Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "Improve routability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
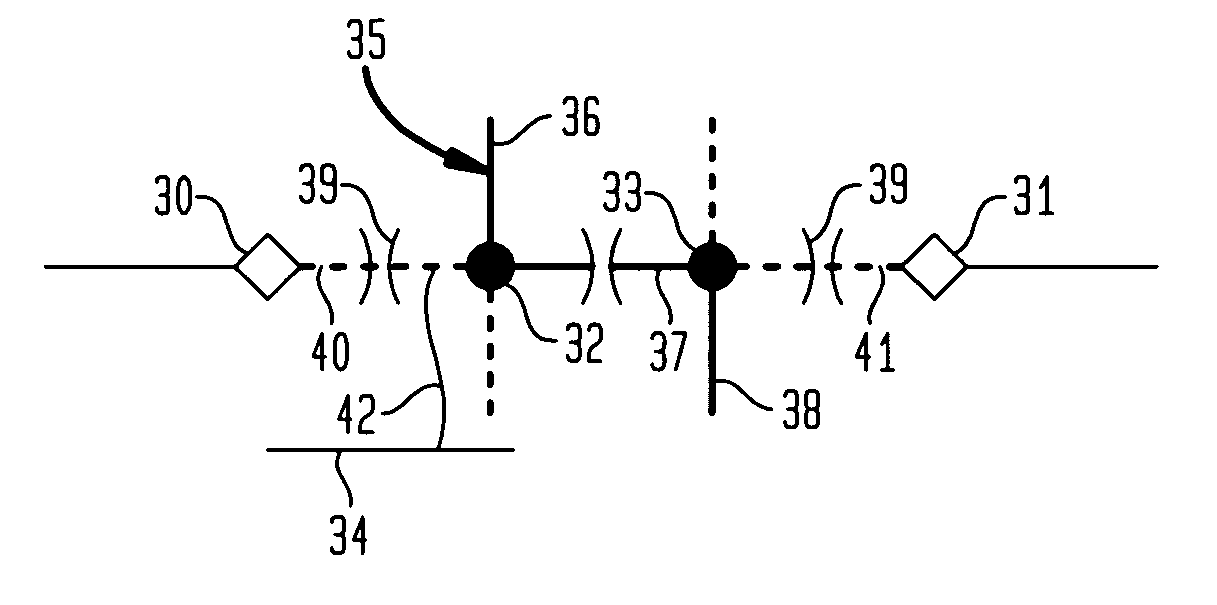
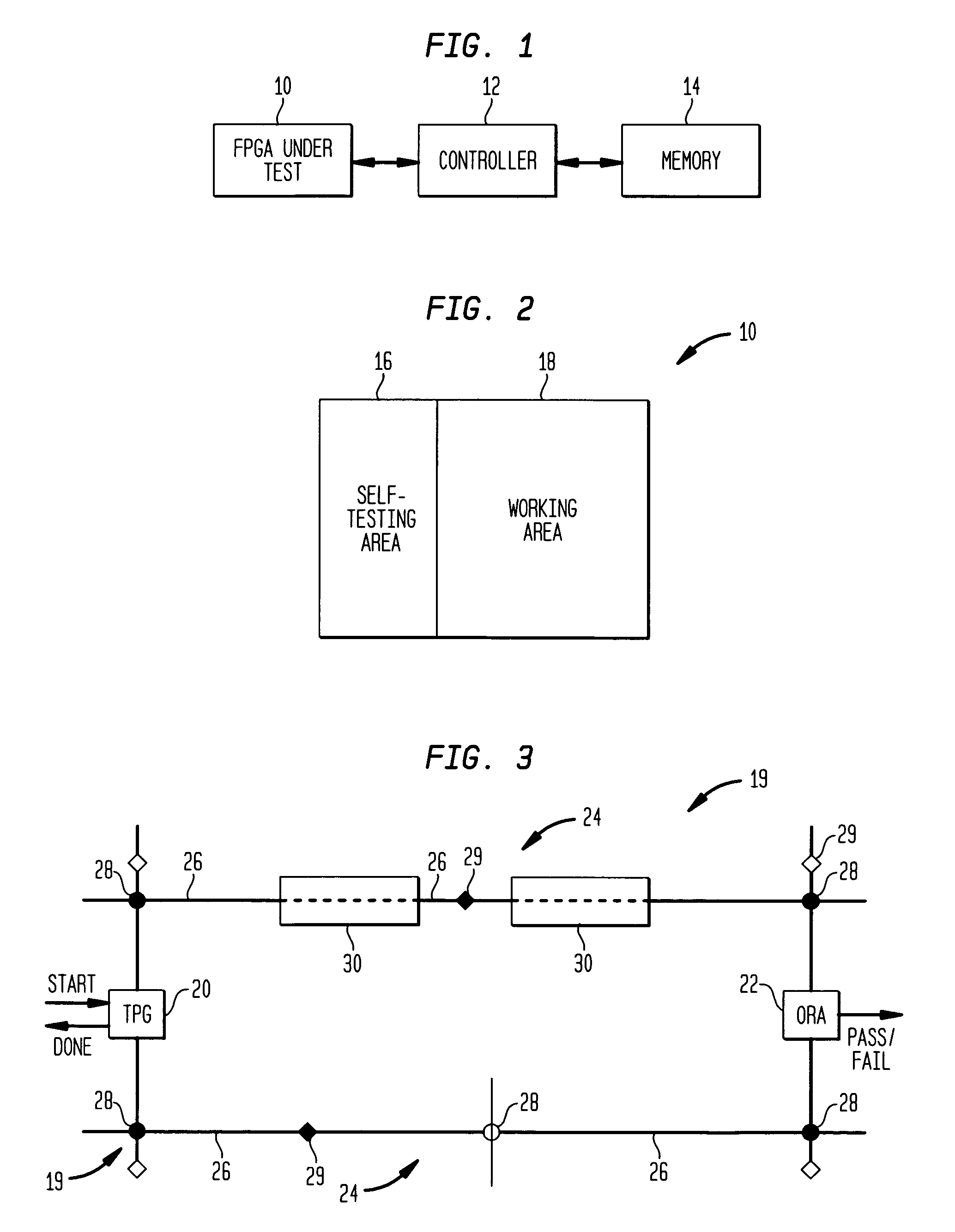
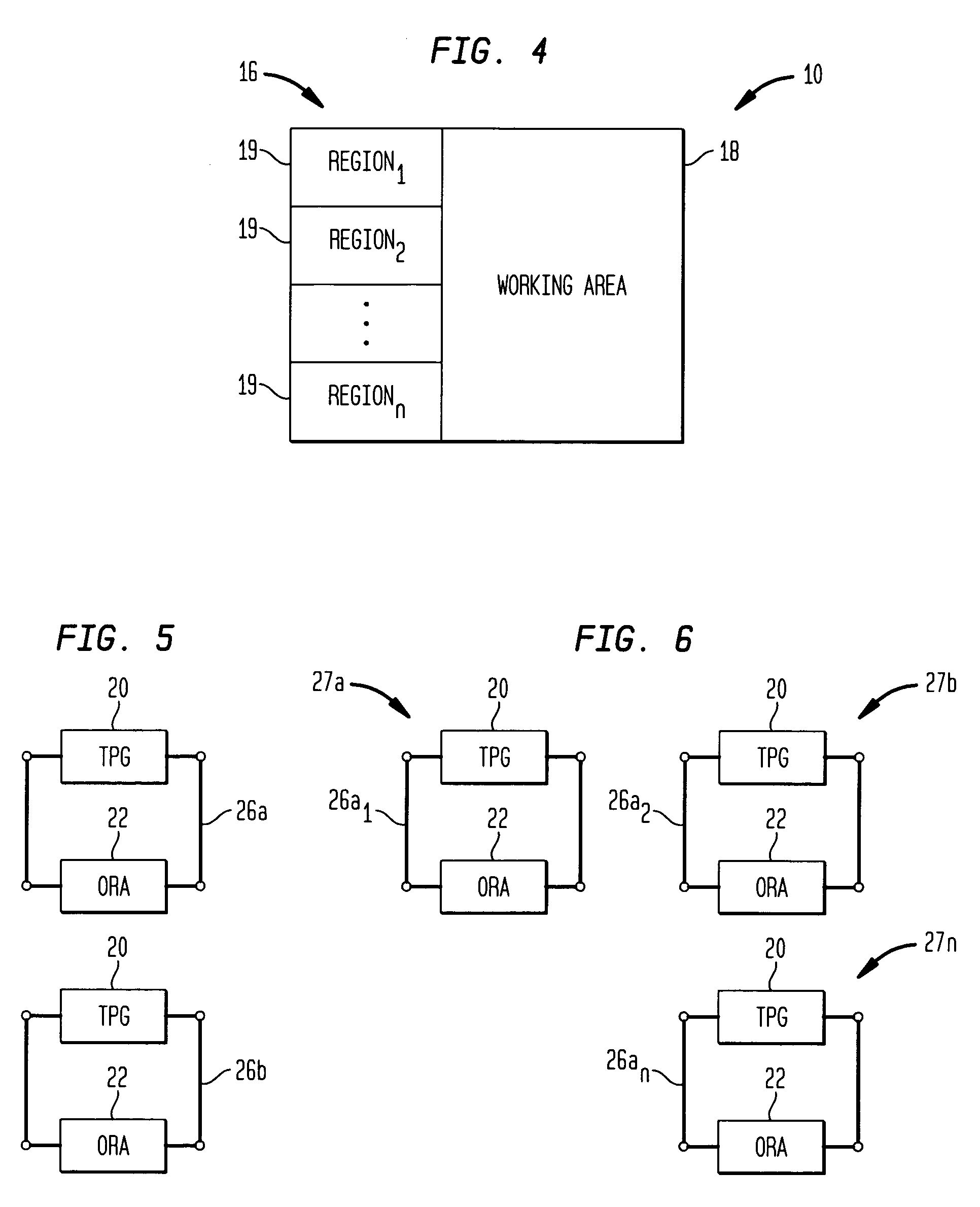
Fault tolerant operation of field programmable gate arrays
ActiveUS6973608B1Extended service lifeMinimize impactElectronic circuit testingRedundant operation error correctionComputer architectureGate array
A method of fault tolerant operation of field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), whether as an embedded portion of a system-on-chip or other application specific integrated circuit, utilizing incremental reconfiguration during normal on-line operation includes configuring an FPGA into a self-testing area and a working area. Within the self-testing area, programmable interconnect resources of the FPGA are tested for faults. Upon the detection of one or more faults within the interconnect resources, the faulty interconnect resources are identified and a determination is made whether utilization of the faulty interconnect resources is compatible with an intended operation of the FPGAs. If the faulty interconnect resources are compatible with the intended operation of the FPGA, utilization of the faulty interconnect resource is allowed to provide fault tolerant operation of the FPGA. If the faulty interconnect resources are not compatible with the intended operation of the FPGA, on the other hand, a multi-step reconfiguration process may be initiated which attempts to minimize the effects of each reconfiguration on the overall performance of the FPGA. In an alternate embodiment, the entire FPGA may be configured as one or more self-testing areas during off-line testing, such as manufacturing testing.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT +1
Heat sink structure with embedded electronic components for semiconductor package
ActiveUS7050304B2Good semiconductor performanceImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
A heat sink structure with embedded electronic components is proposed, wherein a plurality of recessed cavities are formed on a heat sink for embedding the electronic components and receiving at least one semiconductor chip therein. This arrangement enhances electric performance of a semiconductor package with the above heat sink structure and improves heat dissipating efficiency of the semiconductor package.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Array connector having improved electrical characteristics and increased signal pins with decreased ground pins
ActiveUS7137832B2Improve featuresReduce crosstalkCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsConnection contact member materialEngineeringElectrical connector
An electrical connector includes a connector body, a plurality of rows and columns of conductive pins disposed along the length direction and the width direction of the connector body so as to form an array of signal pins located in a pin field, at least two rows of ground pins arranged along at least two sides of the pin field, with no ground pins being arranged in the pin field or between adjacent signal pins. The signal pins are arranged in a stretched pitch and / or staggered configuration to minimize cross-talk and maximize signal pin density and signal-to-ground ratio.
