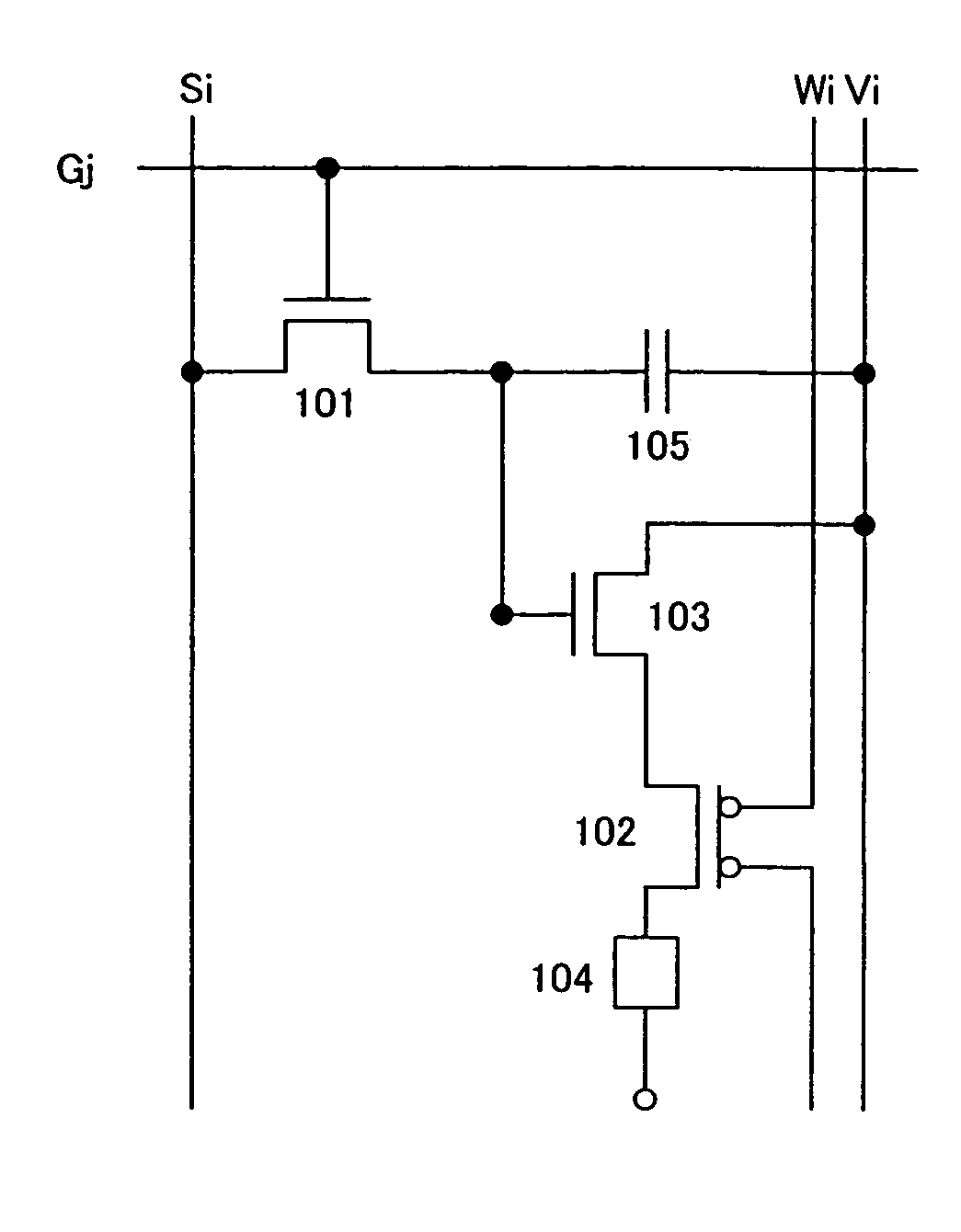
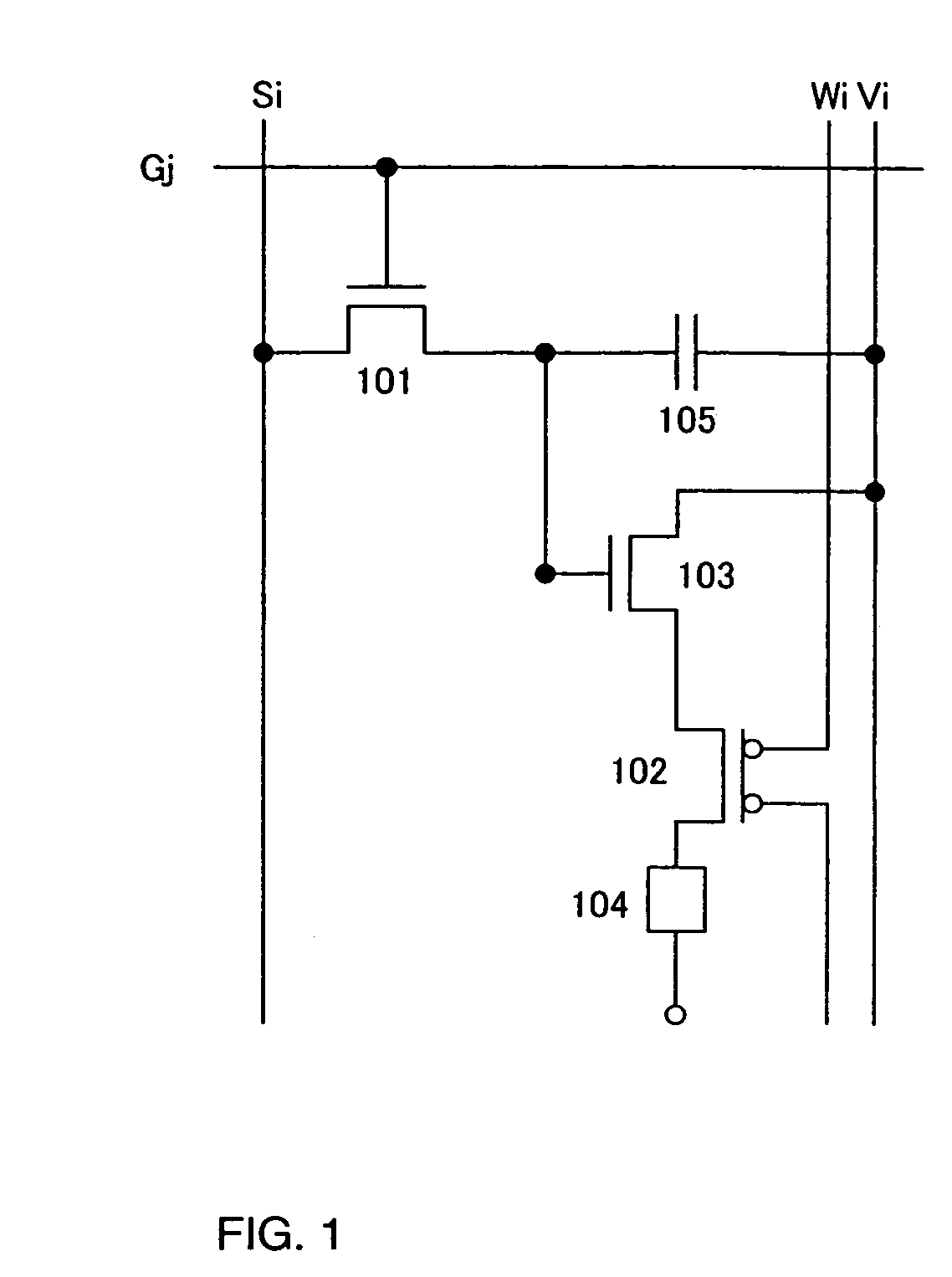
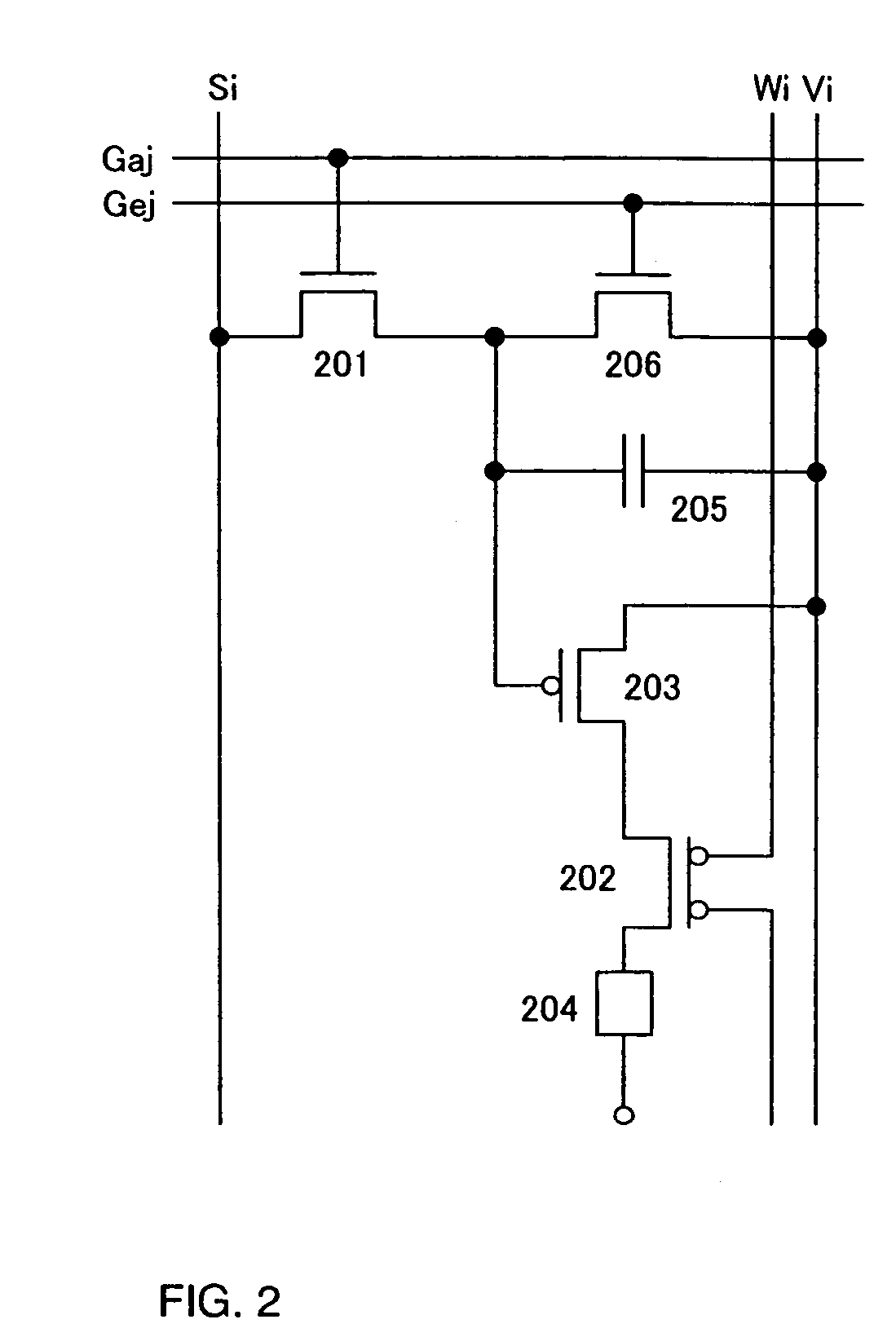
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Luminance variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
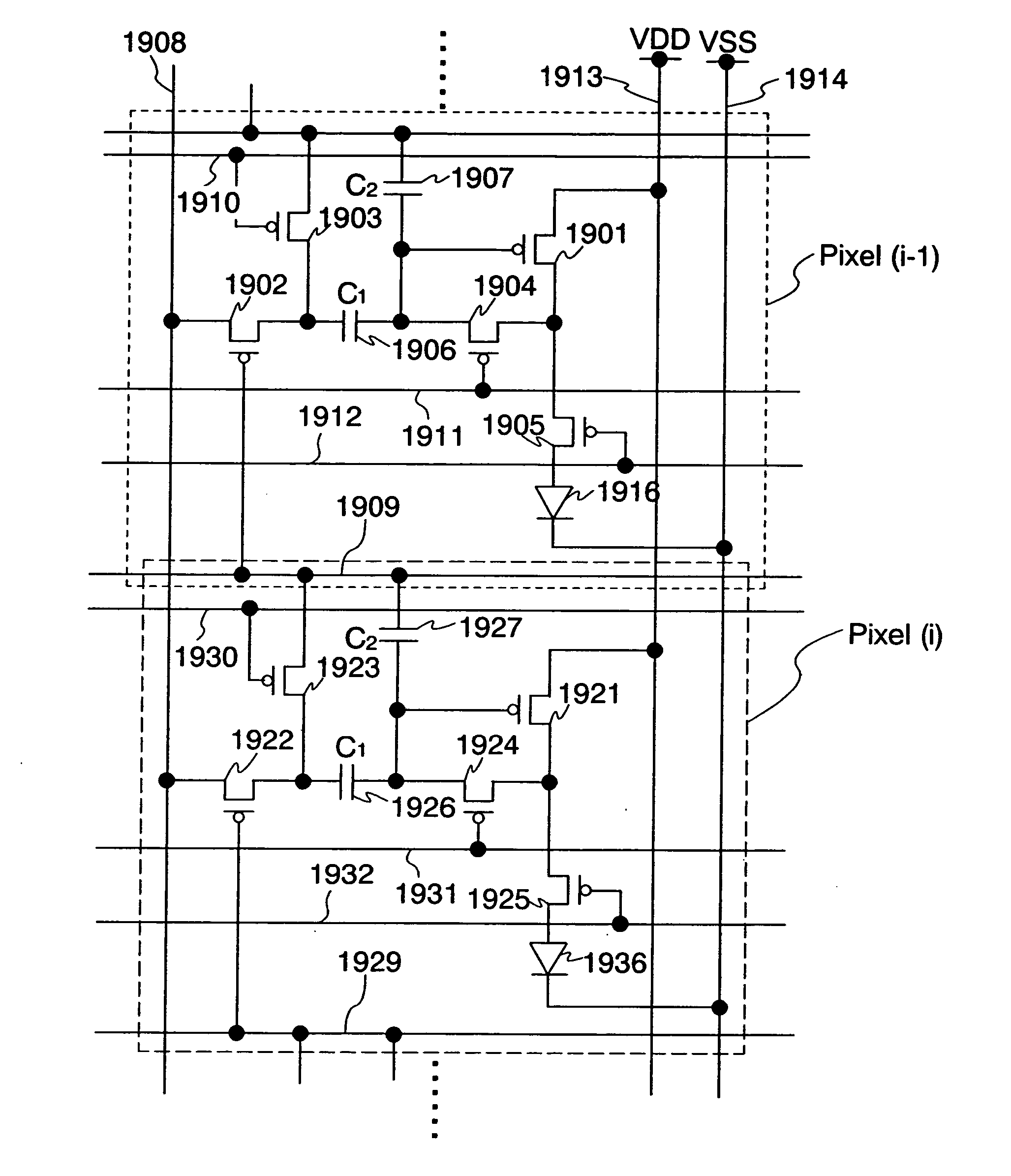
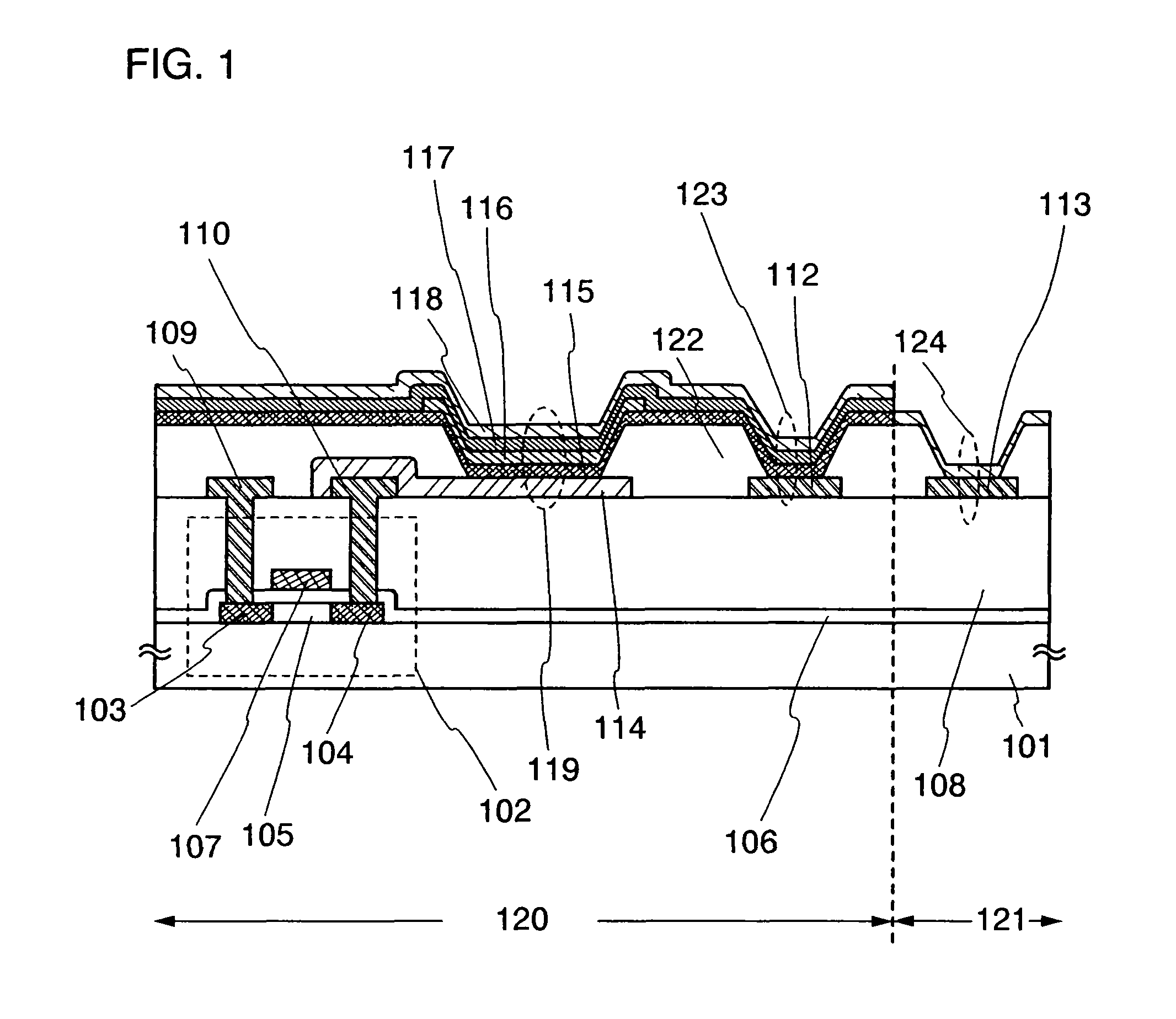
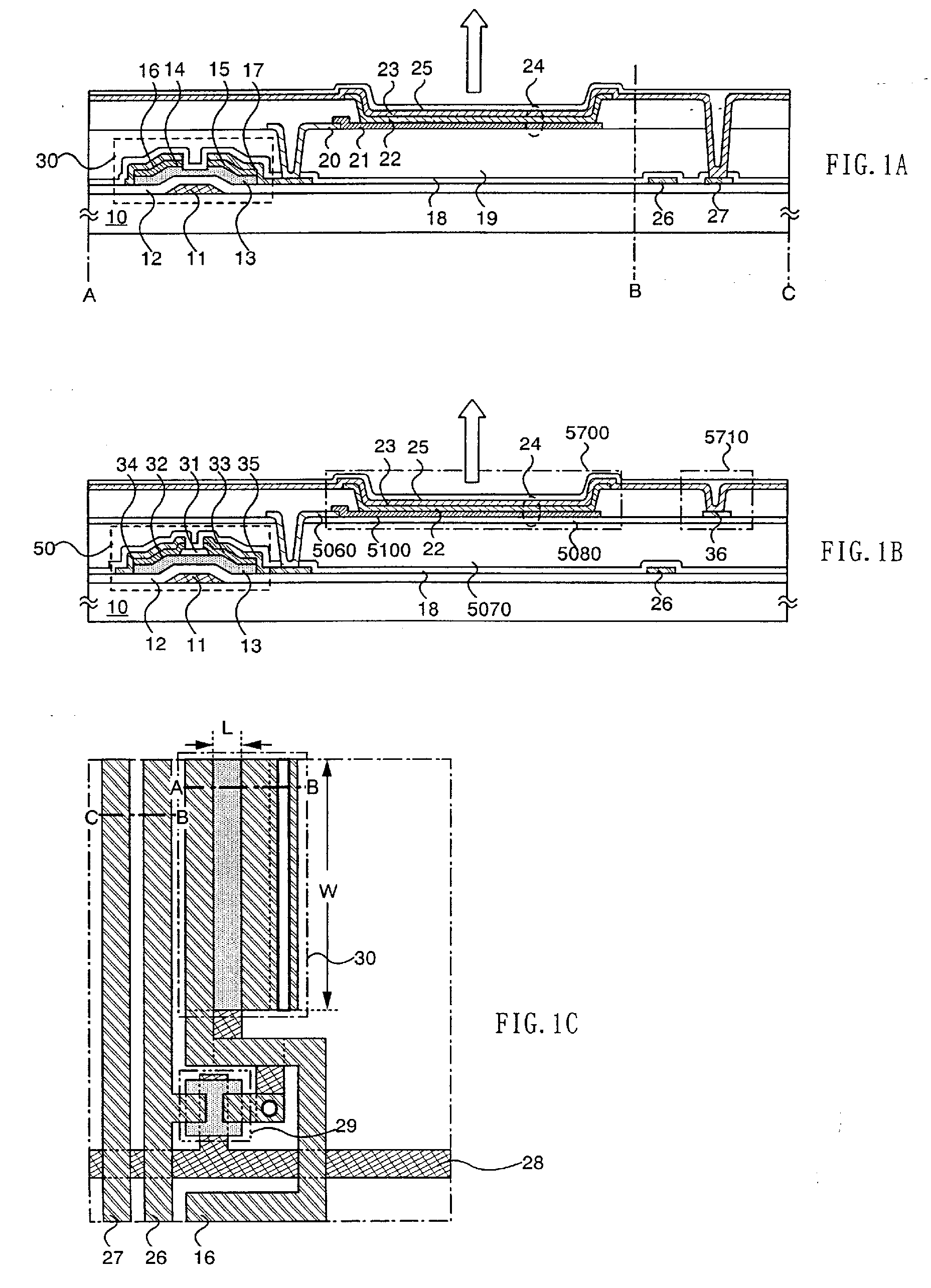
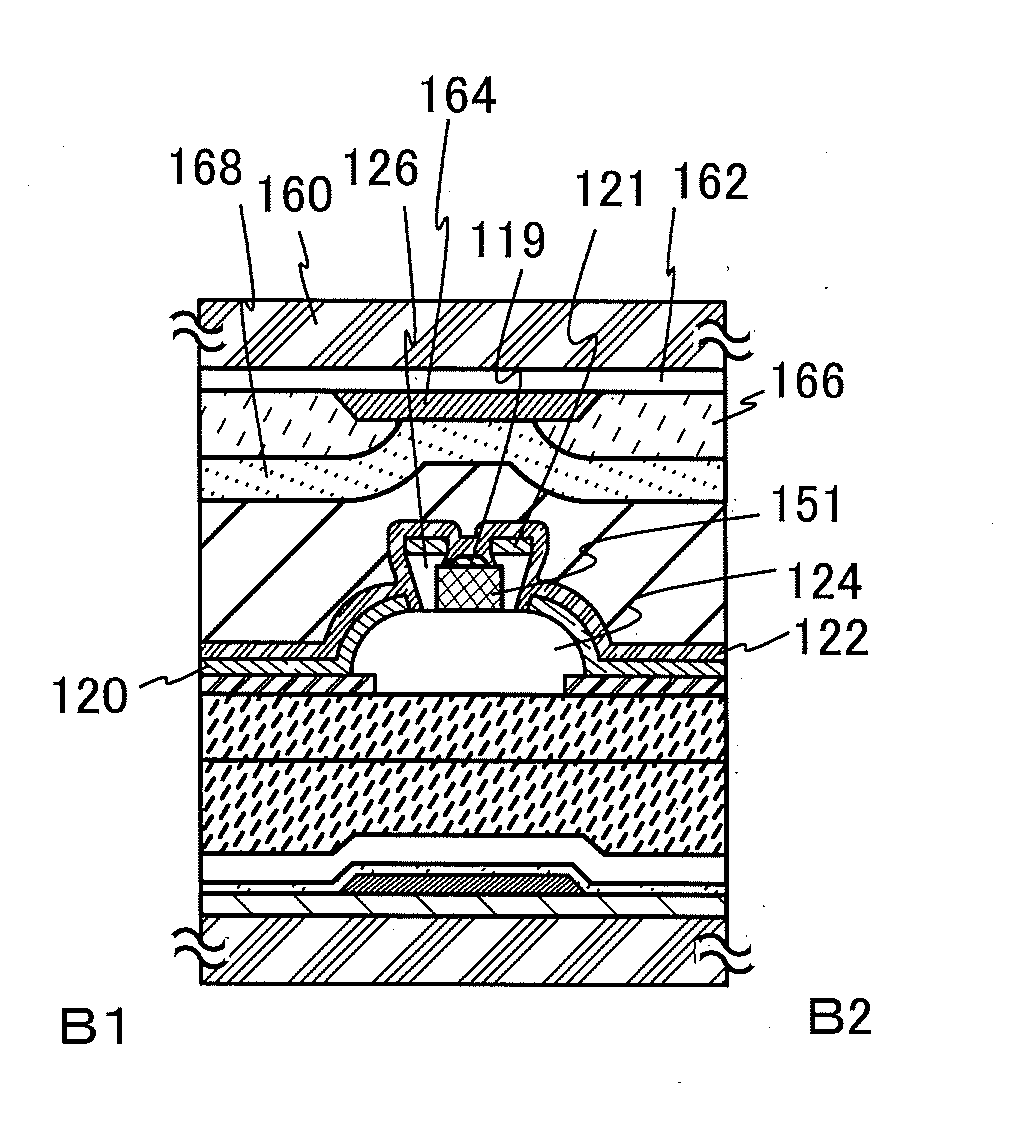
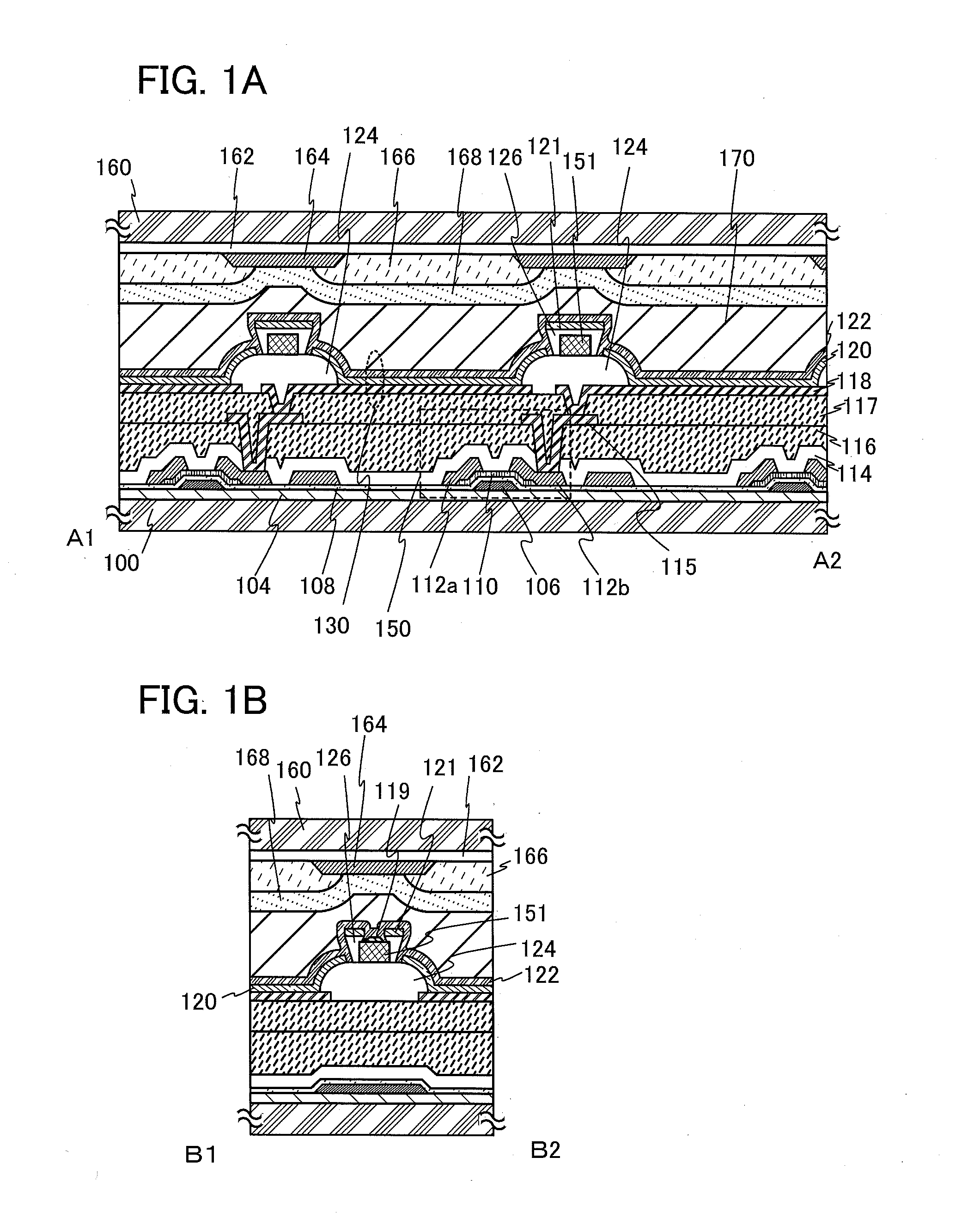
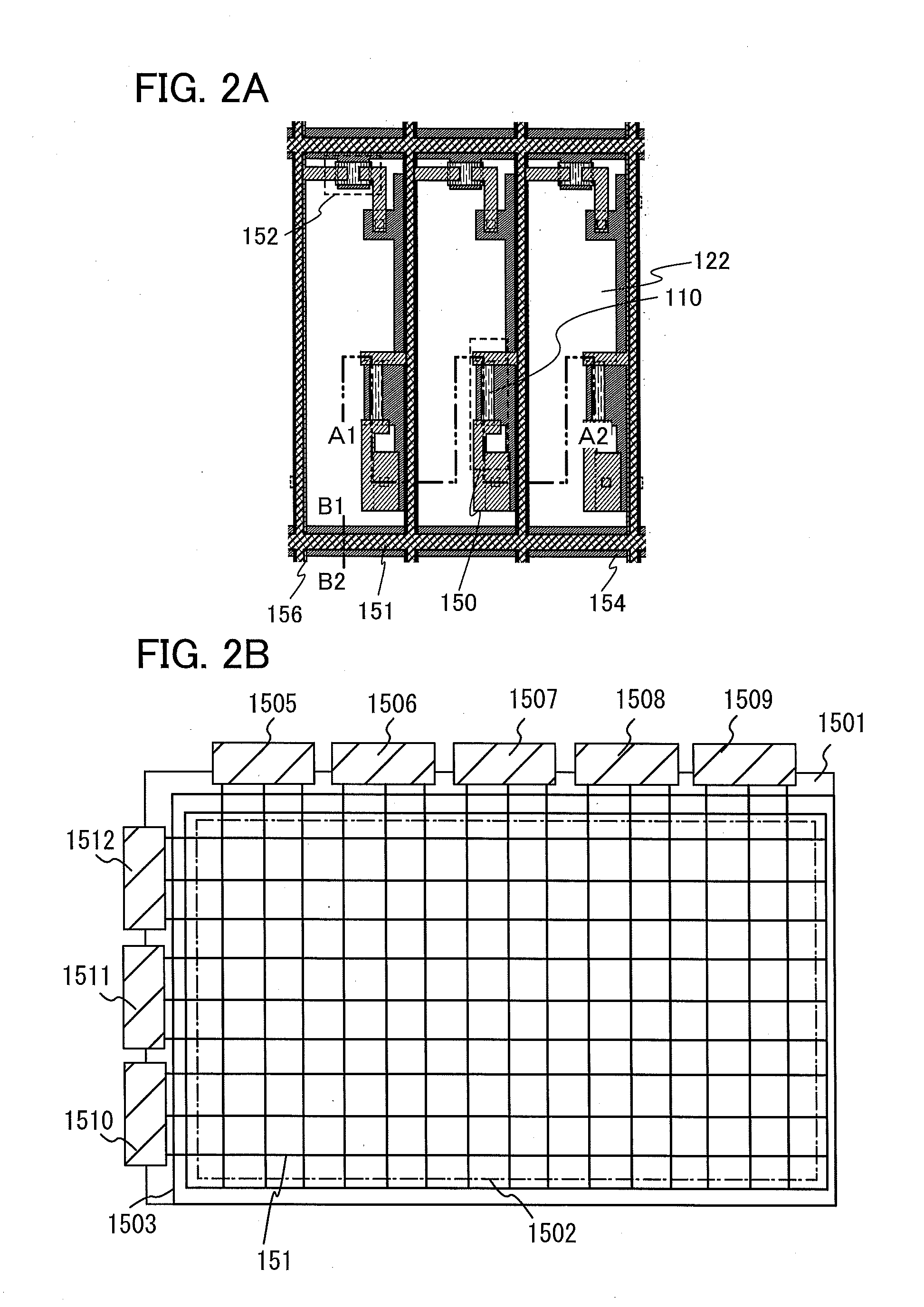
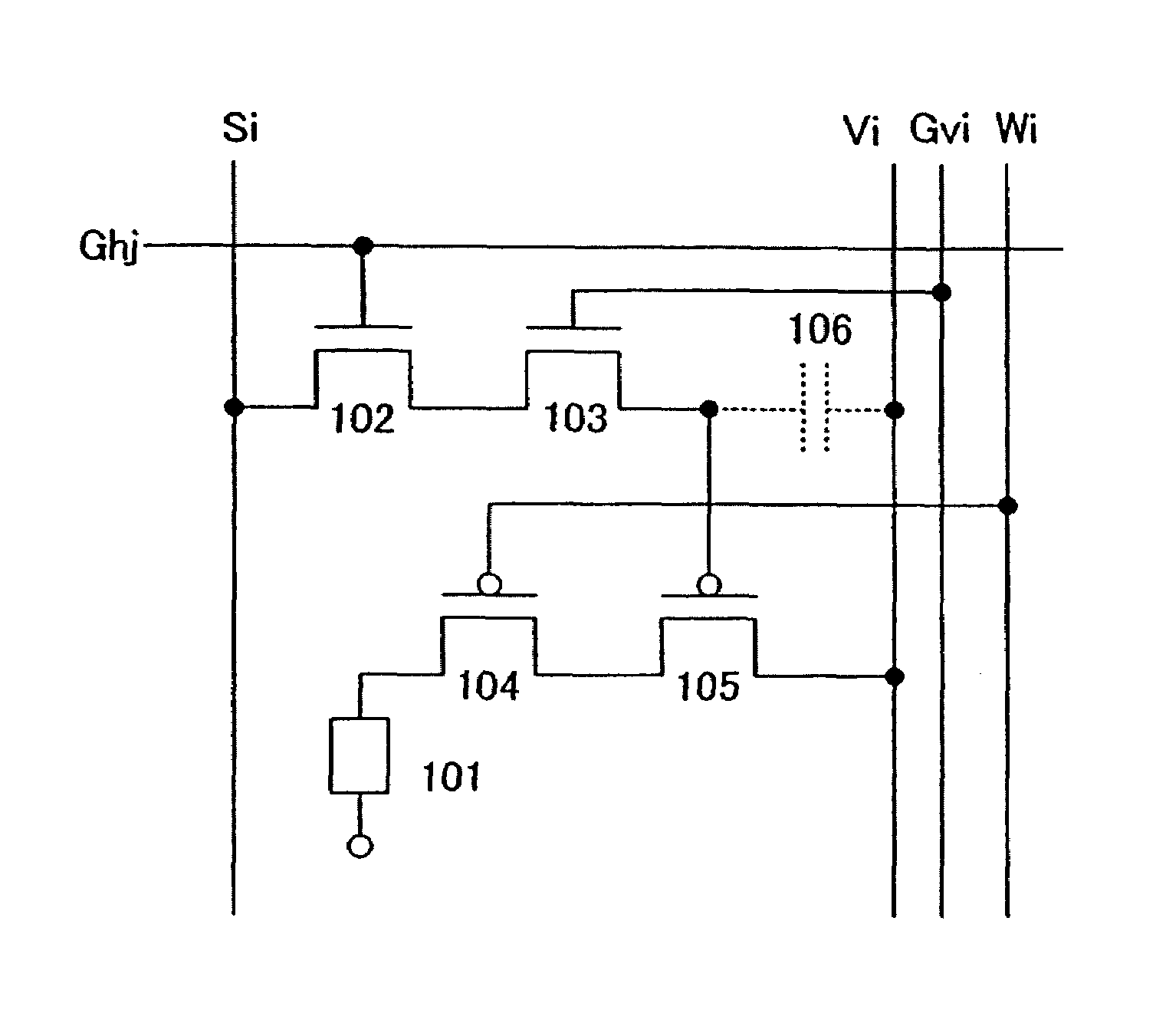
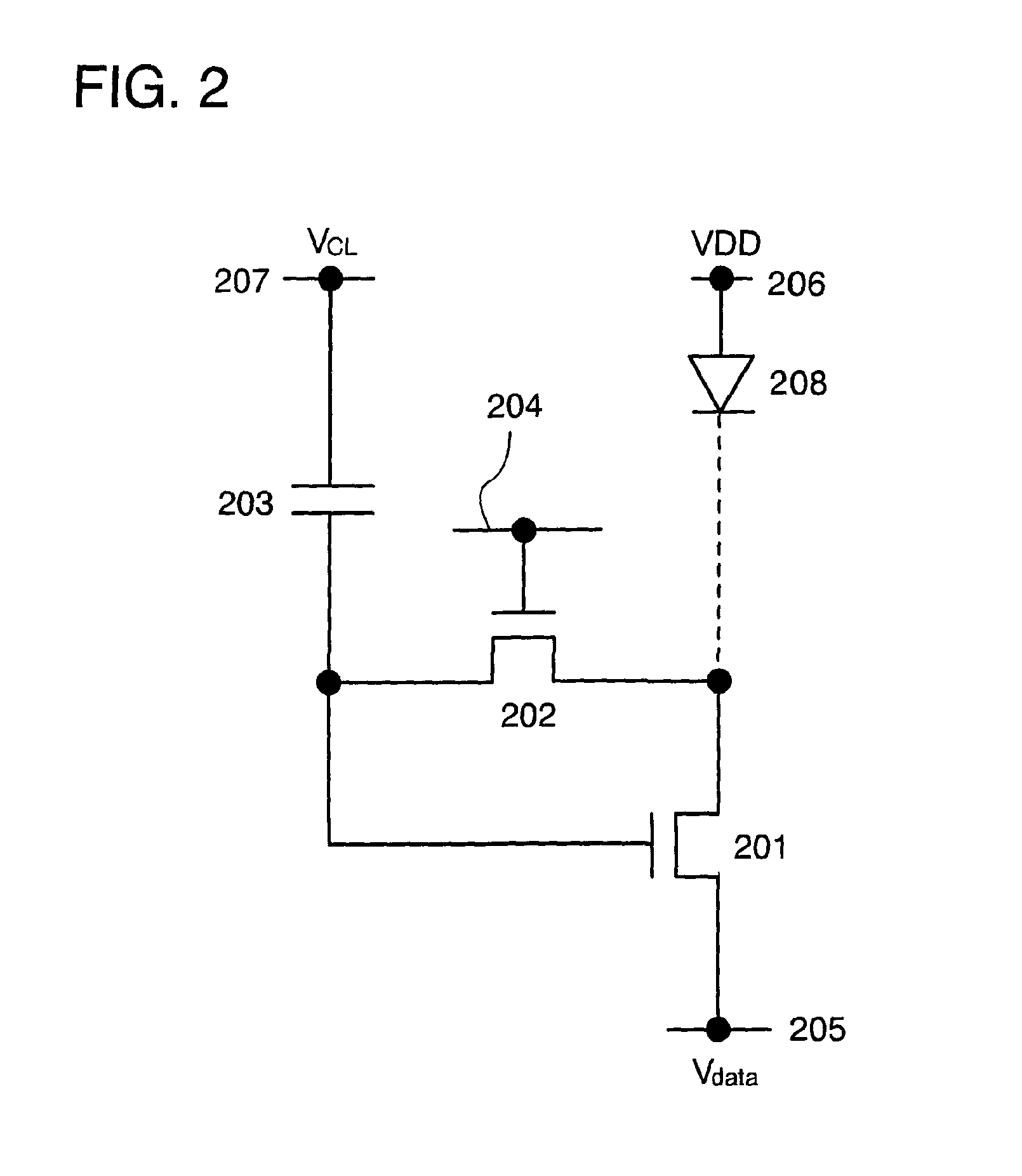
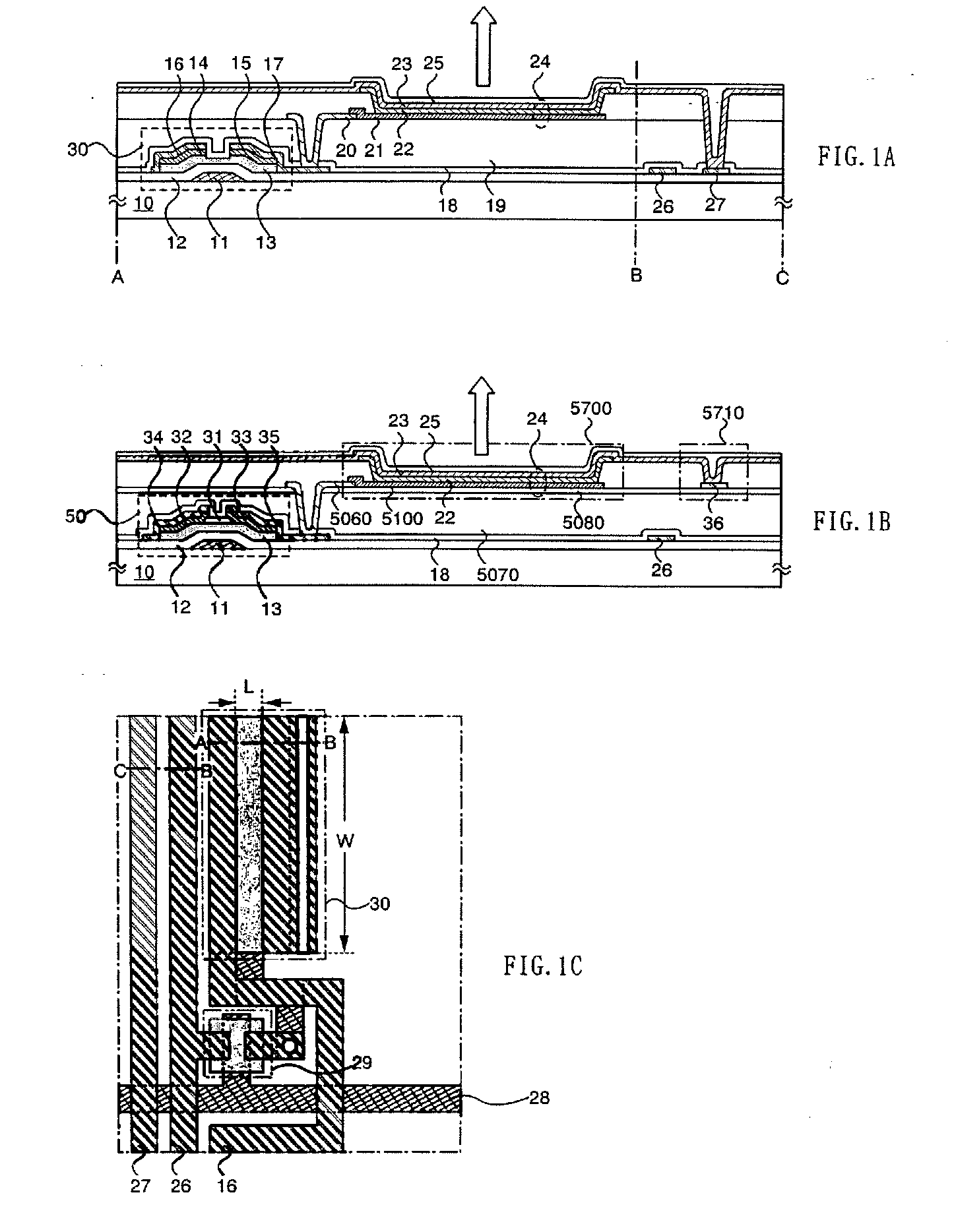
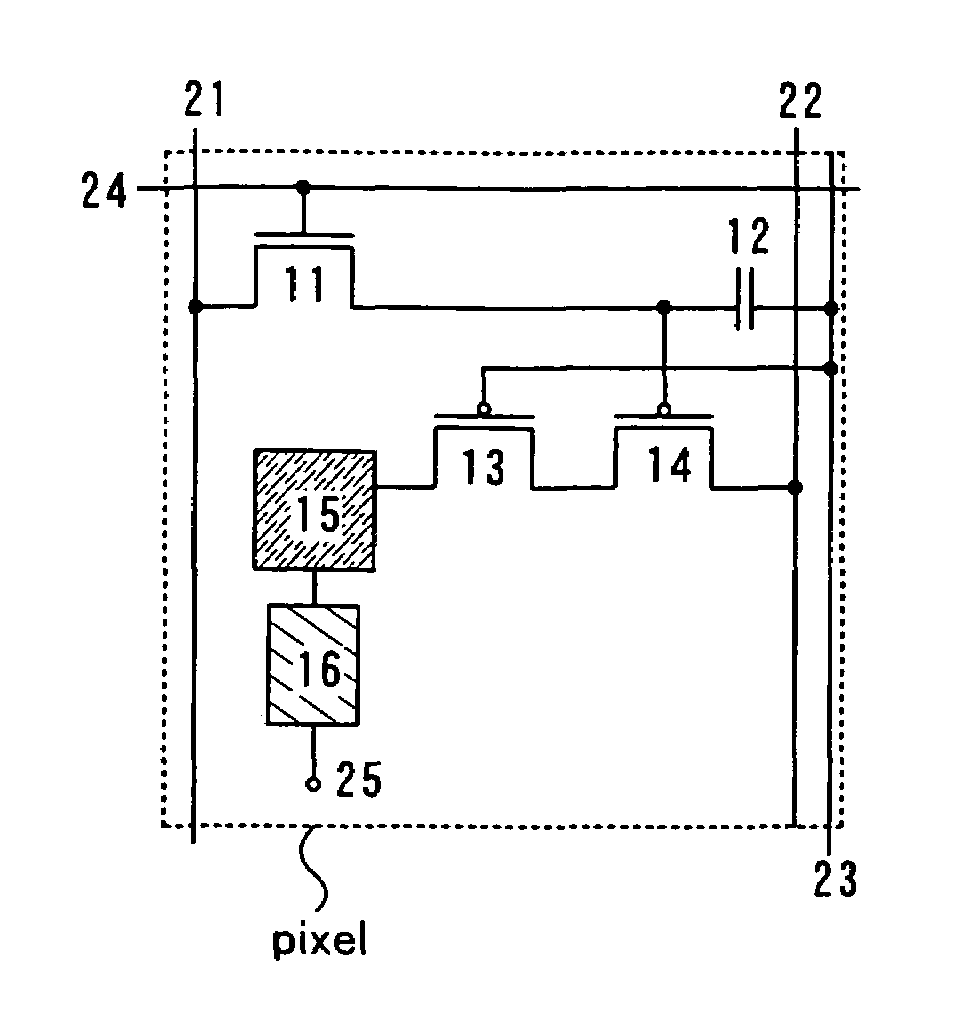
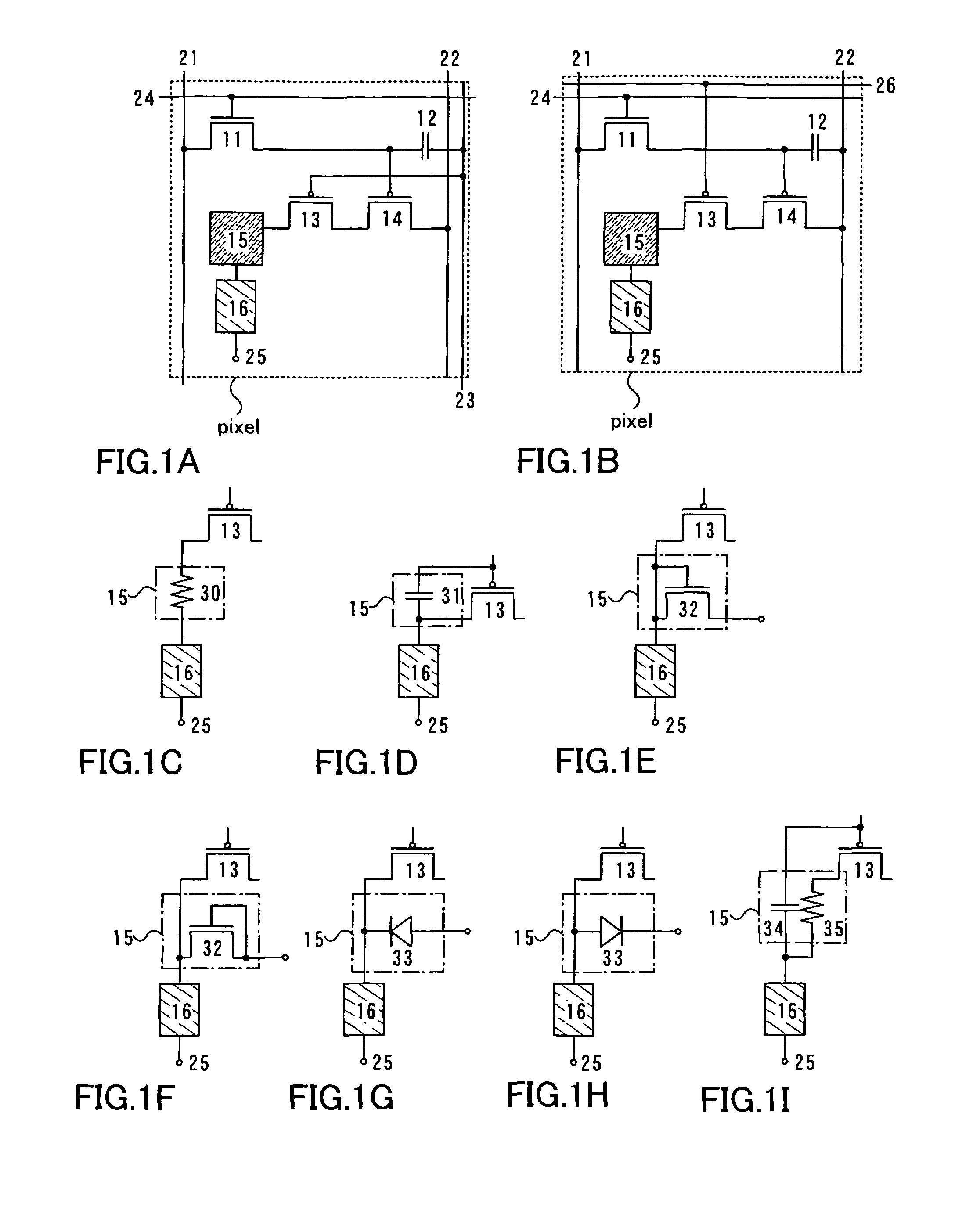
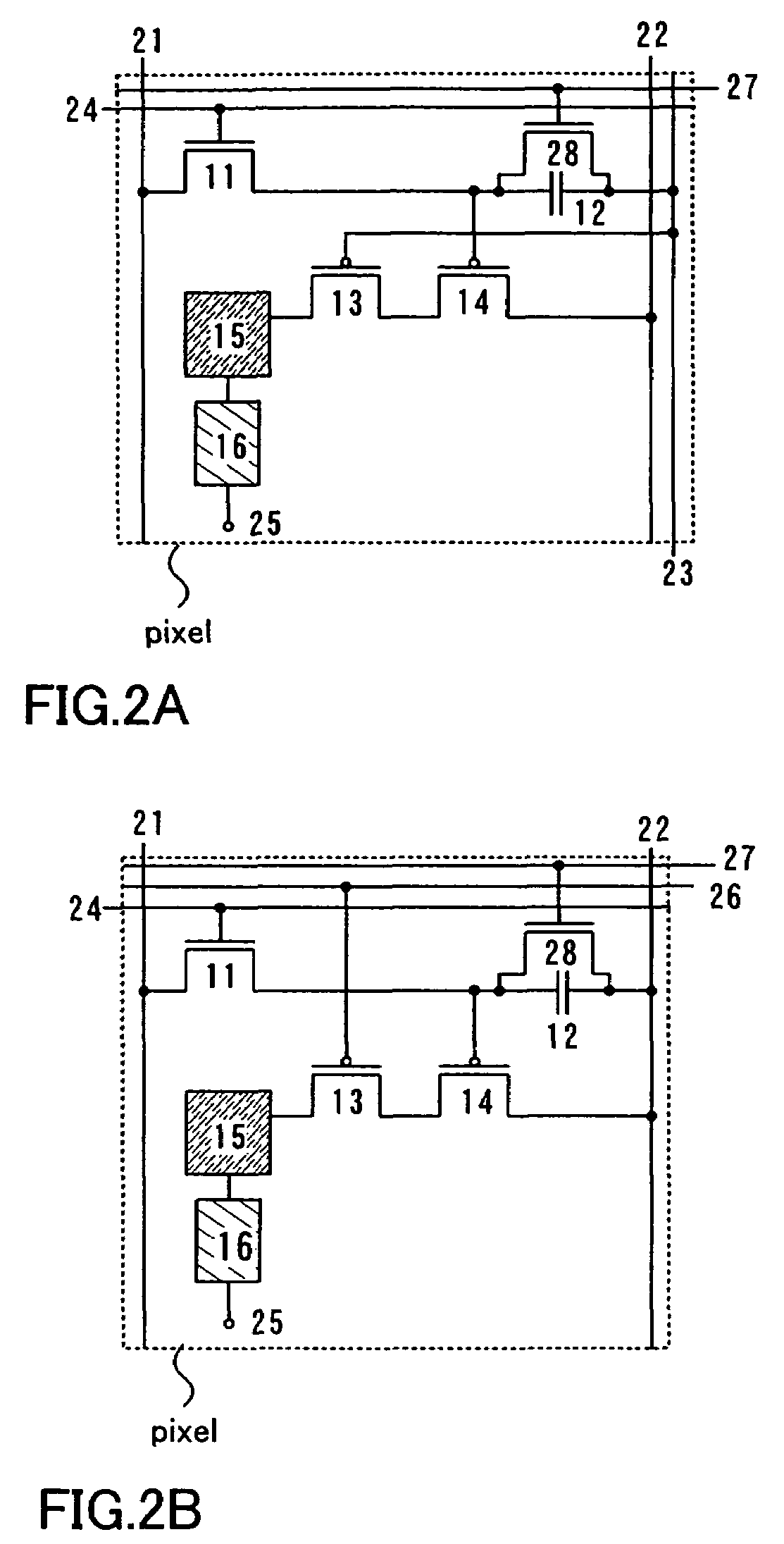
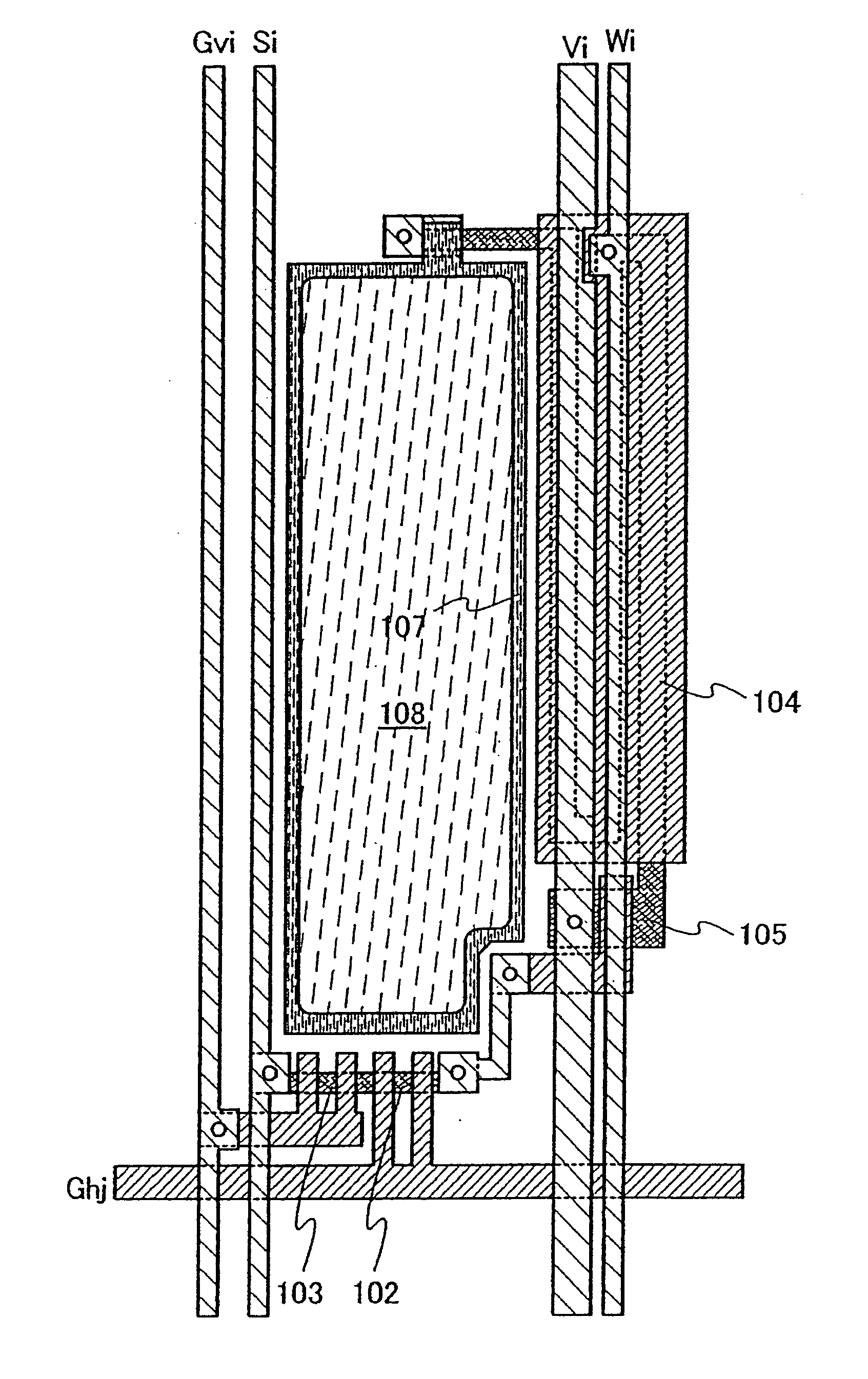
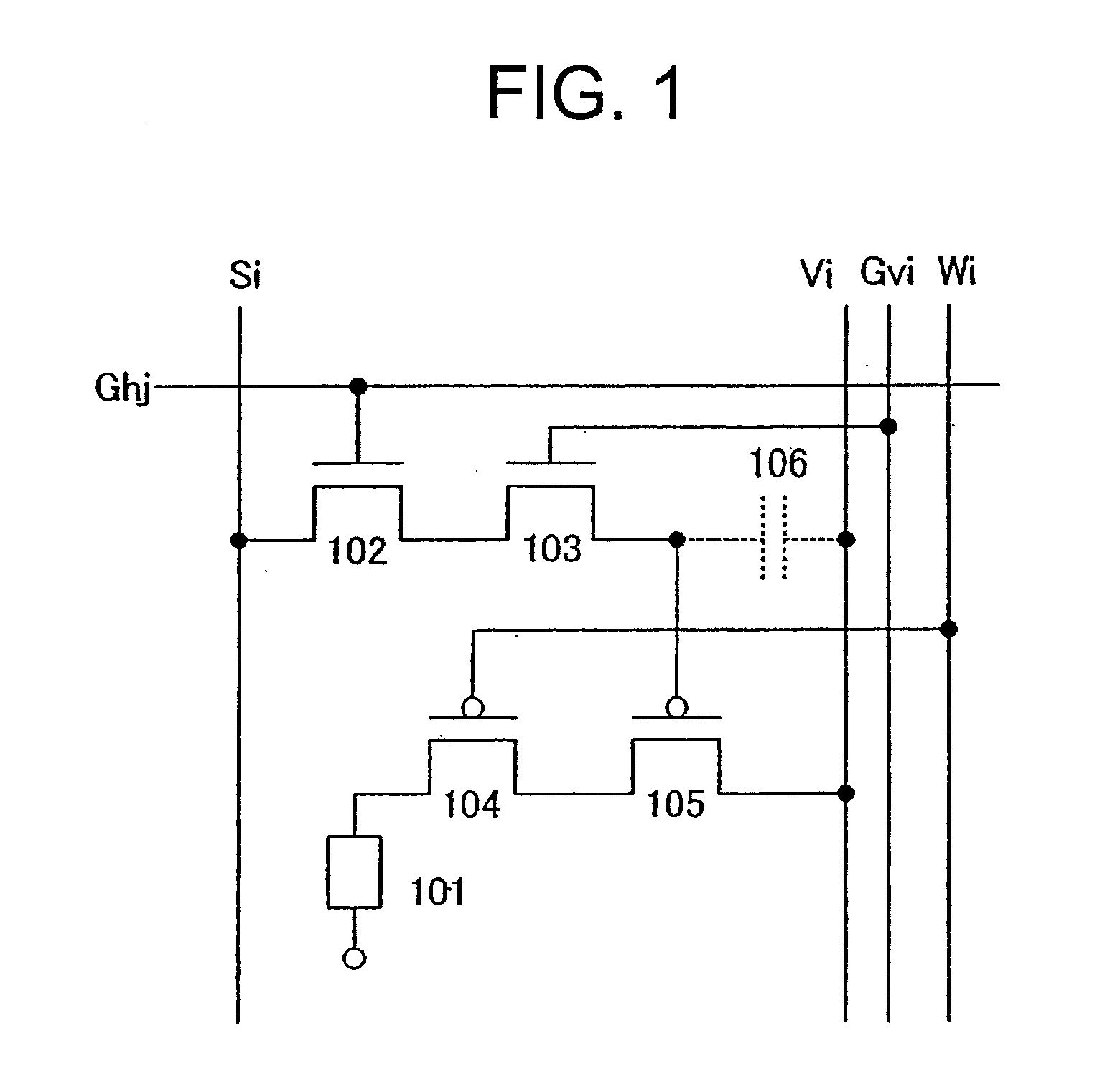
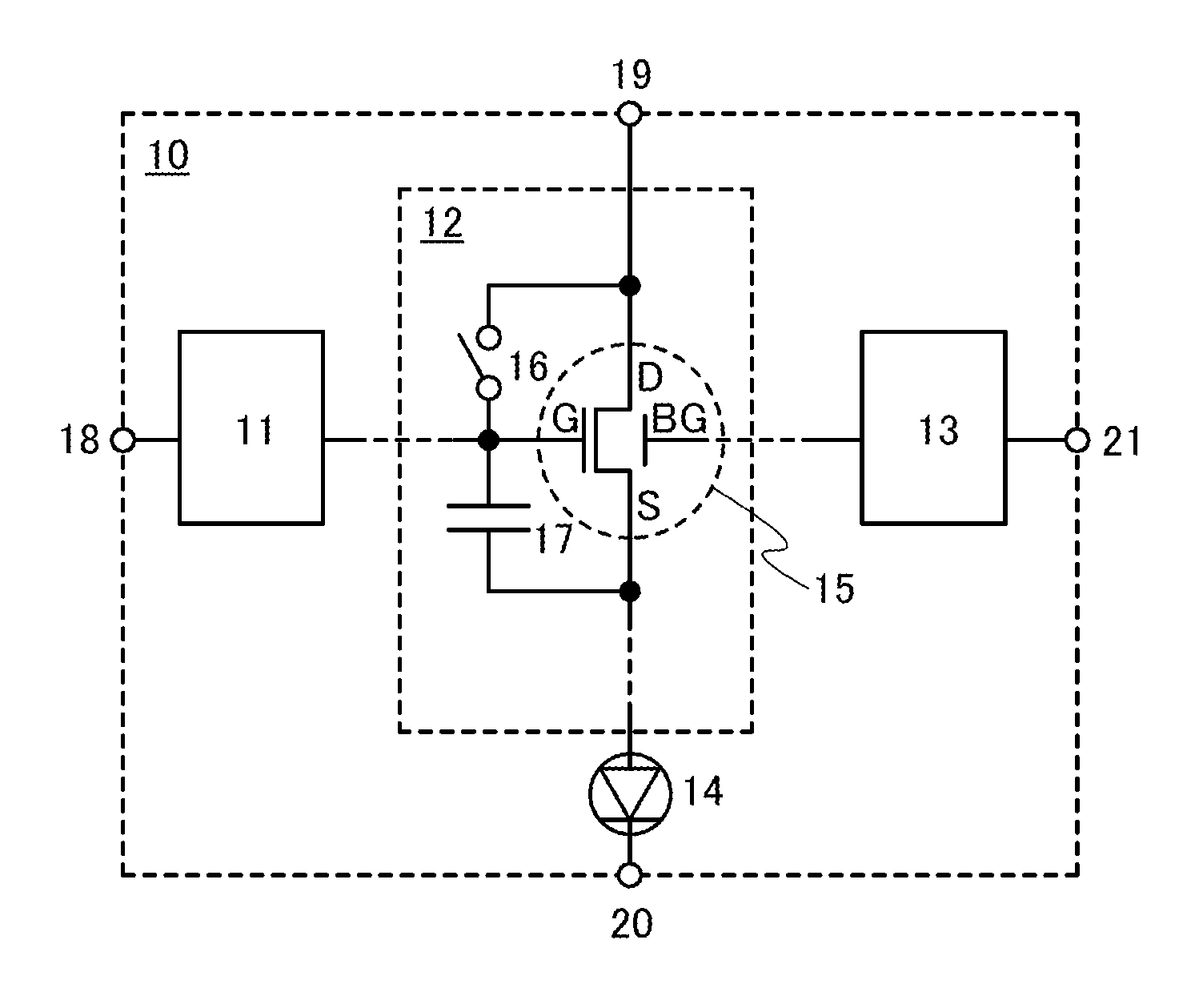
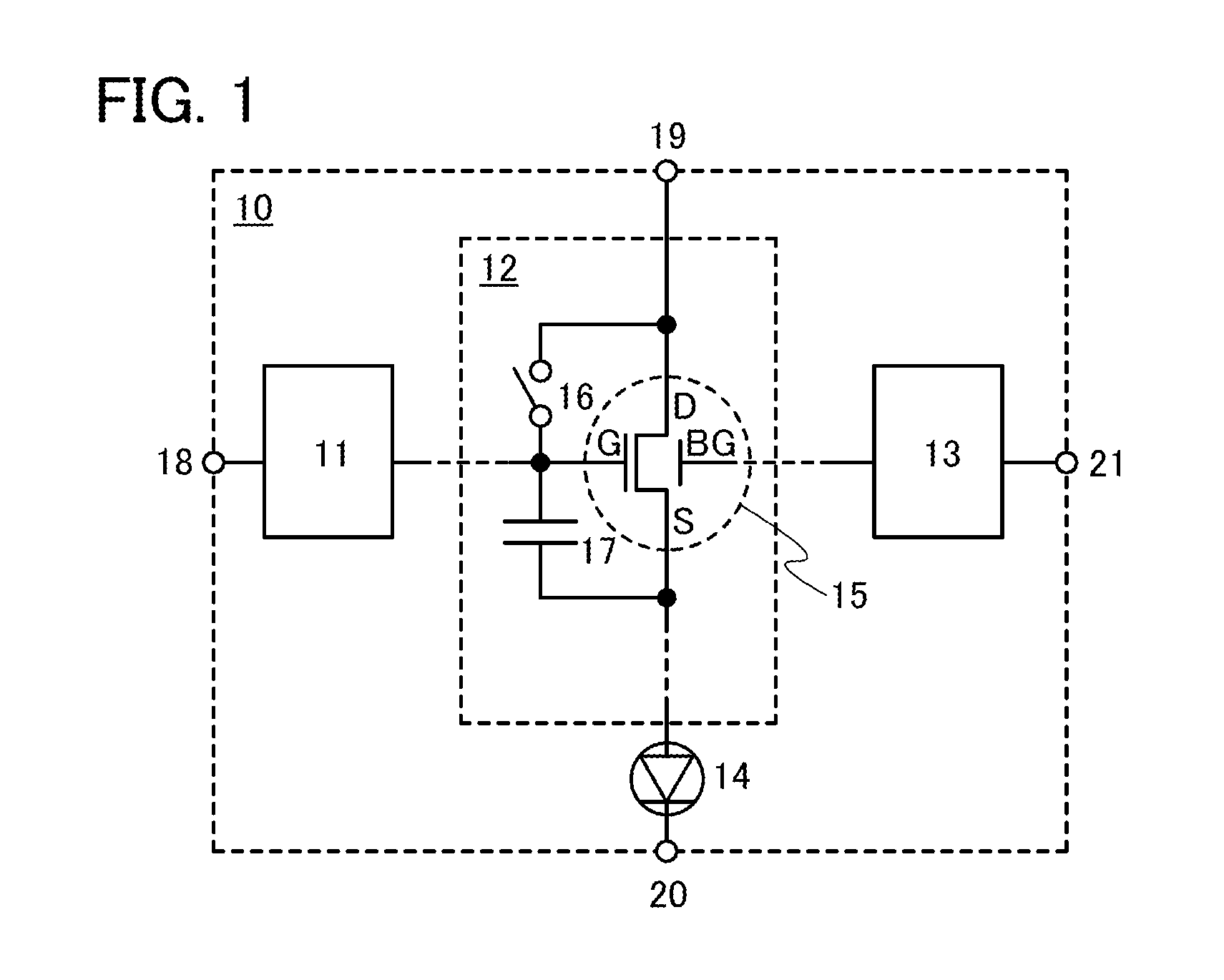
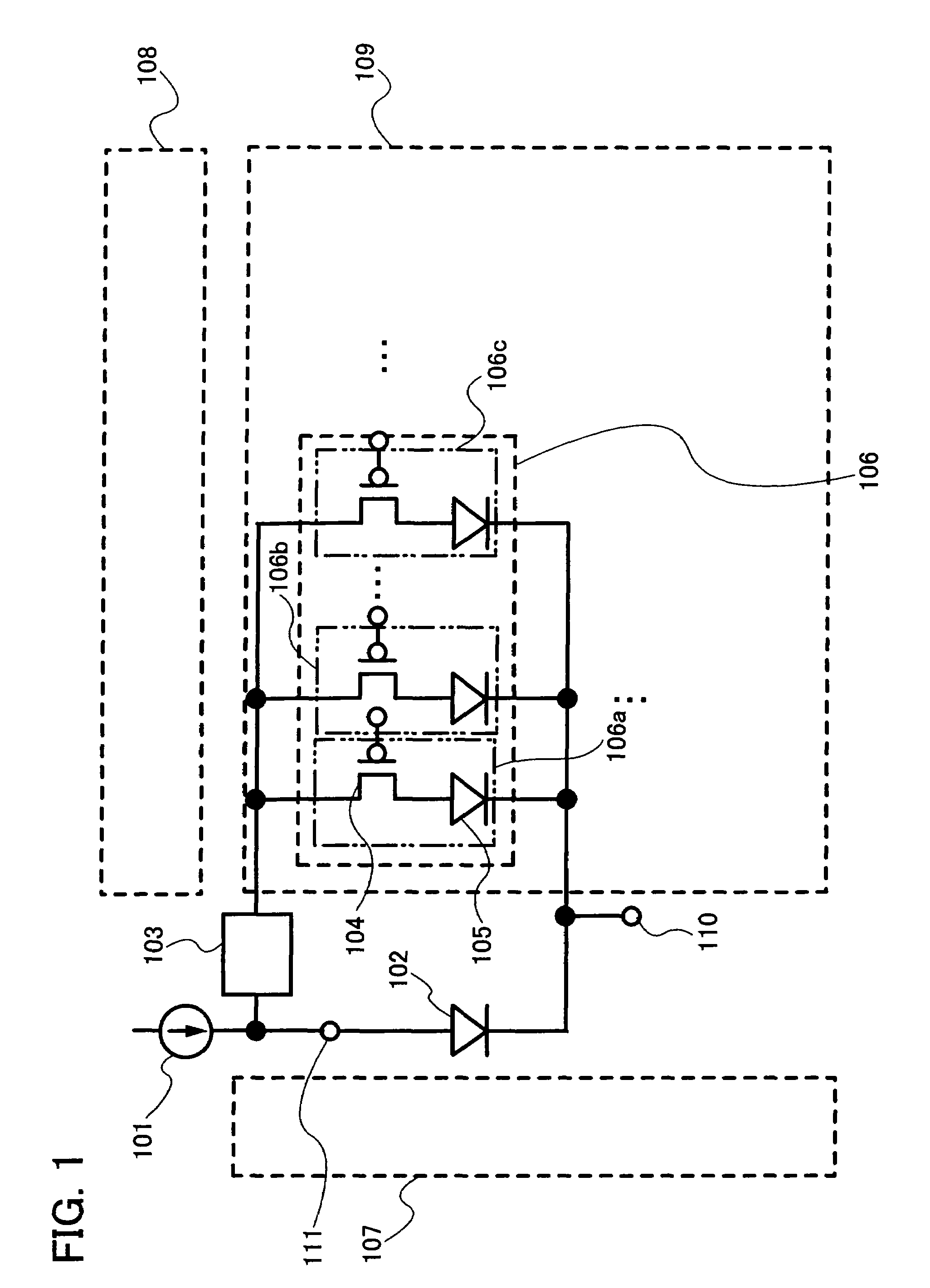
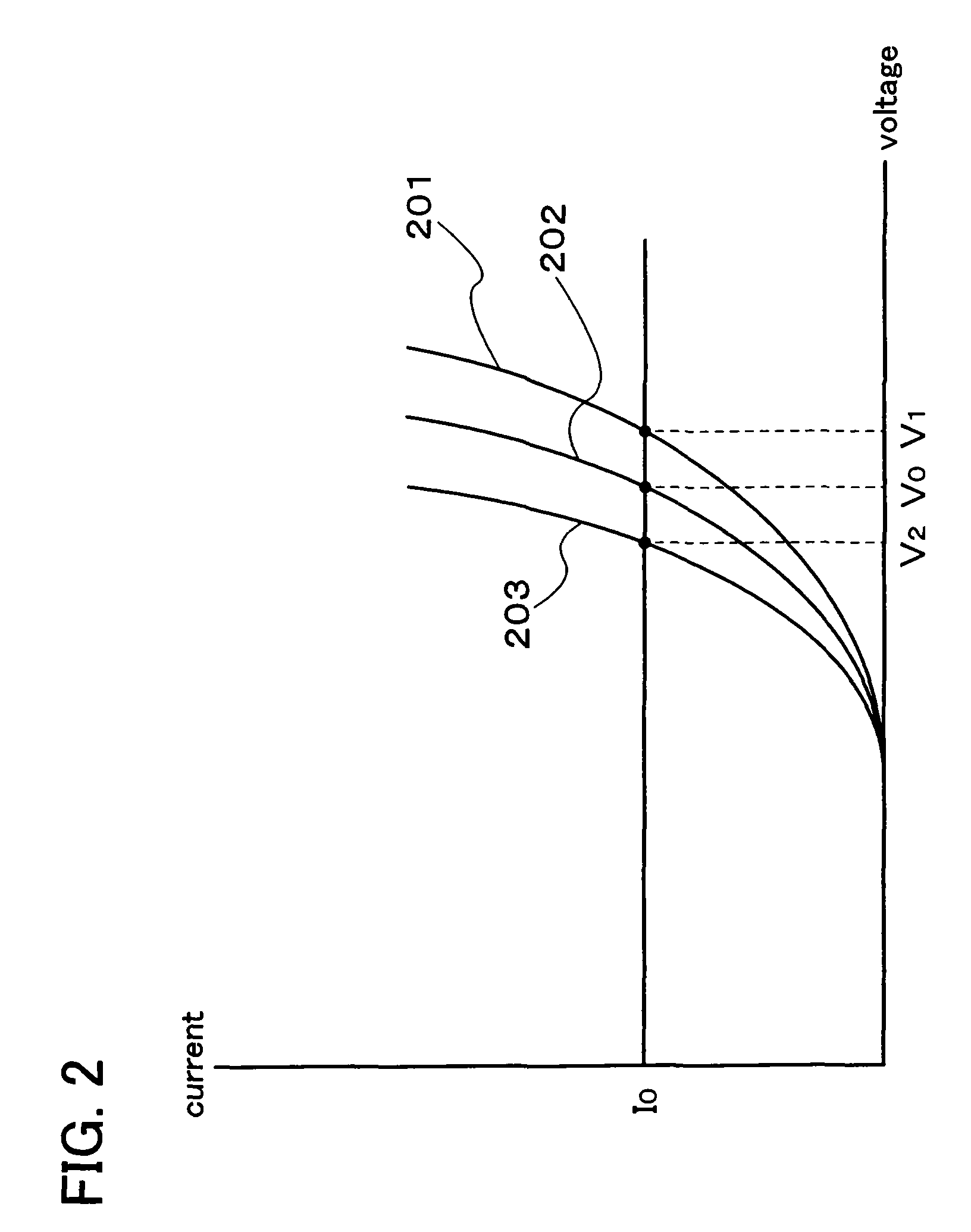
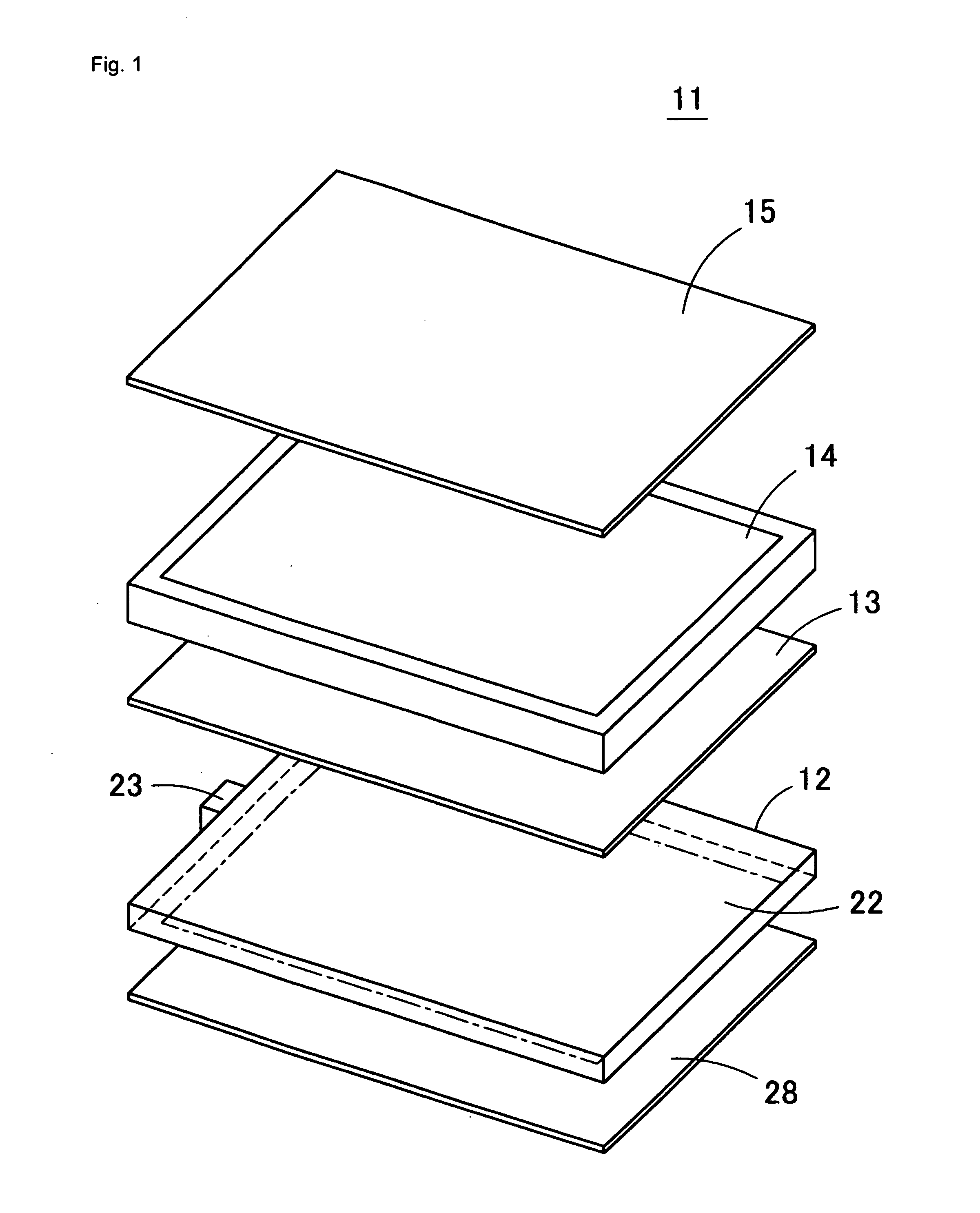
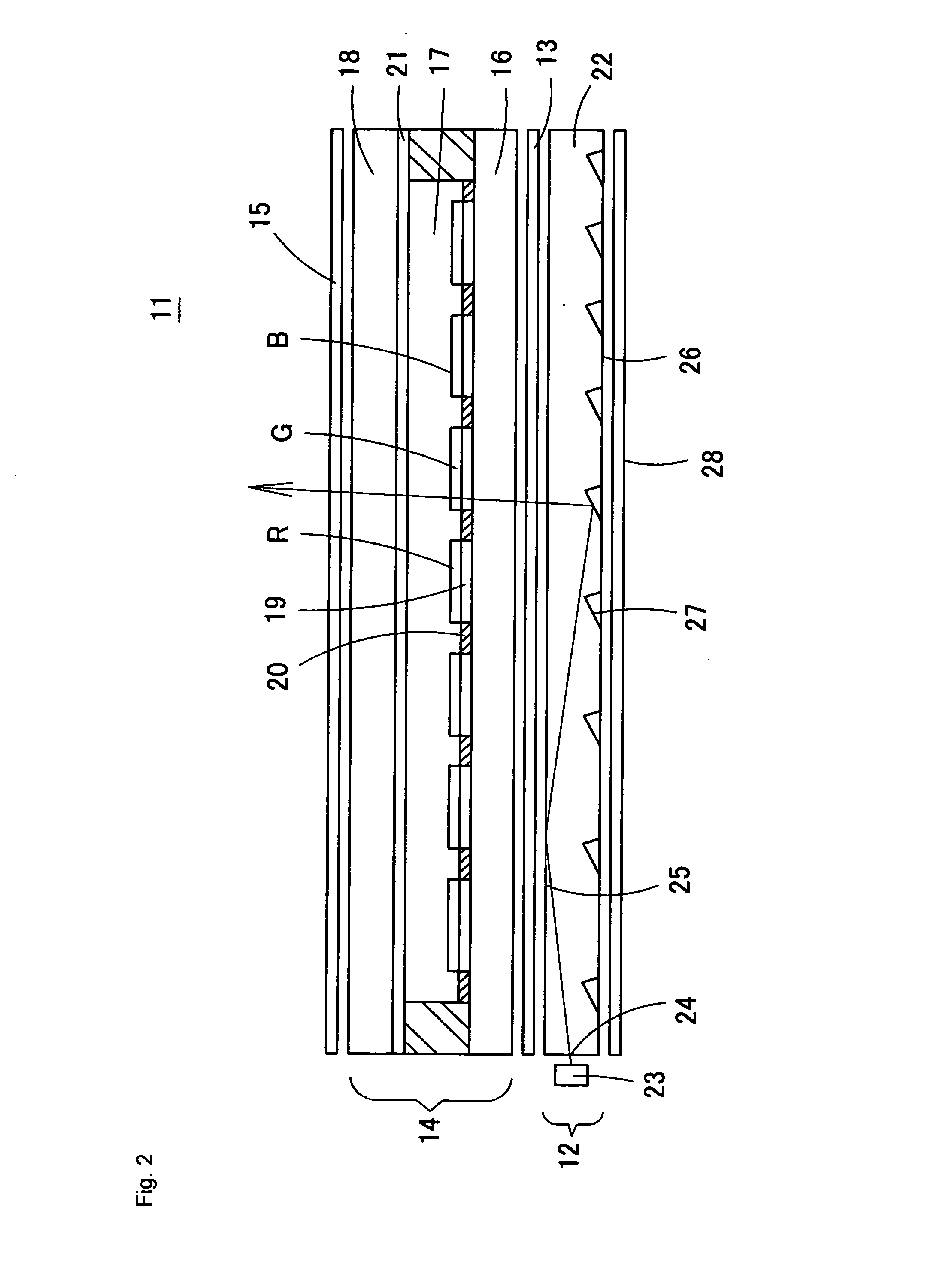
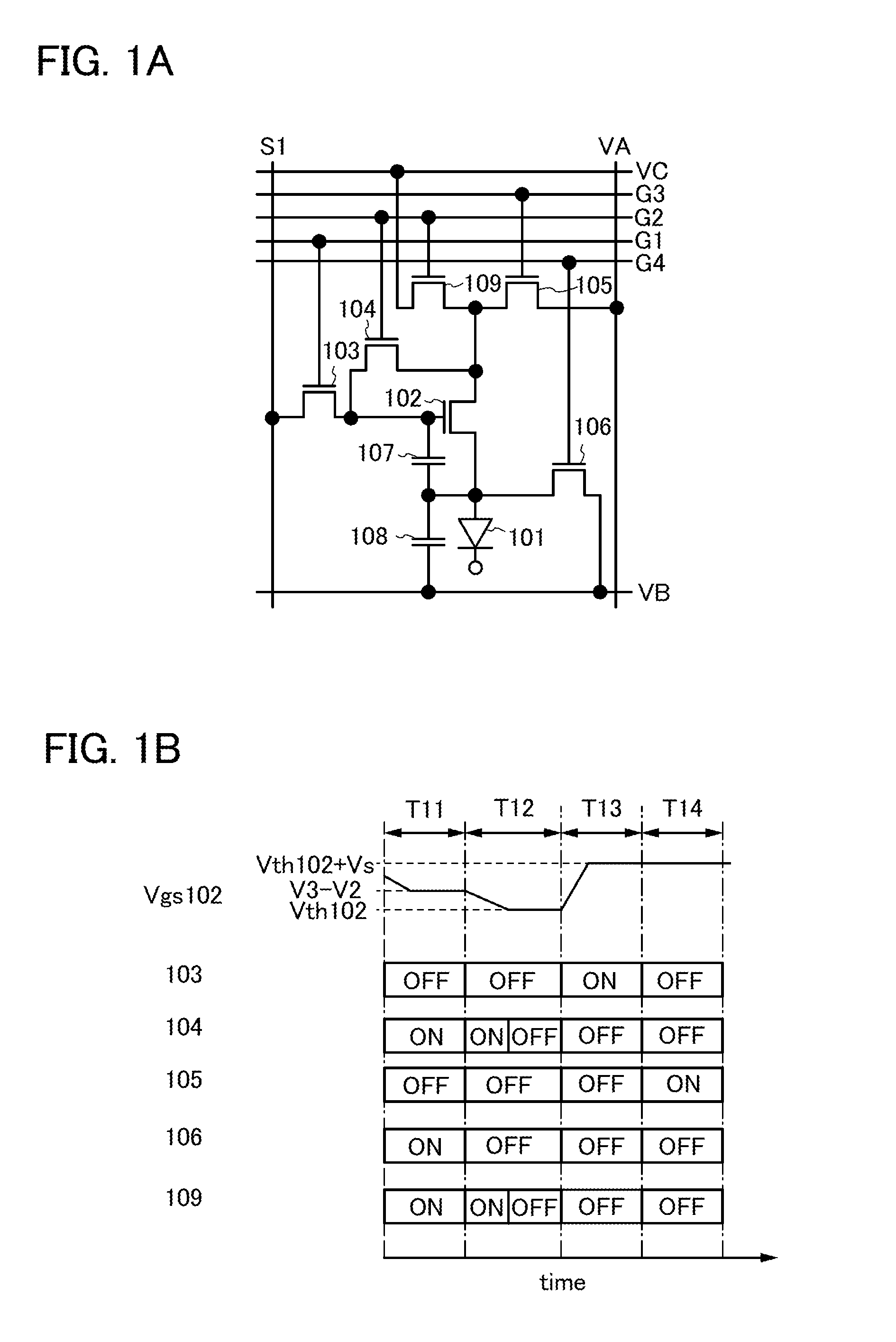
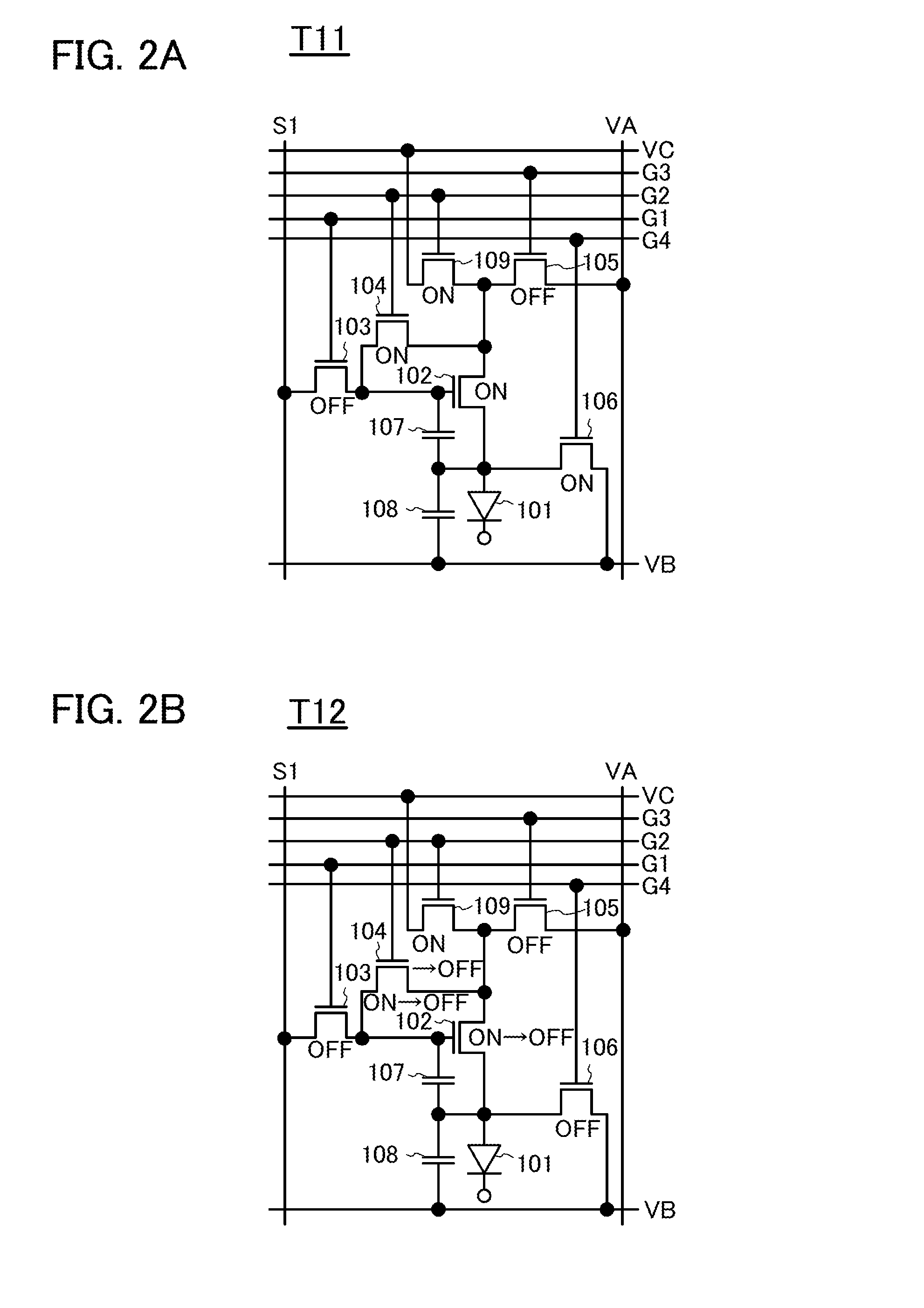
Display device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20070085847A1Reduce luminanceImprove image qualityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesEngineeringDisplay device
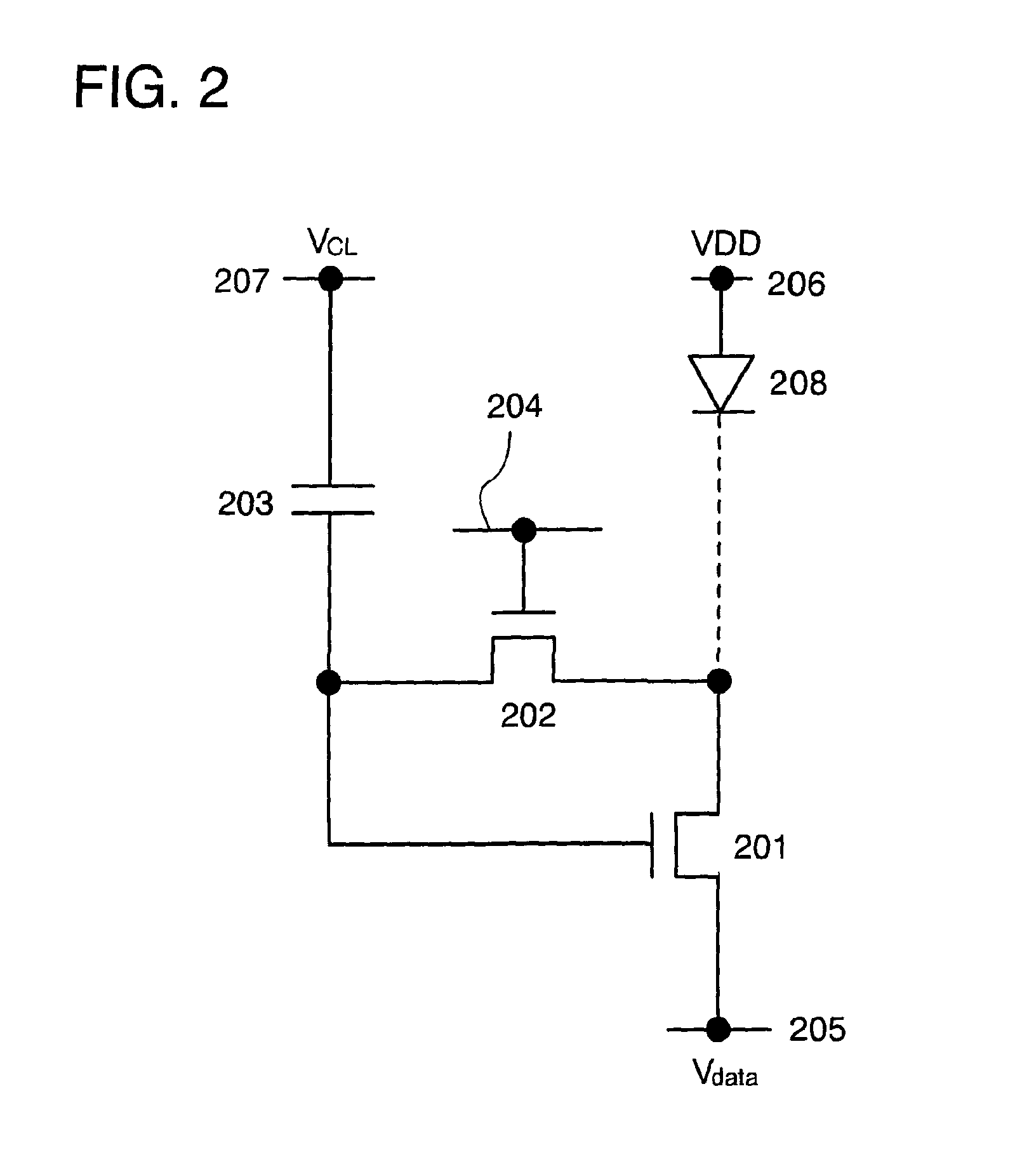
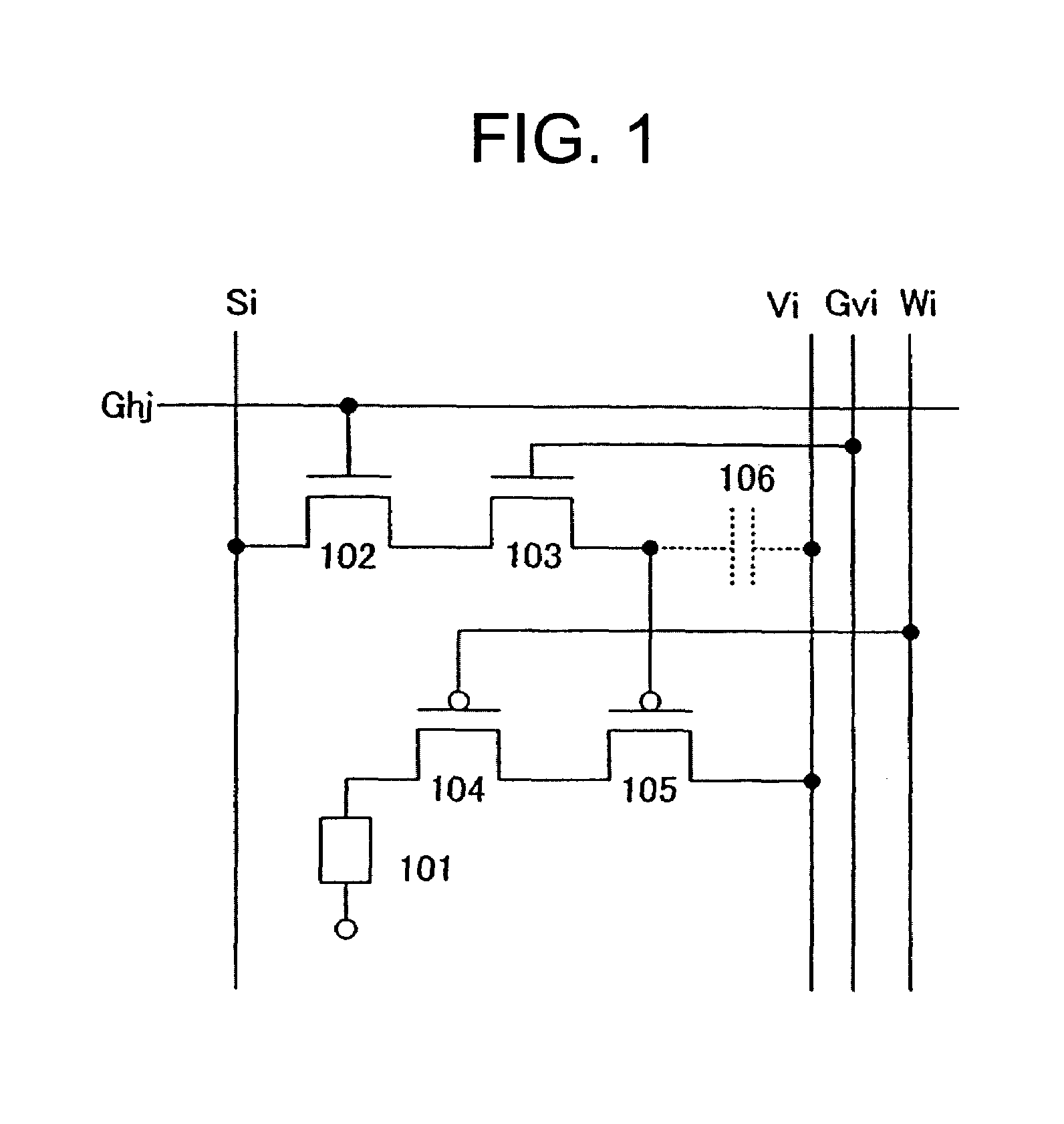
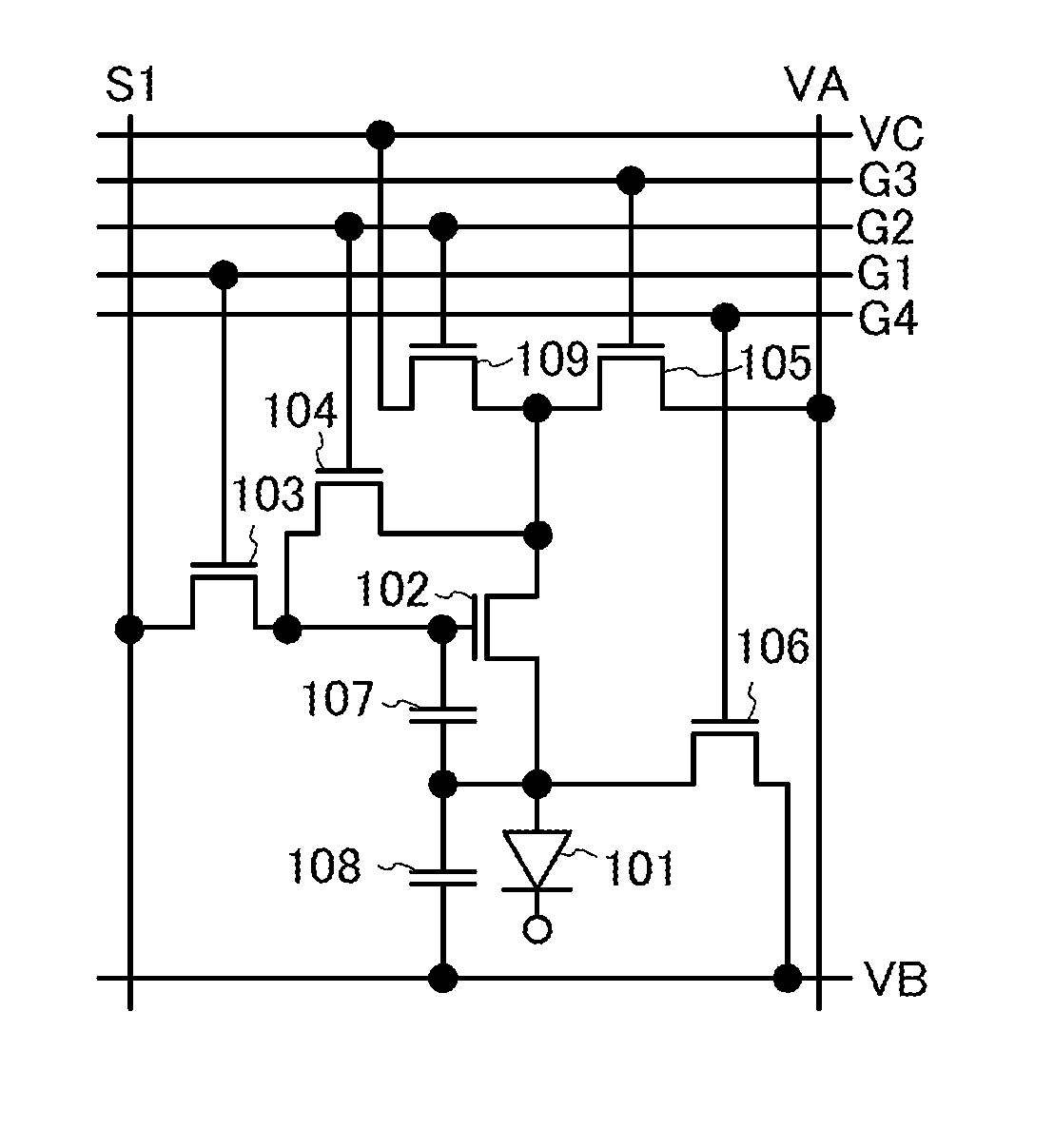
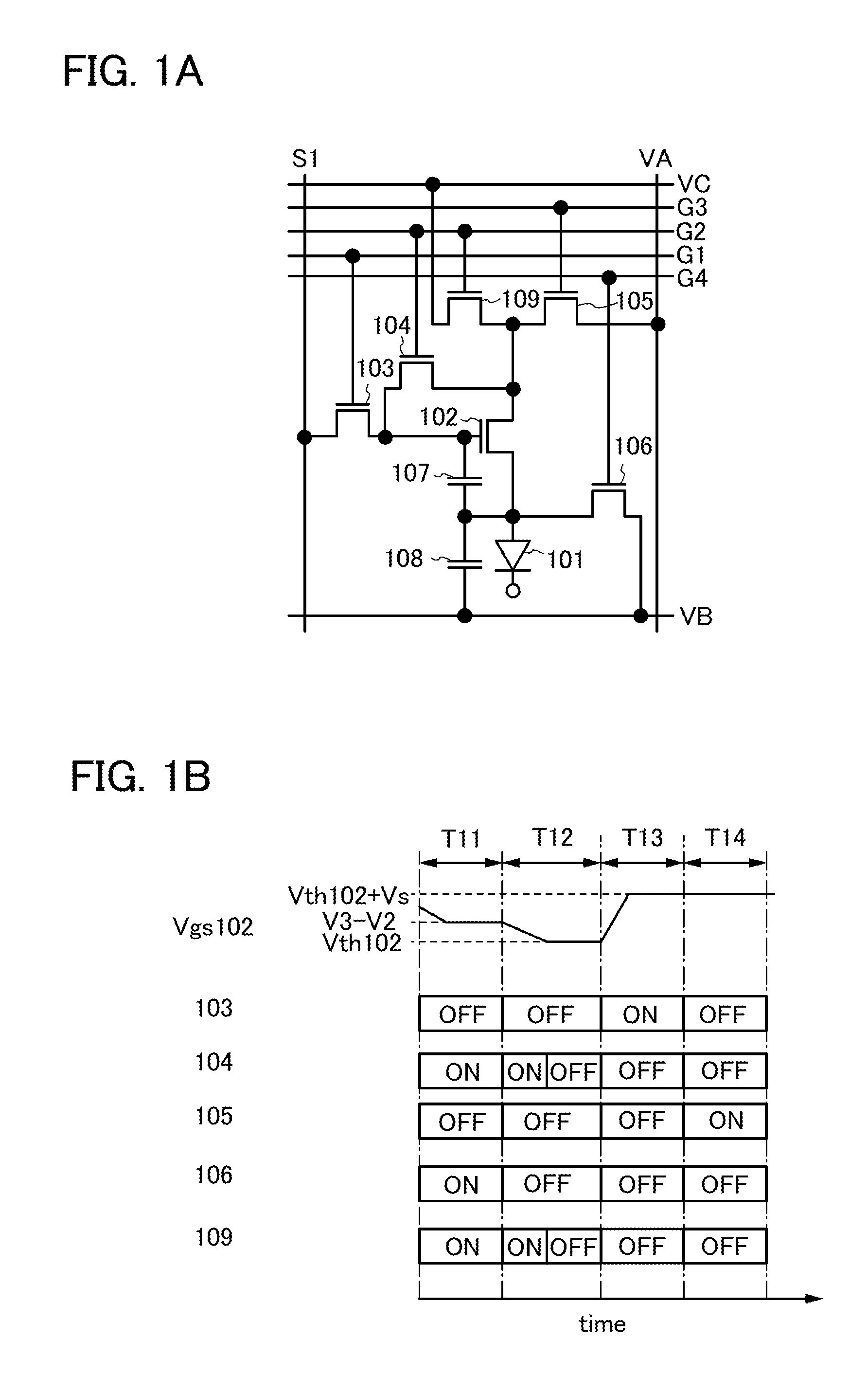
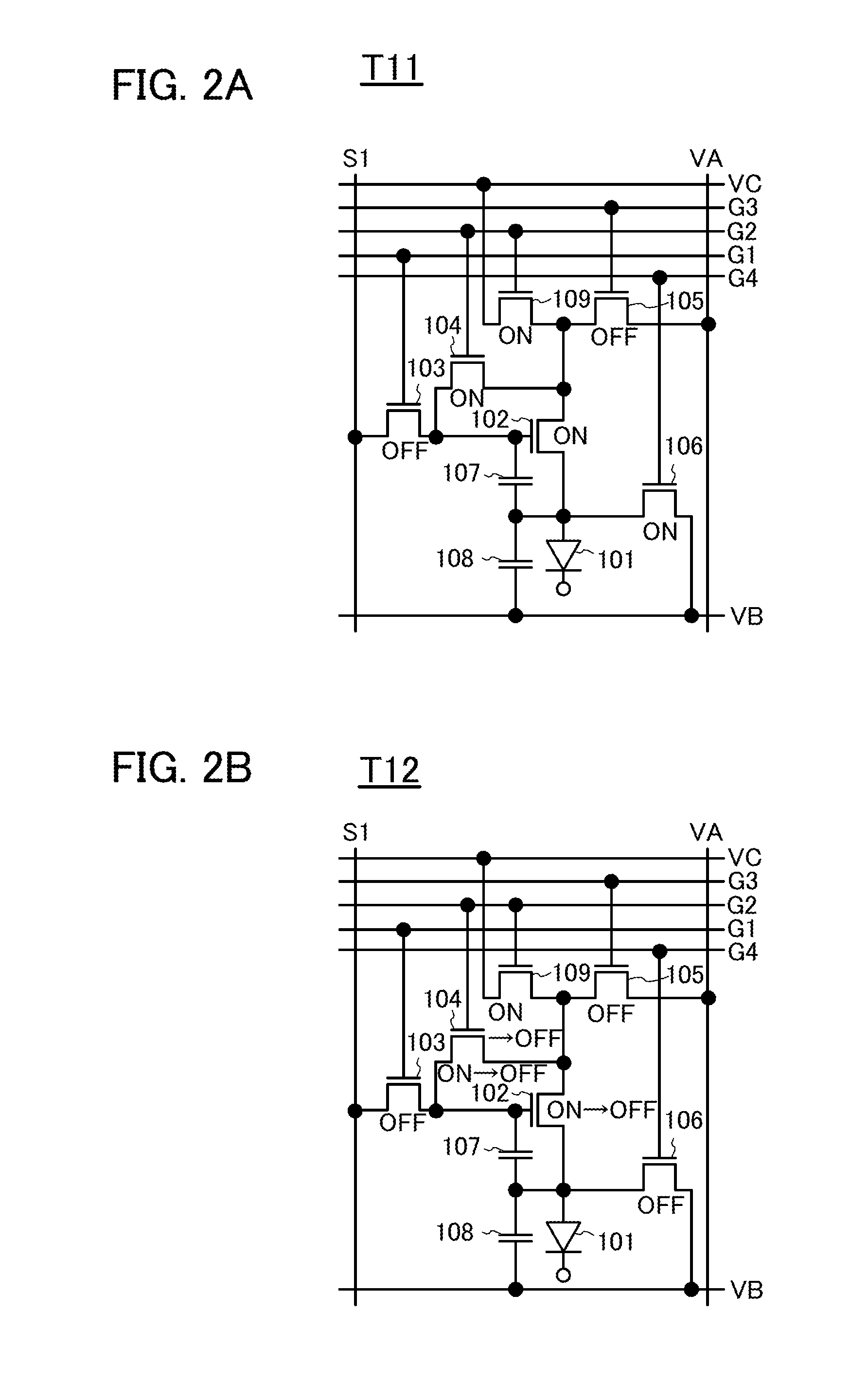
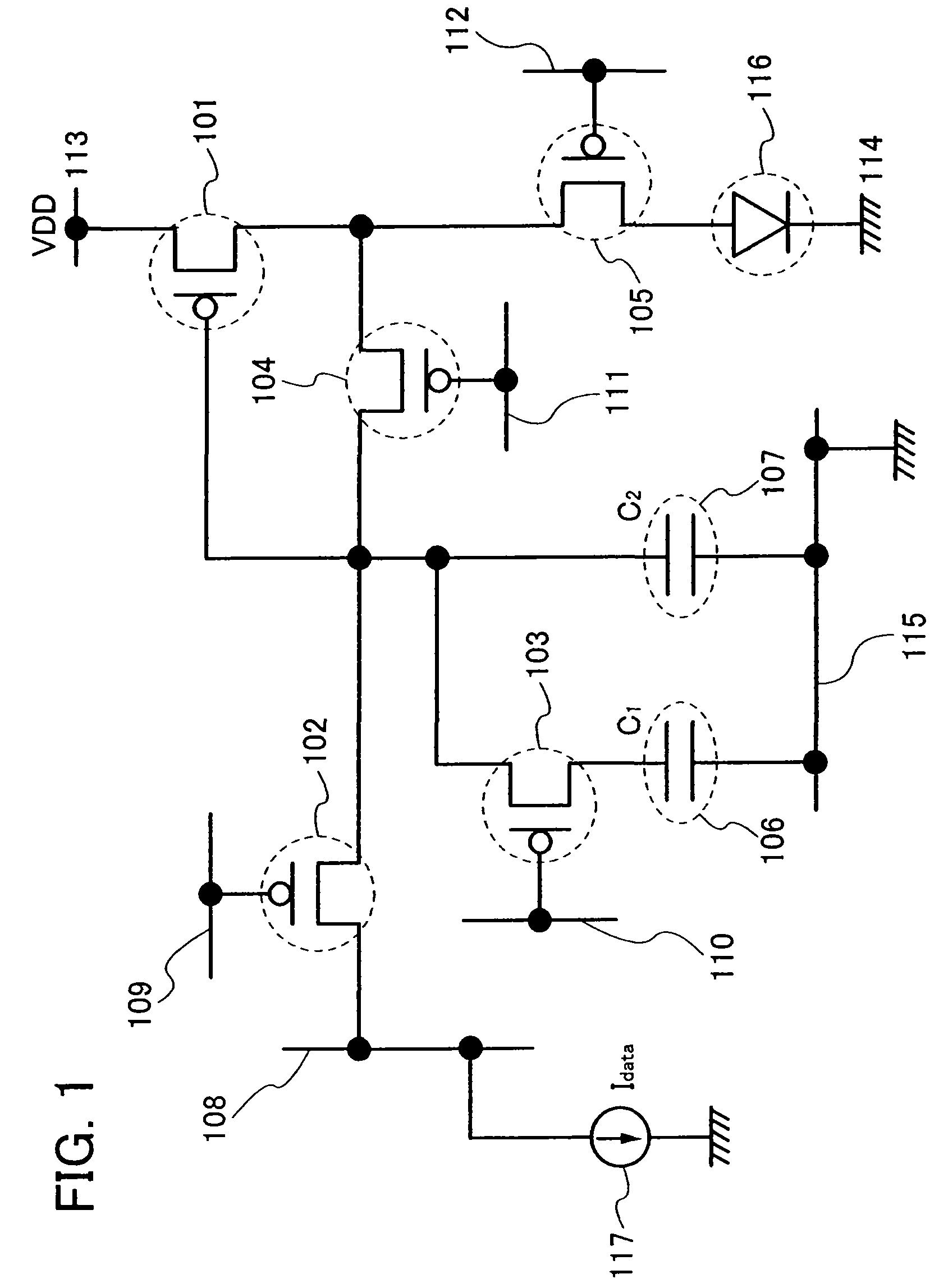
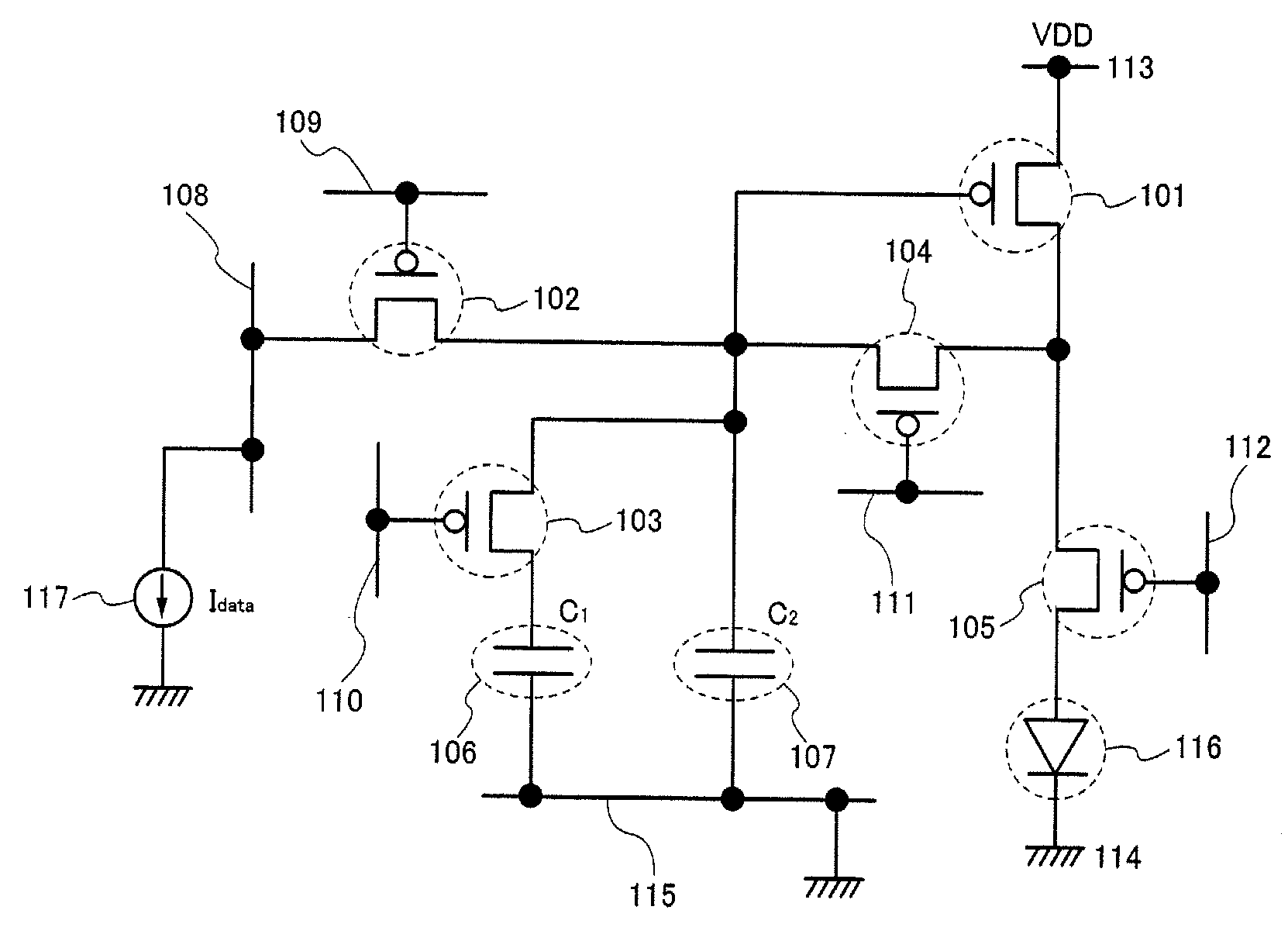
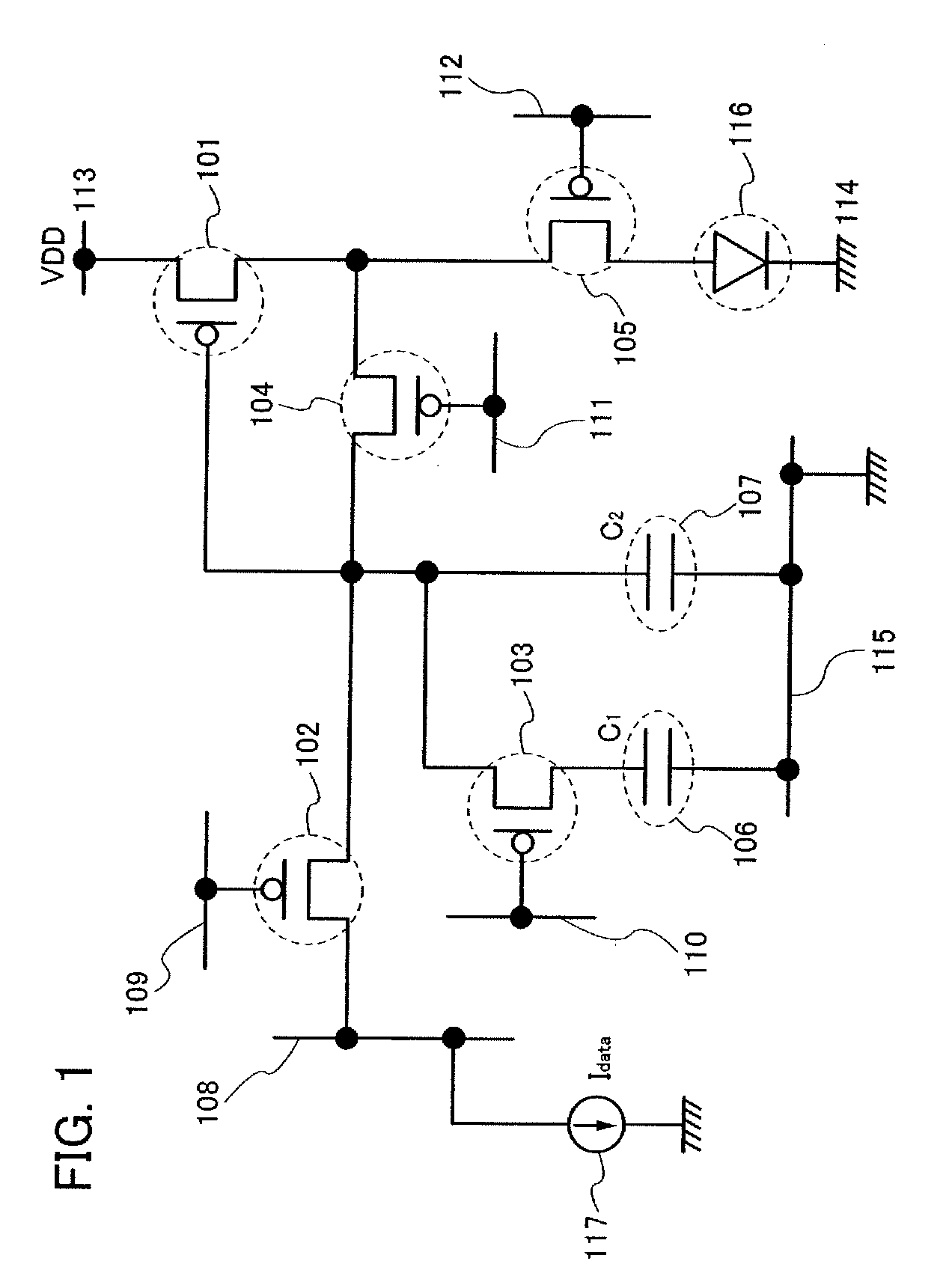
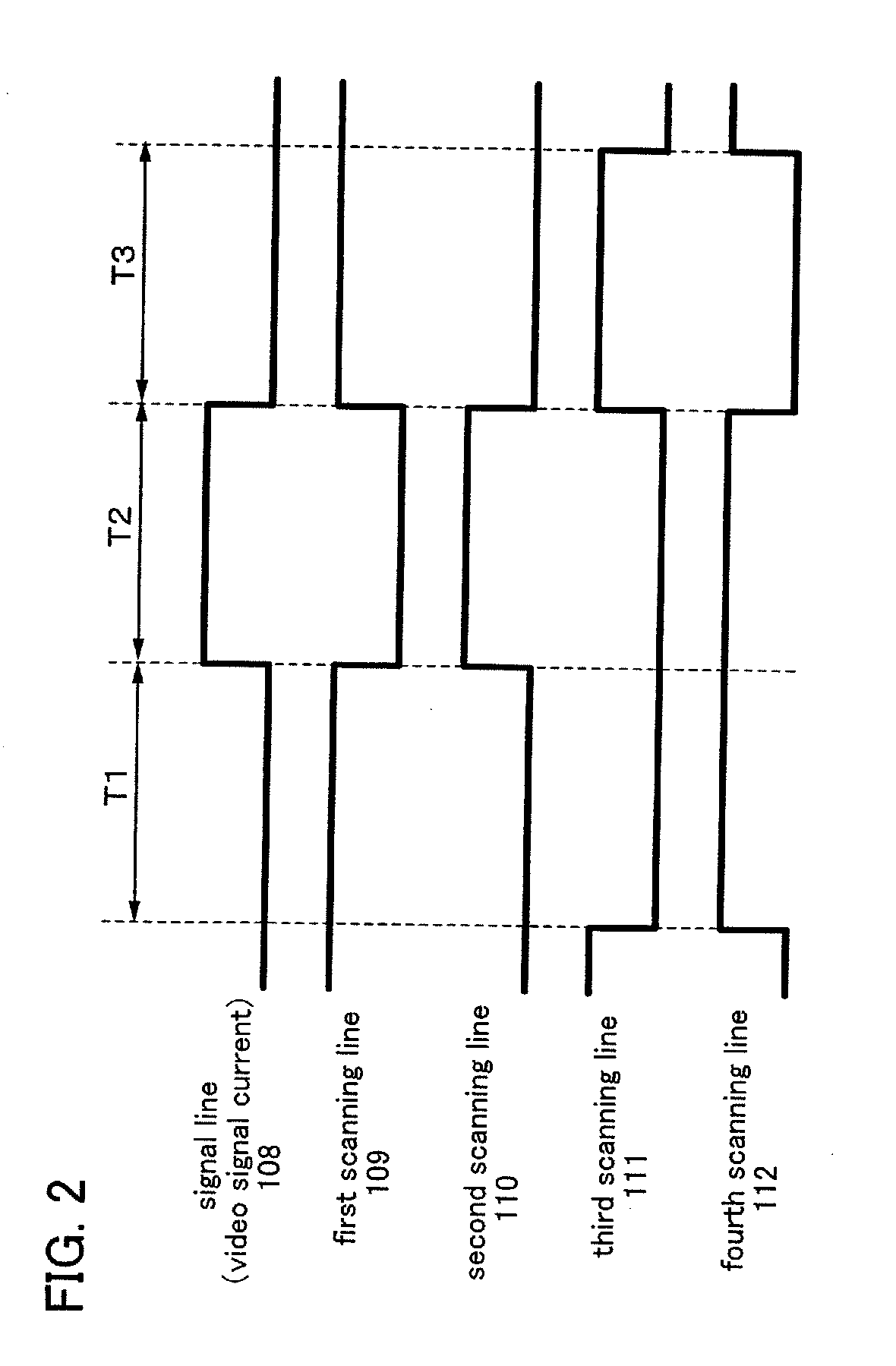
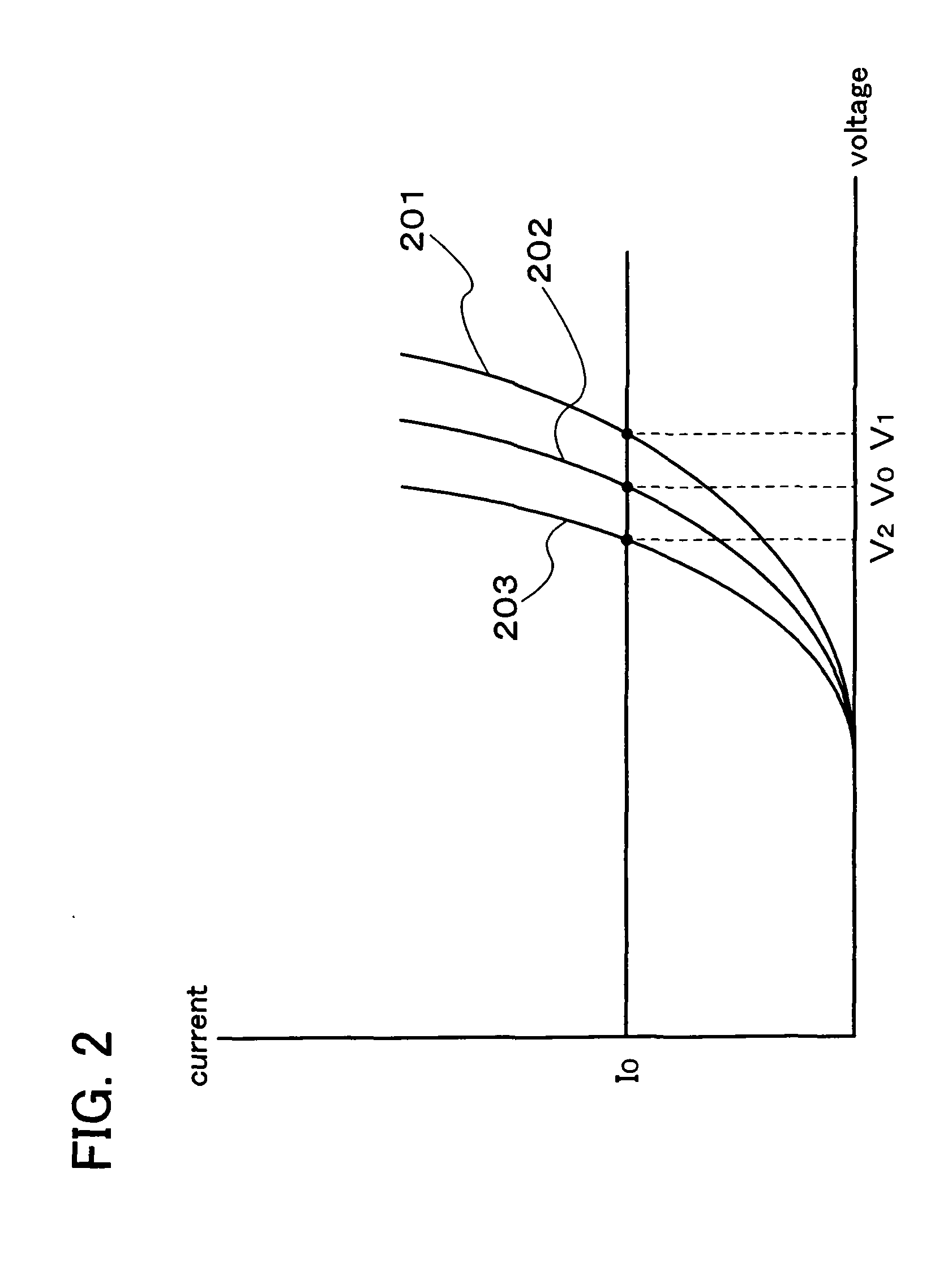
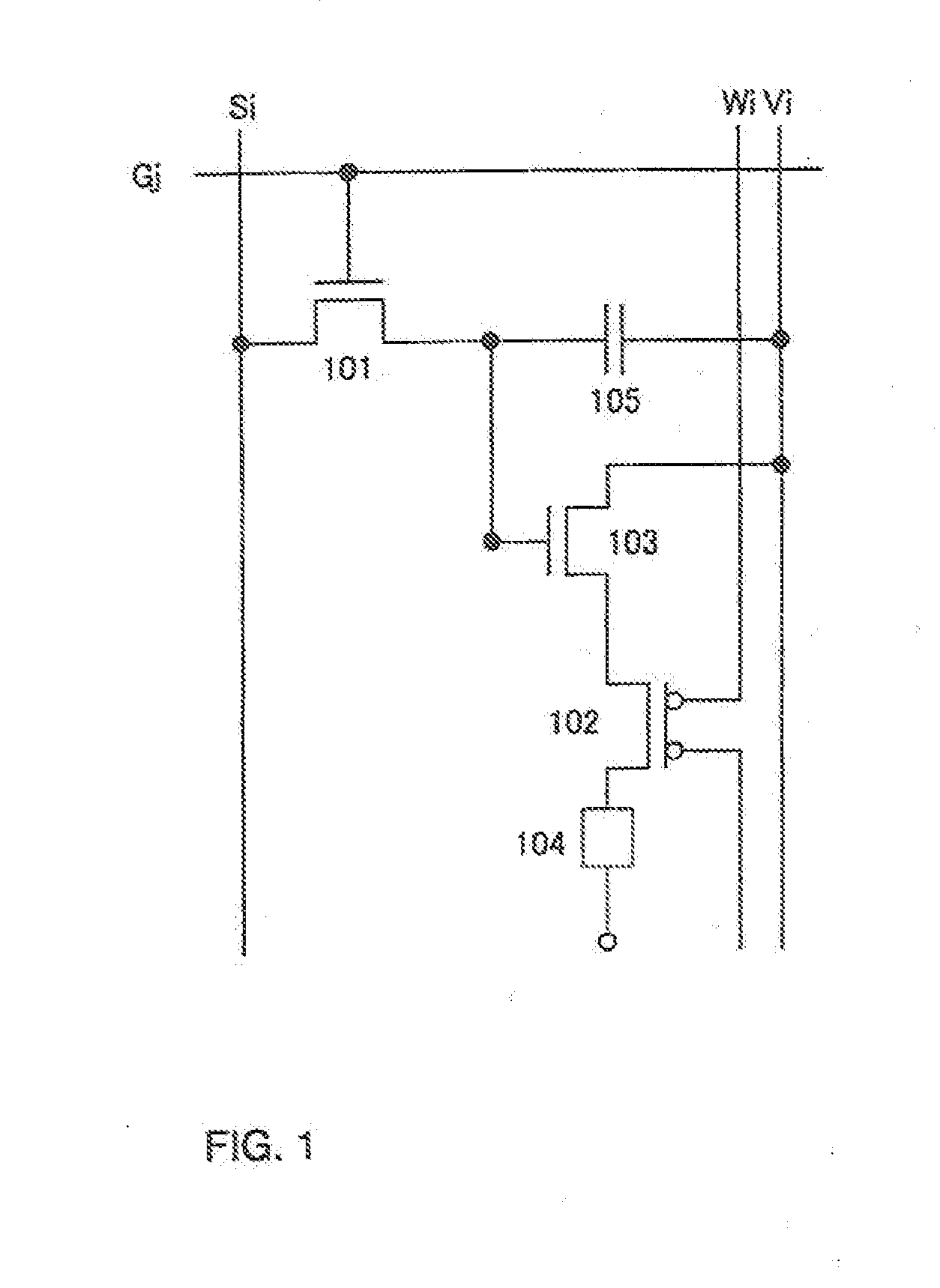
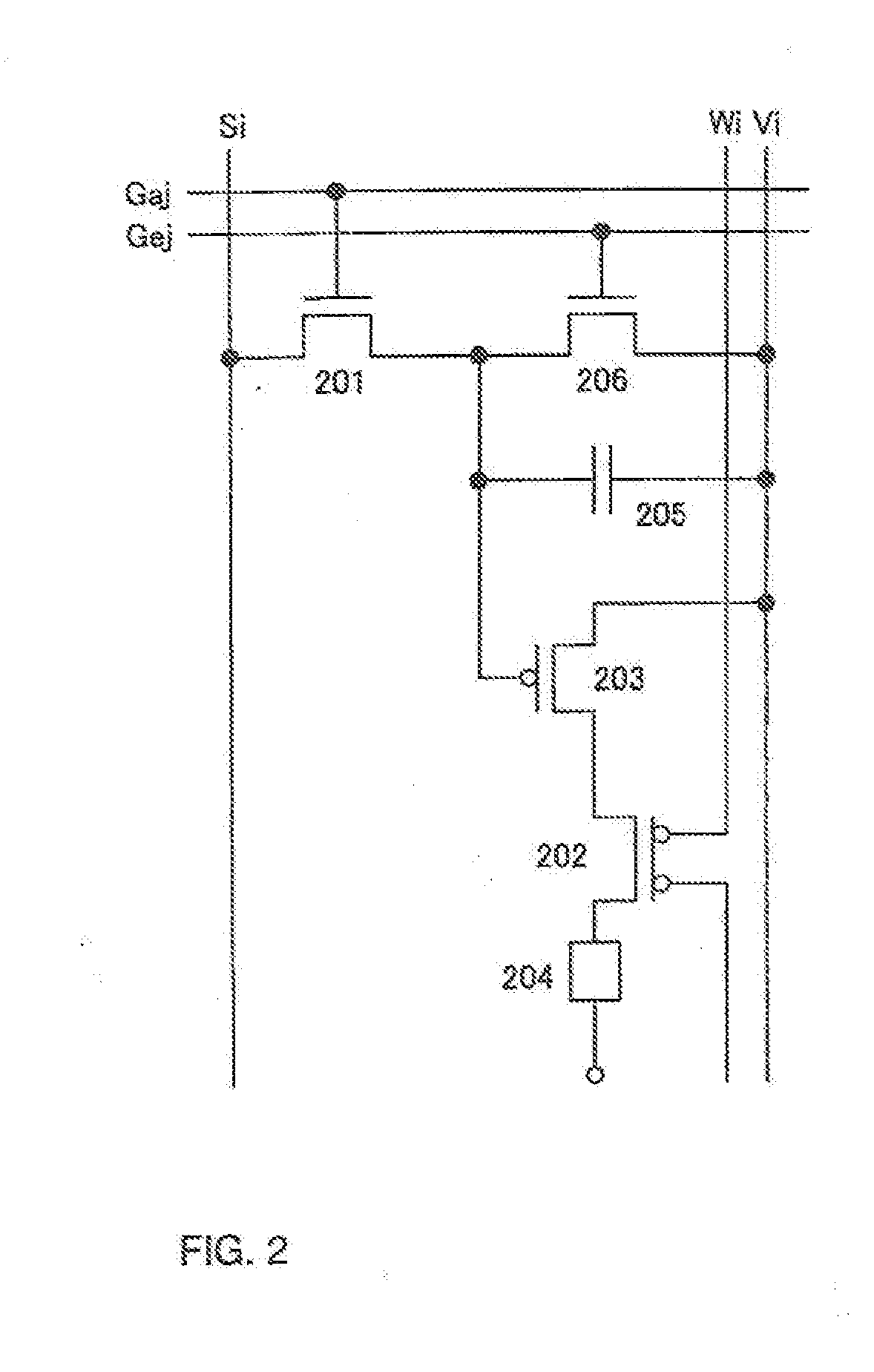
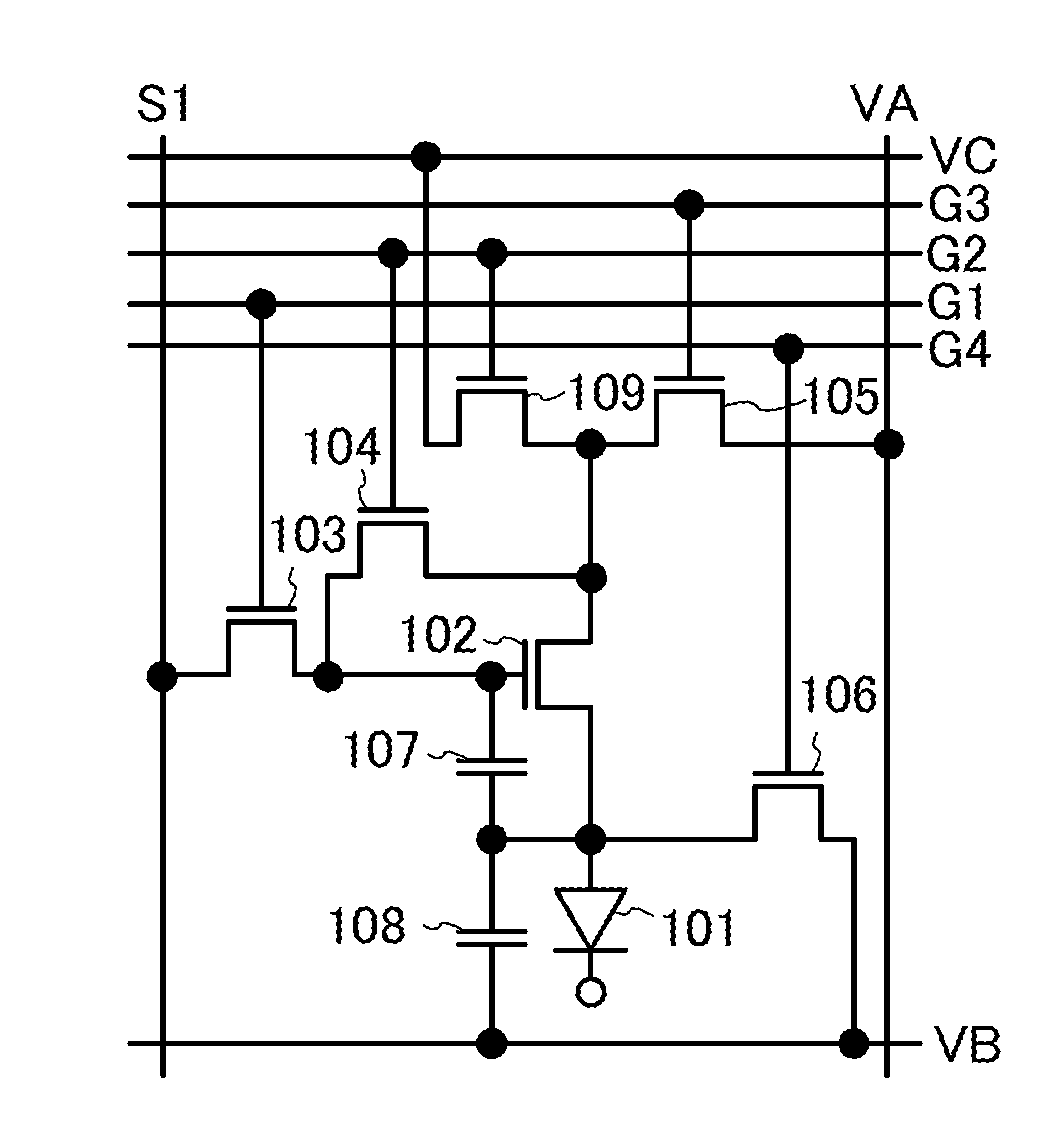
To provide a display device and a driving method thereof, where variations in the threshold voltage of transistors can be compensated and thus variations in luminance of light-emitting elements can be suppressed. In a first period, initialization is performed; in a second period, a voltage based on the threshold voltage of a first transistor is held in first and second storage capacitors; in a third period, a voltage based on a video signal voltage and the threshold voltage of the first transistor is held in the first and second storage capacitors; and in a fourth period, voltages held in the first and second storage capacitors are applied to a gate terminal of the first transistor to supply a current to a light-emitting element, so that the light-emitting element emits light. Through the operation process, a current obtained by compensating variations in the threshold voltage of the first transistor can be supplied to the light-emitting element, thereby variations in luminance can be suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
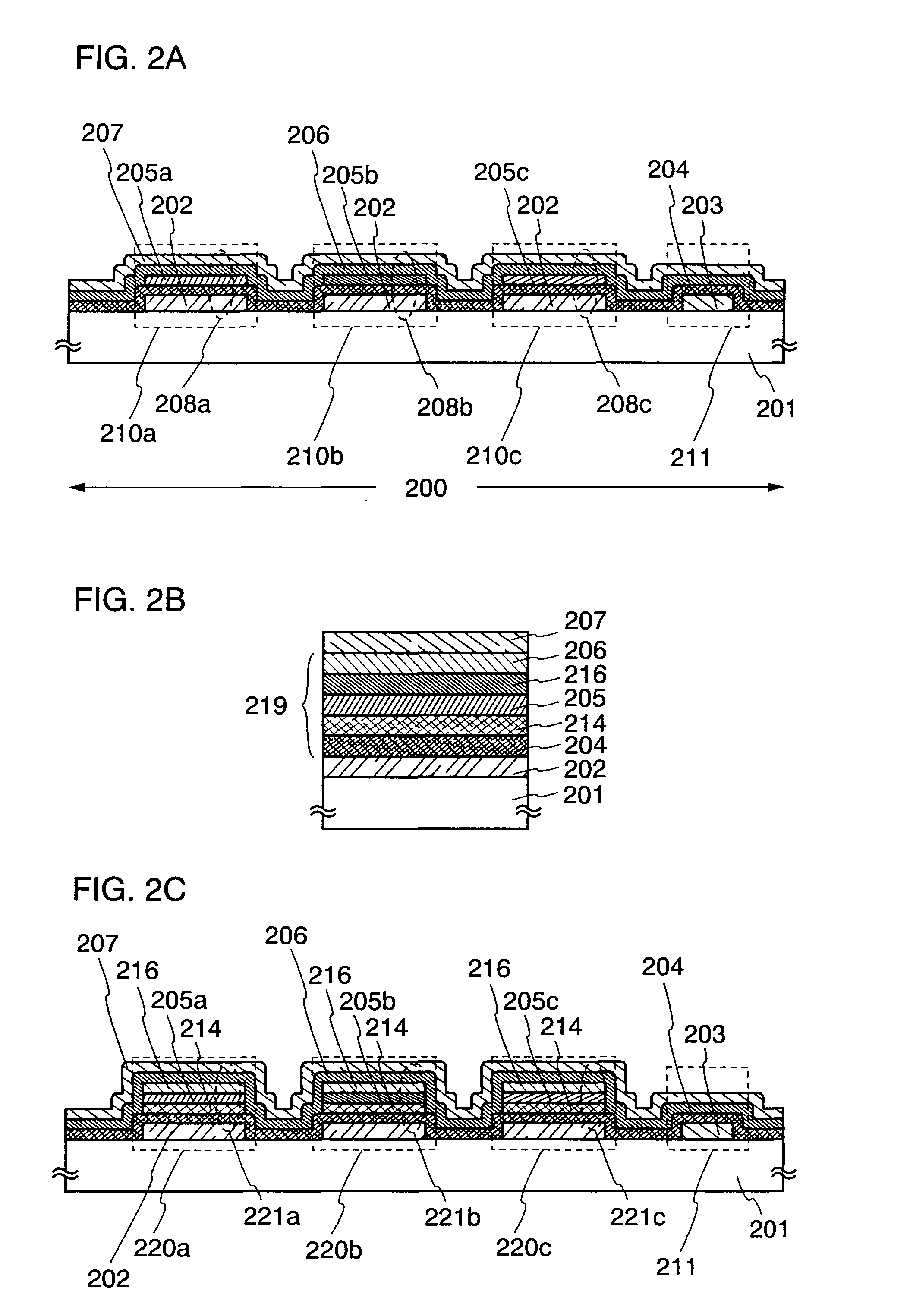
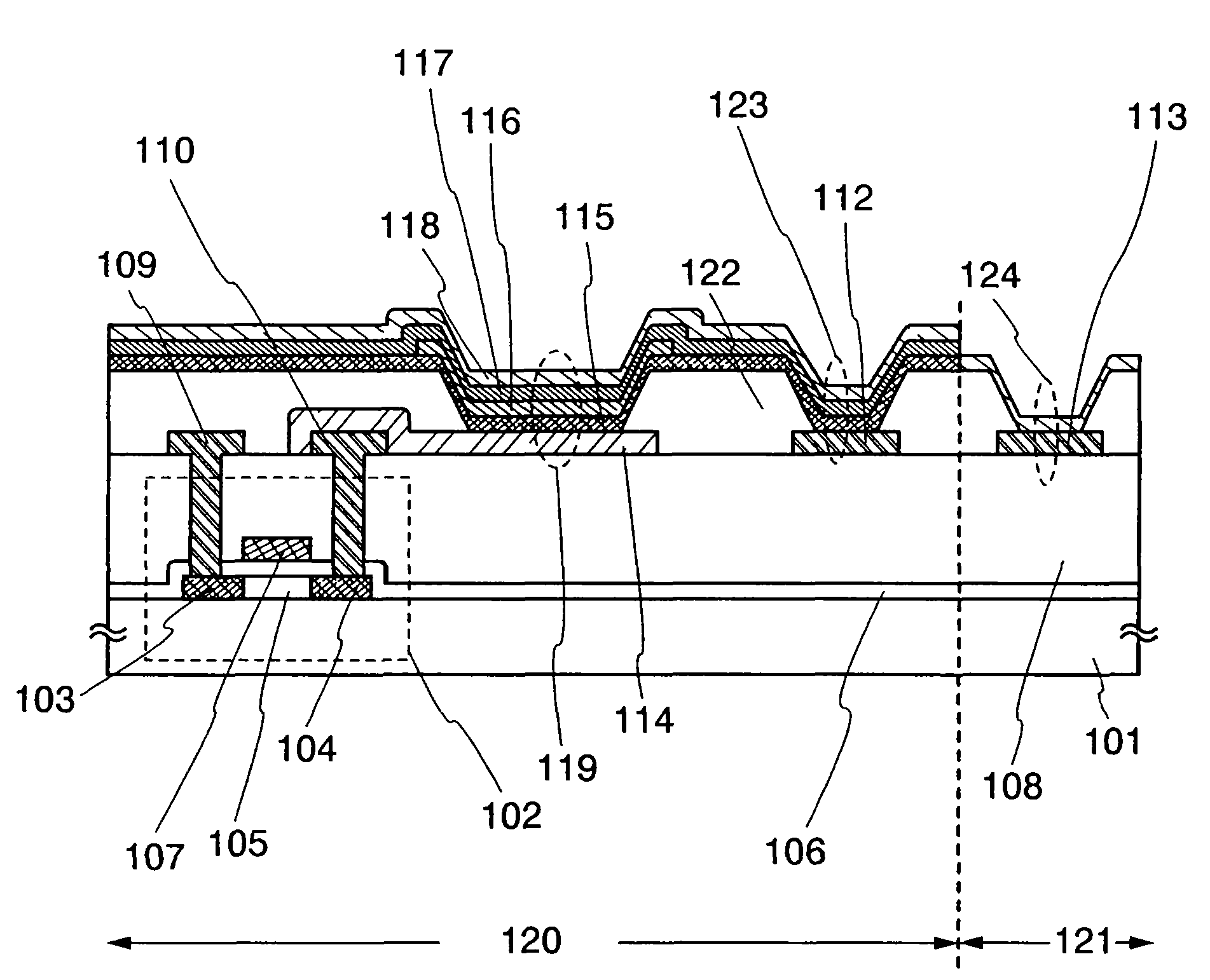
Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070029929A1Reduce variationLuminance variationDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesActive matrixLight emitting device
An active matrix light emitting device of which luminance characteristic does not vary among light emitting elements of respective pixels, and which can be realized even when a panel has higher definition is provided. In the light emitting device, one electrode (a second electrode) of the light emitting element having a layer containing a light emitting material interposed between a first electrode and the second electrode is electrically connected to an auxiliary wiring not only in a peripheral portion but also in a pixel portion. The layer containing a light emitting material has at least a first buffer layer, a light emitting layer, and a second buffer layer. In the pixel portion, either one or both of the first buffer layer and the second buffer layer are interposed between the auxiliary wiring (the first auxiliary wiring) and the second electrode in a connection portion (a first connection portion) where the second electrode and the auxiliary wiring (the first auxiliary wiring) are electrically connected.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
