Buffer insertion to reduce wirelength in VLSI circuits
a buffer and wire length technology, applied in the direction of instruments, geometric cad, computing, etc., can solve the problems of large number of cells, difficult physical design without the aid of computers, and complicated connections between cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
)
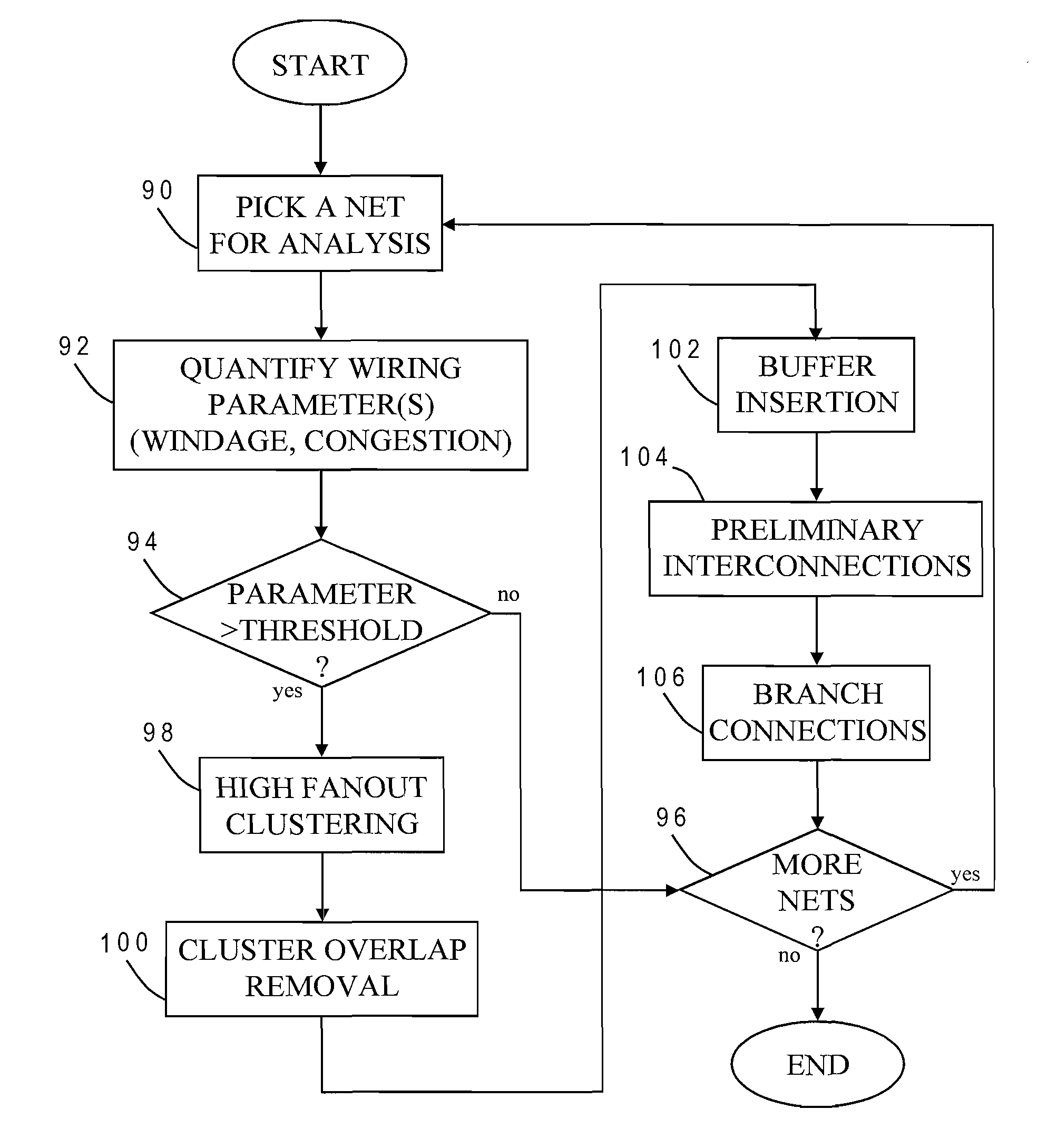
[0030]The present invention provides a novel method for determining buffer insertion locations in a net of an integrated circuit design, and is generally applicable to any type of IC design, such as general-purpose microprocessors, memory units or special-purpose circuitry. The method may be implemented as part of a physical synthesis process which optimizes placement, timing, power consumption, crosstalk effects or other design parameters. As explained more fully below, exemplary embodiment of the present invention utilizes high fanout clustering of net sinks and rewired buffers to produce a more efficient buffered wirelength.