Owner:SAMTEC
Low Inductance Ball Grid Array Device Having Chip Bumps on Substrate Vias
InactiveUS20090289362A1Eliminate couplingReduces bump-to-via current path inductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLow inductance
A high-frequency BGA device (500) with the chip (501) assembled by metal bumps (503) on an insulating substrate (502) with conductive vias (505) and metal traces (504). Chip bumps which serve the high frequency signal terminals are attached directly to the lands (510) on the vias in order to minimize parasitic electrical parameters such as inductance, resistance, and IR drops, thus achieving the required 0.1 nH inductance for each chip terminal. Chip bumps which serve the remaining chip terminals are attached to pads on certain substrate traces. In both cases, the bumps can be attached reliably because the lands on the vias and the pads on the traces are plated with additional metal layers (511, 512), which provide extra thickness as well as a metallurgically suitable surface.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
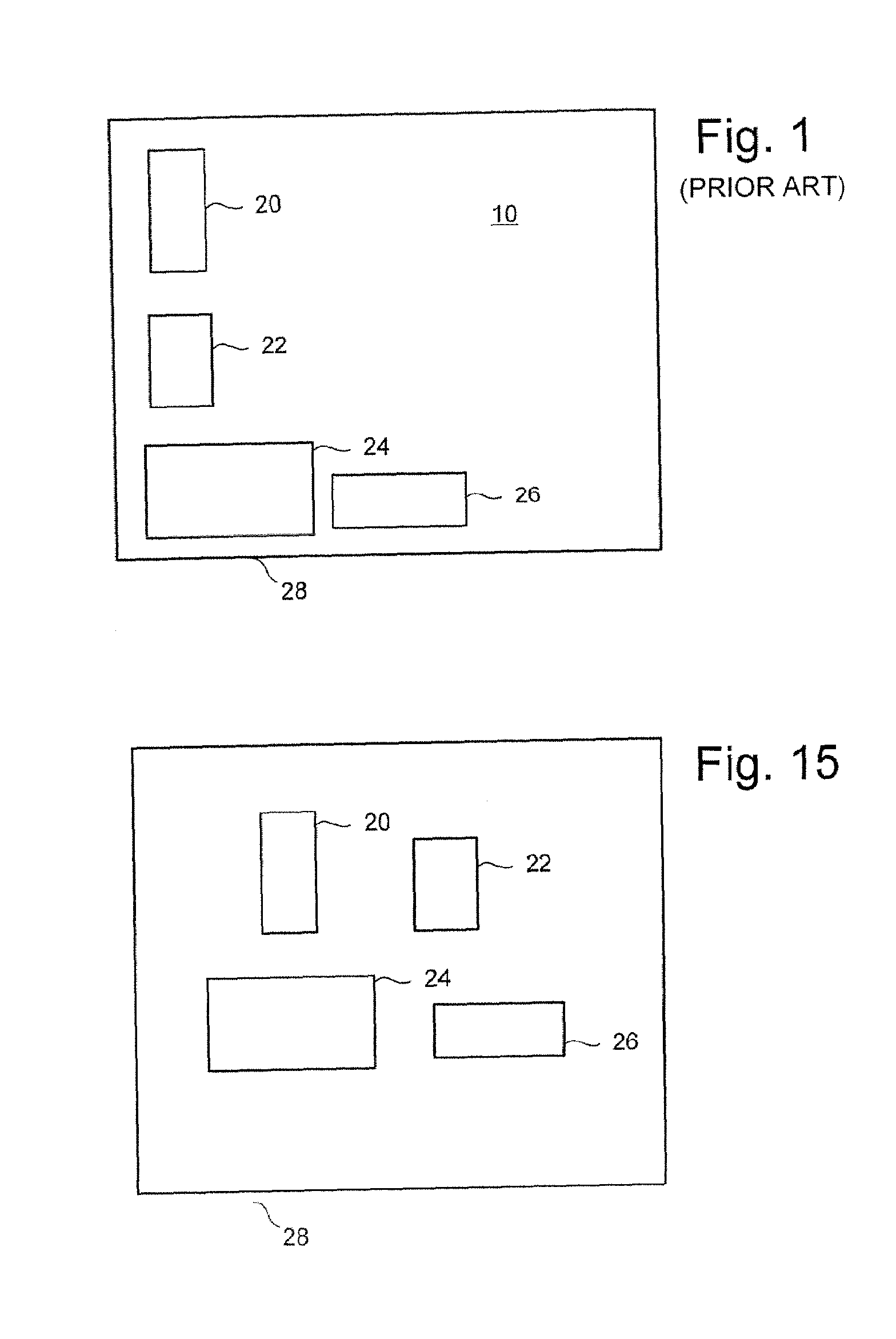
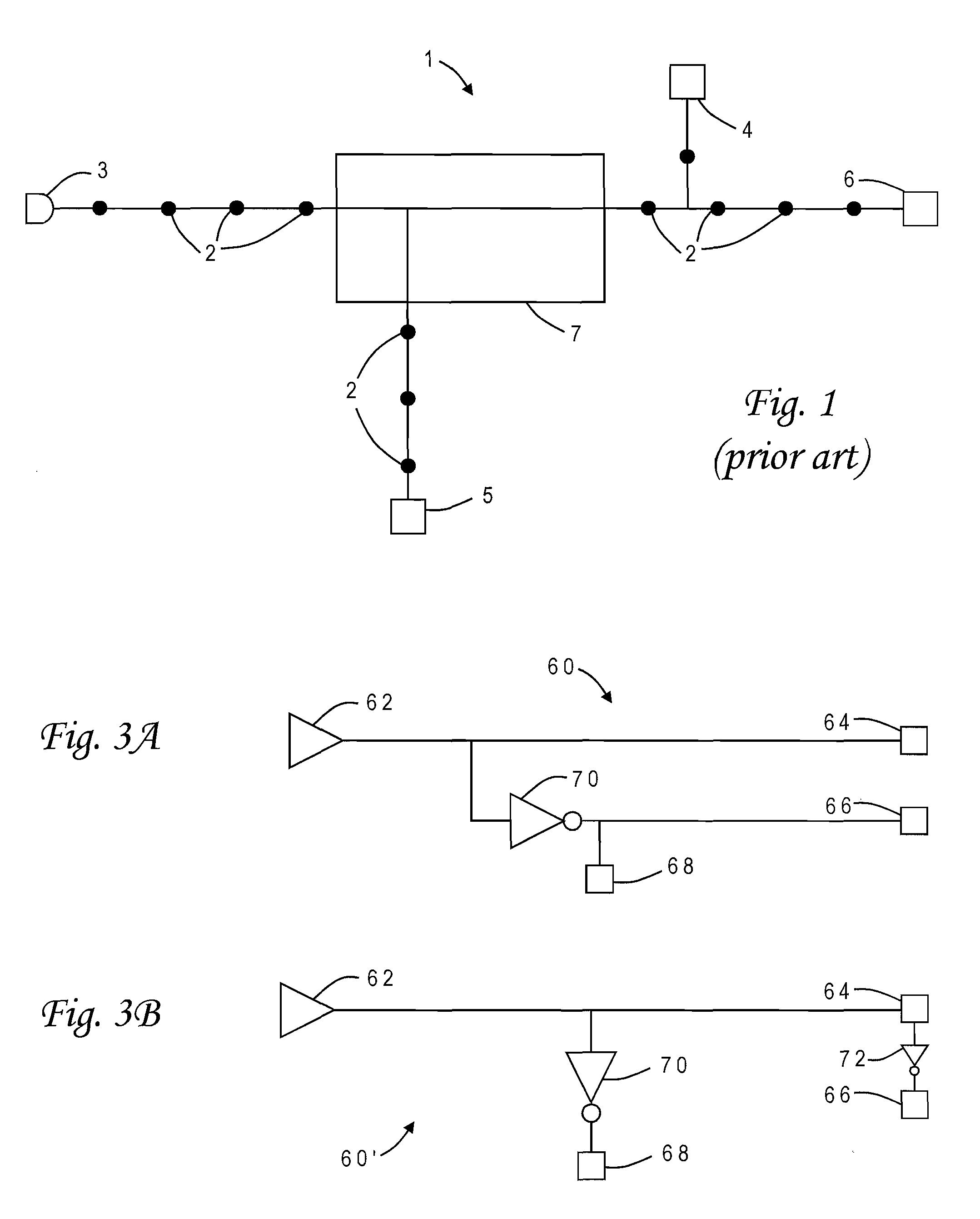
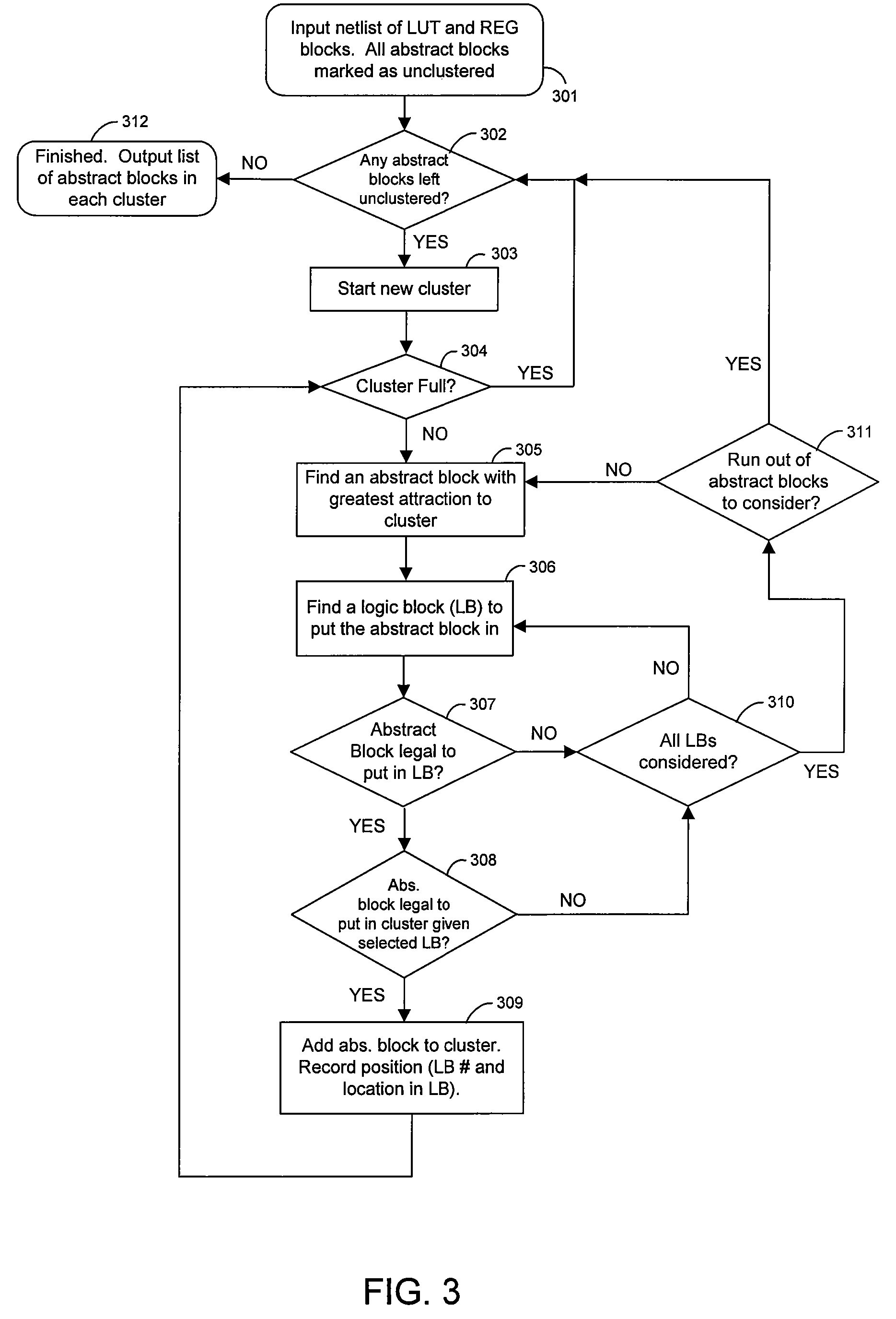
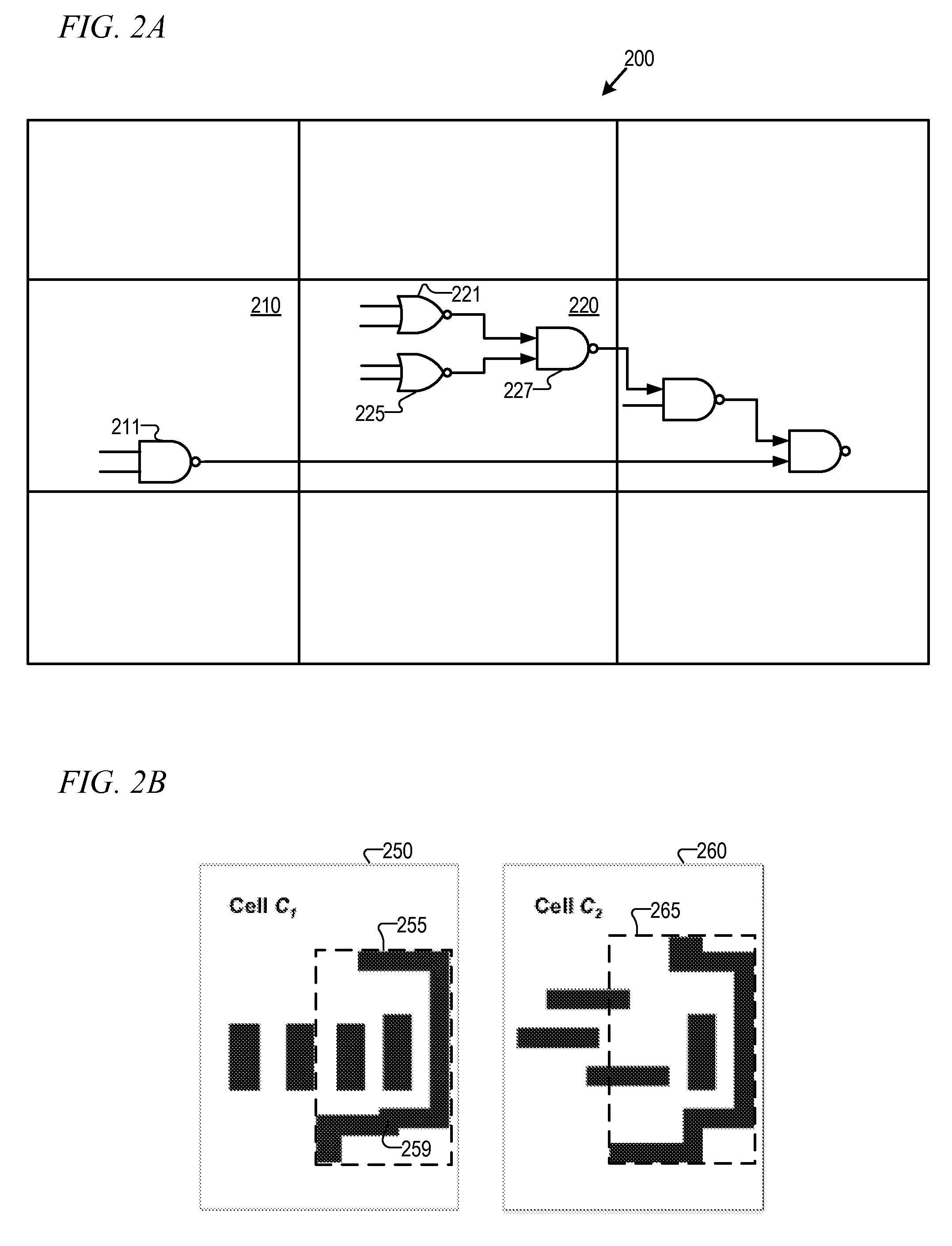
Modifying a design to reveal the data flow of the design in order to create a more favorable input for block placement
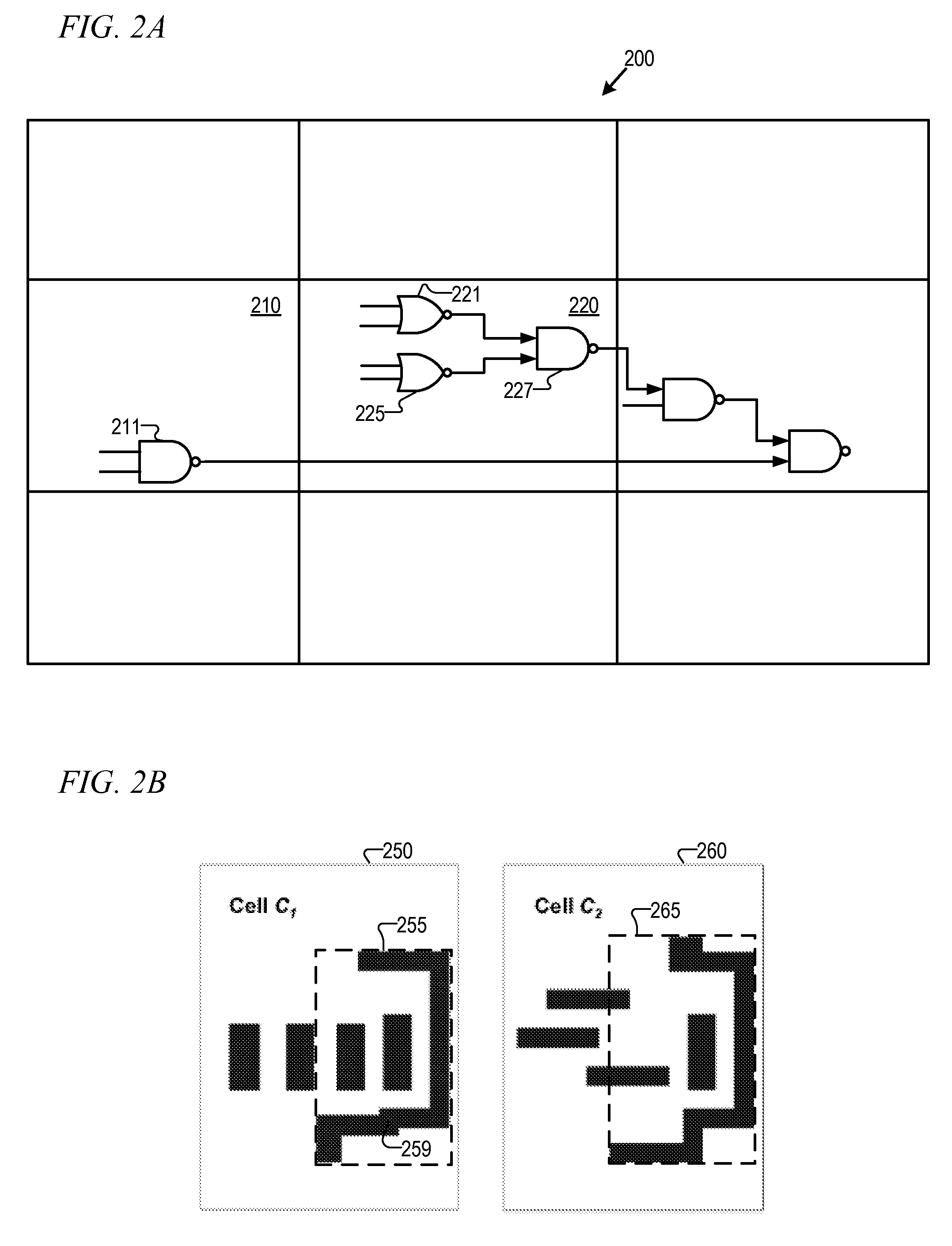
ActiveUS20050183054A1Minimizing wire lengthMinimizing other cost functionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureAND gate
A system is employed for modifying a hierarchical description of a design to reveal the data flow of the design. The modified design provides a more favorable input for block placement. In one embodiment, the modifications includes any one of or a combination of moving hard macros to a higher level of the hierarchical description of the design, flattening modules that are bigger than a threshold, and / or flattening star blocks. Up to three clustering strategies are employed as part of the flattening process, including name-based clustering, external connection based clustering and gate clustering.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
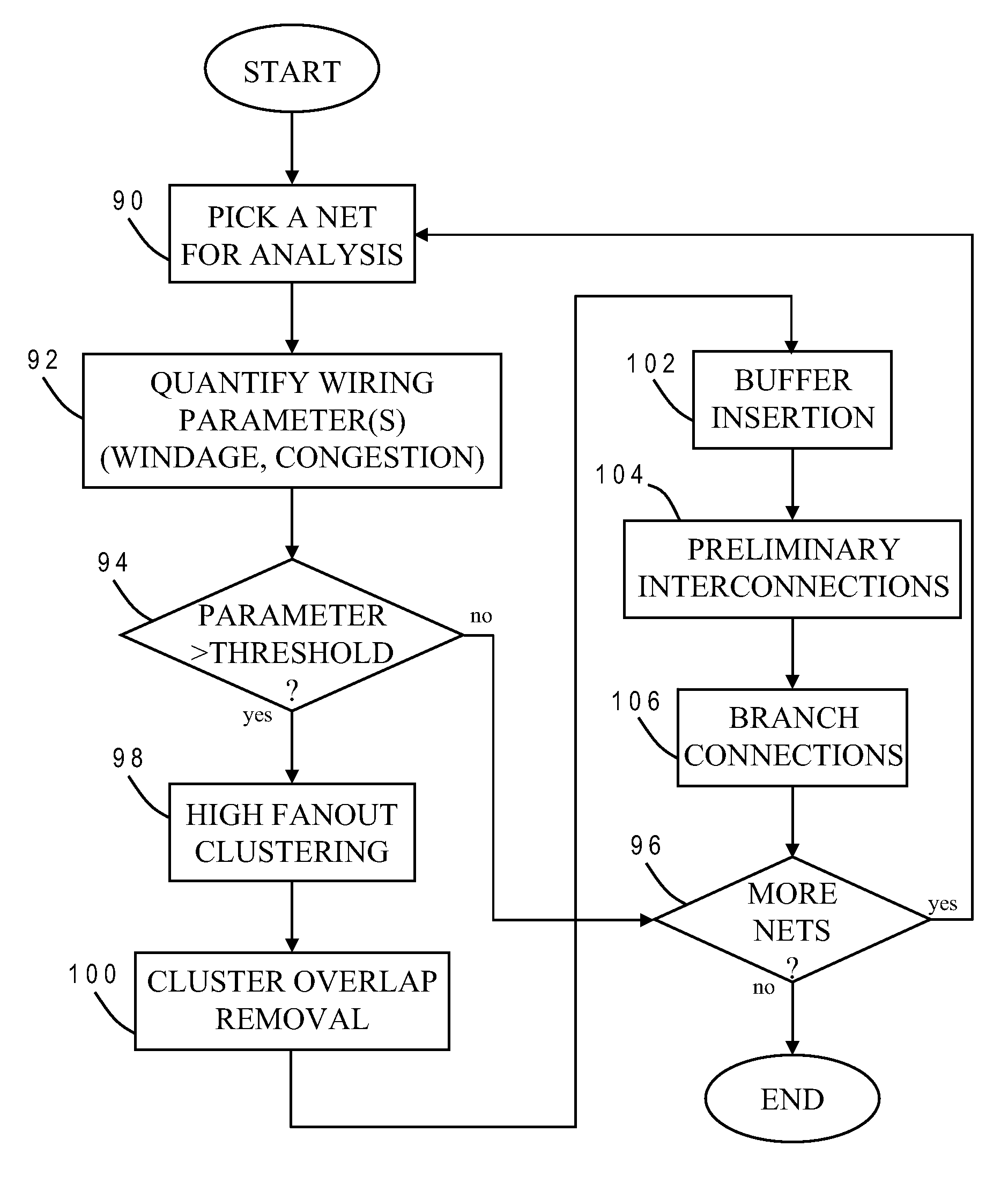
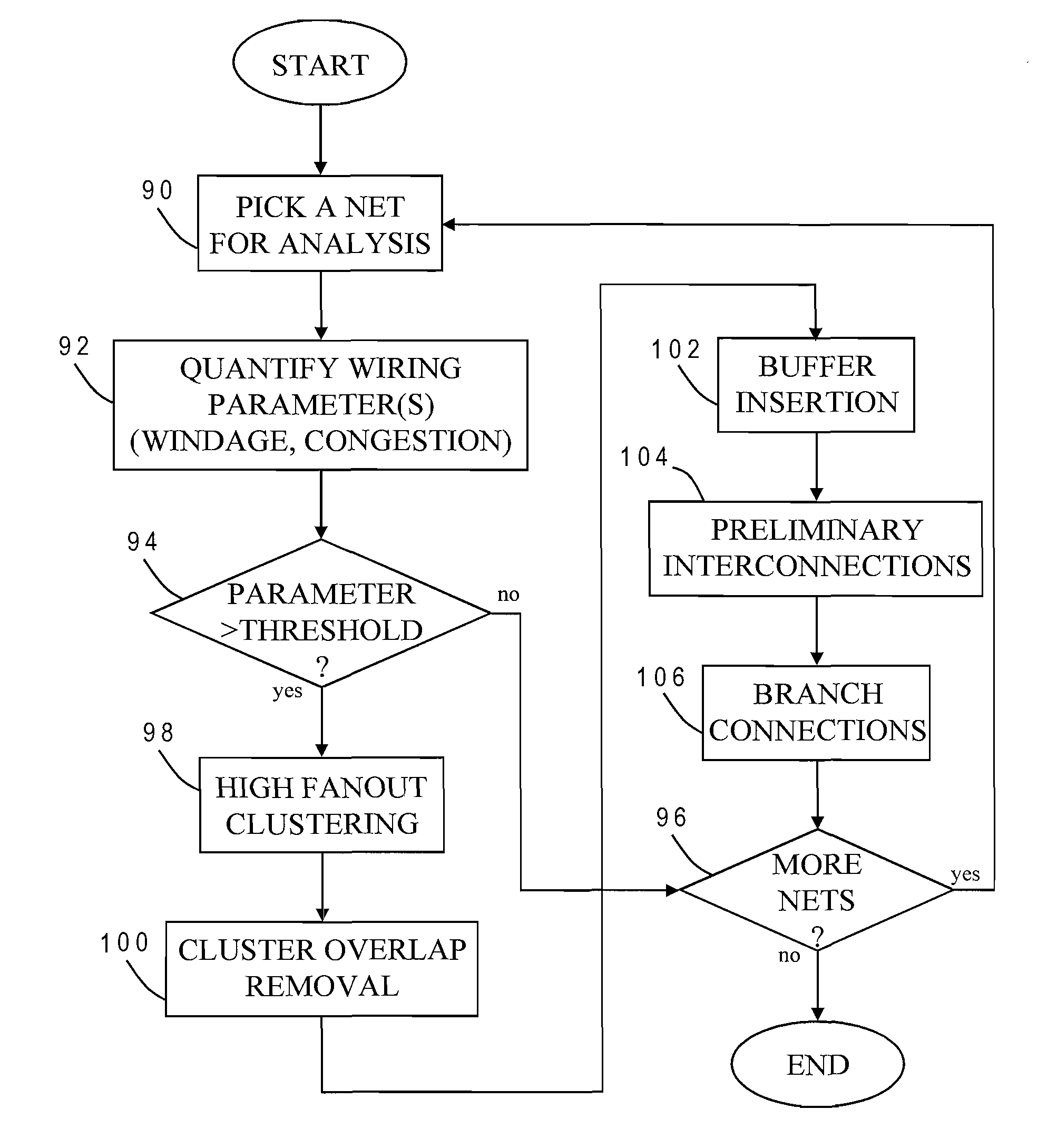
Buffer Insertion to Reduce Wirelength in VLSI Circuits
ActiveUS20070271543A1Simple methodShorten the line lengthGeometric CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingBuffer zone