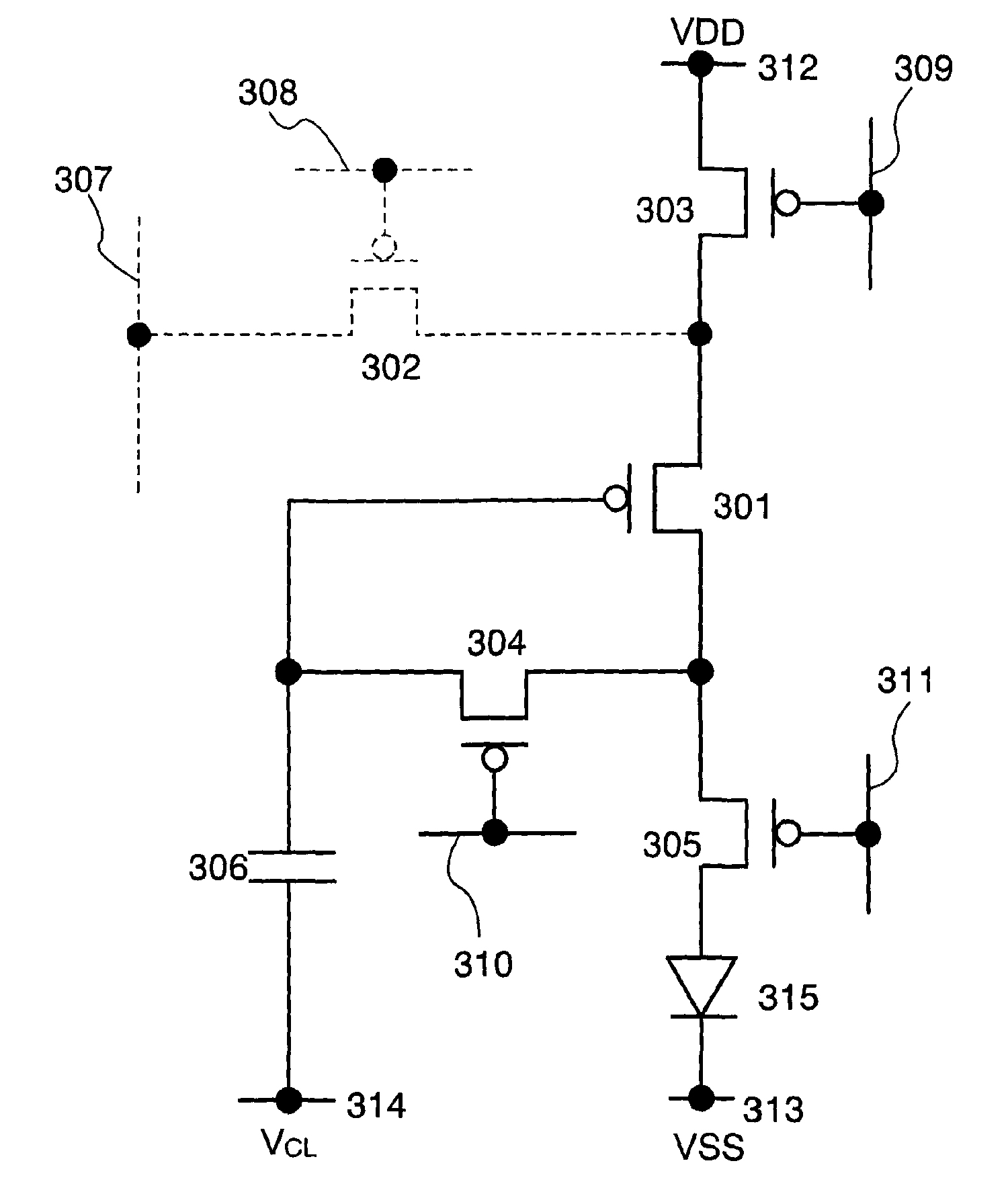
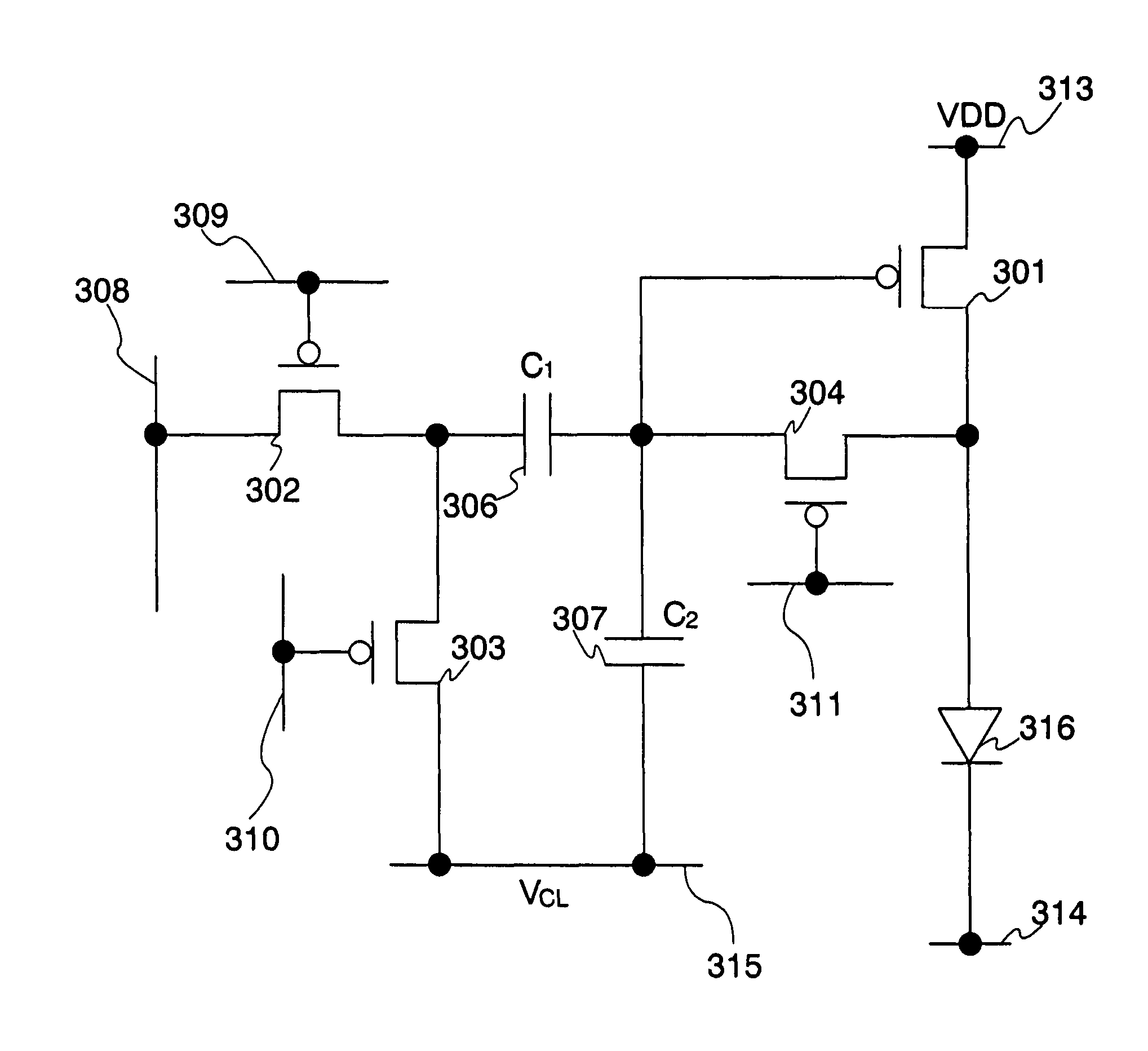
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20080143653A1Reduce variationImprove image qualityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device which can compensate for variations of the threshold voltage of transistors and suppress variations in luminance, and a driving method thereof are provided. Current is supplied to a light emitting element and light is emitted from the light emitting element by following steps: in the first period initial voltage is stored in a storage capacitor; in the second period, voltage based on video signal voltage and the threshold voltage of the transistor is stored in the storage capacitor; and in the third period, the voltage stored in the storage capacitor in the second period is applied to a gate electrode of the transistor. By these operation processes, the current which compensates the effect of the variations of the threshold voltage of the transistor can be supplied to the light emitting element. Therefore, variations in luminance are suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device, driving control circuit and driving method used in same
ActiveUS20070229432A1Reduce blurImage degradationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
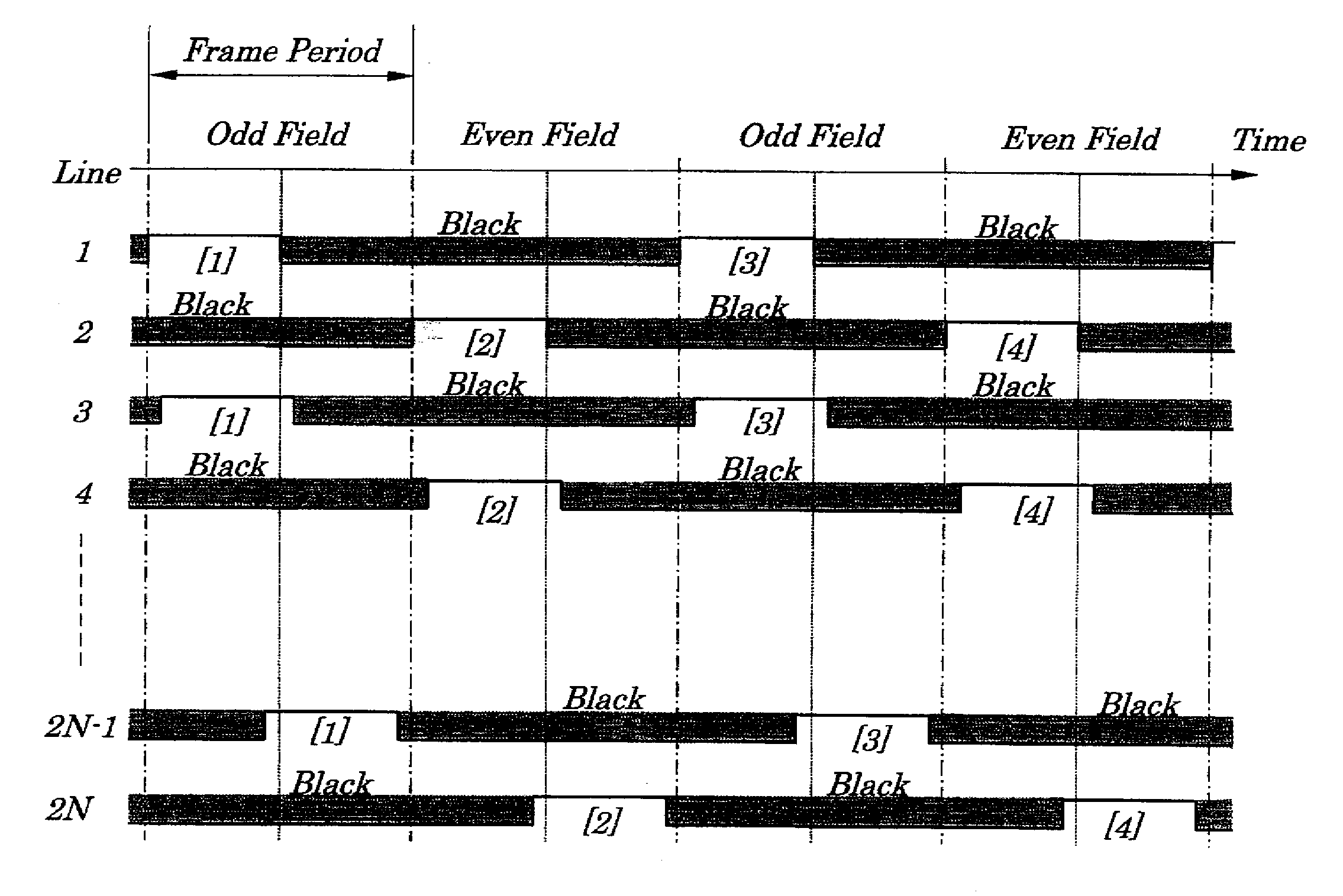
A liquid crystal display device is provided which is capable of improving quality of moving images. A field dividing driving operation is performed in which an odd field during which each of scanning electrodes in odd-numbered rows is sequentially driven and an even field during which each of scanning electrodes in even-numbered rows is sequentially driven occur, alternately and repeatedly, with time width of a refresh rate. In the former half of the odd field, display data is written in each of pixel regions corresponding to scanning electrodes in odd-numbered rows and, in the latter half of the odd field, black data is written in each of the pixel regions corresponding to scanning electrodes in the odd-numbered rows. In the former half of the even field, display data is written in each of pixel regions corresponding to scanning electrodes in the even-numbered rows and, in the latter half of the even field, black data is written in each of pixel regions corresponding to scanning electrodes in the even-numbered rows.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
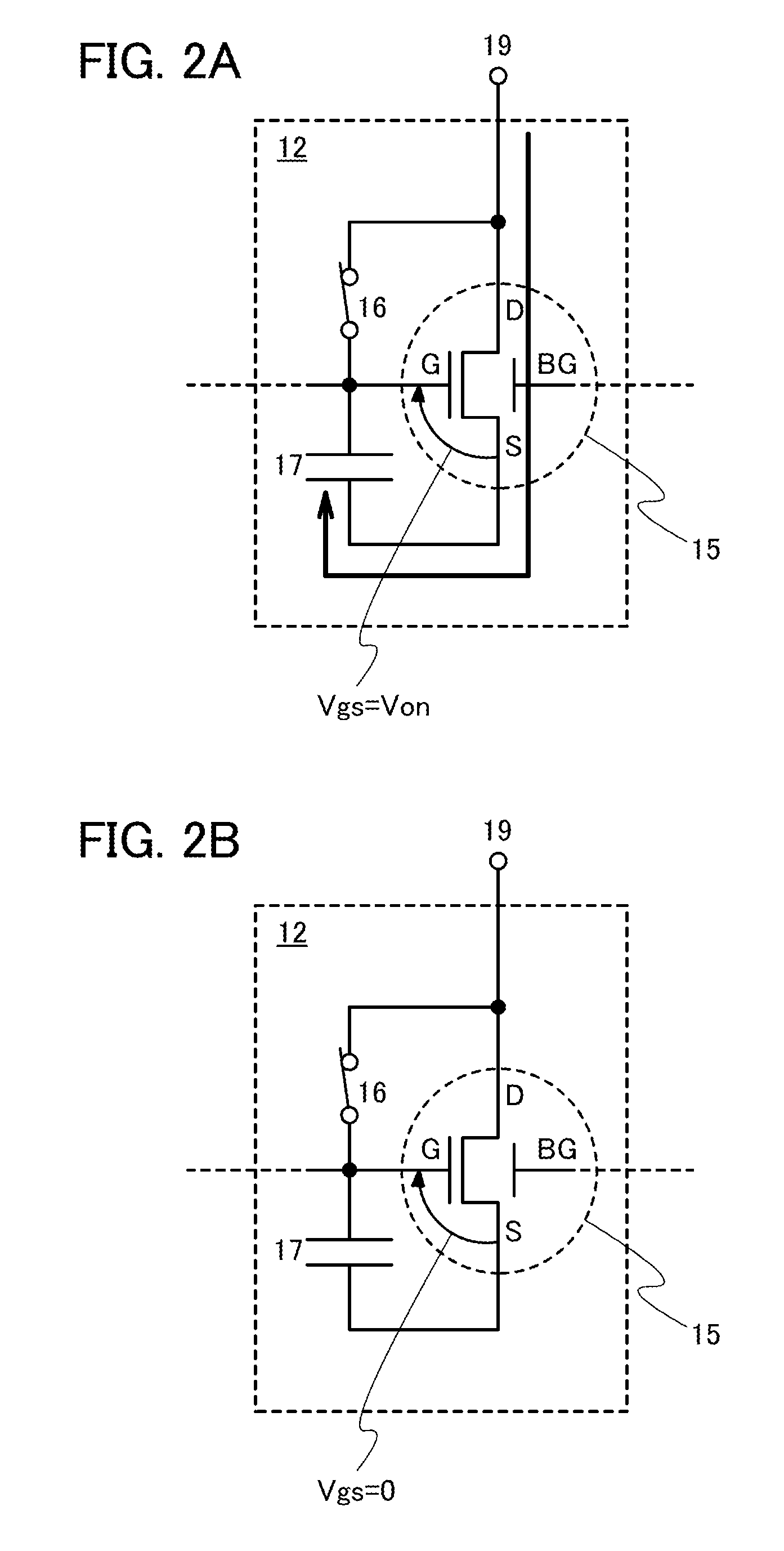
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS20130063413A1Reduce variationLuminance variationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringPower flow
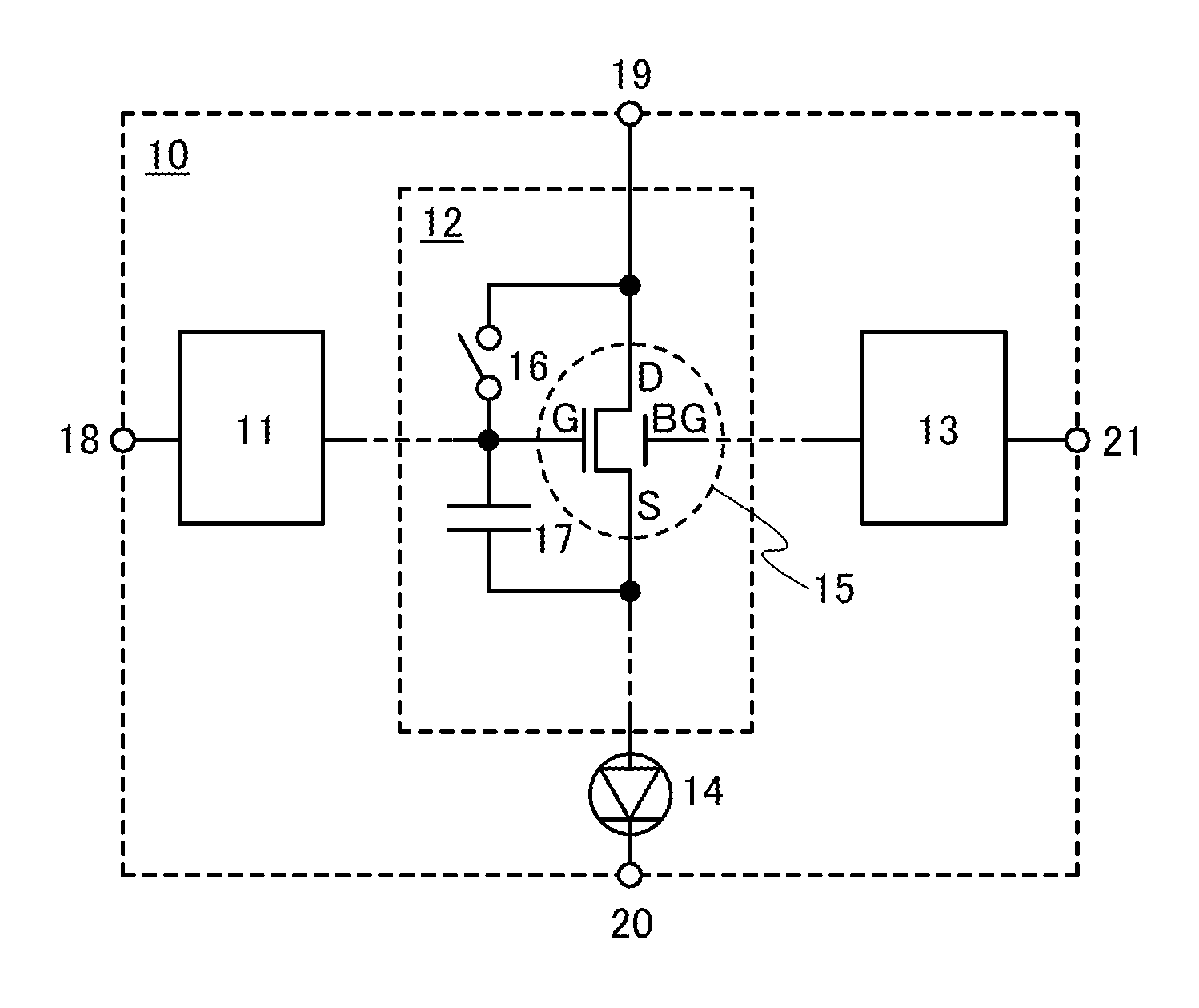
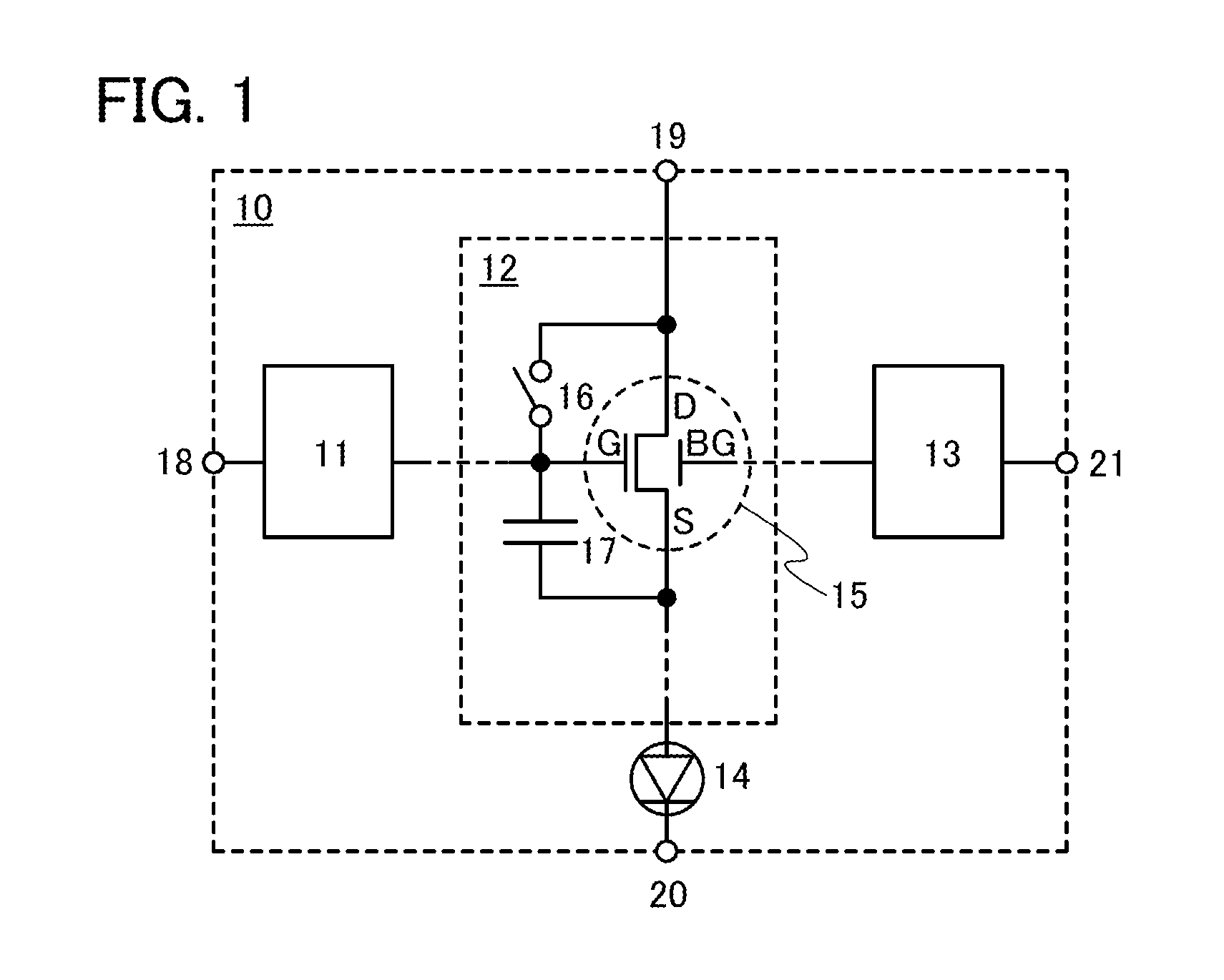
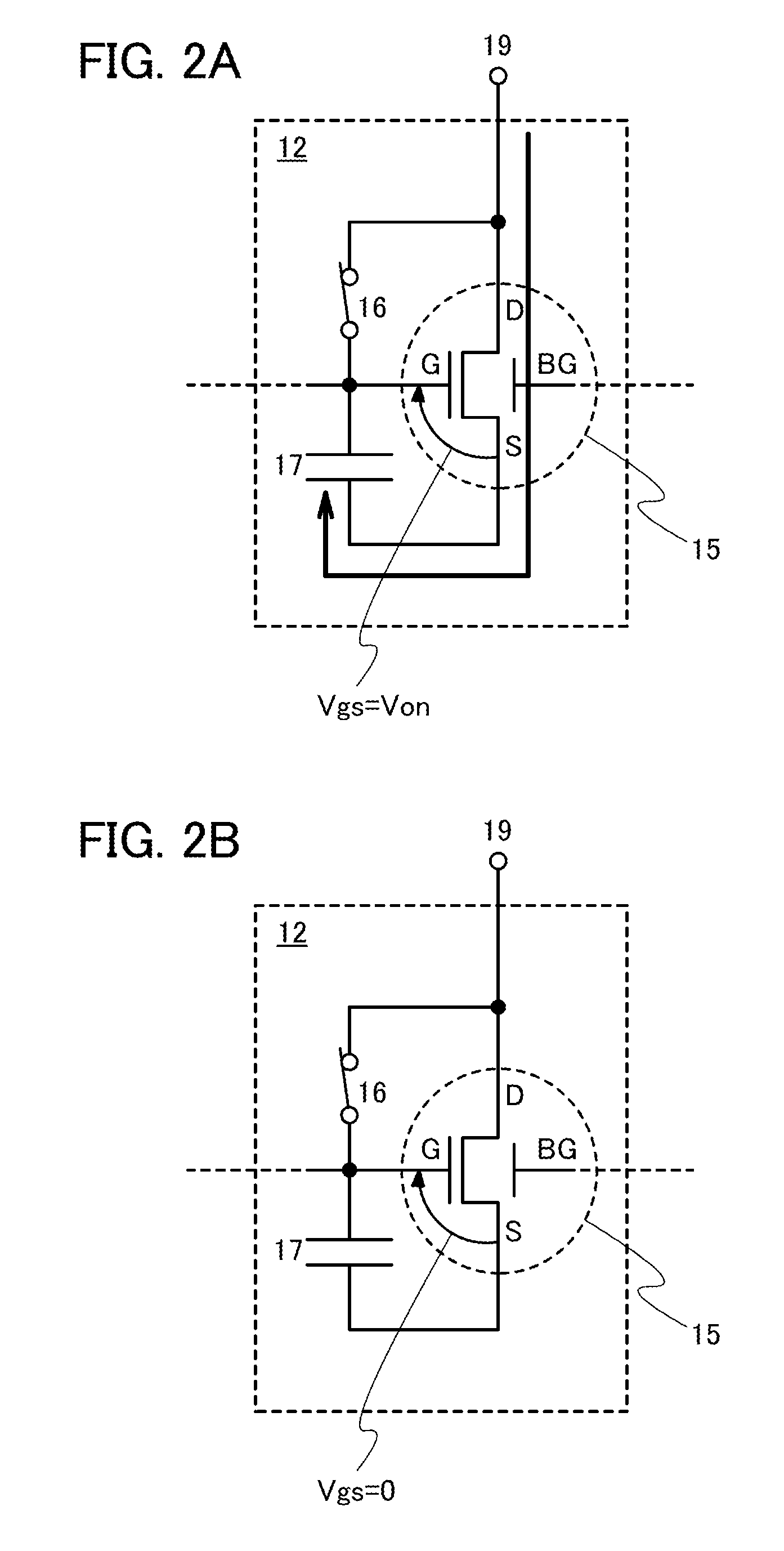
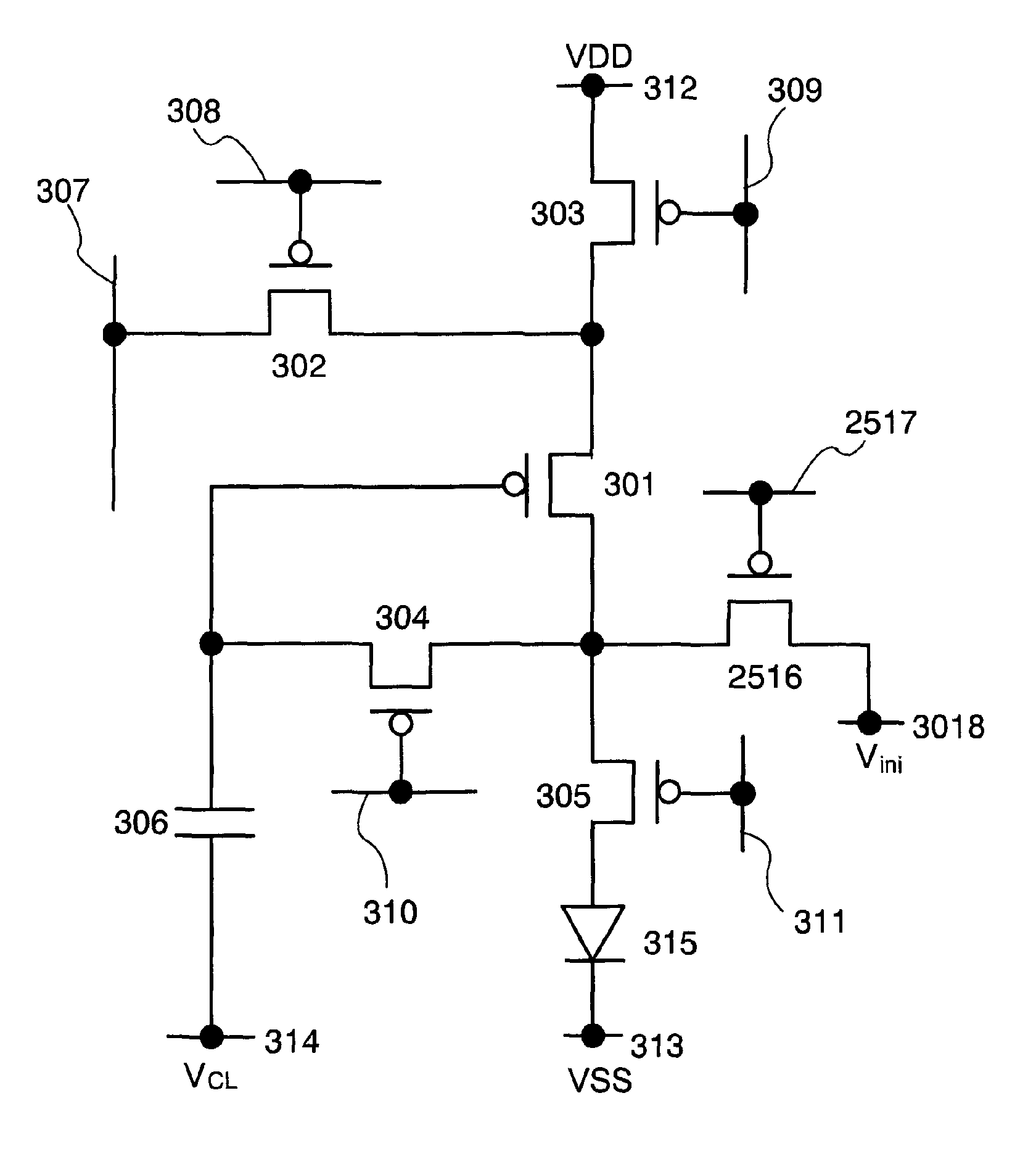
In a light-emitting device, supply of current is controlled using a transistor having a normal gate electrode (a first gate electrode) and a second gate electrode for controlling threshold voltage. The light-emitting device comprises one or more switches for selecting conduction or non-conduction between the first gate electrode and a drain terminal of the transistor. When the threshold voltage of the transistor is acquired, the first gate electrode and the drain terminal of the transistor are brought into conduction with the switch, and the threshold voltage of the transistor is shifted by controlling the potential of the second gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20070222380A1Lower on-resistanceImage quality can be hinderedDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A display device in which variations in luminance due to variations in characteristics of transistors are reduced, and image quality degradation due to variations in resistance values is prevented. The invention comprises a transistor whose channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor, a connecting wiring connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, a light emitting element having a laminated structure which includes a pixel electrode, an electro luminescent layer, and a counter electrode, an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode, and an auxiliary wiring formed in the same layer as a gate electrode of the transistor, a connecting wiring, or the pixel electrode. Further, the connecting wiring is connected to the pixel electrode, and the auxiliary wiring is connected to the counter electrode via an opening portion provided in the insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7994711B2Reduce variationLuminance variationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsActive matrixLight-emitting diode
