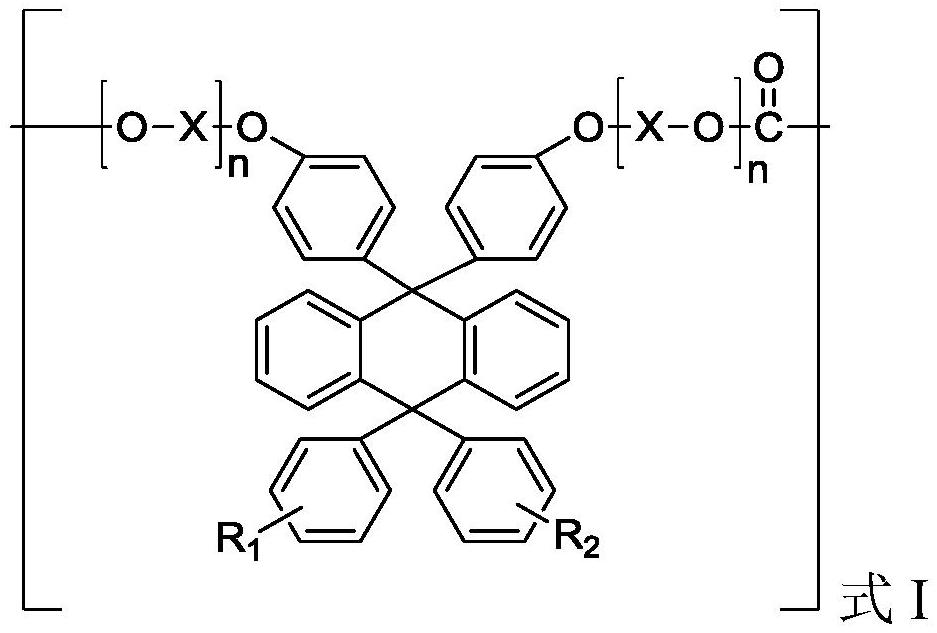
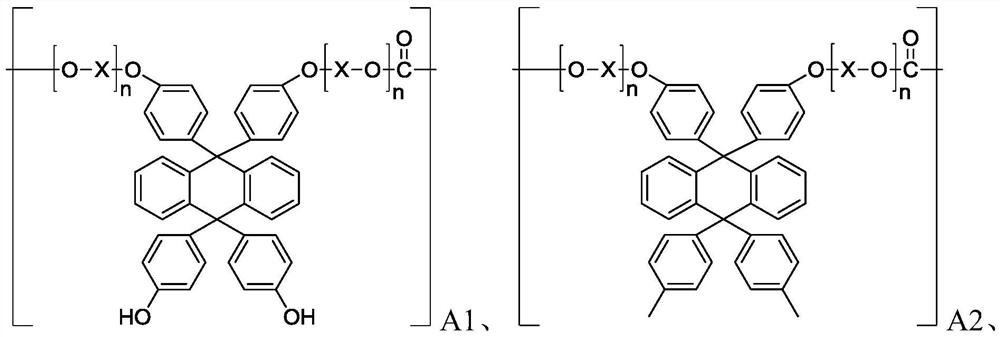
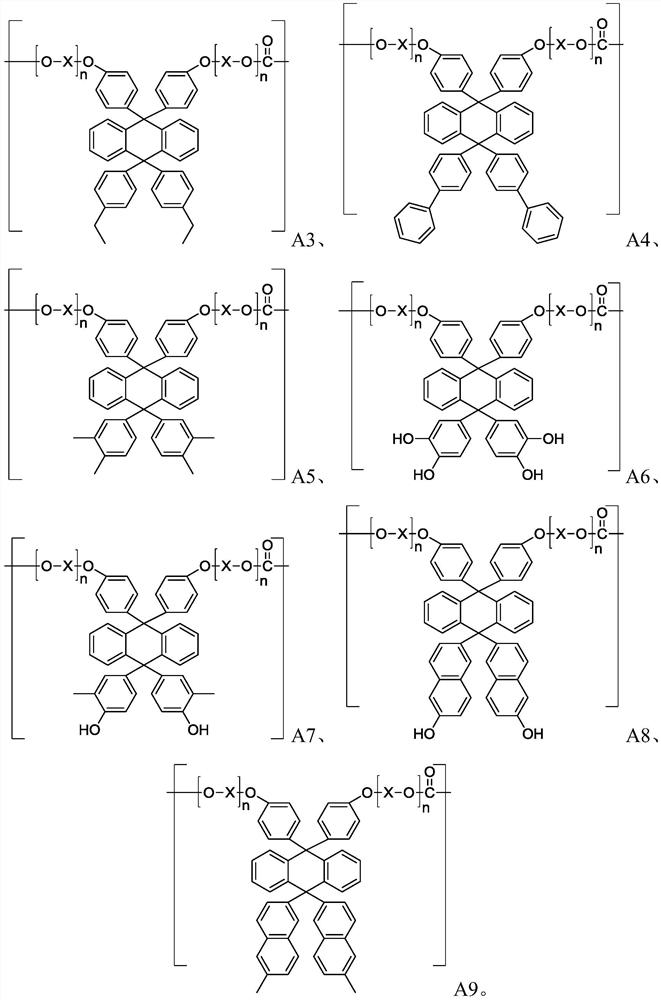
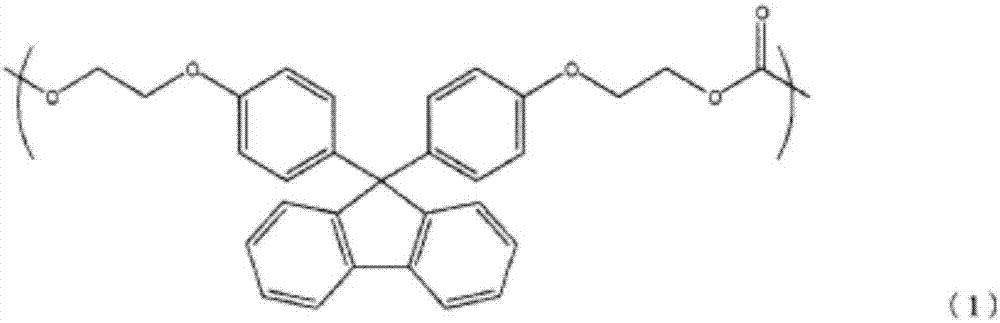
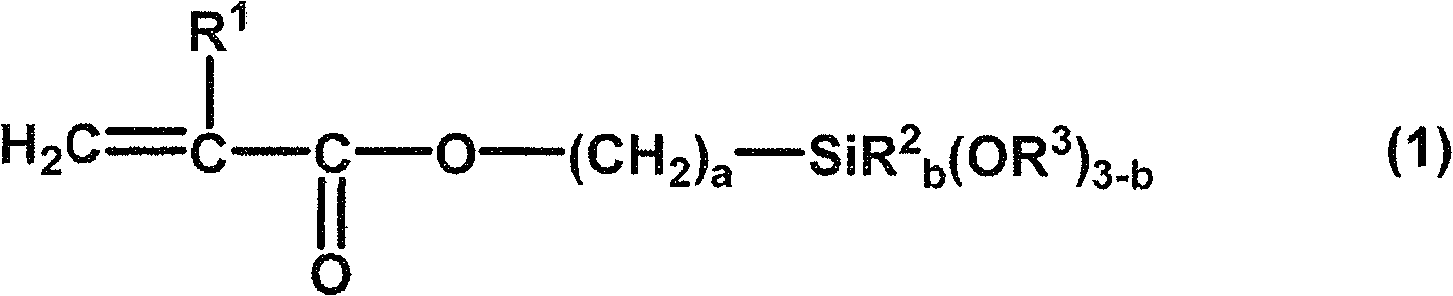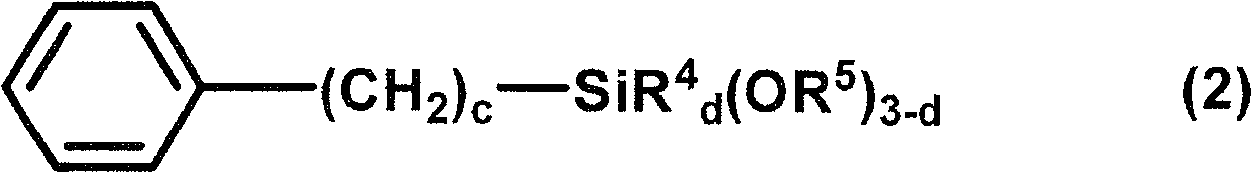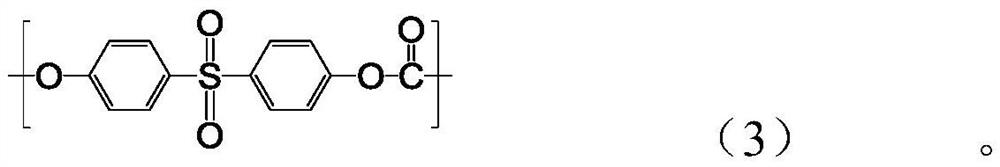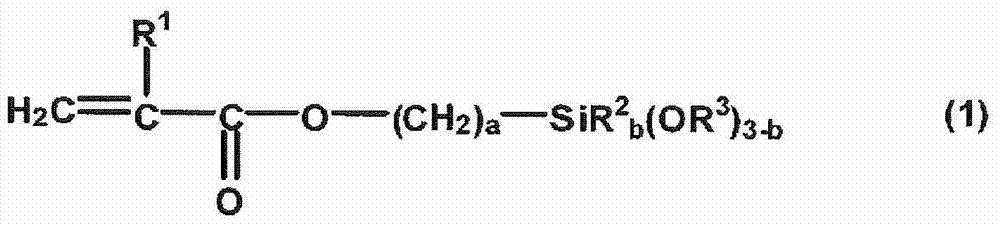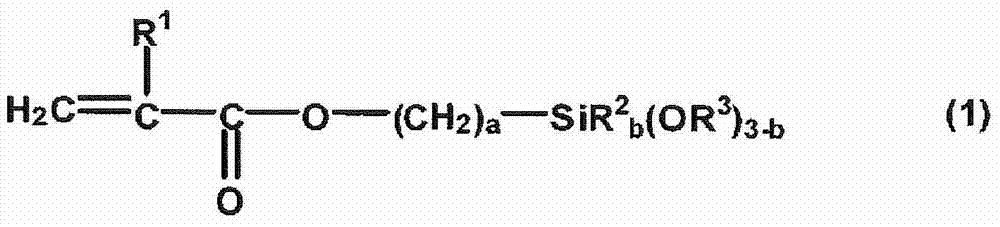Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63results about How to "Low Abbe number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
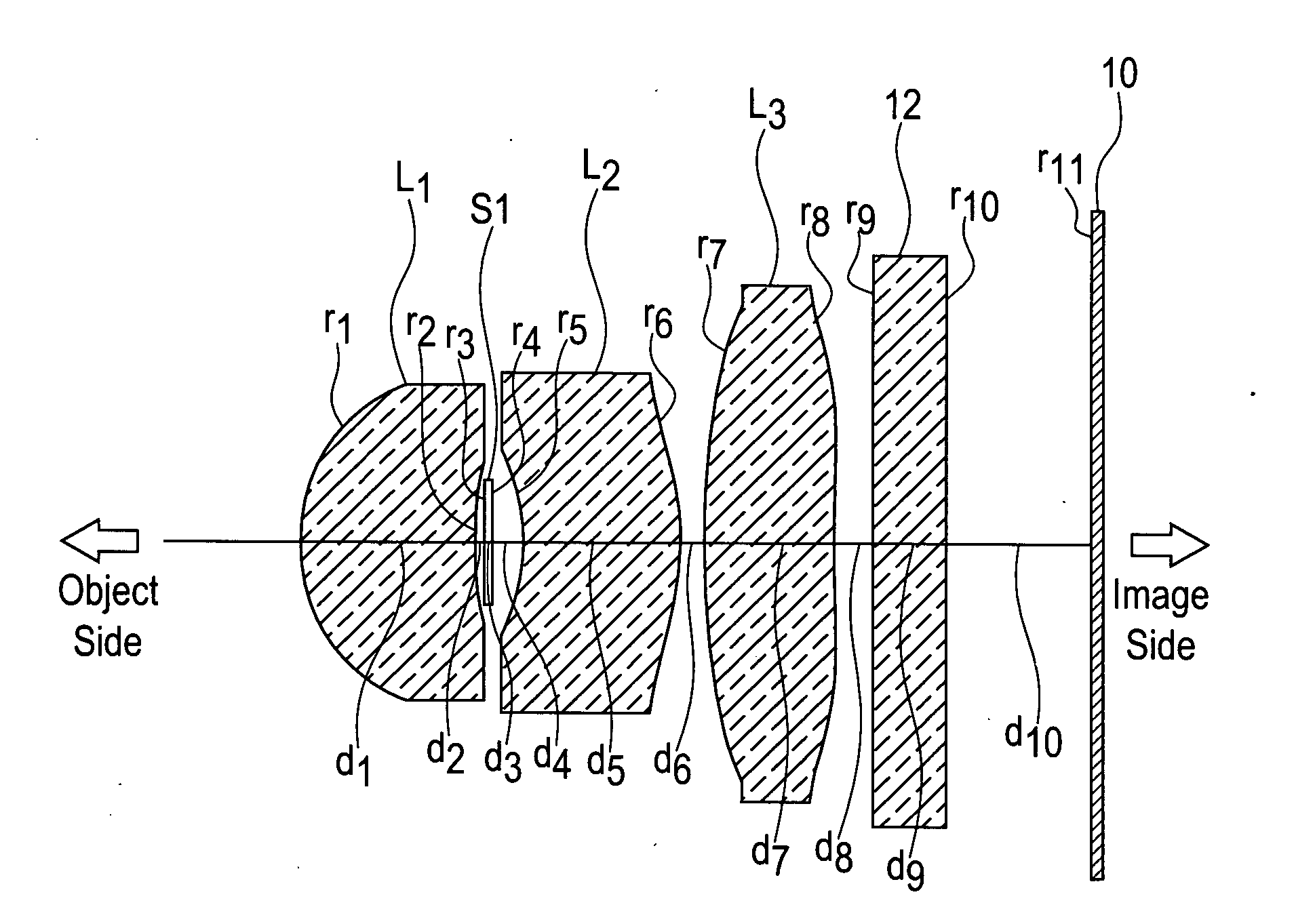
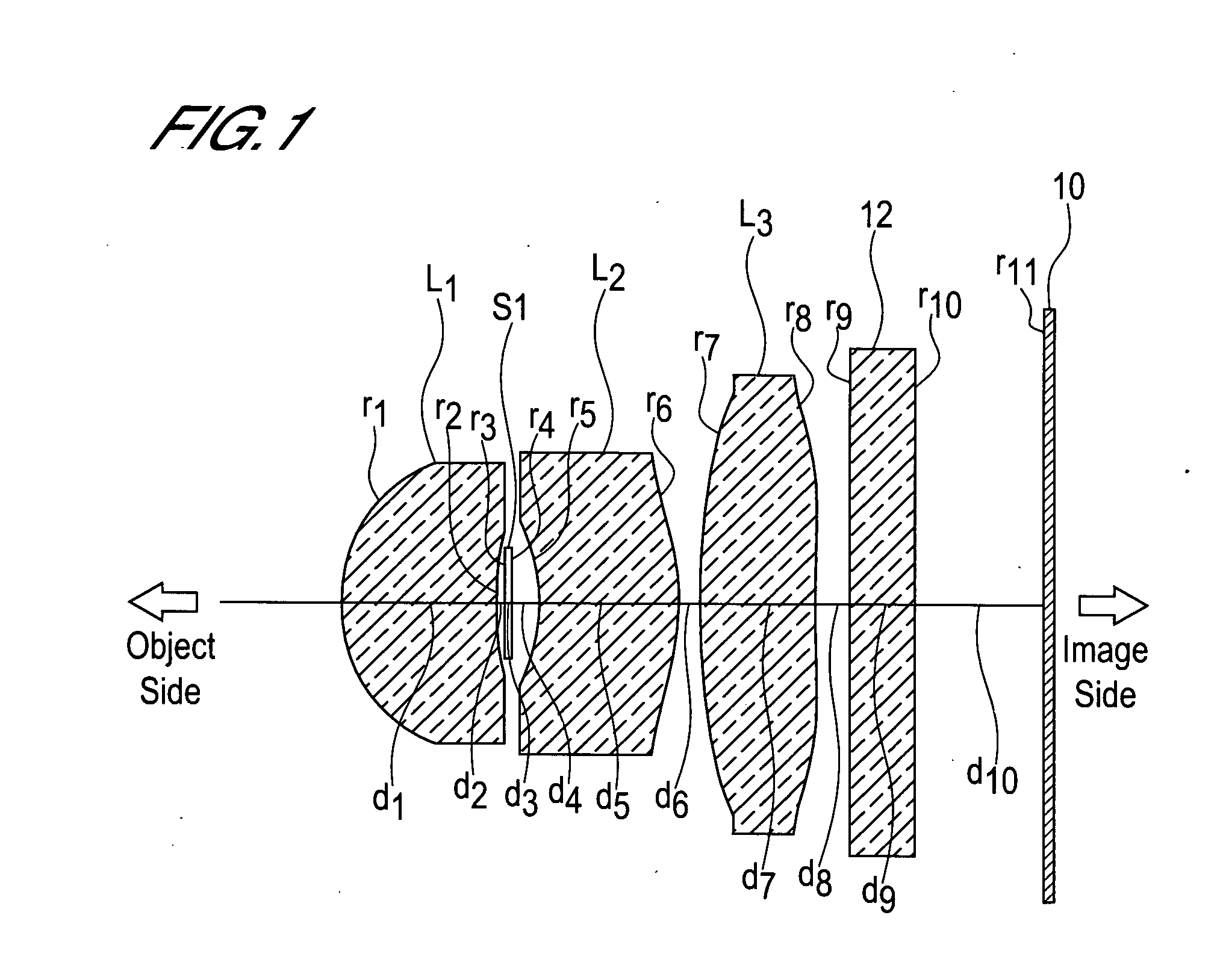
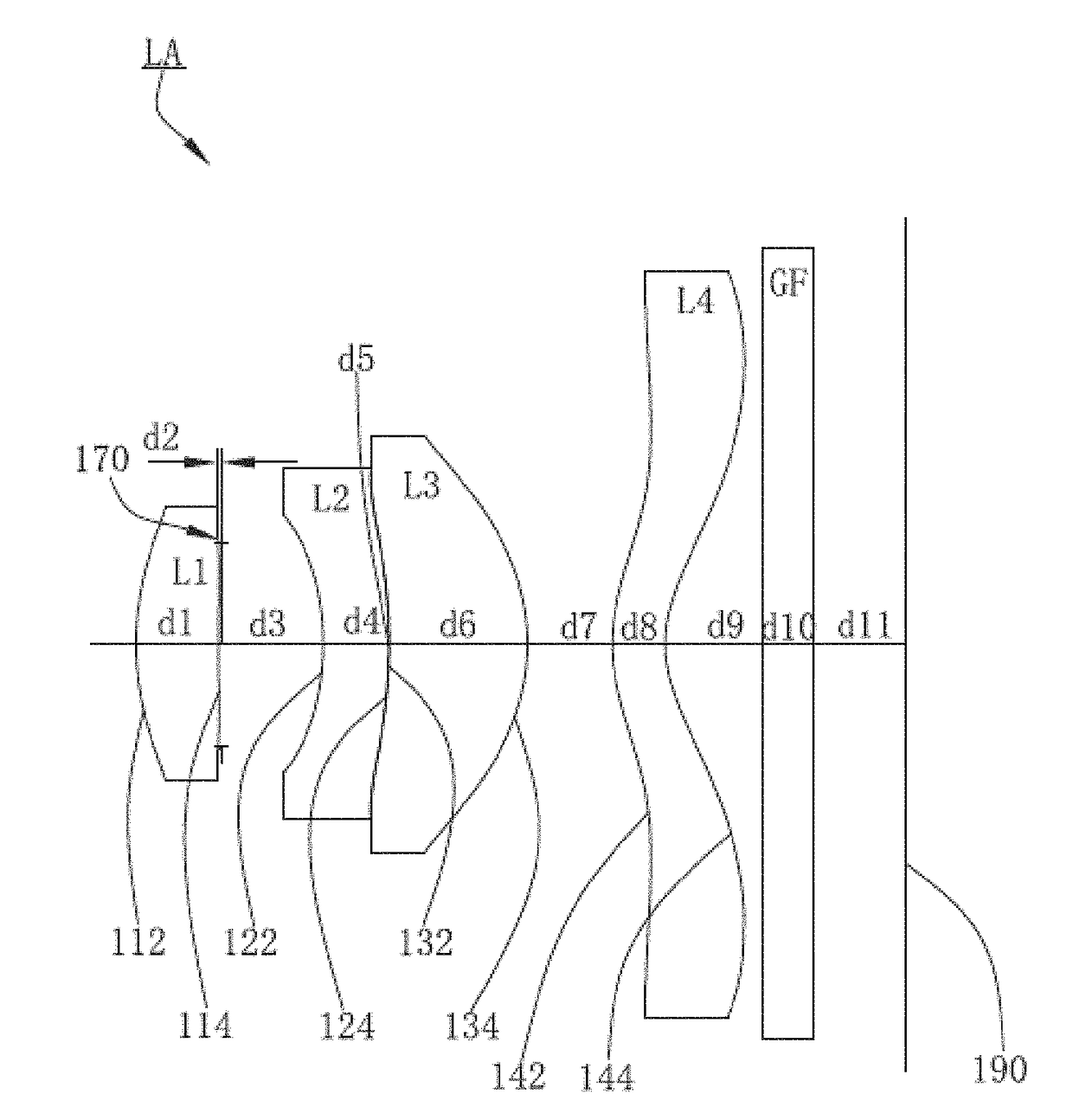
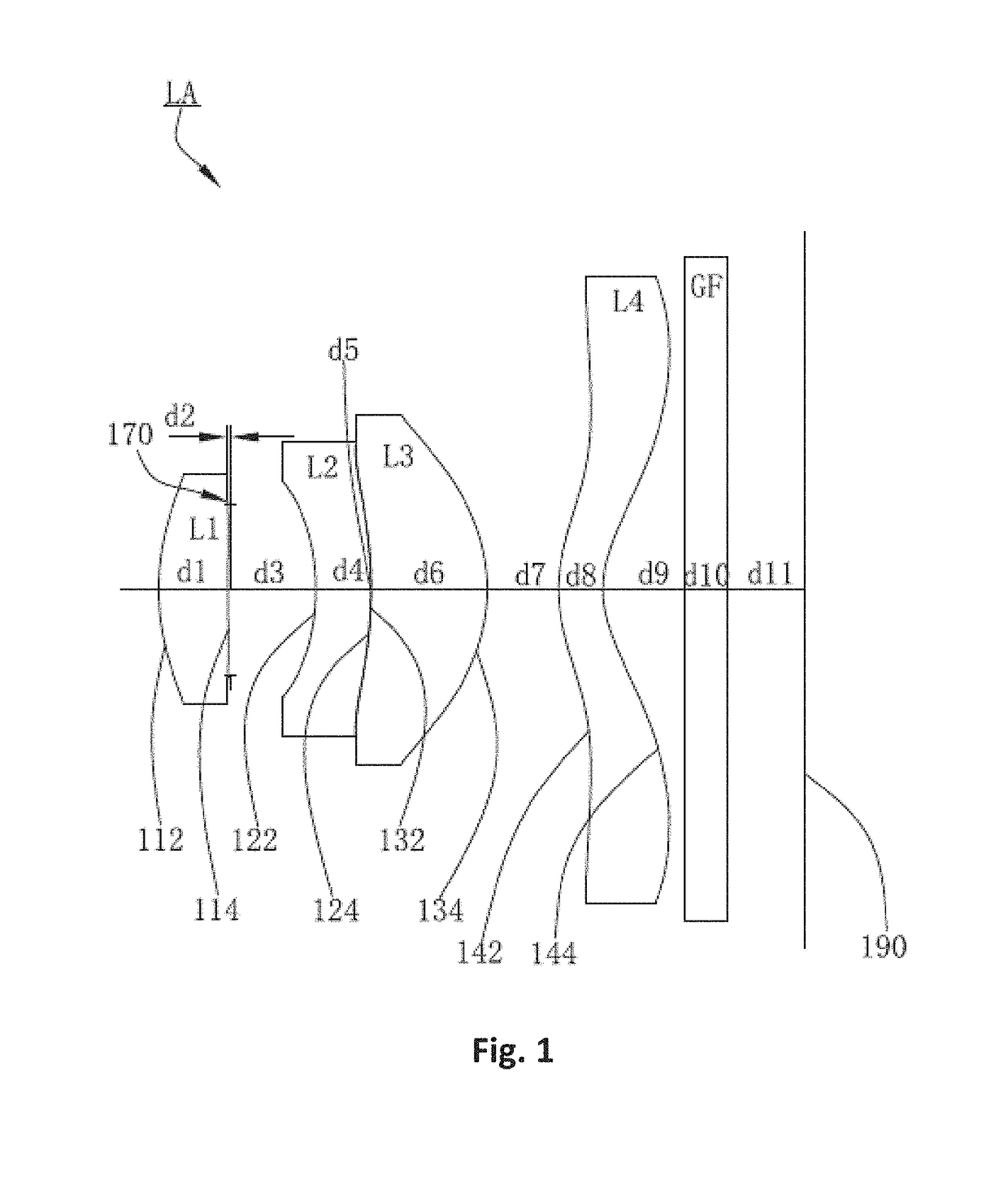
Imaging lens
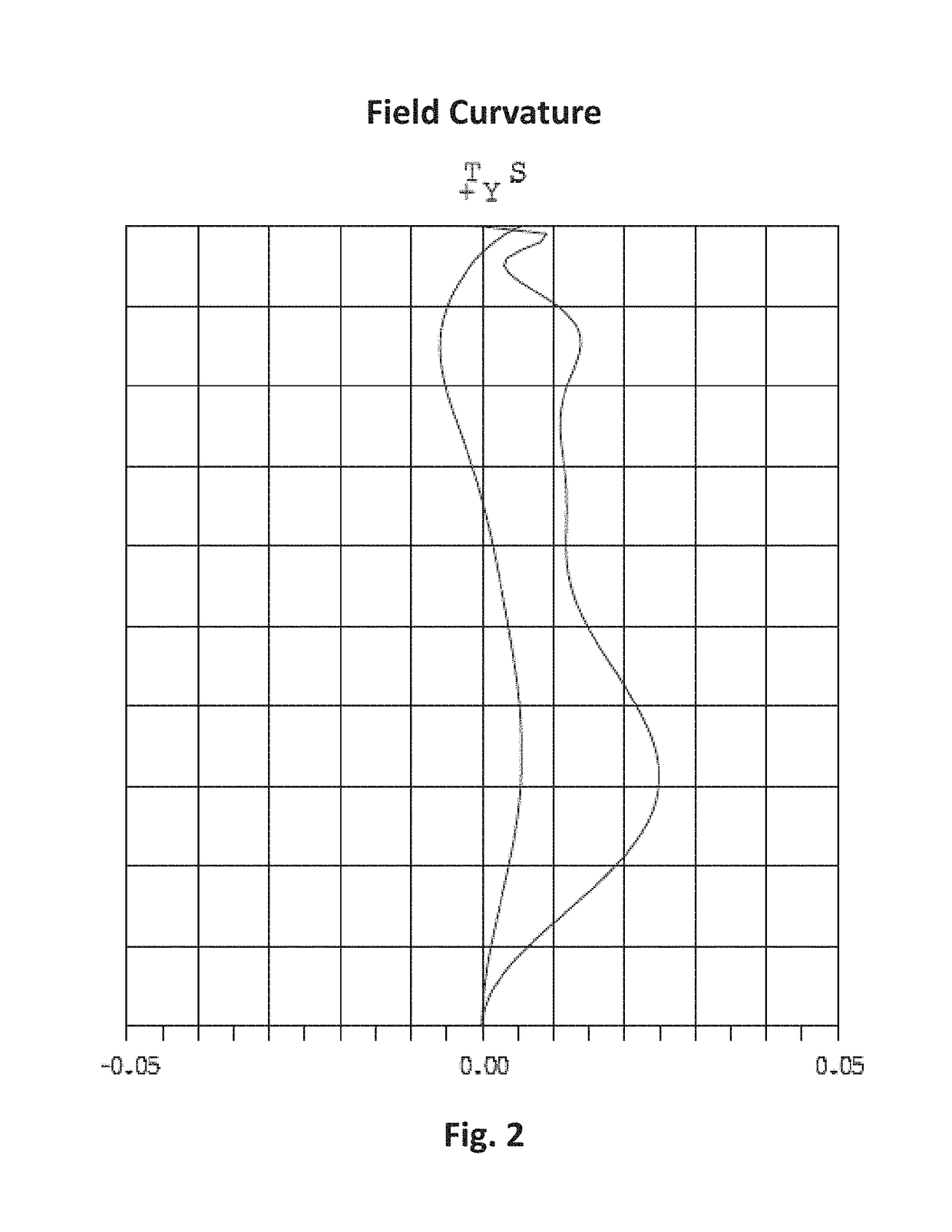
The present invention is an imaging lens in which various aberrations are favorably corrected, the optical length is short, and a sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side. The first lens L1 is a lens having a positive refractive power and a meniscus shape in which the convex surface faces the object side, the second lens L2 is a lens having a negative refractive power and a meniscus shape in which the convex surface faces the image side, and the third lens L3 is a lens in which the convex surface faces the object side. The imaging lens satisfies the following conditions: 0.35<r1 / r2<0.45 (1) 0.07<D2 / f<0.1 (2) 0.01<D4 / f<0.04 (3) 1.00<d / f<1.30 (4) 0.3<bf / f<0.5 (5) where f is the combined focal length of the imaging lens, r1 is the radius of curvature (axial radius of curvature) of the object-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, r2 is the radius of curvature (axial radius of curvature) of the image-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, D2 is the distance between the first lens L1 and second lens L2, D4 is the distance between the second lens L2 and third lens L3, d is the distance (atmospheric) from the object-side surface of the first lens L1 to the imaging surface, and bf is the distance (atmospheric) from the image-side surface of the third lens to the imaging surface.