Wirelength in a net of an integrated circuit design is reduced by forming clusters of sinks to be interconnected, inserting a buffer at each cluster, and providing branch connections between clusters by connecting a sink of one cluster to a buffer of another cluster, to create a buffer tree spanning all sinks. The buffers are inserted at a point on a respective bounding box of a cluster that is closest to a source for the net. A sink that provides a branch connection to the buffer of another cluster is the closest sink to that buffer (except for those sinks in the cluster). Clusters may be formed by examining different pairs of the sinks with different bounding boxes, and identifying one of the pairs whose bounding box has a lowest half-perimeter as the best pair for clustering.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Simplified Substrates for Semiconductor Devices in Package-on-Package Products
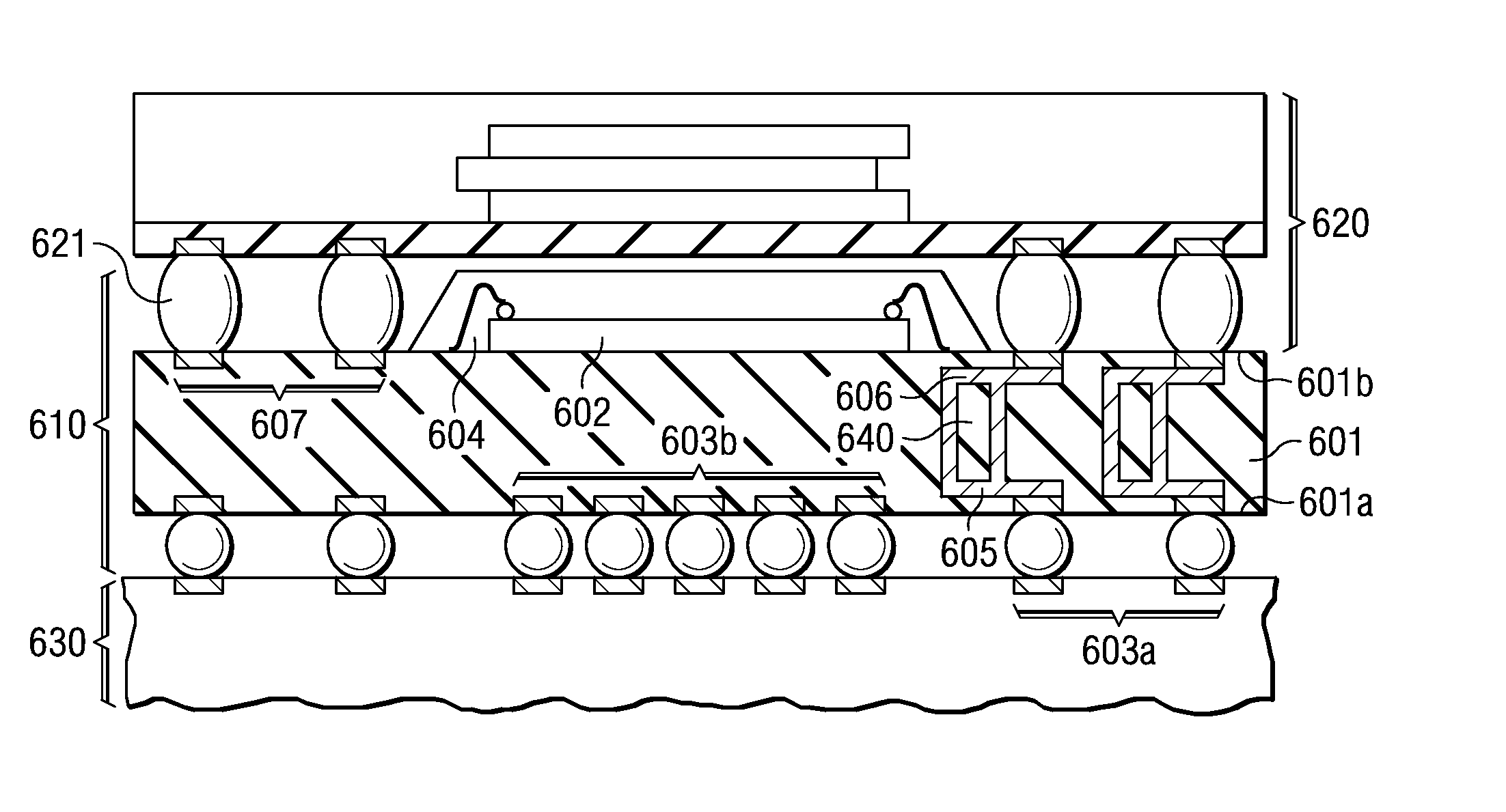
InactiveUS20080258285A1Cost reductionEnhance routabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
An insulating sheet-like substrate (601), which has on one surface (601a) a first patterned metal layer (605) with a first (603a) and a second (603b) array of contact pads. The pads of the first array have a first pitch center-to-center, and each pad has a first perimeter. The pads of the second array have a second pitch center-to-center, and each pad has the first perimeter. The substrate has on its other surface (601b) a second patterned metal layer (606) with a third array (607) of contact pads, which has the first pitch center-to-center, and each pad has a third perimeter. Conductive vias (640) between the first and the second metal layers connect contact pads and have a fourth perimeter; the vias are placed in interstitial locations so that the fourth perimeter does not intersect with the first and third perimeters. Vias in interstitial locations can be provided by disposing the first array and the third array so that the first and third perimeters of respective contact pads are concentrically aligned.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Modifying a design to reveal the data flow of the design in order to create a more favorable input for block placement
ActiveUS7269815B2Easy to placeMinimizing functionComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureAND gate
A system is employed for modifying a hierarchical description of a design to reveal the data flow of the design. The modified design provides a more favorable input for block placement. In one embodiment, the modifications includes any one of or a combination of moving hard macros to a higher level of the hierarchical description of the design, flattening modules that are bigger than a threshold, and / or flattening star blocks. Up to three clustering strategies are employed as part of the flattening process, including name-based clustering, external connection based clustering and gate clustering.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
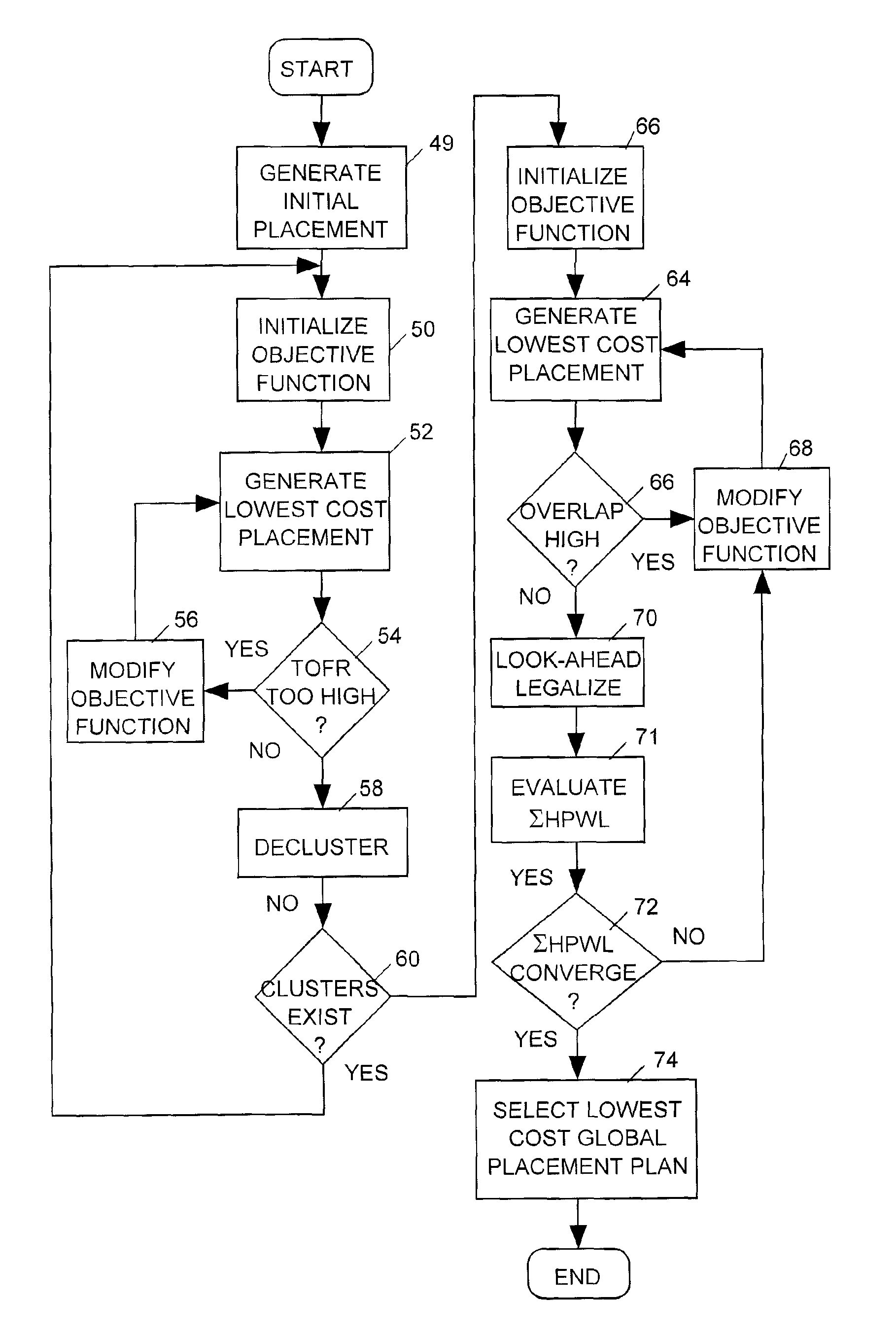
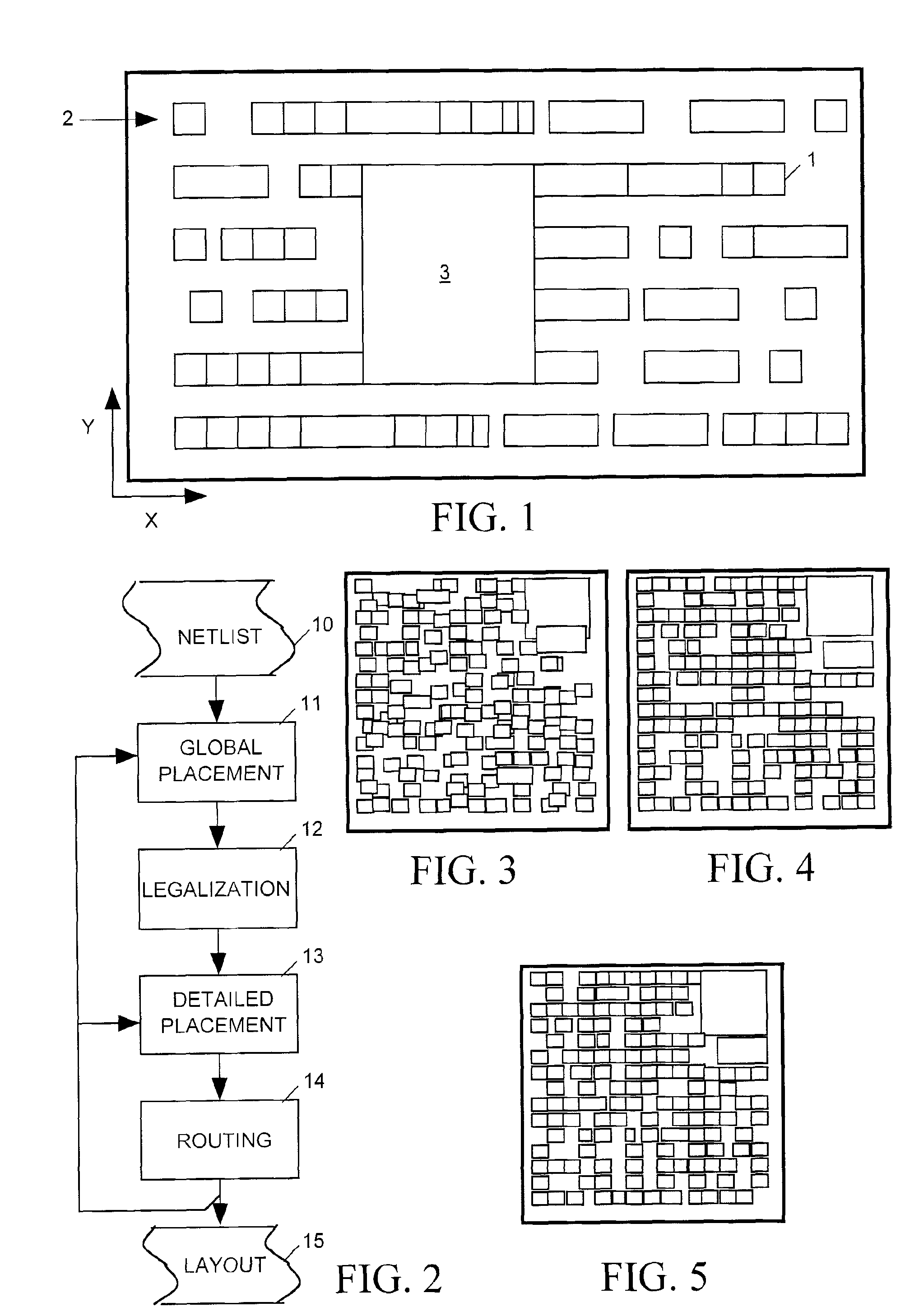
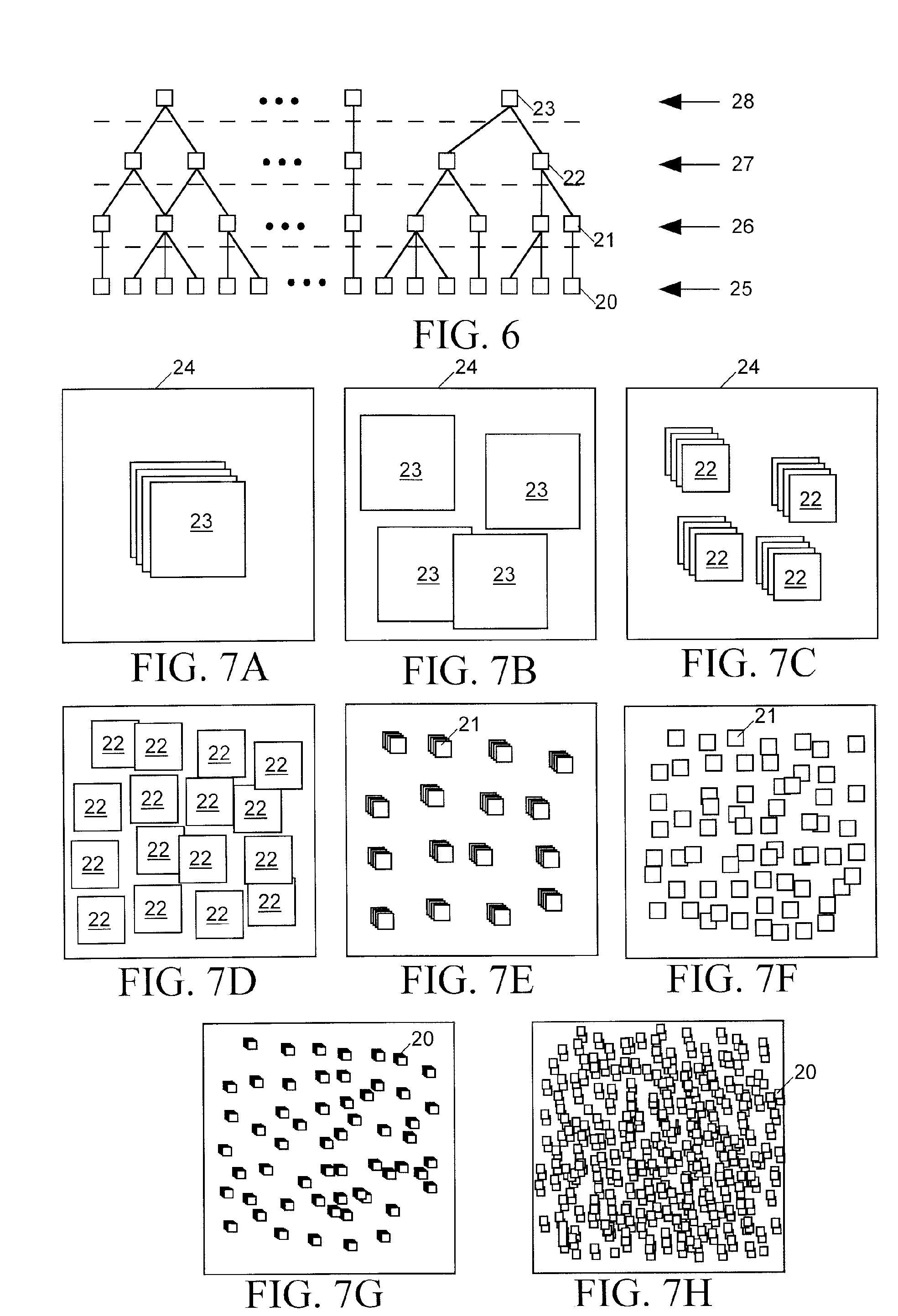
Hierarchy-based analytical placement method for an integrated circuit
ActiveUS7984410B2Improve routabilityMaximizes routabilityComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgram planningTheoretical computer science