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
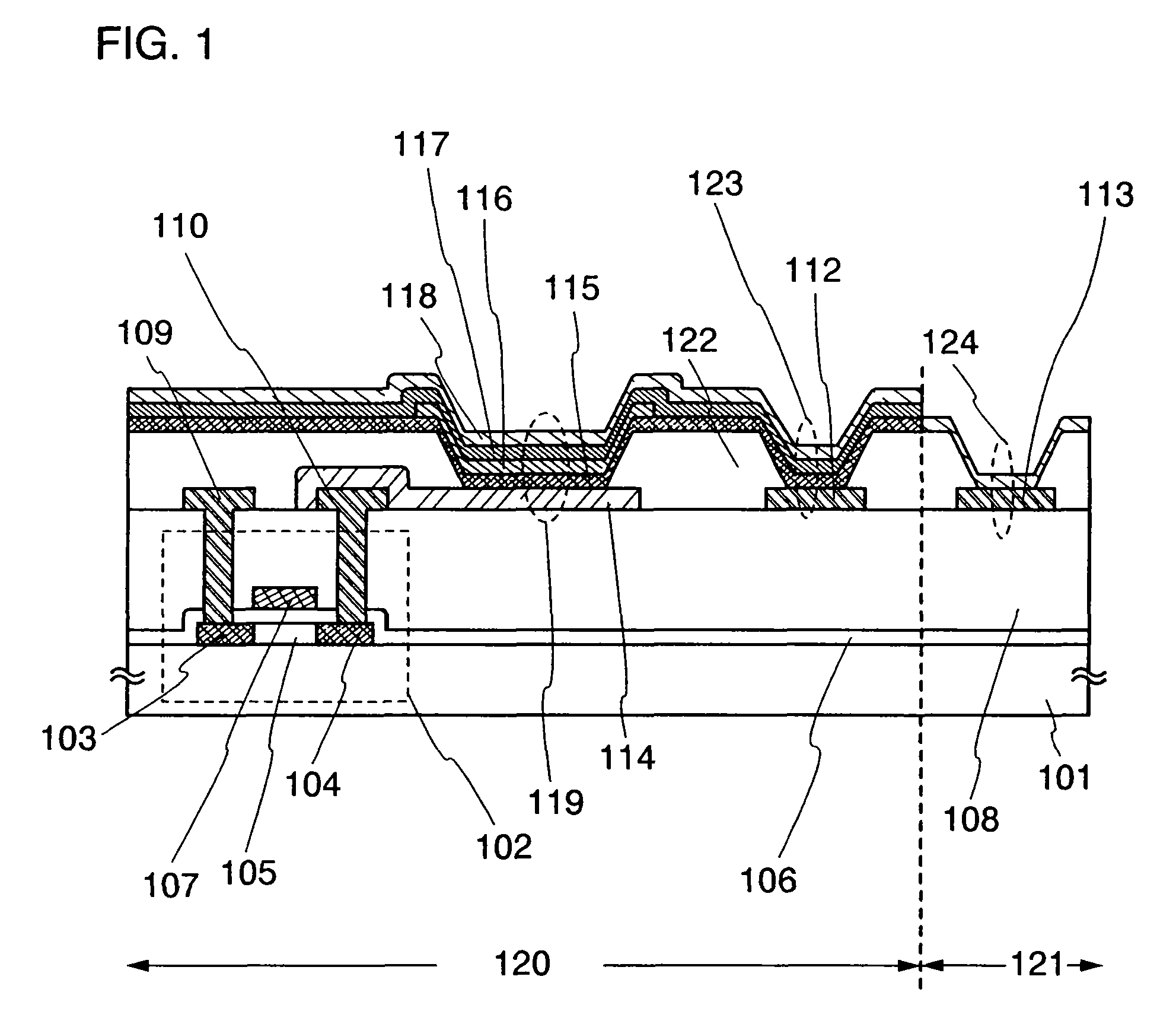
Display Device and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20130299791A1Increase the aperture ratioLarge-area displayElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceAuxiliary electrode
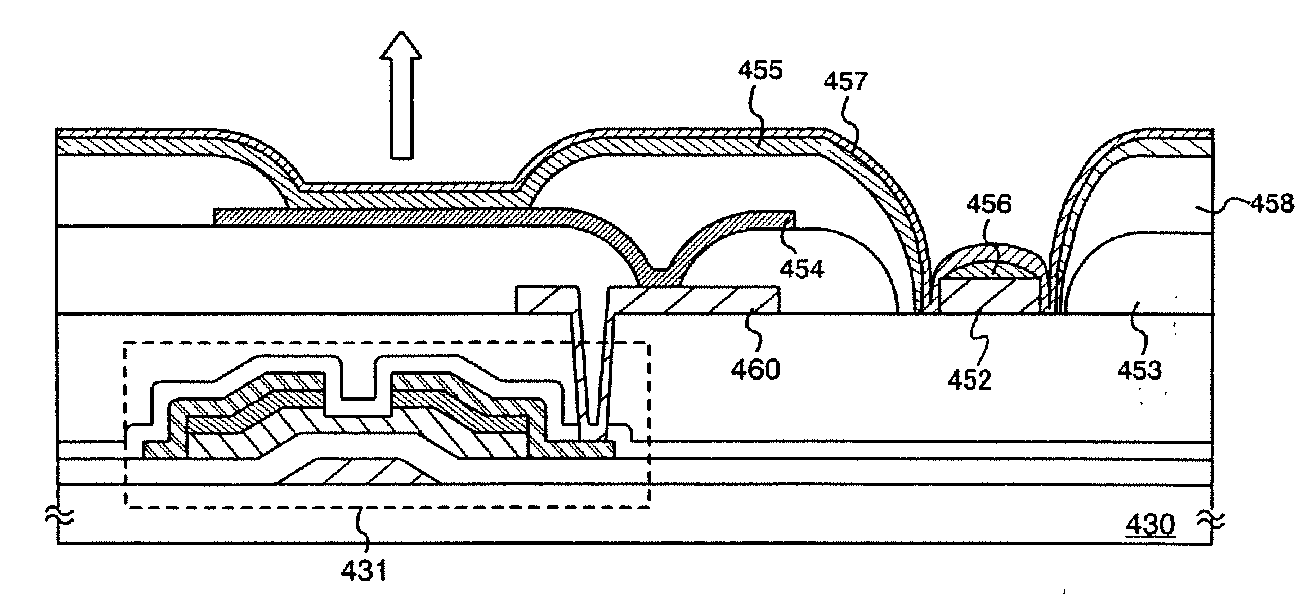
A structure of an EL display device which has an increased display area is provided. Further, a structure of an EL display device which has a high definition display is provided. An auxiliary electrode is formed over a first partition and side surfaces of the auxiliary electrode are covered with a second partition. A top surface of the auxiliary electrode is in contact with the conductive film which is one electrode of a light-emitting element and has a light-transmitting property, which enables a large-area display. Further, even the distance between the adjacent light-emitting elements is shortened, the auxiliary electrode can be provided between the adjacent light-emitting elements, which enables a high definition display.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electroluminescent display having 4 TFTs for rotation between vertical and horizontal image states.
ActiveUS7218294B2Small sizeReduce weightDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesLight emitting deviceLuminescent material
A light emitting device capable of suppressing drop in luminance or luminance unevenness of a light emitting element due to deterioration of an electro luminescent material and capable of switching an image direction vertically to horizontally without a frame memory additionally provided. The light emitting device of the invention comprises in each pixel first to fourth transistors, a light emitting element, and a signal line. The first transistor and the second transistor control the connection between the signal line and a gate of the third transistor, the fourth transistor controls a current value supplied to the light emitting element, and the third transistor selects whether the current is supplied to the light emitting element or not. Further, the first transistor and the second transistor are switched separately.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS8477085B2Reduce variationDecrease in luminanceStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
A display device which can compensate for variations of the threshold voltage of transistors and suppress variations in luminance, and a driving method thereof are provided. Current is supplied to a light emitting element and light is emitted from the light emitting element by following steps: in the first period initial voltage is stored in a storage capacitor; in the second period, voltage based on video signal voltage and the threshold voltage of the transistor is stored in the storage capacitor; and in the third period, the voltage stored in the storage capacitor in the second period is applied to a gate electrode of the transistor. By these operation processes, the current which compensates the effect of the variations of the threshold voltage of the transistor can be supplied to the light emitting element. Therefore, variations in luminance are suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
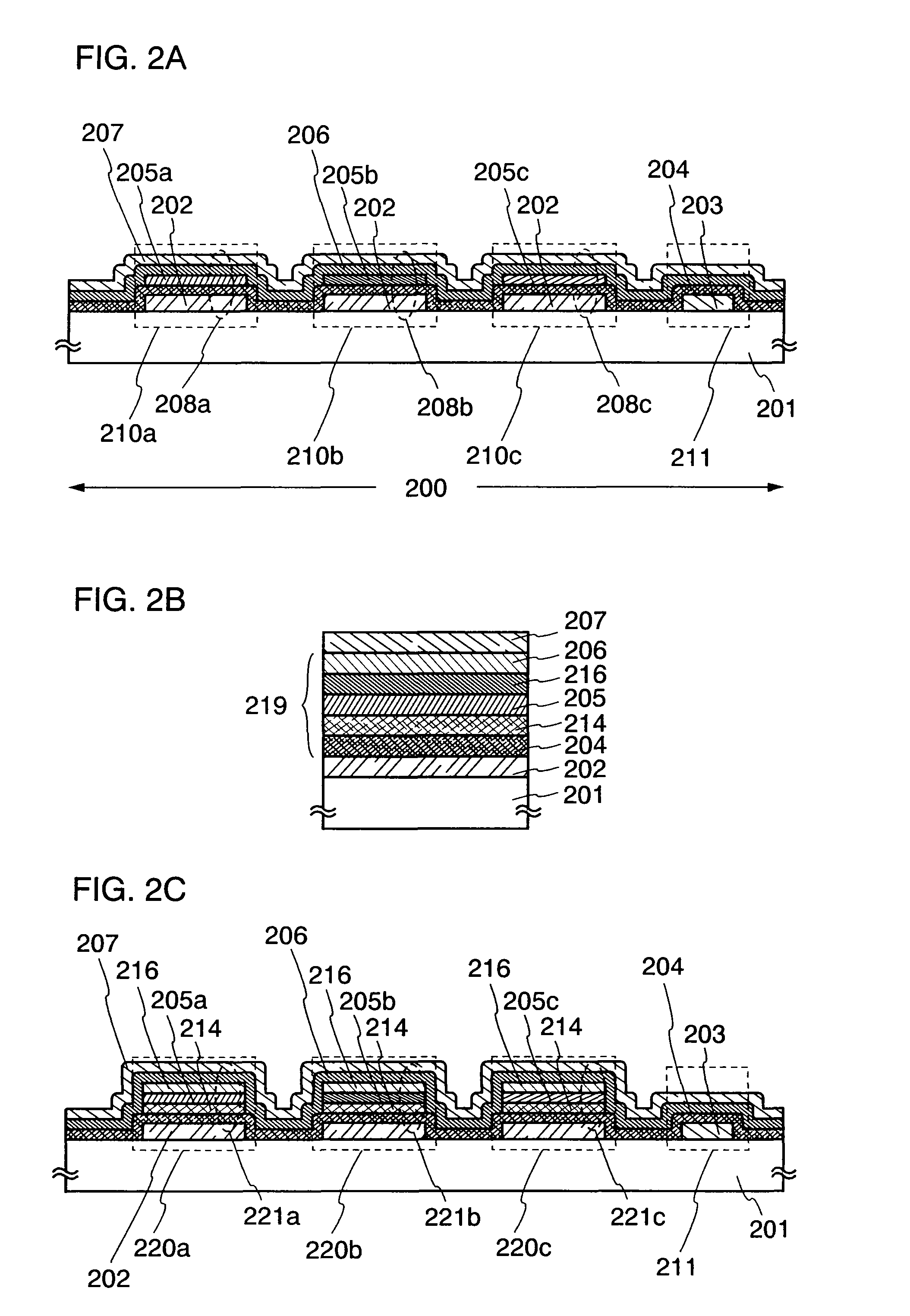
Element substrate and light emitting device
InactiveUS7122969B2High field-effect mobilityLarge amountElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLinear regionEngineering
