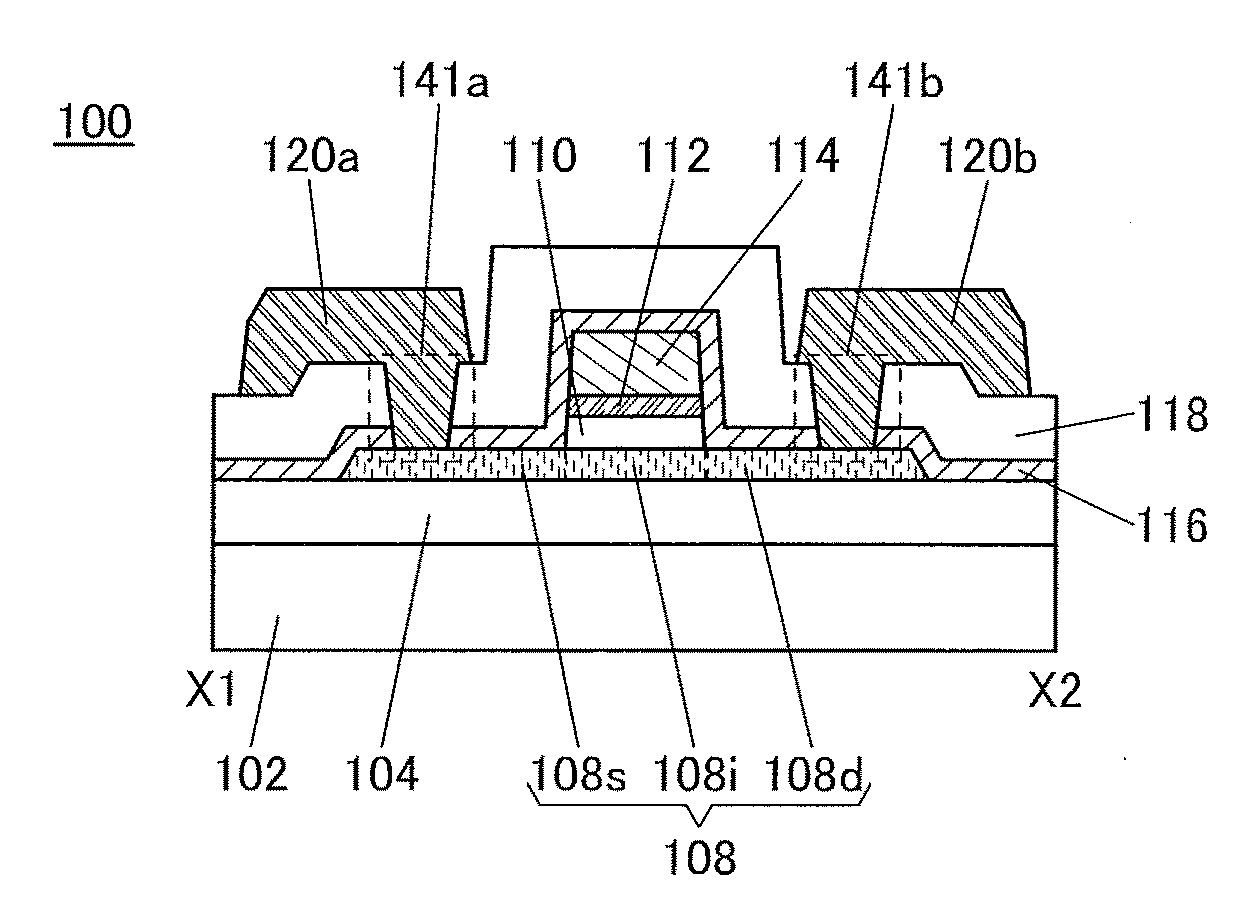
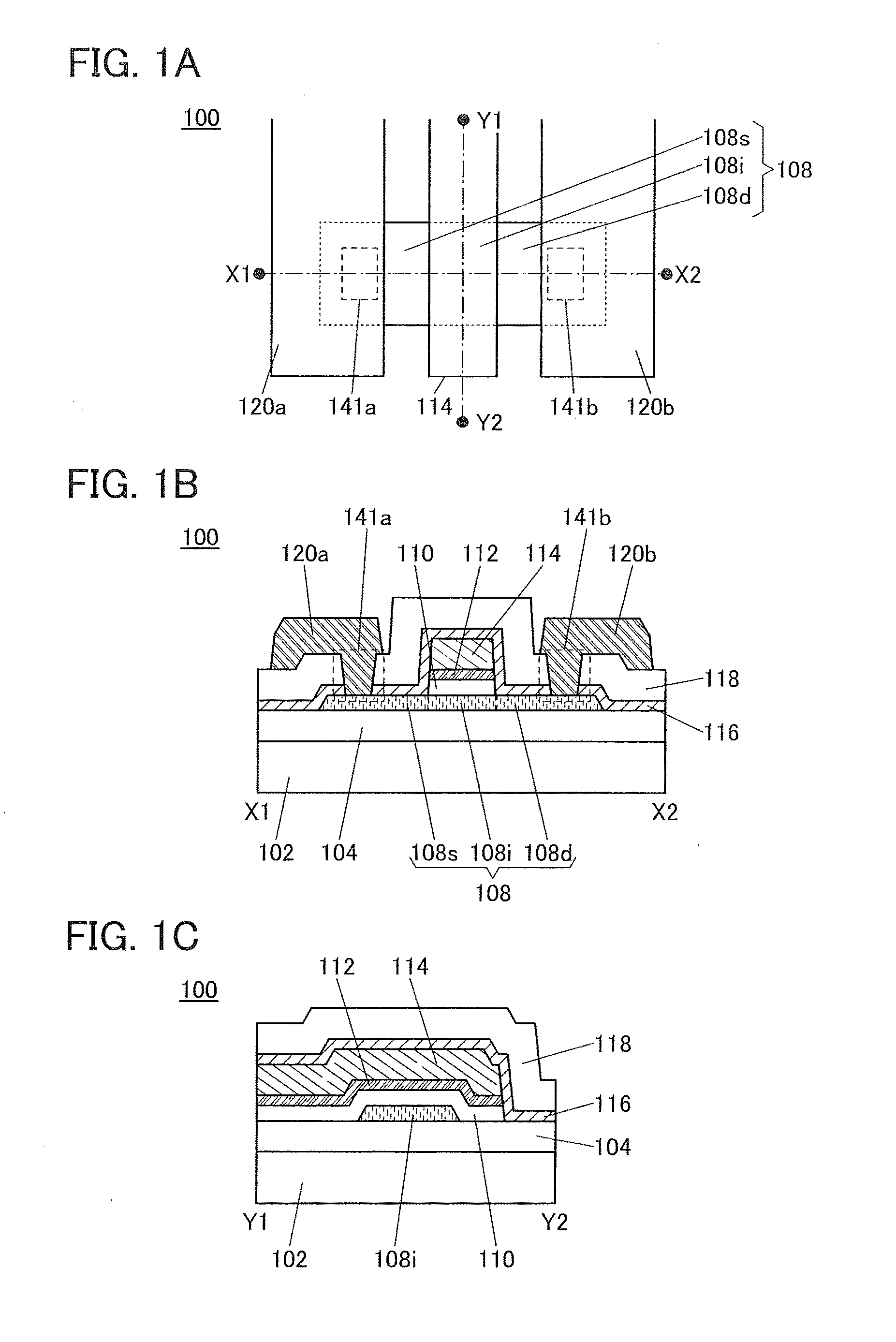
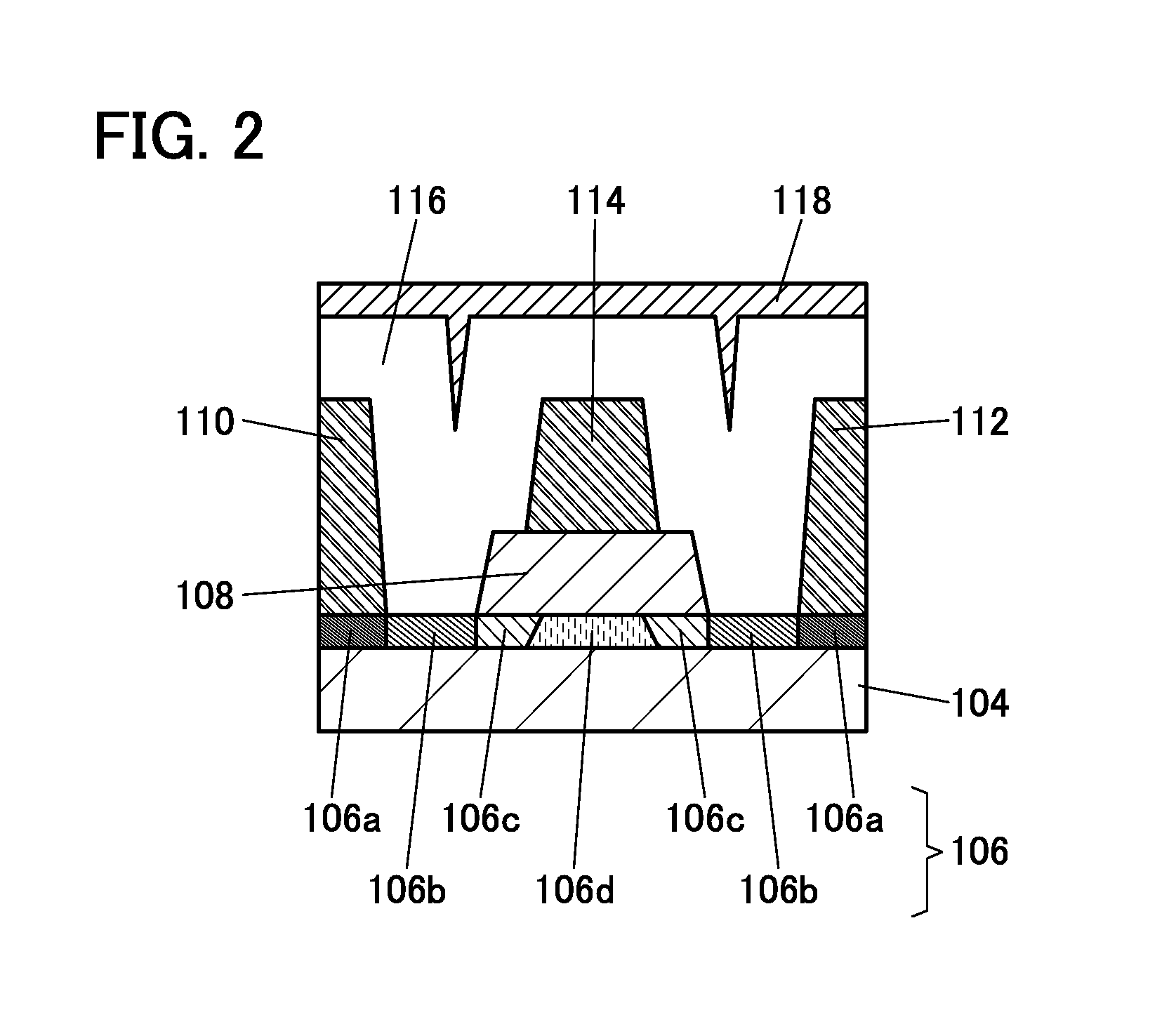
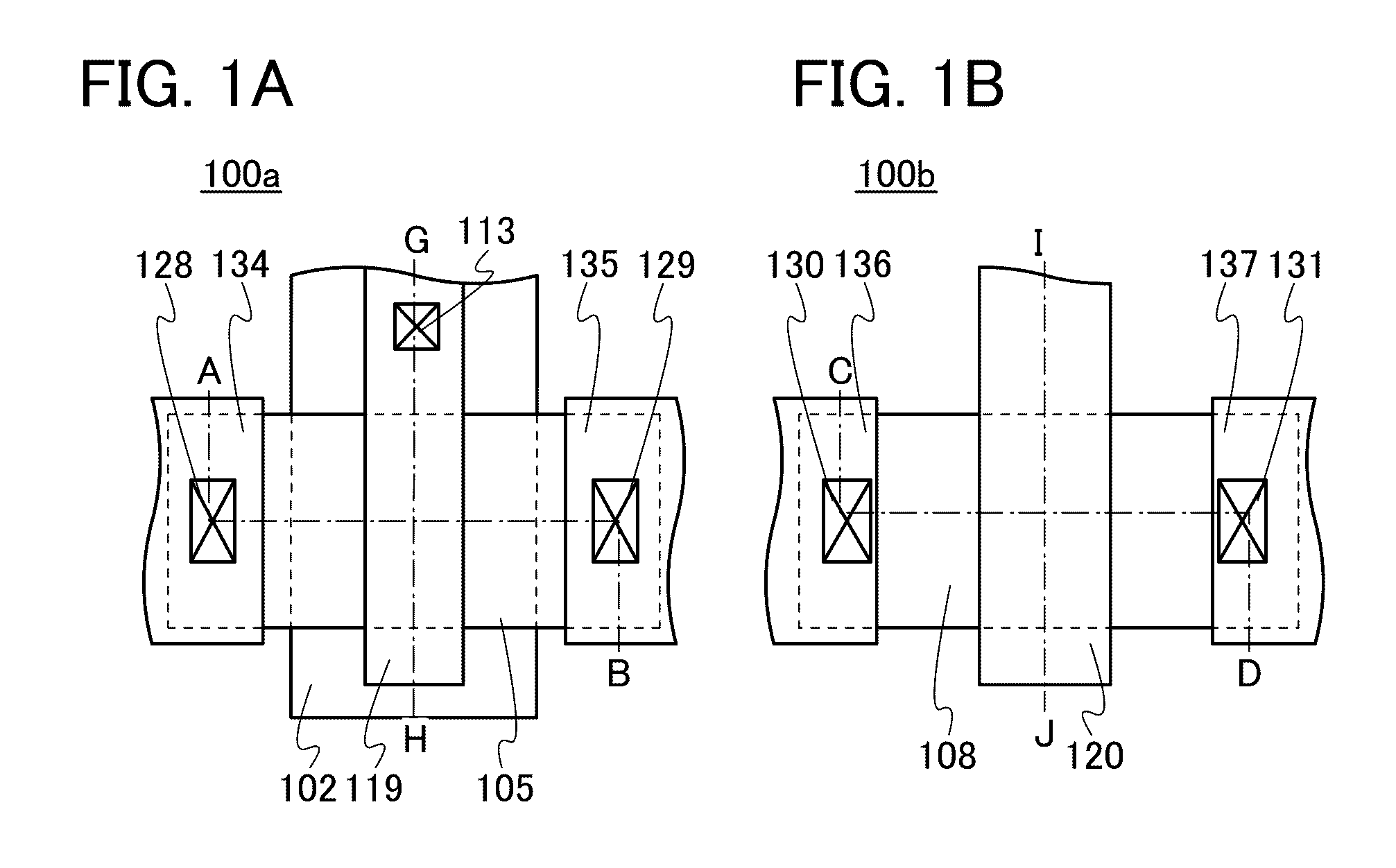
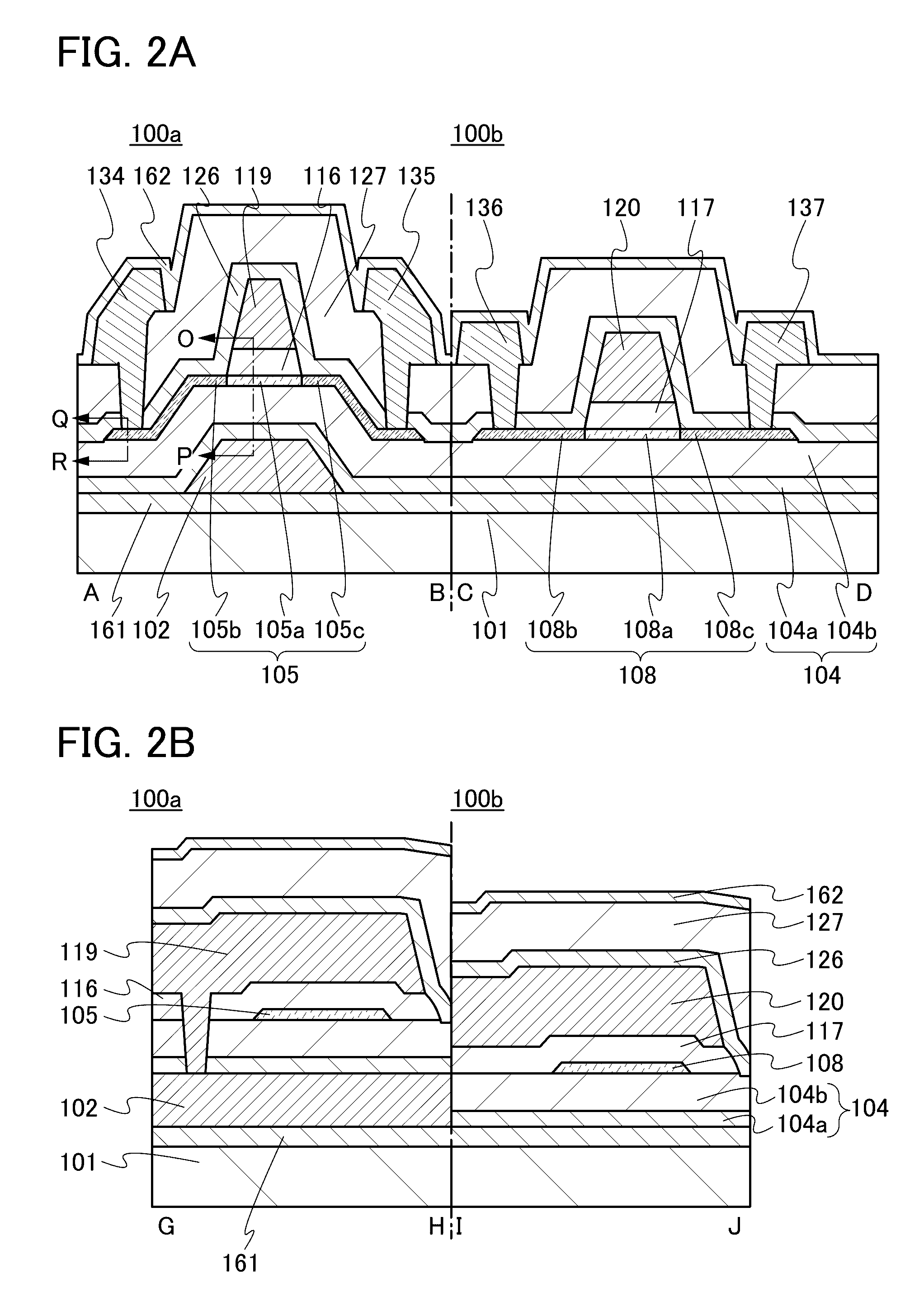
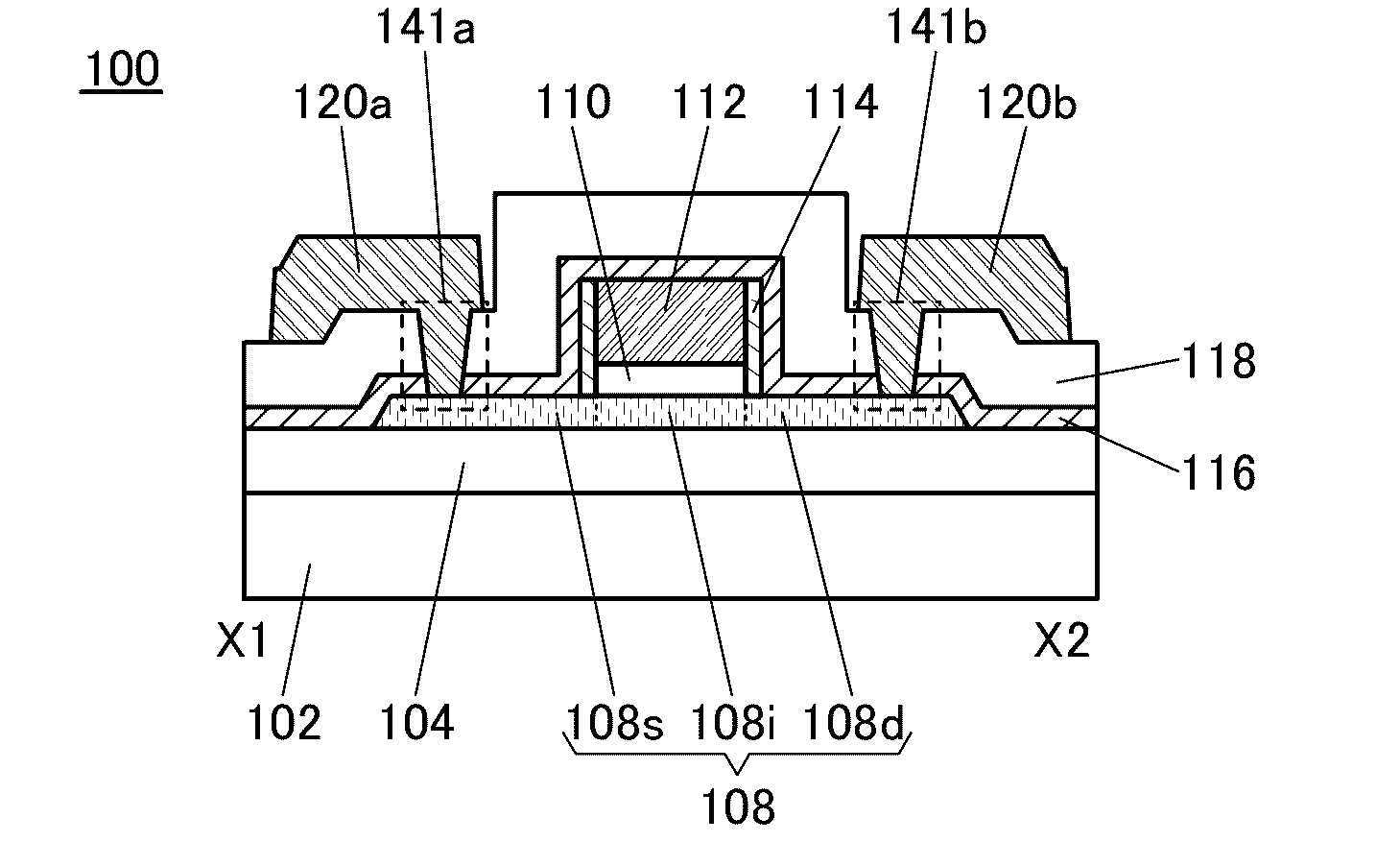
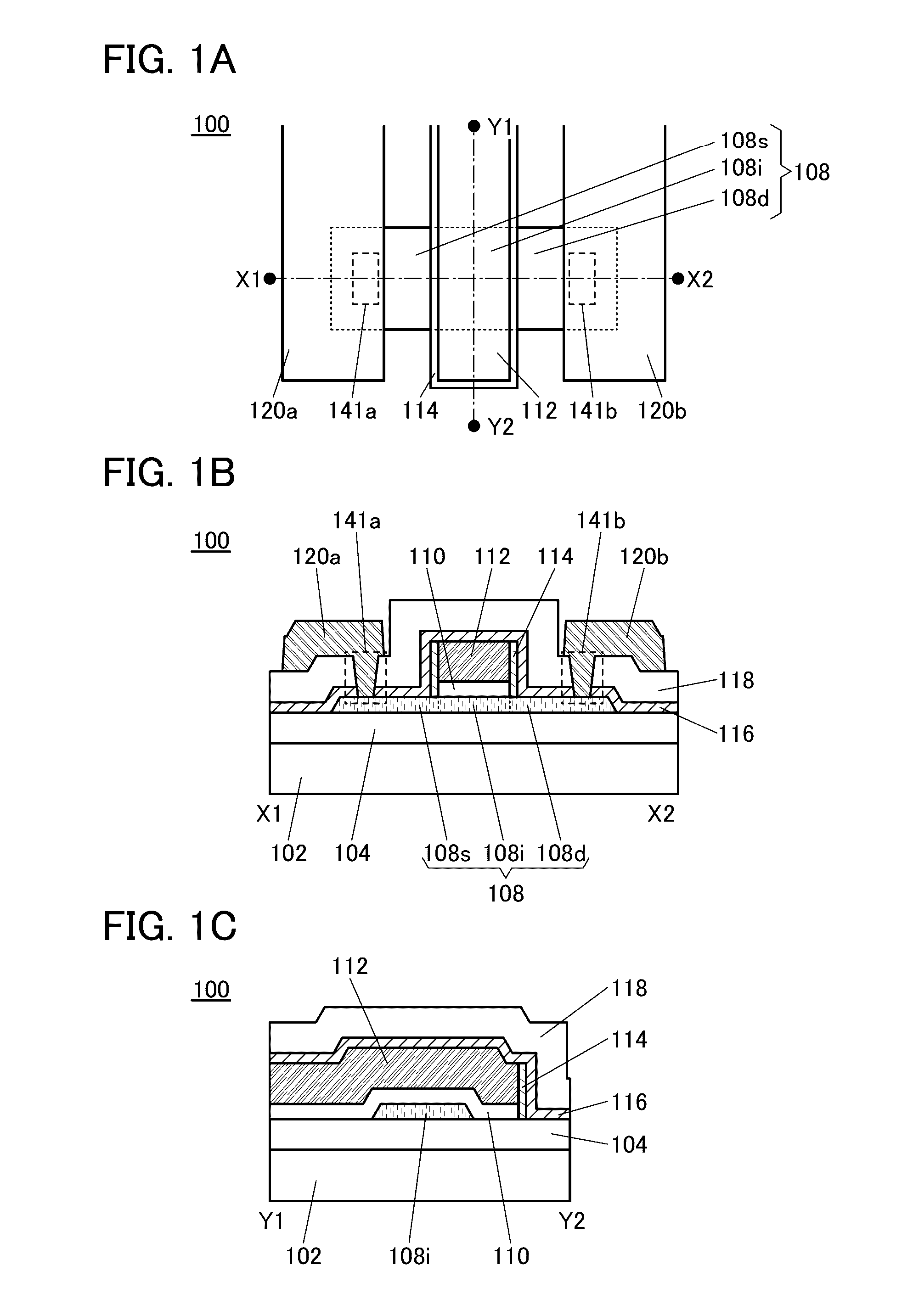
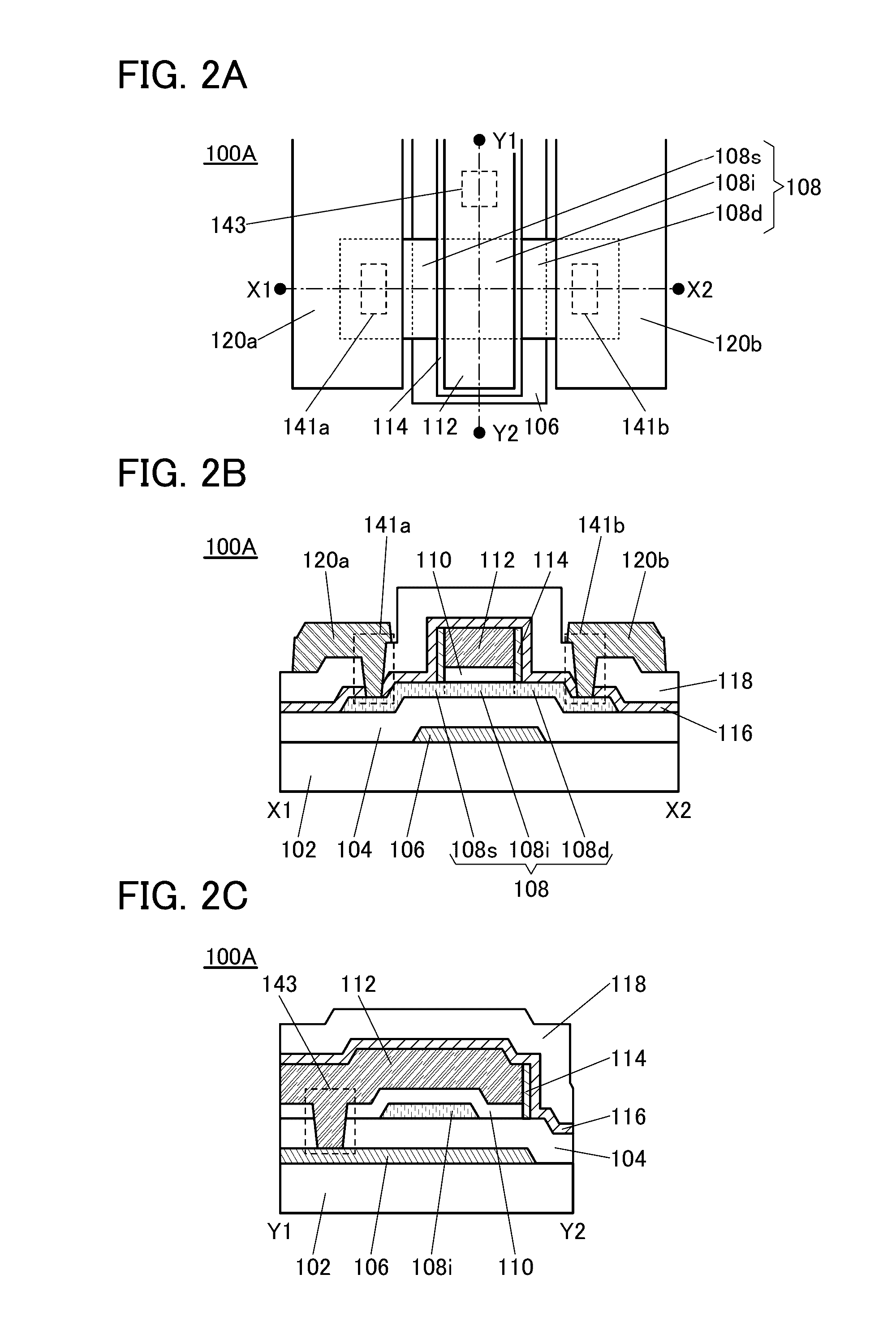
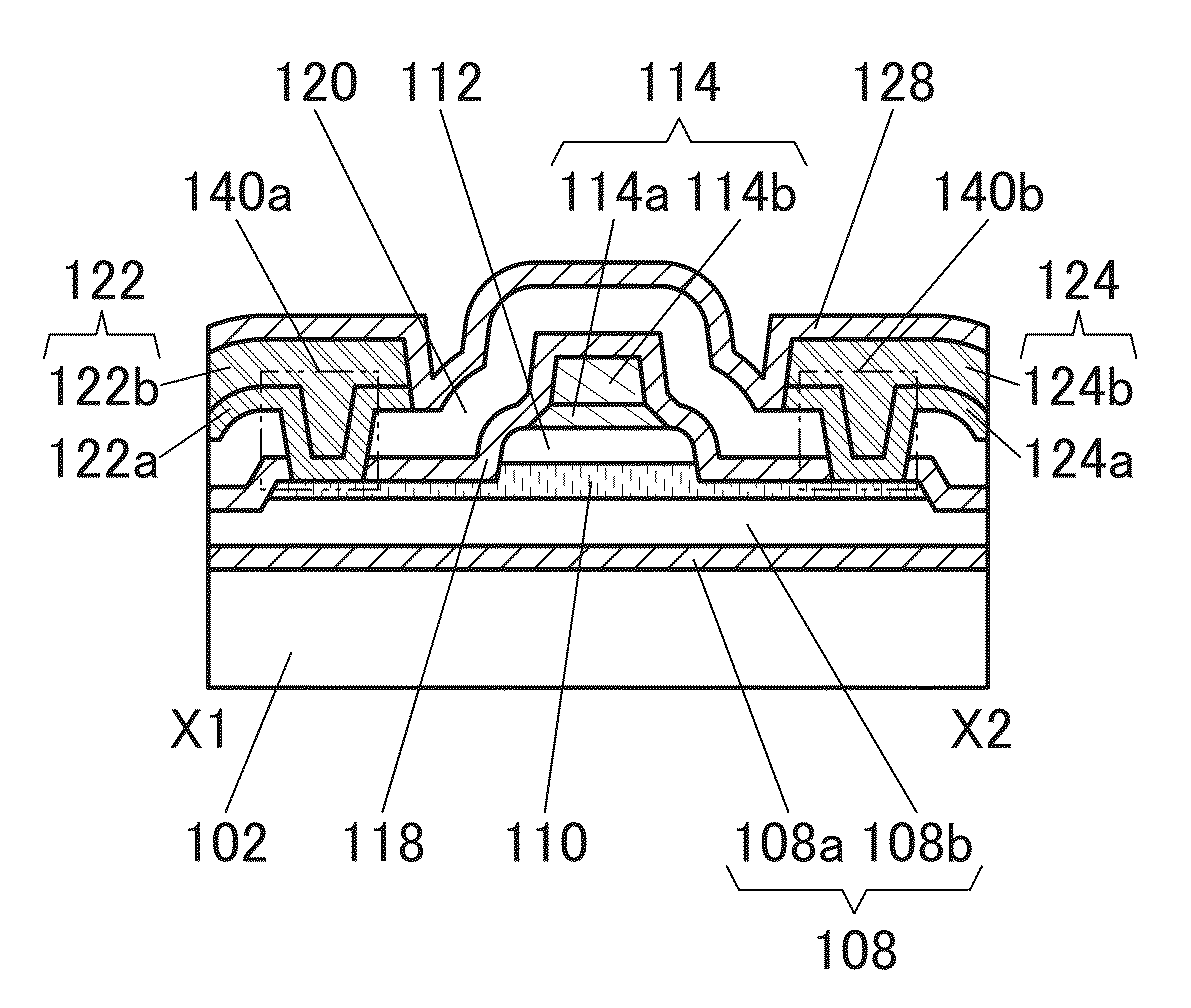
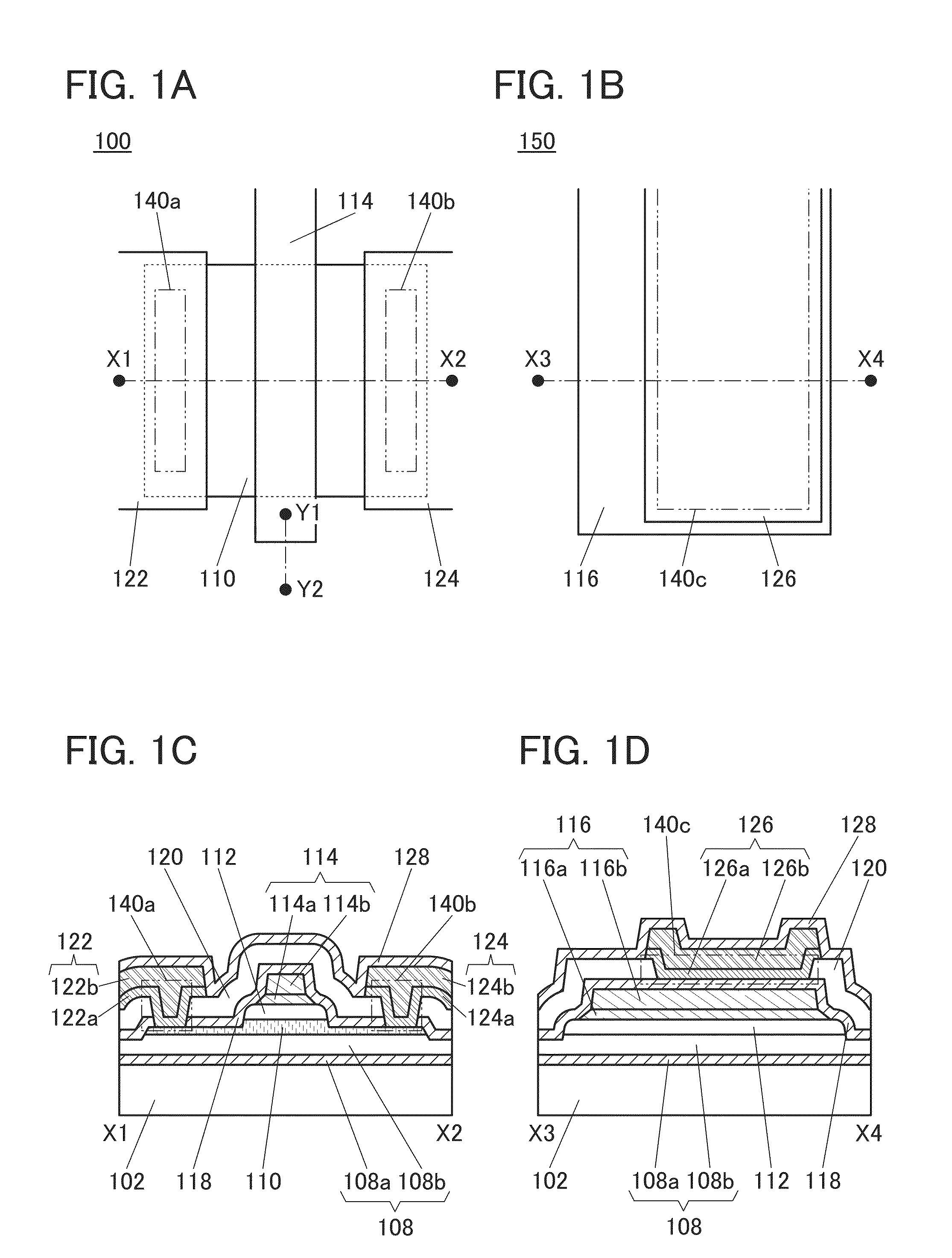
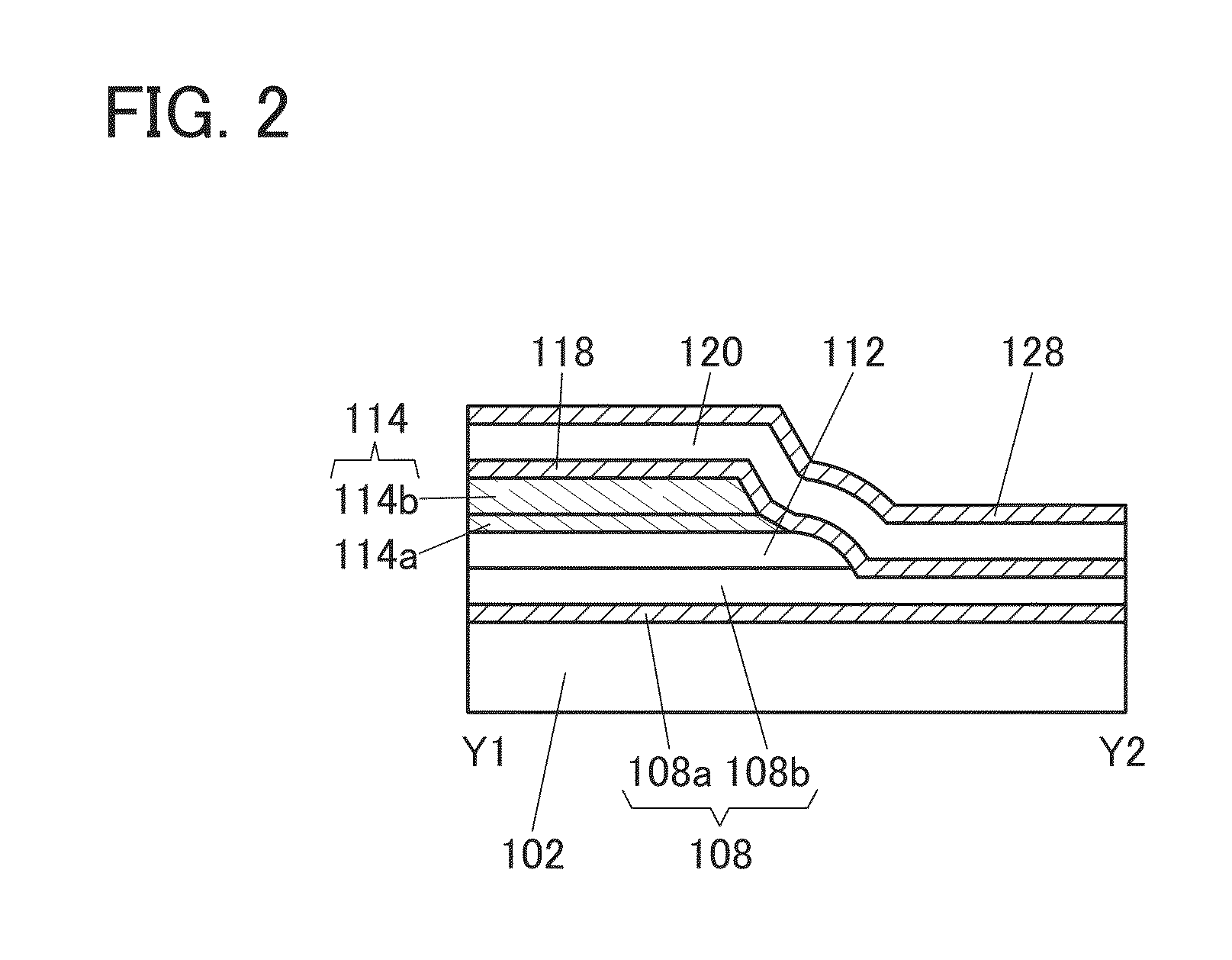
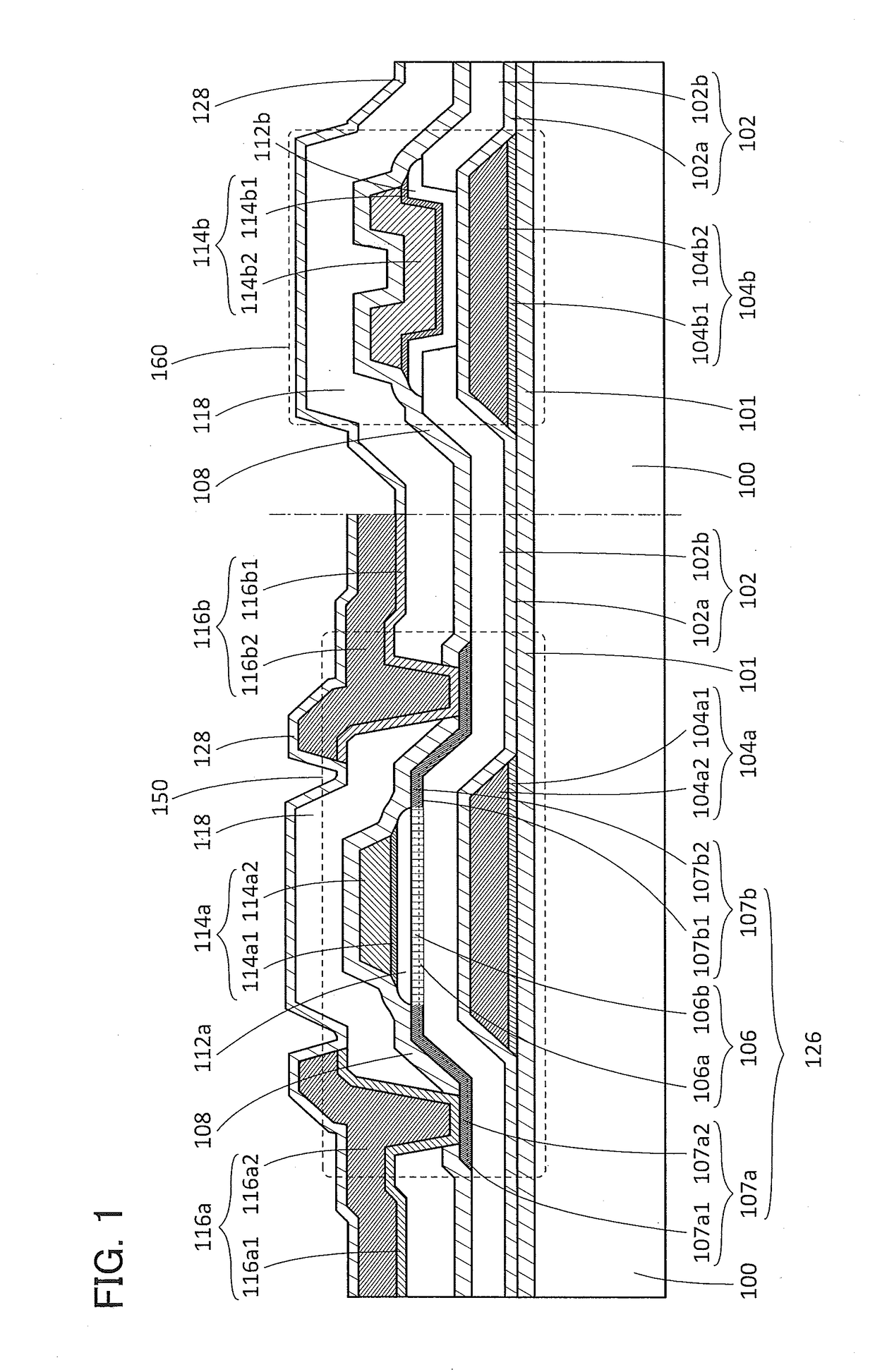
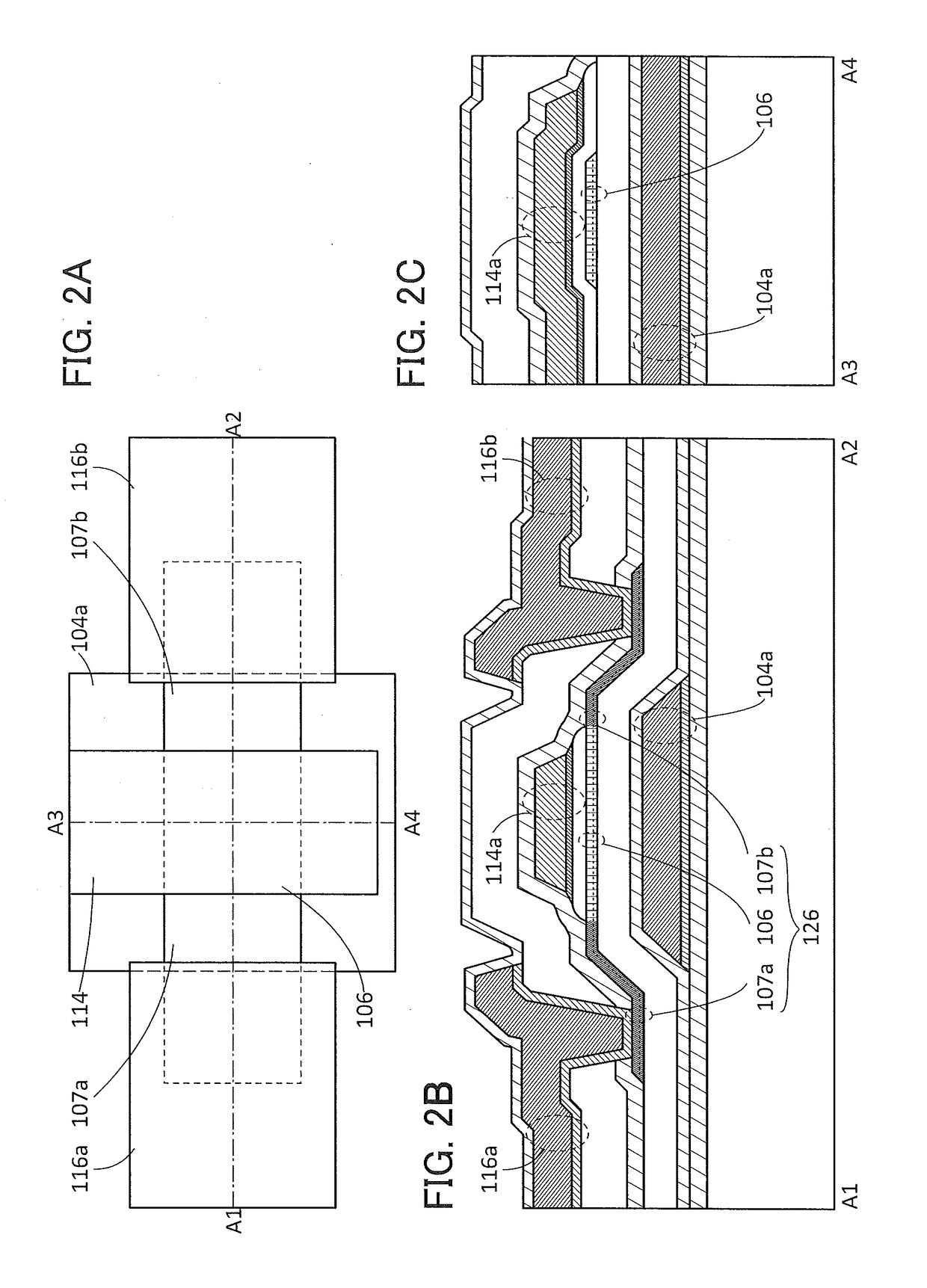
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150228803A1Stable semiconductor characteristicSimple manufacturing processTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitHydrogen
The semiconductor device includes a first transistor provided in a driver circuit portion and a second transistor provided in a pixel portion; the first transistor and the second transistor have different structures. In an oxide semiconductor film of each of the transistors, an impurity element is contained in regions which do not overlap with a gate electrode. The regions of the oxide semiconductor film which contain the impurity element function as low-resistance regions. Furthermore, the regions of the oxide semiconductor film which contain the impurity element are in contact with a film containing hydrogen. Furthermore, the first transistor provided in the driver circuit portion may include the oxide semiconductor film in which a first film and a second film are stacked, and the second transistor provided in the pixel portion may include the oxide semiconductor film which differs from the first film in the atomic ratio of metal elements.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
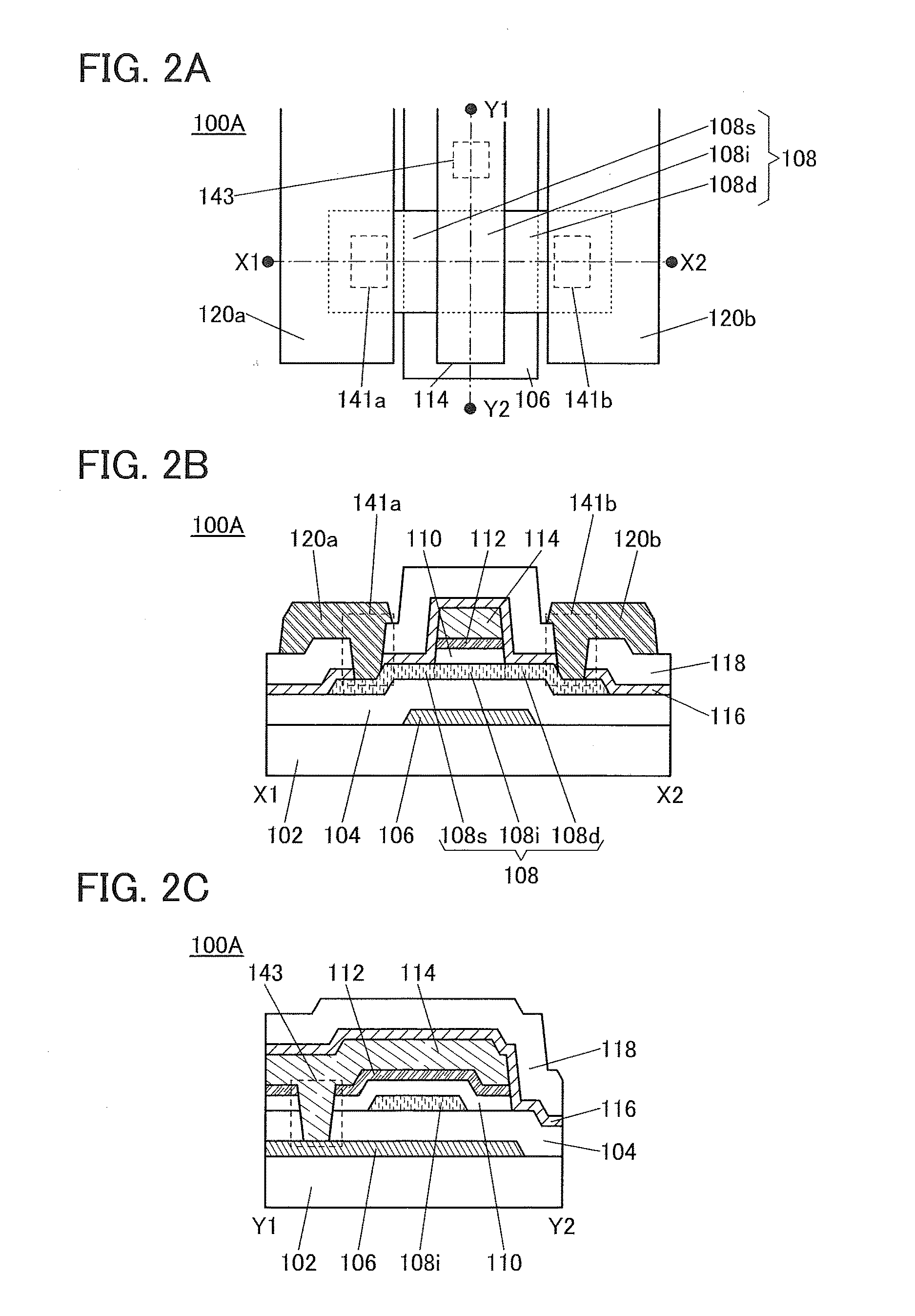
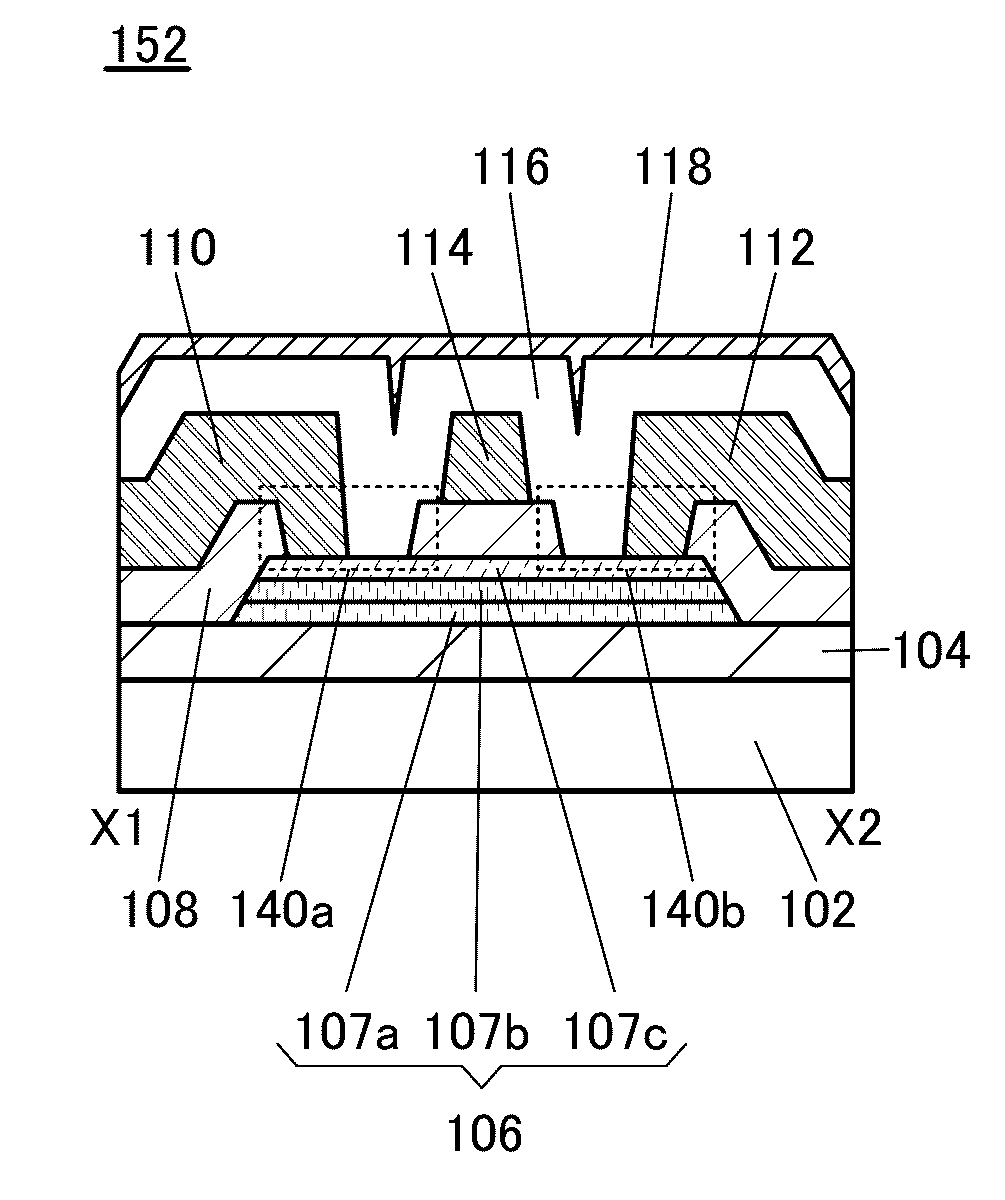
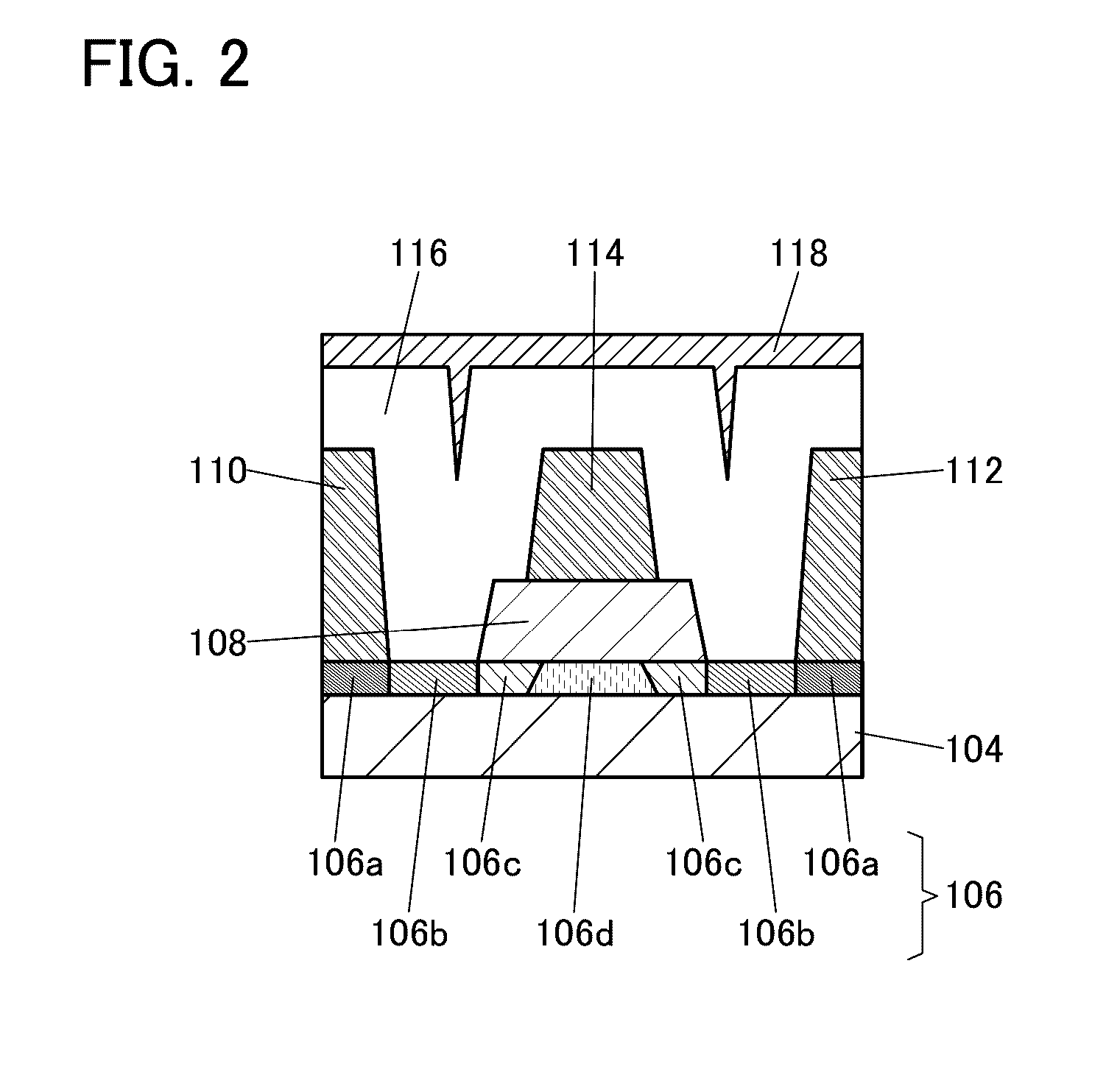
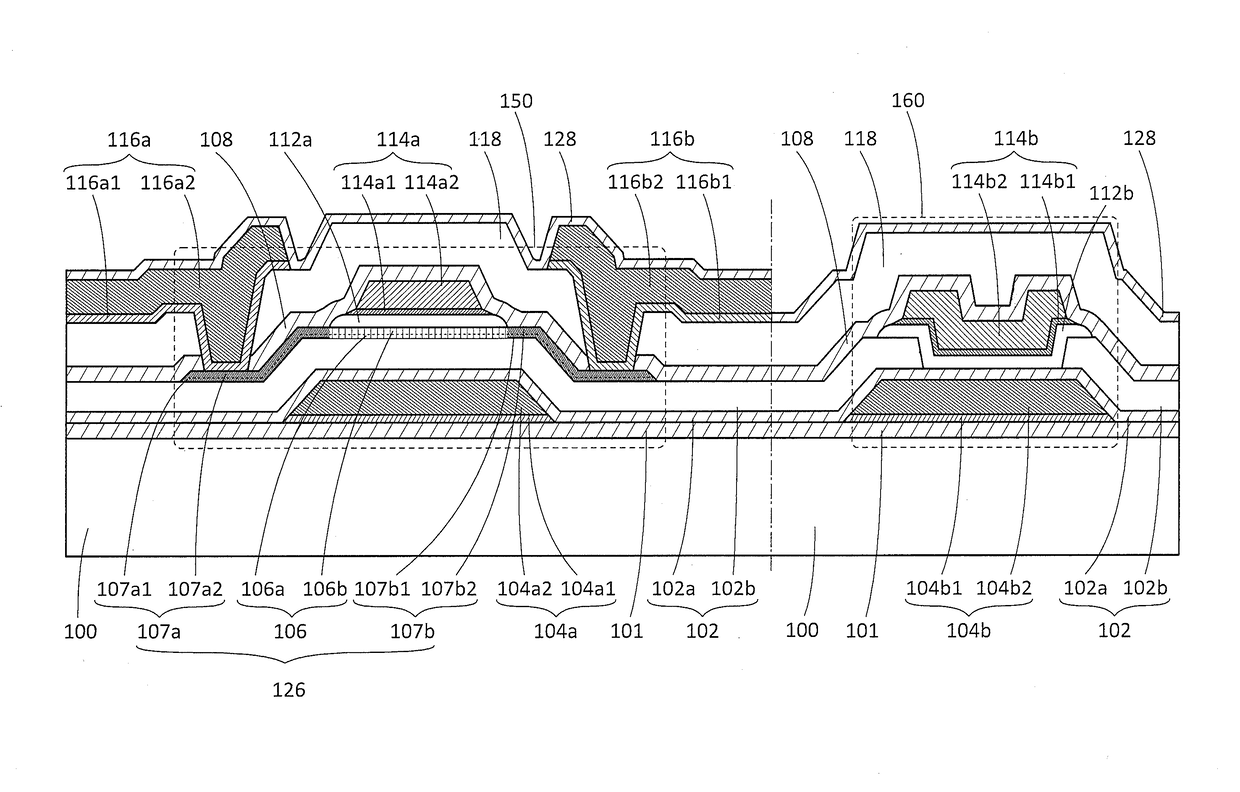
Semiconductor device, display device including the semiconductor device, display module including the display device, and electronic device including the semiconductor device, the display device, and the display module