A placer produces a global placement plan specifying positions of cell instances to be interconnected by nets within an integrated circuit (IC) by initially clusterizing cell instances to form a pyramidal hierarchy of blocks and generating an initial global placement plan specifying a position of each block at a highest level of the hierarchy. The placer then declusterizes the global placement plan by replacing the highest level blocks with their component blocks and then improves the routability of the global placement plan by iteratively moving specified block positions in directions and by distances dynamically determined by analyzing the global placement plan and an objective function having a total wirelength term and having a bin density term reflecting density of blocks in specified areas (bins) of the IC. The placer iteratively repeats the declusterization and routability improvement process until the global placement plan specifies positions of all blocks residing at the lowest level of the hierarchy, with weighting of the bin density term adjusted when necessary during each iteration of the routability improvement process to provide sufficient white space in each bin. The placer employs a look-ahead legalization technique to move low level blocks to legal positions during later iterations of the plan improvement process.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
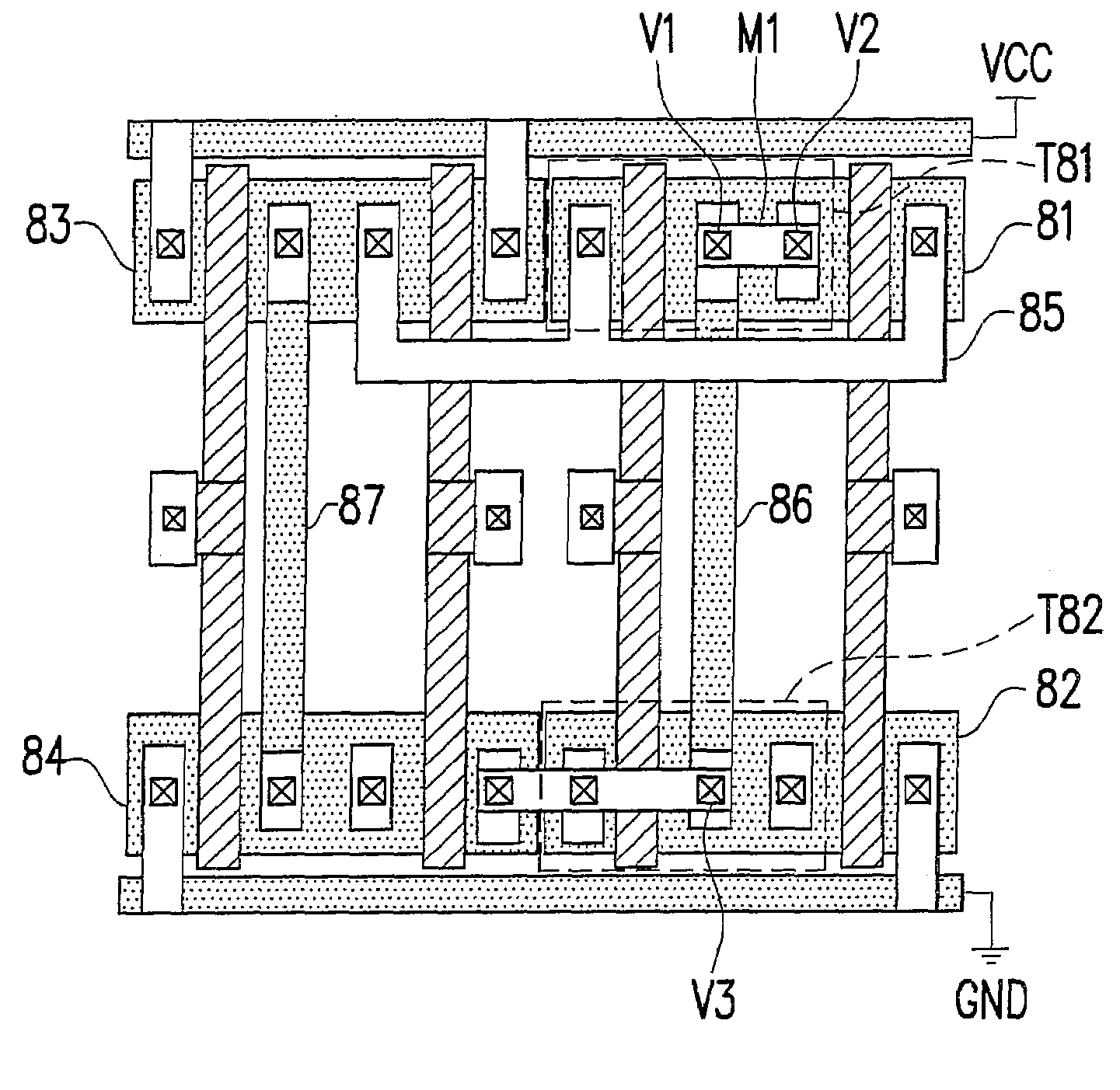
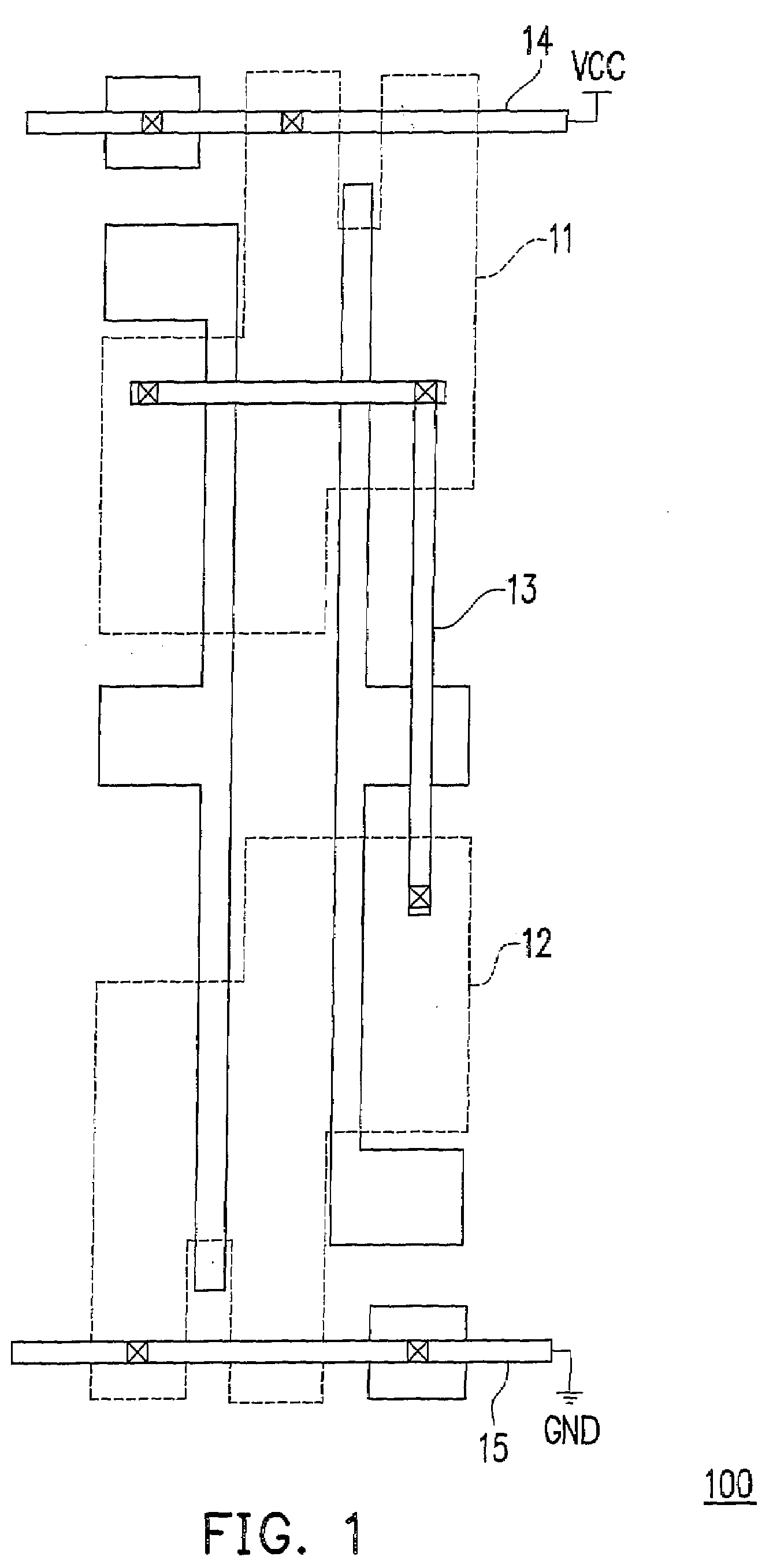
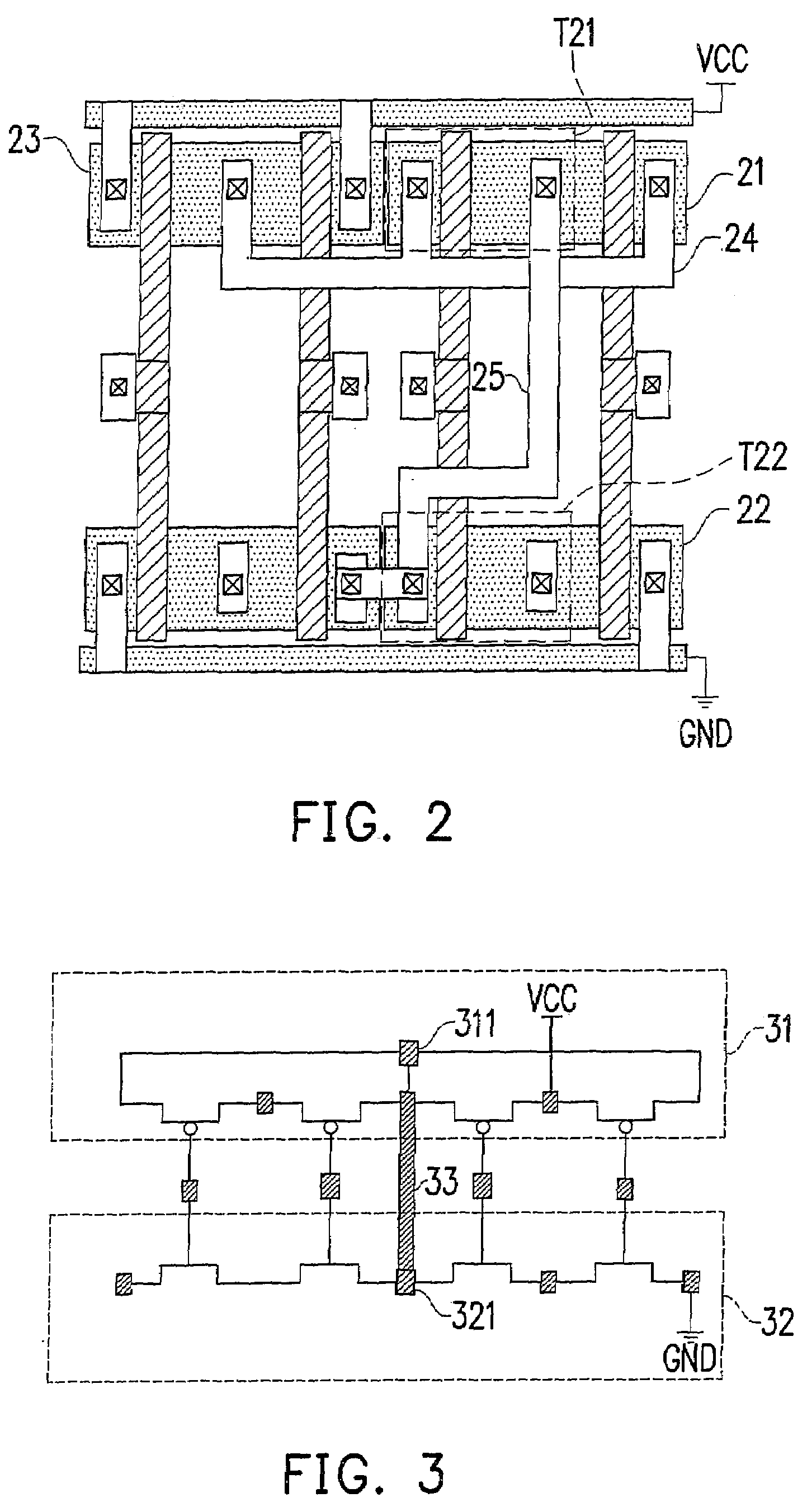
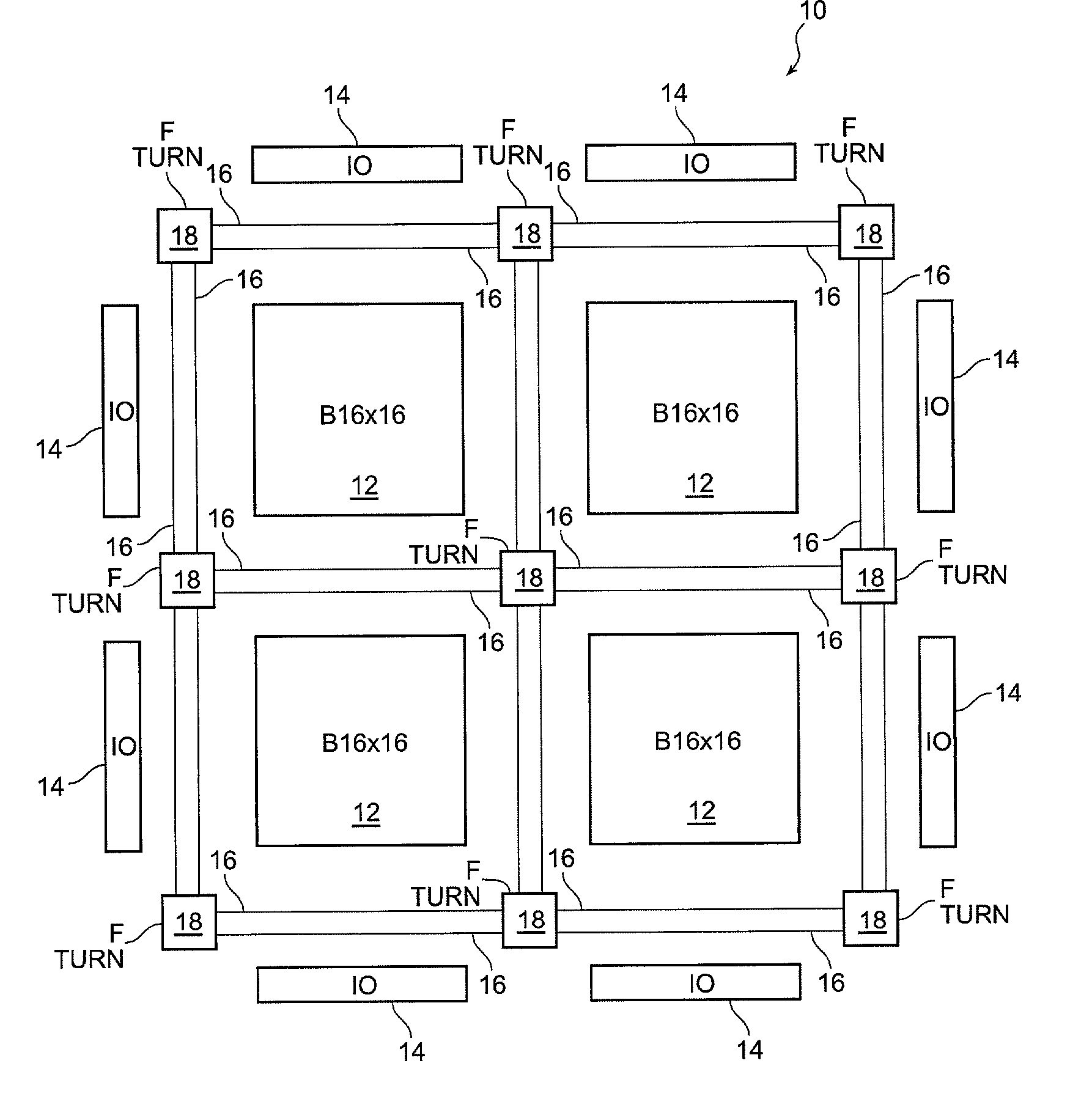
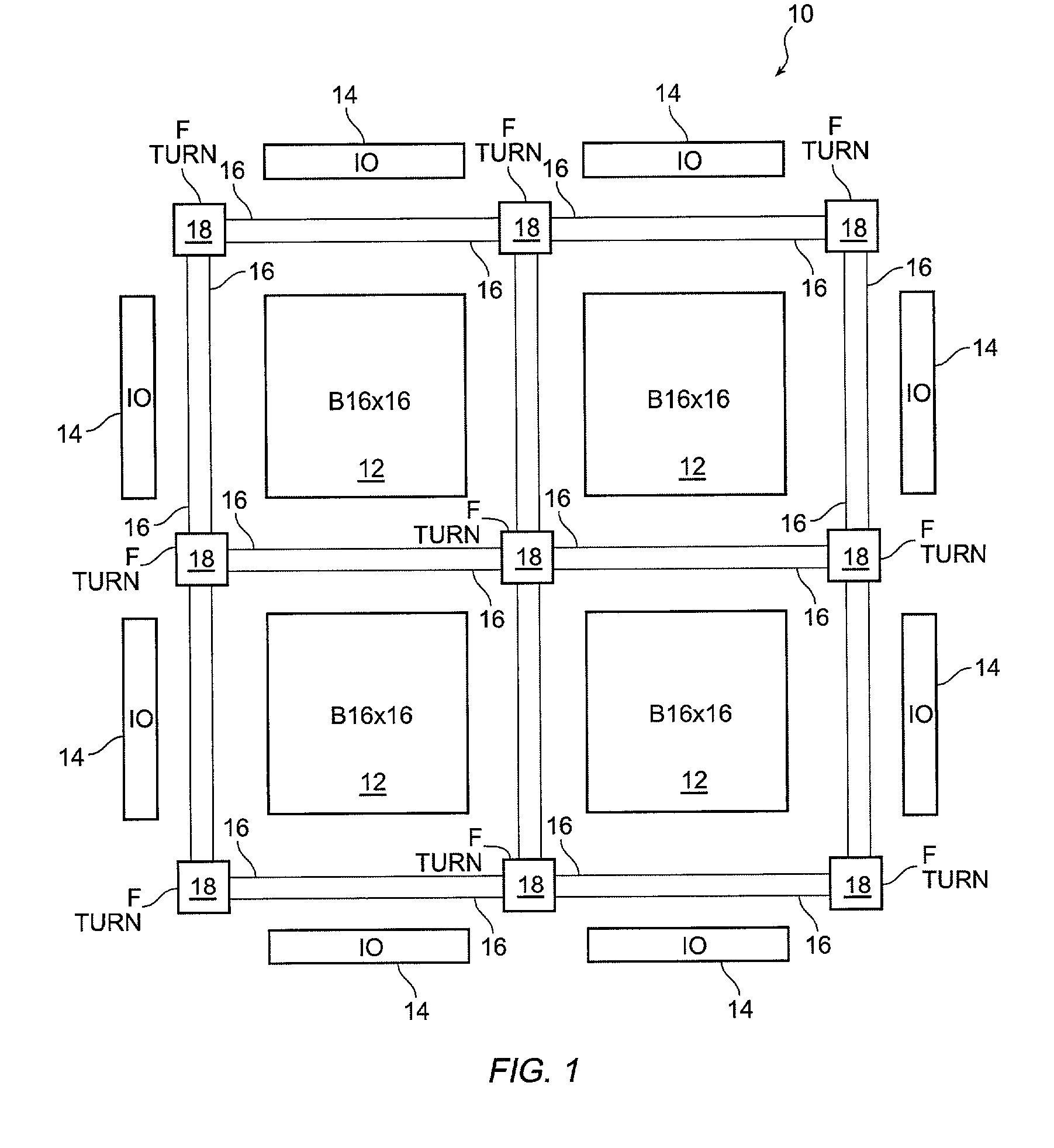
Block connector splitting in logic block of a field programmable gate array
InactiveUS6285212B1Good symmetryEasy to placeSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsFpga architectureElectrical conductor
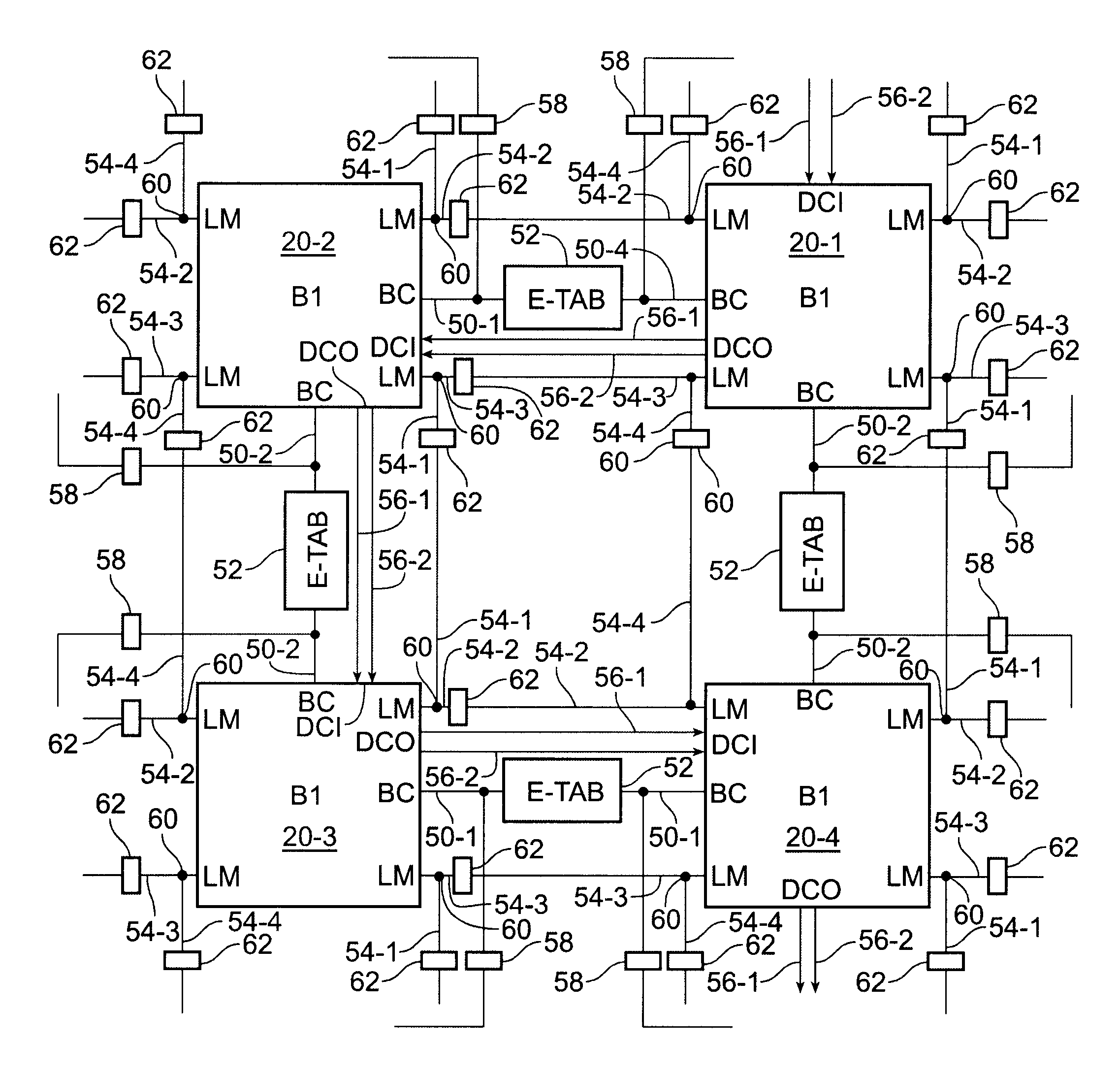
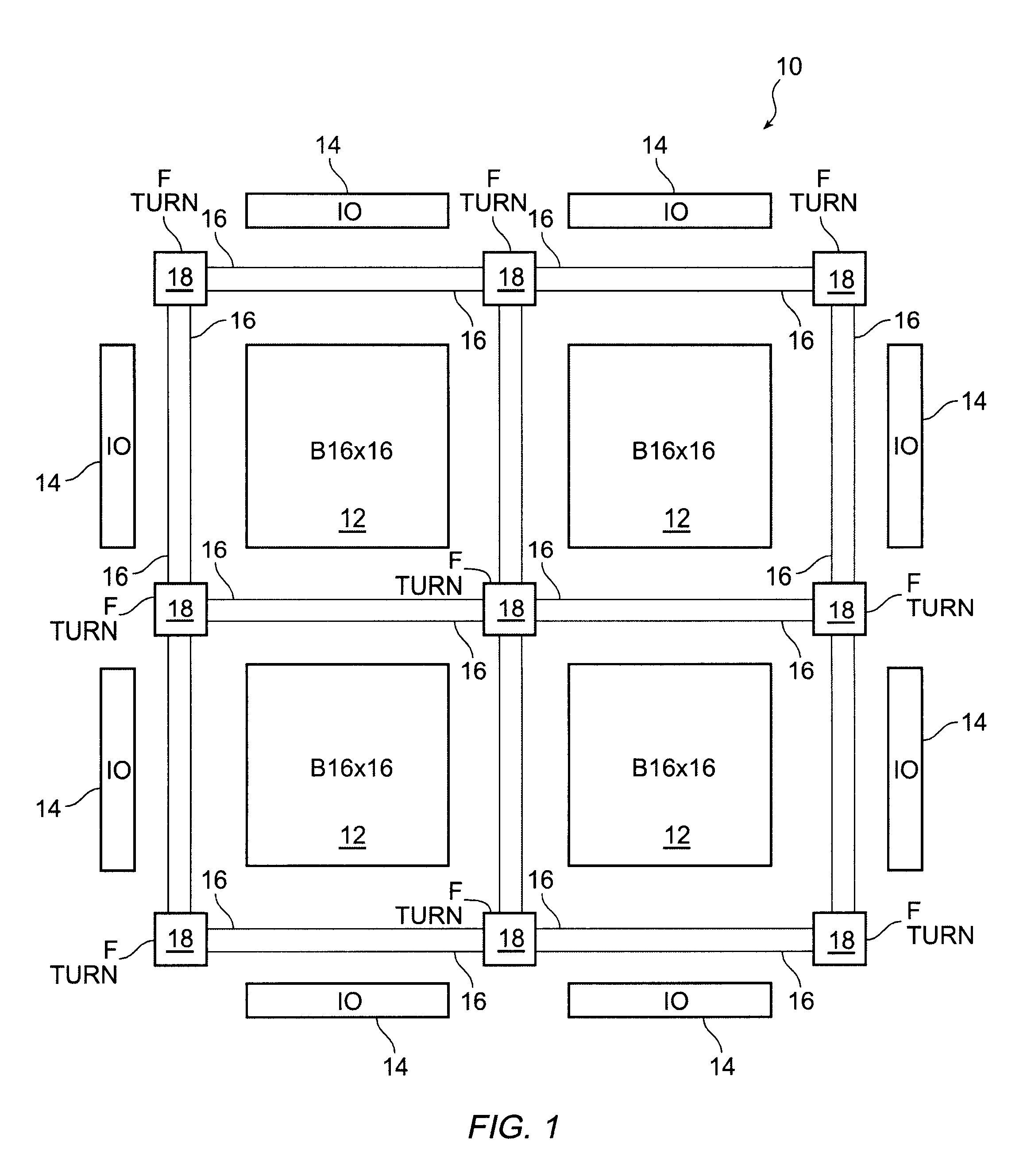
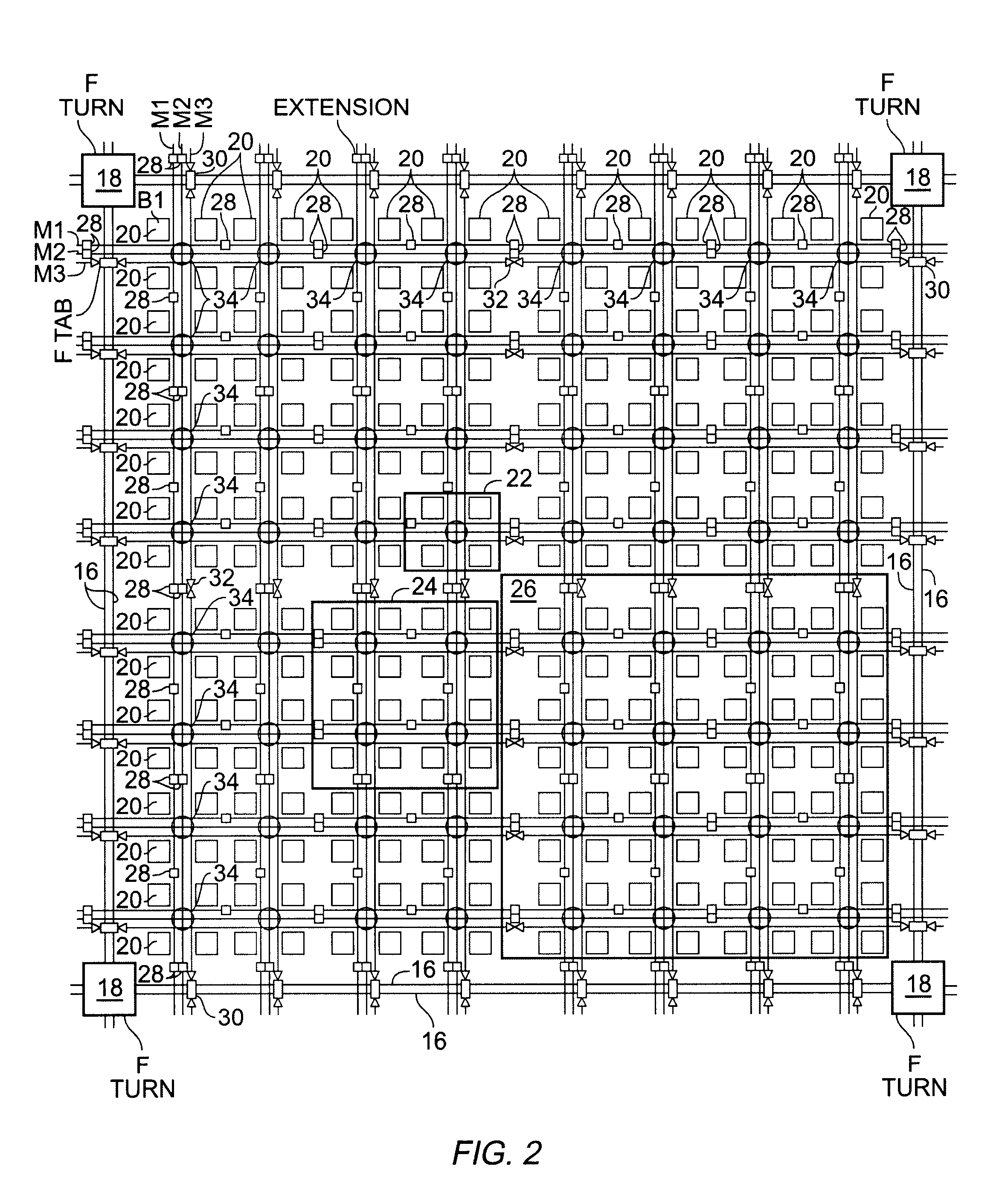
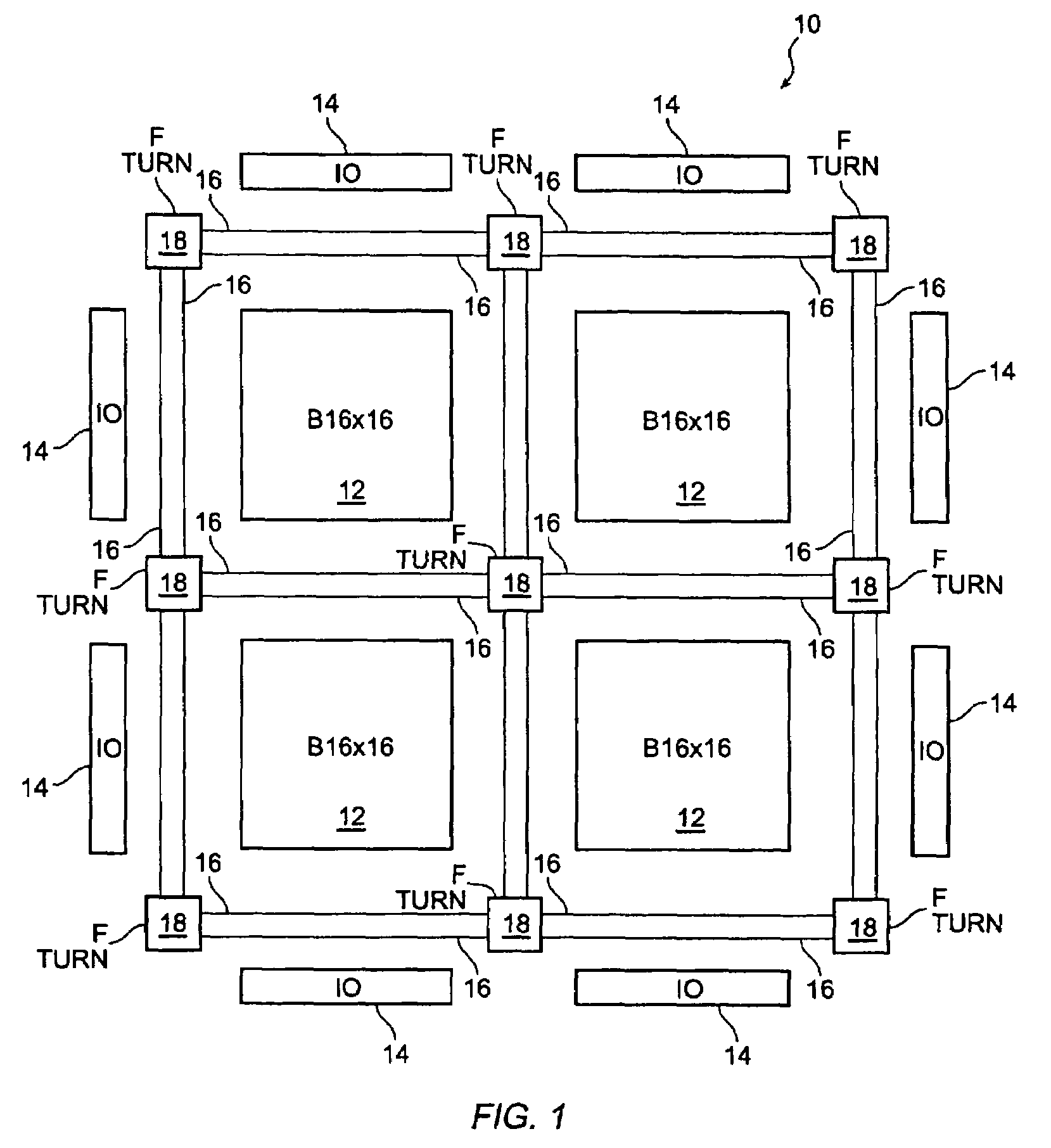
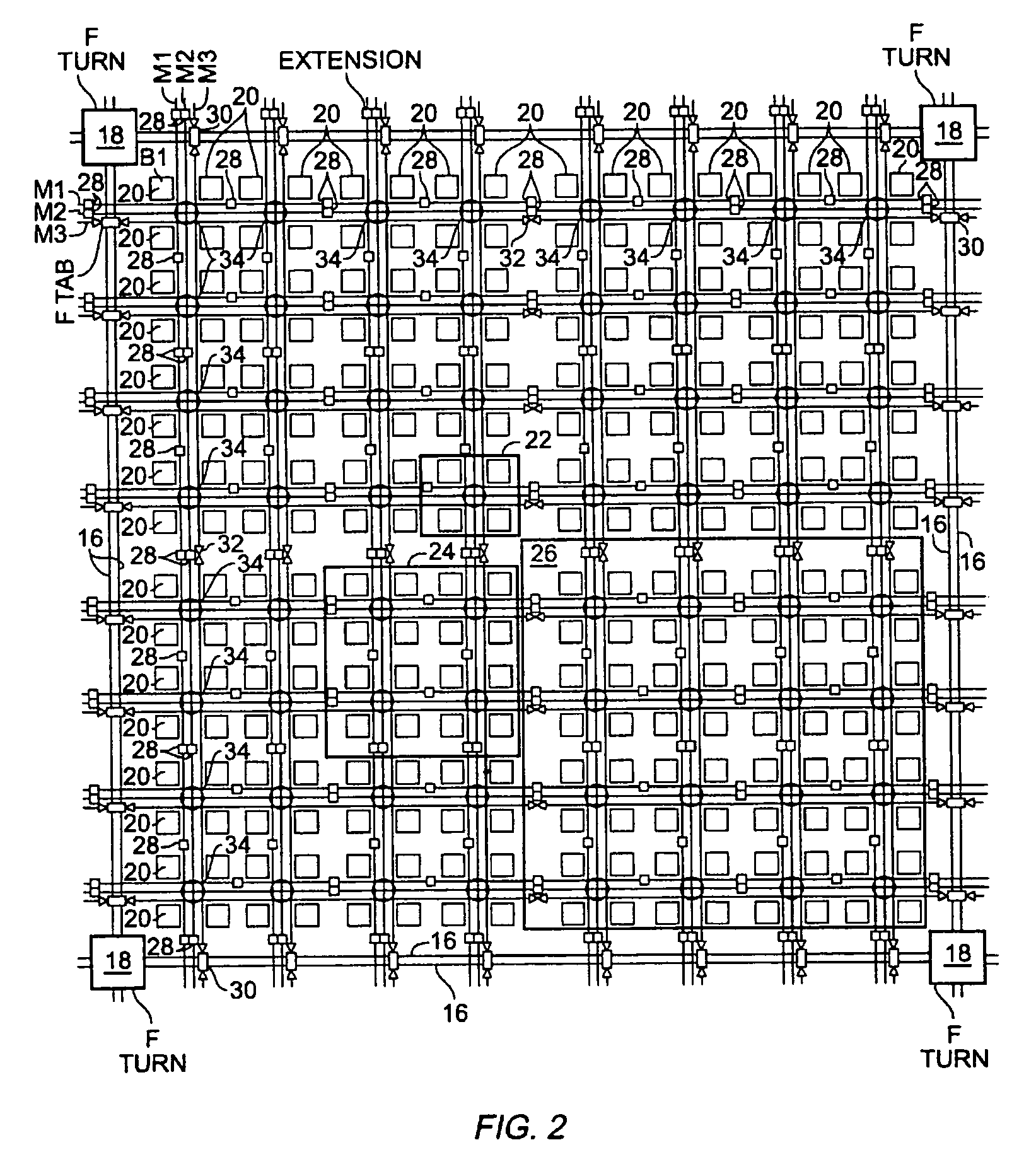
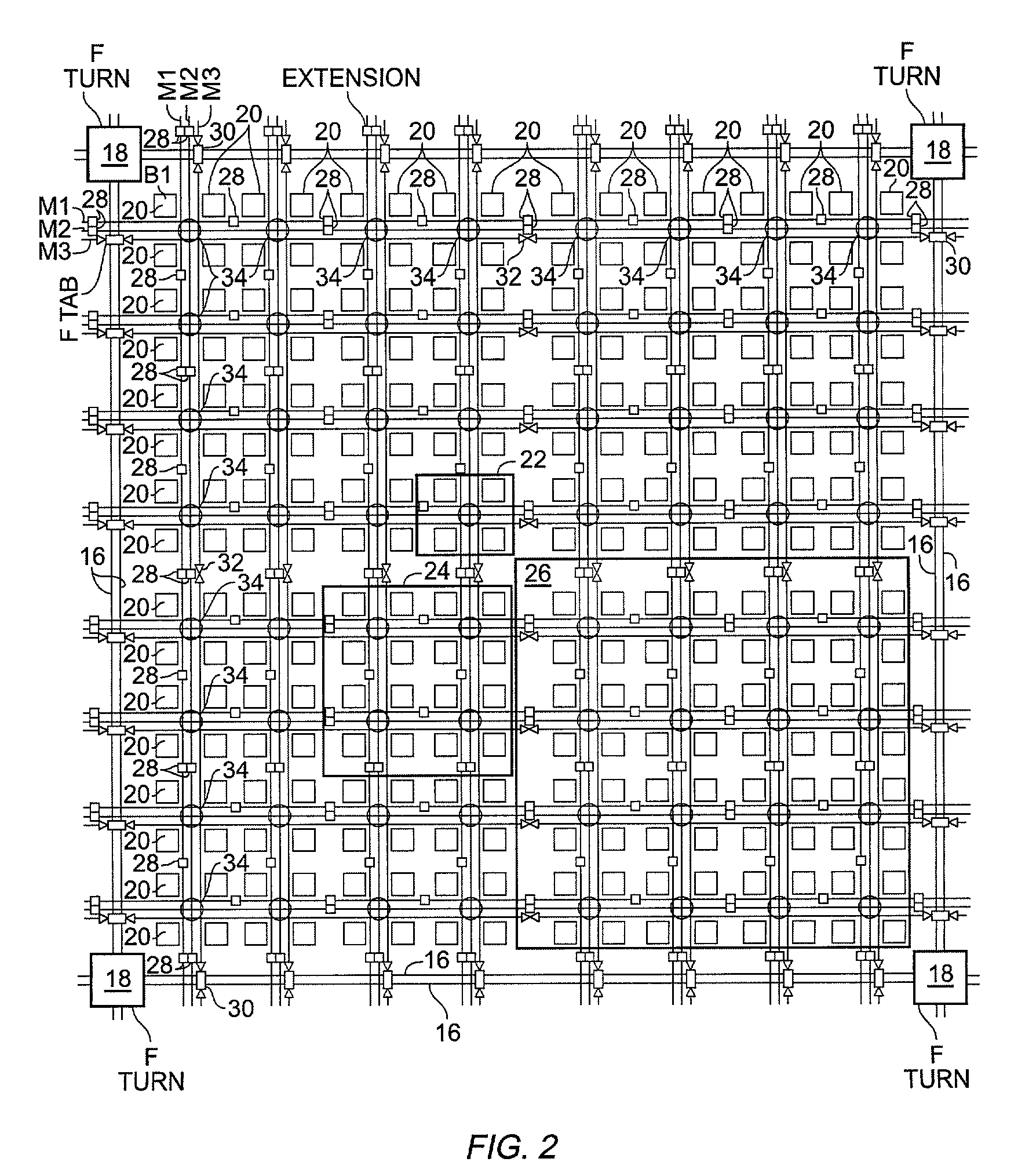
An FPGA architecture has top, middle and low levels. The top level of the architecture is an array of the B16x16 tiles arranged in a rectangular array and enclosed by I / O blocks on the periphery. On each of the four sides of a B16x16 tile, and also associated with each of the I / O blocks is a freeway routing channel. A B16x16 tile in the middle level of hierarchy is a sixteen by sixteen array of B1 blocks. The routing resources in the middle level of hierarchy are expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3 including groups of interconnect conductors. At the lowest level of the semi-hierarchical FPGA architecture, there are block connect (BC) routing channels, local mesh (LM) routing channels, and direct connect (DC) interconnect conductors to connect the logic elements to further routing resources. Within the B1 block, a horizontal BC routing channel is disposed between two upper and two lower clusters of devices, and a vertical BC routing channel is disposed between two clusters of devices on the left side of the B1 block and two clusters of devices