Owner:MILESTONE CO LTD
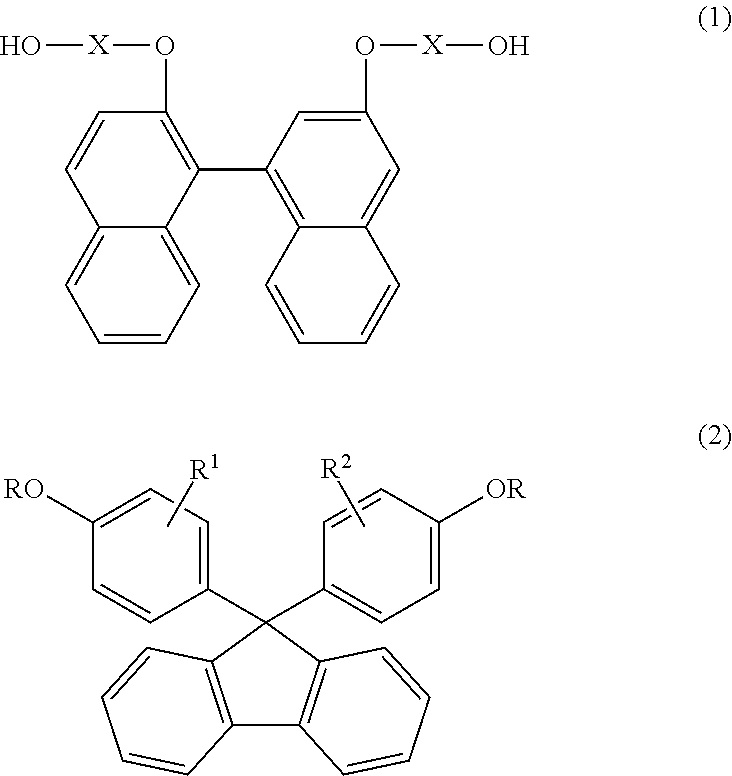
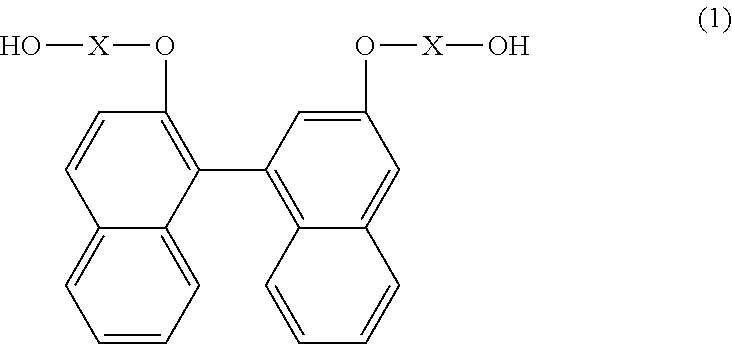
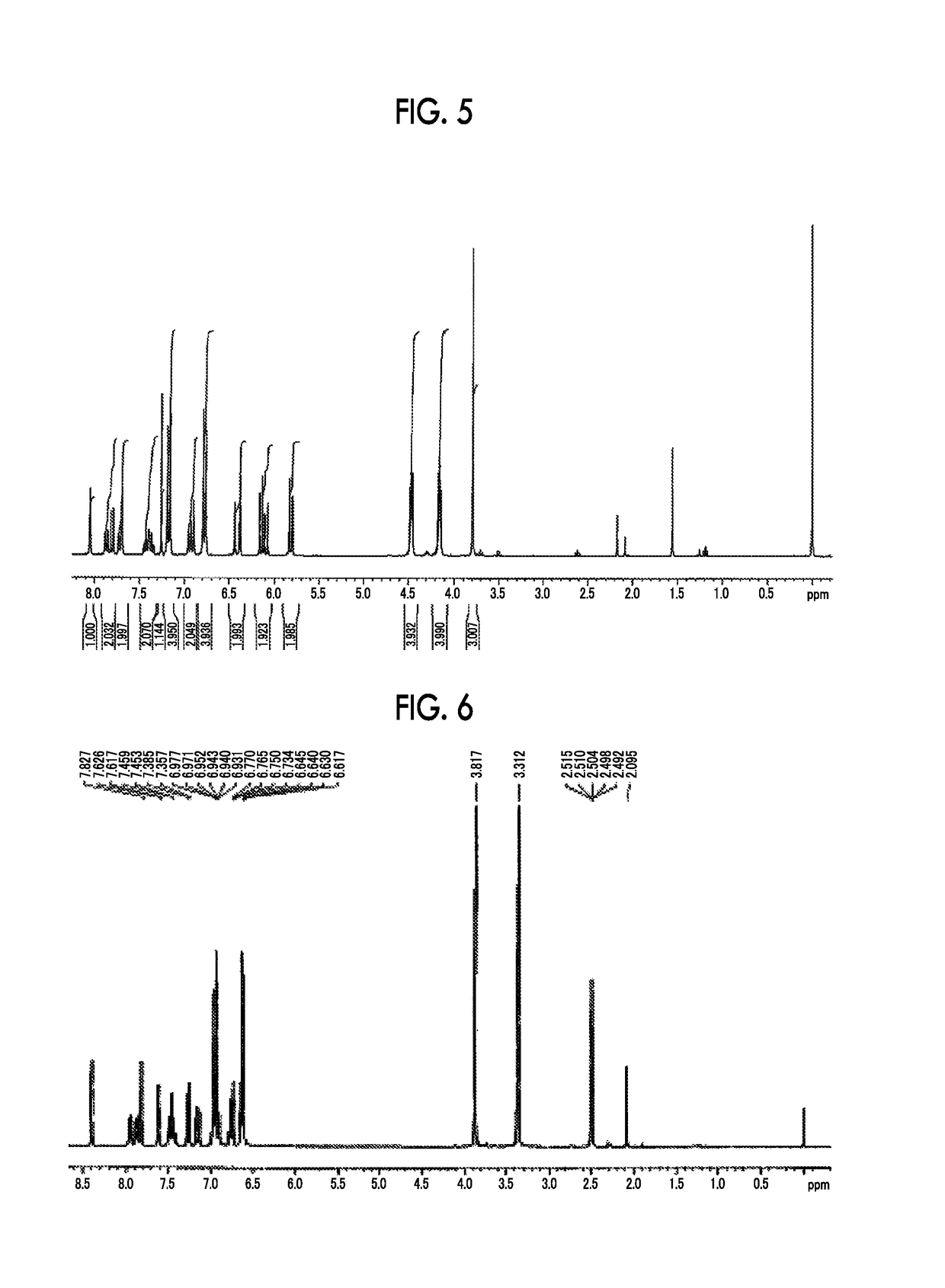
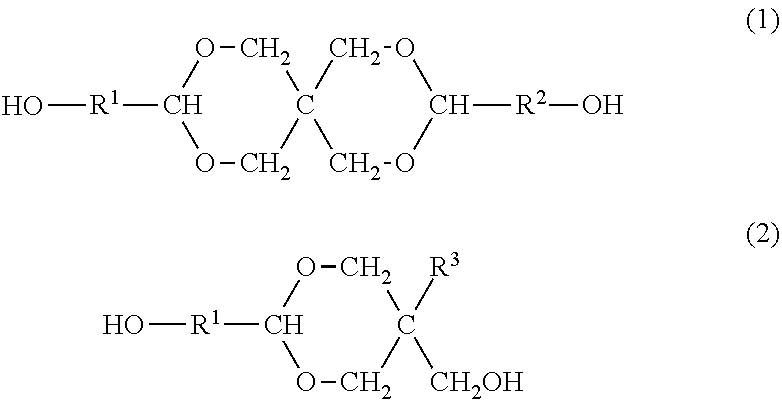
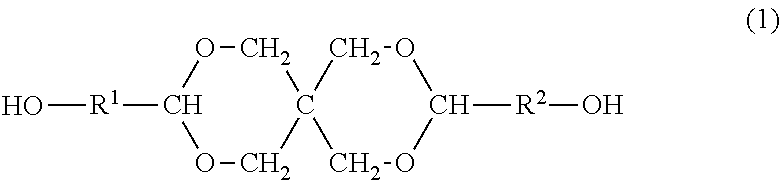
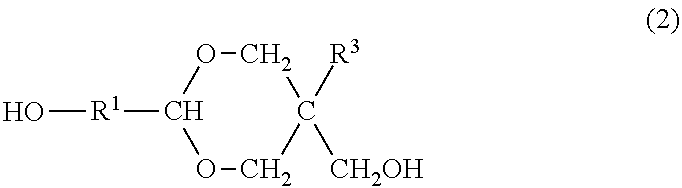
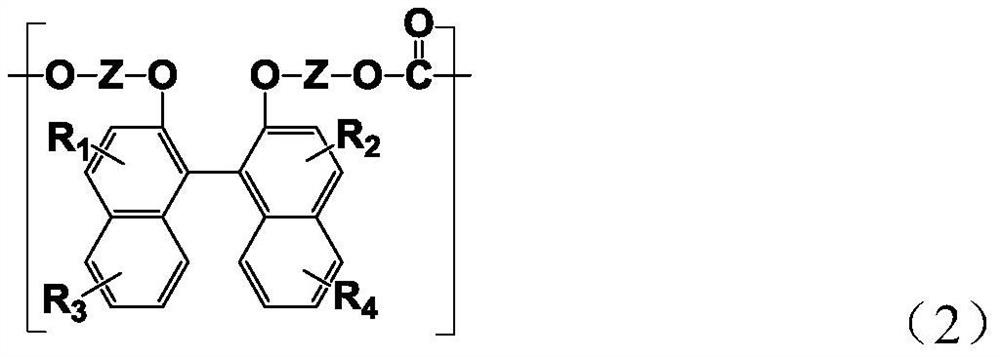
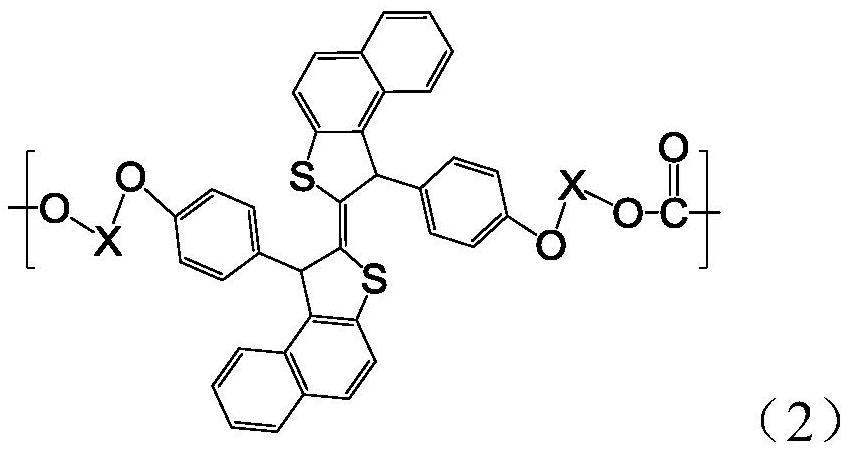
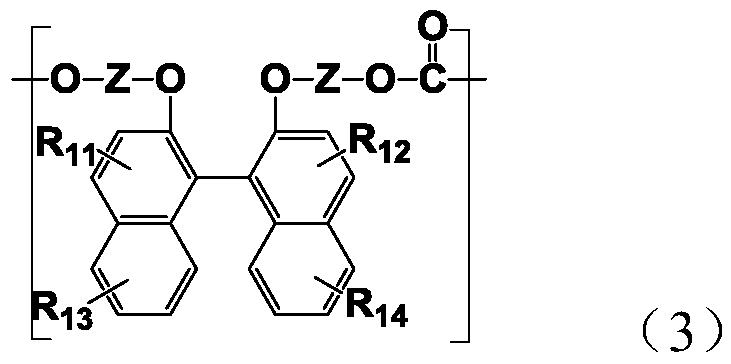
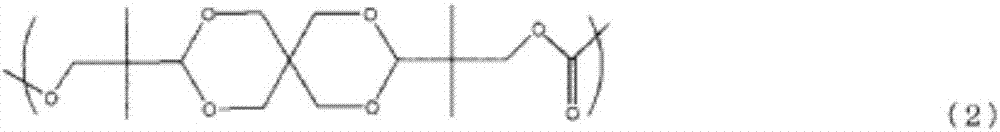
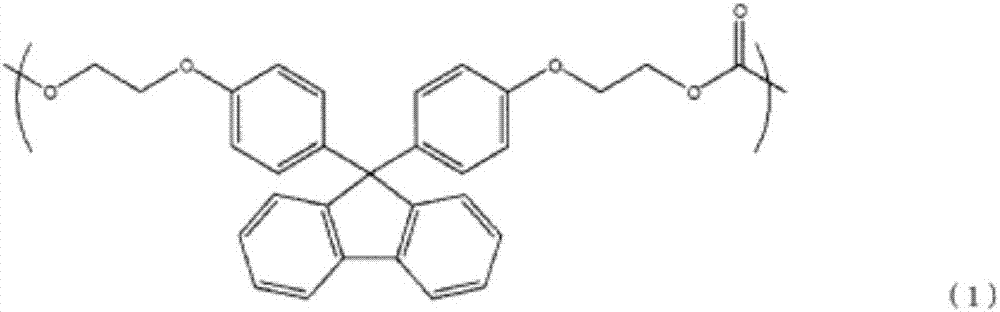
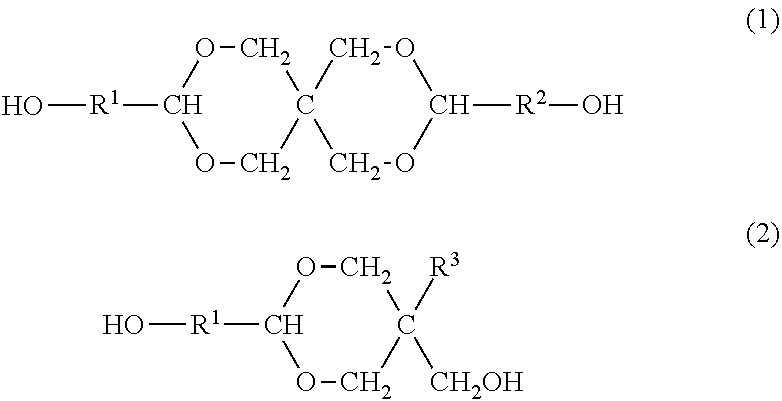
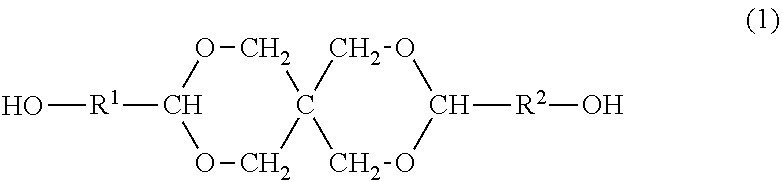
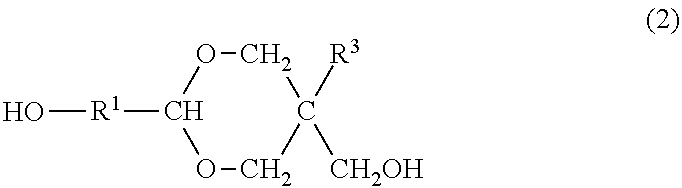
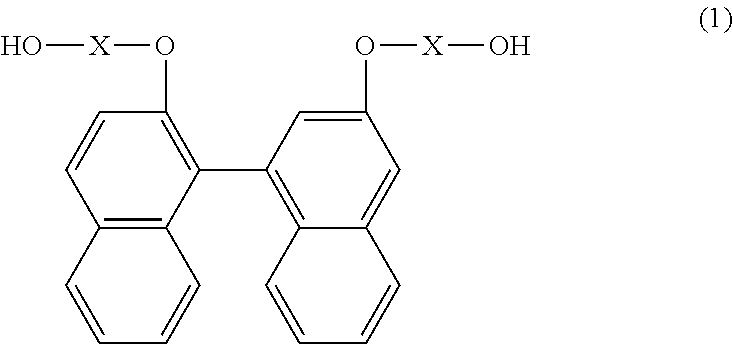
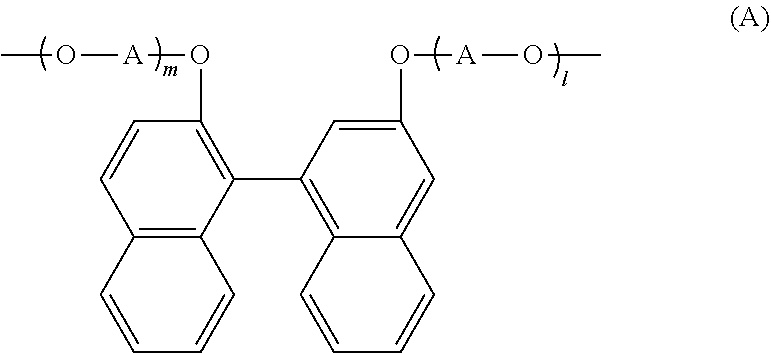
Resin produced by polycondensation, and resin composition
ActiveUS20170044312A1Excellent optical propertiesHigh refractive indexLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationPolyester resinCarboxylic acid
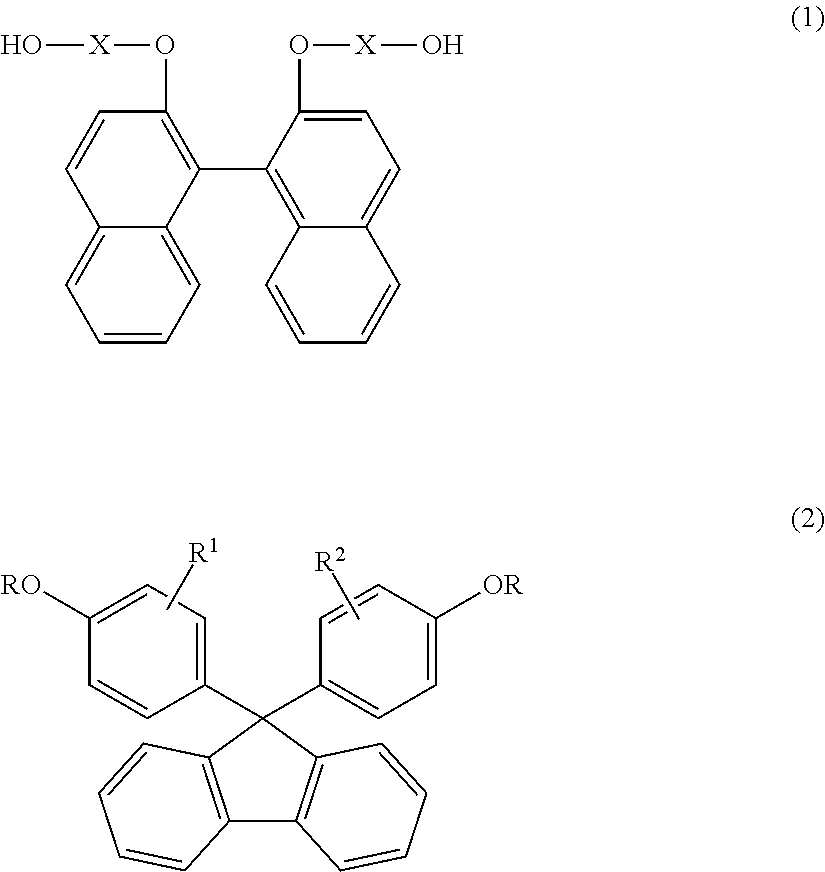
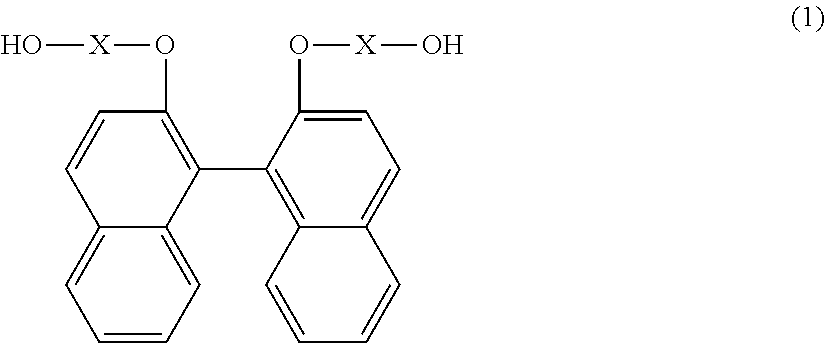
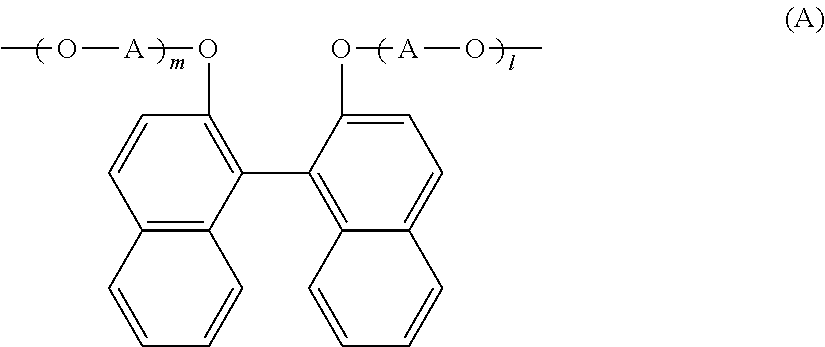
According to one embodiment, a polyester resin is provided, which includes a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (1), a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (2), and a structural unit derived from a dicarboxylic acid or a derivative thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Polarized plate structure
InactiveCN101097269AGood heat resistanceModerate mechanical propertiesPolarising elementsBoard structureOptical film
The present invention relates to a polarized light board structure which is provided with a polarized light layer, a first optical film and a second optical film, the first optical film is formed above the polarized light layer and the second optical film is formed below the polarized light layer, wherein, at least one optical film selected from the first optical film and the second optical film is polymethyl methacrylate optical film. Into the bargain, the optical film is formed by pasting the mixed solution to the polarized light board and doing heat treatment when penetrating the mixed solution and distributing on the substrate to prepare for making have finished, or the optical film is formed by penetrating the mixed solution and distributing on the substrate and doing thermal treatment.