ActiveUS20150221678A1Stable semiconductor characteristicSimple manufacturing processTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceCapacitor
To provide a semiconductor device including a planar transistor having an oxide semiconductor and a capacitor. In a semiconductor device, a transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film, a gate insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film, a gate electrode over the gate insulating film, a second insulating film over the gate electrode, a third insulating film over the second insulating film, and a source and a drain electrodes over the third insulating film; the source and the drain electrodes are electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; a capacitor includes a first and a second conductive films and the second insulating film; the first conductive film and the gate electrode are provided over the same surface; the second conductive film and the source and the drain electrodes are provided over the same surface; and the second insulating film is provided between the first and the second conductive films.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
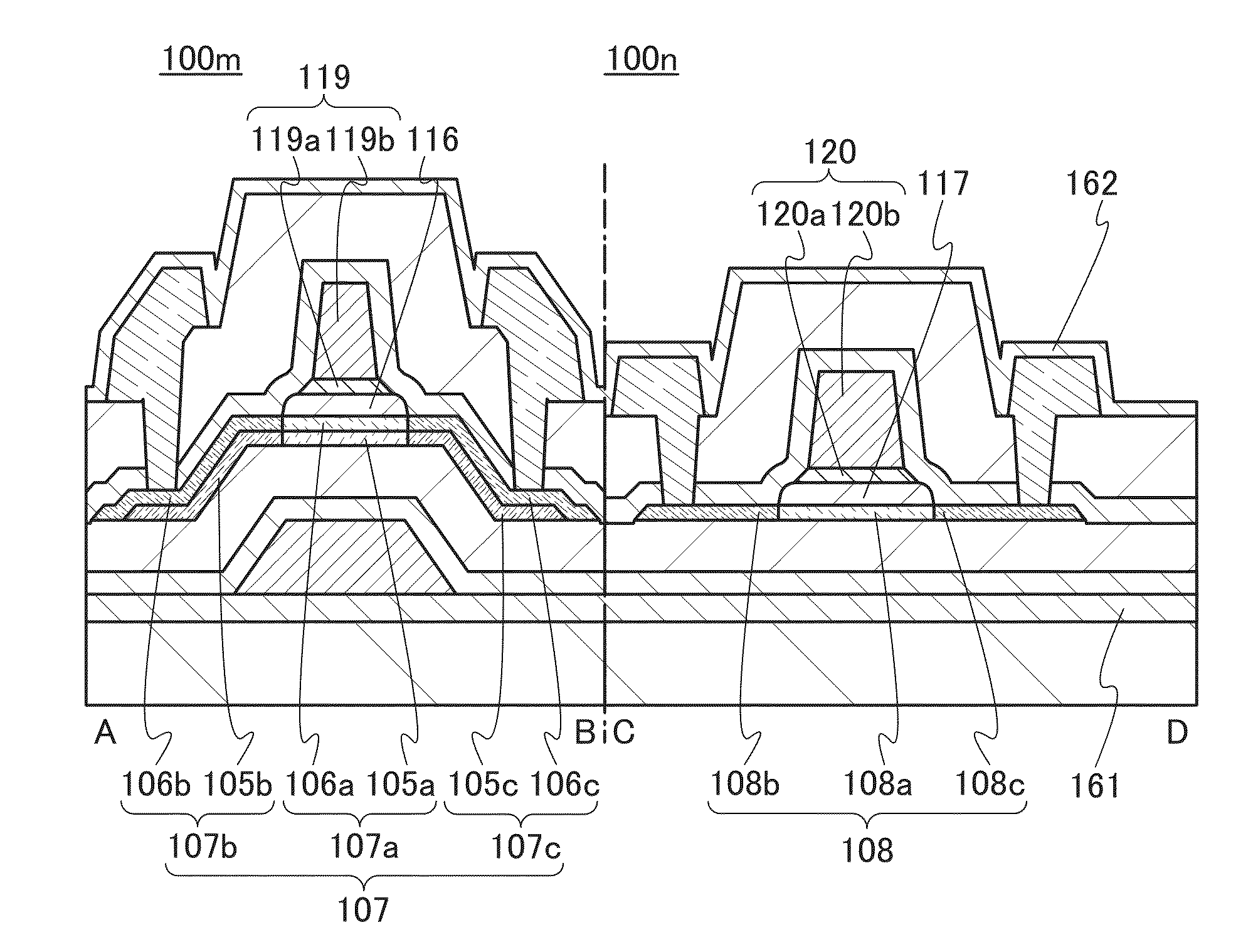
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150228799A1Stable semiconductor characteristicSimple manufacturing processTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitPower semiconductor device
A semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor in which on-state current is high is provided. The semiconductor device includes a first transistor provided in a driver circuit portion and a second transistor provided in a pixel portion; the first transistor and the second transistor have different structures. Furthermore, the first transistor and the second transistor are transistors having a top-gate structure. In an oxide semiconductor film of each of the transistors, an impurity element is contained in regions which do not overlap with a gate electrode. The regions of