on the right side of the B1 block. The BC routing channel forms intersections with the inputs and outputs of the devices in the clusters. The horizontal BC routing channel forms a first diagonally hardwired connection with a routing channel that effectively sends the horizontal BC routing channel in a vertical direction. A second diagonally hardwired connection pairwise shorts the horizontal and vertical BC routing channels to provide dual accessibility to the logic resources in the B1 block from more than one side. Disposed between the first diagonally hardwired connection and the second diagonally hardwired connection is a BC splitting extension which provides a programmable one-to-one coupling between the interconnect conductors of the horizontal BC routing channel on either side of the BC splitting extension.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Block symmetrization in a field programmable gate array
InactiveUS7233167B1Improve routabilityGood symmetryLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsComputation using denominational number representationMultiplexingFpga architecture
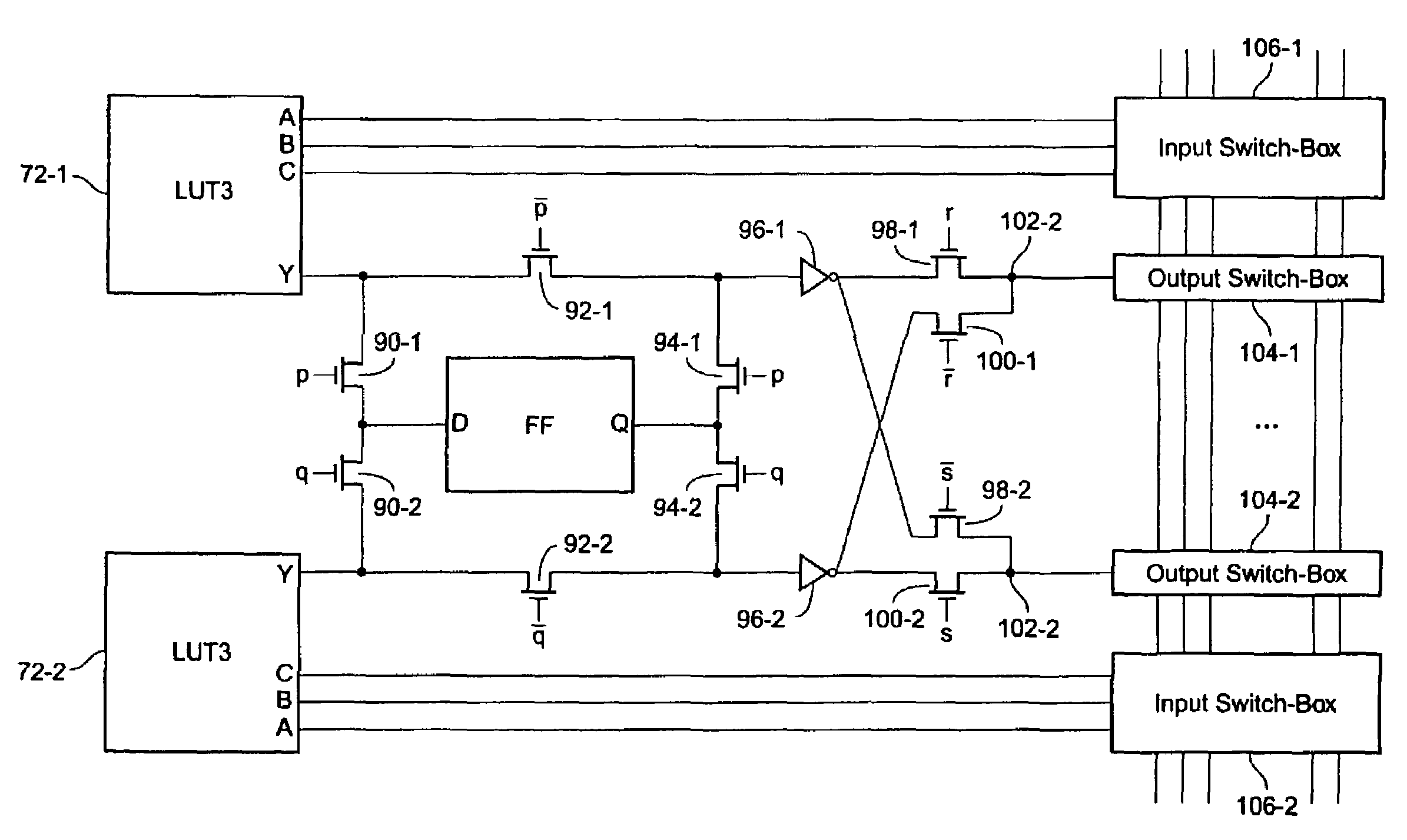
An FPGA architecture has top, middle and low levels. The top level is an array of B16×16 tiles enclosed by I / O blocks. The routing resources in the middle level are expressway routing channels including interconnect conductors. At the lowest level, there are block connect routing channels, local mesh routing channels, and direct connect interconnect conductors to connect the logic elements to further routing resources. Each B1 block includes four clusters of devices. Each of the clusters includes first and second LUT3s, a LUT2, and a DFF. Each of the LUT3s have three inputs and one output. Each of the LUT2s have two inputs and one output. Each DFF has a data input and a data output. In each of the clusters the outputs of the LUT3s are multiplexed to the input of DFF, and symmetrized with the output of the DFF to form two outputs of each of the clusters.
Owner:ACTEL CORP
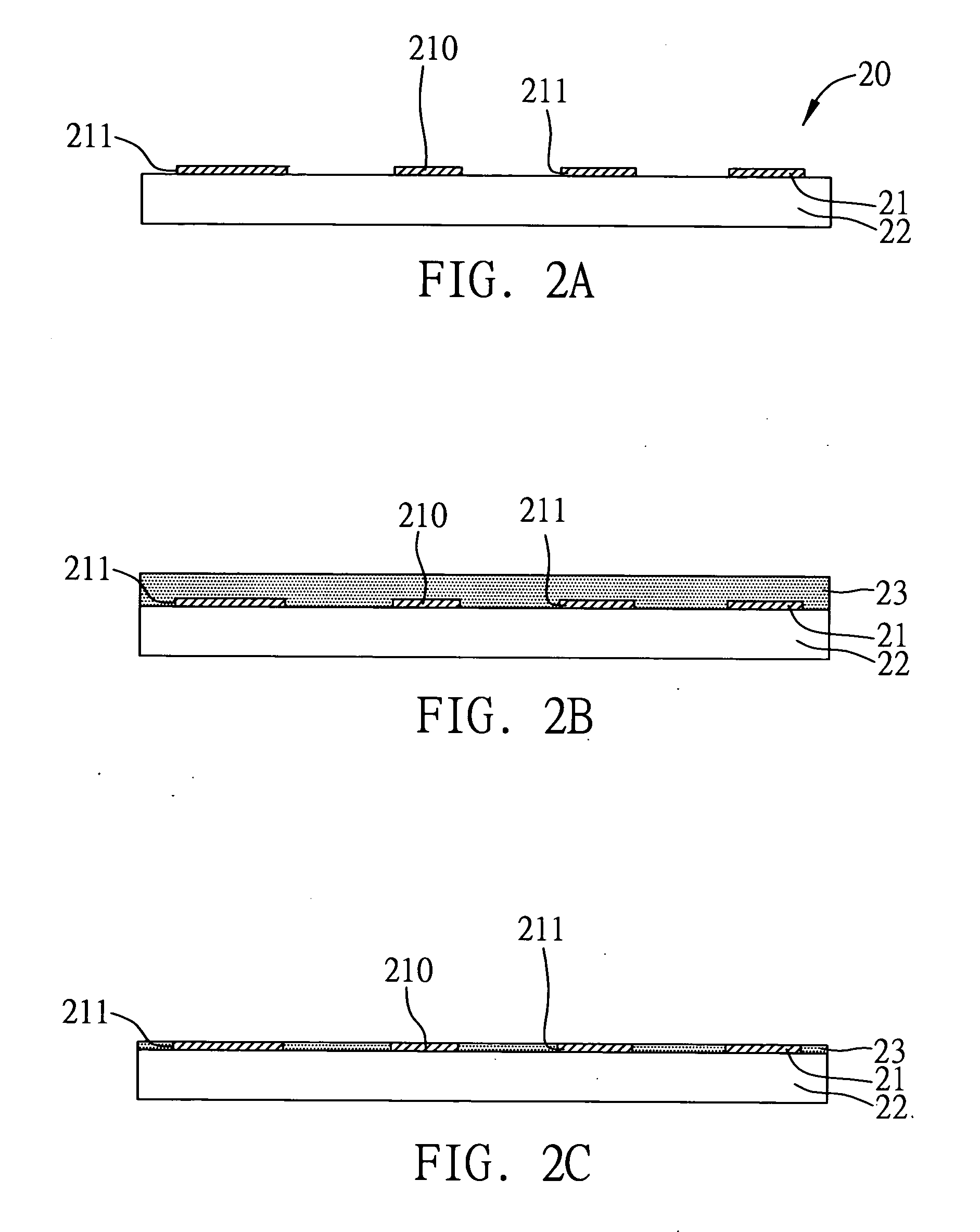
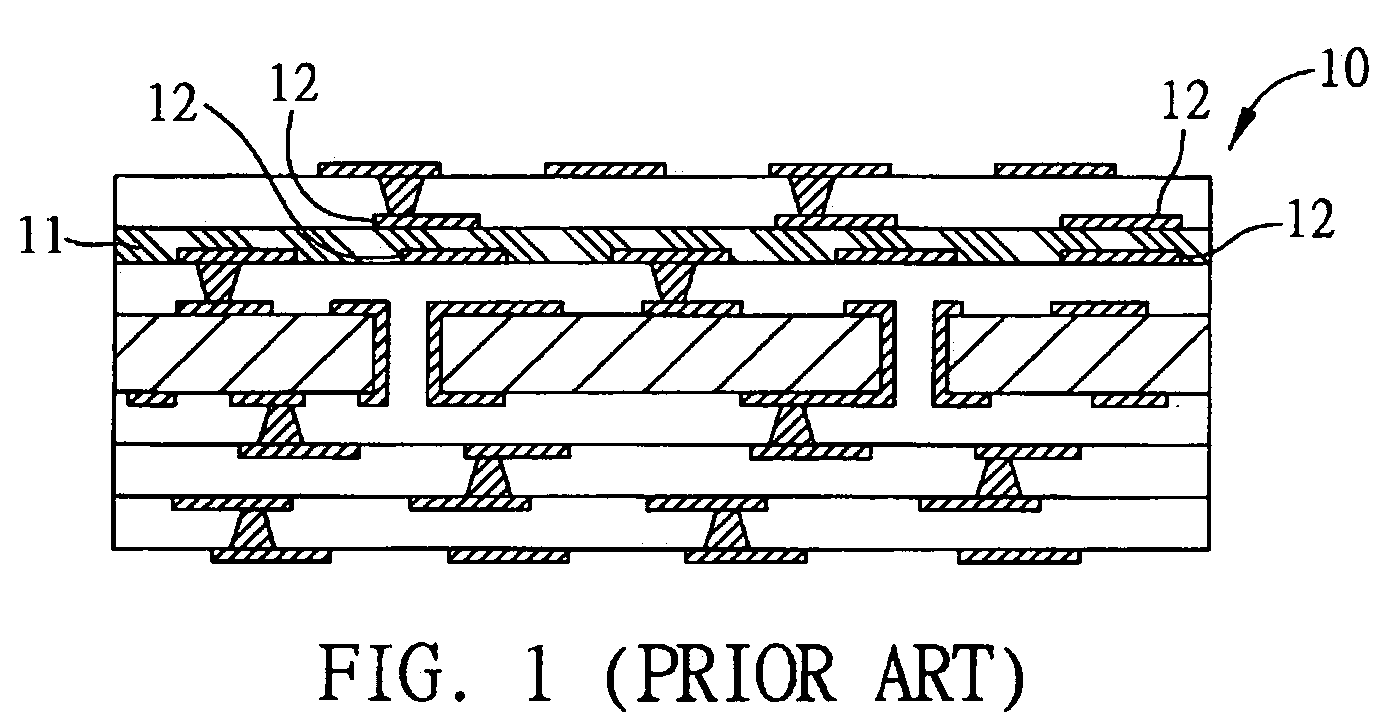
Embedded capacitor structure in circuit board and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050081349A1Improve liquidityEnsure reliabilityElectrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceDielectric layer
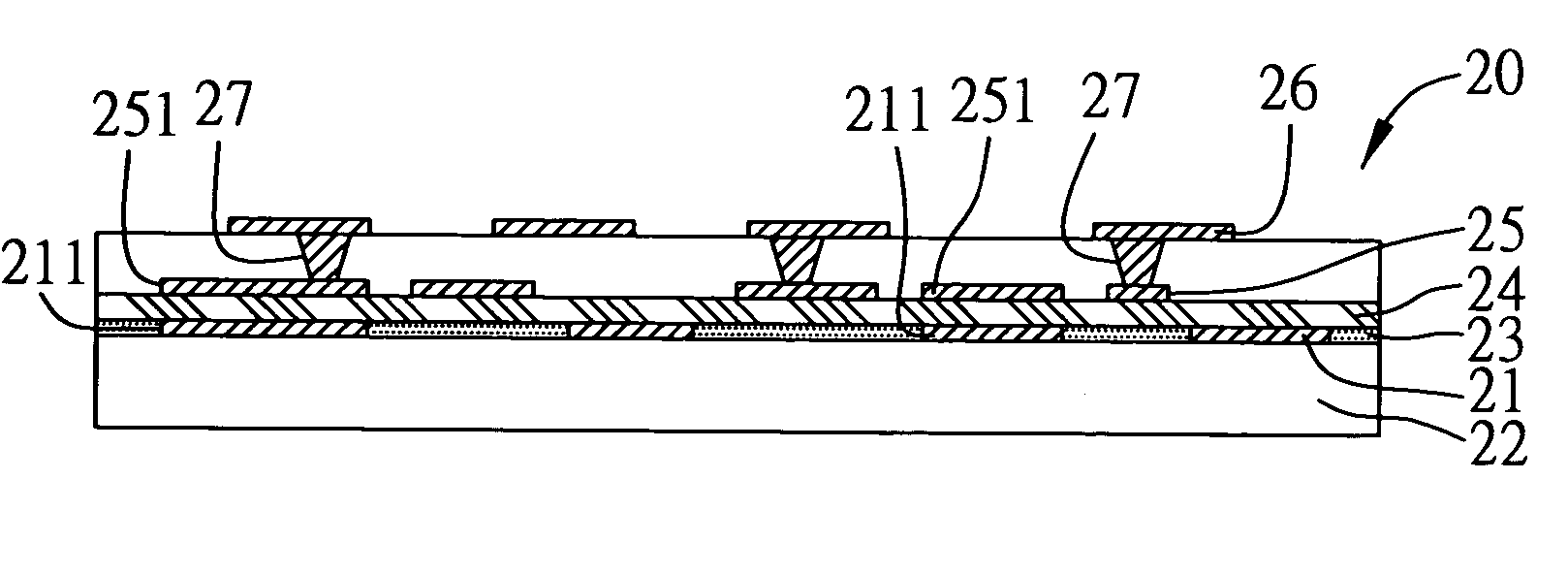
An embedded capacitor structure in a circuit board and a method for fabricating the same are proposed. The circuit board is formed with a first circuit layer on at least one surface thereof, wherein the first circuit layer has at least one first electrode plate for the capacitor structure. Then, a dielectric layer is formed on the first circuit layer and made flush with the first circuit layer. The dielectric layer has a relatively low dielectric constant and good fluidity to effectively fill the spaces between patterned traces of the first circuit later. A capacitive material is deposited on the dielectric layer and the first circuit layer. Finally, a second circuit layer is formed on the capacitive material and has at least one second electrode plate corresponding to the first electrode plate, together with the capacitive material disposed in-between, to form the capacitor structure.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