Owner:OPTIMAX TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Curable composition, cured product, optical component, lens, and compound
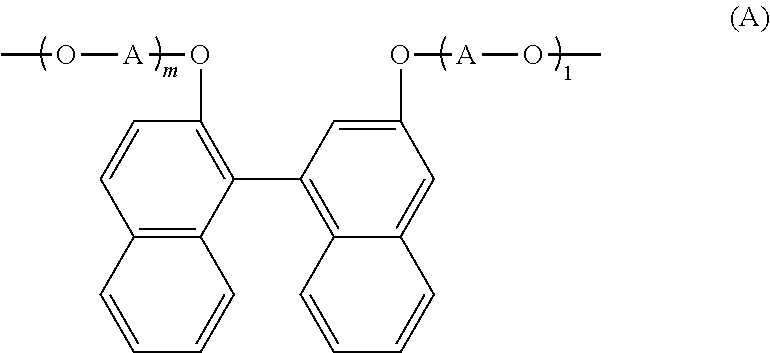
ActiveUS20170342181A1Low Abbe numberIncreased durabilityOrganic chemistryOptical elementsMeth-Viscosity
Disclosed herein are a curable composition which is capable of producing a cured product having a low Abbe's number and increased durability, and a curable composition with suppressed viscosity increase. Provided is a compound represented by General Formula (A). Also provided are a curable composition including a compound represented by General Formula (A), a predetermined (meth)acrylate monomer, and at least one selected from a photoradical polymerization initiator and a thermal radical polymerization initiator; a cured product formed by curing the curable composition; an optical component; and a lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical glass
The invention provides a novel optical glass which has a refractive index (nd) of 1.78 to 2.2 and an Abbe value (νd) of 16 to less than 40 and is suitable for precision mold press molding by virtue of its having a low glass transition temperature, namely, an optical glass which contains by mole in terms of oxides 25 to 60% B2O3, 2 to 45% (in total) TiO2 and Nb2O5 and 1 to 25% WO3 and has a refractive index (nd) of 1.78 to 2.2 and an Abbe value (νd) of 16 to less than 40. Further, the glass contains 5 to 35% La2O3 and 1 to 40% ZnO and has a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 700° C. or below. The optical glass is excellent in meltability, stability and devitrification resistance and has a high refractive index, high light-dispersive power and excellent precision press moldability.