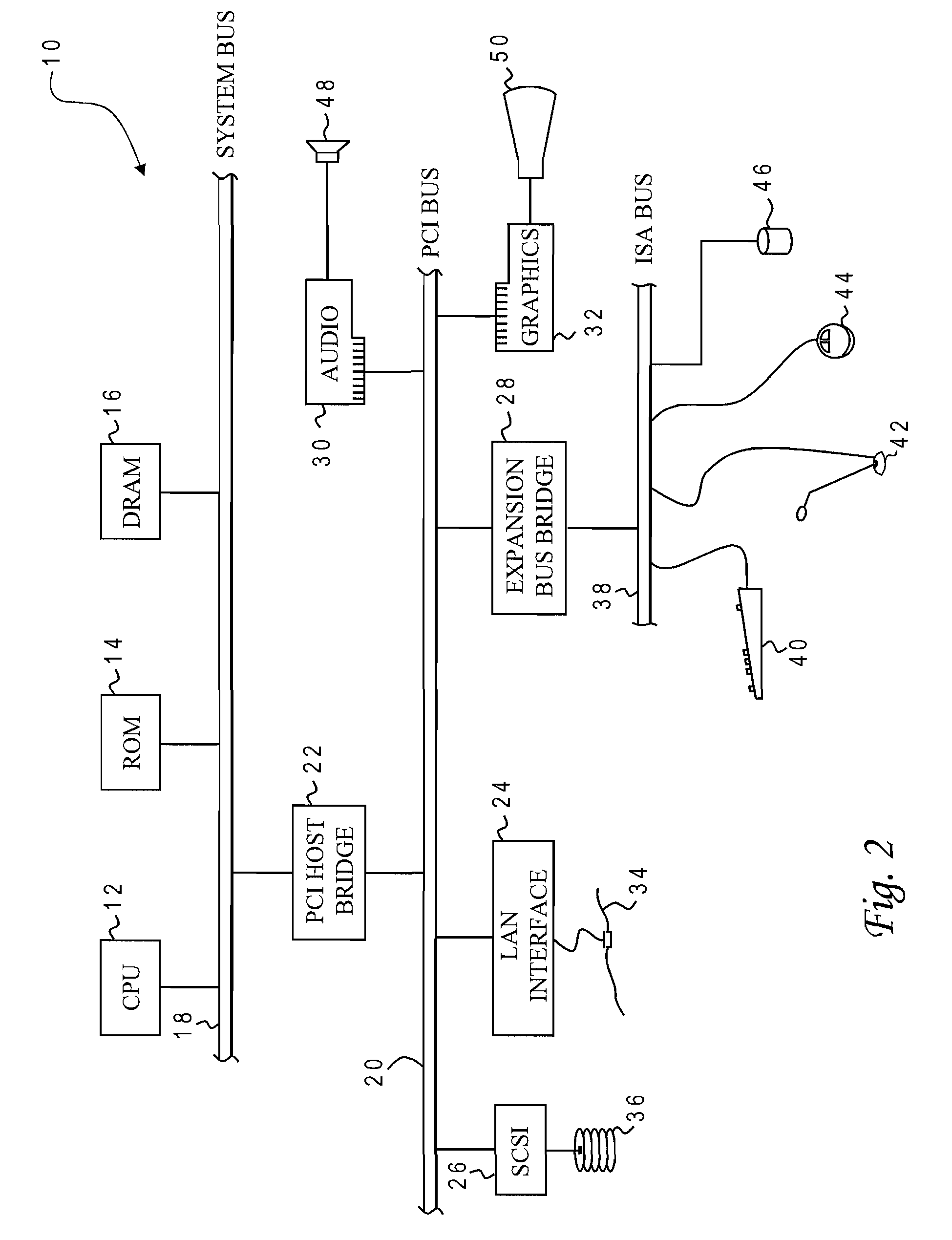
[0031]With reference now to the figures, and in particular with reference to FIG. 2, there is depicted one embodiment 10 of a computer system programmed to carry out the buffer insertion in accordance with one implementation of the present invention. System 10 includes a central processing unit (CPU) 12 which carries out program instructions, firmware or read...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com