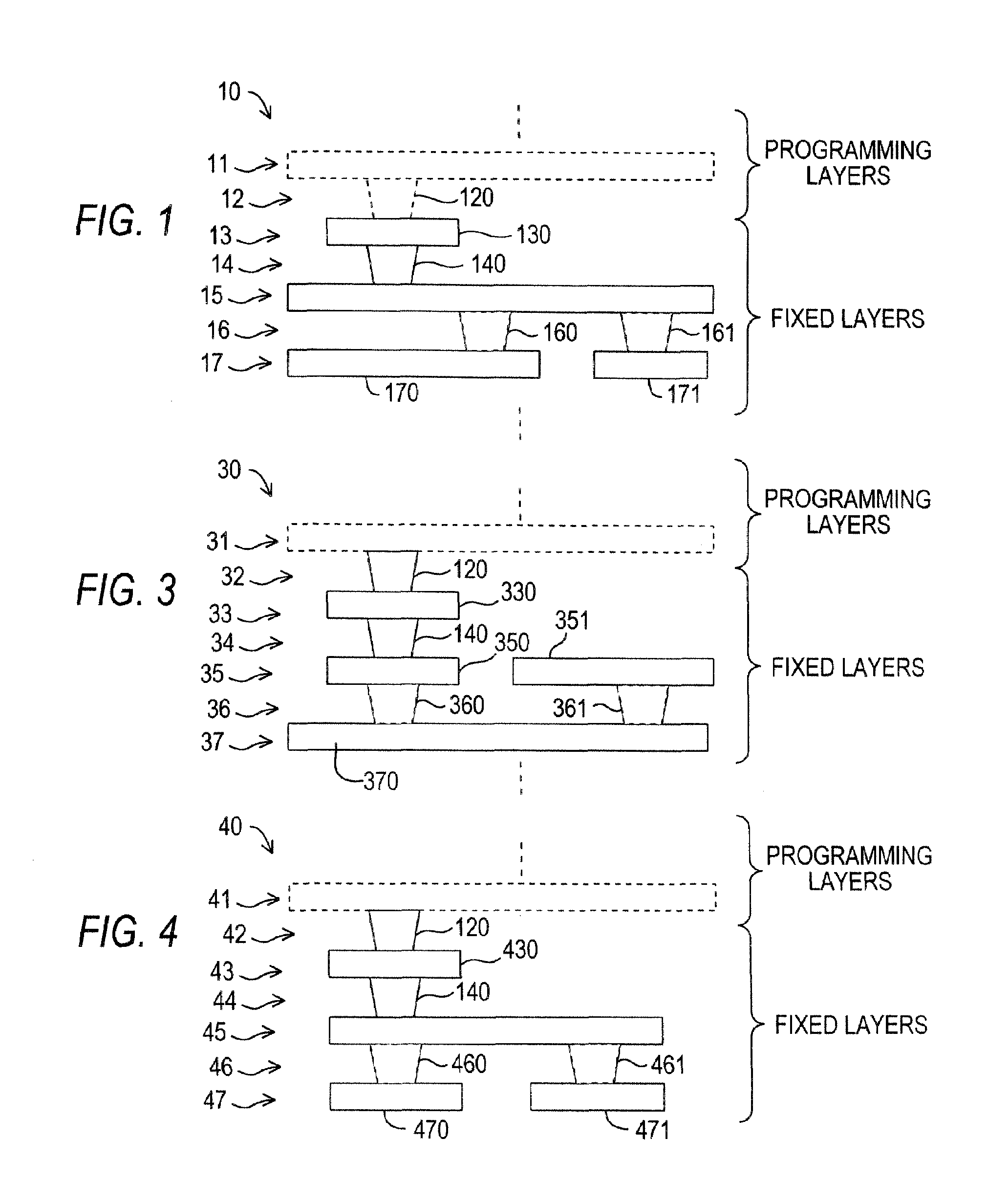
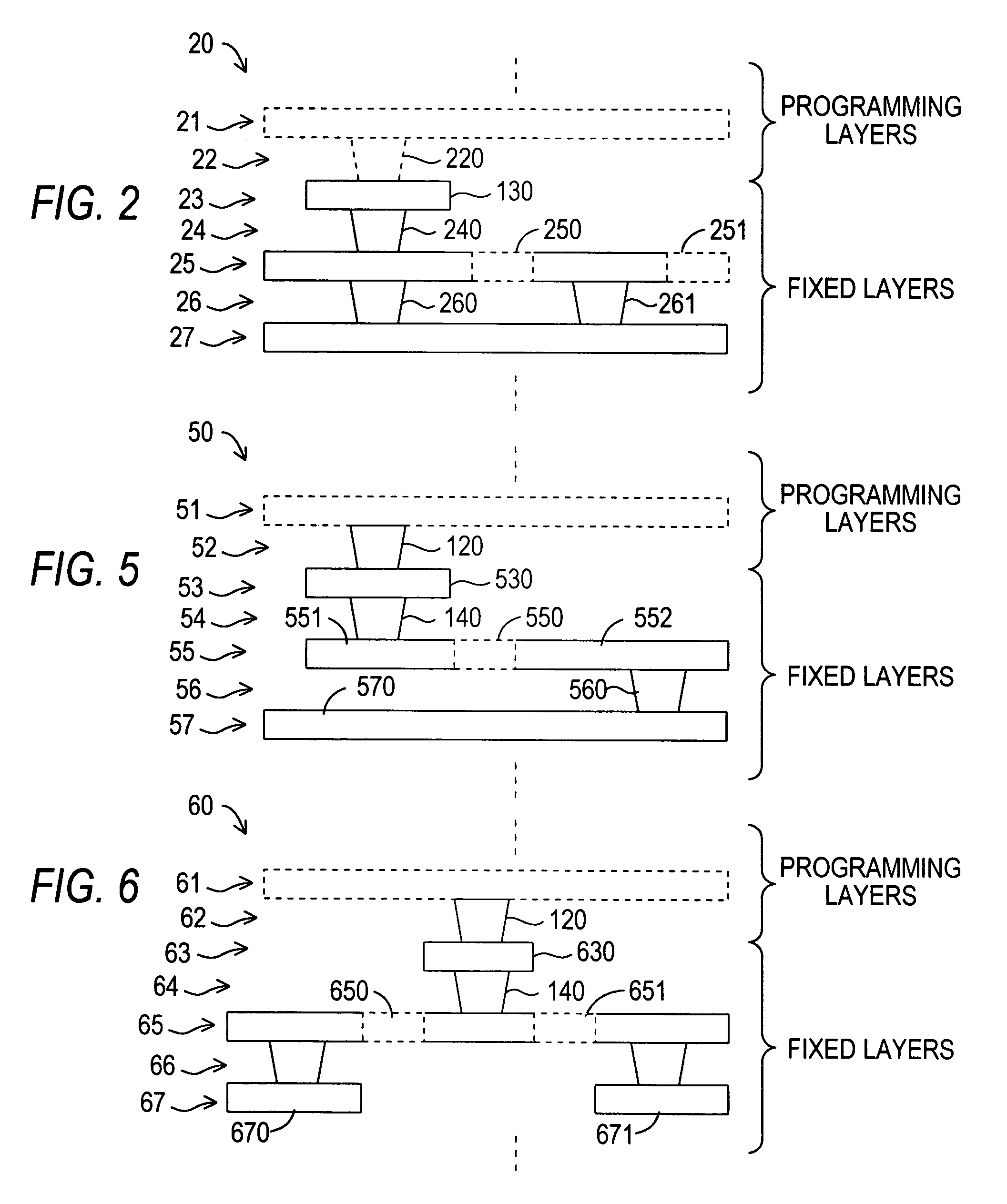
Structured asic layout architecture having tunnel wires
InactiveUS20080116932A1Low costSave routing resourceSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsEngineeringBody region
The present invention discloses a structured ASIC layout architecture, which includes a fixed body region and a programmable layout region. The fixed body region includes a tunnel wire or multiple tunnel wires for providing a function capability or multiple function capability. The programmable layout region is disposed on the fixed body region and is connected to the fixed body region, wherein the programmable layout region utilizes the tunnel wires of the fixed body region to propagate electrical signals.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
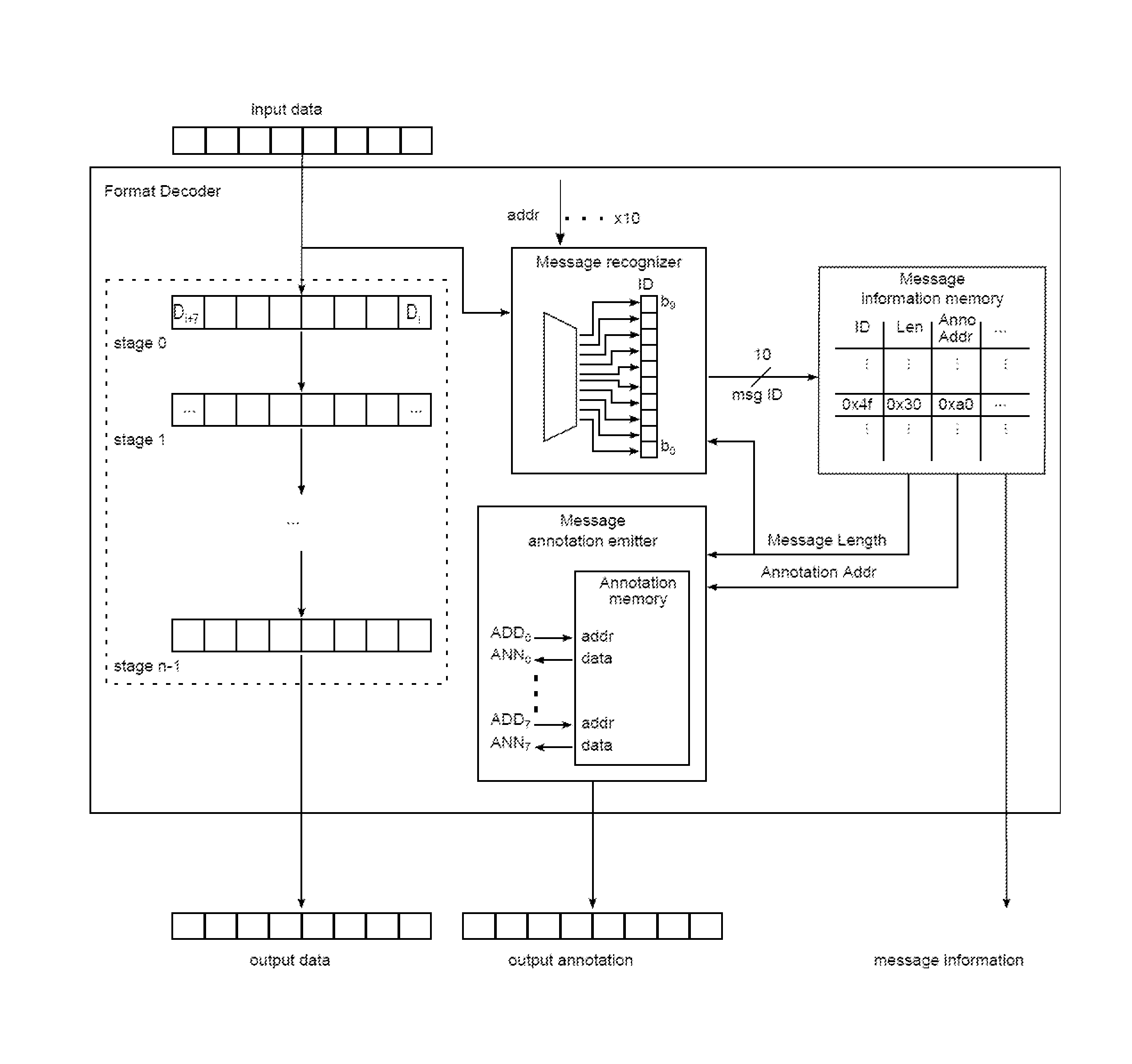
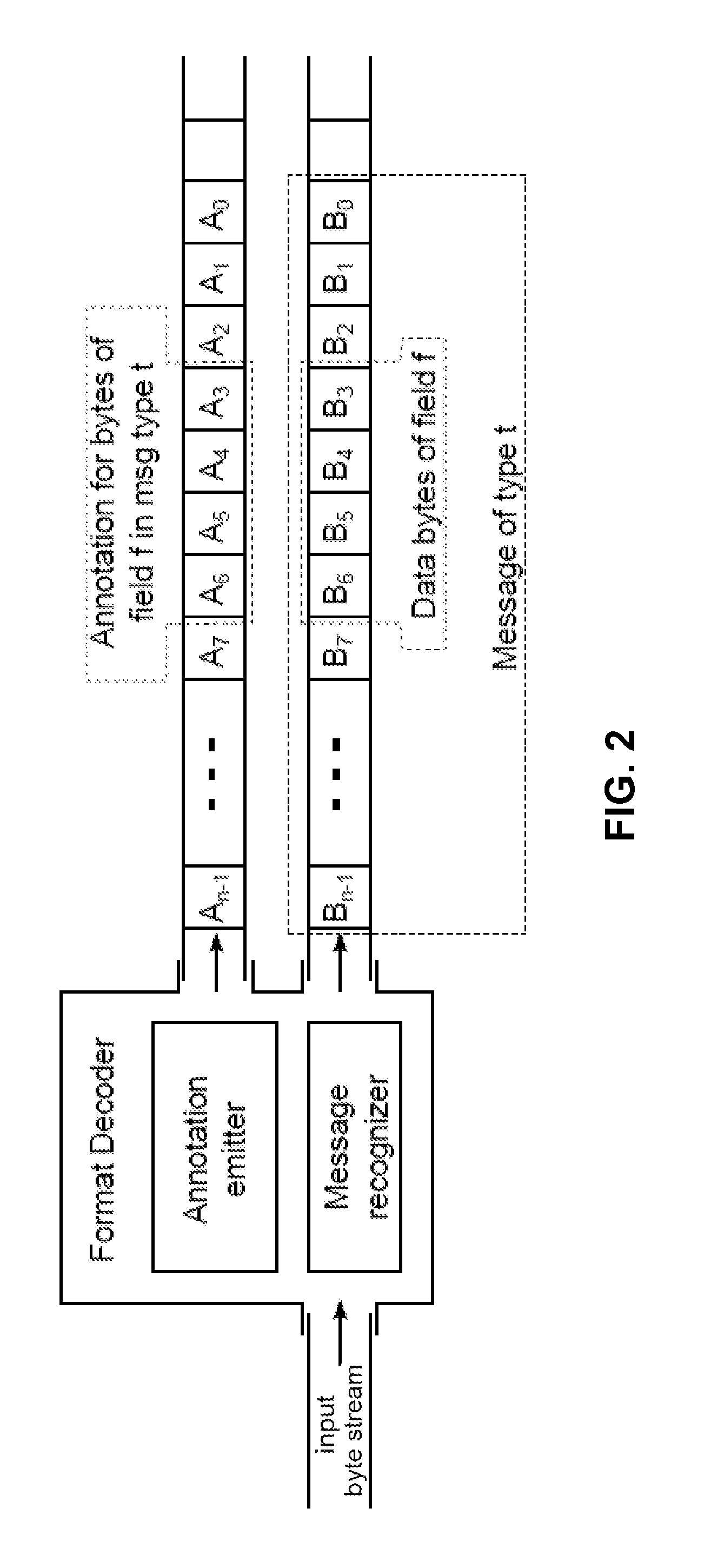
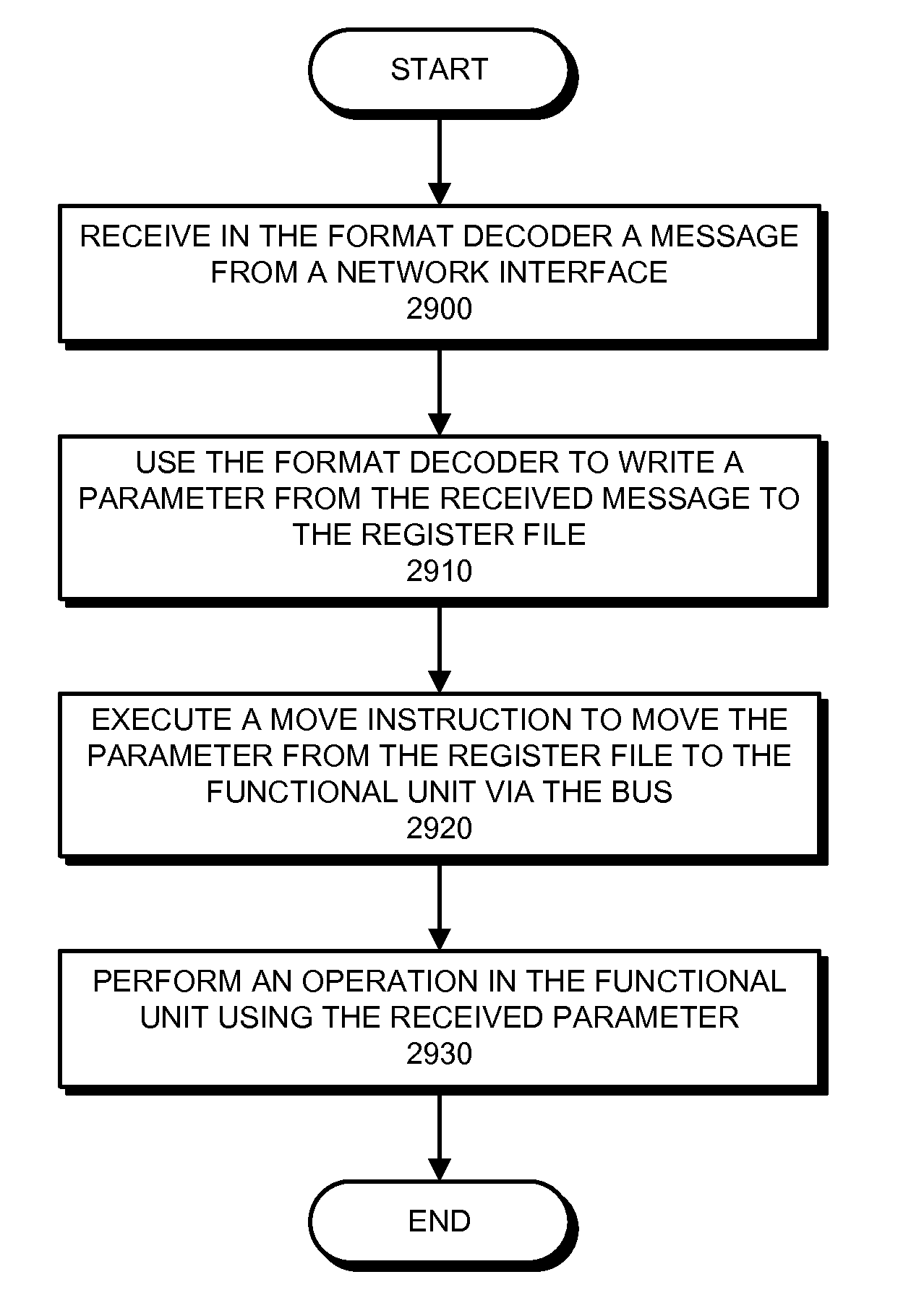
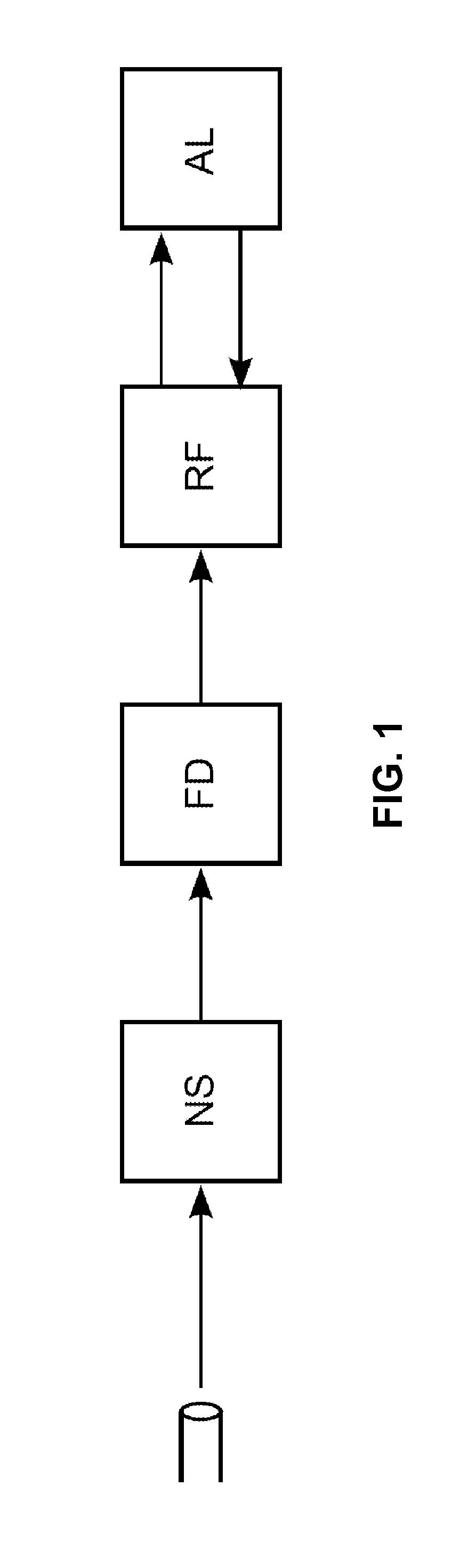
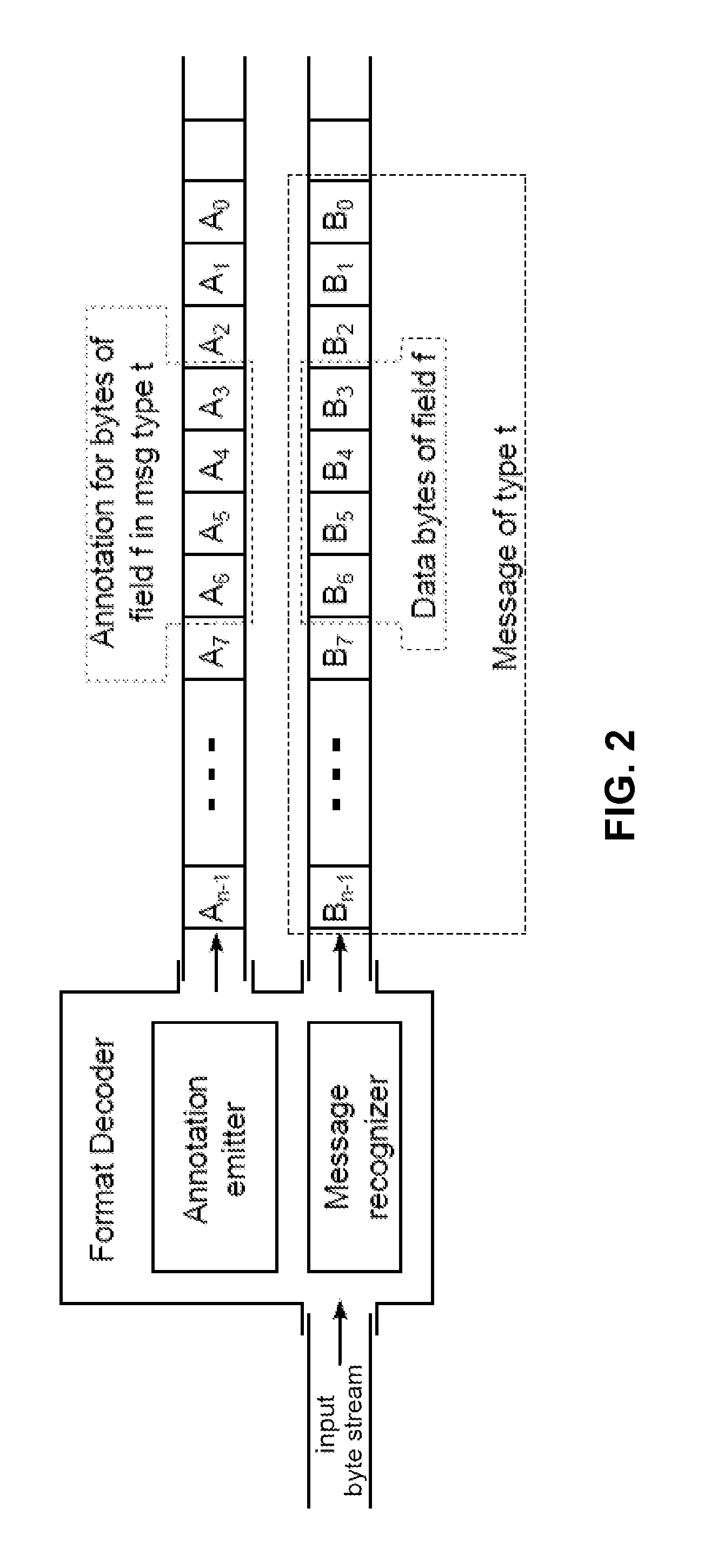
Using a single-instruction processor to process messages
ActiveUS20150193233A1Increase the number ofImprove routabilityRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisProcessor registerOperand
The disclosed embodiments describe single-instruction processors that operates upon messages received from a network interface. A single-instruction processor comprises a register file, a functional unit, a bus connecting the register file and the functional unit, and a format decoder that receives messages from a network interface. This single-instruction processor supports a single instruction type (e.g., a “move instruction”) that specifies operands to be transferred via the bus. During operation, the format decoder is configured to write a parameter from a received message to the register file. A move instruction moves this parameter from the register file to the functional unit via the bus. The functional unit then uses the parameter to perform an operation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Buffer insertion to reduce wirelength in VLSI circuits
InactiveUS20090013299A1Shorten the line lengthImprove routabilityGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingBuffer zone
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
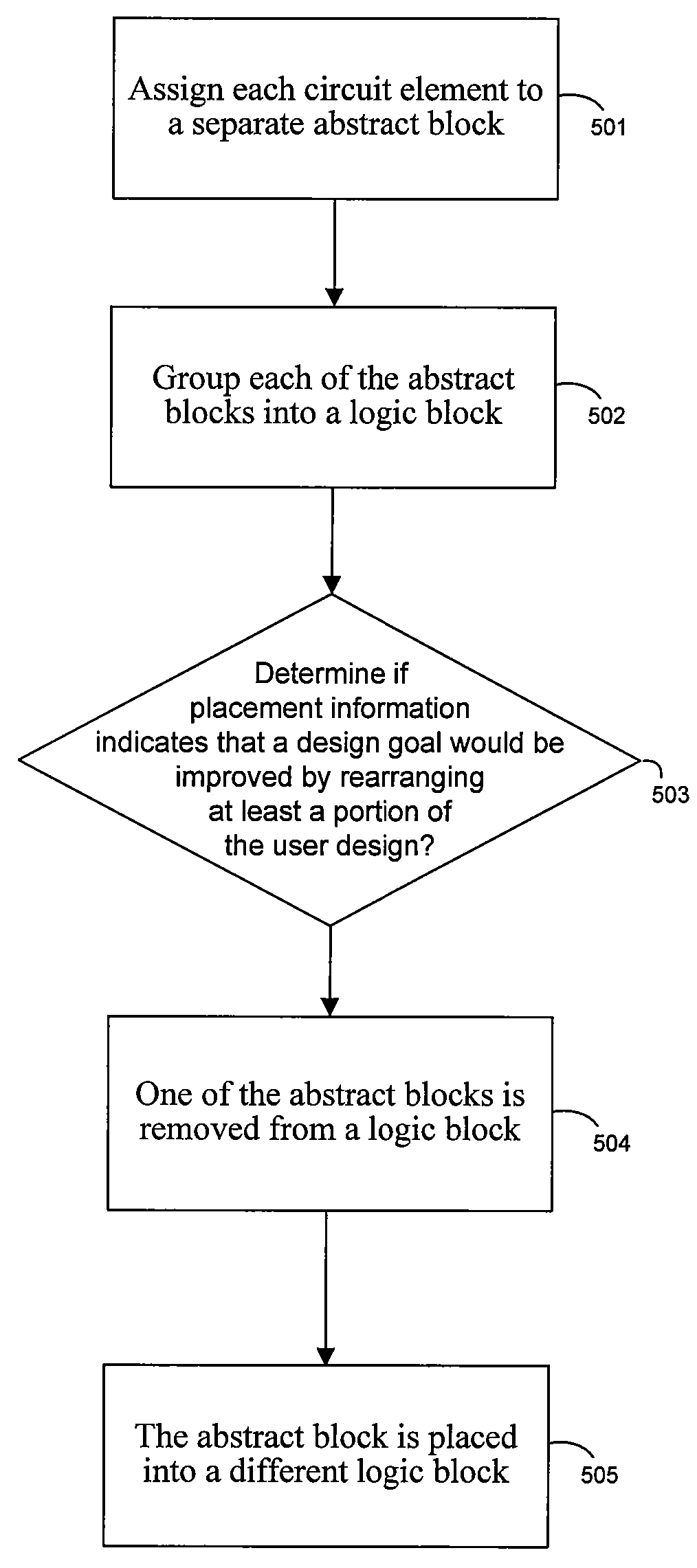
Techniques for grouping circuit elements into logic blocks
InactiveUS7707532B1Improve routabilityProgram controlAerodynamics improvementTheoretical computer scienceComputer science