the oxide semiconductor film which contain the impurity element function as low-resistance regions. Furthermore, the regions of the oxide semiconductor film which contain the impurity element are in contact with a film containing hydrogen. The first transistor provided in the driver circuit portion includes two gate electrodes between which the oxide semiconductor film is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
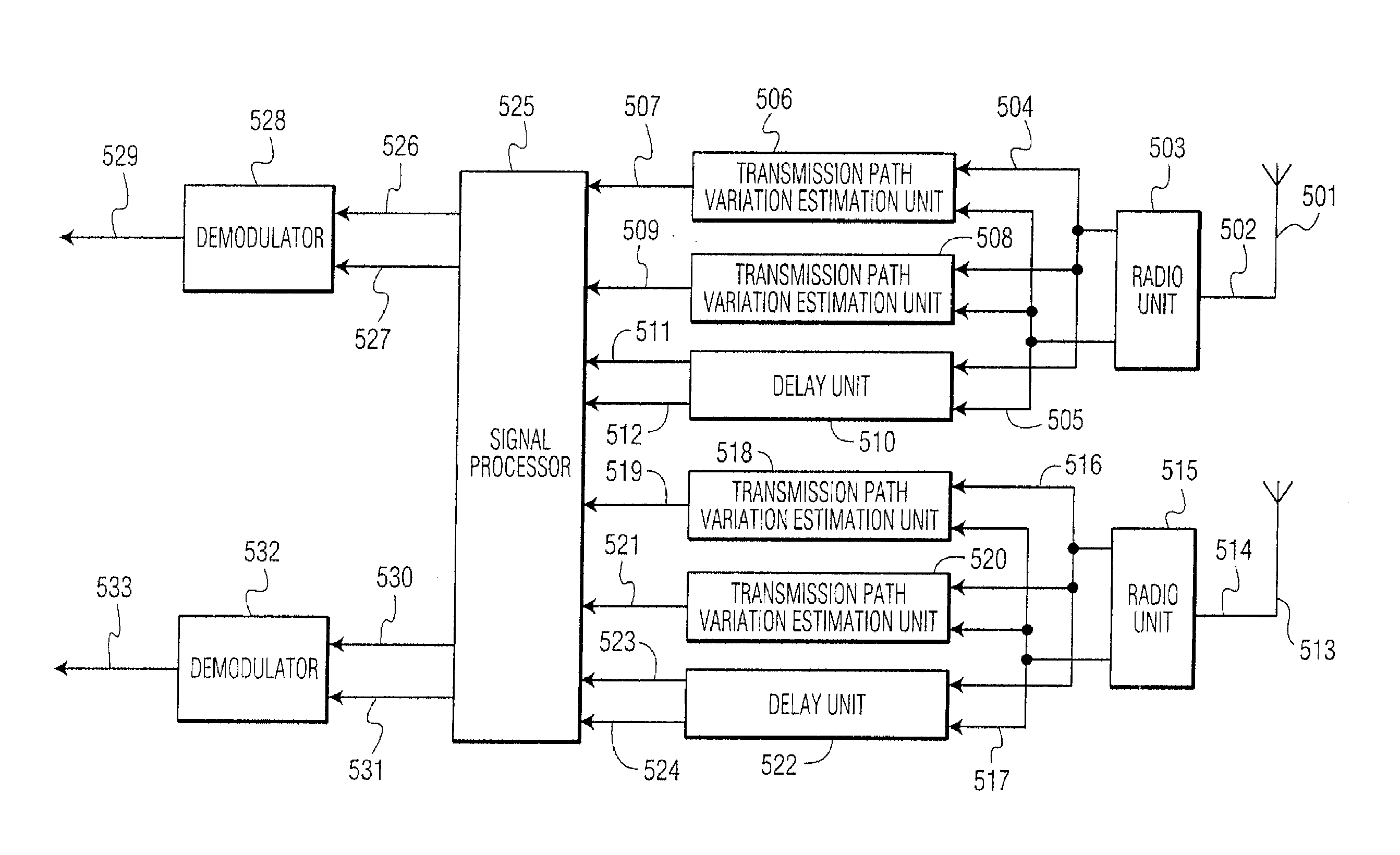
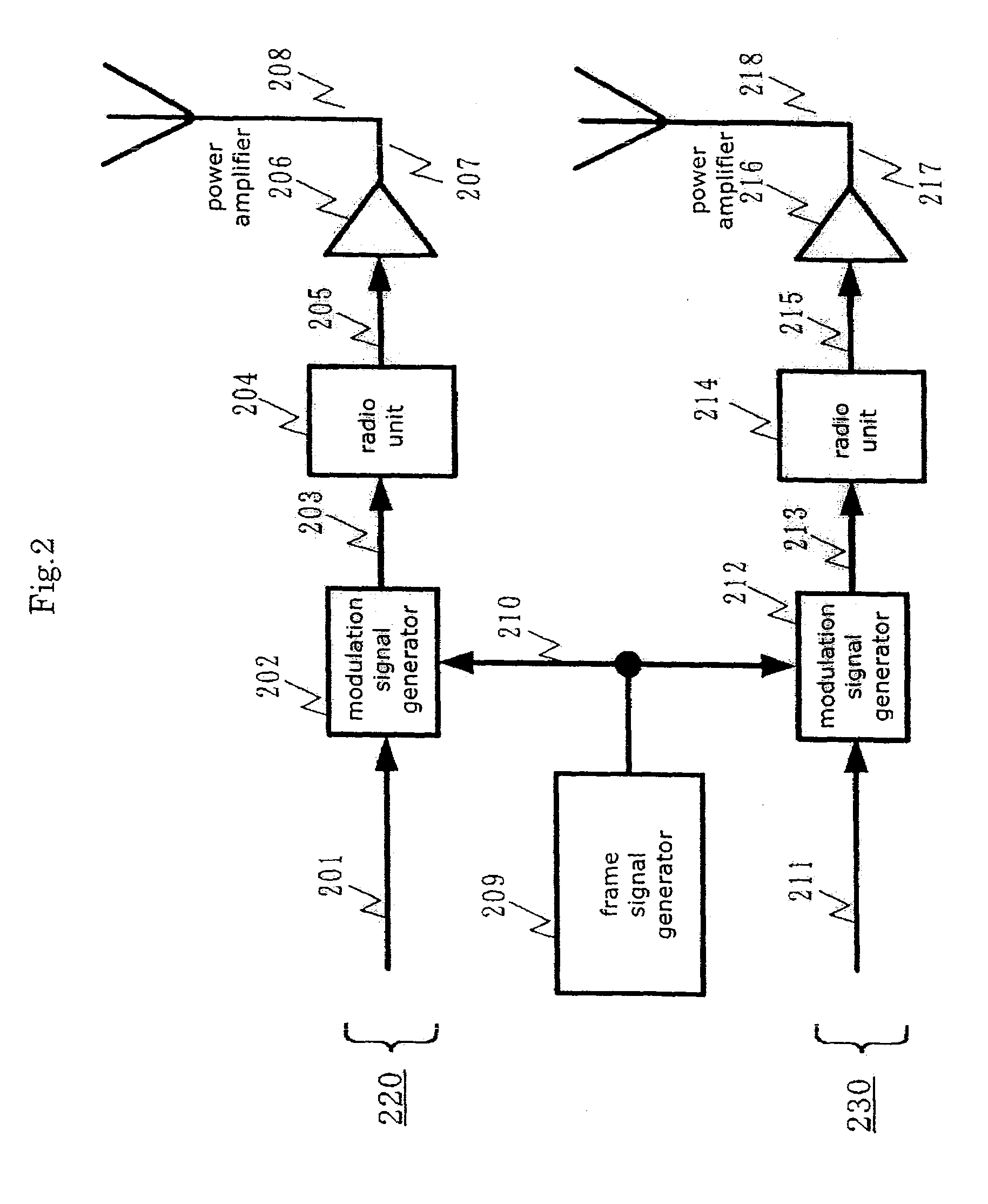
Reception apparatus
ActiveUS7266167B2Estimate channels accuratelySignal delaySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase differenceEngineering
A reception apparatus includes a plurality of antennas for receiving modulation signals of channels in the same frequency band, a received signal strength intensity estimation unit for estimating the reception received signal strength intensity of each reception signal, transmission path fluctuation estimation units for estimating a transmission path fluctuation of each channel of the reception signal, phase difference estimation units for calculating a phase difference of the transmission path fluctuation estimation signal of a predetermined channel of each antenna and outputting it as a phase difference signal, and a signal selection unit for selecting and outputting a reception quadrate baseband signal for isolating a signal of each channel from the reception signals and a transmission path fluctuation estimation signal of each channel. Thus, by isolating and demodulating a plurality of multiplexed modulated signals received, it is possible to improve the data transmission rate.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Reception apparatus
InactiveUS20070165733A1Estimate channels accuratelySignal delaySpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationMultiplexingPhase difference