Owner:OHARA
Optical lens
ActiveUS20110109980A1High refractive indexLow Abbe numberOptical articlesMountingsPolymer scienceRefractive index
An optical lens formed of a polyester resin having a high refractive index, a low Abbe number and good moldability is provided.The optical lens is obtained by injection-molding a polyester resin containing a diol unit containing from 40 to 99% by mol of a unit derived from ethylene glycol and from 1 to 60% by mol of a unit derived from a diol having from 3 to 16 carbon atoms, and a dicarboxylic acid unit containing 50% by mol or more of a unit derived from a naphthalenedicarboxylic acid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
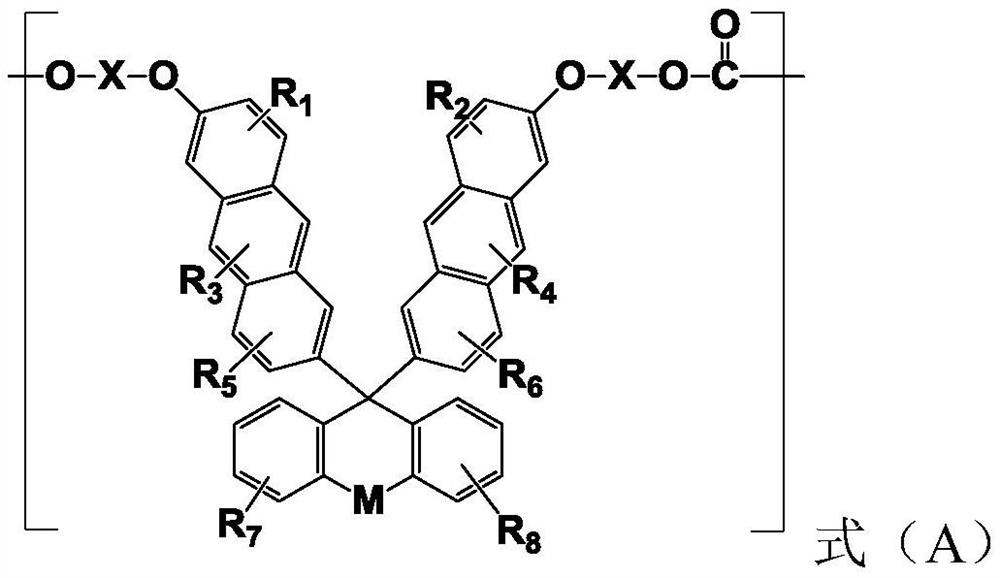
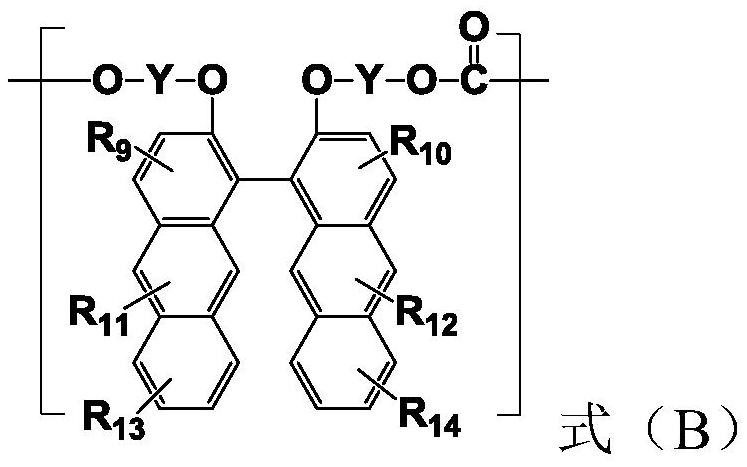
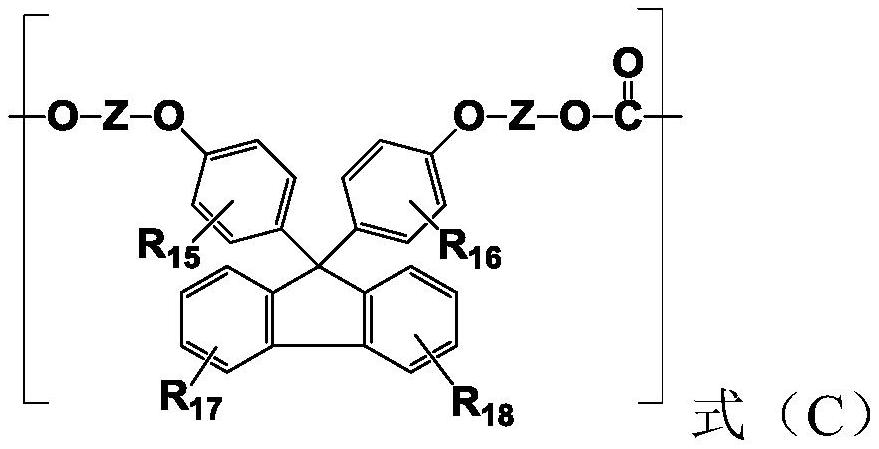
Polycarbonate resin with stable high refractive index as well as preparation method and application of polycarbonate resin
ActiveCN112961336AHigh refractive indexLow Abbe numberOptical elementsPolymer scienceRefractive index
The invention provides stable polycarbonate resin with high refractive index and a preparation method and application thereof. The polycarbonate resin comprises a structural unit as shown in a formula A and optional structural units as shown in a formula B and a formula C. The polycarbonate resin is high in refractive index, good in stability, and capable of meeting the use requirements of optical lenses; the manufacturing method is simple, and has the industrial application prospect.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Curable composition and cured product thereof
InactiveCN102369225AModerate viscosityEasy to operateOptical elementsEnvironmental resistanceSilane compounds
Disclosed is a curable composition having a proper viscosity and excellent handing properties. Also disclosed is a cured article which is characterized by being produced by curing the curable composition, having excellent transparency, heat resistance and environmental resistance and a low Abbe's number, and which, when produced using the curable composition in combination with a material having a high Abbe's number, can have a reduced chromatic aberration. The curable composition is characterized by comprising (a) silica microparticles, (b) a (meth)acrylate compound having at least two ethylenically unsaturated groups and having no ring structure, (c) a (meth)acrylate compound having at least two ethylenically unsaturated groups and also having an aromatic ring structure, and (d) a polymerization initiator, wherein the surfaces of the silica microparticles (a) are treated with a specific silane compound (e) and a specific silane compound (f).
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Optical polycarbonate, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an optical polycarbonate resin for an optical lens, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the polycarbonate resin comprises a structural unit as shown in a general formula (1), and has higher refractive index, better hardness and proper processing temperature. The optical lens prepared from the polycarbonate resin has the advantages of high refractive index,low Abbe number and high stability, so the optical lens can be used in the high-end fields of telescopes, binocular telescopes, unmanned lenses, VR / AR lenses and the like.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Polycarbonate resin, method for producing same, and optical lens
ActiveUS20190241703A1Excellent heat and humidity resistanceLow Abbe numberOptical elementsPolymer scienceRefractive index
The present invention provides a polycarbonate resin having a high refractive index, low Abbe number, and high moist heat resistance. The above problem, according to one embodiment, can be solved by a polycarbonate resin including structural units represented by general formula (1).
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
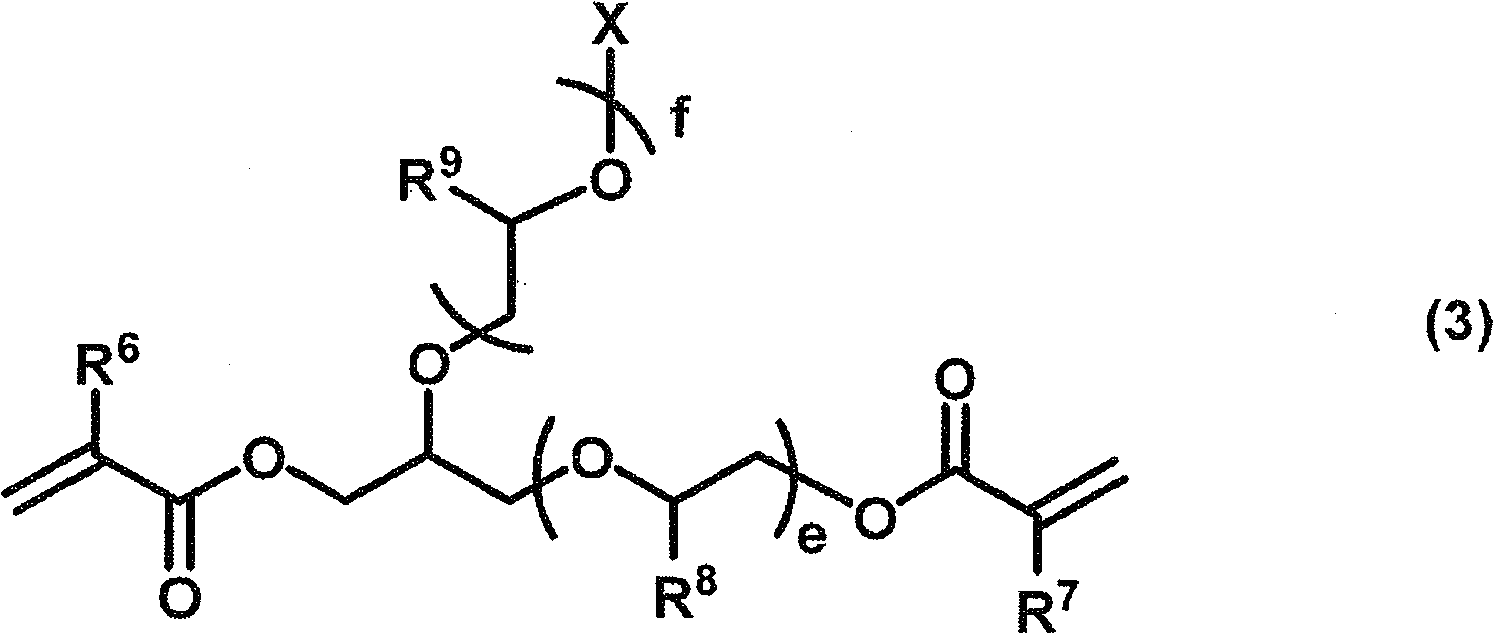
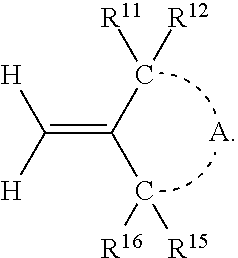
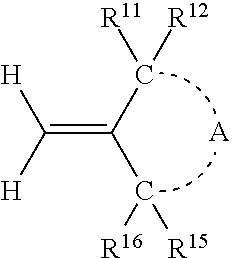
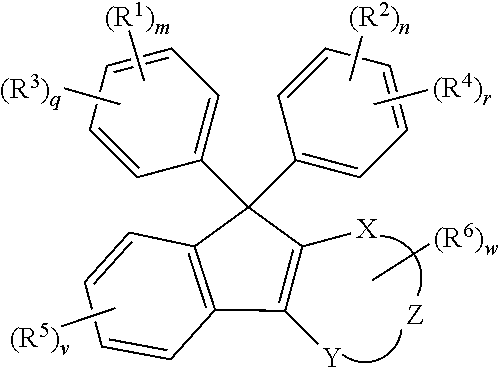
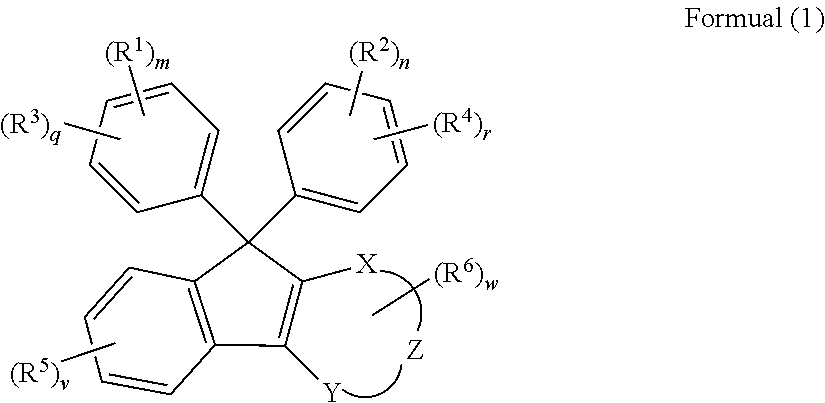
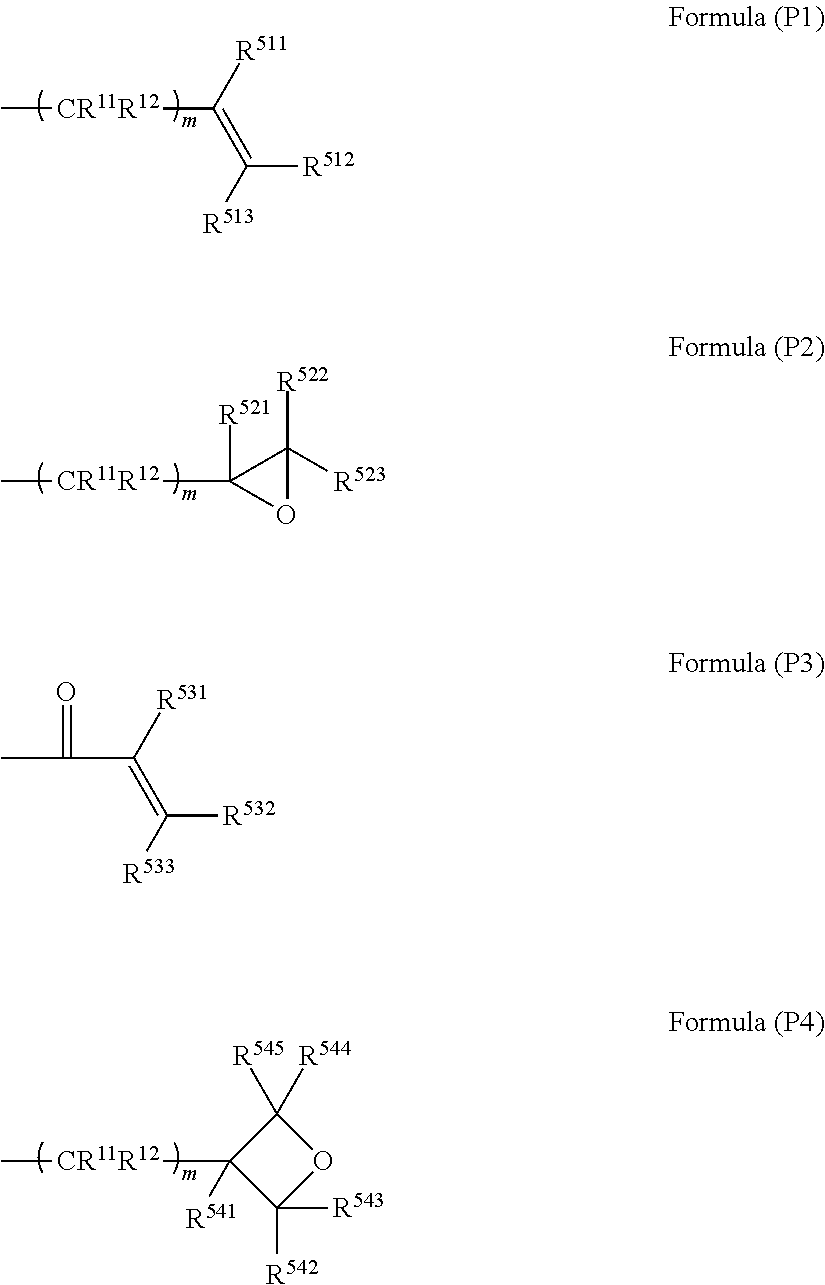
Semi-cured product, cured product and method of manufacturing same, optical component, curable resin composition
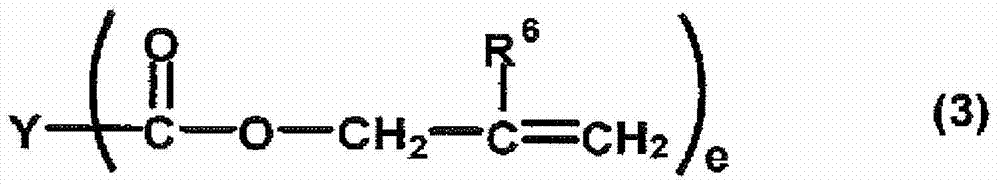