No need of lowering off-current of a switching transistor, fewer luminance variations of a light emitting element between pixels due to characteristic variations of a driving transistor, and less risk of steps due to increase in the number of wirings. A video signal for light emission or non-emission of a pixel is input to a gate of a current controlling transistor operated in a linear region, which is connected in series with the driving transistor, through a switching transistor. Since a voltage Vds between a source and a drain of the current controlling transistor is small, small changes in a voltage Vgs between a gate and a source thereof do not affect a current flowing in a load. The current flowing in the light emitting element is determined by the driving transistor operated in a saturation region, and a fixed potential is input to the gate thereof during light emission.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
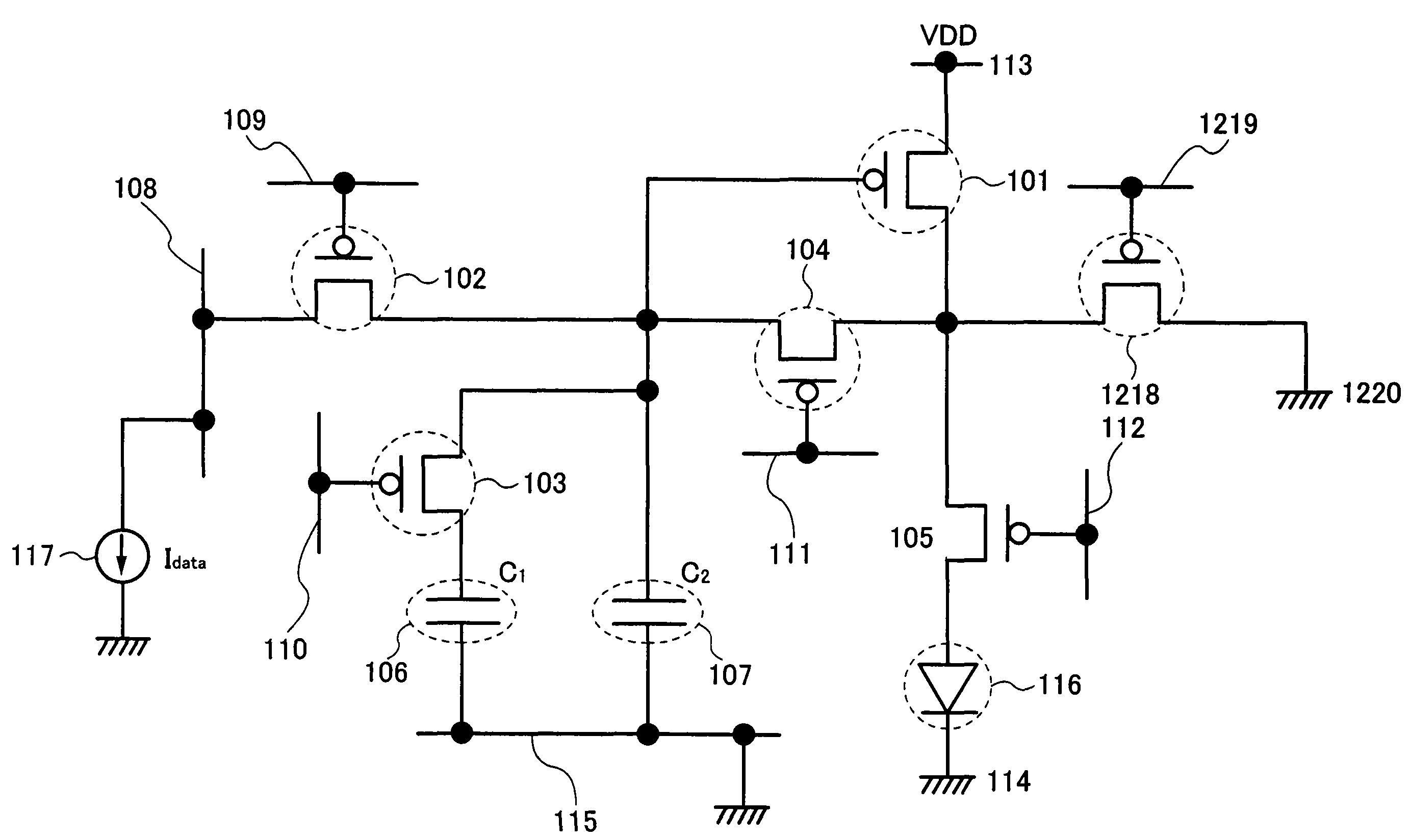
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS20120248435A1Luminance variationTotal current dropStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionEngineering
A light-emitting device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a light-emitting element, a first transistor whose source is electrically connected to an anode of the light-emitting element, a second transistor which controls whether an image signal is input to a gate of the first transistor, a third transistor which controls electrical connection and disconnection between the gate and a drain of the first transistor, a fourth transistor which controls whether a first power supply potential is supplied to the drain of the first transistor, a fifth transistor which controls whether a second power supply potential is supplied to the anode of the light-emitting element, a first capacitor which holds a voltage between the gate and the source of the first transistor, and a second capacitor electrically connected in series with the first capacitor and electrically connected in series with the light-emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display Device and Electronic Apparatus
InactiveUS20080164474A1Lower on-resistanceImage quality can be hinderedStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDisplay device
A display device in which variations in luminance due to variations in characteristics of transistors are reduced, and image quality degradation due to variations in resistance values is prevented. The invention comprises a transistor whose channel portion is formed of an amorphous semiconductor or an organic semiconductor, a connecting wiring connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, a light emitting element having a laminated structure which includes a pixel electrode, an electro luminescent layer, and a counter electrode, an insulating layer surrounding an end portion of the pixel electrode, and an auxiliary wiring formed in the same layer as a gate electrode of the transistor, a connecting wiring, or the pixel electrode. Further, the connecting wiring is connected to the pixel electrode, and the auxiliary wiring is connected to the counter electrode via an opening portion provided in the insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
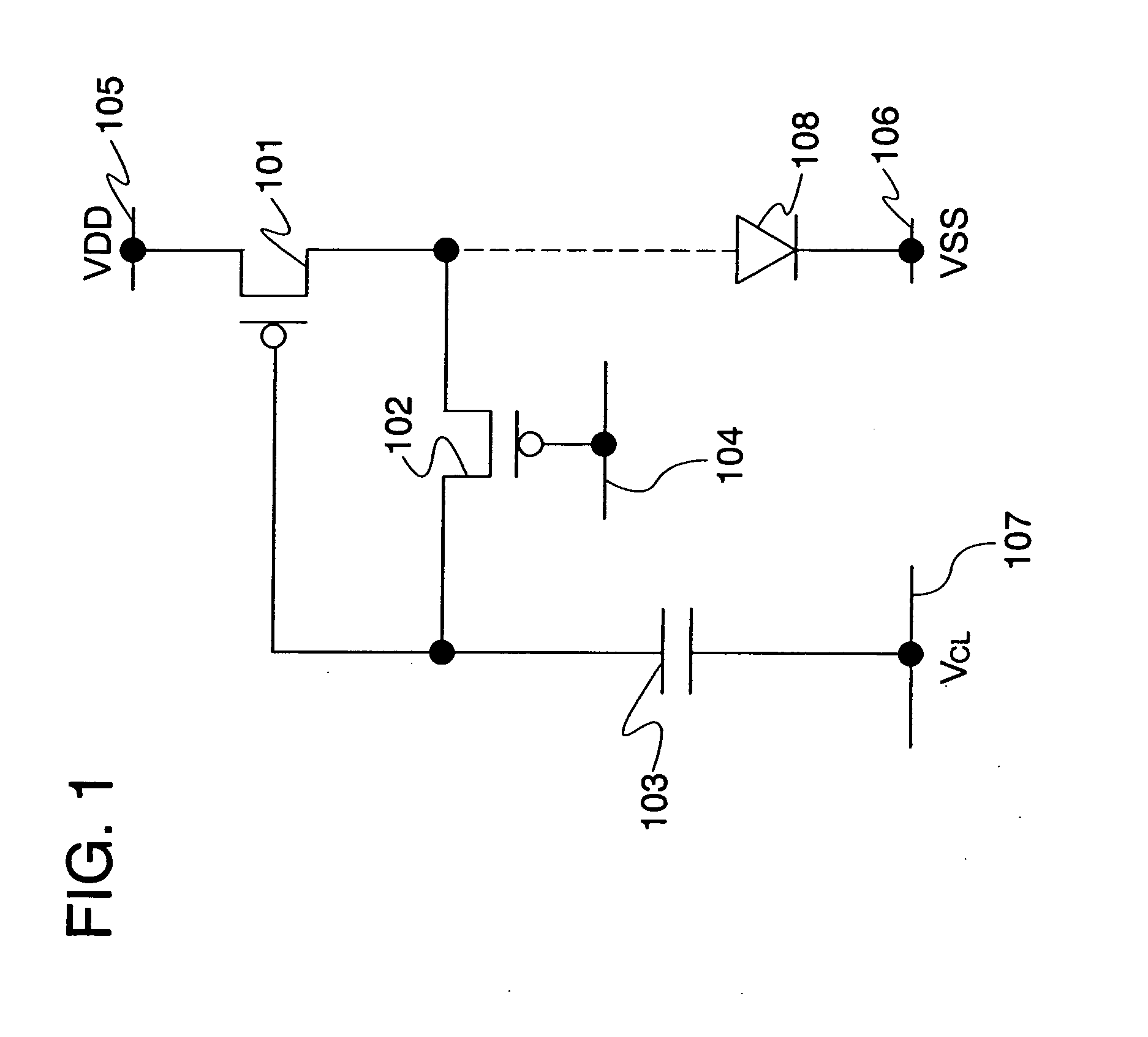
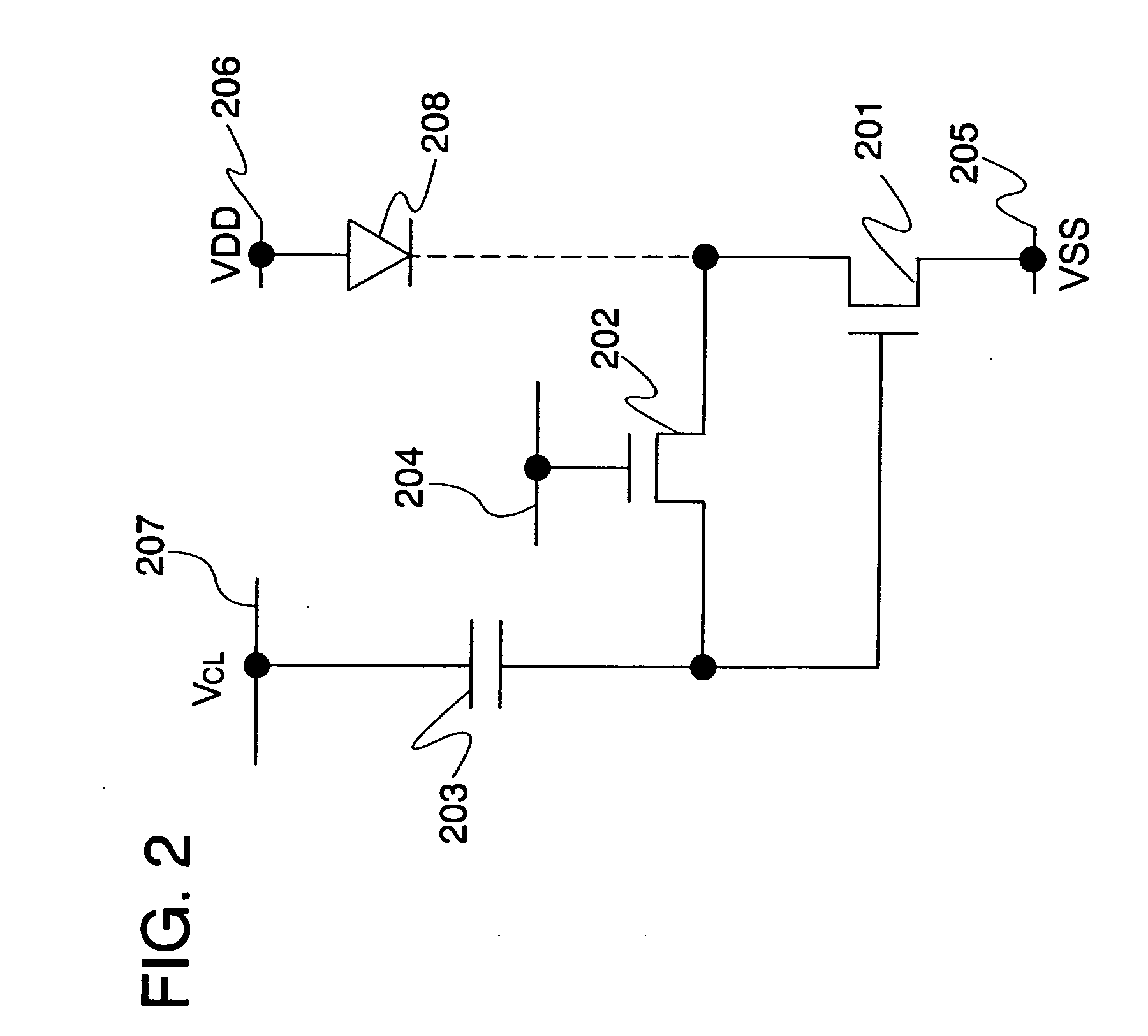
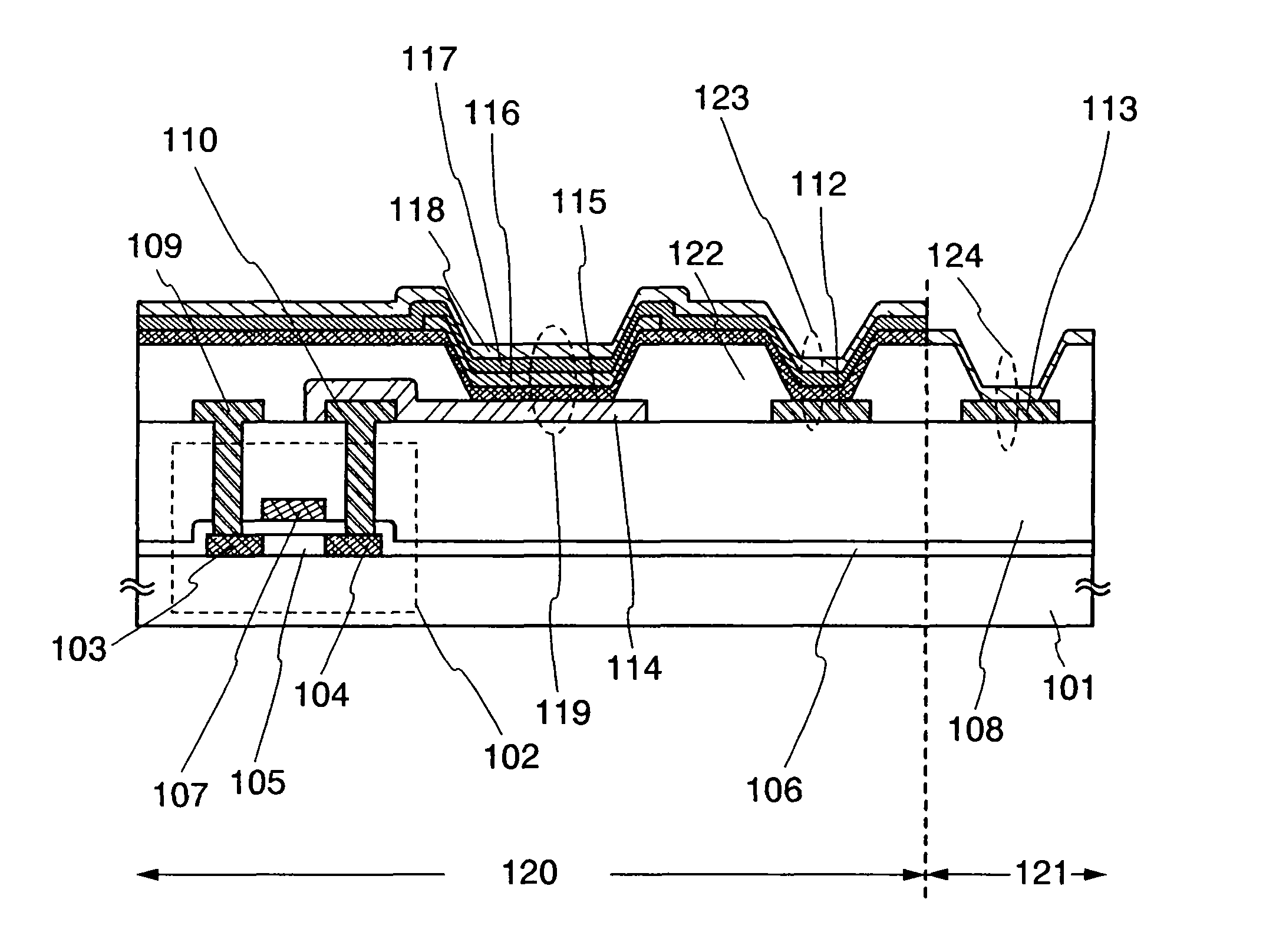
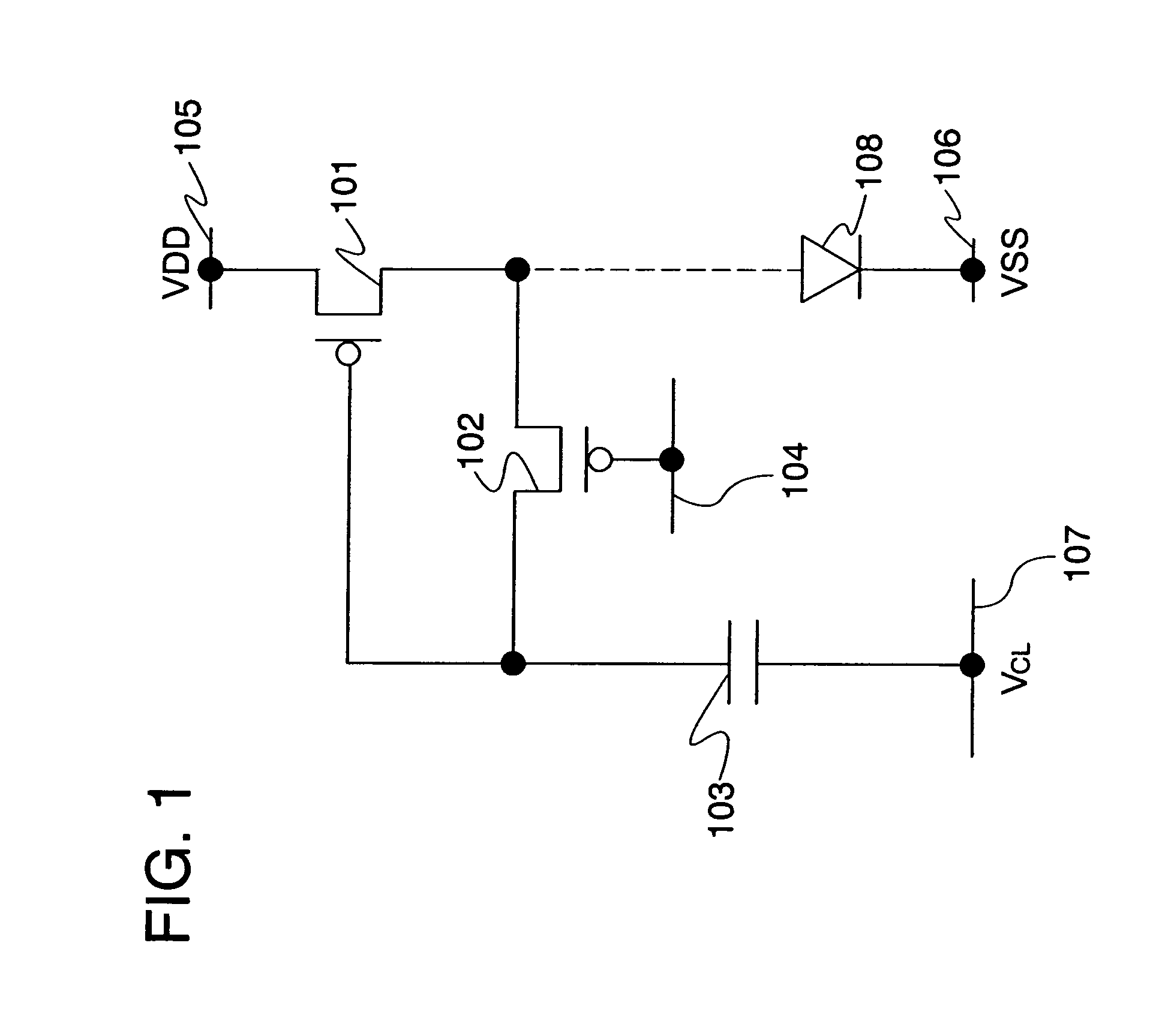
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7247995B2Avoid damageElectrostatic discharge damage during manufacturing steps is preventedTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device in which electrostatic discharge damage during manufacturing steps is prevented. More specifically, a semiconductor device in which electrostatic discharge damage during a step in which the formation of a pixel electrode is completed is prevented. A semiconductor device of the invention comprises a light emitting element, a driving transistor and a protection means disposed between the light emitting element and the driving transistor. The protection means comprises as least one of a resistor element, a capacitor element and a rectifier element. More specifically, the protection means is disposed between a pixel electrode of the light emitting element and a source electrode or a drain electrode of the driving transistor. It is to be noted that the rectifier element is an element having a rectifying function and corresponds to a diode or a transistor whose drain electrode and gate electrode are connected to each other.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting device and electronic apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20070177088A1Luminance can be prevented being loweredLuminance variationStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityLight emitting device