A reception apparatus includes a plurality of antennas for receiving modulation signals of channels in the same frequency band, an received signal strength intensity estimation unit for estimating the reception received signal strength intensity of each reception signal, transmission path fluctuation estimation units for estimating a transmission path fluctuation of each channel of the reception signal, phase difference estimation units for calculating a phase difference of the transmission path fluctuation estimation signal of a predetermined channel of each antenna and outputting it as a phase difference signal, and a signal selection unit for selecting and outputting a reception quadrate baseband signal for isolating a signal of each channel from the reception signals and a transmission path fluctuation estimation signal of each channel. Thus, by isolating and demodulating a plurality of muliplexed modulated signals received, it is possible to improve the data transmission rate.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
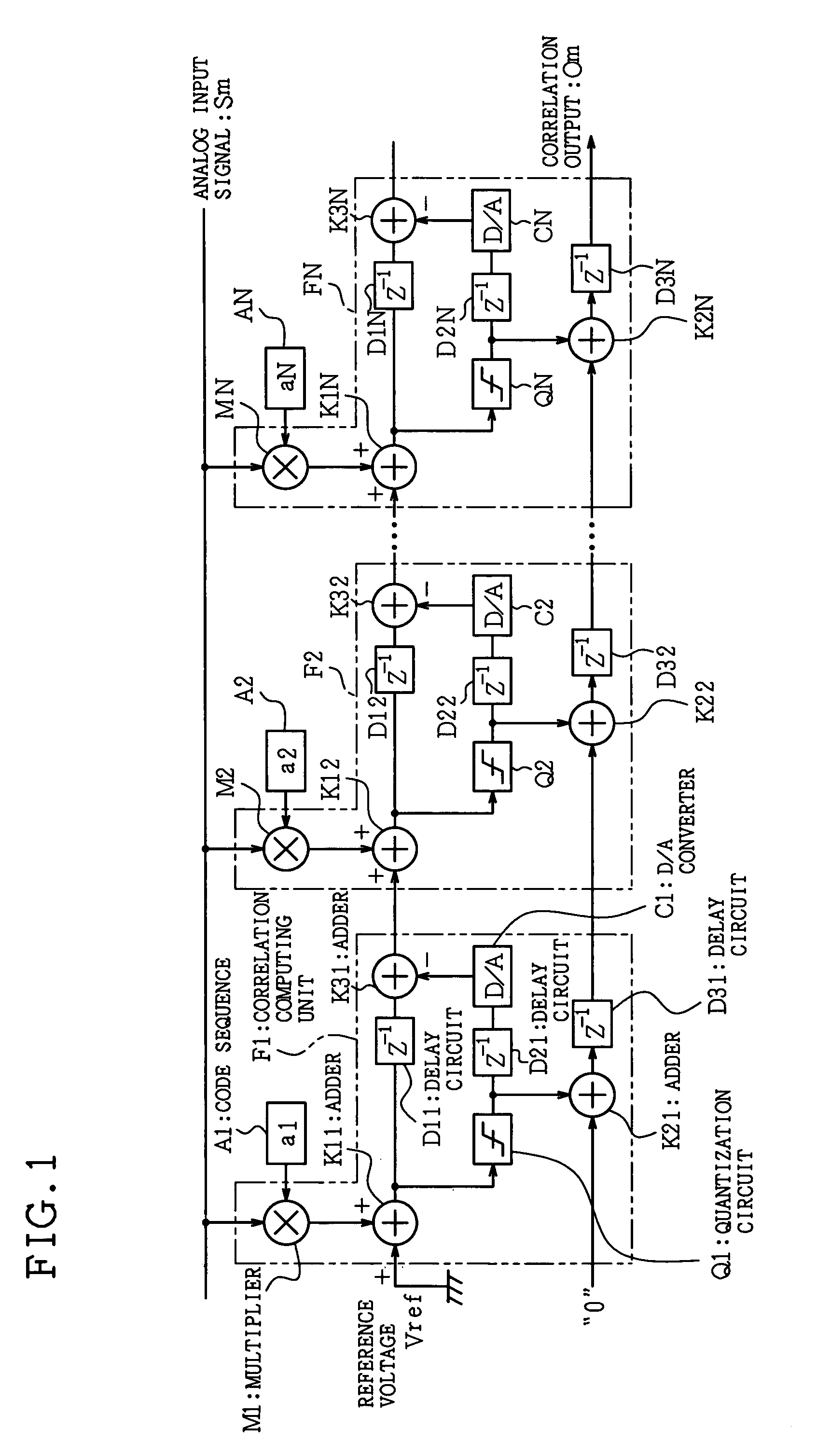
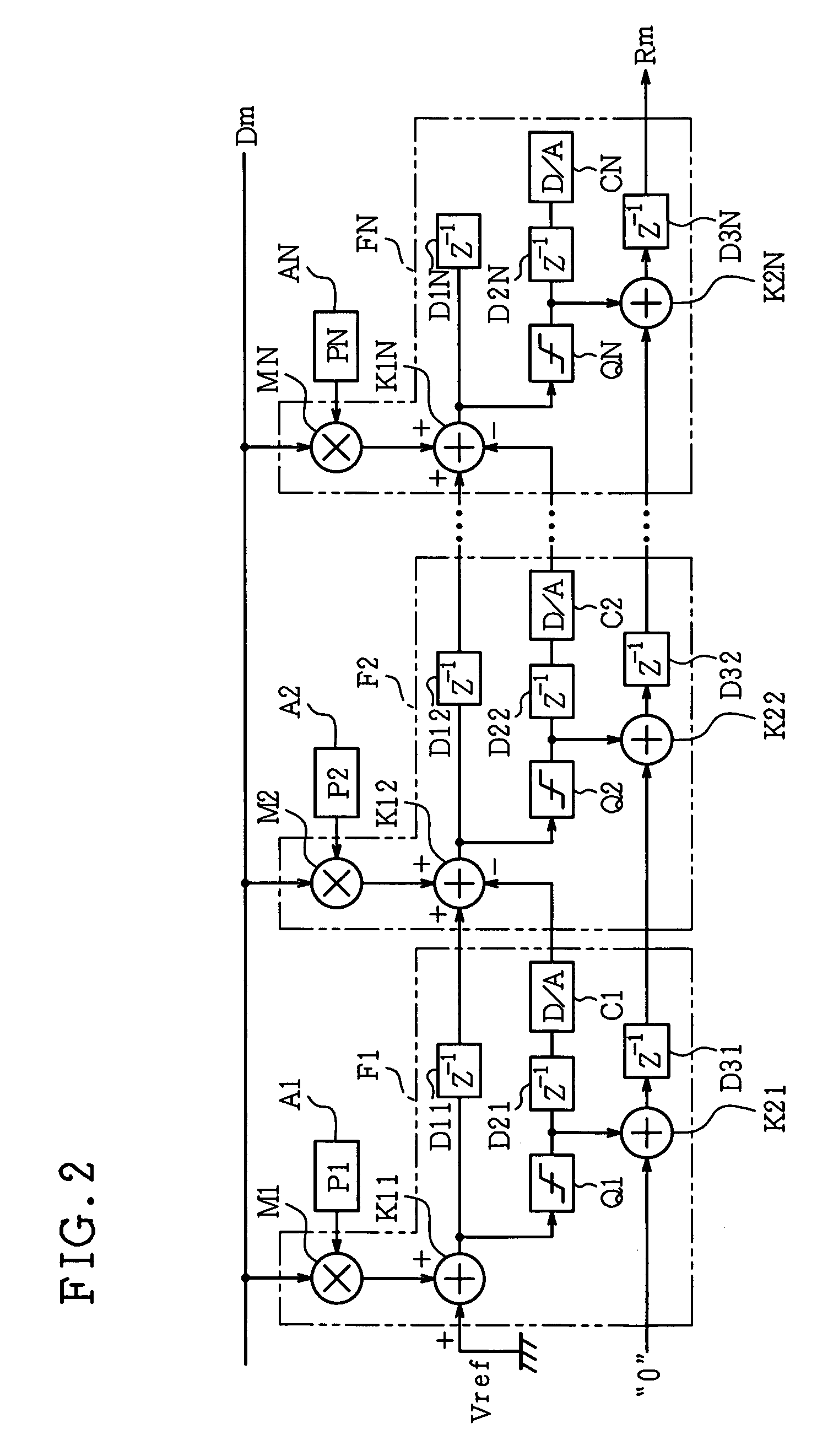
Filter circuit
InactiveUS6983011B1Reduce circuit sizeReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksPower saving provisionsComputer scienceDynamic range
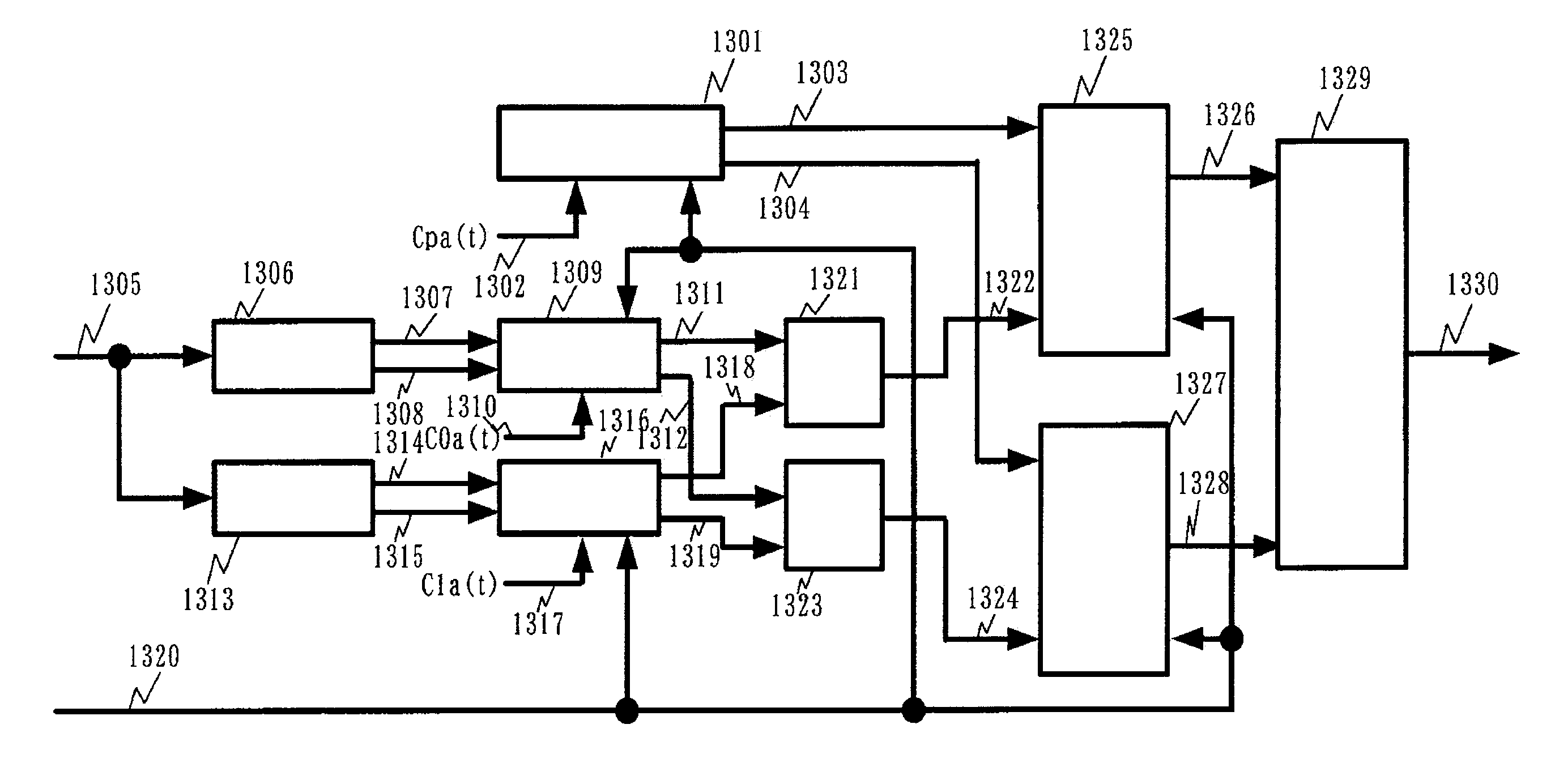
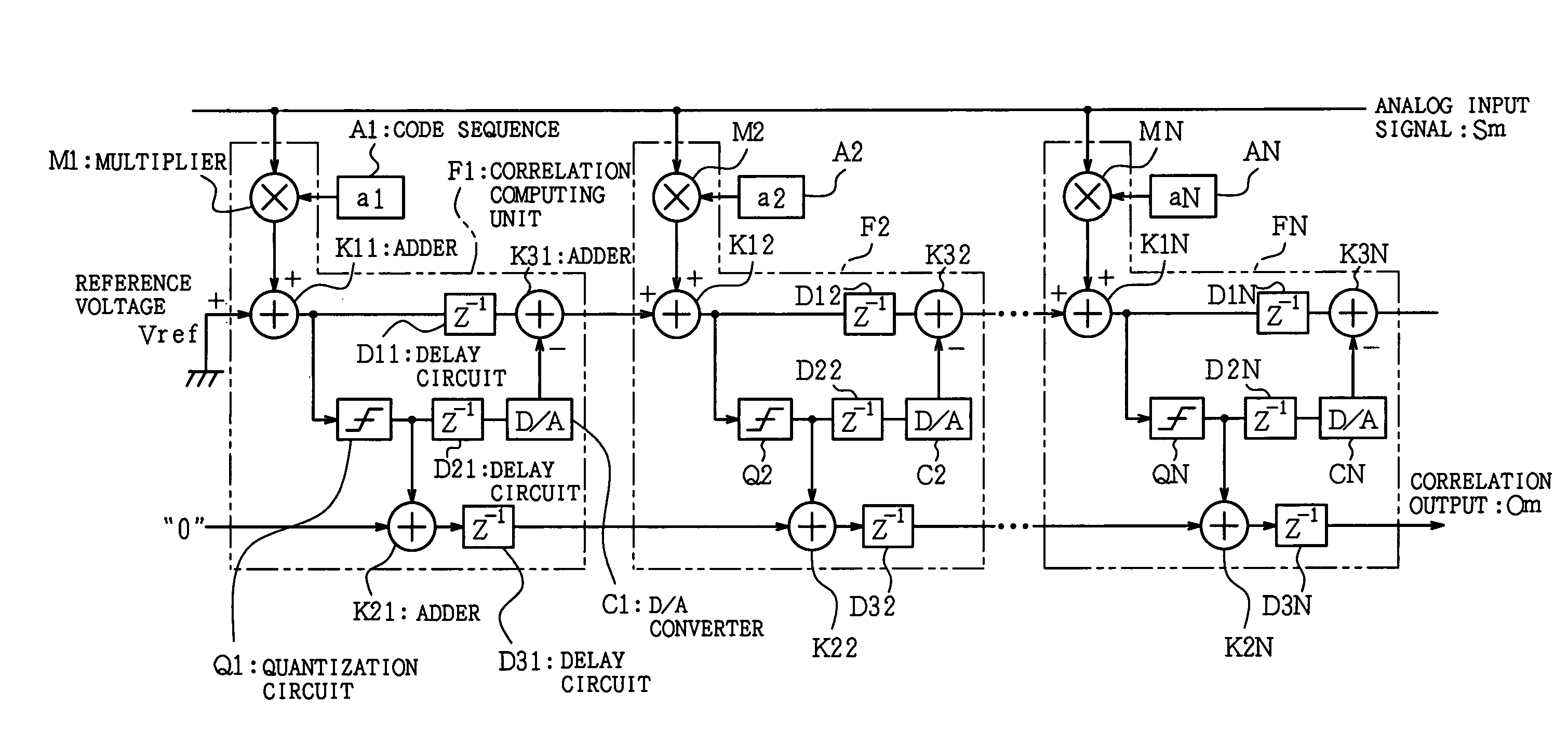
In a filter circuit of the present invention, a partial quantization value is computed by a quantization circuit according to a spread code and others in a unit at an arbitrary stage, where an integrating value is increased. The partial quantization value is successively added by an adder formed by a counter and is transmitted to a unit of the following stage. In an adder of the following stage, an analog residual is computed by subtracting an analog converted value of the partial quantization value, that is obtained by a D / A converter, from the integrating value so as to suppress an increase in the analog cumulative value. With this arrangement, the cumulative value is increased according to an increase in the number of taps, so that an analog adder can reduce power consumption, which is caused by expansion of a dynamic range at the following stage.