Techniques are provided for grouping circuits in a user design for a programmable integrated circuit into logic blocks. A packing tool separates each circuit element into individual abstract blocks and groups the abstract block into logic blocks. A determination is made whether placement information indicates that a design goal would be improved by rearranging at least a portion of the user design. The user design can be rearranged by moving one or more of the abstract blocks into different logic blocks than the ones they were previously grouped with. Circuit elements in the same logic block can be separated and placed into different logic blocks to improve routability of the user design and signal timing.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
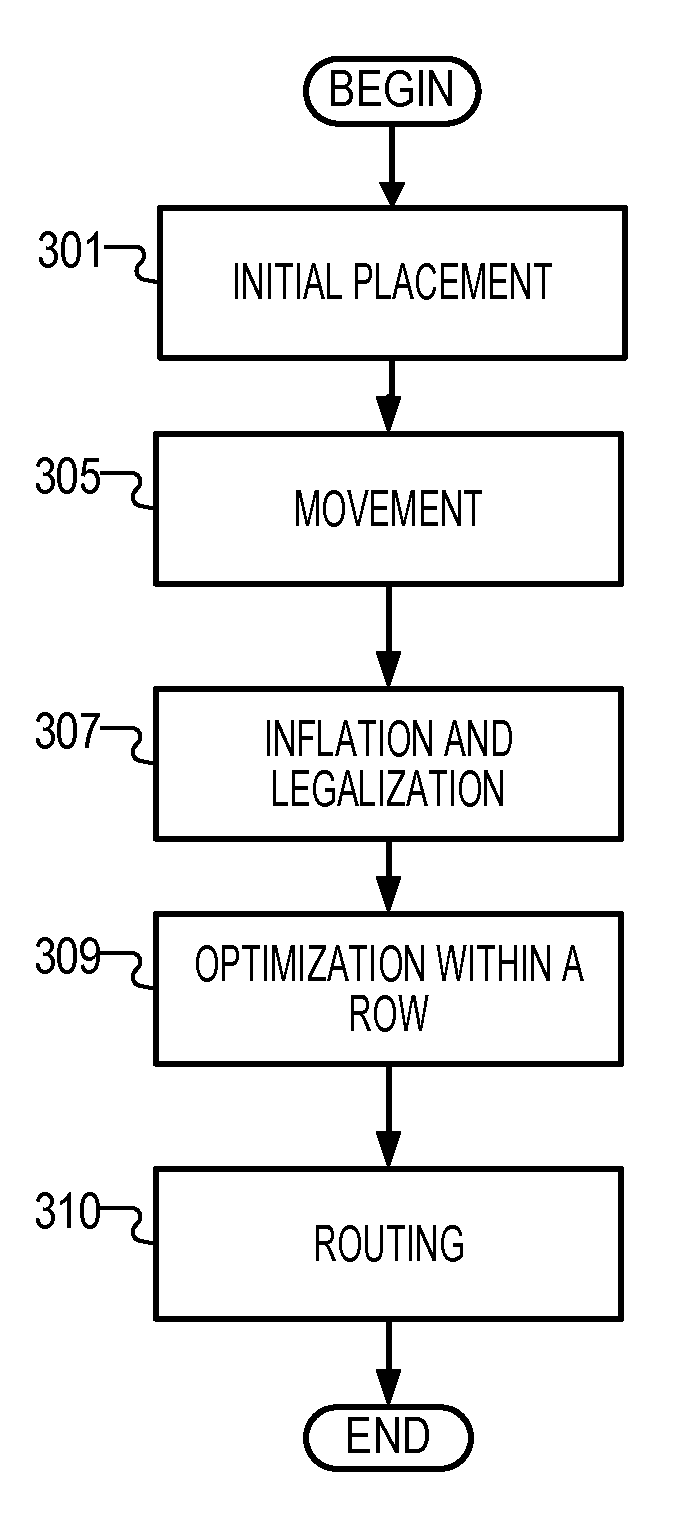
Post-placement cell shifting
InactiveUS8495534B2Detailed routing cost distributionLow costComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData processing systemAlgorithm
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Package stucture and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20160181193A1Increasing routable regionSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorElectronic component
A package structure and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The method includes forming a first wiring layer on a carrier board, forming a plurality of first conductors on the first wiring layer, encapsulating the first wiring layer and the first conductors with a first insulating layer, forming a second wiring layer on the first insulating layer, forming a plurality of second conductors on the second wiring layer, encapsulating the second wiring layer and the second conductors with a second insulating layer, and forming at least one opening in the second insulating layer. The at least one opening extends to a second surface of the first insulating layer, such that at least one electronic component can be disposed in the at least one opening. With forming two insulating layers first followed by forming the at least one opening, there is no need to stack or laminate the substrate that already has an opening, and the electronic component is free of displacement due to any compression. Therefore, a package structure thus fabricated has an increased yield rate.
Owner:PHOENIX PIONEER TECH
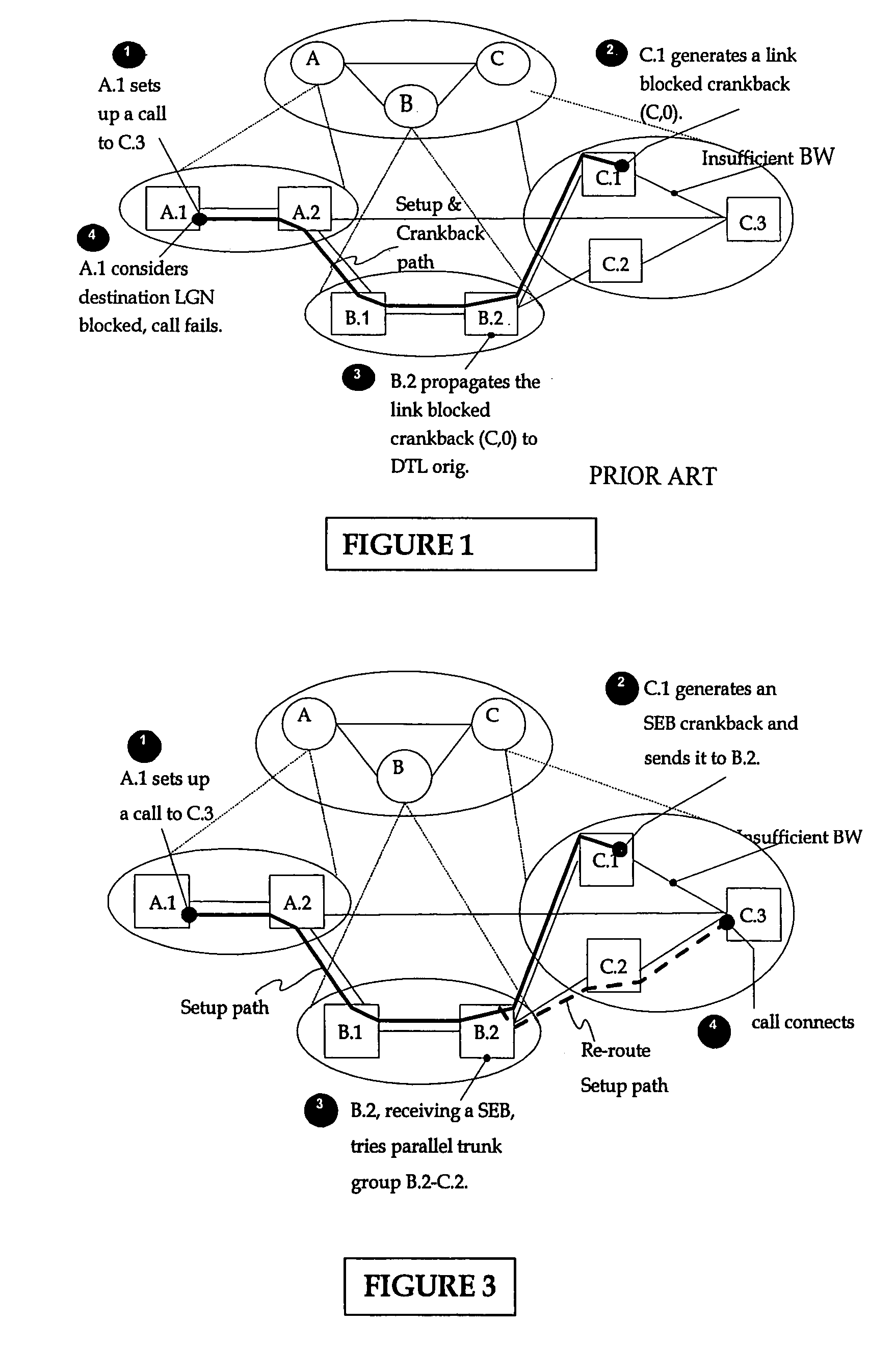
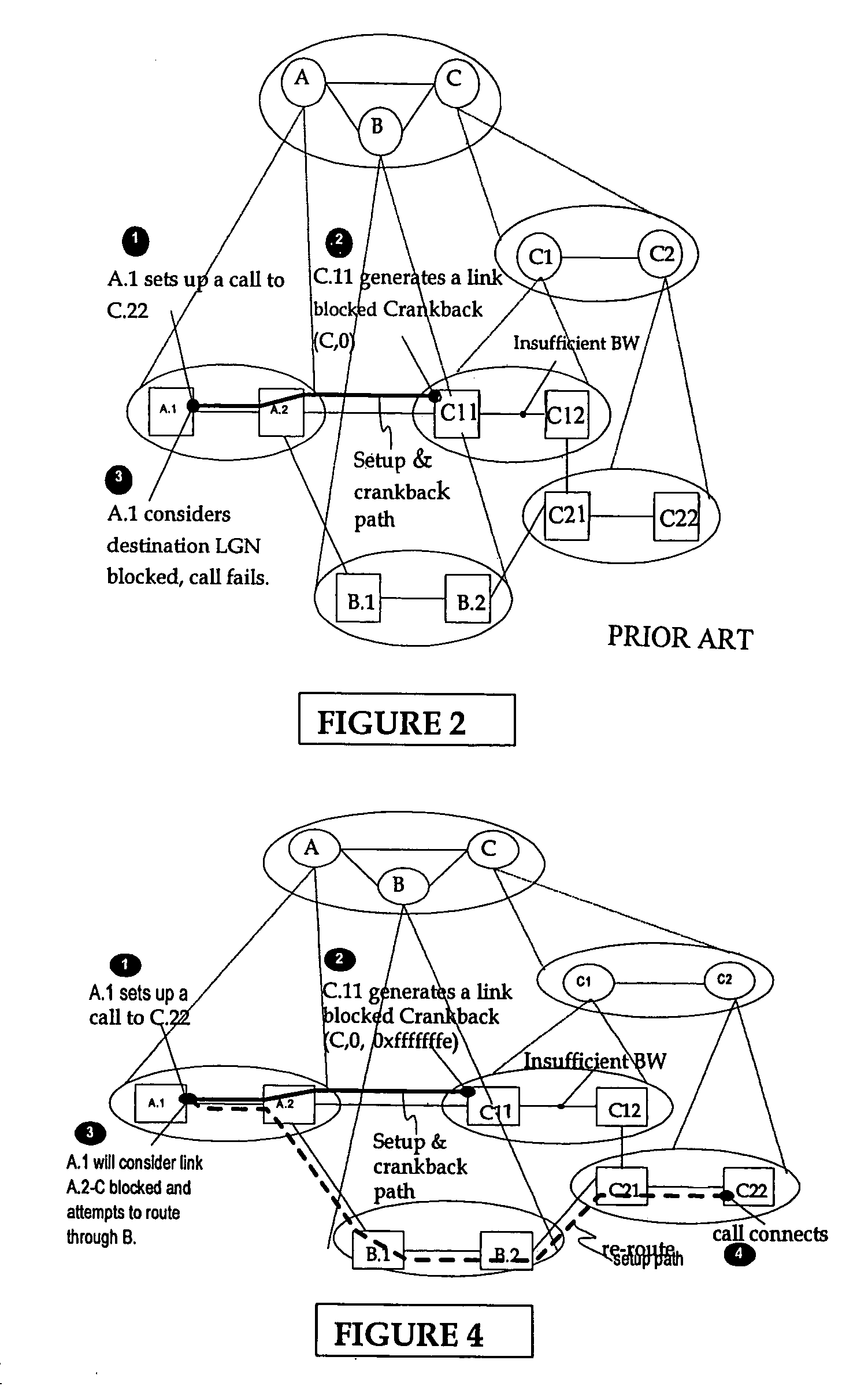
Procedures for improving call routing in PNNI networks
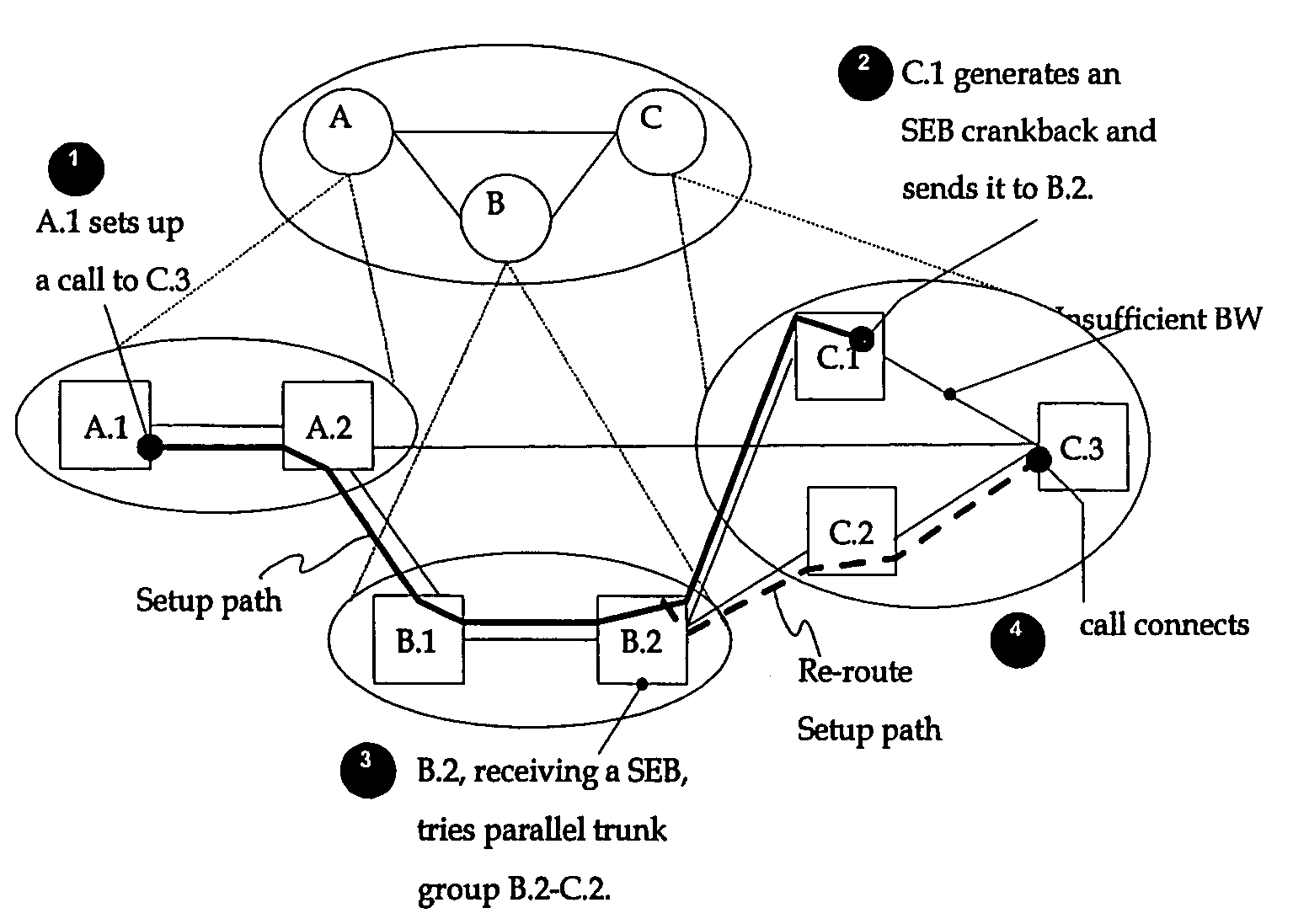
ActiveUS7283467B2Improve routabilityReduce call blockingError preventionTransmission systemsMessage passingComputer science
A method and system for improving call routing in a PNNI network using crankback messaging. A destination logical group node (LGN) blocked crankback procedure is used by entry border nodes, in the event of a failed connection attempt, to instruct preceding routing capable nodes to route the connection over another link. If the entry border node is in the lowest level peer group a Succeeding End Blocked (SEB) crankback message is sent to the preceding routing-capable node. If the entry border node is not in the lowest level peer group, a destination LGN blocked crankback message is sent to the preceding routing-capable node wherein the message has special information to signal the routing node that the link into the destination LGN is blocked.