A curable resin composition comprising a (meth)acrylate monomer having an aromatic ring, a non-conjugated vinylidene group-containing compound represented by the general formula below, and a thermal or a photo-radical polymerization initiator makes it possible to produce a cured product with minimized occurrence of burring during molding and high product yield after molding. The cured product has good heat coloration resistance and low Abbe's number. R11, R12, R15, and R16 represent a substituent and A represents an atomic group necessary for forming a cyclic structure.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical polycarbonate resin, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses optical polycarbonate resin for an optical lens, a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the polycarbonate resin comprises a structural unit shown in a general formula (1), can reach a high refractive index of 1.7 or above and has good hardness and a proper processing temperature. The optical lens prepared from the polycarbonate resin has the advantages of high refractive index, low Abbe number and high stability, so the optical lens can be used in the high-end fields of telescopes, binocular telescopes, unmanned lenses, VR / AR lenses and the like.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Optical polycarbonate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses optical polycarbonate and a preparation method thereof, the optical polycarbonate comprises a structural unit shown in the following general formula (1), and the structural unit can be prepared by reacting a dihydroxy compound corresponding to the structure of the general formula (1) with carbonic acid diester. The obtained polycarbonate resin is high in refractive index and easy to form, and can be applied to the field of optical polycarbonate such as optical lenses.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
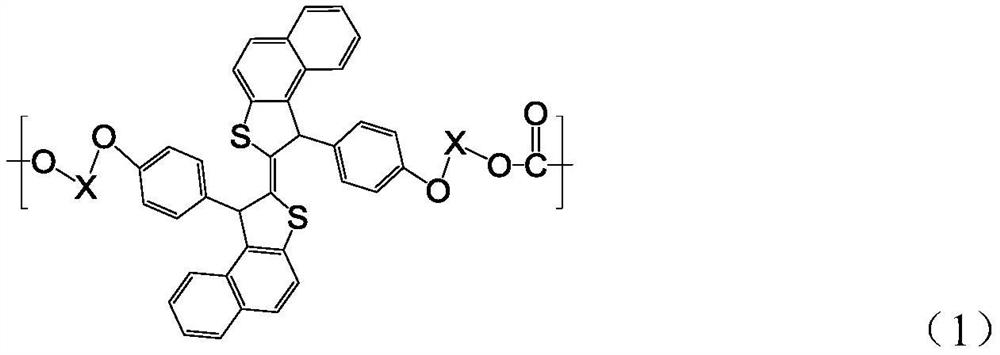
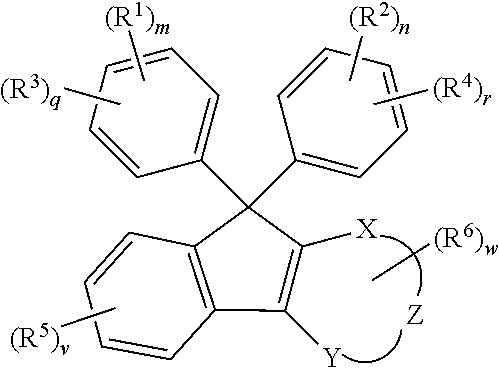
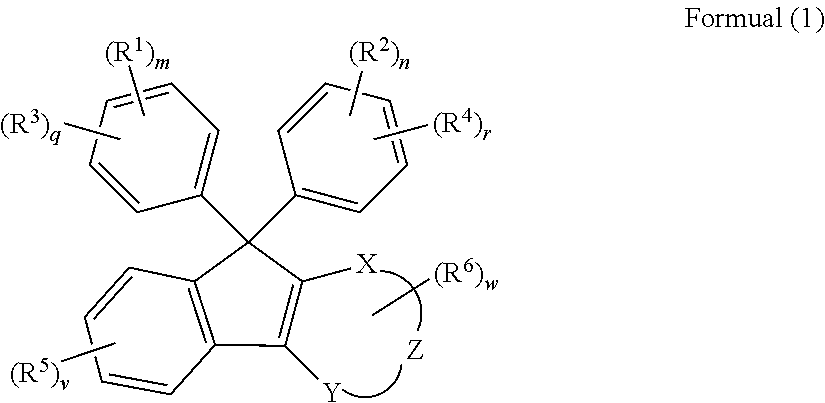
Compound, curable composition, cured product, optical member, and lens
ActiveUS20180305486A1Low Abbe numberHigh abnormal dispersibilityOrganic chemistryOptical elementsMedicinal chemistryAbbe number
A cured product of a compound of the following formula has a low Abbe number and a high abnormal dispersibility. X and Y are O, S, N or S; Z and X—C═C—Y form 5 to 7-membered ring; R1 and R2 represents H, alkoxy, mercapto, thioalkoxy, amino, alkylamino, carboxy, alkylcarbonyloxy, carbamoyloxy or alkoxycarbonyloxy; and R3 to R6 represent substituent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polycarbonate resin, preparation method and formed optical component
ActiveCN112250852AIncrease the number ofImprove thermal stabilityOptical elementsArylPolymer science
The invention provides polycarbonate resin, a preparation method and a formed optical component. The polycarbonate resin comprises polycarbonate with a structural unit as shown in the following formula; In the formula, R1-R2 each independently represents a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, an alkyl group having 1-20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1-20 carbon atoms, a cyclic carbon group having 5-20 carbon atoms, a cyclic carbon oxygen group having 5-20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6-20 carbon atoms, or an aryloxy group having 6-20 carbon atoms; X represents an alkylene group having1-6 carbon atoms; and n is any integer between 1 and 10. The polycarbonate resin prepared by the invention has the advantages of high refractive index, low birefringence and small Abbe number.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
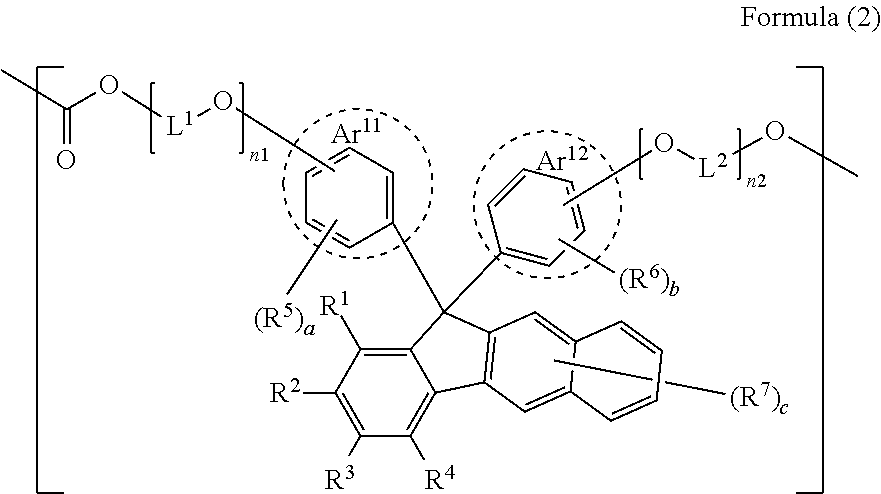
Imaging lens
An imaging lens comprising a polycarbonate that contains formulae (1) and (2) in the proportions indicated below, said imaging lens having a specific refractive index and Abbe number, and having the physical characteristics of a low birefringence and coefficient of water absorption. 50 mol%<=(1)<70 mol%; 30 mol%<(2)<=50 mol%.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
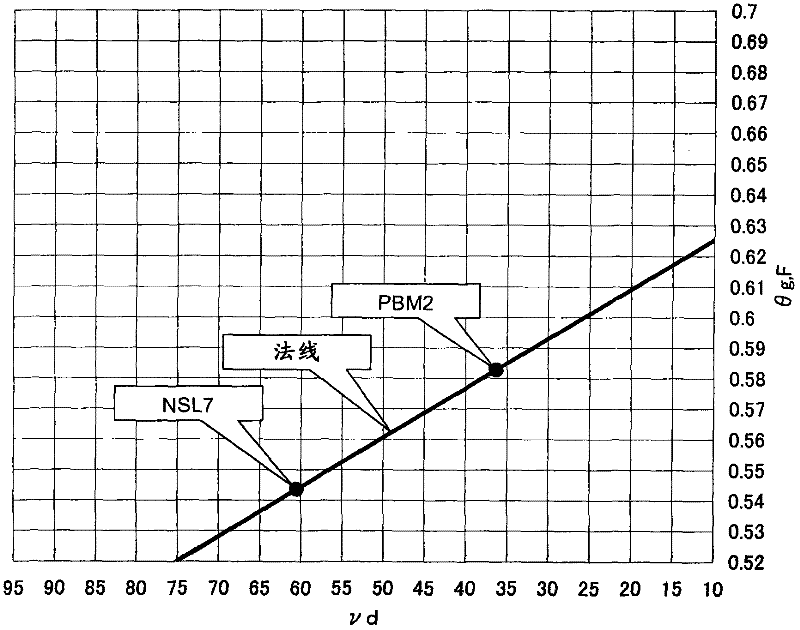
Optical glass, pre-form body and optical element
InactiveCN102603186AIncrease Partial DispersionHigh partial dispersionOptical elementsOptical glassChromatic aberration
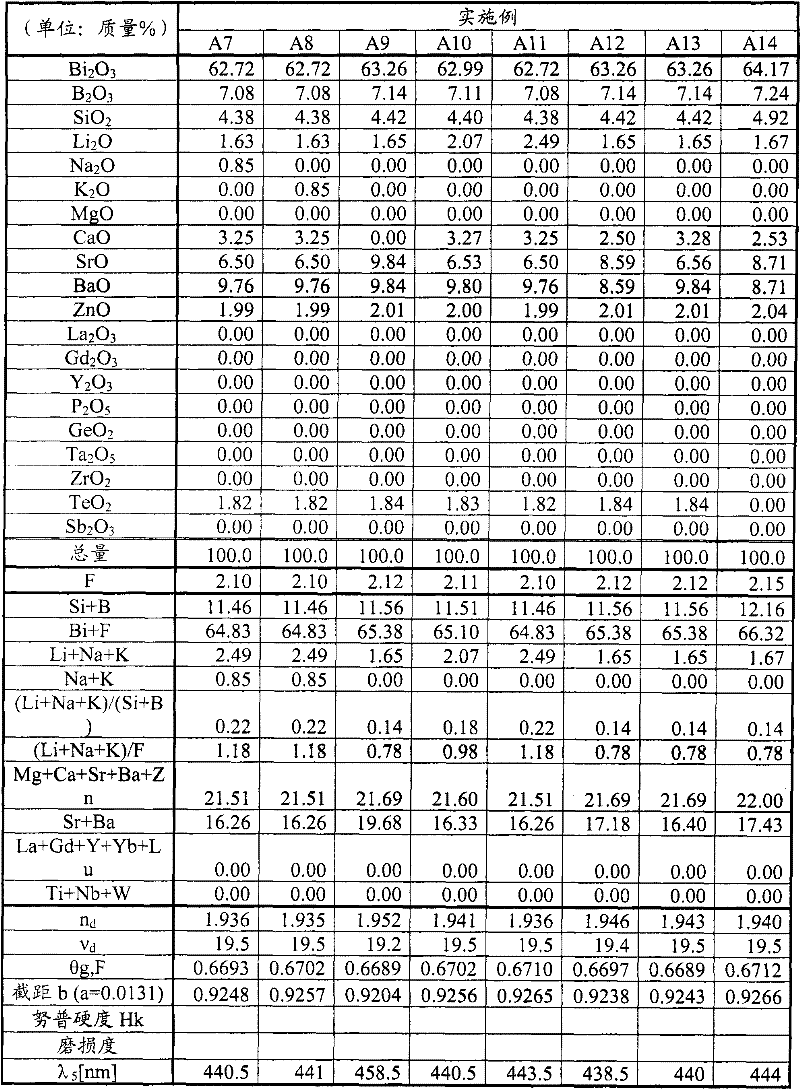
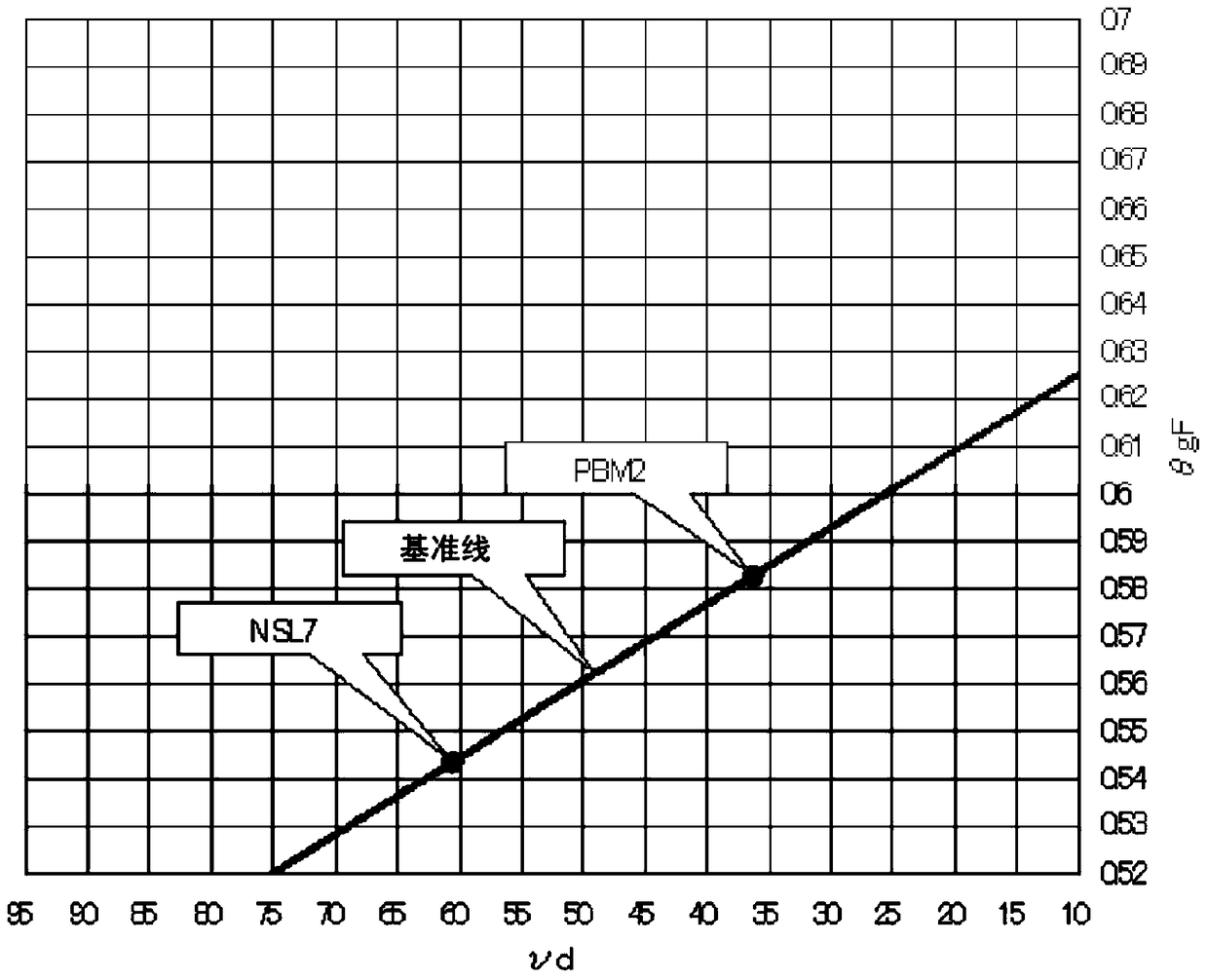
The invention provides an optical glass useful for correcting chromatic aberration of optical elements and a pre-form body using the optical glass. The optical glass satisfies the following conditions: according to components converted into oxide, the optical glass comprises Bi2O2, SiO2 and / or B2O3 and F components; a part dispersion rate [theta g,F] is more than 0.63; an abbe number [vd] is below 27; the part dispersion rate [theta g,F] is greater than -0.0131*[vd]+0.9000.