Owner:SHARP KK
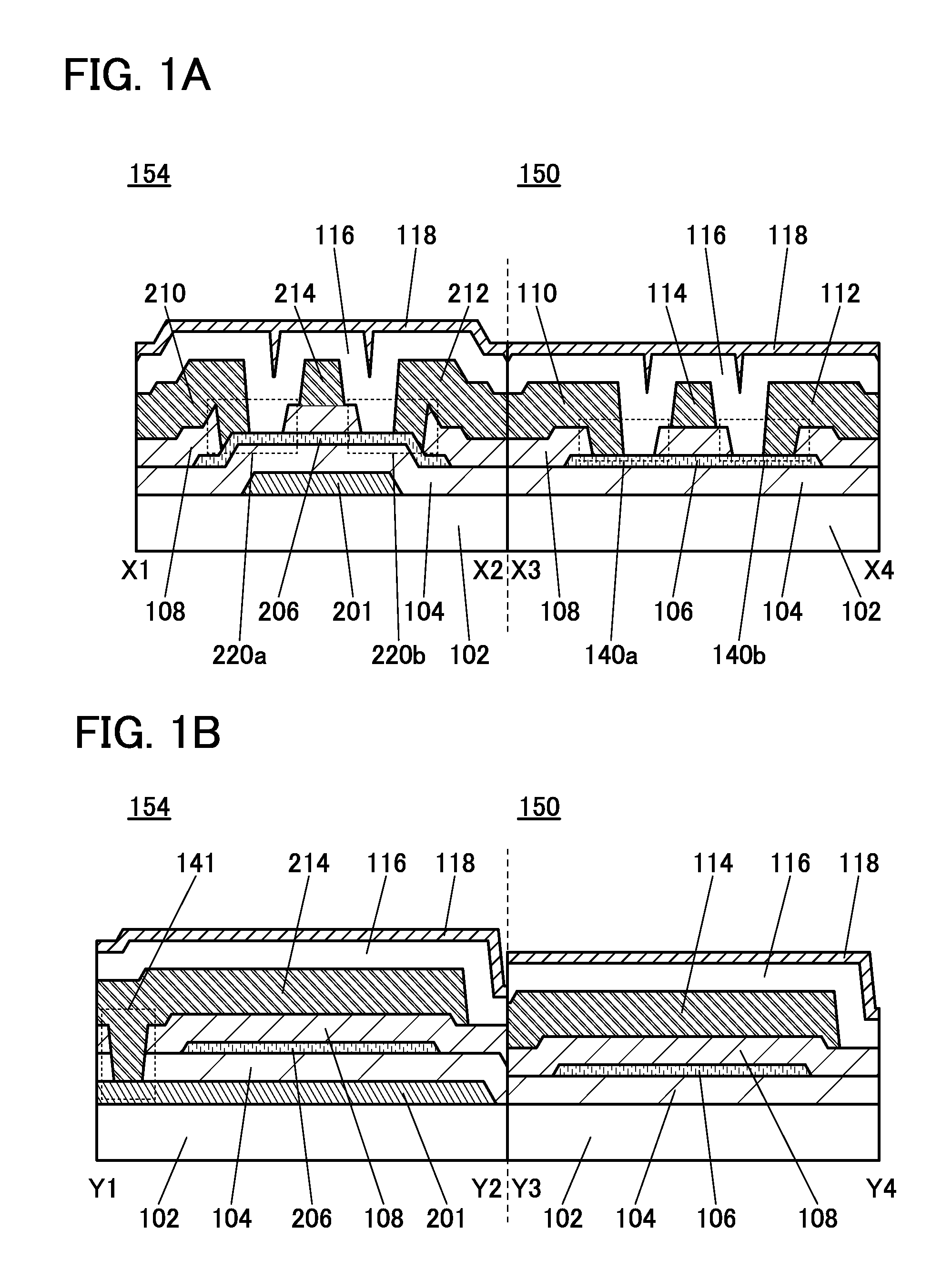
Semiconductor Device, Manufacturing Method Thereof, Module, and Electronic Device
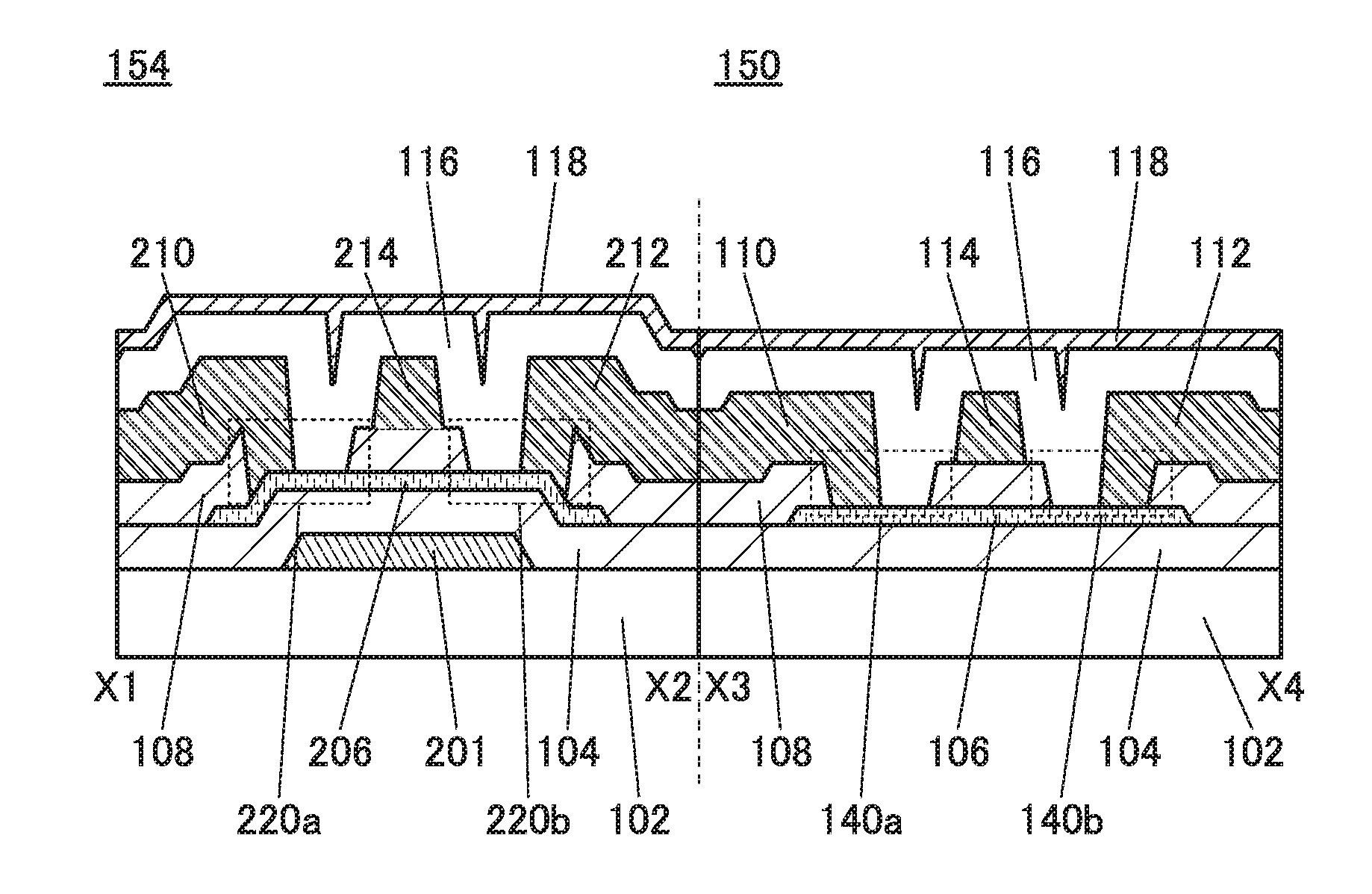
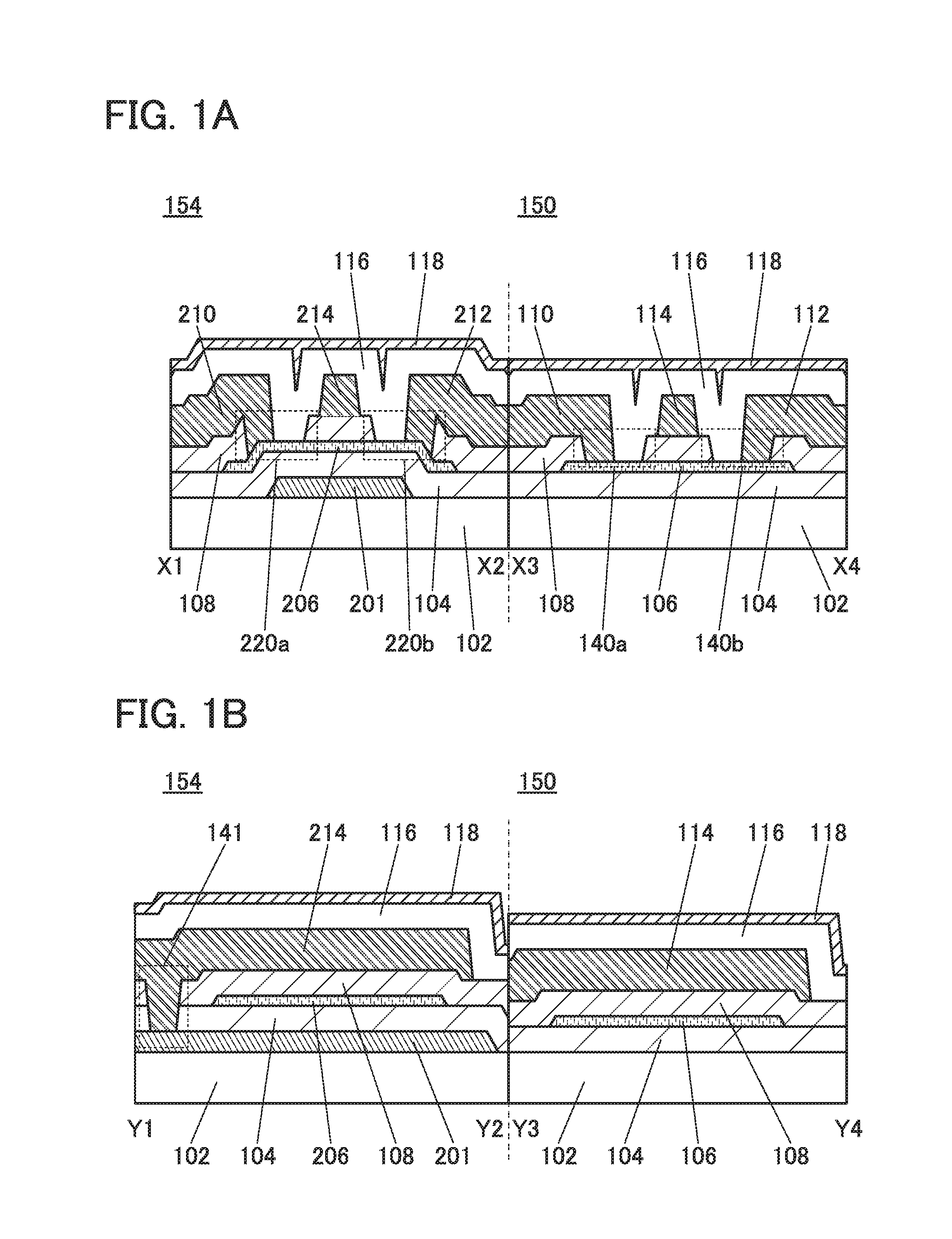
ActiveUS20150221679A1Stable semiconductor characteristicManufacturing processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorCapacitor
A semiconductor device includes a transistor and a capacitor. The transistor includes a first conductive film; a first insulating film including a film containing hydrogen; a second insulating film including an oxide insulating film; an oxide semiconductor film including a first region and a pair of second regions; a pair of electrodes; a gate insulating film; and a second conductive film. The capacitor includes a lower electrode, an inter-electrode insulating film, and an upper electrode. The lower electrode contains the same material as the first conductive film. The inter-electrode insulating film includes a third insulating film containing the same material as the first insulating film and a fourth insulating film containing the same material as the gate insulating film. The upper electrode contains the same material as the second conductive film. A fifth insulating film containing hydrogen is provided over the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
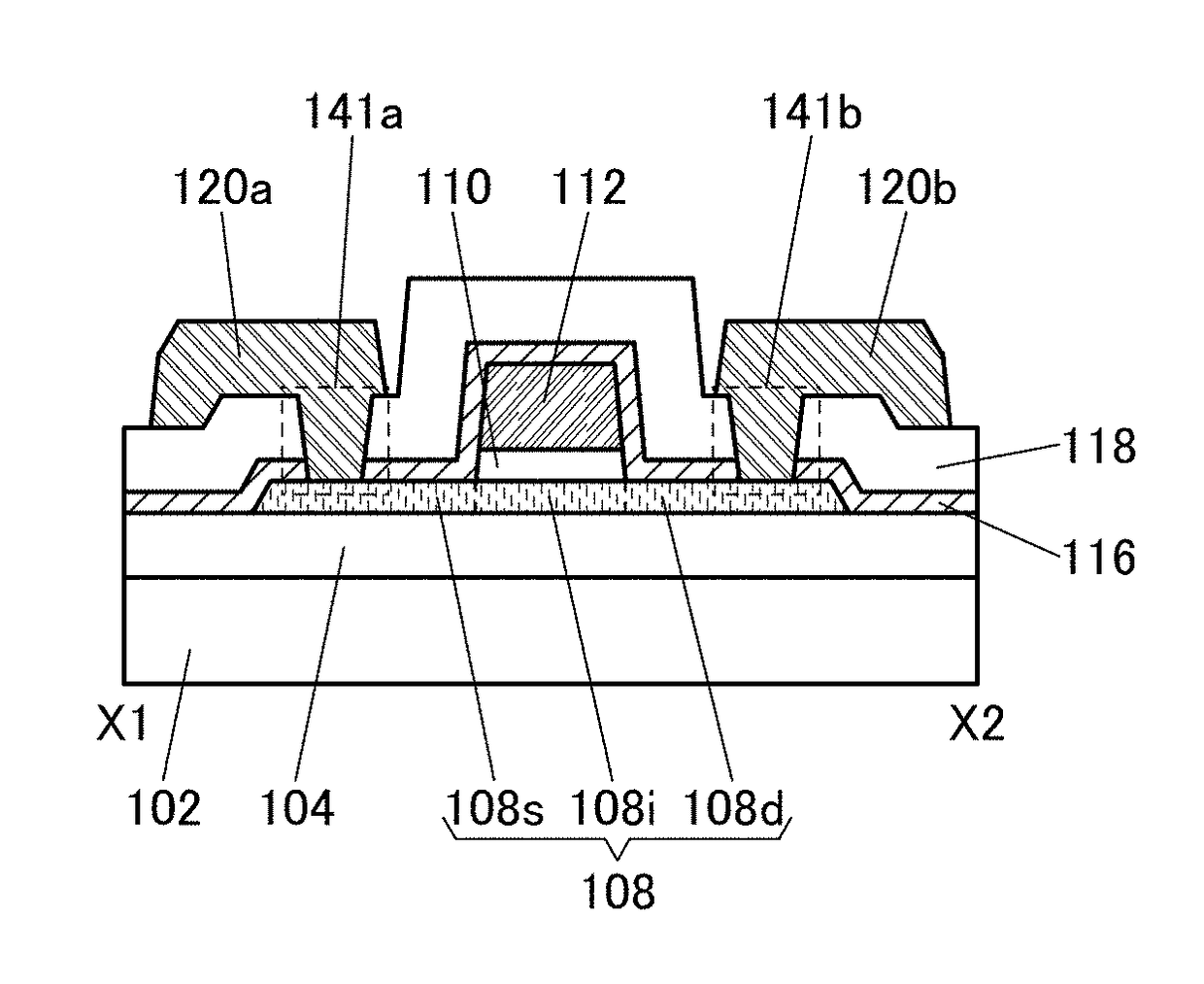
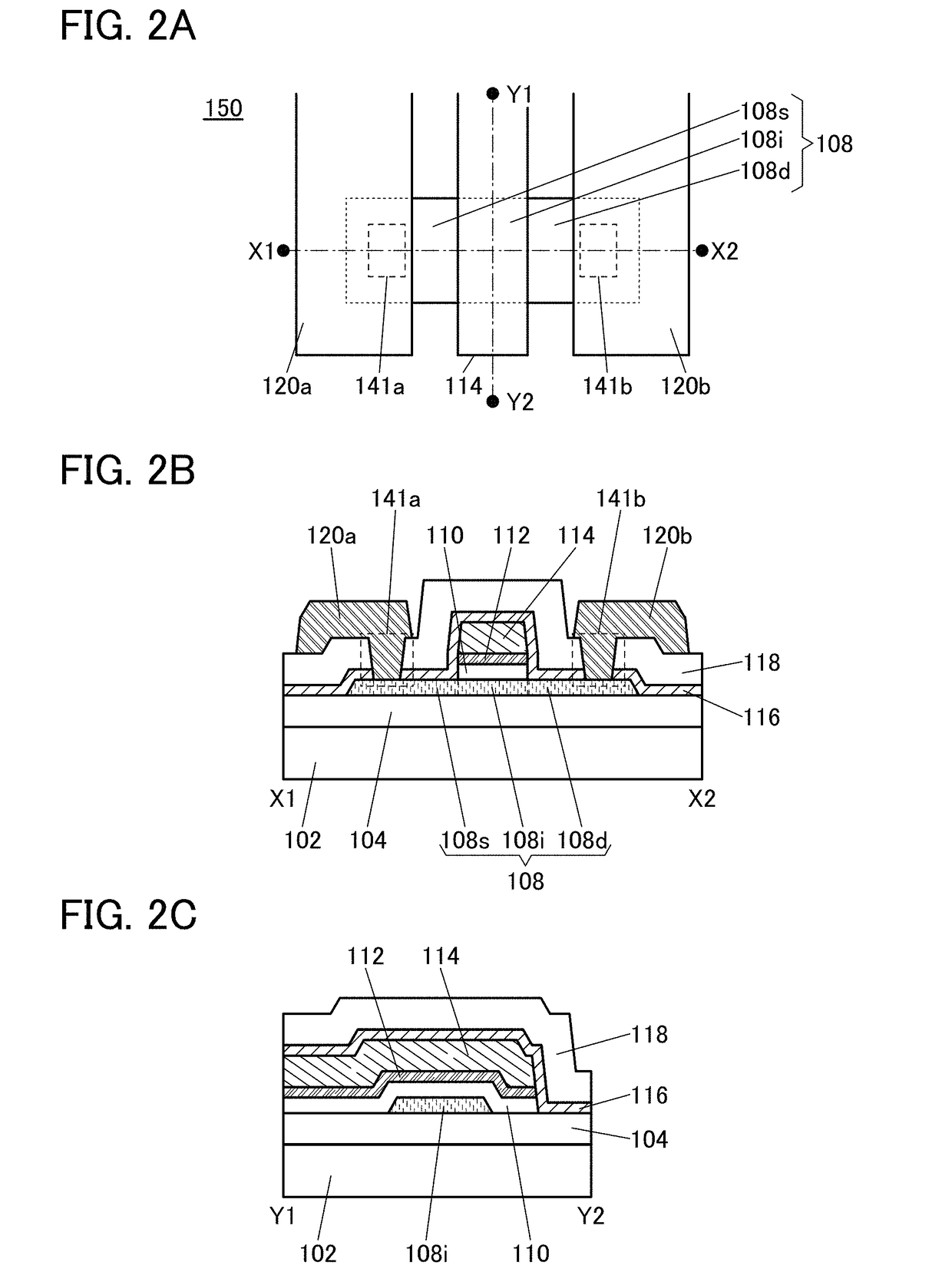
Semiconductor device and display device including the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20160005873A1High on-state currentReduced shutdown currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A change in electrical characteristics can be suppressed and reliability can be improved in a semiconductor device including a transistor having an oxide semiconductor. A semiconductor device includes a transistor, and the transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film over a first insulating film, a gate insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film, a gate electrode over the gate insulating film, a conductive film in contact with a side surface of the gate electrode in a channel length direction, and a second insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film includes a first region overlapping with the gate electrode, a second region overlapping with the conductive film, and a third region in contact with the second insulating film. The third region includes a region having higher impurity element concentration than the second region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20170025544A1Avoid display qualityStable semiconductor characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor deviceOxide semiconductor
In a transistor including an oxide semiconductor, a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. The transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film over a first insulating film; a second insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film; a metal oxide film over the second insulating film; a gate electrode over the metal oxide film; and a third insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film and the gate electrode. The oxide semiconductor film includes a channel region overlapping with the gate electrode, a source region in contact with the third insulating film, and a drain region in contact with the third insulating film. The source region and the drain region contain one or more of hydrogen, boron, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, titanium, and a rare gas.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9412876B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitHydrogen
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150187878A1Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitPower semiconductor device
To provide a semiconductor device including a transistor in which an oxide semiconductor is used and on-state current is high. In a semiconductor device including a first transistor provided in a driver circuit portion and a second transistor provided in a pixel portion, the first transistor and the second transistor have different structures. Furthermore, the first transistor and the second transistor are transistors having a top-gate structure in which conductive films serving as a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode do not overlap. Furthermore, in an oxide semiconductor film, an impurity element is contained in a region which does not overlap with the gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
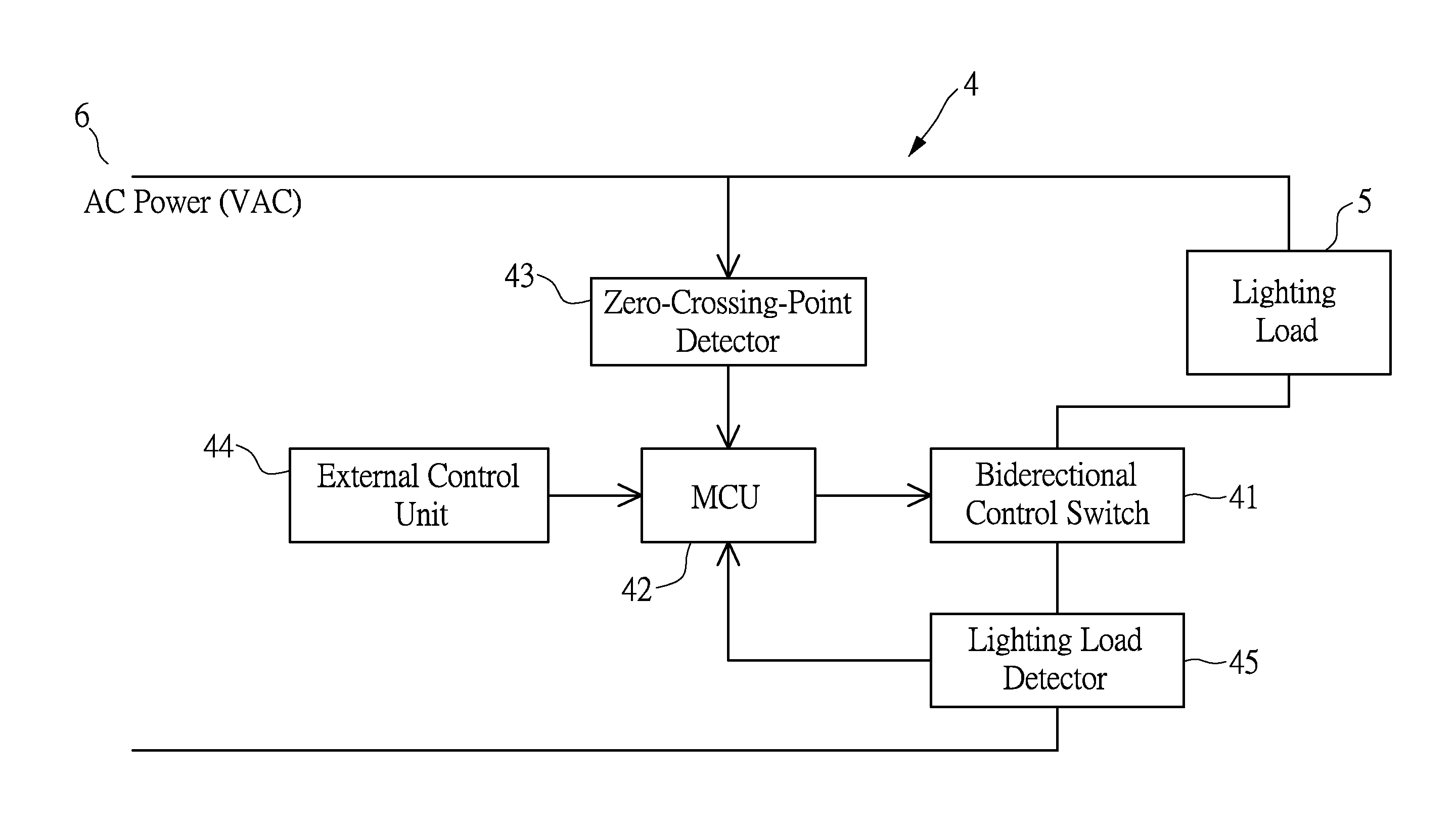
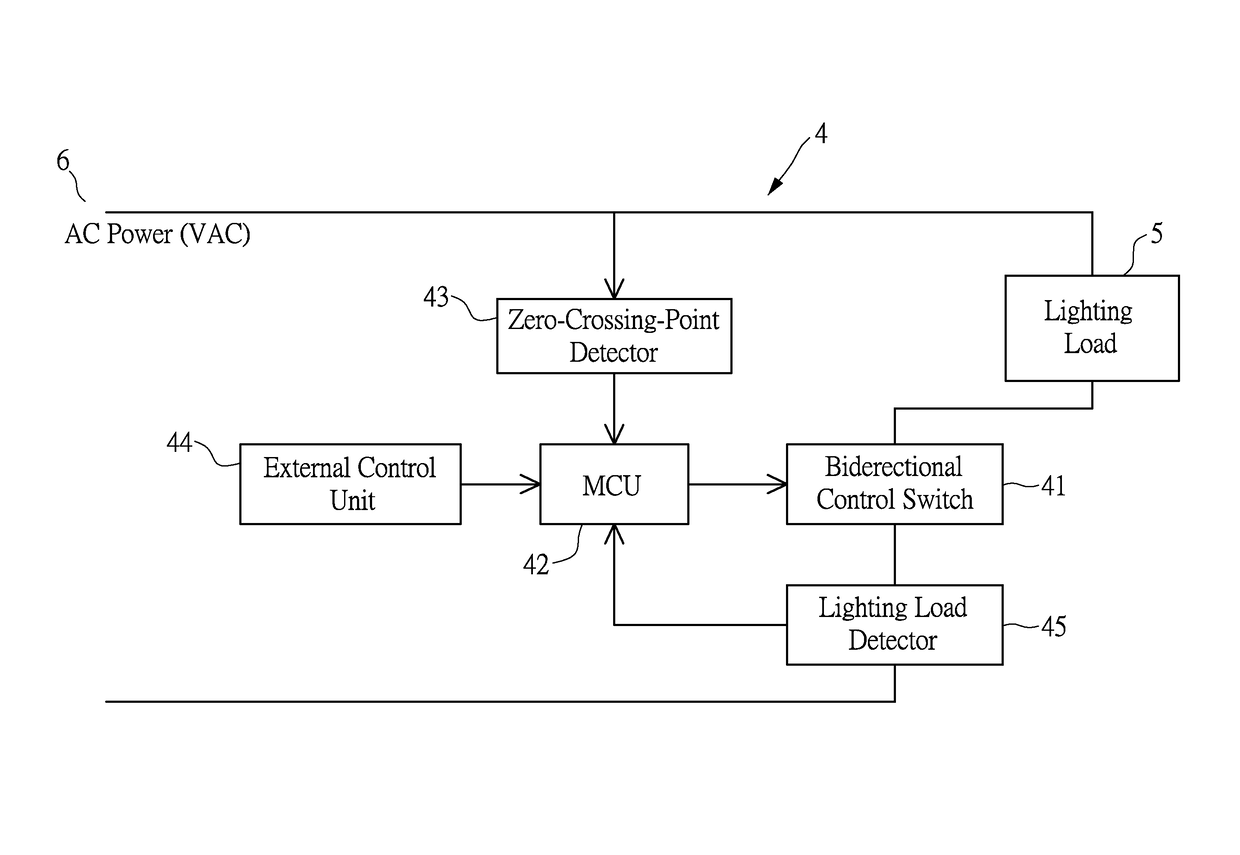
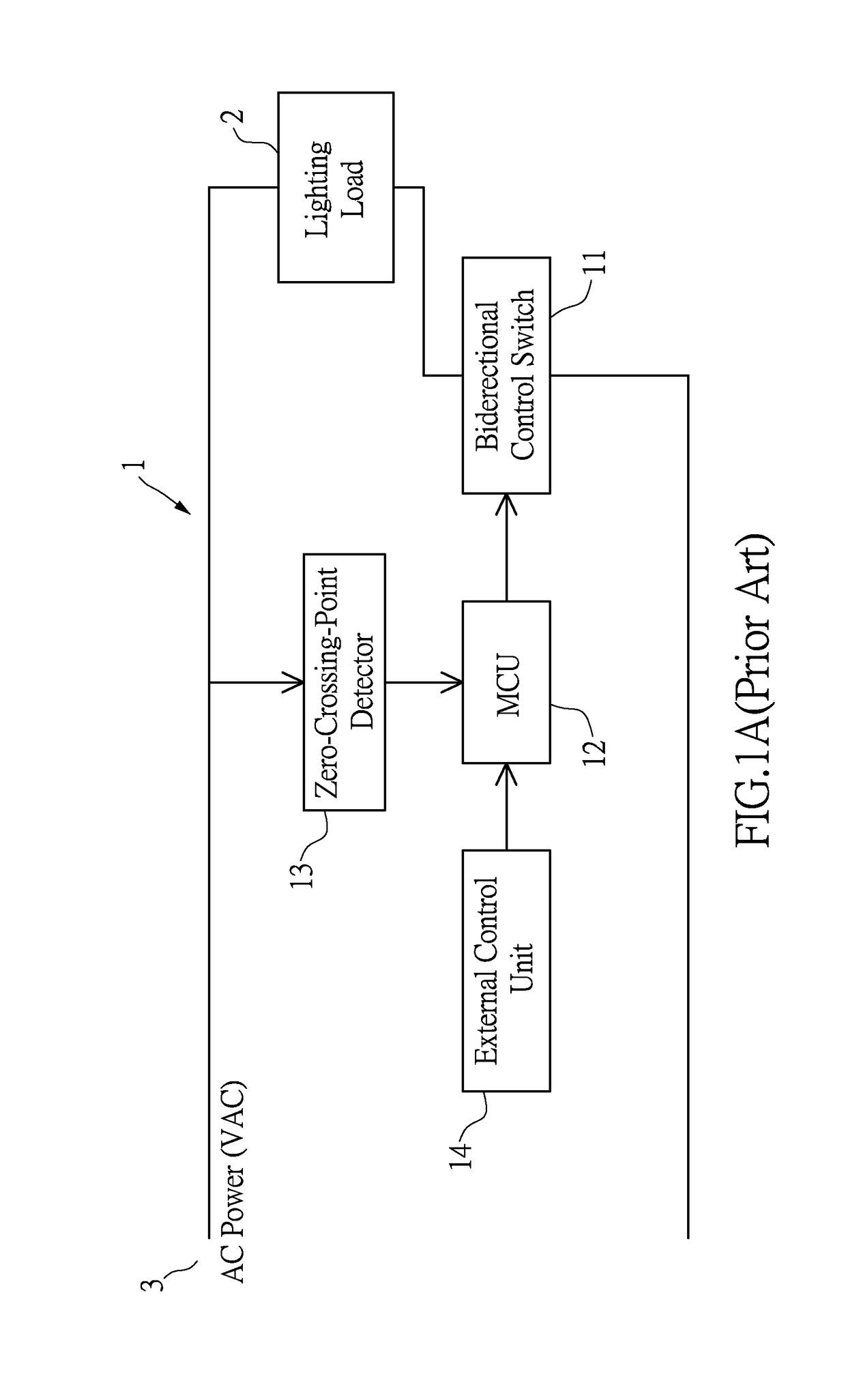
On line automatic detection of the time phase of the threshold voltage of a lighting load and its application in lighting management
ActiveUS20160095187A1Additional time delayEase of overall managementElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementWorking rangeEngineering
The present disclosure discloses a method based on microcontroller circuit and software codes to on line automatically detect the time phase of the threshold voltage of a lighting load in each AC half-cycle. This automatic detection capability enables a dimmer circuit of a lighting apparatus to establish a dimmer working range from the self-detected time phase of threshold voltage of the lighting load. The lighting apparatus can be operated with different types of lighting loads to perform a full dimming range from 0% to 100% of maximum lighting output. Therefore, the dimmer circuit makes possible both the lighting fixtures and the users refrained from dimming difficulties caused by different types of lighting loads with different threshold voltages. The design concept can be extended to manage illuminations in a two-level security light on a simple software basis without resorting to complex electric circuits.