A light emitting device capable of suppressing drop in luminance or luminance unevenness of a light emitting element due to deterioration of an electro luminescent material and capable of switching an image direction vertically to horizontally without a frame memory additionally provided. The light emitting device of the invention comprises in each pixel first to fourth transistors, a light emitting element, and a signal line. The first transistor and the second transistor control the connection between the signal line and a gate of the third transistor, the fourth transistor controls a current value supplied to the light emitting element, and the third transistor selects whether the current is supplied to the light emitting element or not. Further, the first transistor and the second transistor are switched separately.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device and driving method of display device
InactiveUS7737923B2Small sizeReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
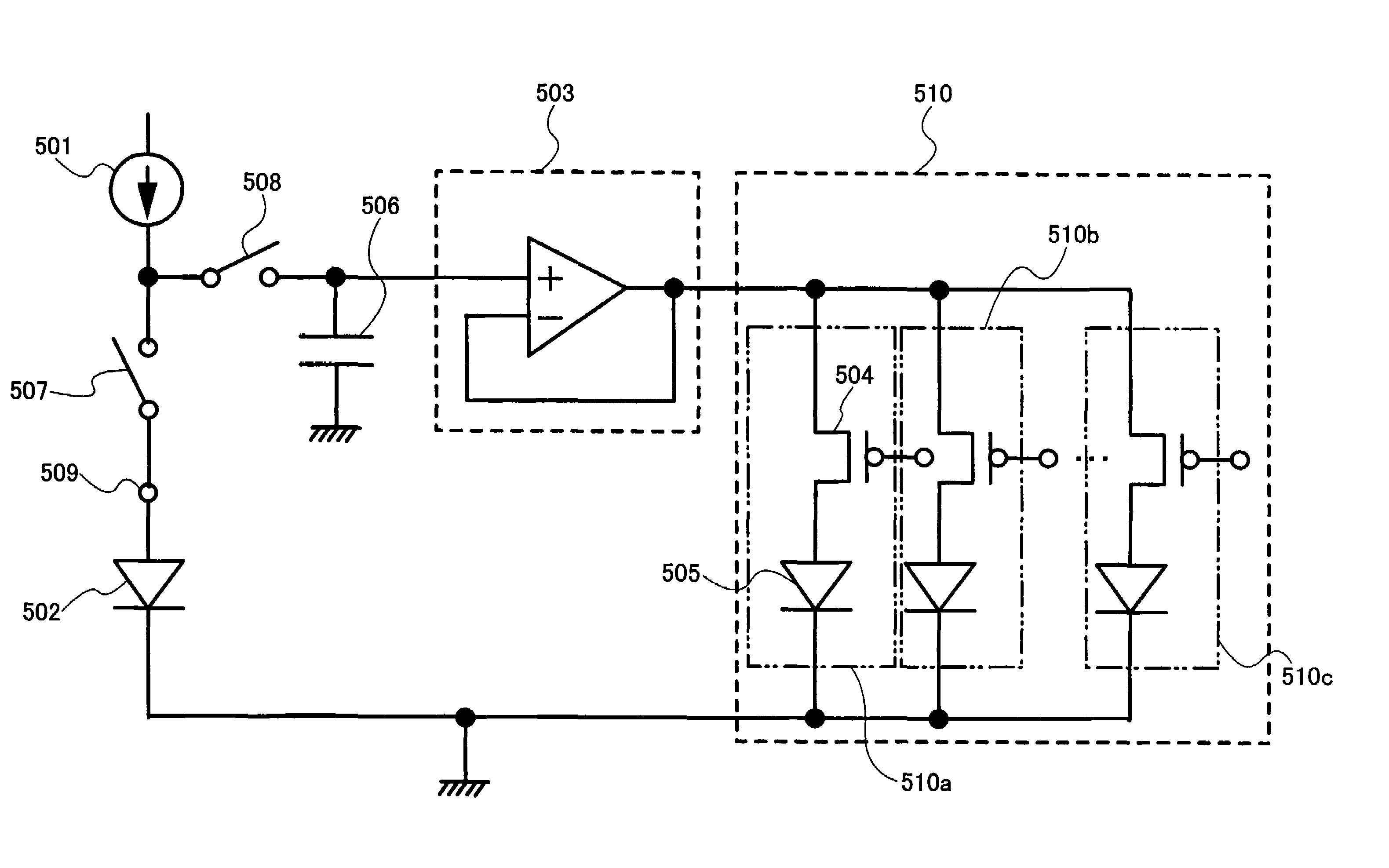
Organic EL display device
InactiveUS20050140607A1Aperture rate be reduceReduce variationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesCharge voltageImage signal
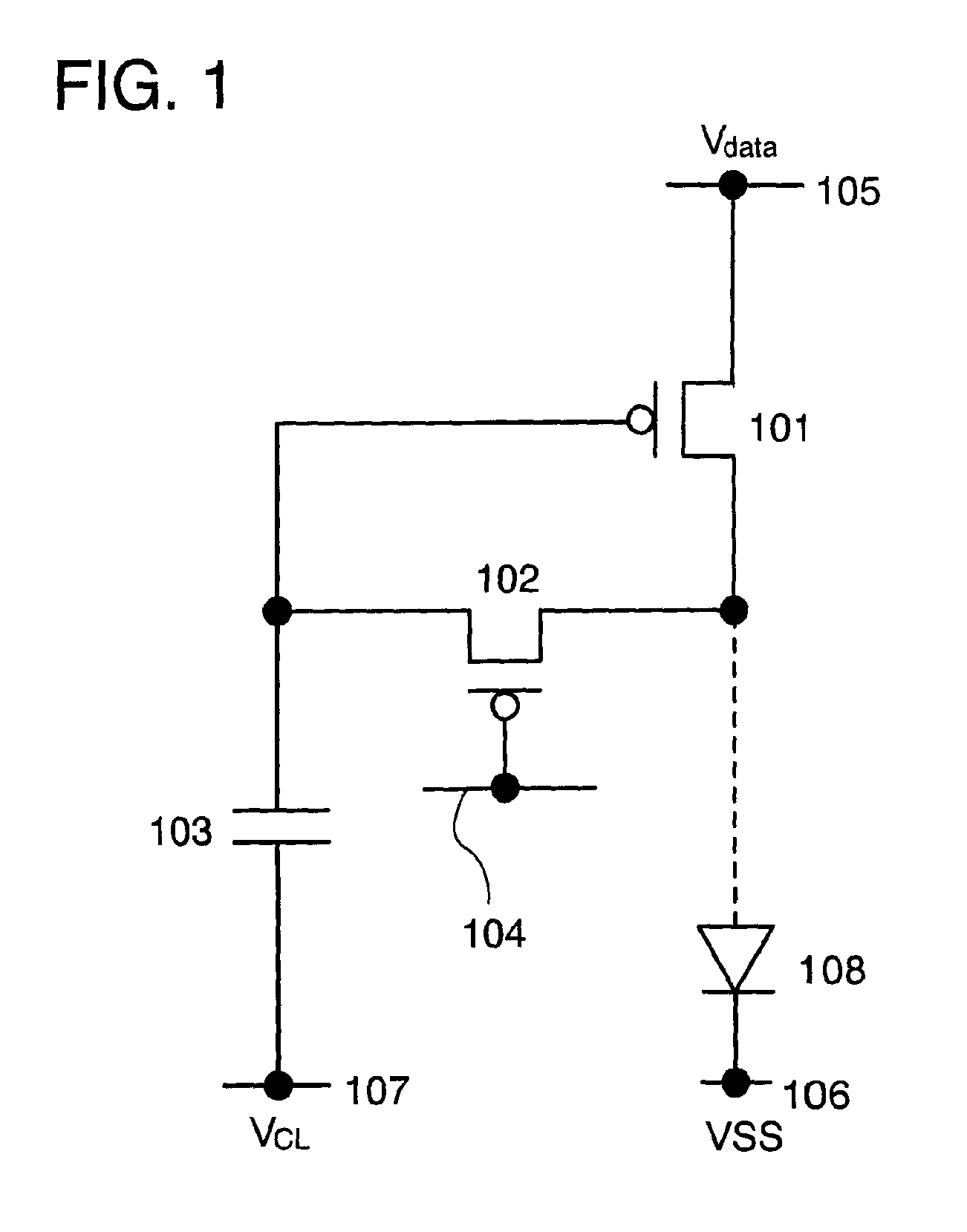
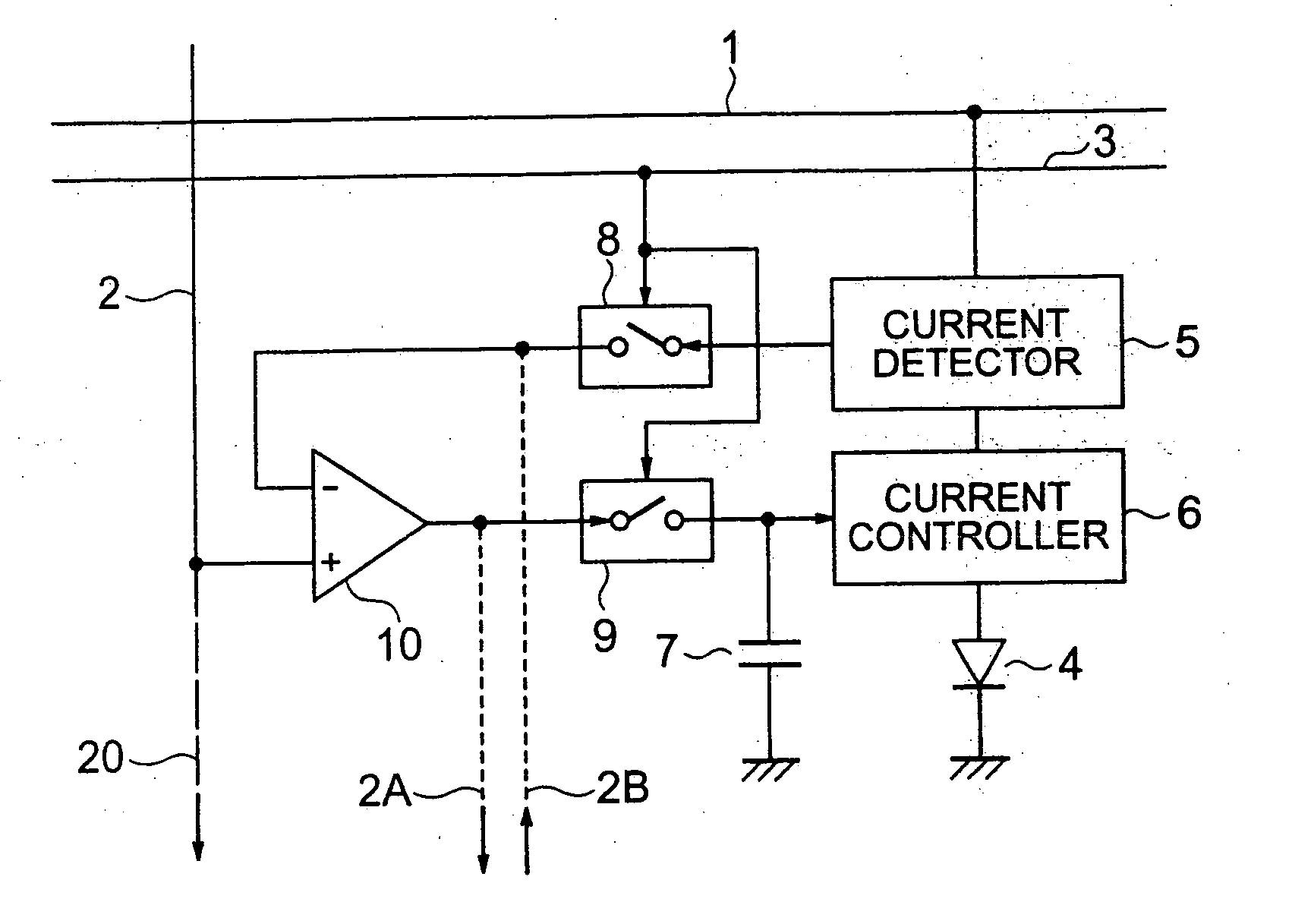
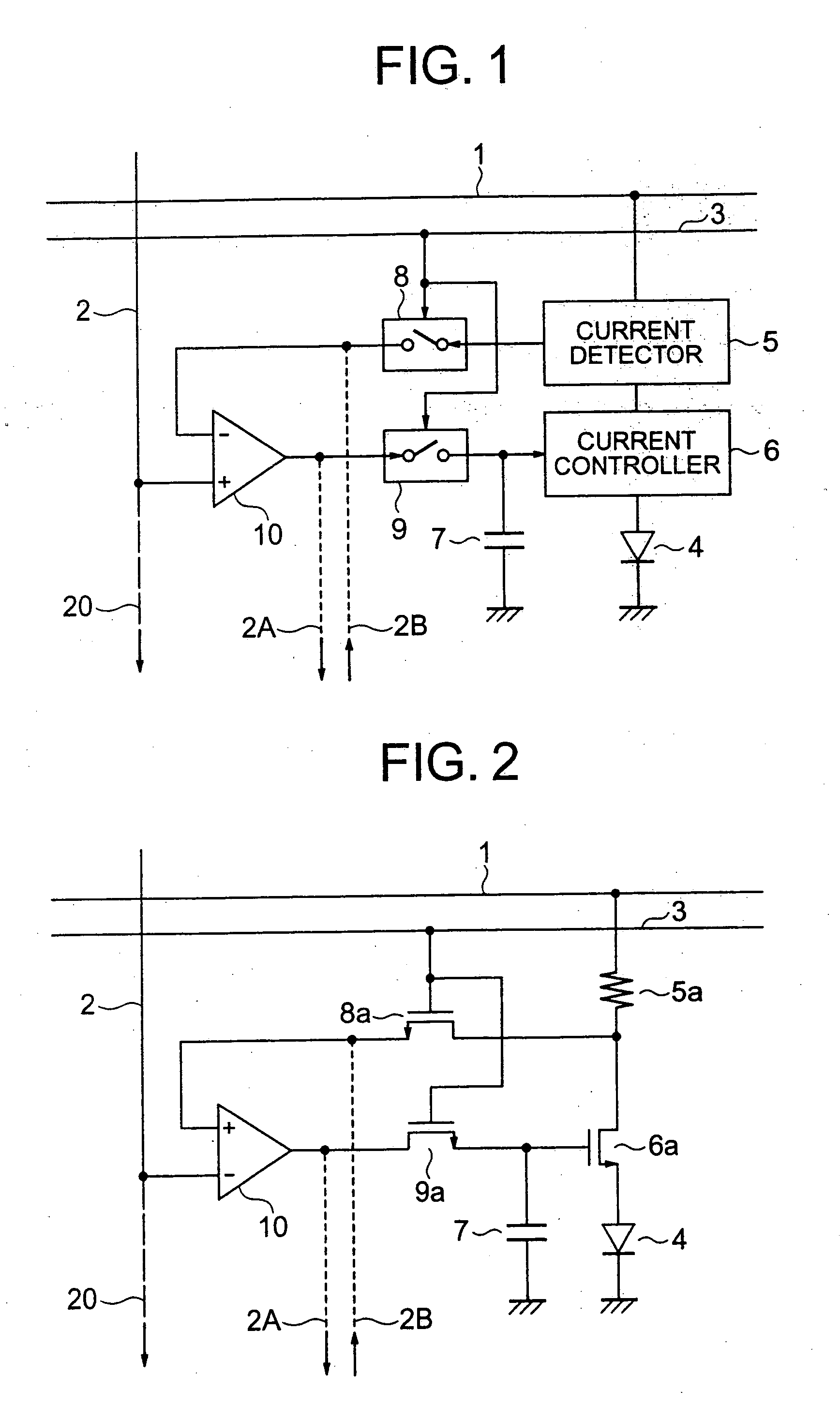
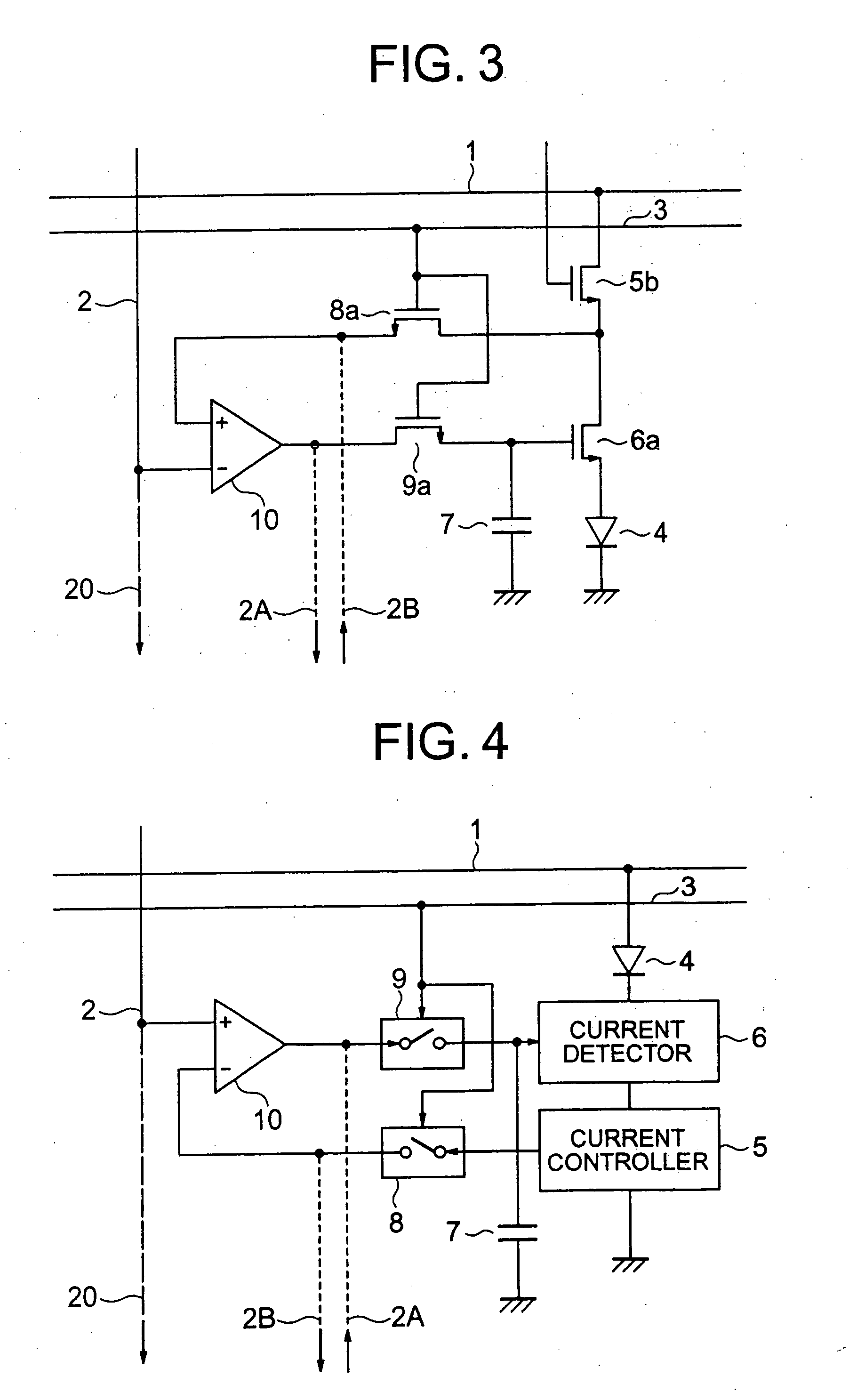
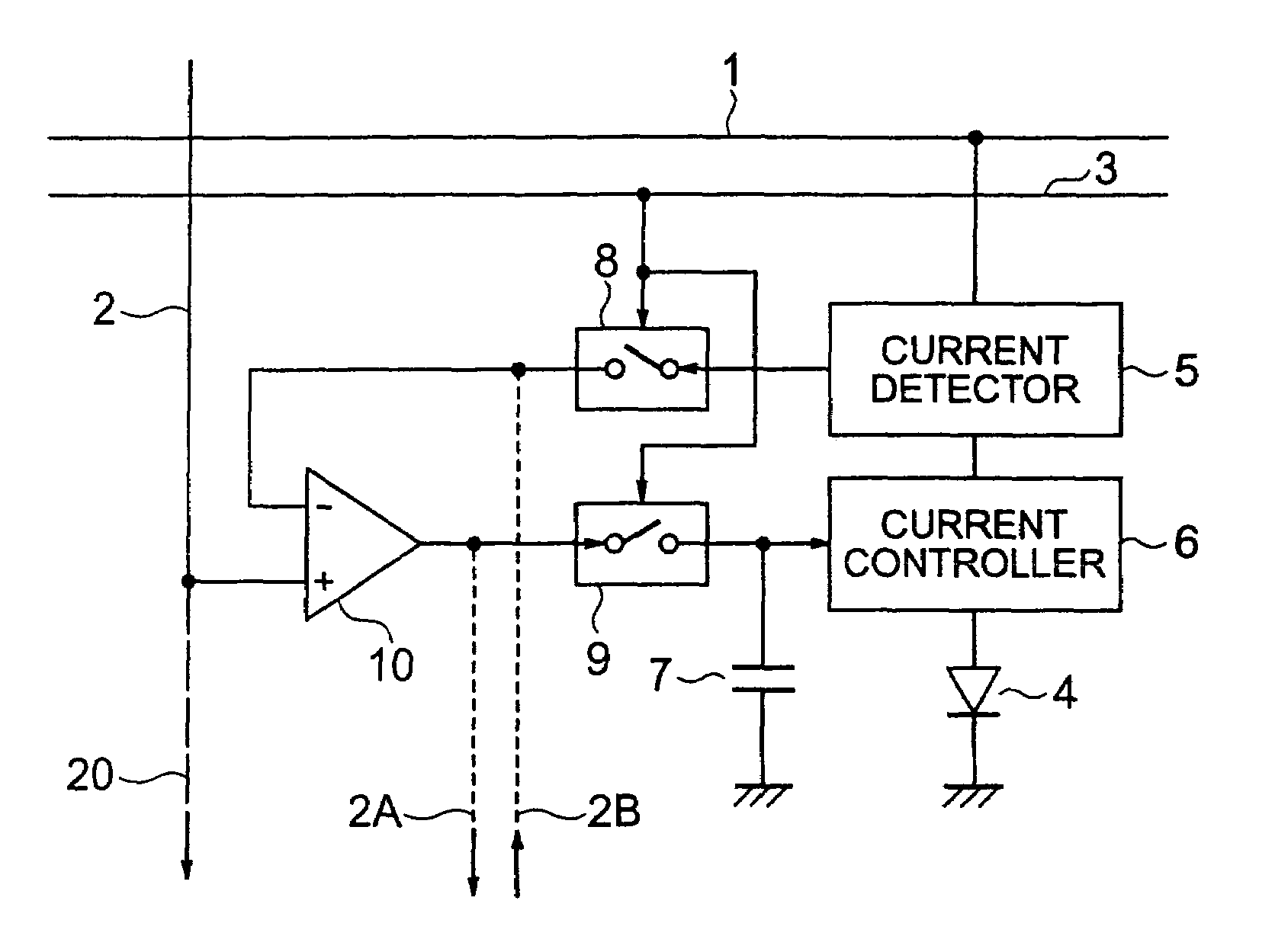
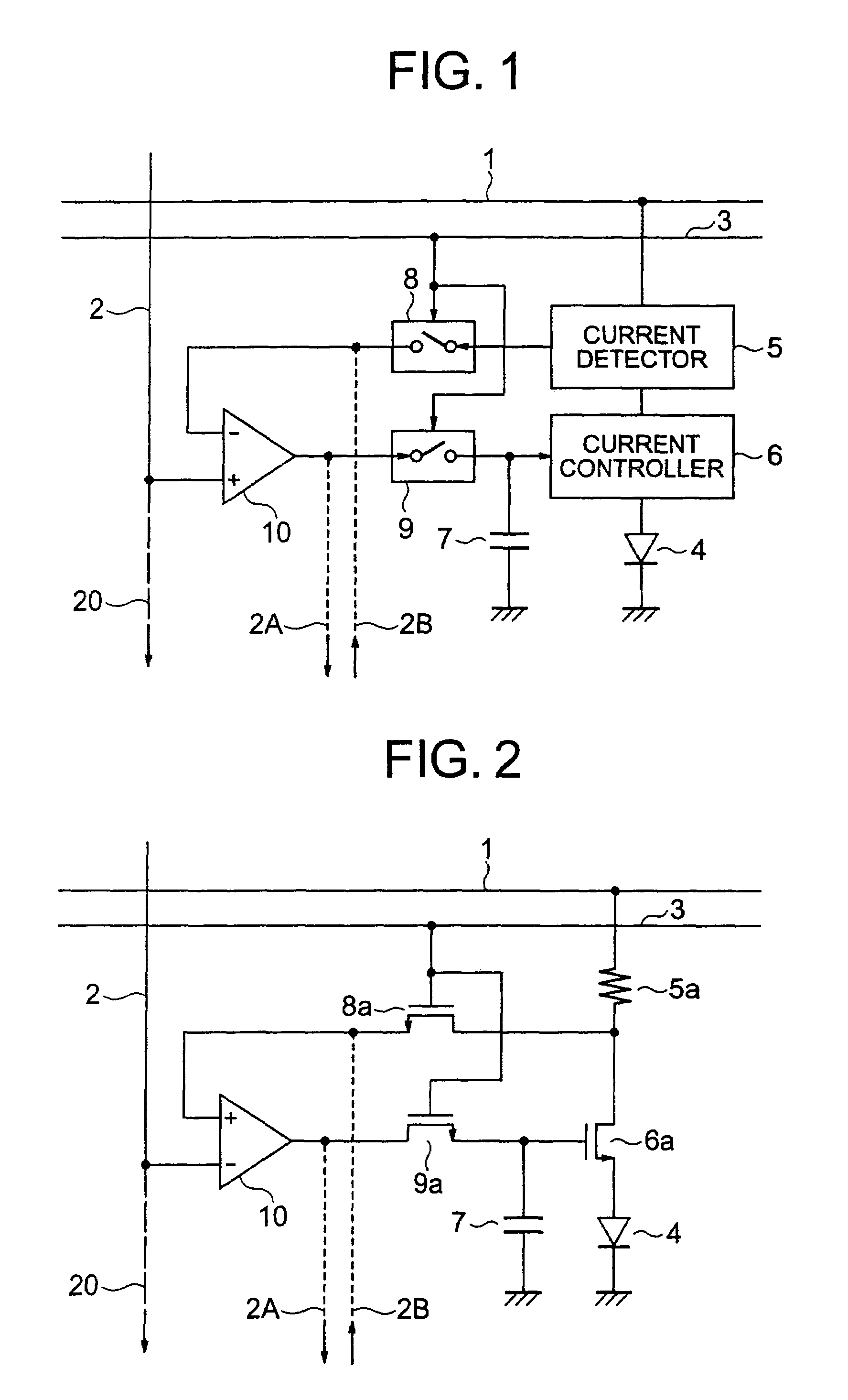
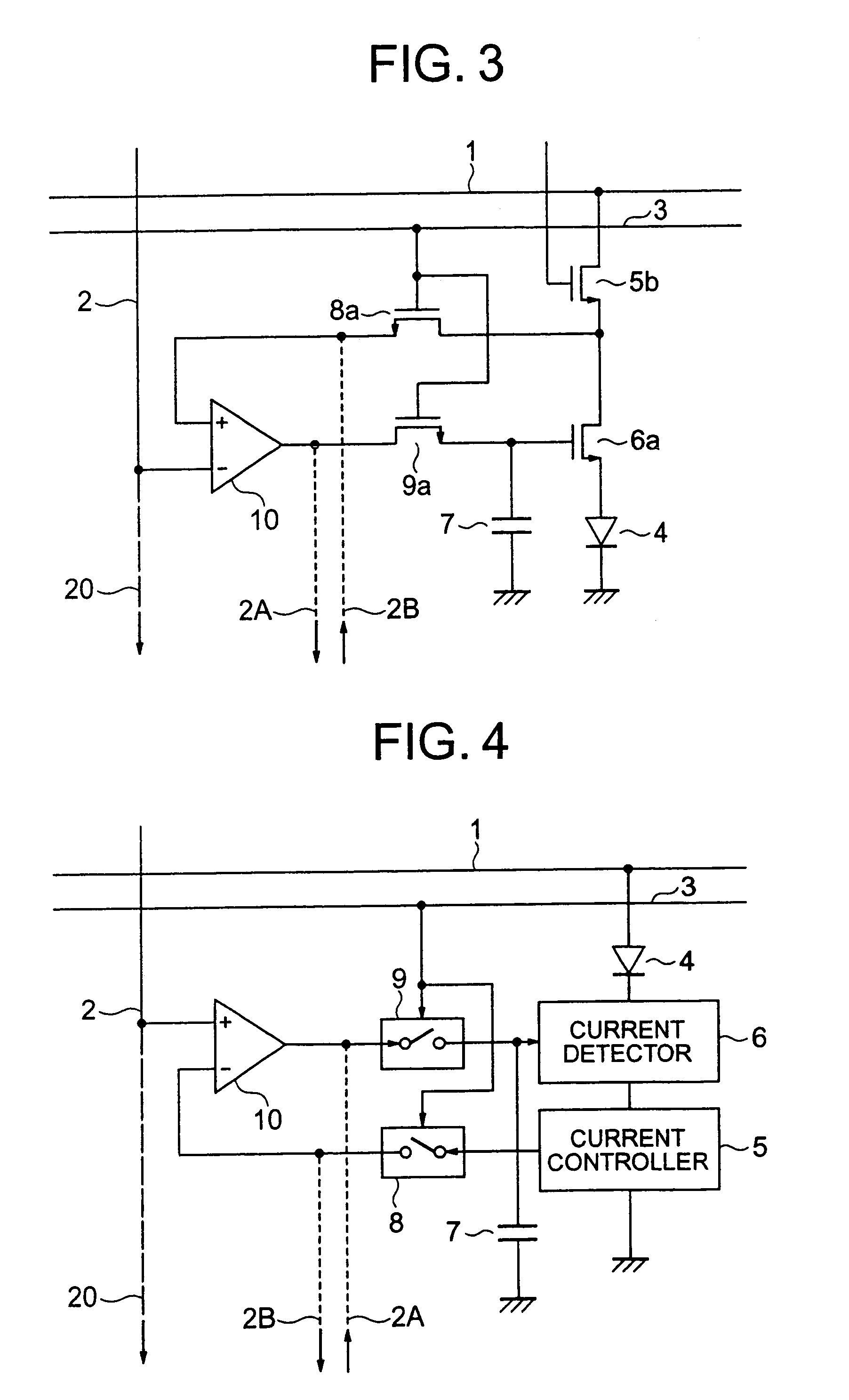
Disclosed is an organic EL display device which includes a light emitter; a current controller controlling a current to be fed to the light emitter; a current detector detecting a value of current flowing through the light emitter as a voltage; a first switching unit switching between transmission and non-transmission of a voltage value corresponding to the detected current; a comparison amplifier comparing and amplifying the voltage value transmitted from the first switching unit to a voltage value corresponding to the image signal; a second switching unit switching between transmission and non-transmission of the voltage value being a result of the comparison and amplification; and an image signal holding capacitor charged / discharged based on the voltage value transmitted from the second switching unit, the current controller controlling the current to be fed to the light emitter based on a charging voltage of the image signal holding capacitor.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
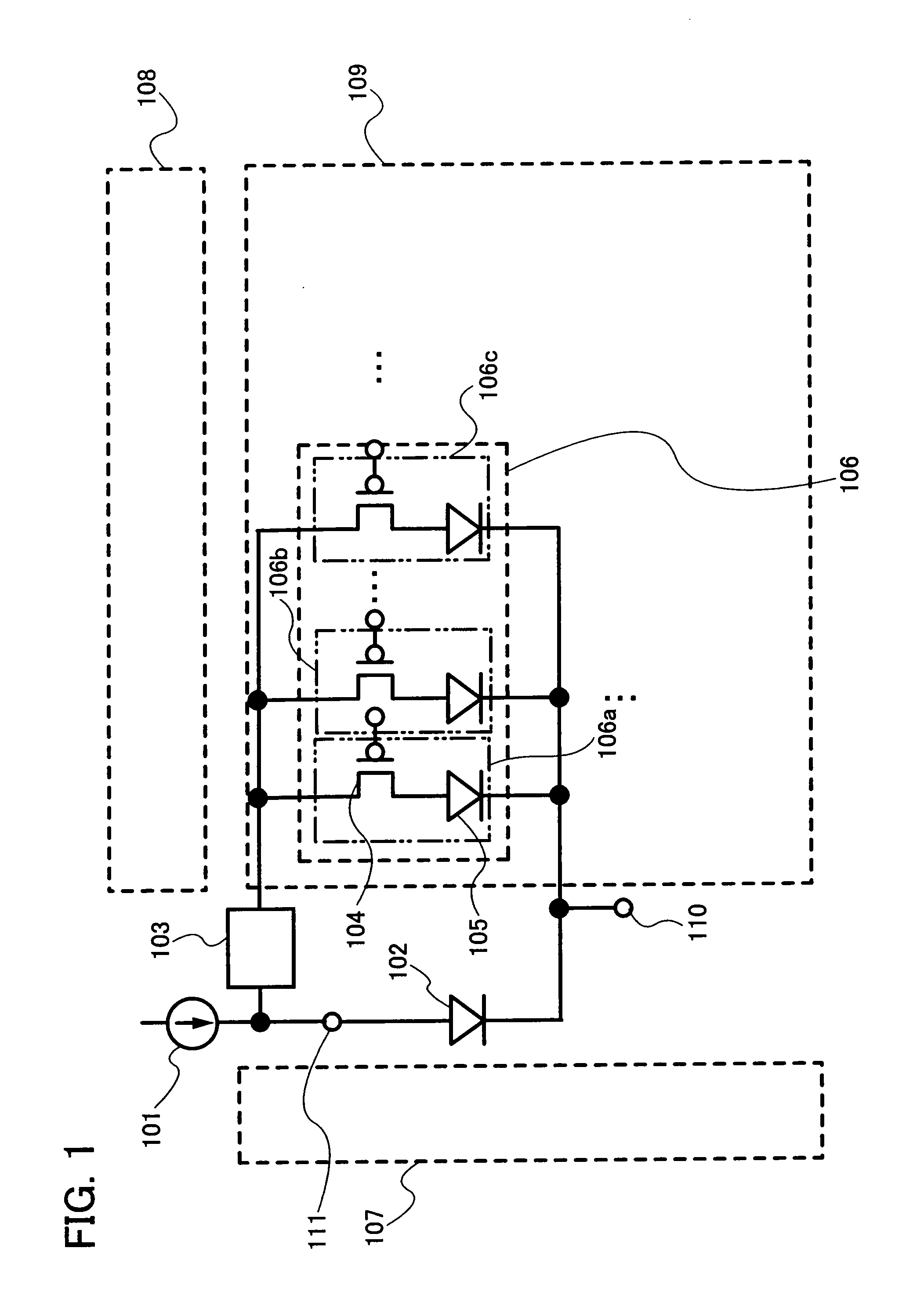
Driving Device for Providing Light Dimming Control of Light-Emitting Element
InactiveUS20090058318A1Suppress in chromaticitySuppress luminescenceElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringControl circuit
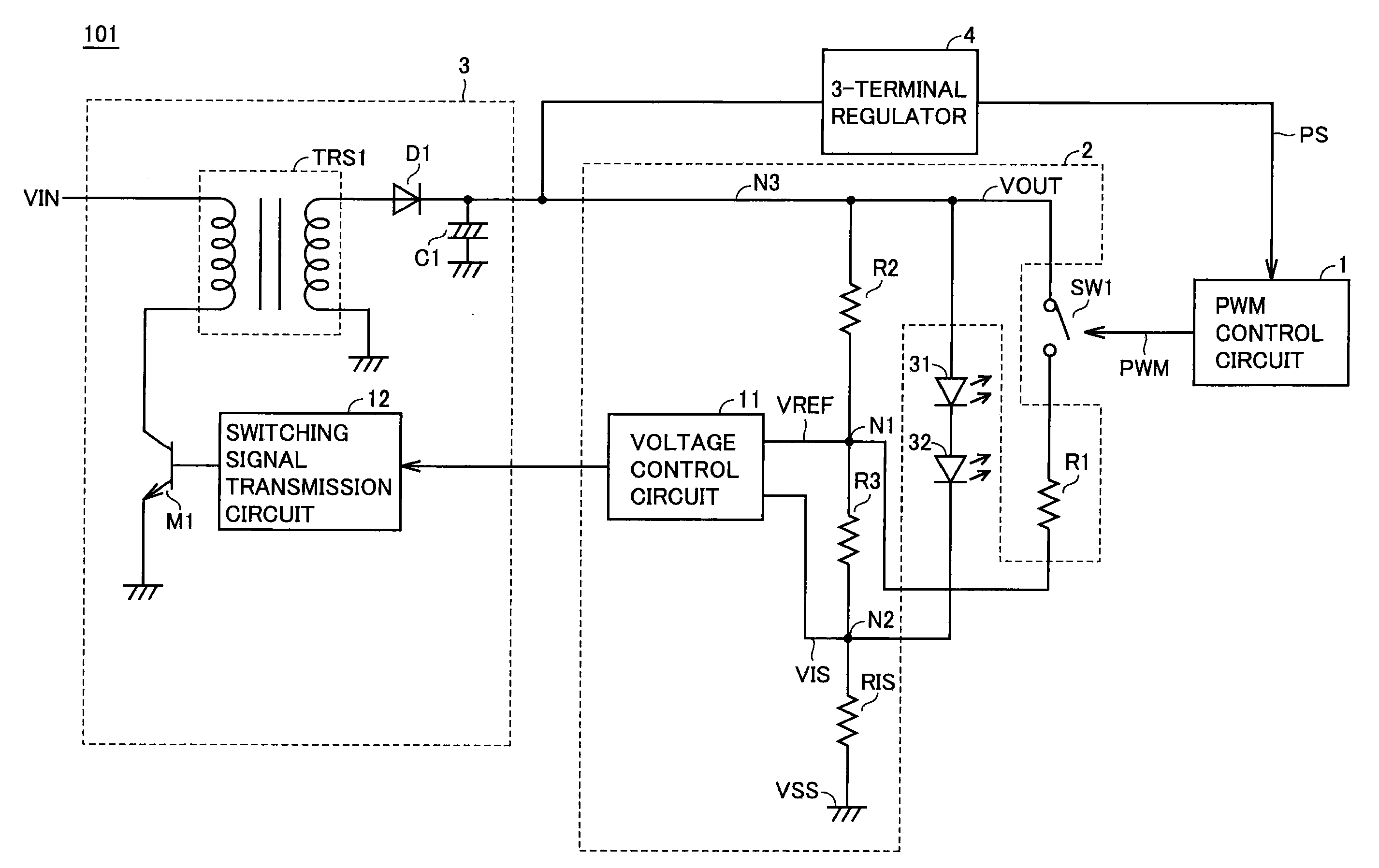
A driving device includes a first switch element to switch between applying or not applying to a light-emitting element a voltage directed to setting the light-emitting element in an ON state, and a constant current control circuit to adjust a current flowing through the light-emitting element when the light-emitting element is in an ON state to a predetermined current value.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Organic EL display device
InactiveUS7027014B2Reduce variationSmall apertureStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierDisplay device