Owner:OHARA
Resin produced by polycondensation, and resin composition
ActiveUS20200190259A1Excellent optical propertiesHigh refractive indexLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationPolymer scienceDicarboxylic acid
According to one embodiment, a polyester resin is provided, which includes a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (1), a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (2), and a structural unit derived from a dicarboxylic acid or a derivative thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
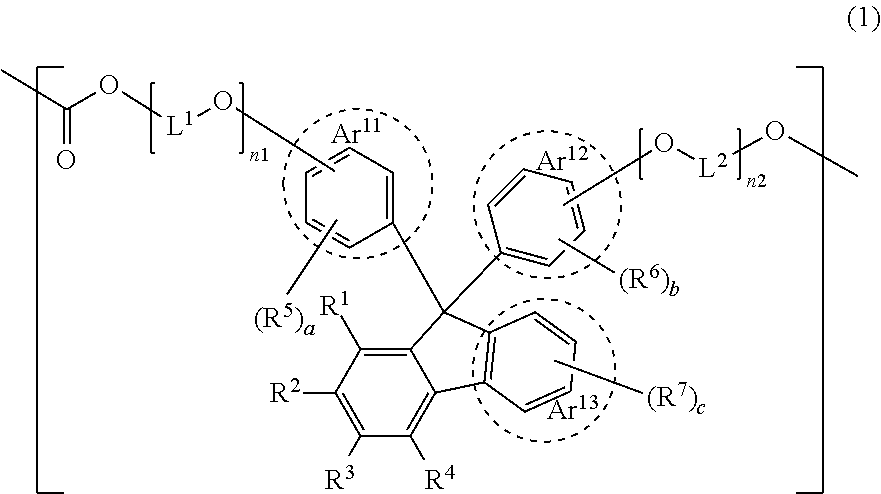
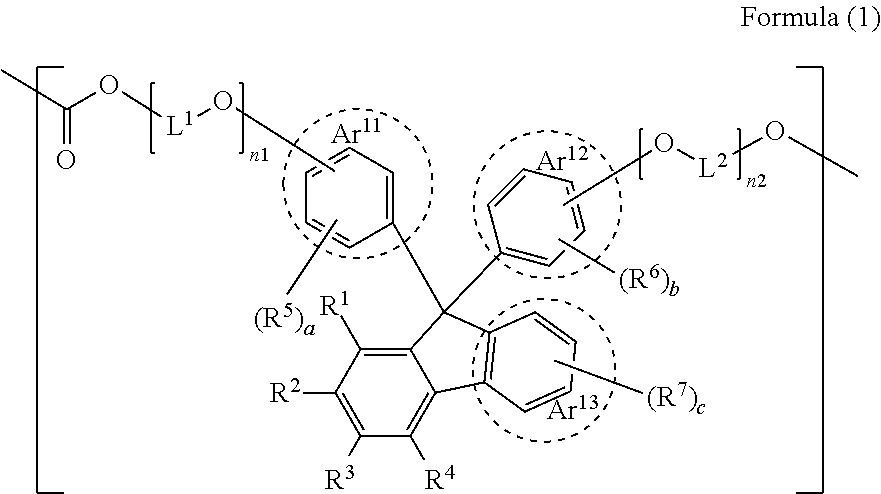
Polycarbonate resin, molded article, optical member, and lens
Disclosed is a polycarbonate resin including a constitutional unit represented by Formula (1). The resin provides a molded article having a sufficiently low Abbe number and excellent durability under high temperature and high humidity. R1 to R4 are a hydrogen atom or a substituent having σp of less than −0.15, R5 to R7 represent a substituent, Ar11 and Ar12 represent an aryl or heteroaryl group, and Ar13 is an aromatic fused ring group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Curable composition and cured product
ActiveUS20180273656A1High Abbe numberImprove crack resistancePigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsMeth-Metal
To provide a curable composition whereby it is possible to obtain a cured product having a high Abbe number and being excellent in transparency, crack resistance and releasability; and such a cured product. A curable composition comprises, in specific ratios, surface-modified metal oxide particles (A) having (meth)acryloyl-group-containing surface-modifying groups on the surface of the metal oxide particles, a compound (B) having a fluorine atom and at least one (meth)acryloyl group, a compound (C) having a urethane bond or —OCH2CH(OH)CH2—, having at least two (meth)acryloyl groups and having a mass-average molecular weight of at least 1,000, a compound (D) having no unsaturated bond-containing ring structure and having at least one (meth)acryloyl group, and a polymerization initiator (E).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
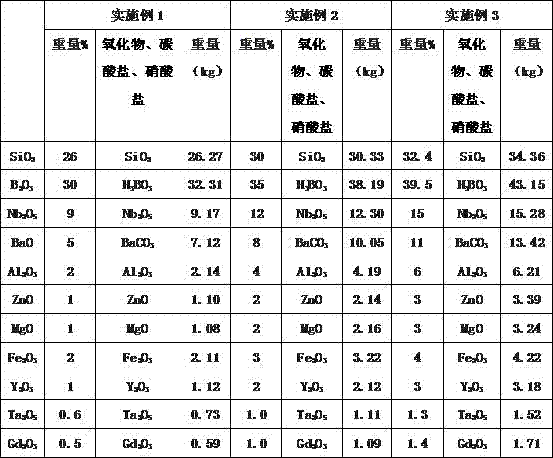
Optical glass
The invention discloses optical glass, which is prepared from the following ingredients (by weight): 26-34% of SiO2, 30-40% of B2O3, 9-15% of Nb2O5, 5-11% of BaO, 2-6% of Al2O3, 1-3% of ZnO, 1-3% of MgO, 2-4% of Fe2O3, 1-3% of Y2O3, 0.6-1.4% of Ta2O5, and 0.5-1.5% of Gd2O3. The content and processing meet the following requirements: total content of SiO2 and B2O3 is between 56% and 73%; total content of Ta2O5 and Gd2O3 is less than or equal to 2.8%; transition temperature Tg is below 650 DEG C; and liquidus temperature LT is not higher than 910 DEG C. Through the above composition, high refractive index and low dispersivity are ensured. In addition, the optical glass of the invention is low-cost, has low density, and has excellent properties such as low tendency towards devitrification, high transmittance and the like. It can be known through the relative grinding hardness FA that the optical glass has good processability. In addition, the glass with high refraction and low Abbe number can make up and correct chromatic aberration to minimize chromatic aberration within the narrowest range, and low-cost operation and batch production can be realized in a stable state.
Owner:合肥协耀玻璃制品有限公司
Optical lens
ActiveUS8233225B2High refractive indexLow Abbe numberOptical articlesMountingsPolymer scienceDicarboxylic acid
An optical lens is obtained by injection-molding a polyester resin containing a diol unit containing from 40 to 99% by mol of a unit derived from ethylene glycol and from 1 to 60% by mol of a unit derived from a diol having from 3 to 16 carbon atoms, and a dicarboxylic acid unit containing 50% by mol or more of a unit derived from a naphthalenedicarboxylic acid.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Curable composition and cured substance thereof
The present invention provides a curable composition, wherein a cured material obtainable by curing the curable composition has excellent transparency, thermal durability and surface hardness and has a small Abbe number. In particular, the present invention provides a curable composition containing (a) silica fine particles; (b) a (meth)acrylate compound having two or more ethylenically unsaturated groups; (c) a (meth)allyl compound having two or more ethylenically unsaturated groups and having an aromatic ring structure; and (d) a polymerization initiator; wherein the surface of the silica fine particles (a) has been treated with a specified silane compound (e) and a specified silane compound (f).
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Camera Lens
A camera lens is disclosed. The camera lens includes, in an order from an object side to an image side, a first lens with a positive refractive power; a second lens with a negative refractive power; a third lens with a positive refractive power; and a fourth lens with a negative refractive power. The camera lens further satisfies specific conditions.