Owner:CHEN CHIA TEH
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9530894B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitHydrogen
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device comprising oxide conductor and display device including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS9837547B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorDisplay device
The reliability of a transistor including an oxide semiconductor can be improved by suppressing a change in electrical characteristics. A transistor included in a semiconductor device includes a first oxide semiconductor film over a first insulating film, a gate insulating film over the first oxide semiconductor film, a second oxide semiconductor film over the gate insulating film, and a second insulating film over the first oxide semiconductor film and the second oxide semiconductor film. The first oxide semiconductor film includes a channel region in contact with the gate insulating film, a source region in contact with the second insulating film, and a drain region in contact with the second insulating film. The second oxide semiconductor film has a higher carrier density than the first oxide semiconductor film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and display device including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170033233A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityTransistorVacuum evaporation coatingNoble gasDevice material
In a transistor including an oxide semiconductor, a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. The transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film over a first insulating film; a second insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film; a gate electrode over the second insulating film; a metal oxide film in contact with a side surface of the second insulating film; and a third insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film, the gate electrode, and the metal oxide film. The oxide semiconductor film includes a channel region overlapping with the gate electrode, a source region in contact with the third insulating film, and a drain region in contact with the third insulating film. The source region and the drain region contain one or more of hydrogen, boron, carbon, nitrogen, fluorine, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, titanium, and a rare gas.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Clamping assembly with integral rail plate
InactiveUS7967267B1Cost-effective constructionPrompt and cost-effective installationCandle holdersDecorative coversPlastic materialsEngineering
A two-piece clamping assembly with an integral rail plate used to rapidly and securely mount a float switch within a fluid collection container for fluid level monitoring. It is usable with both metal and plastic condensate collection pans, and successfully accommodates their differing wall thickness dimensions and different upper edge configurations. When its front and back clamping members are joined together over the top edge, lip, or flange of a pan using one centrally located top fastener, and at least one additional fastener is inserted through the back clamping member until it engages the exterior surface of the pan, the pan's upper edge becomes secured within an inverted J-shaped slot formed between the two clamping members. Vertically-extending internal ribs and horizontally-extending projections strengthen the clamping assembly. Preferred plastic materials also make the clamping assembly impervious to corrosion.
Owner:RECTORSEAL
Semiconductor device with oxide semiconductor film
ActiveUS9356098B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitPower semiconductor device
To provide a semiconductor device including a transistor in which an oxide semiconductor is used and on-state current is high. In a semiconductor device including a first transistor provided in a driver circuit portion and a second transistor provided in a pixel portion, the first transistor and the second transistor have different structures. Furthermore, the first transistor and the second transistor are transistors having a top-gate structure in which conductive films serving as a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode do not overlap. Furthermore, in an oxide semiconductor film, an impurity element is contained in a region which does not overlap with the gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device, display device including the semiconductor device, display module including the display device, and electronic appliance including the semiconductor device, the display device, and the display module
ActiveUS9640669B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceHydrogen
In a semiconductor device including a transistor, the transistor is provided over a first insulating film, and the transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film over the first insulating film, a gate insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film, a gate electrode over the gate insulating film, a second insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film and the gate electrode, and a source and a drain electrodes electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film. The first insulating film includes oxygen. The second insulating film includes hydrogen. The oxide semiconductor film includes a first region in contact with the gate insulating film and a second region in contact with the second insulating film. The first insulating film includes a third region overlapping with the first region and a fourth region overlapping with the second region. The impurity element concentration of the fourth region is higher than that of the third region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device, display device including the semiconductor device, display module including the display device, and electronic device including the semiconductor device, the display device, and the display module
ActiveUS9443876B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
To provide a semiconductor device including a planar transistor having an oxide semiconductor and a capacitor. In a semiconductor device, a transistor includes an oxide semiconductor film, a gate insulating film over the oxide semiconductor film, a gate electrode over the gate insulating film, a second insulating film over the gate electrode, a third insulating film over the second insulating film, and a source and a drain electrodes over the third insulating film; the source and the drain electrodes are electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; a capacitor includes a first and a second conductive films and the second insulating film; the first conductive film and the gate electrode are provided over the same surface; the second conductive film and the source and the drain electrodes are provided over the same surface; and the second insulating film is provided between the first and the second conductive films.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
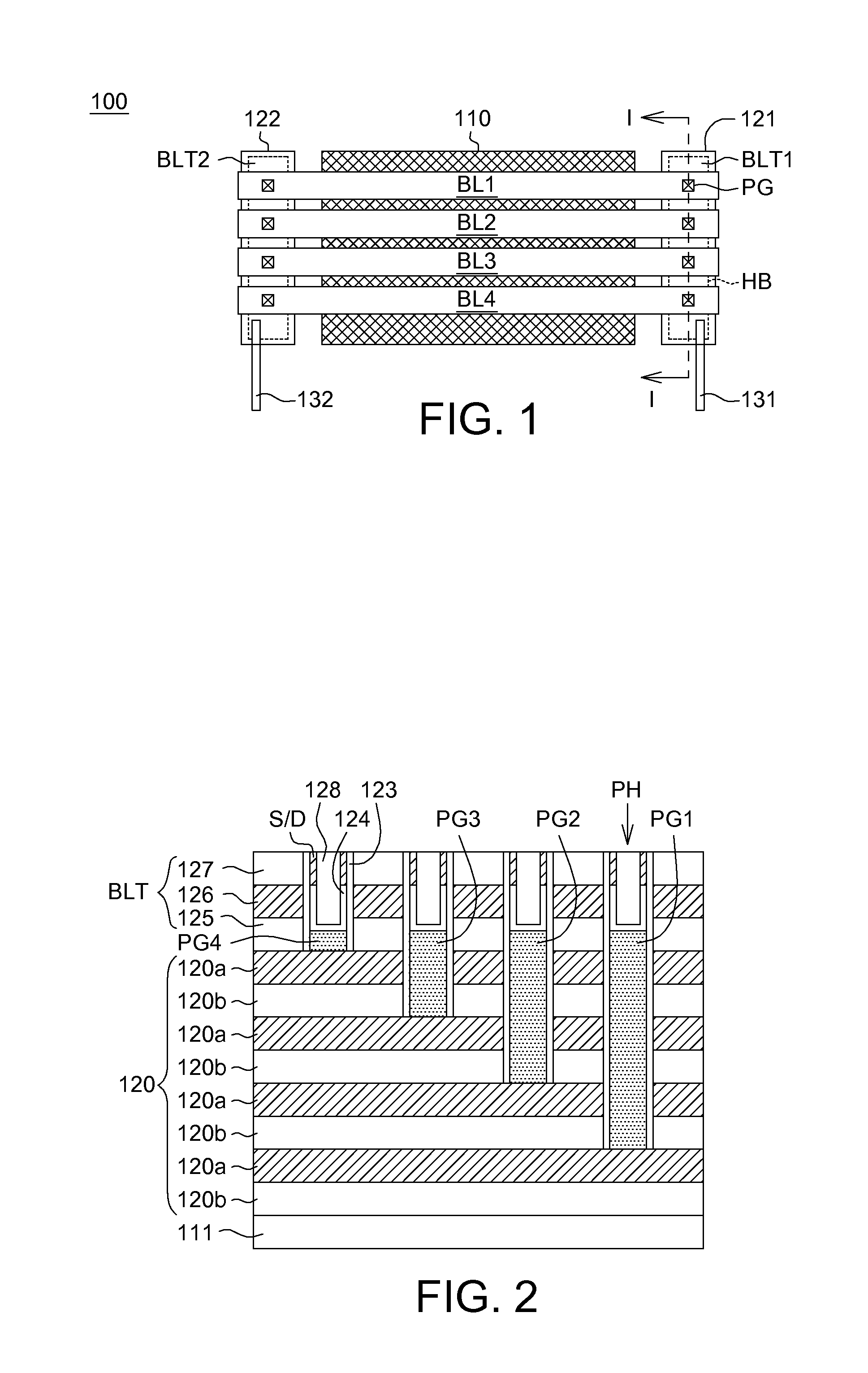
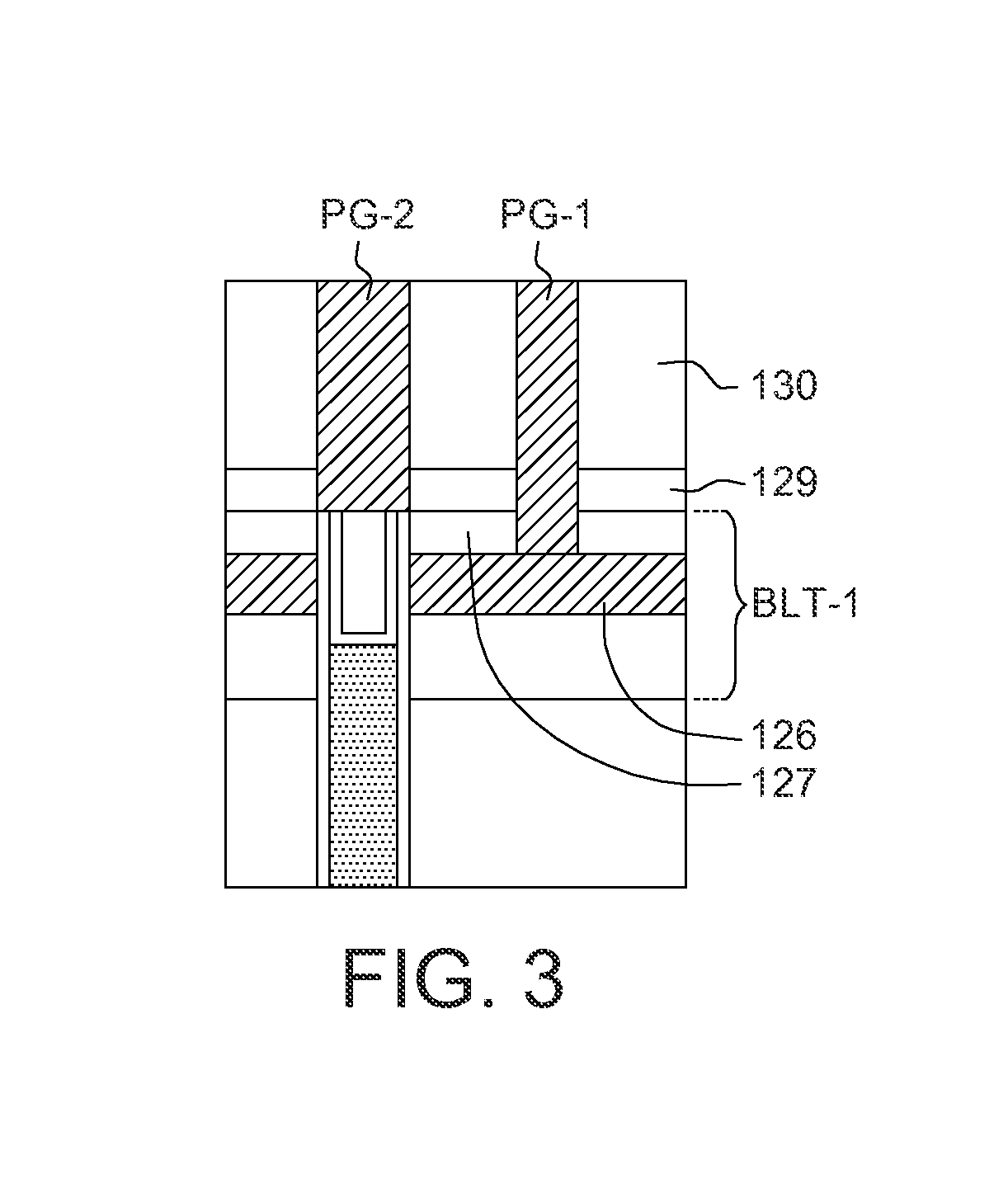
Semiconductor structure with improved capacitance of bit line
ActiveUS8704205B2Increase capacitanceSignal delaySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBit lineCapacitance
A semiconductor structure with improved capacitance of bit lines includes a substrate, a stacked memory structure, a plurality of bit lines, a first stair contact structure, a first group of transistor structures and a first conductive line. The first stair contact structure is formed on the substrate and includes conductive planes and insulating planes stacked alternately. The conductive planes are separated from each other by the insulating planes for connecting the bit lines to the stacked memory structure by stairs. The first group of transistor structures is formed in a first bulk area where the bit lines pass through and then connect to the conductive planes. The first group of transistor structures has a first gate around the first bulk area. The first conductive line is connected to the first gate to control the voltage applied to the first gate.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor and the display device including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS9577110B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesPower semiconductor deviceDisplay device
A novel semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor is provided. In particular, a planar semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor is provided. A semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor and having large on-state current is provided. The semiconductor device includes an oxide insulating film, an oxide semiconductor film over the oxide insulating film, a source electrode and a drain electrode in contact with the oxide semiconductor film, a gate insulating film between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and a gate electrode overlapping the oxide semiconductor film with the gate insulating film. The oxide semiconductor film includes a first region overlapped with the gate electrode and a second region not overlapped with the gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode. The first region and the second region have different impurity element concentrations. The gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode contain the same metal element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, module, and electronic device
ActiveUS9653487B2Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesCapacitorsEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a transistor and a capacitor. The transistor includes a first conductive film; a first insulating film including a film containing hydrogen; a second insulating film including an oxide insulating film; an oxide semiconductor film including a first region and a pair of second regions; a pair of electrodes; a gate insulating film; and a second conductive film. The capacitor includes a lower electrode, an inter-electrode insulating film, and an upper electrode. The lower electrode contains the same material as the first conductive film. The inter-electrode insulating film includes a third insulating film containing the same material as the first insulating film and a fourth insulating film containing the same material as the gate insulating film. The upper electrode contains the same material as the second conductive film. A fifth insulating film containing hydrogen is provided over the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
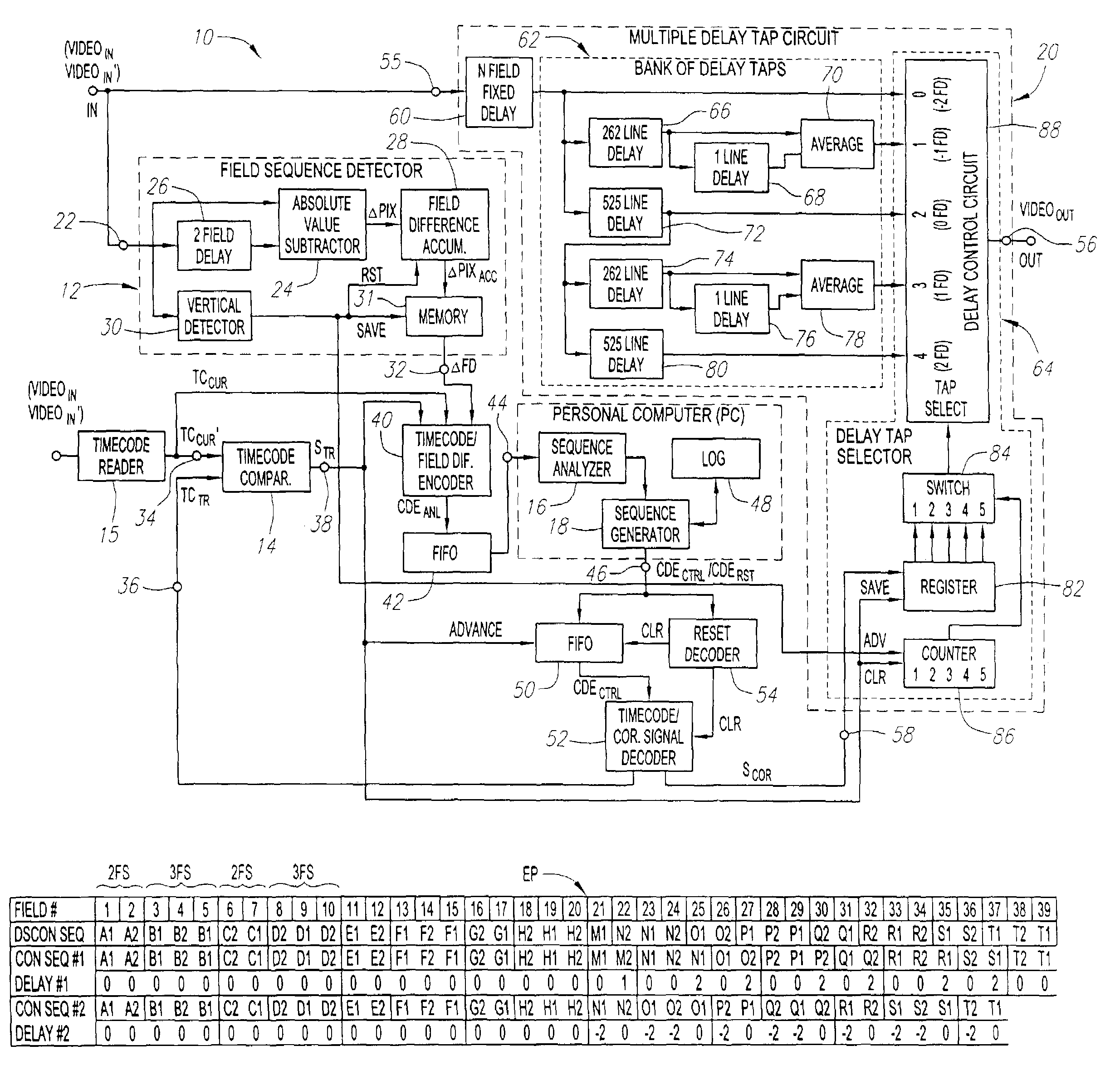
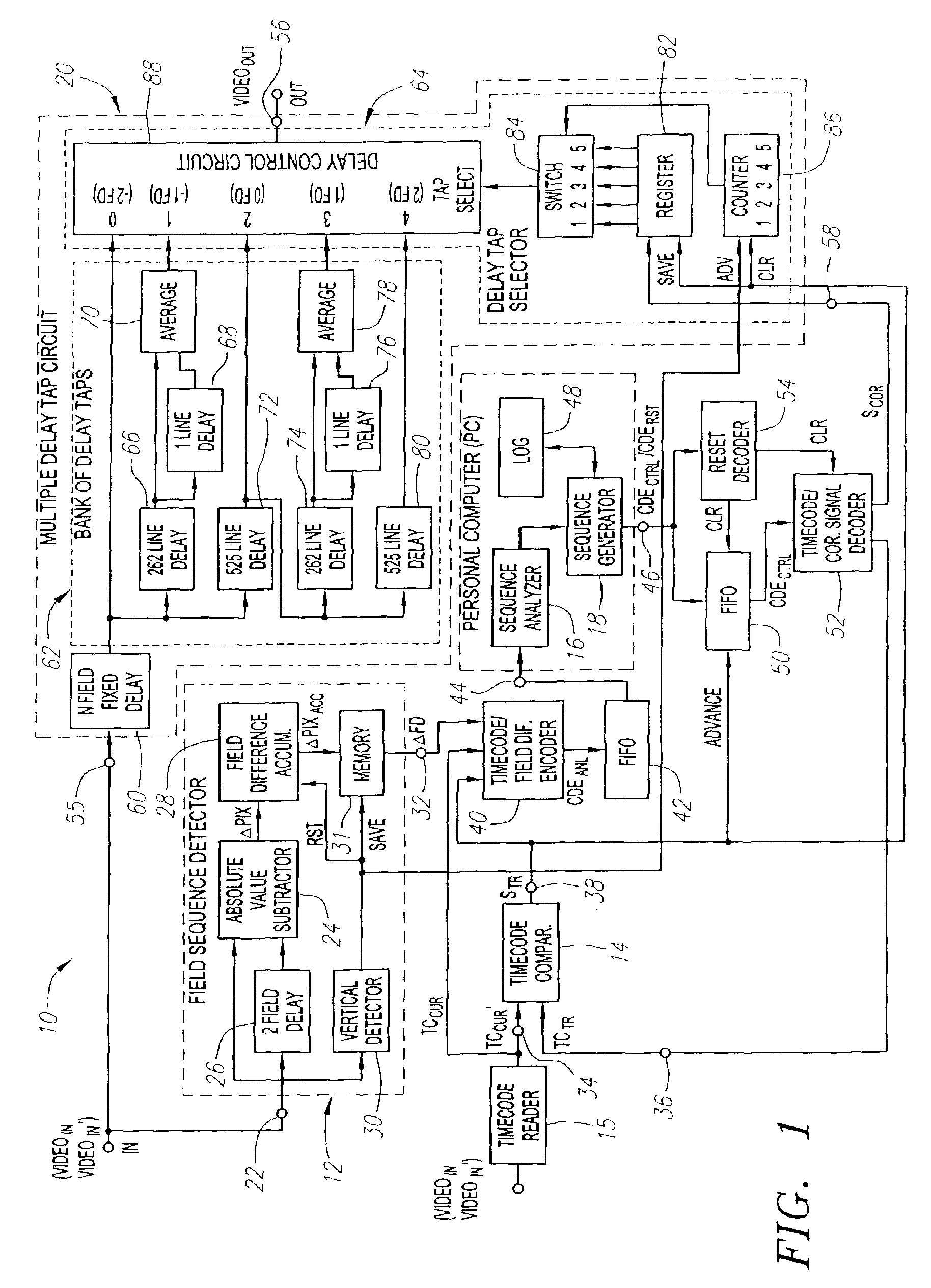
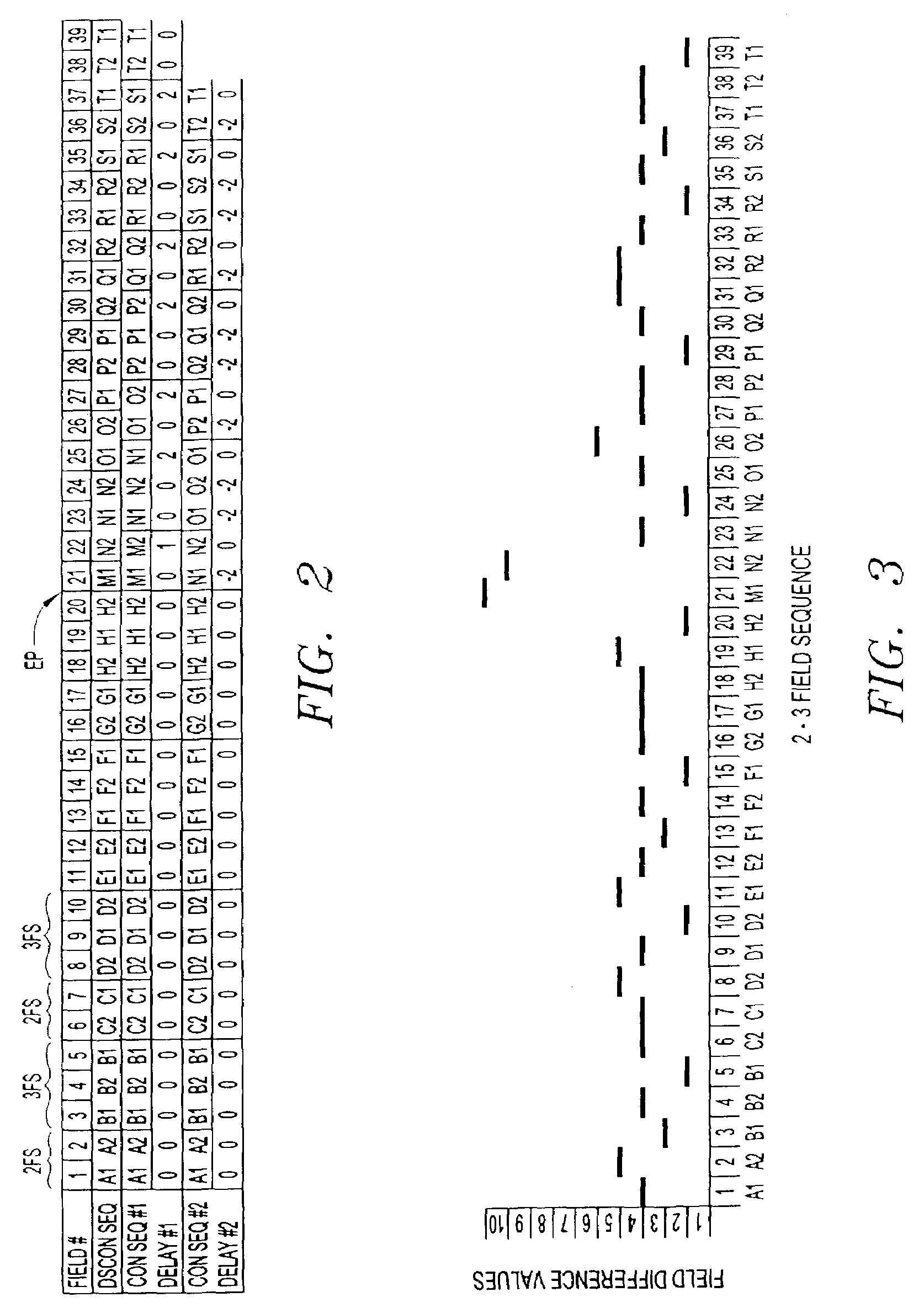
Methods and apparatus for correction for 2-3 field patterns
InactiveUS7139029B2Signal delayMinimize the numberTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSequence analysisComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for allowing a user to correct a discontinuous 2-3 field sequence within a disrupted video signal. A 2-3 field pattern fixer can be operated in a one-pass mode and / or a two-pass mode. In the one-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is used to correct the disrupted video signal as it passes through the 2-3 pattern fixer, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In the two-pass mode, the disrupted video signal is analyzed to generate correction information, which is then stored. This correction information is then used to correct a duplicate of the disrupted video signal, resulting in an undisrupted video signal with a continuous 2-3 field sequence. In this connection, the 2-3 field pattern fixer includes a field sequence detector, a field sequence analyzer, a field sequence generator and a multiple delay tap circuit. The field sequence detector generates field difference values in response to receiving the disrupted video signal. The field sequence analyzer analyzes these field difference values to determine one or more discontinuities within the discontinuous 2-3 field sequence. The field sequence generator generates one or more field sequence correction signals in response to this analysis. The multiple delay tap circuit applies these correction signals to a video signal to generate an undisrupted video signal having a continuous 2-3 field sequence. The 2-3 field pattern fixer can optionally includes a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) memory and a time code comparator, which can be used to store a multitude of the correction signals during the first pass of the two-pass mode, and for synchronizing the application of each of the correction signals to the duplicated disrupted video signal during the second pass of the two-pass mode.