Disclosed is an organic EL display device which includes a light emitter; a current controller controlling a current to be fed to the light emitter; a current detector detecting a value of current flowing through the light emitter as a voltage; a first switching unit switching between transmission and non-transmission of a voltage value corresponding to the detected current; a comparison amplifier comparing and amplifying the voltage value transmitted from the first switching unit to a voltage value corresponding to the image signal; a second switching unit switching between transmission and non-transmission of the voltage value being a result of the comparison and amplification; and an image signal holding capacitor charged / discharged based on the voltage value transmitted from the second switching unit, the current controller controlling the current to be fed to the light emitter based on a charging voltage of the image signal holding capacitor.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Small switch having liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050168421A1Light evenlyInhibit visual variationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriver circuitLiquid-crystal display
A small switch having a liquid crystal display includes an operation button; a liquid crystal display device having a liquid crystal panel for displaying information including characters and / or pictures on the operation button and a printed circuit board on which an IC chip, which serves as a driver circuit for the liquid crystal panel, is mounted, the liquid crystal display device being housed in the operation button; a switch body including a contact mechanism for opening and closing an electrical path by vertically moving the operation button; and backlight sources having different colors. The liquid crystal panel is an antiferroelectric liquid crystal panel. The backlight sources are sequentially turned on at high speed below the antiferroelectric liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal screens having different display contents for every color are displayed in synchronization with the turning on of the backlight sources to achieve multicolor display.
Owner:NKK SWITCHES
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS8957889B2Reduce variationLuminance variationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower flowEngineering
In a light-emitting device, supply of current is controlled using a transistor having a normal gate electrode (a first gate electrode) and a second gate electrode for controlling threshold voltage. The light-emitting device comprises one or more switches for selecting conduction or non-conduction between the first gate electrode and a drain terminal of the transistor. When the threshold voltage of the transistor is acquired, the first gate electrode and the drain terminal of the transistor are brought into conduction with the switch, and the threshold voltage of the transistor is shifted by controlling the potential of the second gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device and electronic apparatus having the display device
InactiveUS7635863B2Luminance variationMonitoring elementStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceInternal resistance
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
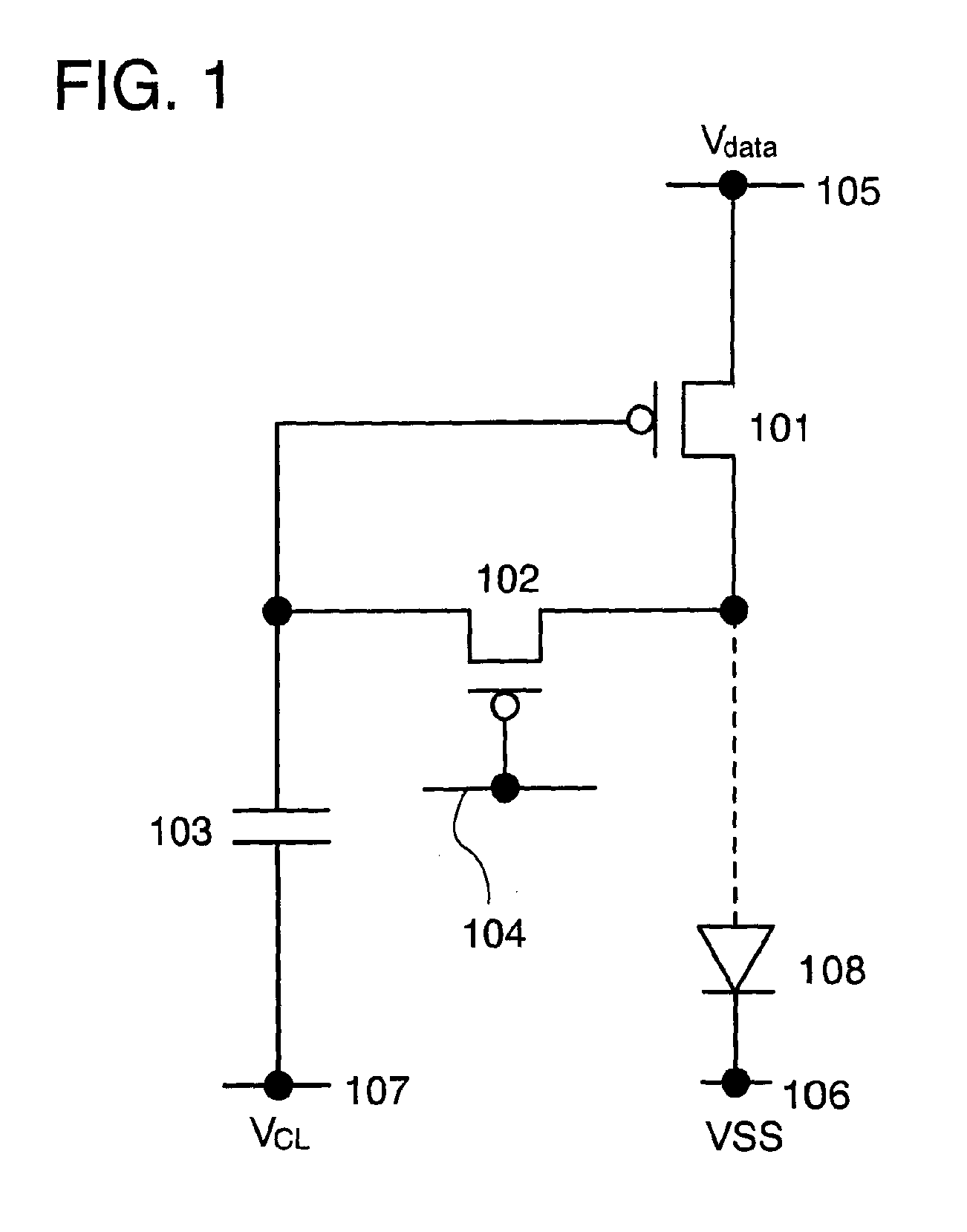
Display device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS8988400B2Reduce variationLuminance variationTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesPower flowDisplay device
To provide a display device and a driving method thereof, where variations in the threshold voltage of transistors can be compensated and thus variations in luminance of light-emitting elements can be suppressed. In a first period, initialization is performed; in a second period, a voltage based on the threshold voltage of a first transistor is held in first and second storage capacitors; in a third period, a voltage based on a video signal voltage and the threshold voltage of the first transistor is held in the first and second storage capacitors; and in a fourth period, voltages held in the first and second storage capacitors are applied to a gate terminal of the first transistor to supply a current to a light-emitting element, so that the light-emitting element emits light. Through the operation process, a current obtained by compensating variations in the threshold voltage of the first transistor can be supplied to the light-emitting element, thereby variations in luminance can be suppressed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