Owner:ALCATEL CANADA
Block connector splitting in logic block of a field programmable gate array
InactiveUS20020011870A1Good symmetryEasy to placeSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsElectrical conductorComputer science
A logic block in a field programmable gate array comprises a plurality of clusters of logic devices. At least one of the logic devices in each of the clusters has an input or an output. A first set of interconnect conductors enters the logic block from a first side and forming a programmable intersection with the input or the output of at least one of the logic devices in each of the clusters. A second set of interconnect conductors enters the logic block from a second side and forming a programmable intersection with the input or output of one of the logic devices in each cluster, the first set of interconnect conductors forming a pairwise hardwired connection with the second set of interconnect conductors. An interconnect conductor splitting extension is disposed between the first set of interconnect conductors and the second set of interconnect conductors.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
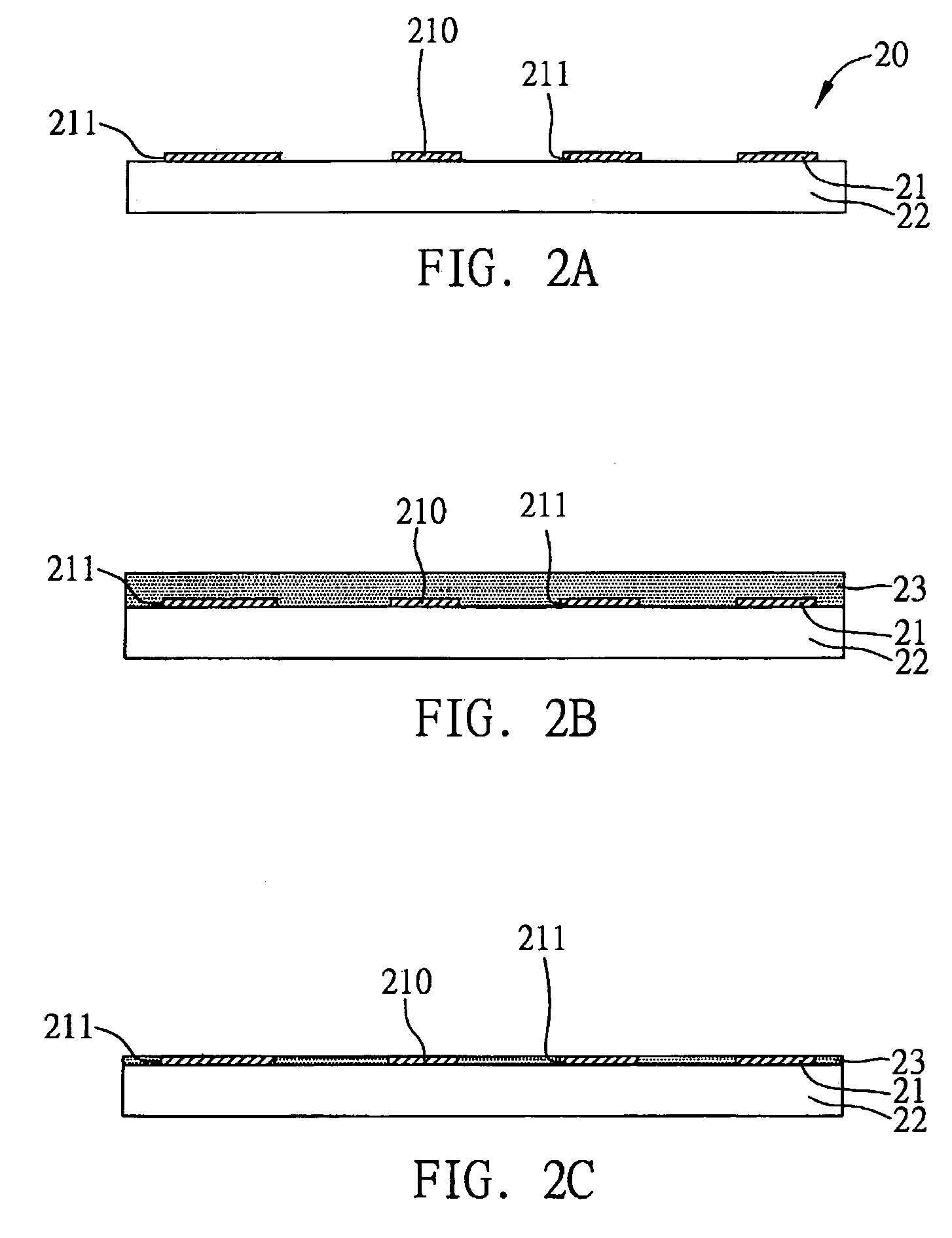
Semiconductor package with enhanced chip groundability and method of fabricating the same
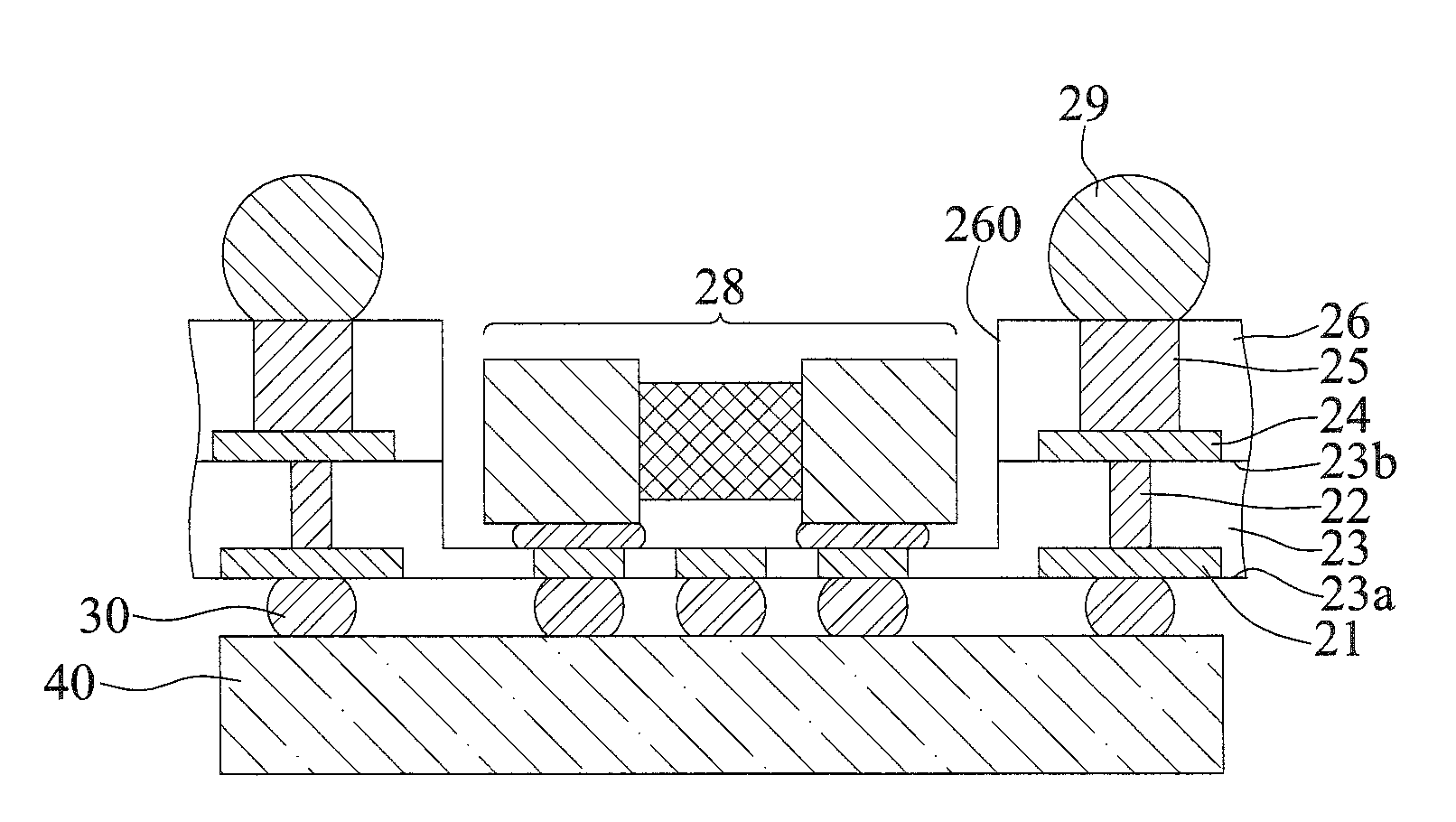
ActiveUS6903441B2Reduce numberEnhance routabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround planeGround line
A semiconductor package and a fabrication method thereof are provided, in which a ground pad on a chip is electrically connected to a ground plane on a substrate by means of an electrically-conductive wall formed over a side surface of the chip and an electrically-conductive adhesive used for attaching the chip to the substrate. Therefore, a wire-bonding process is merely implemented for power pads and signal I / O (input / output) pads on the chip without having to form ground wires on the ground pads for electrical connection purposes. This benefit allows the use of a reduced number of bonding wires and simplifies wire arrangement or routability. And, a grounding path from the chip through the electrically-conductive wall and electrically-conductive adhesive to the substrate is shorter than the conventional one of using ground wires, thereby reducing a ground-bouncing effect and improving electrical performances of the semiconductor package.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
Novel substrate design for semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080246147A1Improve routabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit boardSolder ball
A novel design and method of fabricating a semiconductor device. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention is a flip chip package including a BT substrate. On the side of the substrate facing the die, thin traces are formed of an enhanced conductive material. Conductive bumps such as eutectic solder balls are then mounted on the traces, and the die mounted to the bumps. The die then packaged and mounted to a printed circuit board using, for example, a ball grid array.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Mask-programmable logic device with programmable input/output ports
InactiveUS7304496B2Easy to parallelImprove routabilitySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceMacrocell
A mask-programmable logic device includes a macrocell having an external input / output port for “place-and-route” programming by addition of metallization layers. A programmable “fixed” layer allows the external input / output port to be isolated from the remainder of the macrocell so that it “floats,” allowing signals to be routed through the external input / output port when the macrocell is not in use, to reduce routing blockages. The macrocell also may have at least one internal input / output port, potentially connected to different logic circuits, and a programmable “fixed” layer that can be used to control which internal input / output port is connected to the external input / output port. By thus allowing multiple logic circuits to share a single external input / output port, routing blockages are reduced.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Using a single-instruction processor to process messages
ActiveUS9471316B2Increase the number ofImprove routabilityRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisProcessor registerOperand
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Post-placement cell shifting
InactiveUS20130346938A1Detailed routing cost distributionLow costComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwareCellular Expansion
A computer implemented method for reworking a plurality of cells initially placed in a circuit design. An expander allocates cells to tiles. The expander determines a high detailed routing cost tile class, wherein the high detailed routing cost tile class is a class of tiles that has high detailed routing costs. The expander selects a cell within a tile of the high detailed routing cost tile class to form a selected cell in a selected tile. The expander applies multiple techniques to reposition these cells at new locations to improve the detailed routability. The expander can place an expanded bounding box around the selected cell, wherein the bounding box extends to at least one tile adjacent the selected tile, and repositions the selected cell within the bounding box to form a modified design to improve the detailed routability. The expander may also inflate and legalize those cells.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Mask-programmable logic device with programmable input/output ports
InactiveUS20060279324A1Increase routabilityReduces blockageSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceMacrocell array
A mask-programmable logic device includes a macrocell having an external input / output port for “place-and-route” programming by addition of metallization layers. A programmable “fixed” layer allows the external input / output port to be isolated from the remainder of the macrocell so that it “floats,” allowing signals to be routed through the external input / output port when the macrocell is not in use, to reduce routing blockages. The macrocell also may have at least one internal input / output port, potentially connected to different logic circuits, and a programmable “fixed” layer that can be used to control which internal input / output port is connected to the external input / output port. By thus allowing multiple logic circuits to share a single external input / output port, routing blockages are reduced.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Embedded capacitor structure in circuit board and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20060063325A1Assure planarity and reliabilityIncrease the number ofTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceDielectric layer
An embedded capacitor structure in a circuit board and a method for fabricating the same are proposed. The circuit board is formed with a first circuit layer on at least one surface thereof, wherein the first circuit layer has at least one first electrode plate for the capacitor structure. Then, a dielectric layer is formed on the first circuit layer and made flush with the first circuit layer. The dielectric layer has a relatively low dielectric constant and good fluidity to effectively fill the spaces between patterned traces of the first circuit later. A capacitive material is deposited on the dielectric layer and the first circuit layer. Finally, a second circuit layer is formed on the capacitive material and has at least one second electrode plate corresponding to the first electrode plate, together with the capacitive material disposed in-between, to form the capacitor structure.
Owner:PHOENIX PRECISION TECH CORP
Post-placement cell shifting
InactiveUS20110302544A1Improve detailed routabilityDetailed routing cost distributionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData processing systemAlgorithm
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer program product for reworking a plurality of cells initially placed in a circuit design. An expander allocates cells to tiles. The expander determines a high detailed routing cost tile class, wherein the high detailed routing cost tile class is a class of tiles that has high detailed routing costs. The expander selects a cell within a tile of the high detailed routing cost tile class to form a selected cell in a selected tile. The expander applies multiple techniques to reposition these cells at new locations to improve the detailed routability. The expander can place an expanded bounding box around the selected cell, wherein the bounding box extends to at least one tile adjacent the selected tile, and repositions the selected cell within the bounding box to form a modified design to improve the detailed routability. The expander may also inflate and legalize those cells.
Owner:IBM CORP
Chip and power planning method
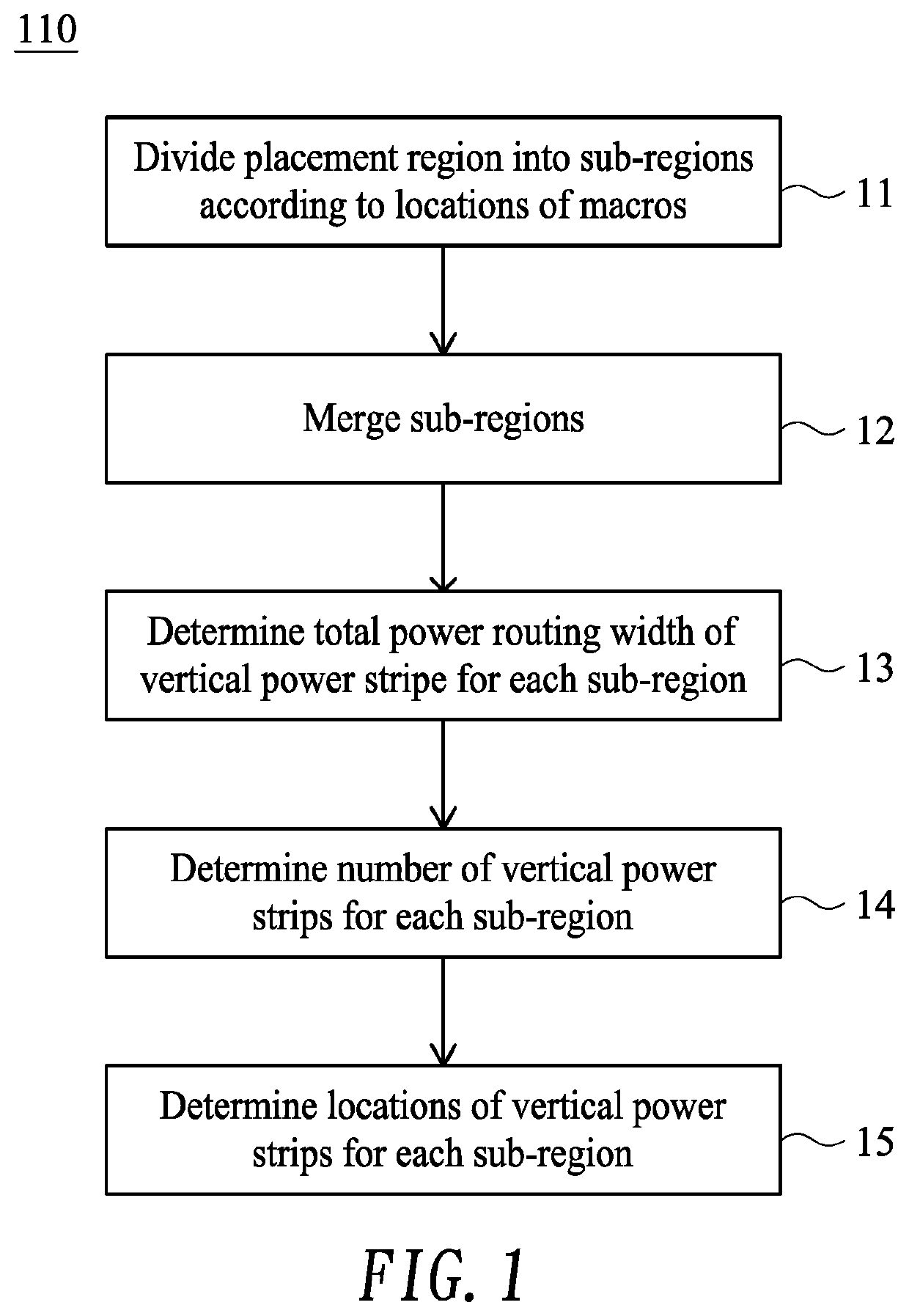
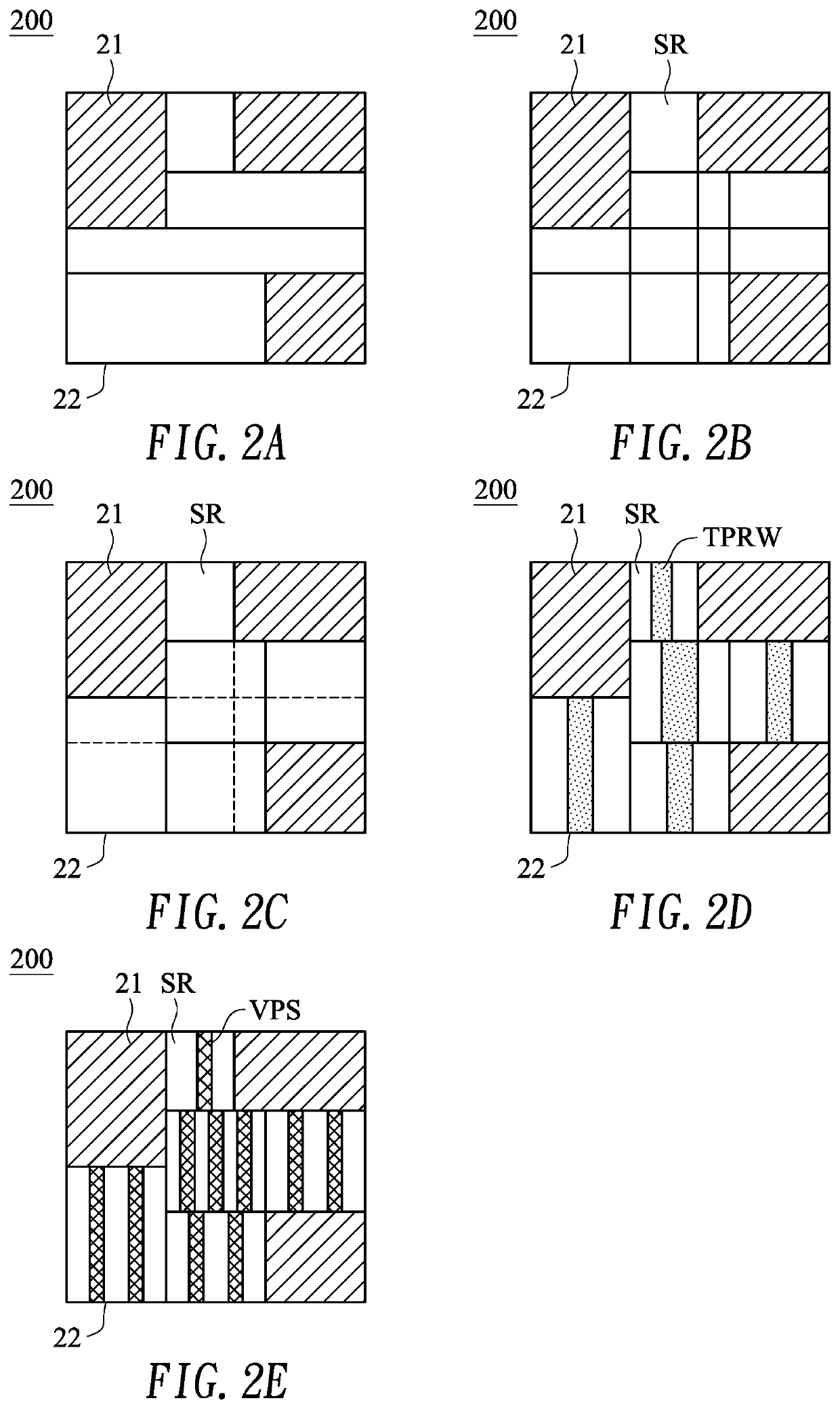
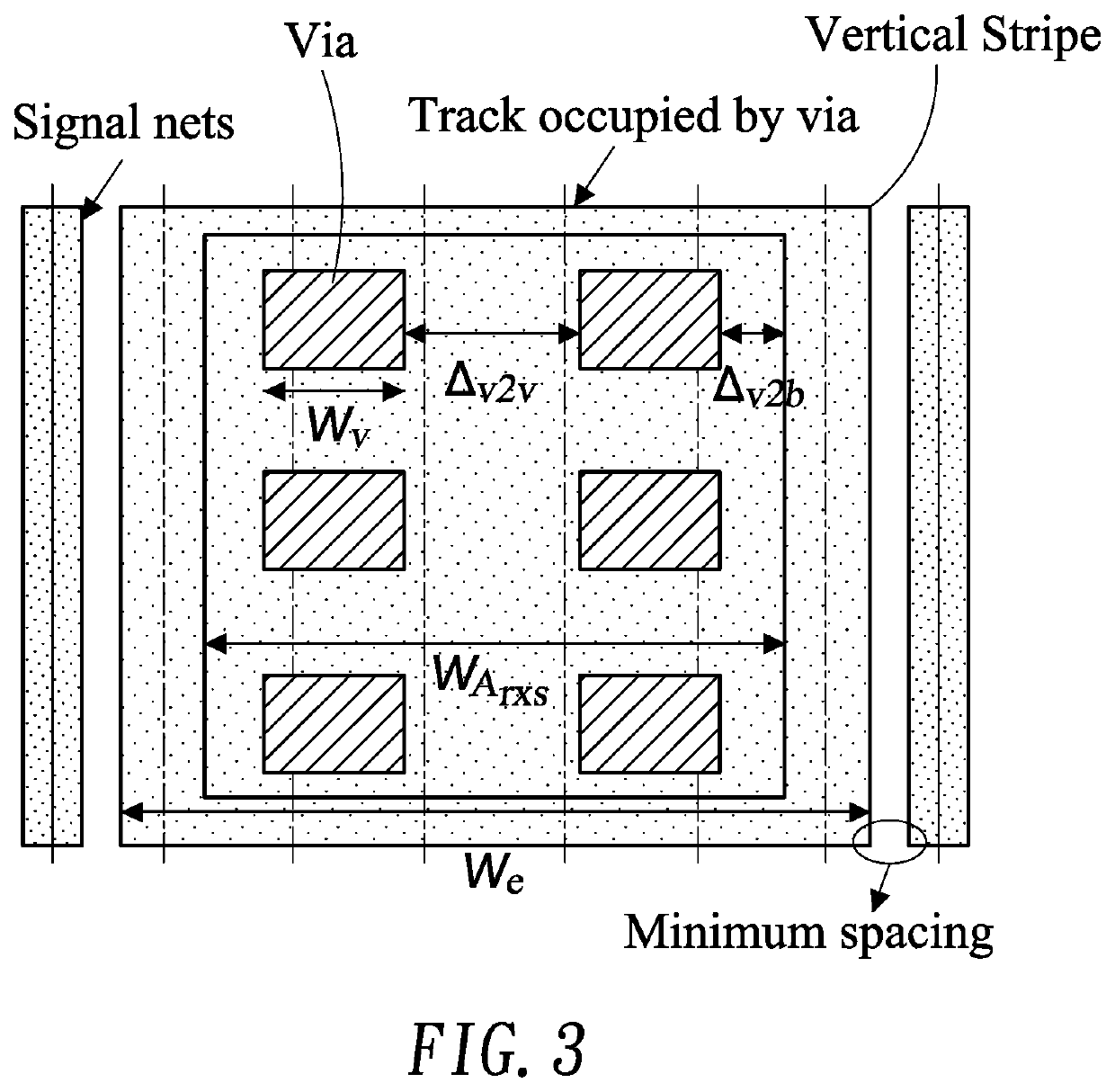
ActiveUS10579765B2Increase contactImprove efficiencyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringComputer science
A chip includes a substrate; macros placed on the substrate, which has a placement region being divided into sub-regions according to locations of the macros; and one or more vertical power stripes (VPSs) disposed in each sub-region. At least one VPS is not aligned with the VPSs of an adjacent higher or lower sub-region.
Owner:NCKU RES & DEV FOUND +1
Package stucture and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS9905503B2Increasing routable regionSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A package structure and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The method includes forming a first wiring layer on a carrier board, forming a plurality of first conductors on the first wiring layer, encapsulating the first wiring layer and the first conductors with a first insulating layer, forming a second wiring layer on the first insulating layer, forming a plurality of second conductors on the second wiring layer, encapsulating the second wiring layer and the second conductors with a second insulating layer, and forming at least one opening in the second insulating layer. The at least one opening extends to a second surface of the first insulating layer, such that at least one electronic component can be disposed in the at least one opening. With forming two insulating layers first followed by forming the at least one opening, there is no need to stack or laminate the substrate that already has an opening, and the electronic component is free of displacement due to any compression. Therefore, a package structure thus fabricated has an increased yield rate.
Owner:PHOENIX PIONEER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com