Owner:ASCENT MEDIA GROUP
On line automatic detection of the time phase of the threshold voltage of a lighting load and its application in lighting management
ActiveUS9655219B2Signal delaySuccessfully controlledElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMicrocontrollerLight equipment
The present disclosure discloses a method based on microcontroller circuit and software codes to on line automatically detect the time phase of the threshold voltage of a lighting load in each AC half-cycle. This automatic detection capability enables a dimmer circuit of a lighting apparatus to establish a dimmer working range from the self-detected time phase of threshold voltage of the lighting load. The lighting apparatus can be operated with different types of lighting loads to perform a full dimming range from 0% to 100% of maximum lighting output. Therefore, the dimmer circuit makes possible both the lighting fixtures and the users refrained from dimming difficulties caused by different types of lighting loads with different threshold voltages. The design concept can be extended to manage illuminations in a two-level security light on a simple software basis without resorting to complex electric circuits.
Owner:CHEN CHIA TEH
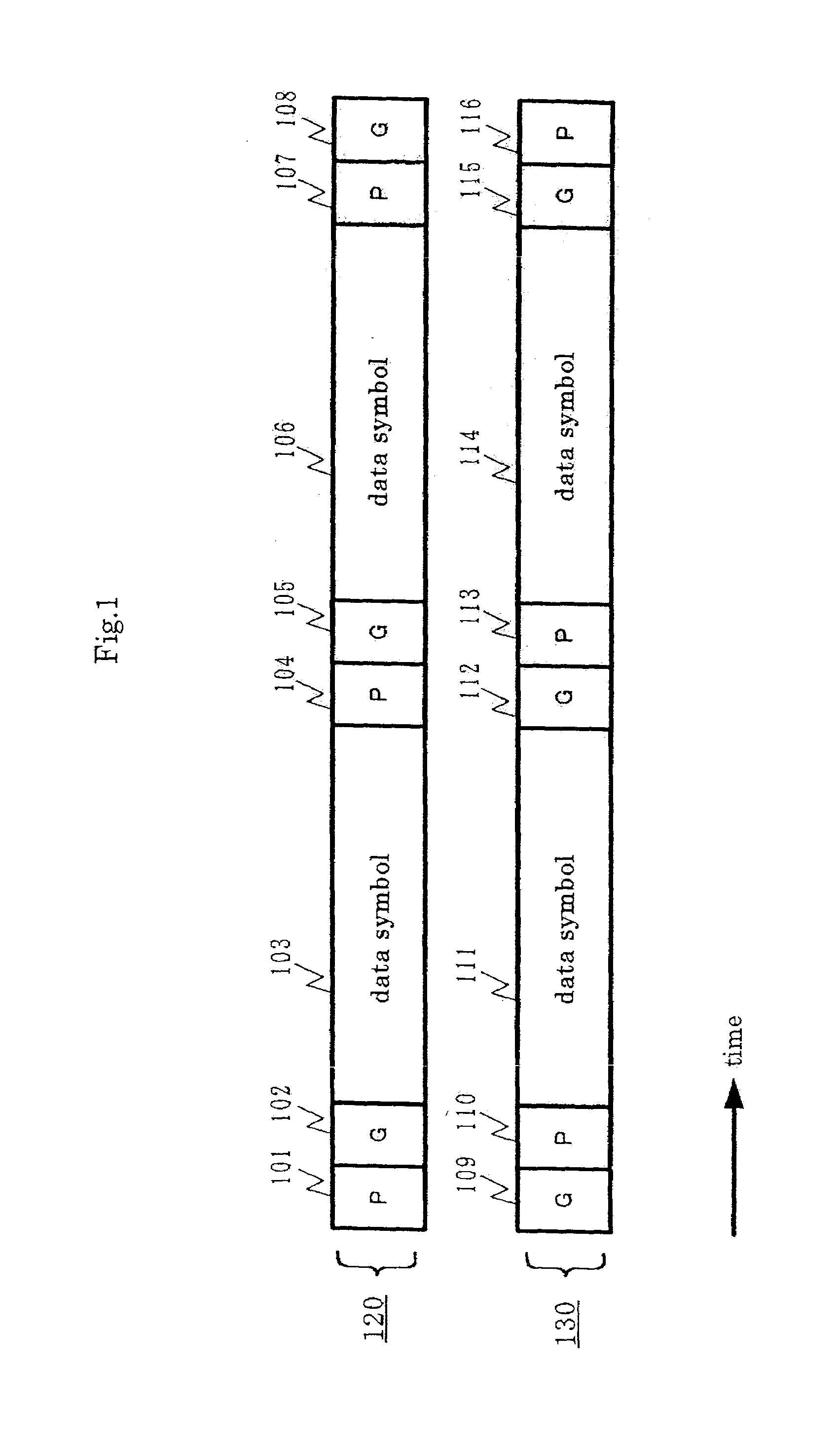
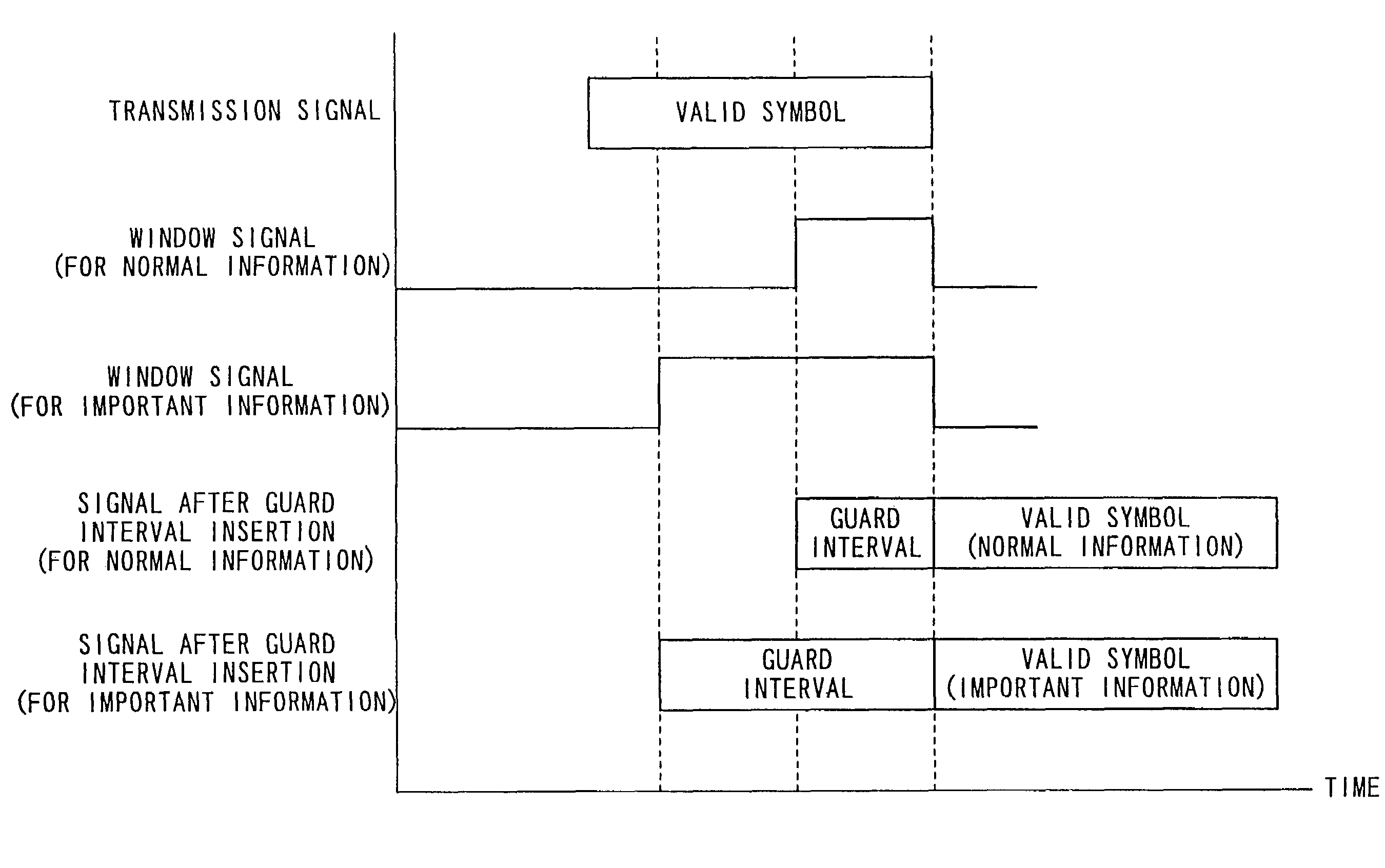
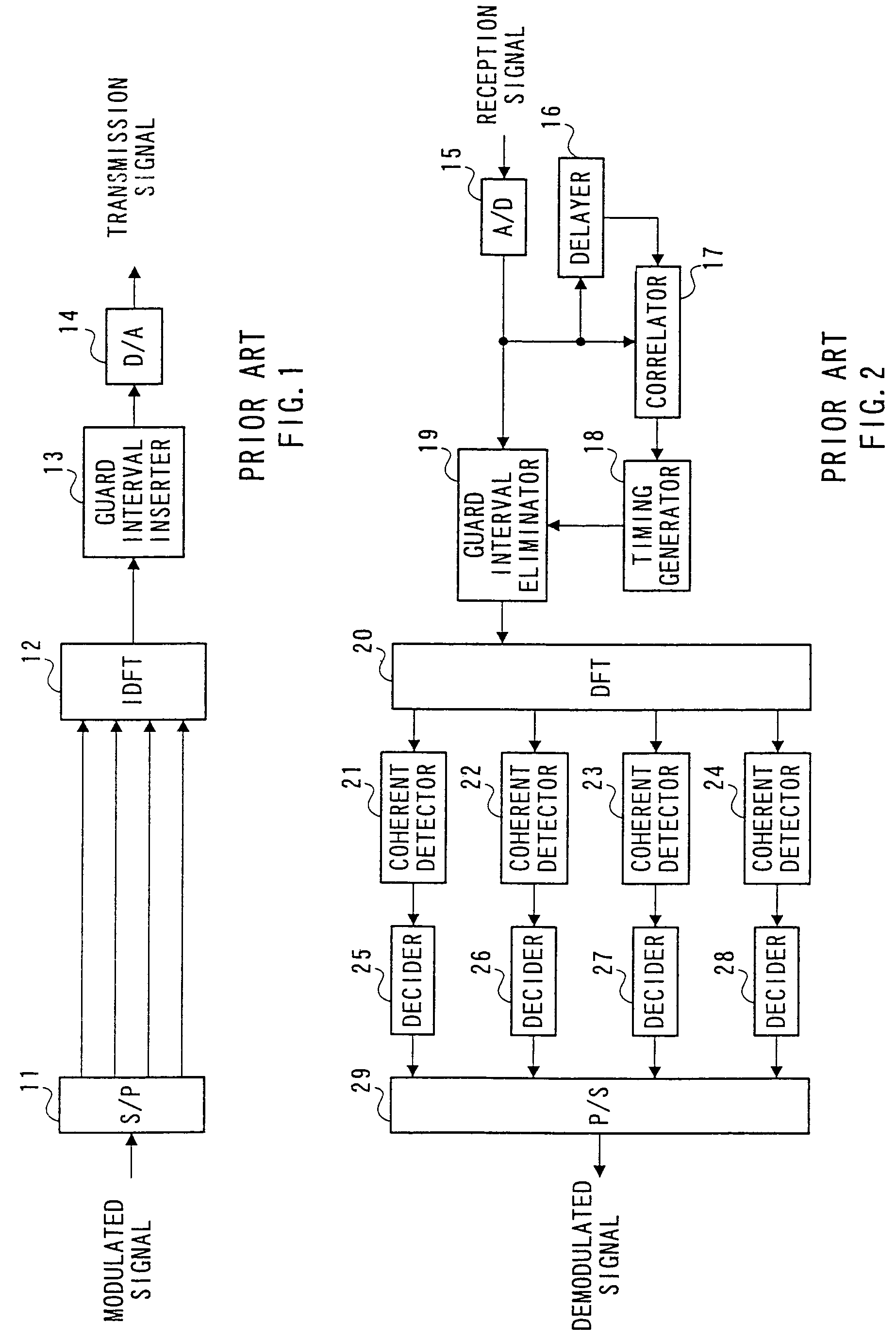
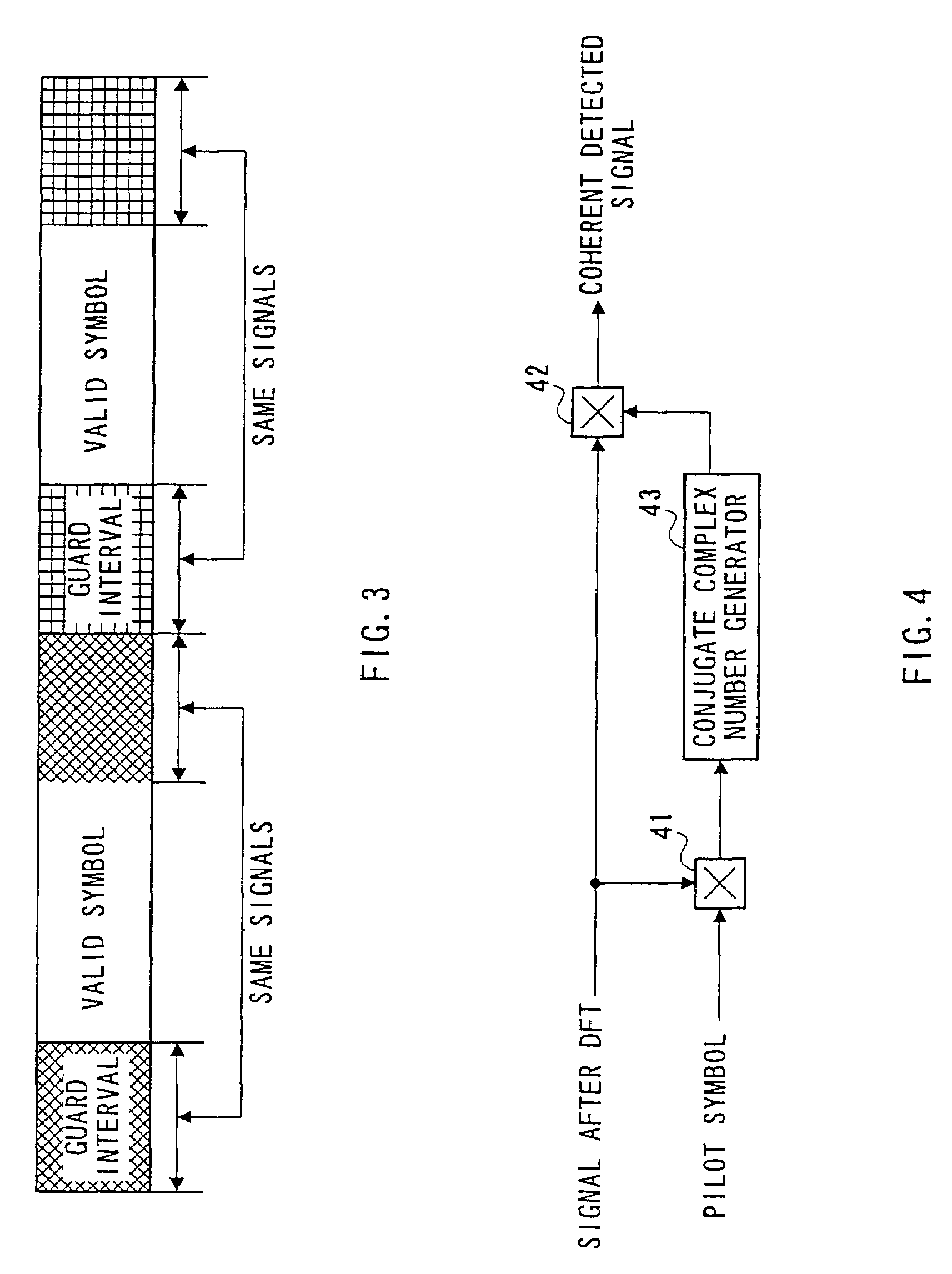
Method and apparatus for setting a guard interval in an OFDM communication
InactiveUS7403471B2Improve transmission efficiencySignal delayFrequency-division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsTelecommunicationsGuard interval
A method and apparatus for setting a guard interval in an OFDM communication. The method includes attaching a part of a first valid symbol to the first valid symbol as a guard interval and attaching a part of a second valid symbol requiring higher channel quality than the first valid symbol, to the second valid symbol as a guard interval, and providing the guard interval of the second valid symbol at a length greater than the guard interval of the first valid symbol.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
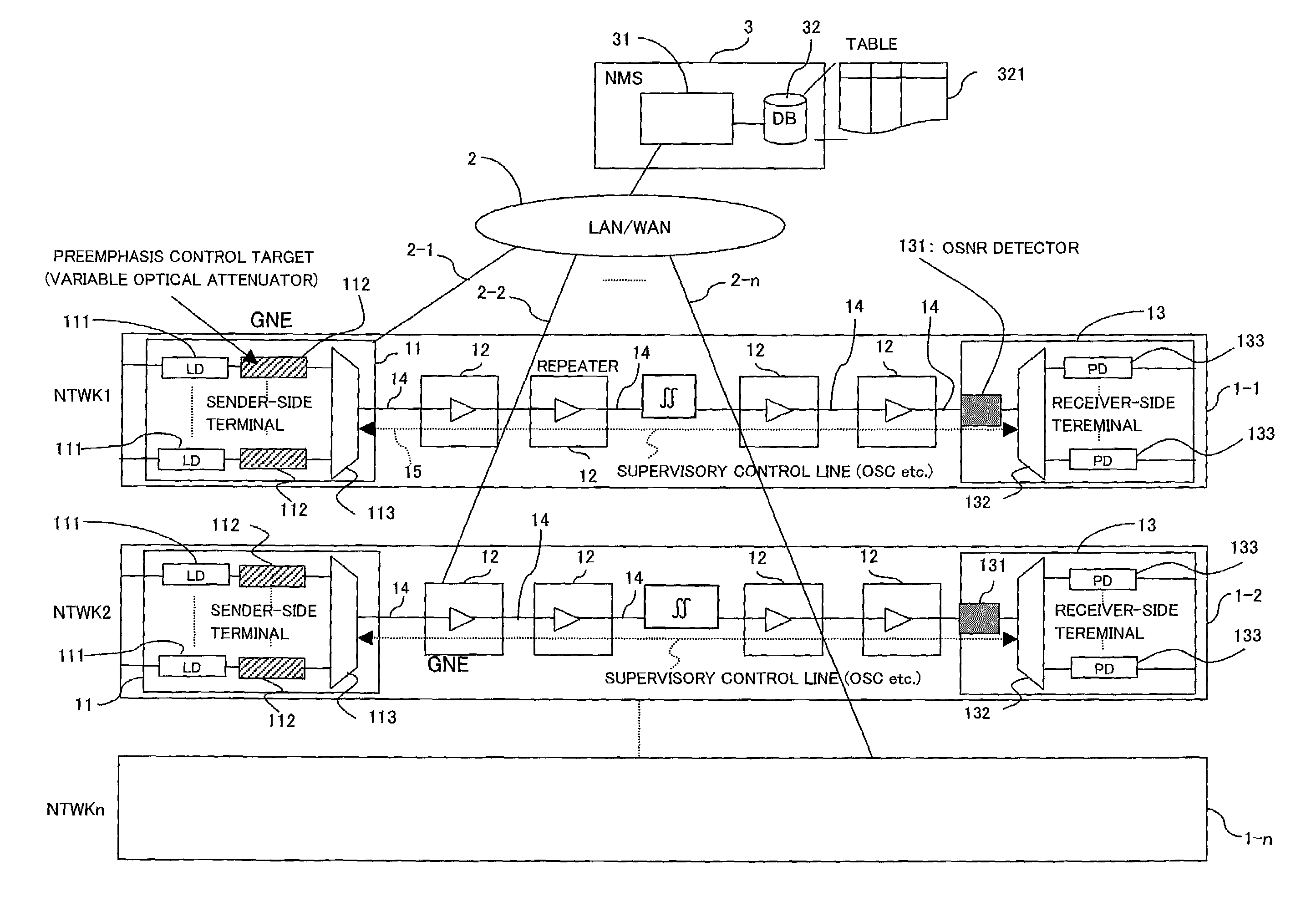
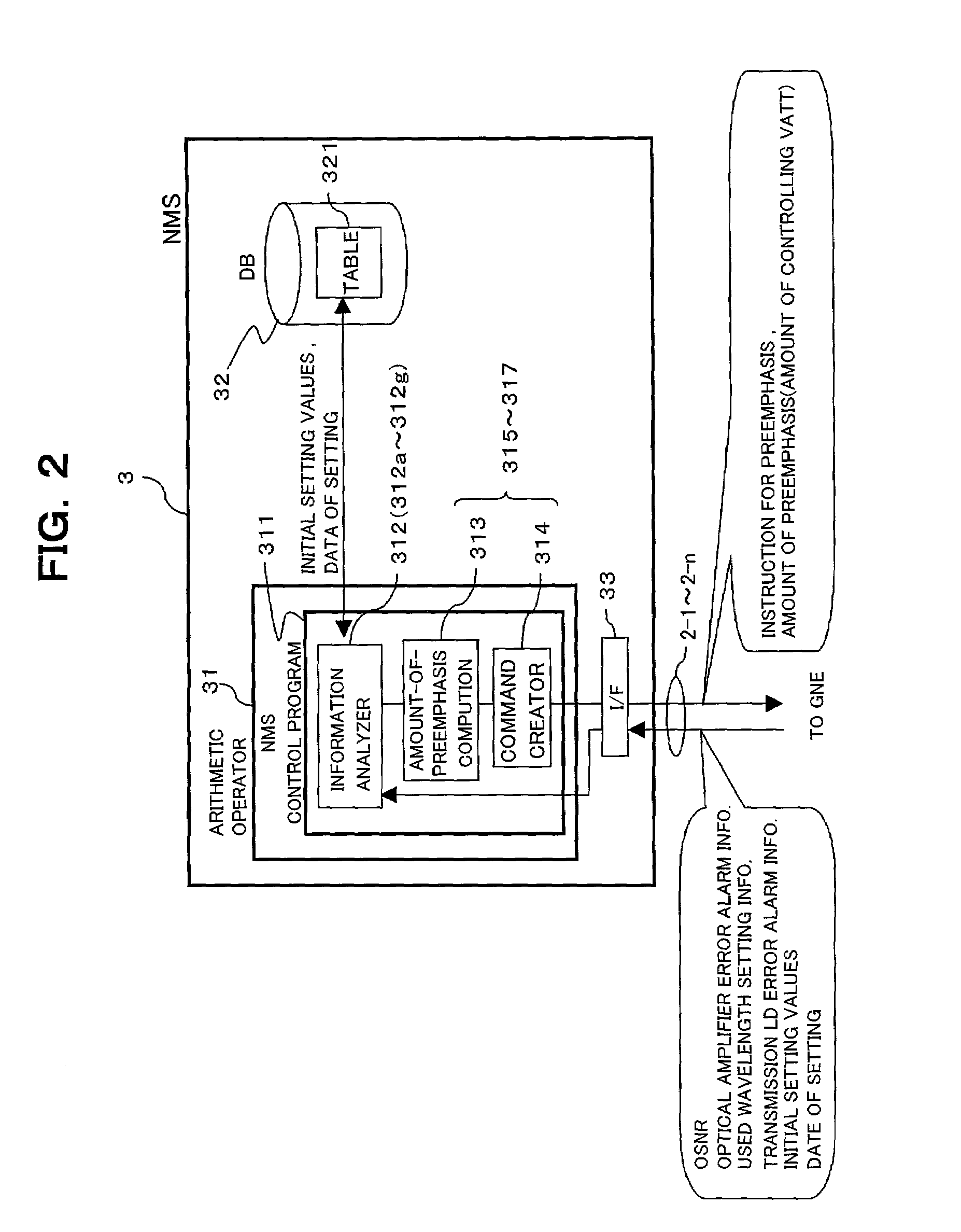
WDM transmission system, central controller for the system, and method for controlling preemphasis in the system
InactiveUS6999680B2Signal delayFacilitate transmissionLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm transmission systemsControl system
A WDM transmission system including a plurality of WDM optical network and a central controller communicably connected to the plural WDM optical network via a plurality of monitor / control lines respectively, the central controller includes variation factor monitoring means for monitoring one or more variation factors of preemphasis on each WDM optical network and preemphasis controlling means for controlling a status of the preemphasis by adjusting the setting for the preemphasis performed on each WDM network via respective one of monitor / control lines. Therefore, preemphasis performed each of the plural WDM optical network can be automatically executed without boosting costs and loads on elements of each WDM optical network. Stabilized transmission of a WDM signal can be performed in each of the plural WDM optical network with ease without manual setting.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Switching device for sharing input/output devices and computer system using the same