License plate lamp
InactiveUS20090196059A1Light utilization efficiencyReduce manufacturing costVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureOptical signallingOptical axisEngineering
A license plate lamp for radiating light to a surface of a license plate attached to a rear end of a vehicle body includes: a lamp body disposed above the license plate; a light emitting diode disposed within the lamp body, the light emitting diode having an optical axis extending in a vertical direction for emitting light toward a license plate located under the light emitting diode; and a control lens provided between the light emitting diode and the license plate for controlling the light emitted by the light emitting diode so that the light is radiated toward a surface of the license plate. The control lens includes a first control portion for radiating the light emitted by the light emitting diode toward an upper end part of the surface of the license plate, and a second control portion located rearward of the first control portion for radiating the light emitted by the light emitting diode toward substantially a whole region of the surface of the license plate.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Display device and driving method of display device
InactiveUS20100245219A1Small sizeReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceCapacitor
One feature of the present invention includes first to third steps of holding a voltage, corresponding to a difference between a voltage applied to a first power supply line and a threshold voltage of a first transistor, between both electrodes of first and second storage capacitors; holding a voltage, corresponding to a difference between a voltage applied to the first power supply line and a gate-source voltage of the first transistor, which is necessary to supply a light-emitting element with a current equivalent to a video signal current inputted into a signal line, between both the electrodes of the second storage capacitor; and applying a voltage based on the voltage held in the first and second storage capacitors in the first and second steps to a gate electrode of the first transistor; therefore, a current is supplied to the light-emitting element through the first transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display, surface light source device, and information device
InactiveUS20070035680A1Luminance variationReduce glareOptical light guidesWaveguidesLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
A liquid crystal display has a light guide plate having a light-emitting plane on its one end surface, a light source arranged on a side surface of the light guide plate, and a liquid crystal panel arranged opposite the light-emitting plane of the light guide plate. Deflection patterns are formed on a surface opposite the light-emitting plane of the light guide plate, and the deflection patterns are arranged so that two independent components on the surface opposite the light-emitting plane of the light guide plate are random. In a certain region on the surface opposite the light-emitting plane, when an average value of the number of the deflection patterns included in each region opposite each pixel of the liquid crystal panel is designated by μn and a standard deviation is designated by σn, their ratio satisfies the relationship: 0<σn / μn≦0.154. Light from the light source introduced into the light guide plate is deflected towards the light-emitting plane by the deflection patterns so as to be emitted from the light-emitting plane. The liquid crystal panel is illuminated by the light emitted from the light-emitting plane.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Display device and electronic apparatus having the display device
InactiveUS20070194314A1Luminance variationMonitoring elementStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesInternal resistanceDisplay device