Owner:AAC OPTICS SOLUTIONS PTE LTD
Polycarbonate resin, method for producing same, and optical lens
ActiveUS20200354516A1Excellent heat and humidity resistanceLow Abbe numberOptical elementsPolymer scienceRefractive index
A polycarbonate resin having a high refractive index, low Abbe number, and high moist heat resistance that includes structural units represented by general formula (1):
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Compound, curable composition, cured product, optical member, and lens
ActiveUS10370473B2Low Abbe numberHigh abnormal dispersibilityOrganic chemistryOptical elementsMedicinal chemistryAbbe number
A cured product of a compound of the following formula has a low Abbe number and a high abnormal dispersibility. X and Y are O, S, N or S; Z and X—C═C—Y form 5 to 7-membered ring; R1 and R2 represents H, alkoxy, mercapto, thioalkoxy, amino, alkylamino, carboxy, alkylcarbonyloxy, carbamoyloxy or alkoxycarbonyloxy; and R3 to R6 represent substituent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Resin produced by polycondensation, and resin composition
ActiveUS10689486B2Excellent optical propertiesHigh refractive indexLight-sensitive devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationPolymer scienceDicarboxylic acid
According to one embodiment, a polyester resin is provided, which includes a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (1), a structural unit derived from a compound represented by general formula (2), and a structural unit derived from a dicarboxylic acid or a derivative thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
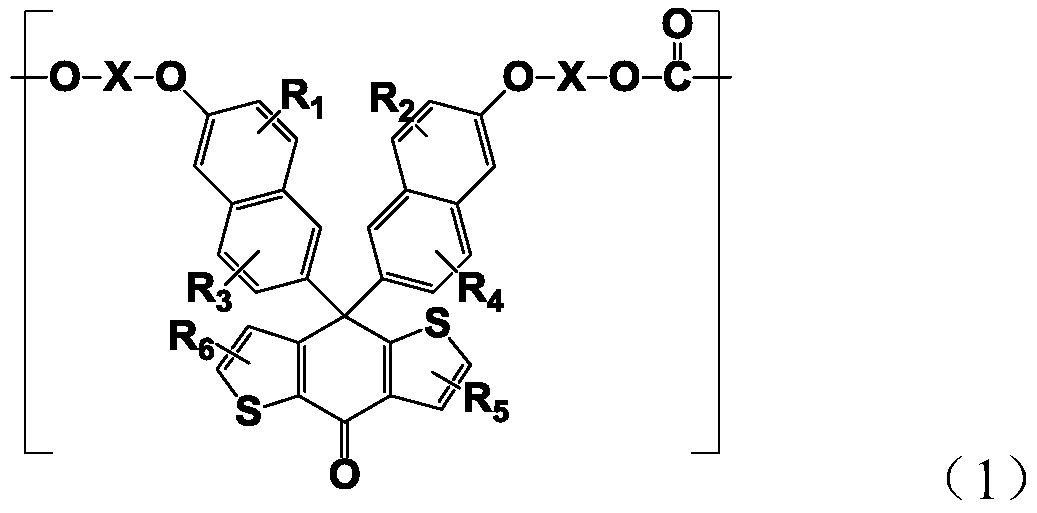
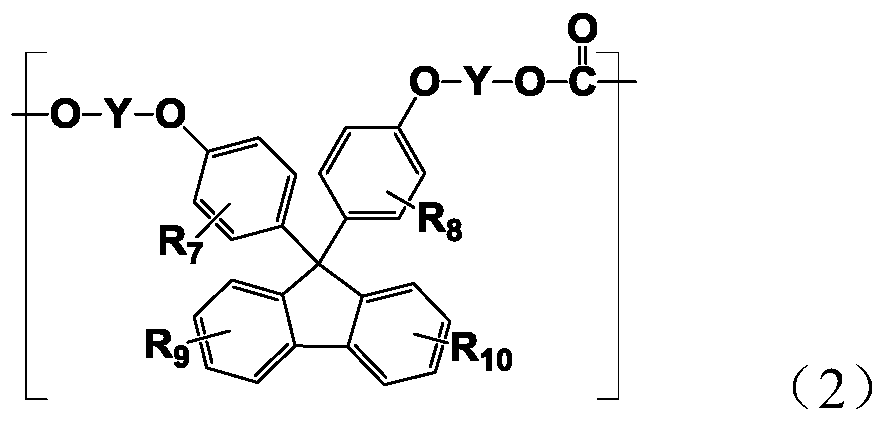
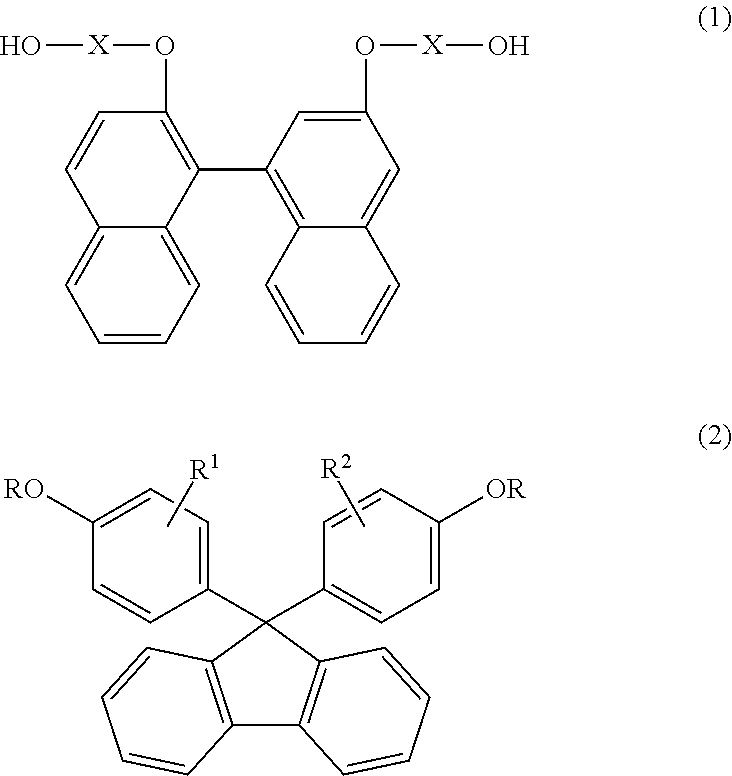
Resin composition and optical lens
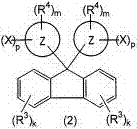
The present invention relates to a resin composition obtained by adding a compound which has polar substituents, is represented by the following formula (2), and includes a 9,9-bisarylfluorene skeleton, to a cycloolefin-based resin having a functional group, the resin composition having a moderate Abbe number. [In the formula, ring Z represents an arene ring; R3 and R4 each represent a substituent; group X represents -[(OR5)n1-Y1] (wherein substituent Y1 represents a hydroxyl, mercapto, glycidyloxy, or (meth)acryloyloxy group, R5 represents an alkylene group, and n1 is 0 or an integer of 1 or larger) or -[(CH2)n2-Y2] (wherein substituent Y2 represents a carboxyl, alkoxycarbonyl, amino, or substituted amino group and n2 is 0 or an integer of 1 or larger); k is an integer of 0-4; m is 0 or an integer of 1 or larger; and p is an integer of 1 or larger.] This resin composition has an Abbe number in an intermediate range (Abbe number of about 28-55) and is useful as an optical lens, etc.
Owner:OSAKA GAS CHEM KK
Curable composition, cured product, optical component, lens, and compound
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical glass, preforms and optical components
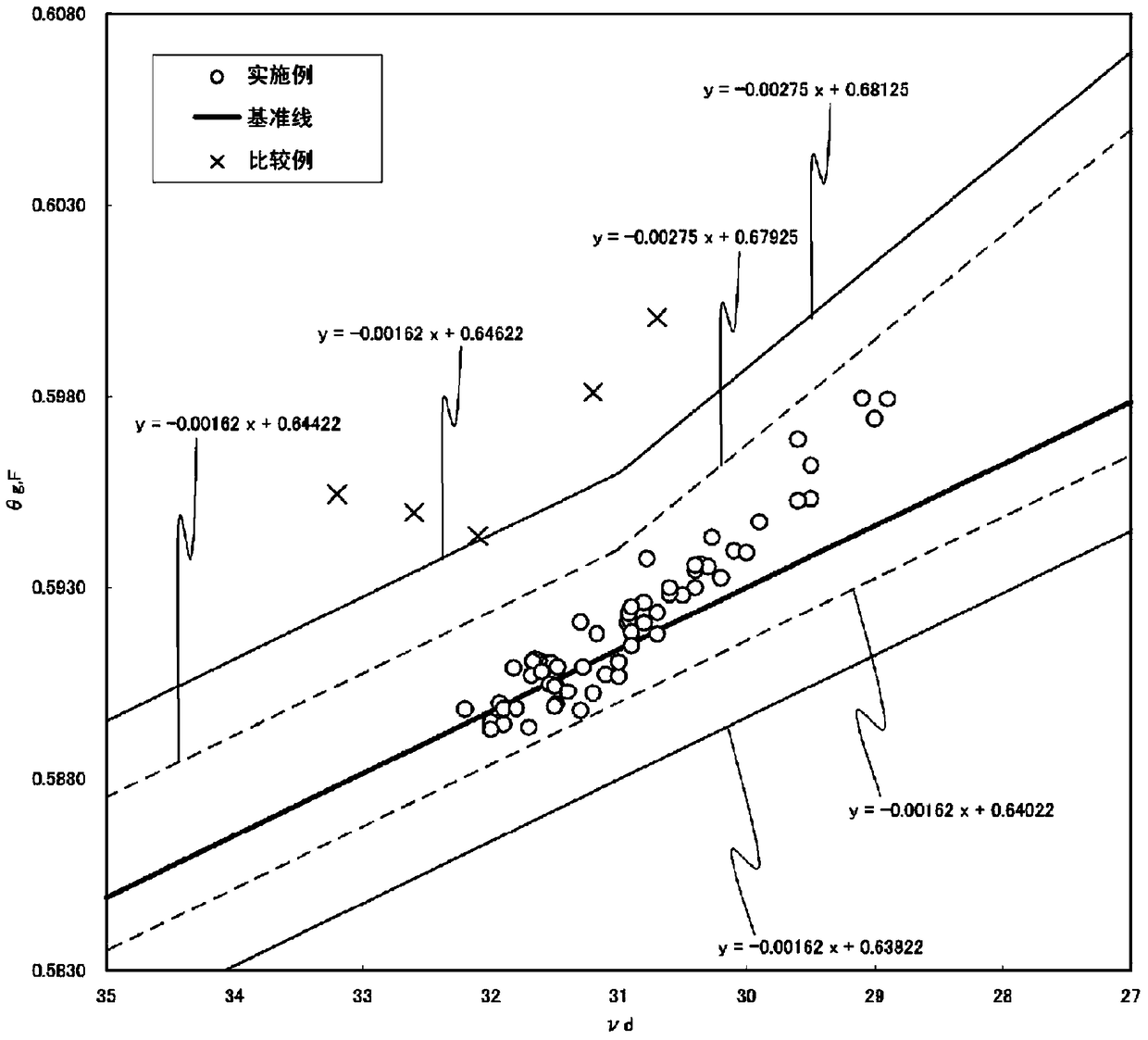
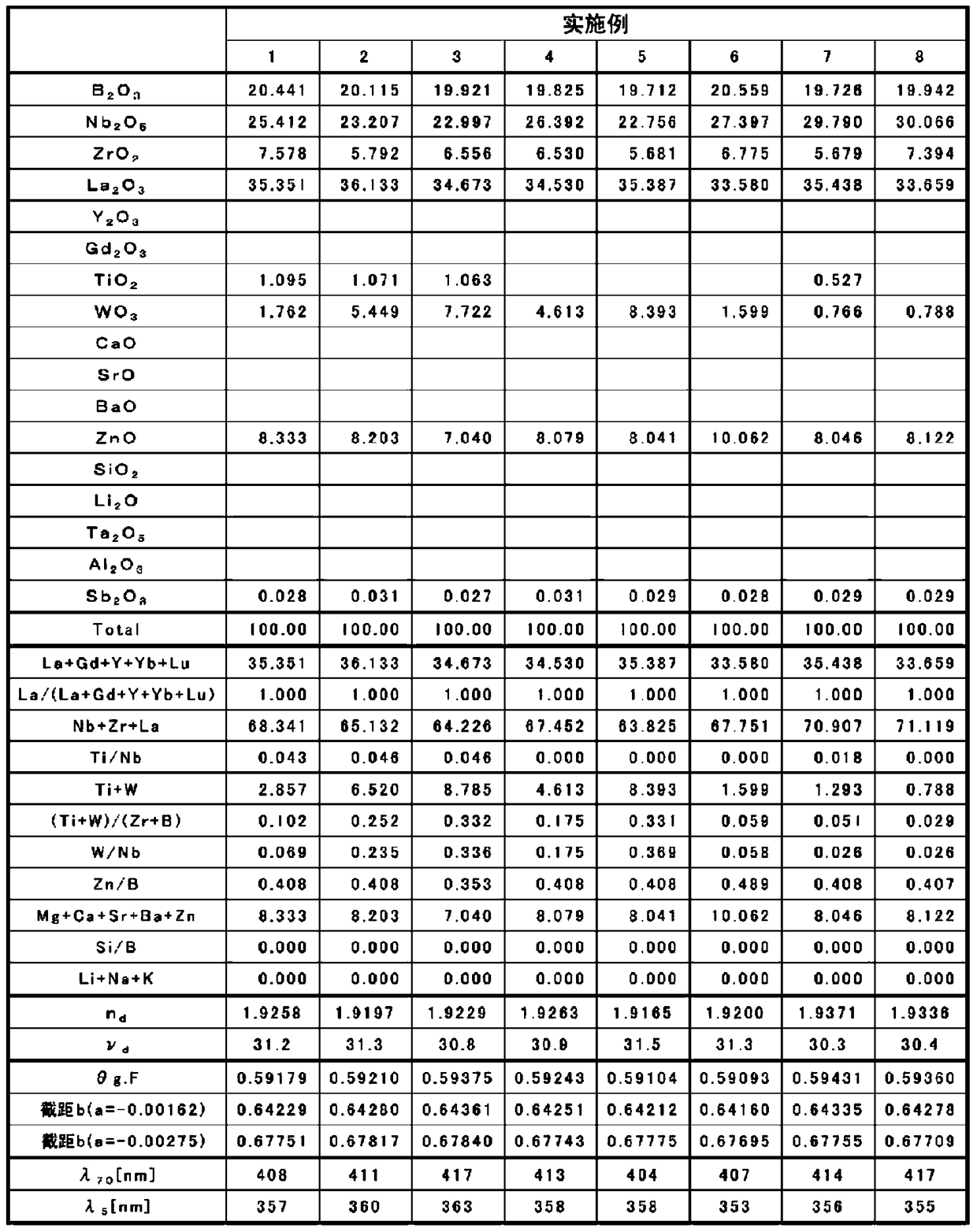
Provided is an optical glass having a small Abbe number (nud), a small partial dispersion ratio (thetag, F), heightened transparency with respect to visible light, and a refractive index (nd) within a desired range. Also provided is a preform and an optical element in which the optical glass is used. The optical glass contains, in terms of mass, 5.0 to 40.0% of an B2O3 component, 15.0 to 60.0% as a sum of the mass of an Ln2O3 component (where Ln is one or more elements selected from the group consisting of La, Gd, Y, and Yb), and 0 to 50.0% of an Nb2O5 component. With respect to the Abbe number (nud), the partial dispersion ratio (thetag, F) satisfies the relationship (-0.00162 × nud + 0.63822) <= (thetag, F) <= (-0.00275 × nud + 0.68125) in the range where nud <= 31, and satisfies the relationship (-0.00162 × nud + 0.63822) <= (thetag, F) <= (-0.00162 × nud + 0.64622) in the range where nud > 31.
Owner:OHARA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com