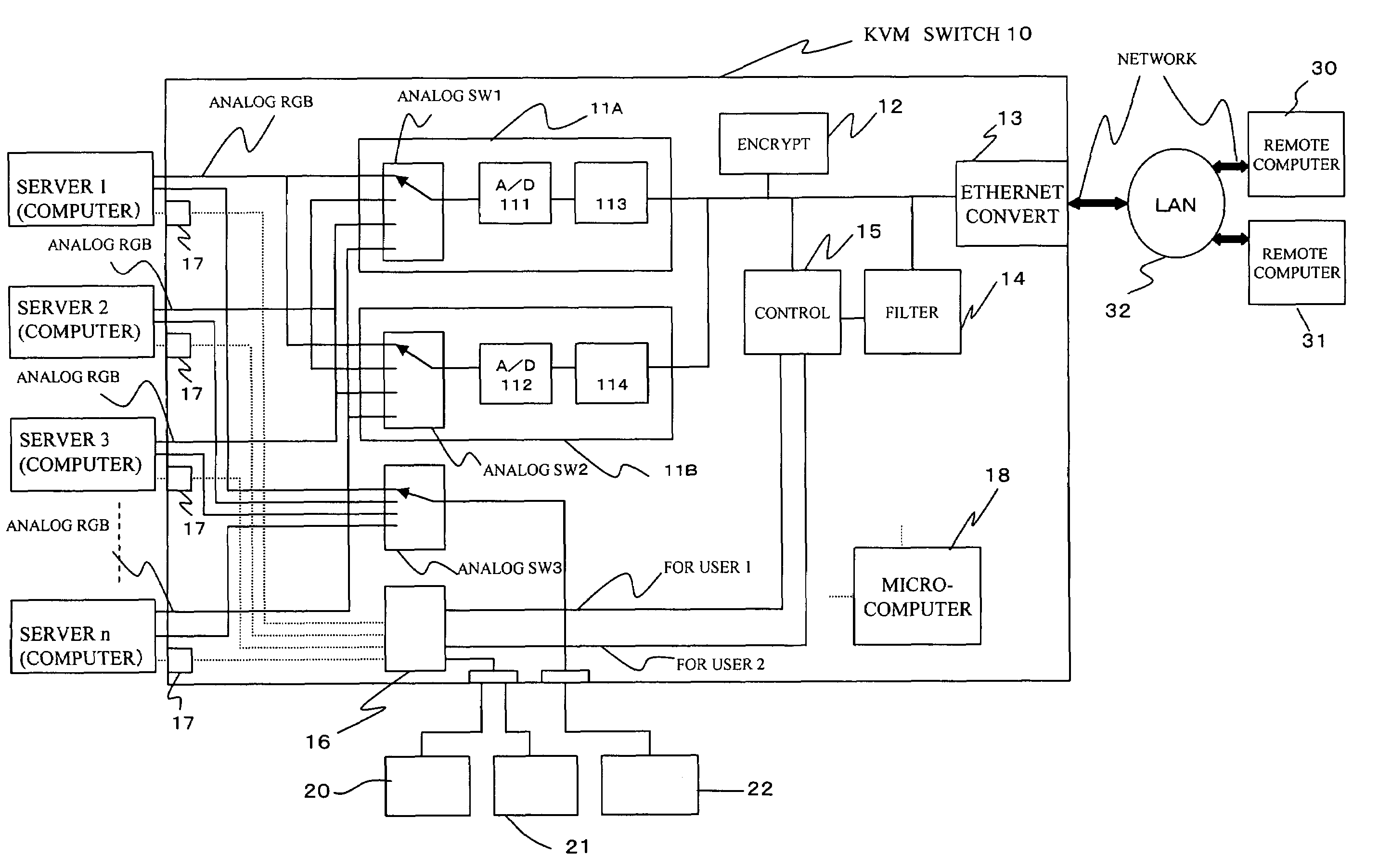
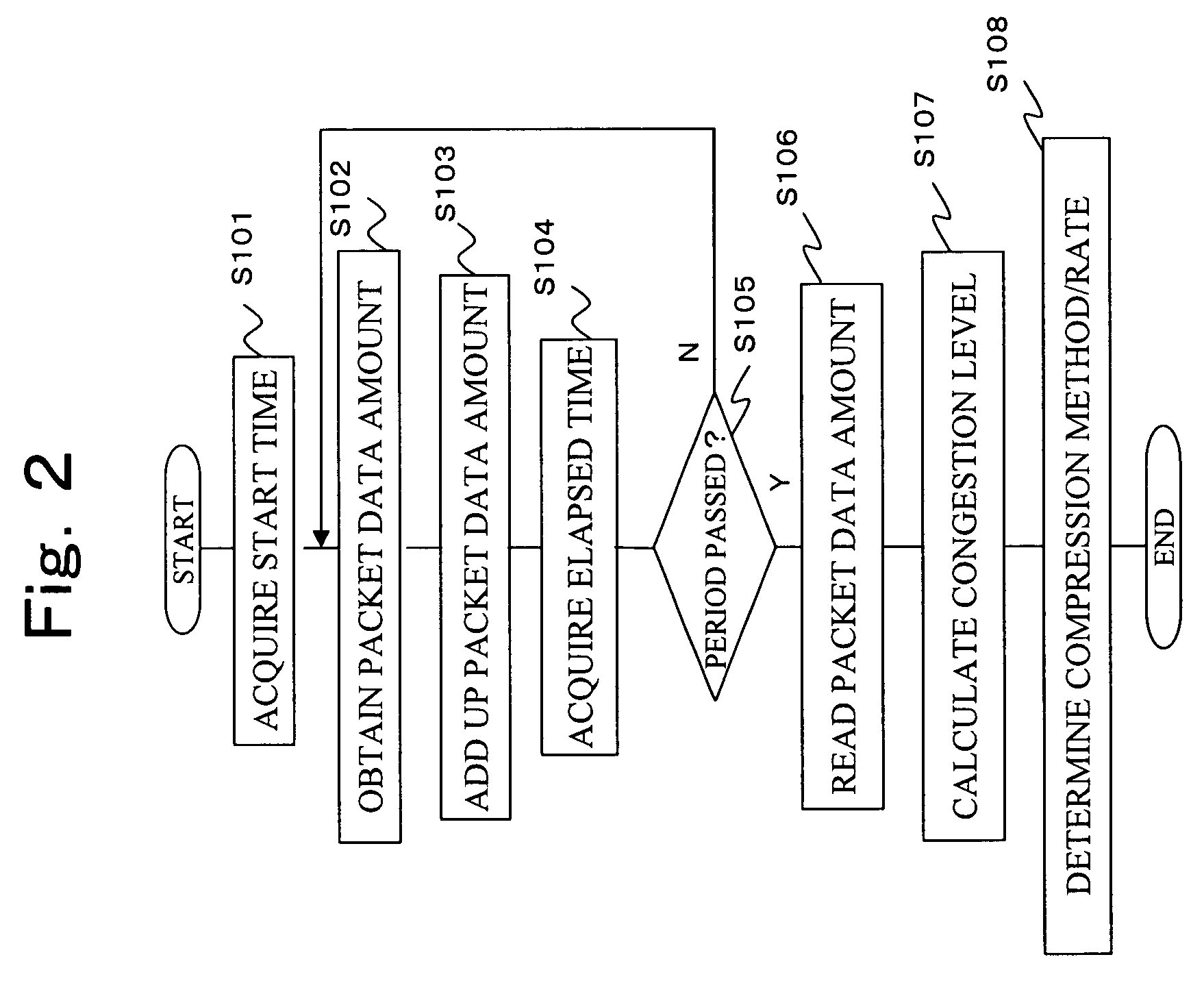
InactiveUS7657106B2Signal delayEnhance the imageCharacter and pattern recognitionData switching by path configurationImage compressionInput/output
A switching device that selectively switches connections to a predetermined terminal among two or more terminals connected to servers, and can be remote-controlled via a network, includes a network interface circuit to be connected to the network, an image processing unit that includes an image compression circuit for compressing image signals outputted from the servers, and a controller that changes a compression method or compression rate to be used at the image compression circuit in accordance with the congestion level of the network.
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20160268441A1Stable semiconductor characteristicImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDriver circuitPower semiconductor device
To provide a semiconductor device including a transistor in which an oxide semiconductor is used and on-state current is high. In a semiconductor device including a first transistor provided in a driver circuit portion and a second transistor provided in a pixel portion, the first transistor and the second transistor have different structures. Furthermore, the first transistor and the second transistor are transistors having a top-gate structure in which conductive films serving as a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode do not overlap. Furthermore, in an oxide semiconductor film, an impurity element is contained in a region which does not overlap with the gate electrode, the source electrode, and the drain electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
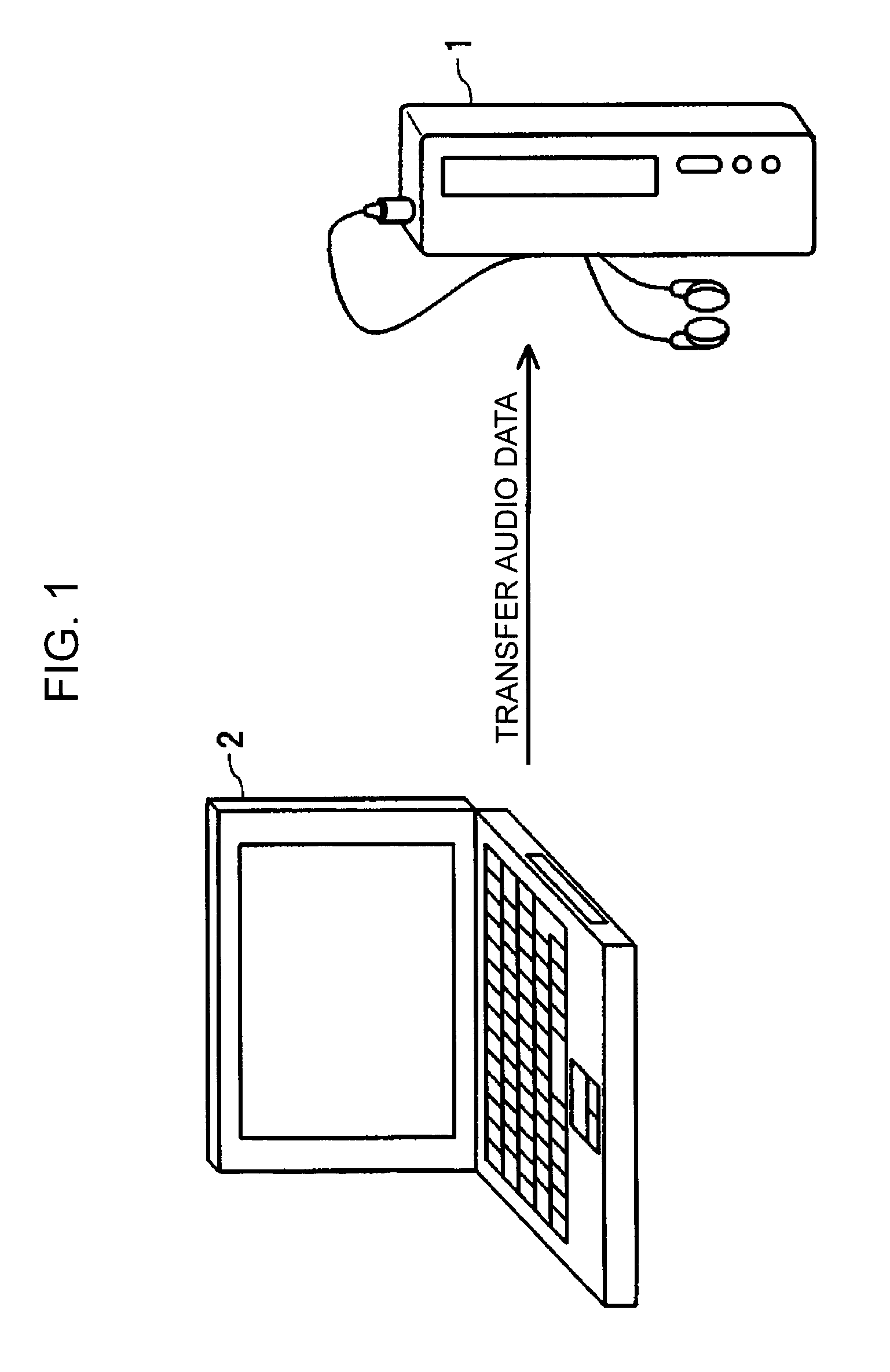
Recording-and-reproducing apparatus, information transfer-and-management method, and recording medium
InactiveUS20050207430A1Eliminate needEasy to useDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationInformation transferExternal interface
A software program of a flash memory loaded into an IC recorder is read and executed by a PC connected to the IC recorder via an external interface and an input-and-output end, so that an information signal, such as audio data held by the PC, is transferred from the PC to the flash memory. Management information about the information signal that is transferred and stored in the flash memory is generated by the software program executed by the PC and stored in the flash memory, so that the IC recorder can use the management information.
Owner:SONY CORP
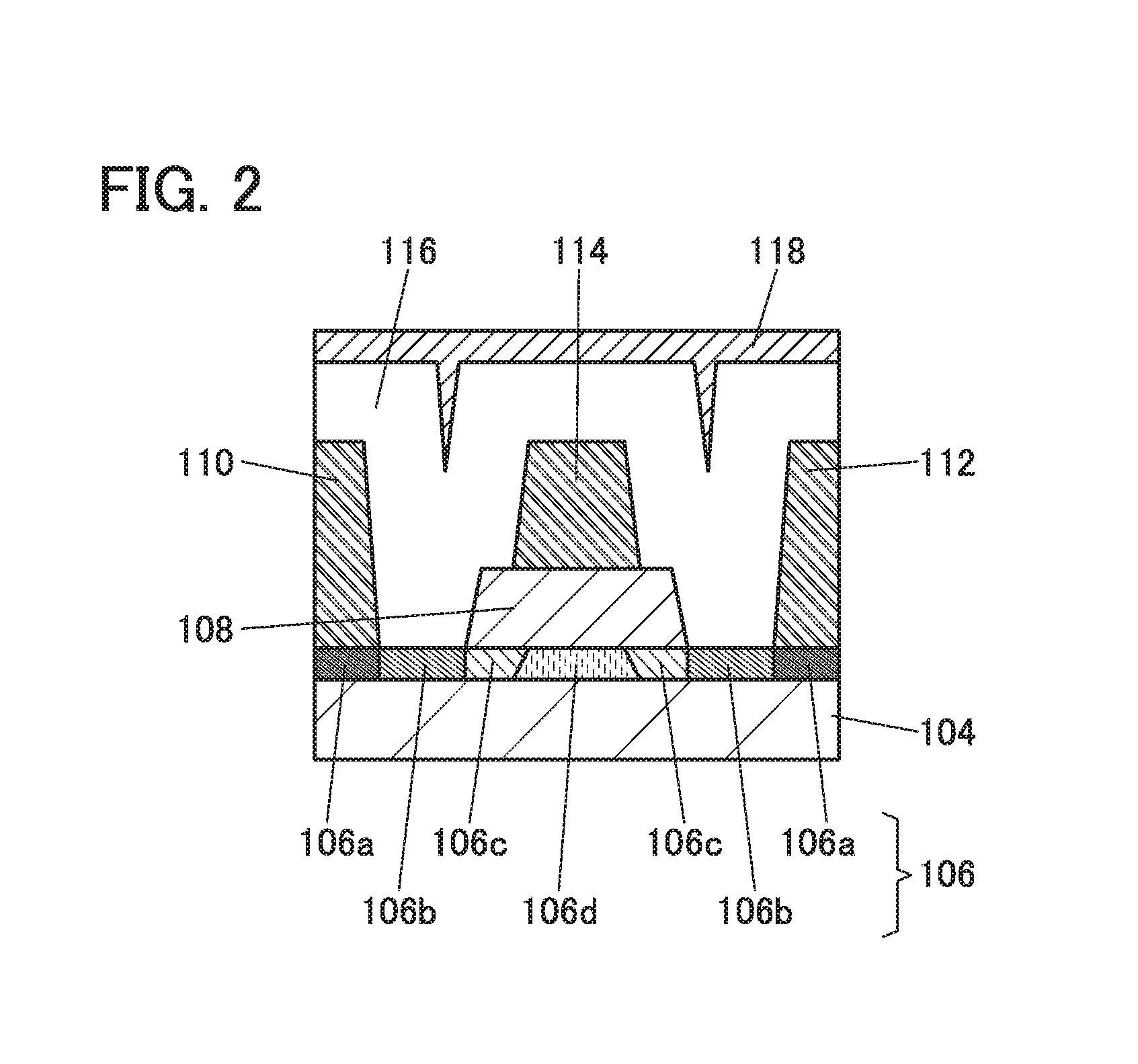
Recording-and-reproducing apparatus, information transfer-and-management method, and recording medium
InactiveUS8055362B2Signal delayTransfer delayDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationInformation transferExternal interface
A software program of a flash memory loaded into an IC recorder is read and executed by a PC connected to the IC recorder via an external interface and an input-and-output end, so that an information signal, such as audio data held by the PC, is transferred from the PC to the flash memory. Management information about the information signal that is transferred and stored in the flash memory is, generated by the software program executed by the PC and stored in the flash memory, so that the IC recorder can use the management information.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com