A light-emitting element has a property that a resistance value (internal resistance) changes in accordance with an environmental temperature. It is an object to downsize a monitoring element which corrects an influence of variations in current value of the light-emitting element, which are caused by an environmental temperature change and a change with time. A pixel includes a plurality of sub-pixels, areas of light-emitting elements provided in the individual sub-pixels are made to be different from each other, and an area of a monitoring element is made to be the same as an area of the light-emitting element in any of the sub-pixels, thereby correcting light-emission of the pixel by the monitoring element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Element Substrate and Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20070241992A1Improve mobilityA large amountElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLinear regionEngineering
No need of lowering off-current of a switching transistor, fewer luminance variations of a light emitting element between pixels due to characteristic variations of a driving transistor, and less risk of steps due to increase in the number of wirings. A video signal for light emission or non-emission of a pixel is input to a gate of a current controlling transistor operated in a linear region, which is connected in series with the driving transistor, through a switching transistor. Since a voltage Vds between a source and a drain of the current controlling transistor is small, small changes in a voltage Vgs between a gate and a source thereof do not affect a current flowing in a load. The current flowing in the light emitting element is determined by the driving transistor operated in a saturation region, and a fixed potential is input to the gate thereof during light emission.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light Emitting Device
InactiveUS20080100227A1Easily rise temperatureLuminance variationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCharge and dischargeSignal lines
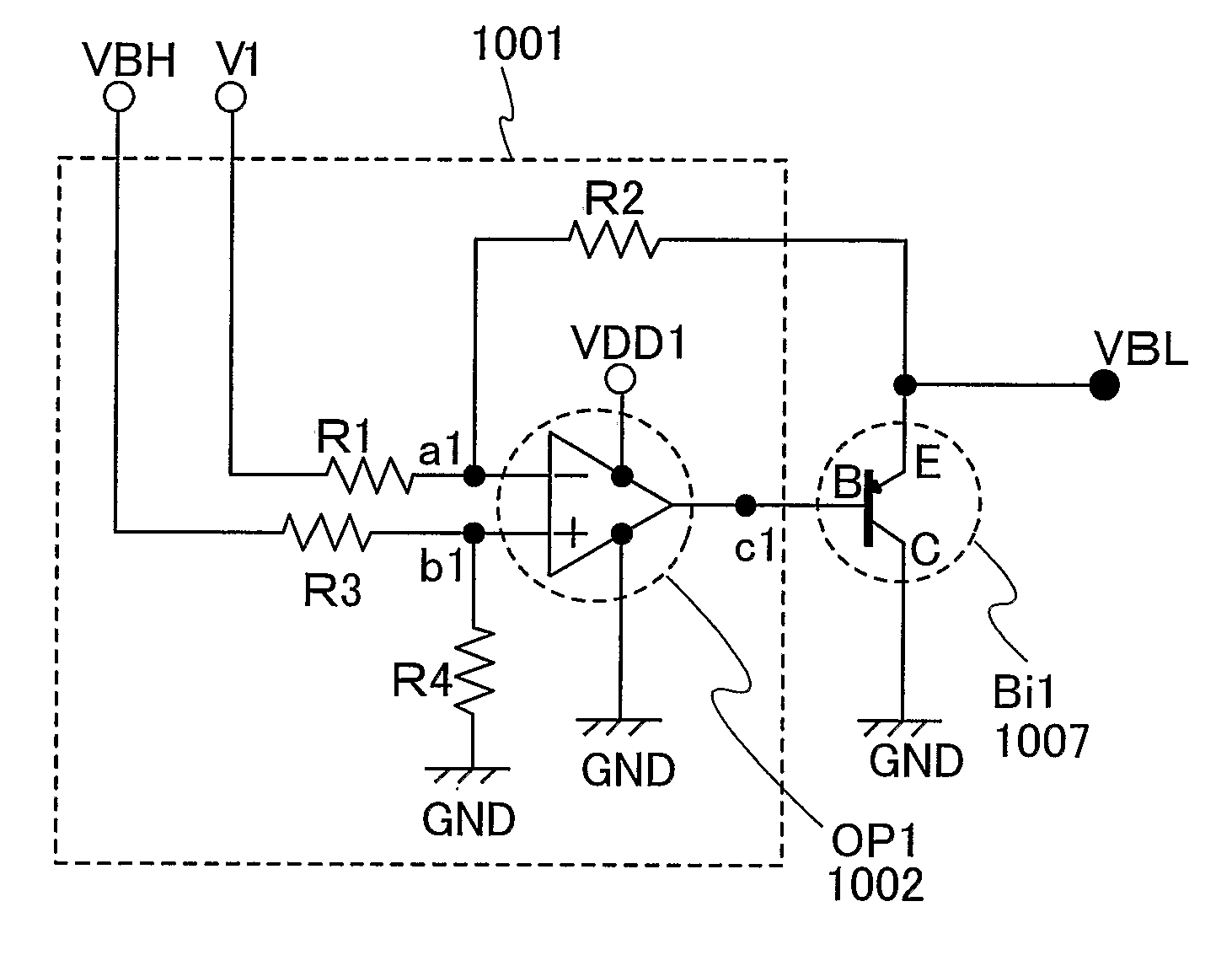
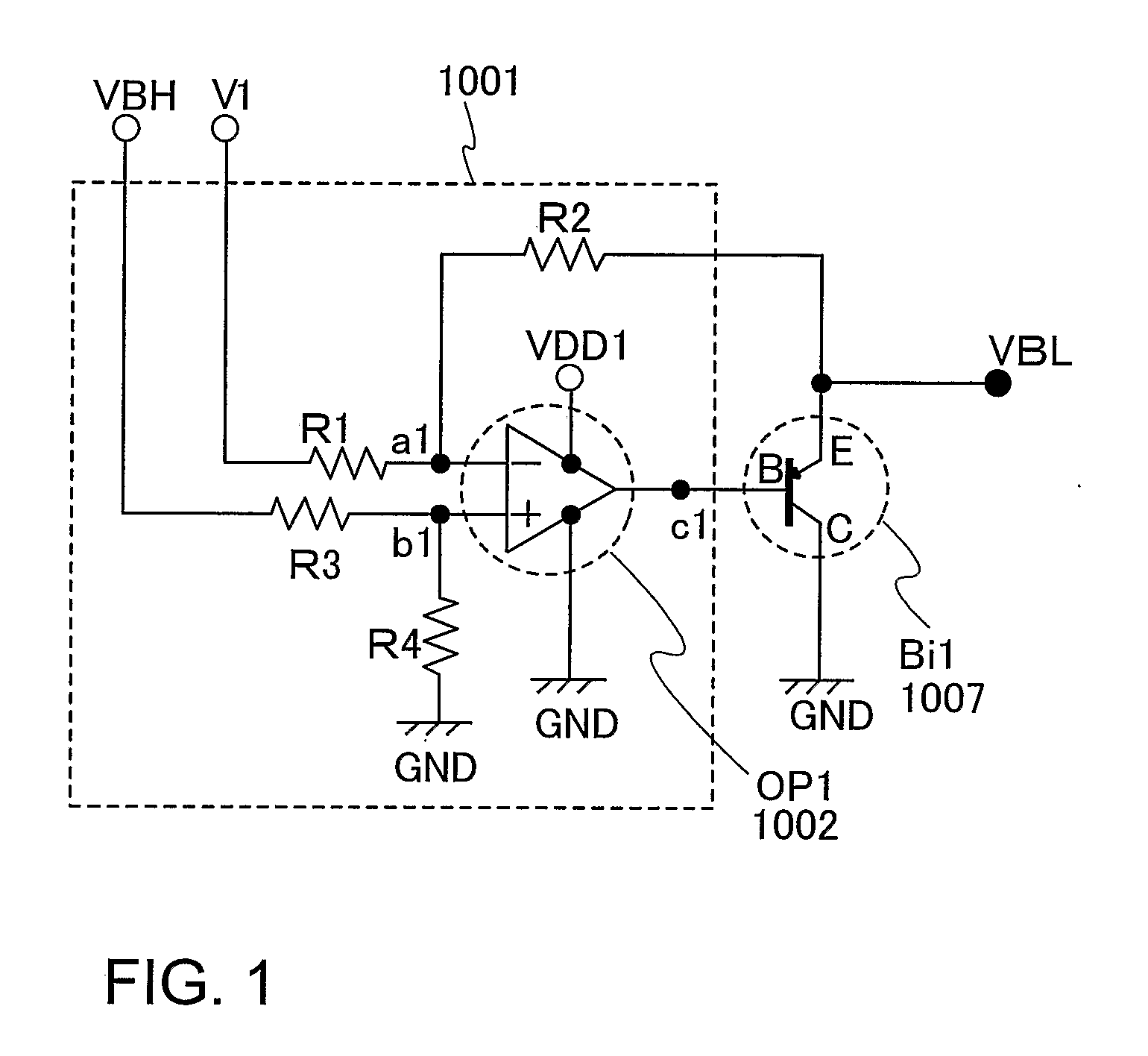
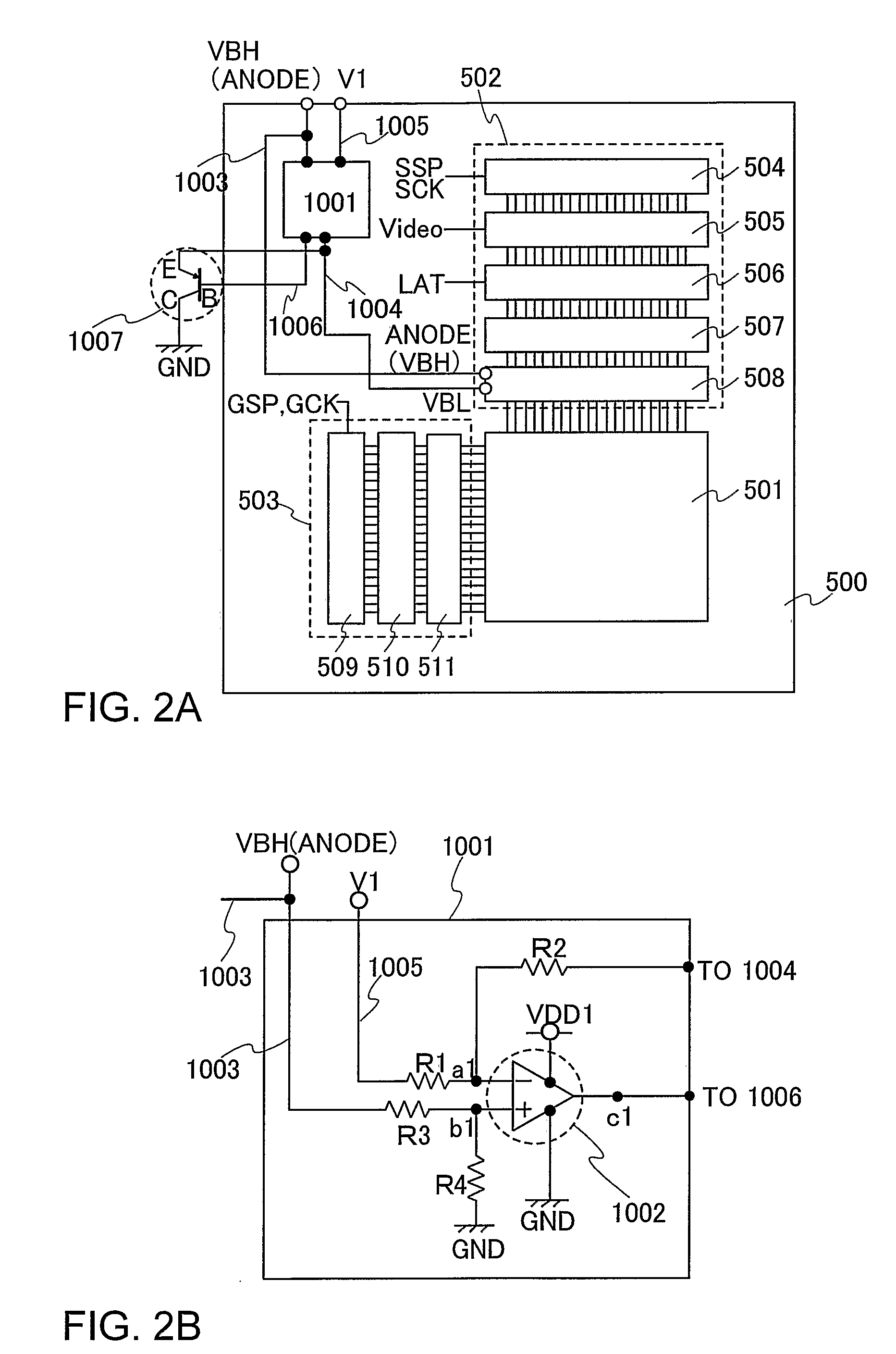
Power consumption required for charging and discharging a source signal line is reduced in an active matrix EL display device. A bipolar transistor (Bi1) has a base terminal B connected to an output terminal c1 of an operational amplifier (OP1), a collector terminal C connected to a low power potential (GND), and an emitter terminal E connected to a resistor R2. A high power potential (VBH) is a potential in synchronization with a high power potential of a light emitting element. A potential of the output terminal c1 of the operational amplifier (OP1) is outputted as a buffer low power potential (VBL). The low power potential (VBL) corresponds to a potential difference between the high power potential (VBH) and a high power potential (V1). Accordingly, the low power potential (VBL) can follow the high power potential (VBH), that is a high power potential of the light emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS9030105B2Total current dropImprove efficiencyStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionEngineering
A light-emitting device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a light-emitting element, a first transistor whose source is electrically connected to an anode of the light-emitting element, a second transistor which controls whether an image signal is input to a gate of the first transistor, a third transistor which controls electrical connection and disconnection between the gate and a drain of the first transistor, a fourth transistor which controls whether a first power supply potential is supplied to the drain of the first transistor, a fifth transistor which controls whether a second power supply potential is supplied to the anode of the light-emitting element, a first capacitor which holds a voltage between the gate and the source of the first transistor, and a second capacitor electrically connected in series with the first capacitor and electrically connected in series with the light-emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com